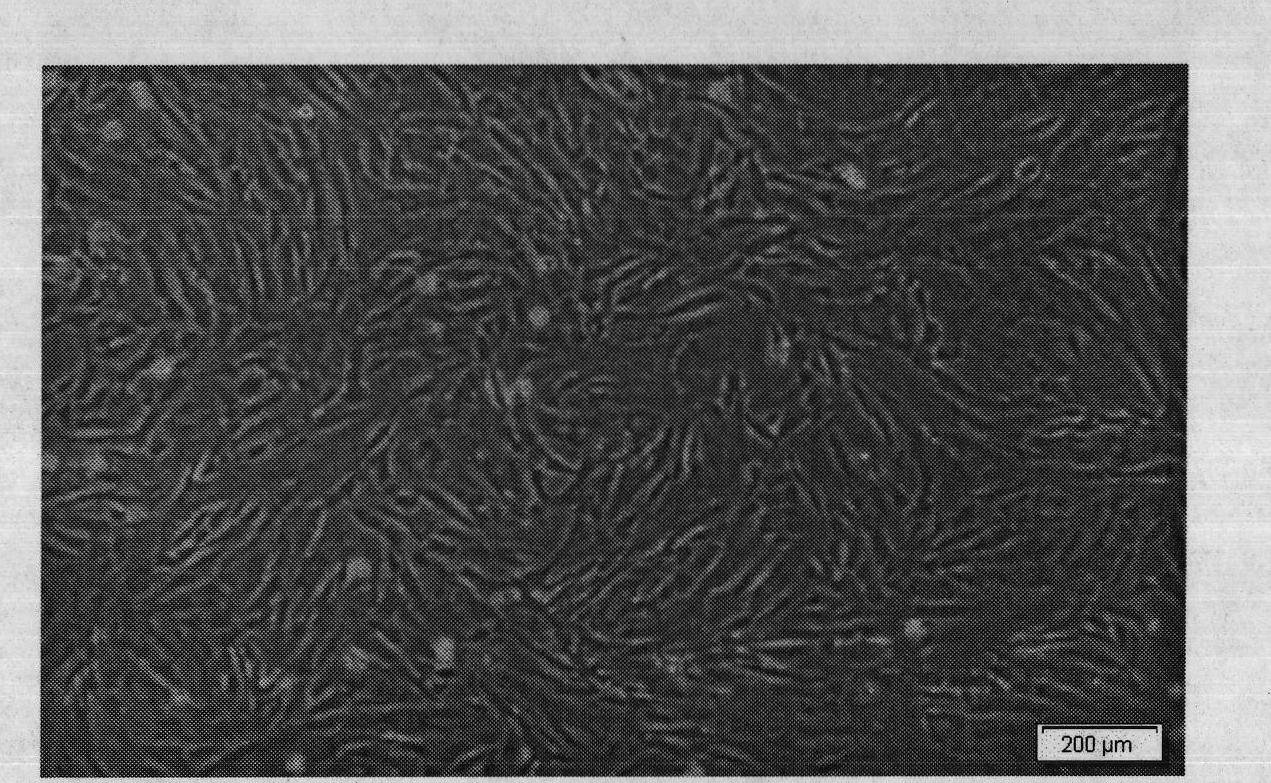
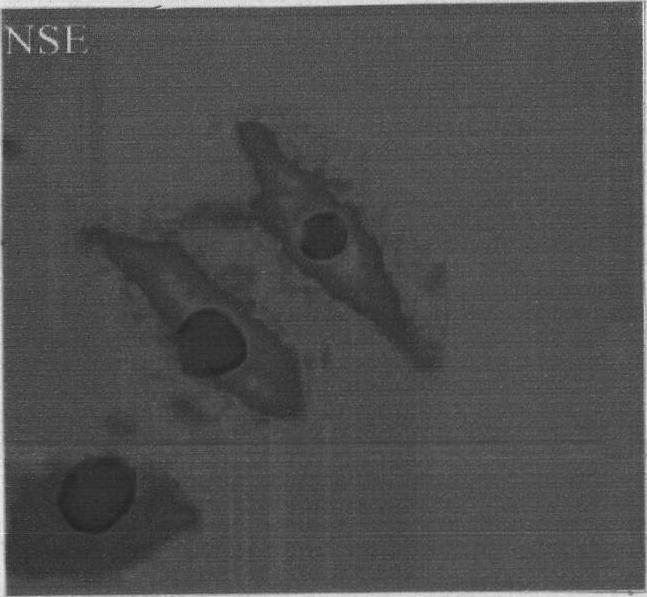
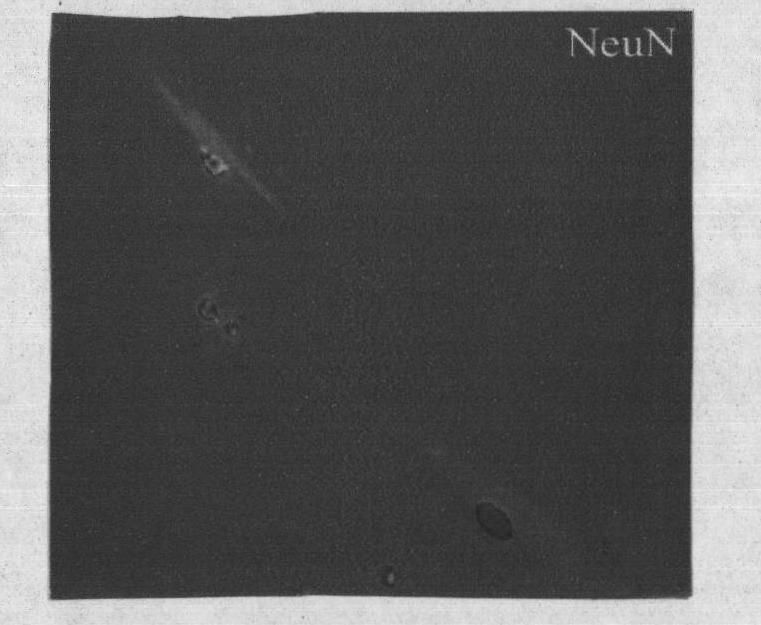
Inducing method for differentiating umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into nerve cells
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and nerve cells, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of cells that cannot be co-cultured, cell separation, and pathogenic pathogens caused by exogenous pathogens, and achieve the effects of saving time, promoting differentiation, and improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] (1) Extraction of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
[0051] This example uses the neonatal umbilical cord authorized by the mother as a source of mesenchymal stem cells.
[0052] The neonatal umbilical cord was washed three times in physiological saline containing 1% double antibody to remove the blood stains on the surface, and then cut into small pieces about 1 cm long. Use ophthalmic scissors to cut the umbilical cord longitudinally along the direction parallel to the blood vessels, and peel off the 2 umbilical arteries and 1 umbilical vein from the umbilical cord. Peel off the amniotic membrane on the surface, wash the Huatong glue part with normal saline containing 1% double antibody for 3 times, and cut it into pieces to about 1mm 3 size. Evenly spread the shredded tissue blocks on the 75cm 2 Place in the culture bottle at room temperature for 5-10 minutes to make the tissue pieces stick tightly. Add 5ml of MSC medium. Place at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultivated ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] (1) Extraction of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
[0069] This example uses the neonatal umbilical cord authorized by the mother as a source of mesenchymal stem cells.
[0070] The neonatal umbilical cord was washed three times in physiological saline containing 1% double antibody to remove the blood stains on the surface, and then cut into small pieces about 1 cm long. Use ophthalmic scissors to cut the umbilical cord longitudinally along the direction parallel to the blood vessels, and peel off the 2 umbilical arteries and 1 umbilical vein from the umbilical cord. Peel off the amniotic membrane on the surface, wash the Huatong glue part with normal saline containing 1% double antibody for 3 times, and cut it into pieces to about 1mm 3 size. Evenly spread the shredded tissue blocks on the 75cm 2 Place in the culture bottle at room temperature for 5-10 minutes to make the tissue pieces stick tightly. Add 5ml of MSC medium. Place at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultivated ...
Embodiment 3
[0085] (1) Extraction of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
[0086] The extraction steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0087] (2) Preparation of four induction media
[0088] Induction medium The basal medium used was Neurobasal (Invitrogen) supplemented with 2V% B27 (Invitrogen).
[0089] The factors added to the four induction media are as follows.
[0090]The first: 5-azacytidine (50uM, Sigma) and Pam 3 CSK 4 (0.1ug / ml, Invivogen)
[0091] The second: bFGF (200ng / ml, Biovison) and Noggin (1ng / ml, Biovison)
[0092] The third: bFGF (200ng / ml, Biovison), RA (50uM, Sigma), FGF8 (1ng / ml, R&D System) and Wnt3a (1ng / ml, R&D System)
[0093] The fourth type: Bmp4 (200ng / ml, R&D System), Shh (500ng / ml, R&D System), RA (50uM, Sigma), NGF (1ng / ml, R&D System) and BDNF (1ng / ml, R&D System)
[0094] (3) Induced differentiation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
[0095] In advance, the 24-well cell culture plate was paved with 100ug / ml laminin (Invitrogen) aqueous s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com