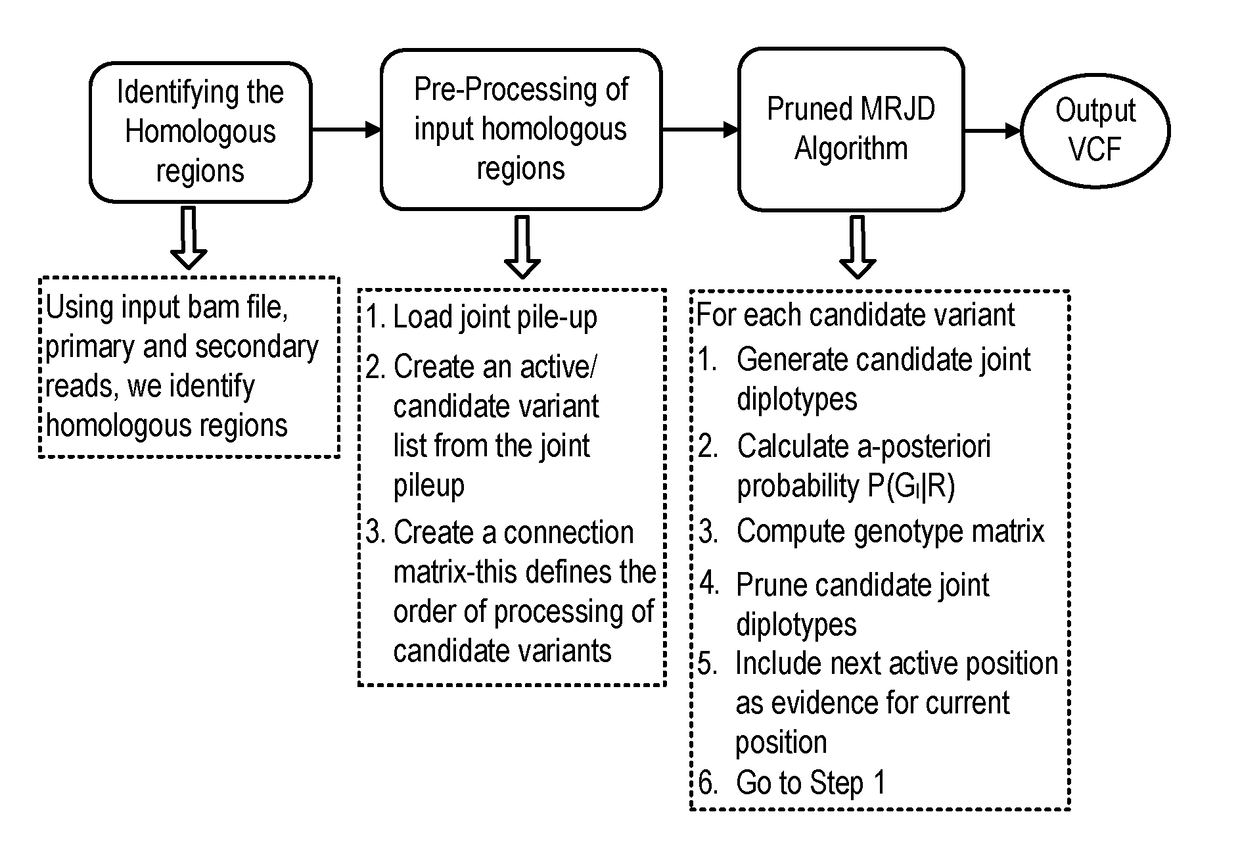
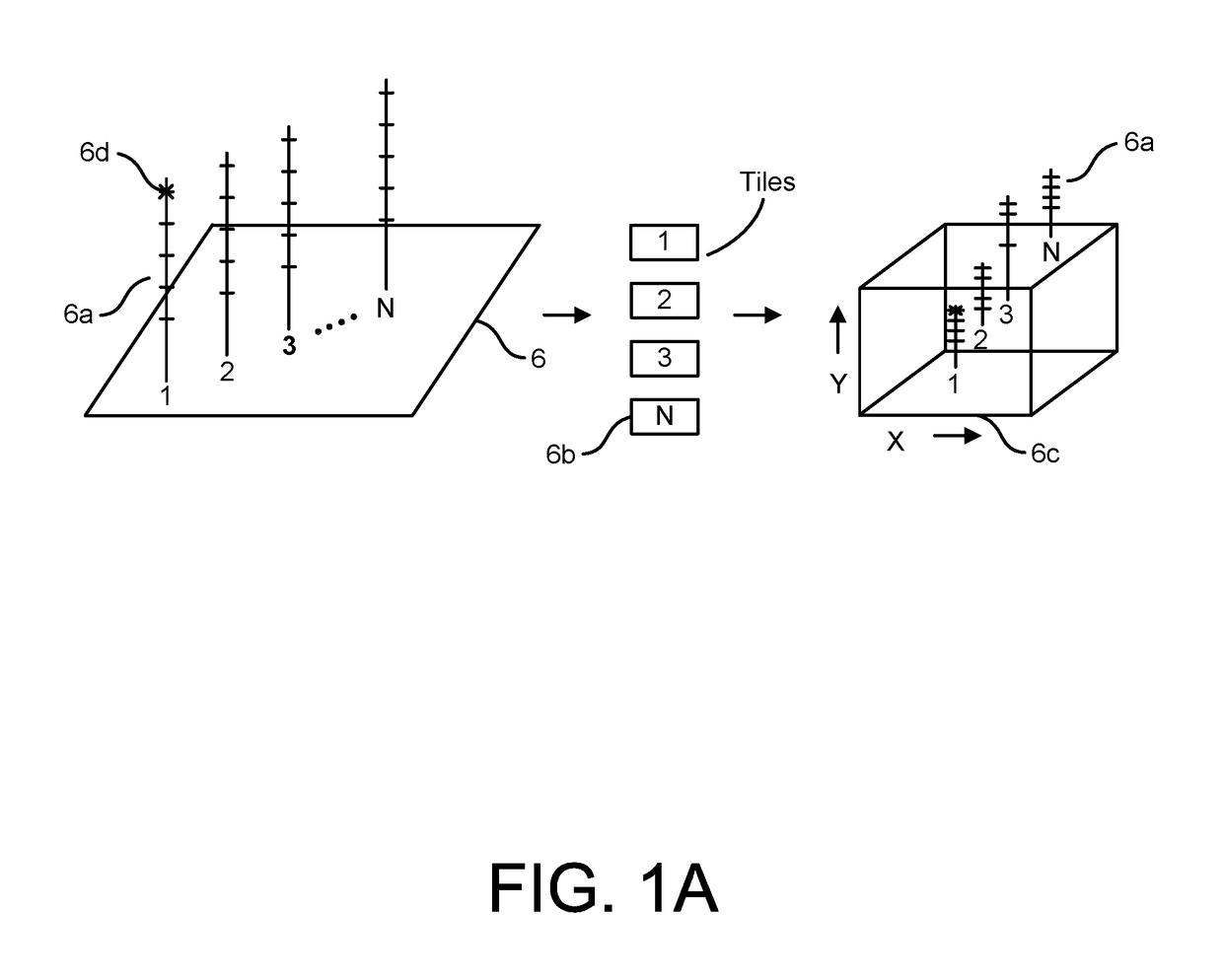
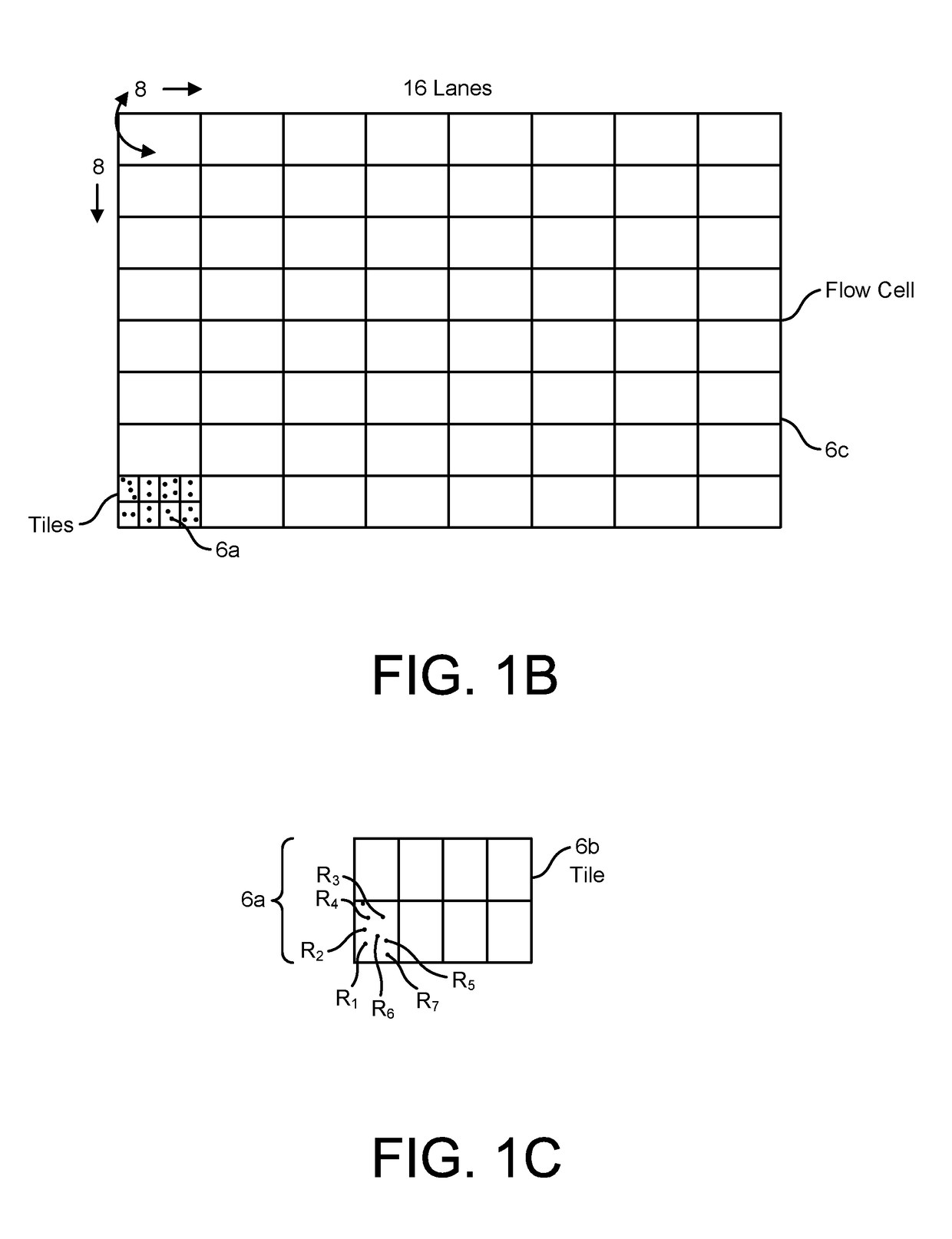
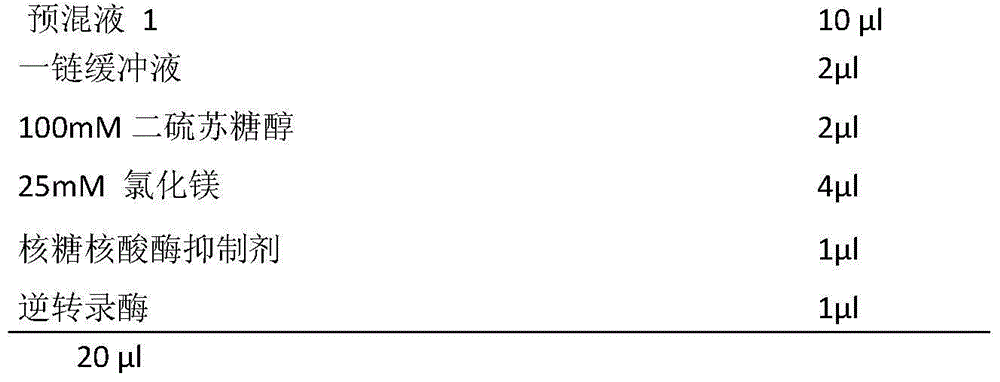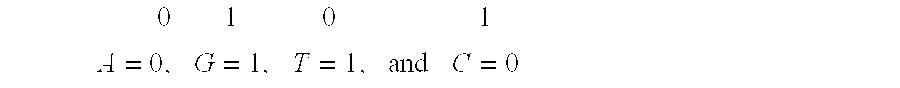Patents
Literature
1455 results about "Bio informatics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioinformatics /ˌbaɪ.oʊˌɪnfərˈmætɪks/ ( listen) is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, computer science, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data.
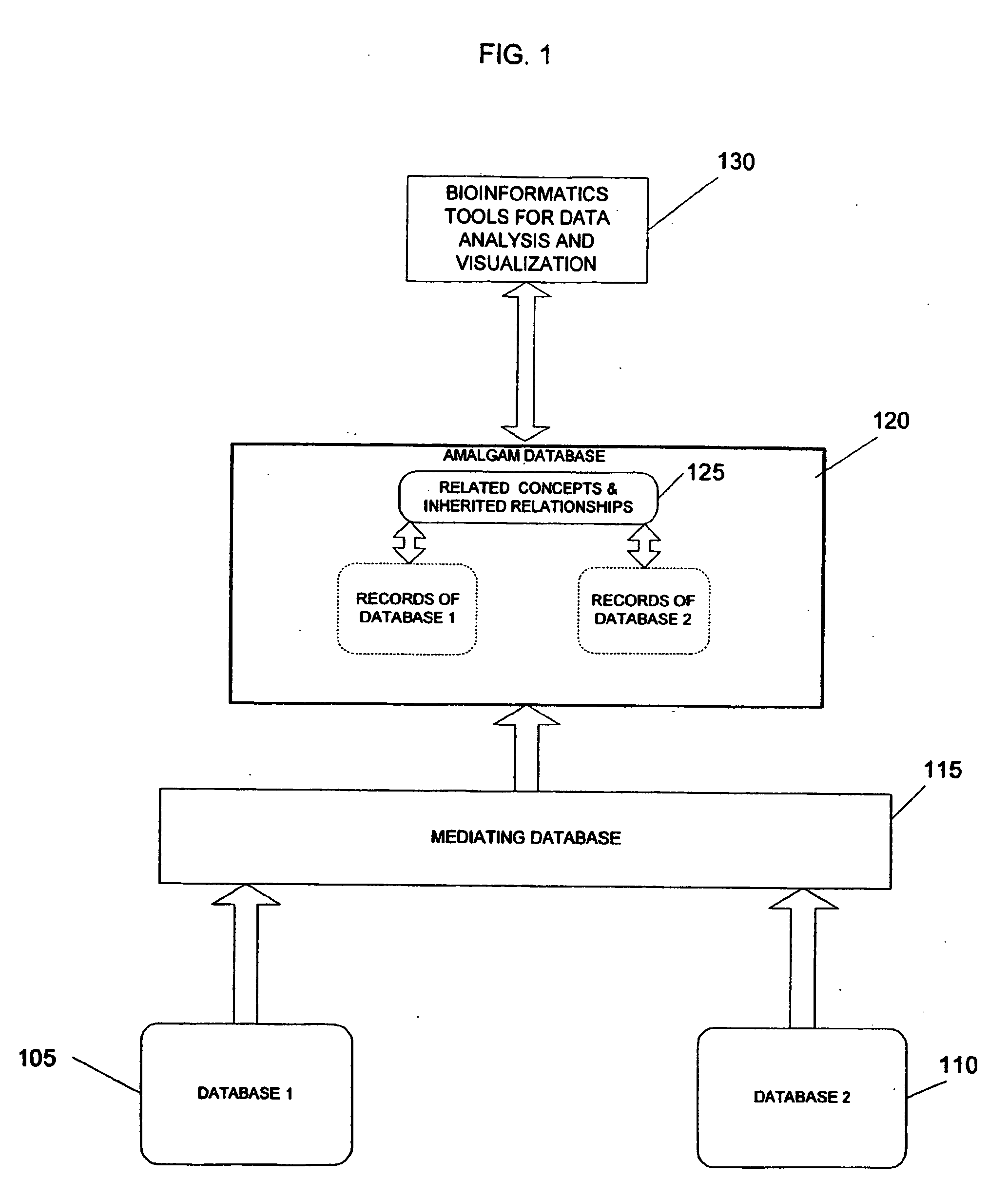
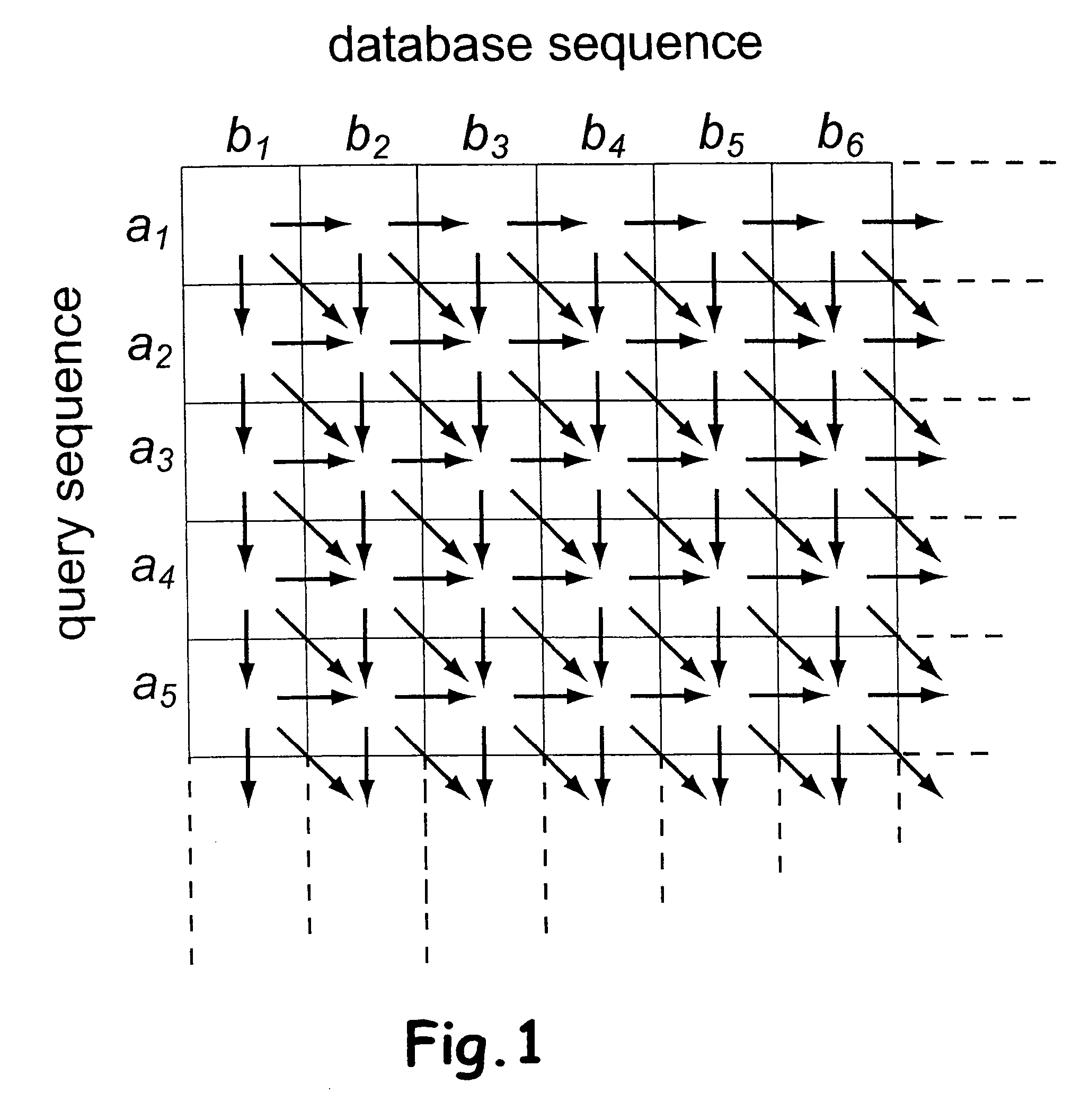
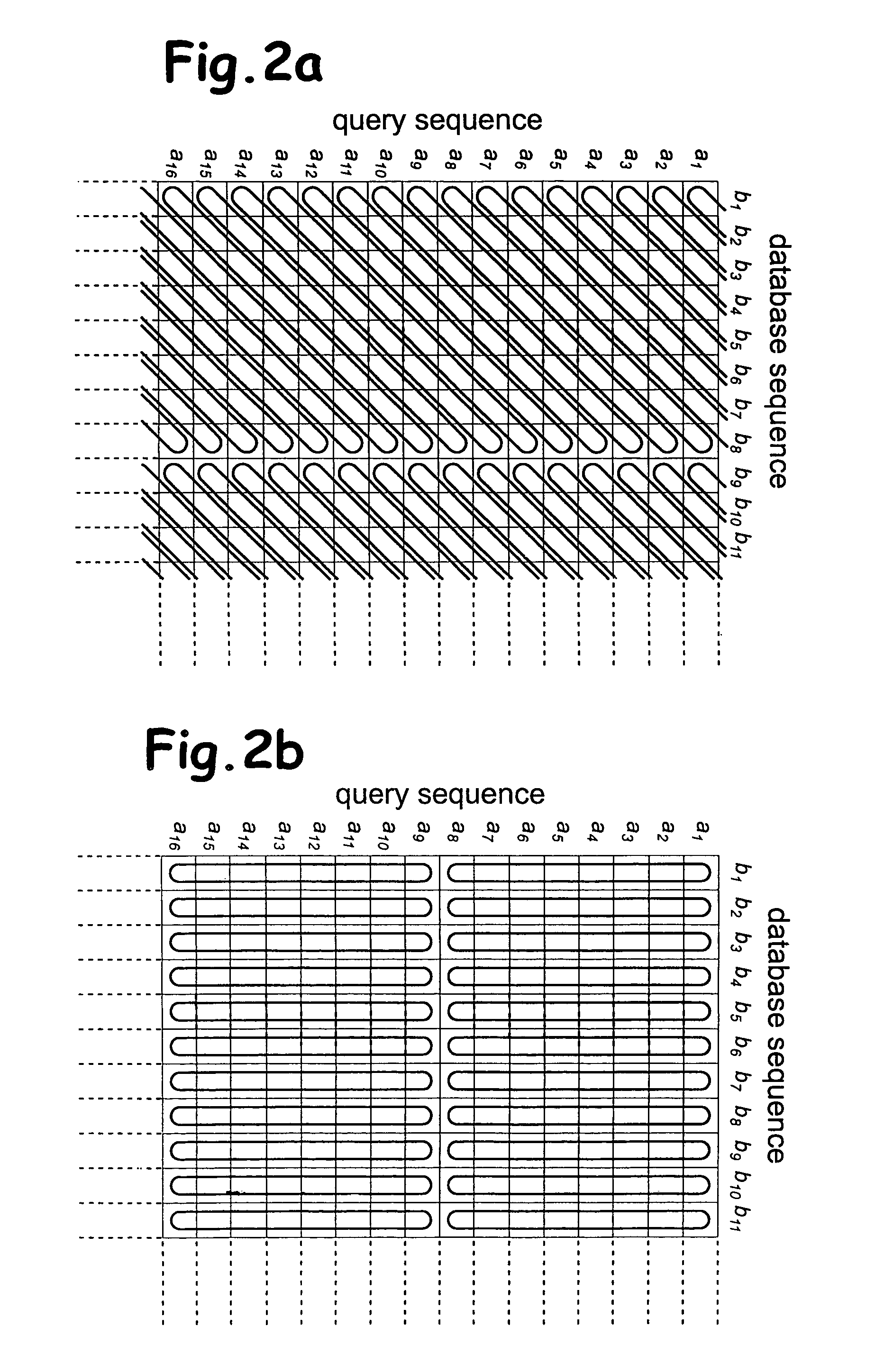
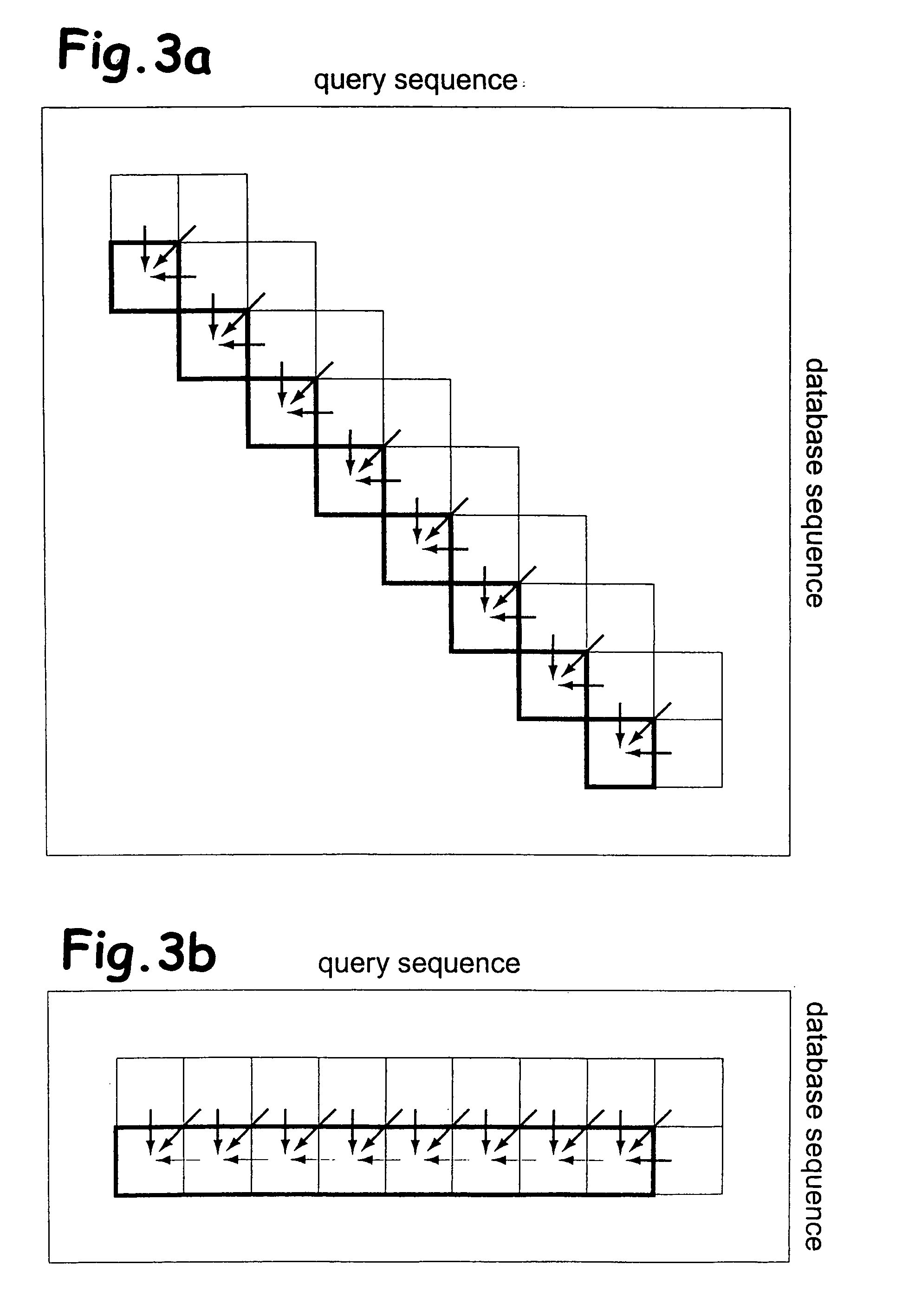
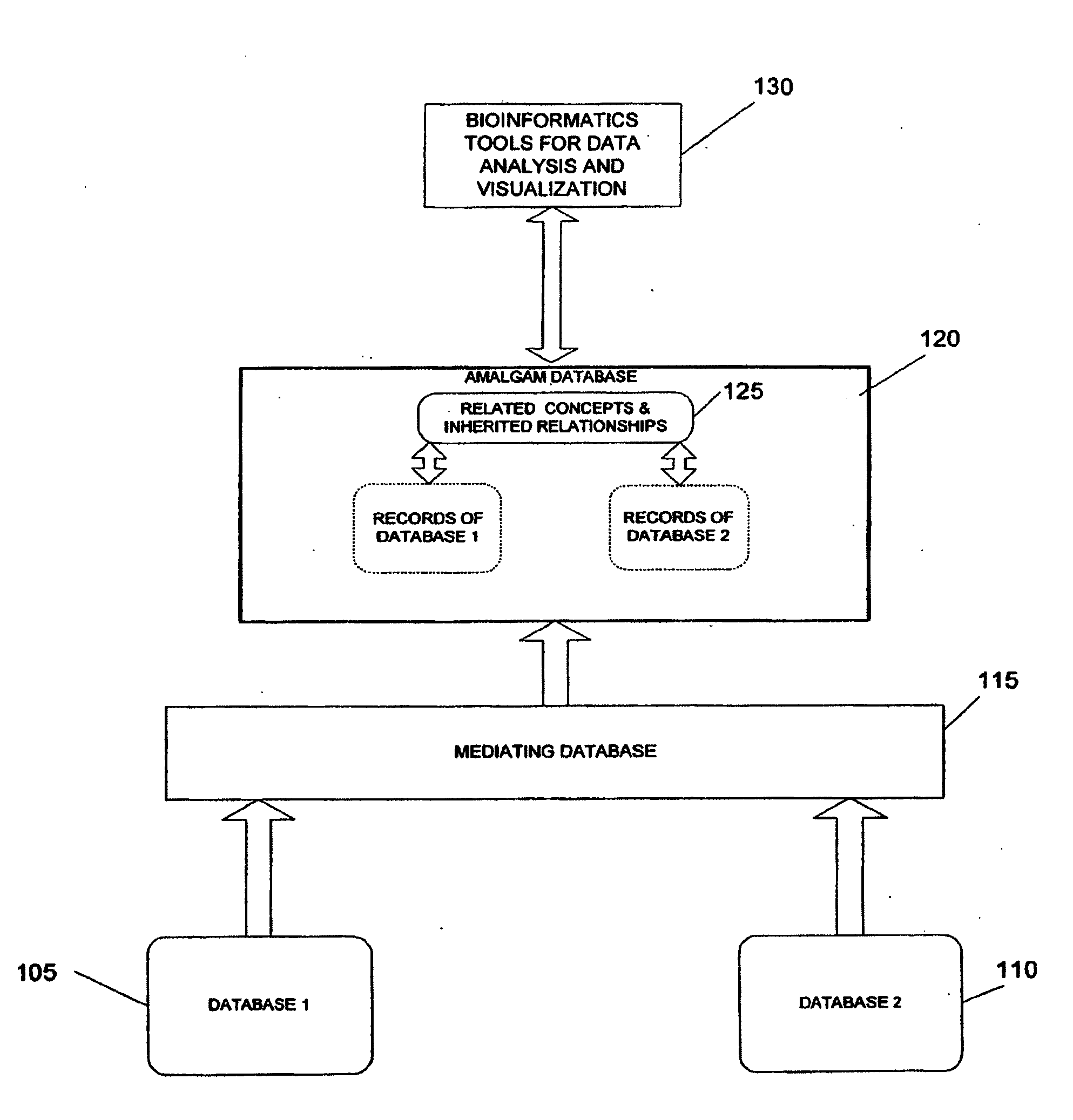
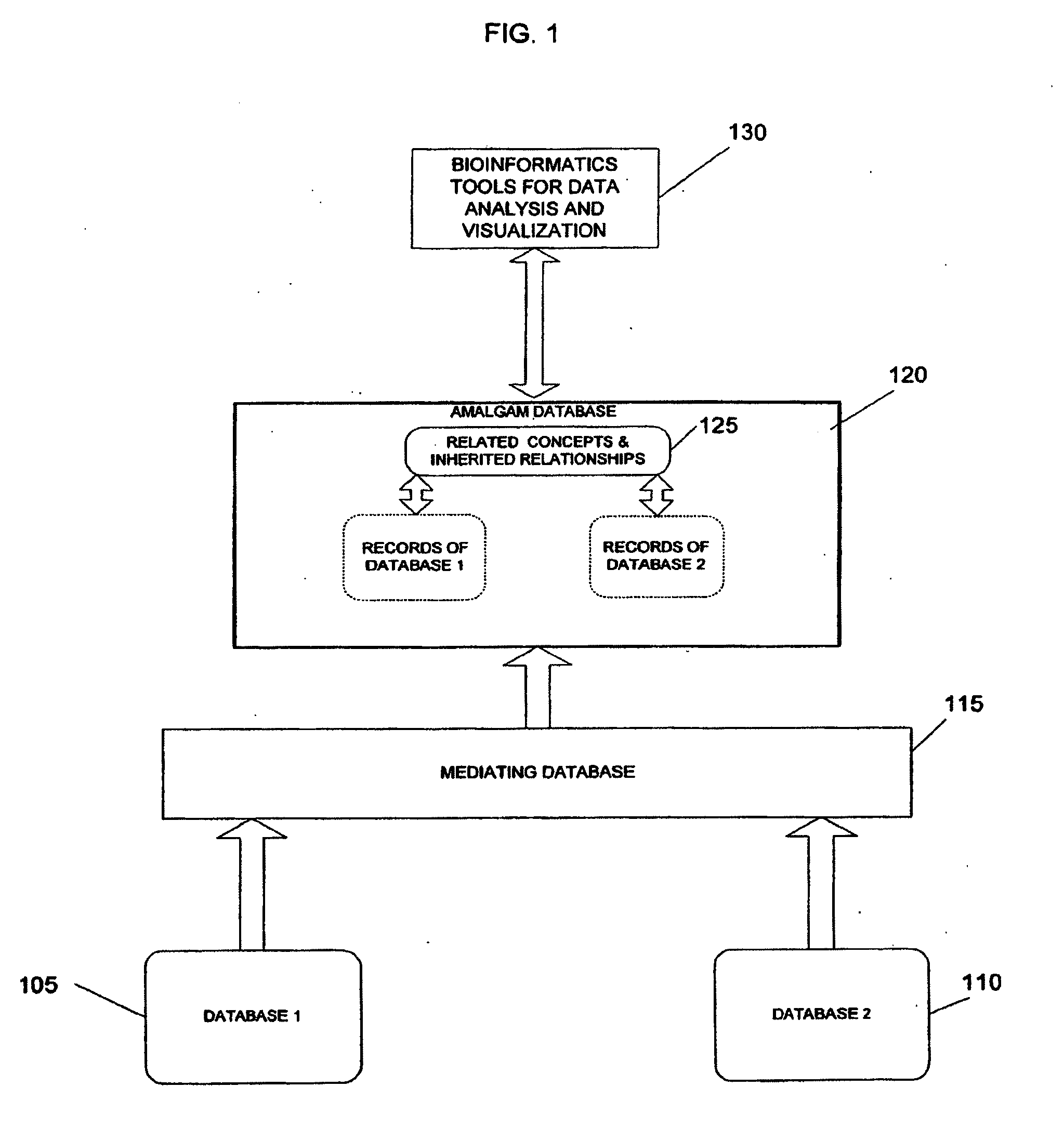
System and method for generating an amalgamated database
InactiveUS20060074991A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderInformaticsBioinformatics databases
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
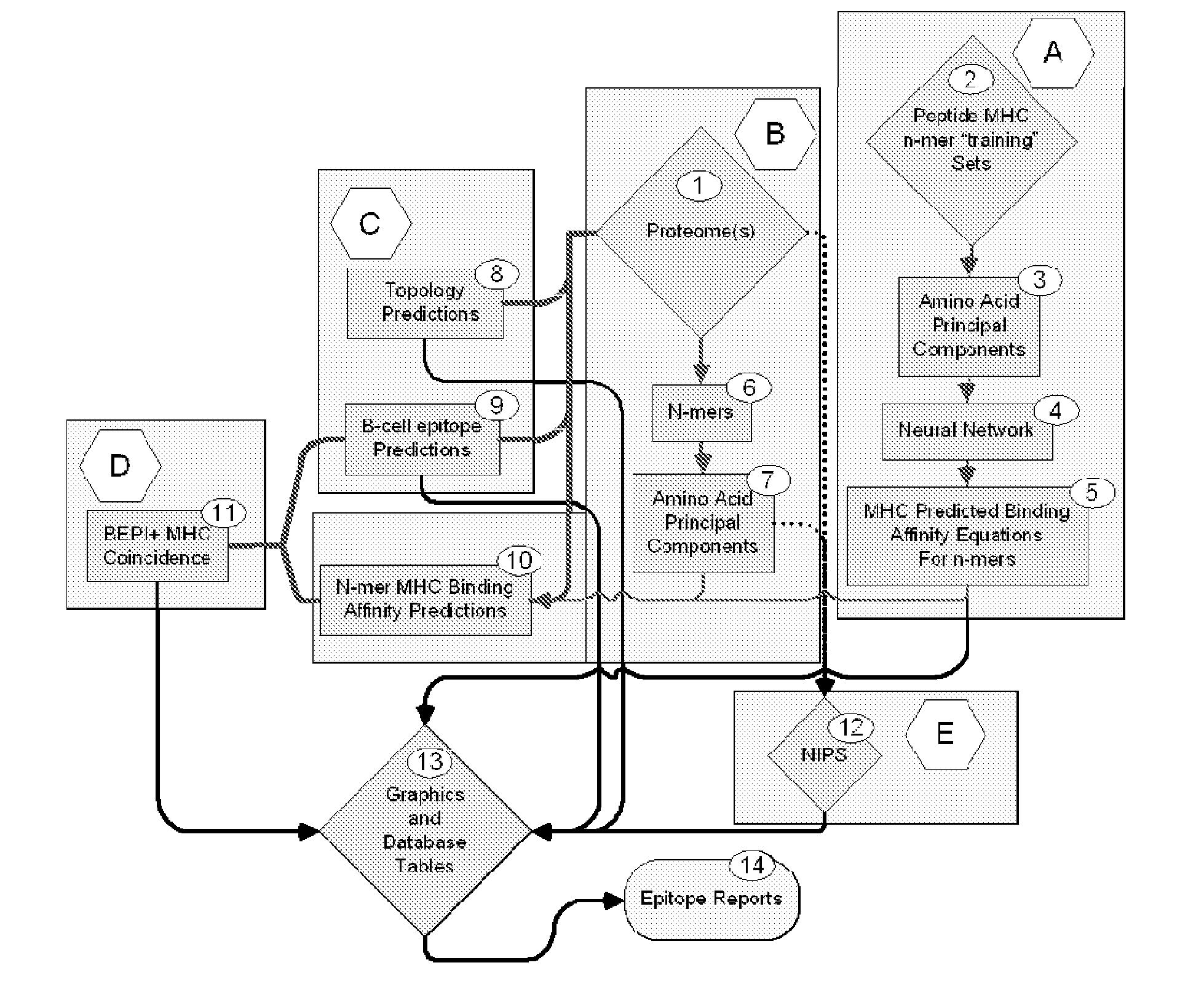
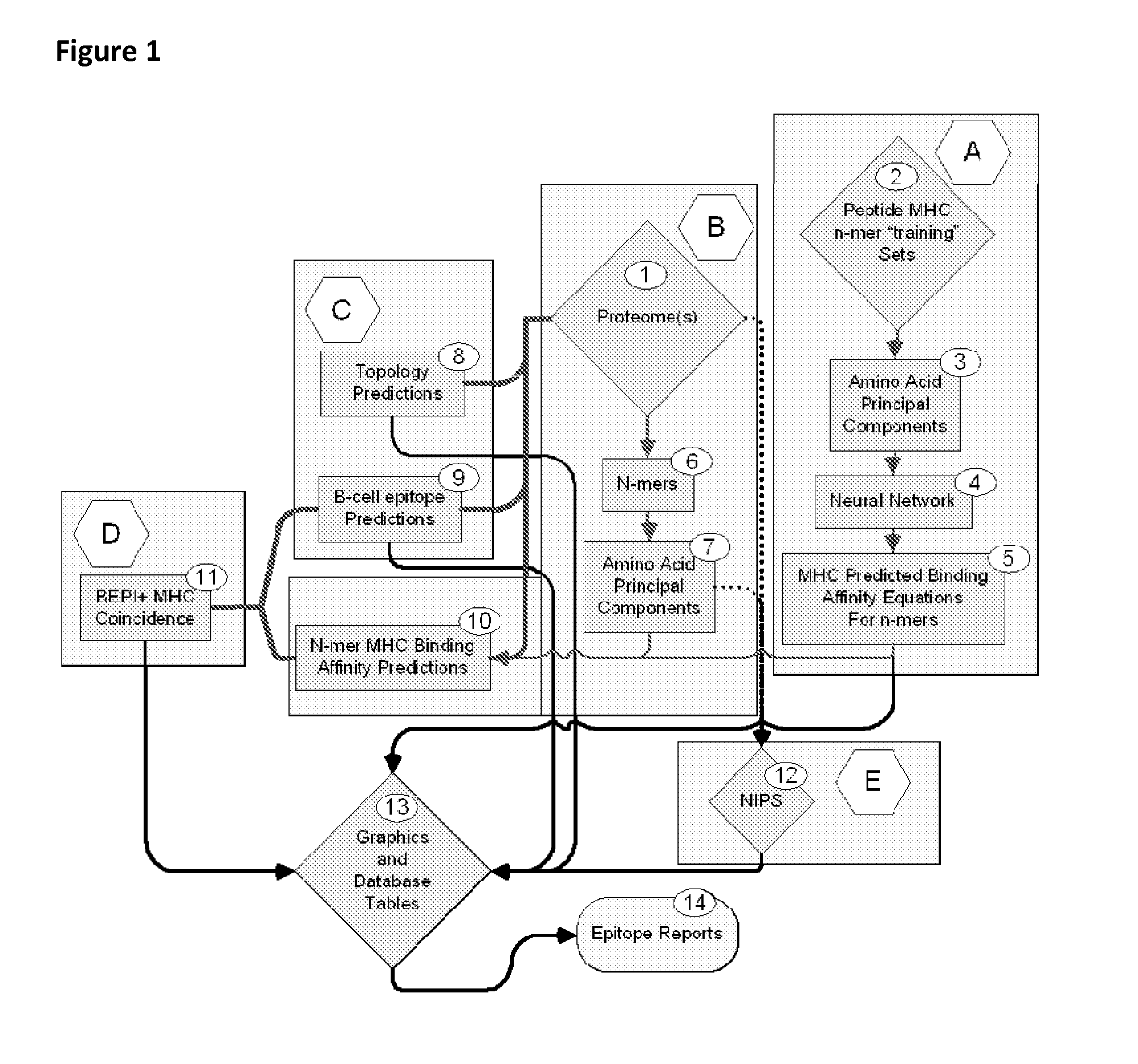
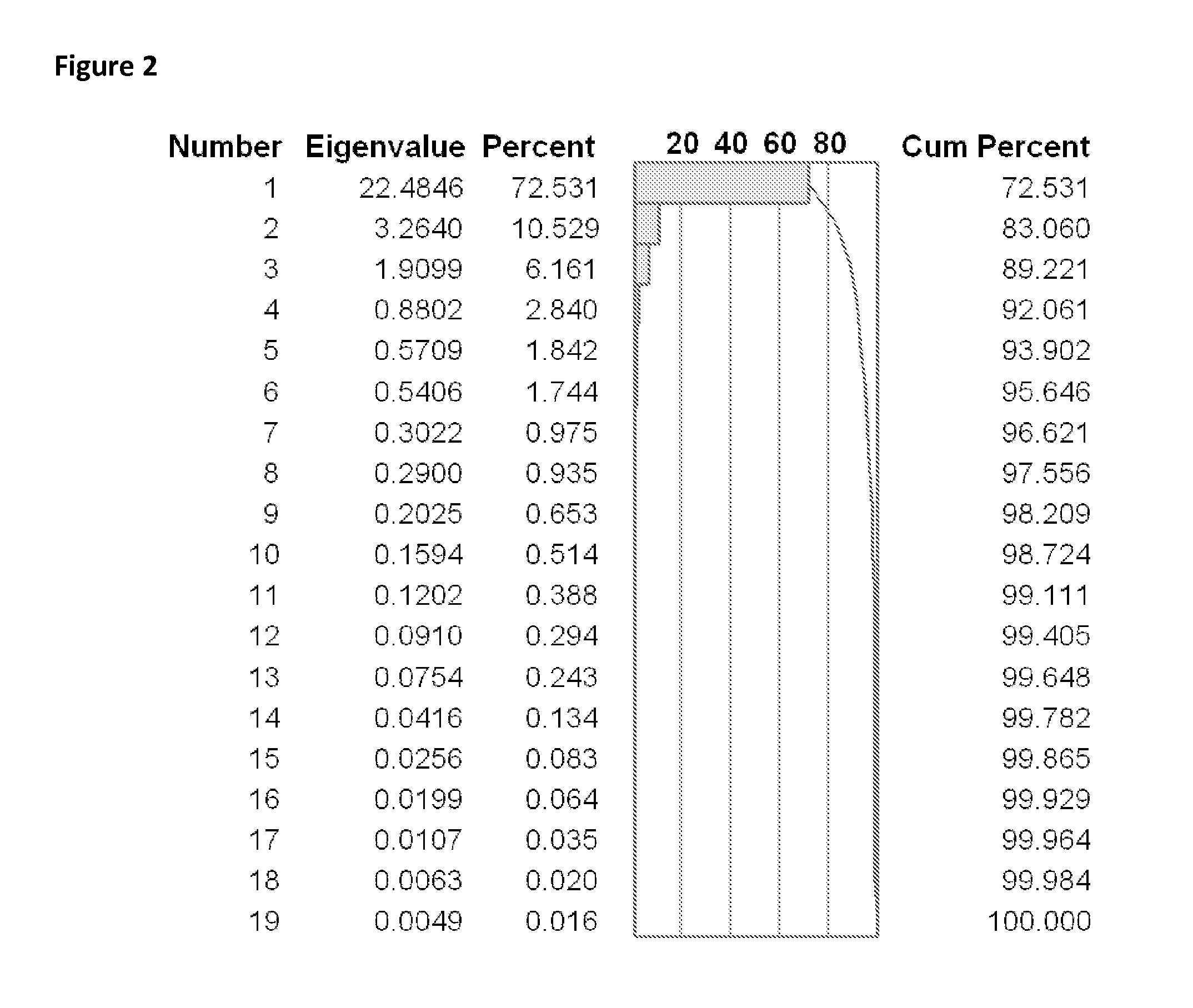
Bioinformatic processes for determination of peptide binding
ActiveUS20130330335A1Increase probabilityHigh responsePeptide/protein ingredientsBiostatisticsEpitopeMicroorganism
This invention relates to the identification of peptide binding to ligands, and in particular to identification of epitopes expressed by microorganisms and by mammalian cells. The present invention provides polypeptides comprising the epitopes, and vaccines, antibodies and diagnostic products that utilize or are developed using the epitopes.
Owner:IOGENETICS
Methods for providing bacterial bioagent characterizing information
InactiveUS7217510B2Easy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementEpidemiological alert systemsMedicineInformatics
The present invention relates generally to the field of investigational bioinformatics and more particularly to secondary structure defining databases. The present invention further relates to methods for interrogating a database as a source of molecular masses of known bioagents for comparing against the molecular mass of an unknown or selected bioagent to determine either the identity of the selected bioagent, and / or to determine the origin of the selected bioagent. The identification of the bioagent is important for determining a proper course of treatment and / or irradication of the bioagent in such cases as biological warfare. Furthermore, the determination of the geographic origin of a selected bioagent will facilitate the identification of potential criminal identity.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
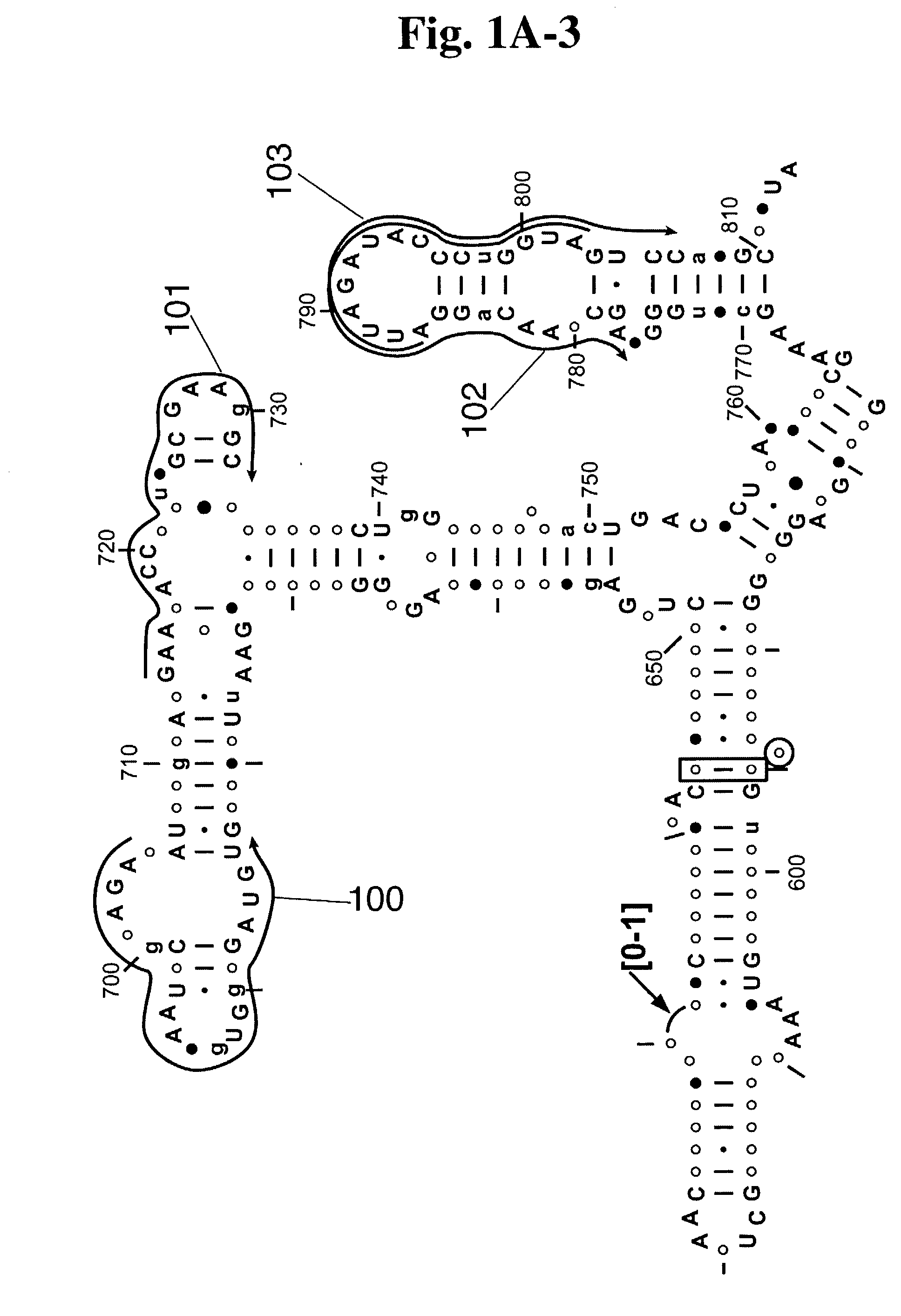
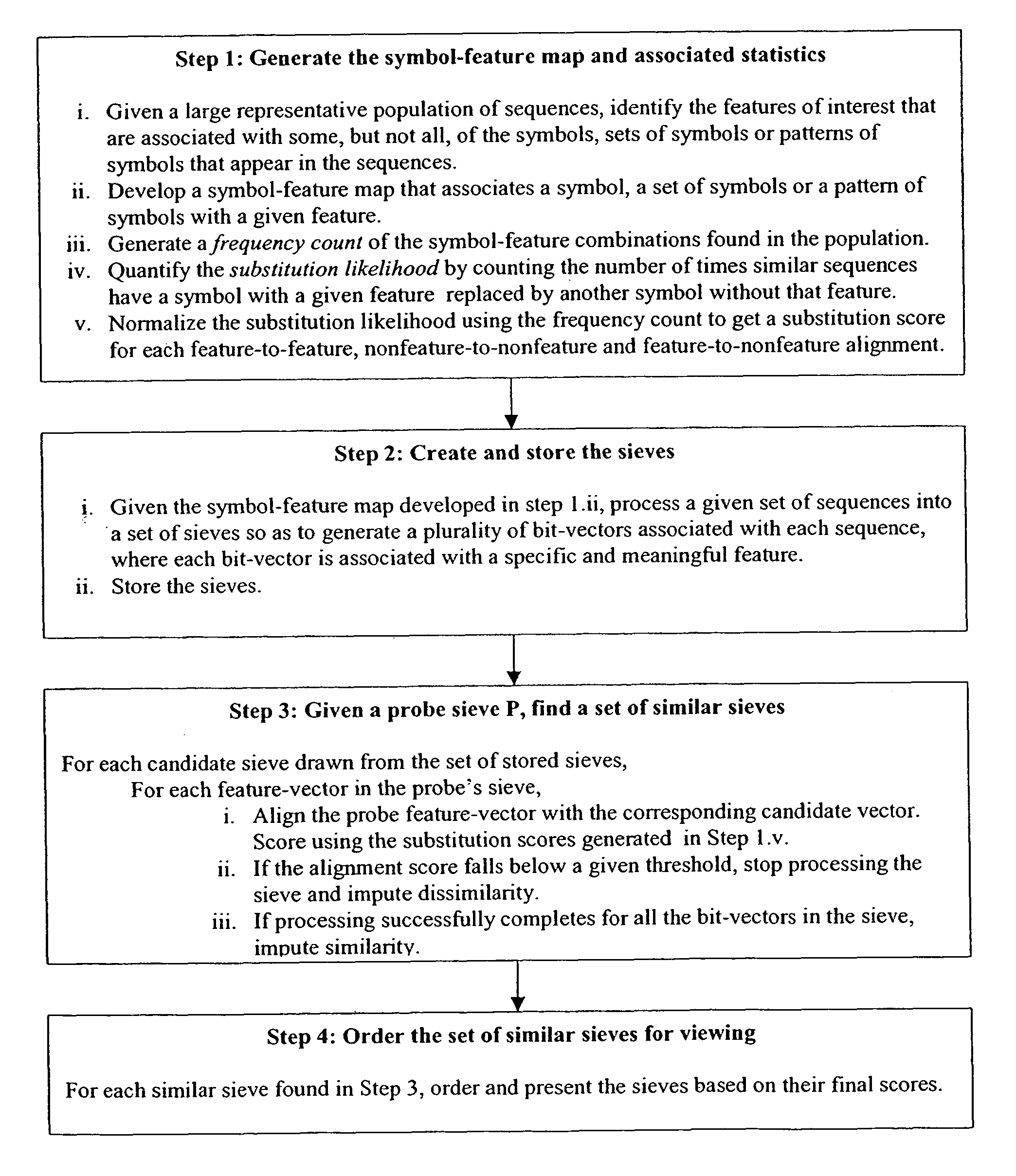
System and method for pattern recognition in sequential data
InactiveUS20050187916A1Easy to useIncrease speedSequence analysisComparison of digital valuesMedical diagnosisSequential data
The present invention is based on the encoding of sequential data or sequences in a novel manner that permits efficient storage and processing of sequential data, as well as methods for searching sequences or databases of sequences. The methods and systems of the current invention may be adapted broadly to various fields of application and to a variety of sequences types. For example, the current invention has broad application including to the fields of bioinformatics, molecular biology, pharmacogenomics, phonetic sequences, lexicographic sequences, signal analysis, game playing, law enforcement, biometrics, medical diagnosis, equipment maintenance and micro-array data analysis.
Owner:ELORET CORP
Determination of optimal local sequence alignment similarity score
InactiveUS7917302B2Low costShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyLocal sequence alignmentProtein function prediction
Sequence alignment and sequence database similarity searching are among the most important and challenging task in bio informatics, and are used for several purposes, including protein function prediction. An efficient parallelisation of the Smith-Waterman sequence alignment algorithm using parallel processing in the form of SIMD (Single-Instruction, Multiple-Data) technology is presented. The method has been implementation using the MMX (MultiMedia eXtensions) and SSE (Streaming SIMD Extensions) technology that is embedded in Intel's latest microprocessors, but the method can also be implemented using similar technology existing in other modern microprocessors. Near eight-fold speed-up relative to the fastest previously an optimised eight-way parallel processing approach achieved know non-parallel Smith-Waterman implementation on the same hardware. A speed of about 200 million cell updates per second has been obtained on a single Intel Pentium III 500 MHz microprocessor.
Owner:SEEBERG ERLING CHRISTEN +1
System And Method For Generating An Amalgamated Database
InactiveUS20090012928A1Semantic analysisUnstructured textual data retrievalInformaticsBioinformatics databases
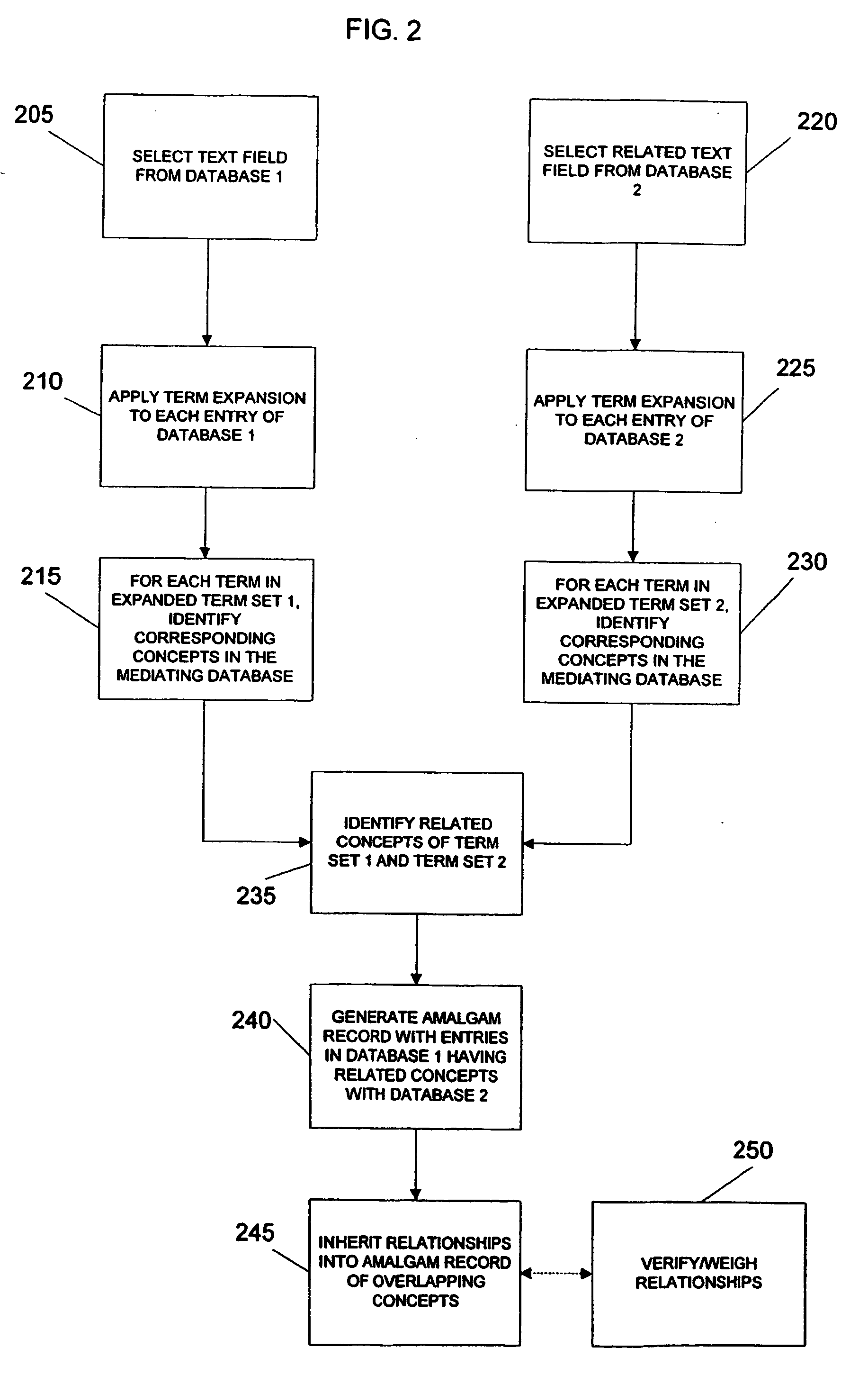
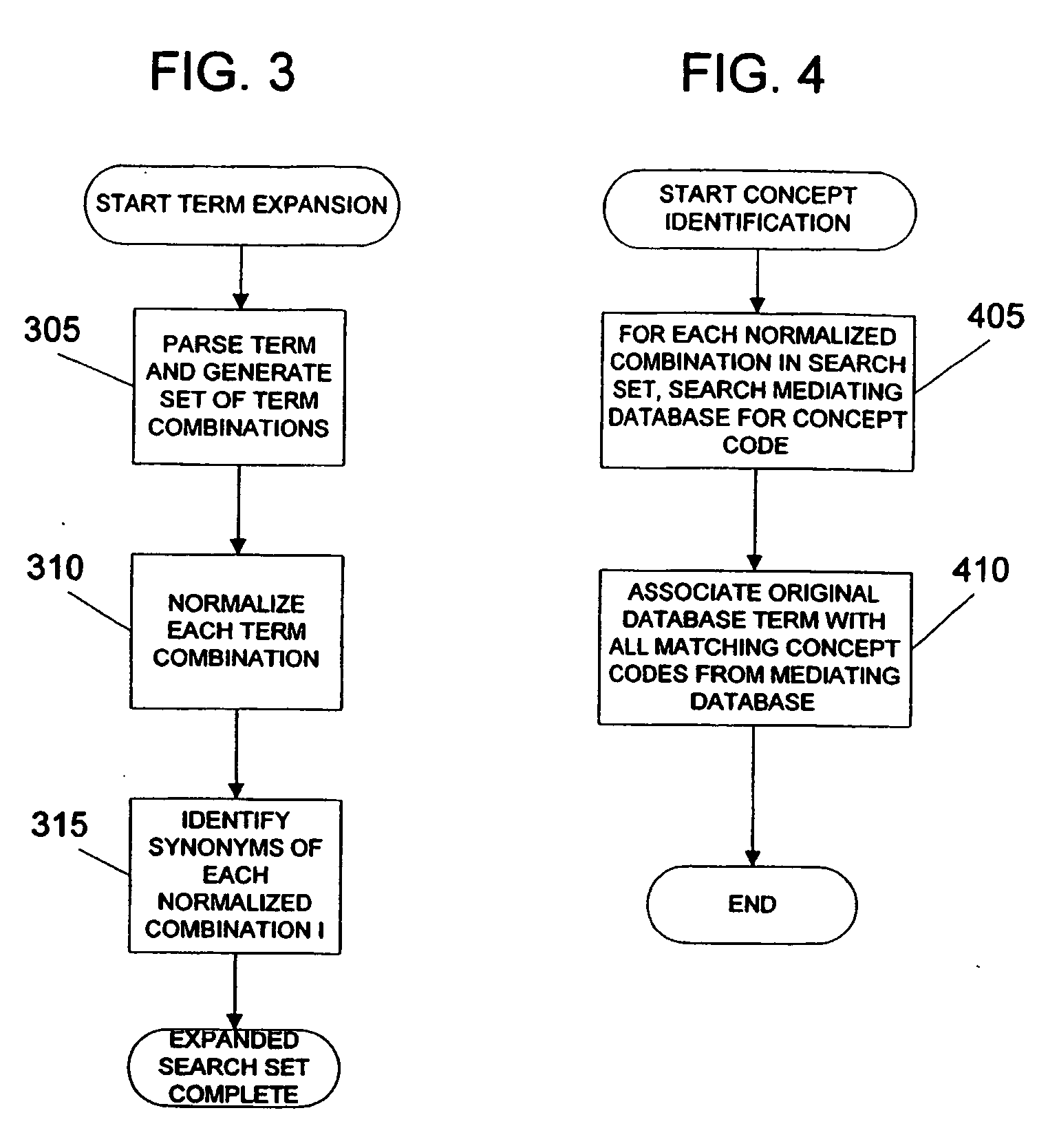
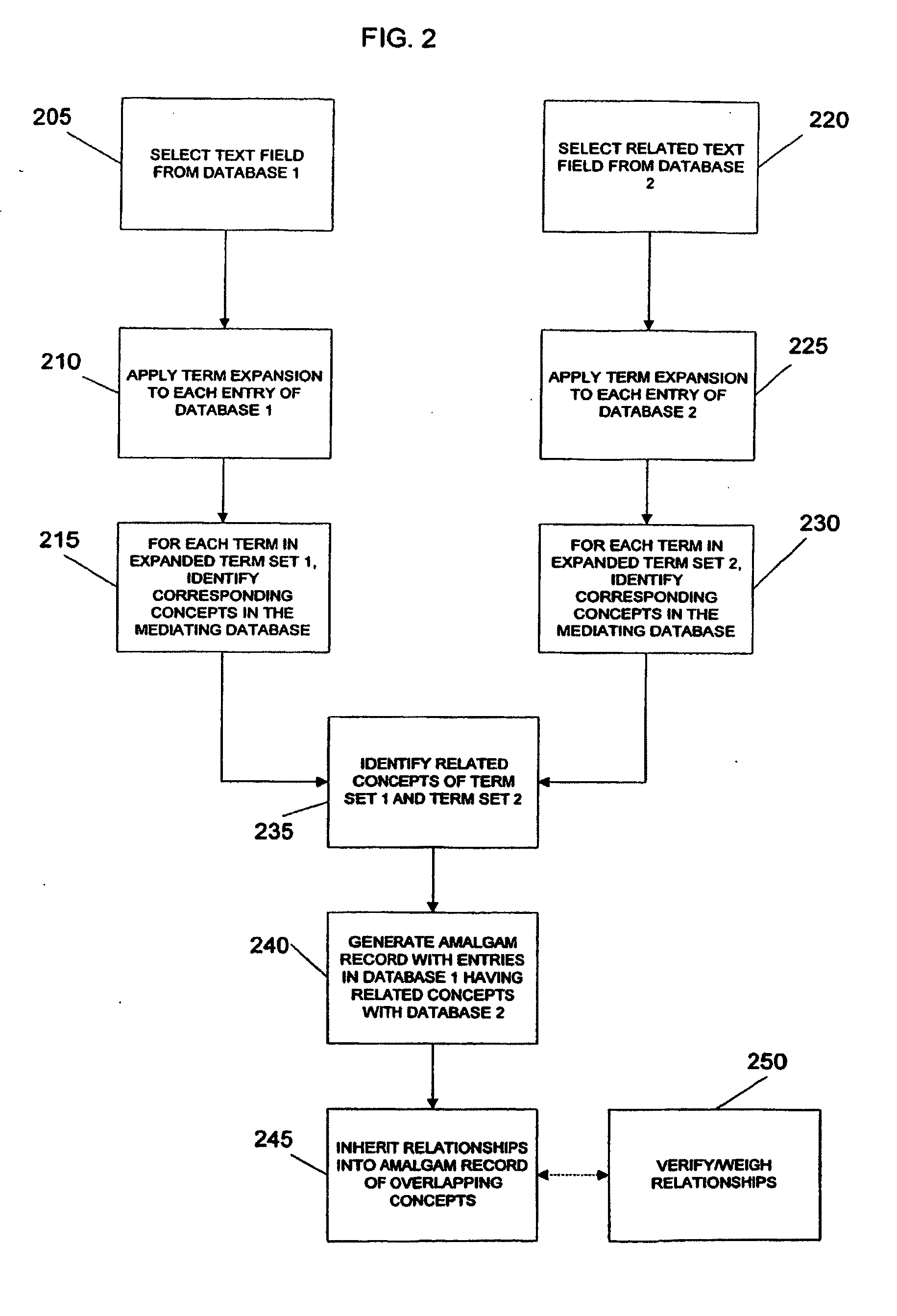
A method for creating an amalgamated bioinformatics database from at least a first database and a second database is presented. Concepts are identified in a first field from the records of the first database. A second field from the records of the second database which has data related to the first field is also identified. A first set of concepts is identified by traversing a mediating database using terms associated with the first field and a second set of concepts is also identified by traversing the mediating database using terms associated with the second field. Either the first set of concepts or the second set of concepts, or both, is identified using non-trivial terminological mapping. The set of related concepts in the first set of concepts and the second set of concepts is identified and a record is generated in the amalgamated bioinformatics database.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
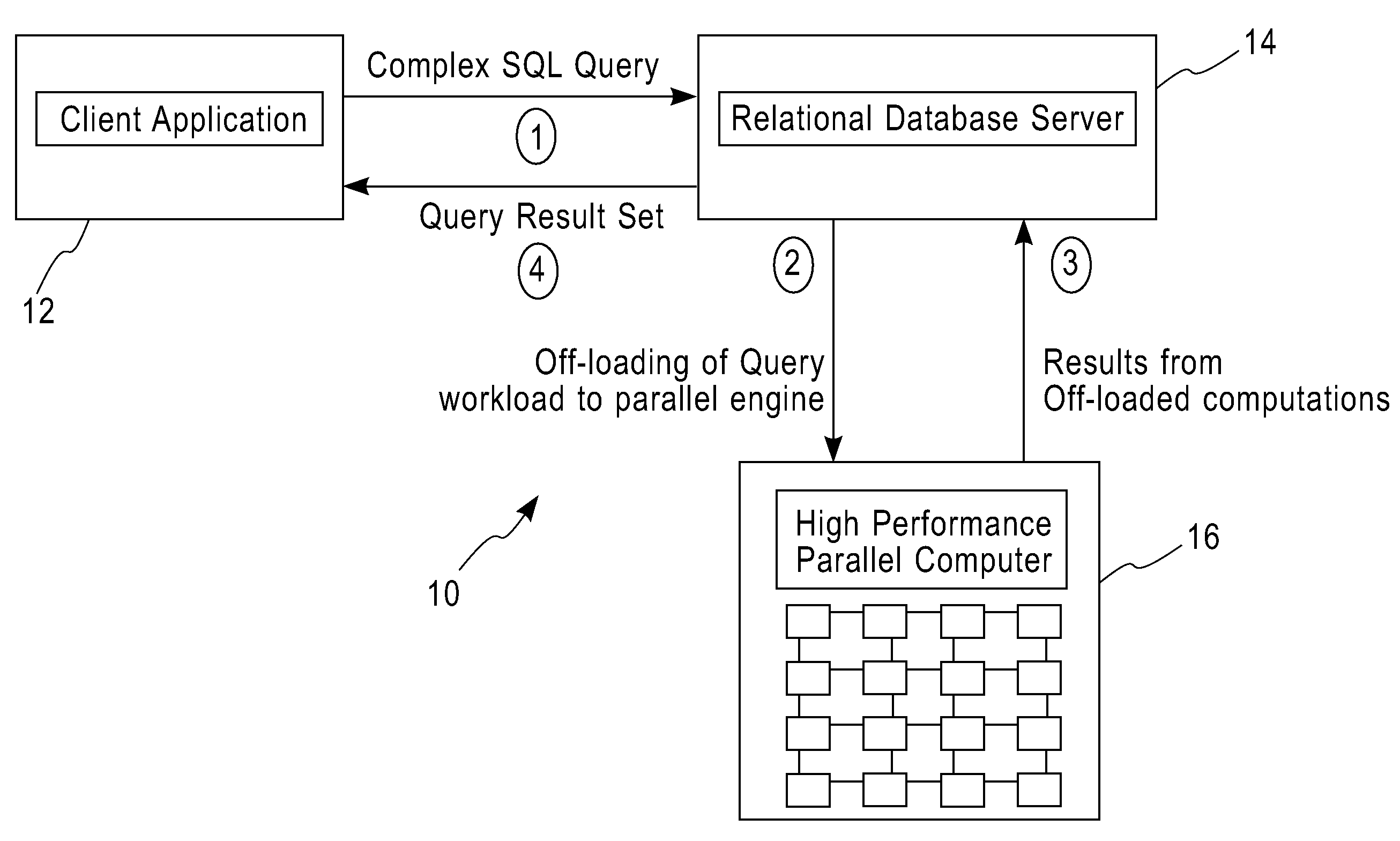
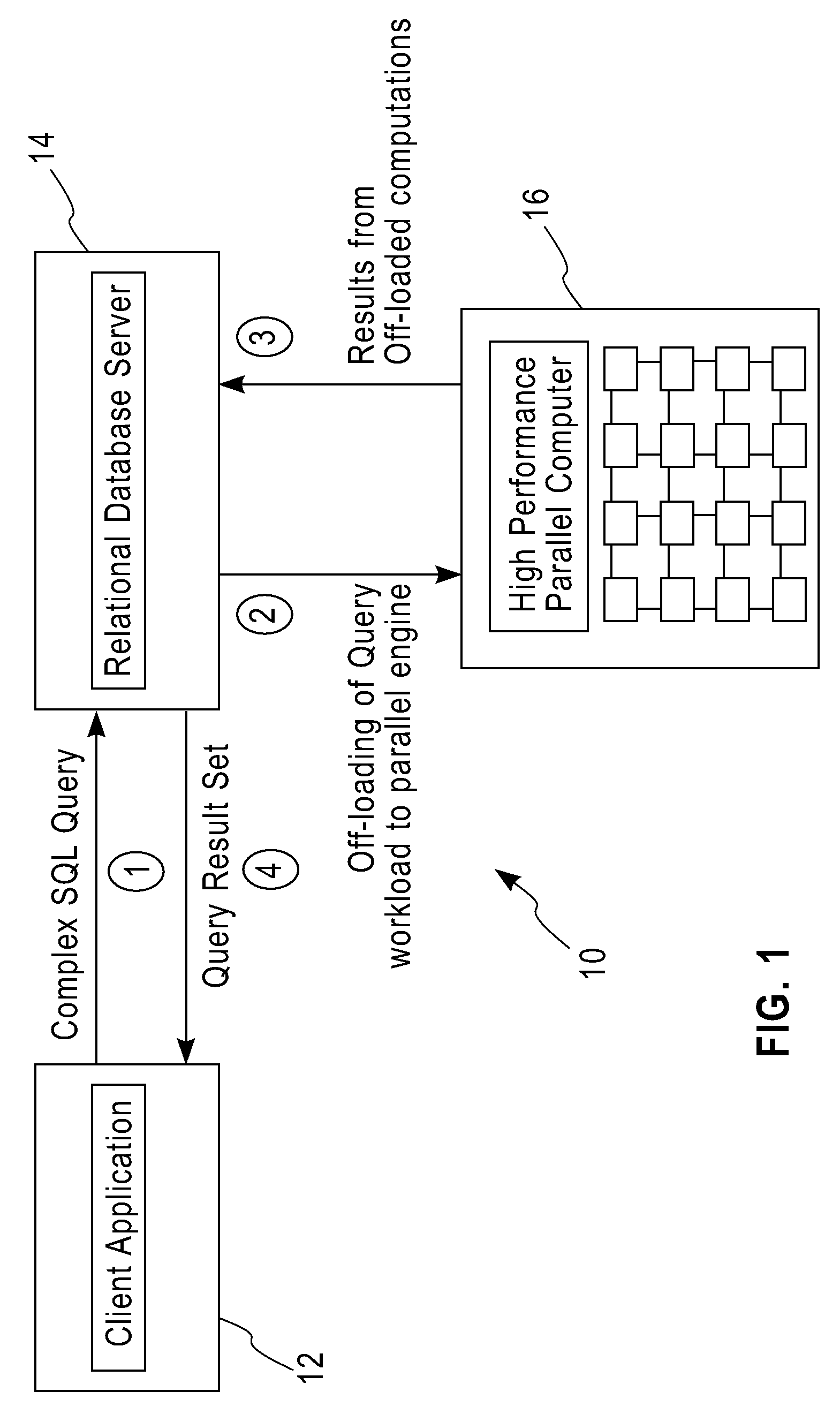
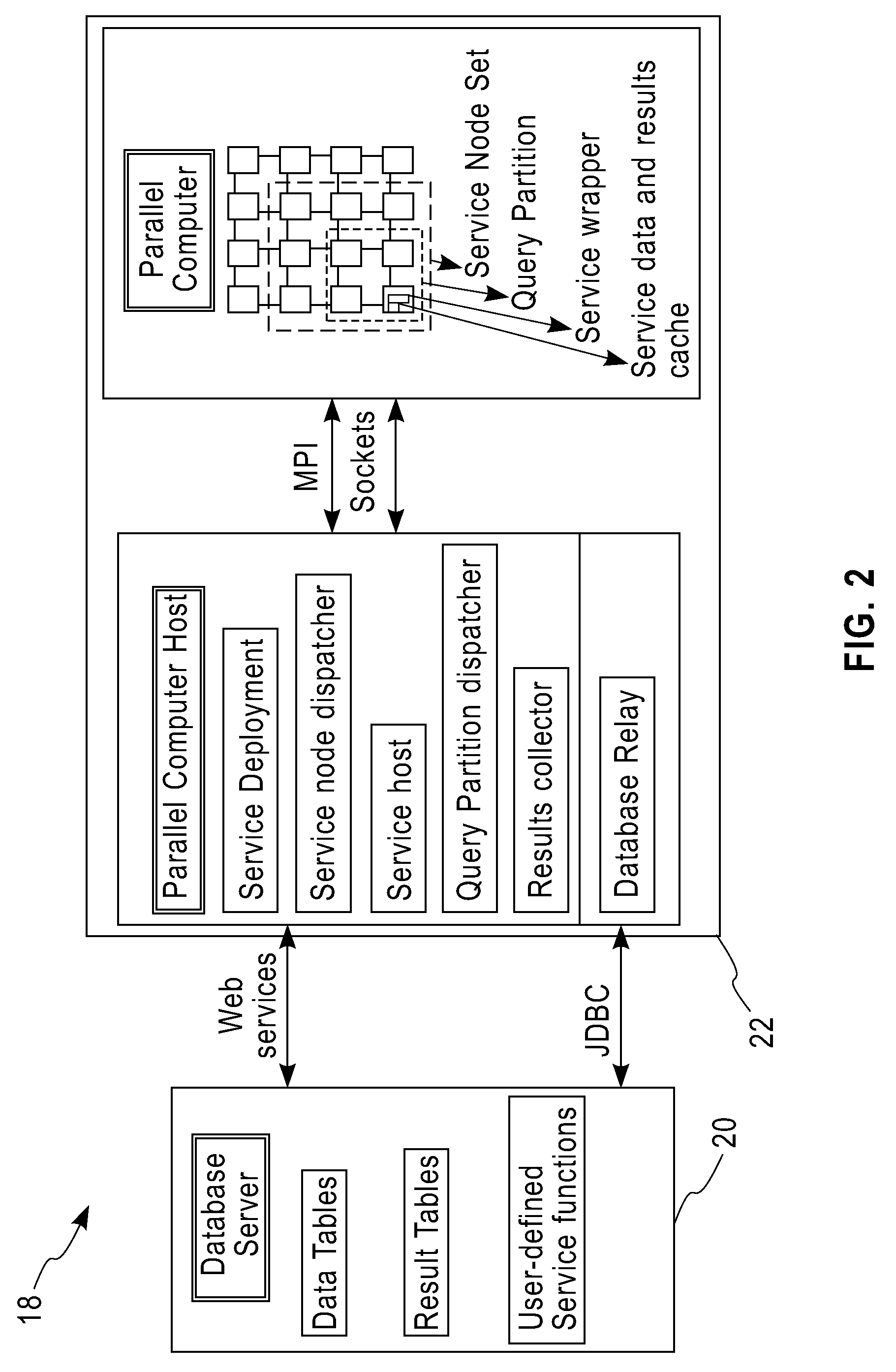
System and method for executing compute-intensive database user-defined programs on an attached high-performance parallel computer
InactiveUS20090077011A1Improve query performanceEasy to guaranteeDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDatabase queryData set
The invention pertains to a system and method for dispatching and executing the compute-intensive parts of the workflow for database queries on an attached high-performance, parallel computing platform. The performance overhead for moving the required data and results between the database platform and the high-performance computing platform where the workload is executed is amortized in several ways, for example,by exploiting the fine-grained parallelism and superior hardware performance on the parallel computing platform for speeding up compute-intensive calculations,by using in-memory data structures on the parallel computing platform to cache data sets between a sequence of time-lagged queries on the same data, so that these queries can be processed without further data transfer overheads,by replicating data within the parallel computing platform so that multiple independent queries on the same target data set can be simultaneously processed using independent parallel partitions of the high-performance computing platform.A specific embodiment of this invention was used for deploying a bio-informatics application involving gene and protein sequence matching using the Smith-Waterman algorithm on a database system connected via an Ethernet local area network to a parallel supercomputer.
Owner:IBM CORP
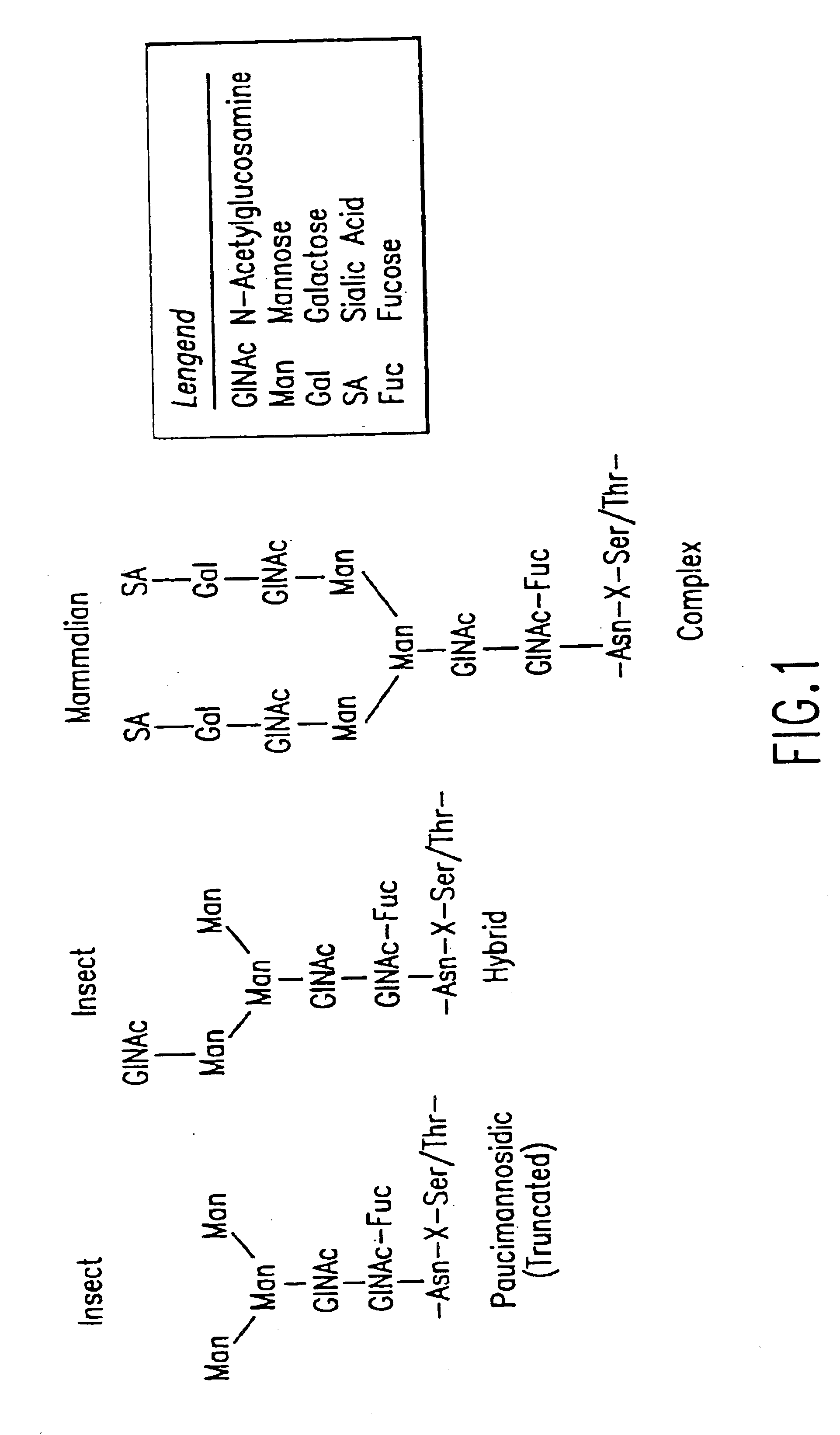
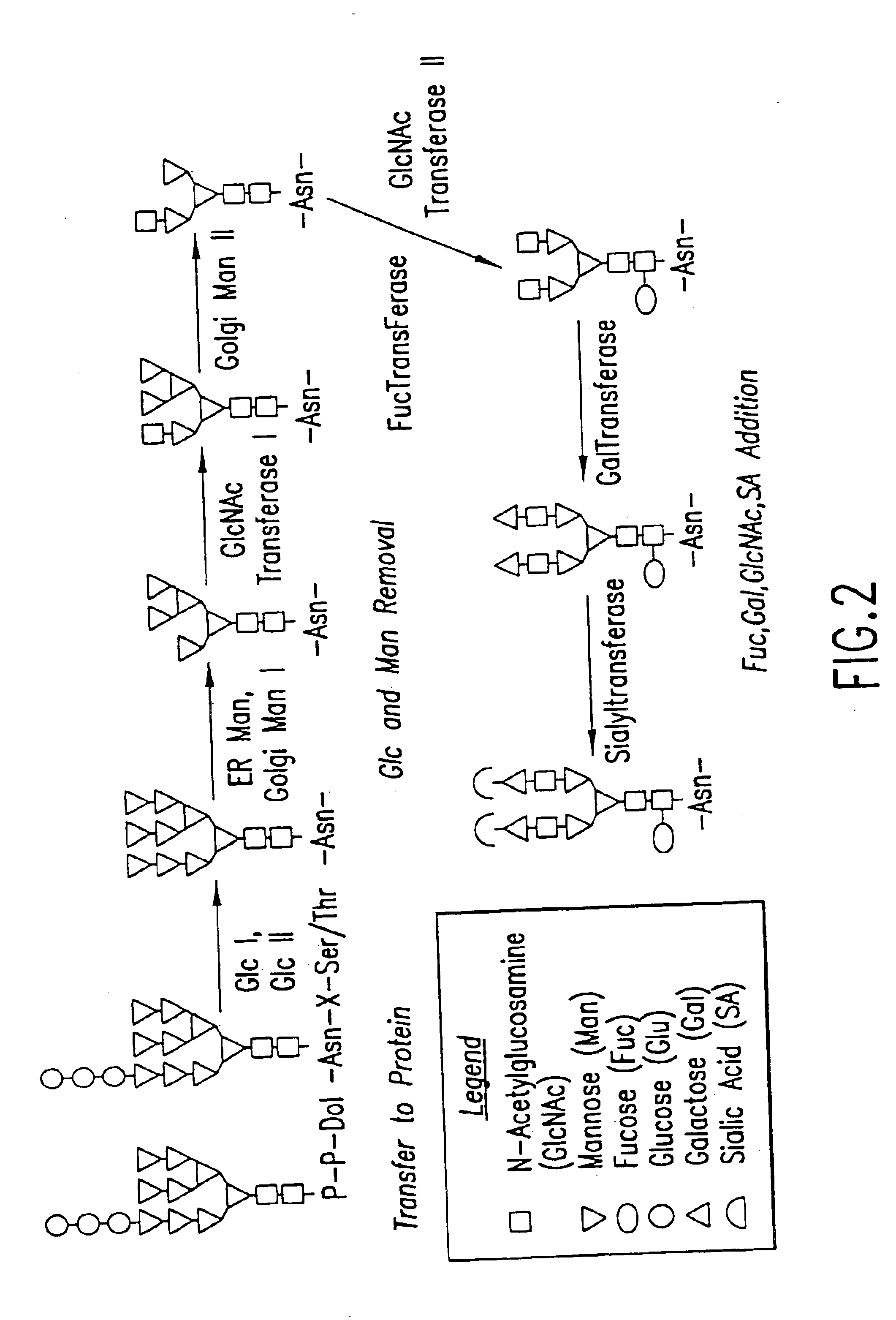
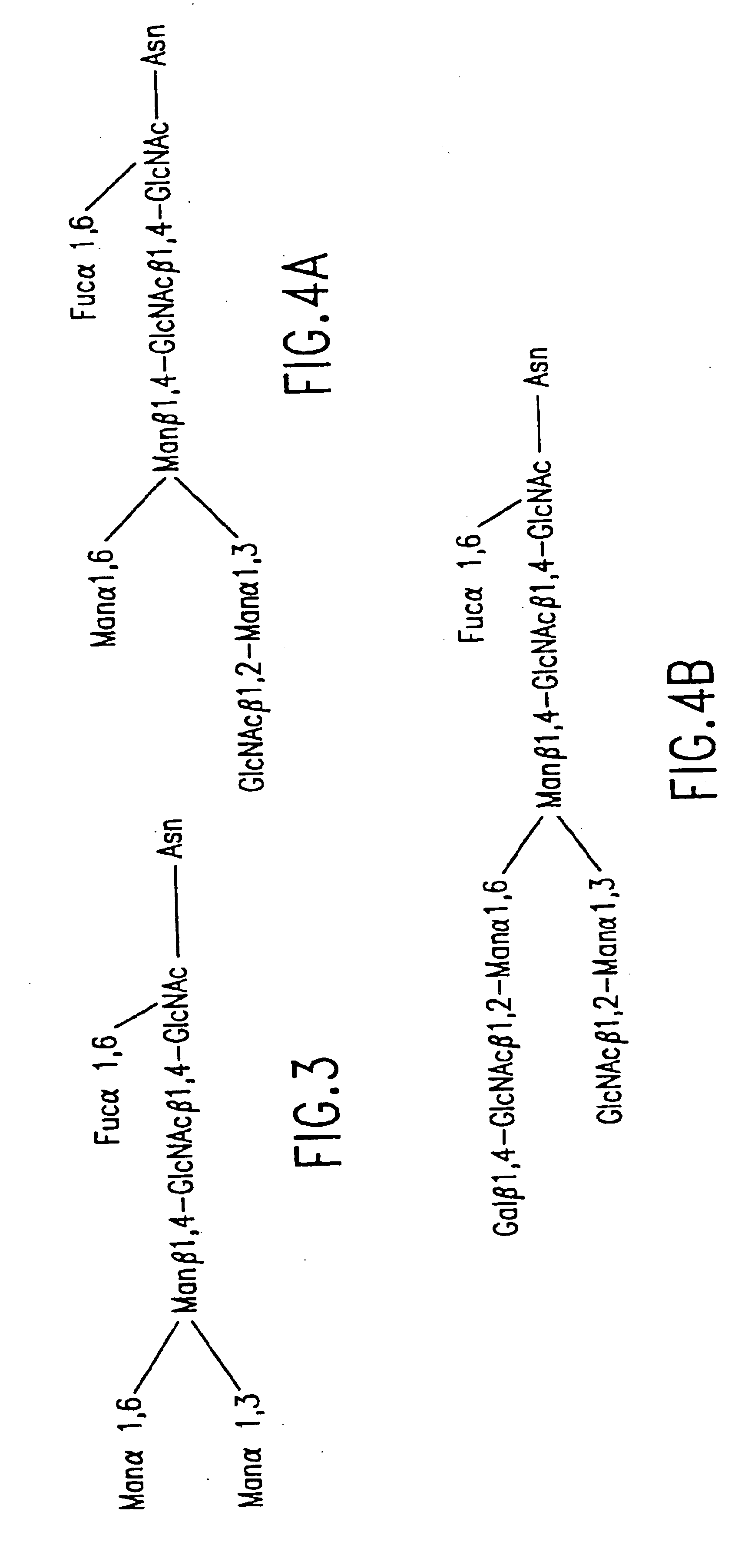
Engineering intracellular sialylation pathways
Methods for manipulating carbohydrate processing pathways in cells of interest are provided. Methods are directed at manipulating multiple pathways involved with the sialylation reaction by using recombinant DNA technology and substrate feeding approaches to enable the production of sialylated glycoproteins in cells of interest. These carbohydrate engineering efforts encompass the implementation of new carbohydrate bioassays, the examination of a selection of insect cell lines and the use of bioinformatics to identify gene sequences for critical processing enzymes. The compositions comprise cells of interest producing sialylated glycoproteins. The methods and compositions are useful for heterologous expression of glycoproteins.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC +1
Response element
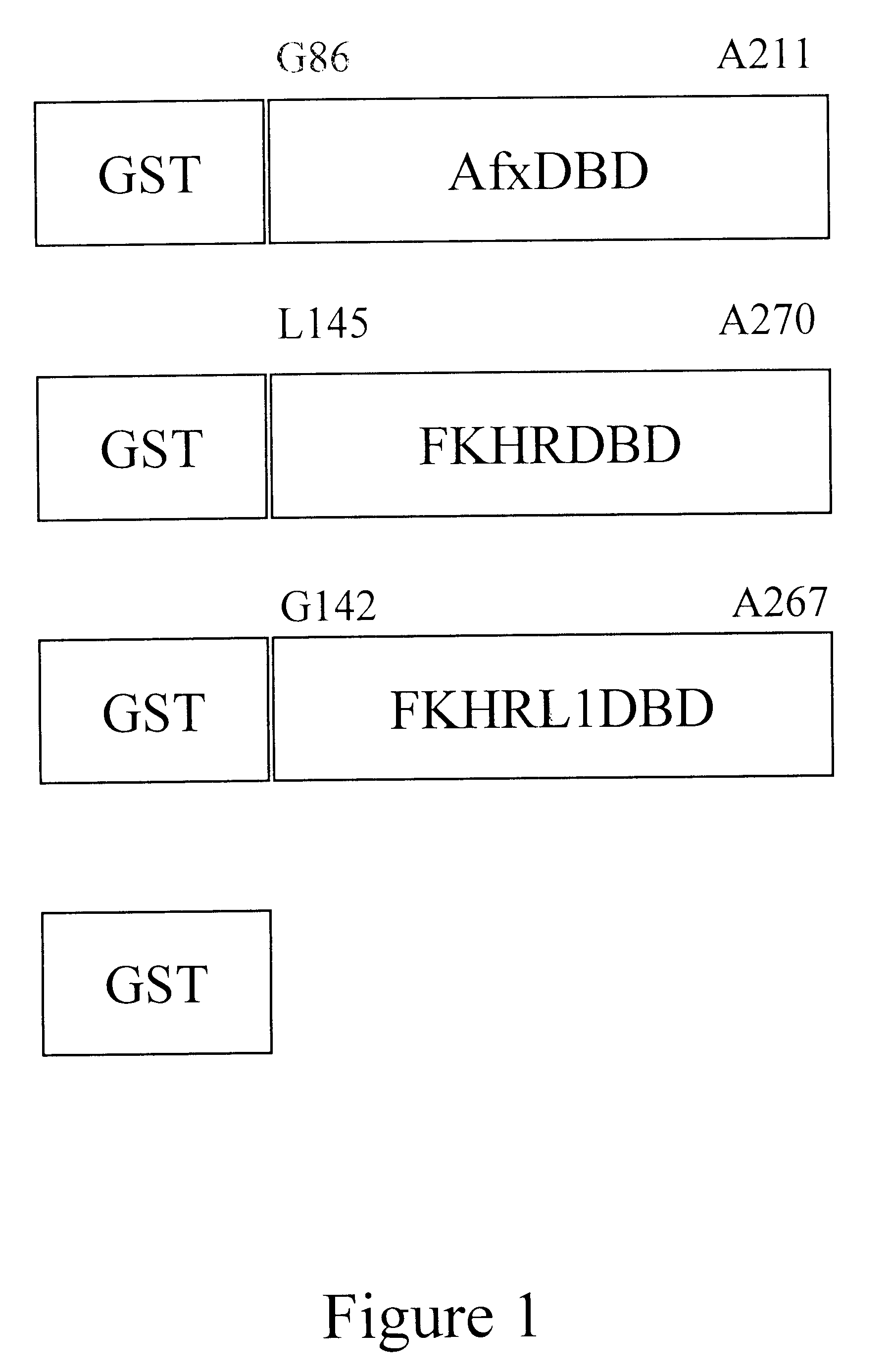
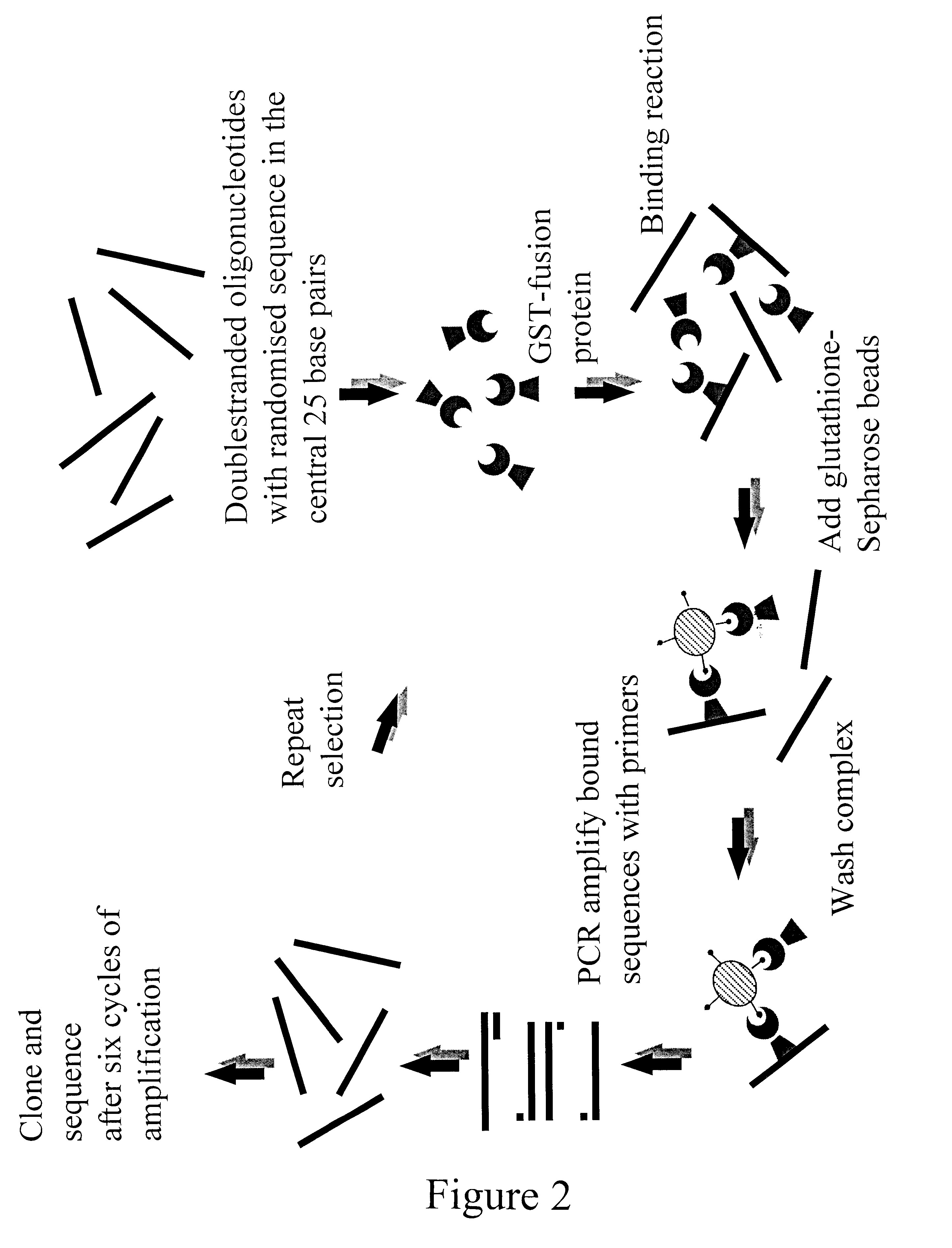
The present invention is directed to a novel Afx response element comprising the nucleotide sequence AACATGTT, said nucleotide sequence having a DNA binding site for the human fork head transkription factor Afx. The invention also relates to the use of the Afx response element in the screening for genes as diabetes drug targets and in the bioinformatic analysis of the human genome, said genes in turn being useful in other screening methods for compounds modifying the insulin receptor signaling pathway. A further aspect of the invention is a vector construct comprising the novel nucleotide sequence, a host cell transformed with said vector construct as well as the fusion protein expressed by said host cell.
Owner:BIOVITRUM AB (PUBL) +1
System, method, and computer program product for extraction, gathering, manipulation, and analysis of peak data from an automated sequencer
InactiveUS20060085139A1High throughput analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologySystems approachesComputer science
The present invention relates to a novel computer program product to extract and gather peak information from an automated sequencer or bioinformatics tool into a peak database, and to manipulate and analyze the peak information within the database.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Time to event data analysis method and system
InactiveUS20120066163A1Increases difference and “ contrast ”Improve efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsParticle separator tubesAnalysis dataTraining phase
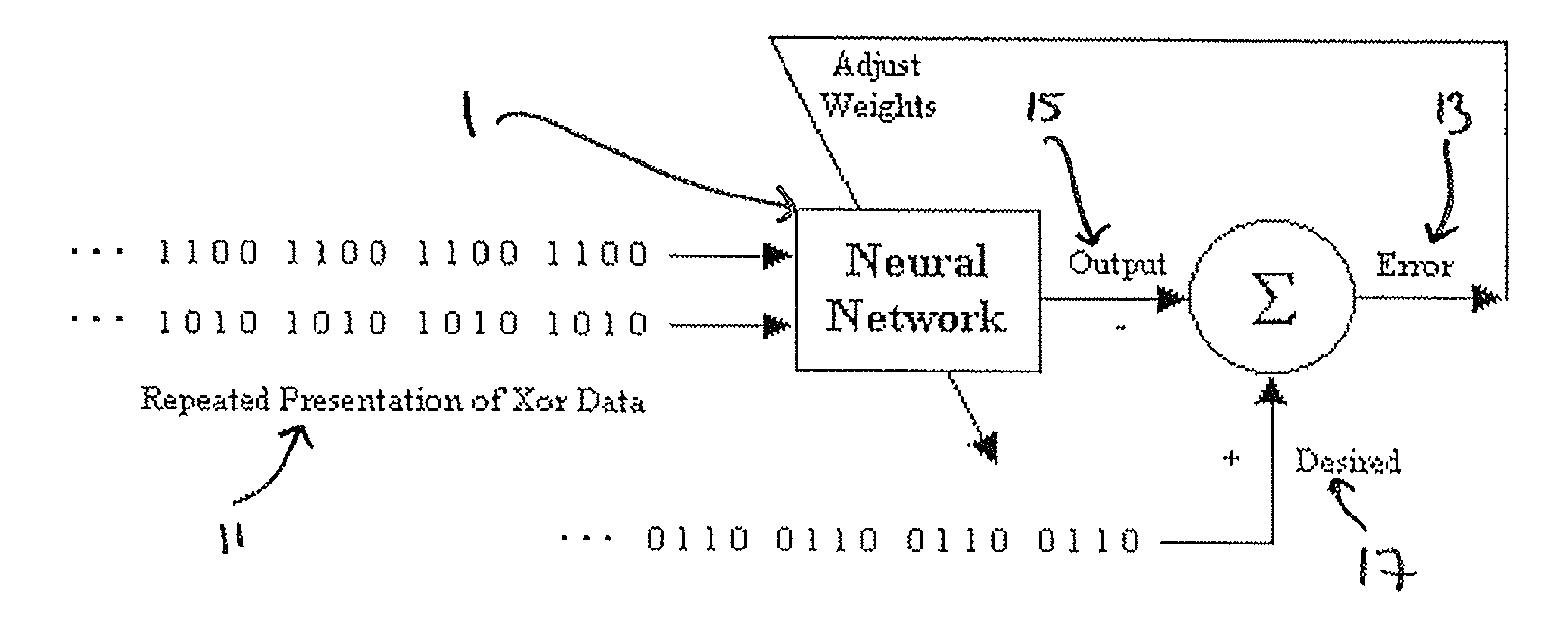
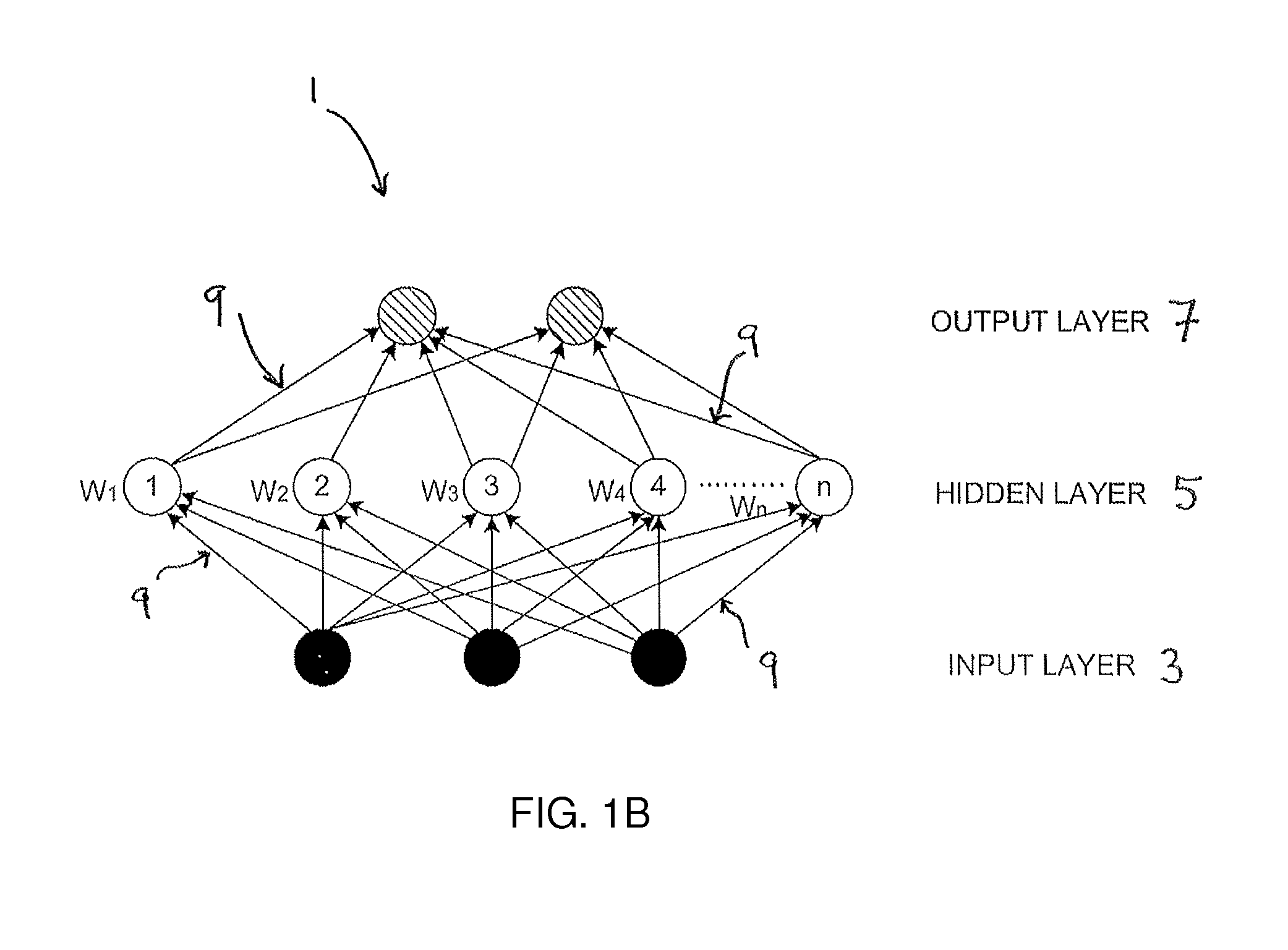
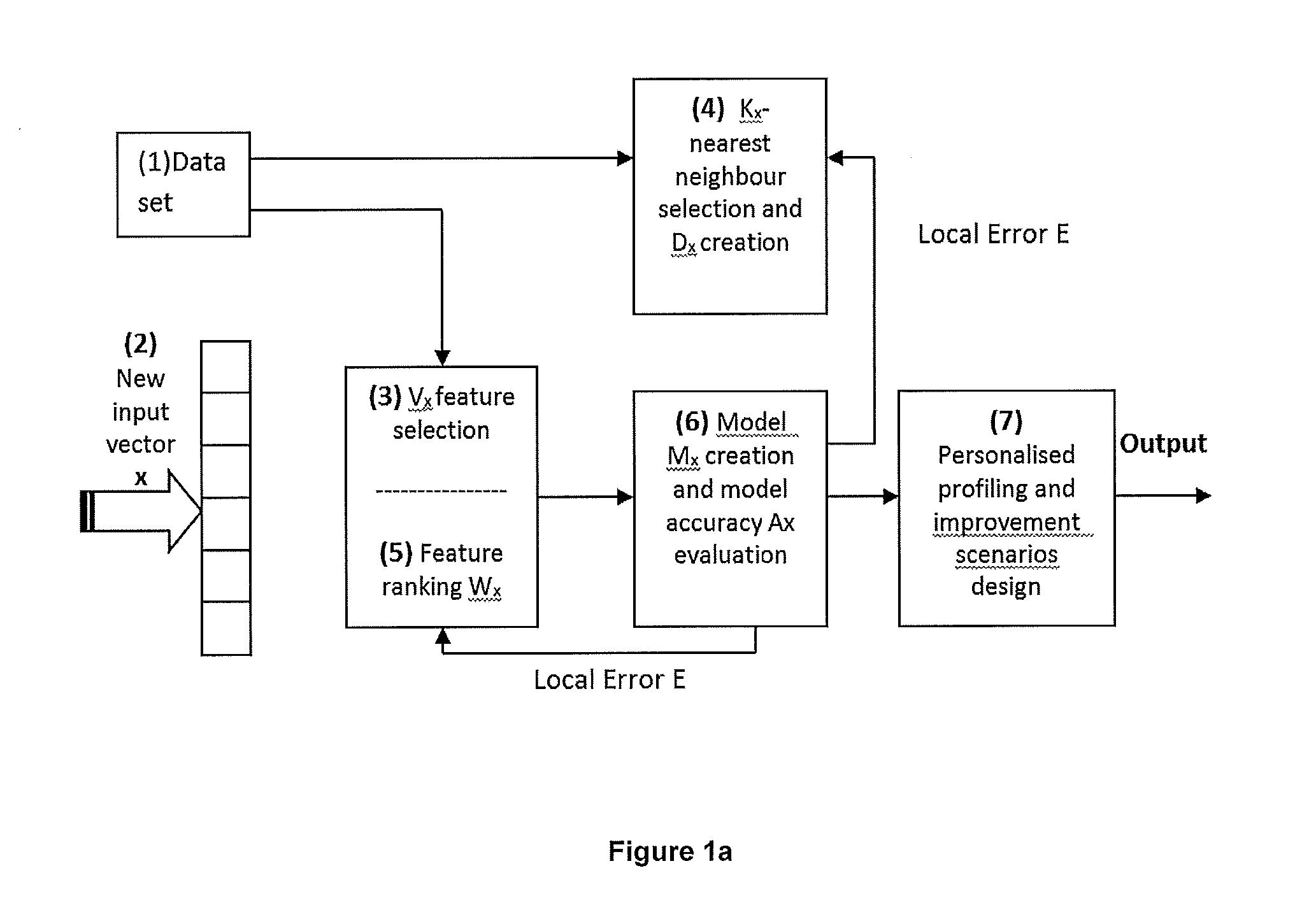
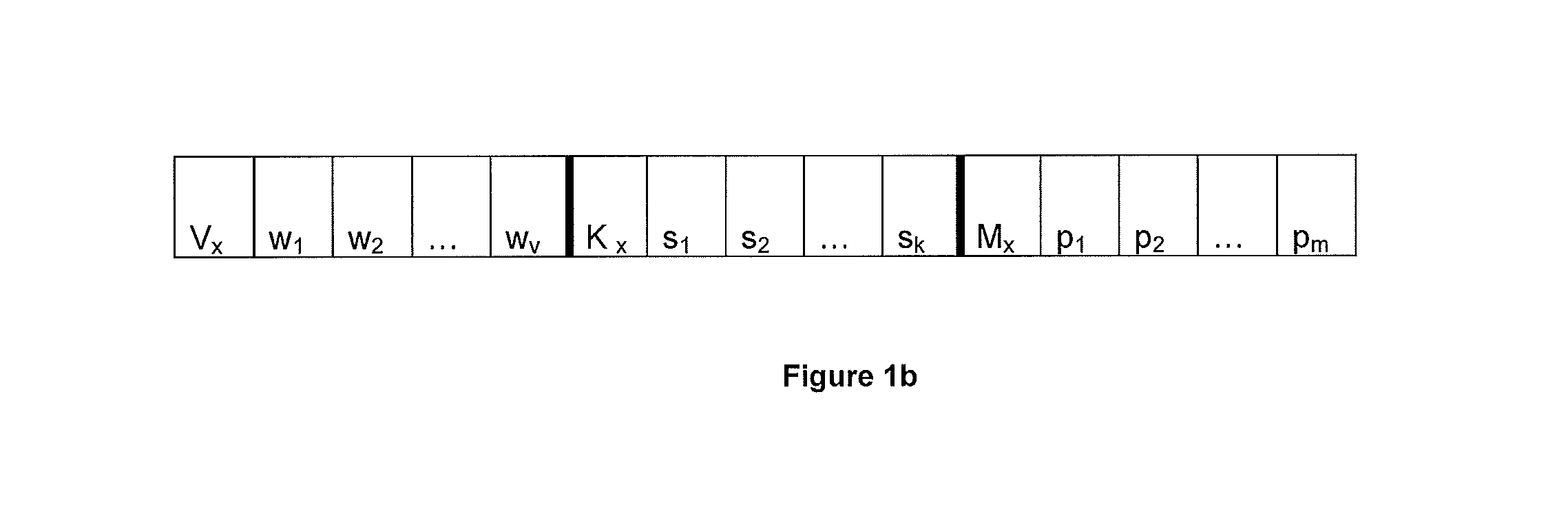
A time to event data analysis method and system. The present invention relates to the analysis of data to identify relationships between the input data and one or more conditions. One method of analysing such data is by the use of neural networks which are non-linear statistical data modelling tools, the structure of which may be changed based on information that is passed through the network during a training phase. A known problem that affects neural networks is the issue of overtraining which arises in overcomplex or overspecified systems when the capacity of the network significantly exceeds the needed parameters. The present invention provides a method of analysing data, such as bioinformatics or pathology data, using a neural network with a constrained architecture and providing a continuous output that can be used in various contexts and systems including prediction of time to an event, such as a specified clinical event.
Owner:NOTTINGHAM TRENT UNIVERSITY
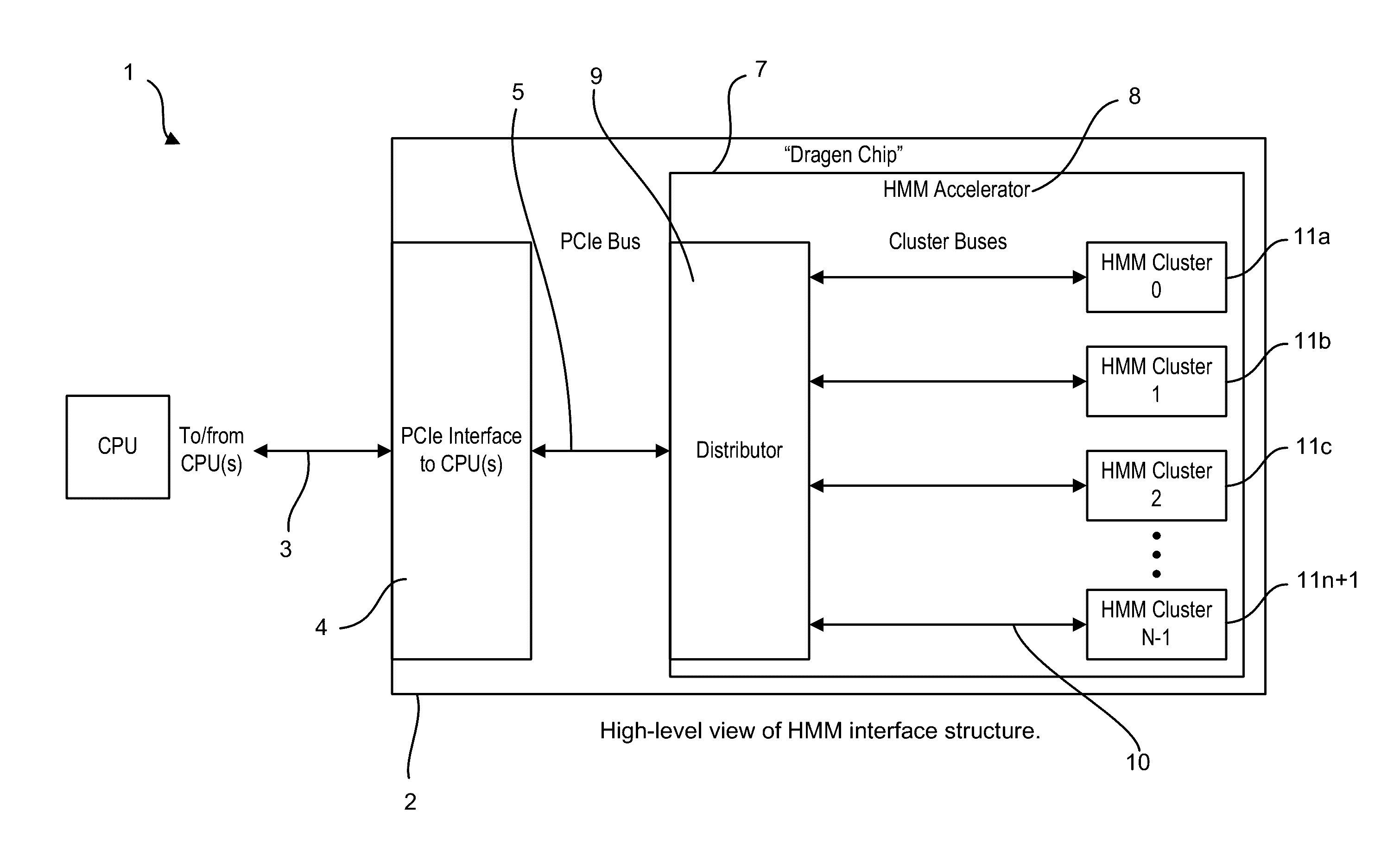
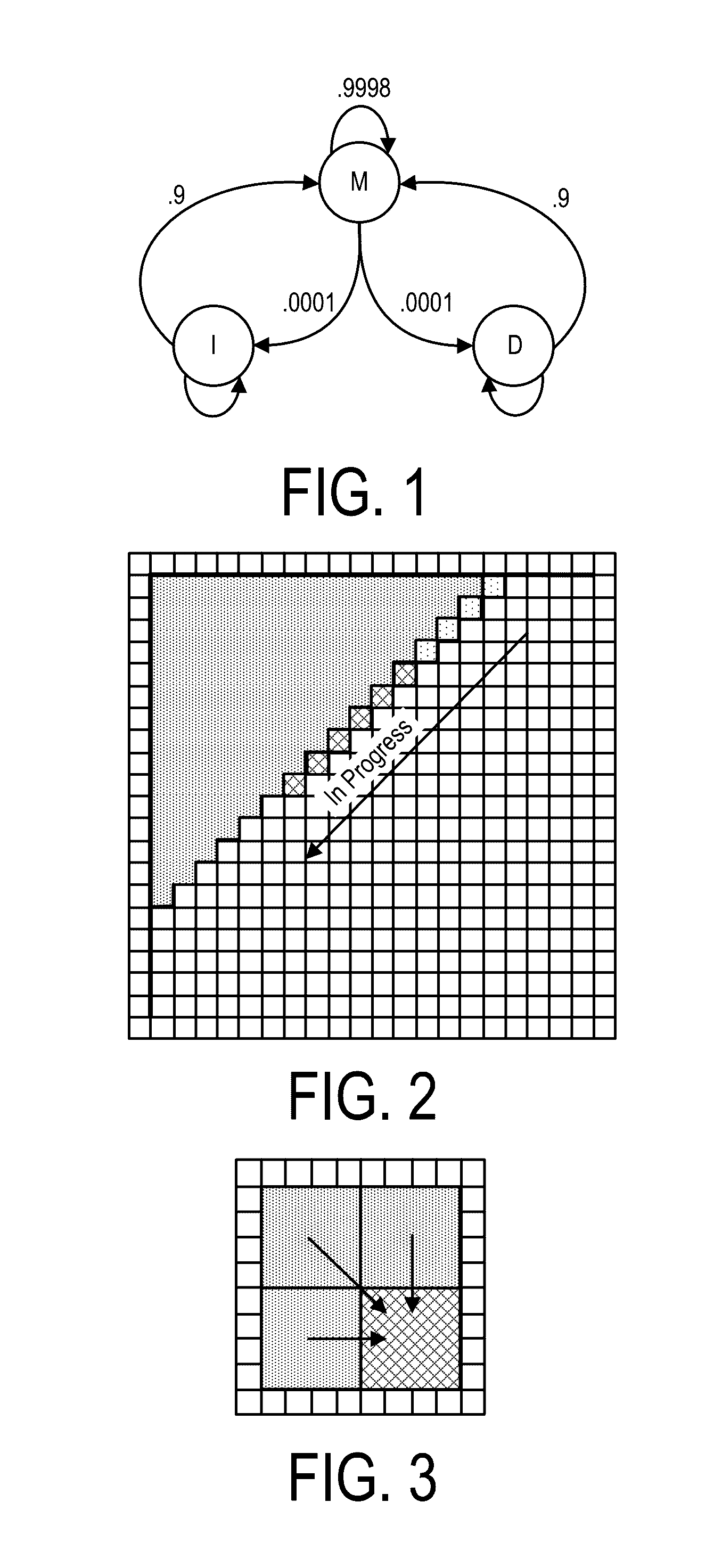
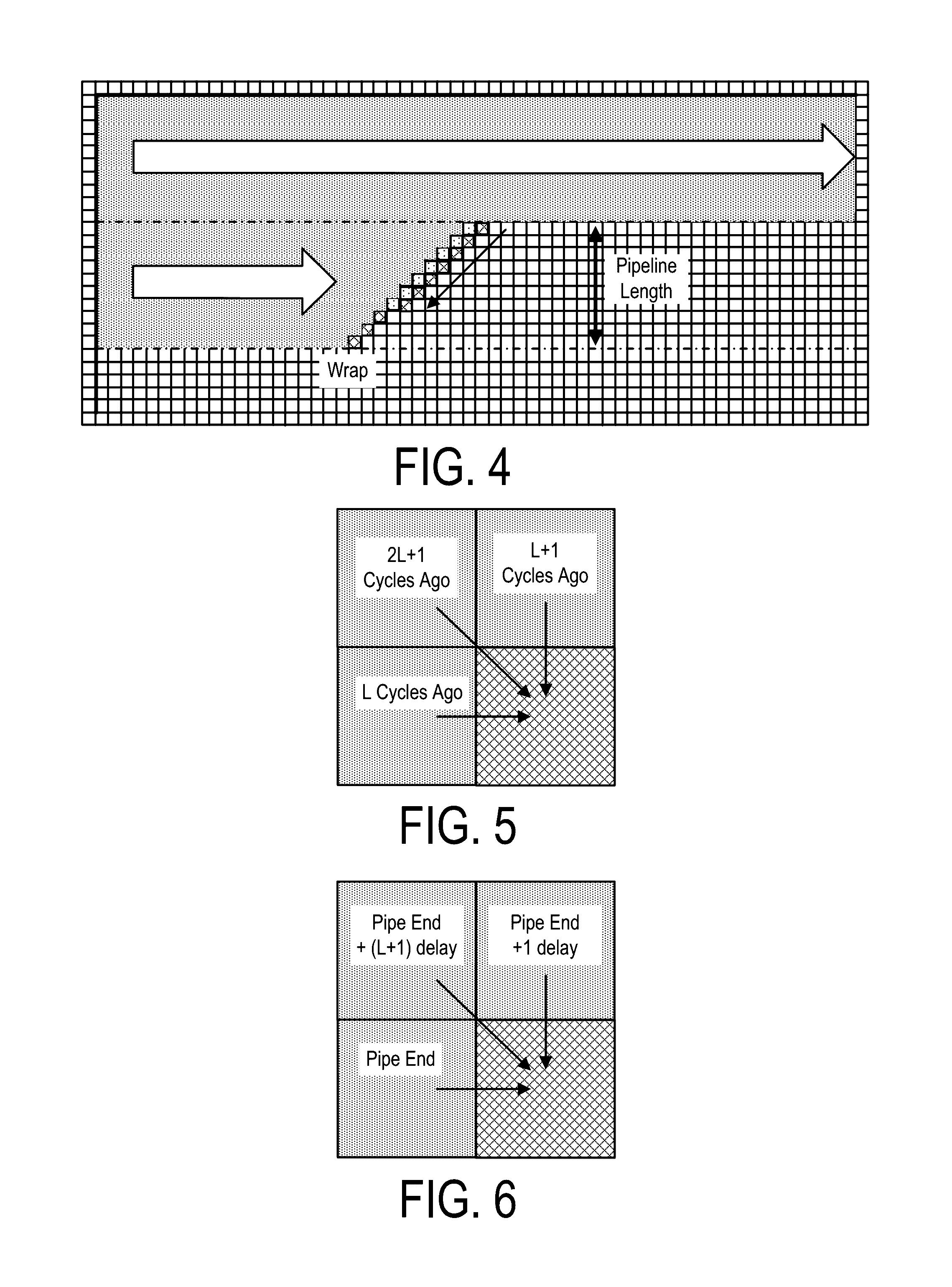
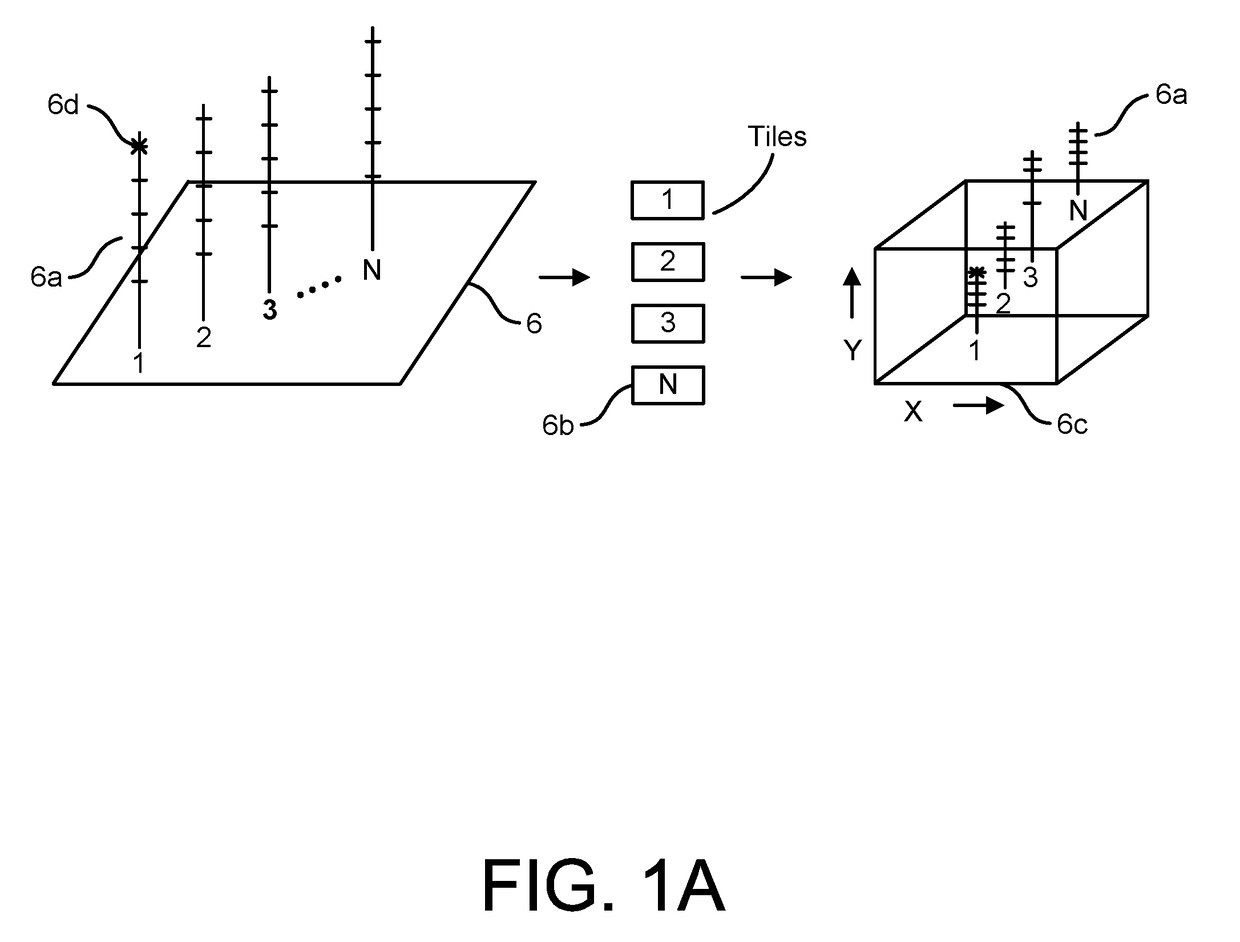
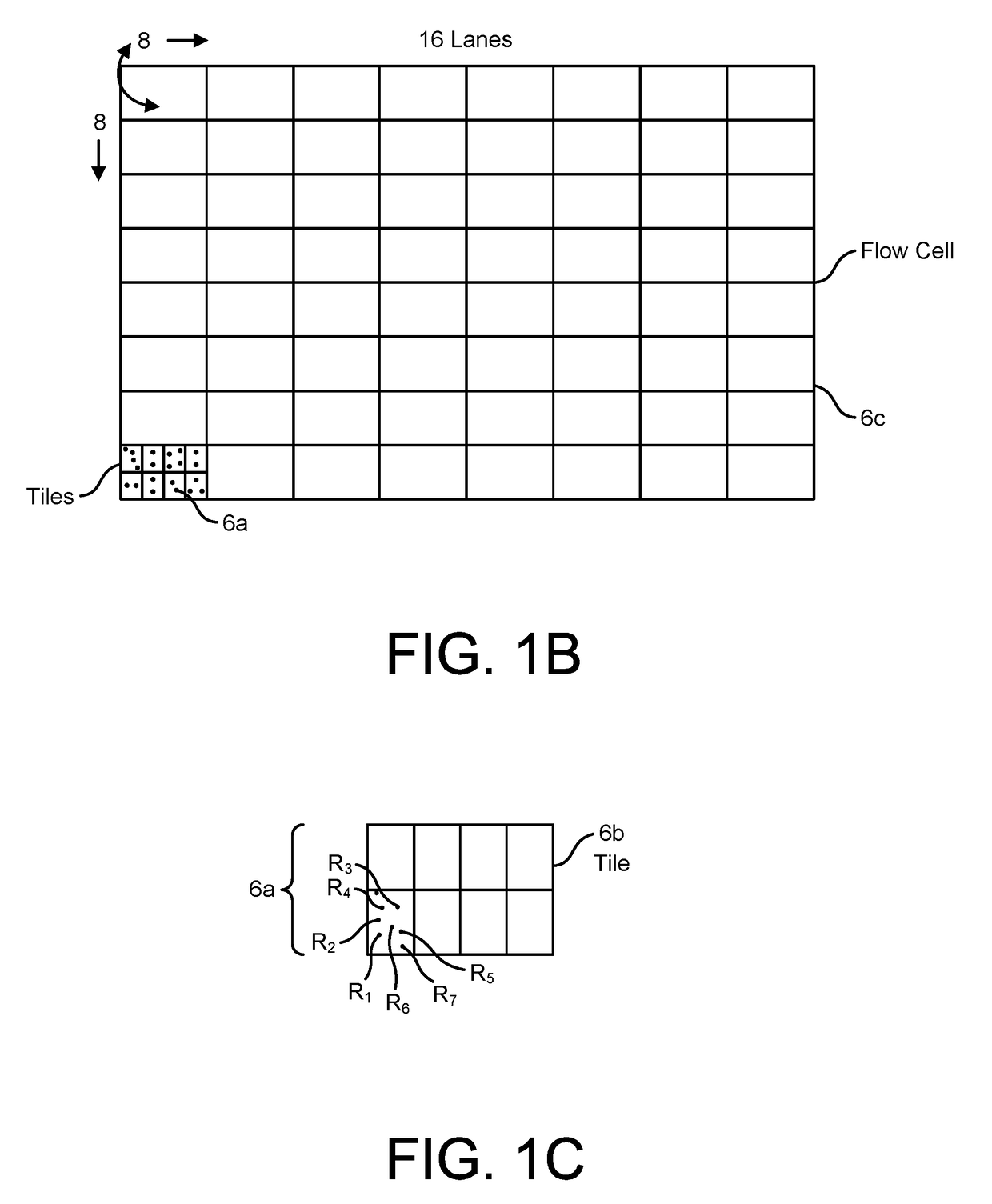
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods executed on an integrated circuit processing platform
ActiveUS20160306922A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyHealth-index calculationTelemedicineElectricityData source
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data includes an integrated circuit formed of a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by physical electrical interconnects. One of the physical electrical interconnects forms an input to the integrated circuit that may be connected with an electronic data source for receiving reads of genomic data. The hardwired digital logic circuits may be arranged as a set of processing engines, each processing engine being formed of a subset of the hardwired digital logic circuits to perform one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis on the reads of genomic data. Each subset of the hardwired digital logic circuits may be formed in a wired configuration to perform the one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods executed on an integrated circuit processing platform
ActiveUS20160306923A1Processing speedProcessed result accuracyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMathematical modelsData sourceGenomic data
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data includes an integrated circuit formed of a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by physical electrical interconnects. One of the physical electrical interconnects forms an input to the integrated circuit that may be connected with an electronic data source for receiving reads of genomic data. The hardwired digital logic circuits may be arranged as a set of processing engines, each processing engine being formed of a subset of the hardwired digital logic circuits to perform one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis on the reads of genomic data. Each subset of the hardwired digital logic circuits may be formed in a wired configuration to perform the one or more steps in the bioinformatics analysis.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
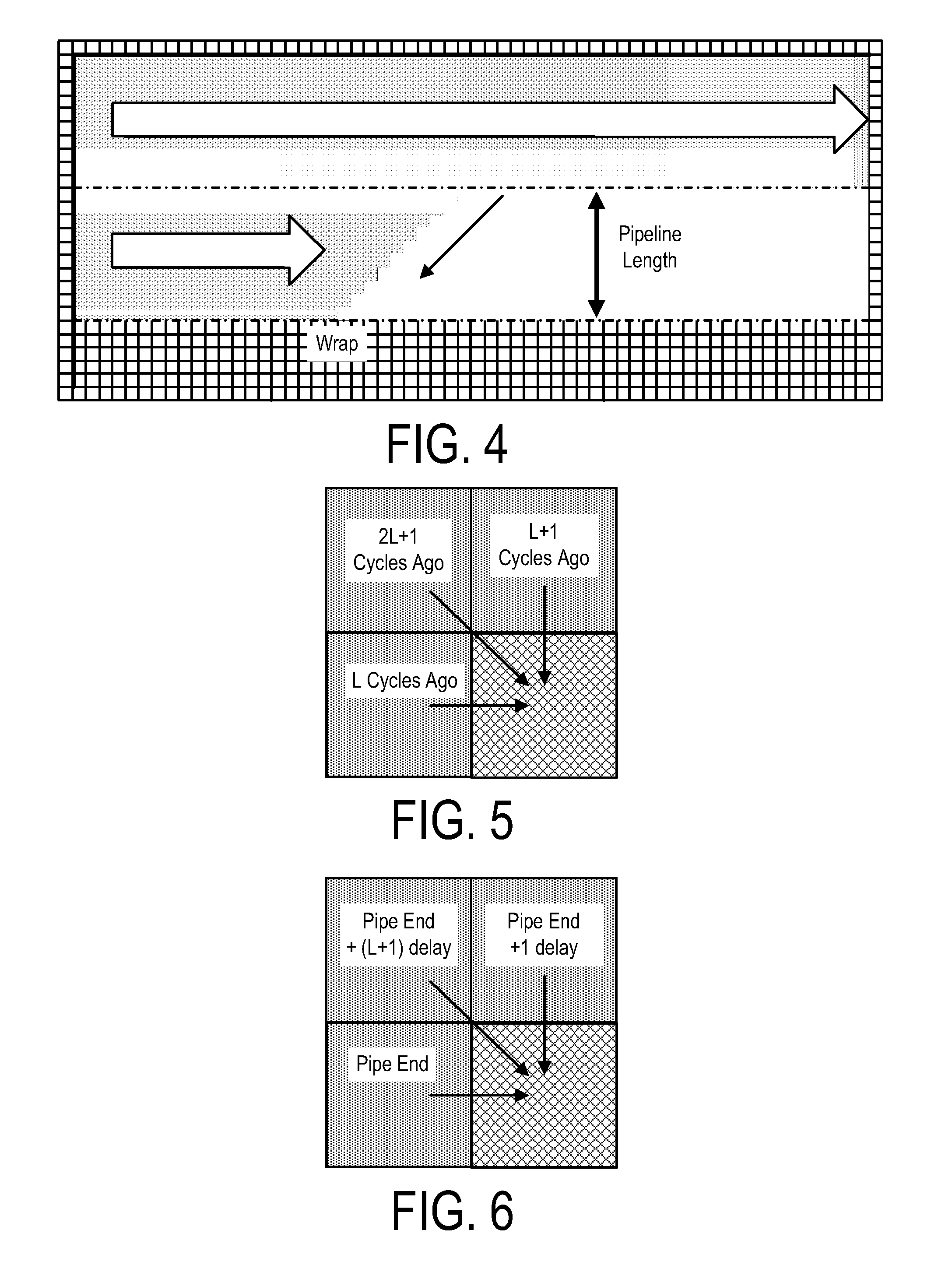
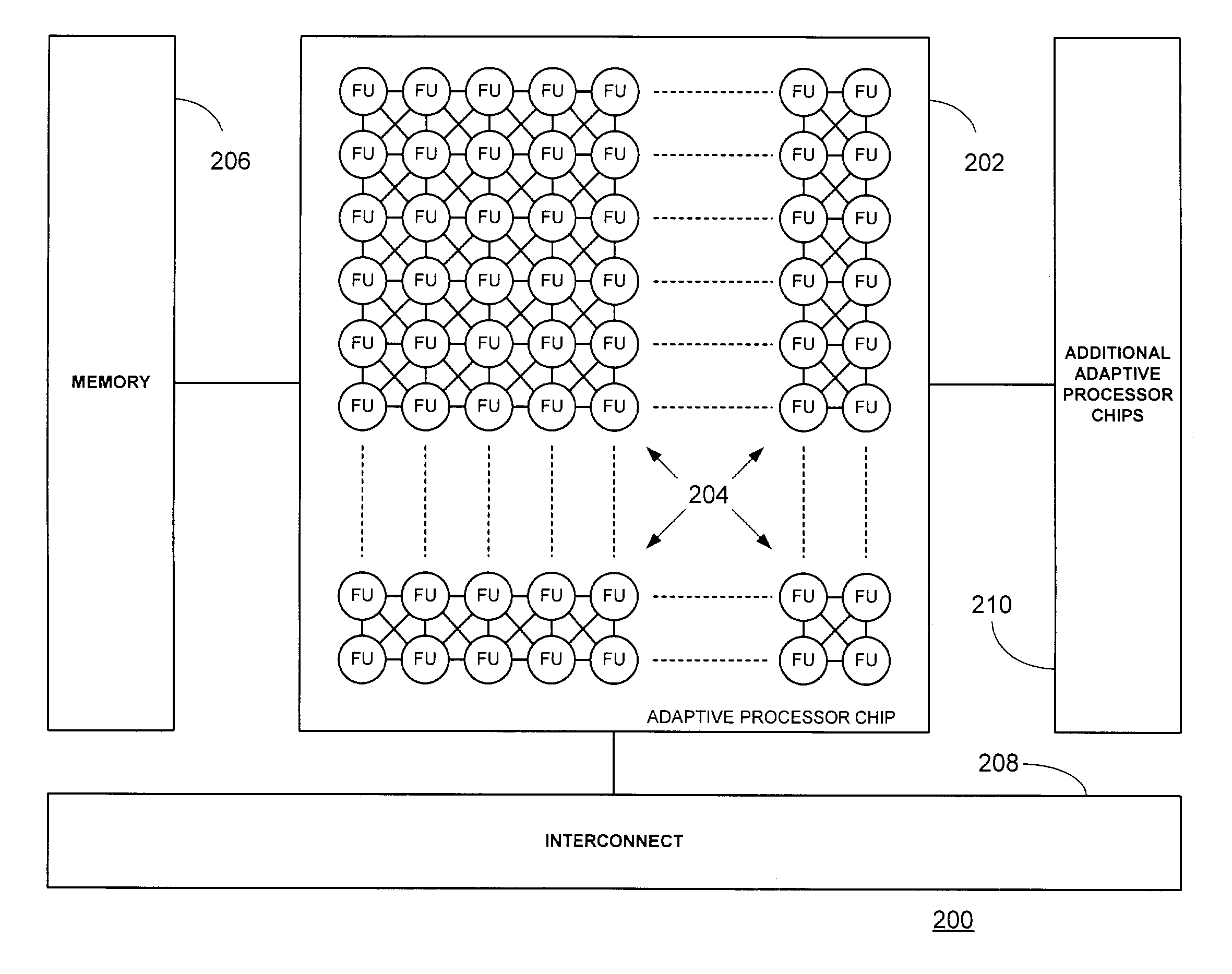
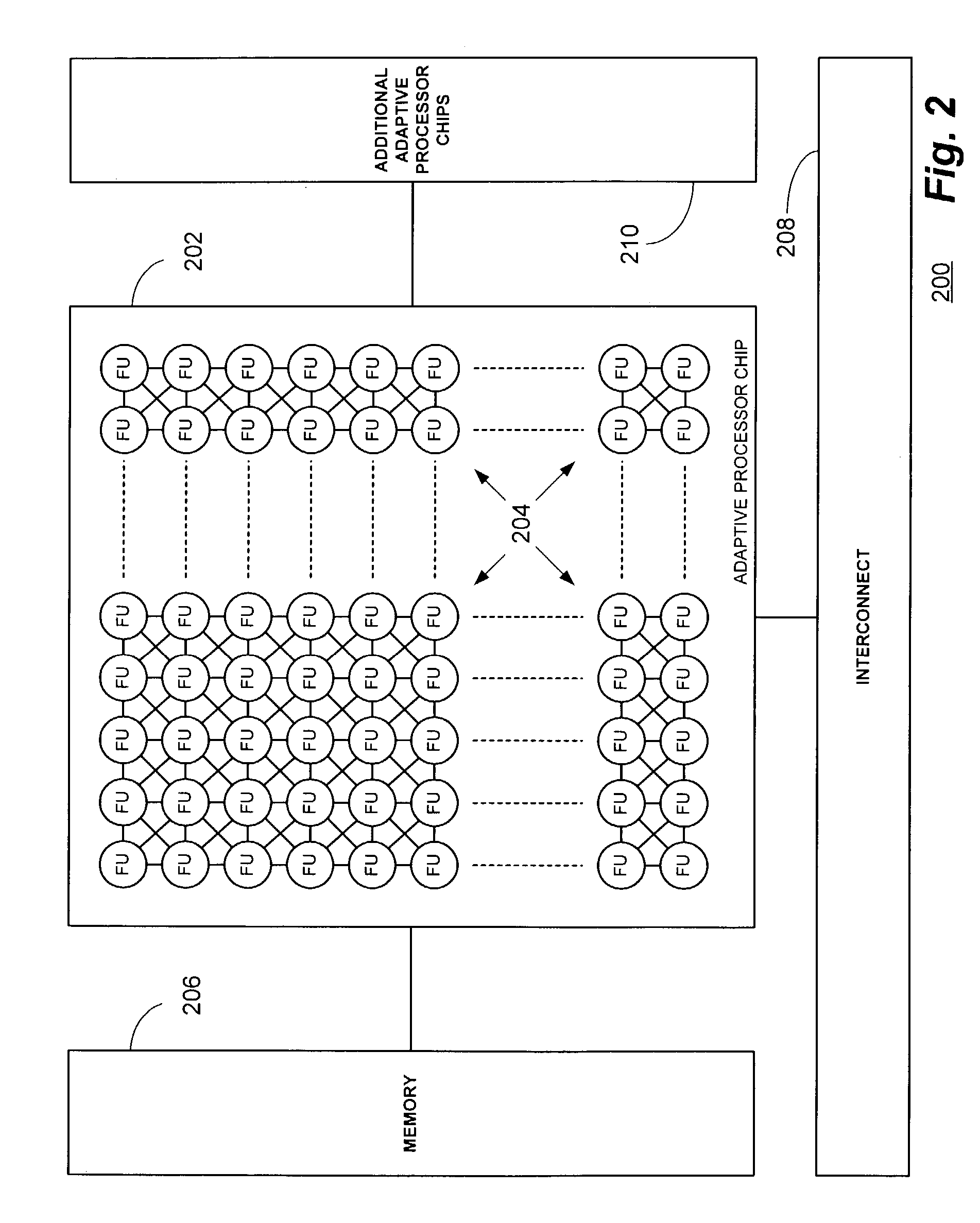
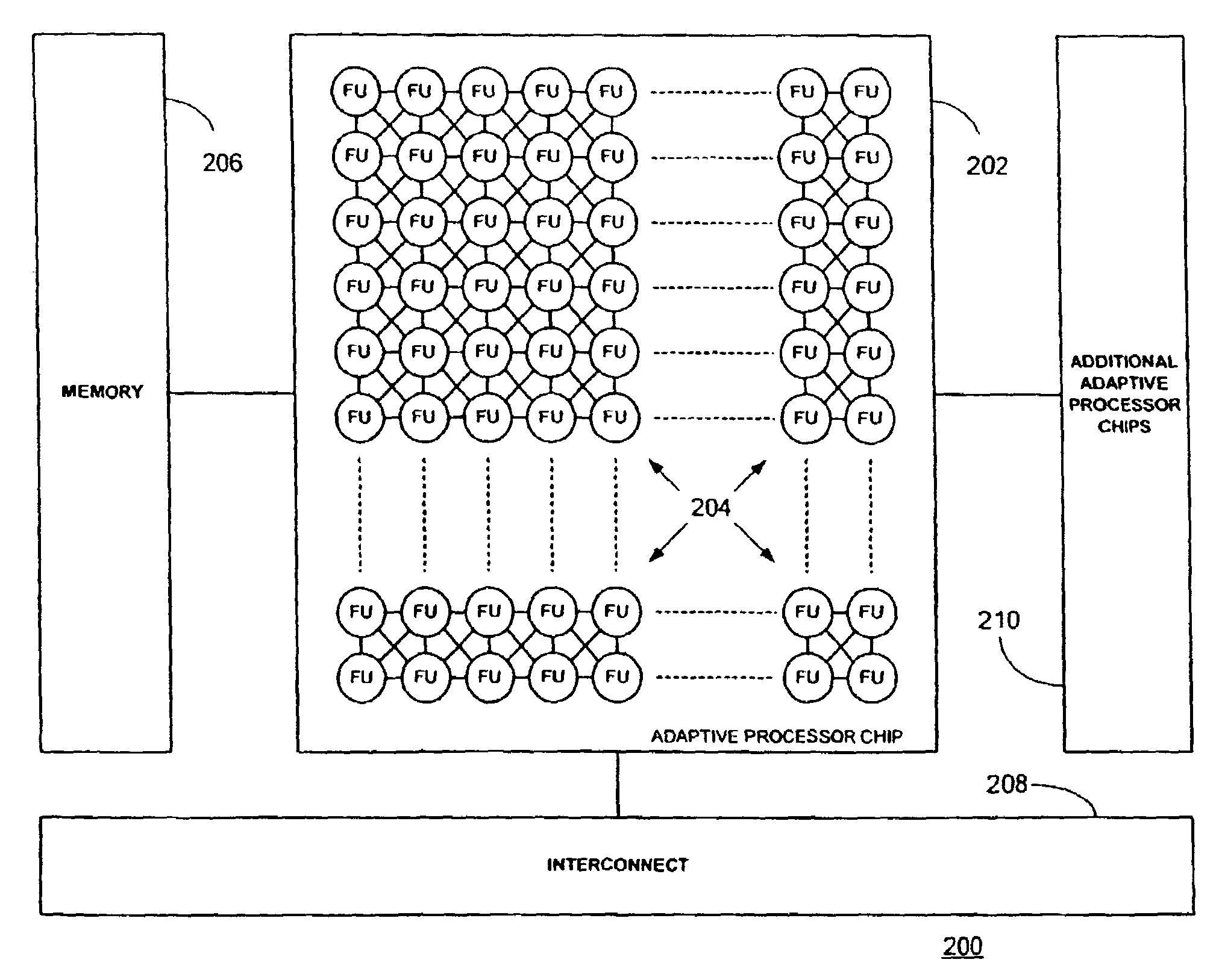
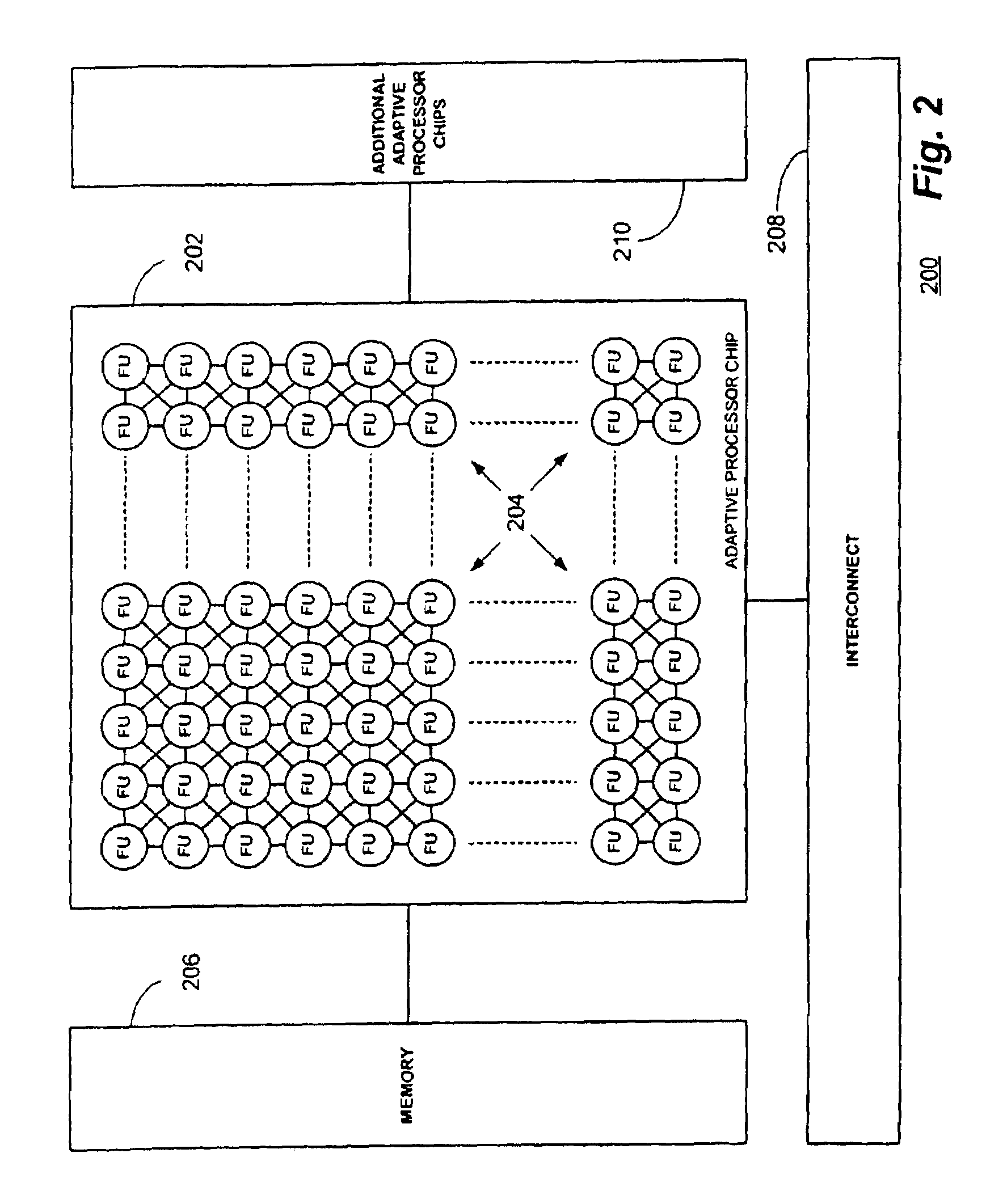
Multi-adaptive processing systems and techniques for enhancing parallelism and performance of computational functions
ActiveUS7225324B2Improve performanceSmall and less-expensiveSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsArchitecture with single central processing unitData processing systemWavefront
Multi-adaptive processing systems and techniques for enhancing parallelism and performance of computational functions are disclosed which can be employed in a myriad of applications including multi-dimensional pipeline computations for seismic applications, search algorithms, information security, chemical and biological applications, filtering and the like as well as for systolic wavefront computations for fluid flow and structures analysis, bioinformatics etc. Some applications may also employ both the multi-dimensional pipeline and systolic wavefront methodologies disclosed.
Owner:SRC COMP
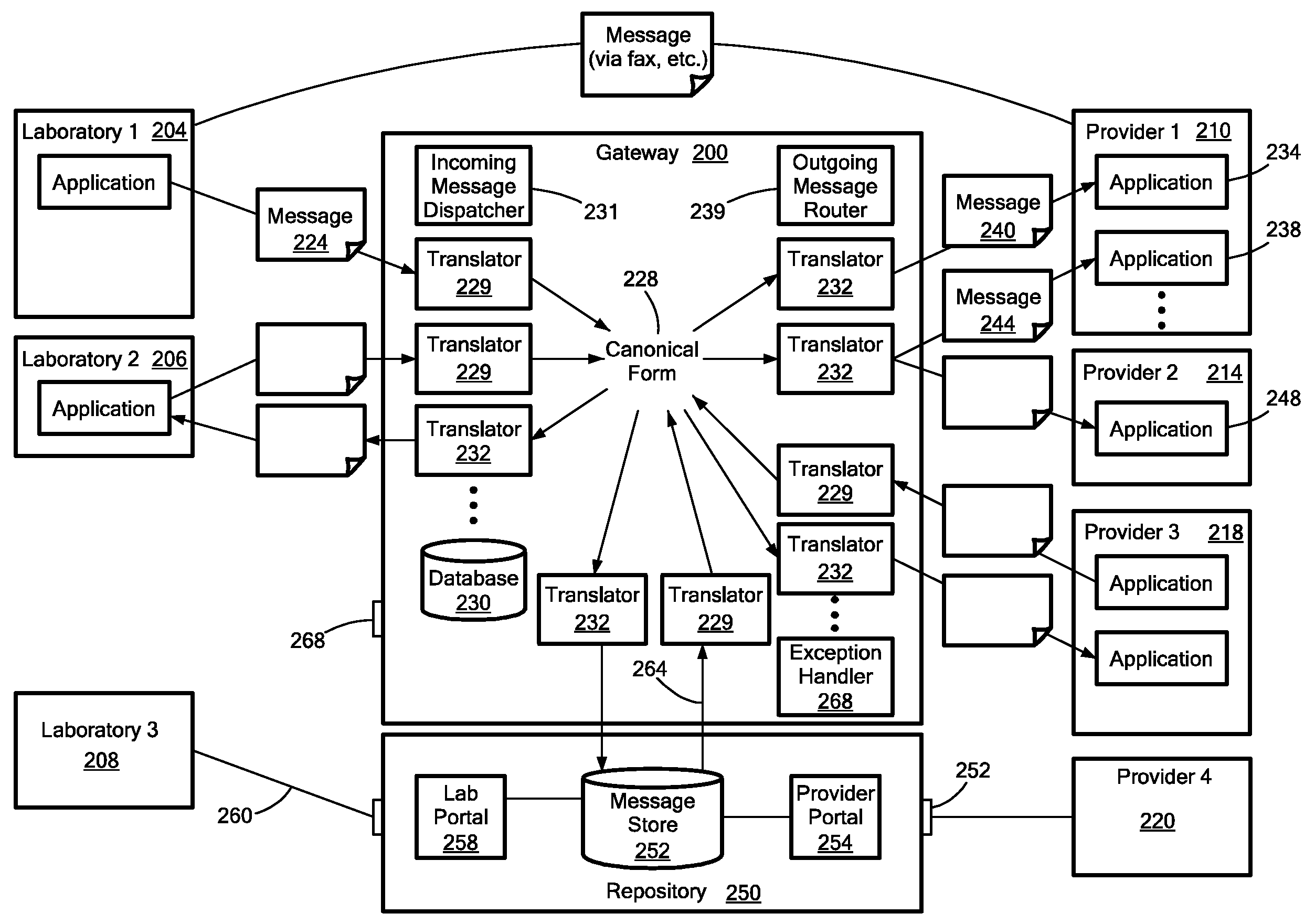
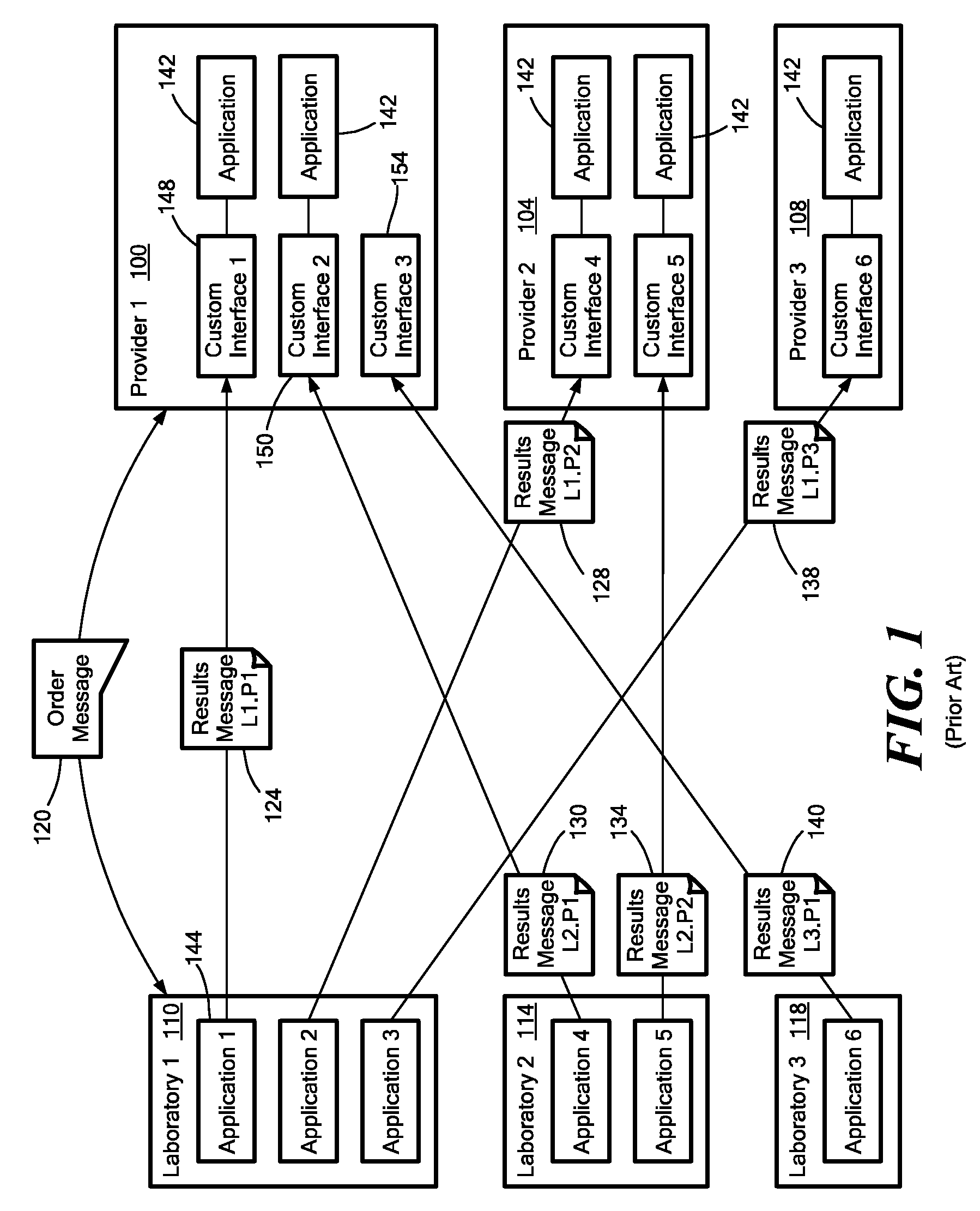
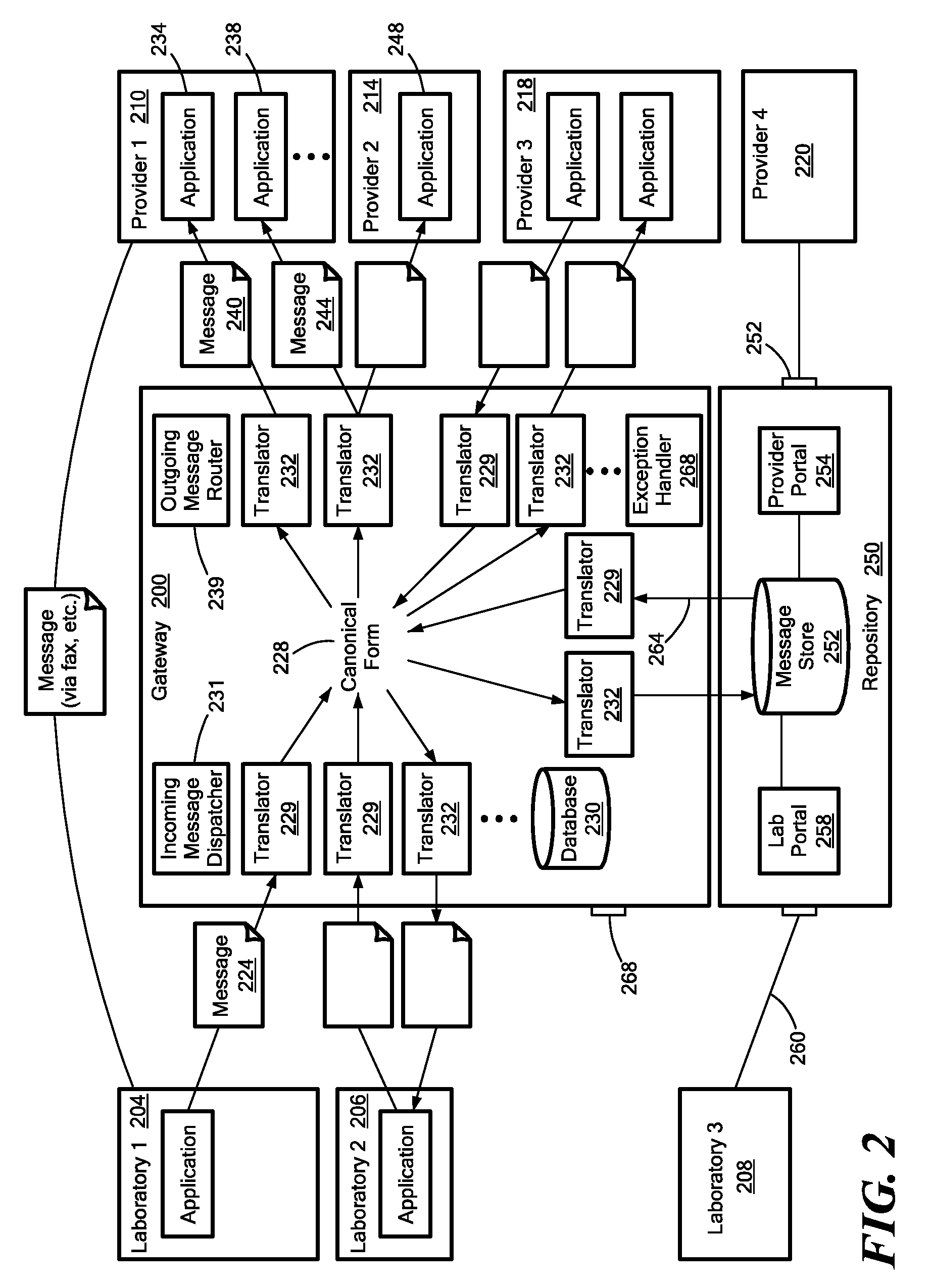
Medical laboratory report message gateway
ActiveUS20080270438A1Fault responseDigital data processing detailsMedical laboratoryBioinformatics databases
A gateway enables medical (including genetic and genomic) laboratories and health care providers (collectively “clients”) to communicate electronic messages with each other without developing and maintaining an interface for each peer. The gateway translates messages sent between the parties. The gateway receives messages from each sender in a form, and containing diagnostic codes, preferred by the sender. For each received message, the gateway ascertains an intended receiving client. Each client may specify one or more receivers (such as applications) that are to receive messages sent to the client, as well as a separate form, and optionally a set of codes, for each receiver. For each receiver, the gateway generates translated messages, according to the receiver's preferred form and / or codes. The gateway sends the translated messages to each of the designated receivers. The gateway may include a validation component to check incoming messages to ensure the messages include required information and that information values are valid or acceptable. The gateway may include an exception handler that notifies a sending client if a message from the client fails to be translated or sent correctly. The gateway may maintain a repository in which the gateway stores copies of messages the gateway sent or would have sent to clients. The gateway provides an interface, such as a secure web interface, to this repository. Clients may access messages or lists of messages, especially messages the clients are not otherwise capable of receiving, through this interface. The gateway may store copies of some of the data that flows through the gateway in a bioinformatics database, which may be automatically analyzed by the gateway or queried for research or patient care purposes.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
System, method, device, and computer program product for extraction, gathering, manipulation, and analysis of peak data from an automated sequencer
InactiveUS20060259248A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologySystems approachesComputer science
The present invention relates to a novel computer program product to extract and gather peak information from an automated sequencer or bioinformatics tool into a peak database, and to manipulate and analyze the peak information within the database.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +2
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods for performing secondary and/or tertiary processing
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data is provided. Particularly, a genomics analysis platform for executing a sequence analysis pipeline is provided. The genomics analysis platform includes one or more of a first integrated circuit, where each first integrated circuit forms a central processing unit (CPU) that is responsive to one or more software algorithms that are configured to instruct the CPU to perform a first set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline. Additionally, a second integrated circuit is also provided, where each second integrated circuit forming a field programmable gate array (FPGA), the FPGA being configured by firmware to arrange a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by a plurality of physical interconnects to perform a second set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline, the set of hardwired digital logic circuits of each FPGA being arranged as a set of processing engines to perform the second set of genomic processing steps. A shared memory is also provided.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
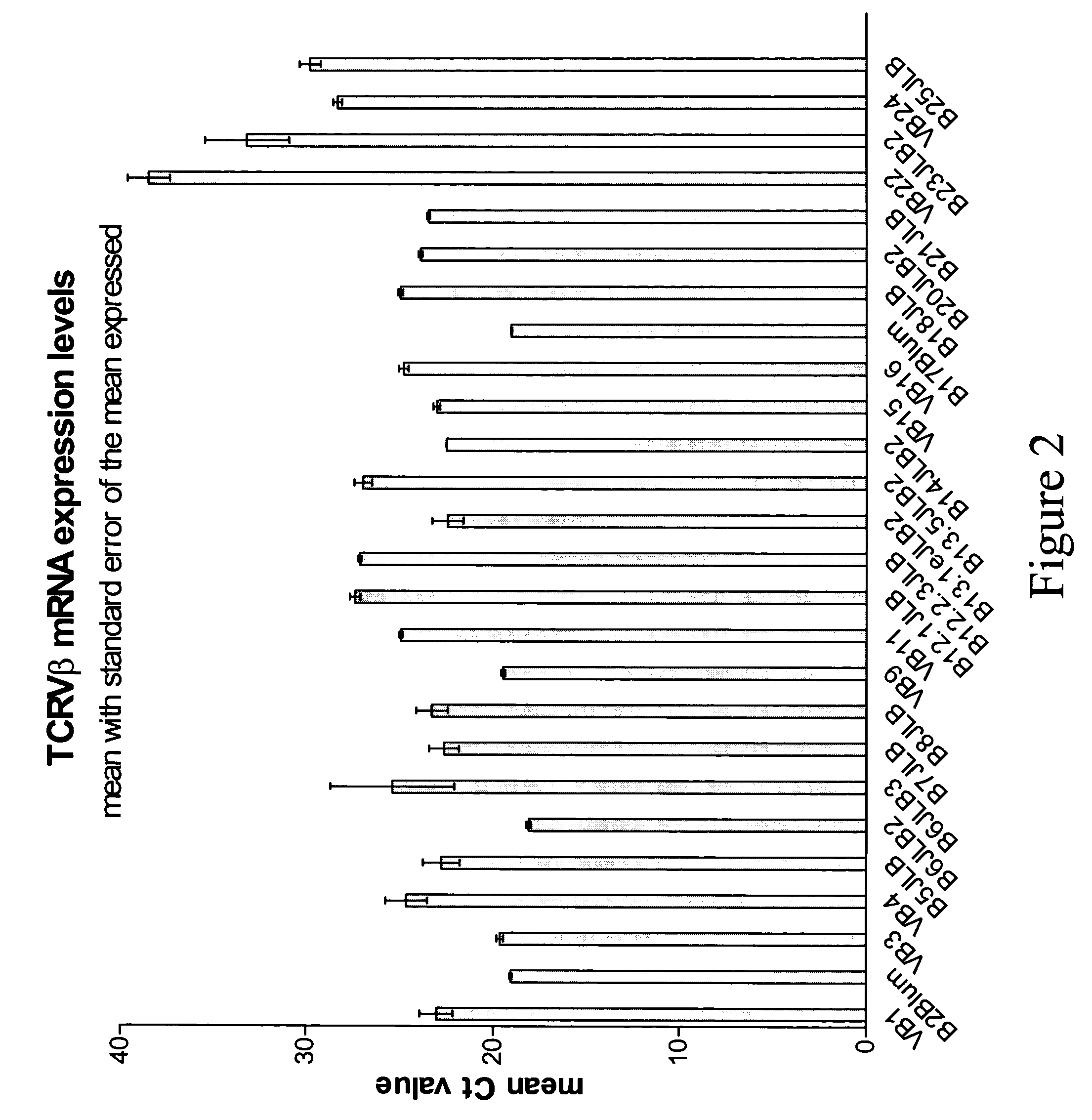
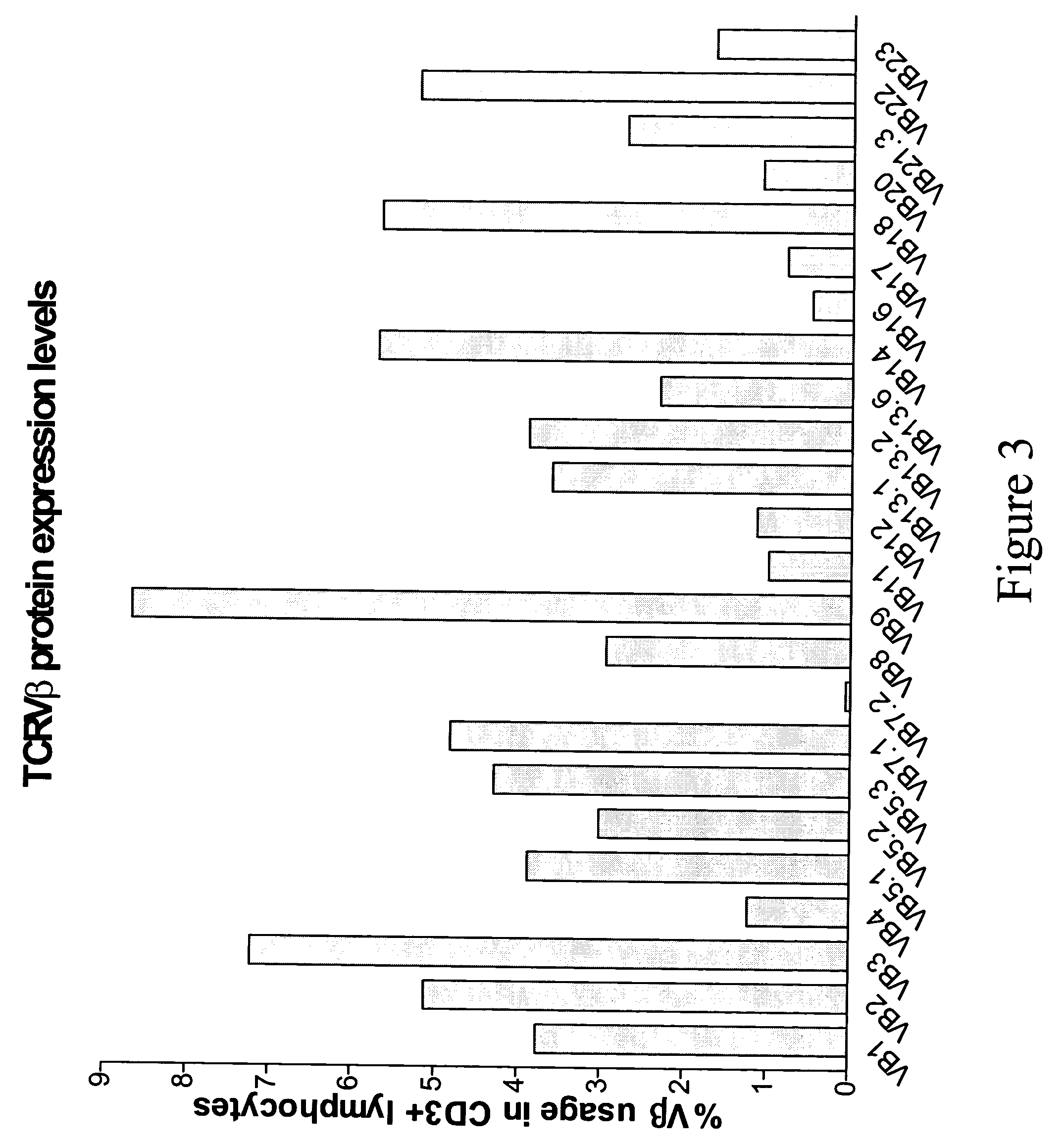
Compositions and methods for the detection of human T cell receptor variable family gene expression
Compositions and methods for the assessment of T cell receptor variable subunits. The present invention provides nucleotide sequences for the evaluation of the expression of TCRV families. These nucleotides sequences were obtained through a bioinformatic investigation of the nucleotide sequences for TCRVα and TCRVβ families. The nucleotide sequences of the present invention uniquely recognize each and every subfamily and allelic member of a particular TCRV family, while at the same time not recognizing the members of any other TCRV family. This unique expression recognition profile of the nucleotide sequences of the present invention provides great utility for the assessment of TCR families in a clinical setting, such as through polymerase chain reactions, gene chip technology, and direct electrophoretic measurement of DNA or RNA.
Owner:BREWER MILLER JAMIE L +1
Multi-adaptive processing systems and techniques for enhancing parallelism and performance of computational functions
InactiveUS7620800B2Improve performanceSmaller and less expensive computer systemsSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsArchitecture with single central processing unitData processing systemStructure analysis
Multi-adaptive processing systems and techniques for enhancing parallelism and performance of computational functions are disclosed which can be employed in a myriad of applications including multi-dimensional pipeline computations for seismic applications, search algorithms, information security, chemical and biological applications, filtering and the like as well as for systolic wavefront computations for fluid flow and structures analysis, bioinformatics etc. Some applications may also employ both the multi-dimensional pipeline and systolic wavefront methodologies disclosed.
Owner:SRC COMP
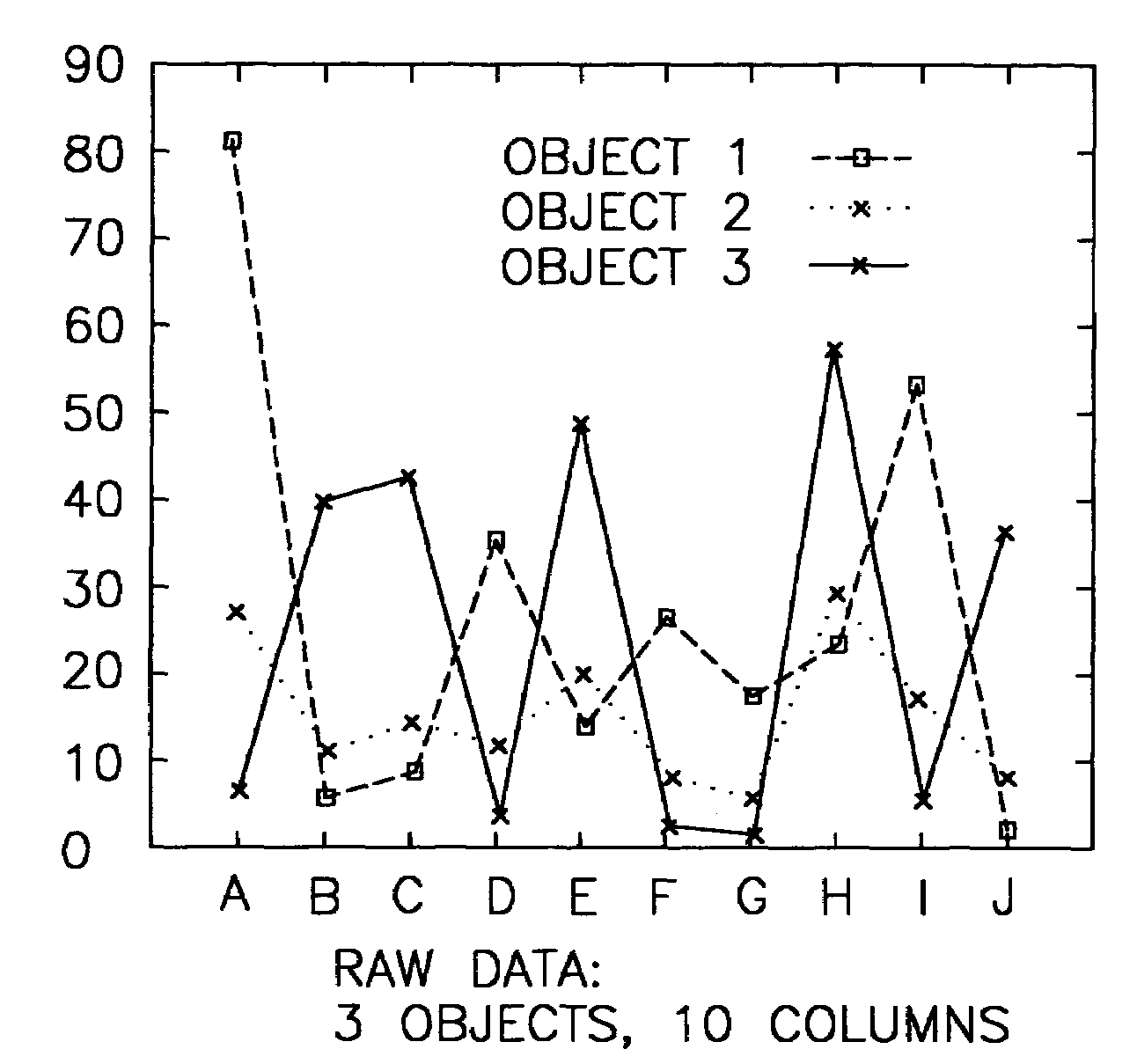
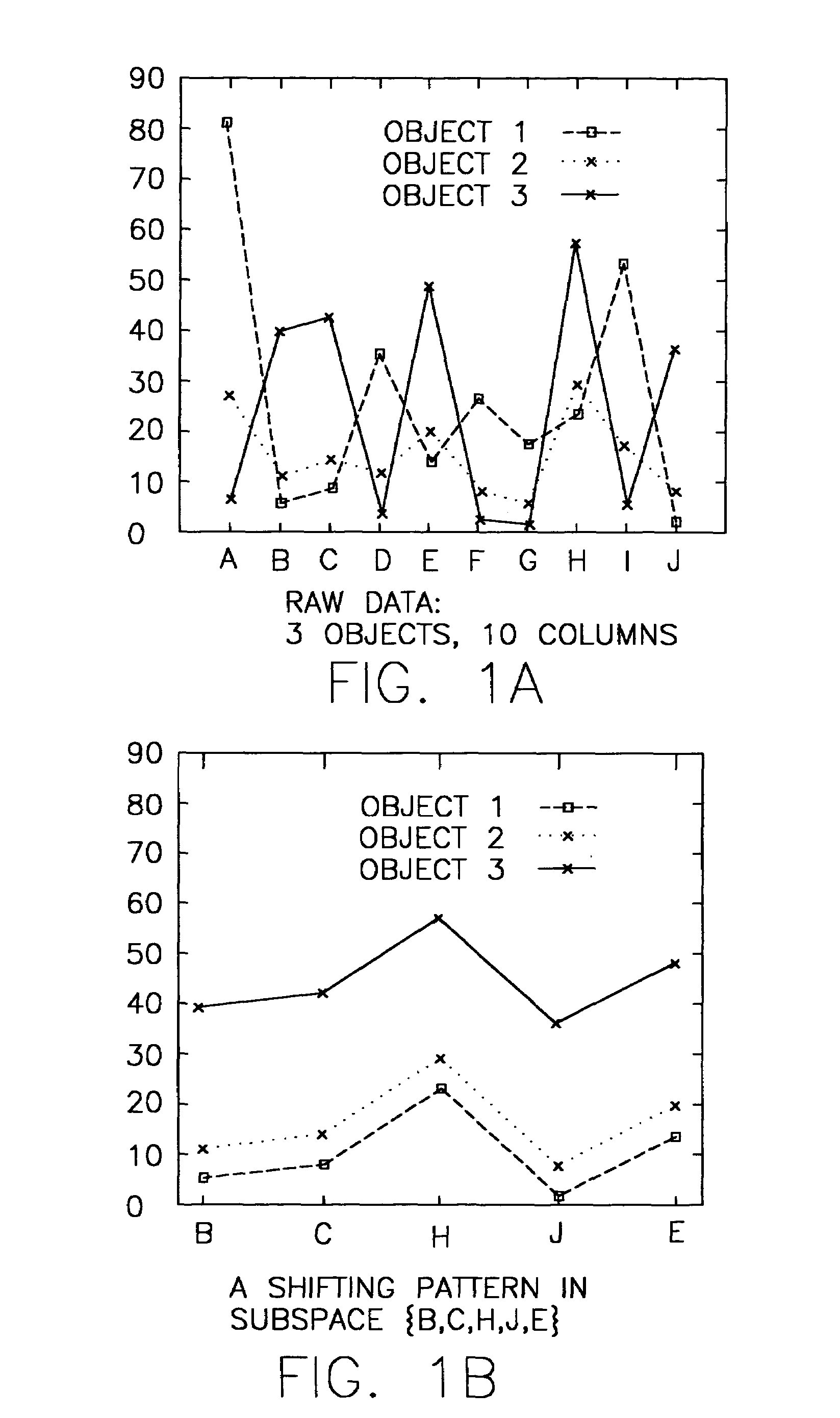
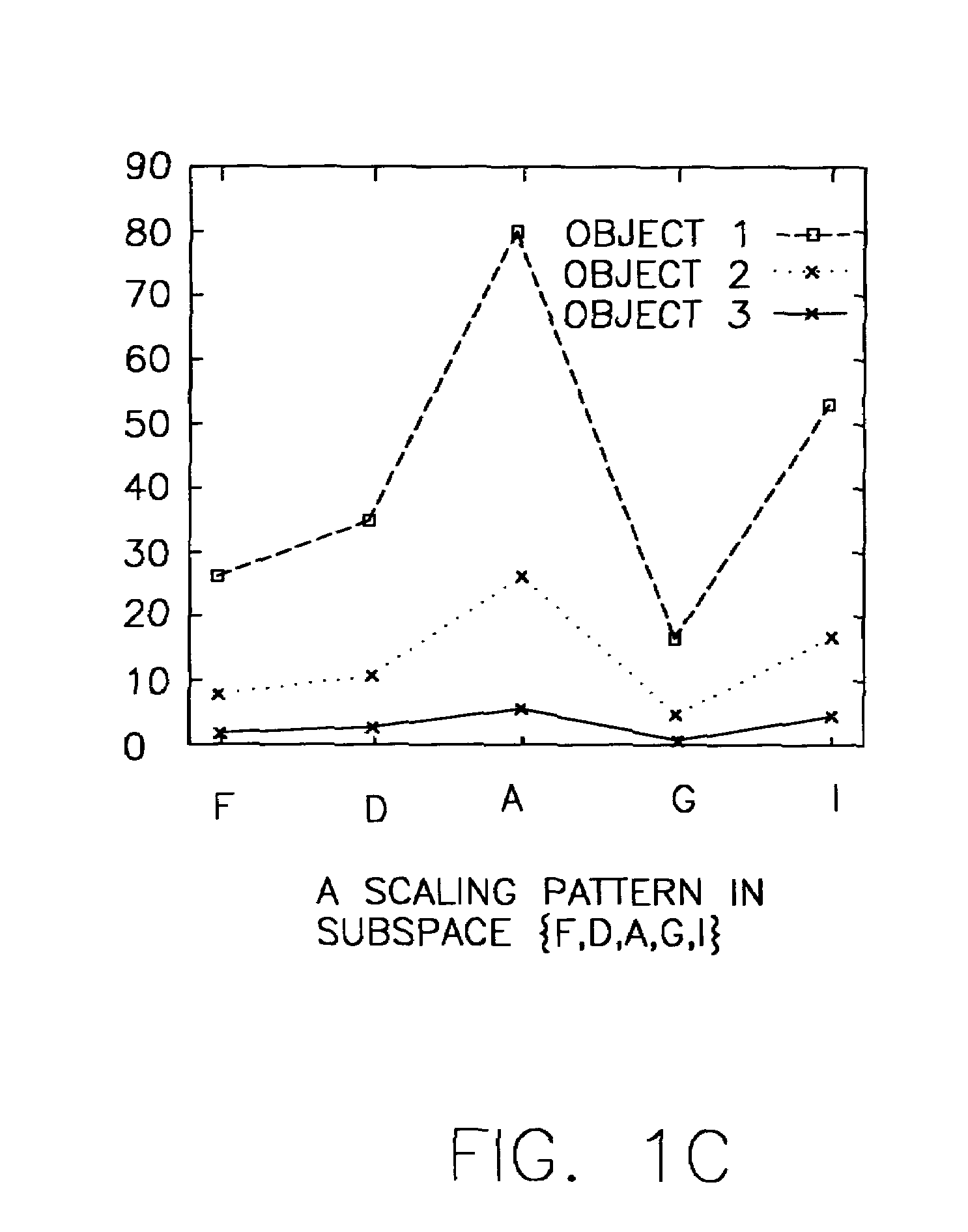
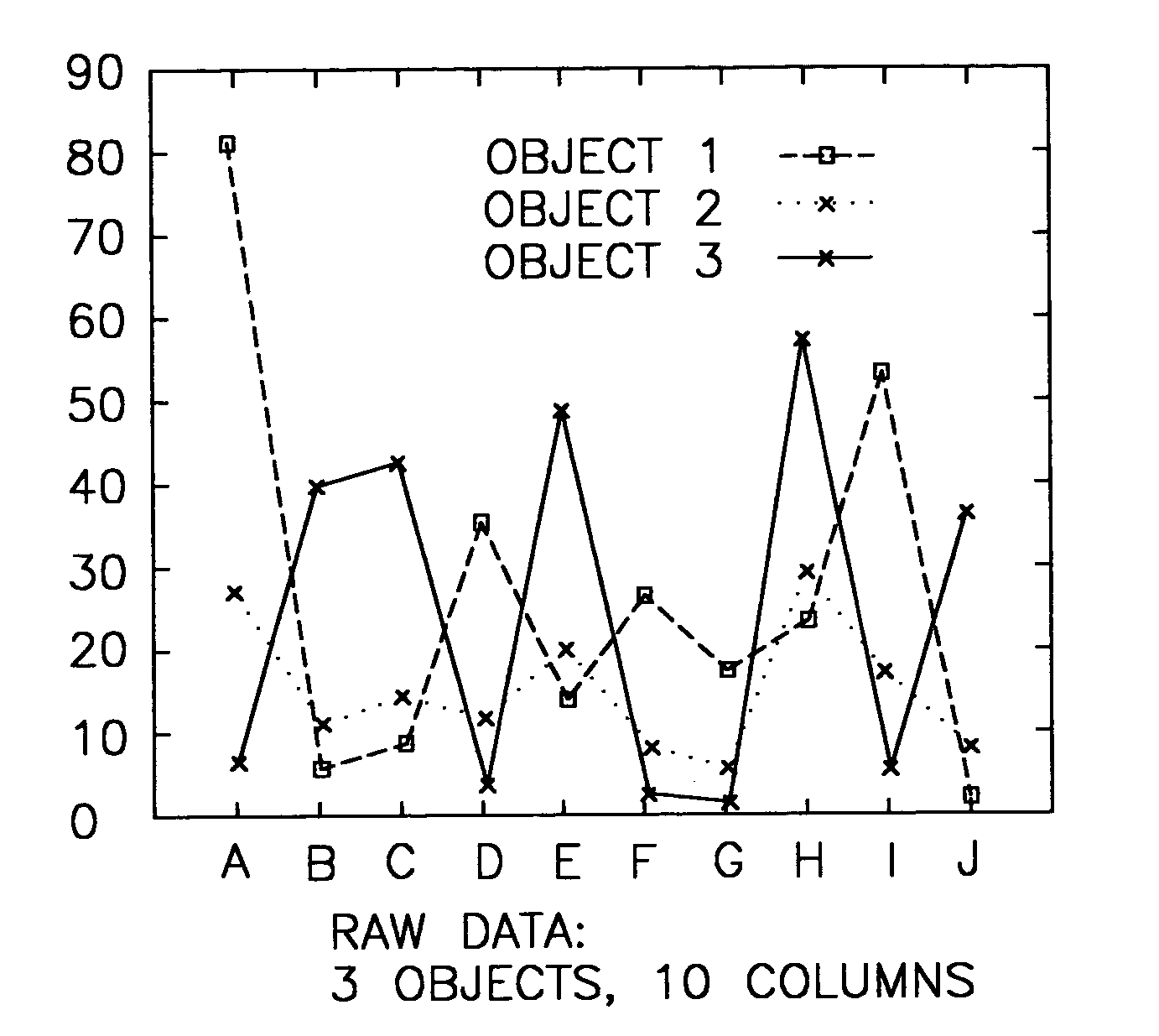
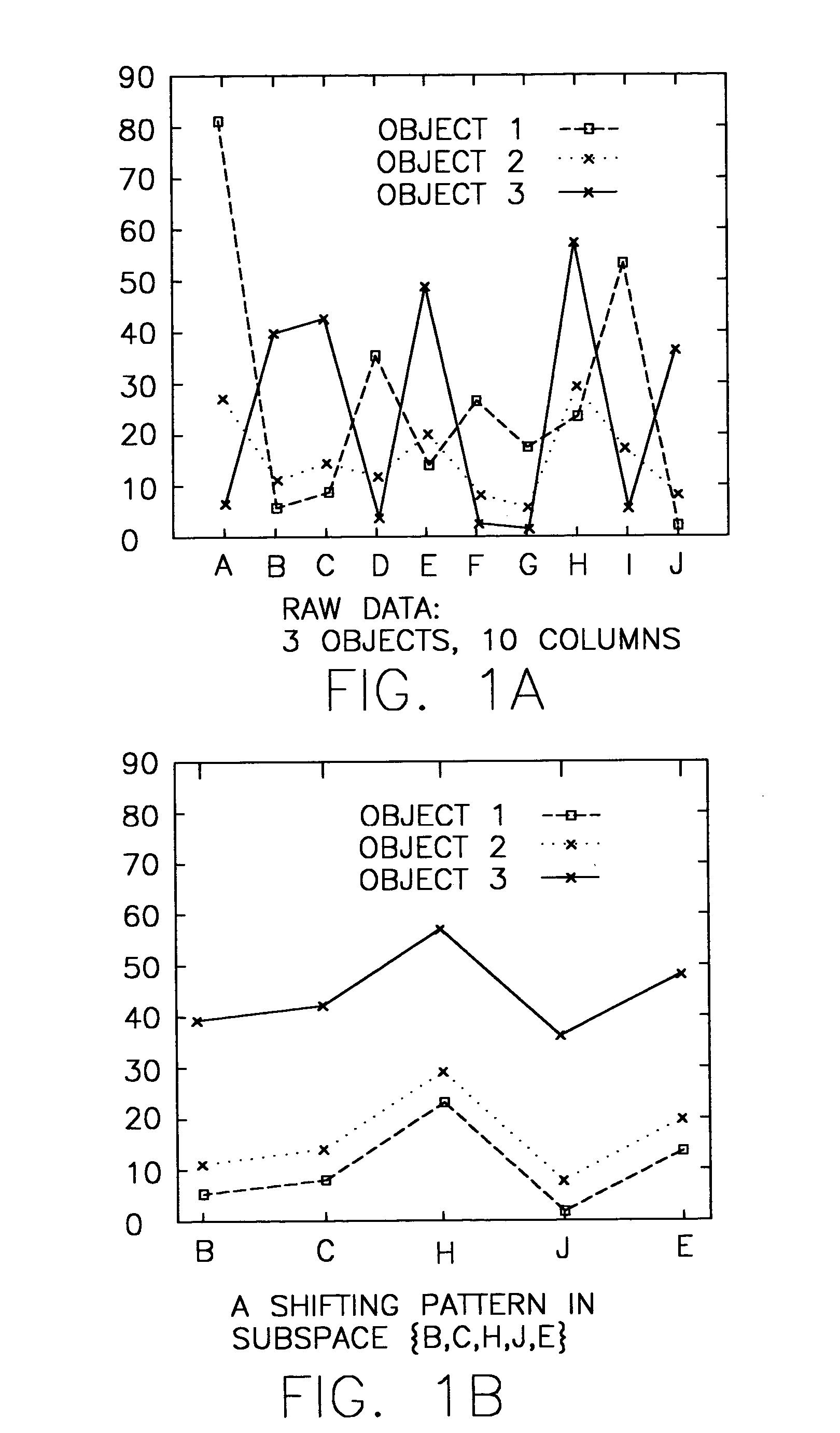
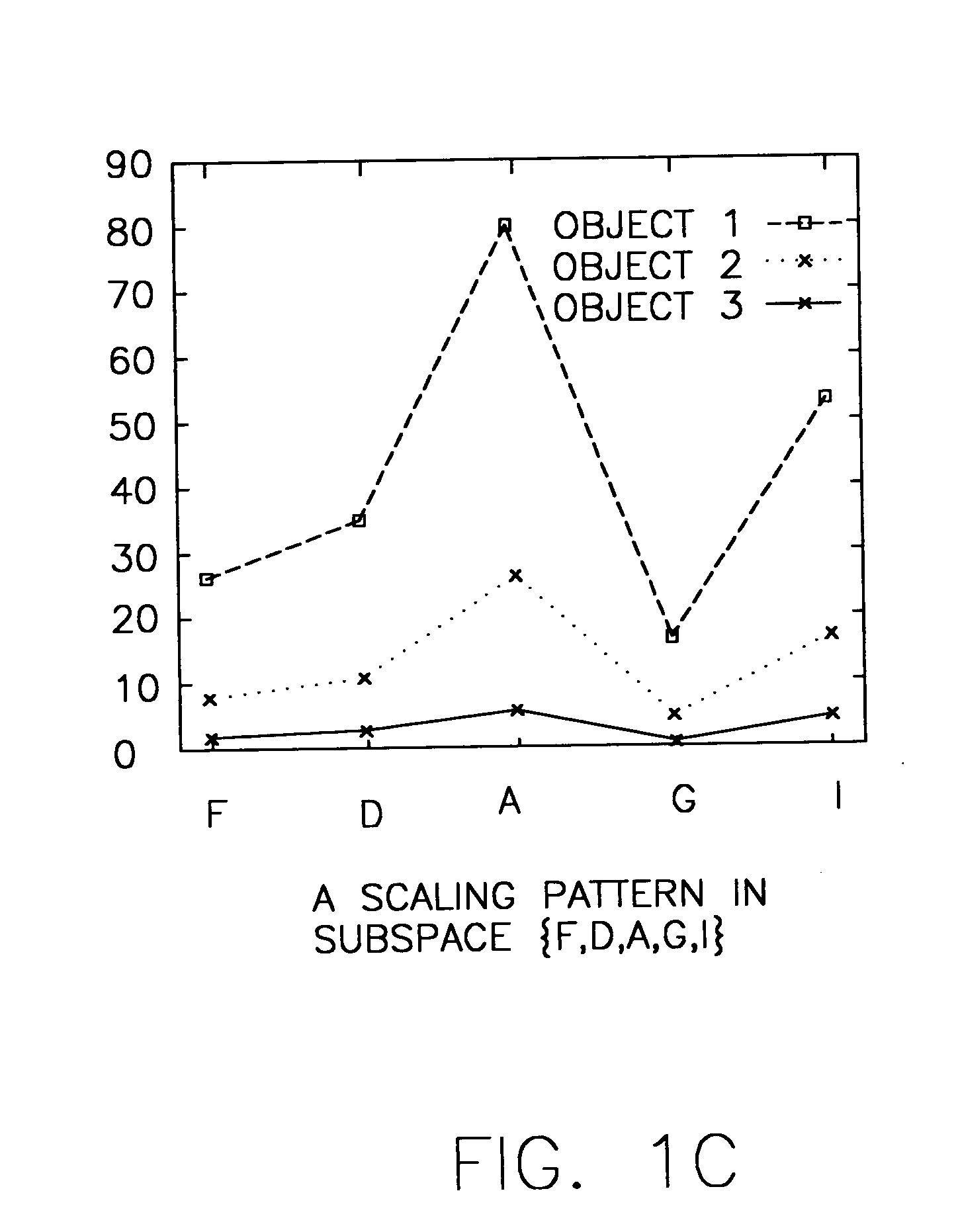
System and method for sequence-based subspace pattern clustering
InactiveUS7565346B2Reduce complexityDigital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setWeb usage analysis
Unlike traditional clustering methods that focus on grouping objects with similar values on a set of dimensions, clustering by pattern similarity finds objects that exhibit a coherent pattern of rise and fall in subspaces. Pattern-based clustering extends the concept of traditional clustering and benefits a wide range of applications, including e-Commerce target marketing, bioinformatics (large scale scientific data analysis), and automatic computing (web usage analysis), etc. However, state-of-the-art pattern-based clustering methods (e.g., the pCluster algorithm) can only handle datasets of thousands of records, which makes them inappropriate for many real-life applications. Furthermore, besides the huge data volume, many data sets are also characterized by their sequentiality, for instance, customer purchase records and network event logs are usually modeled as data sequences. Hence, it becomes important to enable pattern-based clustering methods i) to handle large datasets, and ii) to discover pattern similarity embedded in data sequences. There is presented herein a novel method that offers this capability.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Virus infection detection and identification method based on metagenomics
ActiveCN105112569AHigh detection sensitivityLow initial sample size requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementViral nucleic acidNucleic acid sequence
The invention provides a virus infection detection and identification technology based on metagenomics. The virus infection detection and identification technology based on the metagenomics comprises the four portions of sample preparation, high-throughput sequencing, bioinformatic analysis and result re-checking. In the sample preparation portion, viral nucleic acid is effectively extracted or enriched from detection samples according to the requirements of the virus infection detection and identification technology based on the metagenomics and characteristics of different types of detection samples, and a nucleic acid library which can be used for a next-generation sequencing instrument is established. In the high-throughput sequencing portion, the nucleic acid library established in the sample preparation step is sequenced so to obtain sufficient high-quality nucleic acid sequence information. In the bioinformatic analysis portion, a large number of high-quality nucleic acid sequences obtained in the high-throughput sequencing step is analyzed to further obtain viral component information prompted by the nucleic acid of the samples. In the result re-checking portion, a bioinformatic analysis result and other information, such as technical contrast, are integrated to perform comprehensive study and judgment, finally alternative infection virus is determined, and other technologies, such as PCR, are utilized to perform re-checking.
Owner:INST OF PATHOGEN BIOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Bioinformatic transaction scheme
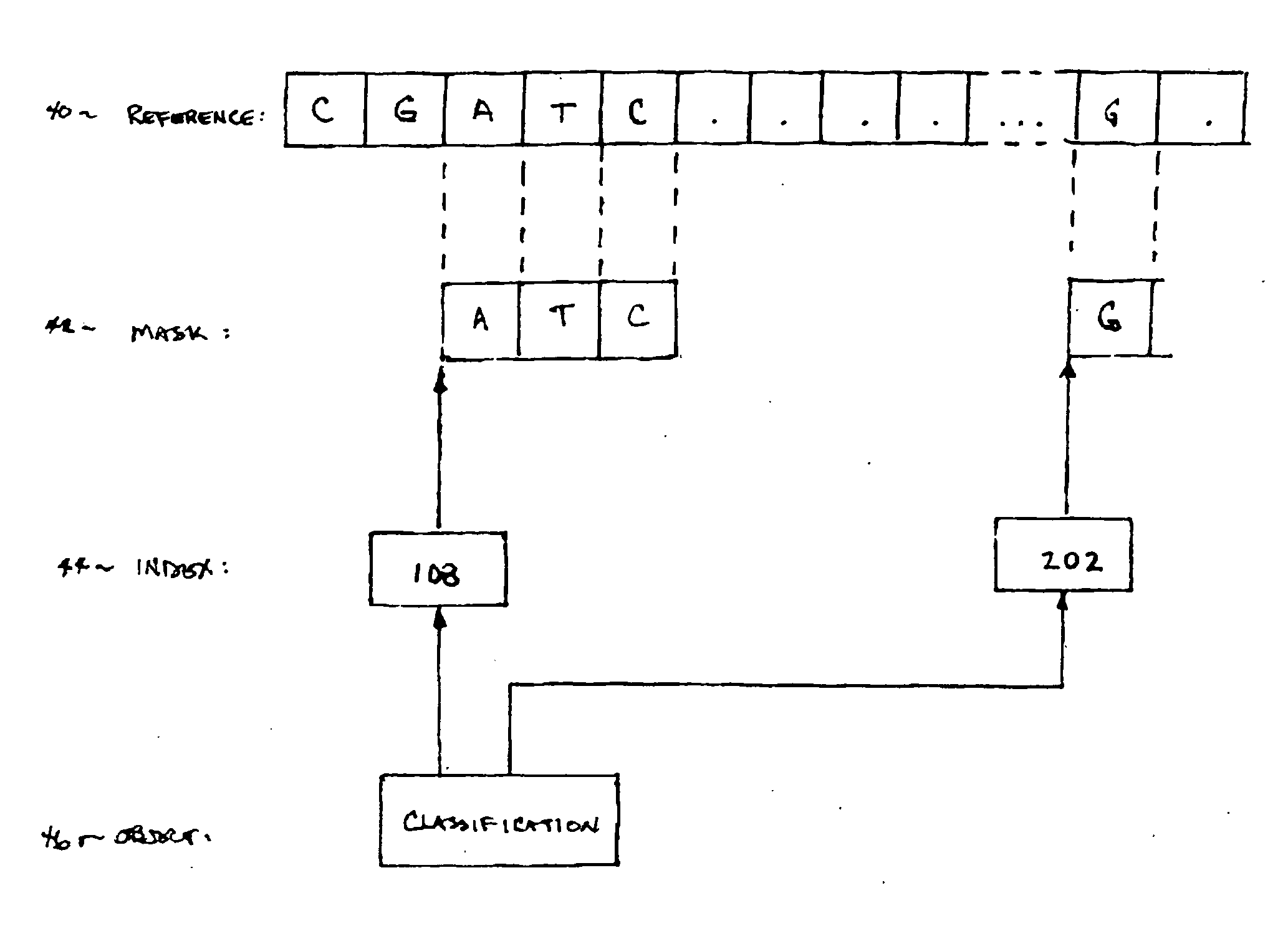
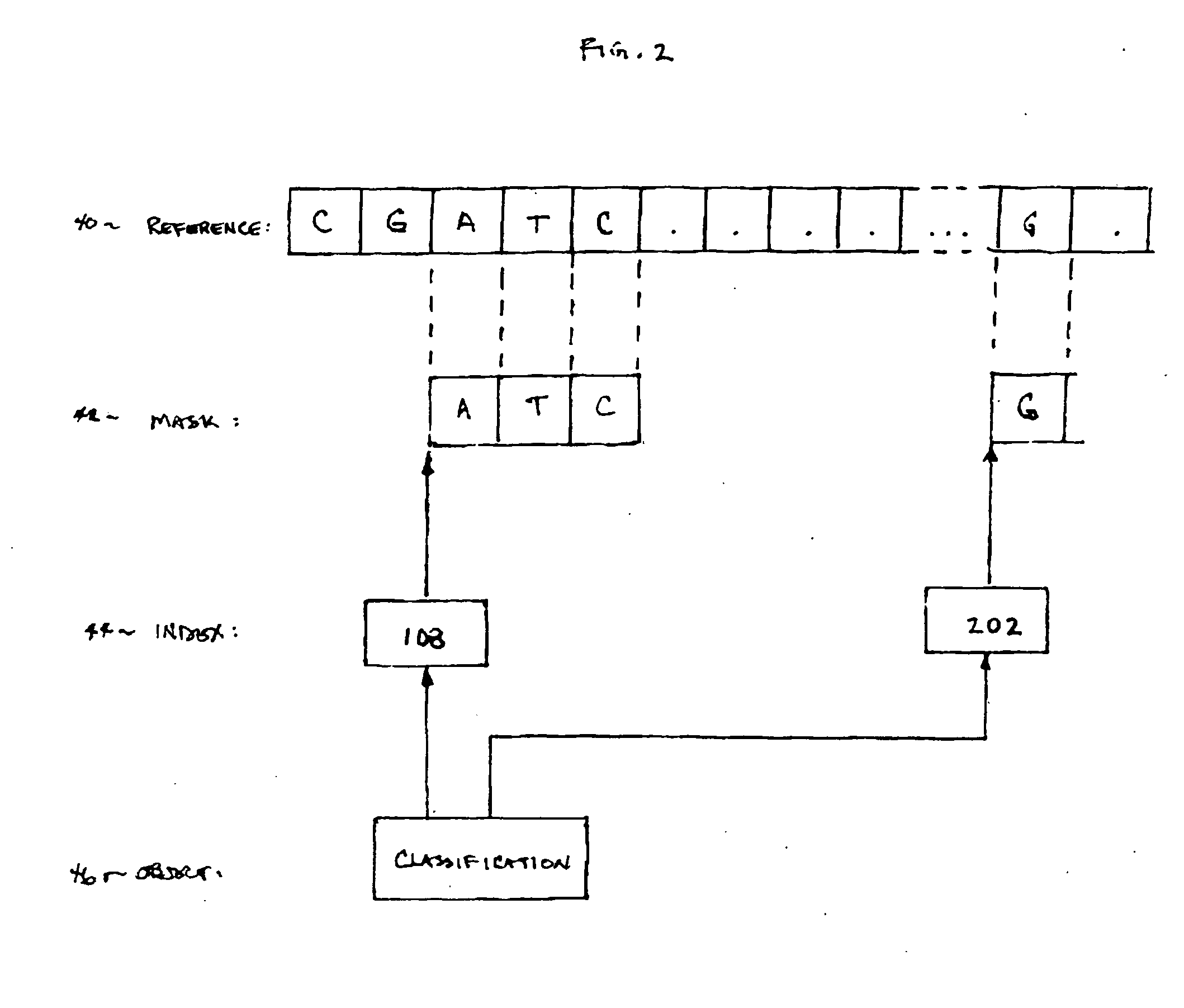
InactiveUS20070061085A1Digital data authenticationSpecial data processing applicationsRisk profilingUser device
Secure network transaction system obtains user-authorized genetic term or bioinformatic profile, and transacts online service according to genetically-based user medical or other risk determined therefrom. Insurance policy, promotional offer, or other service may dynamically address genetically-based condition. Bioinformatic data classifies user per personal mask which filters subset of user genetic sequence. Risk profile may be calculated according to actuarial statistics, genetics and / or heredity using non-discriminatory rules specified for users in temporal or jurisdictional groups. User transactions are modifiable according to bioinformatic data representing genetically-based risk increase or decrease. Data is securely processed, modulated, and stored by network server for remote access and transaction using various portable user devices.
Owner:FERNANDEZ DENNIS S
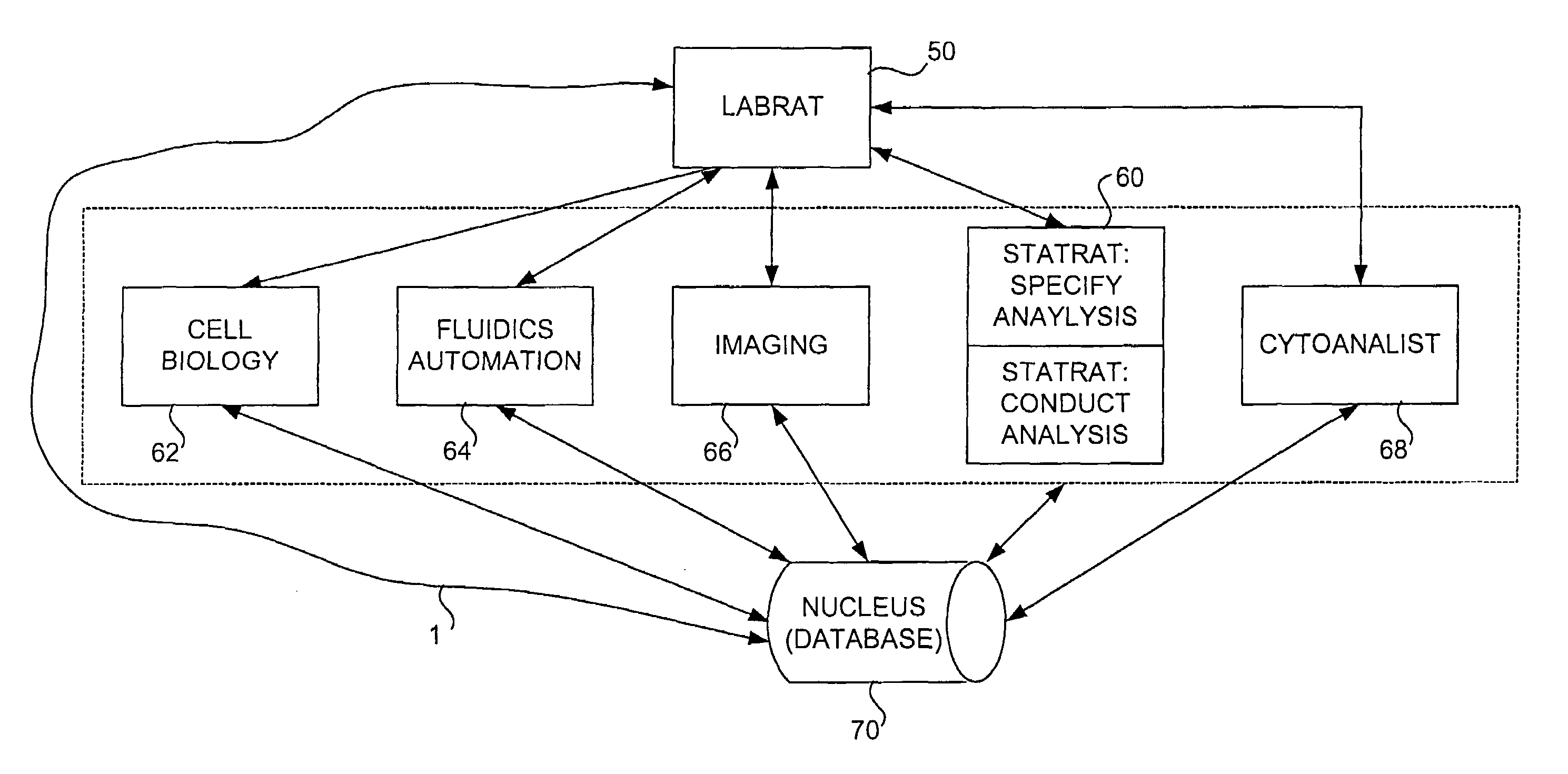
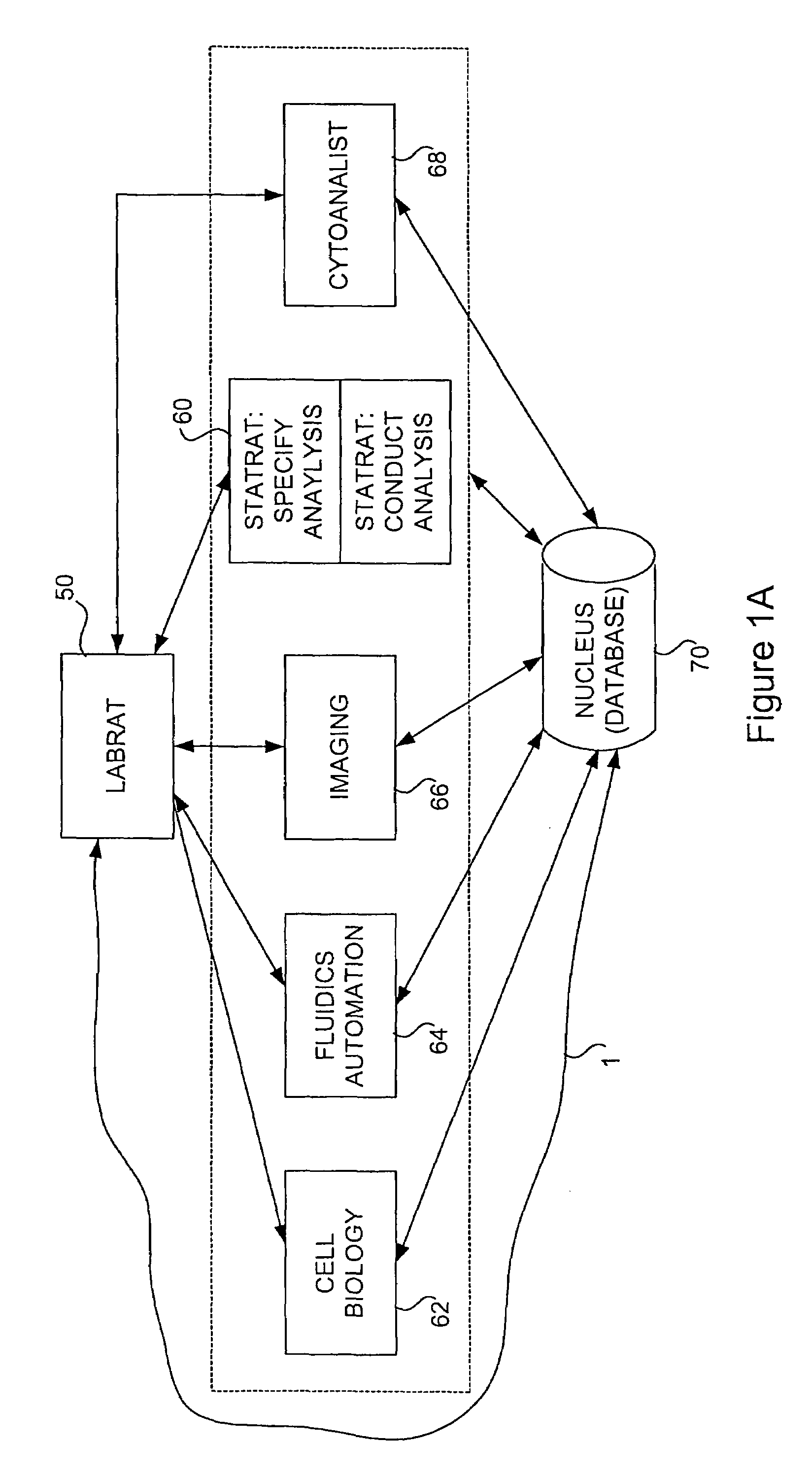
Method and apparatus for automated cellular bioinformatics
InactiveUS6999607B2Facilitate communicationEasy to controlImage enhancementImage analysisMedicineData profiling
An automated system that conducts, monitors, and validates a cell-line-based biological experiment including one or more treatment compounds or other external stimuli. In one preferred embodiment, the system comprises two principal subsystems, and optionally accessory subsystems. A first principal subsystem is an automated laboratory experiment manager for designing the biological experiment, for constructing an assay plate used to conduct the biological experiment, and for managing one or more of the processes that constitute the biological experiment. A second principal subsystem is an automated data analysis manager for analyzing images, for instance produced by the image production system, to detect image data including biological markers and objects, for analyzing the resulting image data to produce biological data, and for analyzing the biological data to produce biological phenotypes and treatment compound signatures.
Owner:CYTOKINETICS INC
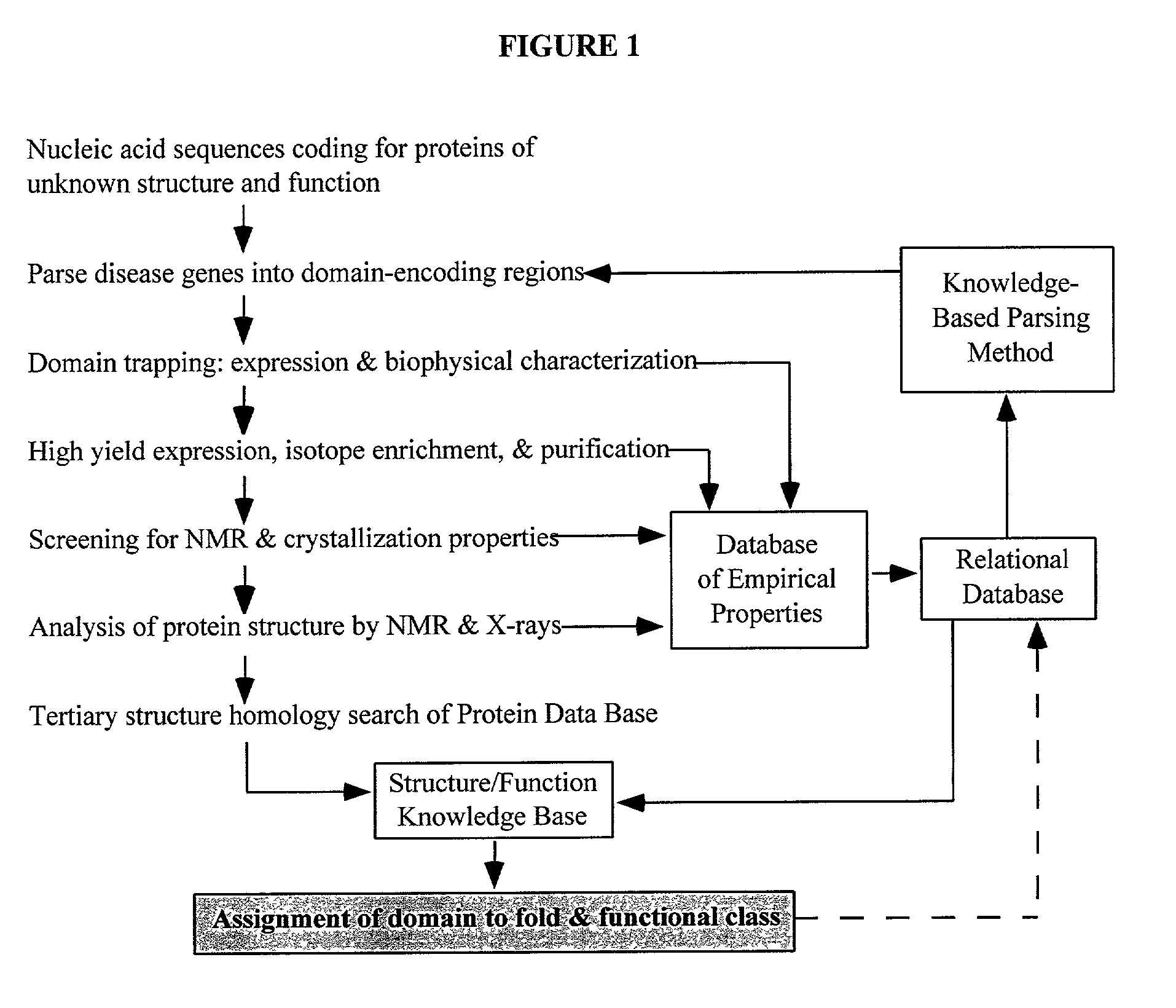
Linking gene sequence to gene function by three dimesional (3D) protein structure determination
InactiveUS20010016314A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFunctional profilingProtein structure
The present invention provides a structure-functional analysis engine for the high-throughput determination of the biochemical function of proteins or protein domains of unknown function. The present invention uses bioinformatics, molecular biology and nuclear magnetic resonance tools for the rapid and automated determination of the three-dimensional structures of proteins and protein domains.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
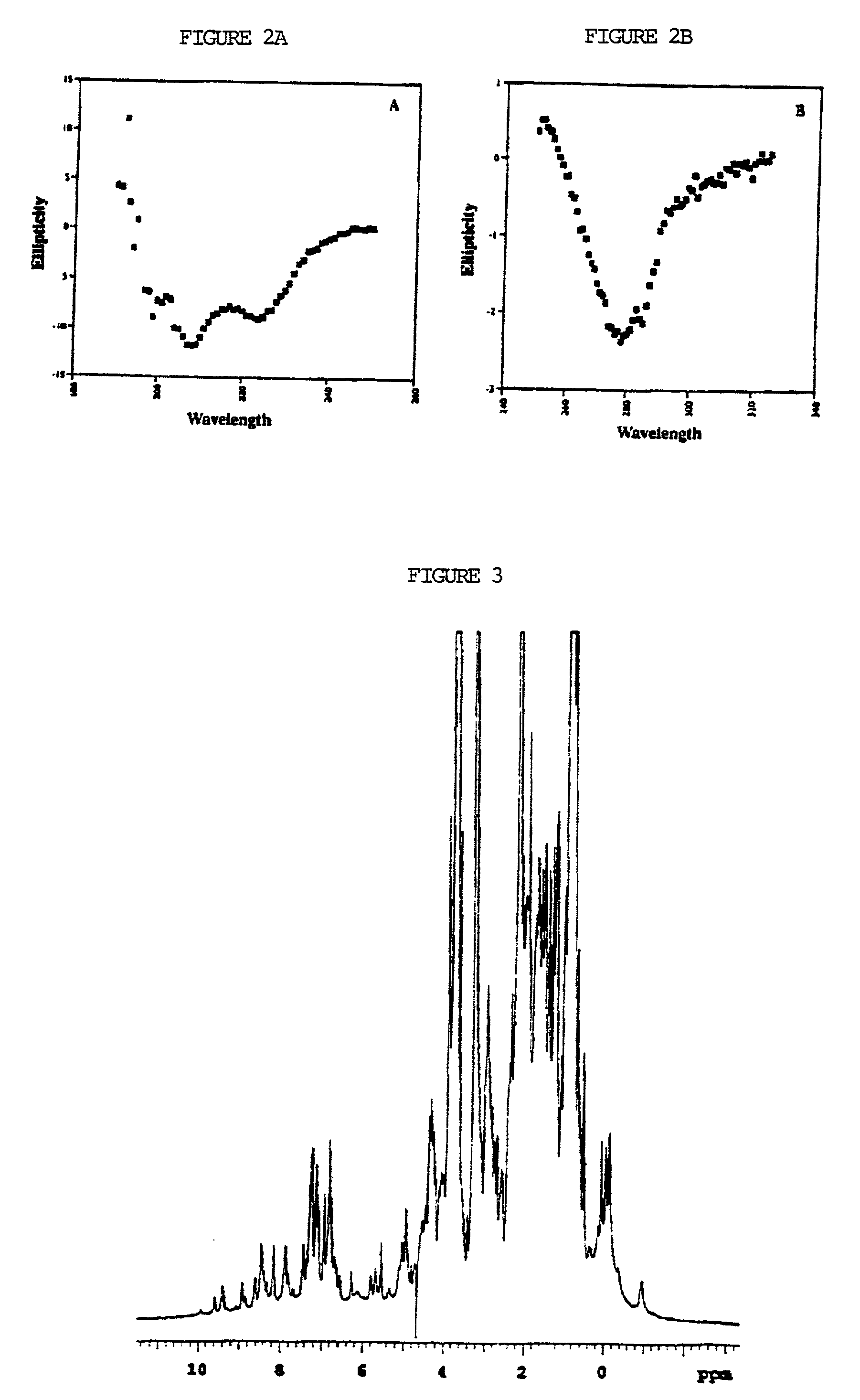
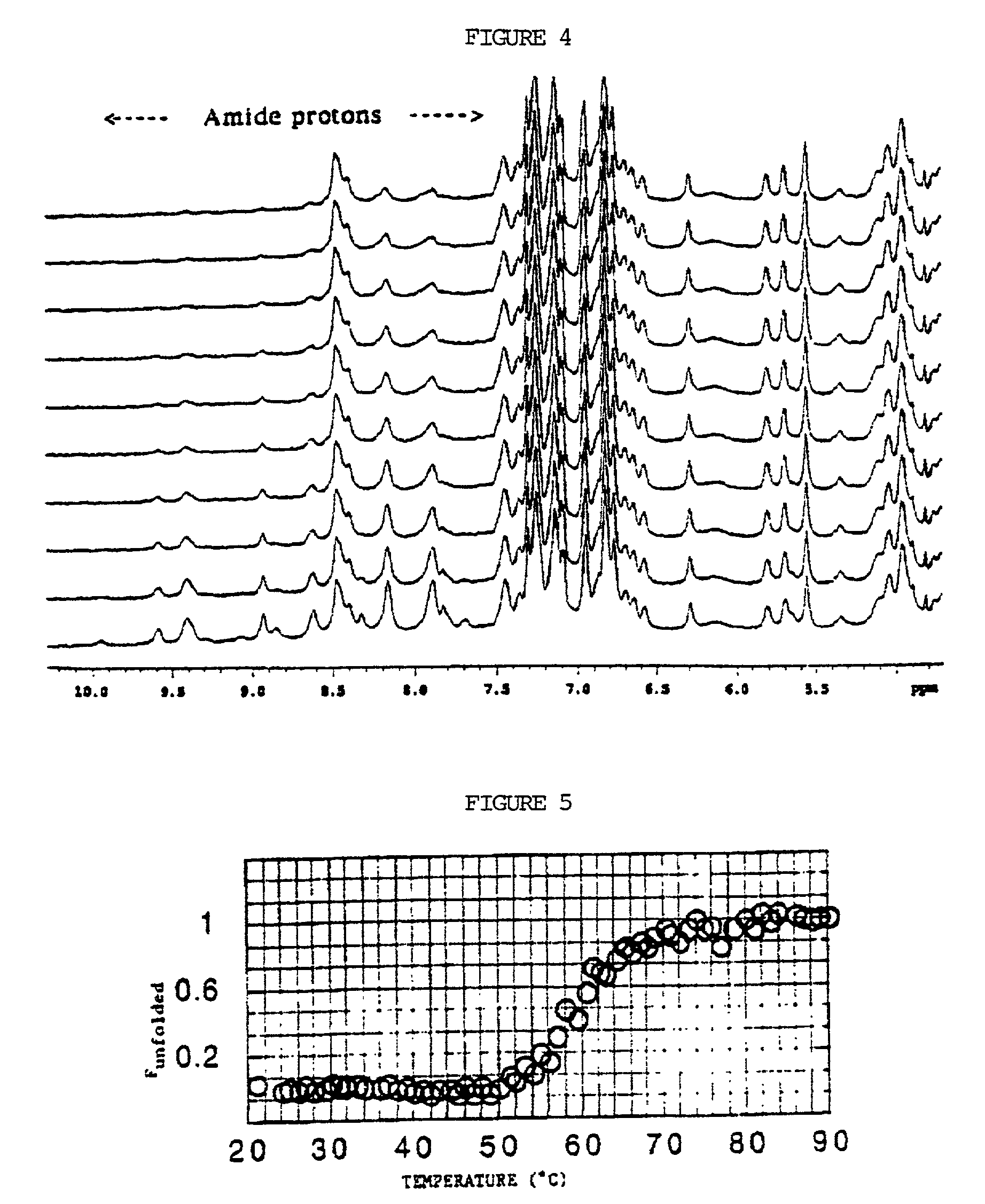
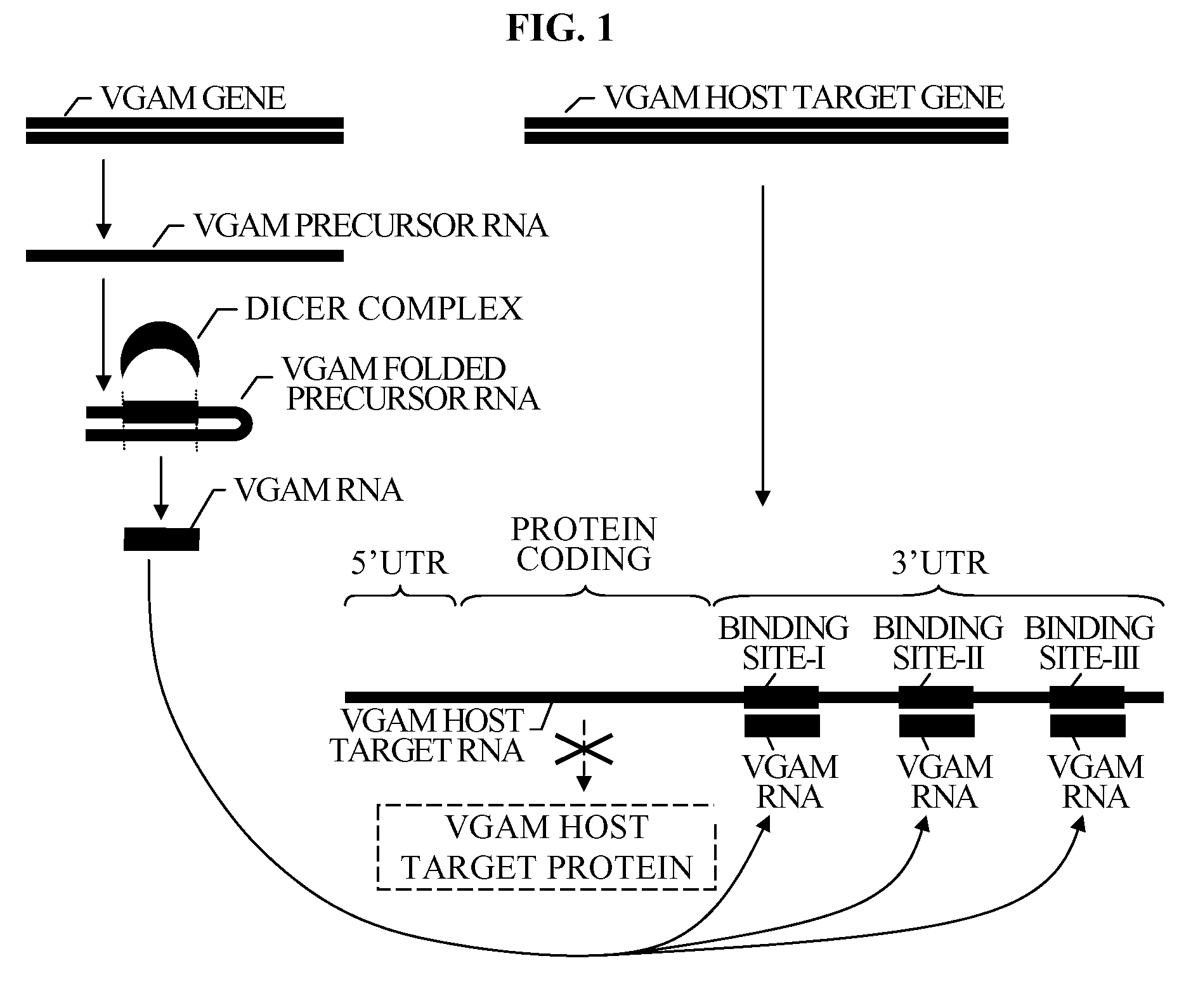
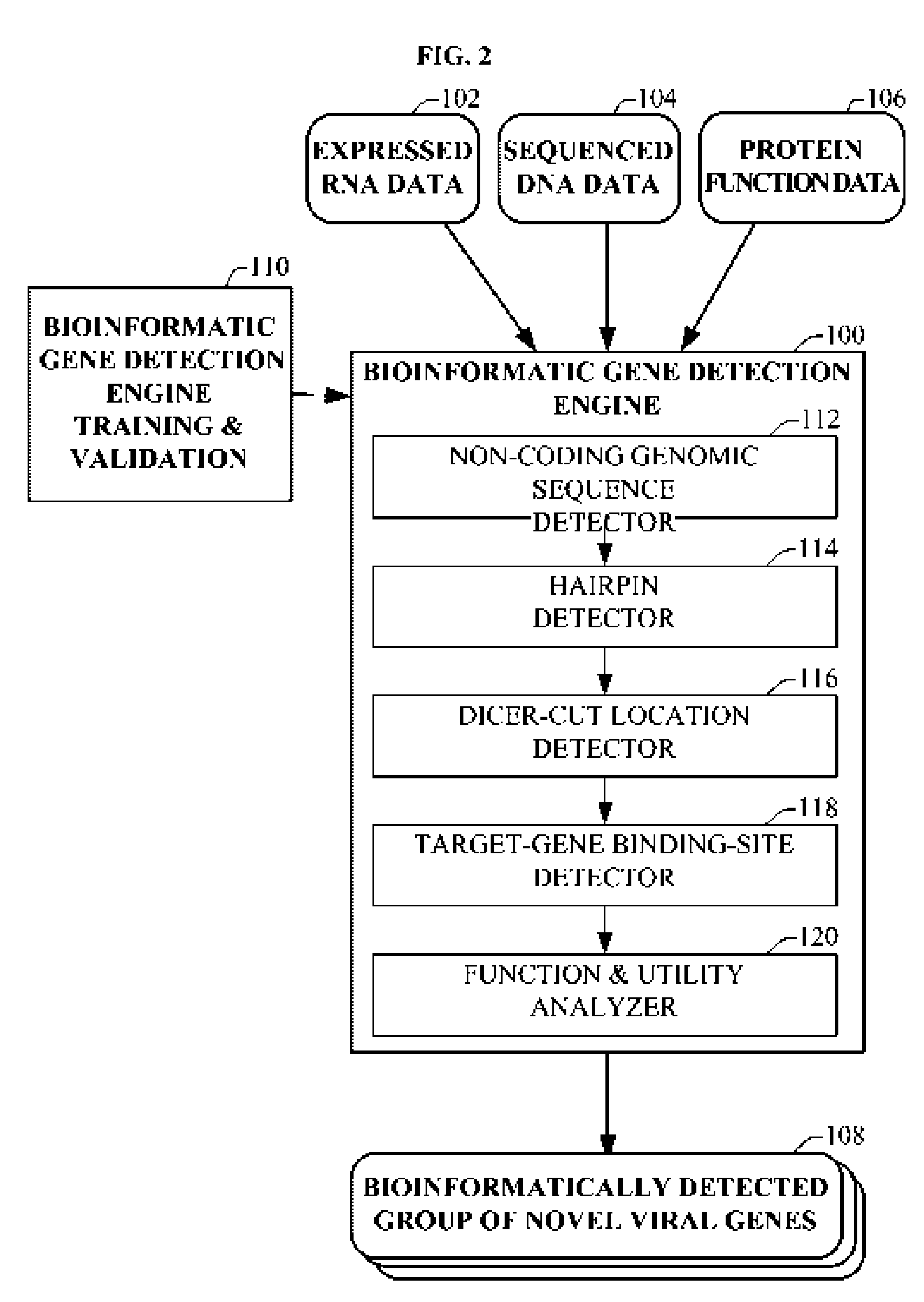
Bioinformatically detectable group of novel HIV regulatory genes and uses thereof
InactiveUS7217807B2Preventing and treating viral diseasesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementViral diseaseOperon
The present invention relates to a group of novel viral RNA regulatory genes, here identified as “viral genomic address messenger genes” or “VGAM genes”, and as “genomic record” or “GR” genes. VGAM genes selectively inhibit translation of known host target genes, and are believed to represent a novel pervasive viral attack mechanism. GR genes encode an operon-like cluster of VGAM genes. VGAM and viral GR genes may therefore be useful in diagnosing, preventing and treating viral disease. Several nucleic acid molecules are provided respectively encoding several VGAM genes, as are vectors and probes, both comprising the nucleic acid molecules, and methods and systems for detecting VGAM genes, and for counteracting their activity.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Systems and methods for subspace clustering
InactiveUS20050278324A1Reduce complexityDigital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setWeb usage analysis
Unlike traditional clustering methods that focus on grouping objects with similar values on a set of dimensions, clustering by pattern similarity finds objects that exhibit a coherent pattern of rise and fall in subspaces. Pattern-based clustering extends the concept of traditional clustering and benefits a wide range of applications, including e-Commerce target marketing, bioinformatics (large scale scientific data analysis), and automatic computing (web usage analysis), etc. However, state-of-the-art pattern-based clustering methods (e.g., the pCluster algorithm) can only handle datasets of thousands of records, which makes them inappropriate for many real-life applications. Furthermore, besides the huge data volume, many data sets are also characterized by their sequentiality, for instance, customer purchase records and network event logs are usually modeled as data sequences. Hence, it becomes important to enable pattern-based clustering methods i) to handle large datasets, and ii) to discover pattern similarity embedded in data sequences. There is presented herein a novel method that offers this capability.
Owner:IBM CORP
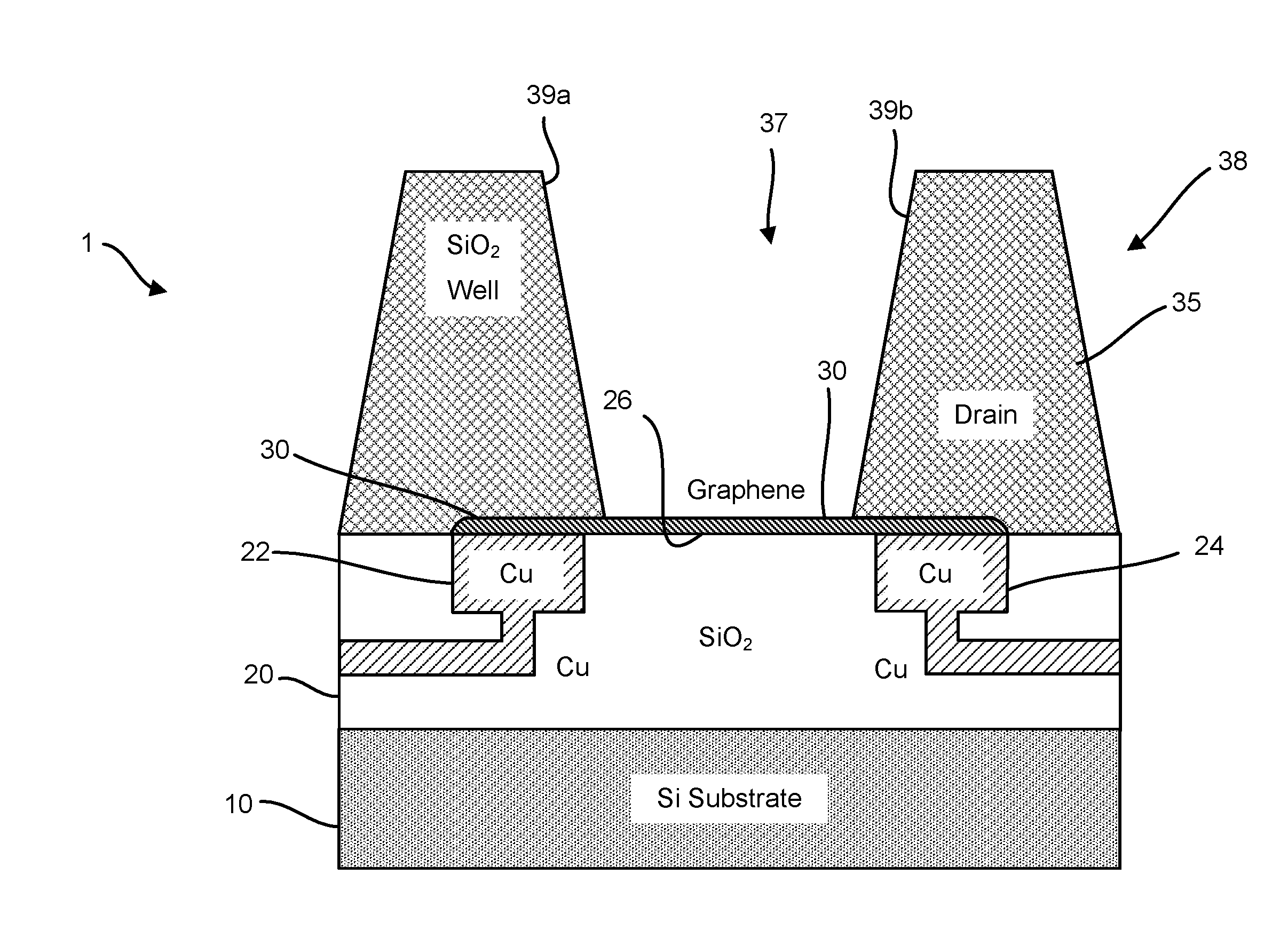
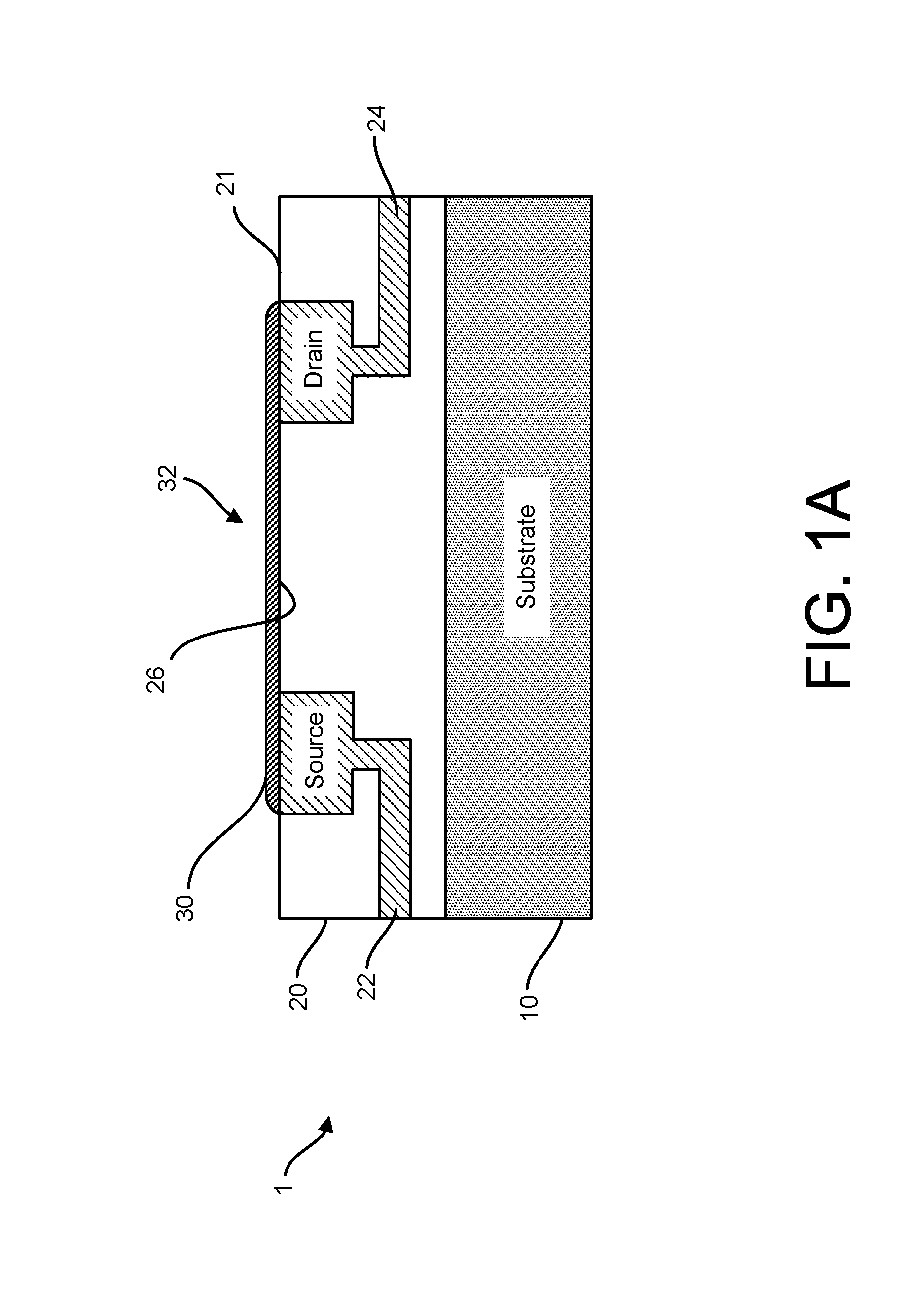
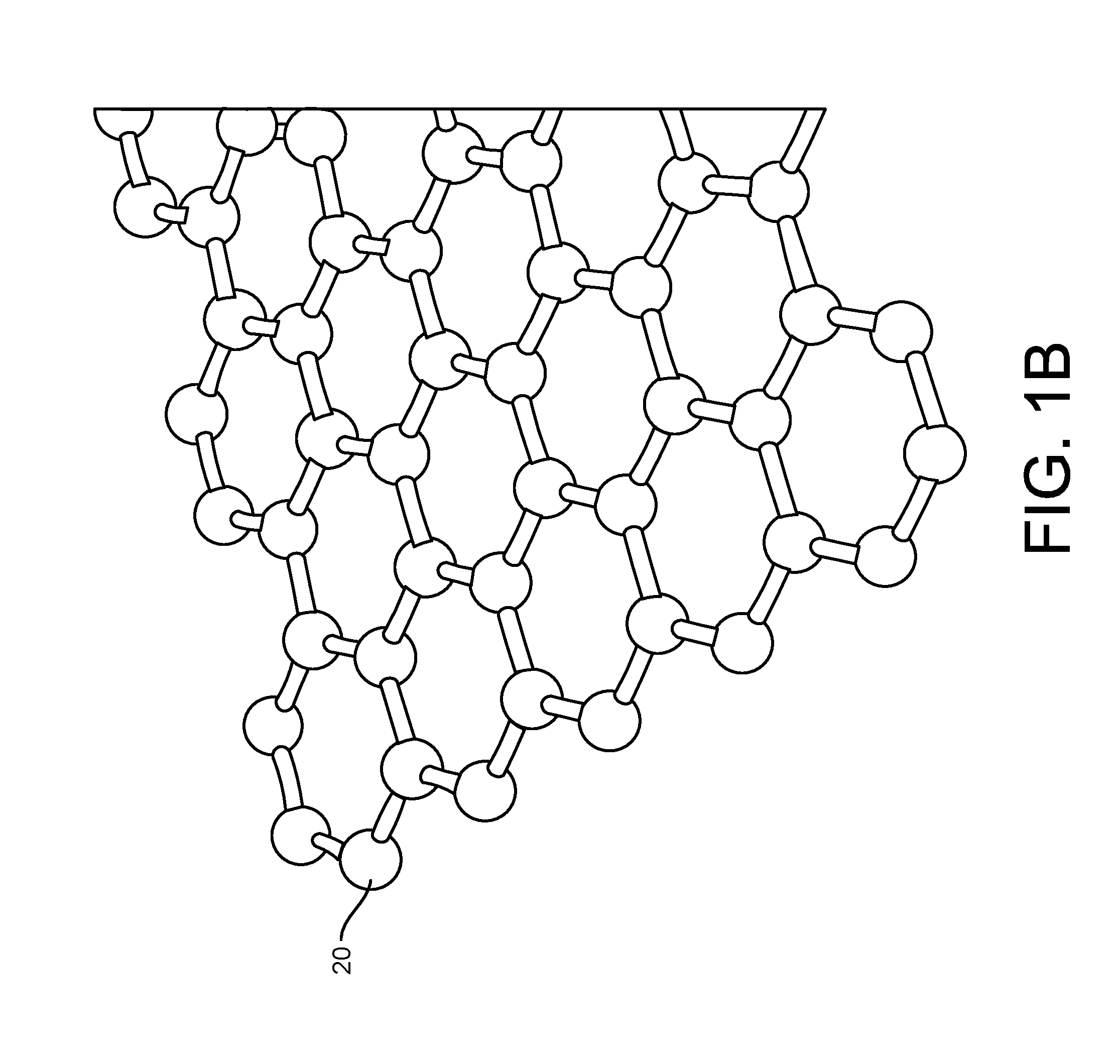
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS20160265047A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementSensor arrayReaction layer
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
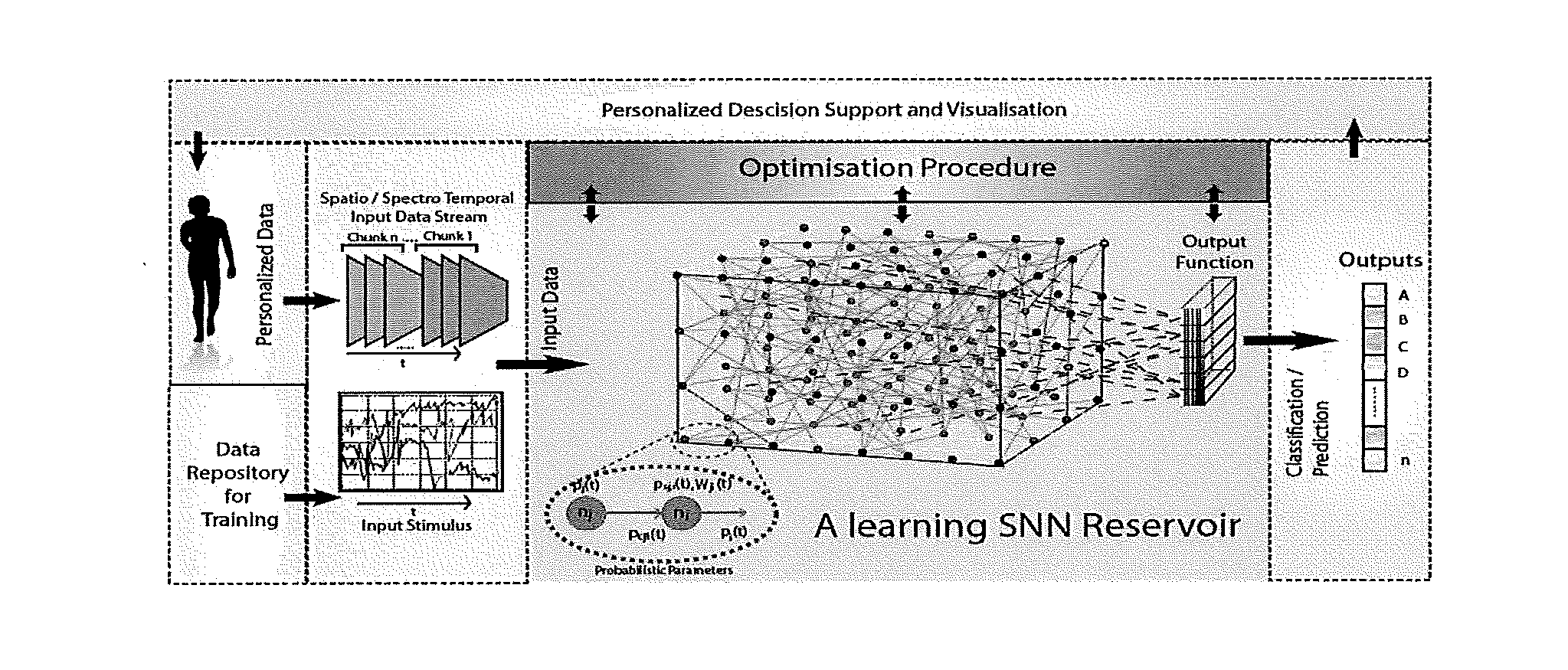
Improved Method And System For Predicting Outcomes Based On Spatio/Spectro-Temporal Data
ActiveUS20160210552A1Improve accuracyShorten the timeDigital computer detailsDigital dataSpike trainSpatiotemporal pattern
This invention involves use of temporal or spatio / spector-temporal data (SSTD) for early classification of outputs that are results of spatio-temporal patterns of data. Classification models are based on spiking neural networks (SNN) suitable to learn and classify SSTD. The invention may predict early events in many applications, i.e. engineering, bioinformatics, neuroinformatics, predicting response to treatment of neurological and brain disease, ecology, environment, medicine, and economics, among others. The invention involves a method and system for personalized modelling of SSTD and early prediction of events based on evolving spiking neural network reservoir architecture (eSNNr). The system includes a spike-time encoding module to encode continuous value input information into spike trains, a recurrent 3D SNNr and an eSSN as an output classification module.
Owner:AUT VENTURES LTD
System and method for pattern recognition in sequential data
InactiveUS8280640B2Easy to useIncrease speedBiological testingComparison of digital valuesSequential dataMedical diagnosis
The present invention is based on the encoding of sequential data or sequences in a novel manner that permits efficient storage and processing of sequential data, as well as methods for searching sequences or databases of sequences. The methods and systems of the current invention may be adapted broadly to various fields of application and to a variety of sequences types. For example, the current invention has broad application including to the fields of bioinformatics, molecular biology, pharmacogenomics, phonetic sequences, lexicographic sequences, signal analysis, game playing, law enforcement, biometrics, medical diagnosis, equipment maintenance and micro-array data analysis.
Owner:ELORET CORP
Bioinformatics systems, apparatuses, and methods for performing secondary and/or tertiary processing
InactiveUS20180121601A1Improve processing speedImprove accuracyInternal/peripheral component protectionProteomicsSequence analysisGenomics
A system, method and apparatus for executing a bioinformatics analysis on genetic sequence data is provided. Particularly, a genomics analysis platform for executing a sequence analysis pipeline is provided. The genomics analysis platform includes one or more of a first integrated circuit, where each first integrated circuit forms a central processing unit (CPU) that is responsive to one or more software algorithms that are configured to instruct the CPU to perform a first set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline. Additionally, a second integrated circuit is also provided, where each second integrated circuit forming a field programmable gate array (FPGA), the FPGA being configured by firmware to arrange a set of hardwired digital logic circuits that are interconnected by a plurality of physical interconnects to perform a second set of genomic processing steps of the sequence analysis pipeline, the set of hardwired digital logic circuits of each FPGA being arranged as a set of processing engines to perform the second set of genomic processing steps. A shared memory is also provided.
Owner:EDICO GENOME
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com