In-situ device for small-angle X-ray scattering experiment
An X-ray, in-situ technology, applied in the field of measuring instruments, can solve the problems of incompatibility with the limited space of synchrotron radiation X-ray scattering line stations, unsuitable samples, low temperature, etc., and achieves good application prospects, simple structure, and high measurement accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
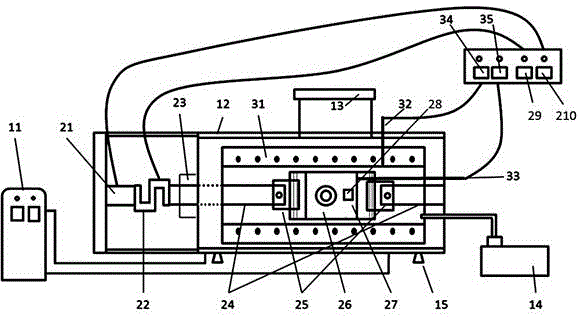
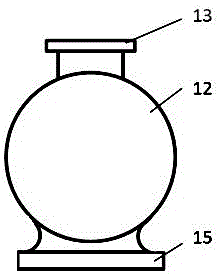
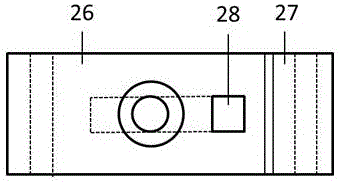
[0031] The basic structure of the in-situ device in this embodiment is as follows figure 1 , figure 2 shown, where figure 2 Left side view of the whole device. The in-situ device can be functionally divided into: vacuum and atmosphere protection system, stress loading and measuring system, temperature loading and measuring system. like figure 1 As shown, the vacuum and atmosphere protection system includes a water cooler 11, an airtight chamber 12, a sample loading flange 13, a vacuum pump 14, and a support 15; the stress loading system includes a power source 21, a stress measurement module 22, and a bellows dynamic seal 23 , transmission rod 24, hinge 25, U-shaped sample holder 26, T-shaped sample holder 27, top-like key 28, power control module 29, stress reading module 210; the temperature loading and measurement system includes a resistance furnace 31. A resistance furnace temperature measurement module 32, a sample temperature measurement module 33, a resistance fu...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The structure of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that the power source 21 selects an electric thrust rod with a rated force of 1 kN and a stroke of 10 mm, the measurement range of the stress measurement module 22 is 0-1 kN, and the measurement accuracy is 2N ; U-shaped sample holding member 26, T-shaped sample holding member 27 and top sample key 28 constitute the sample holding mechanism, which can place samples with a thickness of 3 mm and a width of 8 mm.
[0043] In this example, the stress loading accuracy of the sample can reach 0.1 MPa, the stress loading range is 0~40 MPa, and the temperature loading range is room temperature~1100 o C, the degree of vacuum can reach 2Pa. This embodiment can be used for heating and stressing small-angle X-ray scattering experiments on porous materials and geotechnical samples with low compressive strength but high measurement accuracy.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com