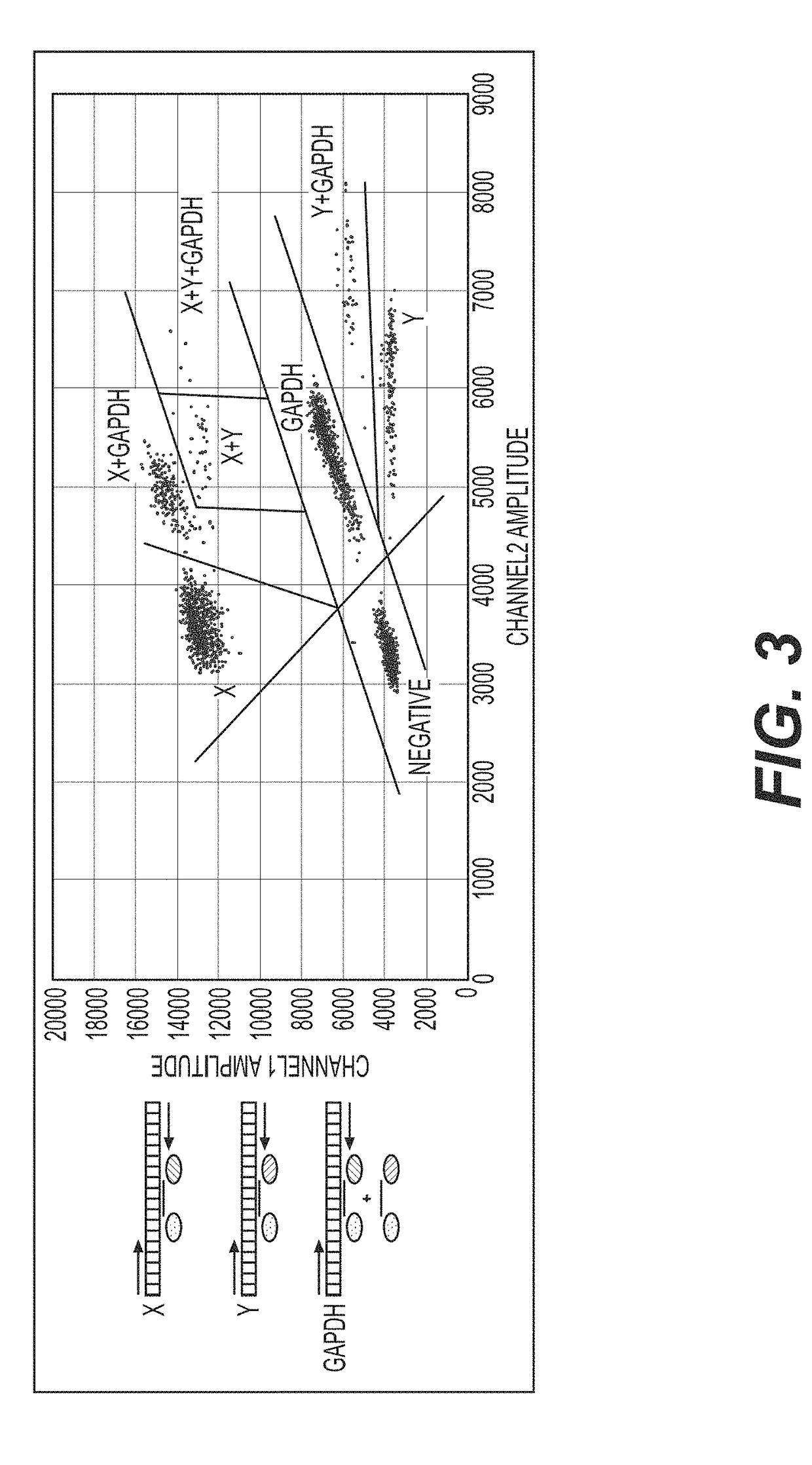
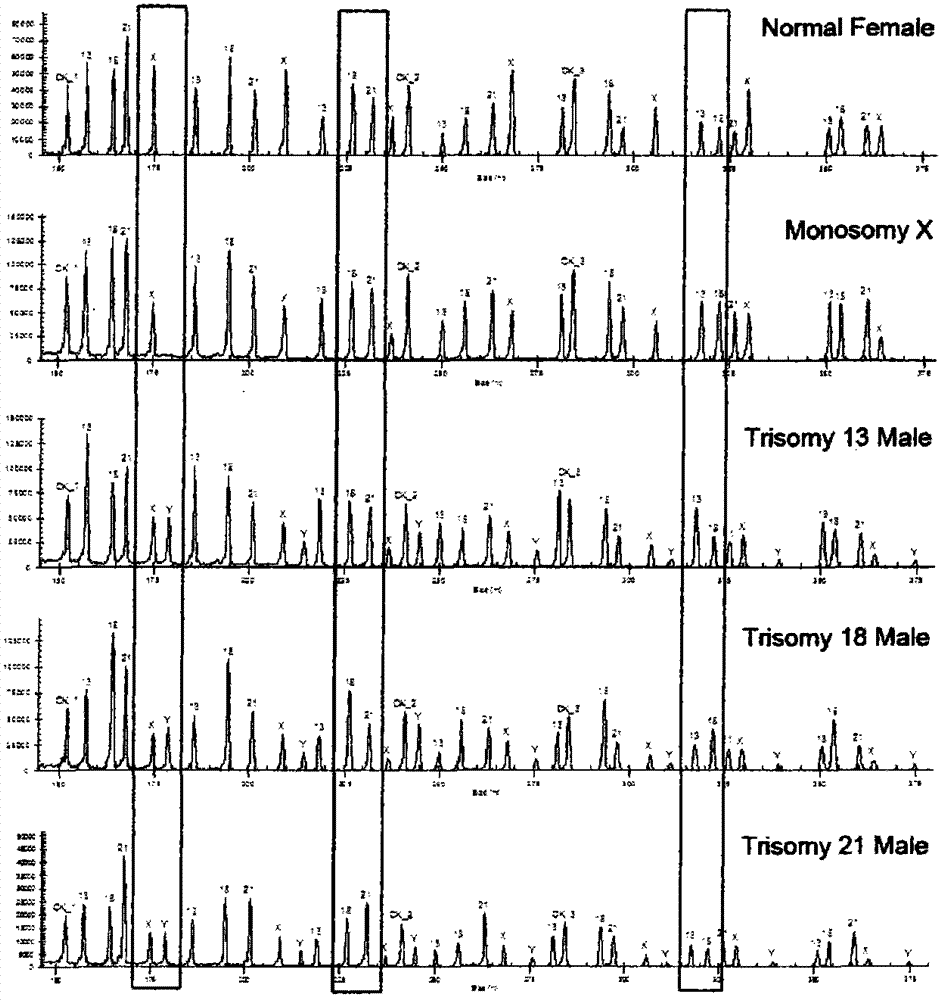
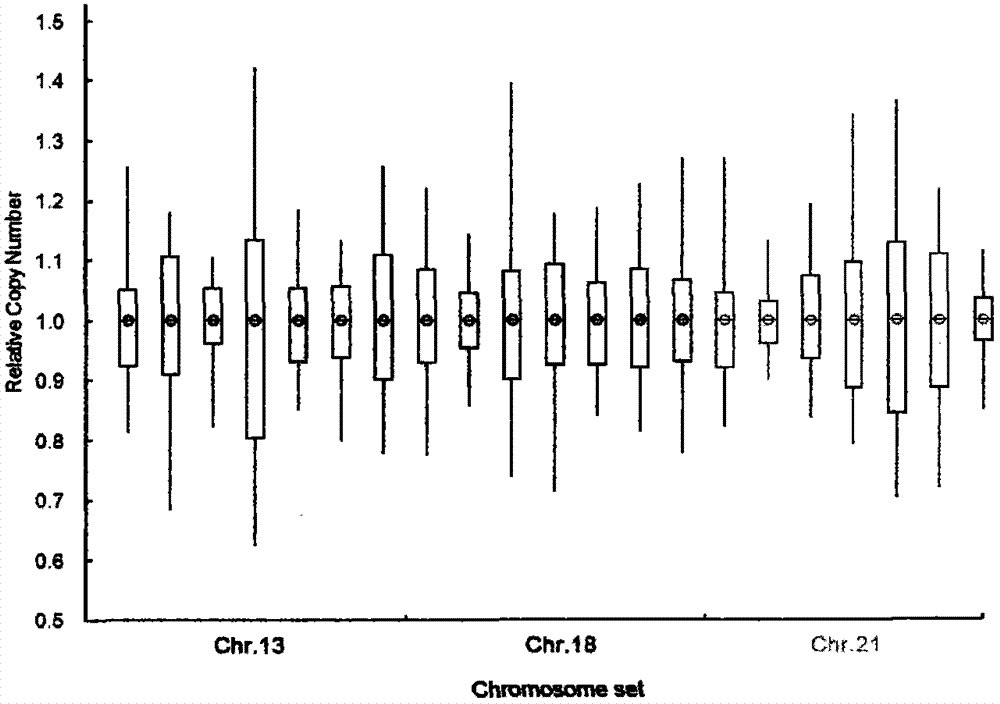
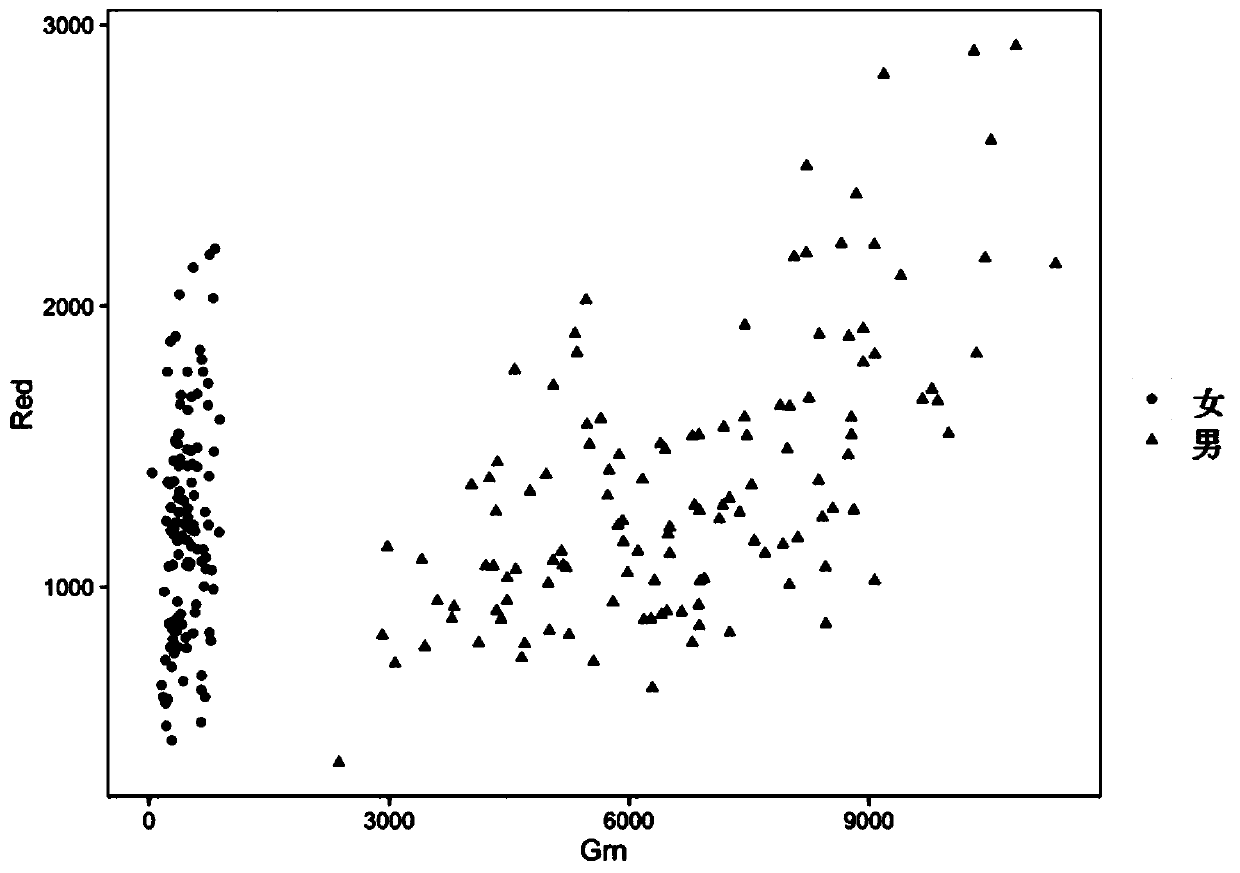
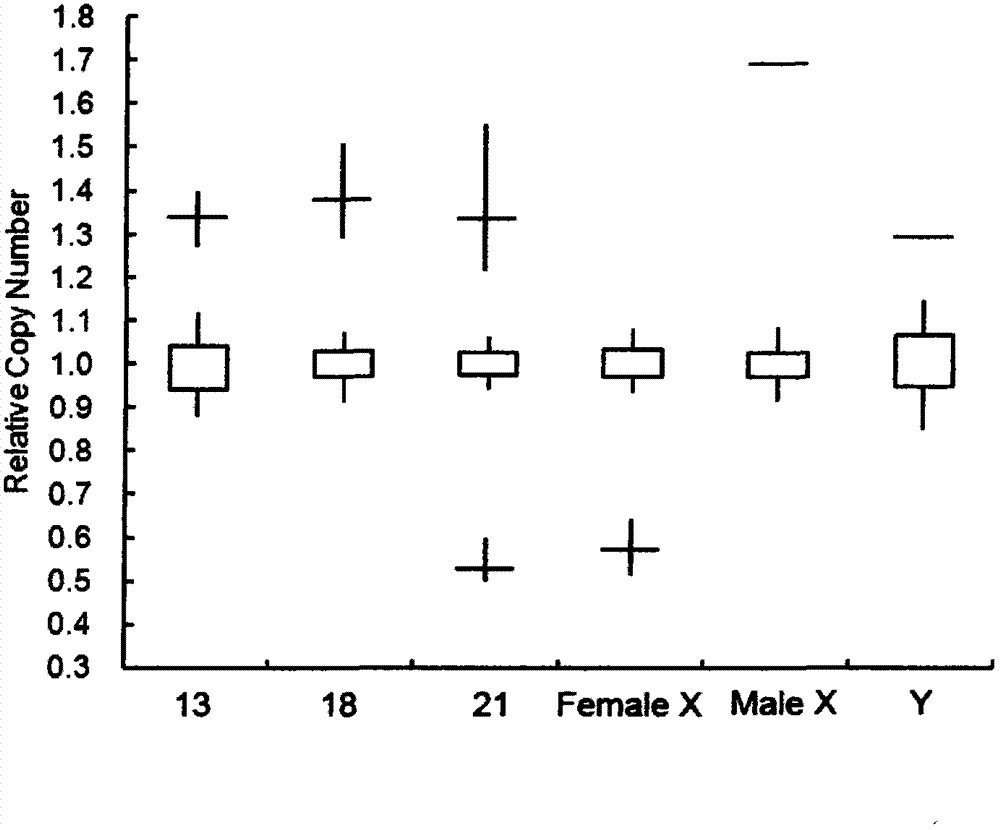Patents
Literature
42 results about "Y chromosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that typically determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which by default triggers male development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest-evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome.
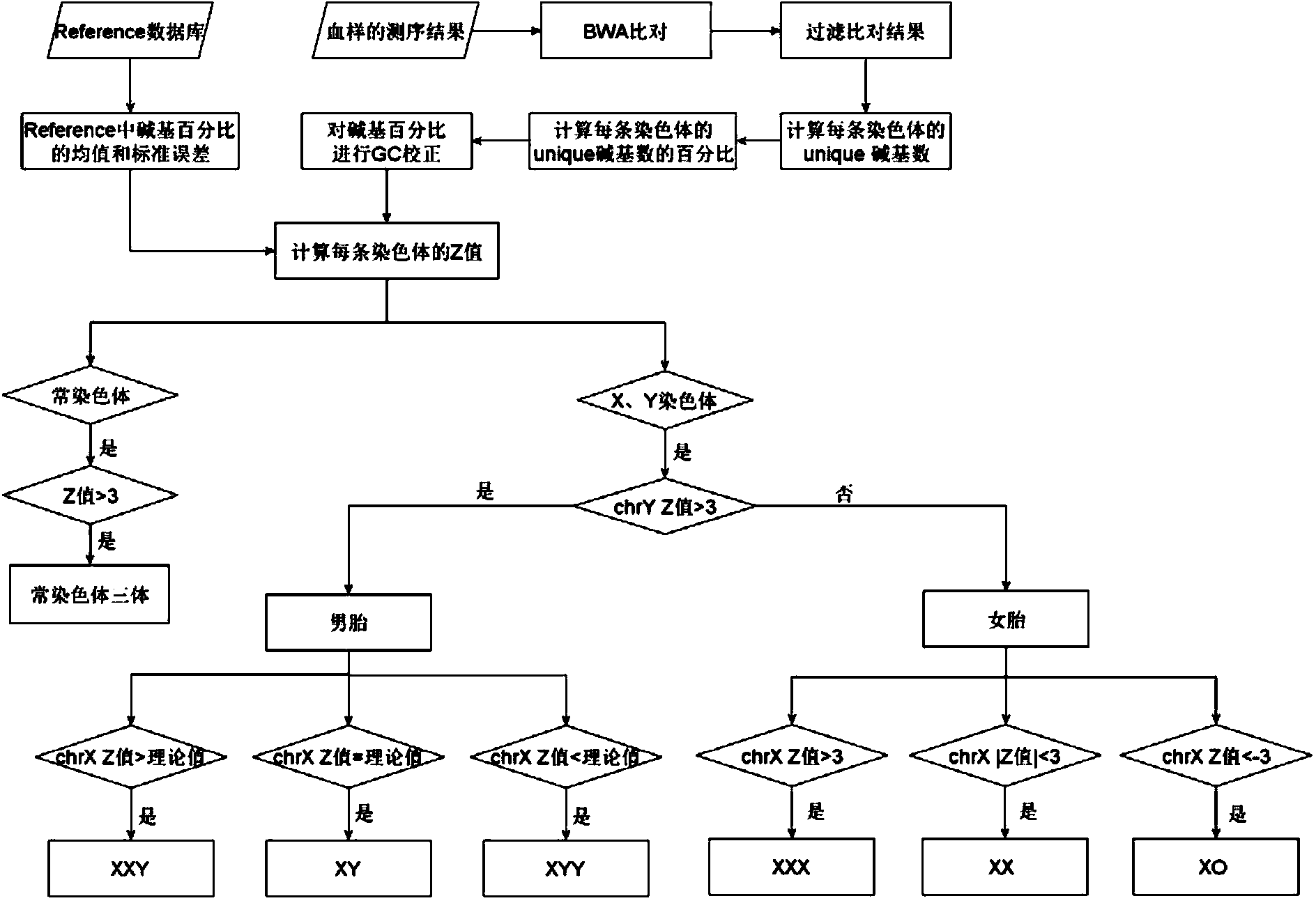
Method and system for noninvasive detection of fetus chromosome aneuploid
ActiveCN103525939AImprove scalabilityBirth rate controlMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsX chromosomeRelational model
The invention belongs to the medical detection field, and discloses a method and a system for noninvasive detection of fetus chromosome aneuploid. The disclosed detection method and system also relate to a method and a system for elimination of sequencing GC preference in chromosomes and among chromosomes and a method and a system used for the relation model of the Z values of X and Y chromosomes in a normal male fetus. Through elimination of influences of sequencing GC preference in chromosomes and among chromosomes, the relation model of the Z values of X and Y chromosomes in a normal male fetus is built, and the determination threshold of difference between the theoretical value and the actual value of the Z value of the X chromosome is built. The accurate detection of fetus chromosome aneuploid, especially sex chromosome aneuploid is achieved.
Owner:BOAO BIOLOGICAL CO LTD
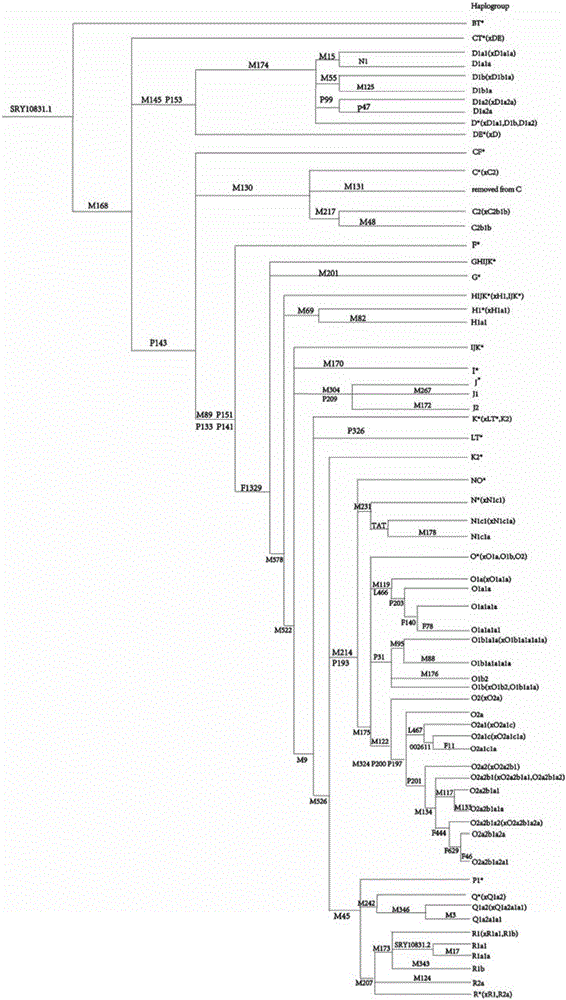
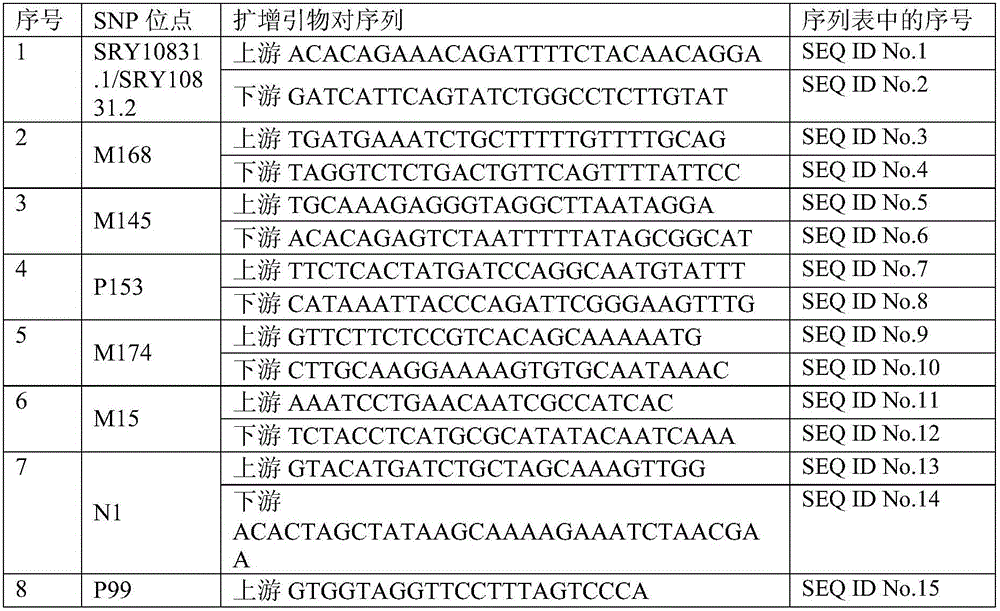
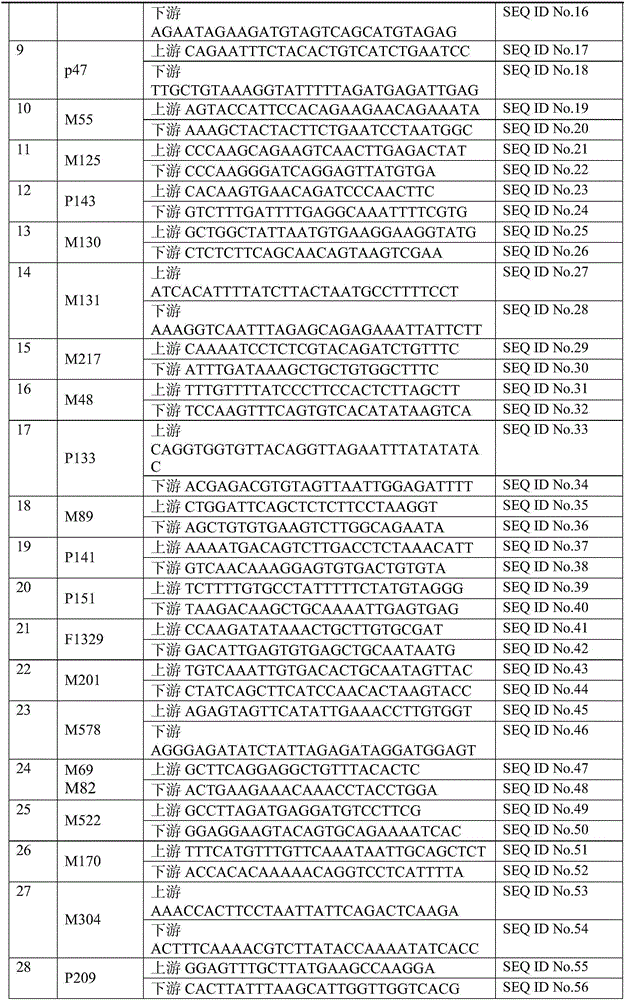
Forensic medicine II sequence testing kit based on 74 gama chromosome SNP genetic markers
ActiveCN106399543AHigh resolutionHigh system resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementY chromosomeForensic science
The invention belongs to the technical field of forensic medicine, and particularly relates to a forensic medicine II sequence testing kit based on 74 gama chromosome SNP genetic markers. The technical problem to be solved is to classify detection materials of Chinese group source at the position of a gama chromosome evolution tree by using the gama chromosome SNP genetic markers. The technical scheme of the invention is forensic medicine II sequence testing kit based on 74 gama chromosome SNP genetic markers, which includes a mixture of 72 pairs of primers for recombination and amplification, thus the detection of 74 pieces of SNP at the same time becomes true. The kit applies single pipe internal recombination and amplification and II sequence testing technology, and thus the genetic typing of 74 pieces of gama chromosome SNP genetic markers of multiple biological detection materials can be obtained in one time; besides, male samples of Chinese group source are correctly affiliated to the branch of the recognized gama chromosome evolution tree.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Amplification composition for detecting abnormal number of chromosomal aneuploid and rapid detection kit
ActiveCN104651488AShort detection cycleHigh speedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationY chromosomeX chromosome
The invention relates to an amplification composition for detecting abnormal number of chromosomal aneuploid and a rapid detection kit, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The amplification composition can be used for amplification detection of STR sites related to 8 21# chromosomes, 6 18# chromosomes, 6 13# chromosomes and 3 X chromosomes and amplification detection of four amelo; all sites can be amplified by a quantitative fluorescent PCR (QF-PCR) technology, so as to detect the abnormal number of 21, 18, 13, X and Y chromosomal aneuploid. According to the kit, detection cycle is short, so the result can be obtained within 5 hours after obtaining the sample; the sensitivity is high; DNA at nanogram level, which is equal to DNA contained in 100 cells, is needed for each detection, so few samples are needed; 1 to 2ml of amniotic fluid can be collected to meet the demand; due to high sensitivity, a chimera containing more than 10% of trisomies can be detected.
Owner:BEIJING MICROREAD GENE TECH
Method for noninvasive antenatal diagnosis through separating fetal nucleated red blood cells from peripheral circulating blood of pregnant woman
InactiveCN105063181AEfficient and specific captureMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseRed blood cell
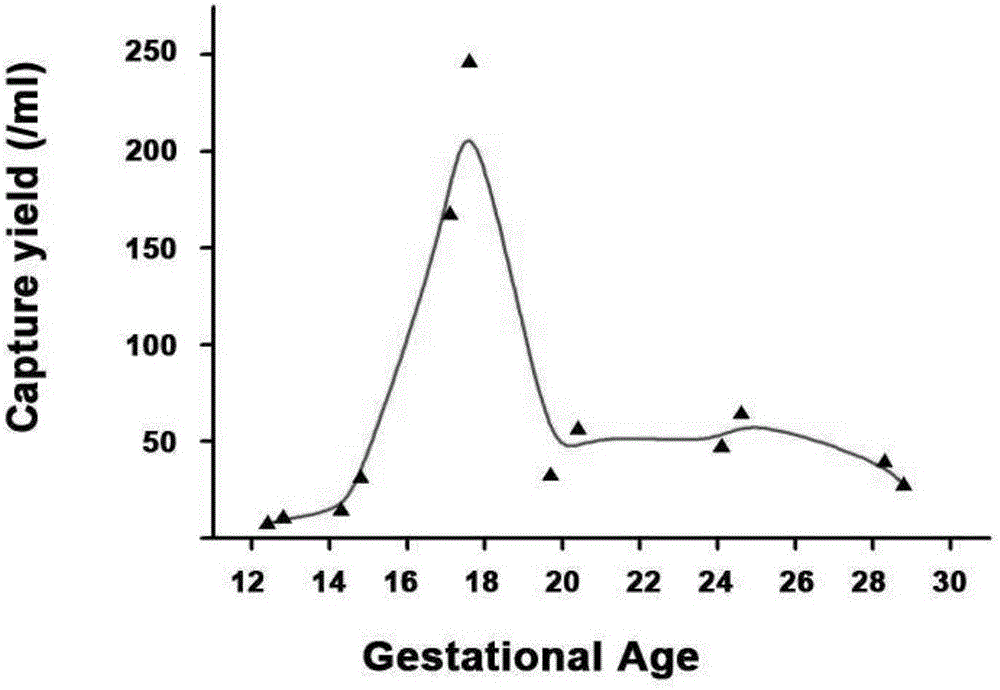
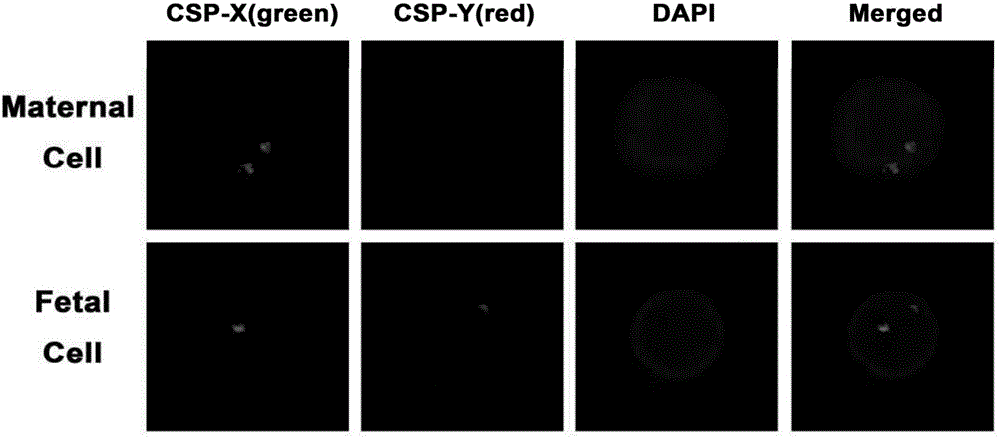
The invention discloses a method for noninvasive antenatal diagnosis through separating fetal nucleated red blood cells from peripheral circulating blood of a pregnant woman. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preprocessing fresh pregnant woman maternal peripheral blood: separating and enriching monocytes containing fetal nucleated red blood cells from maternal peripheral whole blood through a density gradient centrifugation technology; 2, capturing cells: adding a separated monocyte suspension to a substrate chip modified with an antibody, and carrying out standing capturing; and 3, identifying the sex of a fetus: identifying whether the nucleated red blood cells of the captured fetus contain Y chromosome or not by using an FISH probe technology (CSP-X / Y). The method for noninvasive antenatal diagnosis through separating fetal nucleated red blood cells from peripheral circulating blood of the pregnant woman can realize capture and identification of the fetal nucleated red blood cells from the maternal peripheral circulating blood, and allows the FISH analysis to be directly carried out in order to realize noninvasive antenatal diagnosis of the sex or 21-Trisomy syndrome and other chromosome diseases of the fetus.
Owner:石莹
Assay for human DNA for gender determination
ActiveUS20060199217A1Reduce the possibilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementY chromosomeX chromosome
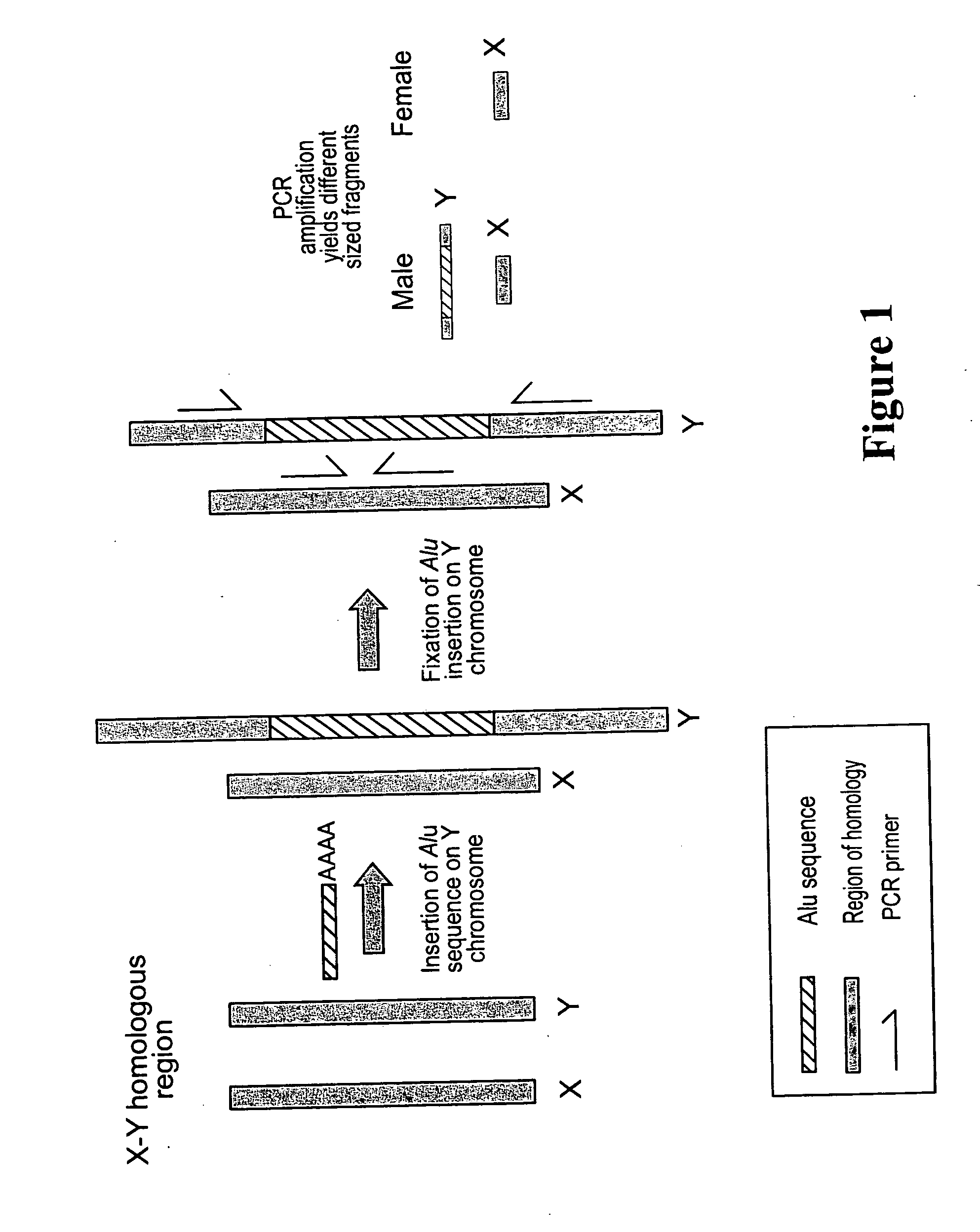
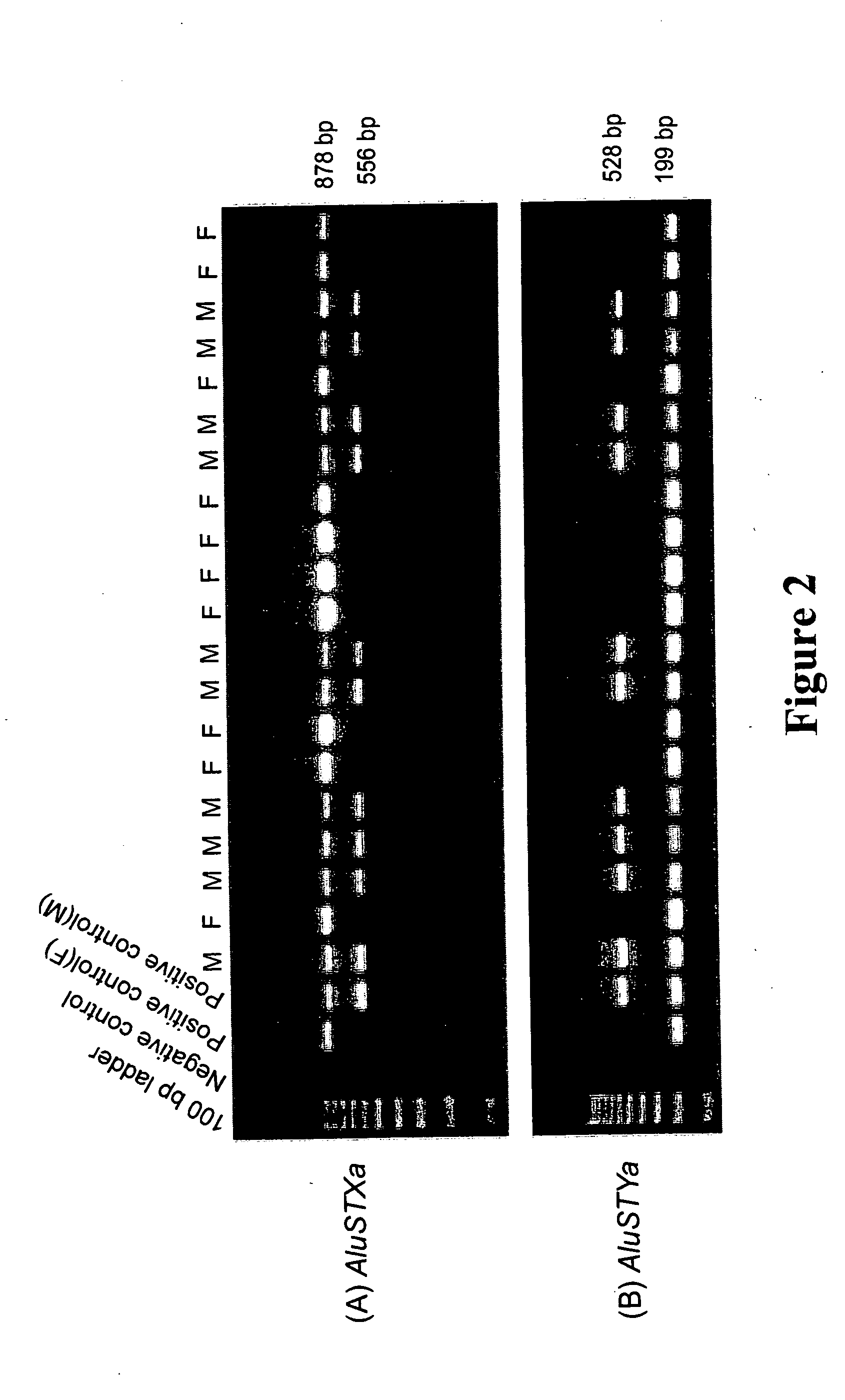
A method for determining gender from a human DNA sample. The loci of Alu element insertion is selected, amplified and evaluated in terms of size of the fragment. The gender assay utilizes AluSTXa for the X chromosome, AluSTYa for the Y chromosome, or both AluSTXa and AluSTYa, to reduce the possibility of error to a negligible quantity. The inserted chromosome yields a large fragment when the homologous region is amplified. The males are distinguished as having two DNA amplicons present, while females have only a single amplicon. The kit adapted for carrying out the method includes a pair of primers to amplify the locus and optionally polymerase chain reaction regents.
Owner:LIFE GENETICS LAB LLC A BODY CORP CHARTERED IN & EXISTING UNDER THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF LOUISIANA +2
Method for identifying sika deer, red deer or other hybridized deer on basis of COI and SRY sequences
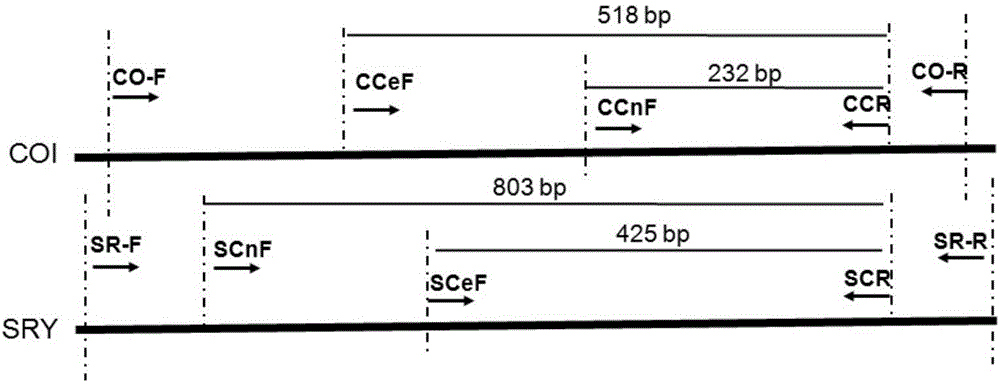
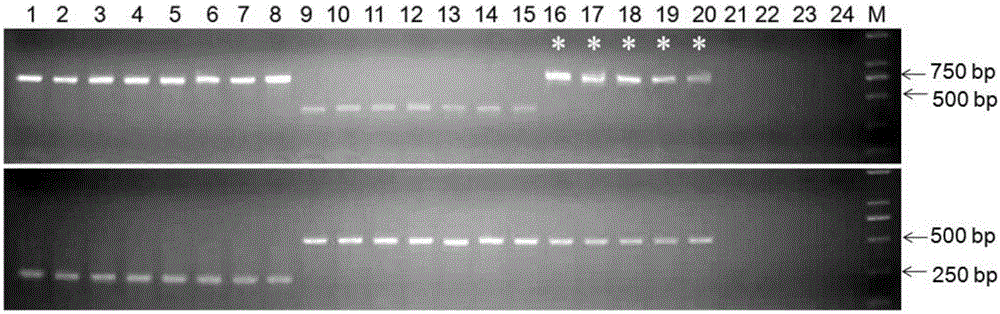
The invention discloses a method for identifying sika deer, red deer or other hybridized deer on basis of COI and SRY sequences. The invention provides the application of a substance for detecting a target site in gene sequences corresponding to a COI gene and an SRY gene in a genome of a to-be-detected sample as well as target nucleotide of the site to preparation of products for detecting whether the to-be-detected sample is sika deer, red deer or other hybridized deer. Two multiple PCR systems are established by utilizing the SRY gene of Y chromosome as an identification mark of a male parent and combining a female parent mark gene COI on the basis of the COI and SRY gene sequences and are used for identifying male and female parent sources of cartialgenous samples, the identification method of the hybridized cartialgenous is initially established, and male and female parent identification of the hybridized deer can be conducted effectively. The method has actual application value on identification of the hybridized cartialgenous, and provides an effective identification method for subsequent quality evaluation of the hybridized cartialgenous.
Owner:华润三九现代中药制药有限公司 +1
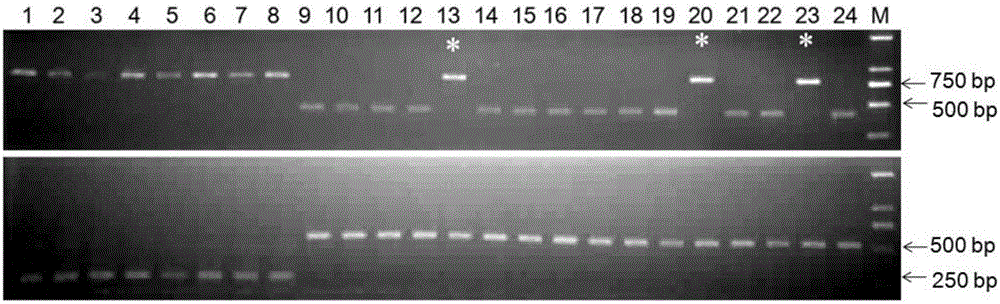
Primer for detecting separation purity of X, Y spermatozoon of cattle
InactiveCN101195842ALow costEasy to operateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDuplex pcrStatistical analysis
The invention provides a primer for detecting the X and Y sperm separation purity. Aiming at a sex-determining gene Sry on a bull Y chromosome, the primer is designed through the PCR mismatching technology. The fragment size can be amplified by 295 bp through the primer, in order to prevent false positive from appearing, a pair of internal control primers C34 is designed through the invention according to a bull autosome 3 reported sequence, the fragment size is amplified by 208bp, dual PCR amplification is performed to single bull sperm through the two pairs of primers, and then the final evaluation is performed to the sperm separation purity according to the statistical analysis to the detection result. The invention provides the technology used for identifying the bull X and Y sperm separation purity with low cost and simple, rapid, and accurate operation, and provides reliable technical support for the popularization and the application of the subsequent sexing semen and the optimization of a sperm separation method.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for generating cloned animals using chromosome shuffling
InactiveUS20040139489A1Population uniformImprove quality controlGenetic material ingredientsGenetic engineeringSpecific chromosomeMammal
The present invention concerns the use of chromosomal replacement techniques in the context of producing cloned and transgenic animals, in order to correct chromosome abnormalities or alter autosomal genotypes, and provide for novel breeding pairs by replacing the sex chromosome in animals to be cloned. Replacement of a sex chromosome, or an X or Y chromosome, will result in animals that are autosomally isogenic and sexually non-isogenic (AISN), with "autosomally isogenic" meaning that the paired sets of autosomes (non-sex chromosomes) in each animal are isogenic or identical. Also included in the invention are animals that are both "autosomally" and "allelically" isogenic whereby each particular pair of chromosomes is internally isogenic or identical within a single animal as well as between animals. Such animals are particularly useful in generating a line of cloned mammals using sexual reproduction, without having to undergo nuclear transfer in order to propagate cloned animals.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Methods and systems for assessing and/or quantifying sperm cell subpopulations bearing a specific genetic signature
ActiveUS20190071725A1Reliable assessmentReliable qualitative and quantitative assessmentMicrobiological testing/measurementY chromosomeX chromosome
Technologies for assessing, quantifying and isolating sperm cell populations and / or subpopulations having specific genetic signatures are provided, as well as methods and systems to assess the efficacy of chromosomal differentiation processes. Compositions for identification and differentiation of X-chromosomes and Y-chromosomes in DNA are also provided.
Owner:ABS GLOBAL
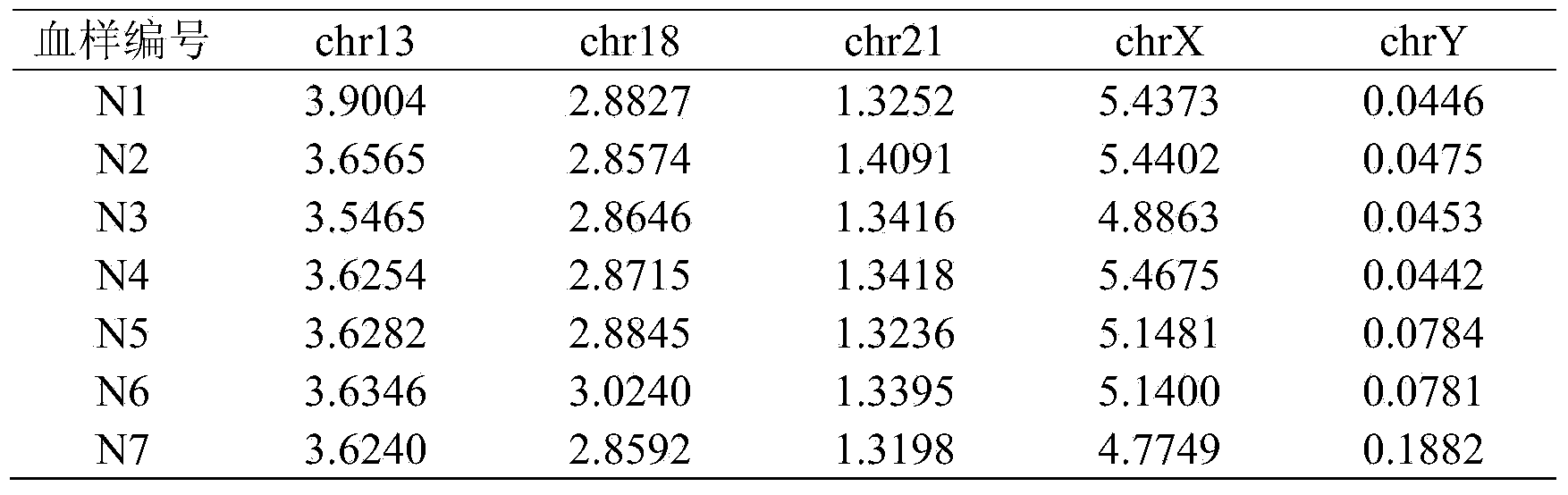
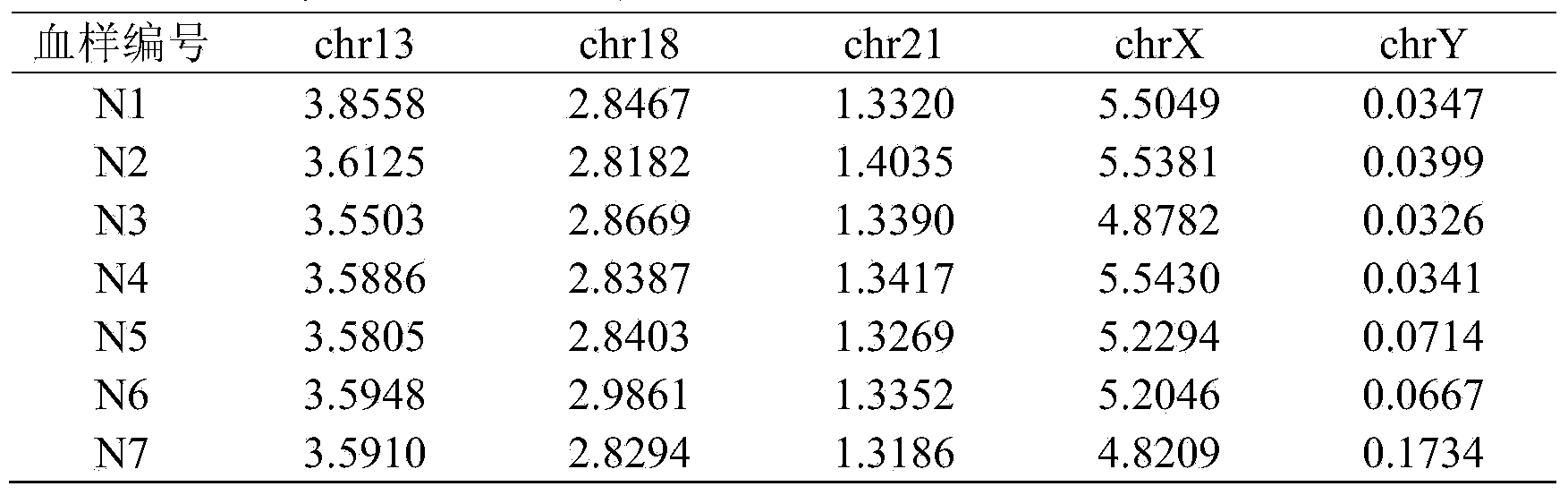
Method for detecting abnormal numbers of five chromosomes
ActiveCN103074416AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementY chromosomeX chromosome
The present invention relates to a method for detecting abnormal numbers of five chromosomes, wherein the method is provided for concurrently detecting aneuploidy of numbers of five chromosomes such as chromosome 21, chromosome 13, chromosome 18, chromosome X and chromosome Y, and comprises: (1) respectively selecting 7 genes from the five chromosomes, and designing 38 pairs of primers based on the selected genes; (2) adopting combinations of the primers to carry out multiplex PCR and capillary electrophoresis; and (3) adopting a software to analyze electrophoresis results.
Owner:NINGBO HEALTH GENE TECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
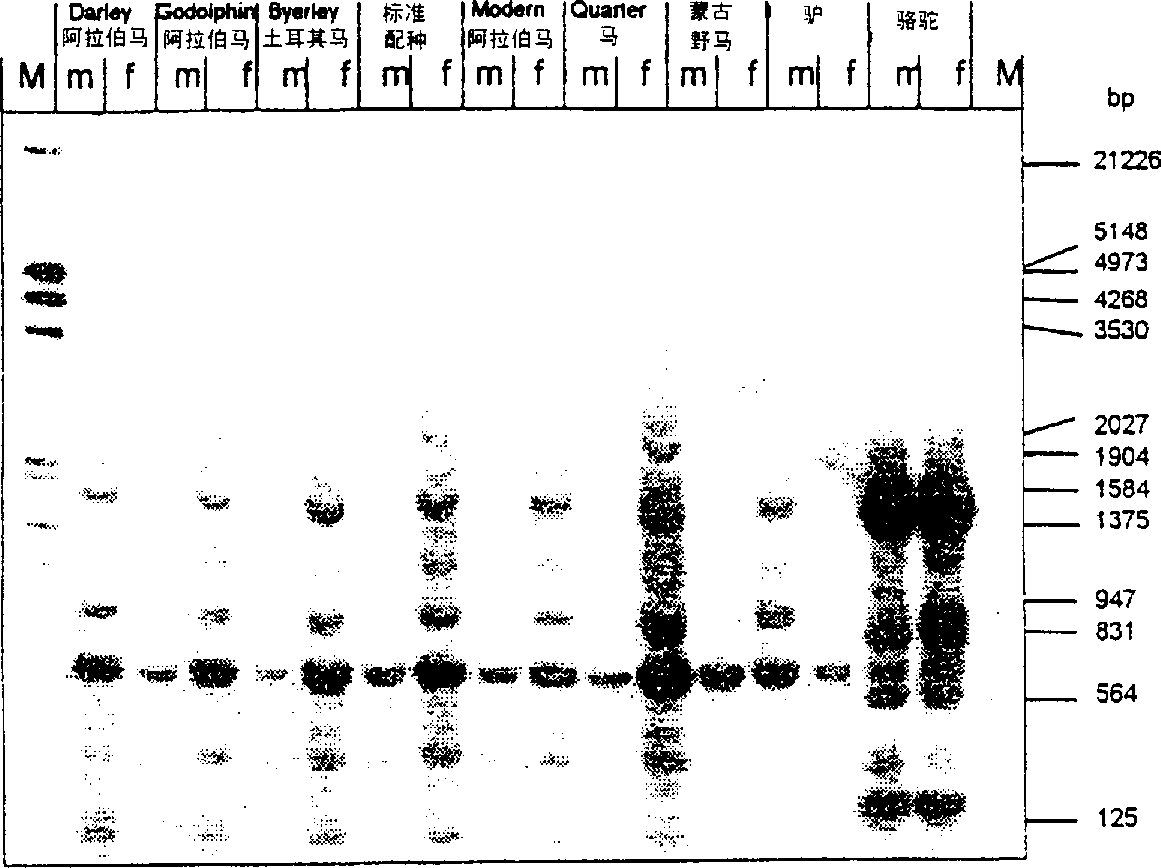
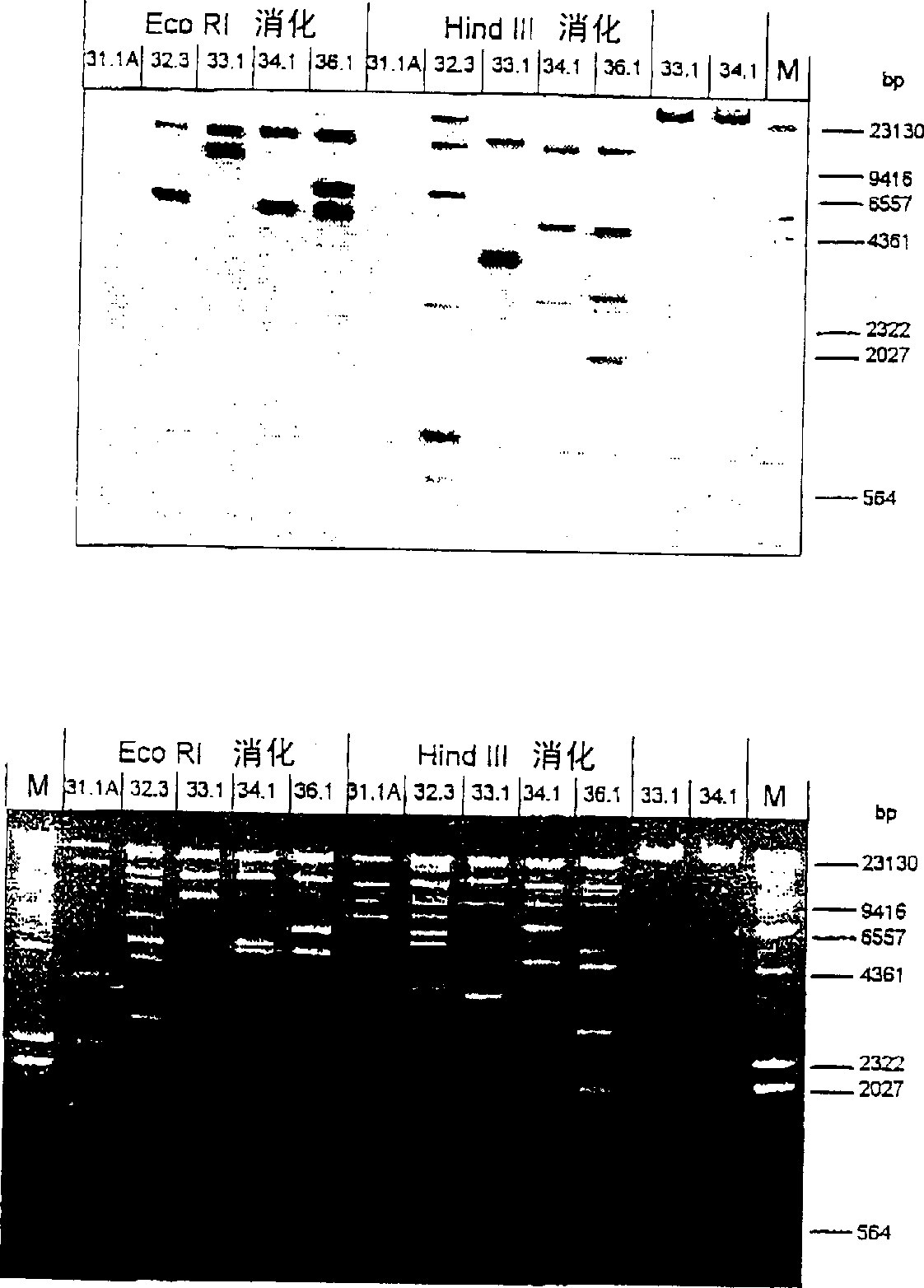
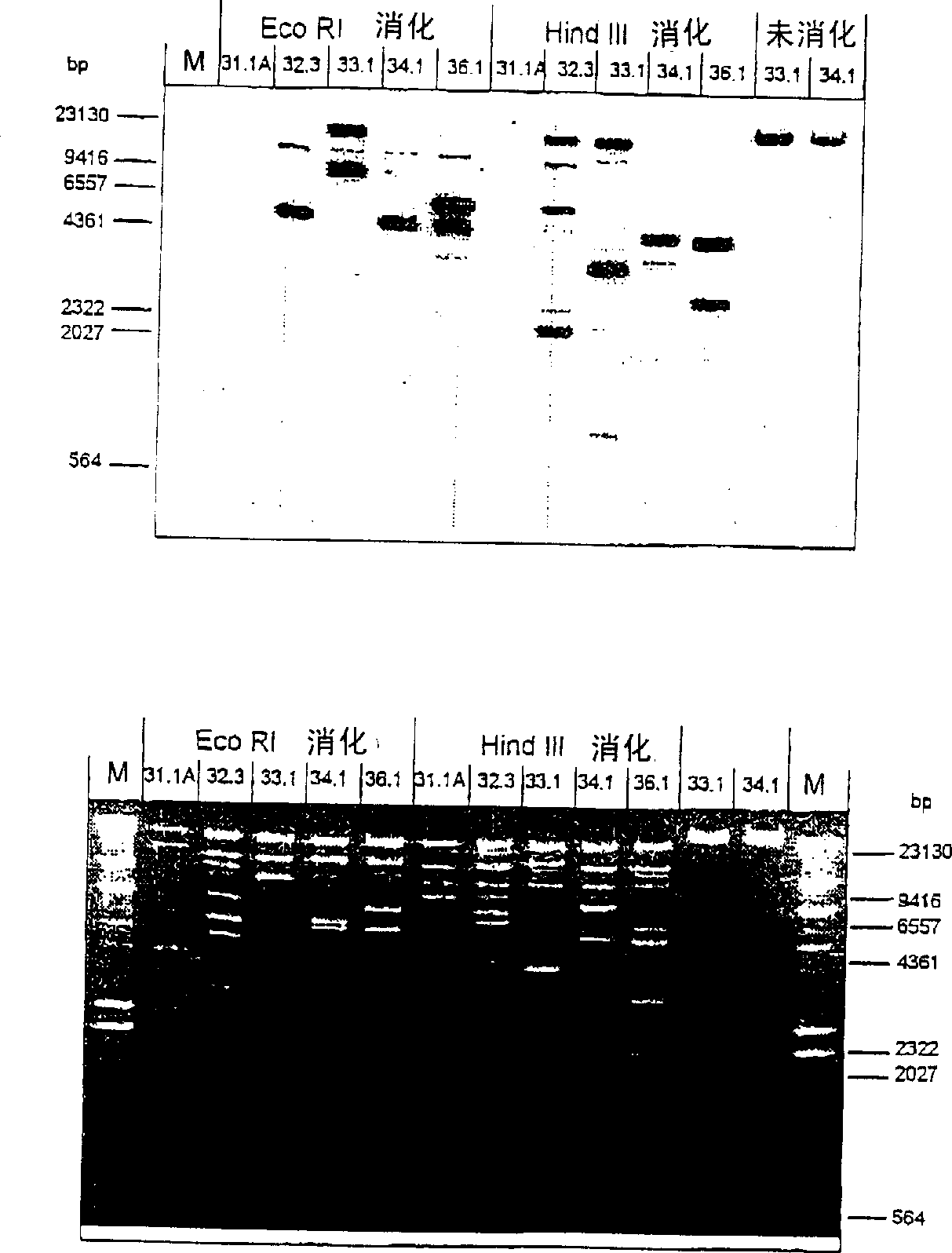
Determination of genetic sex in equine species by analysis of Y-chromosomal DNA sequence
InactiveCN1269831AIncreased sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementY chromosomeDNA
The present invention relates to DNA sequences, probes and primers specific to the Y chromosome of Equus caballus. The present invention also relates to methods for determining the sex of horses, fetal horses, horse embryos or horse cells. The present invention further relates to methods for isolating Y chromosome DNA sequences. .
Owner:WU LI DANCE
Multiple relative real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit for rapidly detecting number of human chromosomes
InactiveCN105861699AEnsure consistencyAvoid mutual interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationY chromosomeX chromosome
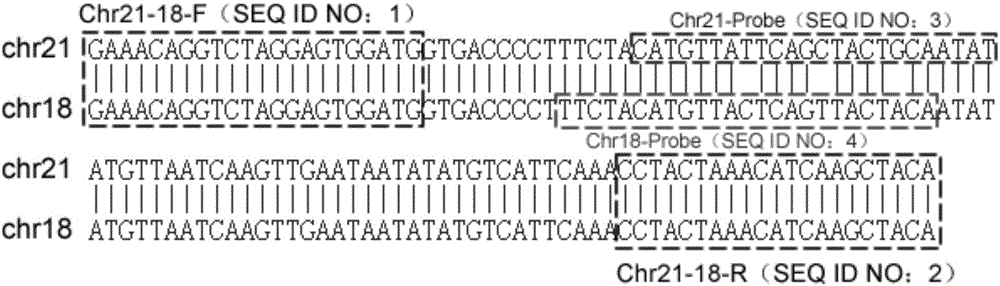
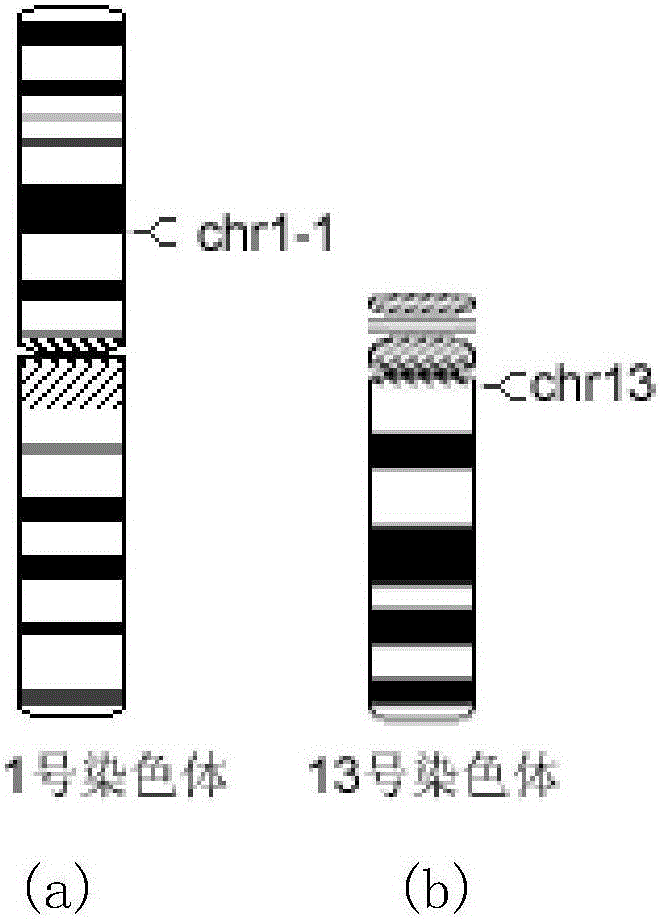
The invention discloses a multiple relative real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit for rapidly detecting the number of human chromosomes. The kit comprises two reaction tubes of a group A reaction system and a group B reaction system, wherein the group A reaction system comprises two pairs of primers and four Taqman probes which are used for detecting repetitive sequences between chromosomes 21 and 18 and repetitive sequences between chromosomes 13 and 1, and are mainly used for detecting the number of chromosomes 13, 18 and 21; the group B reaction system comprises two pairs of primers and four Taqman probes which are used for detecting repetitive sequences between chromosomes 16 and X and repetitive sequences between chromosomes 1 and Y, and are mainly used for detecting the number of chromosomes X and Y. The kit disclosed by the invention is capable of respectively detecting the number of the chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X and Y simultaneously and independently; the results are accurate and reliable; the kit has high sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:孙雷
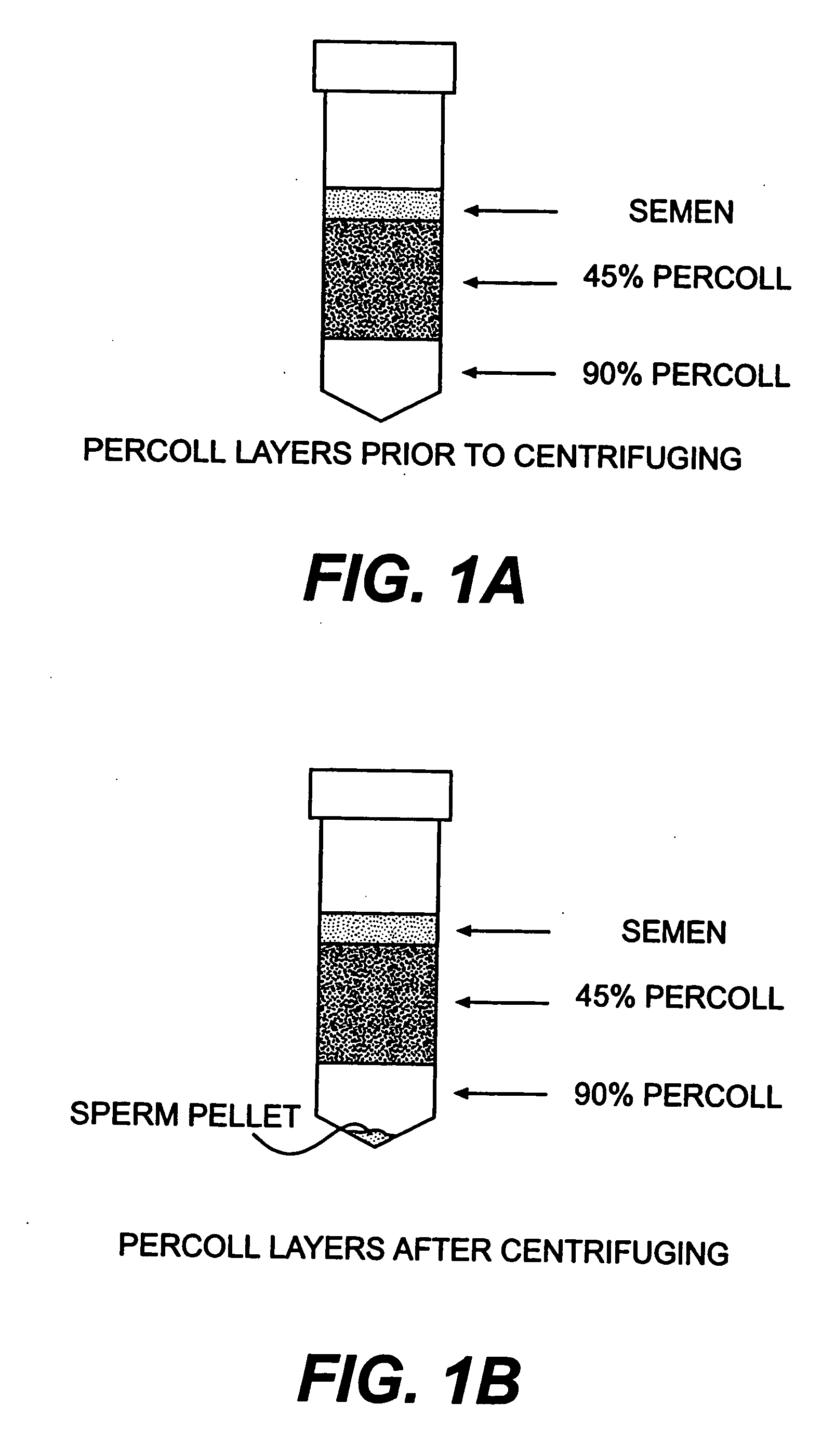
Sperm processing method, apparatus and related media compositions
ActiveUS20180208894A1Preparing sample for investigationDead animal preservationY chromosomeX chromosome
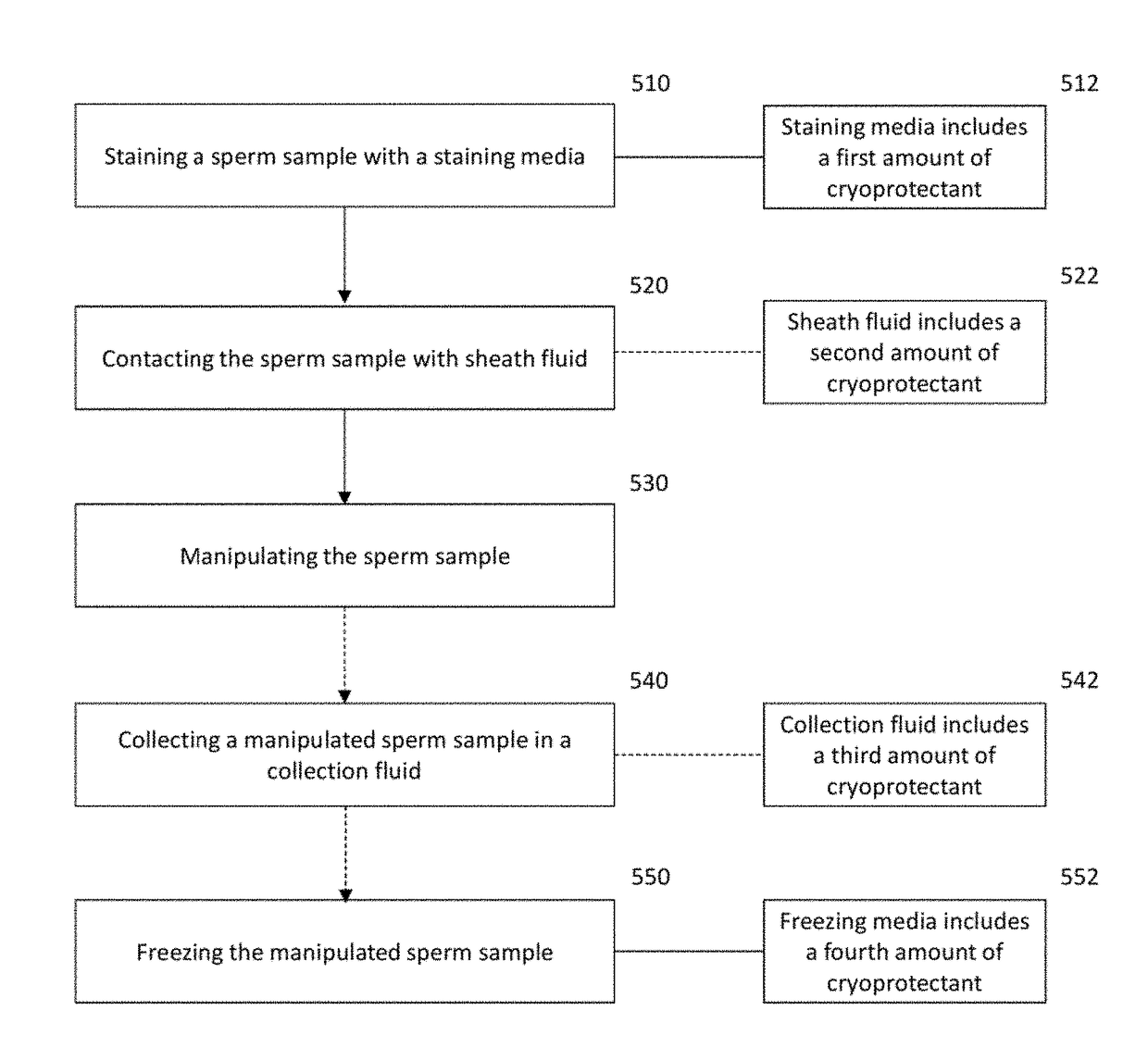
Embodiments of the present invention relate generally to processes, systems, and compositions useful in manipulating a ratio of viable X chromosome bearing sperm to viable Y chromosome bearing sperm in at least one sperm population and useful for preserving the resulting manipulated sperm population. In some embodiments a cryoprotectant may be incorporated into various medias used in manipulating the sperm sample, such as in a staining media, a sheath fluid, and a collection media.
Owner:INGURAN LLC
A method and application for realizing animal sex control based on rbmy gene editing
The invention discloses an animal sex control method based on Rbmy gene editing and application. The method controls animal sex by using CRISPR / Cas9 system to specifically cut Rbmy gene on Y chromosome. Rbmy gene encodes a germ cell specific nucleoprotein, this protein is an important factor related to spermatogenesis, and by cutting Rbmy gene, it is possible to deactivate Rbmy gene, thus Y sperm or fertilized ovum with Y sperm is deactivated and cannot develop into a normal embryo, birth ratio of female animals is finally increased and sex control is achieved. Therefore, sex ratio of animal offspring can be controlled through the method so that the ratio of female animals with better economic value is increased and production efficiency and economic effect are greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Reagent kit for detecting chromosome numerical abnormalities resulting in natural abortion
InactiveCN101407843BLow requirements for testing samplesLower requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementY chromosomeChromosome number abnormality
The invention provides a kit for detecting the abnormal number of chromosomes which causes natural abortion. The kit comprises 7 to 9 groups of multiple PCR primers which can carry out molecule detection and source judging on the abnormal number of 10 types of chromosomes (the chromosomes of number 2, number 13, number 15, number 16, number 18, number 20, number 21, number 22, X and Y); and the detection range covers the common abnormal chromosome types during natural abortion and prenatal diagnosis and the kit has the advantages of high delicacy, high accuracy, low detection cost, and the like.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Detection kit for human Y-chromosomal microdeletion and application of detection kit
InactiveCN108148896AGood typing patternAvoid confusionMicrobiological testing/measurementY chromosomeGenetics
The invention provides a multi-PCR amplification system and detection kit for human Y-chromosomal microdeletion. The system comprises amplification primers comprising following loci with the corresponding sequences from SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.40, wherein the loci comprise 15 Y-chromosomal microdeletion loci (4 in the AZFa region, 4 in the AZFb region, 5 in the AZFc region and 2 in AZFd region),3 sample molecular tag loci (two X-STR loci and one autosomal locus) and 2 gender quality control loci (SRY, ZFX / Y). The 15 Y-chromosomal microdeletion loci use sequence tag loci (STS) specific primers, the 3 sample molecular tag loci use length polymorphism primers, and the 2 gender quality control loci use STS specific primers (EAA / EMQN Y-chromosomal microdeletion related aboratory optimal handbook recommendation detection loci, 2013). The primers are compatible with one another and can react in the same PCR amplification system. In addition, the invention further provides the detection kitcontaining an amplification primer composition container, a PCR reaction mother liquor container and a PCR auxiliary liquid container and application of the detection kit in human Y-chromosomal microdeletion non-diagnostic detection. After DNA extraction, target fragments of 20 genetic marker loci are amplified through a PCR reaction, the cost, labor and time can be remarkably saved, and the workefficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENEDISC BIOTECH CO LTD
Selection of pluripotent cells for production of fertile xy female mice
Methods and compositions are provided for generating F0 fertile XY female animals. The methods and compositions involve making XY pluripotent or totipotent animal cells, in vitro cell cultures, or embryos that are capable of producing a fertile female XY animal in an F0 generation. Such cells, embryos, and animals can be made by silencing a region of the Y chromosome. Optionally, the cells can also be cultured in feminizing medium such as a low-osmolality medium and / or can be modified to decrease the level and / or activity of a Sry protein. Methods and compositions are also provided for silencing a region of the Y chromosome in an XY pluripotent or totipotent animal cell, or in vitro cell cultures, embryos, or animals derived therefrom, by maintaining an XY pluripotent or totipotent animalcell in a feminizing medium. Methods and compositions are also provided for maintaining a population of XY pluripotent or totipotent animal cells in a feminizing medium and selecting cells or clones having increased capabilities for producing a fertile female XY animal in an F0 generation. Methods and compositions are also provided for screening for compounds with feminizing activity or for optimizing concentrations of components in feminizing media.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Multiplex amplification kit for cattle paternity identification and individual identification and application thereof
PendingCN111560442AEasy to identifyComprehensive coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMultiplexY chromosome
The invention discloses a multiplex amplification kit for cattle paternity identification and individual identification and an application thereof. The kit comprises 21 pairs of specific primers for amplifying 20 cattle STR sites and one Amel sex site, the sequences of the specific primers are shown as SEQ ID NO: 1-SEQ ID NO: 42 in a sequence table, and 20 cattle STR sites and one Amel sex site can be amplified at the same time. The invention provides the multiplex amplification kit for cattle paternity identification and individual identification and the application thereof. The kit comprisesan autosomal STR, a Y chromosome STR and an Amel sex site at the same time, the kit is the kit with the most detection sites in the same type of products, can simultaneously amplify and detect 20 cattle STR sites and one cattle sex site in a single tube, has the characteristics of strong specificity, high resolution, accurate typing, high sensitivity and the like, and can completely meet the requirements of cattle paternity identification, individual identification, sex discrimination and the like.
Owner:AGCU SCIENTECH +2
Kit for detecting specific microsatellite locus of sheep Y chromosome and application of kit
The invention discloses a kit for detecting a specific microsatellite locus of a sheep Y chromosome and an application of the kit. The kit comprises 0.6 microliter of to-be-detected sample template DNA, 0.2 microliter of specific microsatellite forward primer, 0.2 microliter of reverse primer, 1 microliter of nucleic acid amplification system 6*Buffer, 0.8 microliter of dNTP, 0.2 microliter of TaqDNA polymerase, and finally adding ddH2O to obtain 10 microliters of mixture. A microsatellite locus is screened out from a specific region of the sheep Y chromosome, and a product can be amplified when the locus is applied to male sheep, but no product is amplified when the locus is applied to a female sheet body. The male sheep group has certain polymorphism by further research, which shows that the locus can be subjected to early embryo sex identification of the sheep, and can also be applied to paternal origin evolution research of the sheep.
Owner:王玉涛
Y-chromosome modification method and application thereof
ActiveCN104450673AImprove breeding efficiencyFermentationPlant genotype modificationY chromosomeAnimal body
The invention discloses a Y-chromosome modification method and an application thereof. The invention discloses an animal Y-chromosome modification method which comprises performing specific suicide component modification on the Y-chromosome of an isolated animal body cell by use of a TALEN method. The Y-chromosome modification method lays a foundation for selectively breeding animals of specific gender and improving the breeding efficiency.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Y-chromosomal microdeletion detection method and primer group
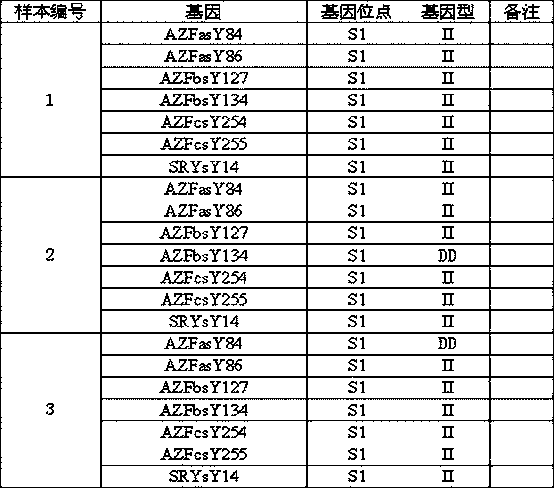
InactiveCN109797210AImprove throughputImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMale infertility
The invention relates to the technical and medical fields of molecular biology genes, in particular to a Y-chromosomal microdeletion detection method and primer group. The nucleotide sequence of sevensequence tag sites of AZFasY84, AZFasY86, AZFasY127, AZFasY134, AZFasY254, AZFasY255 and SRYsY14 is analyzed, corresponding primers are designed, multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on specific sites of genomic DNA in the sample is performed, and finally detection is carried out with the Ion Torrent semiconductor chip sequencing technology. The detection method has the advantages of large flux, high specificity and sensitivity, stable results, good repeatability, fast detection speed and the like; a fast, reliable and accurate new approach is provided for detecting, testing, analyzing and evaluating the genetic aspects of male infertility, and theoretical basis is provided for clinical diagnosis of the diseases.
Owner:上海联吉医学检验所有限公司
A method for efficiently producing Nile tilapia high reproductive rate yy transformed female fish
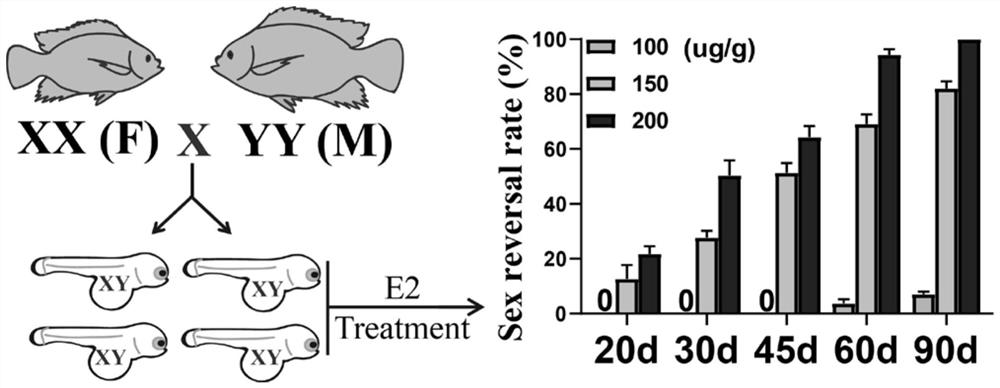
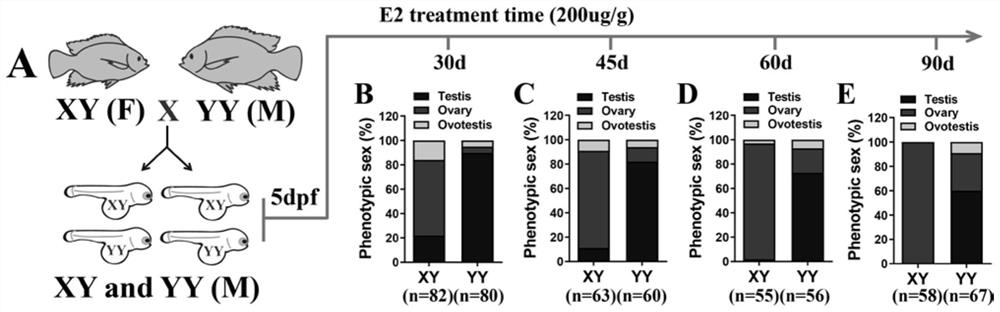
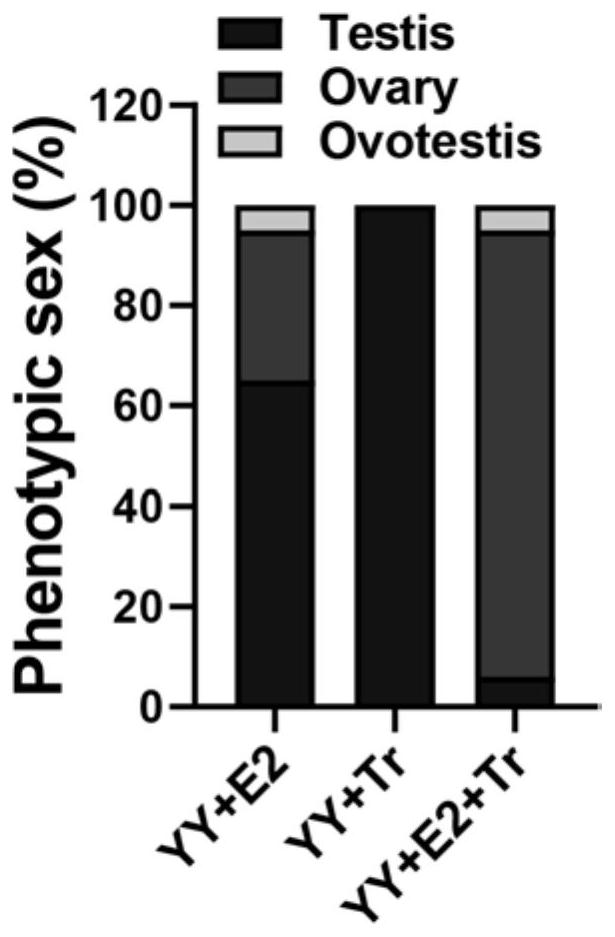
ActiveCN110583539BRealize large-scale productionEfficient productionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAnimal scienceJuvenile fish
The invention relates to a method for efficiently producing YY transformed females of Nile tilapia with a high reproductive rate. Firstly, the XY transformed females are mated with XY males or YY super males, and the offspring are simultaneously fertilized 5 days after fertilization. Soak in estrogen and androgen synthase inhibitors until 10 days after insemination; then feed high-dose hormone-supplemented feed for feminization for 3 months after juveniles open, and use Y chromosome-specific molecular markers to screen out sex chromosomes The transformed female fish with genotype YY were fed with normal feed until 6 months old; then at the age of 6-7 months, the YY transformed female fish were treated with low-dose hormone-supplemented feed, and were raised normally until sexual maturity; finally, the fertile YY transformed female fish were screened out . Fertile YY transformed females are mated with YY super males to establish YY maintenance lines and realize large-scale production of genetic all-male fry, which can significantly increase aquaculture production, reduce aquaculture costs, and reduce the use of hormones. In areas where tilapias invade and flood A large number of YY super male fish can be released for biological control.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Reagent and kit for detecting sexual accompanying hereditary disease of fetus
PendingCN114107481ARealize non-invasive safety detectionImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationY chromosomeGynecology
The invention discloses a reagent and a kit for detecting sex-associated hereditary diseases of fetuses. The reagent for detecting the sex-associated hereditary disease of the fetus comprises a Y chromosome specific primer and a Y chromosome specific probe, an upstream primer of the Y chromosome specific primer is Seq ID No.1, a downstream primer of the Y chromosome specific primer is a sequence shown as Seq ID No.2, and the Y chromosome specific probe is a probe with a fluorescent group at the 5'end and a quenching group at the 3 'end of a sequence shown as Seq ID No.3. According to the reagent for detecting the sex-associated hereditary disease of the fetus, the sex of the fetus can be judged by detecting blood of a pregnant woman, and the sex-associated hereditary disease is detected; the sex-associated hereditary disease related to the gender of the fetus can be found as soon as possible in the early pregnancy stage, and reference is provided for related treatment.
Owner:深圳知因细胞生物科技有限公司
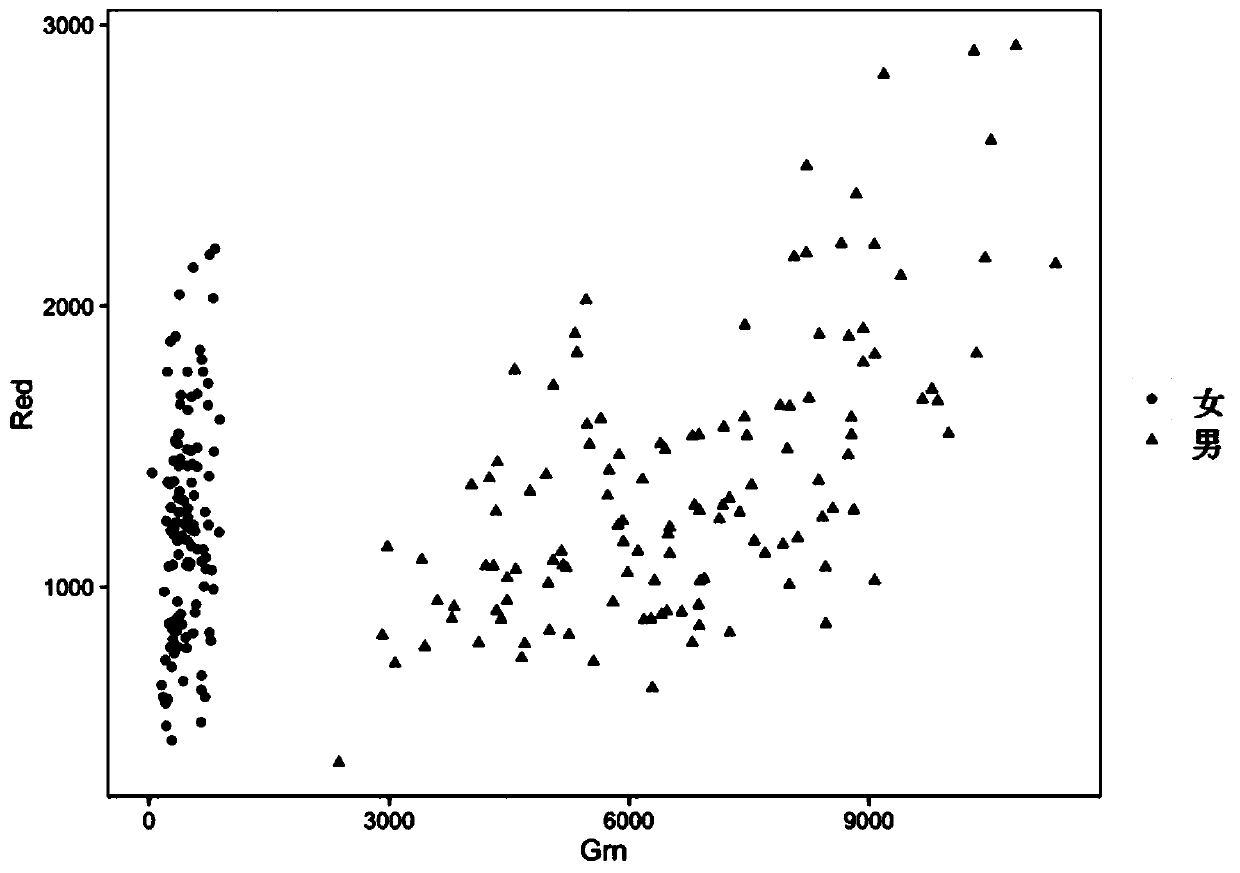
Gender discrimination method based on chip detection of DNA data
The invention discloses a gender discrimination method based on chip detection of DNA data. The gender discrimination method includes the steps: selecting S sites on all sex-related X and Y chromosomes and reading P samples to obtain a P*S size matrix, and screening M sites with large discrimination; establishing a logistic regression model for each site among the M sites, wherein the independentvariables are DNA detection red fluorescence and DNA detection green fluorescence values and the dependent variable value is 0 or 1, representing male and female, and obtaining M regression models andsaving the M regression models; and when predicting a new sample, through the logistic regression models of M sites, obtaining M prediction values between 0 and 1, and calculating the final probability according to the probability interpretation of the logistic regression prediction values. The gender discrimination method based on chip detection of DNA data combines the X and Y chromosomes, andis fully quantified by the method of machine learning, and the gender discrimination result is a value between 0 to 1, thus being able to be compatible with various data cases and making richer discrimination for gender.
Owner:北京各色科技有限公司
Amplification composition and rapid detection kit for detecting abnormal number of chromosomal aneuploidy
ActiveCN104651488BShort detection cycleHigh speedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAmniotic fluidBiology
Owner:BEIJING MICROREAD GENE TECH
Non-invasive fetal sex determination
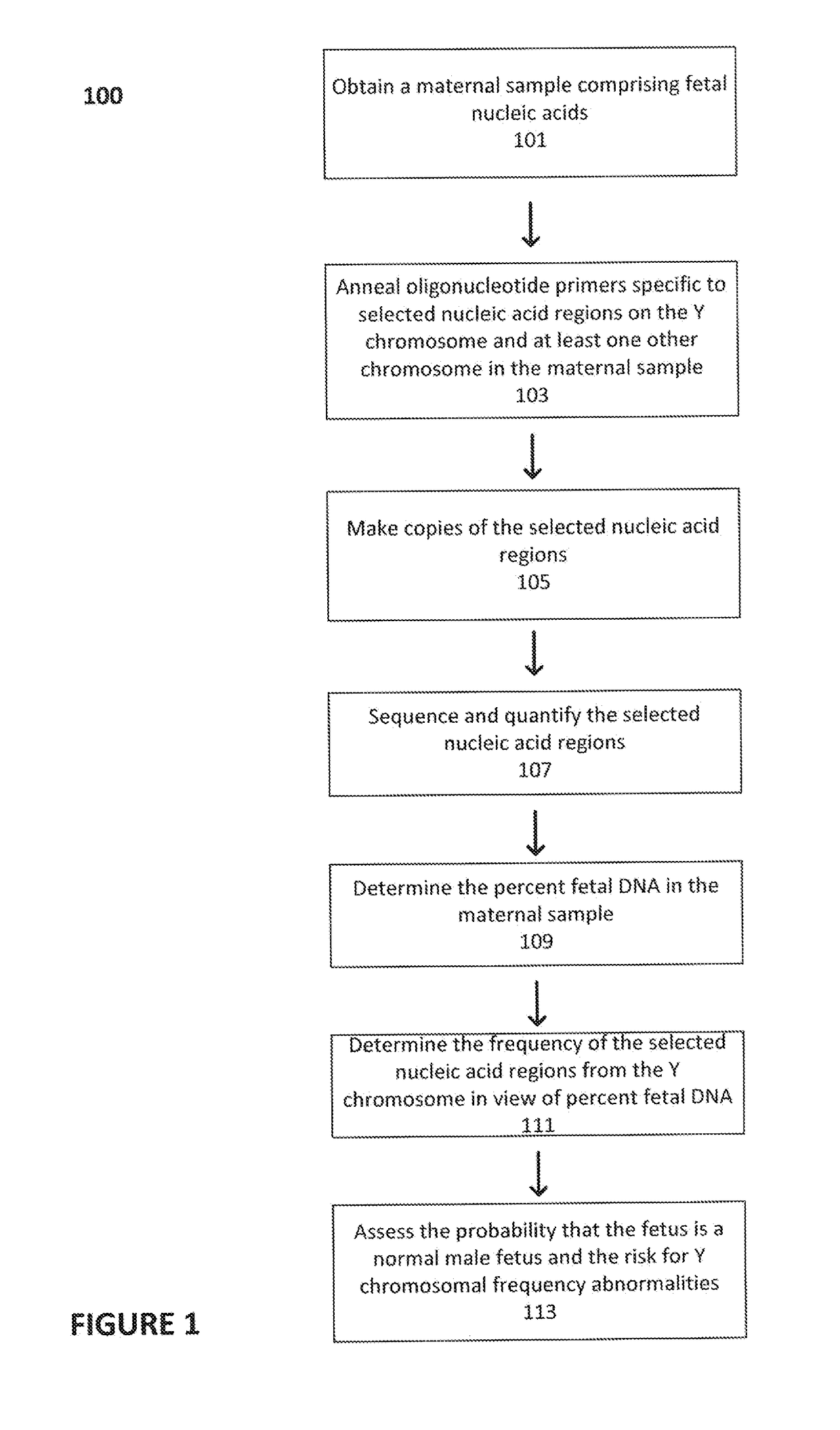
The present invention provides methods for non-invasive determination of sex in a fetus or of Y chromosomal frequency abnormalities—indicative of aneuploidy or sex mosaicisms in a fetus—by detecting and determining the relative contribution genetic sequences from the Y chromosome in view of the percent fetal contribution in a maternal mixed sample.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
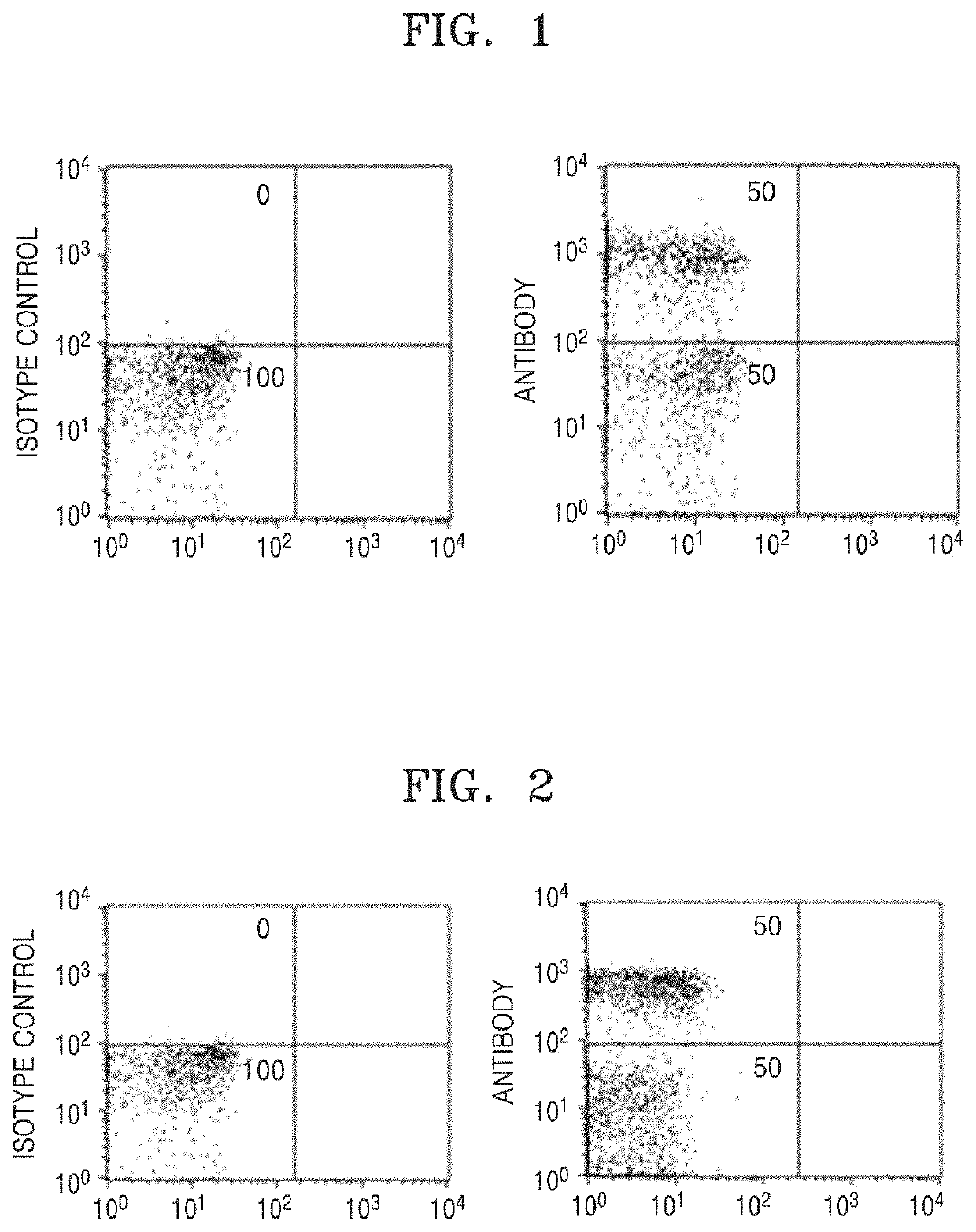
Antibody for determining sex of sperm, and use thereof
ActiveUS10550177B2Easily sorting X chromosome spermsEfficient managementAnimal reproductionCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsY chromosomeAnimal science
Provided are an antibody for sexing sperms and use thereof, and more particularly, a composition for and a method of sexing sperms by using the antibody, and a method of producing an animal of a particular sex. In the present disclosure, it was confirmed that agglutination of Y chromosome sperms may be induced by treatment of the antibody, thereby easily sorting X chromosome sperms and Y chromosome sperms. Therefore, it is possible to produce a large number of customized animals of a particular sex and to selectively produce livestock of a desired sex, and therefore, it is expected to contribute to planed breeding, breeding improvement, and efficient management.
Owner:NURISCI CO LTD
A method for sex identification of mammalian embryos
ActiveCN109402244BSimple knock-inEfficient knock-inMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAGene targetingGene knockin
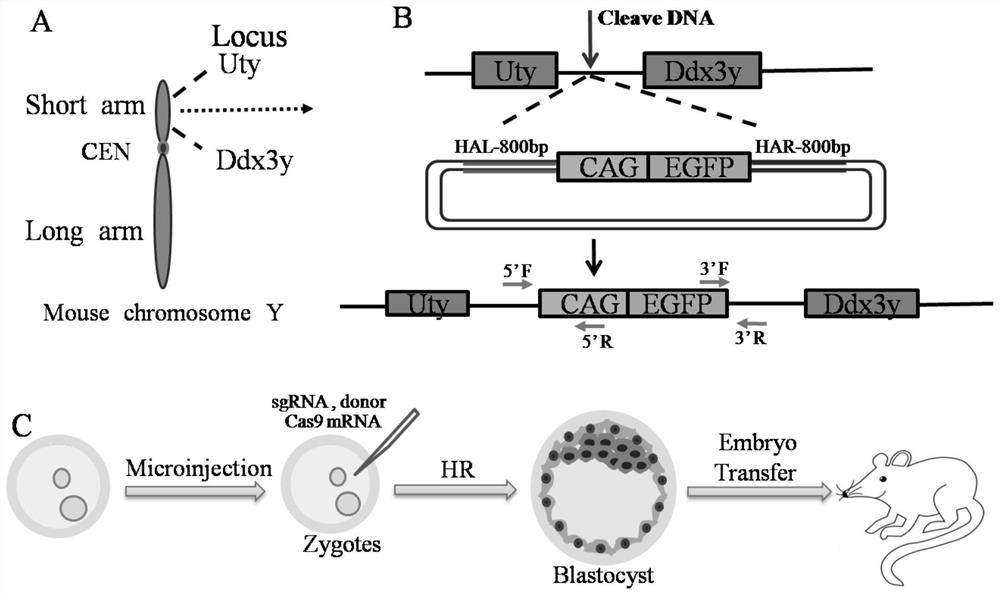
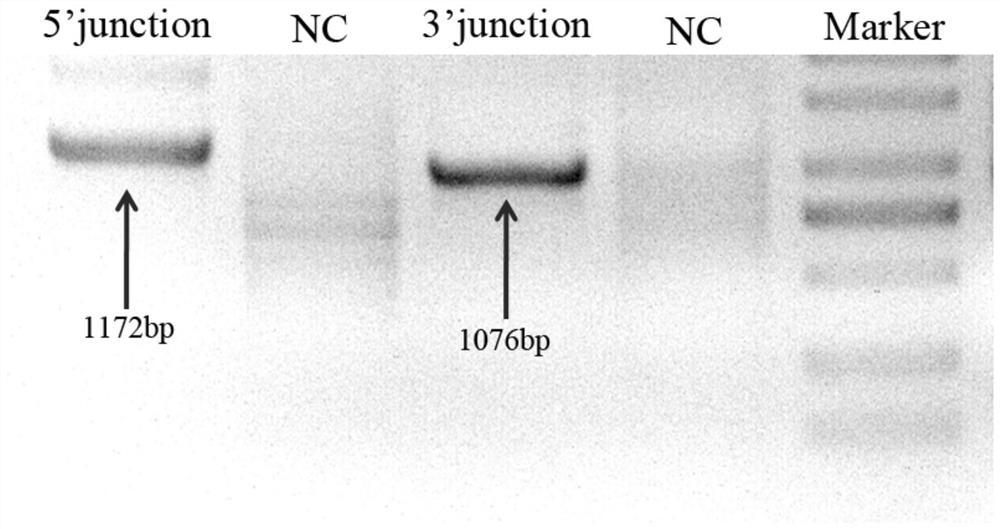
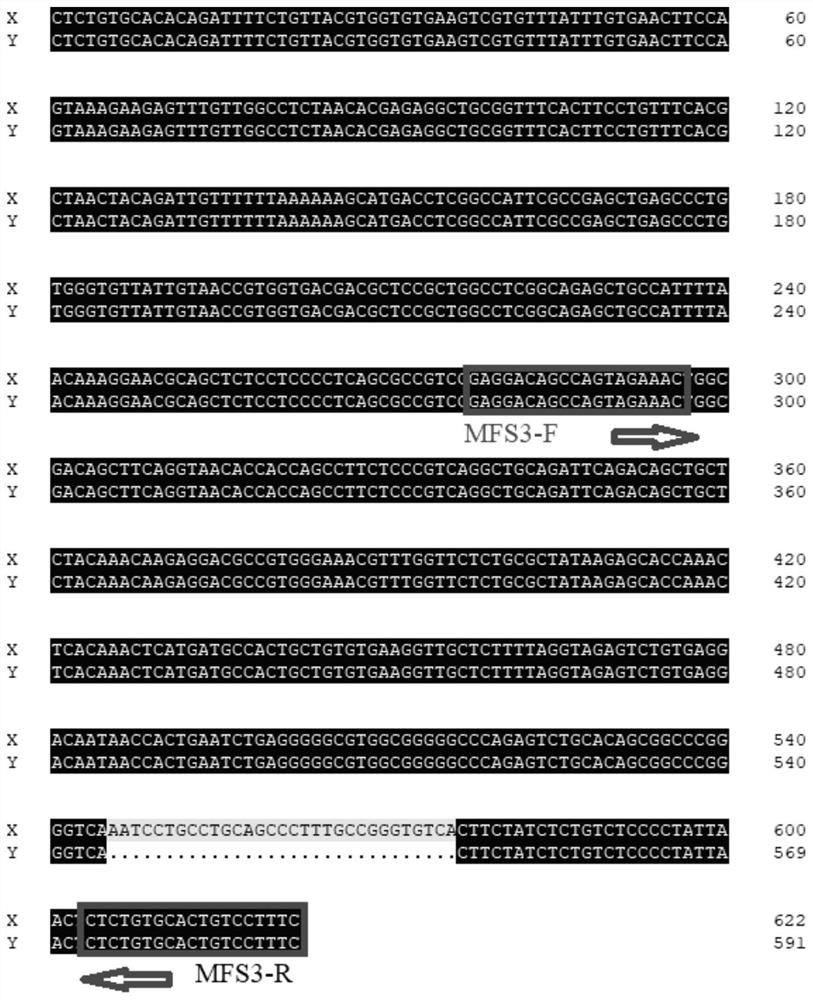
The present invention relates to the technical field of sex identification, in particular to a method for sex identification of mammalian embryos. The present invention accurately identifies the sex of mammalian embryos by inserting a fluorescent reporter gene on the Y chromosome and through the fluorescent expression of the fluorescent reporter gene. Simple, efficient, accurate, and less damage; in the process of constructing a male mammalian model with a fluorescent reporter gene on the Y chromosome, the spacer region located in the Ddx3y and Uty genes is selected as the targeting region for the integration of exogenous genes, reducing the number of gene targeting sites The impact of the selection on the transgenic animal itself; in the gene editing process, the Cas9 protein and the single-guided sgRNA designed according to the gene sequence of the target region can be used to accurately cut the DNA of the target site and target the Ddx3y and Uty genes on the Y chromosome A fluorescent reporter gene is inserted between them, making the gene knock-in method efficient and simple.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Molecular marker for identifying genetic sex of micropterus salmoides and primer pair thereof
PendingCN114717301AIncrease economic benefitsStable identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationY chromosomeZooid
The invention discloses a molecular marker for identifying genetic sex of micropterus salmoides and a primer pair thereof. The sequence of the molecular marker is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and the molecular marker exists on a genetic sex X chromosome of micropterus salmoides and is deleted on a Y chromosome. The sequences of the primer pair are shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 and SEQ ID NO: 3. The primer pair can be used for simply, quickly and stably identifying the genetic sex of different individuals in each population of the micropterus salmoides, including embryos, larvae and adults of the micropterus salmoides. And the accuracy reaches 100%.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Orphan and haploid stem cell line and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN103361304BTypical imprintImprint maintenanceEmbryonic cellsFermentationStem cell lineBlastula
Provided are an androgenetic haploid stem cell line, preparation method and use thereof. Specifically, provided are an androgenetic haploid cell and androgenetic blastula. The nucleus of the cell or the blastula only comprises a haploid autosome and a sex chromosome, the sex chromosome being the X chromosome and containing no Y chromosome. The androgenetic haploid cell of the present application can replace a spermatid as a ligand to generate a fertile animal individual, thus facilitating gene manipulation and being capable of transferring genetic information to the offspring.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com