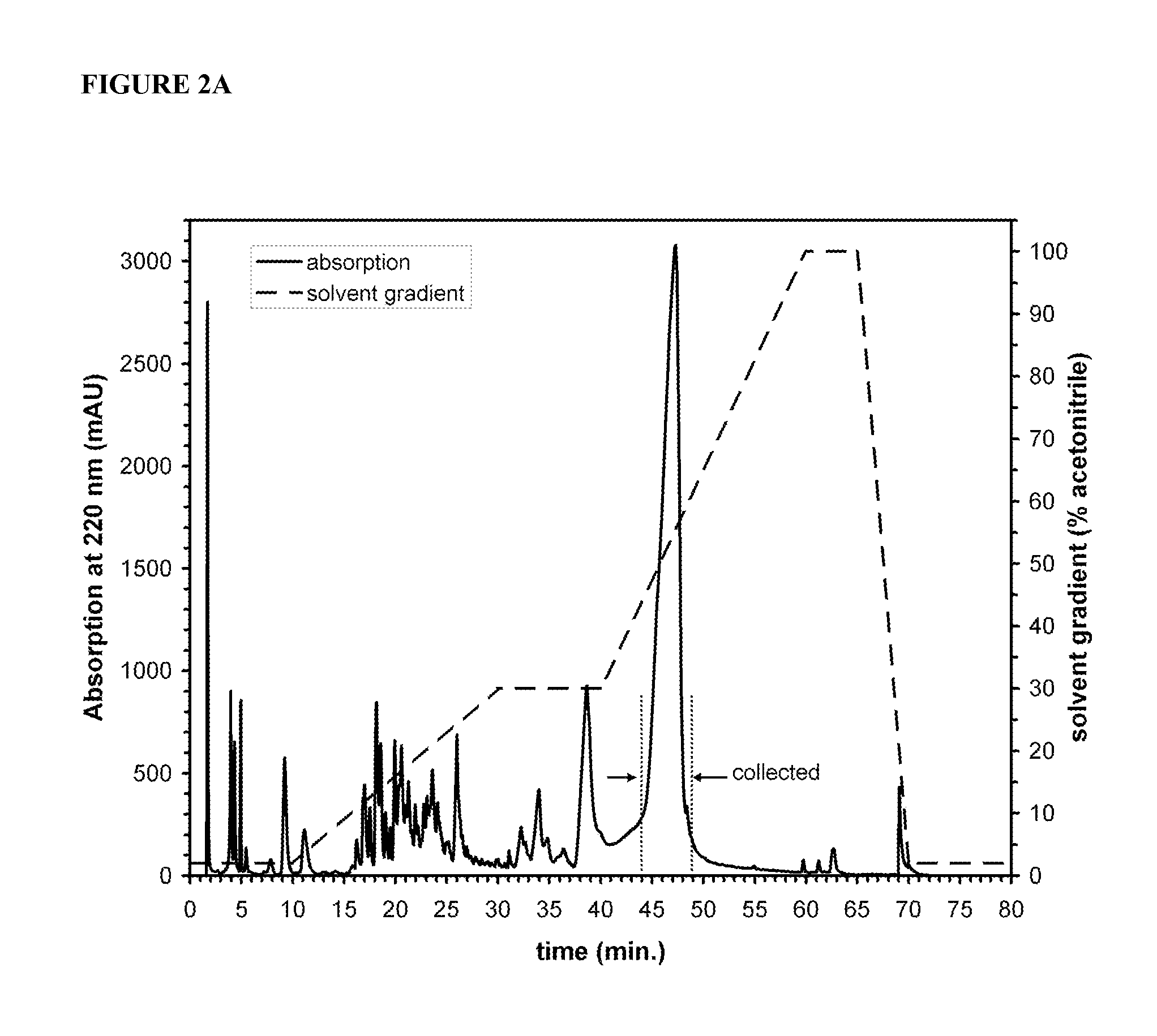
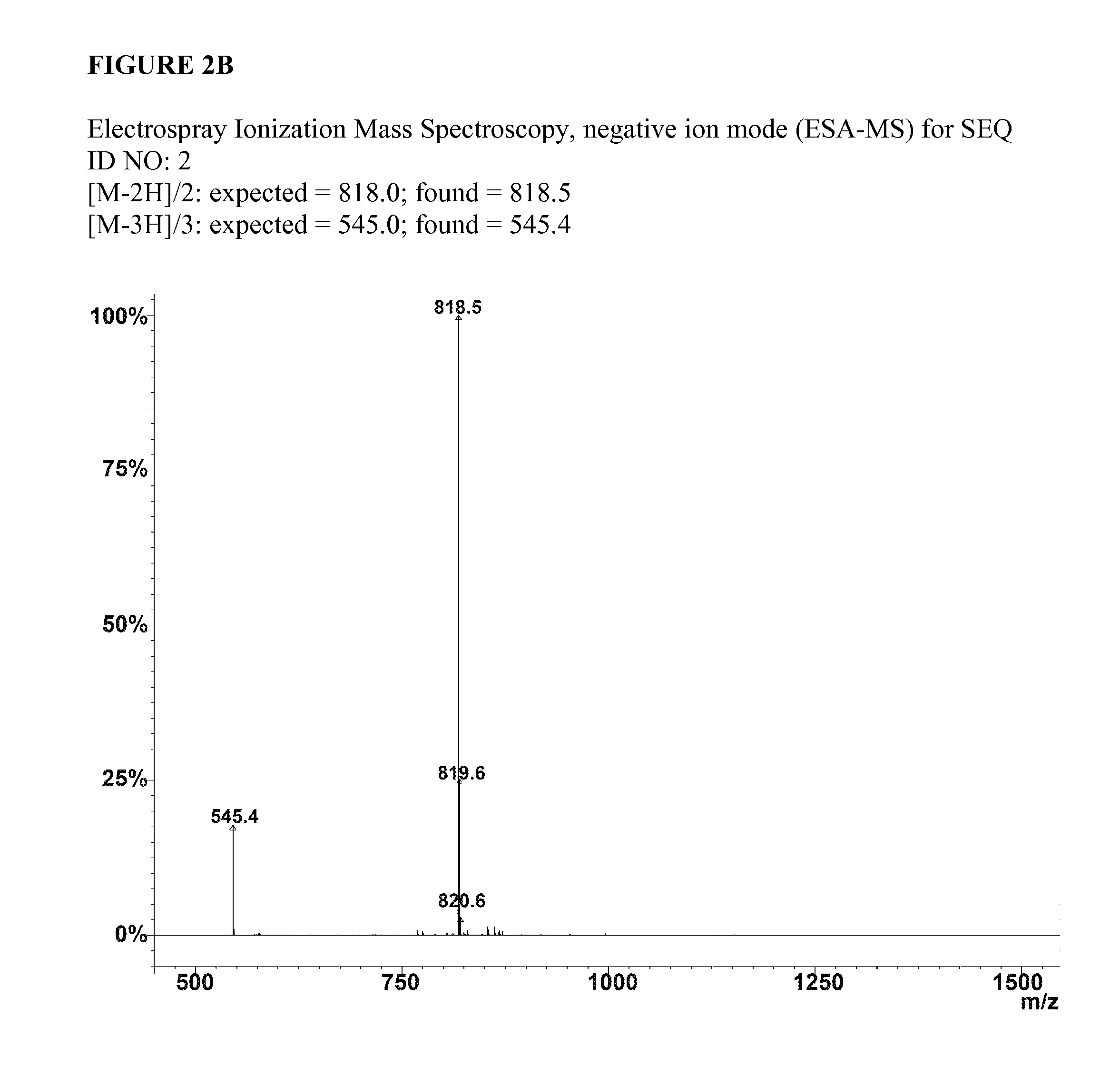
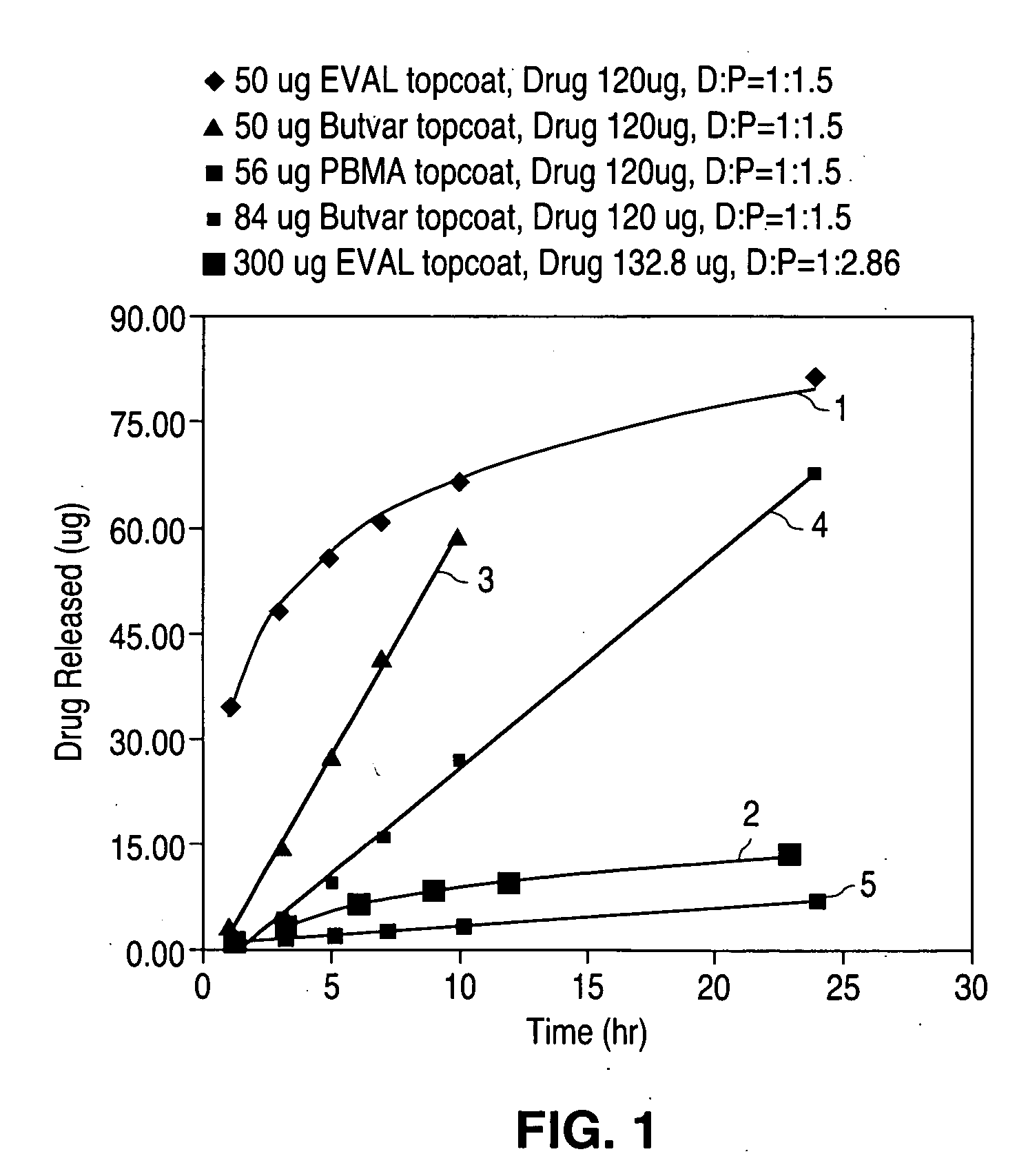
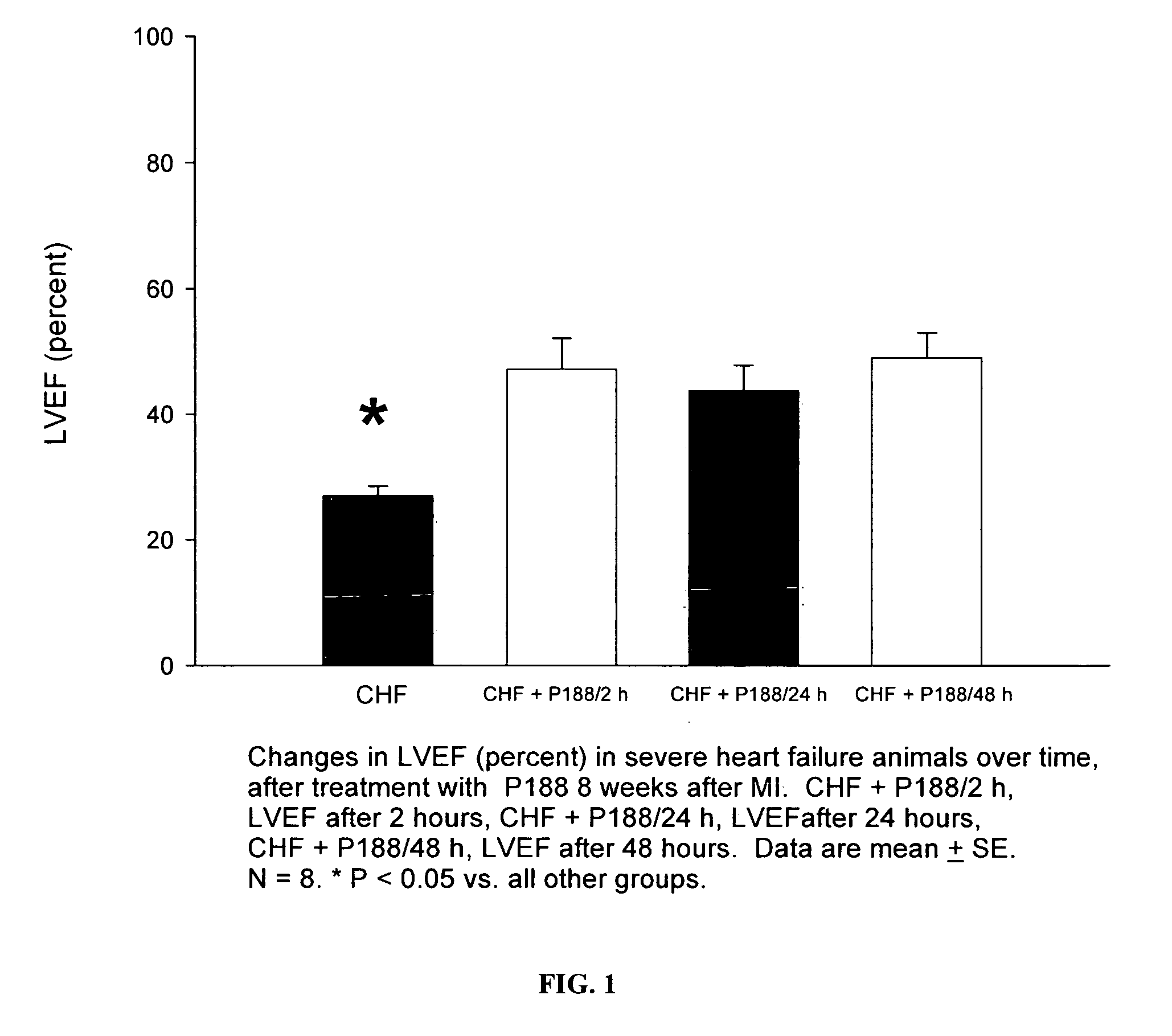
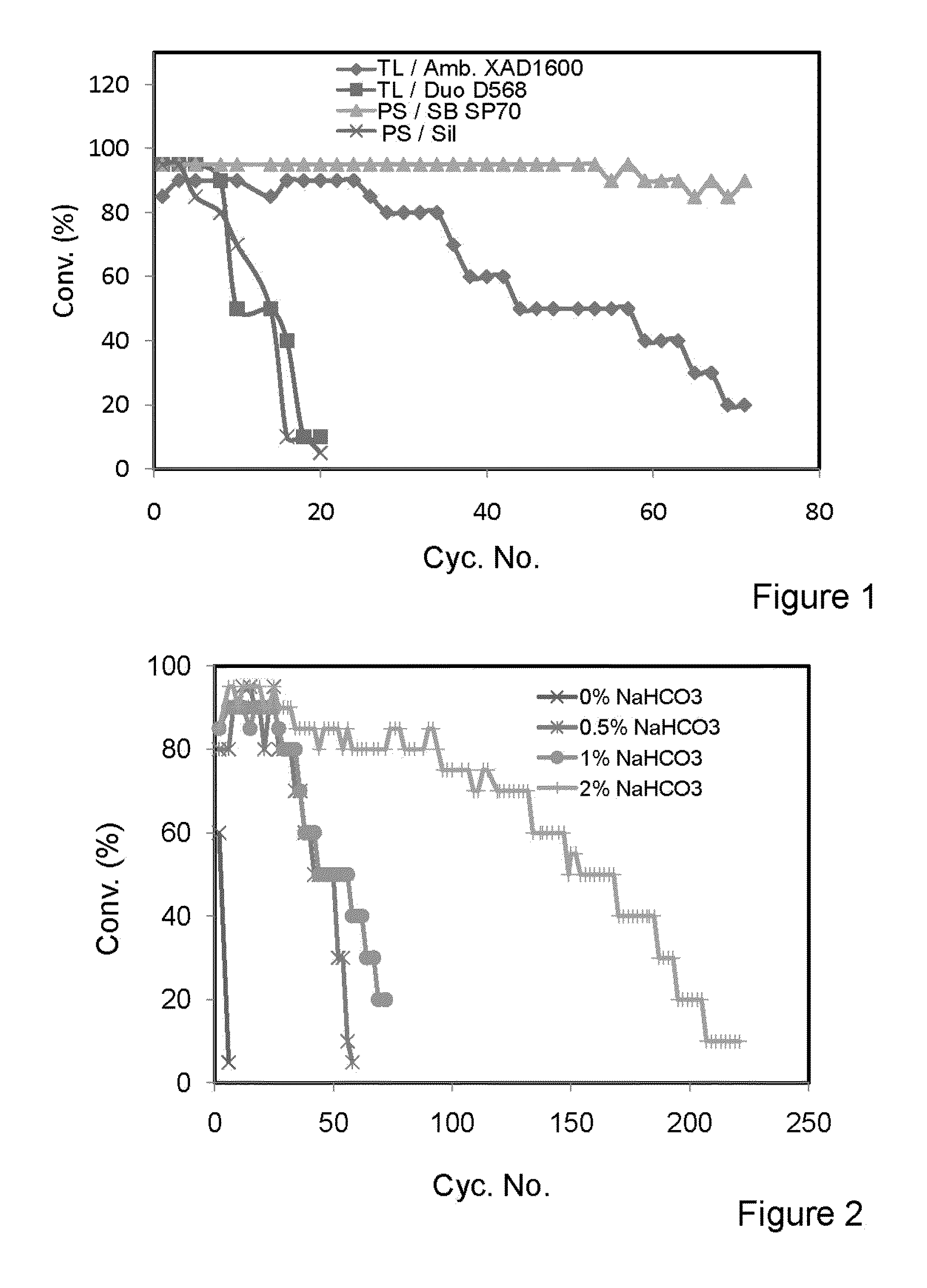
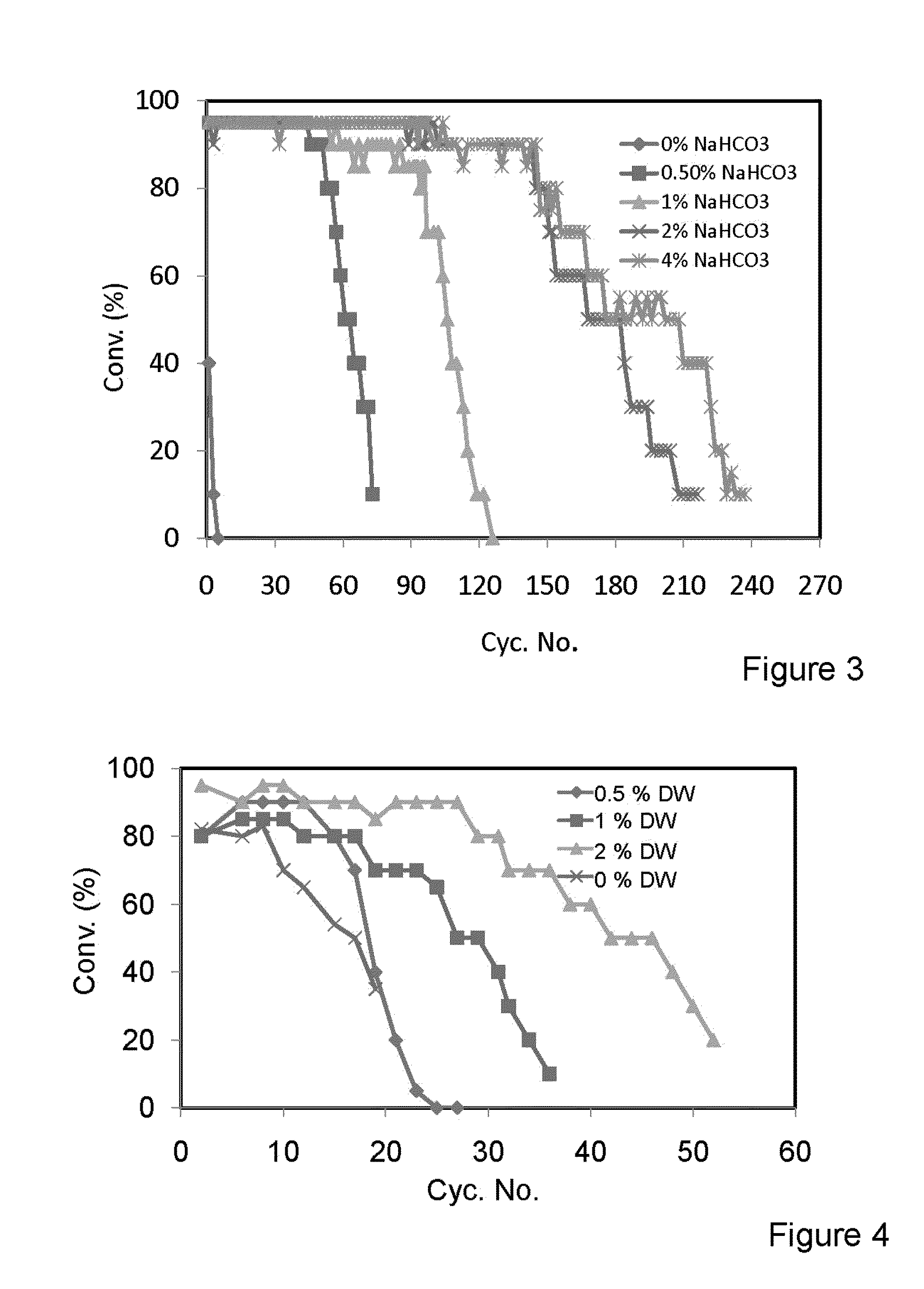
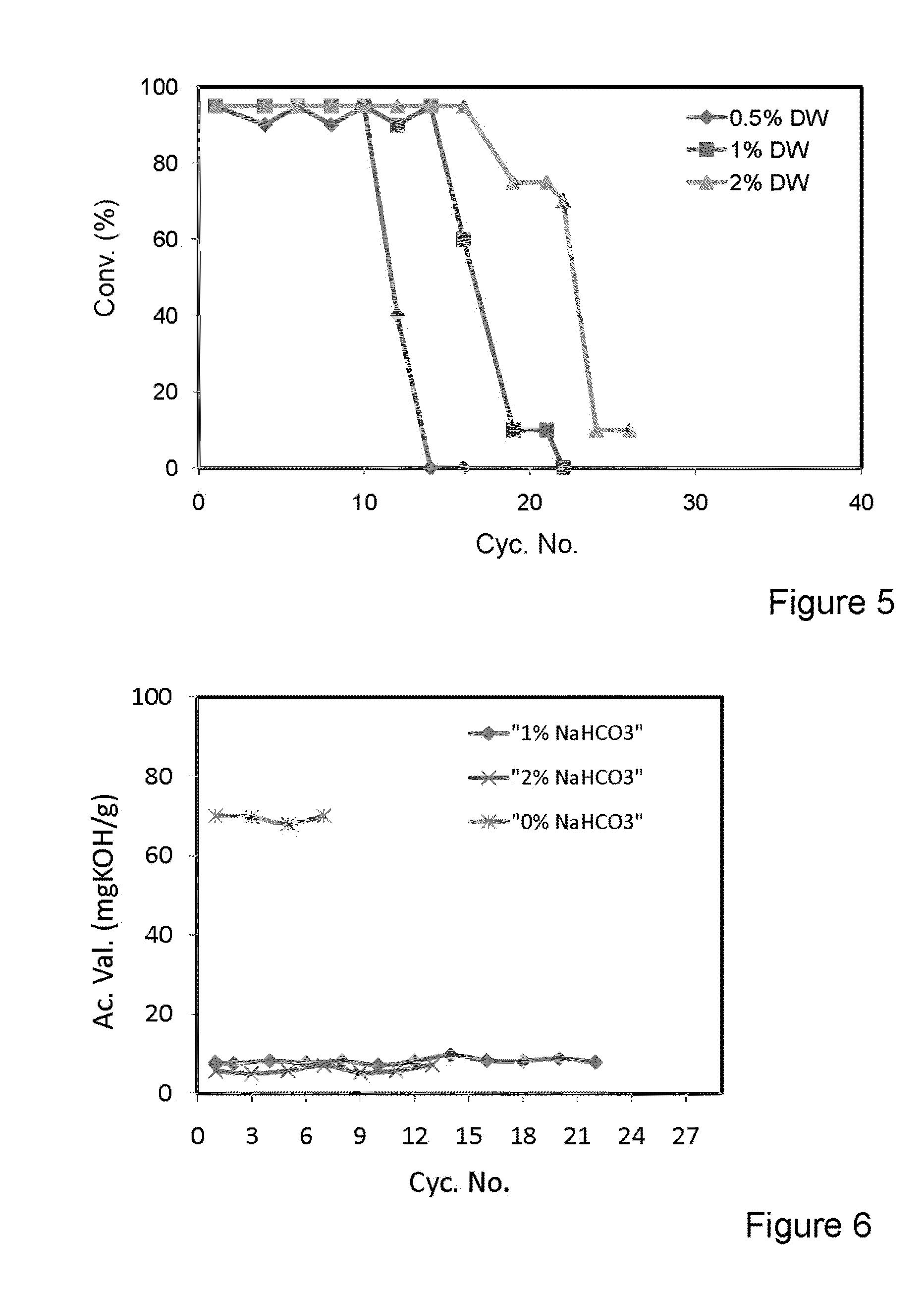
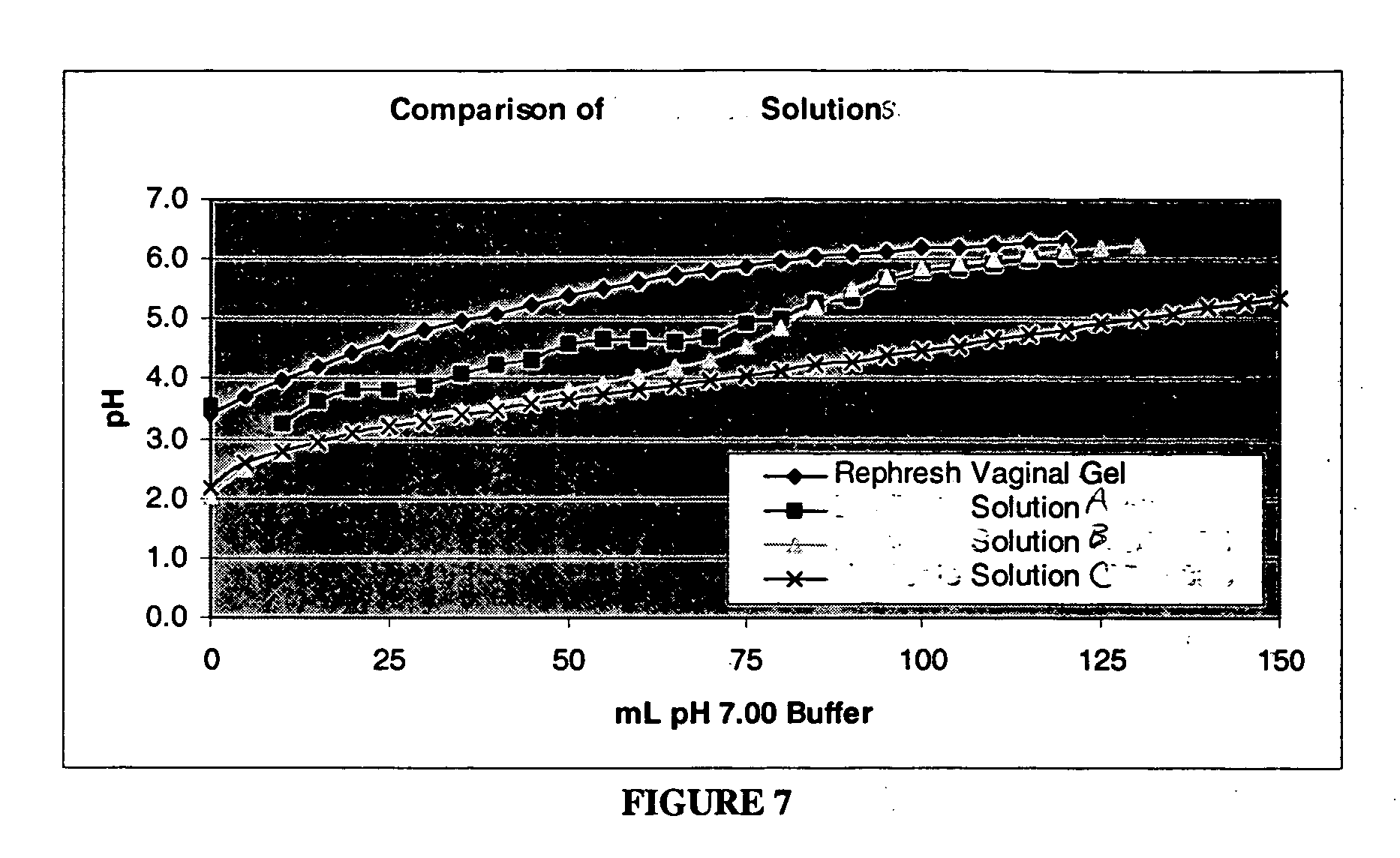
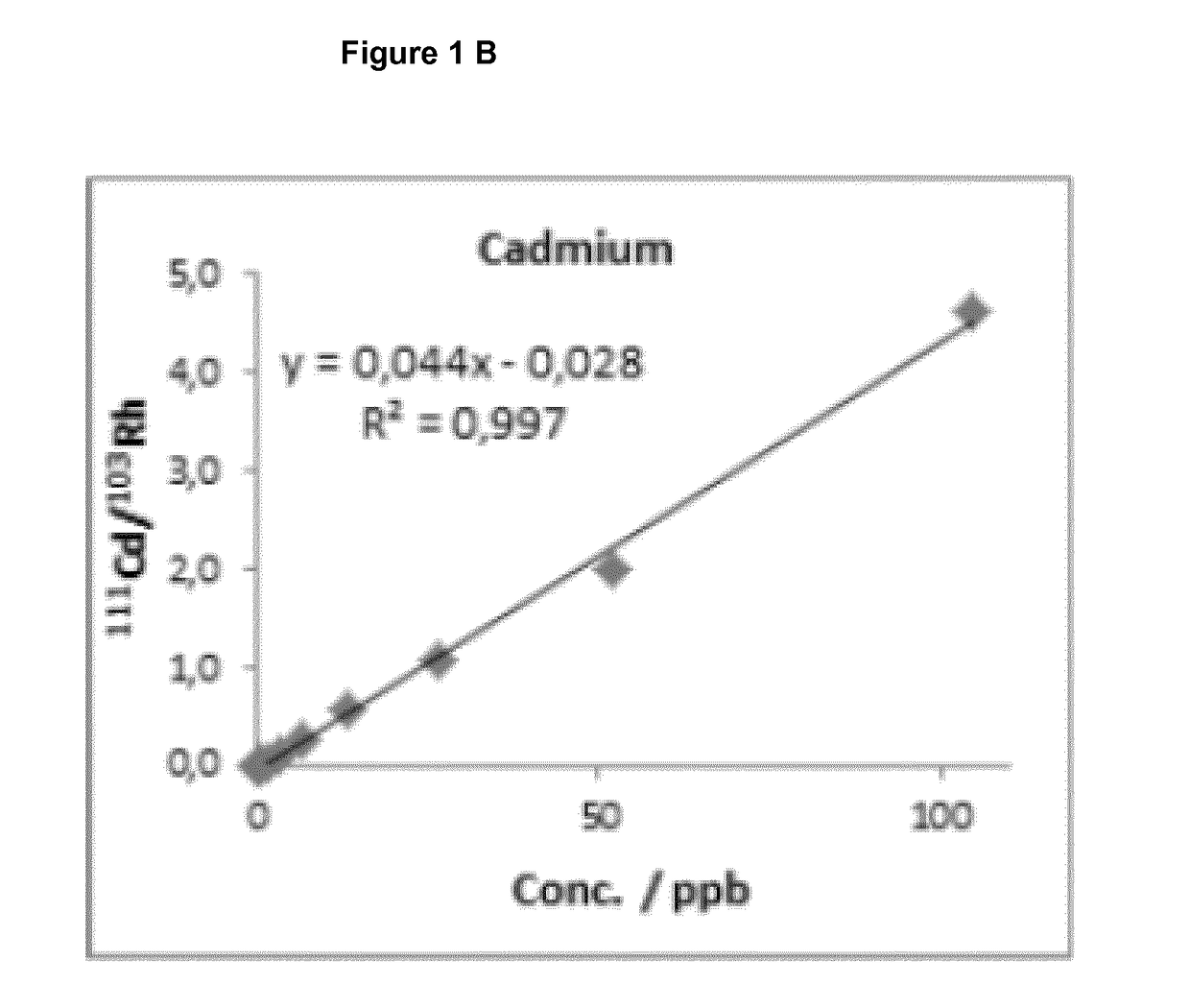
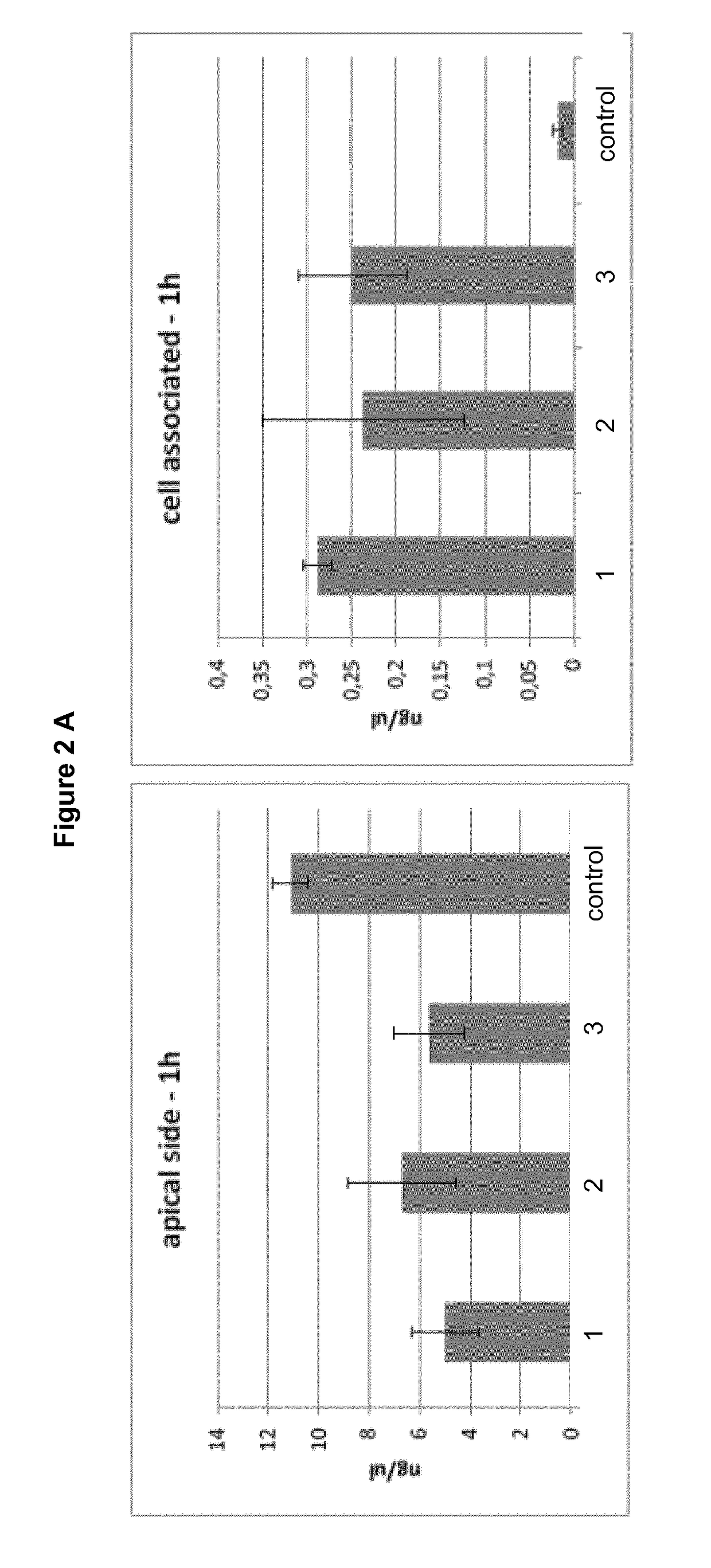
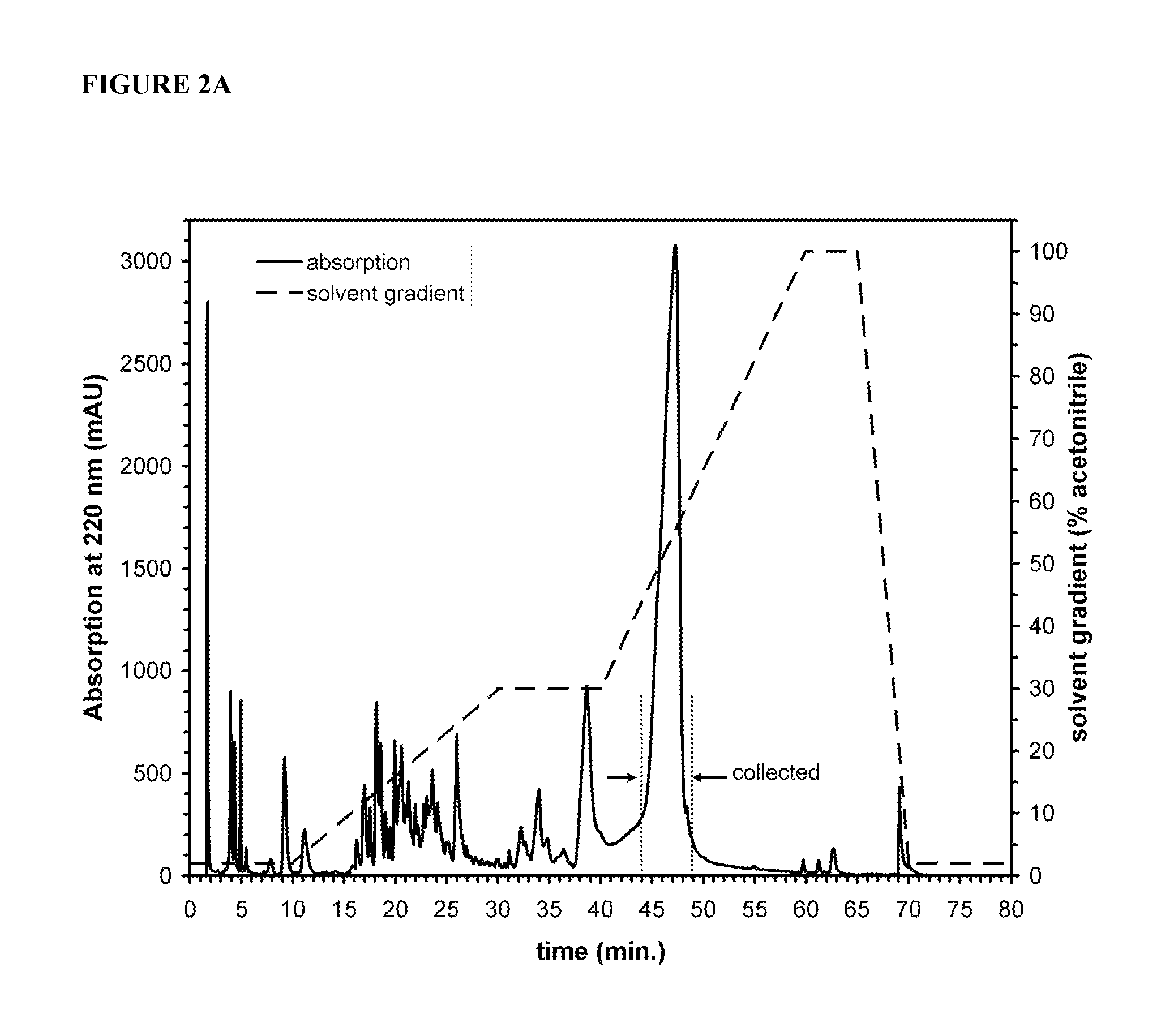
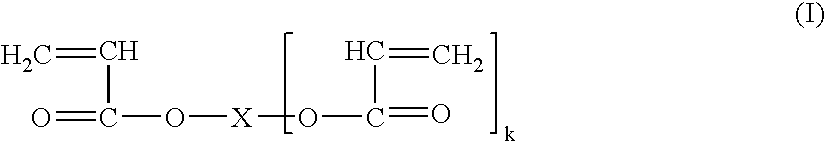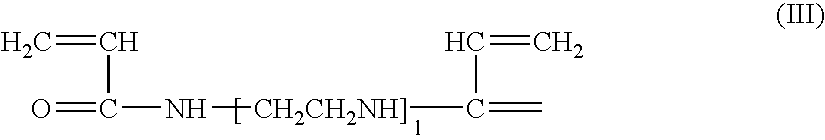Patents
Literature
131 results about "Aqueous buffer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A buffer is an aqueous solution containing a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. A buffer’s pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. It is used to prevent any change in the pH of a solution, regardless of solute.
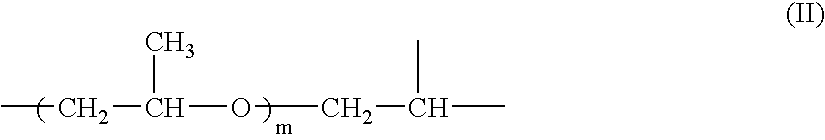
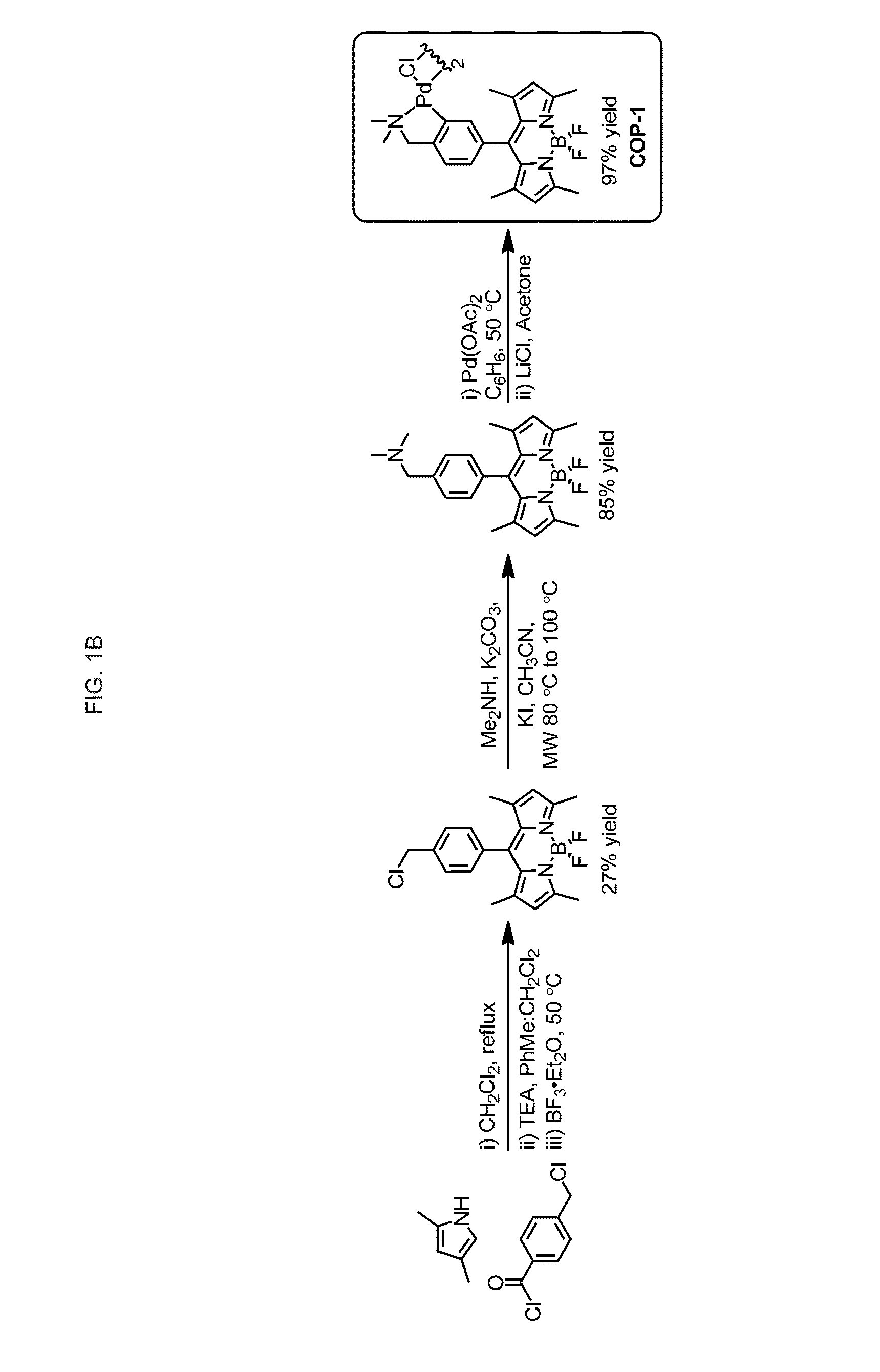
Dynamic coating with linear polymer mixture for electrophoresis
InactiveUS6787016B2Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisAqueous buffer
Compositions and methods are provided for performing capillary electrophoresis using a composition comprising in combination in an aqueous buffered medium a coating polymer and a sieving polymer, where the sieving polymer is more hydrophilic than the coating polymer and is present in greater amount. Of particular interest are uncrosslinked acrylamide polymer mixtures for coating plastic channels and providing sieving for performing DNA separations in microfluidic devices. Polyacrylamide or N,N-dimethyl acrylamide is used with a N,N-dialkyl acrylamide copolymer, either separately or together for sieving and coating, serving as the medium in capillary electrophoresis DNA separations.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Methods for isolating nucleic acids
ActiveUS20050079535A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh concentrationSimple Organic Compounds
A method for purification of a nucleic acid comprising the steps of (a) adsorbing on a substrate the nucleic acid from a composition containing (i) an aqueous buffer, (ii) salts in a high concentration, (iii) a water-miscible, non-acidic organic compound, and (iv) the nucleic acid; ( b) optionally washing with a washing solution the substrate with the adsorbed nucleic acid; (c) contacting the substrate with the adsorbed nucleic acid with a solution containing salts in a lower concentration compared to the composition of step (a), thereby desorbing the nucleic acid from the substrate; (d) separating the solution with the desorbed nucleic acid from the substrate, thereby purifying the nucleic acid; and optionally (e) precipitating the desorbed nucleic acid from the solution of step (d) and isolating the precipitated nucleic acid, thereby further purifying the nucleic acid.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Dosage Form with Impeded Abuse
InactiveUS20090004267A1Prevent crushingPrevent the subsequent abuseOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryWaxBreaking strength
A multiparticulate dosage form formulated to make misuse more difficult containing least one active substance with potential for misuse (A), at least one synthetic or natural polymer (C), optionally at least one natural, semi-synthetic or synthetic wax (D), at least one disintegrant (E) and optionally one or more additional physiologically compatible excipients (B), wherein the individual particles of the dosage form display a breaking strength of at least 500 N and a release of active substance of at least 75% after 45 minutes measured according to Ph.Eur. in the paddle mixer with sinker in 600 ml of aqueous buffer solution with a pH value of 1.2 at 37° C. and 75 rpm.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Dynamic coating with linear polymer mixture for electrophoresis
InactiveUS20020029968A1Sludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisAqueous buffer
Compositions and methods are provided for performing capillary electrophoresis using a composition comprising in combination in an aqueous buffered medium a coating polymer and a sieving polymer, where the sieving polymer is more hydrophilic than the coating polymer and is present in greater amount. Of particular interest are uncrosslinked acrylamide polymer mixtures for coating plastic channels and providing sieving for performing DNA separations in microfluidic devices. Polyacrylamide or N,N-dimethyl acrylamide is used with a N,N-dialkyl acrylamide copolymer, either separately or together for sieving and coating, serving as the medium in capillary electrophoresis DNA separations.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Adhesive sealant composition
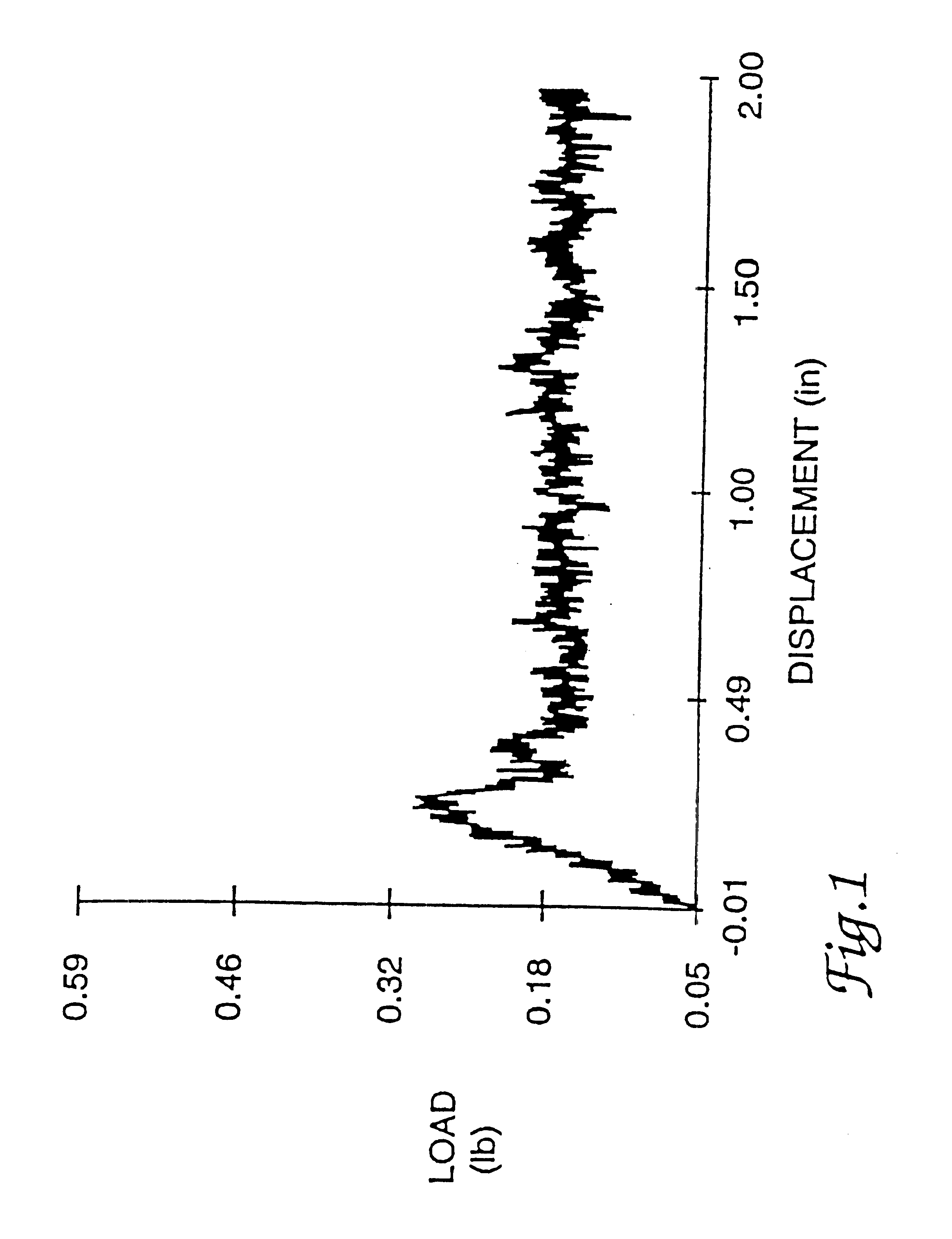
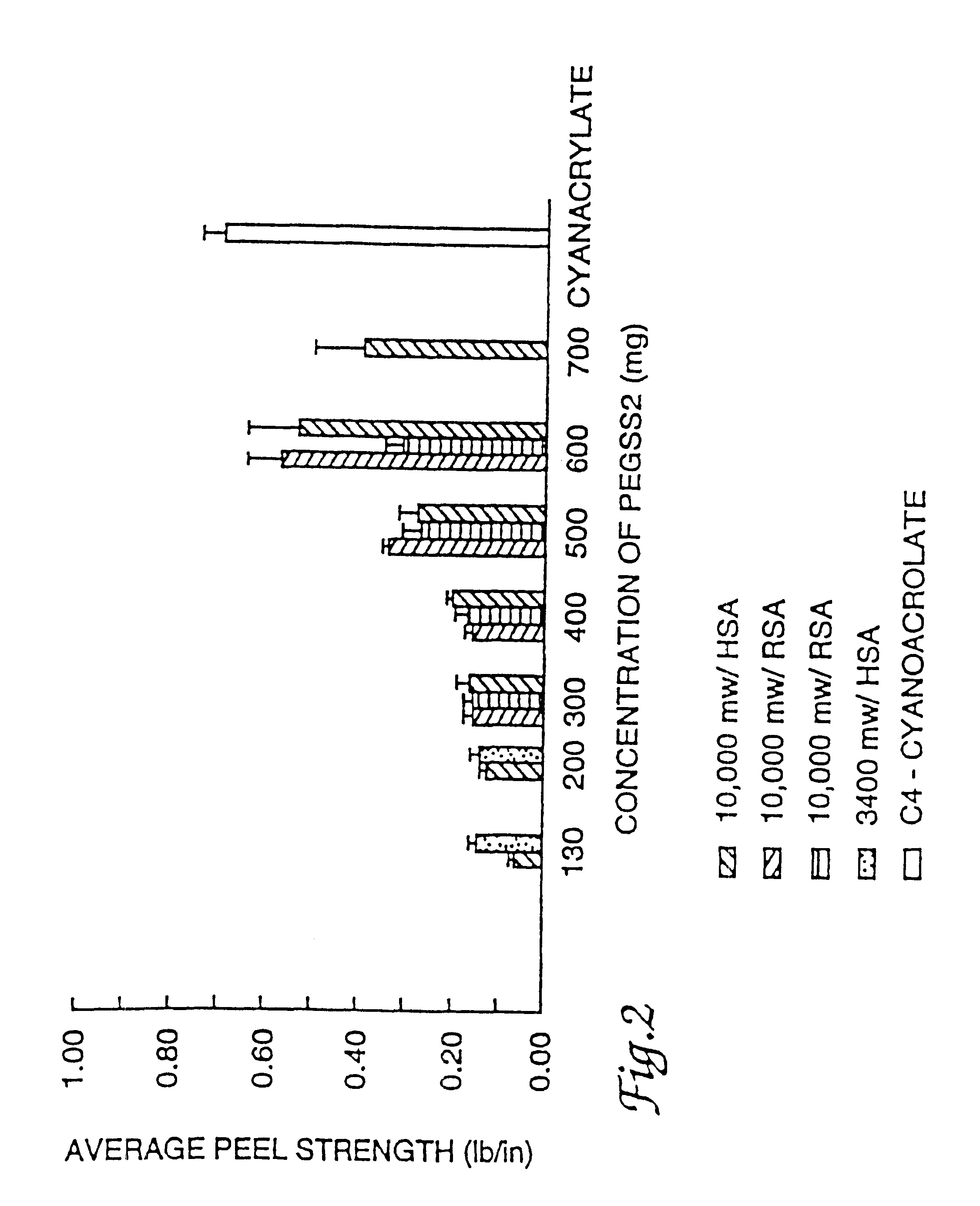
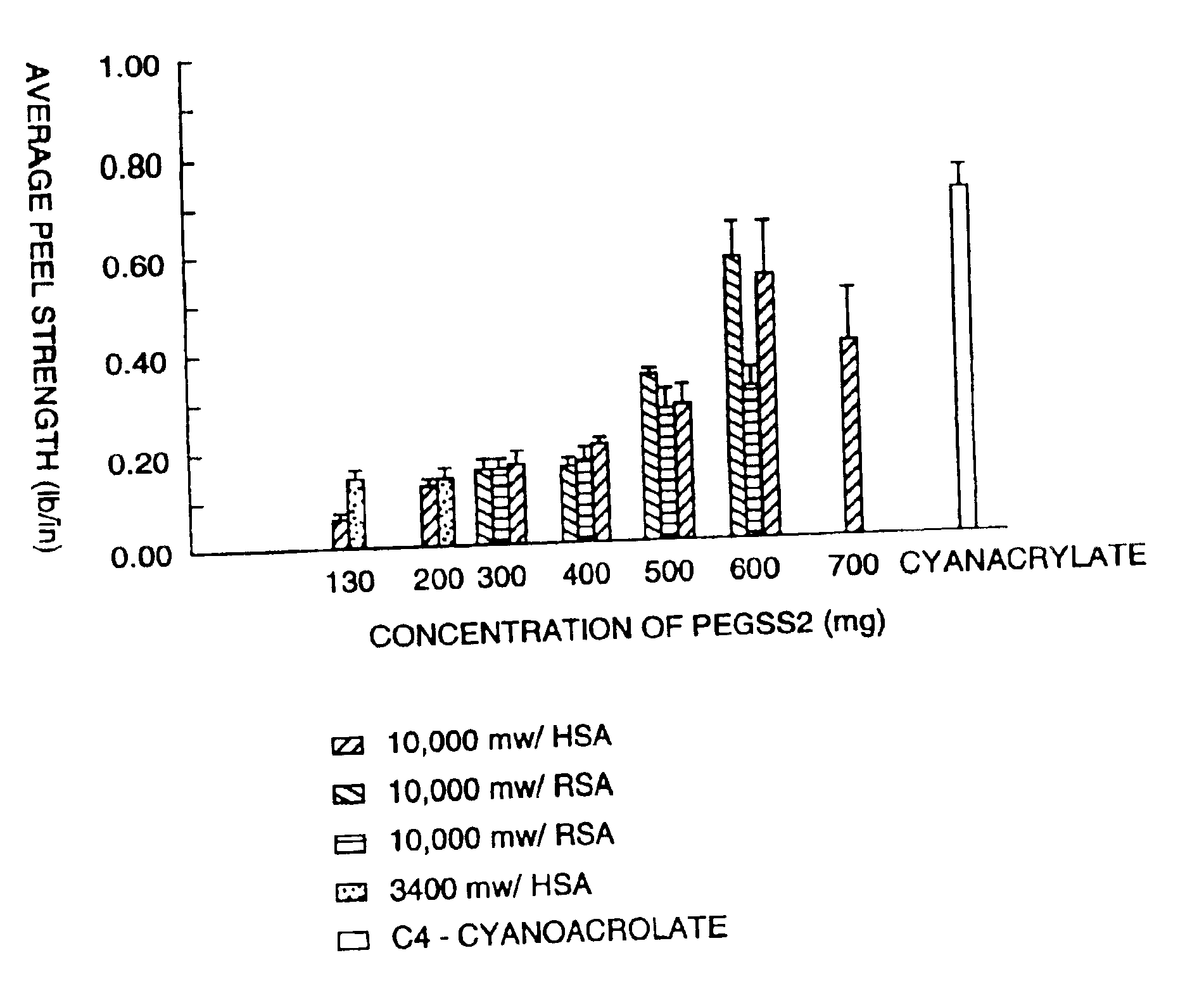
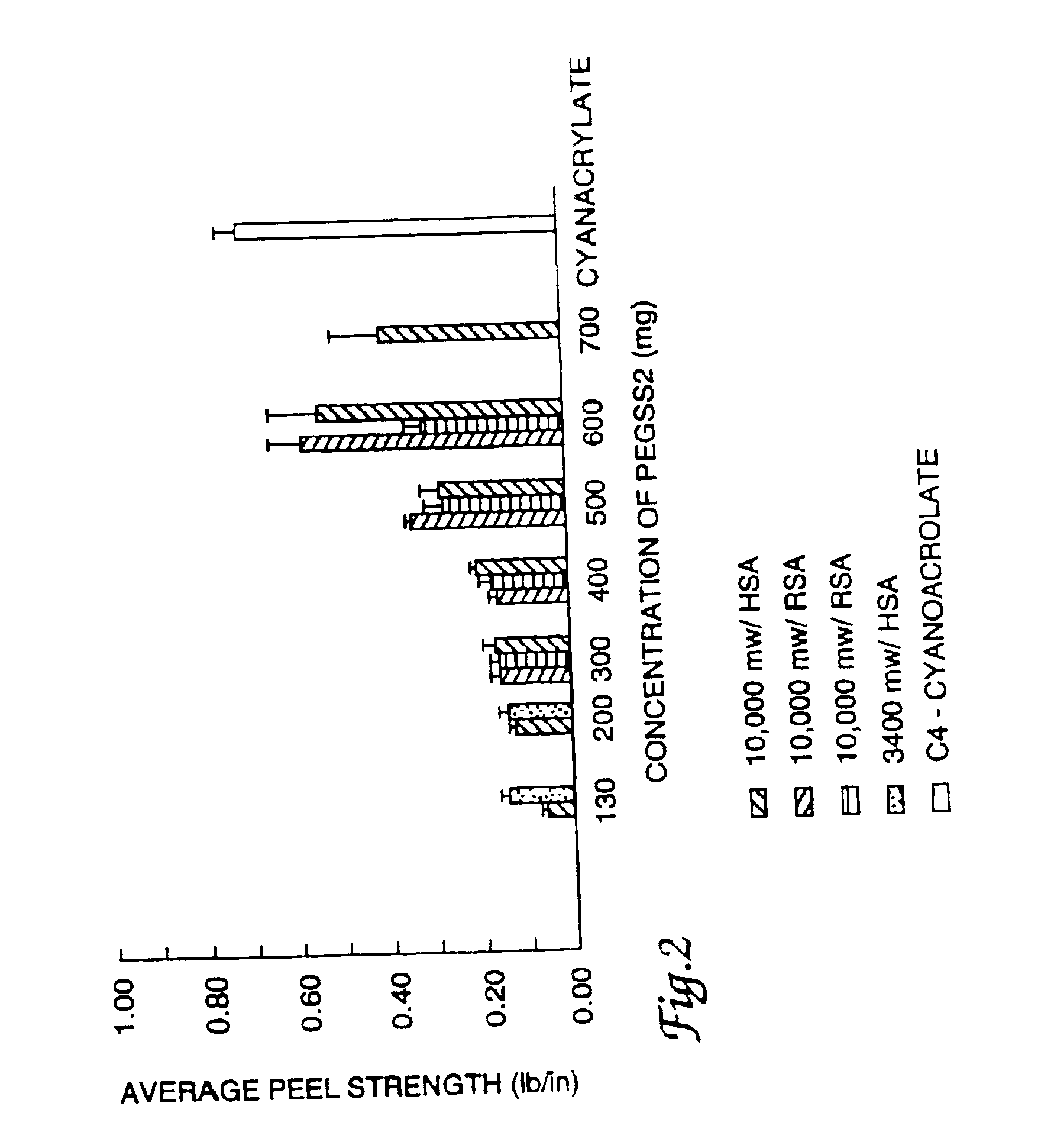
InactiveUSRE38158E1High bonding strengthOrganic active ingredientsNon-fibrous pulp additionAqueous bufferWater soluble
This invention is related to an adhesive composition which may be used to bond or seal tissue in vivo. The adhesive composition is readily formed from a two component mixture which includes a first part of a protein, preferably a serum albumin protein, in an aqueous buffer having a pH in the range of about 8.0-11.0 and a second part of a water-compatible or water-soluble bifunctional crosslinking agent. When the two parts of the mixture are combined, the mixture is initially a liquid which cures in vivo on the surface of tissue in less than about one minute to give a strong, flexible, pliant substantive composition which bonds to the tissue and is absorbed in about four to sixty days. The adhesive composition may be used either to bond tissue, to seal tissue or to prevent tissue adhesions caused by surgery.
Owner:NEOMEND INC
Dosage form with impeded abuse
InactiveUS8722086B2Prevent crushingPrevent the subsequent abuseOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryWaxBreaking strength
A multiparticulate dosage form formulated to make misuse more difficult containing least one active substance with potential for misuse (A), at least one synthetic or natural polymer (C), optionally at least one natural, semi-synthetic or synthetic wax (D), at least one disintegrant (E) and optionally one or more additional physiologically compatible excipients (B), wherein the individual particles of the dosage form display a breaking strength of at least 500 N and a release of active substance of at least 75% after 45 minutes measured according to Ph.Eur. in the paddle mixer with sinker in 600 ml of aqueous buffer solution with a pH value of 1.2 at 37° C. and 75 rpm.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Adhesive sealant composition
This invention is related to an adhesive composition which may be used to bond or seal tissue in vivo. The adhesive composition is readily formed from a two component mixture which includes a first part of a protein, preferably a serum albumin protein, in an aqueous buffer having a pH in the range of about 8.0-11.0 and a second part of a water-compatible or water-soluble bifunctional crosslinking agent. When the two parts of the mixture are combined, the mixture is initially a liquid which cures in vivo on the surface of tissue in less than about one minute to give a strong, flexible, pliant substantive composition which bonds to the tissue and is absorbed in about four to sixty days. The adhesive composition may be used either to bond tissue, to seal tissue or to prevent tissue adhesions caused by surgery.
Owner:NEOMEND INC
Fluorinated surfactants for buffered acid etch solutions
ActiveUS7169323B2Reduce surface tensionSame rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface treatment compositionsEtchingAqueous buffer
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
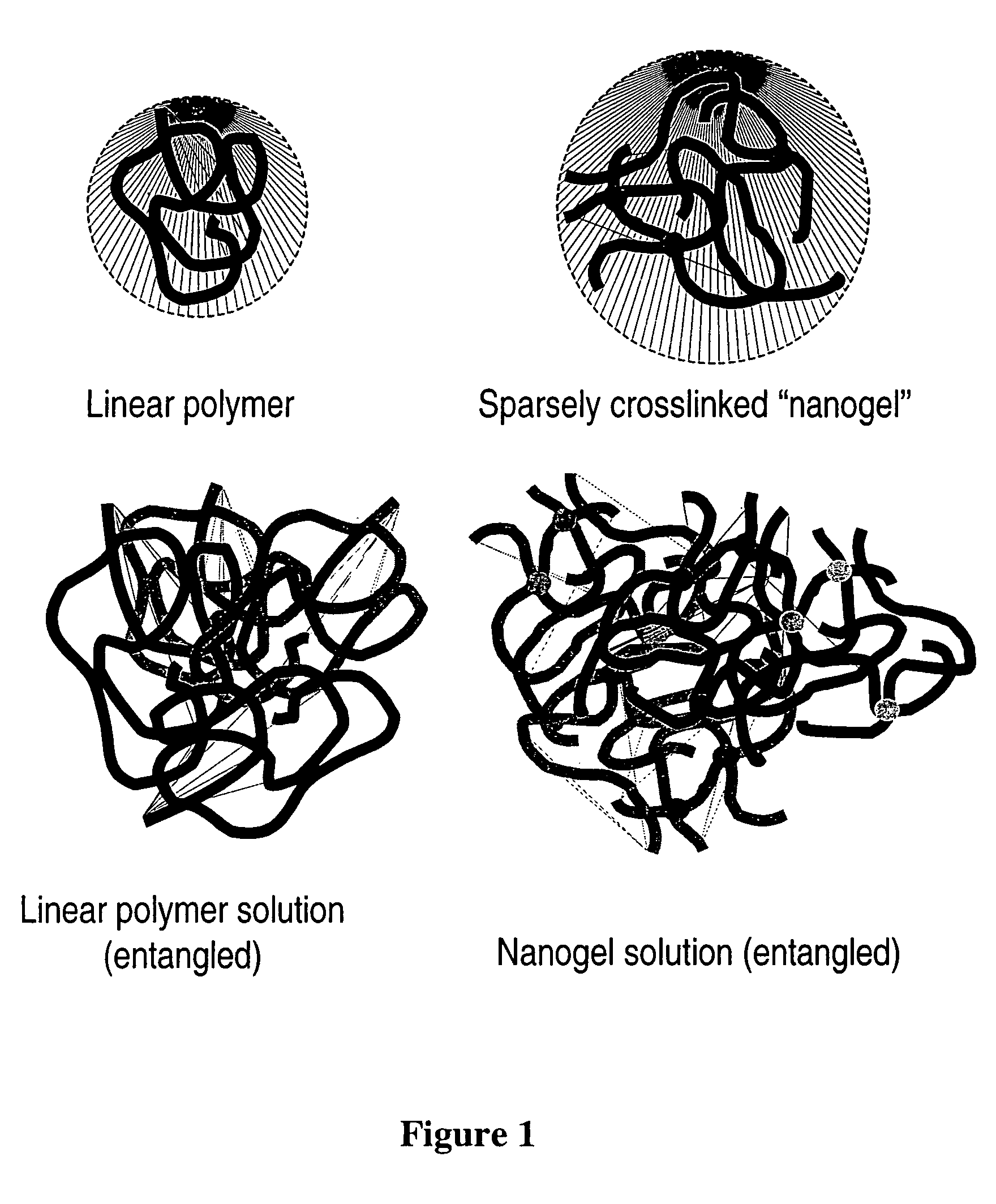
Sparsely cross-linked nanogels: a novel polymer structure for microchannel DNA sequencing
The present invention is generally directed to novel polymeric mateirals for use in the electrophoretic separation of nucleic acids. In particular, the novel polymer materials are sparsely crosslinked nanogels, dissolved in an aqueous buffer to form solutions with moderate to high viscosity. The present invention further provides methods for generating such novel polymers, and related methods of their use.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Electrophoretically Enhanced Detection of Analytes on a Solid Support
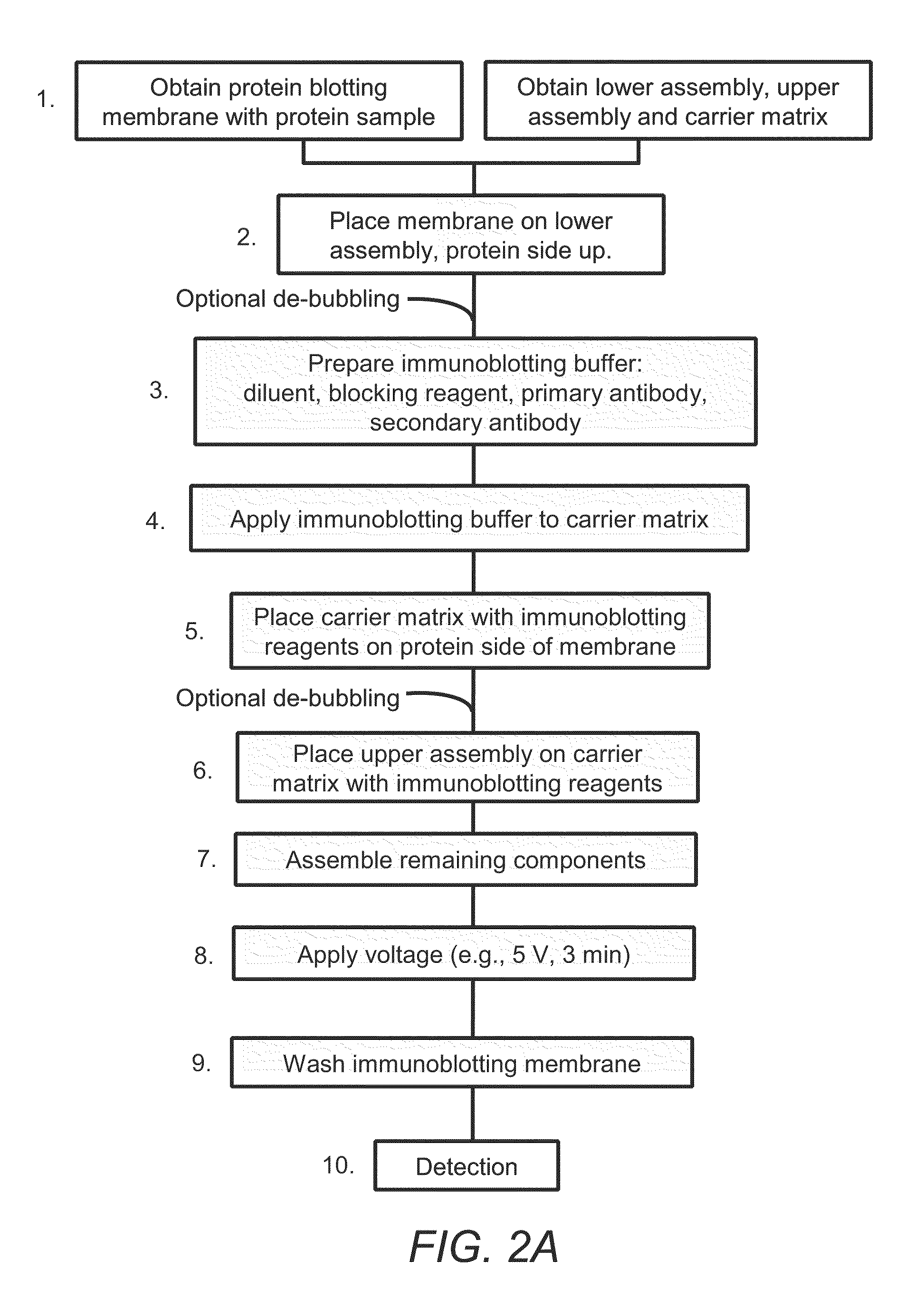
InactiveUS20100044229A1Fast absorptionMinimize absorptionSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectroblottingAnalyte
The present embodiments provide systems, kits and methods suitable for performing dry or substantially dry electro-blotting analyses on immobilized protein or nucleic acid samples. Electro-blotting performed according to the presently described embodiments may include a step whereby detection of one or more immobilized proteins or nucleic acids is electrophoretically accelerated. Methods for performing electro-blotting of immobilized proteins or nucleic acids may include applying an electric voltage to one or more reagents typically used in protein or nucleic acid blotting procedure. The one or more reagents may be absorbed on a suitable carrier matrix. Electro-blotting performed in accordance with the systems and methods described herein may be performed under substantially dry conditions (i.e., with little or no aqueous buffers).
Owner:AVENUE VENTURE OPPORTUNITIES FUND LP AS AGENT +1
Preparation of DNA-containing extract for PCR amplification
Environmental samples typically include impurities that interfere with PCR amplification and DNA quantitation. Samples of soil, river water, and aerosol were taken from the environment and added to an aqueous buffer (with or without detergent). Cells from the sample are lysed, releasing their DNA into the buffer. After removing insoluble cell components, the remaining soluble DNA-containing extract is treated with N-phenacylthiazolium bromide, which causes rapid precipitation of impurities. Centrifugation provides a supernatant that can be used or diluted for PCR amplification of DNA, or further purified. The method may provide a DNA-containing extract sufficiently pure for PCR amplification within 5–10 minutes.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Methods for isolating nucleic acids
ActiveUS7329491B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh concentrationAqueous buffer
A method for purification of a nucleic acid comprising the steps of (a) adsorbing on a substrate the nucleic acid from a composition containing (i) an aqueous buffer, (ii) salts in a high concentration, (iii) a water-miscible, non-acidic organic compound, and (iv) the nucleic acid; (b) optionally washing with a washing solution the substrate with the adsorbed nucleic acid; (c) contacting the substrate with the adsorbed nucleic acid with a solution containing salts in a lower concentration compared to the composition of step (a), thereby desorbing the nucleic acid from the substrate; (d) separating the solution with the desorbed nucleic acid from the substrate, thereby purifying the nucleic acid; and optionally (e) precipitating the desorbed nucleic acid from the solution of step (d) and isolating the precipitated nucleic acid, thereby further purifying the nucleic acid.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
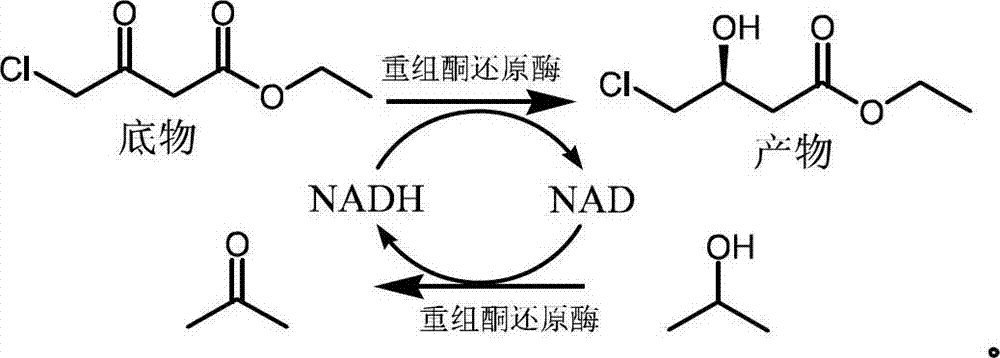
Biological preparation method of (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate ethyl
InactiveCN102925501ASolve too many joinsSolve efficiency problemsMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEthyl butyrateEthyl Chloride
The invention relates to a biological preparation method of (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate ethyl, which uses 4-chloro-3-carbonyl ethyl butyrate as a substrate and enables the substrate to be subjected to asymmetric reduction reaction in the presence of a biological catalyst, a cofactor and a hydrogen donor to produce the (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate ethyl, wherein the biological catalyst is recombinant ketone reductase and the hydrogen donor is isopropyl alcohol; the asymmetric reduction reaction is carried out in a hybrid system of aqueous buffer solution and toluene with pH of 7.0-9.0, and the volume ratio of the aqueous buffer solution to the toluene is 4-20:1. The method provided by the invention solves the problems of requirement of additional coenzyme system, too much added organic solvent, low efficiency of catalyst and high cost in the traditional biological preparation method. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of mild reaction condition, high reaction efficiency and simple operation, and the concentration of the substrate can be increased to 40%, thus improving the preparation efficiency of (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate ethyl and reducing the reaction cost greatly.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
Novel peptide amphiphiles having improved solubility and methods of using same
InactiveUS20090042804A1Improve gelationMaintain good propertiesNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAqueous bufferHuman patient
Disclosed herein are novel peptide amphiphile molecules and compositions discovered to possess improved solubility in aqueous buffers which, in turn, facilitates purification required for pharmaceutical applications, particularly for in vivo administration to human patients. In addition, gels of such peptide amphiphile compositions are shown herein to possess unexpectedly superior gelation kinetics and rheological properties, including an increased mechanical stiffness, which better mimics the mechanical properties of natural central nervous system tissues.
Owner:NANOTOPE
Therapeutic composition and a method of coating implantable medical devices
A method of making a therapeutic composition, as well as the therapeutic composition so made, is disclosed. The method comprises mixing a hydrophobic drug with an aqueous buffer solution and adding a surfactant to the aqueous buffer solution to form the therapeutic composition. A implantable medical device with the therapeutic composition and a method of making a coating for an implantable medical device containing the therapeutic composition is also disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
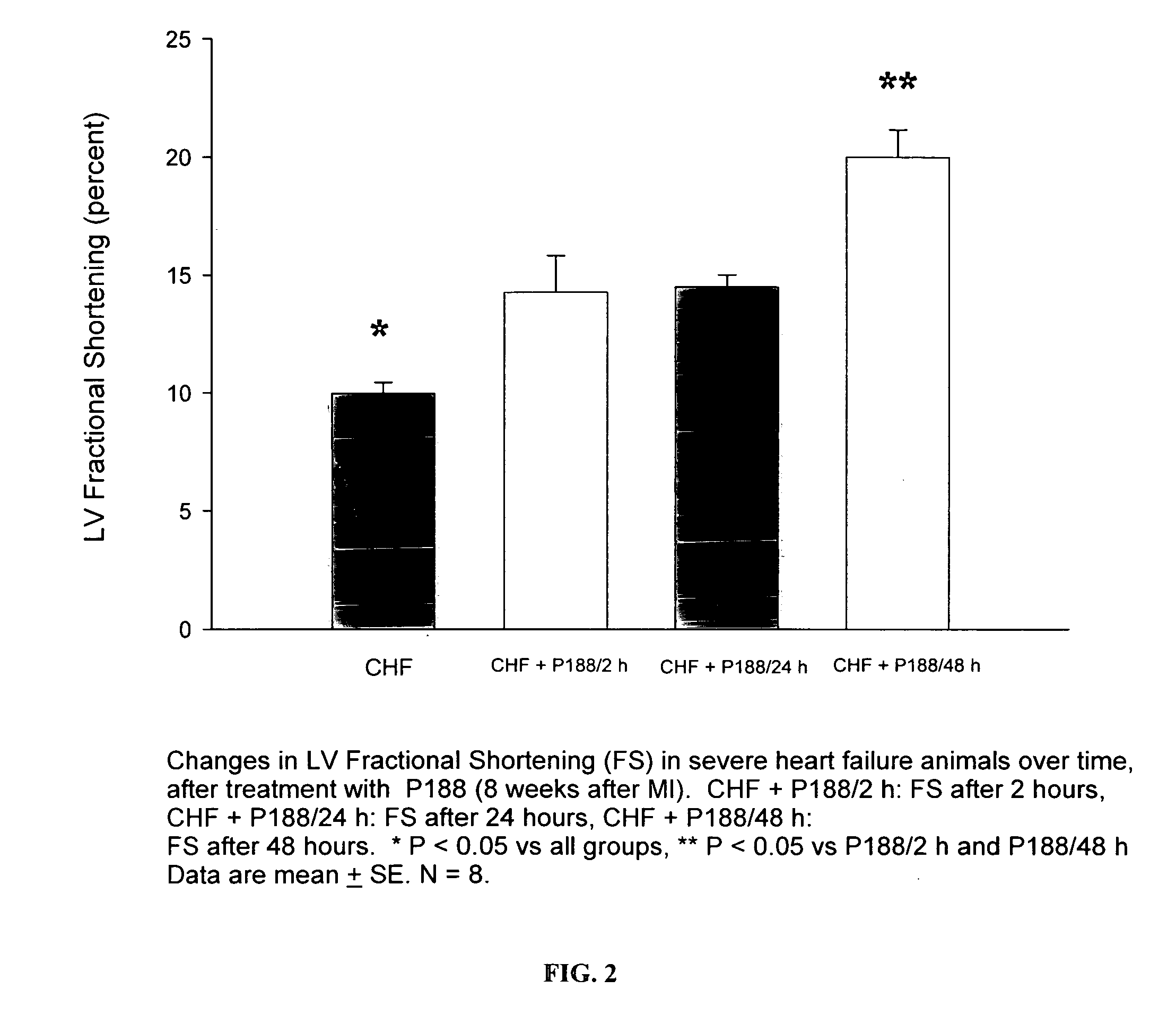
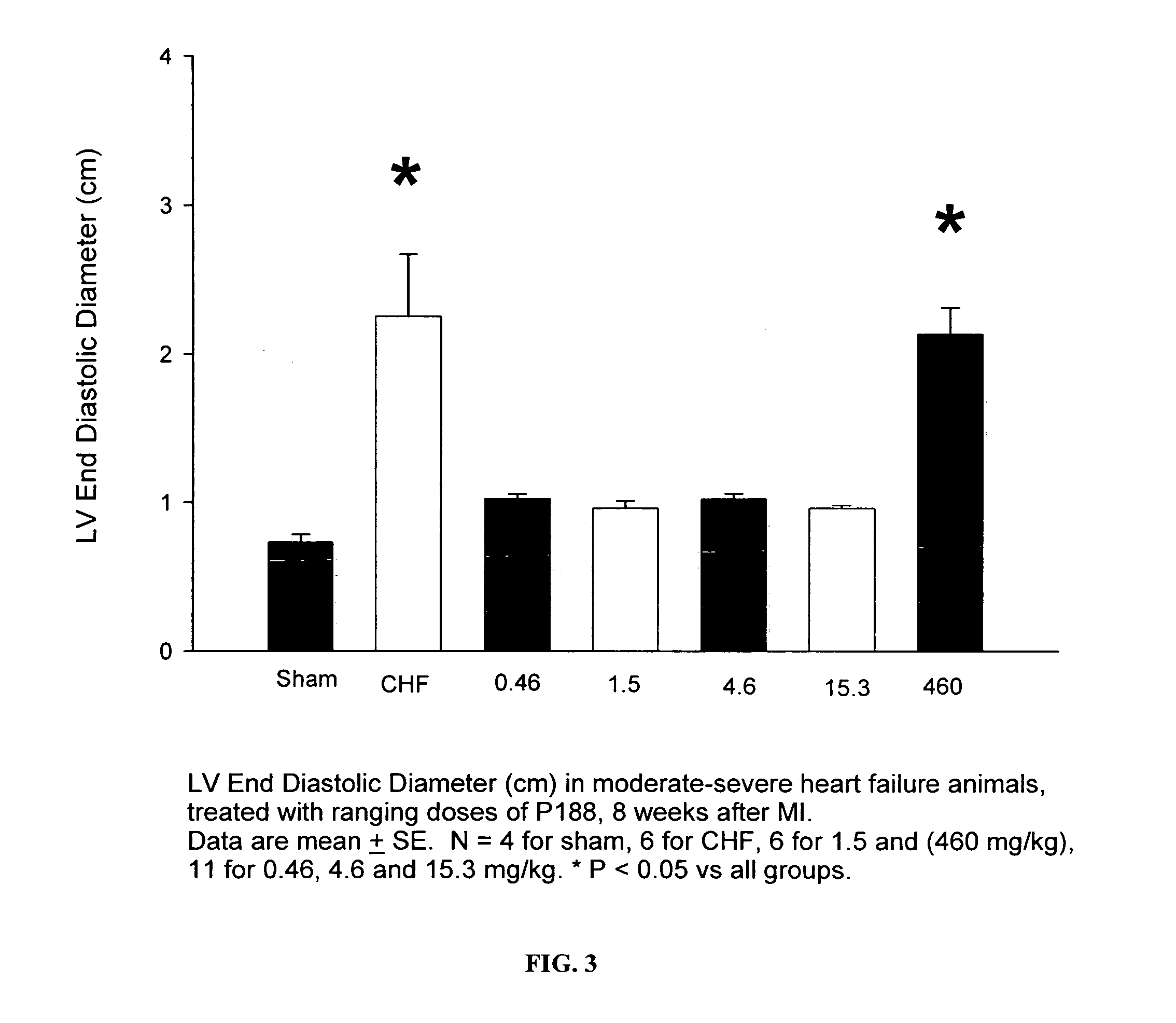
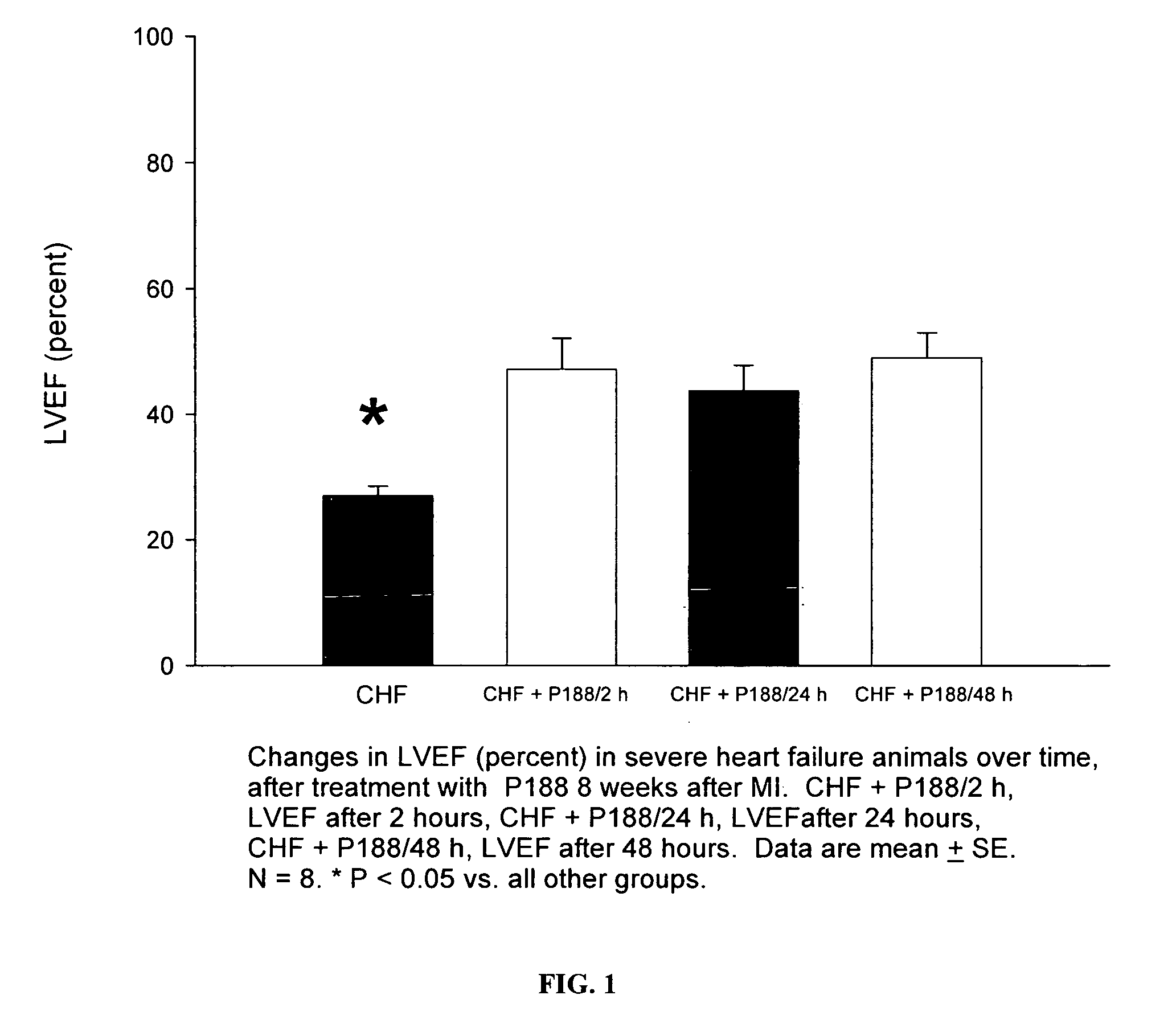
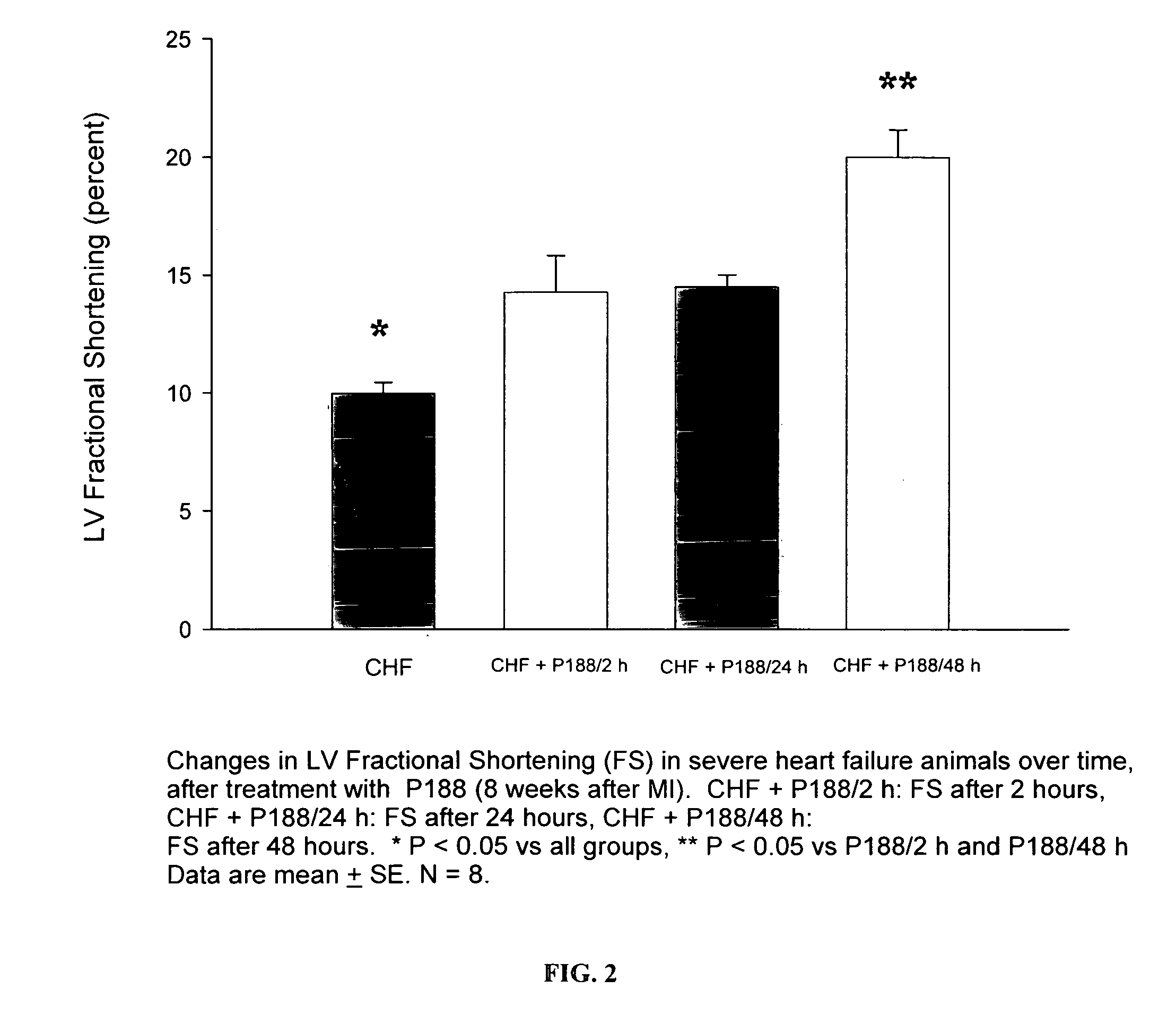
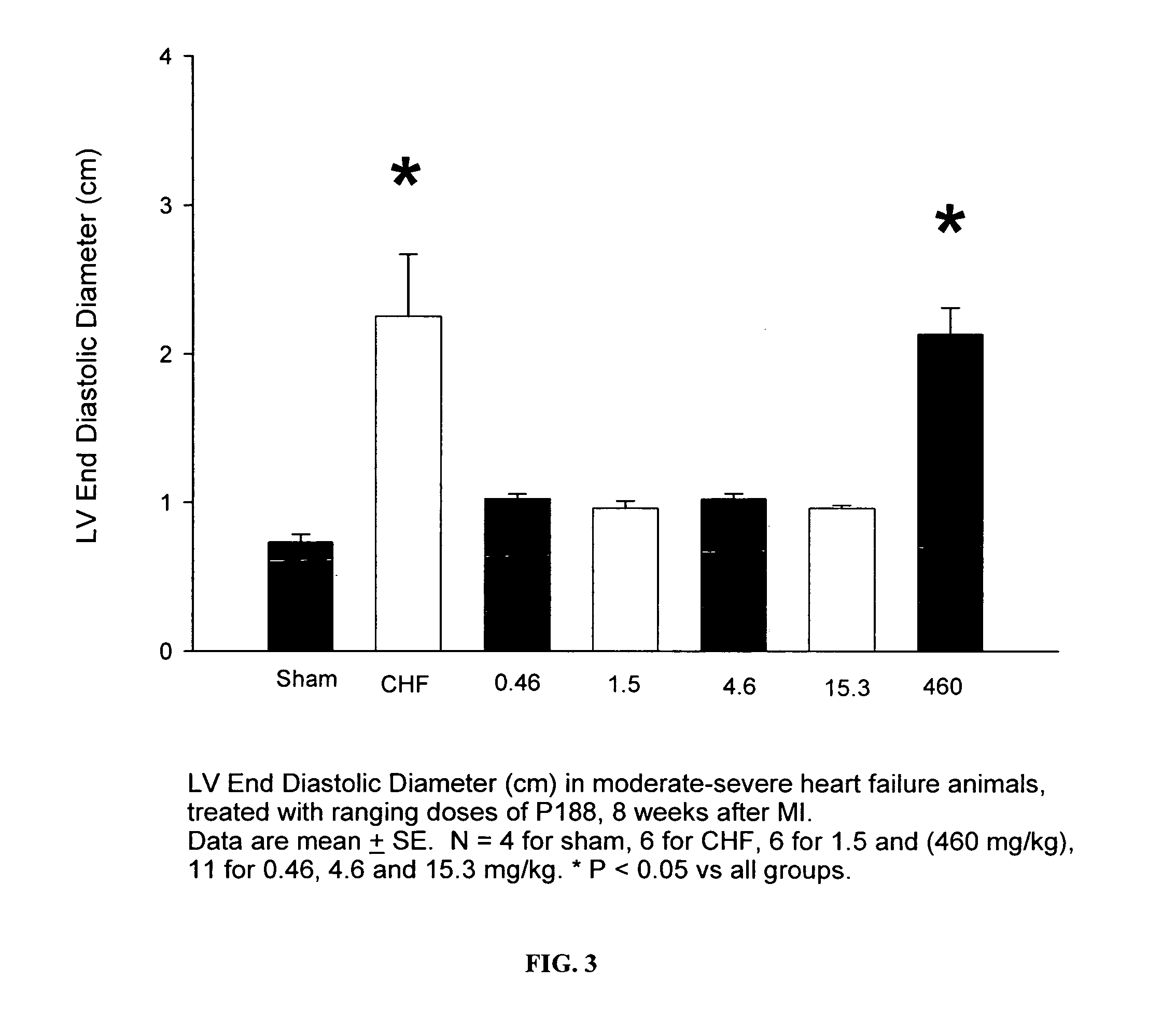
Compositions and Methods for the Treatment of Heart Failure
ActiveUS20100178269A1Significant dysfunctionReduce pressurePharmaceutical delivery mechanismSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsLeft ventricular sizeLeft ventricular ejection
The invention provides a therapeutic composition comprising an aqueous buffer, and a therapeutic agent that improves the functioning of a diseased heart by decreasing left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and simultaneously increasing left ventricular ejection without affecting the blood pressure or heart rate.
Owner:PHRIXUS PHARMA
Water-wettable chromatographic media for solid phase extraction
InactiveUS20050133424A1Simple methodReduce sample preparation timeIon-exchange process apparatusAnalysis using chemical indicatorsHydrophilic monomerOrganic solvent
A method for removing an organic solute from a solution comprises contacting the solution with a polymer formed by copolymerizing one or more hydrophobic monomers and one or more hydrophilic monomers, whereby the solute is adsorbed onto the polymer. The solution can comprise a polar solvent such as a polar organic solvent or water or an aqueous buffer. The hydrophobic monomer can be, for example, divinylbenzene. The hydrophilic monomer can be, for example, a heterocyclic monomer, such as a vinylpyridine or N-vinylpyrrolidone.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Enzymatic transesterification/esterification processes employing lipases immobilized on hydrophobic resins in the presence of water solutions
ActiveUS20130052701A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlcoholAqueous buffer
Disclosed are an enzymatic batchwise or continuous process for the production of fatty acid alkyl esters for use in the biofuels, food and detergent industries and a system therefor. The process utilizes enzymes immobilized on a hydrophobic resin mixed with a fatty acid source and an alcohol or alcohol donor in the presence of an alkaline or mild alkaline aqueous buffer, or in the presence of water or aqueous solution. The production process for fatty acid alkyl esters is carried out by transesterification or esterification simultaneously or sequentially. The biocatalyst activity is maintained with no significant activity losses in multiple uses and also avoids the accumulation of glycerol and water by-products or other hydrophilic compounds on the biocatalyst.
Owner:ENZYMOCORE LTD
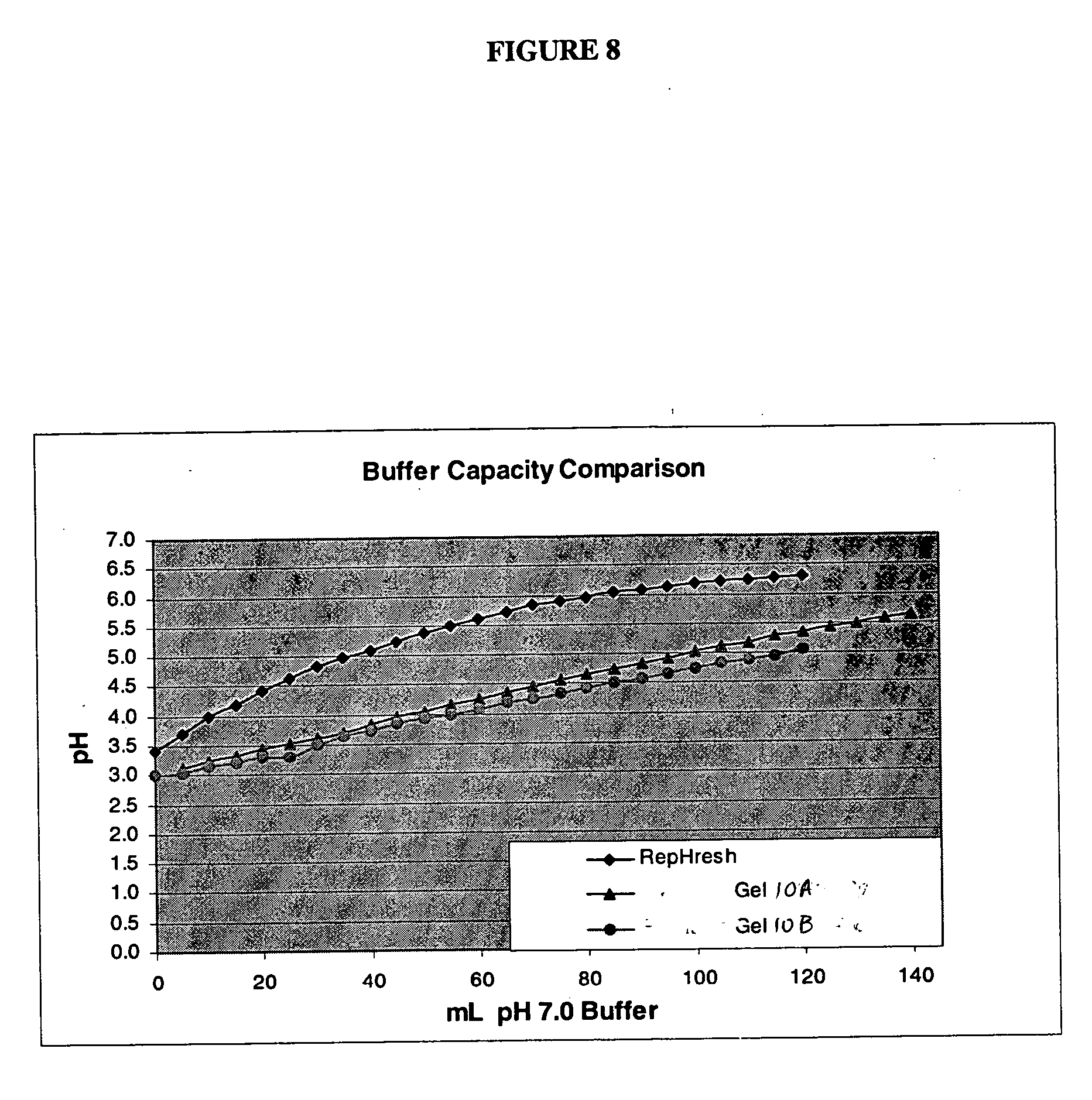
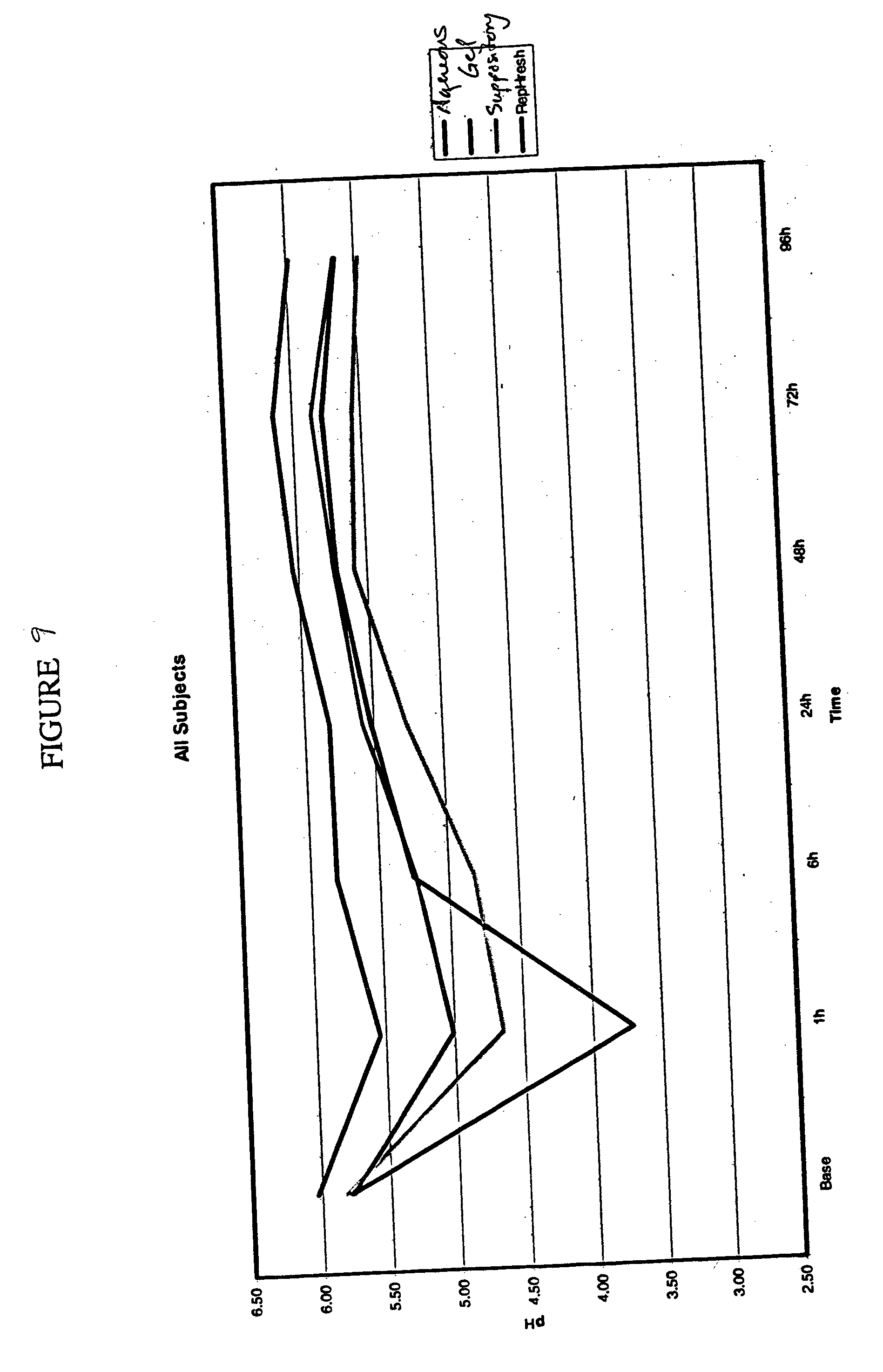
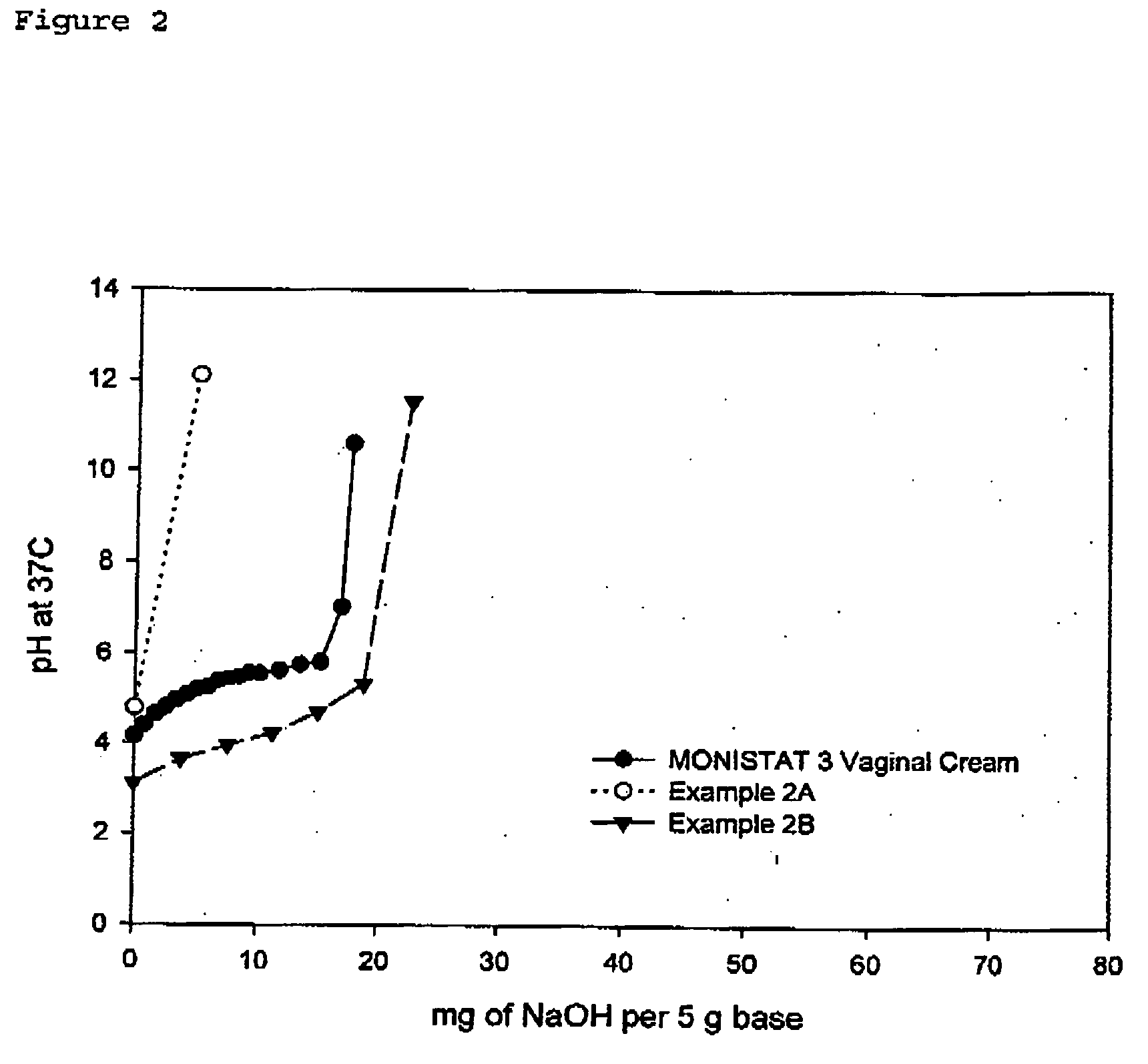
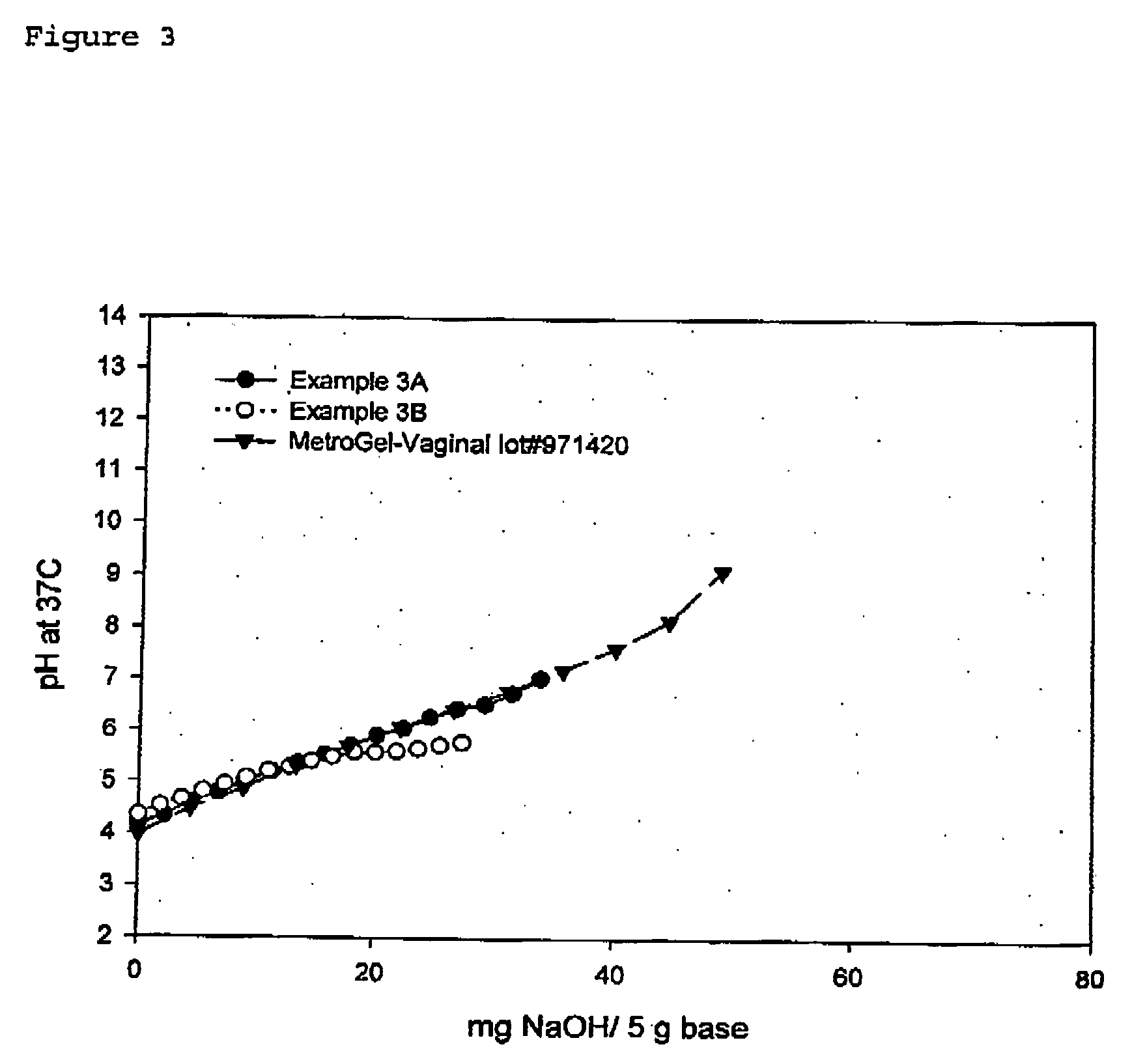
Compositions and methods for reducing vaginal pH
InactiveUS20060105008A1Reducing perceived vaginal odorHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideGynecologyAqueous buffer
This invention relates to aqueous buffered compositions and methods for lowering vaginal pH and reducing the level of self-perceived vaginal odor. Such compositions may be applied to the vaginal area to lower vaginal pH and assist in maintaining such pH over a period of time.
Owner:AHMAD NAWAZ +3
Sparsely cross-linked nanogels: a novel polymer structure for microchannel DNA sequencing
InactiveUS20060074186A1High viscositySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCross-linkAqueous buffer
The present invention is generally directed to novel polymeric mateirals for use in the electrophoretic separation of nucleic acids. In particular, the novel polymer materials are sparsely crosslinked nanogels, dissolved in an aqueous buffer to form solutions with moderate to high viscosity. The present invention further provides methods for generating such novel polymers, and related methods of their use.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Compositions and methods for the treatment of heart failure
ActiveUS8372387B2Function increaseReduce pressurePharmaceutical delivery mechanismSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsHeart failure cellLeft ventricular ejection
Owner:PHRIXUS PHARMA
Apparatus and methods for low temperature small angle x-ray scattering
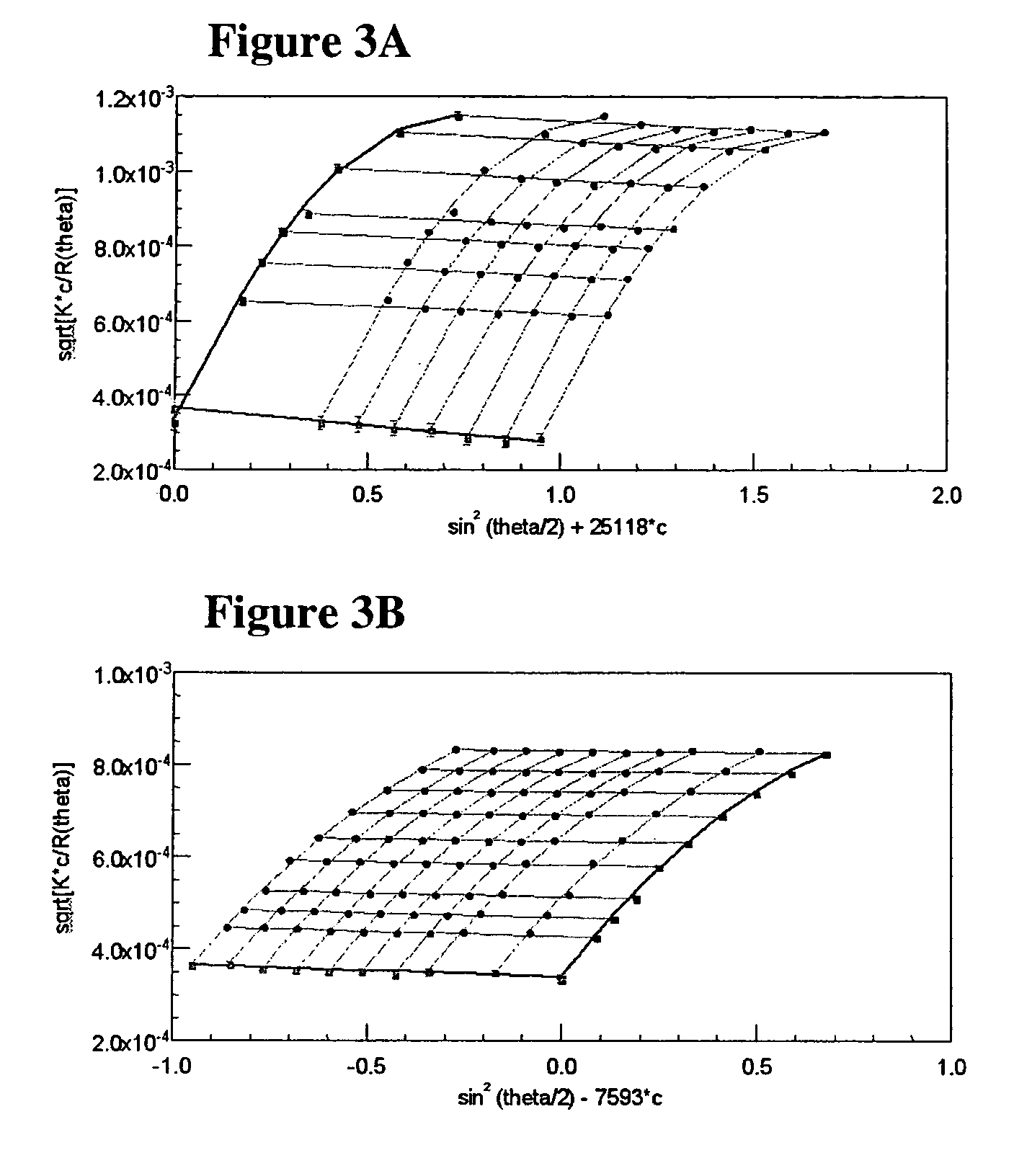
ActiveUS20150233804A1Improve SAXS data qualityFacilitate subtractionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationAqueous bufferSmall-angle X-ray scattering
Apparatus and methods for performing small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) at low (cryogenic) temperatures for determining the structure of and changes in the structure of proteins, DNA, RNA, and other biological molecules and biomolecular assemblies and structures. A cryogenic, small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) application sample holder, includes a sample cell including a base portion and at least two parallel walls disposed on the base, wherein the sample cell has a liquid volume capacity defined by the walls and the base portion of 0.001 to 10 microliters. A method for performing cryogenic SAXS on a sample includes the steps of providing a sample biomolecule solution containing an aqueous buffer, a biomolecule, and a cryoprotectant agent, wherein the cryoprotectant agent comprises up to 60% (w / w) of the biomolecule solution, and other known components as necessary to solubilize and stabilize the biomolecule, in a sample holder of claim 1 or 18, cryogenically cooling the sample solution in the sample holder at a rate equal to or greater than 100 K / sec without ice formation, and examining the cooled sample using small angle X-ray scattering by passing a beam of X-rays through the sample.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for reducing vaginal pH
InactiveUS20060172007A1Reducing perceived vaginal odorHigh antibacterial activityBiocidePowder deliveryGynecologyAqueous buffer
This invention relates to aqueous buffered compositions and methods for lowering vaginal pH and reducing the level of self-perceived vaginal odor. Such compositions may be applied to the vaginal area to lower vaginal pH and assist in maintaining such pH over a period of time.
Owner:AHMAD NAWAZ +3
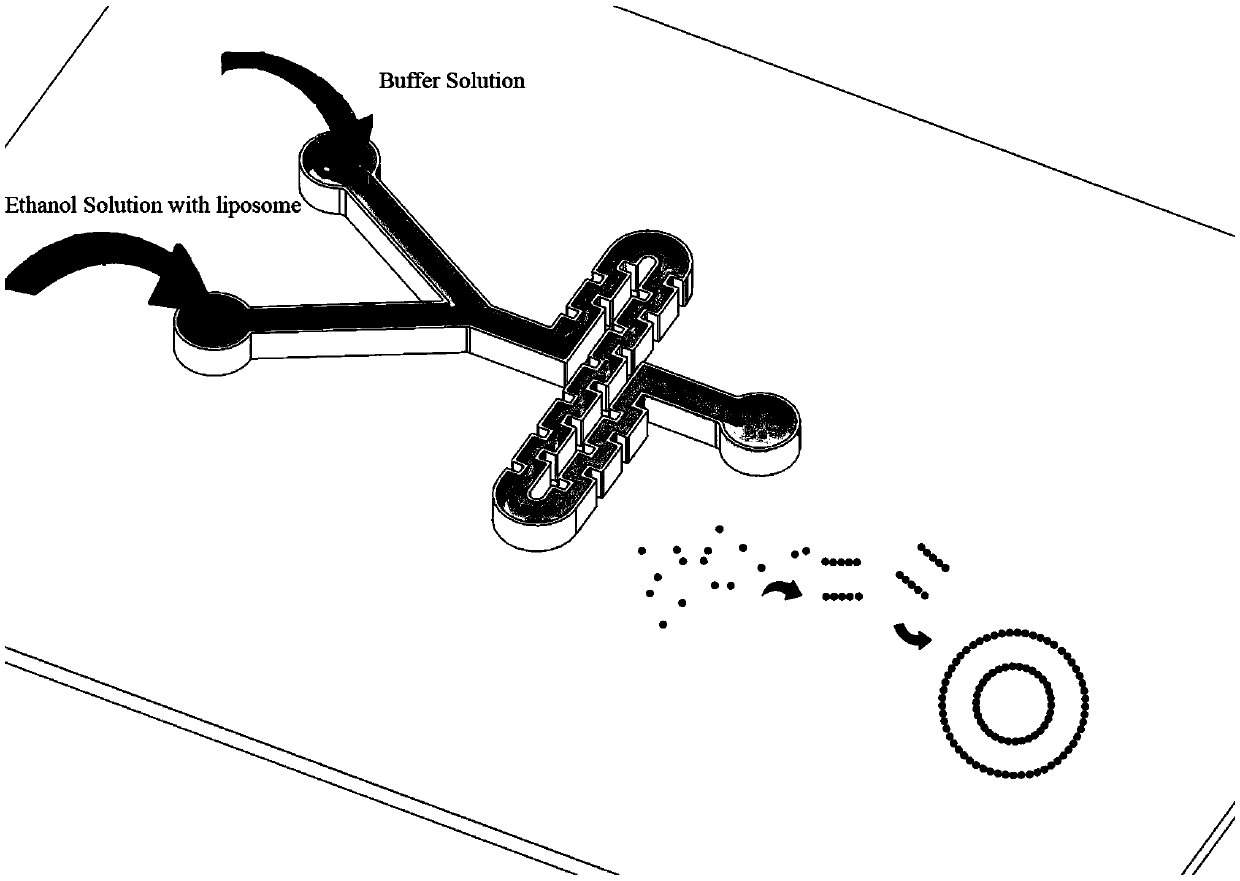
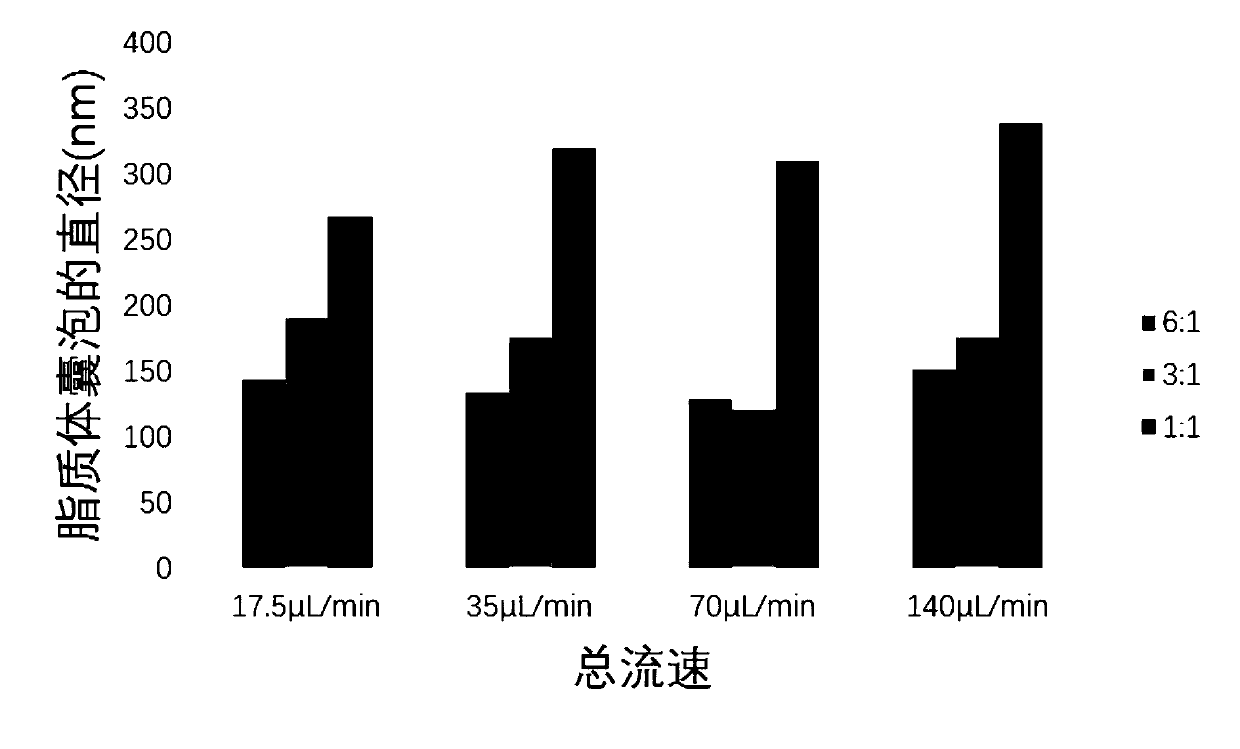
Controllable preparation method of liposome vesicle based on microfluidic device
InactiveCN109603930ALow costPrecisely control the amount addedLaboratory glasswaresPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLiposome VesicleFlow ratio
The invention provides a preparation method of a liposome vesicle based on a microfluidic device. The preparation method comprises the steps of: preparing a microfluidic chip by a soft lithography method; preparing a precursor solution for preparing the liposome vesicle; and using a constant-pressure injection pump to inject the precursor solution into a ''Y''-shaped chip through different injection ports, setting a total flow rate, adjusting the flow ratio of a buffer solution to a phospholipid molecular alcohol solution, and collecting a product at an outlet, wherein the product is the prepared liposome vesicle. The microfluidic chip selected by the invention is a ''Y''-shaped microfluidic chip with a serpentine mixing channel of a square structure, and the chip is prepared by the soft lithography method. By using the chip, based on the principle of self-assembly on an interface, by adjusting the total flow rate and the flow rate ratio of the aqueous buffer solution to the phospholipid molecule ethanol solution, regulation of the size of the liposome vesicle and control on the dimensional uniformity are achieved, and an efficient low-cost method is provided for preparation of artificial cells with uniform properties as well as drug carriers.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for Increasing Signal Intensity in An Optical Waveguide Sensor
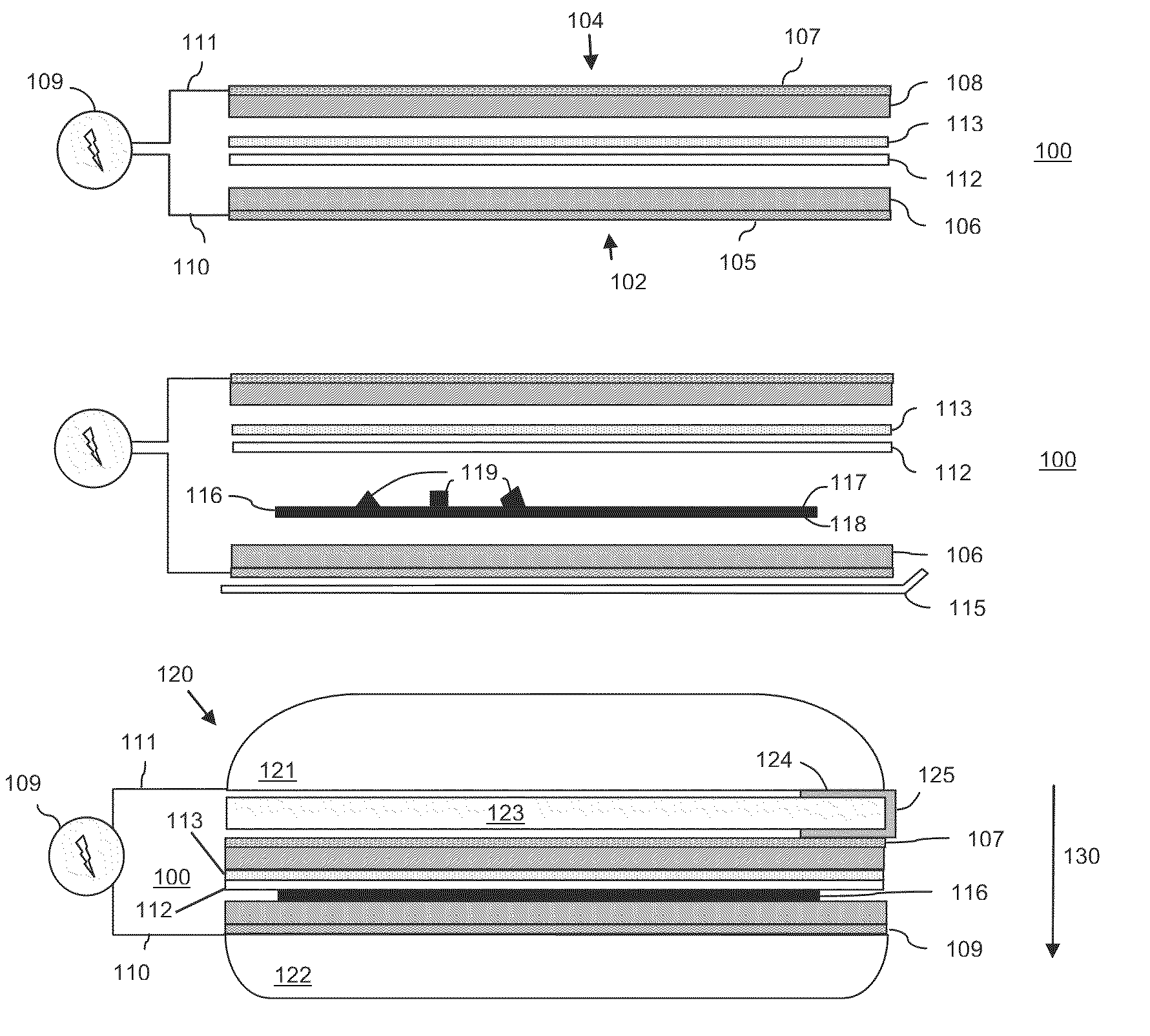
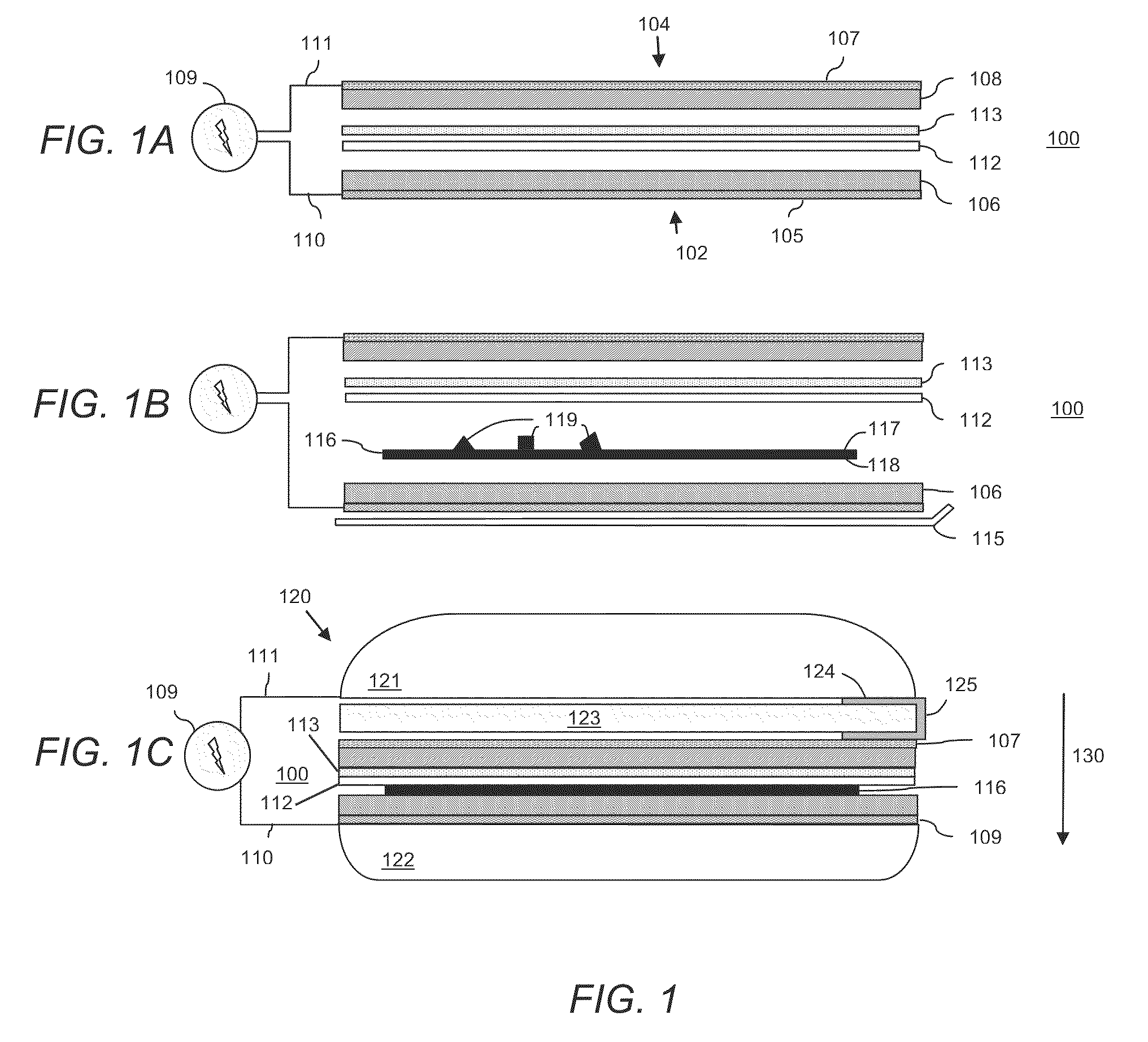
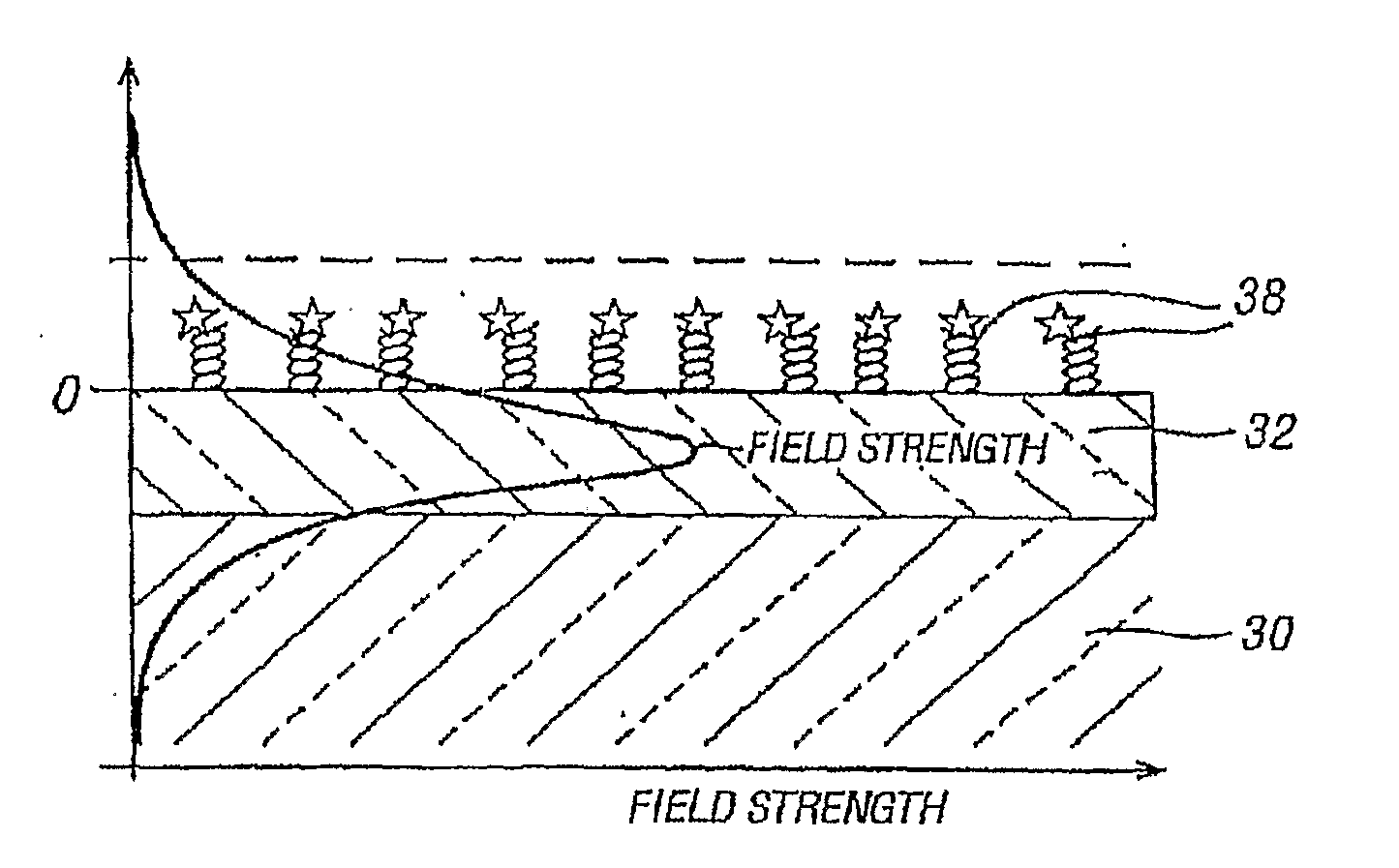
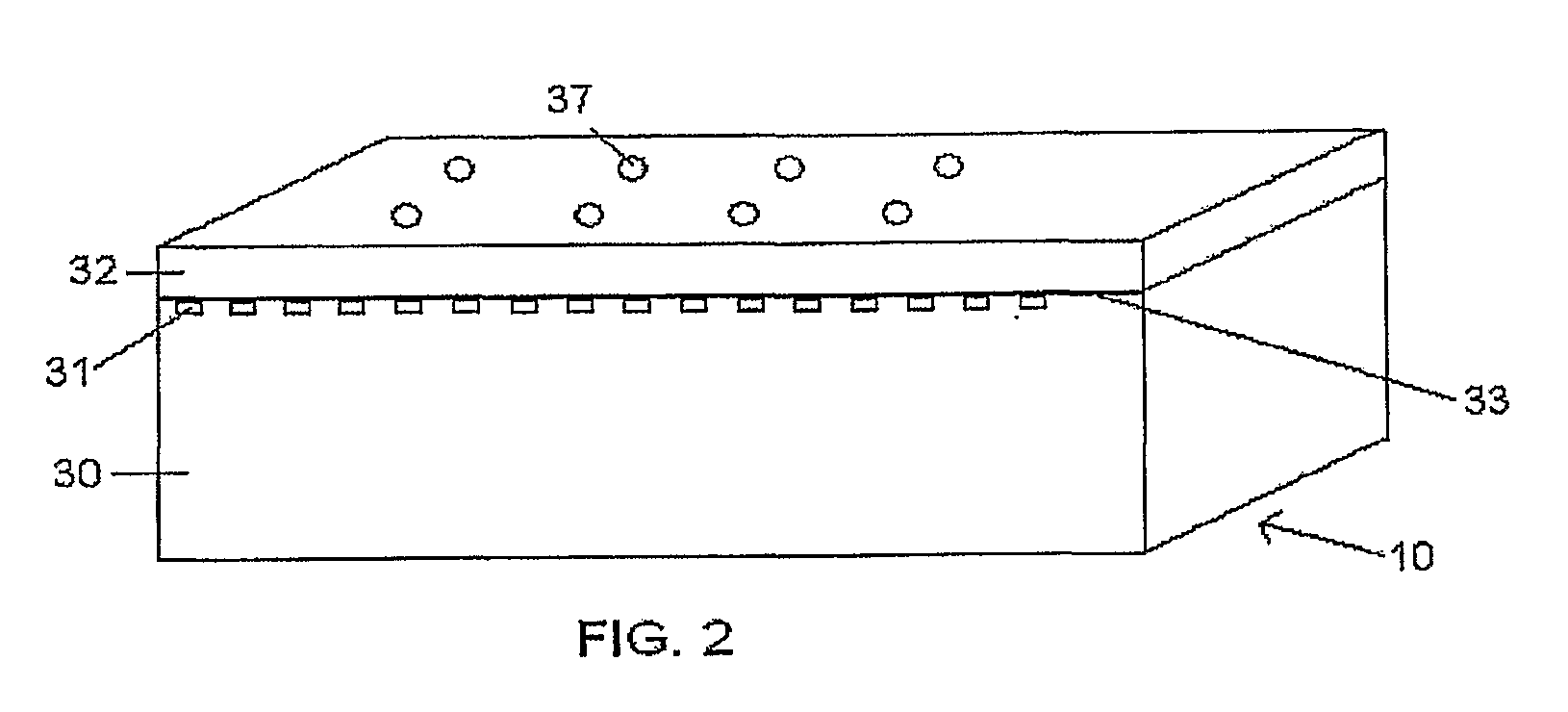
InactiveUS20090034902A1High sensitivityIncrease light intensityMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescenceAqueous buffer
A sensor platform for use in sample analysis comprises a substrate (30) of refractive index m and a thin, optically transparent layer (32) of refractive index (n2) on the substrate, where n2 is greater than n1. The platform includes one of more sensing areas each for one or more capture elements. The platform also includes an immersion fluid with a refractive index n3 greater than an aqueous buffer but less than n2 to enhance the fluorescent signal of an affinity reaction. Also disclosed are an apparatus incorporating the platform and a method of using the platform.
Owner:BAYER TECH SERVICES GMBH
Pharmaceutical formulation having reverse thermal gelation properties for local delivery of nanoparticles
InactiveUS20170340756A1Reduce high temperatureDecreased critical micelle concentrationCompounds screening/testingPowder deliveryEpitopeAqueous buffer
The present invention refers to a pharmaceutical formulation for injection comprising fluorescent nanoparticles as in vivo diagnostics. The present invention relates to an injectable pharmaceutical formulation for human medicine and / or veterinary use, comprising 17% to 20% per weight of poloxamer 407 and 3%-15% per weight of poloxamer 188, 0.10 nM to 10.0 μM fluorescent nanoparticles and water or an aqueous buffer, wherein the pharmaceutical formulation is liquid at 4° C.-32° C. and forms a gel at about 37° C., their use as an in vivo marker and methods of their preparation. The inventive formulation is useful for local control and prevention of spreading / diffusion of nanoparticles, and thus allows full utilization of their quantum physics properties for example as a tool to enable surgical precision of tumor removal; even without tumor specific epitope binding antibodies.
Owner:EXCHANGE IMAGING TECH GMBH
Peptide amphiphiles having improved solubility and methods of using same
InactiveUS8076295B2Improve gelationMaintain good propertiesNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAqueous bufferHuman patient
Disclosed herein are novel peptide amphiphile molecules and compositions discovered to possess improved solubility in aqueous buffers which, in turn, facilitates purification required for pharmaceutical applications, particularly for in vivo administration to human patients. In addition, gels of such peptide amphiphile compositions are shown herein to possess unexpectedly superior gelation kinetics and rheological properties, including an increased mechanical stiffness, which better mimics the mechanical properties of natural central nervous system tissues.
Owner:NANOTOPE
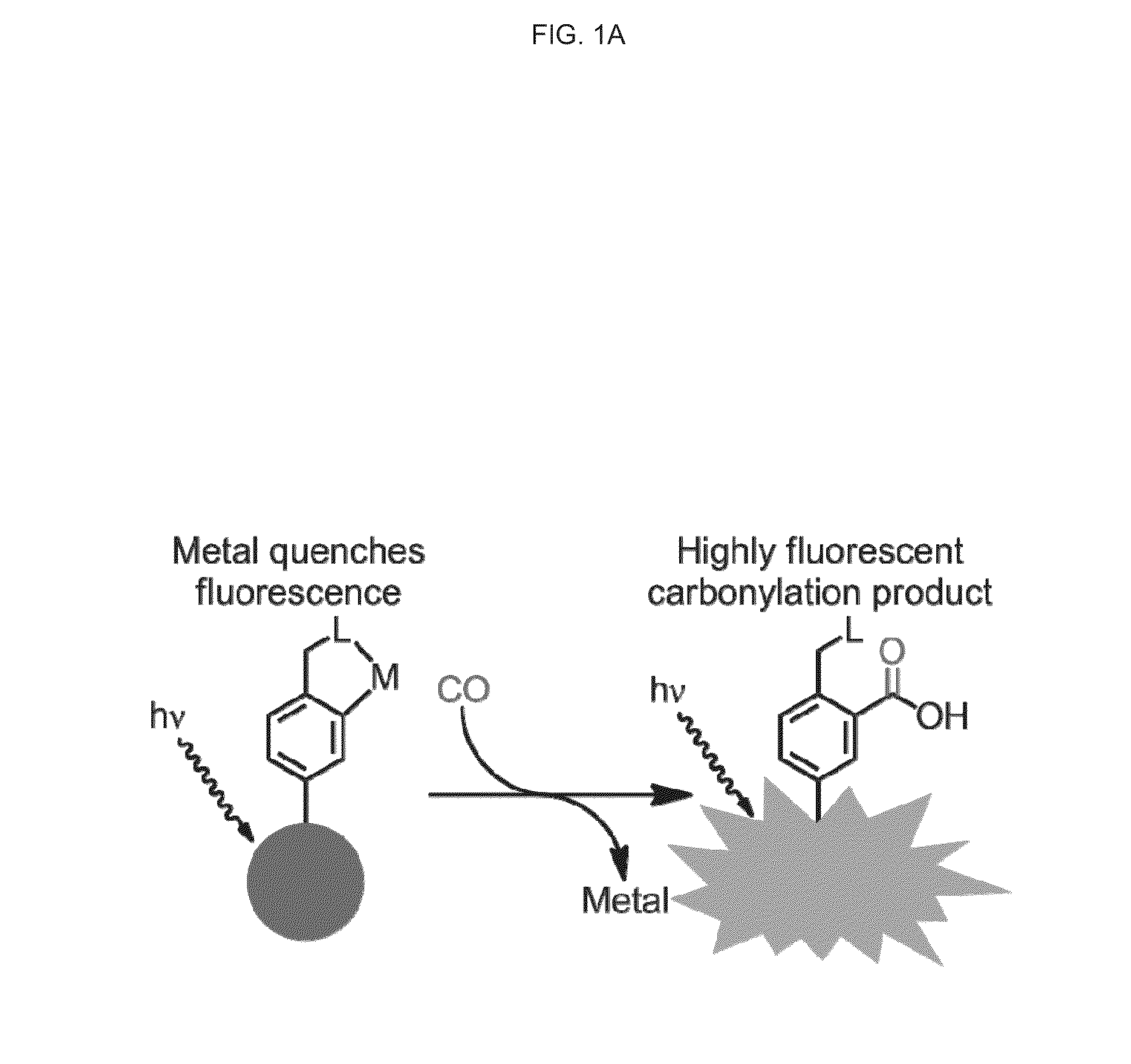
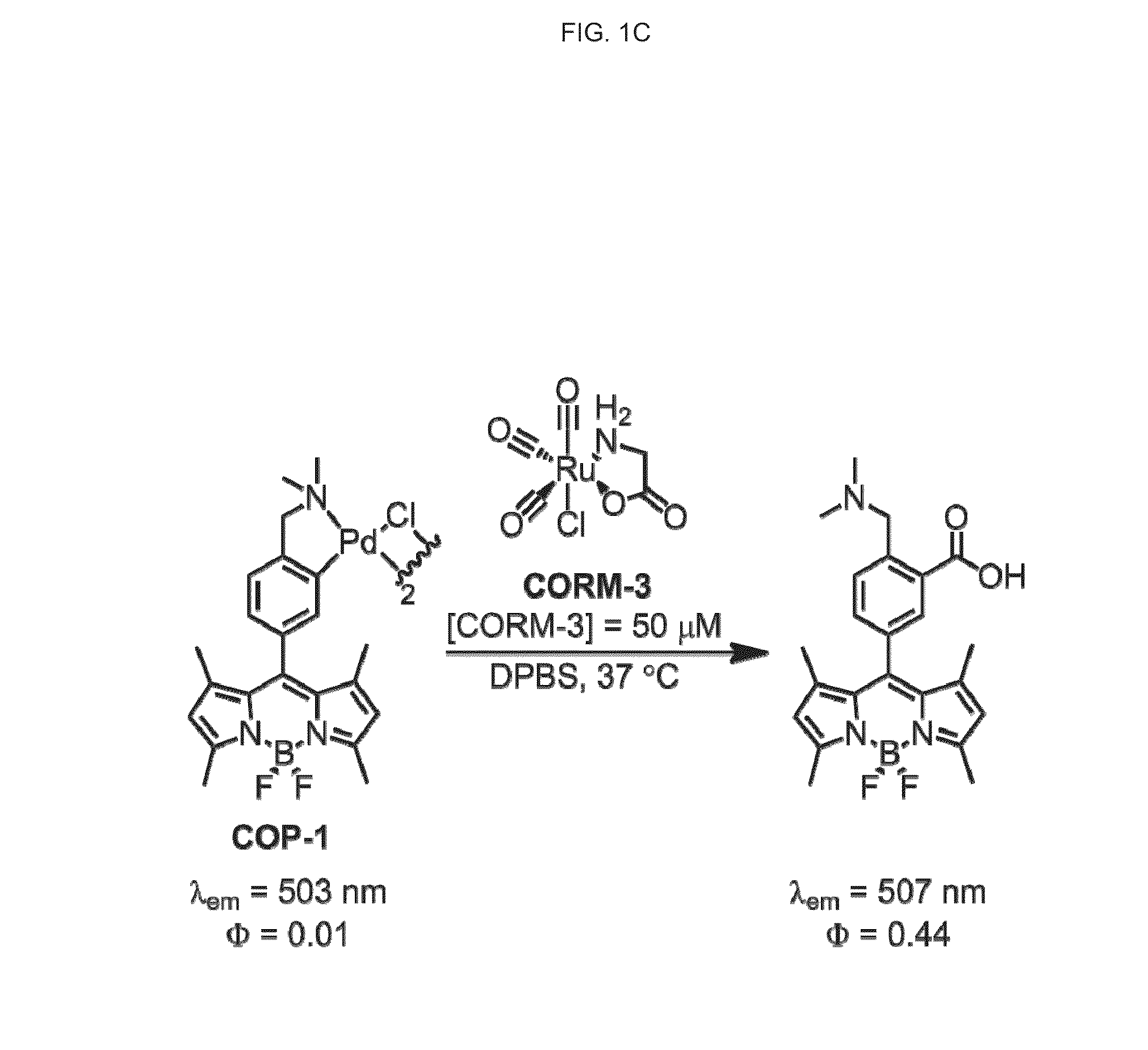
Reaction-based fluorescent probe for selective detection of carbon monoxide using metal-mediated carbonylation
ActiveUS20150057185A1Microbiological testing/measurementPalladium organic compoundsWHOLE ANIMALFluorescence
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a member of the gasotransmitter family that includes NO and H2S and is implicated in a variety of pathological and physiological conditions. Whereas exogenous therapeutic additions of CO to tissues and whole animals have been well studied, the real-time spatial and temporal tracking of CO at the cellular level remains an open challenge. We now report a new type of turn-on fluorescent probe for selective CO detection by exploiting palladium-mediated carbonylation reactivity. The compounds of the invention are capable of detecting CO both in aqueous buffer and in live cells with high selectivity over a range of biologically relevant reactive small molecules, providing a potentially powerful approach for interrogating its chemistry in biological systems.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
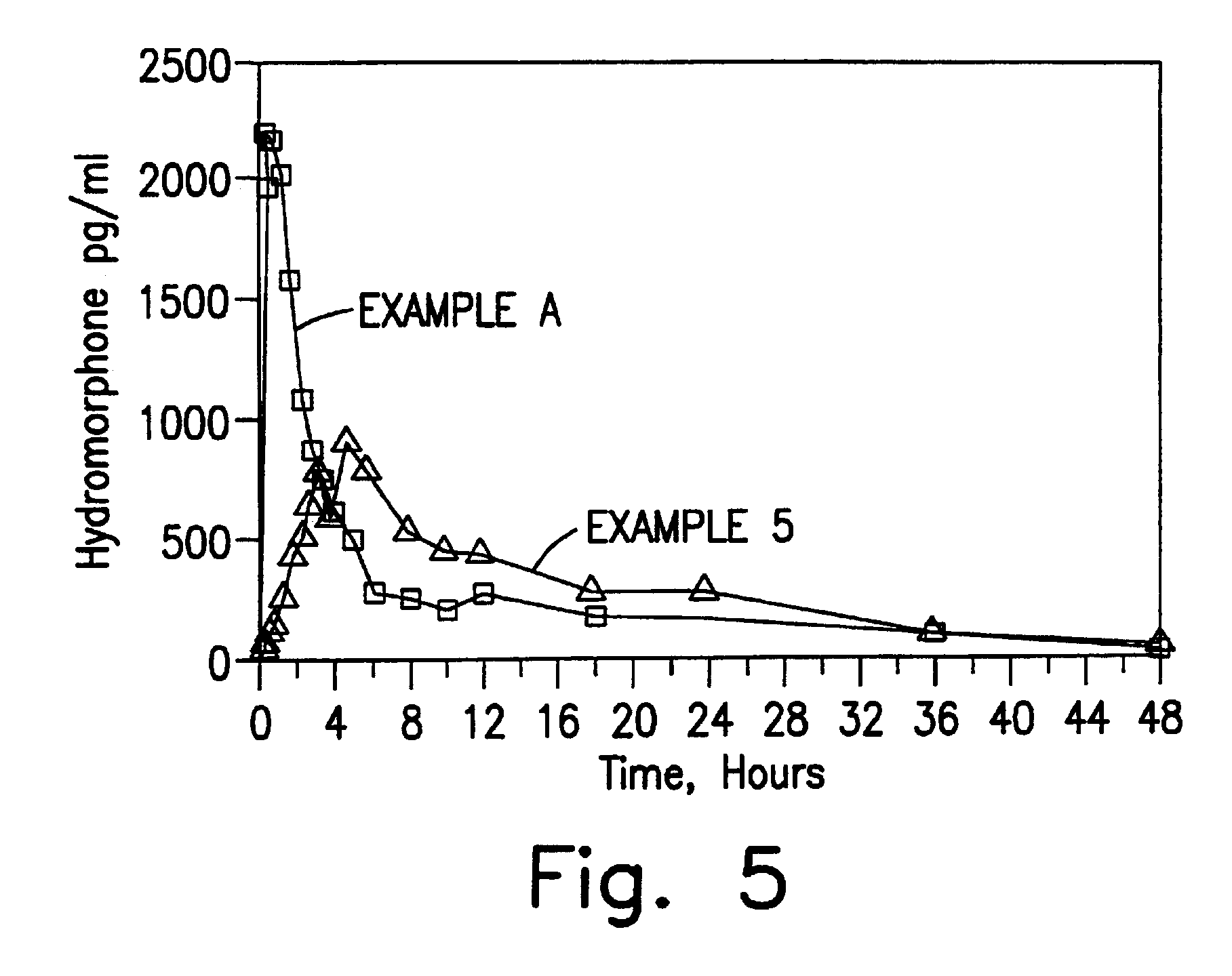
Method of treating humans with opioid formulations having extended controlled release
InactiveUS7740881B1No difference in analgesic efficacyGood effectBiocidePowder deliveryControlled releaseAqueous buffer
Solid controlled-release oral dosage forms comprising a therapeutically effective amount of an opioid analgesic or a salt thereof which provide an extended duration of pain relief of about 24 hours, have a dissolution rate in-vitro of the dosage form, when measured by the USP Paddle Method at 100 rpm at 900 ml aqueous buffer (pH between 1.6 and 7.2) at 37° C. of from about 12.5% to about 42.5% (by wt) opioid released after 1 hour, from about 25% to about 65% (by wt) opioid released after 2 hours, from about 45% to about 85% (by wt) opioid released after 4 hours, and greater than about 60% (by wt) opioid released after 8 hours, the in-vitro release rate being substantially independent of pH and chosen such that the peak plasma level of said opioid analgesic obtained in-vivo occurs from about 2 to about 8 hours after administration of the dosage form.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
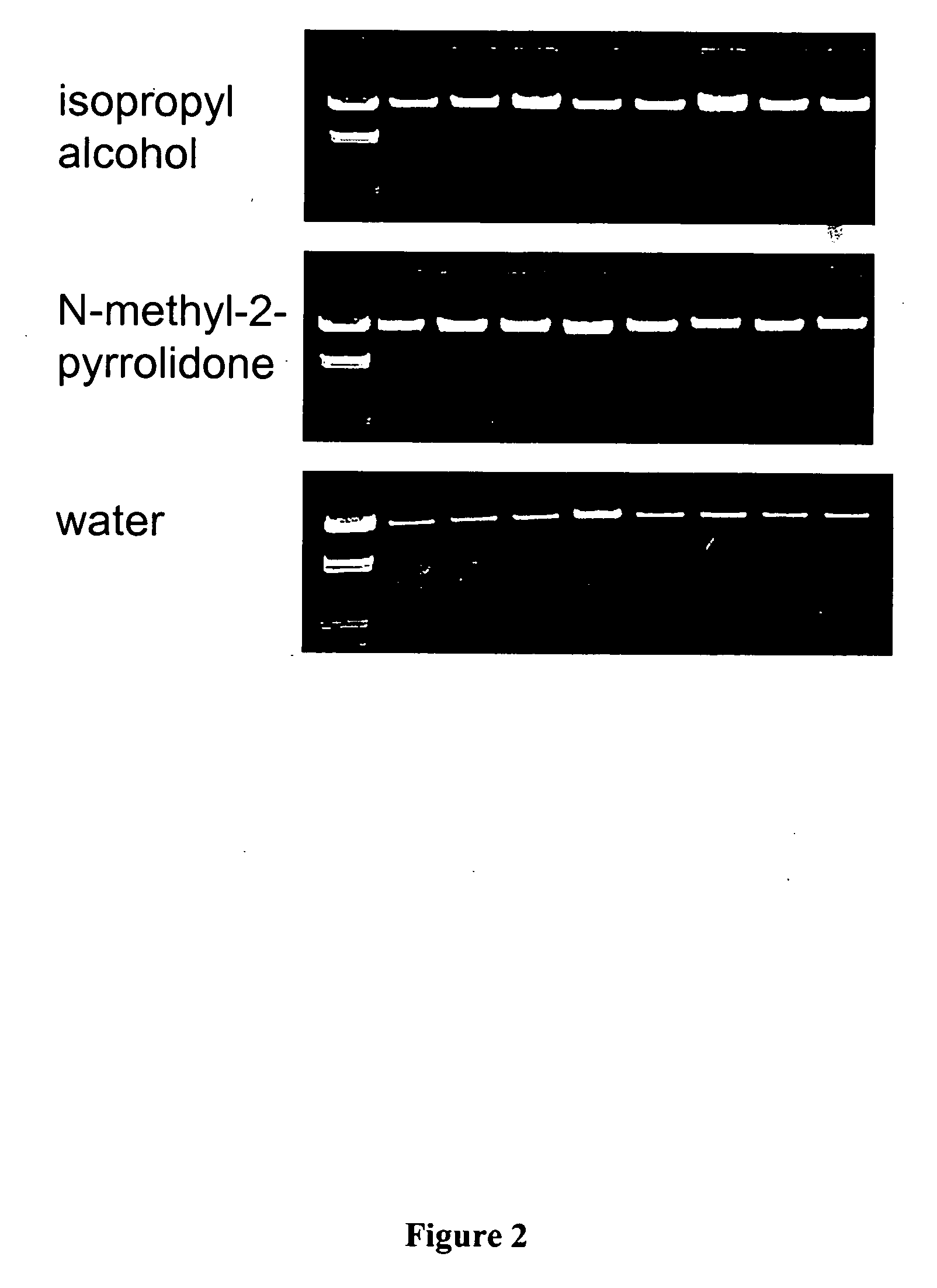
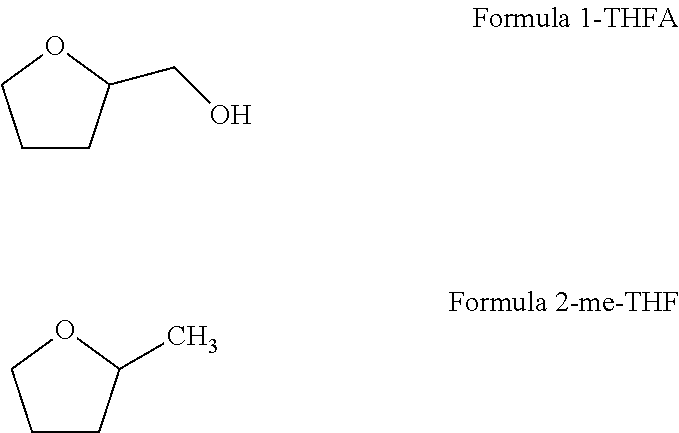
Dewaxing buffer containing a water-soluble organic solvent and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20130189730A1Quickly and efficiently removeReduce protocol timePreparing sample for investigationBiological testingParaffin waxOrganic solvent
Dewaxing buffers containing a water-soluble organic solvent, methods for use thereof, and kits incorporating dewaxing buffers. The dewaxing buffers contain a water soluble organic solvent that has a boiling point of at least 80° C. The dewaxing buffers described herein can be used to quickly and efficiently remove embedding paraffin from slide-mounted tissue sections in an aqueous buffer solution at elevated temperature without fear of paraffin redeposition of the slides. In addition, the dewaxing buffers described herein can be used to perform dewaxing and HIER in a single step, which can substantially reduce protocol time and lower the risk of sample loss or damage.
Owner:RICHARD ALLAN SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com