Method for screening molecular markers correlative with properties based on sequencing technique and BSA (Bulked Segregant Analysis) technique
A sequencing and labeling technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of high price, low accuracy of marker and trait association analysis, low throughput, etc., and achieve development cost reduction, Effects of Marker Development Throughput Improvement and Complexity Reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Population-specific Length Amplified Fragment Sequencing Detection of DNA Molecular Markers
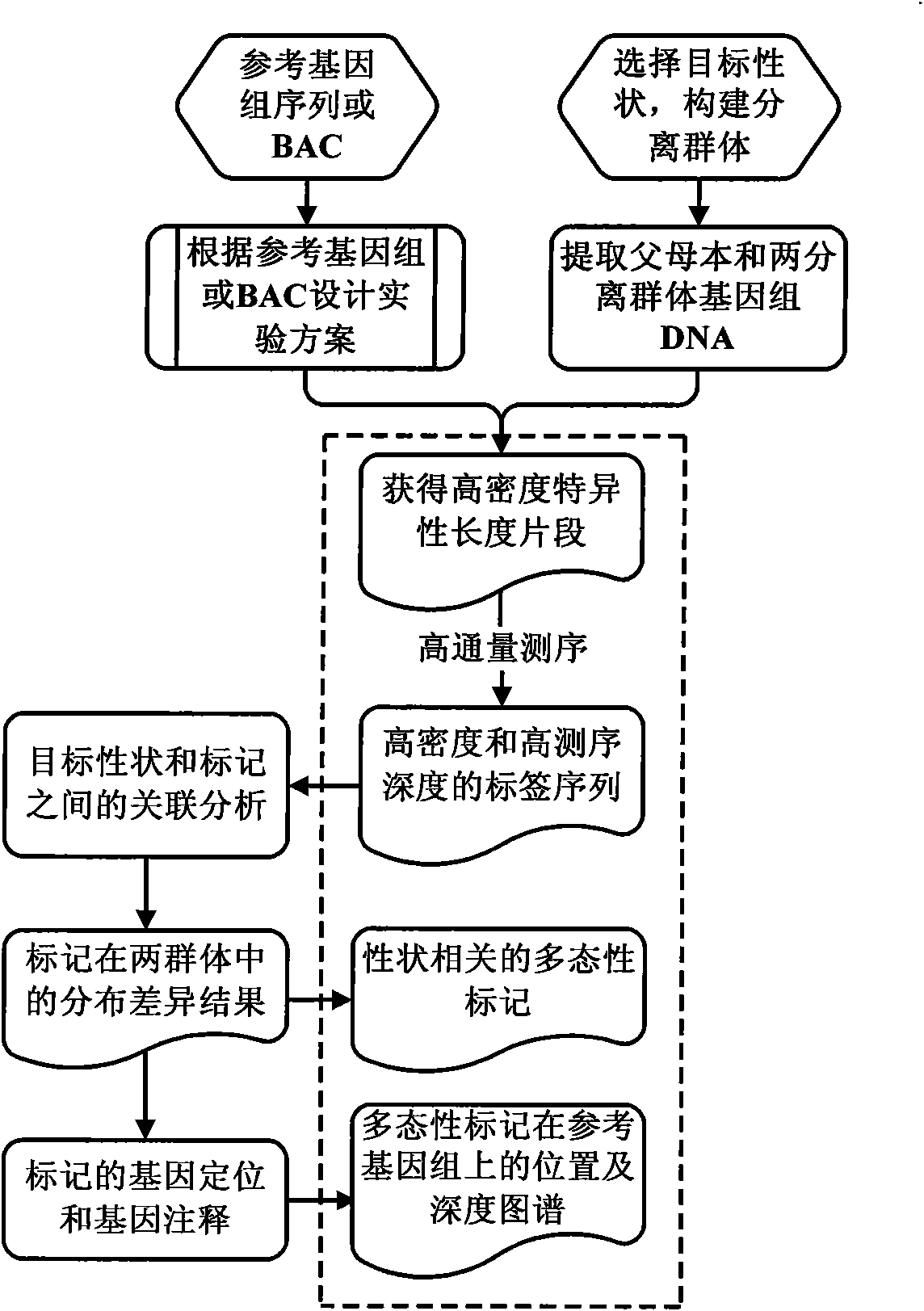
[0028] see figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0029] (1) The objects processed in this embodiment are the DNA samples of the two parents and the DNA samples of the isolated populations after identification; the individual samples in each isolated population should be mixed in the same proportion.
[0030] (2) In this embodiment, the genome or BAC reference sequence of the species to be studied is analyzed, the training parameters are used to find the optimal enzyme combination, and the optimal length of the amplified product is selected to meet the following conditions:
[0031] aThe restriction sites of the enzyme are evenly distributed on the genome;
[0032] b Selecting a specific length of restriction fragments can ensure the number of sequence tags;
[0033] c Select a specific length of restriction fragments to avoid falling in highly repetitive...
Embodiment 2
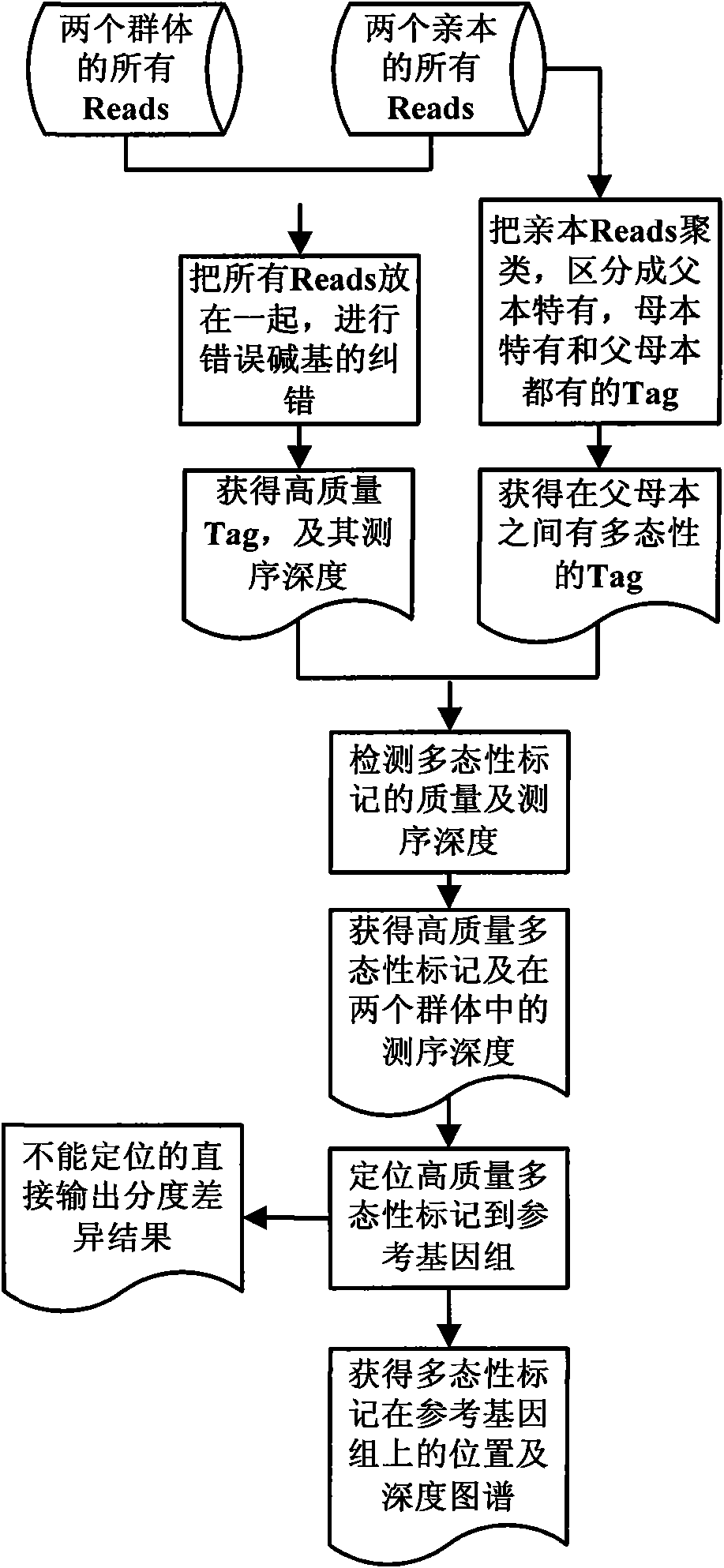
[0043] Example 2 Development of high-density markers and rapid mapping of male sterility trait genes in Chinese cabbage based on high-throughput sequencing
[0044] Including the following steps:
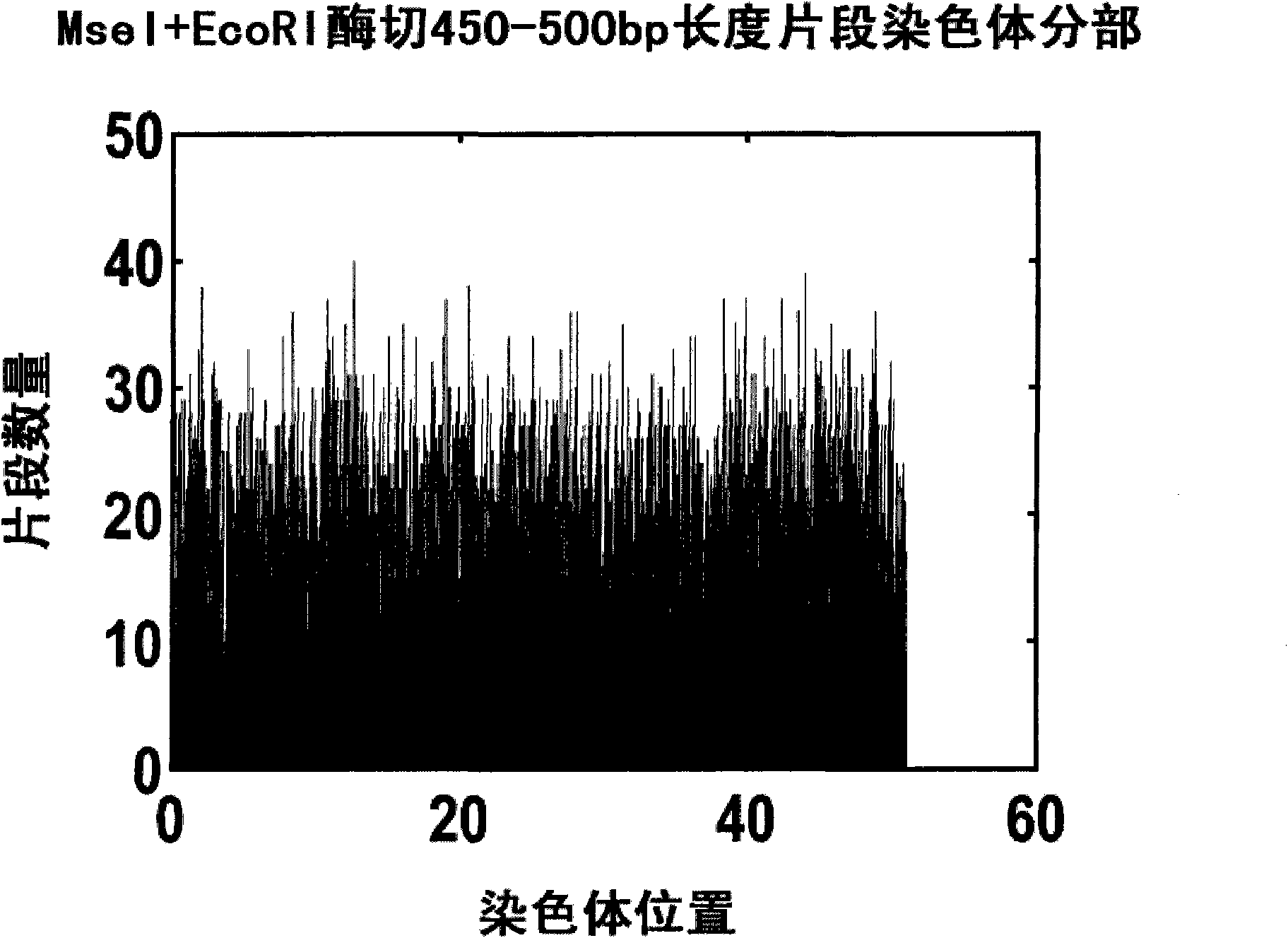
[0045] 1. If Figure 3A Shown is the density distribution map of the 450-500bp length digestion fragments on the chromosome after simulating Ecor1+Msel two enzymes to digest the Chinese cabbage genome reference sequence. After analysis, the 450-500bp length fragment with the highest efficiency is selected, and the length fragment can be evenly distributed on all chromosomes of the genome.
[0046] 2. If Figure 3B Shown is the distribution of the number of 450-500bp length fragments per 100K of the whole genome after simulating Ecor1+Msel two enzymes to digest the Chinese cabbage genome reference sequence. The density of the length segment can also meet the design requirements.
[0047] 3. Through the above analysis, the enzyme digestion parameters of cabbage genome are evaluate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com