Nucleic acid amplification detection method and detection kit for distinguishing DNA from corresponding RNA
A detection method and kit technology, applied in the field of medical detection, can solve the problems of indistinguishability, harsh test conditions, difficult and fast detection, etc., and achieve the effect of simple and fast operation and low operation difficulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0098] Example 1 Verification of specific RNA detection and verification of end conversion template synthesis
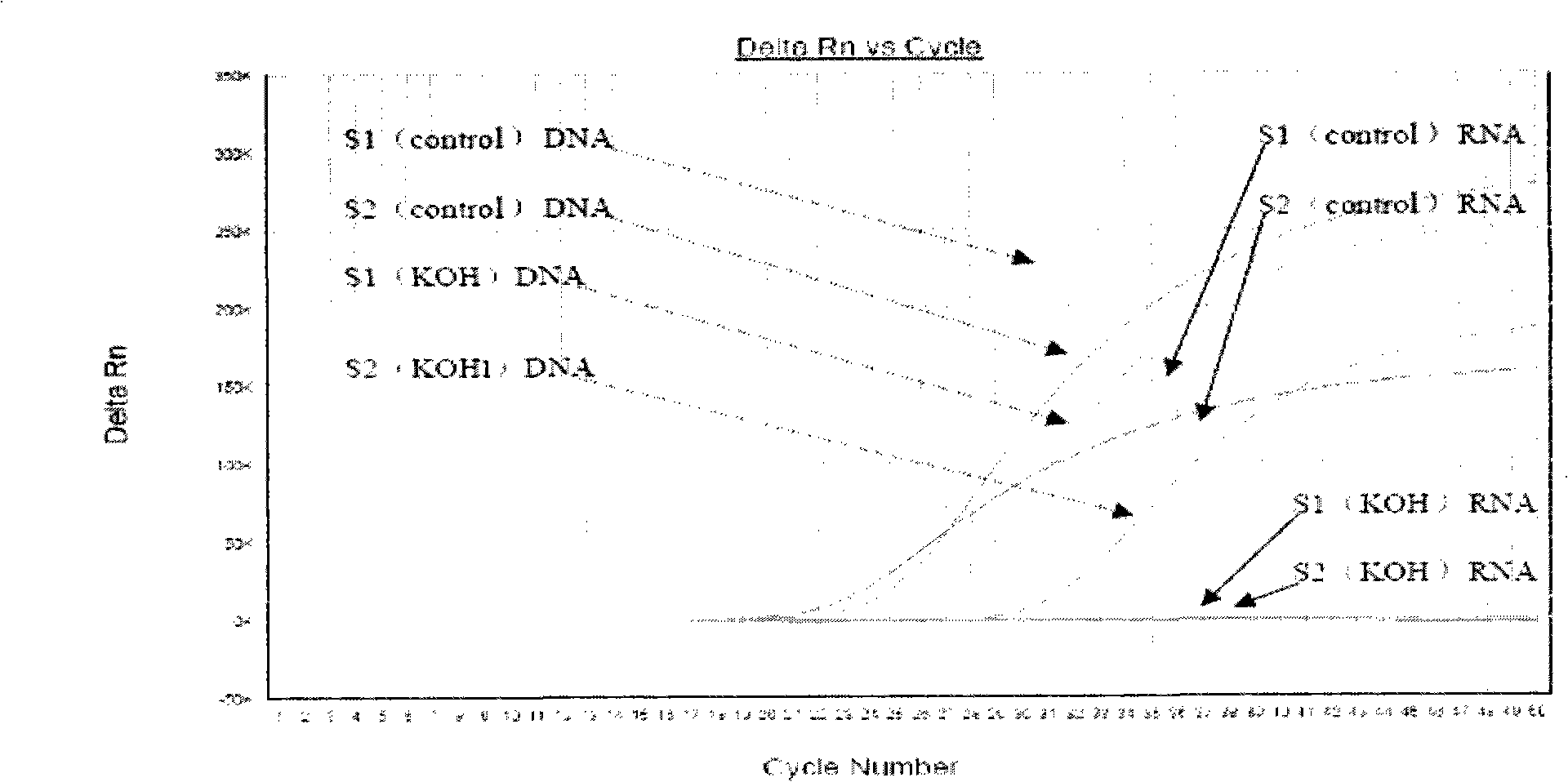
[0099] Freeze-dried BCG from Shanghai Institute of Biological Products, redissolved in 1ml of normal saline, and washed with normal saline 10.
[0100] Doubling serial dilutions were made into serial concentrations. 1:10, 1:100 diluted concentration of BCG samples, take 0.1ml of nucleic acid extraction reagent (column membrane method, Qiagen) to extract and purify the total nucleic acid, use KOH to treat the total nucleic acid (add KOH to the nucleic acid template to a final concentration of 0.3M, 37°C to hydrolyze the RNA for 7 days to completely degrade the RNA), and finally neutralize the pH value to neutral with 1M hydrochloric acid, add water to dilute it about 10 times (acid-base neutralization to generate a higher concentration of salt may bring adverse effects to downstream operations To be on the safe side, dilute it to reduce the salt concentration in the ...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Specificity (MTC specificity) and sensitivity of embodiment 2 kit
[0103] Most of the following mycobacterial strains come from the Institute of Bioinspection (Vaccin Department of China Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products), including: Mycobacterium scrofulaceum (M.scrofulaceum), Mycobacterium kansasii (M.kansassi), intracellular M.intracellulare, M.fortuitum, M.flavescens, M.avium, M.marinum, Di Mycobacterium smegmatis (M.smegmatis), Mycobacterium smegmatis (M.smegmatis), Mycobacterium smegmatis (M. gastri), Mycobacterium toads (M.xenopi), Mycobacterium terrae (M.terrae), Mycobacterium secondary (M.triviale), Mycobacterium abscessus (M.abscessus), Mycobacterium achromosum ( M.nonchromogenic), Mycobacterium tuberculosis human (M.tuberculosis), Mycobacterium bovis (M.bovis), BCG (M.bovisBCG), Mycobacterium simian (M.simiae), Mycobacterium paratuberculosis Bacillus (M.paratuberculosis), M.chelorae.
[0104] In addition, other microorgan...
Embodiment 3
[0106] The same tube detection of embodiment 3 kit and its application
[0107] According to the aforementioned embodiments of the present invention, the primer probe combination SEQ ID NO: 2, 3, 4 and the primer probe combination SEQ ID NO: 8, 9, 10 are assembled into a tube, and the reporter group R1 of its TaqMan MGB probe is selected FAM and R2 choose VIC / HEX, and use the sample extract in Example 2 to detect its chromosomal DNA (IS6110) and 16S rRNA in the same tube, and the results are completely consistent with the results in Example 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com