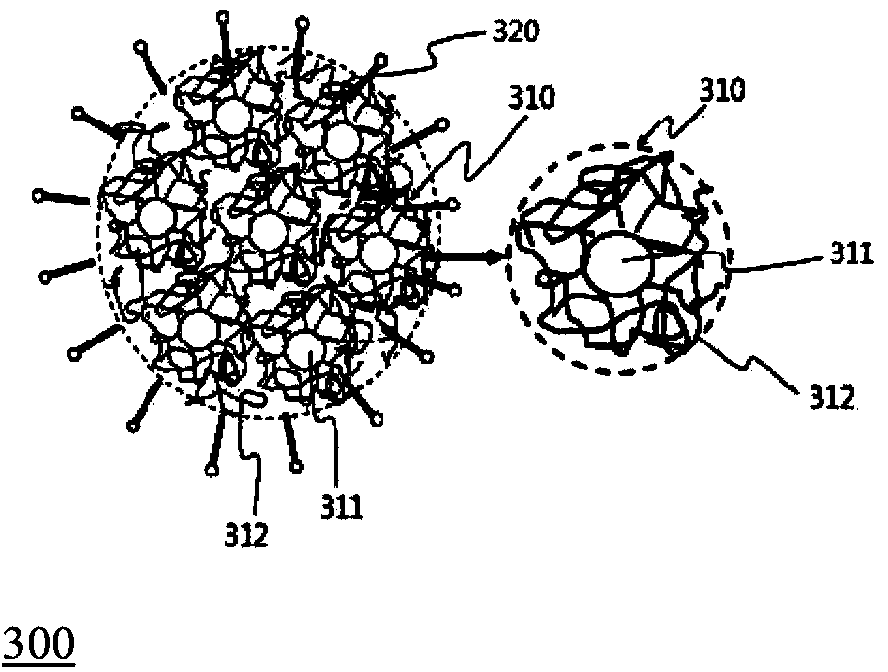
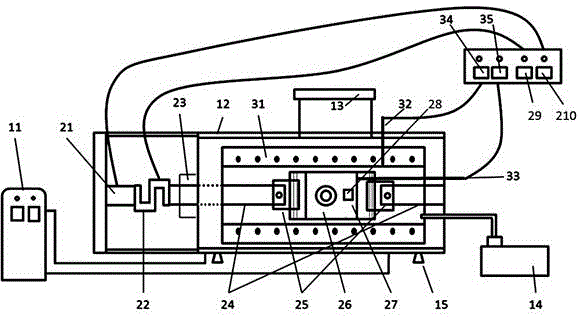
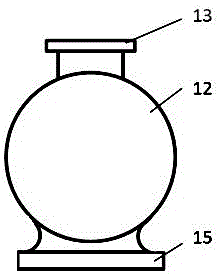
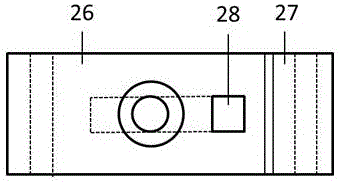
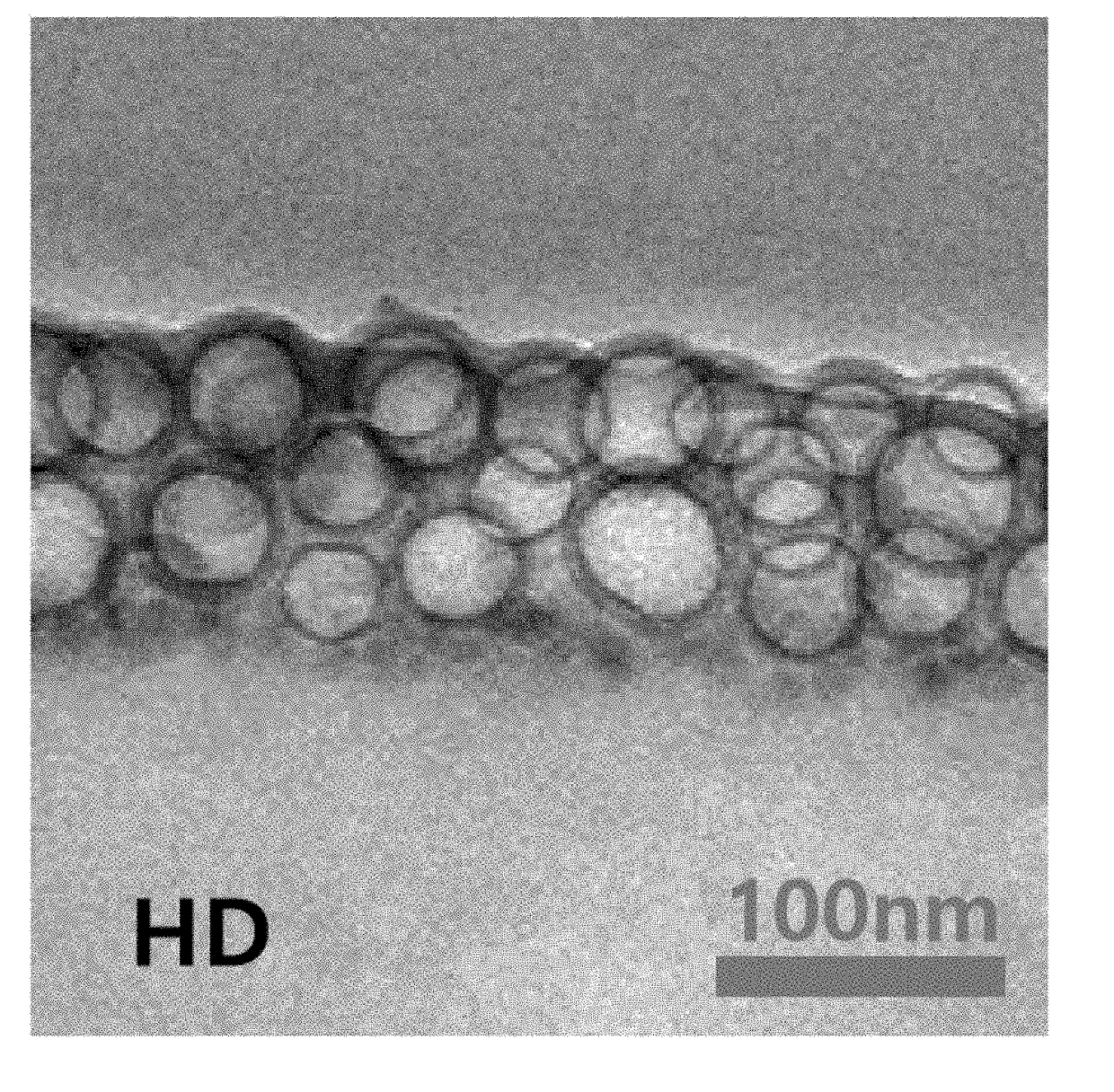
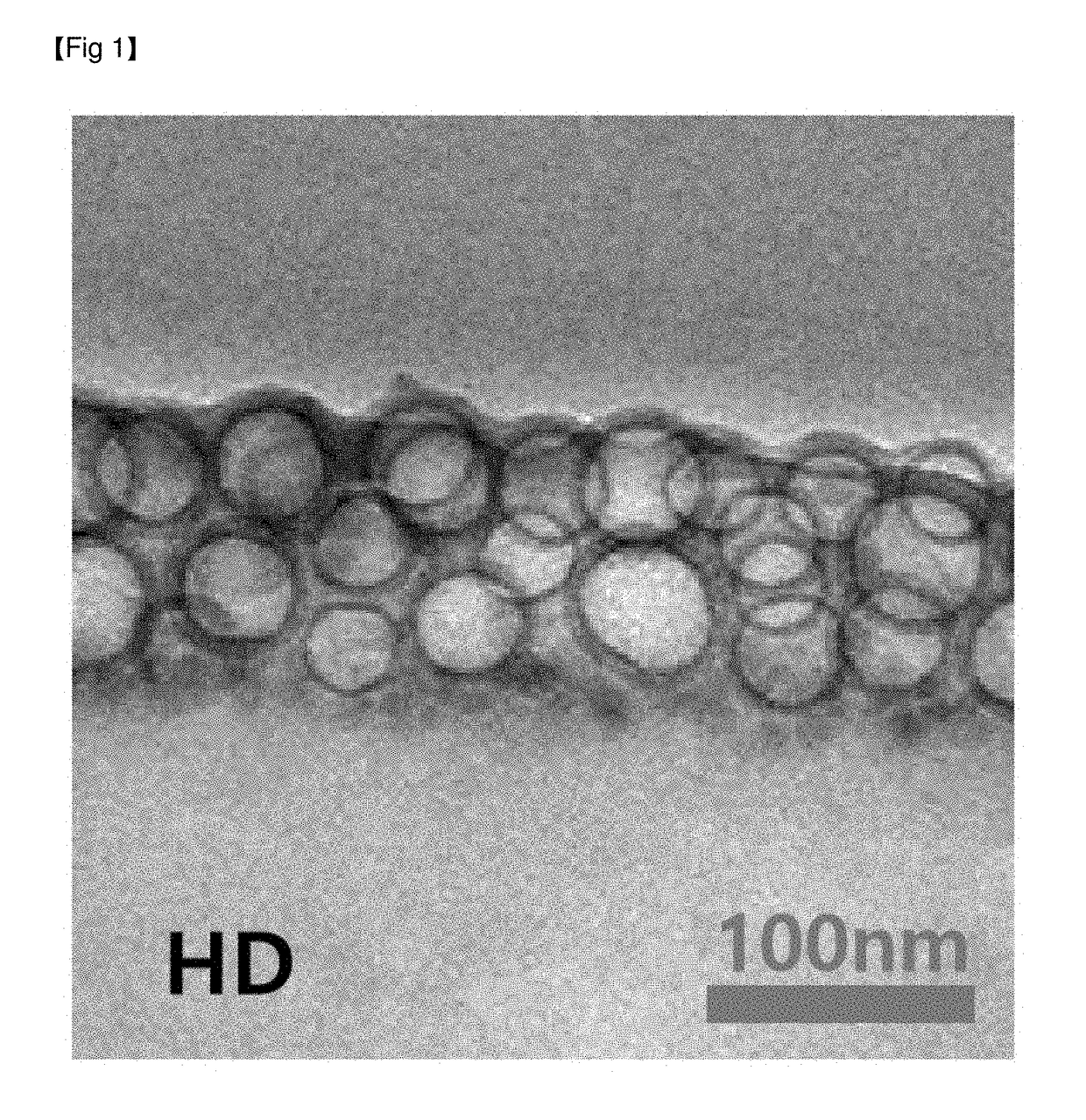
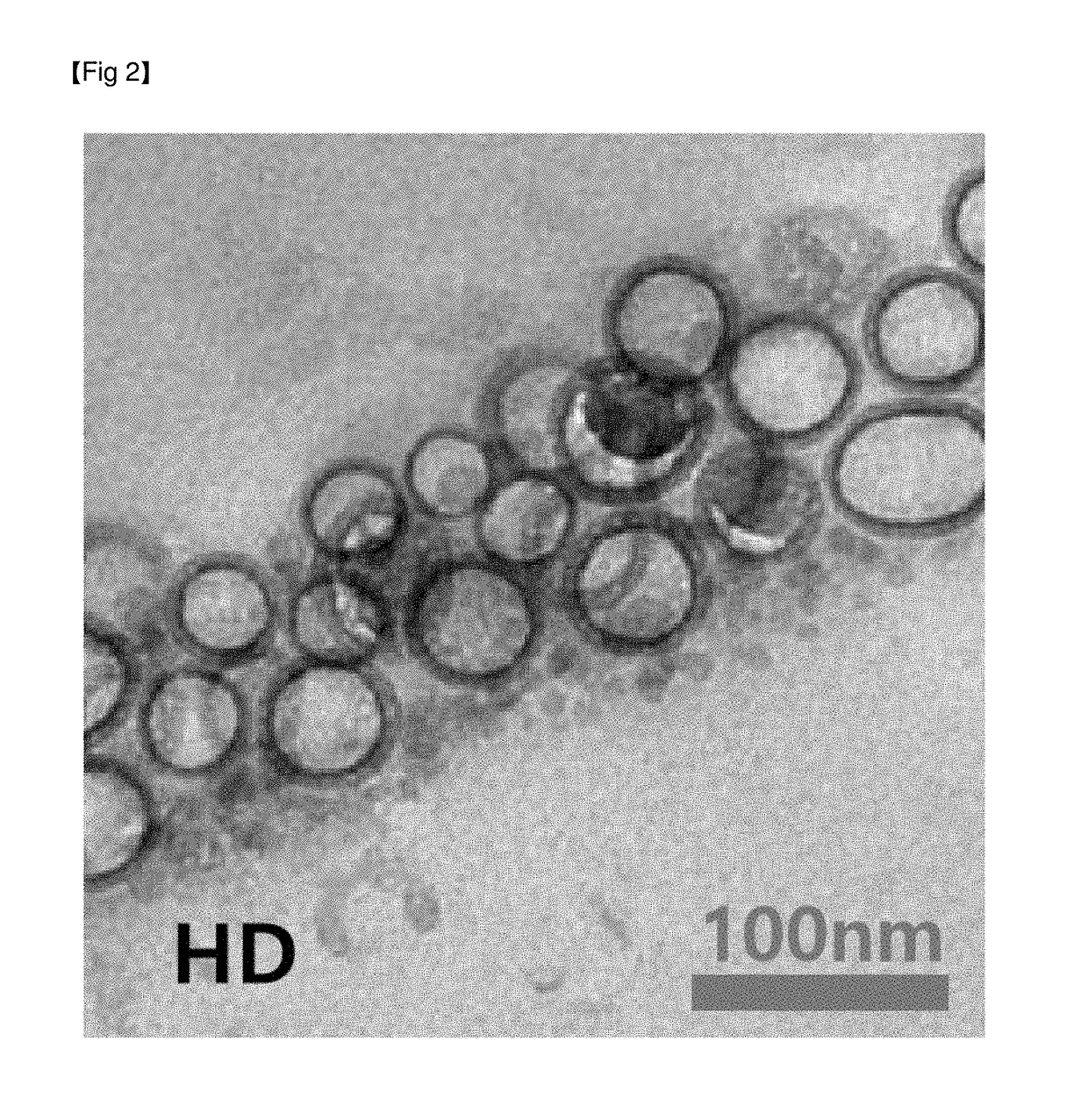
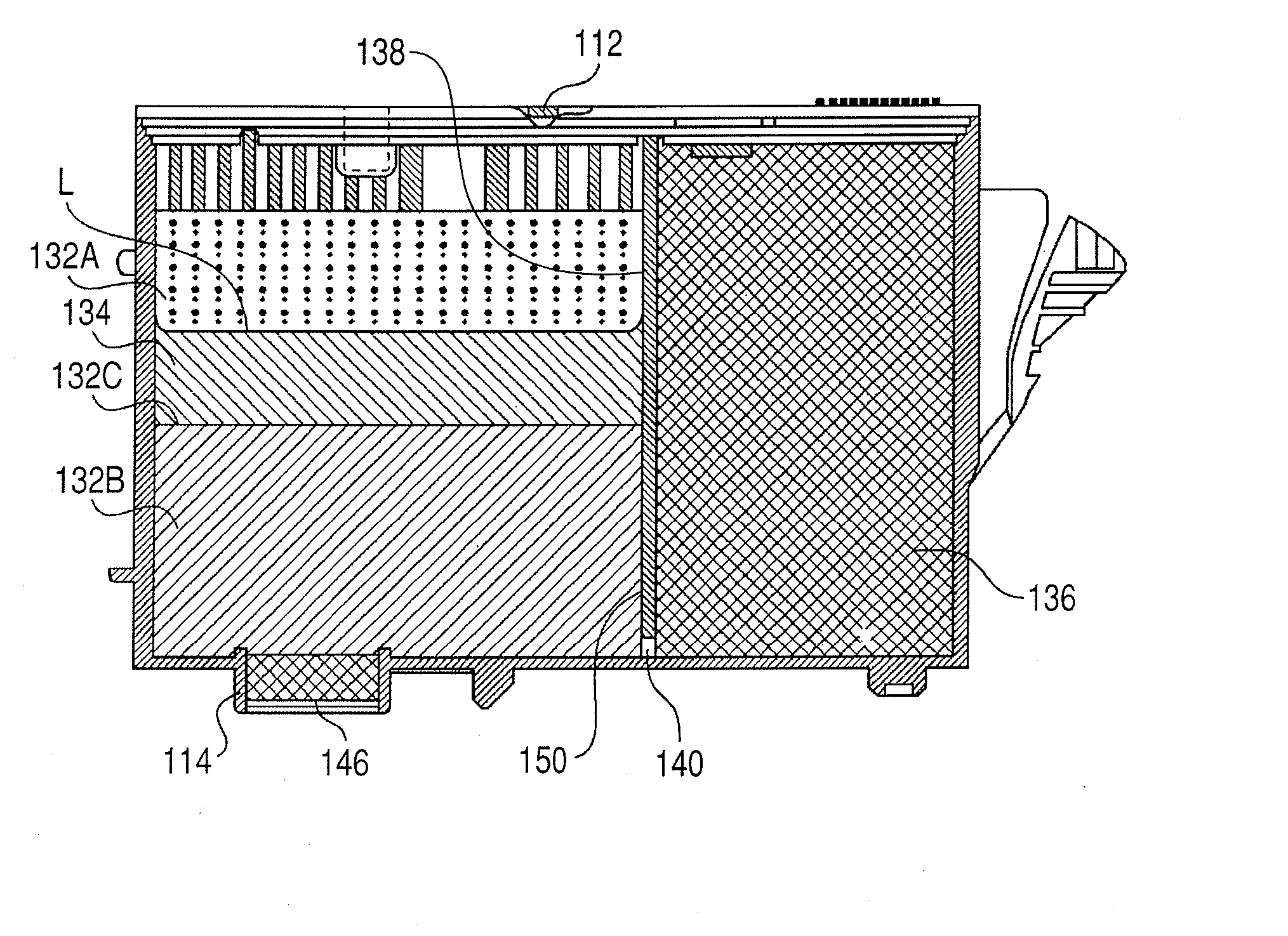
Patents
Literature
91 results about "Small-angle X-ray scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
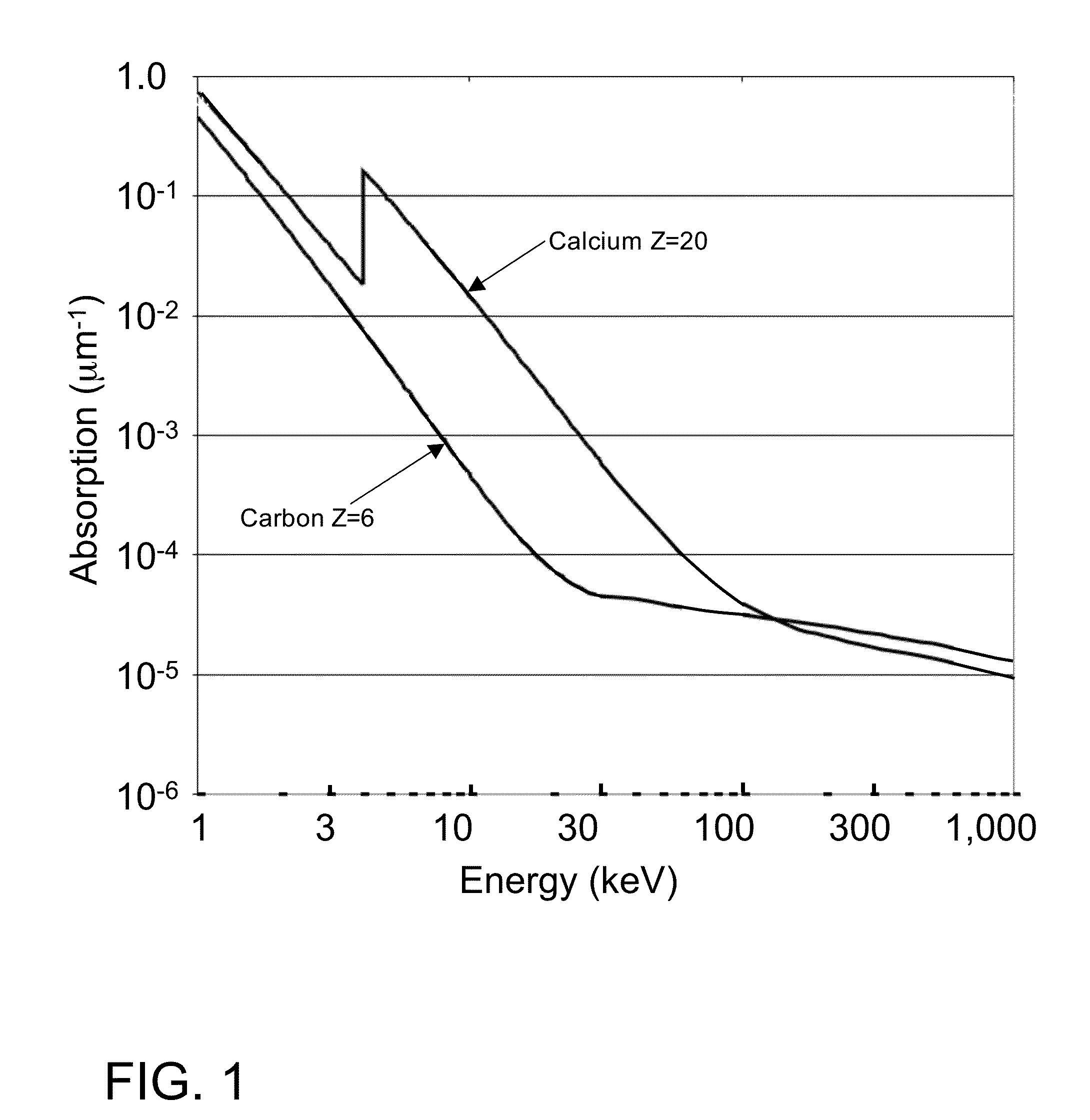
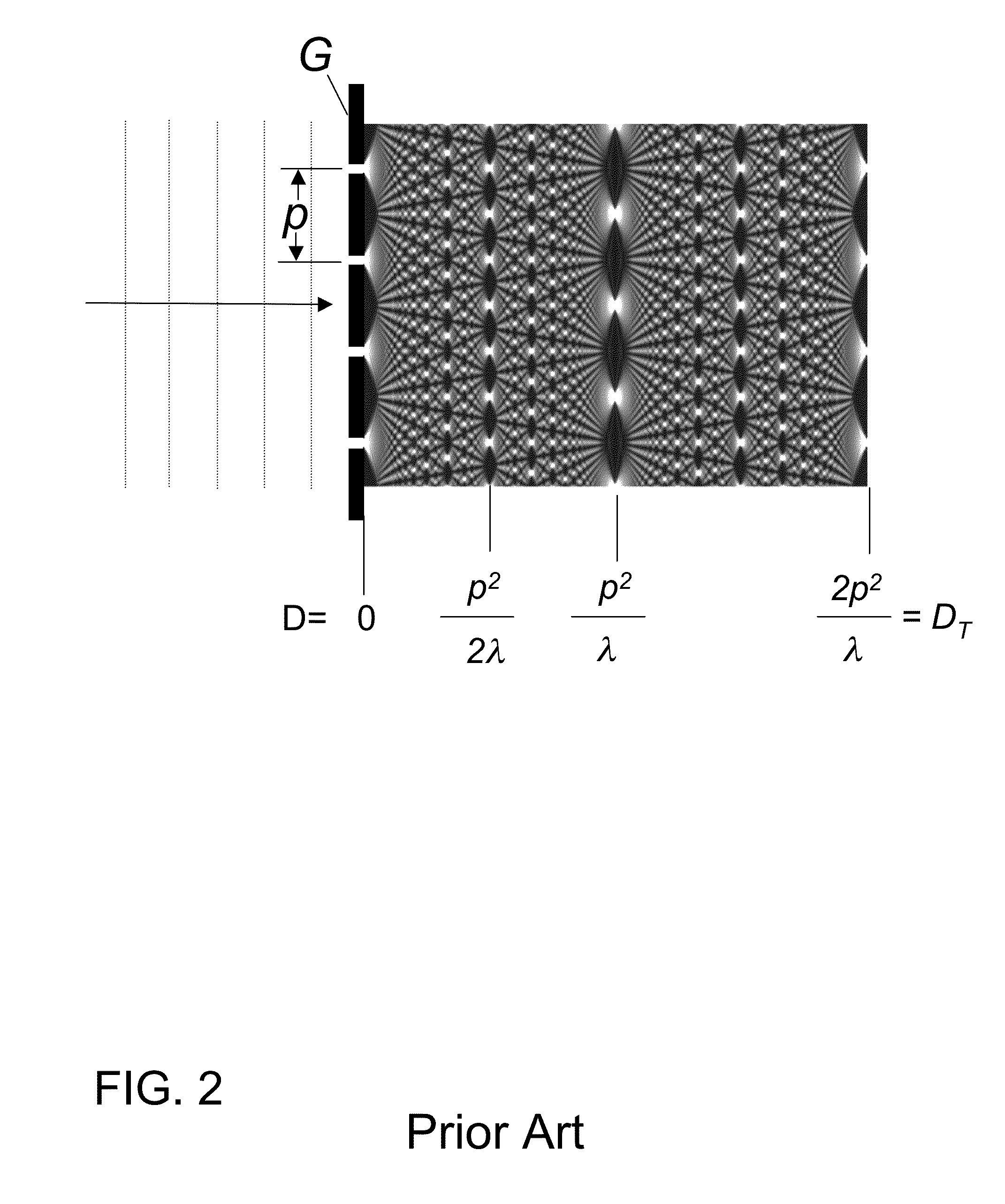
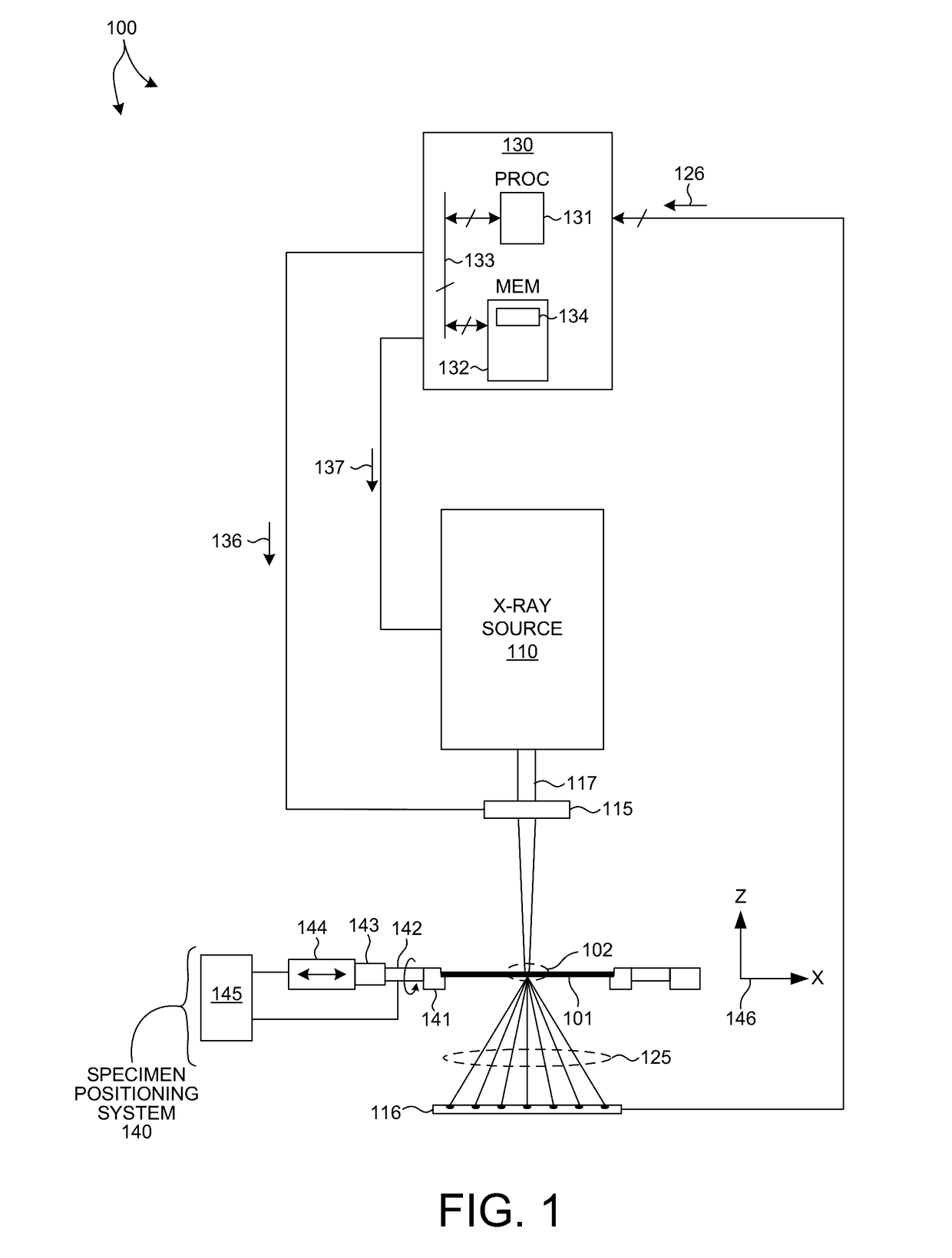
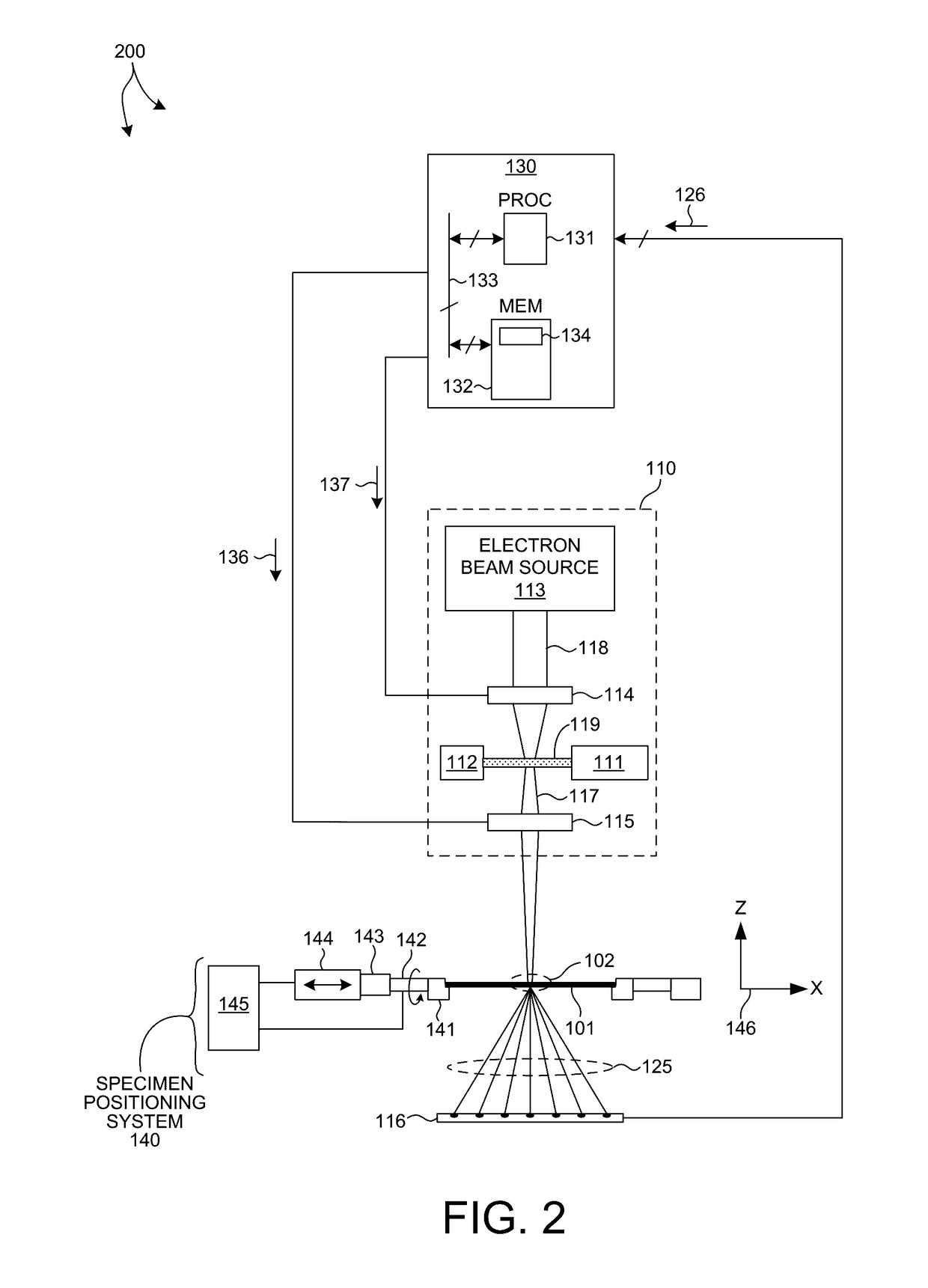
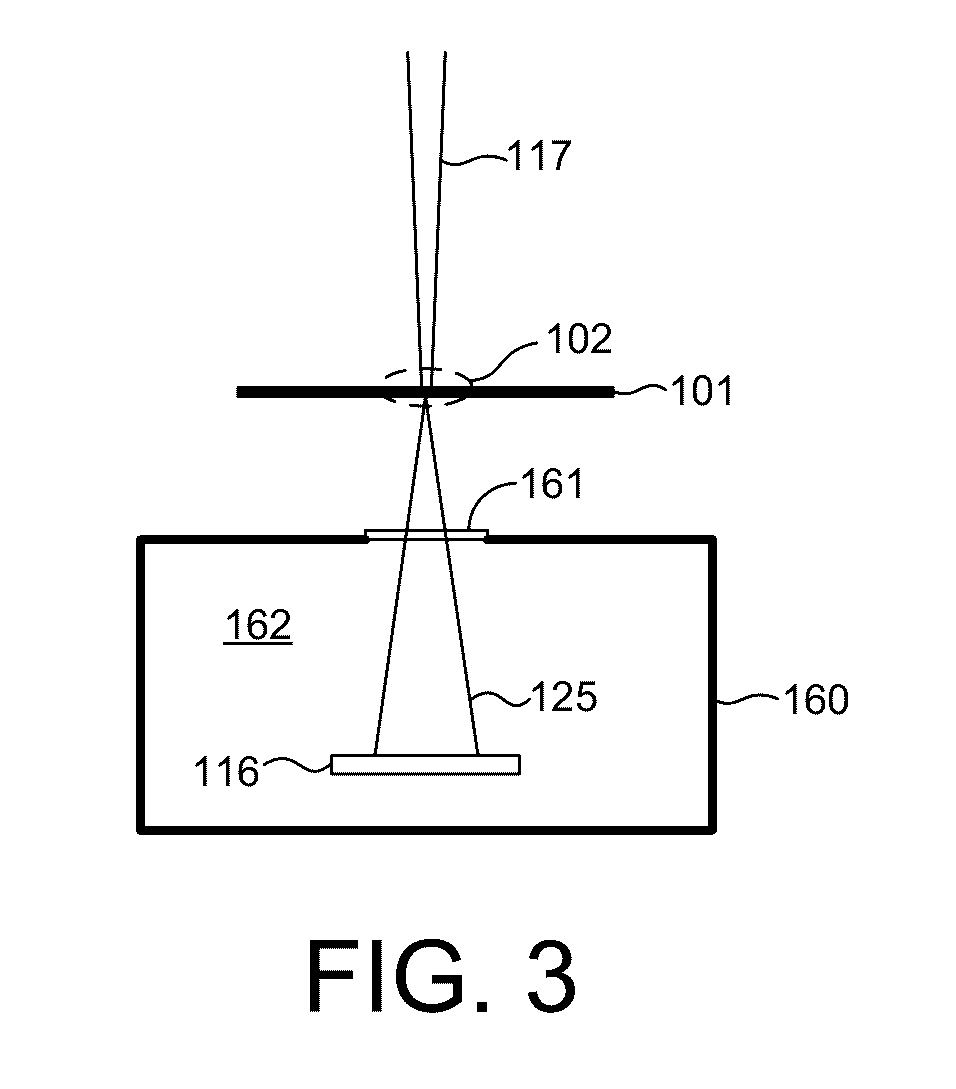
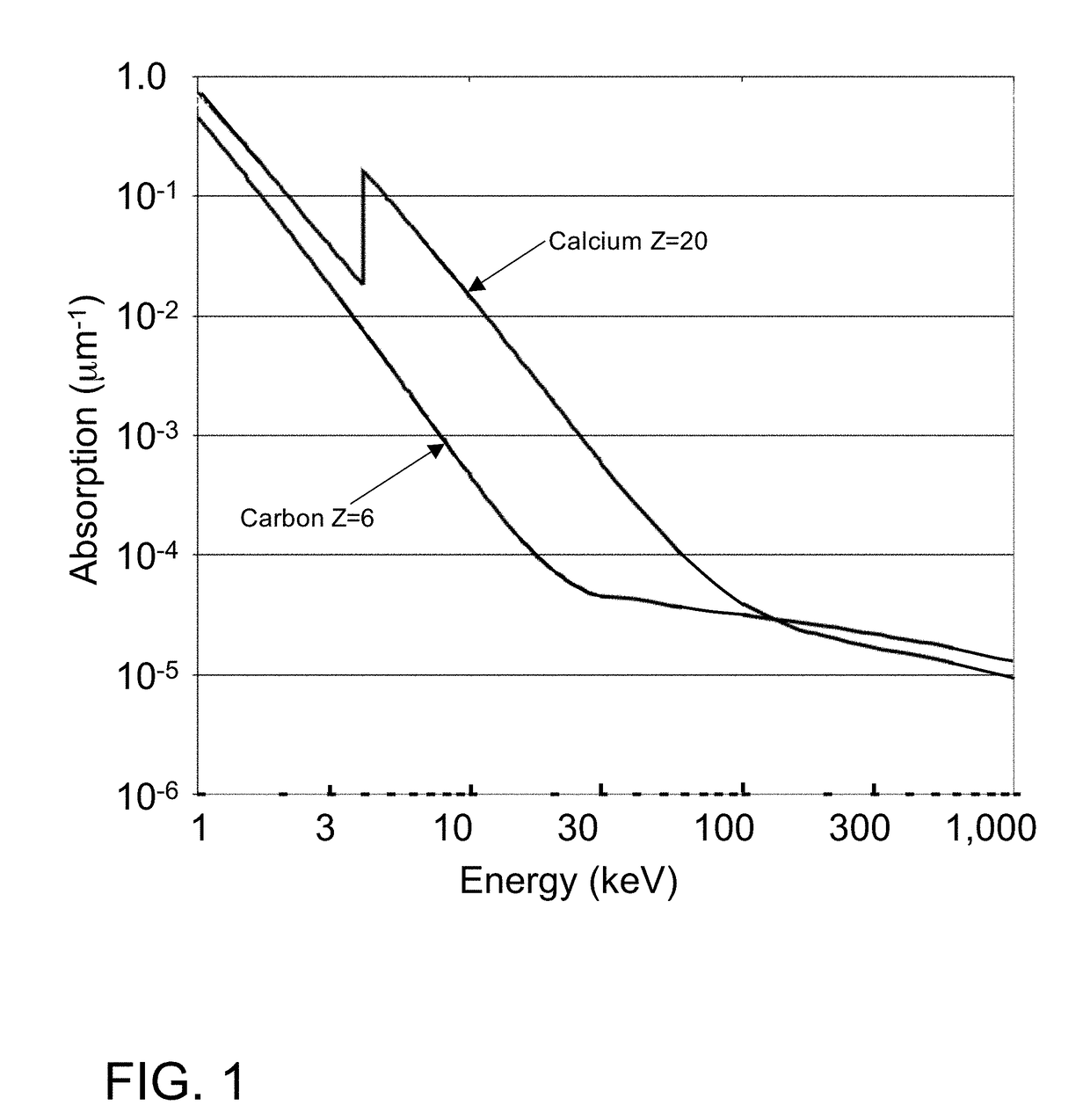
Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) is a small-angle scattering technique by which nanoscale density differences in a sample can be quantified. This means that it can determine nanoparticle size distributions, resolve the size and shape of (monodisperse) macromolecules, determine pore sizes, characteristic distances of partially ordered materials, and much more. This is achieved by analyzing the elastic scattering behaviour of X-rays when travelling through the material, recording their scattering at small angles (typically 0.1 - 10°, hence the "Small-angle" in its name). It belongs to the family of small-angle scattering (SAS) techniques along with small-angle neutron scattering, and is typically done using hard X-rays with a wavelength of 0.07 - 0.2 nm.. Depending on the angular range in which a clear scattering signal can be recorded, SAXS is capable of delivering structural information of dimensions between 1 and 100 nm, and of repeat distances in partially ordered systems of up to 150 nm. USAXS (ultra-small angle X-ray scattering) can resolve even larger dimensions, as the smaller the recorded angle, the larger the object dimensions that are probed.
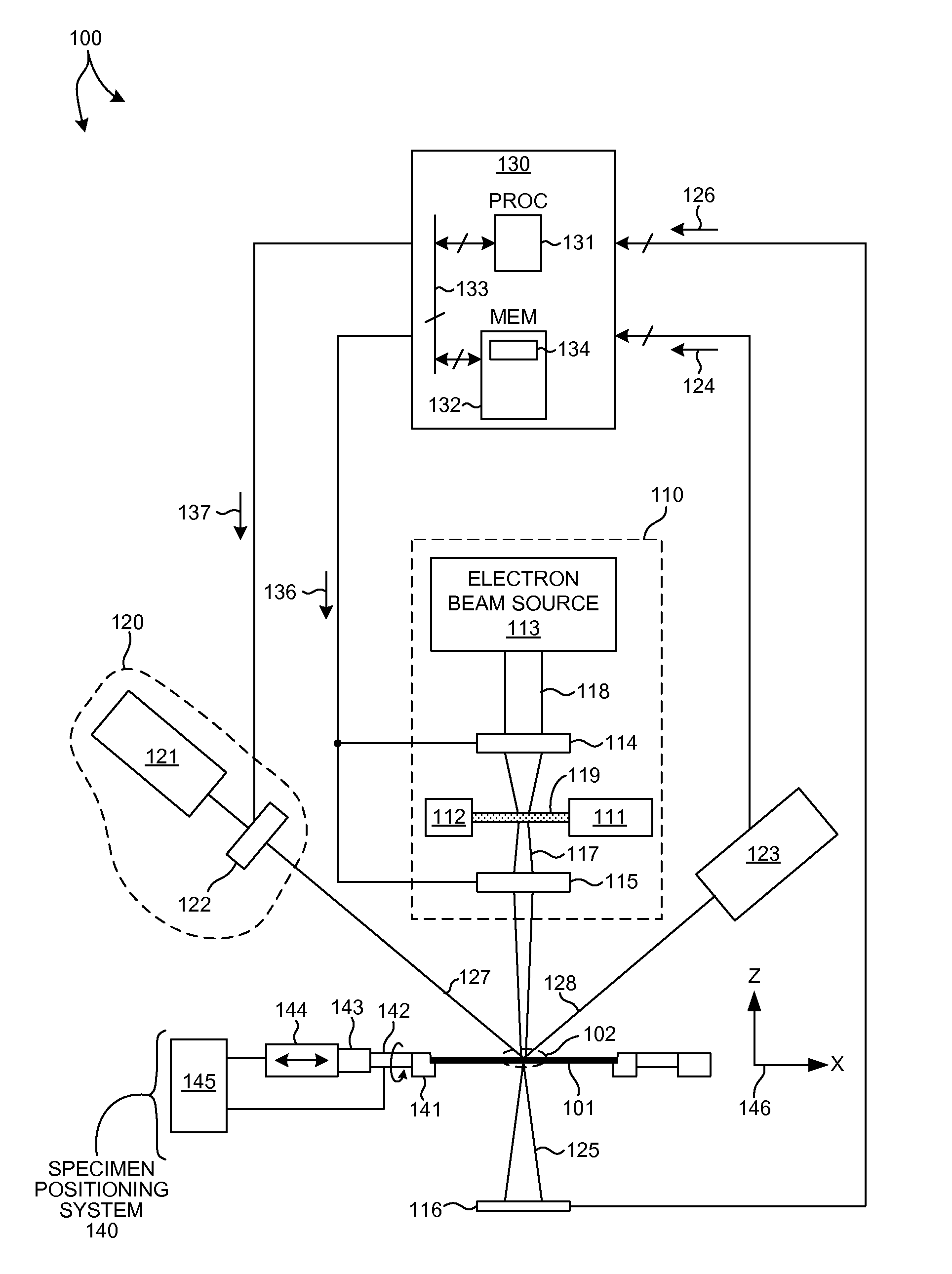
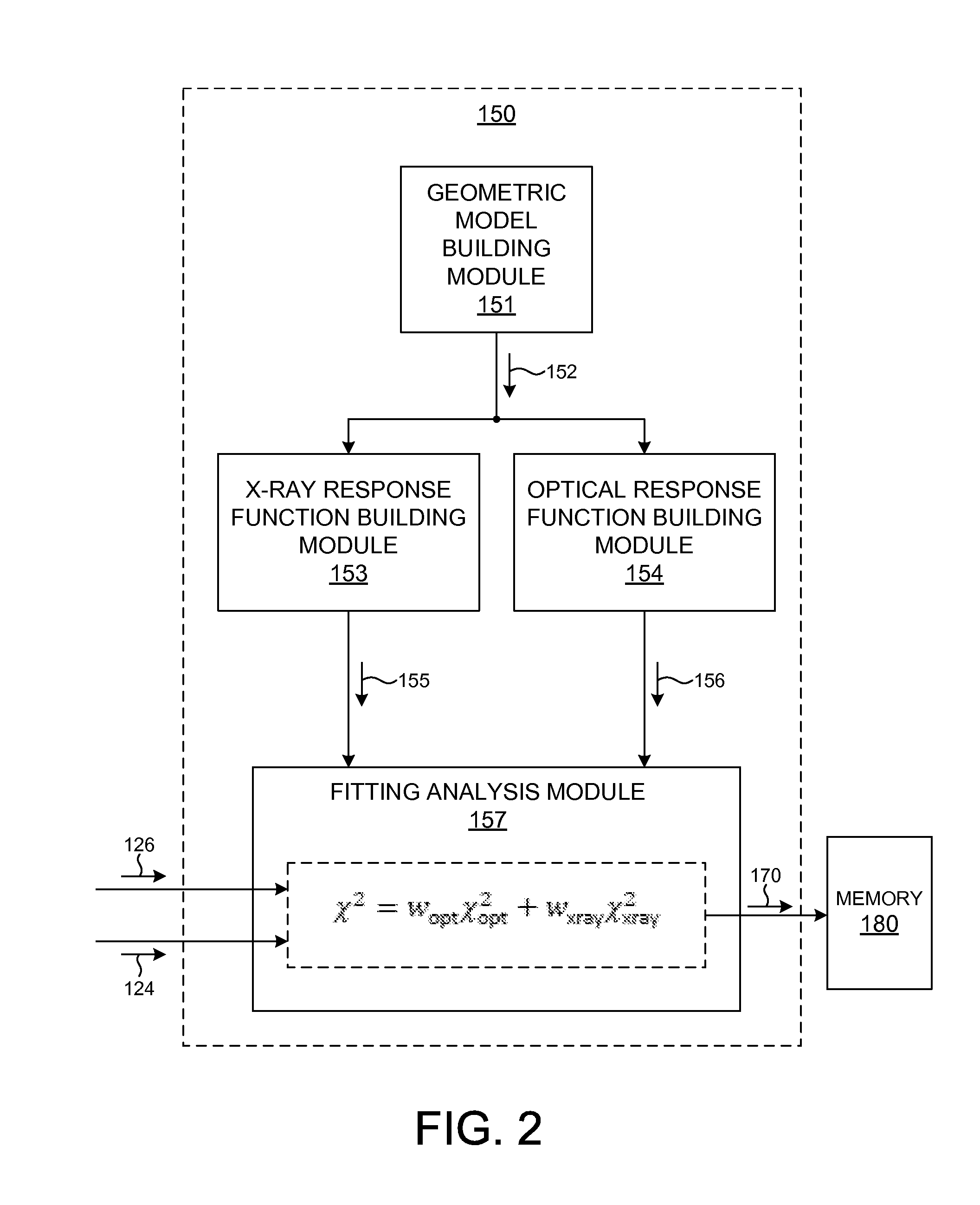
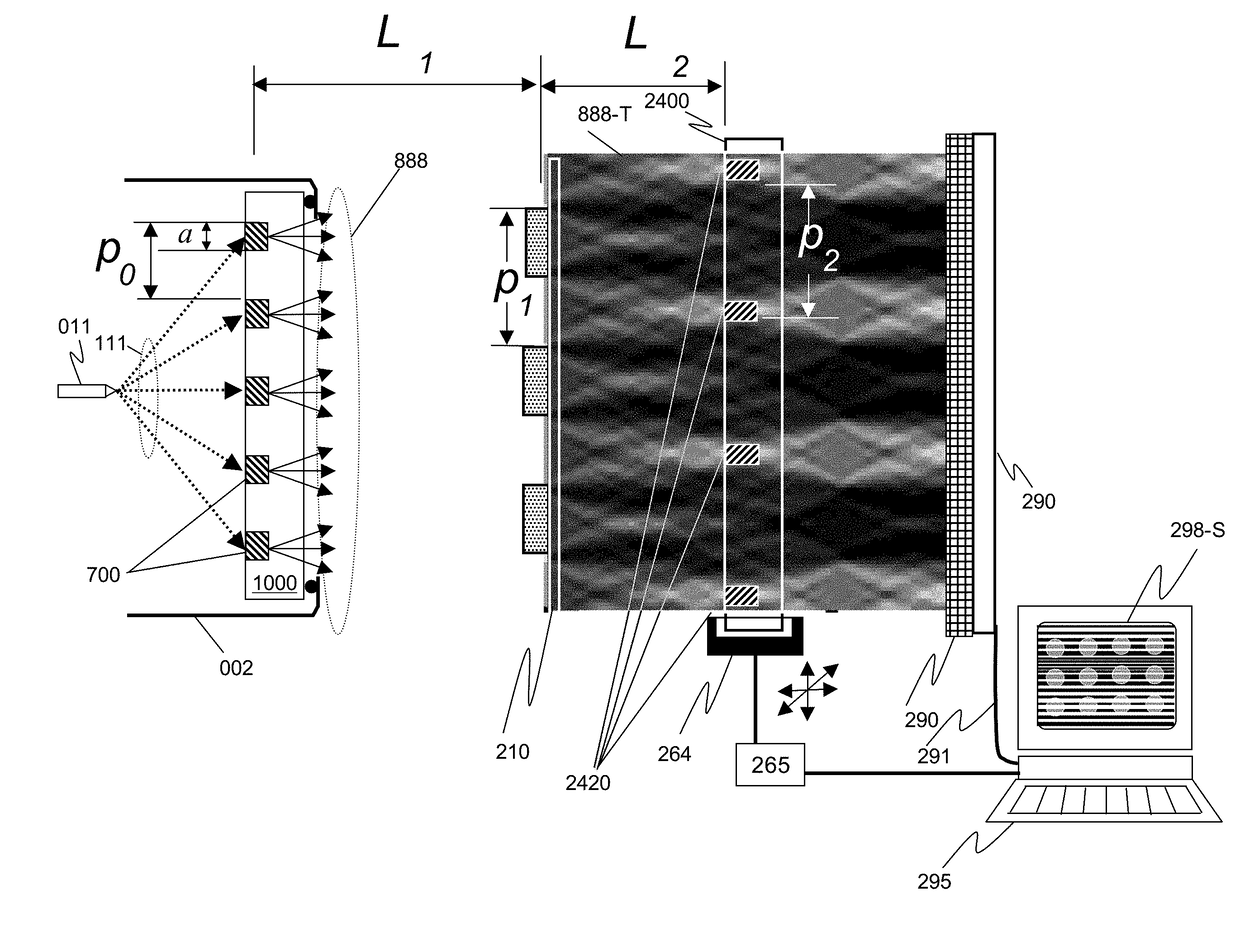
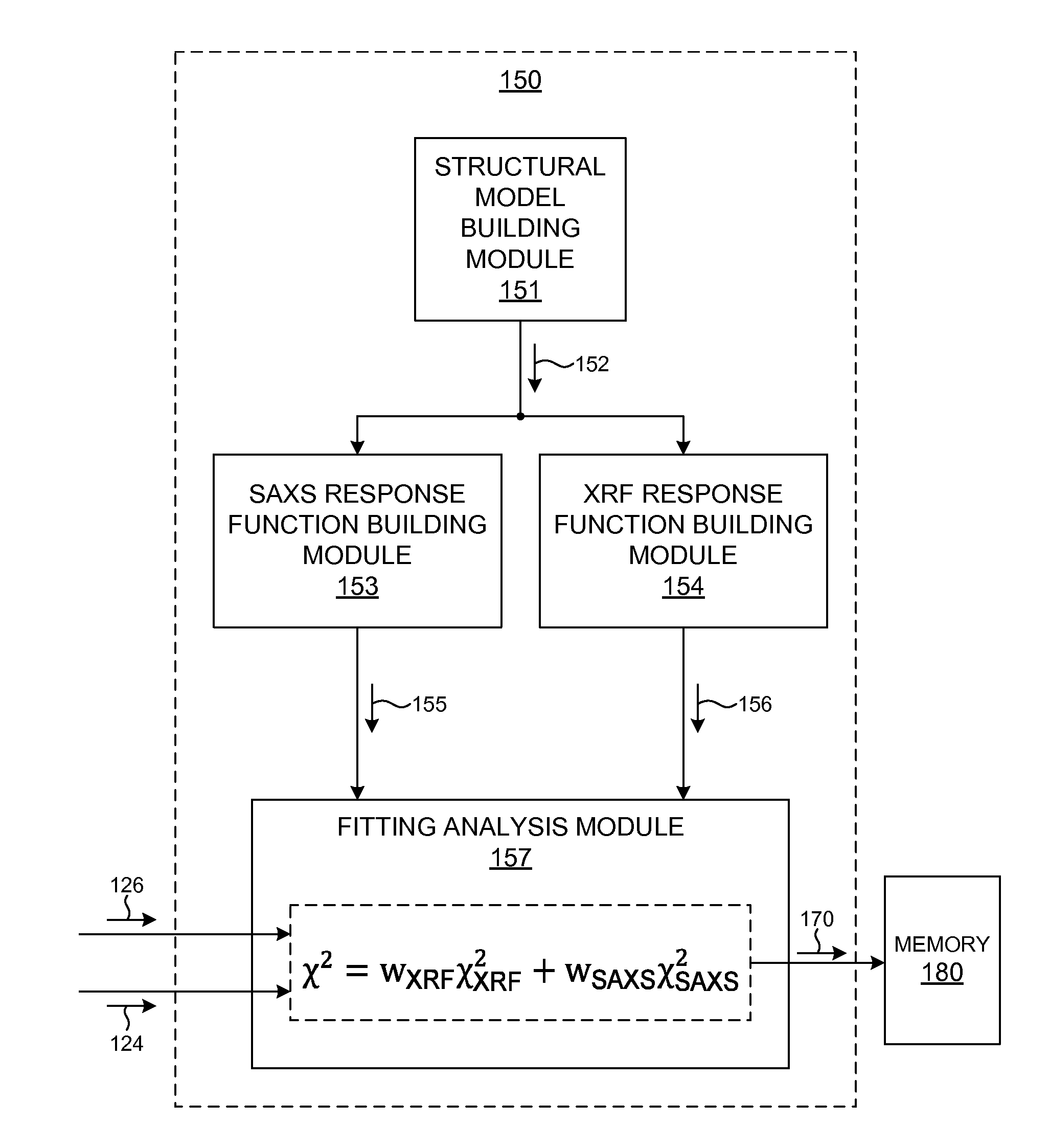
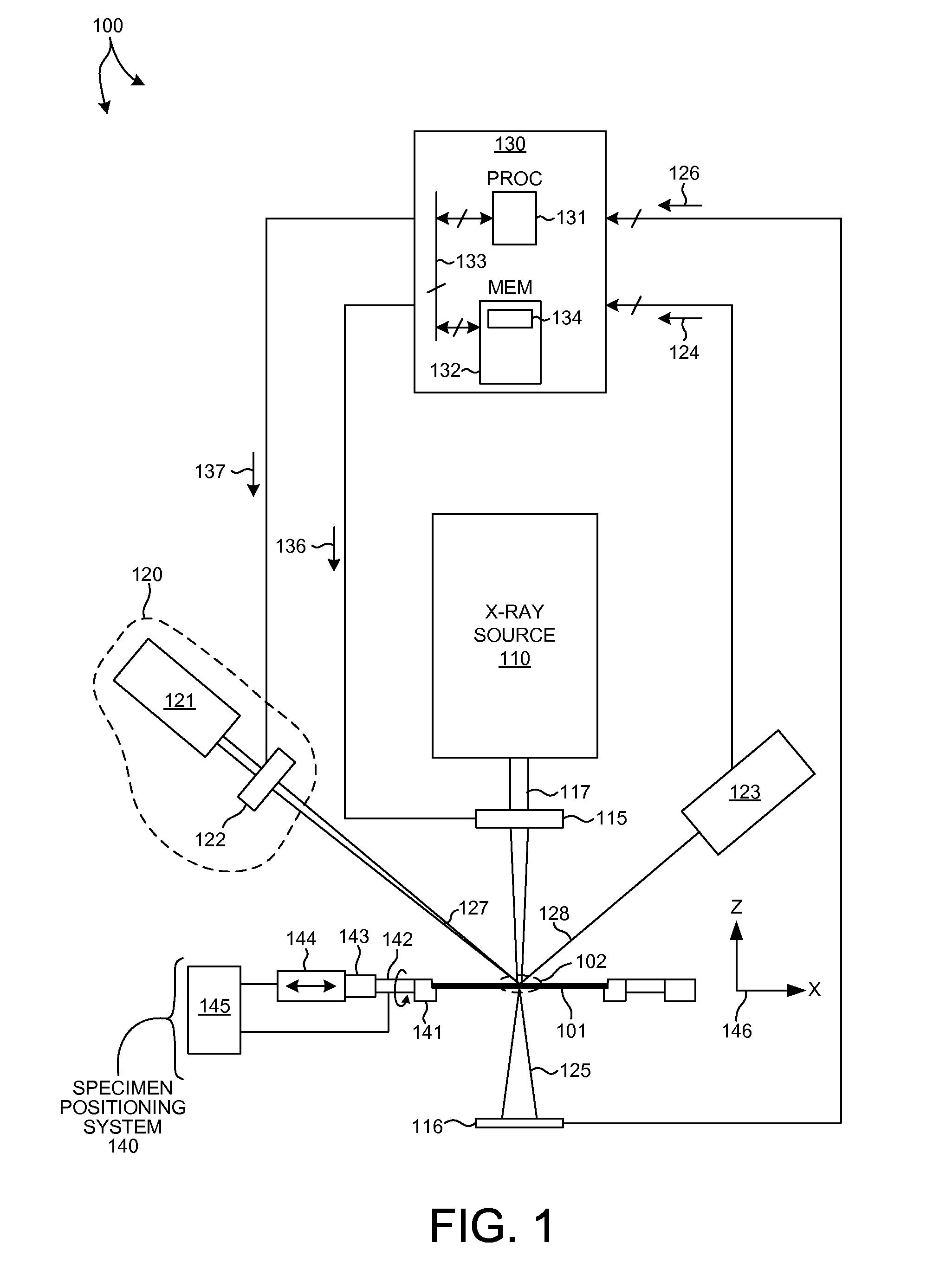
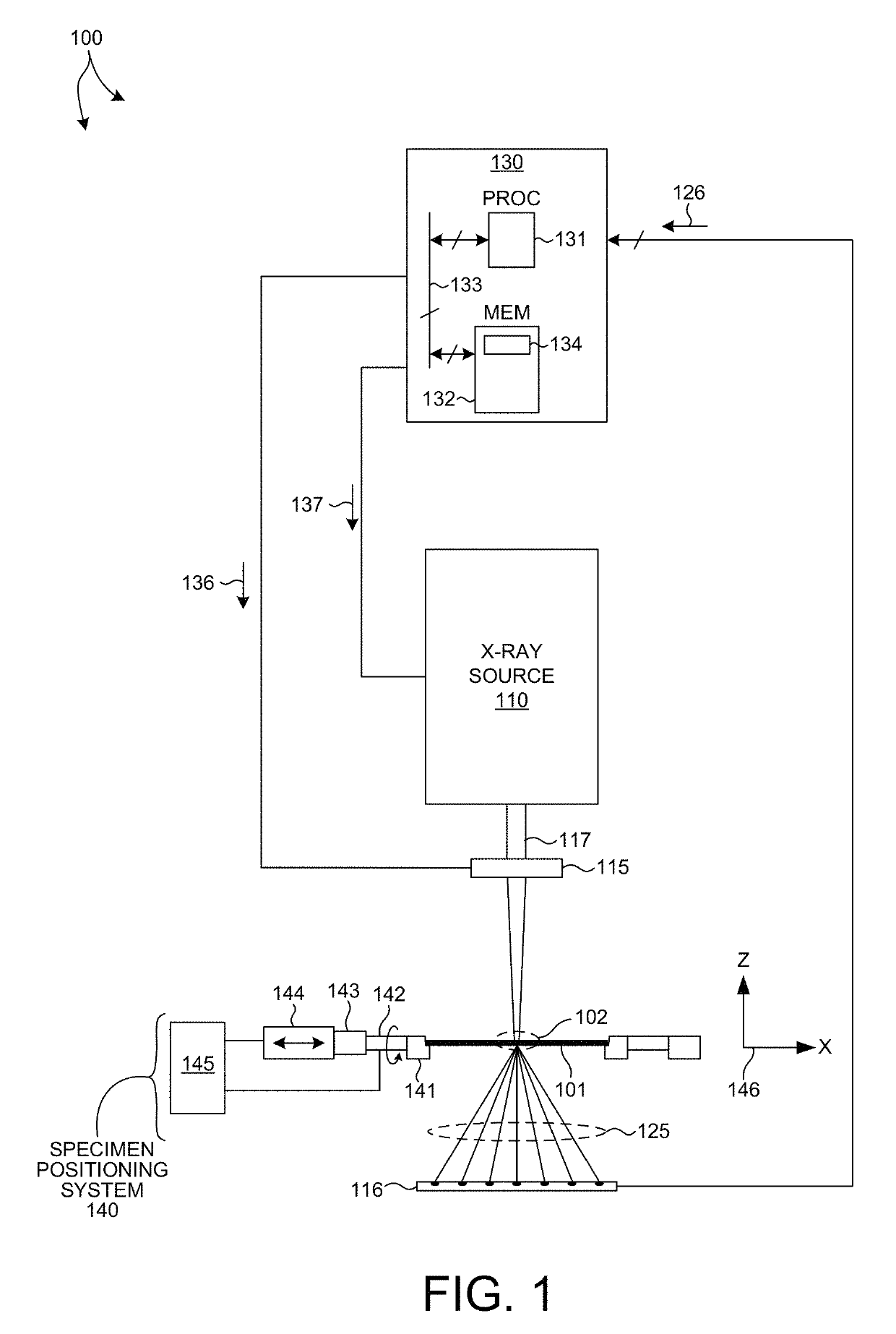
Metrology Tool With Combined X-Ray And Optical Scatterometers
ActiveUS20130304424A1Reduce correlationImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceData setMetrology
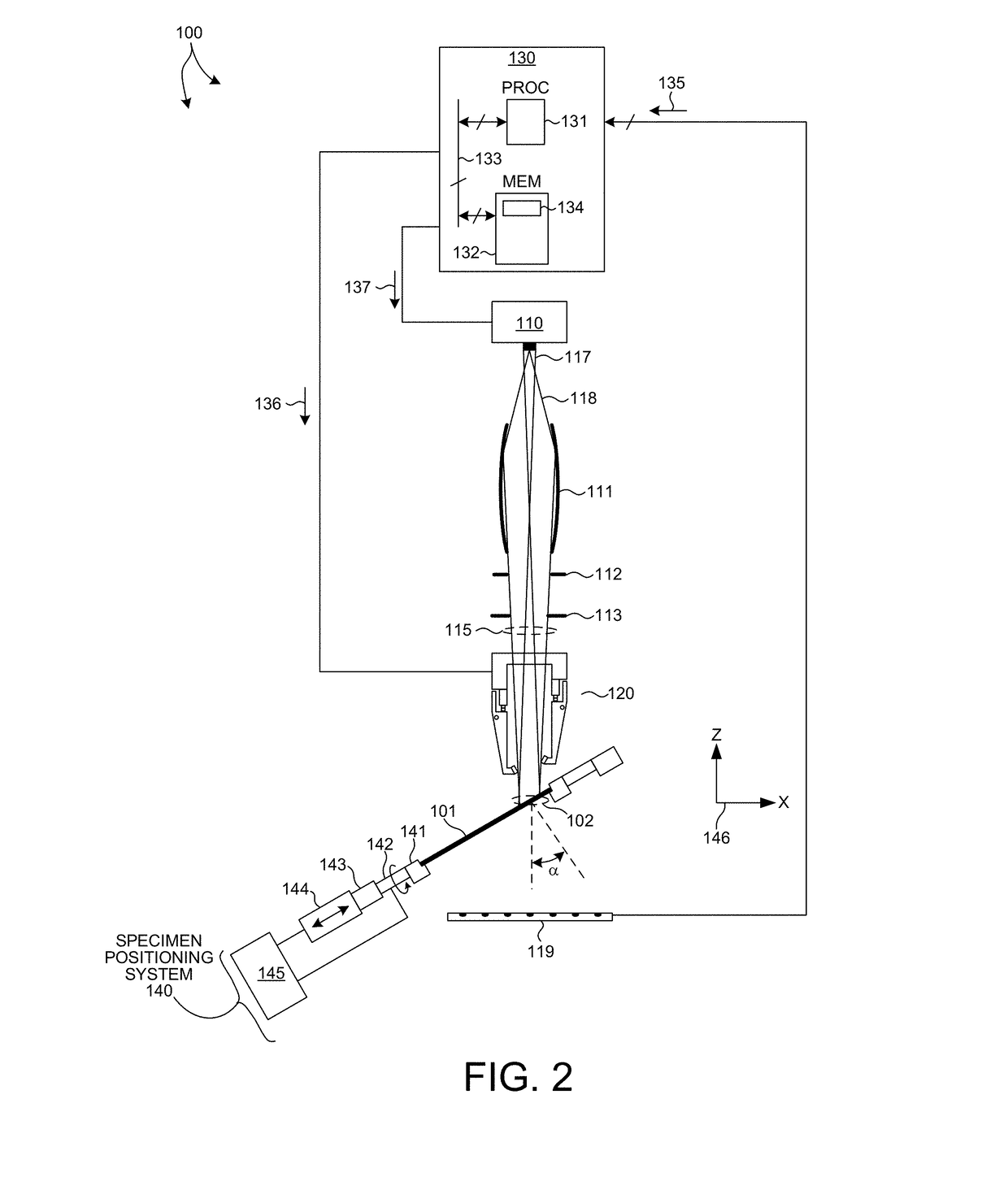
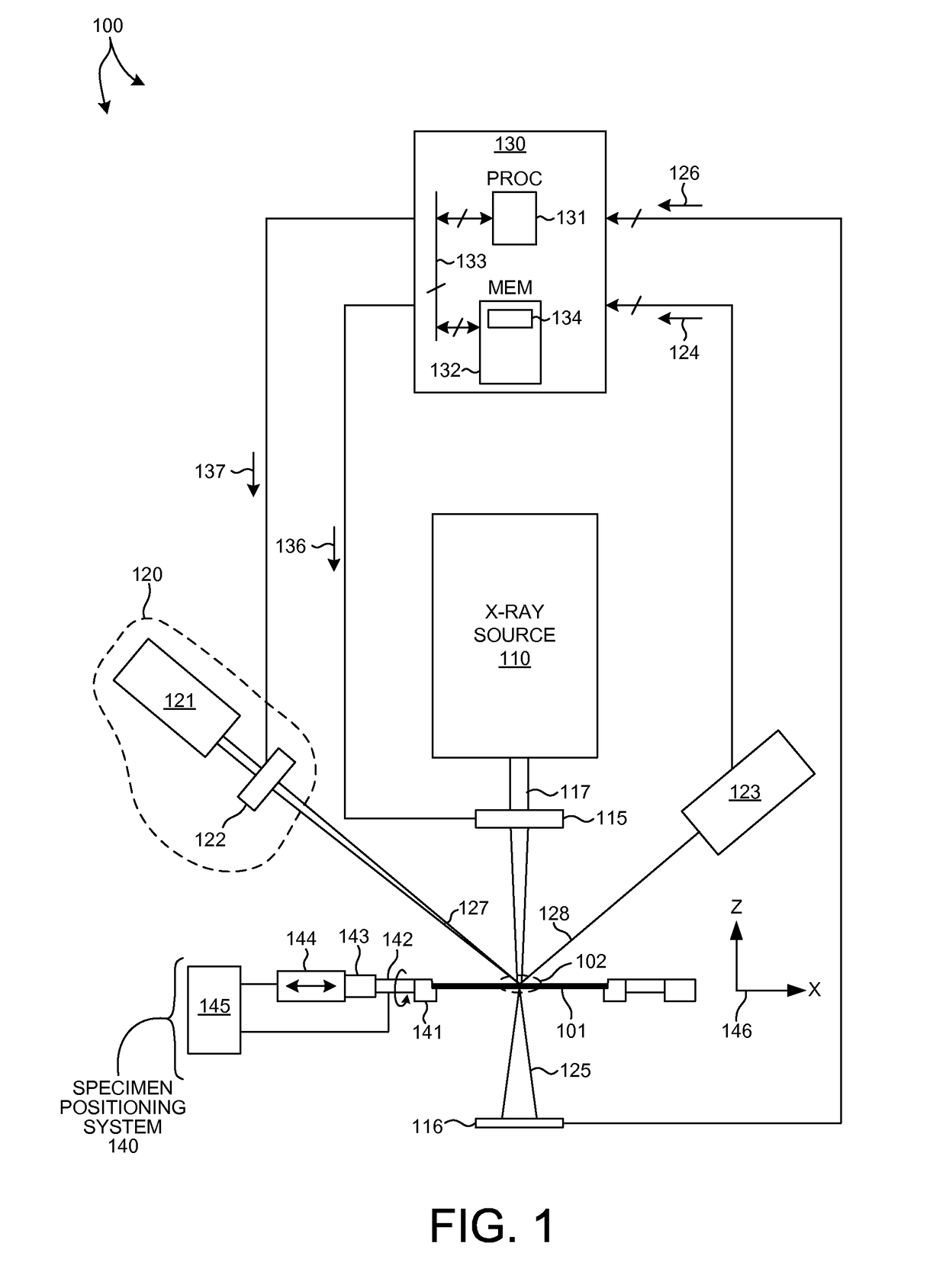
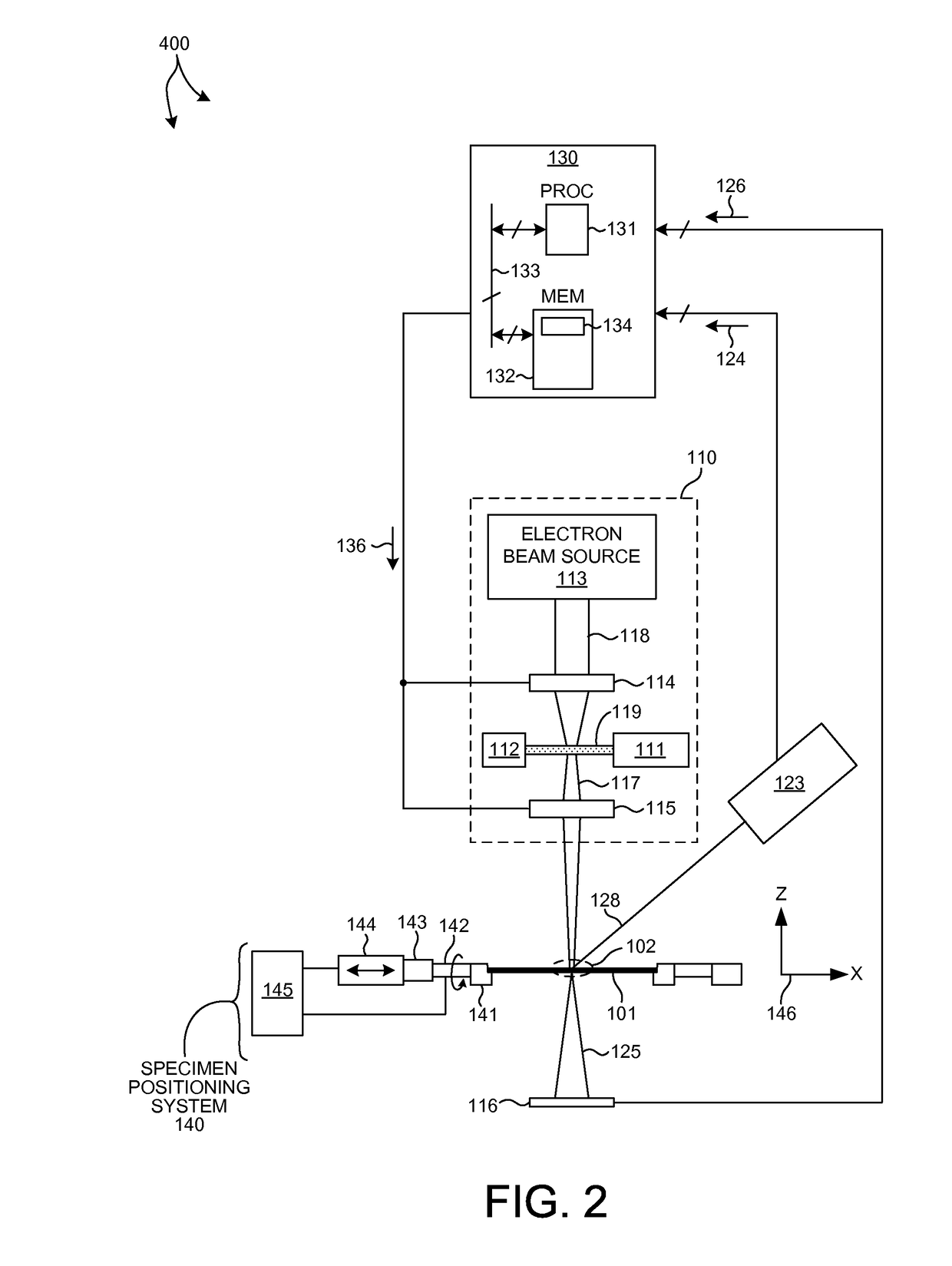
Methods and systems for performing simultaneous optical scattering and small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements over a desired inspection area of a specimen are presented. SAXS measurements combined with optical scatterometry measurements enables a high throughput metrology tool with increased measurement capabilities. The high energy nature of x-ray radiation penetrates optically opaque thin films, buried structures, high aspect ratio structures, and devices including many thin film layers. SAXS and optical scatterometry measurements of a particular location of a planar specimen are performed at a number of different out of plane orientations. This increases measurement sensitivity, reduces correlations among parameters, and improves measurement accuracy. In addition, specimen parameter values are resolved with greater accuracy by fitting data sets derived from both SAXS and optical scatterometry measurements based on models that share at least one geometric parameter. The fitting can be performed sequentially or in parallel.
Owner:KLA CORP
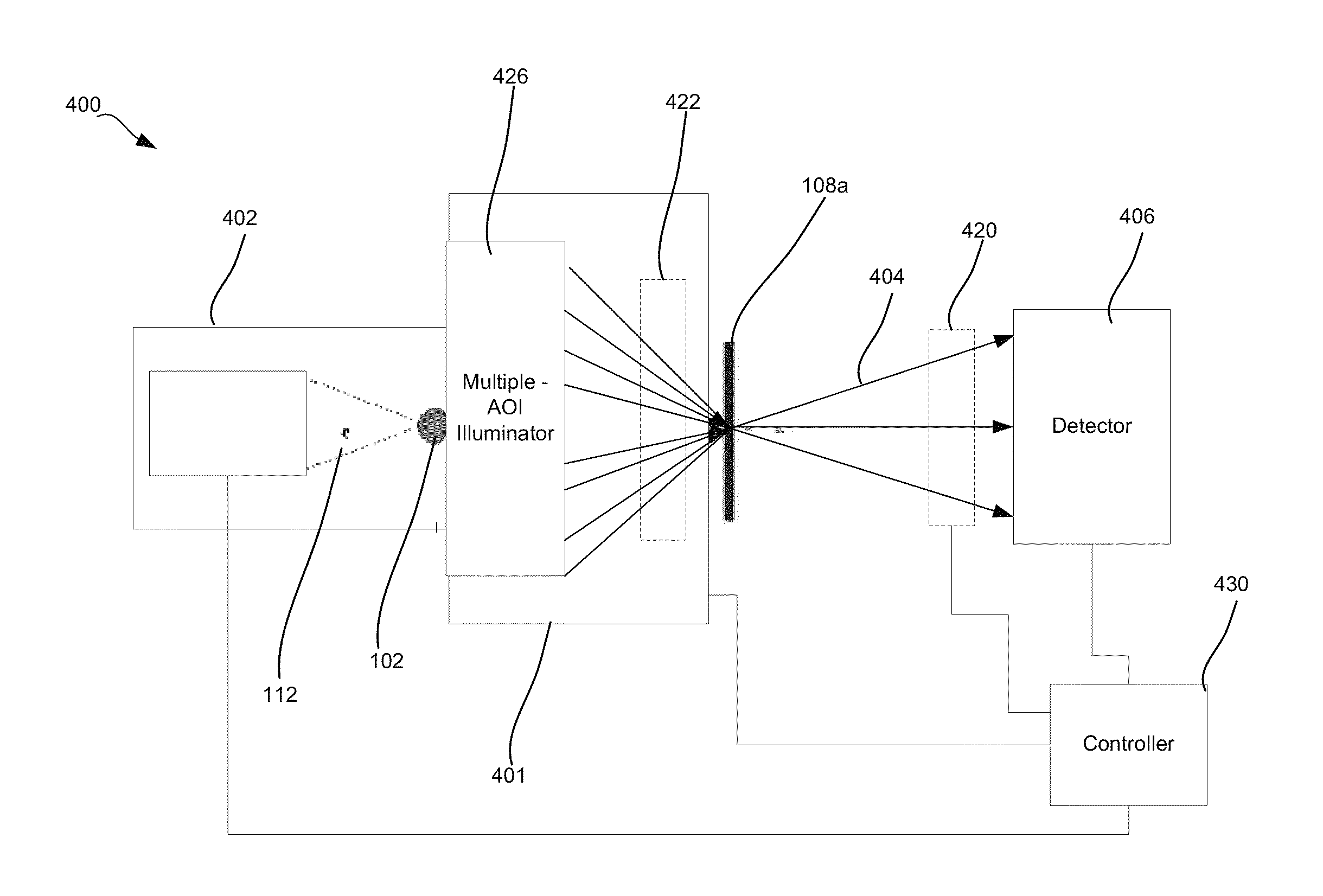
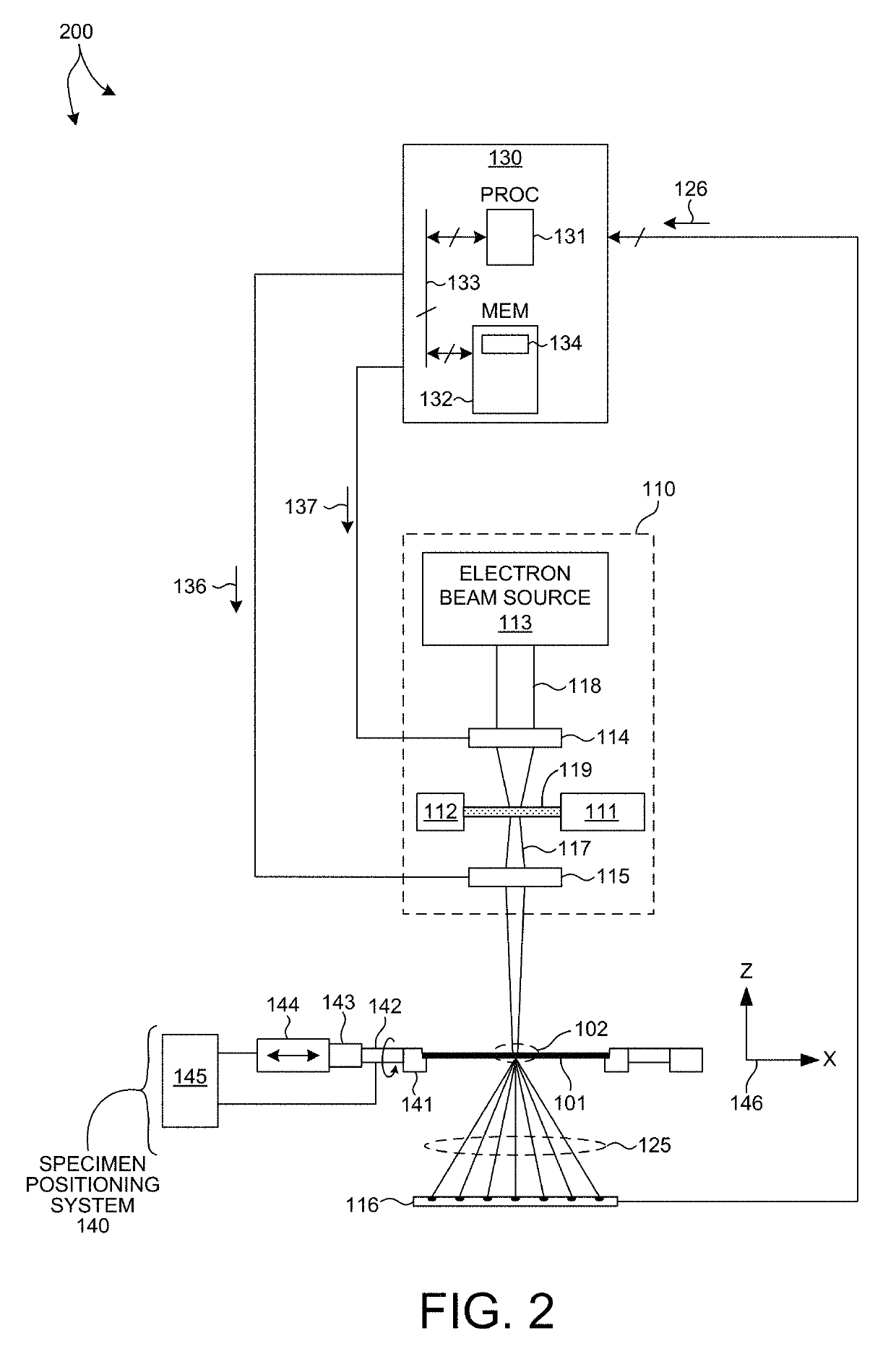
Small-angle scattering x-ray metrology systems and methods
ActiveUS20150110249A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationTesting semiconductor materialsSoft x rayMetrology
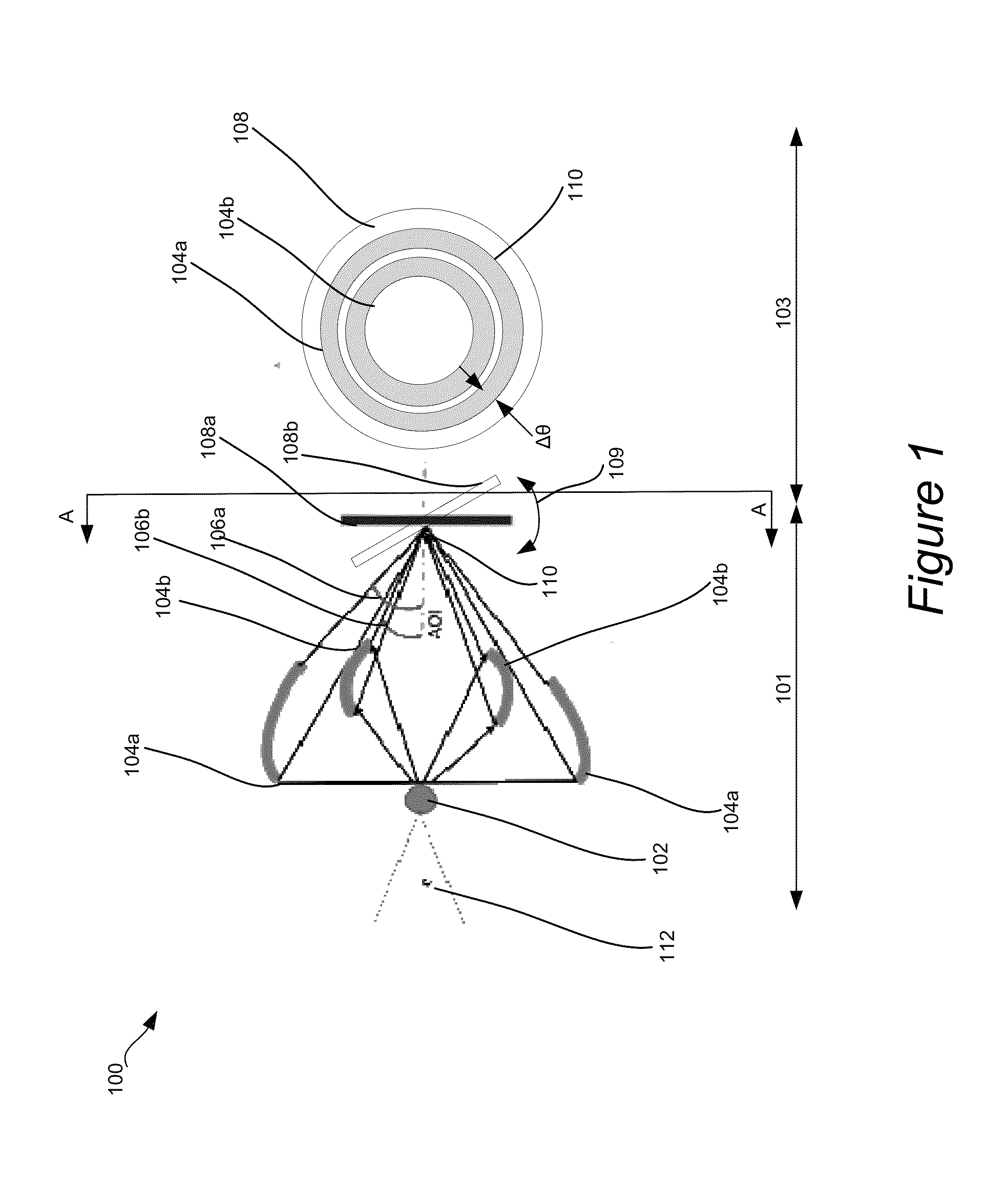
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for performing small angle x-ray scattering metrology. This system includes an x-ray source for generating x-rays and illumination optics for collecting and reflecting or refracting a portion of the generated x-rays towards a particular focus point on a semiconductor sample in the form of a plurality of incident beams at a plurality of different angles of incidence (AOIs). The system further includes a sensor for collecting output x-ray beams that are scattered from the sample in response to the incident beams on the sample at the different AOIs and a controller configured for controlling operation of the x-ray source and illumination optics and receiving the output x-rays beams and generating an image from such output x-rays.
Owner:KLA CORP
X-ray method for the measurement, characterization, and analysis of periodic structures
ActiveUS20150260663A1Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayGrating
Periodic spatial patterns of x-ray illumination are used to gather information about periodic objects. The structured illumination may be created using the interaction of a coherent or partially coherent x-ray source with a beam splitting grating to create a Talbot interference pattern with periodic structure. The object having periodic structures to be measured is then placed into the structured illumination, and the ensemble of signals from the multiple illumination spots is analyzed to determine various properties of the object and its structures. Applications to x-ray absorption / transmission, small angle x-ray scattering, x-ray fluorescence, x-ray reflectance, and x-ray diffraction are all possible using the method of the invention.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
X-Ray Scatterometry Metrology For High Aspect Ratio Structures
ActiveUS20170167862A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyStatic random-access memory
Methods and systems for characterizing dimensions and material properties of high aspect ratio, vertically manufactured devices using transmission, small-angle x-ray scattering (T-SAXS) techniques are described herein. Exemplary structures include spin transfer torque random access memory (STT-RAM), vertical NAND memory (V-NAND), dynamic random access memory (DRAM), three dimensional FLASH memory (3D-FLASH), resistive random access memory (Re-RAM), and PC-RAM. In one aspect, T-SAXS measurements are performed at a number of different orientations that are more densely concentrated near the normal incidence angle and less densely concentrated at orientations that are further from the normal incidence angle. In a further aspect, T-SAXS measurement data is used to generate an image of a measured structure based on the measured intensities of the detected diffraction orders. In another further aspect, a metrology system is configured to generate models for combined x-ray and optical measurement analysis.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
X-ray method for the measurement, characterization, and analysis of periodic structures
ActiveUS9874531B2Lightweight productionIncrease brightnessImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesSoft x rayGrating
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Metrology Tool With Combined XRF And SAXS Capabilities
ActiveUS20150051877A1Reduce correlationHigh measurement accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementMetrologyData set
Methods and systems for performing simultaneous X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) and small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements over a desired inspection area of a specimen are presented. SAXS measurements combined with XRF measurements enables a high throughput metrology tool with increased measurement capabilities. The high energy nature of x-ray radiation penetrates optically opaque thin films, buried structures, high aspect ratio structures, and devices including many thin film layers. SAXS measurements of a particular location of a planar specimen are performed at a number of different out of plane orientations. This increases measurement sensitivity, reduces correlations among parameters, and improves measurement accuracy. In addition, specimen parameter values are resolved with greater accuracy by fitting data sets derived from both SAXS and XRF measurements based on models that share at least one material parameter. The fitting can be performed sequentially or in parallel.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
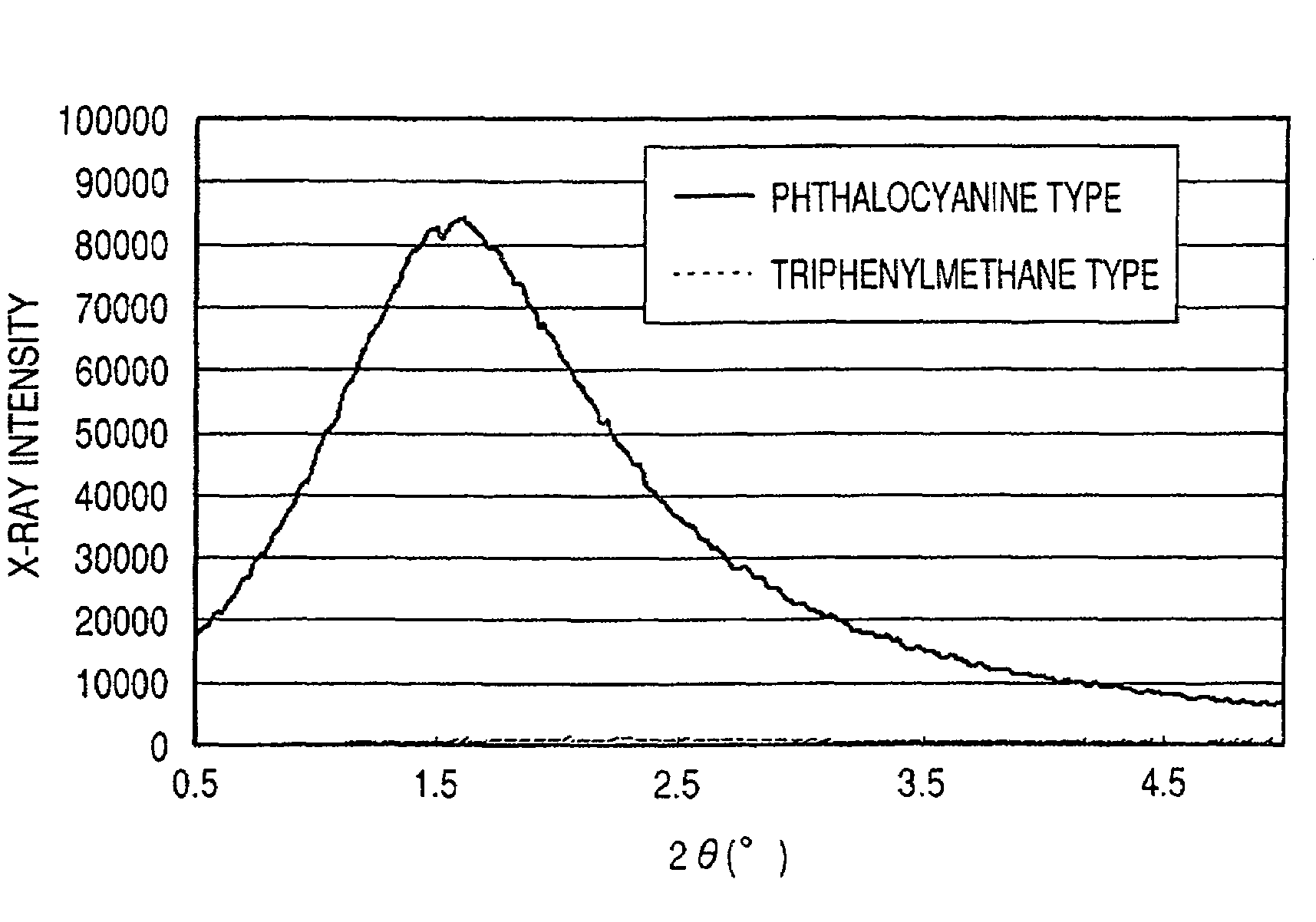
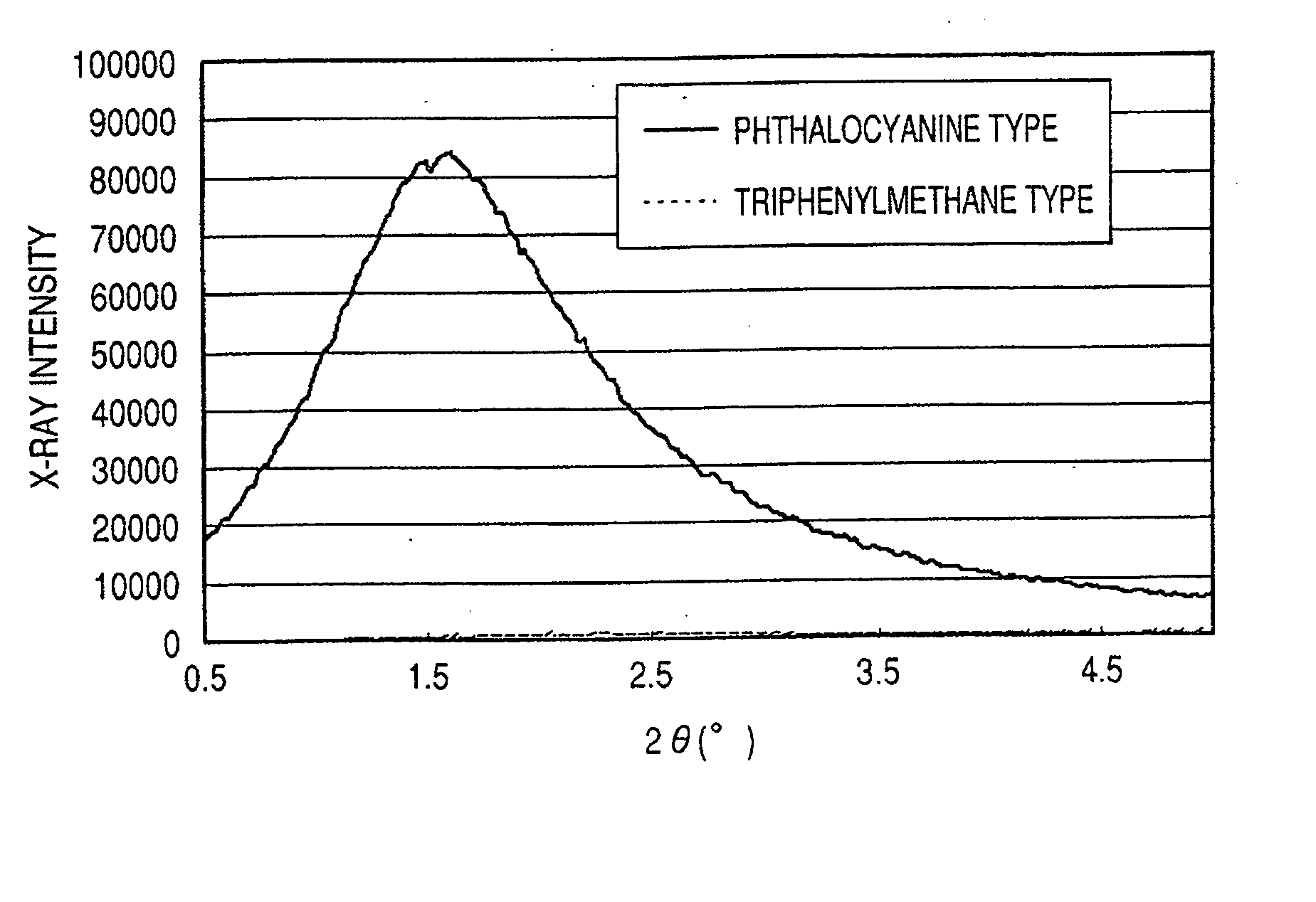
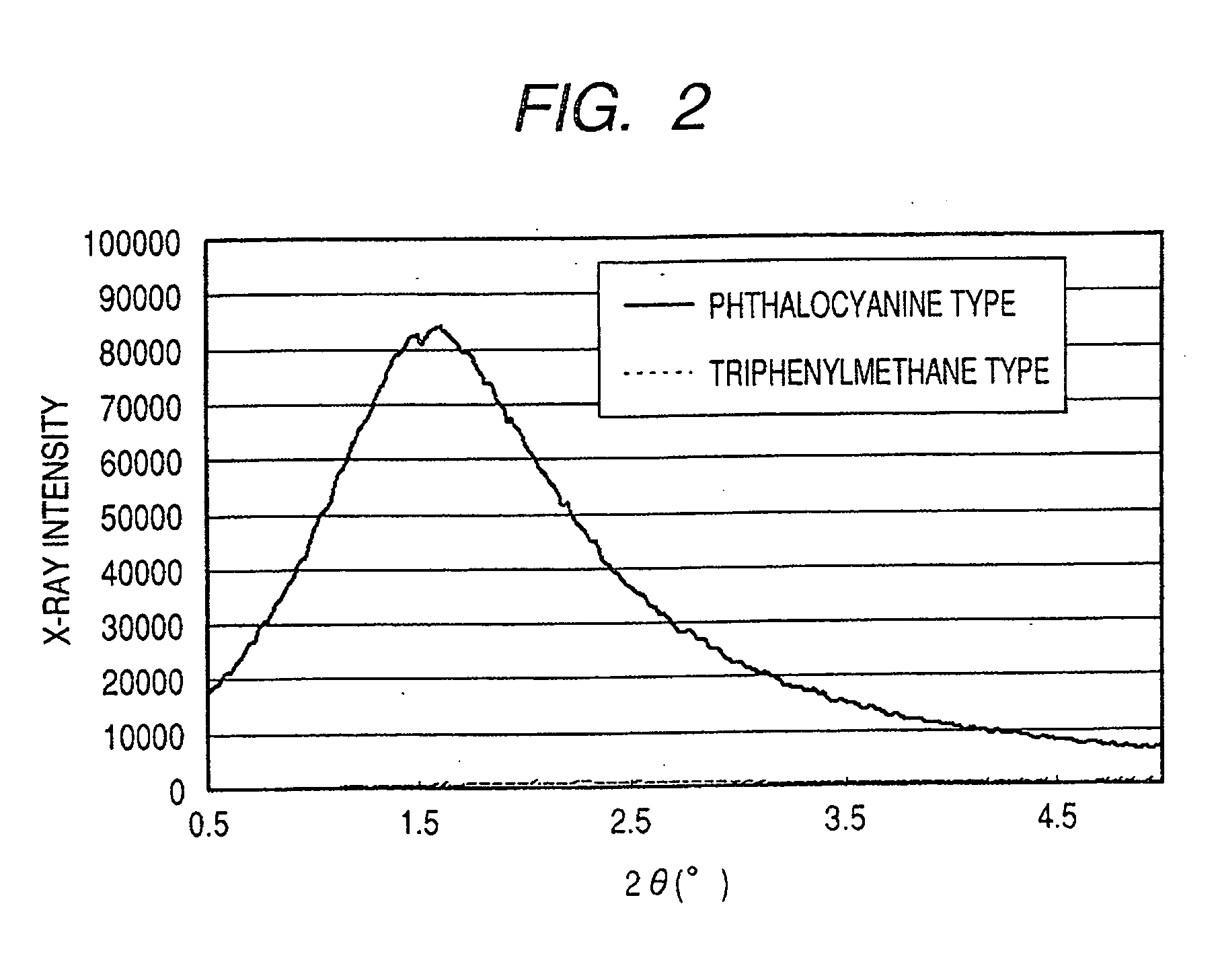
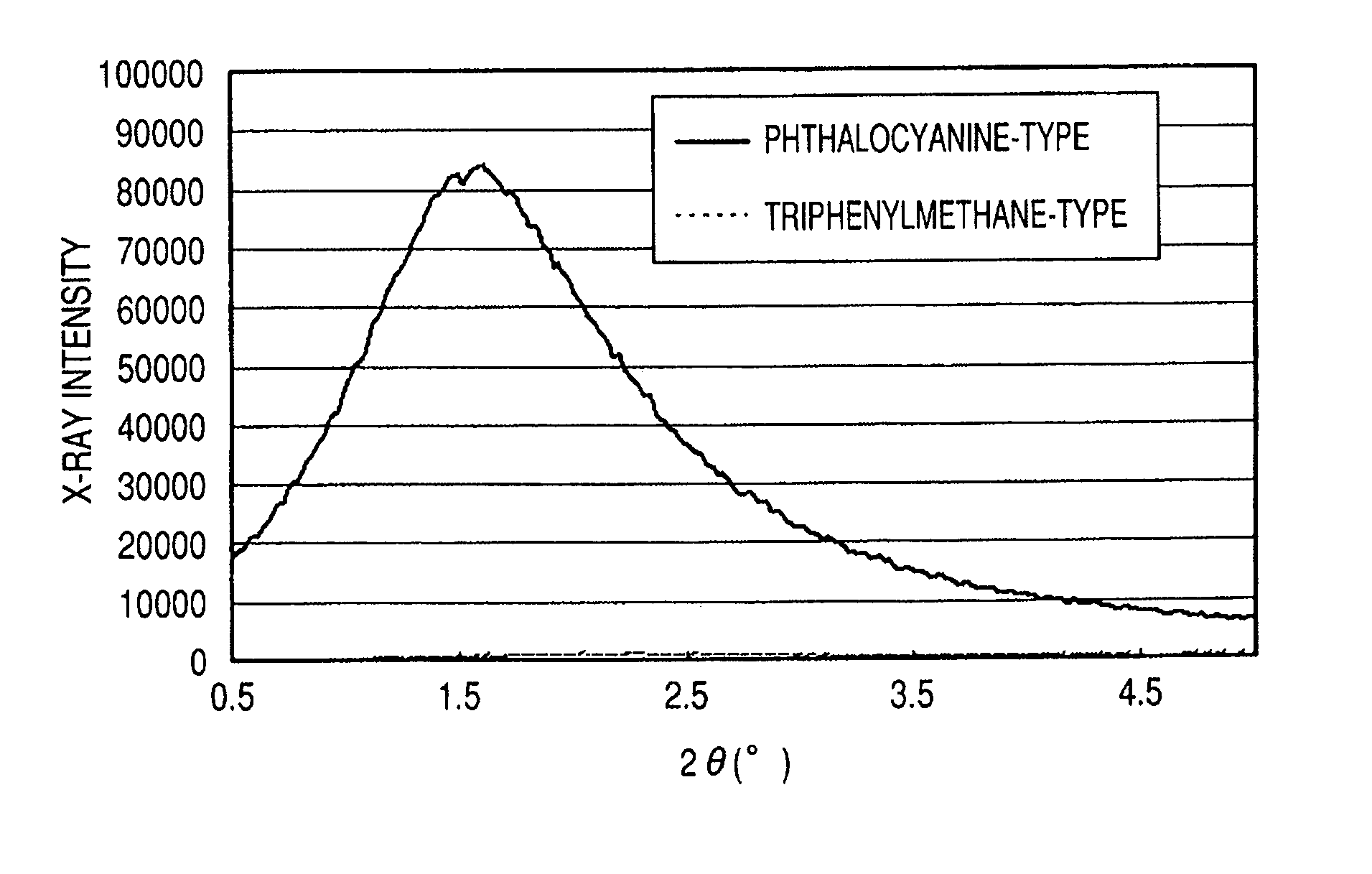
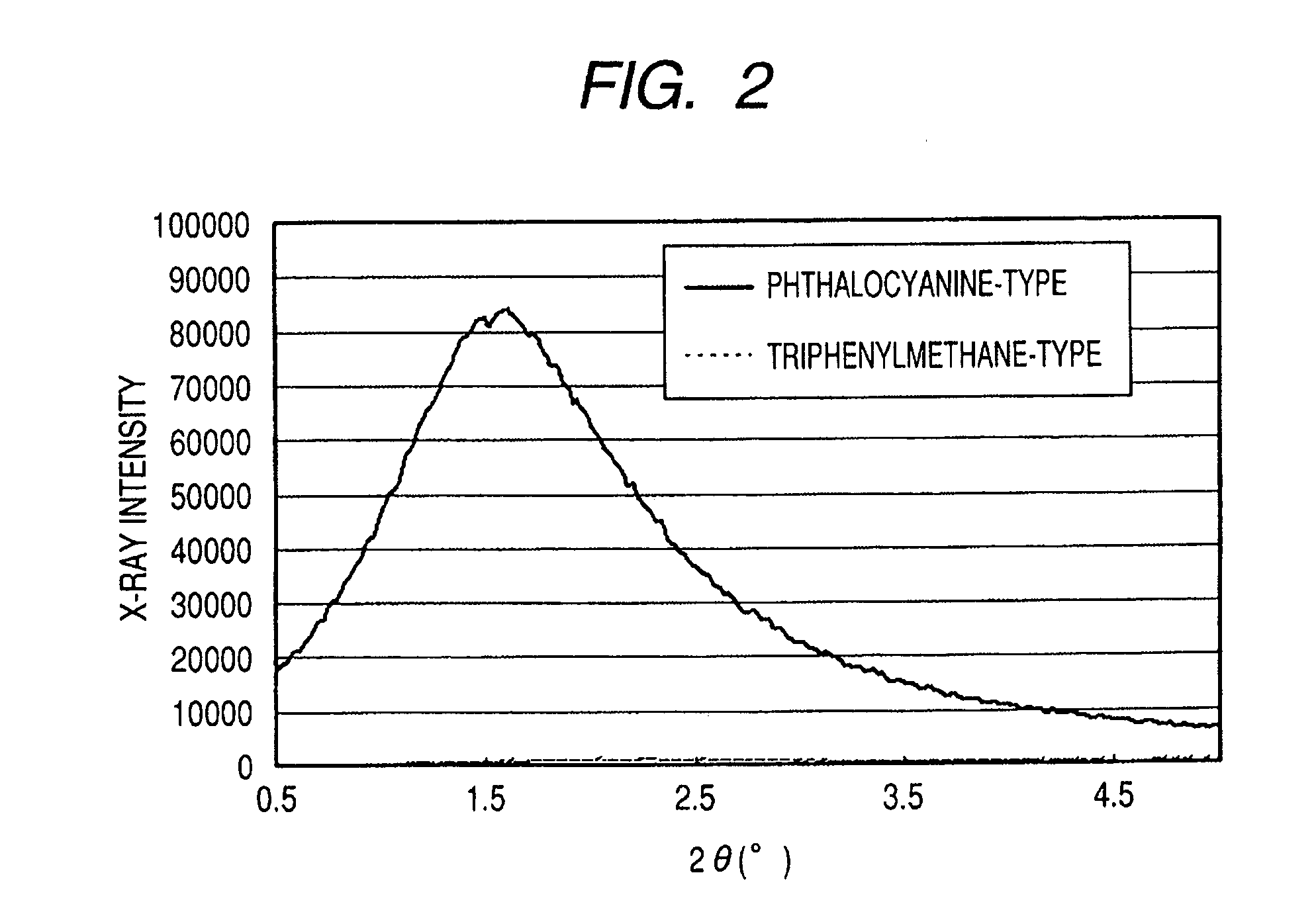
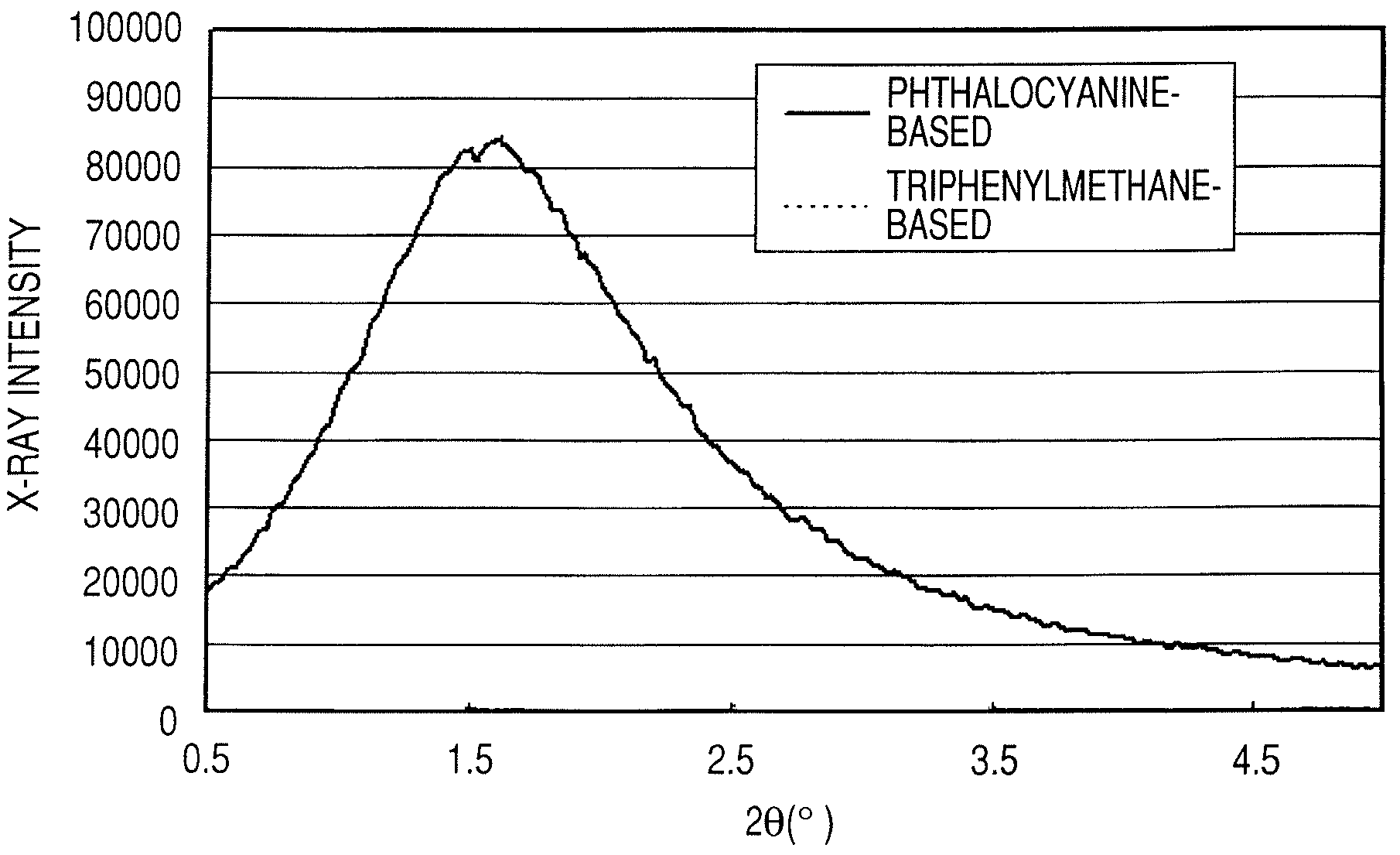
Ink jet ink, ink set, ink jet recording method, ink cartridge, recording unit, and ink jet recording apparatus
ActiveUS7247194B2Good colorIncrease resistanceMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsOrganic solventSmall-angle X-ray scattering
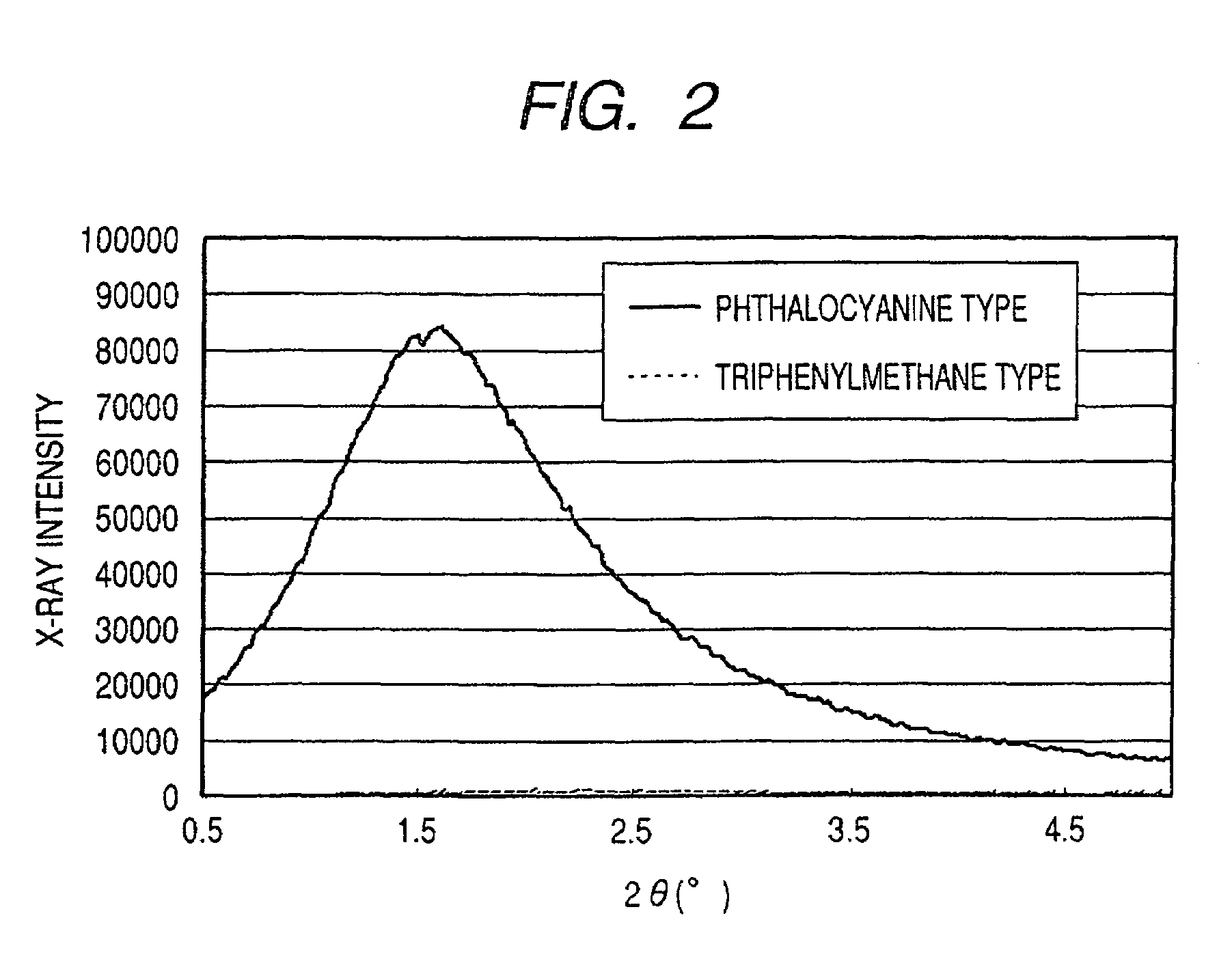
An ink jet ink is disclosed which includes water, a water-soluble organic solvent and a coloring material and has excellent properties. The coloring material is a specific phthalocyanine derivative and is contained in a specific amount in the ink. The water-soluble organic solvent includes a specific amount of 2-pyrrolidone. In addition, a d75 value is in a specific range where the d75 value corresponds to 75% of a dispersion distance distribution, measured by a small angle X-ray scattering method, of molecular aggregates in the ink jet ink whose coloring material concentration is adjusted to 0.5 mass %.
Owner:CANON KK
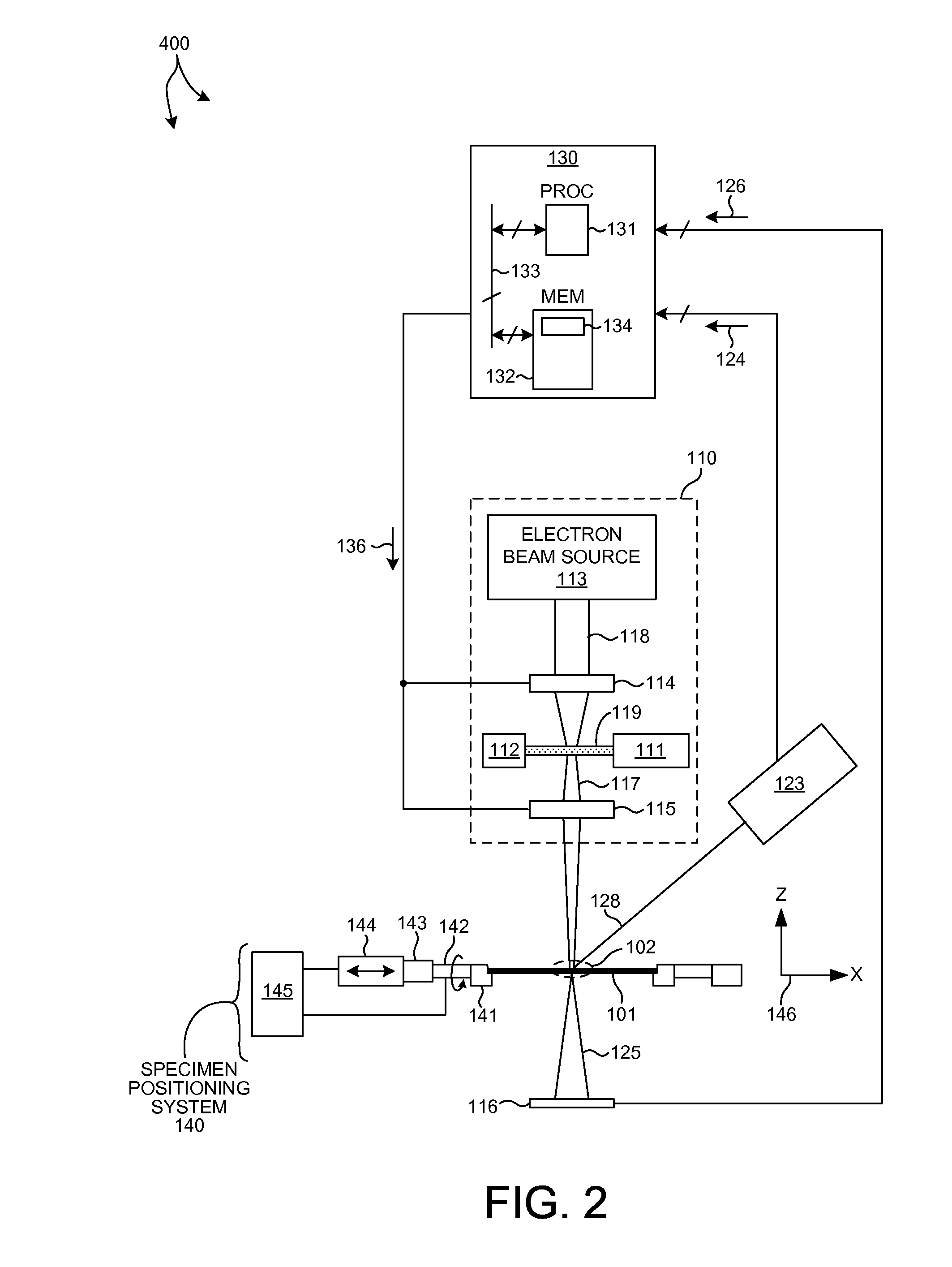
X-ray techniques using structured illumination
ActiveUS20160320320A1Great x-ray fluxEnhanced signalImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesX Ray Emission SpectroscopySmall-angle X-ray scattering
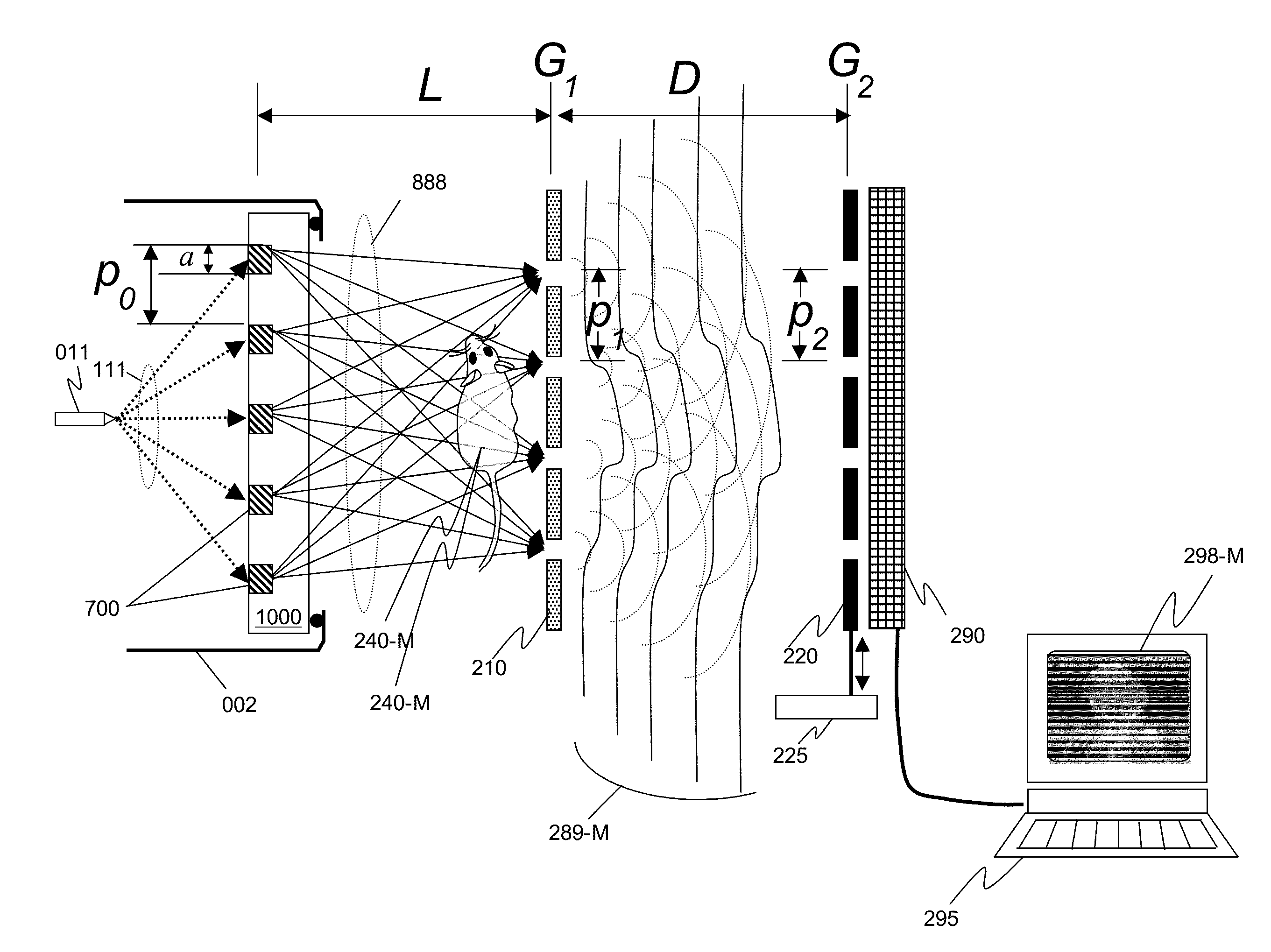
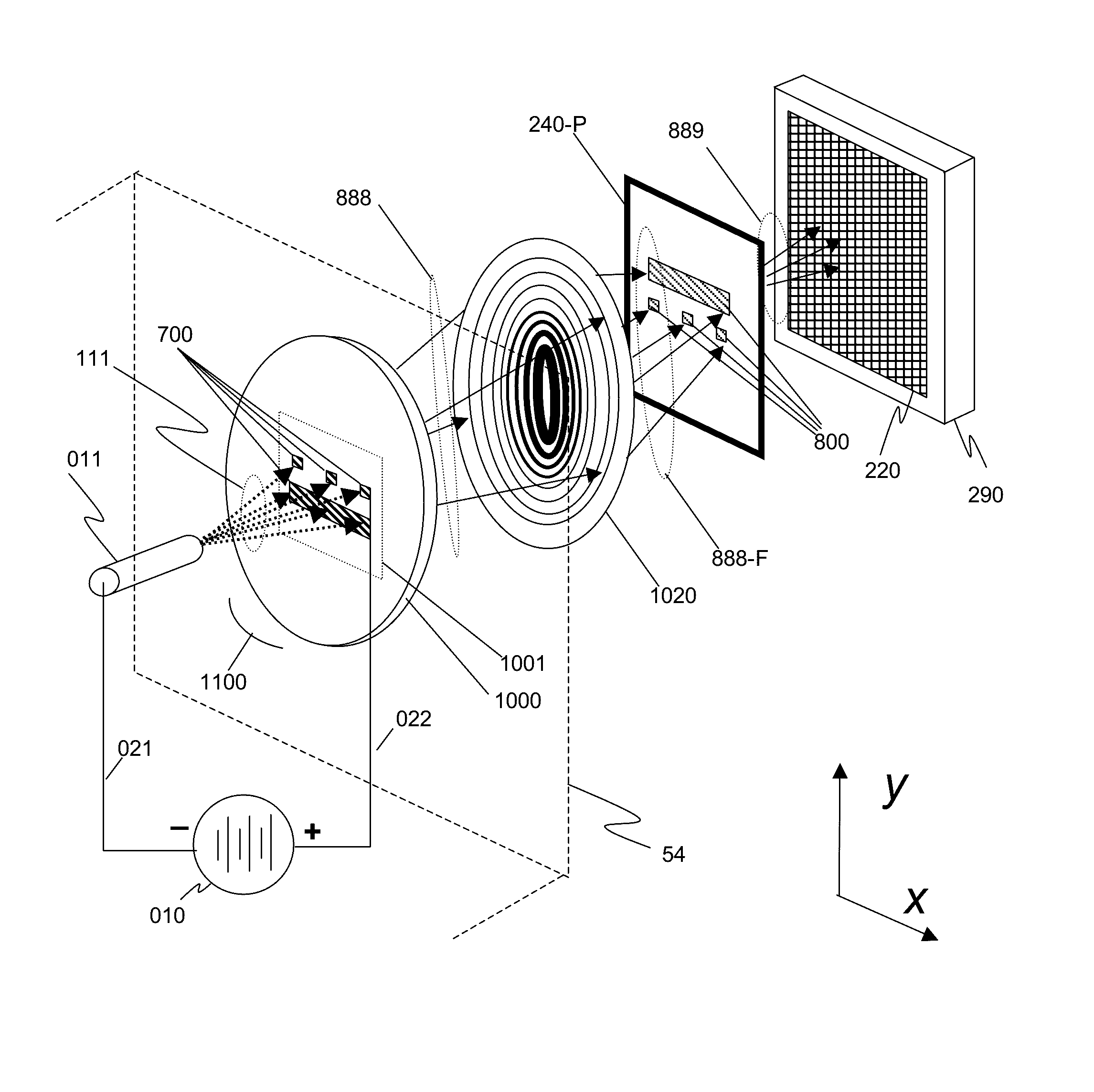
This invention discloses a method and apparatus for x-ray techniques using structured x-ray illumination for examining material properties of an object. In particular, an object with one or more regions of interest (ROIs) having a particular shape, size, and pattern may be illuminated with an x-ray beam whose cross sectional beam profile corresponds to the shape, size and pattern of the ROIs, so that the x-rays of the beam primarily interact only with the ROIs. This allows a greater x-ray flux to be used, enhancing the signal from the ROI itself, while reducing unwanted signals from regions not in the ROI, improving signal-to-noise ratios and / or measurement throughputThis may be used with a number of x-ray measurement techniques, including x-ray fluorescence (XRF), x-ray diffraction (XRD), small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS), x-ray absorption fine-structure spectroscopy (XAFS), x-ray near edge absorption spectroscopy, and x-ray emission spectroscopy.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
X-ray scatterometry metrology for high aspect ratio structures
ActiveUS10352695B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical apparatusDiffraction orderStatic random-access memory
Methods and systems for characterizing dimensions and material properties of high aspect ratio, vertically manufactured devices using transmission, small-angle x-ray scattering (T-SAXS) techniques are described herein. Exemplary structures include spin transfer torque random access memory (STT-RAM), vertical NAND memory (V-NAND), dynamic random access memory (DRAM), three dimensional FLASH memory (3D-FLASH), resistive random access memory (Re-RAM), and PC-RAM. In one aspect, T-SAXS measurements are performed at a number of different orientations that are more densely concentrated near the normal incidence angle and less densely concentrated at orientations that are further from the normal incidence angle. In a further aspect, T-SAXS measurement data is used to generate an image of a measured structure based on the measured intensities of the detected diffraction orders. In another further aspect, a metrology system is configured to generate models for combined x-ray and optical measurement analysis.
Owner:KLA CORP
Ink jet ink, ink set, ink jet recording method, ink cartridge, recording unit, and ink jet recording apparatus
ActiveUS20060102046A1Good colorHigh environmental gas resistanceMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsOrganic solventSmall-angle X-ray scattering
An ink jet ink is disclosed which includes water, a water-soluble organic solvent and a coloring material and has excellent properties. The coloring material is a specific phthalocyanine derivative and is contained in a specific amount in the ink. The water-soluble organic solvent includes a specific amount of 2-pyrrolidone. In addition, a d75 value is in a specific range where the d75 value corresponds to 75% of a dispersion distance distribution, measured by a small angle X-ray scattering method, of molecular aggregates in the ink jet ink whose coloring material concentration is adjusted to 0.5 mass %.
Owner:CANON KK
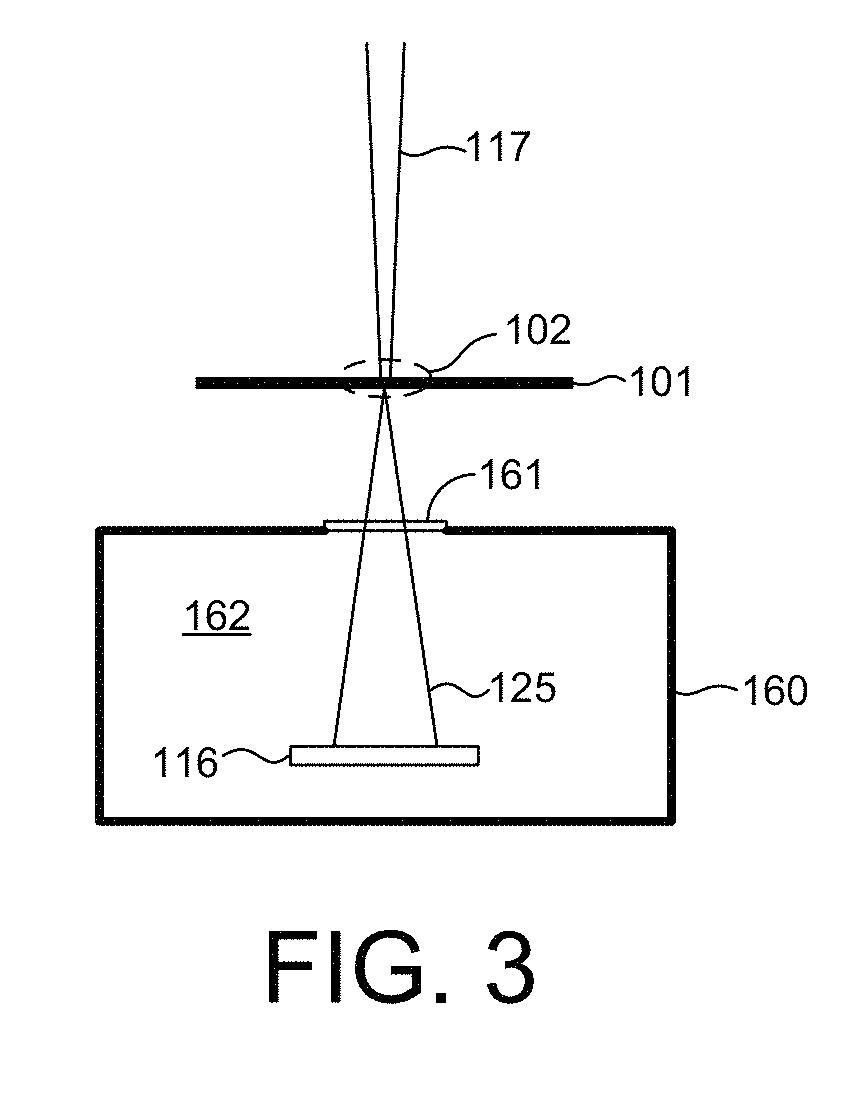
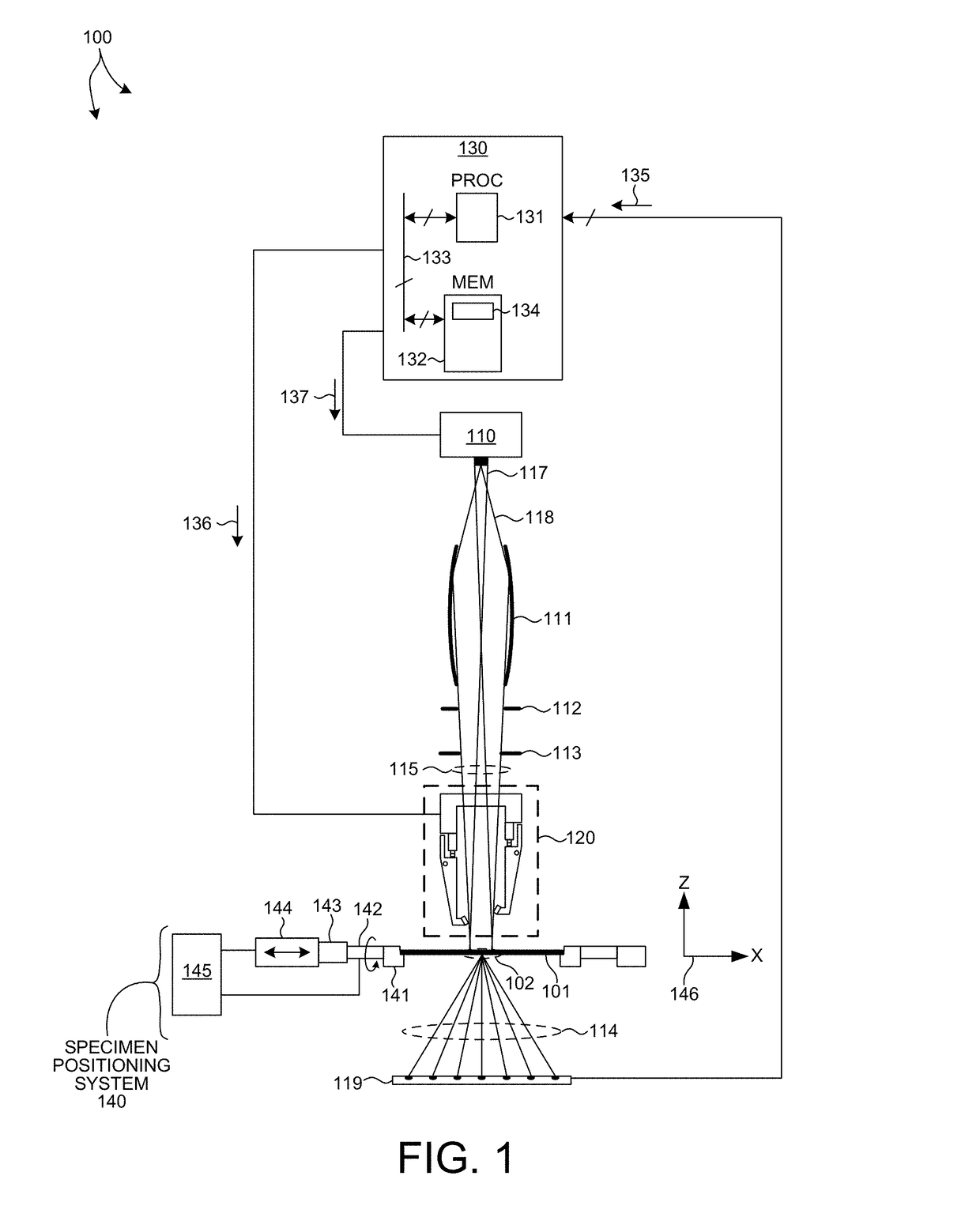
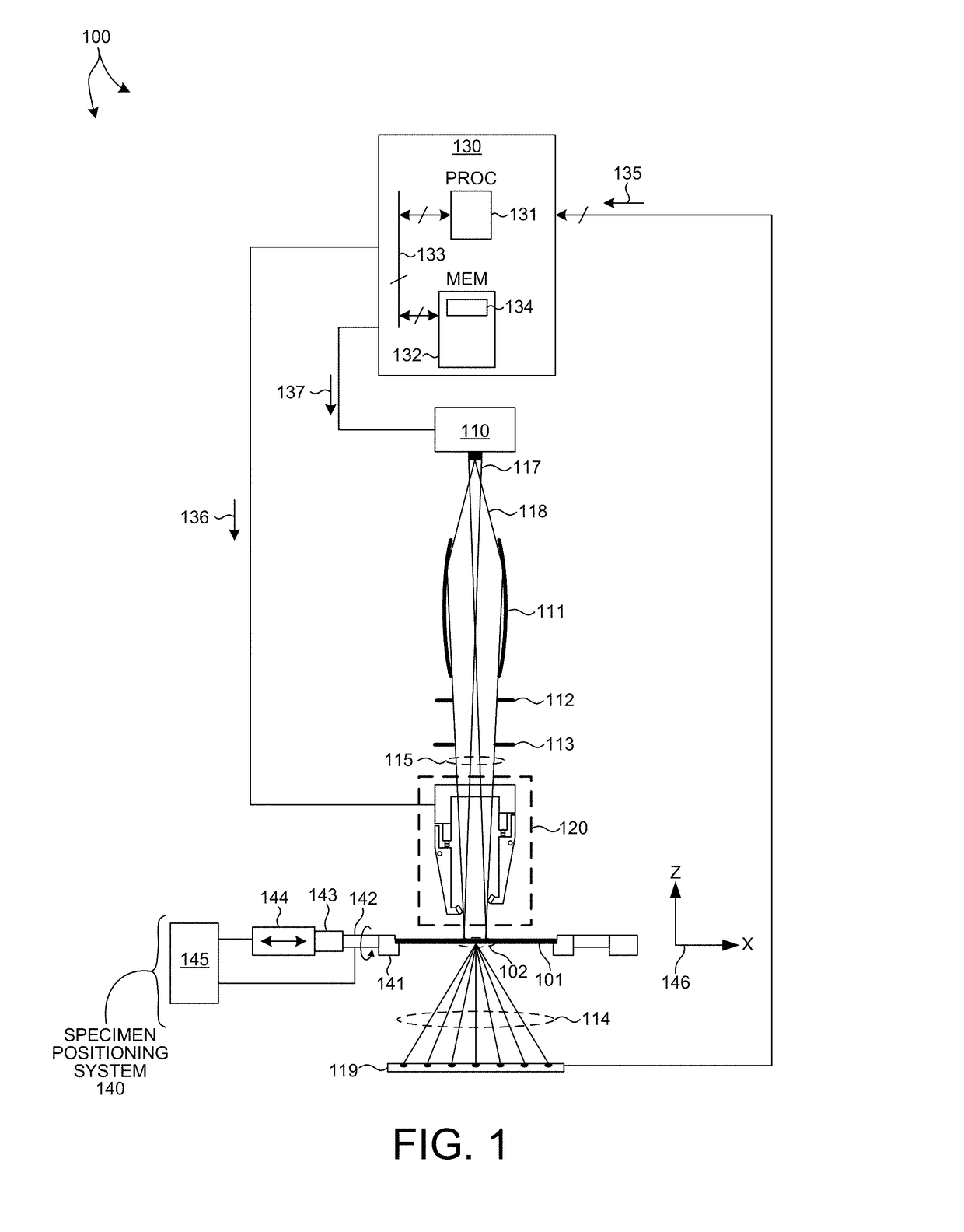
Beam Shaping Slit For Small Spot Size Transmission Small Angle X-Ray Scatterometry
ActiveUS20170307548A1Reduce the impactEffect of beam divergence on beam spot size is minimizedHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSmall-angle X-ray scatteringLight beam
Methods and systems for reducing the effect of finite source size on illumination beam spot size for Transmission, Small-Angle X-ray Scatterometry (T-SAXS) measurements are described herein. A beam shaping slit having a slender profile is located in close proximity to the specimen under measurement and does not interfere with wafer stage components over the full range of angles of beam incidence. In one embodiment, four independently actuated beam shaping slits are employed to effectively block a portion of an incoming x-ray beam and generate an output beam having a box shaped illumination cross-section. In one aspect, each of the beam shaping slits is located at a different distance from the specimen in a direction aligned with the beam axis. In another aspect, the beam shaping slits are configured to rotate about the beam axis in coordination with the orientation of the specimen.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Metrology tool with combined XRF and SAXS capabilities
ActiveUS9778213B2Reduce correlationImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSpecial data processing applicationsMetrologyData set
Methods and systems for performing simultaneous X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) and small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements over a desired inspection area of a specimen are presented. SAXS measurements combined with XRF measurements enables a high throughput metrology tool with increased measurement capabilities. The high energy nature of x-ray radiation penetrates optically opaque thin films, buried structures, high aspect ratio structures, and devices including many thin film layers. SAXS measurements of a particular location of a planar specimen are performed at a number of different out of plane orientations. This increases measurement sensitivity, reduces correlations among parameters, and improves measurement accuracy. In addition, specimen parameter values are resolved with greater accuracy by fitting data sets derived from both SAXS and XRF measurements based on models that share at least one material parameter. The fitting can be performed sequentially or in parallel.
Owner:KLA CORP
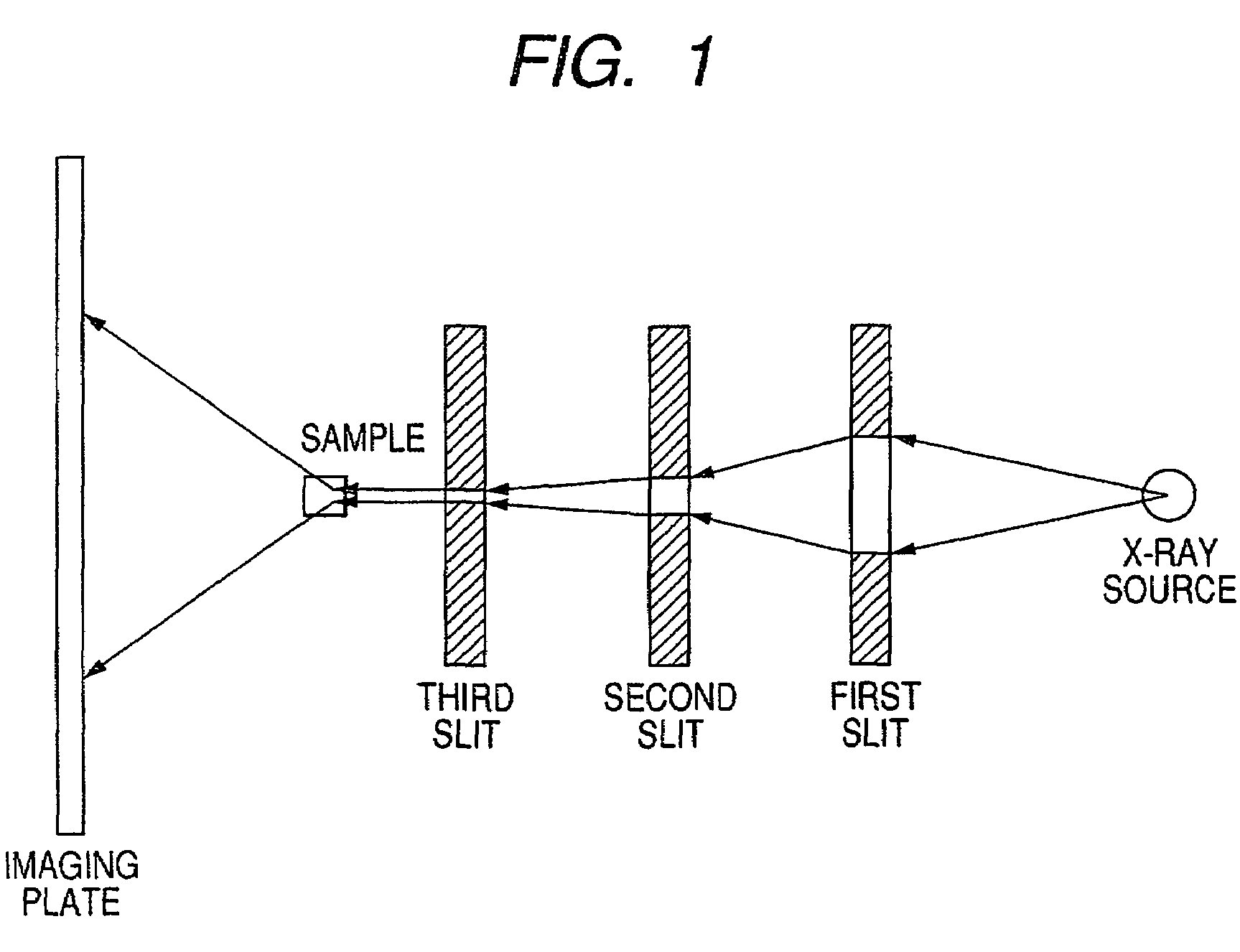
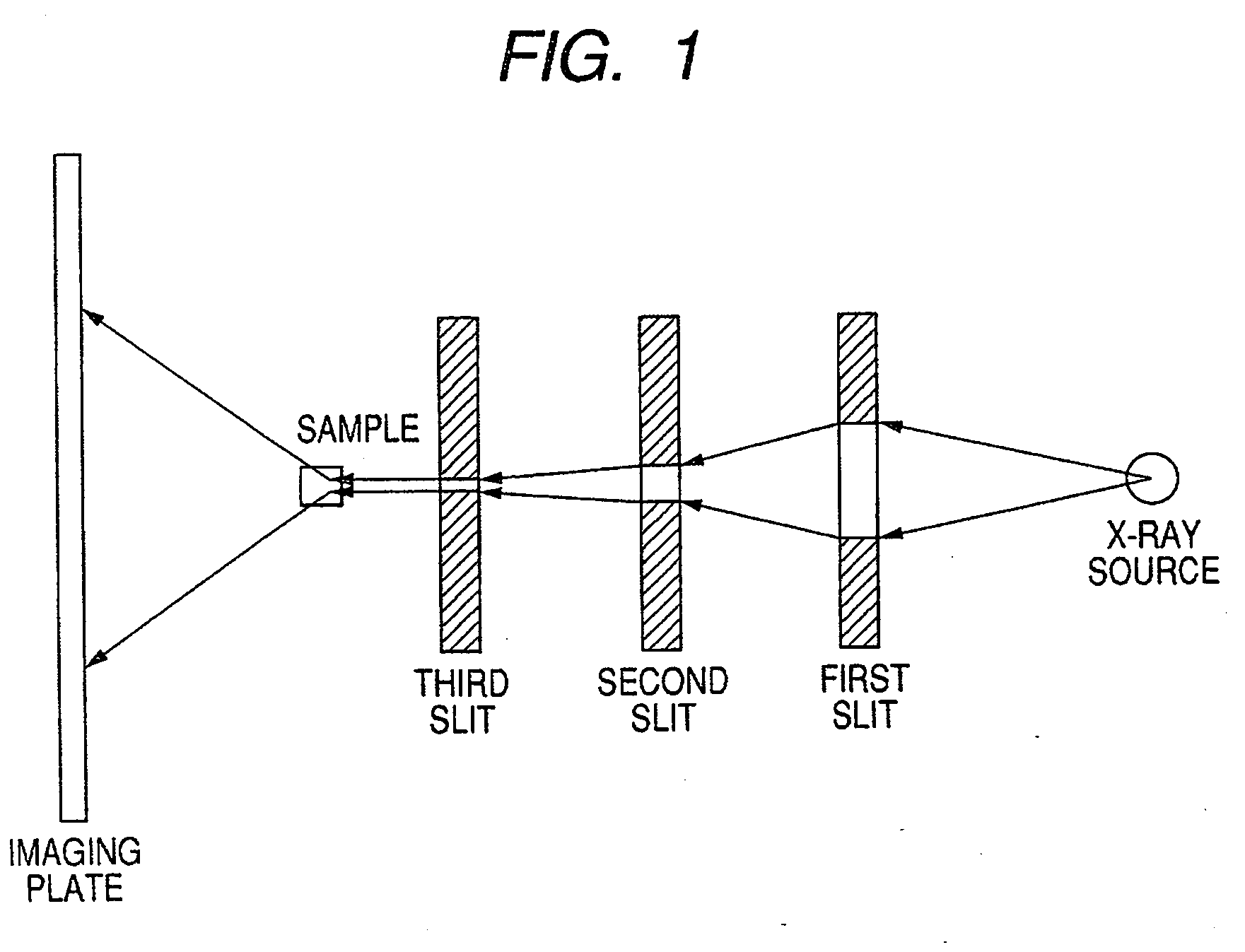
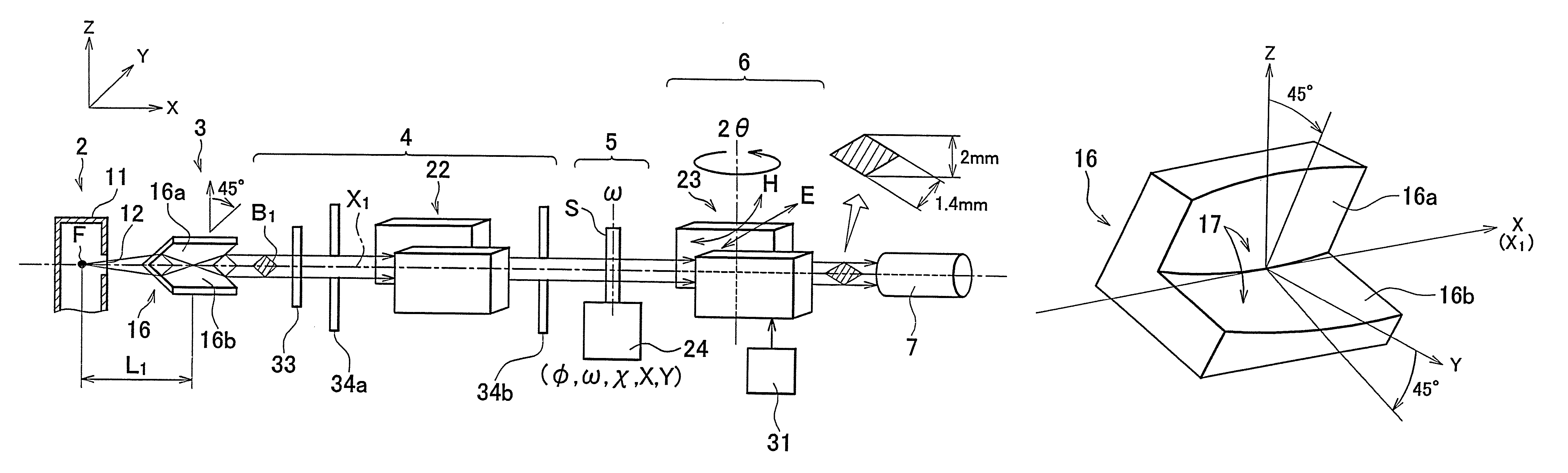
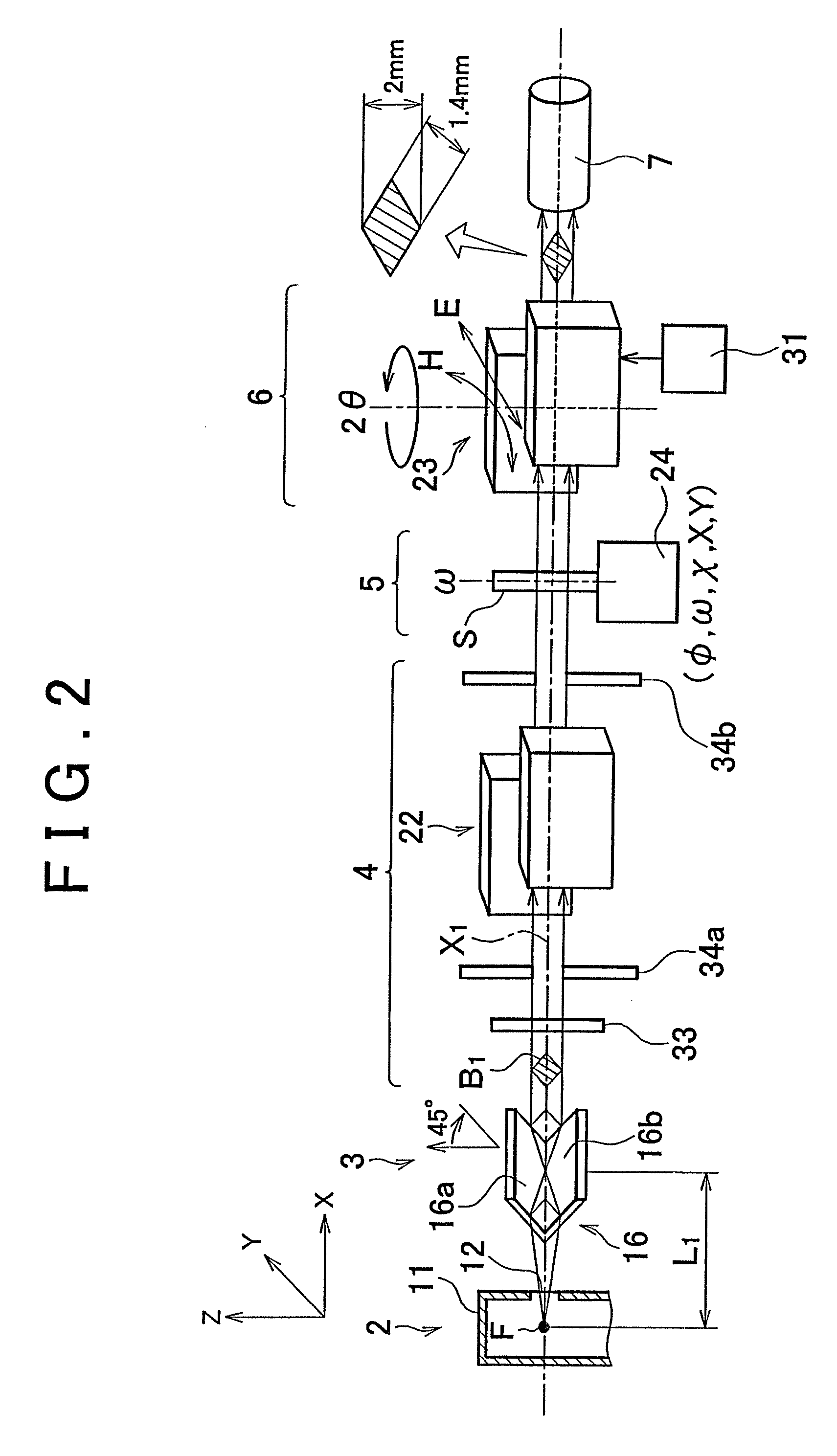
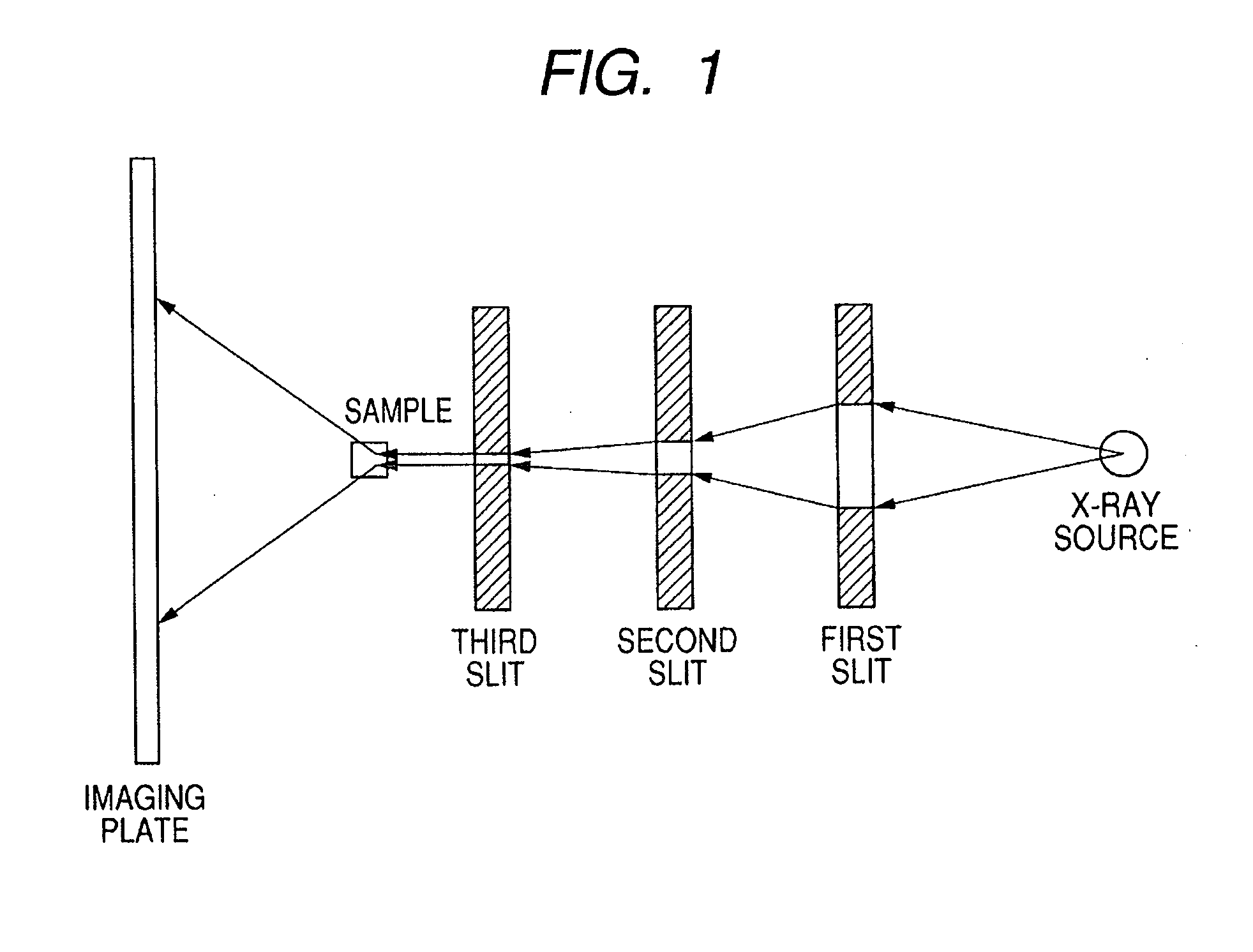
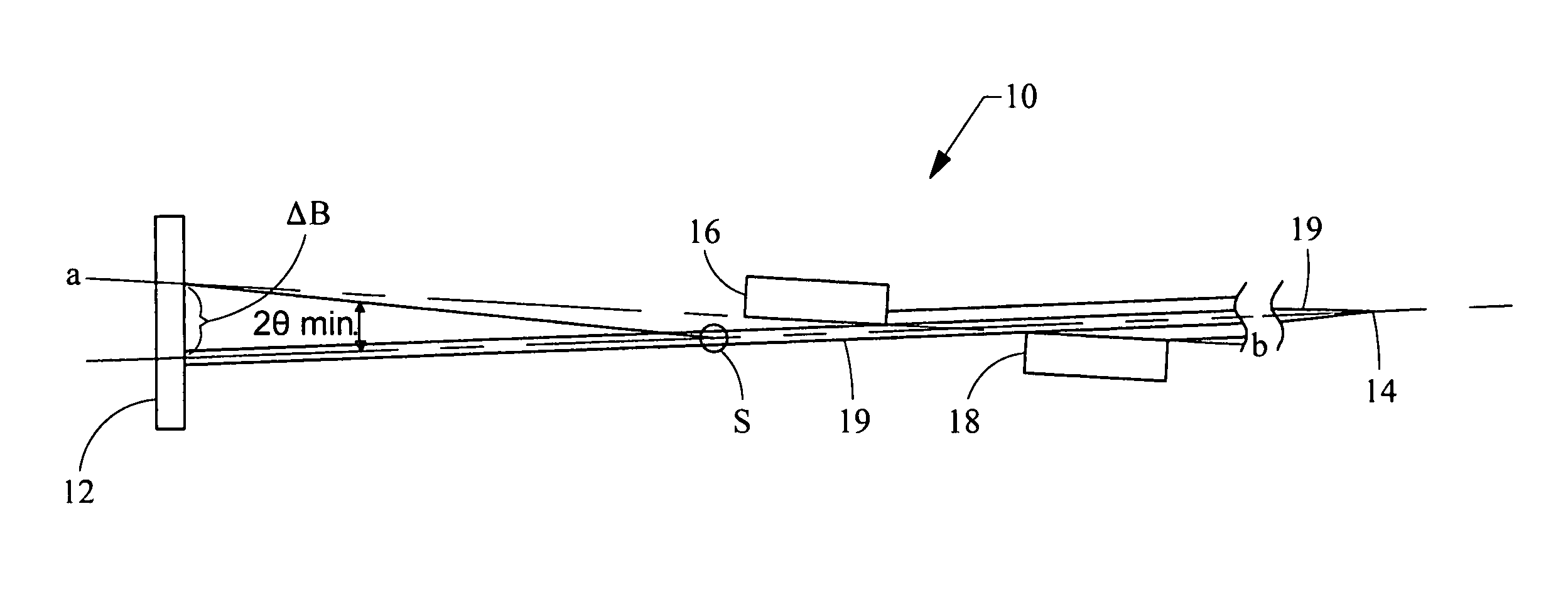
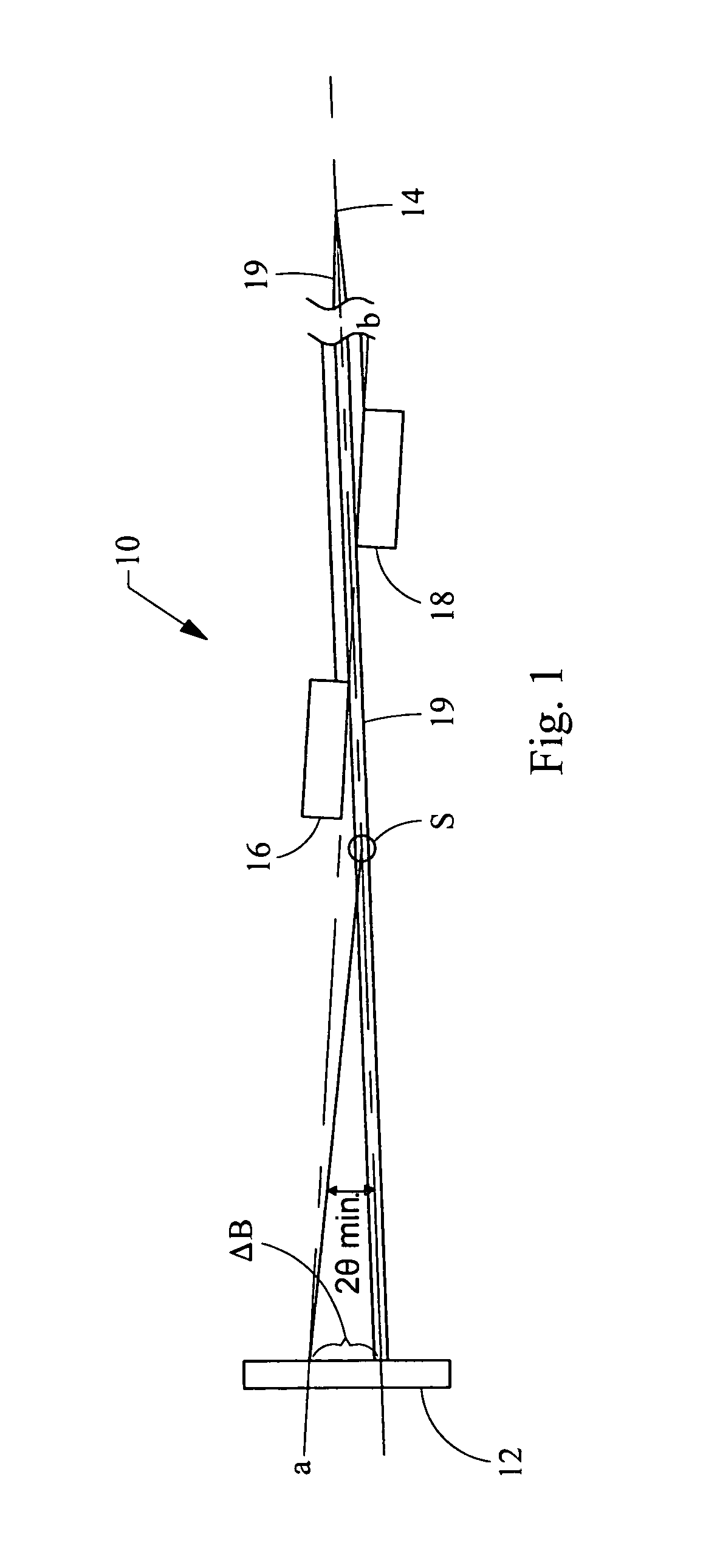
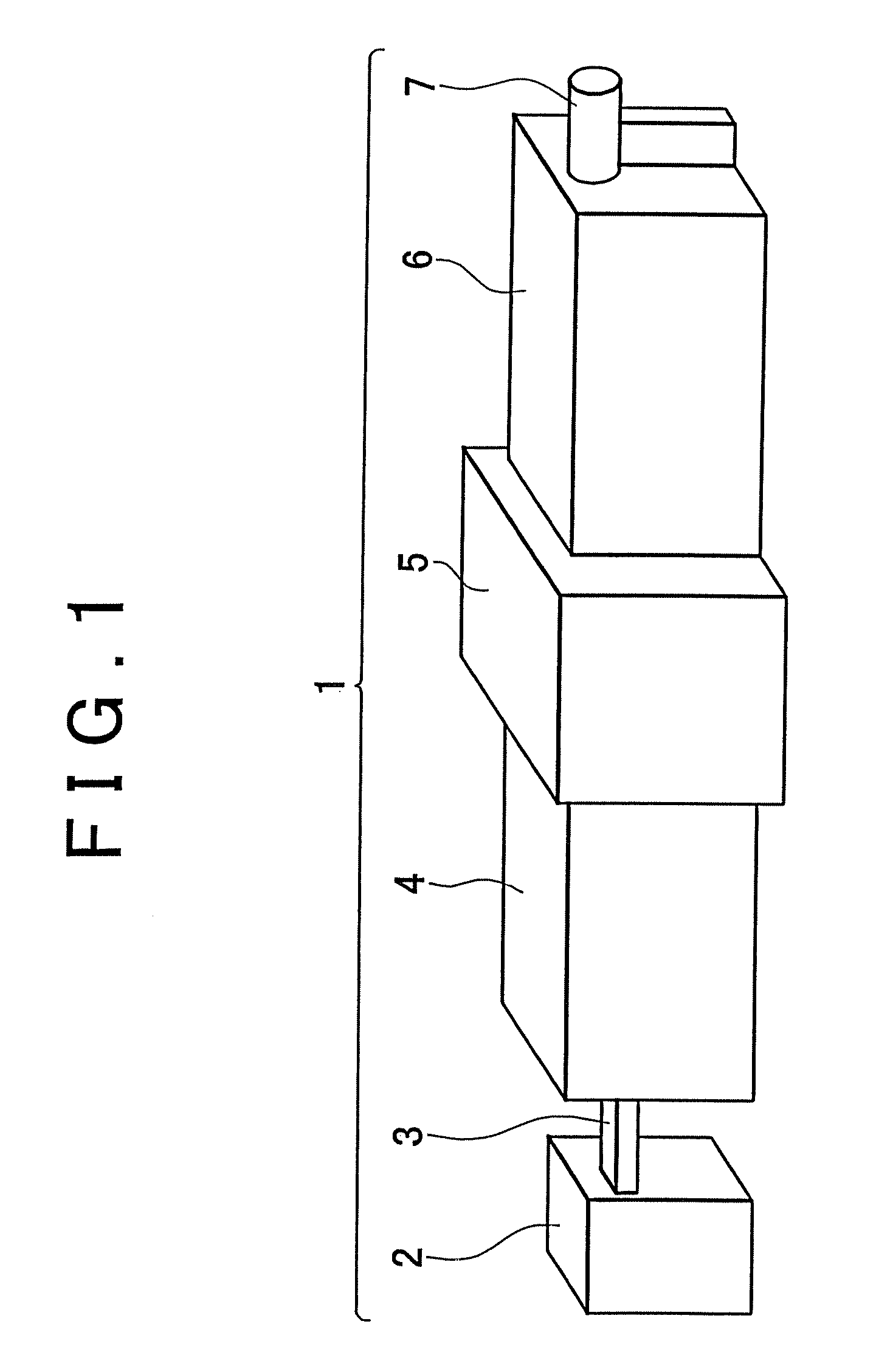
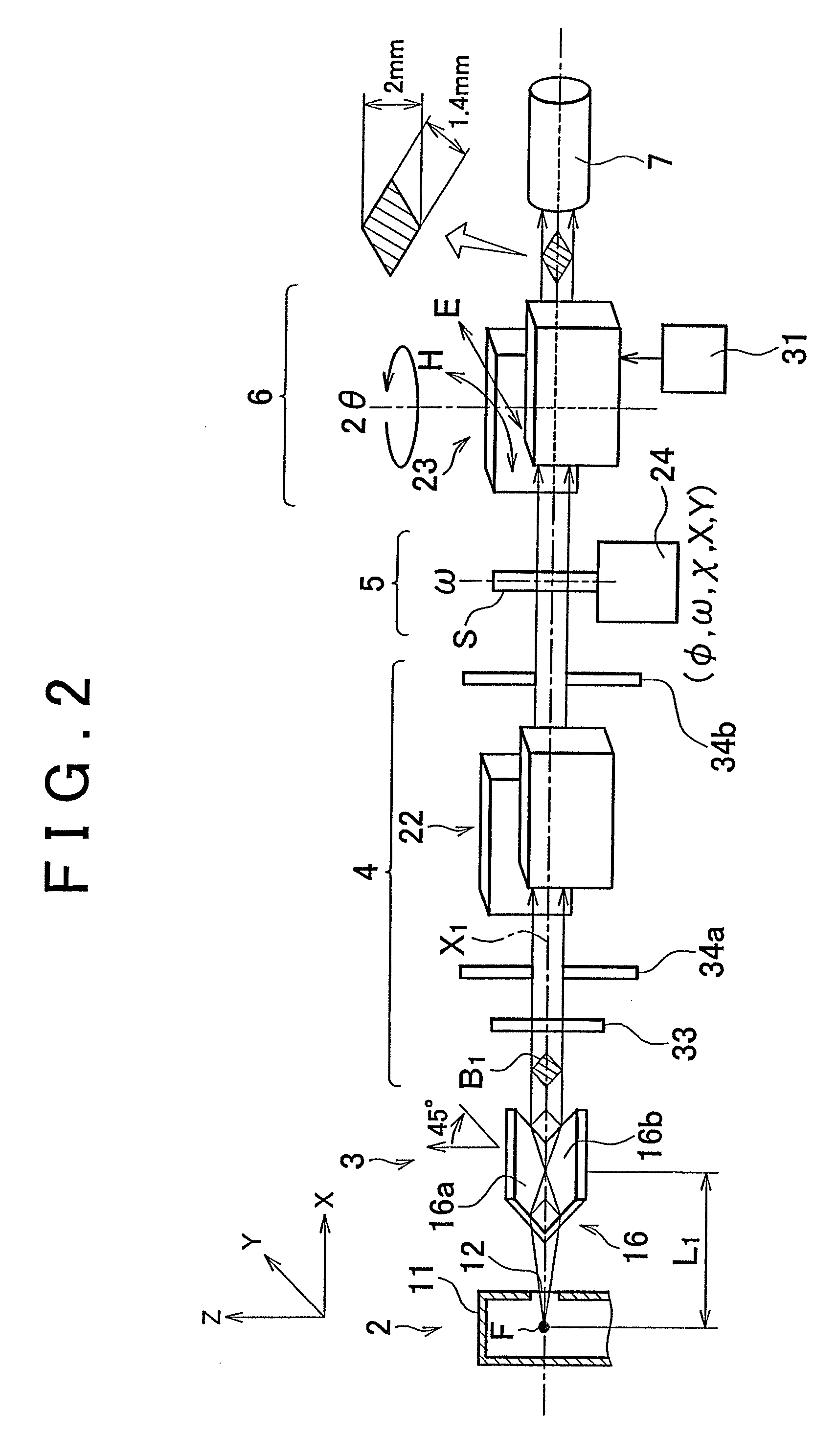
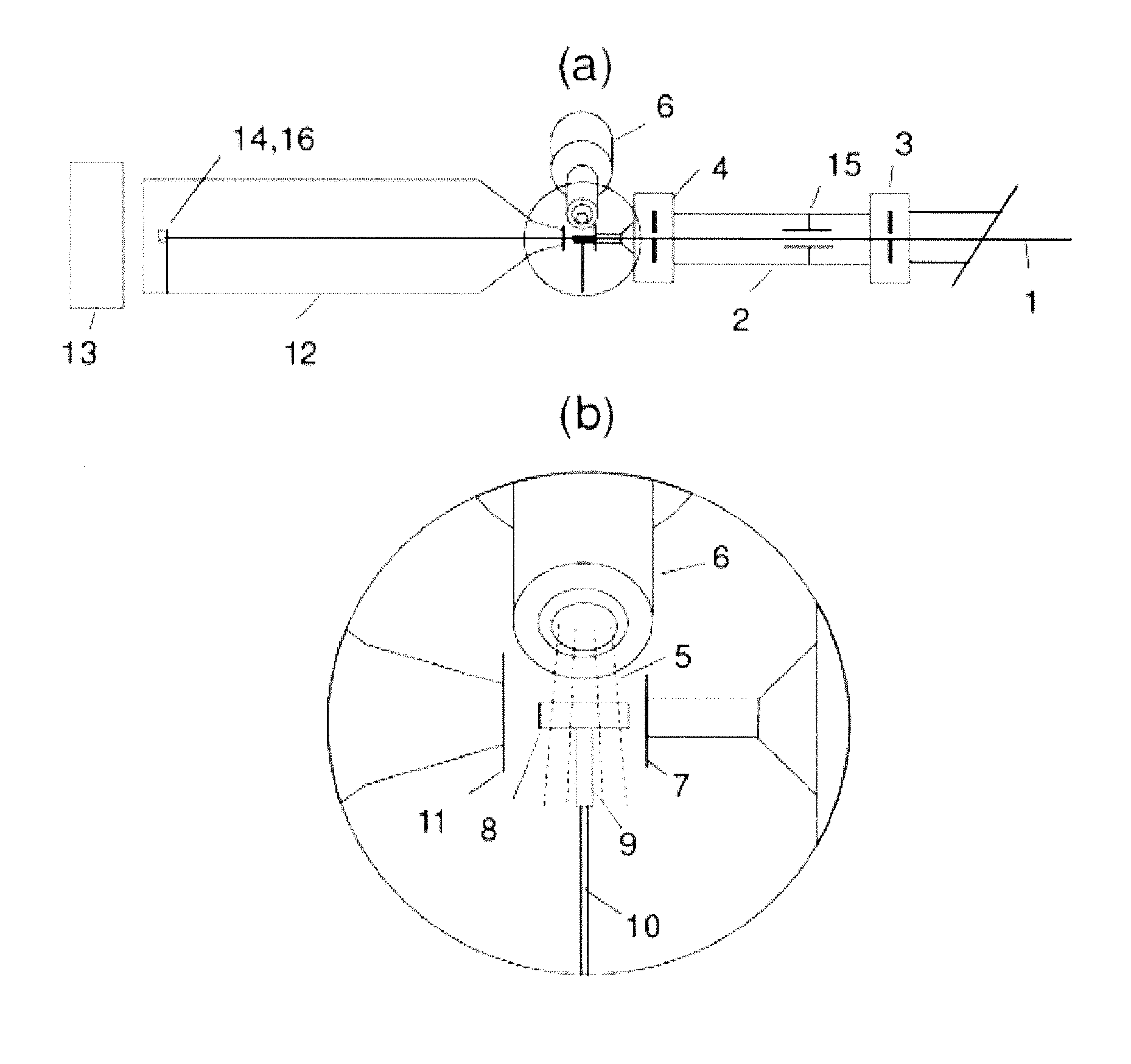
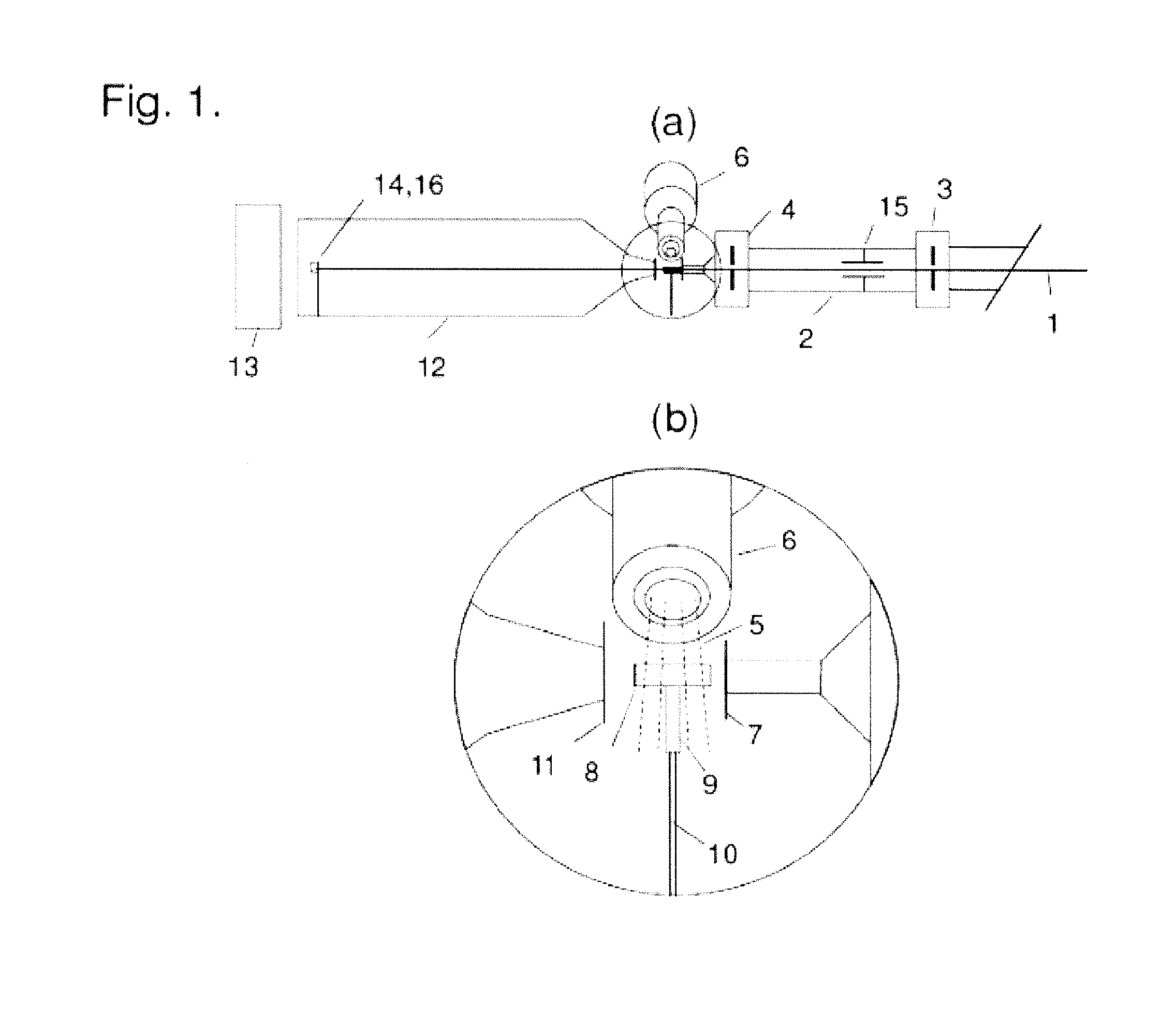
Ultra-small angle x-ray scattering measuring apparatus
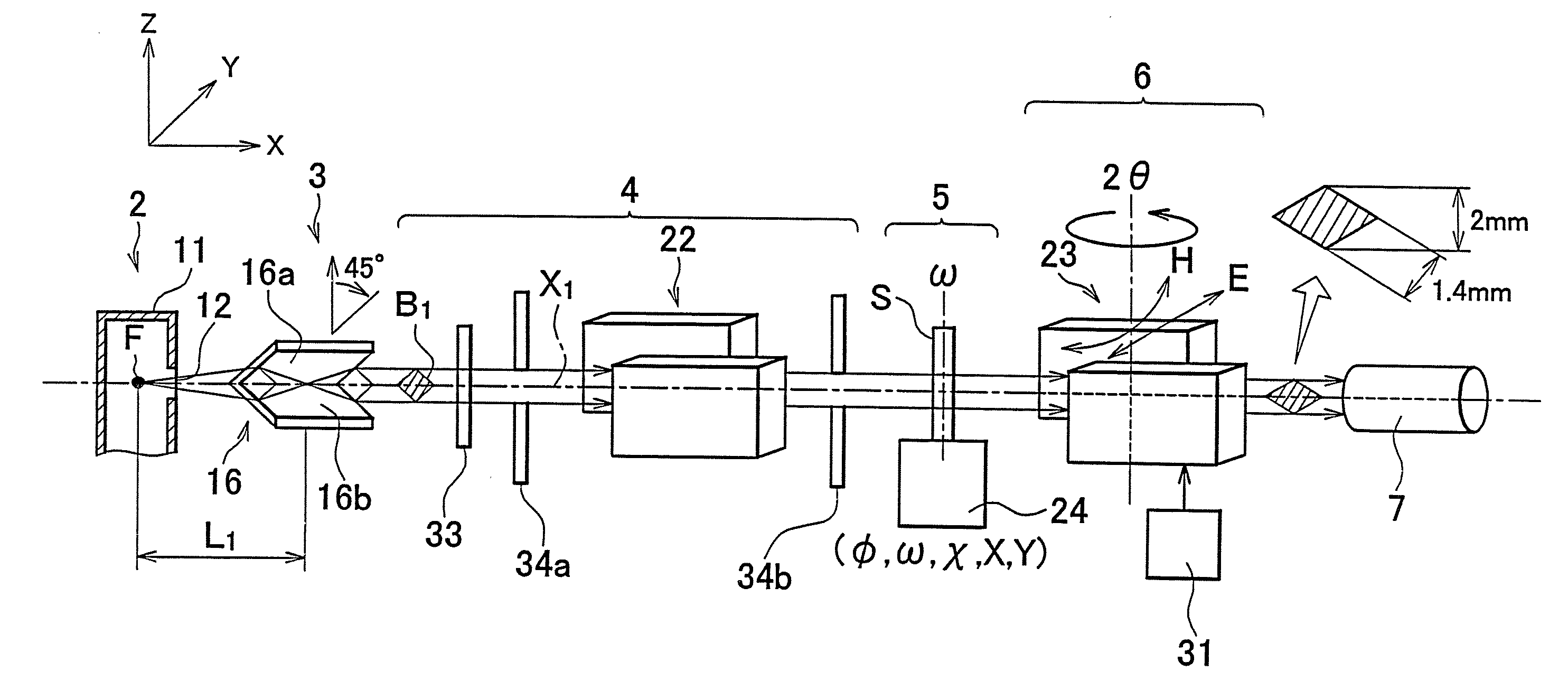
ActiveUS7646849B2Accurate captureSuppressing the smearing phenomenonRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsLattice planeSmall-angle X-ray scattering
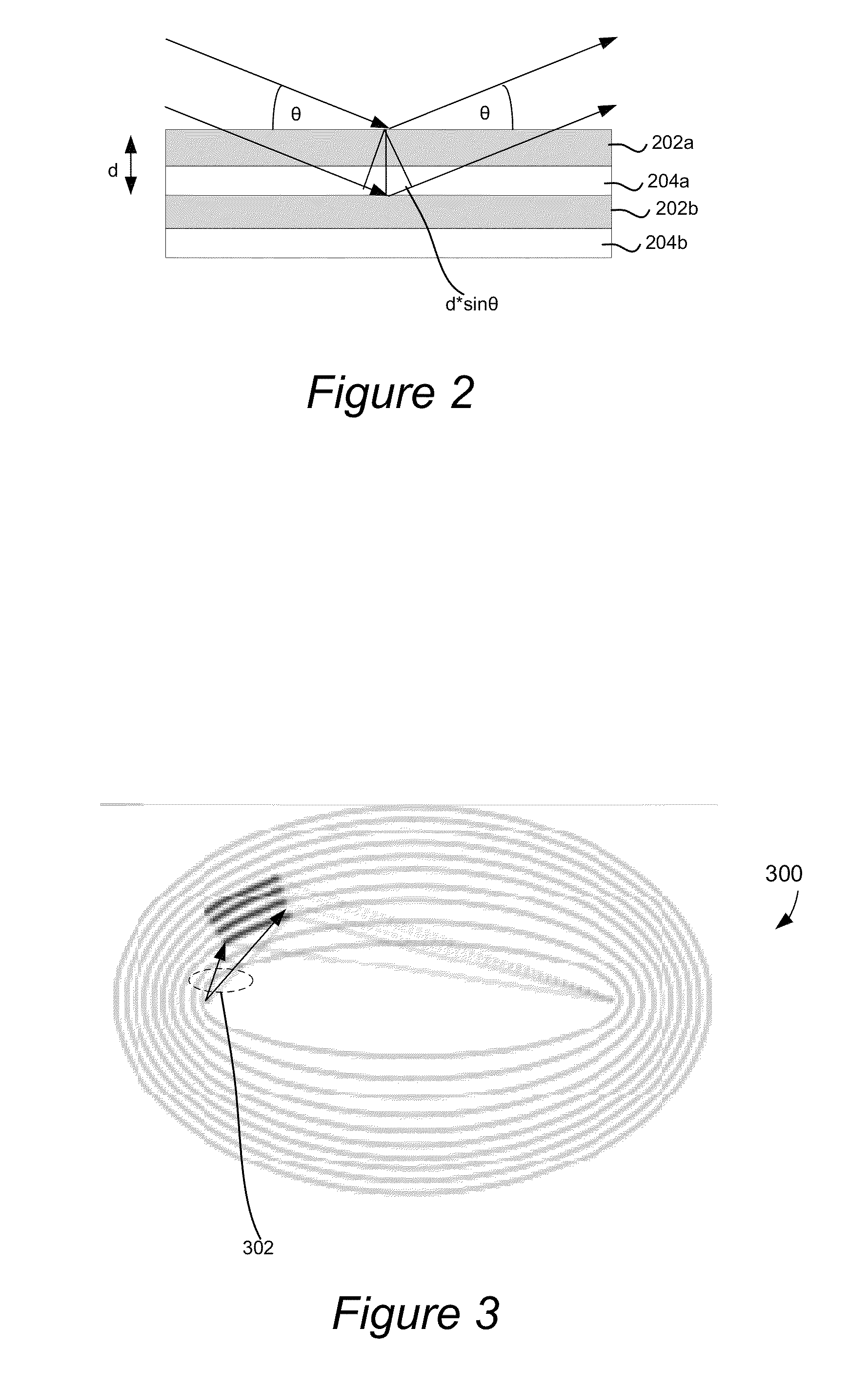
An ultra-small angle X-ray scattering measuring apparatus includes a detector for detecting X-rays emitted from a sample, an X-ray collimating mirror arranged between the X-ray real focus and the sample, a monochromator arranged between the X-ray collimating mirror and the sample and an analyzer arranged between the sample and the detector. The X-ray collimating mirror includes a pair of X-ray mirrors that are arranged orthogonally relative to each other. The X-ray mirrors are multilayer film mirrors and their X-ray reflection surfaces are paraboloidal. The interplanar spacing of lattice planes of each of the multilayer films is continuously changed along the paraboloid so as to meet the Bragg's condition. The monochromator and the analyzer are formed by using a channel-cut crystal. The analyzer is driven to rotate for scanning around a 2θ-axial line and diffracted rays reduced to a spectrum by the analyzer are detected by the detector.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Ink jet ink, ink jet recording method, ink cartridge, recording unit, and ink jet recording apparatus
ActiveUS20060102047A1Excellent in bronze resistanceHigh environmental gas resistanceMeasurement apparatus componentsDuplicating/marking methodsSmall-angle X-ray scatteringPolymer chemistry
There is provided ink jet ink containing at least a coloring material, in which: the coloring material is a compound represented by the following general formula (I) or a salt thereof; a content (weight %) of the coloring material is 3.0 weight % or more with respect to a total weight of the ink jet ink; in a dispersion distance distribution, measured by a small-angle X-ray scattering method, of molecular aggregates in the ink jet ink whose coloring material concentration is adjusted to 3.0 weight %, a dispersion distance d75 value corresponding to 75% of the distribution is 3.0 mass % is 6.50 nm or more and 7.10 nm or less:
Owner:CANON KK
Ink jet ink, ink jet recording method, ink cartridge, ink set and image forming method
ActiveUS7445666B2Good weather resistanceImprove the immunityMeasurement apparatus componentsInksOrganic solventSmall-angle X-ray scattering
An ink jet ink which can form images whose bleeding resistance is high and whose bronzing phenomenon is suppressed, is provided. The ink is an ink jet ink for use together with a pigment ink. The ink jet ink is characterized in that: the ink jet ink contains a coloring material, a polyvalent metal and a water-soluble organic solvent(s); the coloring material is at least a compound represented by the general formula (I); a content (mol / g) of the polyvalent metal is 2.0×10−6 mol / g or more and 4.0×10−4 mol / g or less; a total content (mass %) of the water-soluble organic solvent(s) is 25.0 mass % or more with respect to the total mass of the ink; and in a dispersion distance distribution, measured by a small angle X-ray scattering method, of molecular aggregates in the ink jet ink whose coloring material concentration is adjusted to 0.5 mass %, a dispersion distance d75 value corresponding to 75% of a distribution is 12.60 nm or less.
Owner:CANON KK
X-ray techniques using structured illumination
ActiveUS10401309B2Enhanced signalReducing unwanted signalImaging devicesX-ray tube electrodesX Ray Emission SpectroscopySmall-angle X-ray scattering
Owner:SIGRAY INC
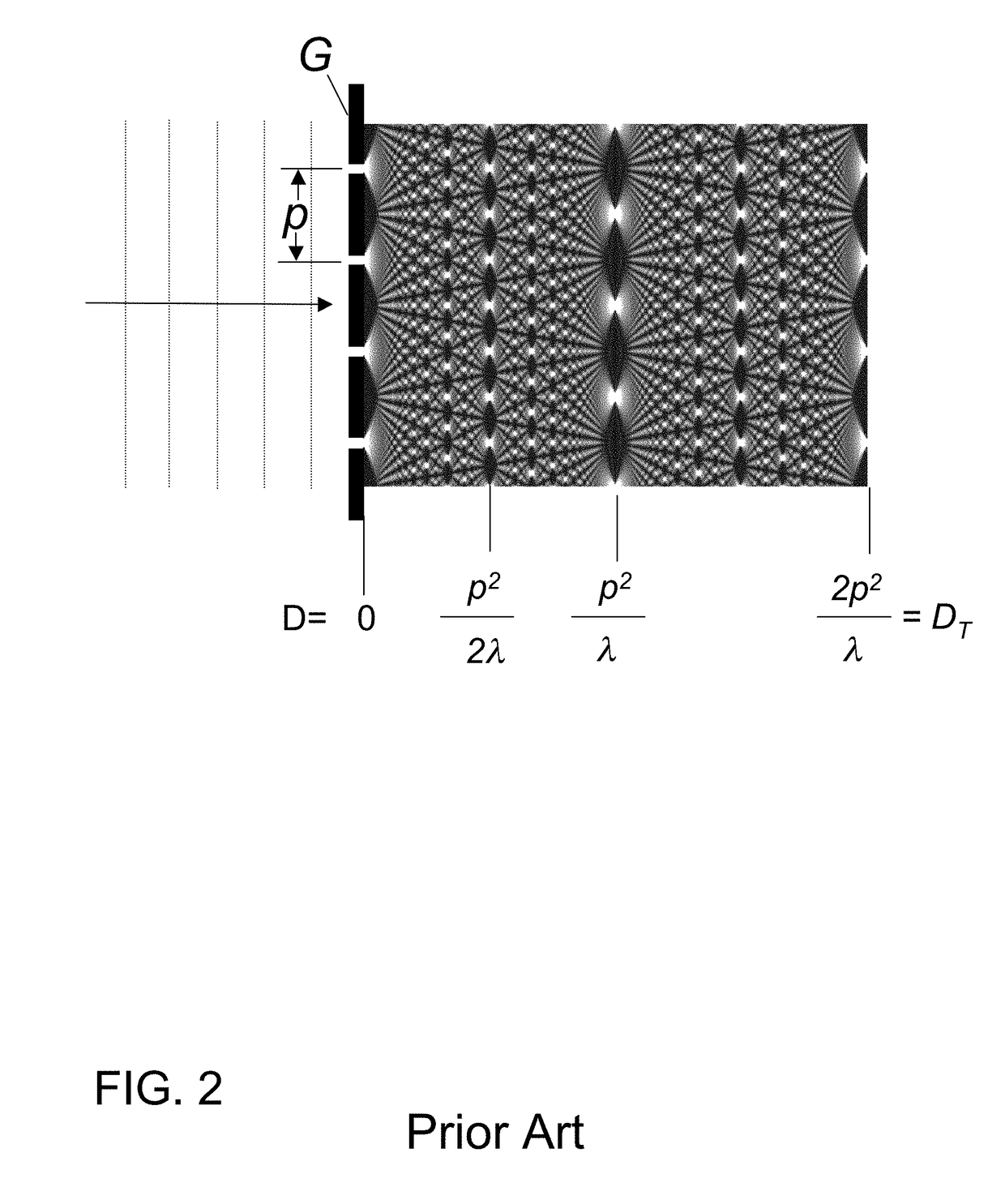
Two-dimensional small angle x-ray scattering camera
ActiveUS7139366B1Wide range of anglesHigh resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSmall-angle X-ray scatteringLight beam
A two-dimensional x-ray scattering camera includes a source, an optic, a detector, and a pair of collimating blocks. The source emits x-ray beams that are reflected by the optic towards a sample. The detector detects scattering from the sample, the pair of collimating blocks is positioned between the optic and the detector to collimate the beam. A bottom surface of one block is substantially parallel a top surface of the other block, and the blocks are rotatable relative to the beam about a pivot. The system forms a two-dimensional beam that is symmetric about the primary beam axis at the detector position, regardless how the beam is collimated by the collimating blocks. The system therefore eliminates smearing and can be used for anisotropic small angle scattering at high resolution and low Qmin.
Owner:OSMIC
Sodium secondary battery
ActiveUS20110135990A1Improve discharge characteristicsEnhanced advantageRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIonSmall-angle X-ray scattering
Disclosed is a sodium secondary battery. The sodium secondary battery comprises a first electrode and a second electrode comprising a carbonaceous material. The carbonaceous material satisfies one or more requirements selected from the group consisting of requirements 1, 2, 3 and 4. Requirement 1: R value (=ID / IG) obtained by Raman spectroscopic measurement is 1.07 to 3. Requirement 2: A value and σA value obtained by small angle X-ray scattering measurement are −0.5 to 0 and 0 to 0.010, respectively. Requirement 3: for an electrode comprising an electrode mixture obtained by mixing 85 parts by weight of the carbonaceous material with 15 parts by weight of poly(vinylidene fluoride), the carbonaceous material in the electrode after being doped and dedoped with sodium ions is substantially free from pores having a size of not less than 10 nm. Requirement 4: Q1 value obtained by a calorimetric differential thermal analysis is not more than 800 joules / g.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Aluminum alloy automobile part
InactiveUS20150218679A1High strengthSuppress in SCC resistanceSuperstructuresNano sizeSmall-angle X-ray scattering
Provided is an automobile part comprising a 7000-series aluminum alloy sheet and provided with both strength and stress corrosion cracking resistance. The automobile part is configured from a 7000-series aluminum alloy sheet having a specific composition, and after artificial aging processing, the grain size distribution of precipitates evaluated by means of a small angle x-ray scattering among the crystal grains of the aluminum alloy plate and the normalized dispersion of the grain size distribution are controlled, resulting in being simultaneously provided with high strength in the form of an 0.2% proof stress of at least 350 MPa, high ductility, and SCC resistance. Also, the automobile part is configured from a 7000-series aluminum alloy sheet having a specific composition, and after artificial aging processing, a specific number density of nanosized precipitates are caused to be present as measured by a transmission electron microscope at 300,000× magnification in the crystal grains of the aluminum alloy plate, resulting in being simultaneously provided with high strength in the form of an 0.2% proof stress of at least 350 MPa, high ductility, and SCC resistance.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
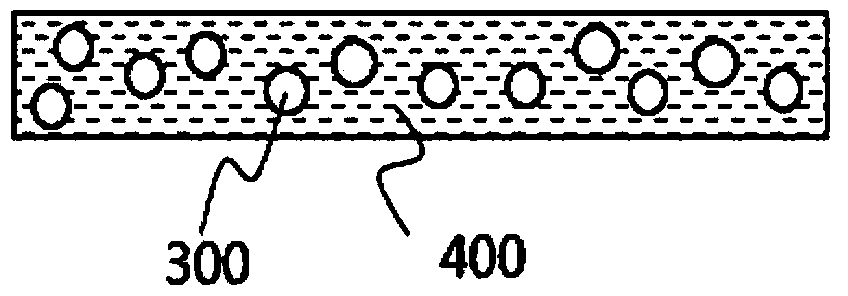
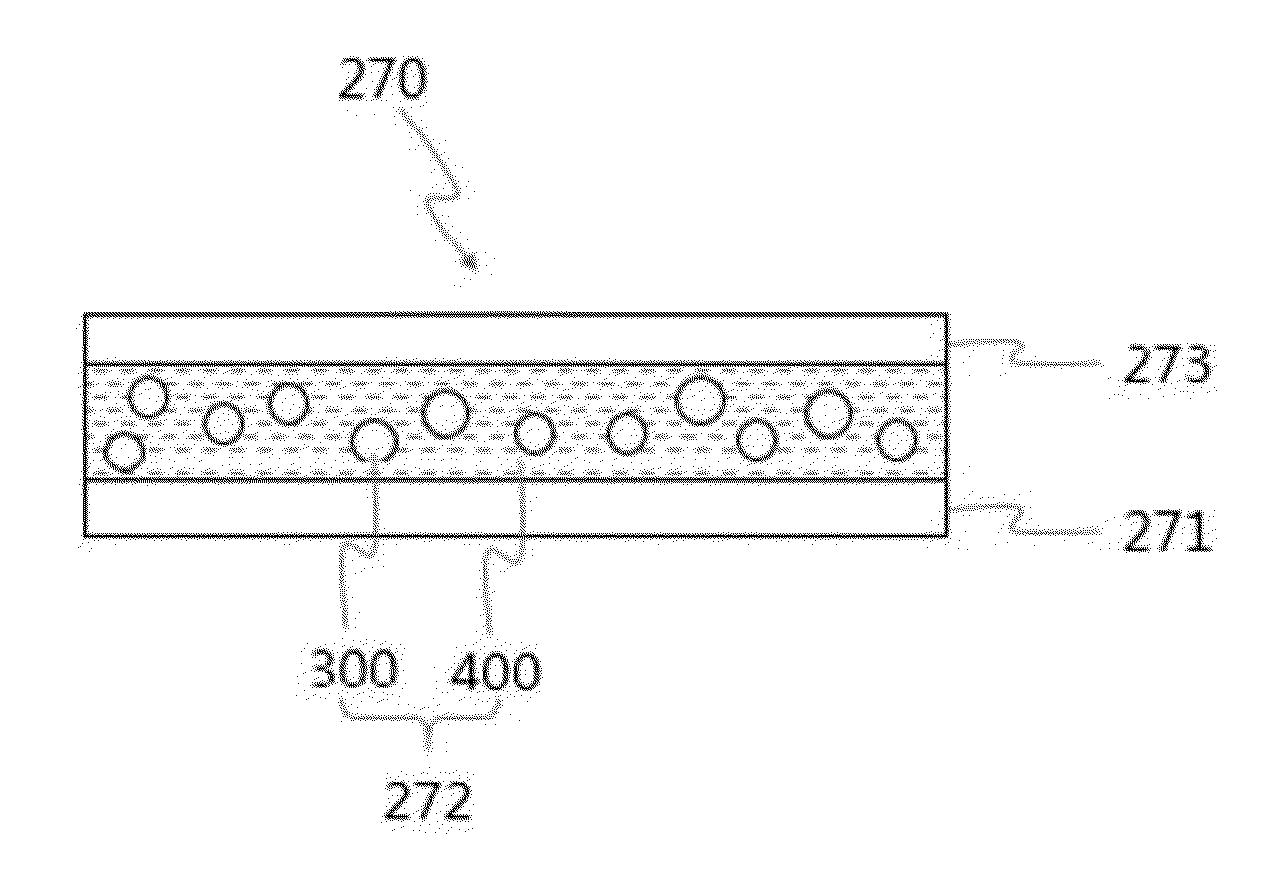
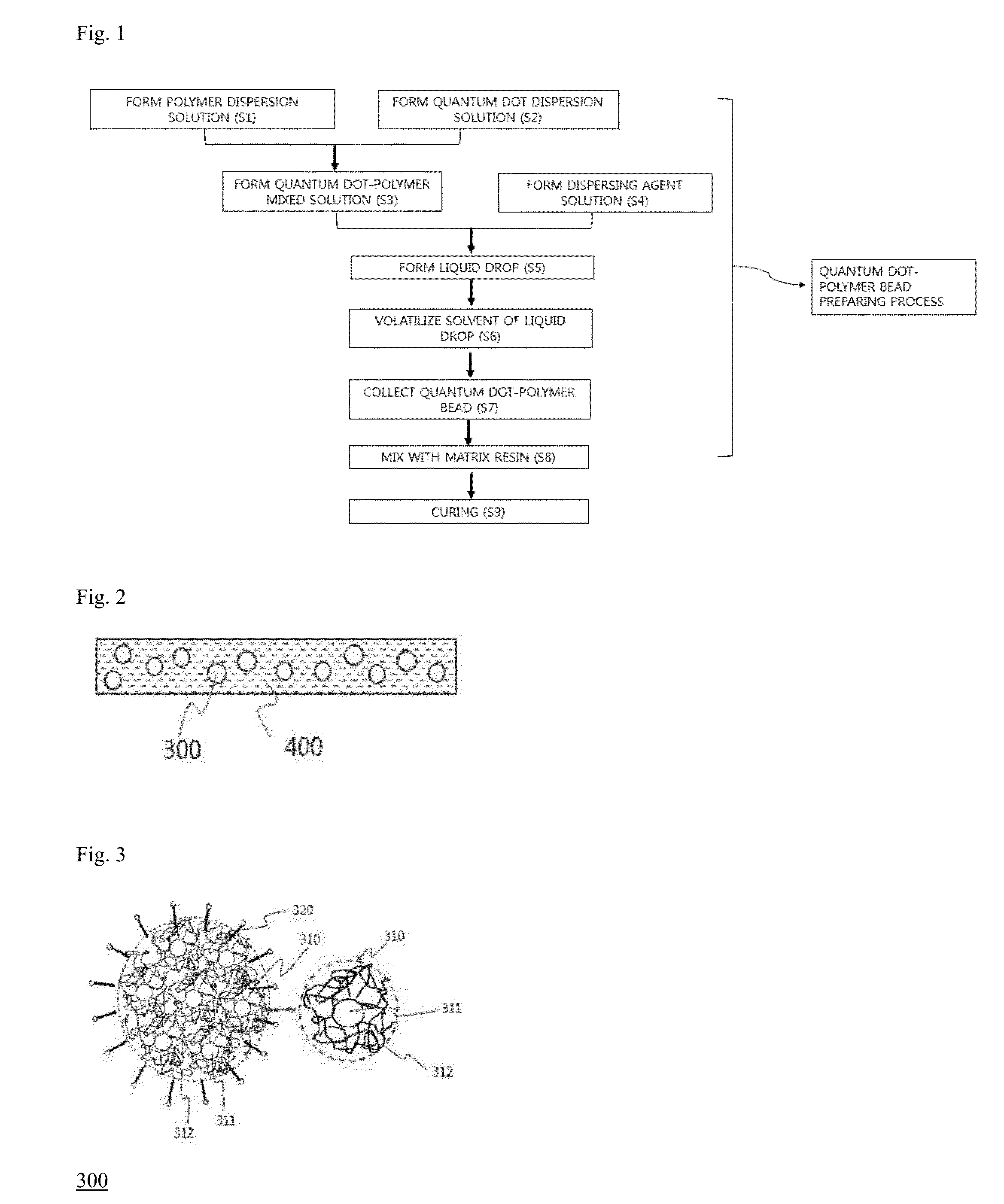
Method for preparing light conversion composite, light conversion film, backlight unit and display device having the same
InactiveCN106195921AElectroluminescent light sourcesSynthetic resin layered productsSmall-angle X-ray scatteringQuantum dot
A light conversion composite including a matrix resin and quantum dot-polymer beads dispersed within the matrix resin. The light conversion composite has a wave number q of 0.0056 angstrom-1 to 0.045 angstrom-1 at a peak point in a scattering intensity graph according to wave numbers measured by using small angle X-ray scattering.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
In-situ device for small-angle X-ray scattering experiment
ActiveCN106290426ASimple structureImprove performanceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSmall-angle X-ray scatteringSpecial design
The invention discloses an in-situ device for small-angle X-ray scattering experiment. The in-situ device comprises a vacuum and atmosphere protection system, a stress load and measurement system and a temperature load and measurement system. Self-alignment of samples during stress load is realized in the stress load system by adopting design of pull-press stress transformation. Special design is adopted in the temperature load and measurement system, wide X-ray channels are realized while uniform of temperature field is guaranteed, and meanwhile, heating temperature of the samples can reach 1100 DEG C. By the arrangement, the in-situ device is simple in structure, reliable in performance, high in measurement accuracy and capable of loading in temperature and stress simultaneously on the samples under the vacuum or atmosphere protection environment. The in-situ device is used in cooperation with a synchrotron-radiation small-angle X-ray scattering line station, in-situ measurement of to-be-measured samples on microscopic deformation, damage and fracture process under the mechanics use environment can be performed, and an effective and reliable measurement method for discovering changes of deformation and microstructure of brittle material samples under the stress is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mesoporous high polymer or carbon/silicon oxide nano-composite material with three-dimensional pore canal structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102380334AImprove stabilityImprove hydrophobicityMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationPtru catalystSmall-angle X-ray scattering
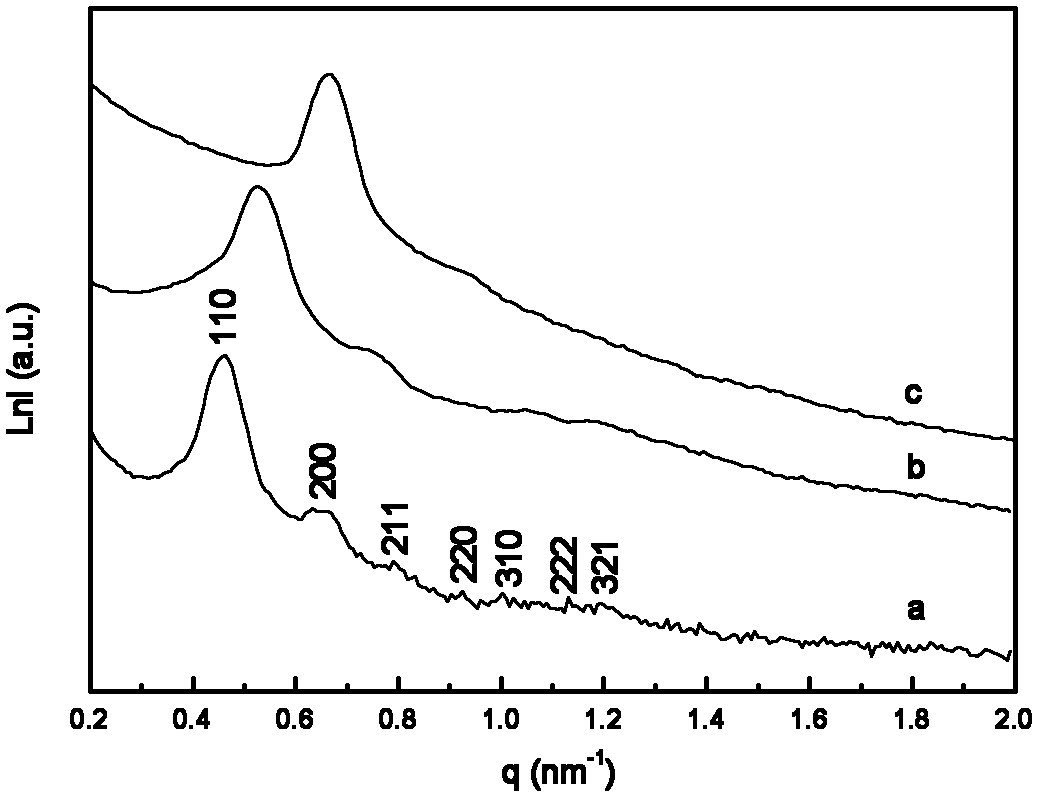
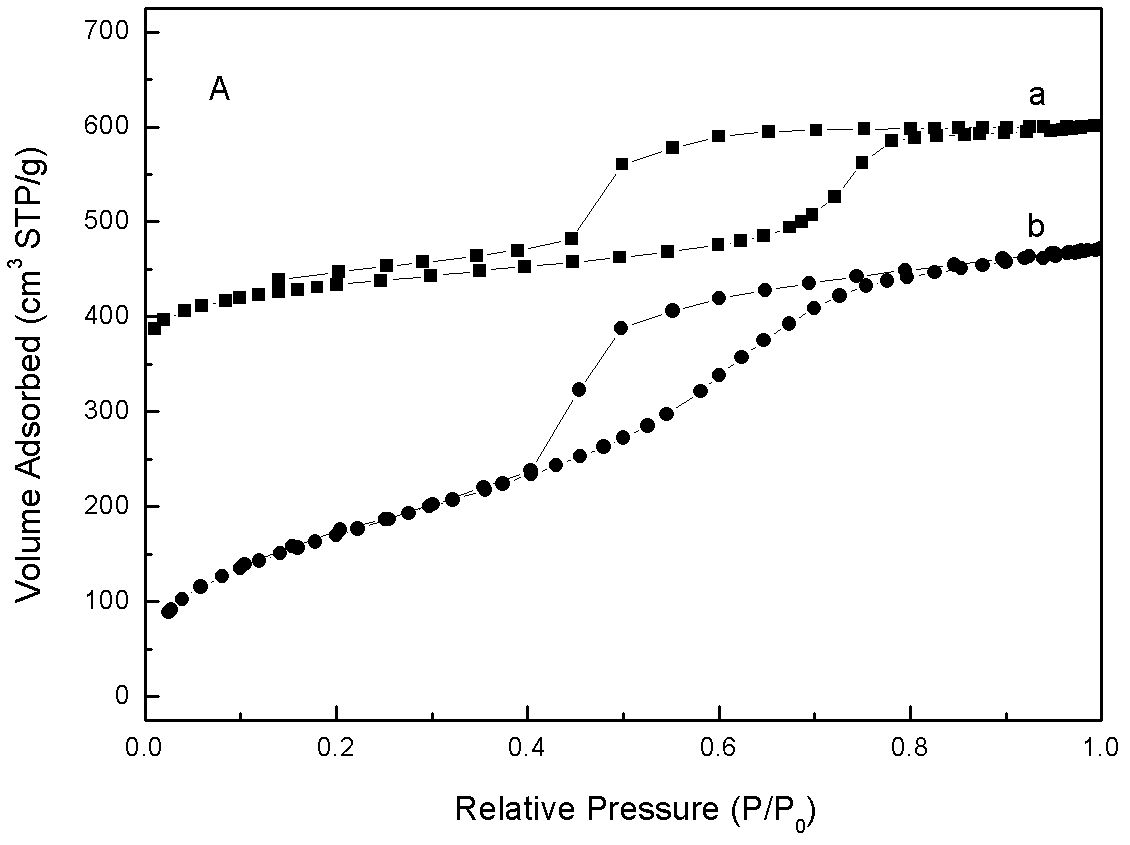
The invention discloses a mesoporous high polymer or carbon / silicon oxide nano-composite material with a three-dimensional pore canal structure. The mesoporous high polymer or carbon / silicon oxide nano-composite material is prepared by mixing PDMS-PEO (Polydimethylsiloxane-Poly Ethylene Oxide) and F127 serving as mixed structure directing agents and a phenolic resin performed polymer Resol serving as a carbon source precursor and reacting to obtain an As-made intermediate, and calcining, wherein crystal diffraction peaks of 110, 200, 211, 220, 310, 222 and 321 are shown in the small angle X ray scattering (SAXS) map of the As-made intermediate, and the q value ratio of the diffraction peaks is shown in the specifications. The specific surface area of the mesoporous carbon / silicon oxide nano-composite material with a three-dimensional cubic Imm pore canal structure is 650-1,600m<2> / g, the pore volume range is 0.45-0.63 cm<3> / g, the pore size is 5.0-6.2 nanometers, and the stability of a mesoporous material framework is up to 900 DEG C. The high polymer or carbon / silicon oxide nano-composite material provided by the invention is particularly suitable for the fields of super capacitor electrode materials, adsorbents, catalyst carriers, separation of biomolecules, gas-sensitive materials, optoelectronic devices, hydrogen storage and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Ultra-Small Angle X-Ray Scattering Measuring Apparatus
ActiveUS20080013685A1Accurate captureSuppressing smearing phenomenonRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsLattice planeSmall-angle X-ray scattering
An ultra-small angle X-ray scattering measuring apparatus includes a detector for detecting X-rays emitted from a sample, an X-ray collimating mirror arranged between the X-ray real focus and the sample, a monochromator arranged between the X-ray collimating mirror and the sample and an analyzer arranged between the sample and the detector. The X-ray collimating mirror includes a pair of X-ray mirrors that are arranged orthogonally relative to each other. The X-ray mirrors are multilayer film mirrors and their X-ray reflection surfaces are paraboloidal. The interplanar spacing of lattice planes of each of the multilayer films is continuously changed along the paraboloid so as to meet the Bragg's condition. The monochromator and the analyzer are formed by using a channel-cut crystal. The analyzer is driven to rotate for scanning around a 2θ-axial line and diffracted rays reduced to a spectrum by the analyzer are detected by the detector.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Method for preparing light conversion composite, light conversion film, backlight unit and display device having the same
InactiveUS20160161065A1Improve luminous efficiencyImproved quantum-dot degradation propertyPoint-like light sourceElectroluminescent light sourcesSmall-angle X-ray scatteringQuantum dot
A light conversion composite including a matrix resin and quantum dot-polymer beads dispersed within the matrix resin. The light conversion composite has a wave number q of 0.0056 Å−1 to 0.045 Å−1 at a peak point in a scattering intensity graph according to wave numbers measured by using small angle X-ray scattering.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
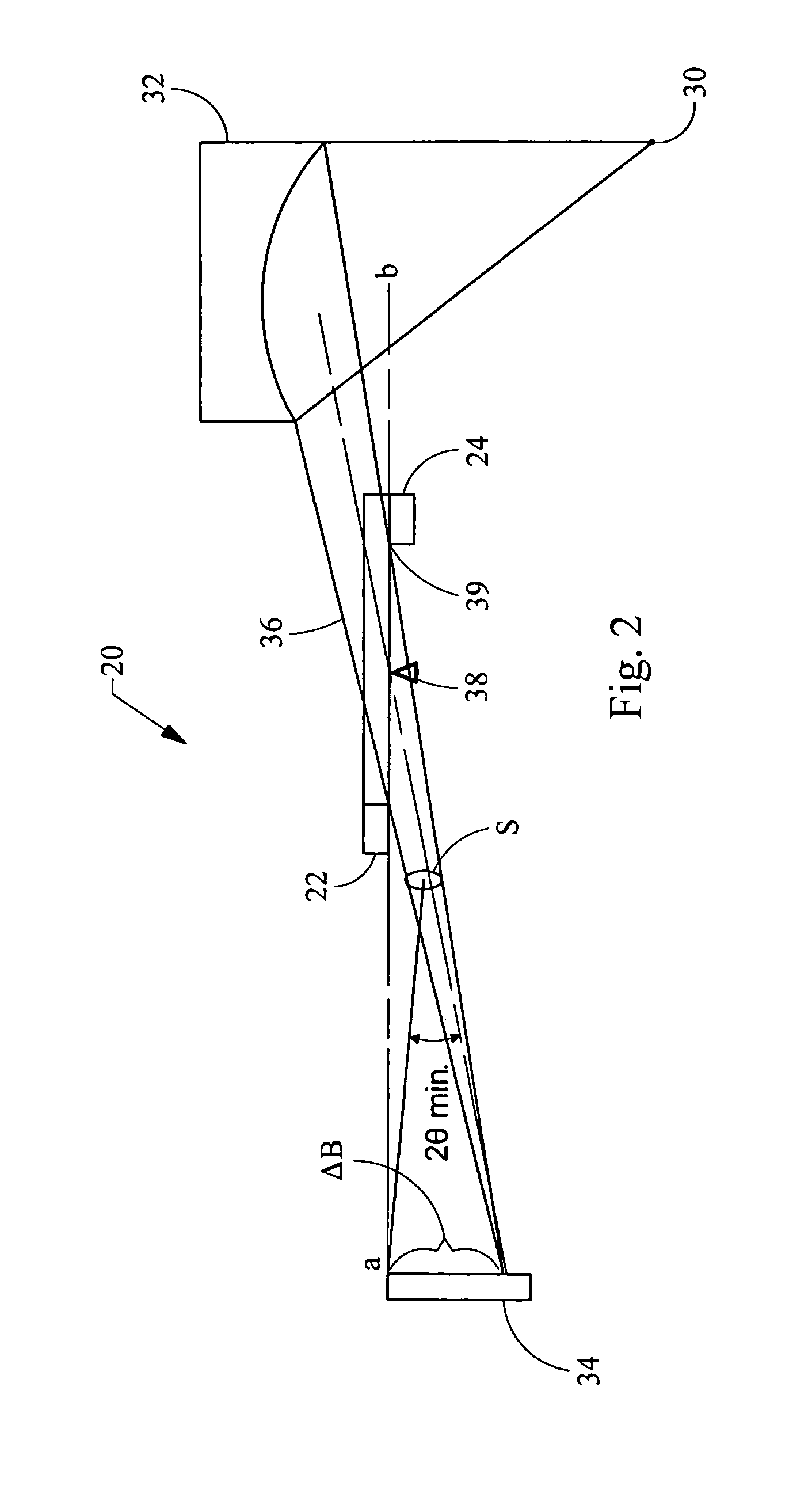
Vertical small angle x-ray scattering system
InactiveUS6956928B2Distance minimizationUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionSmall-angle X-ray scatteringX-ray
A small angle x-ray diffraction scattering system has a vertical orientation, allowing for simplified analysis of liquid samples. The system may function in a beam-up or a beam-down configuration. An x-ray source provides an initial x-ray beam that is directed vertically along a primary beampath to a sample located on a sample support. The small angle scattered x-ray energy travels through a secondary beampath to a detector. The primary and secondary beampaths may be evacuated and separated from a sample chamber by fluid seals. Beam conditioning optics and a collimator may be used in the primary beampath, and a beamstop used in the secondary beampath. The sample chamber may have a microscope or camera, which may be movable, for observing the sample, and a translation stage for moving the sample in at least two dimensions.
Owner:BRUKER AXS
Anti-reflective film
ActiveUS20180231687A1Reduce reflectivityHigh light transmittanceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSynthetic resin layered productsSmall-angle X-ray scatteringComputational physics
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Ink jet ink, ink jet recording method, ink cartridge, ink set and image forming method
ActiveUS20080007606A1Good weather resistanceImproved bleed resistanceMeasurement apparatus componentsInksOrganic solventSmall-angle X-ray scattering
An ink jet ink which can form images whose bleeding resistance is high and whose bronzing phenomenon is suppressed, is provided. The ink is an ink jet ink for use together with a pigment ink. The ink jet ink is characterized in that: the ink jet ink contains a coloring material, a polyvalent metal and a water-soluble organic solvent(s); the coloring material is at least a compound represented by the general formula (I); a content (mol / g) of the polyvalent metal is 2.0×10−6 mol / g or more and 4.0×10−4 mol / g or less; a total content (mass %) of the water-soluble organic solvent(s) is 25.0 mass % or more with respect to the total mass of the ink; and in a dispersion distance distribution, measured by a small angle X-ray scattering method, of molecular aggregates in the ink jet ink whose coloring material concentration is adjusted to 0.5 mass %, a dispersion distance d75 value corresponding to 75% of a distribution is 12.60 nm or less. General Formula (I):
Owner:CANON KK
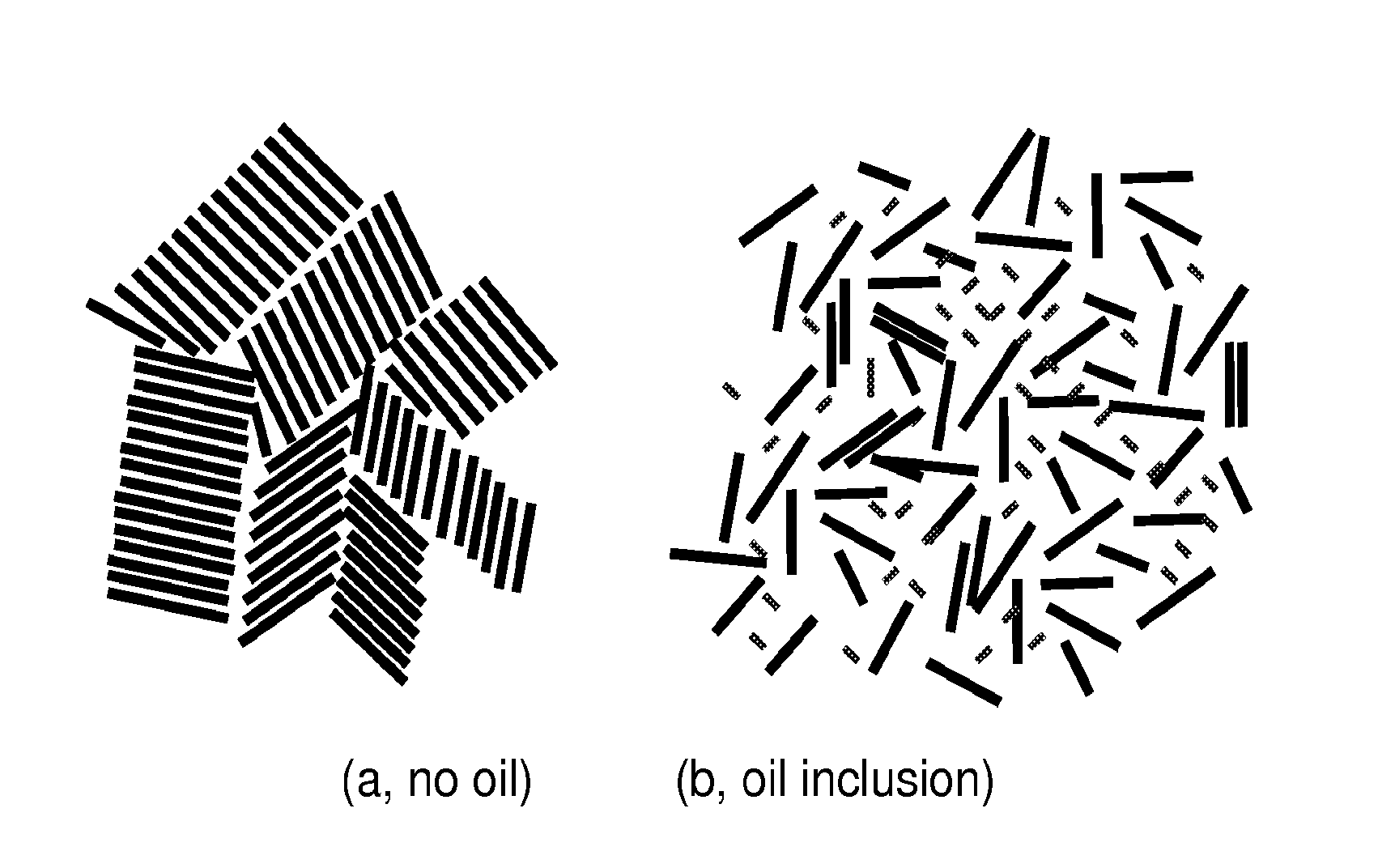
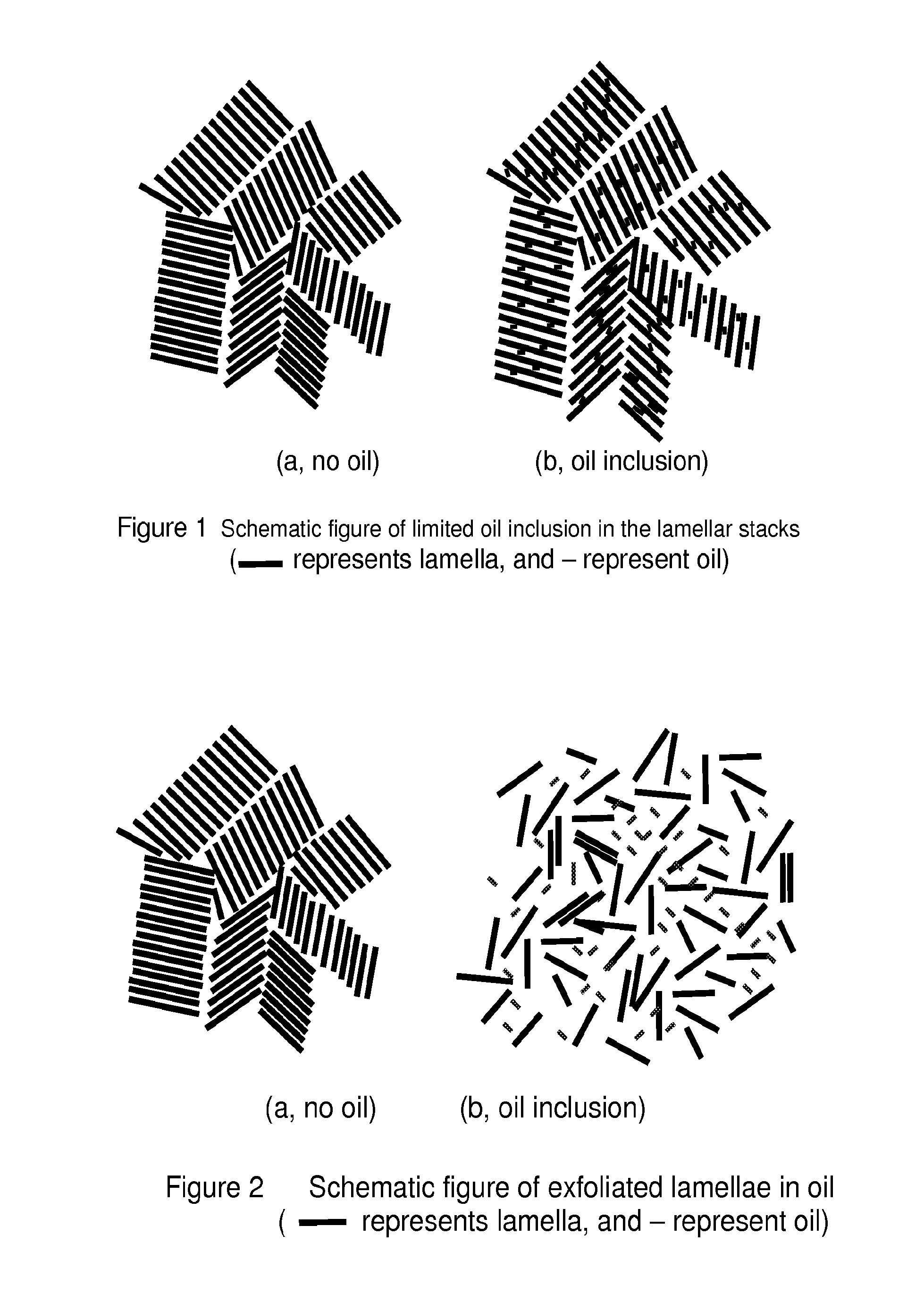
Polymer compositions, methods of making the same, and articles prepared from the same
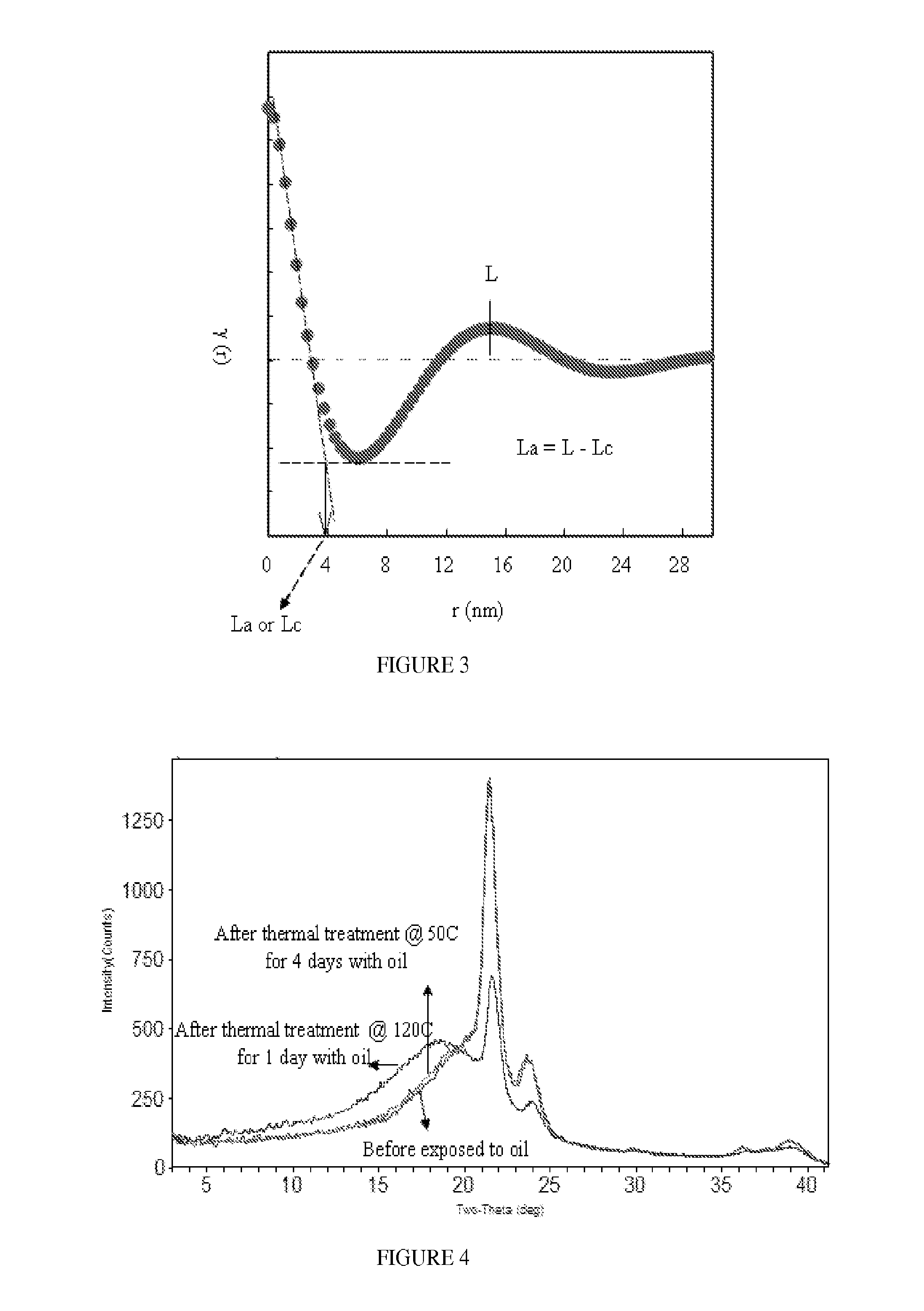
The invention provides a composition comprising a first composition that comprises an ethylene-based polymer and an oil, and wherein the first composition has the following property as determined by small angle x-ray scattering: (Loil−Lno-oil) / Lno-oil>10%, where Loil is the long period of the polymer with oil, and Lno-oil is the long period of the polymer without oil.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Anode active material for secondary battery and method for producing the same, anode and lithium ion battery using the same
InactiveUS20150214548A1New structureNon-metal conductorsConductive materialSmall-angle X-ray scatteringSilicon oxide
To form the silicon oxide-based composite material having new structure as directly obtained by pyrolyzing polysilsesquioxane having specific structure under an inert gas atmosphere, and the formed silicon oxide-based composite material having scattering recognized in a region: 0.02Å−1<q<0.21 Å−1 in a spectrum measured by a small-angle X-ray scattering method, having graphite carbon in which scattering is recognized at 1,590 cm−1 (G band / graphite structure) and 1,325 cm−1 (D band / amorphous carbon), and a peak intensity ratio (ID / IG ratio) of amorphous carbon to crystalline carbon being in a range of 2.0 to 5.0 in a spectrum measured by Raman spectroscopy, and being represented by a general formula SiOxCy (0.5<x<1.8, 1<y<5).
Owner:JNC CORP +1
Apparatus and methods for low temperature small angle x-ray scattering
ActiveUS20150233804A1Improve SAXS data qualityFacilitate subtractionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationAqueous bufferSmall-angle X-ray scattering
Apparatus and methods for performing small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) at low (cryogenic) temperatures for determining the structure of and changes in the structure of proteins, DNA, RNA, and other biological molecules and biomolecular assemblies and structures. A cryogenic, small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) application sample holder, includes a sample cell including a base portion and at least two parallel walls disposed on the base, wherein the sample cell has a liquid volume capacity defined by the walls and the base portion of 0.001 to 10 microliters. A method for performing cryogenic SAXS on a sample includes the steps of providing a sample biomolecule solution containing an aqueous buffer, a biomolecule, and a cryoprotectant agent, wherein the cryoprotectant agent comprises up to 60% (w / w) of the biomolecule solution, and other known components as necessary to solubilize and stabilize the biomolecule, in a sample holder of claim 1 or 18, cryogenically cooling the sample solution in the sample holder at a rate equal to or greater than 100 K / sec without ice formation, and examining the cooled sample using small angle X-ray scattering by passing a beam of X-rays through the sample.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com