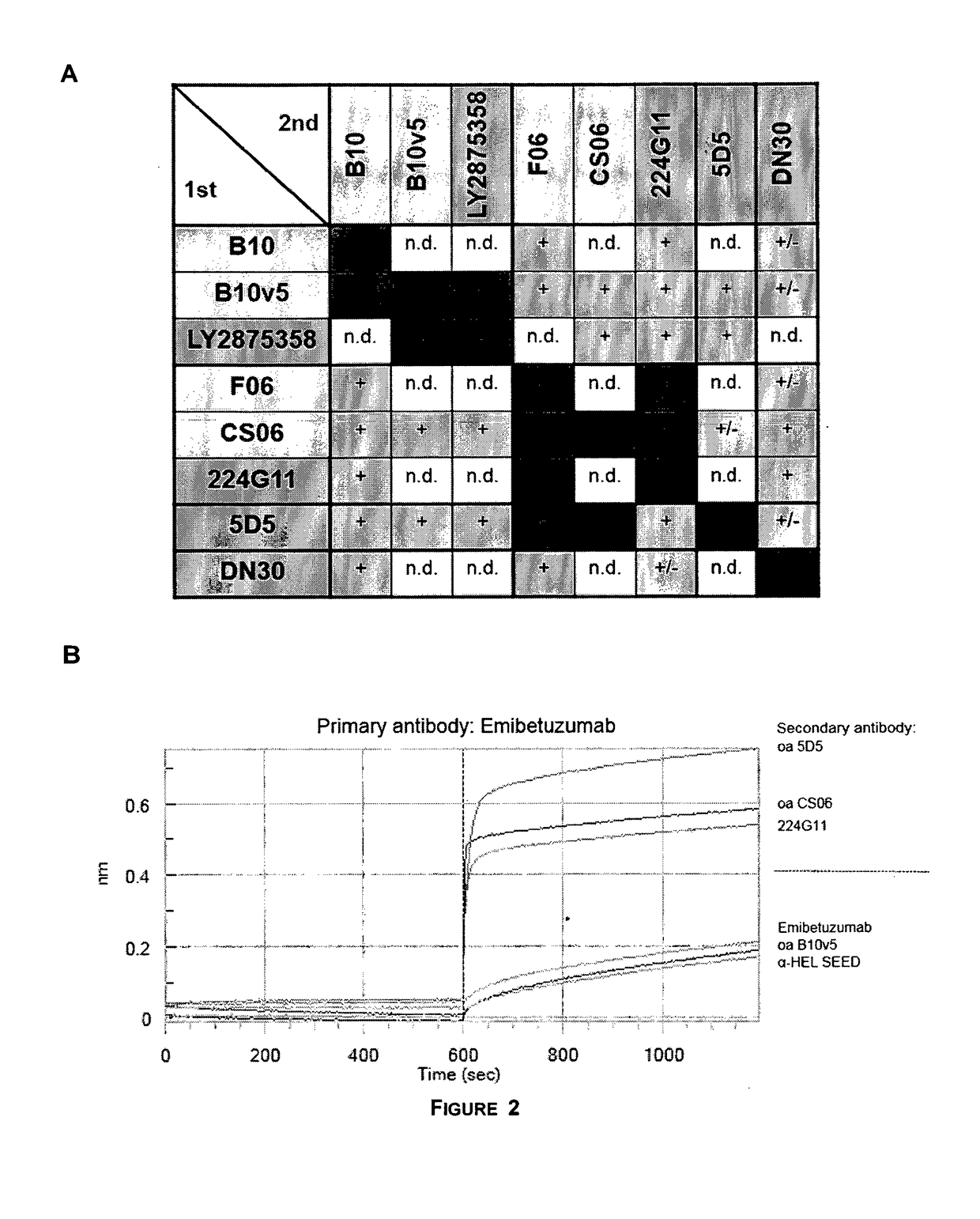
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Immunoglobulin superfamily" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) is a large protein superfamily of cell surface and soluble proteins that are involved in the recognition, binding, or adhesion processes of cells. Molecules are categorized as members of this superfamily based on shared structural features with immunoglobulins (also known as antibodies); they all possess a domain known as an immunoglobulin domain or fold. Members of the IgSF include cell surface antigen receptors, co-receptors and co-stimulatory molecules of the immune system, molecules involved in antigen presentation to lymphocytes, cell adhesion molecules, certain cytokine receptors and intracellular muscle proteins. They are commonly associated with roles in the immune system. Otherwise, the sperm-specific protein IZUMO1, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, has also been identified as the only sperm membrane protein essential for sperm-egg fusion.
Method to screen phage display libraries with different ligands
InactiveUS20040038291A2Immunoglobulin superfamilyLibrary screeningPolyphageImmunoglobulin superfamily
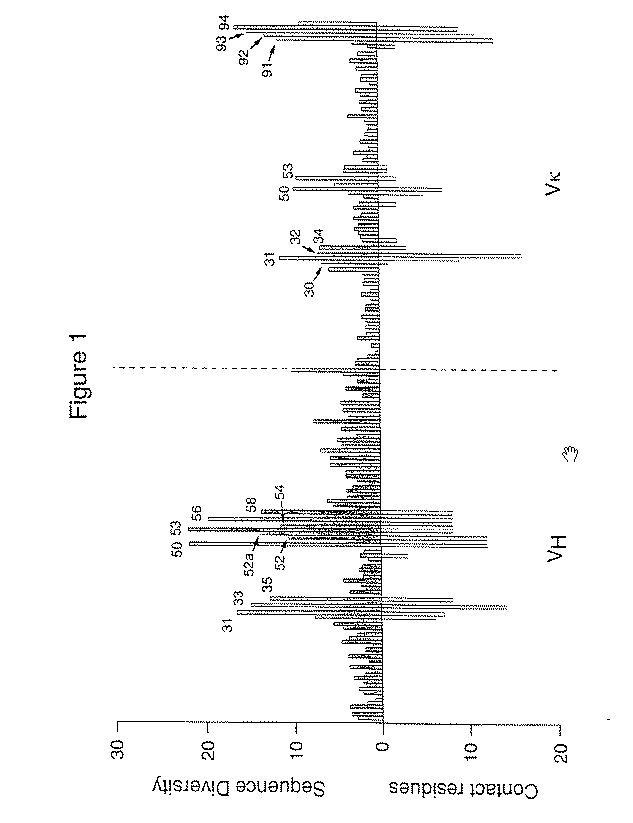
Abstract of the Disclosure The present invention relates to methods for selecting repertoires of polypeptides using generic and target ligands. In particular, the invention relates to a library comprising a repertoire of polypeptides of the immunoglobulin superfamily, wherein the members of the repertoire have a known main chain conformation.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
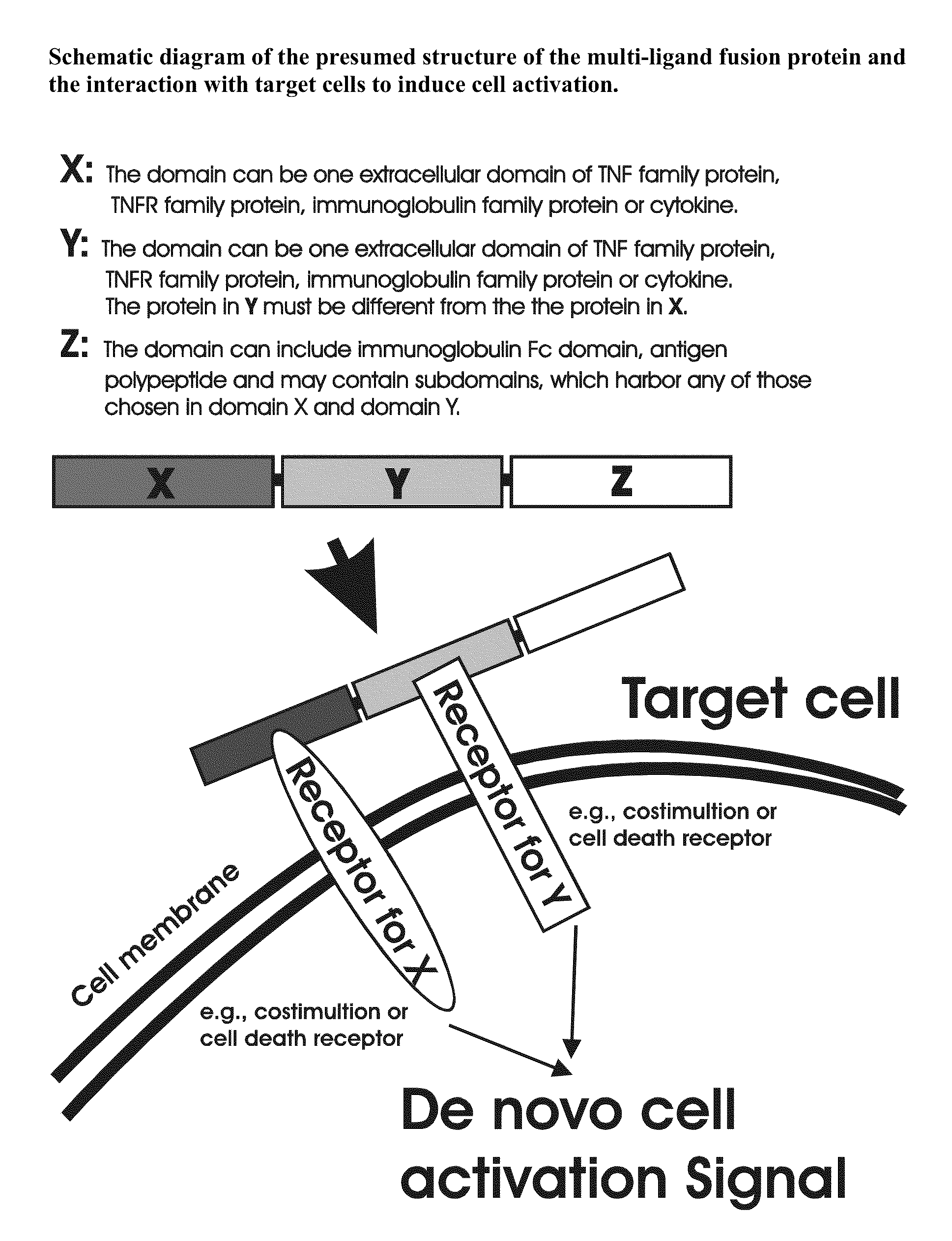
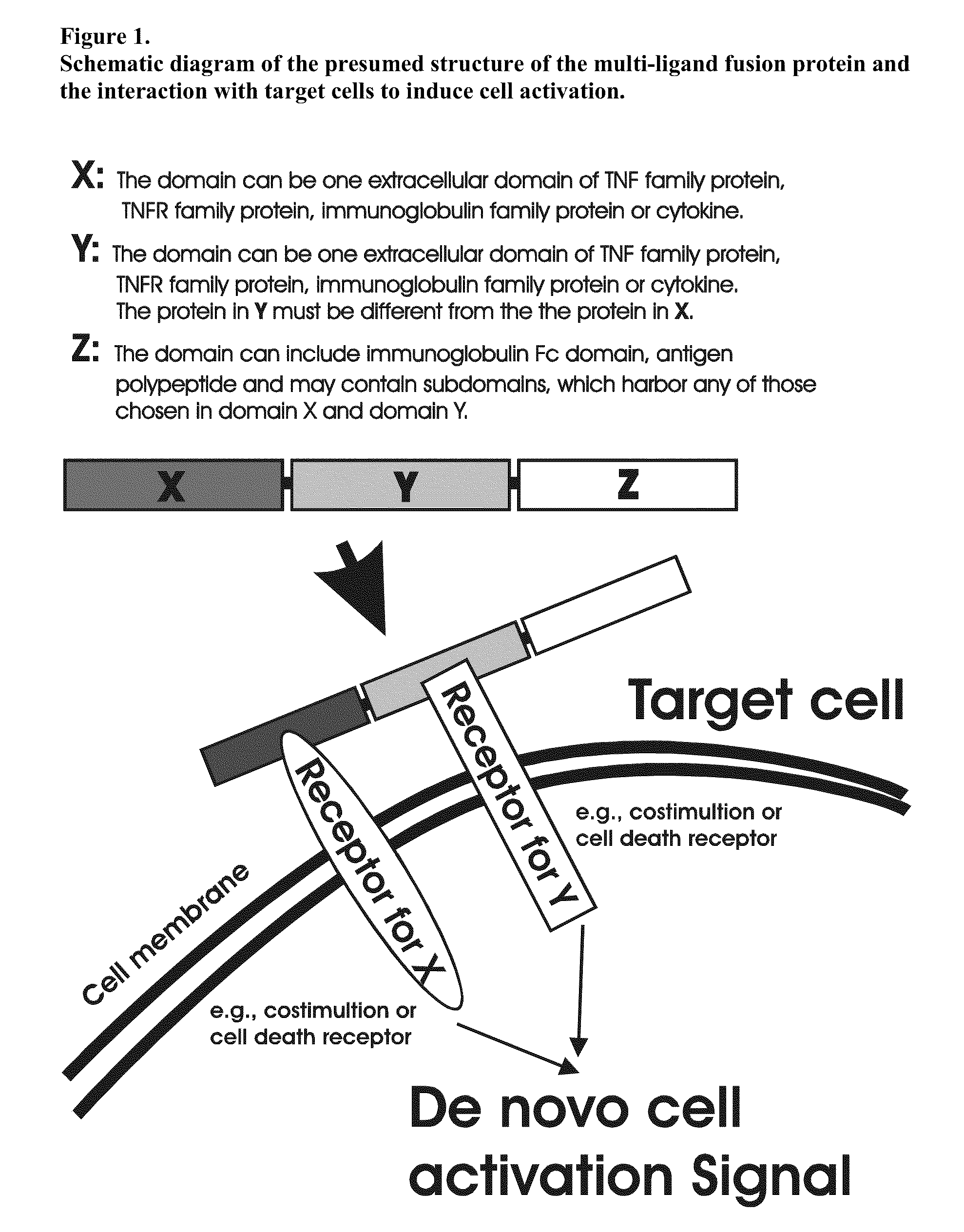
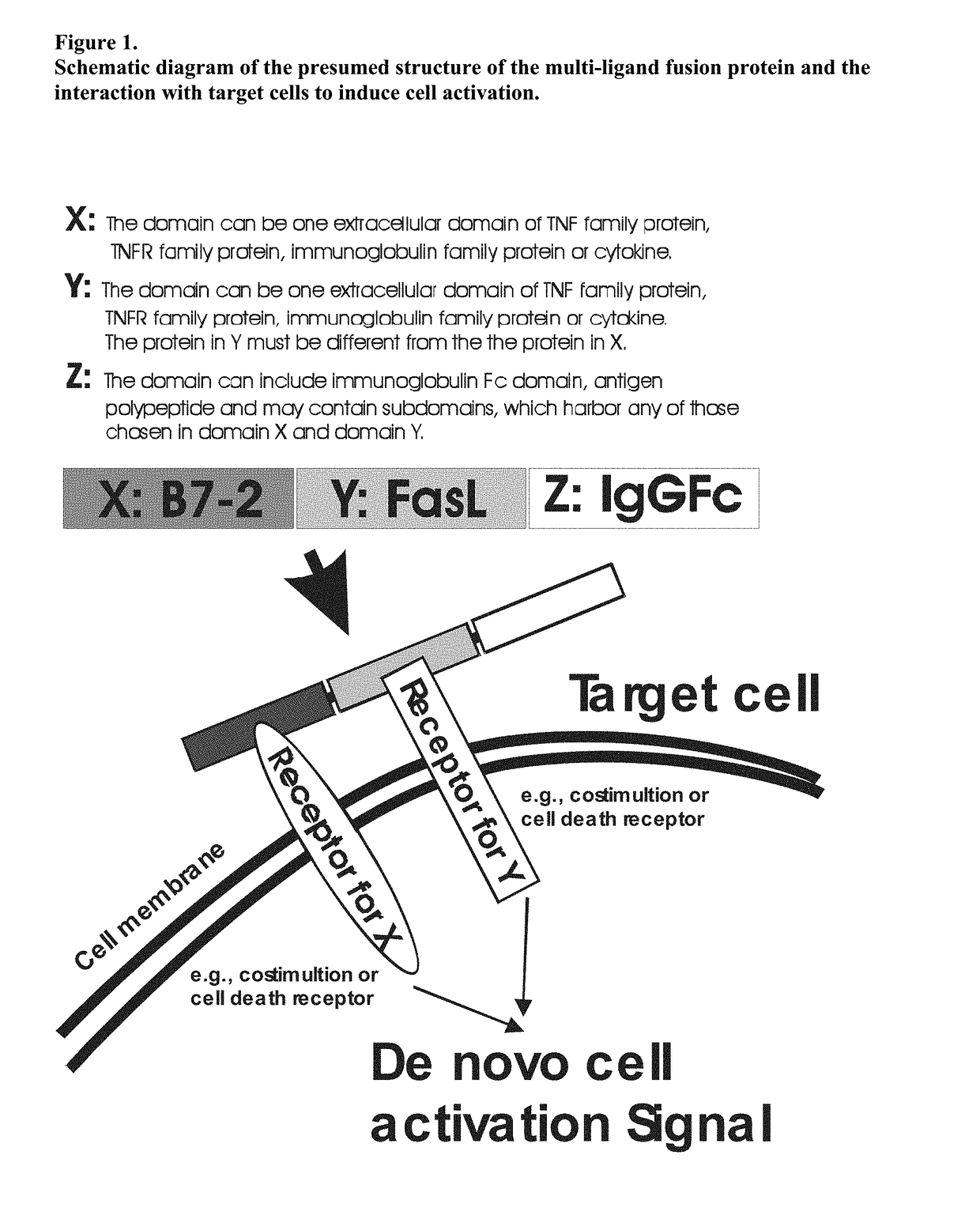
Recombinant multiple domain fusion protein mitogens and use thereof for inducing enhancement or repression of antigen-specific immunity.
ActiveUS20100303811A1Increase heightVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsIMMUNE SUPPRESSANTSAutoimmune responses
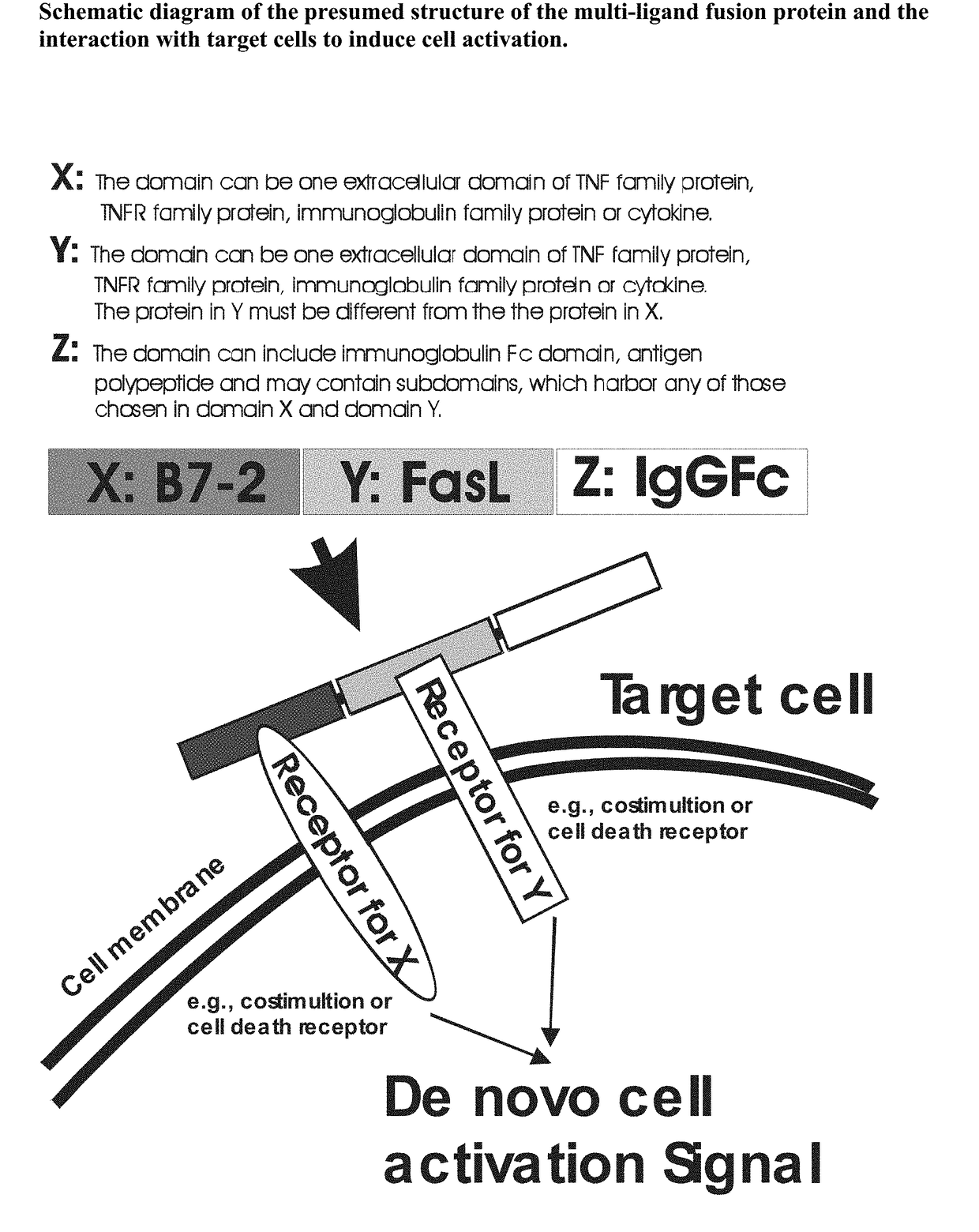
The invention relates to cell stimulatory fusion proteins and DNA sequences, vectors comprising at least two agonists of TNF / TNFR super family, immunoglobulin super family, cytokine family proteins and optional antigen combination. Instructions for use of these proteins and DNA constructs as immune adjuvants and vaccines for treatment of various chronic diseases such as viral infection are also provided. Additionally, the use of these protein and DNA constructs as immune suppressant for treatment of various chronic diseases, such as autoimmunity and organ transplant rejection, is also illustrated.
Owner:OCHI ATSUO
Uses of DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR for inhibiting hepatitis C virus infection
InactiveUS20060198855A1Prevent hepatocellular carcinomaTreating or preventing hepatocellular carcinomaCompound screeningSsRNA viruses positive-senseInfected cellImmunoglobulin superfamily
This invention provides a method of inhibiting HCV infection of a cell susceptible to HCV infection which comprises contacting the cell with an amount of a compound effective to inhibit binding of an HCV envelope glycoprotein to a DC-SIGN protein present on the surface of the cell, so as to thereby inhibit HCV infection of the cell susceptible to HCV infection. This invention provides a method of inhibiting HCV infection of a cell susceptible to HCV infection which comprises contacting the cell with an amount of a compound effective to inhibit binding of an HCV envelope glycoprotein to a DC-SIGNR protein present on the surface of the cell, so as to thereby inhibit HCV infection of the cell susceptible to HCV infection. Compounds of the present invention inhibit HCV infection of cells susceptible to HCV infection. The compounds of the present invention preferably have specificity for preventing or inhibiting infection by HCV and do not inhibit infection by other viruses, such as HIV, that may utilize DC-SIGN or DC-SIGNR for infection. Moreover the compounds of the present invention preferably do not interfere or inhibit members of the immunoglobulin superfamily, in particular, the compounds do not interfere with ICAM-2 or ICAM-3 or with ICAM-2-ilke, or ICAM-3-like molecules.
Owner:PROGENICS PHARMA INC
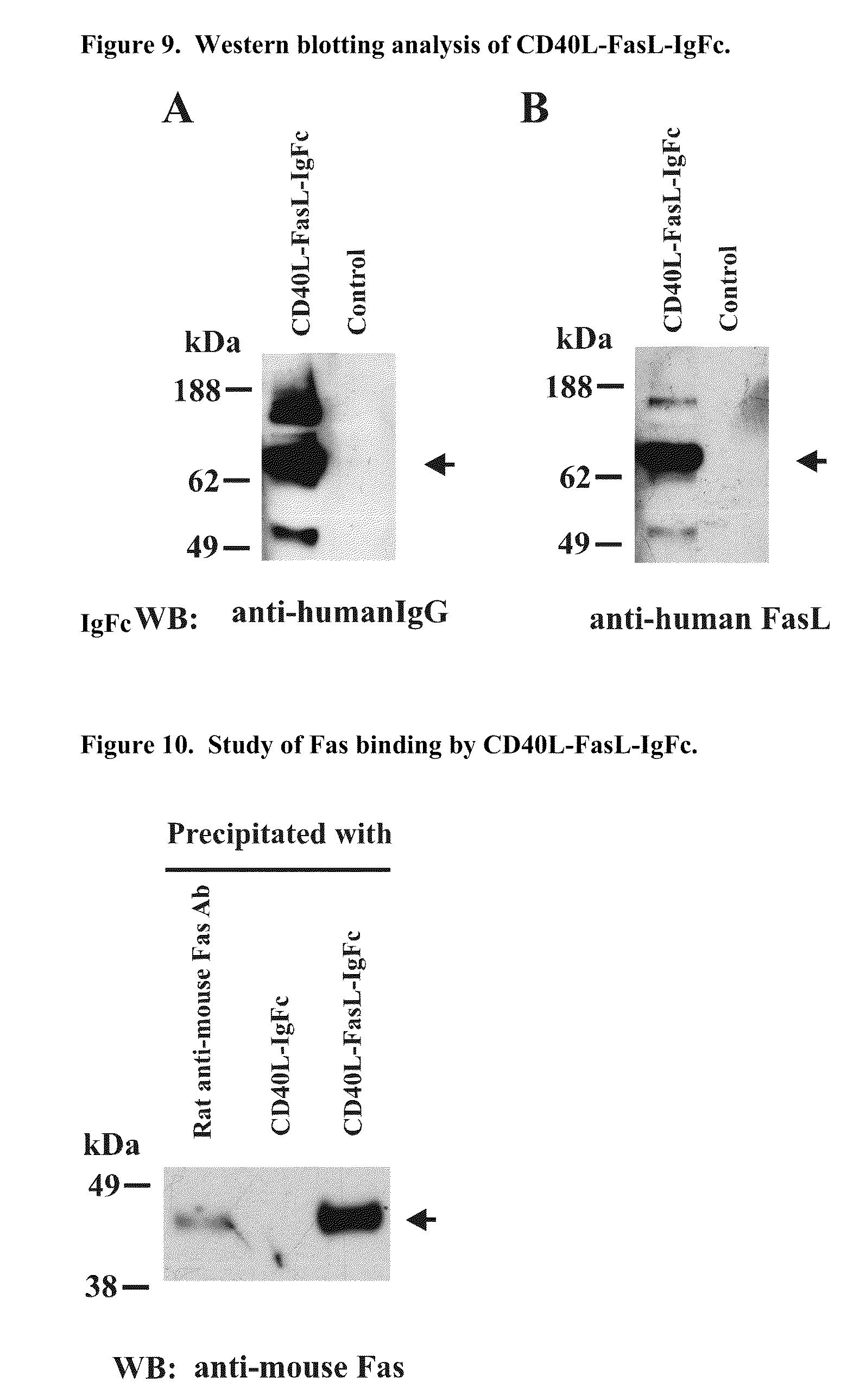
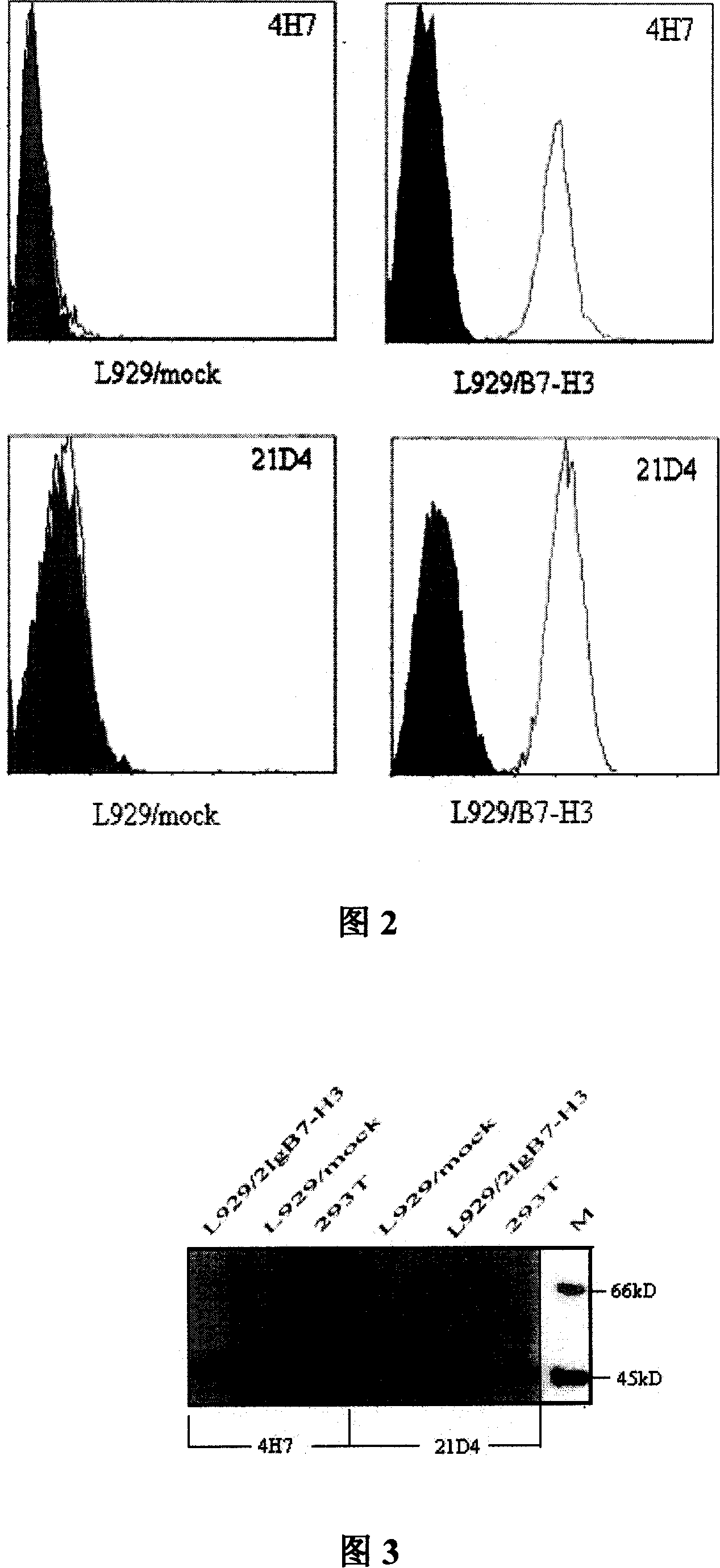
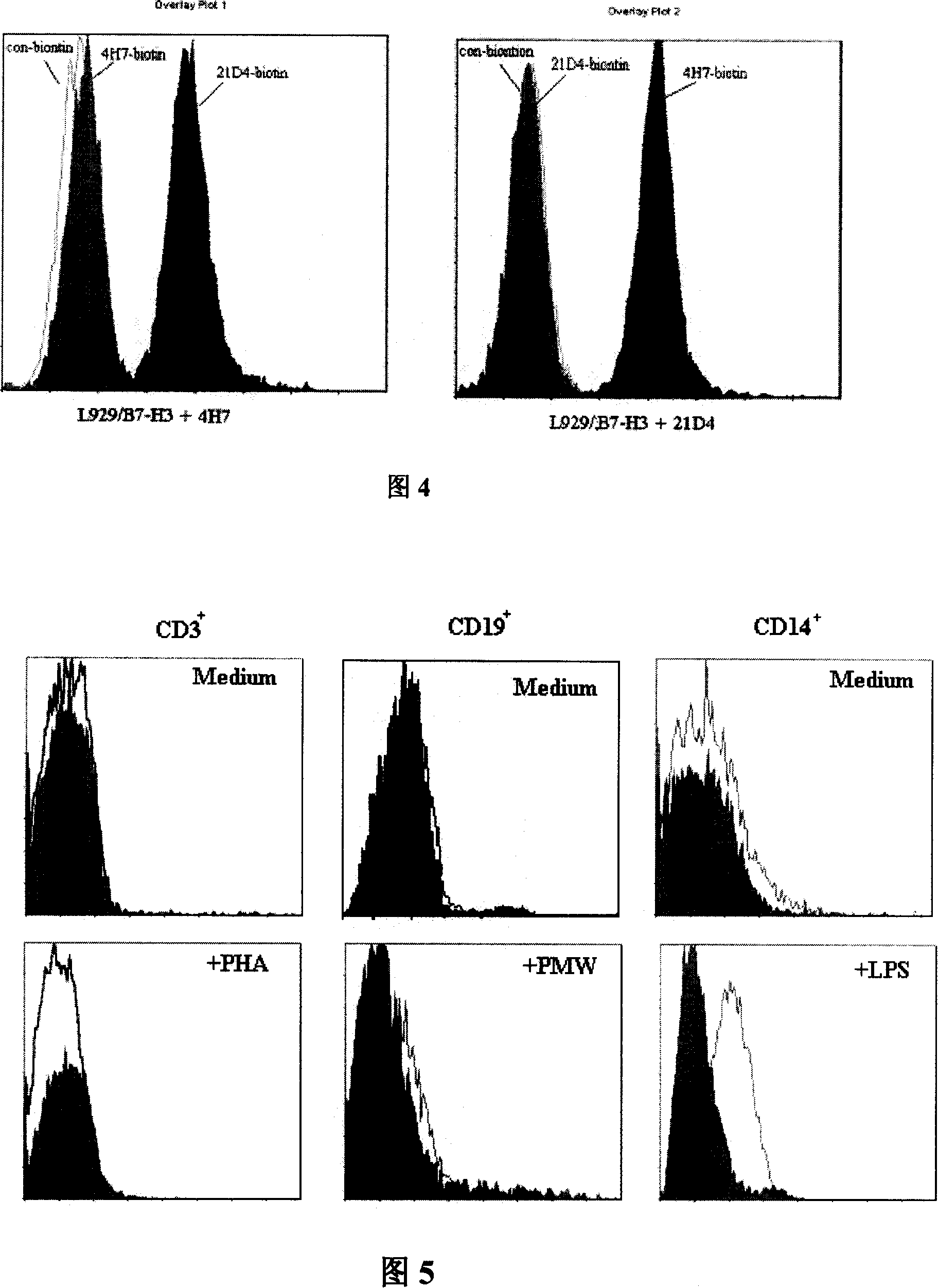
Preparation for anti human B7-H3 monoclonal antibody and application thereof
InactiveCN101104639AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsDendritic cellMonoclonal antibody
The invention relates to binding proteins or polypeptides of a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, specifically relates to an anti-human B7-H3 monoclonal antibodies 4H7 and 21D4, a preparation method of the monoclonal antibodies, and the applications of the monoclonal antibodies in tumor (gastric cancer) prognostic evaluation and in being used as a marked molecule for identification of human dendritic cells (DC).
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for assessing a prognosis and predicting the response of patients with malignant diseases to immunotherapy
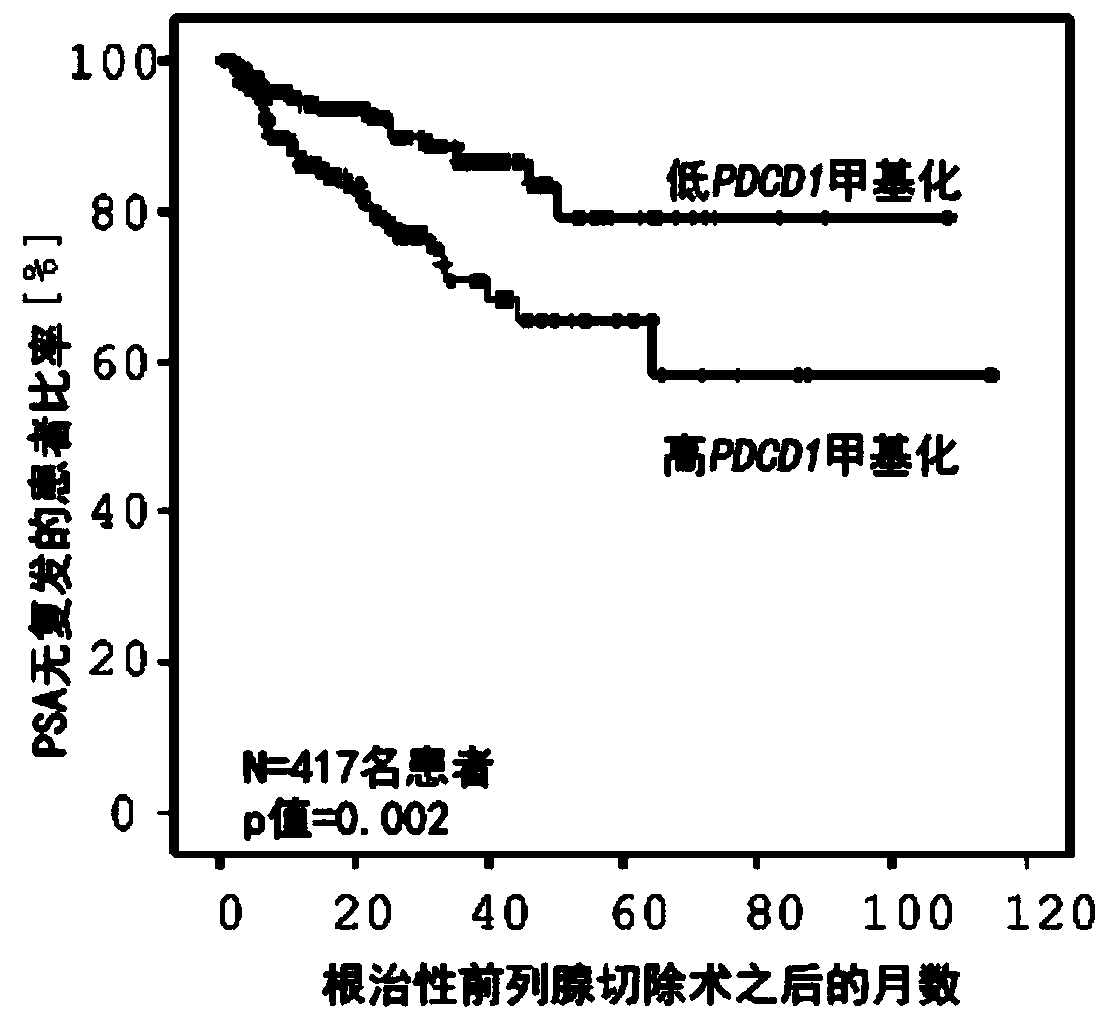
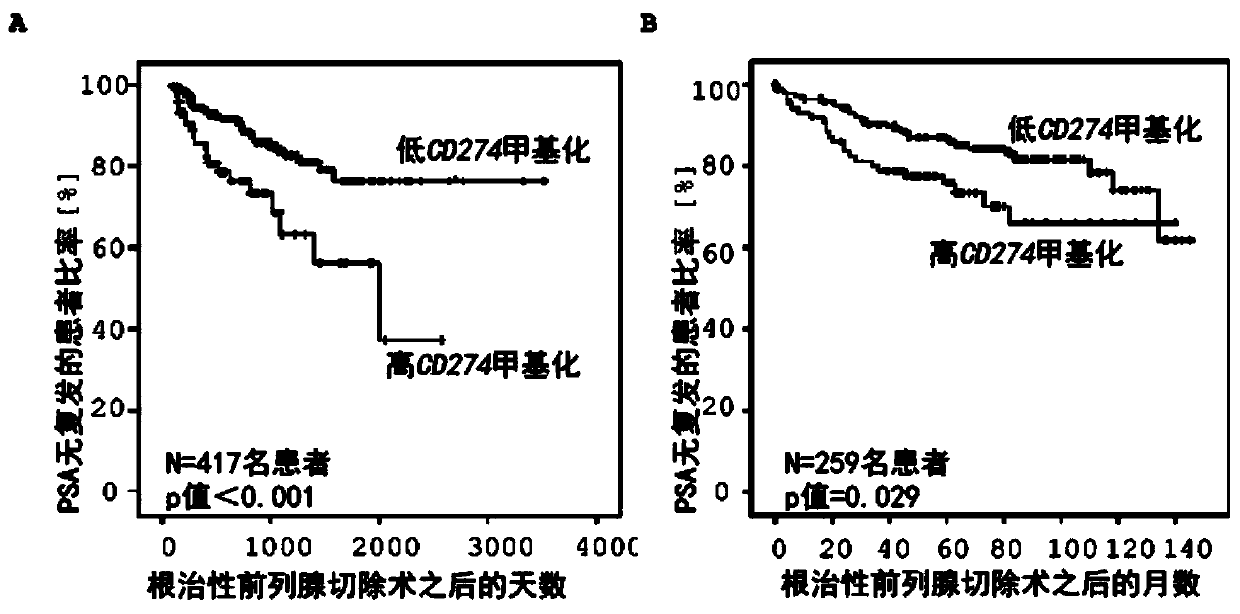
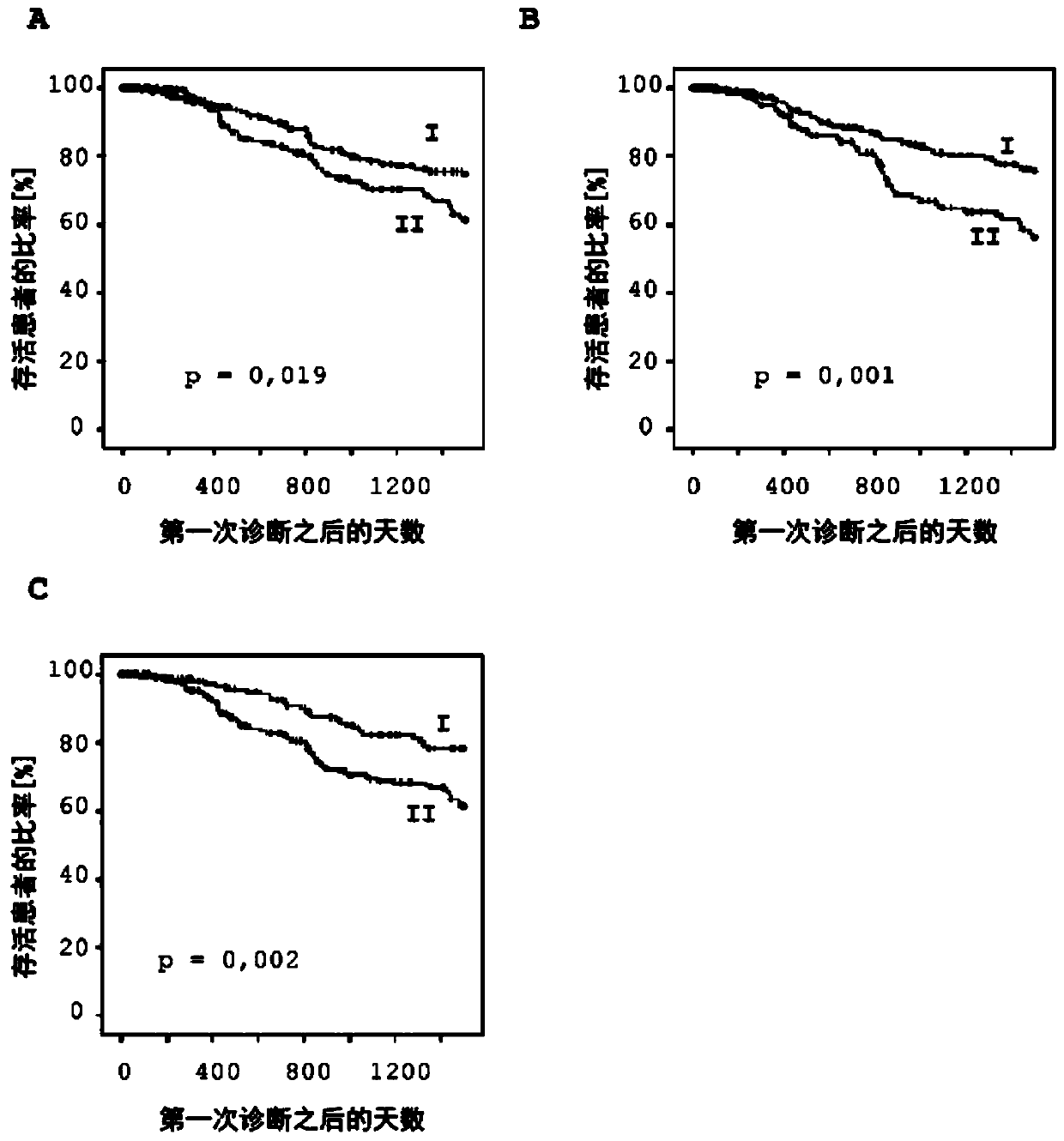
The invention relates to, among others, a method for assessing a prognosis of a patient with a malignant disease and / or for predicting the response of a patient with a malignant disease to immunotherapy. For this purpose, a DNA methylation analysis is carried out on at least one immunoregulatory gene of cells of the malignant disease and / or T lymphocytes which interact with the cells of the malignant disease, said gene coding for an immune checkpoint selected from B7 proteins and the receptors thereof, MHC-peptide complex-binding co-receptors, the members of the tumor necrosis factor receptorsuperfamily TNFRSF9, CD40, TNFRSF4, TNFRSF18, and CD27, the members of the immunoglobulin superfamily TIGIT, BTLA, HAVCR2, BTNL2, and CD48, and the andenosine-binding adenosine 2A receptor.
Owner:迪莫迪特里希
Family of immunoregulators designated leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors (LIR)
InactiveUS20060078564A1Immunoglobulin superfamilySugar derivativesAutoimmune conditionLeukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors
A new family of immunoreceptor molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily, (LIR) polypeptides is described. Disclosed are sequences encoding LIR family members and their deduced amino acid sequences, polypeptides encoded by DNA that hybridize to oligonucleotide probes having defined sequences, processes for producing polypeptides of the LIR family, and antagonistic antibodies to LIR family members. LIR family members can be used to treat autoimmune diseases and disease states associated with suppressed immune function.
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
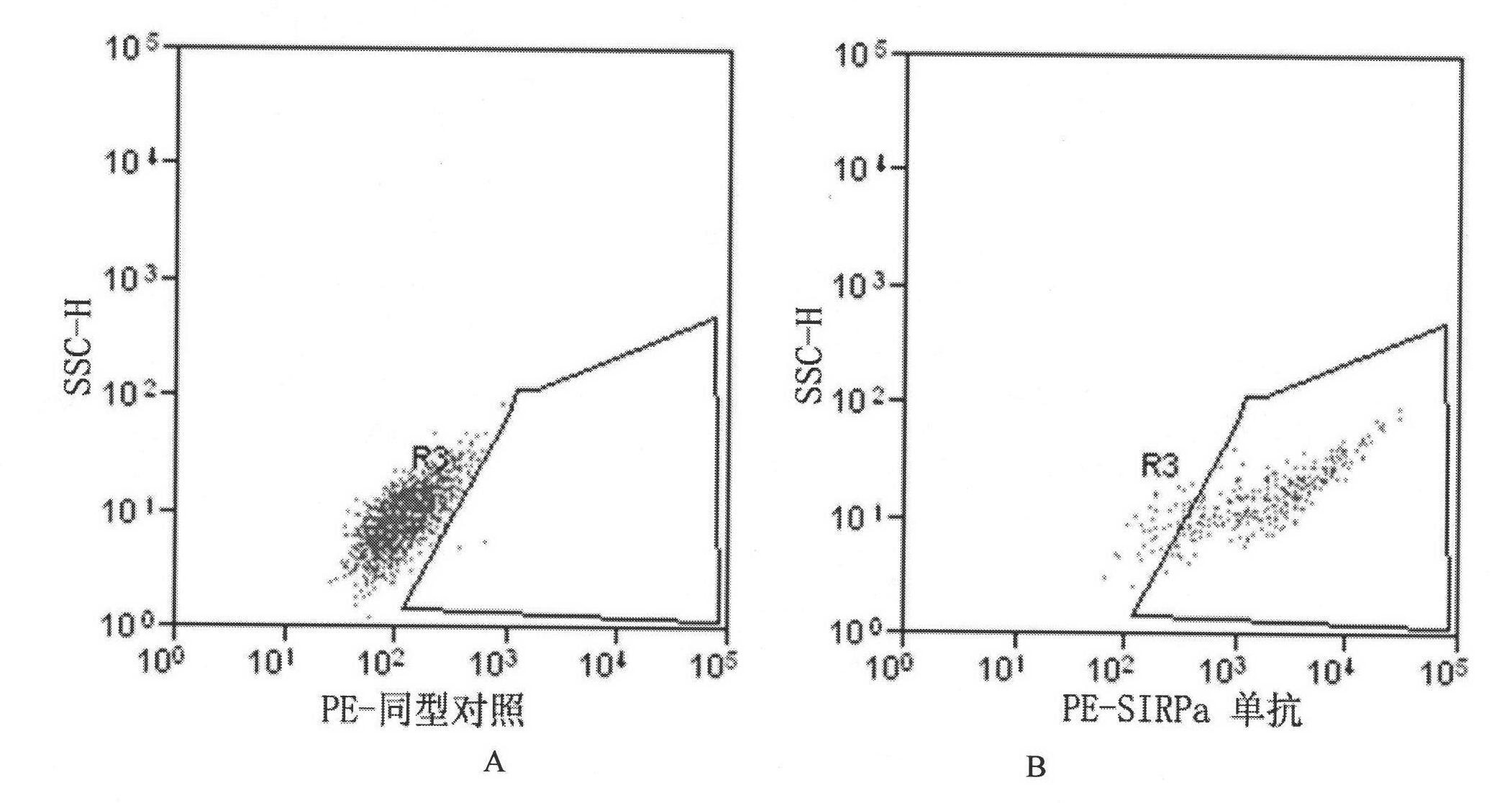
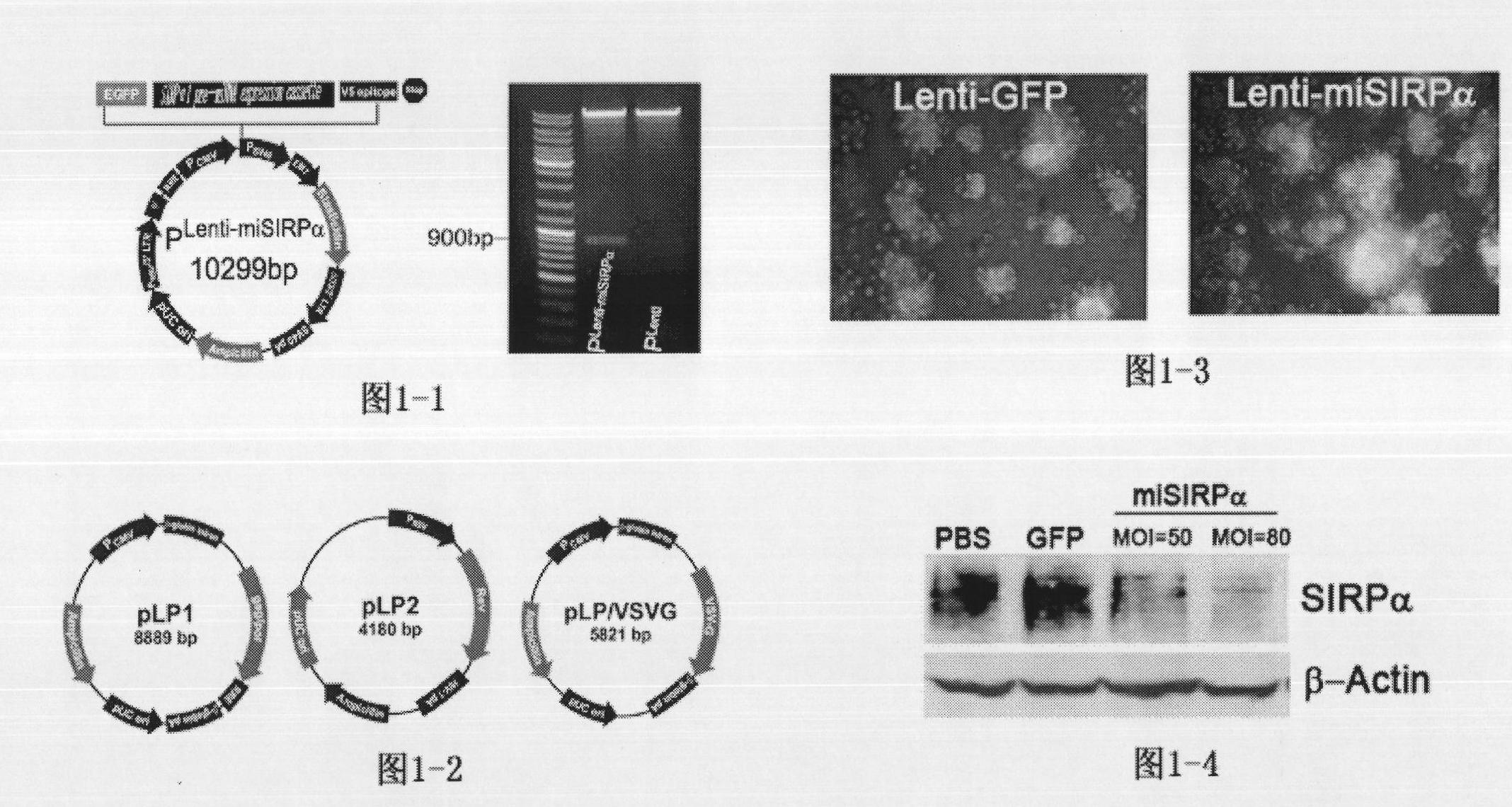
Monoclonal antibody of anti-human SIRPalpha, cell strain, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101880324AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesHuman bodySignal-regulatory protein alpha
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical bioengineering, in particular to a monoclonal antibody of an anti-human signal regulating protein alpha (SIRPalpha), a preparation method and an application. The signal regulating protein alpha (SIRPalpha) is a member belonging to an immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), and tissues are mainly distributed in a medullary system (a macrophage cell, a dendritic cell and the like), therefore, the effect of the SIRPalpha in the immune adjustment of organism has been much accounted gradually. The invention provides the monoclonal antibody of the monoclonal antibody SIRPalpha, which is generated from a hybridoma cell strain with the preserved number of CGMCCNo.3801. The invention also provides the application of the monoclonal antibody in the preparation and detection of the SIRPalpha and in the preparation of drugs for stimulating macrophage TNF-alpha expression of a human body.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
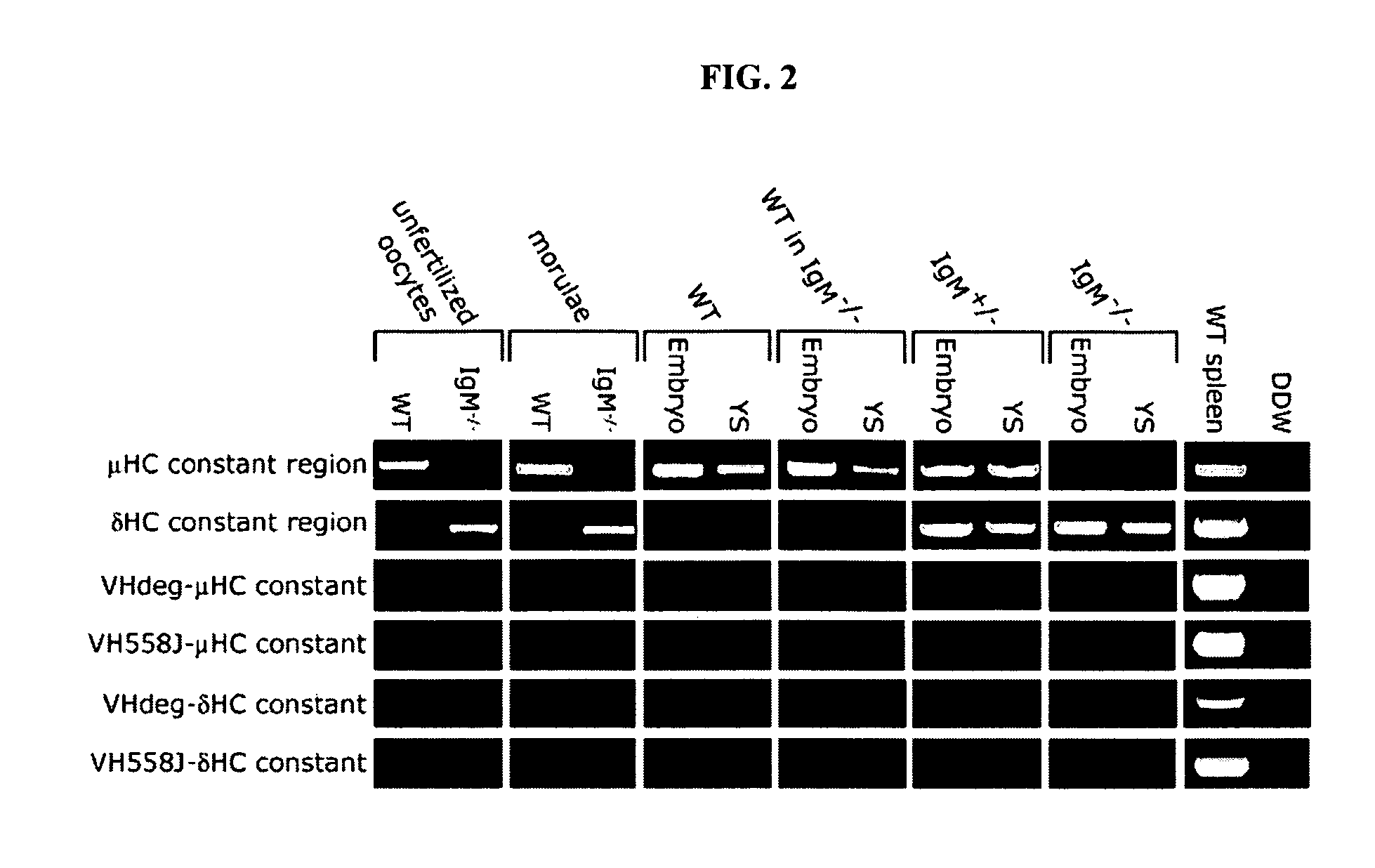
Immunoglobulin heavy chain variants expressed in mesenchymal cells and therapeutic uses thereof
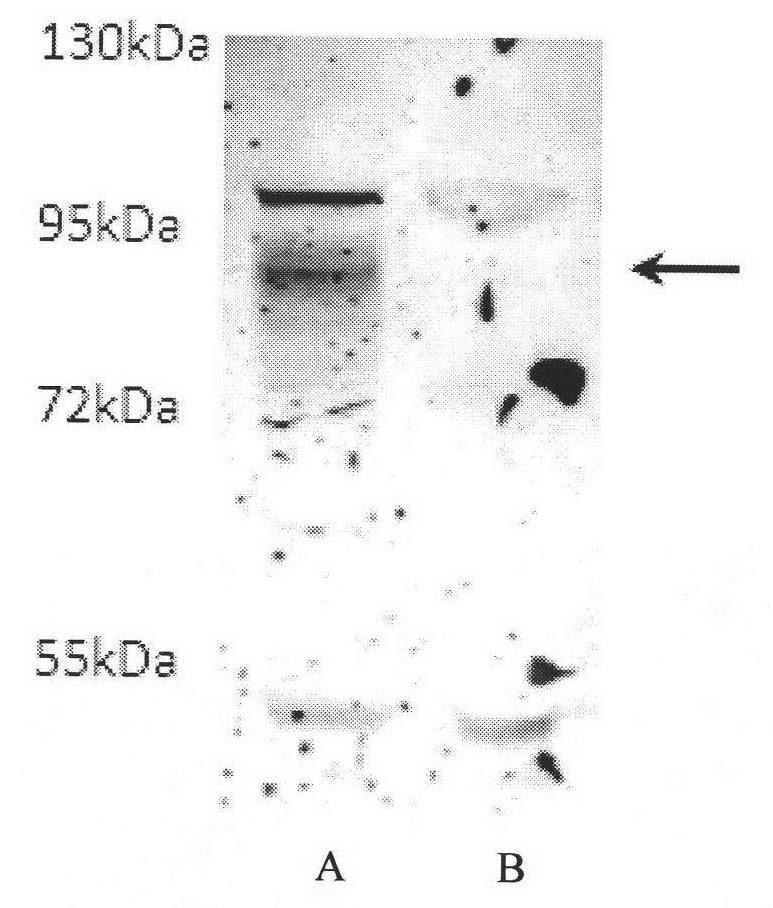
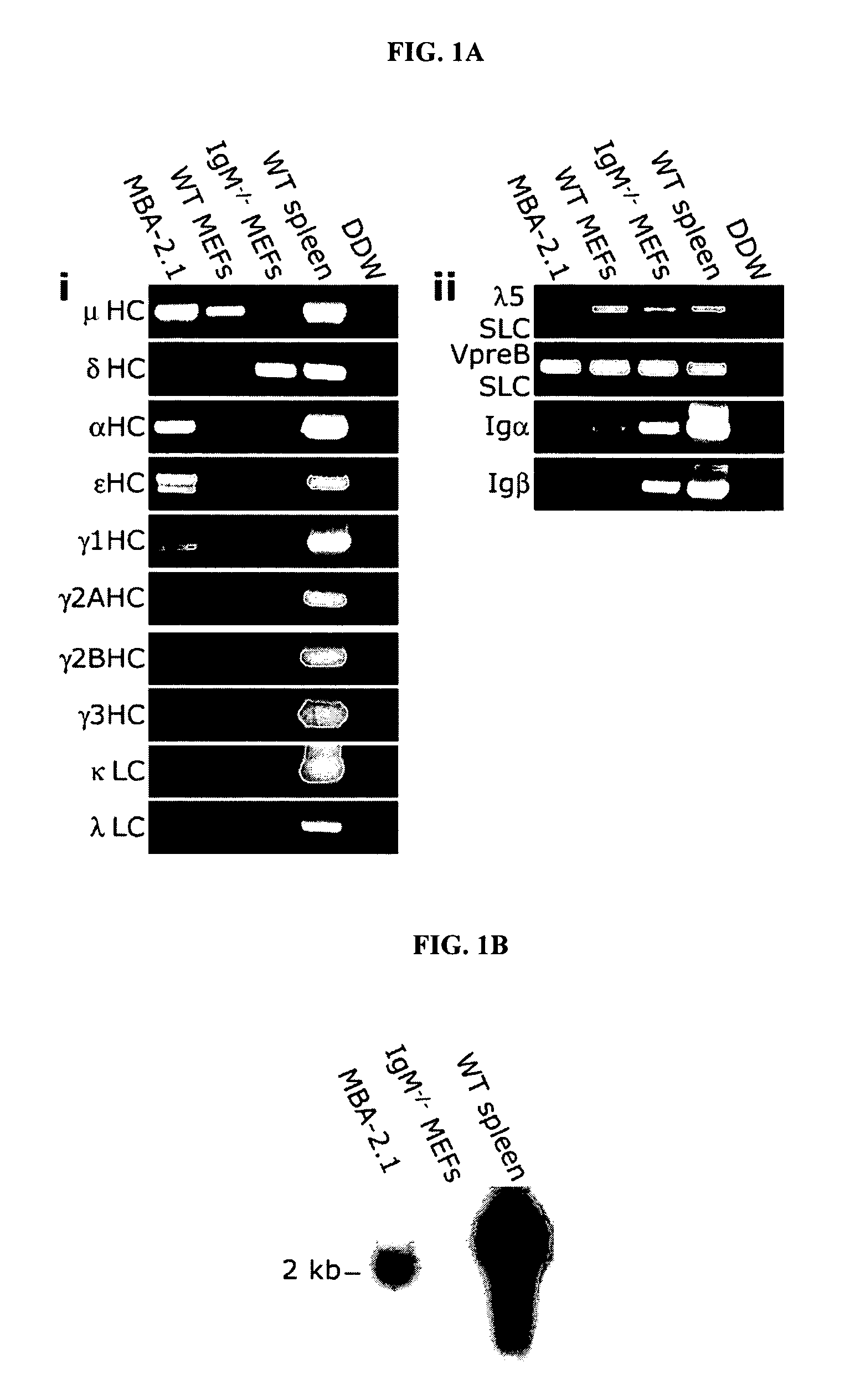
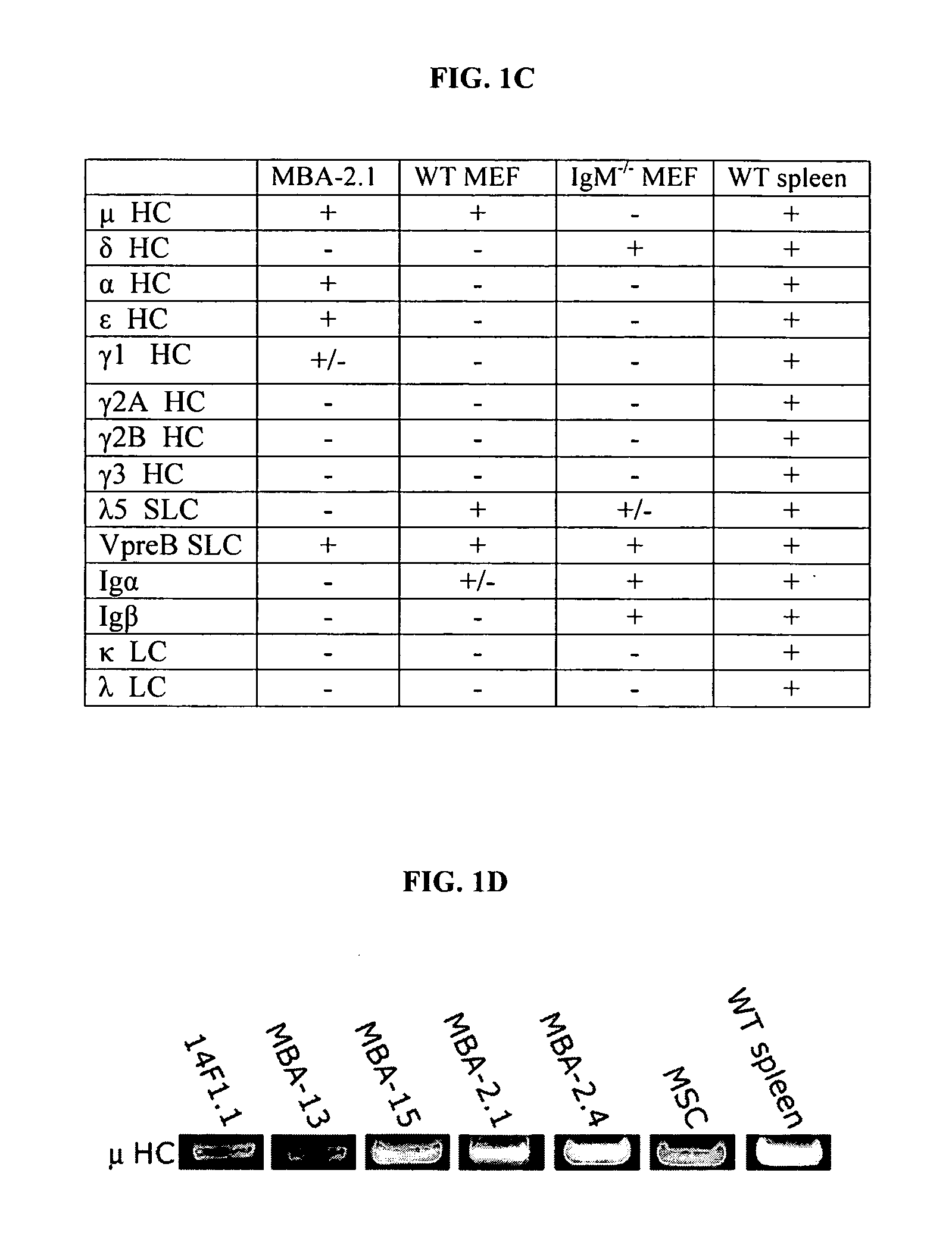
Mesenchymal cells are unexpectedly found to express specific truncated versions of immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily members, Igμ heavy chain and Igδ heavy chain variants. Mesenchymal Ig heavy chain gene products either directly or indirectly control hemopoietic stem cells. Ectopic expression, RNAi or antibody therapy can be used to modulate Ig heavy chain mediated functions.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Family of immunoregulators designated leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors (LIR)
InactiveUS20090226457A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsDiseaseLeukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors
A new family of immunoreceptor molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily, (LIR) polypeptides is described. Disclosed are sequences encoding LIR family members and their deduced amino acid sequences, polypeptides encoded by DNA that hybridize to oligonucleotide probes having defined sequences, processes for producing polypeptides of the LIR family, and antagonistic antibodies to LIR family members. LIR family members can be used to treat autoimmune diseases and disease states associated with suppressed immune function.
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
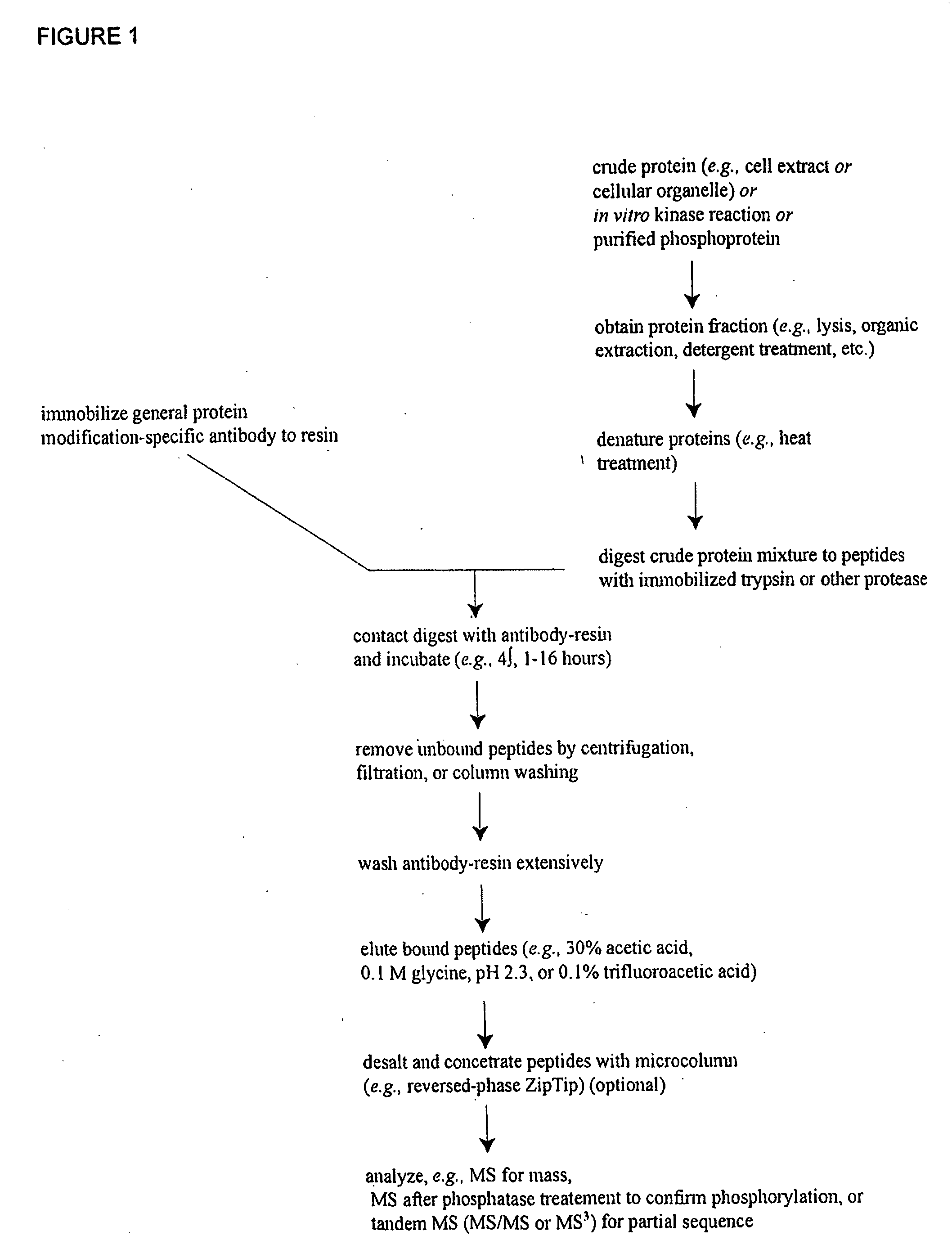
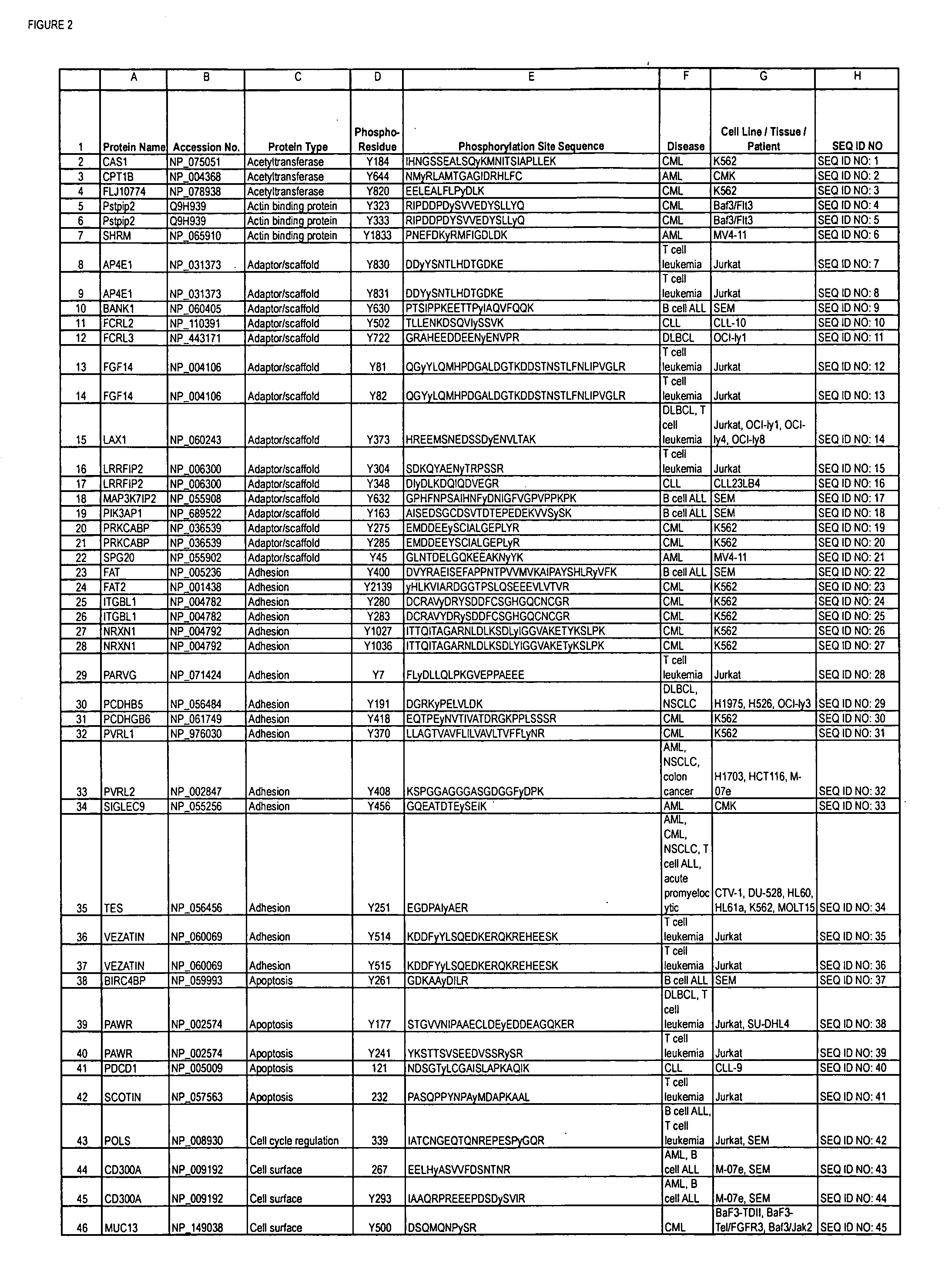
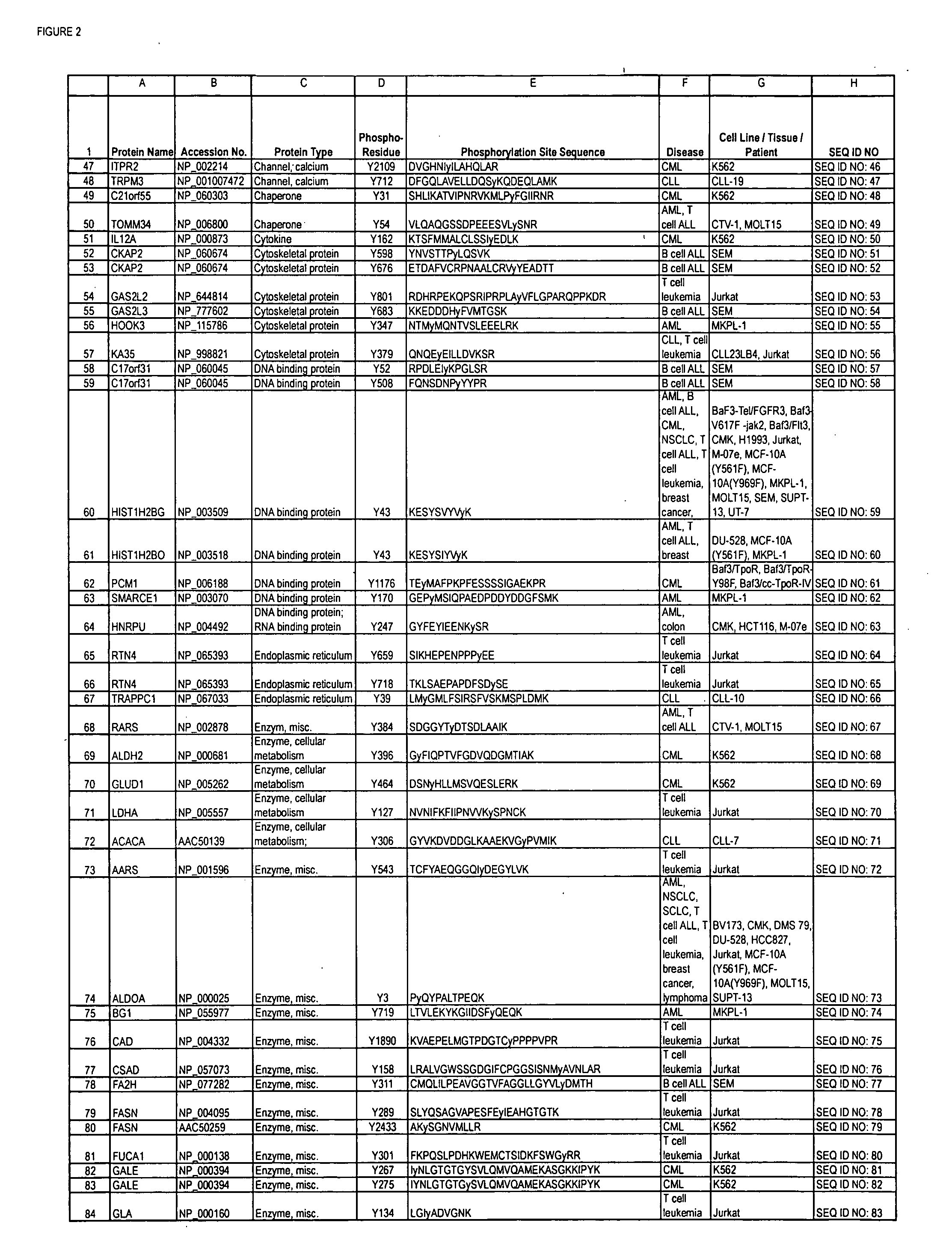
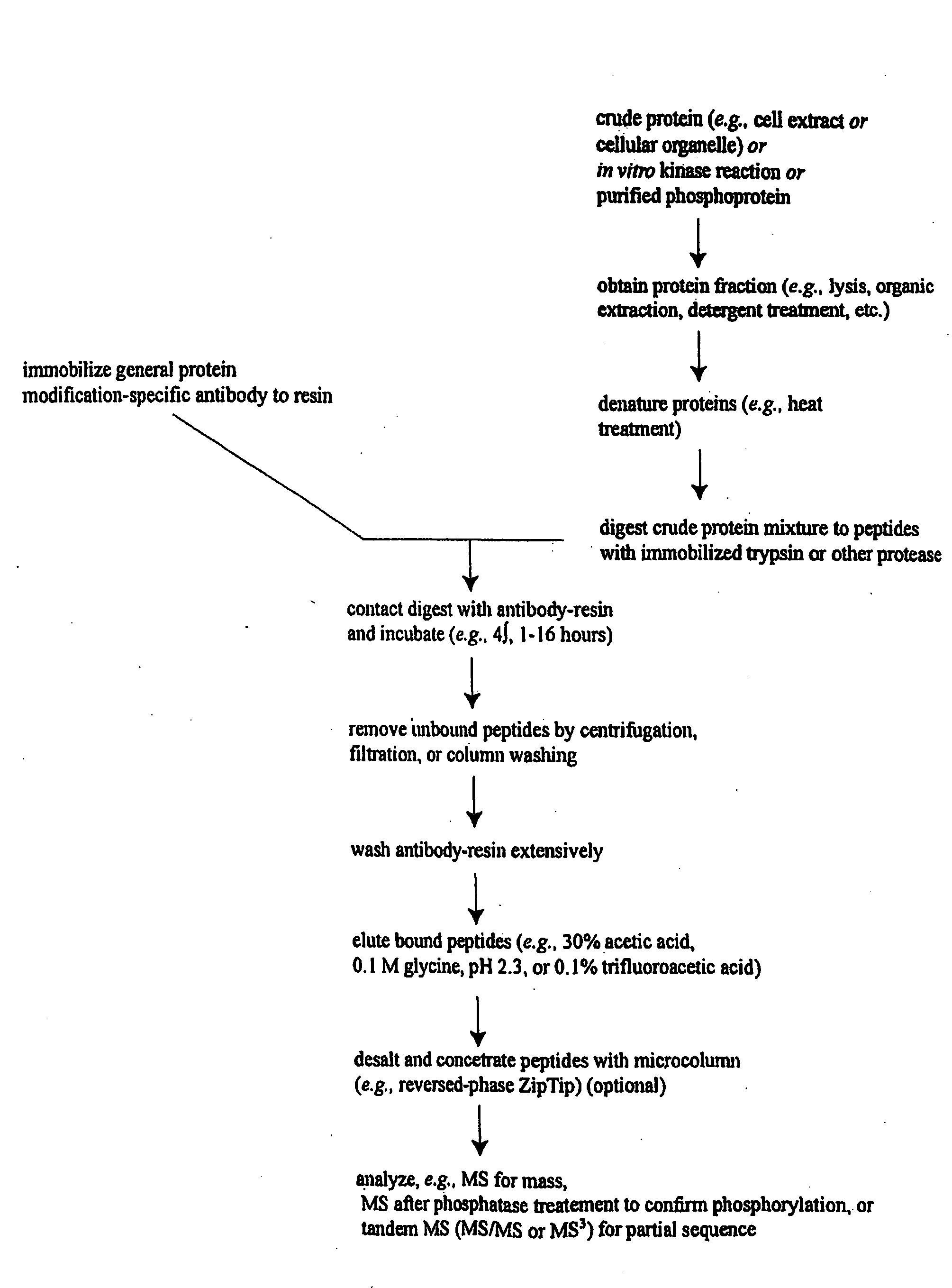
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in Leukemia signaling pathways
ActiveUS20080248490A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingHuman leukemiaADAMTS Proteins
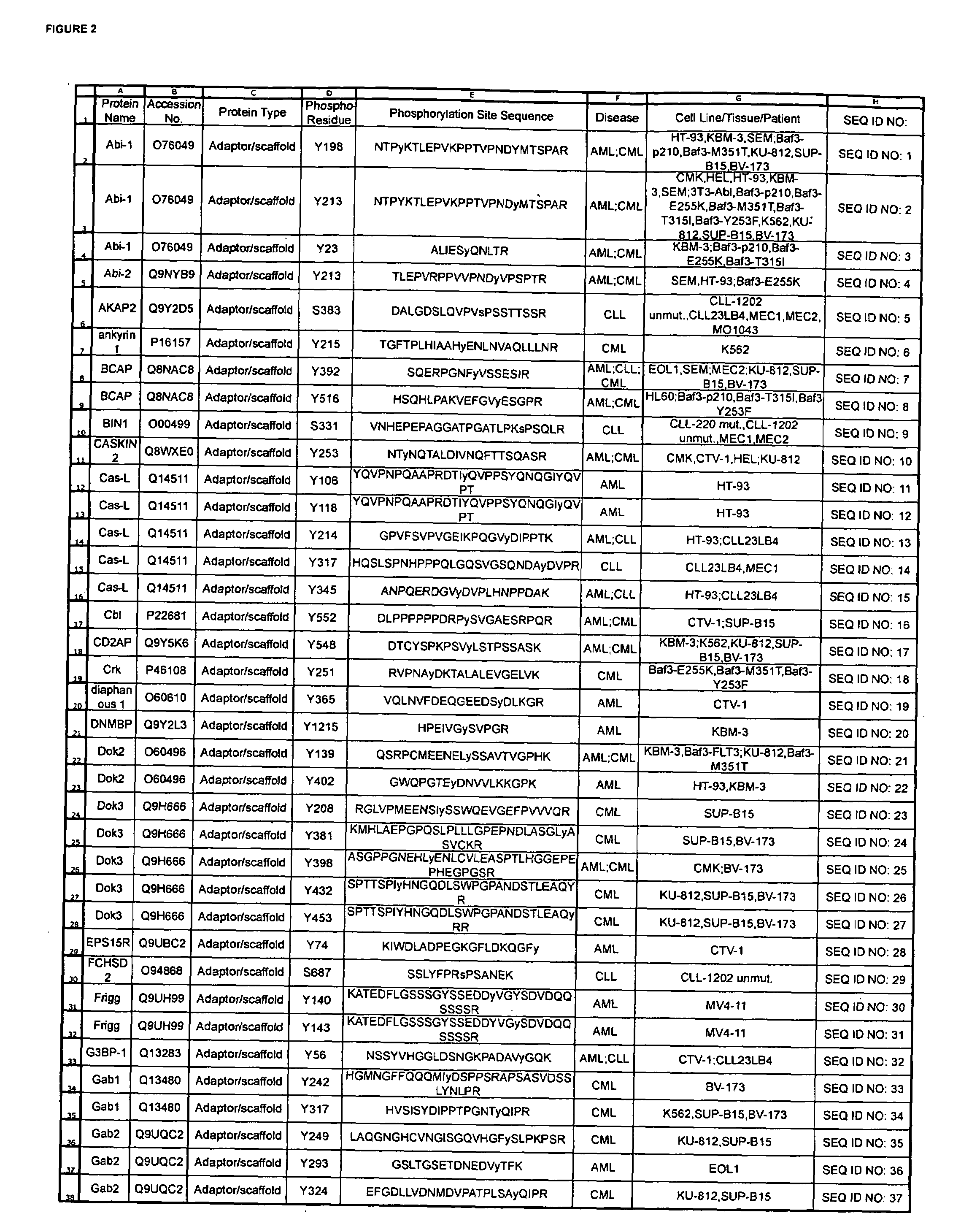
The invention discloses nearly 288 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeletal proteins, Cellular Metabolism enzymes, G Protein / GTPase Activating / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor proteins, Immunoglobulin Superfamily proteins, Inhibitor proteins, Lipid Kinases, Nuclear DNA Repair / RNA Binding / Transcription proteins, Serine / Threonine Protein Kinases, Tyrosine Kinases, Protein Phosphatases, and Translation / Transporter proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Family of immunoregulators designated leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors (LIR)
InactiveUS7014853B2Cell from functioningPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseRIG-I-like receptor
A new family of immunoreceptor molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily, (LIR) polypeptides is described. Disclosed are sequences encoding LIR family members and their deduced amino acid sequences, polypeptides encoded by DNA that hybridize to oligonucleotide probes having defined sequences, processes for producing polypeptides of the LIR family, and antagonistic antibodies to LIR family members. LIR family members can be used to treat autoimmune diseases and disease states associated with suppressed immune function.
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
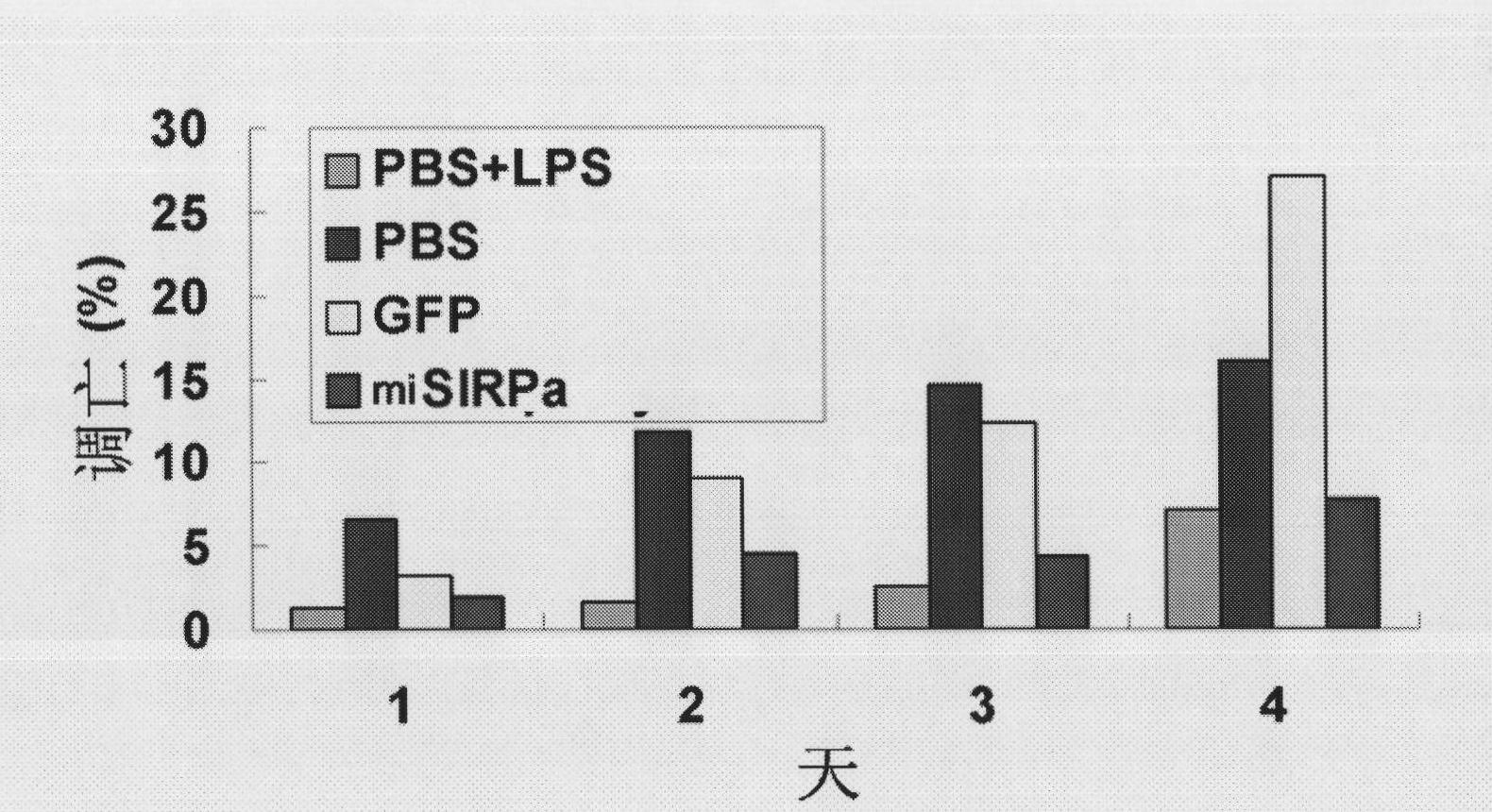
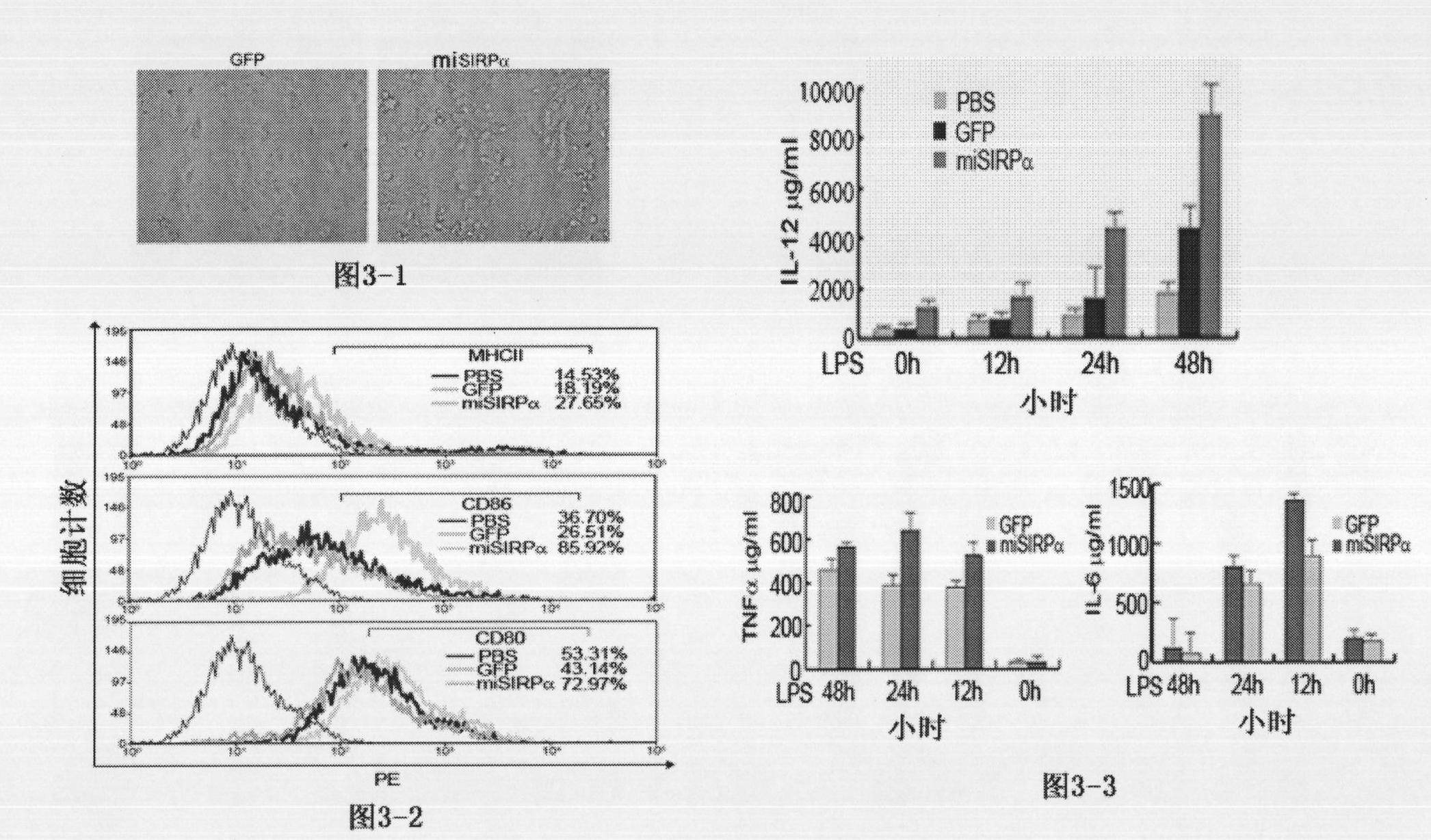
Application of signal adjusting protein alpha in preparation of DC vaccine for preventing and treating tumors
InactiveCN101780283AHigh activityFunction increaseGenetic material ingredientsFermentationAbnormal tissue growthSignal-regulatory protein alpha
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical bio-engineering, and particularly relates to new application of the signal adjusting protein alpha(SIRP alpha). The signal adjusting protein alpha(SIRP alpha) belongs to a member of the immunoglobulin super family(IGSF). In-vitro biological experiments and in-vivo animal experiments prove that in the application of the signal adjusting protein alpha(SIRP alpha) in the preparation of the DC vaccine for preventing and treating tumors of the invention, the SIRP alpha signal path negatively regulates the activity and antigen presentation functions of the DC. The invention further constructs a tumor DC vaccine which can interfere with the SIRP alpha expression by the mediation of a lentiviral vector, and the tumor DC vaccine can obviously improve the DC activation level and the antigen presentation function of the DC and be used for preventing and treating mouse tumors and is a novel tumor vaccine. The invention provides a new idea for clinical treatment application of the SIRP alpha.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
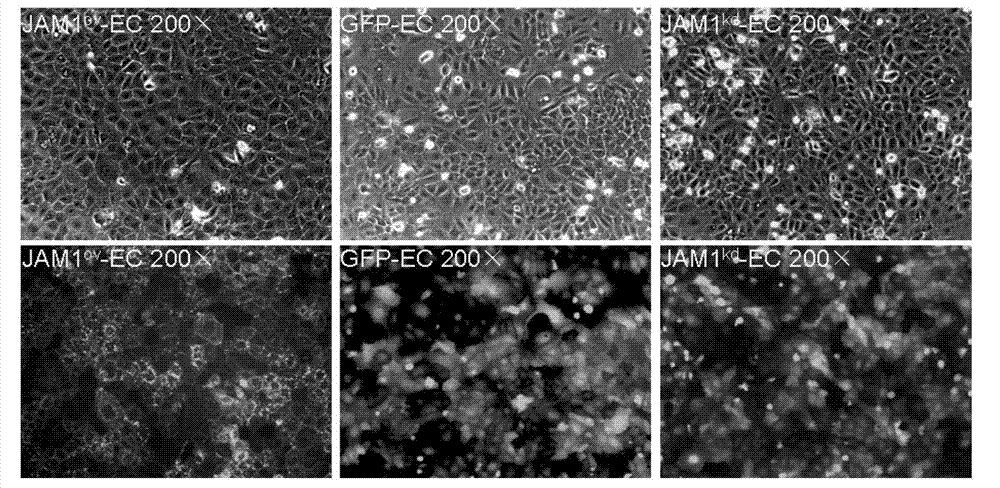
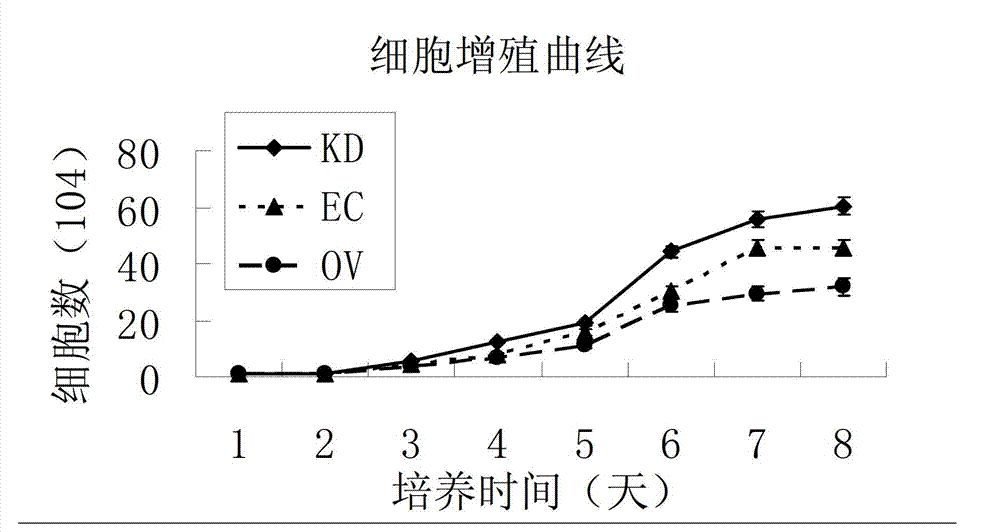
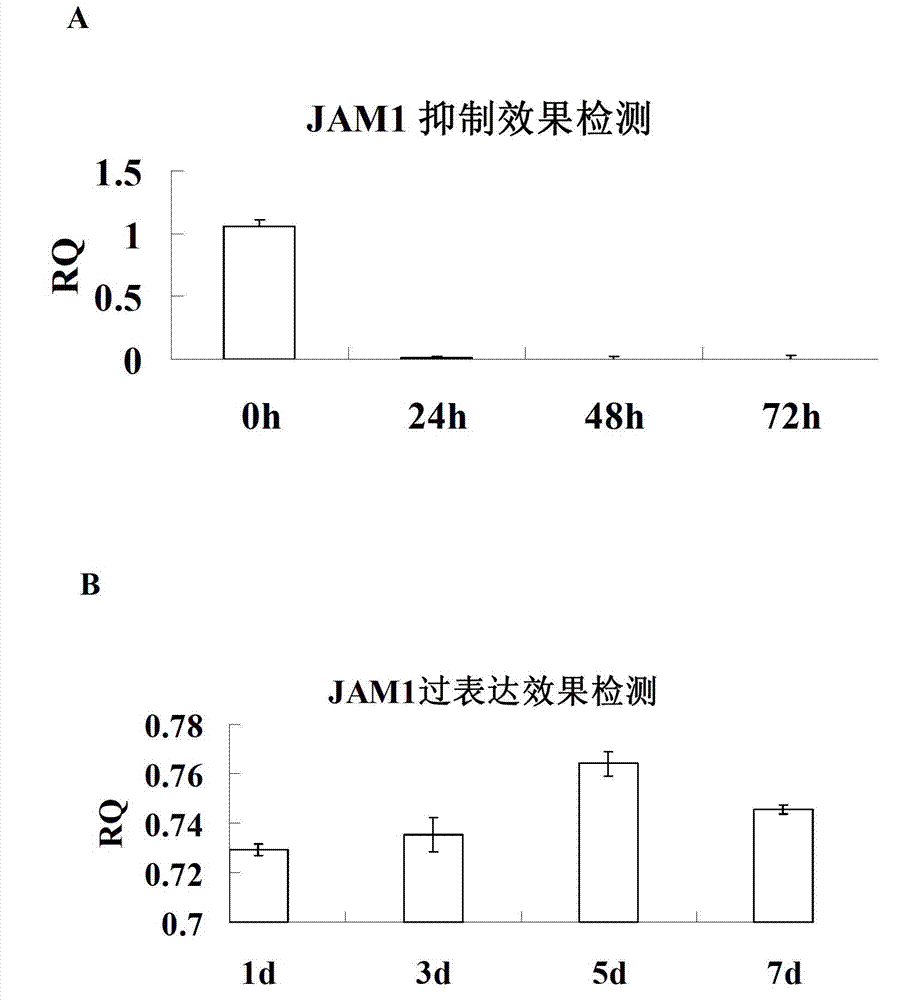
Method for promoting epidermal cell proliferation
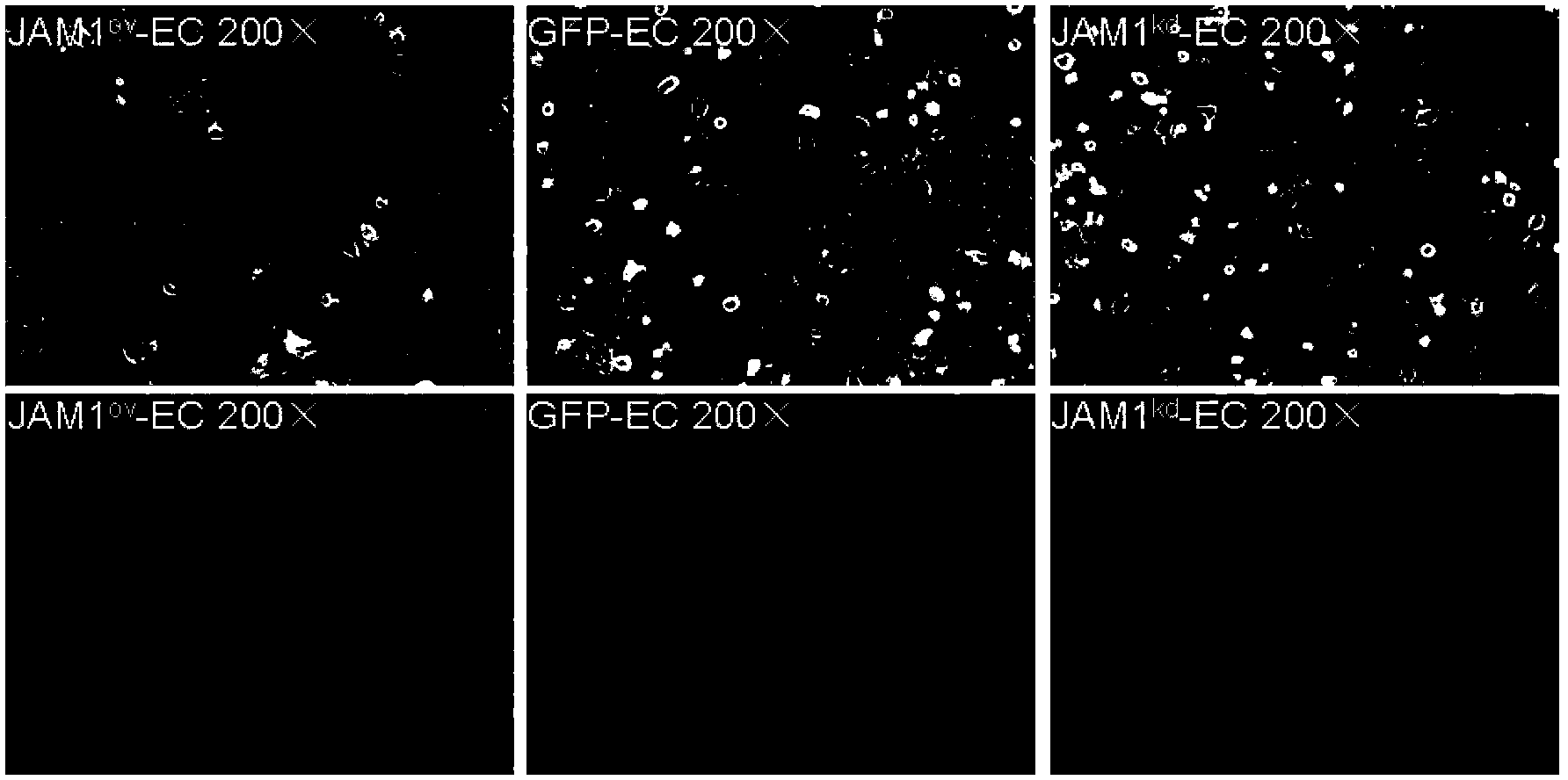
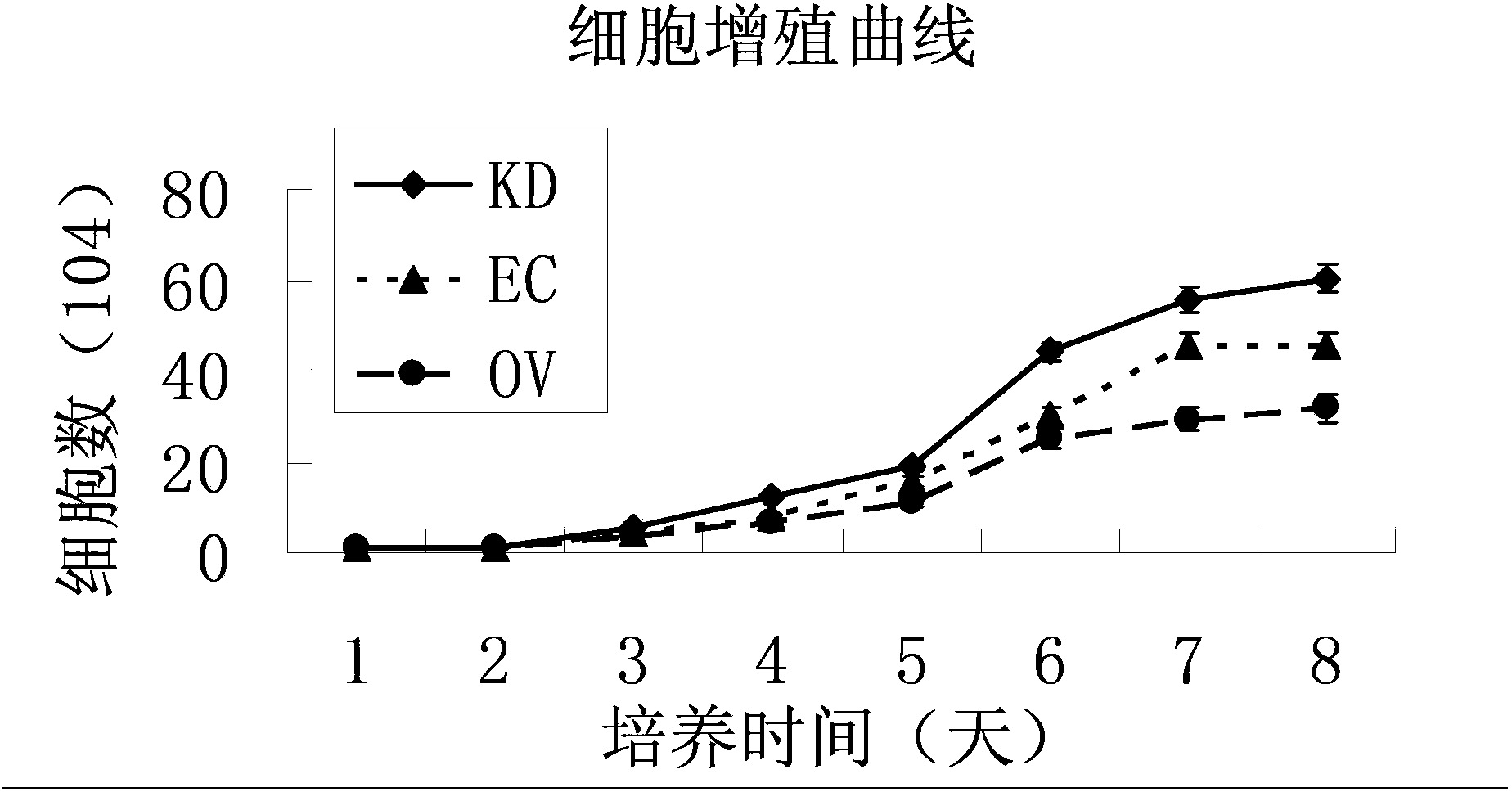
The invention relates to the technical fields of stem cells and gene engineering, and particularly provides a method for promoting epidermal cell proliferation based on gene modification and gene interference with epidermal cells by using a junctional adhesion molecule JAM1 (NM-016946) which is a transmembrane molecule and belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. The invention further provides a low expression epidermal cell of the junctional adhesion molecule JAM1 gene, i.e. JAM1kd-EC, and the proliferation ability of the epidermal cell, the properties and the biological safety of the epidermal cell and the like are detected. The invention further provides a method for promoting epidermal cell proliferation and an application of JAM1kd-EC in wound repair or preparation of skin grafts.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
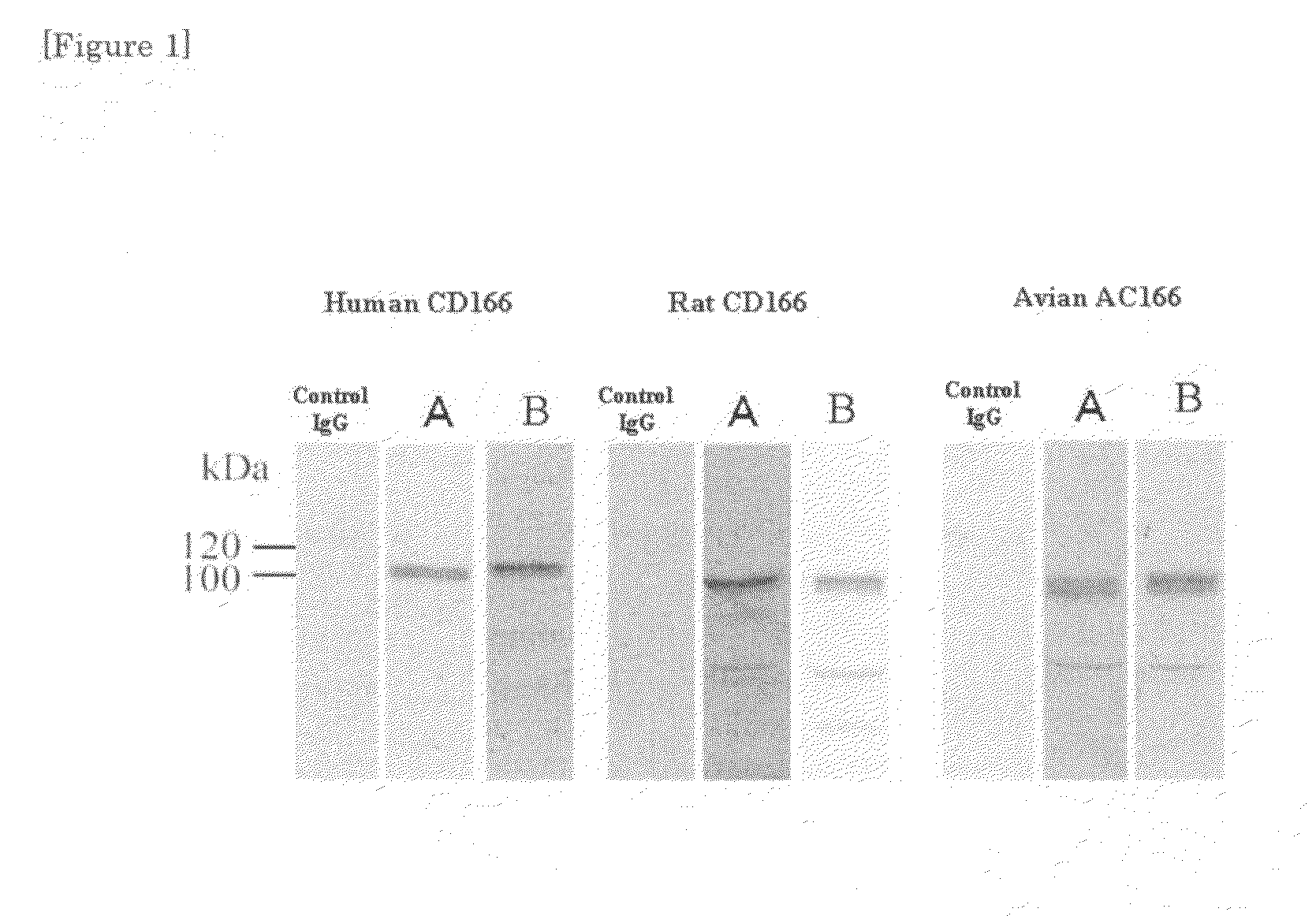
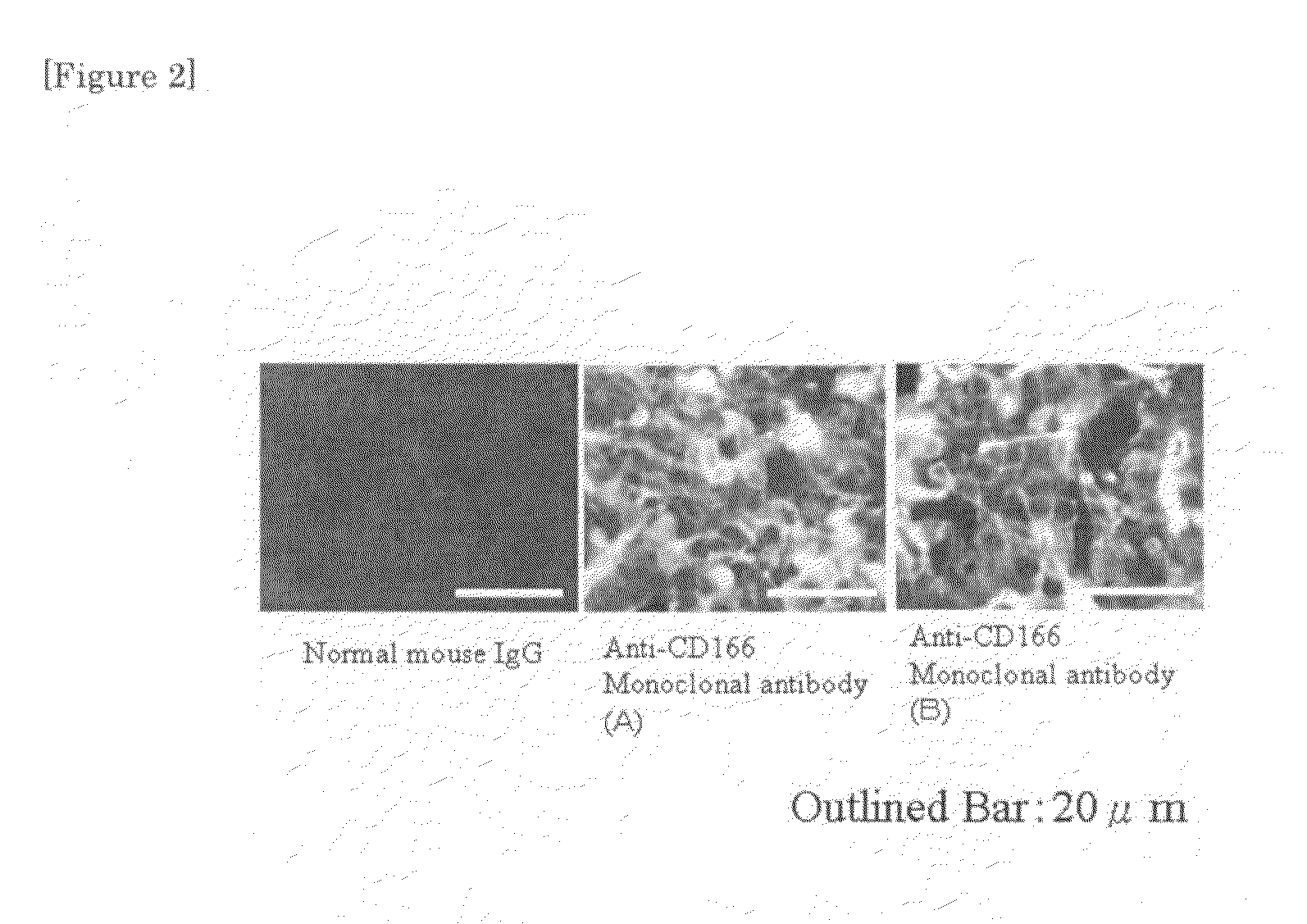
Monoclonal antibody to CD166 and method for production thereof
ActiveUS8003762B2Inhibited intercellular adhesionRestricted motilityAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalImmunoglobulin IgE
CD166 is a cell adhesion molecule belonging to an immunoglobulin superfamily that is expressed in an excessive amount on the tumor surface. If an monoclonal antibody specifically binding to the CD166 is obtained, it becomes possible to suppress growth of tumor cells, detect the cells, and supply a therapeutic drug thereto specifically. However, because the CD166 proteins are very similar to each other among mammals, it was not possible to obtain an antibody to human CD166, by immunizing, for example, mice with the human CD166.The antibody was prepared by immunizing mice with a purified avian CD166 protein. The antibody was found to be adsorbed on human and mouse CD166 proteins in vitro as well as in vivo and to have an action to suppress tumor growth in mice.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Monoclonal antibody of anti-human SIRPalpha, cell strain, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101880324BImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMicroorganism based processesHuman bodySignal-regulatory protein alpha
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical bioengineering, in particular to a monoclonal antibody of an anti-human signal regulating protein alpha (SIRPalpha), a preparation method and an application. The signal regulating protein alpha (SIRPalpha) is a member belonging to an immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), and tissues are mainly distributed in a medullary system (a macrophage cell, a dendritic cell and the like), therefore, the effect of the SIRPalpha in the immune adjustment of organism has been much accounted gradually. The invention provides the monoclonal antibody of the monoclonal antibody SIRPalpha, which is generated from a hybridoma cell strain with the preserved number of CGMCCNo.3801. The invention also provides the application of the monoclonal antibody in the preparation and detection of the SIRPalpha and in the preparation of drugs for stimulating macrophage TNF-alpha expression of a human body.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
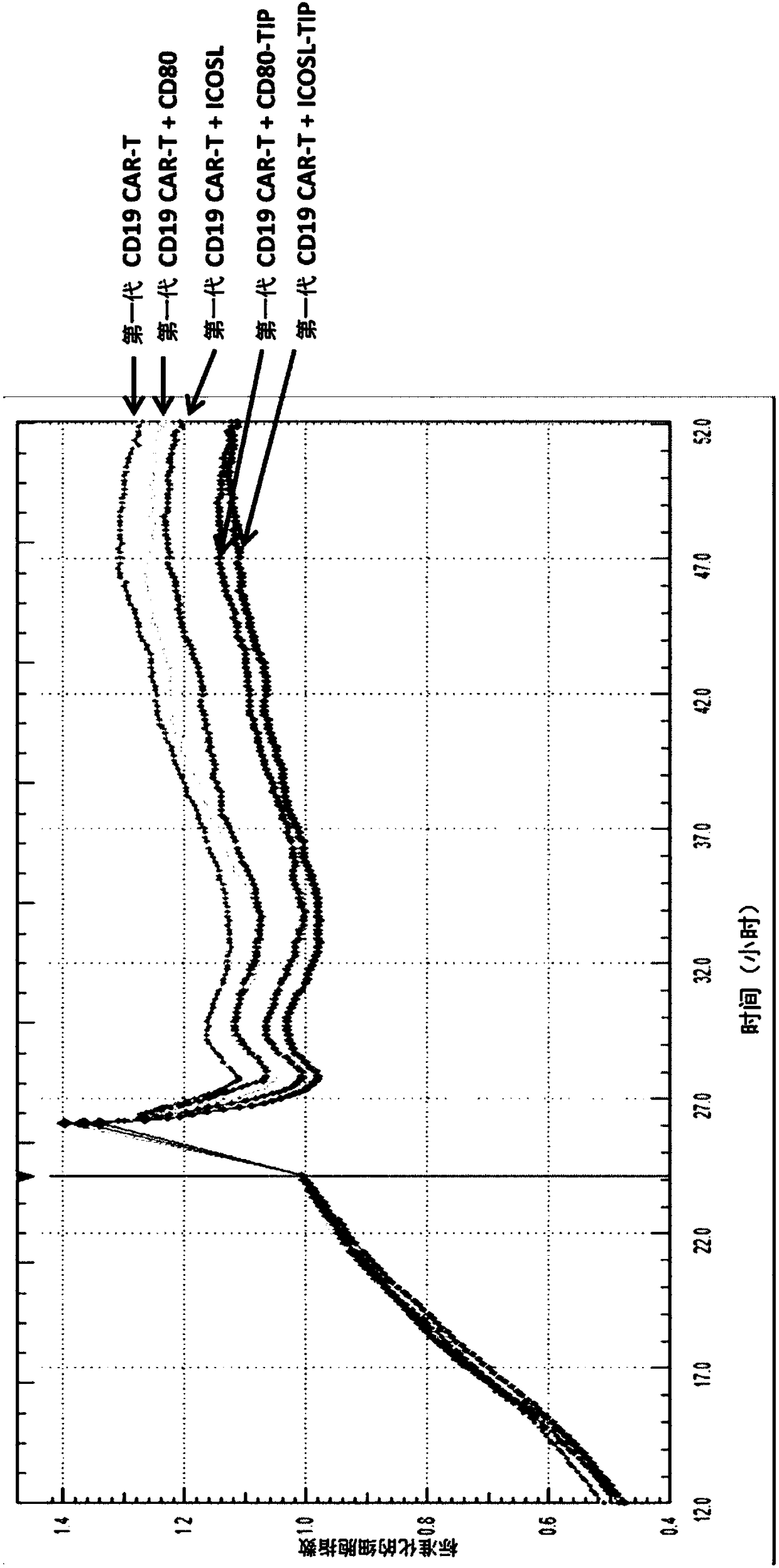
Tunable variant immunoglobulin superfamily domains and engineered cell therapy
Owner:ALPINE IMMUNE SCI INC
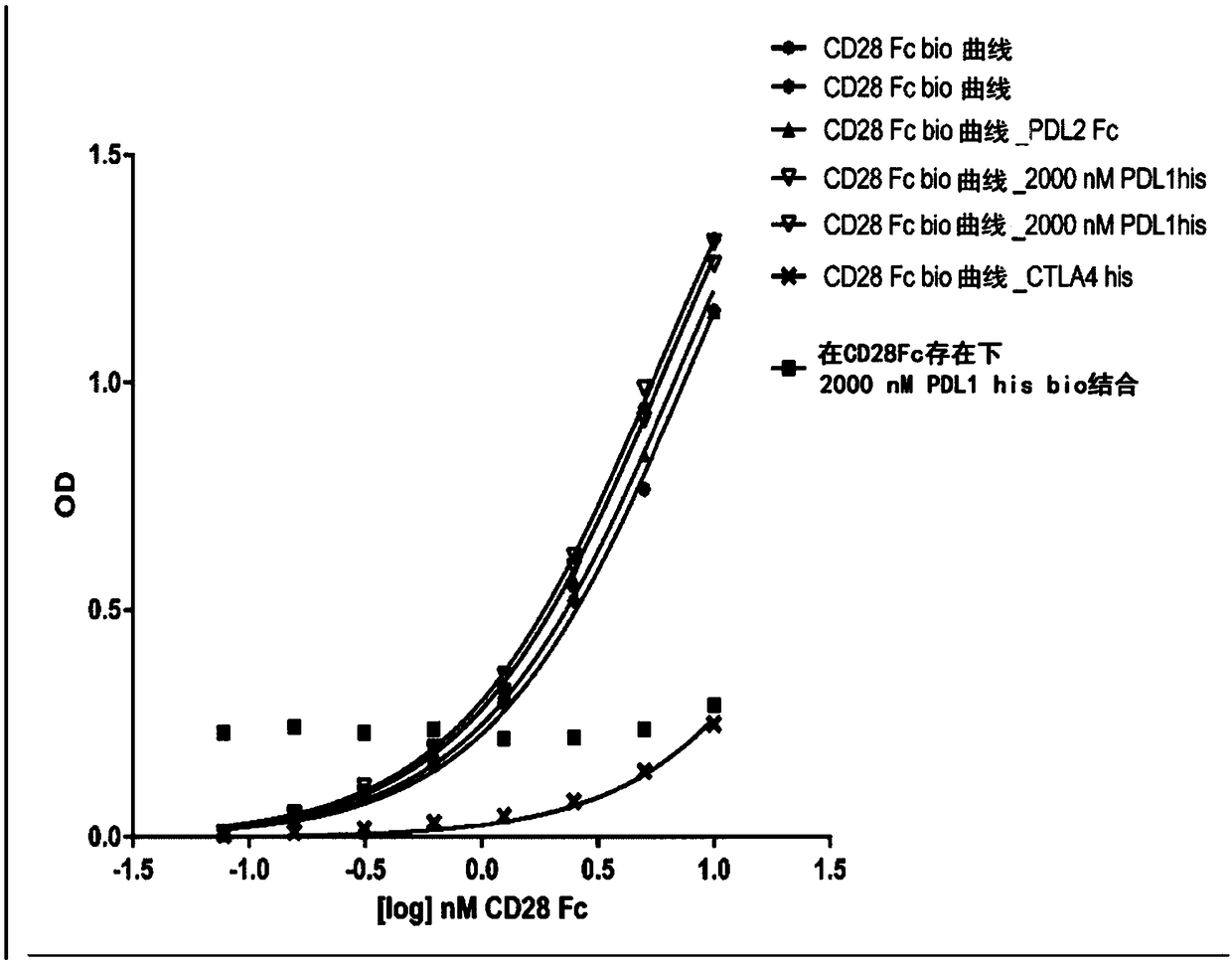
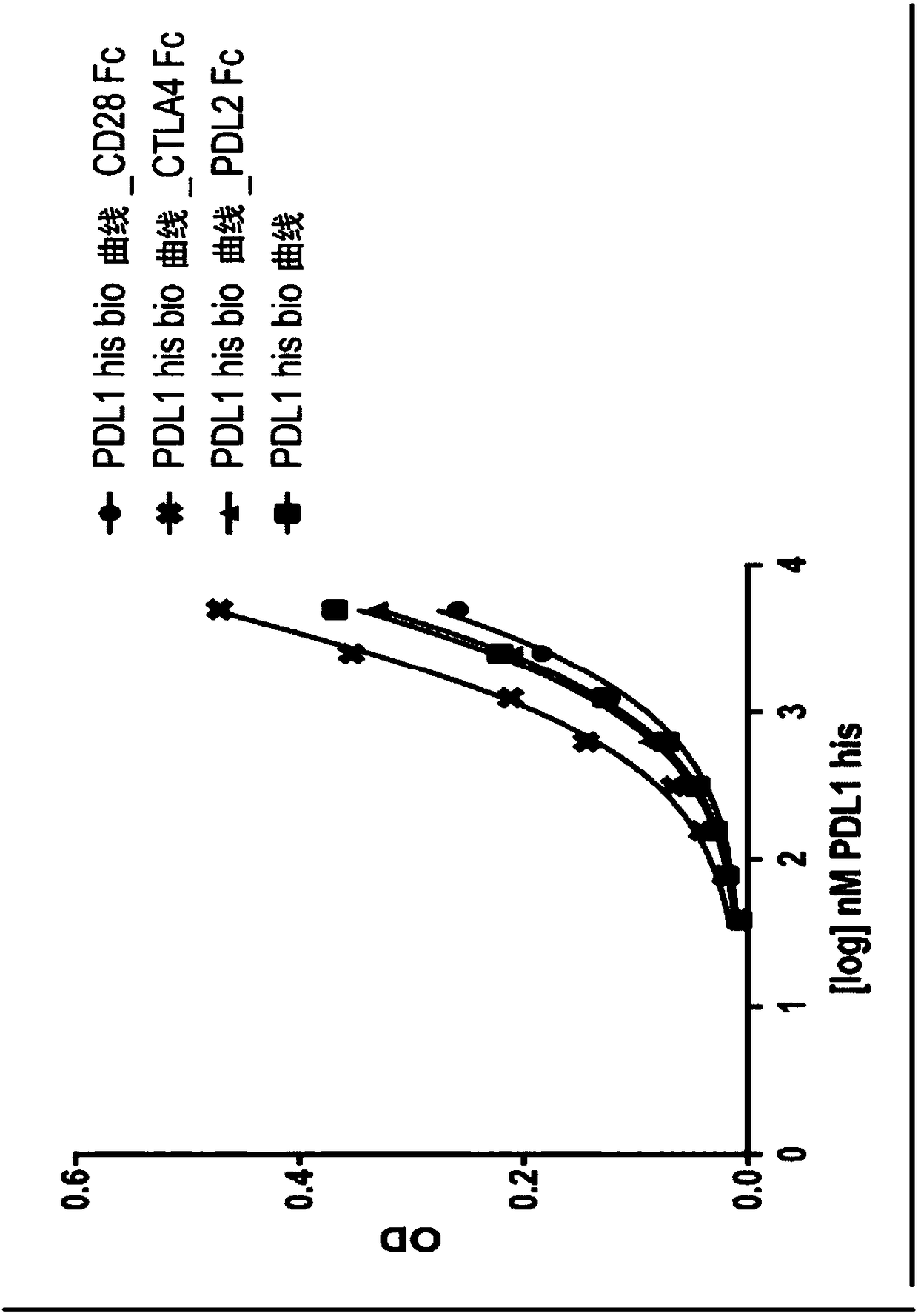
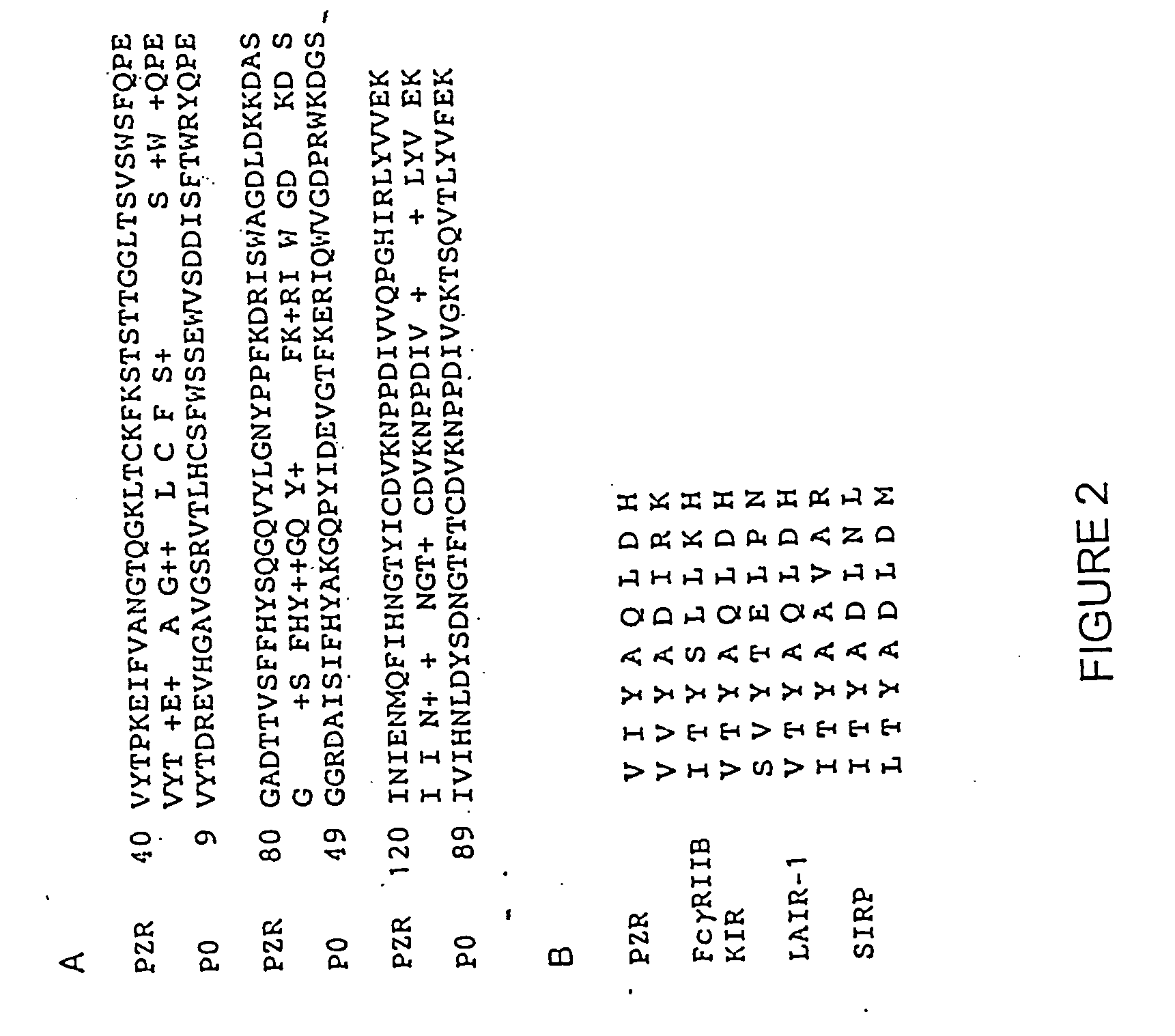
Purified and isolated protein zero related (PZR) and therapeutic and screening methods using same
InactiveUS20060014932A1Animal cellsImmunoglobulin superfamilyImmunoglobulin superfamilyCell signaling
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Biomarker for predicting effects of Anti-pd-1 antibody/Anti-pd-l1 antibody therapy
PendingUS20210002714A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsBiologic markerImmunoglobulin superfamily
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel marker that can be used to predict the effect of anti-PD-1 antibody / anti-PD-L1 antibody therapy with high sensitivity, and use thereof. Provided is a biomarker for predicting the effect of anti-PD-1 antibody / anti-PD-L1 antibody therapy, including an immunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat (ISLR).
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKAI NAT HIGHER EDUCATION & RES SYST
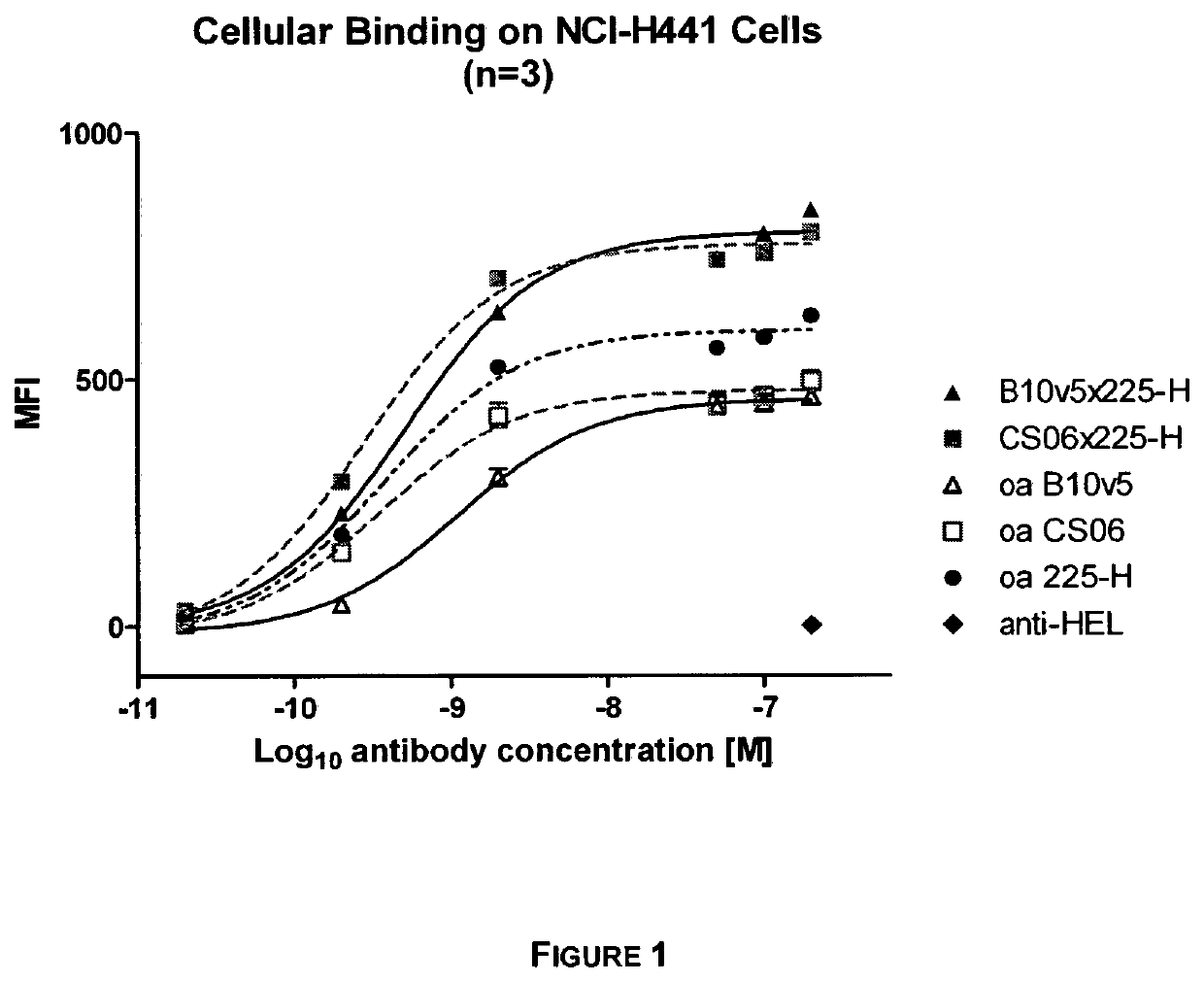
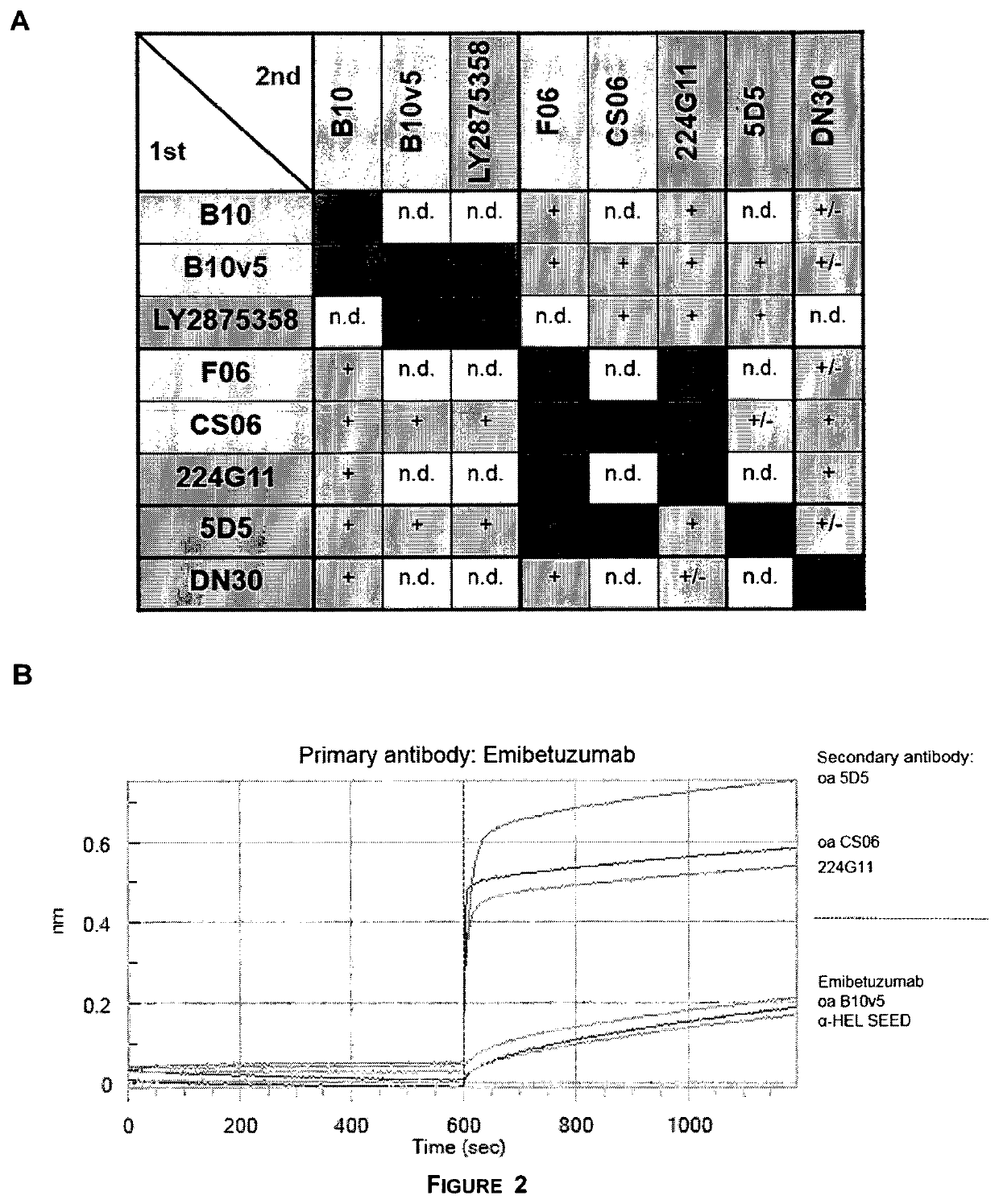
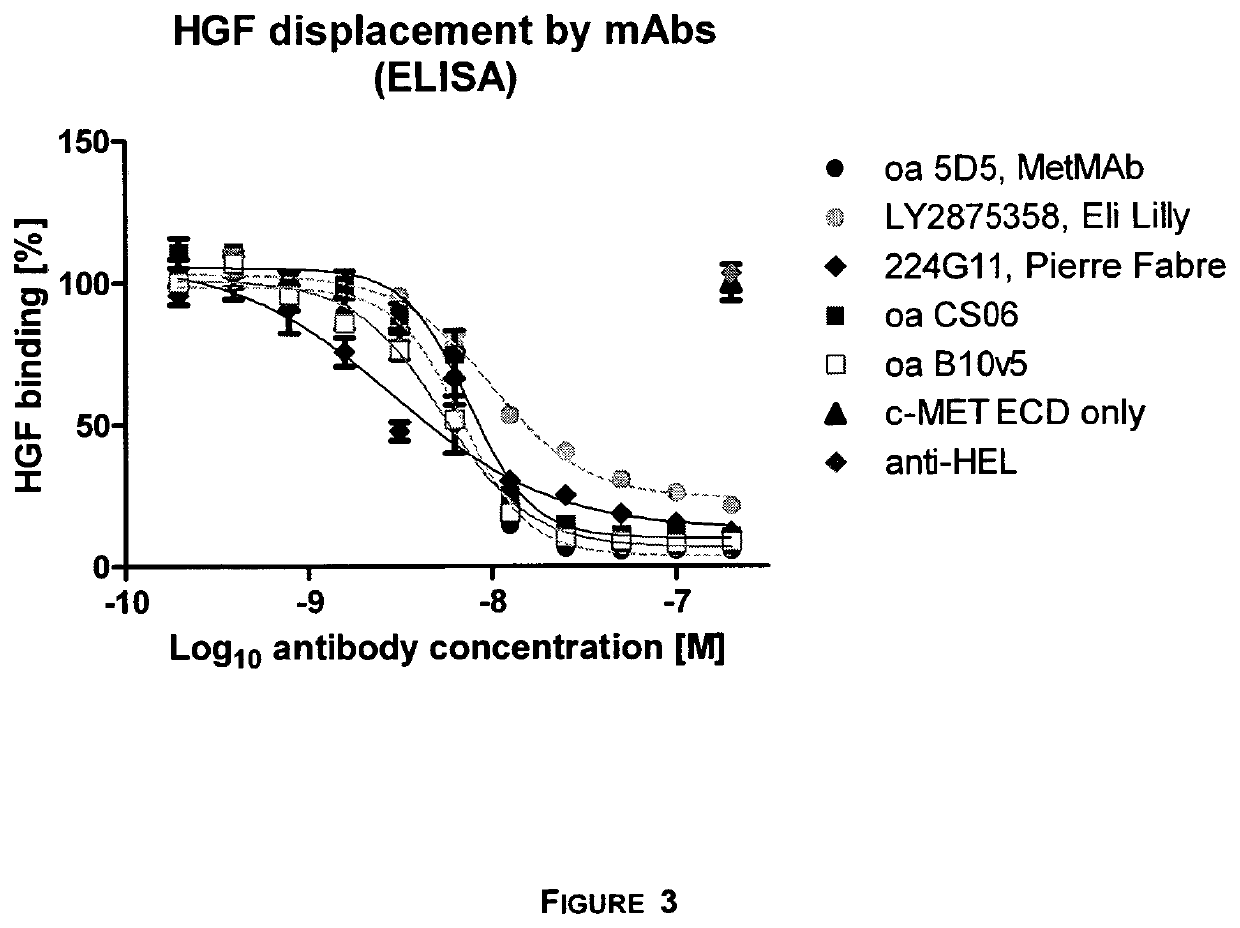
Bi-specific antibodies for enhanced tumor selectivity and inhibition and uses thereof
ActiveUS20180326085A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsInteraction interfaceHybrid protein
A heterodimeric bispecific immunoglobulin molecule includes a first Fab or scFv fragment which specifically binds to EGFR, and a second Fab or scFv fragment which specifically binds to c-MET, and an antibody hinge region, an antibody CH2 domain and an antibody CH3 domain including a hybrid protein-protein interaction interface domain. Each of the interaction interface domains is formed by an amino acid segment of the CH3 domain of a first member and an amino acid segment of the CH3 domain of a second member. The hybrid protein-protein interface domain of the first chain is interacting with the protein-protein-interface of the second chain by homodimerization of a corresponding amino acid segment of the same member of the immunoglobulin superfamily within interaction domains.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Lung cancer marker and applications thereof
InactiveCN106568955AEasy to acceptTraumaIndividual particle analysisDendritic cellTreatment of lung cancer
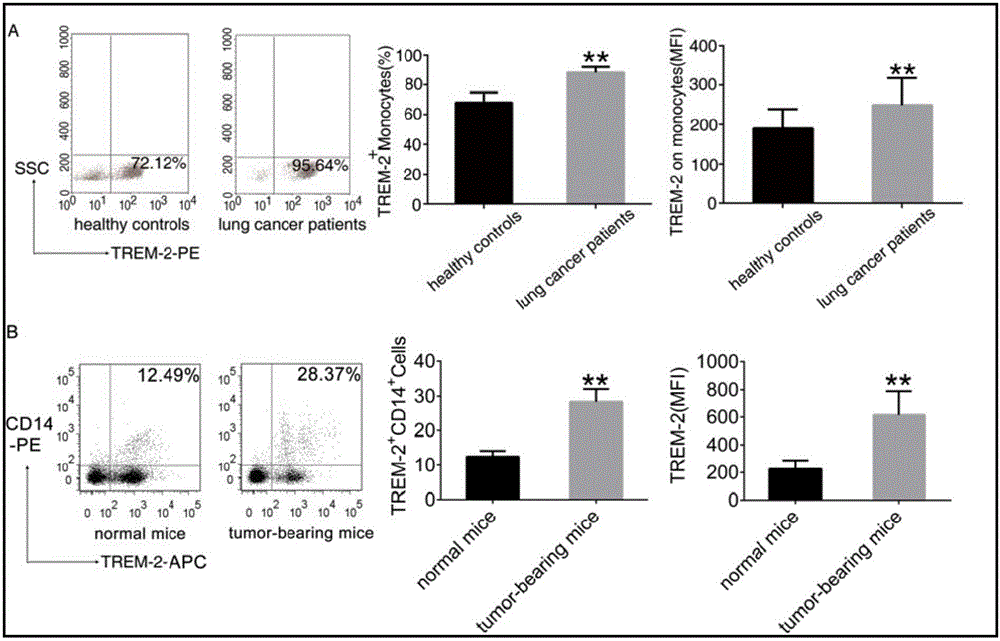
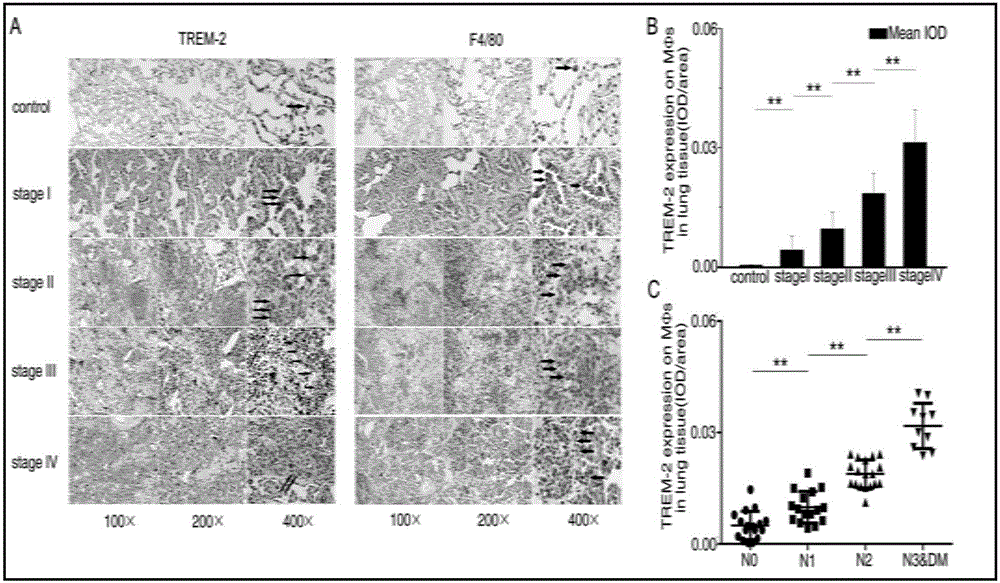
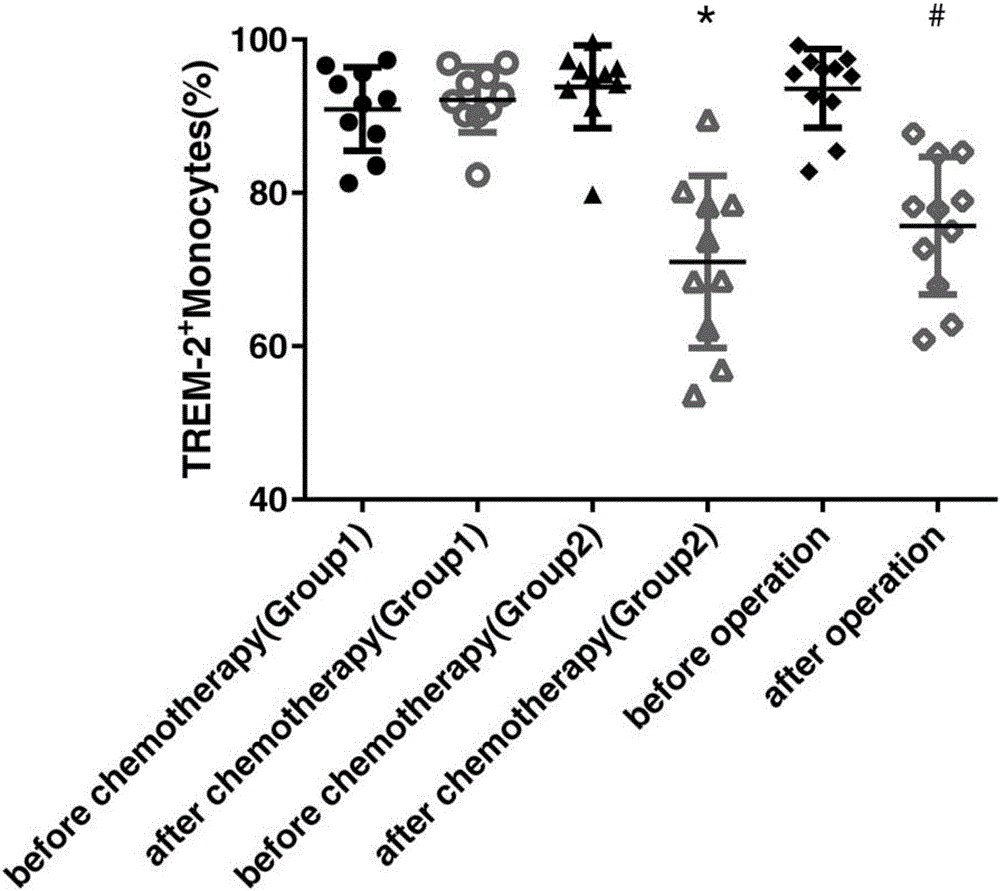
The invention provides a lung cancer marker, which is a TREM-2 protein. The marker is a membrane surface acceptor, which is specifically expressed to myeloid derived dendritic cells and mononuclear macrophage, and belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. The expression of TREM-2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of lung cancer patients and tumor-bearing mice is obviously higher than the expression of TREM-2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of healthy persons and normal mice. The immunohistochemical method detection shows that high expression of TREM-2 exists in the macrophage of lung cancer patients and TREM-2 is in positive correlation with the development of lung cancer. The novel tumor marker (triggering receptors expressed on myeloid cells) namely TERM-2 can be used as a molecular marker of lung cancer diagnosis and treatment, has the advantages of convenience, rapidness, little damage, and easy reexamination, can be easily accepted by the patients, has an important meaning for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
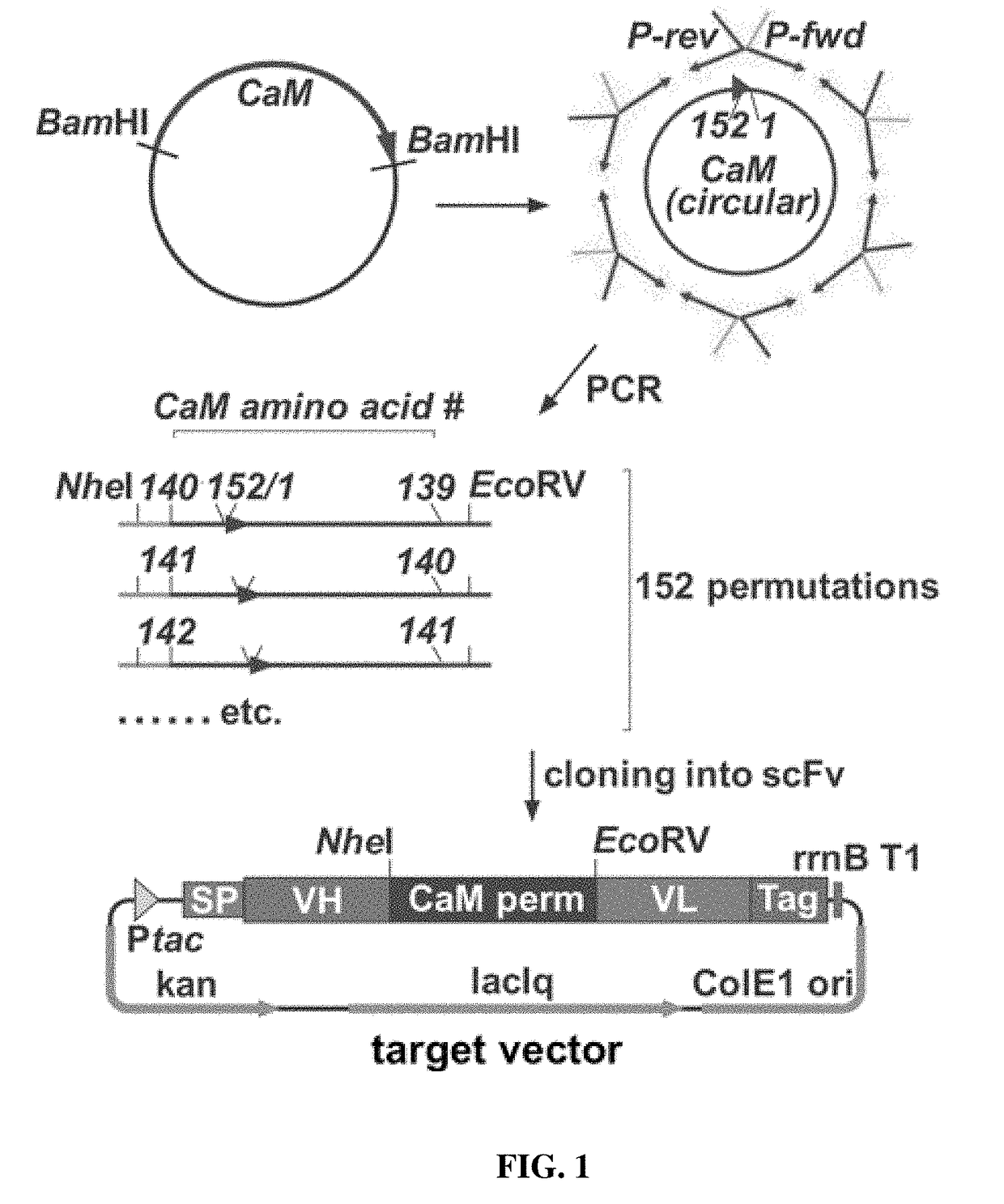
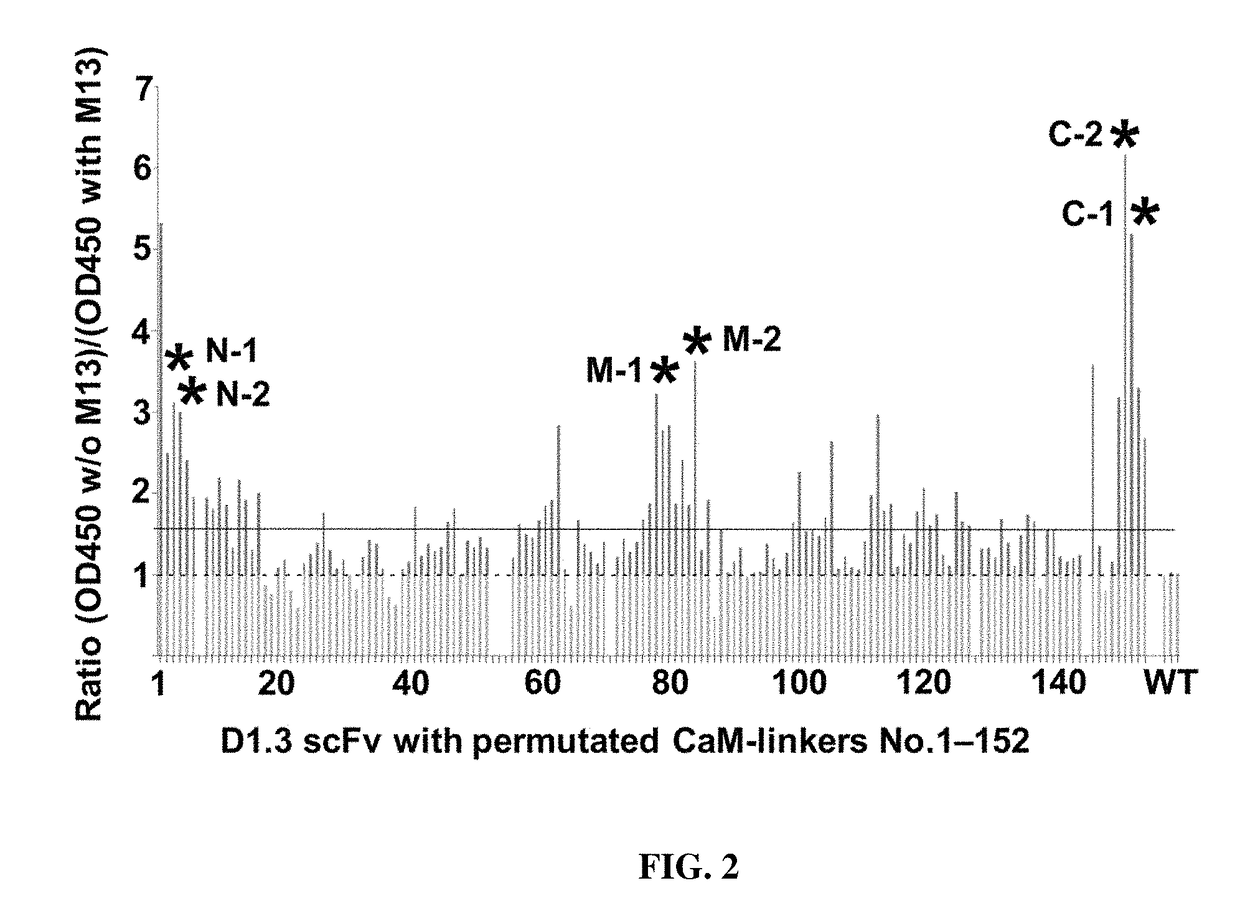
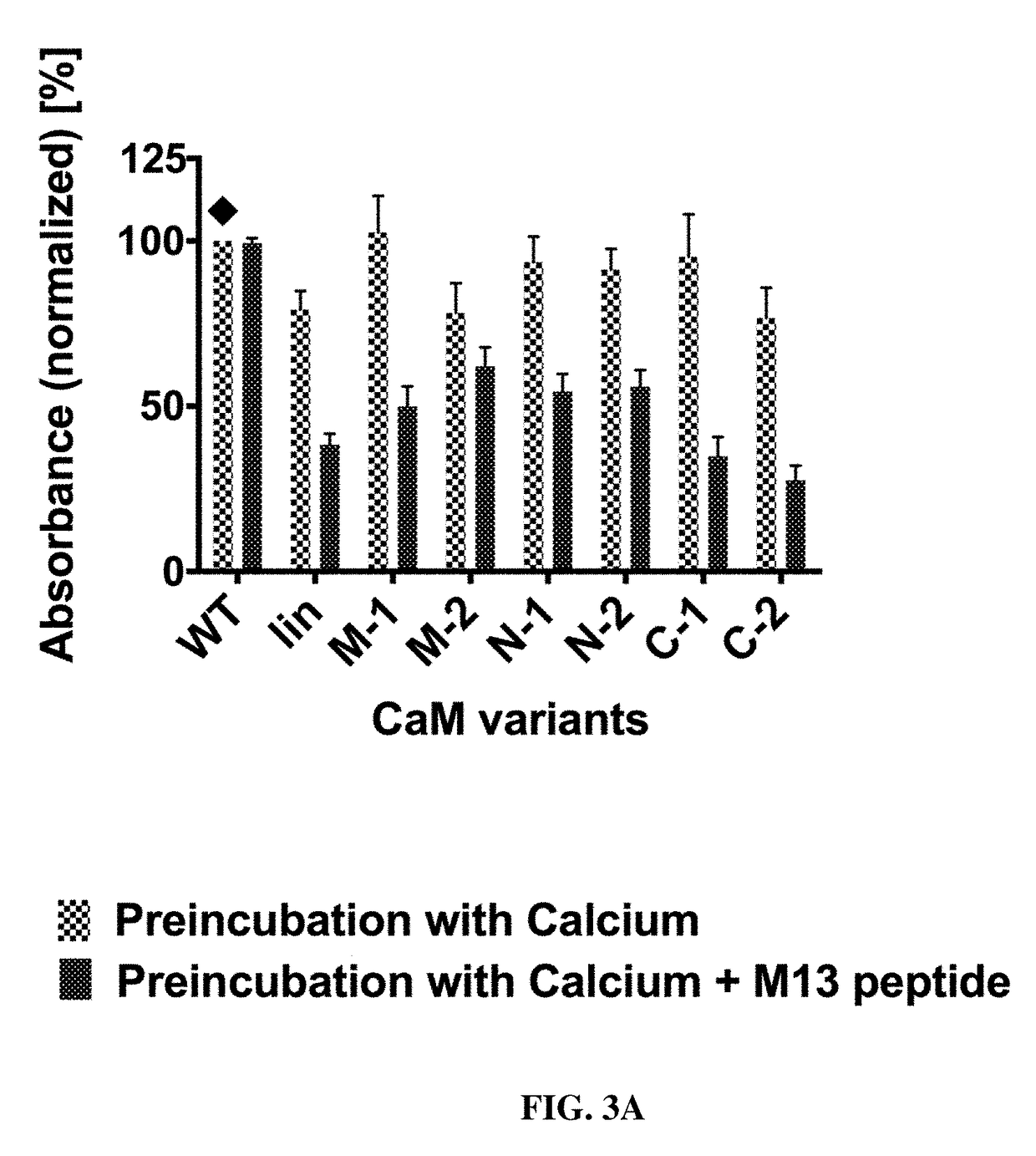
Composition and method for affecting the binding of antigen-binding polypeptides to antigens
ActiveUS10730922B2Strong changeReduce the binding forcePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifTransferasesBinding siteAntigen binding
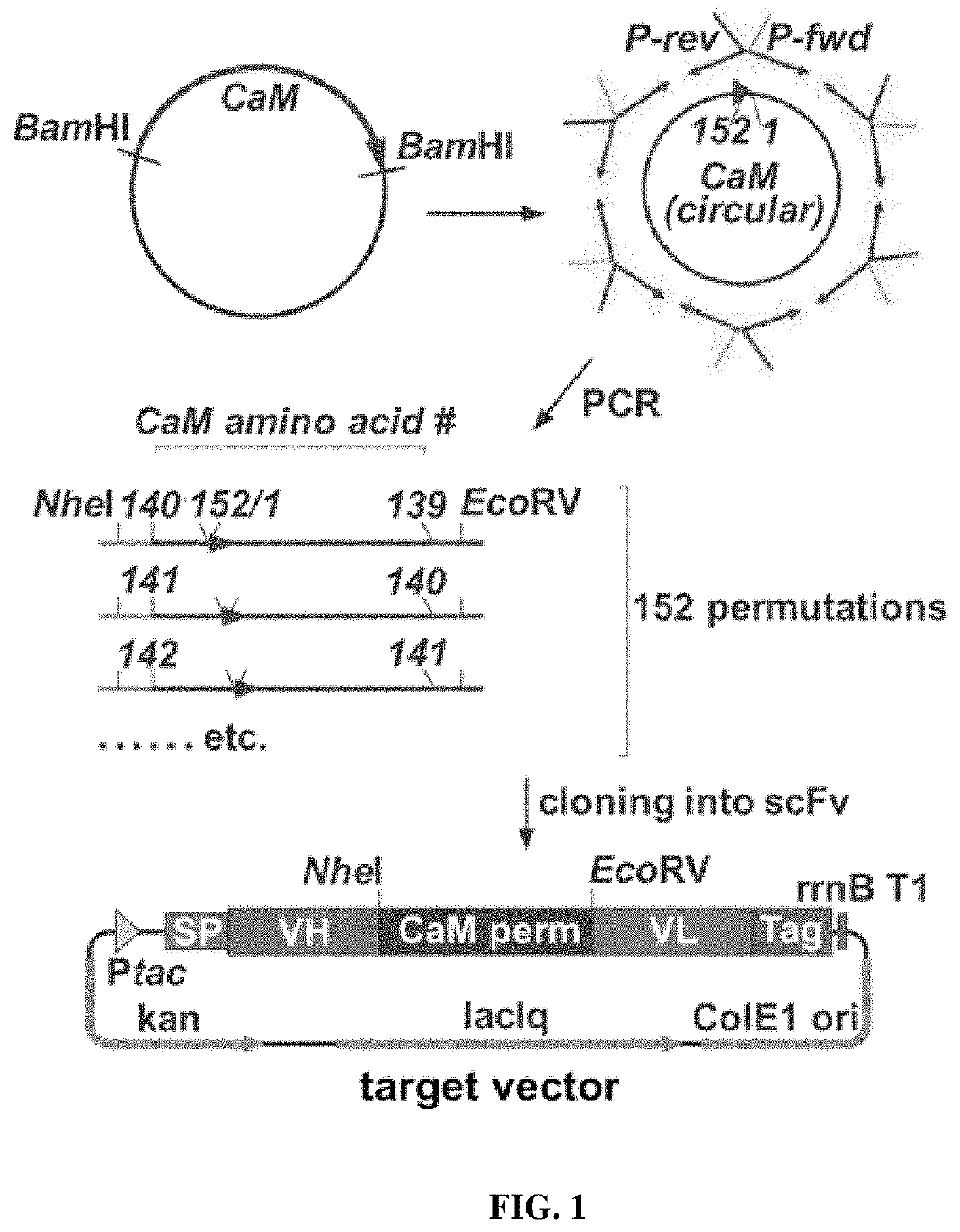
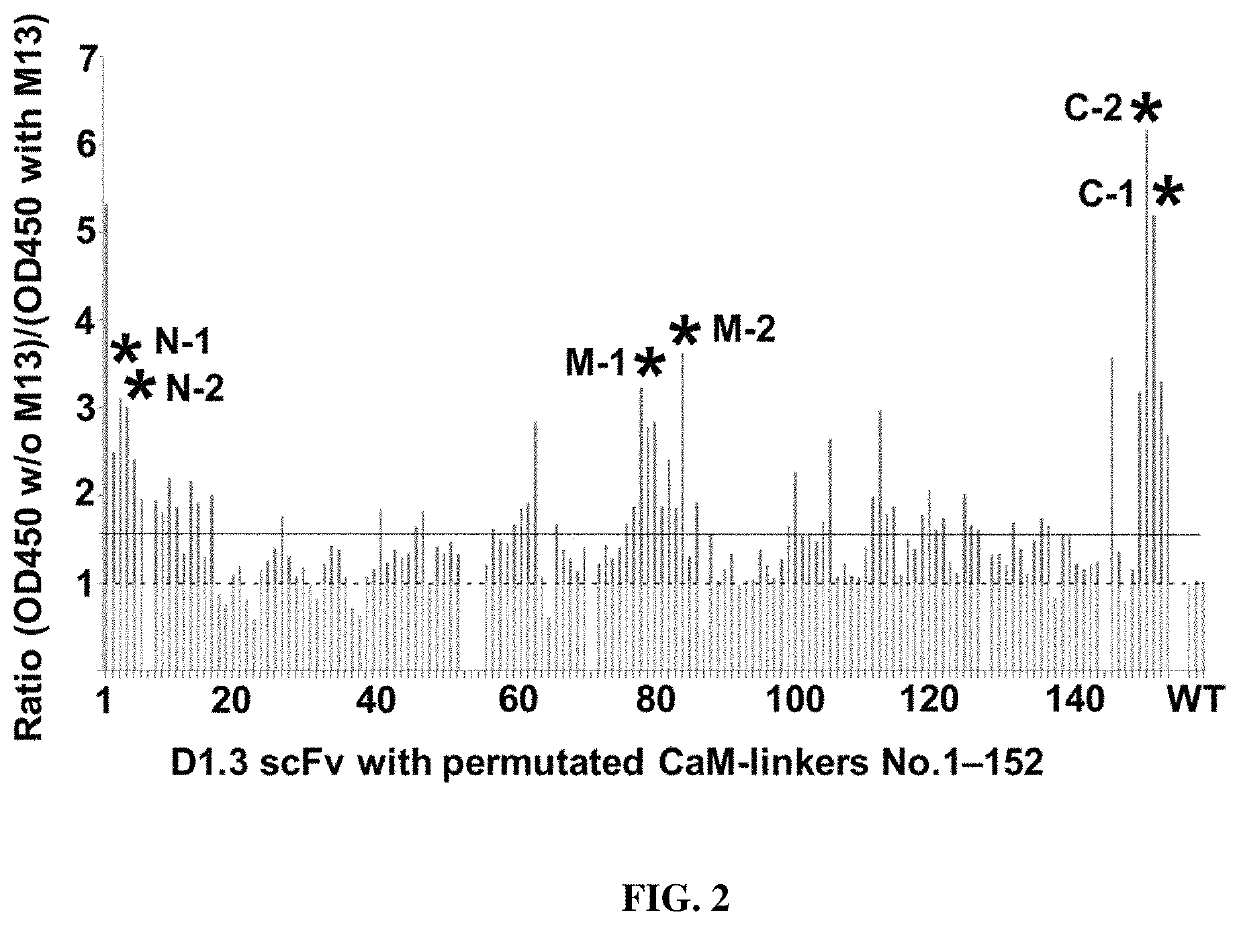
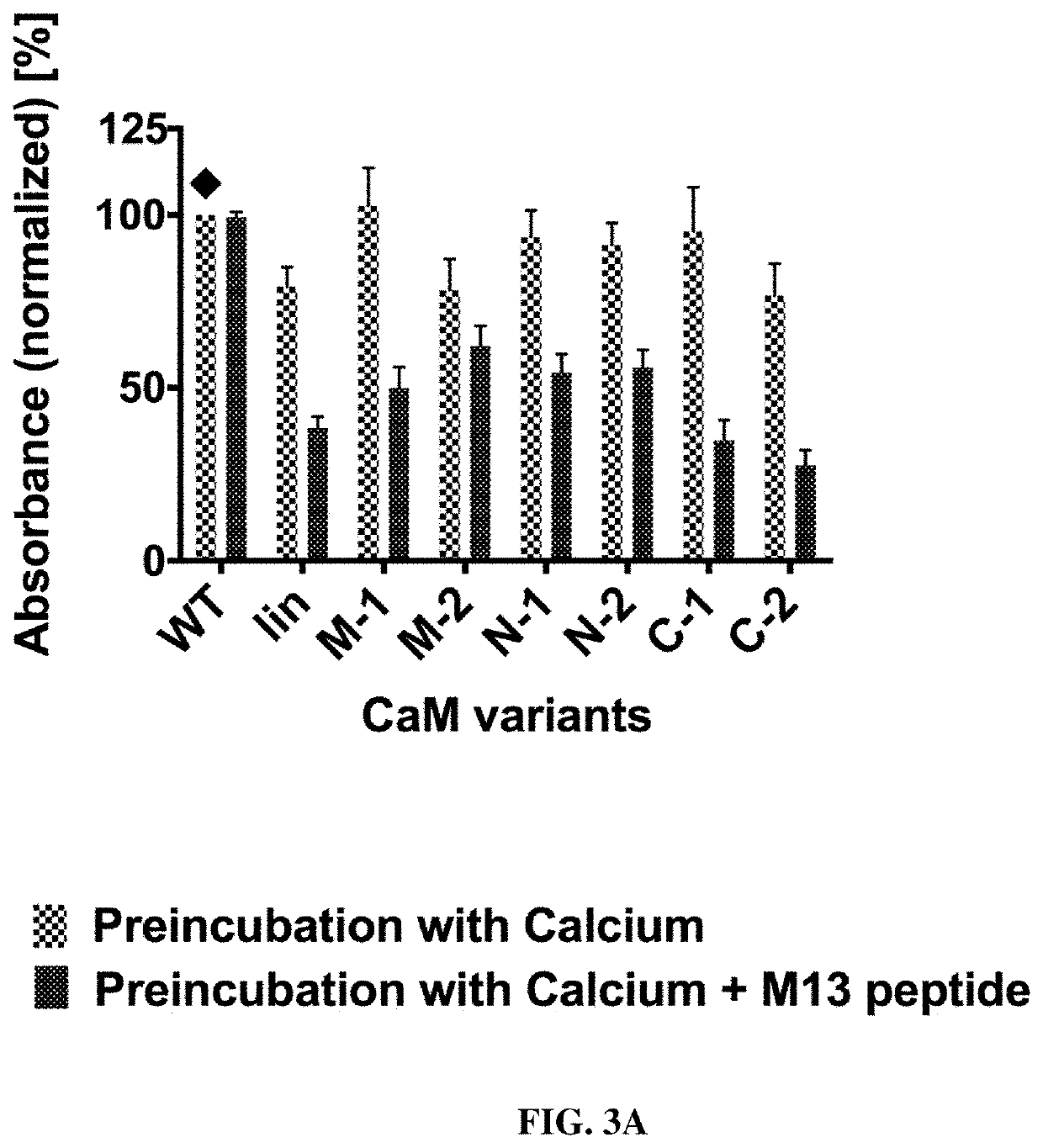
The present invention provides a composition comprising i) a polypeptide comprising calmodulin and two immunoglobulin superfamily domains, wherein said two immunoglobulin superfamily domains are linked via said calmodulin; ii) a calmodulin binding molecule; iii) ions binding to the Ca2+ binding site of calmodulin; wherein the binding of said calmodulin-binding molecule and of said ions to said Ca2+ binding site of calmodulin affects the binding of said polypeptide to an antigen to be bound by said polypeptide. The calmodulin may be a permutated calmodulin. A method for affecting the binding of a polypeptide for an antigen using said composition is also disclosed.
Owner:MABSWITCH INC +1
Recombinant multiple domain fusion protein mitogens and use thereof for inducing enhancement or repression of antigen-specific immunity
ActiveUS9931386B2Improve responseVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsIMMUNE SUPPRESSANTSAutoimmune responses
Owner:OCHI ATSUO
Treatment of cancer metastasis by targeting exosome proteins
PendingUS20220144942A1Reduces and prevents cancer metastasisReduces or prevents cancer metastasisPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenCancer metastasis
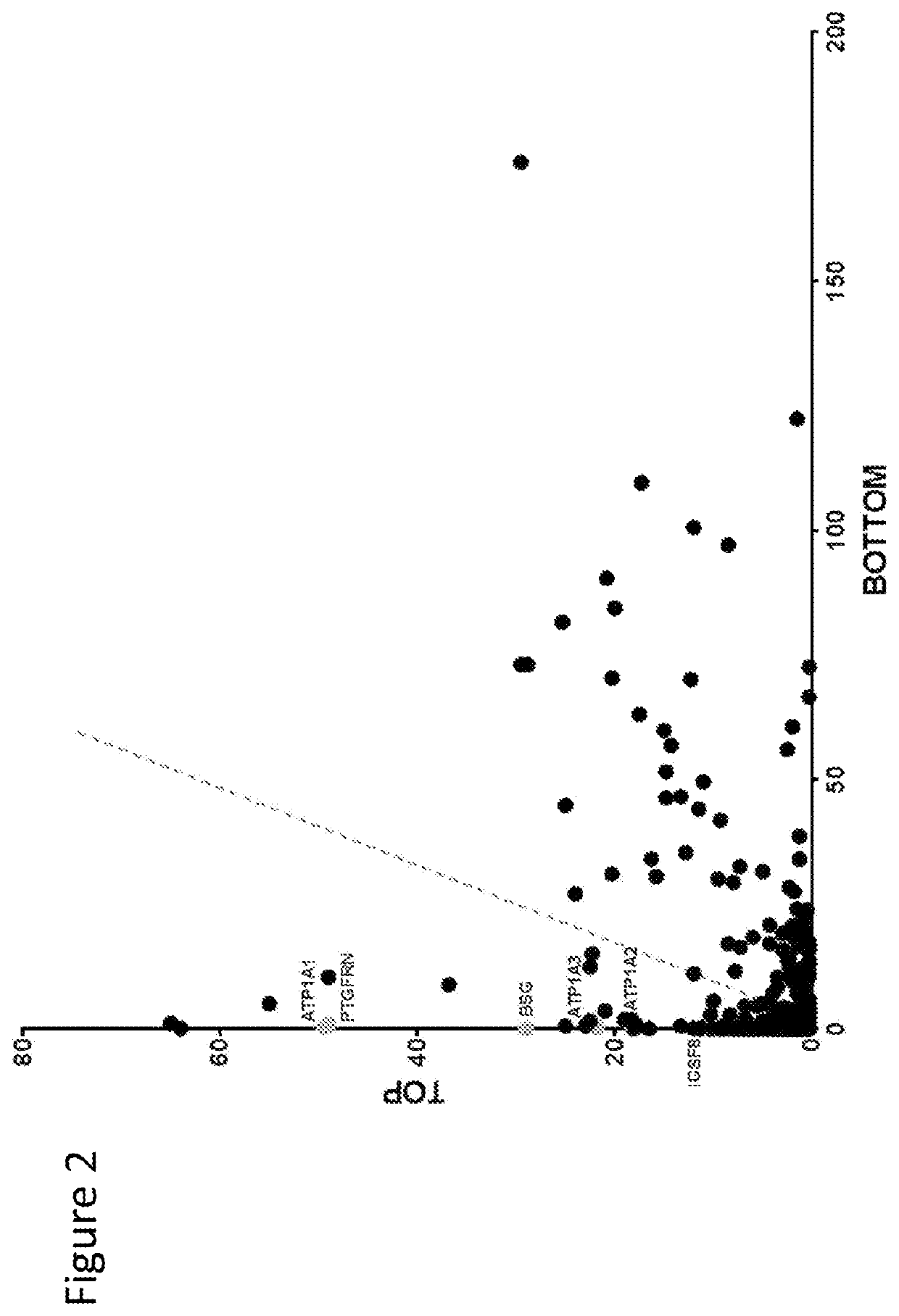
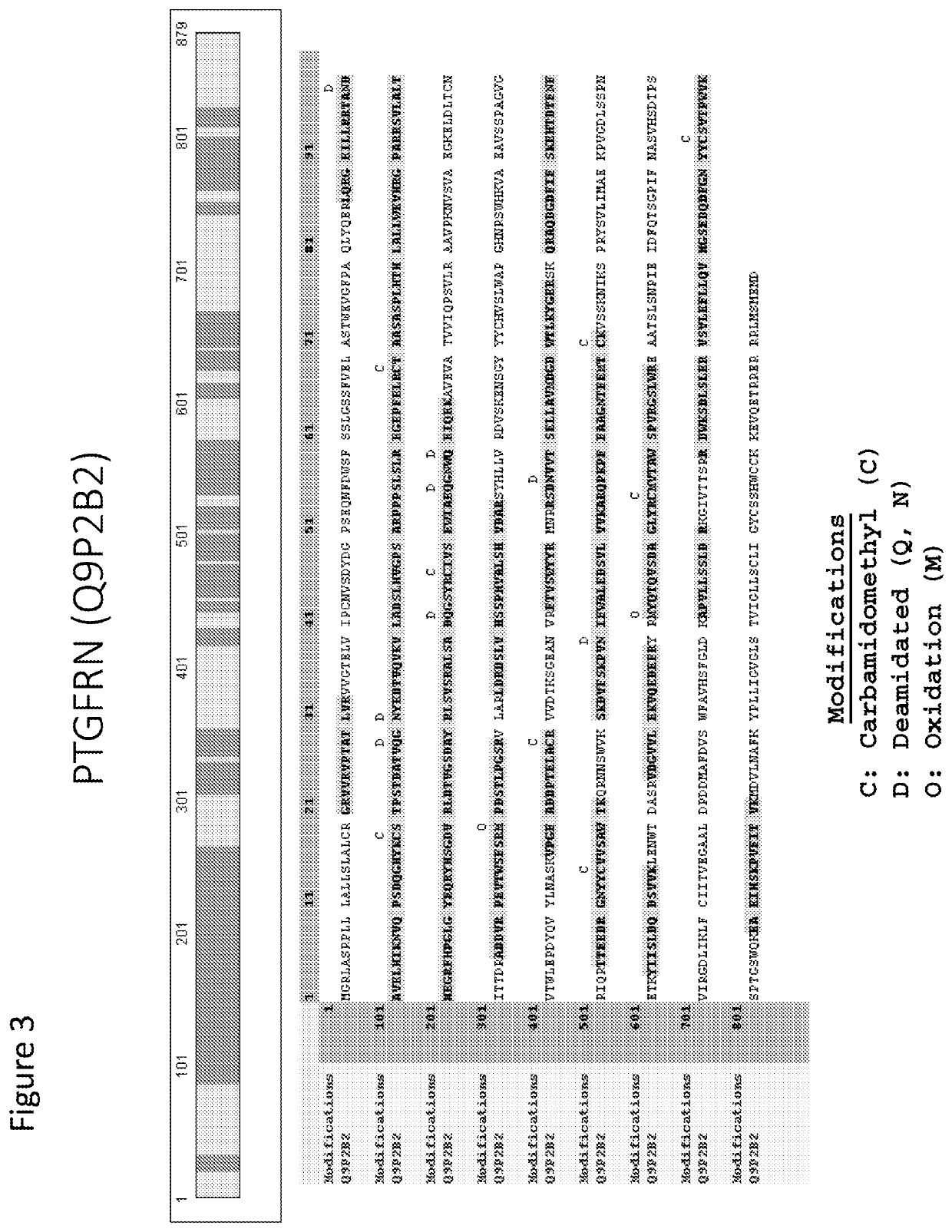
The present disclosure provides a therapeutic method of treating cancer metastasis by inducing clearance of EVs using a binding agent specific to an EV protein. The method utilizes one or more binding agents specific to EV proteins, where the EV proteins are selected from prostaglandin F2 receptor negative regulator (PTGFRN); basigin (BSG); immunoglobulin superfamily member 2 (IGSF2); immunoglobulin superfamily member 3 (IGSF3); immunoglobulin superfamily member 8 (IGSF8); integrin beta-1 (ITGB1); integrin alpha-4 (ITGA4); 4F2 cell-surface antigen heavy chain (SLC3A2); a class of ATP transporter proteins (ATP1A1, ATP1A2, ATP1A3, ATP1A4, ATP1B3, ATP2B1, ATP2B2, ATP2B3, ATP2B4); CD13 (aminopeptidase N); MME (neprilysin), ENPP1 (ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase / phosphodiesterase family member 1); and NRP1 (neuropilin-1). Further provided herein includes a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of cancer metastasis.
Owner:LONZA SALES AG
Bi-specific antibodies for enhanced tumor selectivity and inhibition and uses thereof
ActiveUS11235063B2Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDimerHybrid protein
A heterodimeric bispecific immunoglobulin molecule includes a first Fab or scFv fragment which specifically binds to EGFR, and a second Fab or scFv fragment which specifically binds to c-MET, and an antibody hinge region, an antibody CH2 domain and an antibody CH3 domain including a hybrid protein-protein interaction interface domain. Each of the interaction interface domains is formed by an amino acid segment of the CH3 domain of a first member and an amino acid segment of the CH3 domain of a second member. The hybrid protein-protein interface domain of the first chain is interacting with the protein-protein-interface of the second chain by homodimerization of a corresponding amino acid segment of the same member of the immunoglobulin superfamily within interaction domains.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in leukemia signaling pathways
InactiveUS20090142777A1Animal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansHuman leukemiaADAMTS Proteins
The invention discloses 424 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeletal proteins, Cellular Metabolism enzymes, G Protein / GTPase Activating / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor proteins, Immunoglobulin Superfamily proteins, Inhibitor proteins, Lipid Kinases, Nuclear DNA Repair / RNA Binding / Transcription proteins, Serine / Threonine Protein Kinases, Tyrosine Kinases, Protein Phosphatases, and Translation / Transporter proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Method for promoting epidermal cell proliferation
The invention relates to the technical fields of stem cells and gene engineering, and particularly provides a method for promoting epidermal cell proliferation based on gene modification and gene interference with epidermal cells by using a junctional adhesion molecule JAM1 (NM-016946) which is a transmembrane molecule and belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. The invention further provides a low expression epidermal cell of the junctional adhesion molecule JAM1 gene, i.e. JAM1kd-EC, and the proliferation ability of the epidermal cell, the properties and the biological safety of the epidermal cell and the like are detected. The invention further provides a method for promoting epidermal cell proliferation and an application of JAM1kd-EC in wound repair or preparation of skin grafts.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Recombinant multiple domain fusion protein mitogens and use thereof for inducing enhancement or repression of antigen-specific immunity.
ActiveUS20180200352A1Improve responseSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsIMMUNE SUPPRESSANTSAutoimmune responses
Owner:OCHI ATSUO
Composition and method for affecting the binding of antigen-binding polypeptides to antigens
ActiveUS20180030104A1Improve bindingReduce the binding forcePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifTransferasesBinding siteAntigen binding
The present invention provides a composition comprising i) a polypeptide comprising calmodulin and two immunoglobulin superfamily domains, wherein said two immunoglobulin superfamily domains are linked via said calmodulin; ii) a calmodulin binding molecule; iii) ions binding to the Ca2+ binding site of calmodulin; wherein the binding of said calmodulin-binding molecule and of said ions to said Ca2+ binding site of calmodulin affects the binding of said polypeptide to an antigen to be bound by said polypeptide. The calmodulin may be a permutated calmodulin. A method for affecting the binding of a polypeptide for an antigen using said composition is also disclosed.
Owner:MABSWITCH INC +1
LIR-9, a novel leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
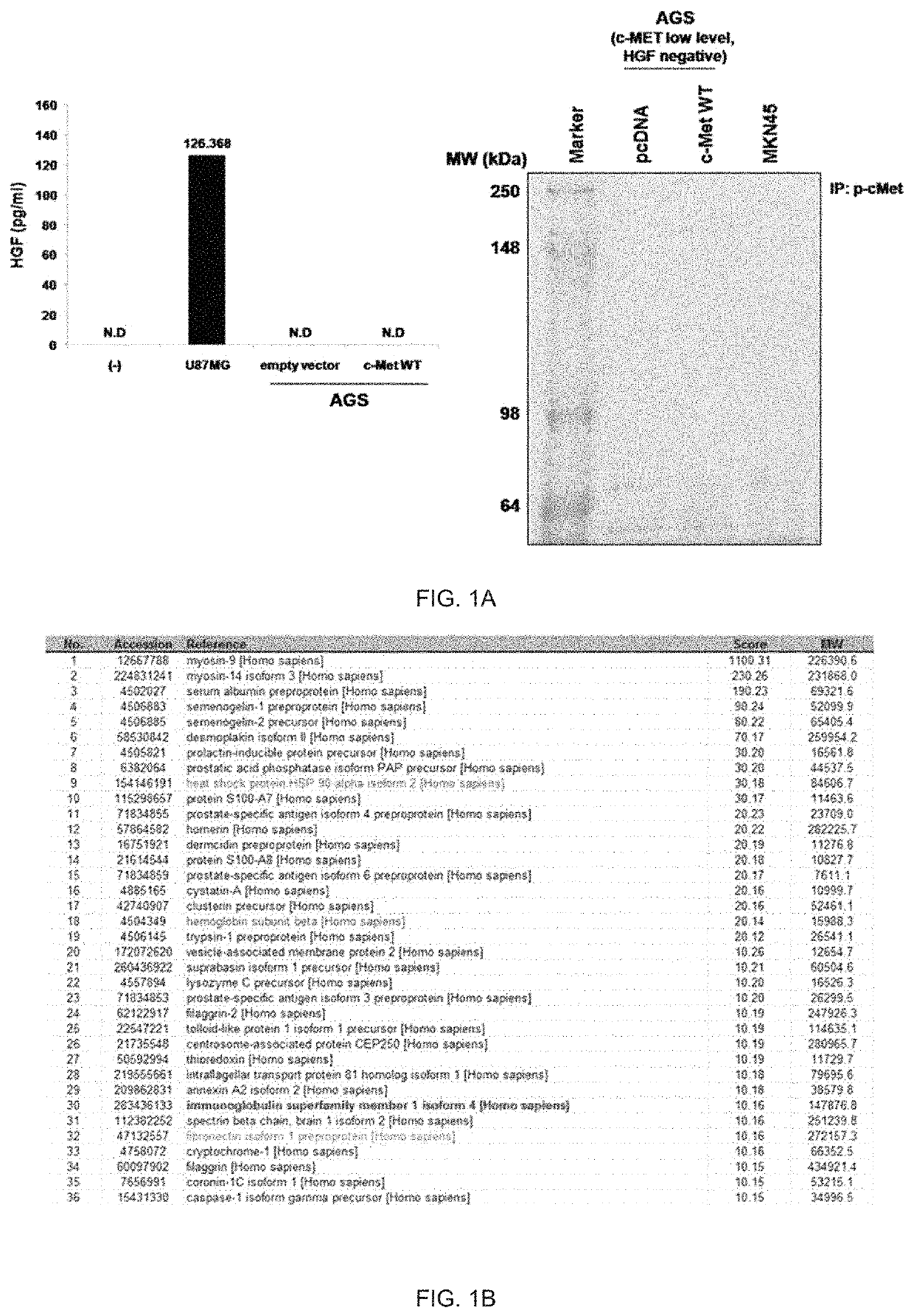
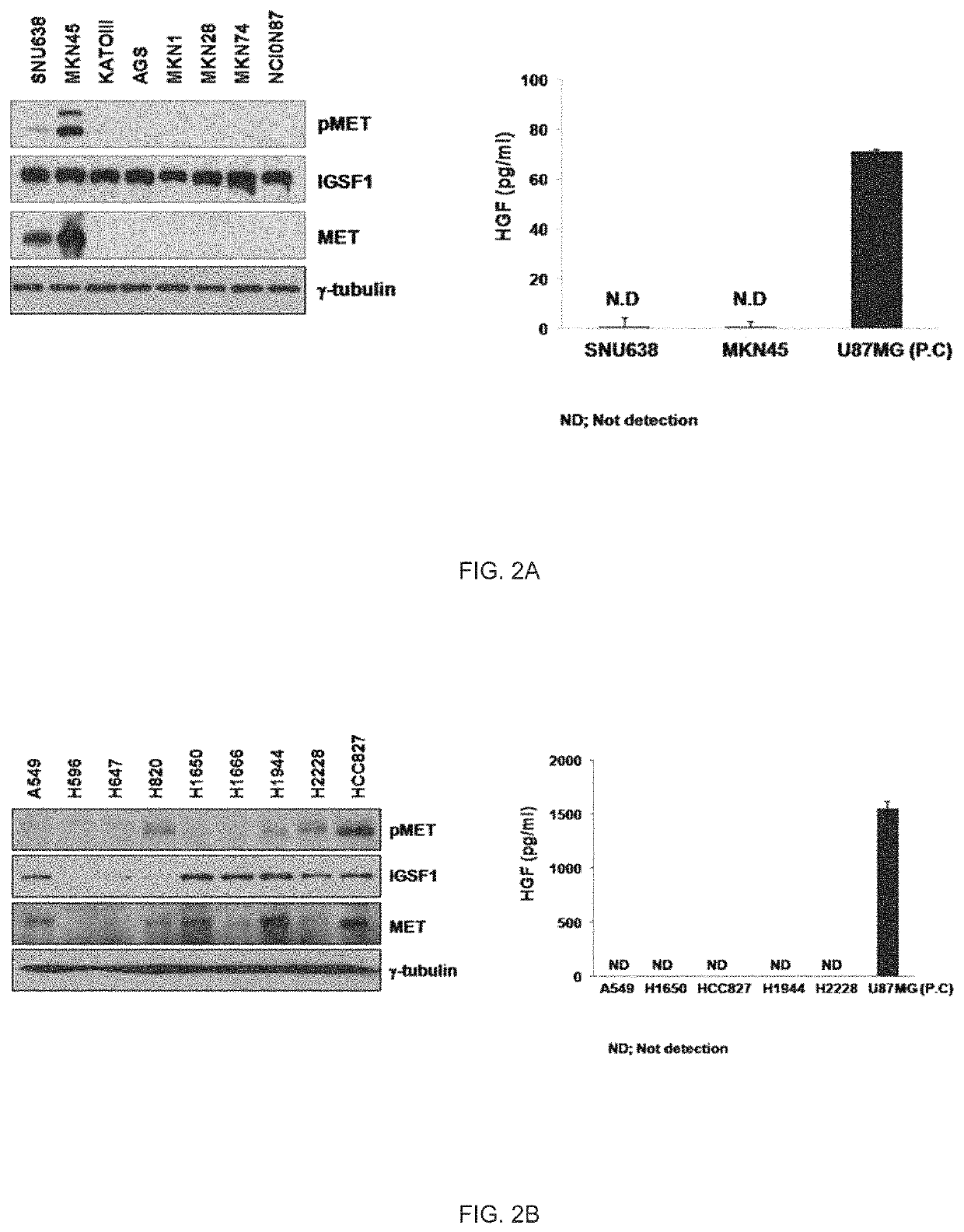
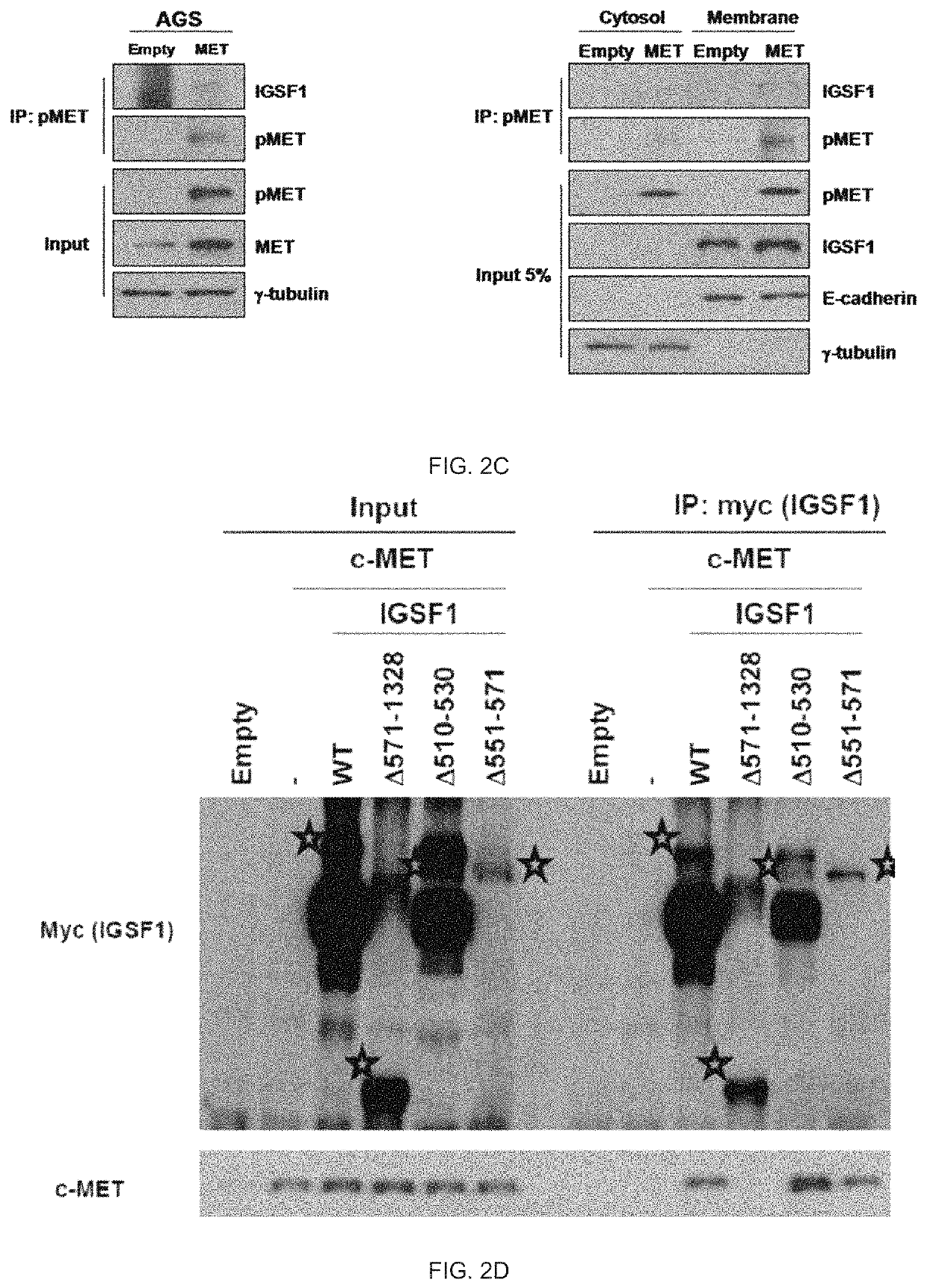
Combination method for treating cancer by targeting immunoglobulin superfamily member 1 (IGSF1) and mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (MET)
ActiveUS11186873B2Reliably determinedHigh therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologic markerImmunoglobulin superfamily
The present invention relates to a biomarker for predicting susceptibility to an MET inhibitor, and a use thereof, and more specifically, the present invention provides a method for predicting susceptibility to the MET inhibitor. According to the present invention, the present invention has an excellent effect of predicting susceptibility to the MET inhibitor for stomach cancer or lung cancer, and thus the present invention may be usefully employed for treating stomach cancer or lung cancer.
Owner:WELLMARKER BIO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com