Patents
Literature
128 results about "Injection Procedure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
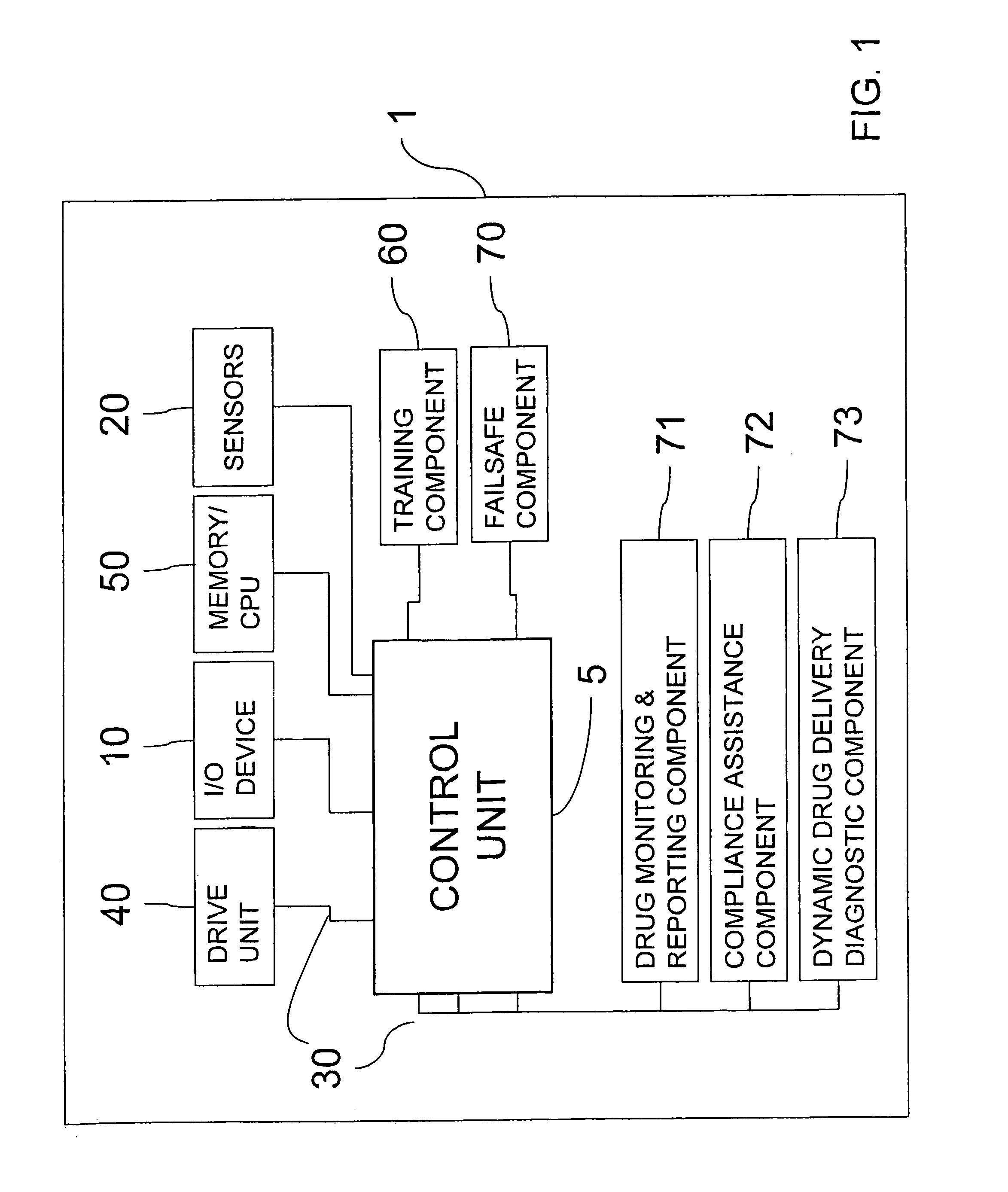
Administration of a drug into a location within the body; this can be achieved either through an established access or via a needle.
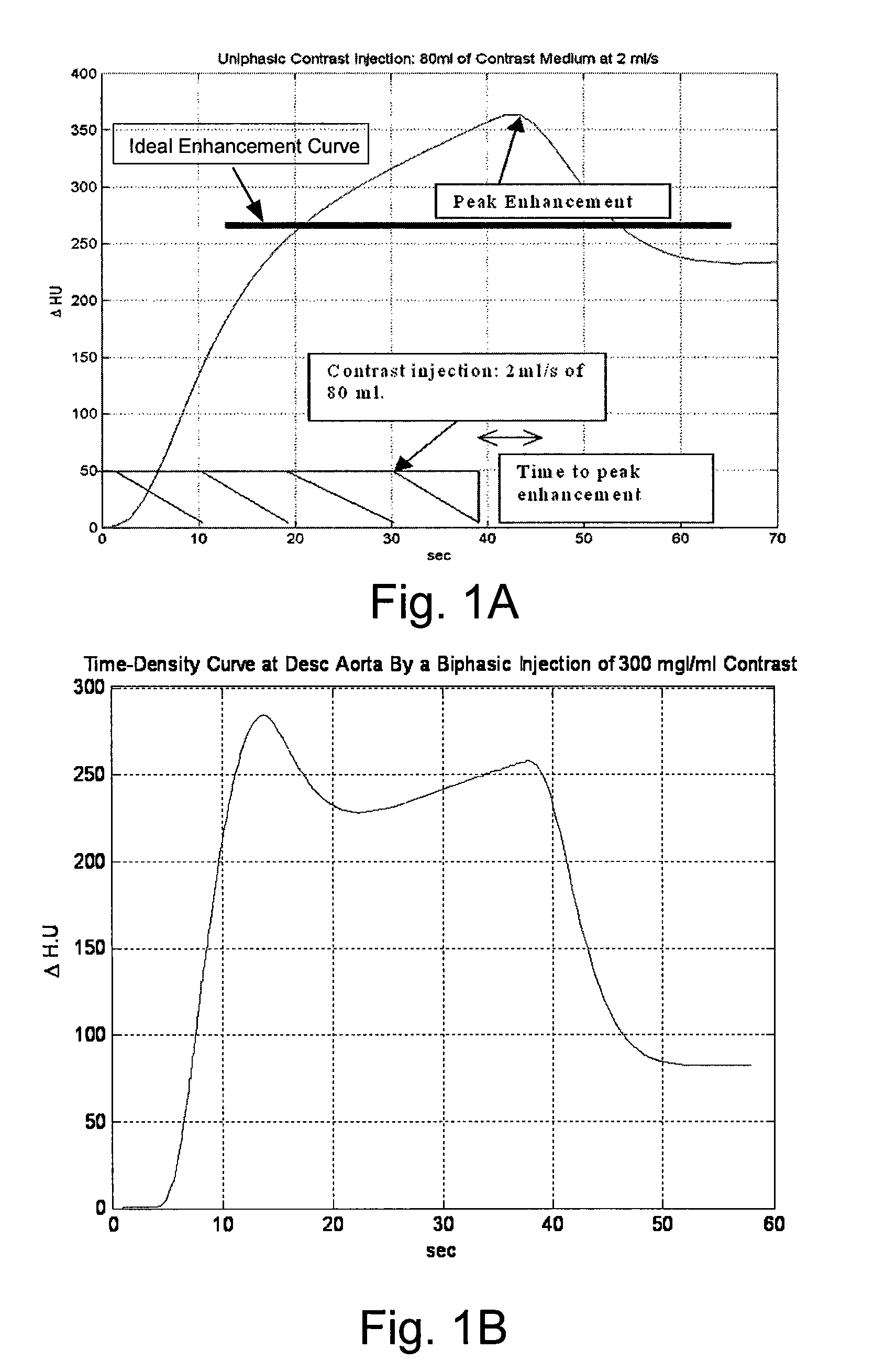
Patient specific dosing contrast delivery systems and methods
InactiveUS6385483B1Improve image qualityMinimum risk and costDrug and medicationsSurgeryMedicineMedical device
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Method and device for painless injection of medication
InactiveUS7637891B2Simple and inexpensive to performSimple and inexpensive to and operateAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesMedication injectionMedical treatment
A device for painlessly injecting medications, and a method for providing a substantially painless injection of medication into a patient that does not require the use of an anesthetic, that does not require the medical personnel to spend a substantial amount of time performing the injection procedure, that is relatively simple and inexpensive to perform and operate, and that provides a relatively high degree of safety for both the medical personnel and for the patient. The injection needle can have an outside diameter greater than 0.20 mm and less than about 0.38 mm. The medicament can be injected painlessly through the needle and into the patient at a substantially constant volumetric flow rate of about 0.05 μL / s to about 50 μL / s.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Injection device
InactiveUS20060258990A1HandlingSimple and safe operationAutomatic syringesMedical devicesRisk strokeSubcutaneous tissue
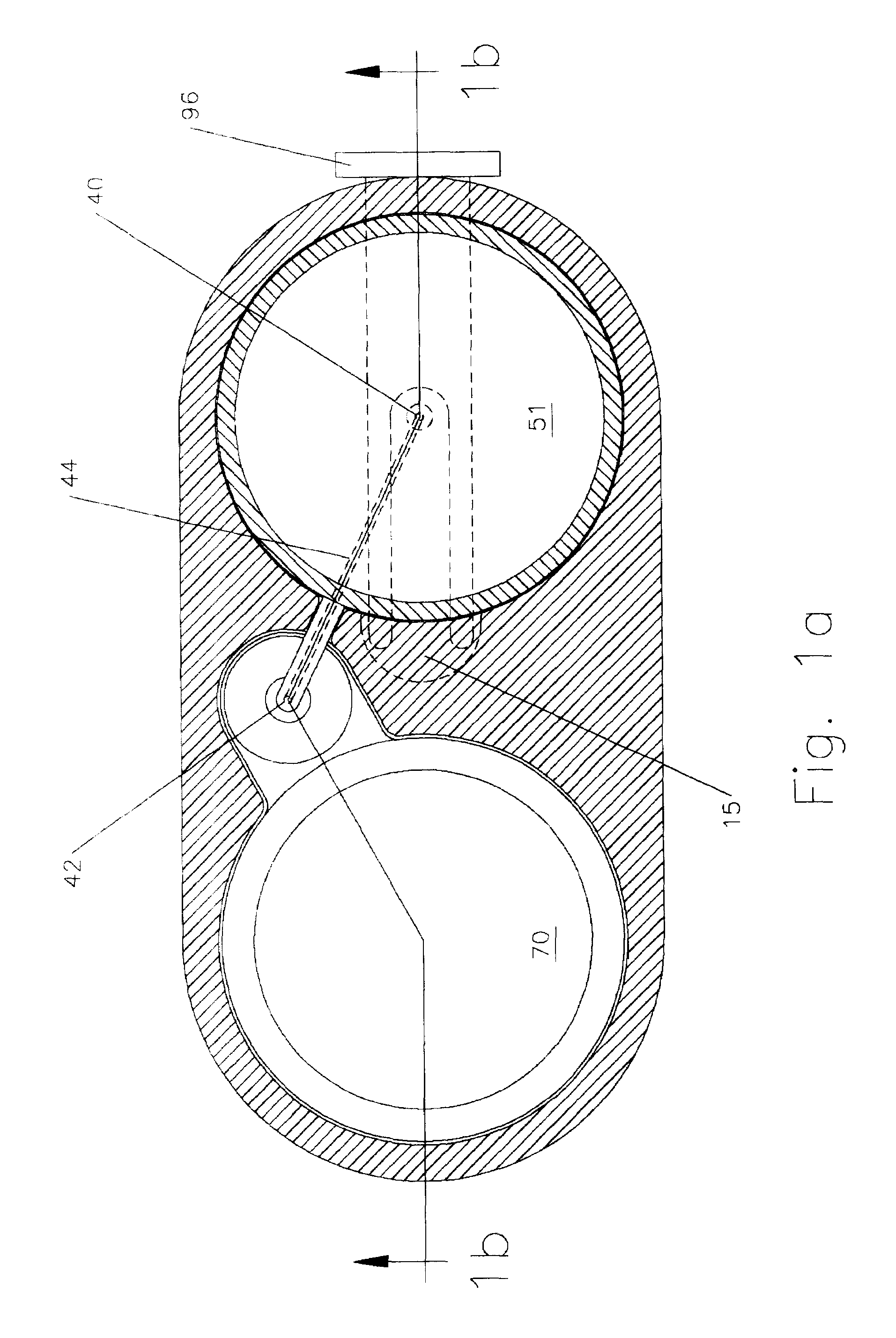
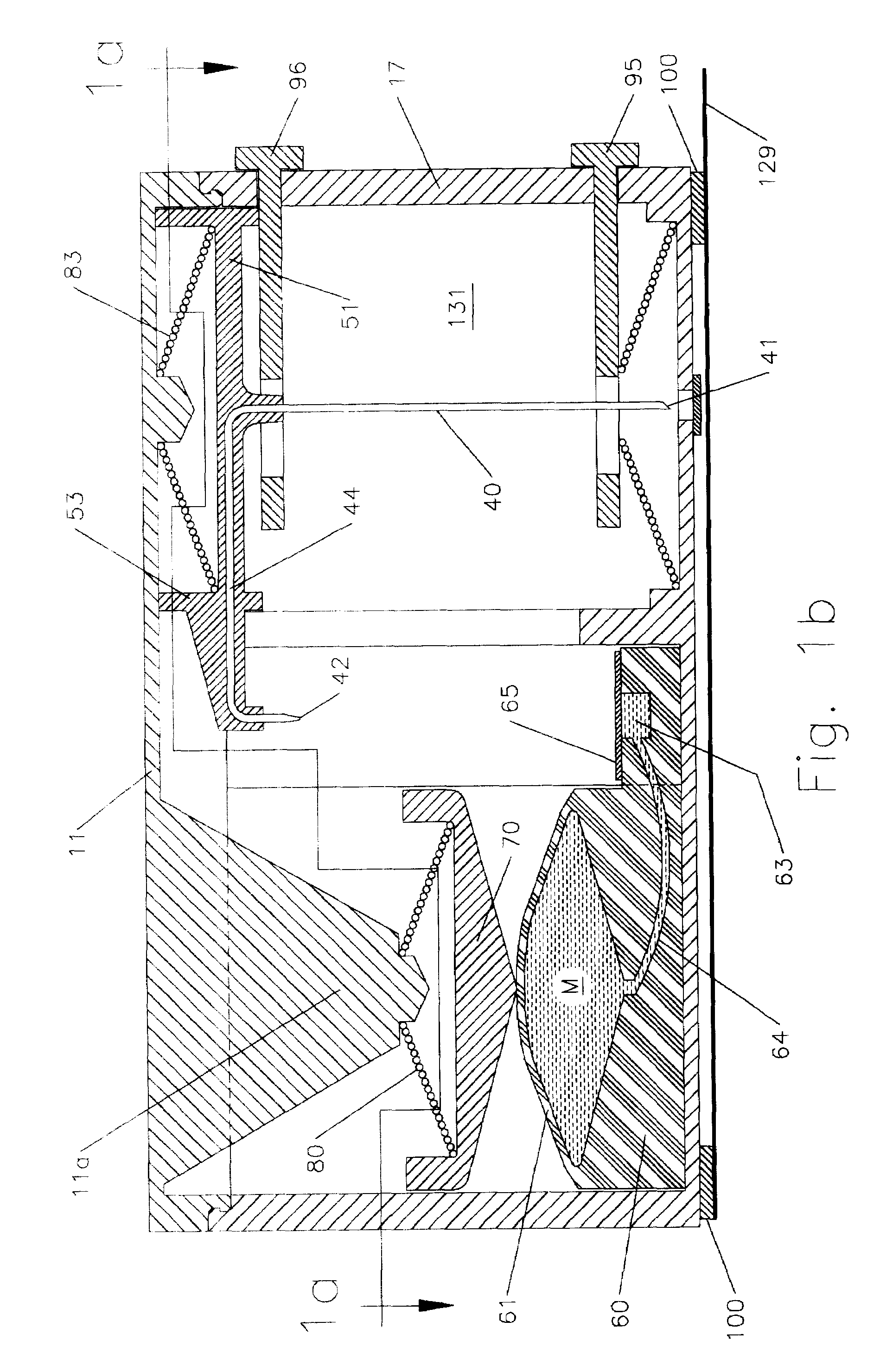
An injection device for a syringe, having a syringe body, a cannula with a needle, a plunger with a plunger rod, and an injection carriage for displacing the syringe body and the plunger, comprises at least one actuating element that acts on the injection carriage to carry out the injection procedure. The actuating element (120, 220, 320) cooperates with components which withdraw the needle (108, 208, 308) from the puncture site once the injection procedure has been completed, using a return stroke (H3) that is applied to the injection carriage. A single, targeted linear movement inserts the needle to a defined depth, injects the medicament and, once the injection has been completed, produces a return stroke which allows the needle to be withdrawn into the housing and thus out from the puncture site. The injection device is advantageously equipped with additional components which produce a delay (TV) between the completion of the injection stroke (H2) and the start of the return stroke (H3). The advantage of said delay is that the pressure that has been produced in the subcutaneous tissue by the injection of the medicament can subside before the needle is withdrawn, thus preventing to a great extent the penetration of the medicament into the insertion channel of the needle. A volume adapter (410) can advantageously be used to predetermine the injection stroke (H2) and thus the quantity of a medicament that is administered during the course of the injection stroke (H2).
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
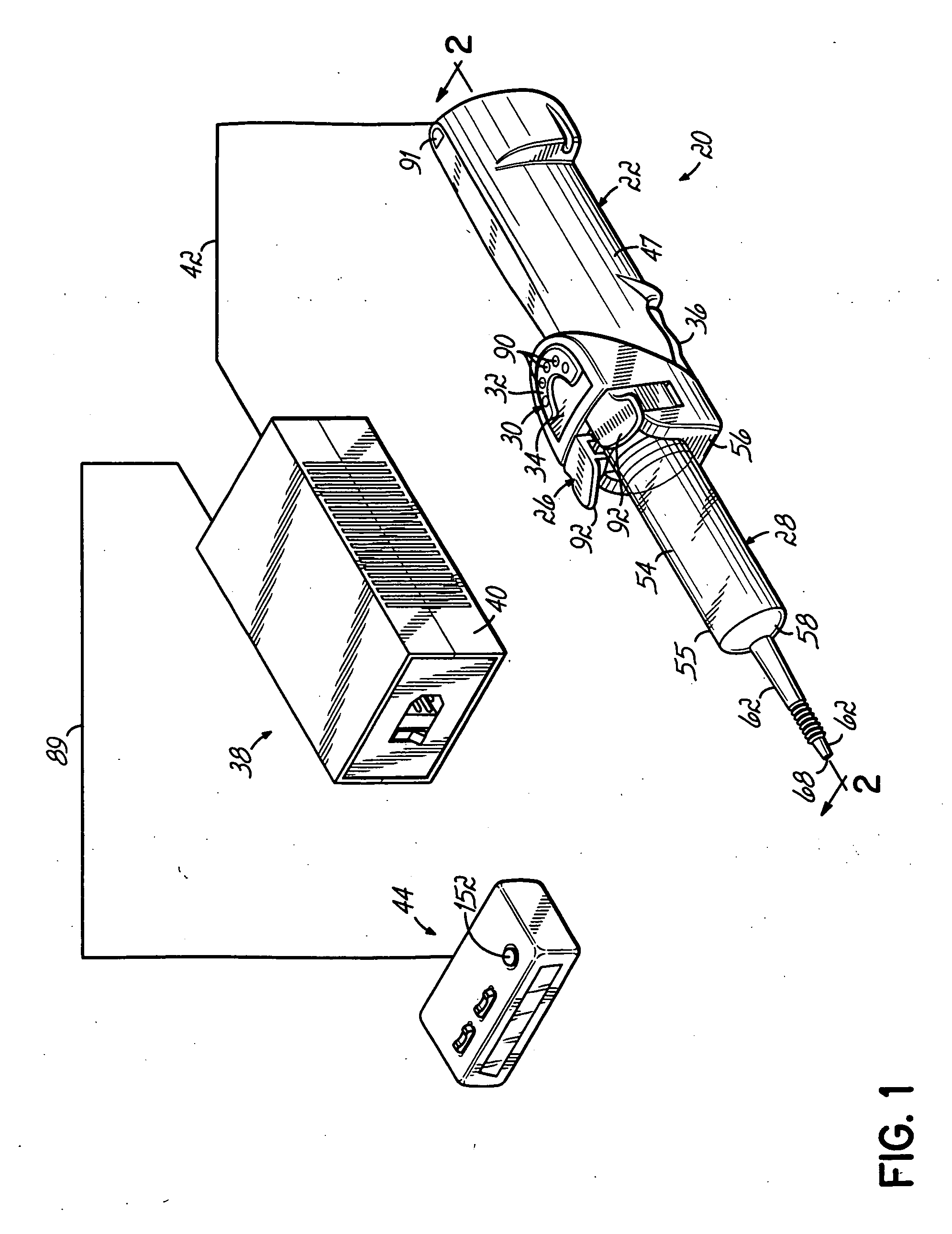
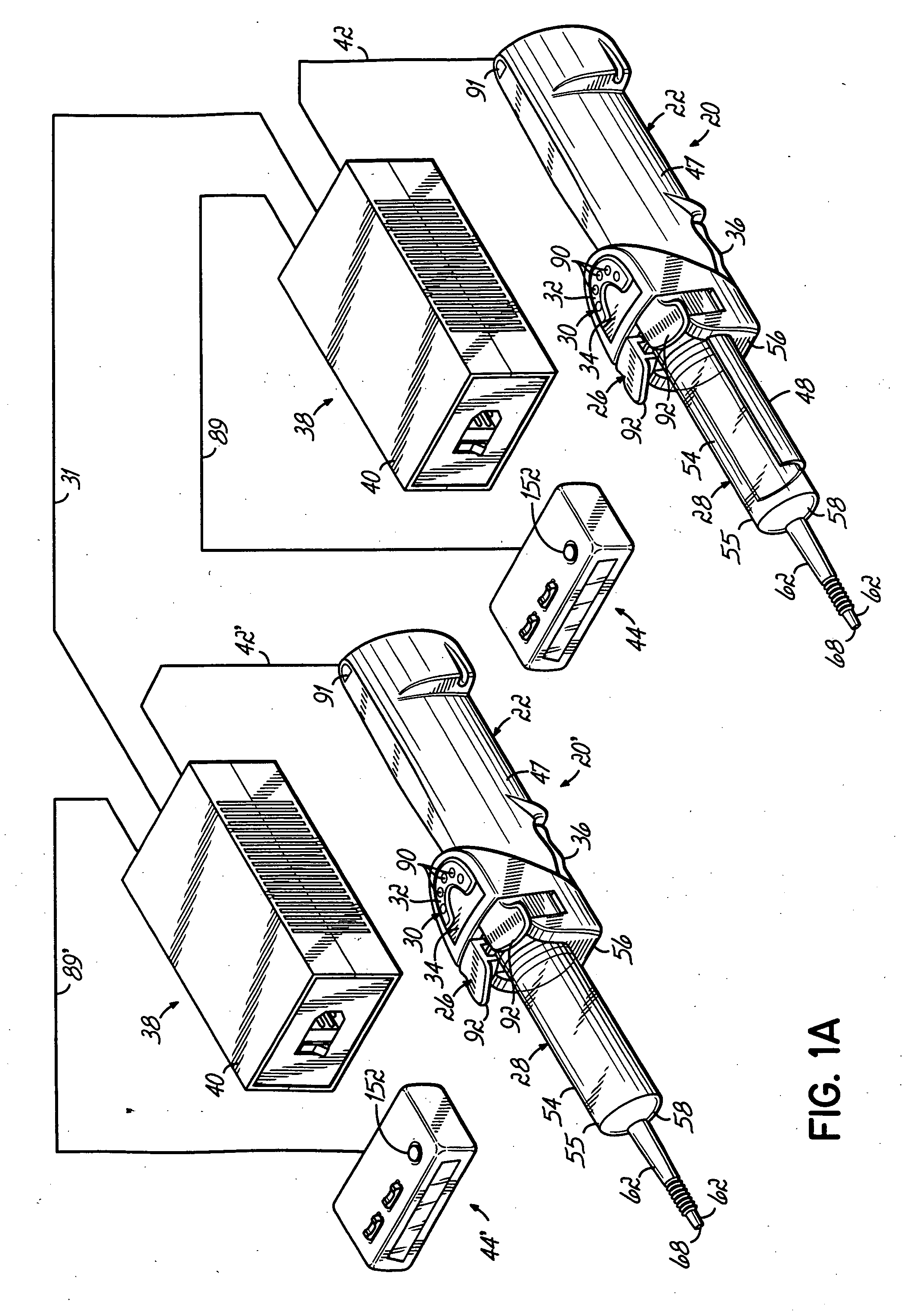
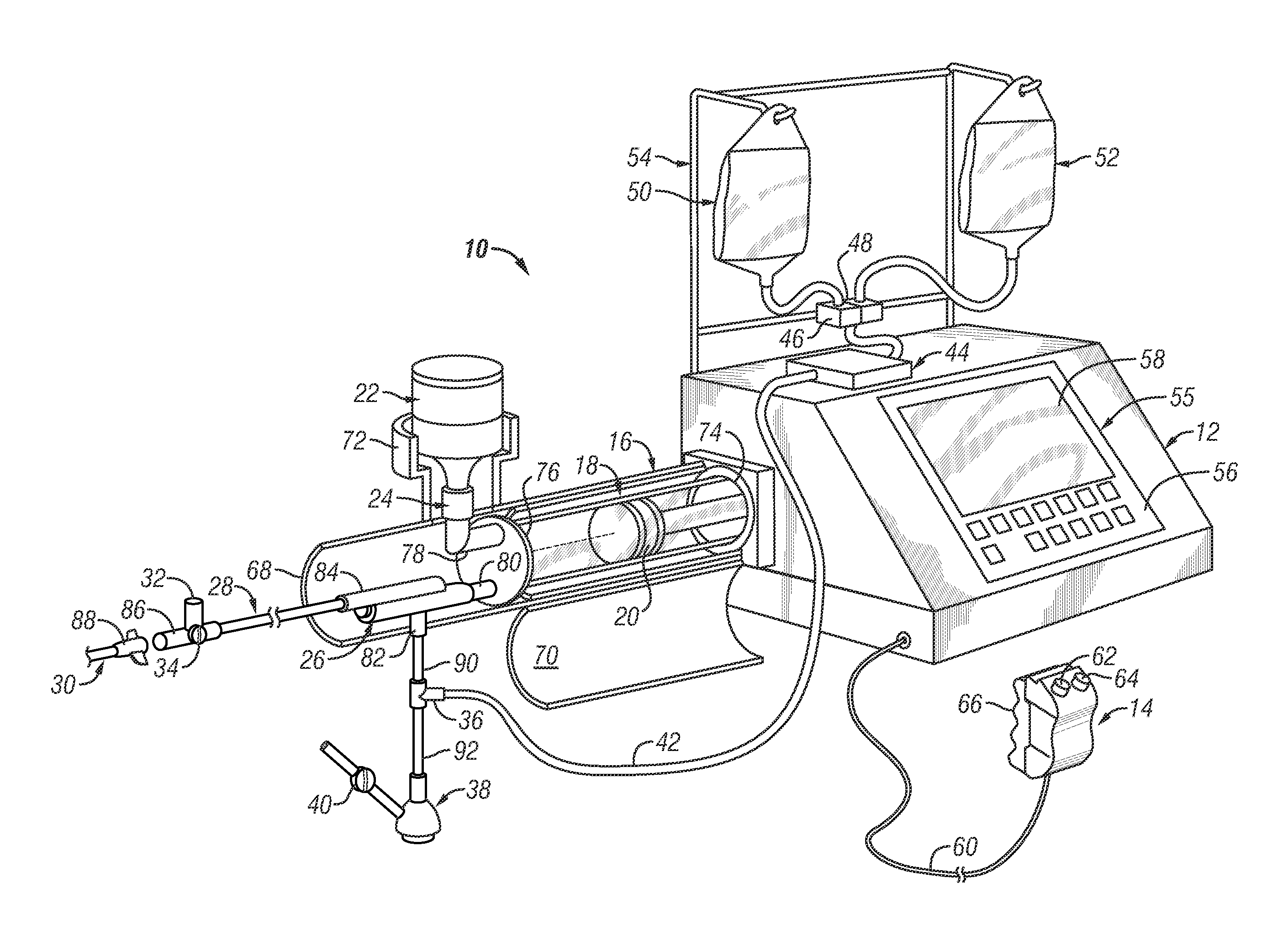
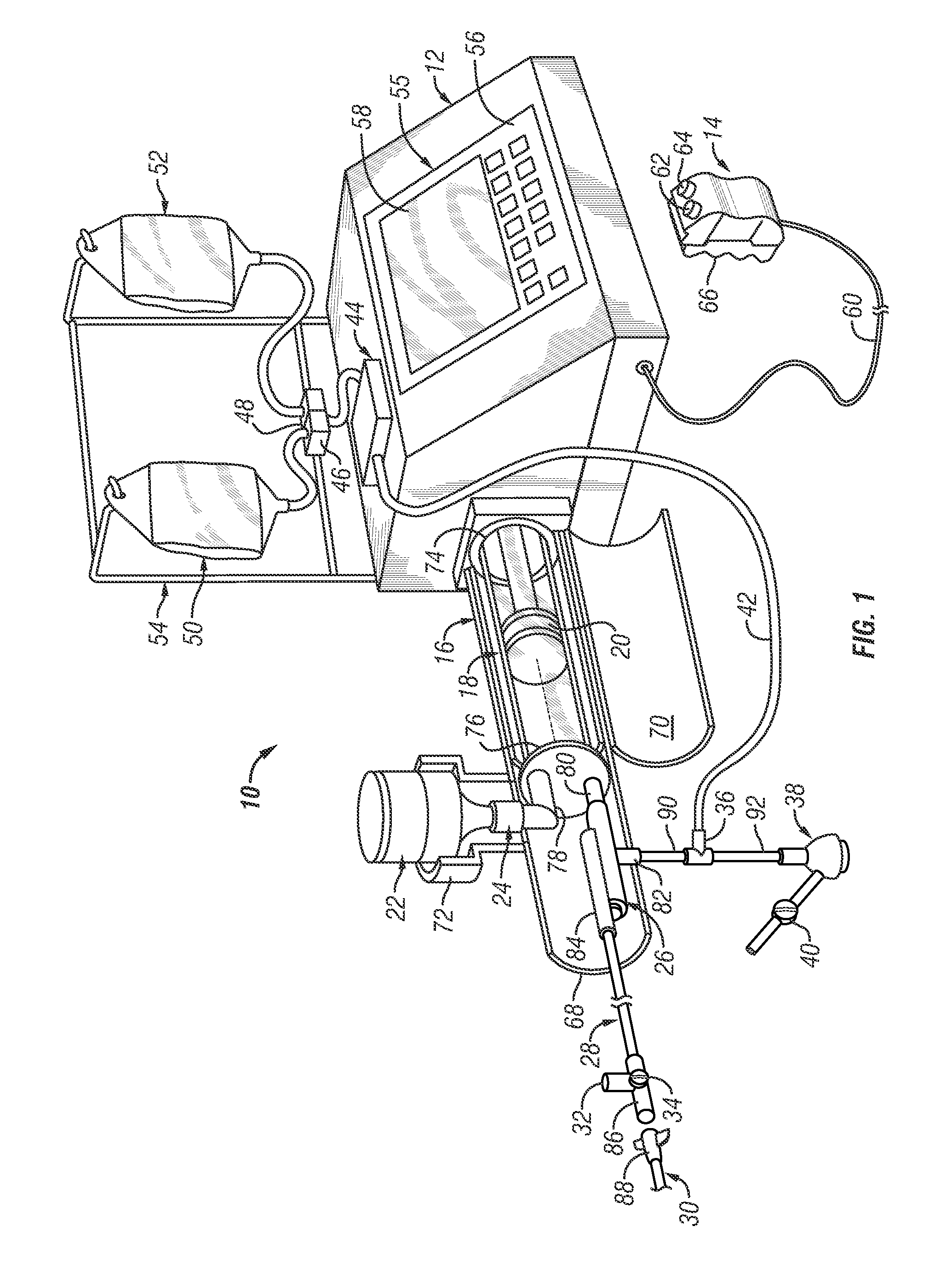
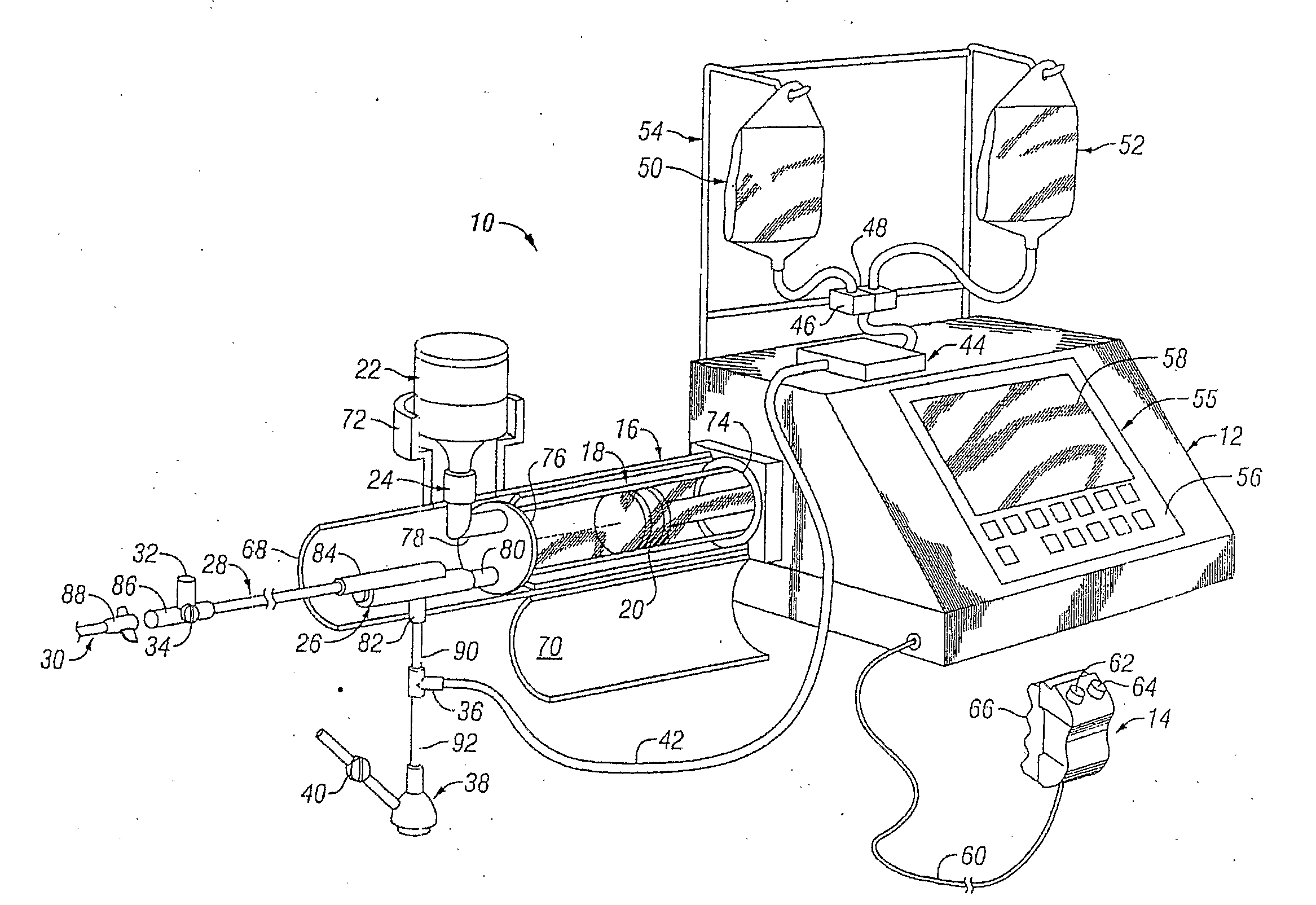
Injector
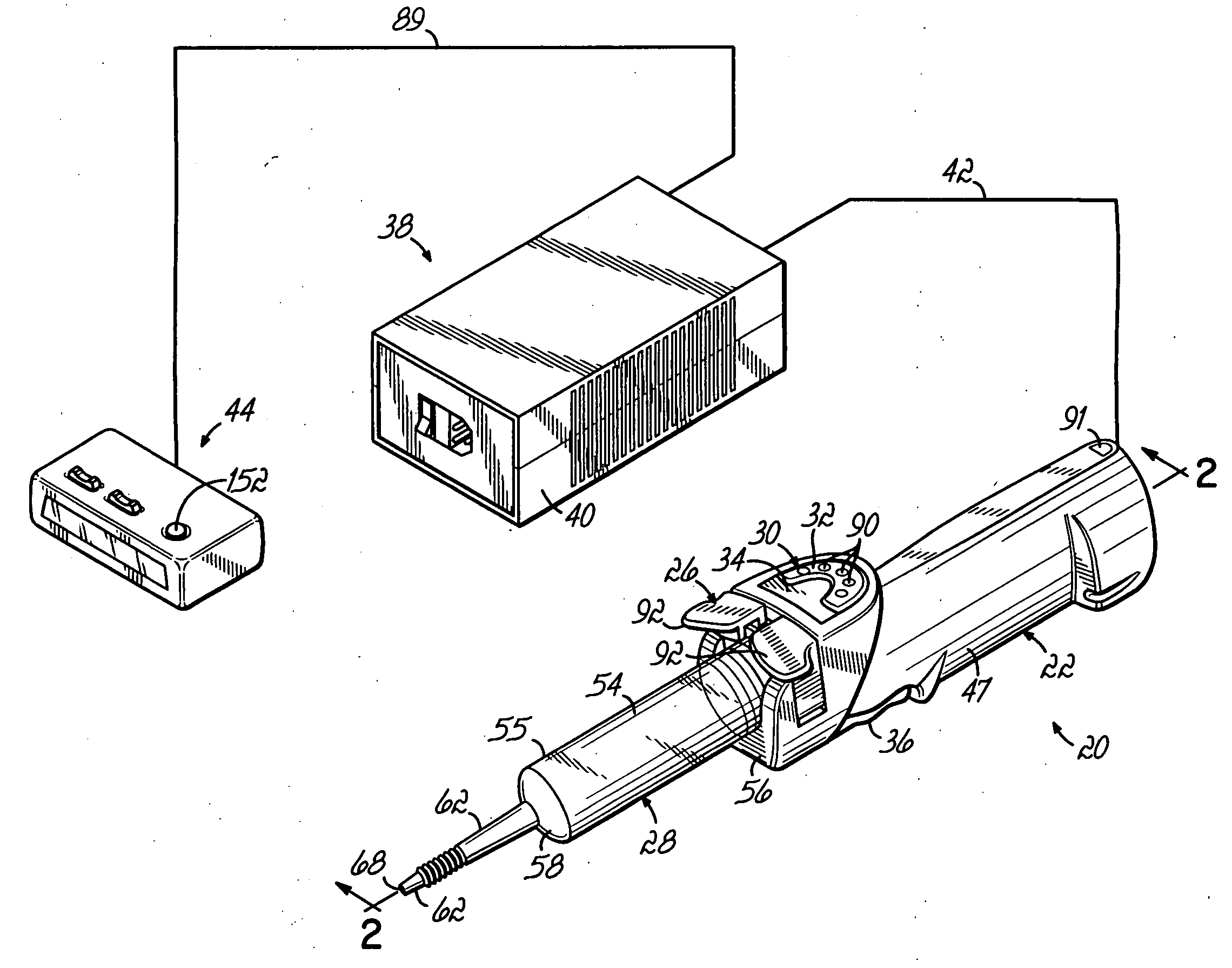
InactiveUS6929619B2Reduces and eliminates power connectionGood adhesionAutomatic syringesMedical devicesAxis of symmetryRadiographic contrast media
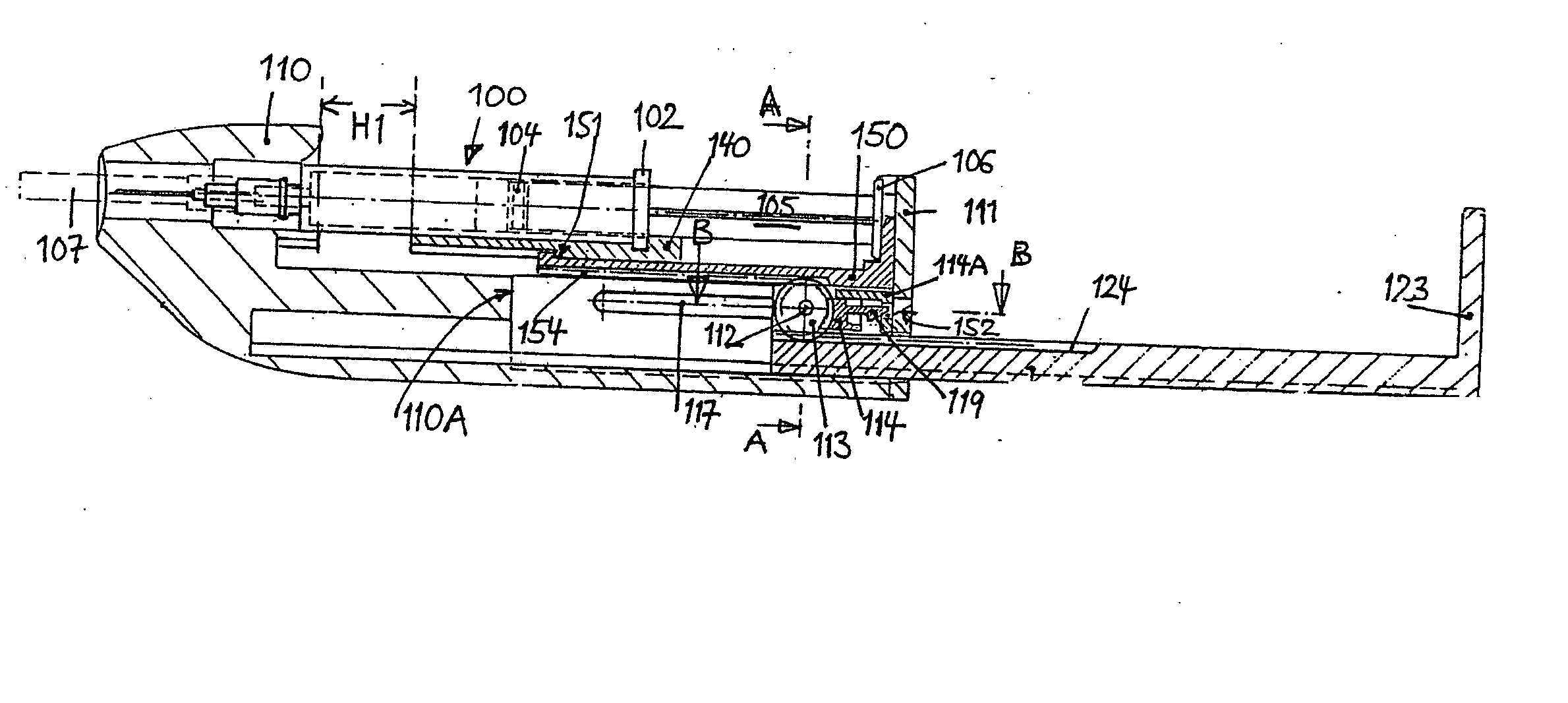
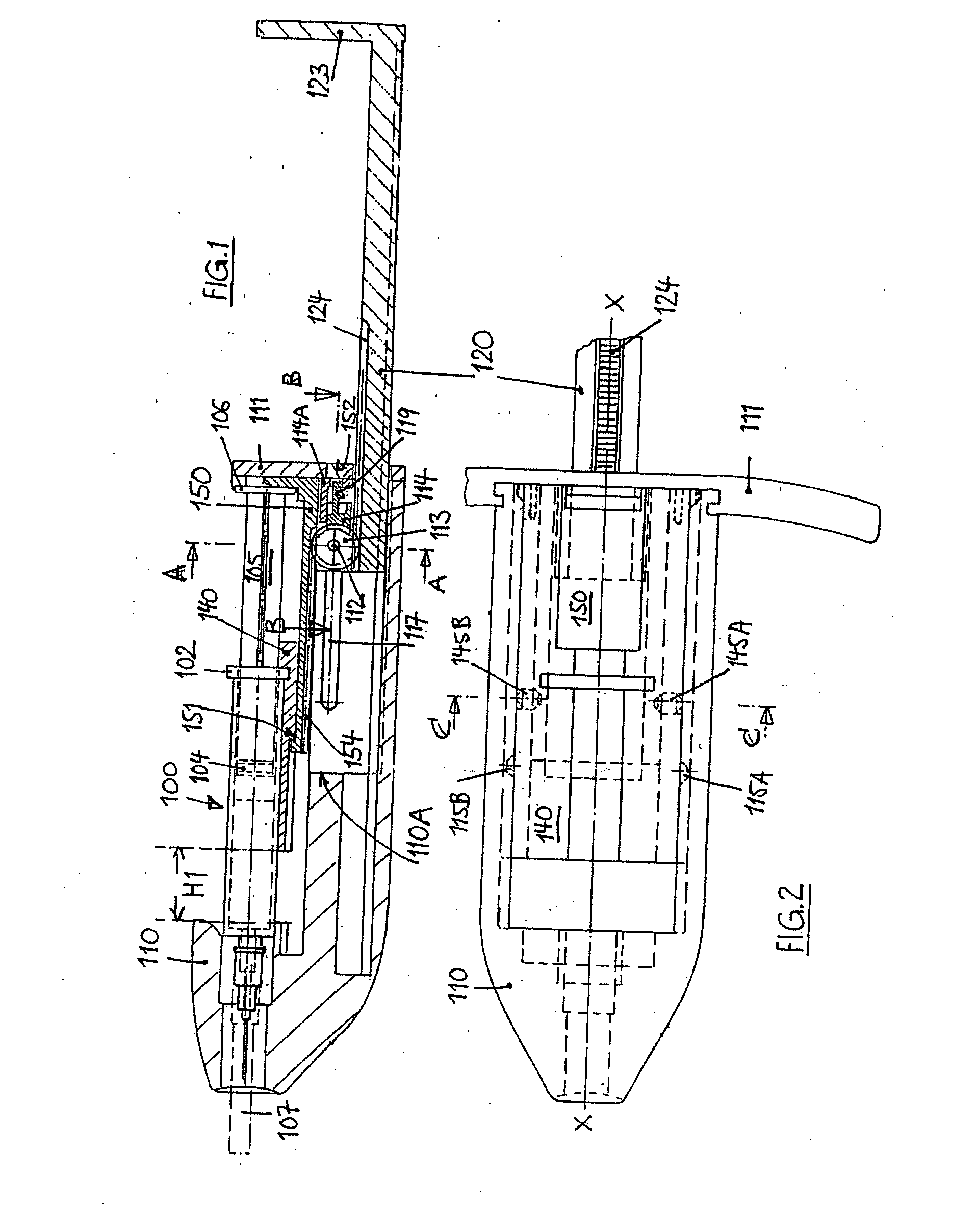
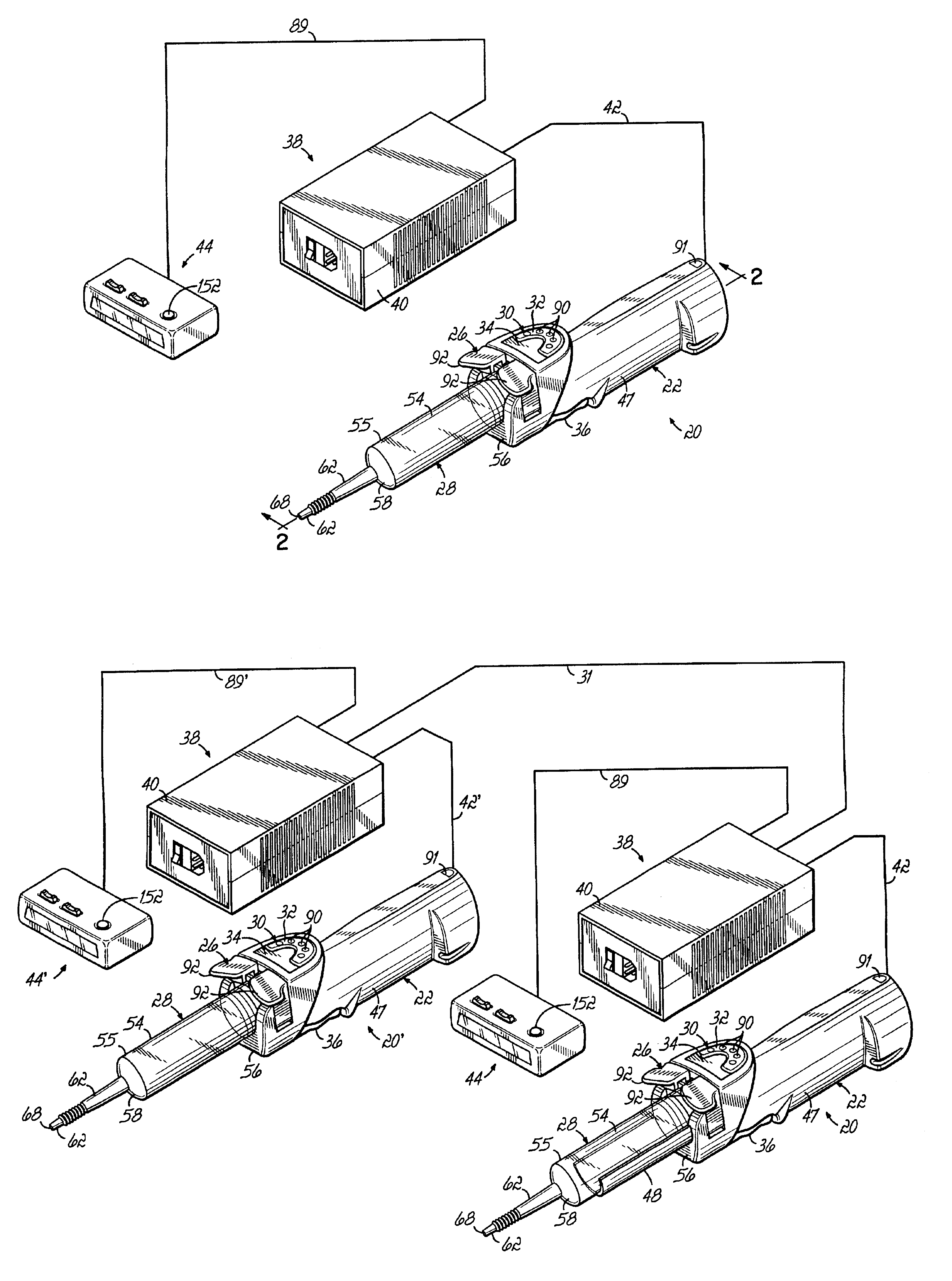
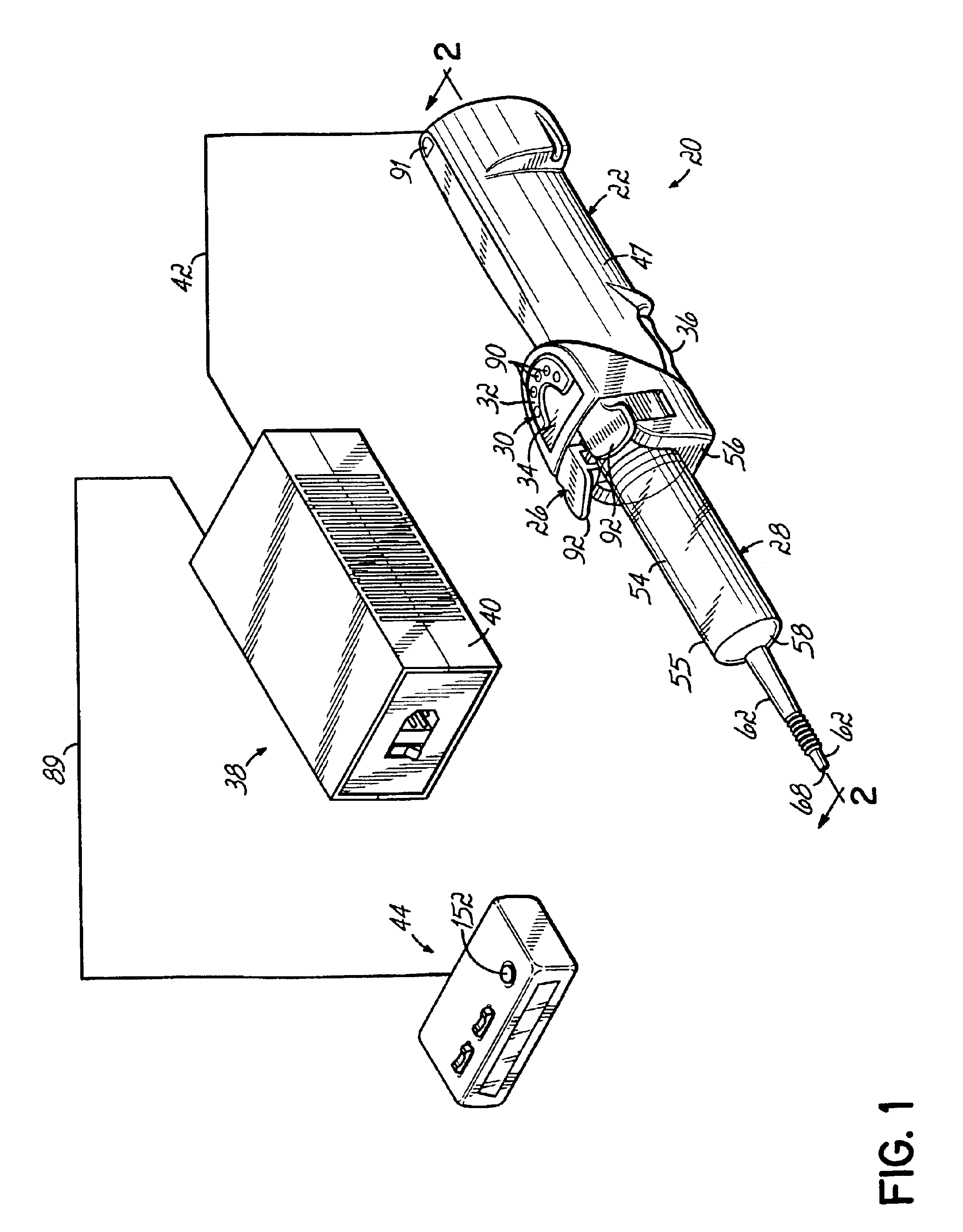
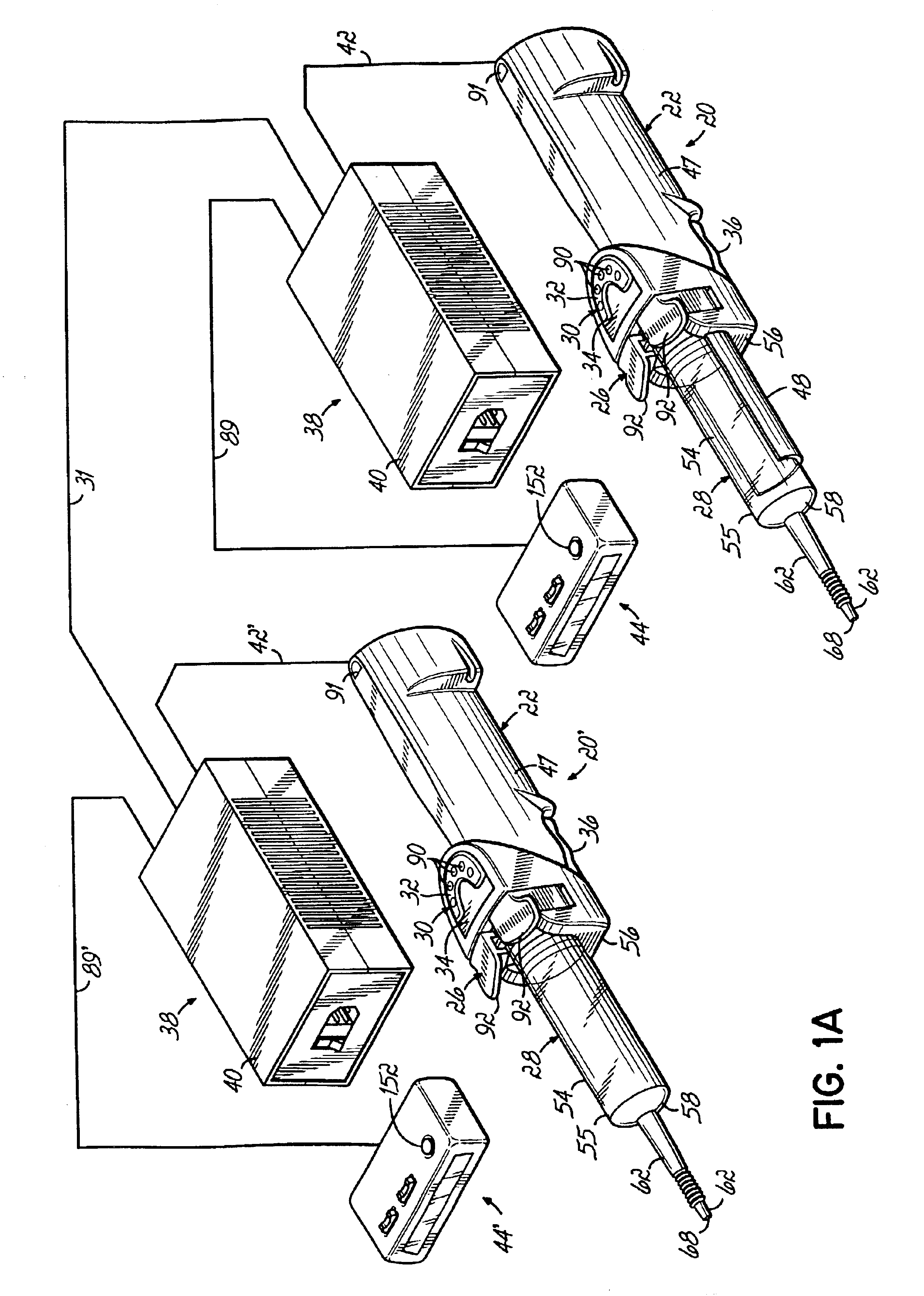
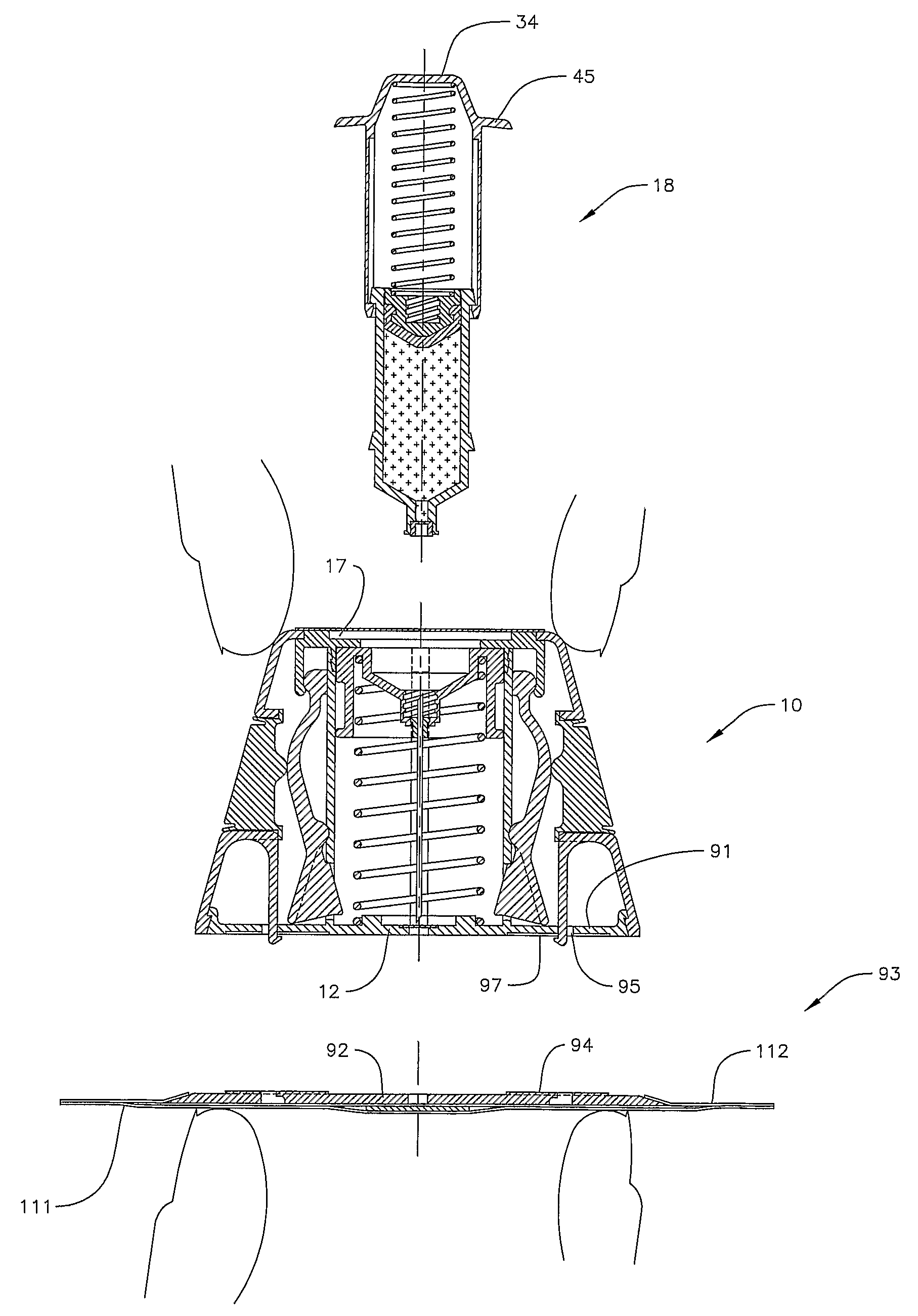
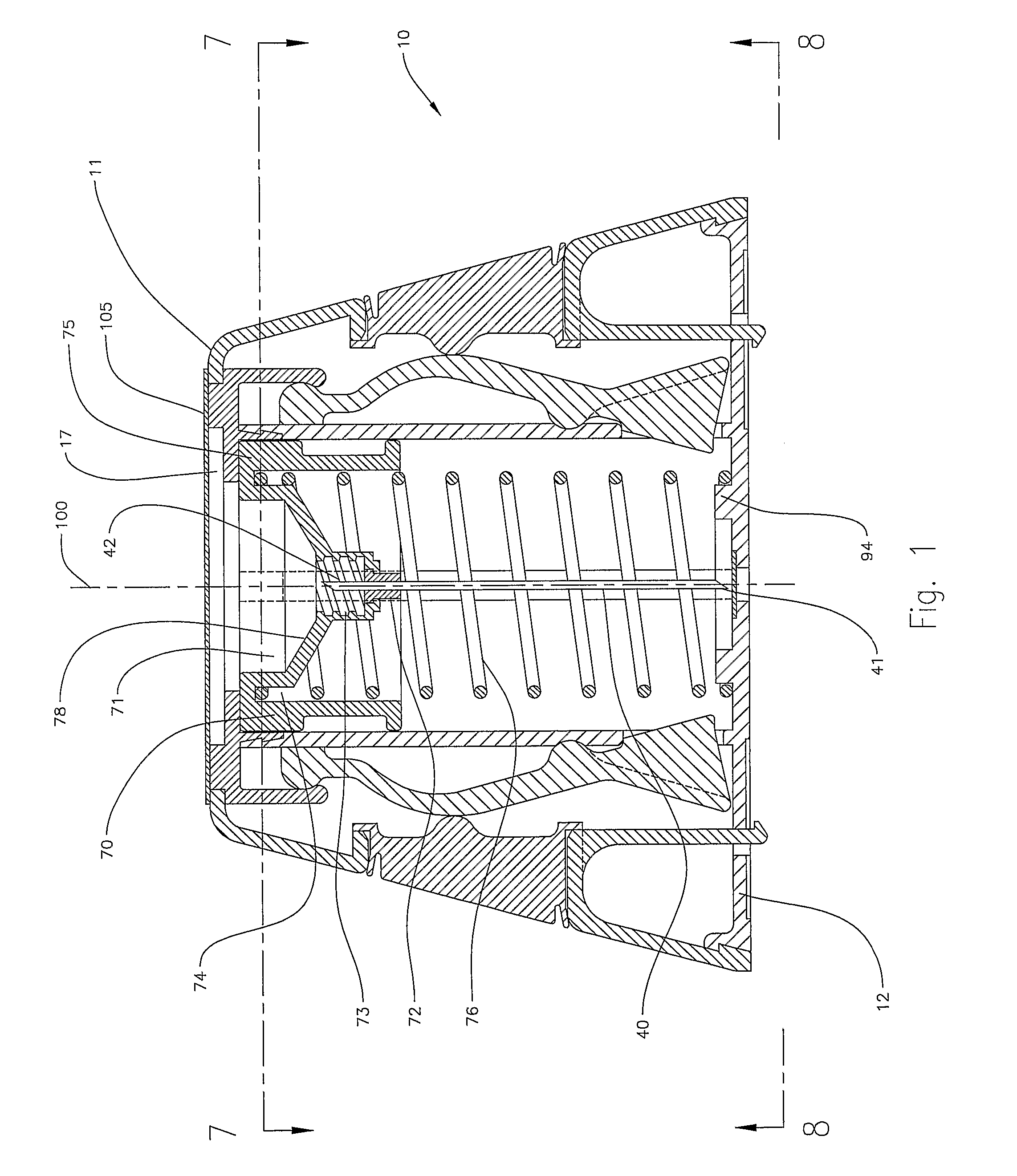
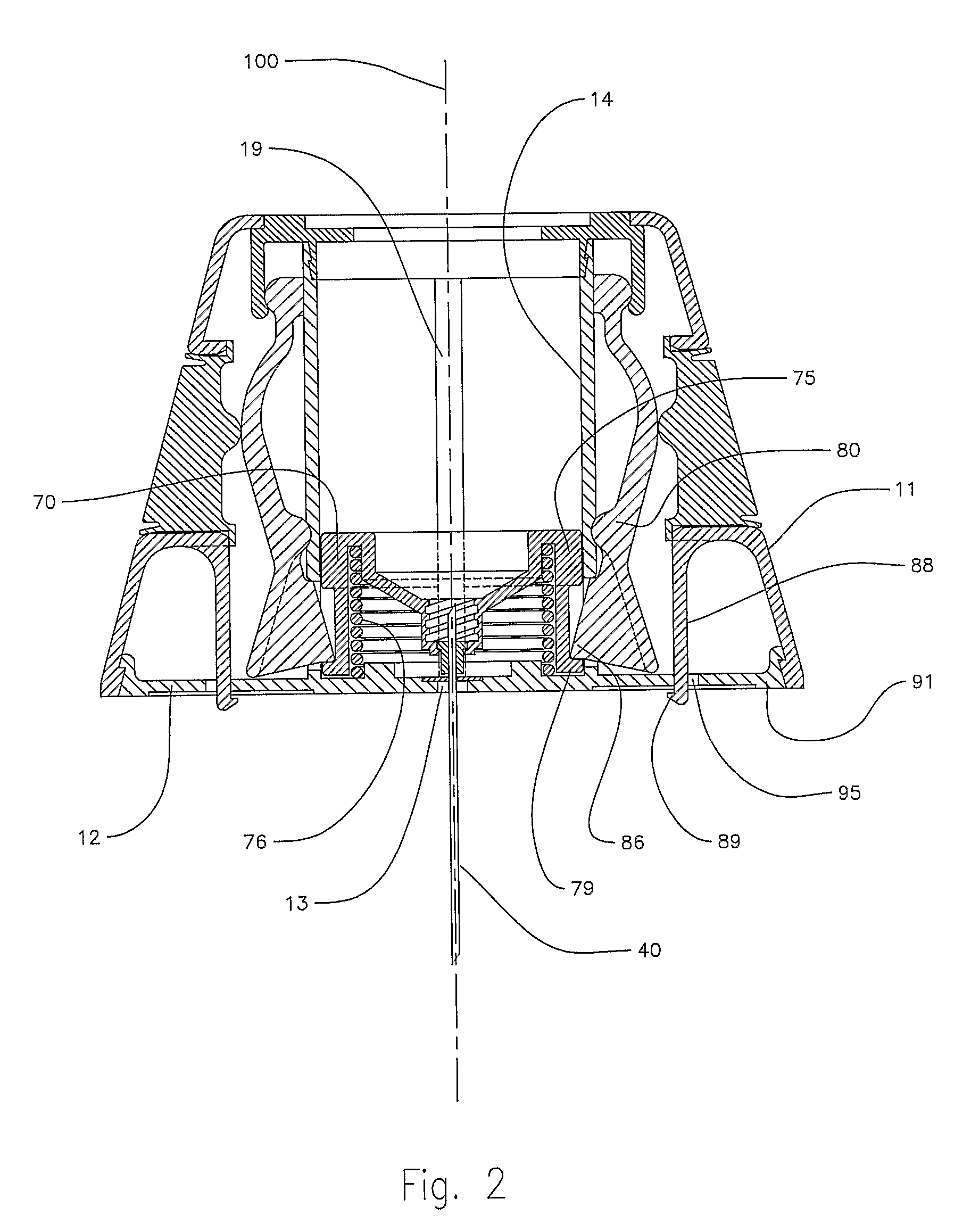
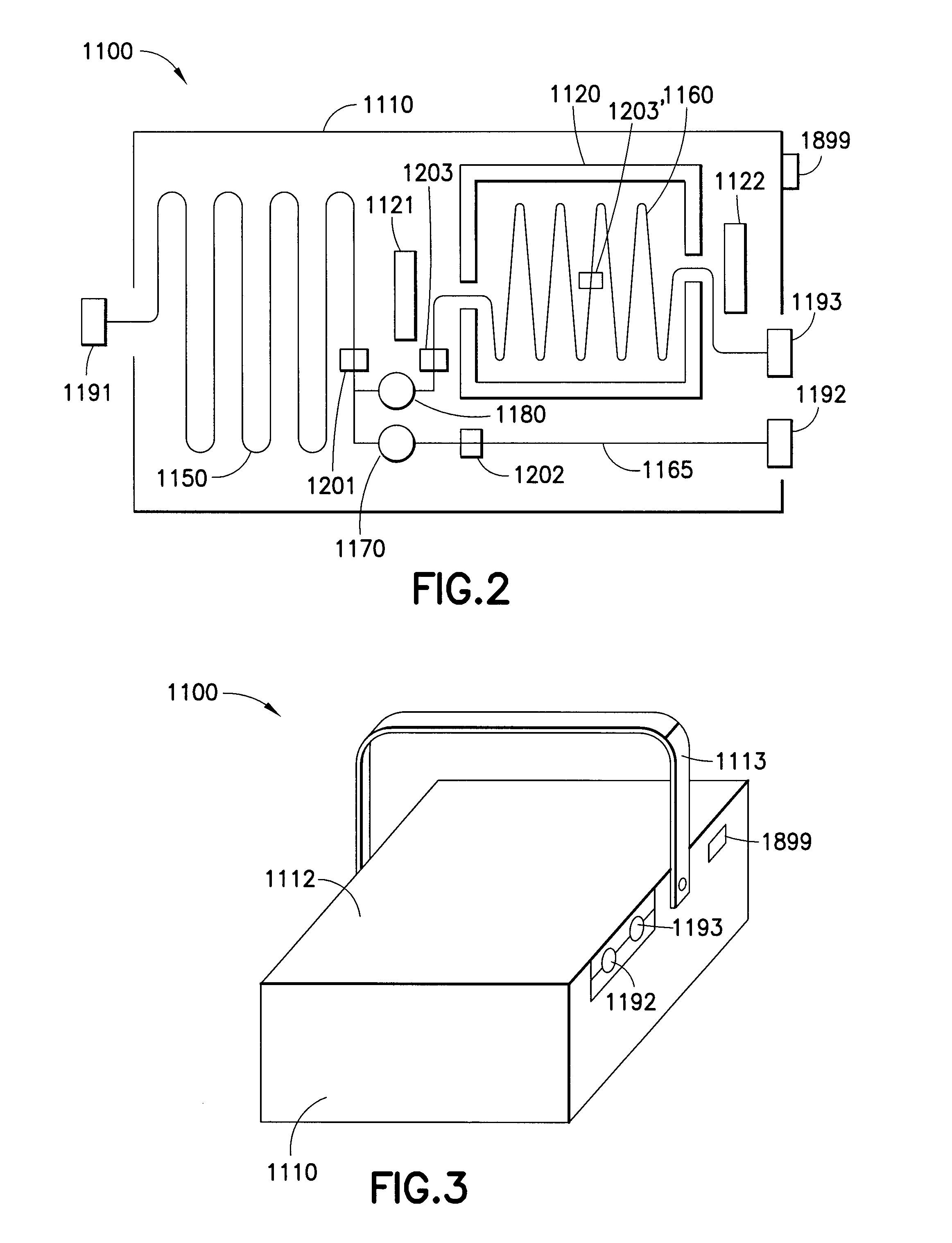
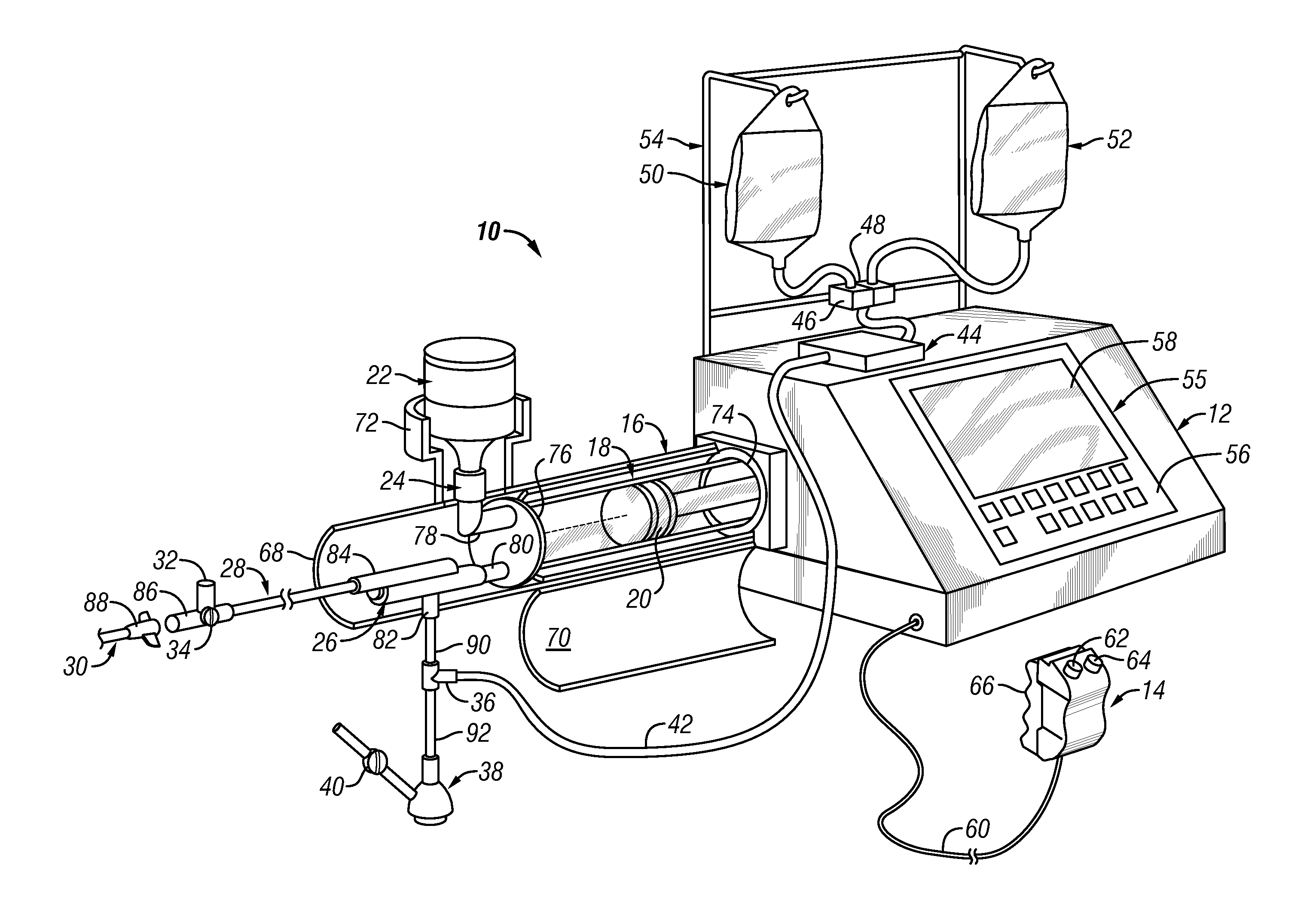
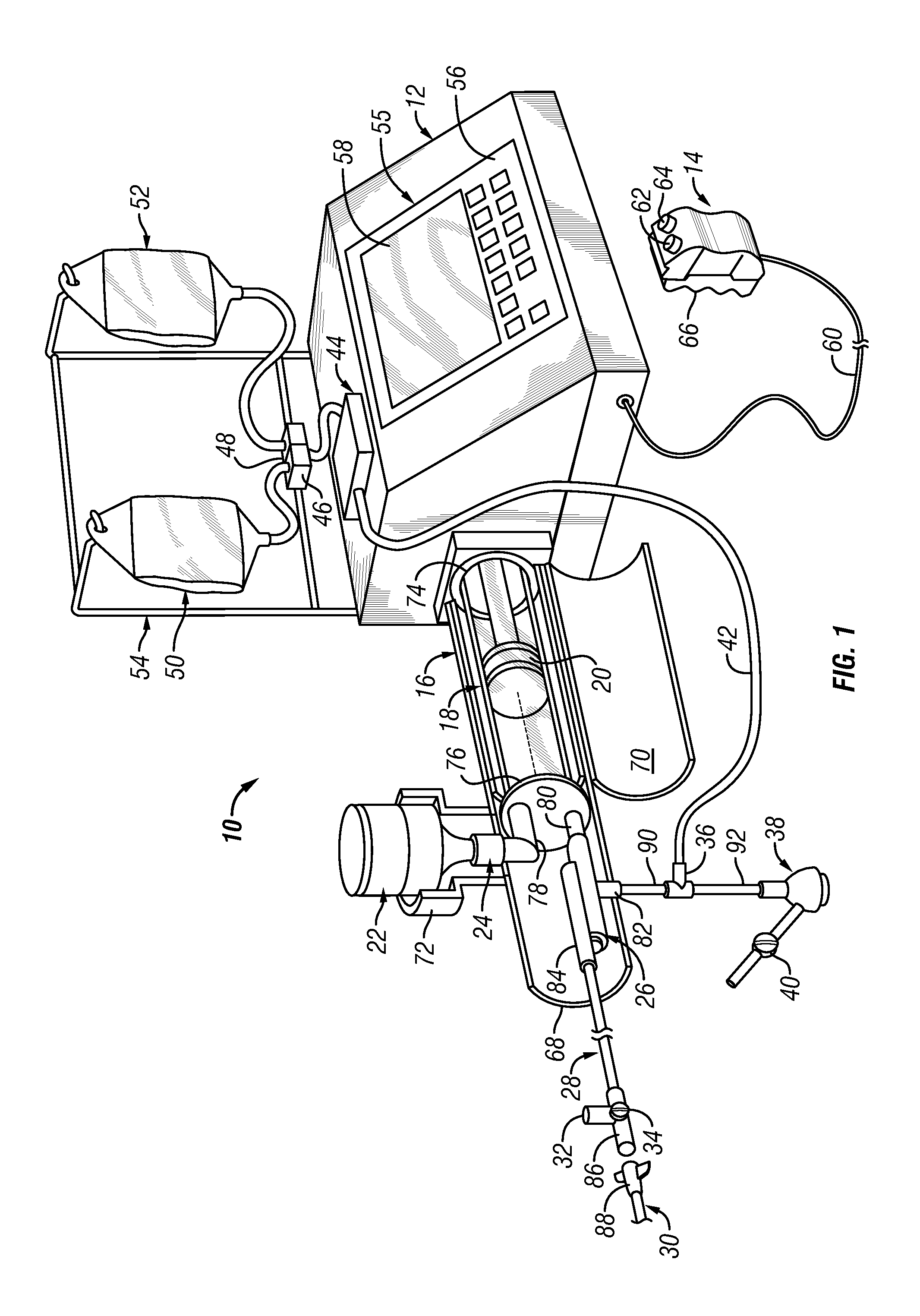
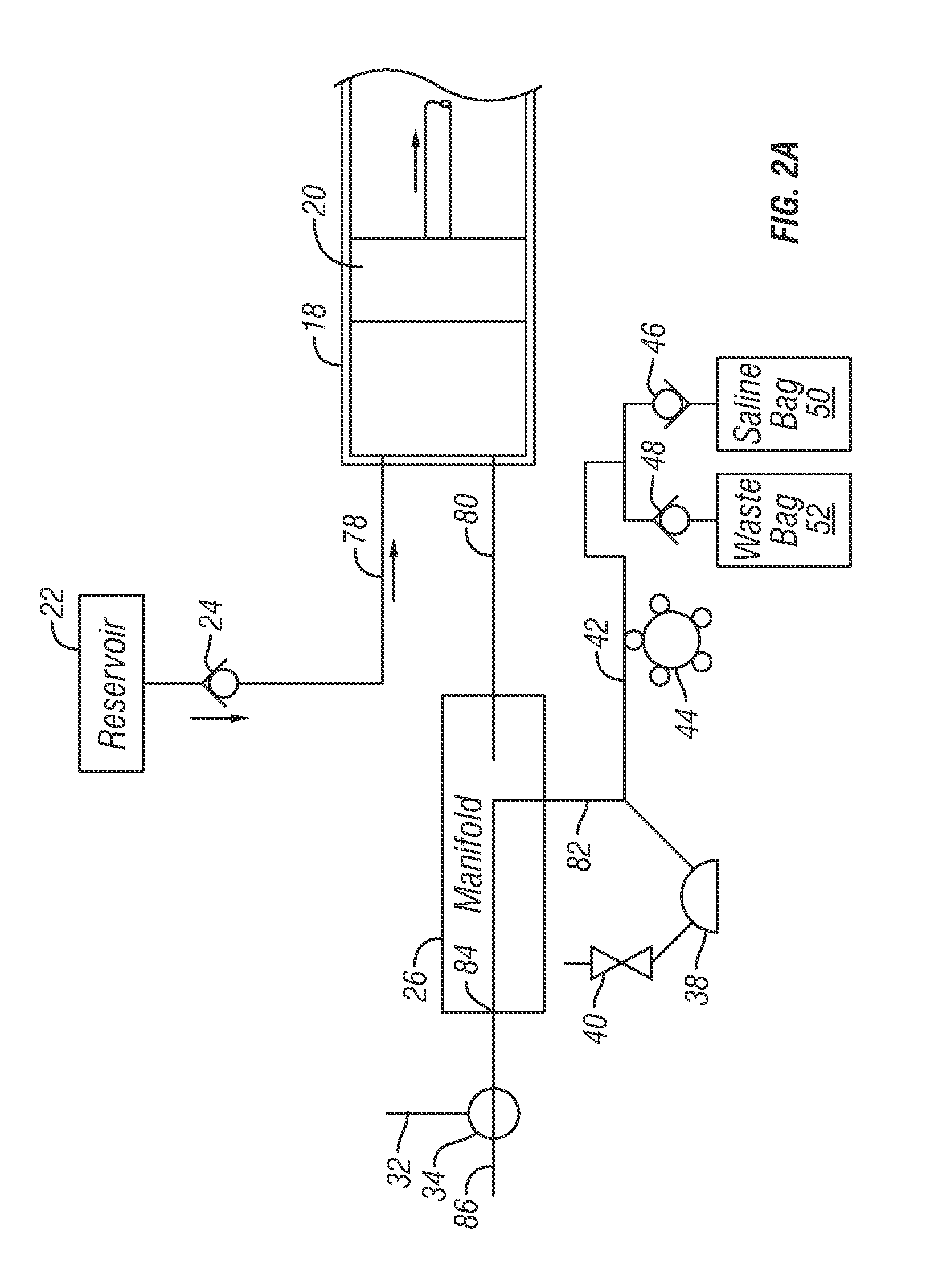
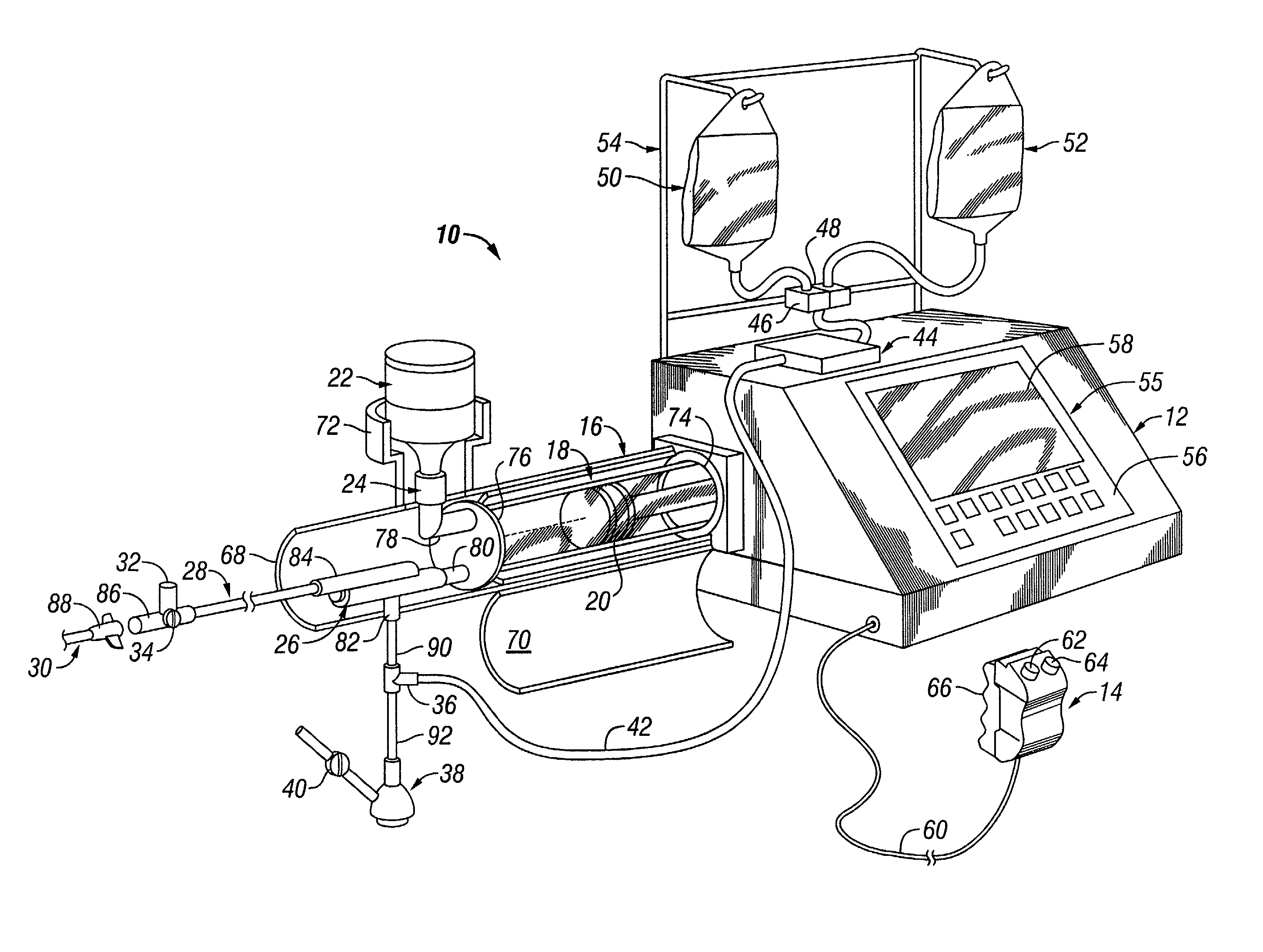
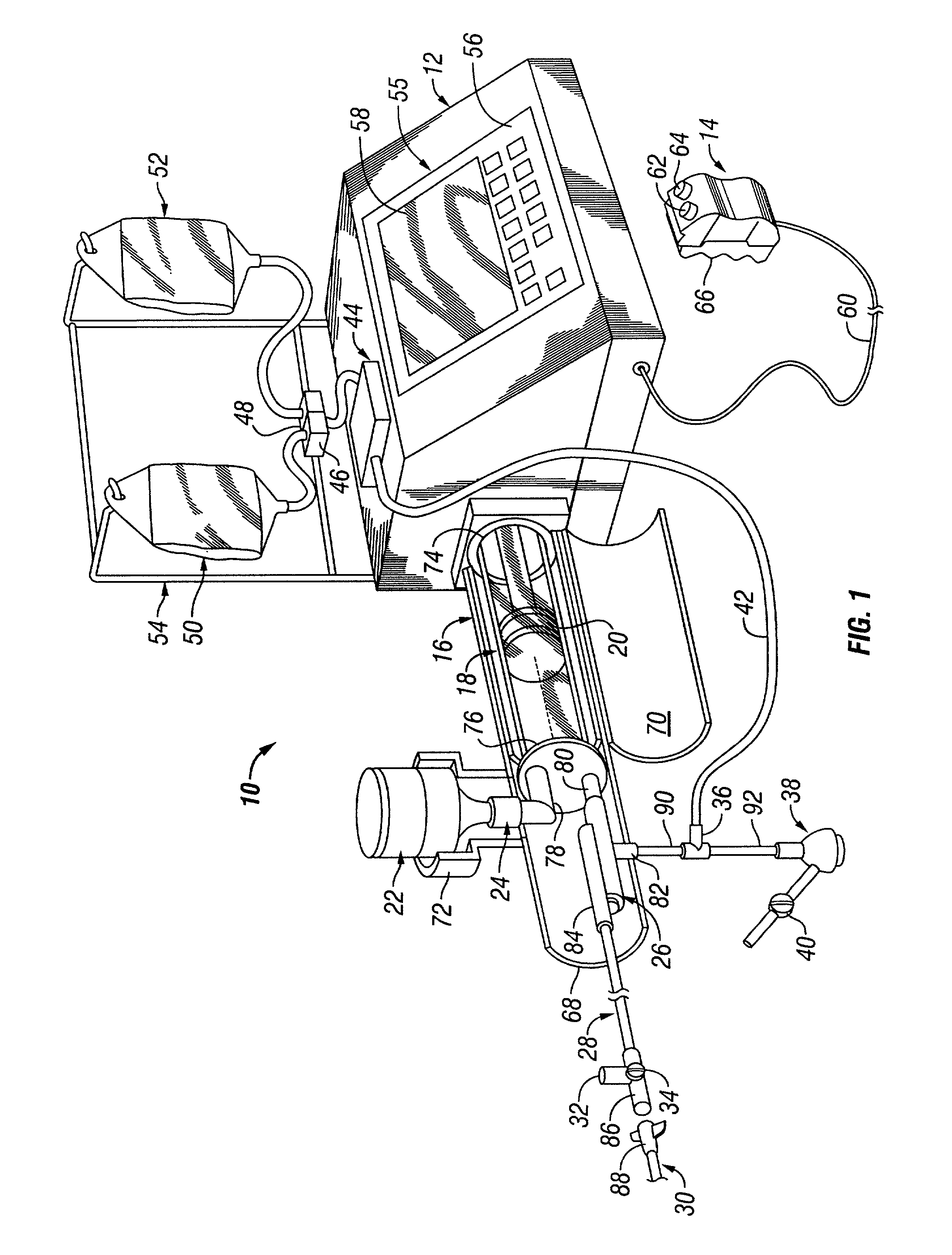
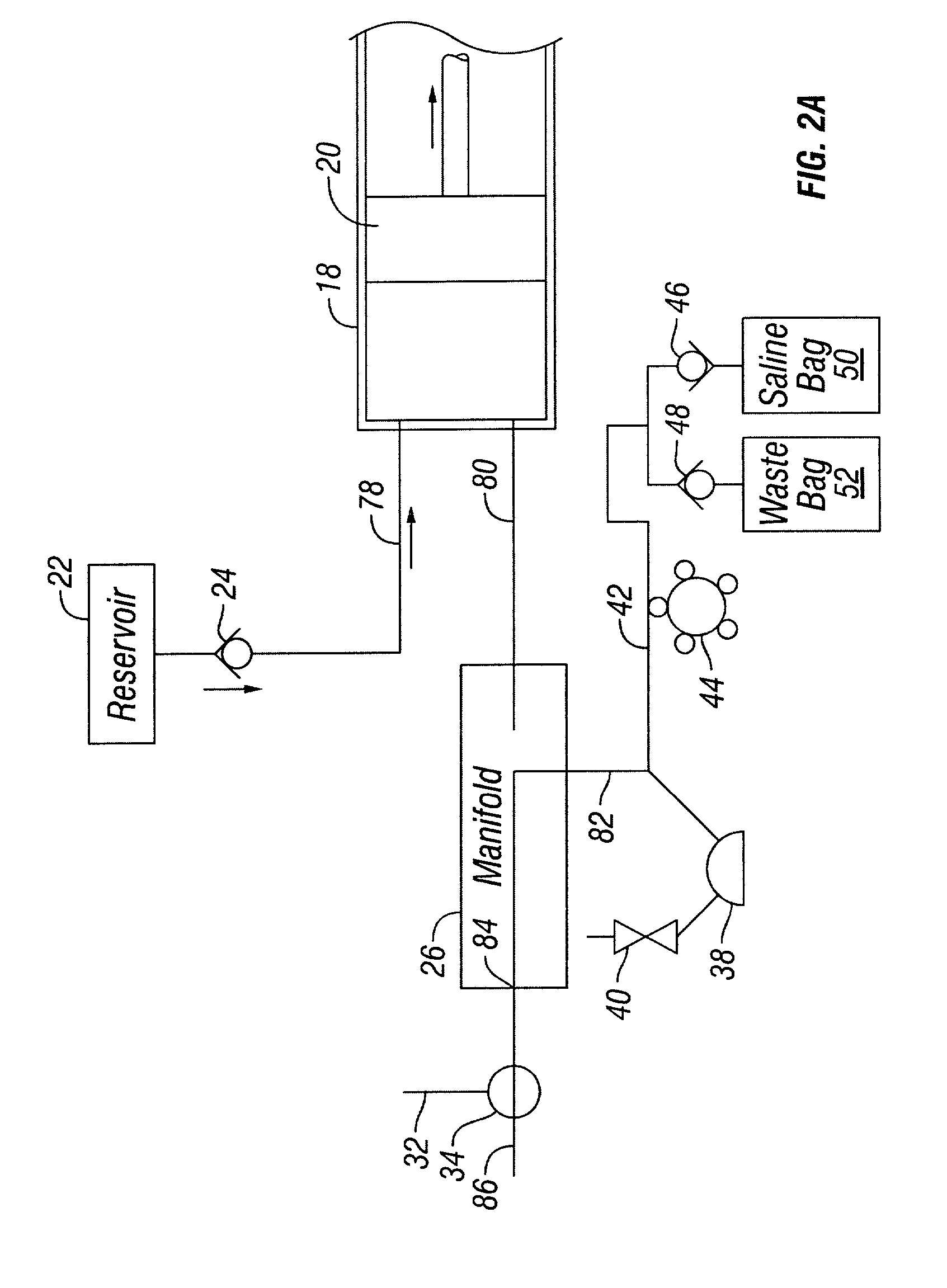
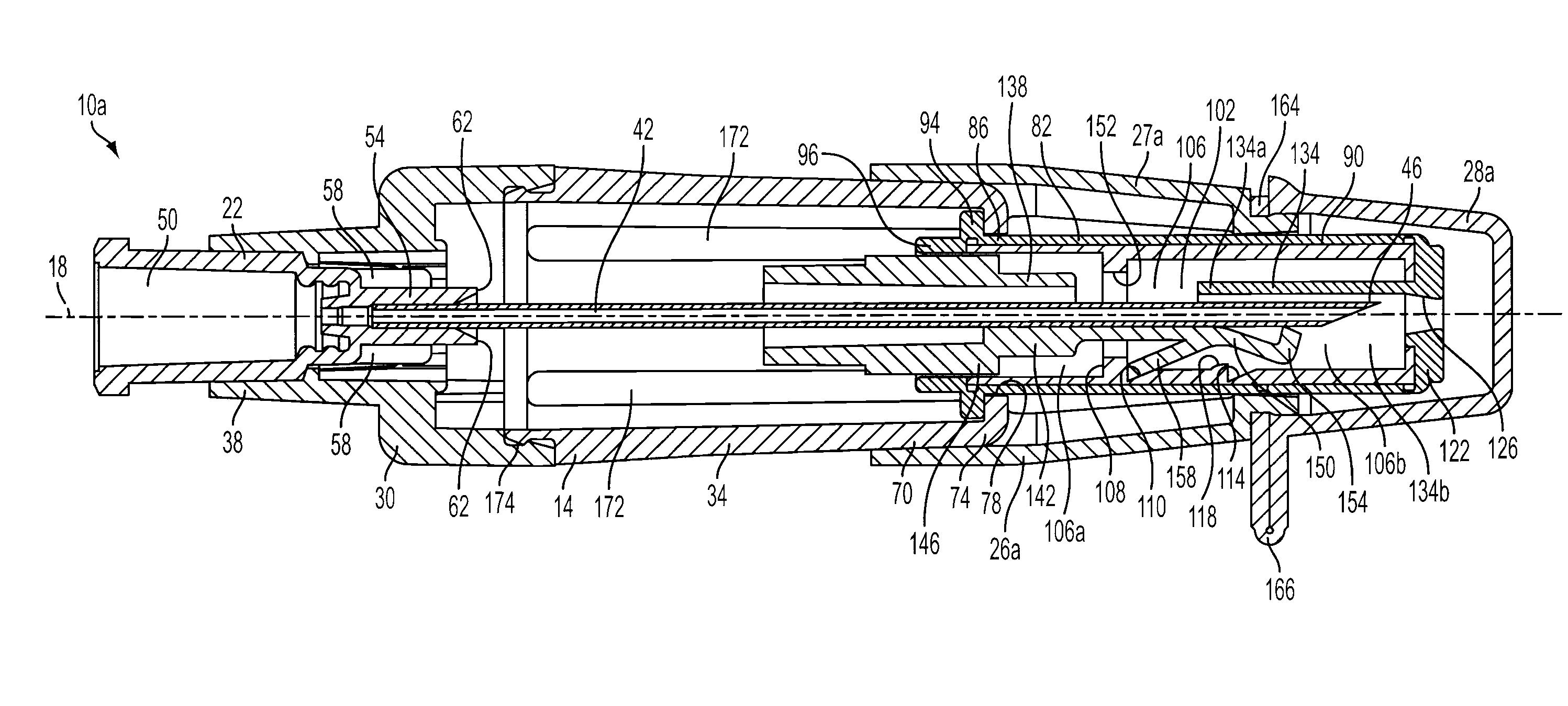
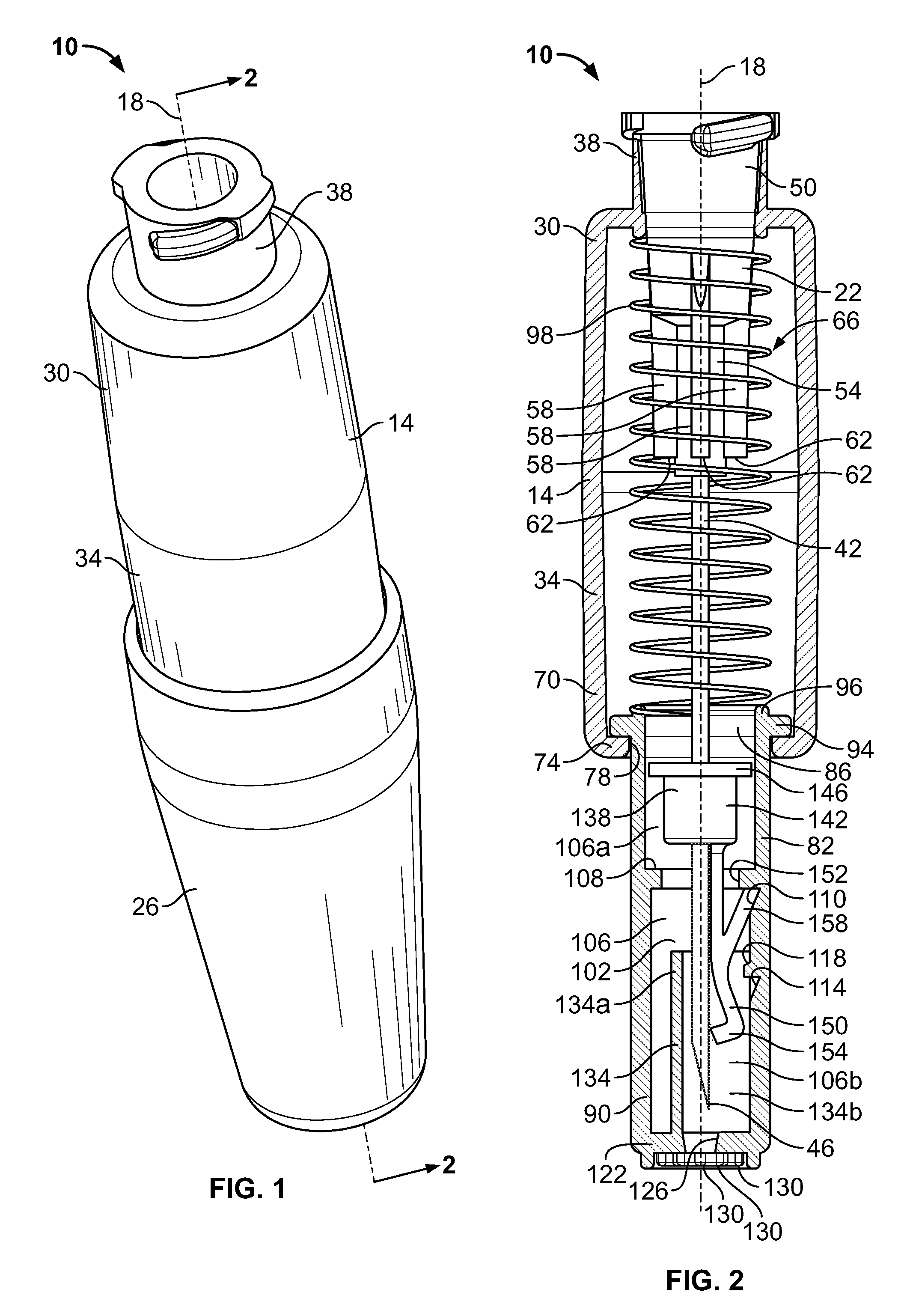
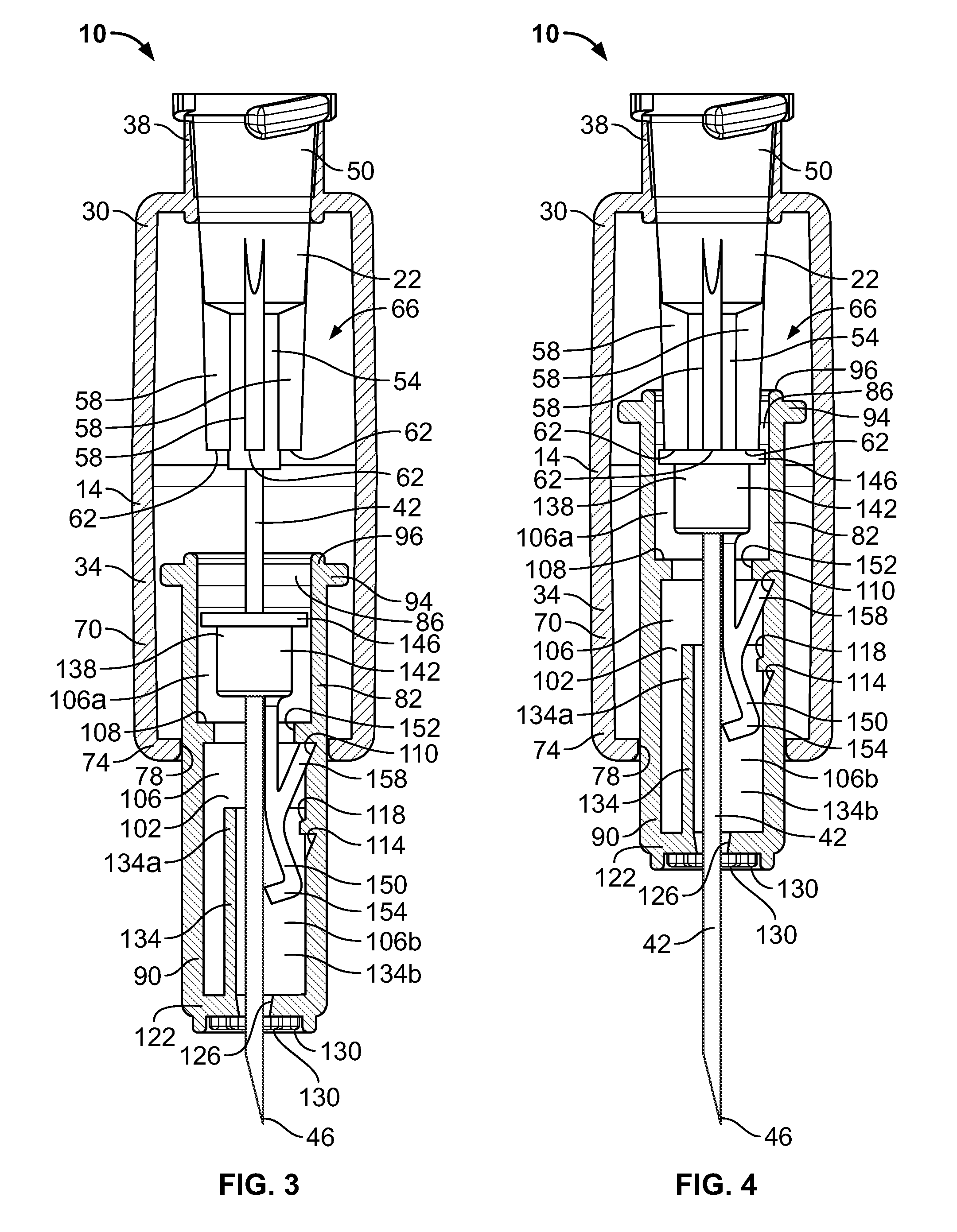
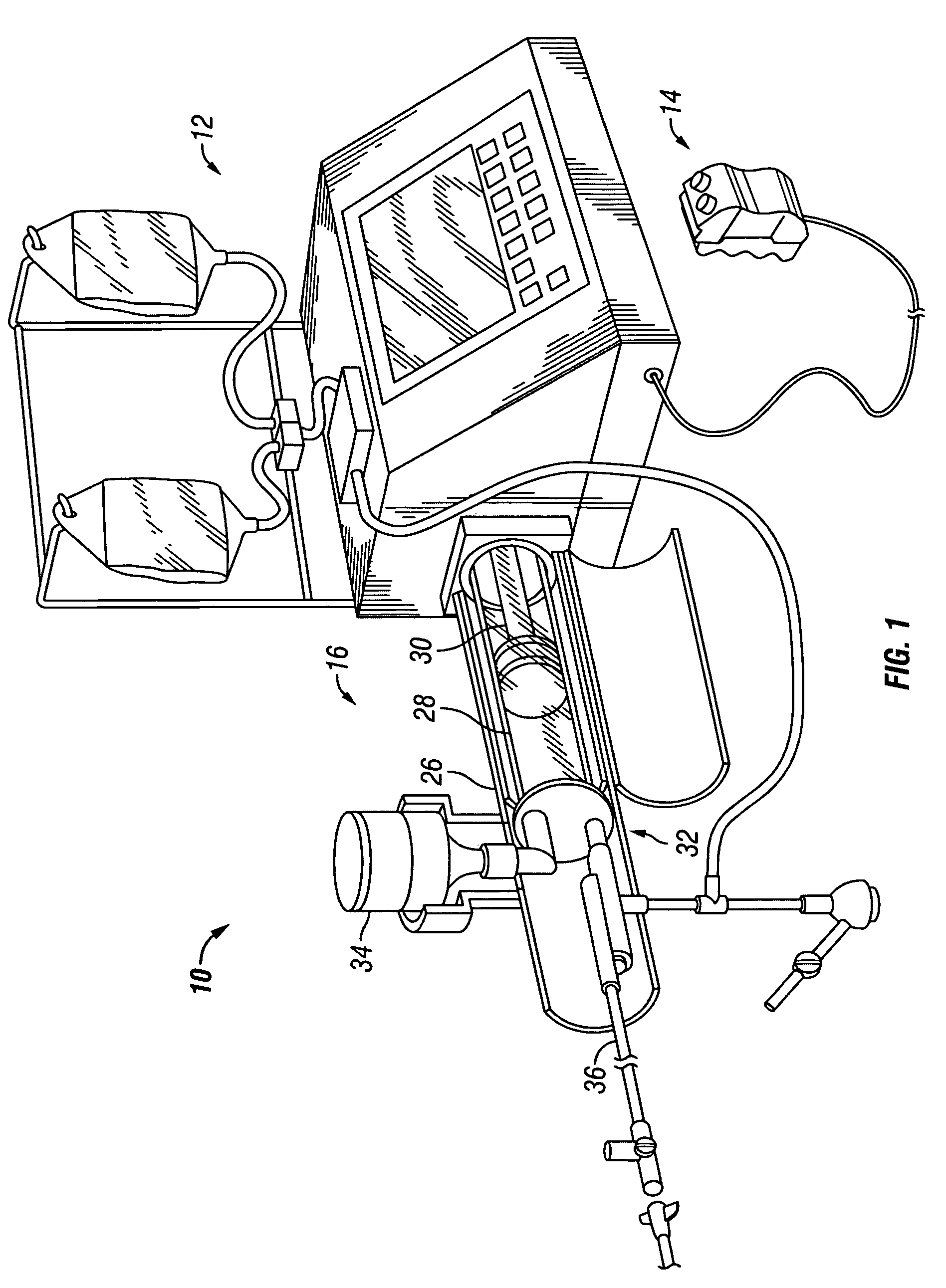
An injector 20 that may be used to deliver radiographic contrast media and / or flushing solution into a patient's vascular system for the purposes such as obtaining enhanced diagnostic x-ray images. The injector includes the following features: (1) a syringe mount 26 for attachment of a syringe 28 to the injector 20; (2) display 34 and controls 90 for volume and flow rates; (3) automatic limiting of the operating pressure of the injector 20 as determined by the selection of a flow rate; (4) a syringe cradle 48 having a warming capability; (5) a purge / retract trigger 36 for control of the injection procedure having intuitive direction (i.e., forward for injecting, reverse for filing), non-contact control transmission through the housing of an injector 20 for an improved seal integrity, a speed lock, and / or the ability to change the concentration and / or flow rate of media or other fluid during an injection procedure; (6) a switch to determine when the drive ram 46 is in a “home” position; (7) a “soft” on / off power switch separate from the injector; and (8) a structure to prevent rotation of the drive ram 46 about its axis of symmetry 76. Additionally, the injector system includes software for the control of various components.
Owner:LIEBEL FLARSHEIM CO
Injection device for administering a vaccine
InactiveUS7670314B2Simple and inexpensive to prepareSimple and inexpensive to and operateAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesMedication injectionInjection device
A manually-powered injection device that self-administers a painless injection. The injection device provides a method for substantially painless injections of vaccine and other medication into a patient that does not require the use of an anesthetic, that does not require the medical personnel to spend a substantial amount of time performing the injection procedure, that is relatively simple and inexpensive to perform and operate, and that provides a relatively high degree of safety for both the medical personnel and for the patient. The injection needle can have an outside diameter greater than 0.10 mm and less than about 0.38 mm. The vaccine or other medicament can be injected painlessly through the needle and into the patient at a substantially constant volumetric flow rate of about 0.05 μL / s to about 50 μL / s, typically over a 3- to 5-minute period of time. The injection device is configured for easy handling, and is manually powered by the use of the hand or fingers of the medical technician, patient or other person.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Self-administration injection system
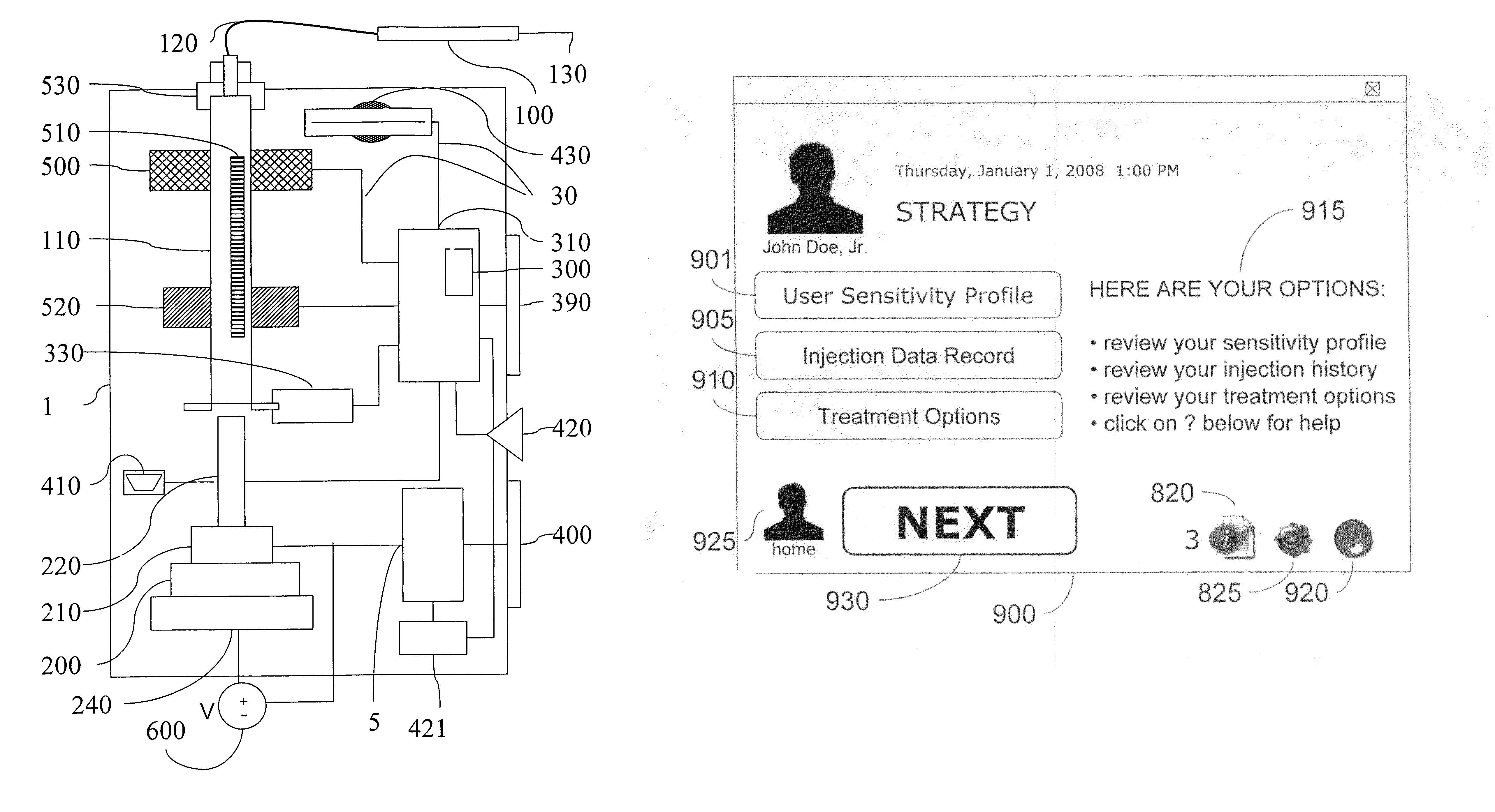
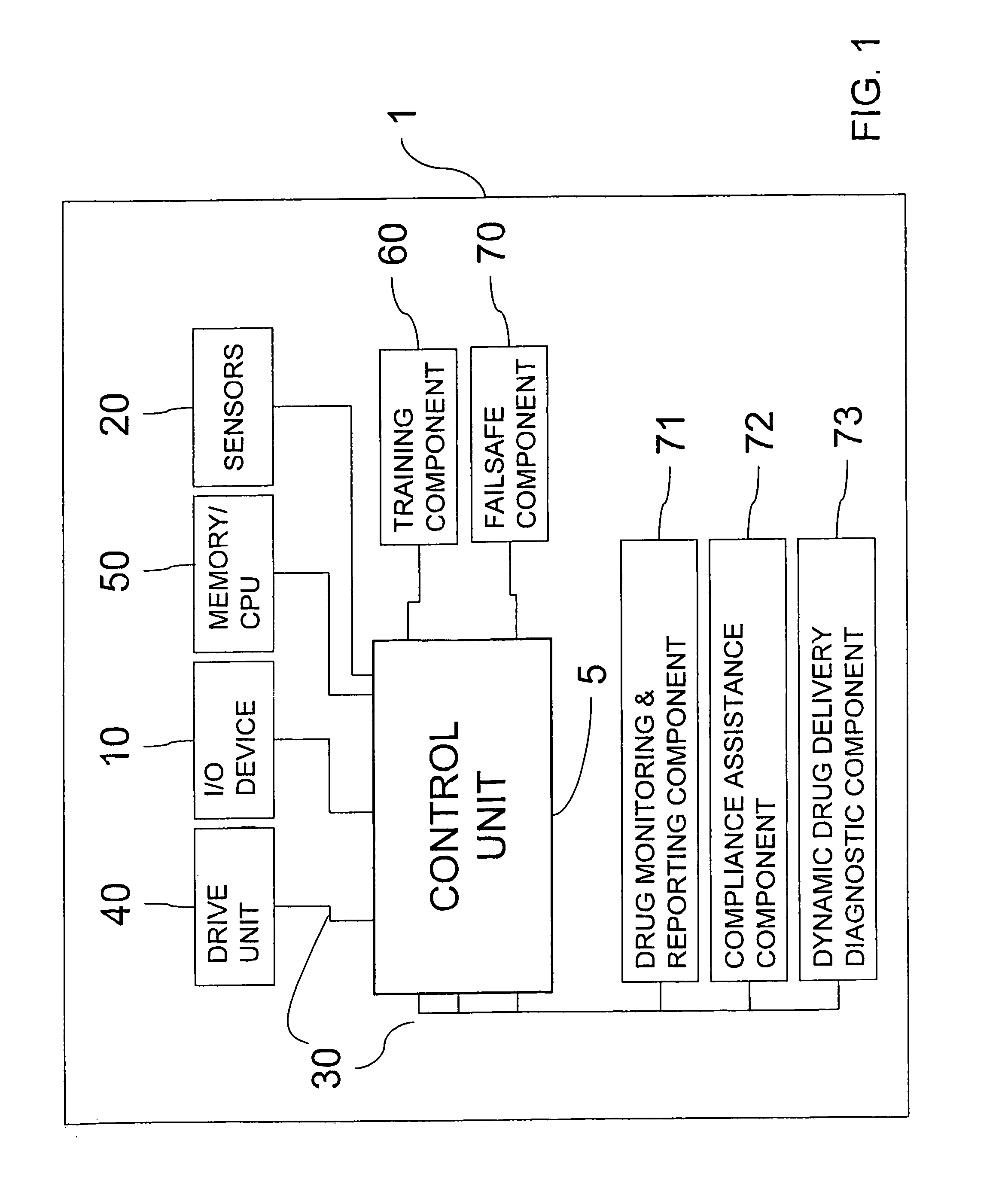
Self-injection system allows a user to inject a drug from a cartridge carrying unique identification information, into any one of a plurality of injection sites. Tissue at each injection site is associated with at least one injection parameter, such as flow-rate, that is different for each site. A scanner reads the identification information of the cartridge and cooperates with a central processing unit to determine the validity of the drug in order to permit an injection procedure to commence. The central processing unit has a memory for storing the different injection parameters and controls a drive unit for driving fluid from the cartridge and through a needle into the selected tissue, at the injection parameter that is associated with the user selected tissue for the injection.
Owner:MILESTONE SCIENTIFIC INC
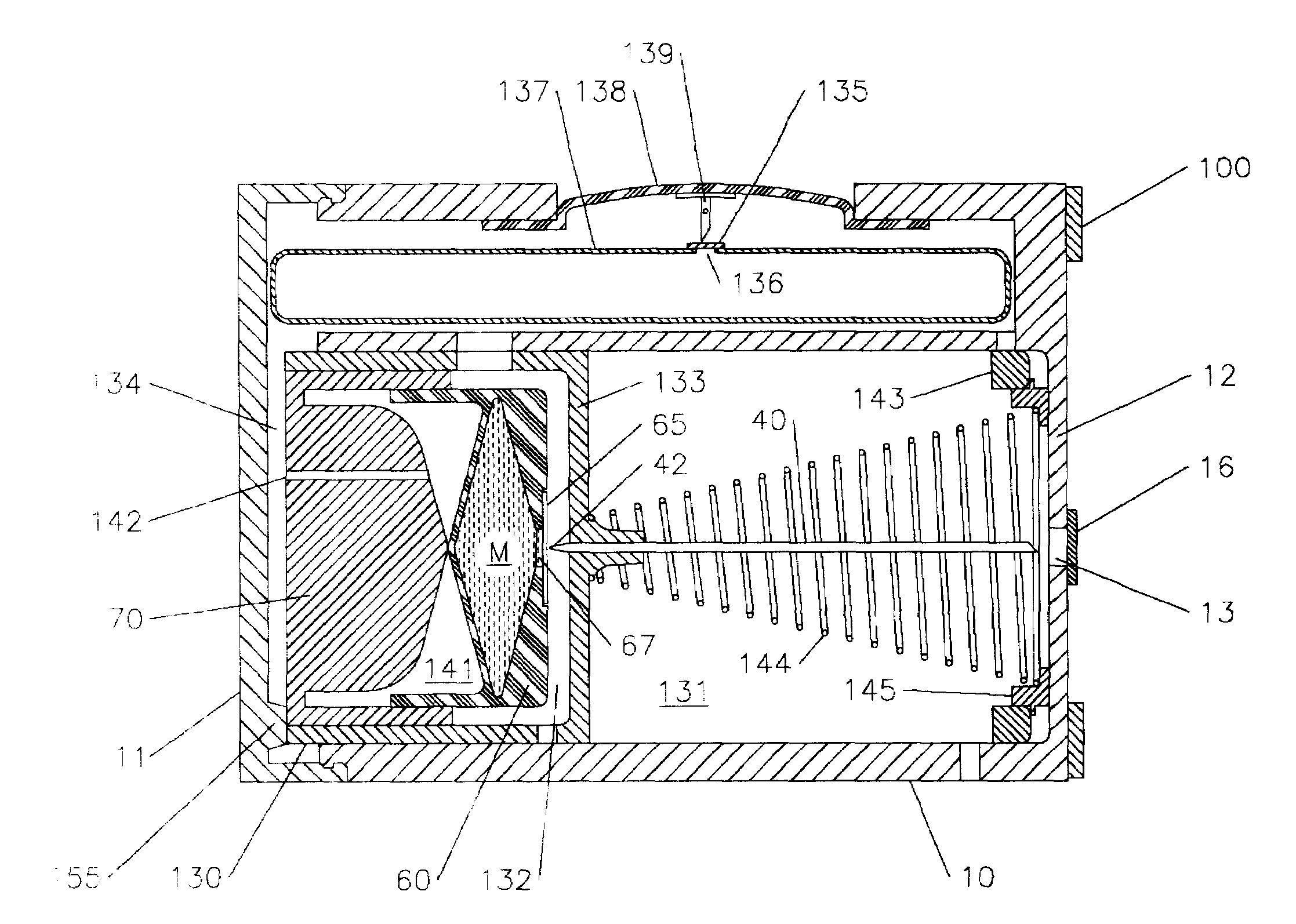
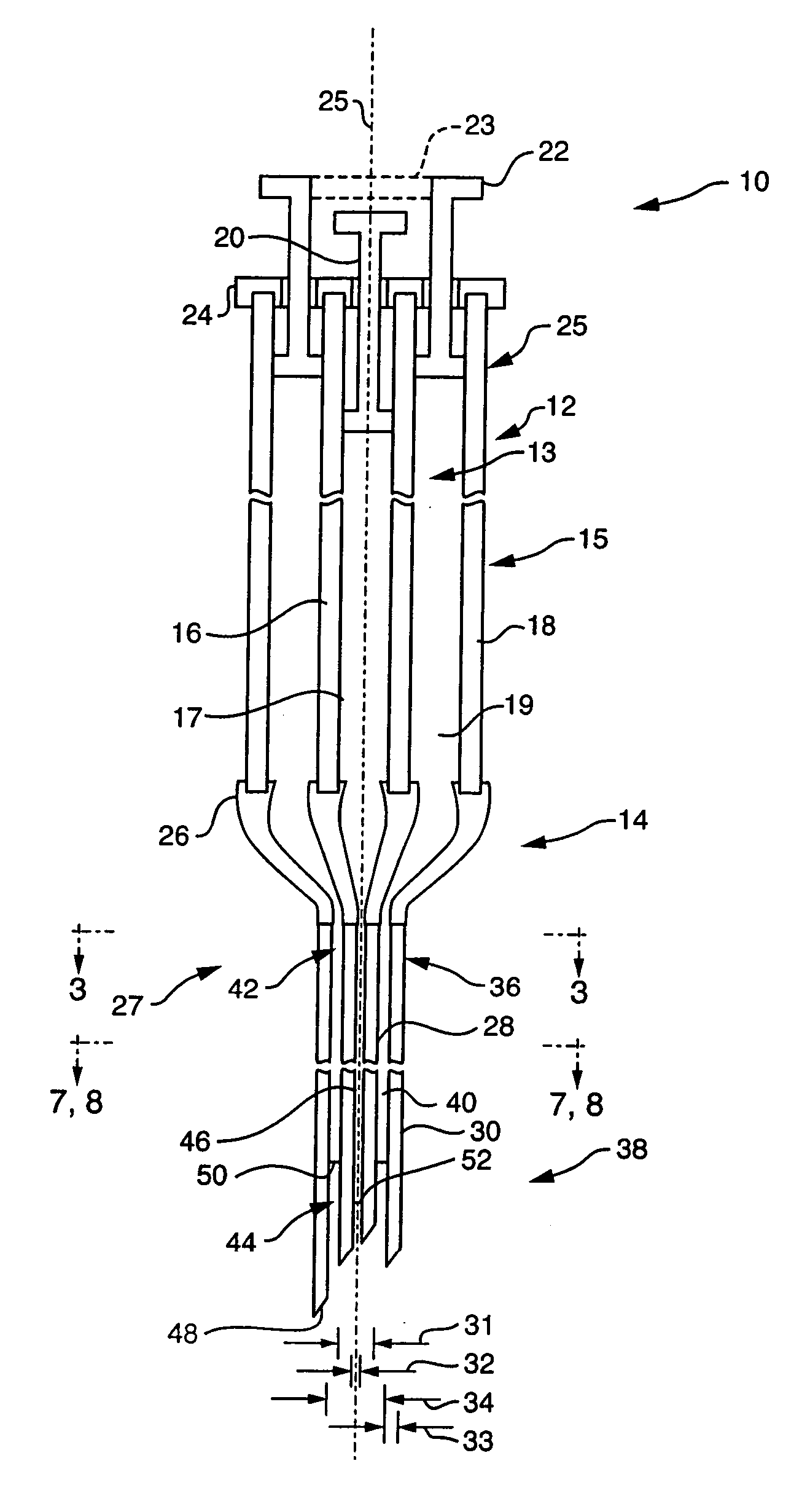
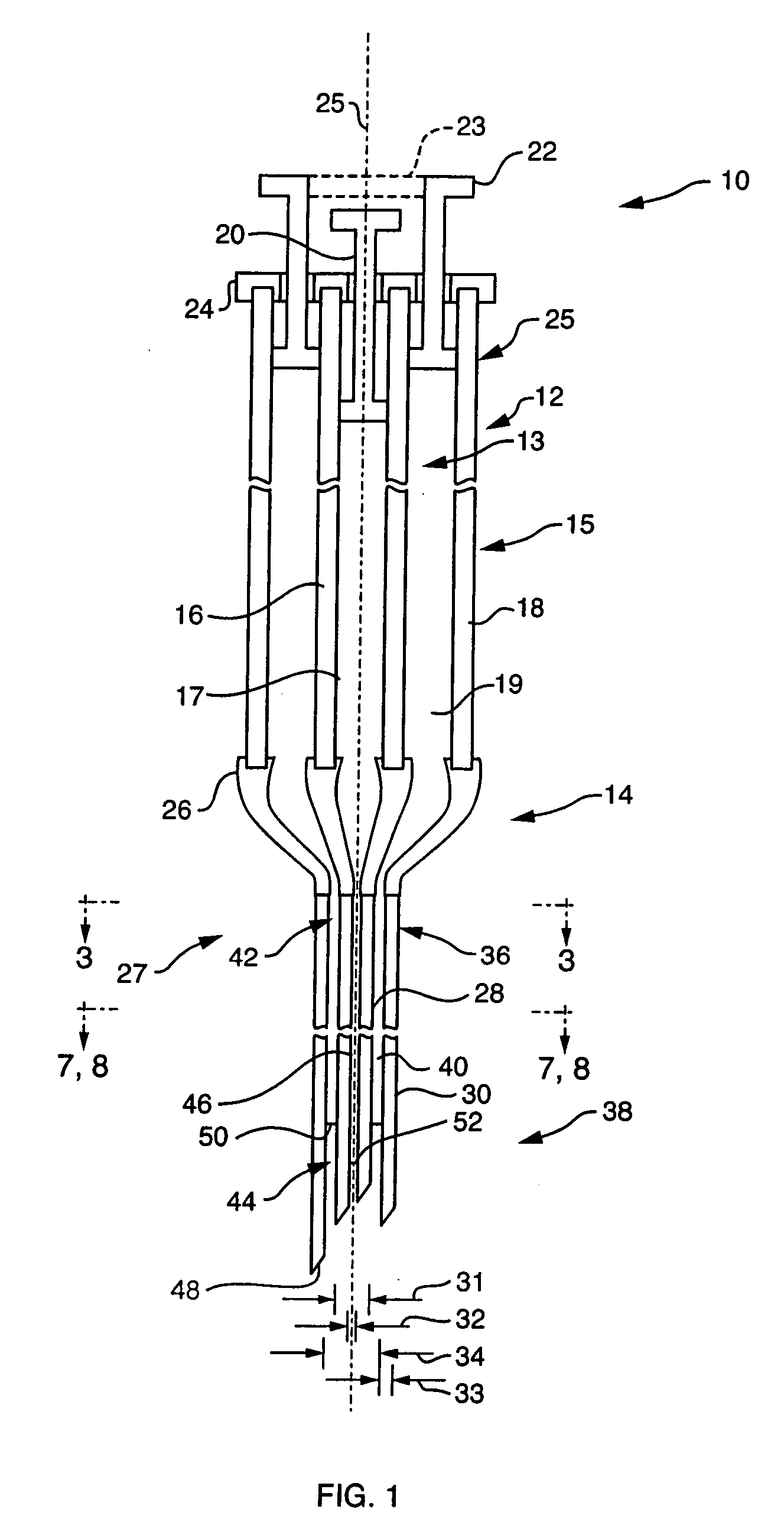
Low-loss multi-lumen injection apparatus
InactiveUS20070073267A1Reduce residual lossInfusion syringesMedical devicesDrug reservoirInjection site
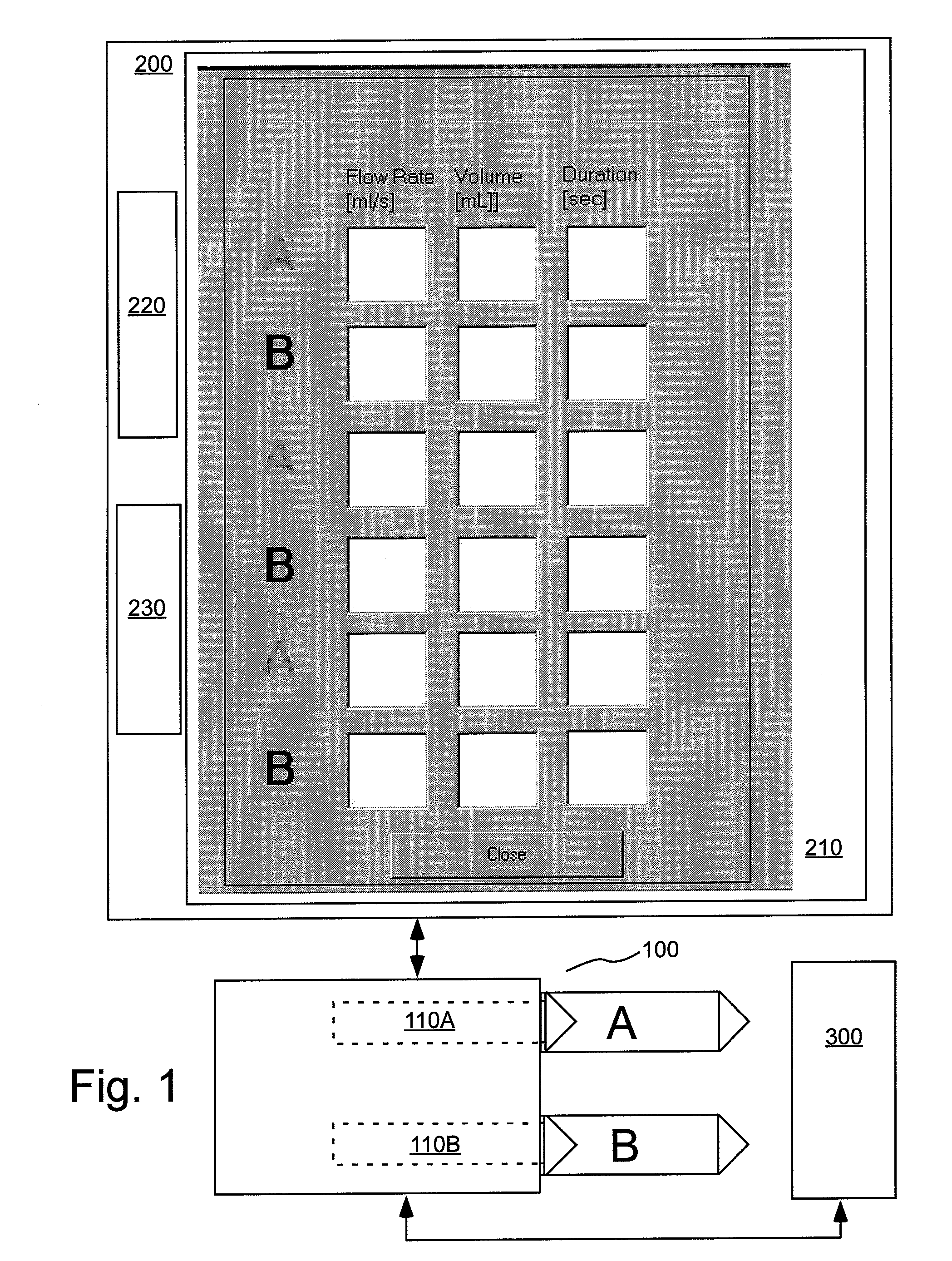
Injection devices, systems and methods are disclosed for injecting two or more medicaments to a patient at a single injection site while preferably minimizing any mixing of the medicaments prior to delivery to the patient. The invention can also be used to sequentially deliver the medicaments to the patient in a repetitive manner. For example, the injection apparatus can sequentially provide a first medicament and then a second medicament to the patient during a first injection procedure. During a second injection procedure, the injection apparatus can again sequentially provide the first medicament and the second medicament to the patient either at the injection site of the first injection procedure or at a different injection site. Multi-lumen manifolds are disclosed for coupling to conventional drug ampoules, to permit the user to sequentially delivery different medicaments via a single skin penetration and to reduce losses associated with usage. Systems including multiple drug reservoirs and filling adaptors are also disclosed.
Owner:MILE CREEK CAPITAL
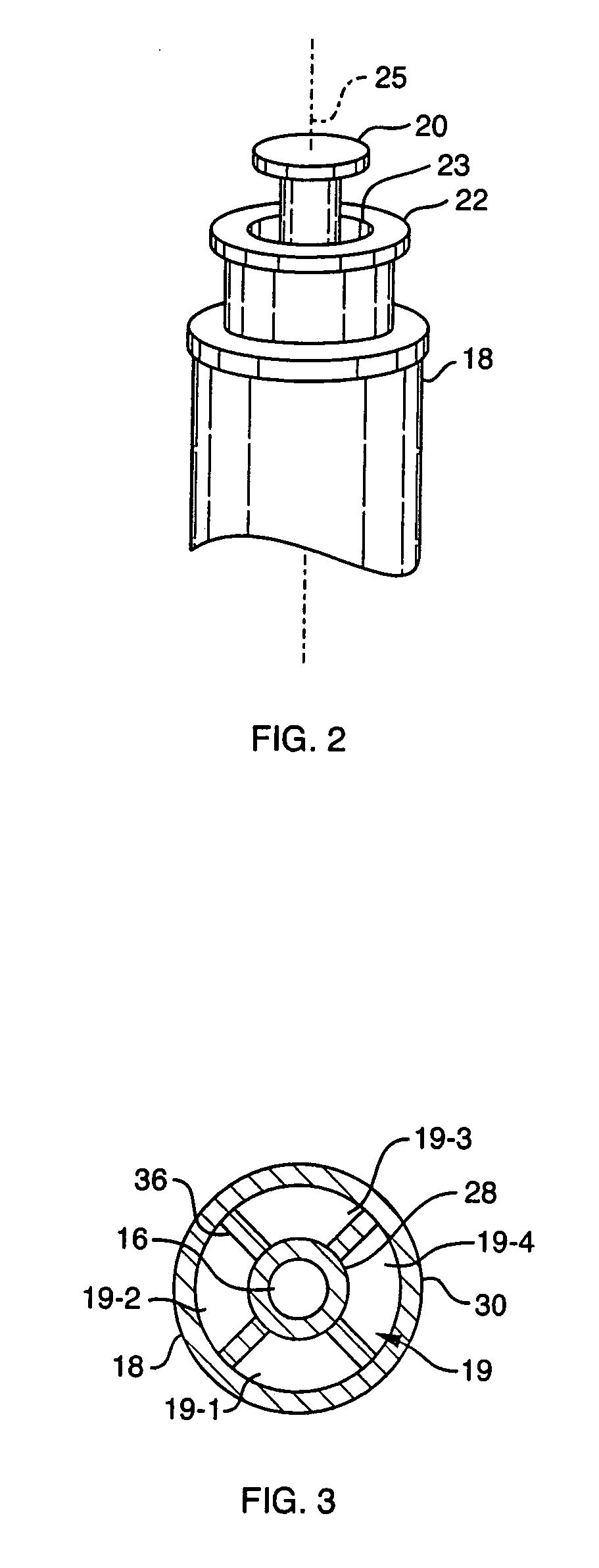
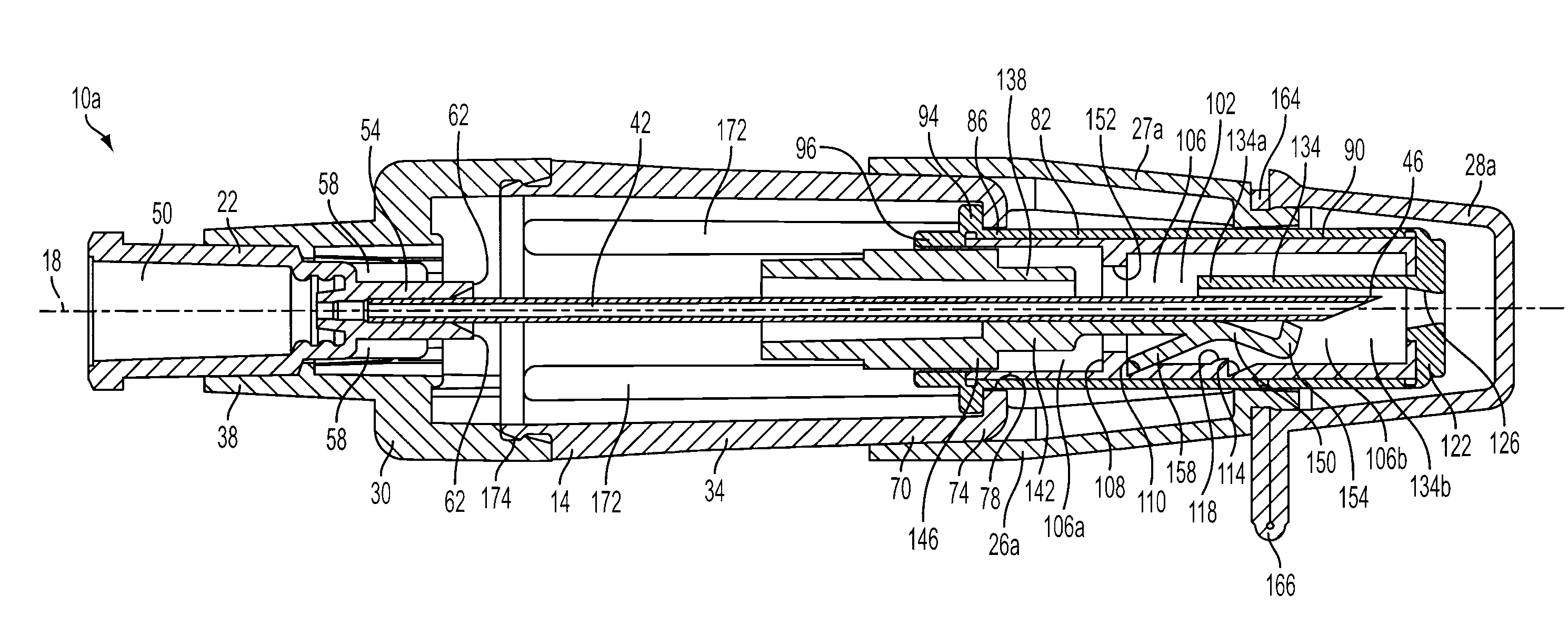
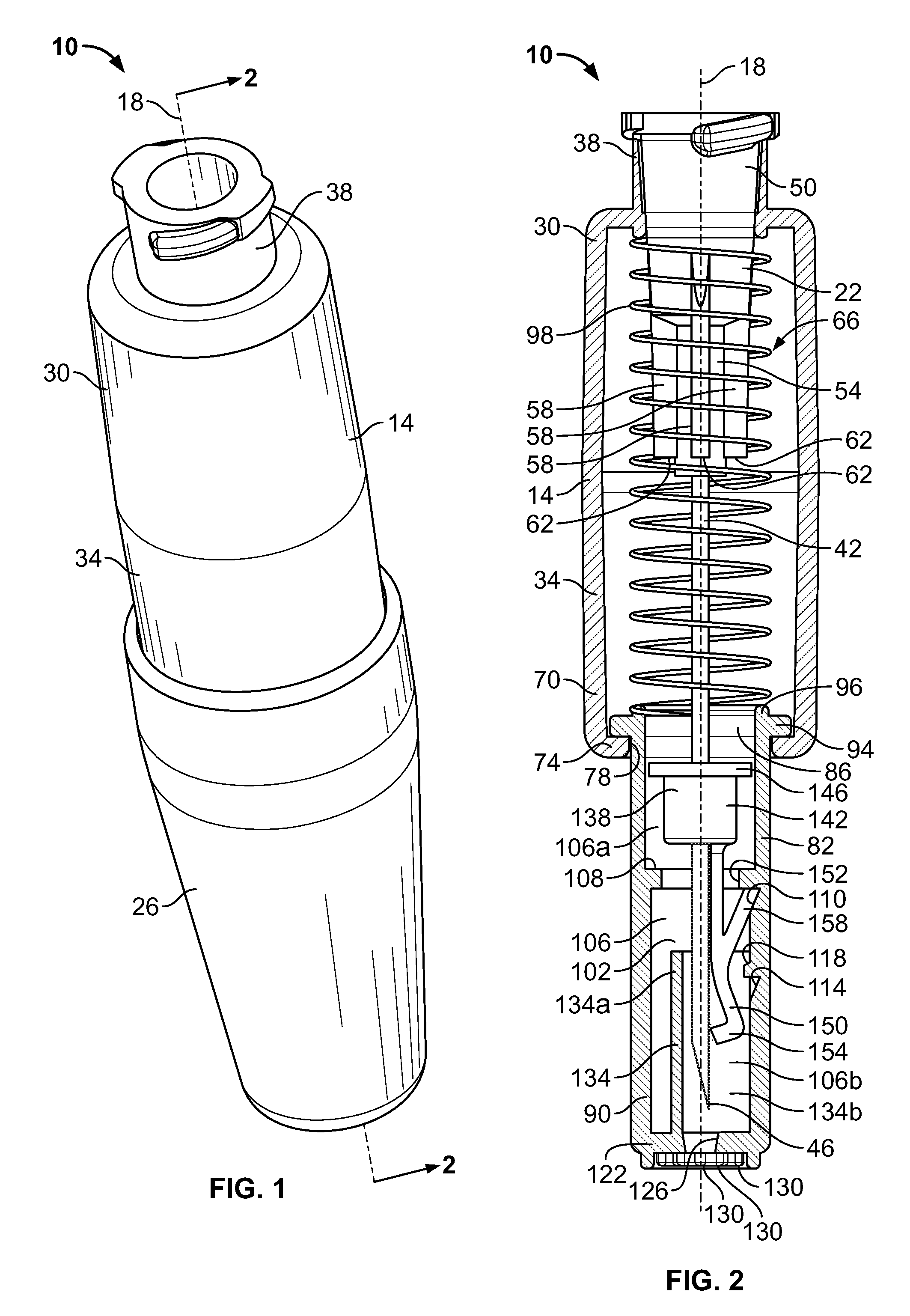
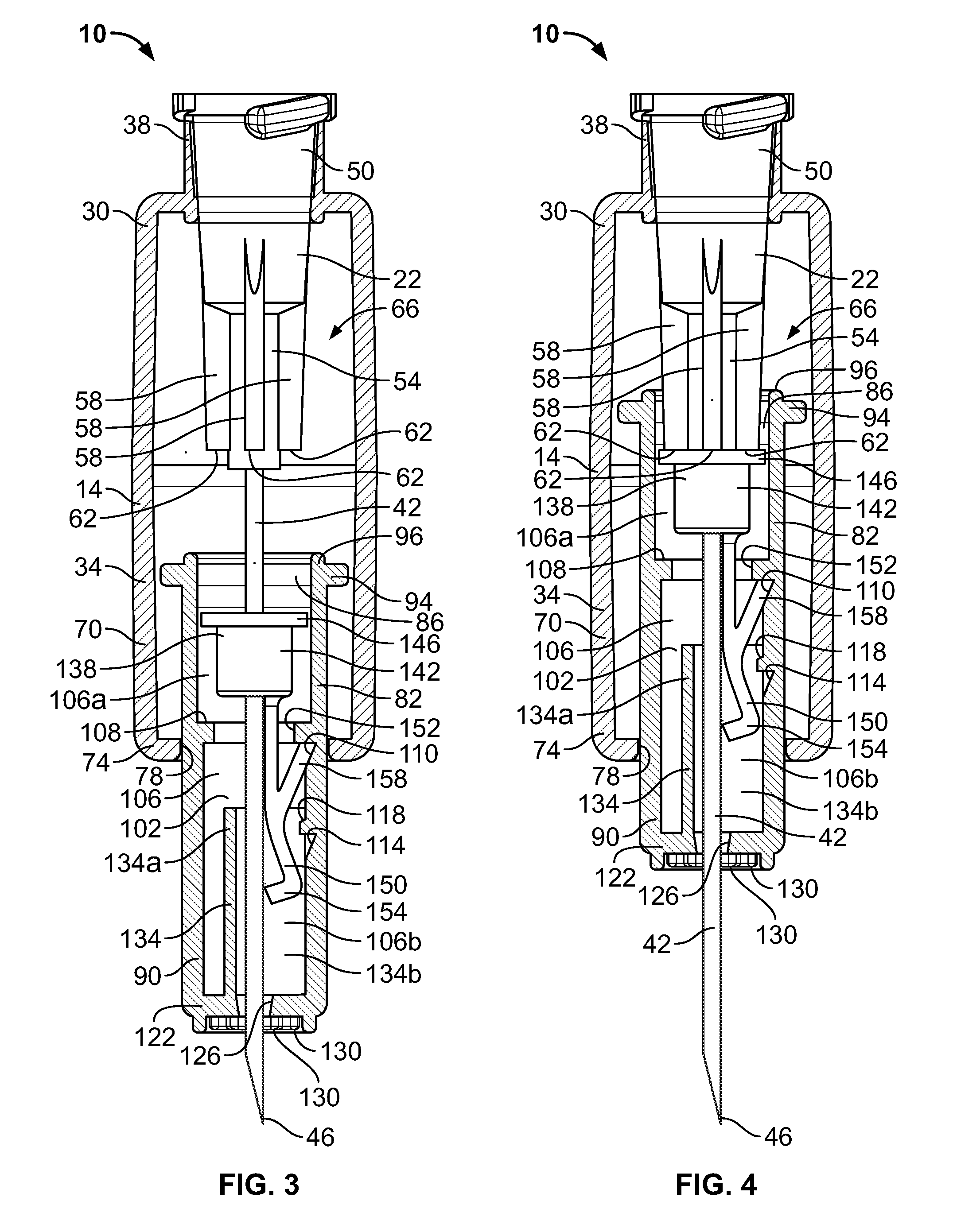
Needle cover assembly for a syringe
A single-use cover assembly that obscures a substantial majority or an entirety of an injection needle from view before, during, and after an injection procedure. The cover assembly includes a housing and a needle sleeve that retracts and extends by sliding axially within the housing. The needle sleeve carries a locking collar that moves from a first position to a second position once the needle sleeve is fully retracted. In the first position the locking collar allows retraction of the needle sleeve from a fully extended position. In the second position, a portion of the locking collar covers a tip of the needle, thereby preventing retraction of the needle sleeve from the fully extended position.
Owner:STA MED
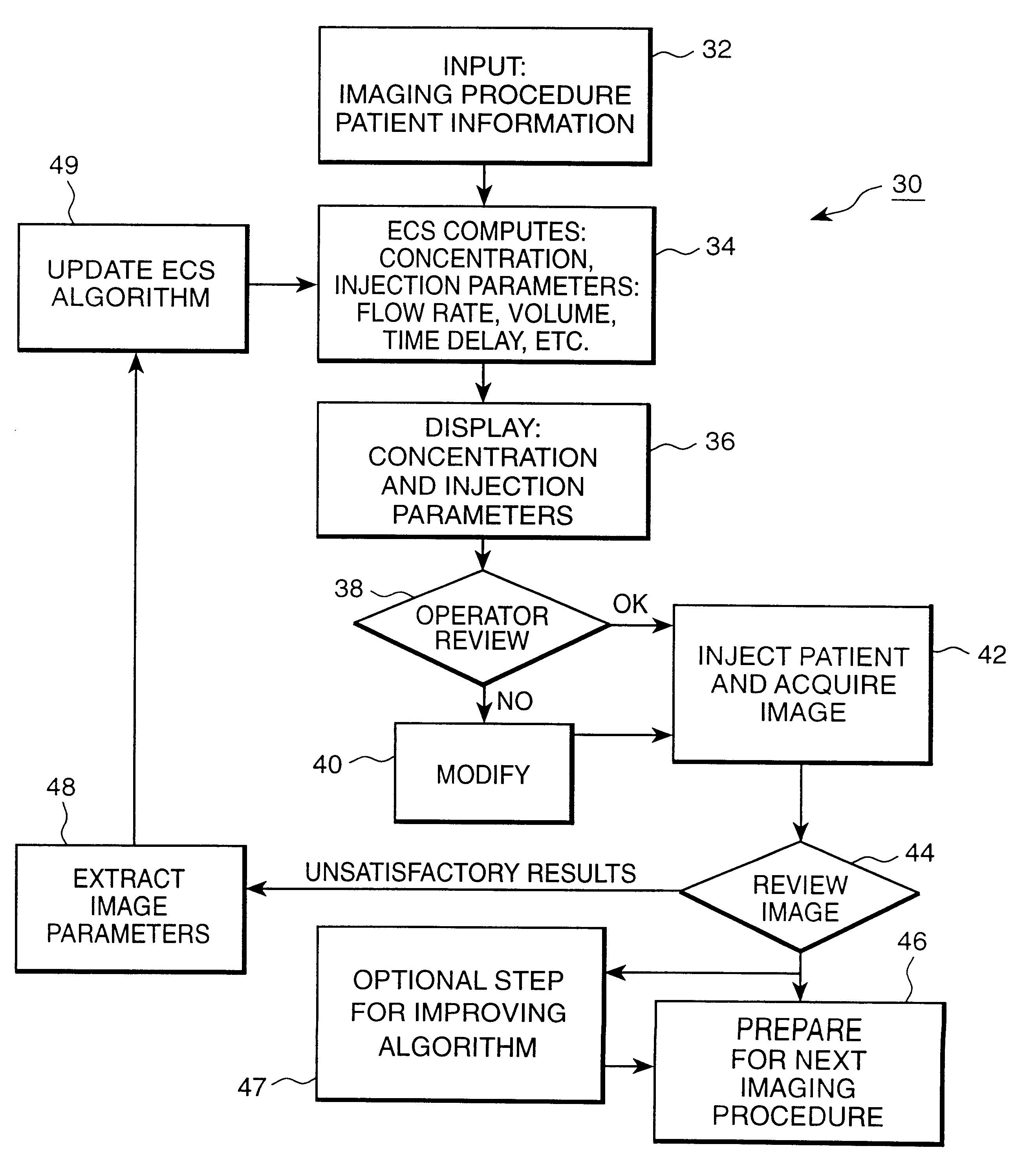
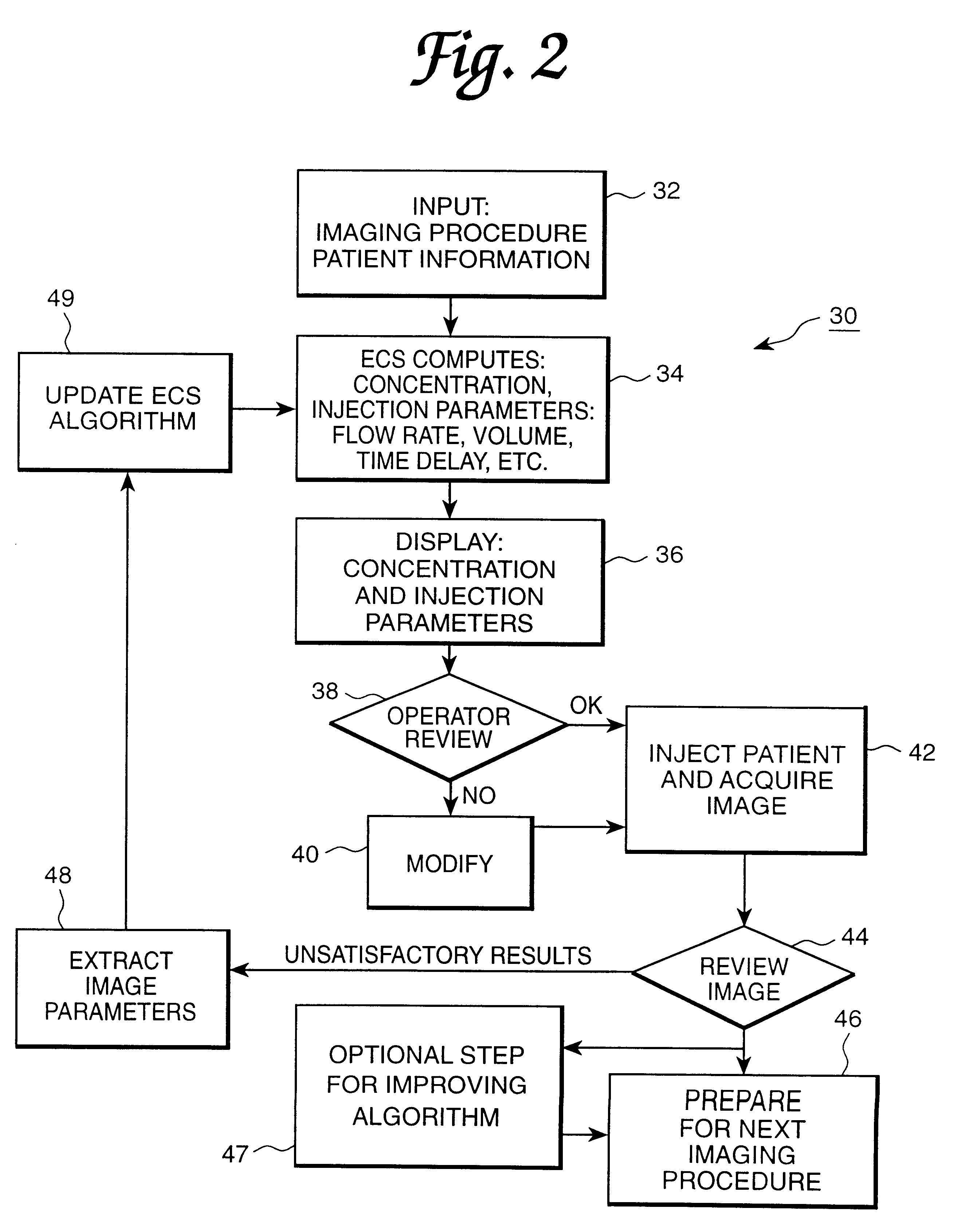
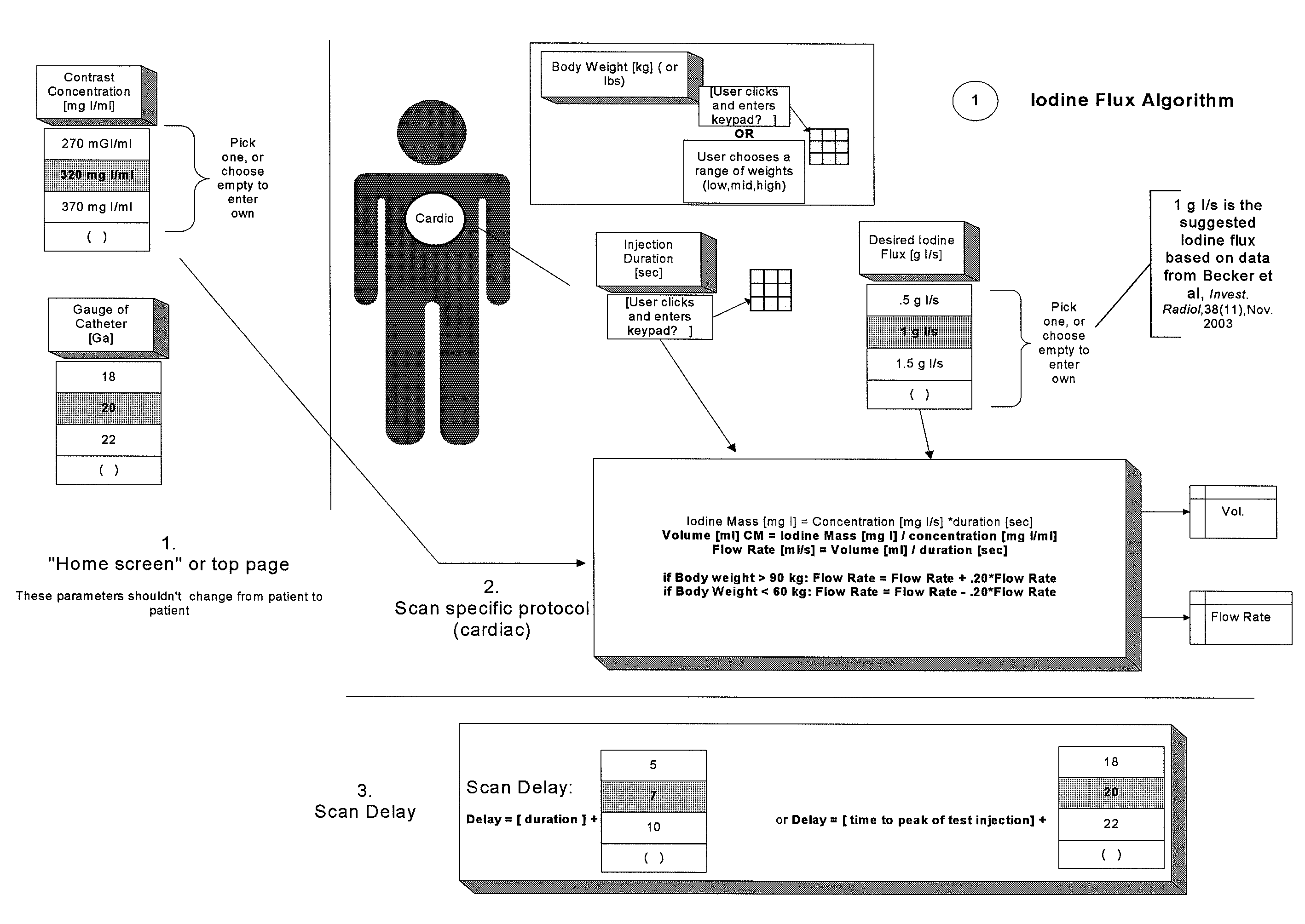
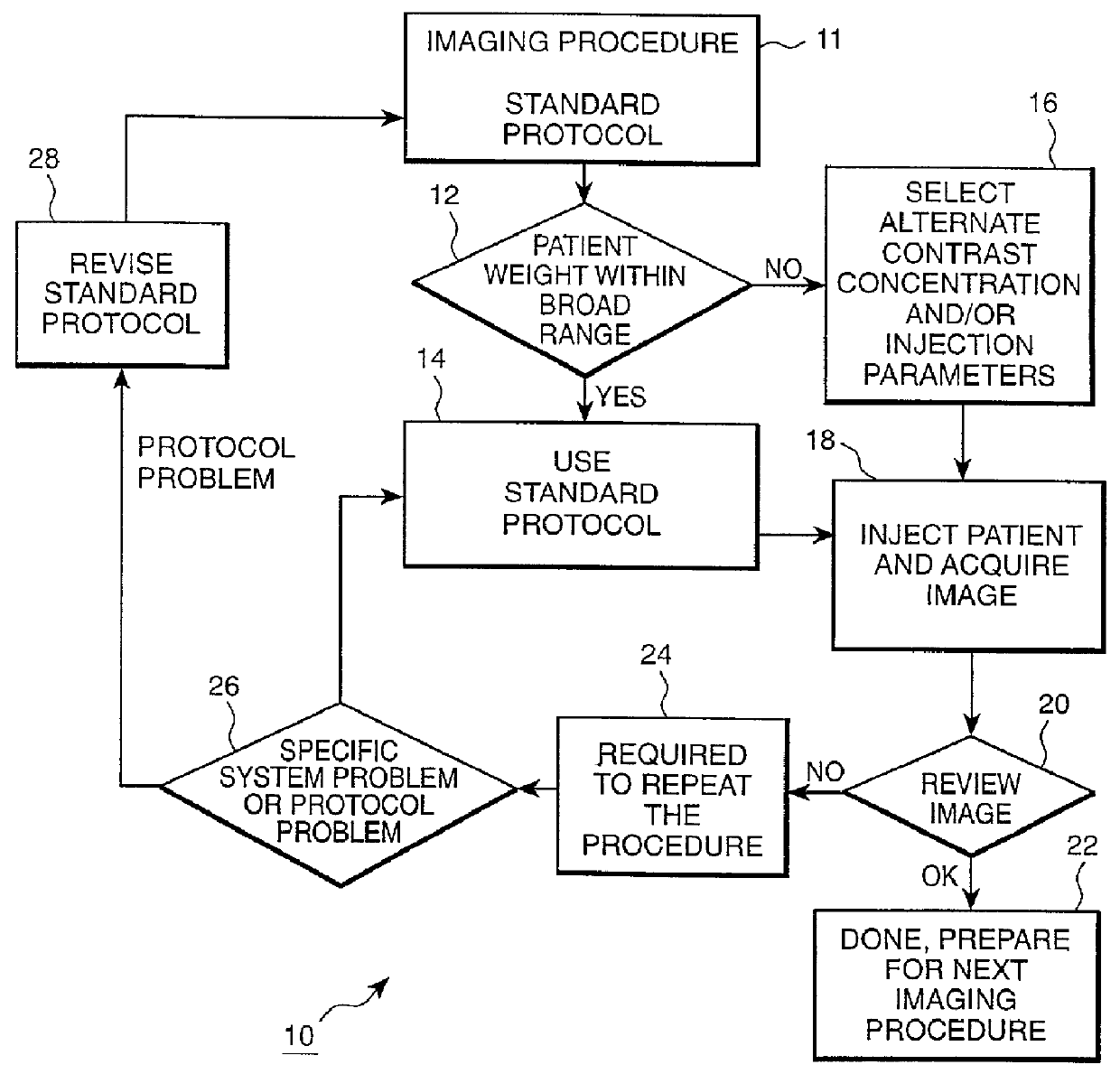
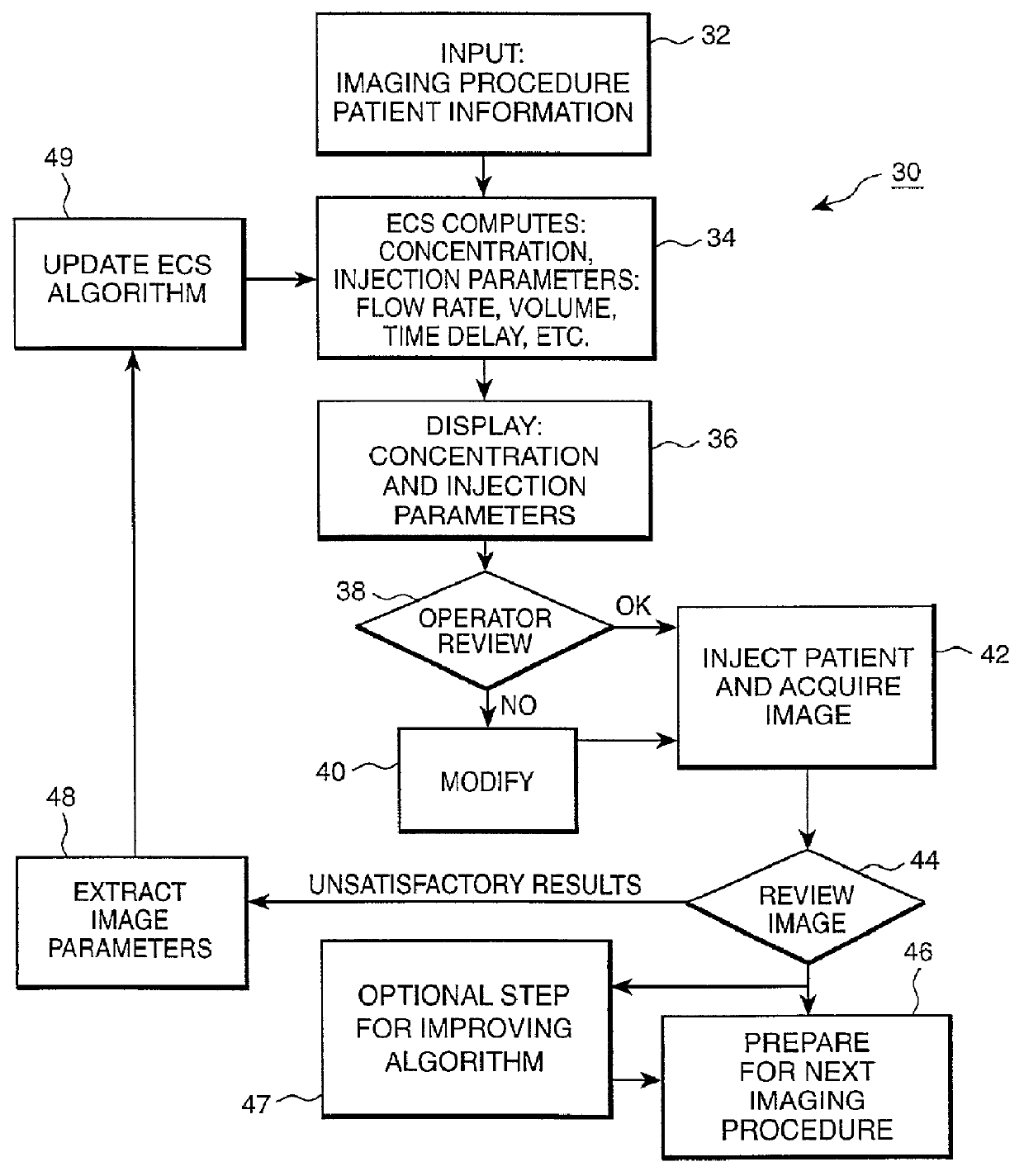
Patient-based parameter generation systems for medical injection procedures
ActiveUS20100113887A1Lower the volumeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDrug and medicationsBody mass indexBiomedical engineering
A system includes a parameter generation system to determine parameters of at least one phase of an injection procedure based at least in part upon a type of the injection procedure. The parameter generator system determines the amount of a pharmaceutical that is to be delivered to a patient at least in part on the basis of the concentration of an agent in the pharmaceutical and at least on part on the basis of a function that depends upon and varies with a patient parameter. The patient parameter can, for example, be weight, body mass index, body surface area or cardiac output. The pharmaceutical can, for example, include a contrast enhancing agent for use in an imaging procedure.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
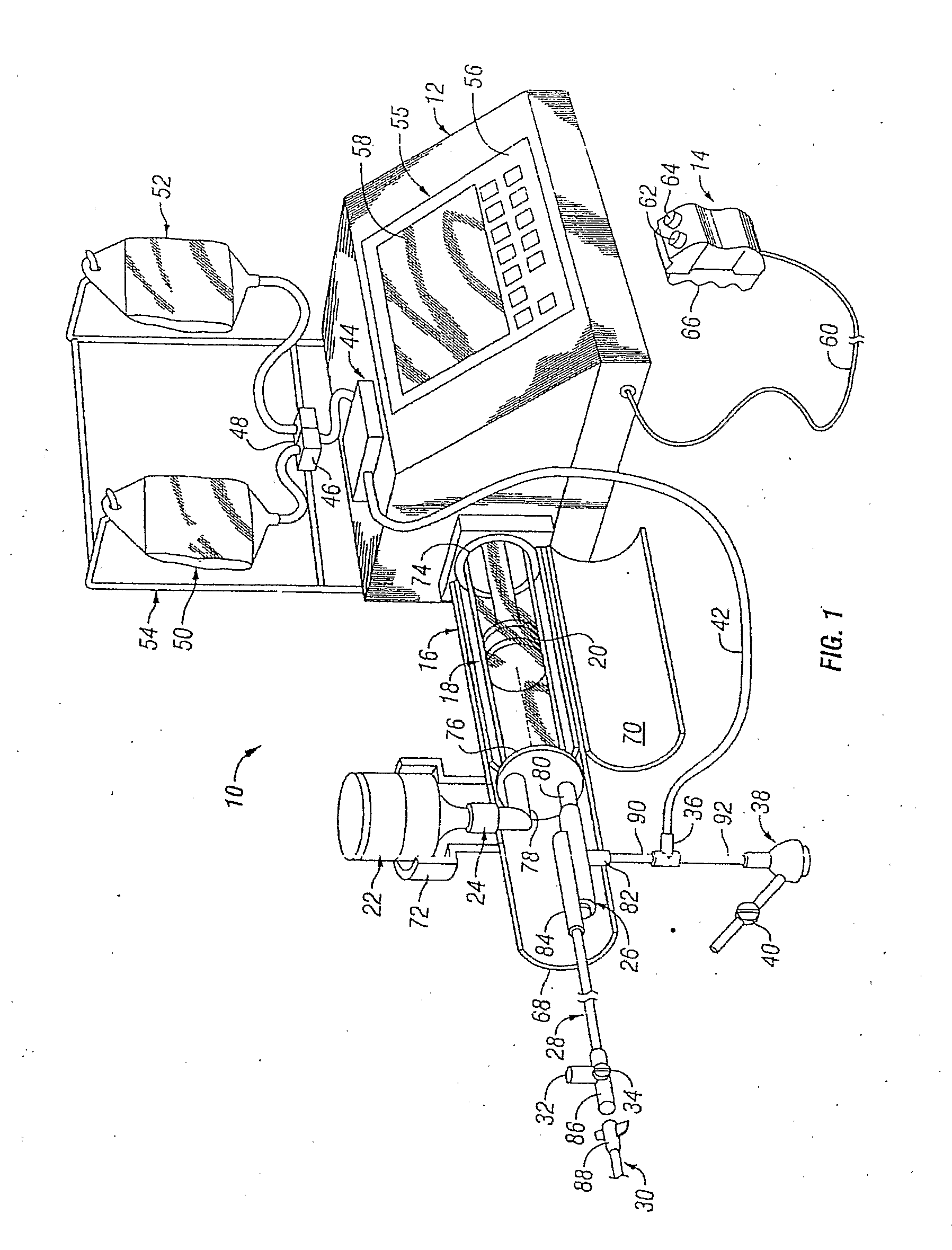
Injector
InactiveUS20050038390A1Reduces and eliminates power connectionGood adhesionAutomatic syringesMedical devicesAxis of symmetryRadiographic contrast media
An injector 20 that may be used to deliver radiographic contrast media and / or flushing solution into a patient's vascular system for the purposes such as obtaining enhanced diagnostic x-ray images. The injector includes the following features: (1) a syringe mount 26 for attachment of a syringe 28 to the injector 20; (2) display 34 and controls 90 for volume and flow rates; (3) automatic limiting of the operating pressure of the injector 20 as determined by the selection of a flow rate; (4) a syringe cradle 48 having a warming capability; (5) a purge / retract trigger 36 for control of the injection procedure having intuitive direction (i.e., forward for injecting, reverse for filing), non-contact control transmission through the housing of an injector 20 for an improved seal integrity, a speed lock, and / or the ability to change the concentration and / or flow rate of media or other fluid during an injection procedure; (6) a switch to determine when the drive ram 46 is in a “home” position; (7) a “soft” on / off power switch separate from the injector; and (8) a structure to prevent rotation of the drive ram 46 about its axis of symmetry 76. Additionally, the injector system includes software for the control of various components.
Owner:LIEBEL FLARSHEIM CO
Apparatus and Methods for Delivery of Fluid Injection Boluses to Patients and Handling Harmful Fluids
ActiveUS20110209764A1Tighter performanceInfusion devicesInternal framesFluid transportDelivery system
A hazardous fluid transport container and a hazardous fluid delivery system are disclosed. The hazardous fluid transport container includes a housing enclosing an at least partially shielded enclosure. First and second fluid path elements are disposed within the housing, with the first fluid path element and second fluid path element fluidly coupled together. A pump unit may be provided for dispensing fluid from the first and second fluid path elements optionally into a third fluid path element. Also, methods for priming the hazardous fluid transport container and for mitigating laminar flow injection bolus spreading are disclosed. Additionally, disclosed is a radioactive fluid transport container for a syringe or other container. The radioactive fluid transport container allows the syringe or container to be used in an injection procedure without removal from the container.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
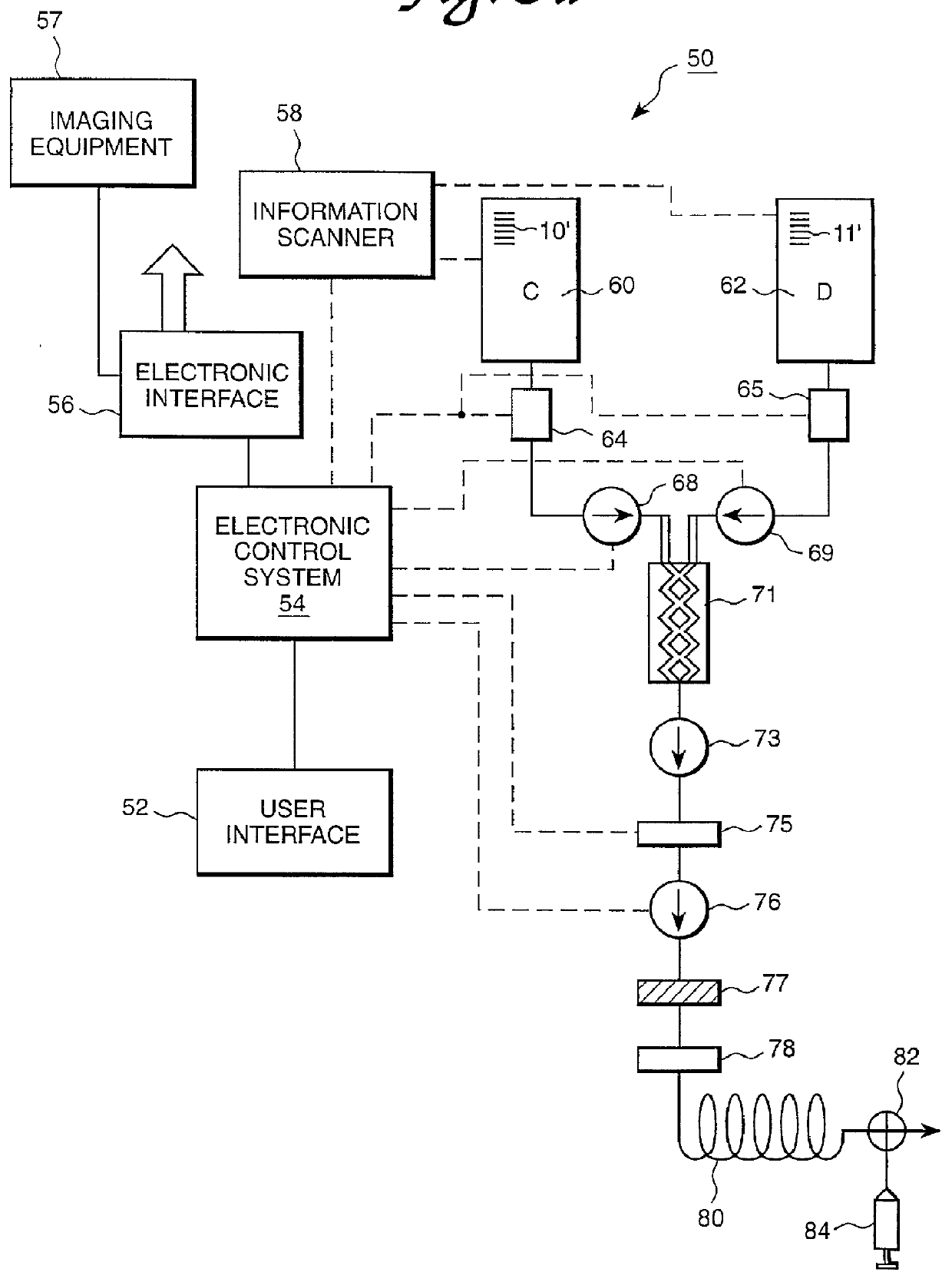
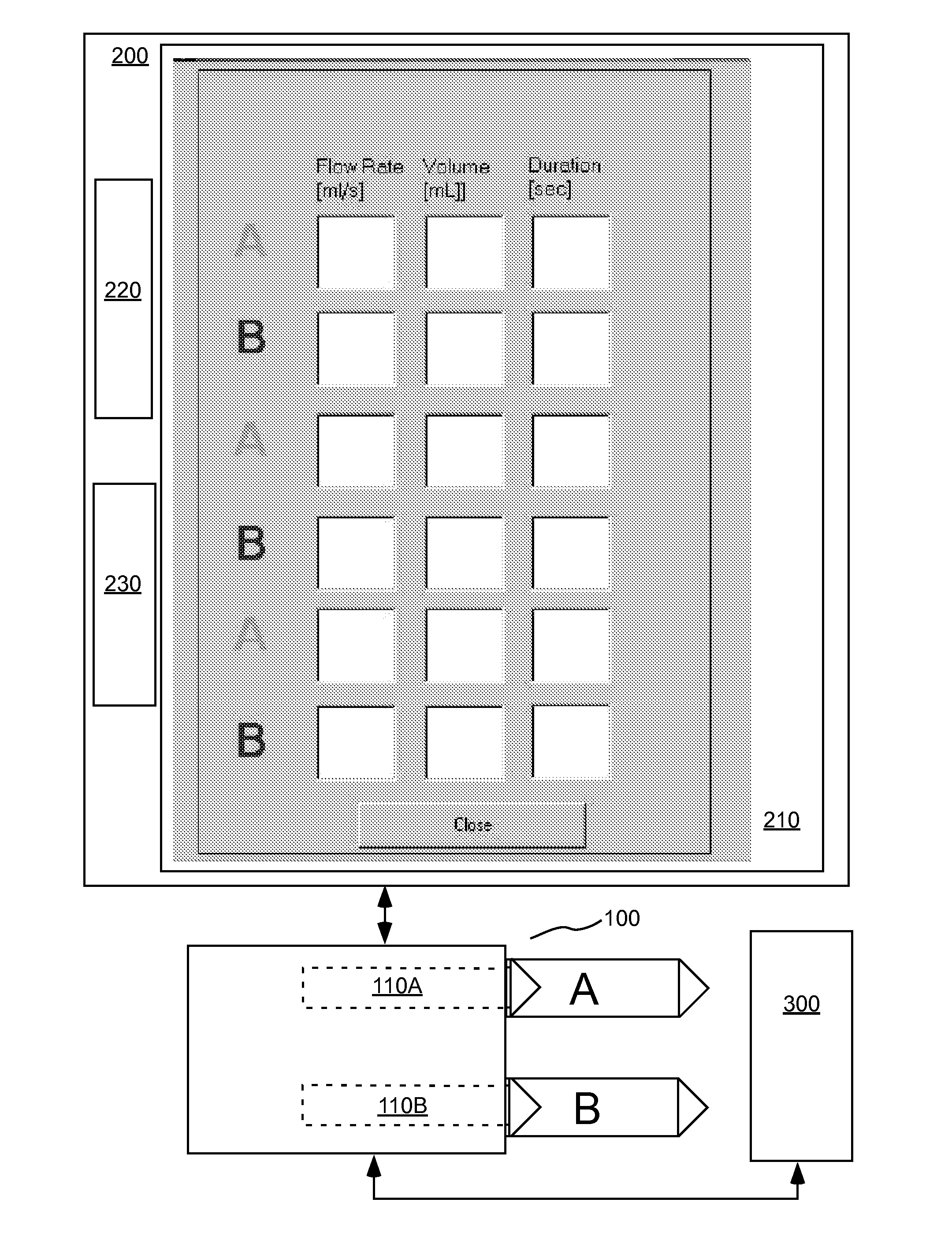
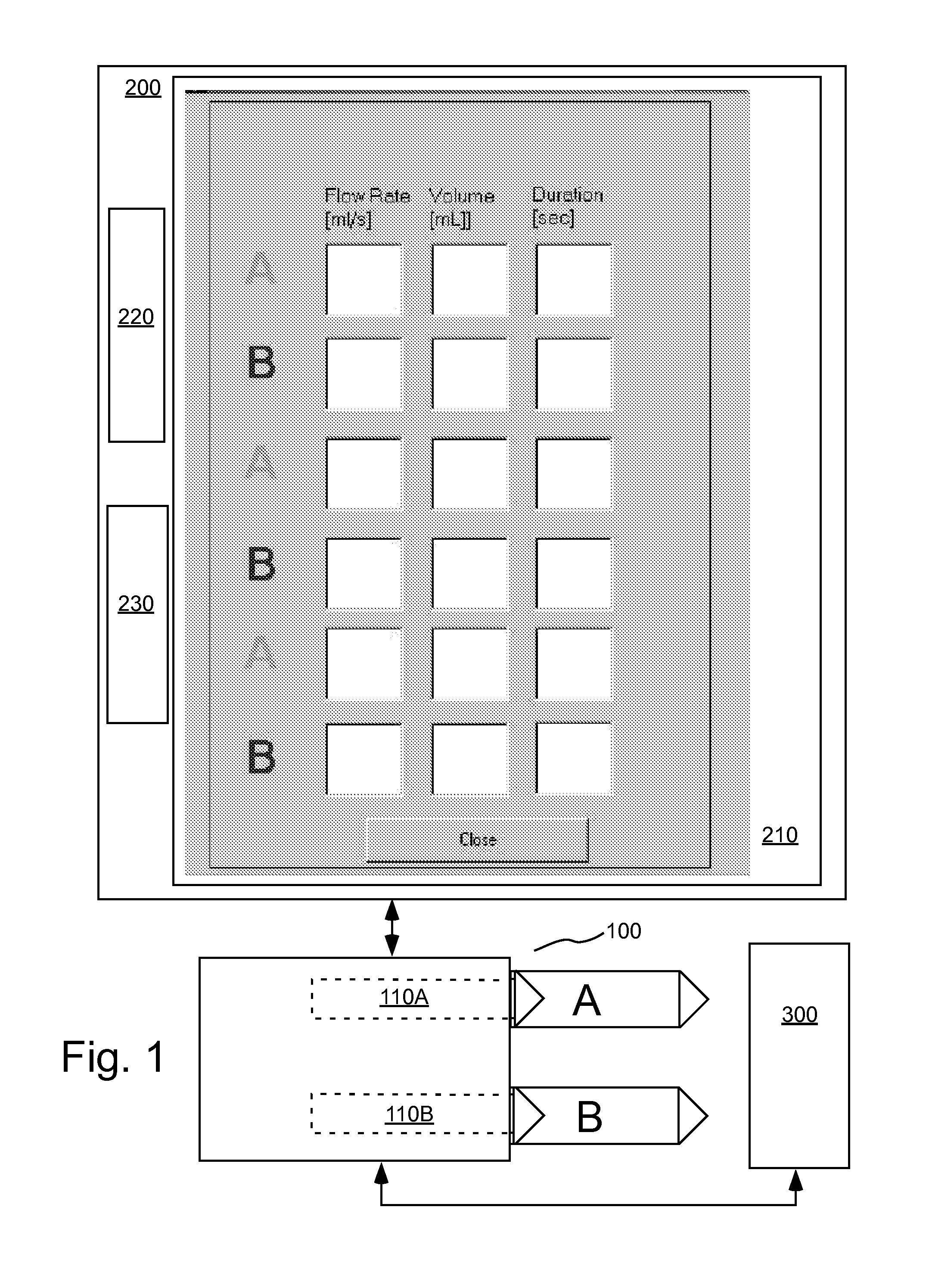
Devices, systems and methods for determining parameters of one or more phases of an injection procedure
ActiveUS20070282263A1Raise the ratioKeep for a long timeElectrocardiographyLocal control/monitoringEngineeringInjection device
A fluid injection apparatus includes at least one pressurizing mechanism and at least a first fluid container (for example, a syringe or a bulk container) operably associated with the at least one pressurizing mechanism. The first fluid container is adapted to contain a first fluid to be injected. The fluid injection apparatus also includes a controller operably associated with the at least one pressurizing mechanism. The controller includes a programming system to allow programming of an injection protocol including, for example, a plurality of phases. At least one parameter generator is provided to determine parameters of at least one of the plurality of phases of the protocol based at least in part upon a type of the injection procedure.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Method and device for painless injection of medication
InactiveUS20100076400A1Simple and inexpensive to performSimple and inexpensive to and operateAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesMedication injectionAnesthetic
A method for providing a substantially painless injection of medication into a patient, including inserting an injection needle having an outside diameter greater than 0.20 mm and less than about 0.38 mm, and injecting a medicament through the needle and into the patient at a substantially constant volumetric flow rate of about 0.05 μL / s to about 50 μL / s that provides a painless injection. The method does not require the use of an anesthetic or that the medical personnel to spend a substantial amount of time performing the injection procedure, is relatively simple and inexpensive to perform and operate, and provides a relatively high degree of safety for both the medical personnel and for the patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
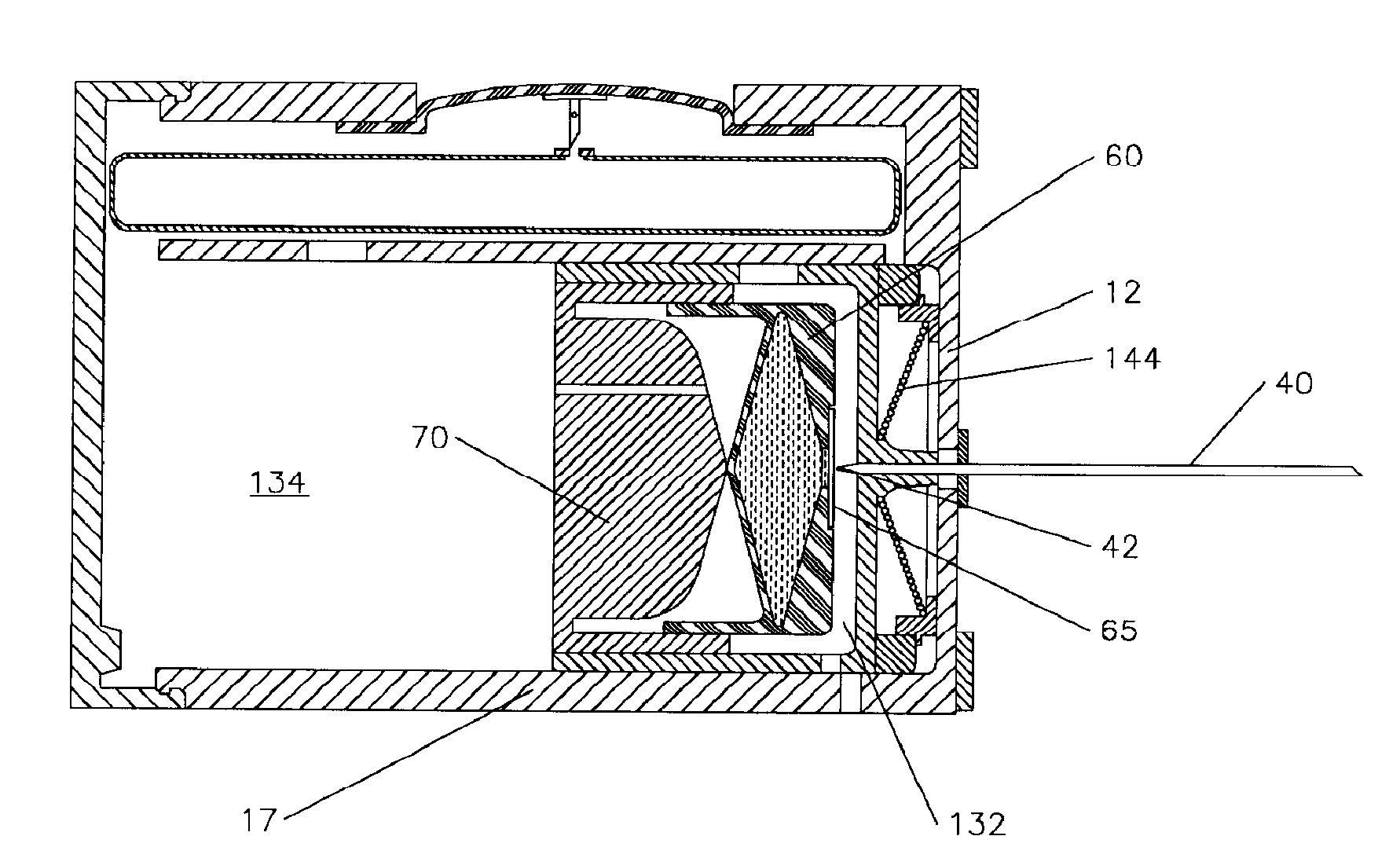
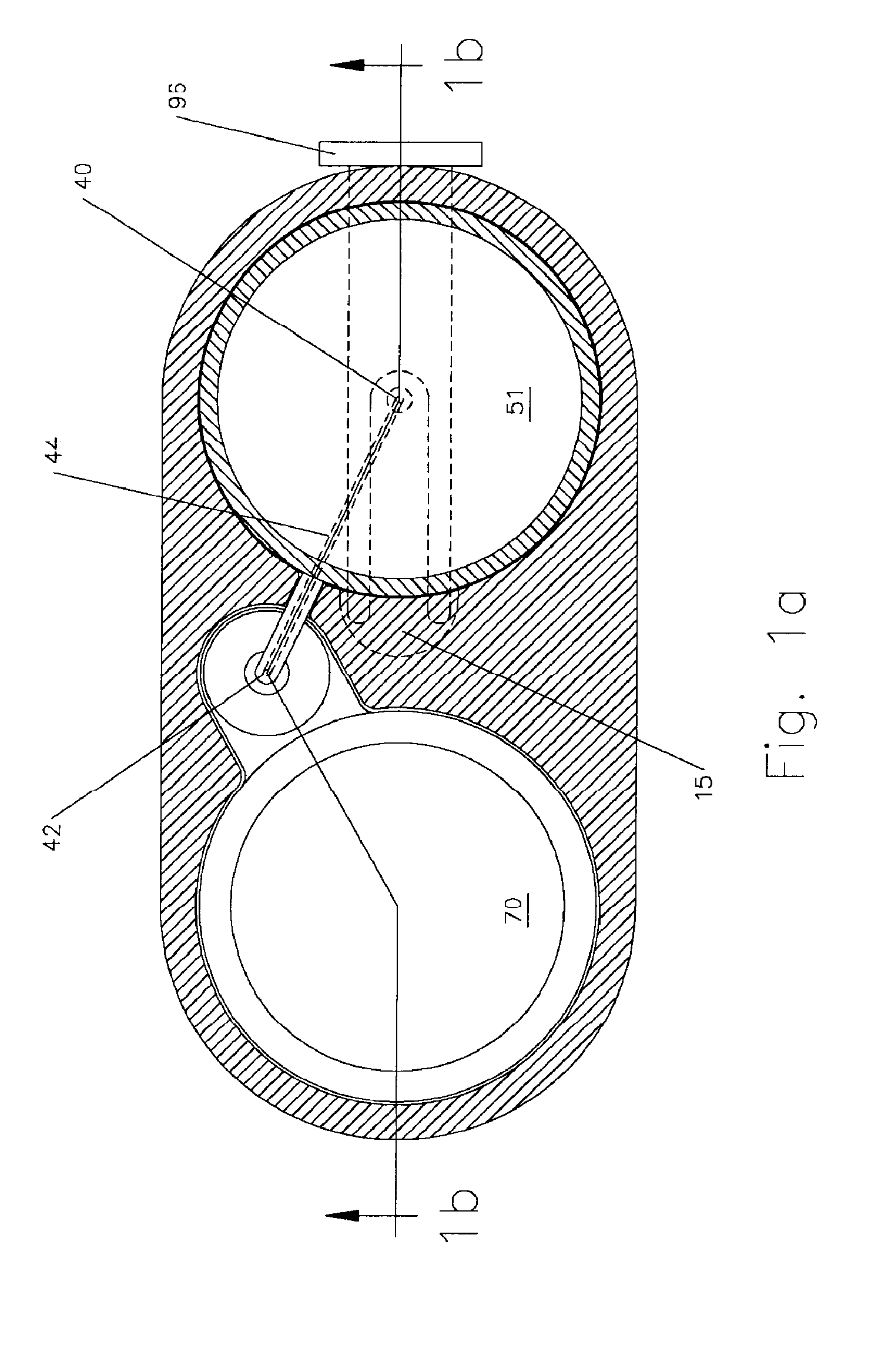
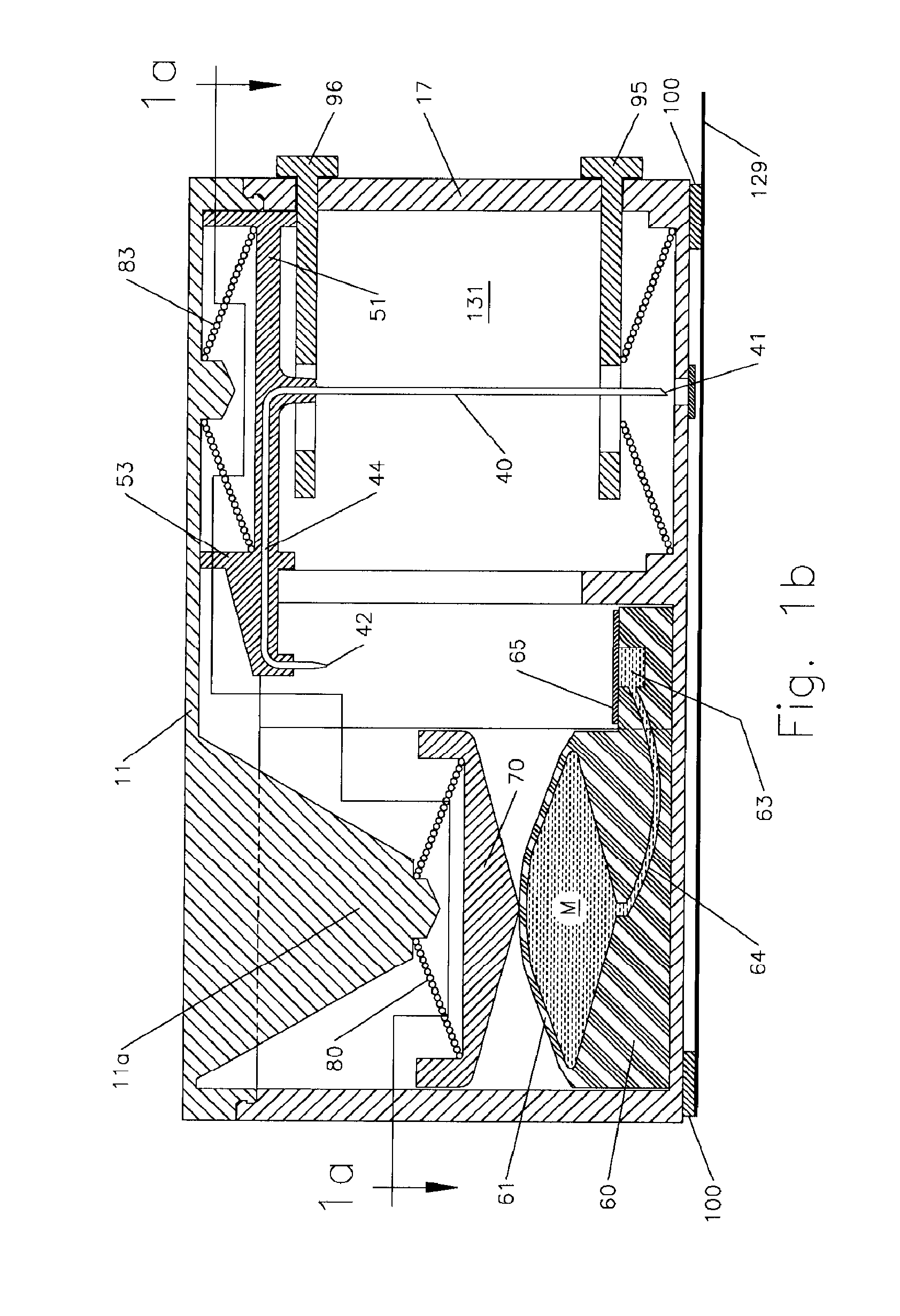
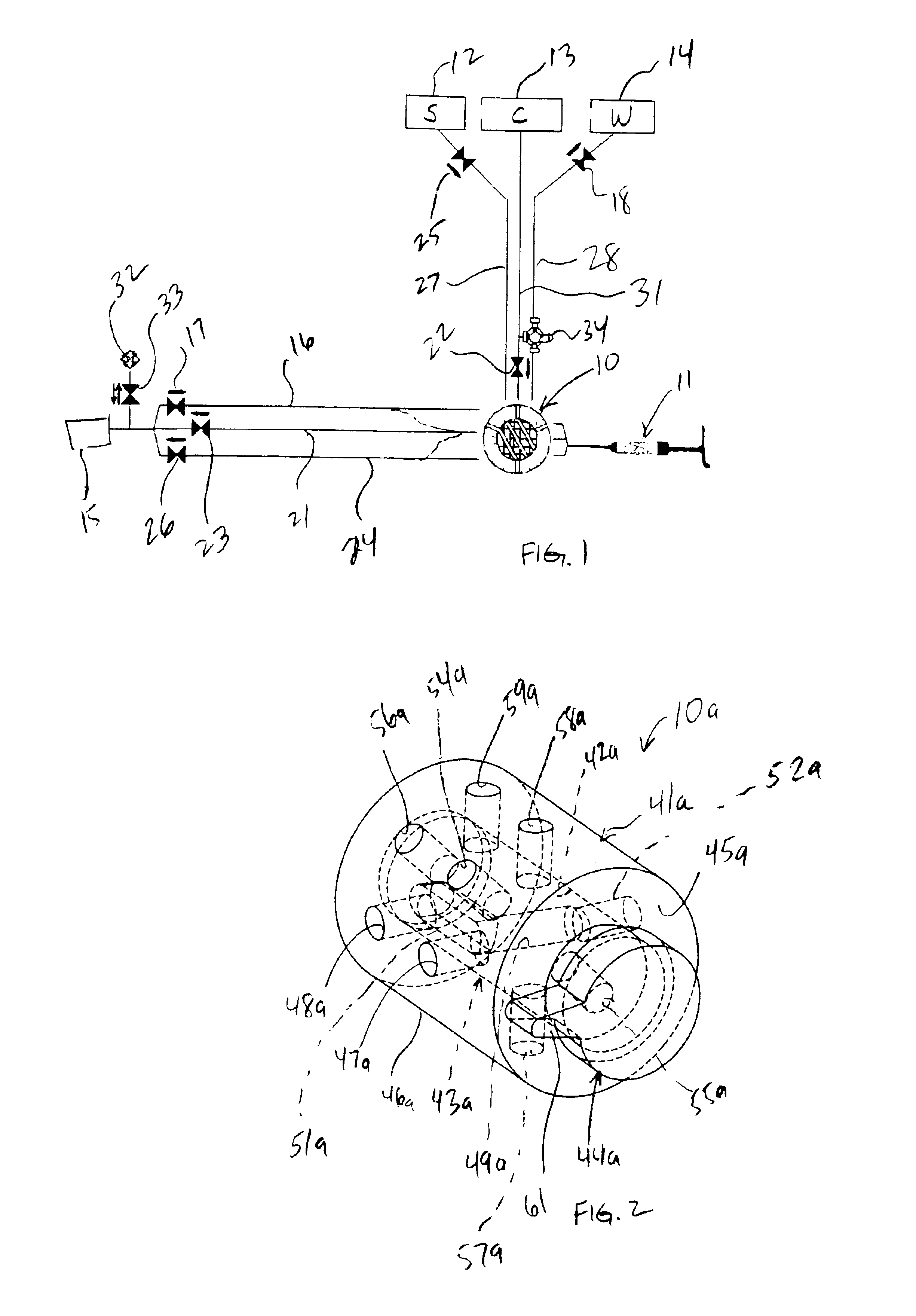
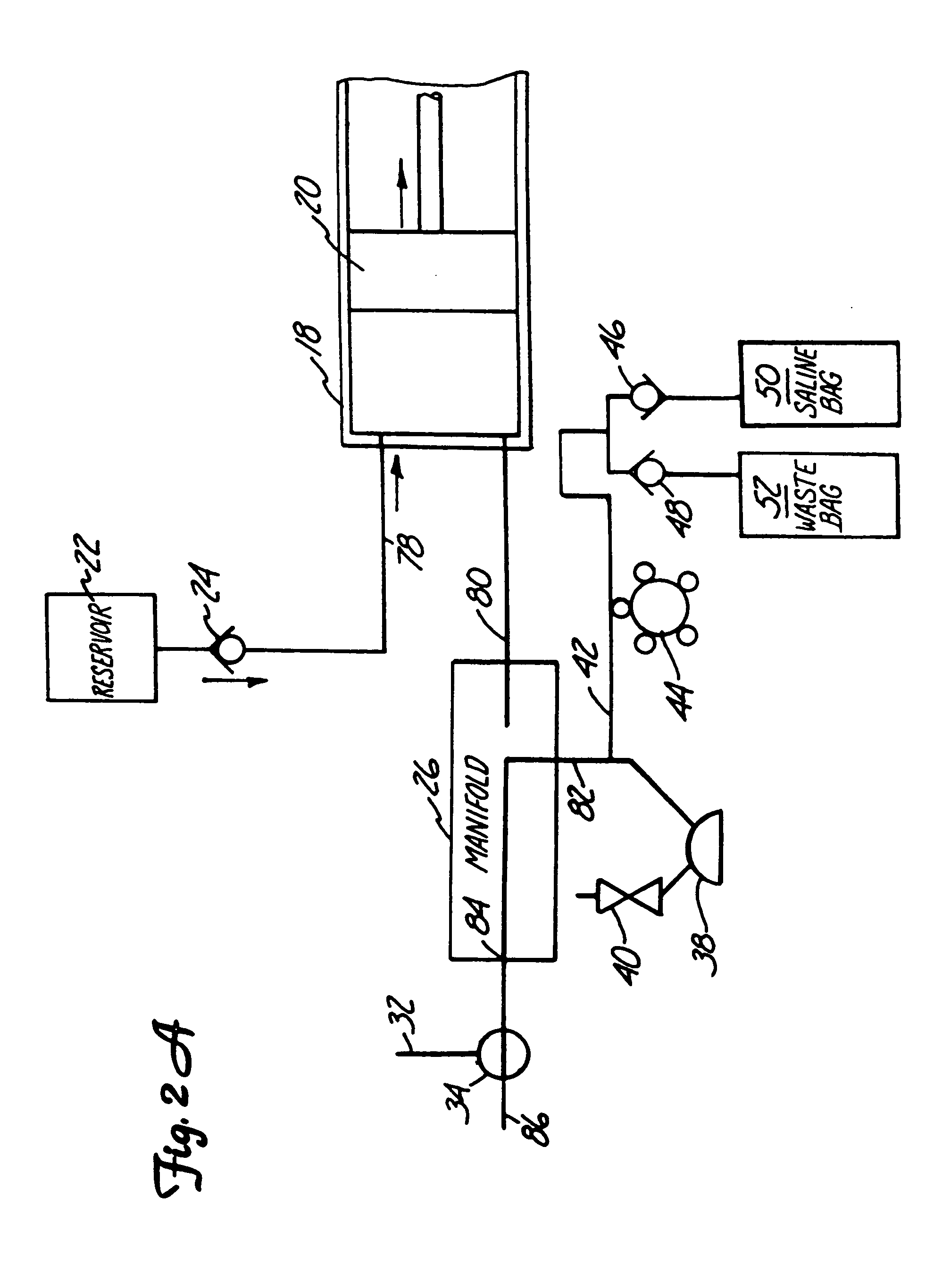
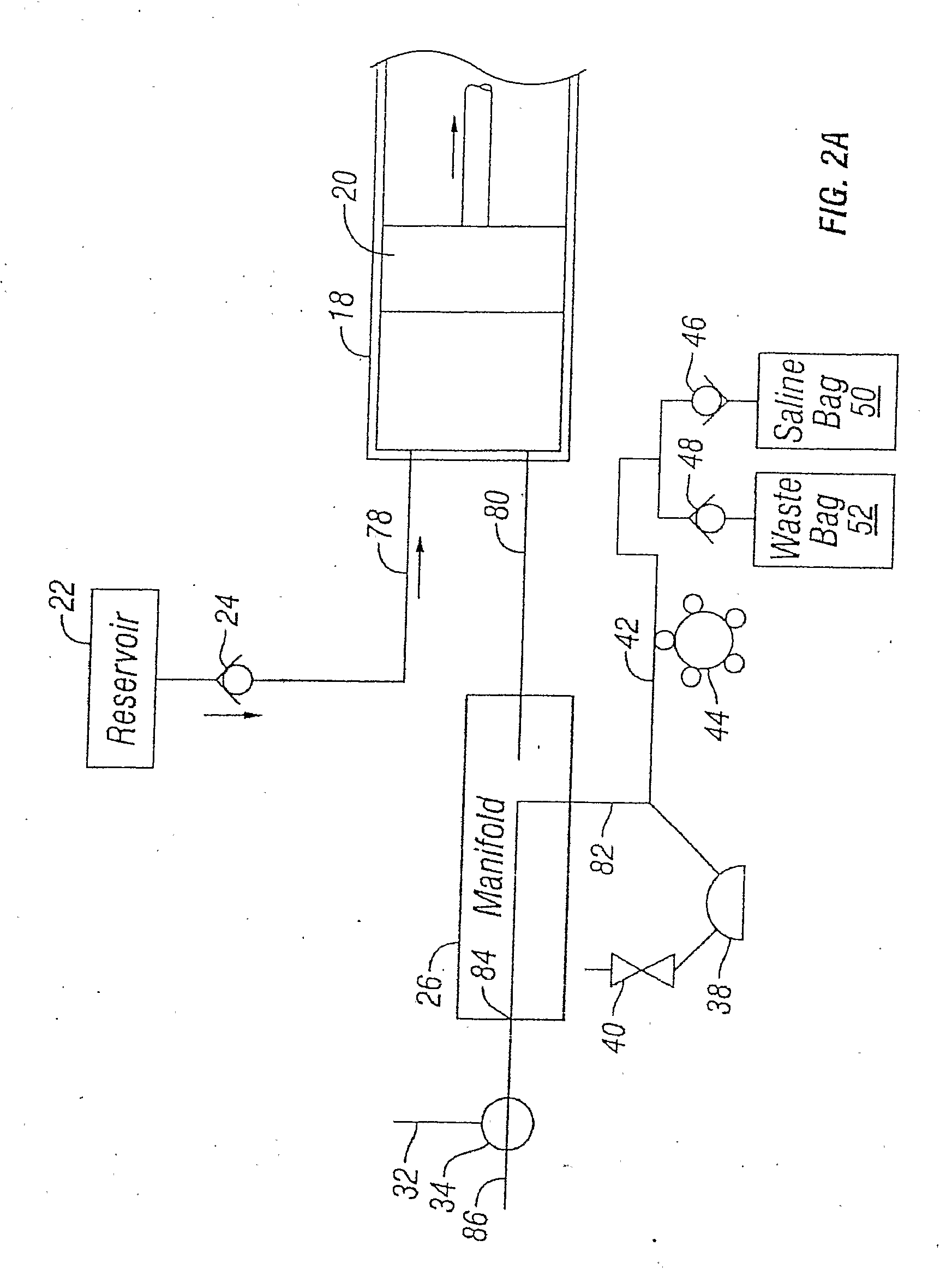
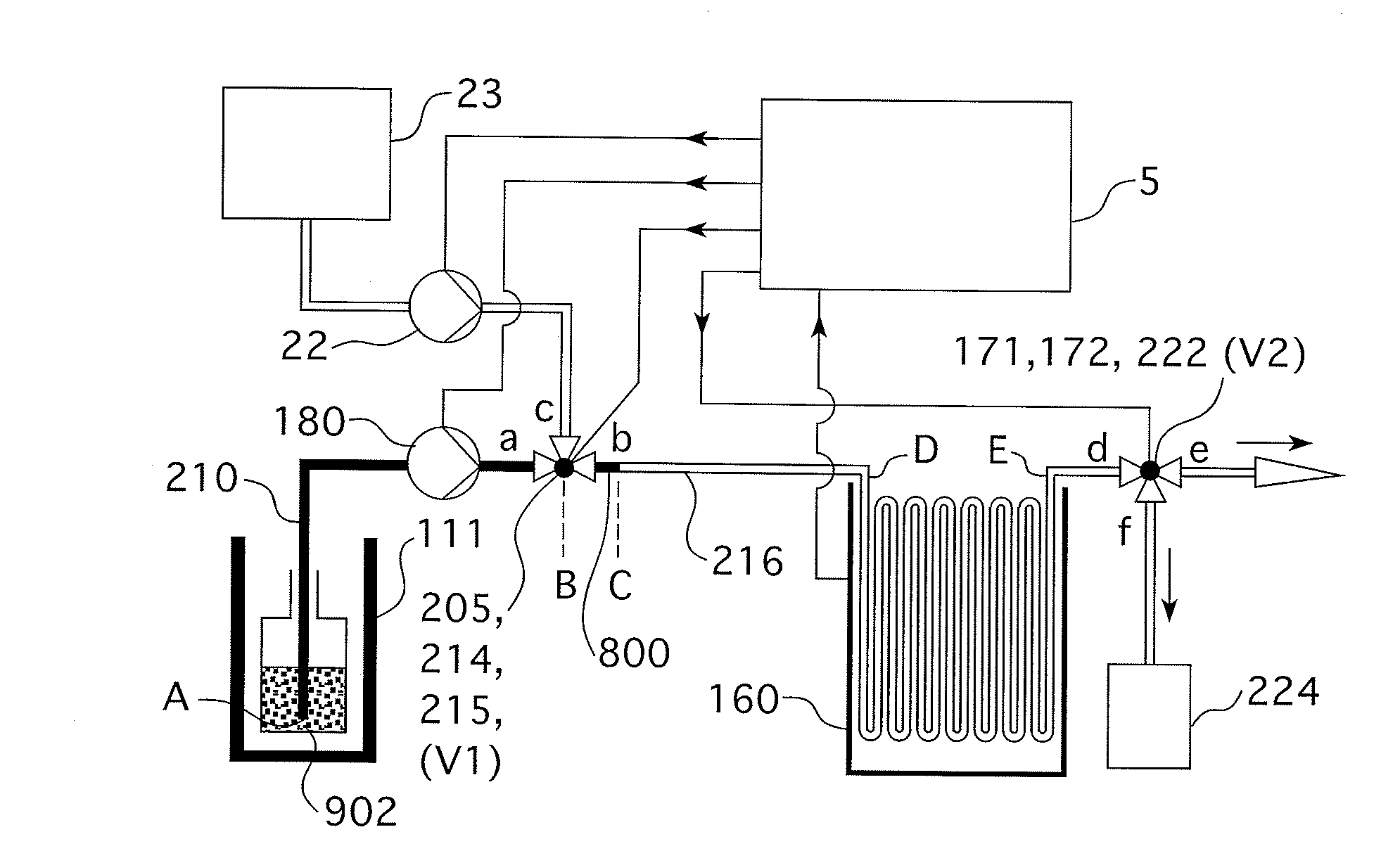
Multiple port fluid control valves
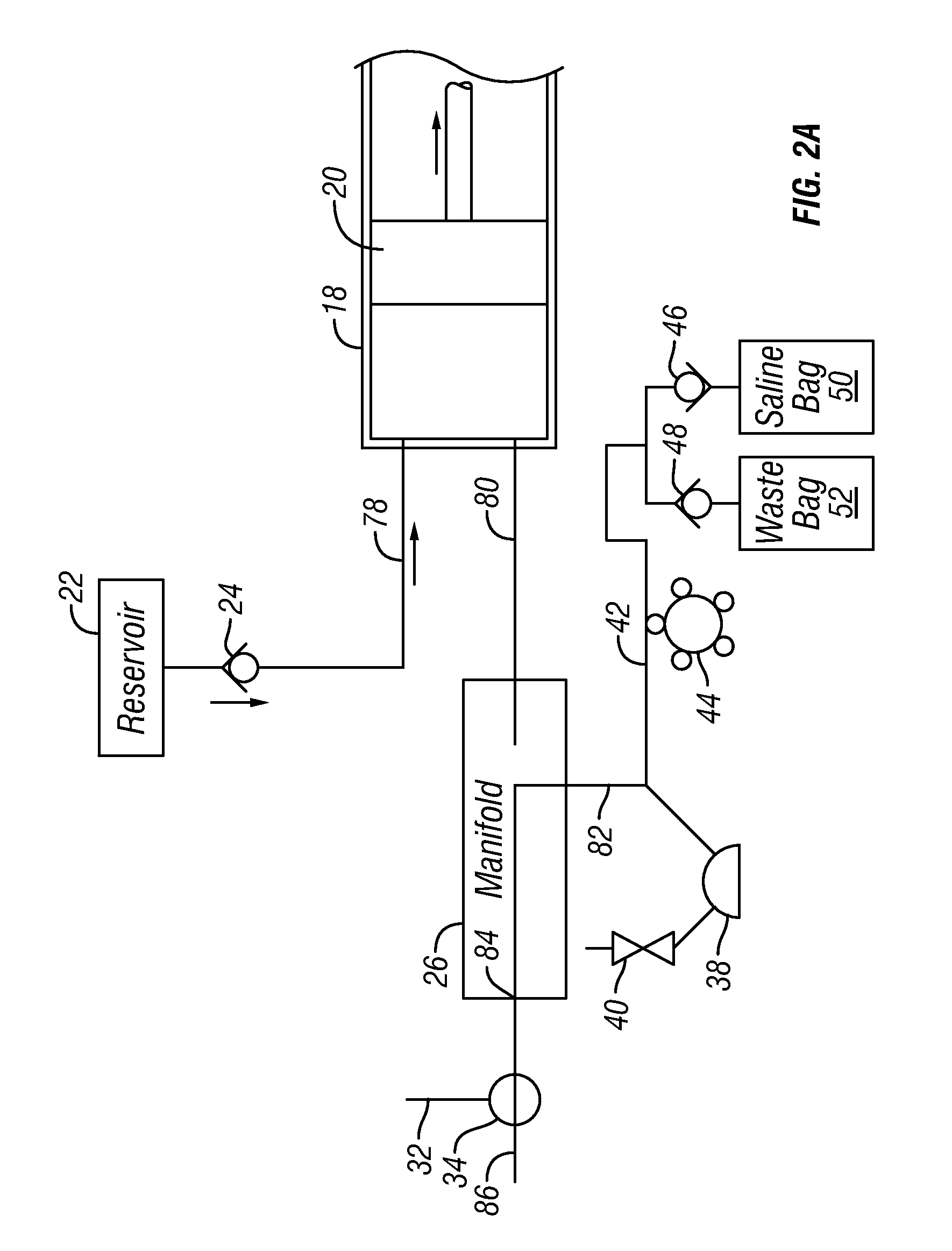
A fluid control valve is disclosed which, with a single valve, can manipulate flow between a saline supply, a contrast supply, a waste dump and a catheter. The control valve includes three primary positions including a contrast position where the valve provides communication between an injector and a contrast supply while isolating the saline supply and catheter. The valve also can be moved to a saline / waste position where the valve provides communication between the injector and the saline supply and / or the waste dump while isolating the contrast supply and catheter. The valve also can be moved to an injection position where the valve provides communication between the injector and the catheter. A single valve provides all three functions. The valve also may provide communication between a pressure transducer and catheter during the saline loading, waste dumping and contrast loading functions. The valve also provides protection or isolation of the pressure transducer during injection procedures.
Owner:MEDLINE INDUSTRIES
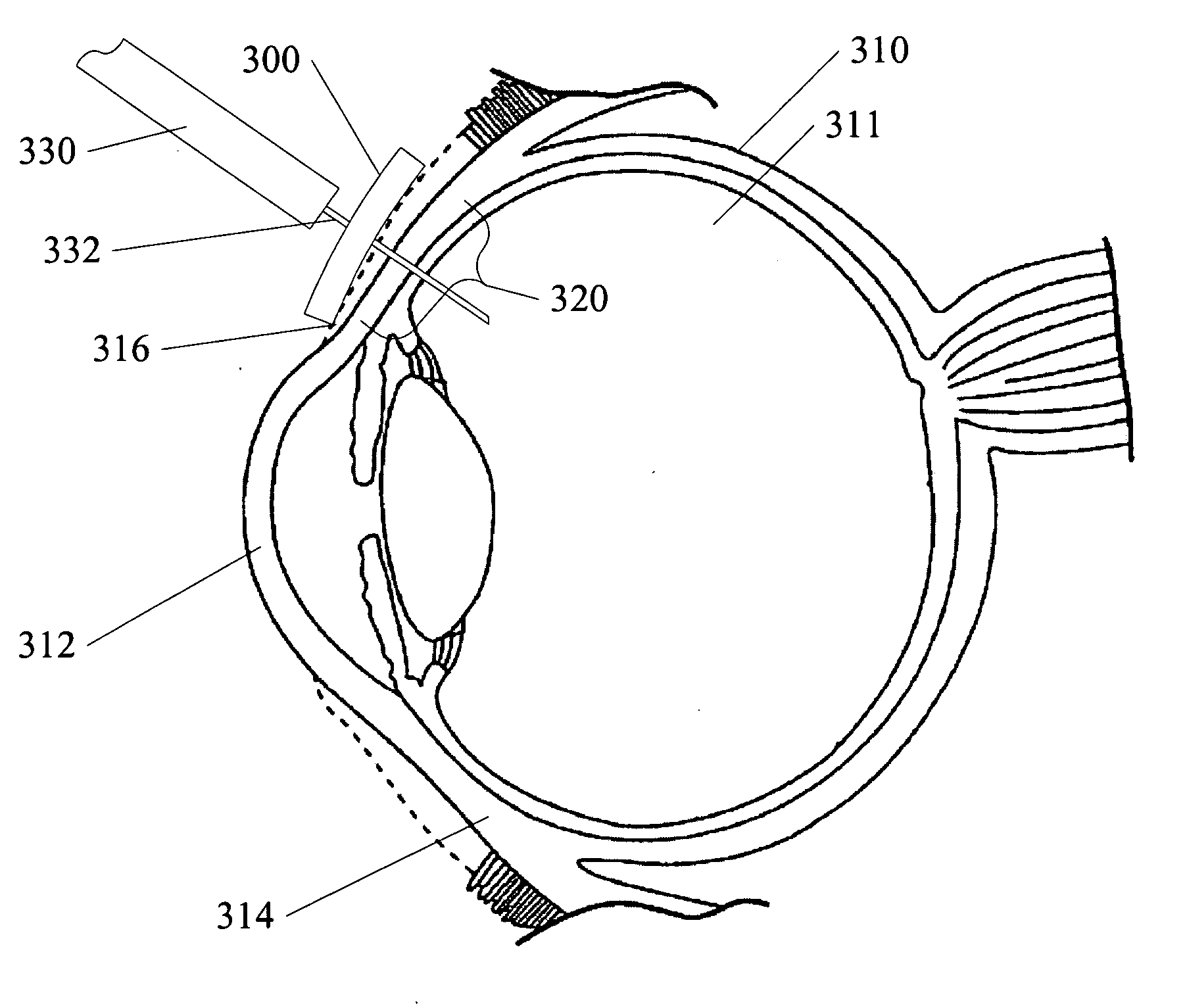
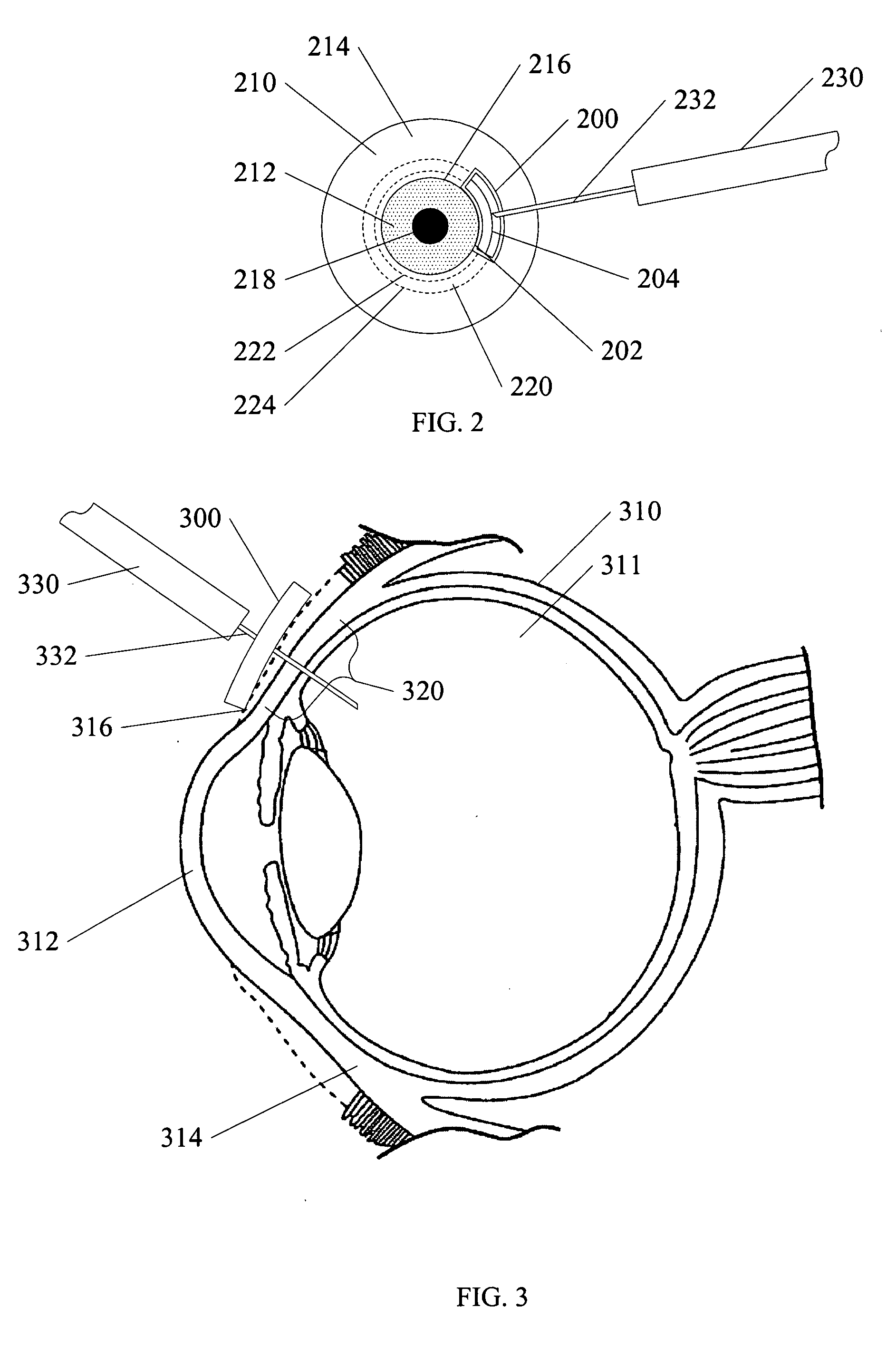
Ocular injection device and method
A device and method for an injection into an eye such as an intravitreal injection is shown. Ocular devices and methods shown provide a reduction in the number of steps involved in an injection procedure. Ocular devices and methods shown also provide consistent and repeatable location of an injection location. Other selected embodiments include integrated structures such as holding portions, or speculum structures that further facilitate an injection procedure.
Owner:WILLIAMS DAVID F
Angiographic injector system with multiple processor redundancy
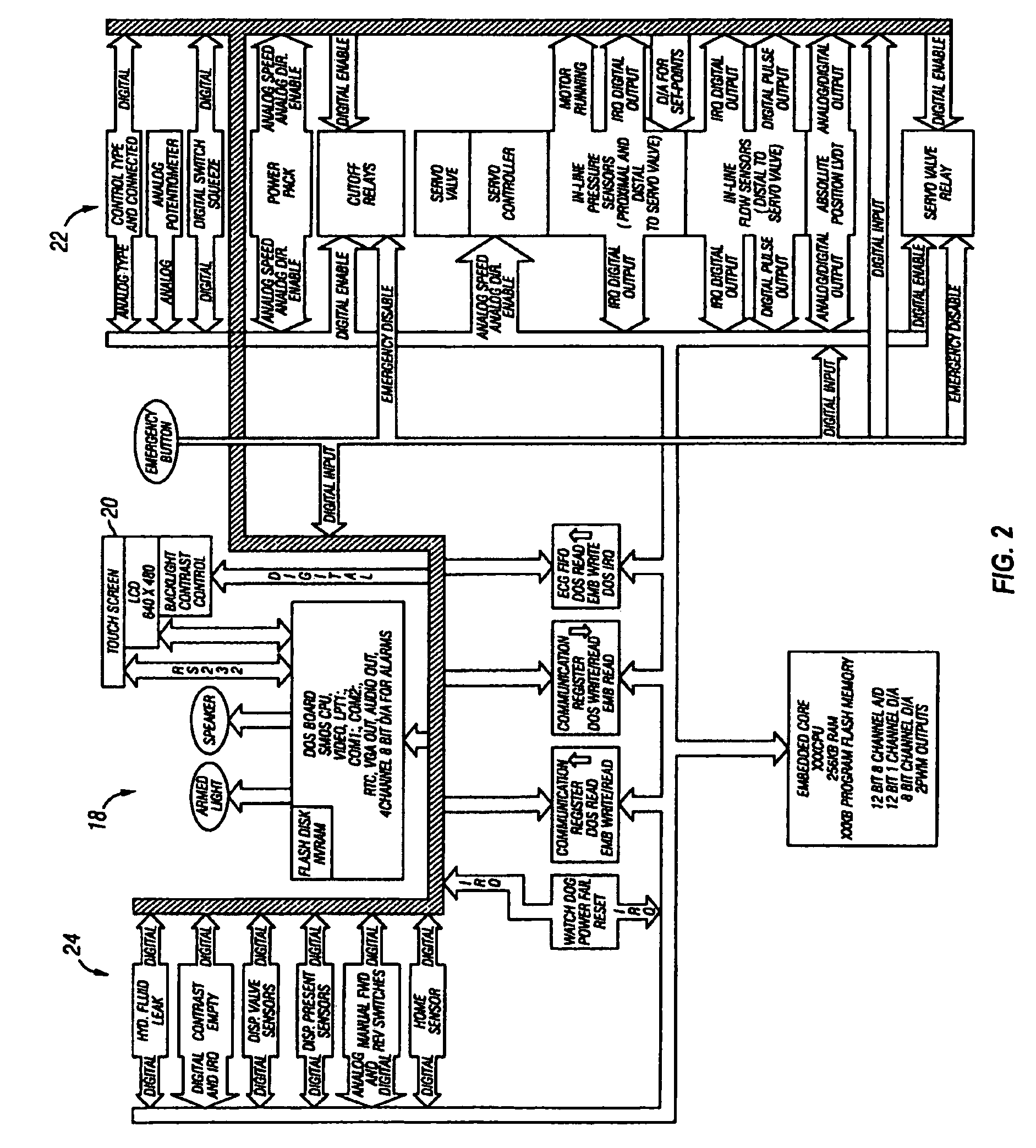
InactiveUS7267666B1Readily and accurately permittedFlexible and user friendlyElectrocardiographySurgeryOperation modeEngineering
An angiographic injector system and a method of controllably delivering medical fluid to a patient from an angiographic injector system are disclosed. A multiple processor control system is used to actively control the injection process and to monitor sensed functions of the system. The multiple processors provide dual redundancy safety circuits for critical control functions such as syringe motor drive speed and current. A motor / servo-amplifier nested control function is also disclosed. A unique method and apparatus are disclosed for establishing injection parameter default values just prior to an injection procedure that are based on physiological values of the patient to be treated. The injector system uses an interactive display panel that presents sequenced set-up screens to the user and which enables the user to select injection procedures, parameters and other modes of operation directly through the interactive panel.
Owner:ACIST MEDICAL SYST
Medical fluid injection system
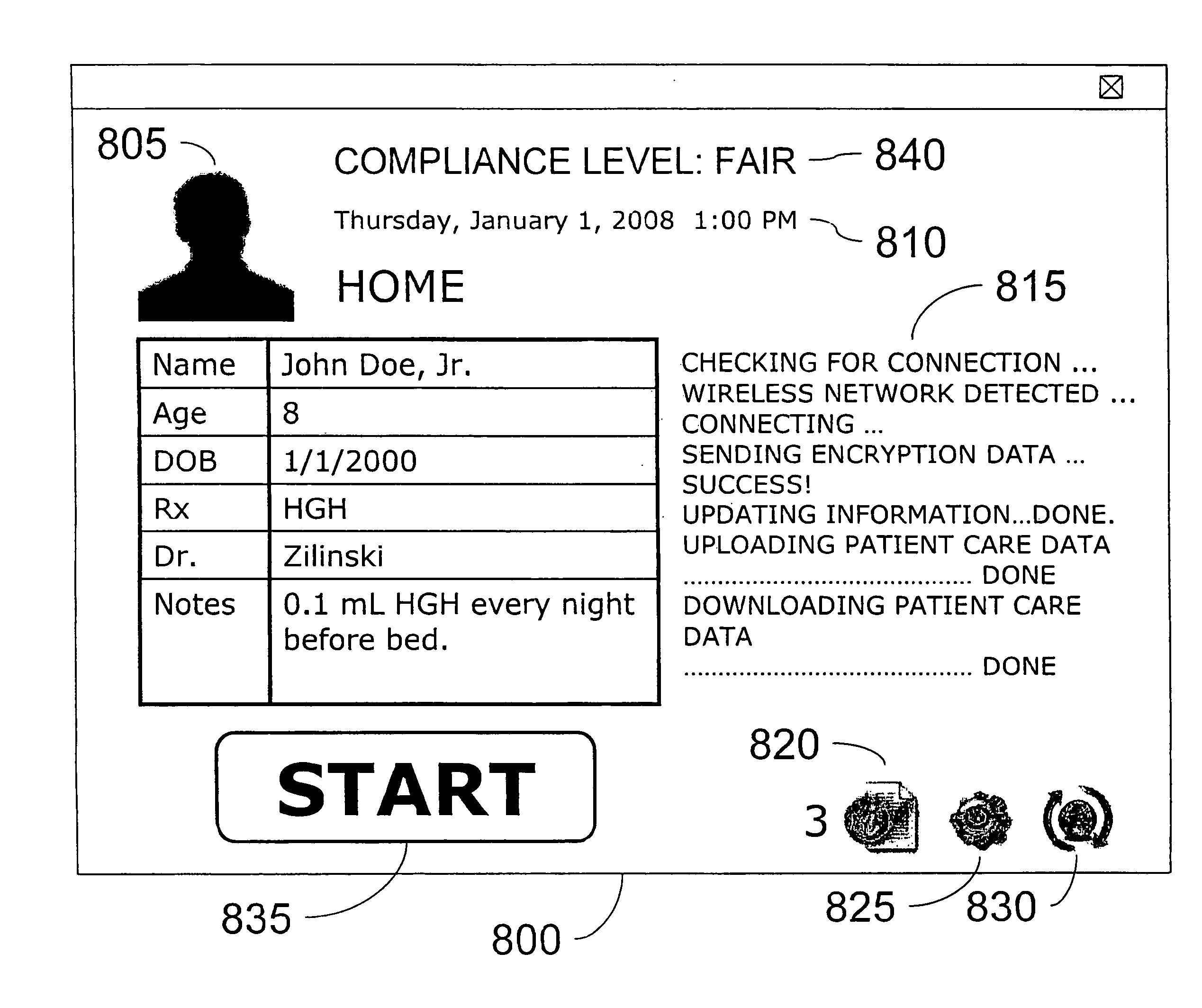
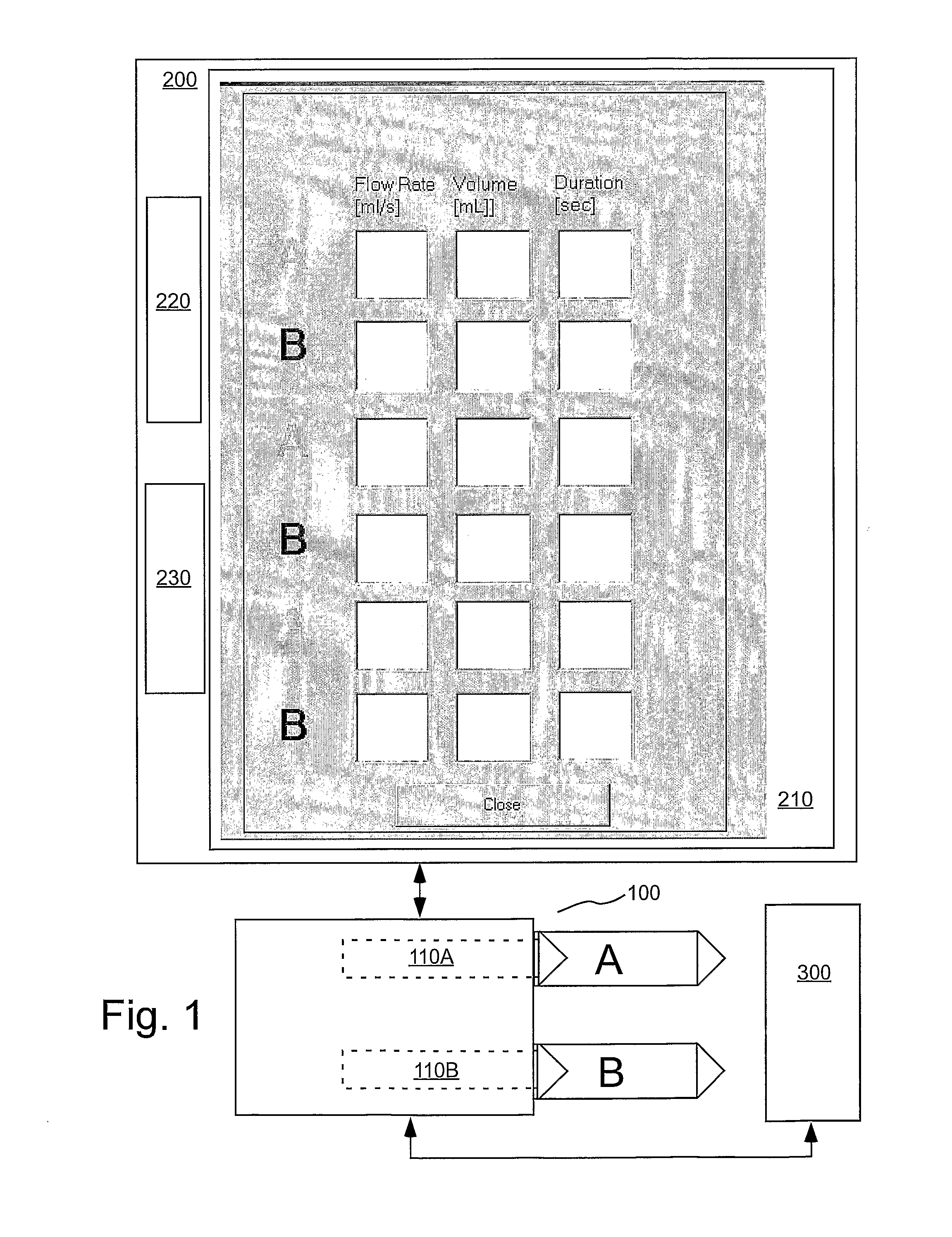
One implementation provides a method to provide injection procedure information in an injection system. In this implementation, the method includes displaying a plurality of different injection procedure options in a user interface of said system, wherein said plurality of different injection procedure options including a cardiac procedure option and a non-cardiac procedure option. The method further includes receiving a user selection of an injection procedure from said displayed plurality of difference injection procedure options, processing a default set of injection parameters based upon said selected injection procedure, and displaying said default set of injection parameters within the user interface of the system prior to an injection.
Owner:ACIST MEDICAL SYST
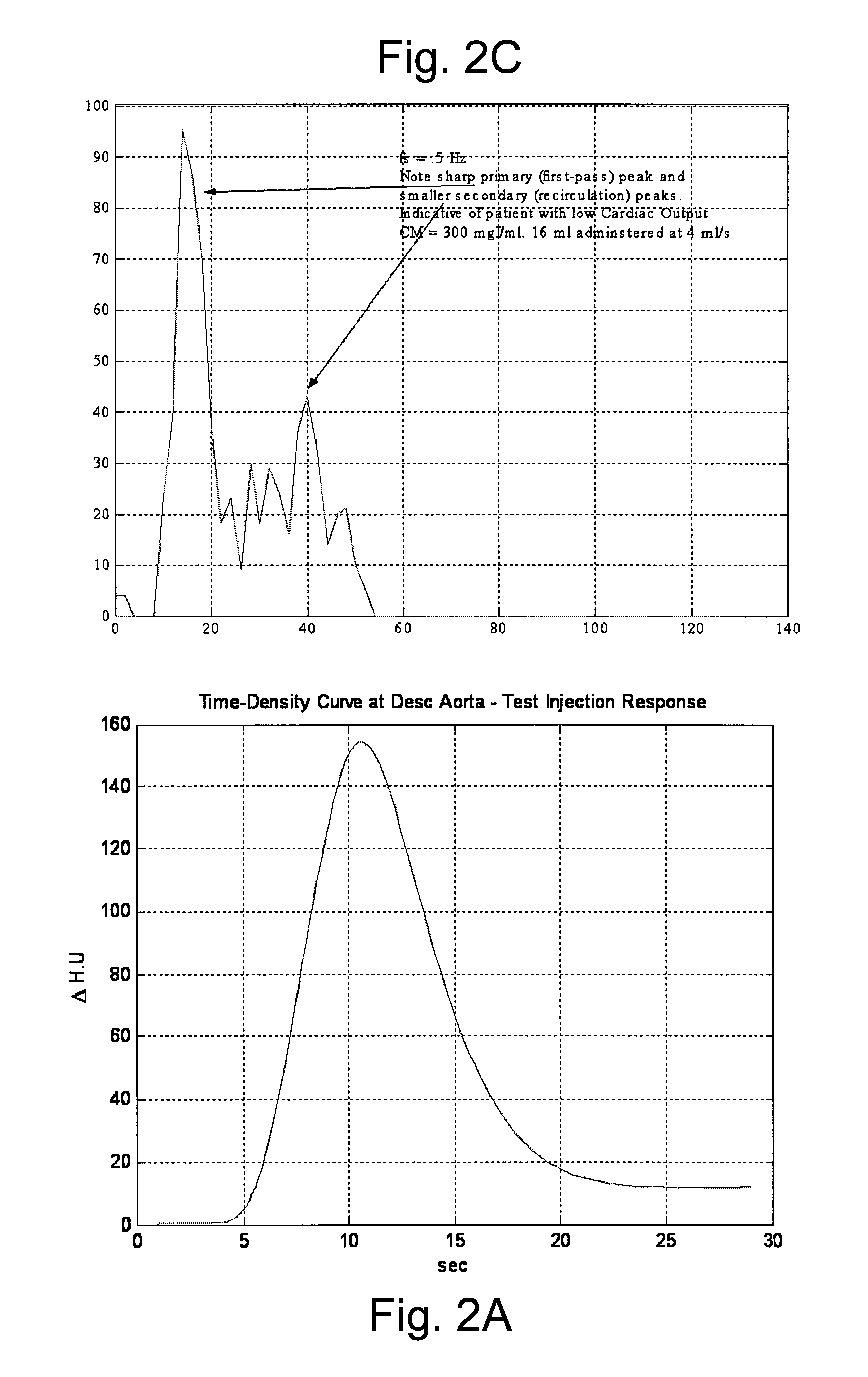
Systems and methods of modeling pharmaceutical propagation in a patient
InactiveUS20070255135A1Reduce contrastIncrease doseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsTime responseMedicine
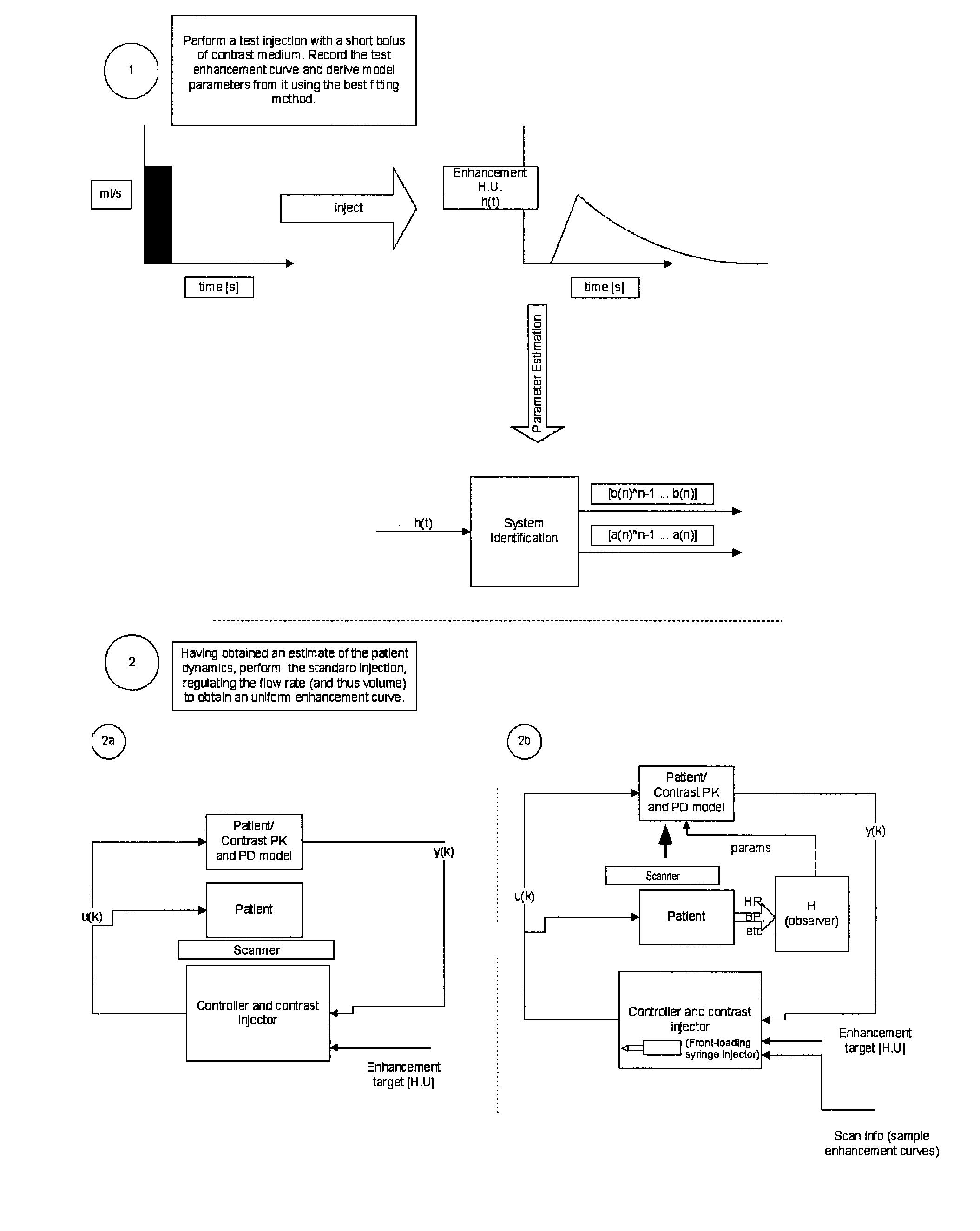
A method of delivering a contrast enhancing fluid to a patient using an injector system, includes determining at least one patient transfer function for the patient based upon data specific to the patient, the at least one patient transfer function providing a time enhancement output for a given input; determining a desired time enhancement output; using the at least one patient transfer function to determine an injection procedure input; and controlling the injector system at least in part on the basis of the determined injection procedure input. The injection procedure input can be determined considering at least one operational limitation or constraint of the injector system. A method of modeling propagation of a pharmaceutical fluid in a patient, includes: collecting data corresponding to a time response curve resulting from injection of the fluid; and determining at least one mathematical model describing the data. The mathematical model can, for example, be a model which is not determined by a continuous or a discrete-time Fourier deconvolution of the data. Further, the injection of fluid by the injector can be controlled at least in part on the basis of the mathematical model.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
System and method for multiple injection procedures on heart vessels
InactiveUS8082018B2Readily and accurately permittedFlexible and user friendlyElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMultiple injectionOperation mode
An angiographic injector system and a method of controllably delivering medical fluid to a patient from an angiographic injector system are disclosed. A multiple processor control system is used to actively control the injection process and to monitor sensed functions of the system. The multiple processors provide dual redundancy safety circuits for critical control functions such as syringe motor drive speed and current. A motor / servo-amplifier nested control function is also disclosed. A unique method and apparatus are disclosed for establishing injection parameter default values just prior to an injection procedure that are based on physiological values of the patient to be treated. The injector system uses an interactive display panel that presents sequenced set-up screens to the user and which enables the user to select injection procedures, parameters and other modes of operation directly through the interactive panel.
Owner:ACIST MEDICAL SYST
Angiographic injector system and method of use
InactiveUS7128729B2Readily and accurately permittedFlexible and user friendlyElectrocardiographyInfusion syringesOperation modeEngineering
An angiographic injector system and a method of controllably delivering medical fluid to a patient from an angiographic injector system are disclosed. A multiple processor control system is used to actively control the injection process and to monitor sensed functions of the system. The multiple processors provide dual redundancy safety circuits for critical control functions such as syringe motor drive speed and current. A motor / servo-amplifier nested control function is also disclosed. A unique method and apparatus are disclosed for establishing injection parameter default values just prior to an injection procedure that are based on physiological values of the patient to be treated. The injector system uses an interactive display panel that presents sequenced set-up screens to the user and which enables the user to select injection procedures, parameters and other modes of operation directly through the interactive panel.
Owner:ACIST MEDICAL SYST
Needle cover assembly for a syringe
Owner:STA MED
Patient specific dosing contrast delivery systems and methods
InactiveUS20010056233A1Improve image qualityMinimum risk and costElectrotherapyDrug and medicationsMedical deviceDelivery system
This invention relates generally to the field of medical devices for delivering contrast media during medical diagnostic and therapeutic imaging procedures and more particularly, this invention relates to improved contrast media delivery systems and methods of use which allow adjustment of contrast media concentration and injection parameters either before or during an injection procedure to provide patient specific dosing of contrast media, thus decreasing the waste and cost of these procedures while increasing their efficiency.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Medical Fluid Injection System
One implementation provides a method to provide injection procedure information in an injection system. In this implementation, the method includes displaying a plurality of different injection procedure options in a user interface of said system, wherein said plurality of different injection procedure options including a cardiac procedure option and a non-cardiac procedure option. The method further includes receiving a user selection of an injection procedure from said displayed plurality of different injection procedure options, processing a default set of injection parameters based upon said selected injection procedure, and displaying said default set of injection parameters within the user interface of the system prior to an injection.
Owner:ACIST MEDICAL SYST
System And Apparatus For Modeling Pressures Generated During An Injection Procedure
InactiveUS20070213662A1Raise the ratioKeep for a long timeElectrocardiographyLocal control/monitoringEngineeringInjection device
A fluid injection apparatus includes at least one pressurizing mechanism and at least a first fluid container (for example, a syringe or a bulk container) operably associated with the at least one pressurizing mechanism. The first fluid container is adapted to contain a first fluid to be injected. The fluid injection apparatus also includes a pressure modeling system adapted to predict a pressure to be generated at one or more points in the injection fluid path during planned injection procedure based upon variables associated with an injection protocol.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Self-administration injection system
Self-injection system allows a user to inject a drug from a cartridge carrying unique identification information, into any one of a plurality of injection sites. Tissue at each injection site is associated with at least one injection parameter, such as flow-rate, that is different for each site. A scanner reads the identification information of the cartridge and cooperates with a central processing unit to determine the validity of the drug in order to permit an injection procedure to commence. The central processing unit has a memory for storing the different injection parameters and controls a drive unit for driving fluid from the cartridge and through a needle into the selected tissue, at the injection parameter that is associated with the user selected tissue for the injection.
Owner:MILESTONE SCIENTIFIC INC
Secondary battery and electrolyte injection method
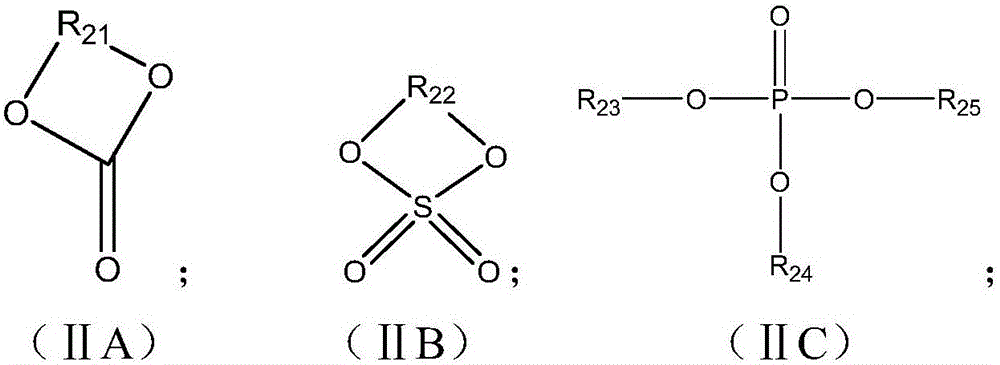
InactiveCN106784589ABalanced High Temperature PerformanceBalance of Mechanical PropertiesCell electrodesSecondary cellsReactive sitePole piece
The invention relates to the field of batteries, in particular to a secondary battery and an electrolyte injection method. The secondary battery is characterized in that a cathode active matter of a cathode pole piece comprises a high-nickel ternary cathode material; an electrolyte consists of an electrolyte S1 in the first injection process and an electrolyte S2 in the second injection process; a filming additive in the electrolyte S1 is an anode filming additive, and a filming additive in the electrolyte S2 is a cathode filming additive. The secondary battery has the advantages that by adding the anode filming additive in the first electrolyte injection process, a good SEI (solid electrolyte interface) is formed at the graphite surface through formation; by adding the cathode filming additive in the second electrolyte injection process, a dense CEI (cathode electrolyte interface) is formed; the active sites at the surface of the high-nickel material are passivated, so as to balance the high-temperature property and dynamic property of the high-nickel secondary battery; the electrolyte injection method is simple, the implementing is easy, and the secondary electrolyte injection procedure is added on the basis of existing procedure.
Owner:CONTEMPORARY AMPEREX TECH CO
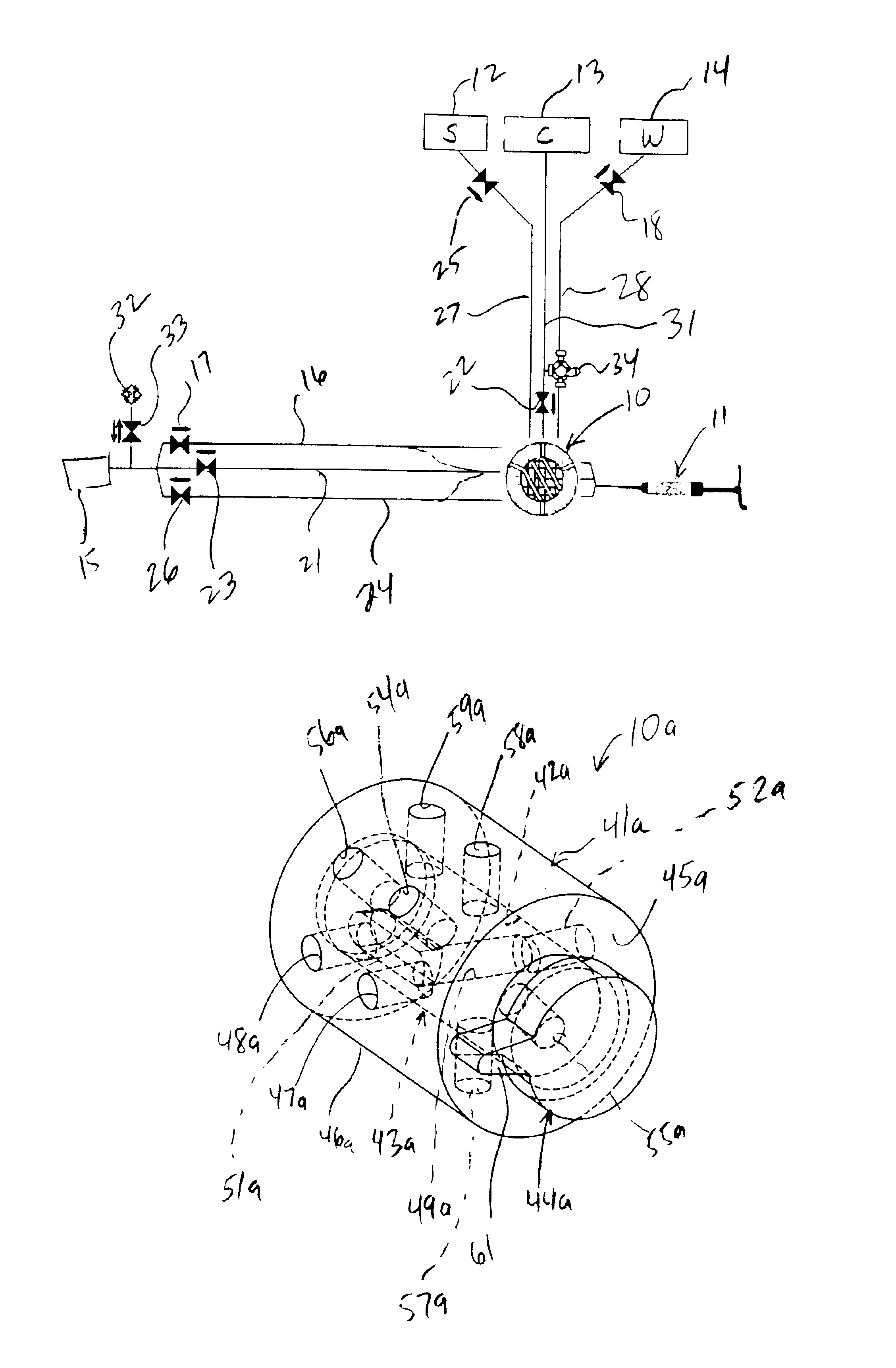
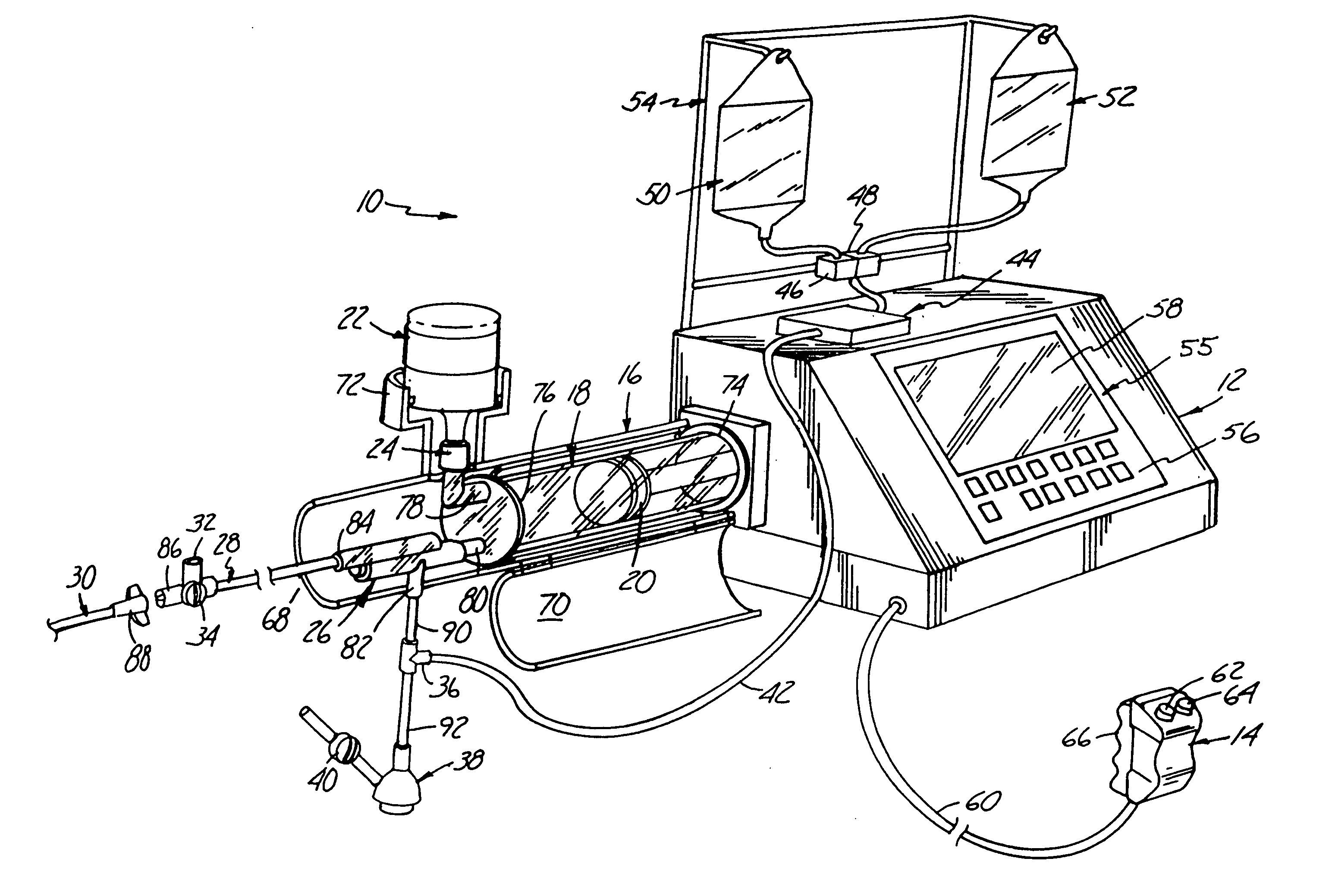
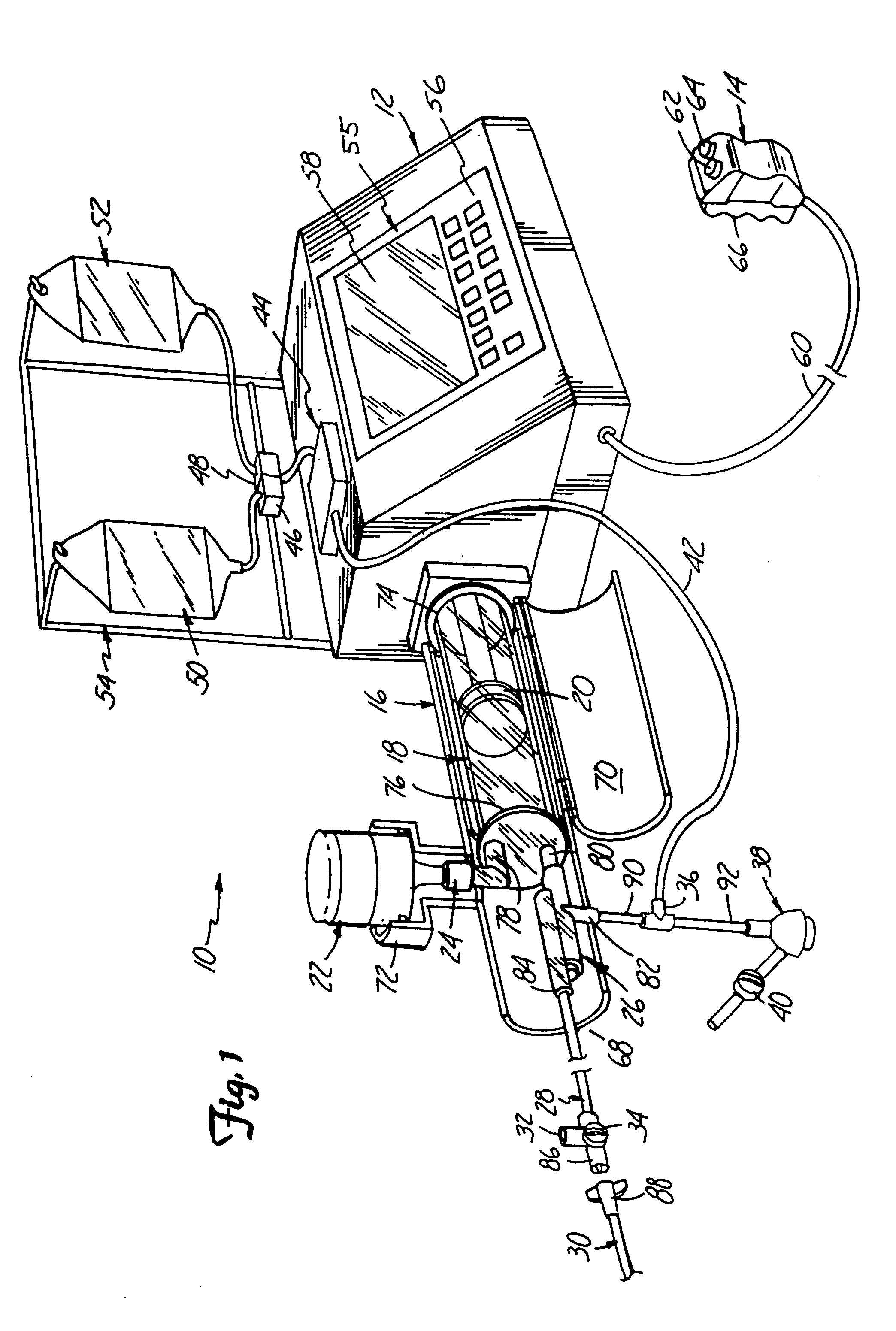
Fluid injector system
InactiveUS7566320B2Free from pollutionCost-effective and safe and efficacious to useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical devicesMultiple useComputer module
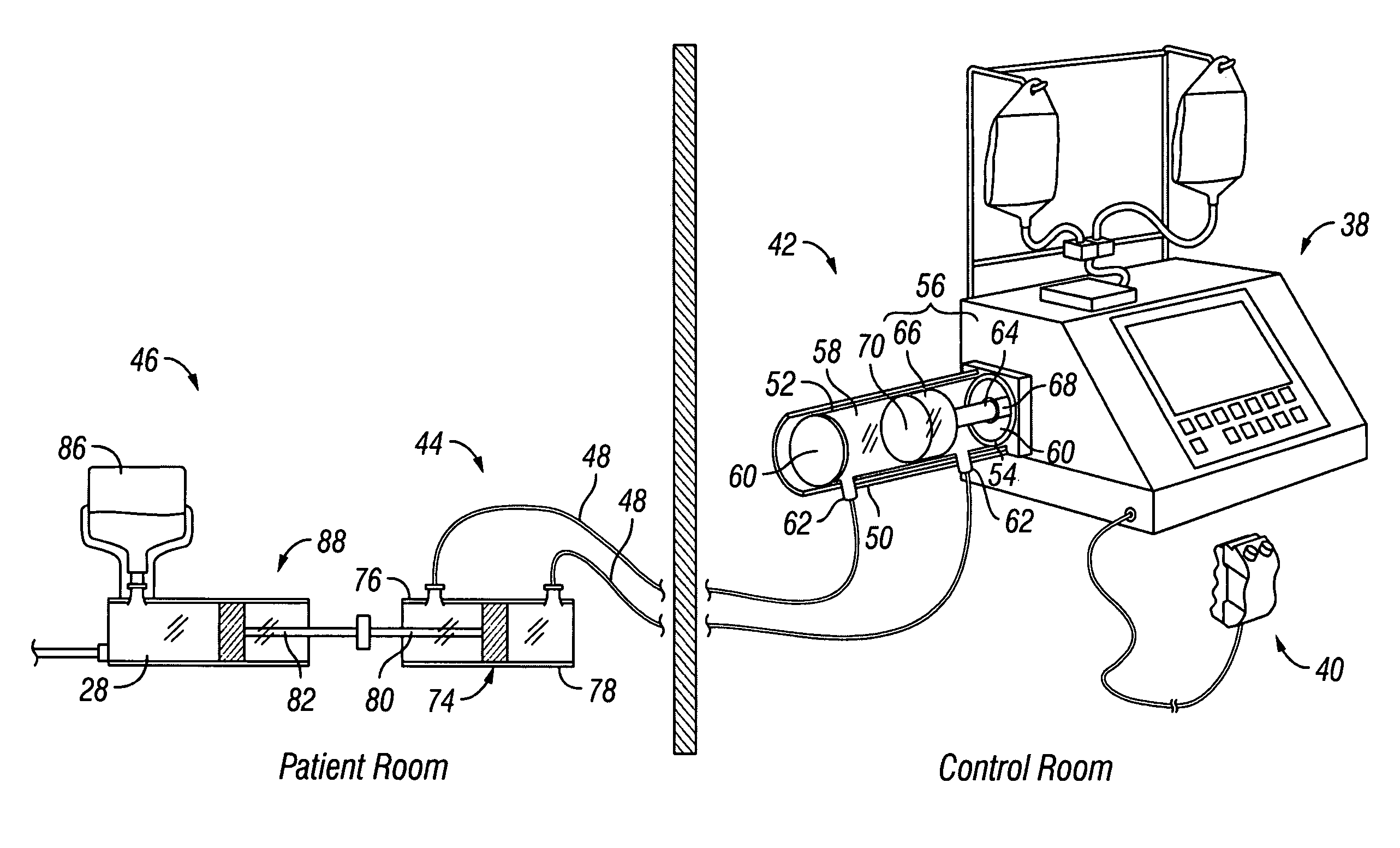
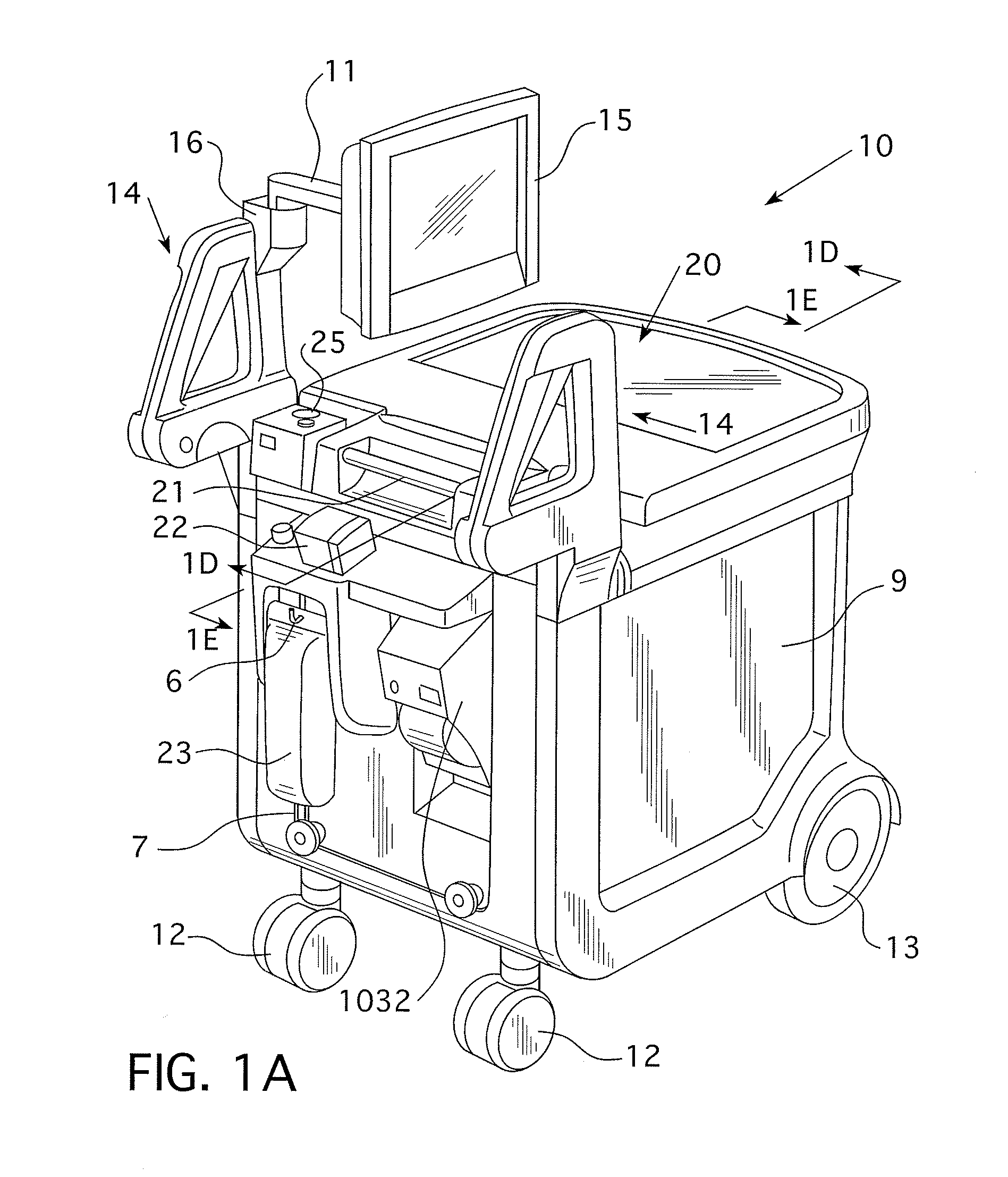
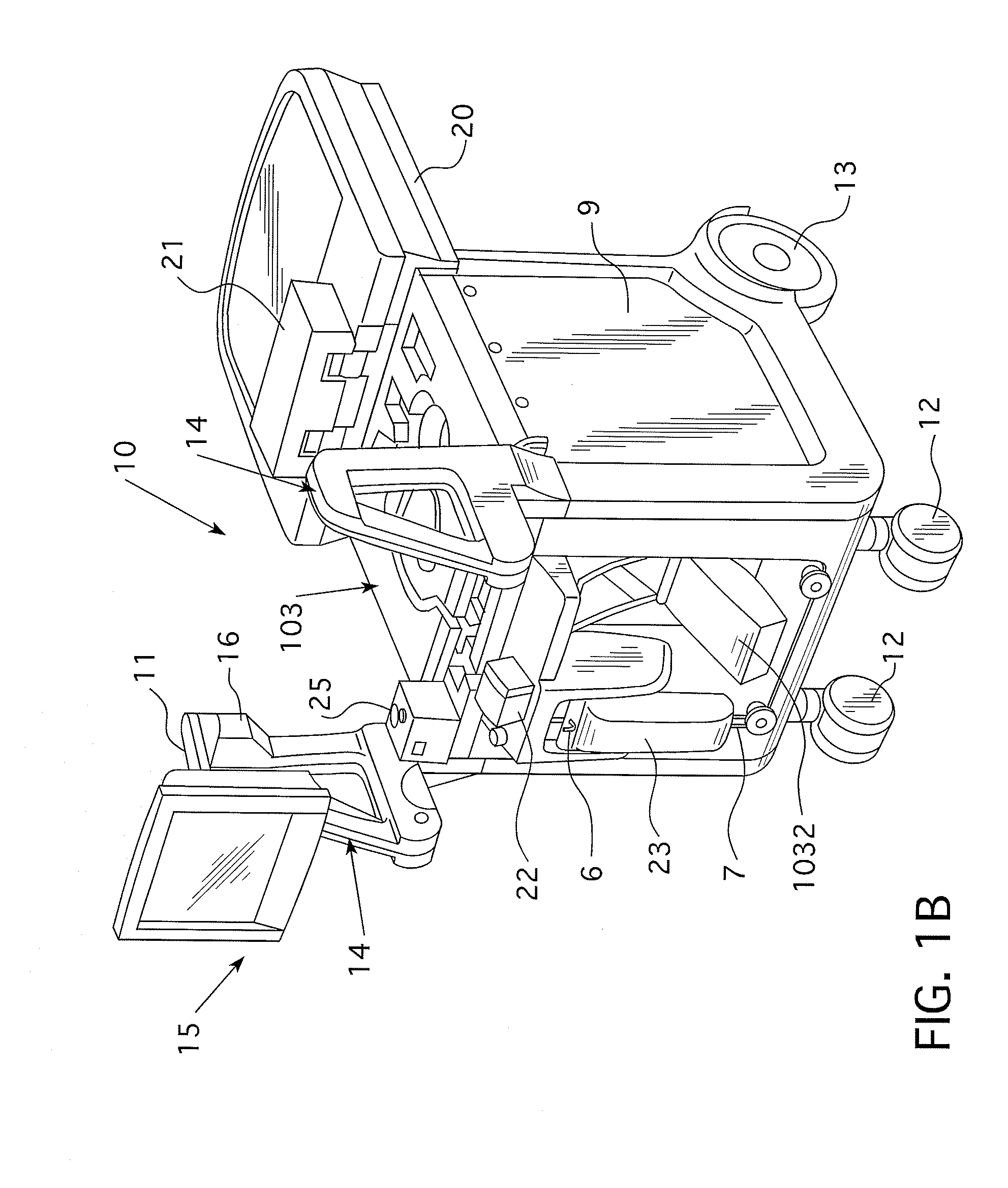
Fluid injector systems used for a variety of imaging and injection procedures are disclosed. The systems may include separate modules or assemblies that may be located in different rooms of a hospital or imaging facility. Various single use and multiple use components may also be used with the modules or assemblies of the system. In addition, the injector system may include hydraulic and / or pneumatic fluid sources to power the system modules of the present invention.
Owner:ACIST MEDICAL SYST
Activity delivery progress monitor
ActiveUS20130079581A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesIsotope delivery systemsRadiopharmaceutical ActivityDelivery system
A system and method for monitoring progress of a radiopharmaceutical injection procedure includes: measuring and monitoring radiopharmaceutical activity of a radiopharmaceutical remaining in at least a portion of a disposable administration set used with a radiopharmaceutical fluid delivery system; and displaying the radiopharmaceutical activity remaining in at least the portion of the disposable administration set to an operator.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Injection system having an agitation mechanism for circulating a fluid medium
InactiveUS7060049B2Reduce the impactReduce impactRotating receptacle mixersTransportation and packagingPeristaltic pumpEngineering
A system for dispensing a medium includes at least a first container to hold the medium, a pressurizing device, such as a pump, in fluid connection with the container for pressurizing the medium, and an agitation mechanism or device to maintain the components of the medium in a mixed state. The container and the pressurizing device can be separate units, as in the case of an bag or bottle in fluid connection with a peristaltic or other type of pump. The container and the pump can also be combined in a single unit, as in the case of a syringe, wherein the syringe barrel of the syringe acts to contain the medium and the syringe plunger pressurizes the medium within the syringe barrel. A method of injecting a multi-component medium includes the step of agitating the medium (for example, as described above) before or during an injection procedure to maintain the components of the medium in a mixed state.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
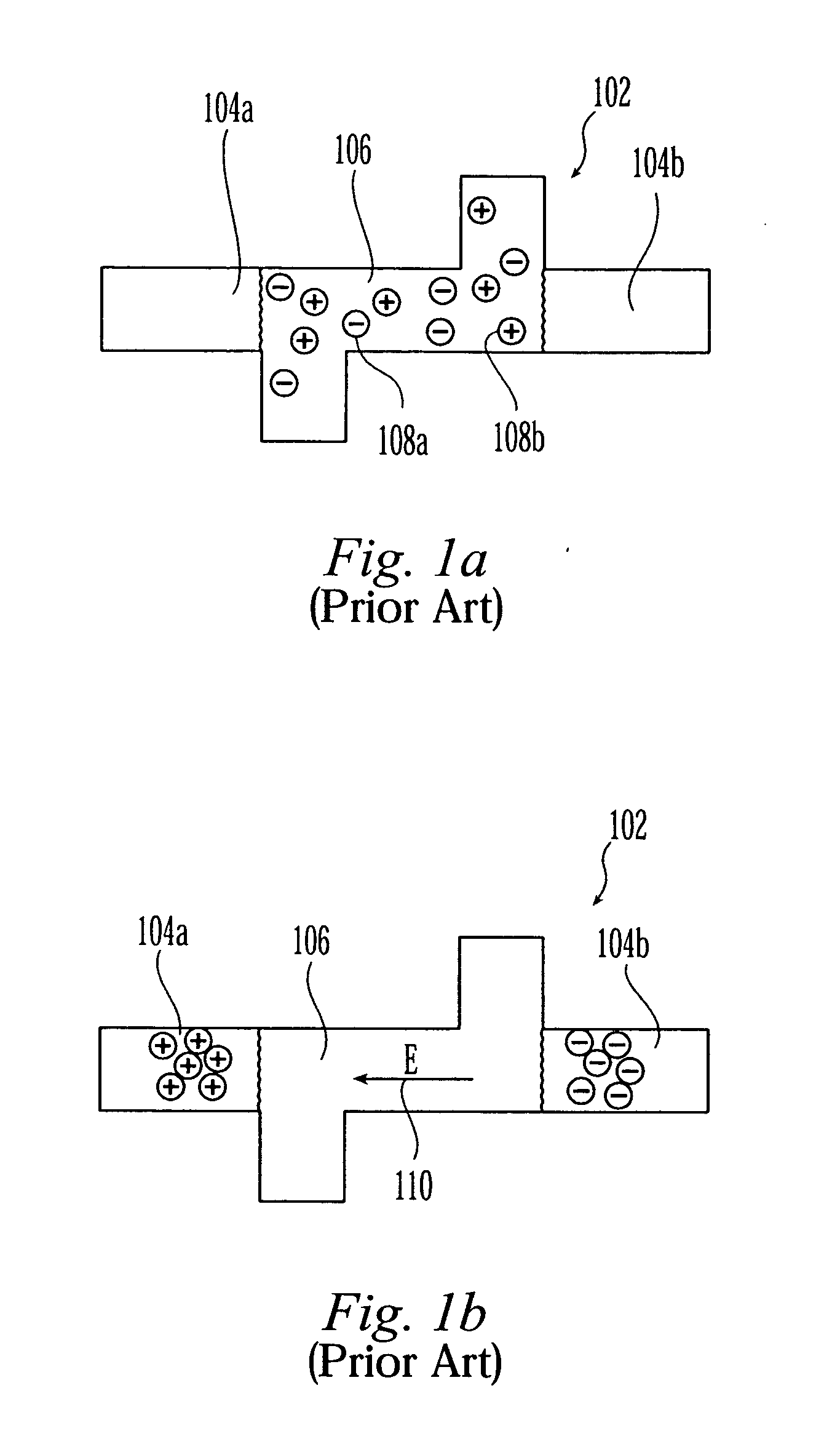
Microfluidic electrophoresis chip having flow-retarding structure
InactiveUS20060042948A1Reducing electrokinetic flow instabilityHigh hydraulic resistanceSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
A capillary electrophoresis device and separation protocol uses a hydraulic resistance-providing structure (HRPS) in the main separation channel to separate the divide the main separate channel into an upstream portion and a downstream portion. The HRPS may take the form of a porous plug, or a solid plug provided with at least one shallow channel. A sample separates and migrates through the porous structure or the shallow channel, upon application of a voltage difference between the upstream and downstream sides. Among other things, the HRPS helps reduce electrokinetic flow in the presence of conductivity gradients and facilitates robust, high-gradient on-chip field amplified sample stacking. The HRPS also enables the use of a pressure-injection scheme for the introduction of a high conductivity gradient in a separation channel and thereby avoids flow instabilities associated with high conductivity gradient electrokinetics. The approach also allows for the suppression of electroosmotic flow (EOF) and benefits from the associated minimization of sample dispersion caused by non-uniform EOF mobilities. An injection procedure employing a single pressure-flow high-conductivity buffer injection step followed by standard high voltage control of electrophoretic fluxes of sample, may be employed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com