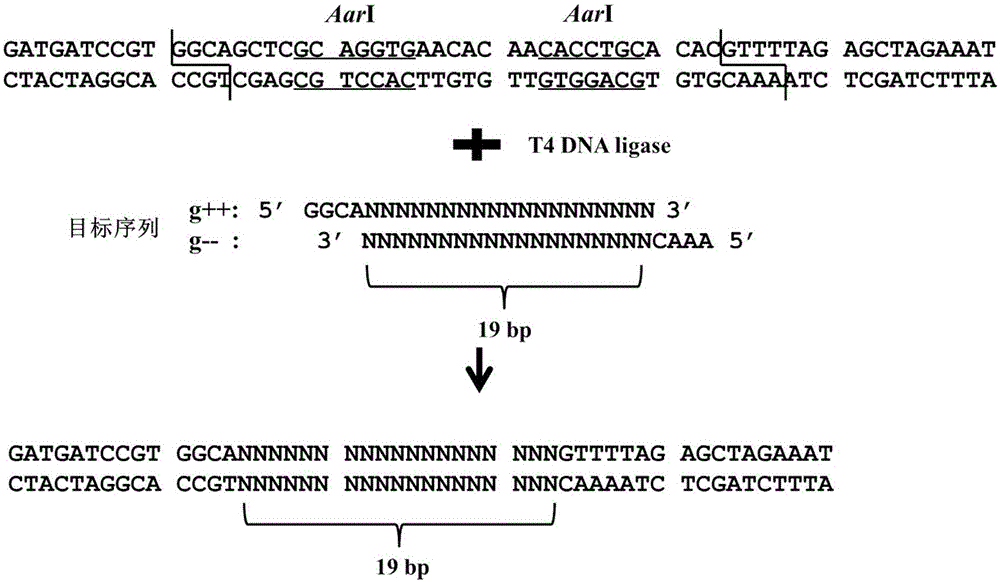
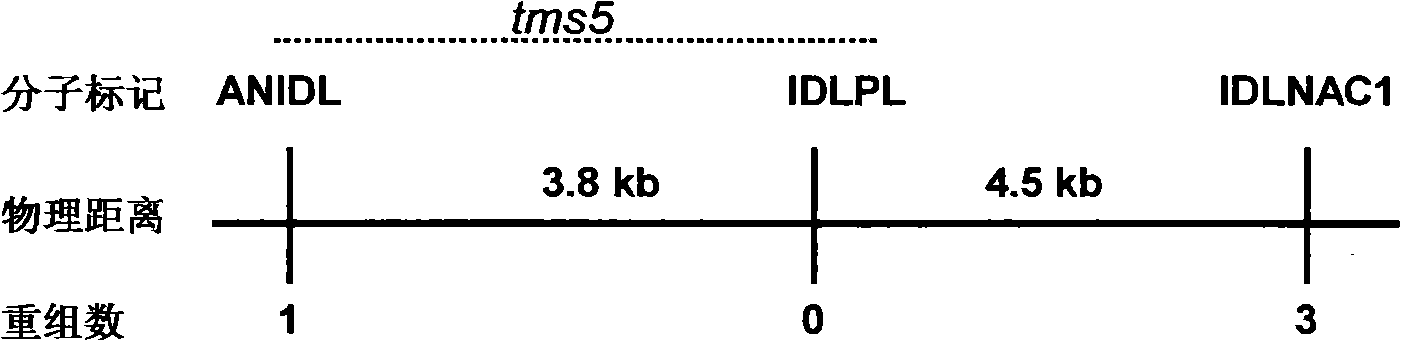
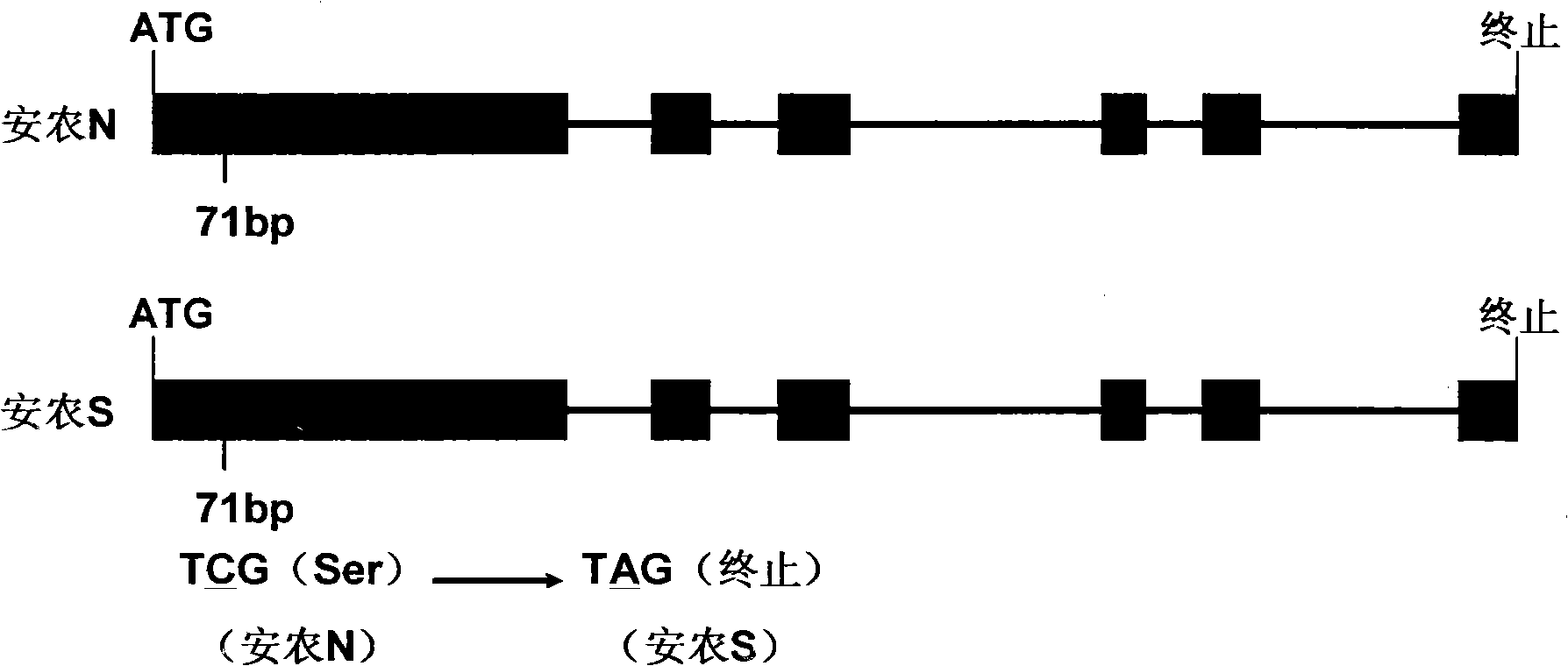
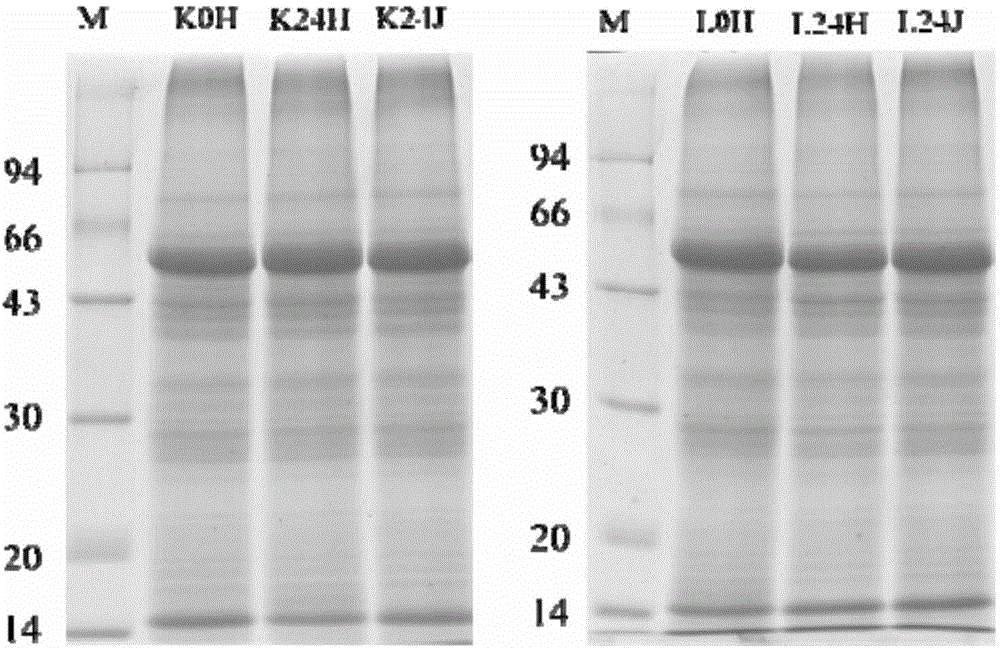
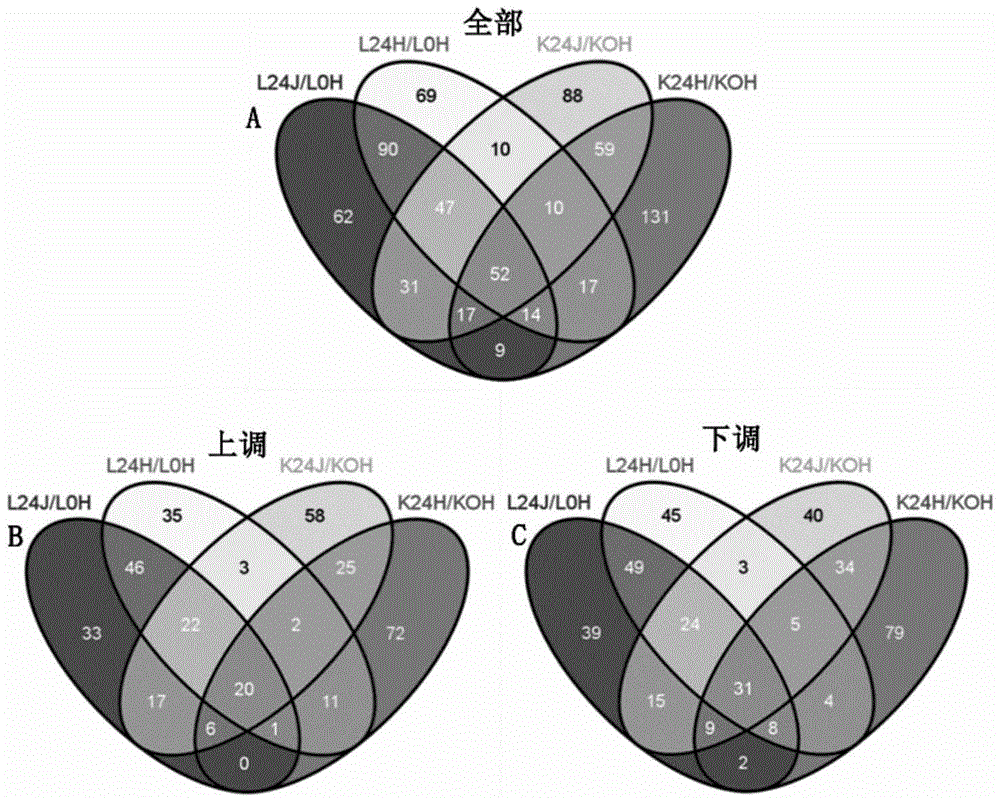
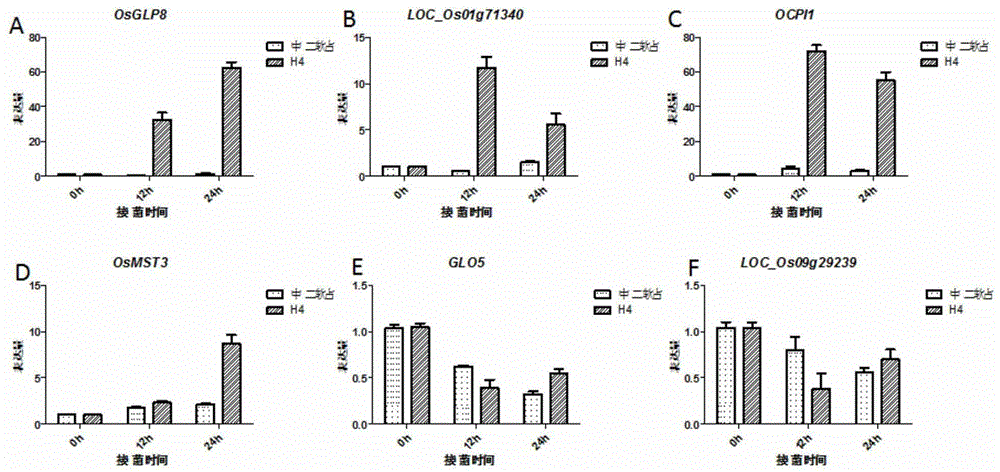
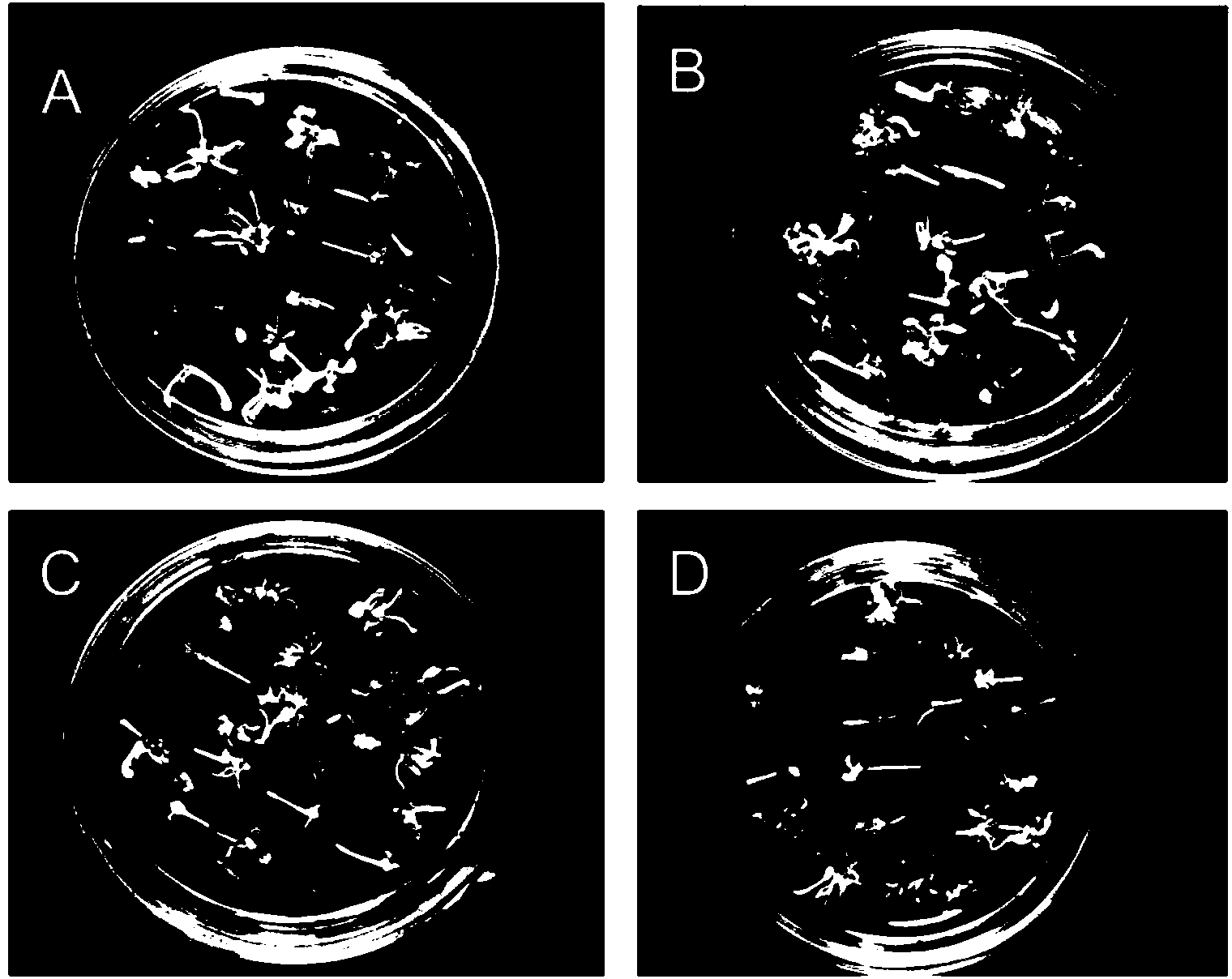
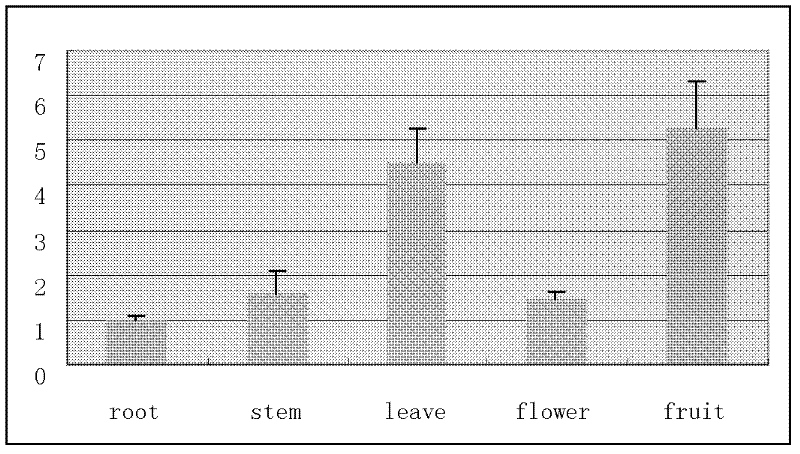
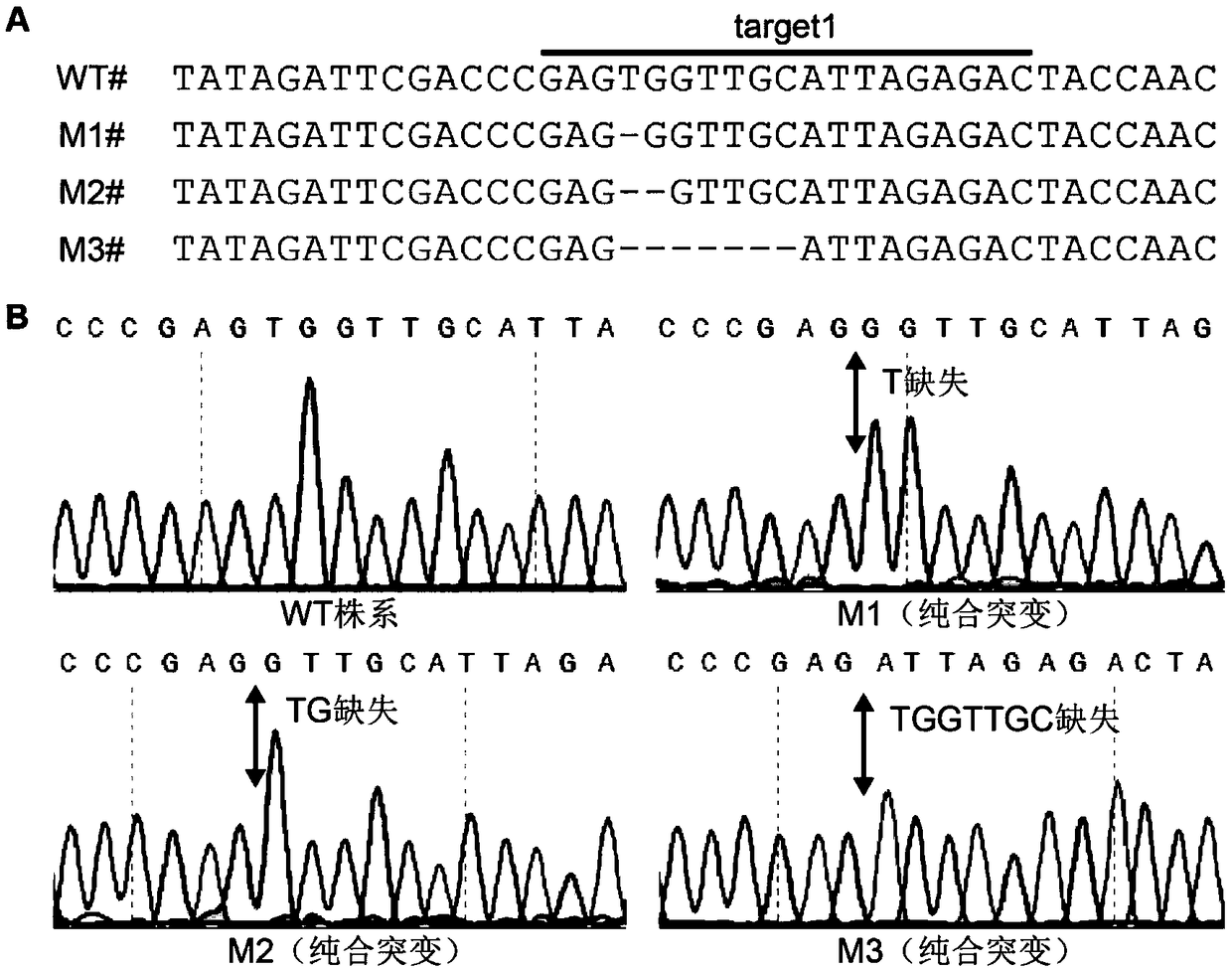
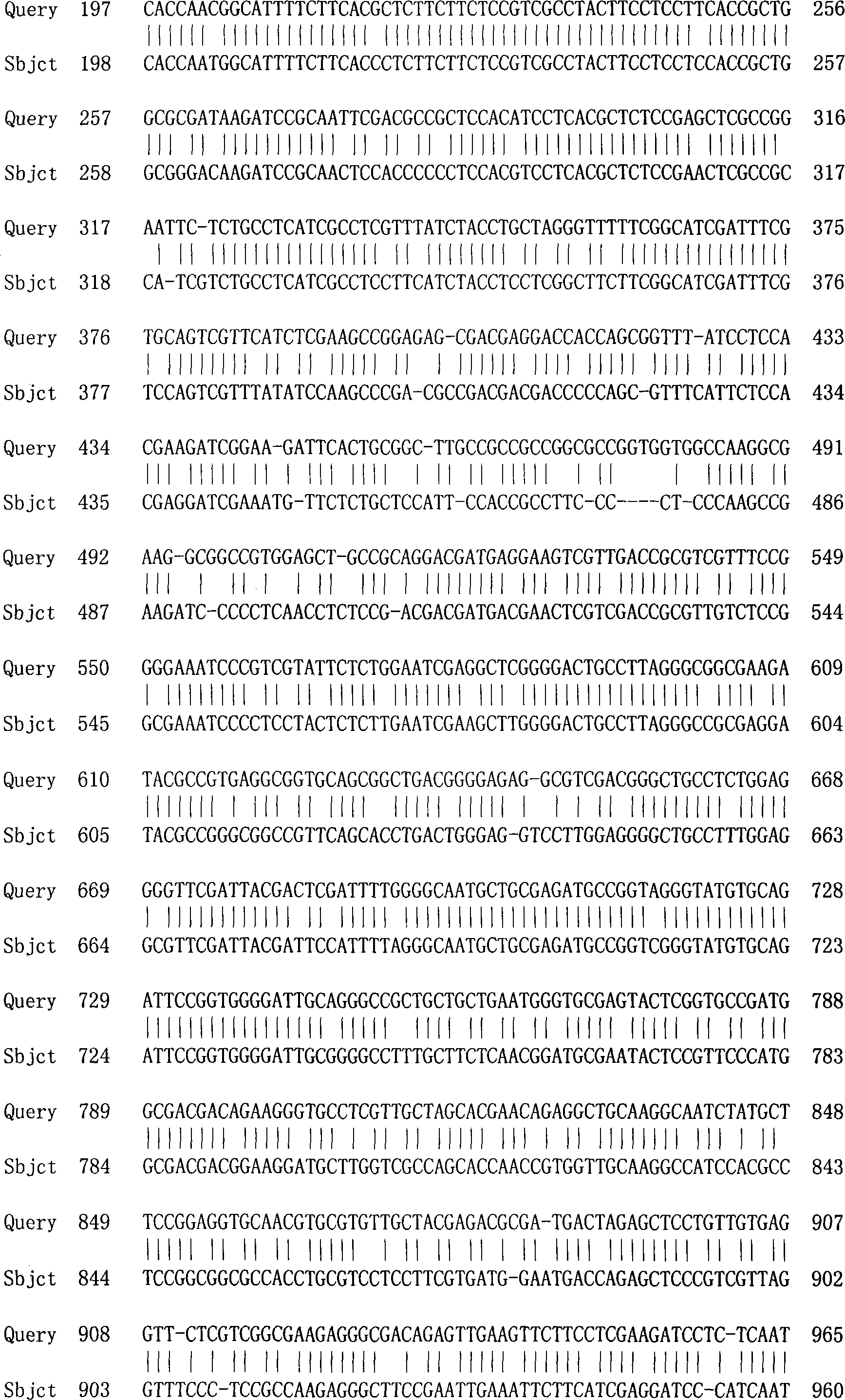
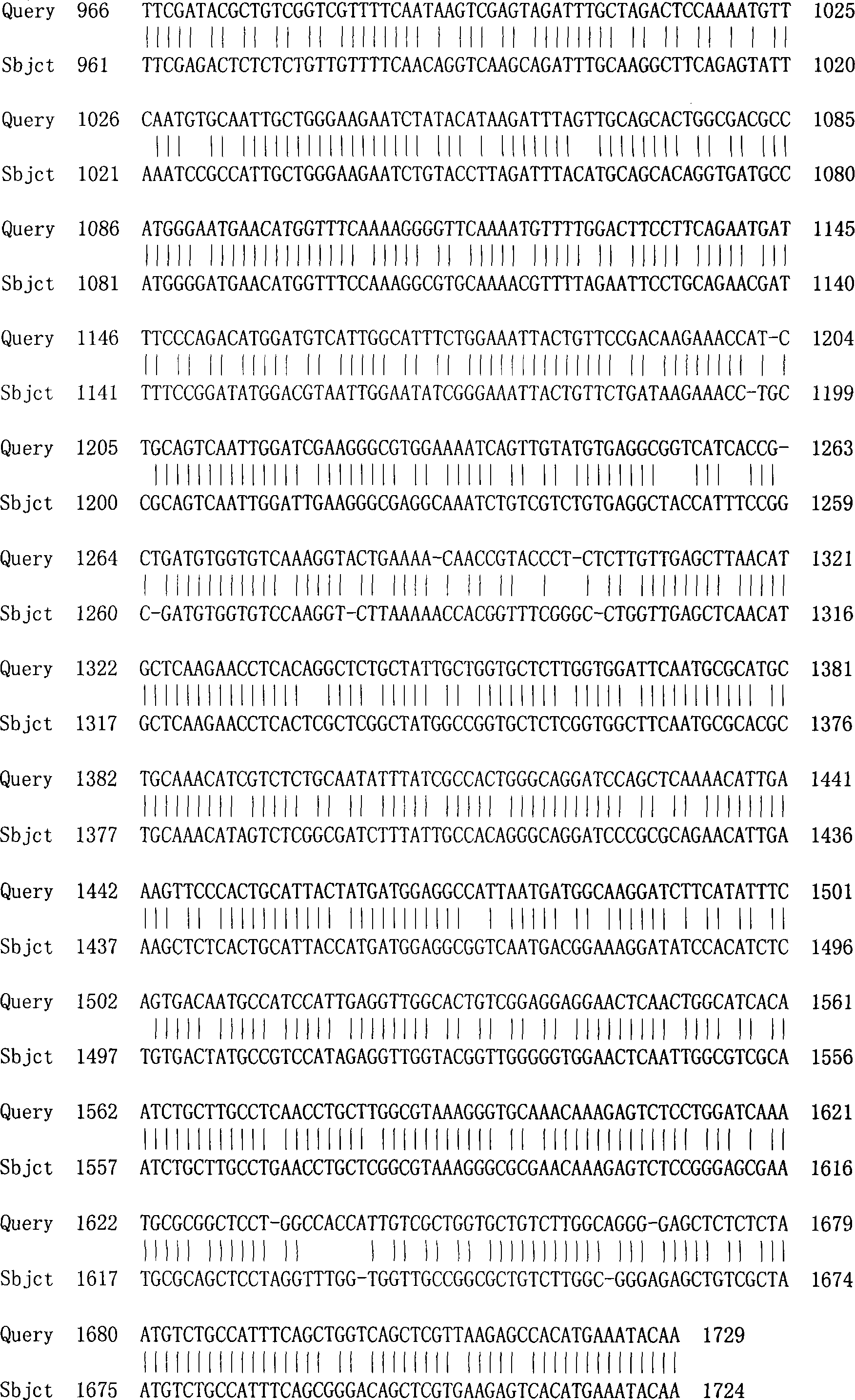
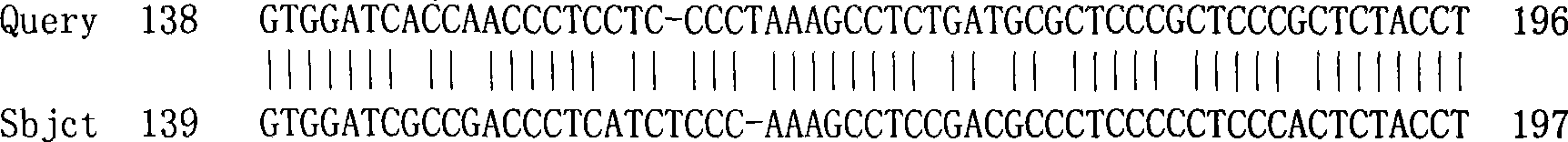Patents
Literature
827 results about "Transgenic technology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transgenic technology consists of the introduction of a defined genetic material into the germline of mice or other animals. This technique has attracted considerable attention, because it has been found to be a very powerful approach for different experimental fields, including molecular and developmental biology as well as medical research.
Method for establishing humanized rat drug evaluation animal model
InactiveCN104593418AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryLarge fragmentEngineered genetic
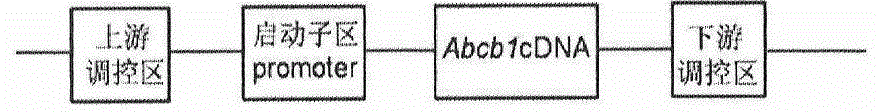
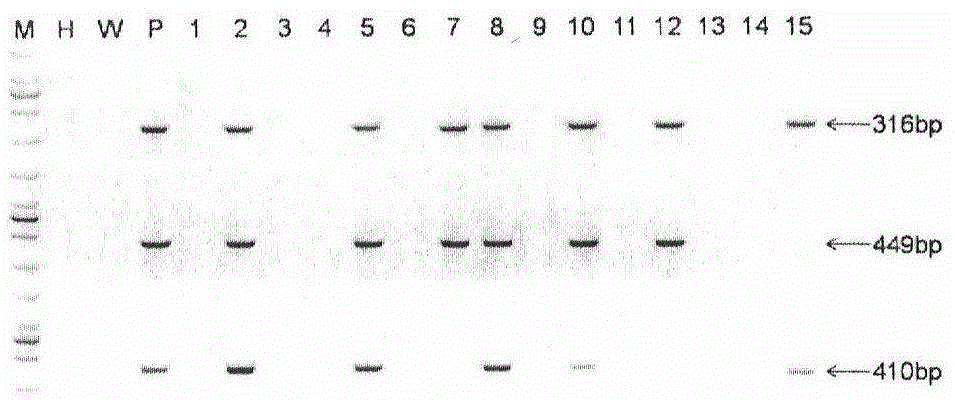
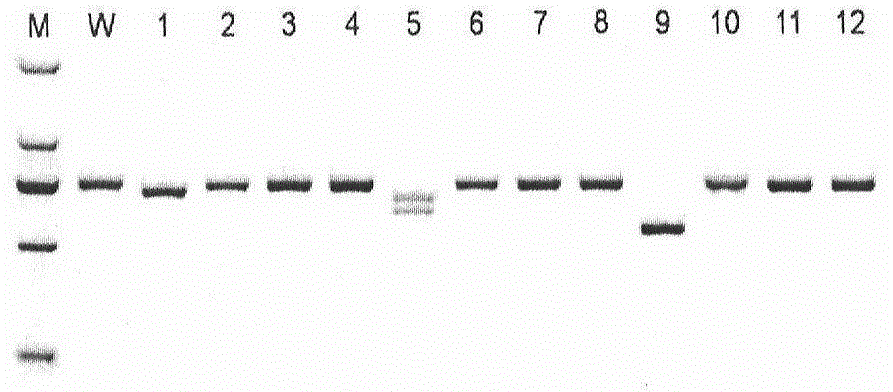
The invention provides a method for establishing a humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. According to the method, a multidrug resistance gene 1 (Abcb1)-knocked-out genetically engineered rat is obtained through a microinjection method by virtue of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology and 153kb bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) fragments containing a humanized Abcb1 promoter and cDNA is simultaneously inoculated into the rat genome through the microinjection method by virtue of a large fragment transgenic technology to obtain a transgenic rat capable of stably expressing human Abcb1 and the genetically engineered rat and the transgenic rat are hybridized to establish the humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. RT-PCR analysis shows that Abcb1 expression profiles of humanized Abcb1 rat are significantly different from those of the rat endogenous Abcb1. The method has the beneficial effects that the humanized rat capable of expressing human Abcb1 is obtained and the rat is used for expressing human Abcb1 genes and has closer expression profiles to those of human so that the model can be well used for the efficacy evaluation of newly developed drugs.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Establishment and application of plant multi-gene knockout vector
ActiveCN105112435AQuick cullingVector-based foreign material introductionTransgenic technologyMutant
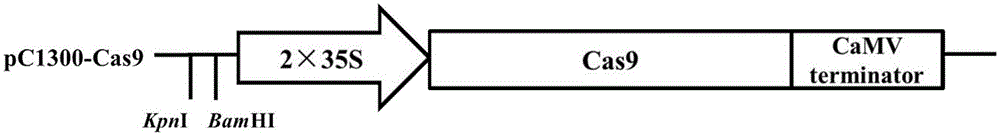
The invention discloses establishment and application of a plant multi-gene knockout vector. A method of the establishment of the plant multi-gene knockout vector comprises the following steps of (1) establishing a binary expression vector pC1300-Cas9; (2) establishing an intermediate vector SK-9RNA; (3) establishing single objective gRNA; and (4) serially connected a plurality of pieces of gRNA and establishing a final binary expression vector. A plurality of gRNA sequences are connected to the binary expression vector of an existing Cas9 sequence by an isocaudamer connecting method, and multiple plant mutants can be obtained by an agrobacterium tumefaciens infected transgenic technology. By an isocaudamer connecting establishment strategy, pieces of gRNA can be combined, and multiple plant mutants can be obtained by transgenosis once, so that an efficient and convenient multiple plant mutants preparing method is established.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Temperature sensing male fertile gene and use thereof
ActiveCN101333533AImprove selection efficiencyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and an application thereof and also discloses a genetic marker of the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene, and provides a protein coded by the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and a carrier containing the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene and a recombinant microorganism. The invention also discloses the application of the thermo-sensitive male fertility gene in cultivating a thermo-sensitive male sterile line and an application of the genetic marker in rice breeding. The thermo-sensitive fertility gene TSSNR is acquired through the map-based cloning technique of Annong S-1 thermo-sensitive sterility gene locus tms5, functions of the gene are validated through transgene experiments, and the transgene technique of RNAi or antisense RNA or the over-expression dominant negative principle is provided, functions of the TSSRZ gene in normal rice varieties are incapable, so as to cultivate the thermo-sensitive male sterile line, and the application value is significant.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
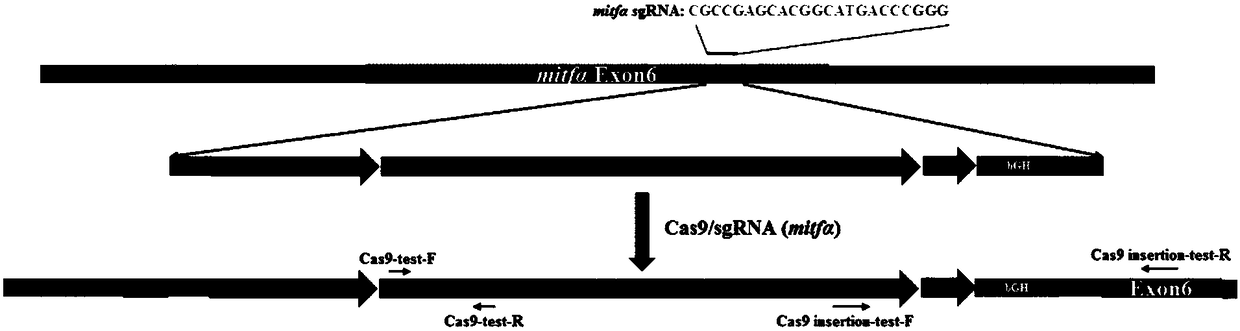
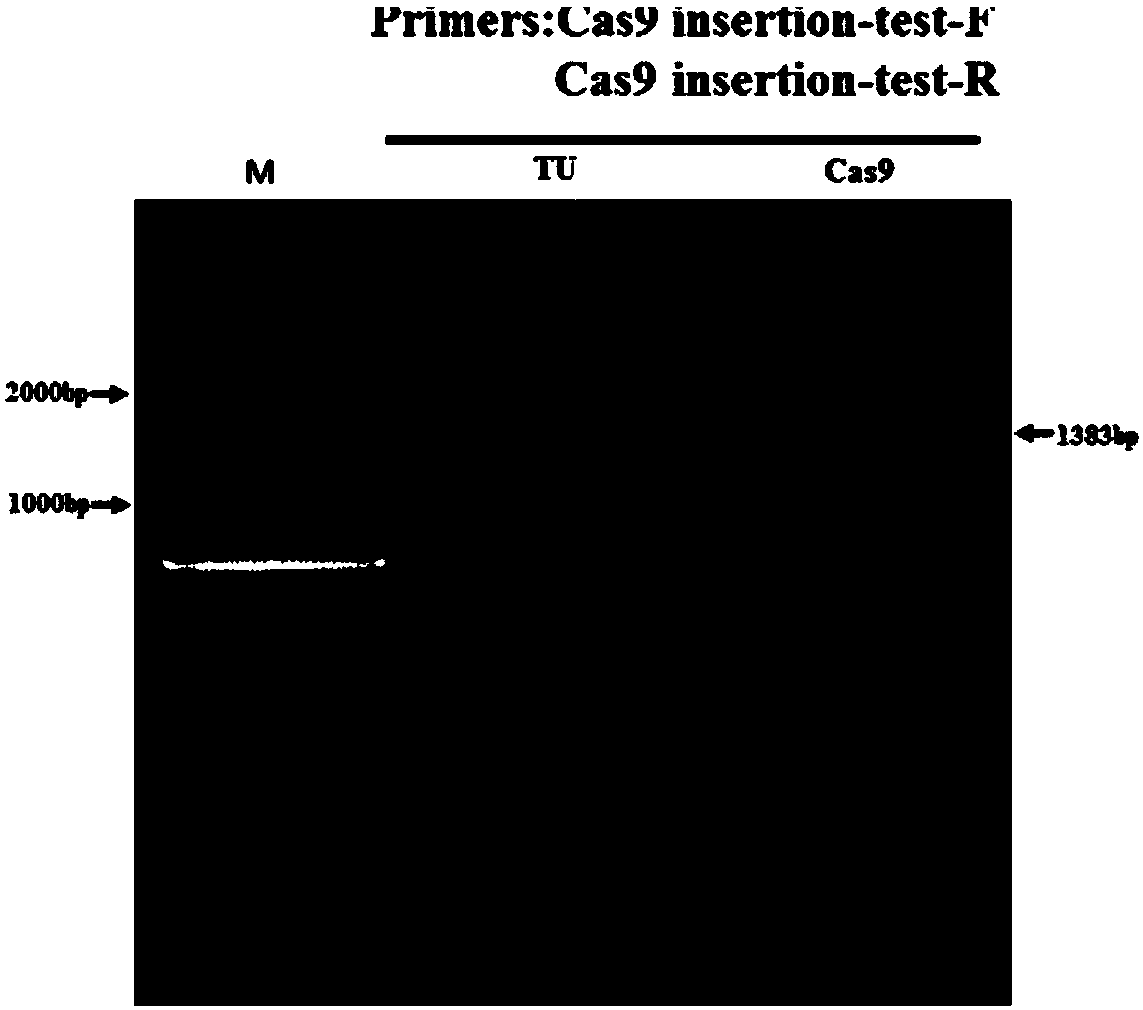
Transgenic zebrafish expressing gene Cas9 and construction method and application of transgenic zebrafish
InactiveCN108251452ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionDiseaseTransgenic technology
The invention relates to a transgenic zebrafish expressing a gene Cas9 and a construction method and the application of the transgenic zebrafish. According to the transgenic zebrafish expressing the gene Cas9, the gene Cas9 is inserted into a gene Mitfa of the zebrafish. The transgenic zebrafish capable of expressing the gene Cas9 is constructed in a targeting way at the fixed point of the pigmentgene Mitfa through the CRISPR / Cas9 transgenic technology, and pigment fading is taken as a mark for screening the homozygous knockout line. Using the transgenic zebrafish to edit a gene Tyr and a gene ZFERV proves that the transgenic zebrafish is more effective in the gene knockout, and a homozygous knockout individual is obtained on the F0 generation. Compared with the application of the traditional CRISPR / Cas9 technology to the zebrafish, the gene editing efficiency of the Cas9 transgenic zebrafish is higher; and a simple effective tool is provided for the large-scale gene screening and theestablishment of a disease model.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Inducing method for differentiating umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into nerve cells
ActiveCN101914493APromote differentiationNo insertion mutationsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to an inducing method for differentiating umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into nerve cells, which comprises the following steps of: cultivating the separated umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in an MSC culture medium to spread a whole culture dish; cultivating the stably-subculturing mesenchymal stem cells in the culture dish which is spread with the extracellular matrix by means of the MSC culture medium to be 70% confluence; and leading the 70% confluent mesenchymal stem cells to sequentially pass through four inducing culture mediums to cultivate, wherein the four inducing culture mediums comprise the following factors of 5-azacytidine+Pam3CSK4, bFGF+Noggin, bFGF+RA+FGF8+Wnt3a, and Bmp4+Shh+RA+NGF+BDNF. The inducing method has the benefit effects of being free of chemical substances with cytotoxicity, transgenic technology and nerve cell co-cultivation, and being high in differentiating efficiency and shorter in time consumption.
Owner:SHANDONG QILU STEM CELL ENG
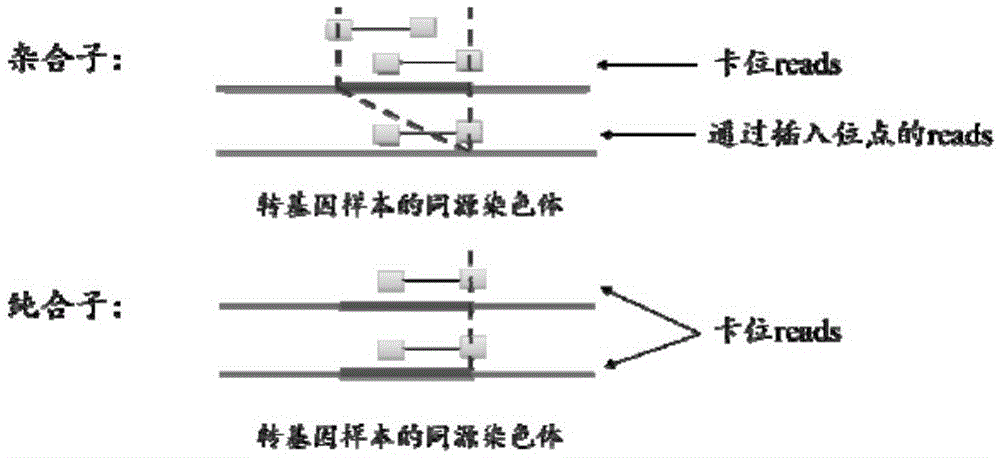
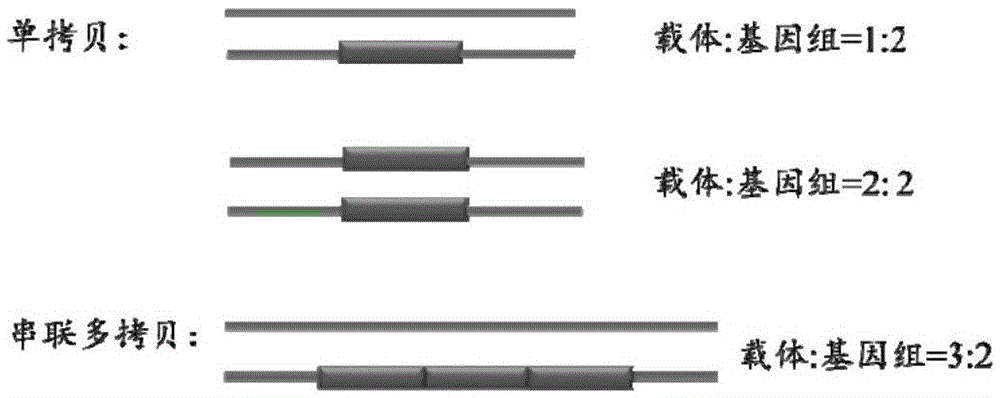
Method for identifying transgenic events through whole genome sequencing data
ActiveCN105631242AAccurate analysisValid identificationProteomicsGenomicsBiological bodyWhole genome sequencing
The invention provides a method for identifying transgenic events through whole genome sequencing data. The method comprises the steps that transgenic events are identified through a bioinformatics means, and the position, direction, copying number and flanking sequence information of foreign fragments inserted into genomes and the homozygous and heterozygous state of transgenic samples can be rapidly and effectively identified. Compared with traditional Genome walking, real-time quantitative PCR and other experiments methods, the method has the advantages that time is short, repeatability is high, the result is stable, and explaining is easier. The method is the most comprehensive in existing transgenic event detection methods, can accurately analyze influences of transgenic events on the living body within a short time, carries out safety evaluation on transgenic animals and plants, and pushes the transgenic technology to be applied in agriculture.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
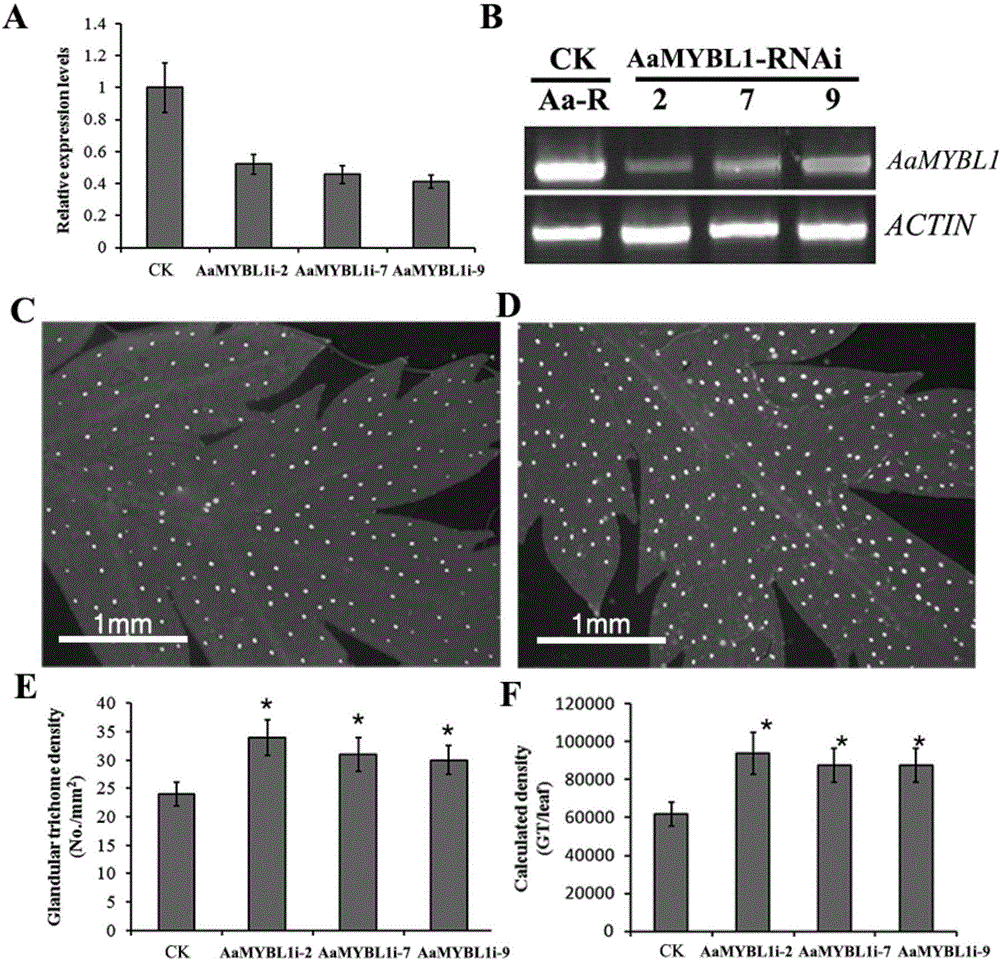
Coding sequence of AaMYBL1 protein of artemisia apiacea and application thereof
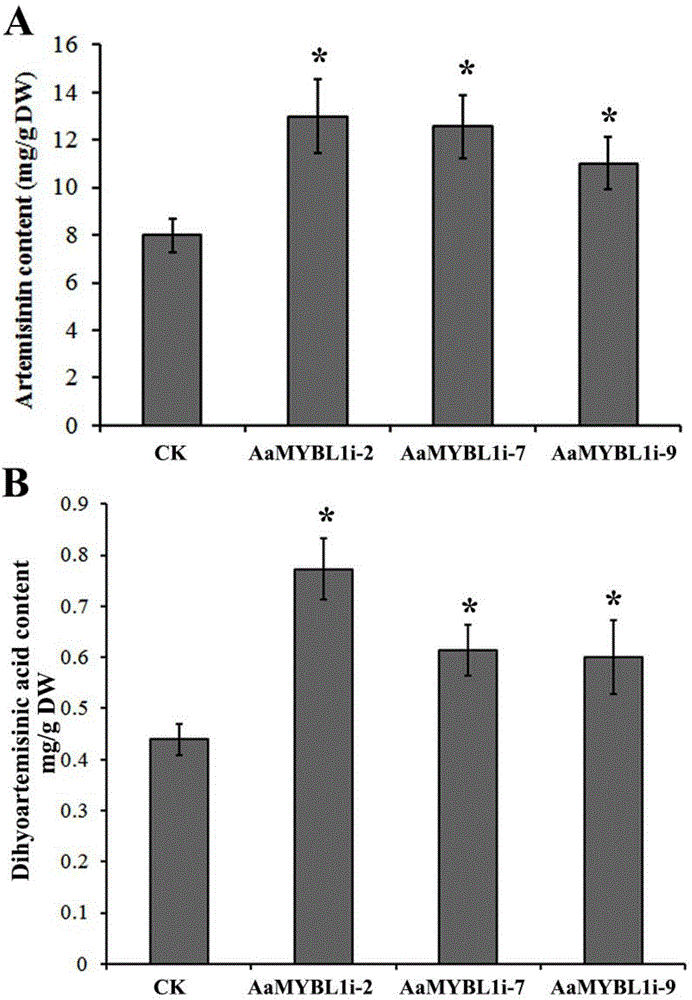
The invention relates to a coding sequence of an AaMYBL1 protein of artemisia apiacea and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence coded by the coding sequence AaMYBL1 of an MYB-like type transcription factor of artemisia apiacea is shown as SEQ ID NO:4. The AaMYBL1 which codes a R3MYB type transcription factor takes part in regulation of density of glandular hairs of artemisia apiacea. An interference vector of the AaMYBL1 transcription factor of artemisia apiacea is transformed into artemisia apiacea by means of the transgenic technology, so that the density of the glandular hairs on the surface of artemisia apiacea can be effectively regulated, thus, the content of artemisinin is improved. The density of the glandular hairs on the surface of a blade of non-transgenic common artemisia apiacea is 24 / square millimeter, and the density of the glandular hairs of a blade of transgenic artemisia apiacea inhibiting AaMYBL1 genetic expression is increased to 34 / square millimeter; the quantity of total glandular hairs of each blade is increased from 61947 to 93683; correspondingly, the content of artemisinin is improved from 8mg / g DW of non-transgenic artemisia apiacea to 12mg / g DW. The coding sequence provided by the invention is of significance for providing a high-yield stable novel medicine source for scaled production of artemisinin.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cloning and application of major gene GS5 capable of controlling width and weight of rice grain
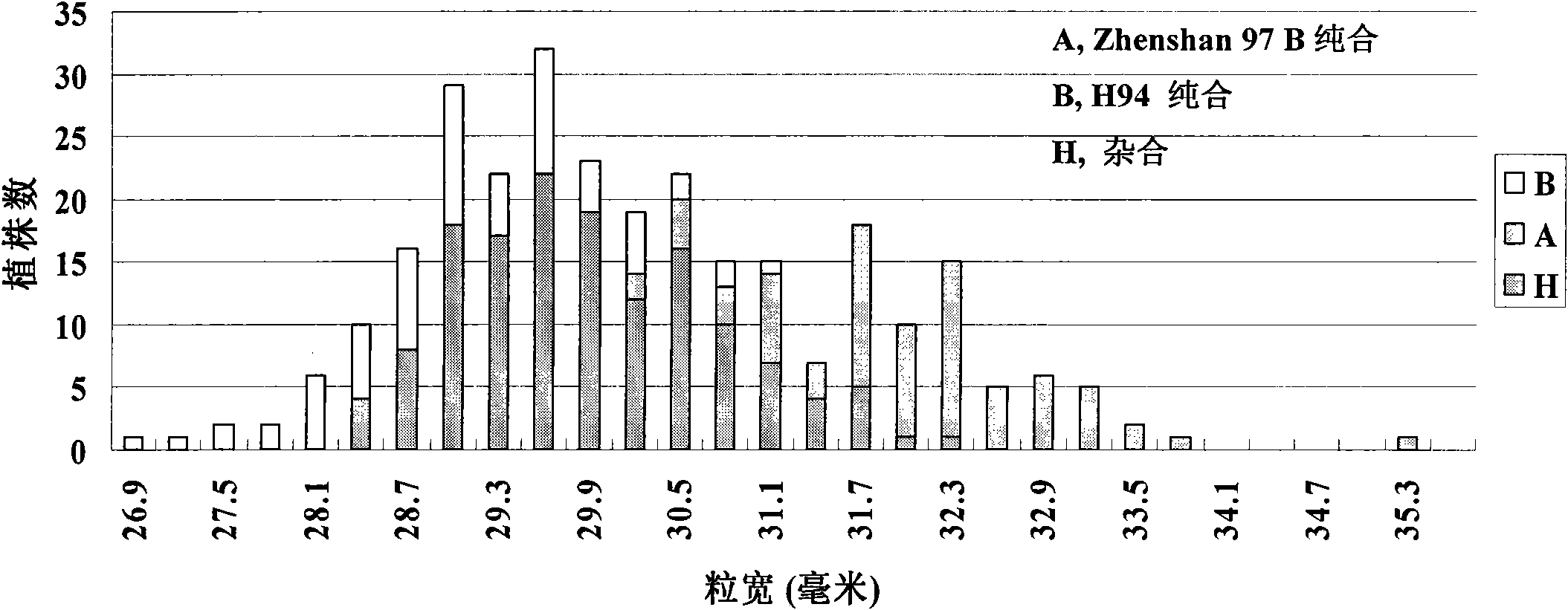
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, disclosing a separated and cloned major gene GS5 capable of controlling the width and the weight of a rice grain and the DNA sequence of the allelic gene of the major gene GS5. The DNA sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 (Zhenshan 97B) and SEQ ID NO.3 (H94) and contains 10 exons. The amino acid sequence of the major gene and the amino acid sequence of the allelic gene are shown as SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.4. By using two large-grain rice varieties and two small-grain rice varieties for comparative sequencing, in an approximately 6.1kb range, 22 common base differences exist between the large-grain variety and the small-grain variety, wherein 18 mutations are in a promoter area, 4 mutations are in a code area and 5 amino acids are caused to be changed. By using a transgenic technology, GS5 transgenic rice plants are obtained and express that the width and the weight of the rice grain are obviously improved when being compared with the control width and the control weight of the rice grain. The character changes are quite coincident with the two genotype expressions of a Zhenshan 97 near-isogenic line and a GS5 near-isogenic line. The invention additionally discloses a method of near-isogenic line breeding, gene cloning and gene transfer and application thereof.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
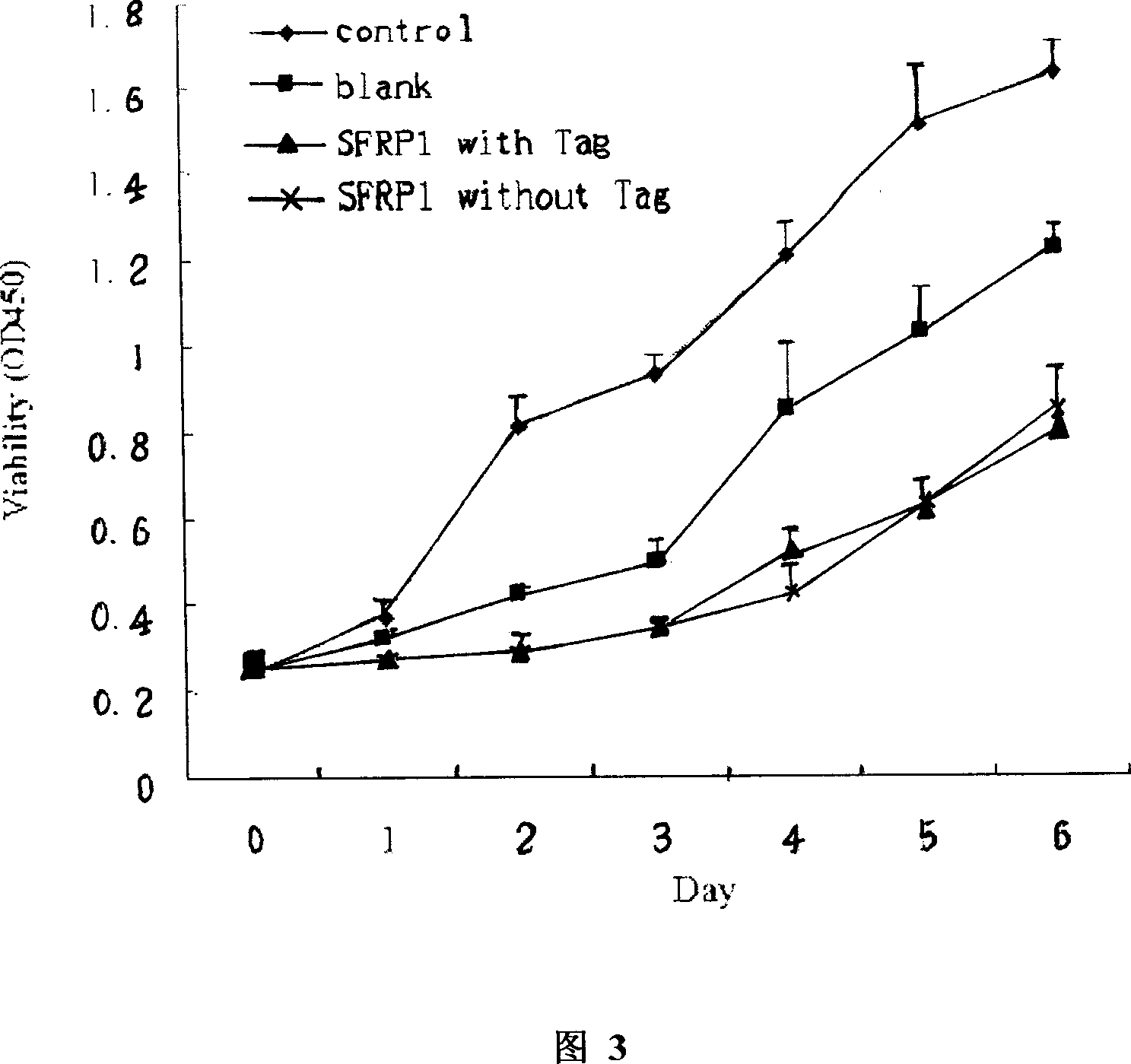
Human SFRP1 gene, its coded protein and application
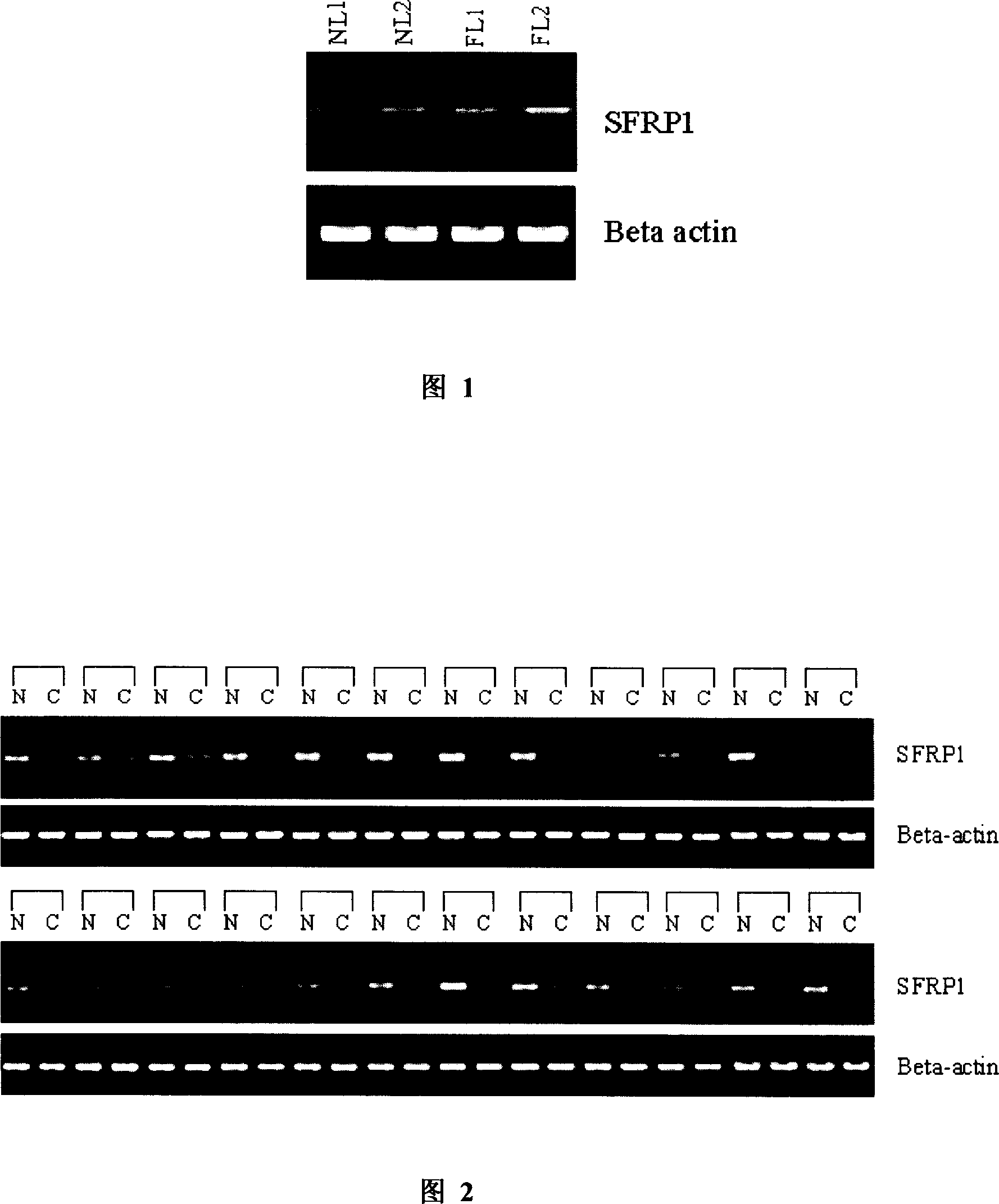
The invention discloses a human SFRP1 gene sequence and coding protein and application in the drug to inhibit tumour from growing, which is characterized by the following: treating or lessening the loss, non-functional or abnormal disease of human SFRP1 protein; making human SFRP2 gene express in the cancer cell through gene-transmitting technology or supplementing human SFRP1 protein in vitro; controlling cancer from breeding and killing cancer cell.
Owner:CHINESE NAT HUMAN GENOME CENT AT SHANGHAI
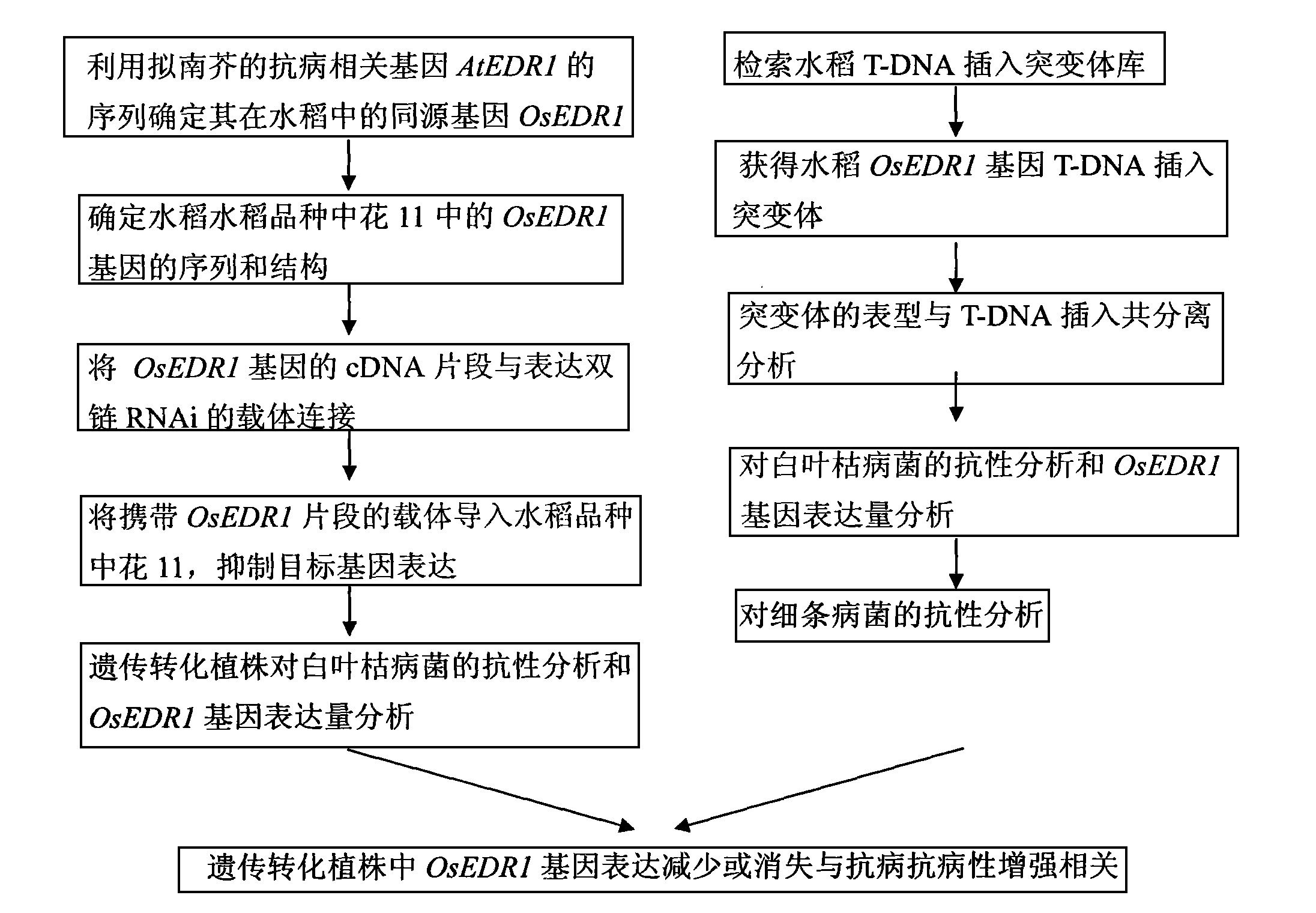
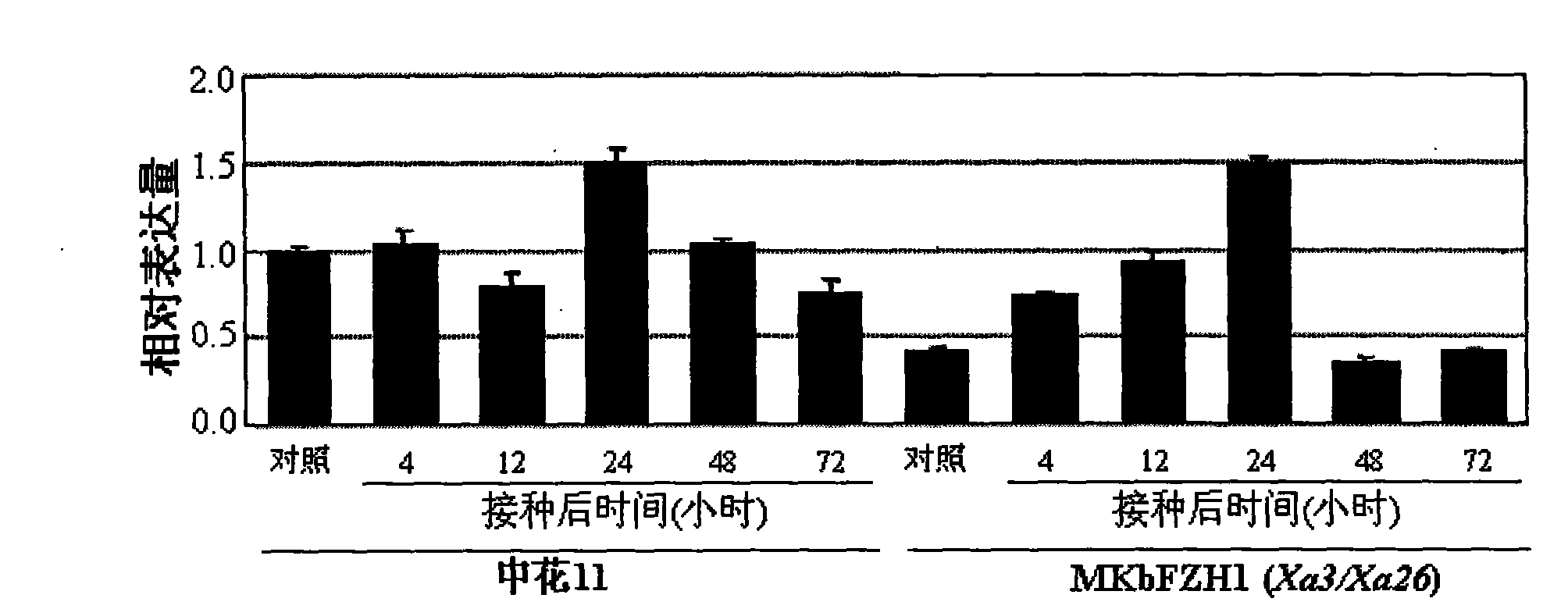
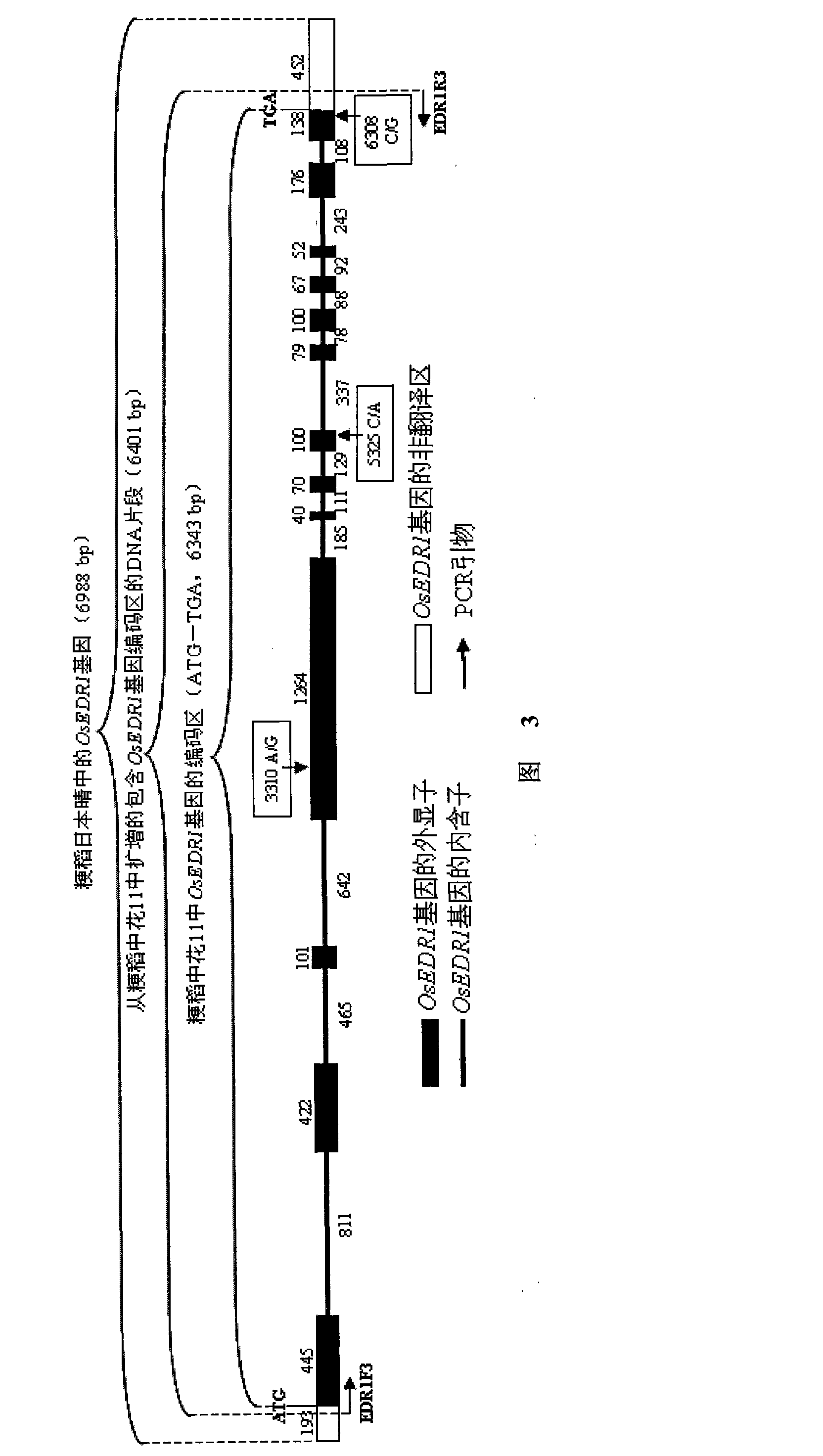
Paddy disease-resistant related gene OsEDR1 and application thereof in improved paddy disease resistance
InactiveCN101514343AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDiseasePlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and more particularly relates to separated clone and functional verification of DNA segments of paddy disease-resistant related gene OsEDR1. By utilizing transgenic technology based on RNA interference (RNAi) principle, part of the DNA segments of the OsEDR1 gene are connected with a vector expressing double-strand RNA to be converted into rice varieties, and the expression of the OsEDR1 gene in the rice varieties can be inhibited. Genetic transformation rice with obviously reduced OsEDR1 gene expression quantity has the remarkably improved resistibility for bacterial blight and bacterial streak disease, so as to prove that the OsEDR1 gene is negative regulatory factor in the reaction of resisting bacterial blight and bacterial streak disease of rice, thus the disease resistance of the rice can be improved by inhibiting the expression of the OsEDR1 gene.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Low-temperature incubation transgene method for cultivated silkworm diapause breed variety
InactiveCN101195833AImprove economyExcellent target traitsMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionDiapauseBombyx mori
The invention relates to a method for a silkworm diapause variety low temperature egg incubation transgene. Silkworm diapause variety next generation graine voltinism is changed in the special egg incubation condition, to ensure that present generation silkworm diapause variety moths obtained under the special egg incubation condition mate, to give birth to non-diapause next generation graine, finally referring to the microinjection transgene method of the non-diapause silkworm eggs embryo, the gene transferring is performed, therefore the obstruction of the silkworm diapause variety transgene technology is expertly broken, and a transgene silkworm is effectively manufactured. The method directly adopts the universal use utility silkworm diapause variety as original material in production, can avoid the long and troublesome breeding process, and directly utilizes the transgene technology to create the good new special silkworm variety with various characteristics, the breeding cycle can be greatly shortened, and massive manpower and physical resources are saved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY +1
Method of researching change of proteome of rice responding rice blast bacterial infection through iTRAQ technology
InactiveCN104820103AQuick and effective screeningStrong disease resistanceBiological testingDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method of researching the change of a proteome of rice responding rice blast bacterial infection through an iTRAQ technology and belongs to the field of plant biotechnology. The method includes following steps: A. extracting a plant materials and leaf protein; B. performing further FASP enzymolysis, peptide fragment marking, SCX classification and LC-MS analysis to the protein sample obtained in the step A; C. performing data query and quantitative analysis to the result after the LC-MS analysis to obtain the change situation of the whole proteome during an interaction process between rice and rice blast bacteria. The method can quickly and effectively screening a candidate gene relative to disease resistance of rice, can be used for researching the candidate gene relative to the disease resistance of the rice well with the proteomics researching method, iTRAQ, which is high-throughput and accurate, can be widely used for researching and developing the characters of plant disease resistance and breeding new plant varieties being strong in disease resistance with combination of the transgenic technology.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Early pickling transgene method for cultivated silkworm diapause breed variety
InactiveCN101195834AImprove economyExcellent target traitsMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionDiapauseAgricultural science
The invention relates to a silkworm diapause variety early pickling transgene method. The hydrochloric dipping treatment is performed to a silkworm diapause ovum, by utilizing a certain time before silkworm egg embryo is developed to a germ band formed, namely, before 2 hours and a half after egg casting, then the embryo microinjection is performed to the graine of diapause treatment canceling, the G0 generation silkworm obtained from the incubation breeding bred to eclosion, the G1 generation silkworms are produced through the idiogamy or the backcross of the silkworms, and labeled and sieved through fluorescence, and therefore the transgene silkworms are effectively manufactured. The method directly adopts the universal use utility silkworm diapause variety as original material in production, can avoid the long and troublesome breeding process, and directly utilizes the transgene technology to create the good new special silkworm variety with various characteristics, the breeding cycle can be greatly shortened, and massive manpower and physical resources are saved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY +1
Transgenic method for cultivated silkworm diapause variety
InactiveCN101503704ABreak through the bottleneckThe method of transgenic technology route is simple and effectiveVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryBiotechnologyDiapause
The invention provides a method for making transgenic silkworms of a silkworm diapause variety. The method comprises the steps of utilizing the relationship between the environmental conditions of a parental generation and the diapause property of filial-generation silkworm eggs and utilizing a generation before transgenic operation to control the environmental conditions of the diapause silkworm variety so as to change the diapause property of a present generation of transgenic operation, performing silkworm-egg embryo microinjection on non-diapause silkworm eggs, utilizing fluorescent protein labeling to screen and making the transgenic silkworms. The method has the advantages of ingeniously breaking through the obstacles of transgenic technology for the silkworm diapause variety and effectively overcoming the defects of the prior transgenic method, and can lay a solid technical foundation for the large-scale application of silkworm transgenic technology in functional gene research, bioreactor development and other practical research.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated cabbage type oilseed rape genetic transformation method
ActiveCN103966258AHigh rate of differentiation of resistant seedlingsGenetic engineeringFermentationHigh concentrationHigh resistance
The invention discloses an agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated cabbage type oilseed rape genetic transformation method. The method comprises the following steps: taking the hypocotyl of a cabbage type oilseed rape seedling, conducting preculture through adopting the lower end of the hypocotyl as an explant, and inducing for production of the callus; infecting the callus explant by adopting agrobacterium tumefaciens carrying target genes, and conducting the co-culture; after the co-culture is conducted on the explant, inducing the explant to generate resistance adventitious buds on a differential medium containing a selective agent; conducting the rooting culture to obtain a resistance seedling. According to the agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated cabbage type oilseed rape genetic transformation method, the lower end of the cabbage type oilseed rape hypocotyl serves as the explant, and the growth conditionis adopted, which is most suitable for cabbage type oilseed rape genetic transformation, and particularly includes the pH value and the high concentration glyphosate differentiation screening method and the low concentration glyphosate differentiation screening method in the co-culture medium, so that the transgenetic seedling with glyphosate resistance is obtained successfully; compared with the prior art, the method has higher resistance seedling differentiation rate, a high efficiency cabbage type oilseed rape regeneration system with glyphosate resistance is built, and a foundation is laid for studying about the transgenic technology of the agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated cabbage type oilseed rape.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
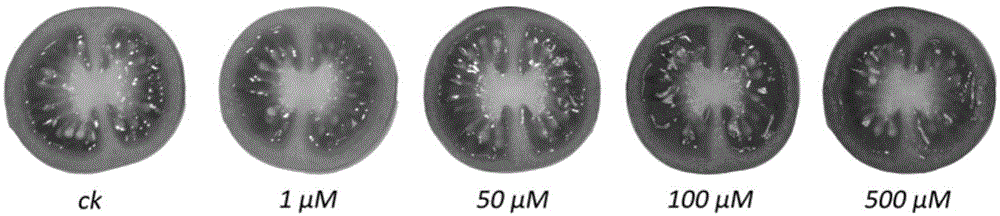
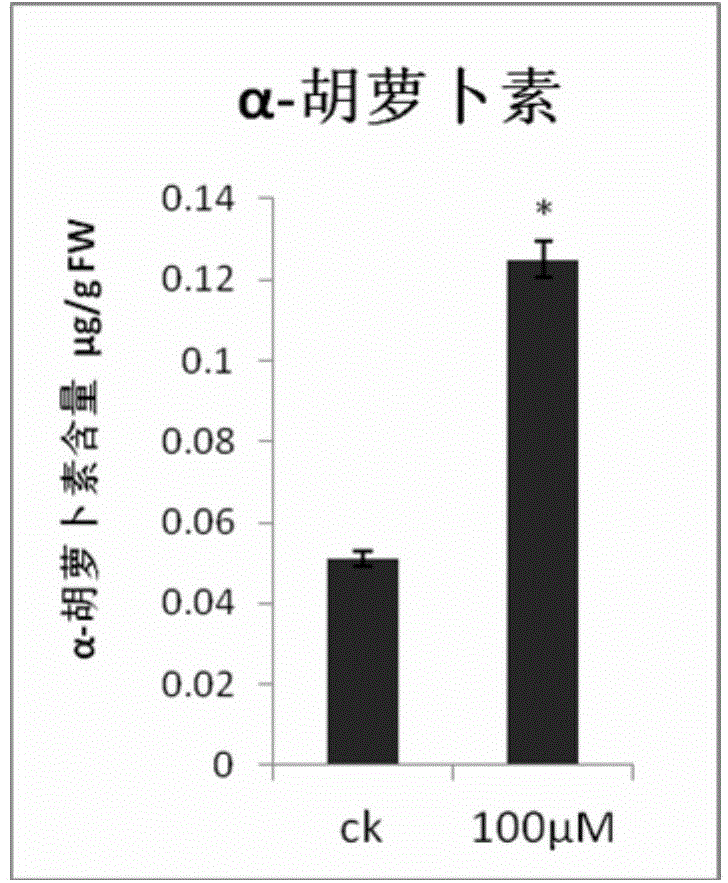
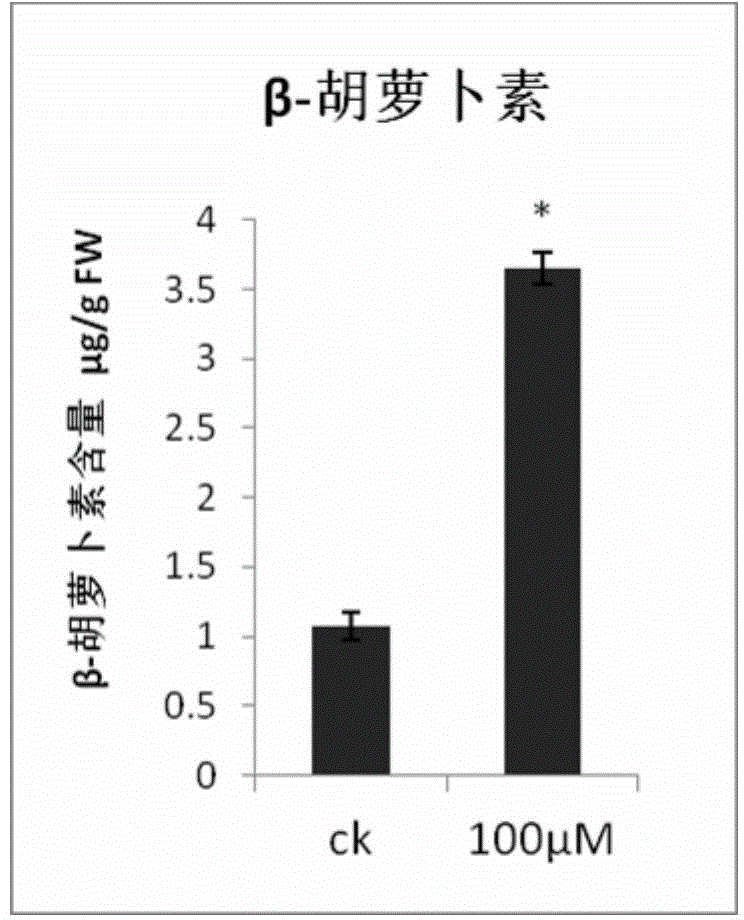
Method for increasing content of carotenoids in tomato fruits
InactiveCN104686215AIncrease alpha-caroteneIncrease beta-carotene contentCultivating equipmentsPlant cultivationBeta-CaroteneAlpha-Carotene
The invention relates to the cultivation of crops, and particularly provides a method for increasing the content of carotenoids in tomato fruits. According to the method, a melatonin solution with a concentration of 50-500 microns per liter is used for spraying tomatoes in a mature green stage. The experimental study results show that the spraying of the melatonin solution for the tomatoes in the mature green stage can increase the contents of alpha-carotene and beta-carotene in the tomato fruits significantly. The method is a non-transgenic technology, and is high in safety, high in efficiency, easy in operation and easy in promotion; the used melatonin solution has the characteristics of convenient preparation and biodegradability.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for creating cultivated silkworm chromatic cocoon by using pigment protein
InactiveCN101255423ASolve technical bottlenecksAchieve diversificationMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionInstabilityHuman health
A colorful silkworm cocoon creation method by pigment protein is disclosed. A pigment protein determining color of coral reed and related marine creature is fusion expressed in bombyx mori silk fibroin by genetic modification of silkworm and especially genetic modification for diapause varieties, so that novel colored silkworm cocoon is created. Exogenous pigment protein is fusion expressed in silk fibroin, and exists stably and uniformly in silk fibroin molecular, so pigment protein will not be lost in silk reeling procedure, and color variety of pigment protein is abundant. The method used by the invention solves two problems of little variety in color of silkworm cocoon and instability in pigment binding, simplifies spinning process of silk fabrics, eliminates harm of dyeing process to silk fiber quality and human health.
Owner:重庆拓桑生物科技有限公司
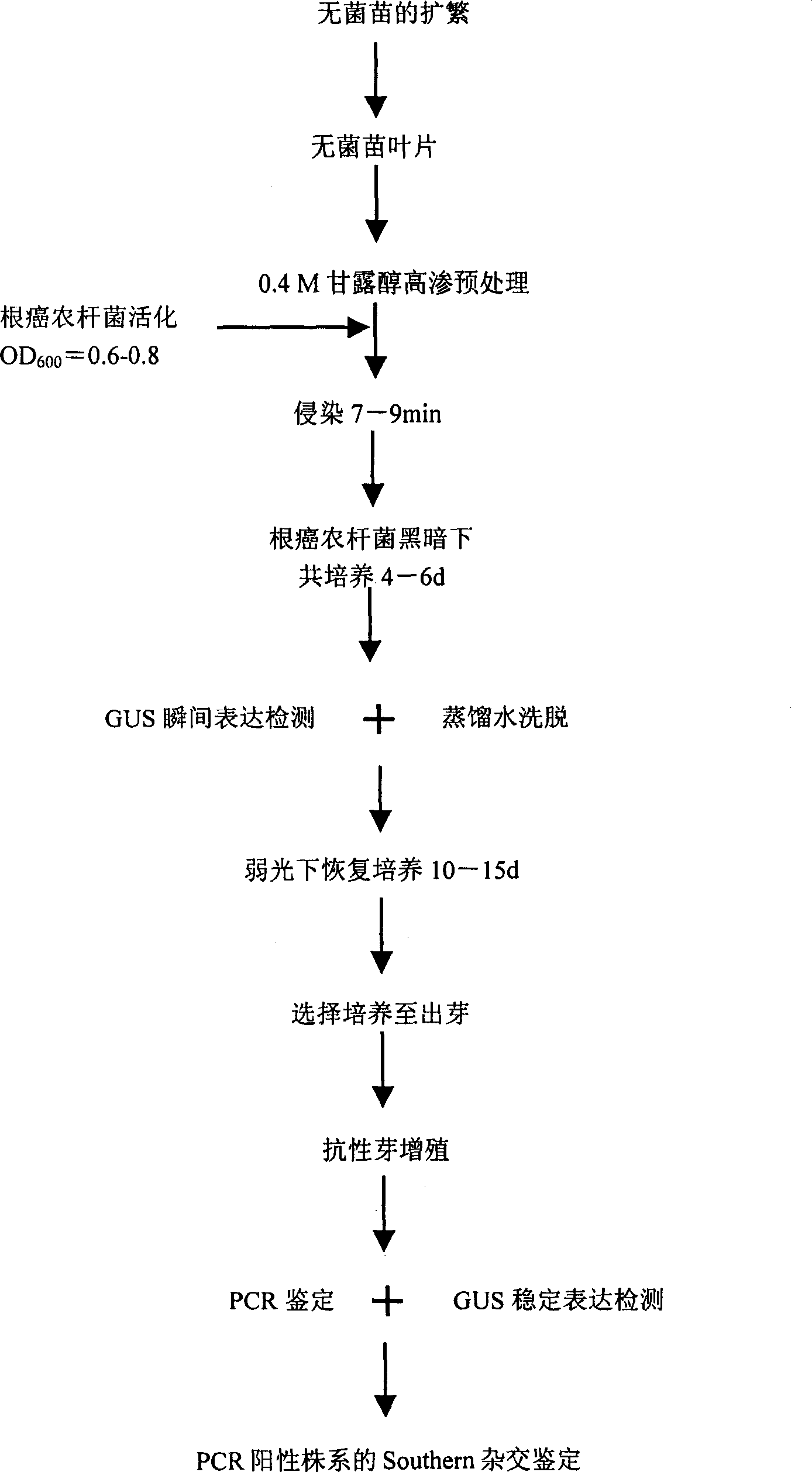
Method for cultivating transgenic sycamore plant mediated by agrobacterium
The present invention belongs to the field of plant transgene technology, and is especially agrobacterium mediating method of cultivating transgenic plant of sycamore as one garden tree. The agrobacterium mediating method includes the steps of genetic transformation, PCR detection and Southern hybridization detection, and features that through agrobacterium mediation to transduce GUS reporter gene to acceptor sycamore, adding kanamycin as selecting agent to the basic culture medium, screening the transformed acceptor cell, PCR detection, GUS gene detection, Southern hybridization and other steps, transgenic plant of sycamore is obtained. The present invention provides technological platform for the genetic improvement of tree, especially sycamore.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for preparing corn type II embryogenic calli
InactiveCN102217533APromote regenerationExcellent agronomic traitsPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsF1 generationTransgenic technology
The invention discloses a method for preparing corn type II embryogenic calli. With the method, a corn inbred line which can produce type II embryogenic calli can be prepared. the method comprises the flowing steps: carrying out selfing among an initial corn inbred line to obtain seeds of an F1 generation; carrying out embryogenic callus induction upon embryos of the F1 generation seeds, such that embryogenic calli are obtained; collecting type II embryogenic calli; carrying out regenerating and cultivating upon the type II embryogenic calli until corn plants are obtained. The obtained corn plants form a target corn inbred line. With type II callus phenotype, the corn material provided by the present invention is easy to regenerate, and the regenerated plants have excellent agronomic properties. According to the present invention, a novel material for present transgenic acceptors is provided, a limitation that presently only non-inbred line Hill are utilized is solved, and the period for cultivating new species of corn by using transgenic technologies is shortened.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
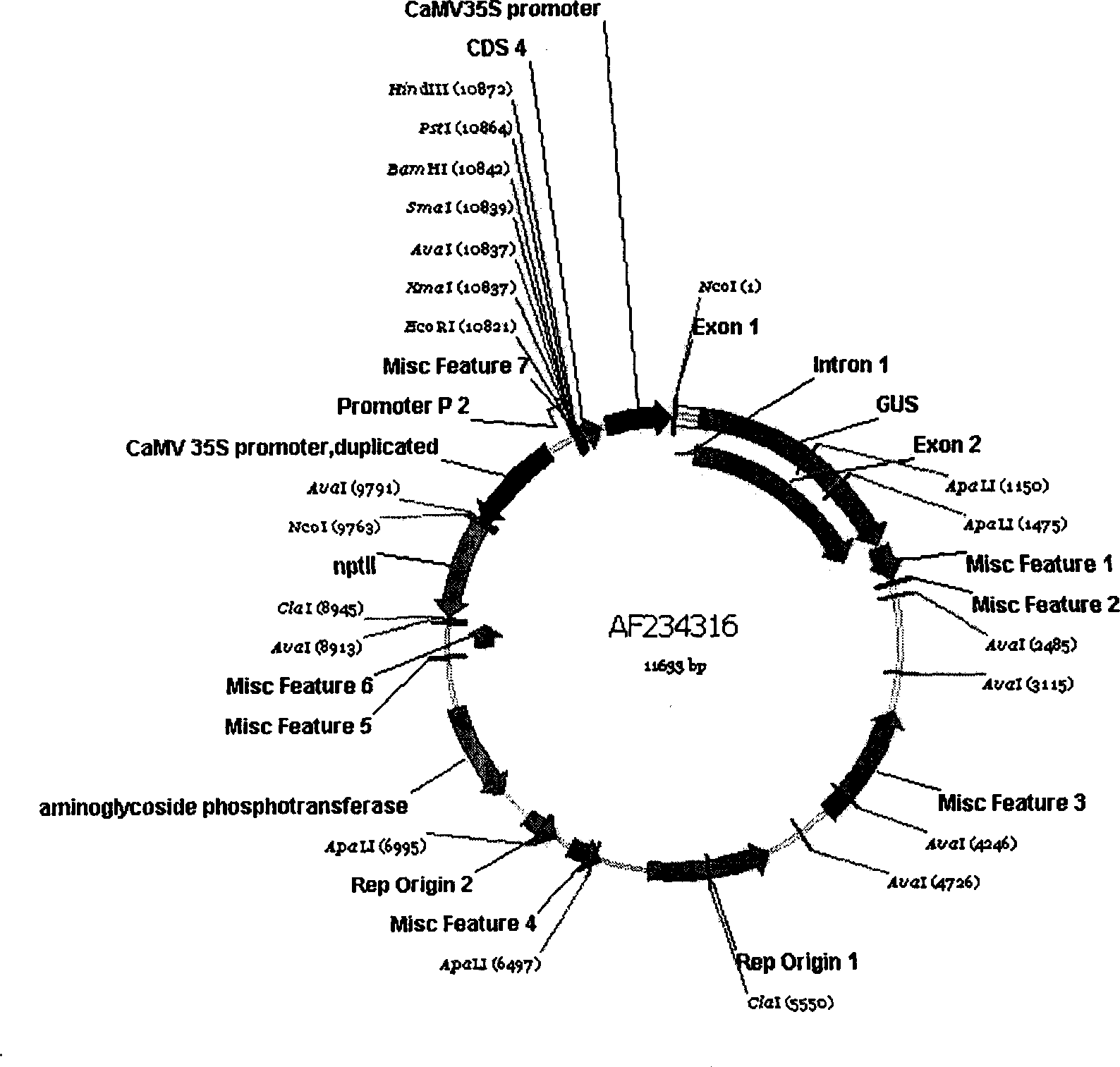
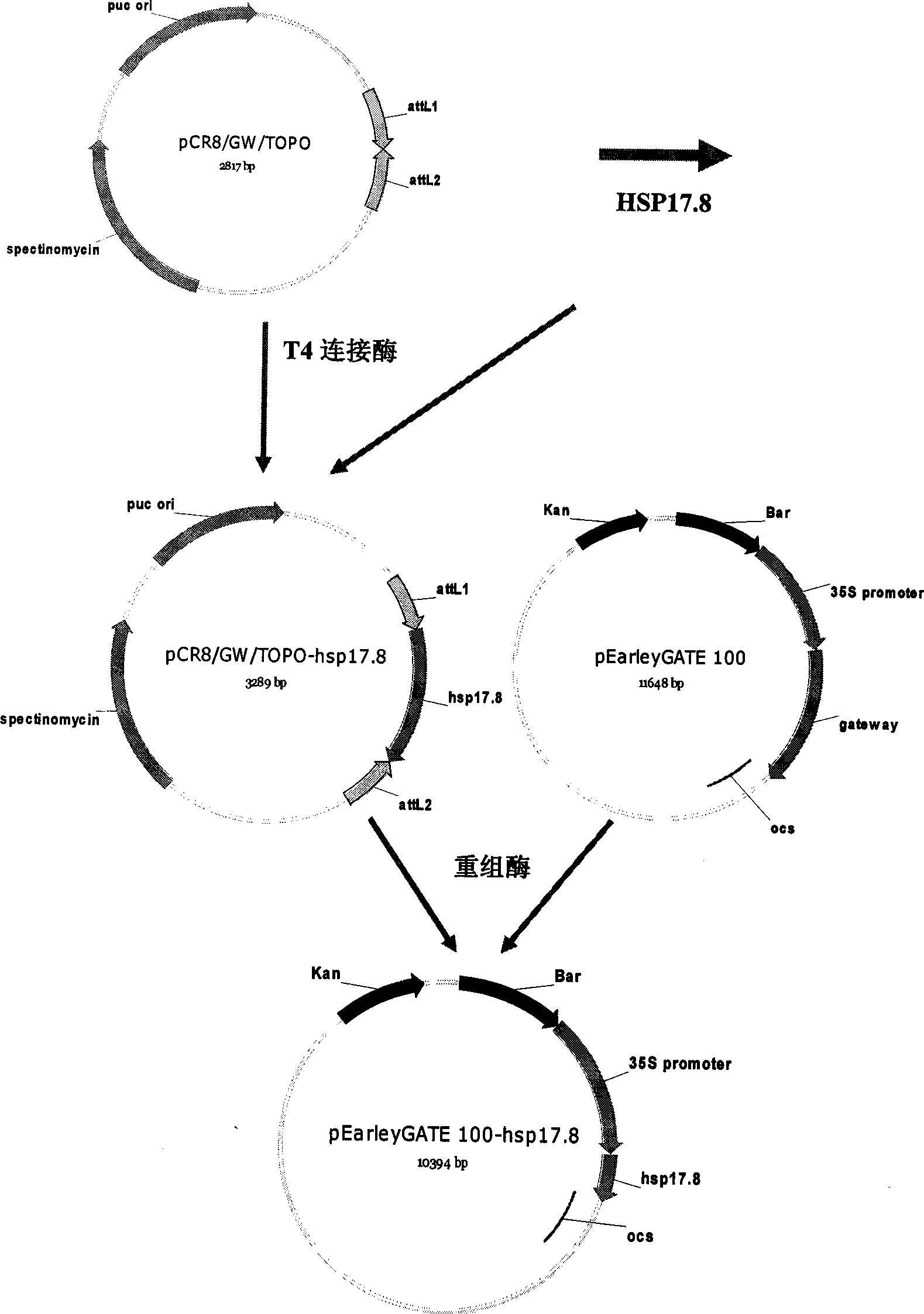
Rape heat shock protein gene HSP17.8 and application thereof
InactiveCN101544983AImprove heat resistanceReduce harmPlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideMutant allele
The invention discloses a rape heat shock protein gene HSP17.8 and application thereof. The invention provides a nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence of the gene, gene sequences which at least have 70 percent homology with a DNA sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in other crops, and mutant alleles or derivatives produced by adding, substituting, inserting or deleting one or more nucleotides. At the same time, the heat shock protein gene also proves that the overexpression of the heat shock protein gene strengthens the heat resistance of arabidopsis at high temperature by means of model plant, namely the arabidopsis through transgenic technology, increases the yield of seeds at high temperature, and improves the yield of the arabidopsis under high temperature stress, so the heat shock protein gene has good application prospect in heat-tolerance breeding of crops.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for constructing lotus regeneration system
ActiveCN104813939ABuild a regenerative systemOvercoming the defect of easily killing lotus embryosPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsShoot apexCataphyll
The invention discloses a method for establishing a lotus regeneration system. The method comprises the following steps: breaking shells of sterilized Guangchang white lotus seeds by using pruning shears; taking out mature lotus nuts (embryos) as explants to culture aseptic seedlings; cutting 2-3mm of stem tips and folded tender leaves (with short petiole) as explants for inducing callus from the aseptic seedlings after 2 months; inducing and differentiating the callus to develop buds after 2 months; after 1 month, cutting off the black callus at the bottom, and proliferating the differentiated seedlings; after 3 months, inducing the differentiated seedlings to develop roots; and strengthening, domesticating and transplanting the rooted tissue culture seedlings after 1 month. By adopting the method, technical basis is provided for transgenic technology of lotus in China, and the inductive callus rate of lotus is increased and the callus is large and stable in size compared with a conventional technique; the propagation coefficients of adventitious buds are increased; as tender leaves of aseptic seedlings of lotus are innovatively taken as explants for inductive callus and are successfully differentiated to obtain seedlings, the material selection of lotus inductive callus is widened, and material guarantee is provided.
Owner:镇江市彩林生态农业观光有限公司
Mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene UGT74AC1 and application thereof
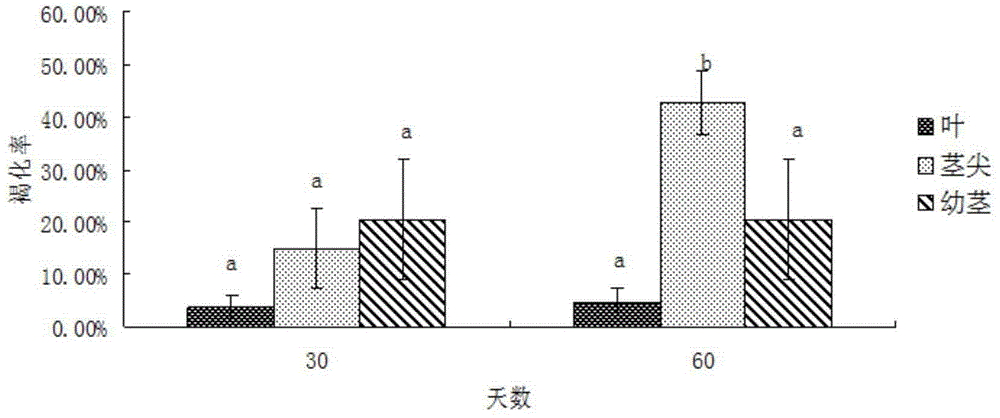
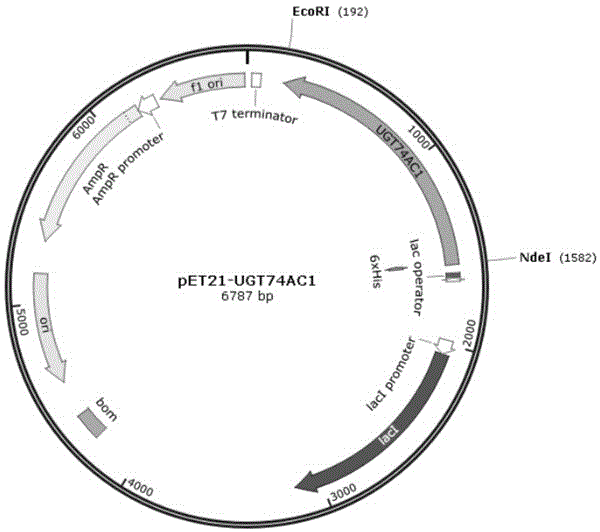
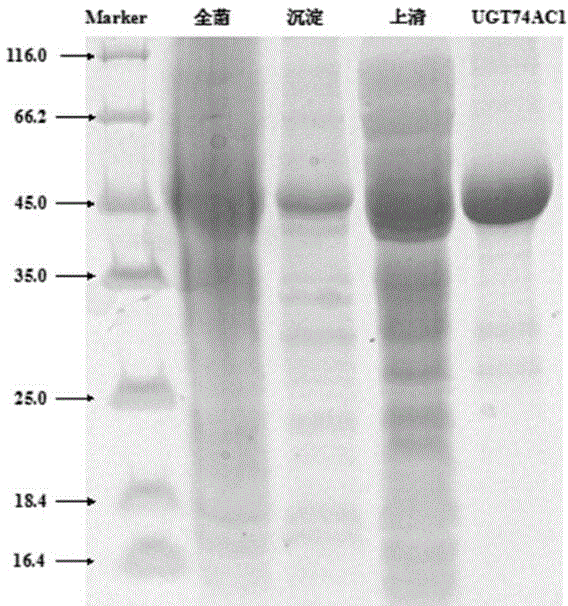
The invention discloses a mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) and application of glycosyltransferase with a gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) code in synthetic mogrosideIE. The glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) has a nucleotide coding sequence shown in SEQIDNO.1 and a peptide sequence shown in SEQIDNO.2. By utilization of an expression of the mangosteen glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) in escherichia coli, the recombinant glycosyltransferase (i)UGT74AC1( / i) can catalyze mogrol and UDP-glucose to react, thereby generating the mogrosideIE. The glycosyltransferase gene (i)UGT74AC1( / i) disclosed by the invention can be applied to the artificial synthesis of the mogrosideIE. Meanwhile, the gene has an important application value in the aspect of improving momordica grosvenori by the utilization of a transgenic technology to improve the content of the mogroside.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
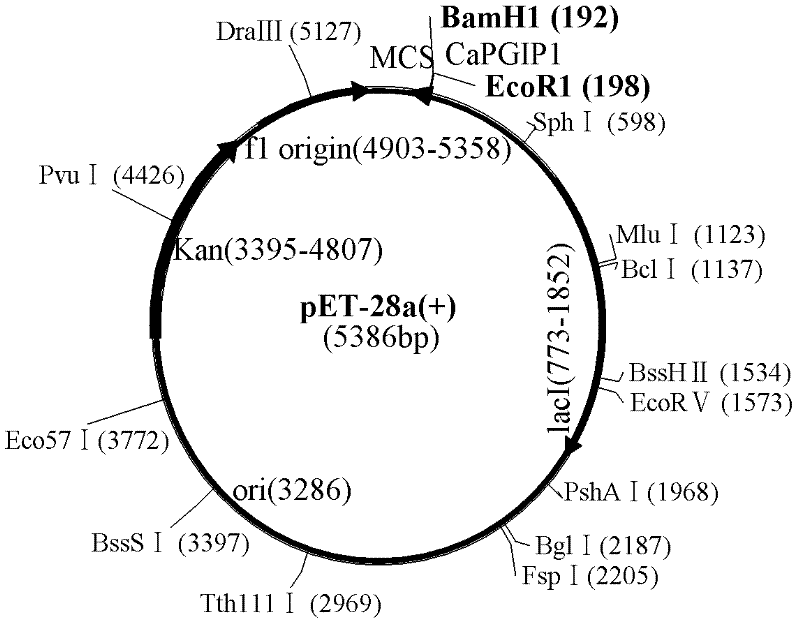
Polygalacturonase arrestin gene CaPGIP1 and disease resistance technology thereof
InactiveCN102250921AImprove disease resistanceReduced disease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumPentagalacturonic acid
The invention belongs to the field of plant biotechnology, in particular provides a polygalacturonase arrestin gene CaPGIP1 cloned from hot pepper, the gene can specially inhibit the activity of polygalacturonase (PGs) secreted by pathogenic bacteria. The invention provides the function verification techniques based on the coding of the gene, such as protein making, enzyme activity testing, gene silencing, transgenic excessive expression and the like and the application of the techniques. Based on the gene and protein operation technology, the CaPGIP1 gene is proved to effectively participate in the defense reaction of hot pepper under the induction of a stress facto, and can inhibit the activity of polygalacturonase (PGs) secreted by various pathogenic bacteria. The gene silence and transgenic technology are further used for proving that the silence or less expression of the gene in the hot pepper reduces the disease resistance of a host, and the excessive expression of the gene in the transgenic tobacco can enhance the resistance; therefore, the gene codes an important disease-resistance related protein. The invention provides an important technological reserve for transforming the polygalacturonase arrestin (PGIP) gene and cultivating a new disease-resistant variety.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Gene transduction method with nano granule as carrier based on ultrasonic intervention guiding
InactiveCN1687427ALow priceEasy to operateImmobilised enzymesOther foreign material introduction processesParticulatesCell wall
A gene transduction method ultrasonic-based, which using the nano particulate as the carrier. It consists of animal transgenic gene method and plant transgenic gene method. The outer gene joins with the particulate with the effect of static form together to form the gene carrier, which can protect the DNA being broken by ultrasonic. The ultrasonic synchronously give effect to particulate gene carrier, cells, organize and apparatus, the carrier can run efficiently through the short period alleyway of cell wall, cell film, core film cell, enables the outer gene constructs with the gene group in cell. This method has a high efficiency, and is provided with convenient manipulation, high efficiency, no request of differential function e.g. other merits. It can be applied widely to these range, animal and plant transgenic technology and genic cure of human being.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for converting cotton germ by agrobacterium with ultrasonic wave aid
InactiveCN101011027AImprove use valueAchieve genetic transformationClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesAgricultural scienceFluorescence
The invention relates to a method for using ultrasonic wave with agricillin to transfer the cotton germ to cultivate gene-transferred cotton. The inventive method comprises that planting the disinfected and skin-removed cotton on the germ-free cultivate medium; removing two fresh blades to be arranged on the germ-free filter paper; adding 10ml of 0.5 OD600nm agricillin solution into the plastic eccentric tube or glass triangle bottle, then putting the germ into the agricillin solution, transferring the treated germ into the share cultivate medium to be cultivated; washes with germ-free water which contains cefradine, absorbs the surface water, to be transferred to the return cultivate medium, under sunlight to be returned and cultivated to obtain the germ; then transfers it to the selecting cultivate medium to obtain the antibody germ; cuts off the antibody germ to be transferred to the rooting cultivate medium to induce the root or transplanted to the cotton stock, to obtain the regenerated gene transferred plant. The invention can improve the instant expression rate of GFP (green fluorescence protein) gene at blast to 100 times, realizes the gene transferred plant of island cotton, and obtain anti-sect cotton. The test has proved that the external gene is stably transferred into the cotton gene to be expressed and generated.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Technology for regulating and controlling Jak-Stat pathway to differentiate, dedifferentiate and rejuvenate cells, and application of technology
PendingCN110423719AAccelerated agingPromote apoptosisCosmetic preparationsVirusesProtein targetCytokine
The present invention belongs to the technical field of cell biology and particularly relates to a technology for regulating and controlling a Jak-Stat pathway to differentiate, dedifferentiate and rejuvenate cells, and an application of the technology. Rejuvenated cell products and / or cell products of different lineage types are obtained by small molecule compound combination, cytokine combination or recombinant protein combination, a gene editing technology and a transgenic technology to quantitatively and / or regularly regulate and control gene or protein targets of the Jak-Stat signaling pathways in cells. The provided technology for regulating and controlling the Jak-Stat signal pathway, and the product / derivatives of the cell product can be used for re-programming cells, tissues, organs and organisms, construct tissue engineering materials, repair damages of tissues and organs of mammals and the aged and degenerated tissues and organs, delay or reverse aging processes of the cells, tissues, organs and organisms, and can be used for immunoregulation of the cells, tissues, organs and organisms.
Owner:YUNNAN JICI INSITUTE FOR REGENERATIVE MEDICINE CO LTD
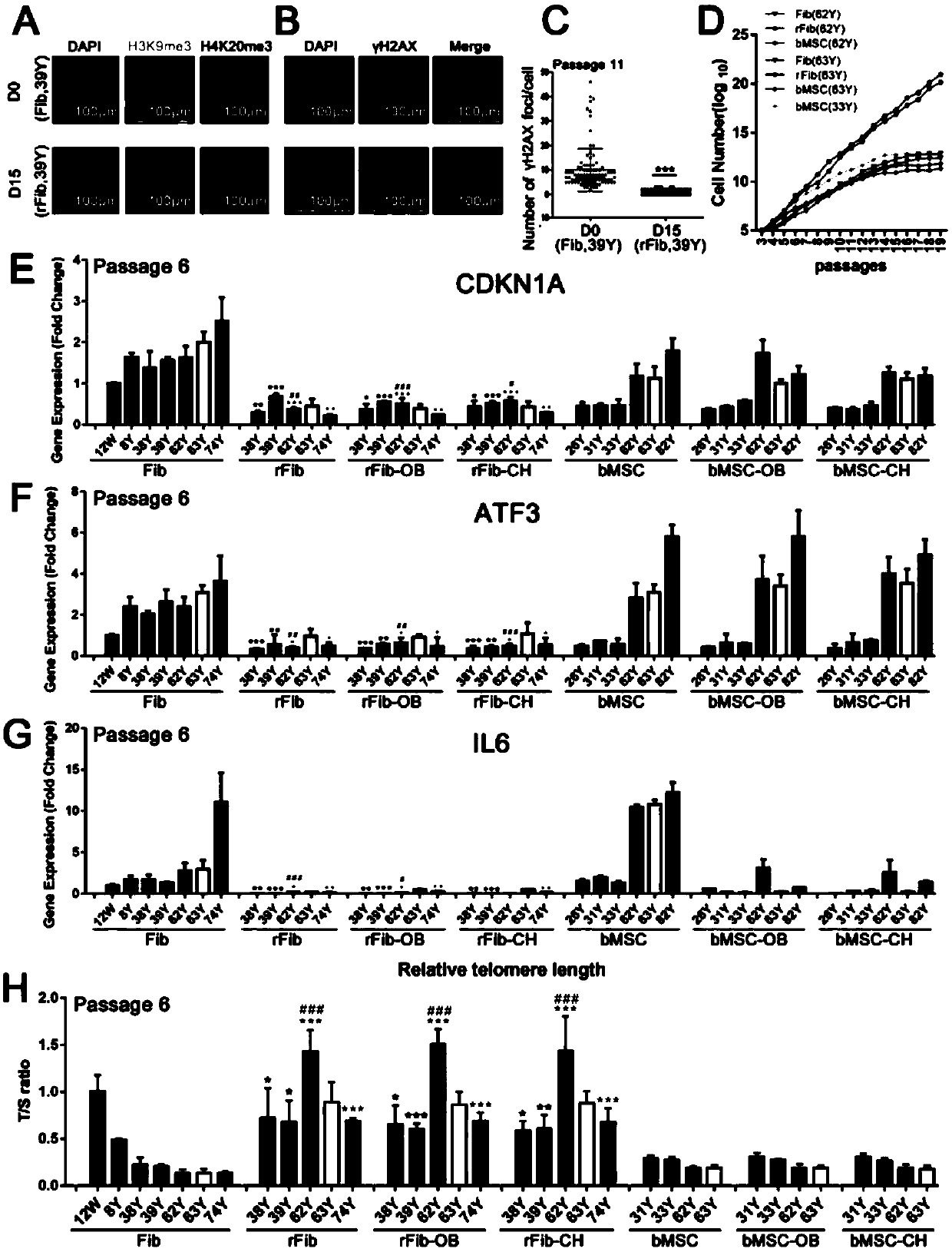
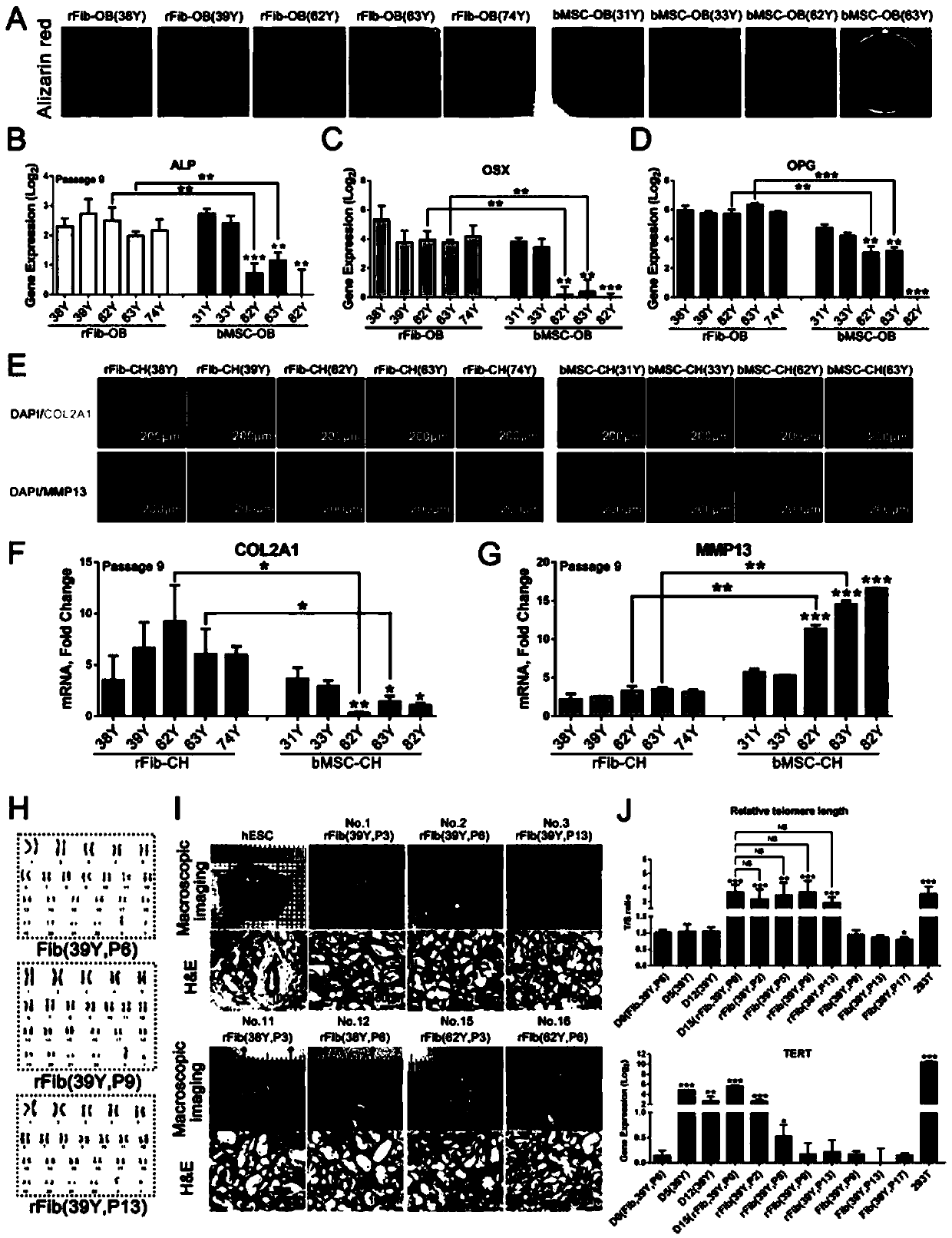
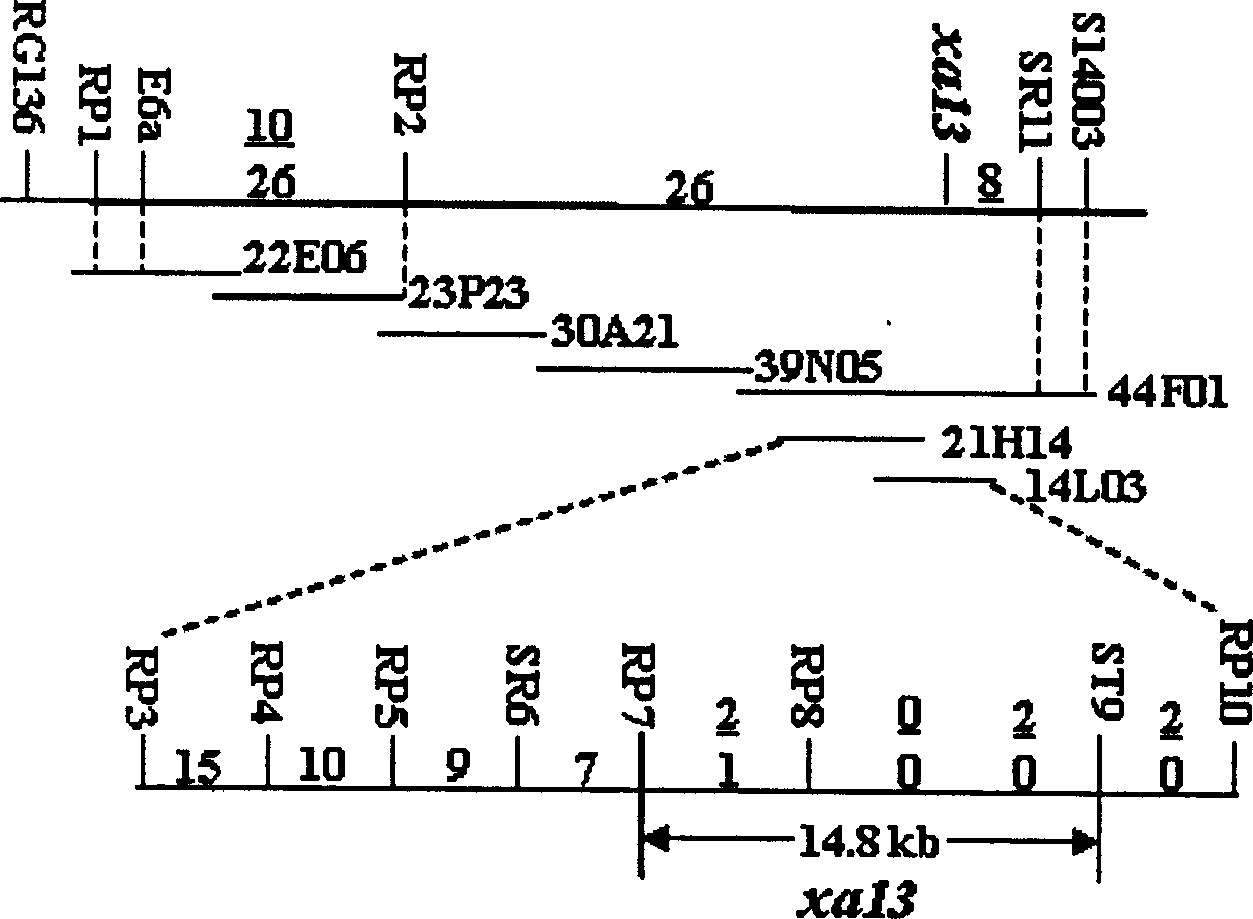
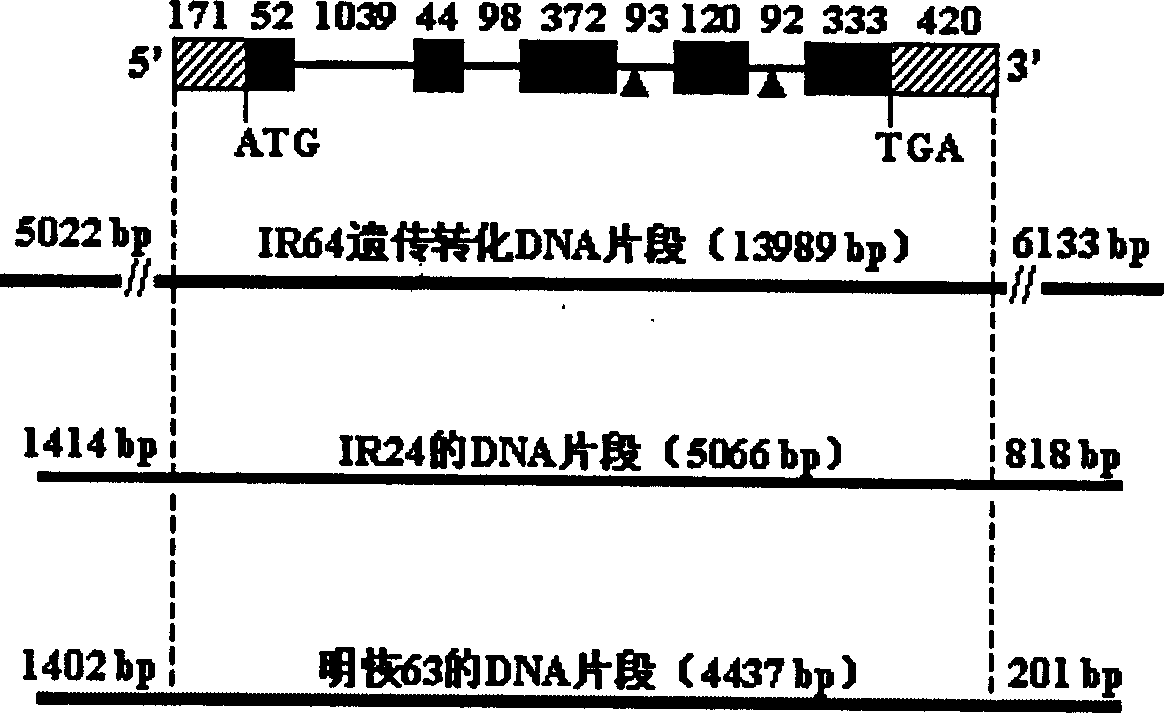
Recessive gene xa13 of rice bacterial blight resistance and its allelic dominant gene xa13
InactiveCN1861791AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceDNA fragmentation
This invention relates to the plant biological technology area, it concretely relates to the separated clone, function testing and application of the two DNA fragments of the bacterial blight of rice recessive gene xa13 and dominant allele gene xa13. The antiviral allele xa13 gene is the function flow mutant of the dominant gene xa13. The mutant of the dominant gene makes the paddy rice generated the resistance of the bacterial blight. Some DNA fragments of the allele and dominant gene are connected with the extraneous regulated sequence and transferred into the paddy rice by the gene transfer technology bases on the RNA interference, and this can resist the function of the dominant gene in the paddy rice and improve the resistance of the bacterial blight of rice. Otherwise, the allele gene xa13 in the paddy rice is suppressed by the RNA technology, and this can improve the resistance of bacterial blight of rice further.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
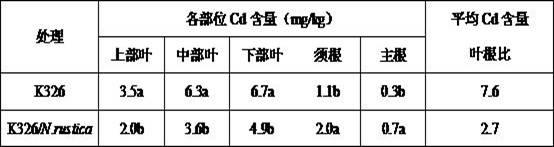
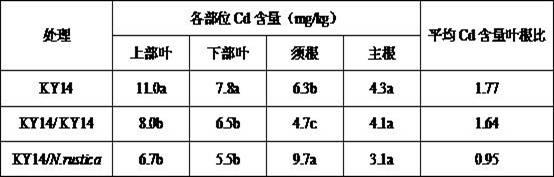
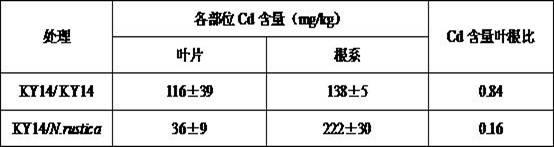
Method for lowering Cd content in tobacco leaves by utilizing grafting technology
InactiveCN102577843AAvoid time-consuming and labor-intensiveNot affected by restrictions on the application of genetically modified technologyHorticultureBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to a method for lowering Cd content in tobacco leaves by utilizing the grafting technology. The method is characterized in that common tobacco is used as scion, rustic tobacco is used as rootstock, and grafting is carried out, and the grafted new tobacco plants have the capability of enriching Cd at the root system of rustic tobacco, and can reduce the transportation of Cd to the above-ground part and reduce the migration of Cd to tobacco leaves, thus the accumulation amount of Cd in the tobacco leaves is lowered. As compared with the traditional tobacco leaf heavy metal content control technique, the method has the following characteristics that (1) the effect of lowering Cd content in the tobacco leaves is obvious; (2) foreign materials are not needed to be added to the soil, thus the soil secondary pollution and the risk of changing the soil ecological environment are avoided; (3) grafting is completed at one time during tobacco nursery stage, thus the problem of wasting time and labor due to multi-time operations during field growth stage of the traditional method is avoided; and (4) the obtained tobacco plants are non-transgenic plants and are not influenced by transgenic technology application limit.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
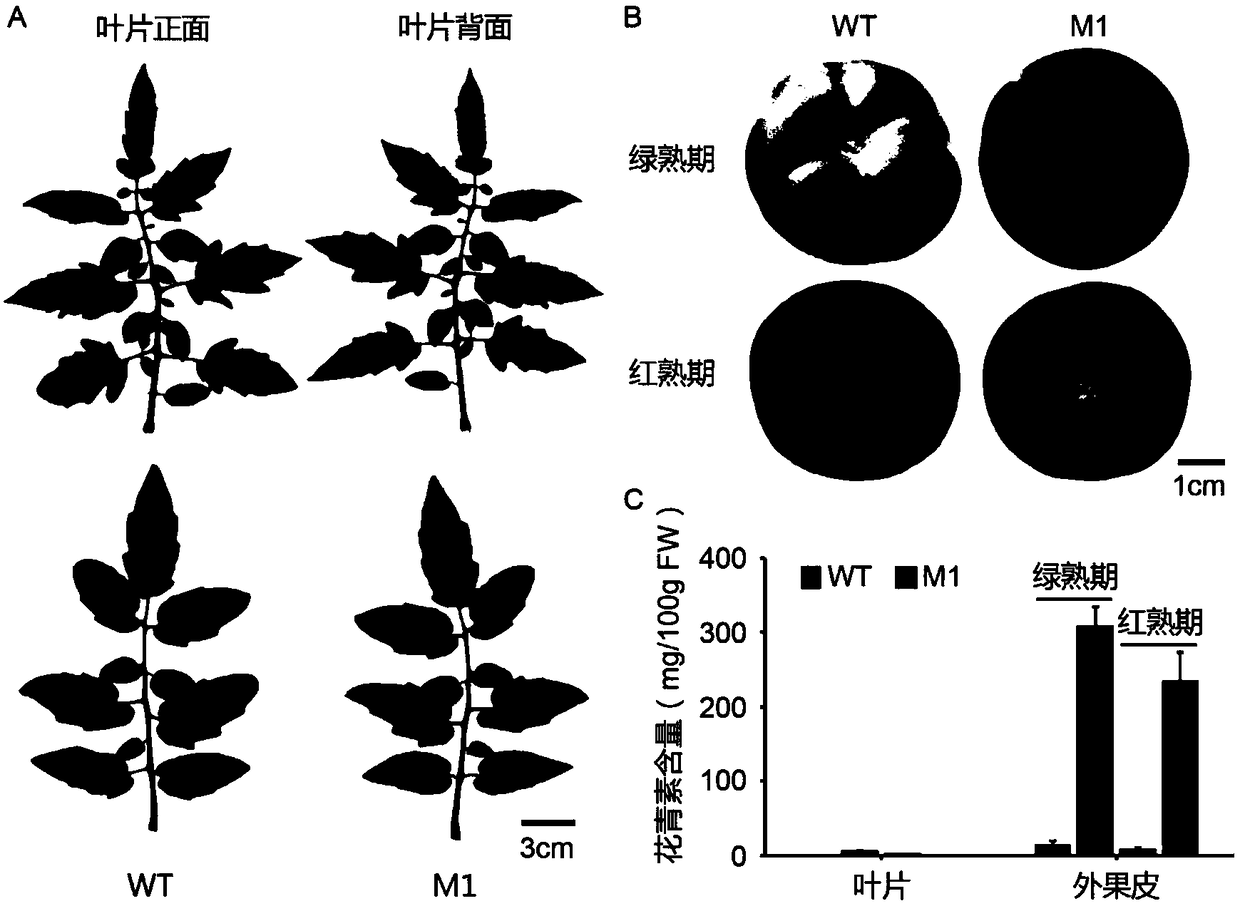
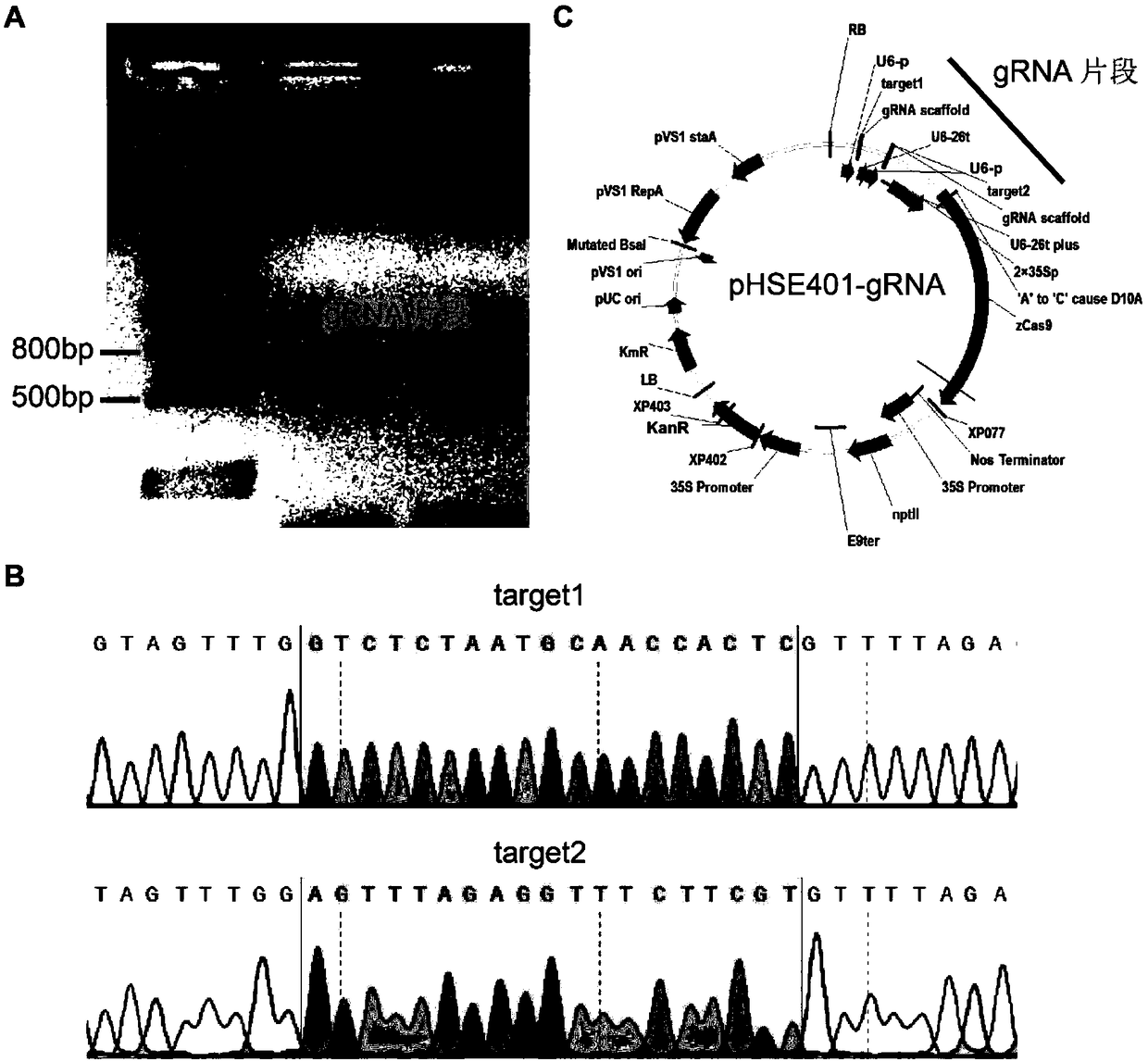
Method and application for creating purple fruit tomato mutant using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing system
ActiveCN109097387AIncrease contentPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceMolecular breeding
The invention discloses a method and application for creating a purple fruit tomato mutant using a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system, and relates to the field of tomato biotechnology and transgenic technology. The method includes constructing a CRISPR / Cas9-gRNA (pHSE401-gRNA) expression vector by designing a mutant target site of SlMYBATV, introducing a cultivated tomato LA1996 containing an Aft site by an agrobacterium-mediated method and conducting kanamycin resistance marker screening to obtain a positive transgenic plant. A strain with homozygous mutation determined by gene sequencing and phenotypic observation and containing no foreign aid gene insertion is a tomato mutant that completely loses the SlMYBATV function and has purple fruit. According to the method and application, the content of anthocyanins in tomato peels can be significantly improved. The method and application have good application prospects in high quality molecular breeding of tomatoes.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Salvia 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl A reductase gene and its coding protein and application
InactiveCN101250544AIncrease contentIncrease productionFungiBacteriaSalvia miltiorrhizaProtein insertion
The invention discloses a salvia 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene, protein which is encoded by the salvia 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene and the use thereof, which fills a gap that the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene is separated and cloned from salvia which is precious traditional Chinese medicine in China. The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene which is provided by the invention has a nucleotide sequence or a homologous sequence which adds, replaces, inserts or losses one or a plurality of nucleotides or allele thereof and the nucleotide sequence which is derived from the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene, which are displayed in the SED ID No.1. The protein which is encoded by the gene has an amino acid sequence or the homologous sequence which adds, replaces, inserts or losses one or a plurality of amino acids, which is displayed in the SEQ ID No.2. The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene which is provided by the invention can increase the content of tanshinone which is a terpenes active component in the salvia through the genetic engineering technology and can be used in research and industrialization for increasing the content of the tanshinone through utilizing the transgenic technology, which is helpful for improving the quality of salvia mi ltiorrhiza and has very good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com