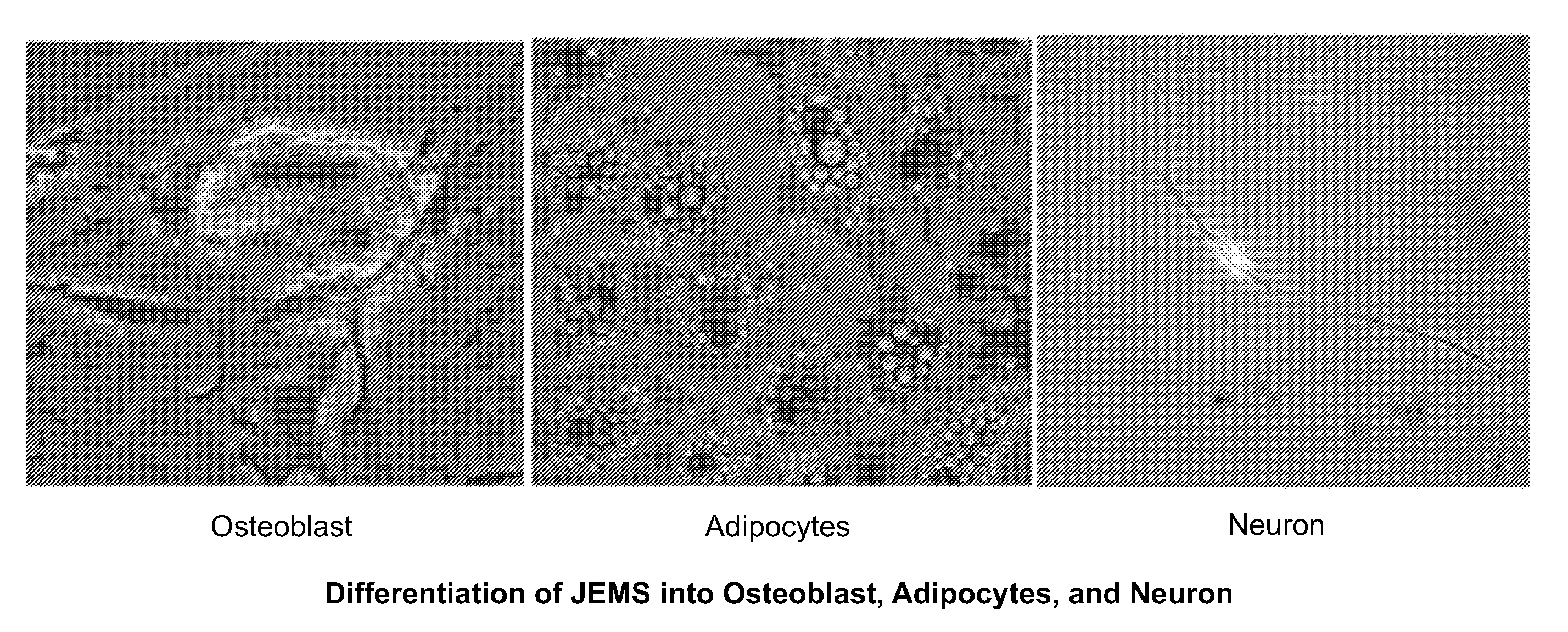
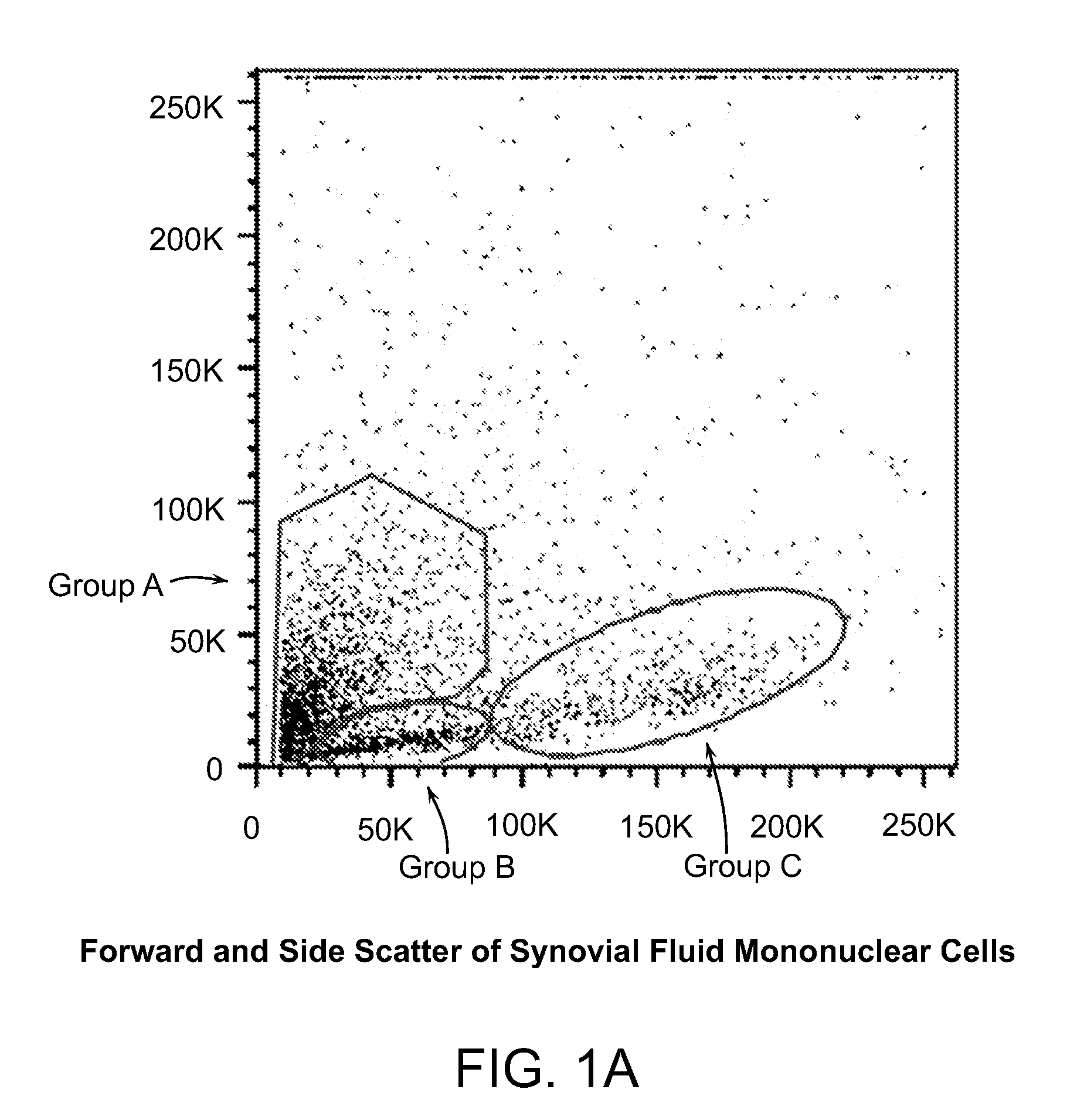
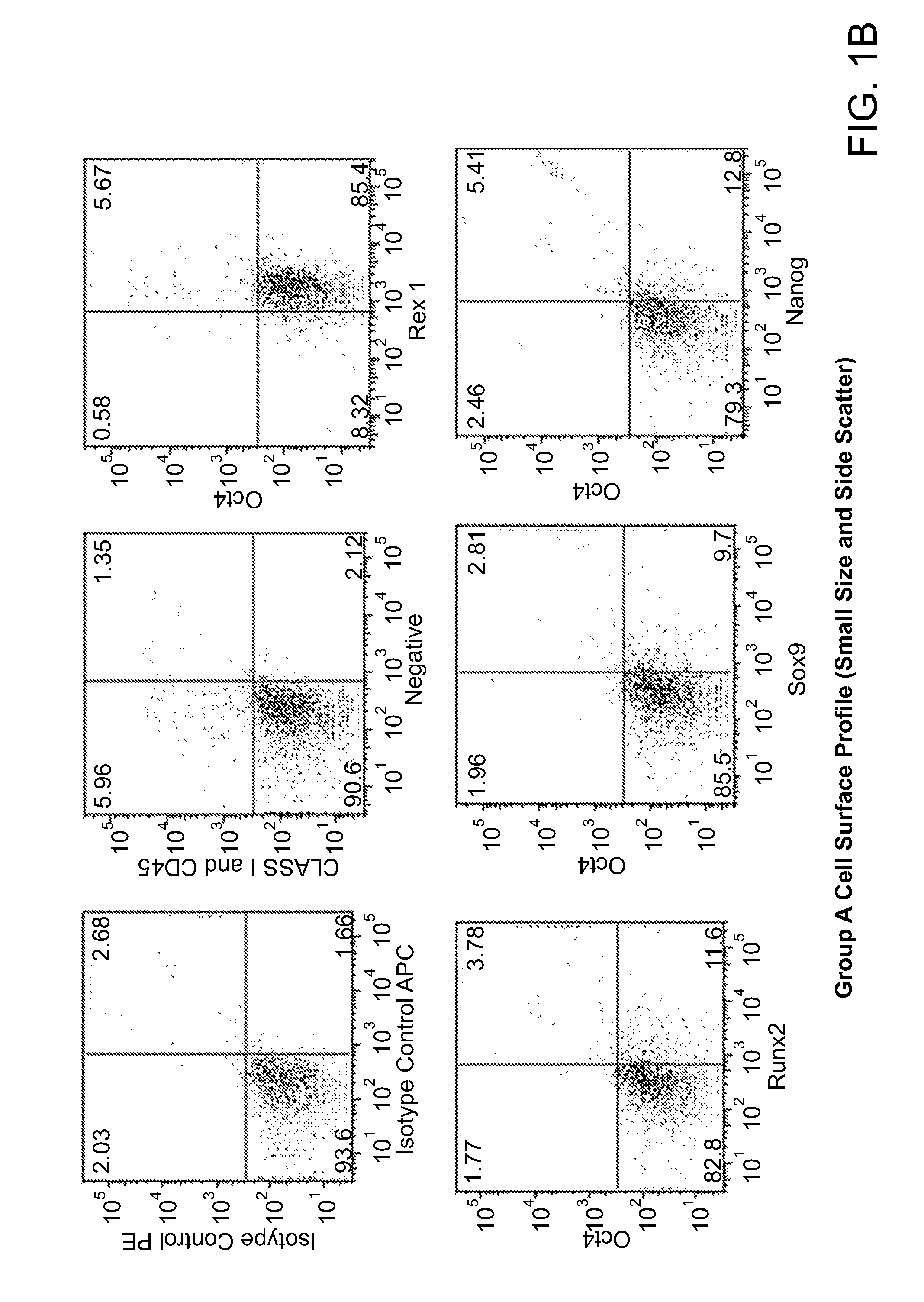
Patents
Literature
97 results about "Ectoderm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
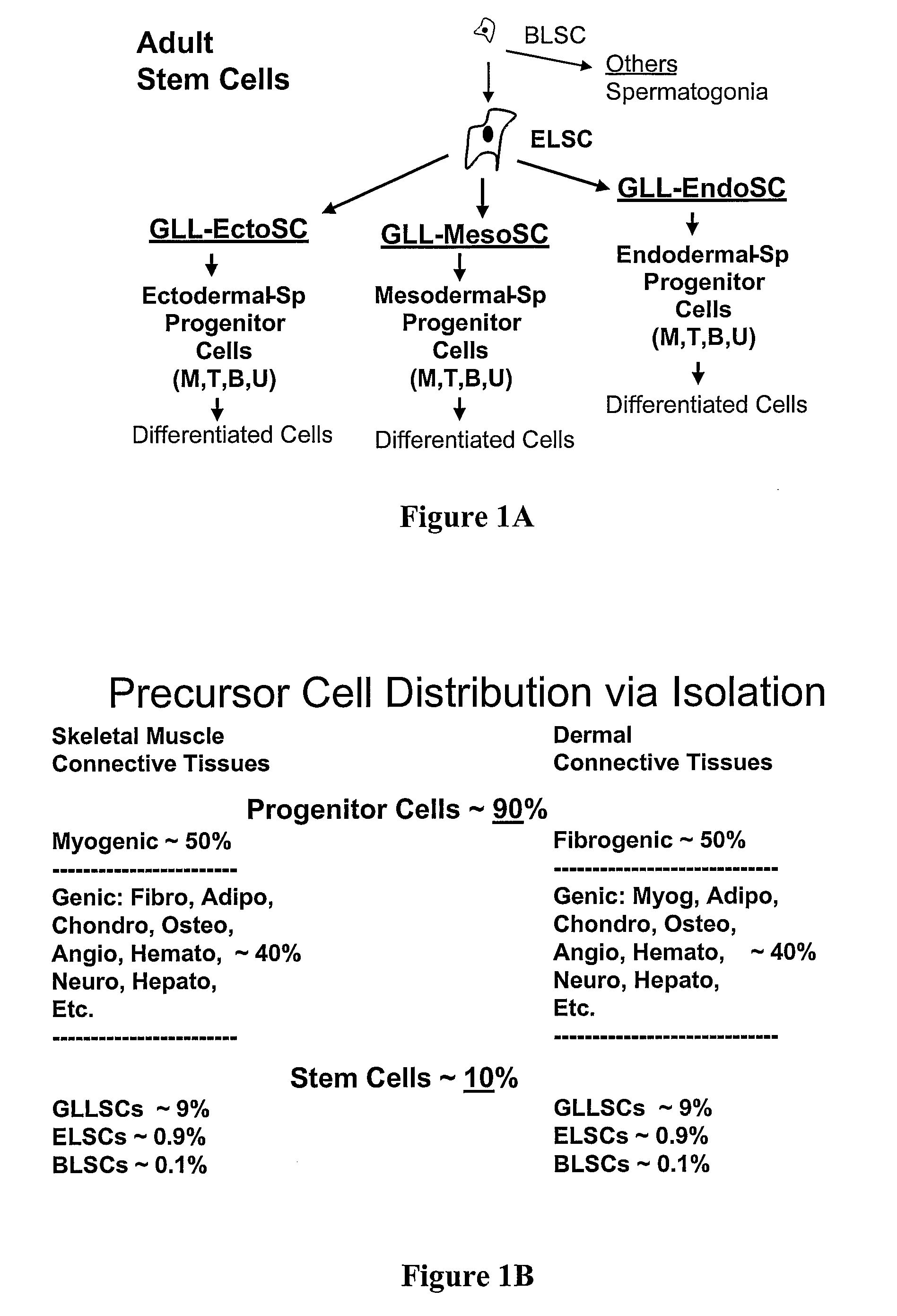
Ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the mesoderm (middle layer) and endoderm (most proximal layer), with the ectoderm as the most exterior (or distal) layer. It emerges and originates from the outer layer of germ cells. The word ectoderm comes from the Greek ektos meaning "outside", and derma, meaning "skin."
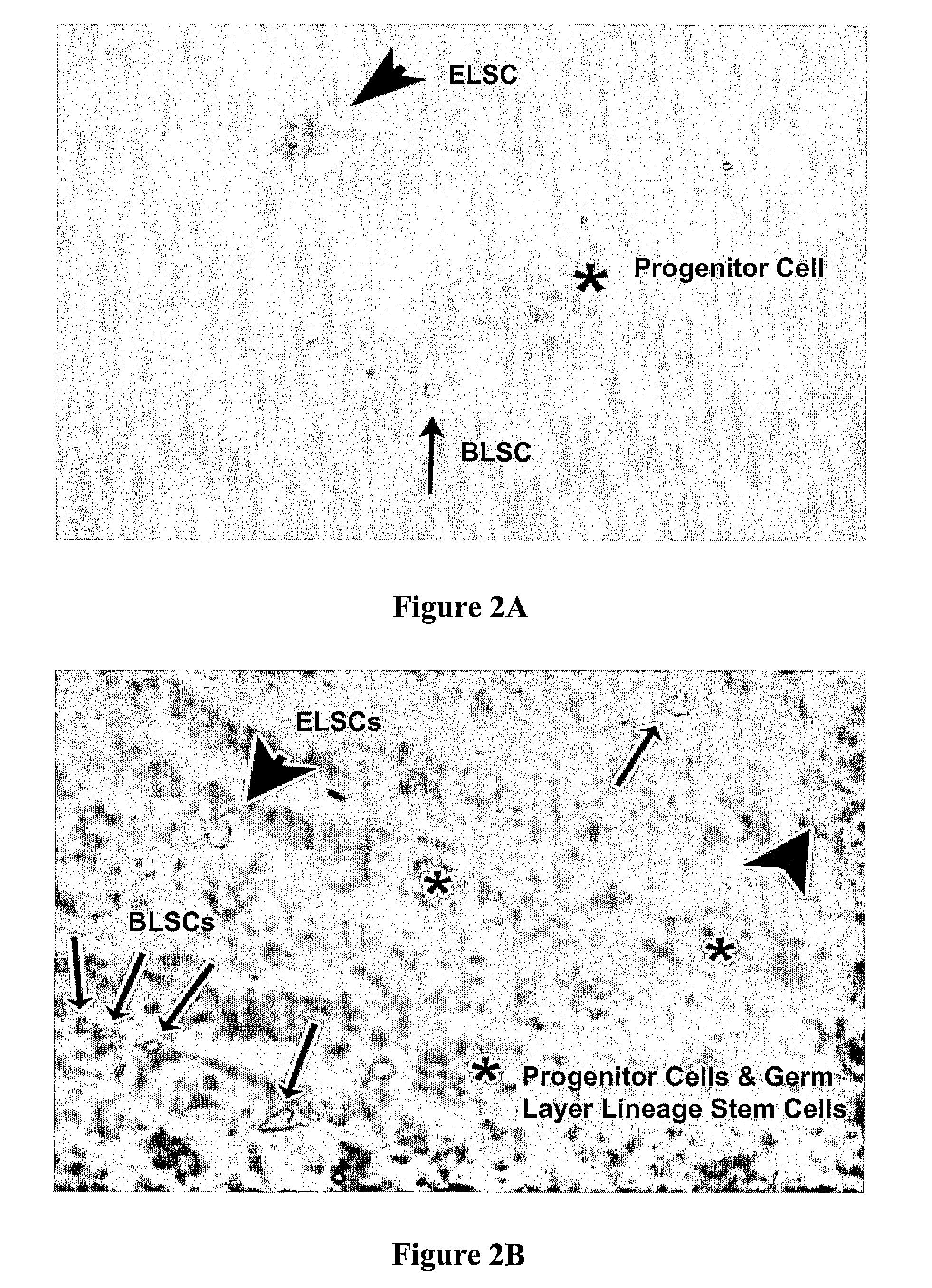
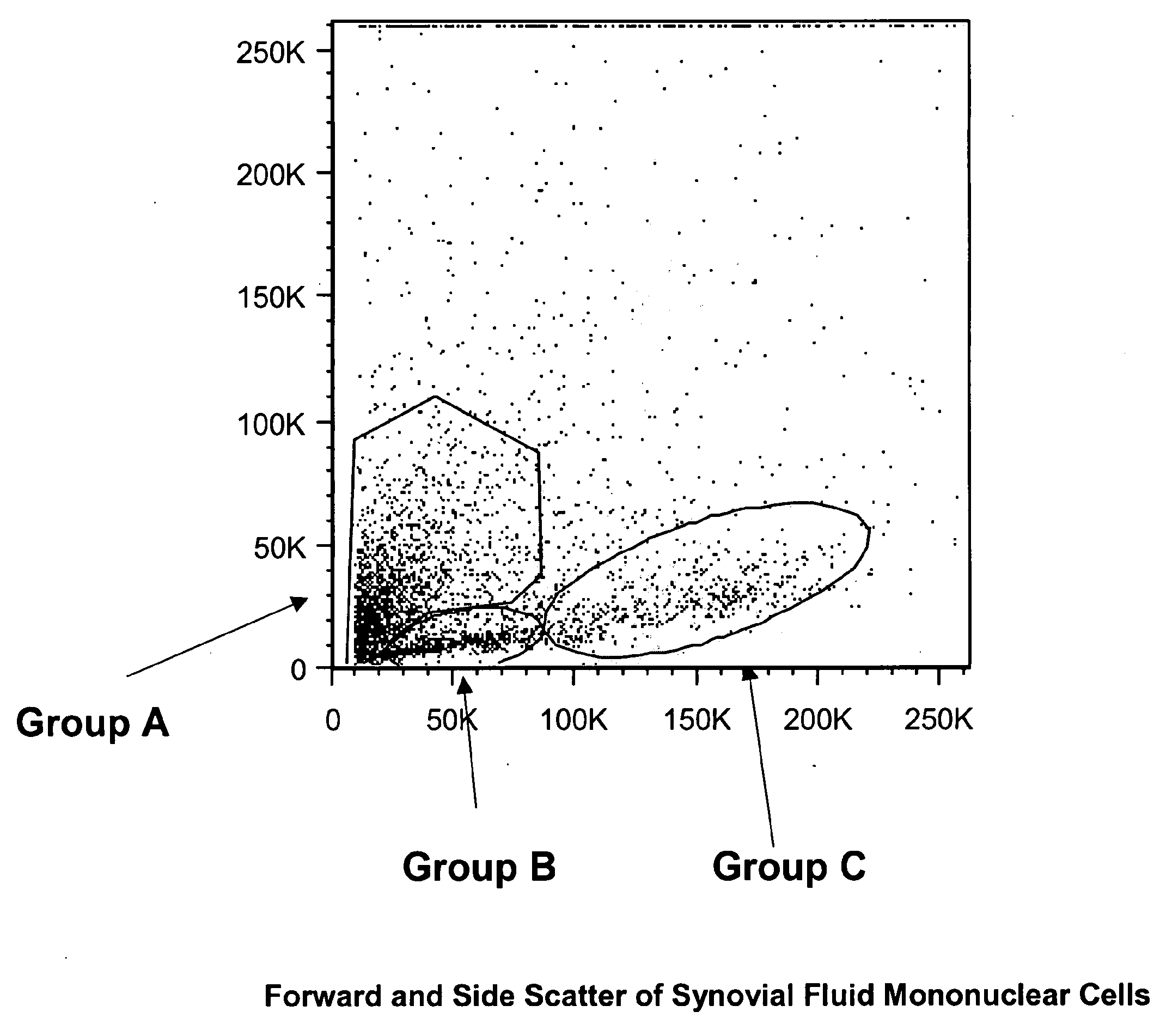
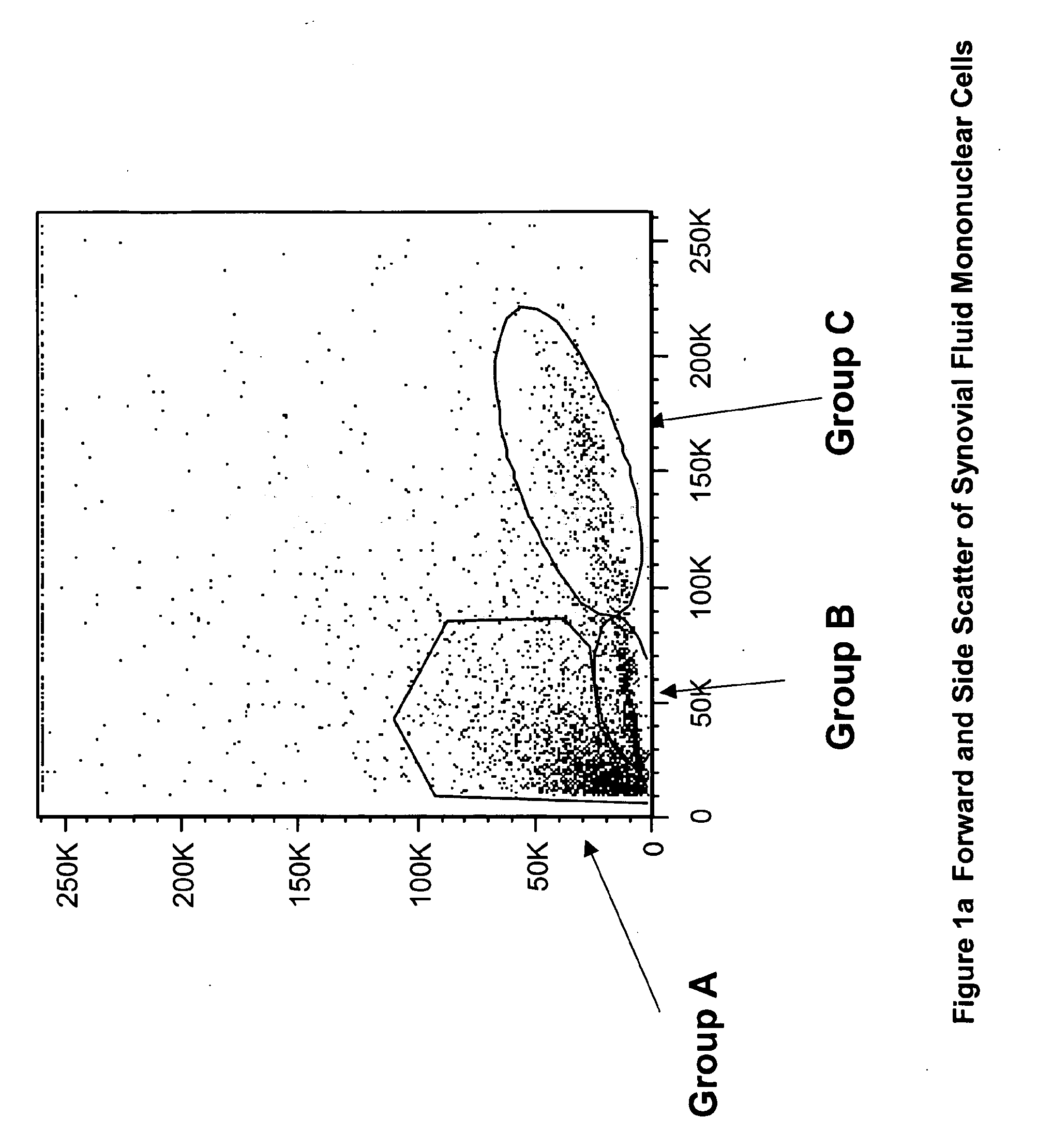
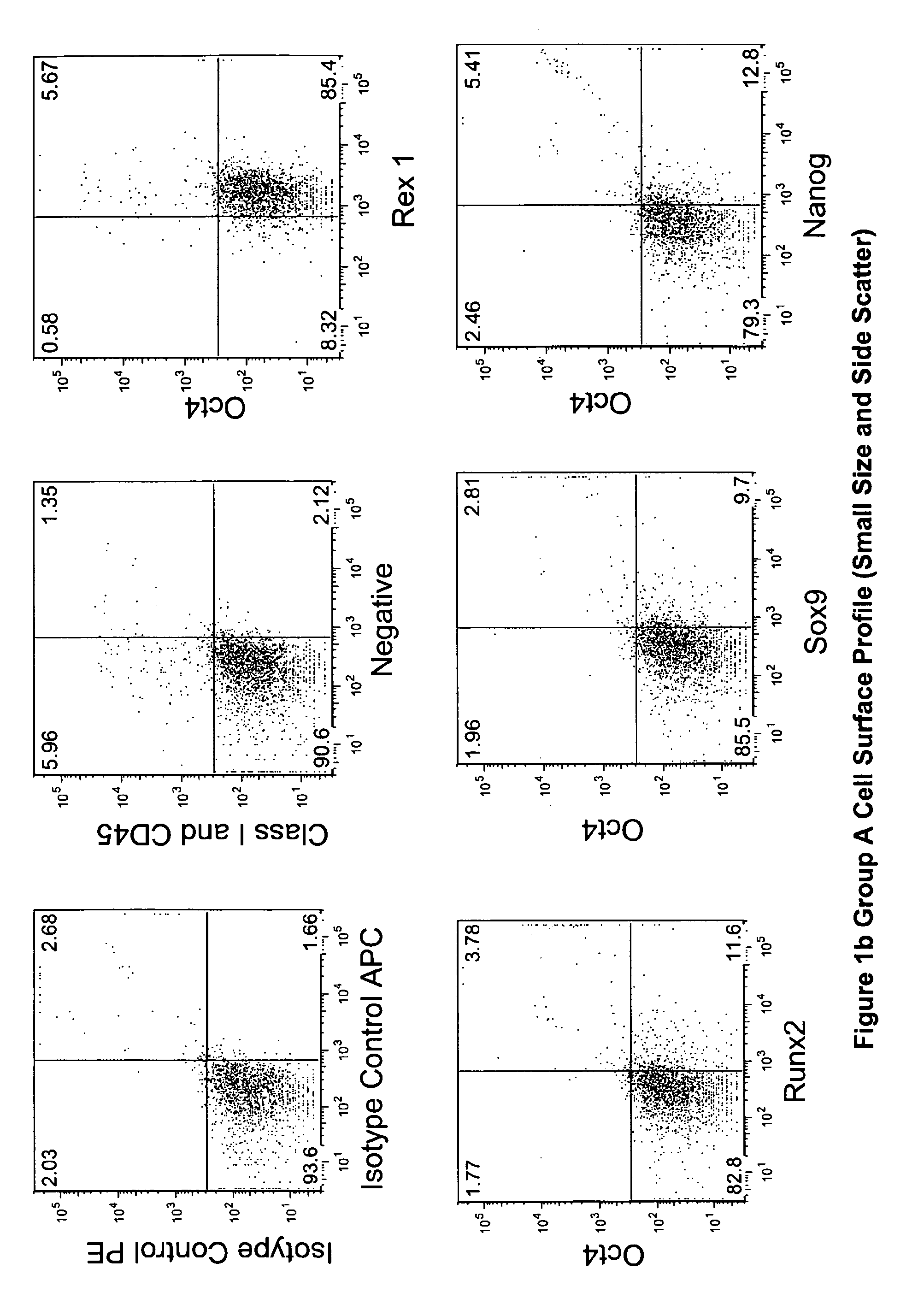
Multipotent amniotic fetal stem cells
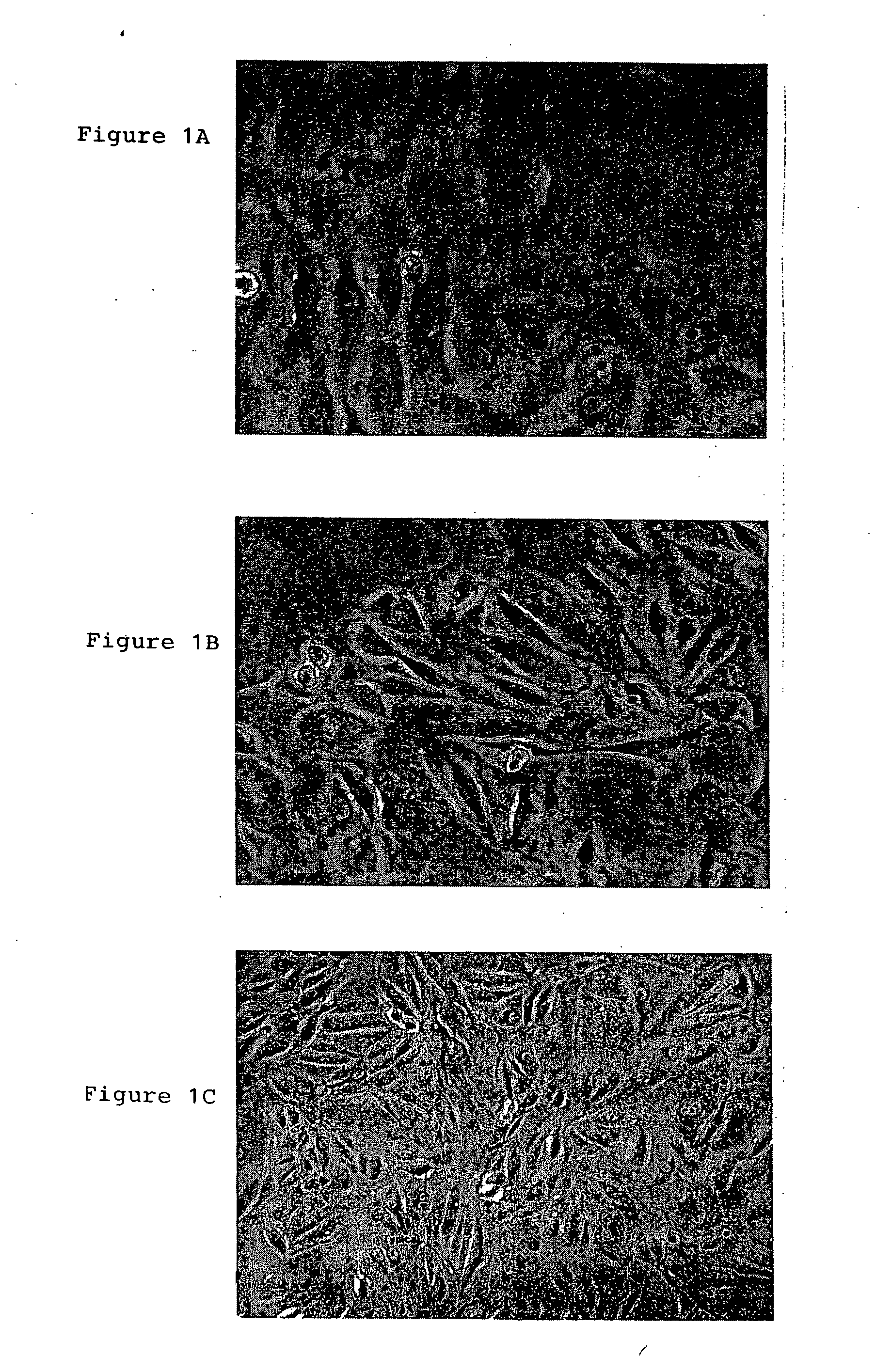
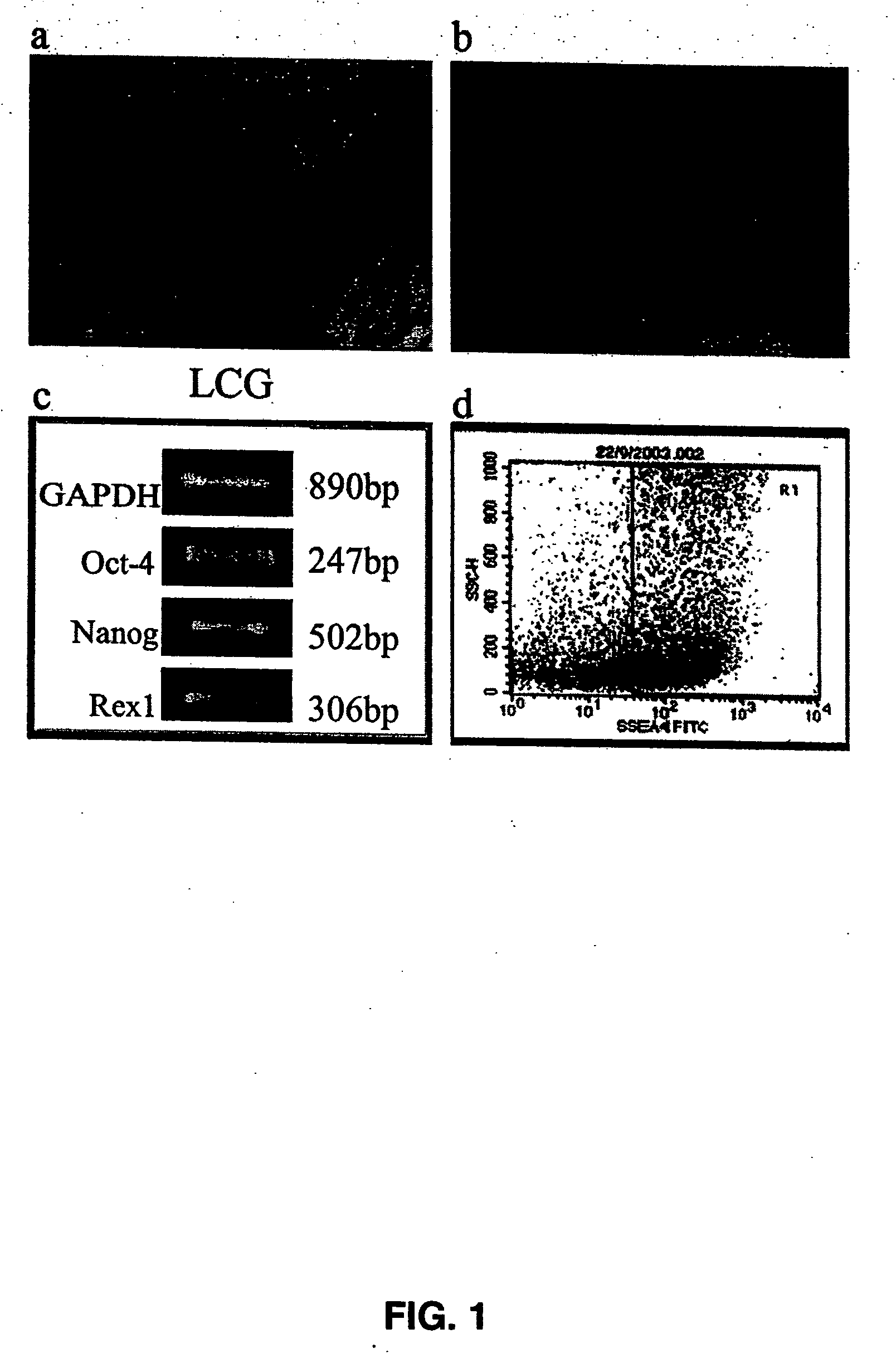
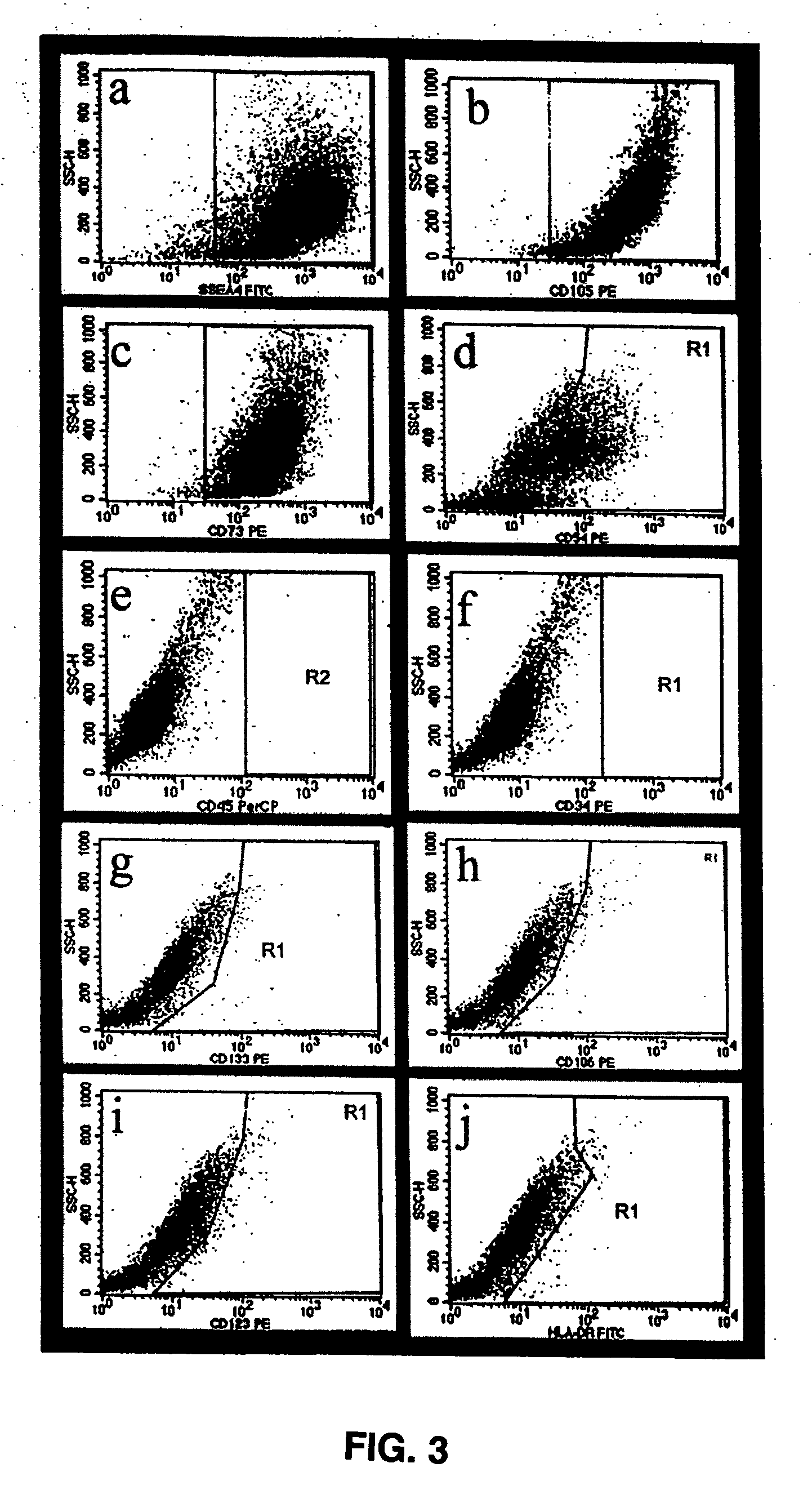
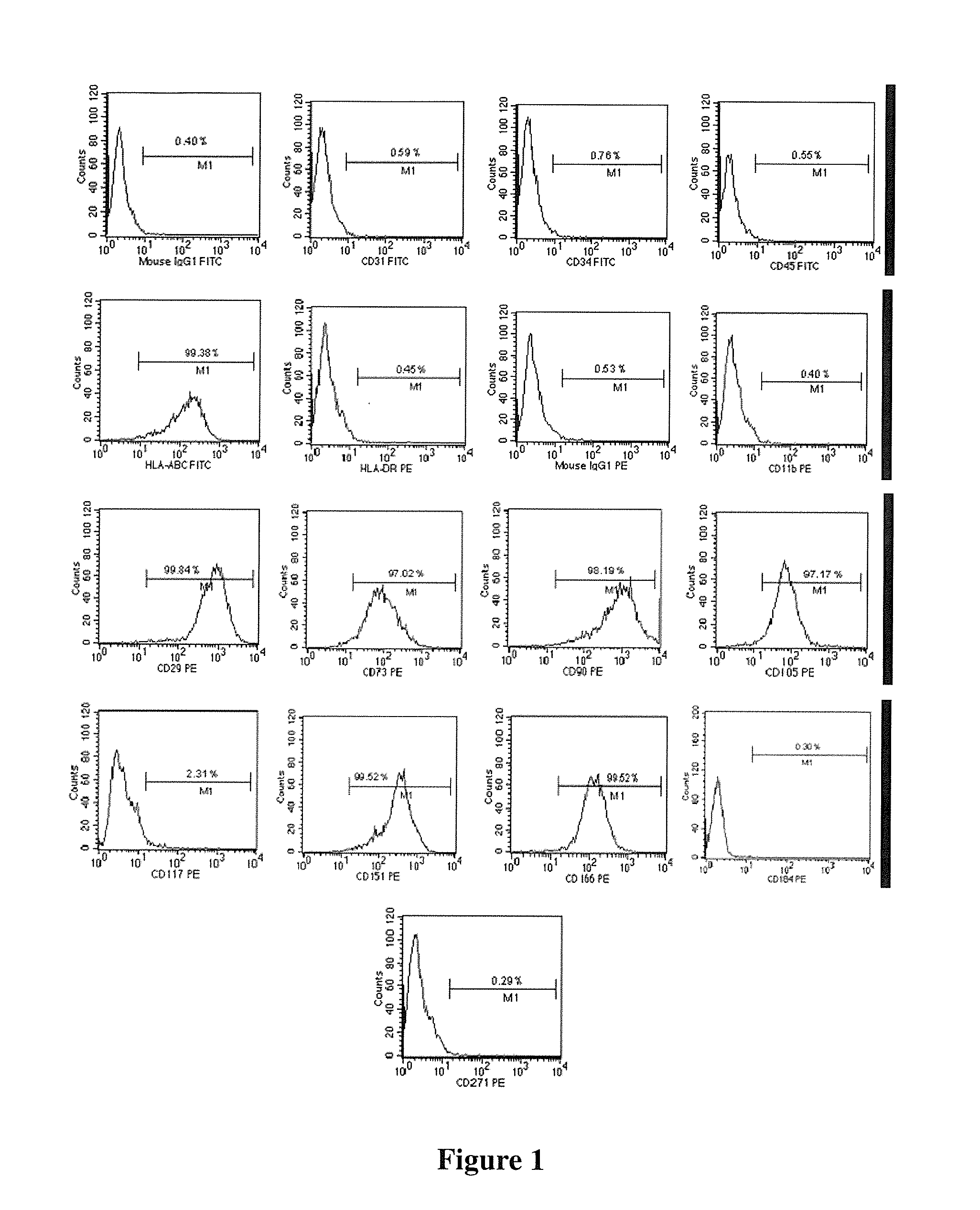
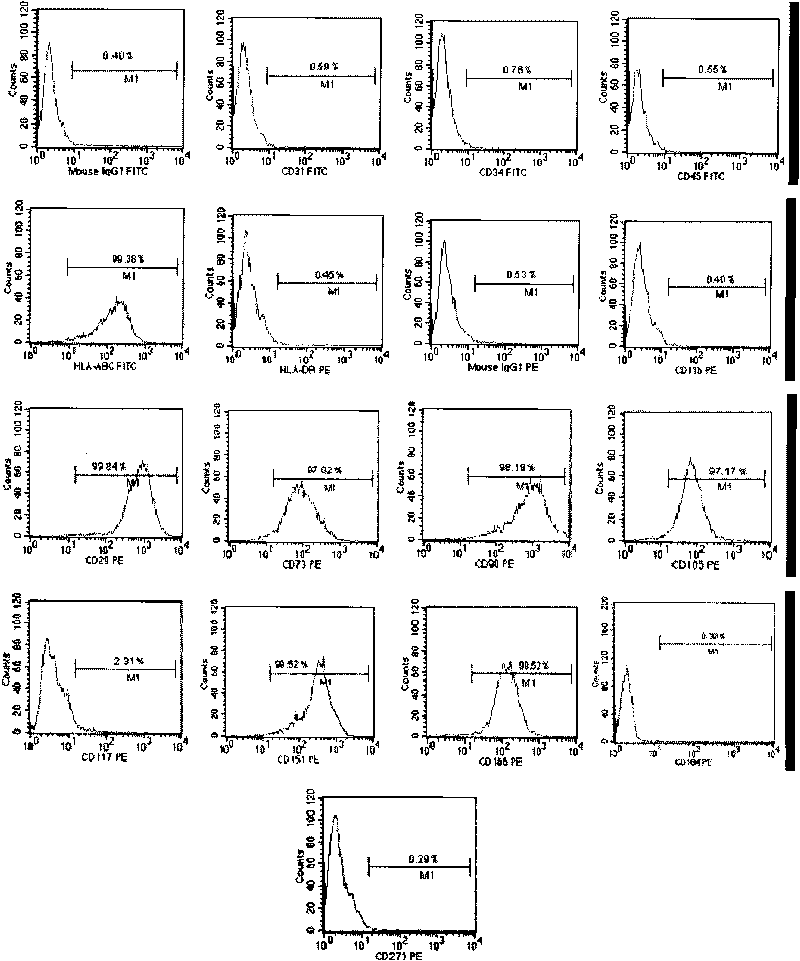
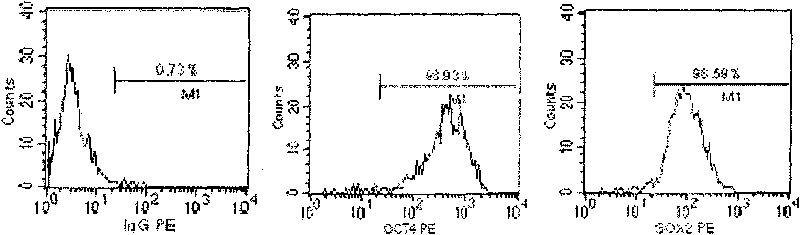
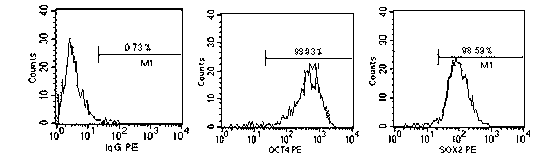
A source of multipotent amniotic fluid / fetal stem cells (MAFSCs) is disclosed. MAFSC are of fetal origin and have a normal diploid karyotype. These cells are characterized by the following cell surface markers: SSEA3, SSEA4, Tra-1-60, Tra-1-81, Tra-2-54, HLA class I, CD13, CD44, CD49b, CD105 and are distinguished by the absence of the antigen markers CD34, CD45, and HLA Class II, but are distinguished from mouse embryonic stem cells in that these cells do not express the cell surface marker SSEA1. MAFSC express the stem cell transcription factor Oct-4. MAFSC cells can be propagated for an indefinite period of time in continuous culture in an undifferentiated state. The MAFSCs have the ability to differentiate in culture in a regulated manner, into three or more subphenotypes. Cells can then be differentiated into endodermal, mesodermal and ectodermal derived tissues in vitro and in vivo. A method for isolating, identifying, expanding and differentiating MAFSCs is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Pluripotent stem cells derived without the use of embryos or fetal tissue
InactiveUS20030113910A1New breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Owner:STEMA
Pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells, compositions, methods and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050255588A1Avoid developmentInhibit progressBone marrow stroma cellsGenetic material ingredientsGerm layerIn vivo
The present invention relates to pluripotent stem cells, particularly to pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells. The invention further relates to methods of purifying pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells and to compositions, cultures and clones thereof. The present invention also relates to a method of transplanting the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention in a mammalian host, such as human, comprising introducing the stem cells, into the host. The invention further relates to methods of in vivo administration of a protein or gene of interest comprising transfecting a pluripotent stem cell with a construct comprising DNA which encodes a protein of interest and then introducing the stem cell into the host where the protein or gene of interest is expressed. The present also relates to methods of producing mesodermal, endodermal or ectodermal lineage-committed cells by culturing or transplantation of the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY
Multipotent stem cells derived from placenta tissue and cellular therapeutic agents comprising the same
InactiveUS20070243172A1Negative immunological responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsGerm layerDisease
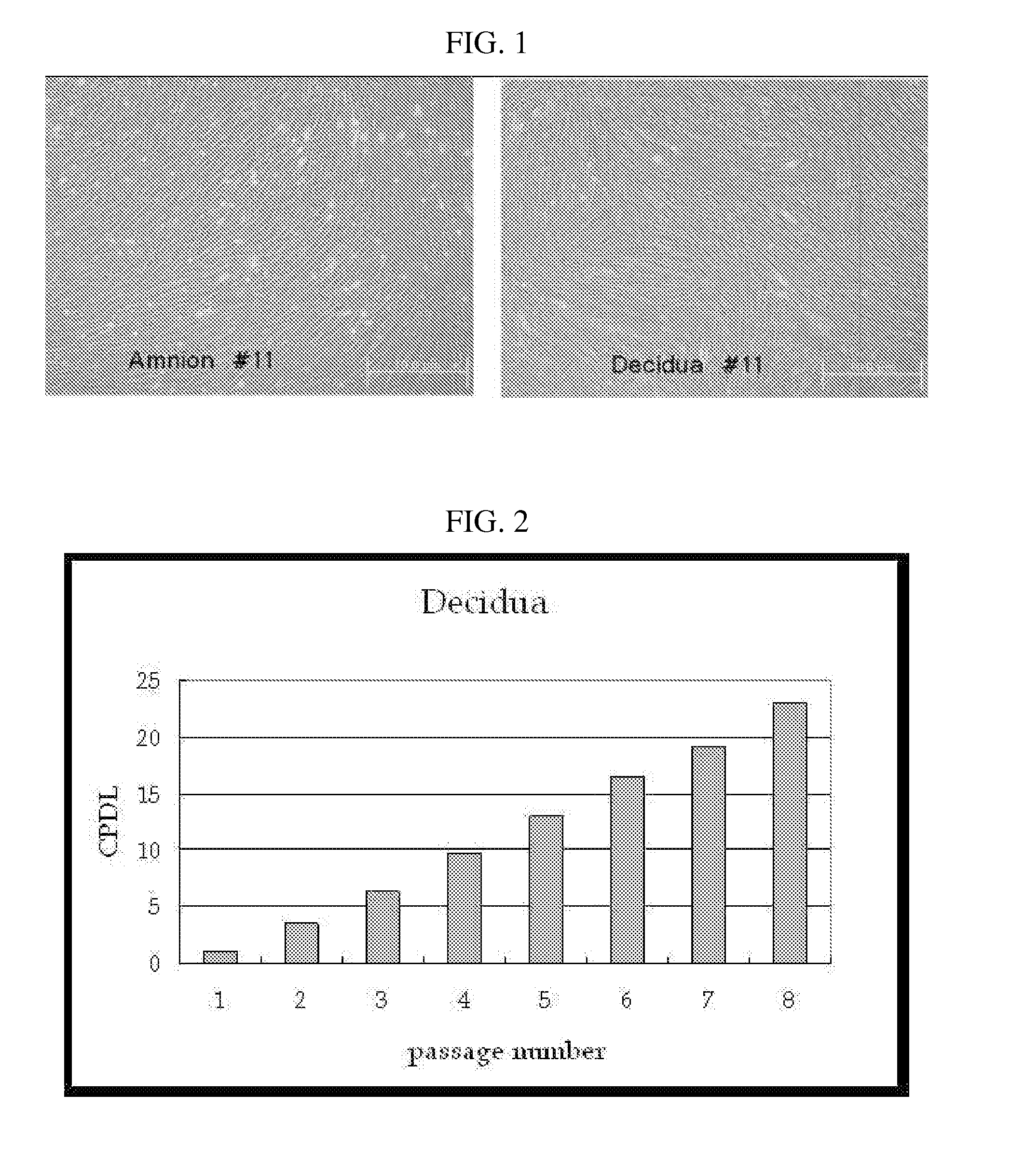
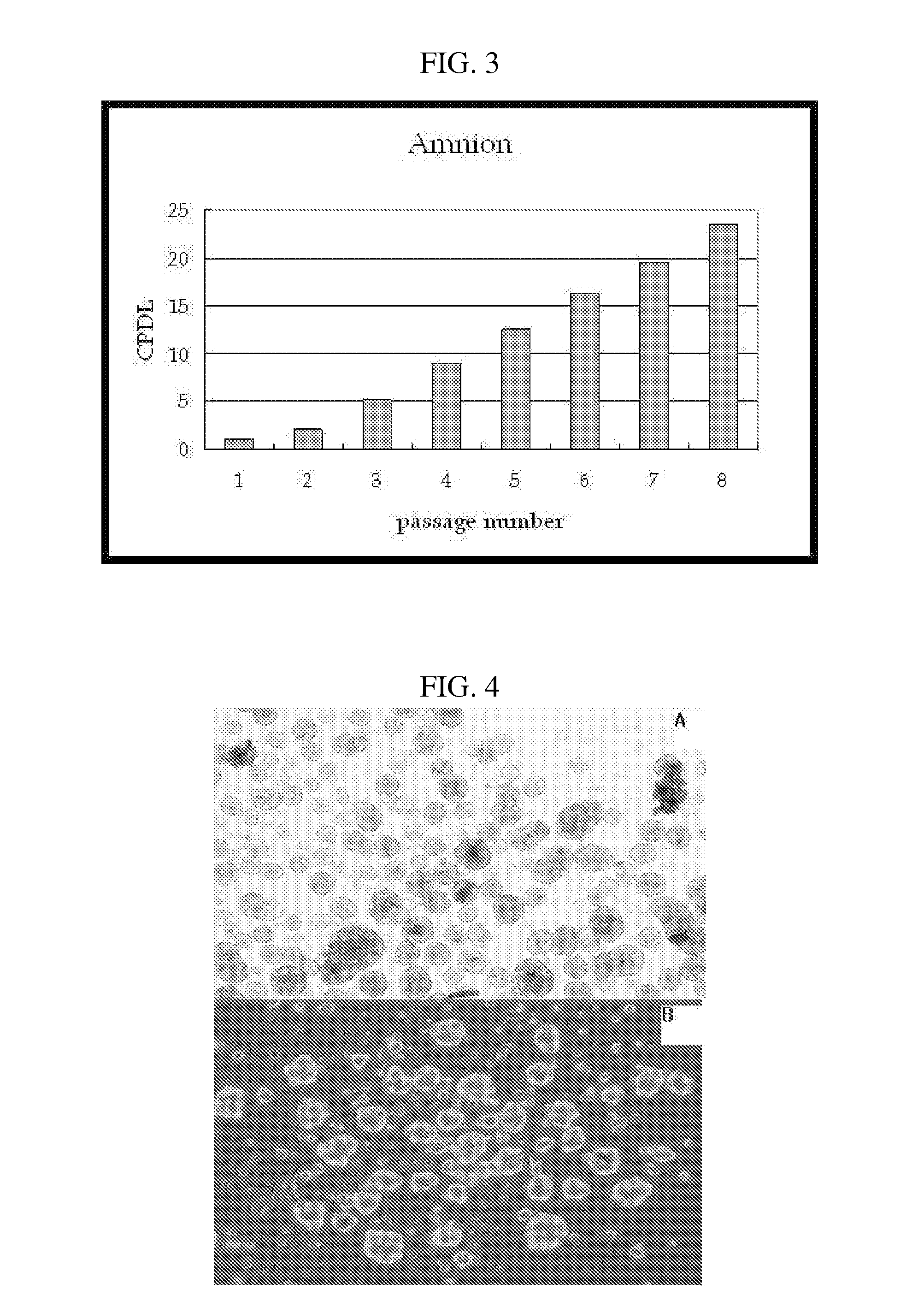
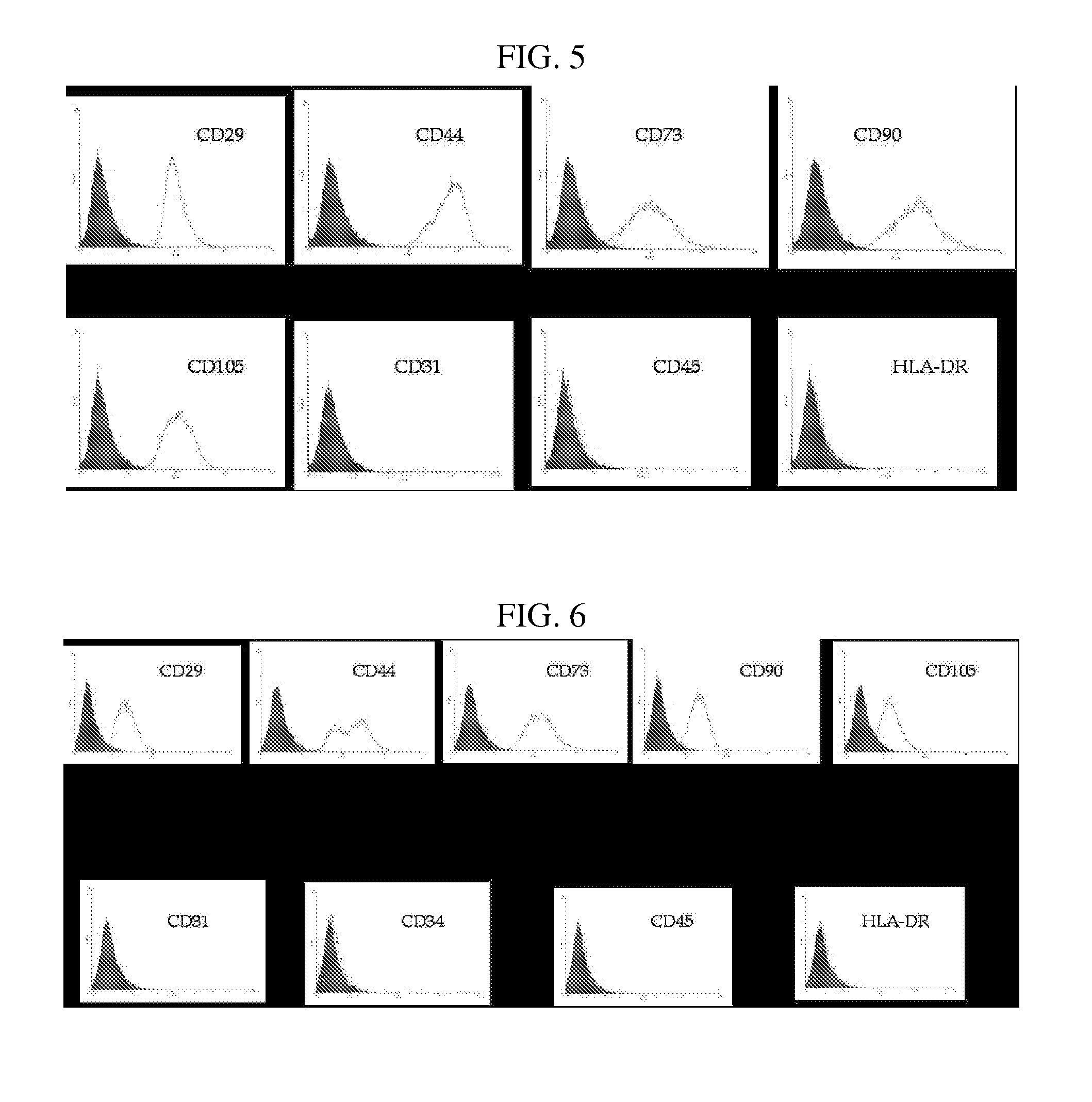
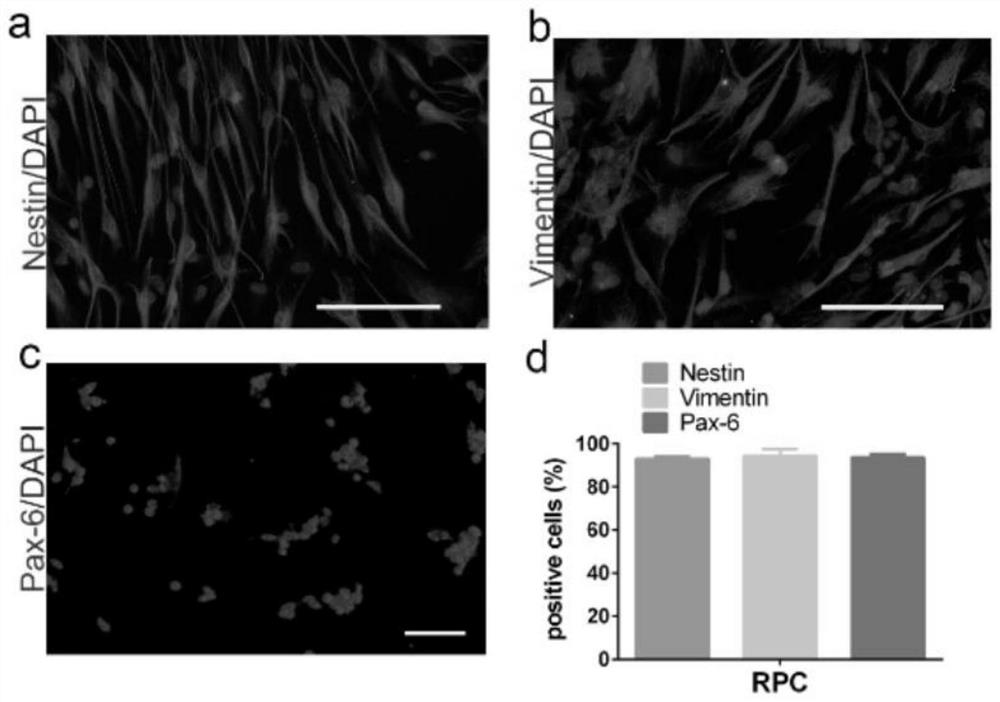
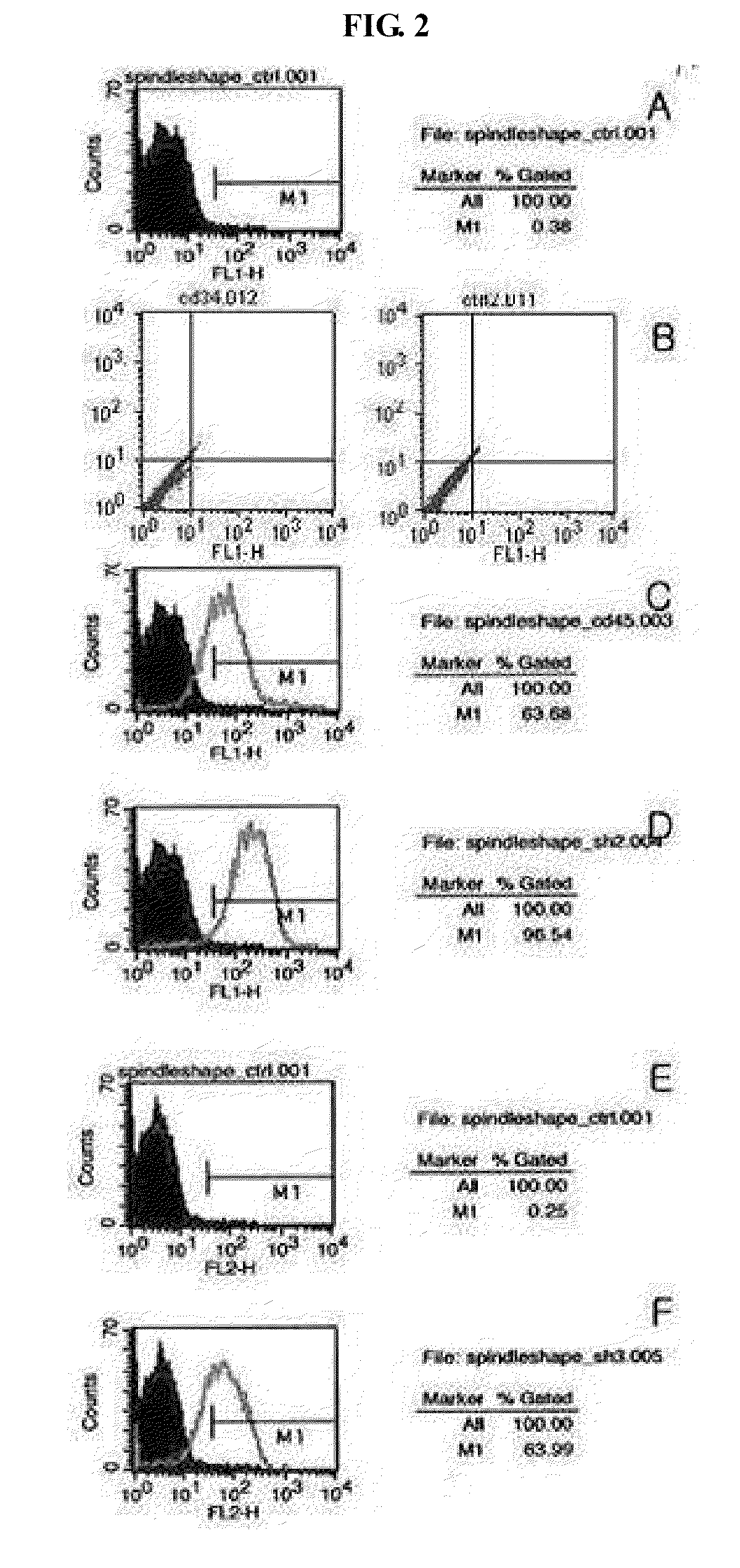
The present invention relates to placenta tissue-derived multipotent stem cells and cell therapeutic agents containing the same. More specifically, to a method for producing placenta stem cells having the following characteristics, the method comprising culturing amnion, chorion, decidua or placenta tissue in a medium containing collagenase and bFGF and collecting the cultured cells: (a) showing a positive immunological response to CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105, and showing a negative immunological response to CD31, CD34, CD45 and HLA-DR; (b) showing a positive immunological response to Oct4 and SSEA4; (c) growing attached to plastic, showing a round-shaped or spindle-shaped morphology, and forming spheres in an SFM medium so as to be able to be maintained in an undifferentiated state for a long period of time; and (d) having the ability to differentiate into mesoderm-, endoderm- and ectoderm-derived cells. Also the present invention relates to placenta stem cells obtained using the production method. The inventive multipotent stem cells have the ability to differentiate into muscle cells, vascular endothelial cells, osteogenic cells, nerve cells, satellite cells, fat cells, cartilage-forming cells, osteogenic cells, or insuline-secreting pancreatic β-cells, and thus are effective for the treatment of muscular diseases, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, nervous diseases, diabetes and the like, and are useful for the formation of breast tissue.
Owner:RNL BIO
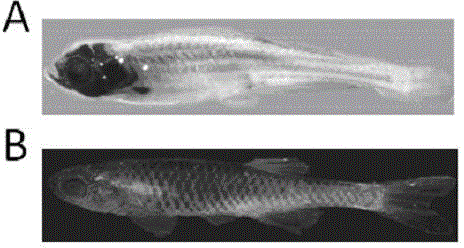
Crispr/Cas9-induced scale-missing zebra fish mode and establishment method
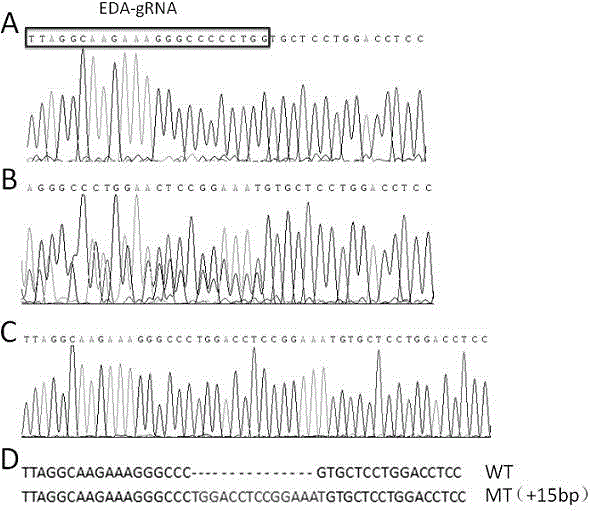
The invention relates to a Crispr / Cas9-induced scale-missing zebra fish mode. The mode is scale-missing zebra fish containing EDA gene exon 4-locus base insertion. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses an establishment method and the application of the Crispr / Cas9-induced scale-missing zebra fish mode. The established scale-missing zebra fish mode has a great application value in functional research of related genes of appendages of the skin, screening of medicines for treating ectoderm dysplasia such as human baldness, and the like.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
Induction of pluripotent stem cells into mesodermal lineages
InactiveUS20080038820A1Promotes commitment and survivalGenetic material ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProgenitorGerm layer
The present invention provides a method of inducing mesoderm derived cells from pluripotent stem cells. In contrast to methods known in the art that are often designed to replicate in vivo events of mesoderm induction, the present invention provides a unique, yet simple, method whereby pluripotent stem cells are mesodermally primed in the presence of factors that concomitantly inhibit the spontaneous differentiation of endoderm and ectoderm during expansion and suspension steps. Exposure and / or adherence of primed aggregates to a extracellular matrix that promotes the commitment and survival of induced mesoderm progenitors, followed by exposure to various mesoderm associated factors, allows for the subsequent induction of such cells into terminally differentiated lineages, such as cardiomyocytes. End products of this induction system will ultimately provide an unlimited source of mesoderm-derived cell types for therapeutic and pharmacological purposes.
Owner:RUDY REIL DIANE ELIZABETH DR +1
Pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells, compositions, methods and uses thereof
The present invention relates to pluripotent stem cells, particularly to pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells. The invention further relates to methods of purifying pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells and to compositions, cultures and clones thereof. The present invention also relates to a method of transplanting the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention in a mammalian host, such as human, comprising introducing the stem cells, into the host. The invention further relates to methods of in vivo administration of a protein or gene of interest comprising transfecting a pluripotent stem cell with a construct comprising DNA which encodes a protein of interest and then introducing the stem cell into the host where the protein or gene of interest is expressed. The present also relates to methods of producing mesodermal, endodermal or ectodermal lineage-committed cells by culturing or transplantation of the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY
Method of inducing and maintaining neuronal cells
InactiveUS20080261879A1Avoid deathPrevent degenerationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsGerm layerNeurulation
The present invention makes available a method for inducing neuronal differentiation and preventing the death or degeneration of neuronal cells both in vitro and in vivo. The subject method stems from the unexpected finding that, contrary to traditional understanding of neural induction, the default fate of ectodermal tissue is neuronal rather than mesodermal and / or epidermal. In particular, it has been discovered that preventing or antagonizing a signaling pathway in a cell for a growth factor of the TGF-β family can result in neuronal differentiation of that cell.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells derived from corneal limbus, methods of isolation and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060216821A1Increase telomerase activityCulture processNervous system cellsGerm layerDisease
The present disclosure describes mammalian pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells (ELSCs) isolated from corneal limbal tissue, a non-embryonic tissue. The ELSCs of the present disclosure are capable of proliferating in an in vitro culture, maintain the potential to differentiate into cells of endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm lineage in culture, and are capable of forming embryoid-like bodies when placed in suspension culture. Thus, these cells possess multi-lineage differentiation potential and self-renewing capability. ELSCs may be a promising therapeutic tool, and may provide new therapeutic alternatives for various diseases, conditions, and injuries.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Pluripotent stem cells, method for preparation thereof and uses thereof
Human pluripotent stem cells which are isolated from cut human umbilical cord or placenta and characteristic of cell surface marker CD151+, OCT4+ and CD184−, can adhere to tissue culture plastic and have the potential to differentiate into three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. Methods of isolating, purifying and culturally expanding of a population of human pluripotent stem cells and uses for treating diseases caused by cell damage or cell aging, and as a kind of carrier cells in gene therapy are provided.
Owner:BEIJING HEALTH & BIOTECH (H&B) CO LTD
Isolation of inner cell mass for the establishment of human embryonic stem cell (hESC) lines
InactiveUS20030104616A1Ensure purityMinimize contaminationMammal material medical ingredientsArtificial cell constructsMidblastulaStem cell line
A method for isolating an inner cell mass comprising the steps of immobilizing a blastocyst stage embryo having a zona pellucida, trophectoderm, and inner cell mass, creating an aperture in the blastocyst stage embryo by laser ablation, and removing the inner cell mass from the blastocyst stage embryo through the aperture. The aperture is through the zona pellucida and the trophectoderm. The laser ablation is acheived using a non-contact diode laser. The inner cell mass removed from the blastocyst stage embryo is used to establish human Embryonic Stem Cell lines.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Non-Embryonic Totipotent Blastomere-Like Stem Cells And Methods Therefor
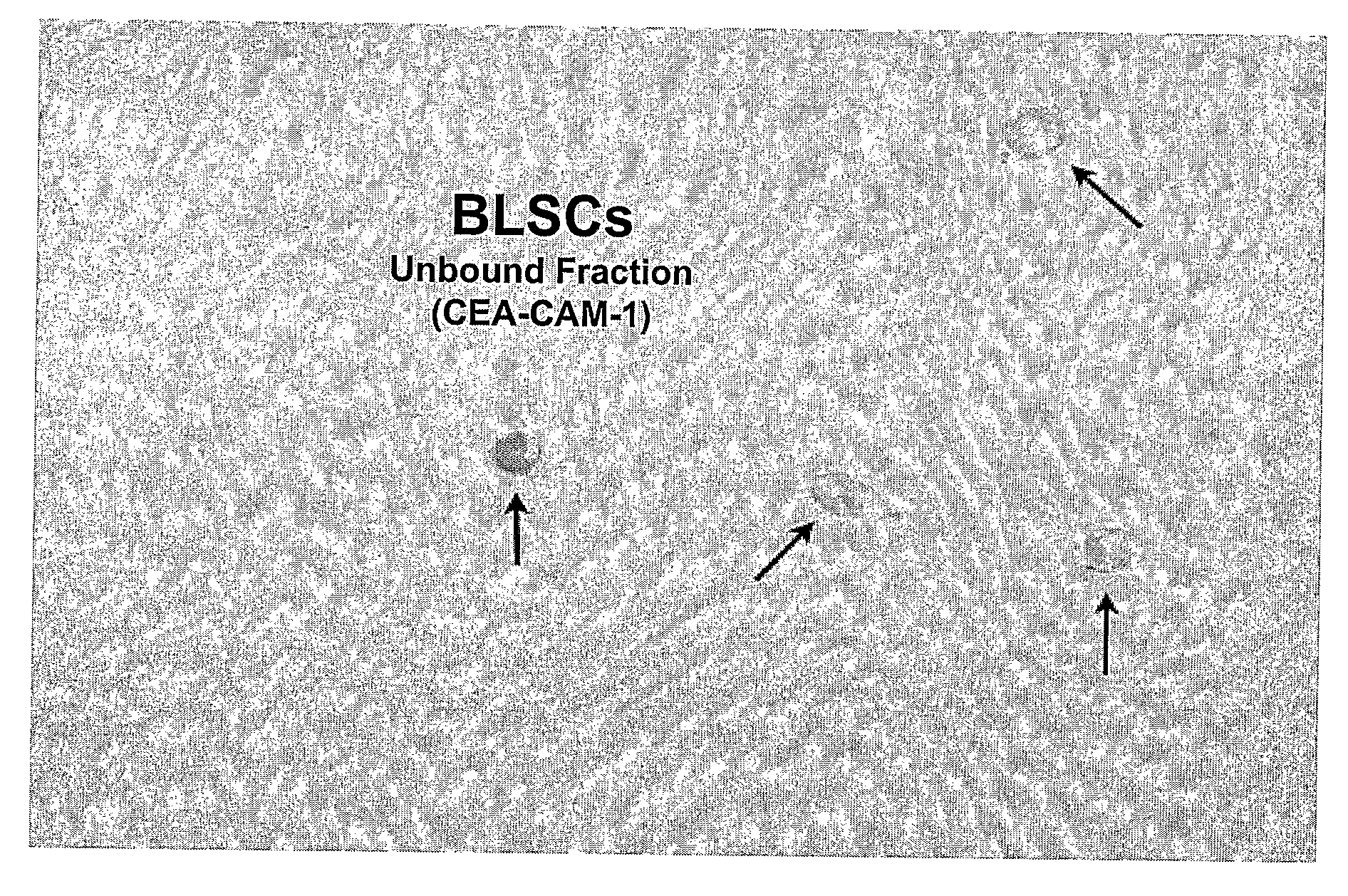
Non-embryonic blastomere-like totipotent stem cells are disclosed. Most preferably, such cells are obtained from various tissues of postnatal mammals (e.g., using tissue biopsied from the mammal), are smaller than 1 μm, have normal karyotype, and do not spontaneously differentiate in serum-free medium without differentiation inhibitors. These non-embryonic blastomere-like totipotent stem cells typically express CD66e, CEA-CAM-1 and telomerase, but do not typically express CD10, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, and SSEA-4. Such blastomere-like totipotent cells can be differentiated into ectodermal, mesodermal, or endodermal tissues, including placental tissues and germ cells. Moreover, when implanted into a mammal, such cells will not be teratogenic.
Owner:MORAGA BIOTECH CORP
Sub totipotential stem cell and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing a population of?human pluripotent stem cells and the application thereof. The preparation of stem cells is characterized by comprising the following steps: CD151<+>, CD31<->, Sox<2+> pluripotent stem cells are separated and collected from human umbilical cord and or placenta tissues; the cells adhere to grow in a culture vessel under a predetermined condition and expand through passage 20 or above to be still stable in gene expression. The population of cells of this invention do not form teratoma after injection into animals. The human pluripotent stem cells highly express CD151, OCT4 and Sox-2 as specific markers of embryonic stem cells, as well as specific markers of epidermic cells, endothelial cells, thrombocytes, dendritic cells, while lack expression of CD31, CD34, CD45 and HLA-II. The pluripotent stem cells are also characterized as being able to adhere to tissue culture plastic and having the potential to differentiate into three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. These pluripotent stem cells are able to be used as carrier cells of gene therapy and for the treatment of diseases caused by cell damage or cell aging. The present invention provides a method of isolating, purifying and culturally expanding of a population of human pluripotent stem cell for preparing the high purity injection preparation. The preparation of stem cells has a good therapeutic effect on the treatment of diseases caused by cell damage or cell aging in animal and human clinical trials. The preparation also has no toxic side effect and no immune rejection.
Owner:BEIJING HEALTH & BIOTECH (H&B) CO LTD
Multipotent stem cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110070205A1Easily attainable embryonic-likePromote wound healingBiocideNervous disorderGerm layerMHC class I
The invention provides a quiescent stem cell having the capacity to differentiate into ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, and which does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 CD90, CD66A, CD66E, CXCR4, CD133 or an SSEA. The invention further provides a proliferative stem cell, which expresses genes including Oct-4, Nanog, Sox2, GDF3, P16INK4, BMI, Notch, HDAC4, TERT, Rex-1, TWIST, KLF-4 and Stella but does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105, CD90, CD66A, CD66E, CXCR4, CD133 or an SSEA. The cells of the invention can be isolated from adult mammals, have embryonic cell characteristics, and can form embryoid bodies. Methods for obtaining the stem cells, as well as methods of treating diseases and differentiated the stem cells, are also provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Multipotent stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100291042A1Easily attainable embryonic-likePromote wound healingBiocidePancreatic cellsDiseaseMHC class I
The invention provides a quiescent stem cell having the capacity to differentiate into ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, and which does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 and CD90. The invention further provides a proliferative stem cell, which expresses genes including Oct-4, Nanog, Sox2, GDF3, P16INK4, BMI, Notch, HDAC4, TERT, Rex-1 and TWIST but does not express cell surface markers including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD44, CD45, CD13, CD34, CD49c, CD73, CD105 and CD90. The cells of the invention can be isolated from adult mammals, have embryonic cell characteristics, and can form embryoid bodies. Methods for obtaining the stem cells, as well as methods of treating diseases and differentiated the stem cells, are also provided.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Culture medium for establishing pig iPS cell line and culture method thereof
InactiveCN103333920AEfficiently obtainedNeat edgesEmbryonic cellsGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyGerm layer
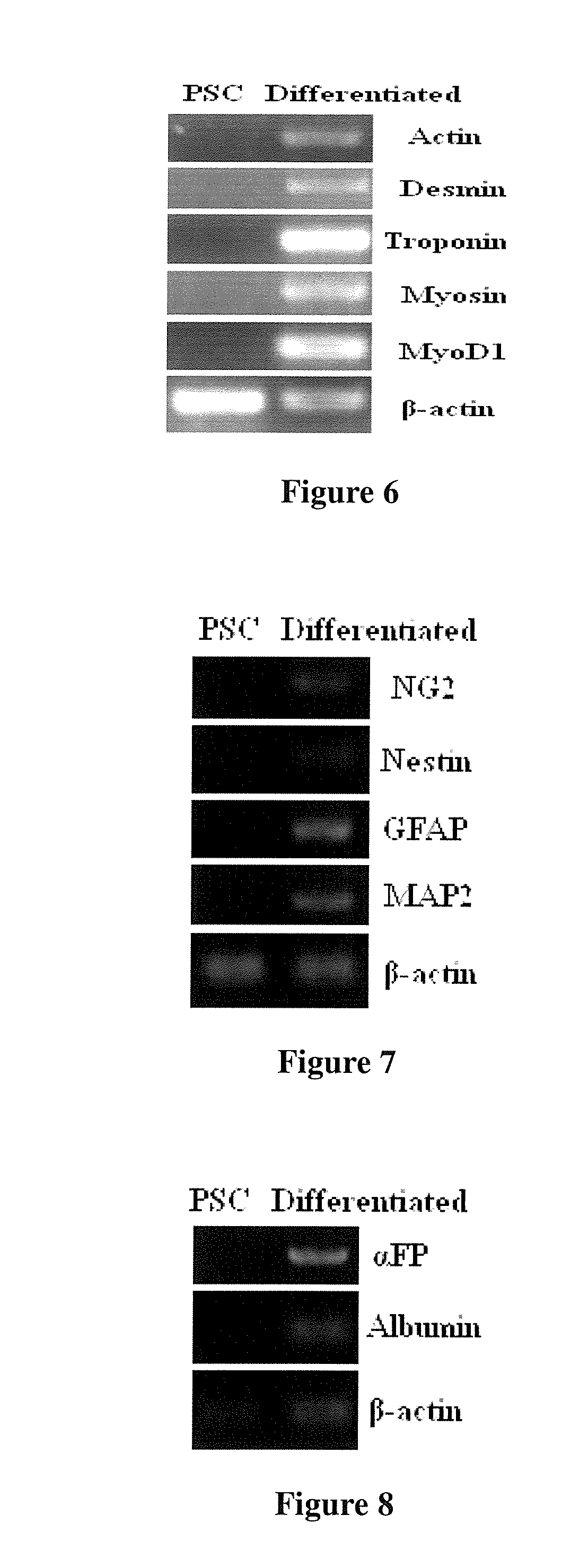
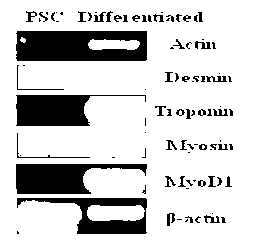
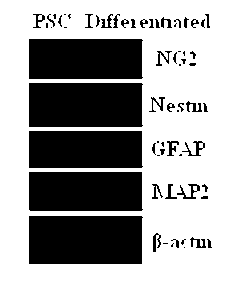
The invention discloses a culture medium for establishing a pig iPS cell line and a culture method thereof. A typical pig iPS cell is obtained in the ninth day through transfection by four transcription factors of OCT4, SOX2, KLF4 and c-MYC and induction culture of the culture medium, and the pig iPS cell can be obtained efficiently. The obtained pig iPS cell clone is flat clone, has a regular edge and is similar to the ES cellular morphology of the human body. According to the pig iPS cell line, the pig iPS cell through subculture keeps the undifferentiated state, shows positive in the AP dyeing displaying result and has a pluripotency mark, and the differentiated cell in vitro expresses NCSTN (entoderm), NESTIN (ectoderm) and DESMIN (mesoblast).
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Preparation method of animal and human primitive pluripotent stem cell, kit and use thereof
ActiveCN105441384AEpidermal cells/skin cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsGerm layerOrgan transplantation
The invention relates to a preparation method of an animal and human primitive pluripotent stem cell, a kit and use thereof. The preparation method of the animal and human primitive pluripotent stem cell provided by the invention includes letting an animal and human primitive ectoderm-like pluripotent stem cell contact at least one MAPK pathway inhibiting factor, at least one WNT signaling pathway regulatory factor, at least one LIF / STAT3 pathway regulatory factor and at least one FGF pathway regulatory factor so as to generate the animal and human primitive pluripotent stem cell. The invention also relates to a composition, medium or kit for preparation of the animal and human primitive pluripotent stem cell, as well as the primitive pluripotent stem cell prepared thereby and its use. The primitive pluripotent stem cell involved in the invention can be used for preparation of the chimeras of different animal and human species and the like, and is expected to be used for disease model establishment, drug testing and organ transplantation, etc.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Induced pluripotent stem cells from human umbilical cord tissue-derived cells
InactiveUS20130157365A1Increase gene expressionArtificial cell constructsDrug compositionsGerm layerUmbilical cord tissue
We have disclosed an induced pluripotent stem cell and the method of preparing the induced pluripotent stem cell from a human umbilical cord tissue-derived cell. More particularly, we have disclosed a human umbilical cord tissue-derived iPS cell which may be differentiated into cells of ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm lineages.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Establishment of a human embryonic stem cell line using mammalian cells
InactiveUS7811817B2Improve matchIncrease valueBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm layerFGF4
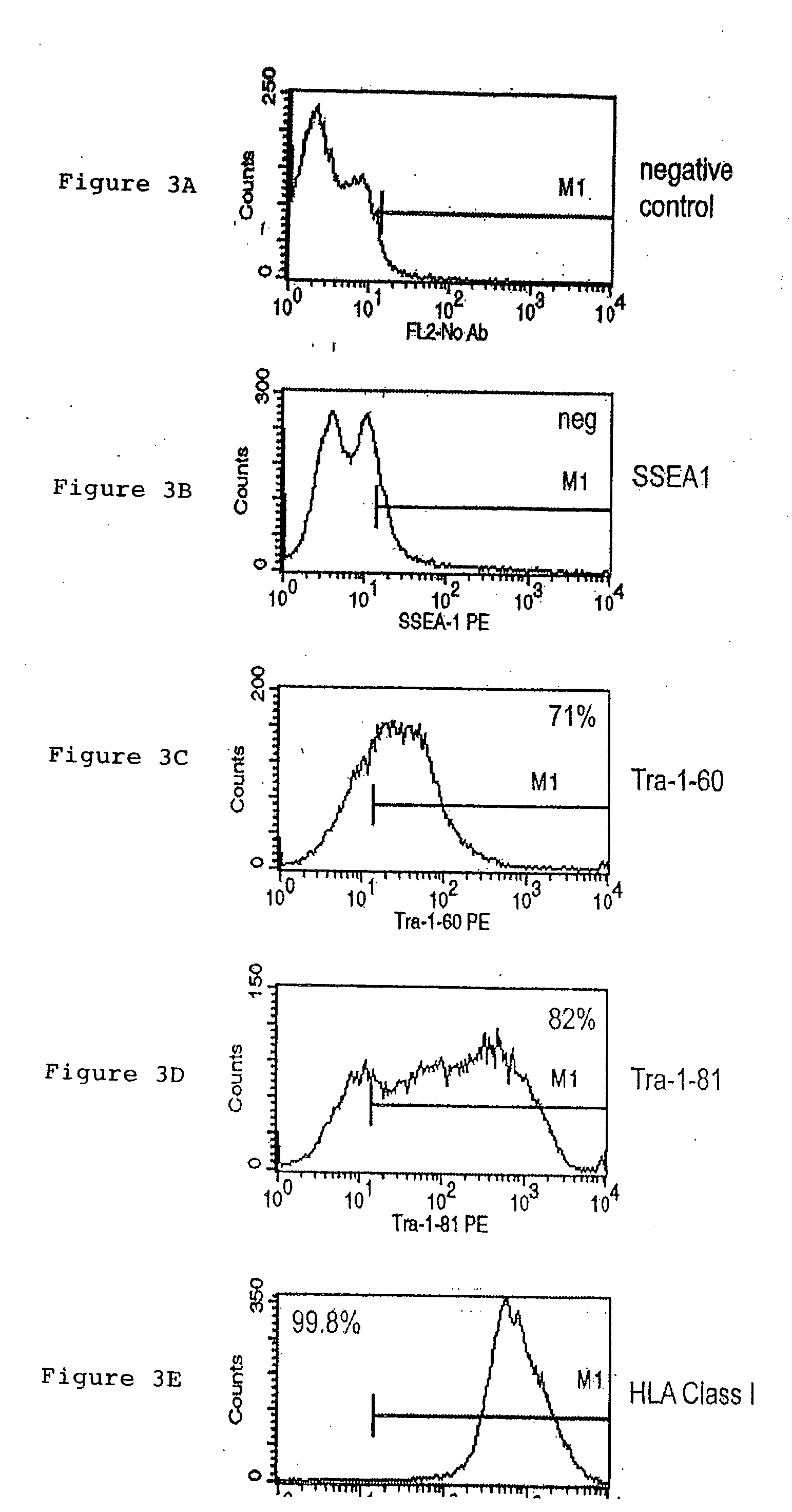
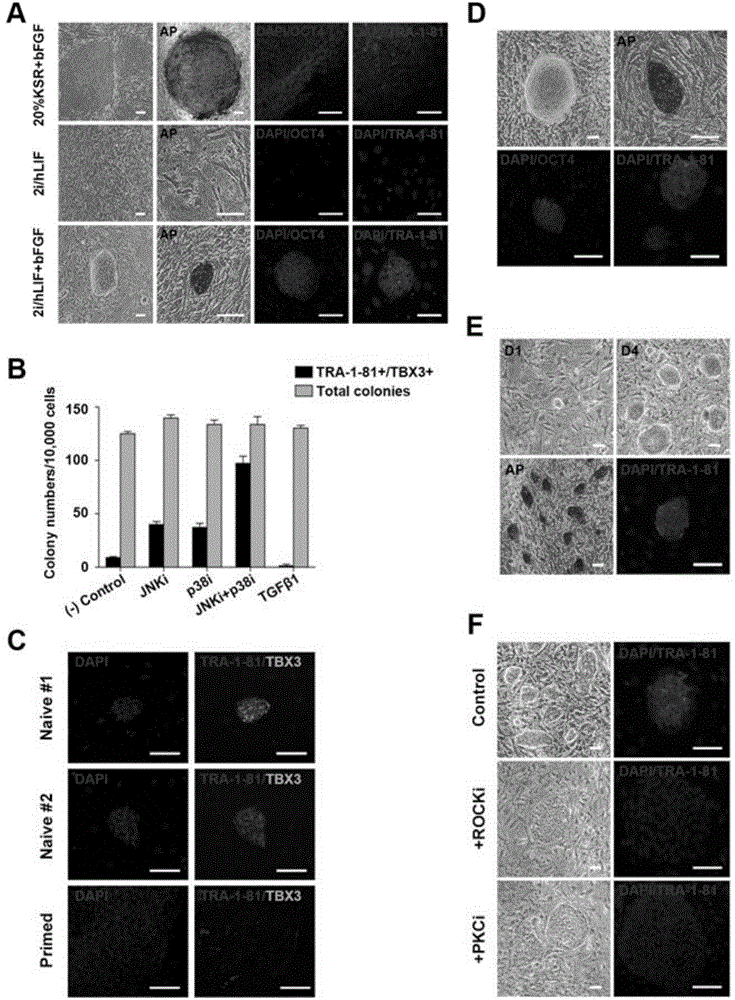
Purified preparations of human embryonic stem cells with certain population-specific characteristics are disclosed. This preparation is characterized by the positive expression of the following pluripotent cell surface markers: SSEA-1 (−); SSEA-4 (+); TRA-1-60 (+); TRA-1-81 (+); alkaline phosphatase (+), as well as a set of ES cell markers including Oct-4, Nanog, Rex1, Sox2, Thy1, FGF4, ABCG2, Dppa5, UTF1, Cripto1, hTERT, Connexin-43 and Connexin-45. The cells of the preparation are negative for lineage specific markers like Keratin 8, Sox-1, NFH (ectoderm), MyoD, brachyury, cardiac-actin (mesoderm), HNF-3 beta, albumin, and PDX1 (endoderm). The cells of the preparation are human embryonic stem cells, have normal karyotypes, exhibit high telomerase activity and continue to proliferate in an undifferentiated state after continuous culture for over 40 passages. The embryonic stem cell line Relicell™ hES1 also retains the ability, throughout the culture, to differentiate into cell and tissue types derived from all three embryonic germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm). Methods for isolating a human embryonic stem cell line are also disclosed.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
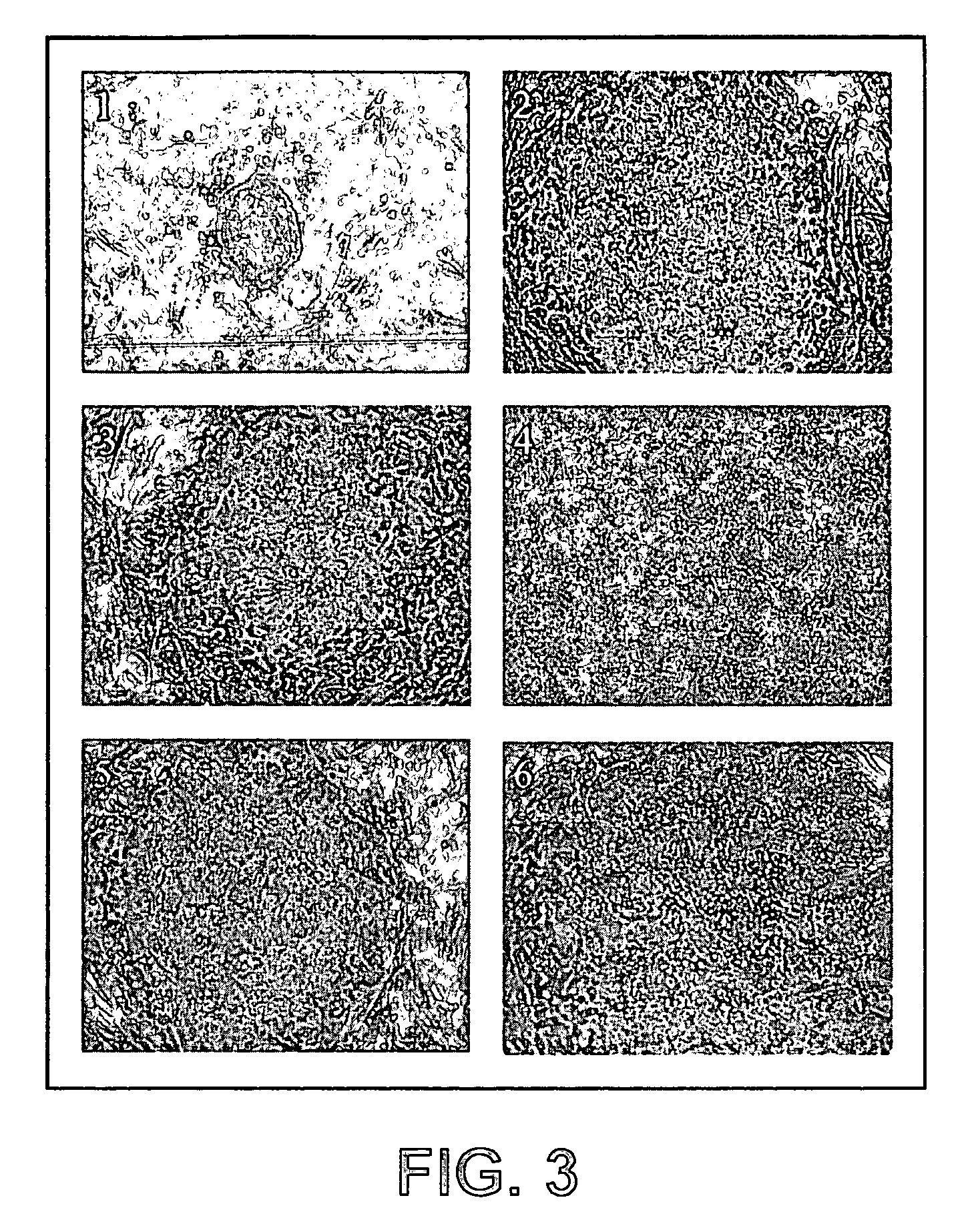
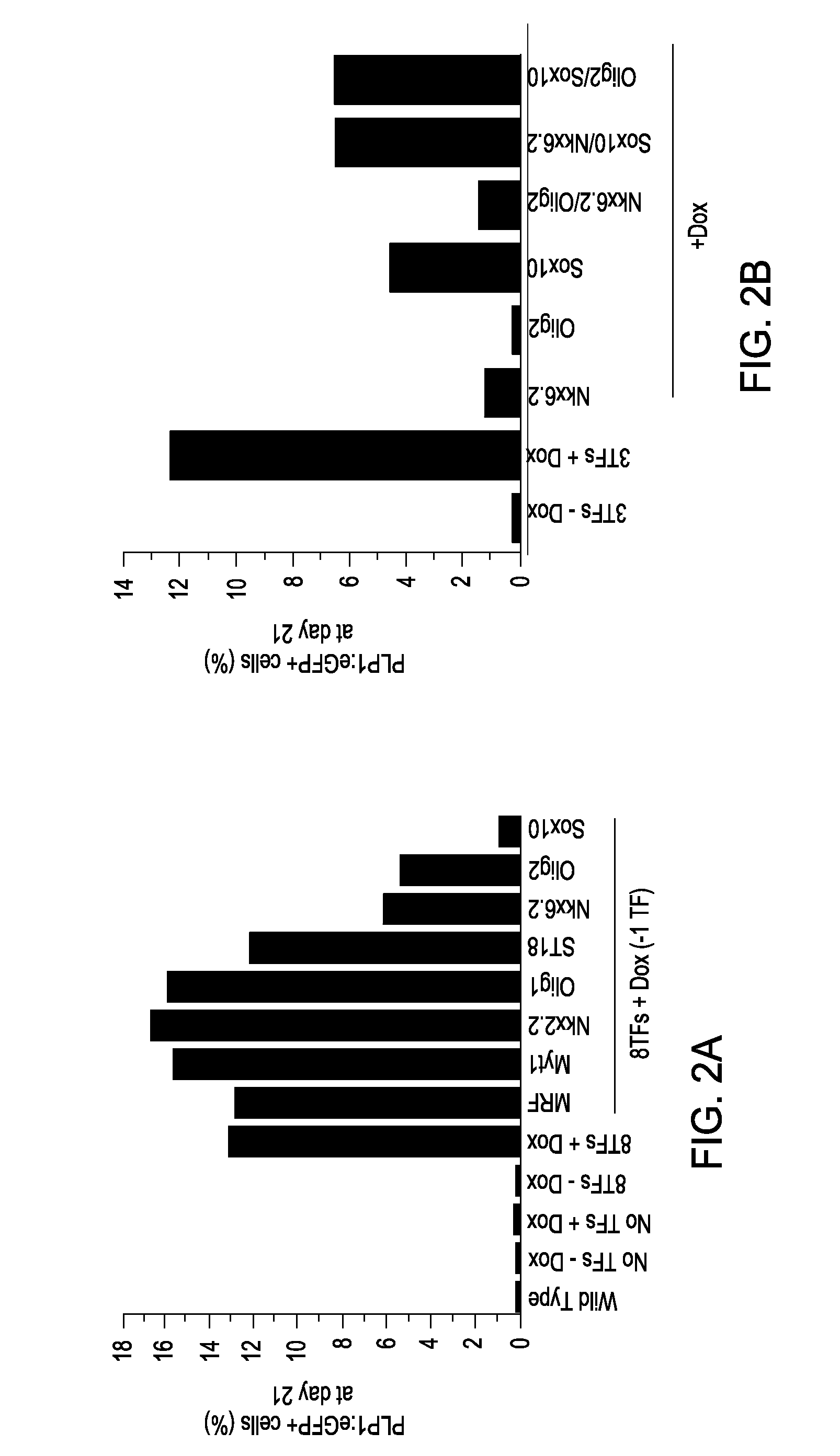
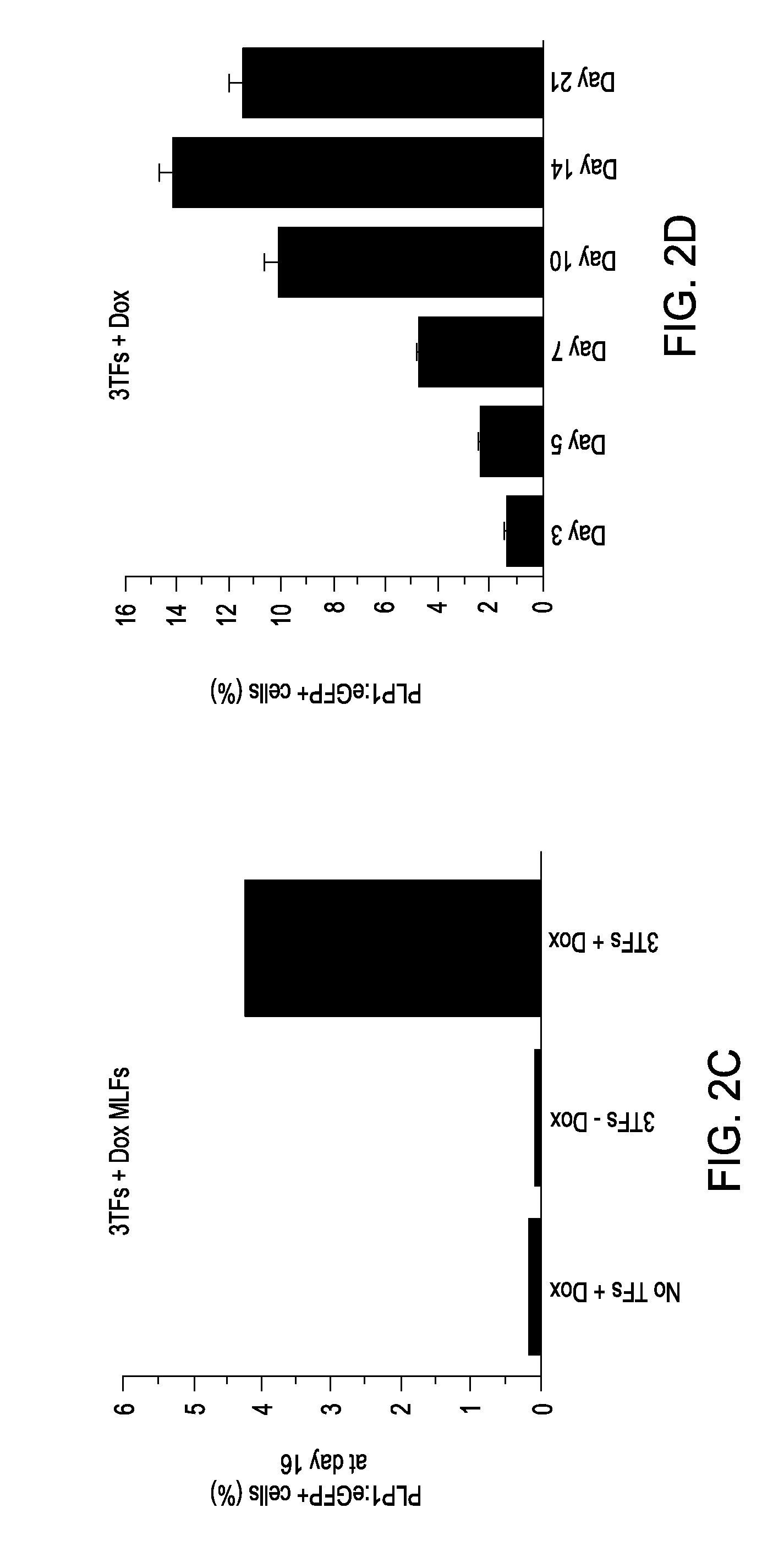
Cell fate conversion of differentiated somatic cells into glial cells
The present invention relates to the reprogramming of differentiated somatic cells, such as those differentiated cells that arise from embryonic mesoderm, into glial cells. Glial cells produced from this reprogramming are functionally equivalent to glial cells that arise from ectodermal origins.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Sub-totipotent stem cell, preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a sub-totipotent stem cell from cut human umbilical cord or placenta, wherein the cell marker is CD151<+>OCT4<+>CD184<->; the cell grows adhering to the wall in a culture container and can differentiate to the body entoderm, mesoblast and ectoderm tissues. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the sub-totipotent stem cell and an application thereof for preparing drug for treating cell injuries or cell aging diseases, and an application thereof as a carrier cell of a gene treatment drug.
Owner:BEIJING HEALTH & BIOTECH (H&B) CO LTD
Methods for preparing human melanocytes from human pluripotent stem cells
The invention relates to an ex vivo method for obtaining a population of human melanocytes derived from human pluripotent stem cells comprising the step consisting of co-culturing human pluripotent stem cells with cells that support ectodermal differentiation in the presence of an agent that stimulates epidermal induction and an agent that stimulates terminal differentiation of keratinocytes. The invention also relates to human melanocytes obtainable by said method and to uses thereof in cell therapy and in screening assays.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Personalized Synthetic Diamond of Different Colours, Obtained From (Living or Dead) Human or Animal Keratin and Production Method Thereof
InactiveUS20080145299A1Polycrystalline material growthUltra-high pressure processesGerm layerHuman body
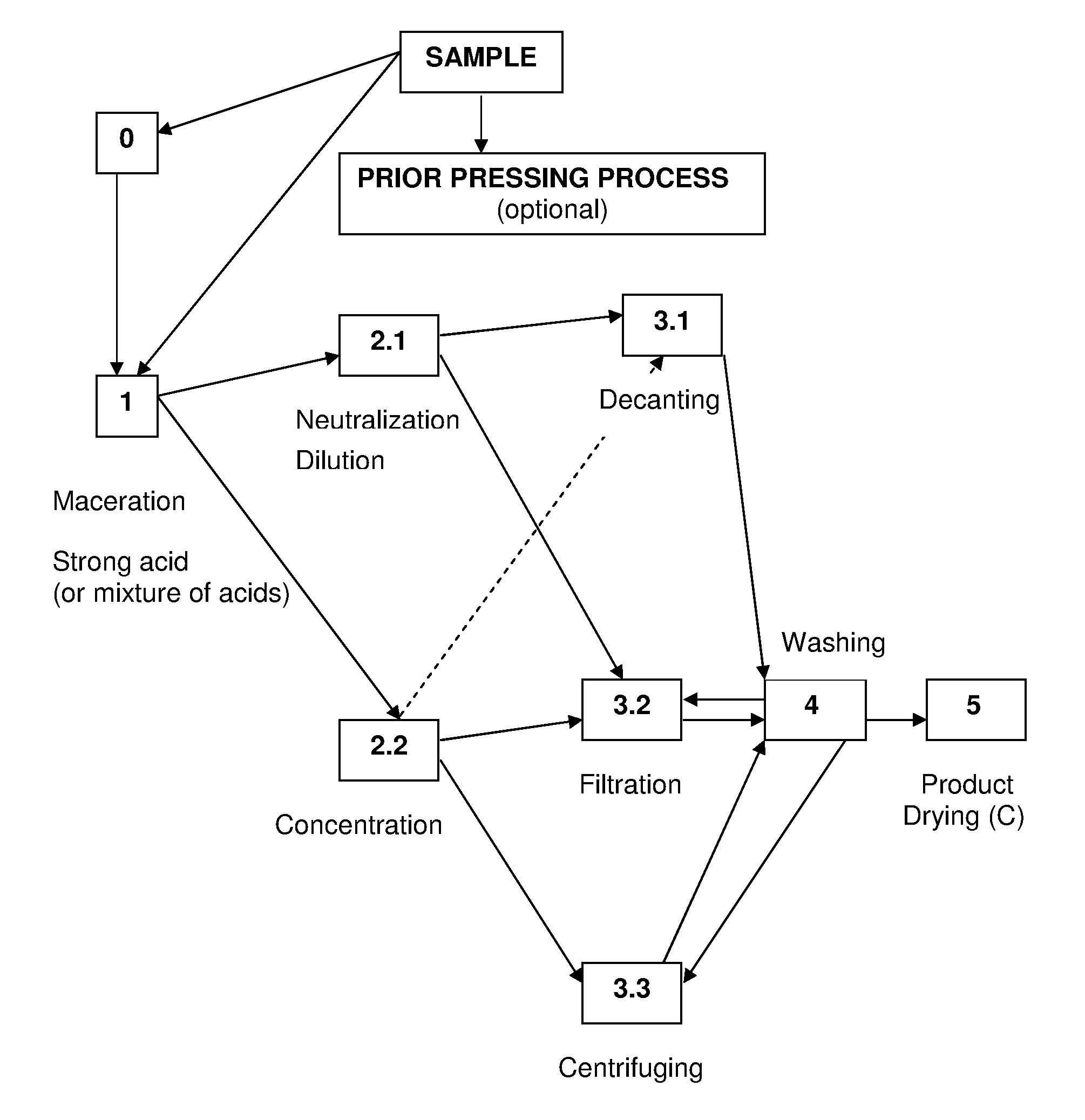
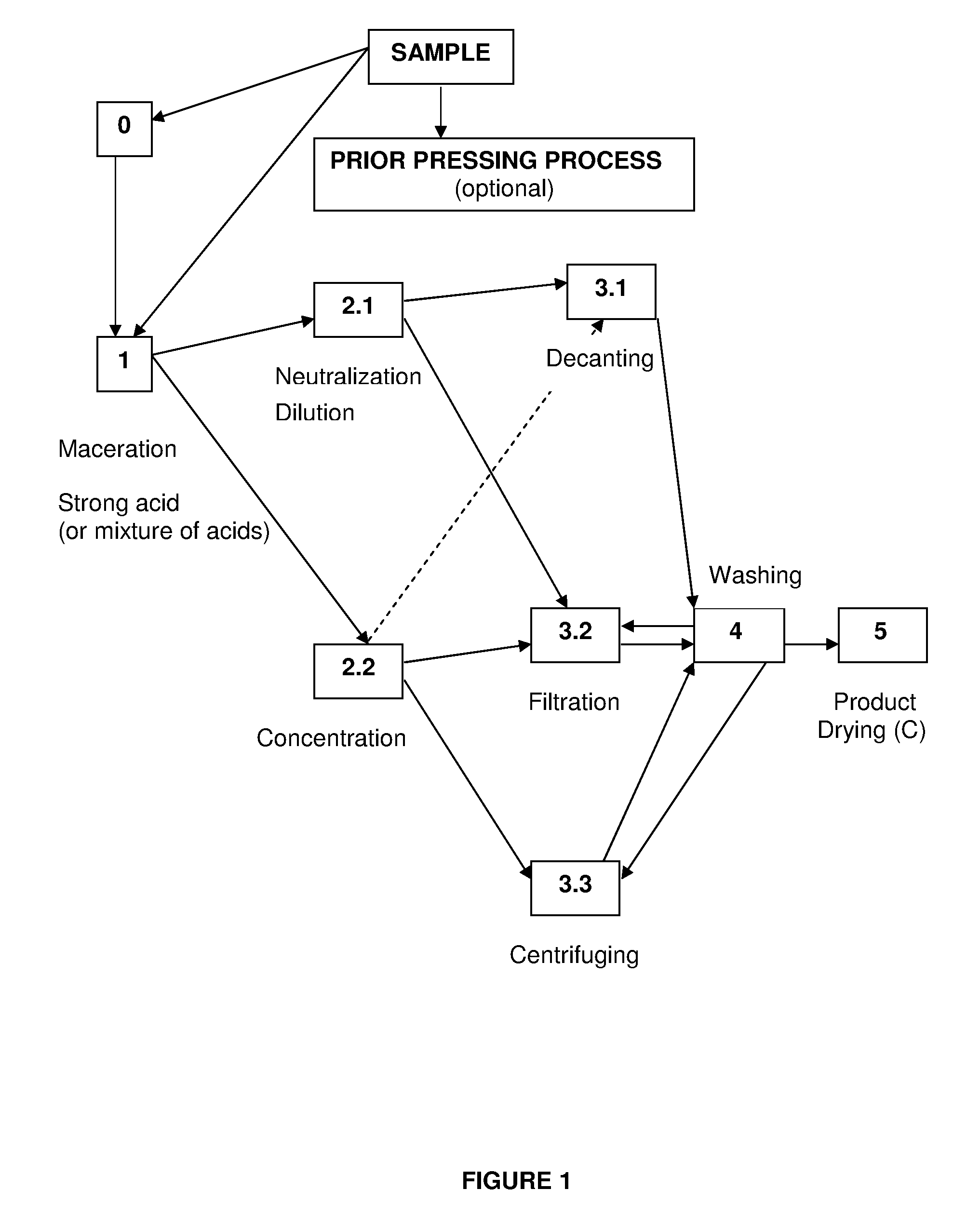
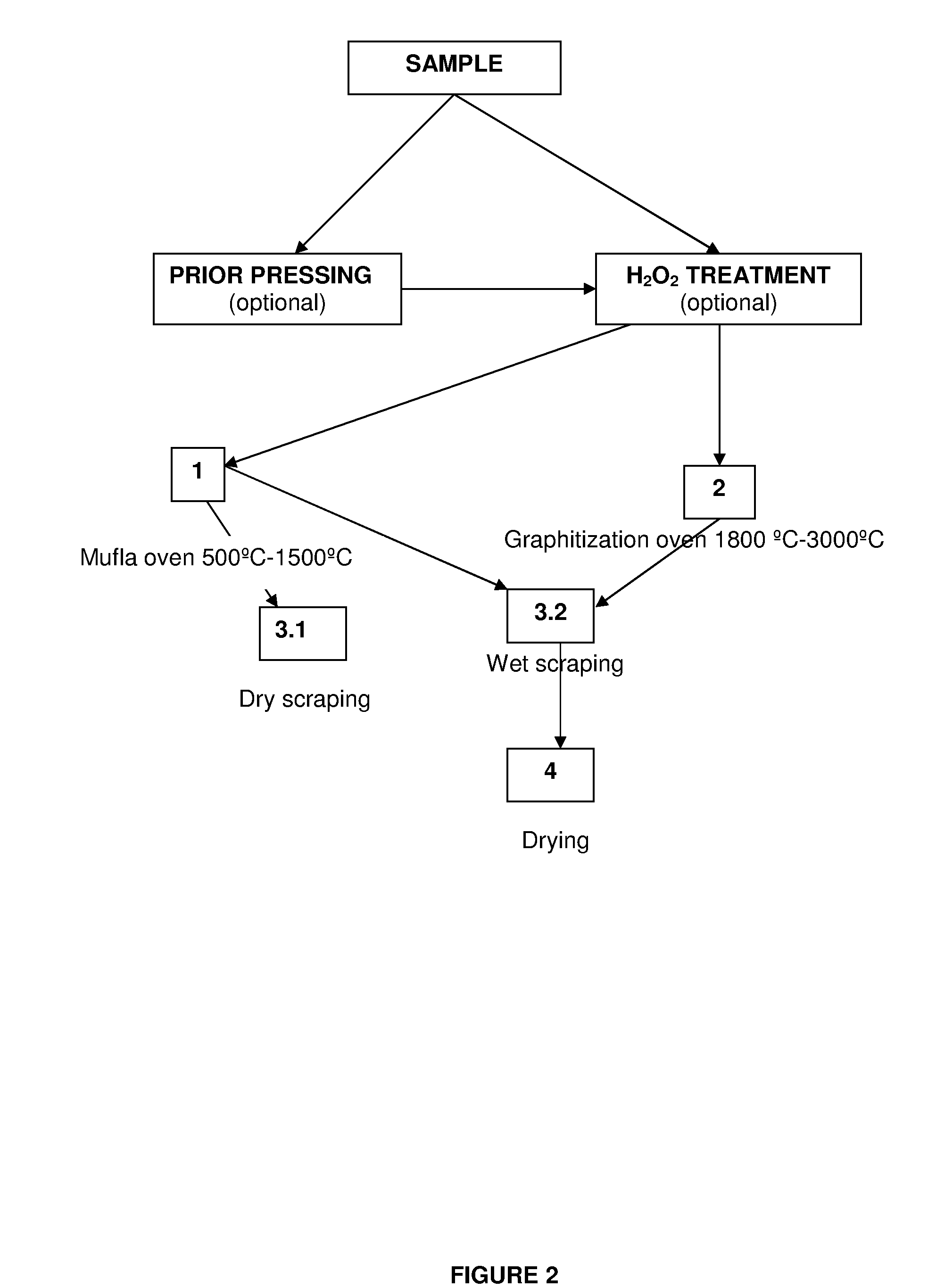
The present invention refers to the provision of a process to manufacture large diamond monocrystals of different colors from carbon obtained from the keratin contained in the ectoderm of many living beings being possible to extract carbon from a human being by cutting a lock of hair and carbonizing it, and then subjecting it to a high pressure high temperature process.
Owner:INST DE MONOCRISTALES
System for inducing nerve stem cell differentiation and inducing method thereof
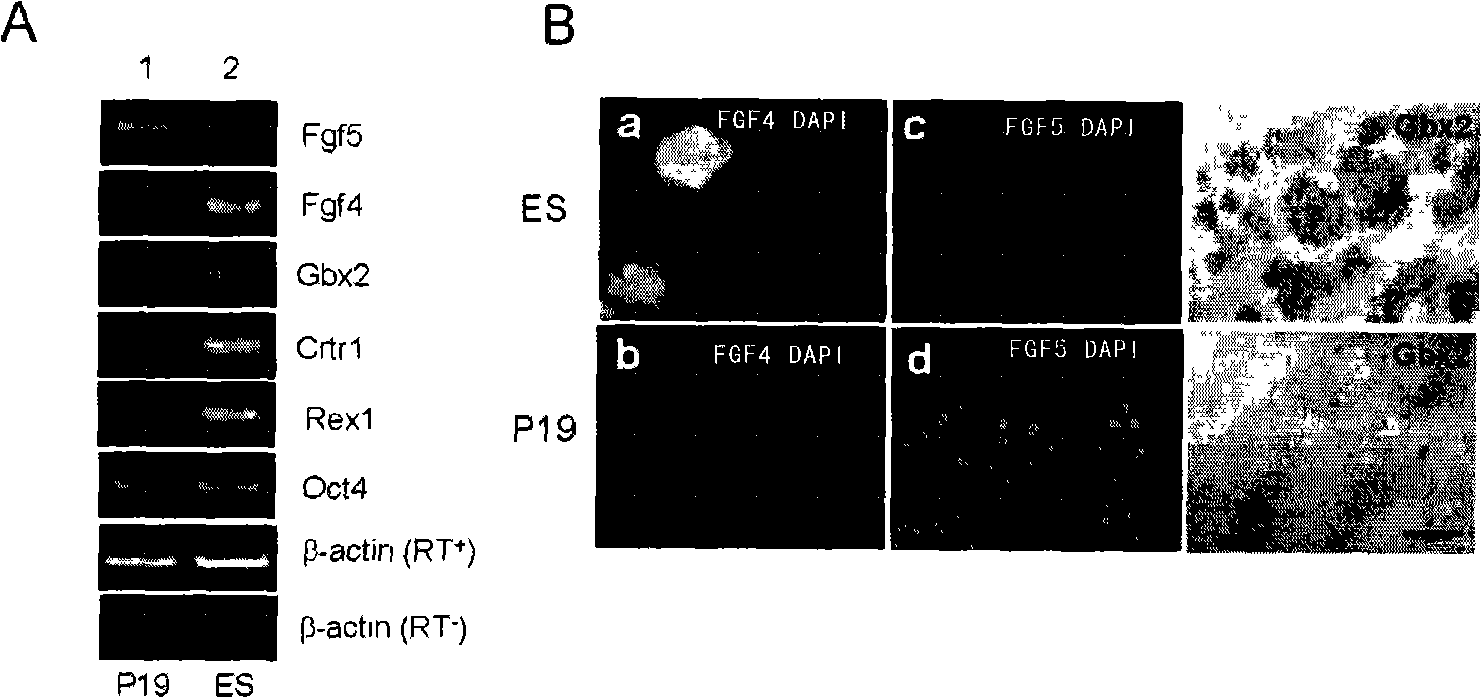
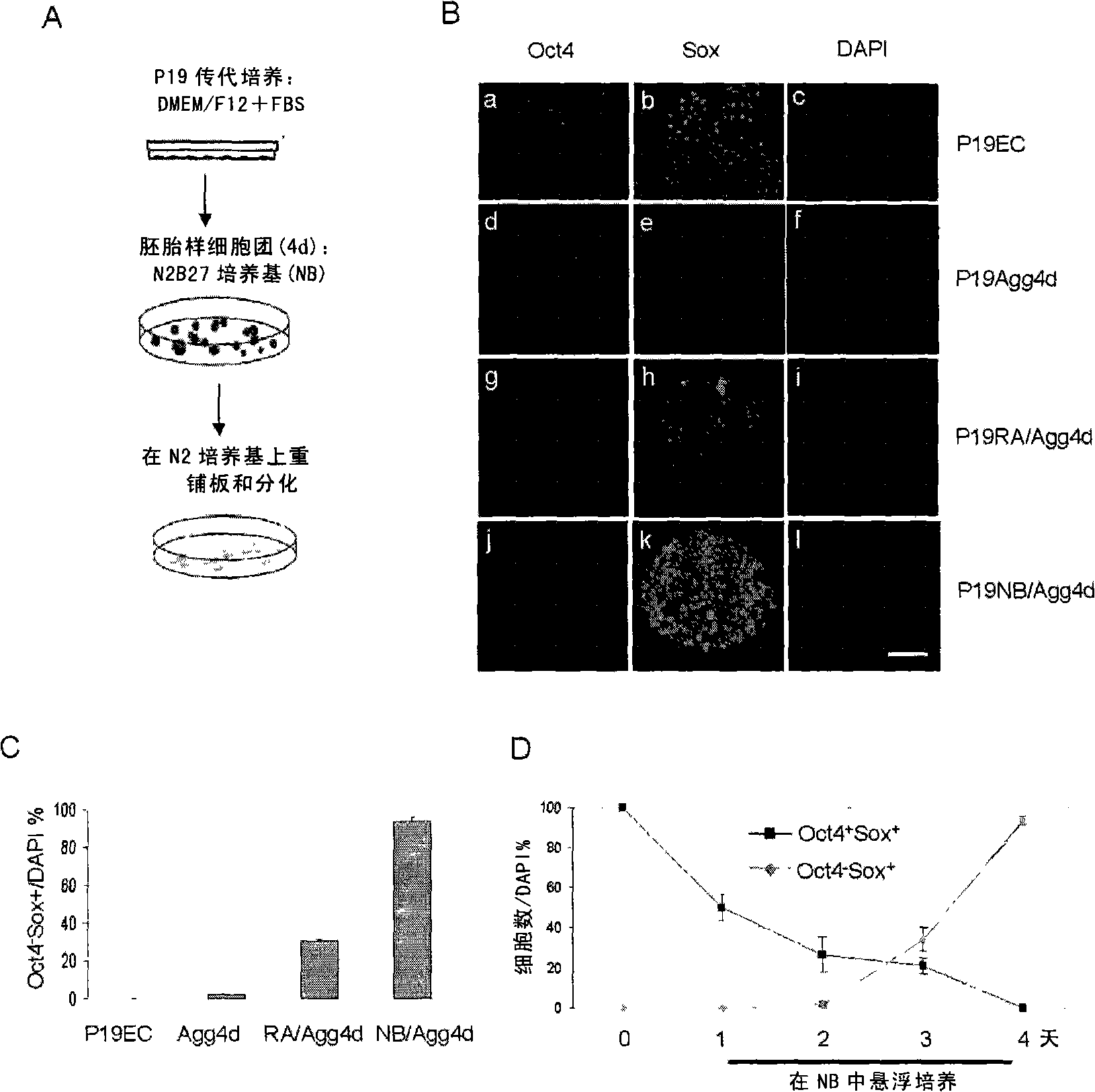
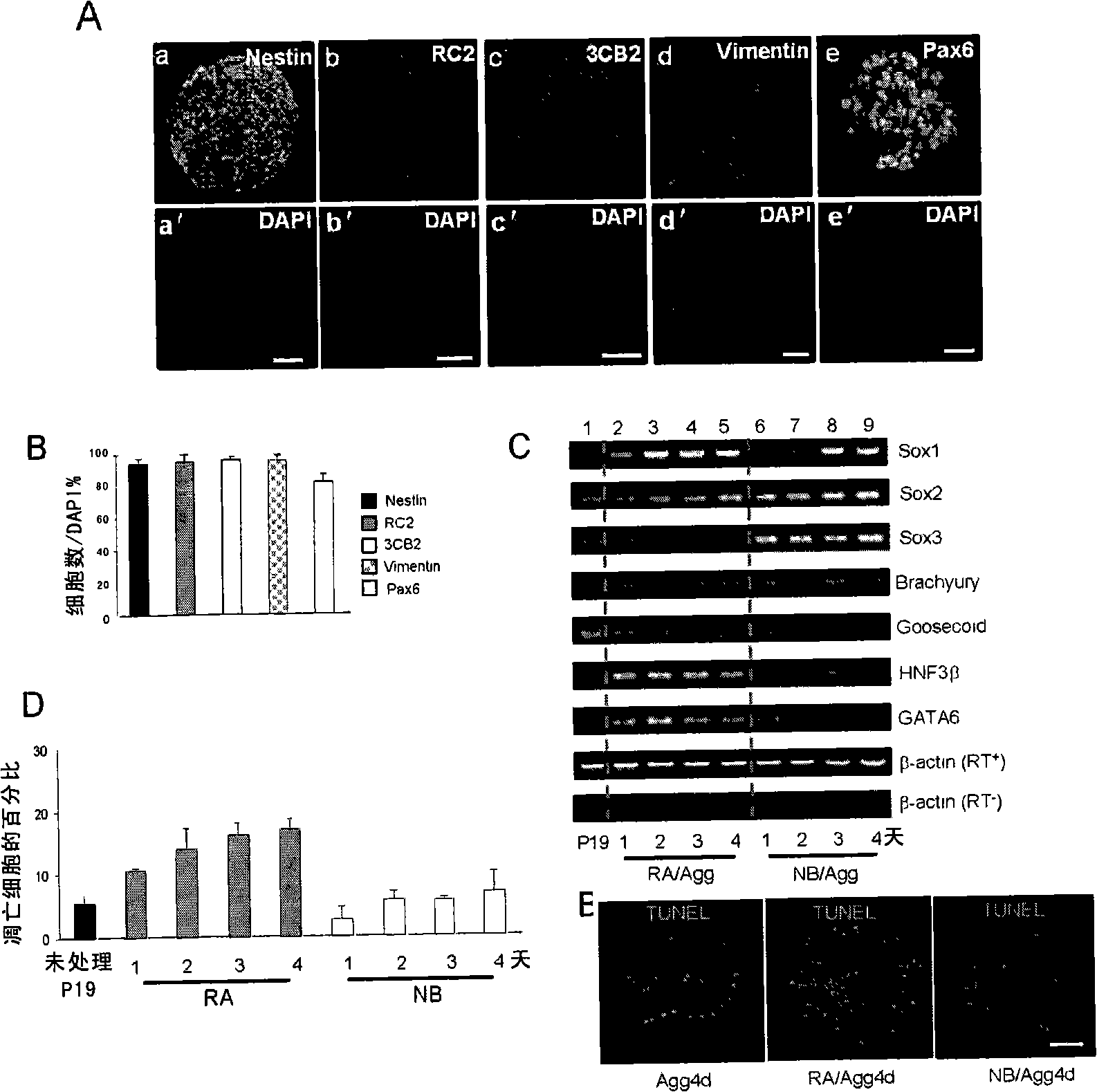
The invention discloses a method for preparing neural stem cells, which comprises a step of inductively culturing P19 cells in N2B27 culture medium to obtain a cell group containing neural stem cells above 94%. The method can culture the P19 cells in an environment without blood serum and retinoic acid, thus suppressing the interference of the blood serum with complex components and preventing the obtained neural stem cells from being transformed posteriorly by retinoic acid. Moreover, the method can directly transform pluripotent stem cells to neutral stem cells without resulting in selective cell apoptosis. The neutral stem cells obtained by the invention have anterior neutral plate characteristics and totipotency, and can well simulate the neurogenesis process in body. Accordingly, the neural stem cells can be used as the research model for analyzing neural induction and neural differentiation process from epiblast to neuroderm, thus providing an ideal path for researching development of embryo after nidation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
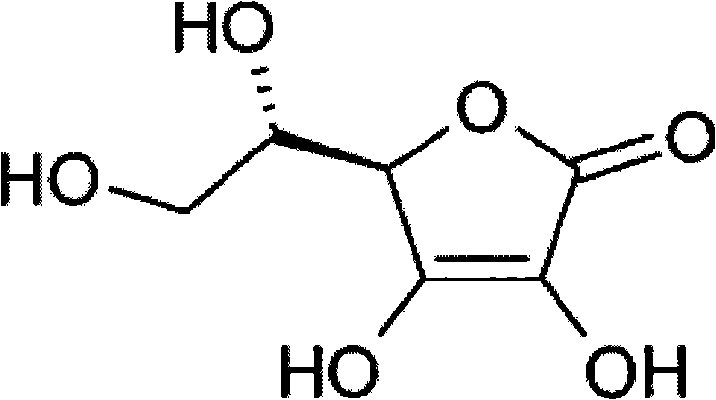
Phenylalanine-derived chiral supramolecular hydrogel and application of phenylalanine-derived chiral supramolecular hydrogel
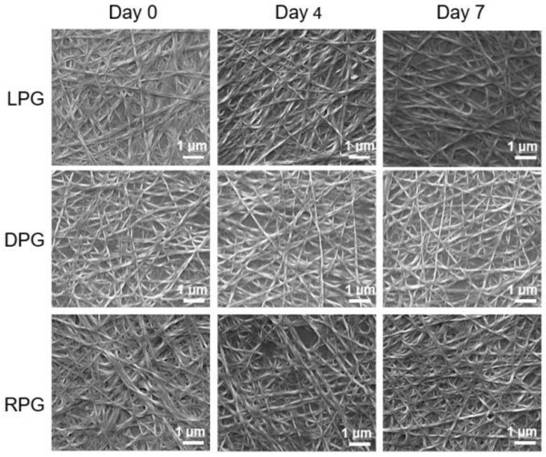
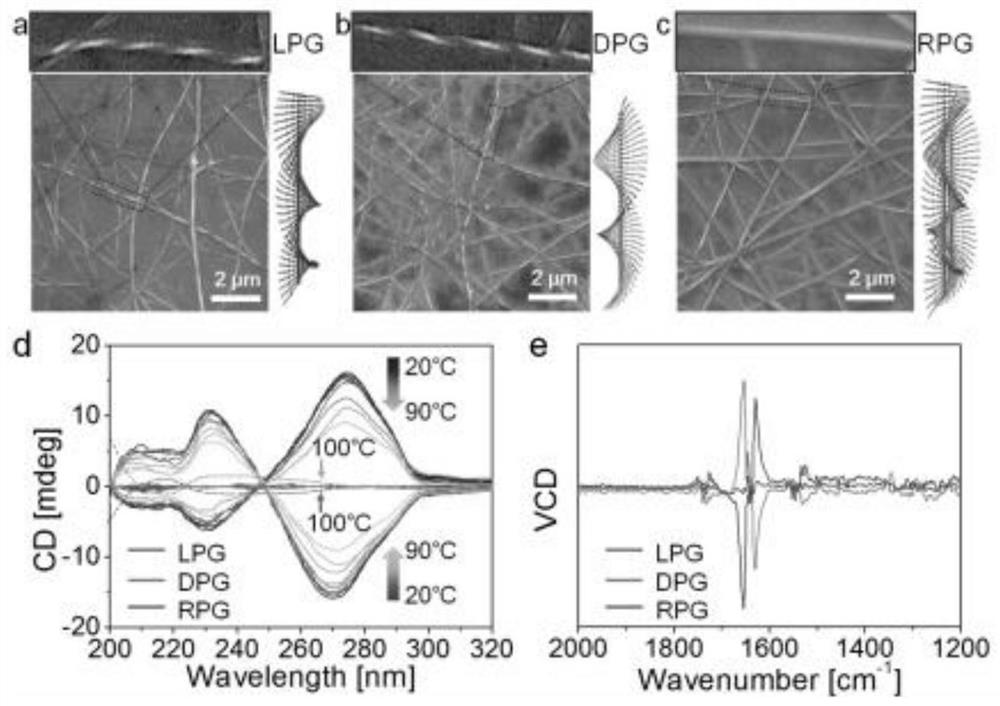
InactiveCN111729622AThere are no defects such as slow transformationEasy to dryOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsNanofiberFiber diameter
The invention discloses phenylalanine-derived chiral supramolecular hydrogel and application thereof, wherein the hydrogel forms a three-dimensional network through physical fiber winding, and the fiber aperture of the hydrogel is about 10 microns. The nanofiber in the LPG gel is in a left-handed spiral shape, and the nanofiber in the DPG gel is in a right-handed spiral shape, and the left and right spiral nanofibers have the same fiber diameter (50 + / - 10 nm) and screw pitch (480 + / - 40 nm). The phenylalanine-derived chiral supramolecular hydrogel is applied to the fields of ophthalmology andneuroscience, and is also applied to stem cells (such as retinal stem cells, neural stem cells and the like) derived from ectoderm.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Multipotent adult stem cells having an ability of oct4 expression derived from umbilical cord blood and method for preparing the same
InactiveUS20090305413A1Negative immunological responseBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsGerm layerDisease
The present invention relates to multipotent adult stem cells expressing Oct4, derived from umbilical cord blood (UCB) and also these cell are expressing CD29, CD31, CD44, simultaneously, a method for preparing the same, and more specifically to multipotent adult stem cells which are obtained by culturing umbilical cord blood-derived monocytes in a medium containing bFGF (basic fibroblast growth factor) and human serum or plasma. In addition, multipotent adult stem cells expressing Oct-4 from UCB are morphologically spindle or round shaped cells Although the stem cells according to the present invention are adult stem cells, they are multipotent and capable of differentiating into ectodermal-, messodermal-, endodermal-originated tissue or cells including osteogenic cells or nerve cells etc, thus they can be effectively used in the treatment of intractable diseases and incurable diseases.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Primate embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050158854A1High nucleus/cytoplasm ratioNervous disorderMetabolism disorderGerm layerSurface marker
A purified preparation of primate embryonic stem cells is disclosed. This preparation is characterized by the following cell surface markers: SSEA-1 (−); SSEA-4 (+); TRA-1-60 (+); TRA-1-81 (+); and alkaline phosphatase (+). In a particularly advantageous embodiment, the cells of the preparation are human embryonic stem cells, have normal karyotypes, and continue to proliferate in an undifferentiated state after continuous culture for eleven months. The embryonic stem cell lines also retain the ability, throughout the culture, to form trophoblast and to differentiate into all tissues derived from all three embryonic germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm). A method for isolating a primate embryonic stem cell line is also disclosed.
Owner:THOMSON
Materials and methods for generating pluripotent stem cells
ActiveCN102725399AEasy to operateLow costNervous disorderEpidermal cells/skin cellsGerm layerEndomesoderm
A method of reprogramming a somatic cell to produce an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell which is capable of differentiating into somatic cells derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm is provided. The aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells and methods of using iPS cell are also provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI ICELL BIOTECH +5
Method for inducing human embryonic stem cells to differentiate to neuroderm
ActiveCN104195102AUniform sizeMaintain high density cultureEmbryonic cellsVitamin CDirected differentiation
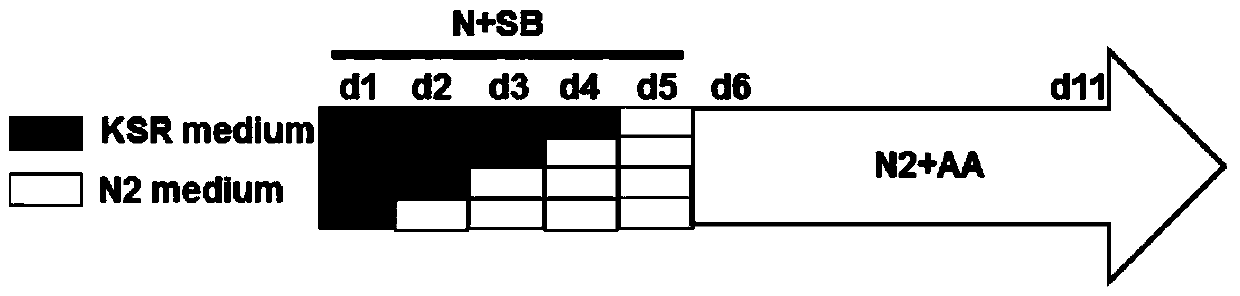
The invention discloses a method for inducing human embryonic stem cells to differentiate to neuroderm. The method comprises the following steps that H9 cells are kept to passage in a cell cluster state, wherein the cell clusters are uniform in size, and high-density culture of the cell clusters can be kept; based on this, two inducing factors of SB431542 and NOGGIN are introduced, a knock out serumreplacer (KSR) culture medium and an N2 culture medium which are determined according to chemical components are used in matched manner according to different proportions at different culture times; and ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is added into the N2 culture medium at induced differentiation later period, so that HESC can be induced within shorter time to differentiate directionally to form an NE cell for expressing a PAX6 protein.
Owner:ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
Kit for predicting birth safety before people-assisted reproduction blastosphere implantation
ActiveCN104561309AReduce the possibilityReduced likelihood of perinatal complicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm layerBlastosphere
The invention discloses a kit for predicting birth safety before people-assisted reproduction blastosphere implantation. The kit comprises products, wherein the products are used for detecting the expression quantity of 97 genes shown in the table 5 and from a cell of a trophectoderm of a people-assisted reproduction blastosphere. If the expression quantity of the 97 genes from the cell of the trophectoderm of a people-assisted reproduction blastosphere meets the evaluation standard, the people-assisted reproduction blastosphere can develop normally and a pregnant woman can have eutocia; otherwise, the people-assisted reproduction blastosphere cannot develop normally, the possibility of affecting baby health and occurring perinatal complication is increased along with the increase of the number of the genes not meeting the evaluation standard, and the transplantation strategy and decision-making are further affected. With adoption of the kit, the possibility of reducing the perinatal complication and the number of babies suffering from illnesses is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING JISHUITAN HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com