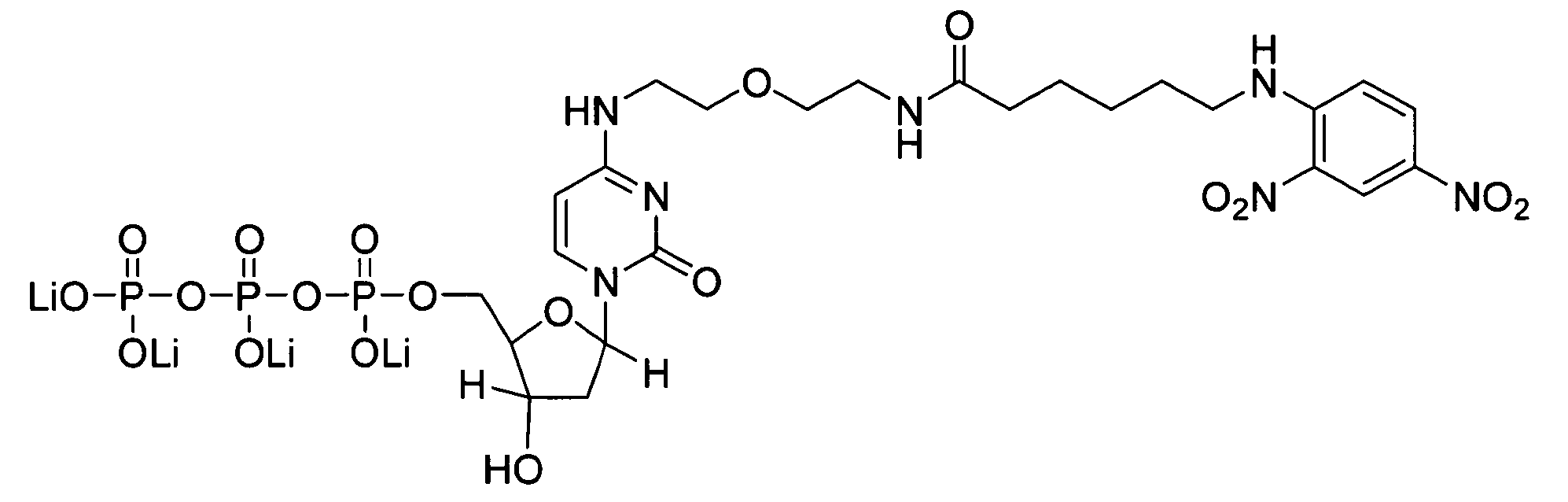
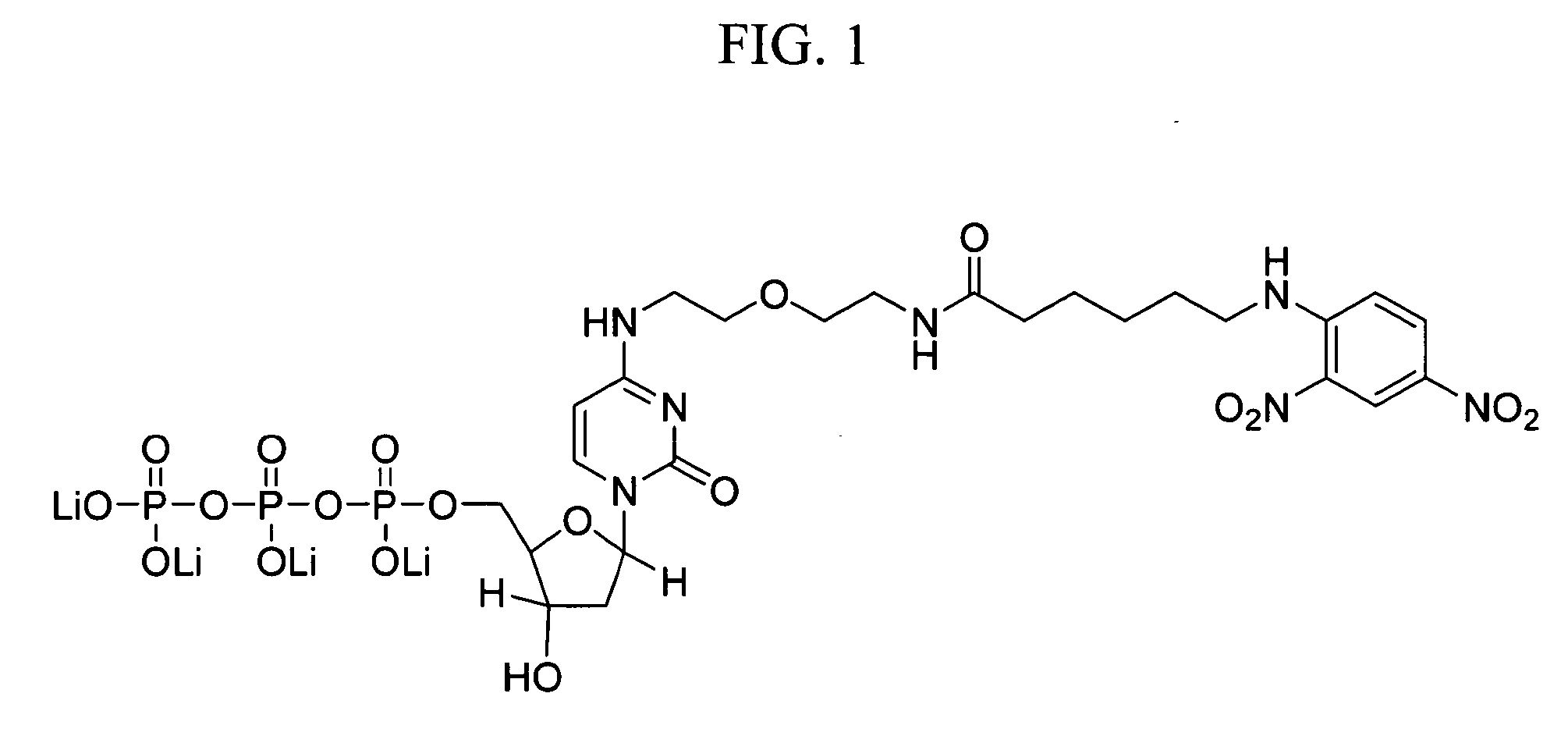
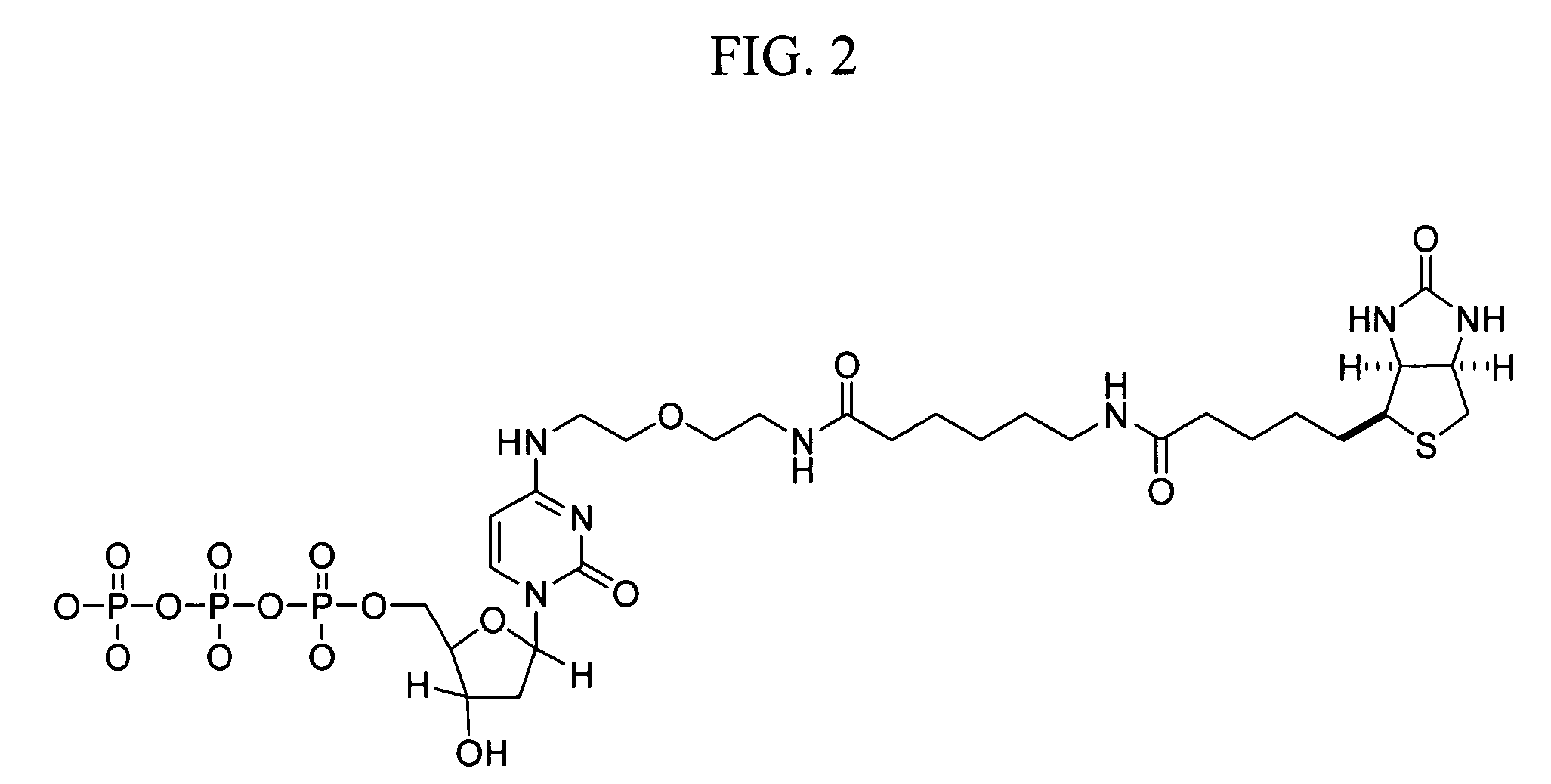
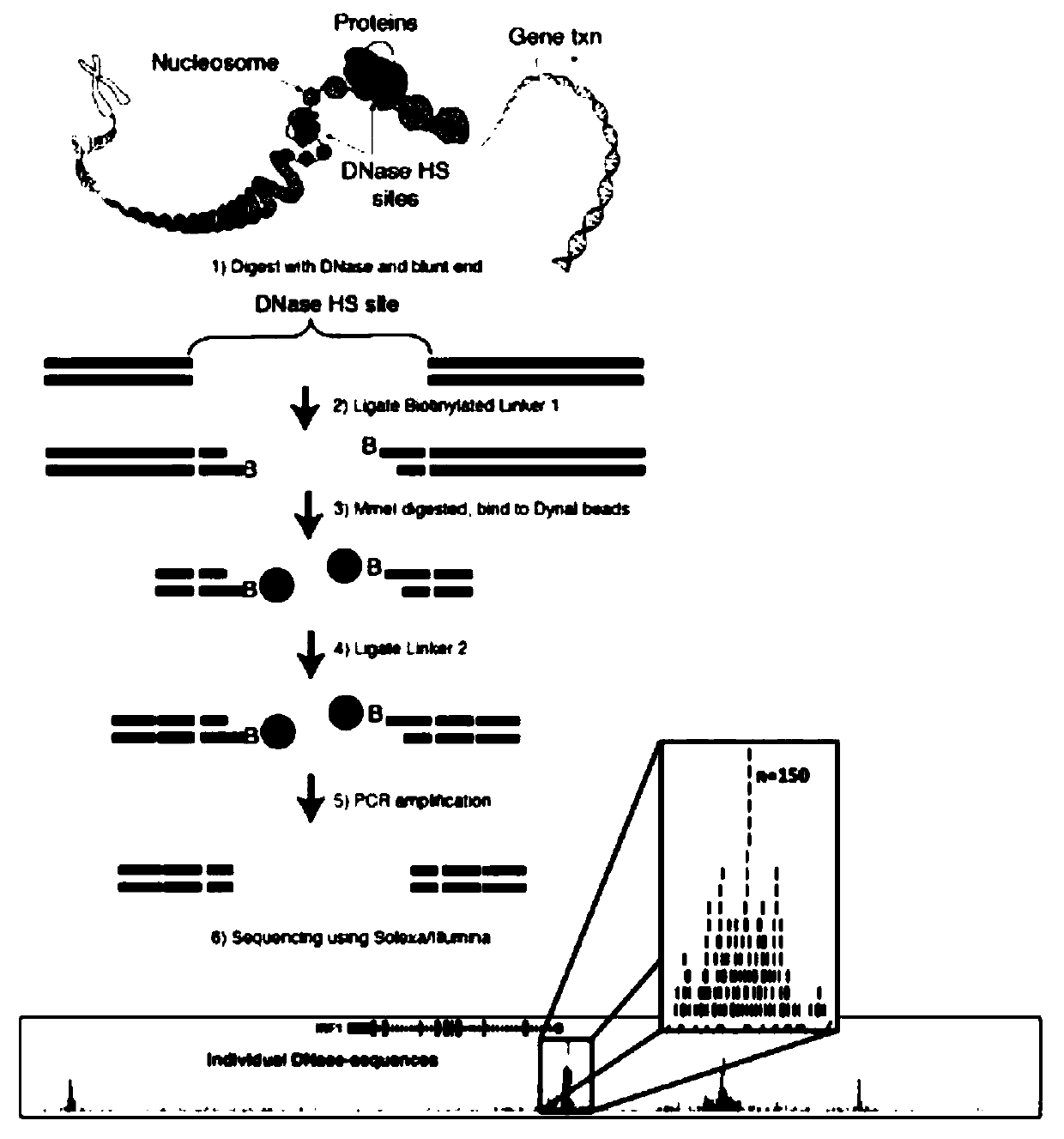
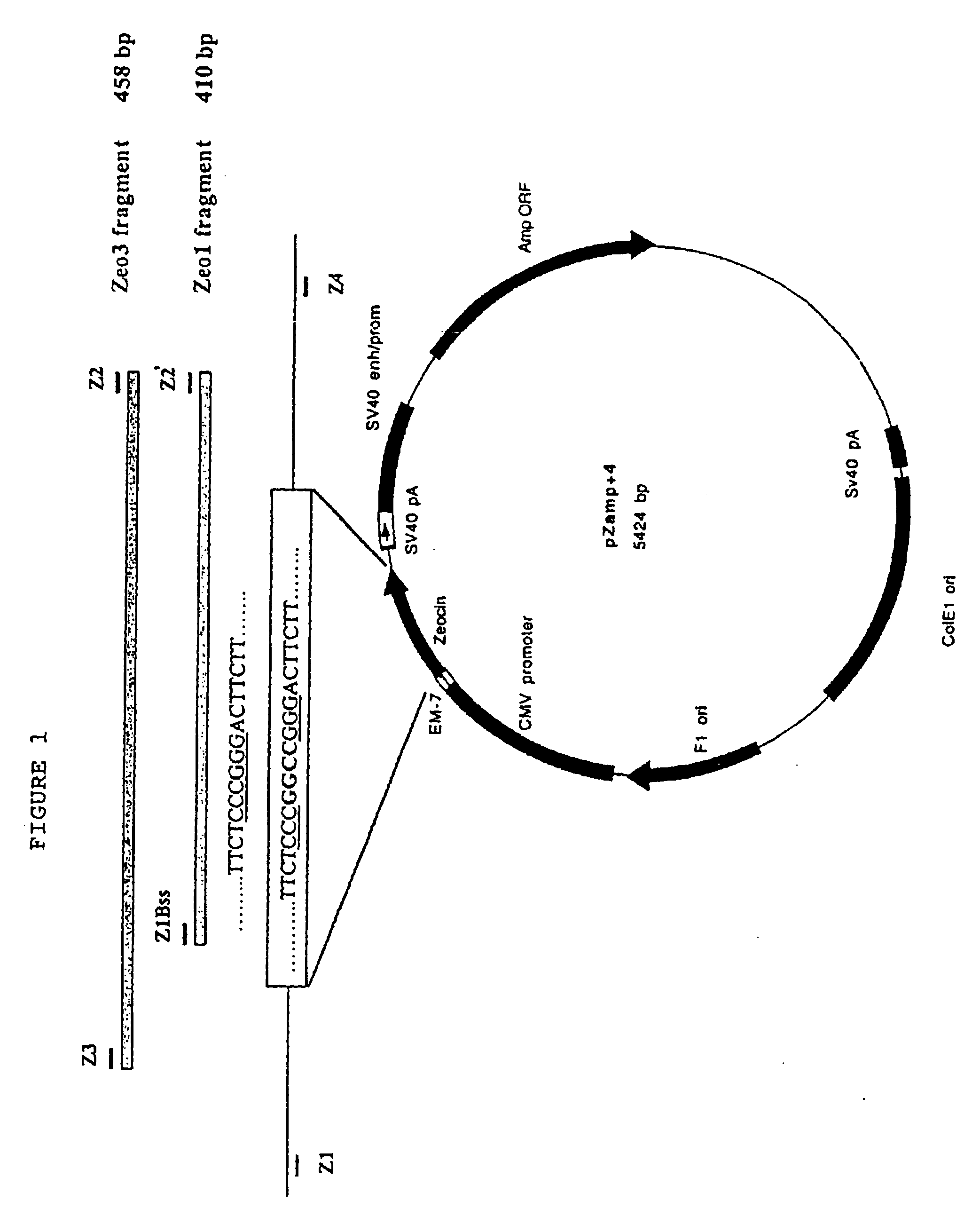
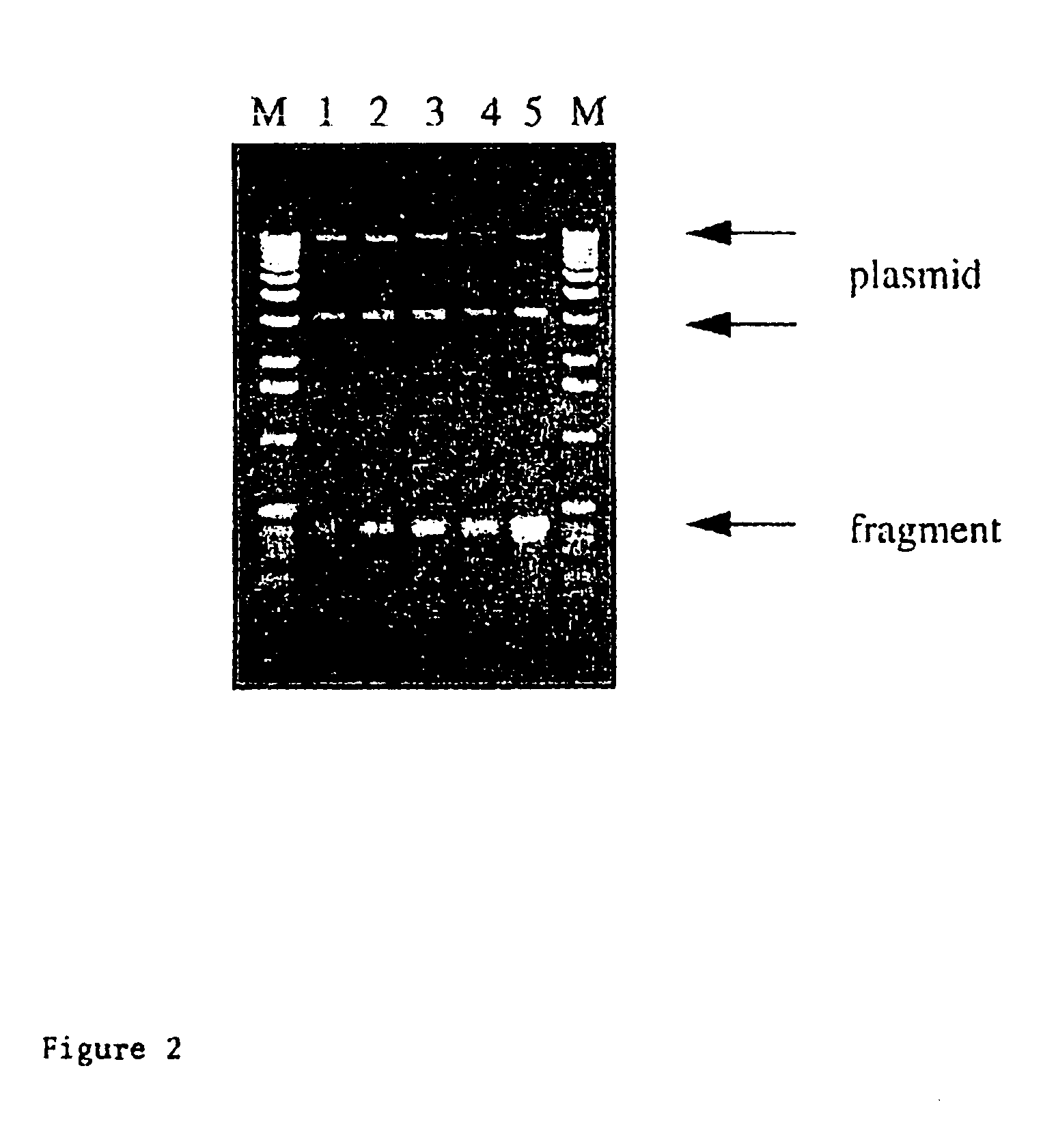
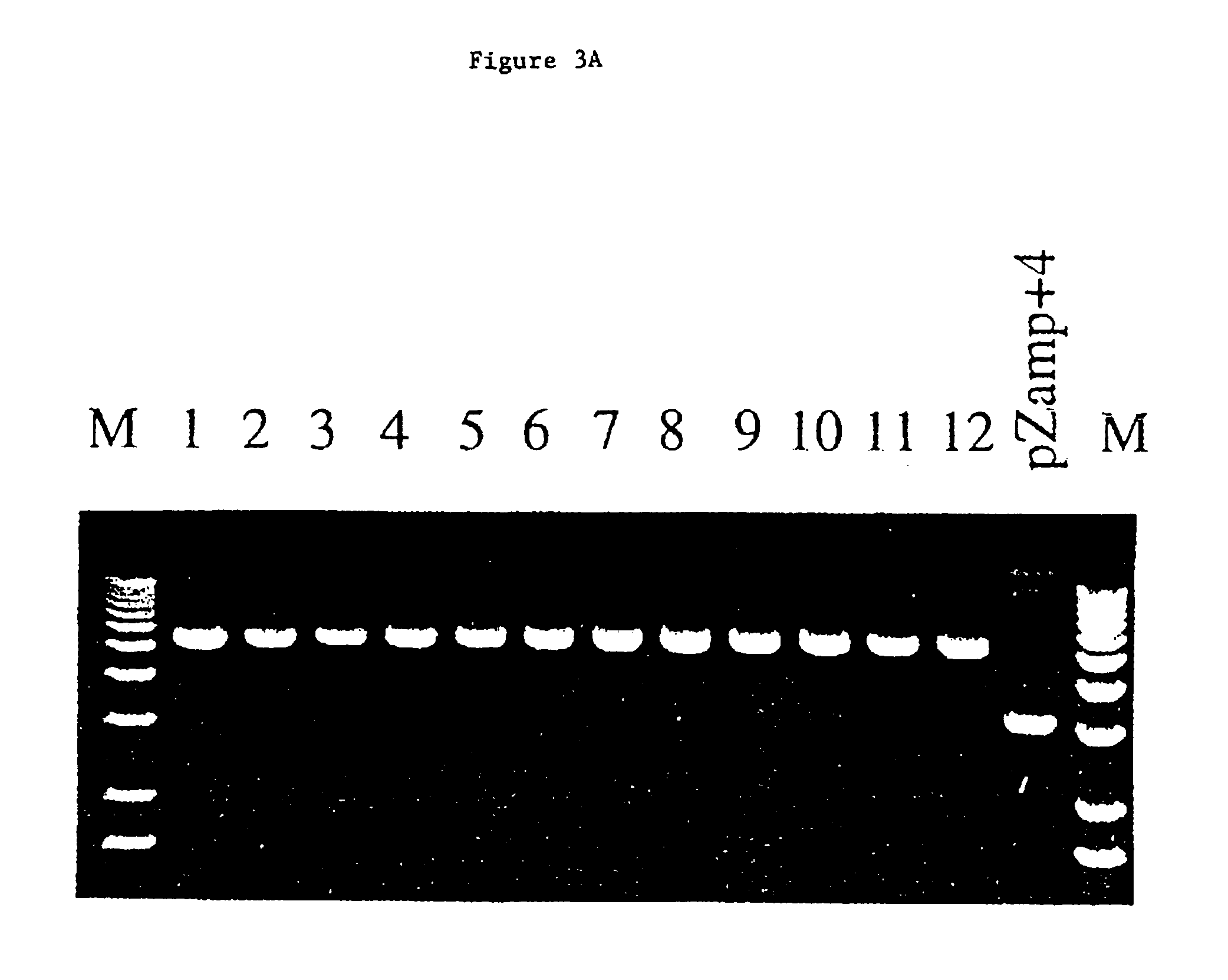
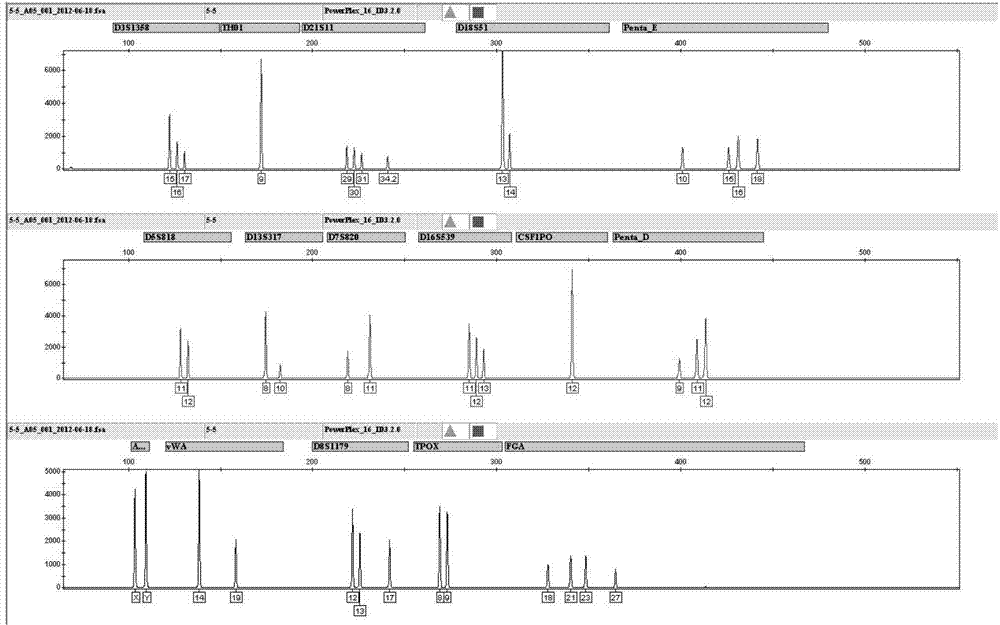
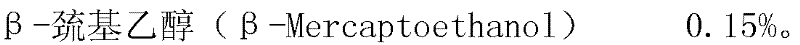Patents
Literature
81 results about "Nuclear DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. Nuclear DNA encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. Nuclear DNA adheres to Mendelian inheritance, with information coming from two parents, one male and one female, rather than matrilineally (through the mother) as in mitochondrial DNA.
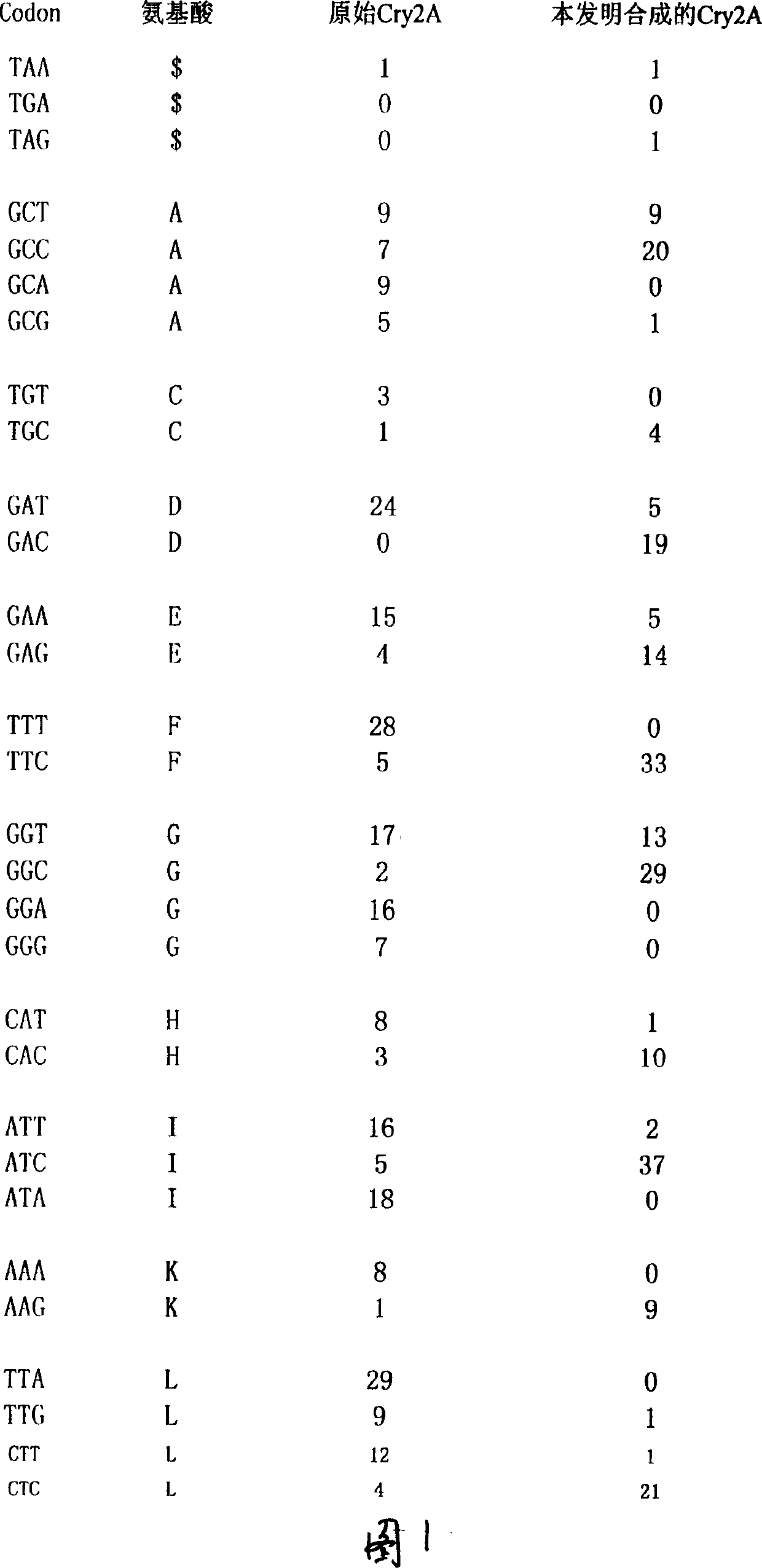
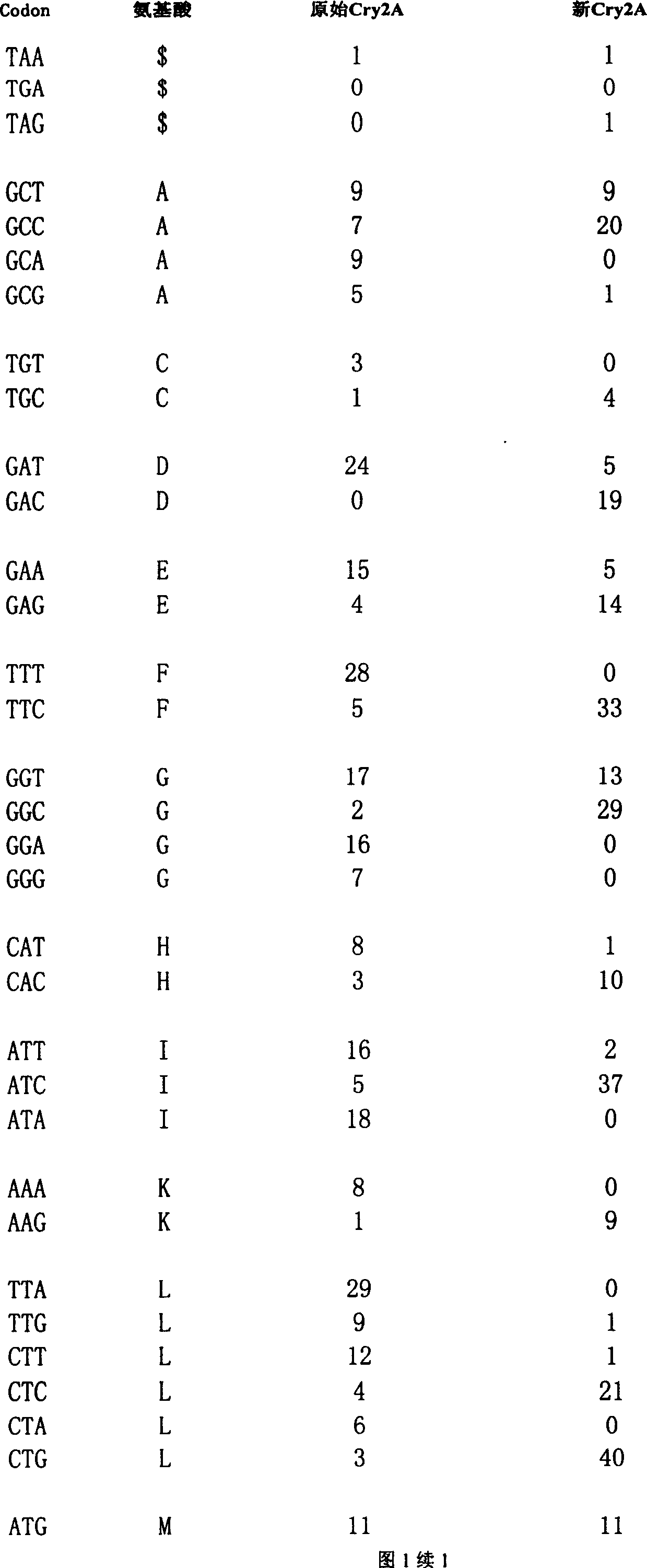
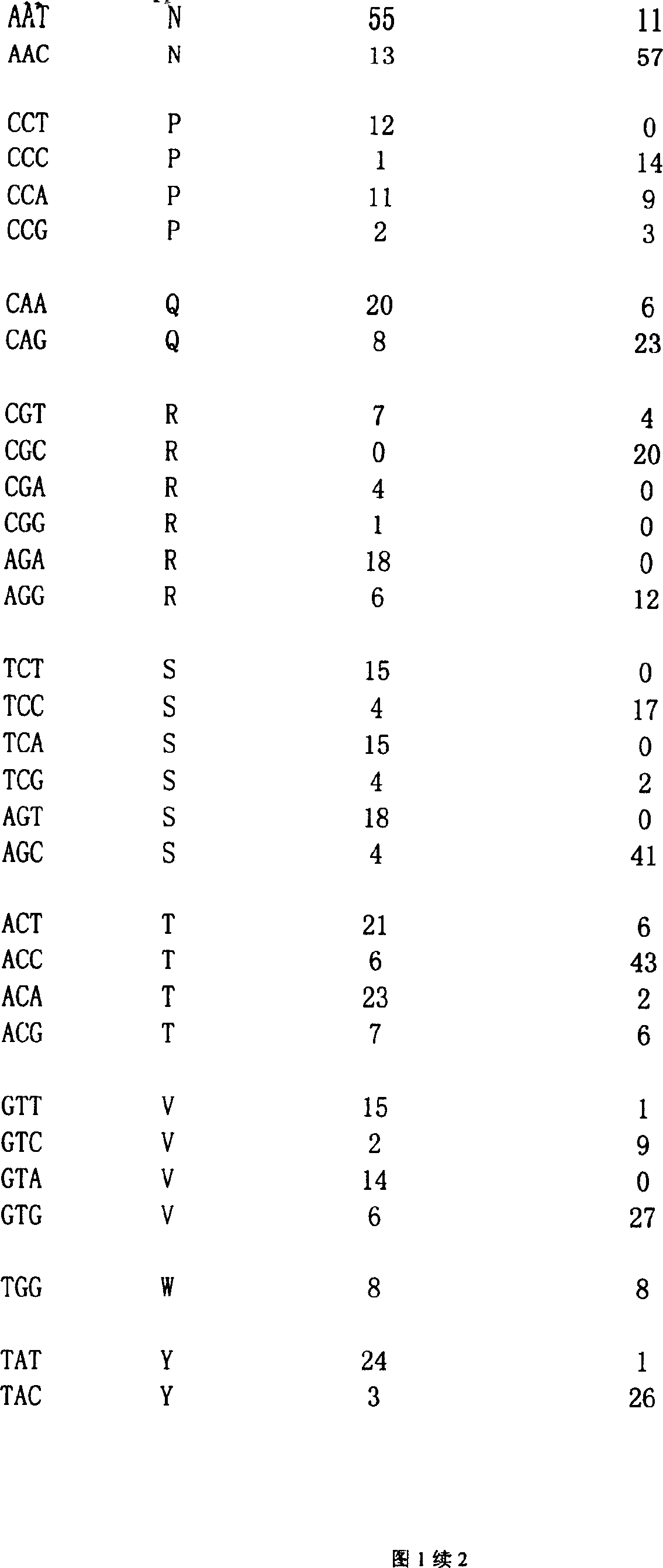
Reforming composite insecticidal crystalline gene Cry2A of bacillus thuringiensis
A Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal protein DNA sequence Cry2A is designed and synthesized. Comparing it with original Cry2A DNA sequence can show that the amino acid components of DNa sequence coding protein are not changed, the application frequency of vegetable preference codon is higher and the AT sequence, reverse reduplicate sequence and indefinable subsequences are eliminated. It can be used for culturing the seed of insect-resisting transgenic plant.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
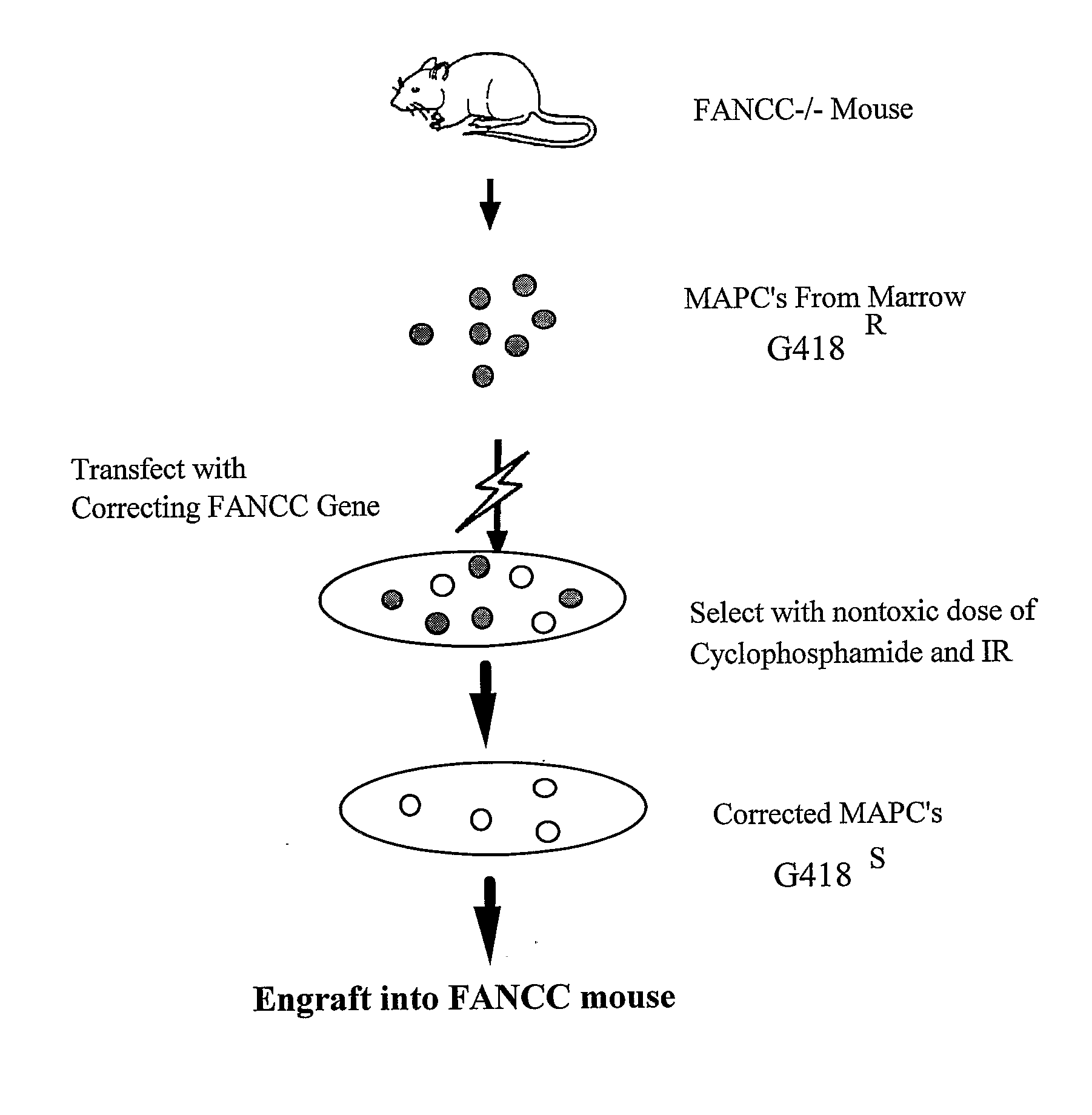
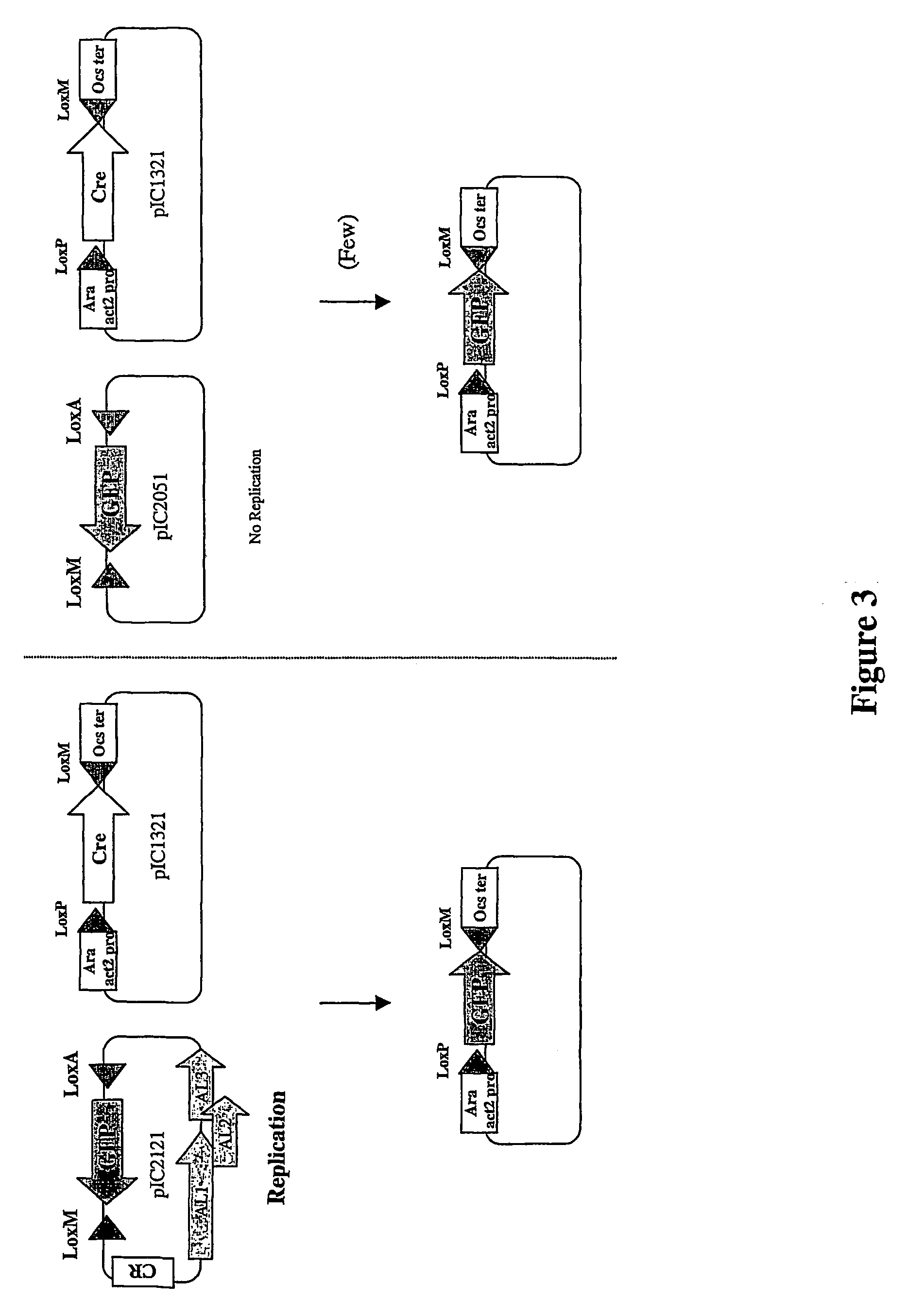
Homologous Recombination in Multipotent Adult Progenitor Cells
InactiveUS20100285590A1Improve the usefulnessIncrease and decrease its productionOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationProgenitorTherapeutic protein
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY
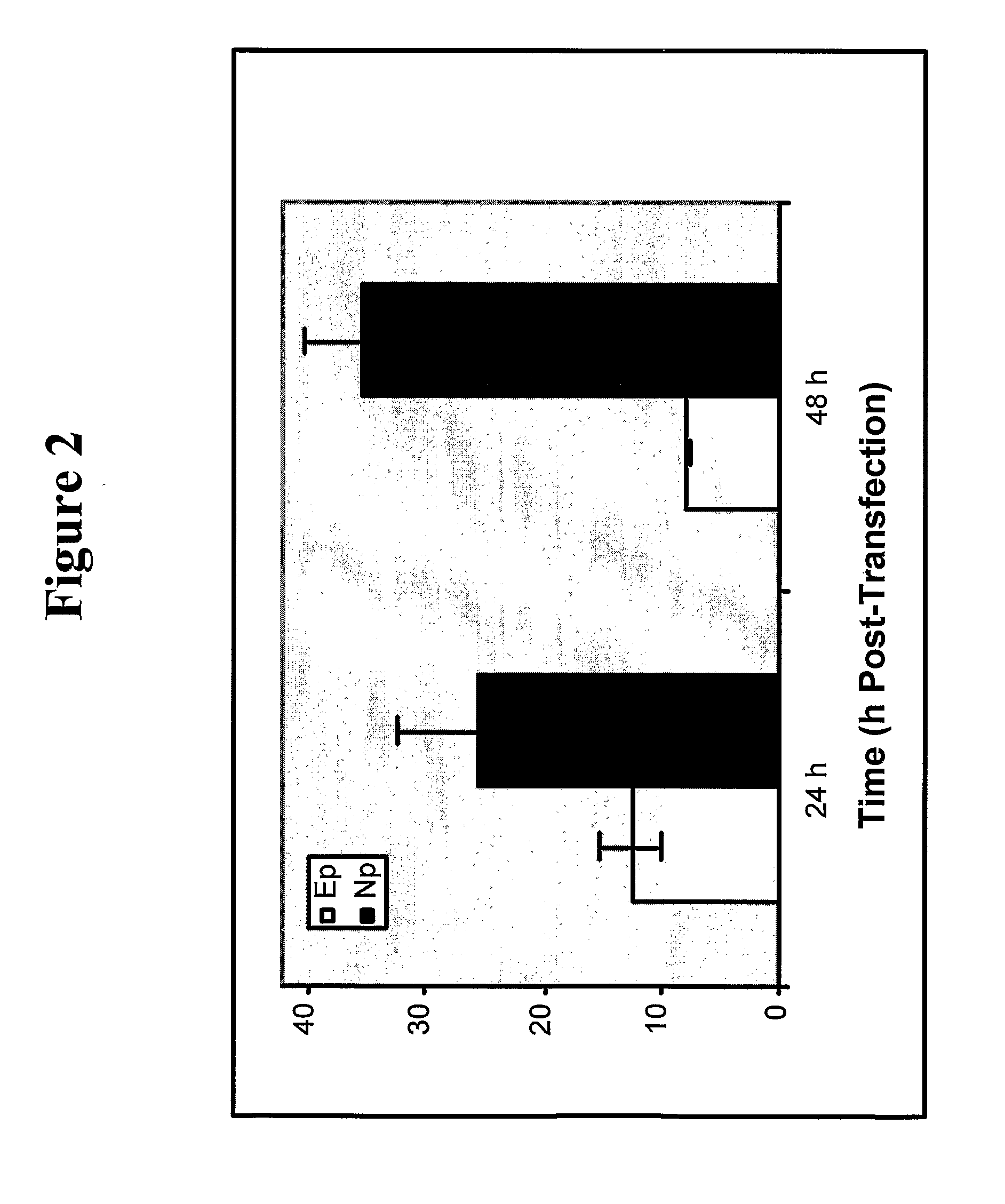
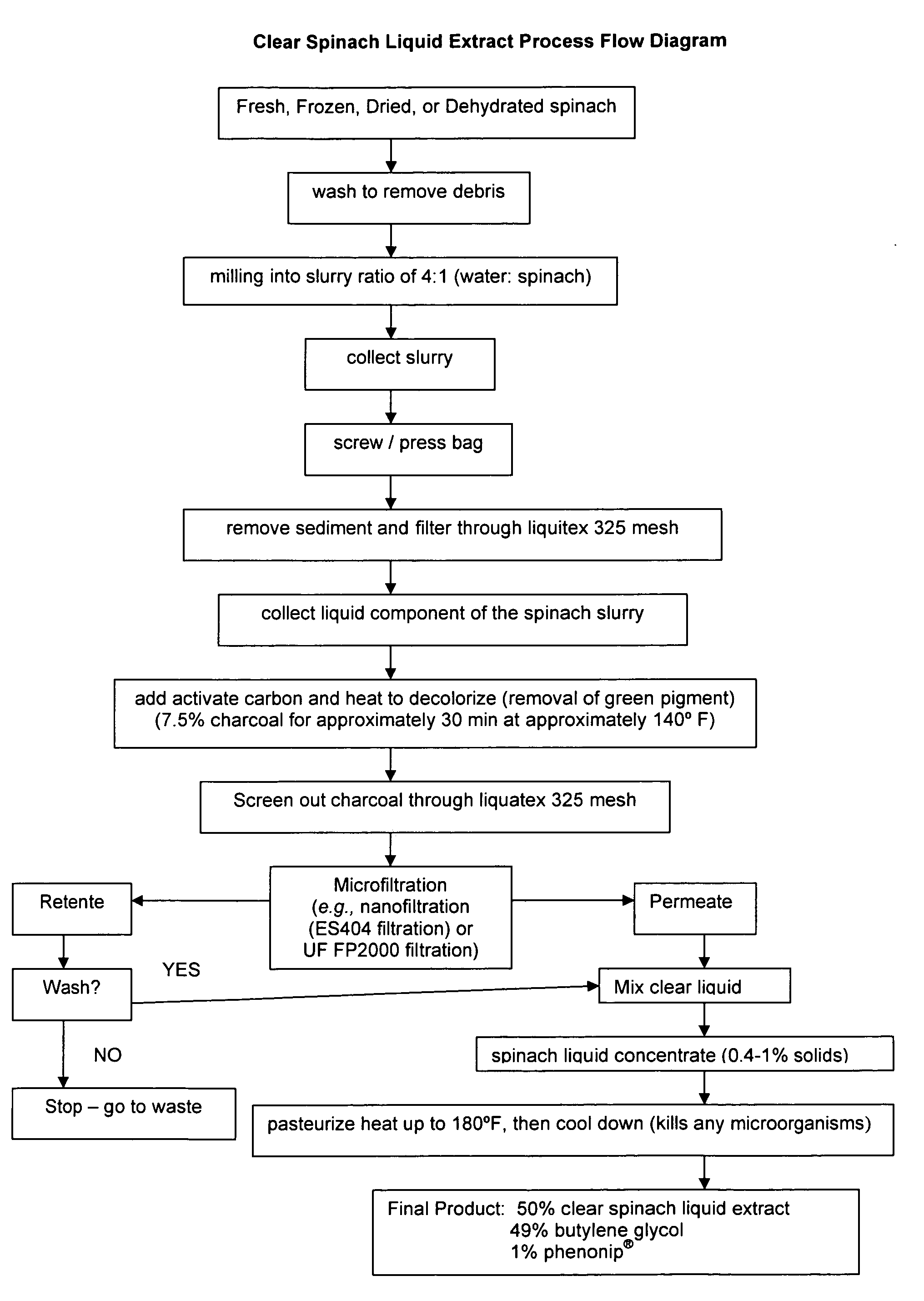
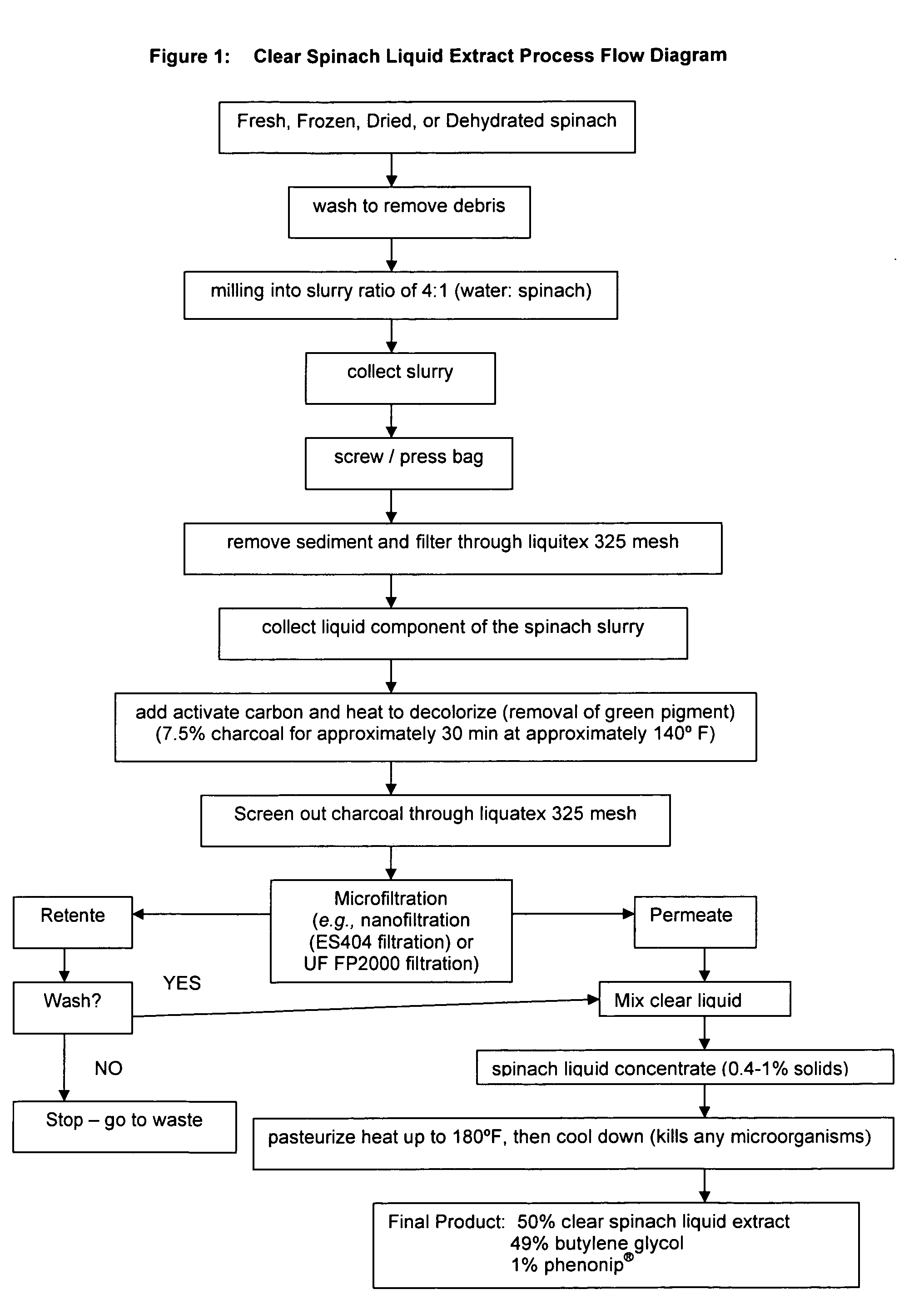
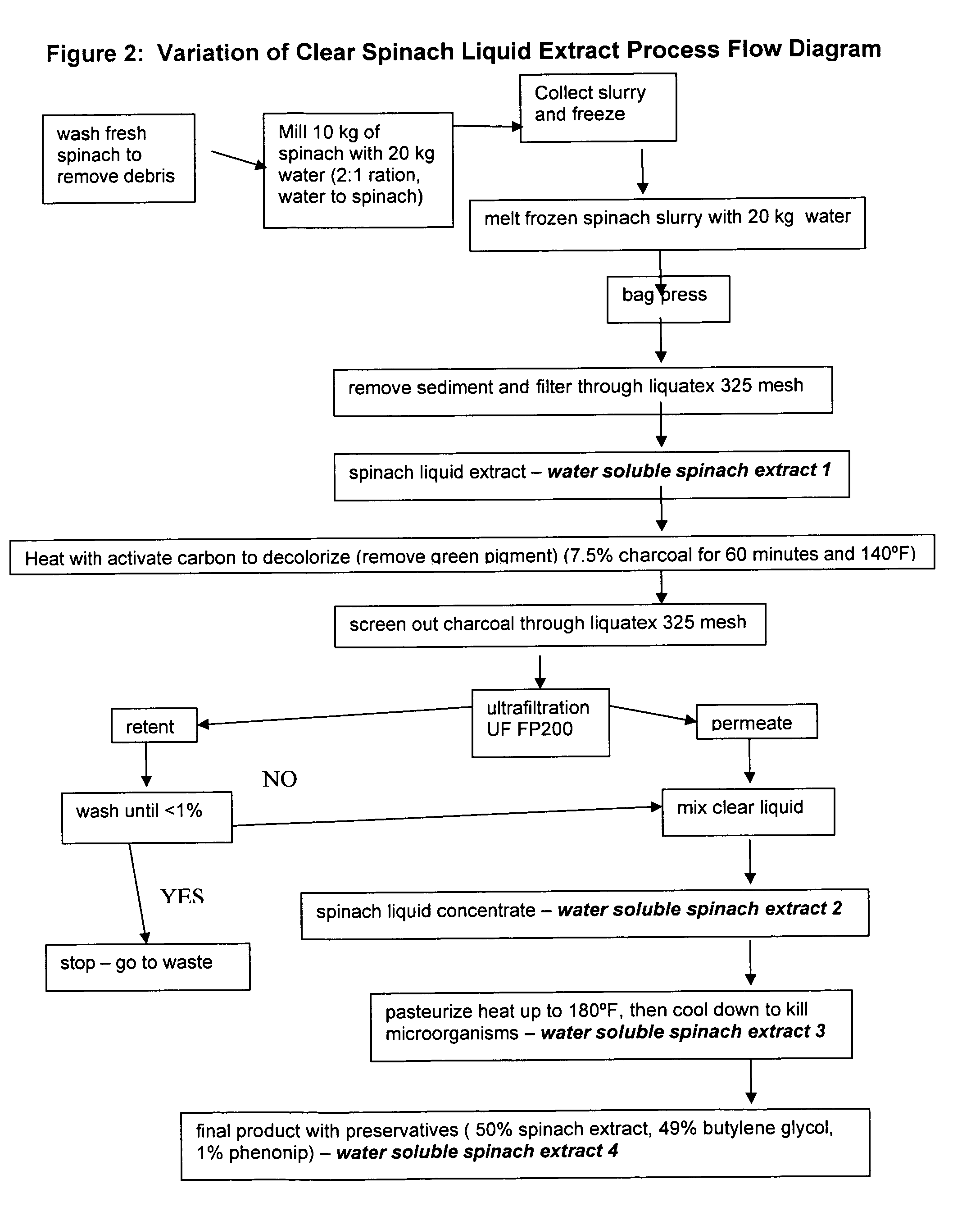
Water soluble extract of spinach for prevention and repair of DNA damage
InactiveUS20080138393A1Prevents and decrease damagePromotes and increases productionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAdjuvantAntioxidant
Compositions comprising a water soluble spinach extract, compositions comprising a water soluble spinach extract, a liposome, a cardiolipin, and at least one antioxidant, compositions comprising a water soluble spinach extract, an extract of Arabidopsis thaliana or of the mustard (Brassica) plant, a liposome, a cardiolipin, and at least one antioxidant, processes for obtaining such compositions, and methods of using such compositions to repair damage to nuclear DNA, mitochondrial DNA, or both, prevent or decrease damage to such DNA from, for example, reactive oxygen species or 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine and / or to repair or prevent mitochondrial damage and loss of membrane fluidity are disclosed. Compositions of the present invention may be topically administered, orally administered or parenterally, such as administration by injection. When topically administered, additives such as penetration enhancers, fragrances, preservatives, moisturizers and cosmetic adjuvants may be included in compositions of the present invention.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Internal control for in situ hybridization
The invention provides a method for monitoring the quality of in situ hybridization analysis of a nuclear DNA target in a tissue or cell sample using a mitochondrial DNA probe as an internal control. The invention also provides a reagent for in situ hybridization detection of a nuclear DNA target and a mitochondrial DNA target in a tissue or cell sample.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
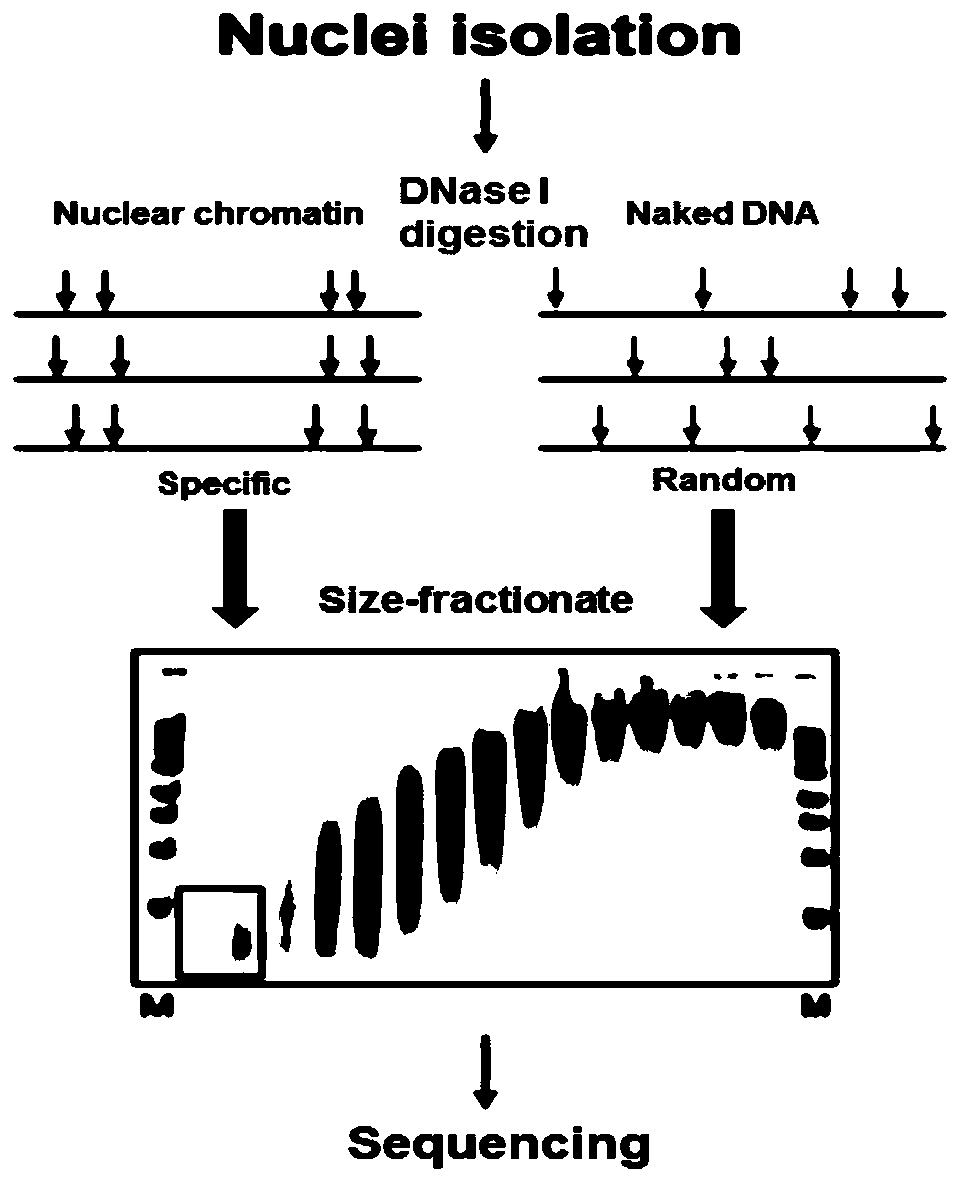
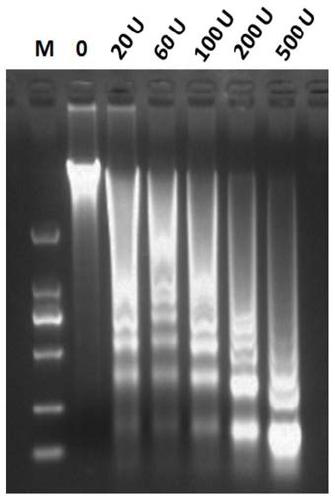
Method for identifying open chromatin sites of plant genomes by using micrococcal nuclease
ActiveCN109706236AImprove visibilityThe method flow is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionMicrococcal nuclease
The present invention discloses a method for identifying open chromatin sites of plant genomes by using micrococcal nuclease. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cross-linking plant material; (2) extracting and purifying cell nucleus of a plant material; (3) subjecting the cell nucleus to enzyme digestion with MNase in different concentrations; (4) detecting MNase digestion effect by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis; (5) selecting appropriate MNase for enzyme digestion of nuclear DNA, performing 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis separation again, recovering DNA fragments, constructinga Illumina sequencing library, and performing sequencing; and (6) performing bioinformatics analysis on the sequencing data, and identifying the whole genome MH loci. The whole method is simple in process and short in time consuming, takes about 2.5 days in one cycle, and is high in visible enzyme digestion effect and suitable for most plant species. The method can be used directly used for identifying the core regions of functional DNA elements.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
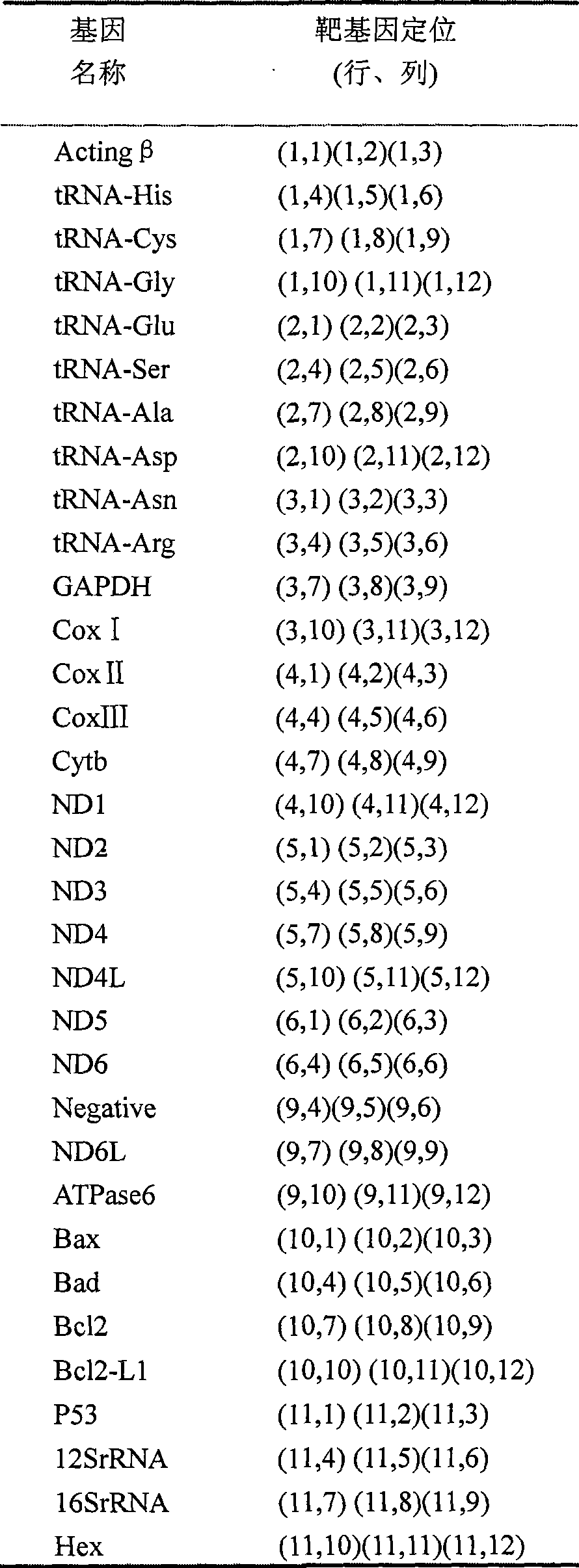
Gene chip for detecting differential expression of human mitochondria gene
InactiveCN101440397AEfficient detectionEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementNuclear DNAMicroarray
The invention discloses a gene chip for detecting the differential expression of human mitochondrial genes. The gene chip is to a glass substrate incubated with probes for detecting the transcriptional abundance of 9 tRNAs, 2 rRNAs and 13 mRNAs encoded by human mitochondrial genes, as well as 5 apoptosis-associated genes encoded by nuclear DNA(nDNA). The gene chip provided by the invention is capable of detecting simultaneously the differential expression of the whole human mitochondrial mtDNA and nDNA under two different conditions, and analyzing the inherent correlation; and the invention represents the minimization and specialization of gene chip technology, and accomplishes the detection on expression of human mitochondrial mtDNA and nDNA efficiently and conveniently.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method of Separating Target DNA from Mixed DNA
The present invention relates to methods of separating target DNA from mixed DNA in a sample. In some embodiments, the target DNA may be viral DNA, prokaryotic DNA, fungal DNA or combinations thereof. In some embodiments the mixed DNA includes target DNA and non-target DNA.
Owner:CANON US LIFE SCIENCES INC
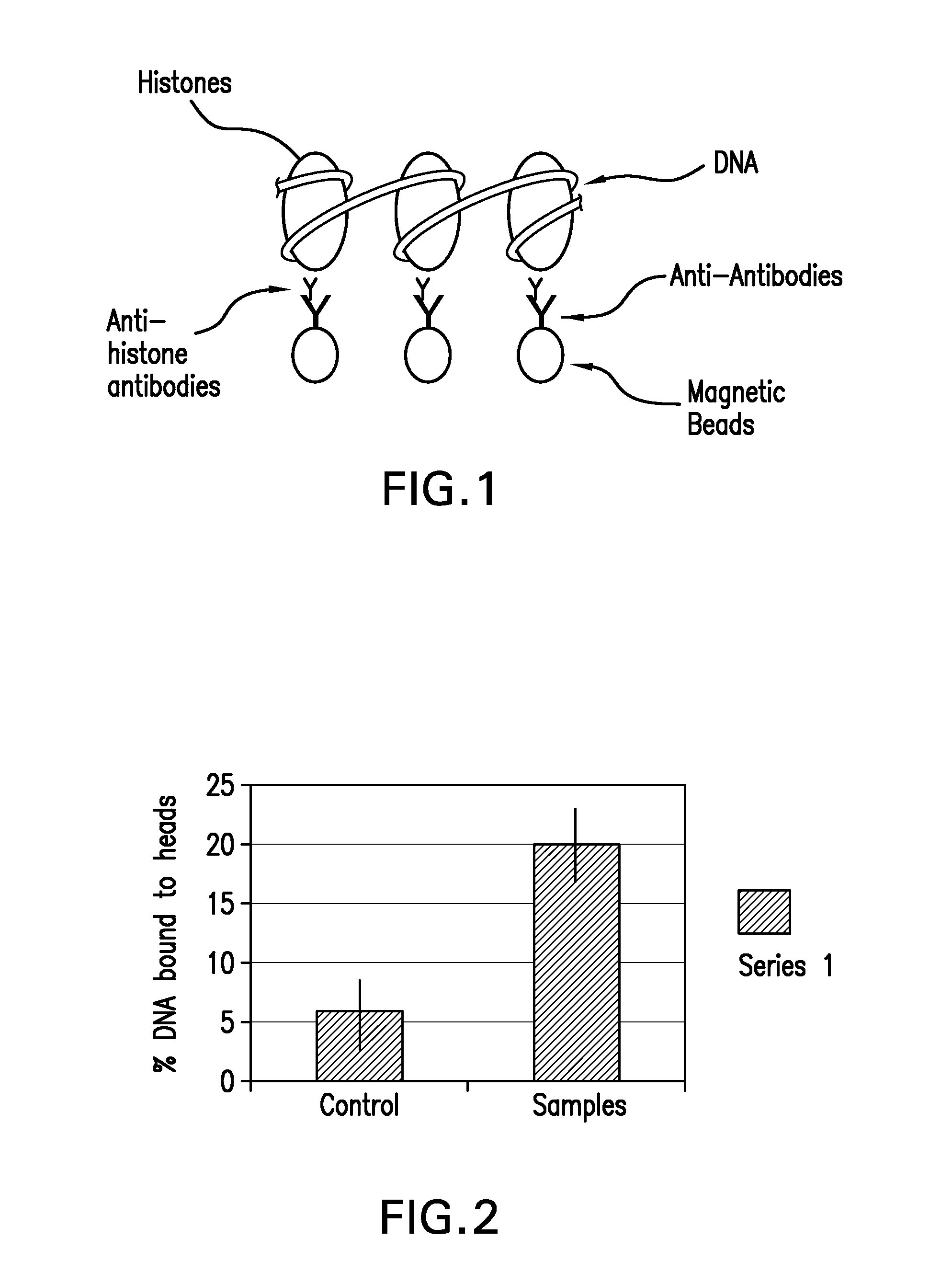
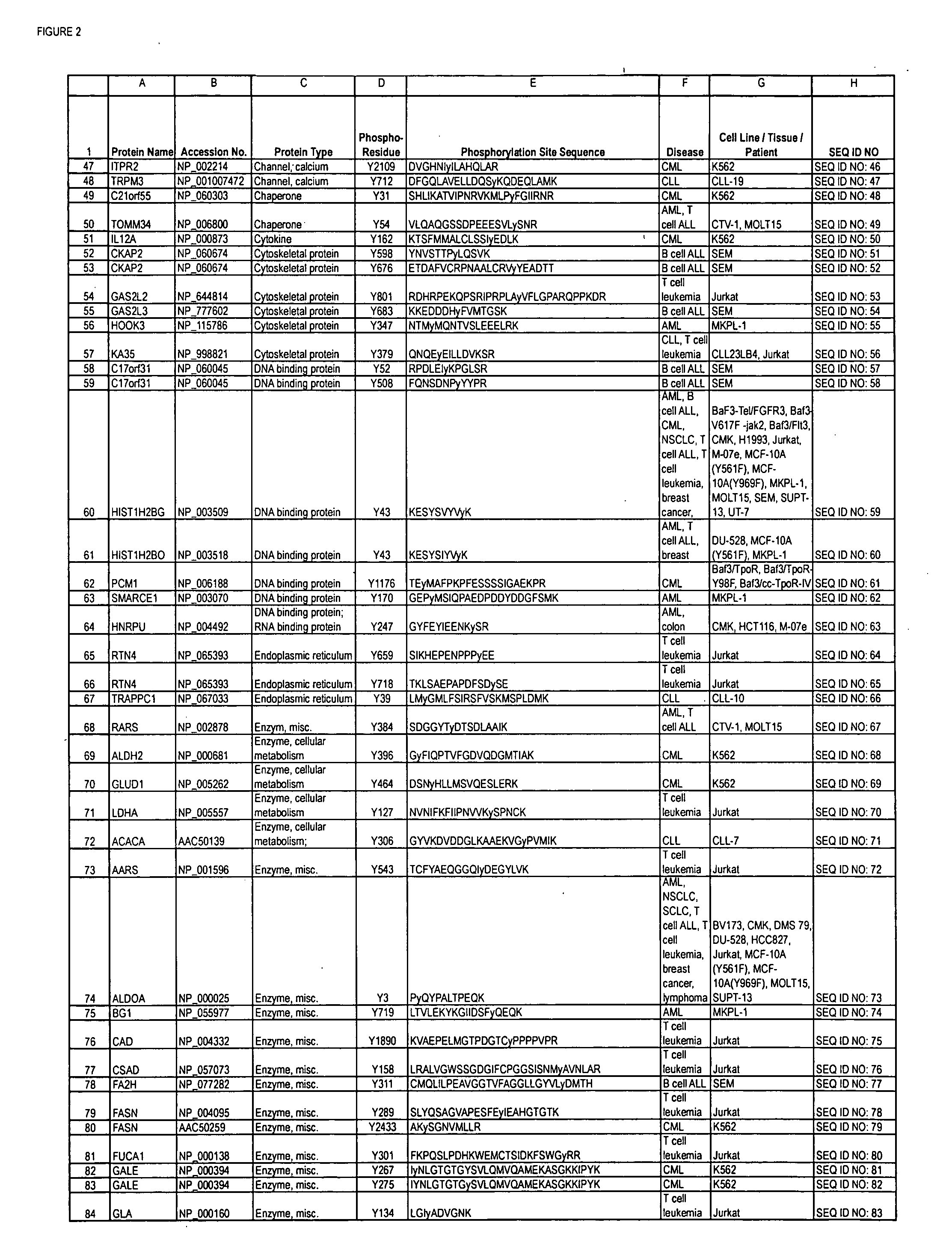
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in Leukemia signaling pathways
ActiveUS20080248490A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingHuman leukemiaADAMTS Proteins
The invention discloses nearly 288 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways underlying human Leukemia, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Cytoskeletal proteins, Cellular Metabolism enzymes, G Protein / GTPase Activating / Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor proteins, Immunoglobulin Superfamily proteins, Inhibitor proteins, Lipid Kinases, Nuclear DNA Repair / RNA Binding / Transcription proteins, Serine / Threonine Protein Kinases, Tyrosine Kinases, Protein Phosphatases, and Translation / Transporter proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Method for extracting nuclear DNA of lotus
The invention discloses a method for extracting the nuclear DNA of a lotus, relating to a method for extracting DNA in the field of molecular biology. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: adding a nucleus extraction buffer solution to etiolated seedling leaves of the lotus, which are grinded into powder, and magnetically stirring, filtering, centrifugalizing and rinsing to obtain apurified nucleus; adding a nucleus lysis buffer solution for water bath at 65 DEG C; extracting through chloroform: isoamylol and precipitating through isopropanol so as to obtain floccus DNA precipitates; and washing through 70% ethanol and drying at room temperature, and then adding a Tris-EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) buffer solution to dissolve the DNA, and preserving at -20 DEG C for later use. The DNA obtained by the invention is the high-quality nuclear DNA of the lotus, has low content of chlorophyll DNA and mitochondrion DNA and contains few polysaccharides, polyphenols, pigments and proteins; and in addition, the invention is suitable for the extraction of the high-quality nuclear DNA needed by the aspects of establishing a BAC (Binary-Analog Conversion) library, sequencing genomes, and the like.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
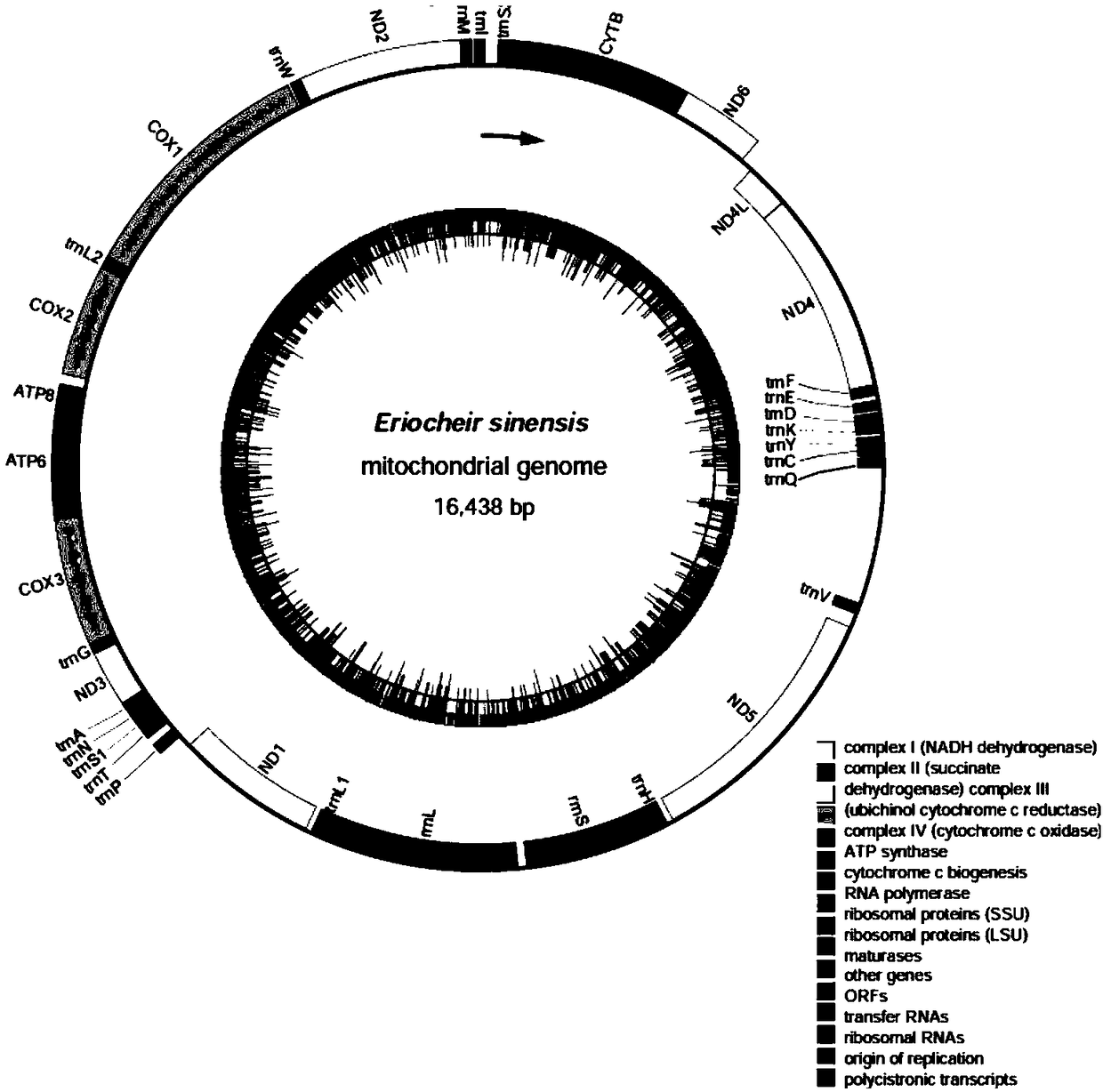
Method for precisely determining mitochondrion whole genome sequence of eriocheir sinensis
ActiveCN109280700AOvercome workloadOvercome costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence designMuscle tissue
The invention relates to a method for precisely determining a mitochondrion whole genome sequence of eriocheir sinensis and the whole genome sequence obtained by using the method. The method comprisesthe following steps of (1) extracting the whole genome DNA in eriocheir sinensis muscle tissues, building a gene library, and performing sequencing by using a second generation sequencing technology;(2) screening a sequencing read segment by referring to the mitochondrion whole genome sequence of closely related species; eliminating nuclear DNA segments; then performing mitochondrion genome splicing; and performing prediction annotation on the protein-coding genes, rRNA and tRNA of the spliced mitochondrion genome; and (3) comparing the spliced mitochondrion genome sequence and the mitochondrion genome sequence of the closely related species; performing PCR amplification on a corresponding second generation sequencing sample according to a conservative region by referring to a mitochondrion whole genome sequence design primer of the closely related species; sequencing a PCR amplification product by using a first generation sequencing technology; and correcting the spliced mitochondrion genome sequence. The method has the advantages of high speed and high accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Nucleic acid amplification detection method and detection kit for distinguishing DNA from corresponding RNA
InactiveCN101948908AEasy to understand the status of growth and reproductionOvercoming detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceReverse transcriptaseNucleic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical detection, in particular relates to a nucleic acid amplification detection method for distinguishing DNA from correspondingly transcribed RNA and provides a corresponding detection kit. The kit comprises pyrolysis solution, nucleic acid extracting solution, lysozyme solution, reverse transcription buffer solution, a reverse transcriptase system, tuberculosis DNA PCR reaction solution, tuberculosis RNA PCR reaction solution and the like, wherein selected primers aim at a section of ITS sequence or IS6110 sequence and a section of 16S rRNA sequence on ribosomal RNA respectively; and a probe is Tagman MGB probe preferably and labeled by different fluorescein. The kit comprises a glycosidase (UNG) component, can judge the relative 16S rRNA content of each bacterium and is used for judging the growth condition of mycobacterium tuberculosis in a sample so as to monitor infection state. The kit is simple, convenient and fast, can specifically detect the RNA and DNA and provides more comprehensive information for clinical use.
Owner:SHANGHAI KEHUA BIO ENG
Auger effect-based cancer therapy method
A method for the treatment of a tumor, comprising administering to a subject a therapeutically effective amount of a complex of a heavy element with a polydentate, pyrrole-containing macrocyclic ligand substituted with charged chemical groups, wherein said complex is capable of bringing said heavy element into close proximity to the nuclear DNA of cells in said tumors, and irradiating said tumor with photons above the K or L shell adsorption edge of said heavy element to elicit the emission of densely ionizing Auger electrons at the level of DNA.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Method for constructing cotton bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library by non-dark cultured leaves
InactiveCN102747427AEasy accessAvoid Bulk GerminationVector-based foreign material introductionLibrary creationLarge fragmentHigh molecular weight dna
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and especially relates to a method for constructing a cotton bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library by non-dark cultured leaves. The method comprises the following steps of 1, selecting cotton leaves, 2, extracting a high-molecular weight nucleus DNA, 3, partly digesting the high-molecular weight nucleus DNA and carrying out selection twice, 4, carrying out recovery, connection and transformation of a large-fragment DNA, and 5, carrying out detection of an insert fragment. The method is suitable for construction of BAC libraries of all cotton materials which comprise cotton materials having low seed amounts and persistent cotton materials having no seed.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for extracting mitochondrial DNA of cotton
InactiveCN102121000ALittle mechanical damageHigh puritySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationMitophagyPhenol
The invention discloses a method for extracting mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of cotton. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) homogenizing cotton, and centrifuging and collecting precipitate; (2) removing nuclear DNA, adding ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) solution, and centrifuging to obtain the precipitate; (3) adding buffer solution, and centrifuging to obtain mitochondria; (4) adding lysis solution and acetate solution, centrifuging, collecting supernatant, and extracting by using chloroform-isoamylol; (5) adding acetate solution and absolute ethanol, centrifuging to obtain the precipitate, and washing by using ethanol; (6) dissolving in triisopropylphenylsulfonyl (Tris)-EDTA (TE); (7) removing ribonucleic acid (RNA) and protein, extracting by using Tris saturated phenol-chloroform-isoamylol, and centrifuging and collecting the supernatant; and (8) adding the acetate solution and the ethanol, and centrifuging to obtain the precipitate; and washing by using the ethanol to obtain the mitochondrial DNA. Aiming at defects of the conventional extraction of the mitochondrial DNA, the conventional cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) method is improved, and the extraction conditions are optimized by adjusting the time and times of centrifugation, changing reagents, increasing extraction and washing times, and the like. On the basis of ensuring that the mechanical damage degree of the mitochondria is minimum, the nuclear DNA, phenols and polysaccharides outside the mitochondria are effectively removed, pollution rate is reduced, the purity and the quality of the mitochondrial DNA are improved, and the mitochondrial DNA can meet the requirement of subsequent experiments of the gene engineering of the cotton mitochondria.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
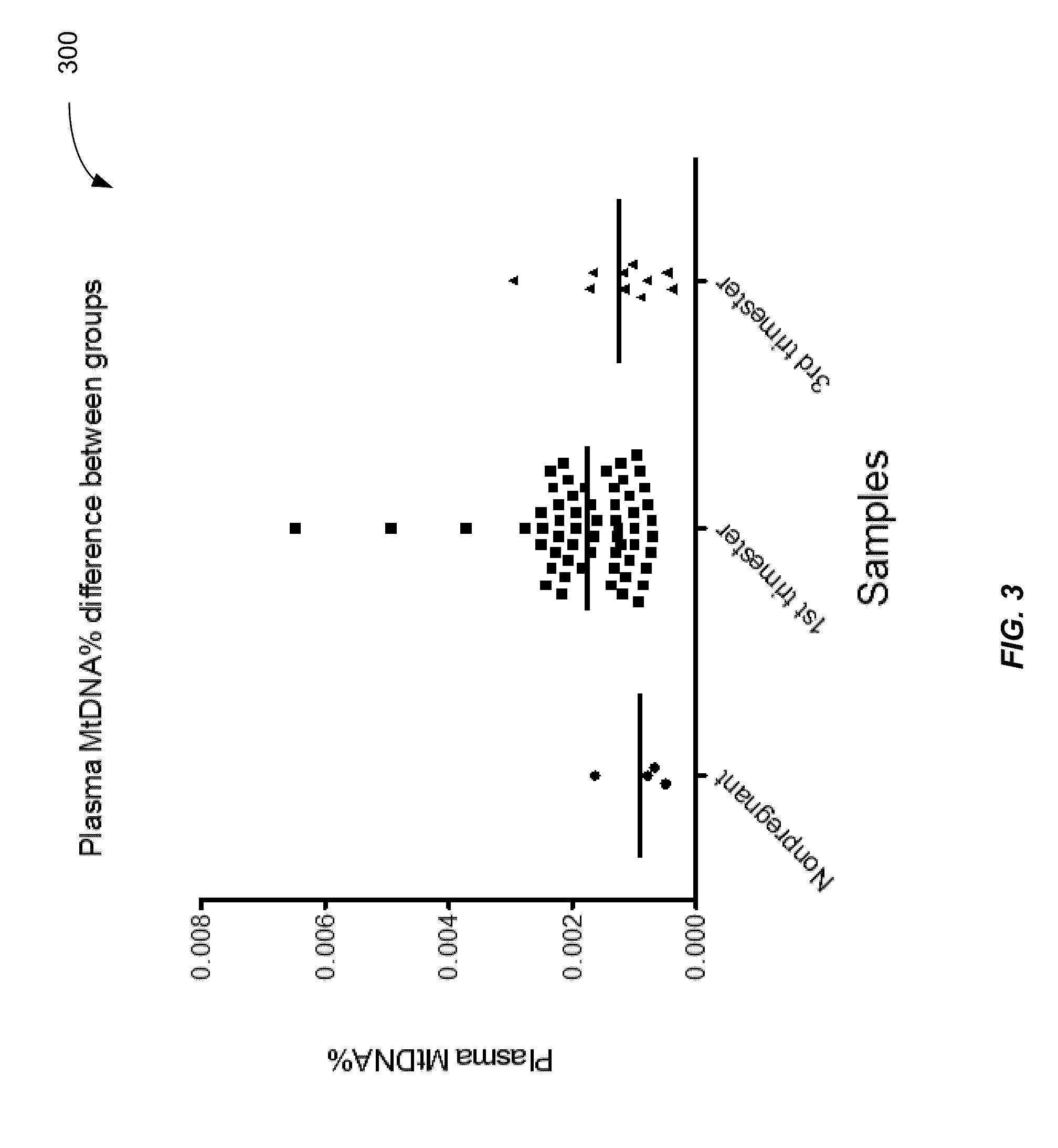
Applications of plasma mitochondrial DNA analysis
ActiveUS20160203260A1Reduce cost of measurementAccurately determineMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAbnormal tissue growthTissues types
An amount of mitochondrial DNA molecules relative to an amount of nuclear DNA molecules is determined in a biological sample, and the relative amount is used for various purposes, e.g., screening, detection, prognostication or monitoring of various physiological and pathological conditions. As examples, an amount of mitochondrial DNA can be used to estimate a concentration of DNA of a tissue type, such as a fetal DNA concentration, tumor DNA concentration, or a concentration of DNA in the biological sample derived from a non-hematopoietic tissue source. Sequencing techniques can be used to determine a mitochondrial DNA concentration in a sample for an accurate detection of a level of cancer. A level of an auto-immune disease is also determined using a relative amount of mitochondrial DNA molecules compared nuclear DNA molecules.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for rapidly measuring nuclear DNA content
InactiveCN102181534AEasy to observeAccurate diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingColor imageFeulgen stain
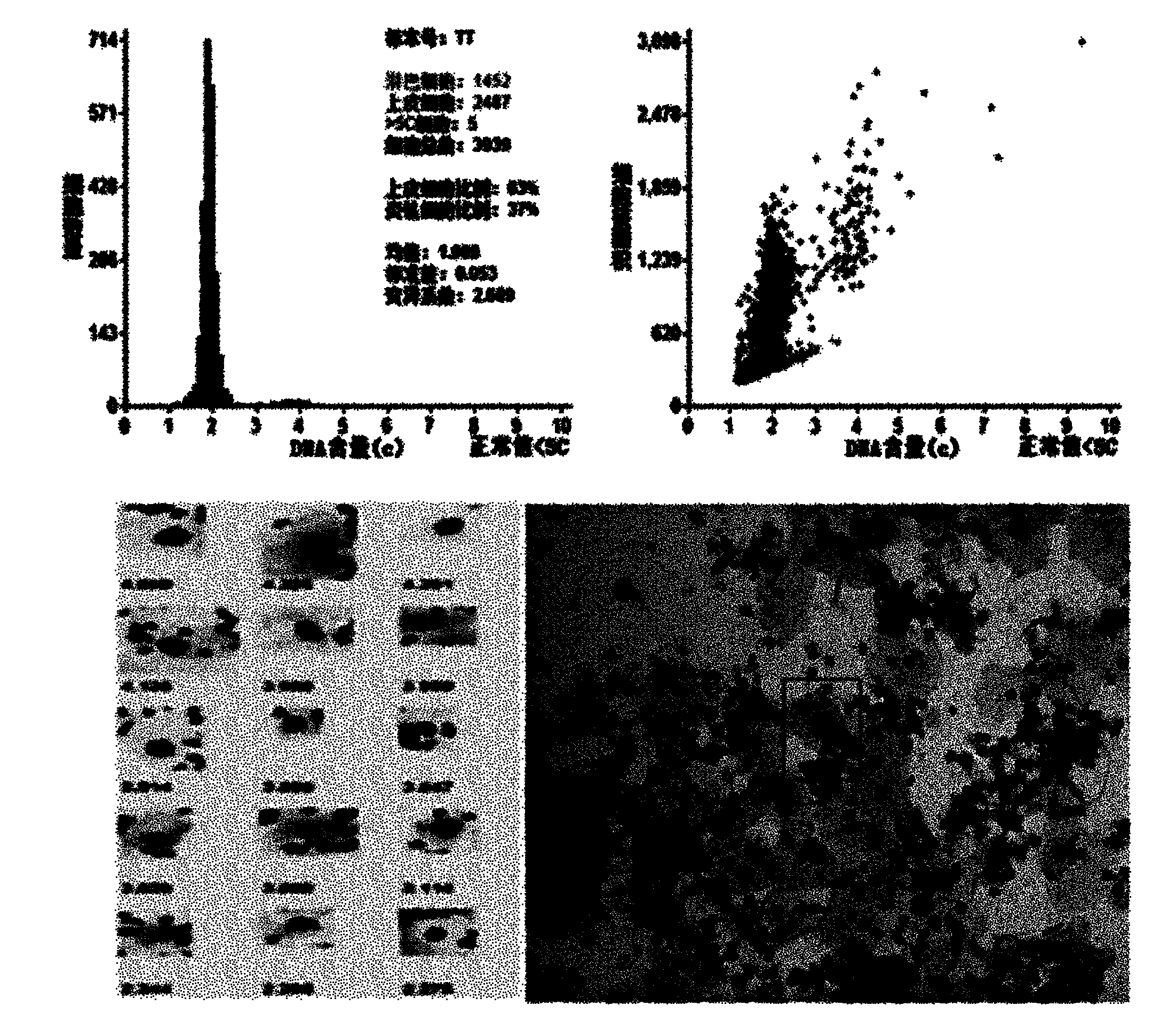
The invention relates to a method for rapidly measuring nuclear DNA content. The method comprises the following steps: Feulgen dyeing is performed on the nucleus, then EA50 or eosin is used to dye the cytoplasm, after two-step dyeing, a computer image analysis system is adopted to scan a sample on a glass slide, the grayness is obtained to perform registration with a color image; the cells in the field of vision are classified according to the morphological characteristics of the cells, normal lymphocytes are selected as the standard cells for calculating the DNA content; and the epithelial cells in each field of vision are selected, the DNA content of each epithelial cell on the glass slide is calculated according to the DNA content of the standard cells, the positions of the epithelial cells are recorded, and a cell picture is stored. A grayscale image and a color image in the same area of field of vision are provided for the analysis of the computer image analysis system, and the color image is provided for morphological observation and physician review. By adopting the method, the nuclear DNA content can be measured rapidly and the clinician can observe the cell morphology conveniently.
Owner:WUHAN LANDING INTELLIGENCE MEDICAL CO LTD
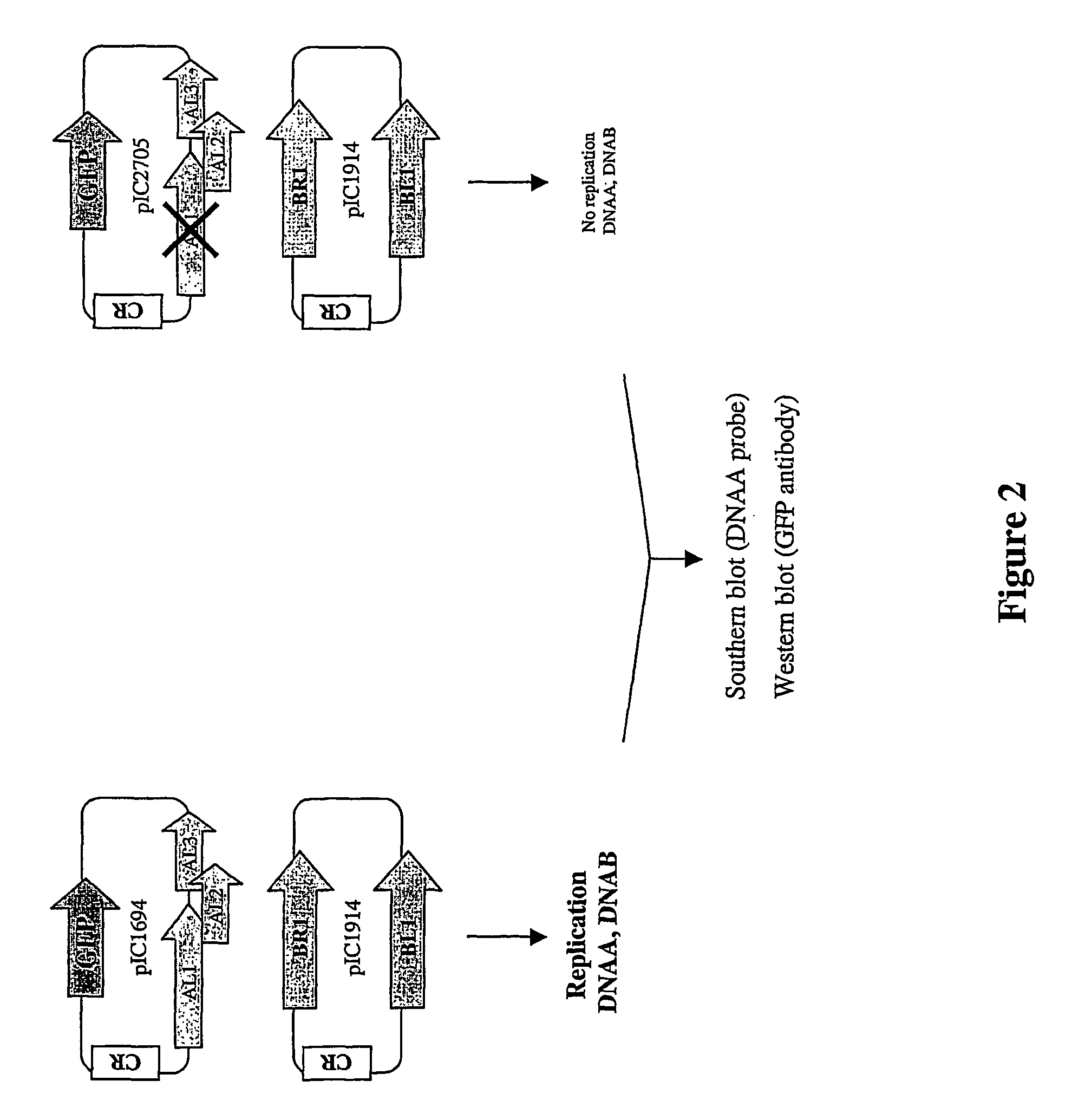
Expression vector system and a method for optimization and confirmation of DNA delivery and quantification of targeting frequency
InactiveUS6916611B2Microbiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAExpression vectorNuclear DNA
An expression vector system comprising a pair of expression vectors constructed from a wild-type and a mutant version of a maker, reporter or selection gene, and a method for optimization and confirmation of DNA delivery and of gene targeting and for quantification of targeting frequency. Novel prokaryotic / eukaryotic DNA vectors used for DNA delivery and gene targeting assessment and targeting frequency quantification.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for distinguishing individual in mixed seminal stain by single sperm capture and mitochondrial DNA typing
InactiveCN103757095ARealize detectionSolve the problem of personal identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisSemen
A method for distinguishing individuals in mixed seminal stain by single sperm capture and mitochondrial DNA typing mainly solves the technical problems in the prior art that DNA content can not meet the requirements of routine mixed seminal stain test and that complete individual genetic information can not be provided. The method is realized by the steps of single sperm capture, DNA extraction from the single sperms, nested amplification on mt DNA HV I zone, DNA sequence analysis of the products from two amplifications and sperm concentration and autosome STR detection. According to the invention, single sperm mitochondrial DNA with personal characteristics is employed as a detection index, the mixed semen from different individuals is distinguished according to individual semen, and then nuclear DNA detection is carried out, thereby successfully solving the problem of recognizing individuals in mixed sample with components from different individuals. The characteristic of abundant mitochondrial DNA content of single sperm is utilized to meet the requirements of mitochondrial DNA detection by PCR technology; and a plurality of sperms with mitochondrial DNA of the same type are collected for realizing nuclear DNA detection, in order to achieve the purpose of individual identification.
Owner:中国医科大学
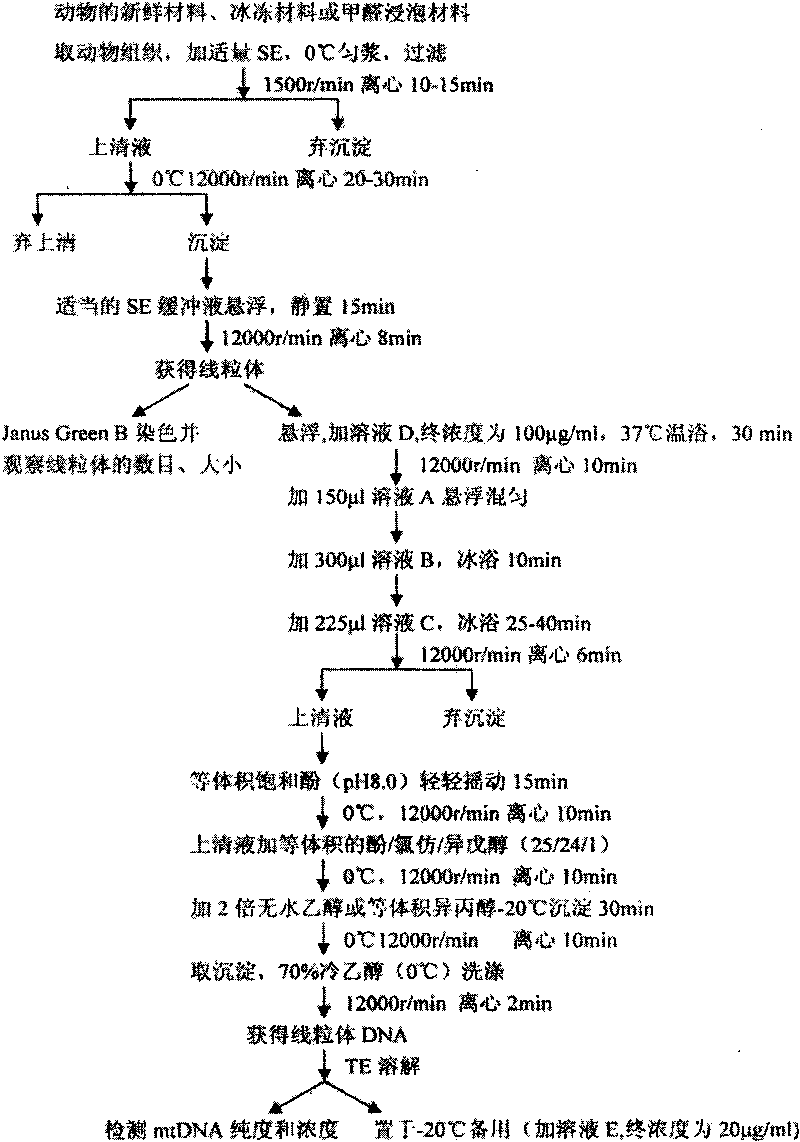
Method for extracting and purifying animal mitochondria DNA
InactiveCN101717772AHigh purityEnzyme digestionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationPurification methodsDigestion
The invention discloses a method for extracting animal mitochondria DNA, which has the innovativeness that a DNasel digestion step is added on the basis of alkaline denaturation to eliminate residual nuclear DNA; and an RNase digestion step is added to remove residual RNA. The mitochondria DNA extracted by the method has high purity. The electrophoretic detection shows that an electrophoretic band is a clear, regular and uniform band; and the background is clear, and the conditions such as the trailing of macromolecular DNA and front-end RNA and the like do not occur near a sample application pore.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
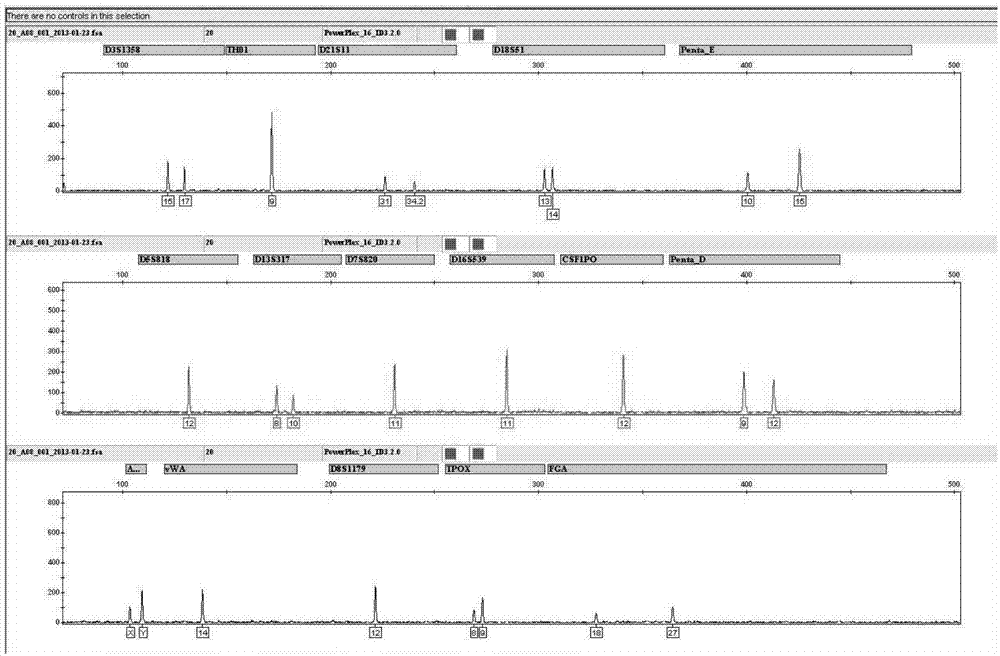
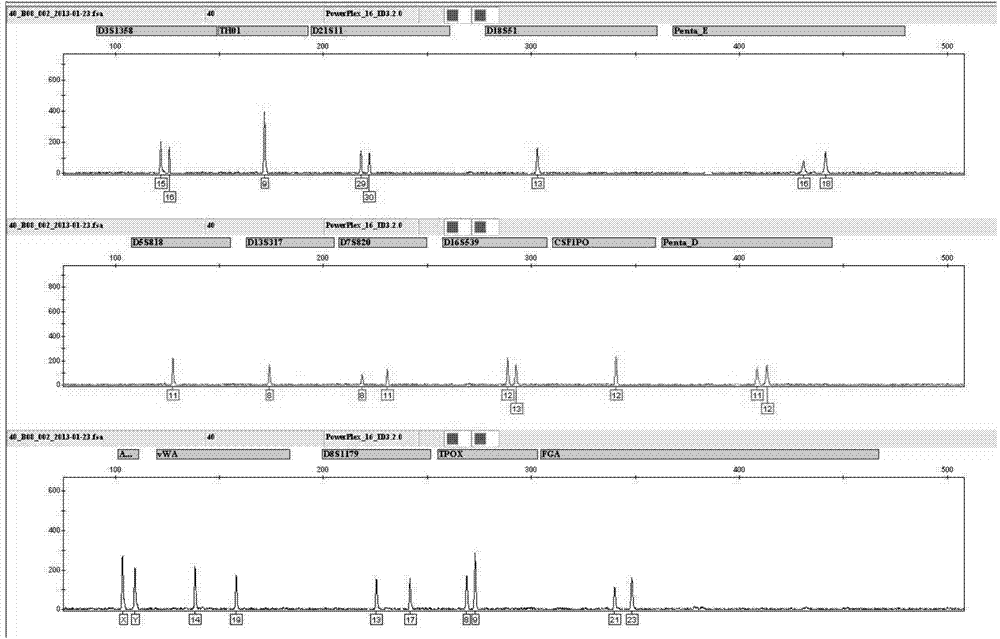
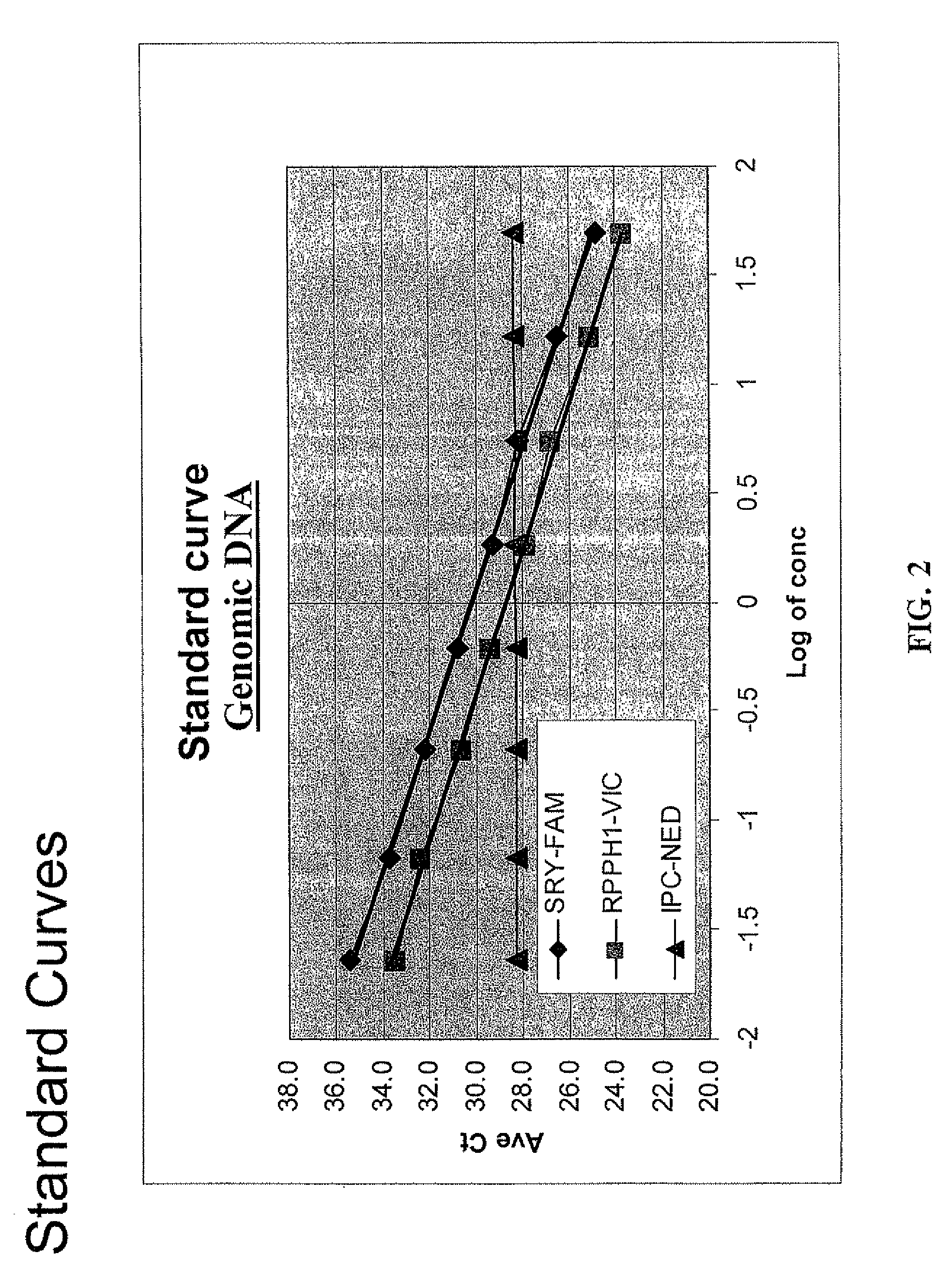
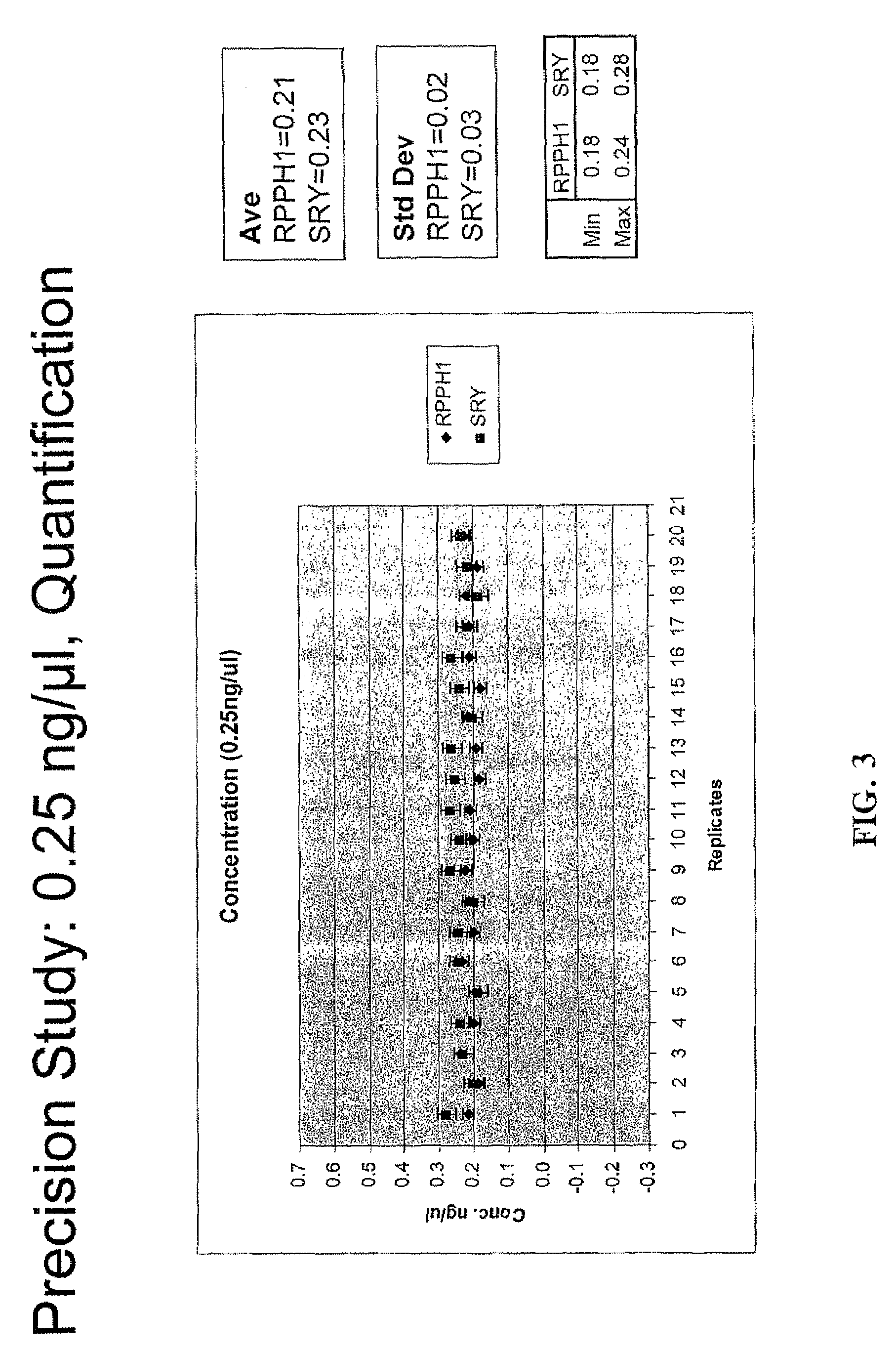
Multiplex compositions and methods for quantification of human nuclear DNA and human male DNA and detection of PCR inhibitors
ActiveUS8012691B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular TechniqueQuantification methods
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
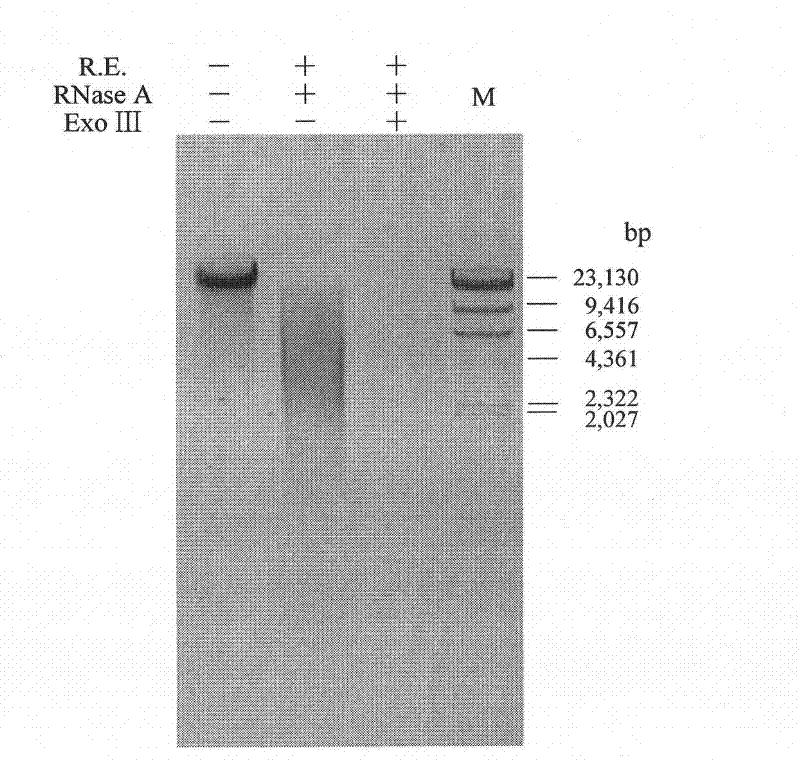
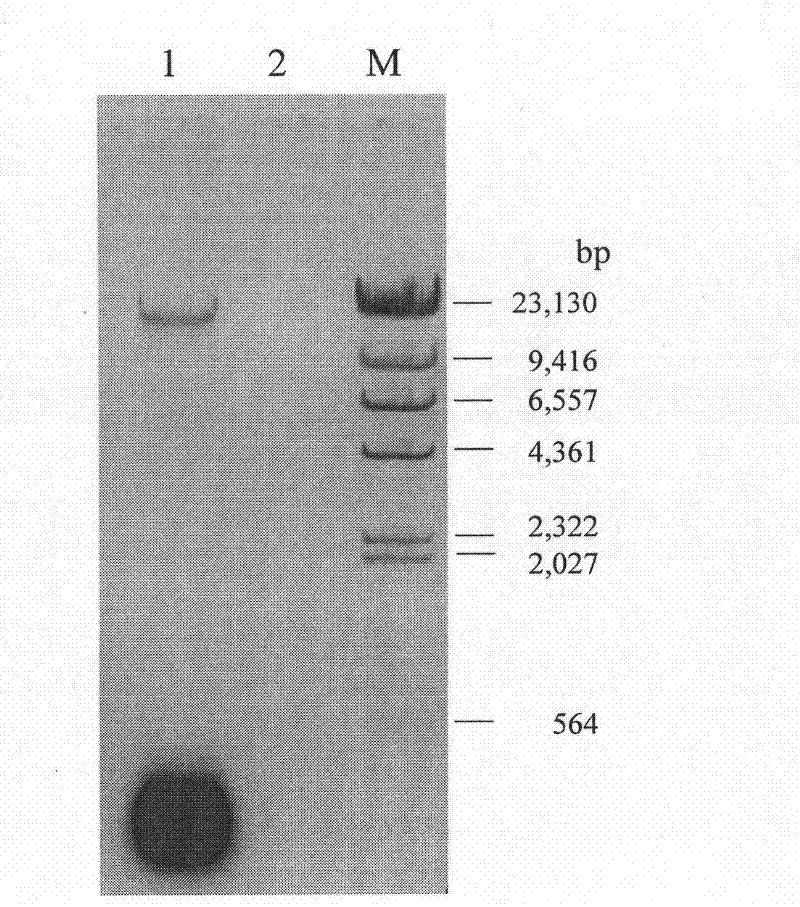
Human mitochondrial DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) purification method
InactiveCN102417903AHigh puritySimple and fast operationDNA preparationPurification methodsExonuclease III
The invention relates to a human mitochondrial DNA purification method. The method utilizes the joint action of restriction endonucleases (Bg1 II and Dra III), ribonuclease A and exonuclease III to degrade nuclear DNA and RNA (Ribonucleic acid) residues in genome DNA or mitochondrial DNA crude extract, so that high-purity mitochondrial DNA can be obtained. The method is widely applicable to the purification of human mitochondrial DNA samples, the purity is high, and the method is easy to operate, takes short time, and can meet the requirement of each technology in the mitochondria research field on the high purity of mitochondrial DNA.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Method for extracting and purifying columnar high-purity animal mtDNA
InactiveCN101717773AHigh purityEnzyme digestionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationPurification methodsElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a method for extracting and purifying a columnar high-purity animal mtDNA. In the method, an alkaline denaturation method is taken as a basis and improved by adding a DNaseI digestion step to eliminate the residue of nuclear DNA, and by adding a RNase digestion step to eliminate the residue of RNA; a column chromatography is adopted to replace a phenol extraction method for purifying the mtDNA to solve the problems of phenol toxicity and residue thereof. The mitochondrial DNA obtained by the method has high purity; and electrophoresis detection displays that an electrophoresis band is clear, neat and even with clear background and without the situations of macromolecular DNAs near sample application holes, front-end DNA trailing, and the like.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
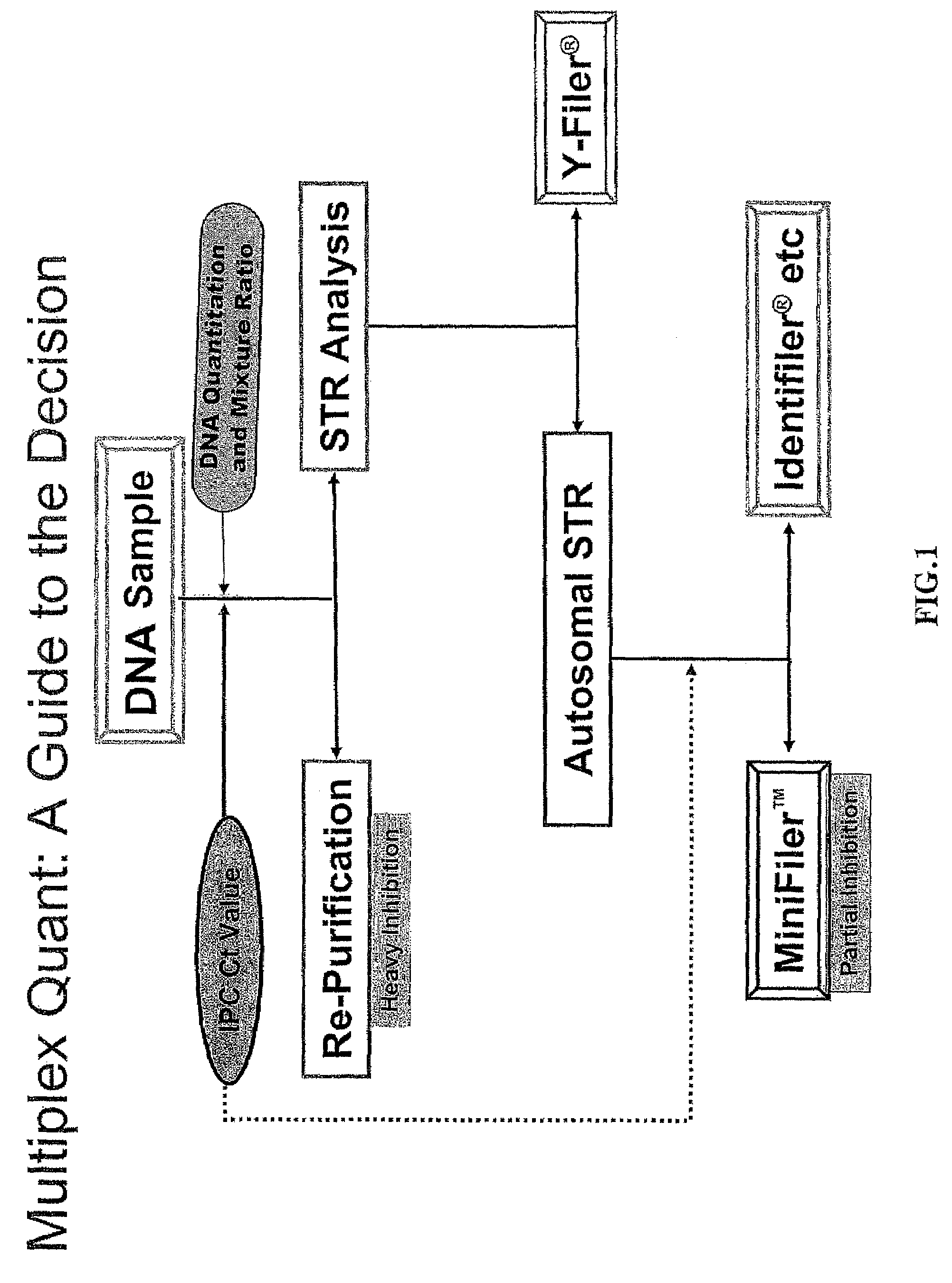
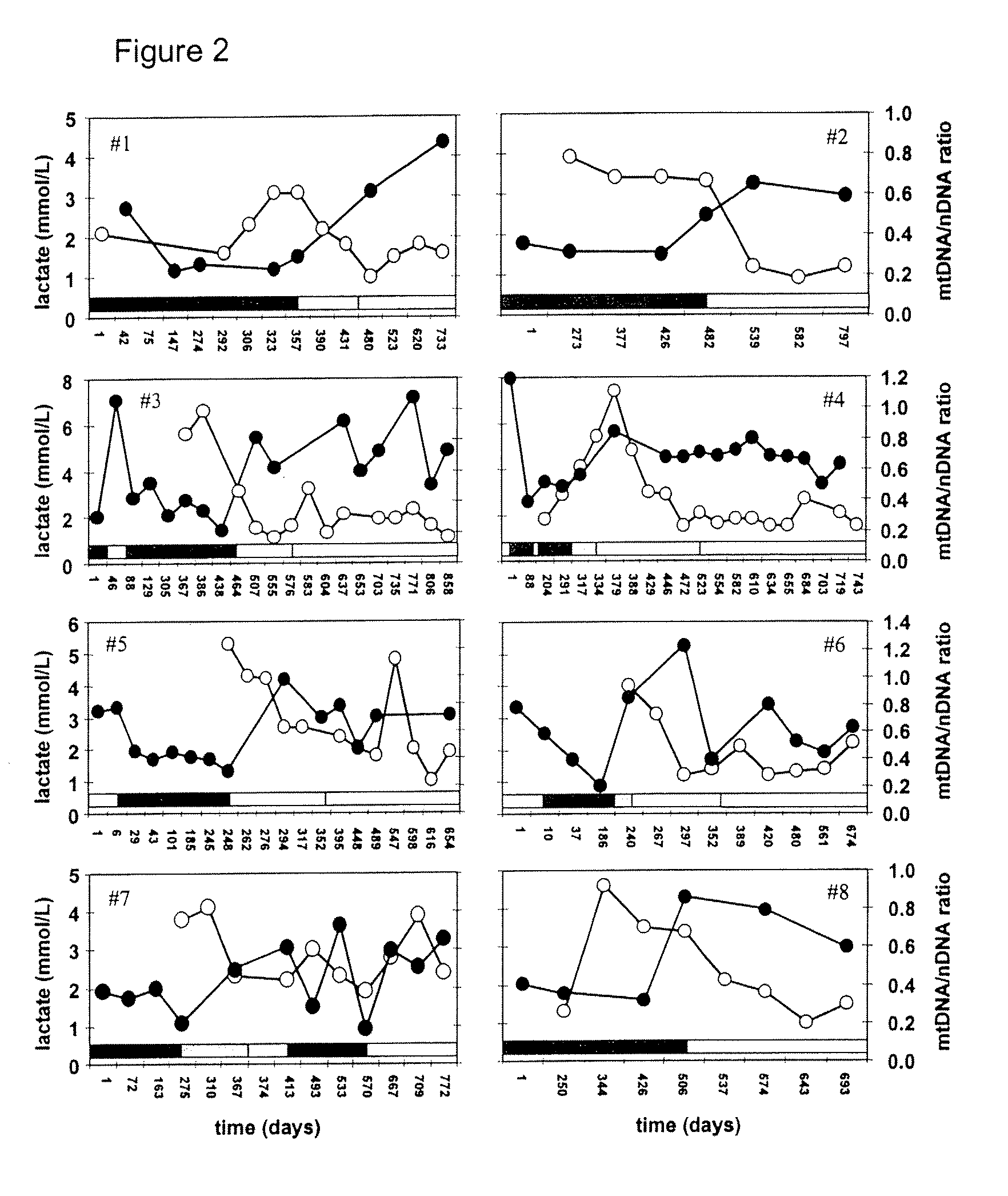
Pharmacological Applications of Mitochondrial DNA Assays
InactiveUS20090053697A1Nervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug treatmentNucleic acid
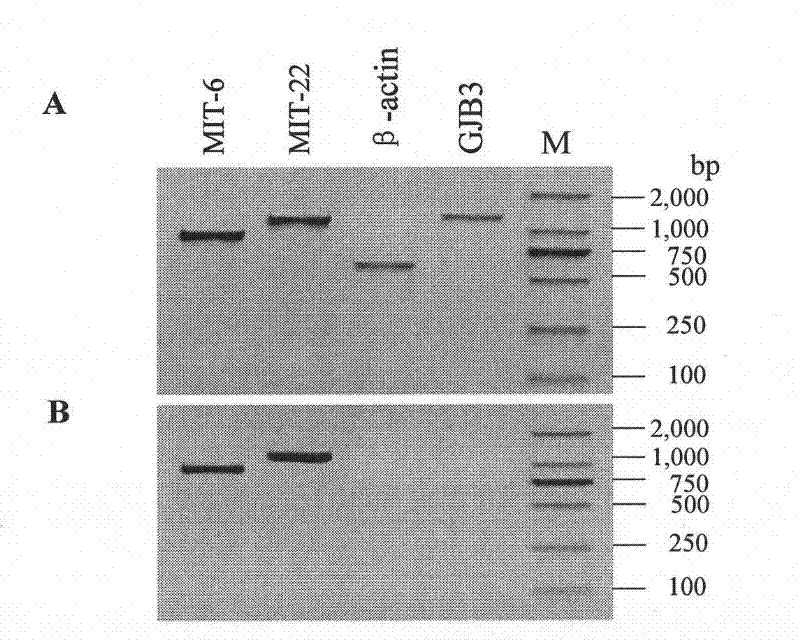
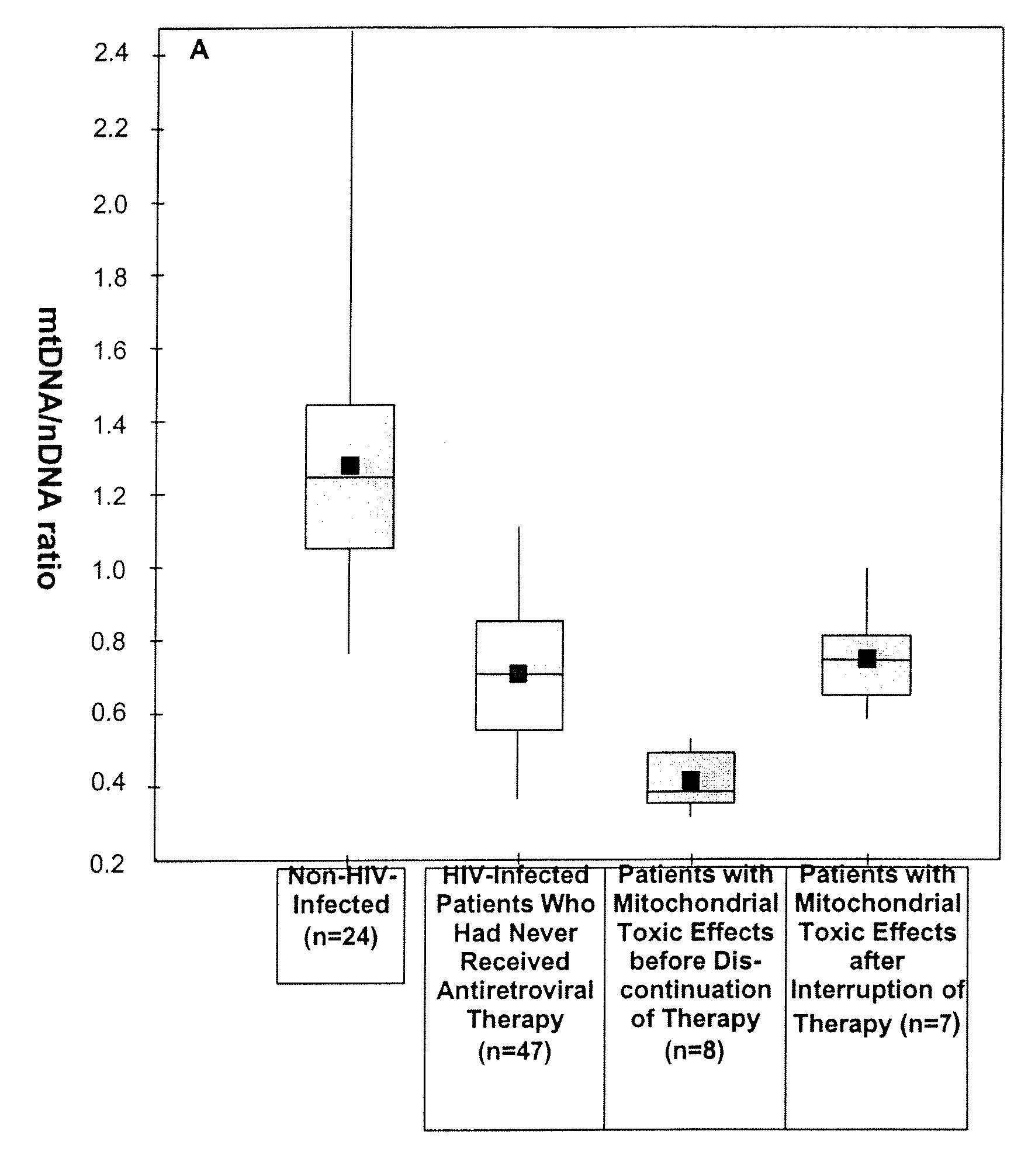
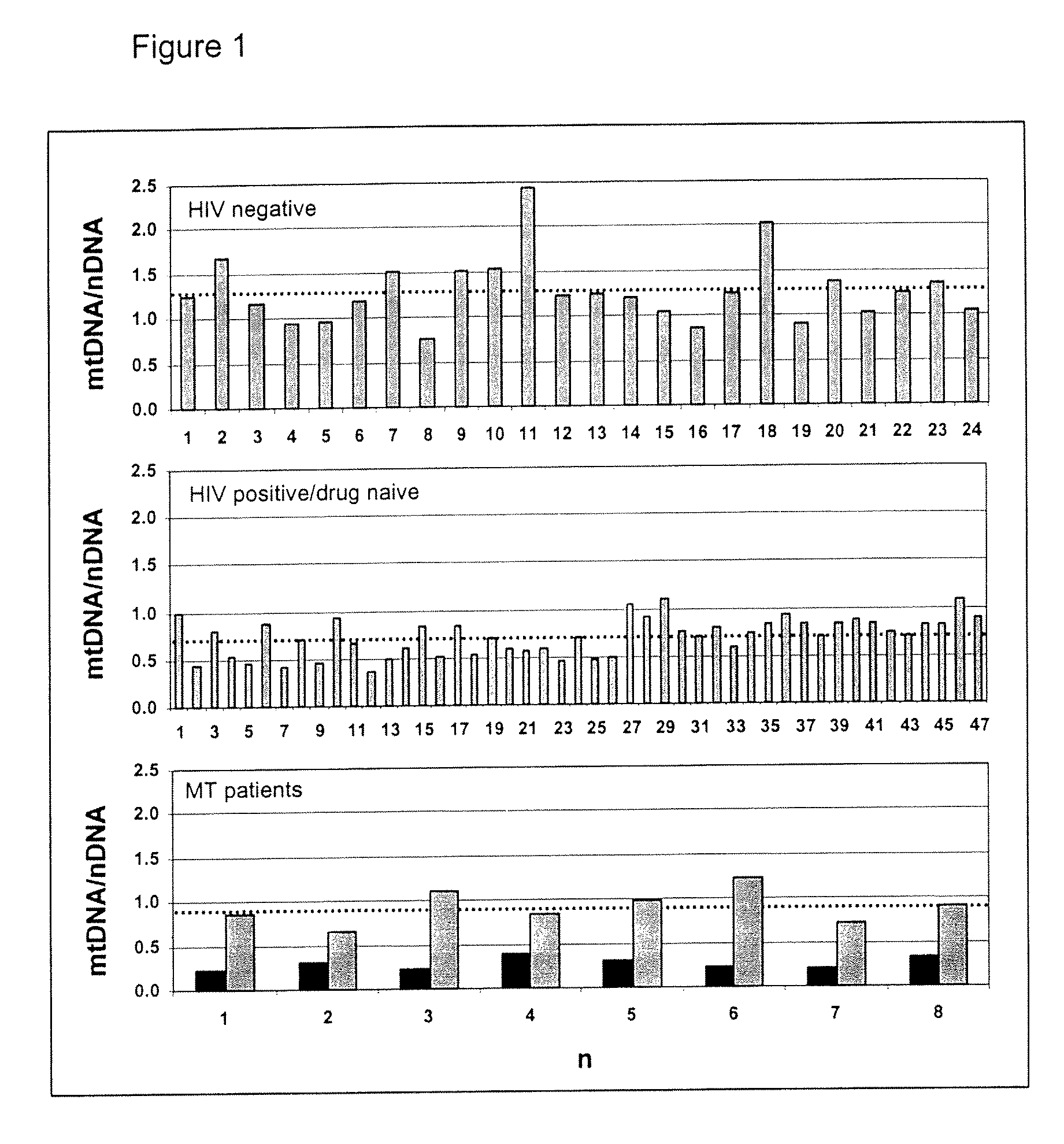
The invention provides assays to determine the relative amount of mitochondrial DNA in a subject, such as a subject undergoing drug treatment. The subject may for example be a human patient undergoing treatment for an HIV infection with a nucleic acid precursor such as a nucleoside or nucleotide analogue. The assays of the invention may include PCR assays, such semi-quantitative or quantitative PCR involving the co-amplification of a mitochondrial sequence and a reference sequence, such as a genomic sequence. Information from such assays may be evaluated to provide a ratio of mithchondrial DNA to nuclear DNA in the cells of the subject.
Owner:COTE HELENE +2
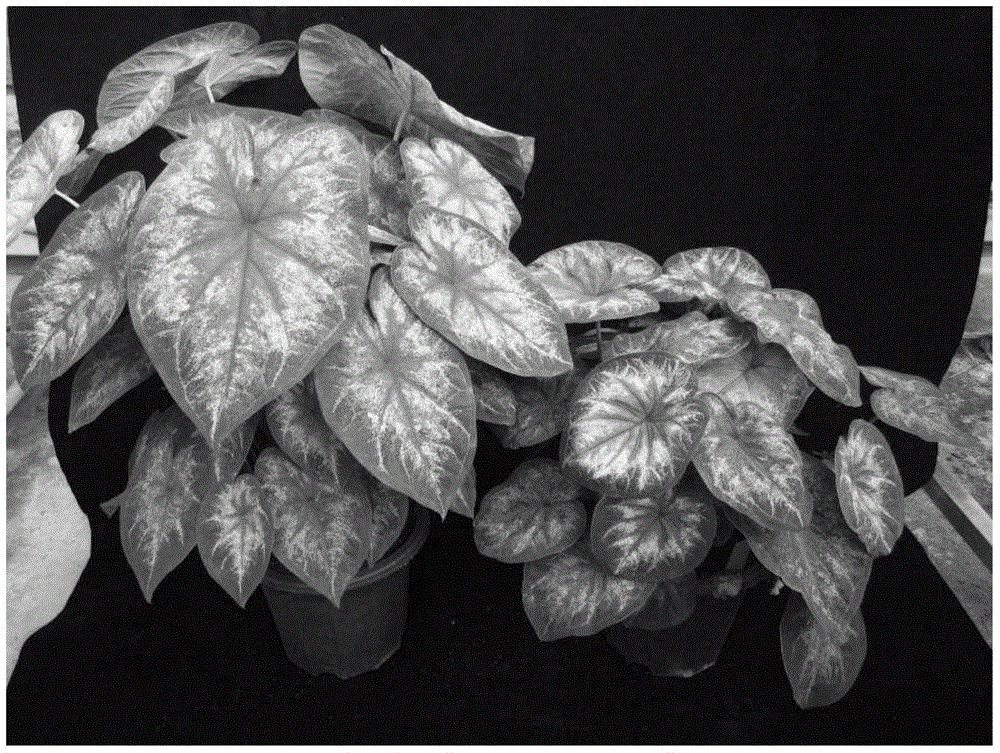
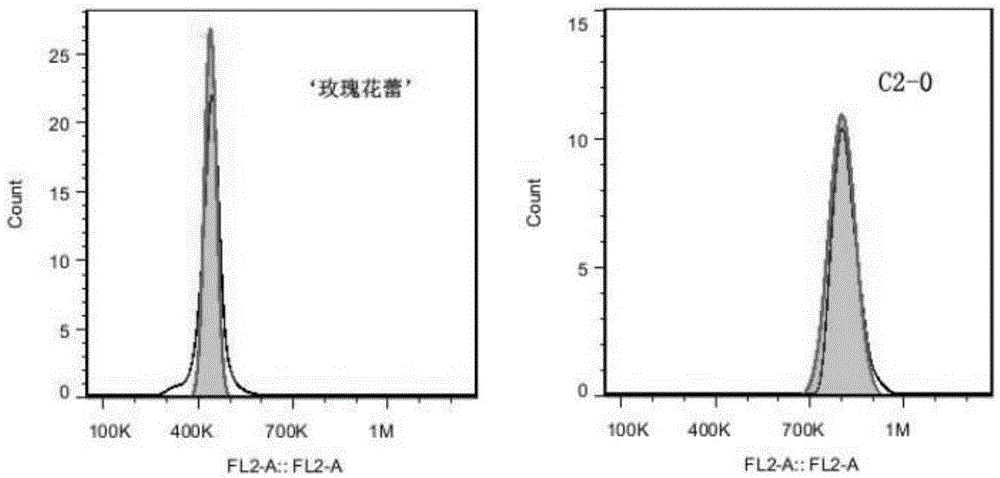
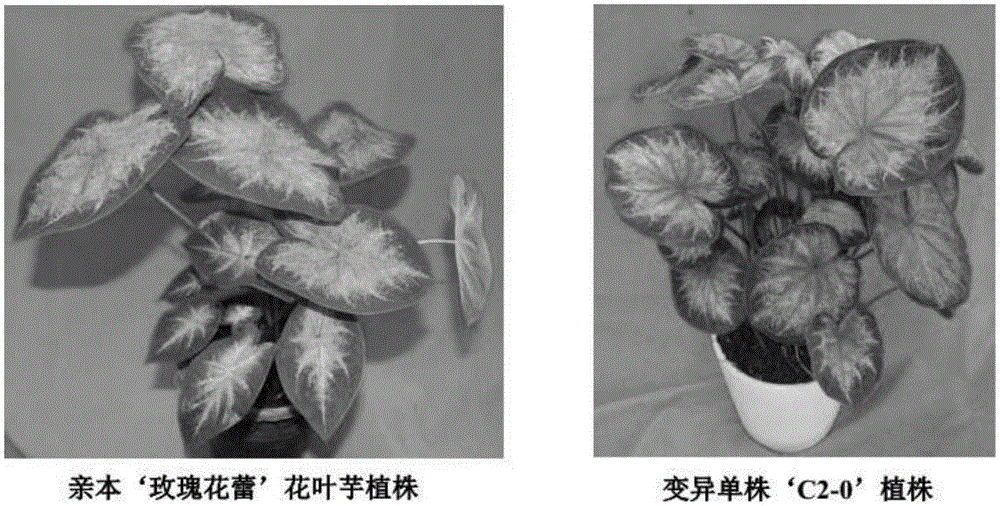
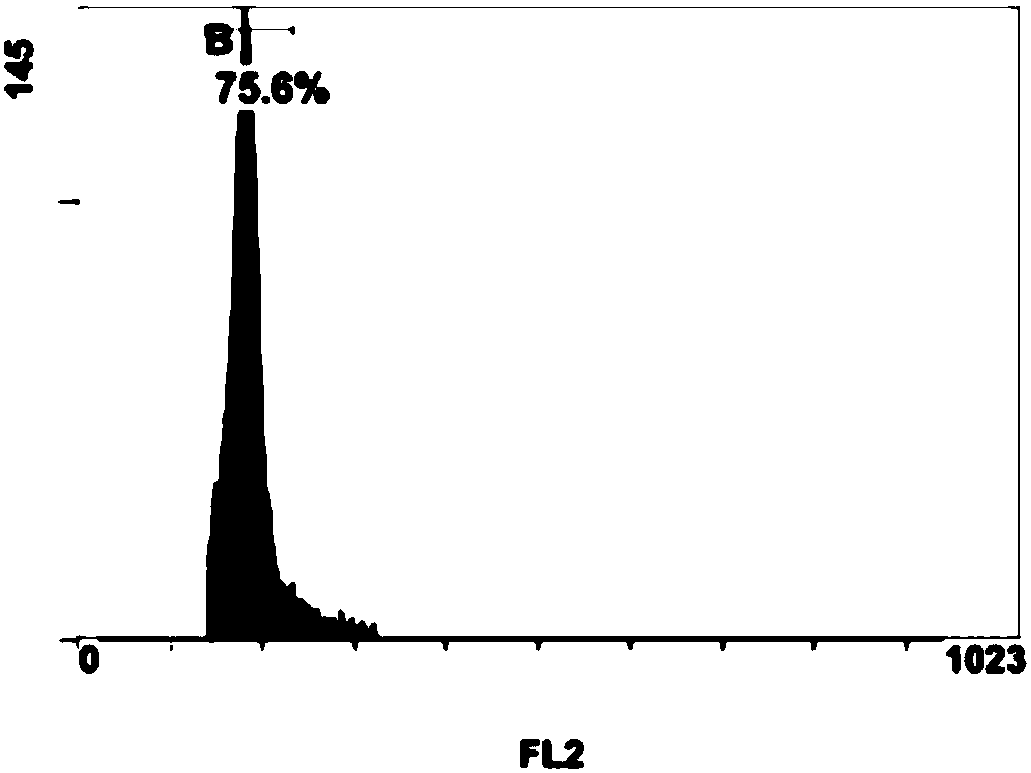
Breeding method for somaclonal variation of caladium bicolor
InactiveCN105557525AImprove stabilityHigh speedHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySomaclonal variation
The invention discloses a breeding method for somaclonal variation of caladium bicolor, and belongs to the technical field of genetic breeding of flowers. The method comprises the steps that a tissue culture rapid propagation system of a parent is built in a callus induction way; variant plants with special characters are screened out of offspring groups and numbered, the content of relative nuclear DNA of the variant plants is detected, and when the peak value position of the variant plants is 1.6 to 2.2 times that of the parent, the corresponding plants are determined as preferable plants of the caladium bicolor; a clonal offspring group of the preferable plants is built, multi-year multi-point experimental research is carried out on the main characters of the offspring group, the specificity, consistency and stability of the preferable plant offspring group are verified, and finally the preferable plants are determined as a new variety of the caladium bicolor. According to the method, good variant plants of the caladium bicolor can be effectively obtained, the variant plants can be stabilized fast, an operating method is simple and convenient, the breeding cycle is shortened, and breeding efficiency is improved.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL HORTICULTURE RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
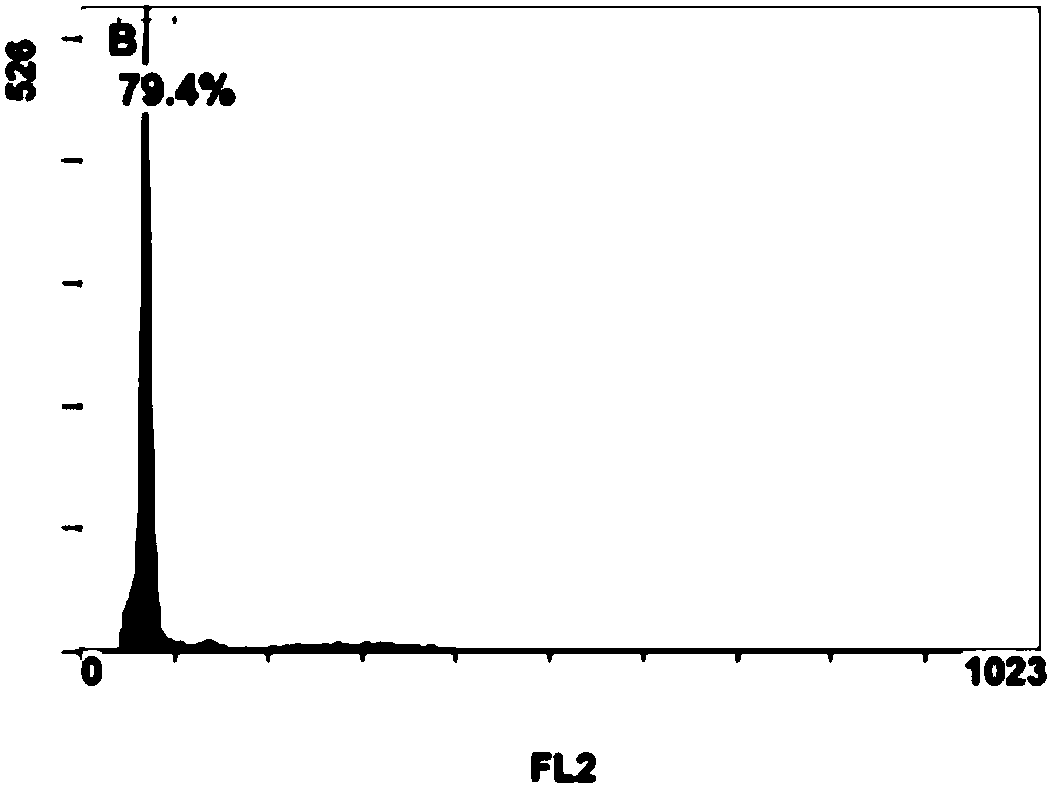
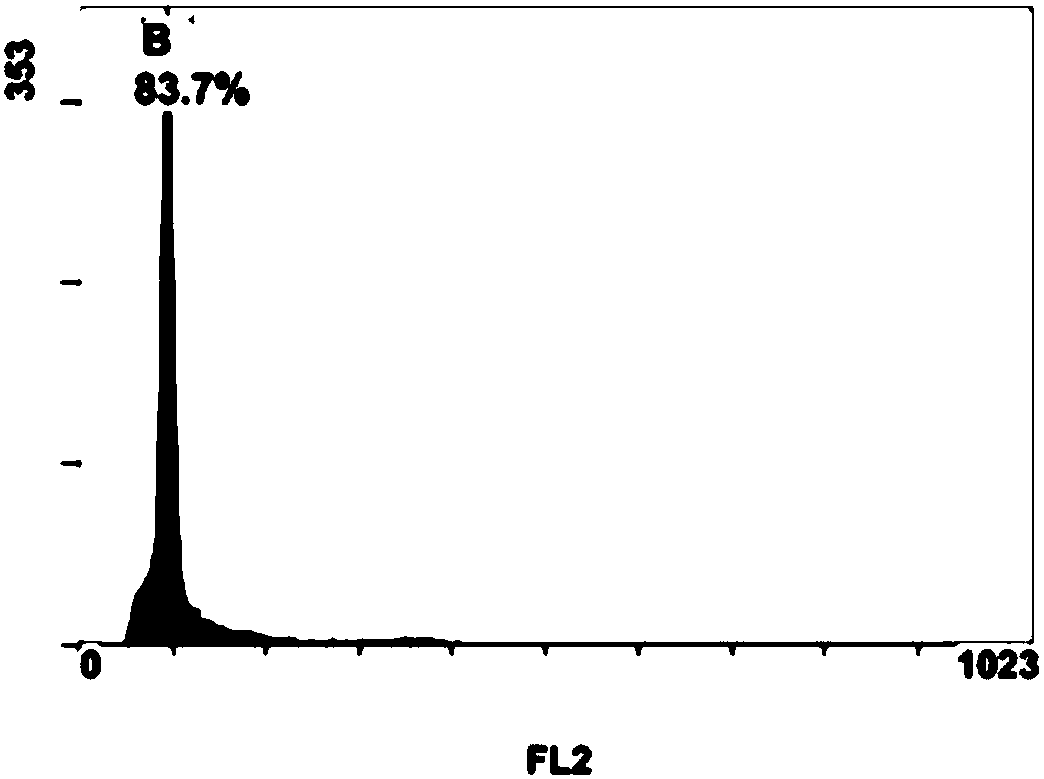
Preparation method of flow cytometry water lily sample and cell lysis buffer solution
InactiveCN107603883AEnsure stabilityPrevent agglutinationPreparing sample for investigationMicroorganism lysisStainingTissue sample
The invention discloses a preparation method of a flow cytometry water lily sample and a cell lysis buffer solution, and relates to the field of flow cytometry detection. The preparation method of theflow cytometry water lily sample, disclosed by the invention, comprises a lysing step and a staining step, wherein in the lysing step, a water lily tissue sample is lysed, filtered and centrifuged toobtain cell nuclei to be dyed, and in the staining step, the cell nuclei to be dyed are stained to obtain dyed cell nuclei. By the preparation method, the improved cell lysis buffer solution is usedfor treating the water lily tissue sample, and the cell lysis buffer solution can remove residual cytoplasmic fragments from the complete cell nuclei of water lily, maintain the stability of the cellnuclei in a suspension, prevent agglutination, protect DNA from degradation and provide a suitable environment for specific nuclear DNA chemical staining, so that negative effects of cytoplasmic components on staining are effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Construction method for cold-resistant transgenic tobaccos based on fatty acid desaturase gene
The invention provides a construction method for cold-resistant transgenic tobaccos based on a fatty acid desaturase gene. The construction method comprises the following steps: firstly, amplifying out stearoyl carrier protein desaturase gene (SAD) of spinach by virtue of an RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) process, and connecting the stearoyl carrier protein desaturase gene to a plant genetic transformation carrier pBI121; cloning and recombining a correct carrier by virtue of nucleotide sequence analysis and transforming the correct carrier into agrobacterium tumefaciens LBA4404; transforming tobacco aseptic seedling explants by the agrobacterium tumefaciens containing recombinant plasmids by virtue of a leaf disc method, screening out a kanamycin resistant plant and transplanting the kanamycin resistant plant into a flower pot, and collecting seeds after the kanamycin resistant plant is mature; sowing the seeds on an MS culture medium containing kanamycin to germinate and grow; extracting nuclear DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from leaves of the kanamycin resistant plant to carry out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection, dot blotting and Southern cross identification; and finally, by taking molecularly-identified positive transgenic tobaccos as experimental materials, carrying out conductivity measurement and chlorophyll content measurement respectively under low temperature stress, wherein the cold resistance of SAD transgenic tobaccos is obviously improved.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Site-targeted transformation using amplification vectors
ActiveUS8058506B2Highly versatileImprove efficiencyBryophytesSugar derivativesOrigin of replicationPlant cell
A process of causing a targeted integration of DNA of interest into a plant cell nuclear genome, comprising; i) providing plant cells with an amplification vector, or a precursor thereof, capable of autonomous replication in plant cells, said vector comprising; a) DNA sequence(s) encoding an origin of replication functional in plant cells, b) DNA sequence(s) necessary for site-specific and / or homologous recombination between the vector and a host nuclear DNA, and c) optionally, further DNA of interest; ii) optionally providing conditions that facilitate vector amplification and / or cell to cell movement and / or site-specific and / or homologous recombination, and iii) selecting cells having undergone recombination at a predetermined site in the plant nuclear DNA.
Owner:ICON GENETICS
Method for correcting human genome damage through micro nutrient substances according to genetic background
InactiveCN105200125ALower levelMaintain stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGenomicsHuman DNA sequencing
The invention relates to a method for correcting human genome damage through micro nutrient substances according to the genetic background and belongs to the technical field of nutrition genomics and medical genetics application. The method comprises the steps that peripheral blood of an individual is sampled, the levels of folate of the blood, serum VB12 and serum Hcy are detected, nuclear DNA is extracted, the MTHFR C677T and A1298C genetypes and the genome damage condition of the individual are combined, and micro nutrient substance intervention suggestions are given to the individual with the high genome damage according to reference values (the folate of erythrocyte is higher than 700 nM, the serum folate is higher than 34 nM, the serum VB12 is higher than 300 pM, and the serum Hcy is lower than 8 micrometers) at which various blood micro nutrient substances maintain the stability of genomes, so that the heredity damage of the individual is corrected, and the stability of the genomes is maintained. The strategy is beneficial to preventing cardiovascular diseases and reducing the risk factor of genome damage related diseases.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Reforming composite insecticidal crystalline gene Cry2A of bacillus thuringiensis
A Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal protein DNA sequence Cry2A is designed and synthesized. Comparing it with original Cry2A DNA sequence can show that the amino acid components of DNa sequence coding protein are not changed, the application frequency of vegetable preference codon is higher and the AT sequence, reverse reduplicate sequence and indefinable subsequences are eliminated. It can be used for culturing the seed of insect-resisting transgenic plant.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
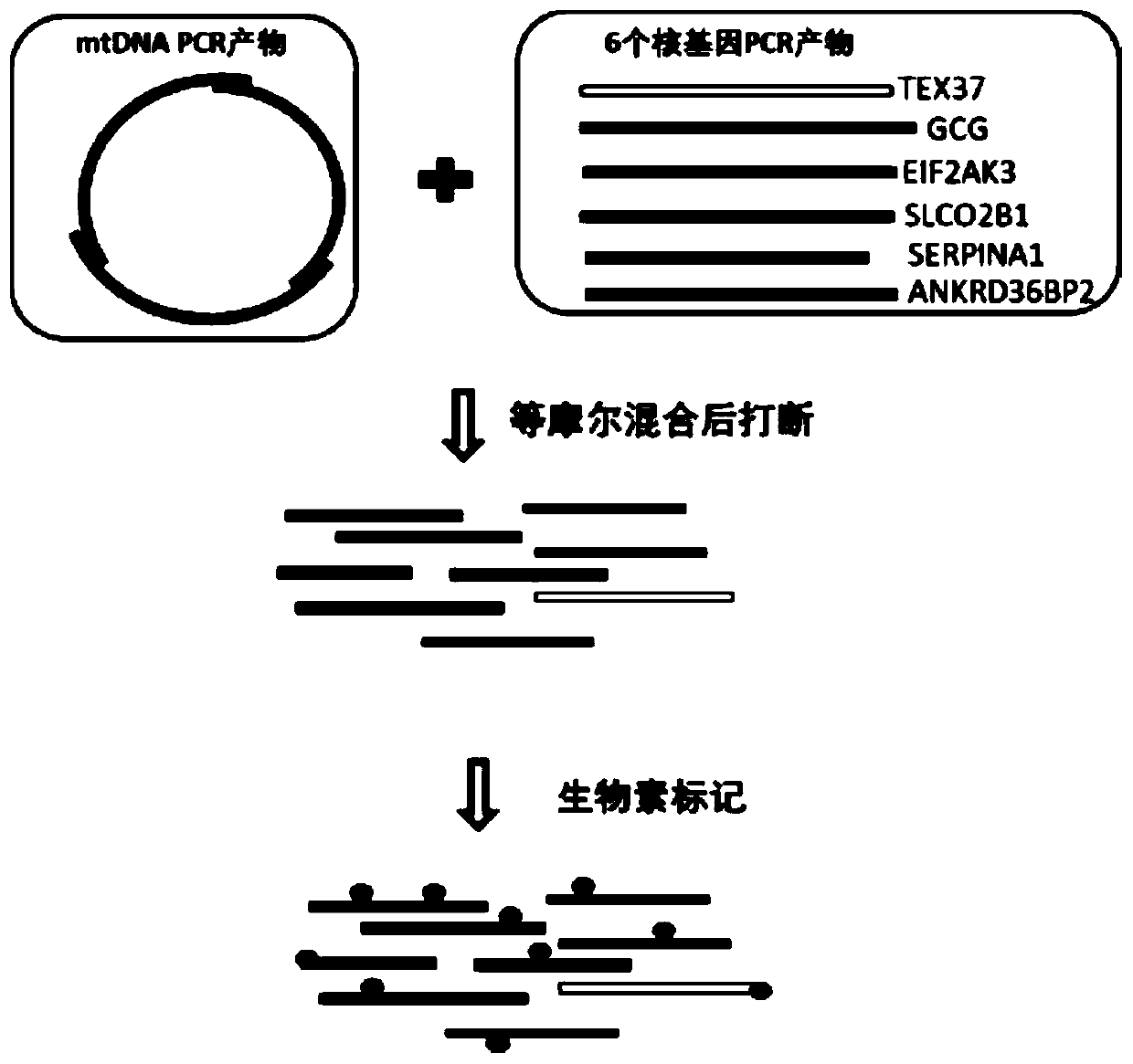
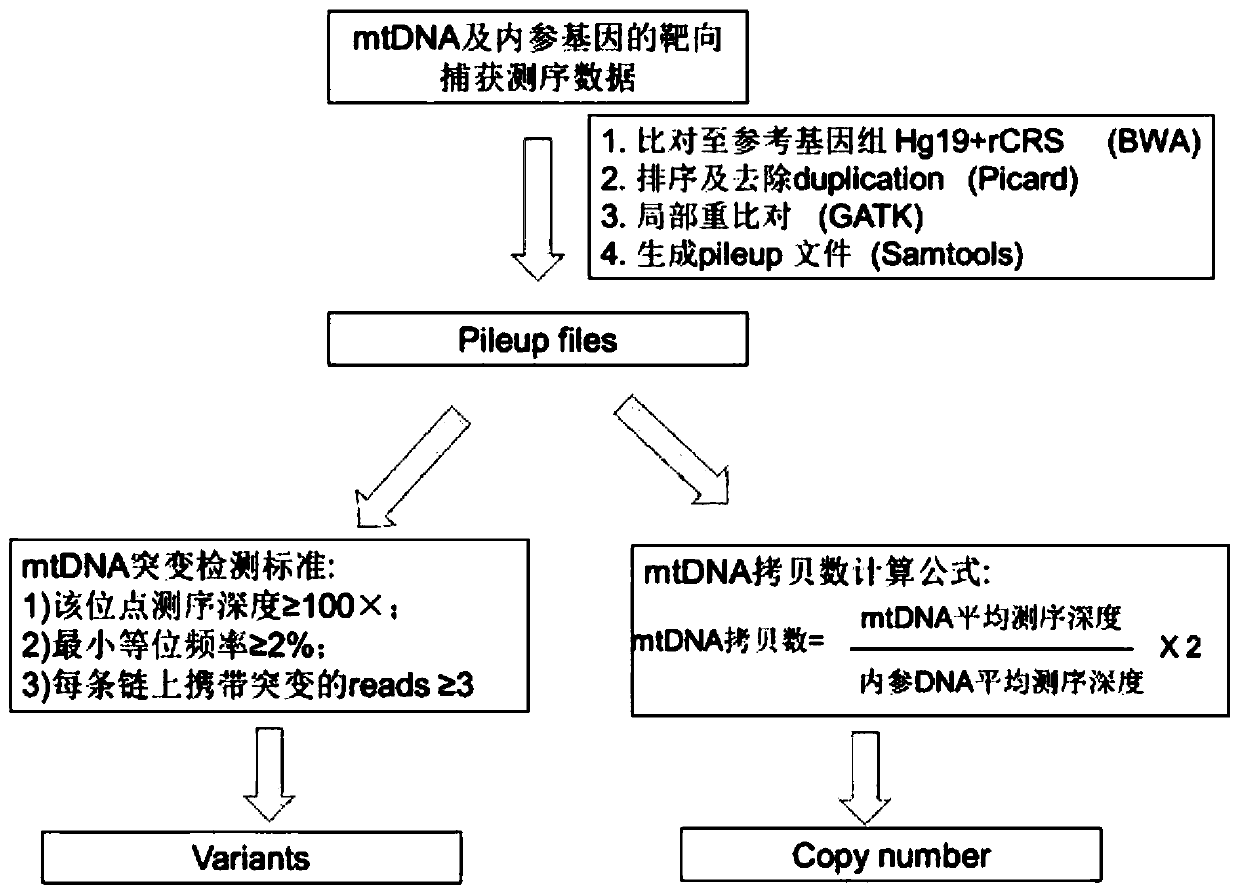
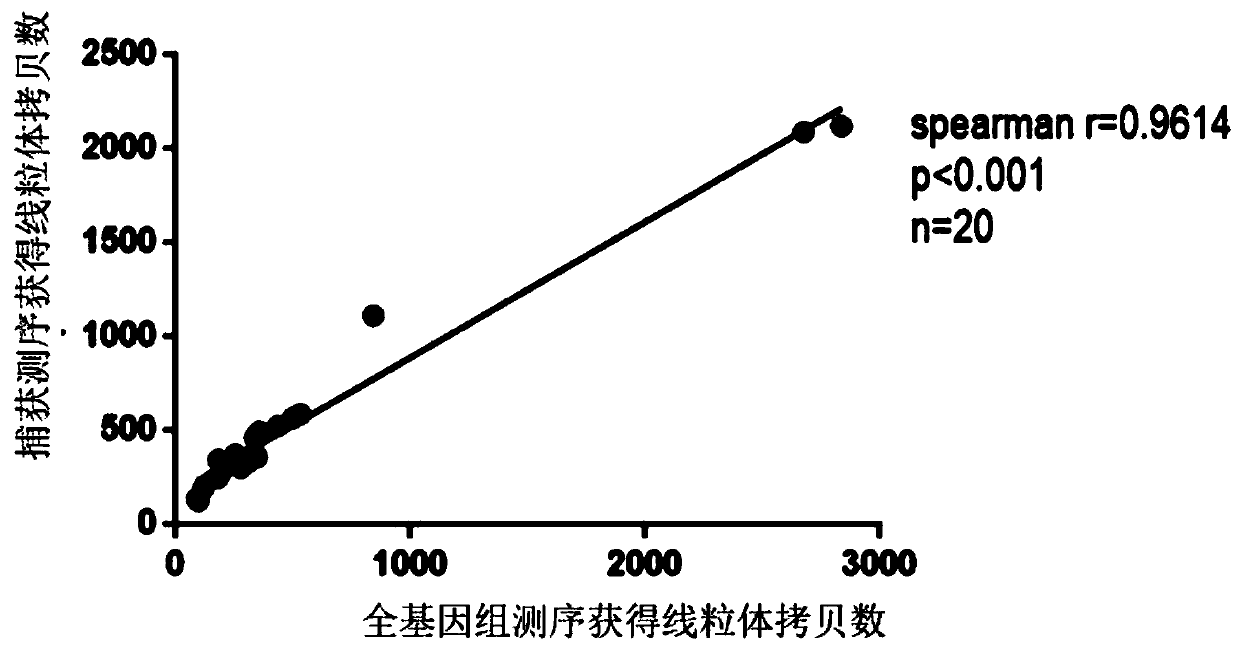
Method for simultaneously detecting copy number and mutation of mtDNA based on NGS
PendingCN110241191AAccurate detectionOvercoming problems such as poor accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementWhole genome sequencingDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting the copy number and mutation of mtDNA based on NGS. A capture probe of mitochondrion DNA and 6 reference DNA fragments is prepared, the mitochondrion DNA and references in a whole-genome sequencing library are captured, sequencing data is analyzed by utilizing a bioinformatics technology, and simultaneous accurate detection of mitochondrial genome mutation and the copy number is realized. The method specifically comprises the following steps of 1, PCR amplification; 2, probe preparation; 3, capture sequencing; 4, bioinformatics analysis. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the low-frequency mutation and the copy number of the mitochondrion DNA can be accurately detected in the capture sequencing process, the DNA demand is reduced, precious DNA samples are saved, the experiment operation is simplified, and the detection cost is greatly reduced. Six nuclear DNA fragments are randomly selected as the references in the preparation process of the probe, the problem that capture sequencing data is used for calculating the copy number in the prior art and accordingly the accuracy is poor is solved, and the accuracy of related research results is improved.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com