Brown planthopper resistant gene in rice and use thereof
An anti-BPH gene technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problem of not yet cloning the anti-BPH gene, etc., and achieve the effect of improving resistance, good effect and clear function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1: Positional cloning of Bph14 gene
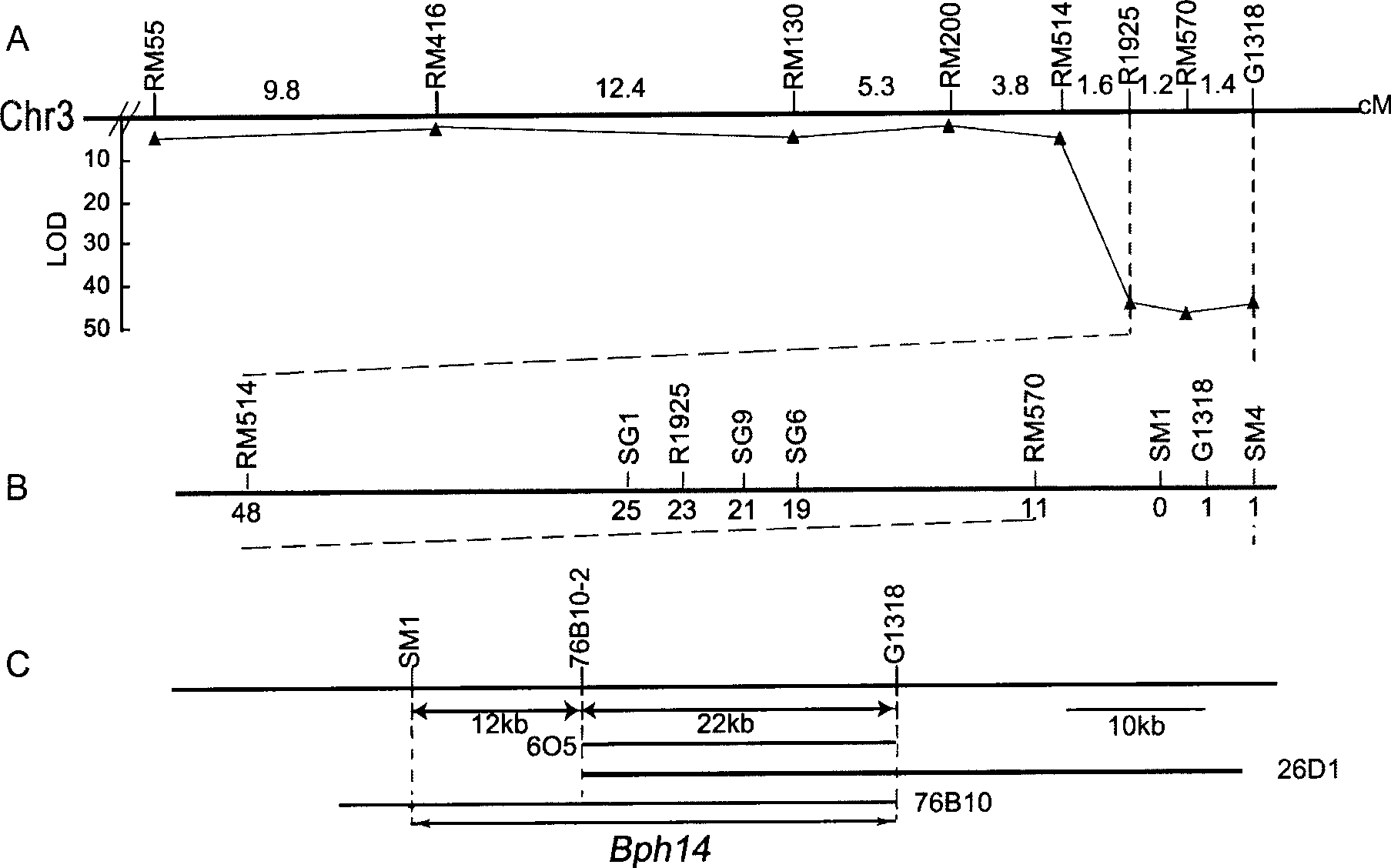
[0052] 1. Preliminary positioning results of Bph14
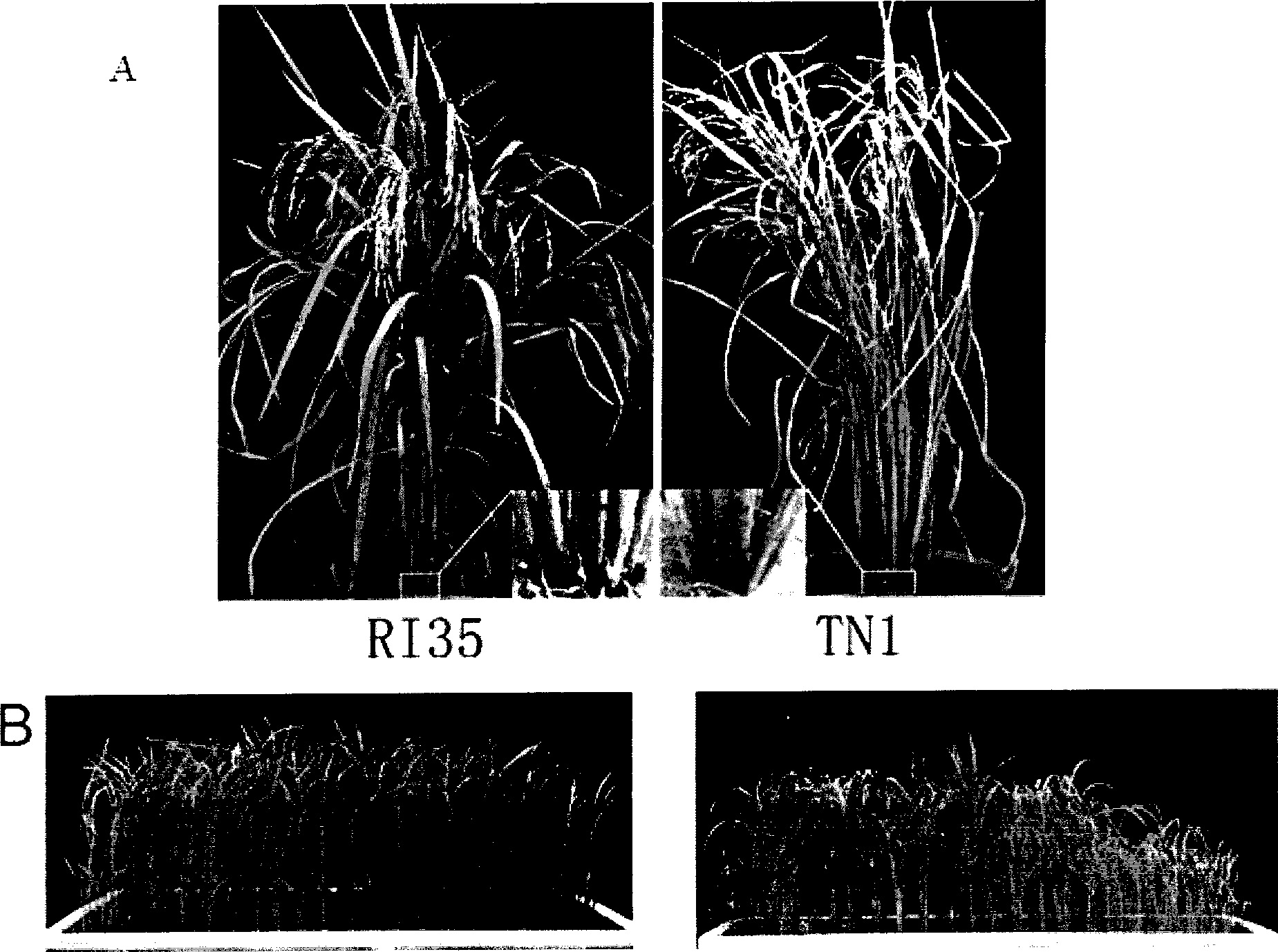
[0053] The brown planthopper-resistant rice material RI35 (Hao PY, Liu CX, Wang YY, Chen RZ, TangM, Du B, Zhu LL, He GC (2008) Herbivore-induced callose deposition on the sieve plates of rice: an important mechanism for host resistance. PlantPhysiology 146: 1810-1820) was crossed with a brown planthopper-susceptible rice variety (Taichung Local No. 1, TN1, purchased from the National Rice Germplasm Bank) to construct a Bph14-containing F 2 group. To identify F 2 To locate the N. lugens resistance phenotype of each individual plant in the population, the seedling stage group method was used to investigate the resistance performance of each individual plant in the population (see figure 1 B). f 2 The insect resistance level of a single plant is according to the corresponding F 2-3 The average value of the insect resistance level of all individual plants in the famil...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2: Functional verification and application of Bph14 gene
[0070] 1. Construction of genetic transformation vector
[0071] The vector used was pCAMBIA1301 (purchased from Center for the Application of Molecular Biology to International Agriculture, Australia). According to the results of genome sequencing, design primers (5'cg gaattc ctccctgactgaagaagagaagag3',5'cg gaattc tgctagctgtgattctcttatgatg3'), which includes an EcoRI adapter, amplifies the genome of insect-resistant rice B5 (Z. Huang et al., Identification and mapping of two brown planthopper resistance genes in rice. Theor Appl Genet, 2001, 102: 929-934). The total volume of the PCR reaction is 50 μl: 1 μl DNA, 5 μl 10× buffer, 1 μl 10 mM dNTP, 3 μl each of 10 μM primers, 1 U high-fidelity Taq enzyme; reaction program: 94°C for 2 minutes, 94°C for 15 seconds, 58°C for 30 seconds, 72°C for 7 minutes and 30 seconds, total 30 cycles; the product was purified by adding 1 / 10 volume of 3mM NaAC and 2× v...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3: Molecular marker-assisted selection of brown planthopper-resistant rice with Bph14 gene
[0078] According to the genome sequence and cDNA sequence of the Bph14 gene, multiple pairs of SSR-marked or STS-marked primers can be designed. In this example, the primer pair 5'ctgctgctgctctcgtattg3' and 5'cagggaagctccaagaacag3' were used as marker primers to breed rice with insect resistance function, and the length of the amplified fragment was 172bp. Genomic DNA of insect-resistant rice, insect-susceptible varieties and their hybrid and backcross progeny plants is extracted, and after PCR amplification with primers designed for the Bph14 gene sequence, molecular marker detection is carried out by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Among the hybrid progeny plants, those with the same PCR band pattern as the insect-resistant rice (the amplified product contains a 172bp fragment) are the selected plants containing the Bph14 gene (such as figure 2 ). The insect res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com