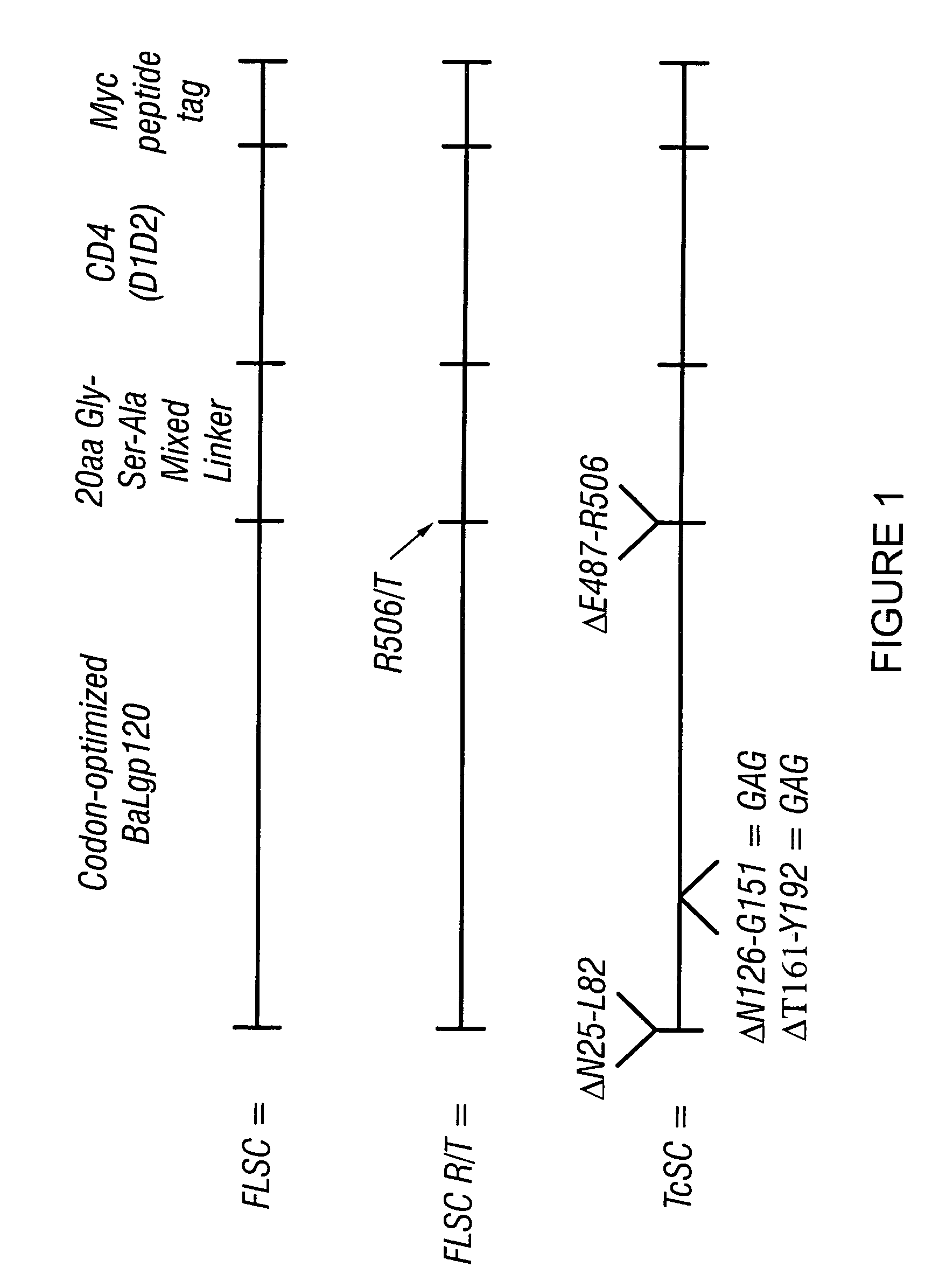
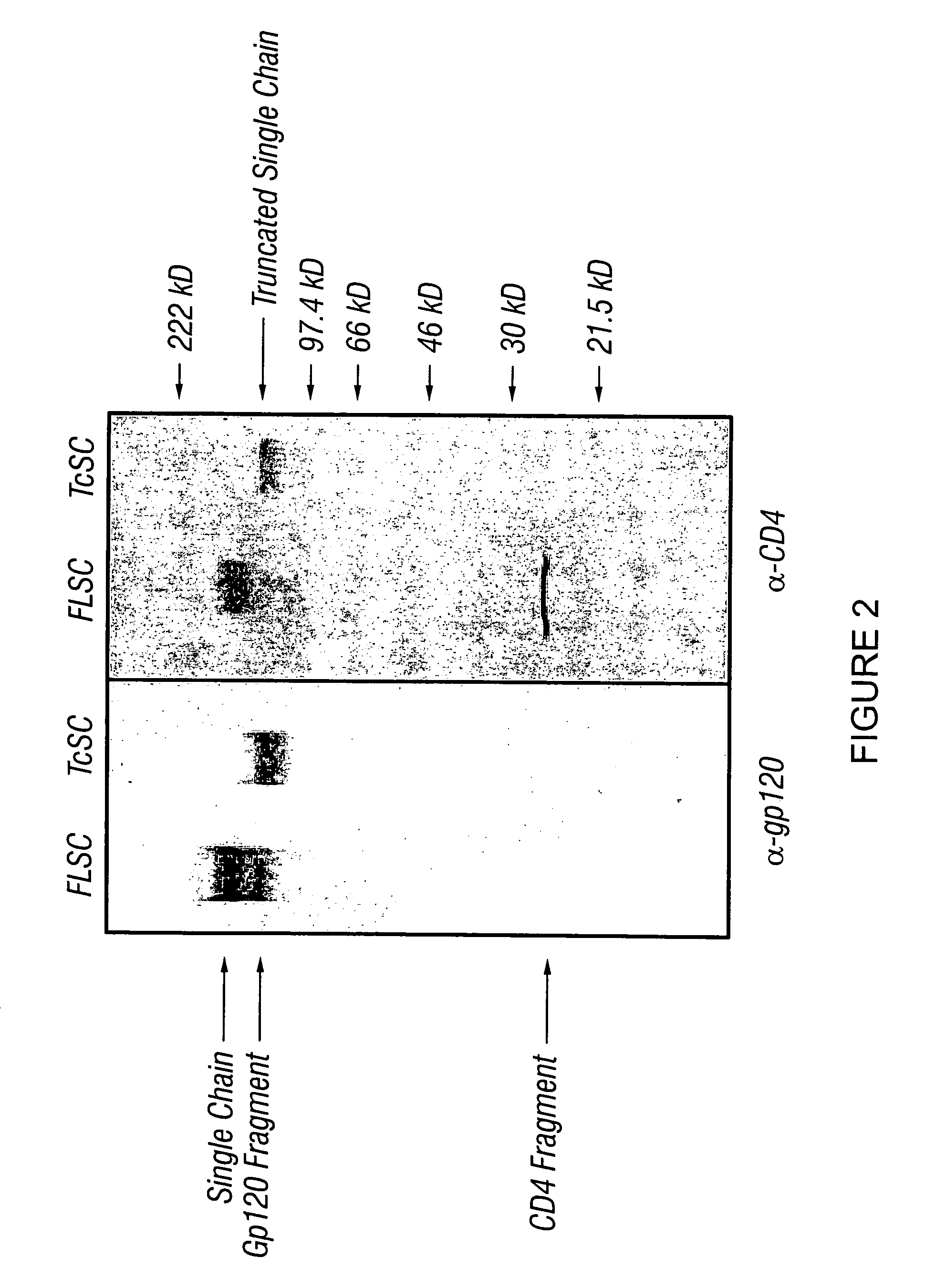
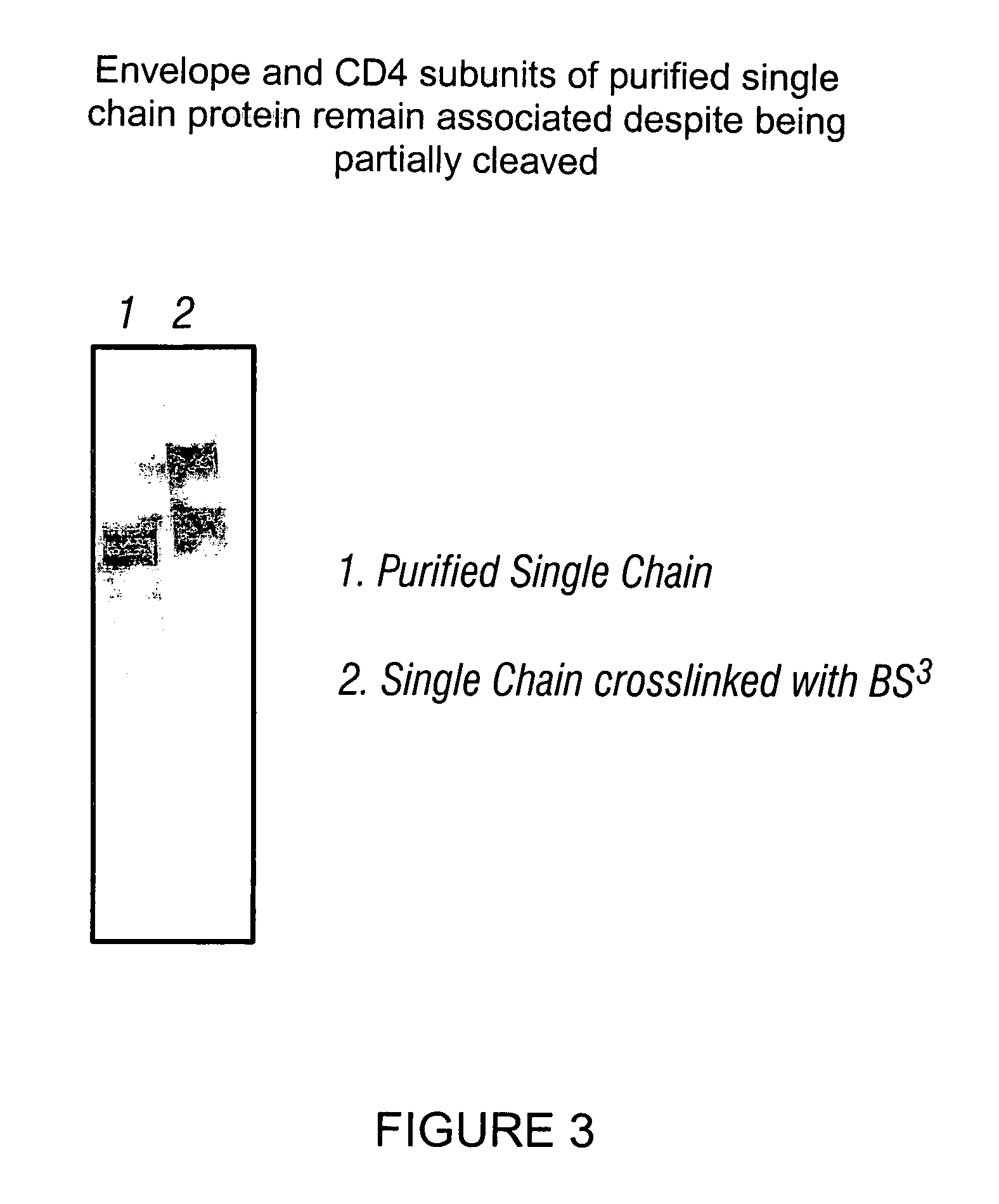
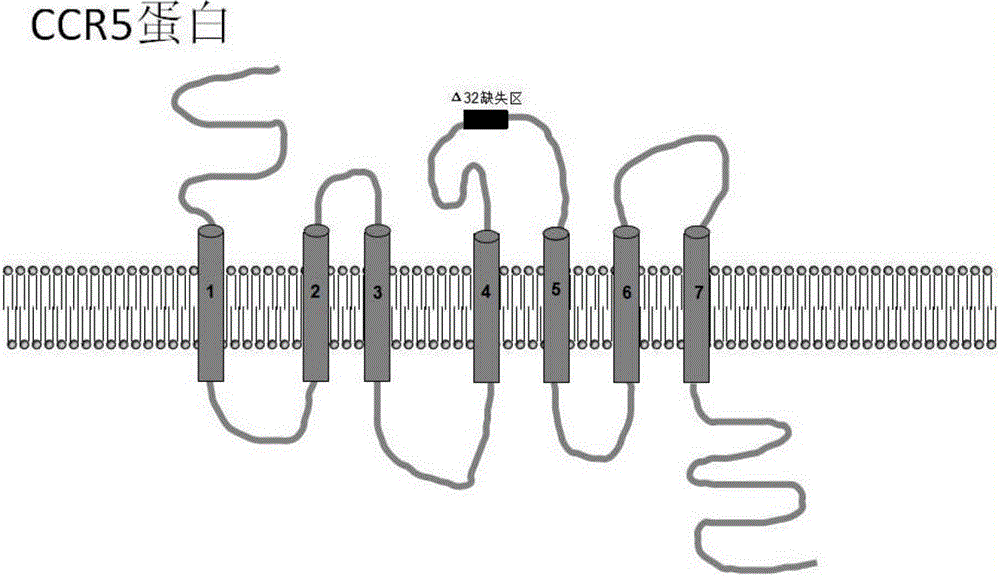
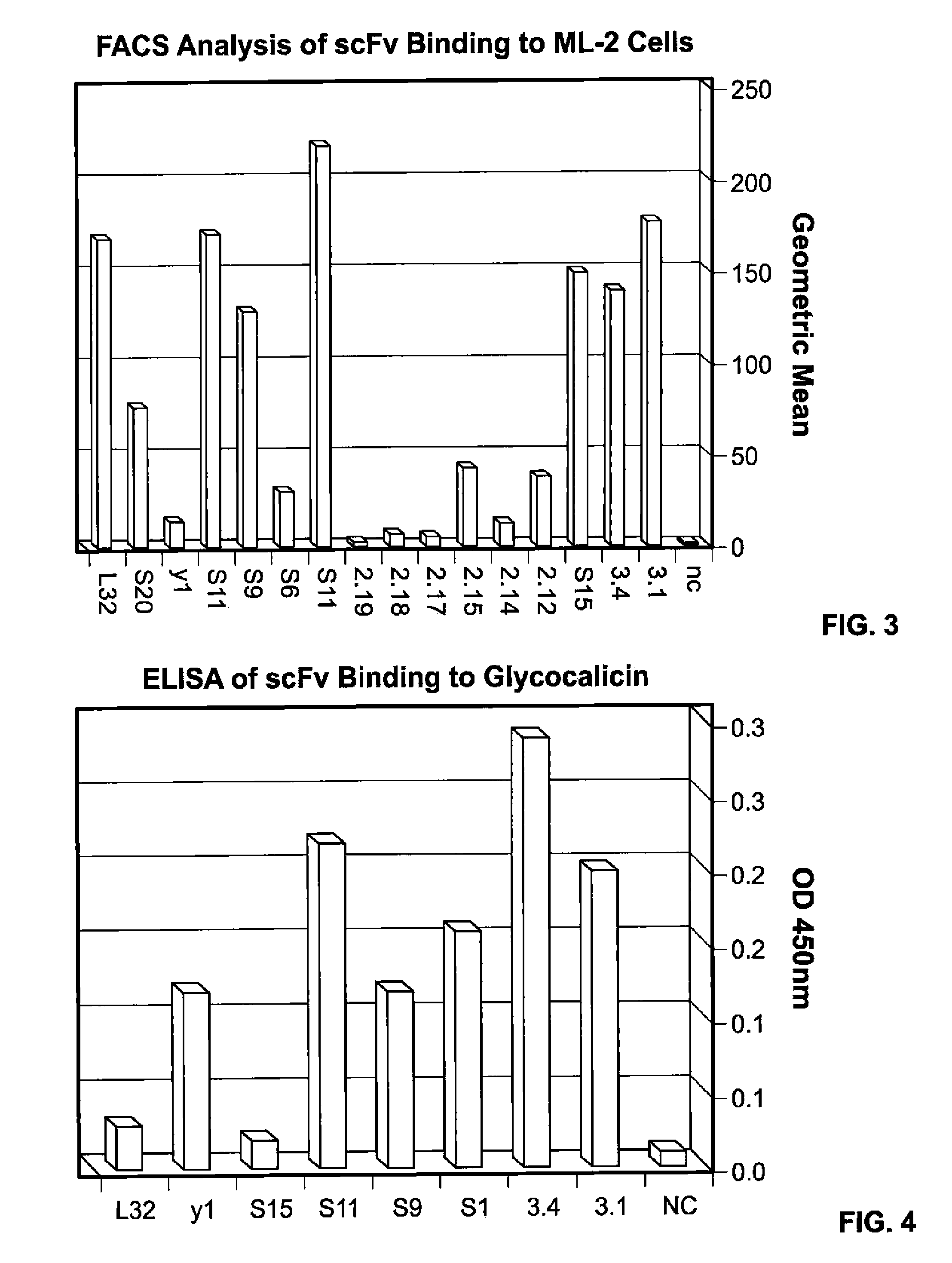
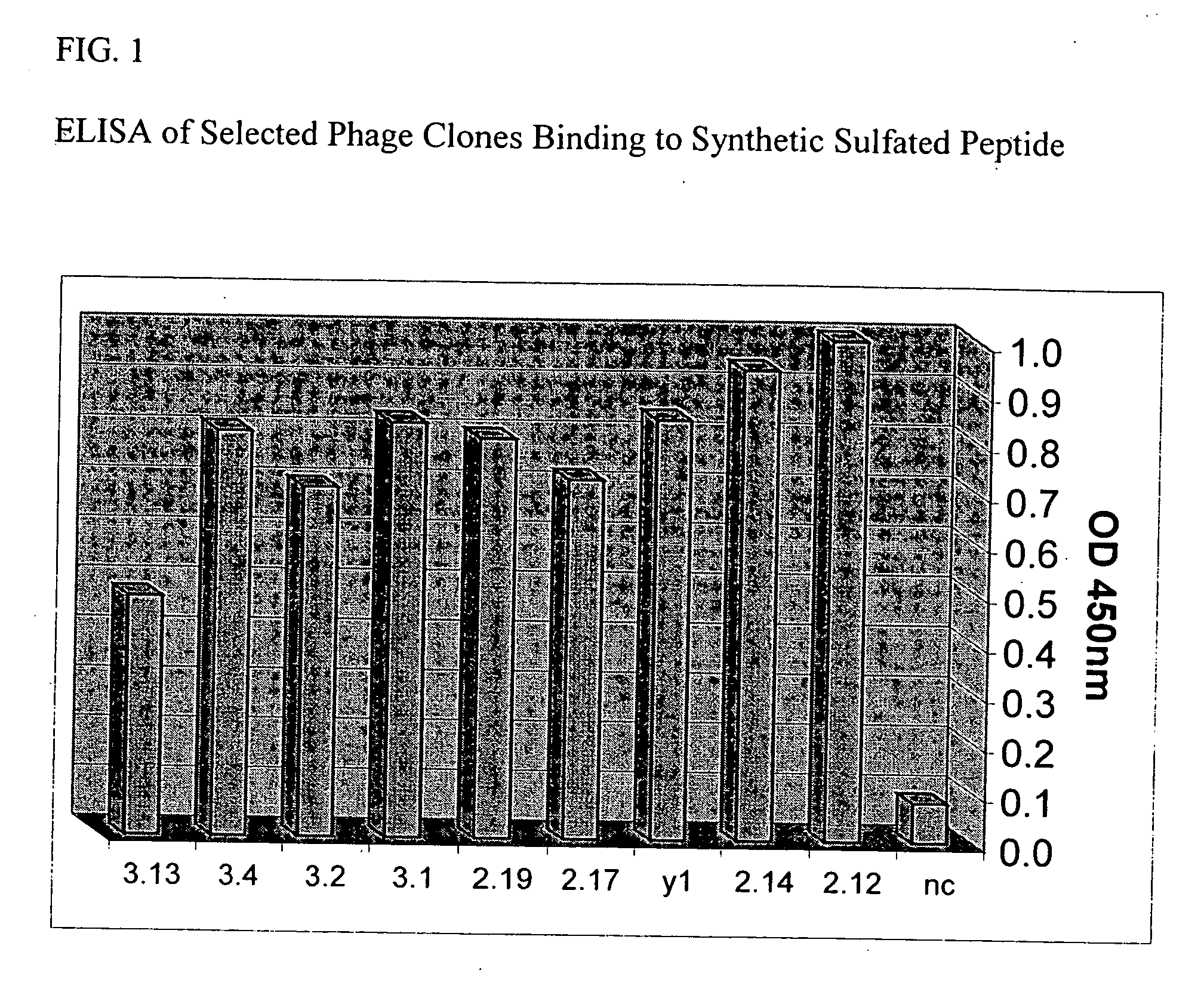
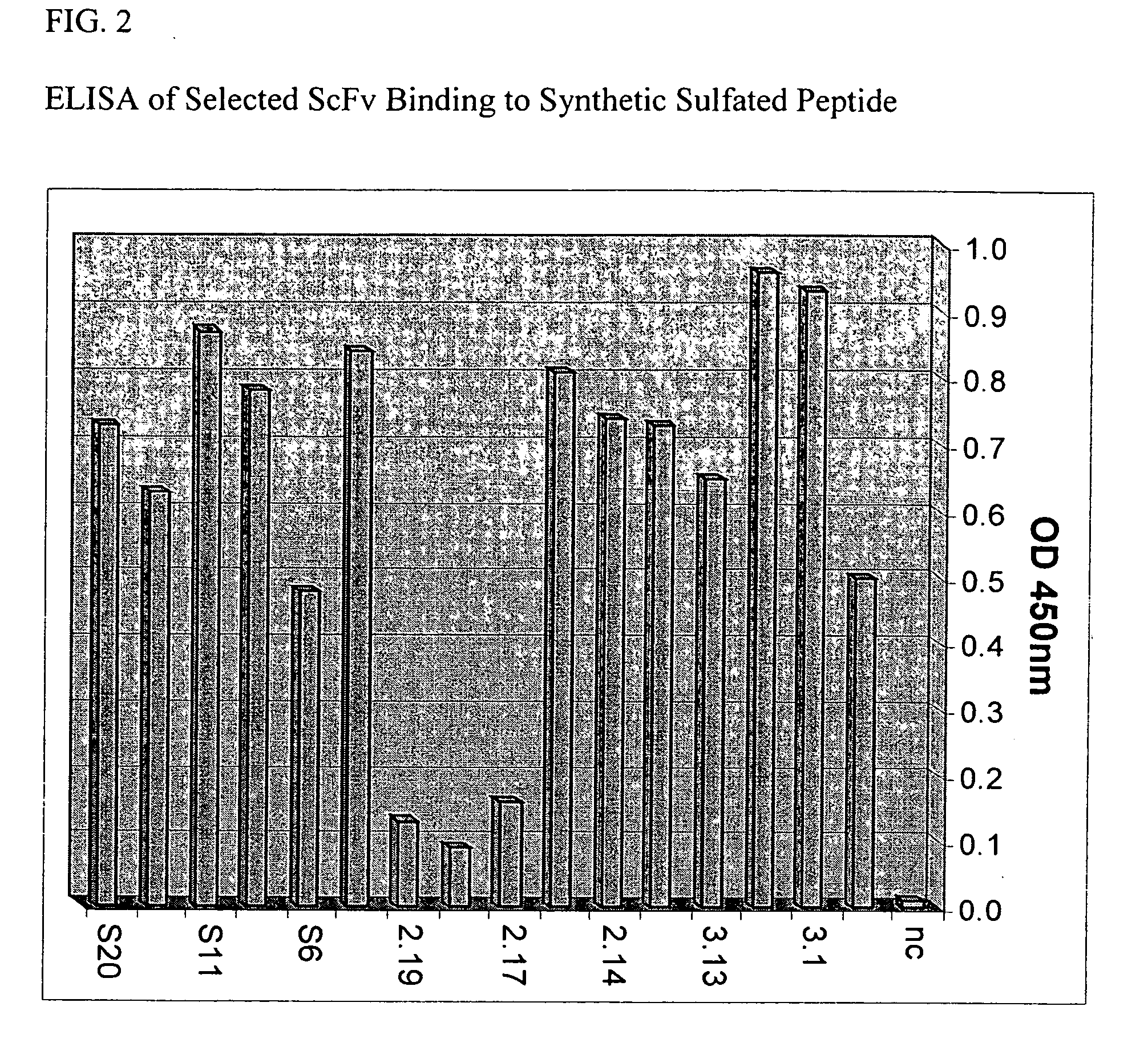
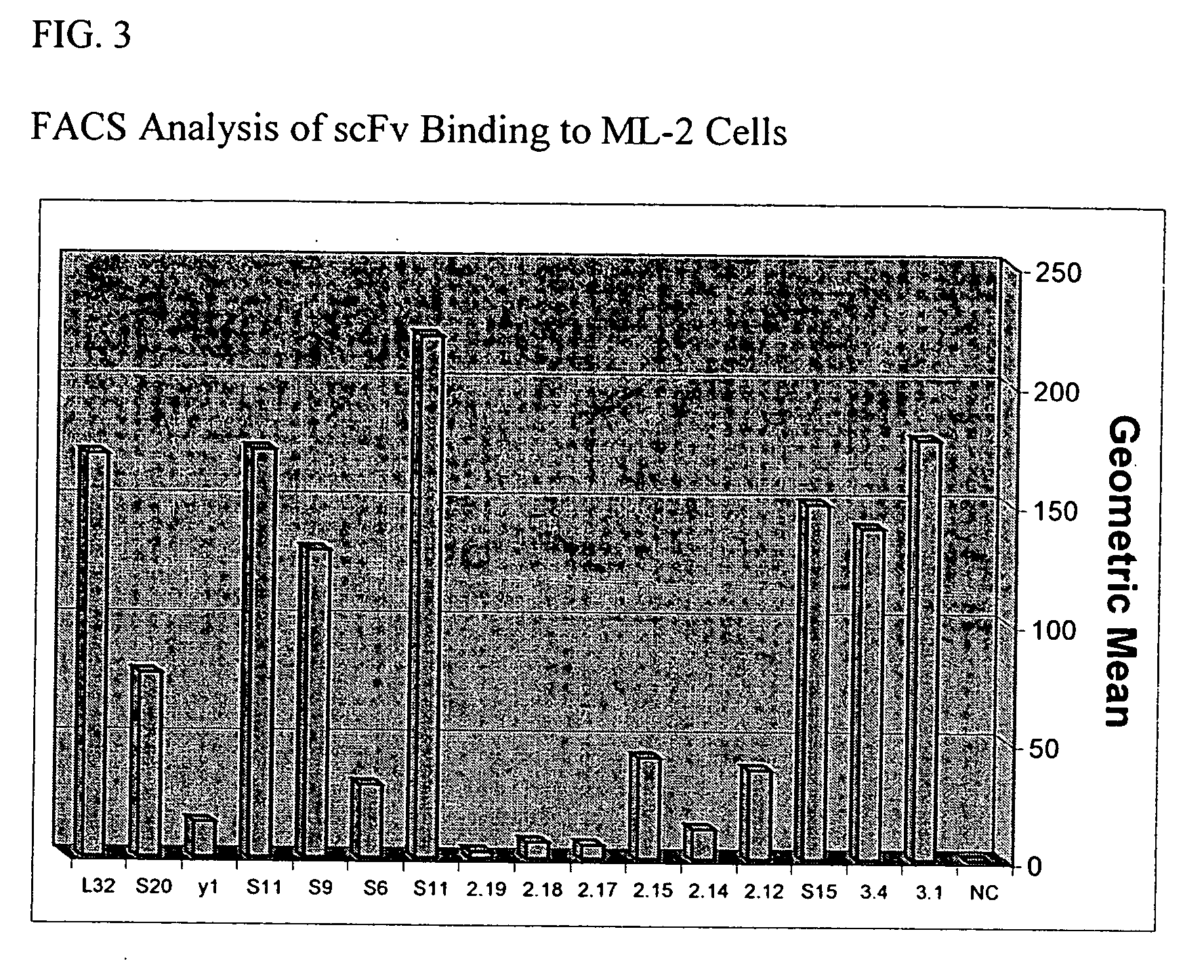
Patents
Literature
83 results about "Co-receptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A co-receptor is a cell surface receptor that binds a signalling molecule in addition to a primary receptor in order to facilitate ligand recognition and initiate biological processes, such as entry of a pathogen into a host cell.
Prevention and treatment of HCV infection employing antibodies that inhibit the interaction of HCV virions with their receptor
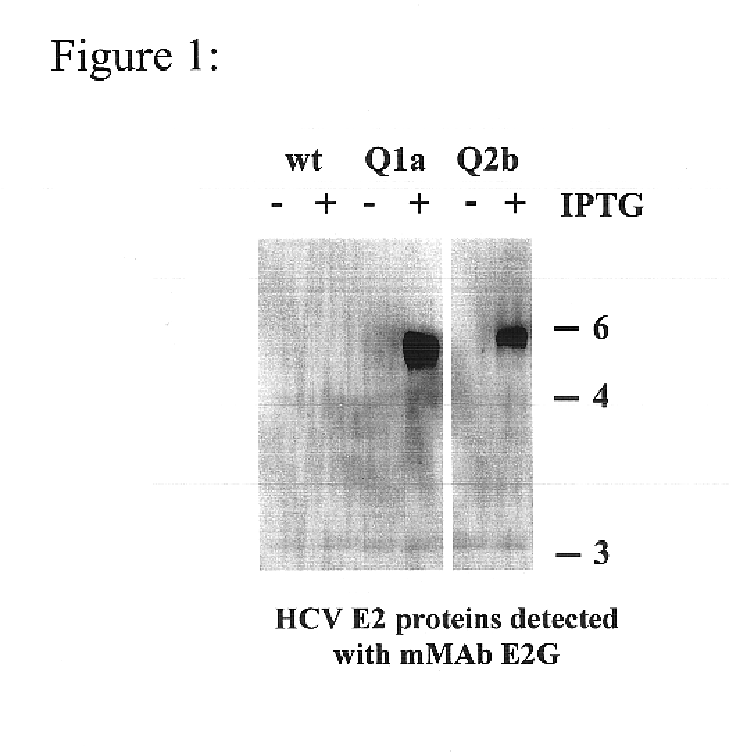
Human monoclonal antibodies binding to epitopes common to type 1 and 2 HCV are provided, as well as conformationally conserved HCV E2 2a and 2b proteins. Compositions comprising the antibodies find use in diagnosis and therapy. The antibodies recognize conformational epitopes that are conserved across multiple genotypes of HCV. Thus the antibodies have the potential to be useful in the prevention and treatment of the majority of HCV infections. A subset of the antibodies (CBH-2, CBH-5, CBH-7, CBH-8C, CBH-8E, and CBH-11) have the ability to prevent the binding of HCV E2 proteins of multiple genotypes to human CD81, a possible co-receptor for HCV infection. A subset of the antibodies (CBH-2 and CBH-5) have been shown to inhibit the binding of HCV virions (as opposed to purified E2 protein) to human CD81. A further subset of the antibodies (CBH-4D, CBH4B, CBH-8C, and CBH-9) have been shown to prevent HCV envelope mediated fusion using an HCV psuedotype system.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Combinatorial selection of phosphorothioate single-stranded DNA aptamers for TGF-beta-1 protein
InactiveUS20050239134A1Increased proliferationPrevent proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsDNA AptamersTgf β signalling
The present invention includes the selection and isolation of thioaptamers that target the signaling protein TGF-β1, compositions of such thioaptamers and the use of such thioaptamers to either block or enhance signal transduction of the TGF-β1 protein and thus function as, e.g., immunomodulatory agents. Thioaptamers may also be targeted alone or in combination with other thioaptamers against the ligand, the receptors, the ligand trap protein(s) and / or the co-receptors to modulate TGF-β signaling pathway.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
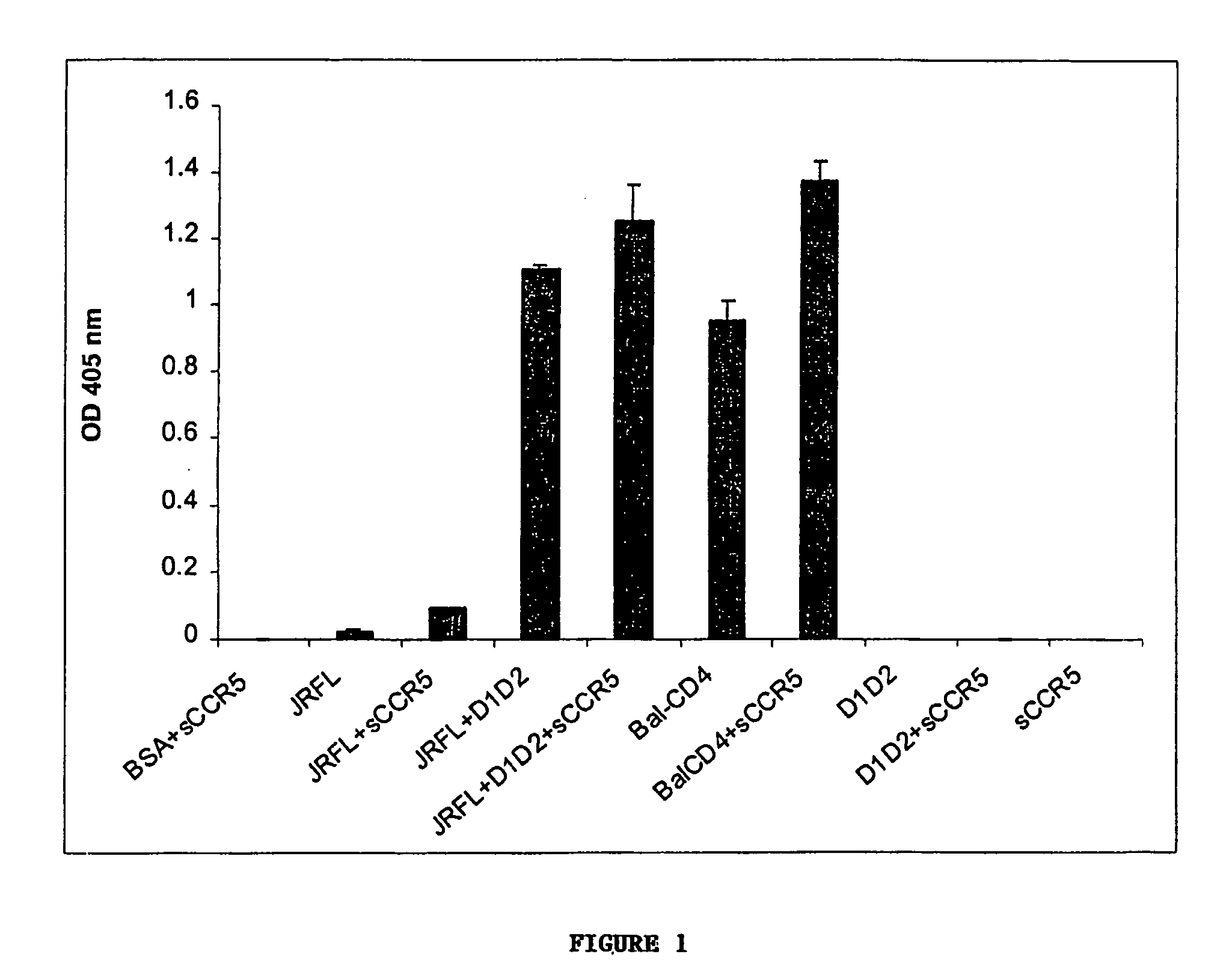
Virus coat protein/receptor chimeras and methods of use
InactiveUS7311920B1Sufficient amountMethod can be usedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCXCR4Immunodeficiency virus
The invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising a virus coat sequence and a receptor sequence that can interact with each other to form a complex that is capable of binding a co-receptor. Such chimeric molecules therefore exhibit functional properties characteristic of a receptor-coat protein complex and are useful as agents that inhibit virus infection of cells due to occupancy of co-receptor present on the cell, for example. In particular aspects, the chimeric polypeptide includes an immunodeficiency virus envelope polypeptide, such as that of HIV, SIV, FIV, FeLV, FPV and herpes virus. Receptor sequences suitable for use in a chimeric polypeptide include, for example, CCR5 and CXCR4 sequences.
Owner:MARYLAND BIOTECH INST UNIV OF
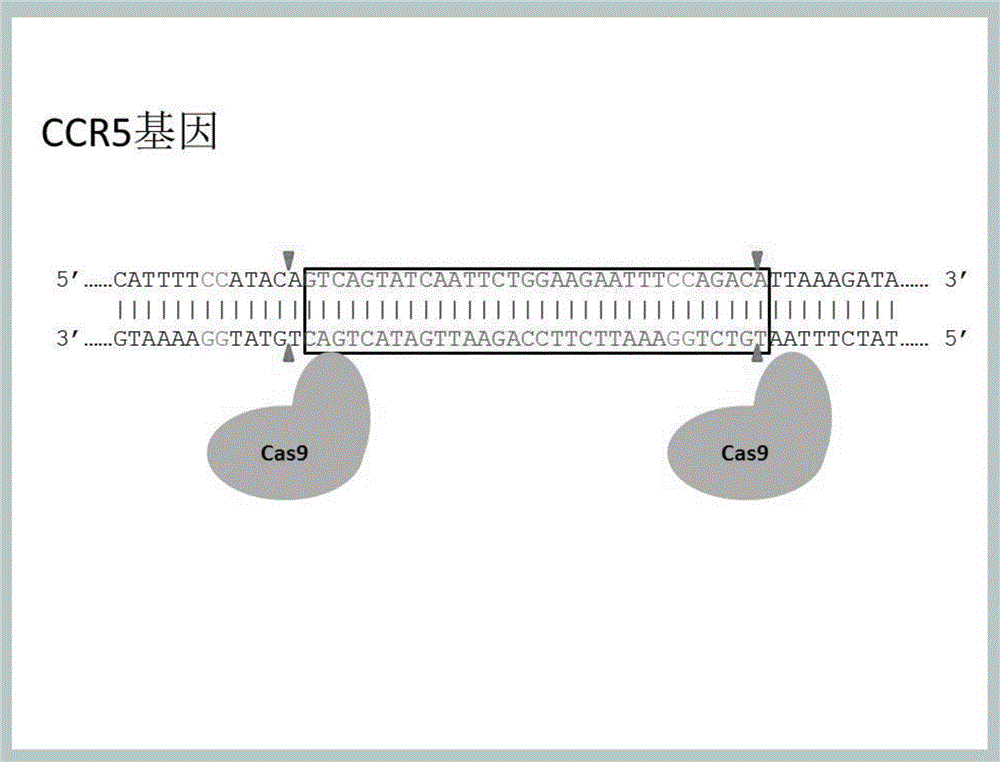
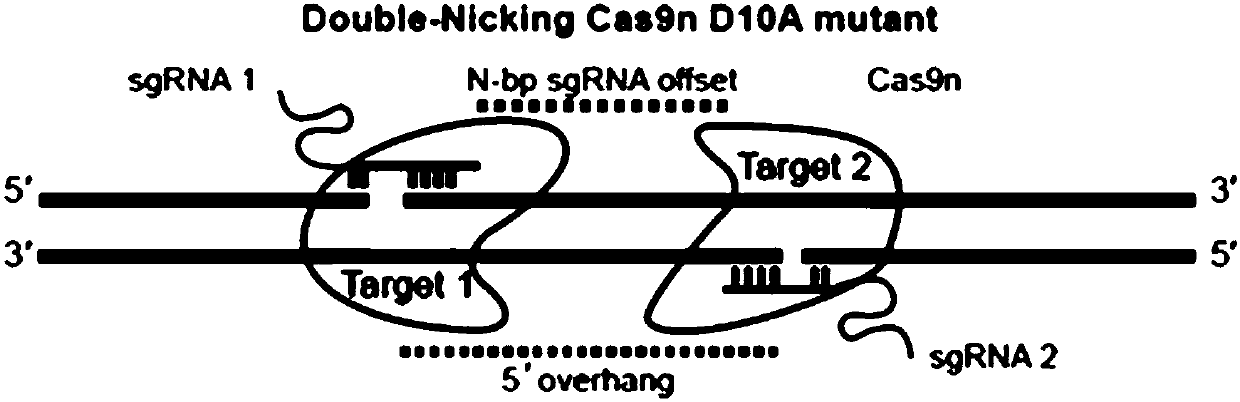
Method for inducing CCR5-delta32 deletion with genome editing technology CRISPR-Cas9
The invention relates to a method for successfully inducing cell chemokine receptor CCR5 genes to be mutated into CCR5-delta32 deletion-type genes with a new genome editing technology CRISPR-Cas9. CCR5 is an important receptor for human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) to invade personal host cells. CCR5-delta32 deletion means deletion of 32 basic groups occurs in a CCR5 coding region, so that the sequence after the 185th amino acid is changed, and early termination occurs. CCR5-delta32 biallelic-gene homozygous deletion has natural resistance to HIV infection, and can not be infected by HIV. By means of the method, a slow virus packaging system and the CRISPR technology are used at the same time; as the slow virus infecting host range is wide, the method can be applied to cells such as bone marrow stem cells and CD4T cells, and the CCR5-delta32 deletion-type genes hopefully become medicine for treating acquired immune deficiency syndrome or other diseases.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
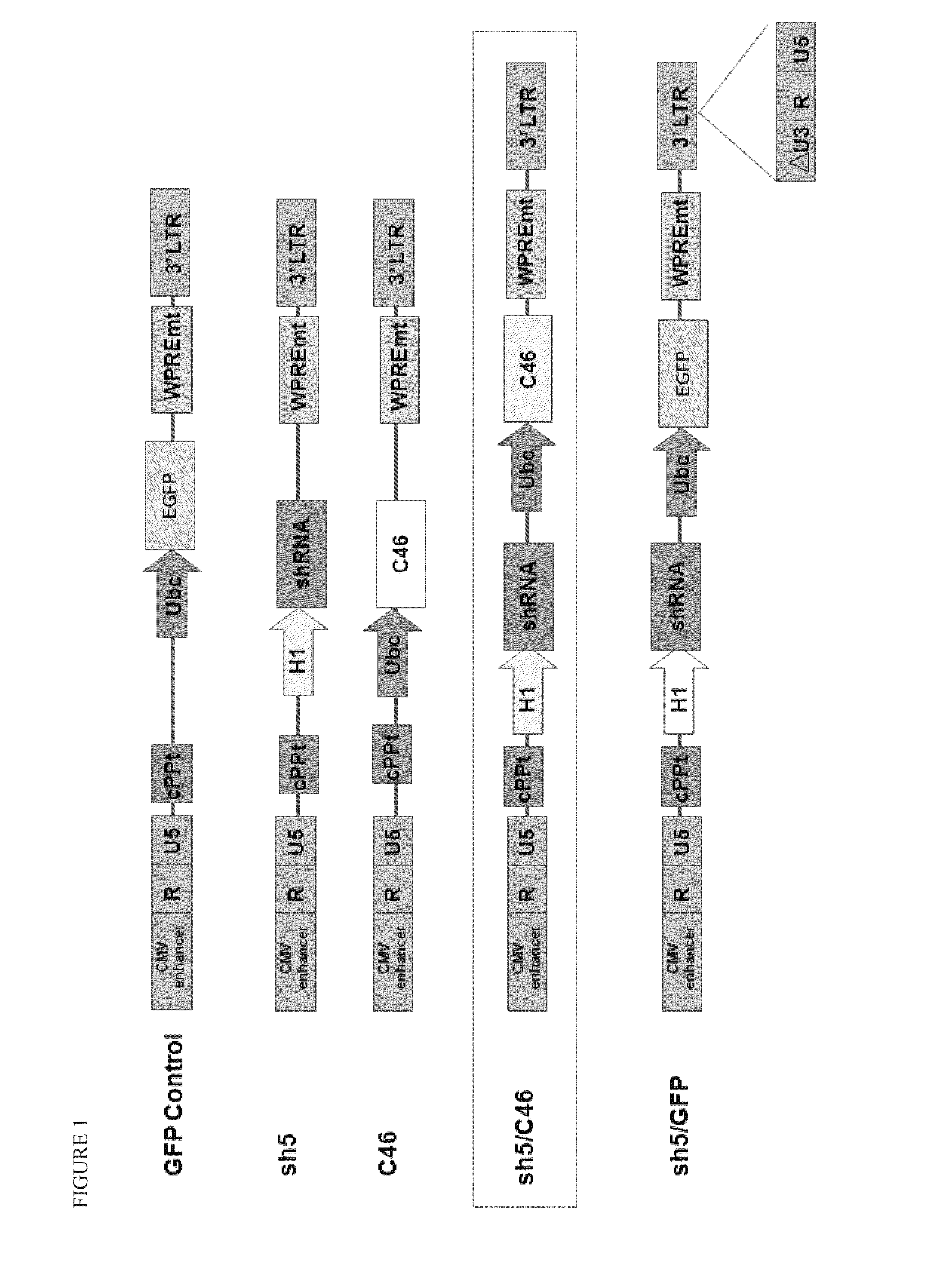
Dual vector for inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus
The present invention provides an expression vector for preventing or inhibiting HIV entry, fusion or replication in mammalian cells. In particular, the invention provides a recombinant retroviral vector that encodes an inhibitor of a HIV co-receptor, such as CCR5 or CXCR4, and a protein that inhibits HIV fusion to target cells and / or HIV replication. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising such constructs and methods of use thereof to prevent or treat HIV infection in a patient are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
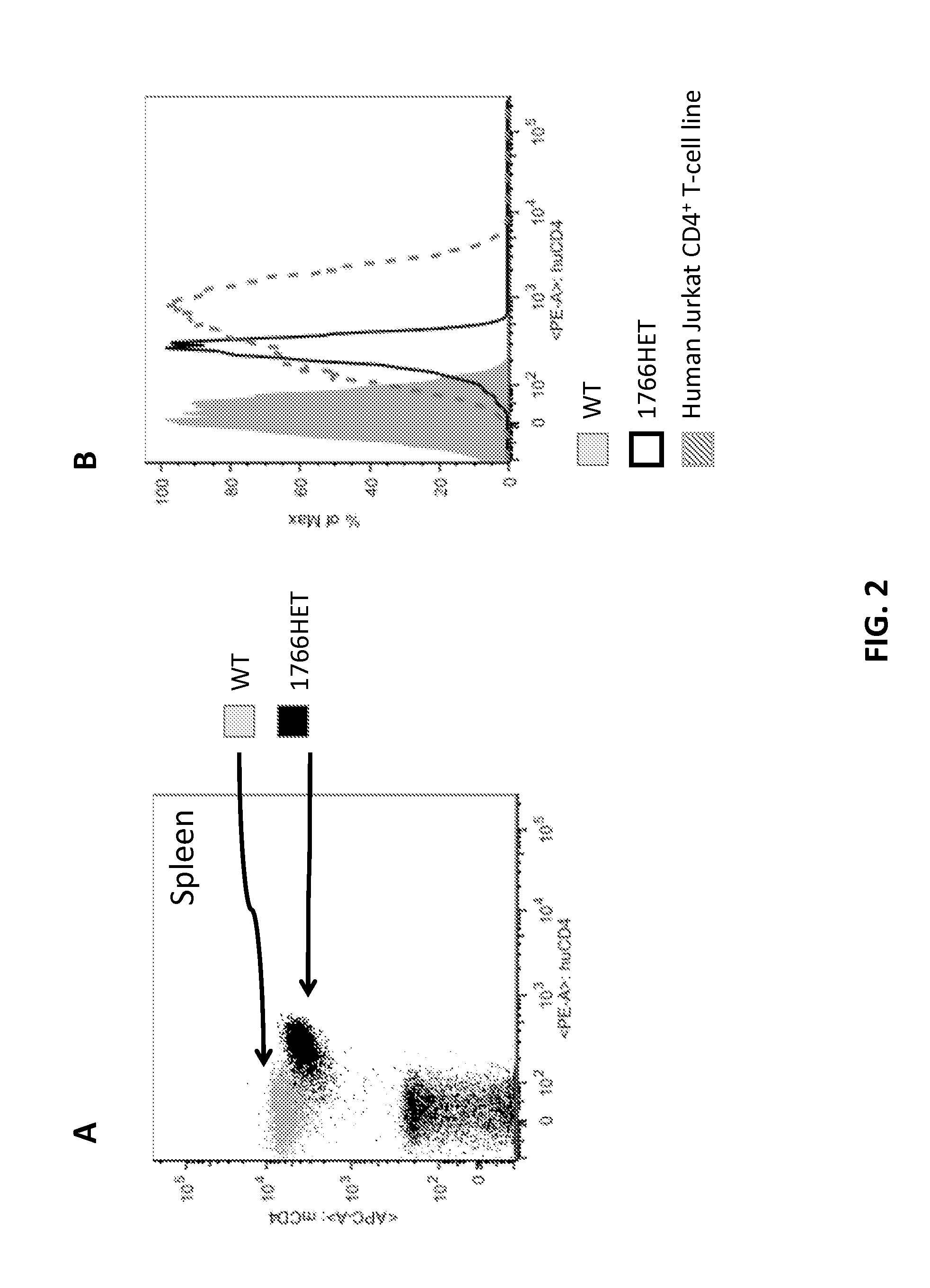
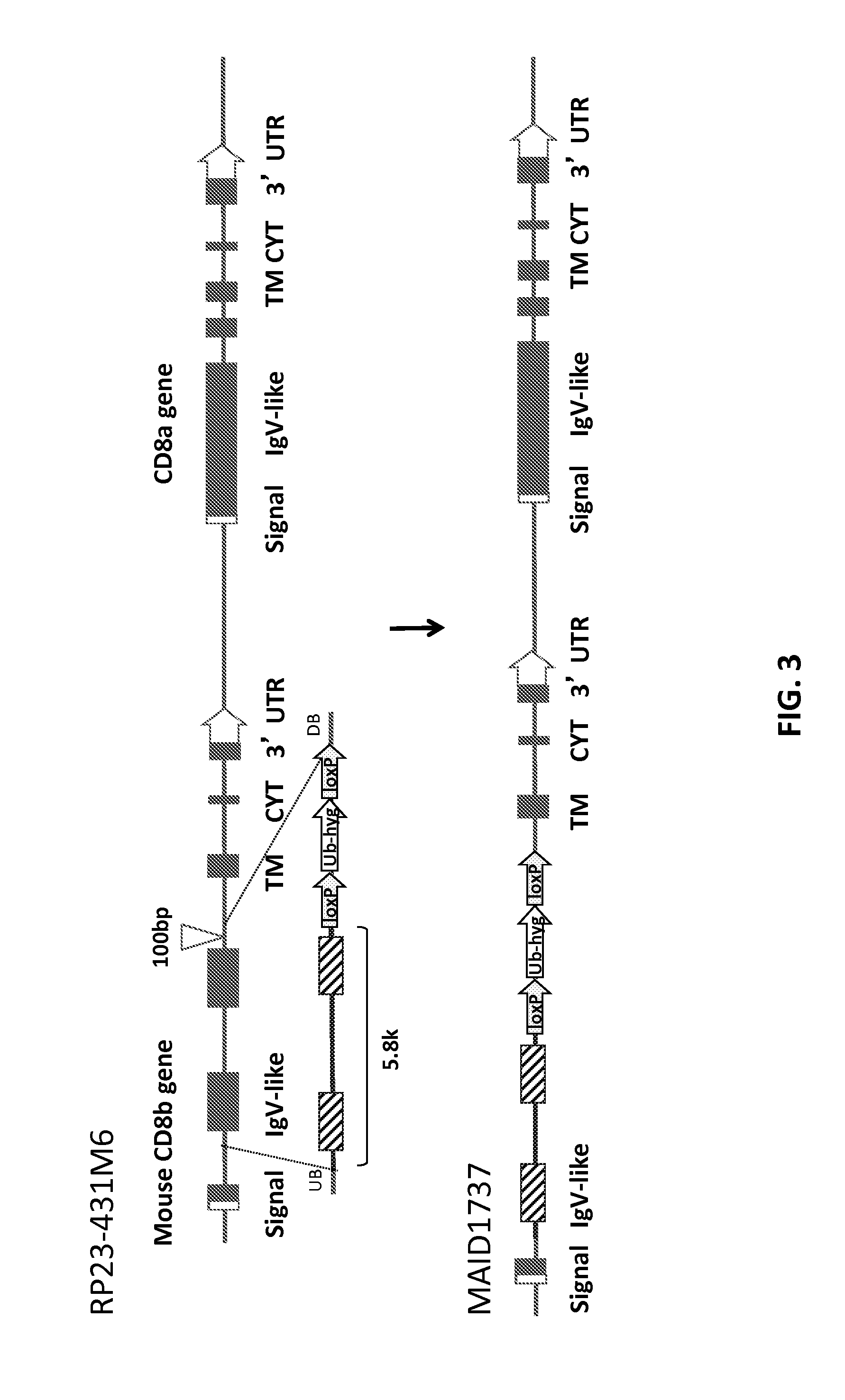
Humanized t cell co-receptor mice
The invention provides genetically modified non-human animals that express chimeric human / non-human T cell co-receptor polypeptides (e.g., CD4, CD8α, CD8β), as well as embryos, cells, and tissues comprising the same. Also provided are constructs for making said genetically modified animals and methods of making the same.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Combination therapy comprising the use of protein kinase C modulators and Histone Deacetylase inhibitors for treating HIV-1 latency
InactiveUS20100166806A1Adverse propertyPrevent HIV-1-induced cytotoxicityBiocideOrganic chemistryReverse transcriptaseHydroxamic acid
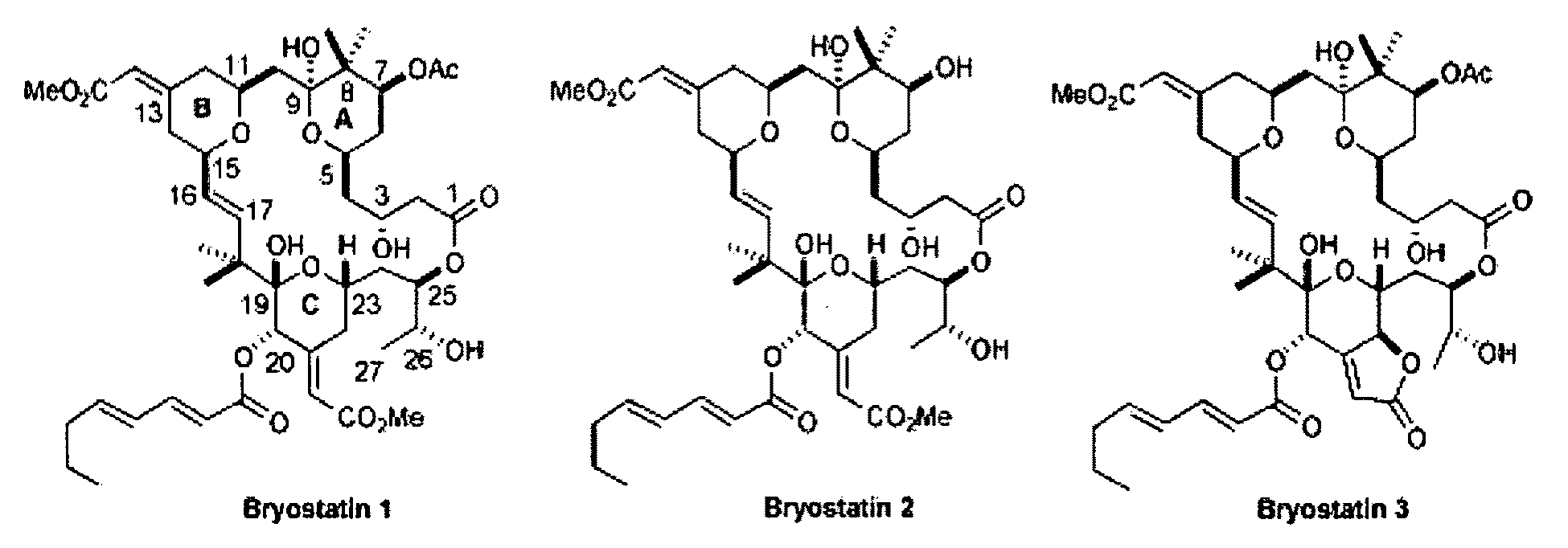
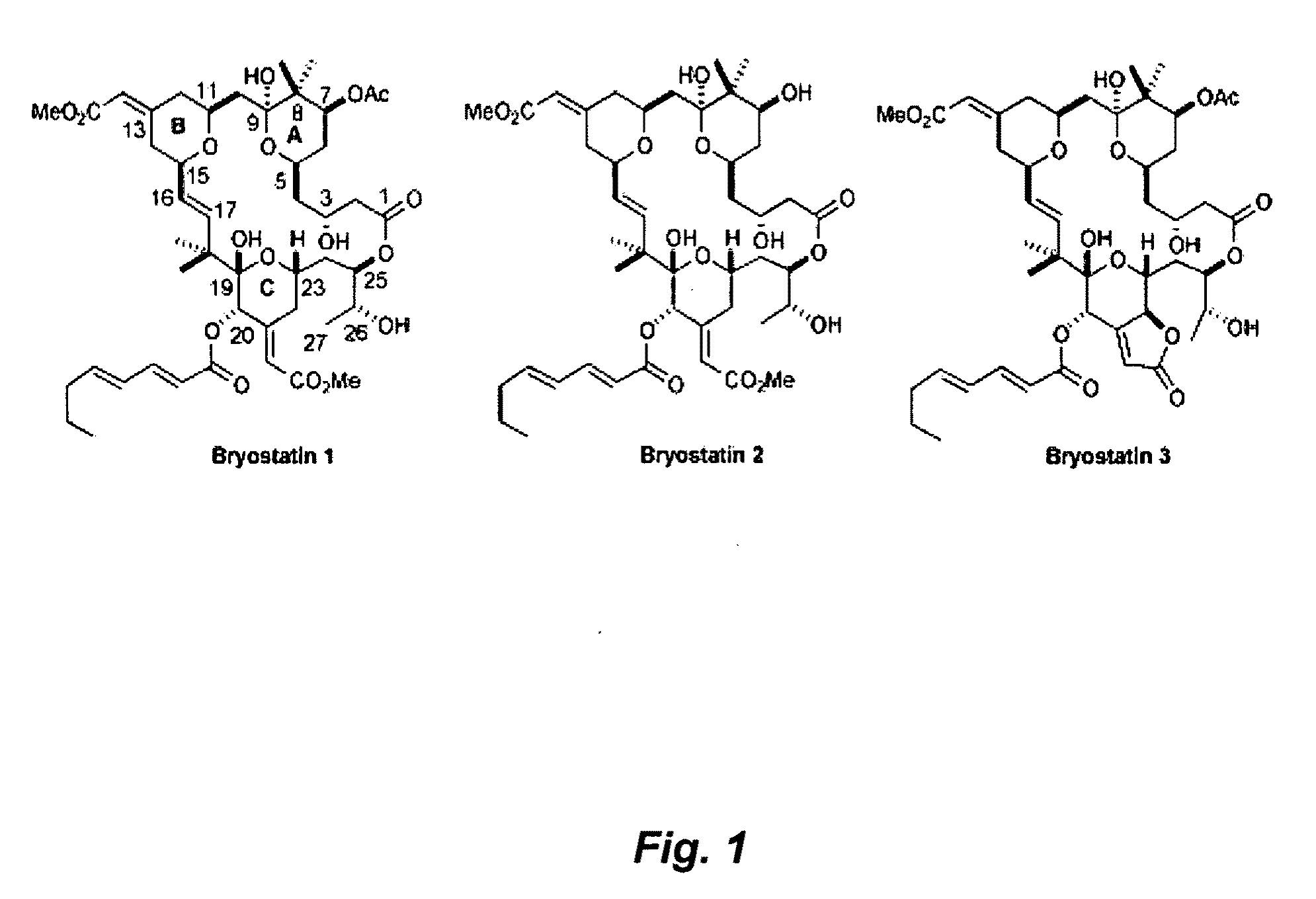
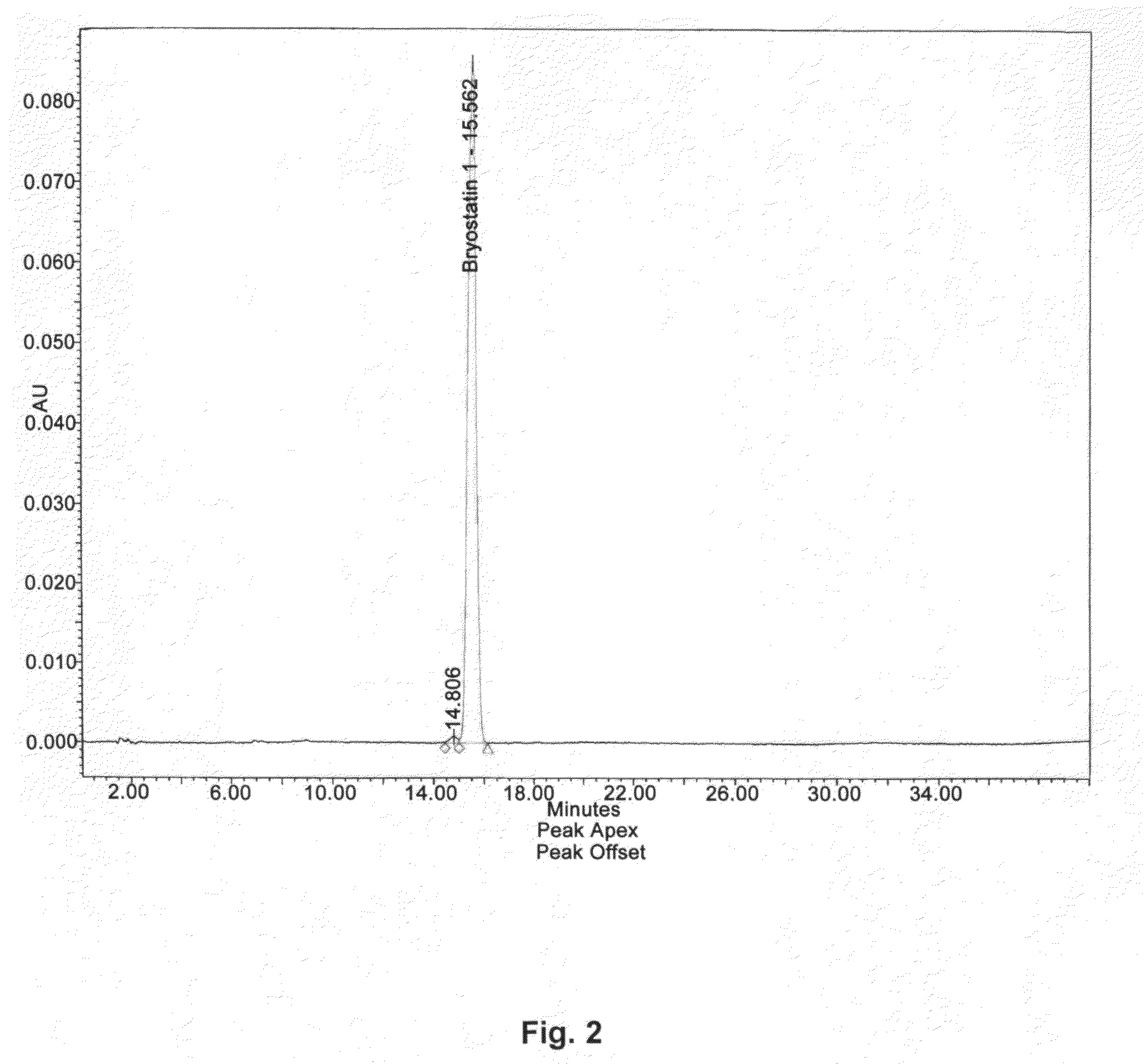
The invention relates to a combination of treatments, more particularly a combination treatment for HIV-1 infection. The present invention is directed to the use of bryostatin-1 and their natural and synthetic derivatives for AIDS therapy, in particular to the use of bryostatins in combination with other active drugs such as Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors and anti-retrovirals, for the treatment of HIV-1 latency. According to the present invention, we provide a combination therapy for the treatment of HIV-1 latency which employs bryostatin-1 (and analogues) and one of the following HDAC inhibitors; valproic acid, butyrate derivatives, hydroxamic acids and benzamides. While HDACi can be used in continuous dosing protocol, bryostatins can be used following a cyclical dosing protocol. Bryostatins can be formulated in pharmaceutical acceptable carriers including nanoparticles, phospholipids nanosomes and / or biodegradable polymer nanospheres. This combination therapy needs to be used in patients treated with antiretroviral therapy (HIV-1 protease inhibitors, HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors, HIV-1 integrase inhibitors, CCR5 co-receptor inhibitors and fusion inhibitors).
Owner:APHIOS
GRNA, expression vector, knockout system and kit for knocking out CXCR4 gene
InactiveCN107893074AEffective knockoutHigh feasibilityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNACXCR4Co-receptor
The invention discloses a gRNA, a knockout system and a kit for knocking out CXCR4 gene. A target site with high cutting efficiency is screened, the gRNA specifically targeting a target gene is designed and prepared, the CXCR4 gene can be effectively knocked out by CRISPR-Cas9 technology, HIV virus co-receptor CXCR4 on cell surface can be knocked out by CRISPR-nickase gene editing technology, theoff-target efficiency can be greatly reduced under the premise of effective CXCR4 gene knockout, the feasibility of clinical use is improved, and security risks can be reduced.
Owner:广东赤萌医疗科技有限公司
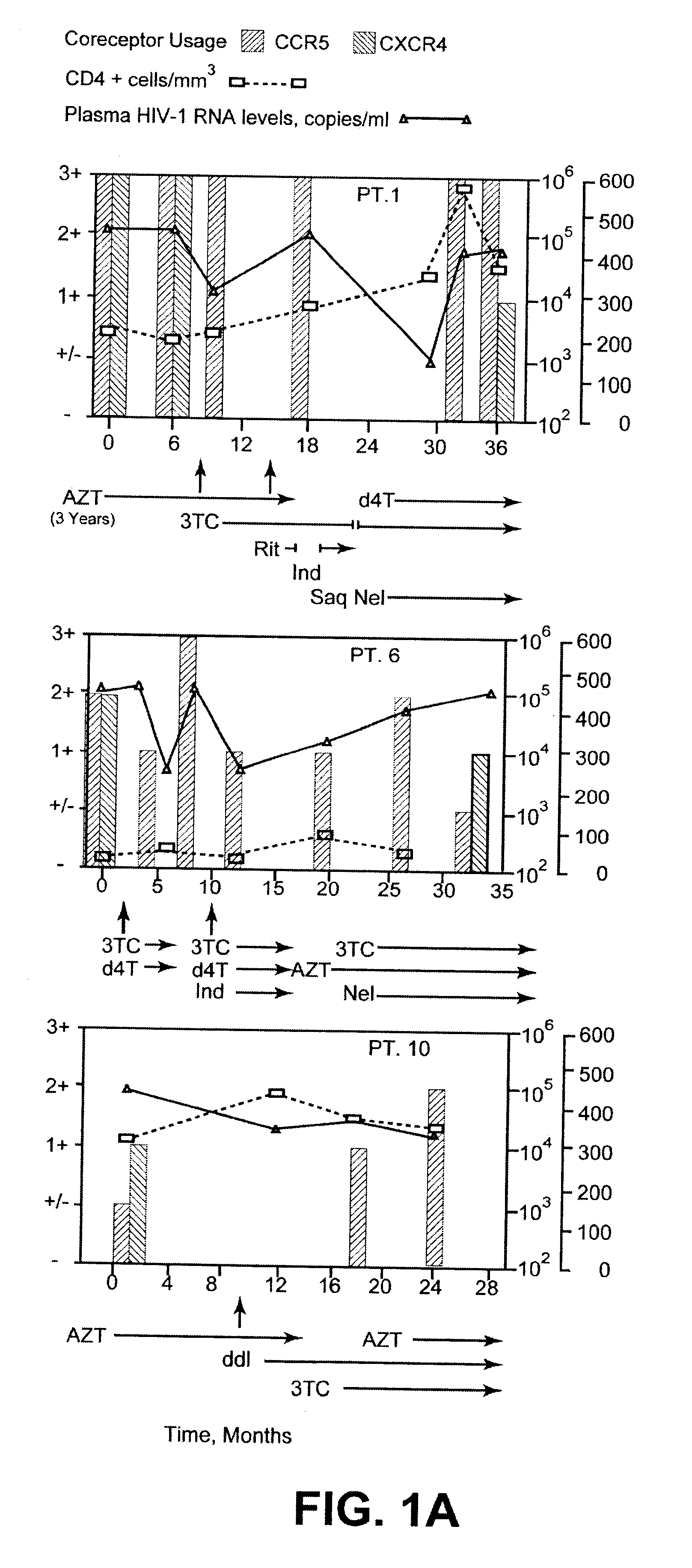
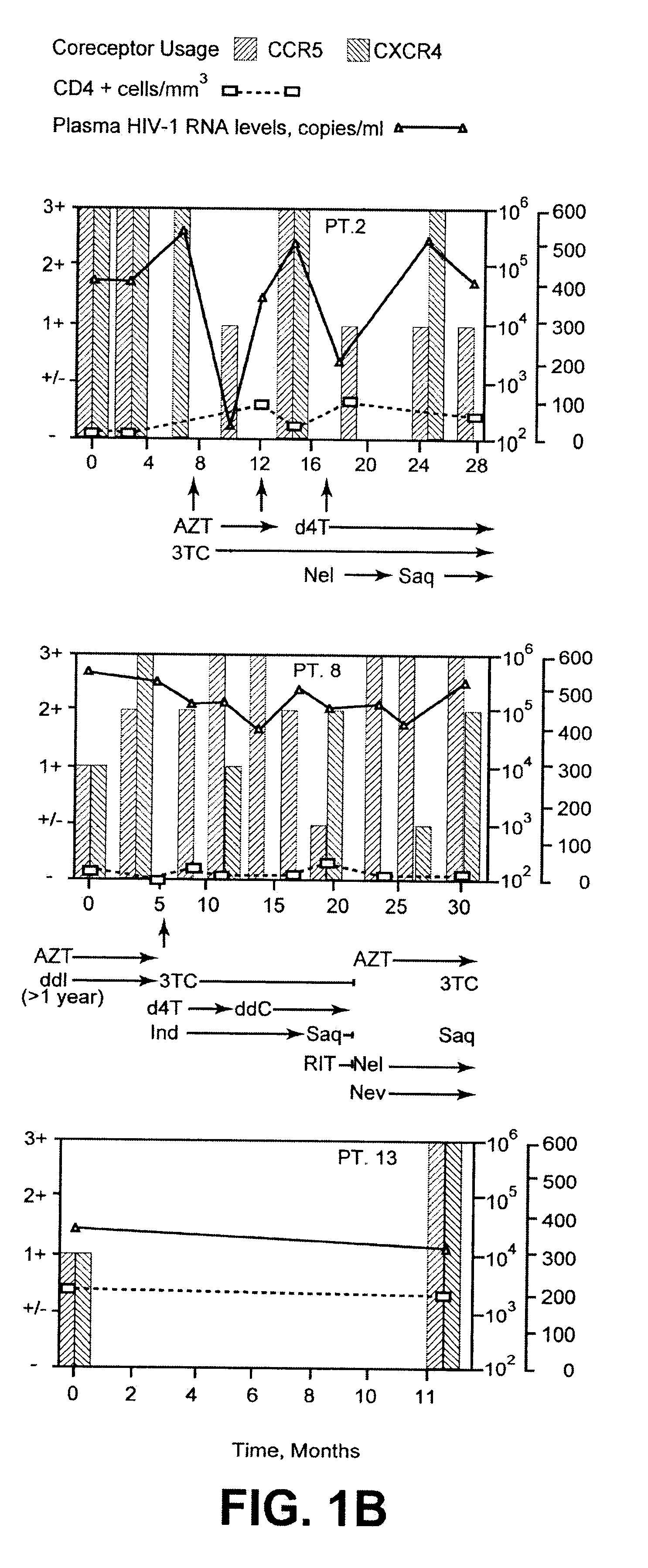
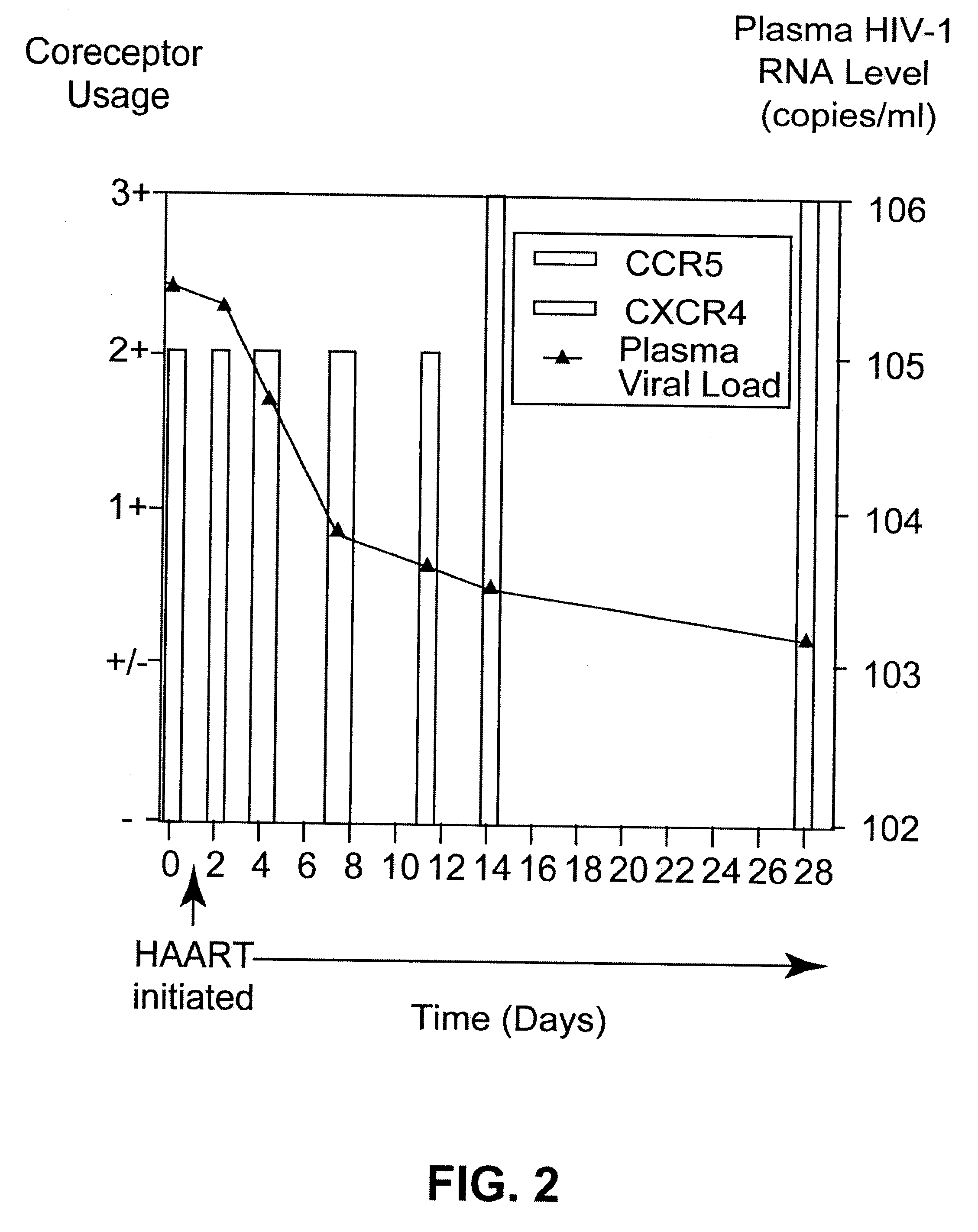
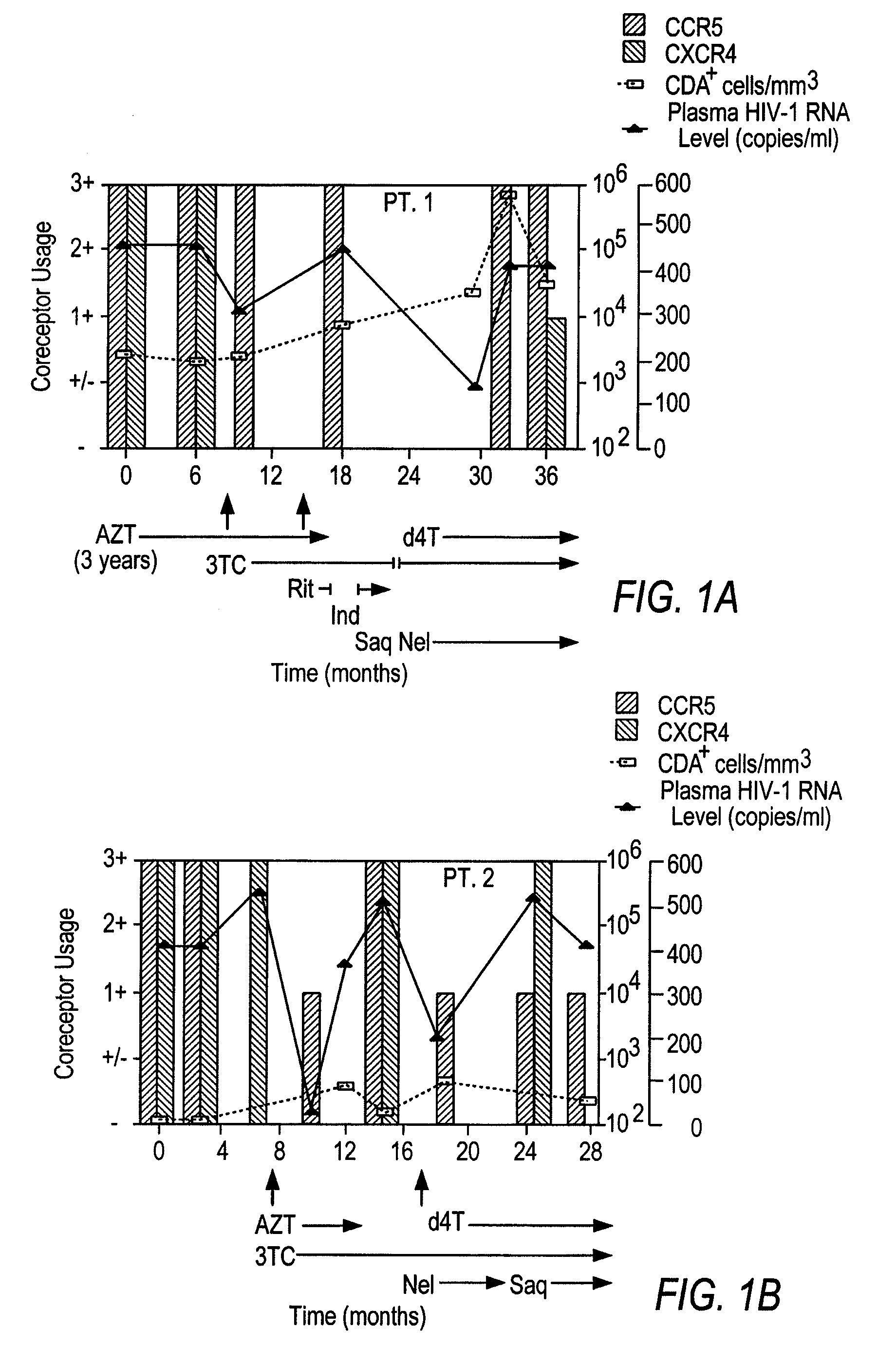
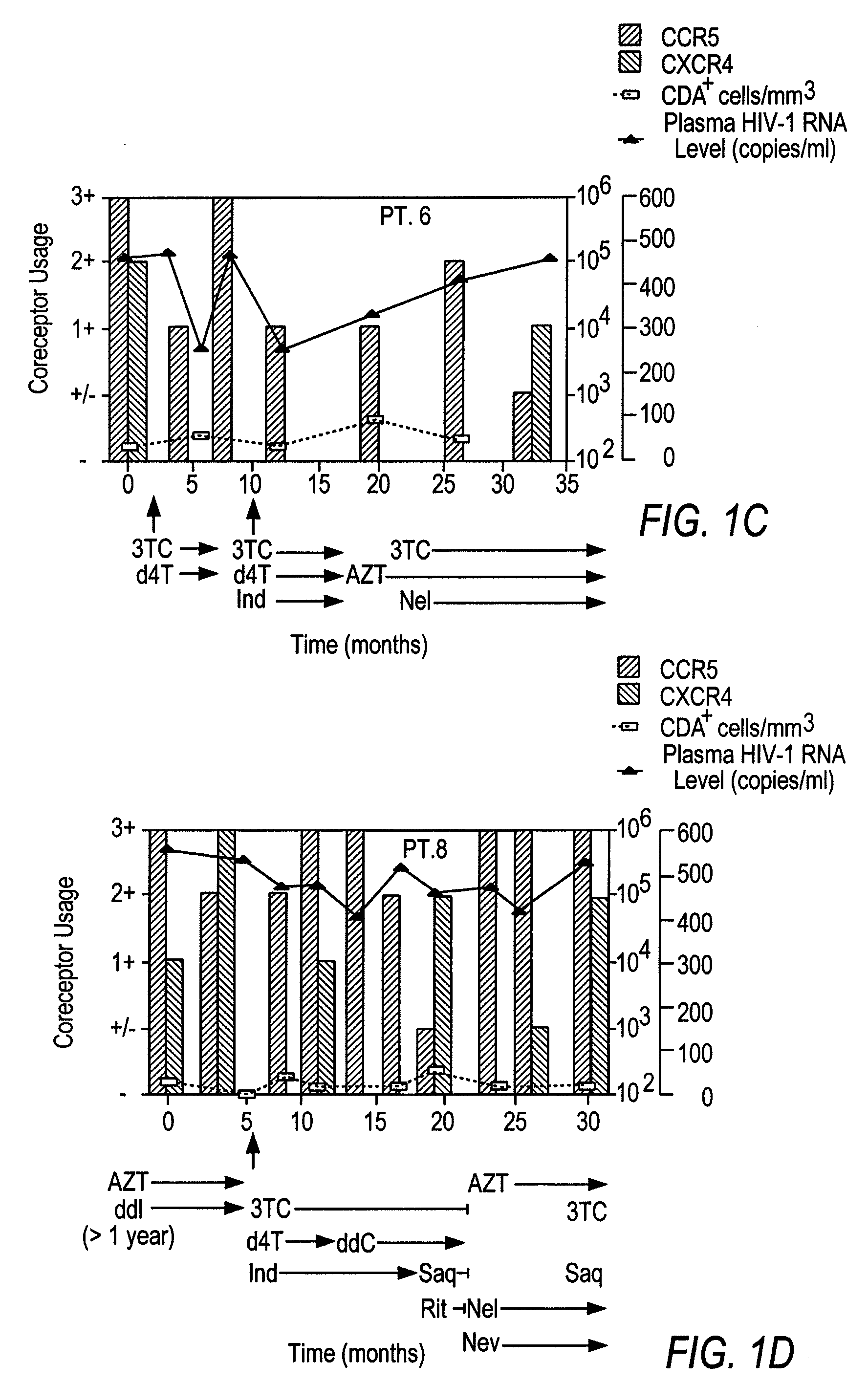
Analysis of HIV-1 coreceptor use in the clinical care of HIV-1-infected patients
InactiveUS6727060B2Accurate predictionMore effectivenessMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsImmunodeficiency virusHIV positives
A change in viral tropism occurs in many HIV positive individuals over time and can be indicated by a shift in coreceptor use from CCR5 to CXCR4. The shift in coreceptor use to CXCR4 has been shown to correlate with increased disease progression. In patients undergoing HAART, the predominant populations of virus can be shifted back to CCR5-mediated entry after the CXCR4-specific strains have emerged. The present invention relates to a diagnostic method to monitor coreceptor use in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. The present invention further relates to a diagnostic method applied to HIV-positive individuals undergoing HAART to monitor the suppression of CXCR4 specific strains. The diagnostic methods can be used to assist in selecting antiretroviral therapy and to improve predictions of disease prognosis over time.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
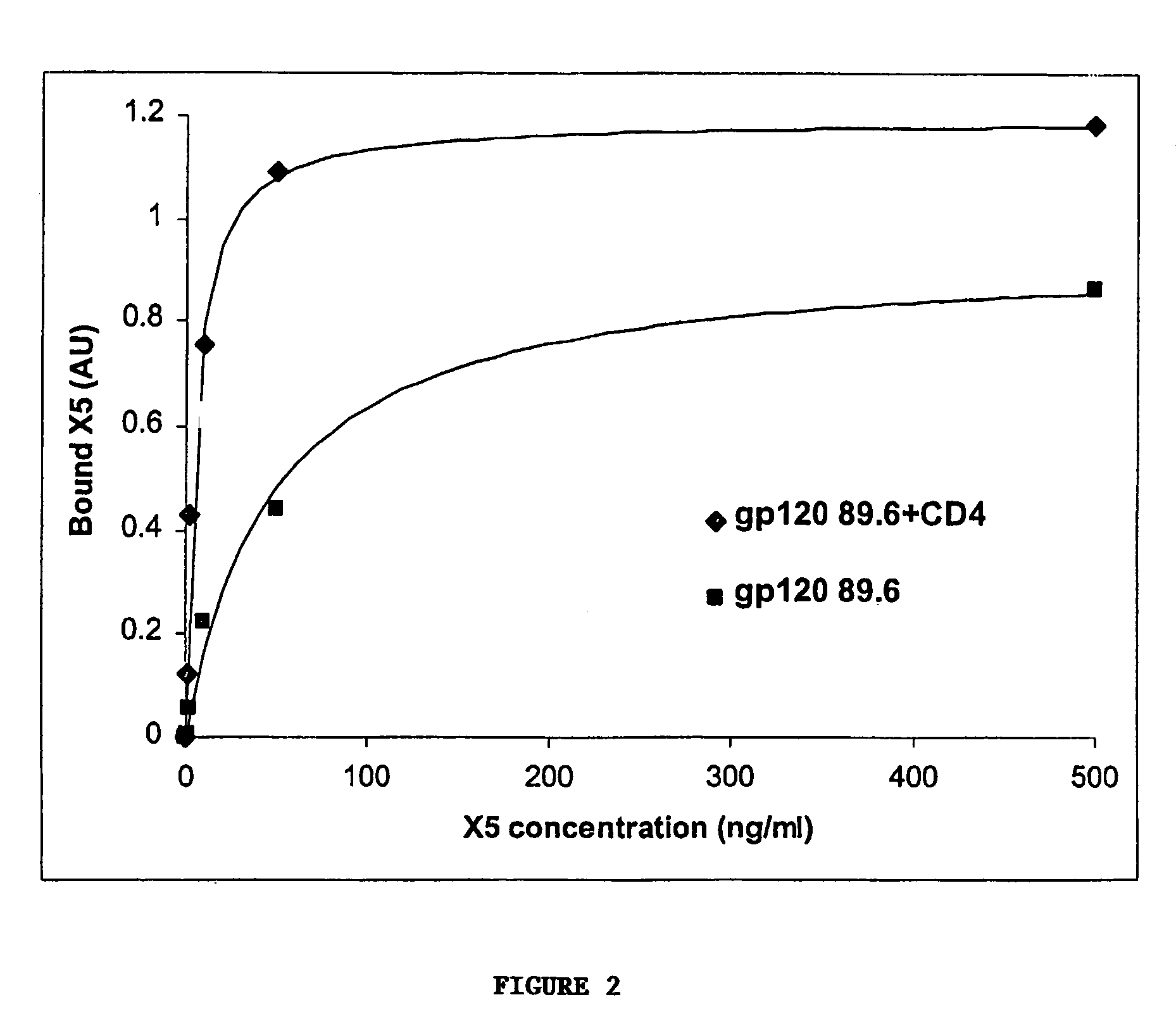
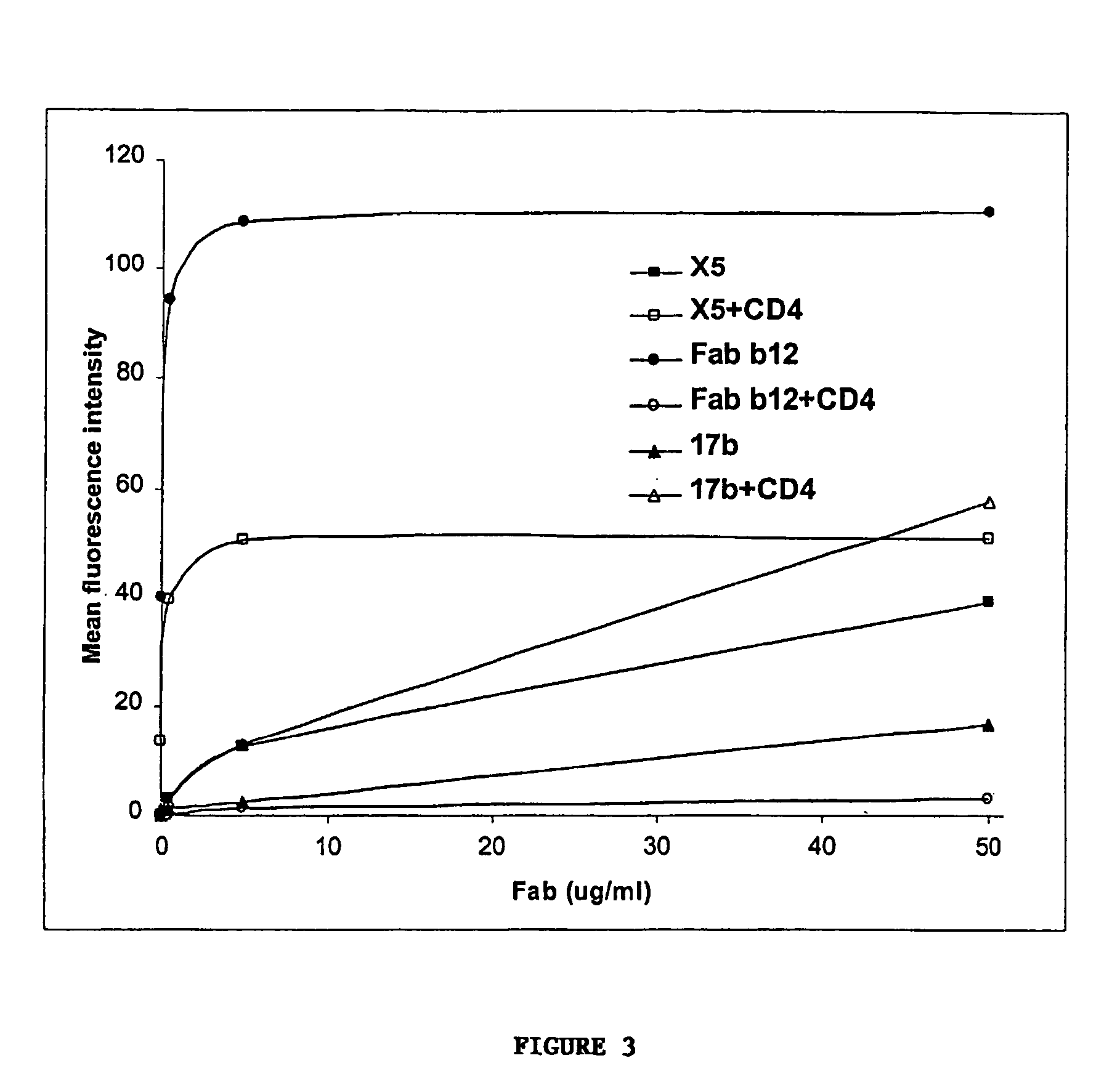
Broadly cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus selected by Env-CD4-co-receptor complexes
InactiveUS7223844B2Increase exposurePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody fragmentsMammal
The present invention features antibodies and antibody fragments that specifically bind a CD4-inducible HIV gp120 epitope that is enhanced by binding a co-receptor for HIV, such as CCR5 or CXCR4, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies or antibody fragments. The invention also features nucleic acids encoding the antibodies or antibody fragments, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the nucleic acids encoding the antibodies or antibody fragments, vectors comprising the nucleic acids, and cells comprising the vectors. The invention further features methods of identifying antibodies or antibody fragments with broadly neutralizing activity against HIV. The invention also features methods of inhibiting HIV entry into cells and methods of inhibiting replication of HIV in mammals, using the antibodies and nucleic acids of the invention.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
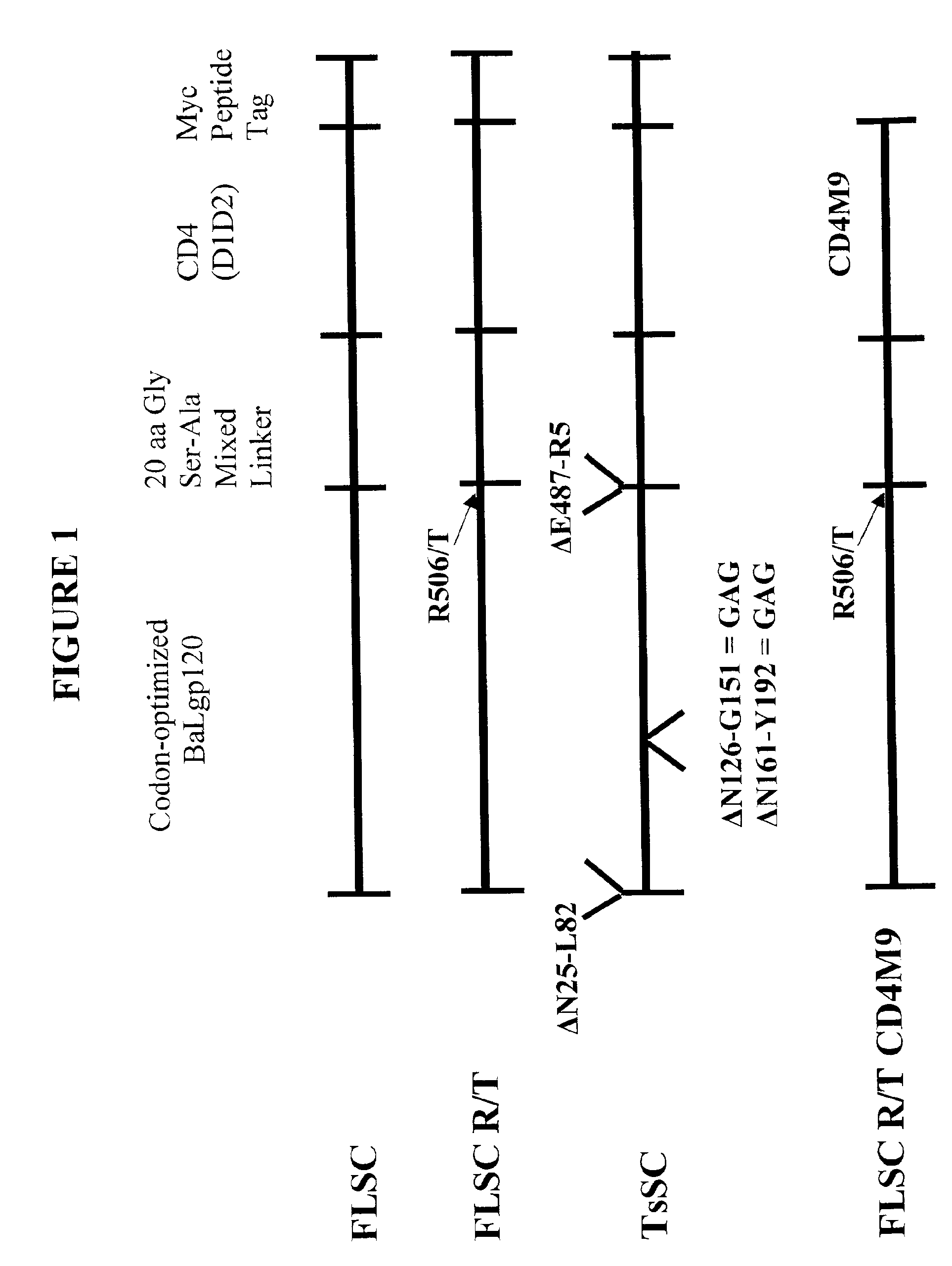
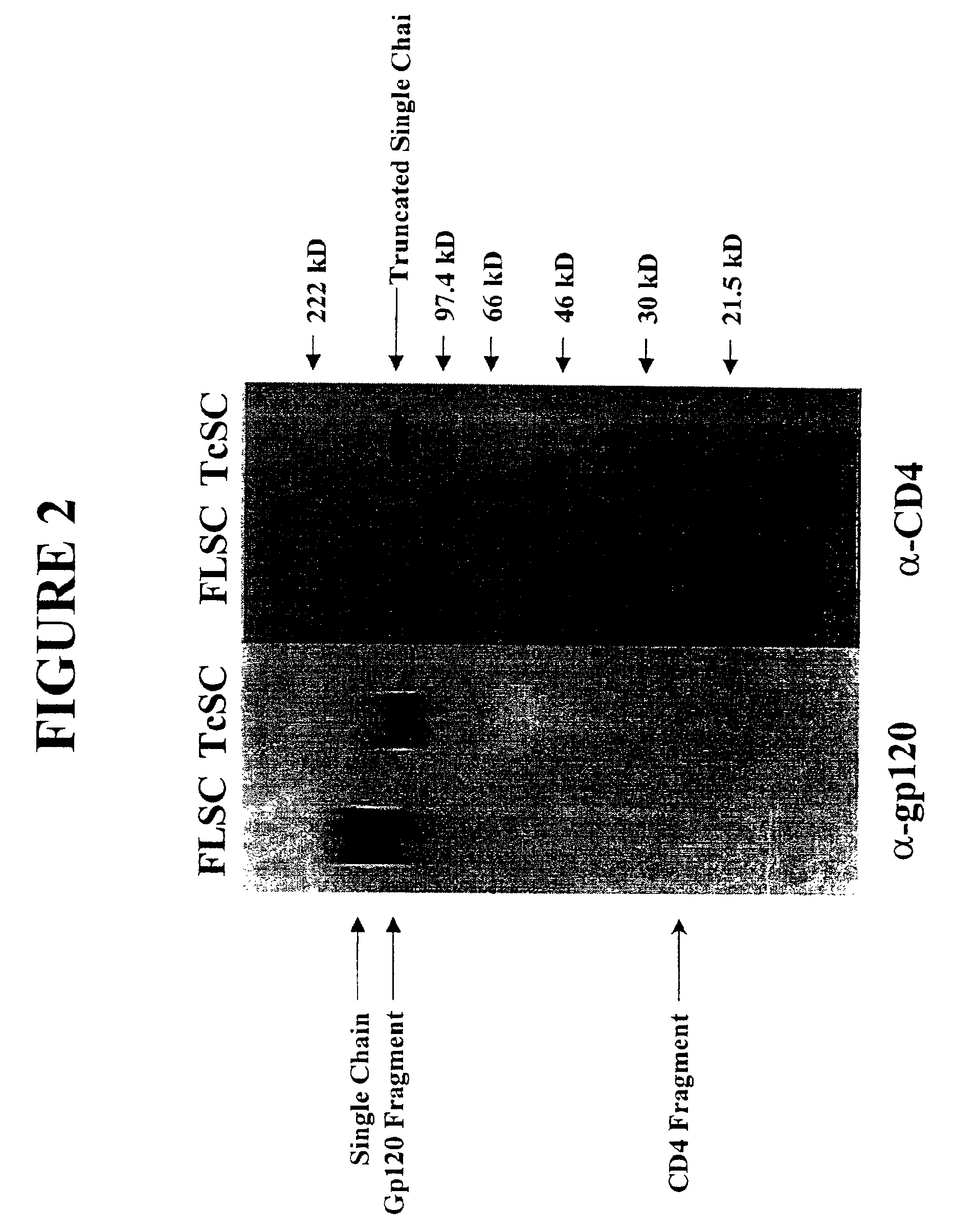
Virus coat protein/receptor chimeras and methods of use
InactiveUS6908612B2Raise the potentialAvoid virus infectionOrganic active ingredientsFungiImmunodeficiency virusHerpes simplex virus DNA
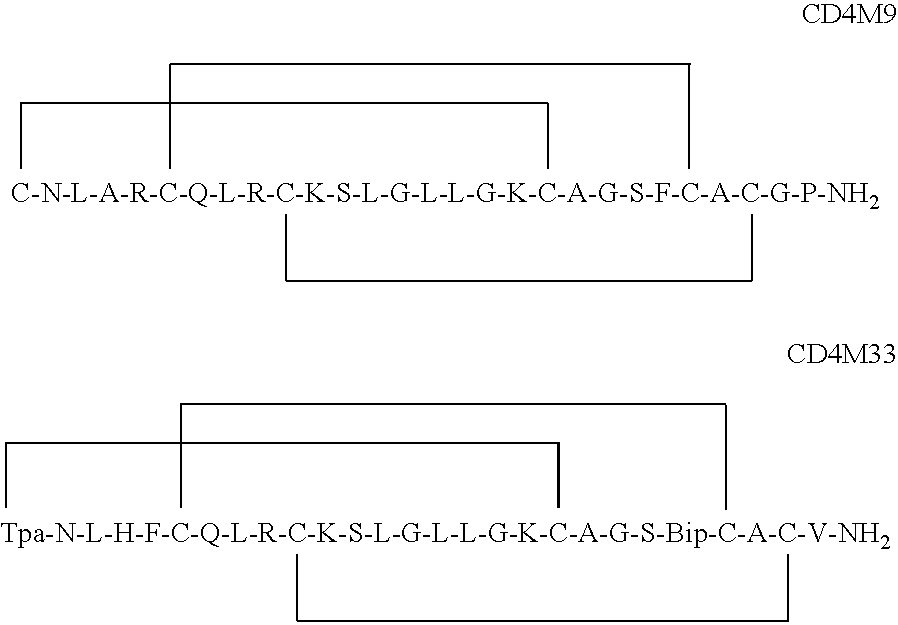
The invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising a virus coat sequence and a receptor sequence that can inter-act with each other to form a complex that is capable of binding a co-receptor. Such chimeric molecules therefore exhibit functional properties characteristic of a receptor-coat protein complex and are useful as agents that inhibit virus infection of cells due to occupancy of a co-receptor present on the cell. In particular aspects, the chimeric polypeptide includes an immunodeficiency virus envelope polypeptide, such as that of HIV, SIV, FIV, FeLV, FPV and herpes virus. Receptor sequences suitable for use in a chimeric polypeptide include, for example, CD4 D1D2 and CD4M9 sequences.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF BIOTECH INST
Dual vector for inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS20160243169A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCXCR4Immunodeficiency virus
The present invention provides an expression vector for preventing or inhibiting HIV entry, fusion or replication in mammalian cells. In particular, the invention provides a recombinant retroviral vector that encodes an inhibitor of a HIV co-receptor, such as CCR5 or CXCR4, and a protein that inhibits HIV fusion to target cells and / or HIV replication. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising such constructs and methods of use thereof to prevent or treat HIV infection in a patient are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
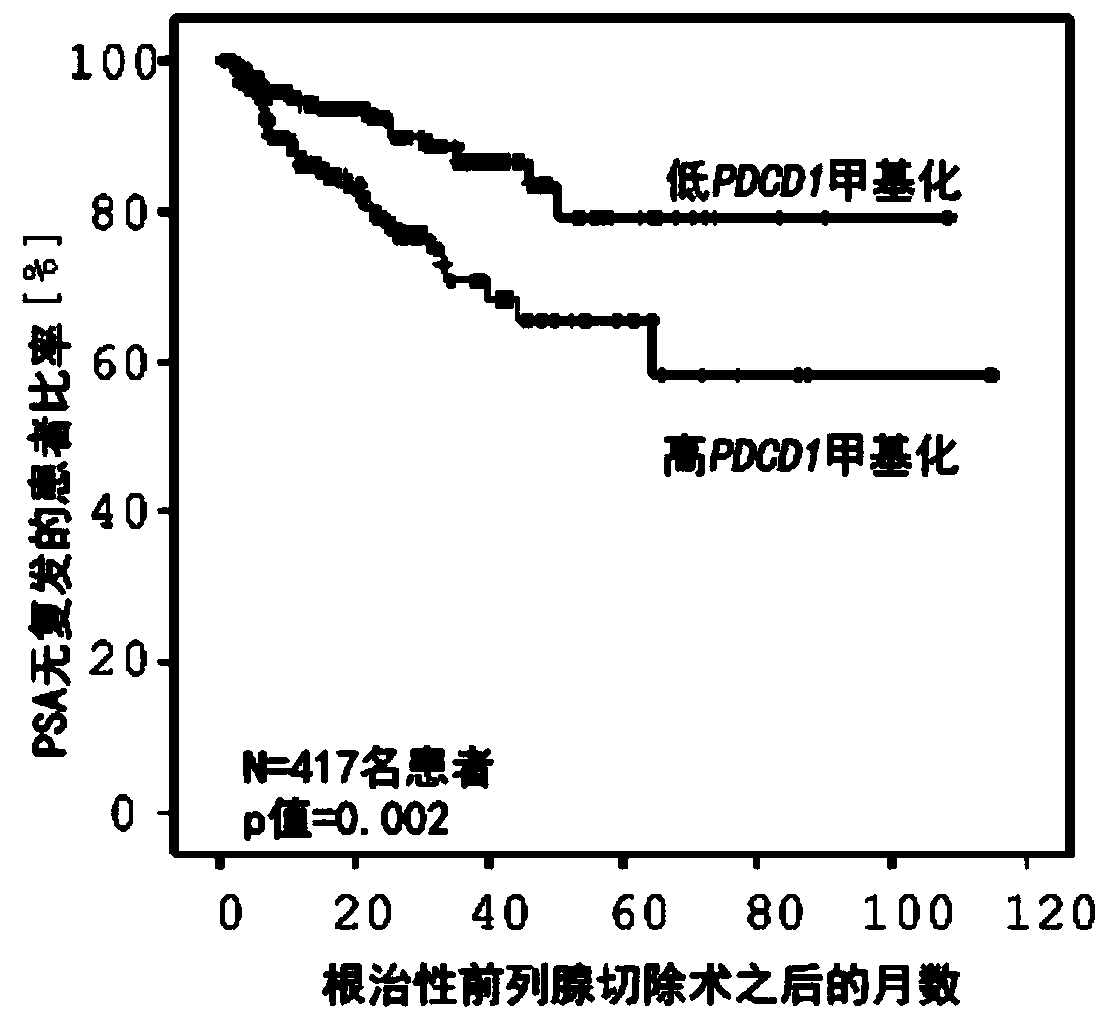
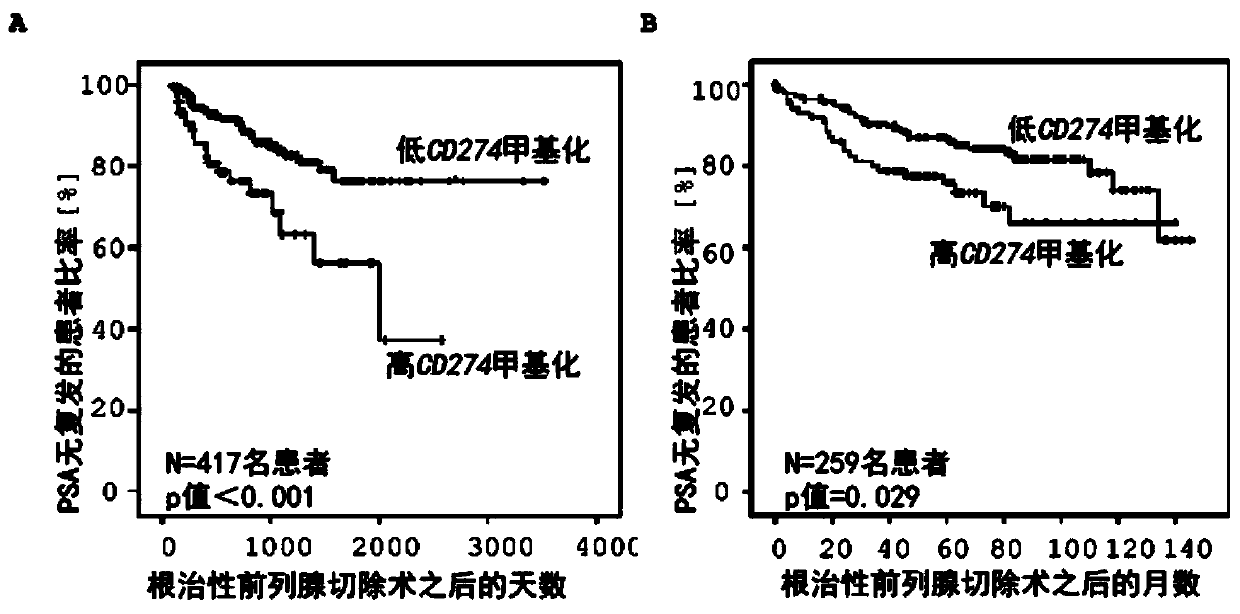
Method for assessing a prognosis and predicting the response of patients with malignant diseases to immunotherapy
The invention relates to, among others, a method for assessing a prognosis of a patient with a malignant disease and / or for predicting the response of a patient with a malignant disease to immunotherapy. For this purpose, a DNA methylation analysis is carried out on at least one immunoregulatory gene of cells of the malignant disease and / or T lymphocytes which interact with the cells of the malignant disease, said gene coding for an immune checkpoint selected from B7 proteins and the receptors thereof, MHC-peptide complex-binding co-receptors, the members of the tumor necrosis factor receptorsuperfamily TNFRSF9, CD40, TNFRSF4, TNFRSF18, and CD27, the members of the immunoglobulin superfamily TIGIT, BTLA, HAVCR2, BTNL2, and CD48, and the andenosine-binding adenosine 2A receptor.
Owner:迪莫迪特里希
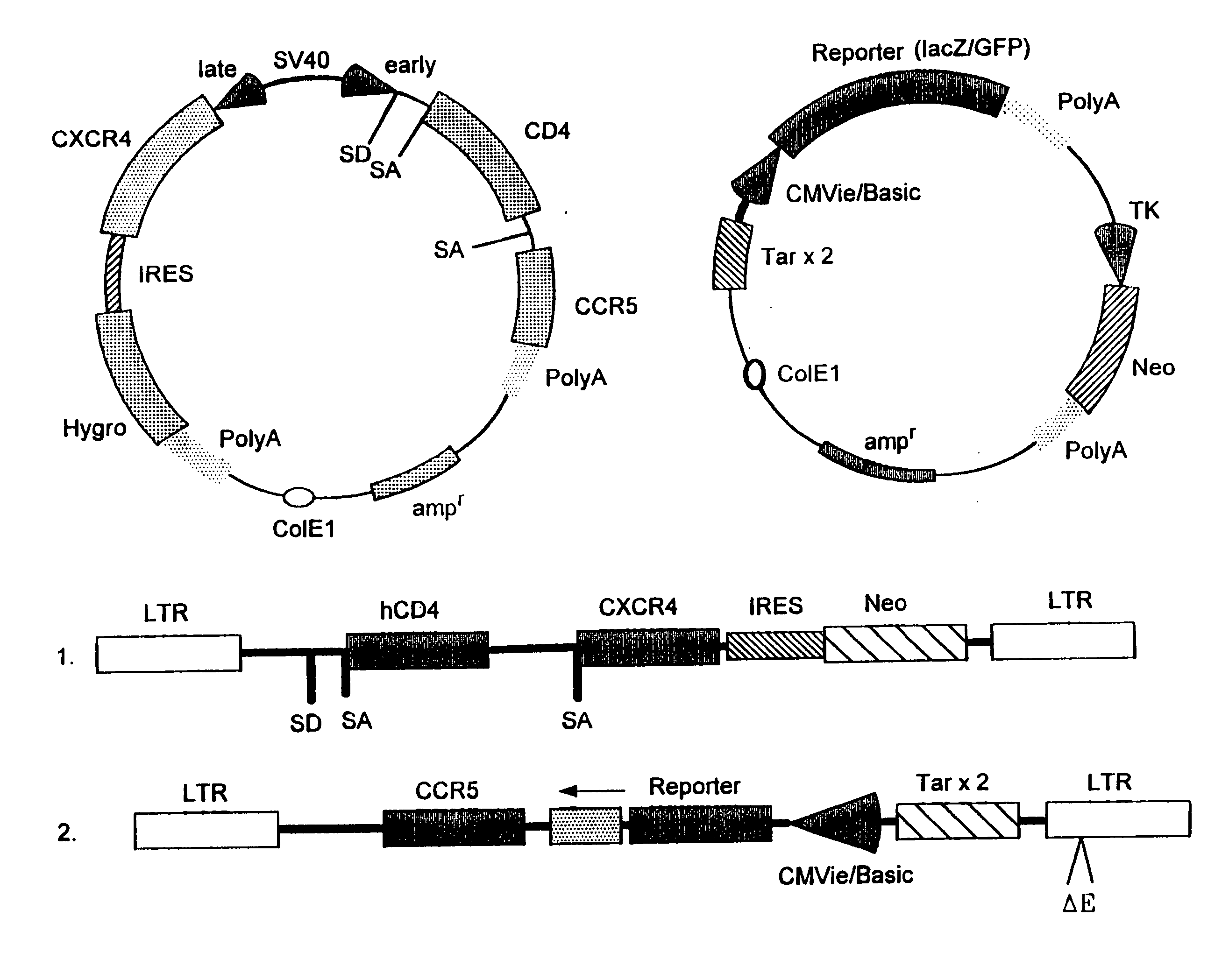
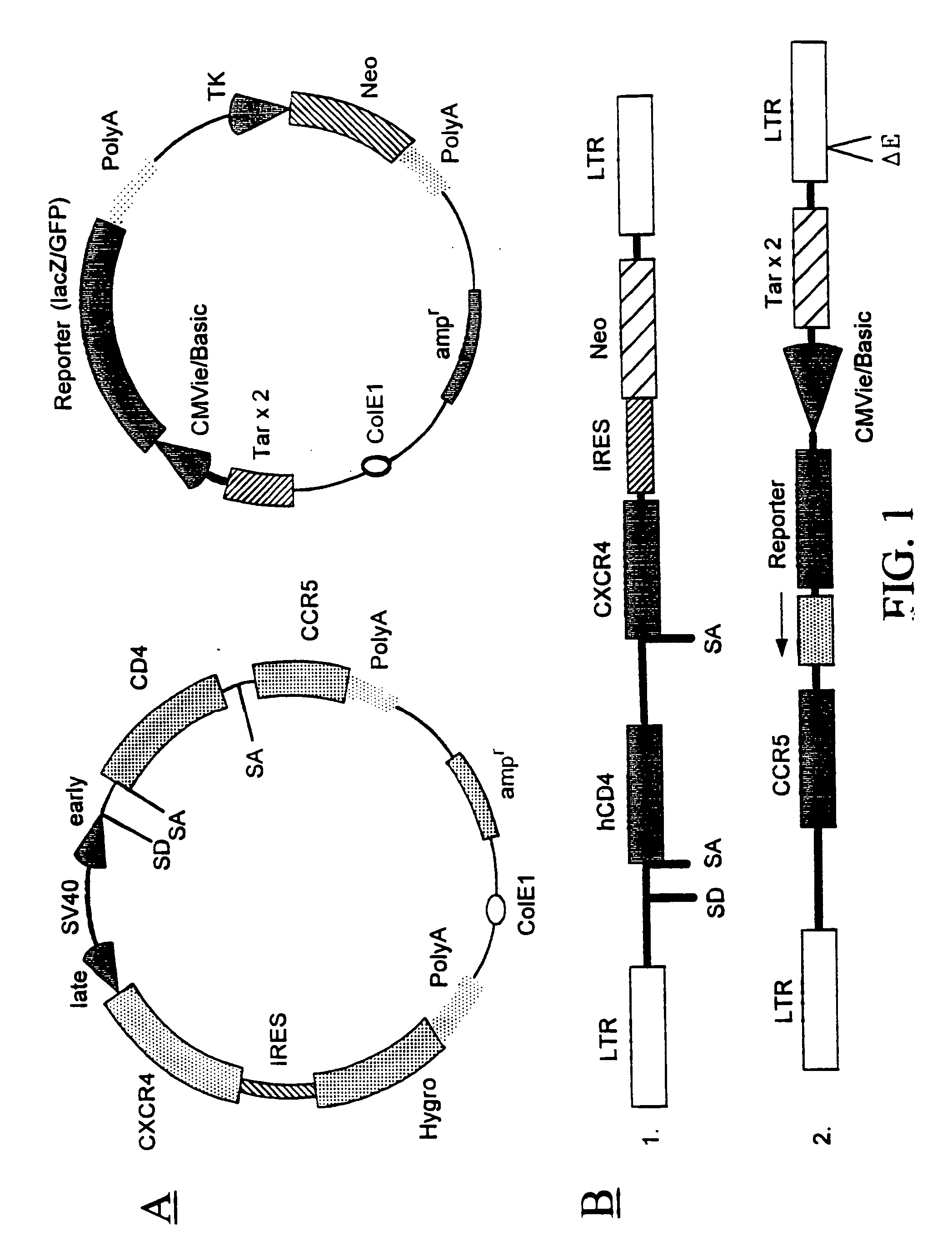
Methods of monitoring HIV drug resistance using adenoviral vectors
InactiveUS20020168345A1Easy to produceEasy maintenanceVirusesDiagnosticsInfected cellProtein regulation
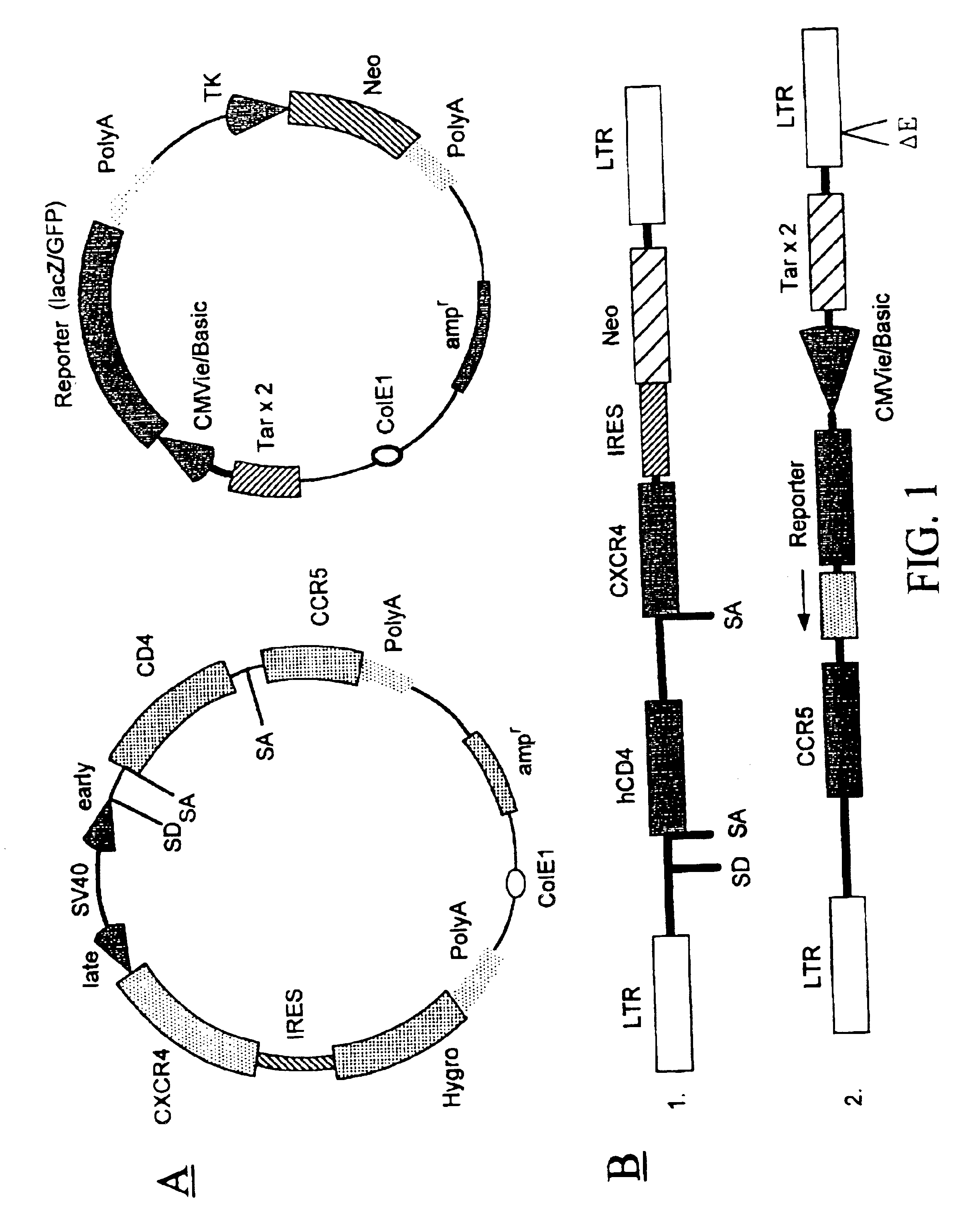
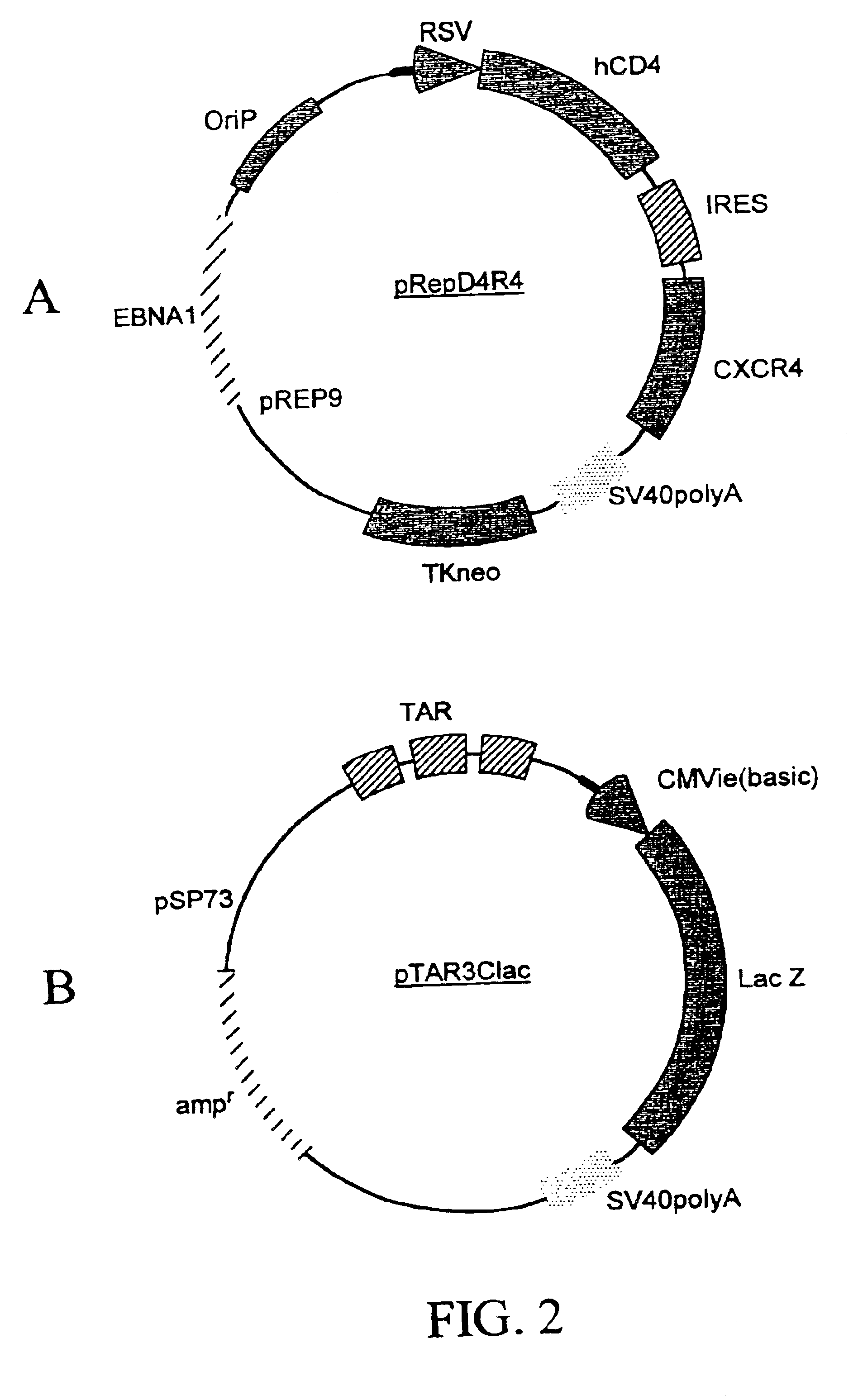
Recombinant expression vectors and methods are provided for detecting HIV and monitoring HIV drug resistance. The method comprises: taking a culture of cells; adding a recombinant viral vector into the culture to transduce the cells, the recombinant viral vector comprising a reporter sequence comprising a reporter gene whose expression is regulated by a protein specific to HIV viruses which is expressed from a genome of an HIV virus upon infection of a cell in the culture that is transduced by the recombinant viral vector, and a receptor sequence comprising CD 4 and one or more coreceptor genes, expression of the coreceptor genes facilitating productive infection of the transduced cell and enabling HIV virus which has infected the transduced cell to replicate and infect non-infected cells in the culture of the cells transduced by the recombinant viral vector; infecting the transduced cells with a sample containing HIV; adding one or more anti-HIV agents to the cell culture; and detecting a change in a level of expression of the reporter gene in cells.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Simultaneous Delivery of Receptors and/or Co-Receptors for Growth Factor Stability and Activity
InactiveUS20090220588A1Reduce capacityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsFactor iiCo delivery
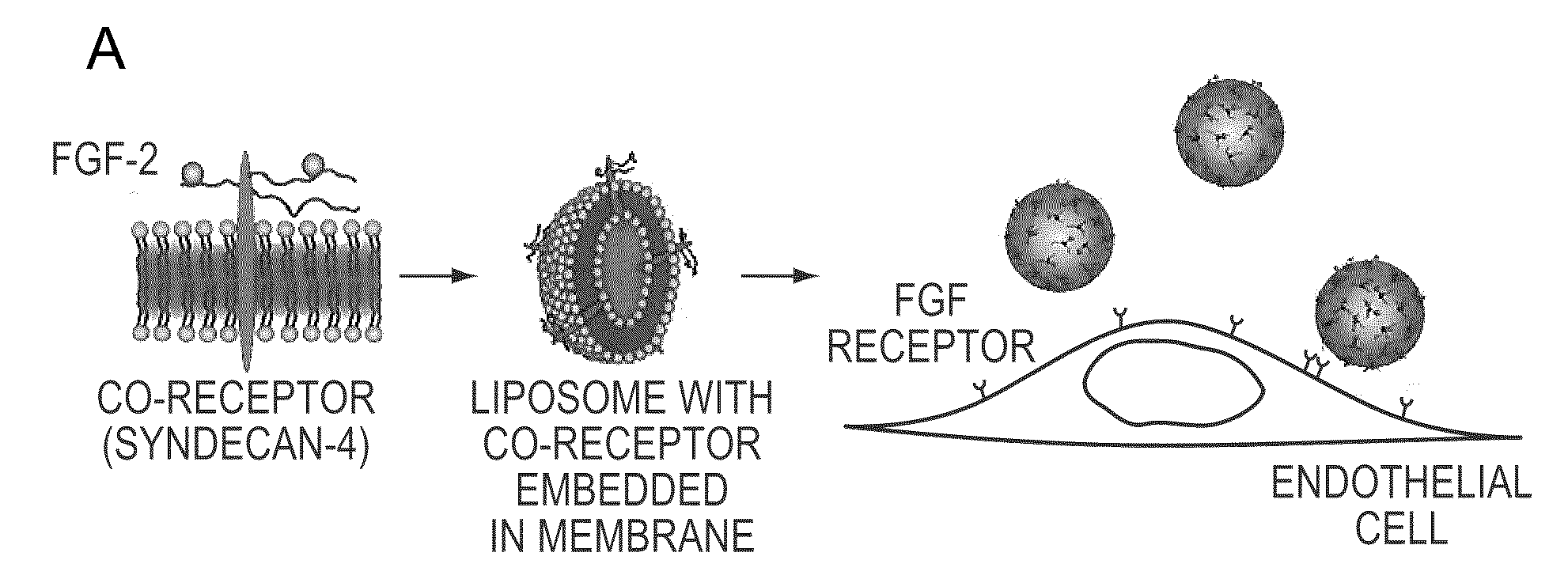
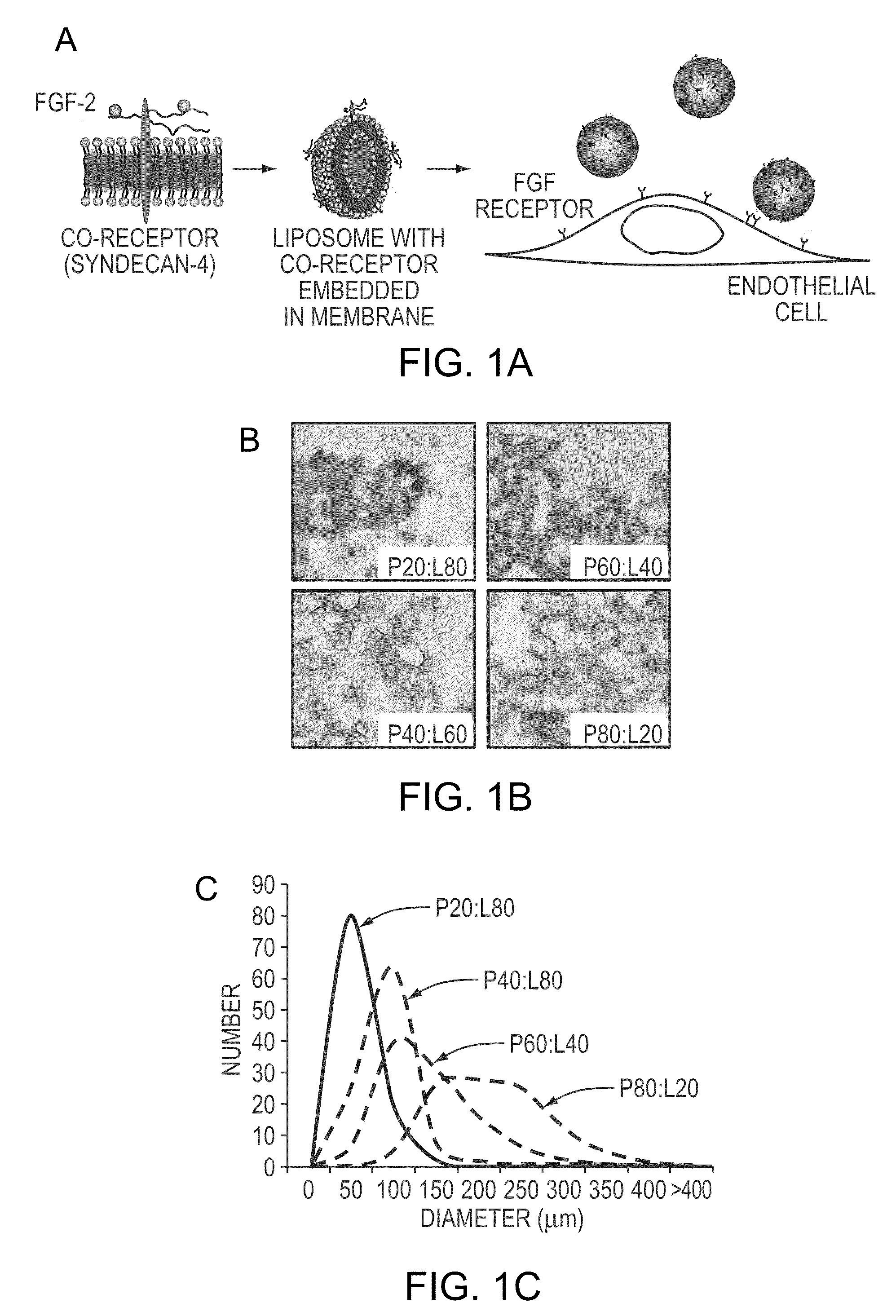
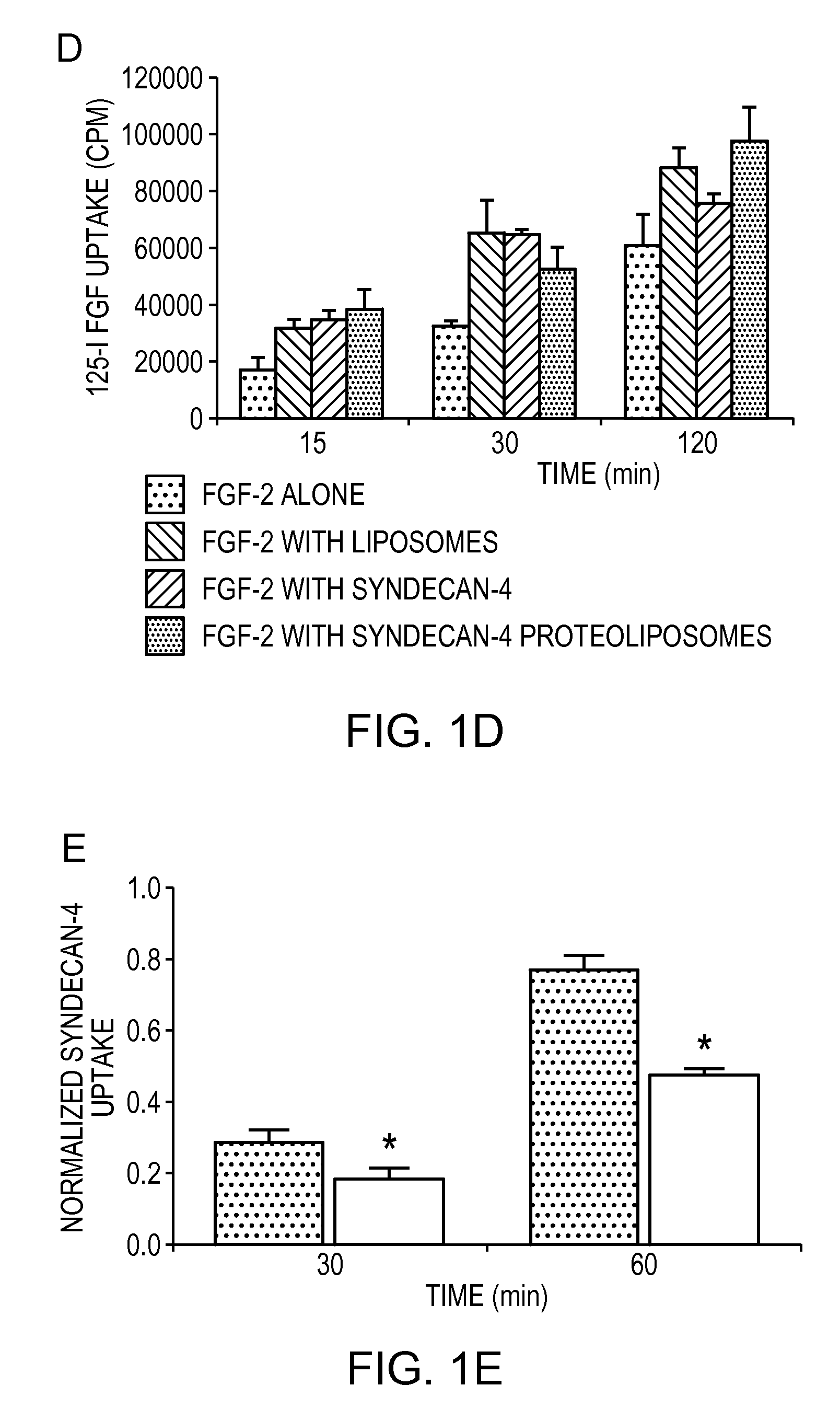
The compositions and methods of the present invention relate to the co-delivery of a molecule and a polypeptide to cells to improve the therapeutic efficacy of the molecules. In one embodiment of the invention, the invention may improve delivery of growth factors by co-delivering these growth factors with their receptors and co-receptors, such as syndecans. Co-delivery of growth factors with syndecans, for example, may protect growth factors from proteolysis, enhance their activity, and target the growth factors to the cell surface to facilitate growth factor signaling. This novel approach to growth factor therapy could be extended to other systems and growth factors enabling the enhancement of multiple signaling pathways to achieve a desired therapeutic outcome.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
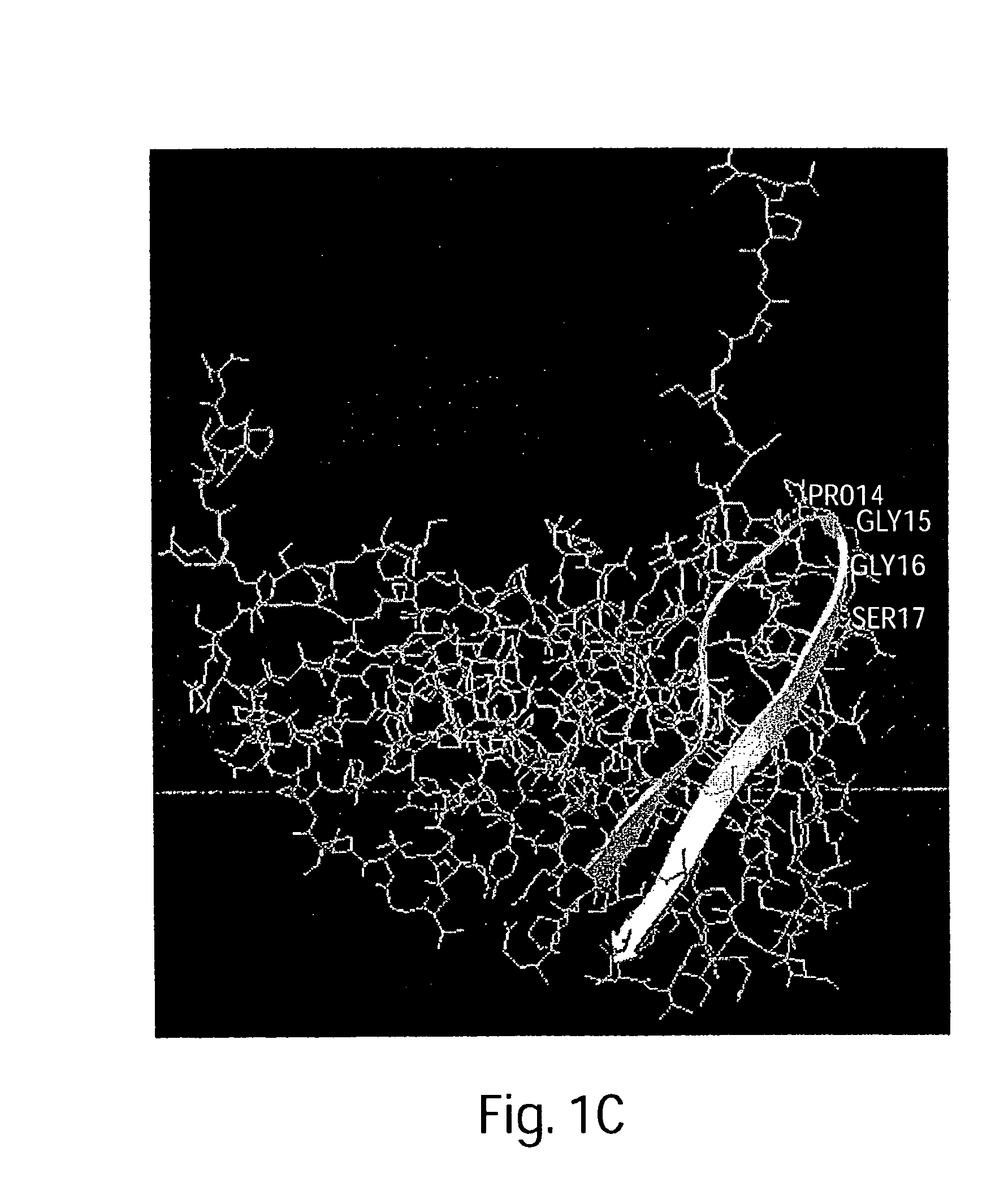
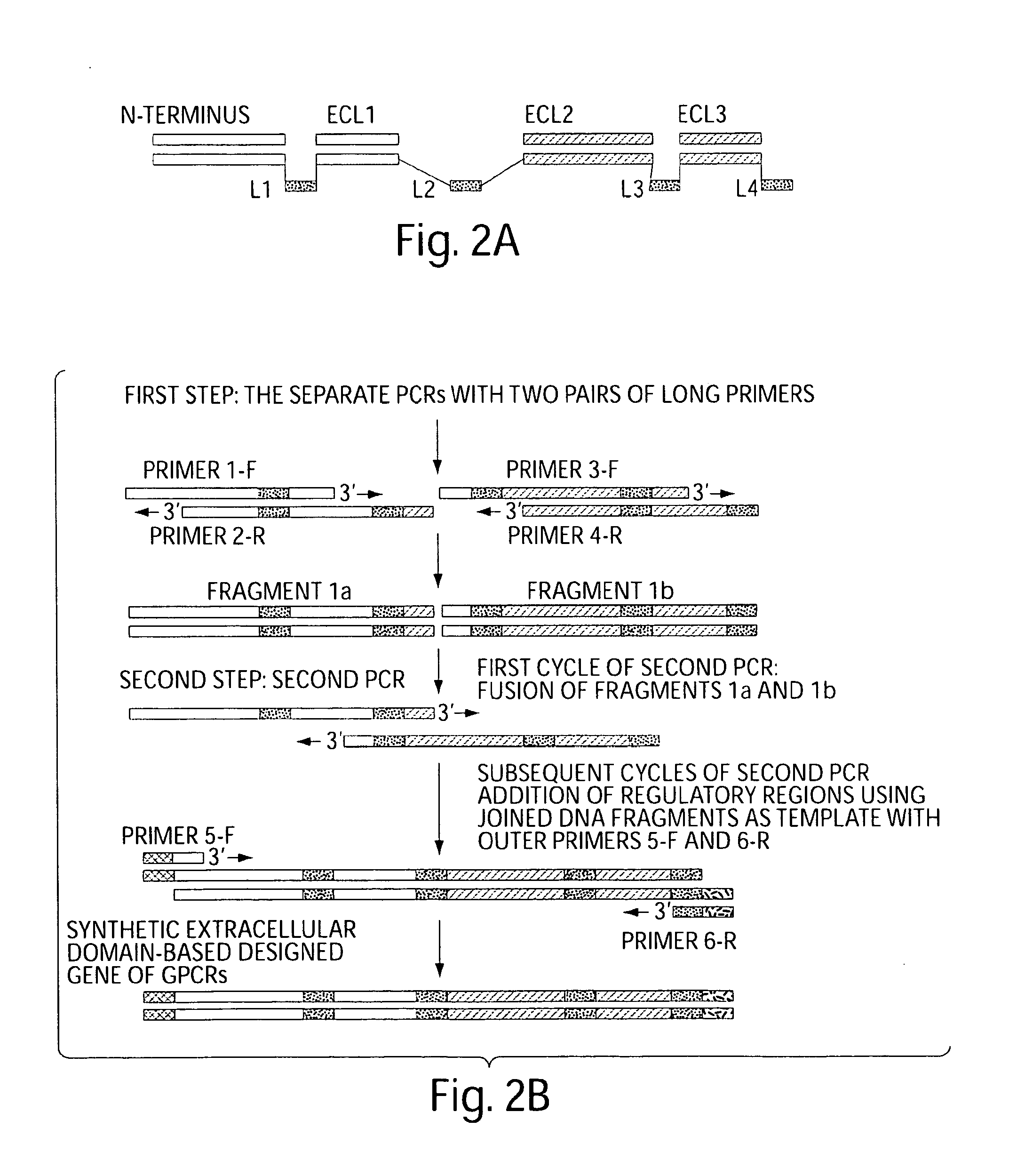
Strategy for cloning and expressing the extracellular domains of receptors as soluble proteins
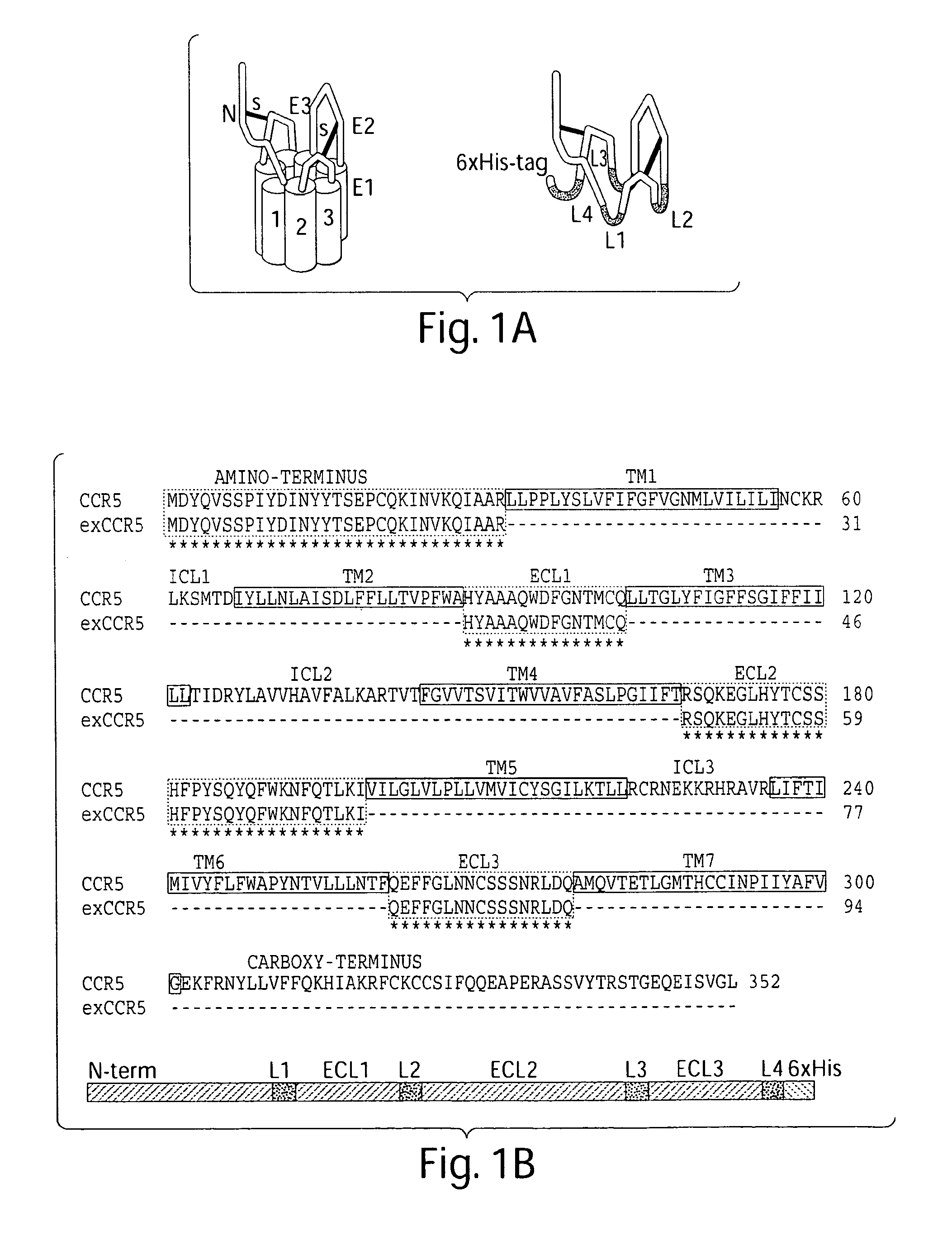
The present invention relates generally to soluble G protein-coupled receptor constructs. More specifically, the invention relates to soluble chemokine receptors, and soluble HIV co-receptors in particular. The invention is generally useful for designing and constructing soluble GPCR, which may be used to identify binding molecules. The invention also relates to methods of treating and / or preventing a disease or disorder associated with impaired function of such a receptor. The invention thus provides compositions and methods for therapeutic applications, such as vaccine.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Method for testing drug susceptibility of HIV
InactiveUS20040106136A1Convenient and cost-effective and ultra sensitiveImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHIV receptor
Methods, compositions and kits are provided for testing susceptibility of HIV to drug treatment, such as drug resistance of HIV and inhibition of HIV replication by a drug candidate. In one aspect of the invention, a method is provided for detecting drug resistance of HIV contained in a sample from an individual infected with HIV. In one embodiment, the method employs an indicator cell line which over-expresses CD4 and one or more co-receptors for HIV such as CXCR4 and CCR5 at high levels to render the cells susceptible to productive infection of various strains, subtypes or clades of HIV from both laboratory and clinical isolates. The methods, compositions and kits can be used for high throughput screening of HIV patient samples, anti-HIV agents, and for designing customized HIV therapy.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
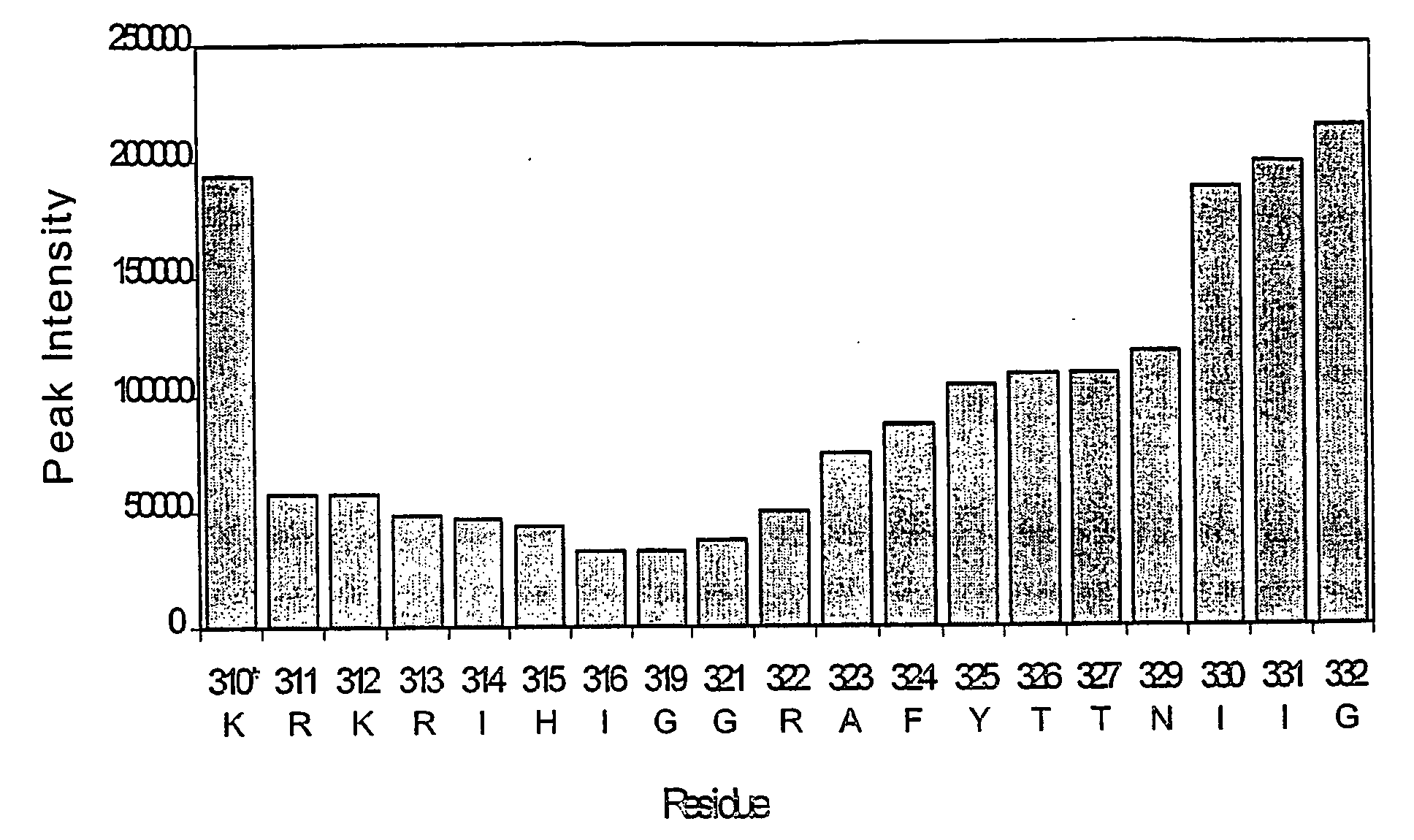
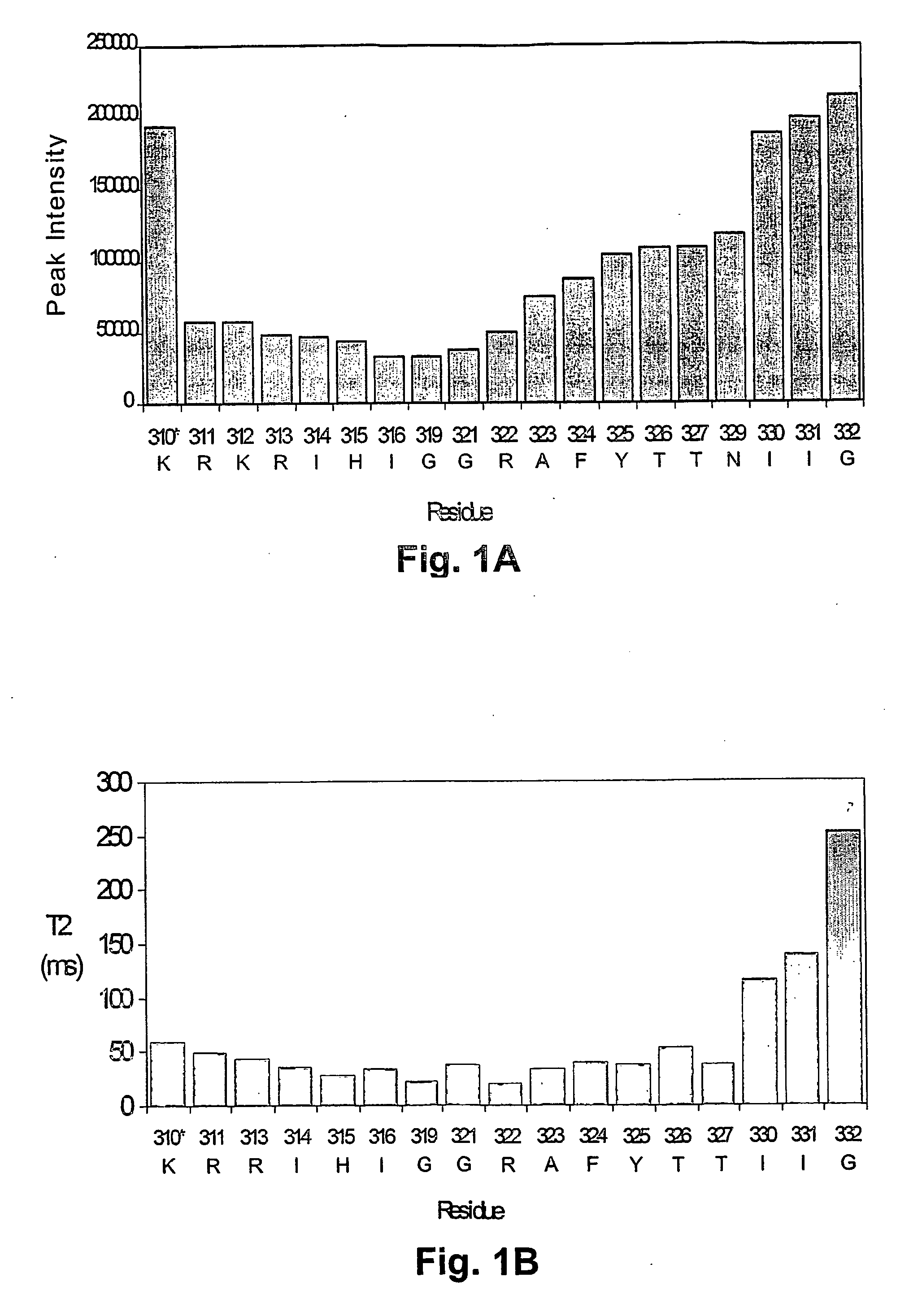
Hcv coreceptor and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20090098123A1Prevents and mitigates interactionReduce retentionPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCo-receptorProtein function
The invention relates to the discovery that the Claudin-1 protein functions as a co-receptor for entry of HCV into cells. Methods of inhibiting, preventing or mitigating HCV infections by inhibiting HCV interactions with Claudin-1 are provided. Methods of identifying agents or compounds that interfere with HCV interactions with Claudin-1 are also provided. Finally, useful kits, cell culture compositions, agents, and compounds related to the inhibition of HCV interactions with Claudin-1 are also disclosed.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
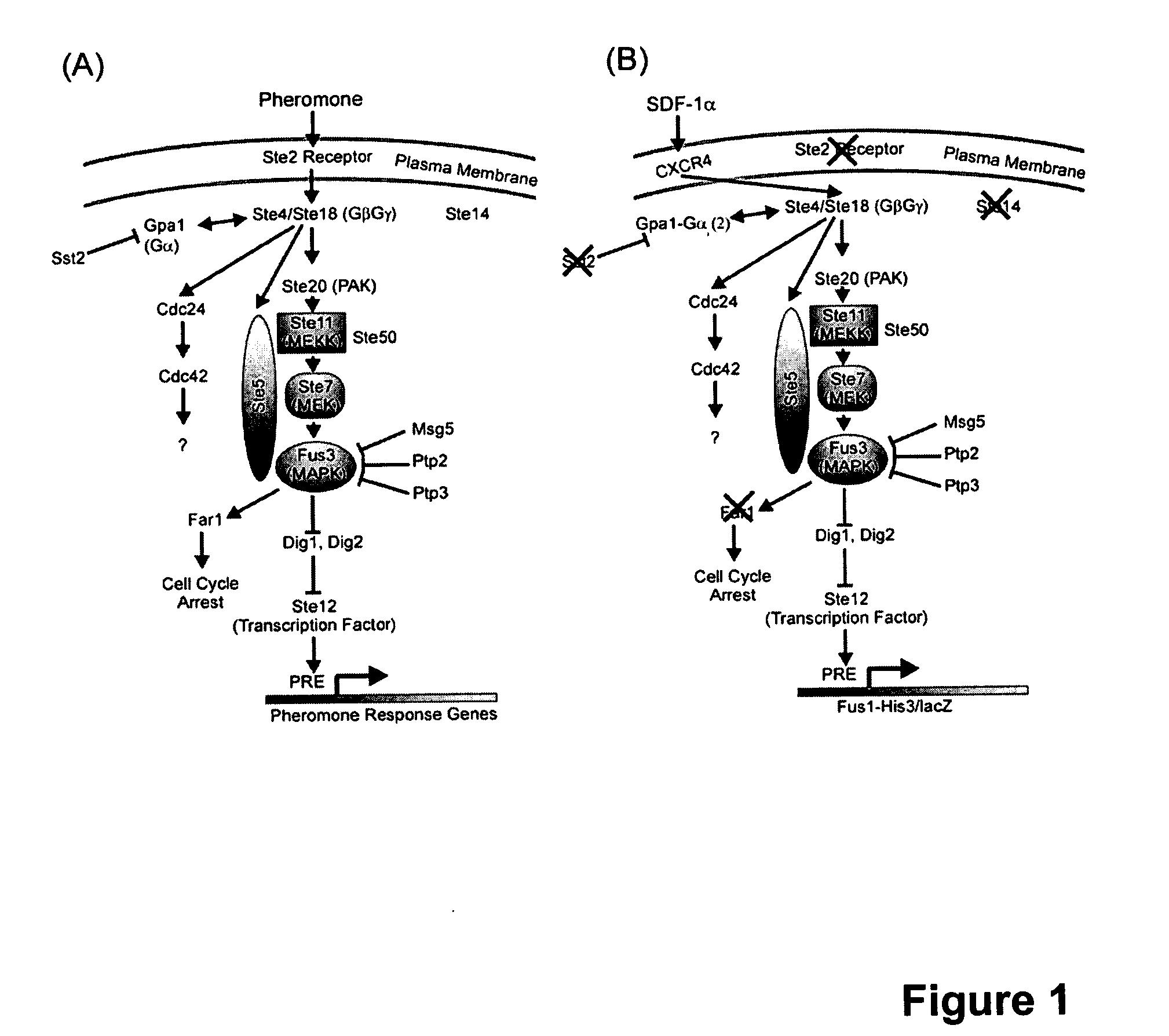
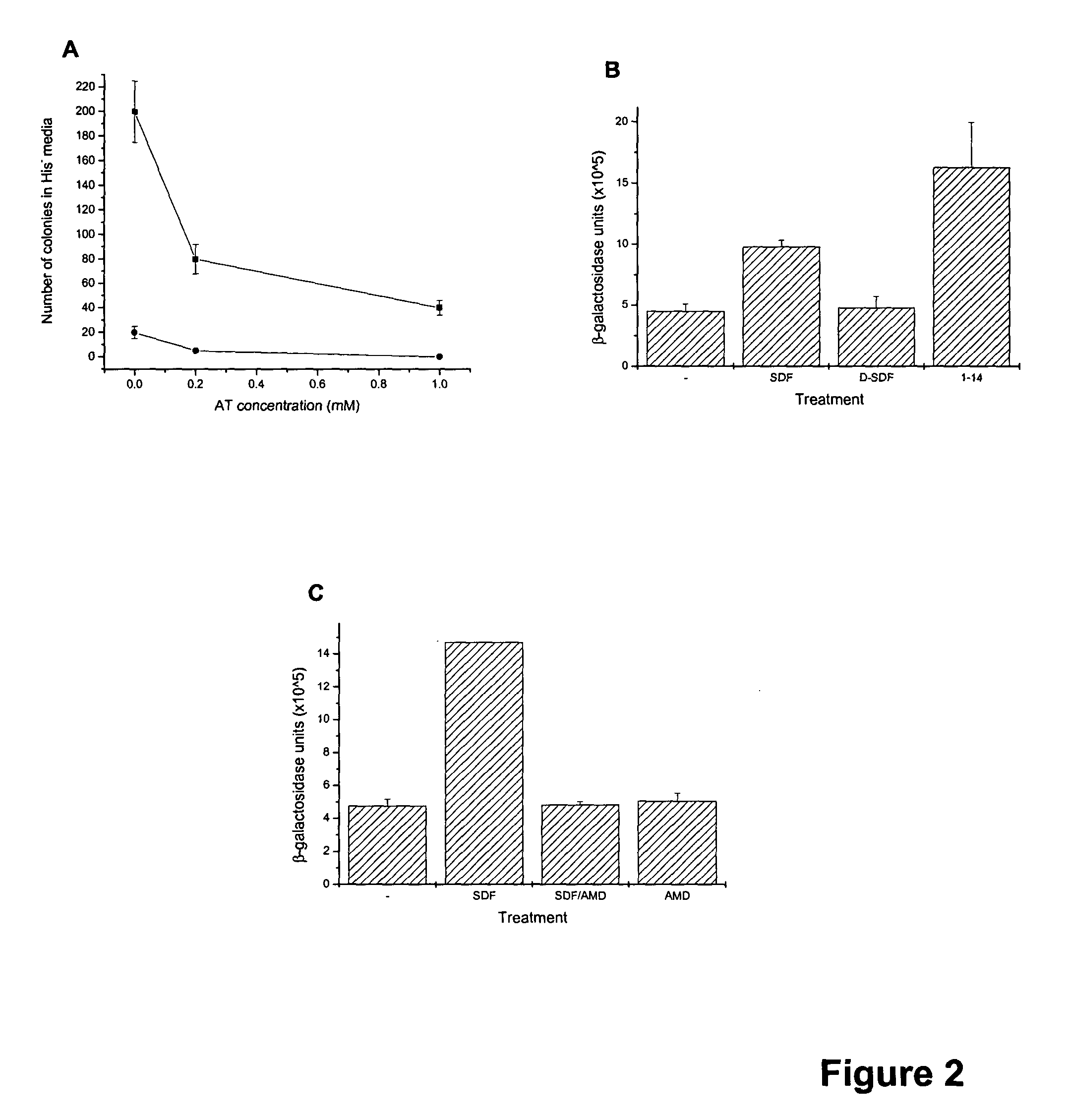
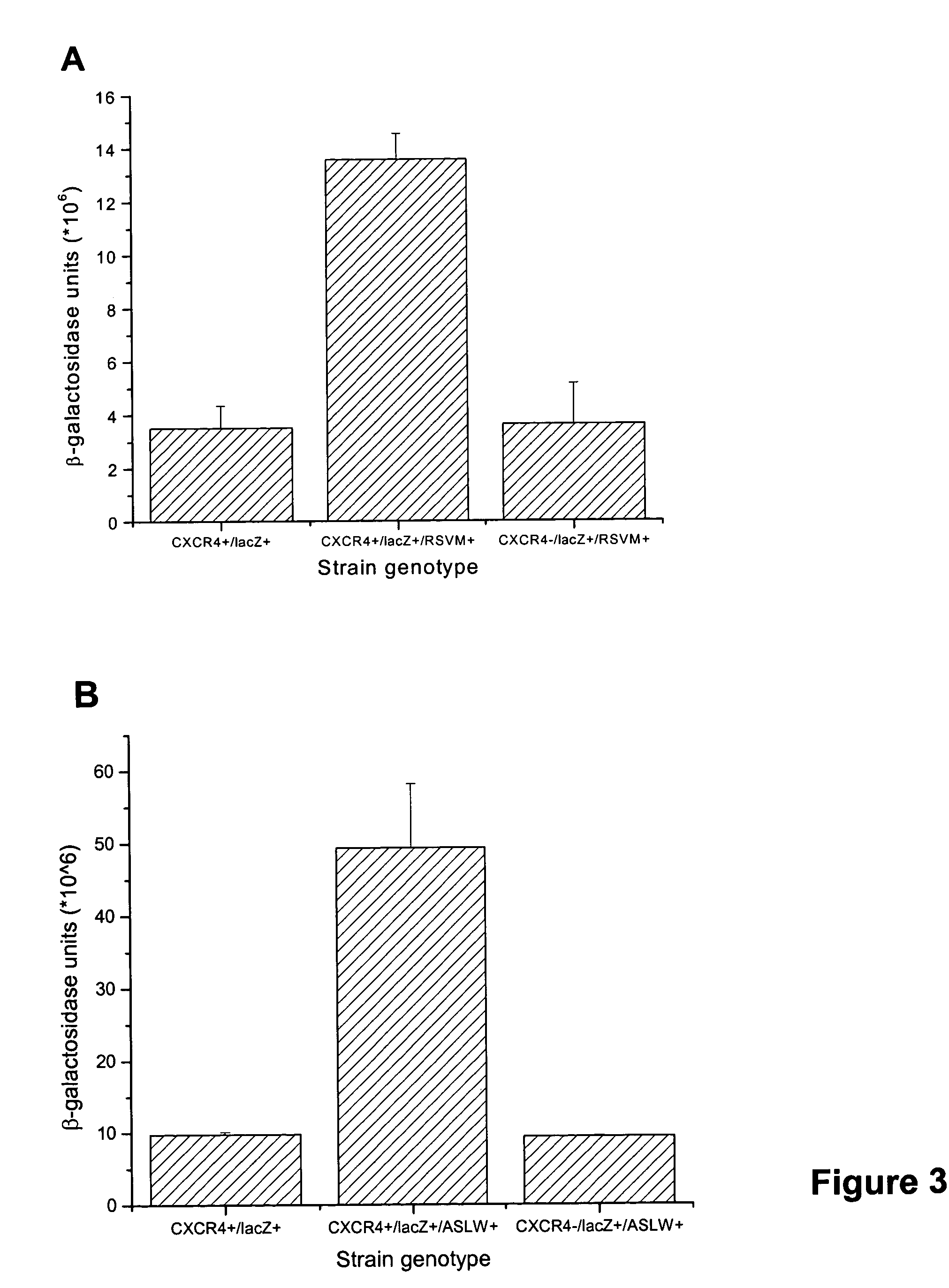
Identification of allosteric peptide agonists of CXCR4
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a co-receptor for T-tropic strains of HIV-1. A number of small molecule antagonists of CXCR4 are in development, but all are likely to lead to adverse effects due to the physiological function of CXCR4. To prevent these complications, allosteric agonists may be therapeutically useful as adjuvant therapy in combination with small molecule antagonists. A synthetic cDNA library coding for 160,000 different SDF-based peptides was screened for CXCR4 agonist activity in a yeast strain expressing functional receptor. Peptides that activated CXCR4 in an autocrine manner induced colony formation. Two peptides, designated RSVM and ASLW, were identified as novel agonists that are insensitive to the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100. In chemotaxis assays using the acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line CCRF-CEM, RSVM behaves as a partial agonist and ASLW as a superagonist. The superagonist activity of ASLW may be related to its inability to induce receptor internalization. In CCRF-CEM cells, the two peptides are also not inhibited by another CXCR4 antagonist, T140, or the neutralizing monoclonal antibodies 12G5 and 44717.111. These results suggest that alternative agonist binding sites are present on CXCR4 that could be screened to develop molecules for therapeutic use.
Owner:LOLIS ELIAS +3
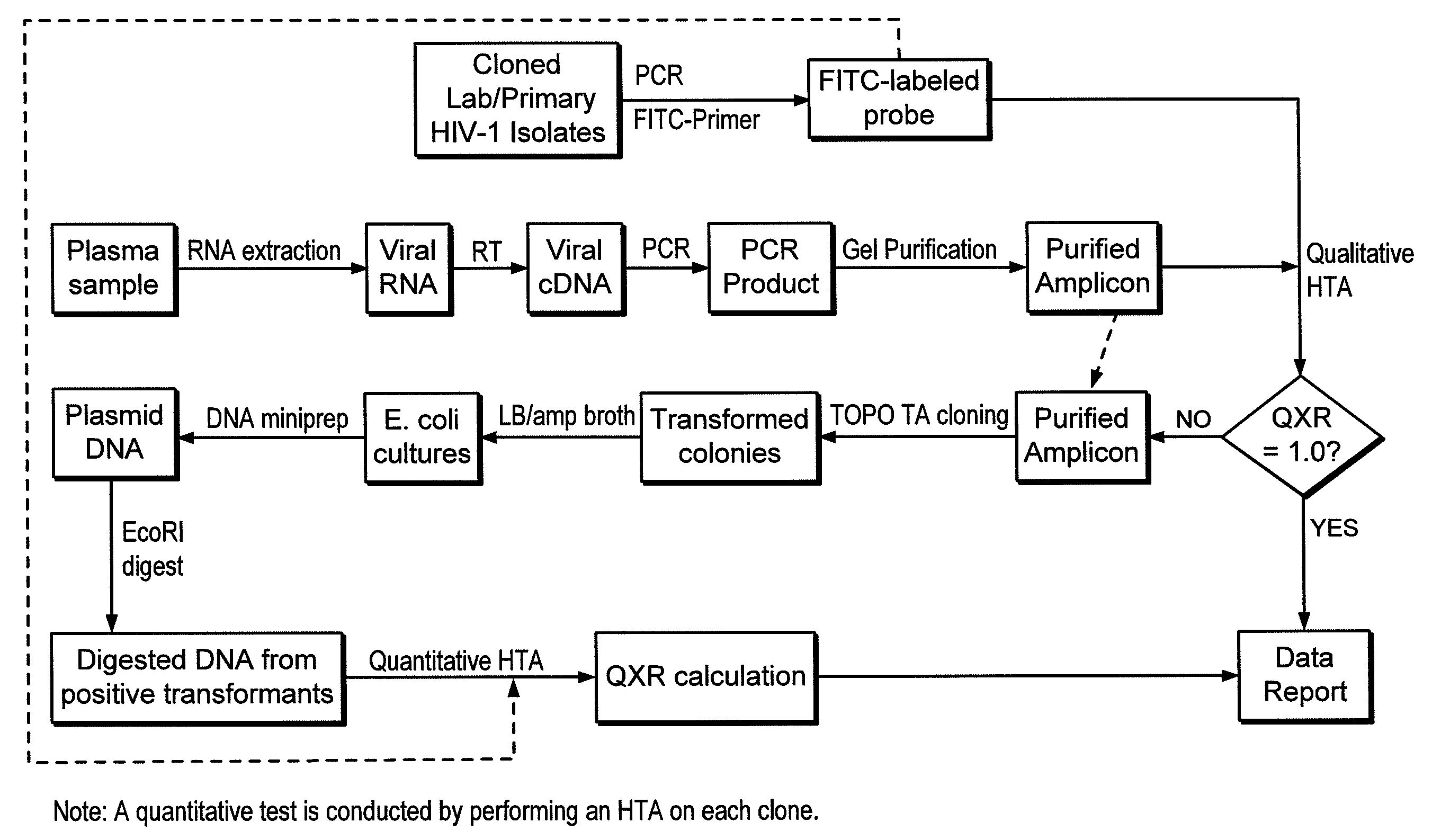
Heteroduplex tracking assay
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Methods of using pHHLA2 to co-stimulate T-cells
InactiveUS20070053903A1Improve transcription efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsT cellCo-receptor
The invention provides pHHLA2 co-receptor polypeptides and functional fragments, antibodies to same, isolated polynucleotides encoding same, vectors containing the polynucleotides, cells containing the vectors. Methods of making and using these co-stimulatory pHHLA2 co-receptors molecules are also disclosed.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Constrained Hiv V3 Loop Peptides as Novel Immunogens and Receptor Antagonists
InactiveUS20080206264A1Potent and broad activitySuppress infectivityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCyclic peptideDisease
The present invention provides constrained peptides and other organic molecules, that mimic the three dimensional characteristics of the HIV-1 V3 loop peptide when bound by a highly potent human neutralizing monoclonal antibody specific for a V3 conformational epitope, which structure is determined by NMR. Methods for screening for, and designing such molecules are disclosed. These molecules are useful as immunogens for inducing broadly-neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1 as well as antagonists for inhibiting the binding of HIV-1 to the relevant co-receptors, and may therefore be used in method of preventing or treating HIV-1 infection and disease.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Virus coat protein/receptor chimeras and methods of use
InactiveUS8183354B2Raise the potentialAvoid virus infectionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCXCR4Immunodeficiency virus
The invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising a virus coat sequence and a receptor sequence that can inter-act with each other to form a complex that is capable of binding a co-receptor. Such chimeric molecules therefore exhibit functional properties characteristic of a receptor-coat protein complex and are useful as agents that inhibit virus infection of cells due to occn-panty of co-receptor present on the cell, for example. In particular aspects, the chimeric polypeptide includes an immunodeficiency virus envelope polypeptide, such as that of HIV, SIV, FIV, FeLV, FPV and herpes virus. Receptor sequences suitable for use in a chimeric polypeptide include, for example, CCR5 and CXCR4 sequences.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
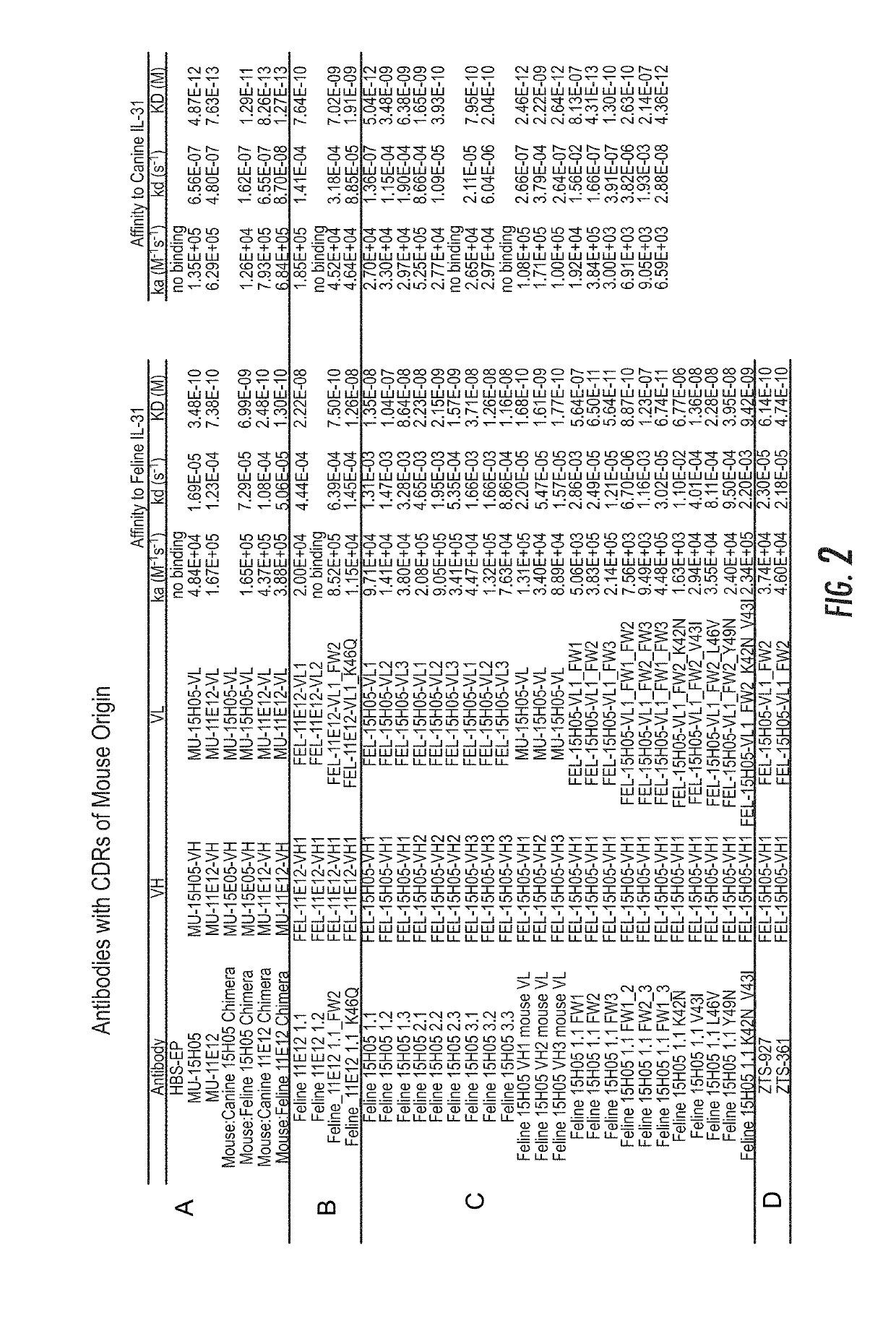
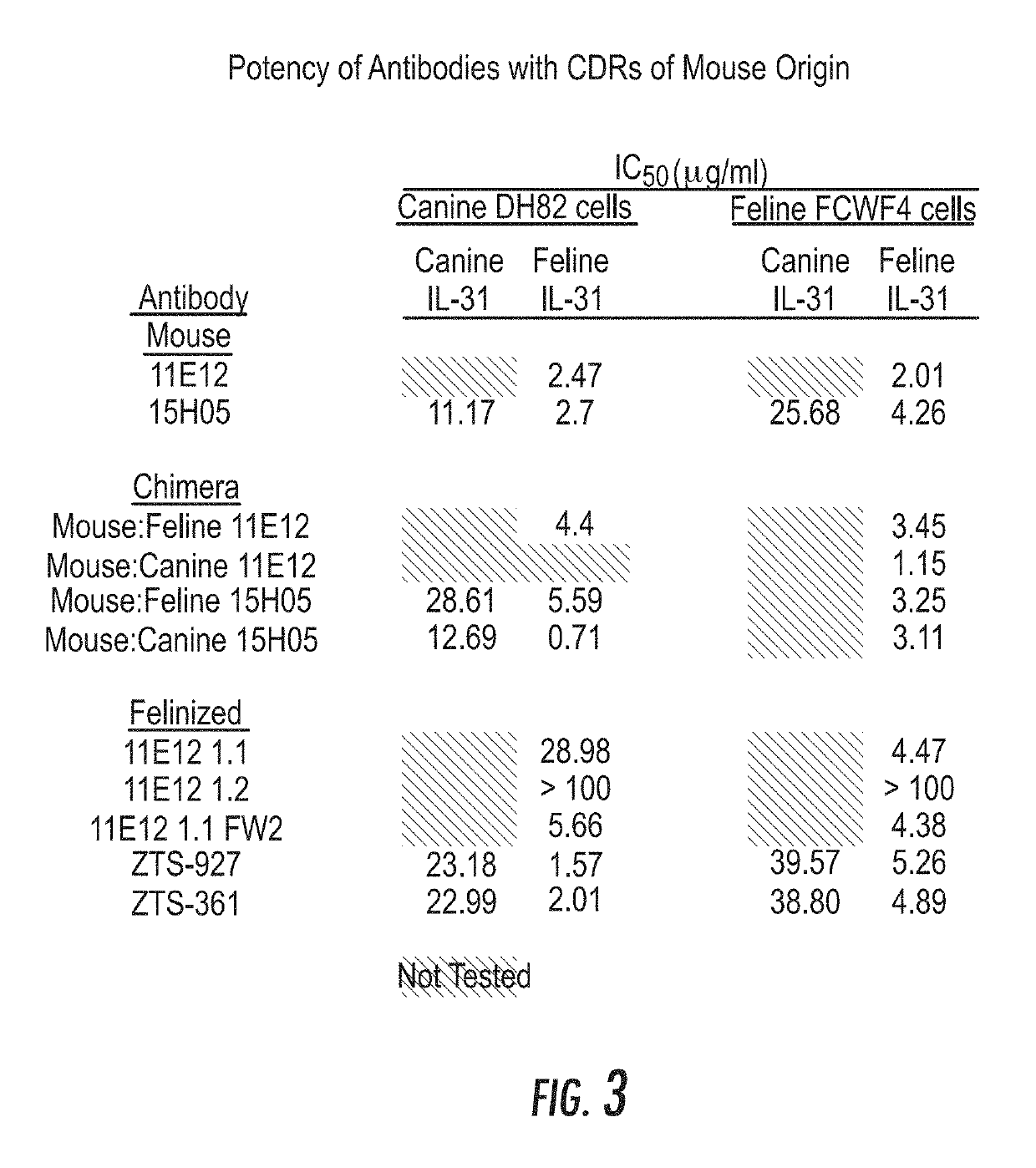
Interleukin-31 monoclonal antibodies for veterinary use
ActiveUS20190284272A1Improve consistencyQuality improvementBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsEpitopeInterleukin 31
A monoclonal antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof is provided that specifically binds to a region on a mammalian IL-31 protein involved with interaction of the IL-31 protein with its co-receptor, wherein the binding of said antibody to said region is impacted by mutations in a 15H05 epitope binding region selected from: a region between about amino acid residues 124 and 135 of a feline IL-31 sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 157 (Feline_IL31_wildtype); a region between about amino acid residues 124 and 135 of a canine IL-31 sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 155 (Canine_IL31); and a region between about amino acid residues 118 and 129 of an equine IL-31 sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 165 (Equine_IL31). Such antibodies can be in the form of veterinary compositions useful for treating IL-31-mediated disorders in cats, dogs, or horses.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Method for producing recombinant cells for detecting HIV
InactiveUS6967076B2Versatile and efficientVirusesGenetic material ingredientsInfected cellProtein regulation
Recombinant expression vectors and methods are provided for detecting HIV and monitoring HIV drug resistance. The method comprises: taking a culture of cells; adding a recombinant viral vector into the culture to transduce the cells, the recombinant viral vector comprising a reporter sequence comprising a reporter gene whose expression is regulated by a protein specific to HIV viruses which is expressed from a genome of an HIV virus upon infection of a cell in the culture that is transduced by the recombinant viral vector, and a receptor sequence comprising CD 4 and one or more coreceptor genes, expression of the coreceptor genes facilitating productive infection of the transduced cell and enabling HIV virus which has infected the transduced cell to replicate and infect non-infected cells in the culture of the cells transduced by the recombinant viral vector; infecting the transduced cells with a sample containing HIV; adding one or more anti-HIV agents to the cell culture; and detecting a change in a level of expression of the reporter gene in cells.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Peptide mimotopes of the cd3 t-cell co-receptor epsilon chain and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190070248A1Optimization of binding propertyGenerate and inhibit immune responseImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenBinding domain
The present invention provides molecules that mimic antigenic determinants of the CD3 (cluster of differentiation 3) T-cell co-receptor epsilon chain (CD3ε). These molecules compete with CD3ε for binding to a CD3ε binding domain. e.g. a CD3ε binding domain of an antibody, and are capable of detecting antibodies against CD3ε. The mimotopes of the invention may be used to generate or inhibit immune responses in animals and preferably humans. Additionally, they may serve as tools for anti-CD3ε antibody purification and the detection of anti-CD3ε antibodies in biological samples.
Owner:JPT PEPTIDE TECH +1
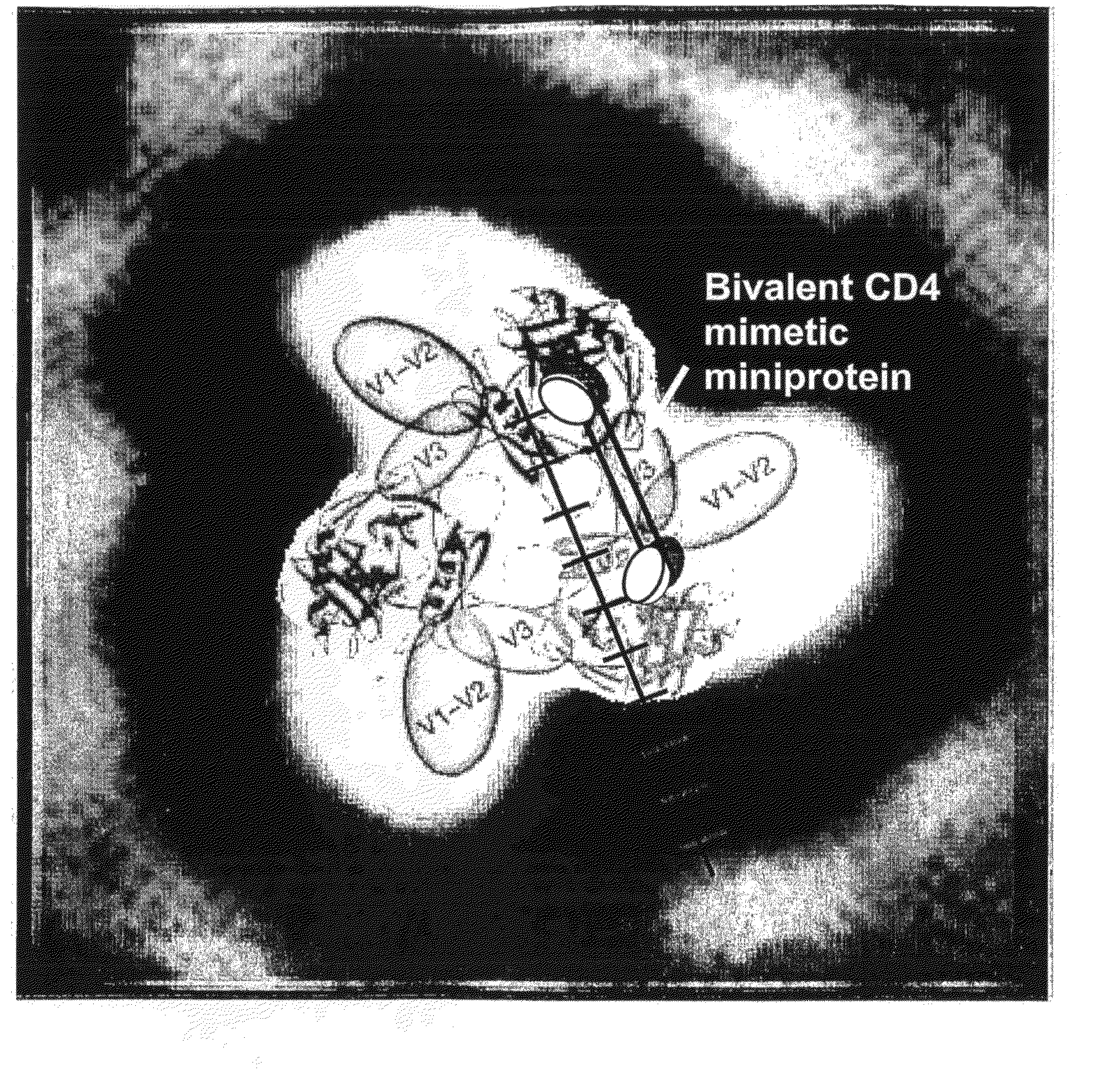
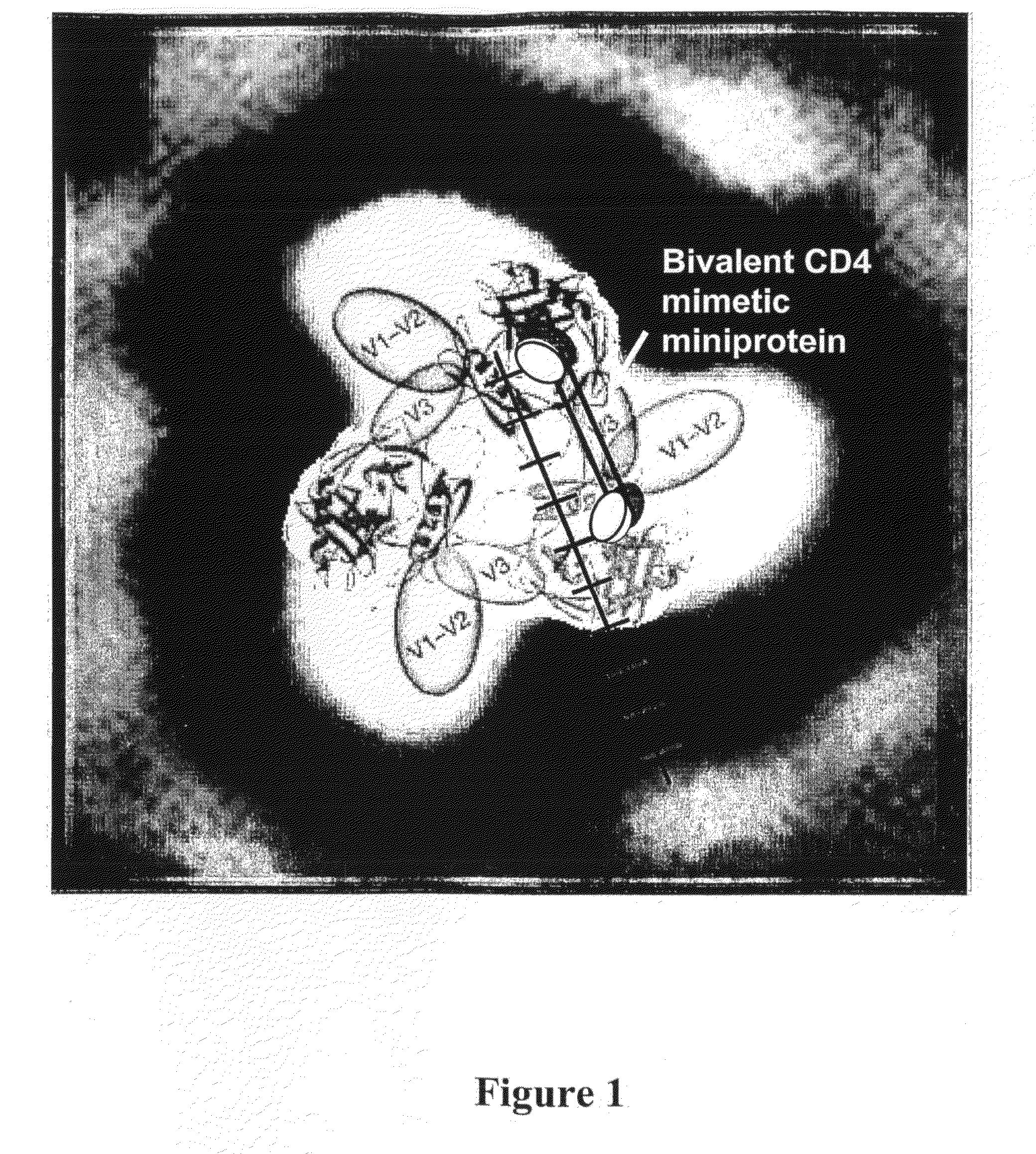
Constrained HIV envelope-based immunogen that simultaneously presents receptor and coreceptor binding sites
The present invention relates to a soluble binding complex comprising a soluble gp120 trimer, in which only two gp120 protomers have CD4 binding sites occupied by interconnecting CD4 mimetic moieties, thereby allowing for the exposure of CD4-induced epitopes on the mimetic-bound protomers and an unoccupied CD4 binding site on the third gp120 protomer.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
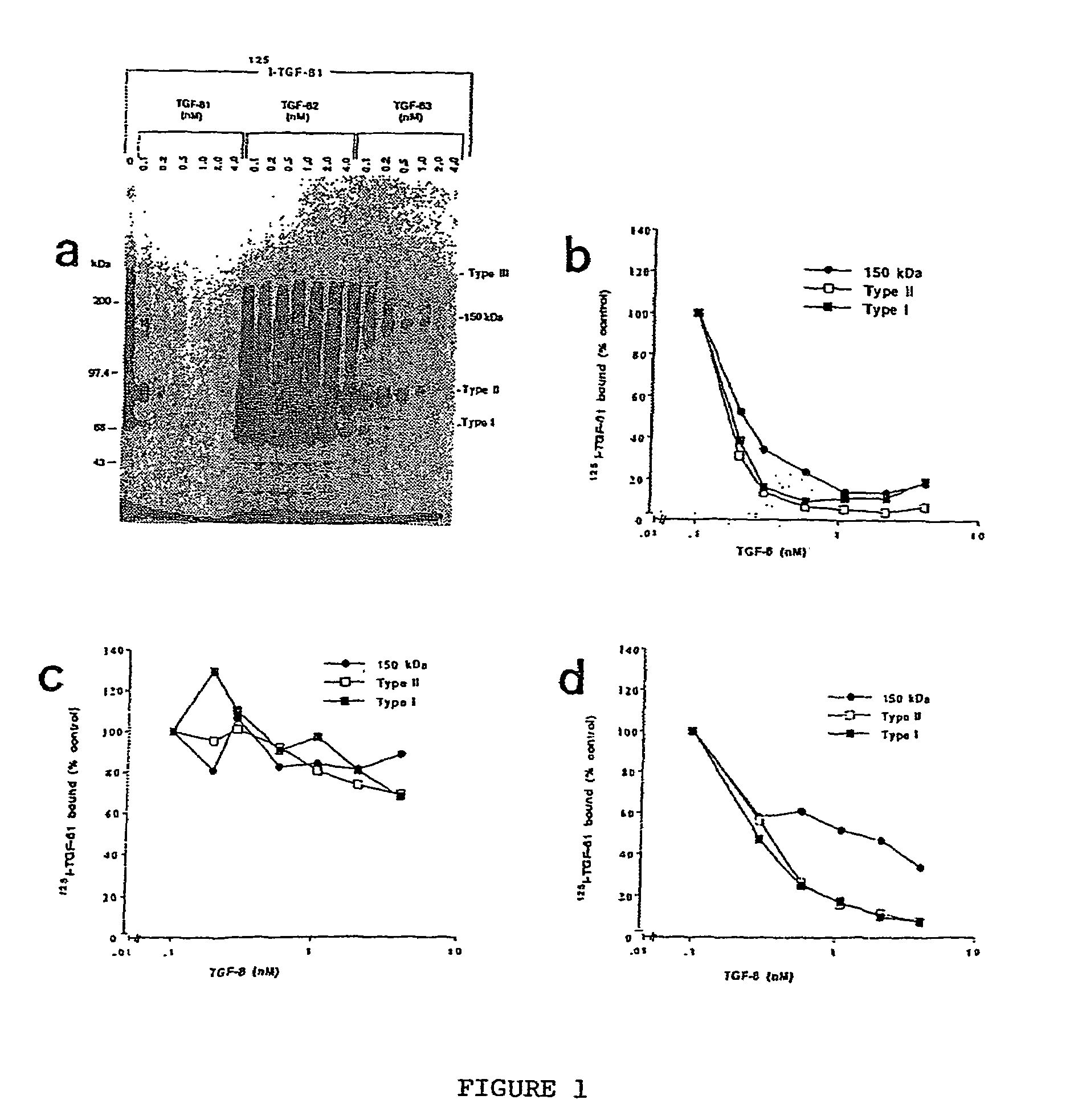
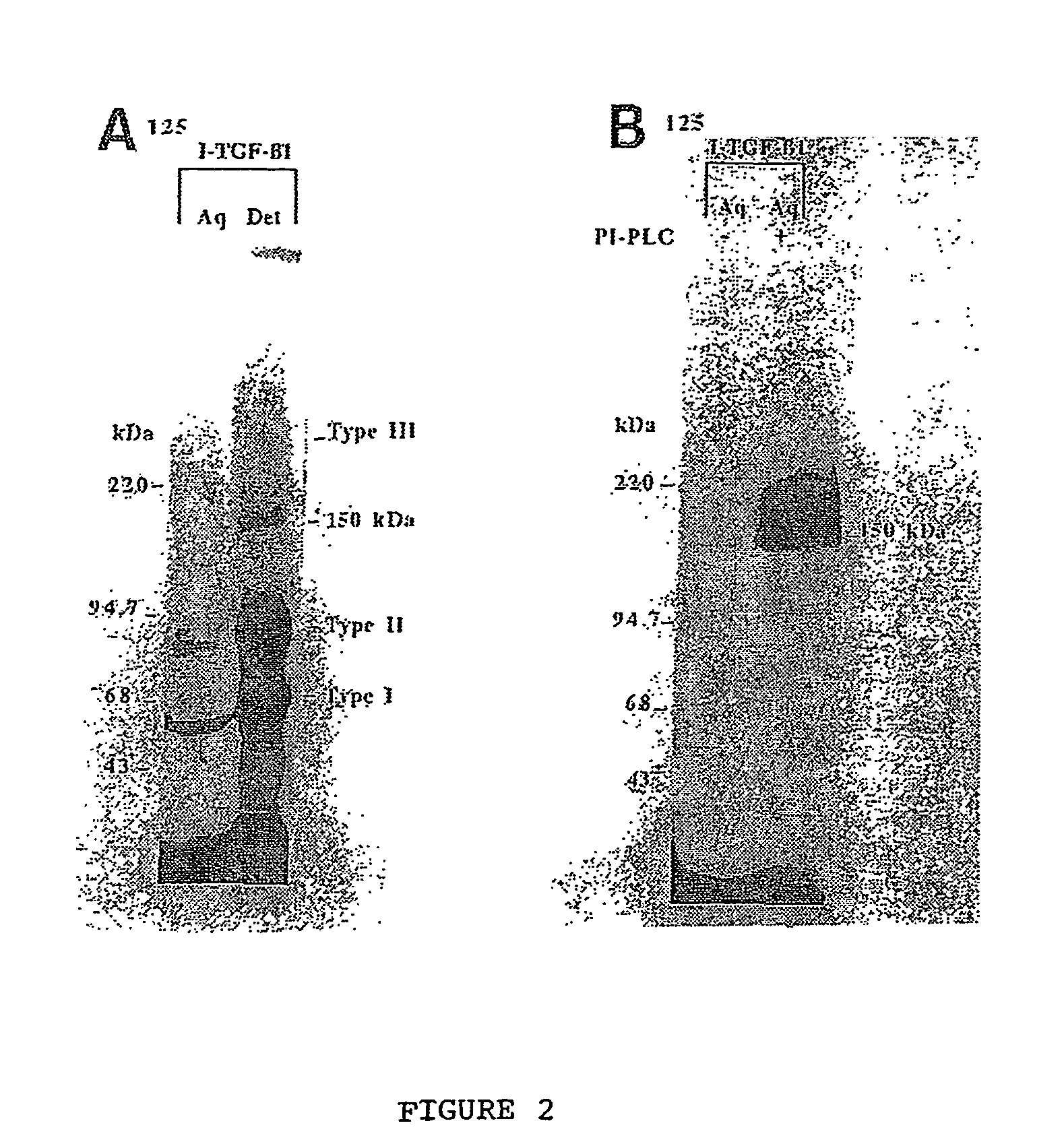
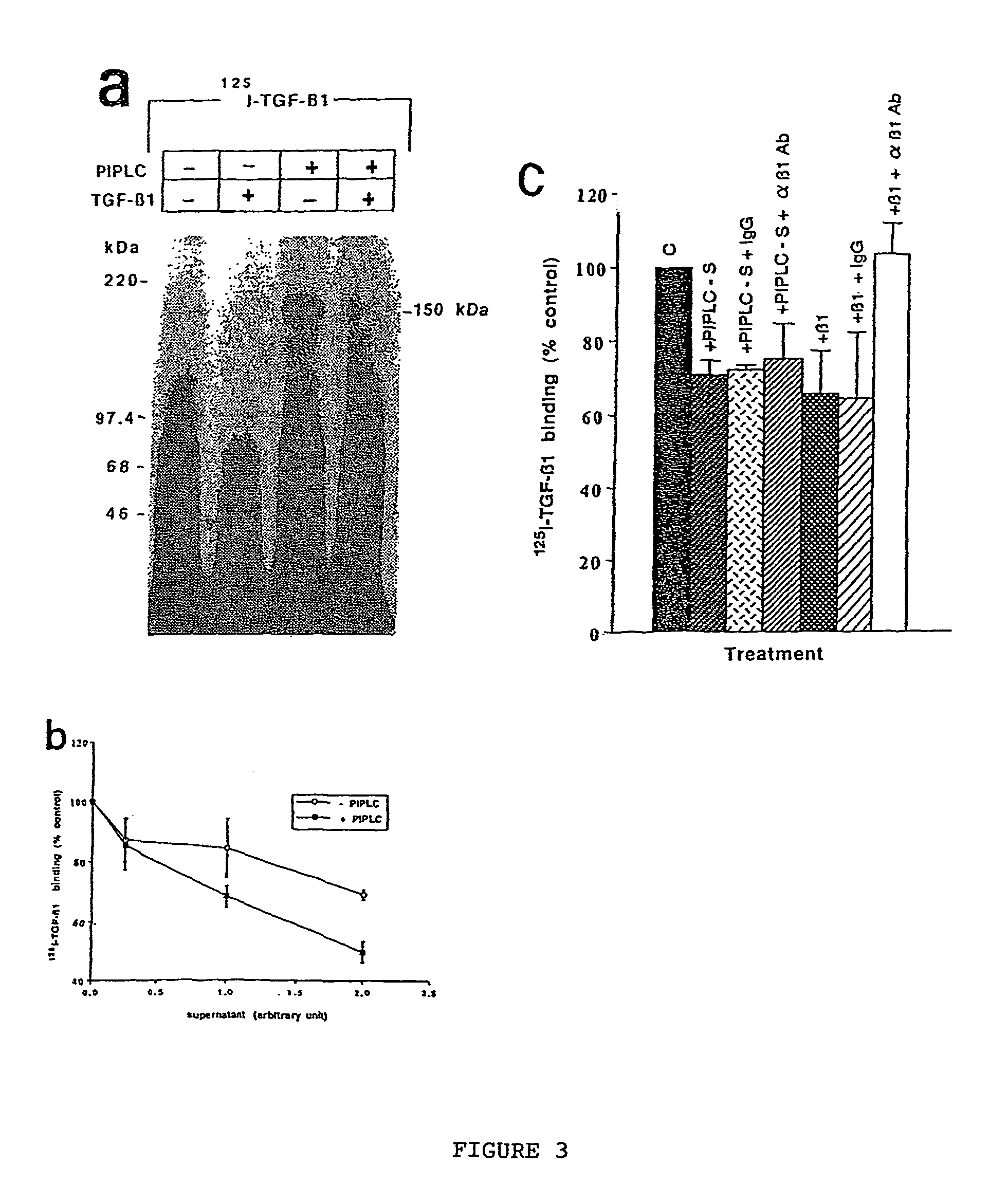
150 KDA TGF-B1 accessory receptor acts a negative modulator of TGF-B signaling
The present invention relates to a TGF-β1 binding protein called r150. This protein has a GPI-anchor contained in r150 itself and not on a tightly associated protein and that it binds TGF-β1 with an affinity comparable to those of the signaling receptors. Furthermore, the released (soluble) form of this protein binds TGF-β1 independent of the types I and II receptors. Also, the soluble form inhibits the binding of TGF-β to its receptor. In addition, evidence that r150 is released from the cell surface by an endogenous phospholipase C is provided. Also, the creation of a mutant human keratinocyte cell line with a defect in GPI synthesis which displays reduced expression of r150 is described. Our results using these mutant keratinocytes suggest that the membrane anchored form of r150 is a negative modulator of TGF-beta responses. These findings, taken together with the observation that r150 forms a heteromeric complex with the signaling receptors, suggest that this accessory receptor in either its membrane anchored or soluble form may antagonize TGF-β responses in human keratinocytes. Experiments with mutants confirmed that TGFβ1 activity can be modulated when the expression of the accessory receptor r150 is silenced. The complete nucleic acid and deduced amino acid sequences are now provided. The r150 cloned nucleic acid was used to study overexpression of r150. When r150 gene is overexpressed, TGFβ responses are increased. r150 and its derivatives or precursors (fragments, variants and nucleic acids encoding the same) will find a broad clinical utility, knowing that TGFβ1 is an important cytokine.
Owner:9406 2668 QUEBEC INC
Antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080274100A1Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCXCR4HIV receptor
The present invention provides antibodies or fragments thereof that bind to co-receptor CCR5 or CXCR4.
Owner:BEN LEVY RACHEL +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com