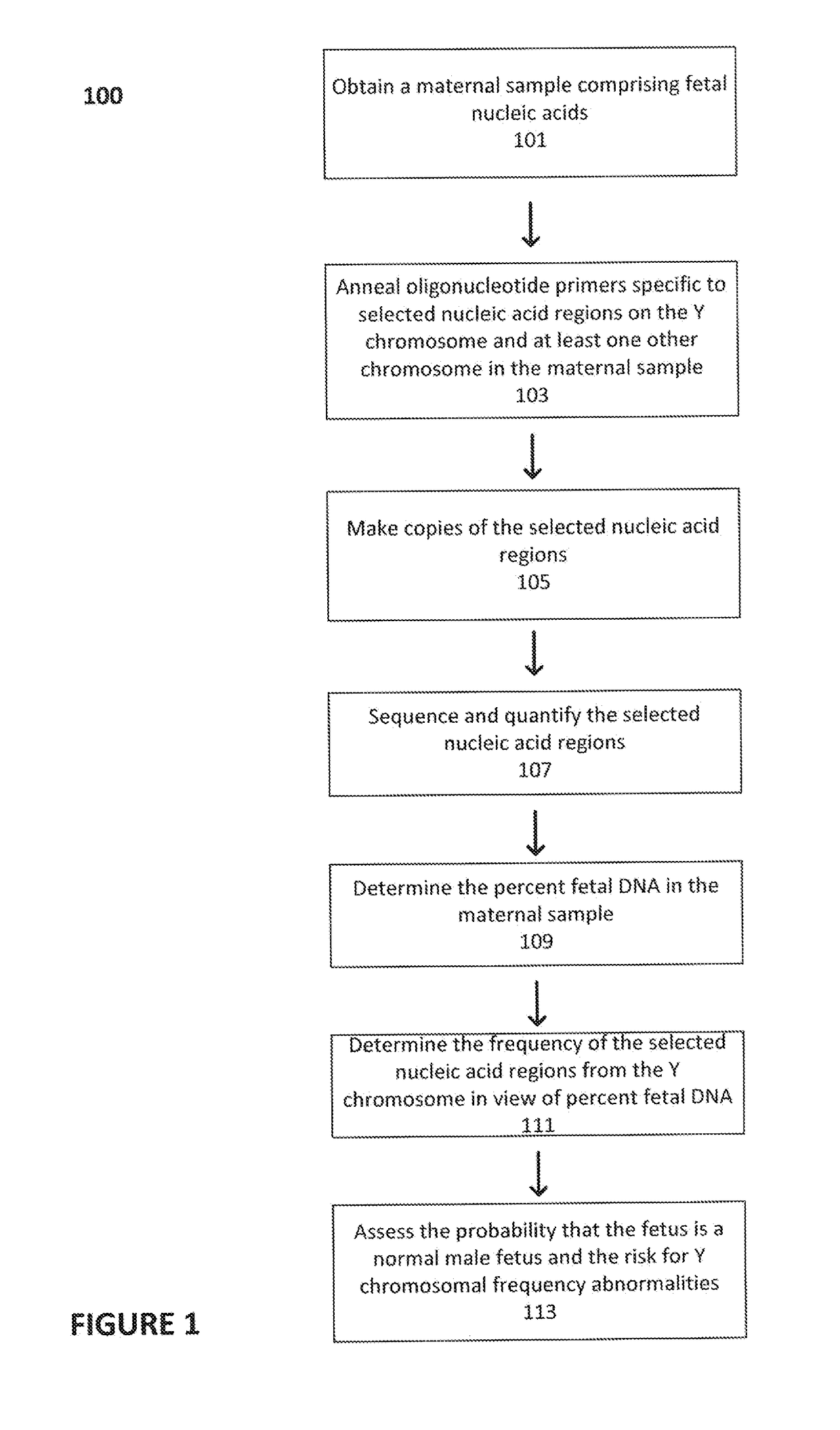
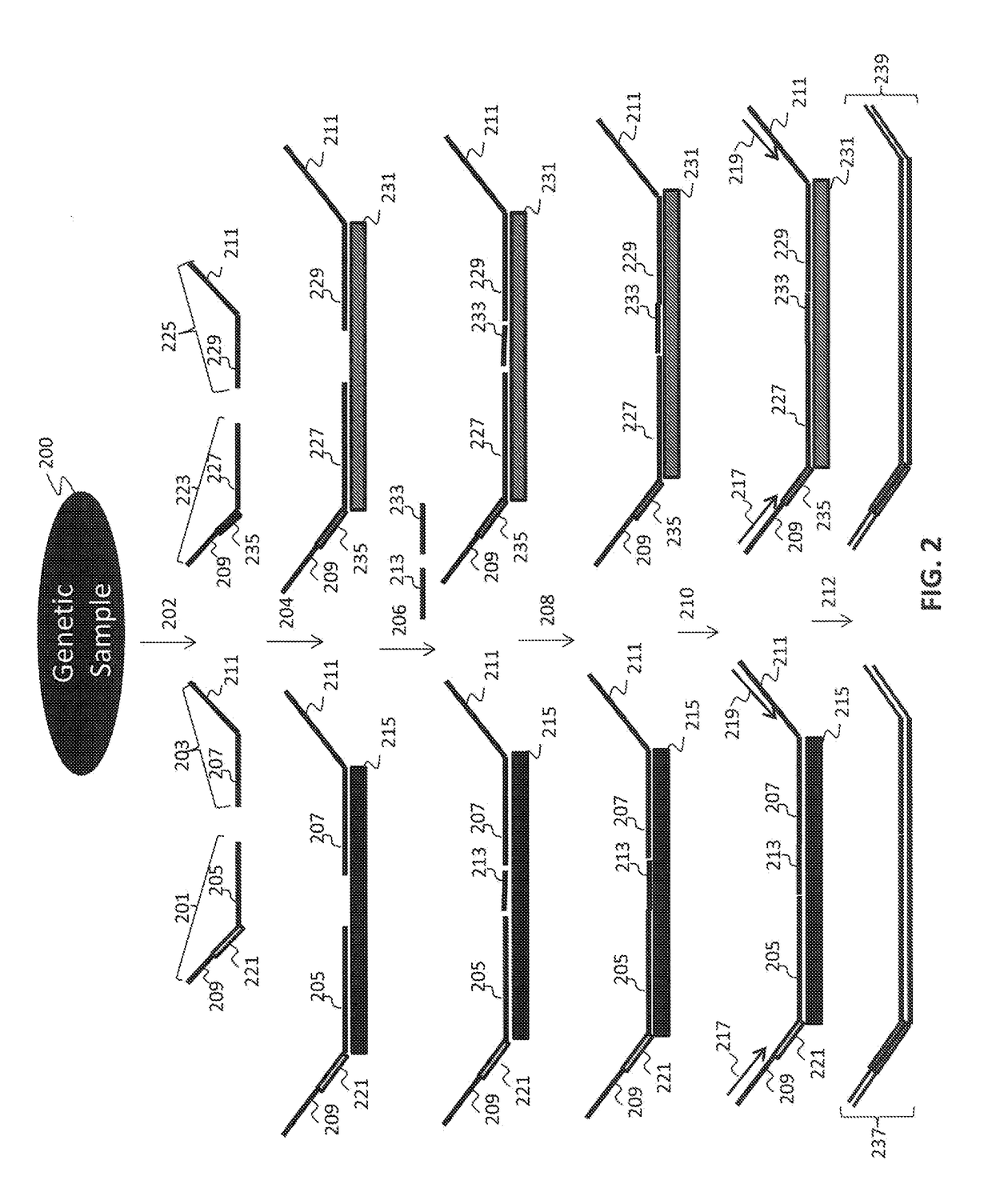
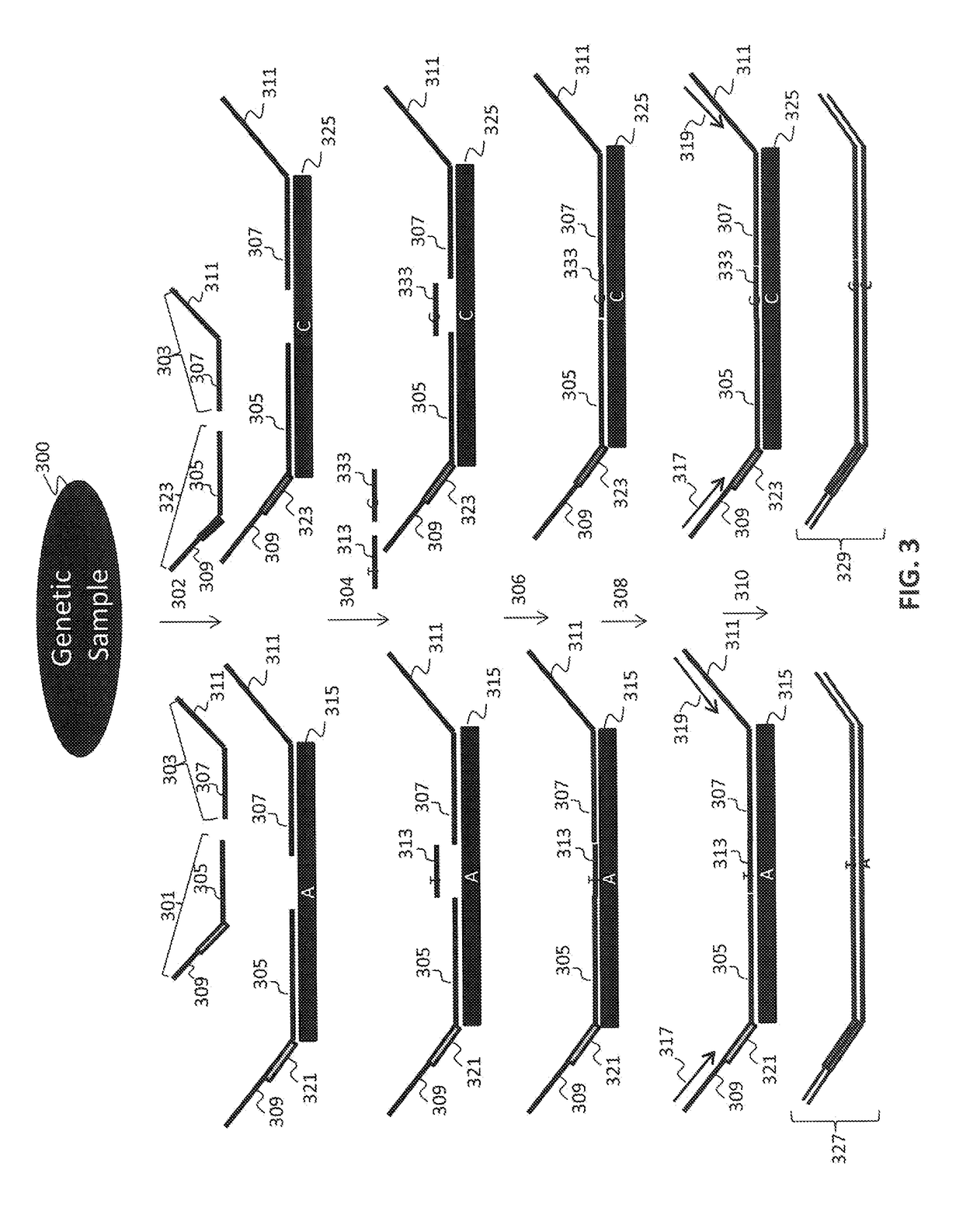
Non-invasive fetal sex determination
a fetal sex and non-invasive technology, applied in the field of non-invasive sex determination, can solve the problem of inherently inefficient random or shotgun sequencing methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
of Y Chromosome Frequency Abnormalities Using Non-Polymorphic Sites in Chromosome-Specific Genomic Regions
[0153]In a first embodiment, assays directed against a specific genomic regions on the Y chromosome were used to identify the presence or absence of a Y chromosome frequency abnormality. The present assay system allowed the identification of the presence or absence of such an abnormality in the DNA of multiple individuals using a highly multiplexed system.
[0154]Multiple interrogations were prepared using oligonucleotides complementary to or derived from the Y chromosome (chrY), and chromosomes 13, 18 and 21 (chr13, chr18 and chr21). All oligonucleotides used in the tandem ligation formats were synthesized using conventional solid-phase chemistry. The oligos of the first fixed set and the bridging oligonucleotides were synthesized with 5′ phosphate moieties to enable ligation to 3′ hydroxyl termini of adjacent oligonucleotides. Thirty-two non-polymorphic assays were developed on ...
example 2
on of DNA for Use in Tandem Ligation Procedures
[0155]Genomic DNA from subjects was obtained from Coriell Cell Repositories (Camden, N.J.) and fragmented by acoustic shearing (Covaris, Woburn, Mass.) to a mean fragment size of approximately 200 bp.
[0156]The DNA was biotinylated using standard procedures. Briefly, the Covaris fragmented DNA was end-repaired by generating the following reaction in a 1.5 ml microtube: 5 ug DNA, 12 μl 10×T4 ligase buffer (Enzymatics, Beverly Mass.), 50 U T4 polynucleotide kinase (Enzymatics, Beverly Mass.), and H20 to 120 μl. This was incubated at 37° C. for 30 minutes. The DNA was diluted using 10 mM Tris 1 mM EDTA pH 8.5 to desired final concentration of ˜0.5 ng / μl.
[0157]5 μl DNA was placed in each well of a 96-well plate, and the plate sealed with an adhesive plate sealer and spun for 10 seconds at 250×g. The plate was then incubated at 95° C. for 3 minutes, and cooled to 25° C., and spun again for 10 seconds at 250×g. A biotinylation master mix was p...
example 3
Amplification of Ligated Products
[0163]The polymerized and / or ligated nucleic acids were amplified using universal PCR primers complementary to the universal sequences present in the first and second fixed sequence oligos hybridized to the nucleic acid regions of interest. 25 μl of each of the reaction mixtures of Example 3 were used in each amplification reaction. A 50 μL universal PCR reaction consisting of 25 μL eluted ligation product plus 1× Pfusion buffer (Finnzymes, Finland), 1M Betaine, 400 nM each dNTP, 1 U Pfusion error-correcting thermostable DNA polymerase, and primer pairs with sample tags used to uniquely identify individual samples prior to pooling and sequencing. The PCR was carried out under stringent conditions using a BioRad Tetrad™ thermocycler.
[0164]10 μl of universal PCR product from each of the samples were pooled and the pooled PCR product was purified using AMPure™ SPRI beads (Beckman-Coulter, Danvers, Mass.), and quantified using Quant-iT™ PicoGreen, (Invit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com