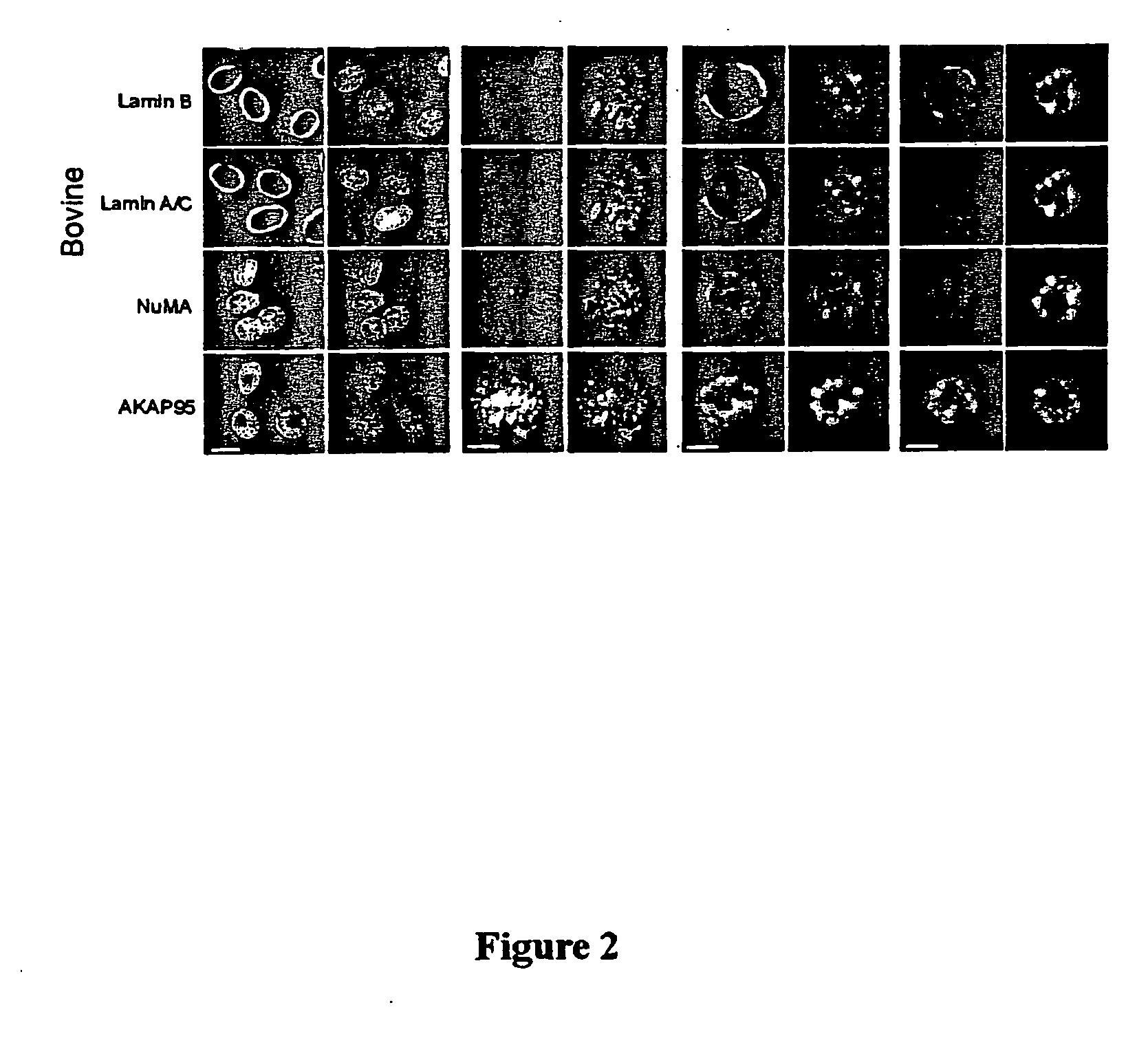
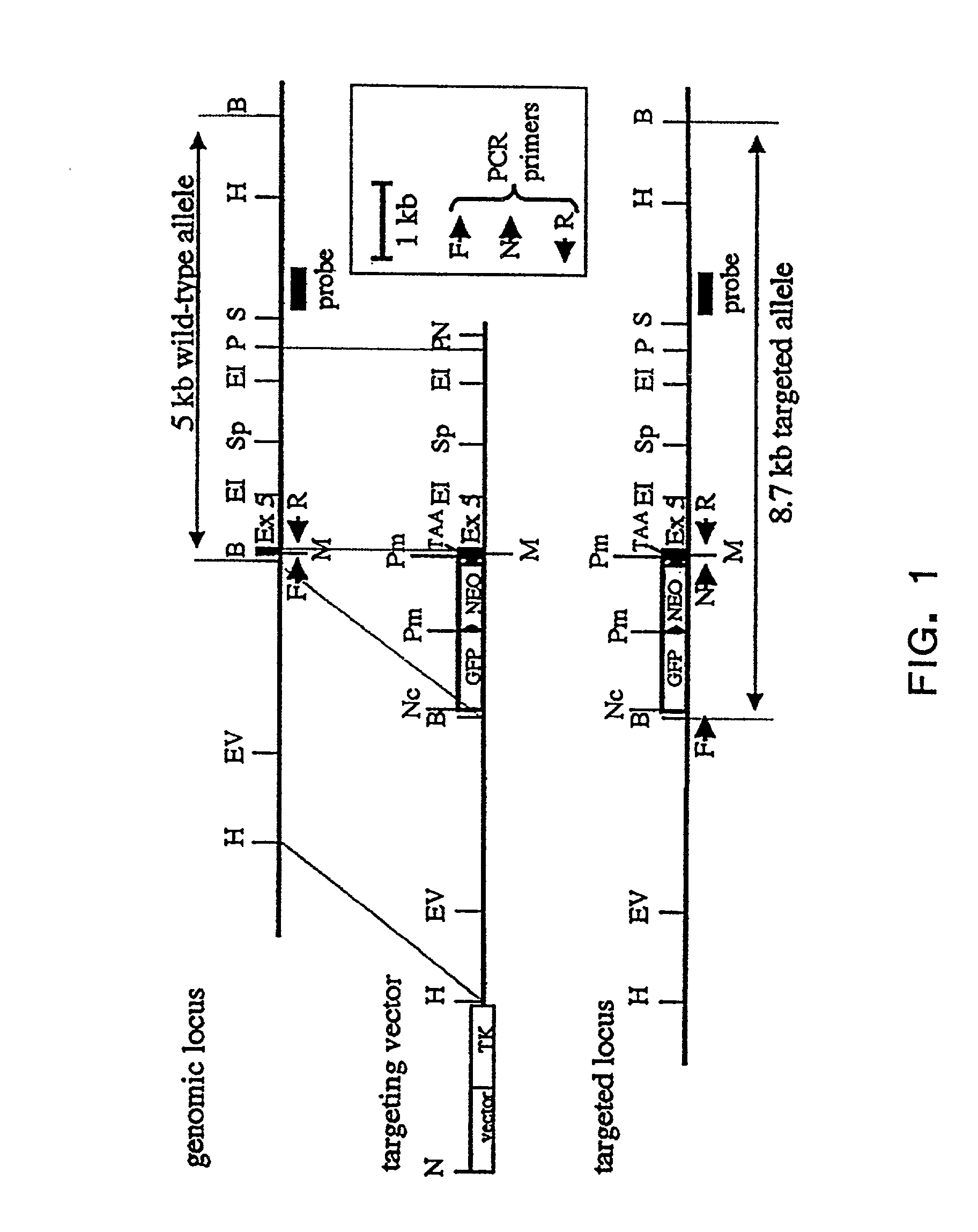
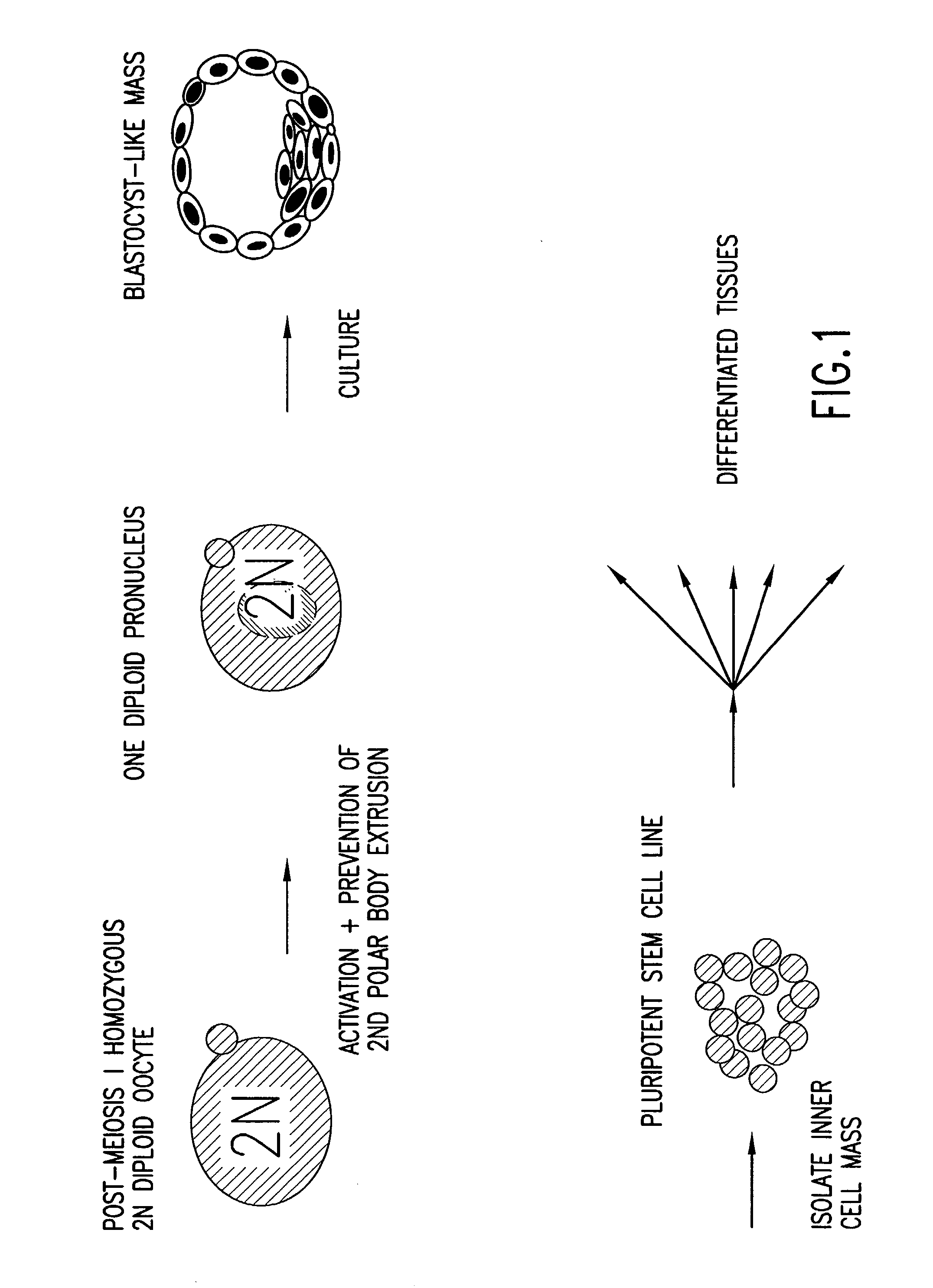
Patents
Literature
383results about "New breed animal cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
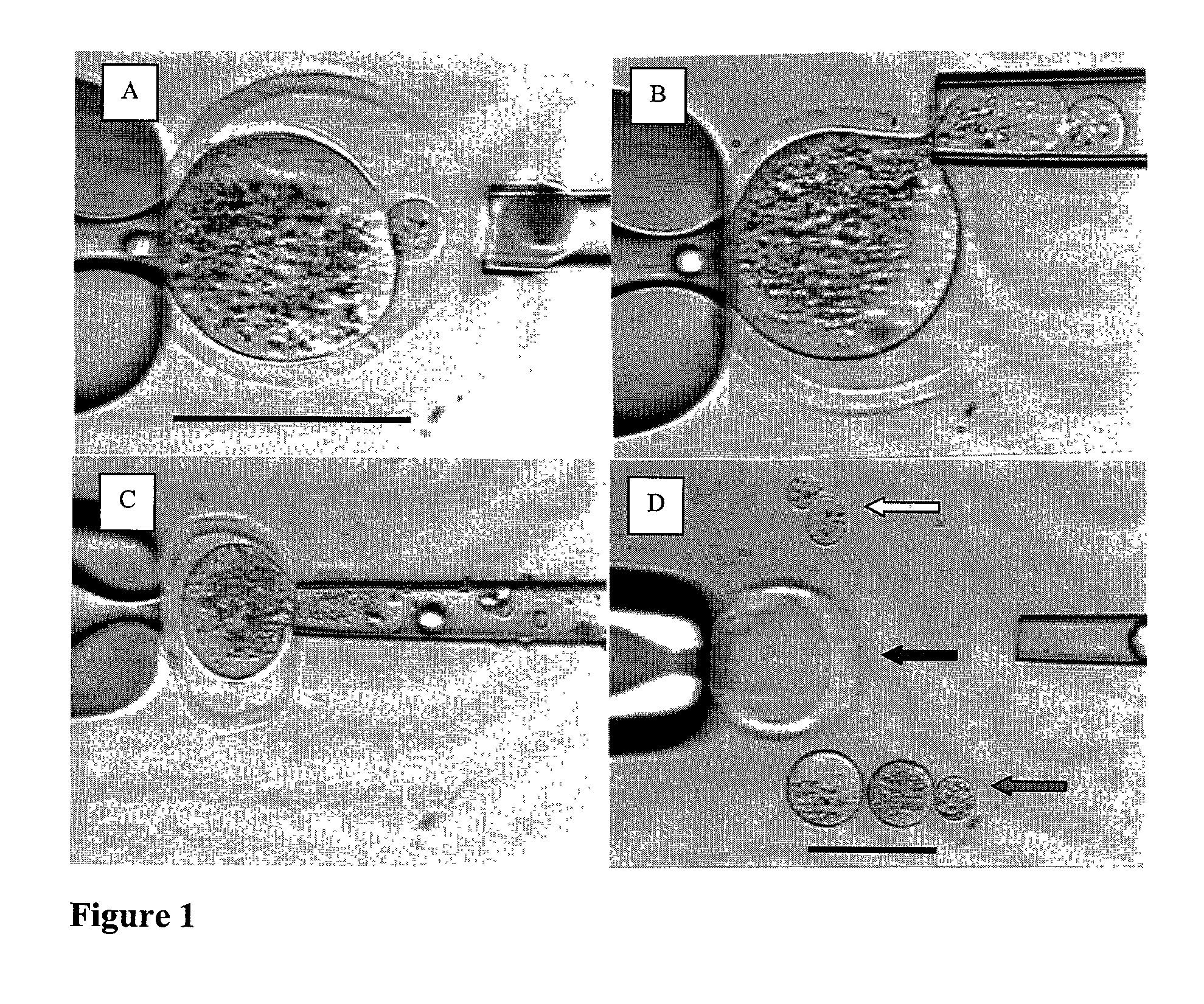
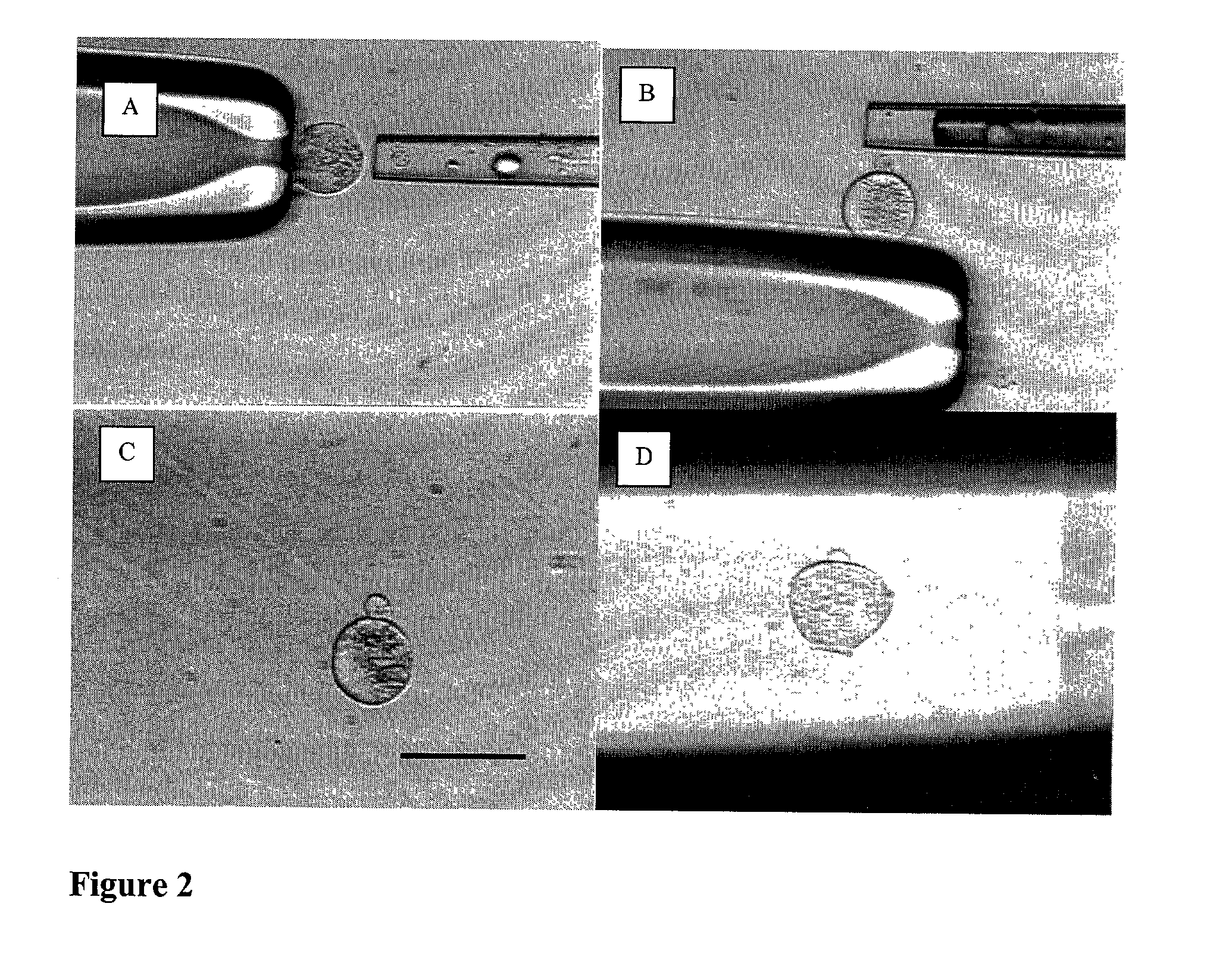
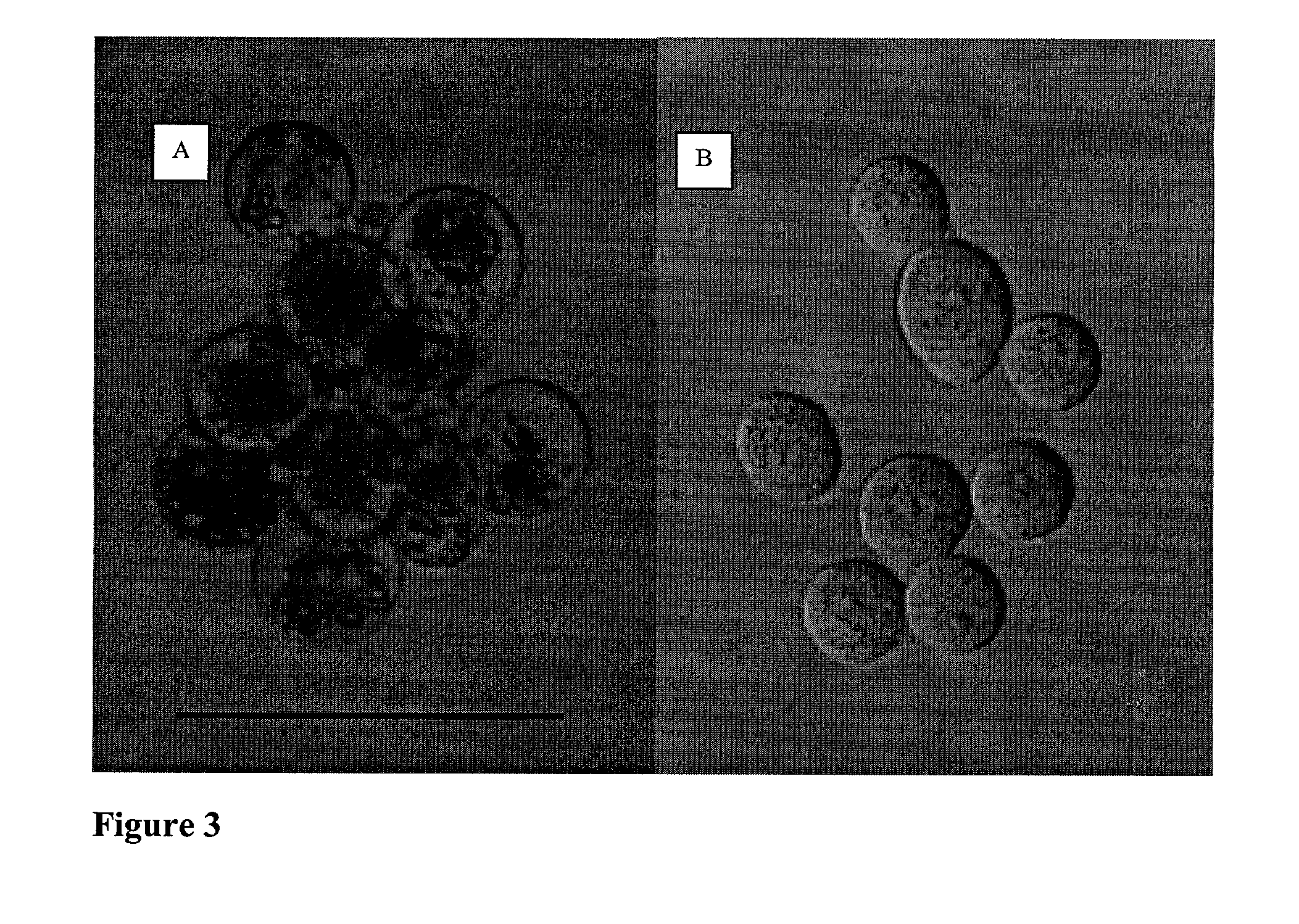
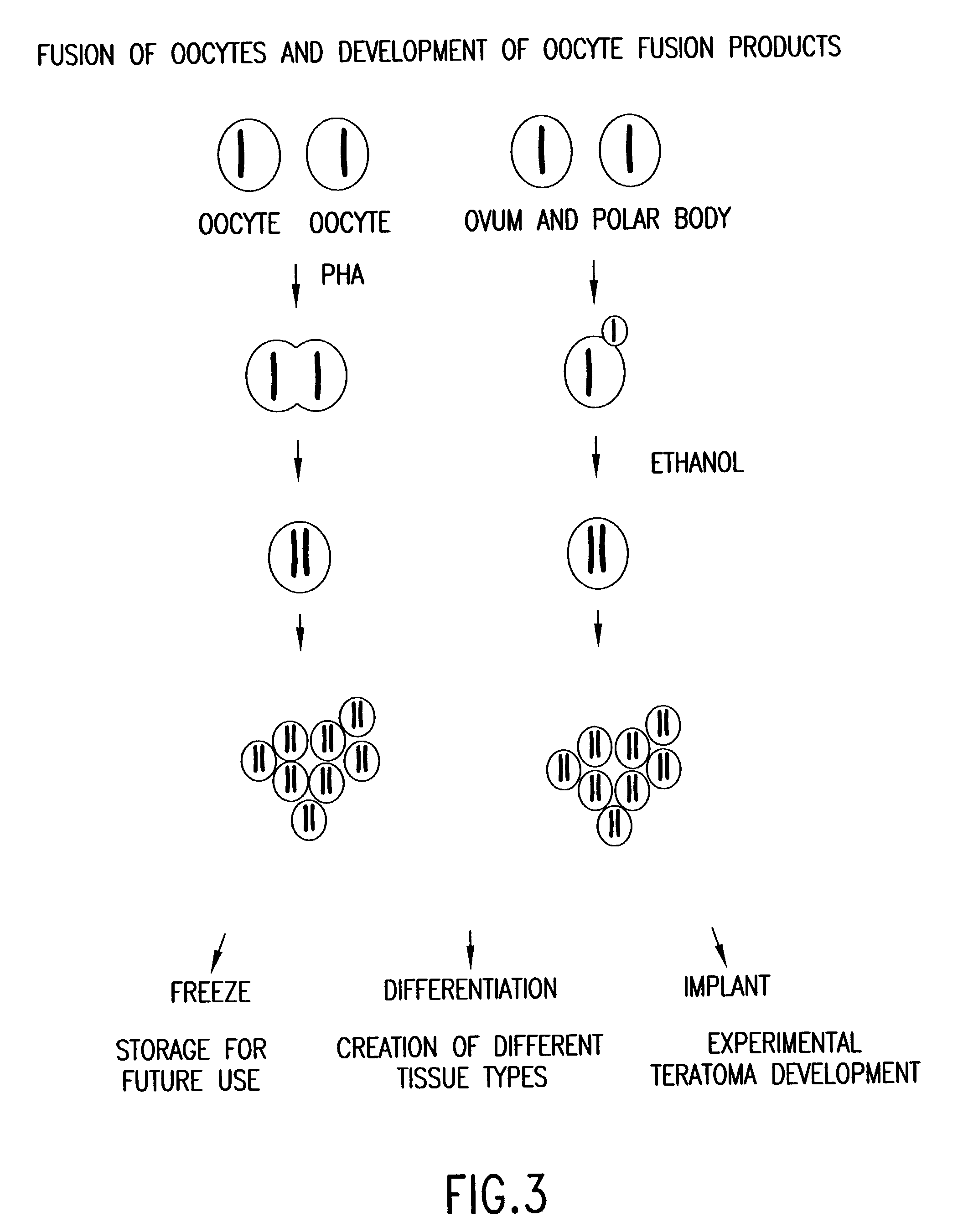
CICM cells and non-human mammalian embryos prepared by nuclear transfer of a proliferating differentiated cell or its nucleus
InactiveUS6235970B1Simple procedureSimplifying and facilitating procedureNervous disorderMuscular disorderPresent methodNuclear transfer
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of the same species as the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring, and for production of isogenic CICM cells, including human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic mammalian embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST
Pluripotent stem cells derived without the use of embryos or fetal tissue
InactiveUS20030113910A1New breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Owner:STEMA
Gynogenetic or androgenetic production of pluripotent cells and cell lines, and use thereof to produce differentiated cells and tissues
InactiveUS20040014206A1Rejection is prevented and reducedEliminate, orMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPrimateEmbryo
Methods for obtaining pluripotent (embryonic stem) cells from parthenogenetic embryos, especially primates, are provided. These cells are useful for producing differentiated cells, tissues and organs, especially human and non-human primate cells, tissues and organs.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Cloning pigs using donor nuclei from non-quiescent differentiated cells
InactiveUS6235969B1Superior genotypes of pigsSpeed up genetic progressNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyPresent method
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated pig cell nuclei into enucleated pig oocytes is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic pig embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
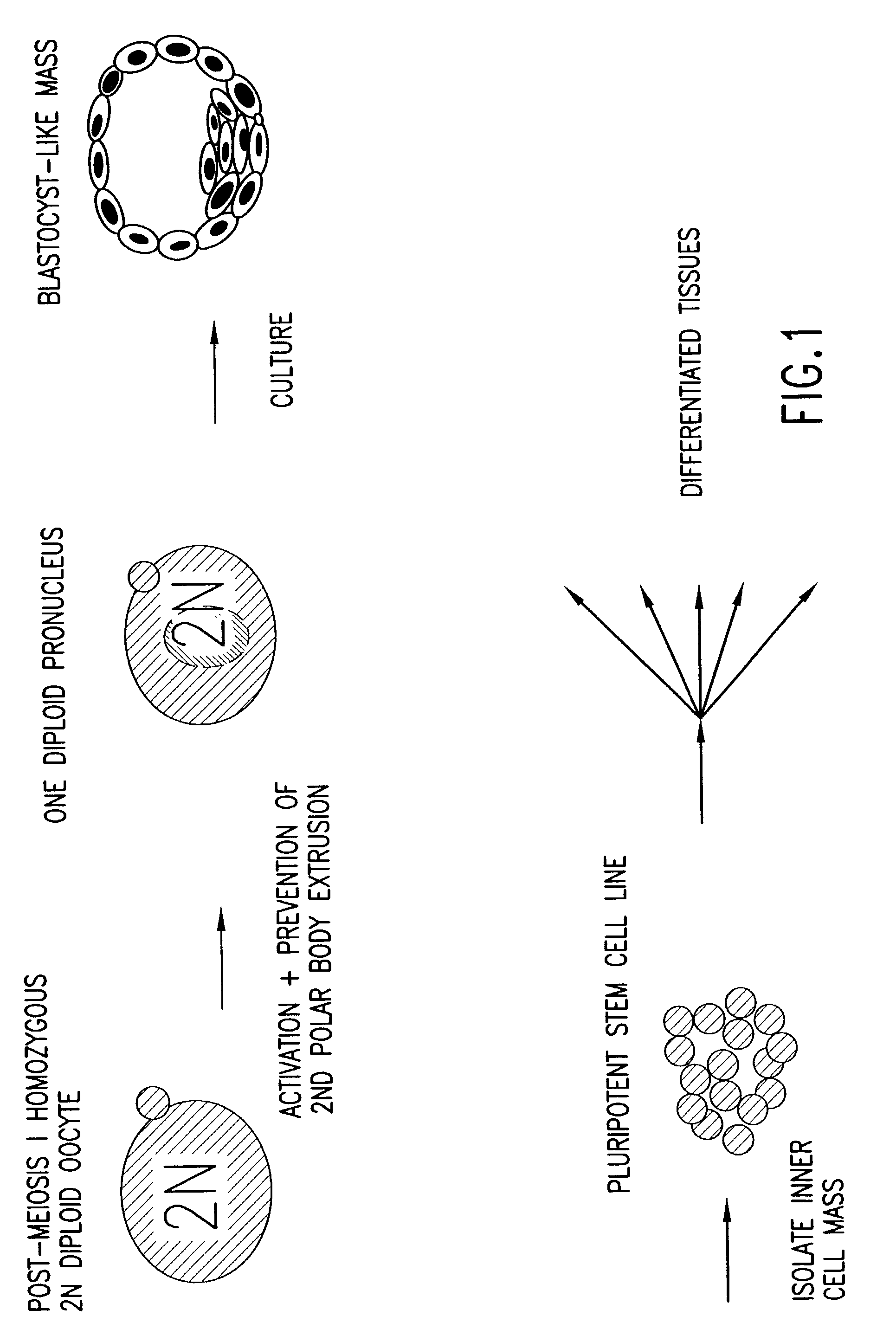
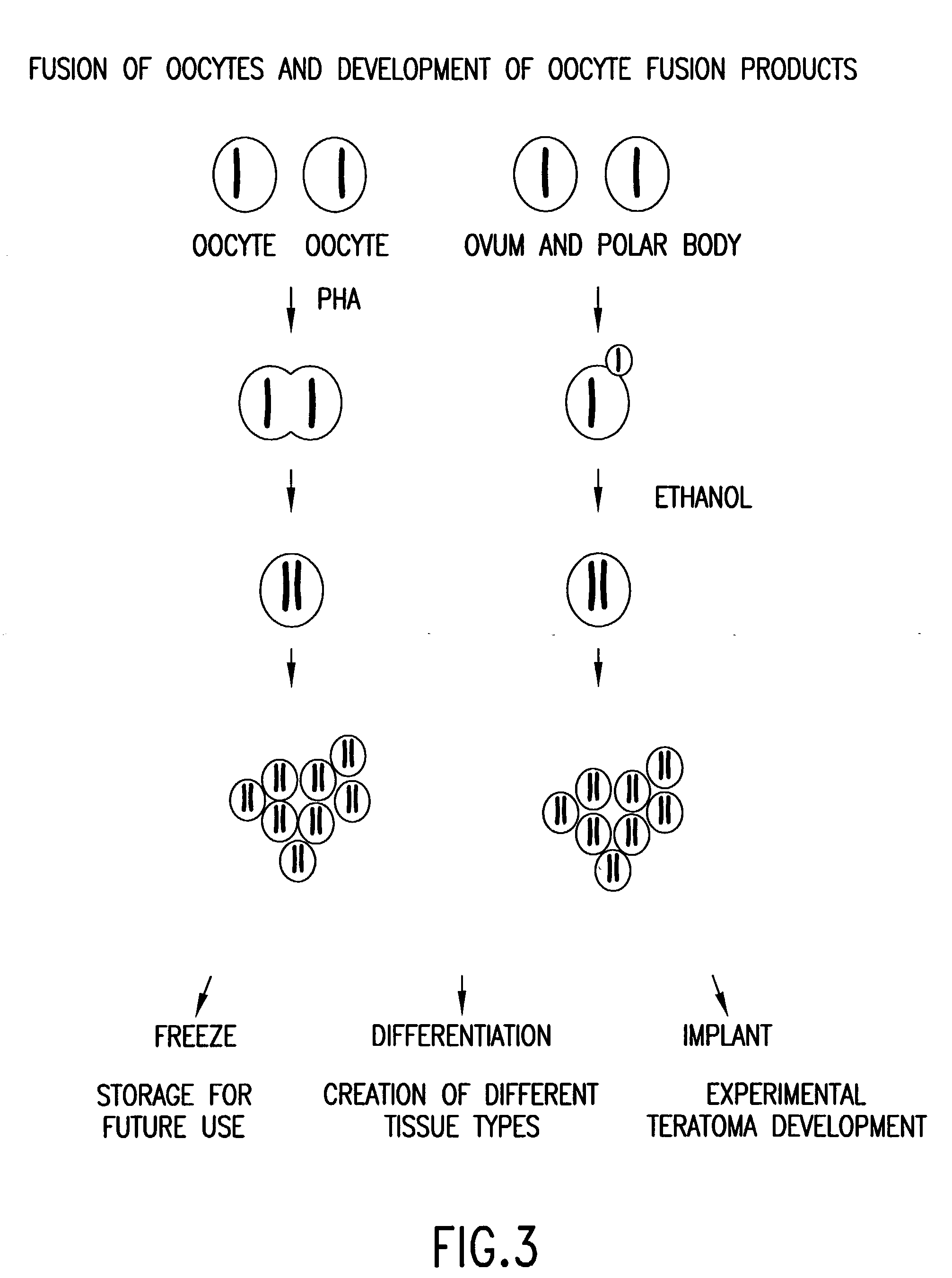
Isolated homozygous stem cells, differentiated cells derived therefrom, and materials and methods for making and using same
The present invention discloses and describes pluripotent homozygous stem (HS) cells, and methods and materials for making same. The present invention also provides methods for differentiation of HS cells into progenitor (multipotent) cells or other desired cells, groups of cells or tissues. Further, the applications of the HS cells disclosed herein, include (but are not limited to) the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases (for example, genetic diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, endocrine-related disorders and cancer), traumatic injuries, cosmetic or therapeutic transplantation, gene therapy and cell replacement therapy.
Owner:STEMRON
Cloning using donor nuclei from a non-quiesecent somatic cells
InactiveUS6215041B1Superior genotypes of cowsSpeed up genetic progressNew breed animal cellsPeptide/protein ingredientsEmbryoSomatic cell
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF A PUBLIC INSTION OF HIGHER EDUCATION OF THE COMMONWEALTH OF MASSACHUSETTS AS REPRESENTED BY ITS AMHERST CAMPUS
Method of rapid production of hybridomas expressing monoclonal antibodies on the cell surface
The present invention relates to genetically altered hybridomas, myelomas and B cells. The invention also relates to utilizing genetically altered hybridomas, myelomas and B cells in methods of making monoclonal antibodies. The present invention also provides populations of hybridomas and B cells that can be utilized to make a monoclonal antibody of interest.
Owner:ABEOME CORP +1
Assay utilizing multipotent adult stem cells
The present invention relates generally to mammalian multipotent adult stem cells (MASC), and more specifically to methods for obtaining, maintaining and differentiating MASC to cells of multiple tissue types. Uses of MASC in the therapeutic treatment of disease are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
Genetic characterization and prognostic significance of cancer stem cells in cancer
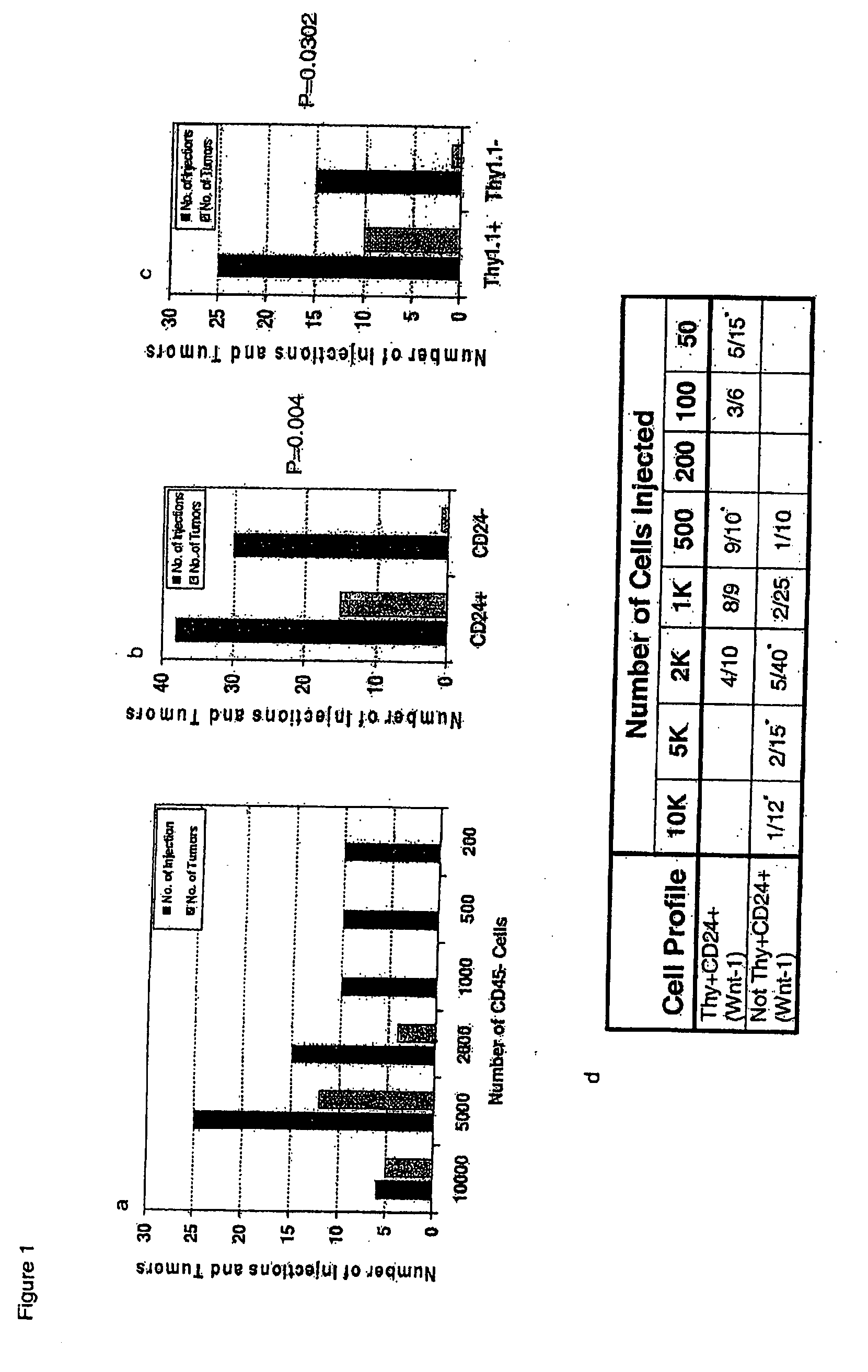
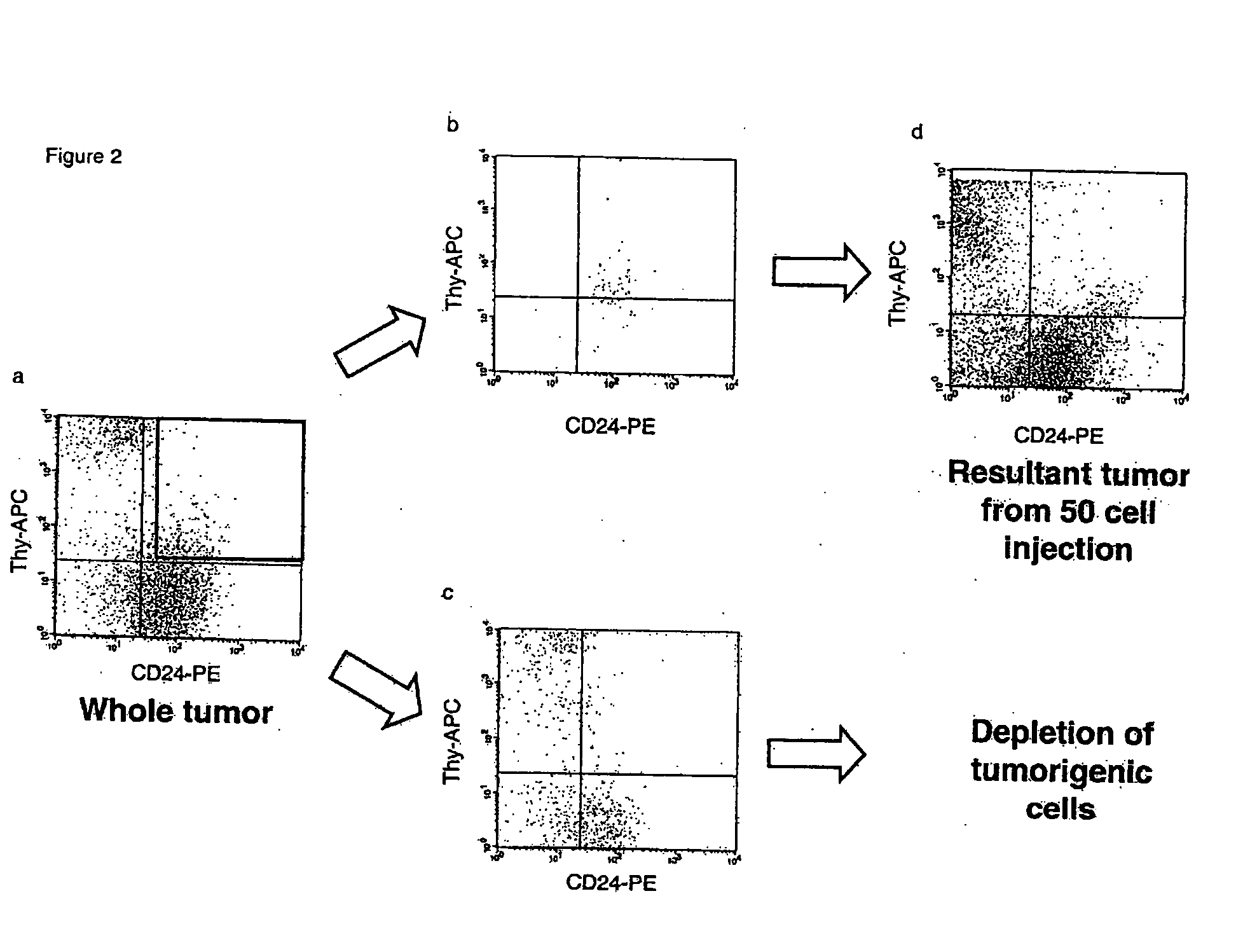
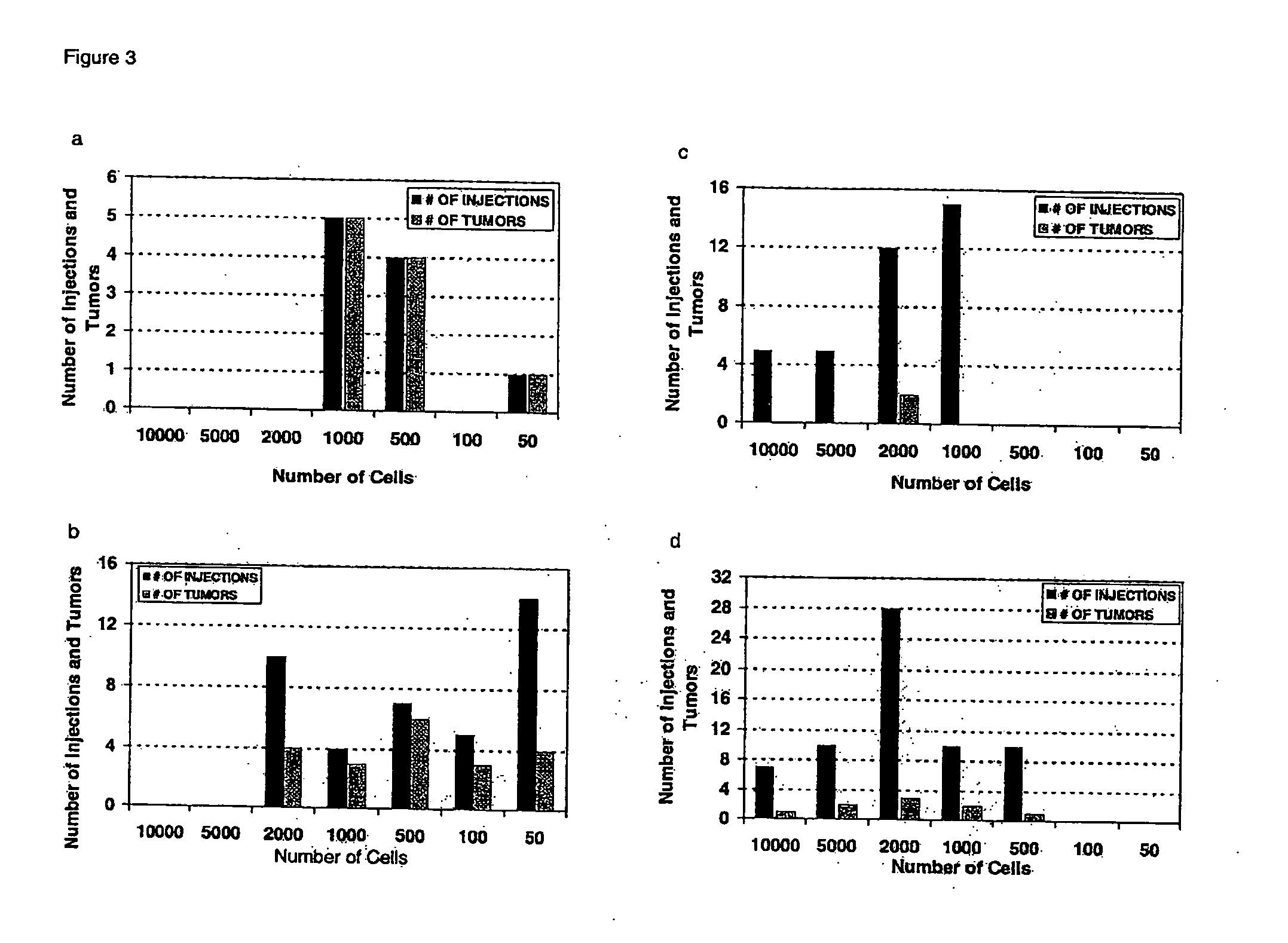
InactiveUS20070220621A1Predictive of survivalReduce spreadNew breed animal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementSolid tumorGene expression
The present invention is related to the identification of cancer stem cells using the MMTV-Wnt-1 transgenic mouse model. These cancer stem cells have a gene expression signature that allows them to be distinguished from their non-tumorigenic counterparts. Moreover, the gene expression pattern can also predict survival in a diverse group of solid tumors.
Owner:CLARKE MICHAEL F +2
Embryonic or stem-like cell lines produced by cross species nuclear transplantation
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor cell nuclei into enucleated oocytes of a species different from the donor cell is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for the production of isogenic embryonic stem cells, in particular human isogenic embryonic or stem cells. These embryonic or stem-like cells are useful for producing desired differentiated cells and for introduction, removal or modification, of desired genes, e.g., at specific sites of the genome of such cells by homologous recombination. These cells, which may contain a heterologous gene, are especially useful in cell transplantation therapies and for in vitro study of cell differentiation.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Treatment of infertility
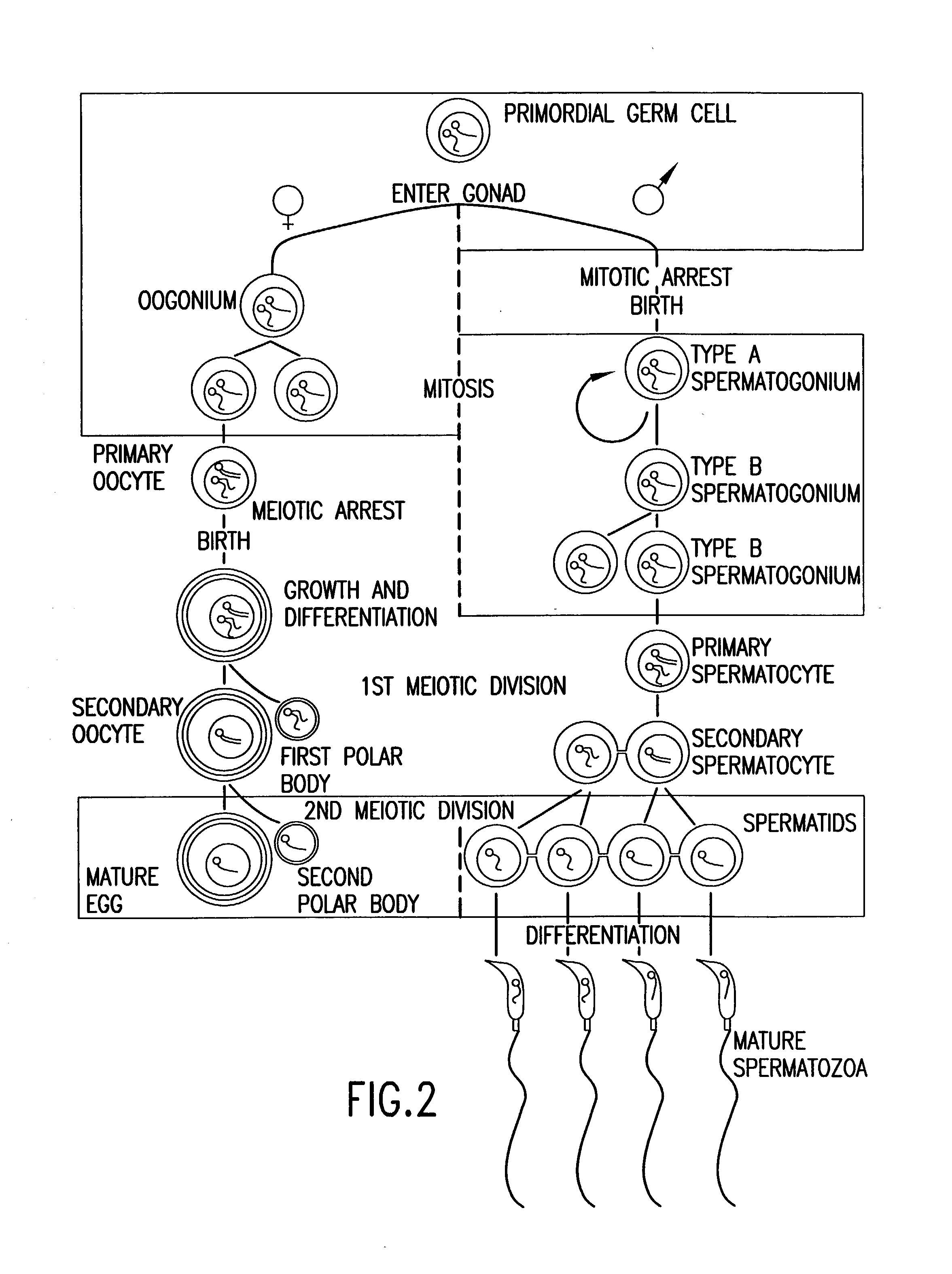
InactiveUS6585982B1Easy to optimizeIVF can be improved substantiallyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMeiosisInfertility
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Stem cell-derived endothelial cells modified to disrupt tumor angiogenesis
InactiveUS20060024280A1Enhance the ability of the endothelial cells to disrupt and inhibit tumor angiogenesisHigh sensitivityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthTumor angiogenesis
The present invention provides cloned, genetically modified, endothelial cells, and the stem cells from which they are derived, which are produced by somatic cell nuclear transfer. The invention further provide novel therapeutic methods in which such cells are administered to a patient with tumors to inhibit and / or disrupt angiogenesis of the tumors, thereby inhibiting tumor growth and killing tumor cells.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Muir-Torre-like syndrome in Fhit deficient mice
InactiveUS20060075511A1Drug screeningNucleic acid vectorParanasal Sinus CarcinomaGastrointestinal cancer
The invention provides nonhuman transgenic animals with a disrupted FHIT gene. The invention further provides transgenic mice in which one or both Fhit alleles have been inactivated. Preferably, the Fhit-deficient mice develop multiple tumors of both visceral and sebaceous origin, similar to those of Muir-Torre familial cancer syndrome. The present invention further relates to the generation of these transgenic mice and their use as model systems to study the effects of carcinogenic agents in promoting clonal expansion of neoplastic cells in cancers, preferably gastrointestinal cancers of which Muir-Torre syndrome is a subset. The invention further relates to testing therapeutic agents for their efficacy in the prevention and treatment of cancer, preferably gastrointestinal cancer.
Owner:CROCE CARLO +1
Therapeutic reprogramming, hybrid stem cells and maturation
InactiveUS20050170506A1Minimal oxidative damageTherapeutic applicationNew breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsCell lineageReprogramming
Therapeutically programmed cells and methods for making such cells are provided. Therapeutically programmed cells are stem cells which have been matured such that they represent either a more differentiated state or a less differentiated state after contact with stimulatory factors. The therapeutically reprogrammed cells are suitable for cellular regenerative therapy and have the potential to differentiate into more committed cell lineages. Additionally, hybrid stem cells suitable for therapeutic reprogramming and cellular regenerative therapy are provided.
Owner:PRIMEGEN BIOTECH LLC
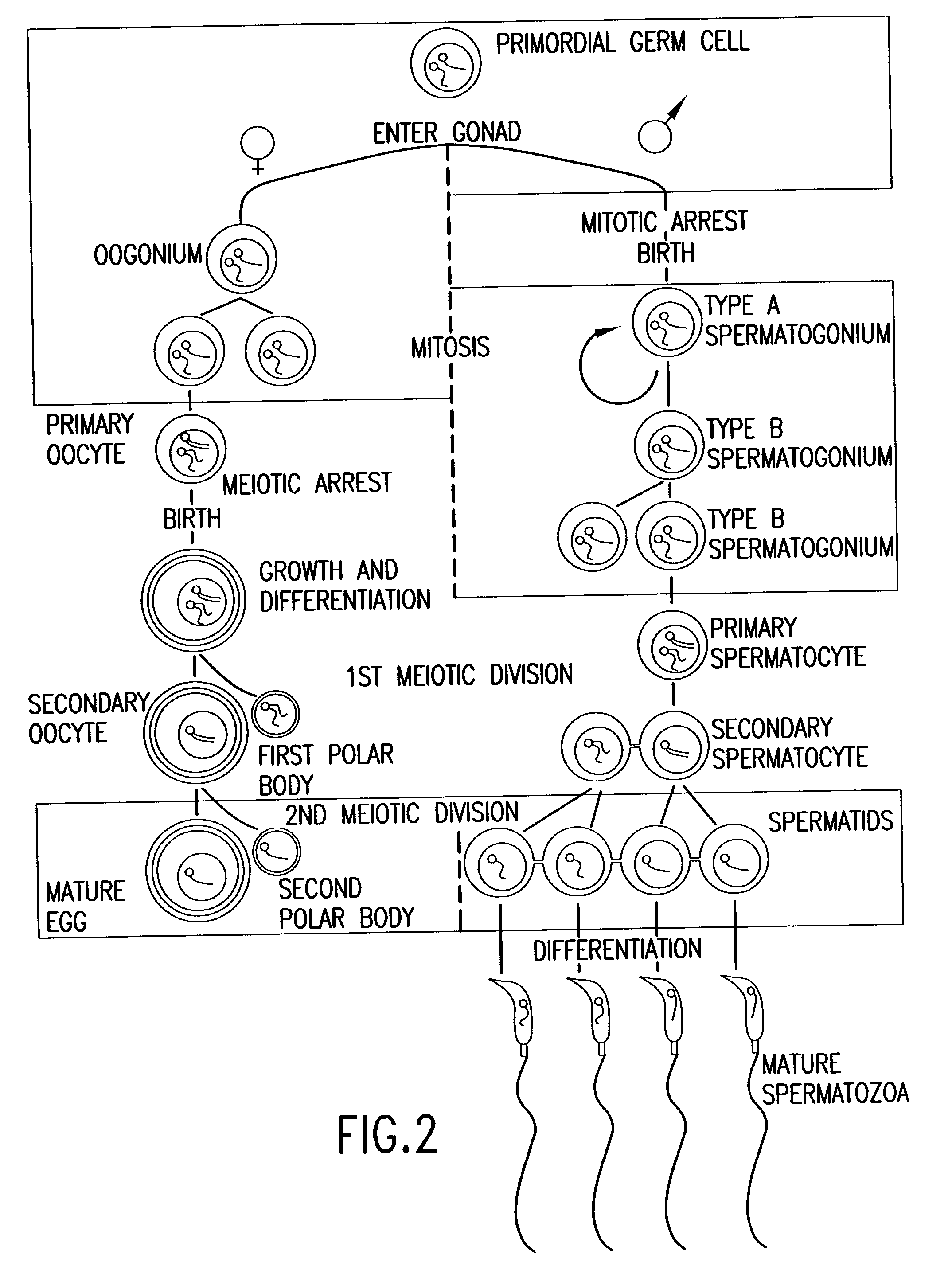
Use of haploid genomes for genetic diagnosis, modification and multiplication
InactiveUS20040146865A1Combination becomes very largeSimple methodNew breed animal cellsGenetically modified cellsNuclear transferEmbryo
Methods for propagating haploid genomes of male or female origina and genetic screening and modification thereof are provided. These haploid genomes may be used to produce haploid embryos, and embryonic stem-like cells and differentiated cells. Also, these haploid genomes and cells containing, may be used as nuclear transfer donors to produce diploid nuclear transfer units. These diploid NT units e.g., human NT units, may be used to obtain pluripotent cells and differentiated cells and tissues.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
Humanized t cell co-receptor mice
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express chimeric human / non-human T cell co-receptor polypeptides (e.g., CD4, CD8α, CD8β), as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the same. Also provided are constructs for making said genetically modified animals and methods of making the same.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
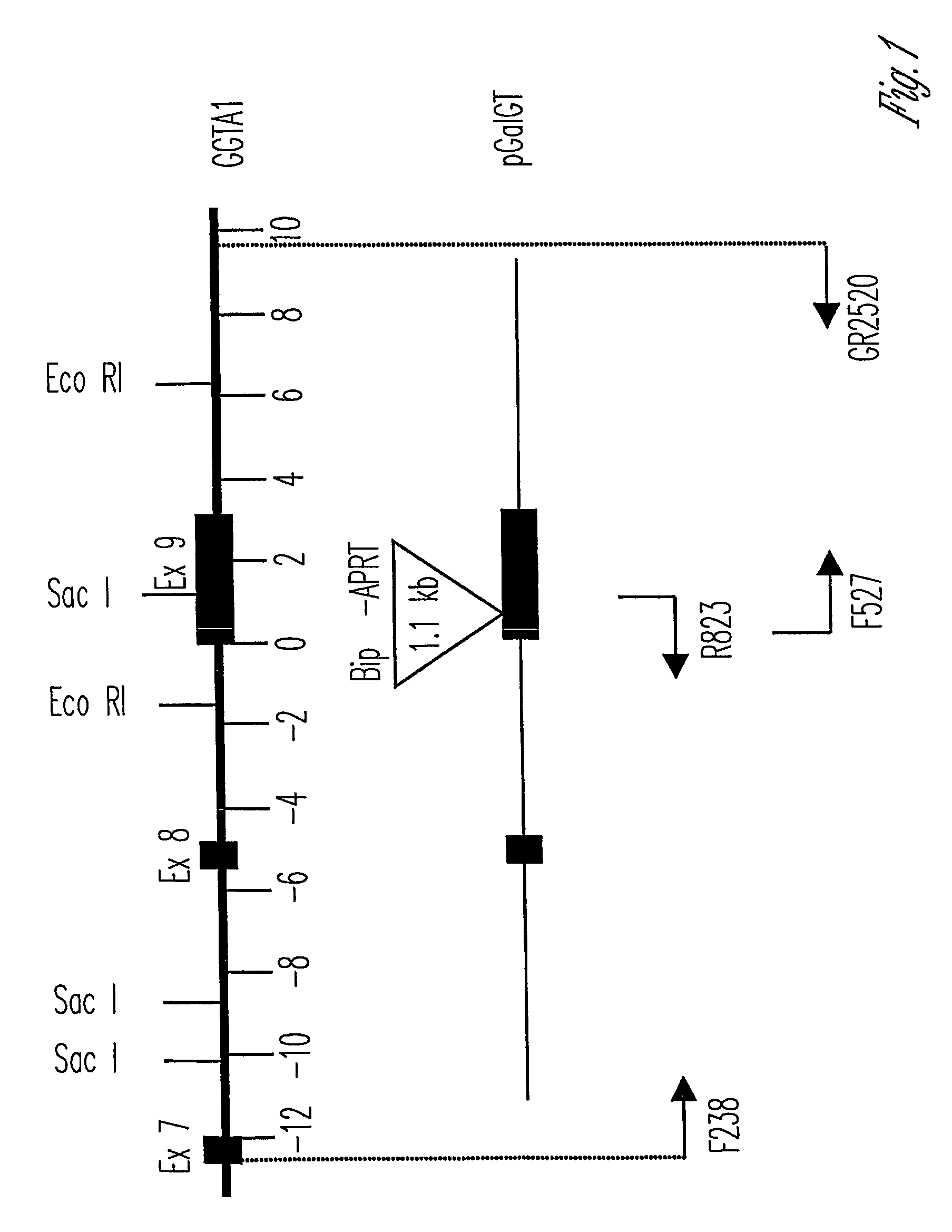
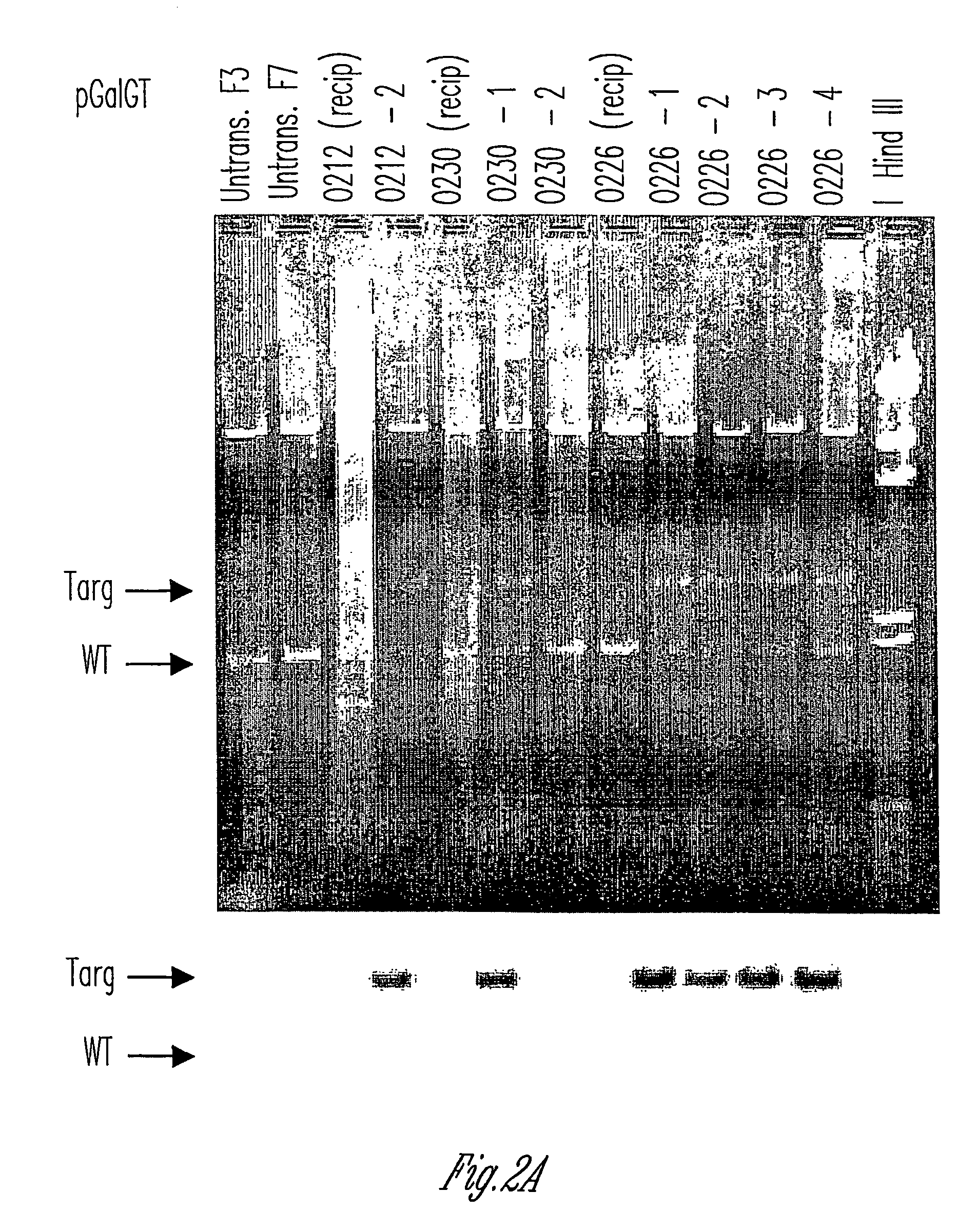
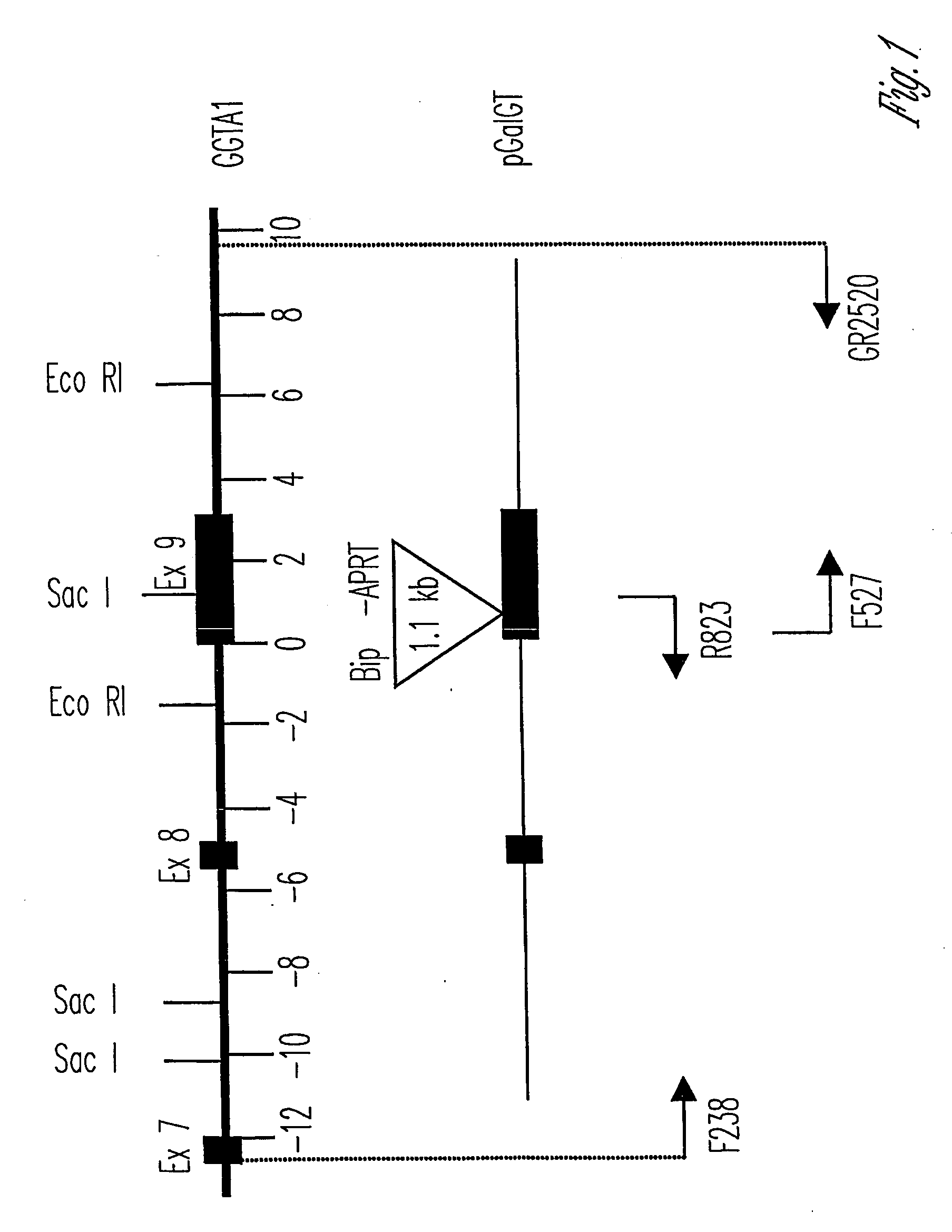
Alpha(1,3)-galactosyltransferase knockout swine, tissues and organs
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides viable gene knockout swine including swine in which the α(1,3)-galactosyltransferase gene has been disrupted, methods for making such swine, and methods of using the tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS +1
Knockout swine and methods for making the same
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of non-human animals. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic manipulation of non-human animals to be used for xenotransplantation. The invention provides viable gene knockout swine including swine in which the α(1,3)-galactosyltransferase gene has been disrupted, methods for making such swine, and methods of using the tissues and organs of such swine for xenotransplantation.
Owner:IMMERGE BIOTHERAPEUTICS +1
Methods for cloning mammals using reprogrammed donor chromatin or donor cells
InactiveUS20060212952A1Improve completenessImprove survivabilityNew breed animal cellsRecombinant DNA-technologyReprogrammingMammal
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Muir-torre-like syndrome in Fhit deficient mice
The invention provides nonhuman transgenic animals with a disrupted FHIT gene. The invention further provides transgenic mice in which one or both Fhit alleles have been inactivated. Preferably, the Fhit-deficient mice develop multiple tumors of both visceral and sebaceous origin, similar to those of Muir-Torre familial cancer syndrome. The present invention further relates to the generation of these transgenic mice and their use as model systems to study the effects of carcinogenic agents in promoting clonal expansion of neoplastic cells in cancers, preferably gastrointestinal cancers of which Muir-Torre syndrome is a subset. The invention further relates to testing therapeutic agents for their efficacy in the prevention and treatment of cancer, preferably gastrointestinal cancer.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Isolated homozygous stem cells, differentiated cells derived therefrom, and materials and methods for making and using same
The present invention discloses and describes pluripotent homozygous stem (HS) cells, and methods and materials for making same. The present invention also provides methods for differentiation of HS cells into progenitor (multipotent) cells or other desired cells, groups of cells or tissues. Further, the applications of the HS cells disclosed herein, include (but are not limited to) the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases (for example, genetic diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, endocrine-related disorders and cancer), traumatic injuries, cosmetic or therapeutic transplantation, gene therapy and cell replacement therapy.
Owner:STEMRON
Method for generating cloned animals using chromosome shuffling
InactiveUS20020174449A1Population uniformImprove quality controlNew breed animal cellsFermentationSpecific chromosomeMammal
The present invention concerns the use of chromosomal replacement techniques in the context of producing cloned and transgenic animals, in order to correct chromosome abnormalities or alter autosomal genotypes, and provide for novel breeding pairs by replacing the sex chromosome in animals to be cloned. Replacement of a sex chromosome, or an X or Y chromosome, will result in animals that are autosomally isogenic and sexually non-isogenic (AISN), with "autosomally isogenic" meaning that the paired sets of autosomes (non-sex chromosomes) in each animal are isogenic or identical. Also included in the invention are animals that are both "autosomally" and "allelically" isogenic whereby each particular pair of chromosomes is internally isogenic or identical within a single animal as well as between animals. Such animals are particularly useful in generating a line of cloned mammals using sexual reproduction, without having to undergo nuclear transfer in order to propagate cloned animals.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Muir-torre-like syndrome in Fhit deficient mice
The invention provides nonhuman transgenic animals with a disrupted FHIT gene. The invention further provides transgenic mice in which one or both Fhit alleles have been inactivated. Preferably, the Fhit-deficient mice develop multiple tumors of both visceral and sebaceous origin, similar to those of Muir-Torre familial cancer syndrome. The present invention further relates to the generation of these transgenic mice and their use as model systems to study the effects of carcinogenic agents in promoting clonal expansion of neoplastic cells in cancers, preferably gastrointestinal cancers of which Muir-Torre syndrome is a subset. The invention further relates to testing therapeutic agents for their efficacy in the prevention and treatment of cancer, preferably gastrointestinal cancer.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Universal donor cells
InactiveUS6916654B1Inhibition of activationHigh degreePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsClass II major histocompatibility complex geneT cell
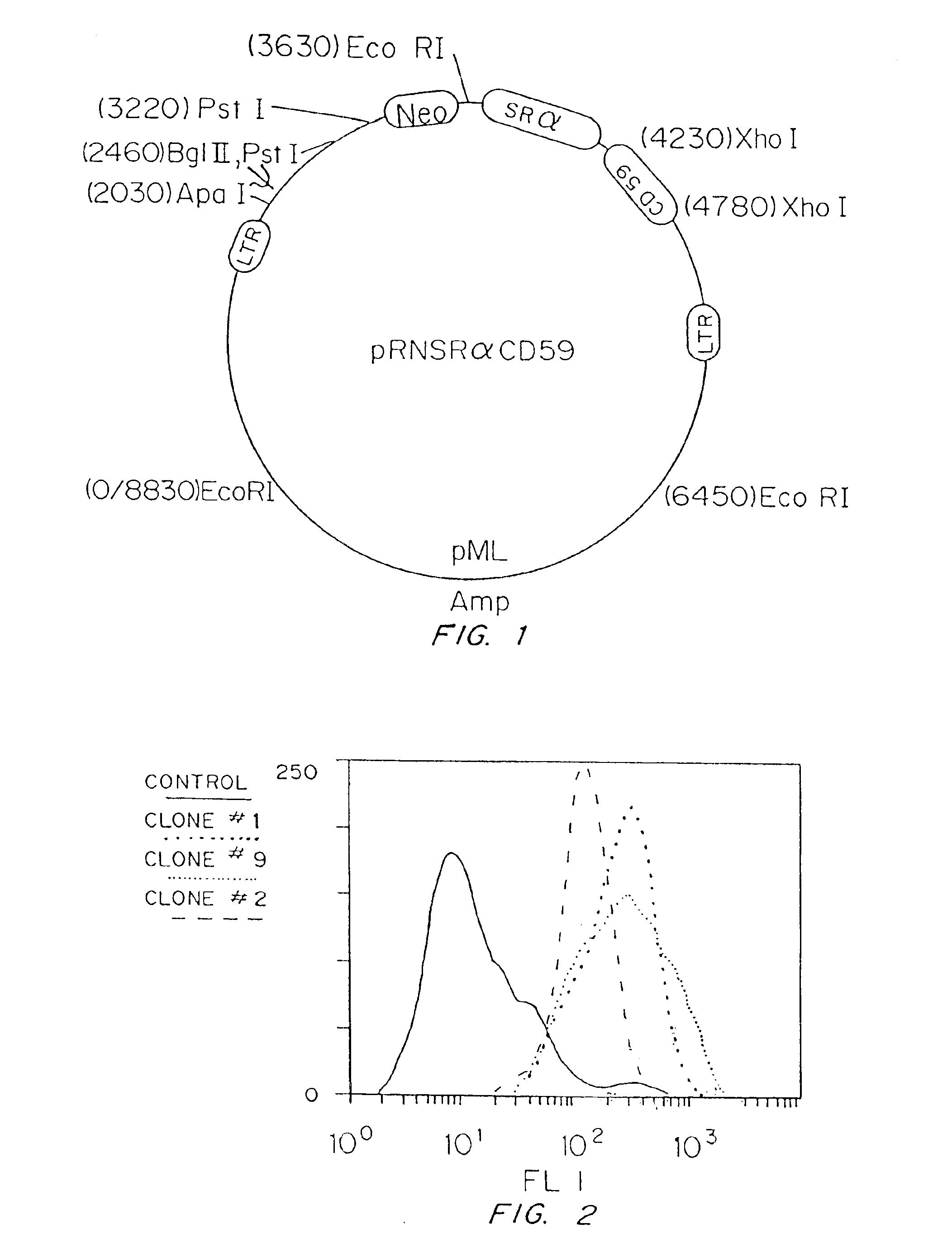
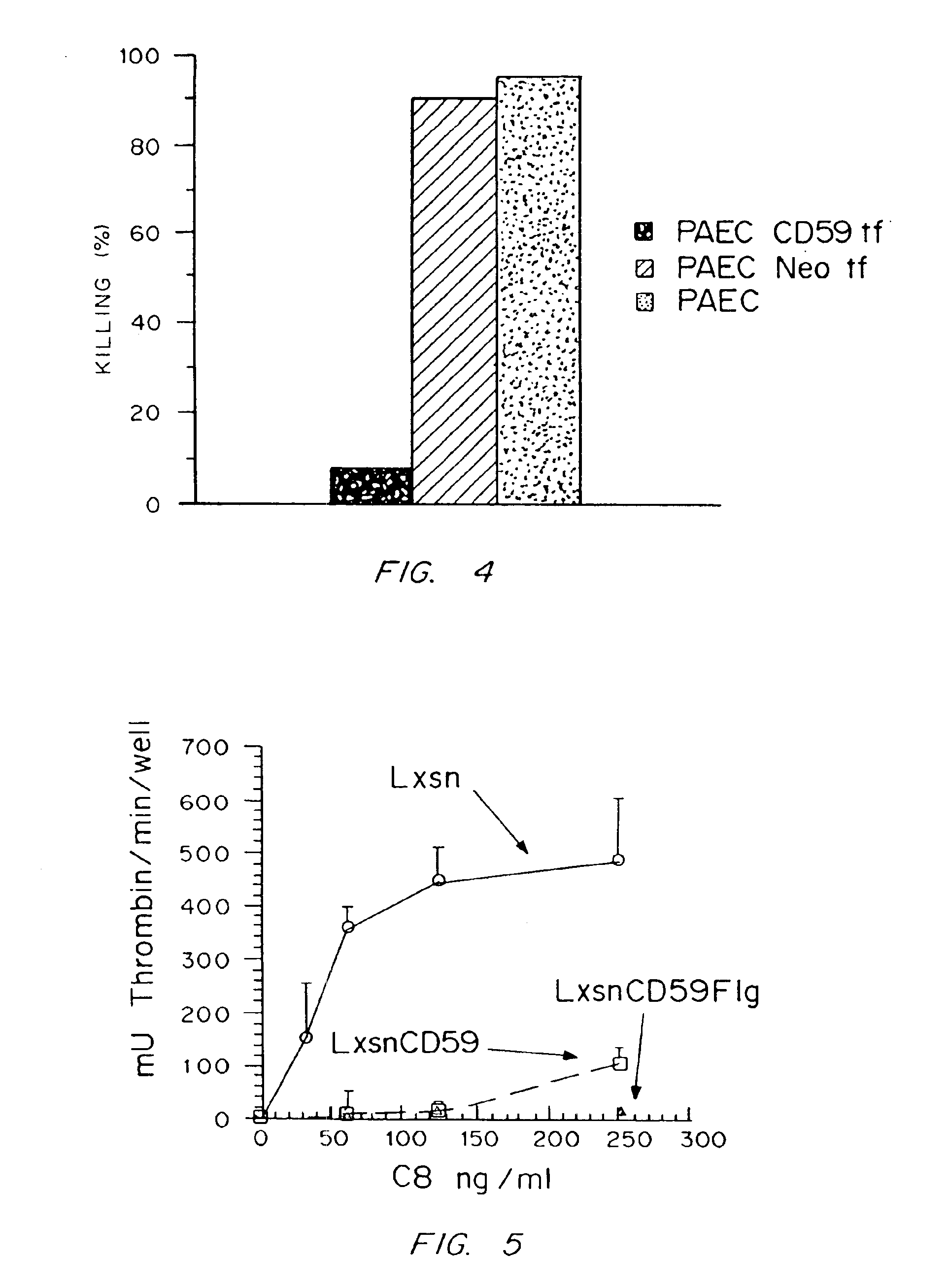
Genetically engineered cells are provided which can serve as universal donor cells in such applications as reconstruction of vascular linings or the administration of therapeutic agents. The cells include a coding region which provides protection against complement-based lysis, i.e., hyperacute rejection. In addition, the cell's natural genome is changed so that functional proteins encoded by either the class II or both the class I and the class II major histocompatibility complex genes do not appear on the cell's surface. In this way, attack by T-cells is avoided. Optionally, the cells can include a self-destruction mechanism so that they can be removed from the host when no longer needed.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND +1
Gynogenetic or androgenetic production of pluripotent cells and cell lines, and use thereof to produce differentiated cells and tissues
InactiveUS20030129745A1Rejection is prevented and reducedEliminate, orMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPrimateEmbryo
Methods for obtaining pluripotent (embryonic stem) cells from parthenogenetic embryos, especially primates, are provided. These cells are useful for producing differentiated cells, tissues and organs, especially human and non-human primate cells, tissues and organs.
Owner:ROBL JAMES M +2
Method for producing immortalised antibodies-secreting cells
A method for producing immortalized antibody-secreting cells, comprising: (a) providing a transgenic animal having antibody-secreting cells capable of expressing one or more transgenes, wherein the antibody-secreting cells are in a non-immortalized state in the absence of a stimulus and are capable of changing to an immortalized state by means of the transgenes or transgenes upon exposure of the cells to the stimulus; (b) extracting the antibody-secreting cells from the animal; and (c) exposing the antibody-secreting cells to the stimulus, thereby immortalizing the antibody secreting cells by means of the transgene or transgenes.
Owner:GRANTA BIOTECH
Methods for enhancing embryo viability
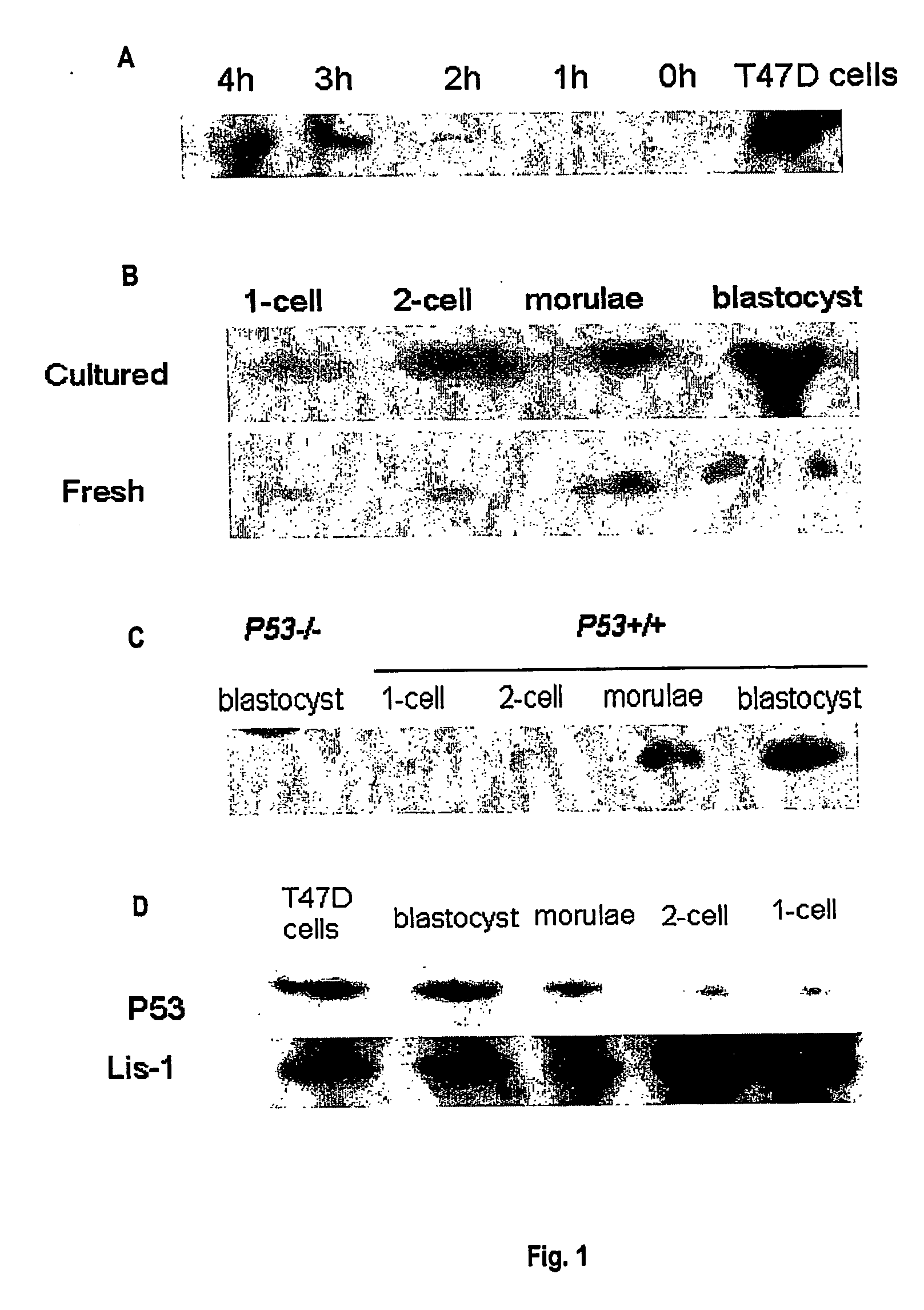
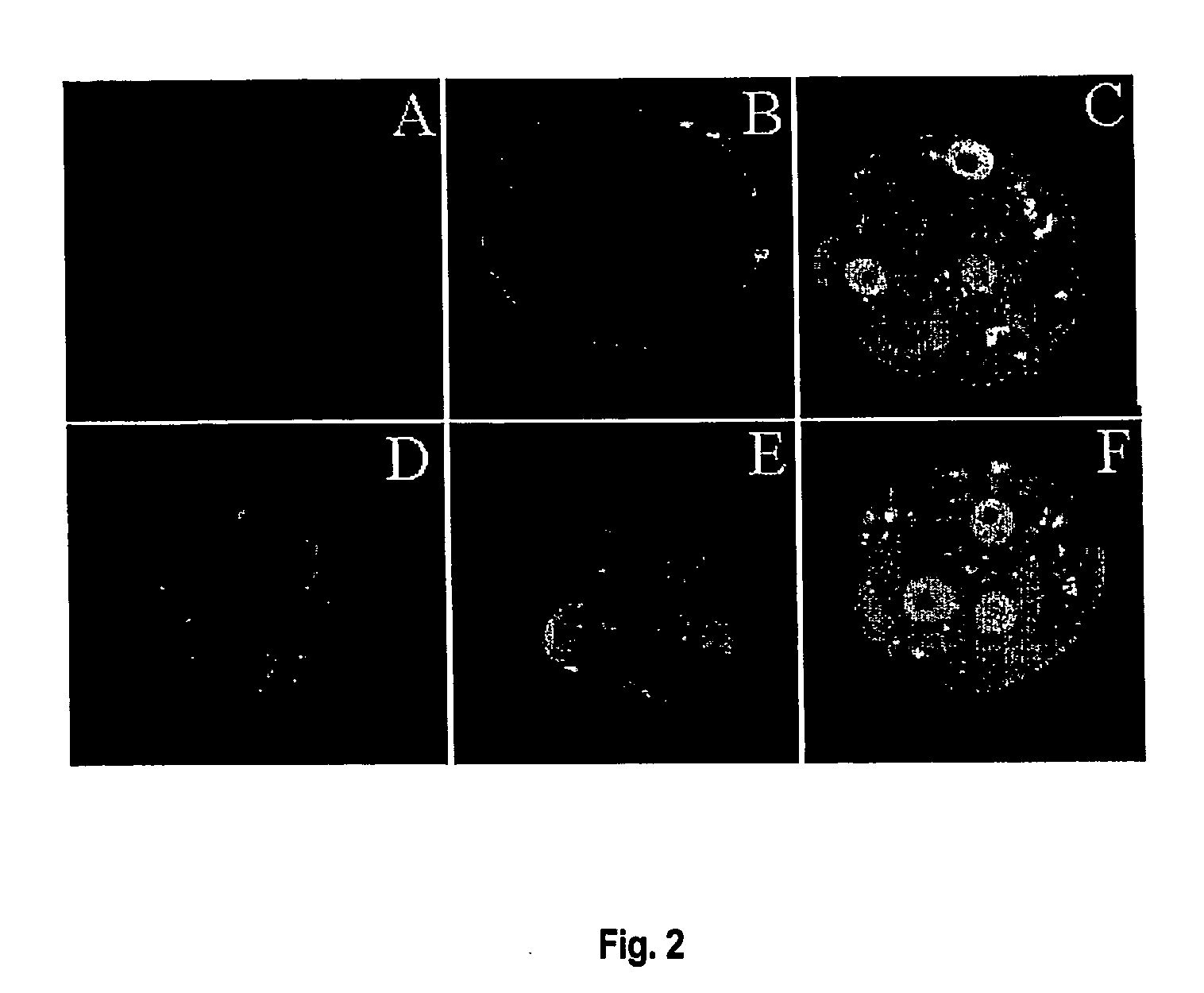
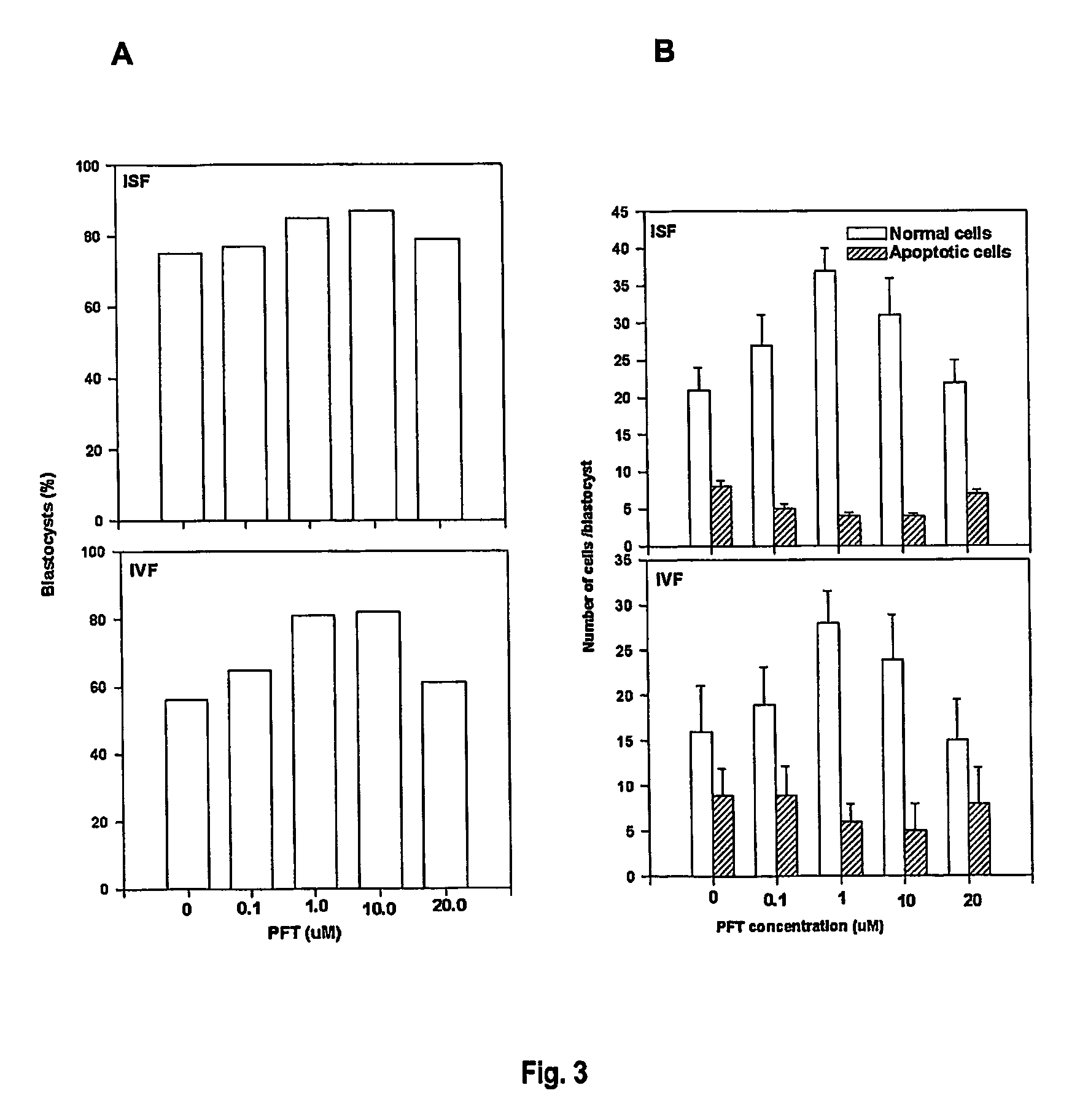
InactiveUS20070006332A1Enough timeImprove pregnancy rateOrganic active ingredientsP53 proteinEmbryoBiology
Owner:BIOLOGICAL RESOURCES
Method for sex biasing spermatozoa
InactiveUS20050114915A1Improve abilitiesRaise the potentialNew breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsCell bindingBiology
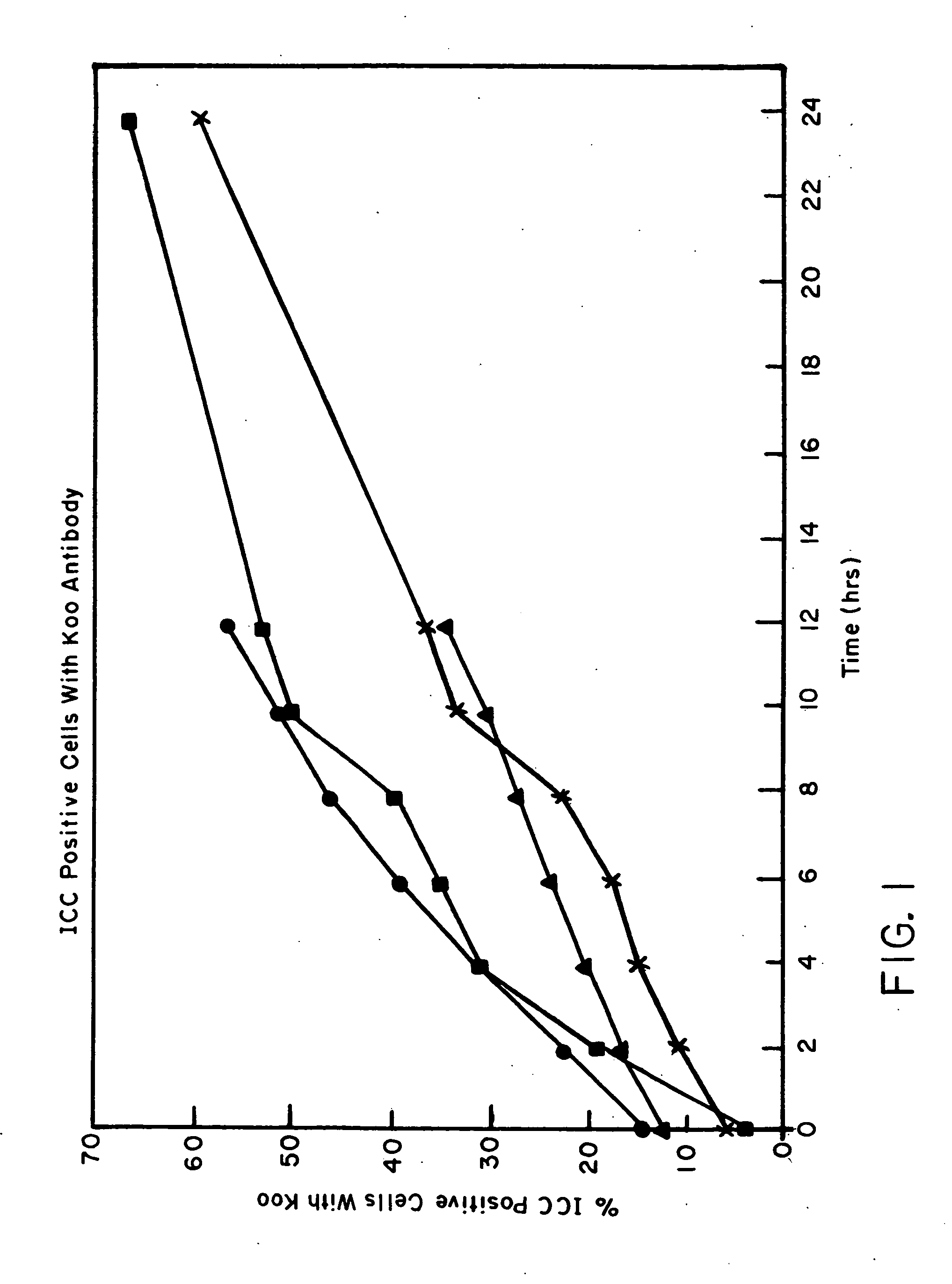
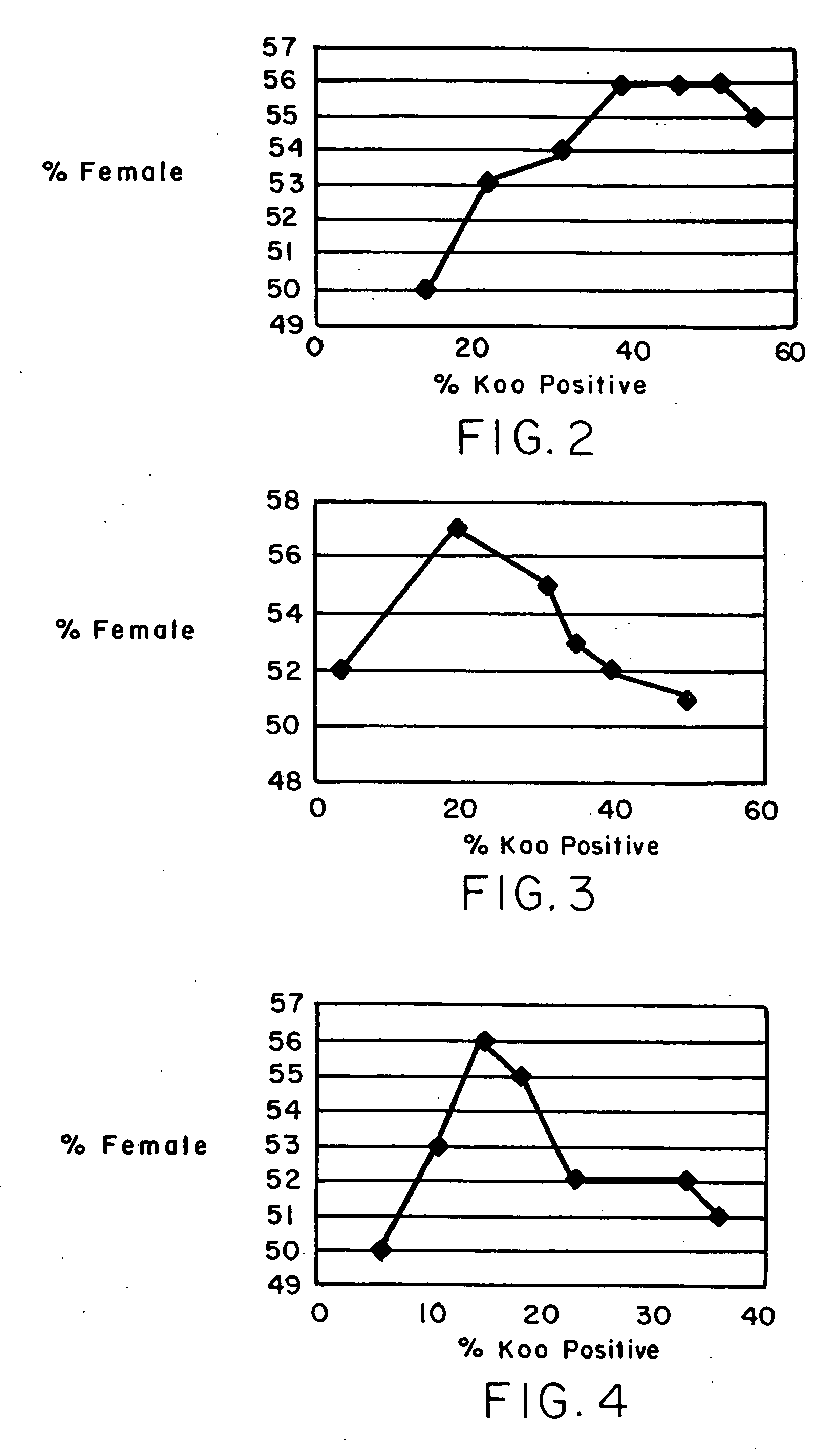
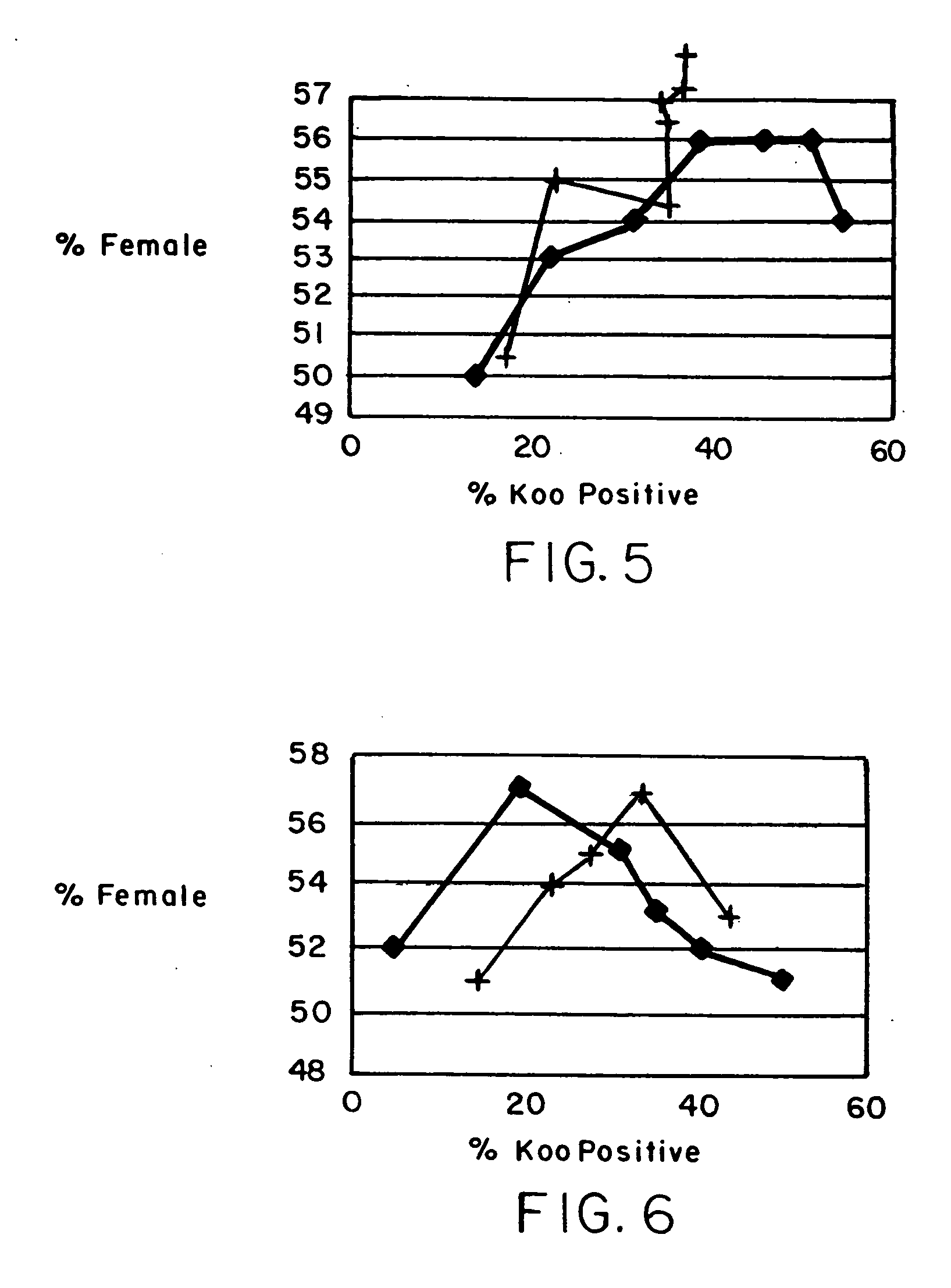
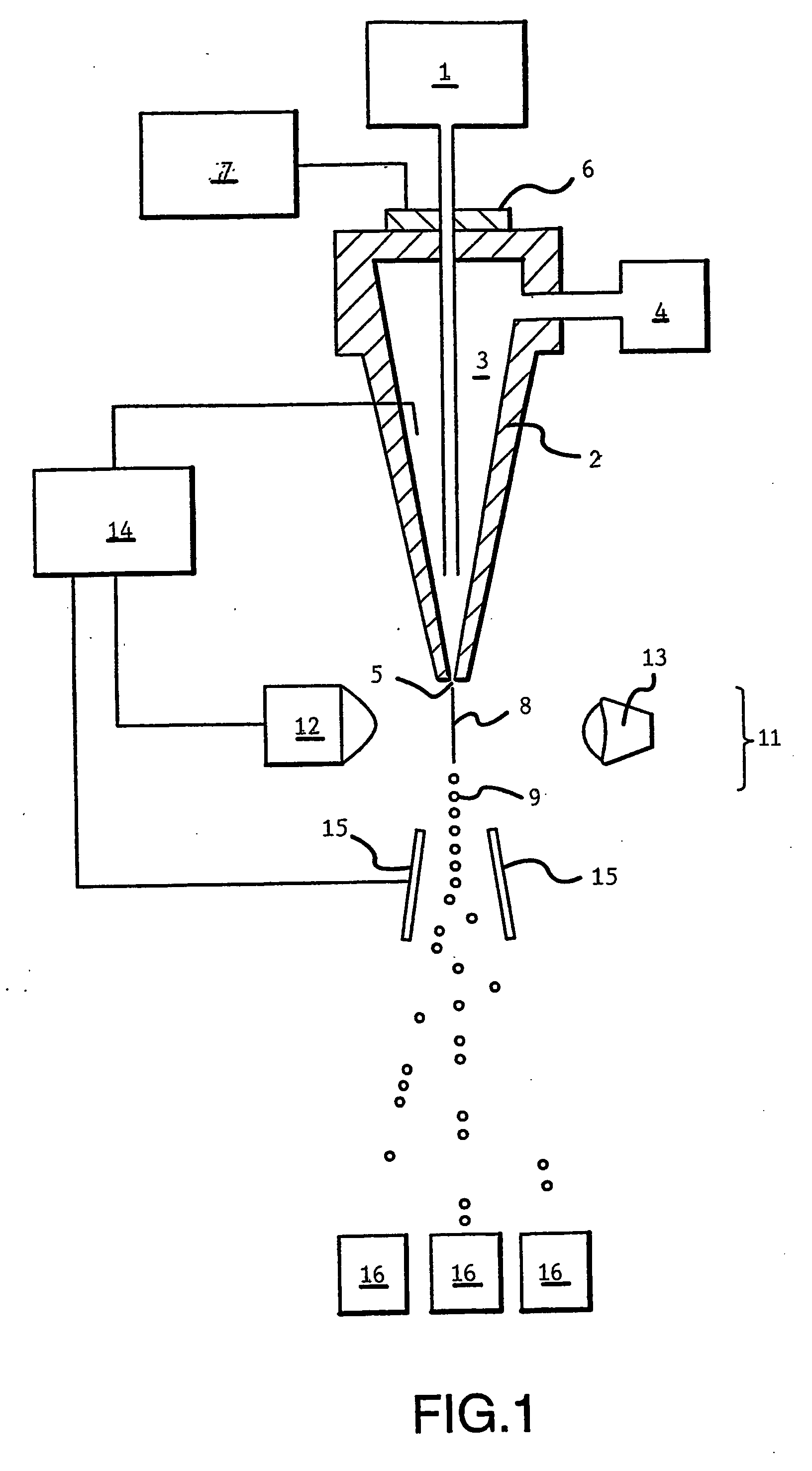
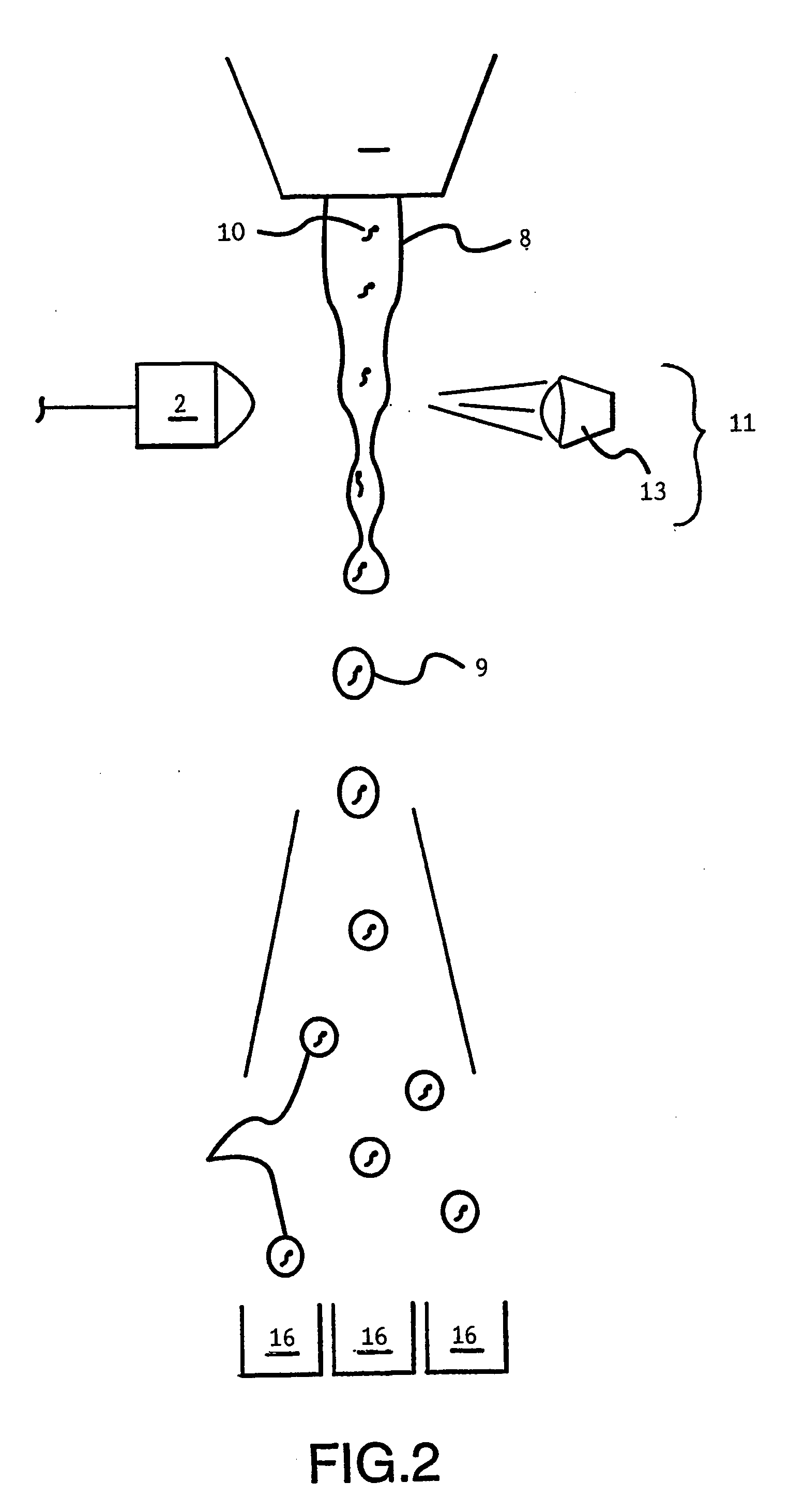
A method is described for treating a specimen of semen containing sperm cells to increase the relative number of sperm cells of a desired sex type in a treated specimen to increase the potential for conceiving an offspring of the desired sex. A specimen of semen is treated after a predetermined time to increase the relative ability of a at least a portion of the semen to conceive an offspring of the desired sex. The treatment preferably comprises contacting the sperm cells with an agent that preferentially effects sperm cells of a selected sex type. In some preferred embodiments, the semen is separated into two components. A first component has a higher number of sperm of the desired sex type than sperm of a non desired sex type and a second component has a higher number of sperm of the non desired sex type relative to sperm of the desired sex type. In one embodiment, the separating step is performed after a predetermined percent of the sperm cells exhibit a punctate pattern, which is capable of determination by labeling the sperm cells with Koo antibody and determining the percent of cells labeled. In another embodiment, the separating step is performed after waiting for a time determined by locating a maximum in the curve obtained by plotting percent female cells determined by FISH against percent Koo positive cells, determining the time at which the maximum percent female cells occurs, and beginning the following step no earlier than about one hour before the time of the maximum percent female cells. In yet another embodiment, the separating step is performed after waiting for a period of time between about 2 hours and about 24 hours after collection of the ejaculate. Preferably, in the separating step, the sperm is contacted with a cell binding agent, permitting the sperm of the non desired sex type to preferentially bind to the cell binding agent, and the cell binding agent with preferentially bound sperm of the non desired sex type is separated from non bound sperm.
Owner:VICAM
Methods and compositions for the generation of antibodies
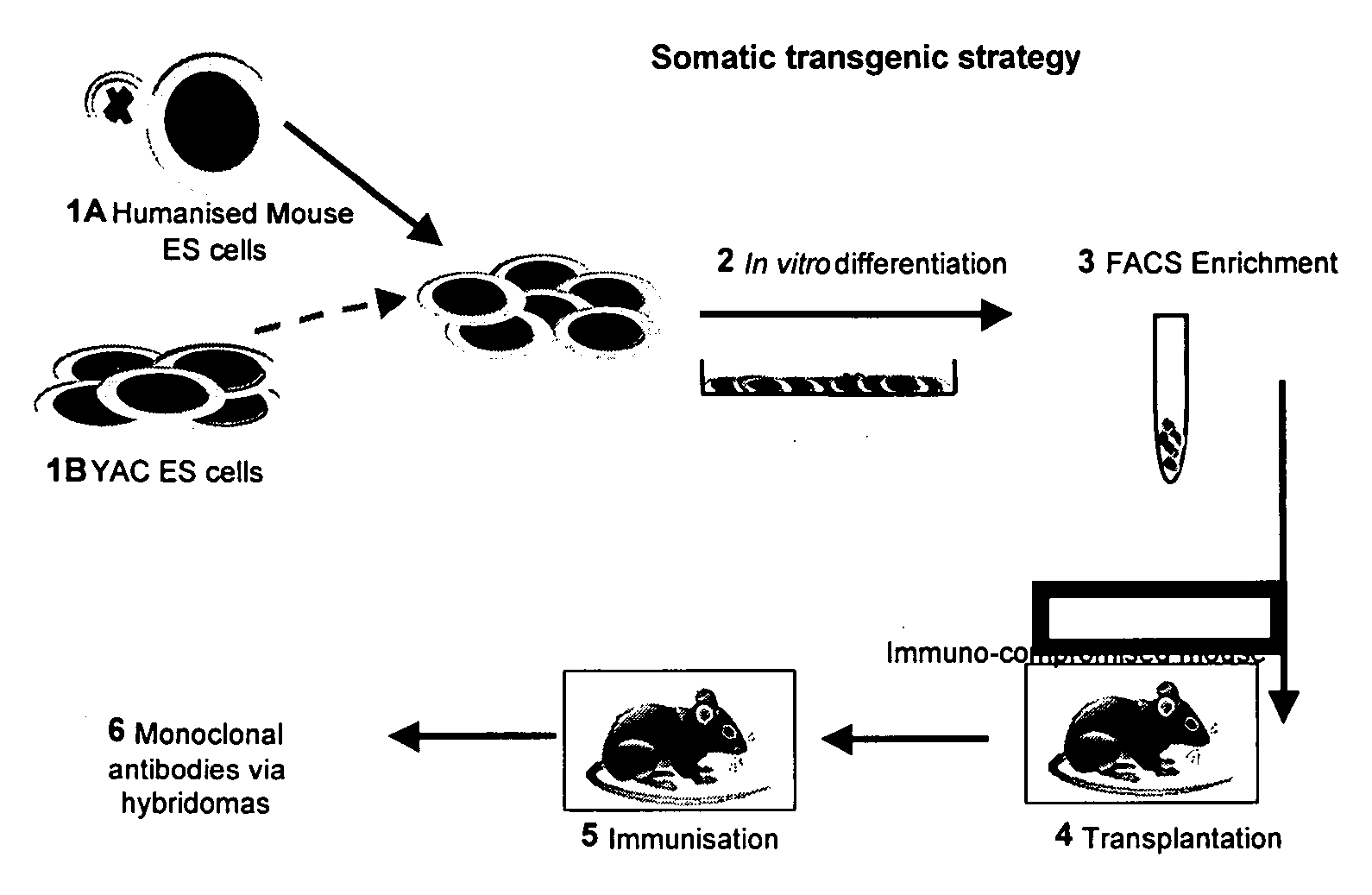
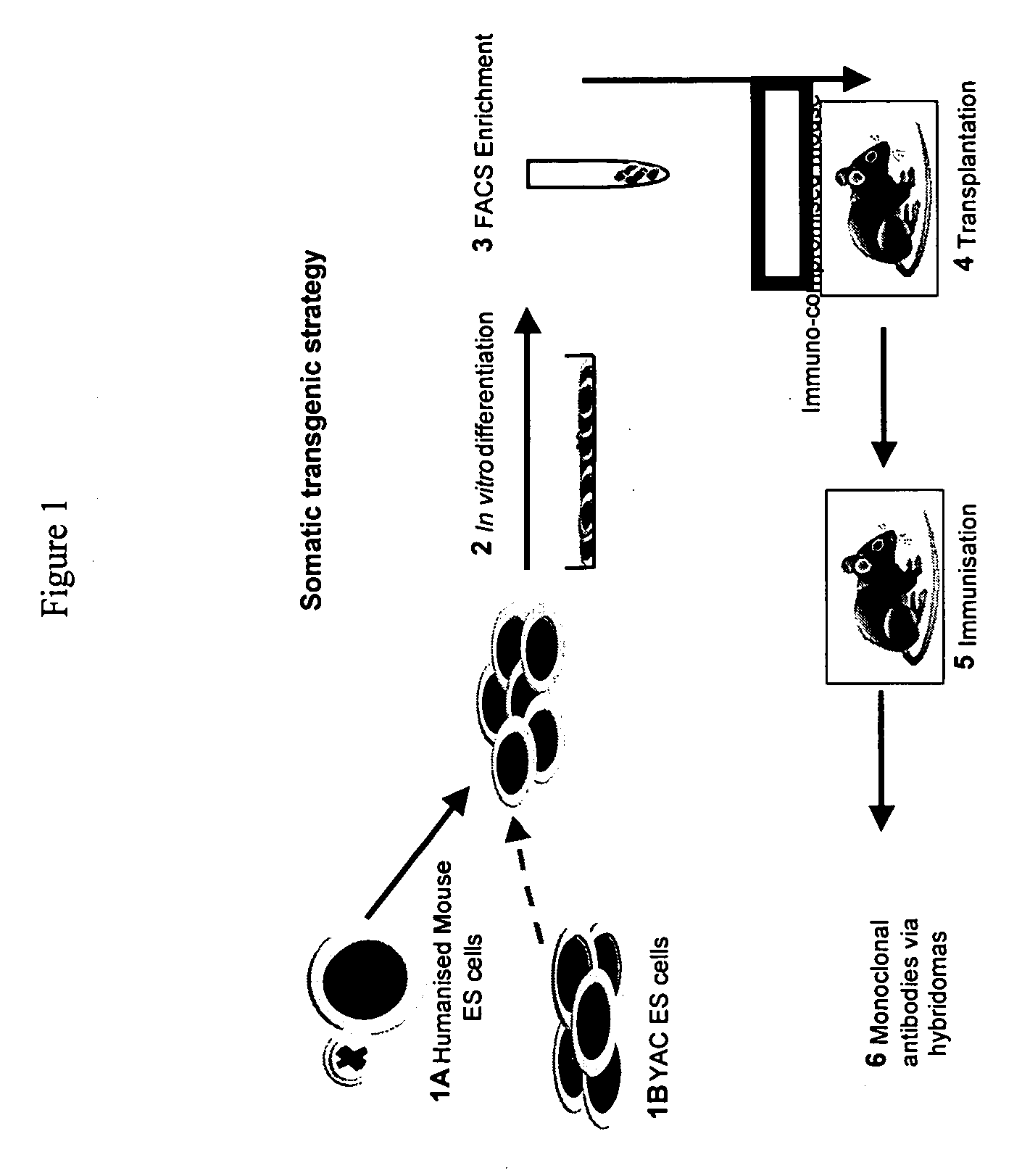
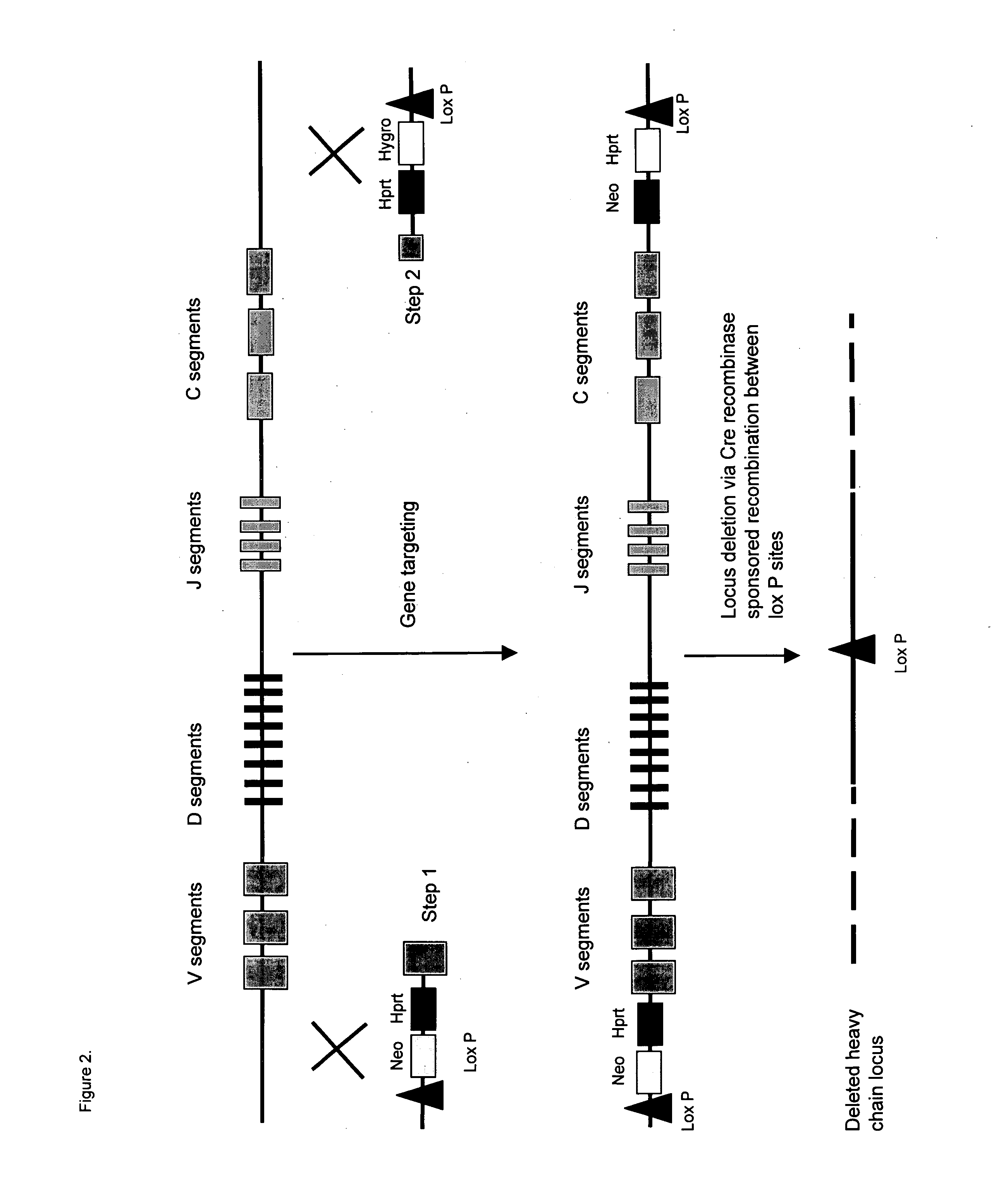
InactiveUS20060156422A1Efficient and functional route of cell deliveryAvoid problemsAnimal cellsNew breed animal cellsMonoclonal antibodyGenetically modified animal
The present invention relates to a novel method for the generation of monoclonal antibodies. In particular the invention relates to a novel method for the generation of monoclonal antibodies from non-human somatic transgenic animals. Uses of antibodies generated using the method of the invention are also described.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com