Patents
Literature
1612 results about "Capillary electrophoresis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a family of electrokinetic separation methods performed in submillimeter diameter capillaries and in micro- and nanofluidic channels. Very often, CE refers to capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE), but other electrophoretic techniques including capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE), capillary isoelectric focusing (CIEF), capillary isotachophoresis and micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) belong also to this class of methods. In CE methods, analytes migrate through electrolyte solutions under the influence of an electric field. Analytes can be separated according to ionic mobility and/or partitioning into an alternate phase via non-covalent interactions. Additionally, analytes may be concentrated or "focused" by means of gradients in conductivity and pH.
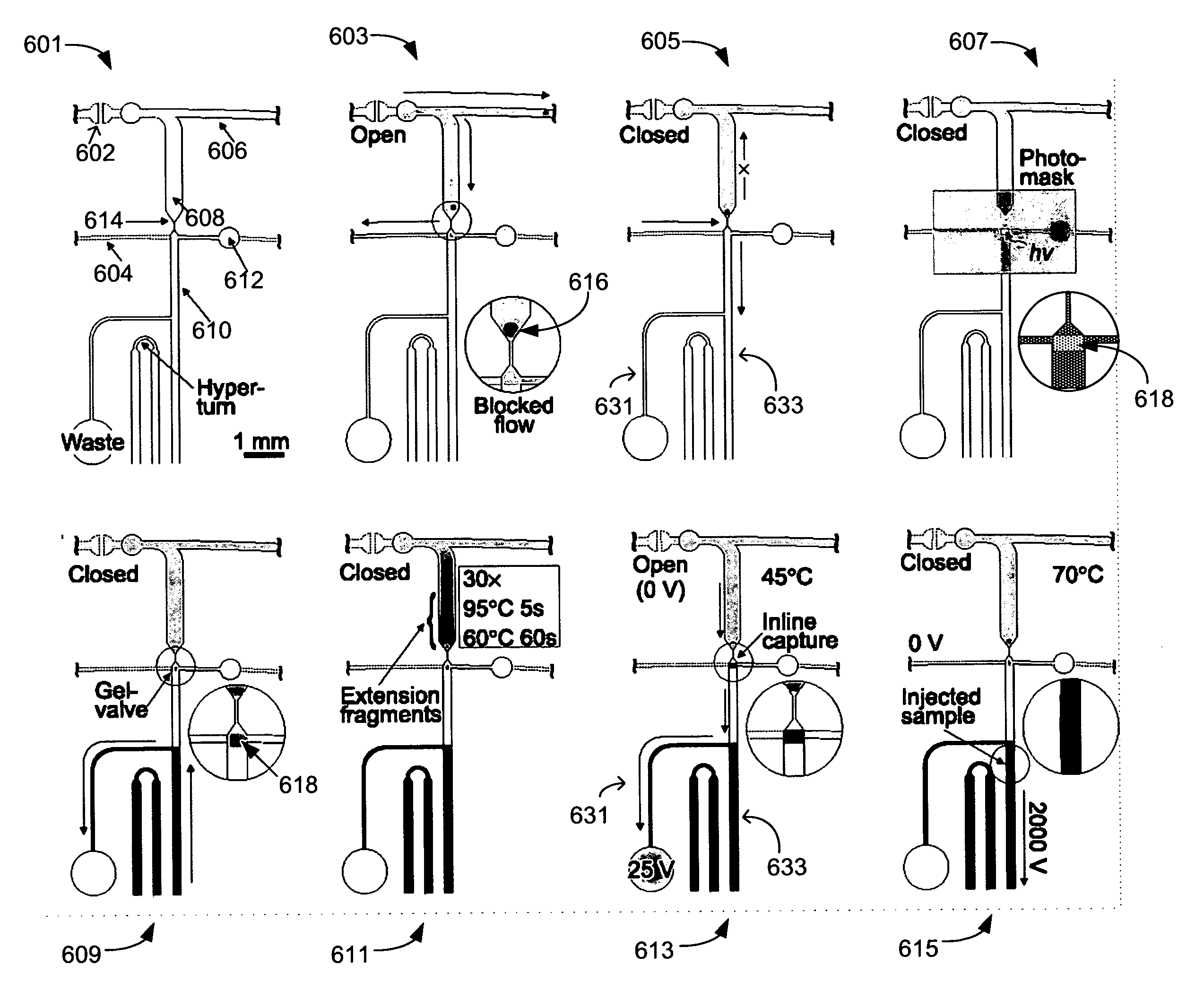
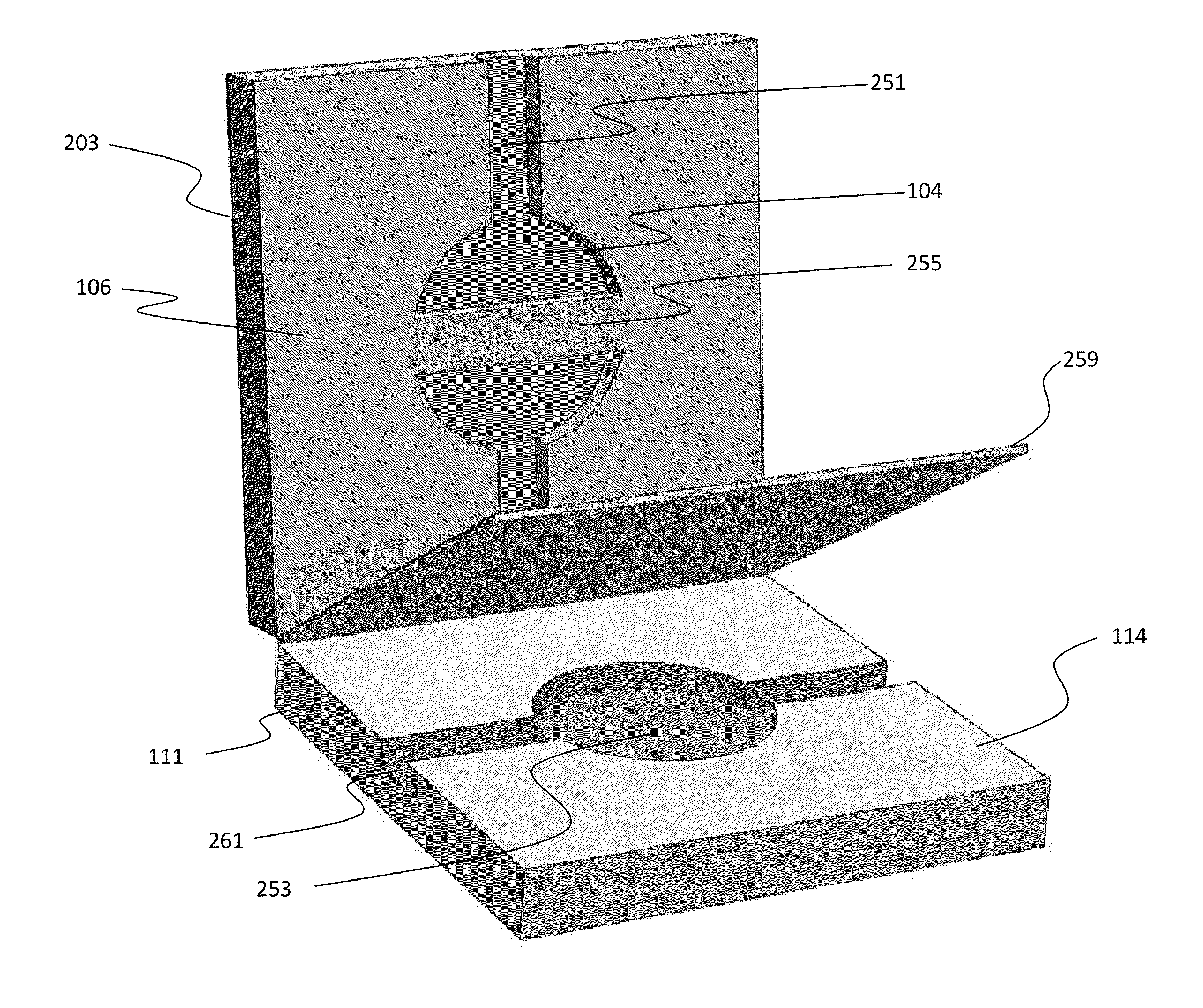
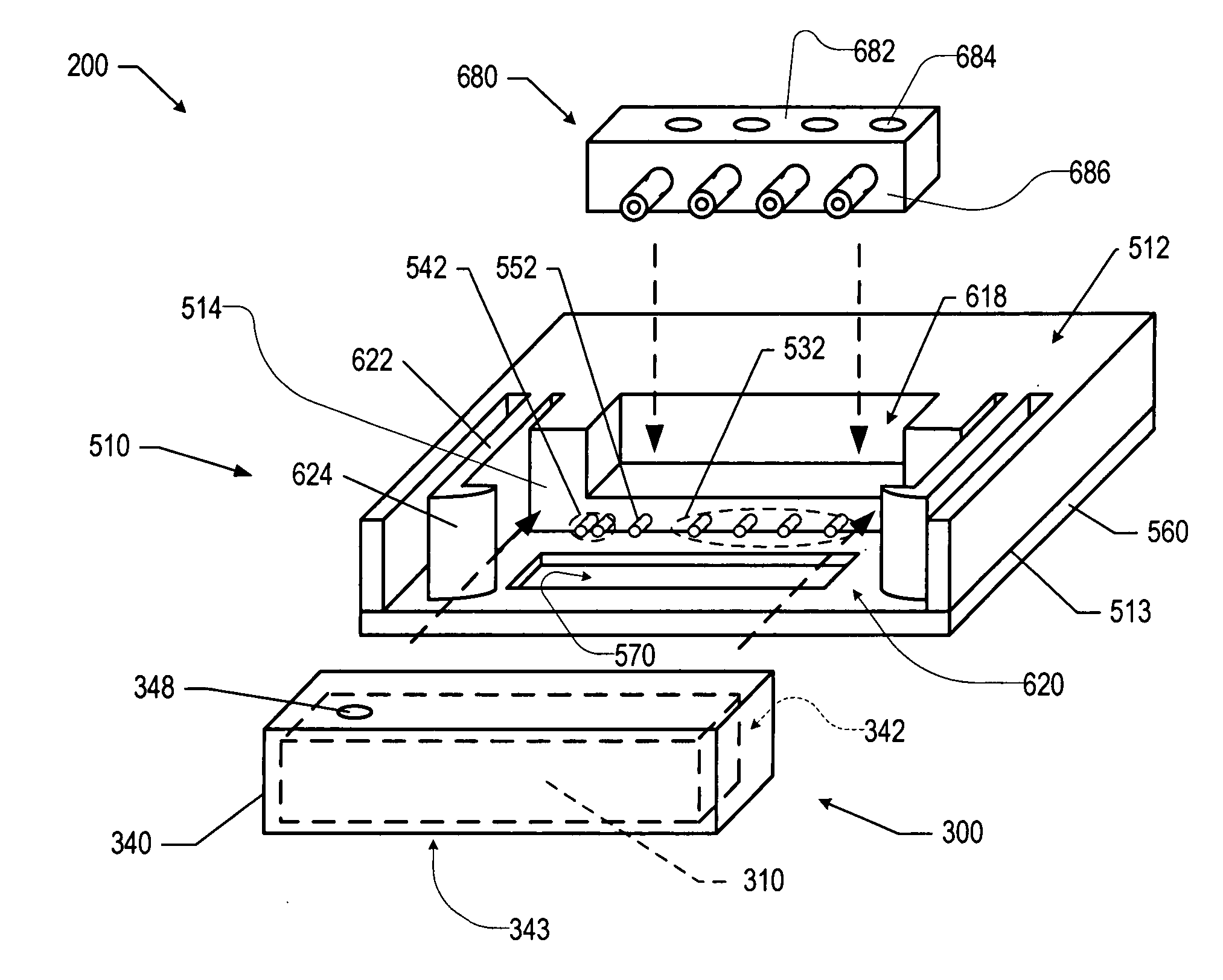
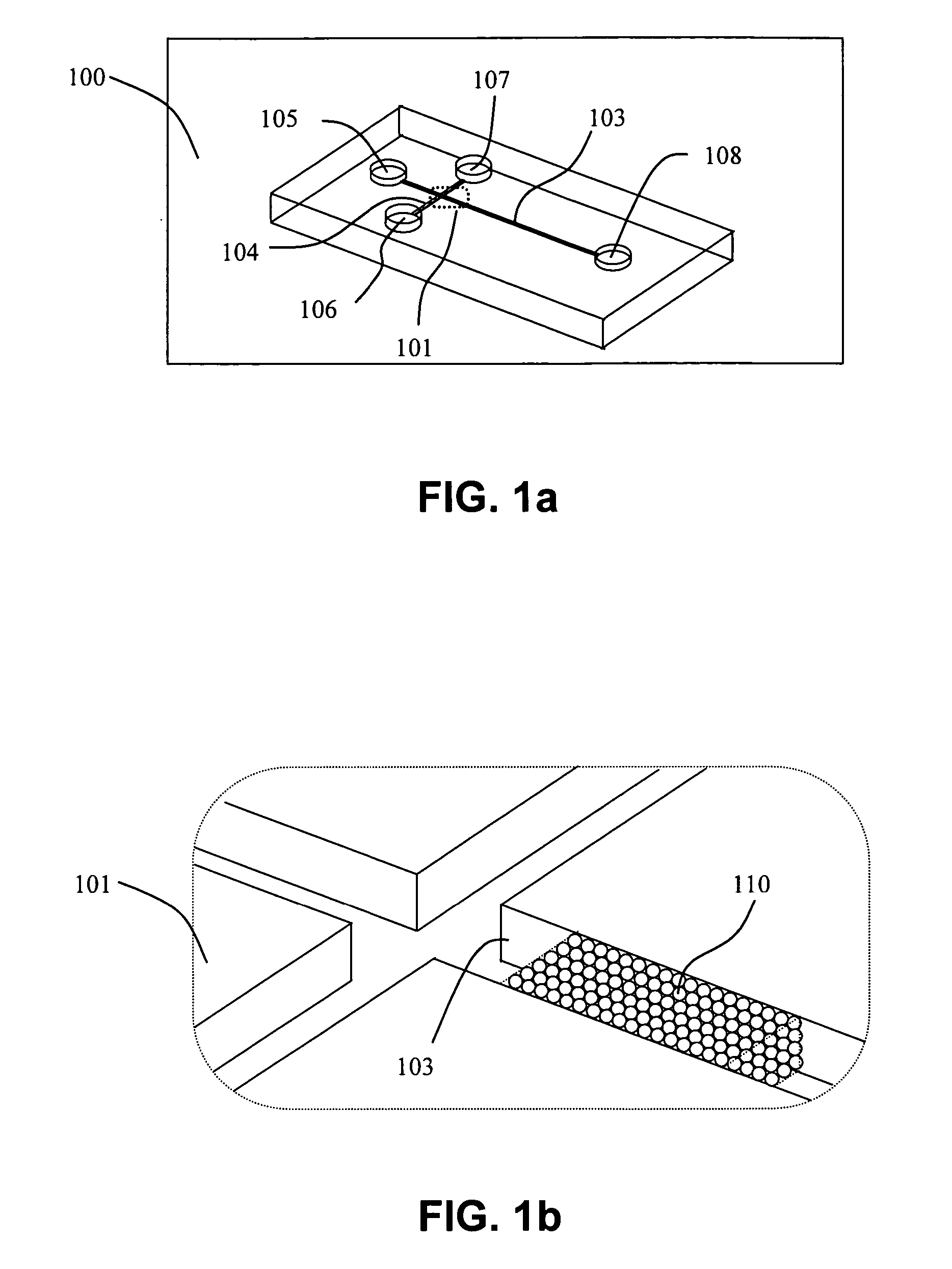
Inline-injection microdevice and microfabricated integrated DNA analysis system using same
InactiveUS20090035770A1Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
Methods and microfluidic circuitry for inline injection of nucleic acids for capillary electrophoresis analysis are provided. According to various embodiments, microfabricated structures including affinity-based capture matrixes inline with separation channels are provided. The affinity-based capture matrixes provide inline sample plug formation and injection into a capillary electrophoresis channel. Also provided are methods and apparatuses for a microbead-based inline injection system for DNA sequencing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Universal sample preparation system and use in an integrated analysis system
ActiveUS20110005932A1Optical radiation measurementSludge treatmentSample purificationCapillary Tubing
The invention provides a system that can process a raw biological sample, perform a biochemical reaction and provide an analysis readout. For example, the system can extract DNA from a swab, amplify STR loci from the DNA, and analyze the amplified loci and STR markers in the sample. The system integrates these functions by using microfluidic components to connect what can be macrofluidic functions. In one embodiment the system includes a sample purification module, a reaction module, a post-reaction clean-up module, a capillary electrophoresis module and a computer. In certain embodiments, the system includes a disposable cartridge for performing analyte capture. The cartridge can comprise a fluidic manifold having macrofluidic chambers mated with microfluidic chips that route the liquids between chambers. The system fits within an enclosure of no more than 10 ft3. and can be a closed, portable, and / or a battery operated system. The system can be used to go from raw sample to analysis in less than 4 hours.
Owner:INTEGENX
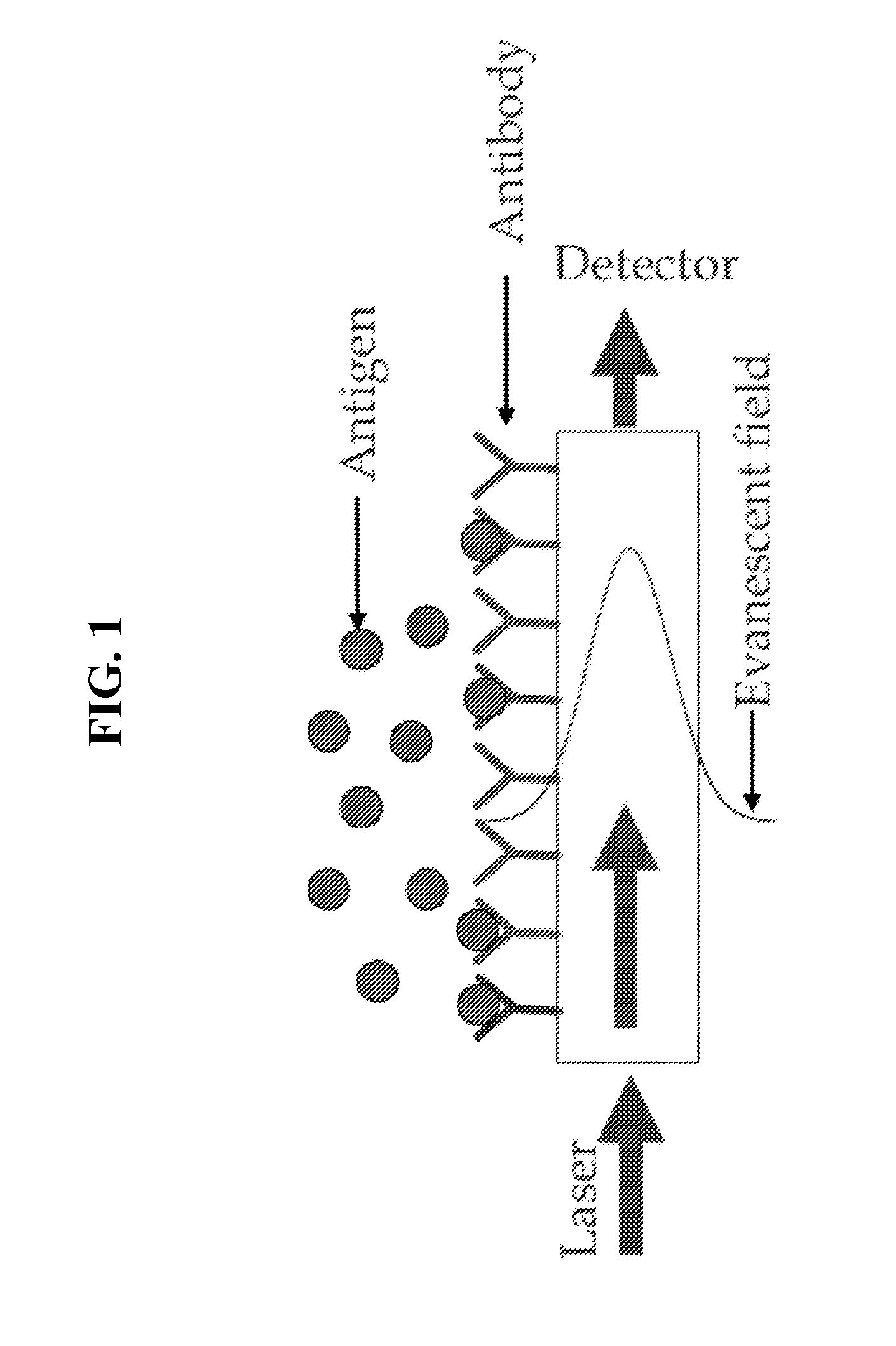
Methods and apparatus for pathogen detection and analysis
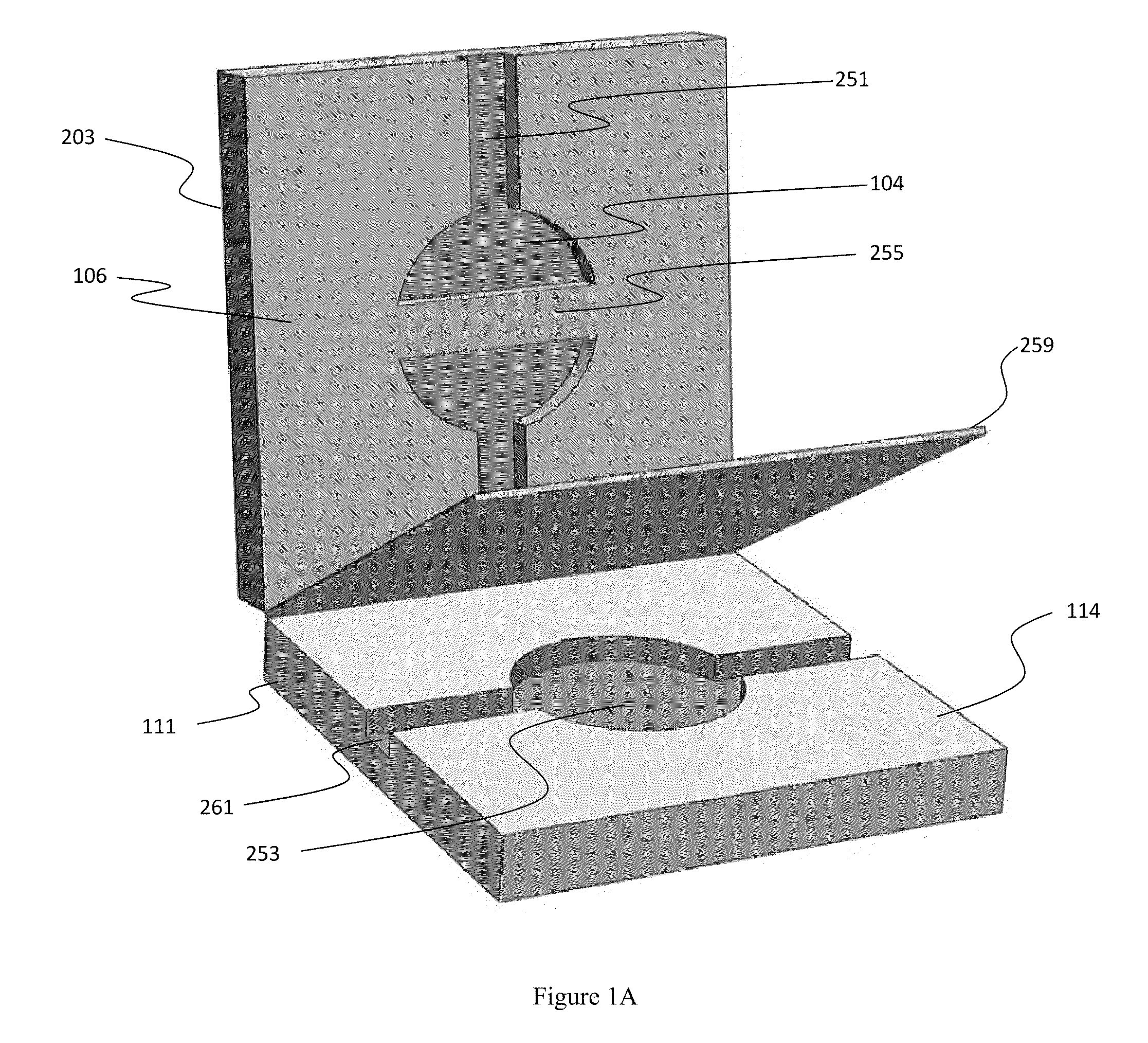
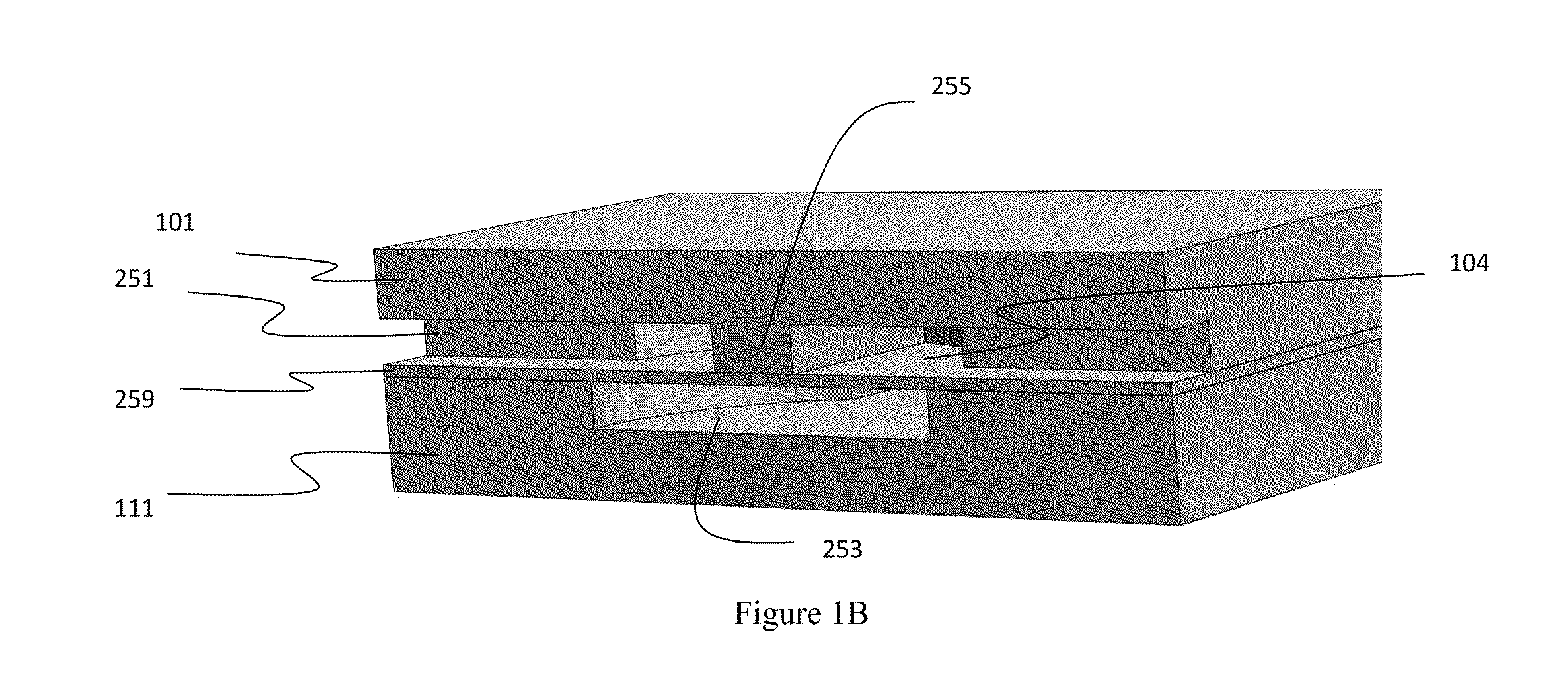
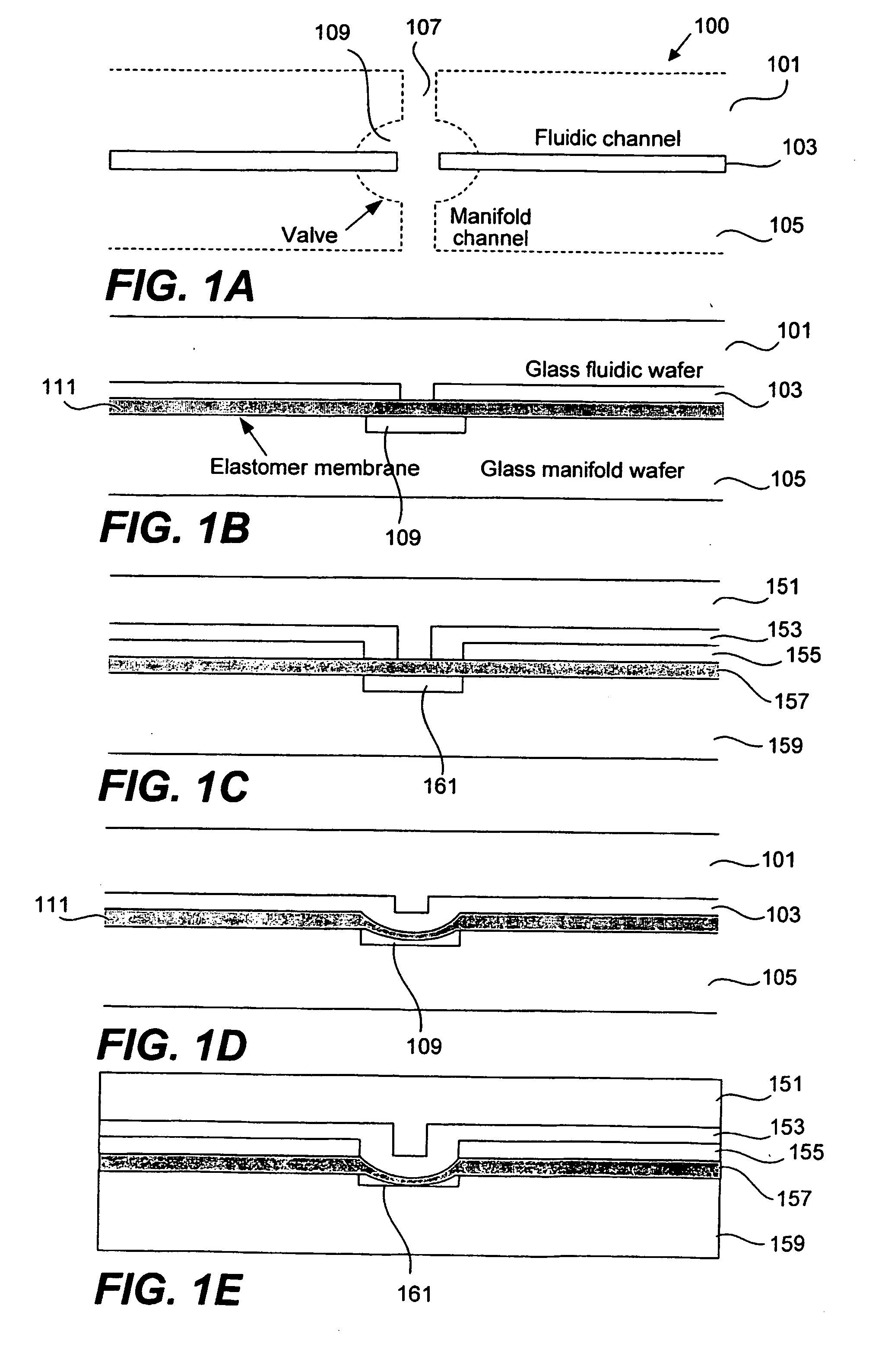
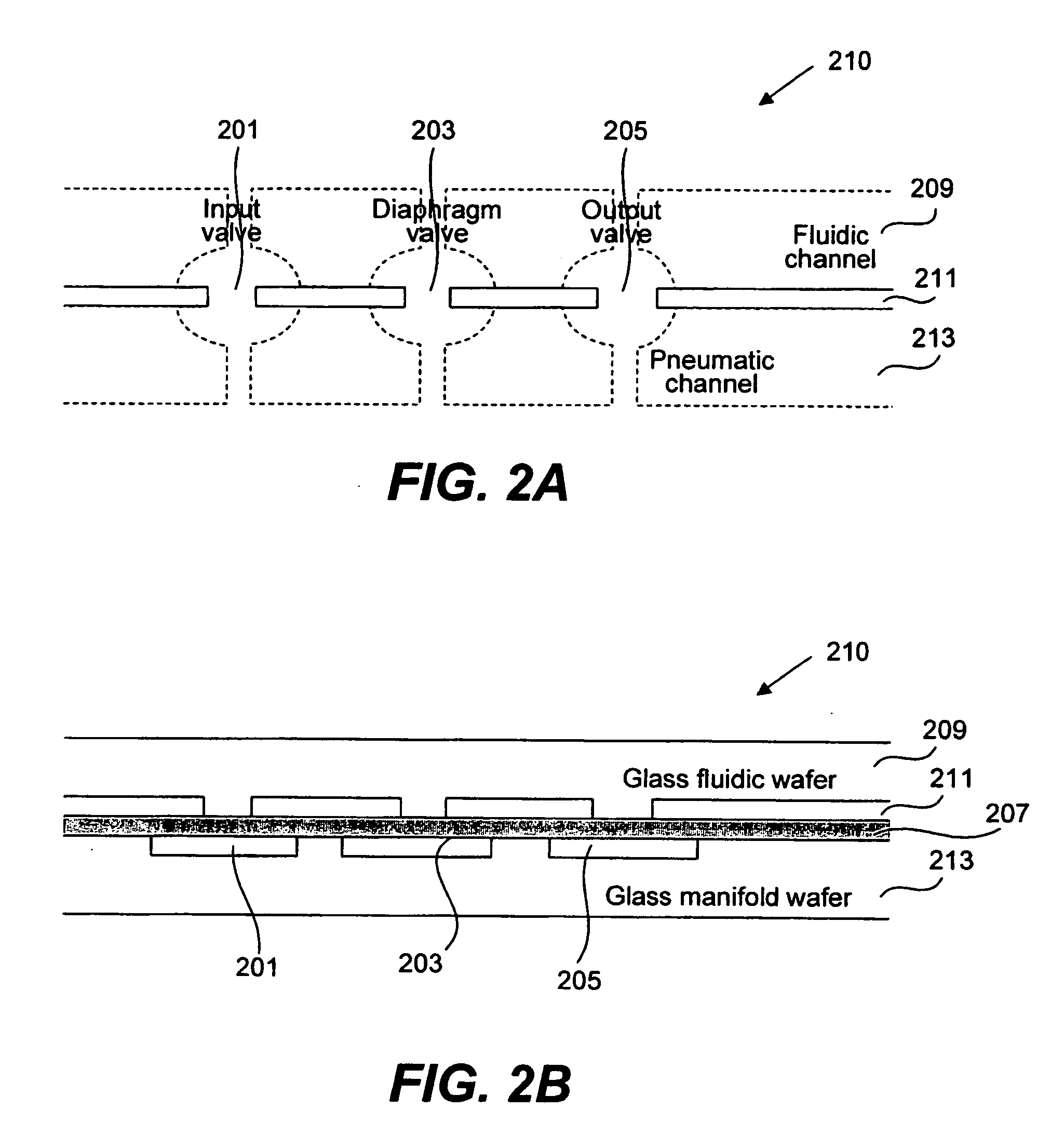
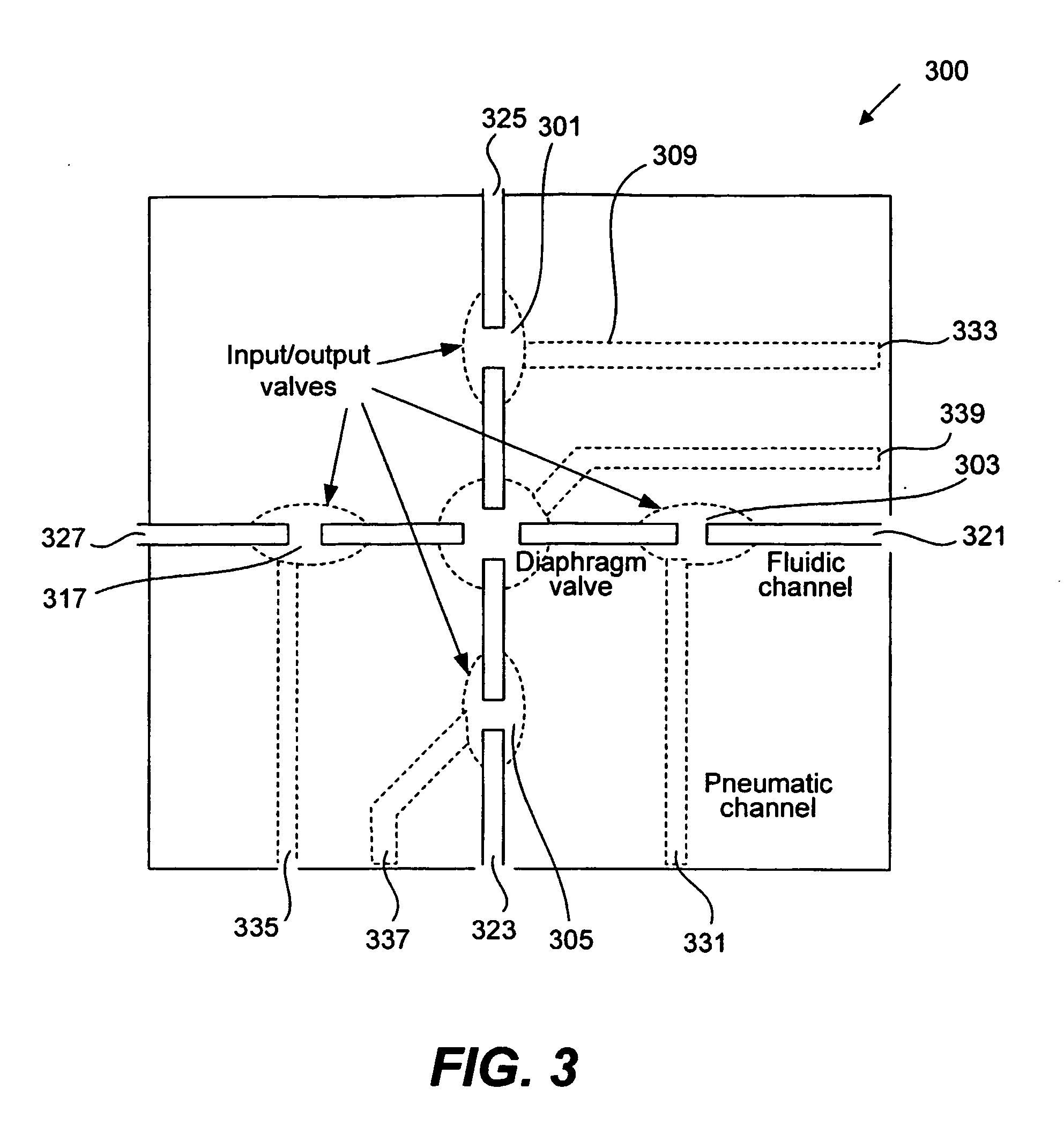
Methods and apparatus for implementing microfluidic analysis devices are provided. A monolithic elastomer membrane associated with an integrated pneumatic manifold allows the placement and actuation of dense arrays of a variety of fluid control structures, such as structures for isolating, routing, merging, splitting, and storing volumes of fluid. The fluid control structures can be used to implement a pathogen detection and analysis system including integrated immunoaffinity capture and analysis, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and capillary electrophoresis (CE) analysis. An analyte solution can be input into the device and pumped through a series of immunoaffinity capture matrices in microfabricated chambers having antibodies targeted to the various classes of microbiological organisms such as bacteria, viruses and bacterial spores. The immunoaffinity chambers can capture, purify, and concentrate the target for further analysis steps.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dynamic coating with linear polymer mixture for electrophoresis
InactiveUS6787016B2Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisAqueous buffer
Compositions and methods are provided for performing capillary electrophoresis using a composition comprising in combination in an aqueous buffered medium a coating polymer and a sieving polymer, where the sieving polymer is more hydrophilic than the coating polymer and is present in greater amount. Of particular interest are uncrosslinked acrylamide polymer mixtures for coating plastic channels and providing sieving for performing DNA separations in microfluidic devices. Polyacrylamide or N,N-dimethyl acrylamide is used with a N,N-dialkyl acrylamide copolymer, either separately or together for sieving and coating, serving as the medium in capillary electrophoresis DNA separations.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Electrochemical detector integrated on microfabricated capilliary electrophoresis chips
InactiveUS6045676AMinimizes the effect of interference from applied electrophoresis fieldsAccurately and conveniently placed, robust and sensitiveCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesElectrochemical detectorCapillary electrophoresis
A microfabricated capillary electrophoresis chip which includes an integral thin film electrochemical detector for detecting molecules separated in the capillary.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi-color multiplexed analysis in a bio-separation system
InactiveUS6870165B2Low costSensitive highOptical radiation measurementSludge treatmentCapillary electrophoresisFluorescence
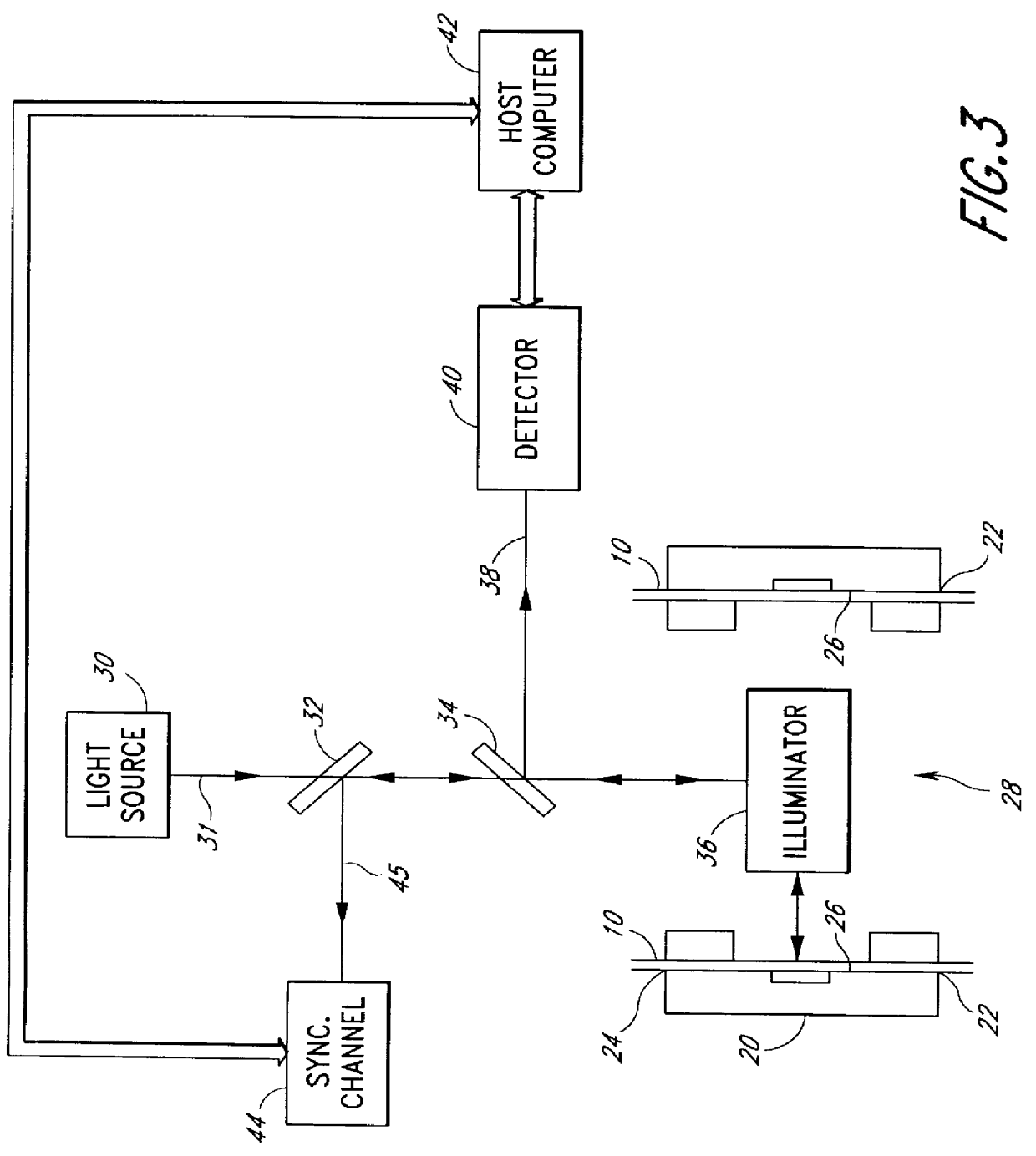
A multi-channel and multi-color bio-separation detection method and apparatus in which a single detector is coupled to a plurality of radiation sources, in a one detector / many radiation sources configuration. Each radiation source directs radiation at a detection zone of a single separation channel, and a single detector is applied to detect light emissions from the detection zones associated with several radiation sources. The radiation sources are activated to direct radiation at the detection zone in a predetermined sequence and further in a cyclic manner, with the detector output synchronized to the radiation sources by a controller. Bio-separation may be conducted simultaneously in all the channels in parallel, with detection time-staggered and / or time multiplexed with respect to the light sources. In one embodiment, low cost light emitting diodes may be used as radiation sources. In another aspect, the detection scheme is configured for radiation induced fluorescence detection in an capillary electrophoresis instrument.
Owner:QIAGEN SCIENCES LLC
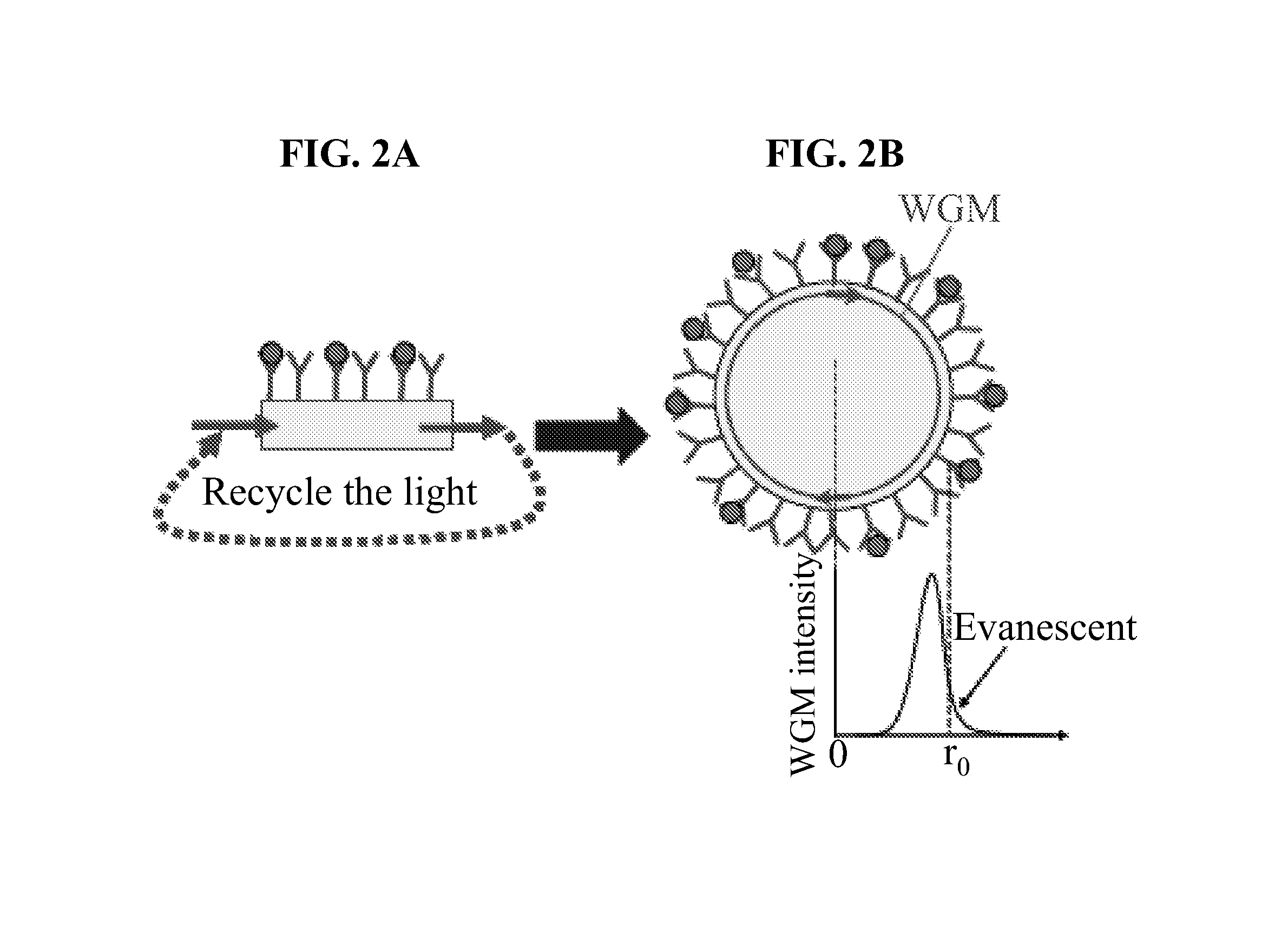
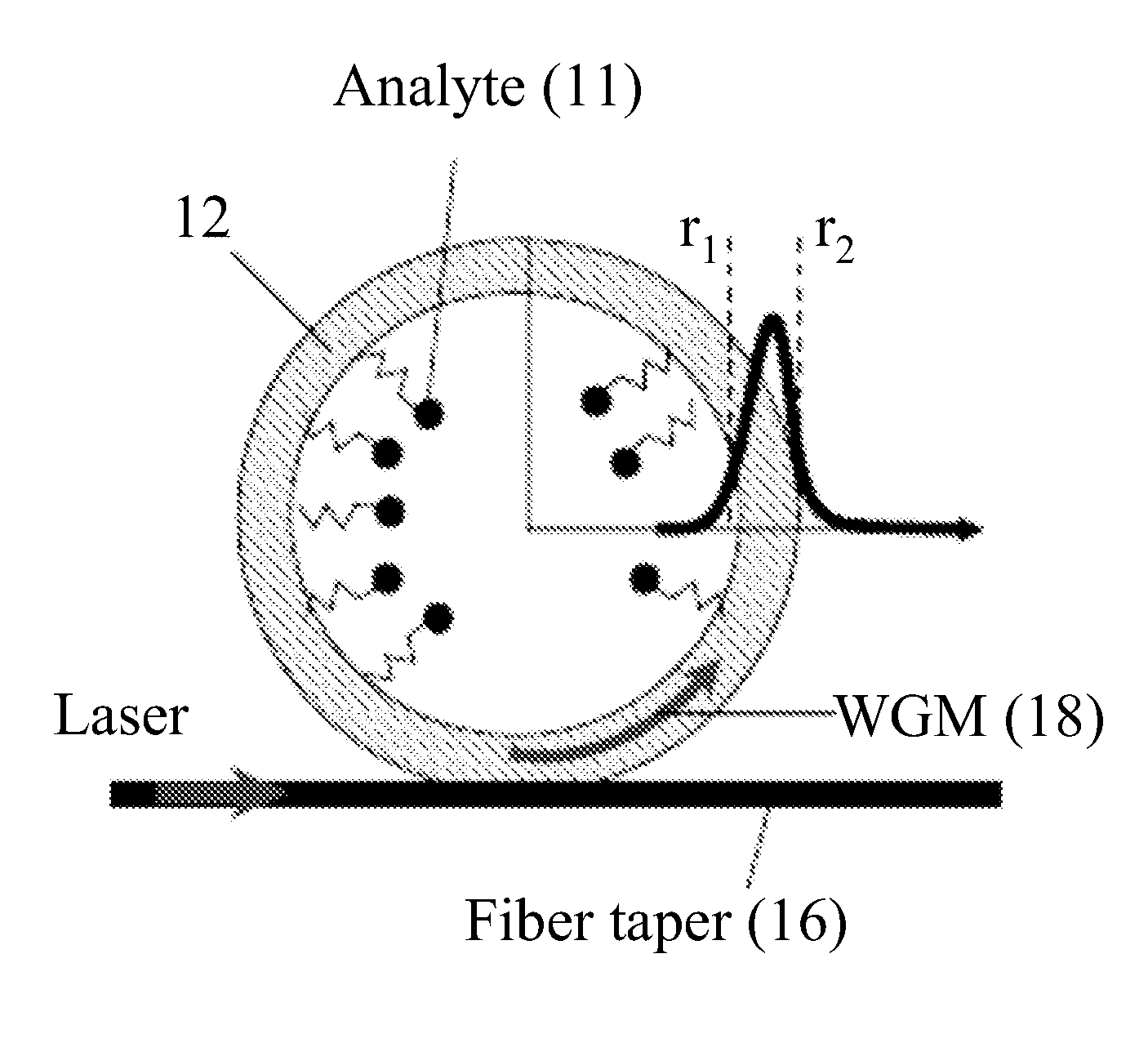
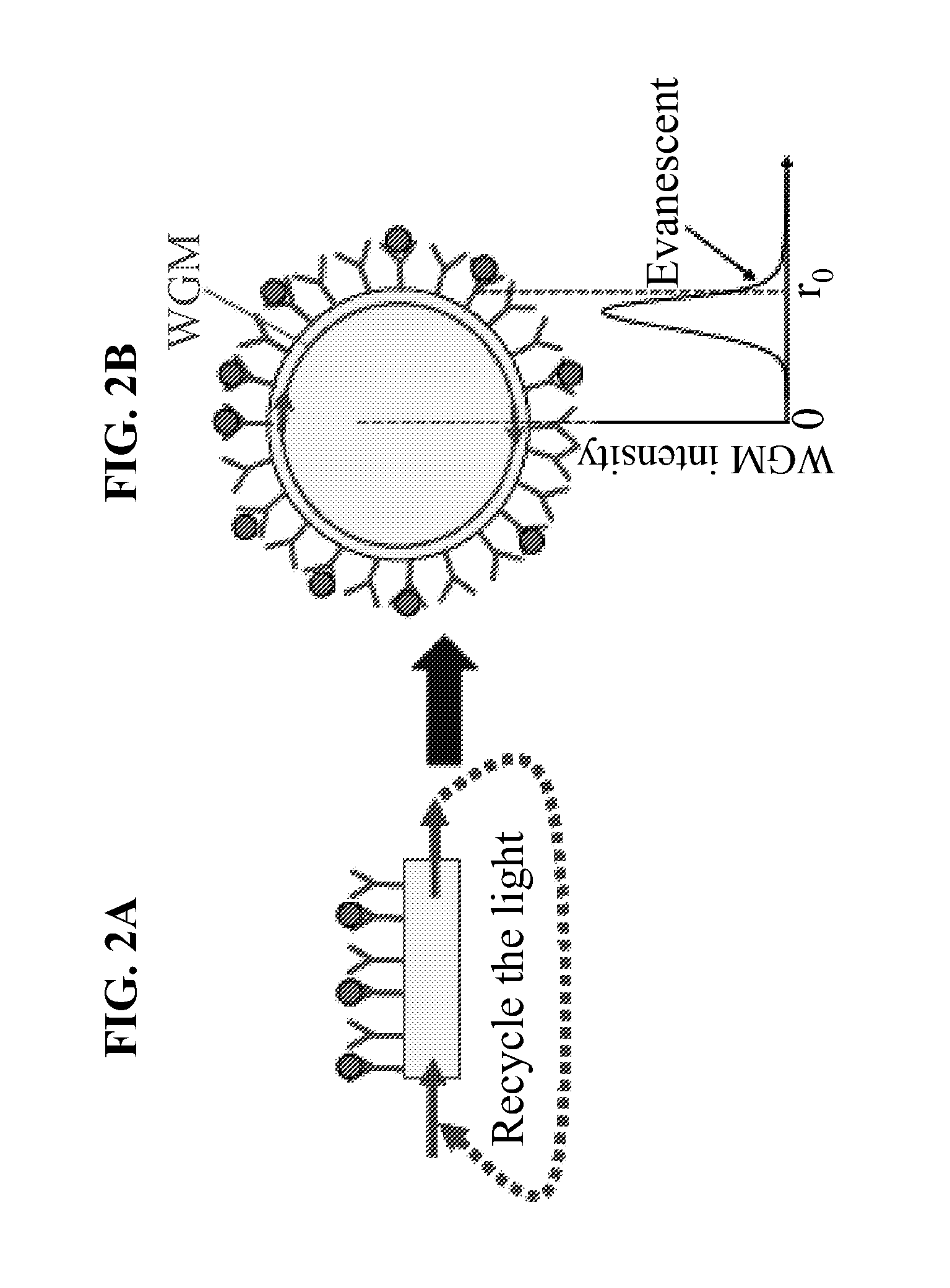
Hollow Core Optical Ring Resonator Sensor, Sensing Methods, and Methods of Fabrication
InactiveUS20070237460A1High sensitivityLow sample consumptionMaterial analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesTarget analysisWhispering gallery
The present invention is directed to hollow core optical ring resonators (HCORRs), methods of fabricating HCORRs, and methods of using HCORRs in sensing applications. In particular, the evanescent field and whispering gallery modes of the HCORRs may be used to detect a target analyte within the hollow core of the HCORR. Other features of the present invention include utilizing the HCORR as part of a multiplex sensing device, including using the HCORR in capillary electrophoresis and chromatography applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
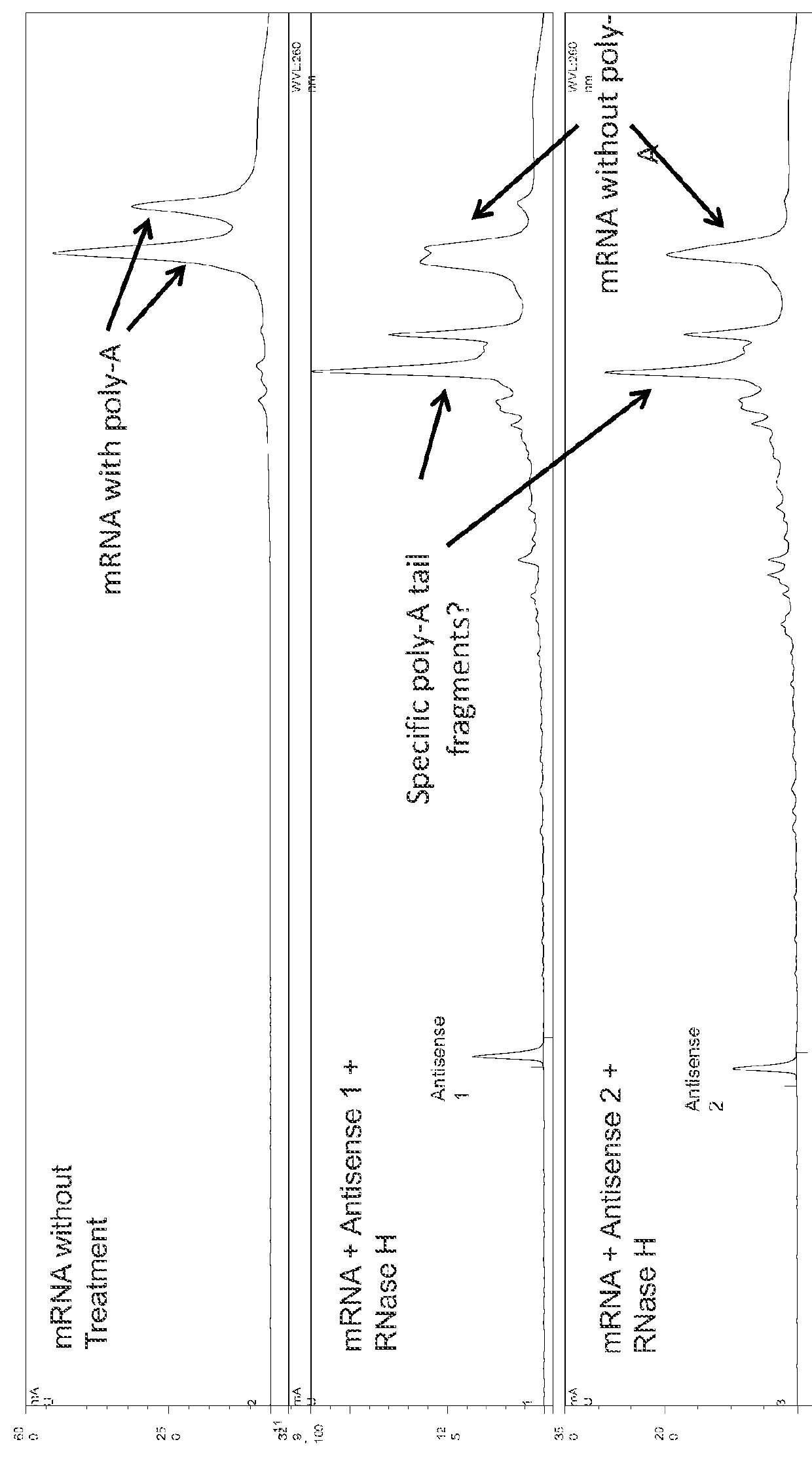
Characterization of mRNA molecules
InactiveUS20160032273A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisReverse transcriptase
The present invention describes methods for the characterization of mRNA molecules during mRNA production. Characterizing mRNA includes processes such as oligonucleotide mapping, reverse transcriptase sequencing, charge distribution analysis, and detection of RNA impurities. Oligonucleotide mapping includes using an RNase to digest antisense duplexes from an RNA transcript, and then subjecting the digested RNA to reverse phase HPLC, anion exchange HPLC, and / or mass spectrometry analysis. Reverse transcriptase sequencing involves reverse transcription of an RNA transcript followed by DNA sequencing. Charge distribution analysis can comprise procedures such as anion exchange HPLC, or capillary electrophoresis. Detection of impurities includes detecting short mRNA transcripts, RNA-RNA hybrids, and RNA-DNA hybrids.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
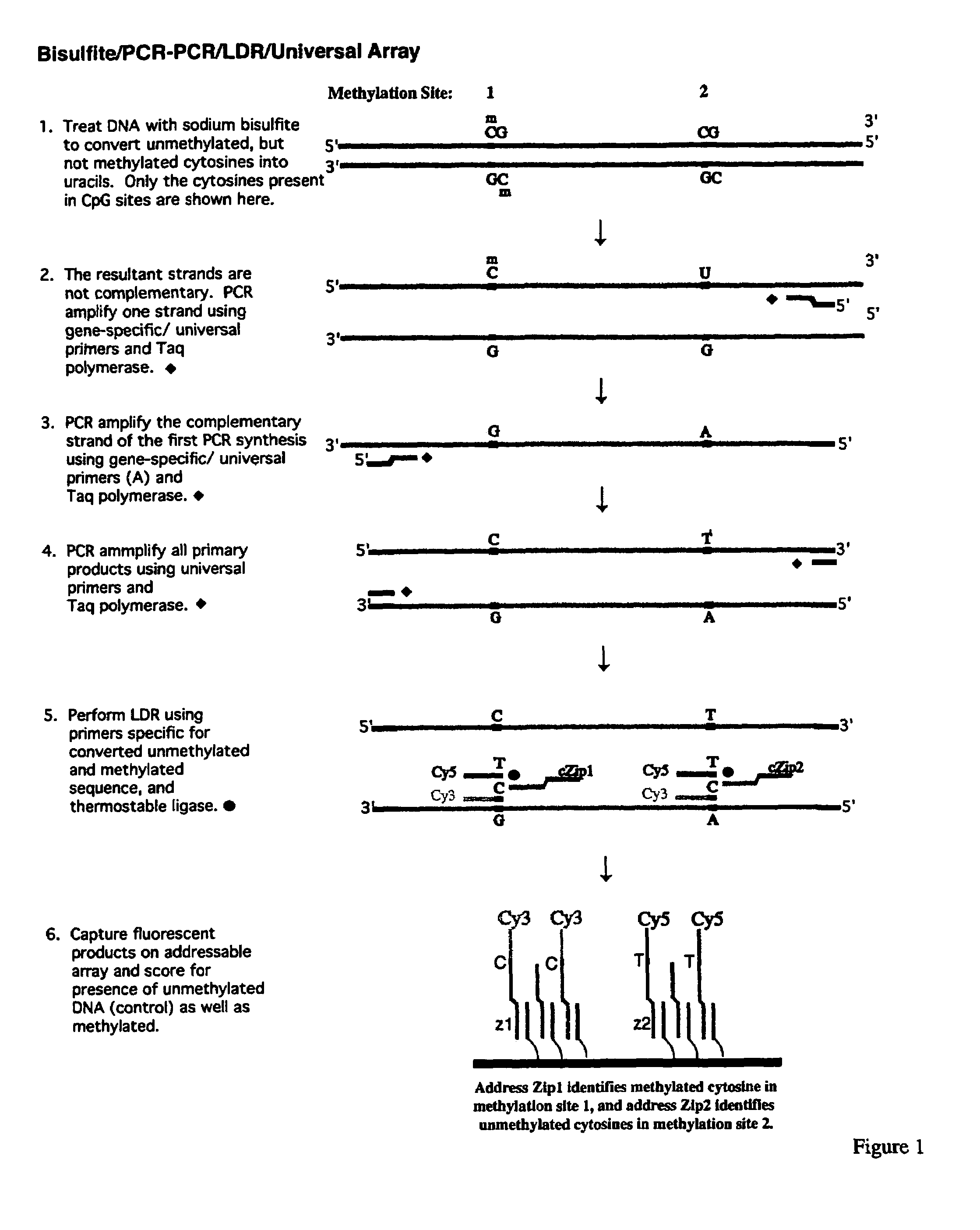
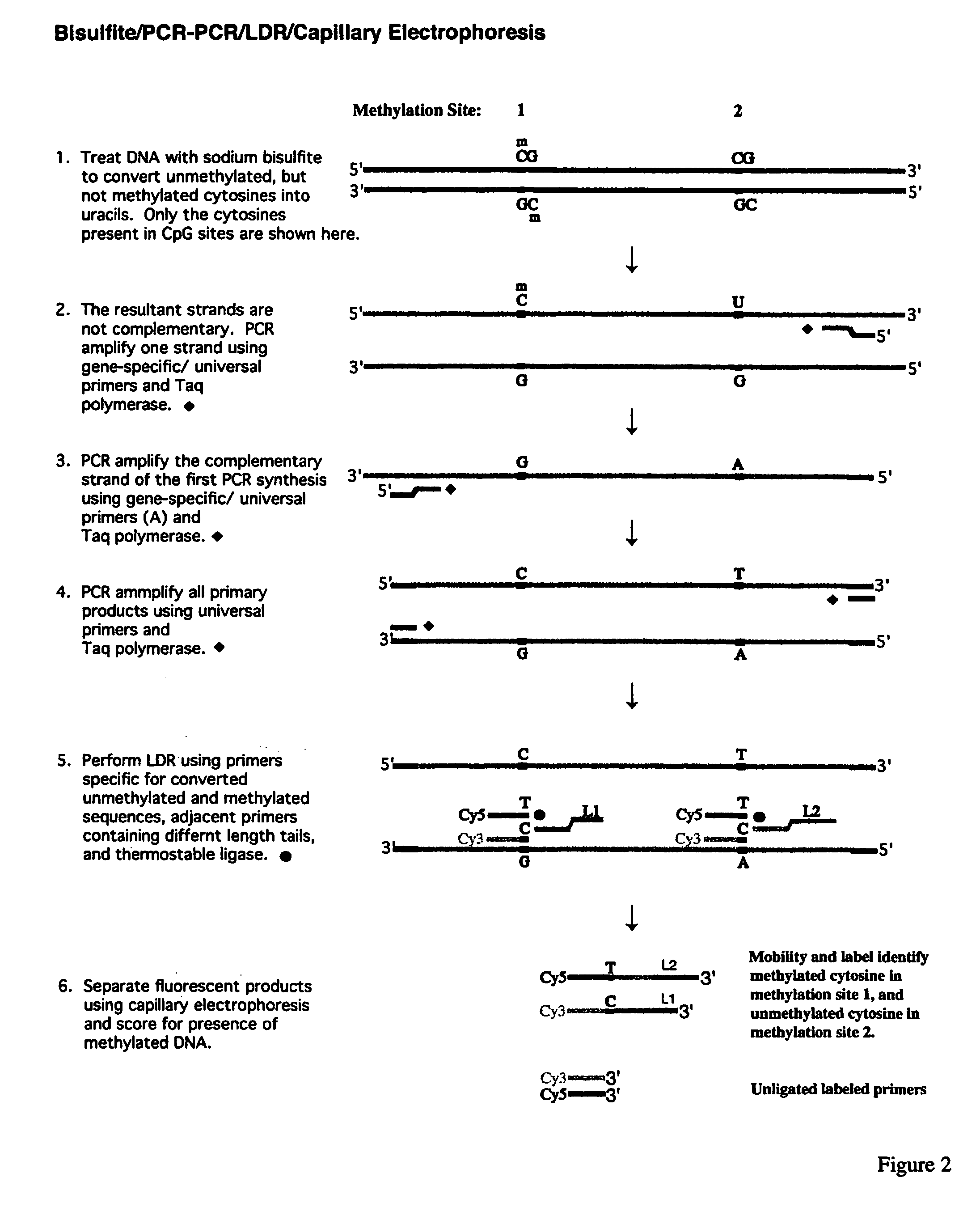
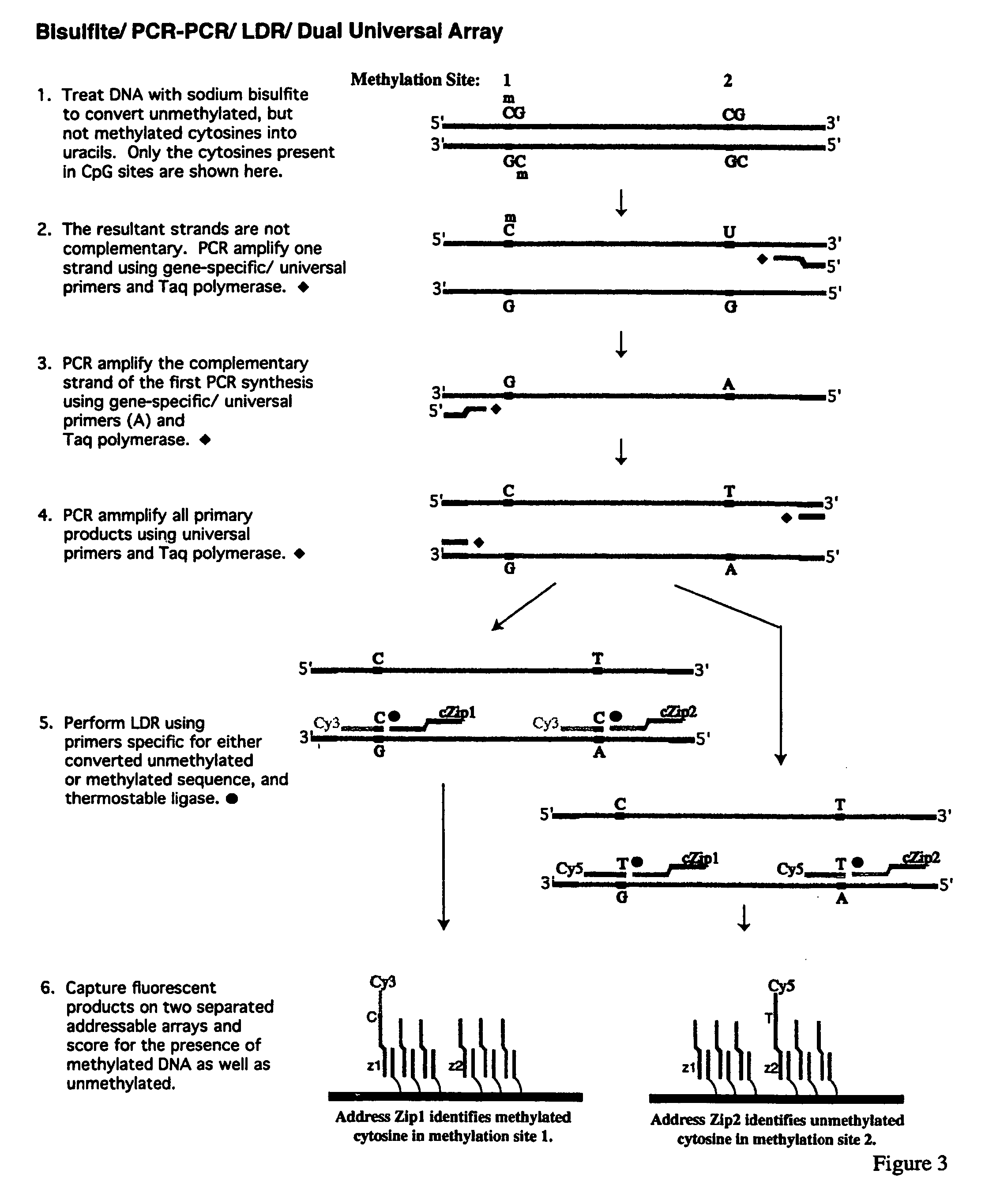
Method for detection of promoter methylation status
InactiveUS7358048B2Precise “ molecular signature ”Accurately methylation statusMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
The present invention relates to the detection of promoter methylation status using a combination of either modification of methylated DNA or restriction endonuclease digestion, multiplex polymerase chain reaction, ligase detection reaction, and a universal array or capillary electrophoresis detection.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
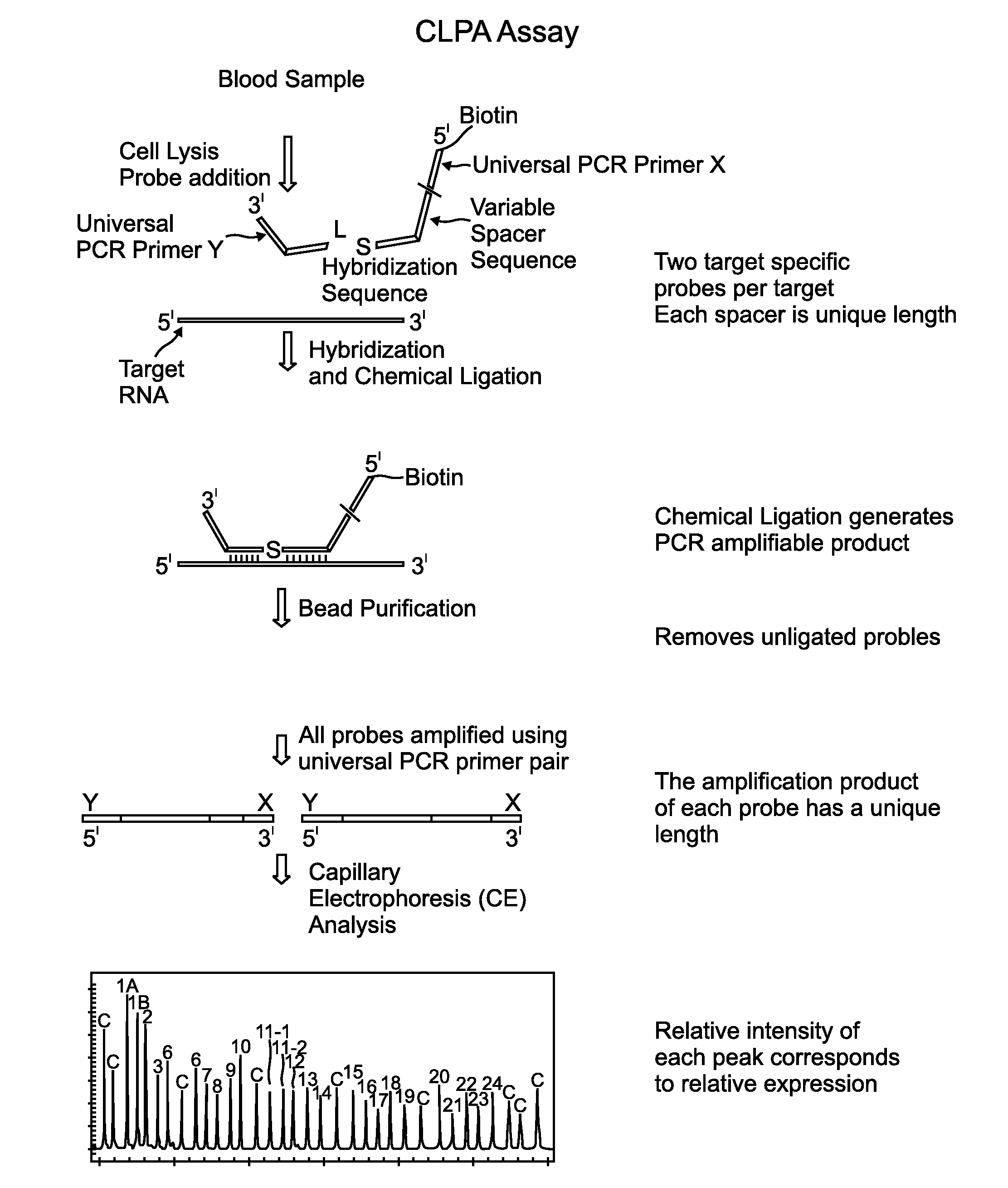
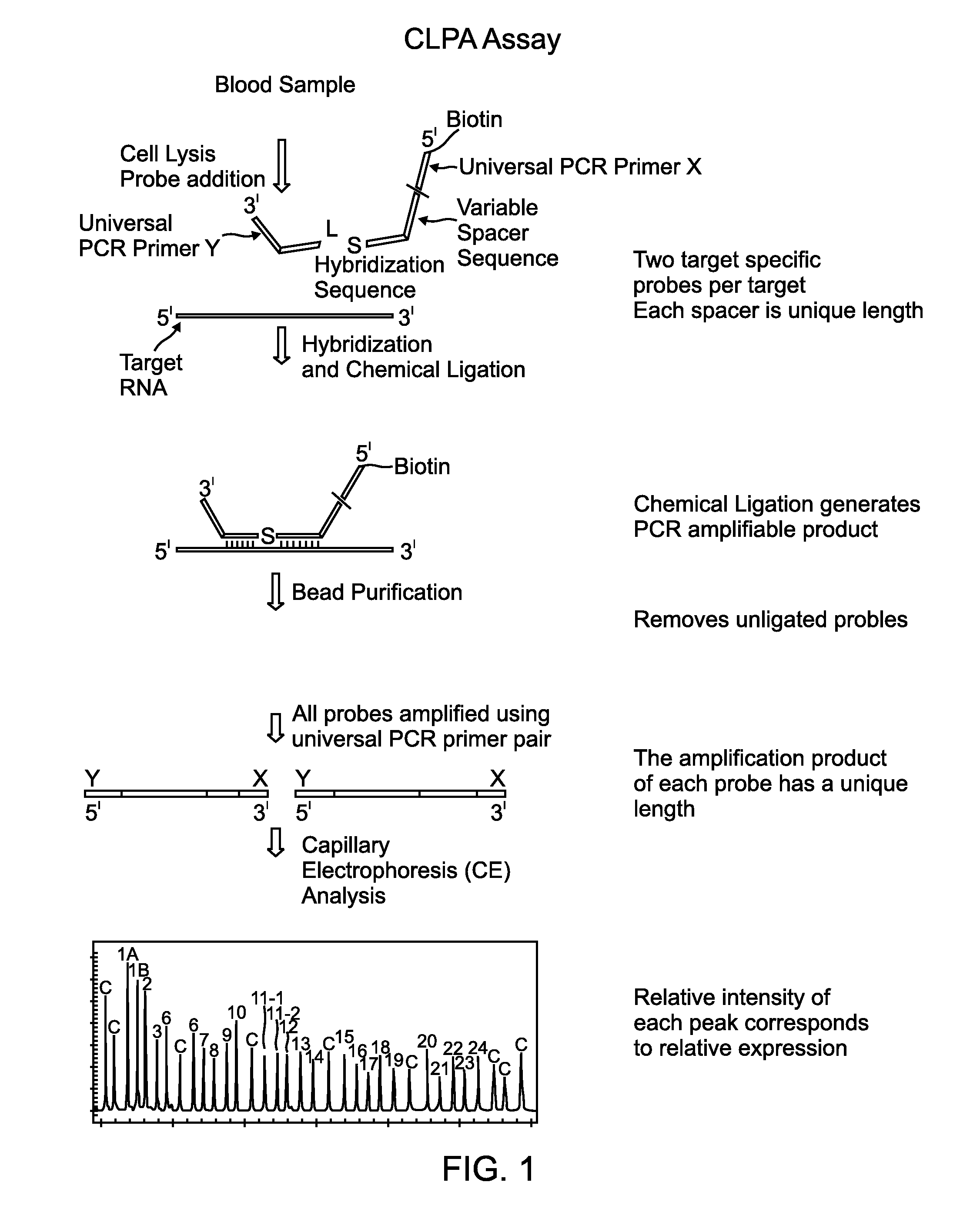
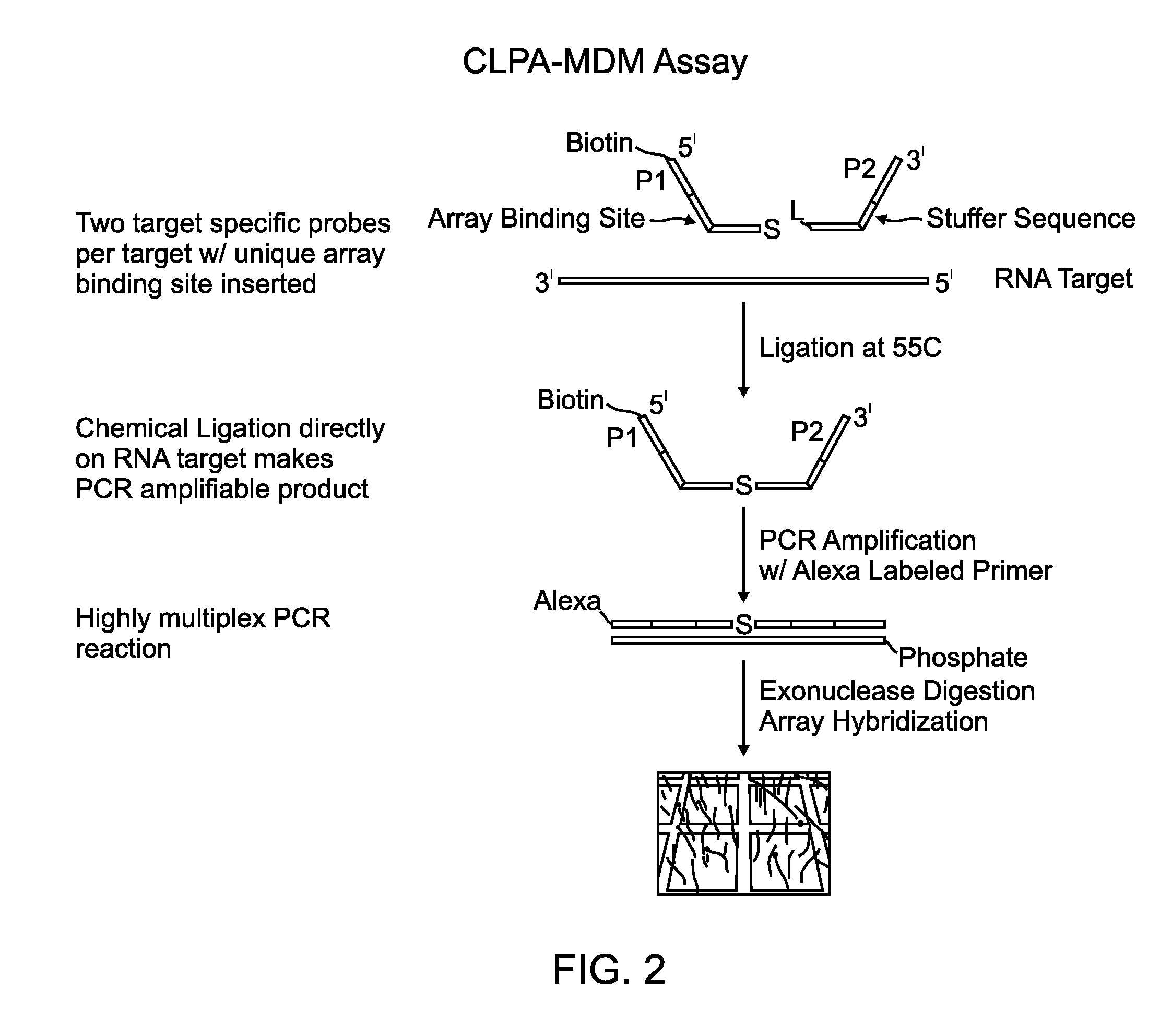
Chemical ligation dependent probe amplification (CLPA)
ActiveUS20100267585A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical ligationCapillary electrophoresis
The present invention provides compositions, apparatuses and methods for detecting one or more nucleic acid targets present in a sample. Methods of the invention include utilizing two or more oligonucleotide probes that reversibly bind a target nucleic acid in close proximity to each other and possess complementary reactive ligation moieties. When such probes have bound to the target in the proper orientation, they are able to undergo a spontaneous chemical ligation reaction that yields a ligated oligonucleotide product. In one aspect, the ligation product is of variable length that correlates with a particular target. Following chemical ligation, the probes may be amplified and detected by capillary electrophoresis or microarray analysis.
Owner:DXTERITY DIAGNOSTICS
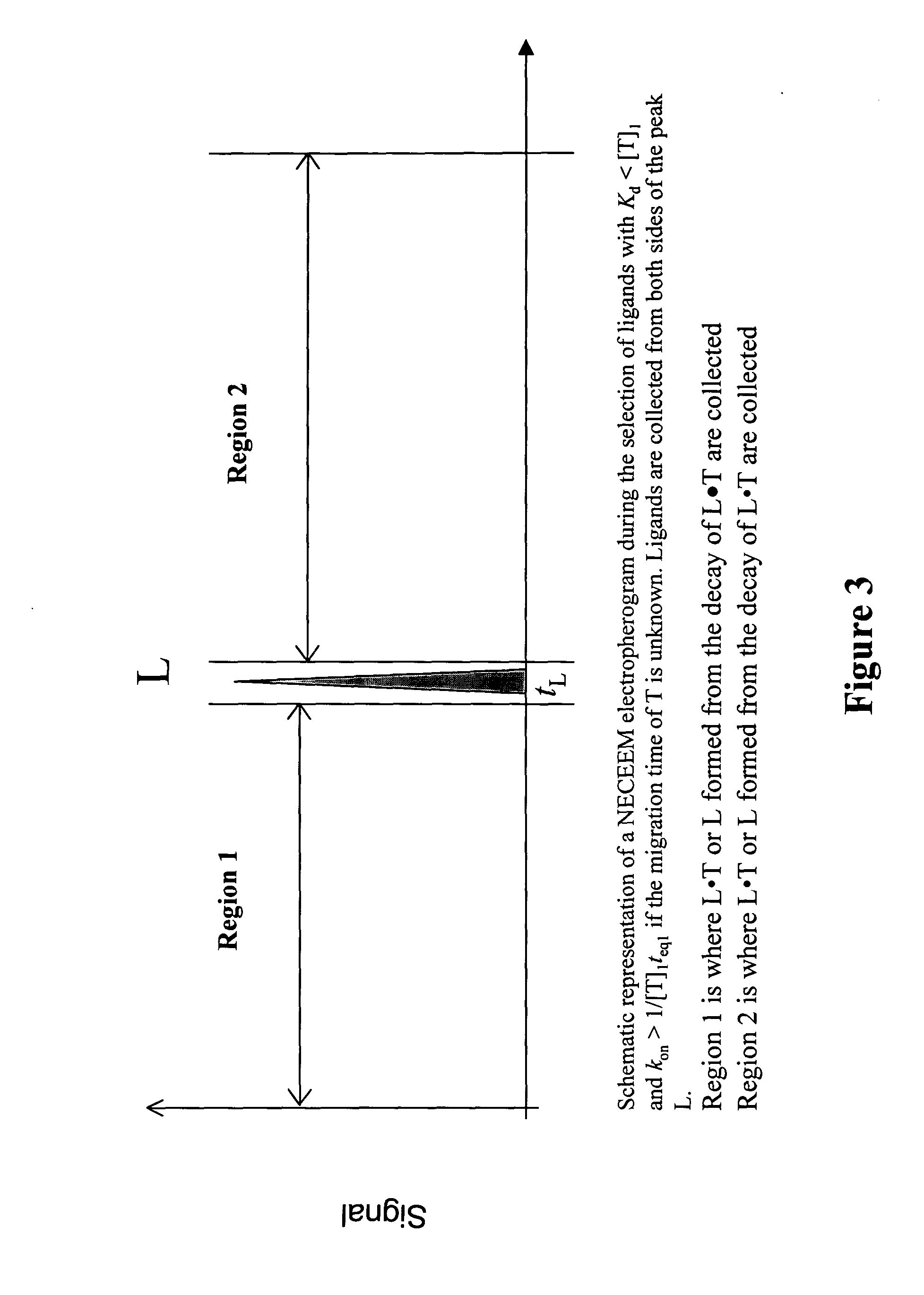
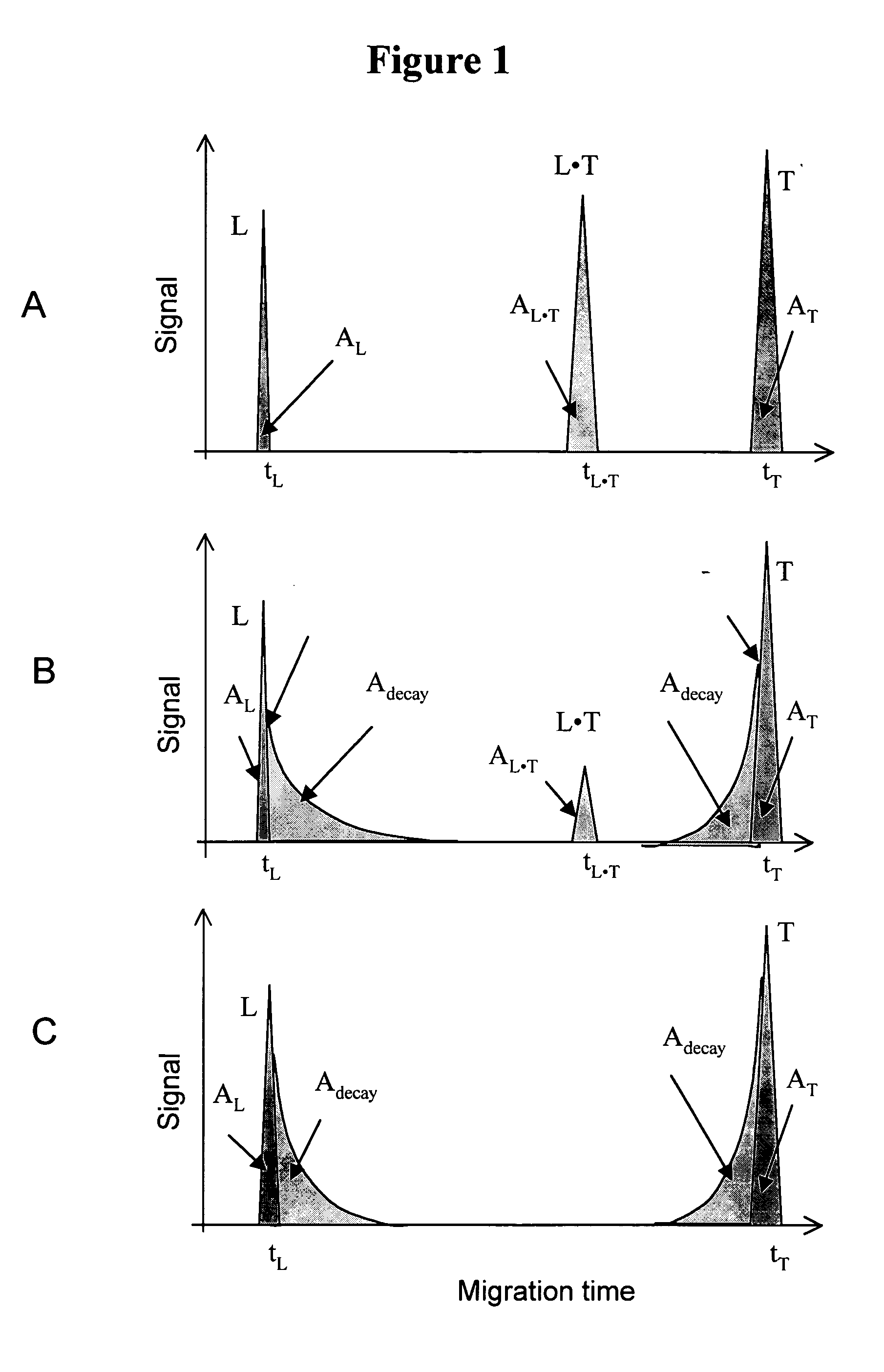
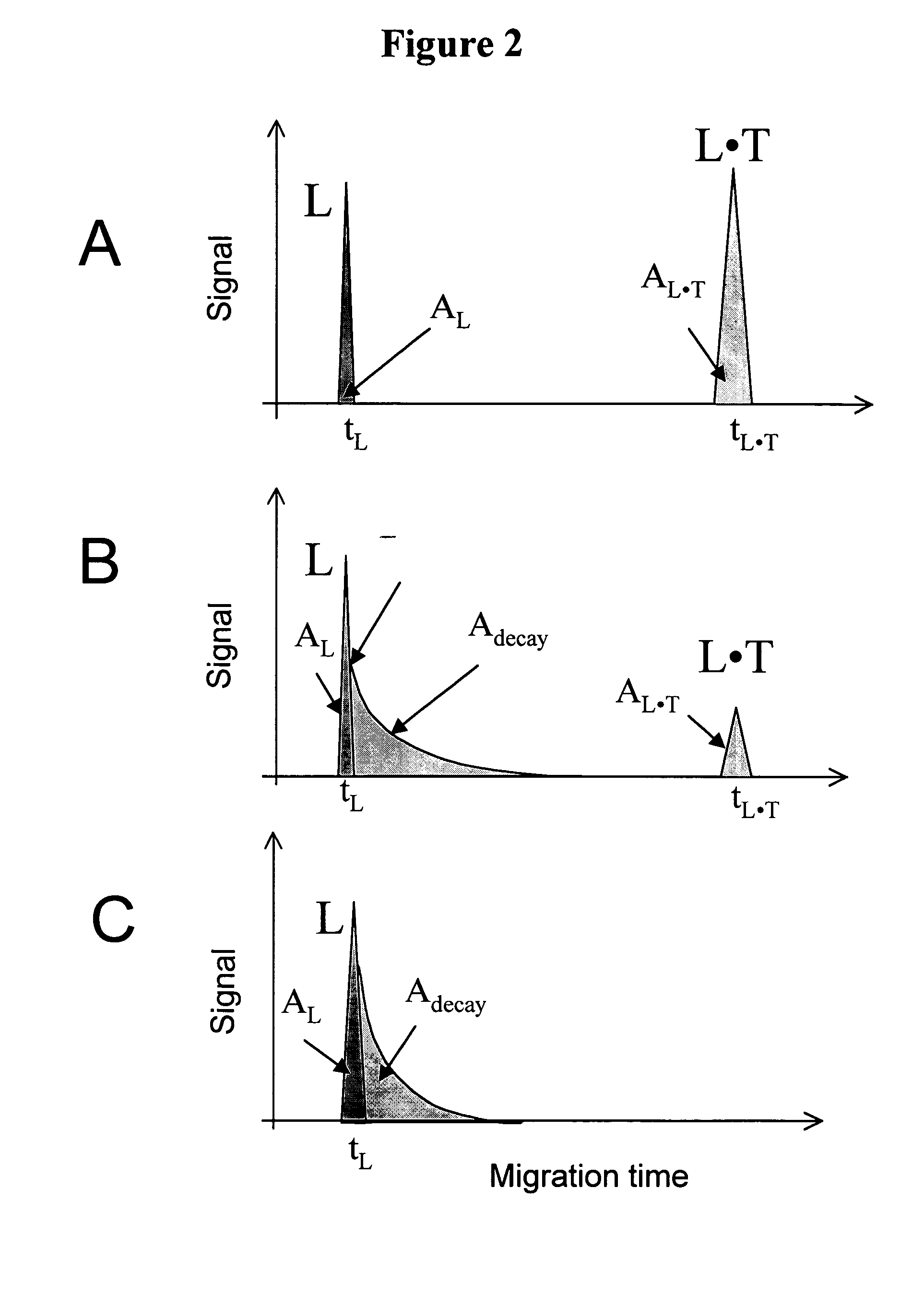
Non-equilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures (NECEEM) - based methods for drug and diagnostic development
ActiveUS20050003362A1Enhances electrophoretic separationEasy to separateCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSolid substrateNucleotide Aptamers
The invention discloses a Non-Equilibrium Capillary Electrophoresis of Equilibrium Mixtures (NECEEM) method and NECEEM-based practical applications. The NECEEM method is a homogeneous technique, which, in contrast to heterogeneous methods, does not require affixing molecules to a solid substrate. The method of the invention facilitates 3 practical applications. In the first application, the method allows the finding of kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of complex formation. It advantageously allows for revealing two parameters, the equilibrium dissociation constant, Kd, and the monomolecular rate constant of complex decay, koff, in a single experiment. In the second practical application, the method of this invention provides an approach for quantitative affinity analysis of target molecules. It advantageously allows for the use of affinity probes with relatively high values of koff. In the third practical application, the method of this invention presents a new and powerful approach to select target-binding molecules (ligands) from complex mixtures. Unique capabilities of the method in its third application include but not limited to: (a) the selection of ligands with pre-determined ranges of kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of target-ligand interactions, (b) the selection of ligands present in minute amounts in complex mixtures of biological or synthetic compounds such as combinatorial libraries of oligonucleotides, and (c) the selection of ligands for targets available in very low amounts. In particular, the method of this invention provides a novel approach for the selection of oligonucleotide aptamers. The NECEEM-based method can be used for discovery and characterization of drug candidates and the development of new diagnostic methods.
Owner:KRYLOV SERGEY
Dynamic coating with linear polymer mixture for electrophoresis
InactiveUS20020029968A1Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisAqueous buffer
Compositions and methods are provided for performing capillary electrophoresis using a composition comprising in combination in an aqueous buffered medium a coating polymer and a sieving polymer, where the sieving polymer is more hydrophilic than the coating polymer and is present in greater amount. Of particular interest are uncrosslinked acrylamide polymer mixtures for coating plastic channels and providing sieving for performing DNA separations in microfluidic devices. Polyacrylamide or N,N-dimethyl acrylamide is used with a N,N-dialkyl acrylamide copolymer, either separately or together for sieving and coating, serving as the medium in capillary electrophoresis DNA separations.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
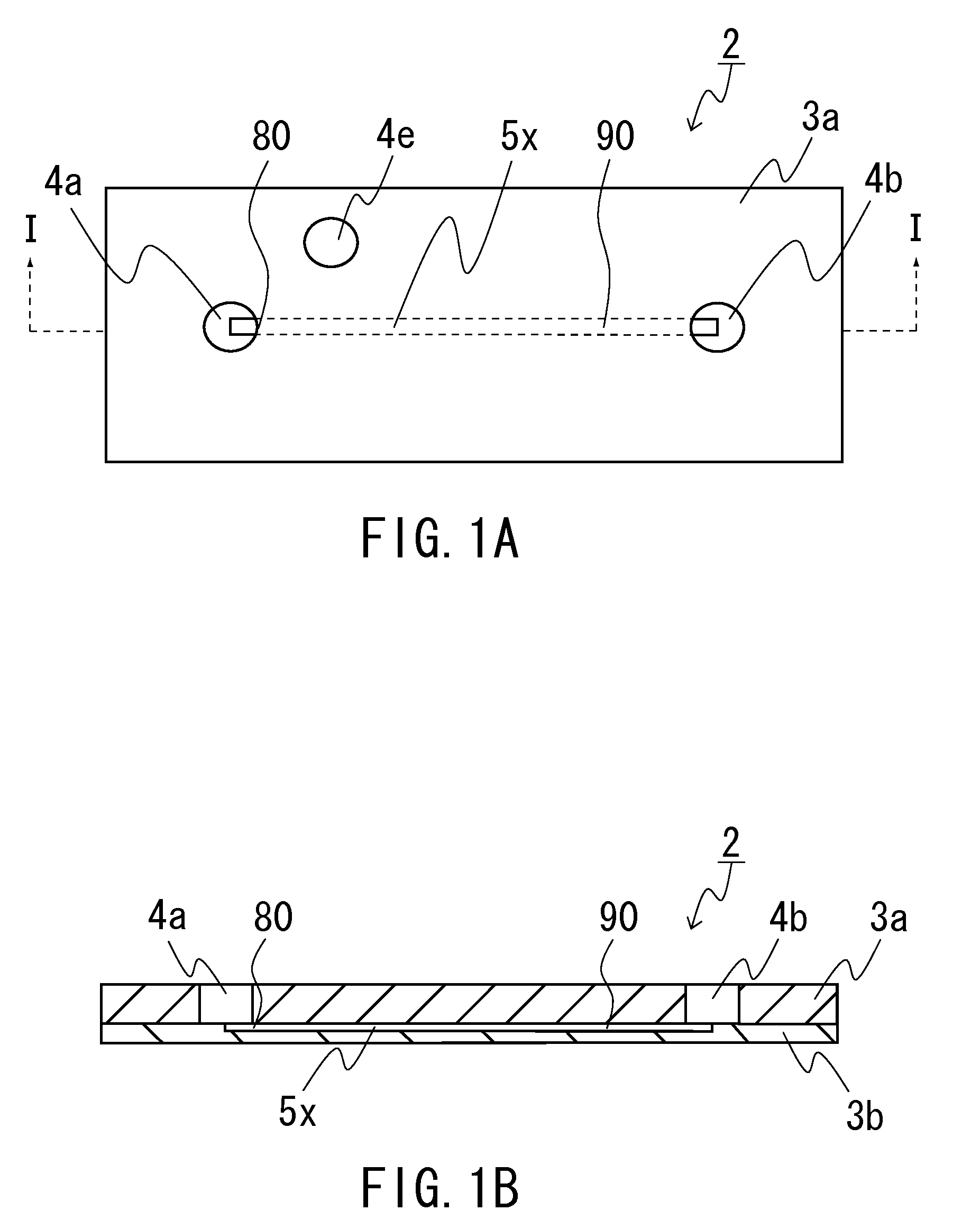
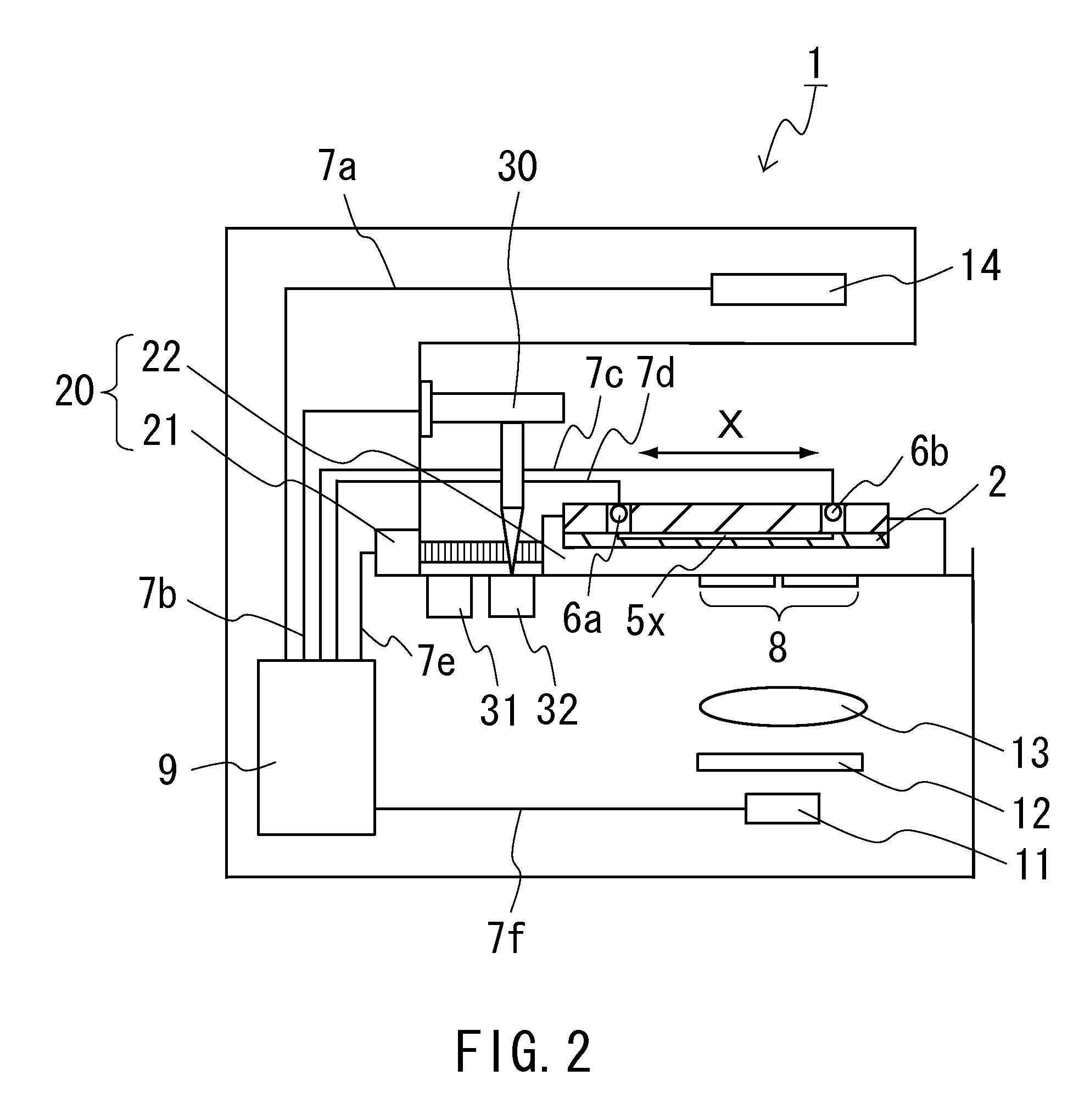
Analysis apparatus for capillary electrophoresis
ActiveUS20100181199A1Fast and accurate analysisSmall sizeCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
A capillary electrophoresis analysis apparatus is provided for analyzing samples by a capillary electrophoresis method that allows for rapid and highly accurate separation and detection.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Microfluidic chip for capillary electrophoresis separation and chemiluminescence detection
InactiveCN101692047AImprove separation efficiencyHigh sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceDispersed particle separationCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a microfluidic assay chip integrated capillary electrophoresis separation with chemiluminescence detection. The microfluidic chip consists of a buffer solution storage tank, a sample liquid storage tank, a sample waste liquid tank, a waste liquid tank, a sheath flow storage tank, a sample introduction channel, a separation channel, a sheath flow channel and a detection channel. A terminal of the separation channel and a starting point of the detection channel are communicated with the sheath flow channel. A chemiluminescence reagent enters the detection channel through the sheath flow channel; and when compositions to be assayed after the capillary electrophoresis separation of the chip meets the chemiluminescence reagent at a connecting point of the separation channel and the detection channel, the compositions are mixed with chemiluminescence reagent in the detection channel and then undergo luminous reaction. The inside of the separation channel is provided with a microporous plug to prevent the chemiluminescence reagent from flowing backwards into the separation channel under the driving of pressure difference so as not to influence electrophoresis separation. The microfluidic assay chip has the characteristics of high separation efficiency, high detection sensitivity, simple structure, small volume, light weight, convenient operation and the like, and is ideal to prepare a portable micro total separation system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
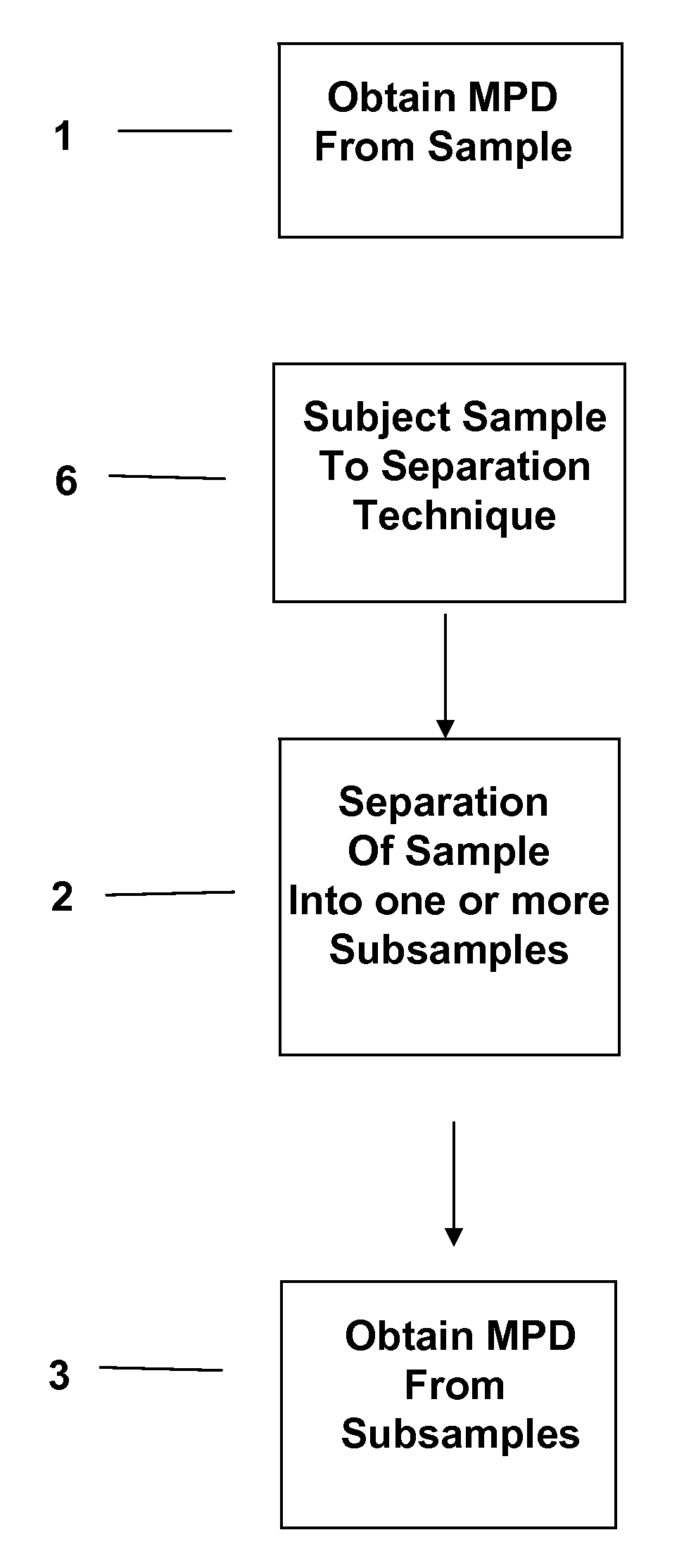
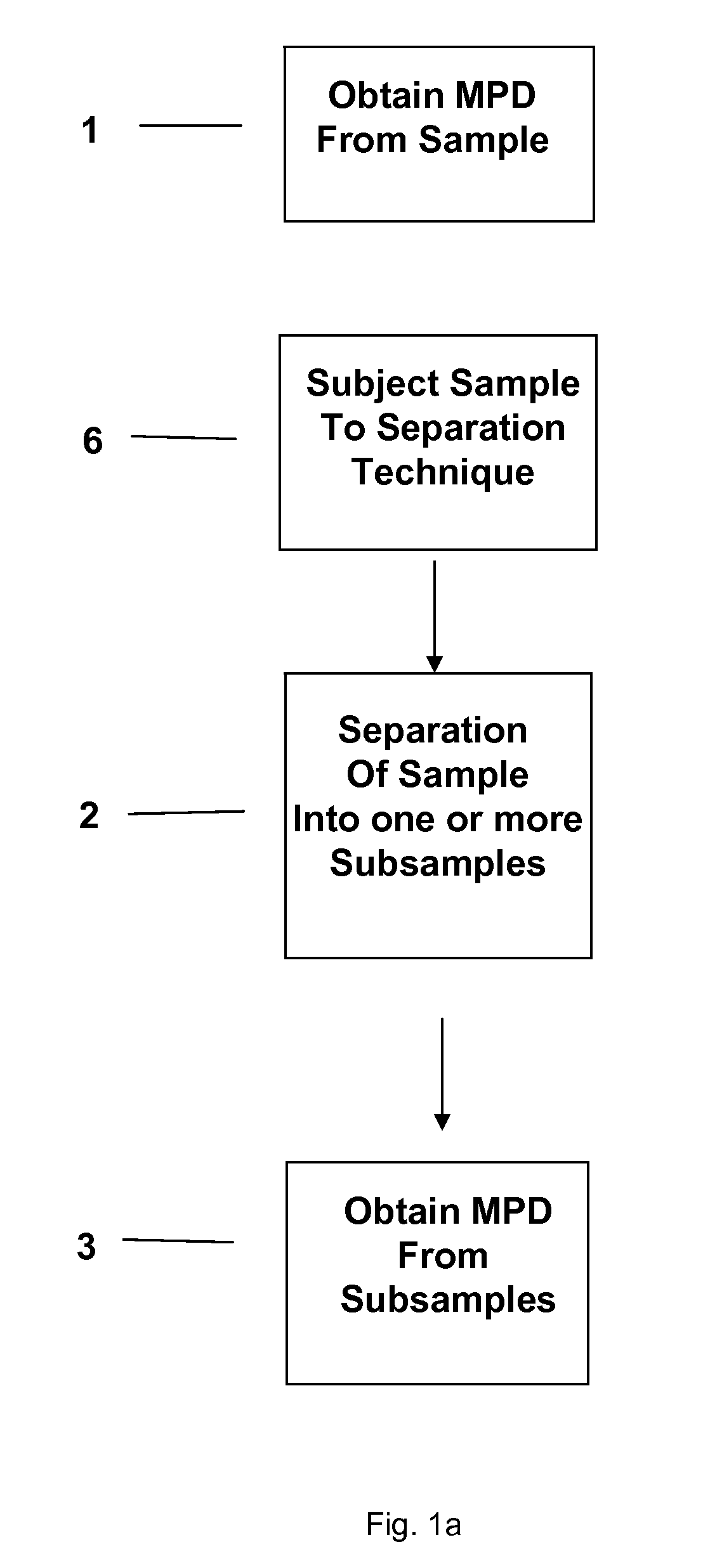
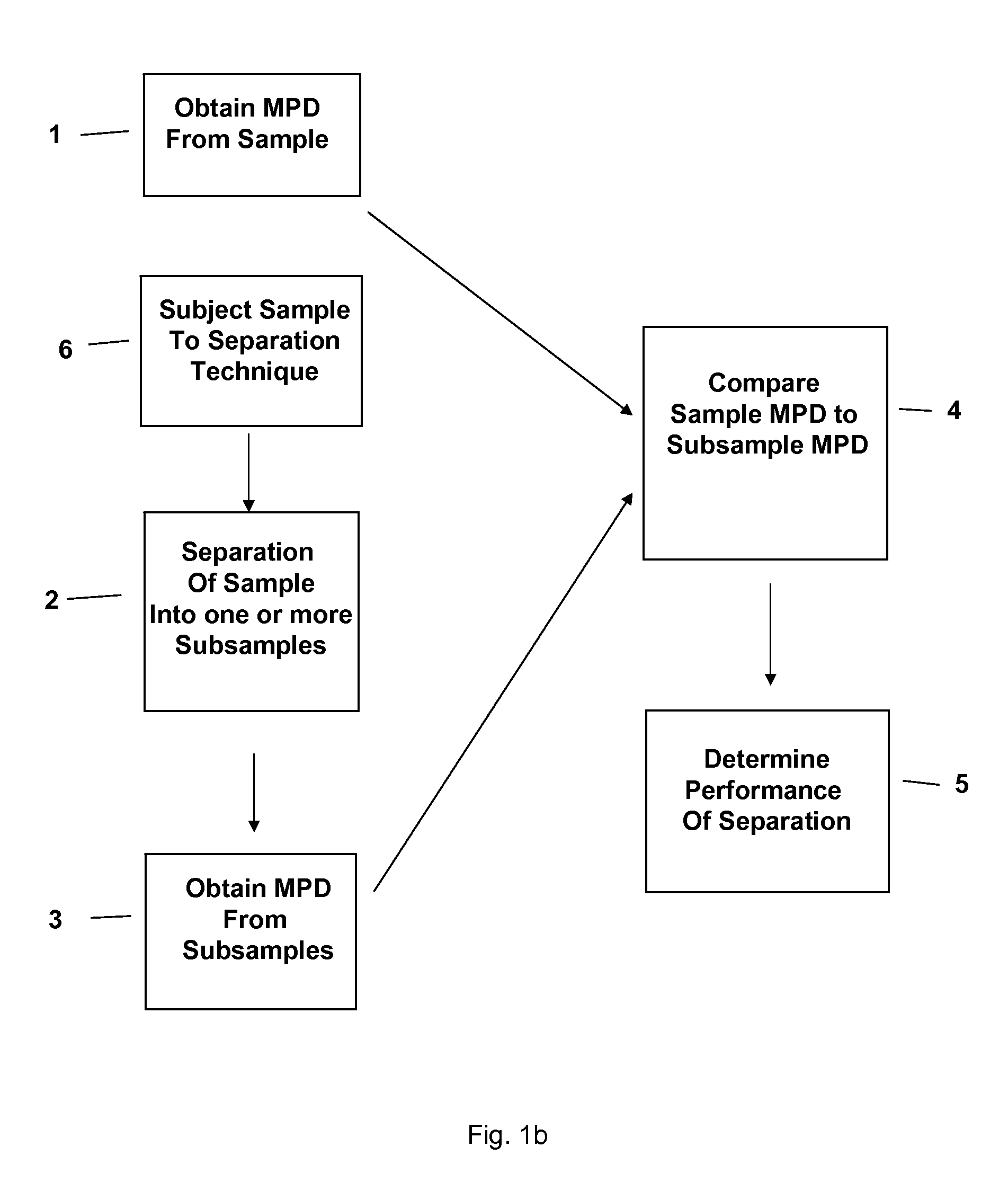
Separation technology method and identification of error
InactiveUS20100050737A1Optical radiation measurementParticle separator tubesCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
The present invention relates to a method and accompanying device for separating a known or unknown sample into one or more subsamples. By comparing the subsample's measurement profile data to the sample measurement profile data, the performance of the separation can be determined. The separation could be chromatography [such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), or the like], electrophoresis [such as capillary electrophoresis (CE) or the like], or another separation technique. The measurement profile data could be ultraviolet / visible (UV / Vis) spectra, mass spectra (MS), or another measurement technique.
Owner:WOLTERS ANDREW MARK
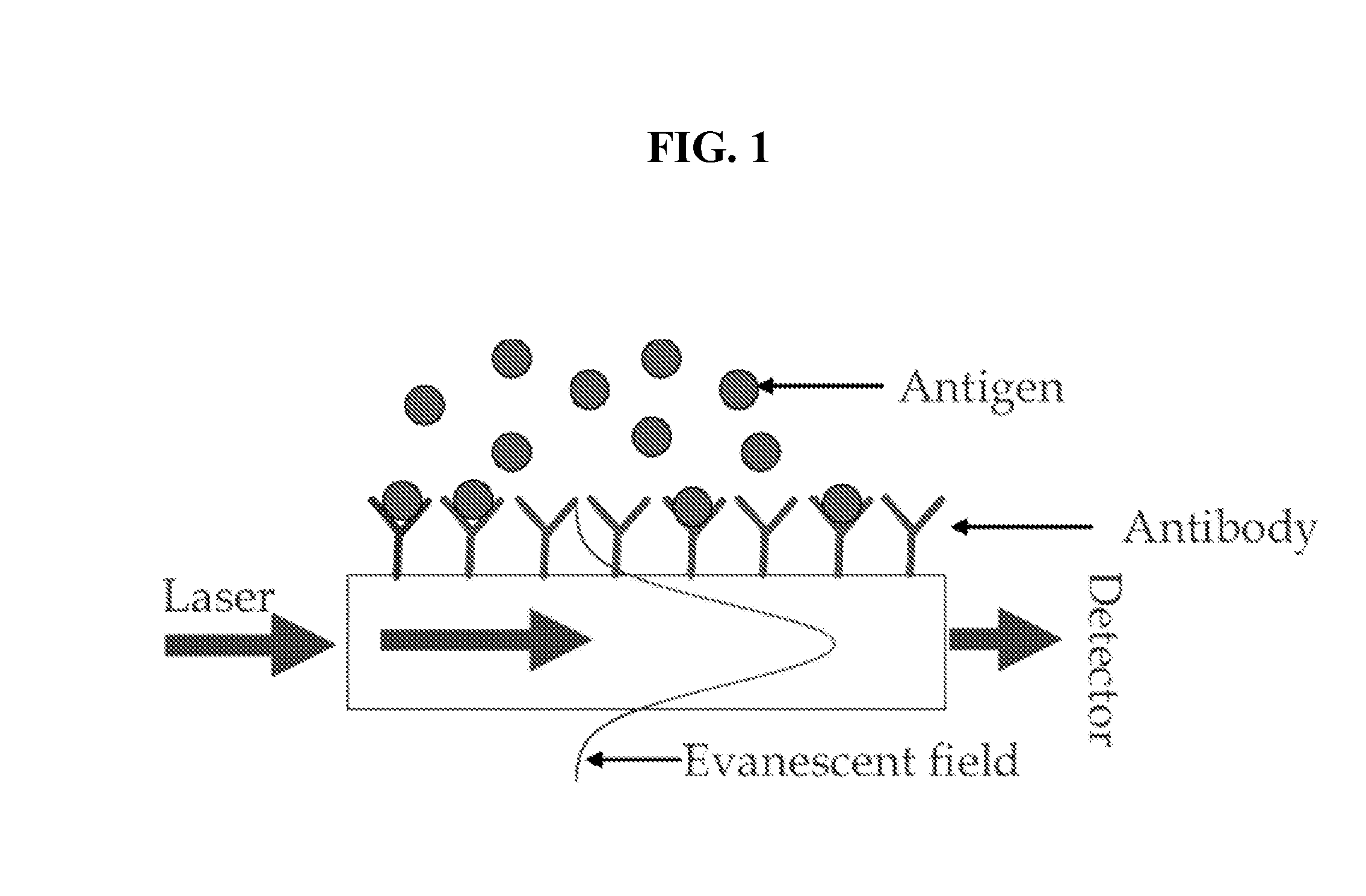
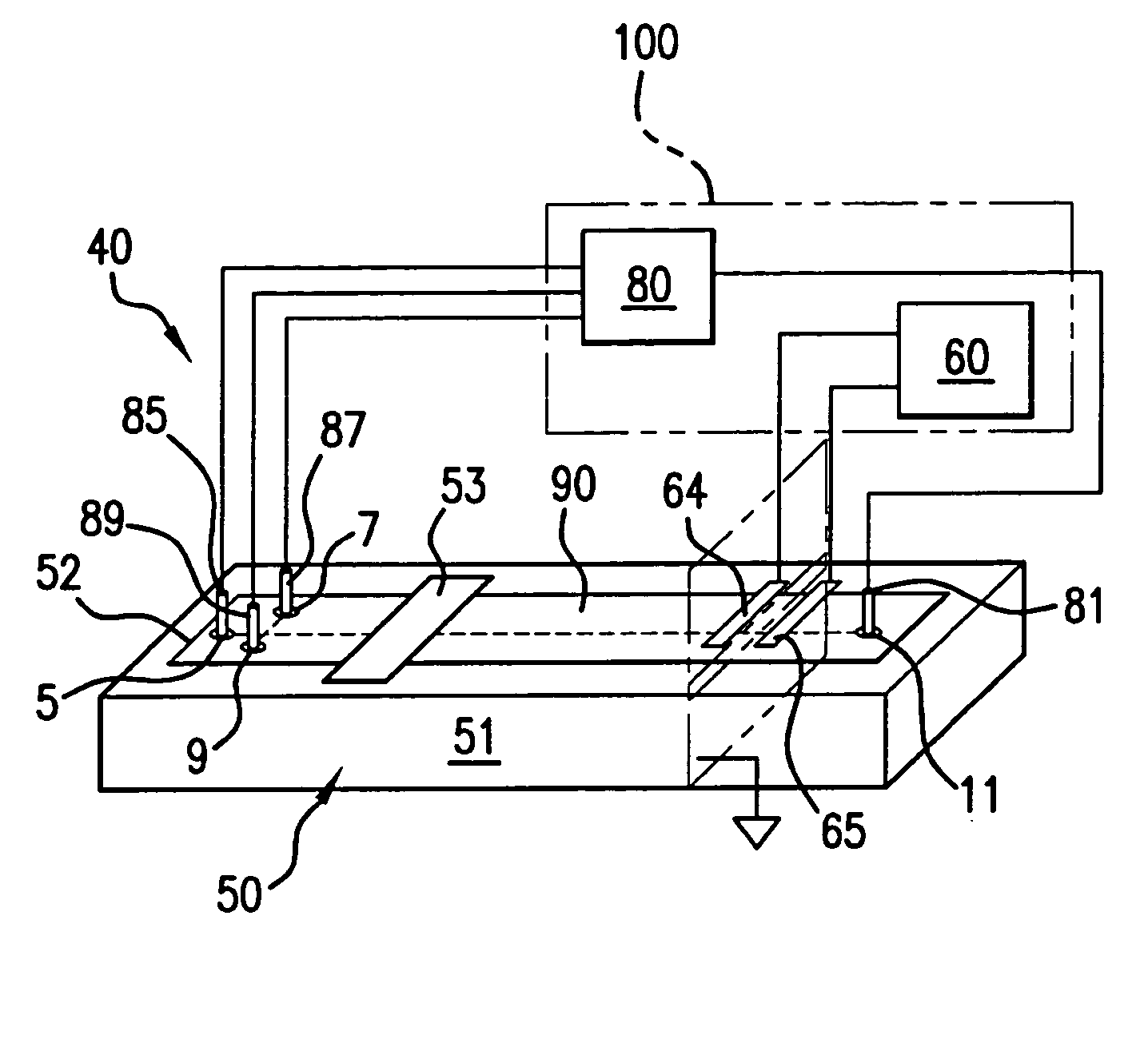
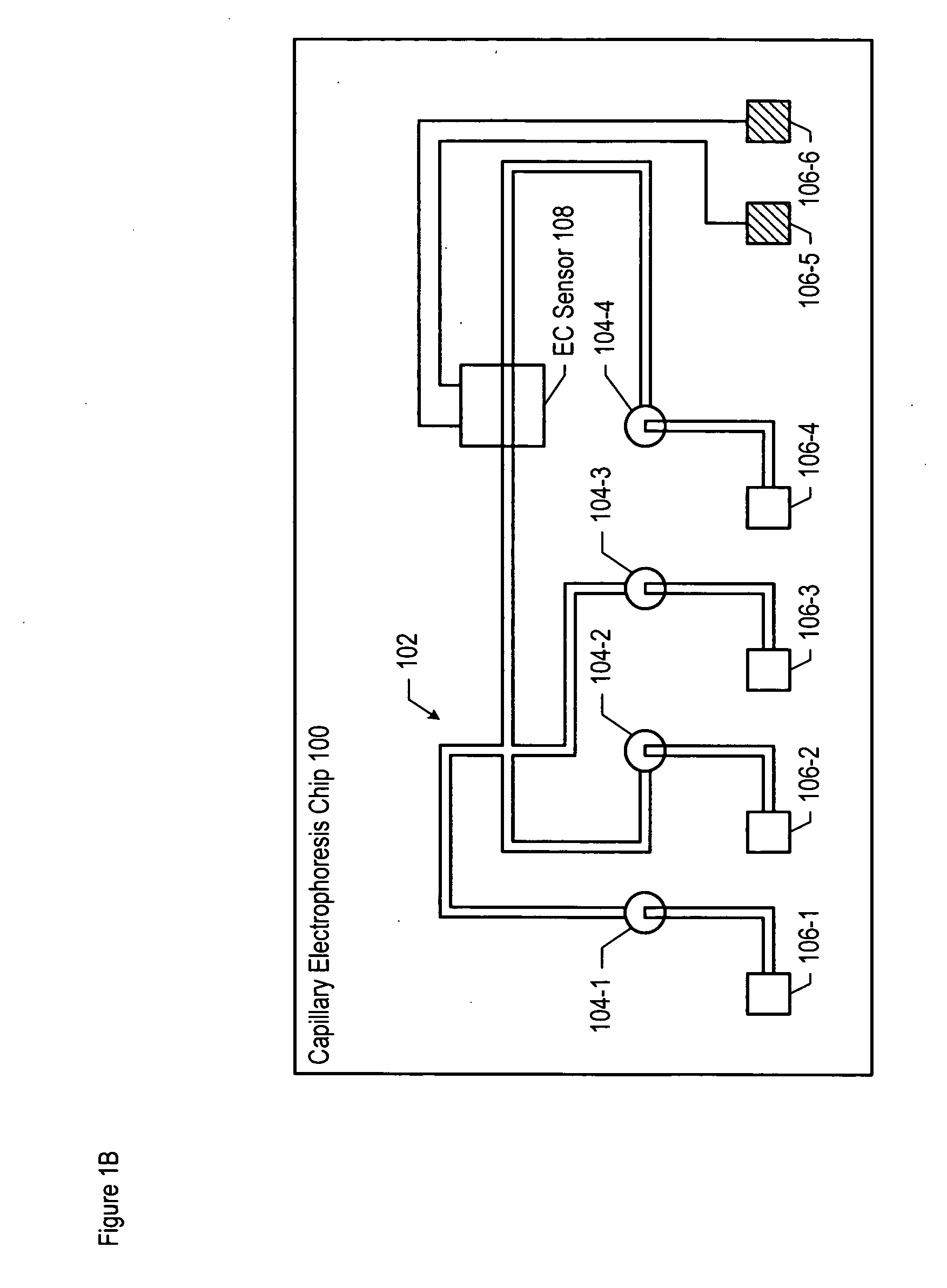
Method and apparatus for performing high-voltage contactless conductivity (HV-CCD) electrophoresis
InactiveUS20050109621A1Reduce adhesionSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementAnalyteCapillary electrophoresis
A chip-based capillary electrophoresis assembly including: a holder including a frame for removably receiving a chip; a capillary electrophoresis microchip dimensioned to fit onto the holder, and comprising a body and a separation channel defined in the body; and a pair of adhesive detection electrodes integrated with an electronic conductometric detection circuit, wherein the assembly is assemblable by disposing the capillary electrophoresis microchip on the holder and removably placing the adhesive electrodes on the microchip body near the separation channel. A label-free analyte conductometric detection method and a label-free capillary electrophoresis immunoassay method are also described.
Owner:HAUSER PETER C
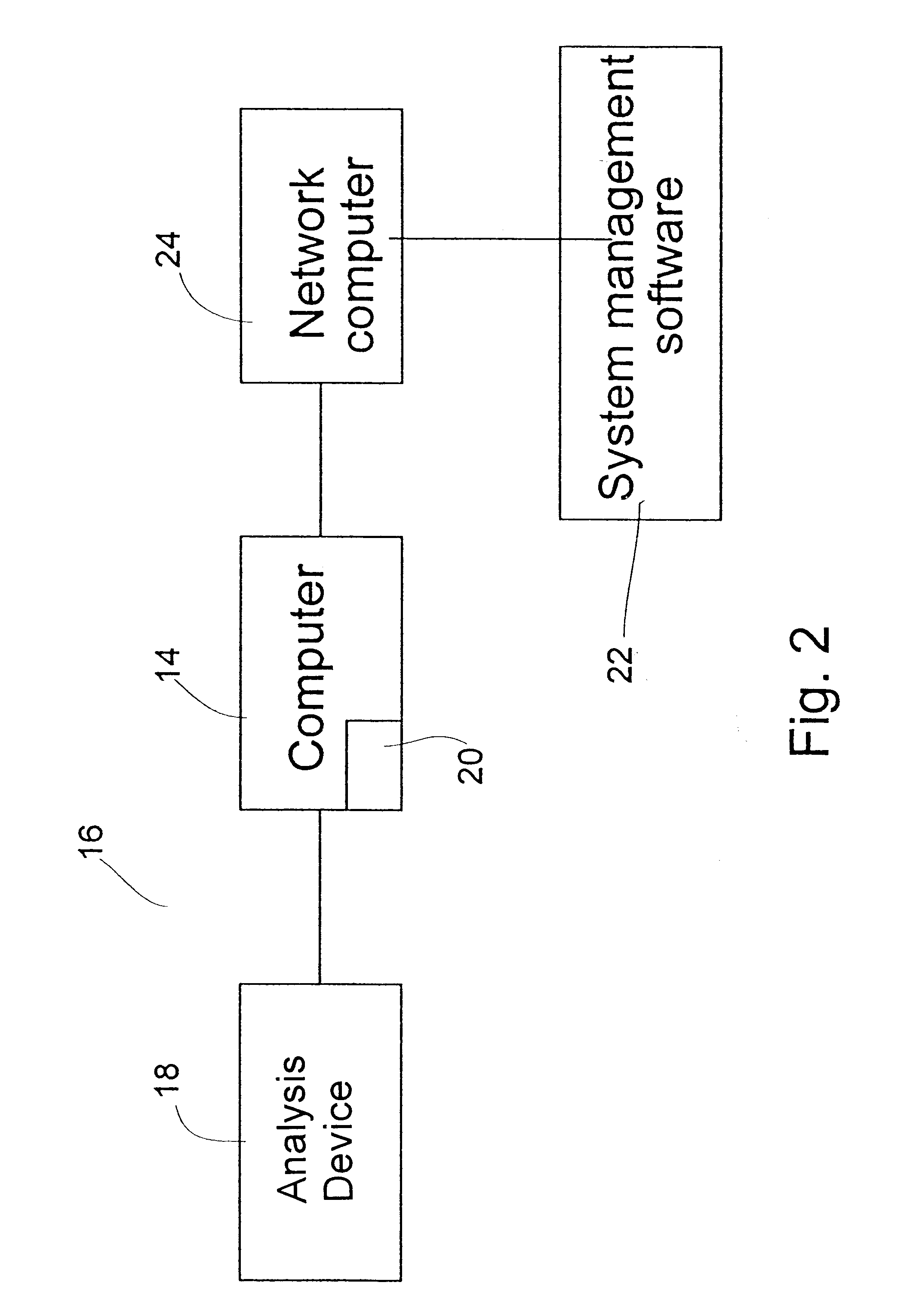
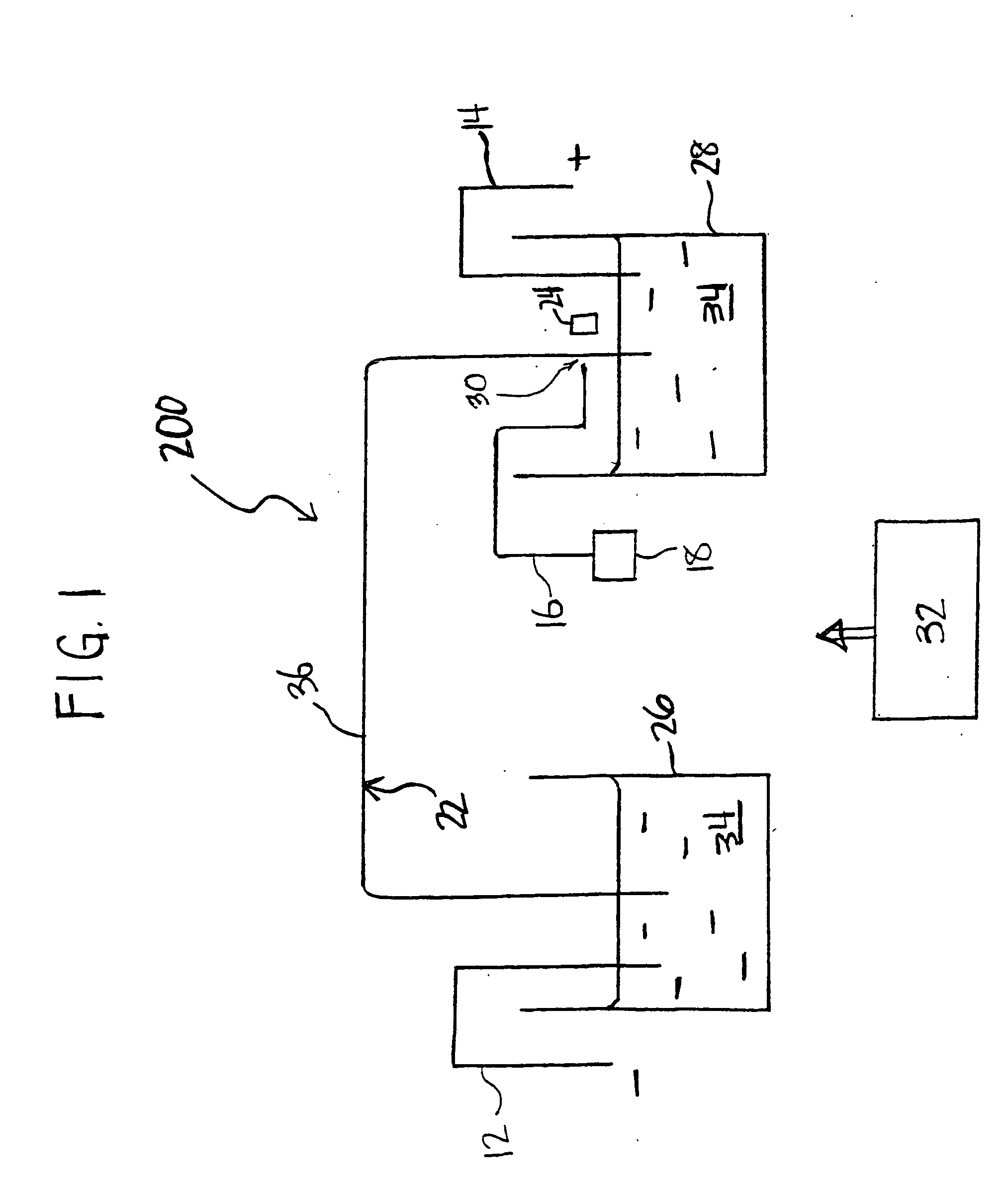
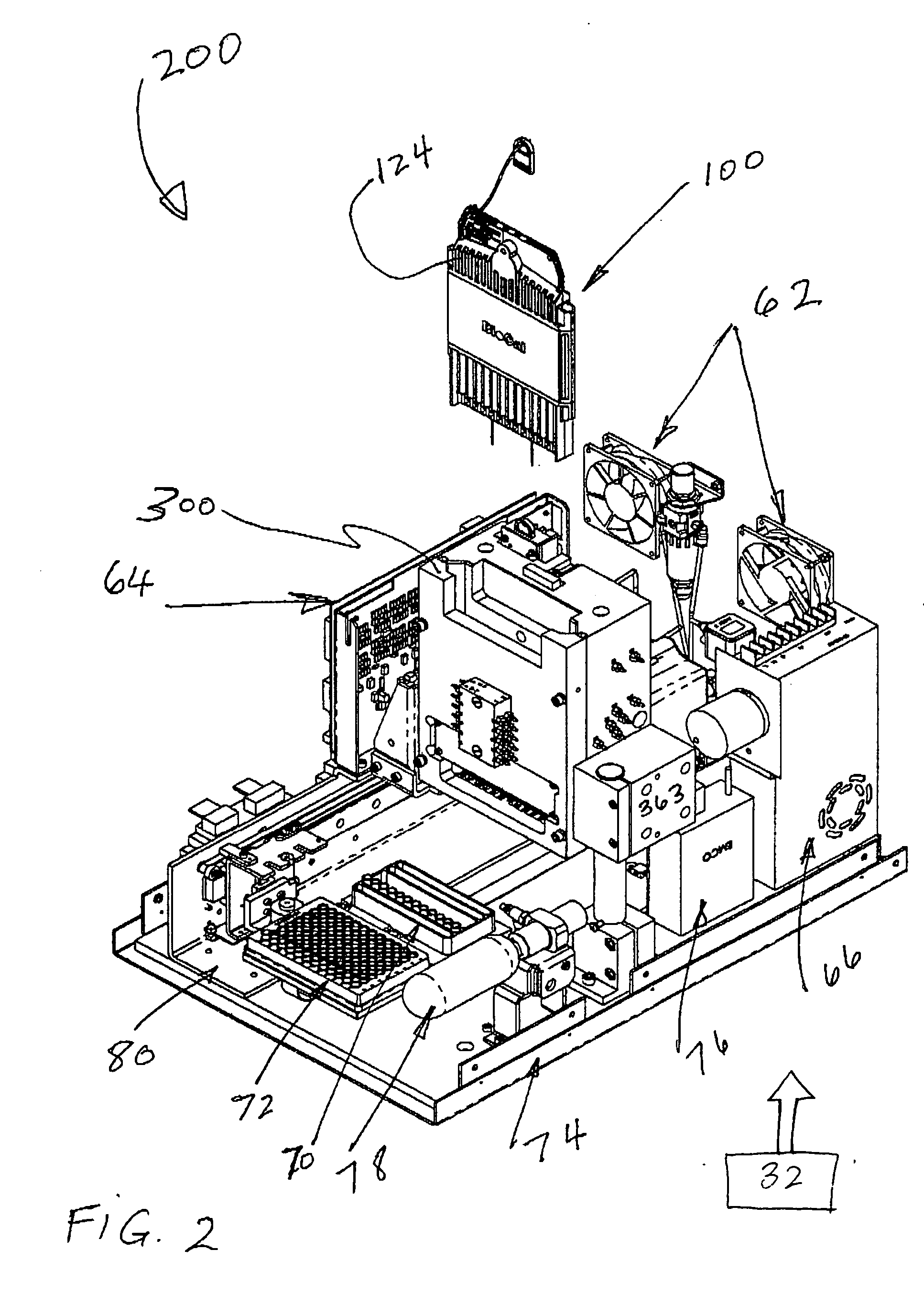
System and method for device monitoring
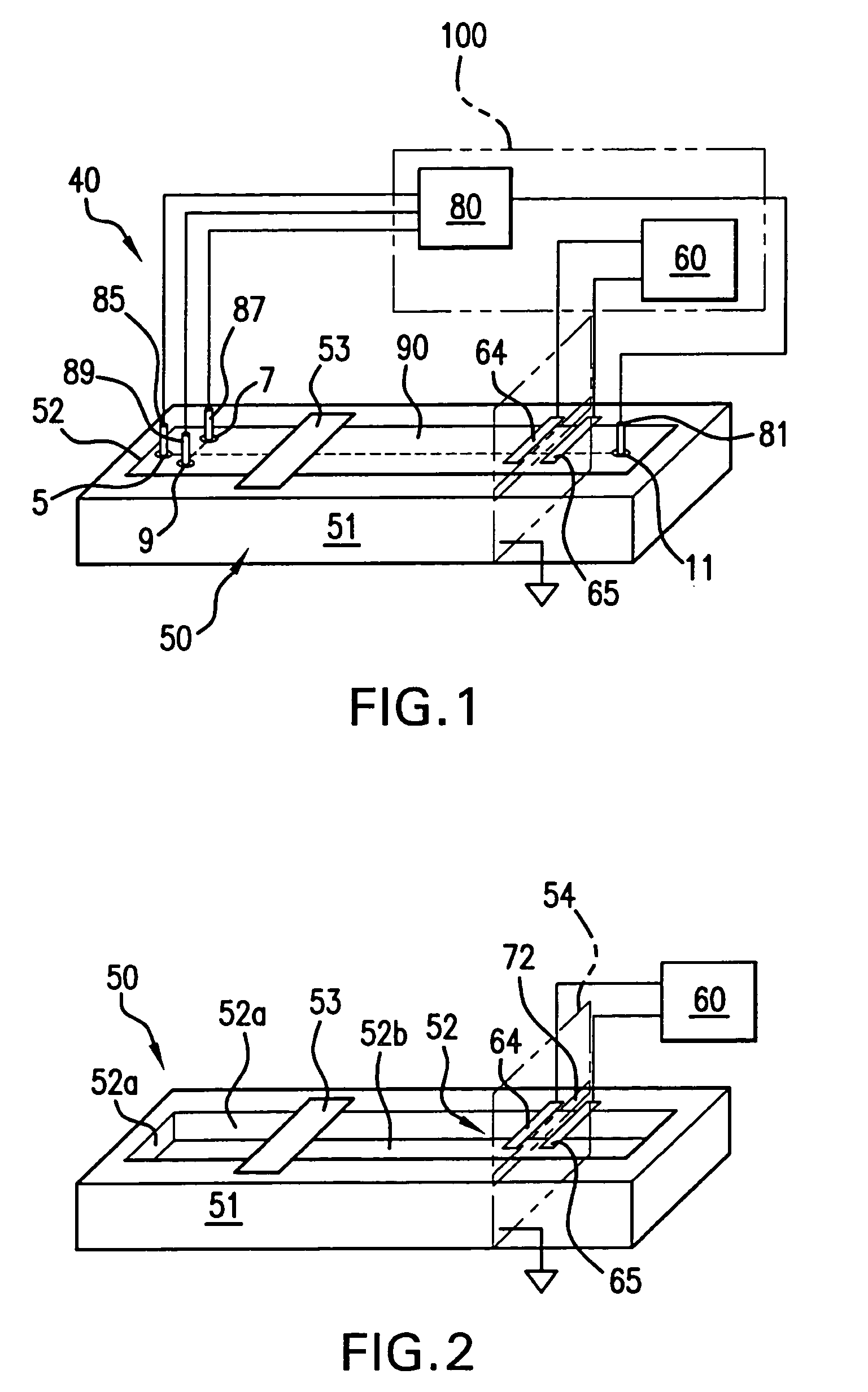
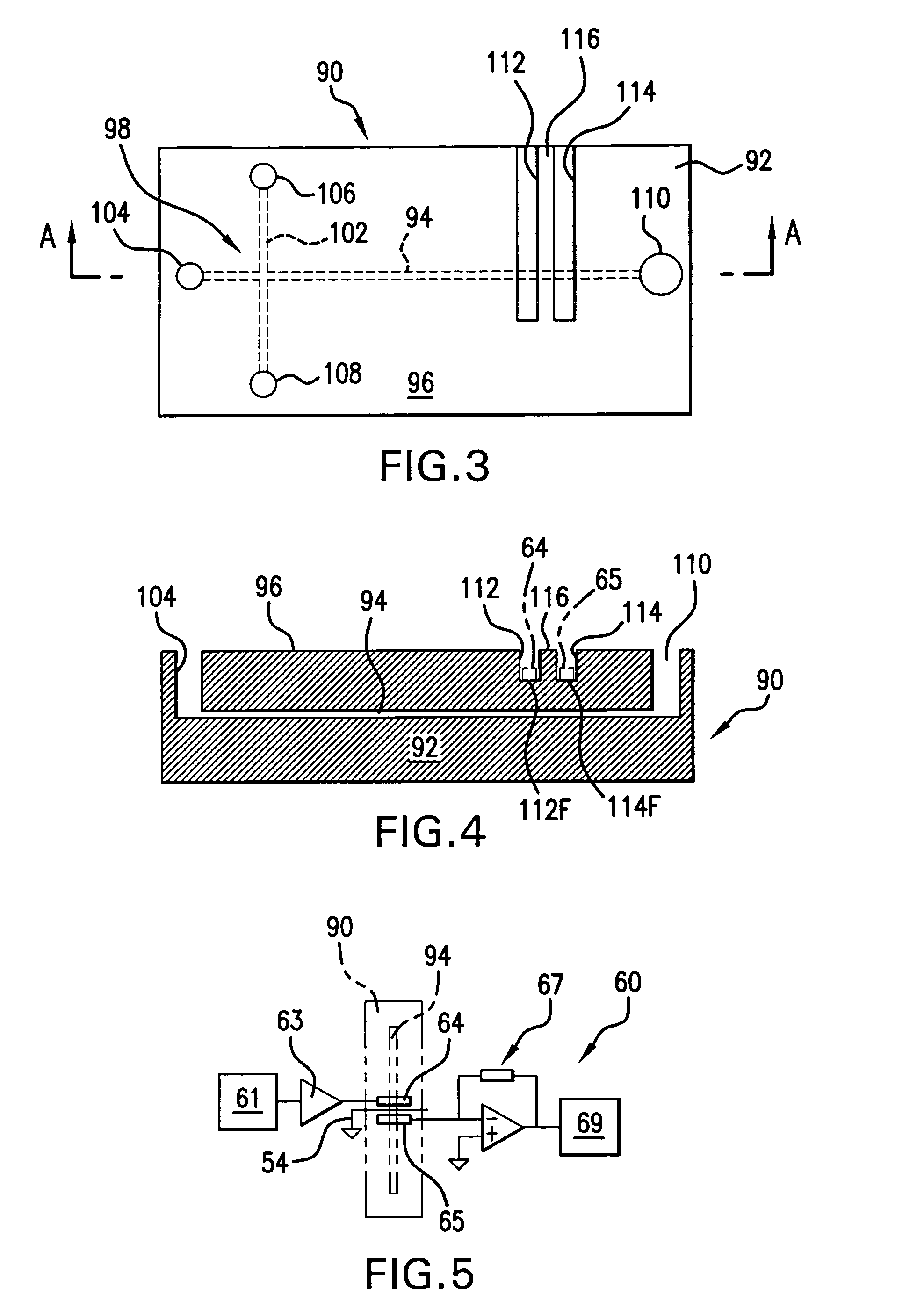
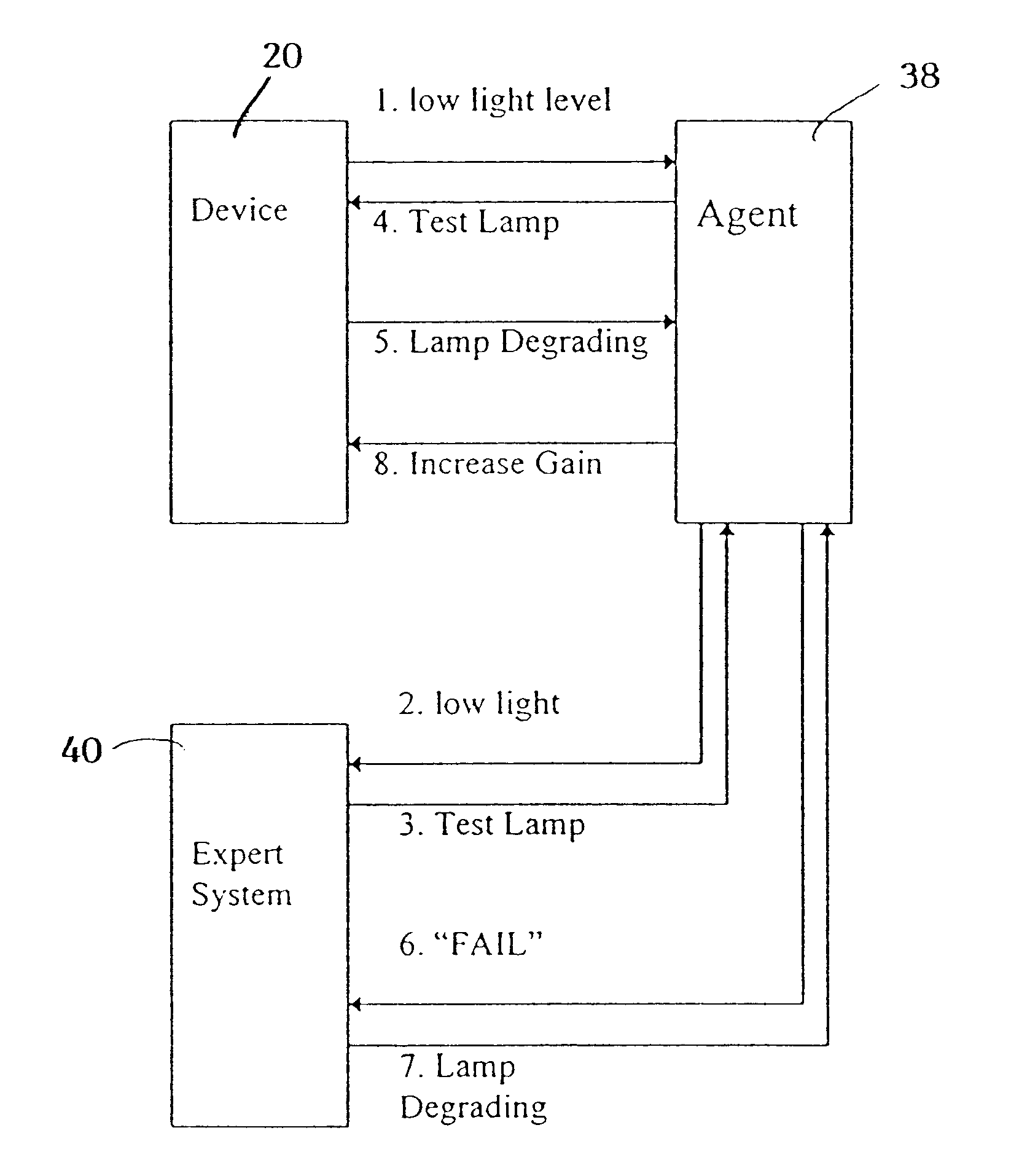
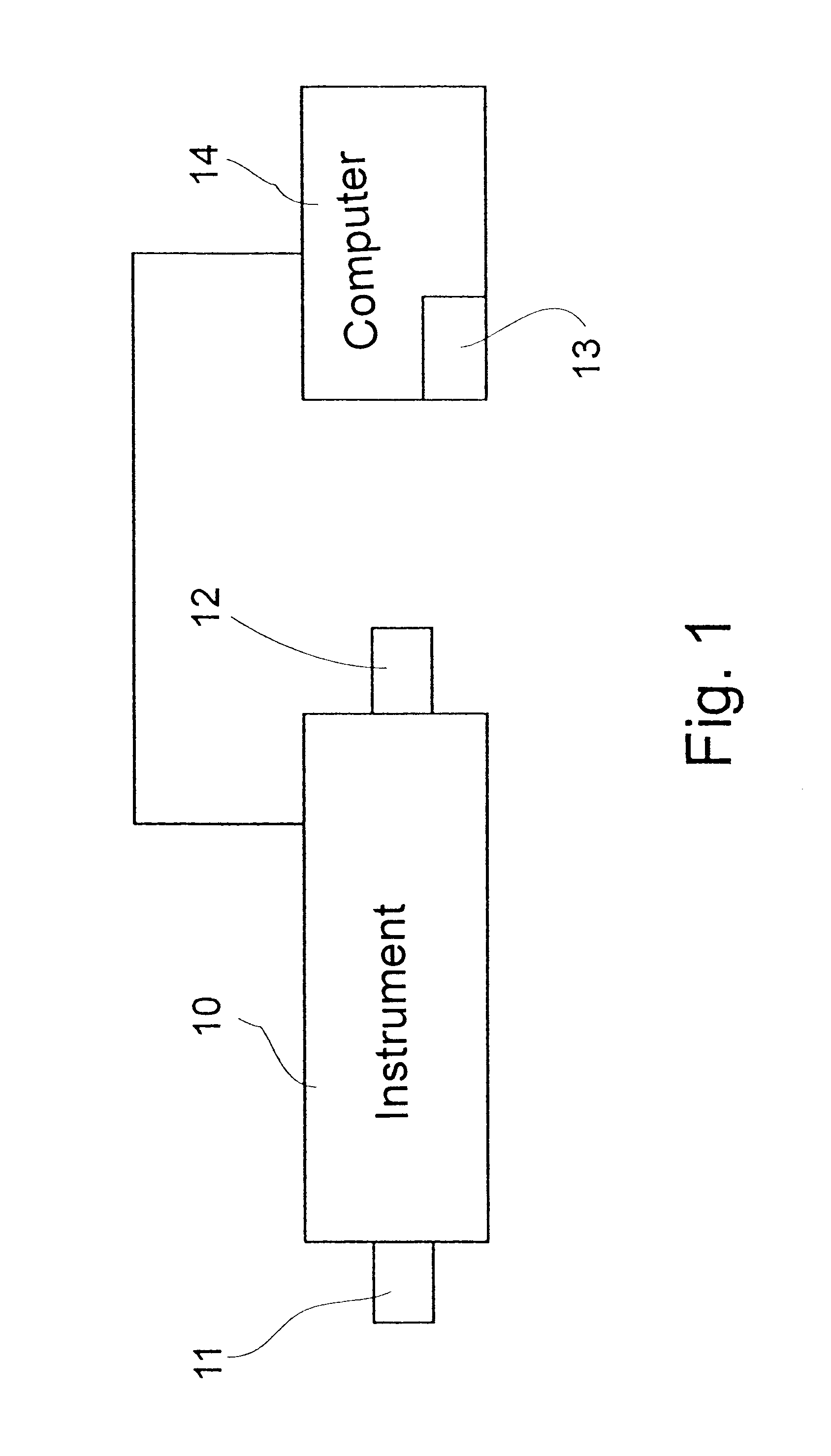
InactiveUS6584430B1Local control/monitoringDigital computer detailsCapillary electrophoresisSystems management
A system for monitoring the state and performance of an analysis device, such as a capillary electrophoresis instrument. The system includes software for operating the analysis device and system management software for monitoring the device, generating a report on the state of the device and selecting an appropriate response based on this report. The response can include altering the function of one or more parts of the device, or signaling the need for a repair to be performed, for example.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
System and Method For the Separation of Analytes
InactiveUS20100155243A1Low costImprove efficiencyElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityAnalyte
A separation module operates to fractionate or separate an analyte into fractions according to pI, i.e., pI bands, utilizing capillary isoelectric focusing (“CIEF”) within a first microchannel. The fractions are stacked to form plugs, the number of which is determined by a number of parallel second microchannels integrally connected to the first microchannel, into which the fractions are directed according to the buffer characteristics found in each of the individual microchannels. Within the microchannels the plugs are separated into proteins according to a different chemical property, i.e., “m / z,” utilizing capillary electrophoresis (“CE”).
Owner:LEIDOS +1
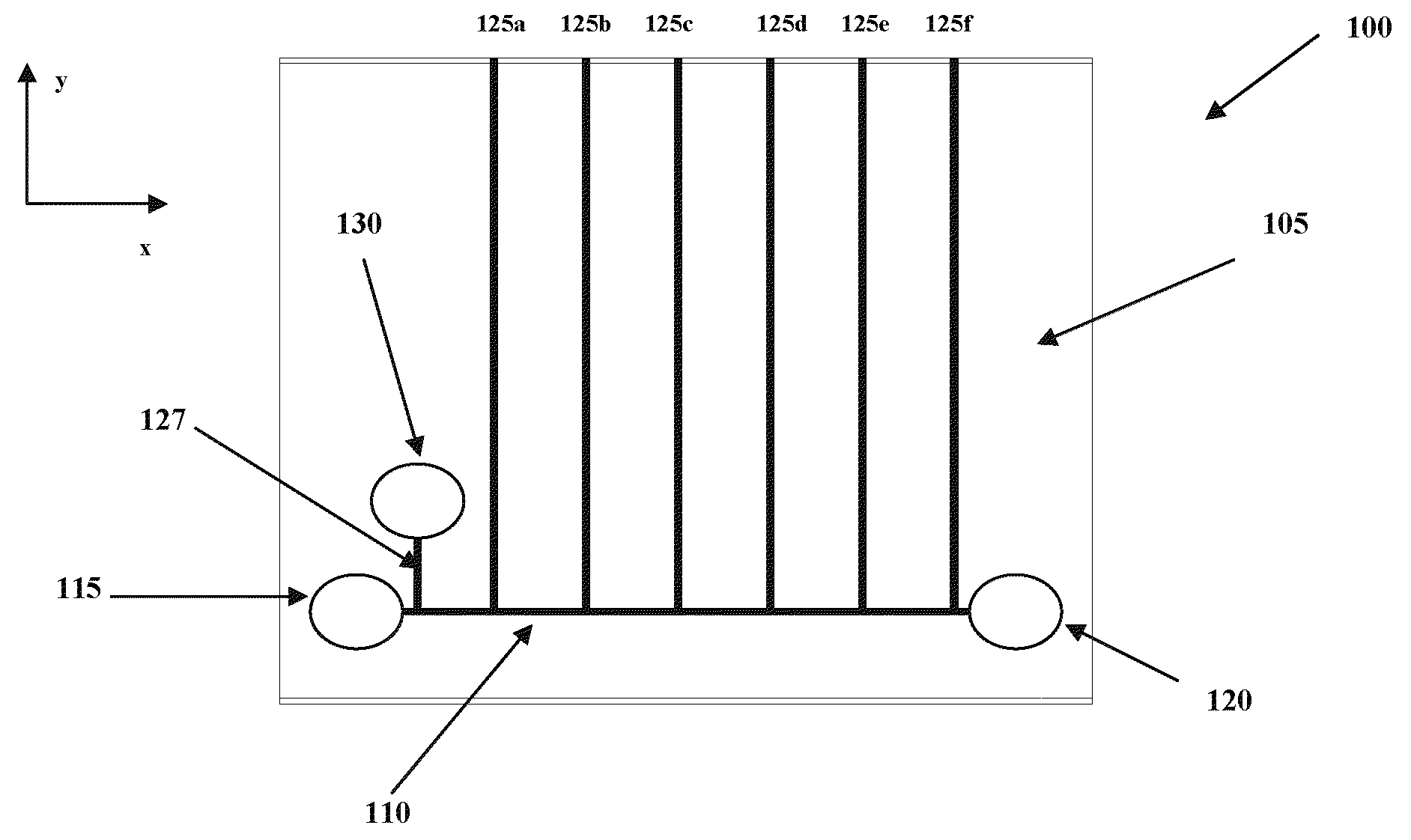
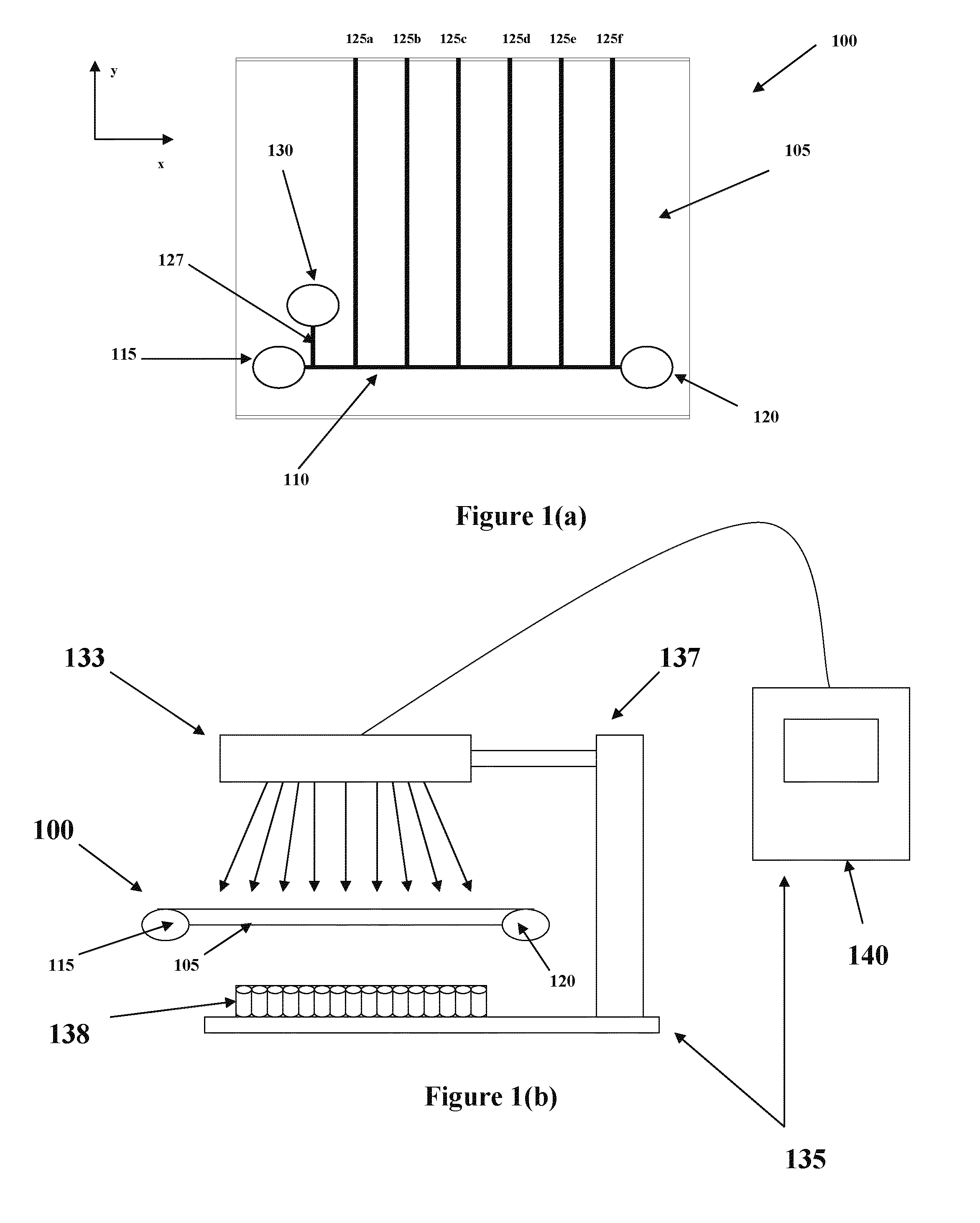
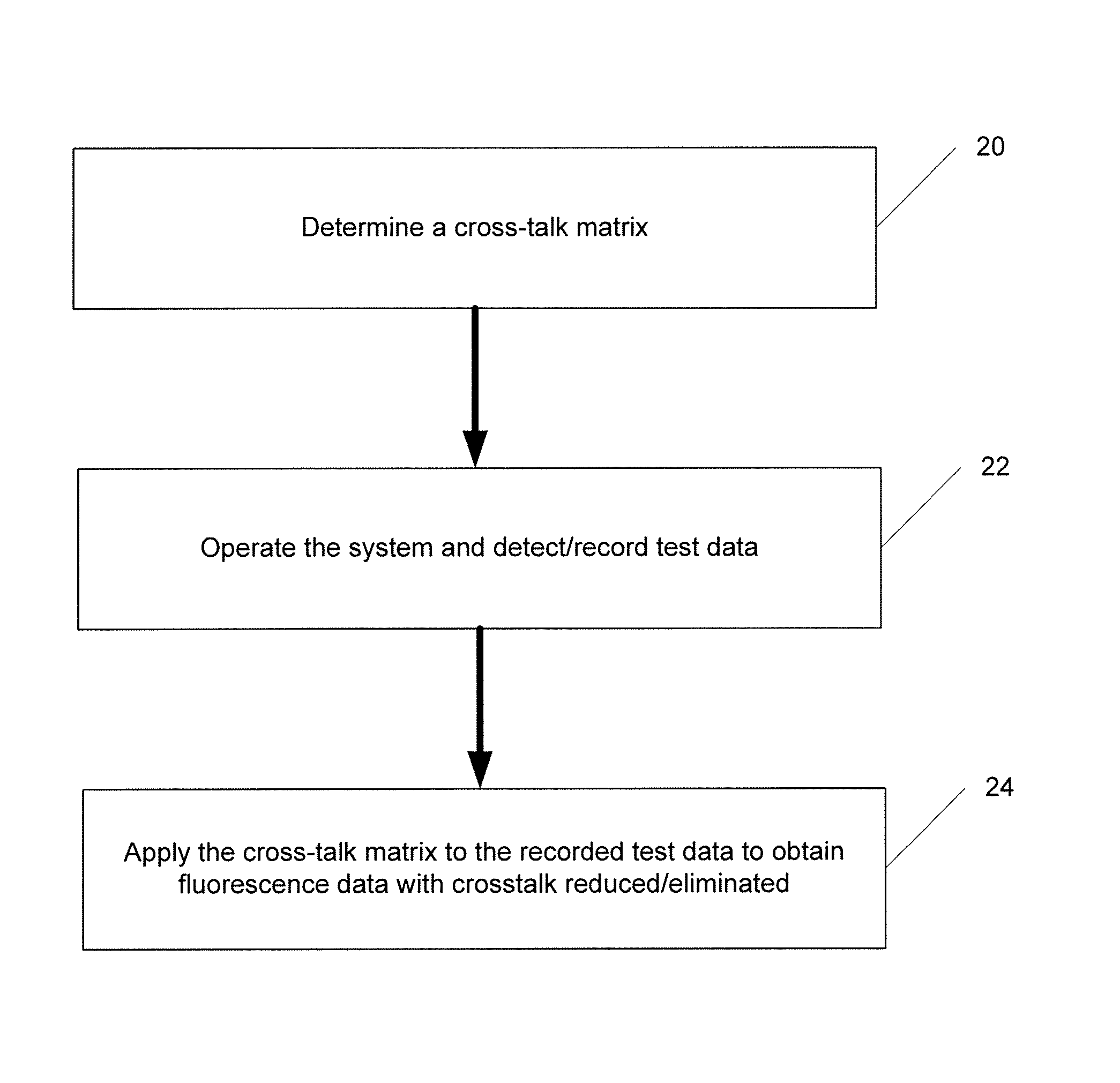
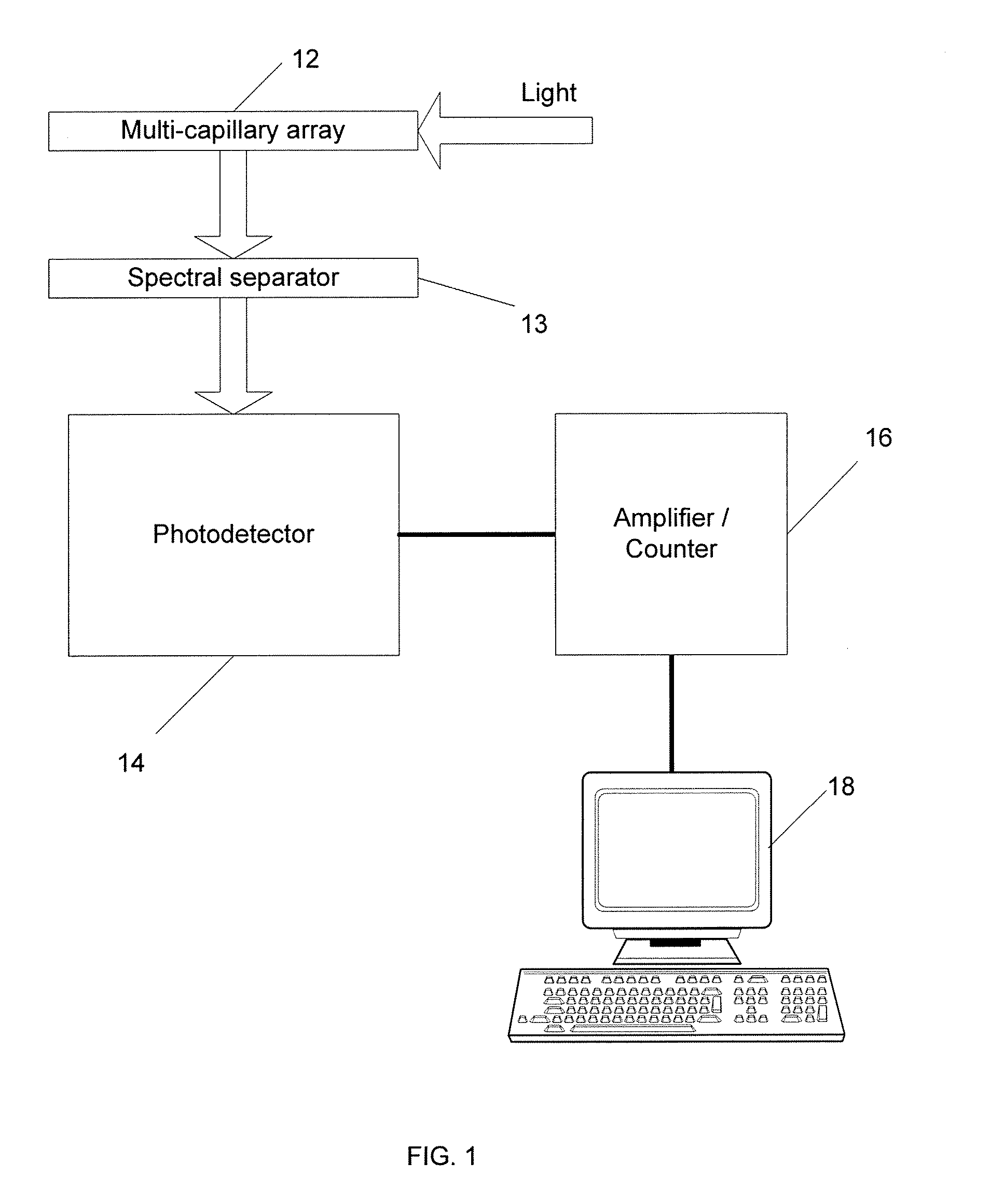
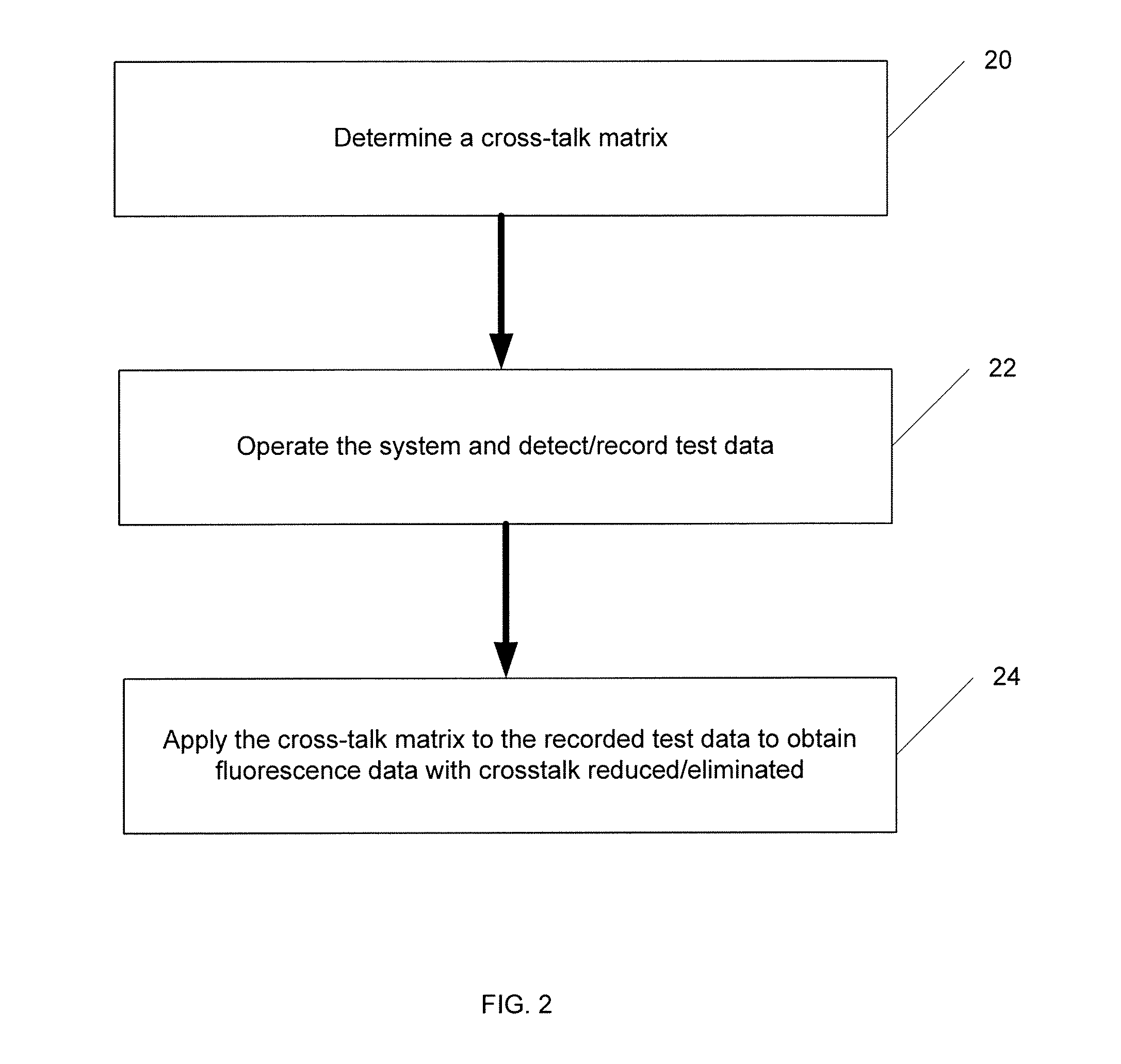
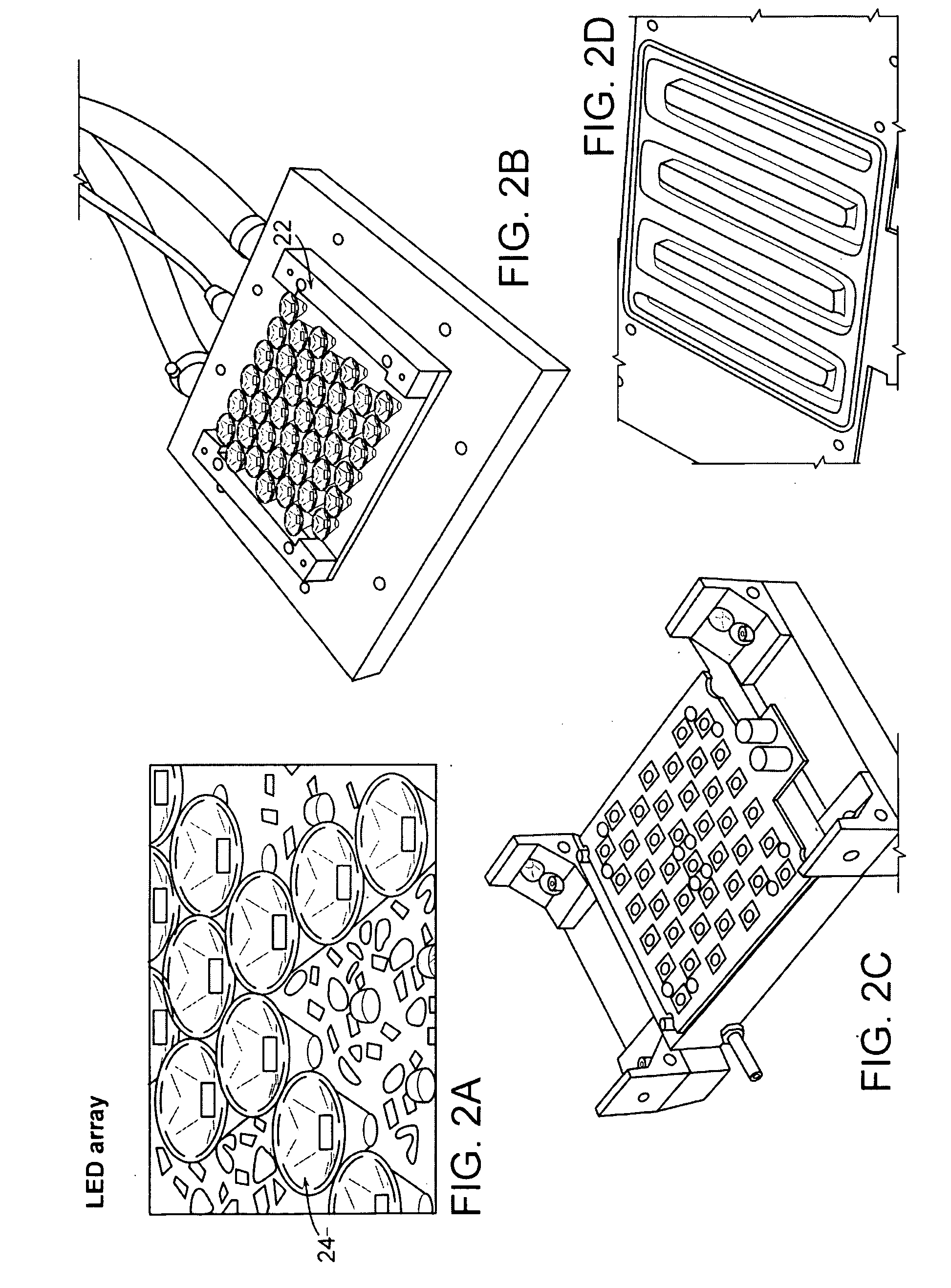
System And Method For Cross-Talk Cancellation In A Multilane Fluorescence Detector
InactiveUS20070194249A1Improve collection efficiencyGreat freedomRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotometryCapillary electrophoresisFluorescence
The present invention is directed to a system and method for cross-talk cancellation for multi-lane fluorescence detectors. The invention may be implemented in accordance with a variety of systems, including systems for multi-capillary electrophoresis. The present invention is based on a special calibration procedure for determination of a channel cross-talk matrix and enables an accurate separation of the fluorescence emitted from individual capillary lanes. The proposed method for cross-talk calibration and removal is very useful for design and development of multi-lane single photon counting detection systems.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Hollow core optical ring resonator sensor, sensing methods, and methods of fabrication
InactiveUS7693369B2High sensitivityReduce consumptionMaterial analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesTarget analysisWhispering gallery
The present invention is directed to hollow core optical ring resonators (HCORRs), methods of fabricating HCORRs, and methods of using HCORRs in sensing applications. In particular, the evanescent field and whispering gallery modes of the HCORRs may be used to detect a target analyte within the hollow core of the HCORR. Other features of the present invention include utilizing the HCORR as part of a multiplex sensing device, including using the HCORR in capillary electrophoresis and chromatography applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Universal sample preparation system and use in an integrated analysis system
ActiveUS8394642B2Raman/scattering spectroscopyHeating or cooling apparatusCapillary electrophoresisAnalyte
The invention provides a system that can process a raw biological sample, perform a biochemical reaction and provide an analysis readout. For example, the system can extract DNA from a swab, amplify STR loci from the DNA, and analyze the amplified loci and STR markers in the sample. The system integrates these functions by using microfluidic components to connect what can be macrofluidic functions. In one embodiment the system includes a sample purification module, a reaction module, a post-reaction clean-up module, a capillary electrophoresis module and a computer. In certain embodiments, the system includes a disposable cartridge for performing analyte capture. The cartridge can comprise a fluidic manifold having macrofluidic chambers mated with microfluidic chips that route the liquids between chambers. The system fits within an enclosure of no more than 10 ft3. and can be a closed, portable, and / or a battery operated system. The system can be used to go from raw sample to analysis in less than 4 hours.
Owner:INTEGENX
Universal interface for a micro-fluidic chip
InactiveUS20060163069A1Improve performanceEasy accessImmobilised enzymesSludge treatmentDocking stationElectricity
An integrated capillary electrophoresis system comprising a universal interface is disclosed. The universal interface includes one or more of the following structural elements: a chip assembly that receives a capillary electrophoresis CE chip; a fluidic interface for coupling fluids between the chip assembly and external sources or destinations; a first electrical interface for coupling power from an external source to the chip assembly; a second electrical interface for coupling electrical signals from the chip assembly to external analysis electronics; an optical interface for coupling optical signals between the chip assembly and external sources or destinations; and a docking station for uniting and spatially locating the various other structural elements.
Owner:OCTROLIX
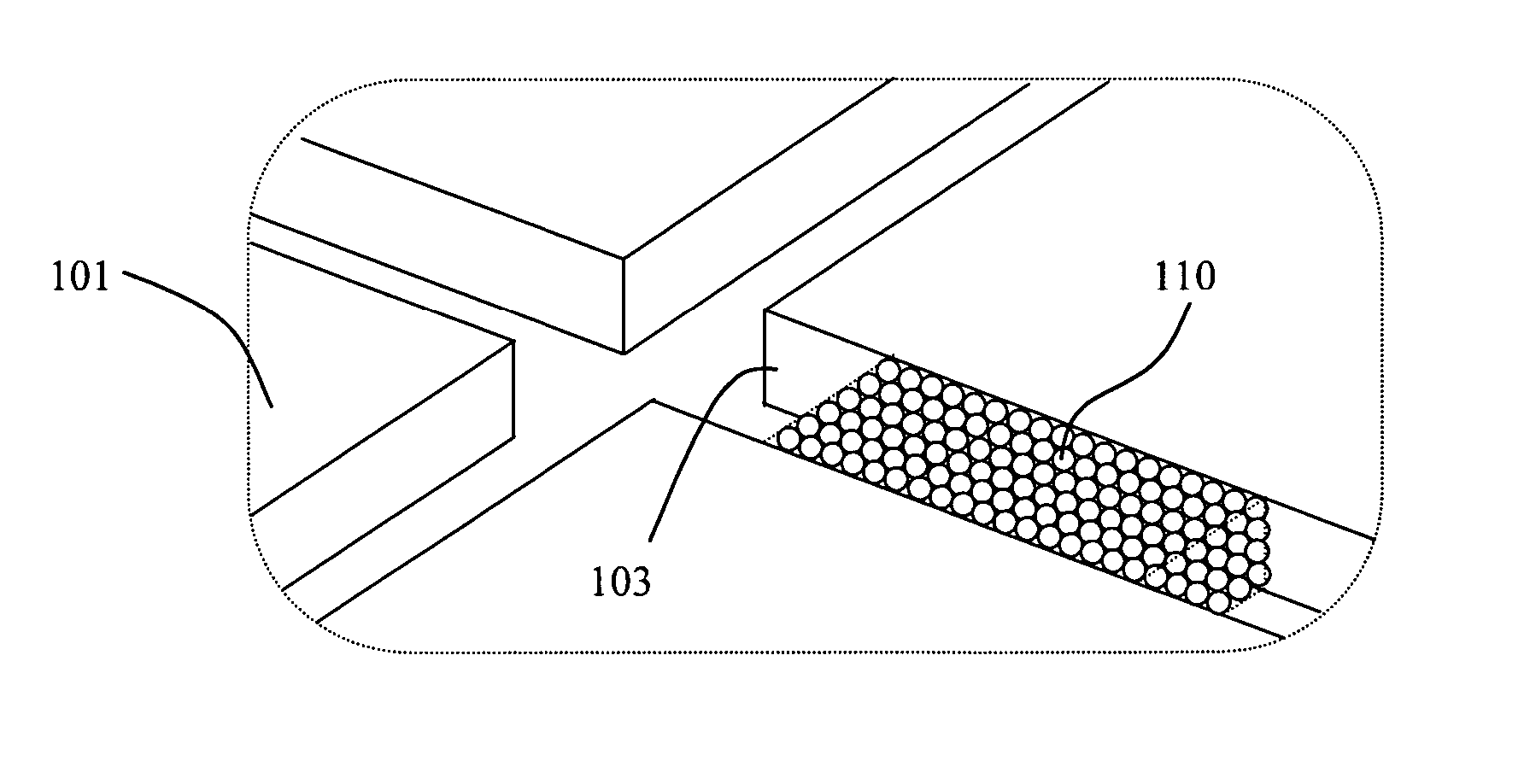
Fully packed capillary electrophoretic separation microchips with self-assembled silica colloidal particles in microchannels and their preparation methods
InactiveUS20060147344A1Rapid and improved separationEnhanced interactionComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
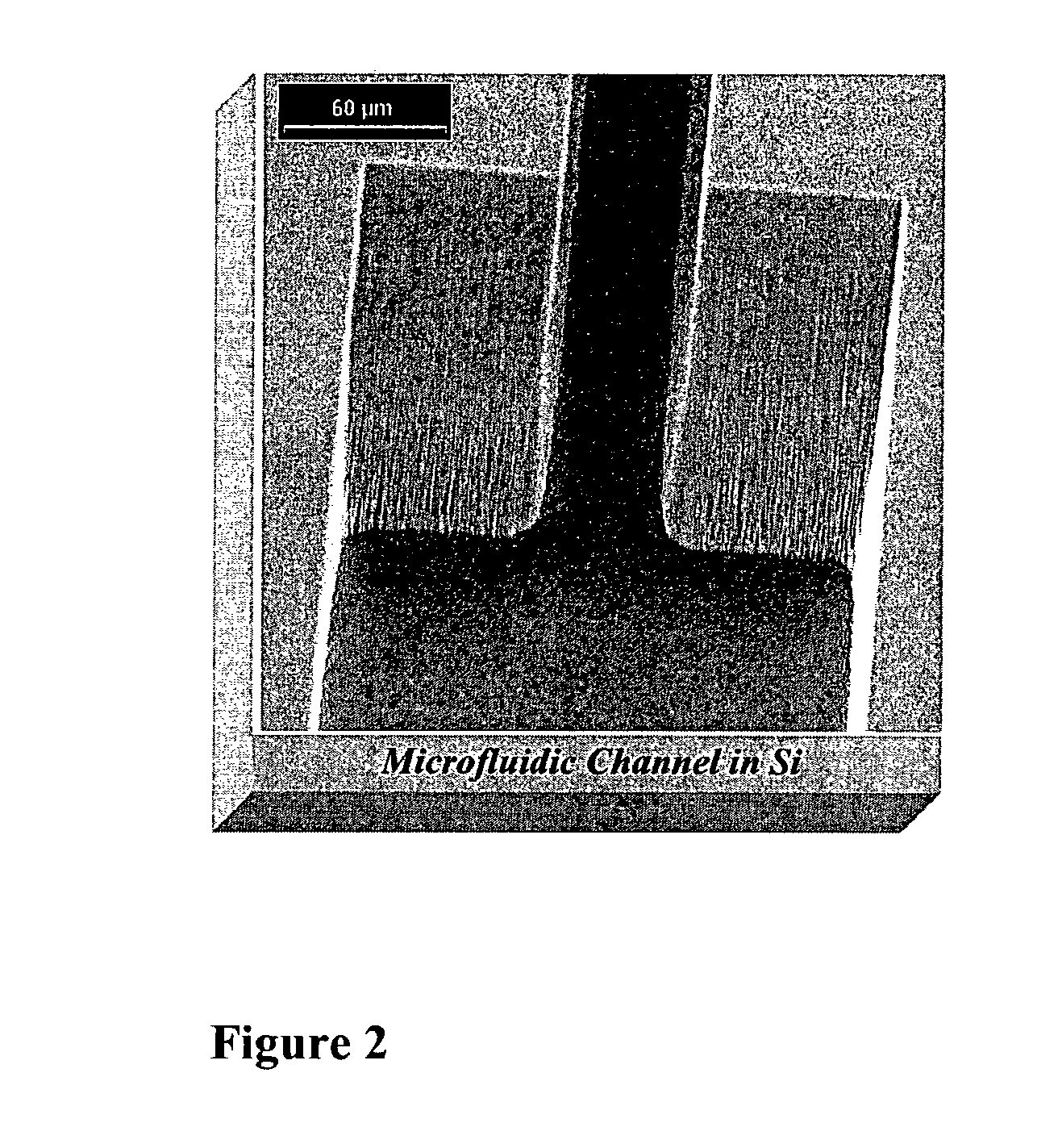
A novel CEC column preparation method for various forms of CEC separation using selectively or fully packed microchannels with self-assembled silica colloidal particles is disclosed. The method relies on the three dimensional uniform silica colloidal packing through selective regions or whole channels resulting in uniform EOF and reproducibility. The fully packed capillary electrophoretic separation microchip is inherently suited for a handheld system since it exploits uniquely fully packed separation channels to achieve better separation efficiency and stability. The fully packed capillary electrophoretic separation microchip can be easily fabricated using low-cost, rapid manufacturing techniques, and can provide high performance for CEC separation with various chromatographic stationary support packing, functionalized surface of packed beads. The fully packed microchannels with self-assembled silica colloidal particles can be applied for preparation of a built-in submicron filter. Embodiments of the present invention address a significant challenge in the development of disposable CEC microchips, specifically, providing a reliable solution for preparation of the CEC separation column in a device that may be immediately applied for a variety of CEC applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
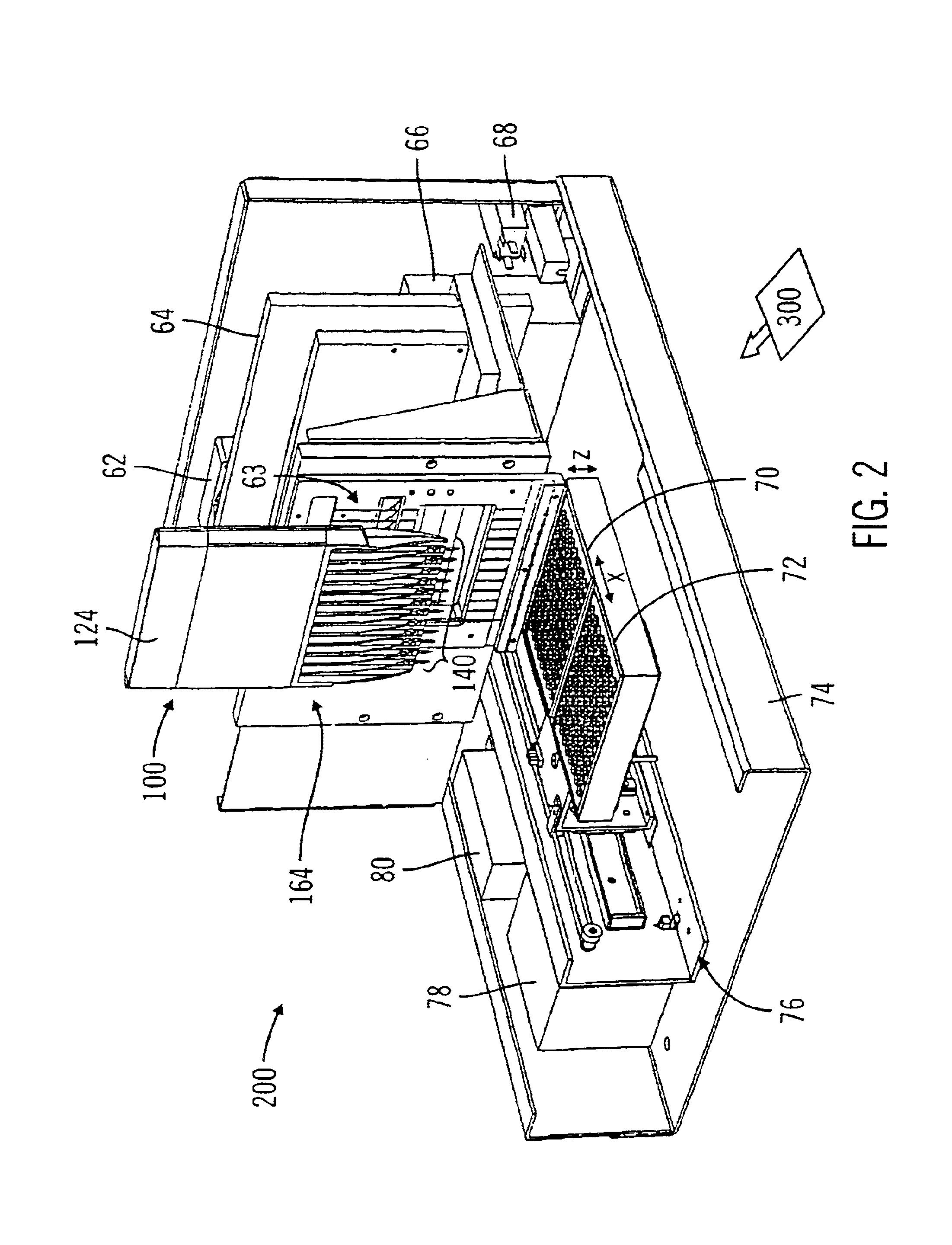
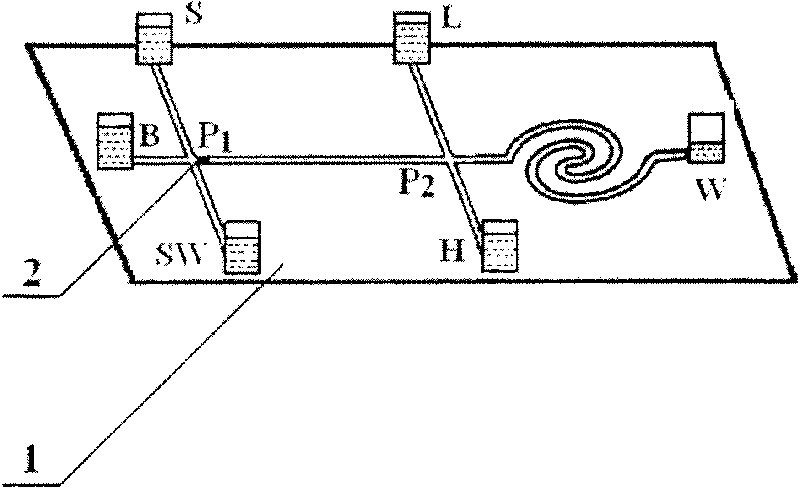
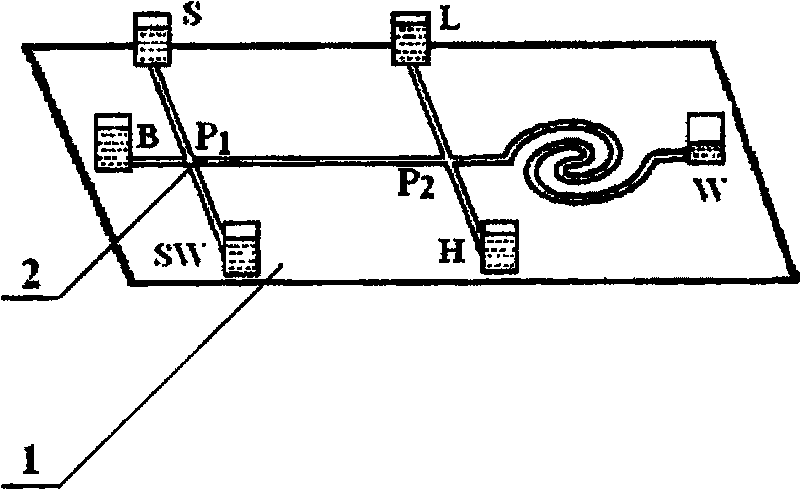
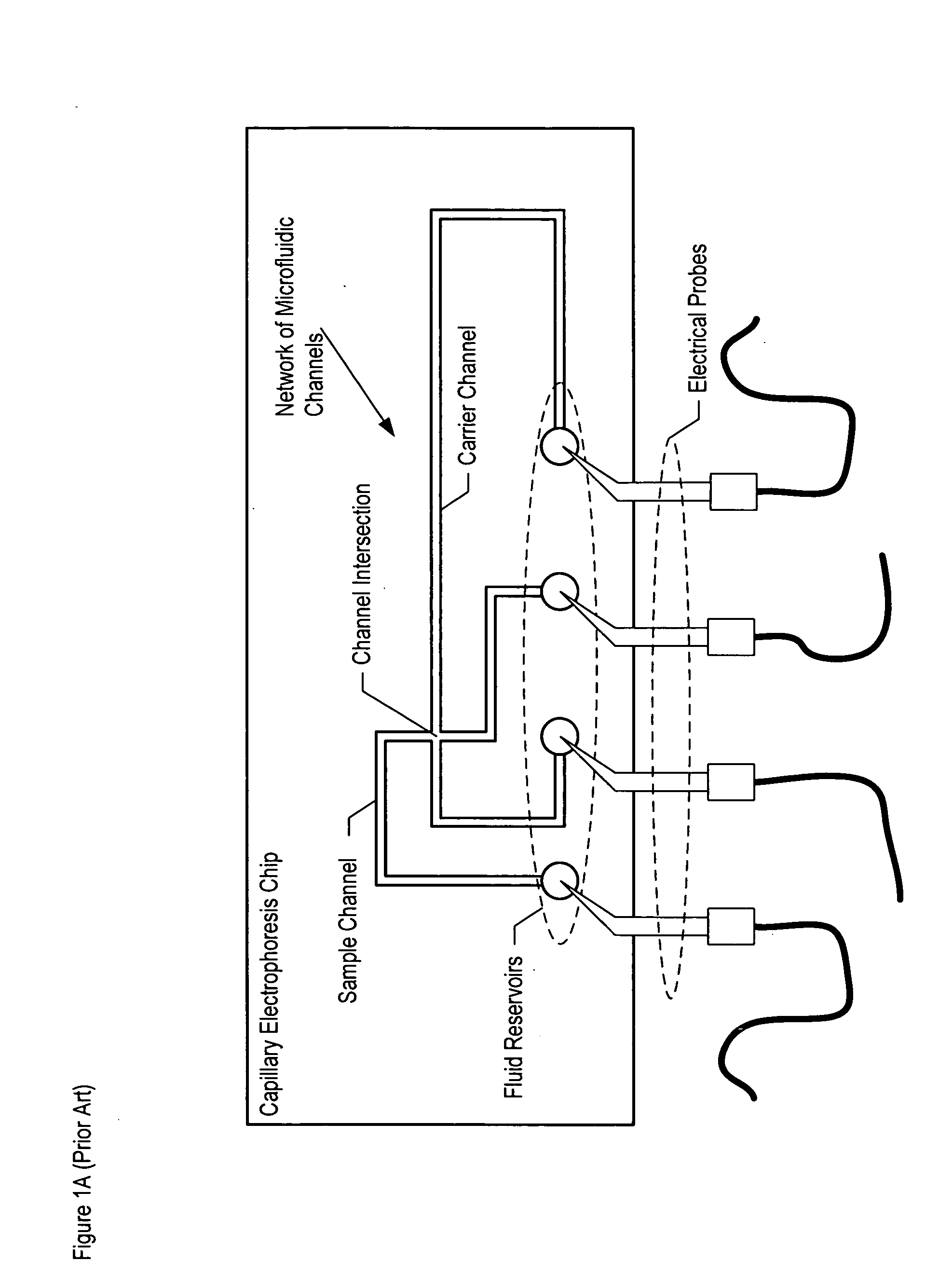
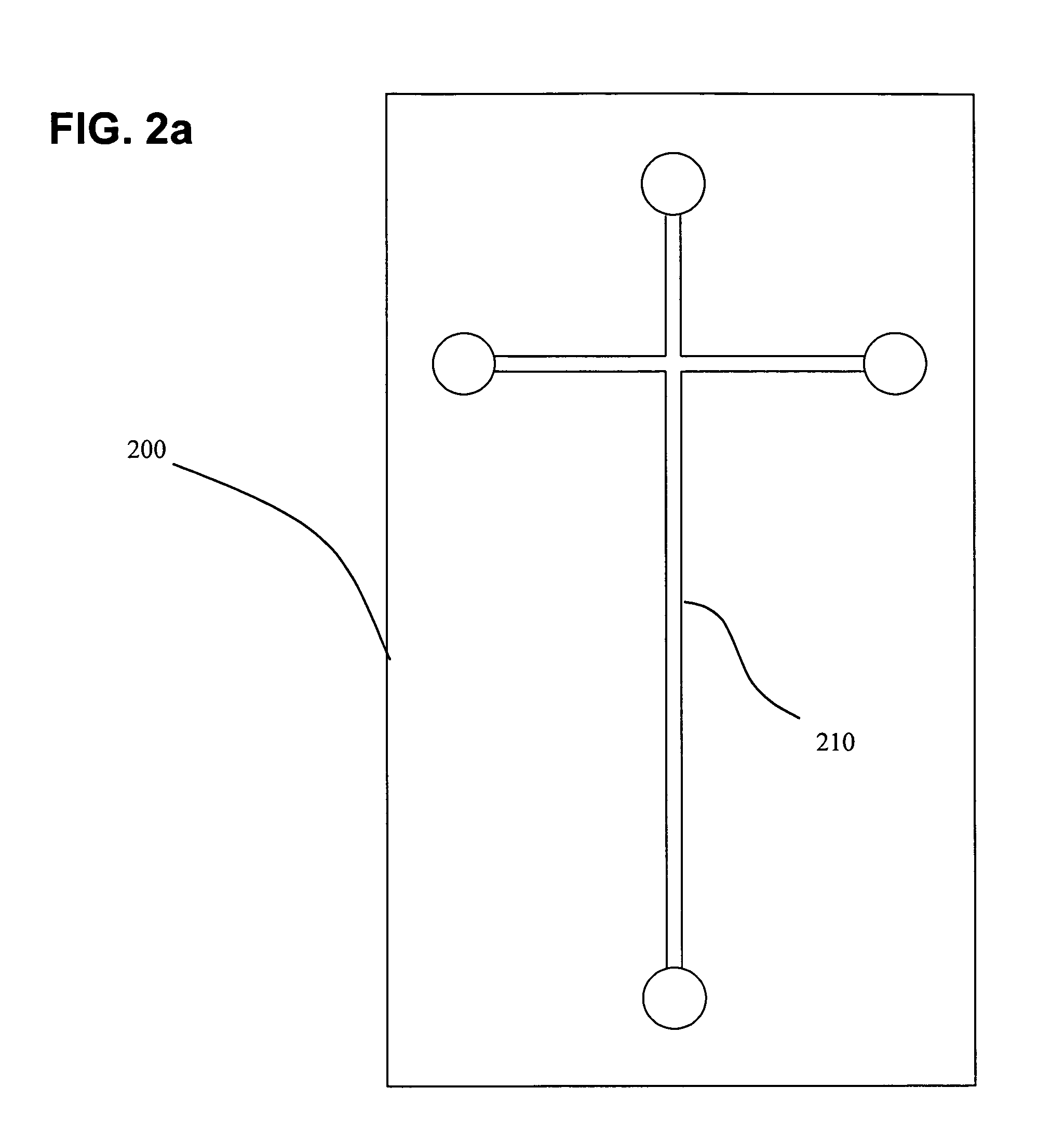
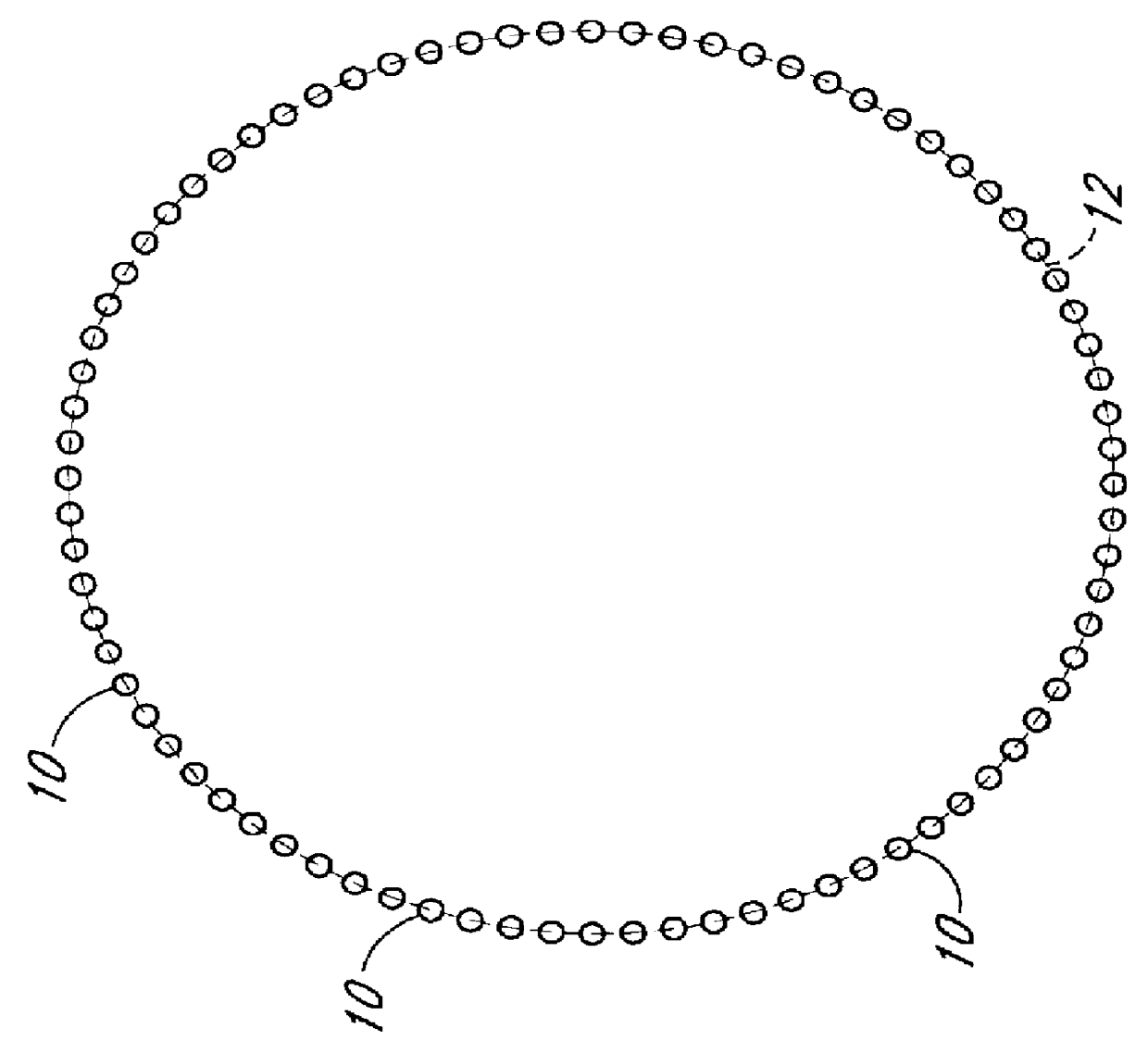
Capillary electrophoresis apparatus and method
InactiveUS6103083ASludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
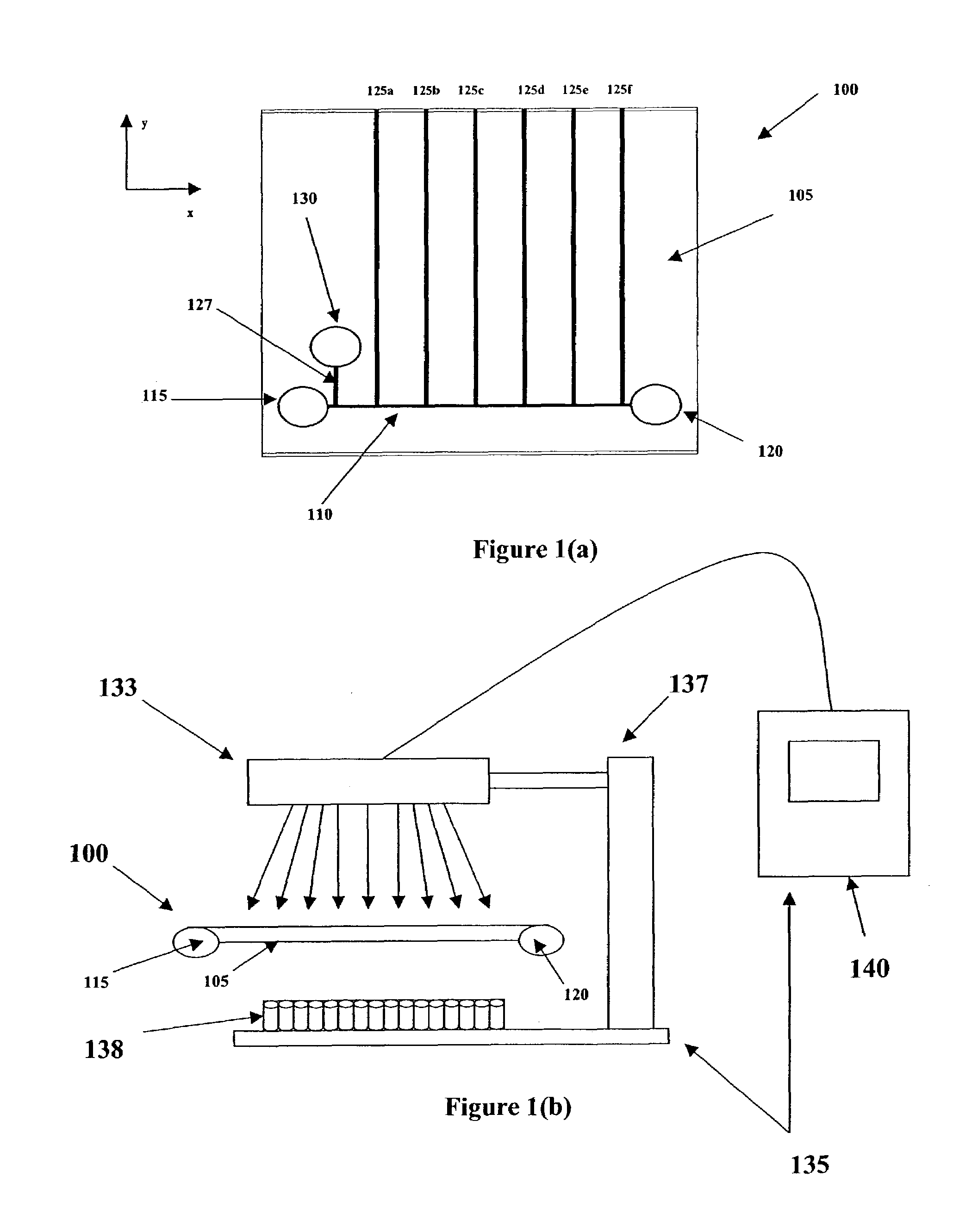
The present invention relates to an electrophoresis apparatus having a plurality of capillaries arranged in a plane such that a curving contour is formed by the intersection points of each of the capillaries with the plane. The apparatus may be used to determine the sequence of nucleic acids. The present invention also relates to methods of using the electrophoresis apparatus and methods of making the electrophoresis apparatus.
Owner:TECHLDG
Interfacing Capillary Electrophoresis to a Mass Spectrometer via an Impactor Spray Ionization Source
ActiveUS20150021469A1Reduce interfaceEliminate the problemComponent separationSamples introduction/extractionAnalyteCapillary electrophoresis
A mass spectrometer is disclosed comprising a separation device arranged and adapted to emit an eluent over a period of time. The separation device preferably comprises a Capillary Electrophoresis (“CE”) separation device. The mass spectrometer further comprises a nebuliser and a target. Eluent emitted by the separation device is nebulised, in use, by the nebuliser wherein a stream of analyte droplets are directed to impact upon the target so as to ionise the analyte to form a plurality of analyte ions.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Micromixer with overlapping-crisscross entrance
InactiveUS20050232076A1Improve the mixing effectSemi-permeable membranesFlow mixersCapillary electrophoresisShortest distance
The micromixer with overlapping-crisscross entrance incorporated with the grooved microchannel, is used effectively for mixing two or more fluid streams. The X-shape overlapping-crisscross inlet ports wherein two microfluidic channels contact over a small area, allow the fluid streams flow through and create the tumbling inside the micromixer. Then merging with some patterned grooves on the walls also induces swirling motion. As a result, the folding and stretching effects of the flow are augmented to amplify the fluid mixing of two or more streams of the inlet fluids within a relative short distance in the micromixer. All of the flow streams are actuated with either pressure driven by a syringe pump or capillary electrophoresis. The present invention is applicable for micro total analysis systems and drug delivery systems.
Owner:YANG JING TANG
Microfluidic electrophoresis chip having flow-retarding structure
InactiveUS20060042948A1Reducing electrokinetic flow instabilityHigh hydraulic resistanceSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
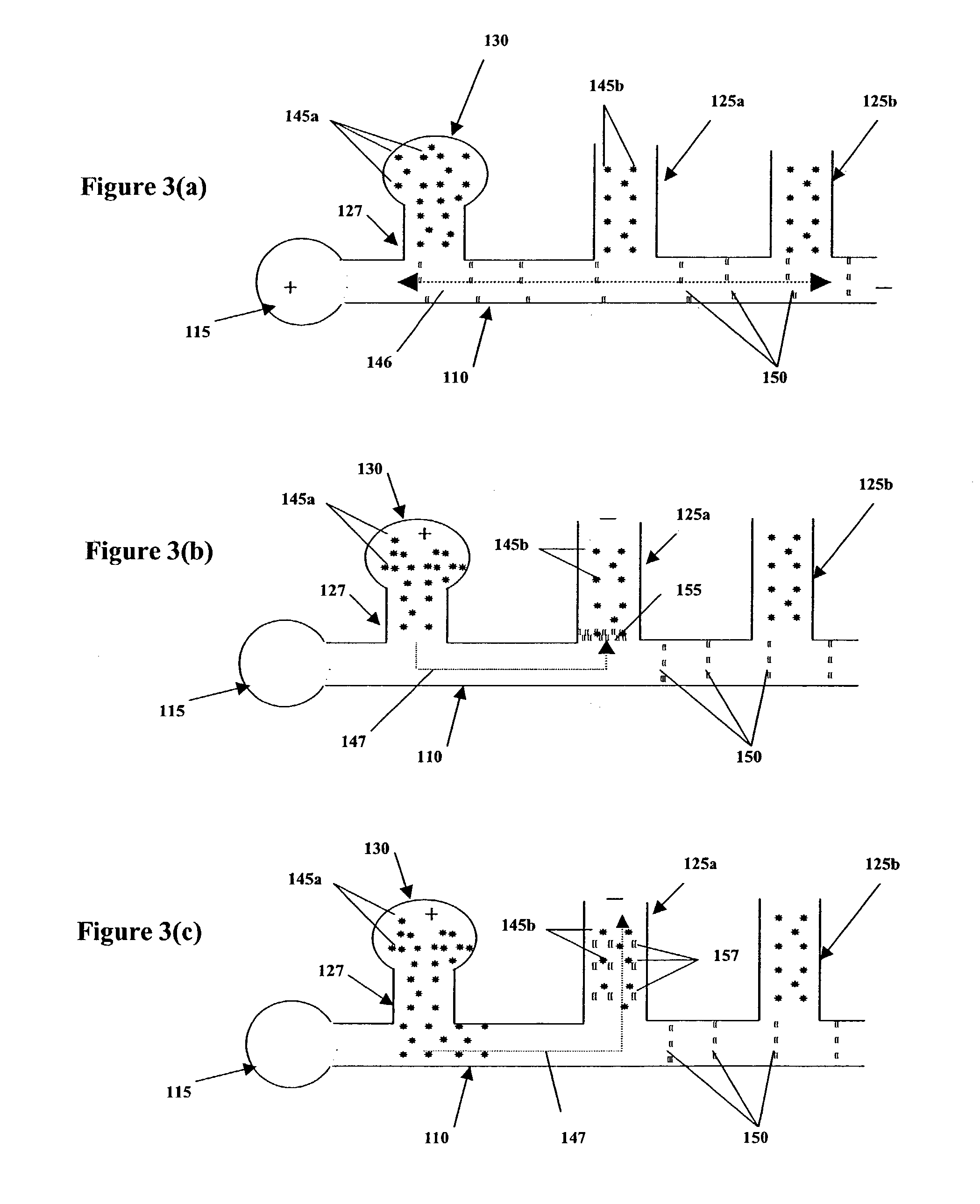
A capillary electrophoresis device and separation protocol uses a hydraulic resistance-providing structure (HRPS) in the main separation channel to separate the divide the main separate channel into an upstream portion and a downstream portion. The HRPS may take the form of a porous plug, or a solid plug provided with at least one shallow channel. A sample separates and migrates through the porous structure or the shallow channel, upon application of a voltage difference between the upstream and downstream sides. Among other things, the HRPS helps reduce electrokinetic flow in the presence of conductivity gradients and facilitates robust, high-gradient on-chip field amplified sample stacking. The HRPS also enables the use of a pressure-injection scheme for the introduction of a high conductivity gradient in a separation channel and thereby avoids flow instabilities associated with high conductivity gradient electrokinetics. The approach also allows for the suppression of electroosmotic flow (EOF) and benefits from the associated minimization of sample dispersion caused by non-uniform EOF mobilities. An injection procedure employing a single pressure-flow high-conductivity buffer injection step followed by standard high voltage control of electrophoretic fluxes of sample, may be employed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
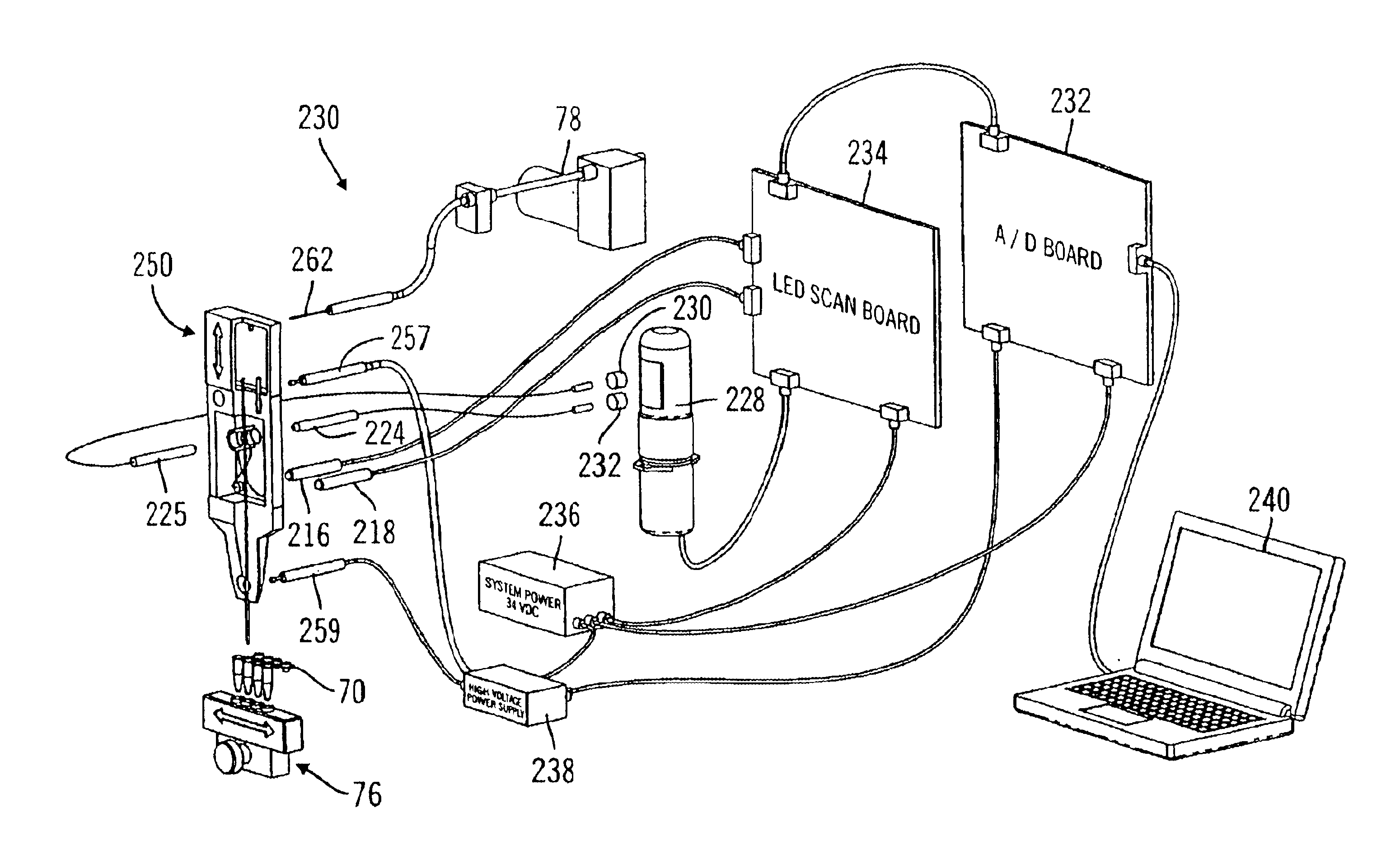
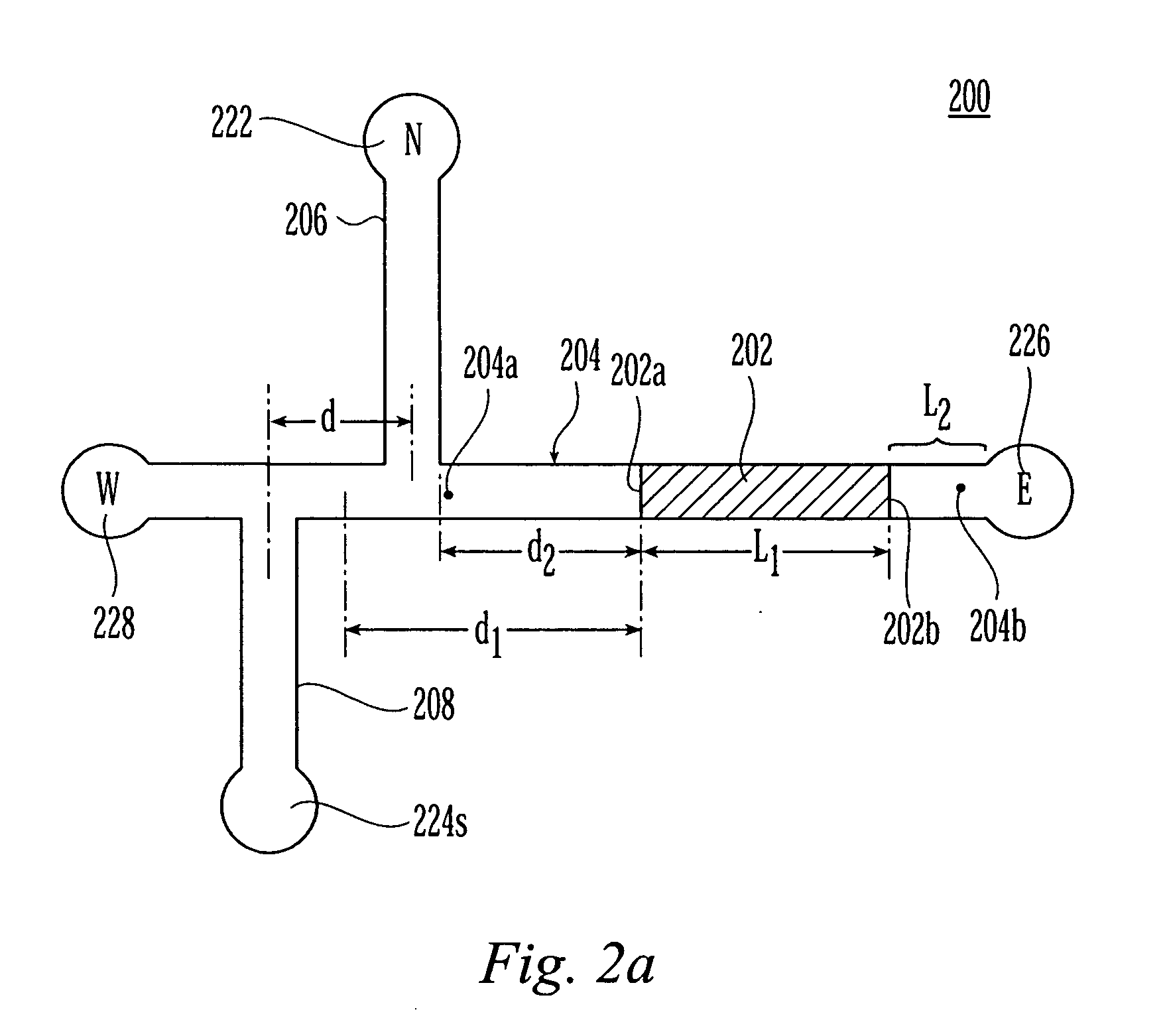
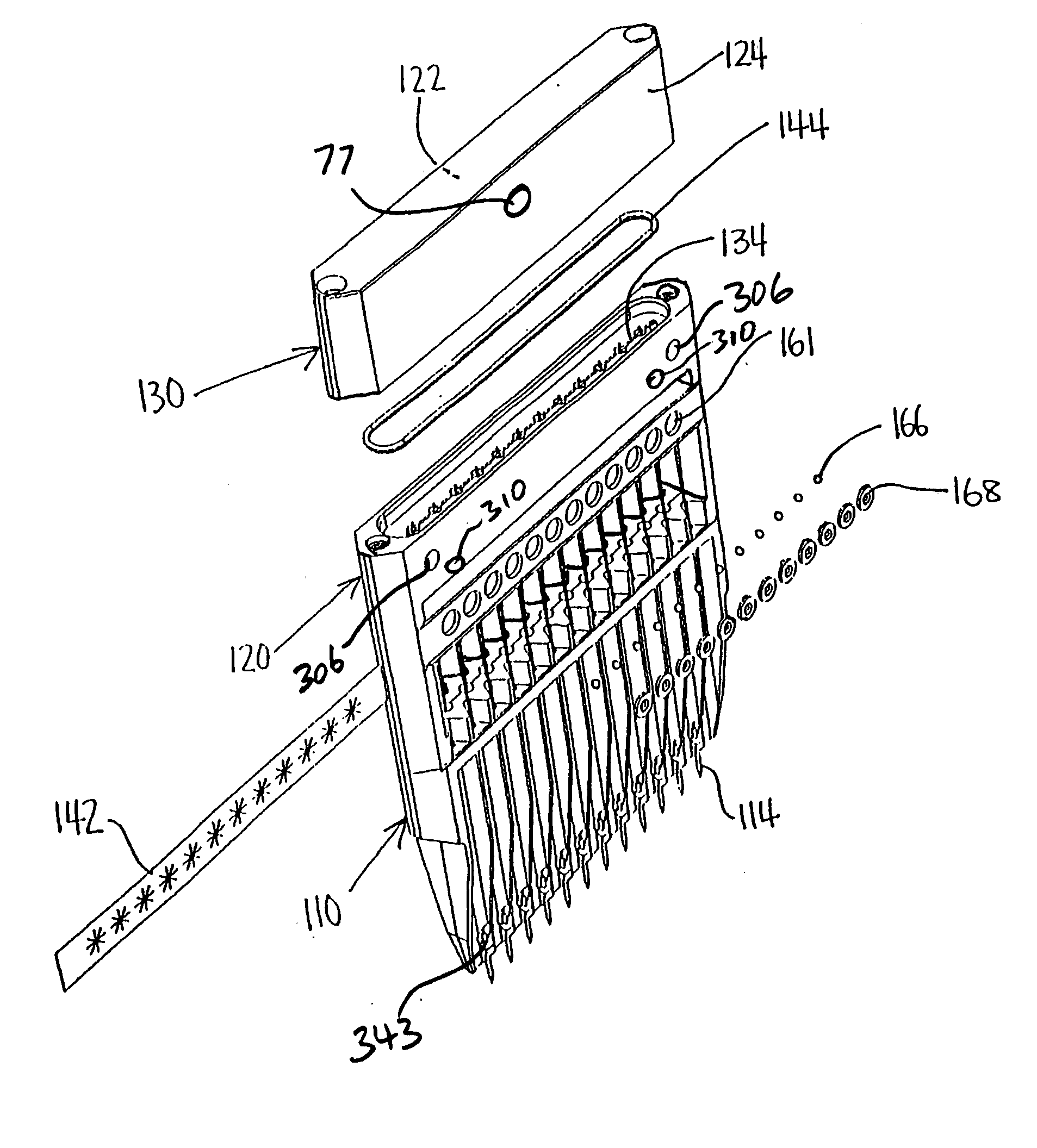
Multi-capillary electrophoresis cartridge interface mechanism
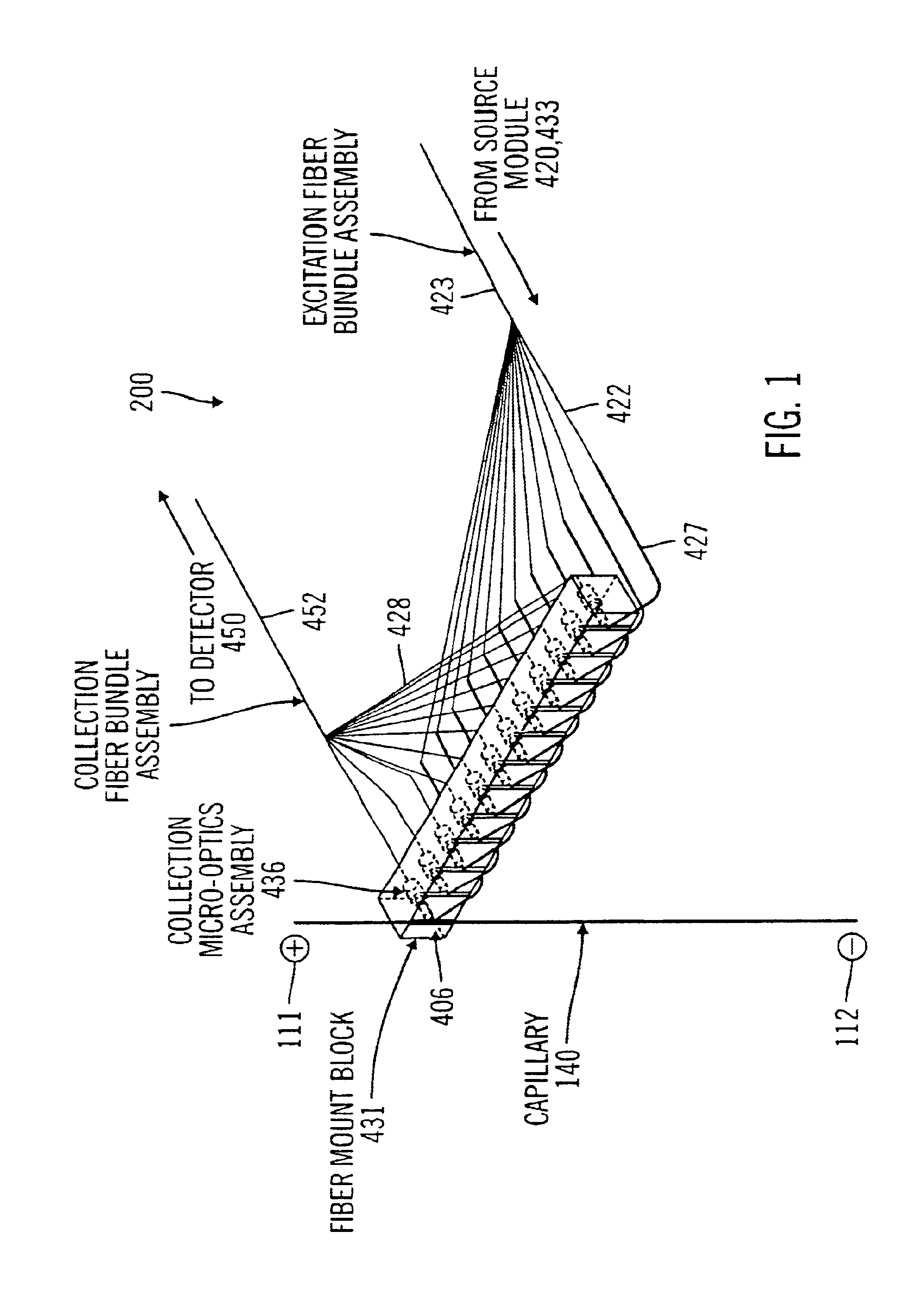
ActiveUS20050016852A1Precise positioningReliable implementationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCapillary electrophoresisMagnetic tape
The present invention provides for an interface mechanism in a bio-separation instrument that makes interface connections to a multi-channel cartridge. The interface mechanism precisely positions the cartridge in relation to the support elements in the instrument (e.g., high-voltage, gas pressure, incident radiation and detector), and makes automated, reliable and secured alignments and connections between various components in the cartridge and the support elements in the supporting instrument. The interface mechanism comprises pneumatically or electromechanically driven actuators for engaging support elements in the instrument to components on the cartridge. After the cartridge has been securely received by the interface mechanism, the connection sequence is initiated. The interface provides separate high voltage and optical connections for each separation channel in the cartridge, thus providing channel-to-channel isolation from cross talk both electrically and optically.
Owner:QIAGEN SCIENCES LLC
System and method for the separation of analytes
InactiveUS7655477B1Easy to separateLow costMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityCapillary electrophoresis
A separation module operates to fractionate or separate an analyte into fractions according to pI, i.e., pI bands, utilizing capillary isoelectric focusing (“CIEF”) within a first microchannel. The fractions are stacked to form plugs, the number of which is determined by a number of parallel second microchannels integrally connected to the first microchannel, into which the fractions are directed according to the buffer characteristics found in each of the individual microchannels. Within the microchannels the plugs are separated into proteins according to a different chemical property, i.e., “m / z,” utilizing capillary electrophoresis (“CE”).
Owner:LEIDOS +1
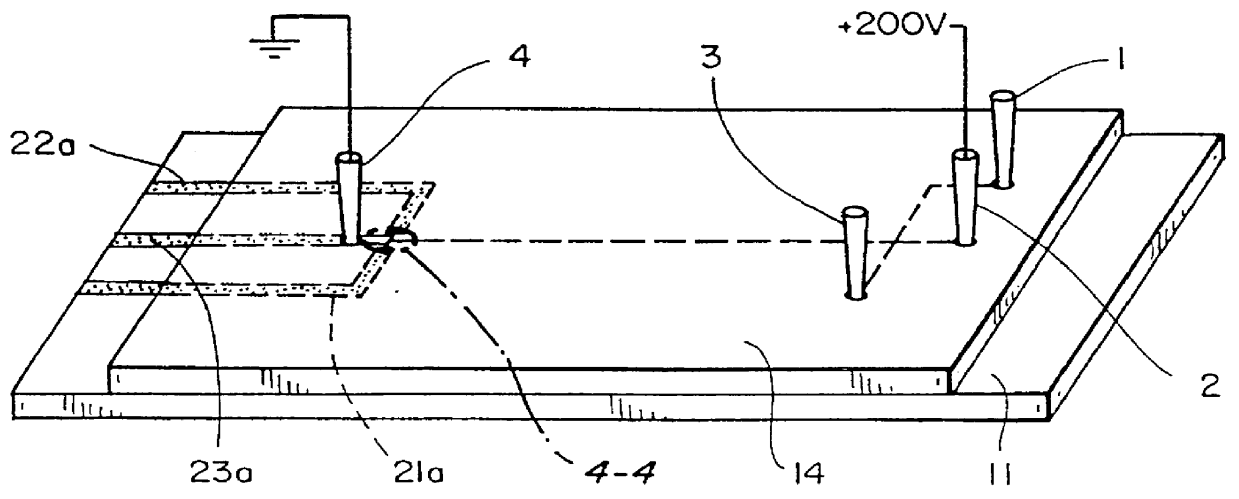
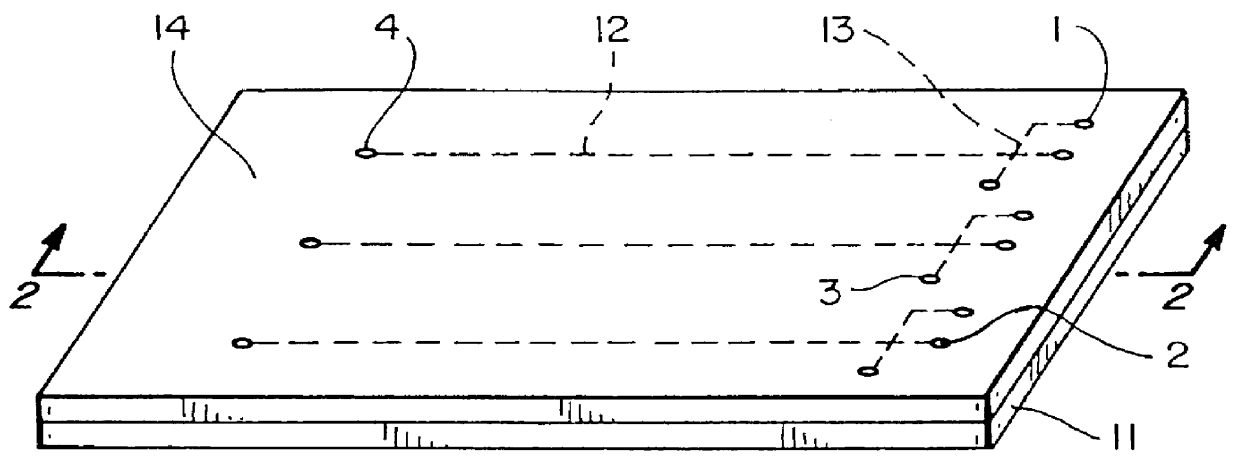
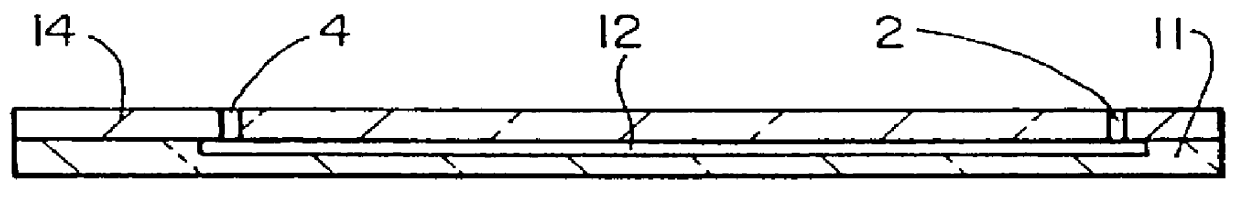
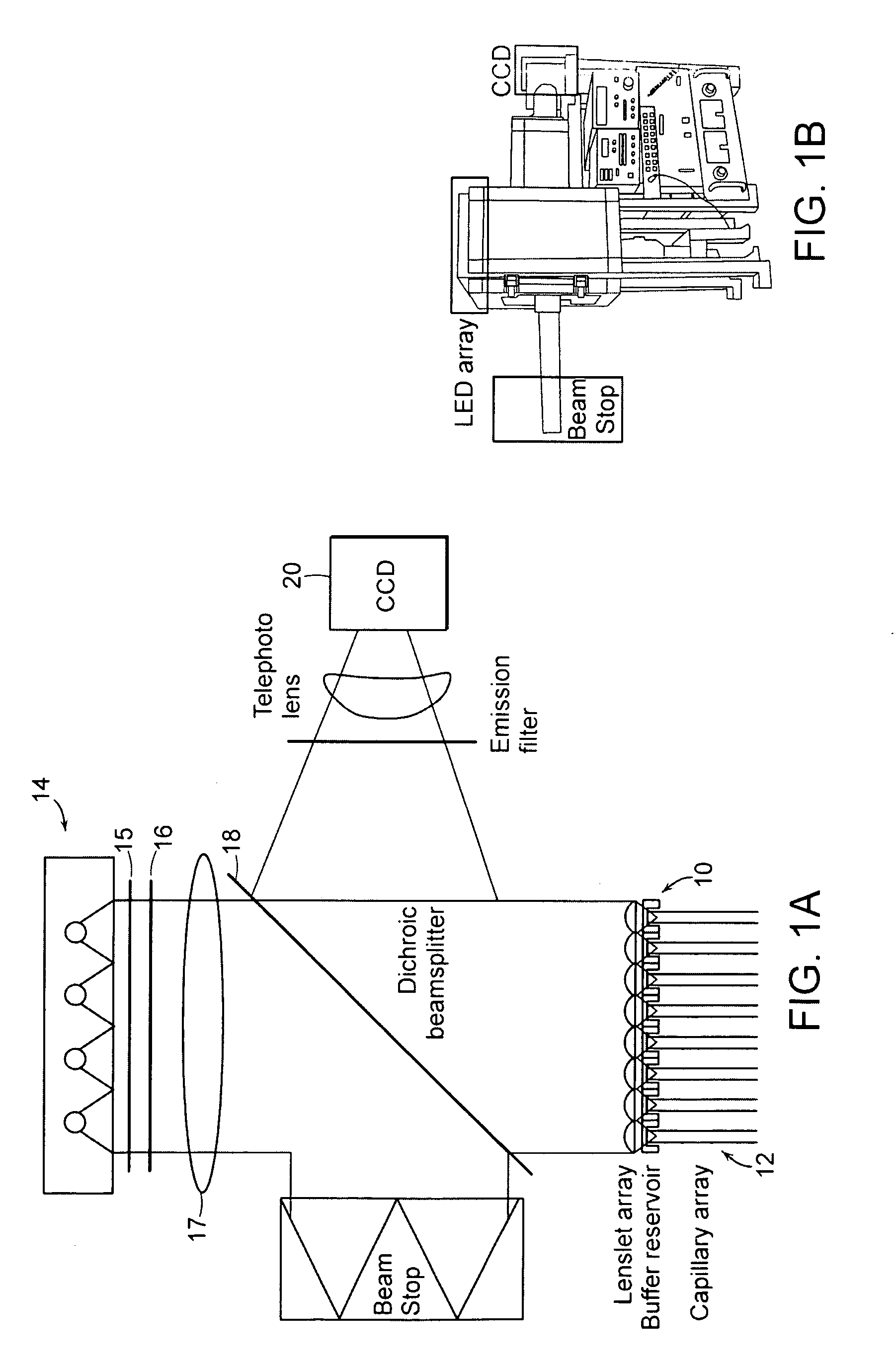
End-column fluorescence detection for capillary array electrophoresis
InactiveUS20060176481A1Easy to collectSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
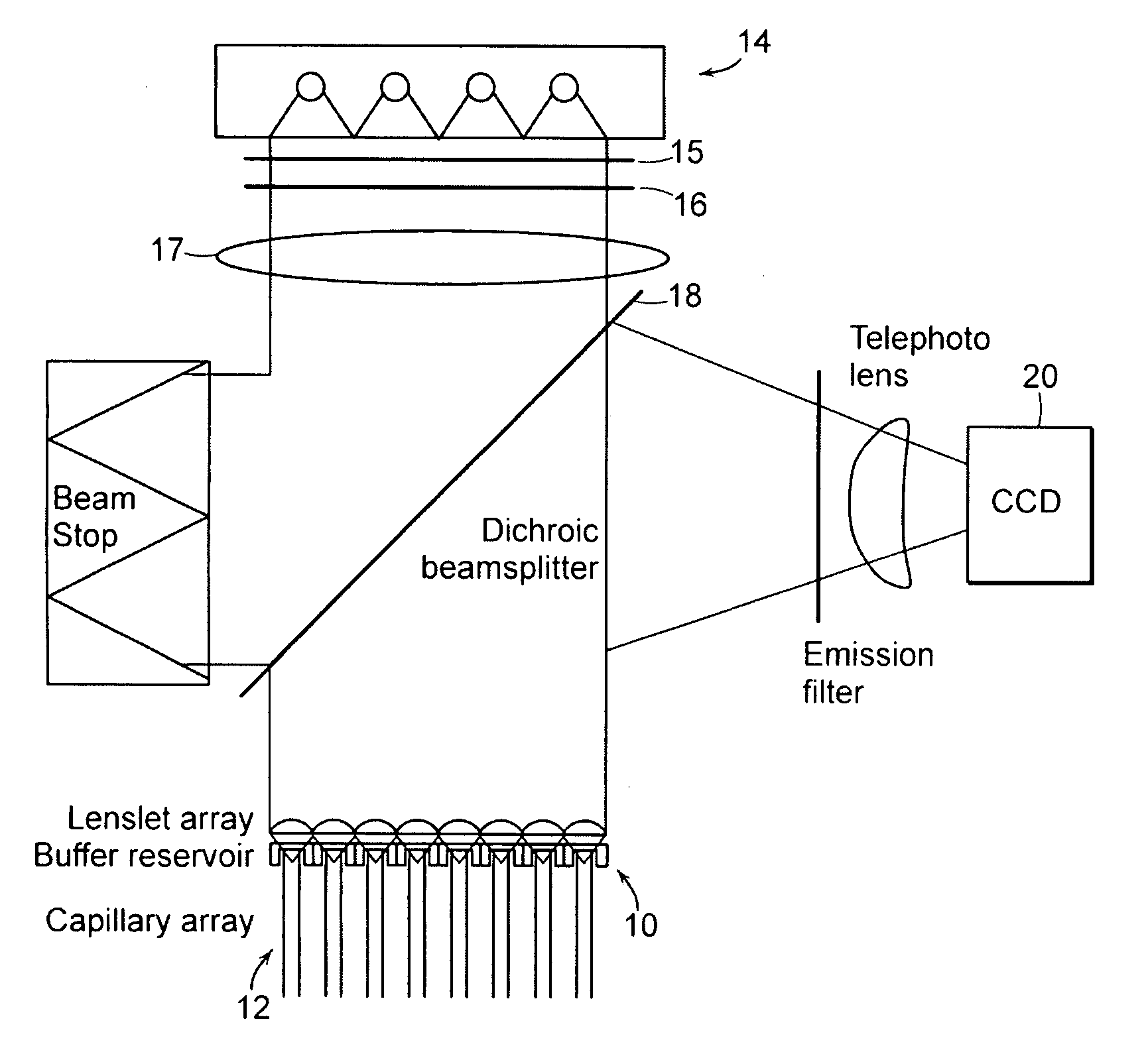
A massively parallel electrophoresis system comprised of capillaries, with means for parallel imaging of the capillary ends. The capillaries are aligned with parallel longitudinal axes and a set of ends that are substantially coplanar. The electrophoresis system has a source of excitation radiation for illuminating the ends while an imaging optical arrangement places substantially coplanar loci, one per capillary, within a focal region of the imaging optical arrangement. A detector module receives electromagnetic radiation that is emitted by fluorophores within the capillaries upon excitation by the excitation radiation and transmitted to the detector module by way of the imaging optical arrangement. A manifold may terminate the array of electrophoresis capillaries, wherein the manifold has a platen with a plurality of recessions for receiving each of a the ends of the array of capillaries, and a septum disposed adjacent to the platen for penetration by the ends of the array of capillaries when inserted into the platen. Electrophoresis products may be separated by segregating effluent from one or more capillaries of the array.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com