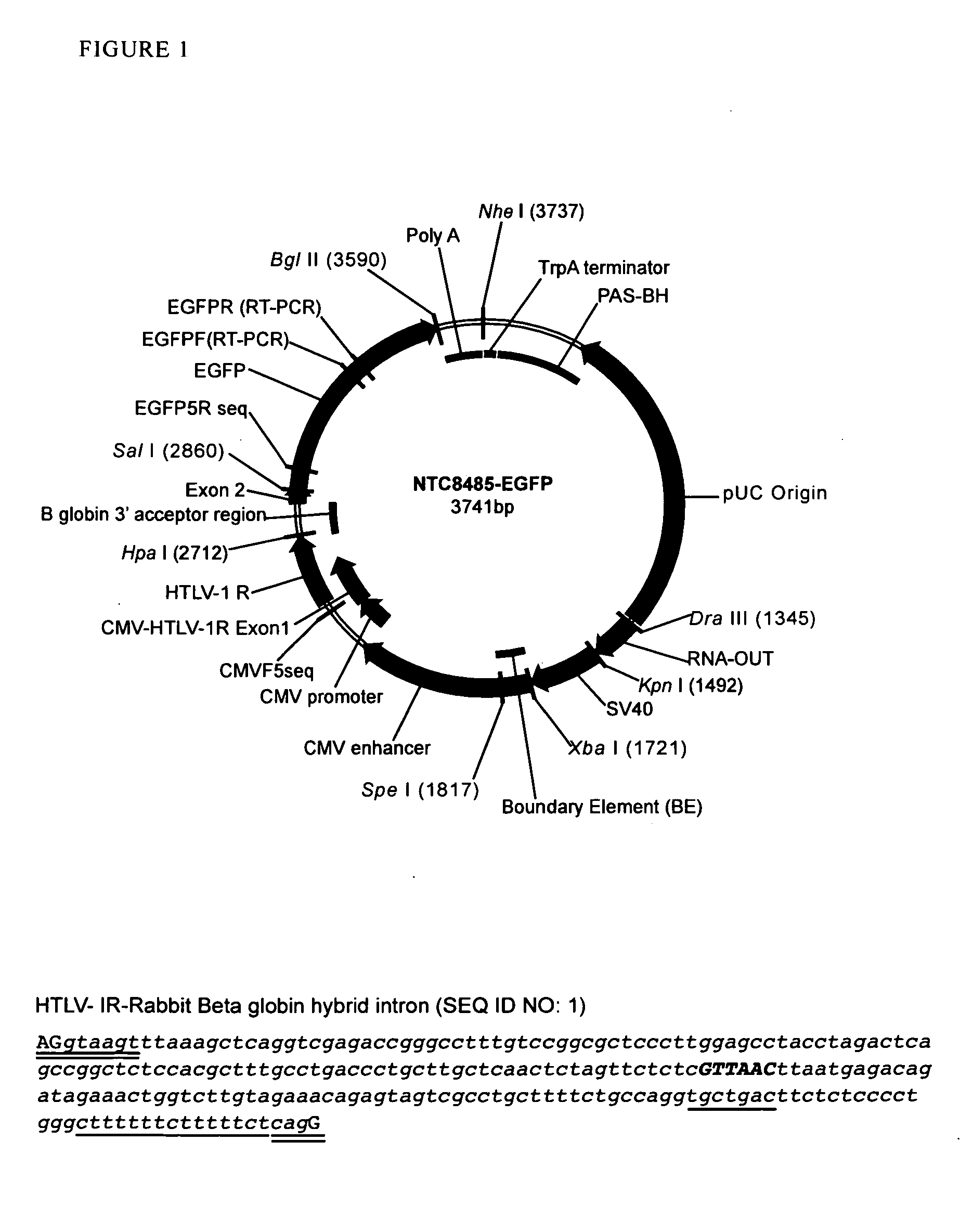
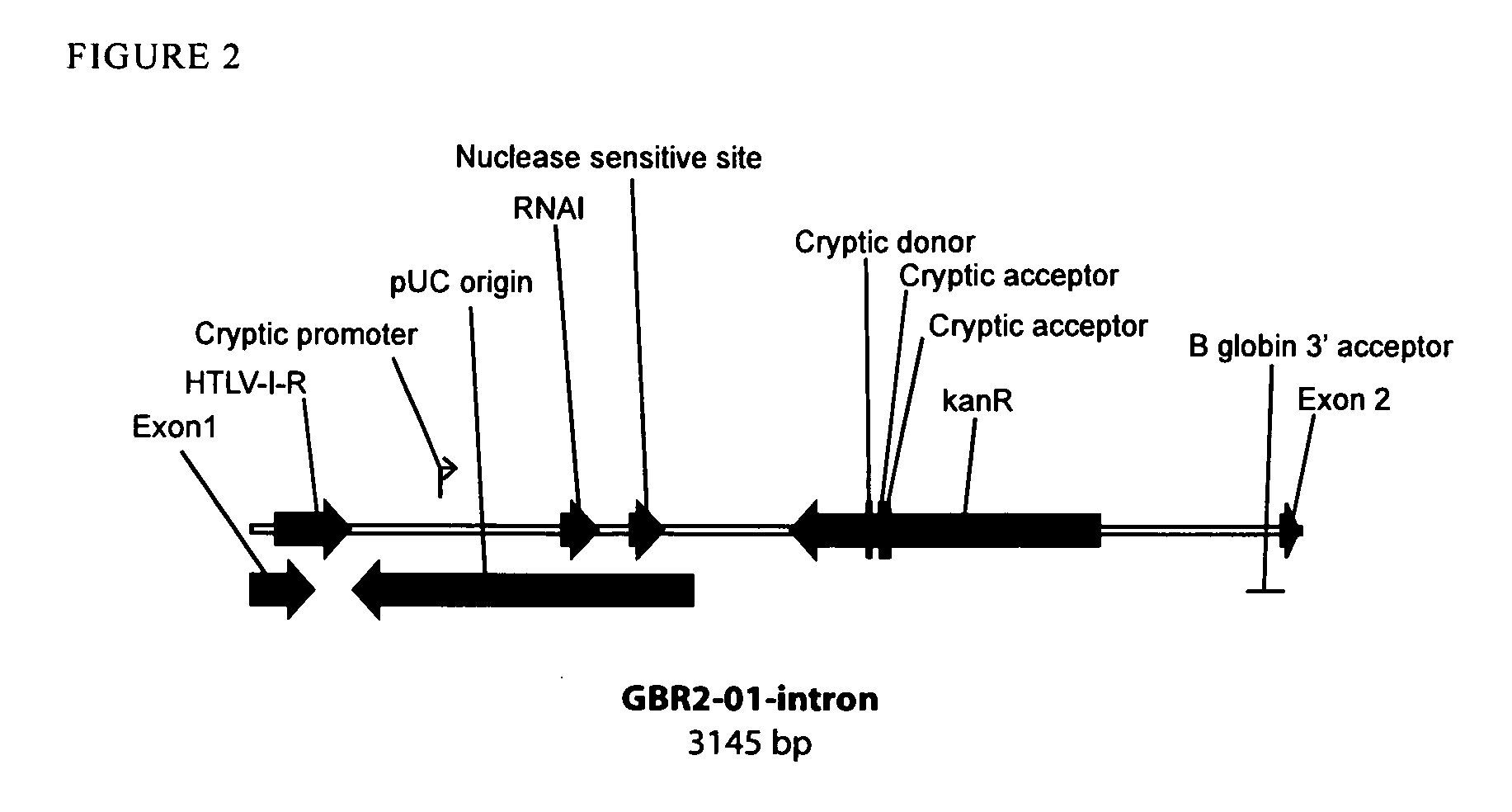
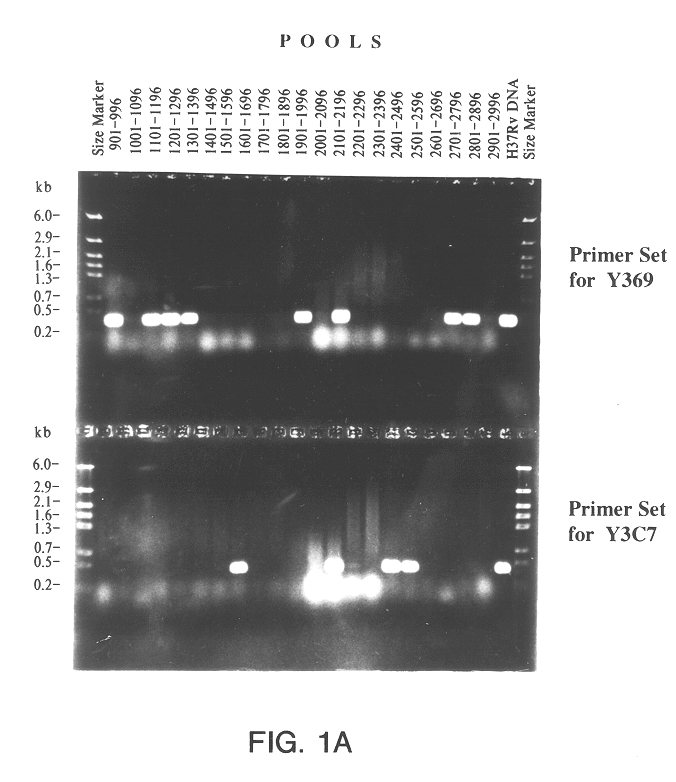
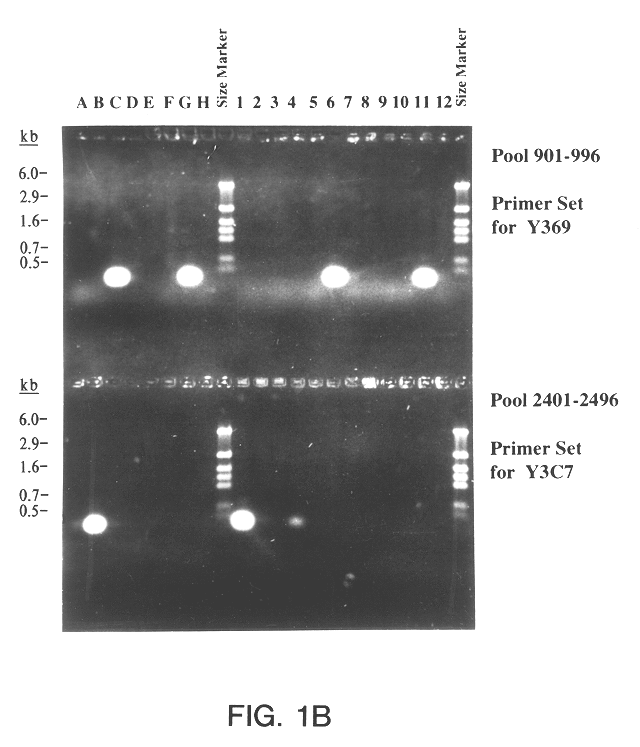
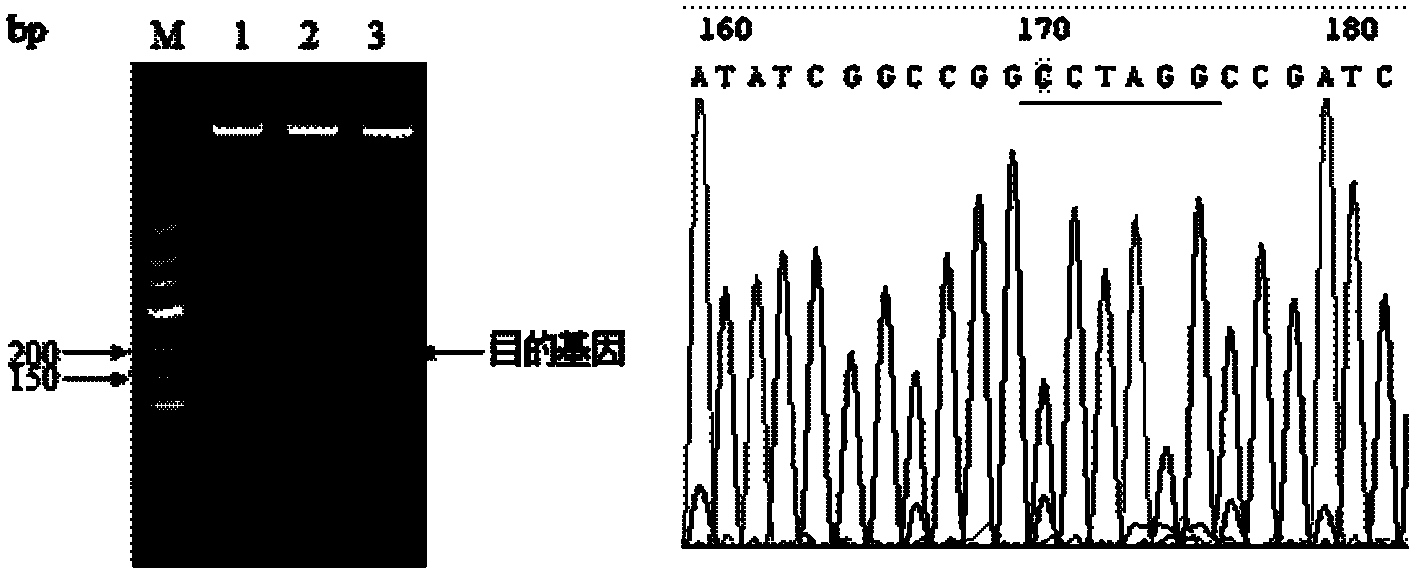
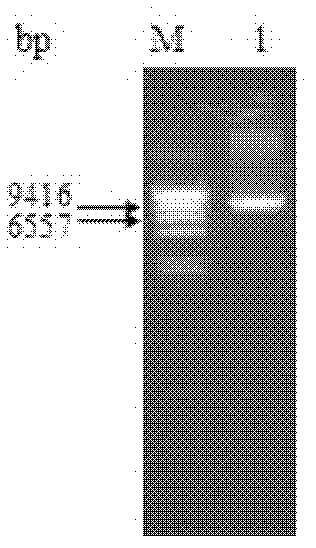
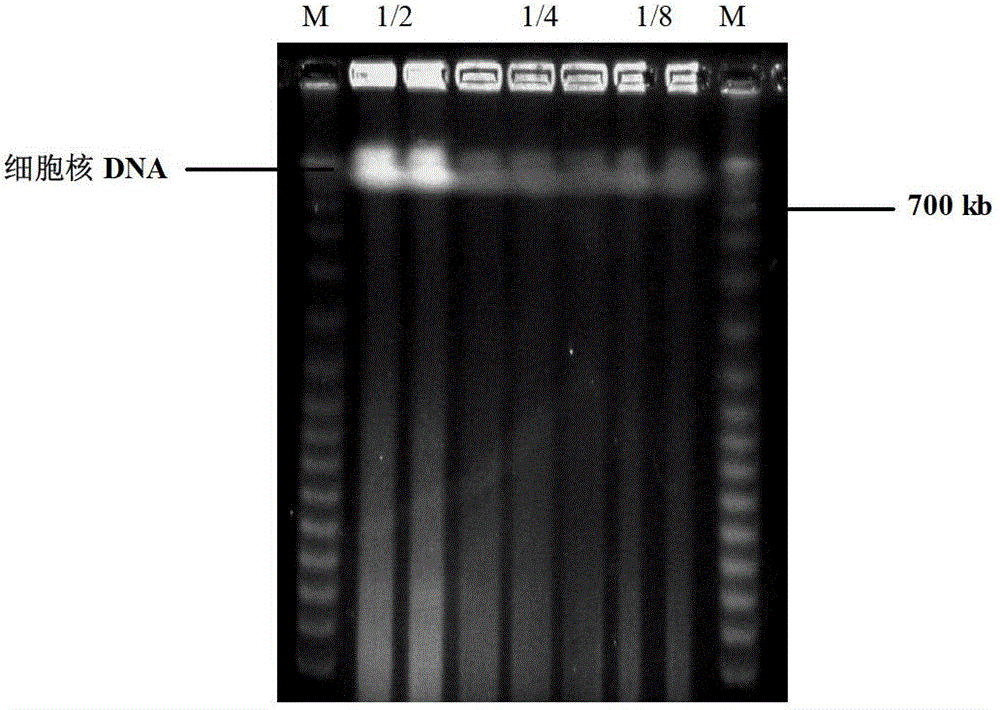
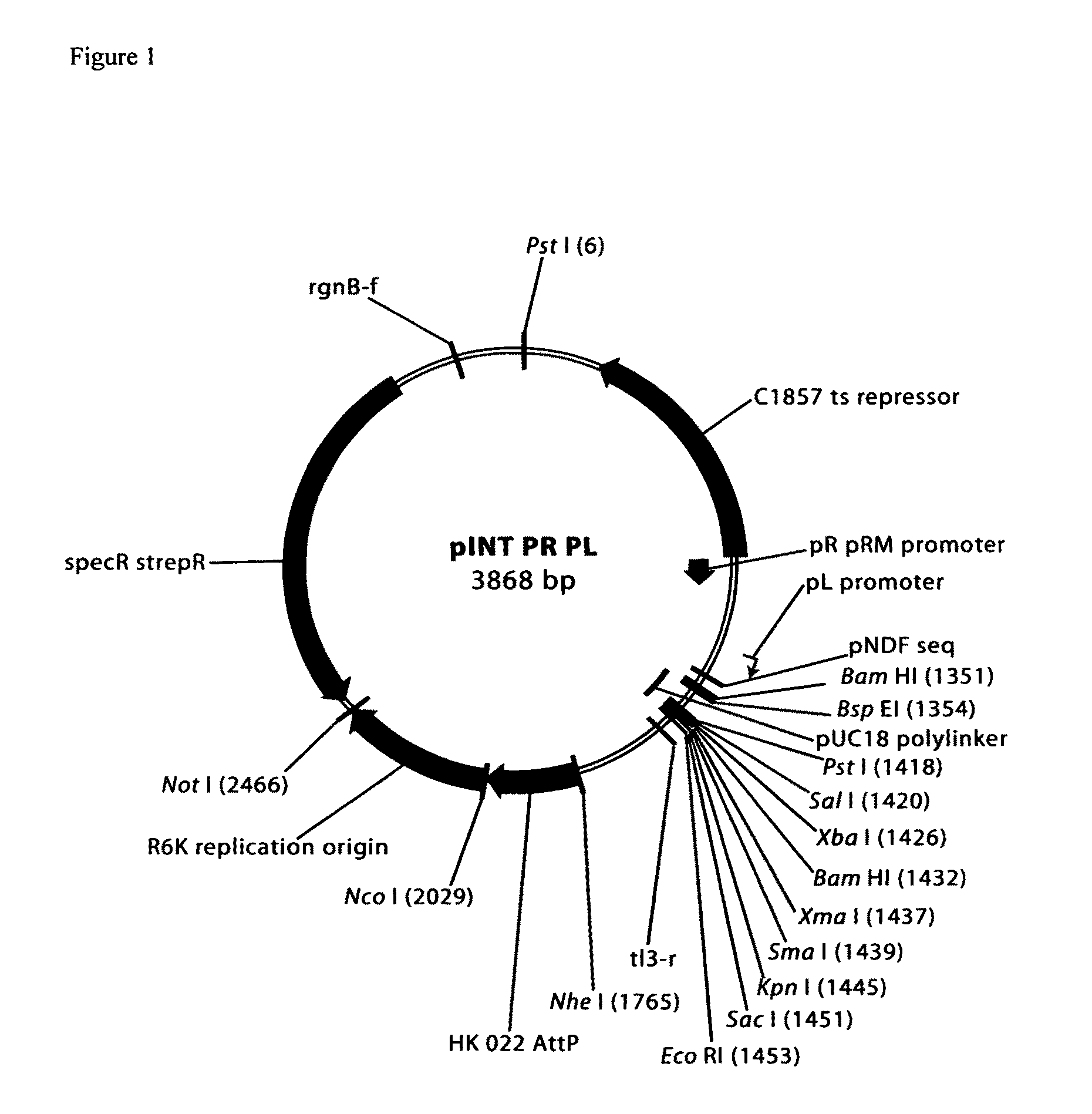
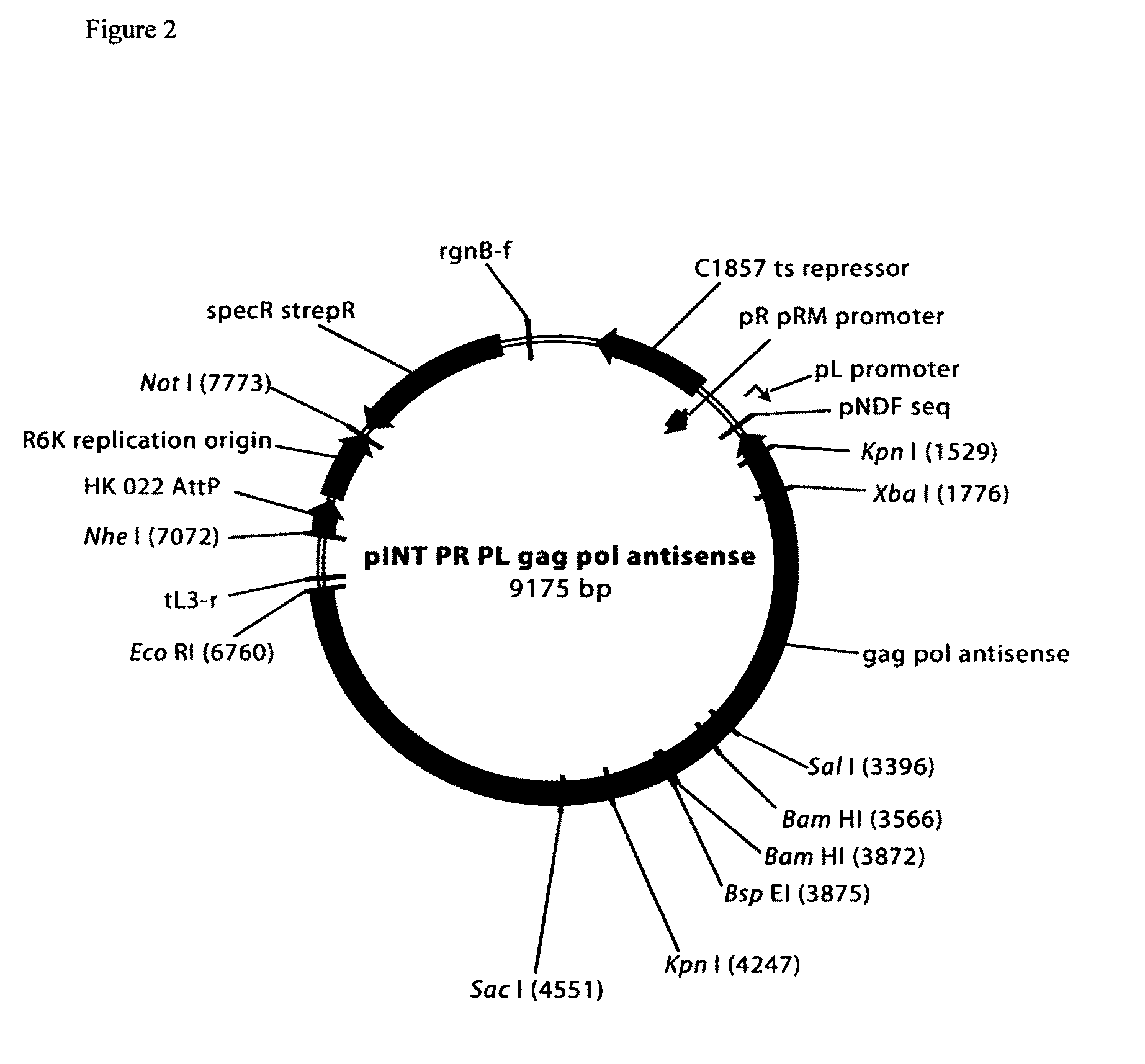
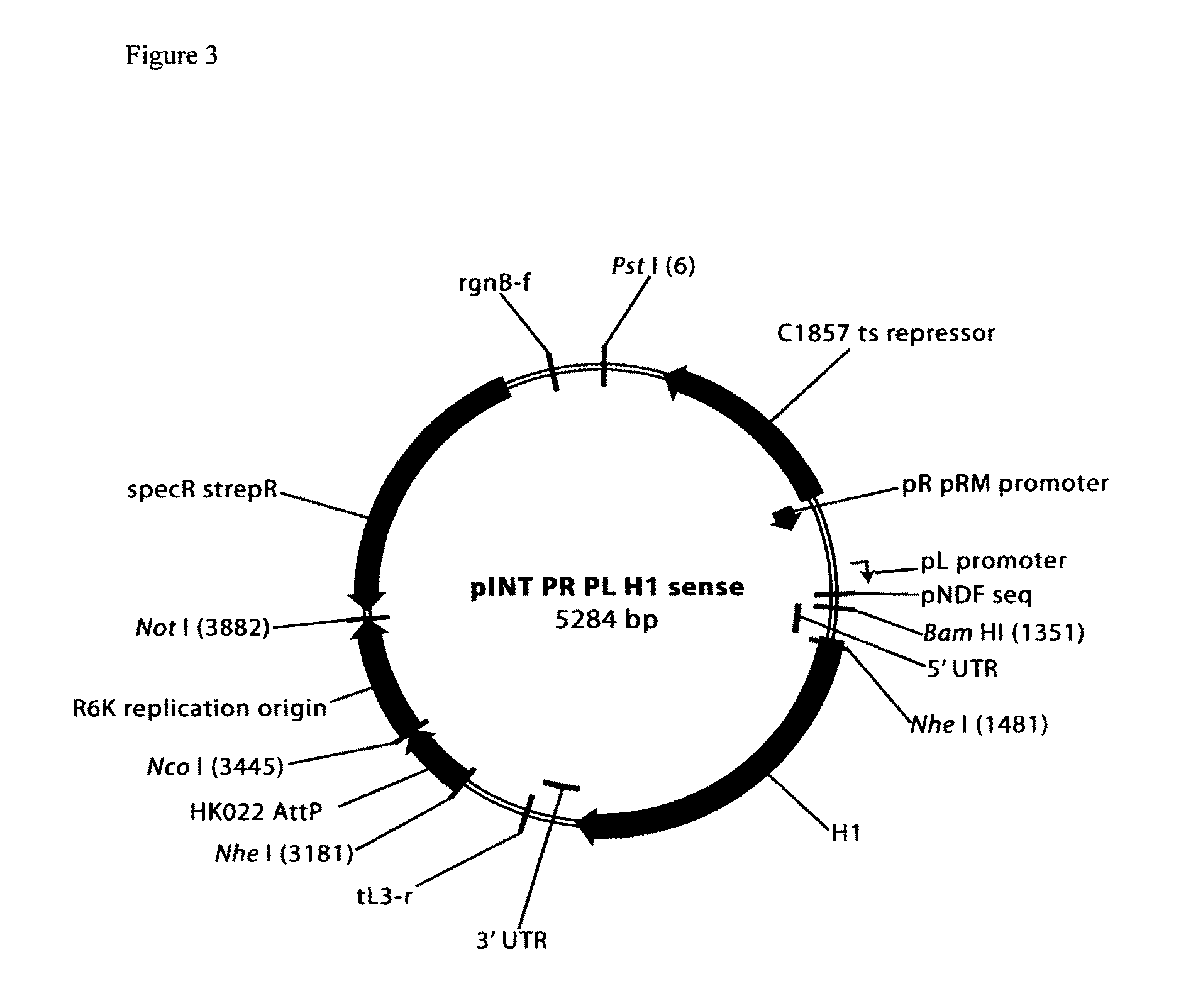
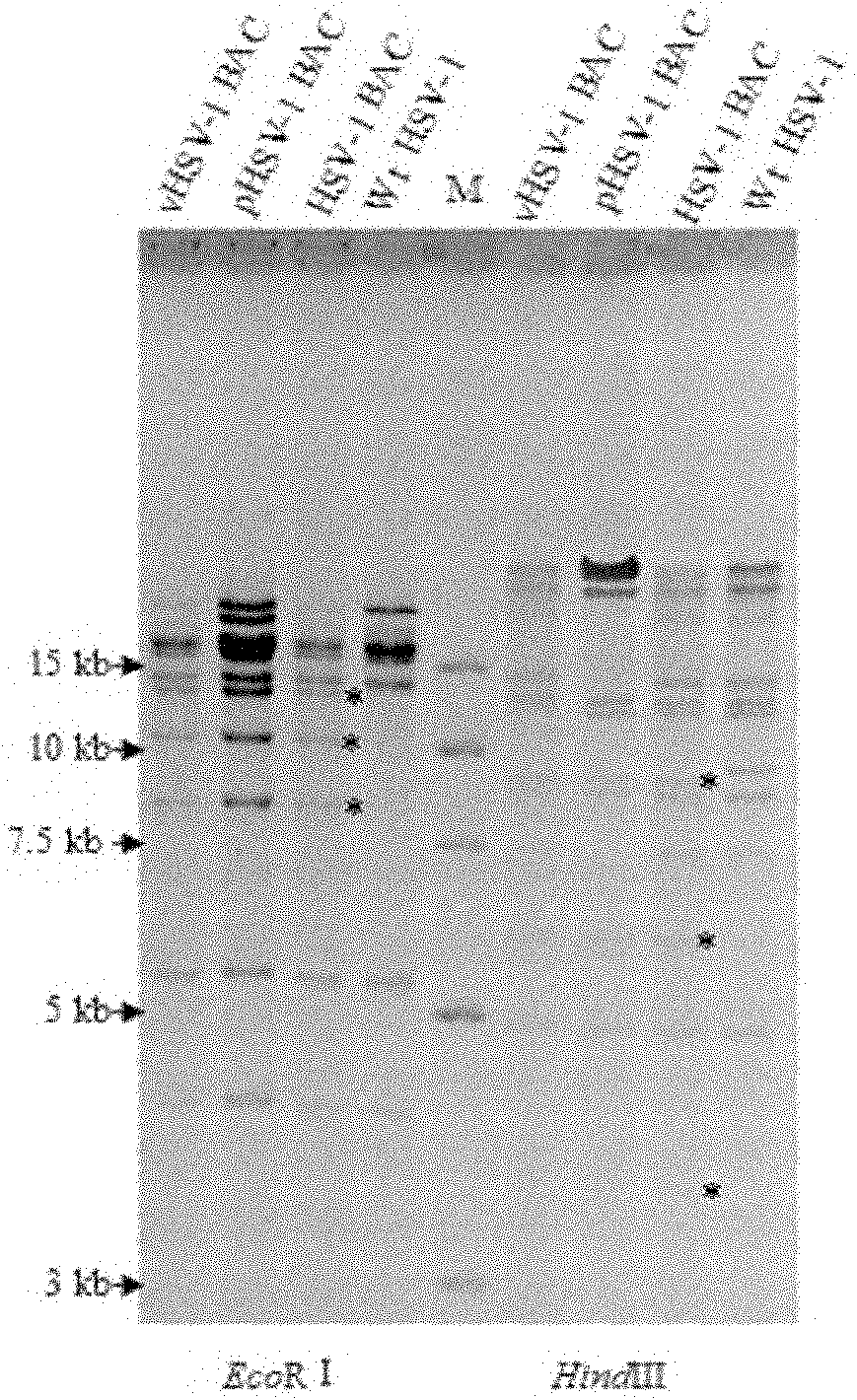Patents
Literature
93 results about "Bacterial artificial chromosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) is a DNA construct, based on a functional fertility plasmid (or F-plasmid), used for transforming and cloning in bacteria, usually E. coli. F-plasmids play a crucial role because they contain partition genes that promote the even distribution of plasmids after bacterial cell division. The bacterial artificial chromosome's usual insert size is 150–350 kbp. A similar cloning vector called a PAC has also been produced from the DNA of P1 bacteriophage.
Comparative mapping and assembly of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS7809509B2Improve accuracyImprove completenessMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesNucleic acid sequencingBacterial artificial chromosome
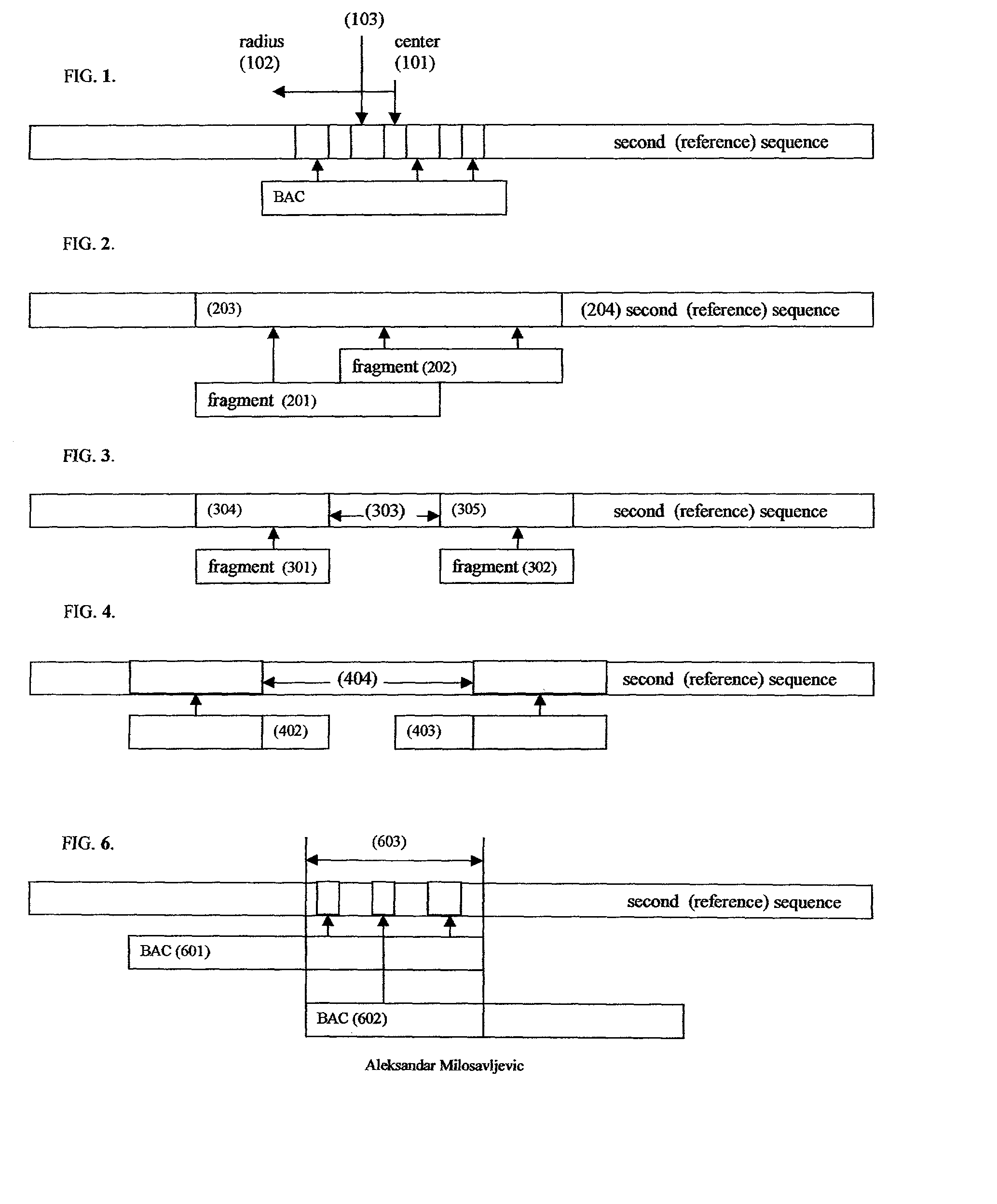
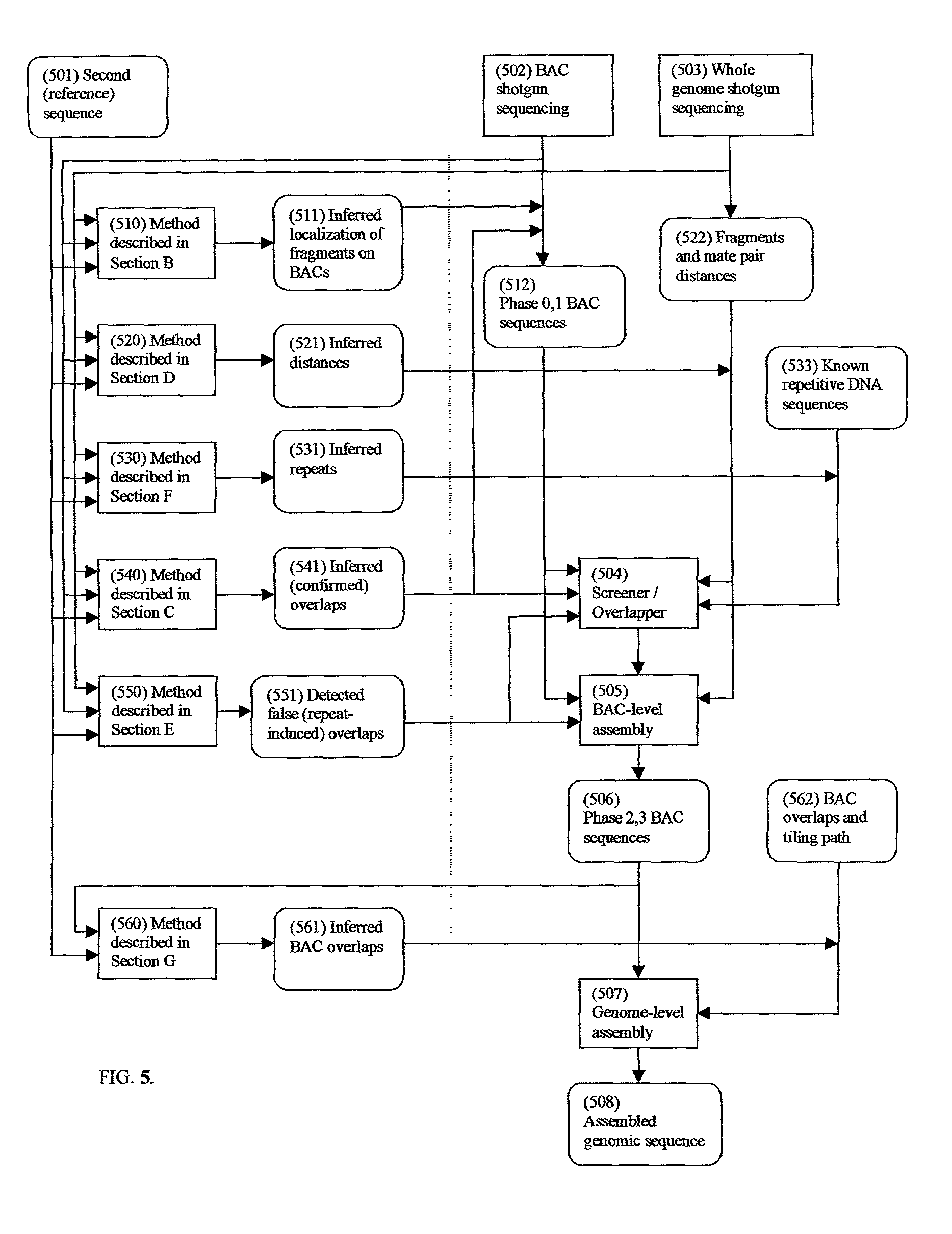
A method for assembling nucleic acid sequence fragments is disclosed. The fragments are assembled using information about their relative position inferred by comparison of the fragments against a known sequence of a related nucleic acid (FIG. 3). Additionally, the method localizes fragments to bacterial artificial chromosomes (FIG. 1) and determines relative position of bacterial artificial chromosomes using sequence comparison information (FIG. 6). The method utilizes the information about relative orientation, mutual distance, fragment localization to bacterial artificial chromosomes, and relative position of bacterial artificial chromosomes to constrain the assembly process (FIG. 5), thus resulting in a more accurate assembly requiring fewer sequencing reactions.
Owner:IP GENESIS
Method for establishing humanized rat drug evaluation animal model
InactiveCN104593418AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryLarge fragmentEngineered genetic
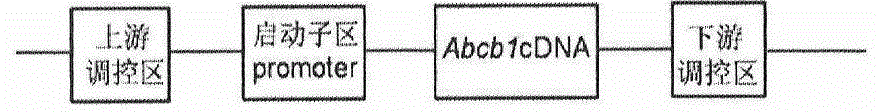
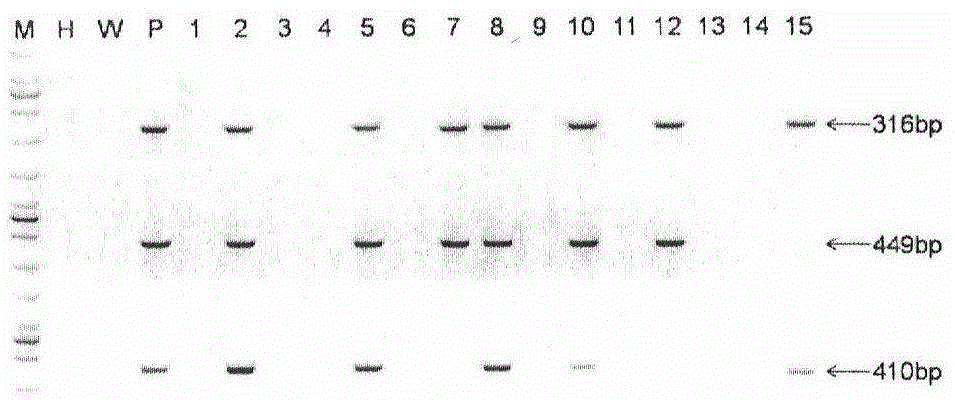
The invention provides a method for establishing a humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. According to the method, a multidrug resistance gene 1 (Abcb1)-knocked-out genetically engineered rat is obtained through a microinjection method by virtue of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology and 153kb bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) fragments containing a humanized Abcb1 promoter and cDNA is simultaneously inoculated into the rat genome through the microinjection method by virtue of a large fragment transgenic technology to obtain a transgenic rat capable of stably expressing human Abcb1 and the genetically engineered rat and the transgenic rat are hybridized to establish the humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. RT-PCR analysis shows that Abcb1 expression profiles of humanized Abcb1 rat are significantly different from those of the rat endogenous Abcb1. The method has the beneficial effects that the humanized rat capable of expressing human Abcb1 is obtained and the rat is used for expressing human Abcb1 genes and has closer expression profiles to those of human so that the model can be well used for the efficacy evaluation of newly developed drugs.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for isolating a polynucleotide of interest from the genome of a mycobacterium using a BAC-based DNA library application to the detection of mycobacteria
InactiveUS6183957B1Reducing potential for recombinationAvoiding lethal overexpressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideGenomic DNA
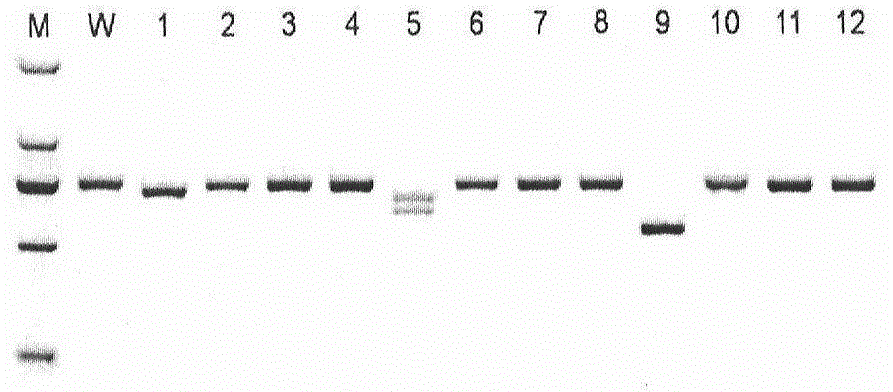
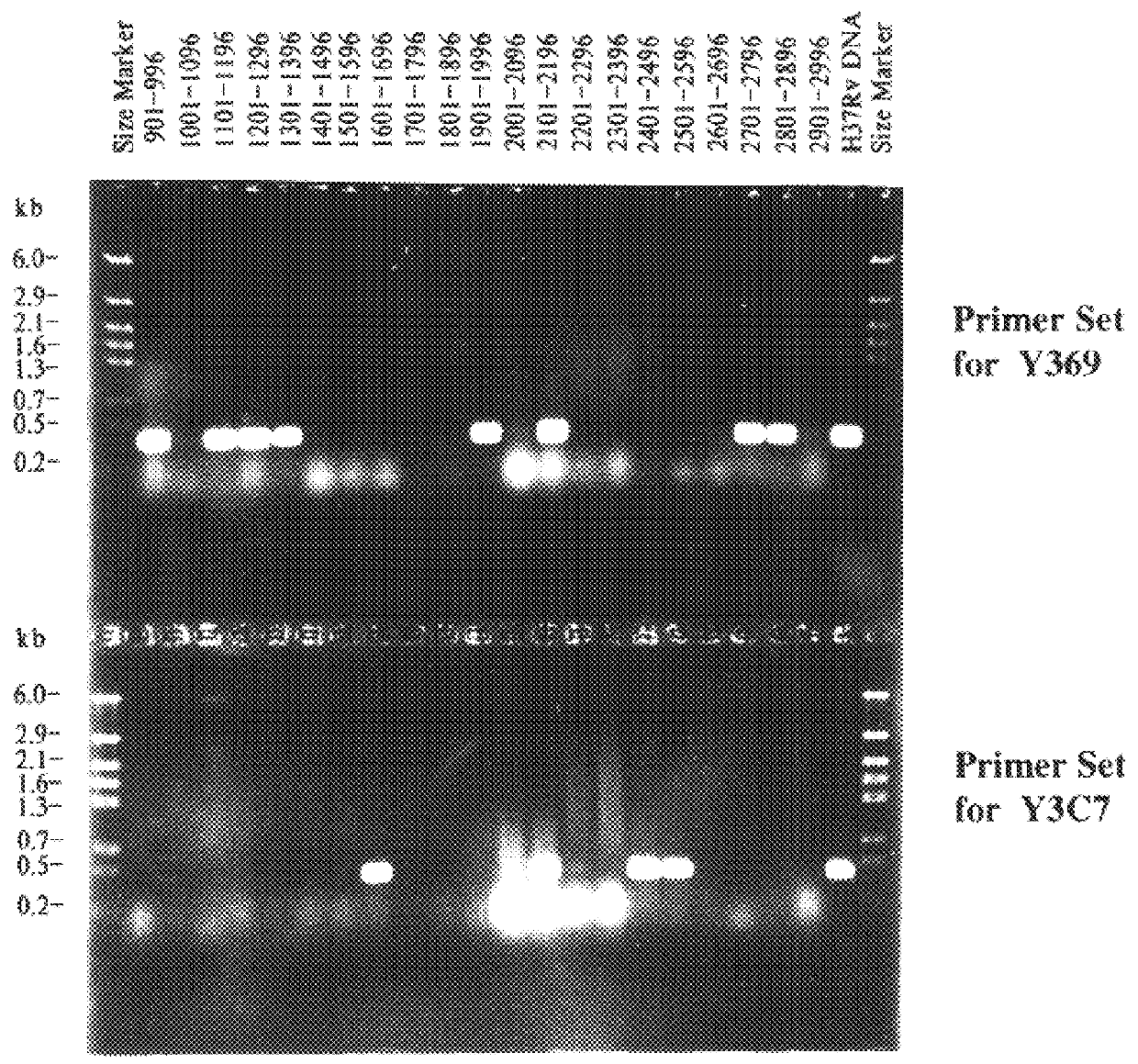
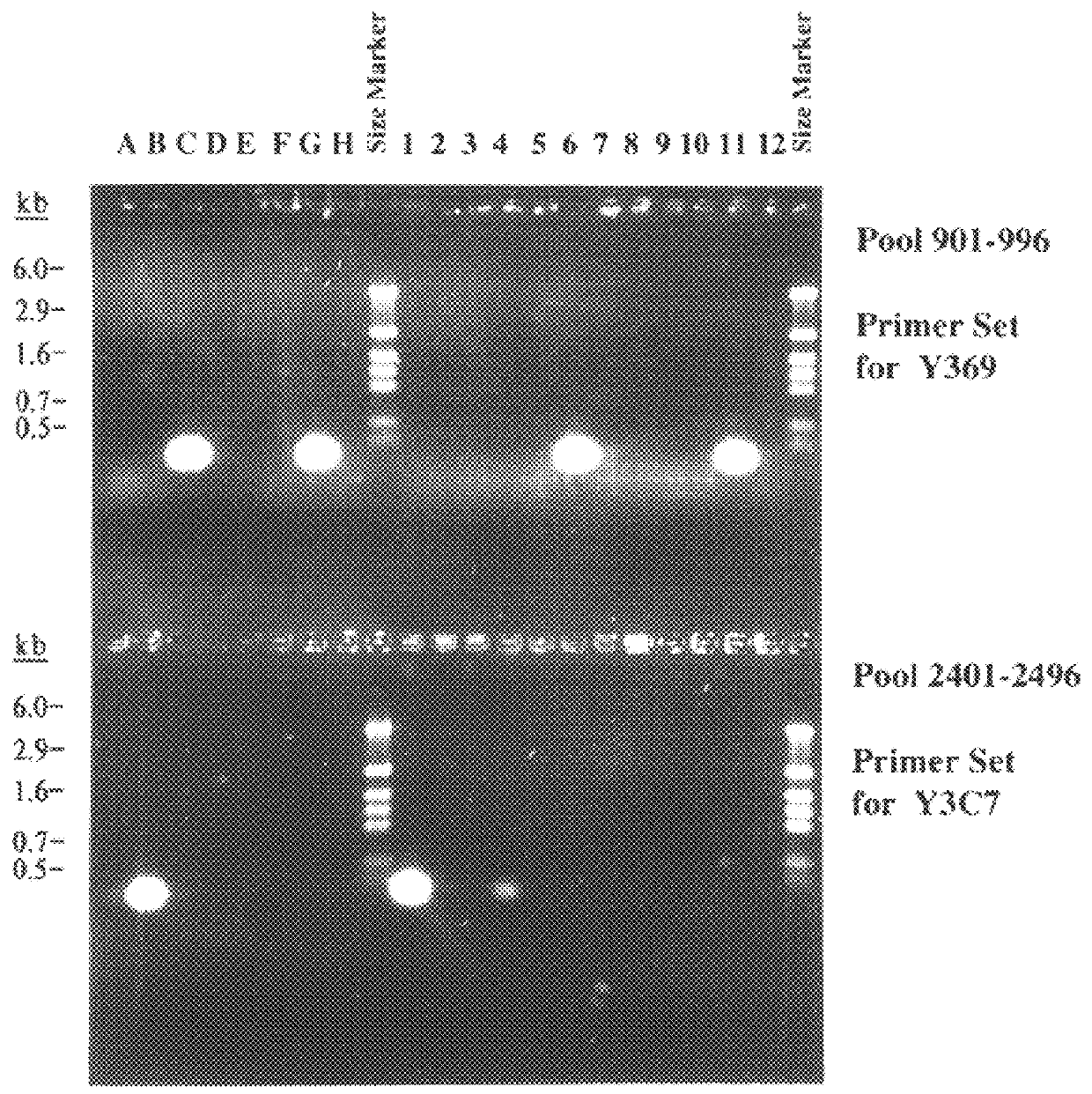
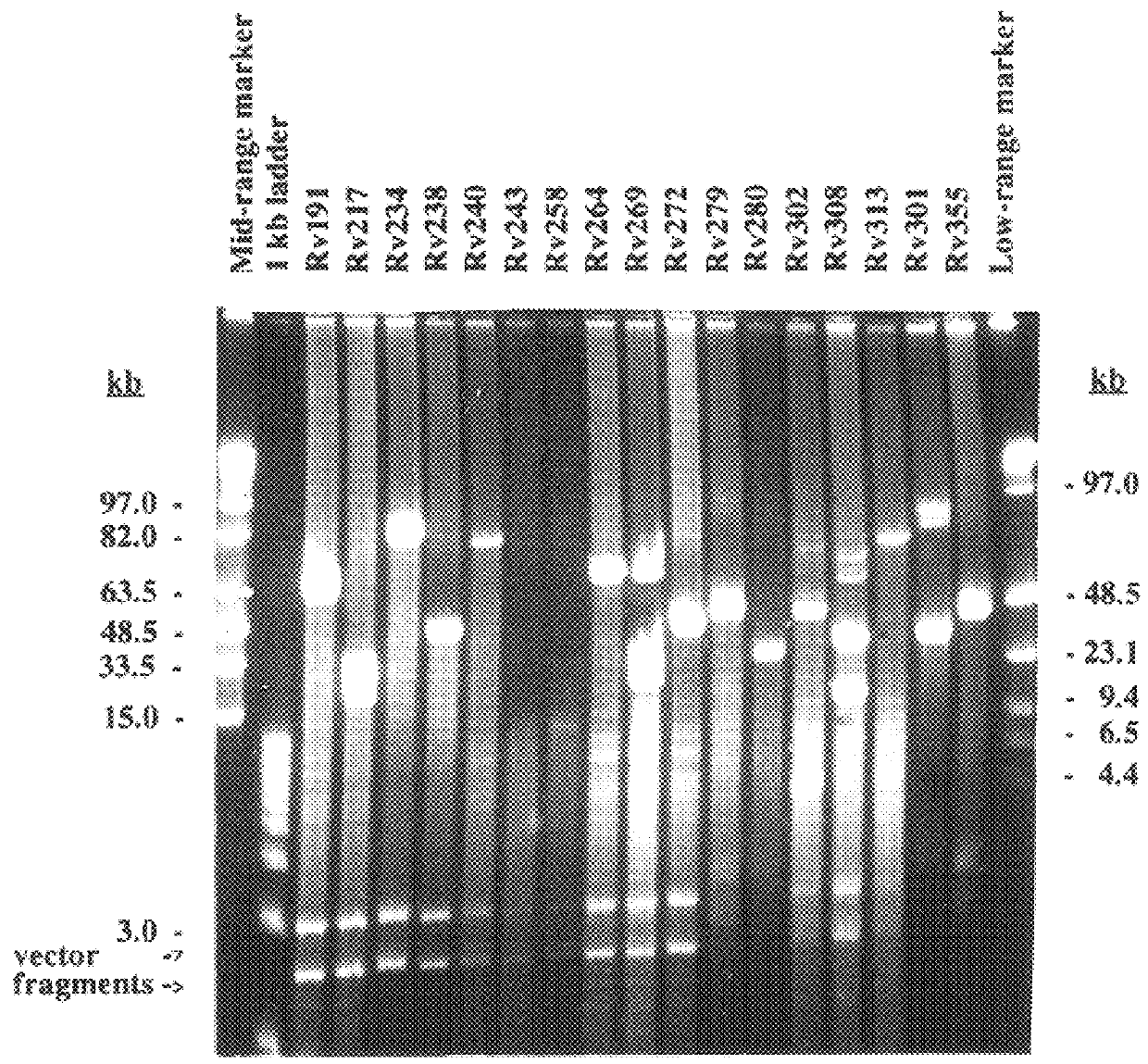
The present invention relates to a method for isolating a polynucleotide of interest that is present in the genome of a first mycobacterium strain and / or is expressed by the first mycobacterium strain, where the polynucleotide of interest is also absent or altered in the genome of a second mycobacterium strain and / or is not expressed in the second mycobacterium. The method comprises: (a) contacting the genomic DNA of the first mycobacterium strain under hybridizing conditions with the DNA of a least one clone that belongs to a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) genomic DNA library of the second mycobacterium strain, and (b) isolating the polynucleotide of interest that does not form a hybrid with the DNA of the second mycobacterium strain. This invention further pertains to a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Rv genomic DNA library, as well as a Mycobacterium bovis BCG strain Pasteur genomic DNA library, and the recombinant BAC vectors that belong to those genomic DNA libraries. This invention also relates to a method, as well as a kit, for detecting a nucleic acid of a mycobacterium in a biological sample.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Establishing method of bacterial artificial chromosome recombinant duck plague virus rescue system platform and application
InactiveCN105802922ALower titerDoes not affect the replication cycleVirus peptidesNucleic acid vectorBacteroidesRecombinant vaccines
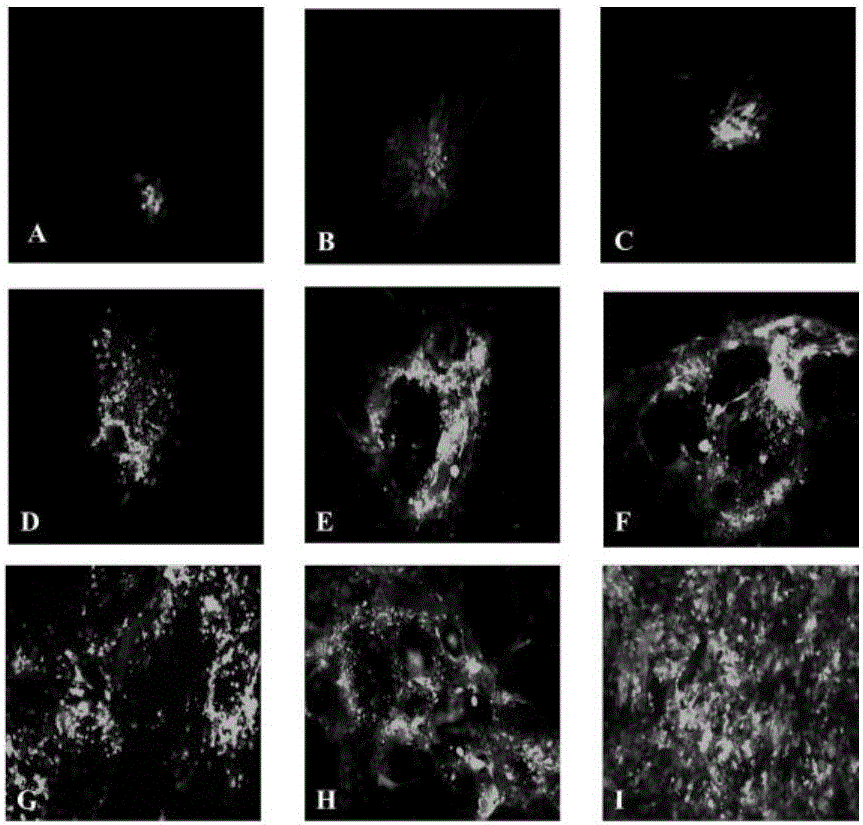
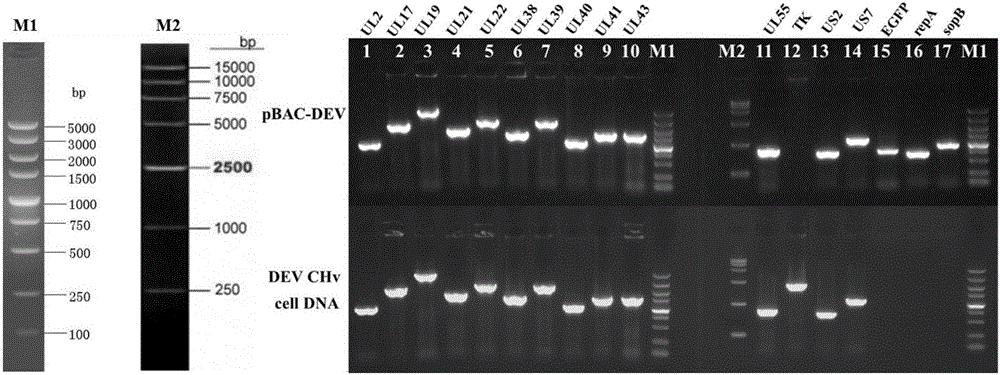
The invention discloses an establishing method of a bacterial artificial chromosome recombinant duck plague virus rescue system platform and application of the platform. A bacterial artificial chromosome recombinant duck plague virus is obtained by inserting a recombinant duck plague virus transfer vector pUC18 / EGFP-TKAB-BAC11 in a TK domain, wherein the recombinant duck plague virus transfer vector contains a TK gene left-right homologous arm, a reporter gene EGFP and a bacterial artificial chromosome core function component. By means of the platform, the in-vitro biologics characteristics of a UL55 gene-deleted strain established through an inside-bacterium two-step RED recombination method and a back mutation strain and parent strain of the UL55 gene-deleted strain are quite close; the functions are not related to positioning of a UL26.5 gene in a cell. The method is beneficial to development of pathogenic mechanism and gene function research of DPV CHv and is beneficial to the duck plague virus prevention and the research and application of recombinant duck plague virus vaccines of other poultry infectious diseases based on the platform; in addition, due to the fact that the recombinant virus carries a TK deletion mark and an EGFP gene, a mark vaccine can be developed to clinically distinguish a wild virus and a recombinant vaccine virus.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
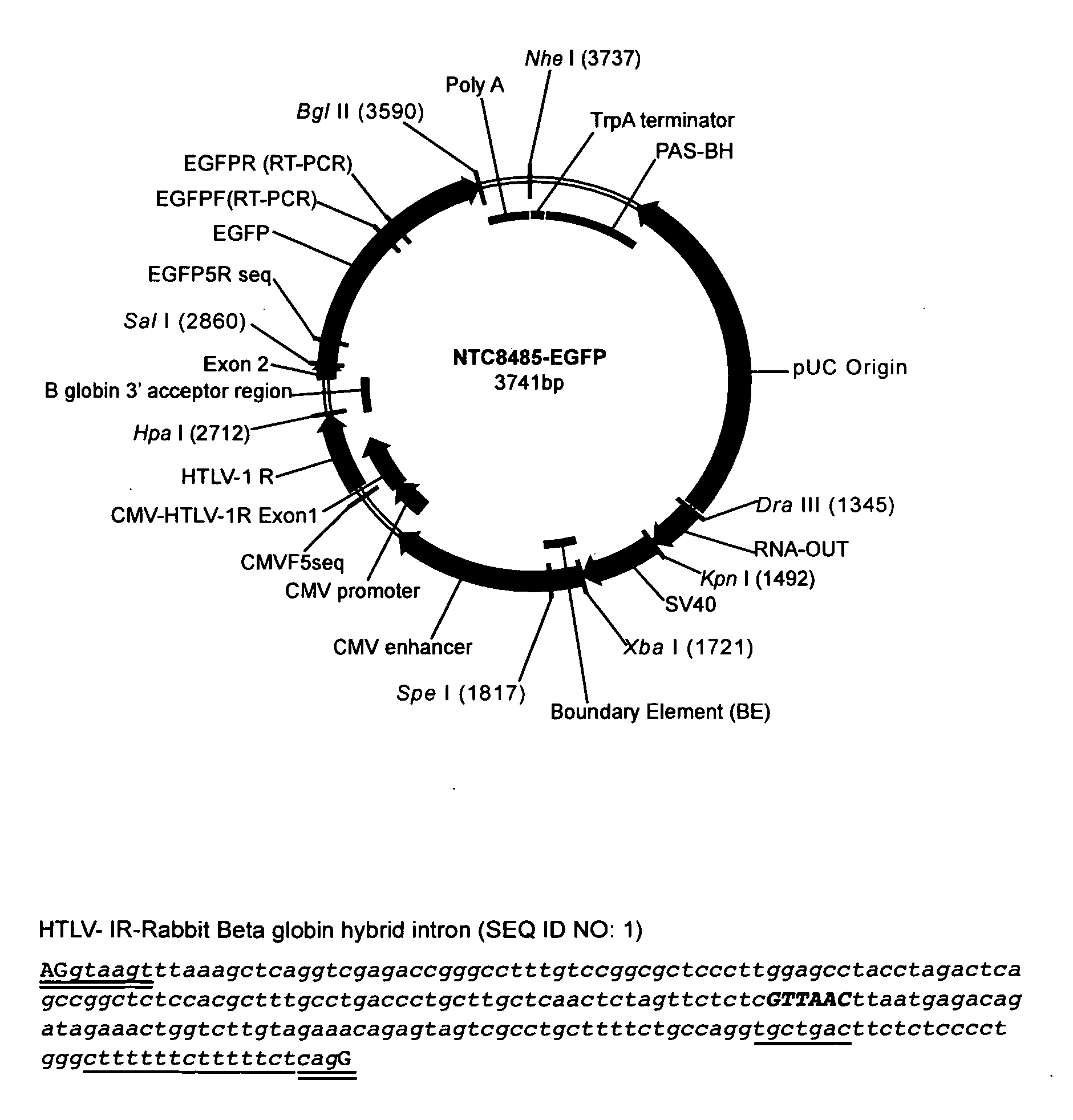
Replicative minicircle vectors with improved expression
ActiveUS20150275221A1Efficient preparationImproved in vivo expressionGenetic material ingredientsNucleic acid vectorBacteriophageViral vector
The present invention relates to the production and use of covalently closed circular (ccc) recombinant DNA molecules such as plasmids, cosmids, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), bacteriophages, viral vectors and hybrids thereof, and more particularly to vector modifications that improve expression of said DNA molecules.
Owner:ALDEVRON LLC
Method for isolating a polynucleotide of interest from the genome of a mycobacterium using a bac-based DNA library: application to the detection of mycobacteria
InactiveUS6492506B1Reducing potential for recombinationInhibit overexpressionSugar derivativesBacteriaCDNA libraryNucleotide
A method for isolating a polynucleotide of interest that is present in the genome of a first mycobacterium strain and / or is expressed by the first mycobacterium strain, where the polynucleotide of interest is also absent or altered in the genome of a second mycobacterium strain and / or is not expressed in the second mycobacterium. The method includes (a) contacting the genomic DNA of the first mycobacterium strain under hybridizing conditions with the DNA of a least one clone that belongs to a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) genomic DNA library of the second mycobacterium strain, and (b) isolating the polynucleotide of interest that does not form a hybrid with the DNA of the second mycobacterium strain. This invention further pertains to a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain H37Rv genomic DNA library, as well as a Mycobactetium bovis BCG strain Pasteur genomic DNA library, and the recombinant BAC vectors that belong to those genomic DNA libraries. This invention also relates to mycobacterial nucleic acids, and methods and kits for using these nucleic acids to detect mycobacteria in a biological sample.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
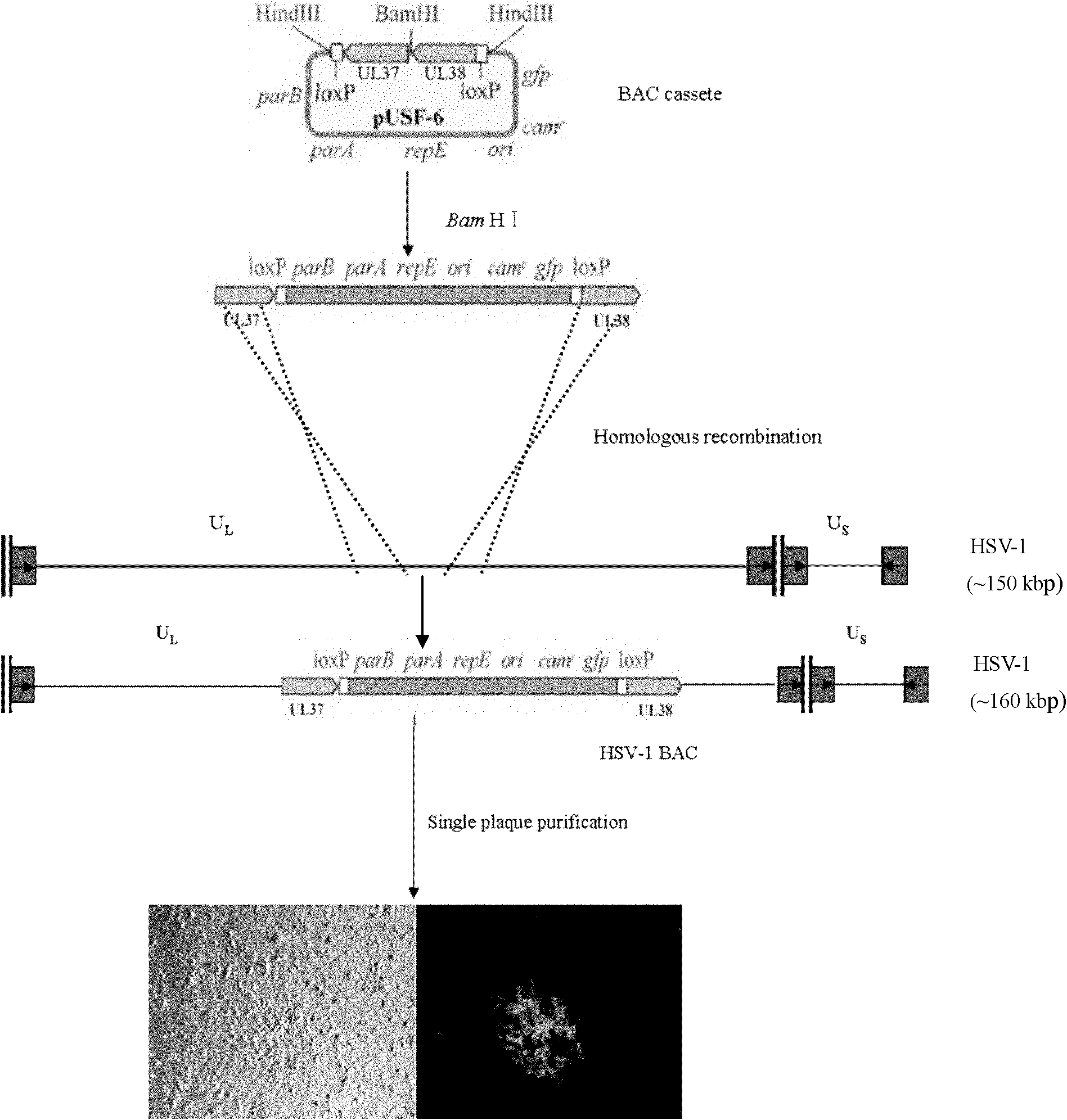
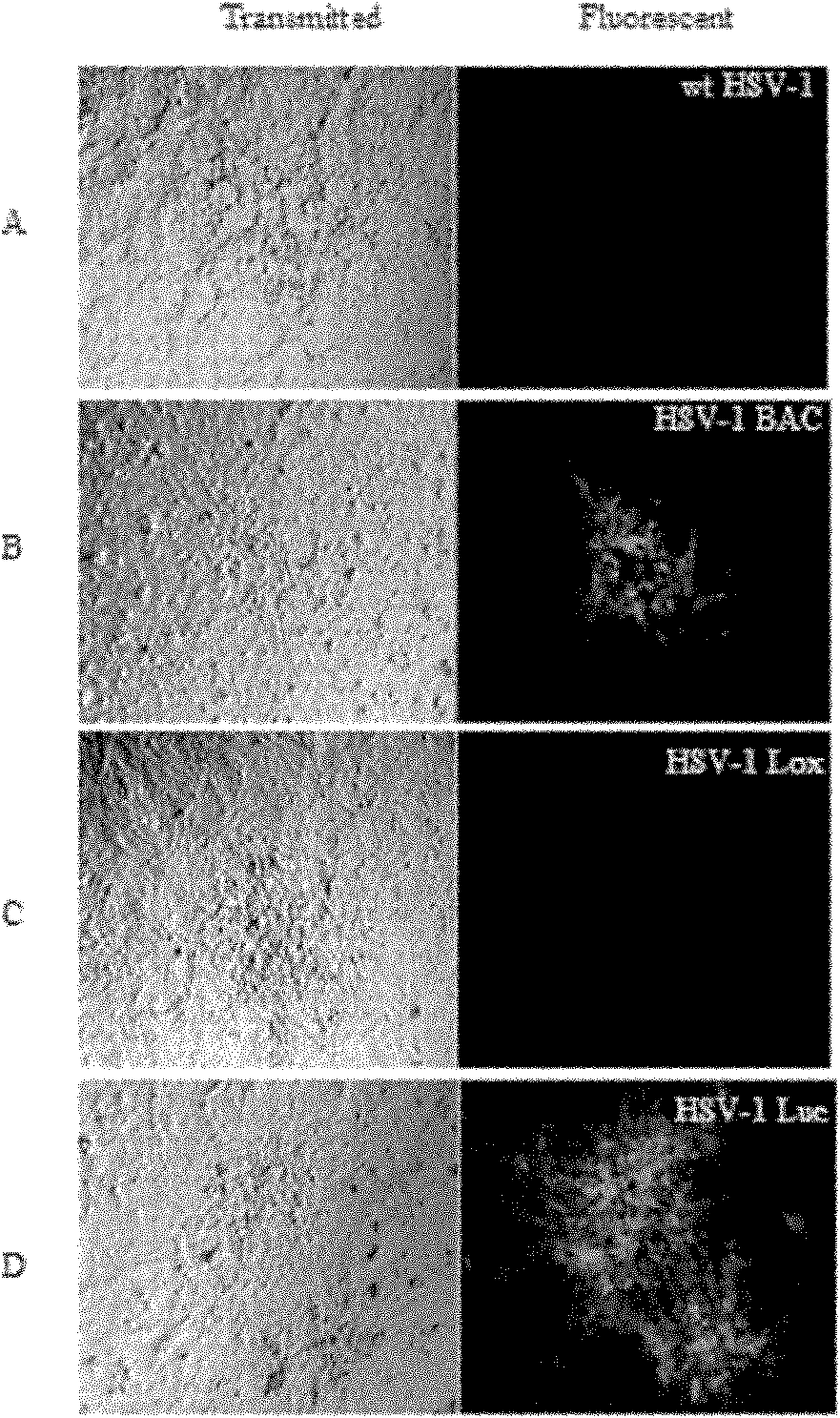
Method for constructing HSV-1 BAC system carrying luciferase report genes
InactiveCN101979598AEliminate the hassle of titrationStable passageMicrobiological testing/measurementViruses/bacteriophagesTransfer vectorBacterial artificial chromosome
The invention discloses a method for constructing an HSV-1 BAC (herpes simplex virus I bacterial artificial chromosome) system carrying luciferase report genes. The method comprises the following steps of: A, constructing a system, namely (1) designing primers according to HSV-1 F strain sequences, (2) constructing transfer vectors, (3) constructing recombinant viruses, (4) purifying plaques, (5) identifying the recombinant viruses, (6) constructing recombinant BAC, (7) saving the recombinant viruses and (8) measuring a growth curve; and B, constructing a Luciferase stable expression system, namely (1) designing amplified Luciferase-Hygr primers, (2) amplifying fragments by using high-fidelity KOD enzyme, (3) electrically transforming pHSV-1 BAC to E.coliDY380, (4) electrically transforming the reclaimed DNA fragments into pHSV-1 BAC / DY380 electrically-transformed competent cells, (5) identifying, (6) picking DY380 monoclone, (7) extracting BAC plasmids, (8) saving the viruses, and (9) performing half quantification on the viruses in vitro for the HSV-1 BAC Luc recombinant virus infected cells. The method is simple, feasible and convenient to operate, can modify the virus genomes in vitro, and also can perform half quantification on the virus particles in vitro.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
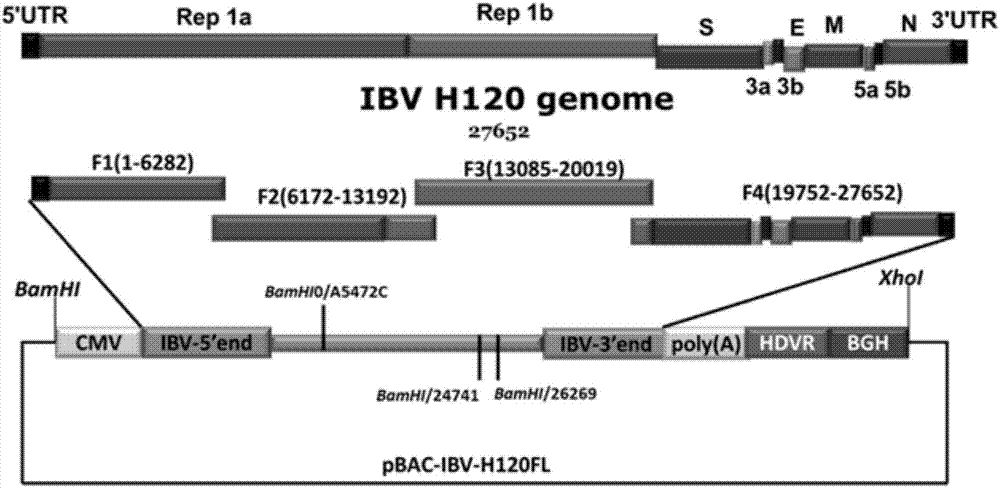
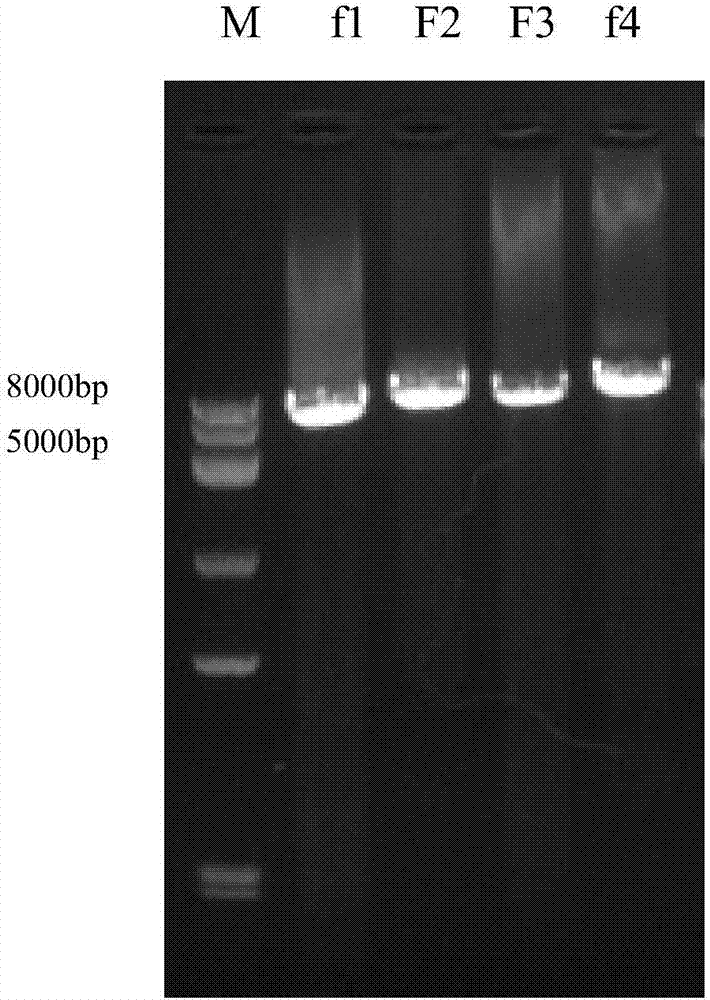
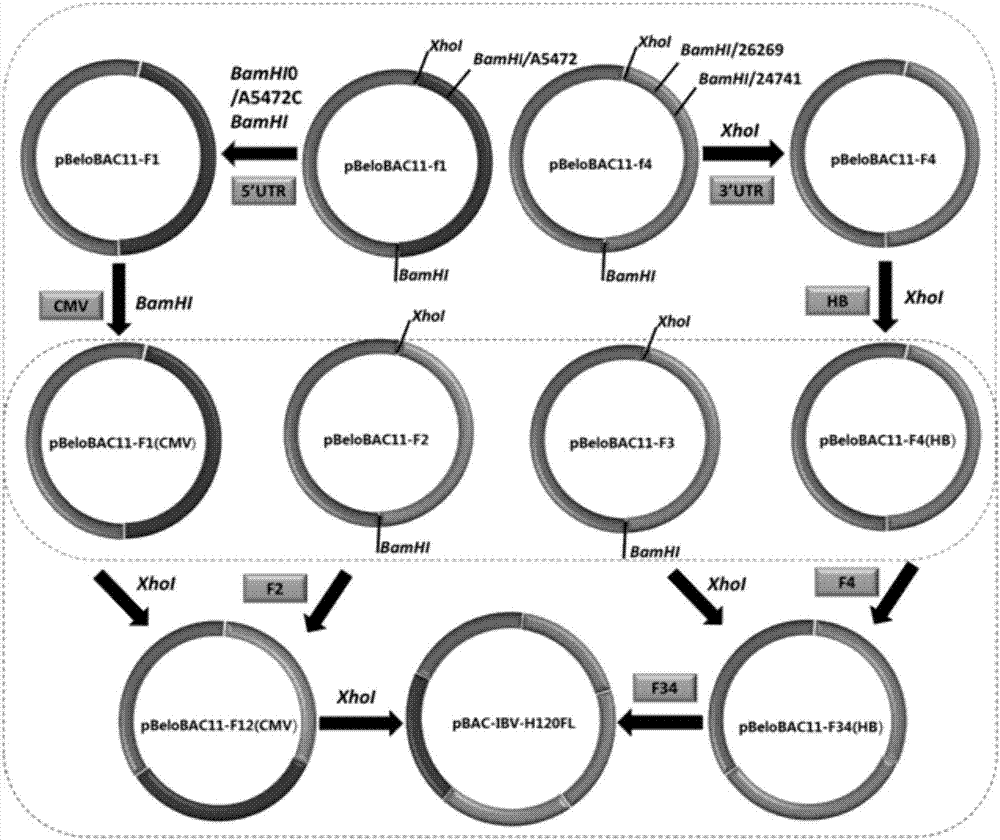
Method for quickly constructing IBV (Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus) reverse genetic strain
ActiveCN107190022AEasy to operateHigh rate of positive clonesSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicroorganism based processesEmbryoIn vitro study
The invention discloses a method for quickly constructing an IBV (Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus) reverse genetic strain, and belongs to the technical field of coronavirus reverse genetics. The constructing method comprises the following steps: quickly completing construction containing IBV genomic full-strength cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) clone by taking a BAC (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome) vector as a framework and applying an in-vitro homologous recombination technology, directly transfecting cells by a constructed recombinant plasmid, and transcribing in the cells, thus obtaining a transcript having infectivity; completing virus packaging; inoculating SPF (Specific Pathogen Free) chick embryo to a mixed solution of the cells and a culture medium and passing from generation to generation, thus obtaining the IBV reverse genetic strain. The constructing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple operation and high positive cloning efficiency, the obtained IBV reverse genetic strain has passage stability, and an effective tool is provided for researching pathogenesis of the virus in vitro, developing a novel vaccine and the like; according to the method disclosed by the invention, transcription is carried out in the cells by utilizing a CMV (Cytomegalovirus) promoter added on a 5' terminal, and the rescue efficiency of the virus is greatly increased by utilizing an HDVR (Hepatitis Delta Virus Ribozyme) sequence added on a 3' terminal.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for efficiently producing recombinant proteins in mammary glands by utilizing artificial chromosomes
ActiveCN102199624AIntegrity guaranteedHigh expressionHydrolasesFermentationHigh level expressionPosition effect
The invention provides a method for efficiently producing recombinant proteins in mammary glands by utilizing artificial chromosomes (including BAC, PAC and YAC). In the method, a recombinant technology is adopted to completely replace target genes on artificial chromosomes of mammary gland-specific expressed proteins (including as1-casein, beta-casein, beta lactoglobulin, rabbit or mouse whey acidic protein and the like) of a mammal with an exogenous gene, so that the exogenous gene obtains an intact regulatory sequence of a mammary gland high-level expression target gene, the 'position effect' is avoided, the higher-level expression of human lysozyme or other recombinant proteins in the mammary glands can be realized, the success rate of transgenic breeding is improved, and the cost forproducing and purifying the recombinant proteins at a later stage can be saved at the same time.
Owner:WUXI KINGENEW BIOTECHNOLOGY LIMITED COMPANY
Method of recombination and agents useful for same
InactiveCN1331748AHomologous recombinationOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaRecBCDNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates generally to a method for the recombination of at least two nucleic acid sequences and agents useful for same. More particularly, the present invention contemplates a method of recombining, in a host cell which expresses the recBCD nuclease or a functional derivative thereof, a circular nucleic acid sequence with a linear nucleic acid sequence. The method of the present invention is useful, inter alia, for the modification of bacterial artificial chromosomes by homologous recombination with a linear DNA sequence.
Owner:THE MURDOCH INST
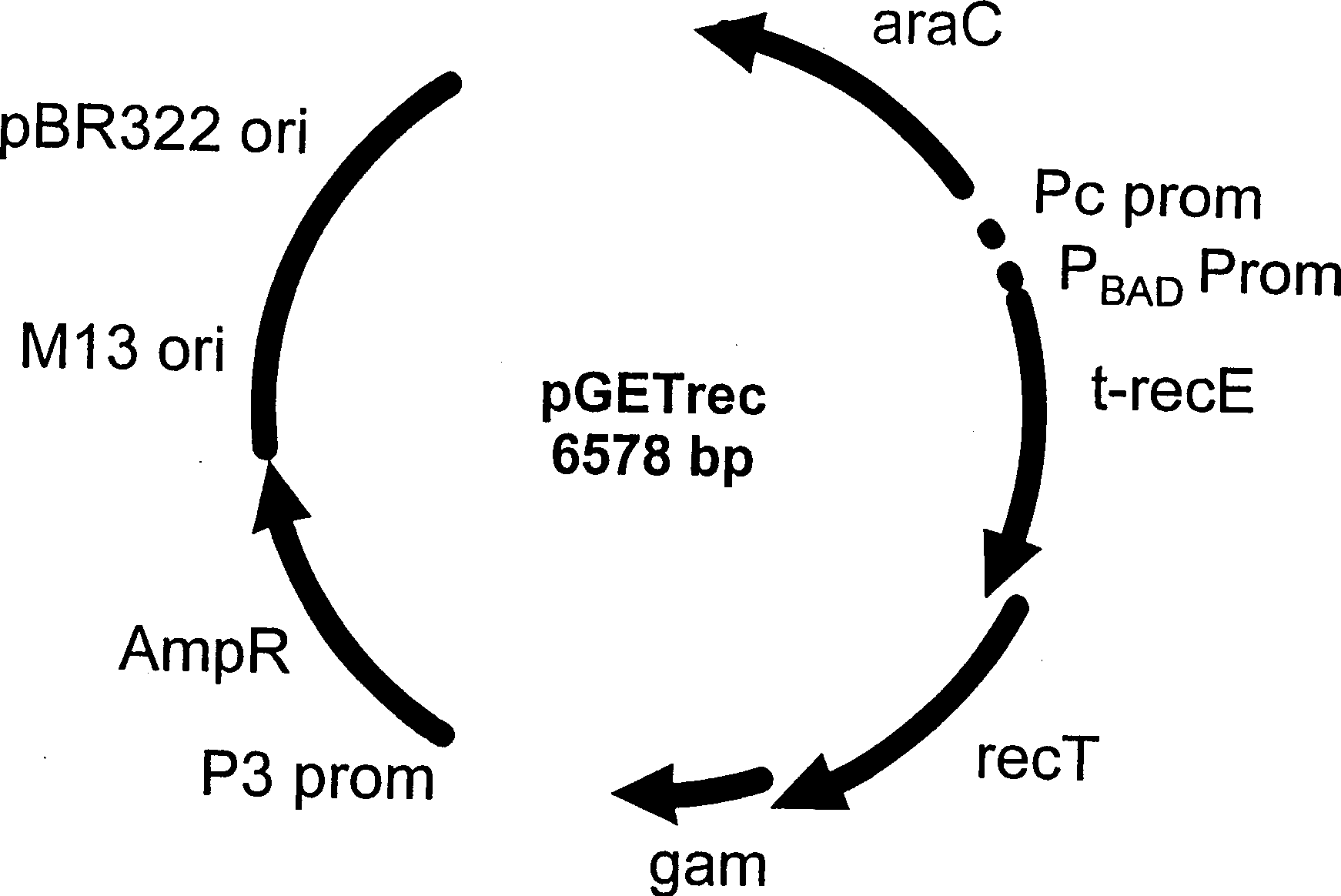
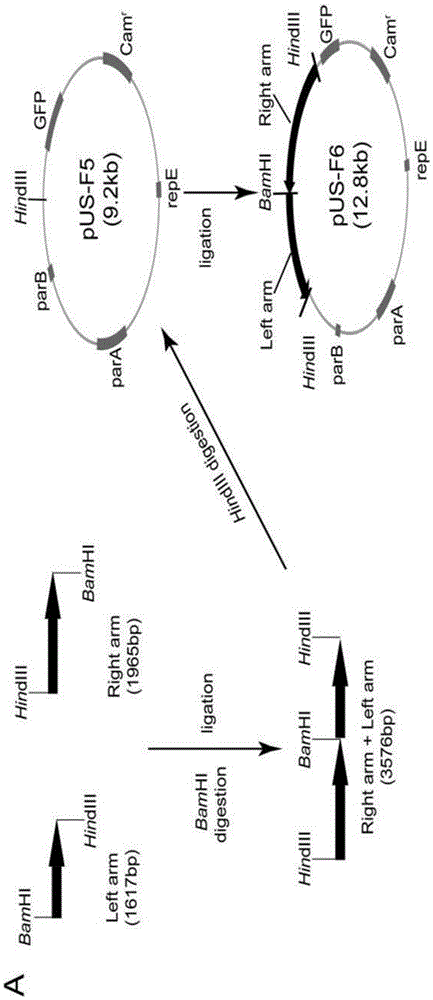
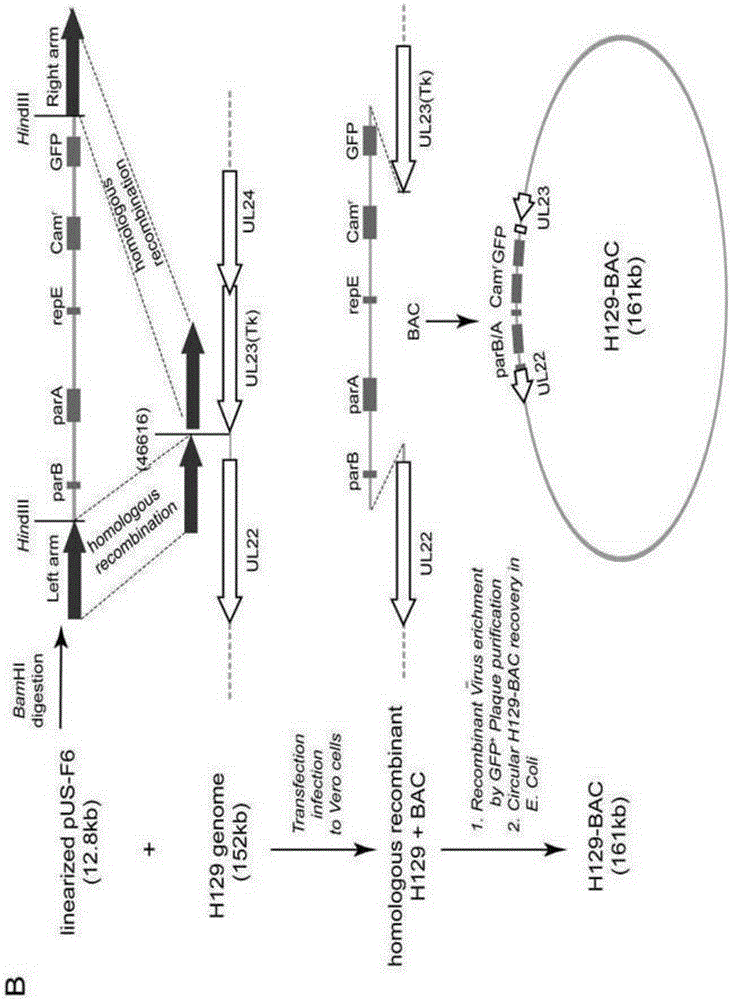
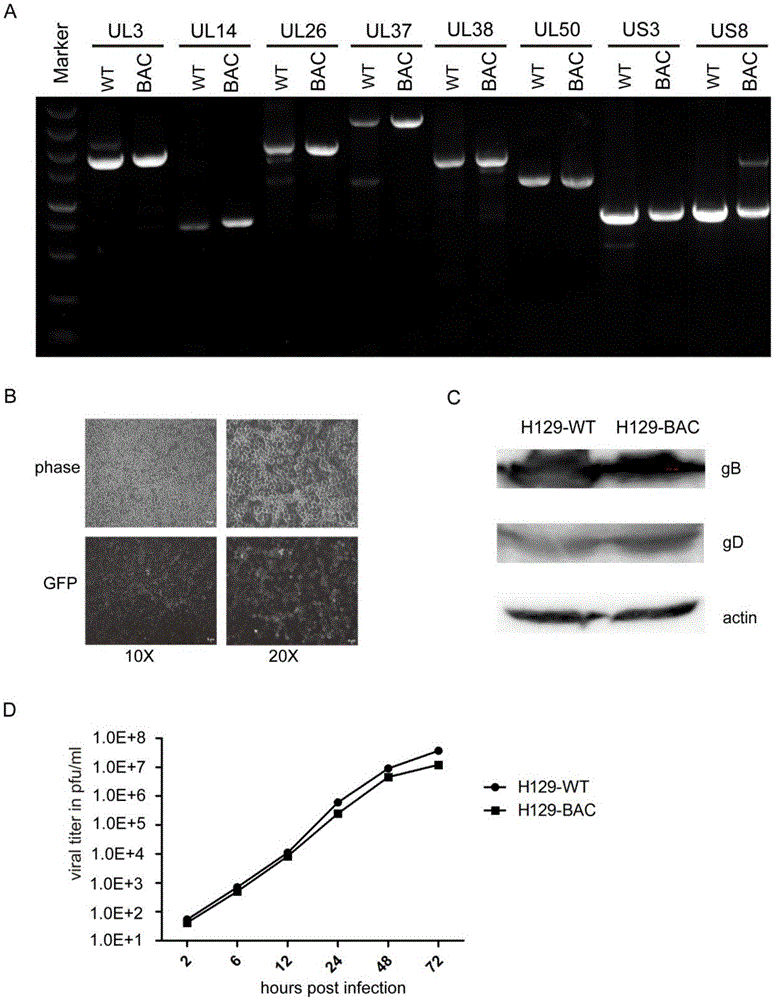
Construction method and application of HSV1-H129-BAC and mutant thereof
ActiveCN105567618ASmall molecular weightDoes not affect structure and functionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHerpes simplex virus DNAMutant
The invention relates to the biotechnical field, and concretely relates to an HSV1-H129-BAC and a mutant thereof. The above virus and the mutant thereof carry a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), can keep low-copy number self-replication in specific bacteria, and solve the disadvantages of unable long-term preservation, unable self-replication and inconvenient molecular biologic mutation reconstruction due to too large herpes virus genomes. The virus and the mutant thereof also carry a GFP reporter gene, and substantially develop the application prospect of the herpes virus as a tool virus. The invention also provides a construction method of the H129-BAC and the mutant thereof. The method allows H129 to be reconstructed in order to obtain H129-BAC and endows the H129-BAC with more mutant types; and the construction method, the H129 and the mutant thereof form a genetic modification platform with high application possibility.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
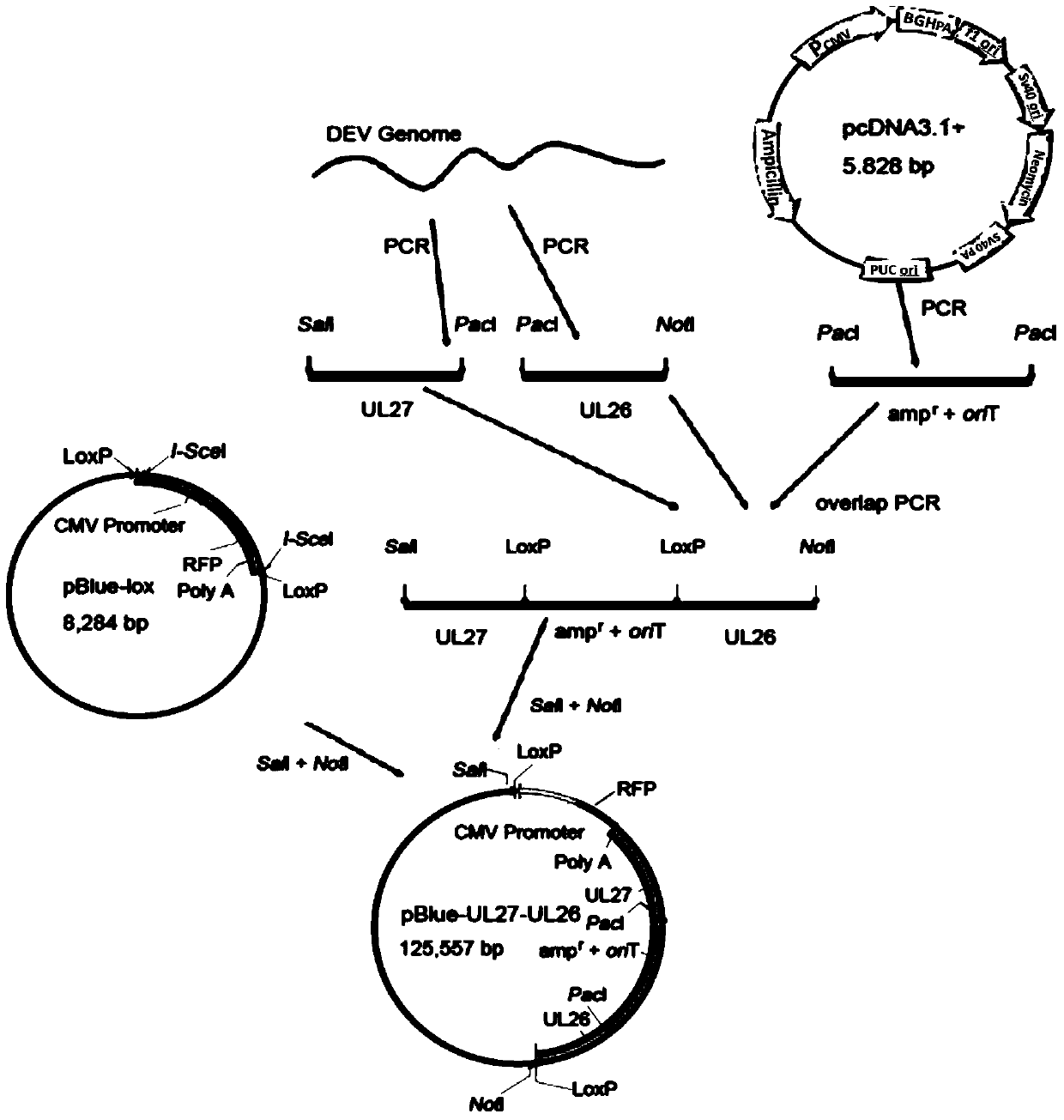
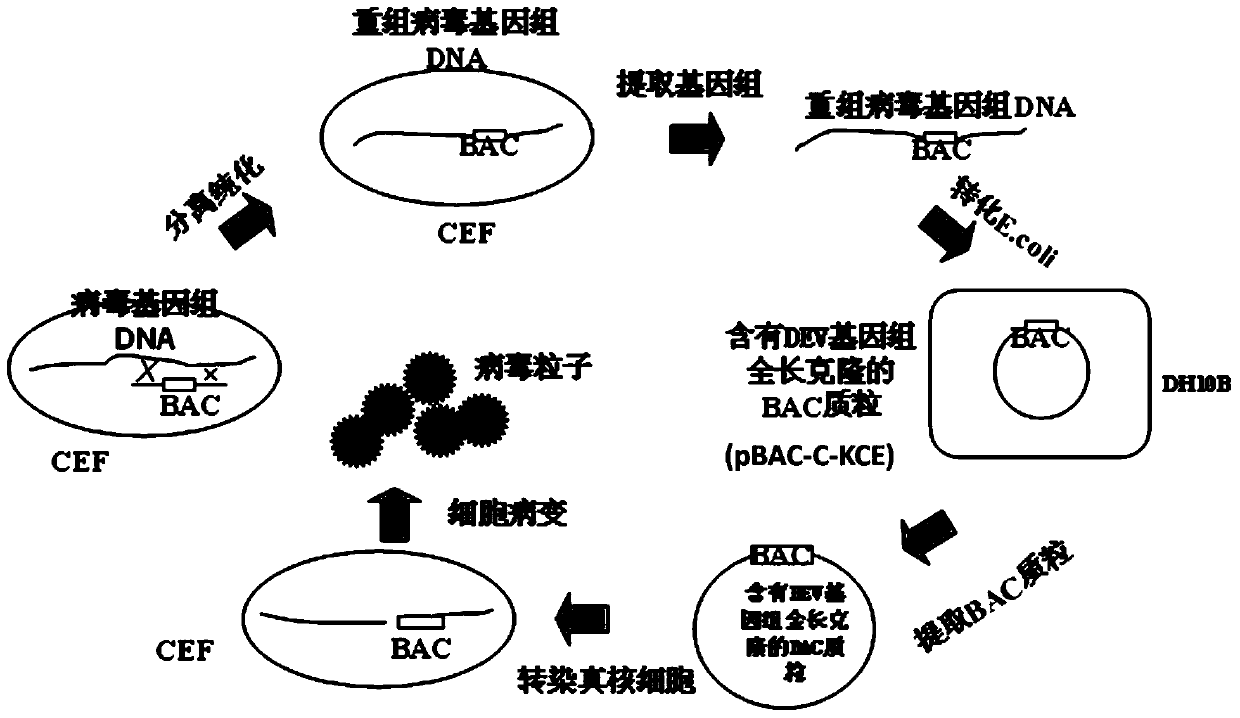
Construction method and use of duck enteritis virus bacterial artificial chromosome
InactiveCN103497967AShort cycleThere is no cross-species transferViruses/bacteriophagesVector-based foreign material introductionDuck enteritis virusEngineered genetic
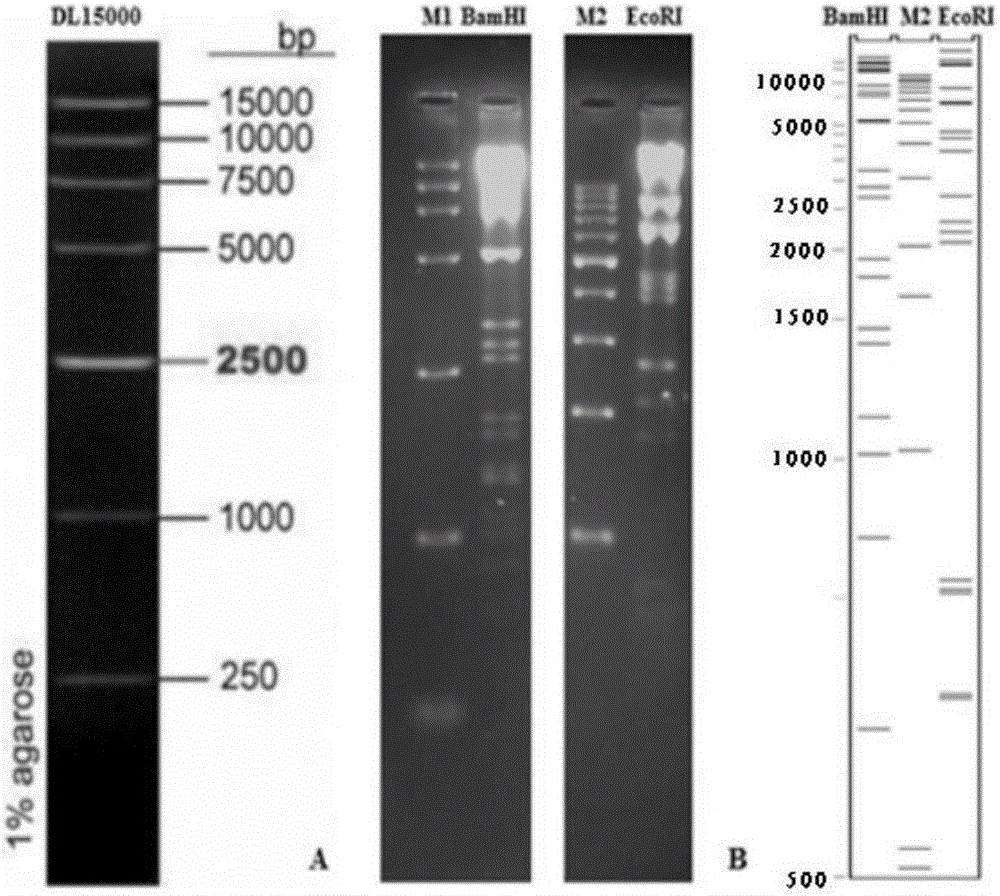
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal gene engineering and relates to a construction method and a use of a duck enteritis virus bacterial artificial chromosome. Through cloning, a duck enteritis virus bacterial artificial chromosome pBAC-C-KCE plasmid is obtained, is preserved in the China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) and has an accession number of CCTCC NO: M2013377. The invention also discloses the use of the duck enteritis virus bacterial artificial chromosome pBAC-C-KCE in recombinant duck enteritis virus packaging.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
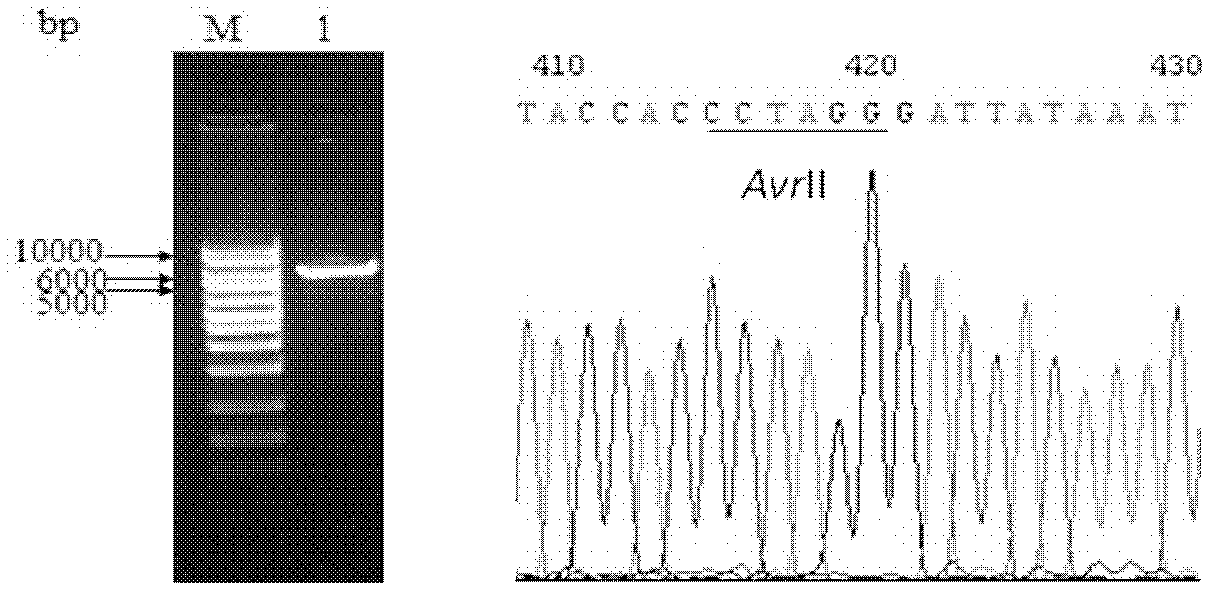
Construction method for linearized shuttle vector BmBacmid
The invention discloses a construction method for a linearized shuttle vector BmBacmid. The construction method comprises the following steps of: 1) constructing a pBacAvrII2 vector containing two AvrII loci; 2) constructing a pBACAvrII2 vector containing bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), namely designing a pair of primers of which two ends contain FseI loci, amplifying a segment of the BAC on DH10BacBacmid, and inserting into the pBacAvrII2 vector to obtain the pBACAvrII2 vector; and 3) constructing the linearized shuttle vector BmBacmid, namely amplifying the segment of the BAC through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) by taking the pBACAvrII2 vector as a template, co-transfecting bombyxmori cells by using the PCR product and linearized BmBacPAK, performing homologous recombination in the bombyxmori cells to generate recombinant virus, thus obtaining the linearized shuttle vector BmBacmid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for constructing cotton bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library by non-dark cultured leaves
InactiveCN102747427AEasy accessAvoid Bulk GerminationVector-based foreign material introductionLibrary creationLarge fragmentHigh molecular weight dna
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and especially relates to a method for constructing a cotton bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) library by non-dark cultured leaves. The method comprises the following steps of 1, selecting cotton leaves, 2, extracting a high-molecular weight nucleus DNA, 3, partly digesting the high-molecular weight nucleus DNA and carrying out selection twice, 4, carrying out recovery, connection and transformation of a large-fragment DNA, and 5, carrying out detection of an insert fragment. The method is suitable for construction of BAC libraries of all cotton materials which comprise cotton materials having low seed amounts and persistent cotton materials having no seed.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacterial strains with improved plasmid stability
ActiveUS20100233814A1Improve production yieldHigh copy numberFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBacteroidesBacterial strain
The present invention relates to the propagation of covalently closed circular recombinant DNA molecules such as plasmids, cosmids, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), bacteriophages, viral vectors and hybrids thereof, and more particularly is strain modifications that improve strain viability, plasmid stability, plasmid production yield, and plasmid-directed protein production yield, using said DNA molecules in fermentation culture.
Owner:ALDEVRON LLC
Double-stranded cyclic dna capable of proliferating as a bacterial e coli chromosome
InactiveUS20050106733A1Easy to modifyEasy to produceBacteriaInactivation/attenuationEscherichia coliGenomic DNA
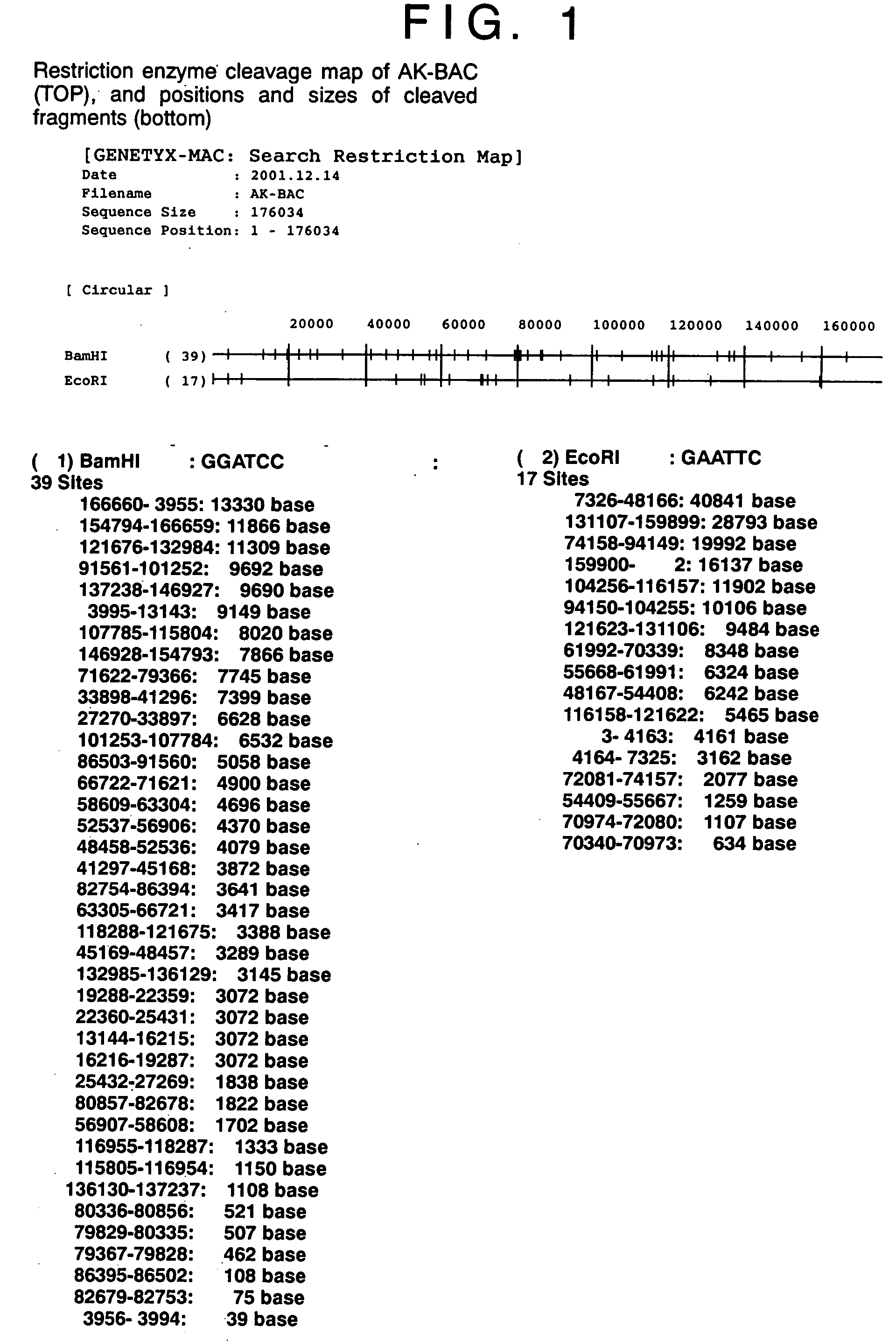
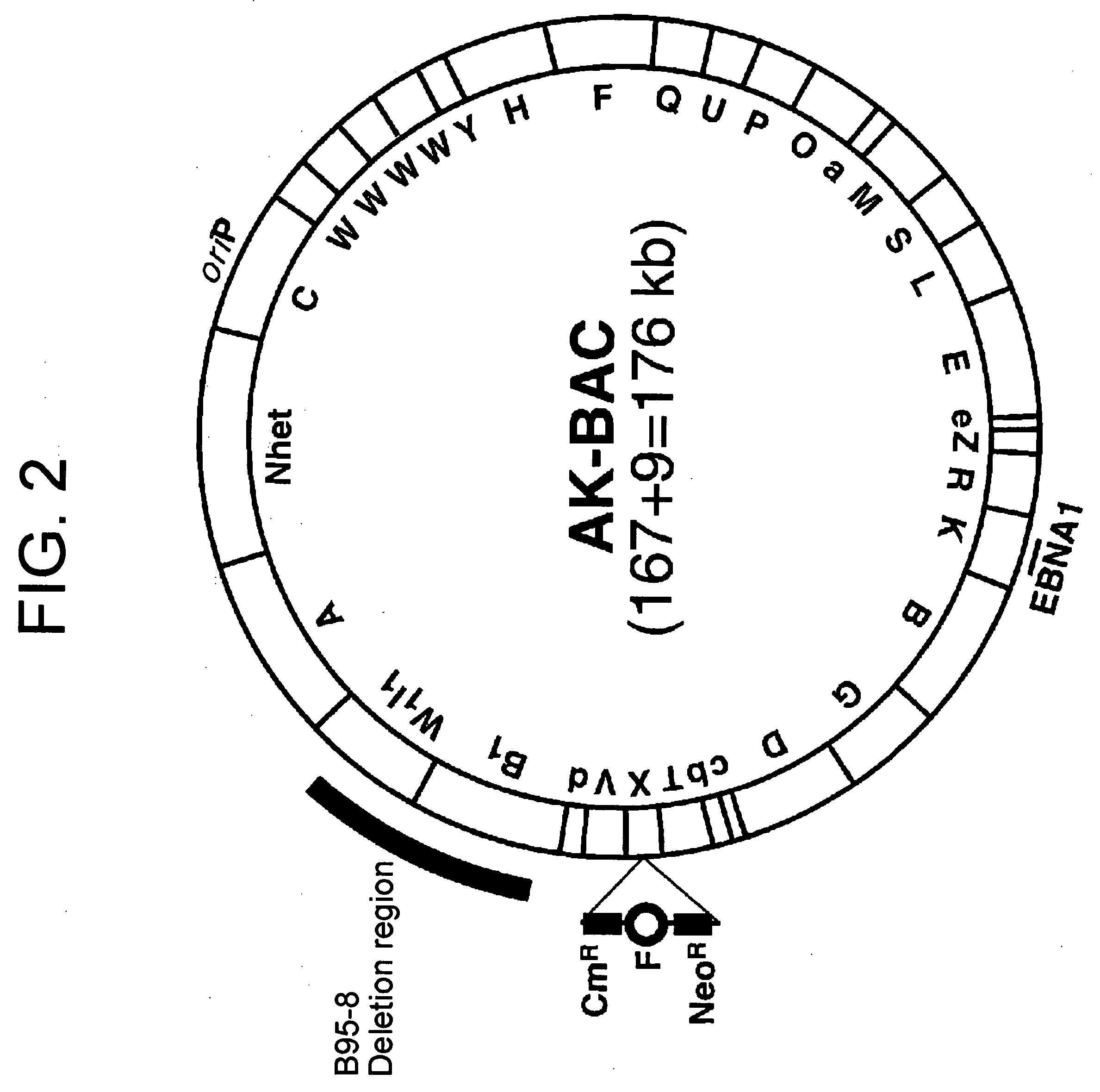
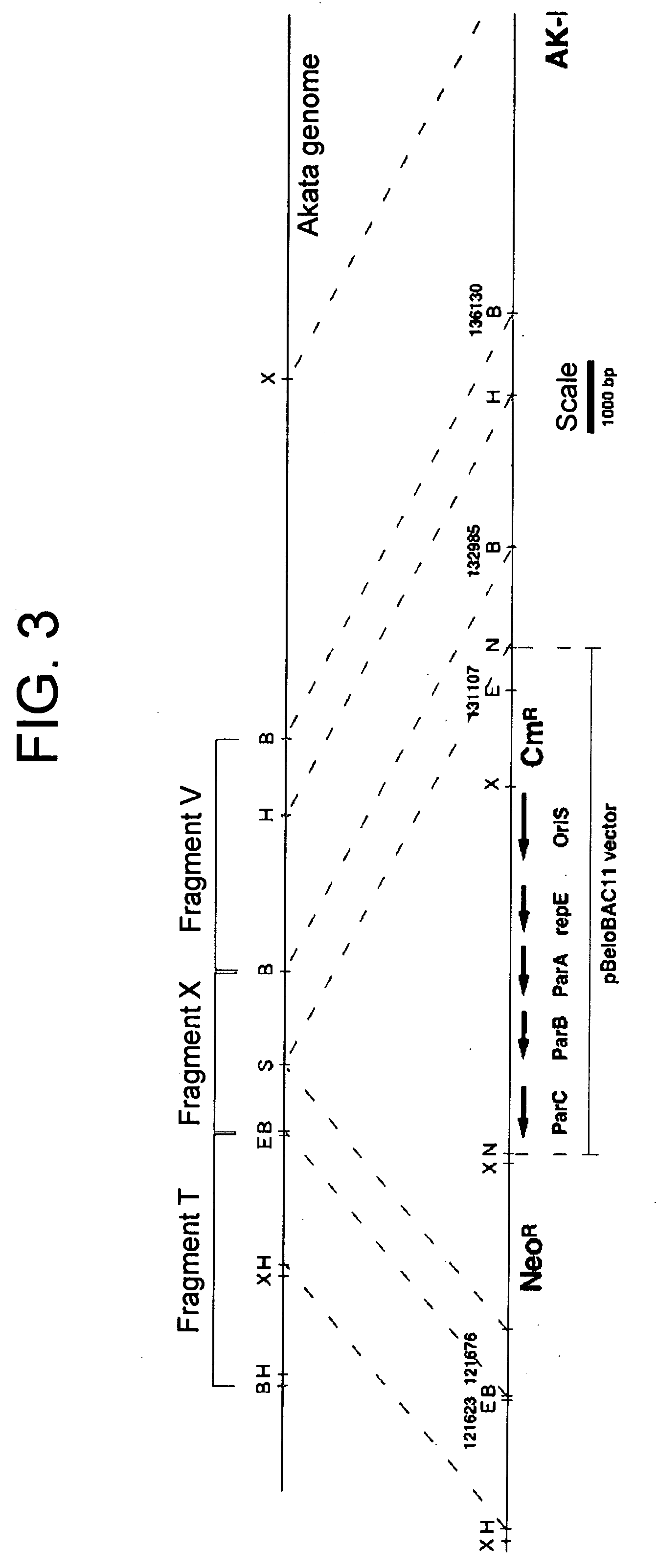
(PROBLEM) To establish a system enabling modification and proliferation of EB virus circular DNA in Escherichia coli and large-scale production of recombinant EB virus virions in the cells. (Means for Resolution) The present invention enables modification and proliferation of a circular EB virus genome derived from Akata cells in Escherichia coli by inserting a DNA sequence of a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) into a circular EB virus DNA in Akata cells via homologous recombination. The recombinant EB virus can be produced in a large quantity by introducing the resulting genomic DNA into Akata cells.
Owner:EVEC
Method for cultivating transgenic plant
InactiveCN101736013ARaise the possibilityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSaccharumSucrose
The invention discloses a method for cultivating transgenic plant. Recombined binary bacteria artificial chromosome containing foreign DNA is introduced into agrobacterium, so as to obtain recombined agrobacterium; the obtained recombined agrobacterium is subject to suspension by the following solution and then converted into the target plant: solvent is water, solute is non-ionic surfactant nonyl phenol polyoxyethylene ether or Sillwet L-77 and cane sugar; wherein the volume percent concentration of the nonyl phenol polyoxyethylene ether or Sillwet L-77 is 0.05-0.1%, and mass percent concentration of the cane sugar is 5%. By utilizing the method of the invention, foreign DNA segment as high as 75kb can be introduced into the target plant, thus the possibility that gene cluster related toinversion resistance (especially related to salt tolerance) is transformed into the target plant is greatly improved, thereby laying the foundation for cultivating salt tolerant plant.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel high-resolution quantitative multicolor fluorescent in-situ hybridization method and application thereof
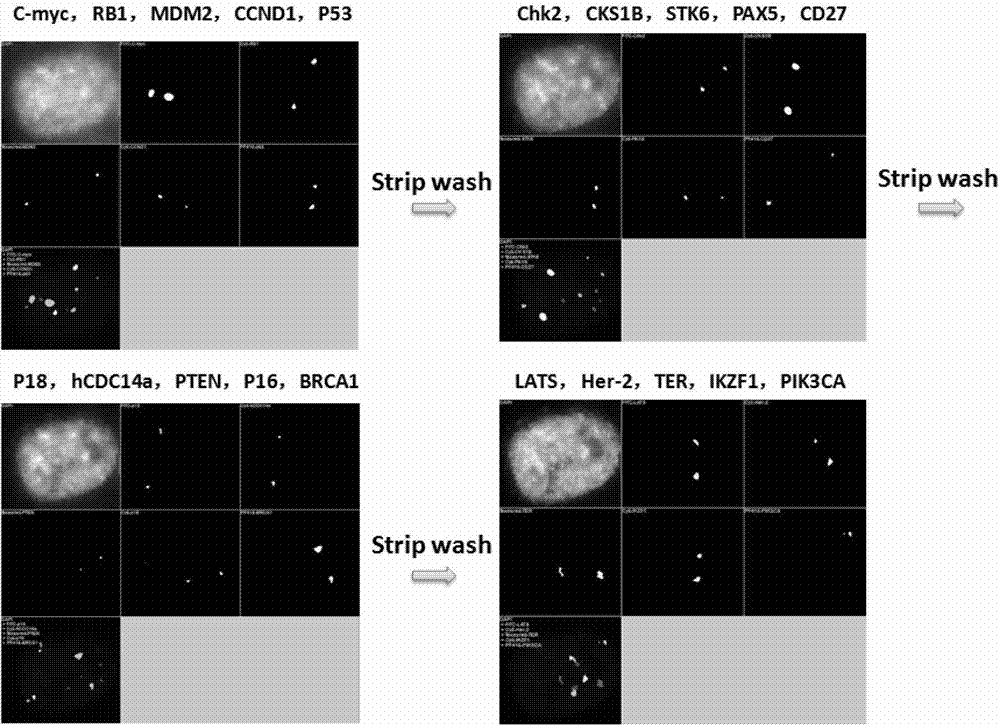
InactiveCN103114128AApplicable clinical researchImprove signal-to-noise ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseBacterial artificial chromosome
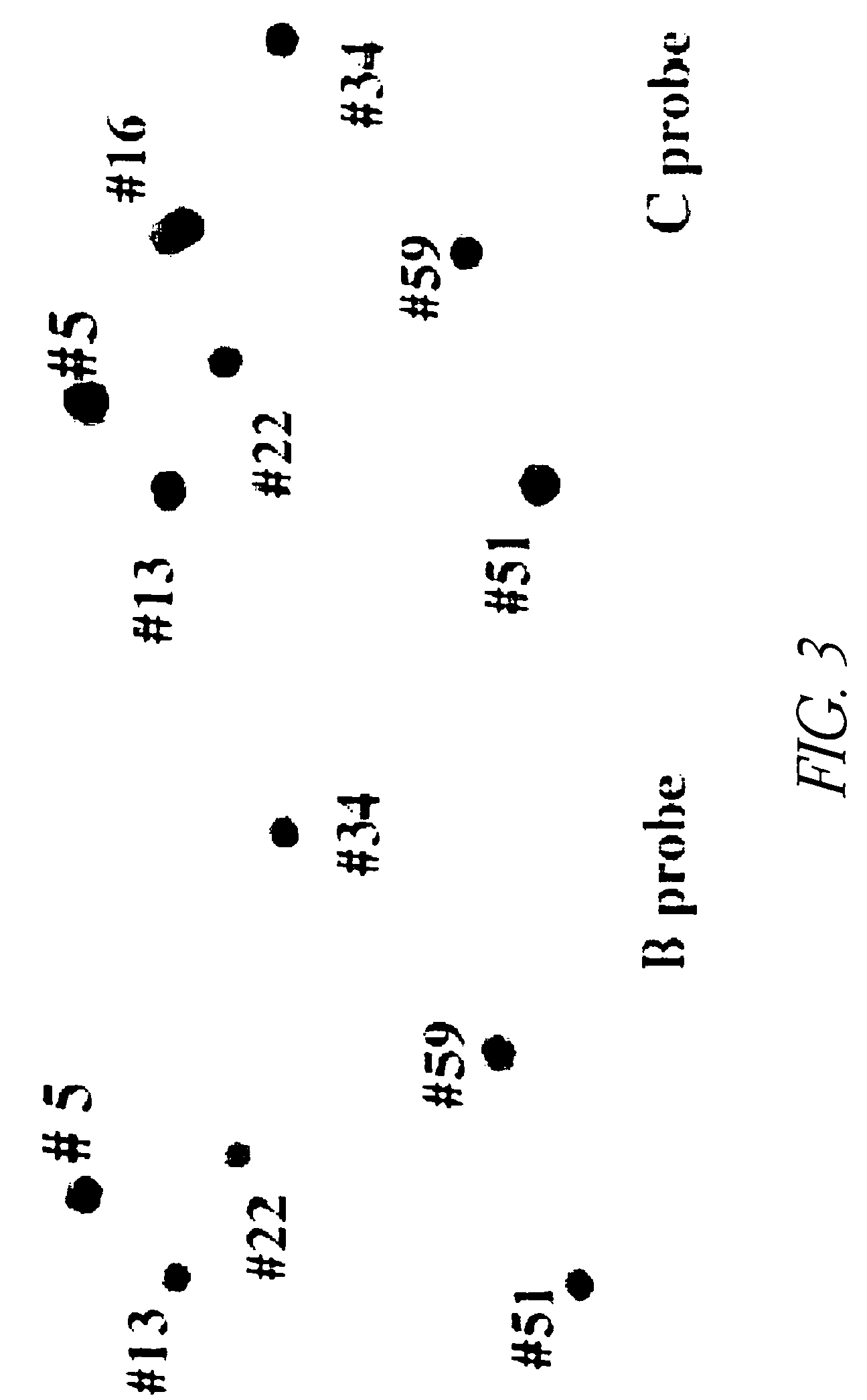
The invention relates to a novel high-resolution quantitative multicolor fluorescent in-situ hybridization method and application thereof. The method provided by the invention is implemented in a way that: a fluorescein label BAC (bacterial artificial chromosome) probe is adopted, and a continuous fluorescent in-situ hybridization method (probe elution rehybridization) is utilized; and after the hybridization each time, fluorescent information in six optical filter channels DAPI, Spectrum GreenTM, Cy3TM v1, Texas Red, Cy5 and PF-415 are acquired under a fluorescent microscope, and a computer automatic fluorescent visual field relocation method is utilized to accurately locate all the acquired images for all slices to the same visual field, thereby simultaneously analyzing 5-20 genes of a single normal or tumor cell. The method provided by the invention can screen and verify multiple gene mutants on the unicell level, and can be used for distinguishing different subtypes of multiple diseases as well as further classification of the same subtype of disease.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Bacterial strains with improved plasmid stability
ActiveUS9012226B2High copy numberImprove production yieldFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBacteroidesBacterial strain
The present invention relates to the propagation of covalently closed circular recombinant DNA molecules such as plasmids, cosmids, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), bacteriophages, viral vectors and hybrids thereof, and more particularly is strain modifications that improve strain viability, plasmid stability, plasmid production yield, and plasmid-directed protein production yield, using said DNA molecules in fermentation culture.
Owner:ALDEVRON LLC
Cloning of transgenic unglulates comprising artificial chromosomes
ActiveUS7652192B2Improve efficiencyIncrease volumeNew breed animal cellsFermentationNuclear transferEmbryo
The invention is directed in part to totipotent cells that have one or more artificial chromosomes; processes for producing such cells; processes for using such cells (e.g., nuclear transfer); transgenic embryos and transgenic animals cloned from such cells; and processes for producing such embryos and animals.
Owner:SAB LLC
Recombinant herpesvirus of turkey (HVT) and preparation method thereof
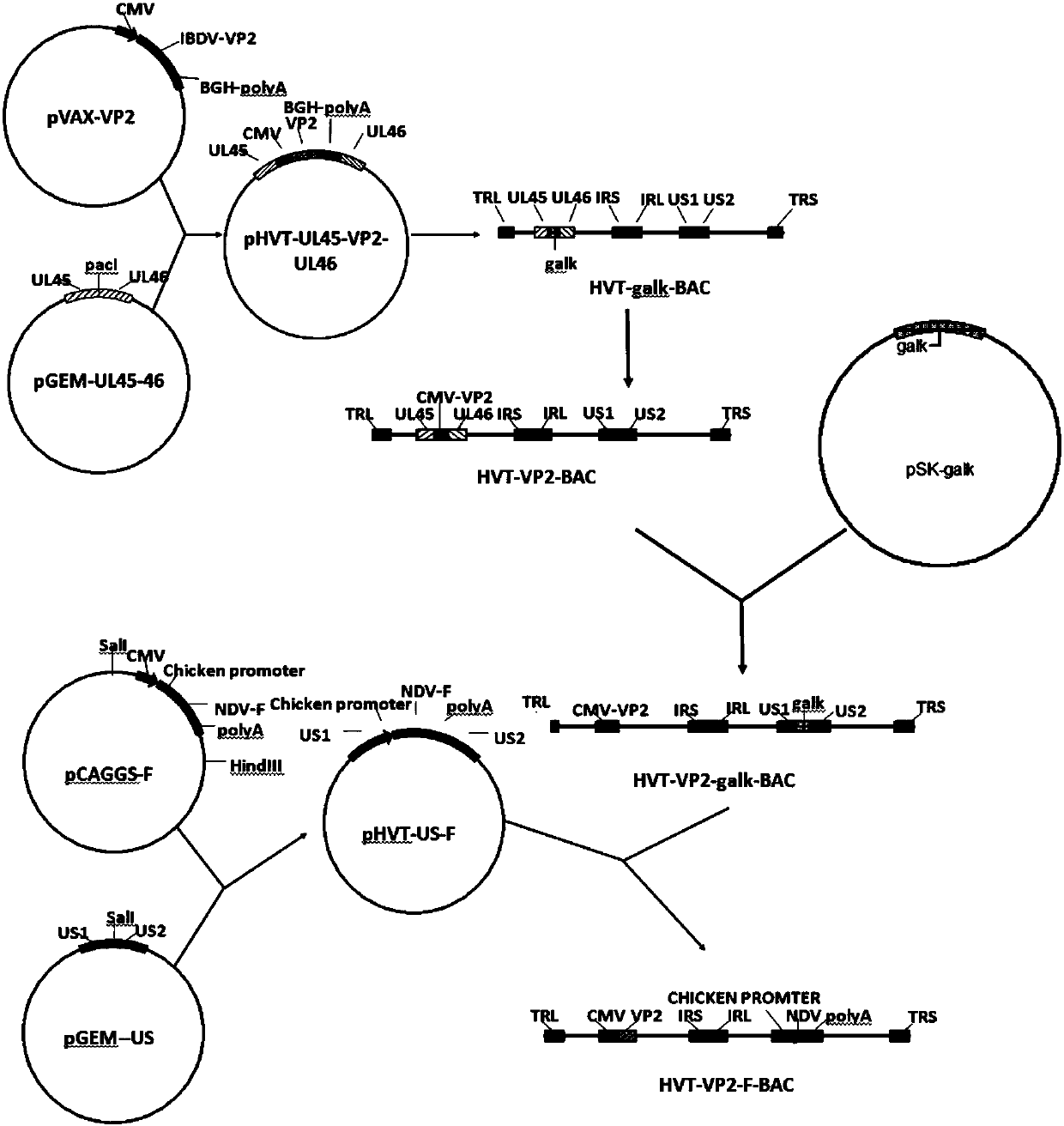
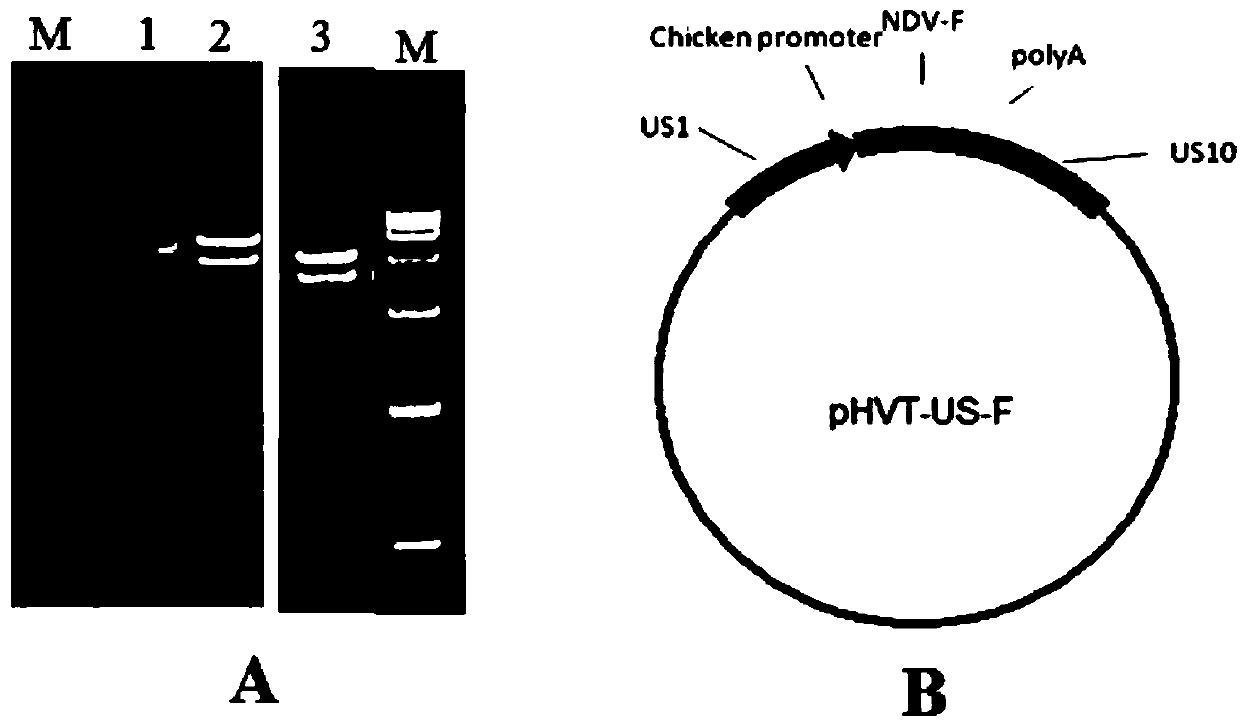
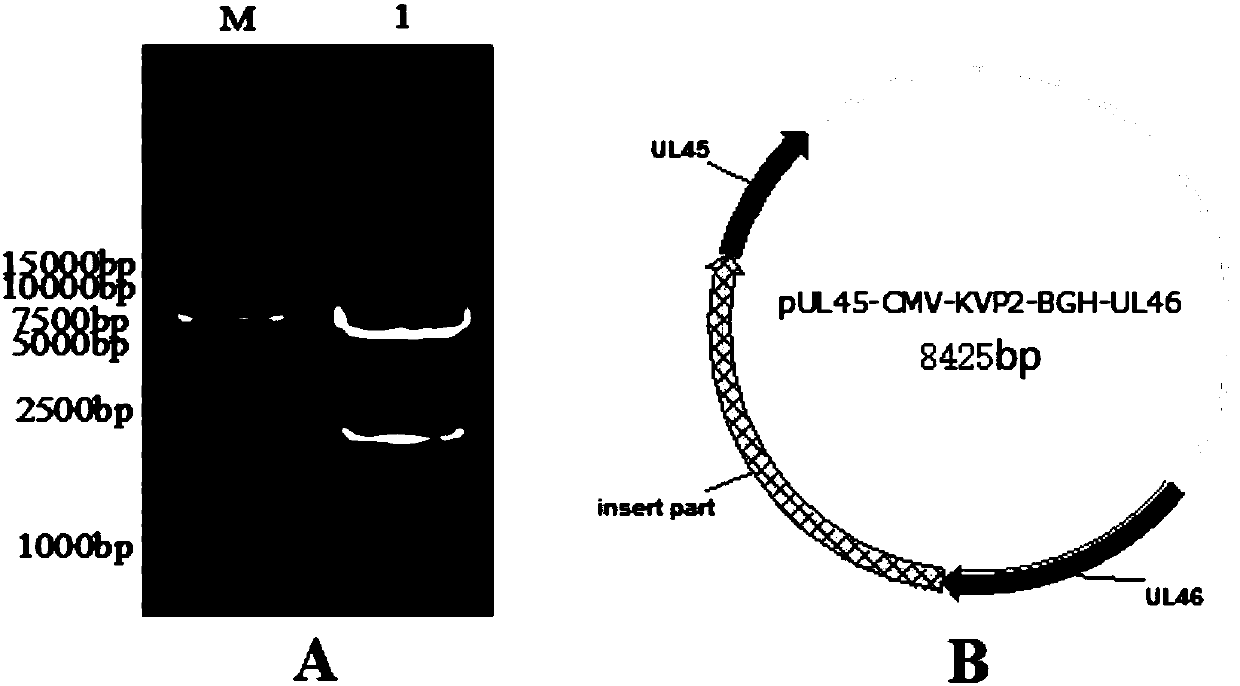
InactiveCN107815469AReduce manufacturing costSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesAntigenBacterial artificial chromosome
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and in particular discloses a recombinant herpesvirus of turkey (HVT). The recombinant HVT is capable of simultaneously expressing NDV and IBDVprotective antigen genes, and is a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) based on the HVT. The construction method comprises the following steps: inserting a VP2 gene expression cassette of an infectious bursal disease virus LX strain under regulation of a cytomegalovirus promoter CMV into a UL45-46 non-essential region of the HVT genome by utilizing a gene recombination technology; and insertingan F gene expression cassette of a newcastle diseases virus PX02 / 3 strain under regulation of a chicken beta-actin promoter pec into another non-essential region US1-10 of the HVT genome. The recombinant herpesvirus of turkey is a recombinant triplet poultry vaccine candidate strain capable of controlling Marek's disease of chickens and effectively resisting Newcastle disease and infectious bursaldisease.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
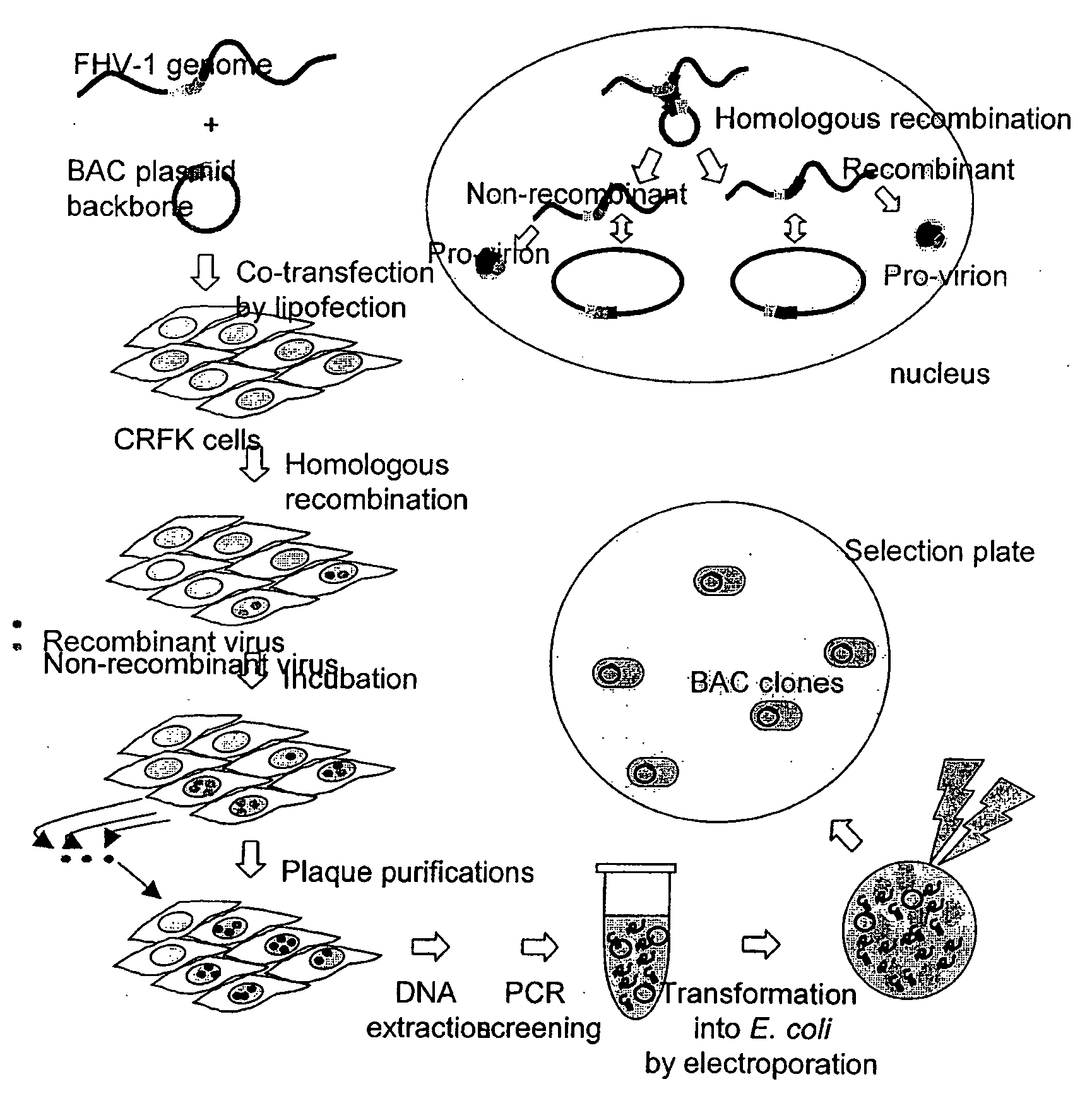
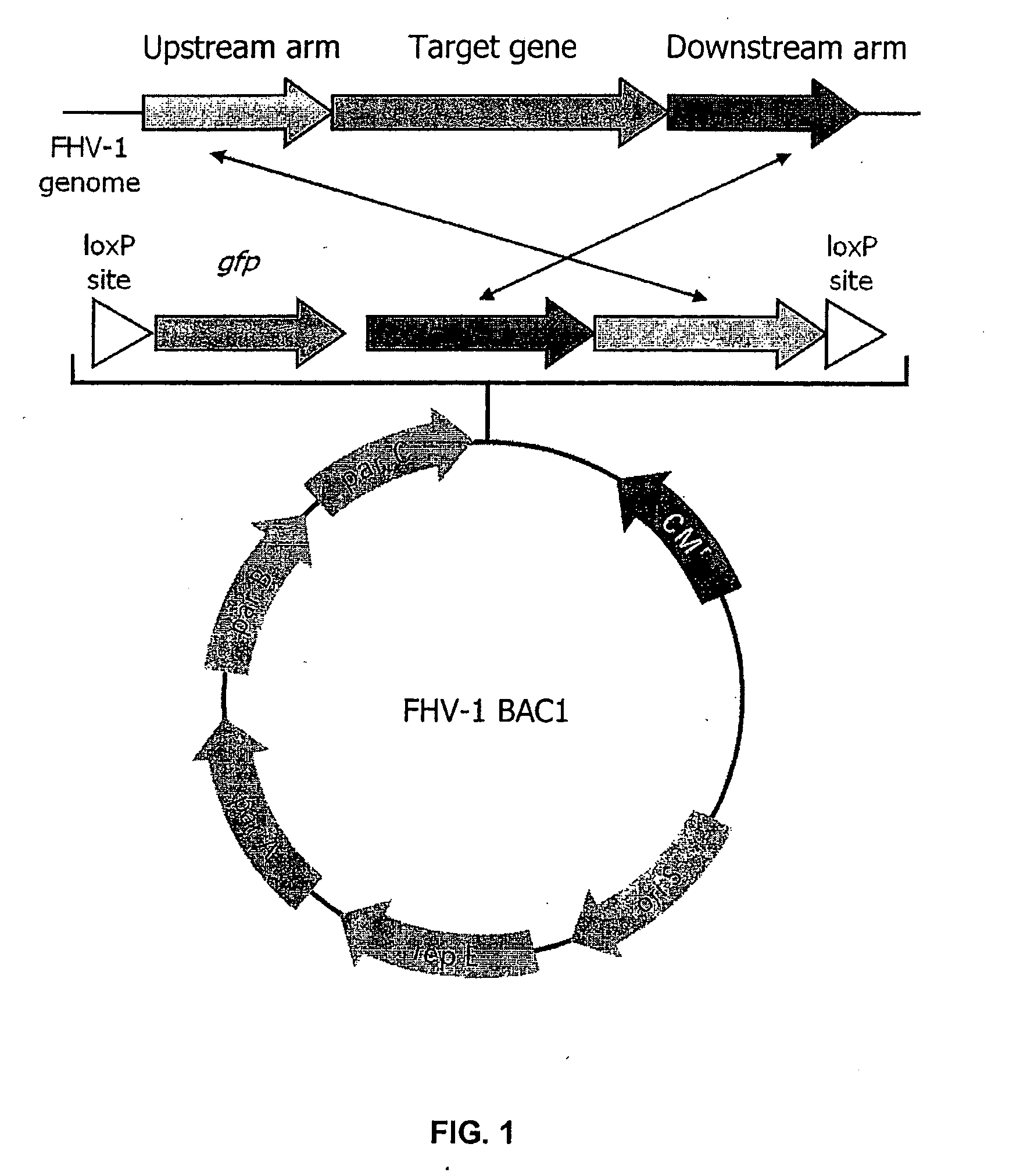
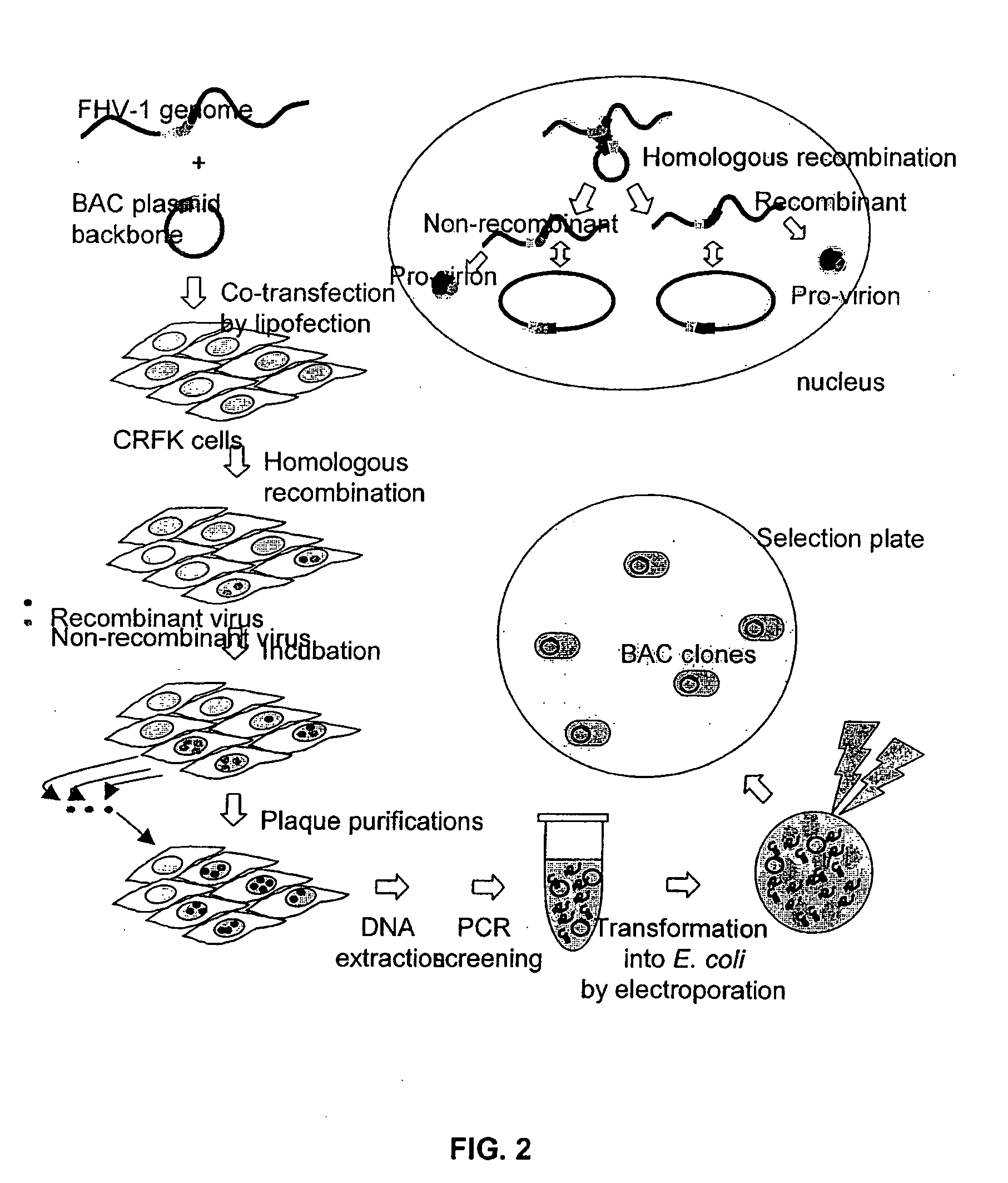
Bacterial Artificial Chromosome Containing Feline Herpes Virus Type 1 Genome and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20100291142A1Fast and efficient manipulationAnimal cellsViral antigen ingredientsFeline herpesvirus type 1Virus type
The present invention relates to recombinant feline herpes virus type 1 (FHV-1) nucleic acids and proteins. In particular the present invention provides compositions comprising the full length FHV-1 genome or portions thereof, and infectious FHV-1 virions produced therefrom. The FHV-1 compositions are suitable for use in inducing an immune response in inoculated subjects and for use in identifying agents that attenuate FHV-1 infection.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
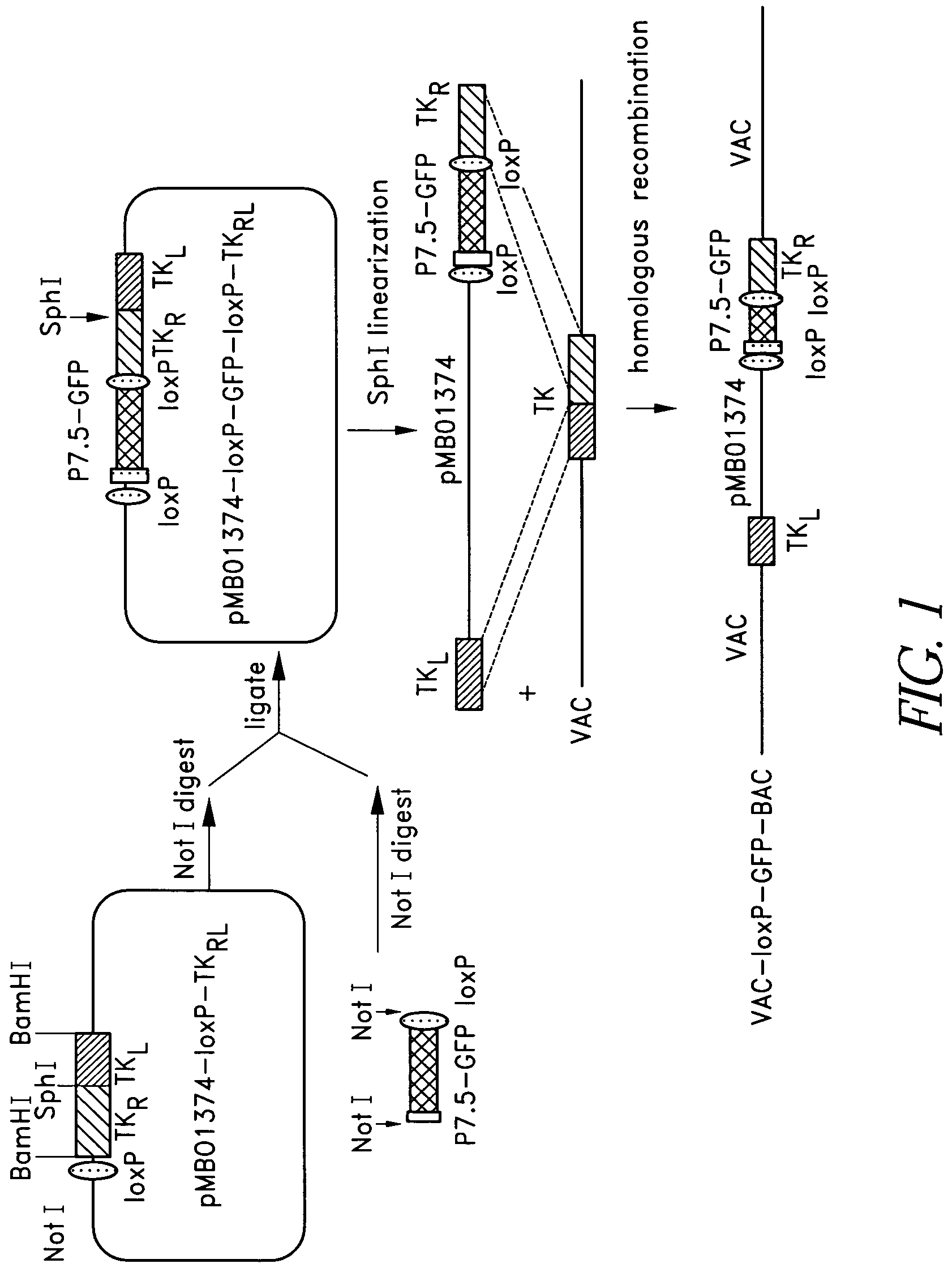
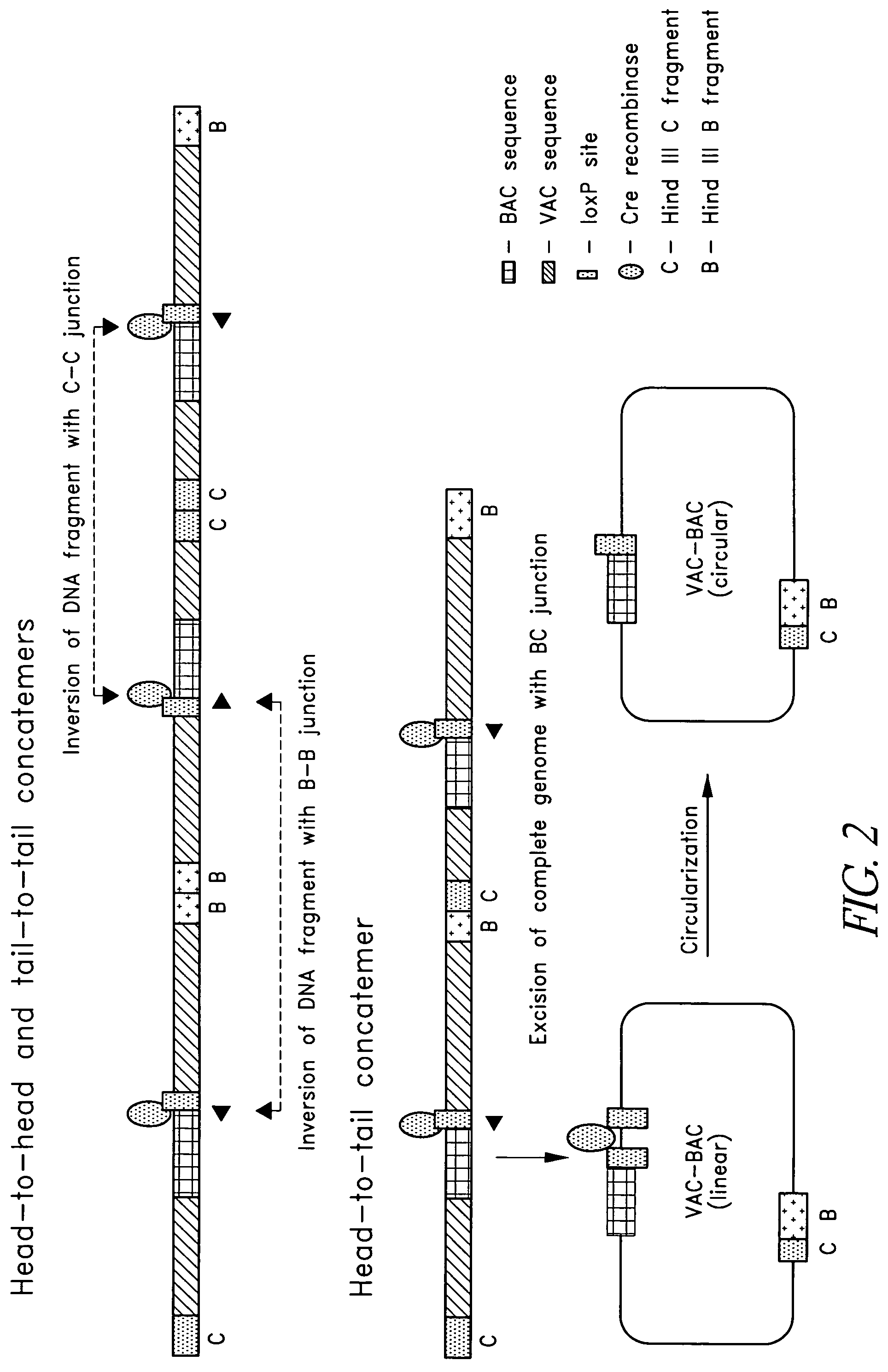
VAC-BAC shuttle vector system
ActiveUS7494813B2Improving immunogenicityImprove securitySsRNA viruses positive-senseBacteriaShuttle vectorBacterial artificial chromosome
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC THE
Herpes simplex virus type 1 carrier system, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103589754AWeak toxicityImprove securityGenetic material ingredientsFermentationEscherichia coliBacterial artificial chromosome
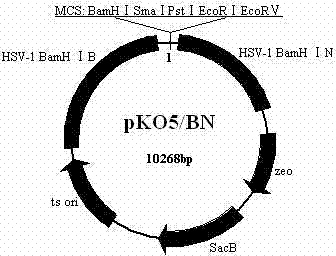
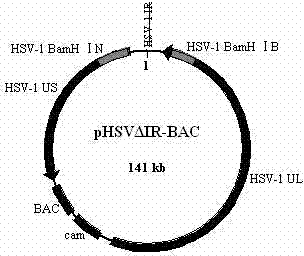
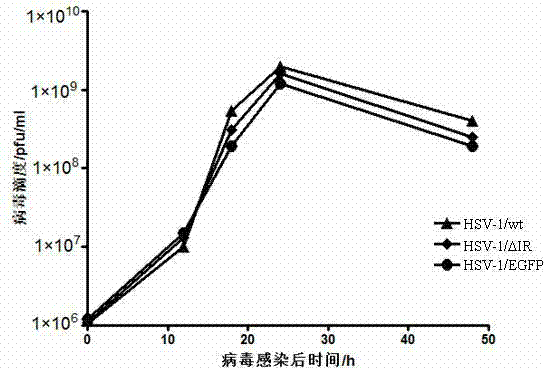
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a herpes simplex virus type 1 carrier system, and a preparation method thereof. The carrier system comprises a shuttle plasmid by taking DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment at two sides of an inverted repeat sequence (IR) inside HSV-1 (herpes simplex virus type 1) as homologous recombinant arms, and a bacterial artificial chromosome plasmid pHSV delta IR-BAC (bacterial artificial chromosome) containing IR zone deleted HSV-1 genome. The method for preparing recombinant HSV-1 by using the carrier system comprises the following steps: firstly, cloning a target DNA fragment into pKo5 / BN to obtain a recombinant shuttle plasmid; secondly, electro-transforming escherichia coli containing pHSV delta IR-BAC by using the recombinant shuttle plasmid, and screening to obtain recombinant bacteria; finally, extracting the recombinant DNA from the recombinant bacteria, transfecting Vero cells, and purifying to obtain recombinant HSV-1. The carrier system is high in security, can accommodate 30Kb of exogenous DNA, and can construct optional replication type recombinant HSV-1 capable of expressing a plurality of target genes.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Method for improving cell transfection efficiency through utilization of bacterial artificial chromosome homologous recombination
InactiveCN103352050AGood reorganization effectImprove the efficiency of transfecting integrated cellsVector-based foreign material introductionNucleofectionHost cell filopodium
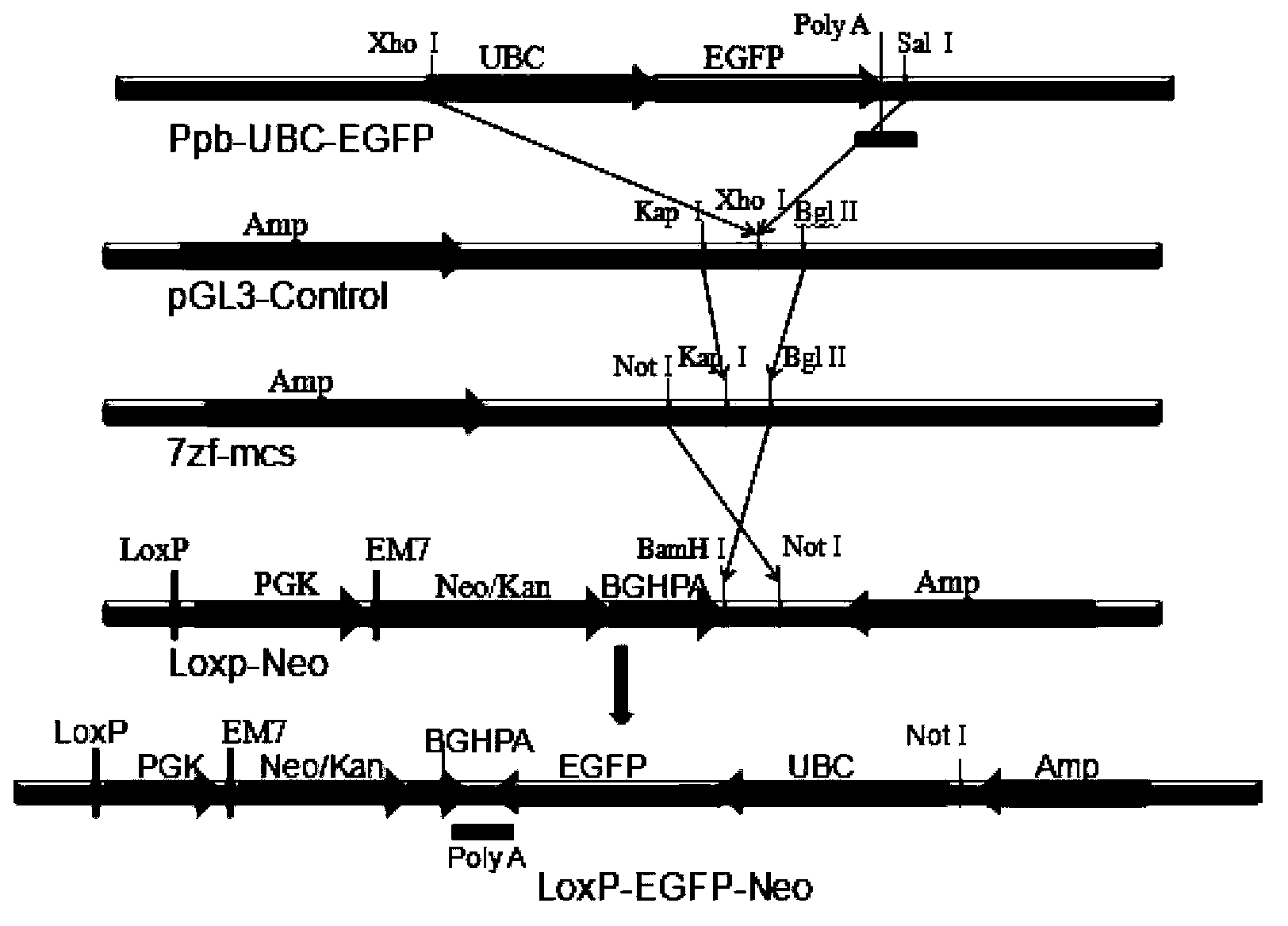
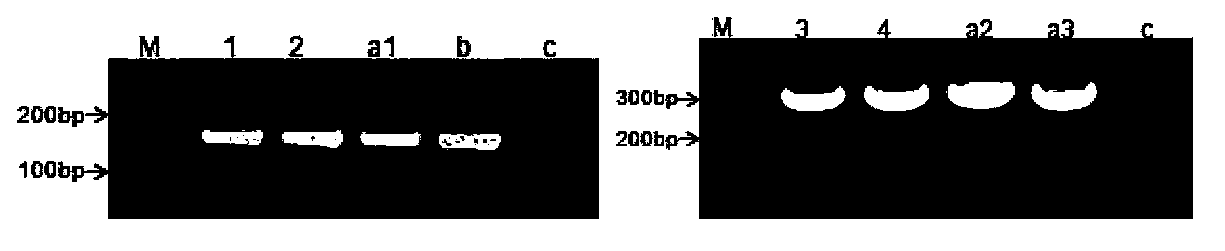
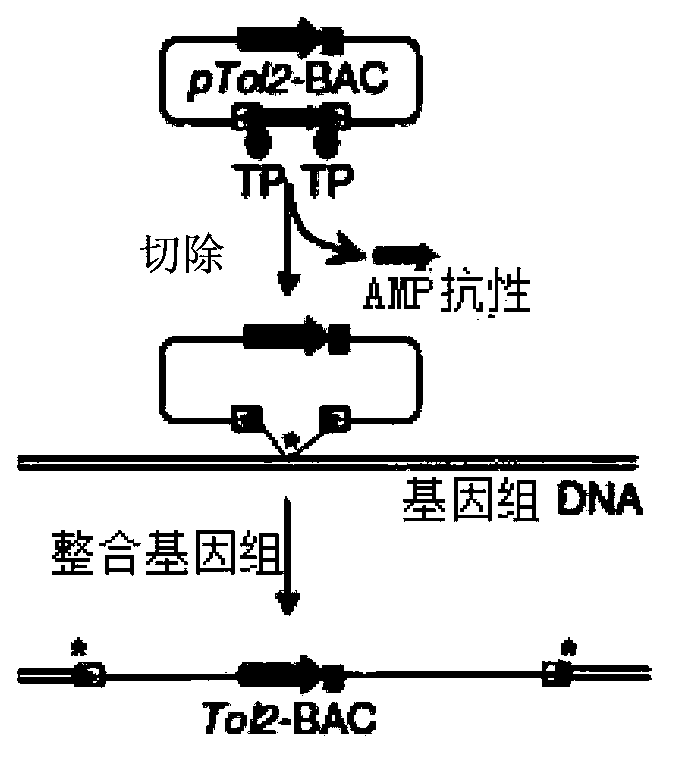
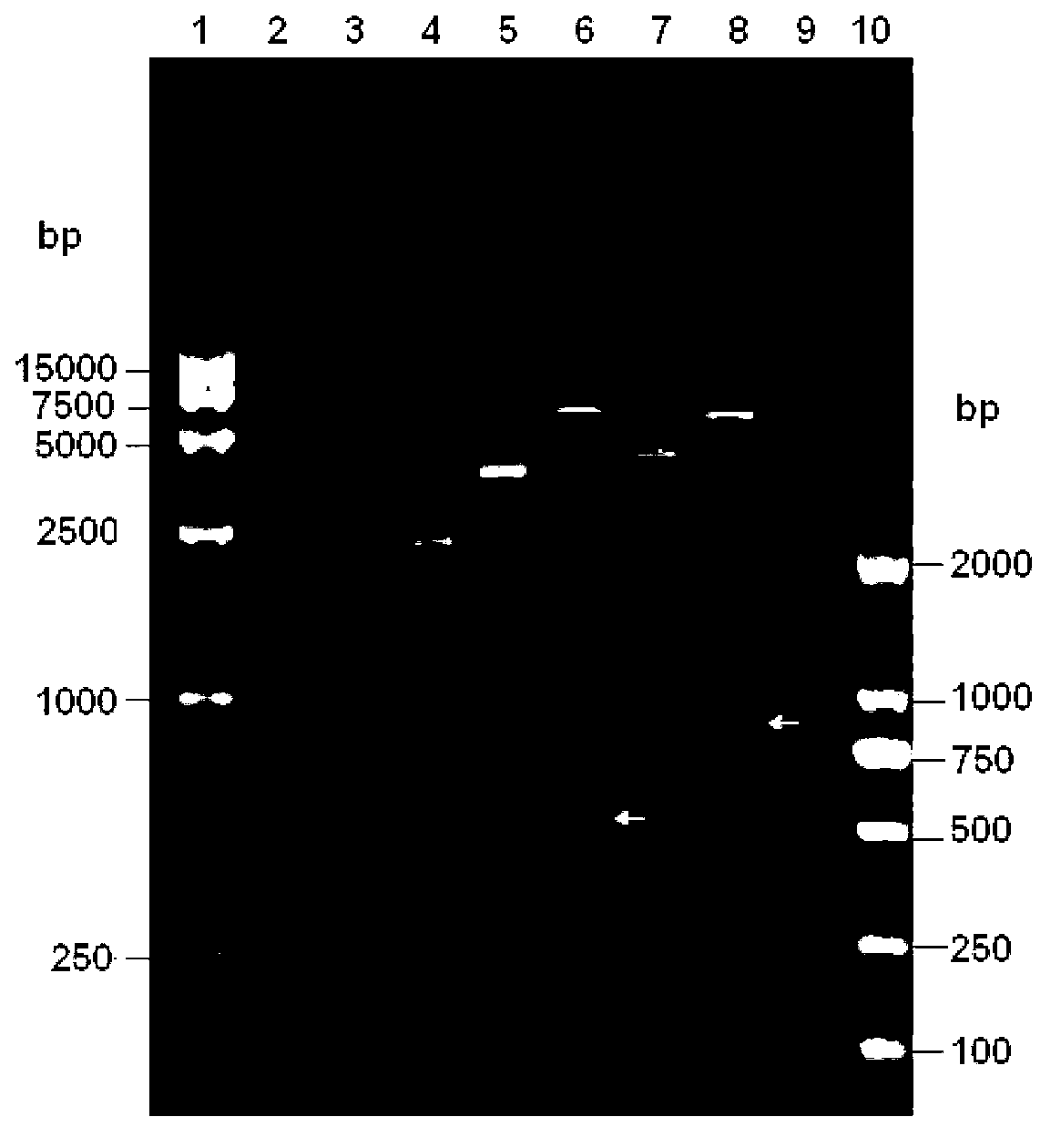
The invention provides a method for improving cell transfection efficiency through utilization of bacterial artificial chromosome homologous recombination. Homologous recombination of BAC containing target genes is carried out through use of pABRG recombinant plasmid, then through use of nucleofection technology, the recombined BAC transfects host cells, through adoption Tol2 transposon optimized by mammal codons, so that the recombined BAC containing the target genes is integrated in to host cell genomes. Through successful construction of eGFP marker gene containg human UBC promoter and BAC carrier of eukaryotic screening resistant neo gene, wherein both ends of the carrier being provided with Loxp components, preparation for marking and resistibility removing after cell transfection are ready. In addition, transfection efficiency of electrotransfection BAC-Tol2-eGFP carrier can reach 1%-6%, the highest transfection efficiency can reach 10%, and a complete set of experimental routes and methods for use and operation of large mammalian BAC are provided.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Chimeric virus, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103205460AHigh titerImproving immunogenicityViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesFull length cdnaSerotype
The invention discloses an infectious Japanese encephalitis virus clone which is a recombinant vector including full-length cDNA of genome of a Japanese encephalitis virus attenuated strain SA14-14-2. The invention further discloses a chimeric virus and application thereof and a bacterial artificial chromosome as represented by SEQ ID No. 1. The chimeric virus provided by the invention can grow and proliferate on a plurality of cells used for production of human vaccines and show similar growth characteristics, is applicable to production of four serotype Dengue vaccines and has the advantages of strong immunogenicity, high antibody titer, good application prospects and a high industrial application value.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGICAL PROD +1
Respiratory syncytial virus expression vectors
ActiveUS10227569B2SsRNA viruses negative-senseAnimal cellsNucleic acid sequencingRespiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
In certain embodiments, the disclosure relates to vectors containing bacterial nucleic acid sequences and a paramyxovirus gene. Typically, the expression vector comprises a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), and a nucleic acid sequence comprising a respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) gene in operable combination with a regulatory element and optionally a reporter gene.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
Bacteria artificial chromosome plasmid extraction method
InactiveCN1570099AHigh yieldImprove the efficiency of extracting BAC DNABacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionAcetic acidPotassium acetate
A method for extracting BAC plasmid is provided. In the existing method, the solutionII uses NaOH, SDS and dd.H2O as material, in which NaOH mol concentration is 0.4N, SDS concentration is 0.8%, the solutionIII uses 5M potassium acetate 60ml, glacial acetic acid 28.5ml, H2O 11.5ml as material. The invention changes the solution II and solution III, which promote the BAC DNA extraction efficiency. The adoption of TB culture medium promotes greatly the yield. Only one centrifuging tube is used in the invention, which save the labor and time.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Fungal artificial chromosomes, compositions, methods and uses therfor
ActiveUS20170211077A1Reduced expression levelAlter protein structureMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorOrigin of replicationBiotechnology
Fungal artificial chromosome (FAC) vectors are disclosed. A vector can be replicated in a bacterial or a fungal host, and can comprise an insert of heterologous DNA up to about 500 kilobases. A vector can be used for cloning and expressing a secondary metabolite (SM) gene cluster. An insert sequence can be modified by homologous recombination. A vector can be a plasmid comprising bacterial and fungal origins of replication, as well as bacterial and fungal selection marker genes. Also disclosed are vectors that can be integrated into a fungal genome, and dual function vectors which can be replicated in a bacterial or a fungal host and can also be integrated into a fungal genome. Also disclosed are methods of generating plasmid libraries including vectors comprising intact SM gene clusters.
Owner:INTACT GENOMICS INC
Method for screening molecular markers correlative with properties based on sequencing technique and BSA (Bulked Segregant Analysis) technique
ActiveCN101886132BIncreased development throughputIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementBulked segregant analysisFunctional genes
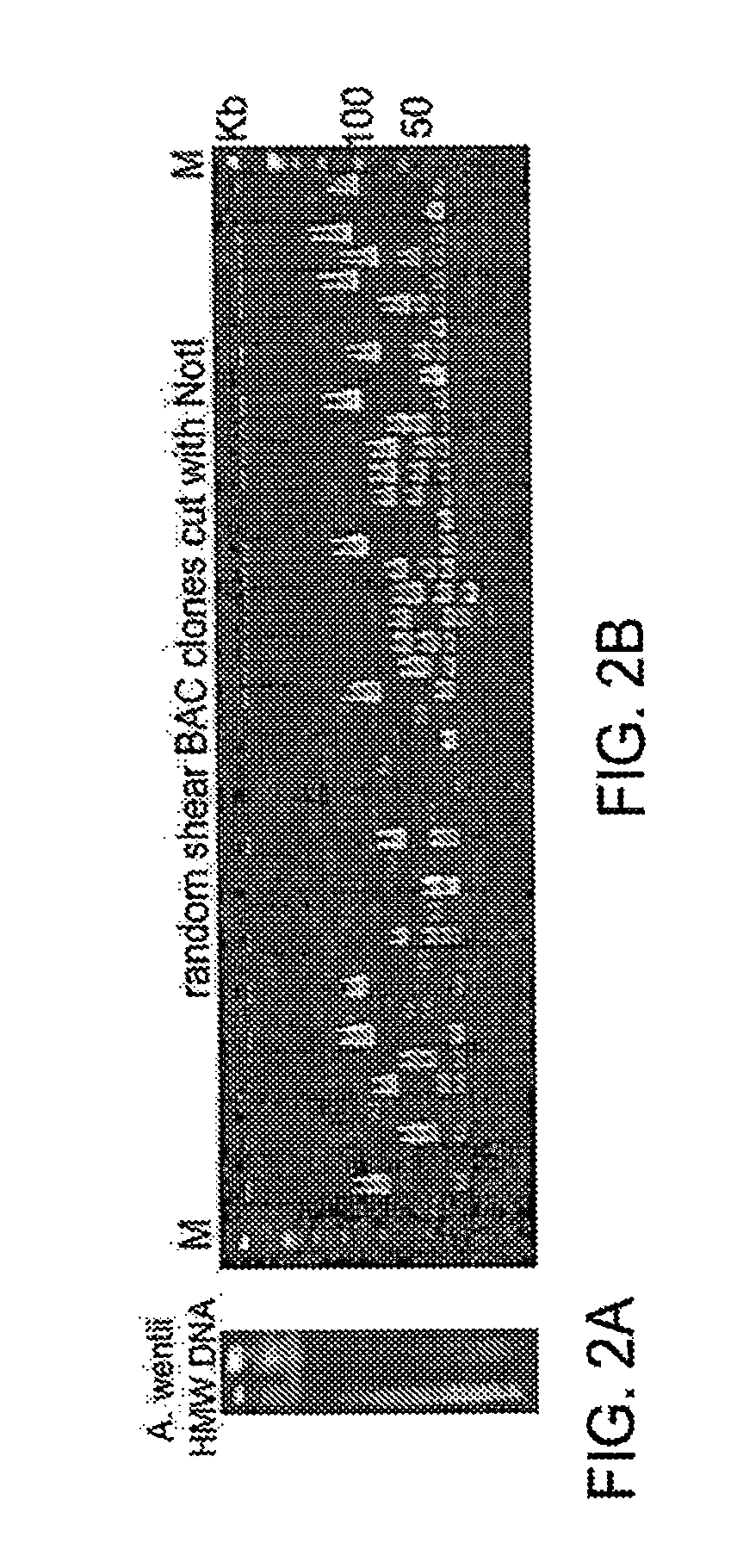
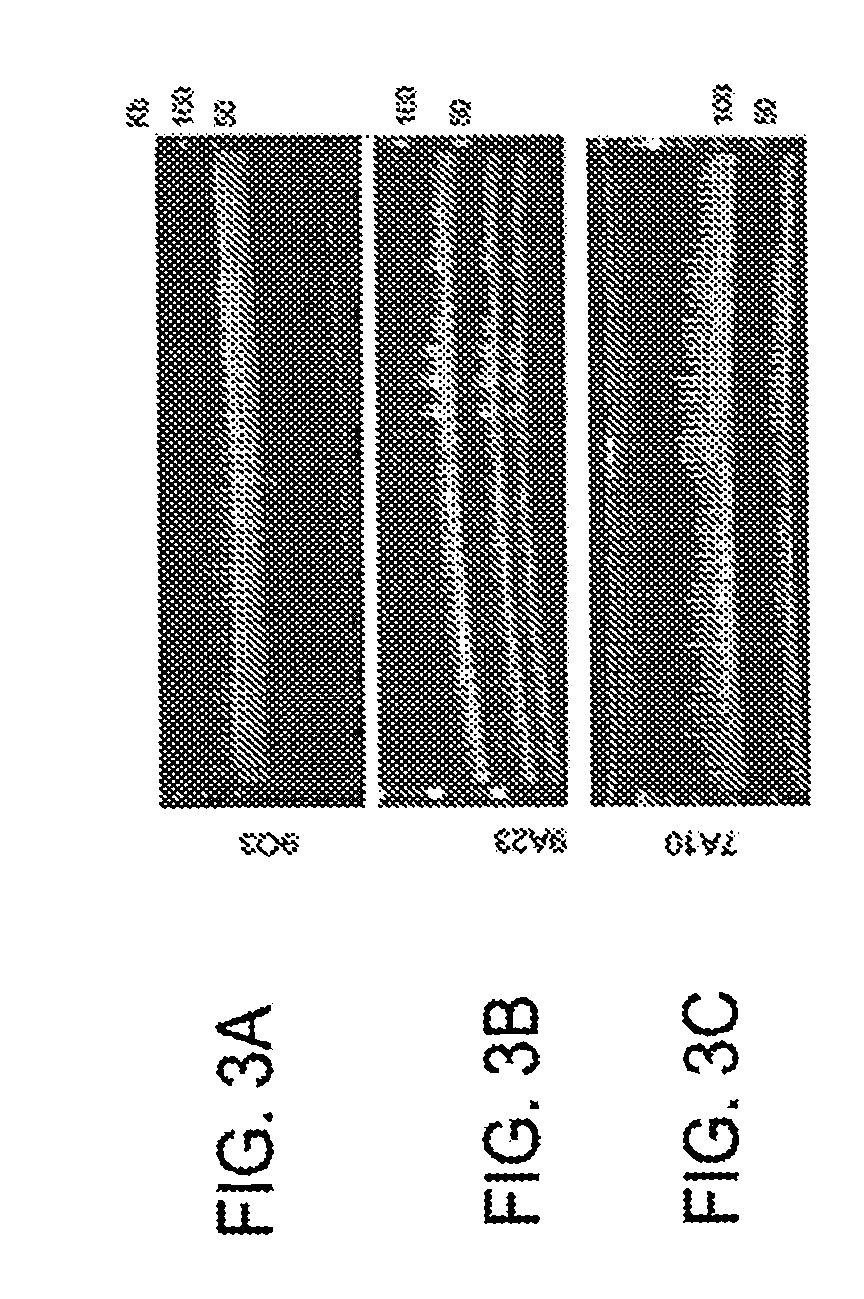
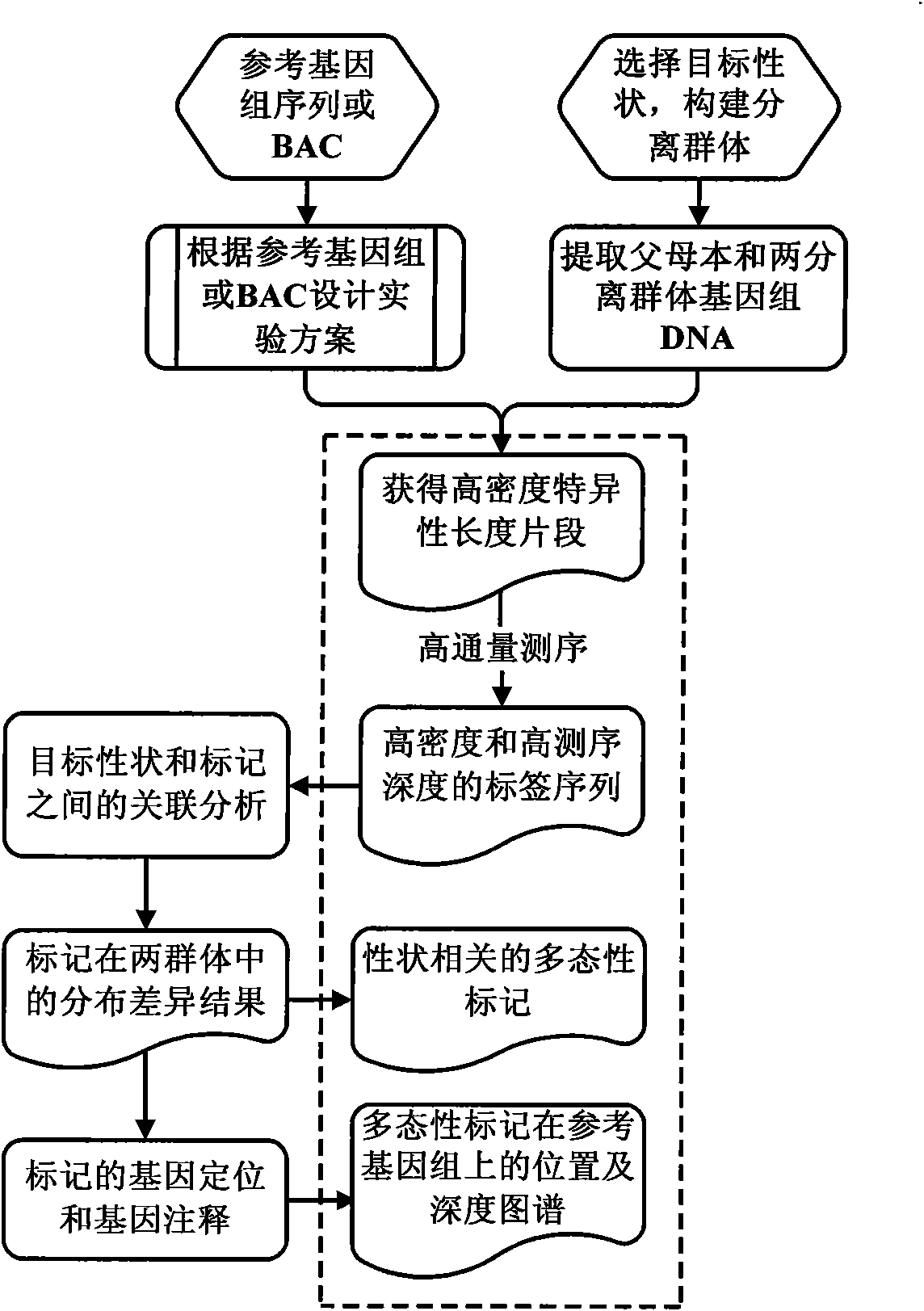
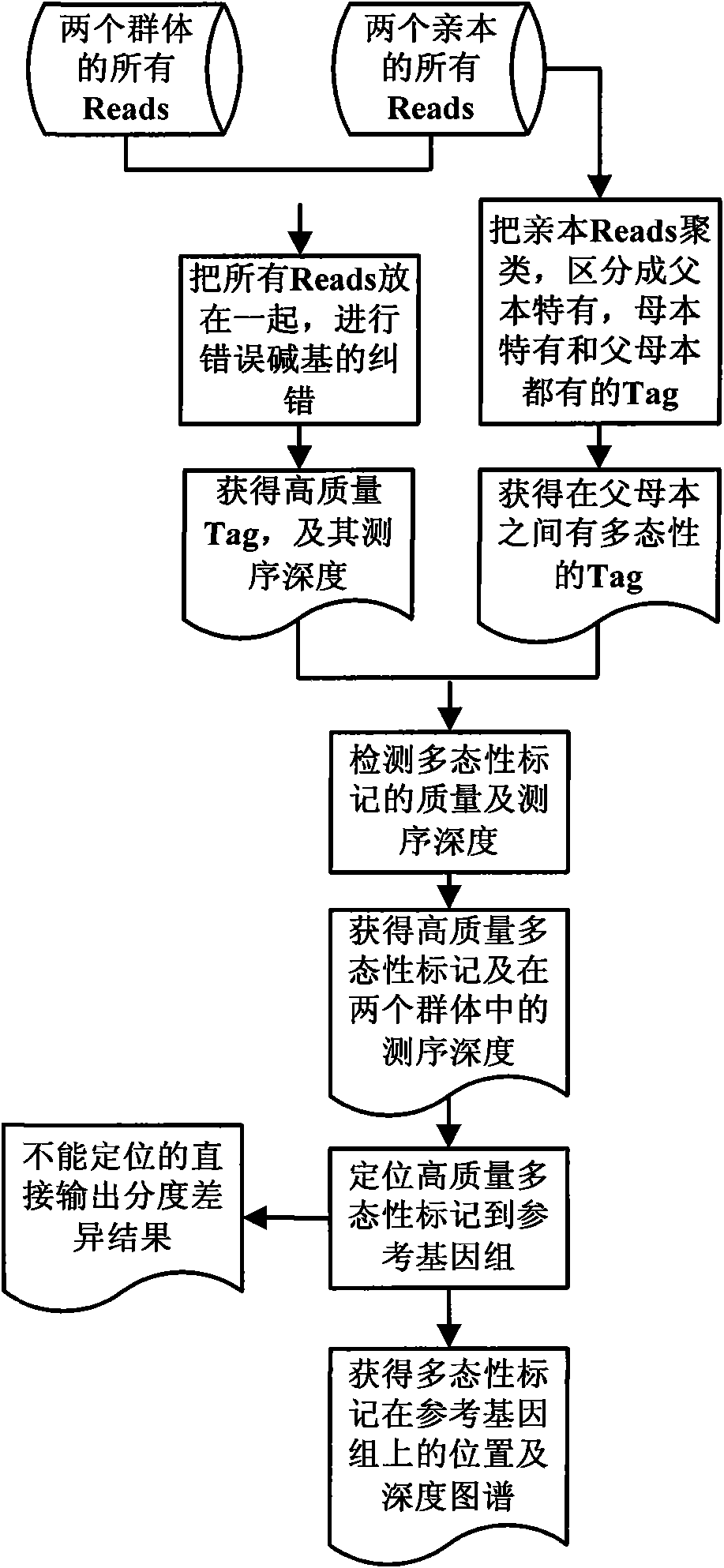
The invention provides a method for screening DNA molecular markers closely correlative with properties, which is mainly used for identifying DNA molecular markers correlative with properties by combining super bulked segregant analysis (BSA) with a high throughput sequencing technique. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out parameter training to data comprising different species genomes or BAC (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome) sequences and the like by utilizing a bioinformatics method to find out an optimal marker sequencing scheme for improving the development efficiency of the markers; carrying out correlative analysis to bulked segregant sequencing results to detect the molecular markers correlative with the properties and position back to the genomes or BAC, and then precisely positioning candidate functional genes through the high-density property-correlative molecular markers. Compared with the traditional method, the method has the advantages of greatly improving throughput and greatly reducing cost. The method can be used for carrying out marker positioning to large groups and directly determining the linkage between the markers and the target properties, has high reliability and accuracy of correlative analysis, and is mainly applied to the aspects of marker development and gene positioning, such as crop molecular breeding and the like.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com