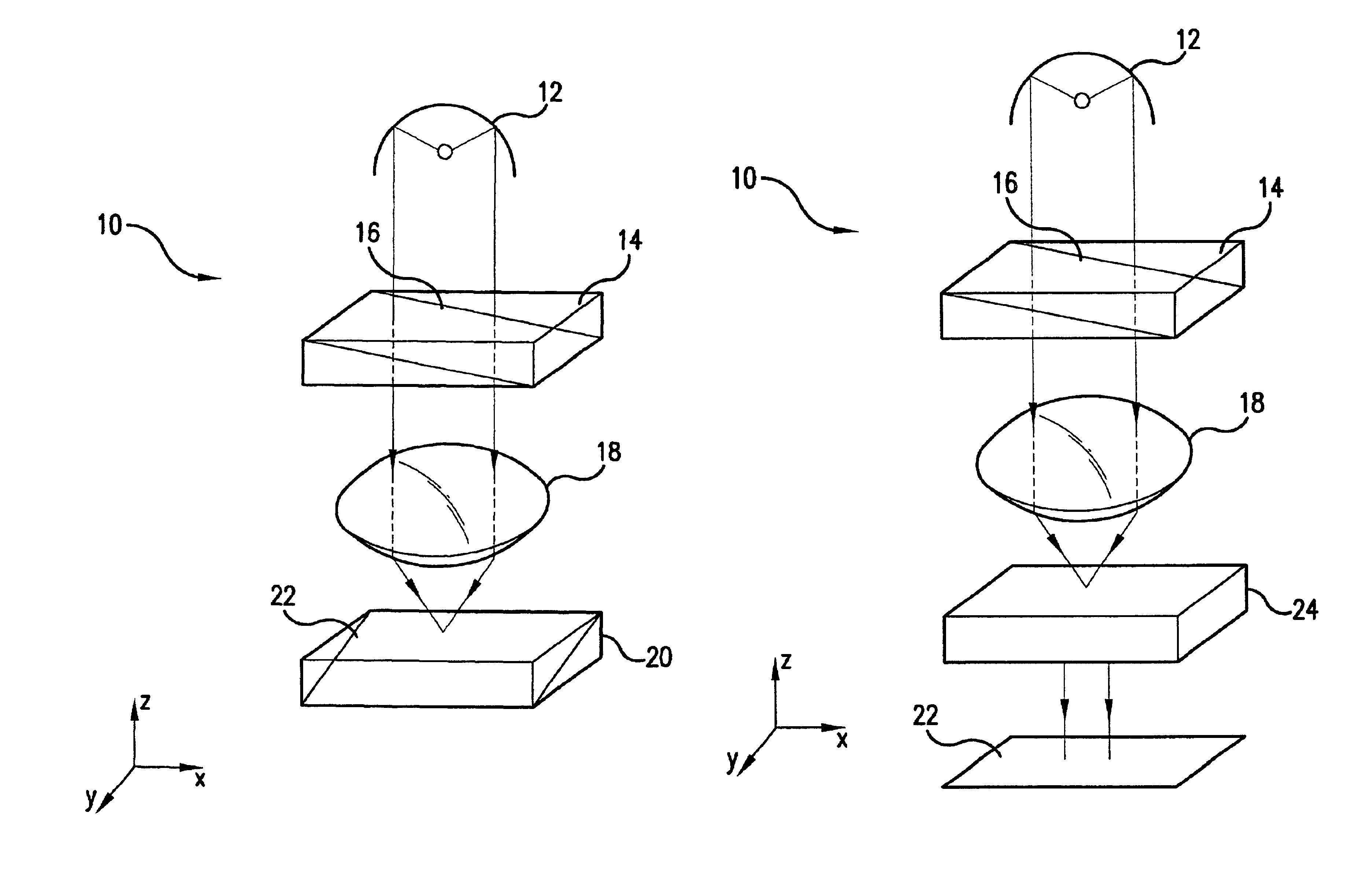
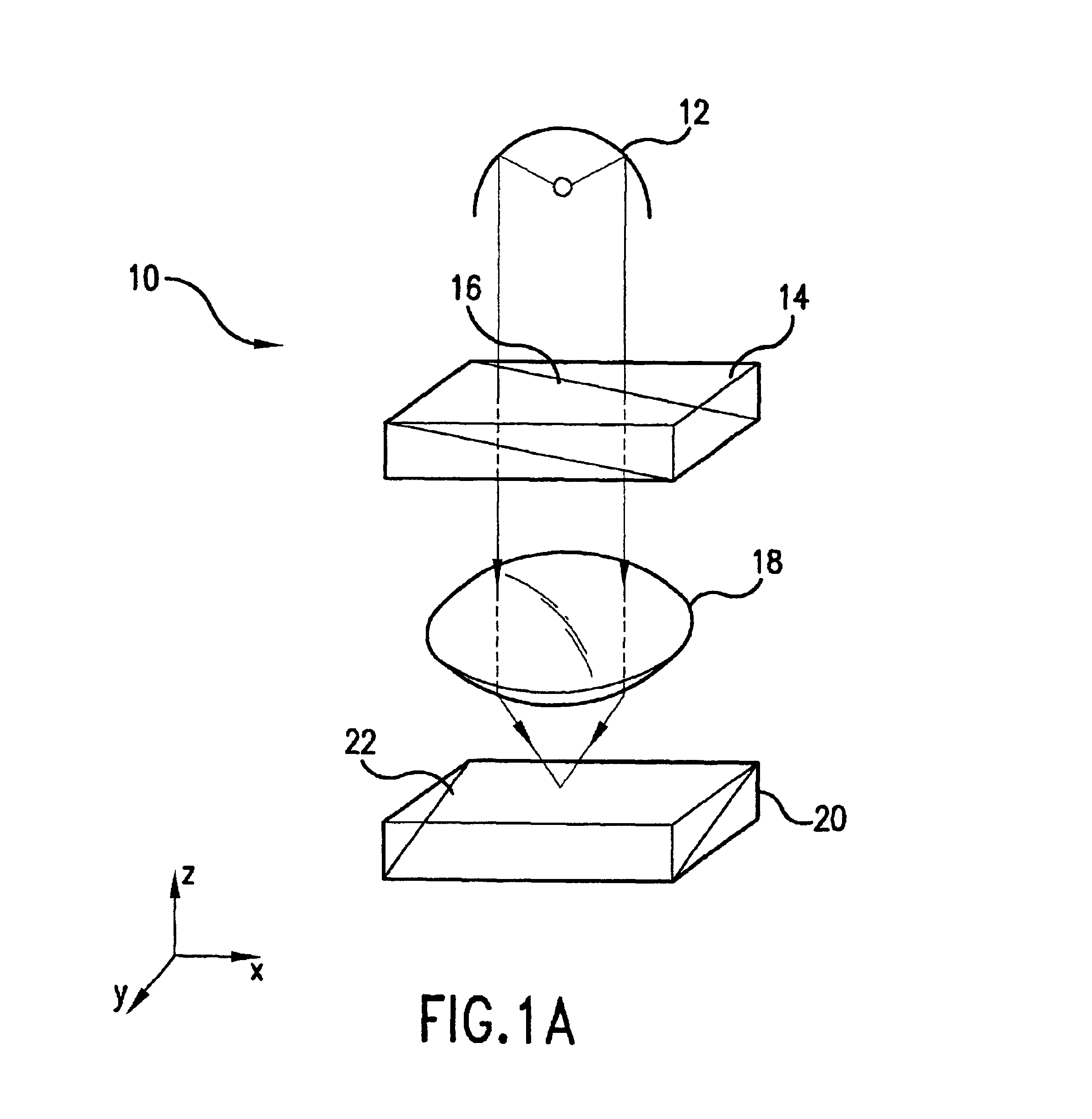
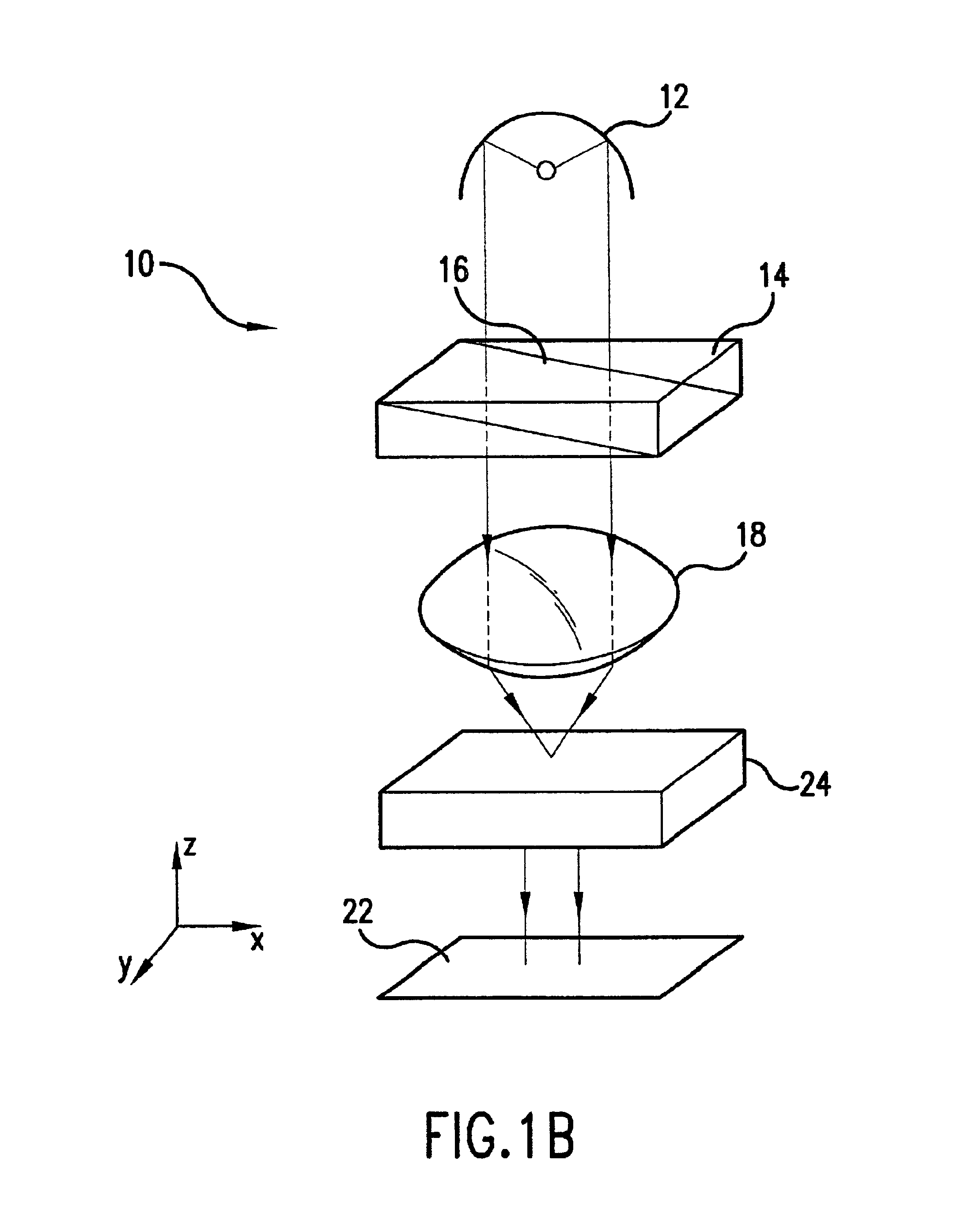
Patents
Literature
59results about How to "Faster data acquisition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
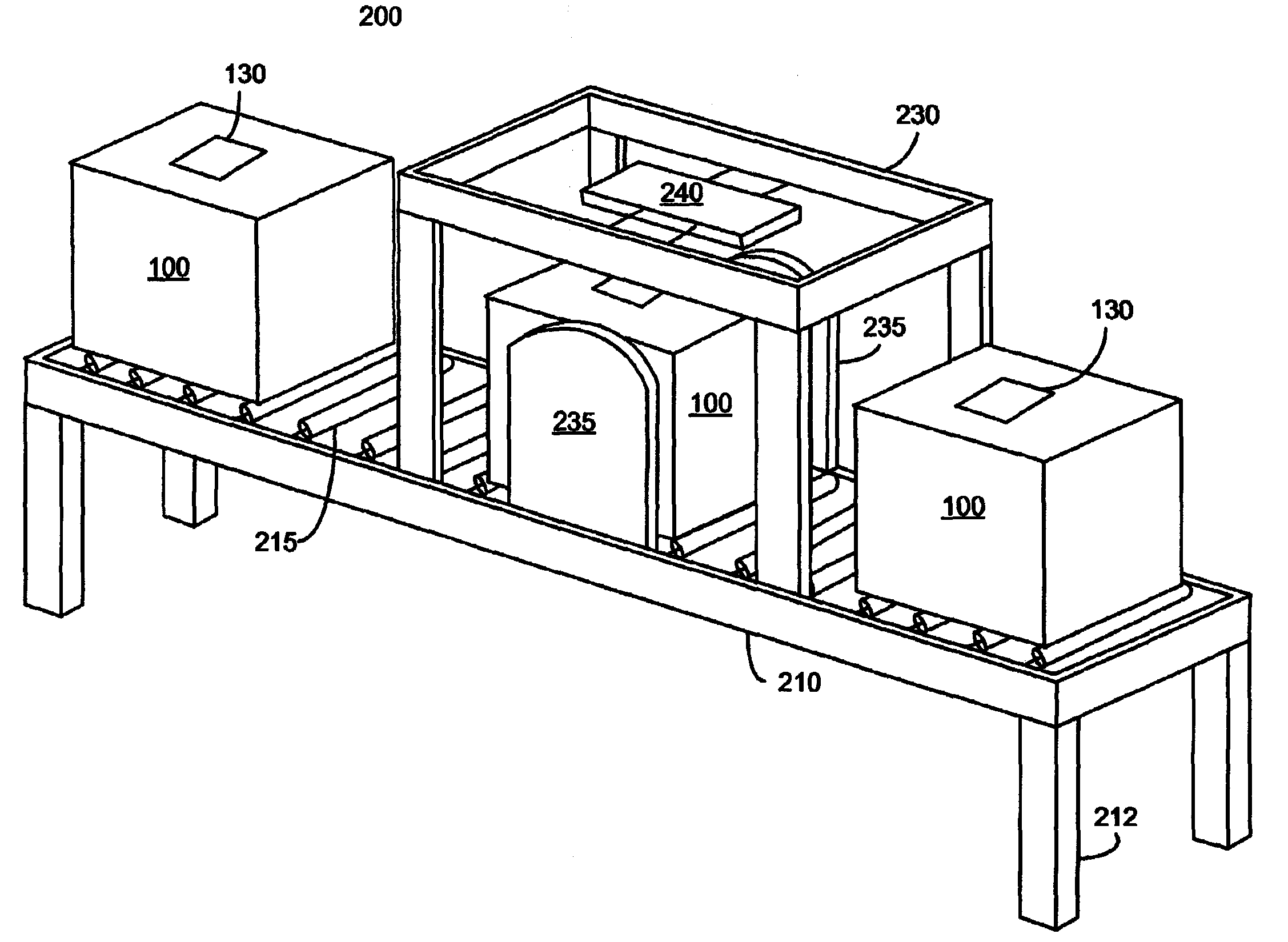
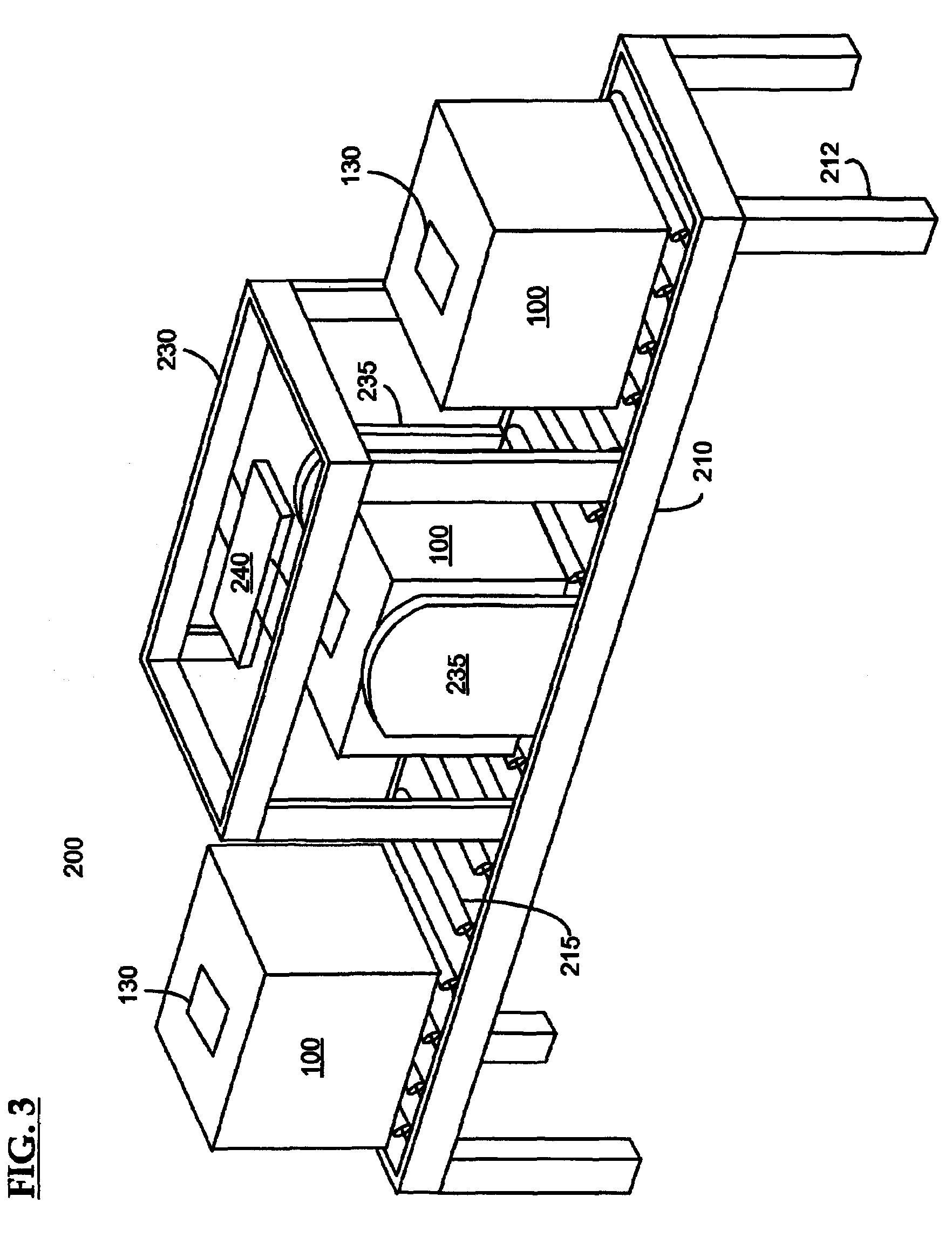
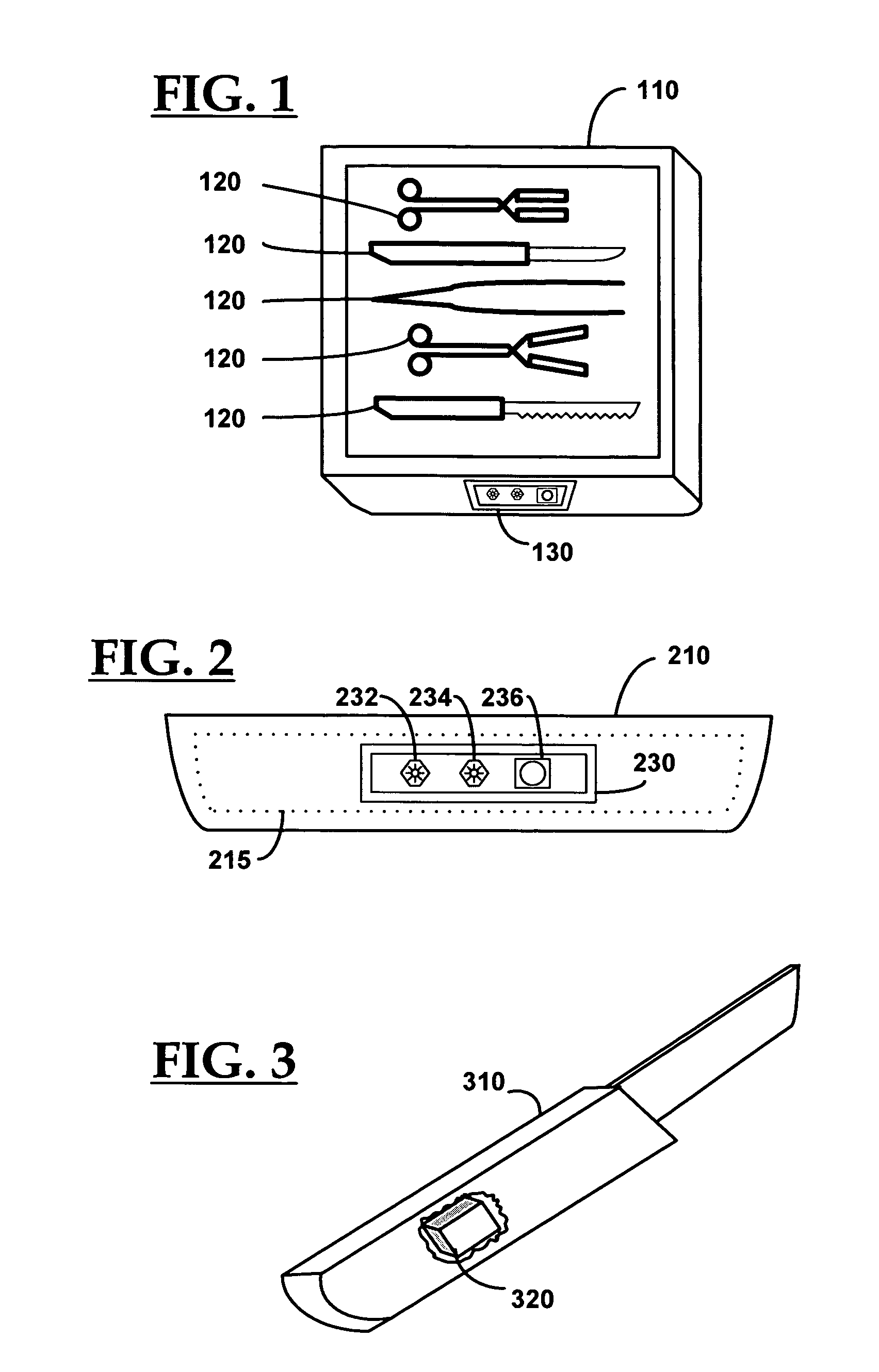
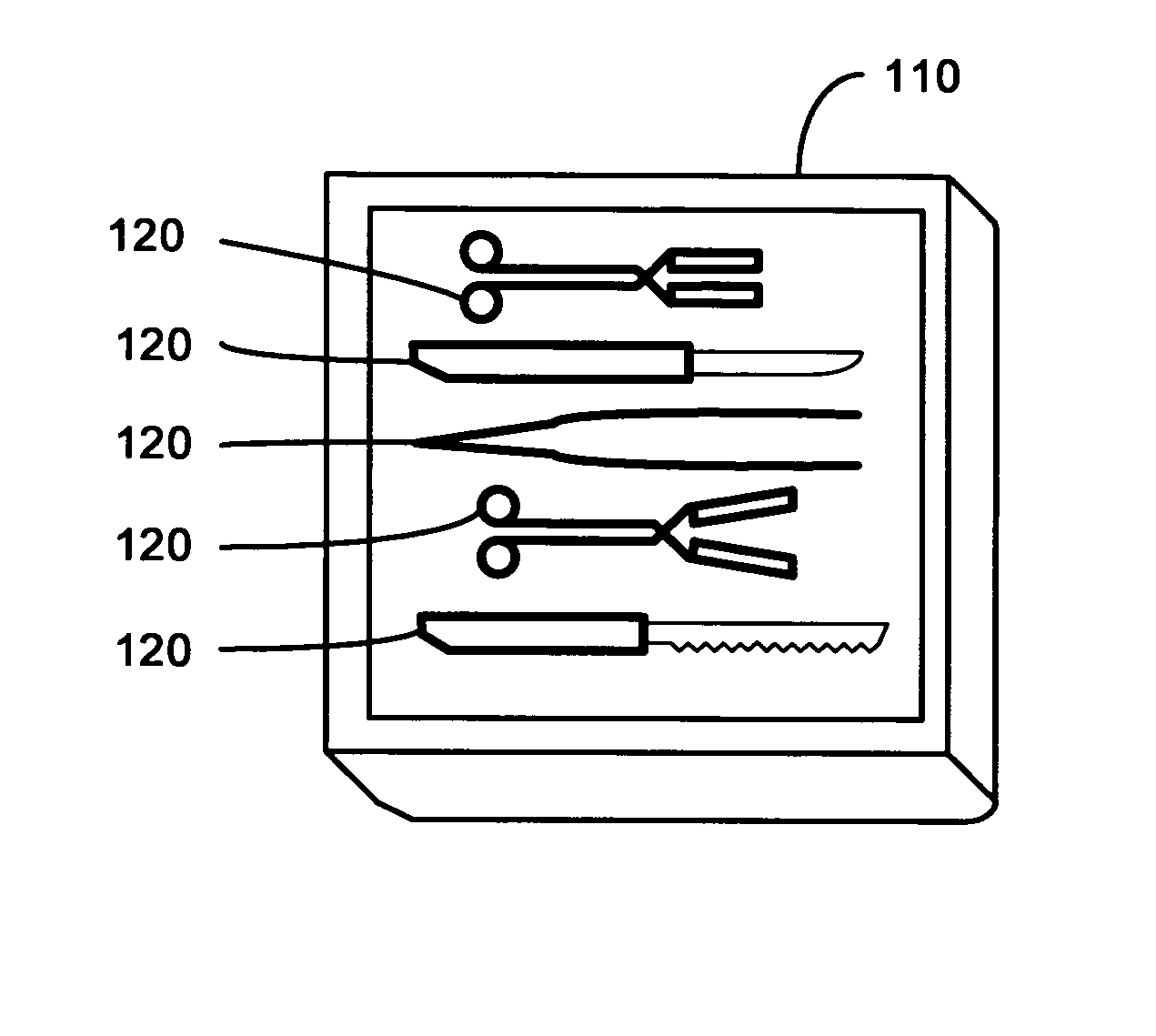
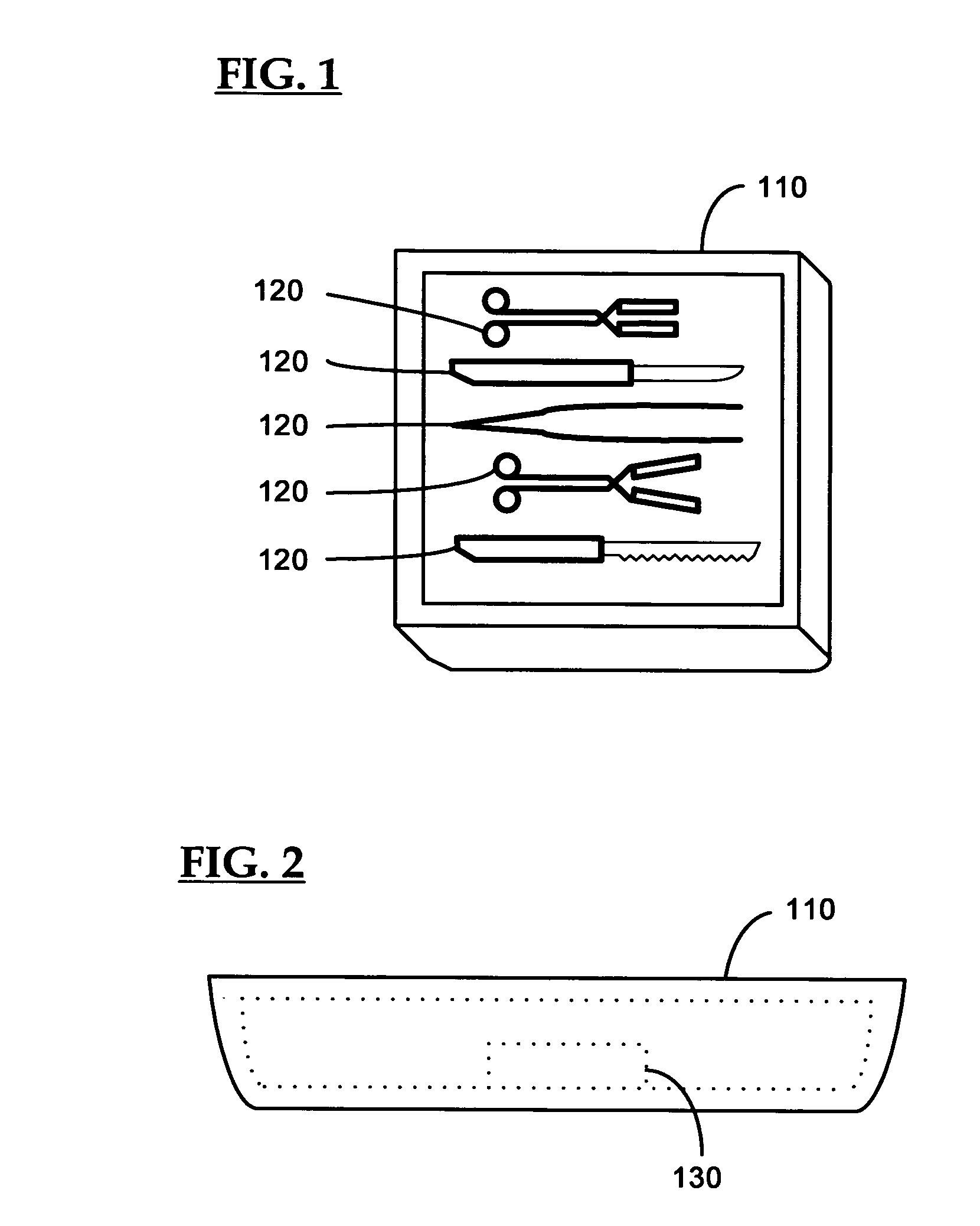
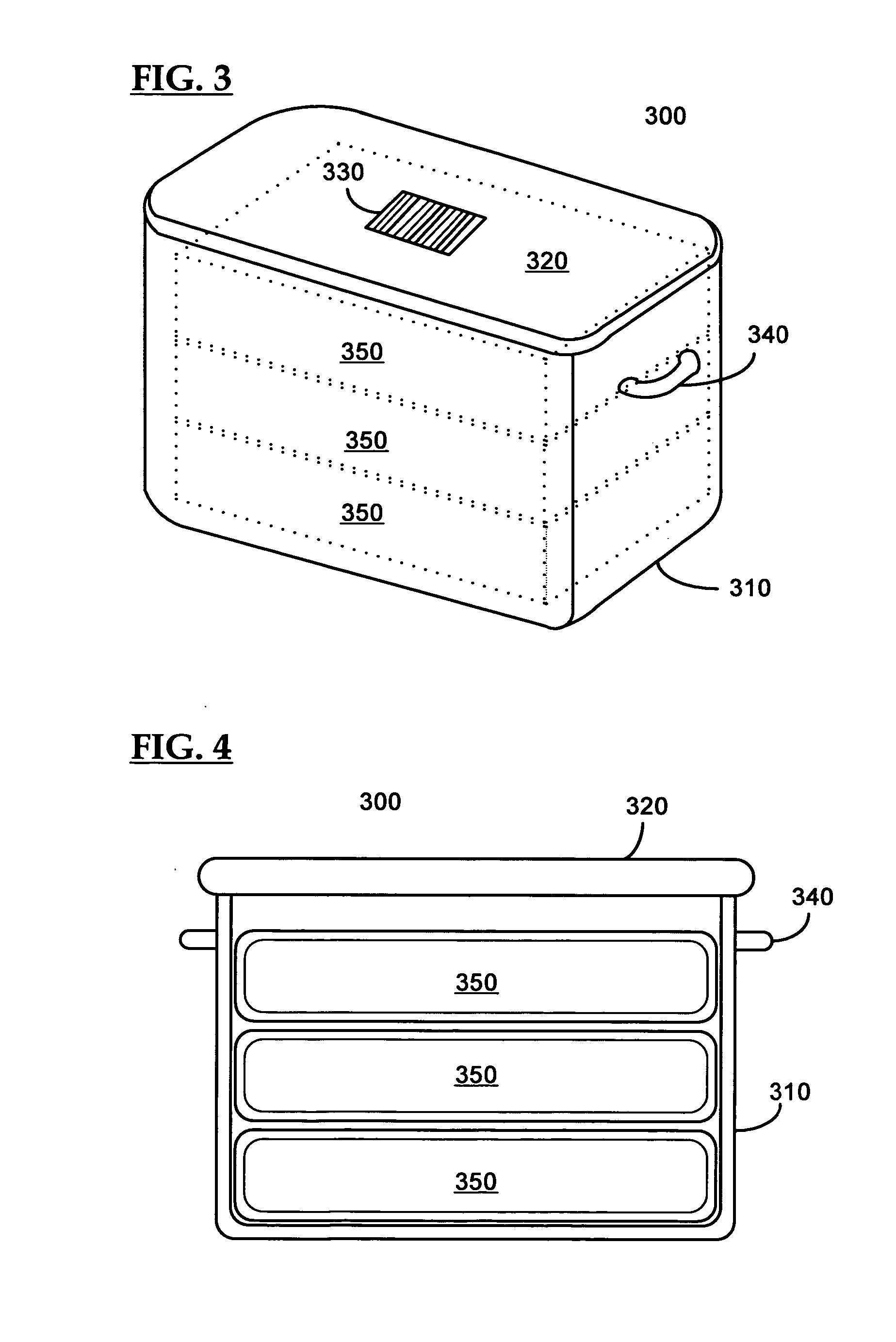
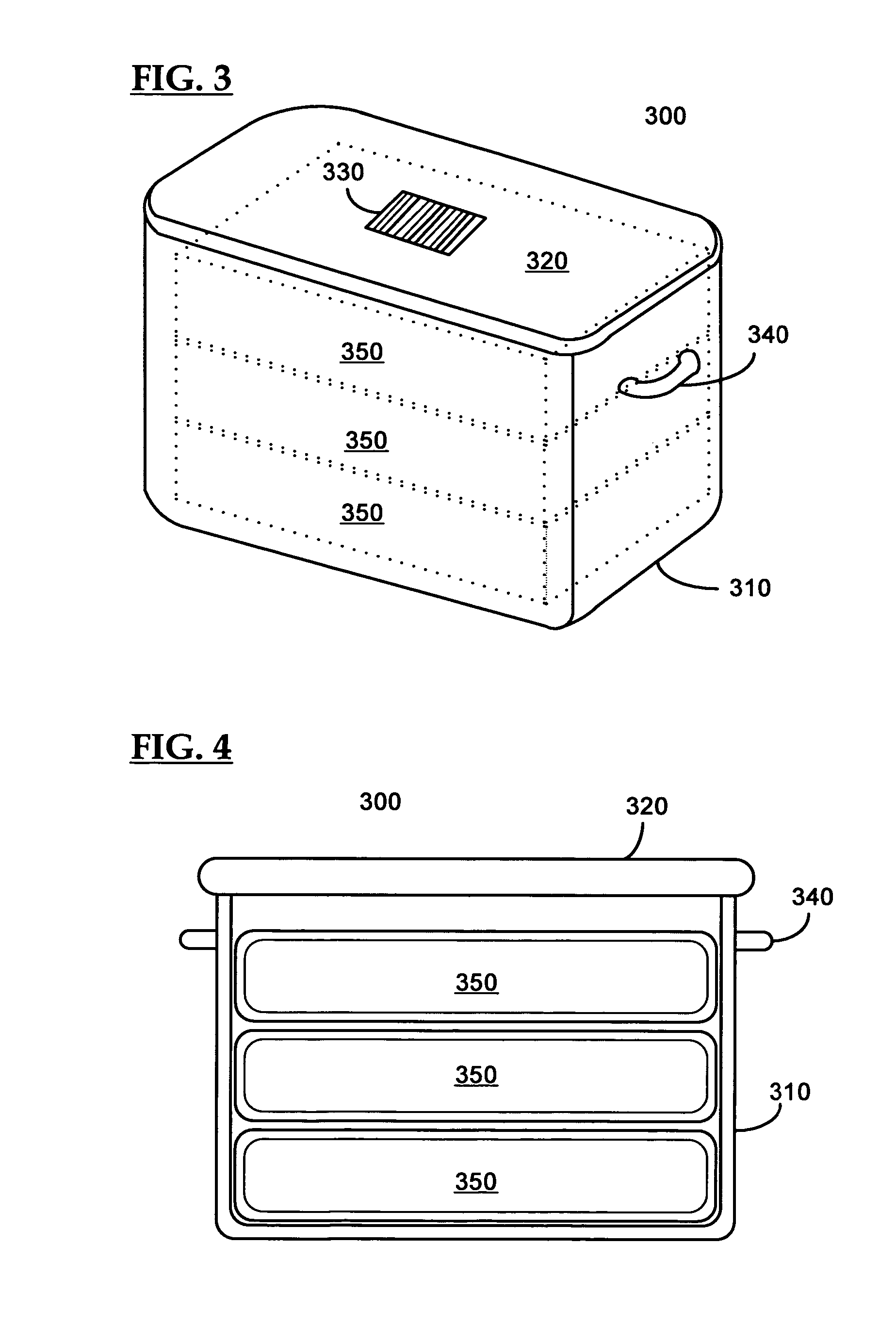
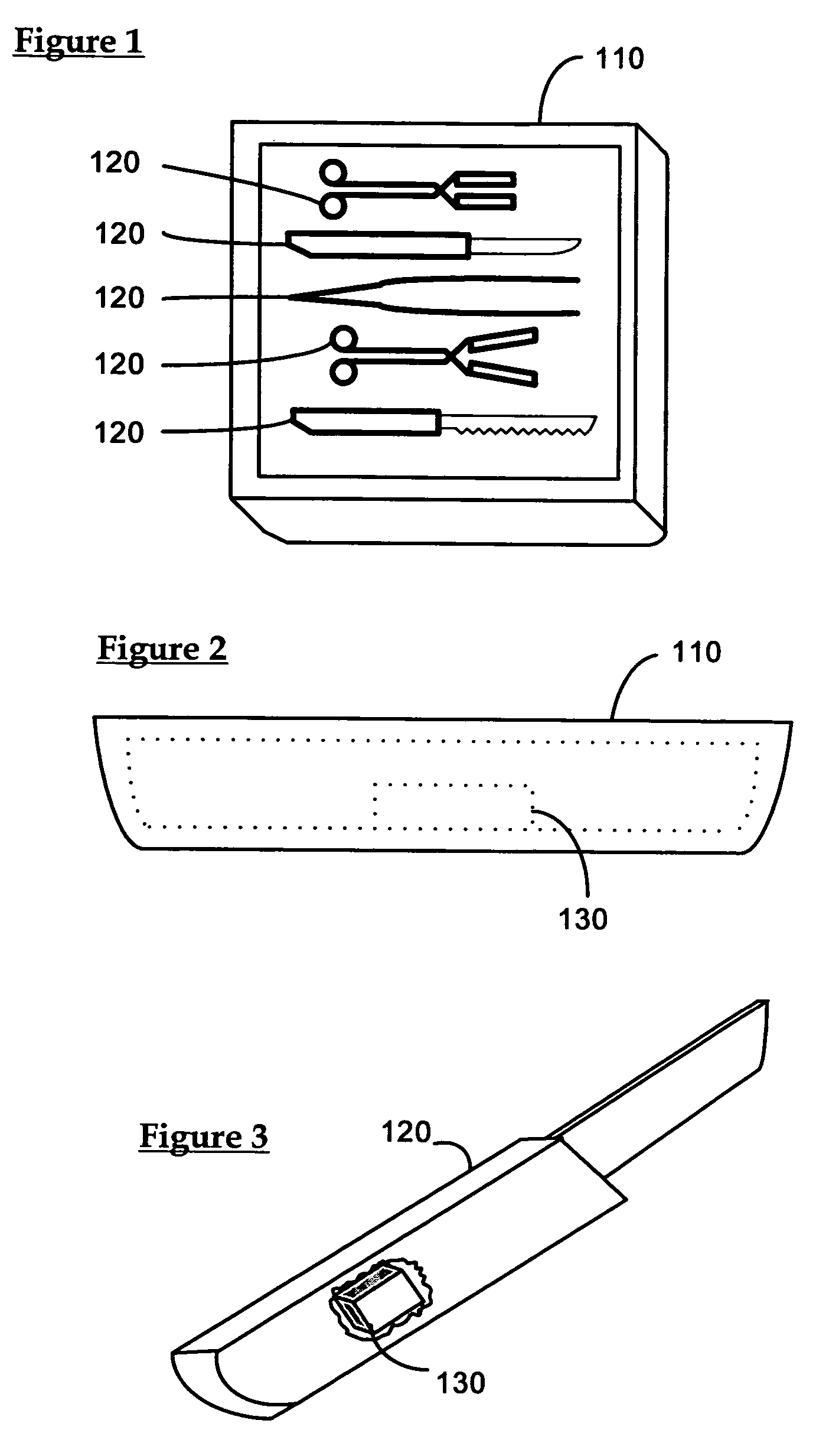
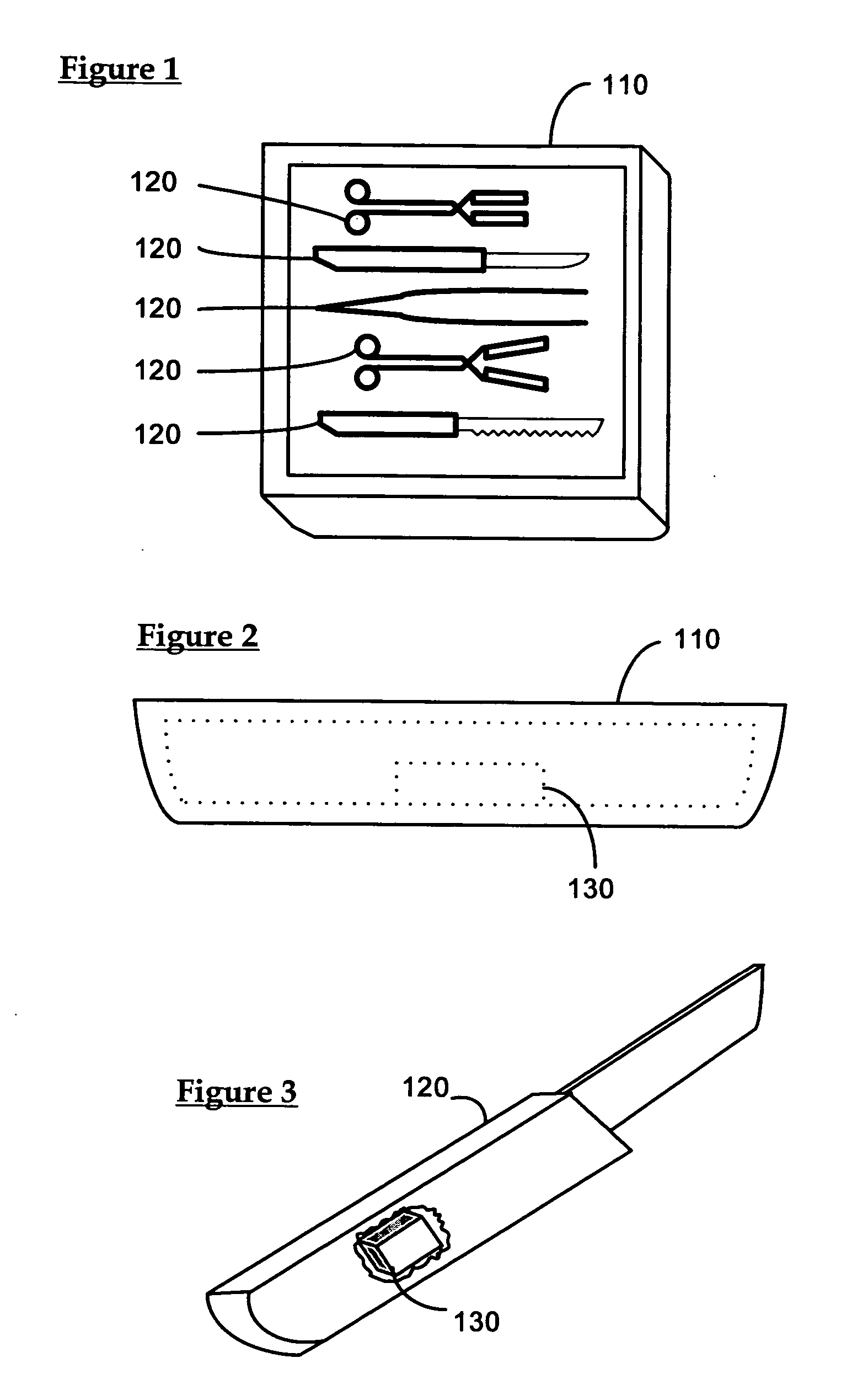
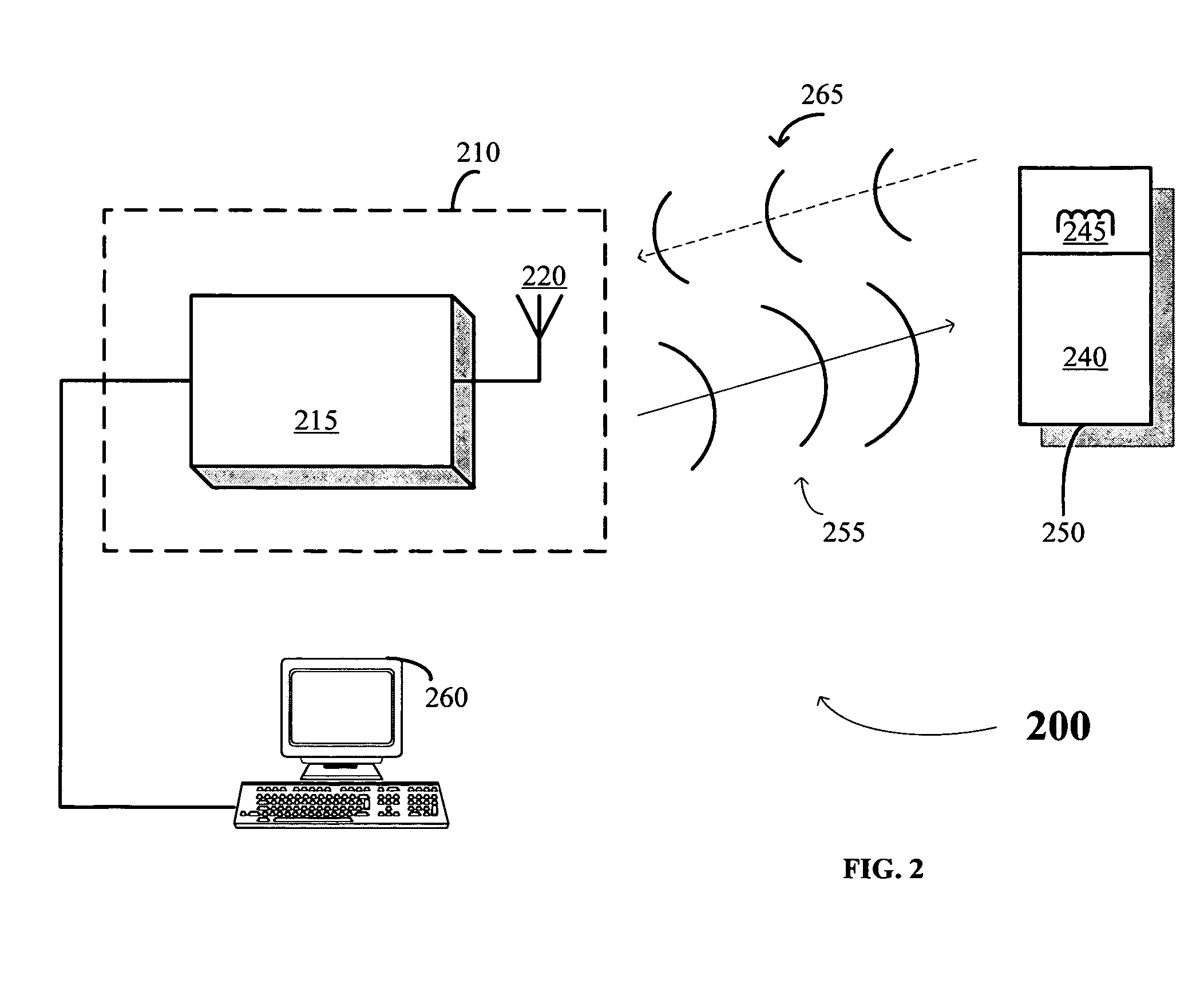
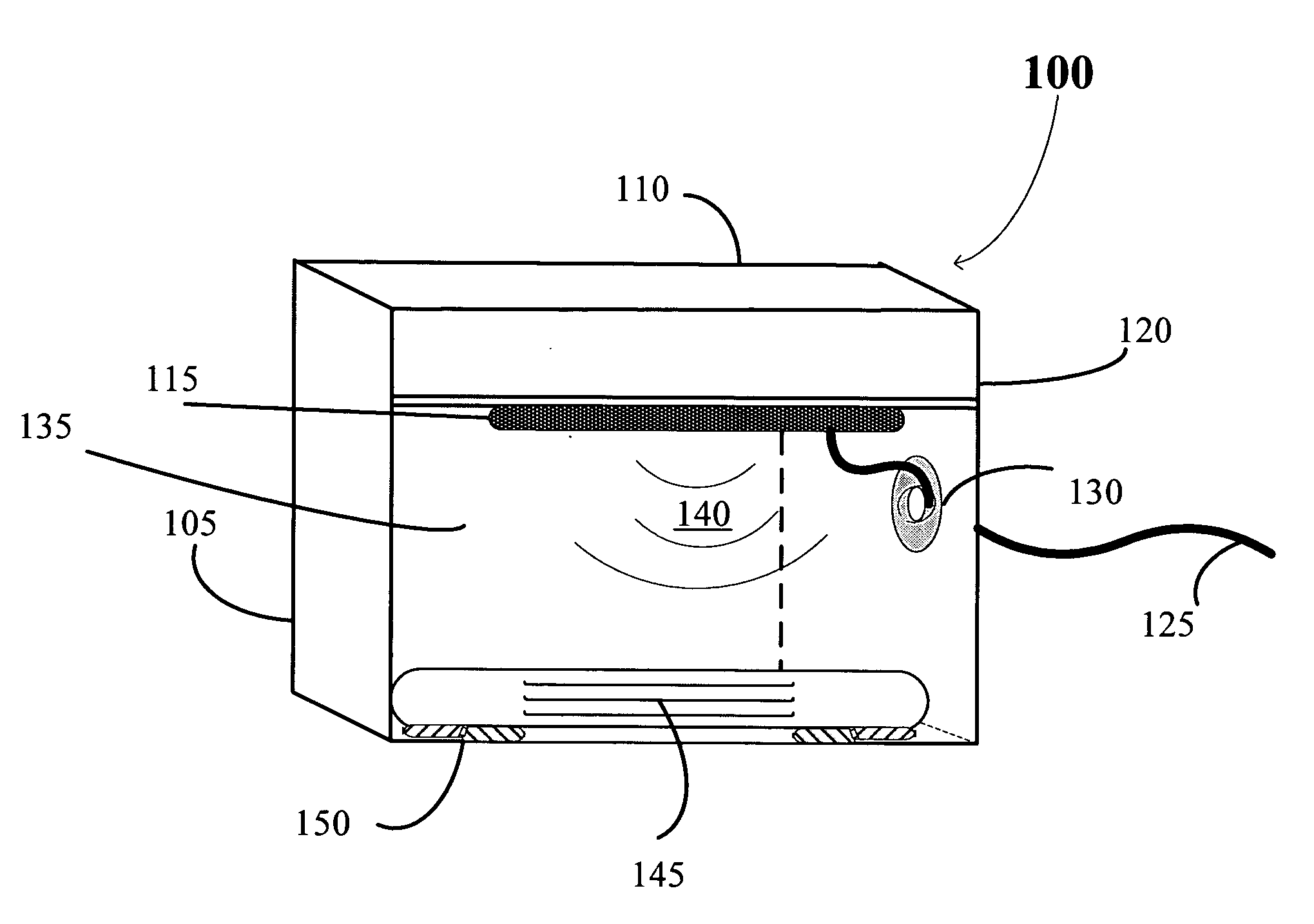
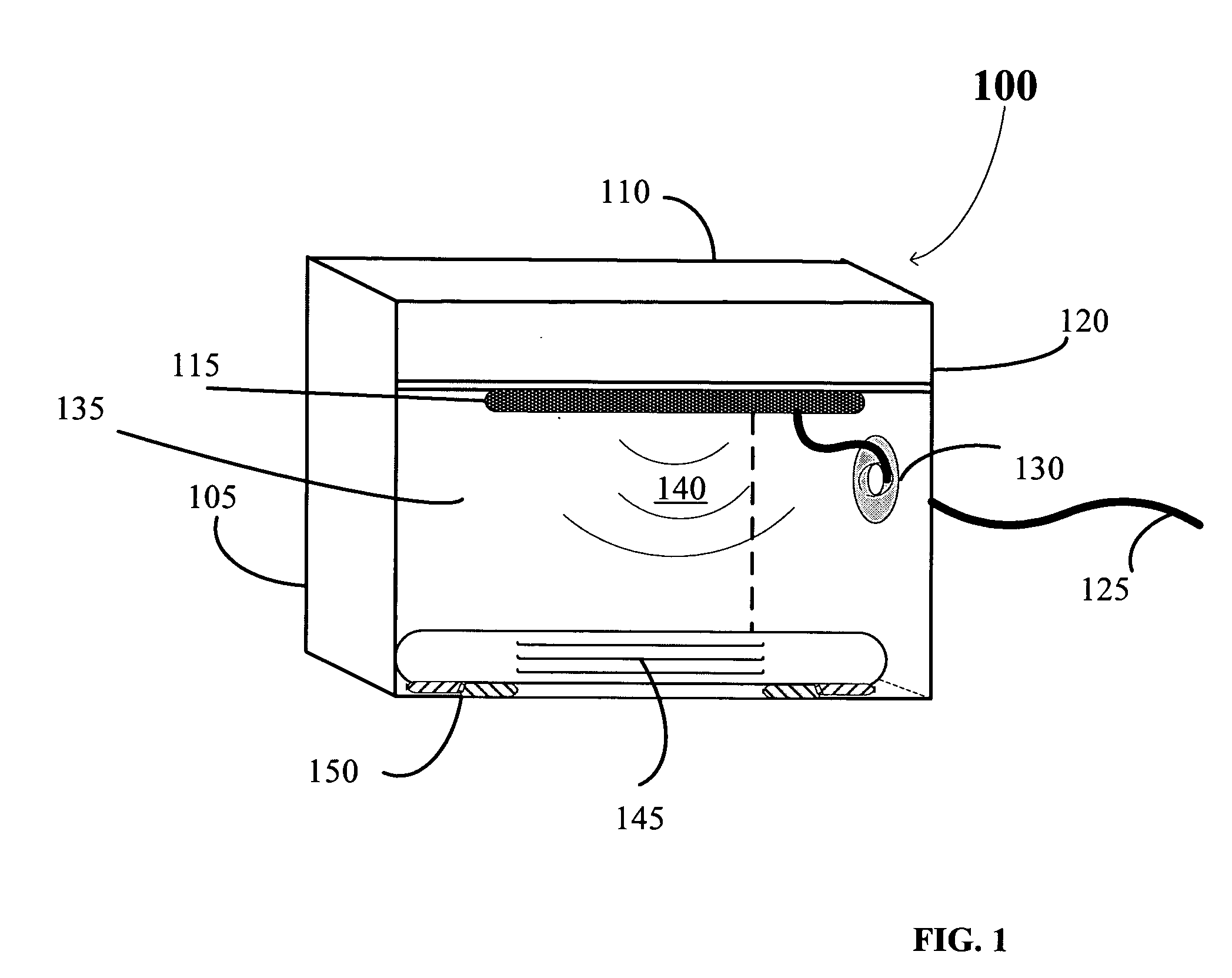
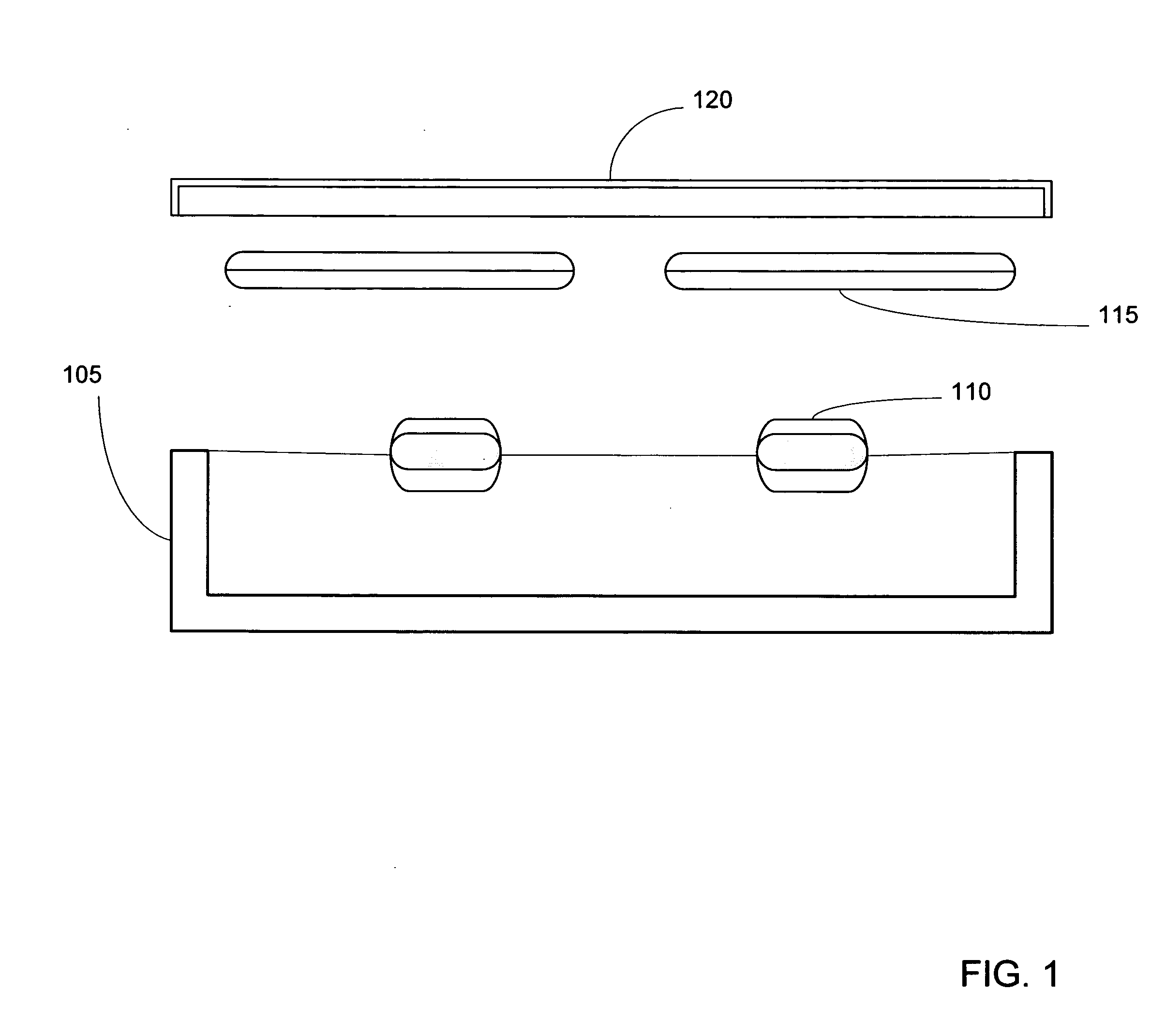
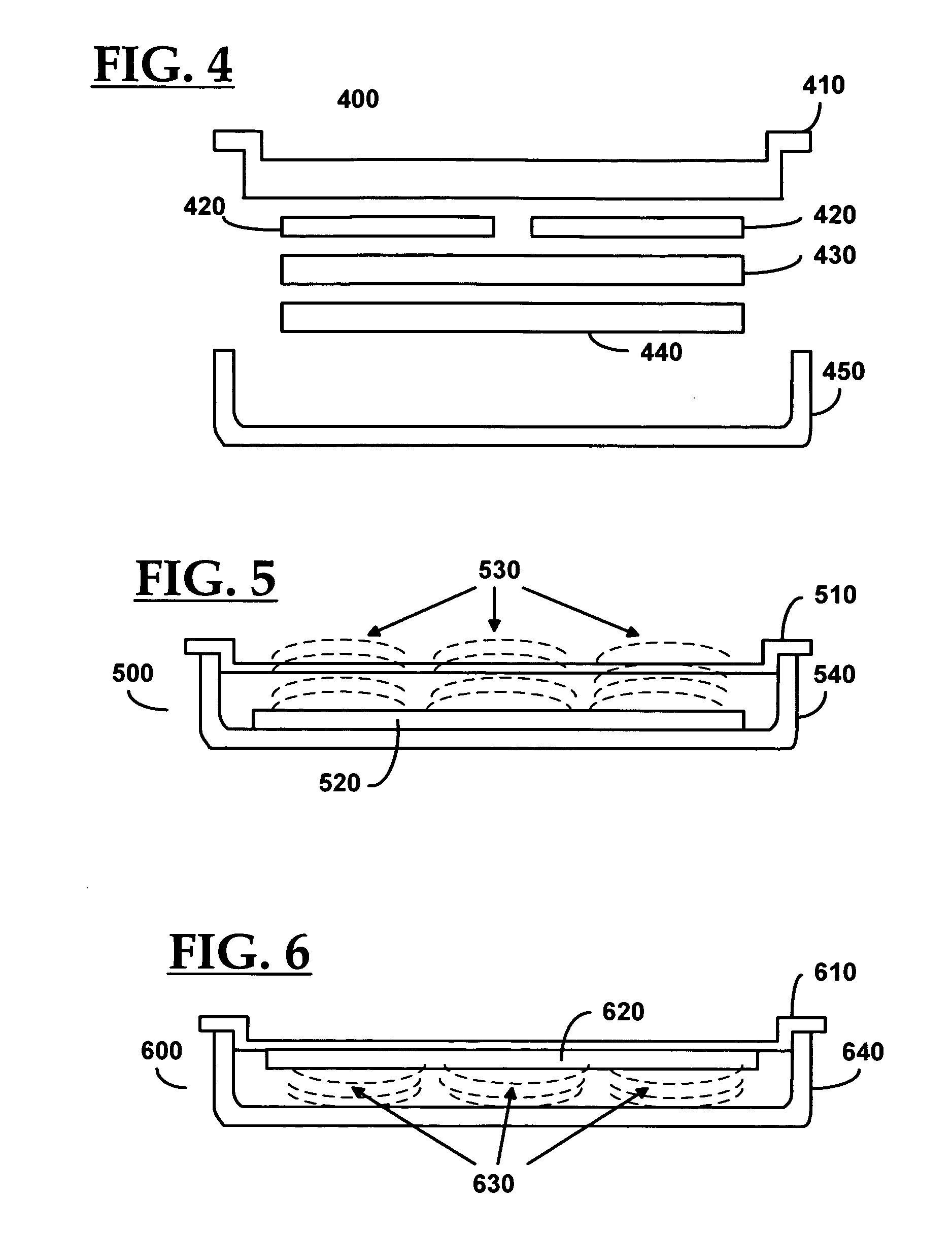
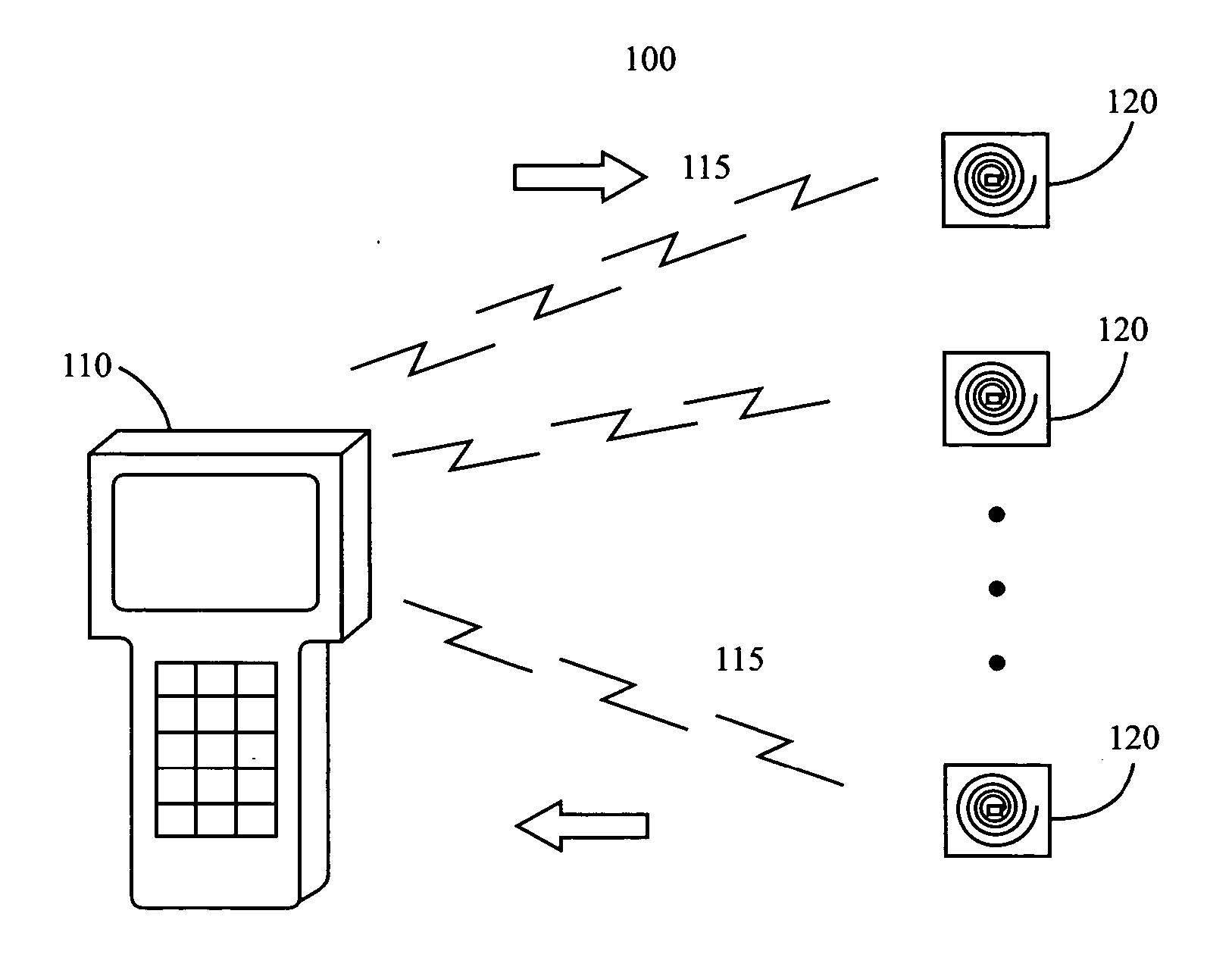
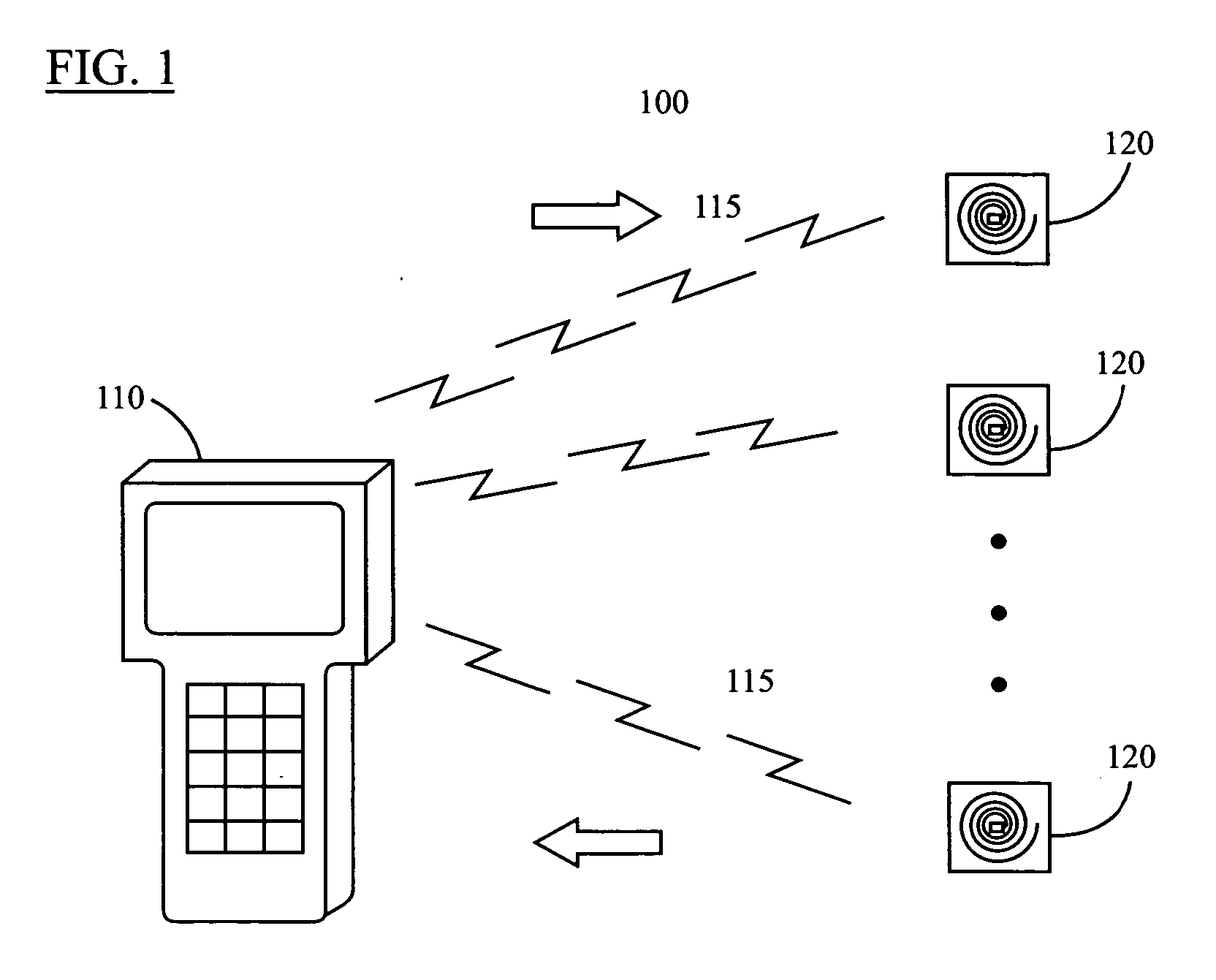
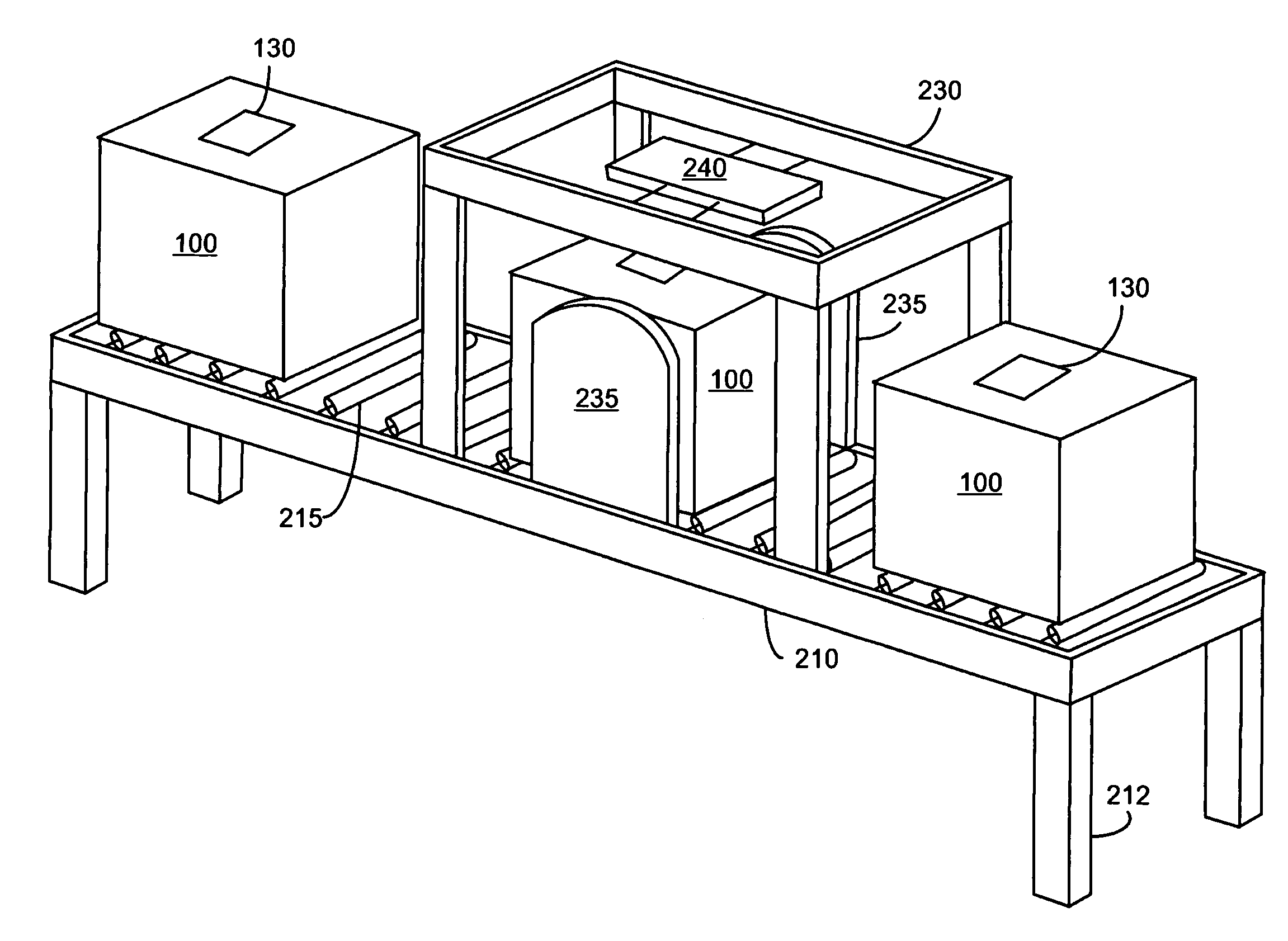
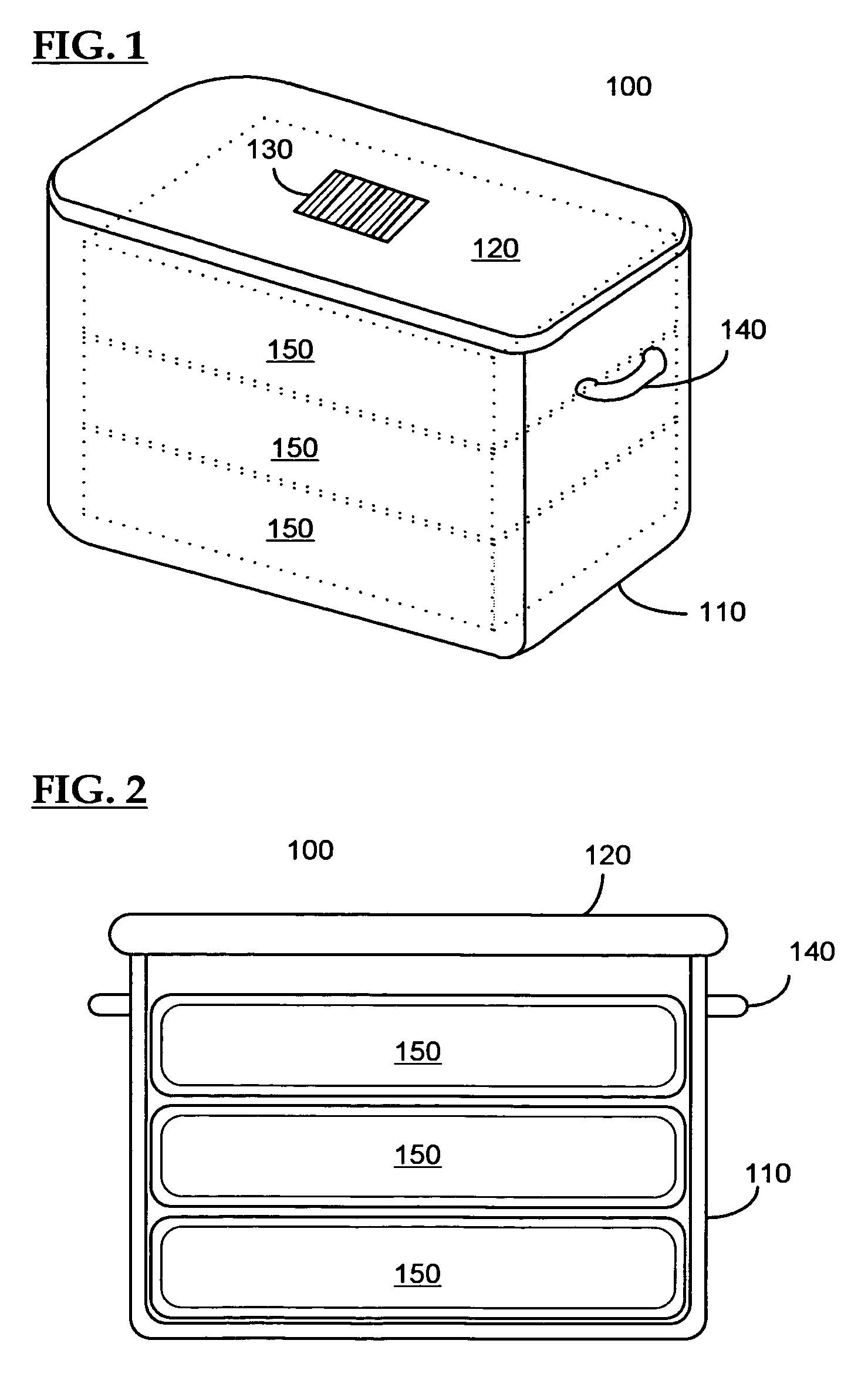
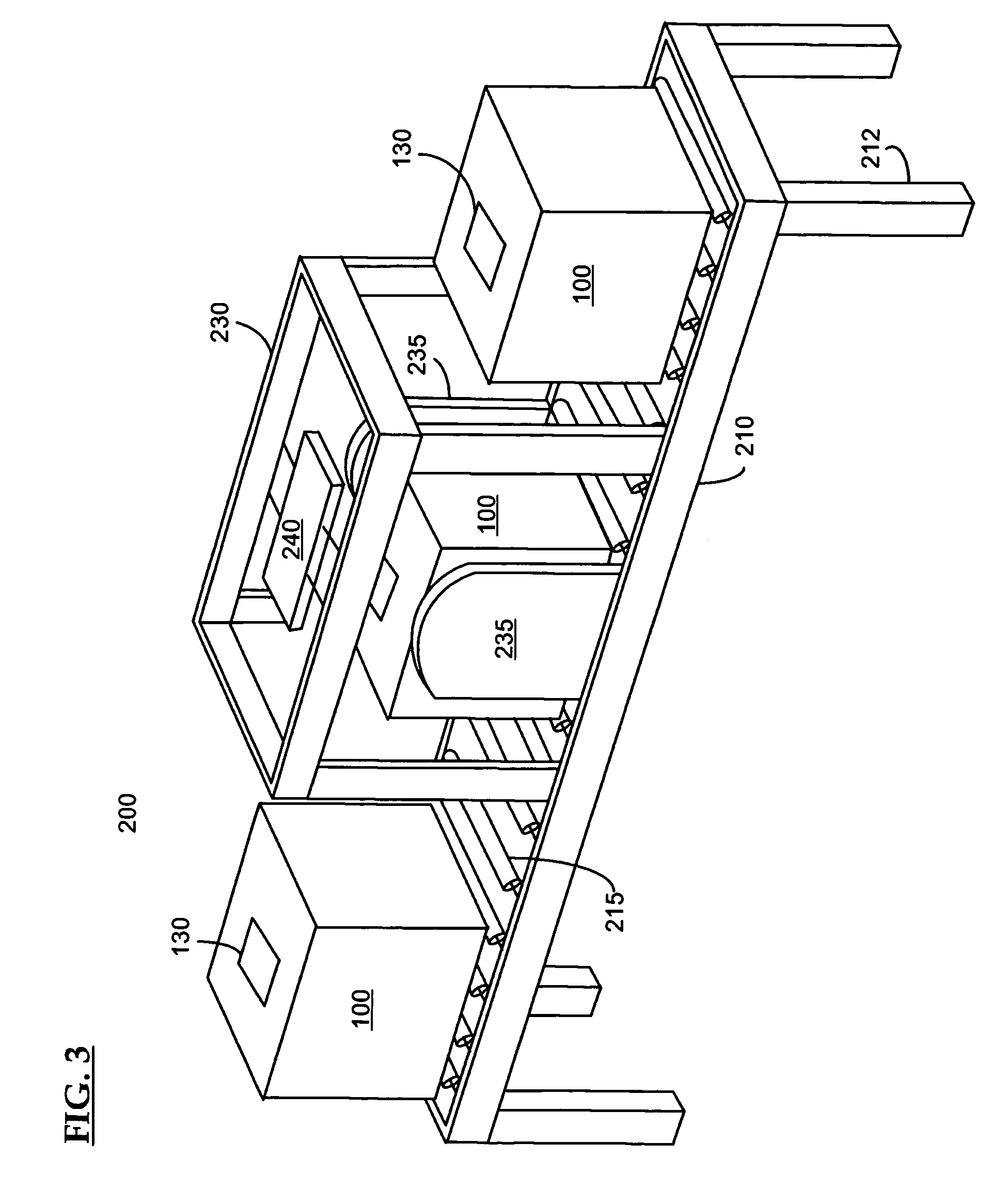
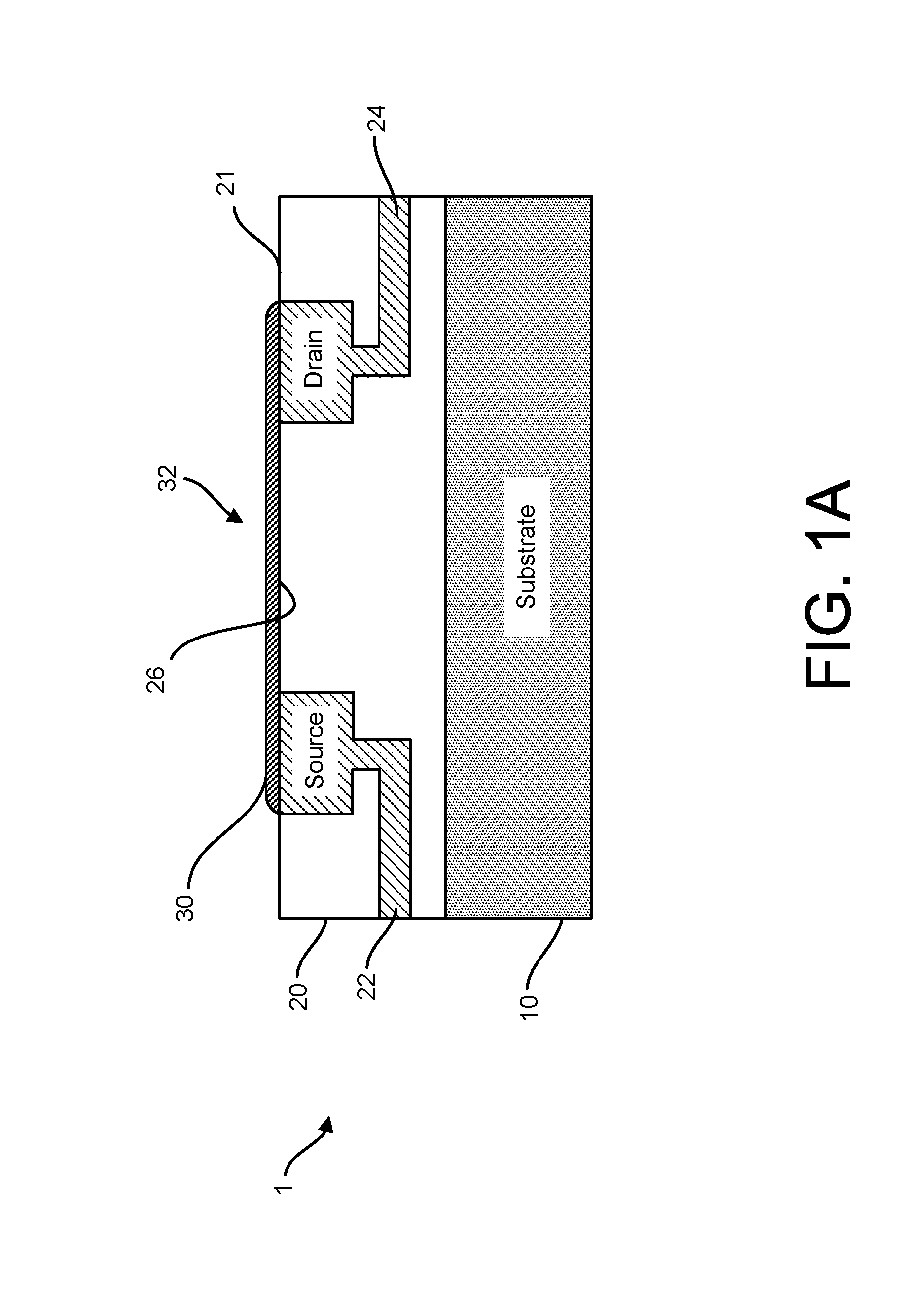
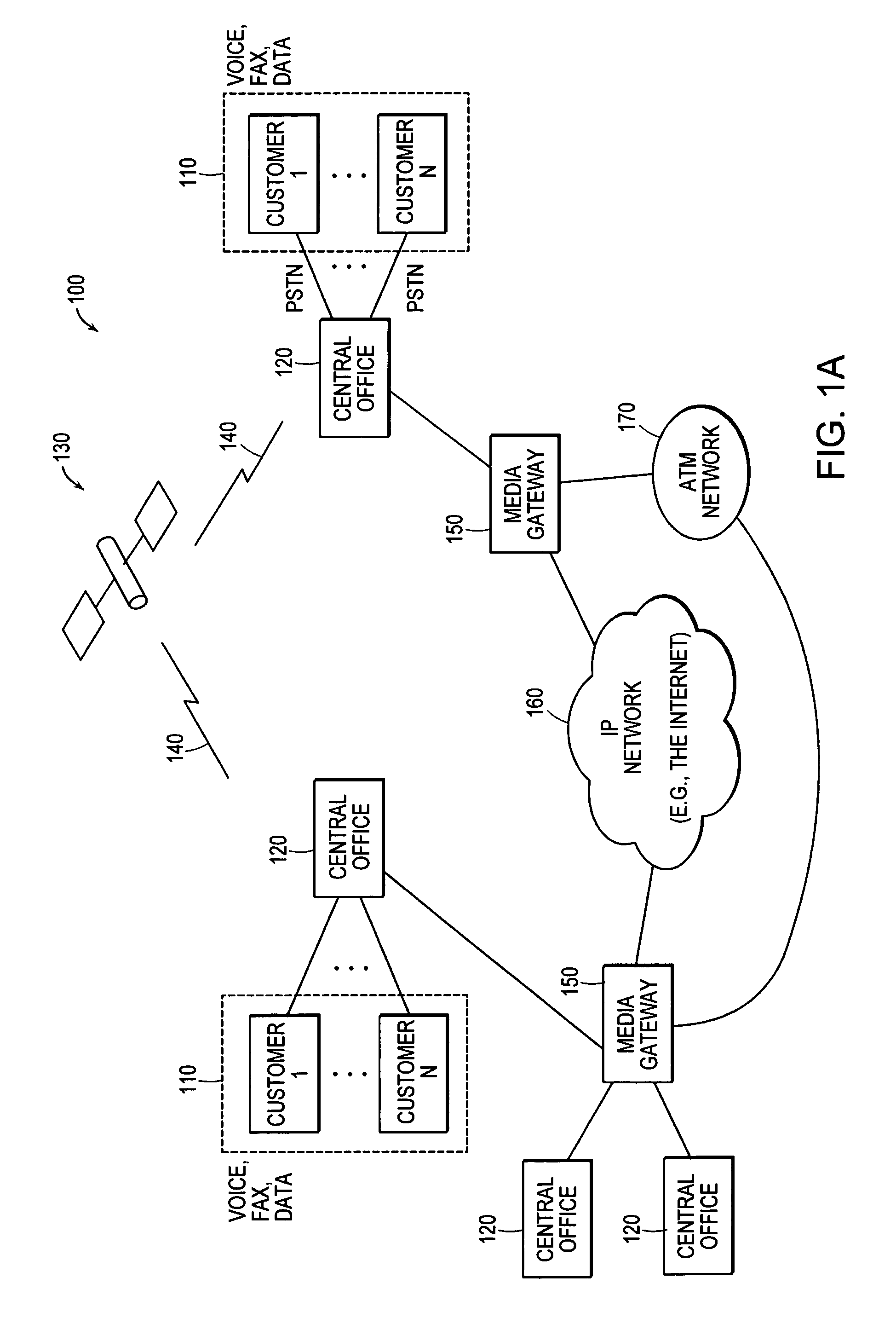
Control system for an RFID-based system for assembling and verifying outbound surgical equipment corresponding to a particular surgery
ActiveUS7492261B2Accurate and rapid processingImprove throughputLogisticsElectric signalling detailsUser inputControl system
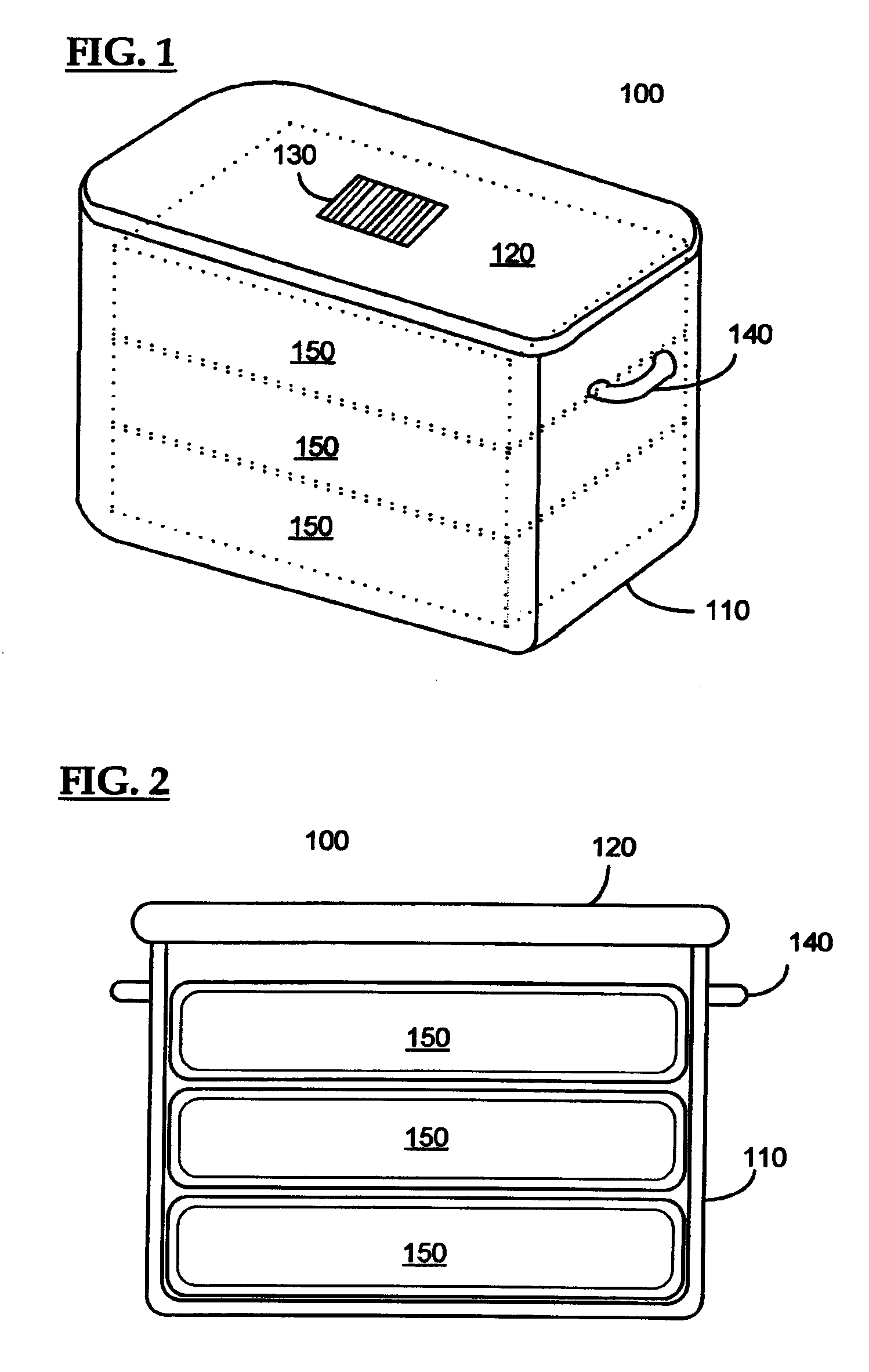
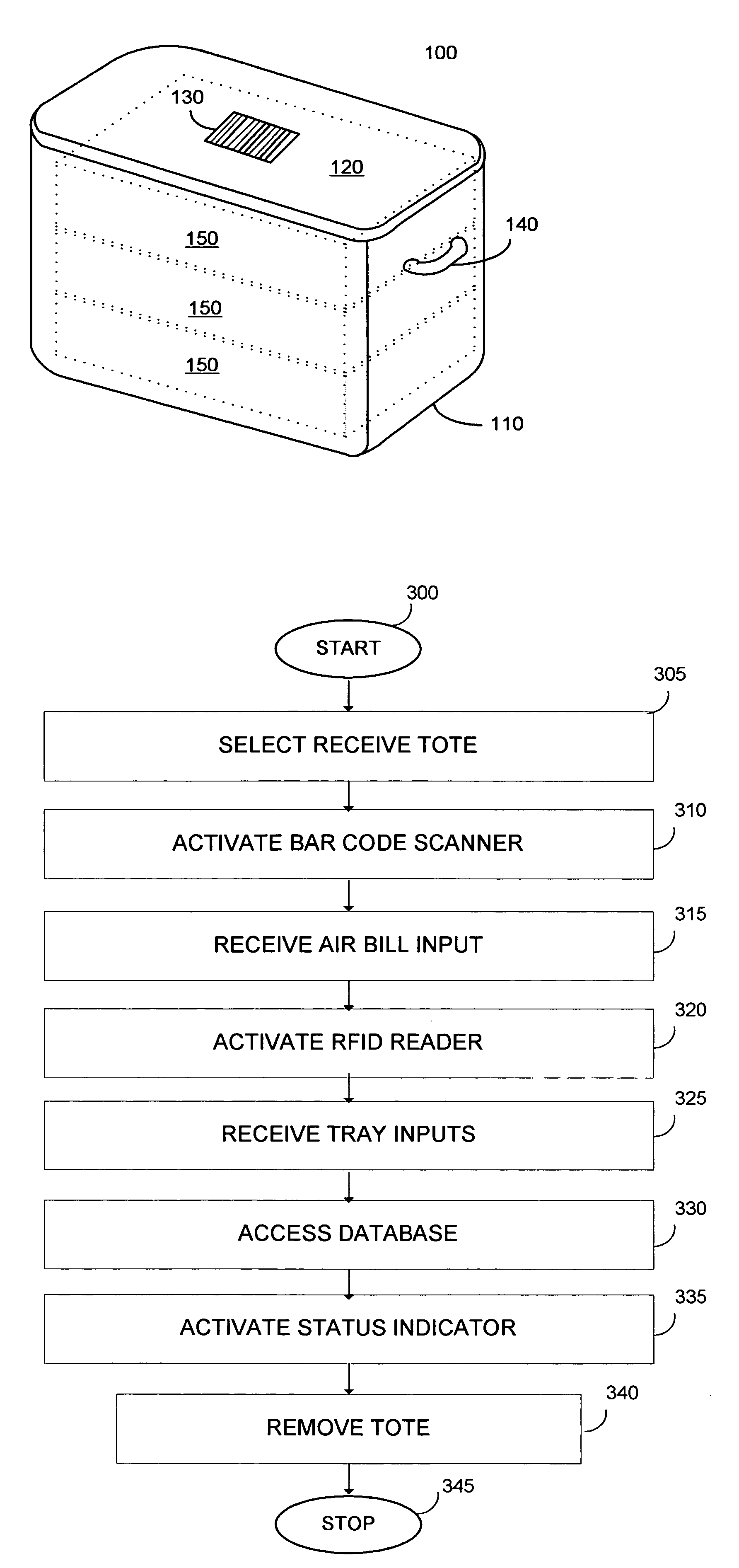
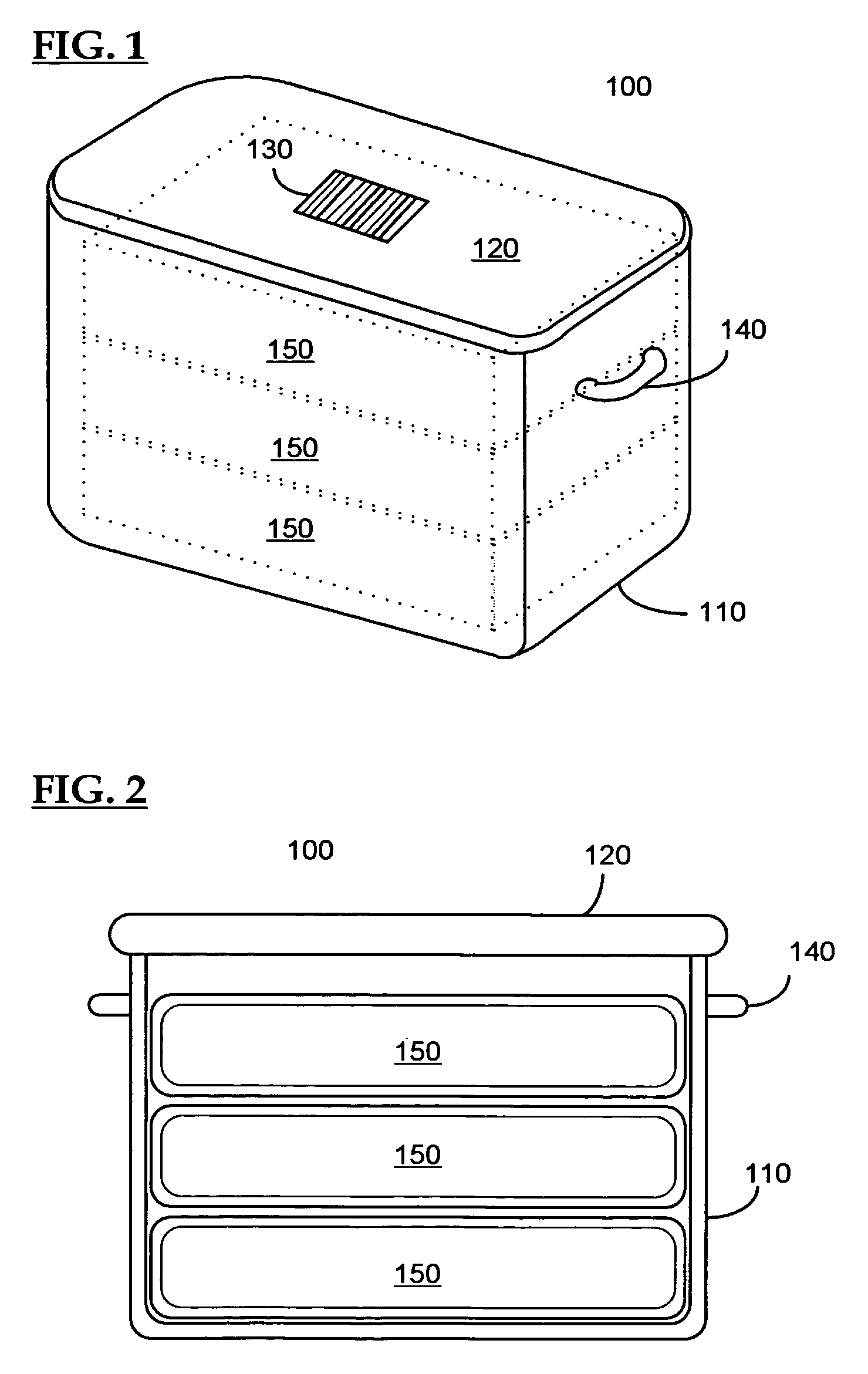
A control system for an RFID-based system for assembling and verifying outbound surgical equipment corresponding to a particular surgery. A user enters a identification number of a surgery. The control system queries a database of surgery information and outputs a list of required surgical equipment, such as surgical instrument sets. An operator uses the list to pick instrument sets for loading into a shipping tote. Each set is tagged with an RFID inventory tag that stores identification information for that set such as a set name and ID number. The shipping tote is passed through an RFID reader and identification data read from the tags is compared against the identification data for sets required for that surgery. A status indicator is activated to alert a user as to whether the surgery is complete that is, all expected sets are present, or that exception handling is required. The control system updates a database such as an ERP system to reflect that the surgery including the required sets has shipped—and the sets are inventoried out to the intended recipient.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
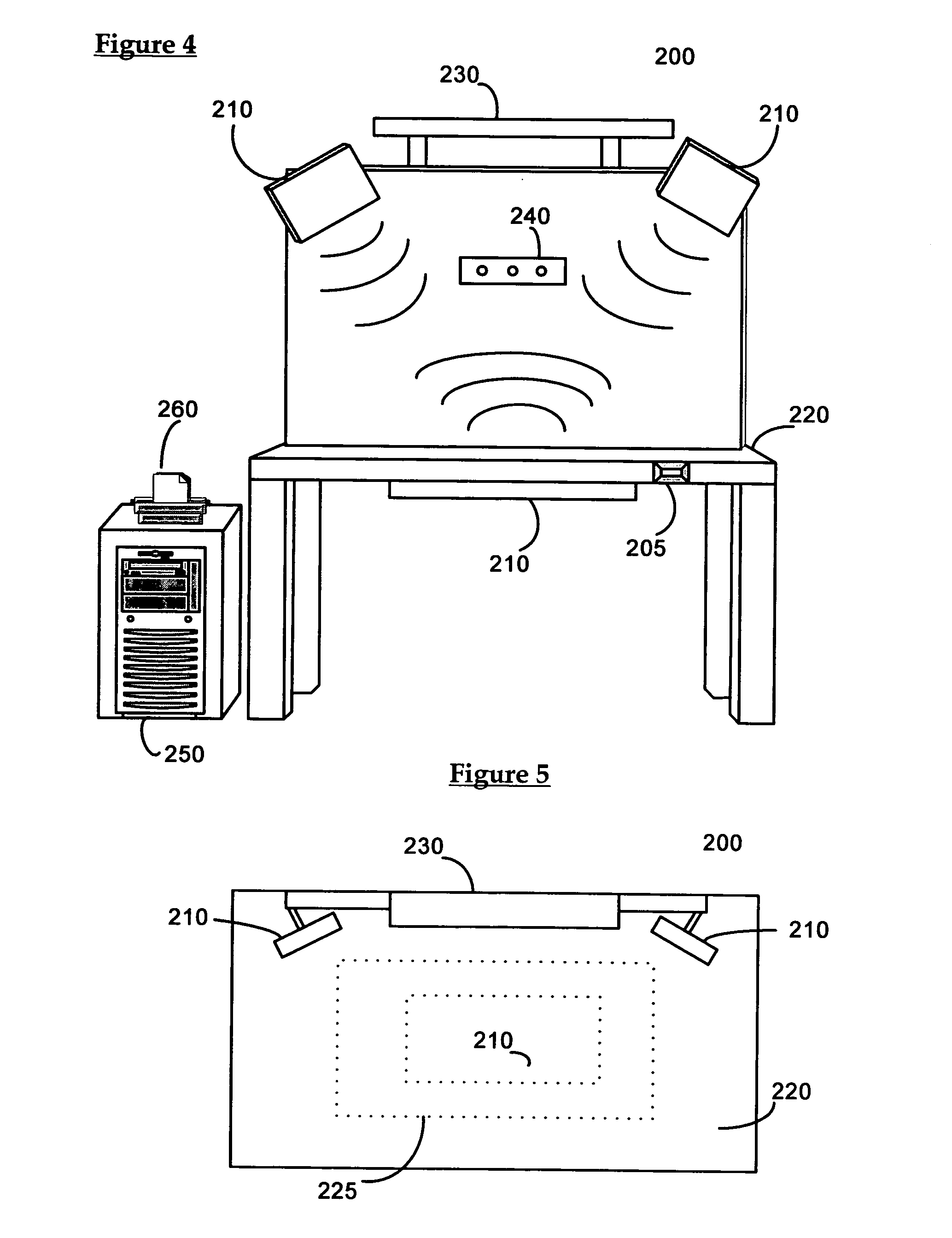
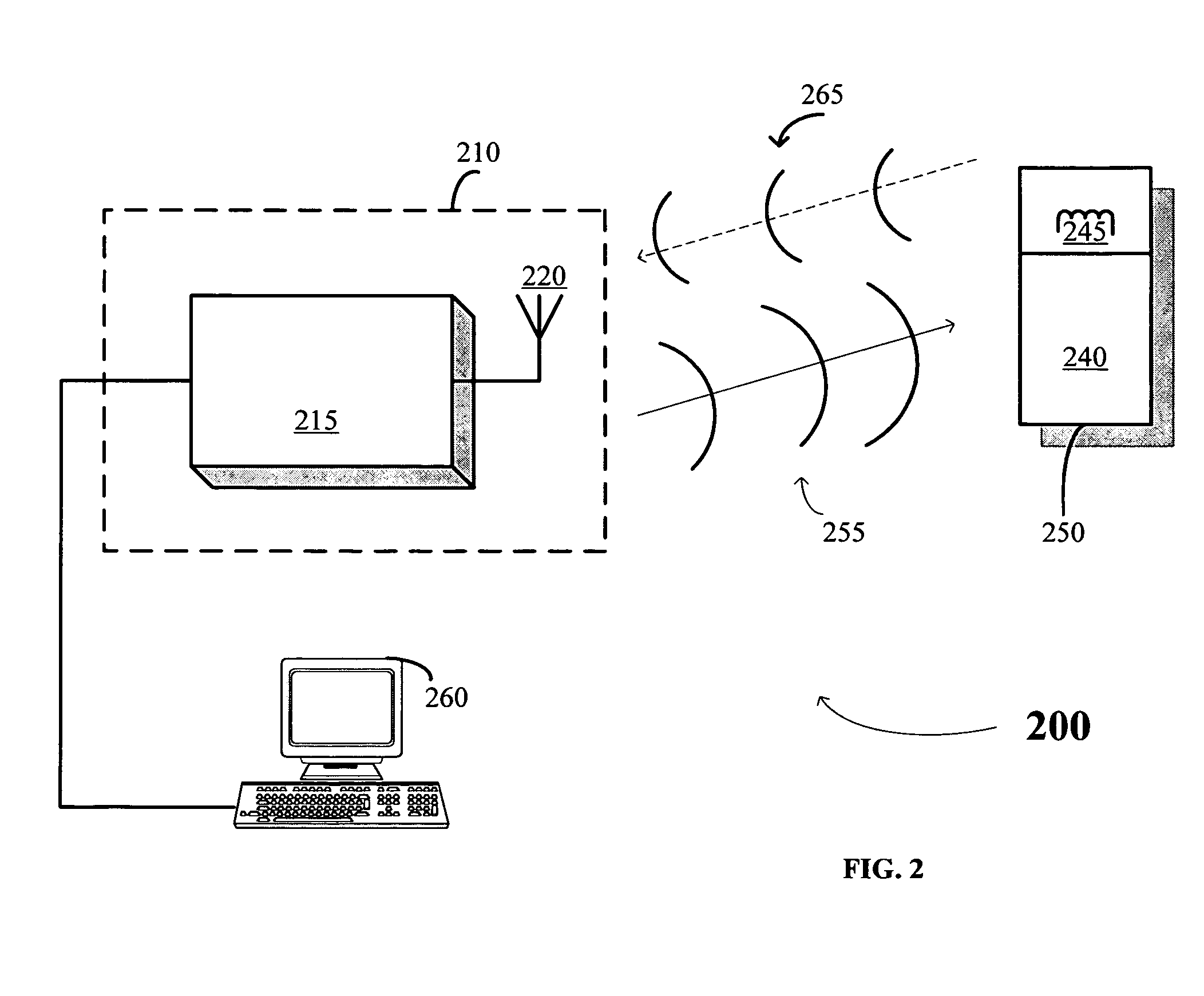
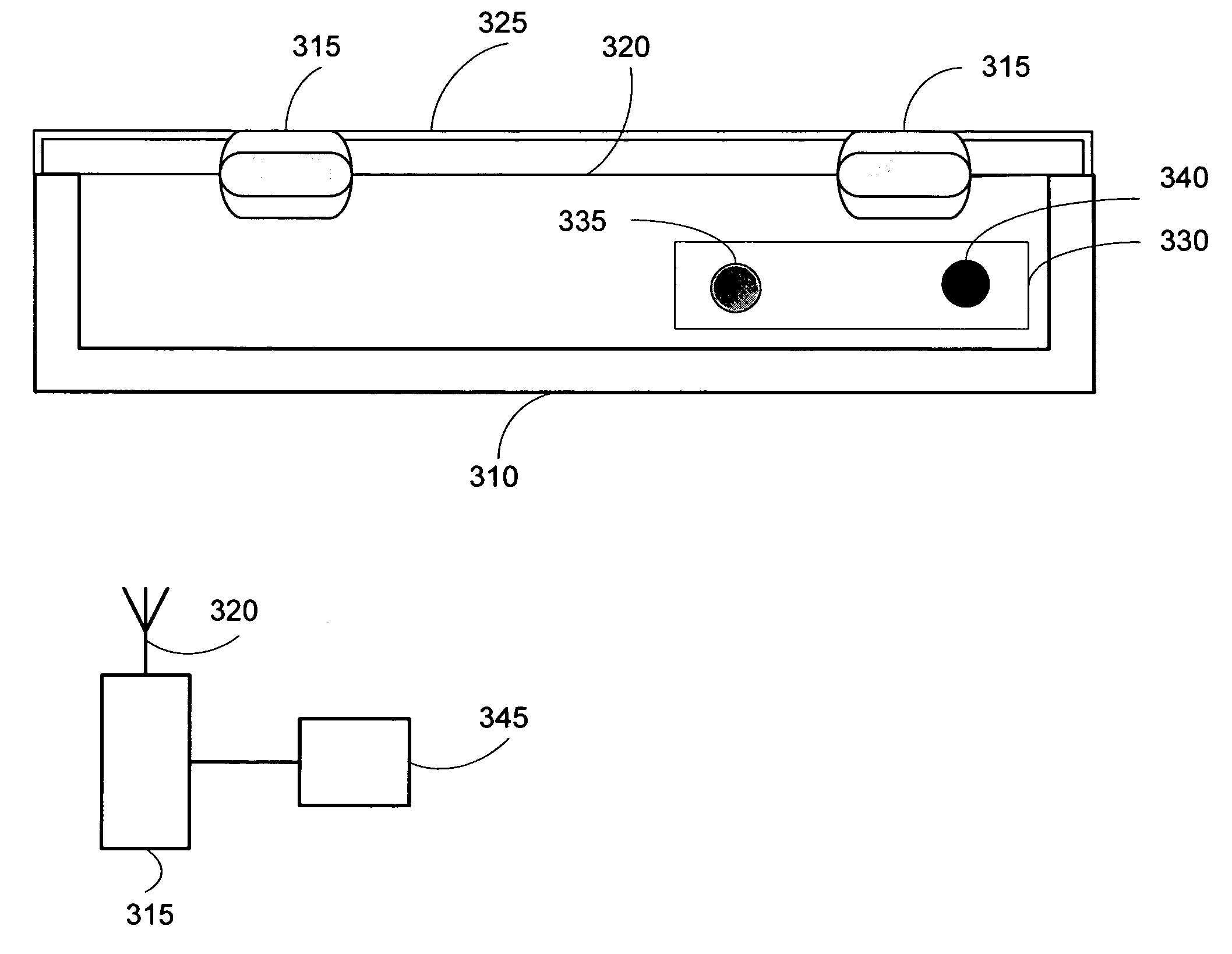
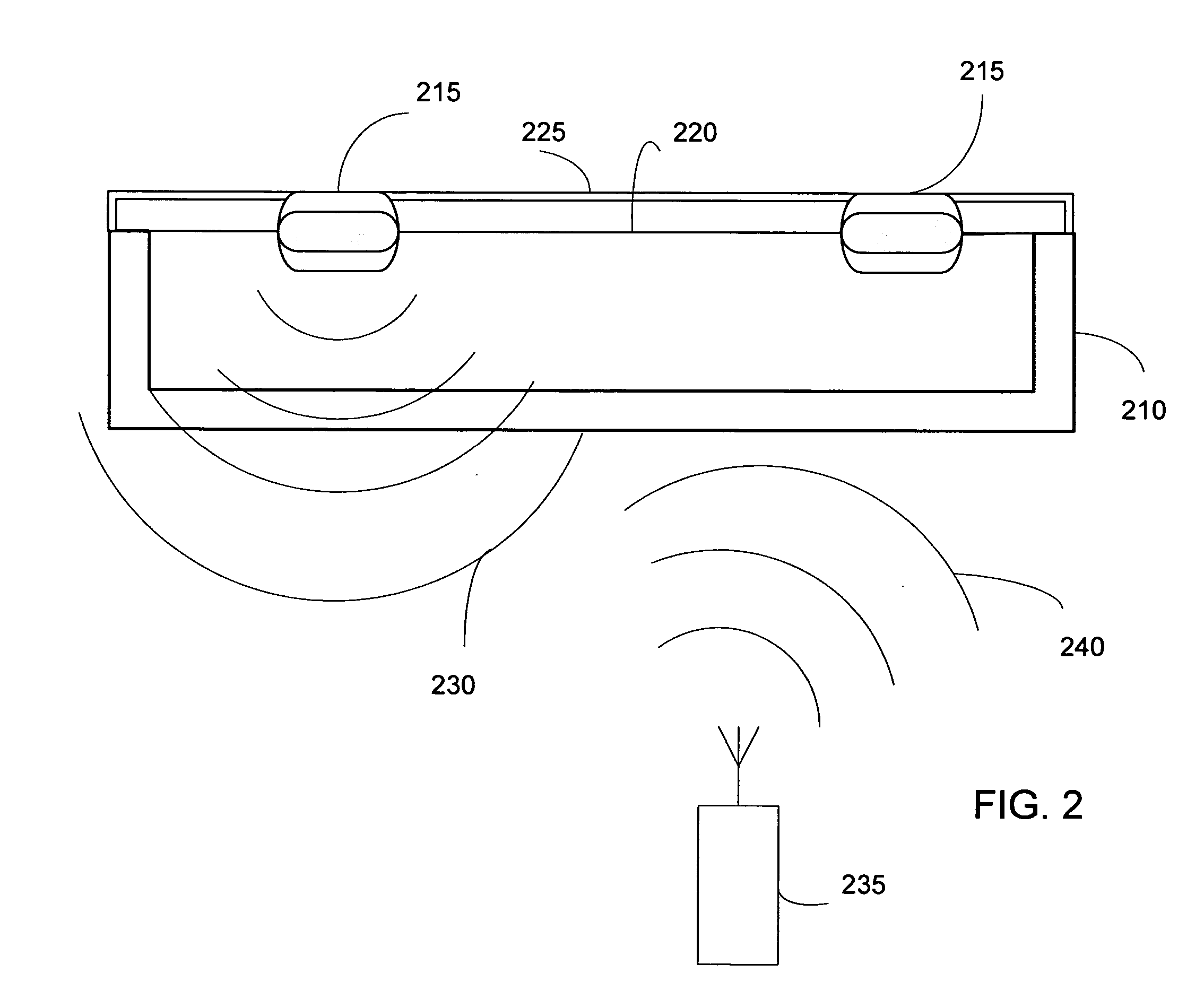
Smart instrument tray RFID reader
ActiveUS7362228B2Accurate and rapid trackingReduce processing costsSurgical furnitureDispensing apparatusEngineeringWorkstation
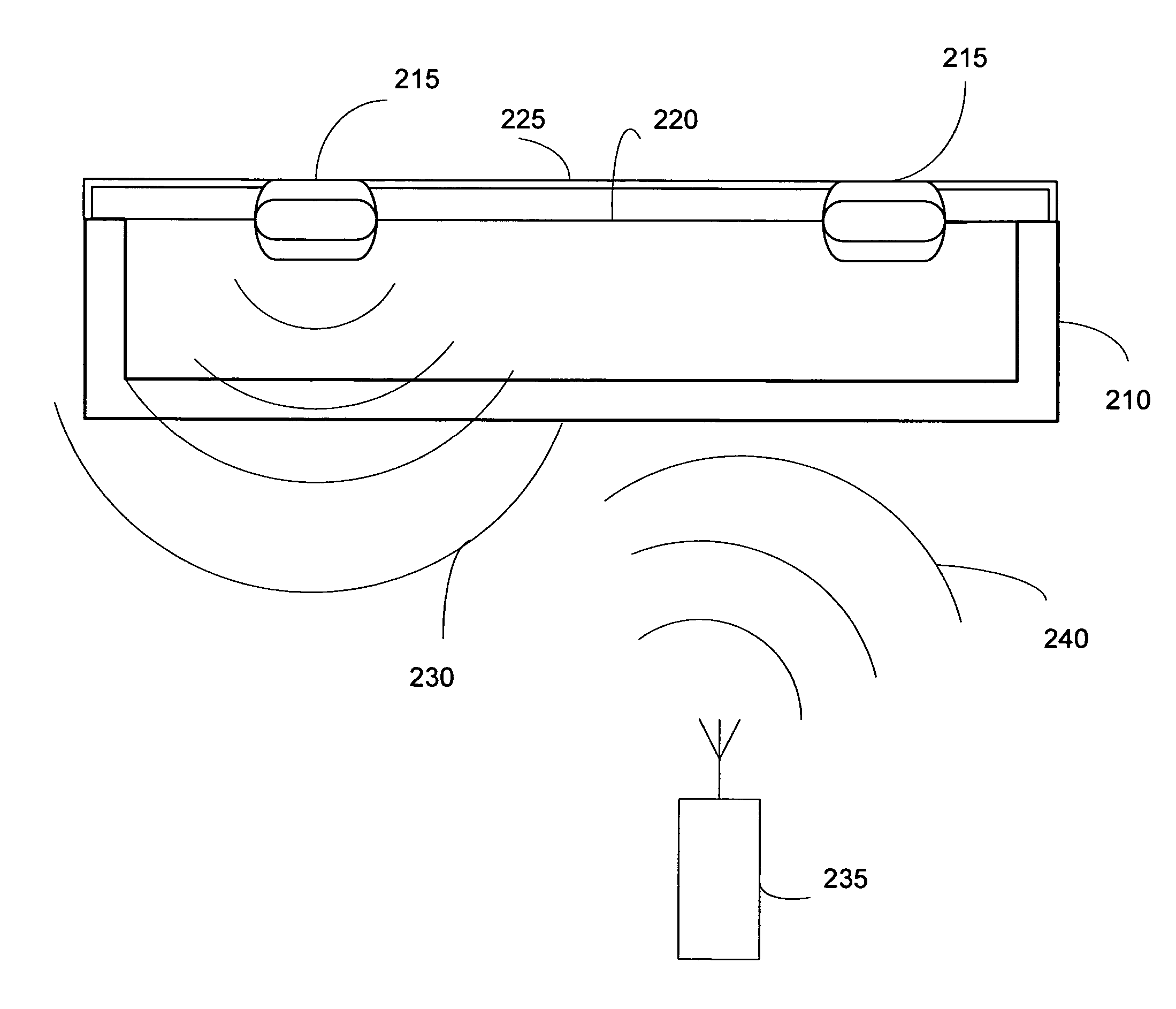
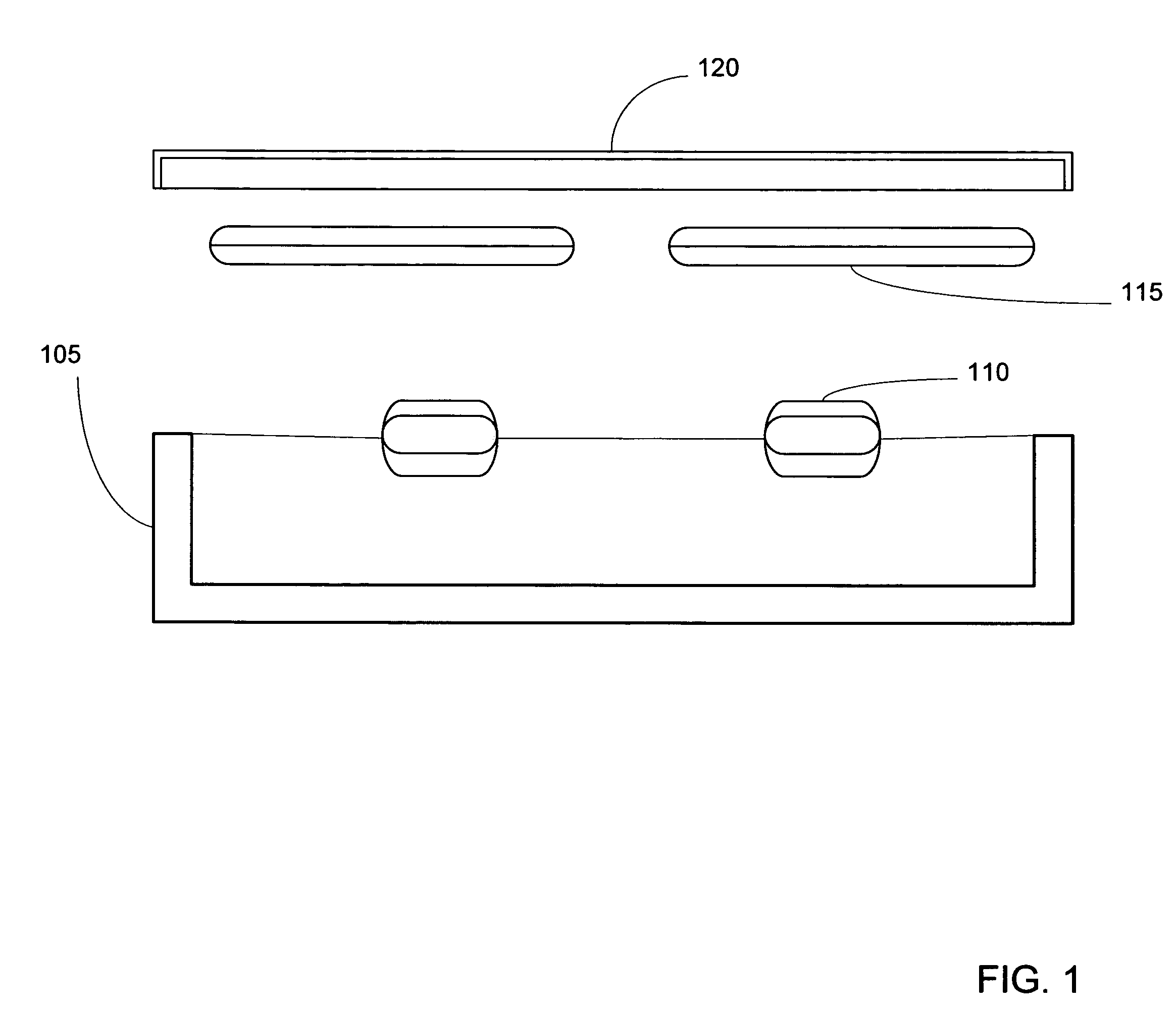
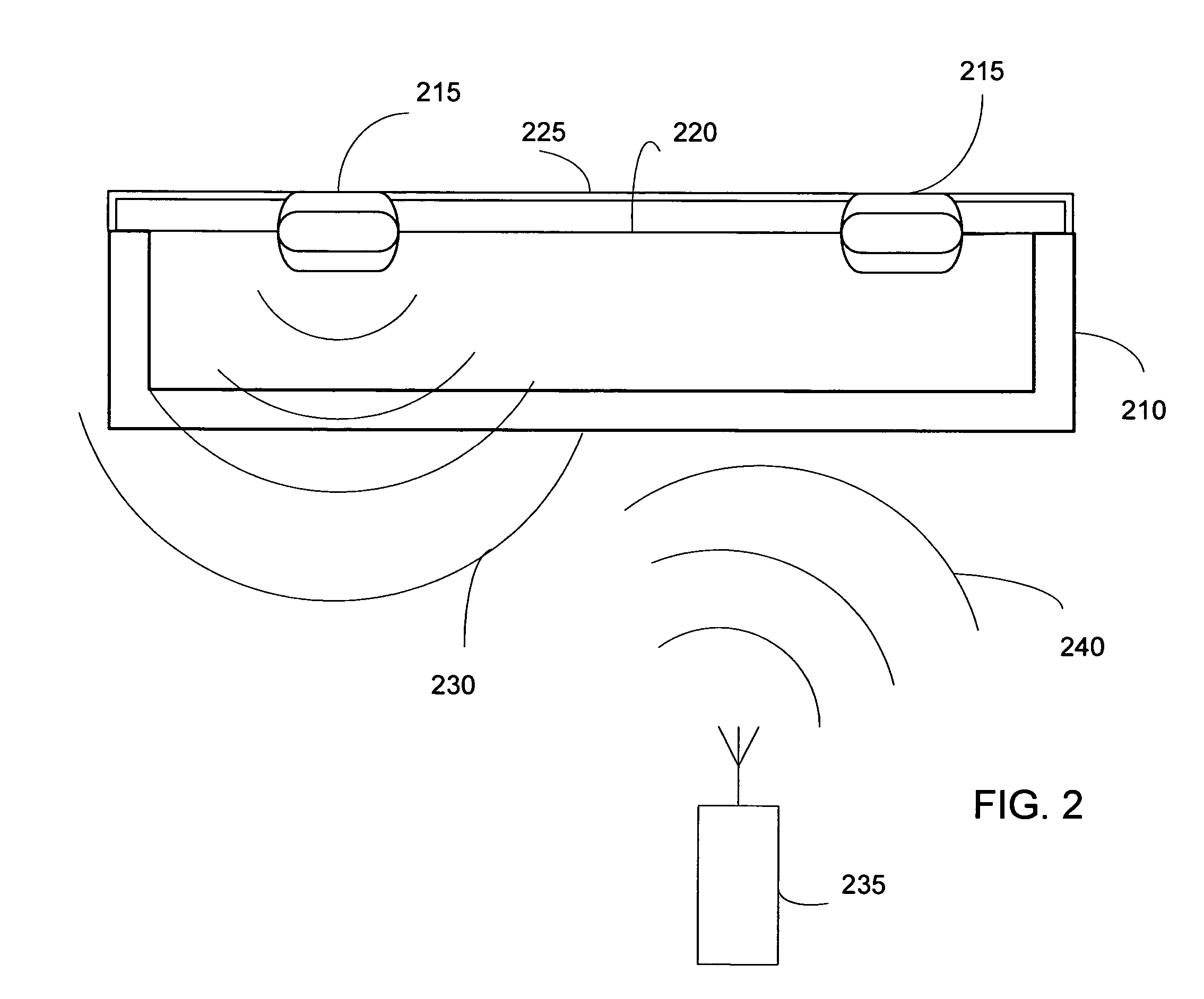
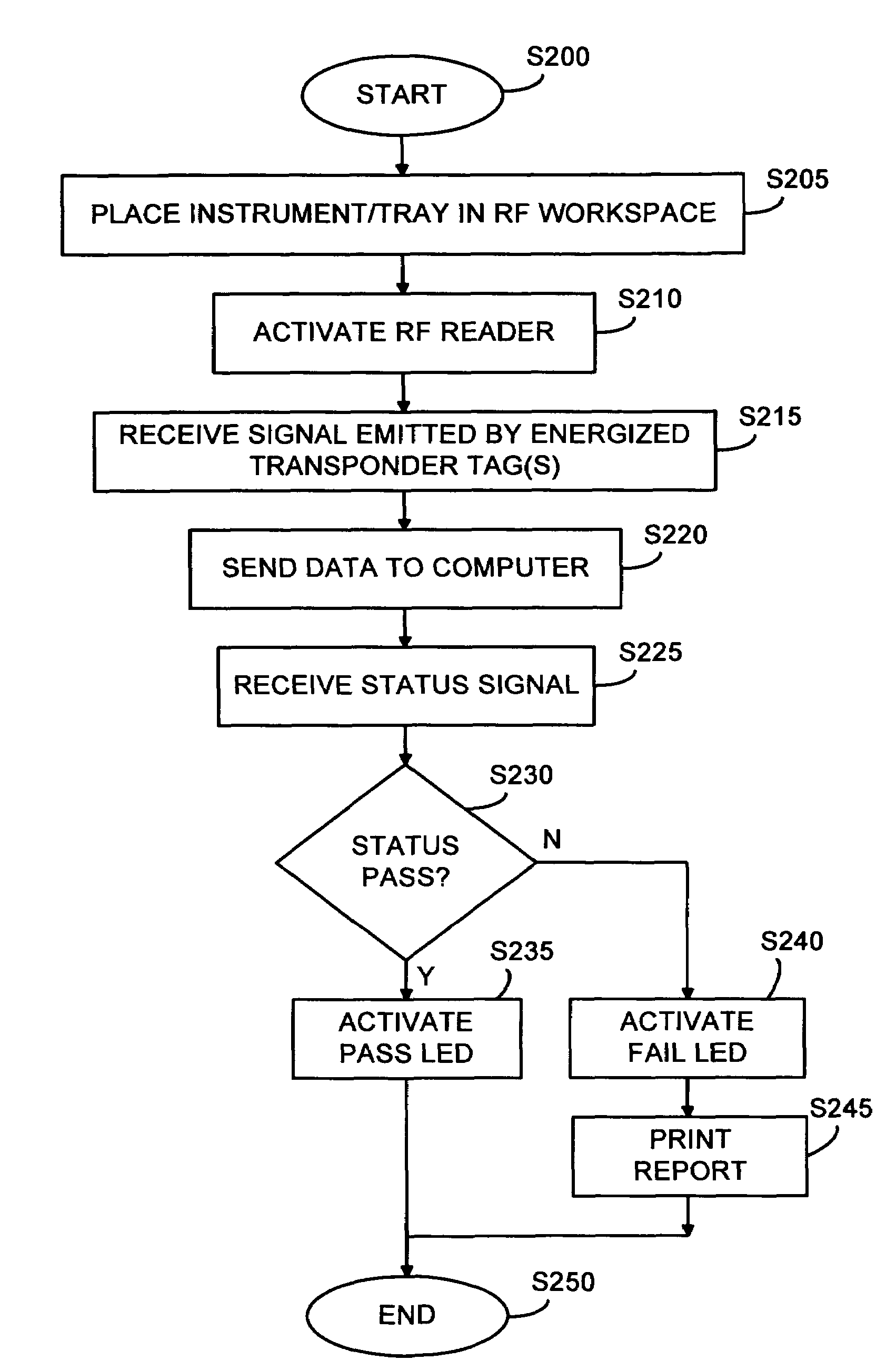
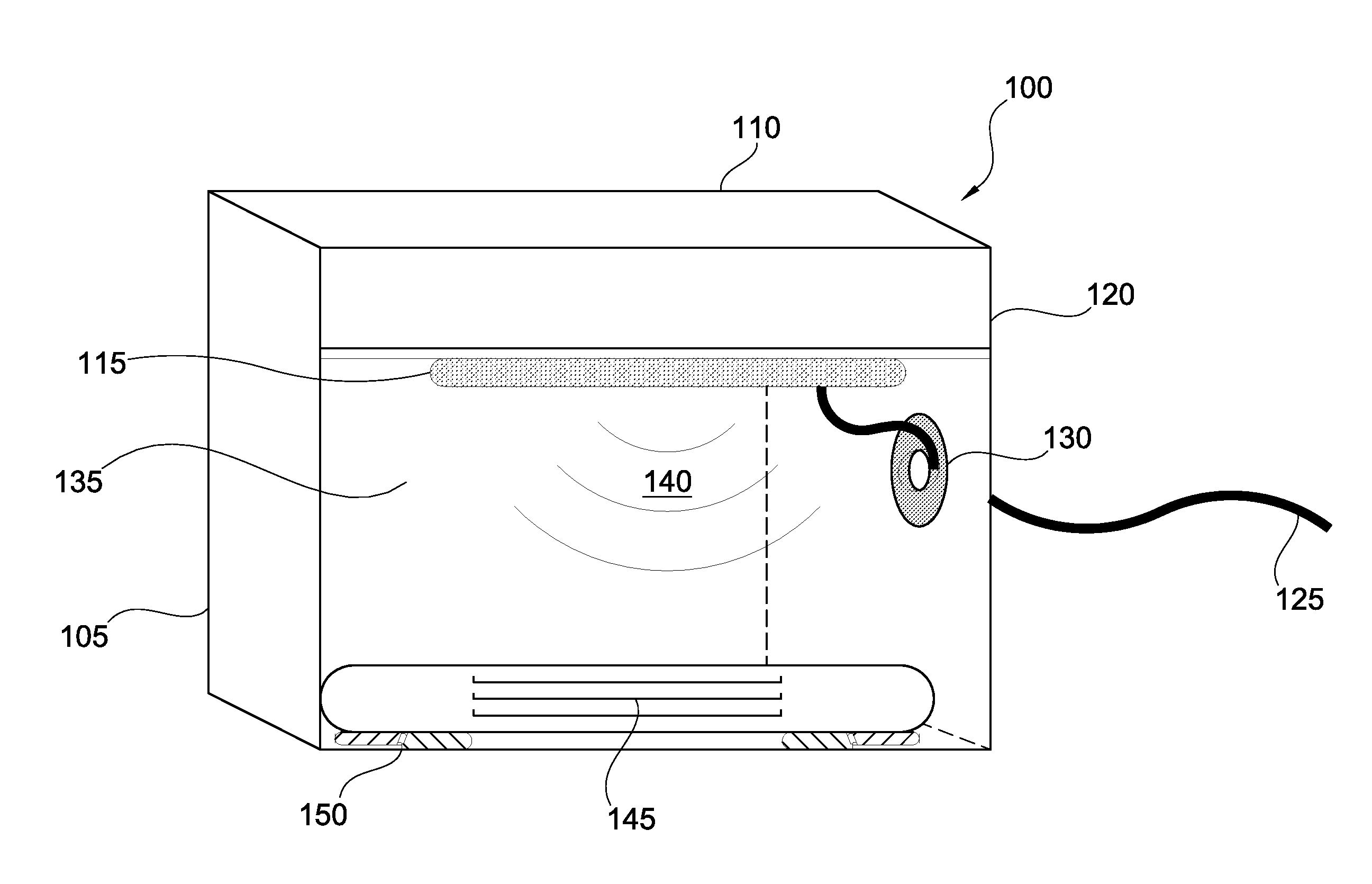
A radio frequency identification (RFID) workstation reader for RFID-enabled surgical instruments and surgical instrument trays and a method of using a RFID workstation reader to read RFID-enabled surgical instruments and surgical instrument trays is disclosed. The method, apparatus, and system enable individual instruments or a surgical instrument tray containing several surgical instruments to be quickly and efficiently inventoried and tracked. An instrument or instrument tray is placed on the workstation reader. An RF field generated by a plurality of antennae, causes RFID tags embedded in or attached to the instrument or instrument tray to emit a signal containing item specific identification information stored in the tags. The information is received by a control circuit and passed to a computer for data analysis. A status LED is illuminated on the workstation reader based on the results of the data analysis. The method, apparatus, and system can track, inspect, and verify inbound and outbound surgical instrument kits, and help to assess the surgical instruments' and trays' duty life cycle usage.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
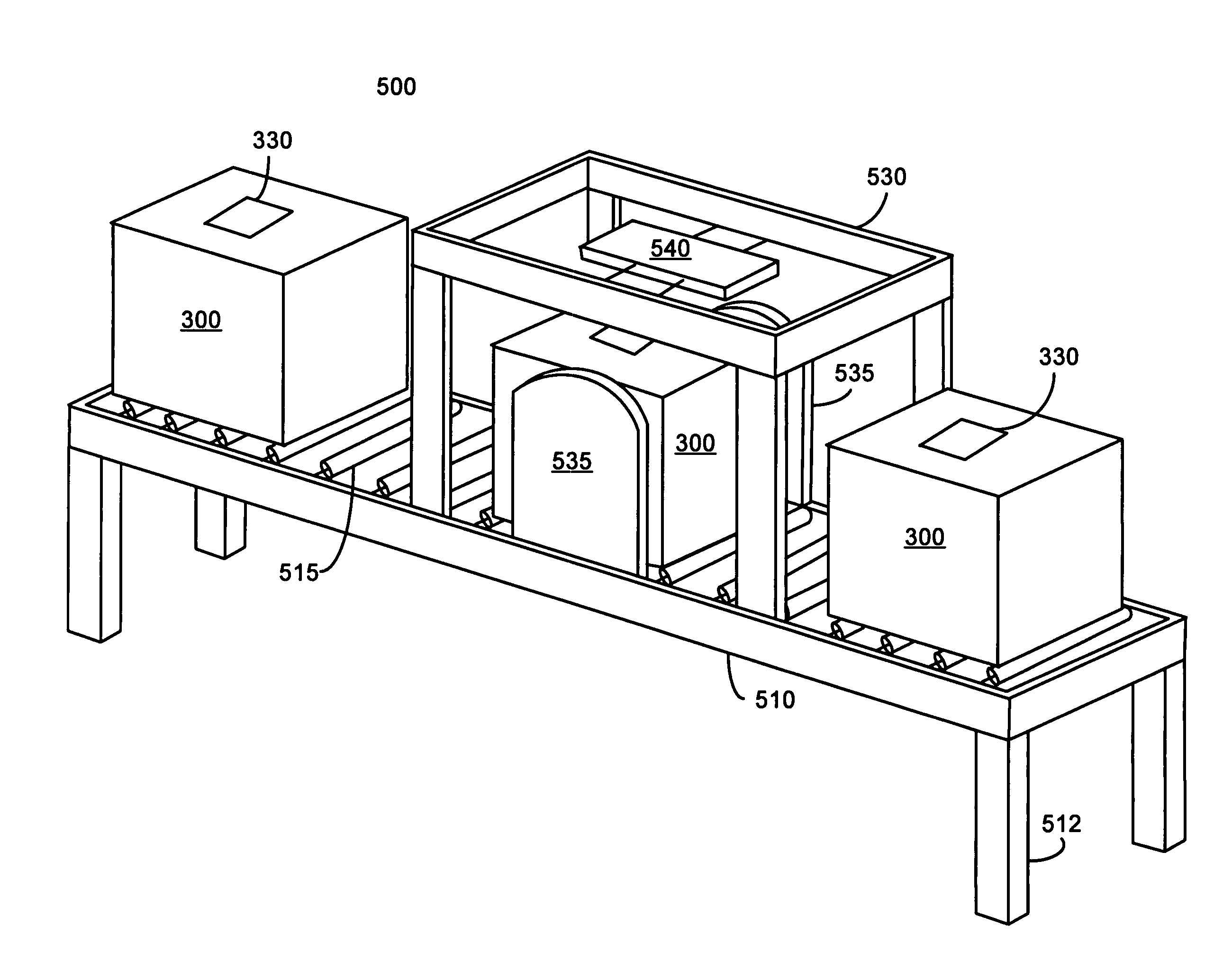
Surgical instrument tray shipping tote identification system and methods of using same
ActiveUS20060109105A1Reduce processing costsAccurate and rapid trackingLogisticsElectric signalling detailsTransceiverBarcode
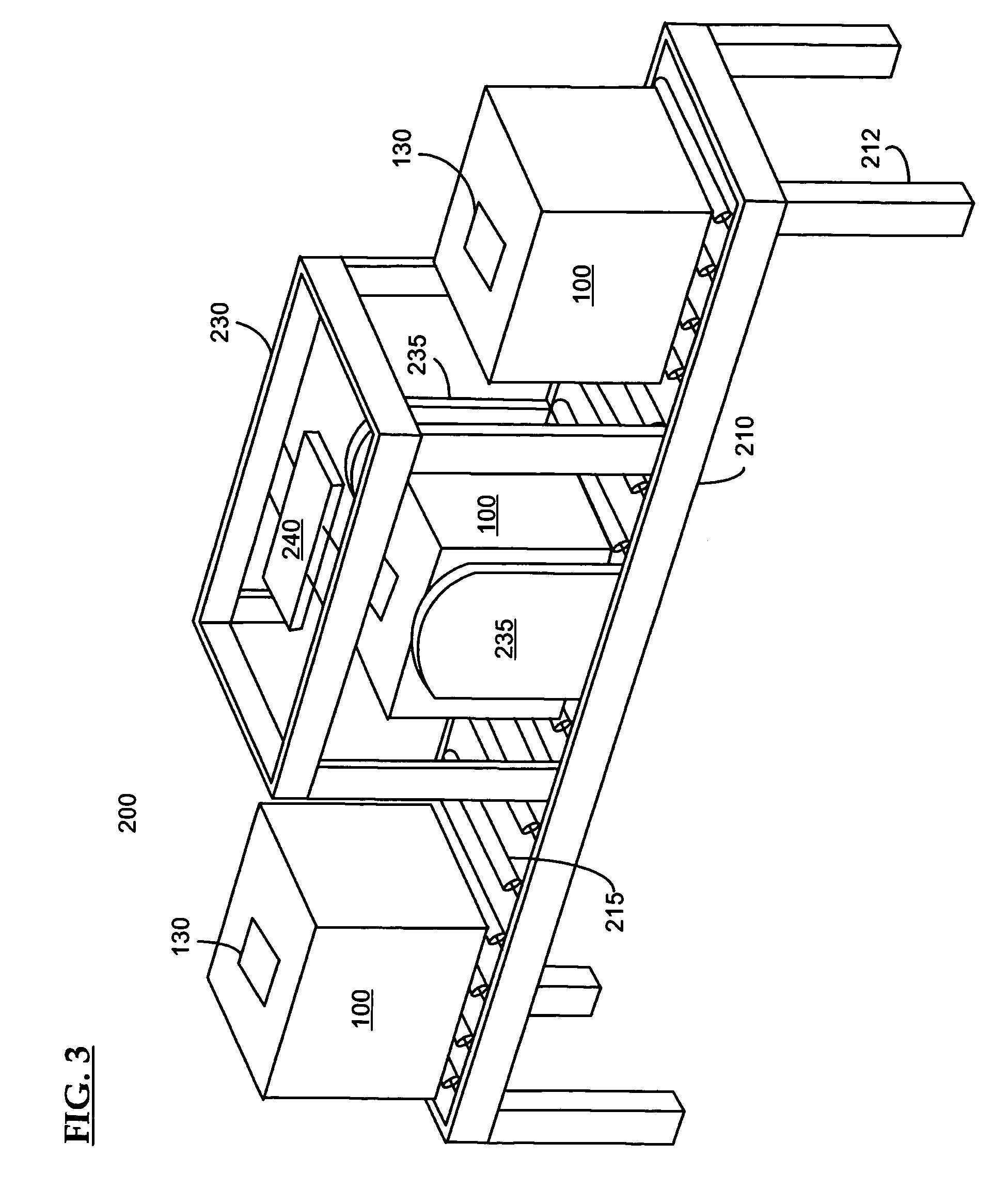
A surgical instrument tray shipping tote identification system is provided. During transit to or from a medical facility, processing center, distribution center or other location, multiple surgical instruments trays are placed in an instrument tray shipping tote. Each instrument tray includes at least one RFID transponder tag storing identification information about that tray. The shipping tote has a bar coded shipping label affixed to one surface generated at the point of origin. When the tote arrives at the distribution center, it is placed on a conveyor system that includes a reading station having an RFID transceiver and a bar code reader. Information read from the RFID transponder tags and the bar code label is transmitted by a controller to an external database to check for any off-nominal status indicators. Once this check is performed, an indication is sent back to the controller and an appropriate indicator on the identification system is activated.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Surgical instrument tray shipping tote identification system and methods of using same
ActiveUS7227469B2Accurate and rapid trackingReduce processing costsLogisticsElectric signalling detailsTransceiverBarcode
A surgical instrument tray shipping tote identification system is provided. During transit to or from a medical facility, processing center, distribution center or other location, multiple surgical instruments trays are placed in an instrument tray shipping tote. Each instrument tray includes at least one RFID transponder tag storing identification information about that tray. The shipping tote has a bar coded shipping label affixed to one surface generated at the point of origin. When the tote arrives at the distribution center, it is placed on a conveyor system that includes a reading station having an RFID transceiver and a bar code reader. Information read from the RFID transponder tags and the bar code label is transmitted by a controller to an external database to check for any off-nominal status indicators. Once this check is performed, an indication is sent back to the controller and an appropriate indicator on the identification system is activated.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Smart instrument tray RFID reader
ActiveUS7118029B2Reduce processing costsImprove verification accuracySurgical furnitureDiagnosticsWireless lanEngineering
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
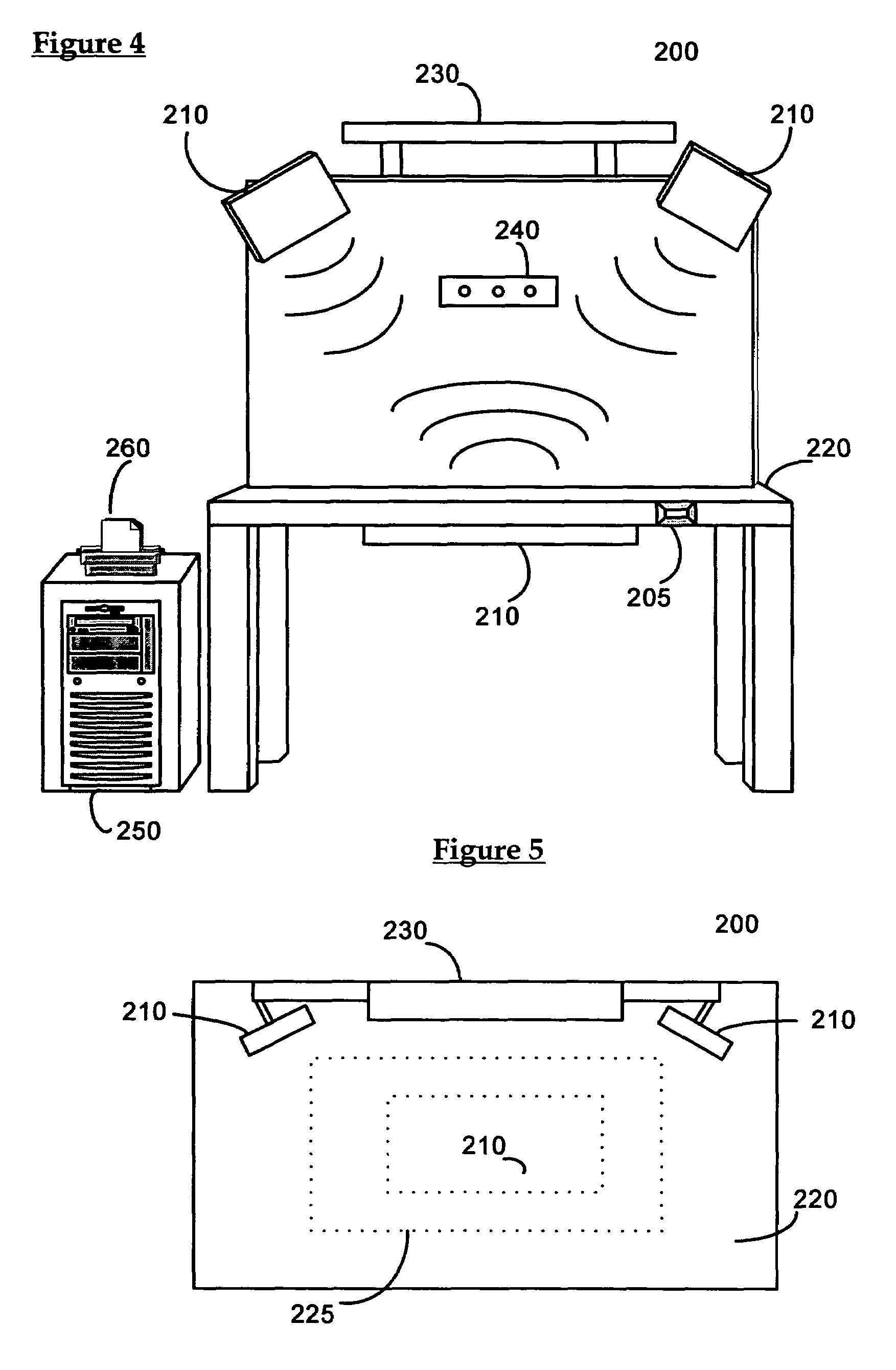
Workstation RFID reader for surgical instruments and surgical instrument trays and methods of using same
ActiveUS7268684B2Accurate and rapid trackingReduce processing costsSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsEngineeringWorkstation
A radio frequency identification (RFID) workstation reader for RFID-enabled surgical instruments and surgical instrument trays and a method of using a RFID workstation reader to read RFID-enabled surgical instruments and surgical instrument trays. The method, apparatus, and system enable individual instruments or a surgical instrument tray containing several surgical instruments to be quickly and efficiently inventoried and tracked. An instrument or instrument tray is placed on the workstation reader. An RF field generated by a plurality of antennae, causes RFID tags embedded in or attached to the instrument or instrument tray to emit a signal containing item specific identification information stored in the tags. The information is received by a control circuit and passed to a computer for data analysis. A status LED is illuminated on the workstation reader based on the results of the data analysis. The method, apparatus, and system can track, inspect, and verify inbound and outbound surgical instrument kits, and help to assess the surgical instruments' and trays' duty life cycle usage.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Workstation RFID reader for surgical instruments and surgical instrument trays and methods of using same
ActiveUS20060119481A1Reduce processing costsAccurate and rapid trackingSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsEngineeringWorkstation
A radio frequency identification (RFID) workstation reader for RFID-enabled surgical instruments and surgical instrument trays and a method of using a RFID workstation reader to read RFID-enabled surgical instruments and surgical instrument trays is disclosed. The method, apparatus, and system enable individual instruments or a surgical instrument tray containing several surgical instruments to be quickly and efficiently inventoried and tracked. An instrument or instrument tray is placed on the workstation reader. An RF field generated by a plurality of antennae, causes RFID tags embedded in or attached to the instrument or instrument tray to emit a signal containing item specific identification information stored in the tags. The information is received by a control circuit and passed to a computer for data analysis. A status LED is illuminated on the workstation reader based on the results of the data analysis. The method, apparatus, and system can track, inspect, and verify inbound and outbound surgical instrument kits, and help to assess the surgical instruments' and trays' duty life cycle usage.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
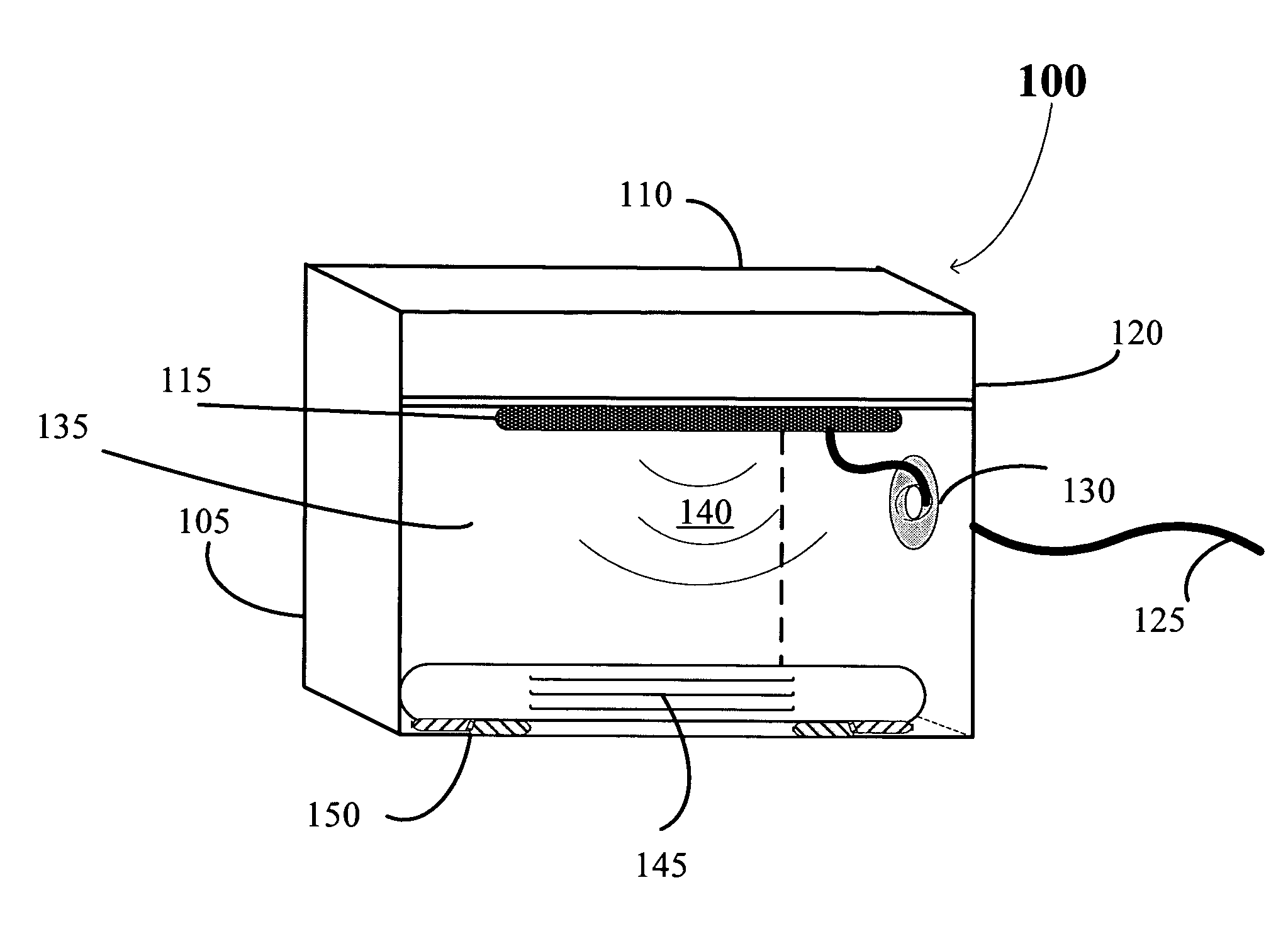
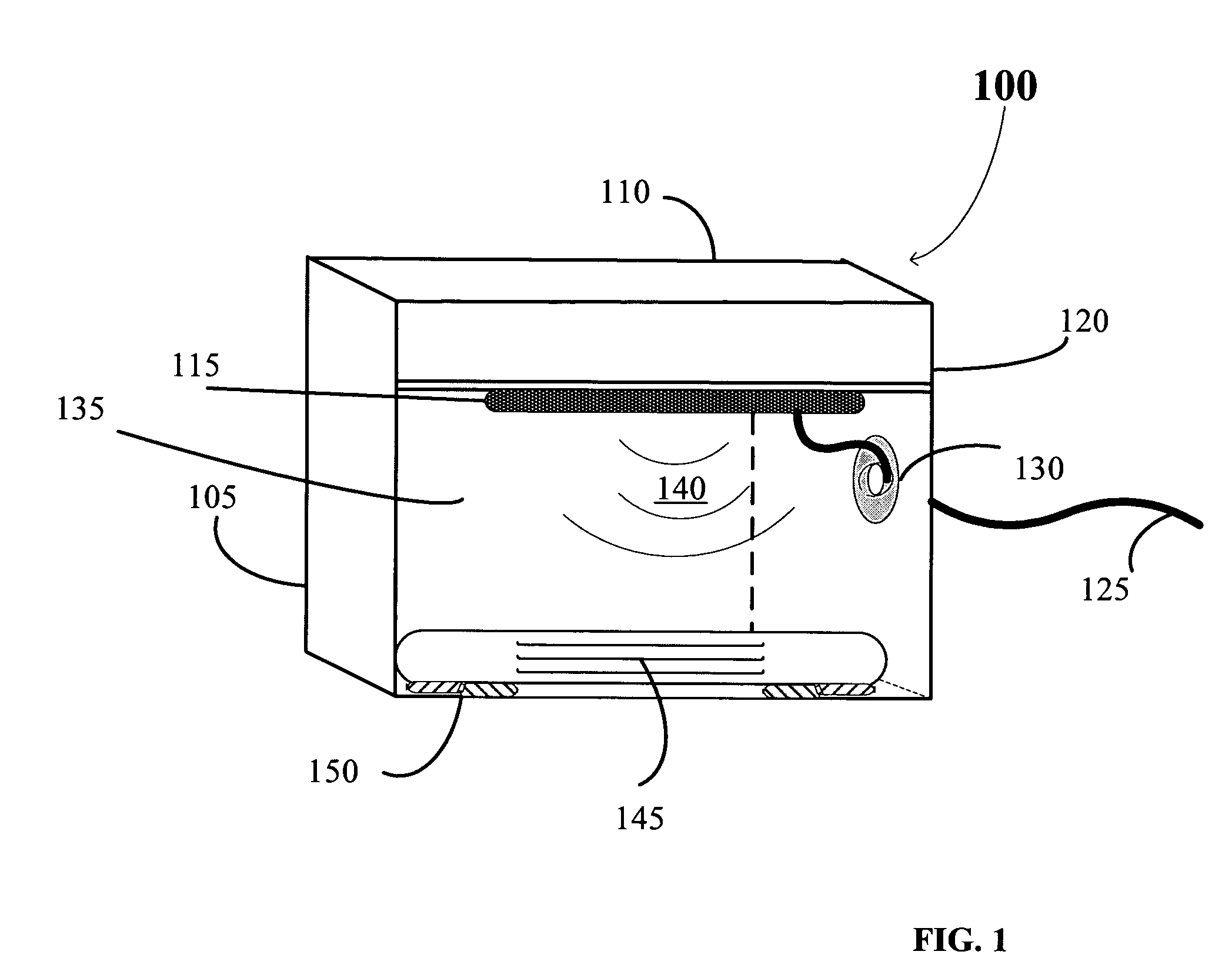
Automated pass-through surgical instrument tray reader
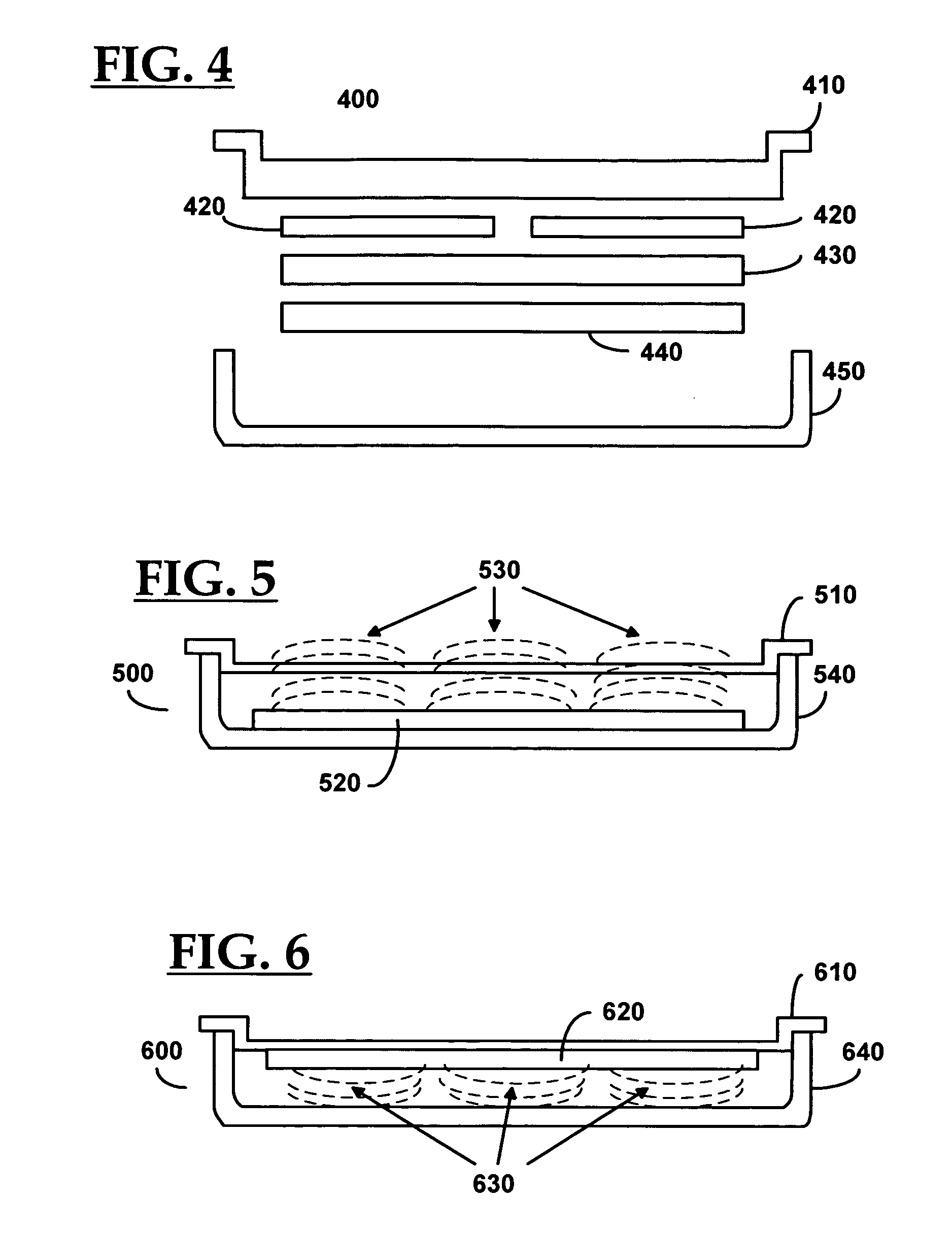
ActiveUS7644016B2Reduce processing costsEfficient collectionElectric signal transmission systemsSurgical furnitureData terminalEngineering
An apparatus and method for interrogating and automatically identifying a radio-frequency tagged surgical instrument tray and its contents of RFID-tagged surgical instruments are disclosed. The surgical instrument tray and its contents come into contact with an RF signal transmitted by the RFID reader, and as a result, the RFID tags affixed on the instrument tray and the surgical instruments respond by transmitting back to the RFID reader data pertaining to the history of the surgical instruments. A data terminal, which is connected to the RFID reader, may contain data pertaining to the radio frequency tagged surgical instruments during packaging, and during the return of the surgical instrument trays to the packager, identifies the surgical instruments.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Automated pass-through surgical instrument tray reader
ActiveUS20060043177A1Cost reductionReduce processing costsElectric signal transmission systemsSurgical furnitureRadio frequencyInstrument tray
An apparatus and method for interrogating and automatically identifying a radio-frequency tagged surgical instrument tray and its contents of RFID-tagged surgical instruments are disclosed. The surgical instrument tray and its contents come into contact with an RF signal transmitted by the RFID reader, and as a result, the RFID tags affixed on the instrument tray and the surgical instruments respond by transmitting back to the RFID reader data pertaining to the history of the surgical instruments. A data terminal, which is connected to the RFID reader, may contain data pertaining to the radio frequency tagged surgical instruments during packaging, and during the return of the surgical instrument trays to the packager, identifies the surgical instruments.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Smart instrument tray RFID reader
ActiveUS20060043179A1Reduce processing costsInterference problemSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsEngineeringElectromagnetic field
A method and apparatus for automatically identifying the contents of an instrument tray by use of a radio-frequency tag (RFID) is disclosed. The method, apparatus, and system enable the instrument tray to receive an interrogation signal from a reader and to respond to the interrogation signal with a code comprised of its identifying information as well as its contents of radio frequency tagged instruments. Both the instrument tray and / or the reader may be coupled by a proximity electromagnetic field, an inductive coupling, or may be units of a wireless LAN system such as a wireless fidelity local area network. The interrogation signal interrogates the tray to ascertain its contents, and the tray in turn transmits a signal to the reader to inform the reader of its contents. The method, apparatus, and system can track, inspect, and verify inbound and outbound surgical instrument trays and kits, to assess, for example, the surgical instruments' and trays' duty life cycle usage.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Smart instrument tray RFID reader
ActiveUS20060244593A1Reduce processing costsAccurate and rapid trackingSurgical furnitureDispensing apparatusEngineeringWorkstation
A radio frequency identification (RFID) workstation reader for RFID-enabled surgical instruments and surgical instrument trays and a method of using a RFID workstation reader to read RFID-enabled surgical instruments and surgical instrument trays is disclosed. The method, apparatus, and system enable individual instruments or a surgical instrument tray containing several surgical instruments to be quickly and efficiently inventoried and tracked. An instrument or instrument tray is placed on the workstation reader. An RF field generated by a plurality of antennae, causes RFID tags embedded in or attached to the instrument or instrument tray to emit a signal containing item specific identification information stored in the tags. The information is received by a control circuit and passed to a computer for data analysis. A status LED is illuminated on the workstation reader based on the results of the data analysis. The method, apparatus, and system can track, inspect, and verify inbound and outbound surgical instrument kits, and help to assess the surgical instruments' and trays' duty life cycle usage.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
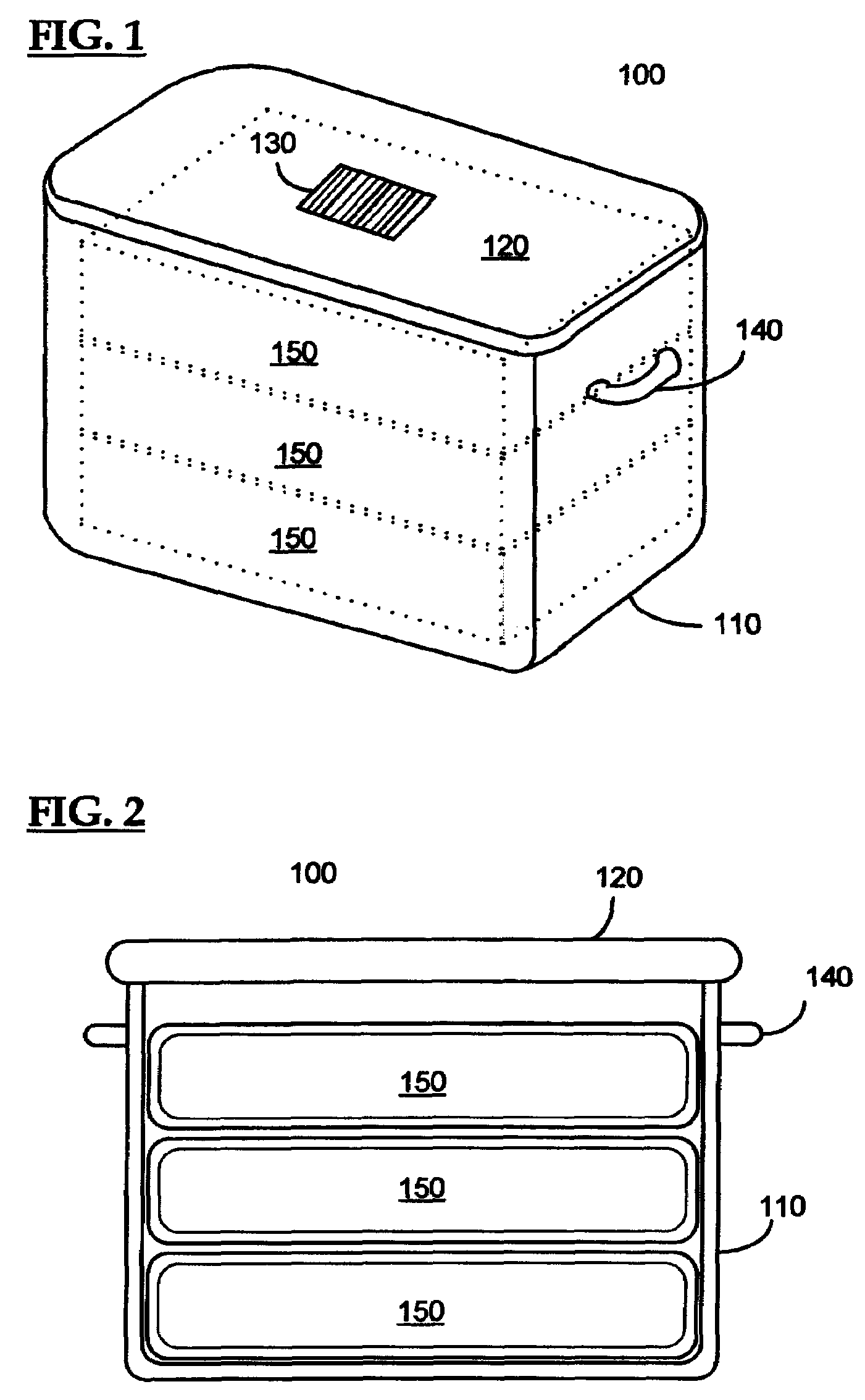
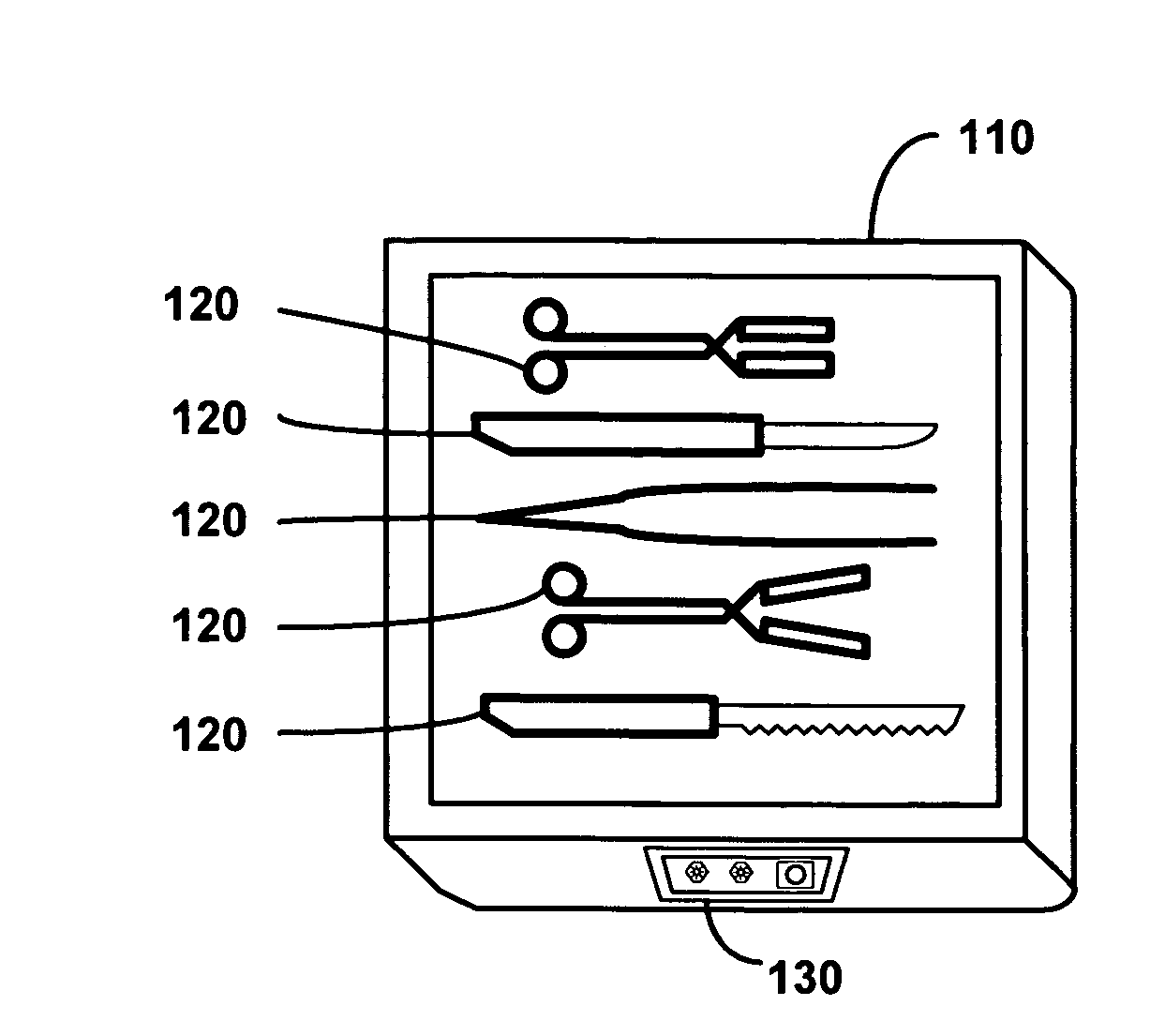
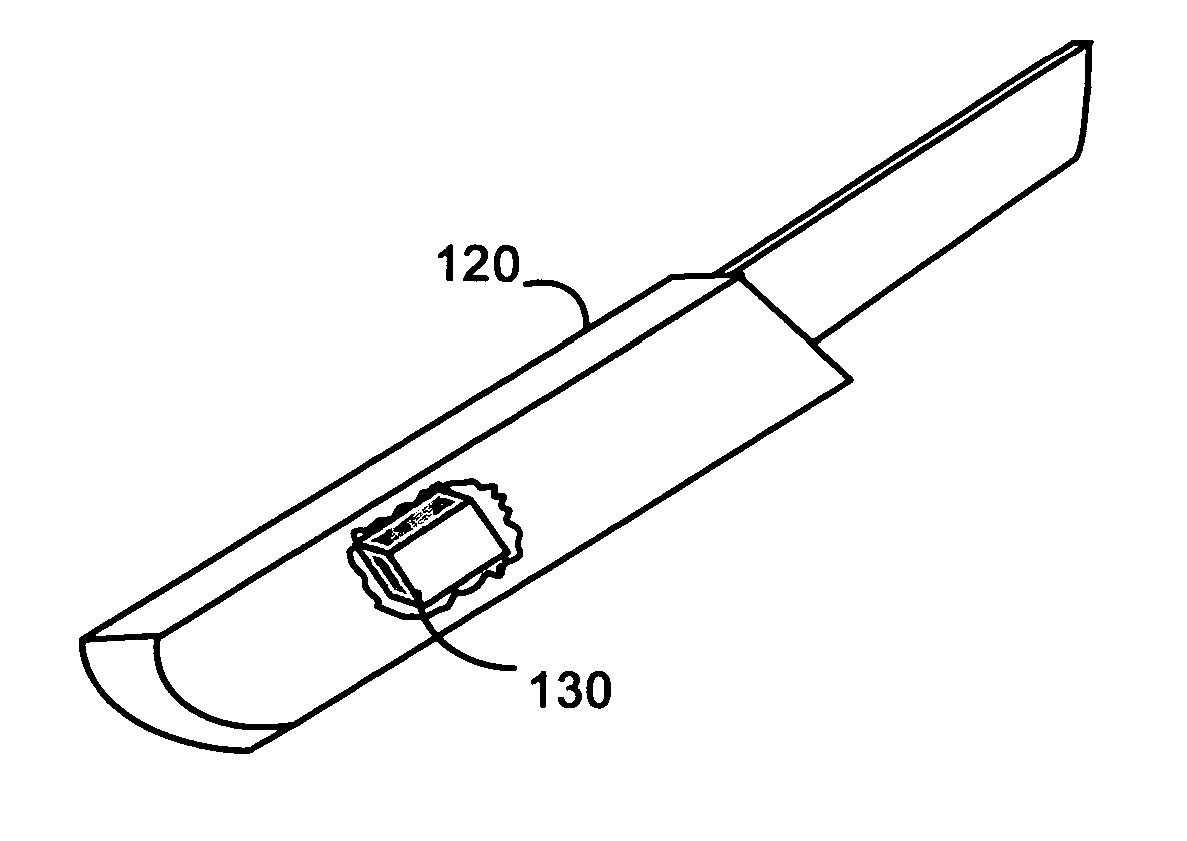
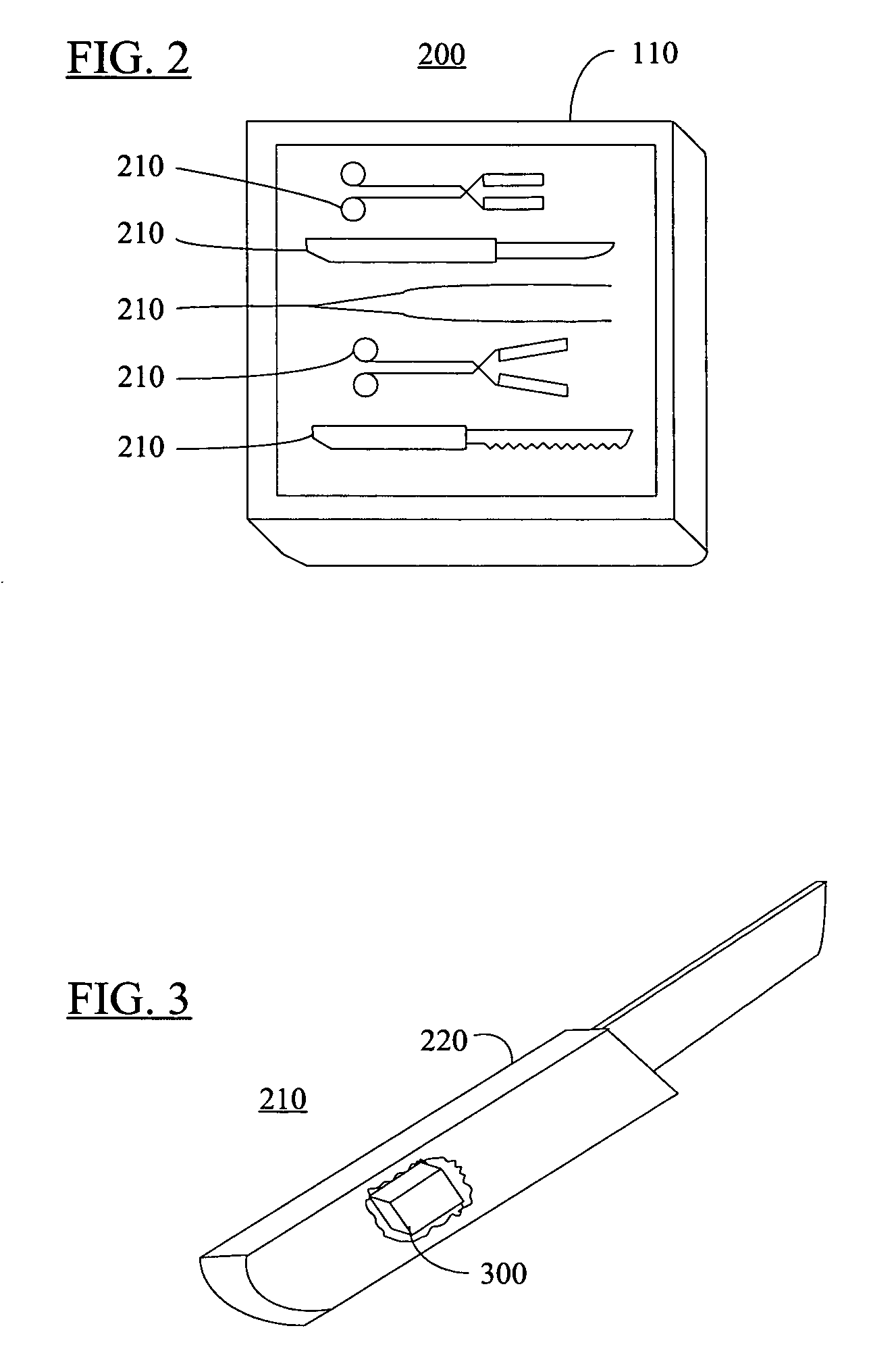
Method and apparatus for surgical instrument identification
ActiveUS20060244652A1Reduce processing costsOvercomes shortcomingSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsEngineeringOperating life
Systems and methods for identifying surgical instruments by use of radio-frequency identification tags (RFID) are disclosed. In the systems and methods, each of a plurality of surgical instruments is provided with at least one RFID transponder tag storing identification information associated with the corresponding instrument. The tag may be adhered to, embedded, or potted within a portion of the instrument. Using an RFID reading device, a user may interrogate the tag, thereby identifying the particular instrument. This identification information may be used to index a database and retrieve a data record unique to that instrument. The systems and methods allow a user to track, inspect, and verify inbound and outbound surgical instruments, to assess, for example, the surgical instruments' duty life cycle usage.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Systems and methods for processing surgical instrument tray shipping totes
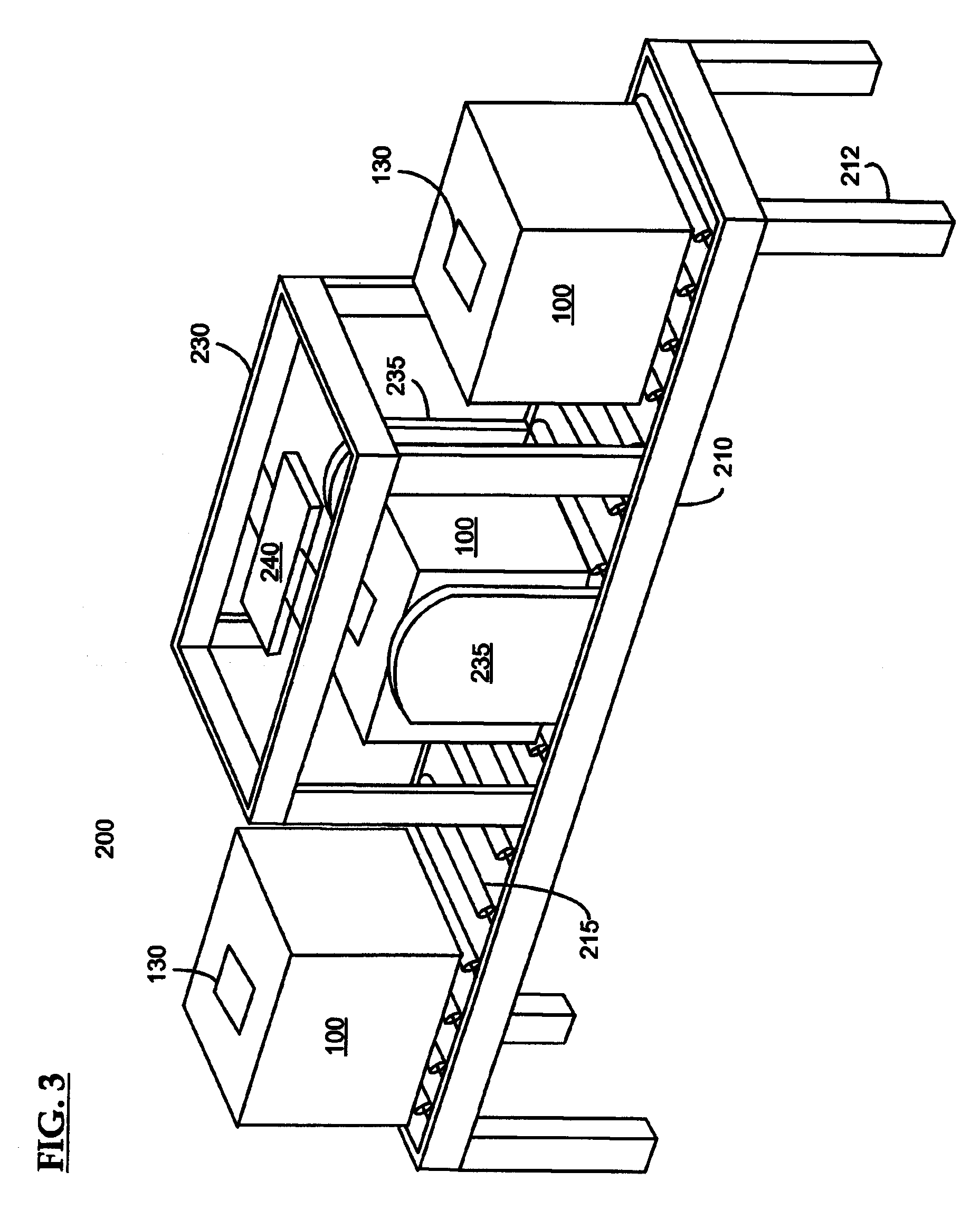
ActiveUS7492257B2Accurate and rapid trackingImprove throughputLogisticsCommerceControl systemEngineering
Systems and methods for processing surgical instrument tray shipping totes. A control system is adapted to control a bar code reader module, an RFID module, a database module and an interface module. The control system provides functionality adapted to process incoming and outgoing surgical instrument shipping totes containing one or more RFID-enabled surgical instrument trays. A database, ERP system or other system in communication with the control system alerts the operator of the status of an incoming tote and / or trays contained in the tote to increase processing efficiency and speed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
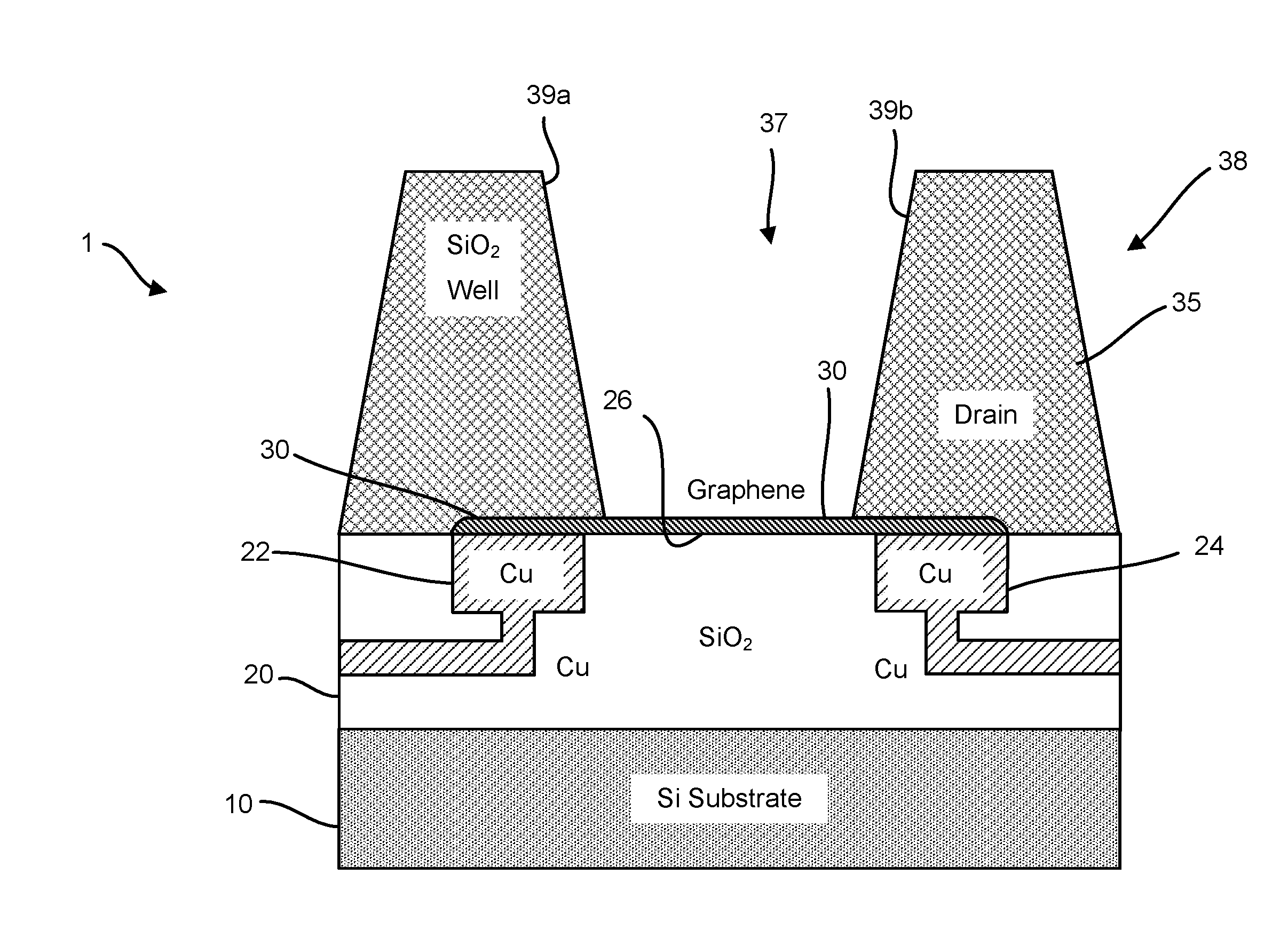
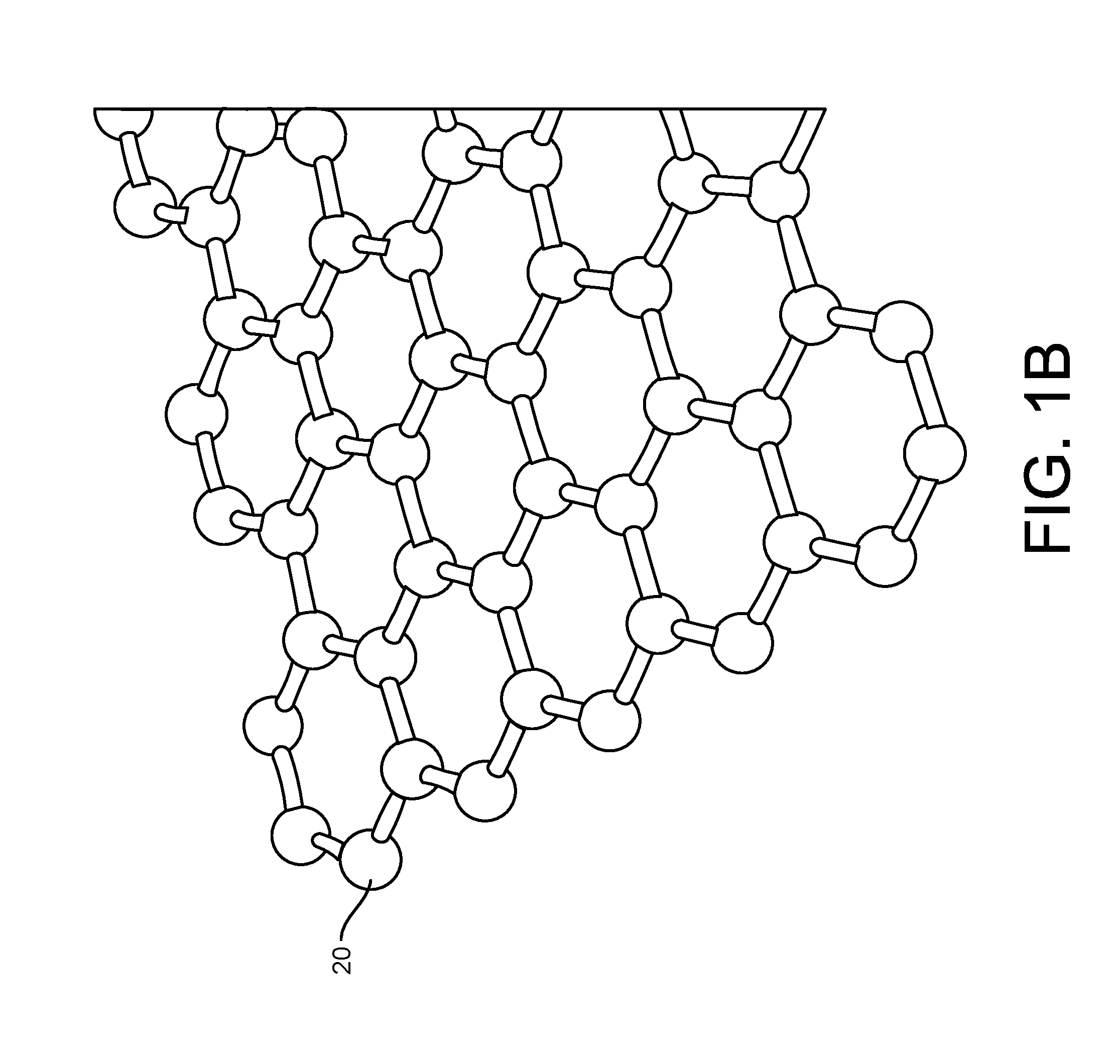
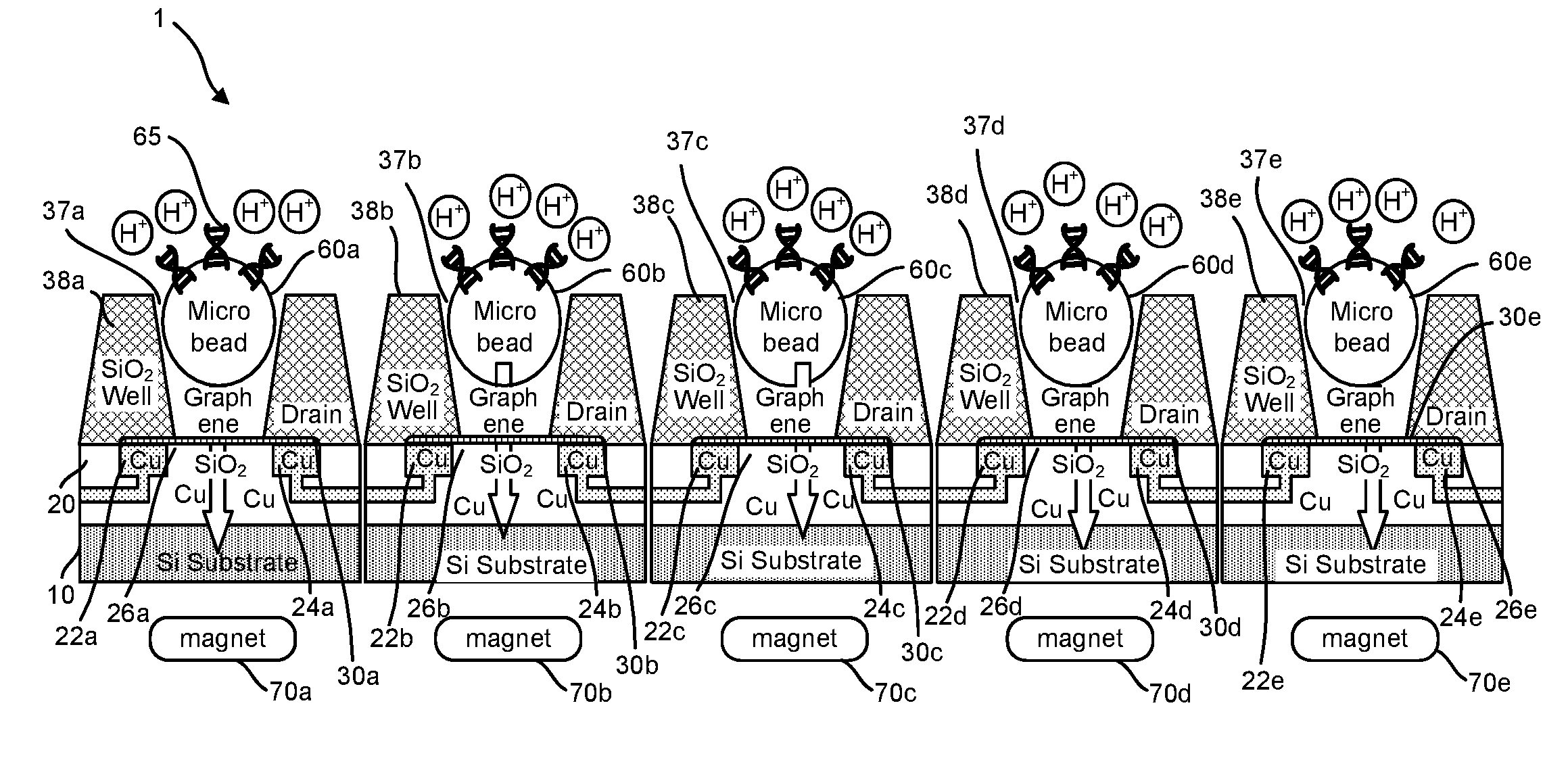
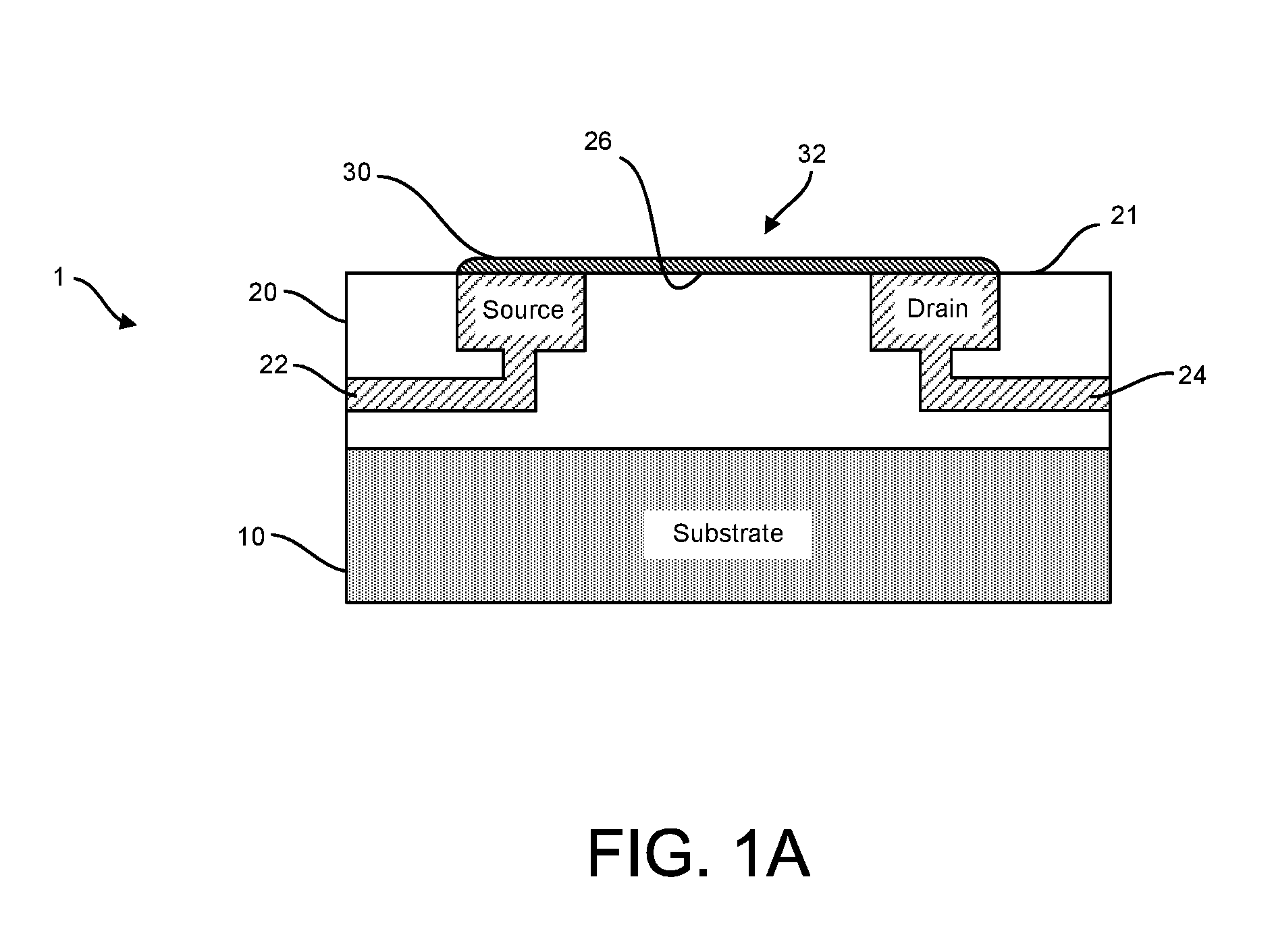
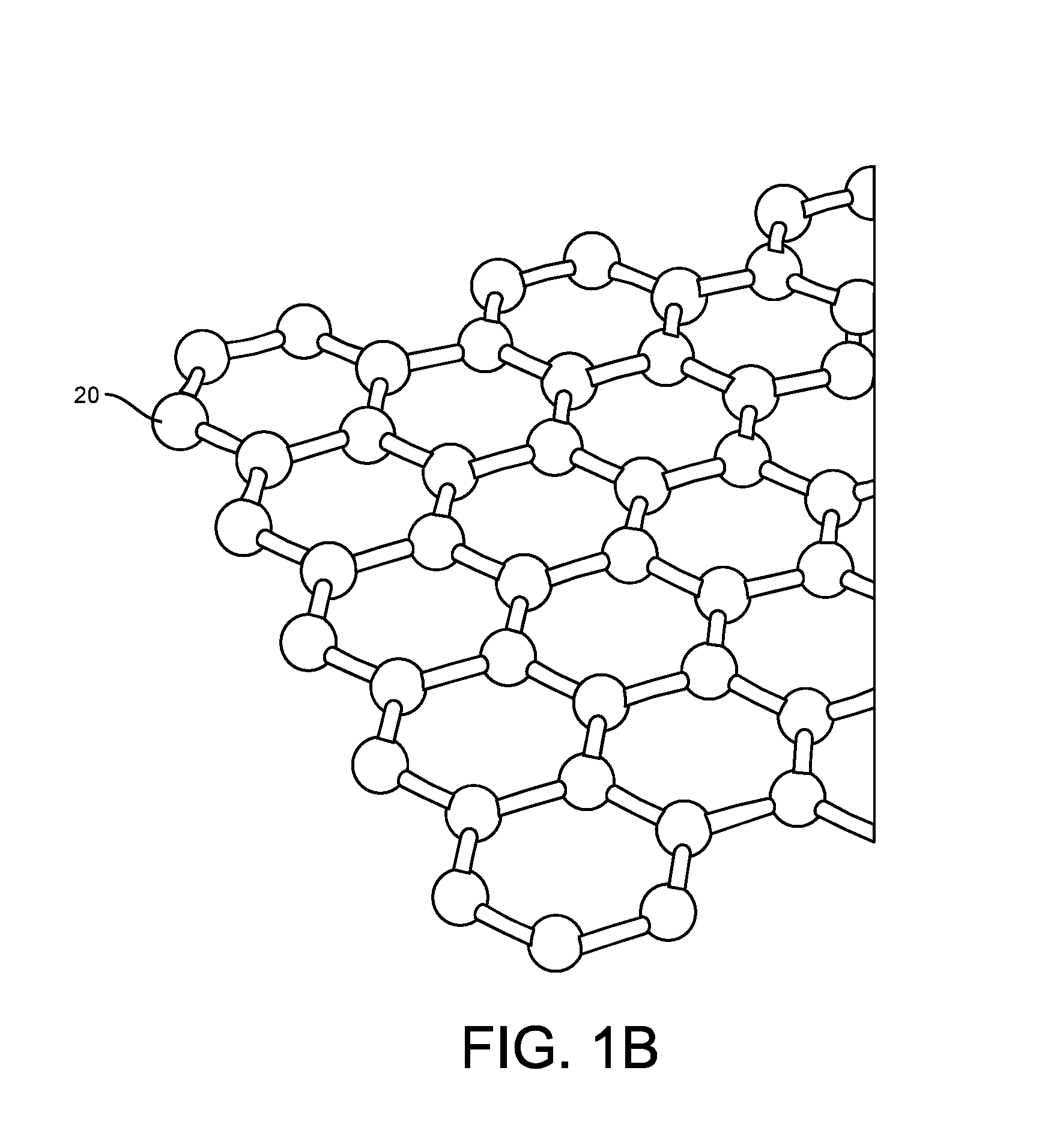
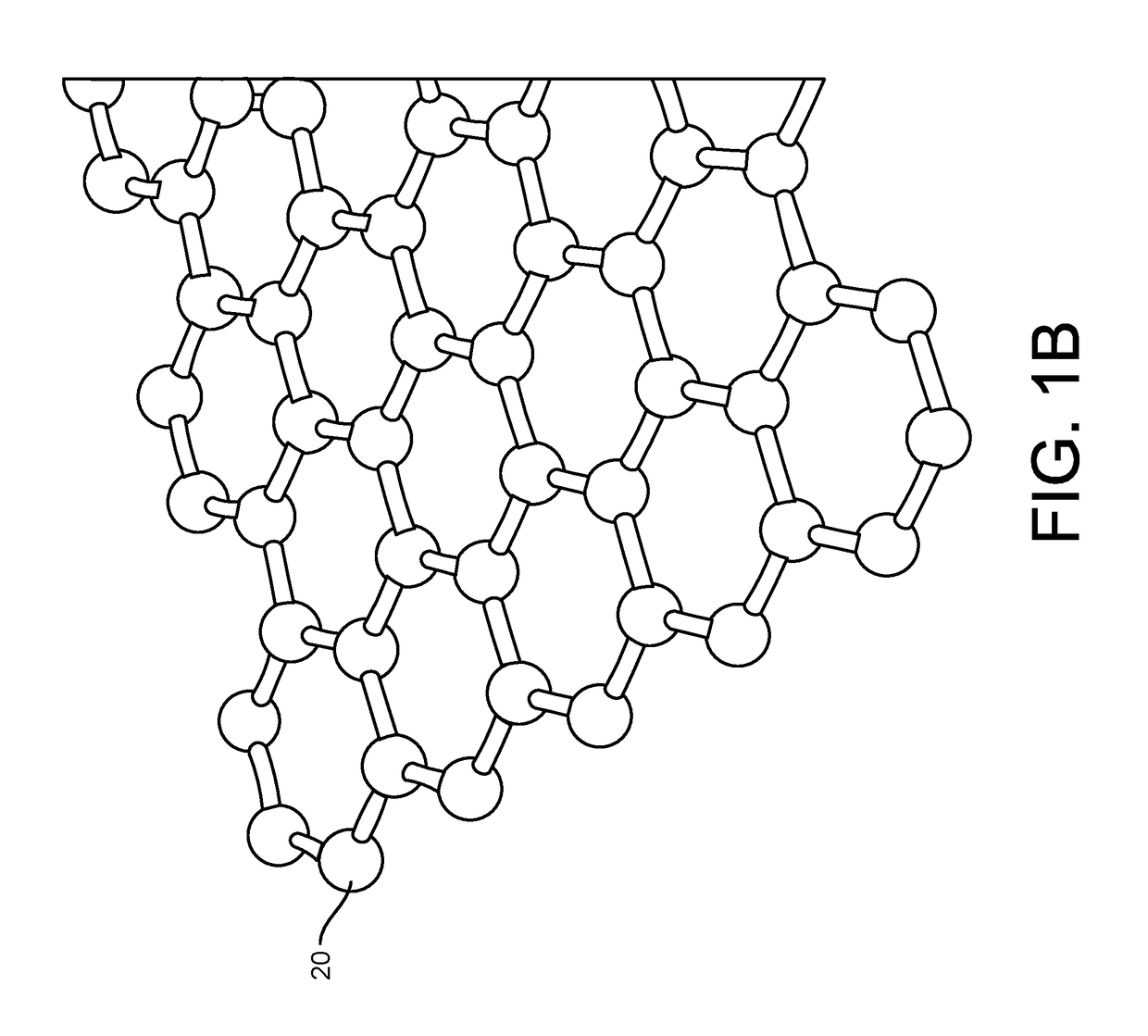
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
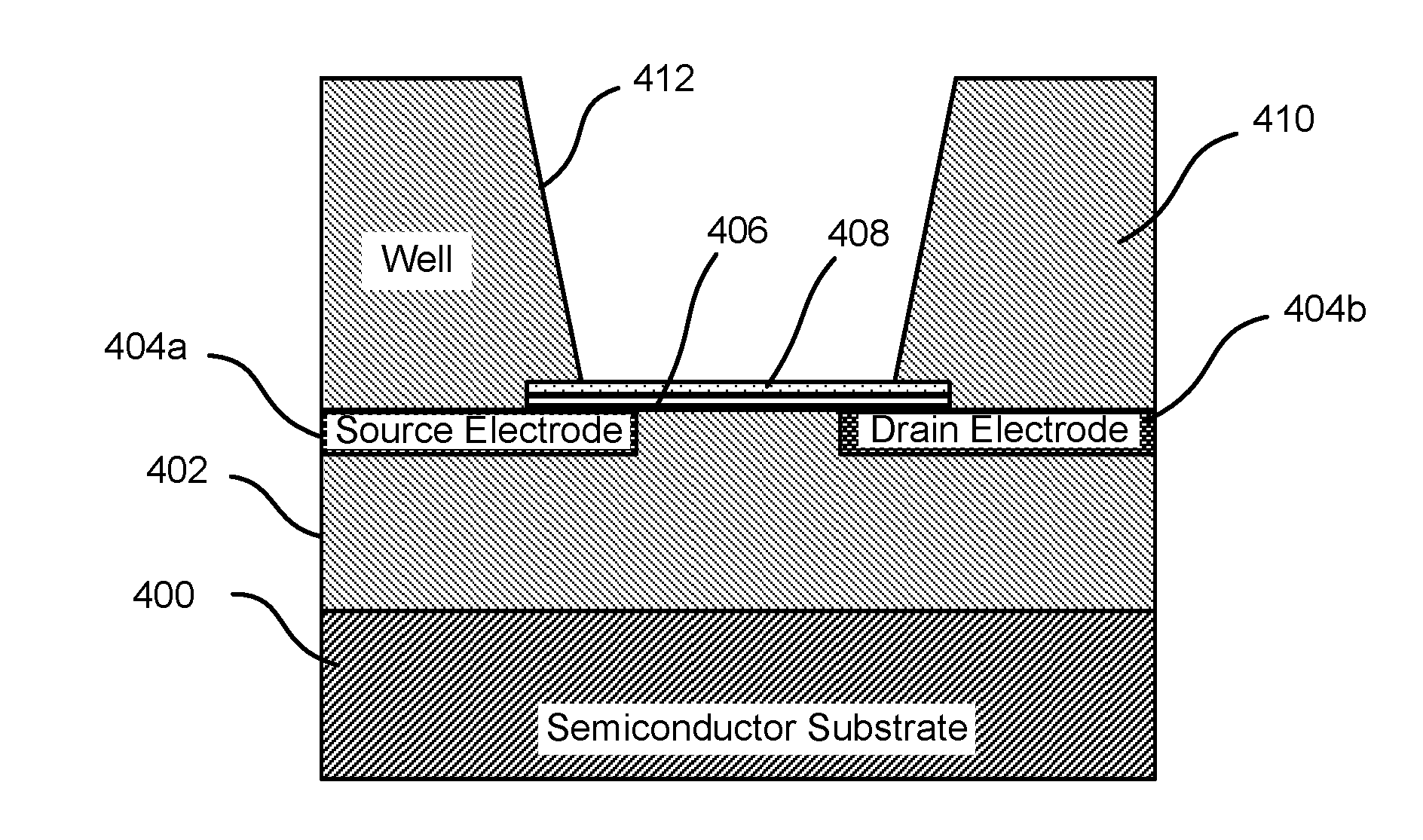
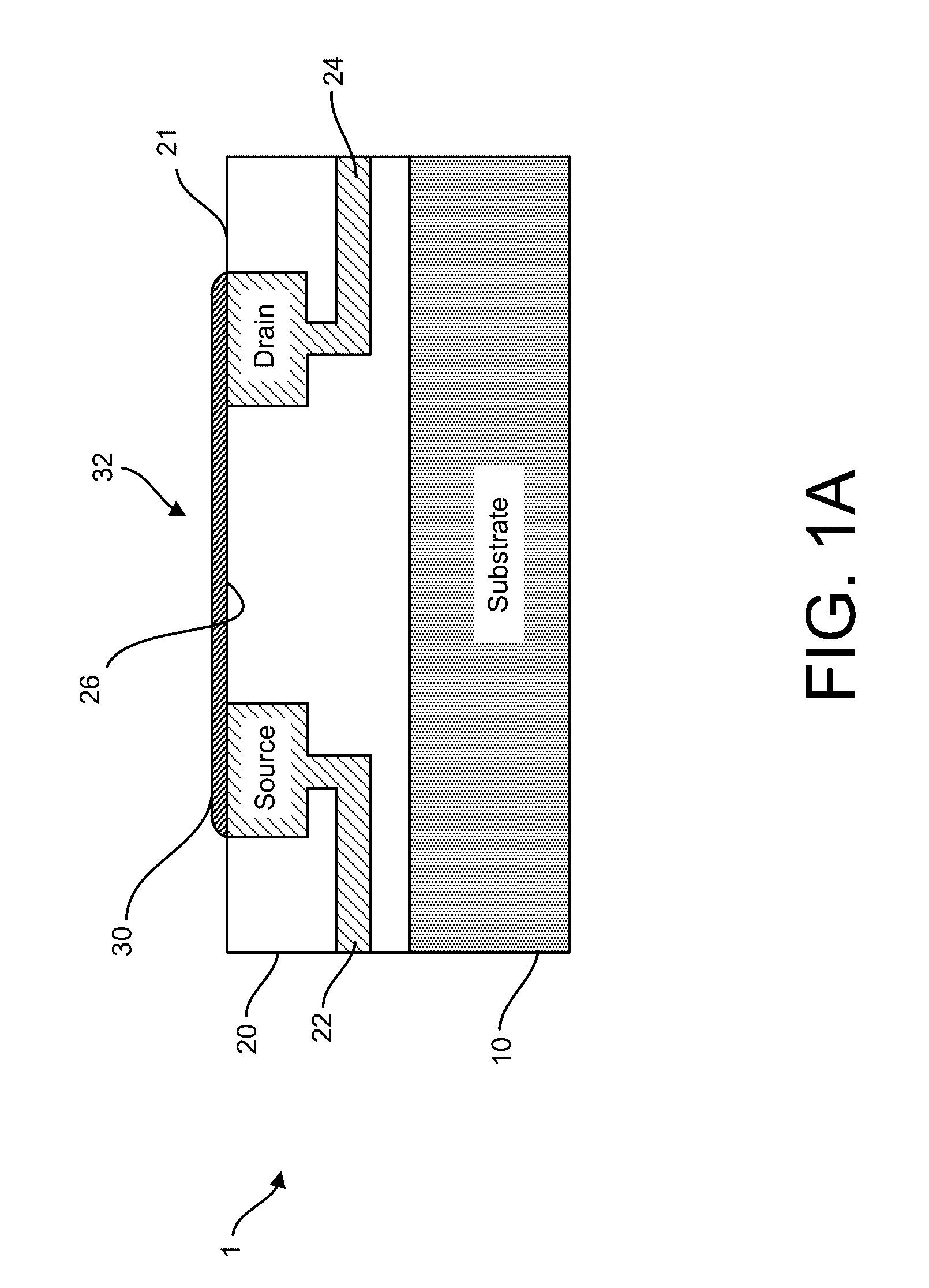
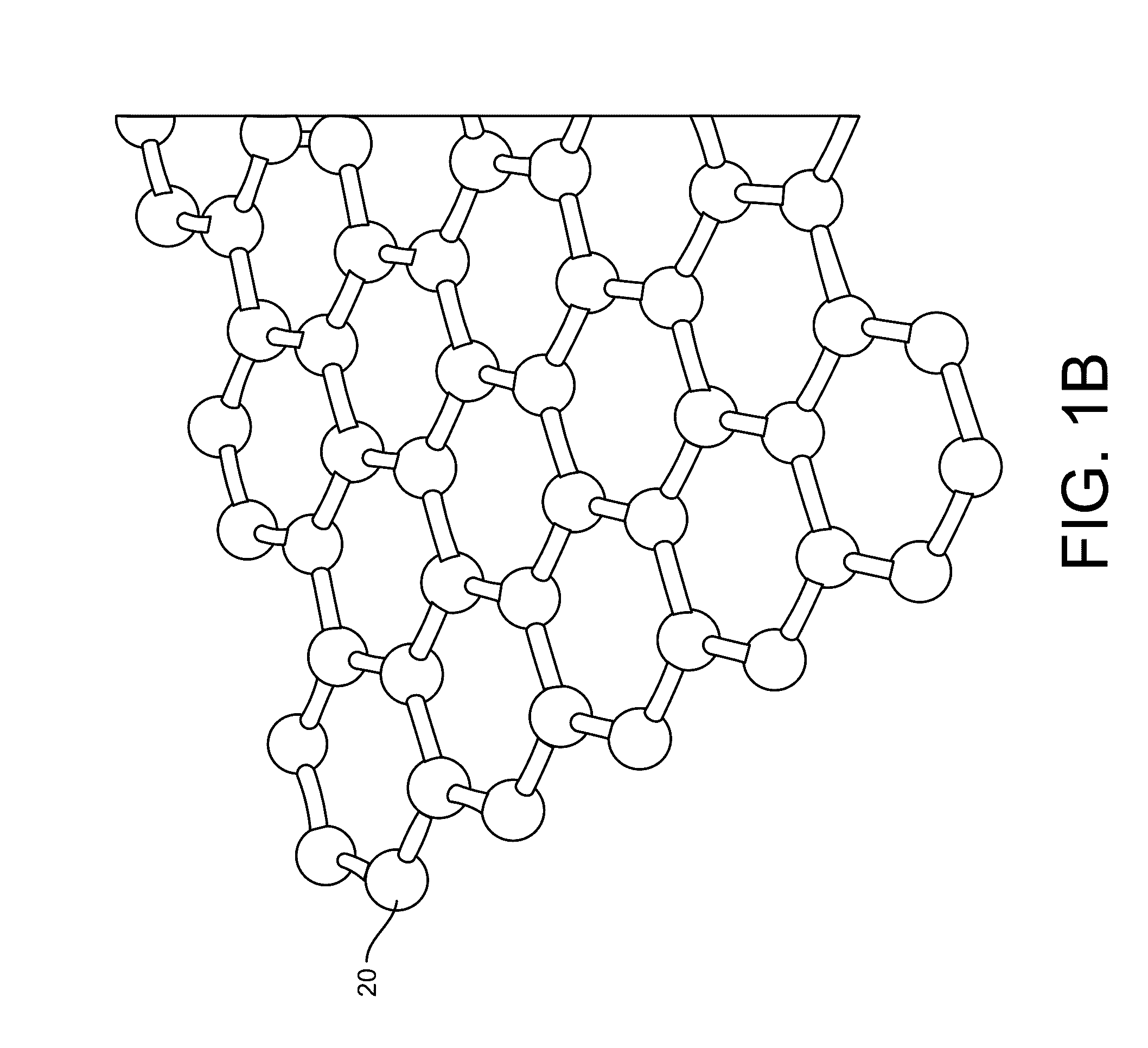
ActiveUS20160265047A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementSensor arrayReaction layer
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
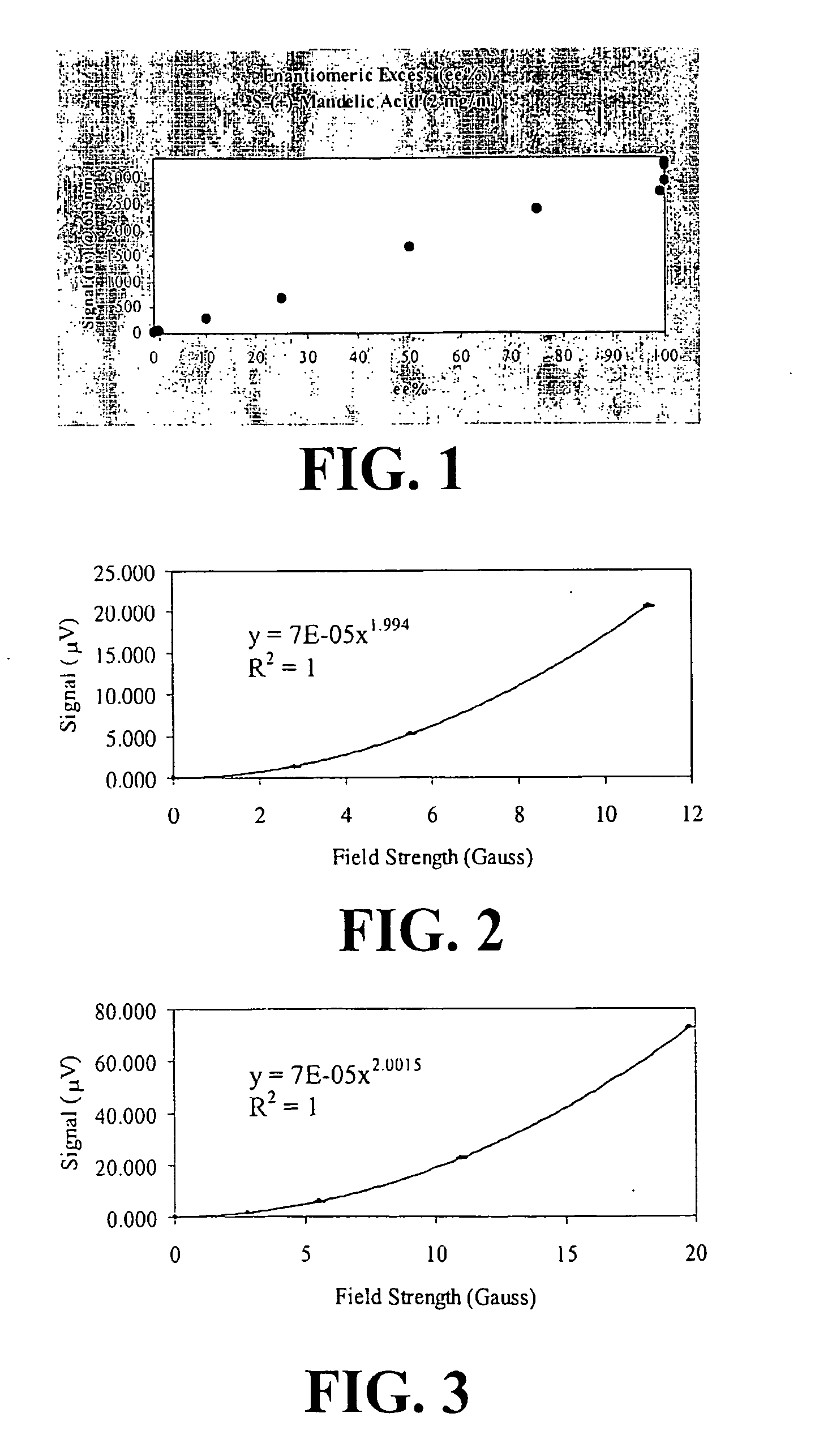
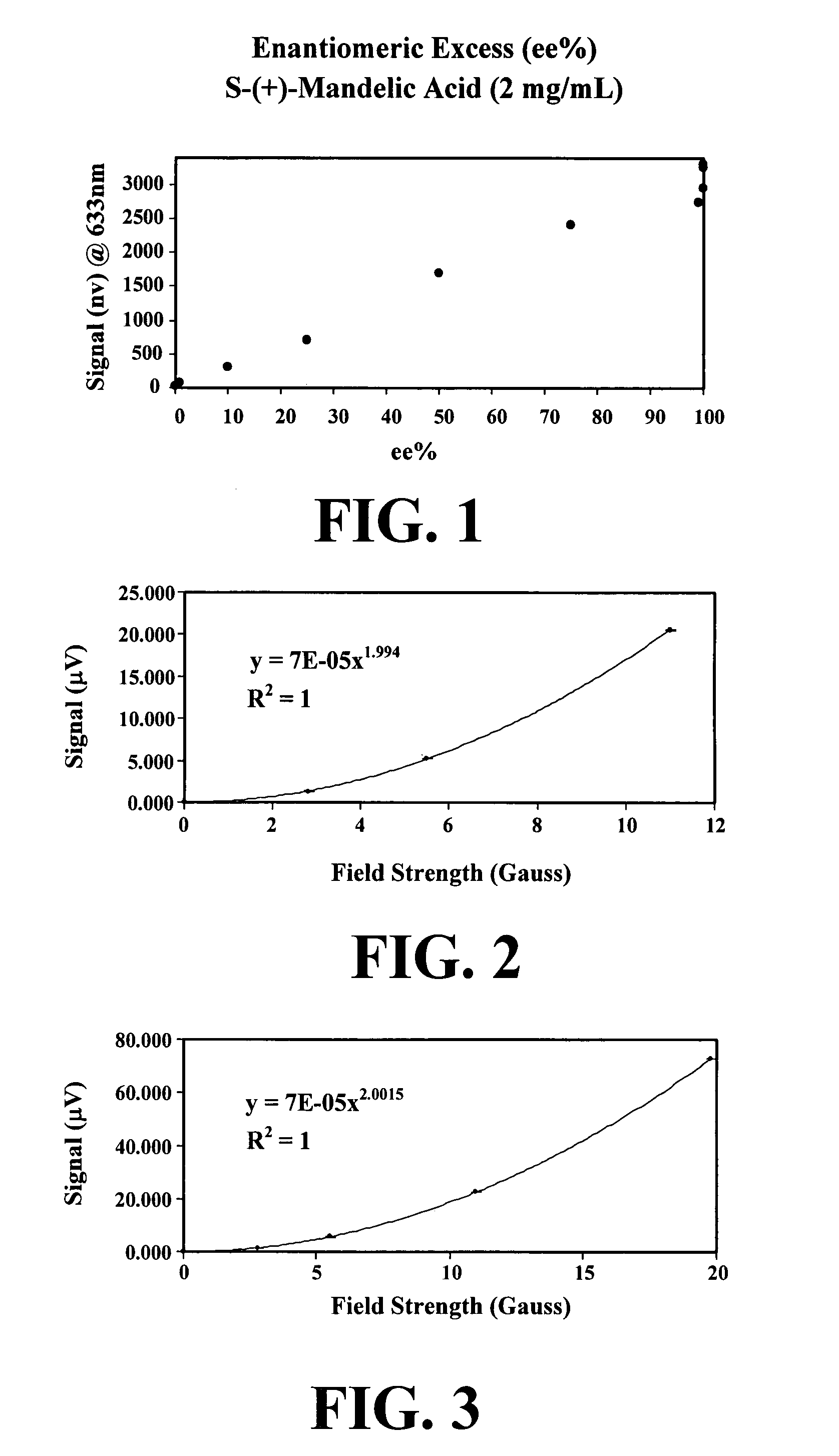
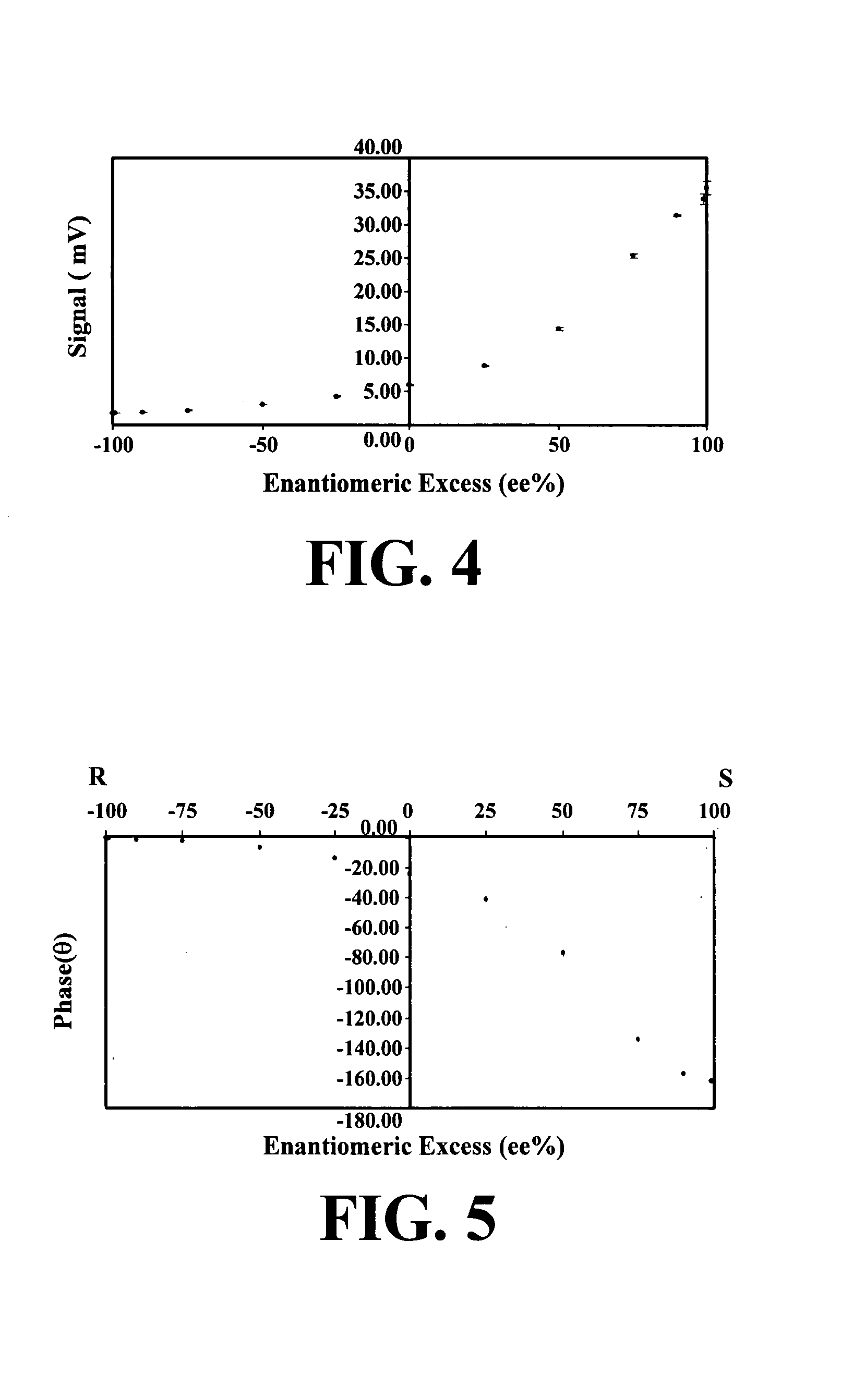
High-throughput chiral detector and methods for using same
InactiveUS20050094144A1Rapid and accurate and large-scale screeningEasy to measurePolarisation-affecting propertiesLight polarisation measurementAnalyteOptical property
A new generation polarimetry apparatus and methodology is disclosed, which involve passing polarized light through a sample including a chiral analyte, where the analyte is under the influence of a periodically varying magnetic field. The apparatus also utilizes optical heterodyne detection and lock-in detection at higher order harmonics of the magnetic field modulation frequency to improve sensitivity and detection limits of optical properties of chiral analytes.
Owner:GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Analytical scanning evanescent microwave microscope and control stage
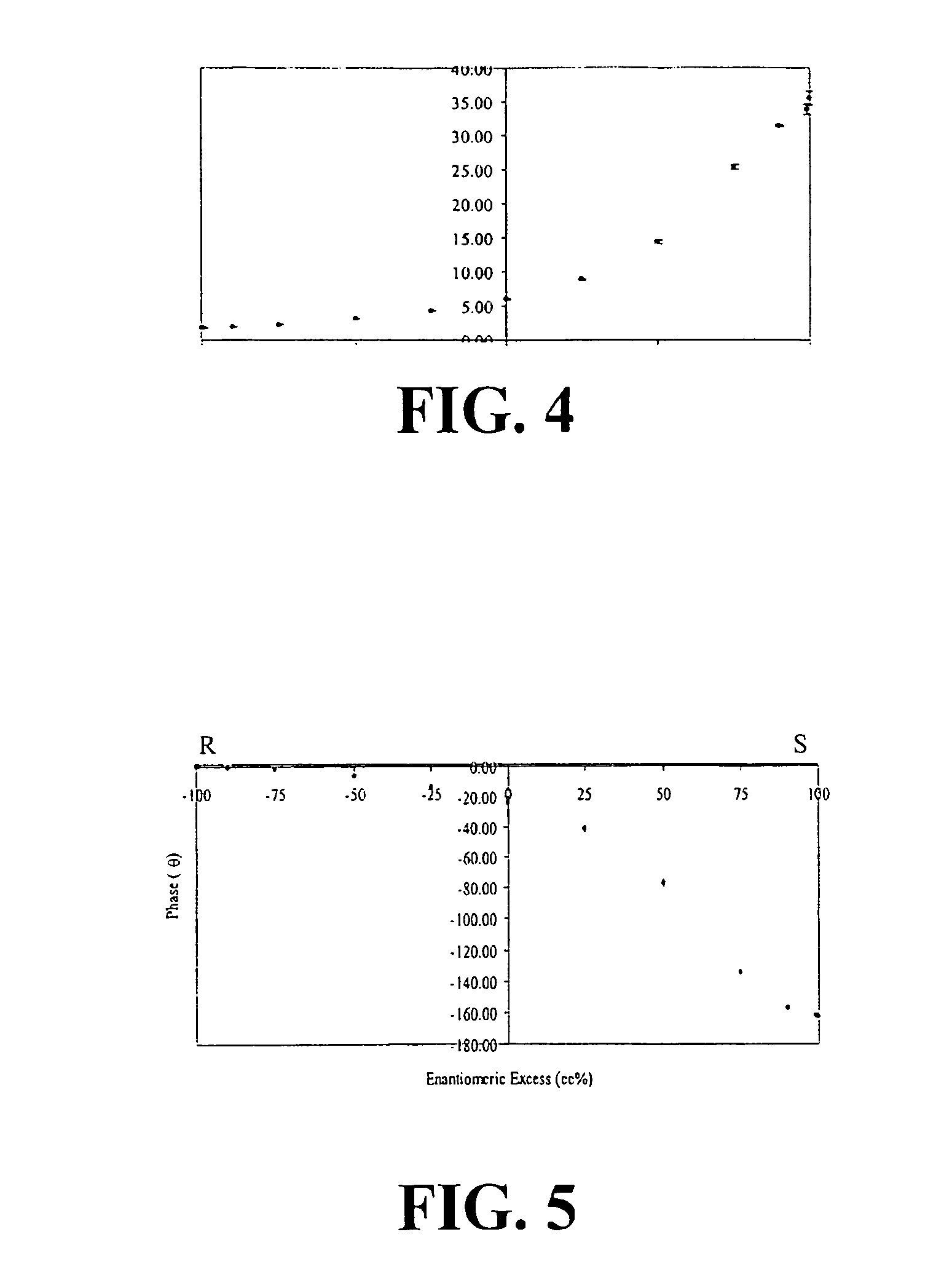
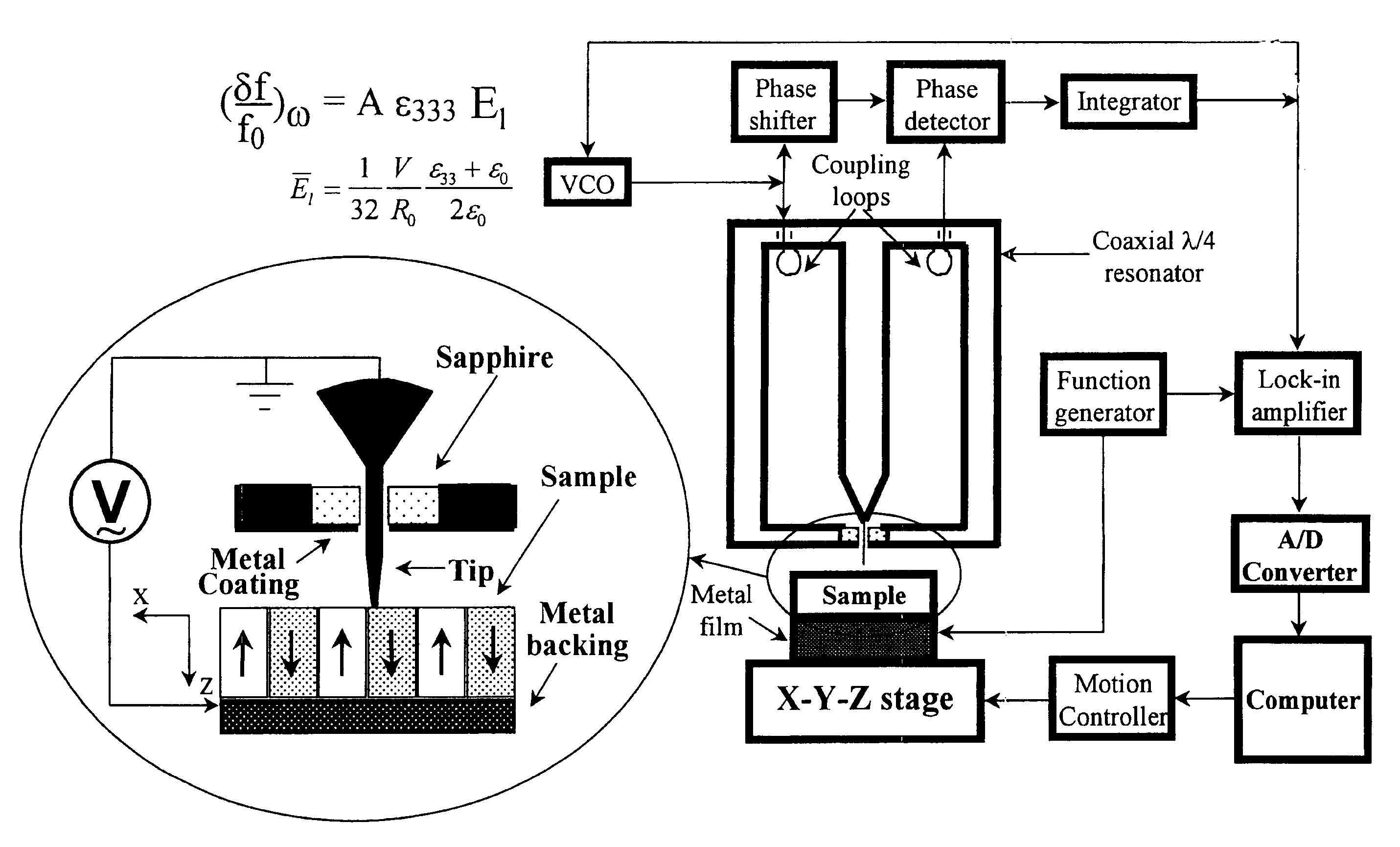
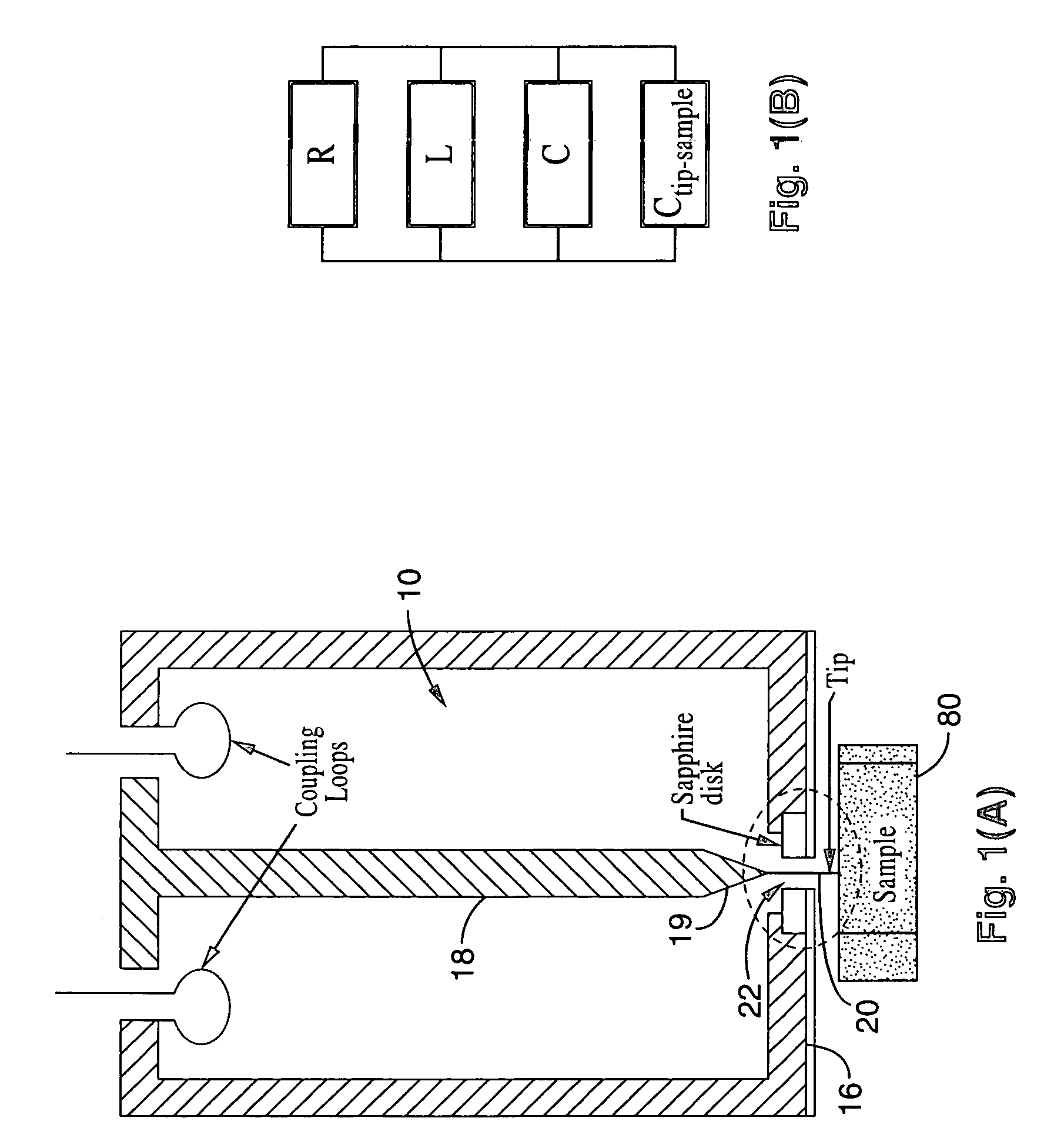
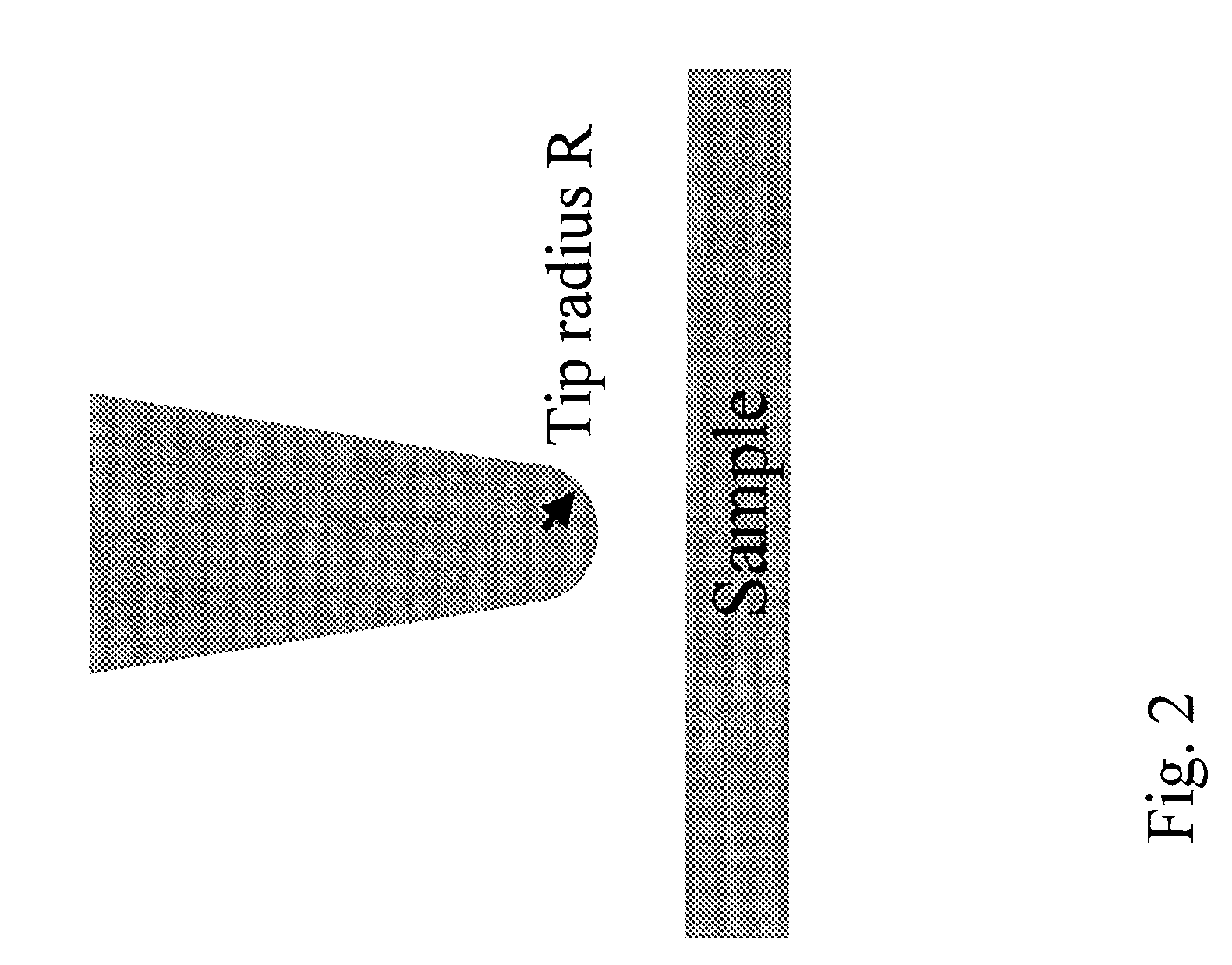
InactiveUS7550963B1Faster data acquisitionResistance/reactance/impedenceNanoopticsDielectricElectricity
A scanning evanescent microwave microscope (SEMM) that uses near-field evanescent electromagnetic waves to probe sample properties is disclosed. The SEMM is capable of high resolution imaging and quantitative measurements of the electrical properties of the sample. The SEMM has the ability to map dielectric constant, loss tangent, conductivity, electrical impedance, and other electrical parameters of materials. Such properties are then used to provide distance control over a wide range, from to microns to nanometers, over dielectric and conductive samples for a scanned evanescent microwave probe, which enable quantitative non-contact and submicron spatial resolution topographic and electrical impedance profiling of dielectric, nonlinear dielectric and conductive materials. The invention also allows quantitative estimation of microwave impedance using signals obtained by the scanned evanescent microwave probe and quasistatic approximation modeling. The SEMM can be used to measure electrical properties of both dielectric and electrically conducting materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS20170018626A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerSensor array
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
Control system for an rfid-based system for assembling and verifying outbound surgical equipment corresponding to a particular surgery
ActiveUS20070001839A1Improve throughputReduce errorsLogisticsElectric signalling detailsControl systemSurgery procedure
A control system for an RFID-based system for assembling and verifying outbound surgical equipment corresponding to a particular surgery. A user enters a identification number of a surgery. The control system queries a database of surgery information and outputs a list of required surgical equipment, such as surgical instrument sets. An operator uses the list to pick instrument sets for loading into a shipping tote. Each set is tagged with an RFID inventory tag that stores identification information for that set such as a set name and ID number. The shipping tote is passed through an RFID reader and identification data read from the tags is compared against the identification data for sets required for that surgery. A status indicator is activated to alert a user as to whether the surgery is complete that is, all expected sets are present, or that exception handling is required. The control system updates a database such as an ERP system to reflect that the surgery including the required sets has shipped—and the sets are inventoried out to the intended recipient.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
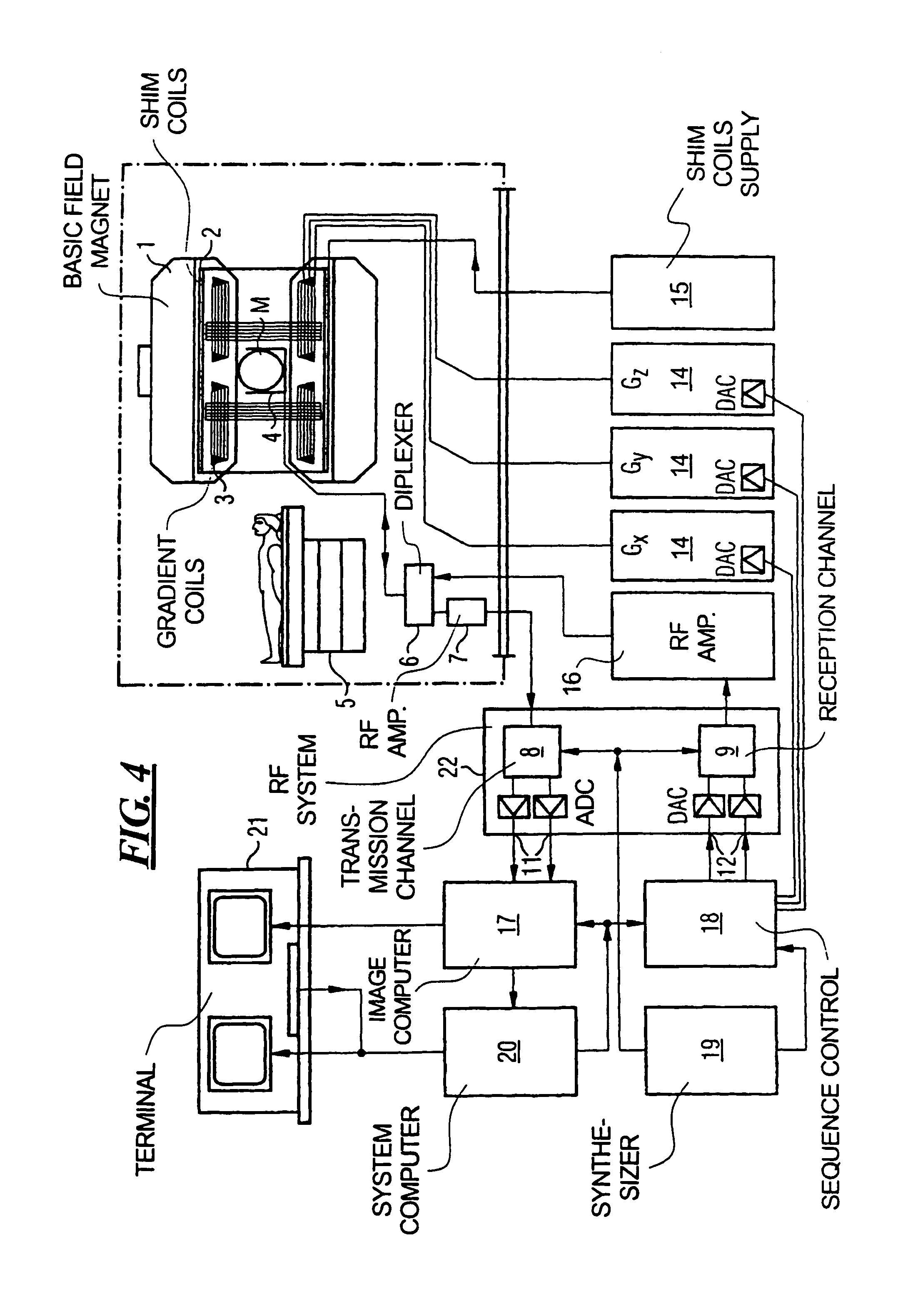
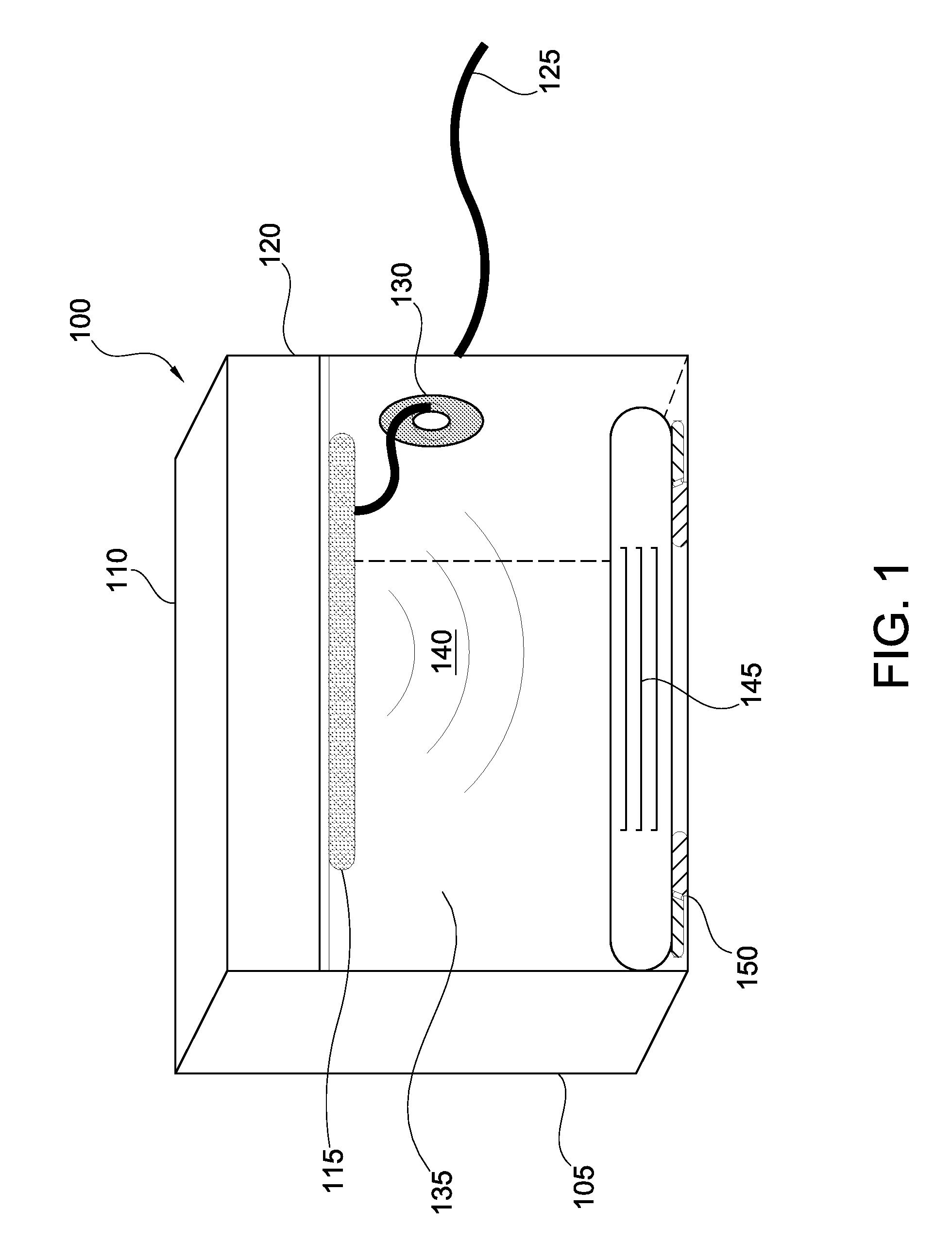
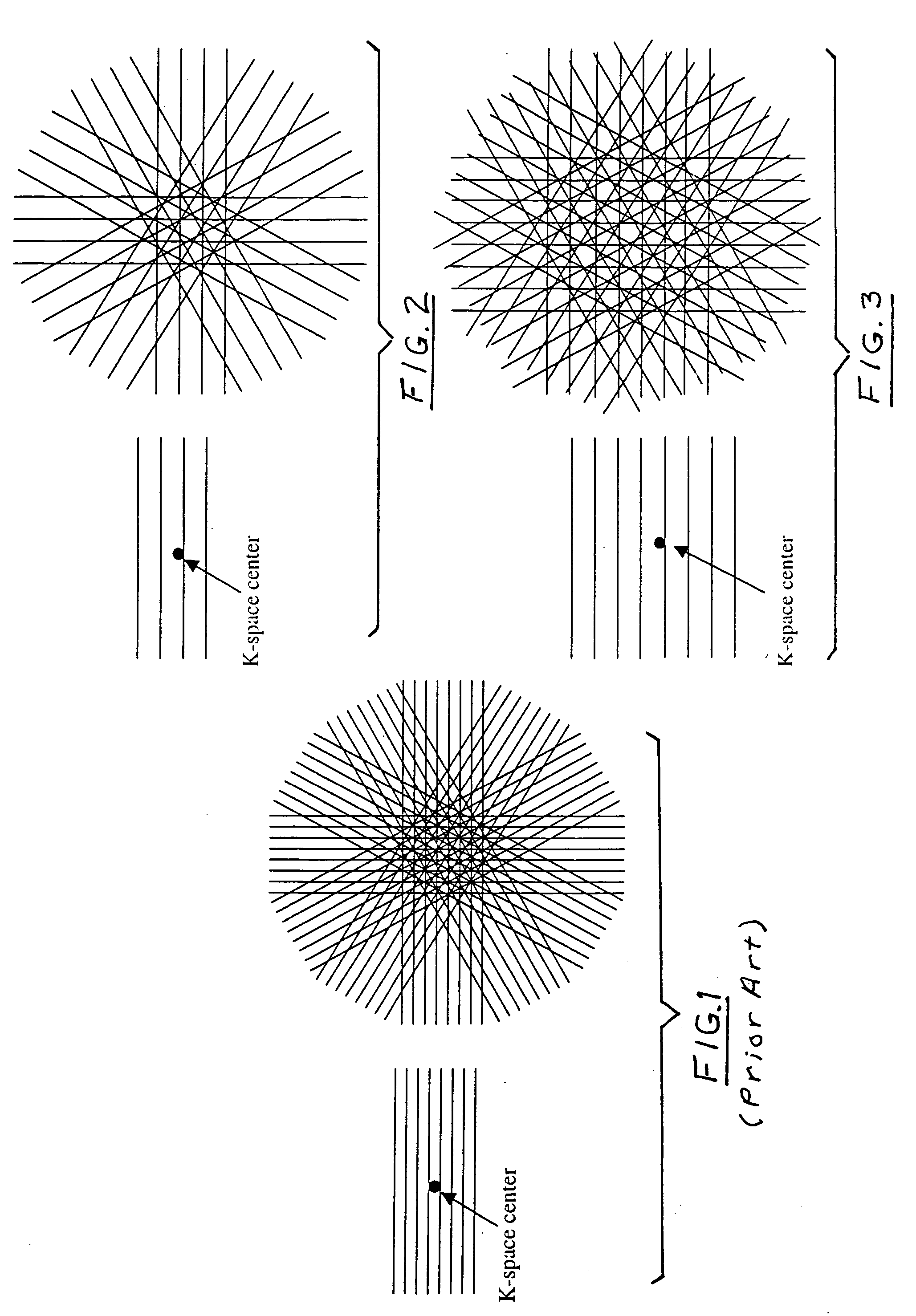
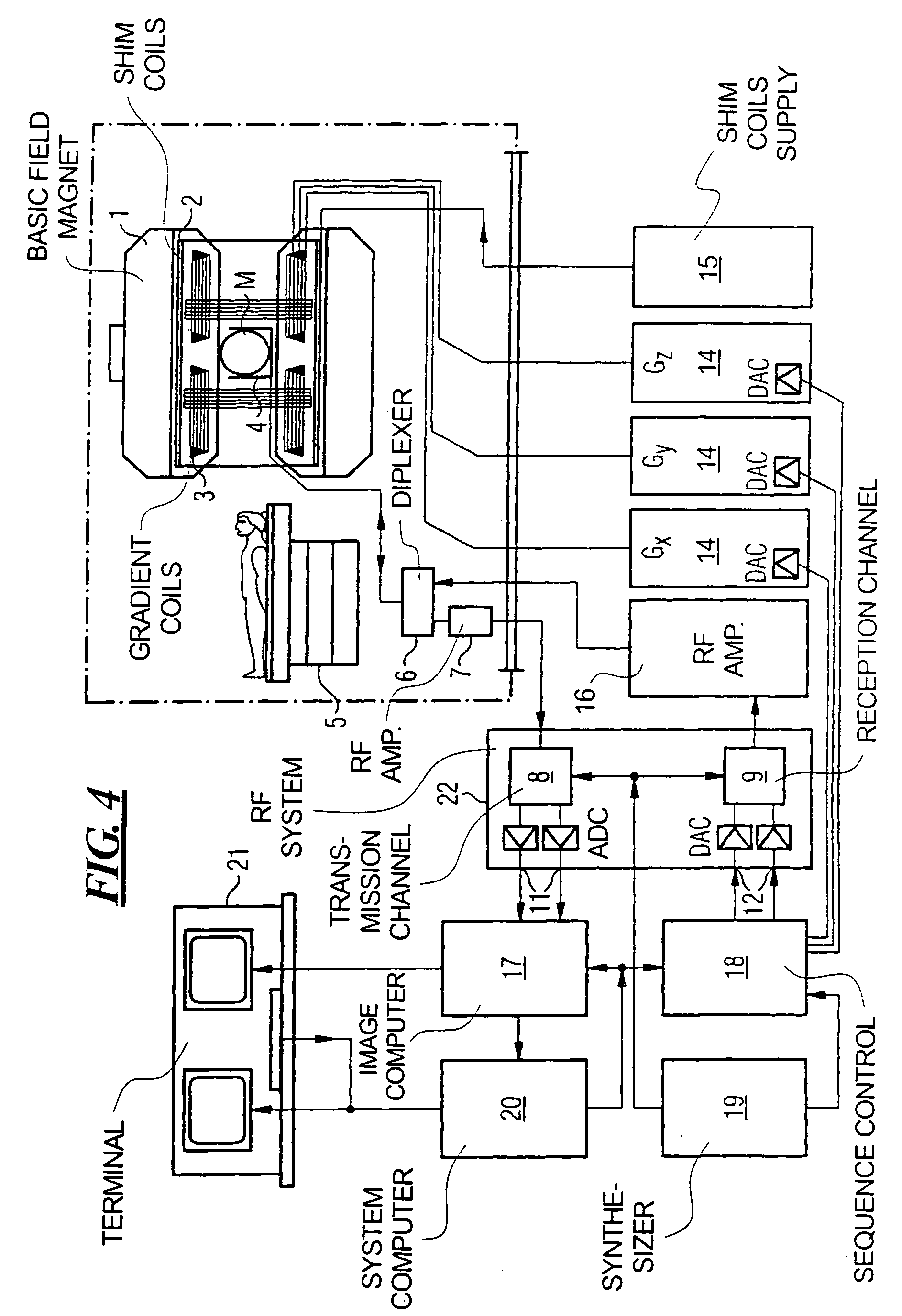
MRI method and apparatus for faster data acquisition or better motion artifact reduction
InactiveUS7102348B2Reduce disadvantagesKeep for a long timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonancePropeller
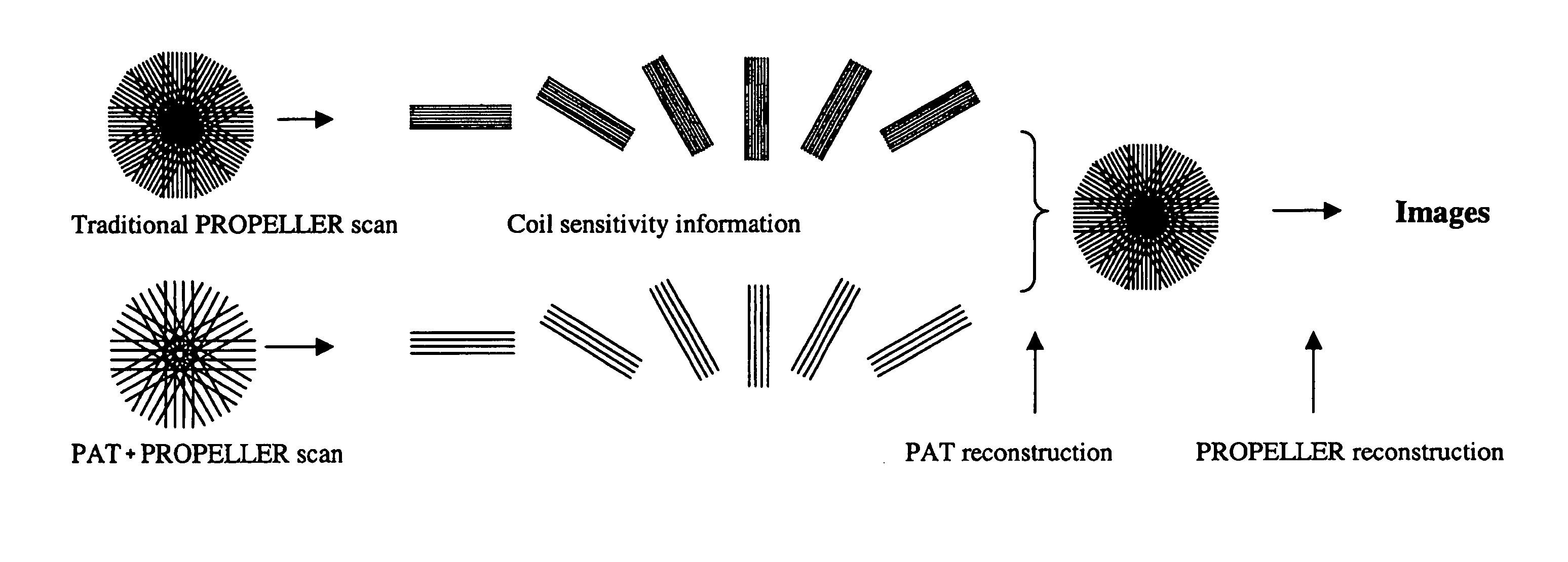
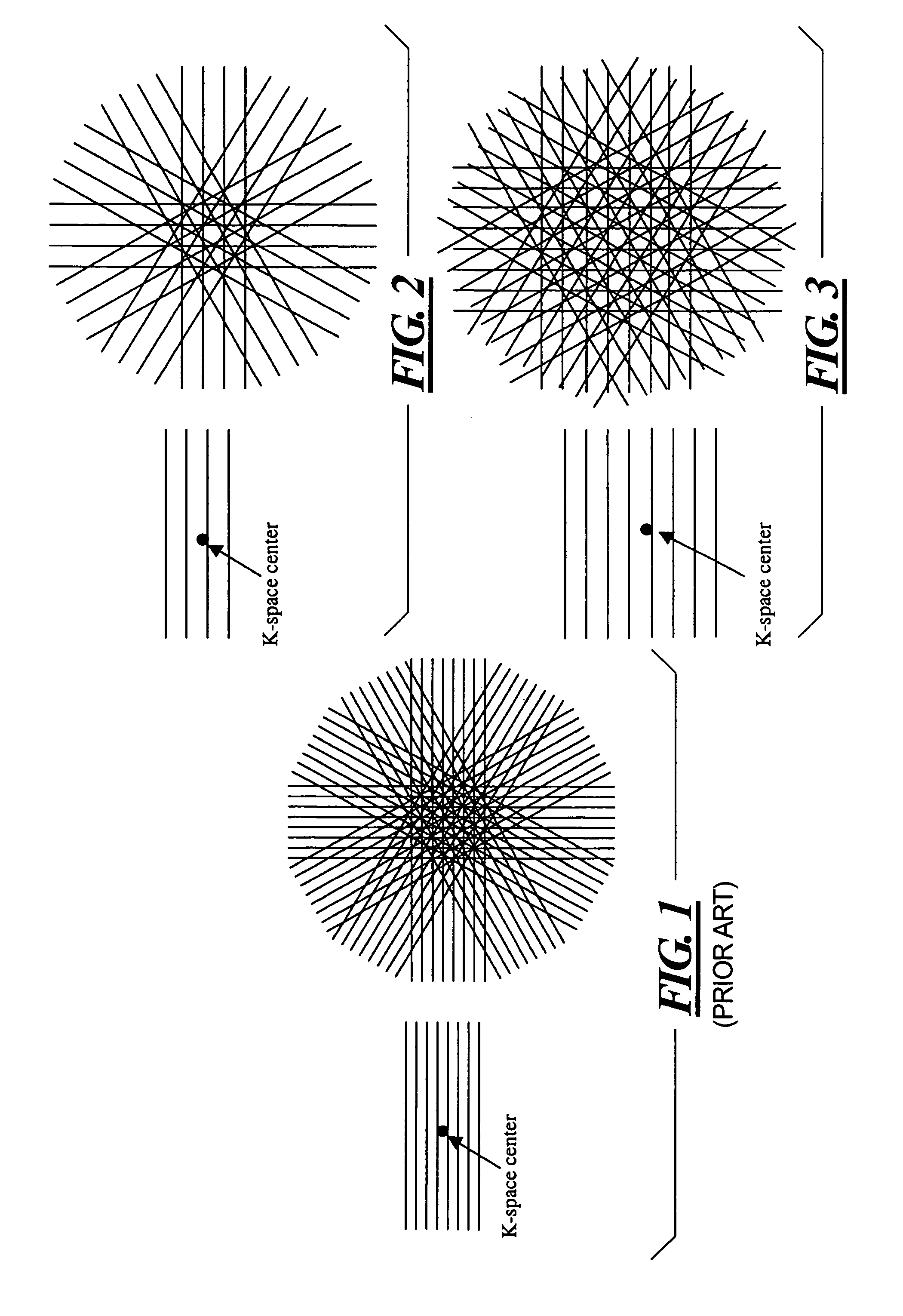
In a method and apparatus for generating a magnetic resonance image, raw magnetic resonance data are acquired from a subject for each of a number of PROPELLER strips using, for each strip, multiple magnetic resonance reception coils in a partial acquisition technique (PAT), and the raw data in said PROPELLER strips are entered into k-space according to the PROPELLER scan. A PAT reconstruction of the data in k-space is conducted dependent on the respective sensitivities of the reception coils, and a PROPELLER reconstruction of the data in k-space is conducted after the PAT reconstruction for generating a magnetic resonance image of the subject.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Graphene FET devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS9618474B2Faster data acquisitionImprove accuracyTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerSensor array
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
Systems and methods for processing surgical instrument tray shipping totes
ActiveUS20060145856A1Accurate and rapid trackingImprove throughputLogisticsCommerceControl systemEngineering
Systems and methods for processing surgical instrument tray shipping totes. A control system is adapted to control a bar code reader module, an RFID module, a database module and an interface module. The control system provides functionality adapted to process incoming and outgoing surgical instrument shipping totes containing one or more RFID-enabled surgical instrument trays. A database, ERP system or other system in communication with the control system alerts the operator of the status of an incoming tote and / or trays contained in the tote to increase processing efficiency and speed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Automated Pass-Through Surgical Instrument Tray Reader
ActiveUS20100108761A1Reduce processing costsEfficient collectionElectric signal transmission systemsSurgical furnitureData terminalEngineering
An apparatus and method for interrogating and automatically identifying a radio-frequency tagged surgical instrument tray and its contents of RFID-tagged surgical instruments are disclosed. The surgical instrument tray and its contents come into contact with an RF signal transmitted by the RFID reader, and as a result, the RFID tags affixed on the instrument tray and the surgical instruments respond by transmitting back to the RFID reader data pertaining to the history of the surgical instruments. A data terminal, which is connected to the RFID reader, may contain data pertaining to the radio frequency tagged surgical instruments during packaging, and during the return of the surgical instrument trays to the packager, identifies the surgical instruments.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
MRI method and apparatus for faster data acquisition or better motion artifact reduction
InactiveUS20060028206A1Reduce disadvantagesKeep for a long timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceData acquisition
In a method and apparatus for generating a magnetic resonance image, raw magnetic resonance data are acquired from a subject for each of a number of PROPELLER strips using, for each strip, multiple magnetic resonance reception coils in a partial acquisition technique (PAT), and the raw data in said PROPELLER strips are entered into k-space according to the PROPELLER scan. A PAT reconstruction of the data in k-space is conducted dependent on the respective sensitivities of the reception coils, and a PROPELLER reconstruction of the data in k-space is conducted after the PAT reconstruction for generating a magnetic resonance image of the subject.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
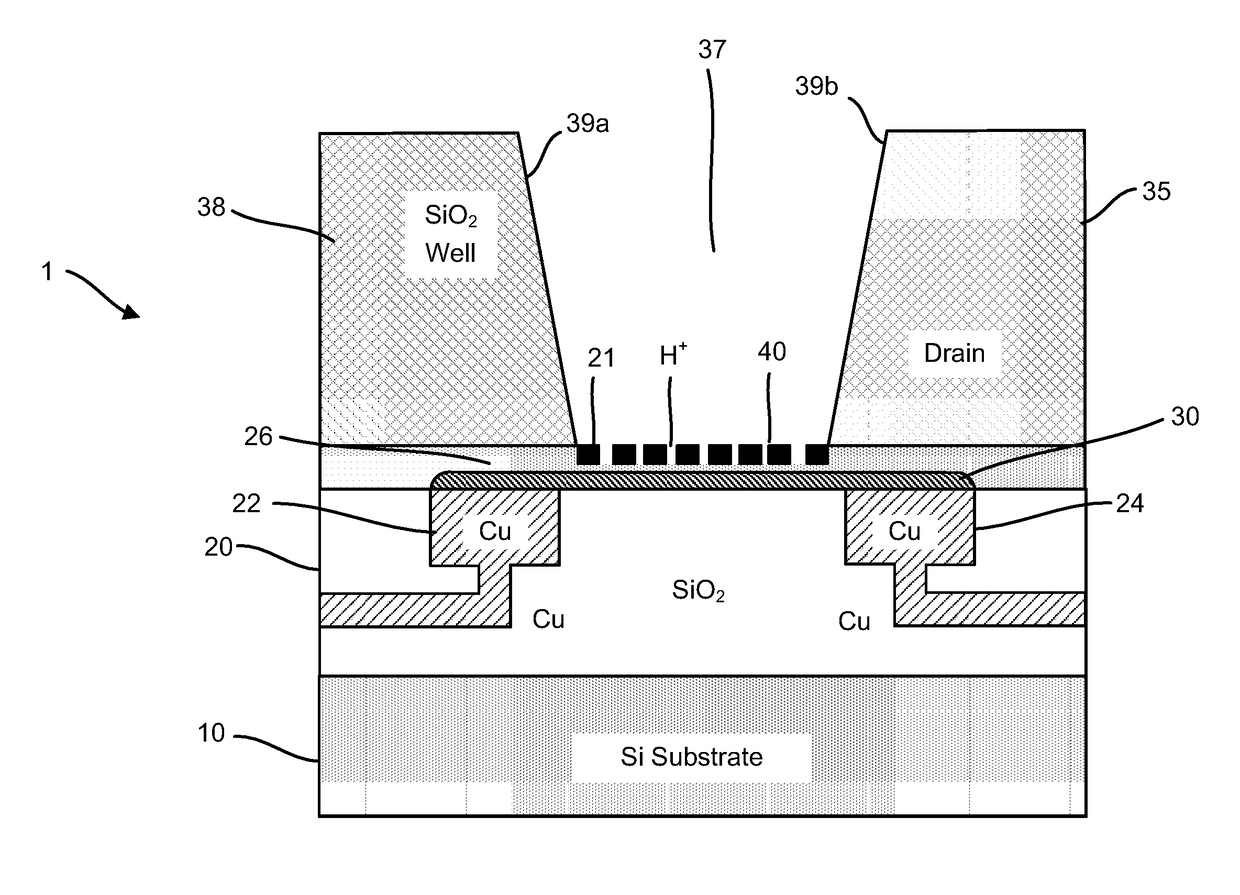
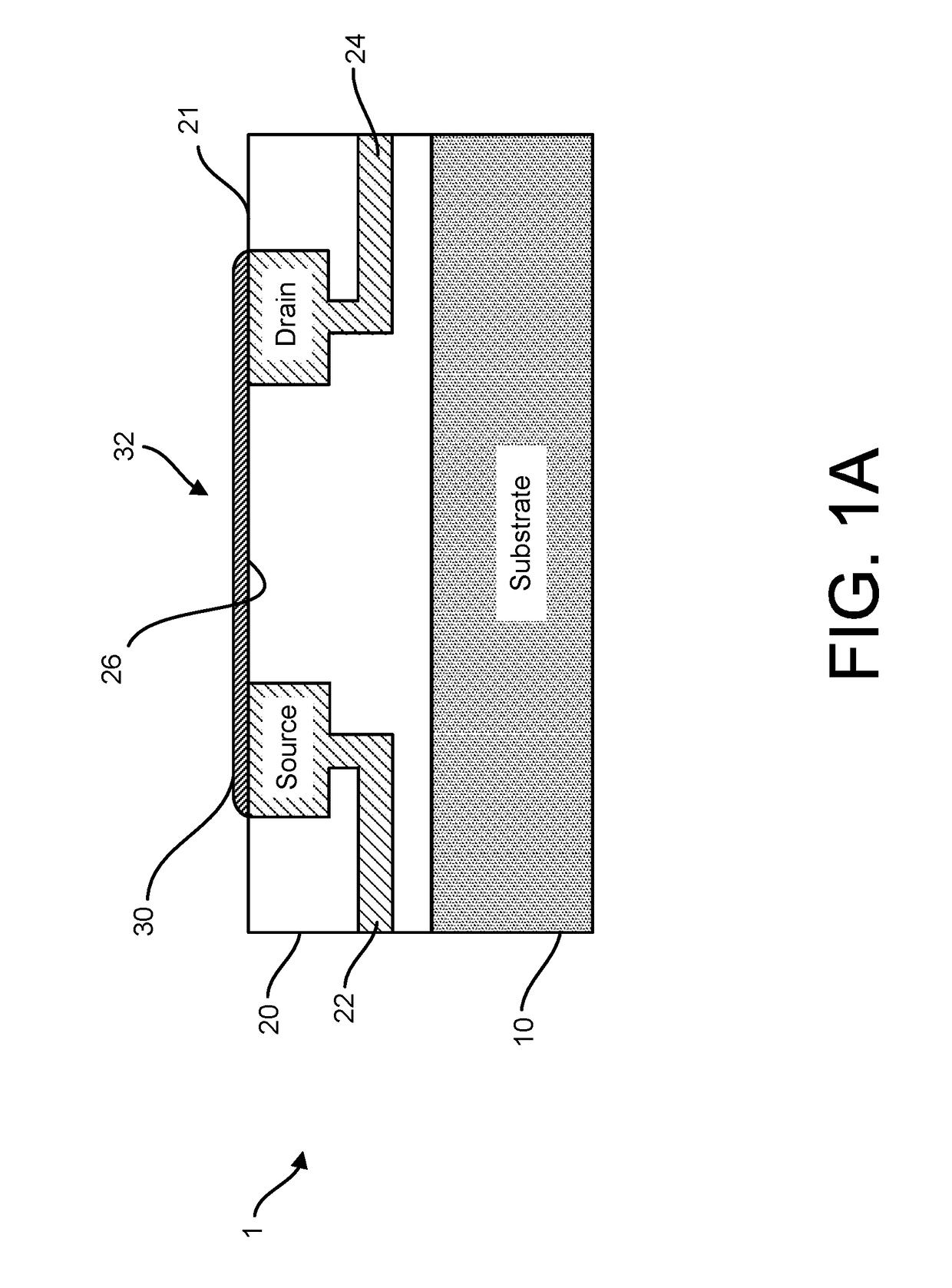
ActiveUS20170053908A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteConductive materials
Provided herein are integrated circuits for use in performing analyte measurements and methods of fabricating the same. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. The methods for fabricating the integrated circuits include steps of depositing an insulating layer on a semiconducting substrate, and forming trenches in the insulating dielectric layer. Conductive material may be deposited in the trenches to form electrodes, and the insulating layer may be conditioned so that the electrodes protrude above the insulating layer. A 2D material, such as graphene, may be deposited on the electrodes to form a channel between the electrodes.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
High-throughput chiral detector and methods for using same
InactiveUS7301633B2Rapid and accurate and large-scale screeningDetection morePolarisation-affecting propertiesLight polarisation measurementOptical propertyAnalyte
A new generation polarimetry apparatus and methodology is disclosed, which involve passing polarized light through a sample including a chiral analyte, where the analyte is under the influence of a periodically varying magnetic field. The apparatus also utilizes optical heterodyne detection and lock-in detection at higher order harmonics of the magnetic field modulation frequency to improve sensitivity and detection limits of optical properties of chiral analytes.
Owner:GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method and Apparatus for Surgical Instrument Identification
InactiveUS20100176925A1Reduce processing costsOvercomes shortcomingSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsEngineeringSurgical device
Systems and methods for identifying surgical instruments by use of radio-frequency identification tags (RFID) are disclosed. In the systems and methods, each of a plurality of surgical instruments is provided with at least one RFID transponder tag storing identification information associated with the corresponding instrument. The tag may be adhered to, embedded, or potted within a portion of the instrument. Using an RFID reading device, a user may interrogate the tag, thereby identifying the particular instrument. This identification information may be used to index a database and retrieve a data record unique to that instrument. The systems and methods allow a user to track, inspect, and verify inbound and outbound surgical instruments, to assess, for example, the surgical instruments' duty life cycle usage.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
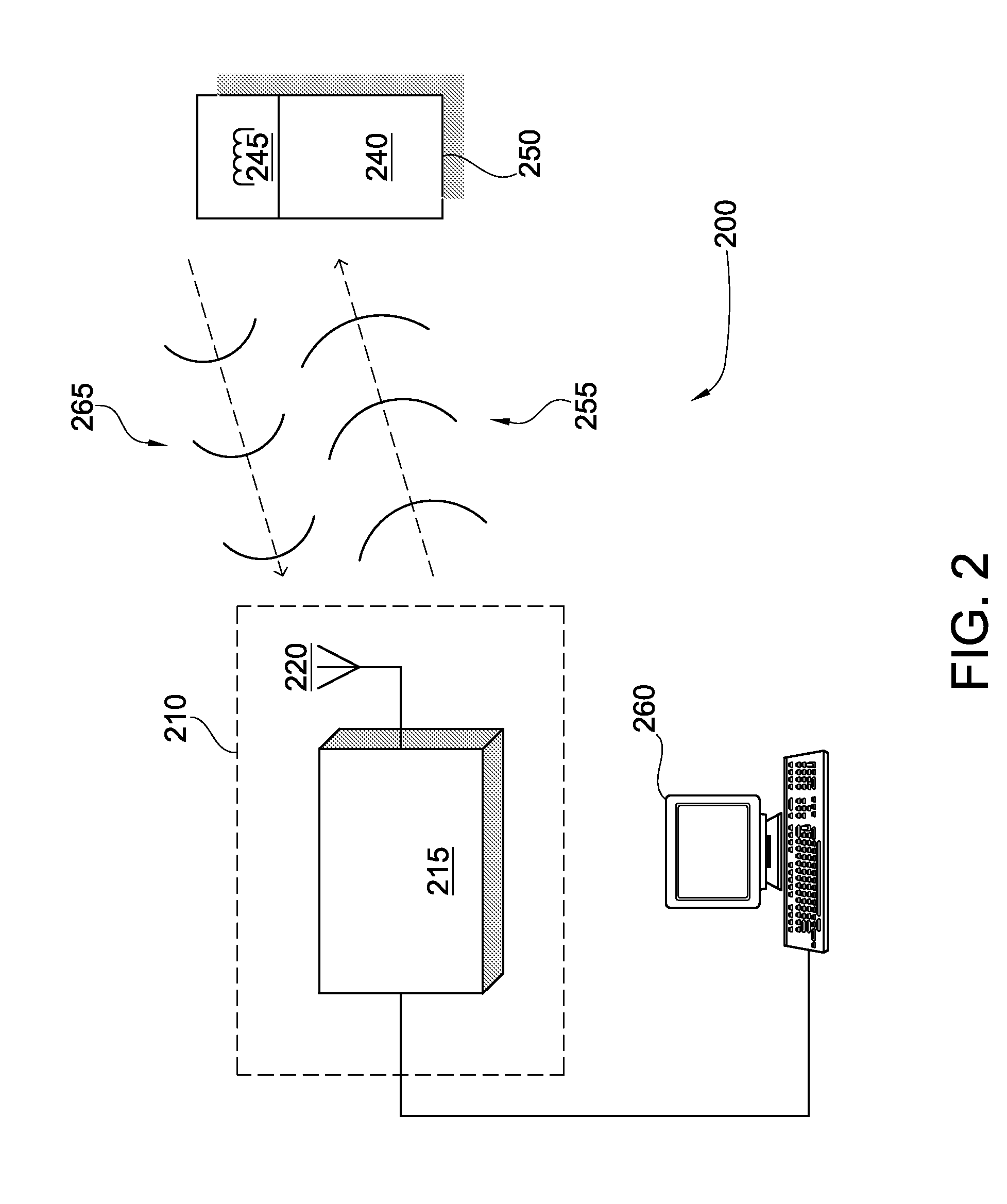
Hand-held optical scanner for real-time imaging of body composition and metabolism
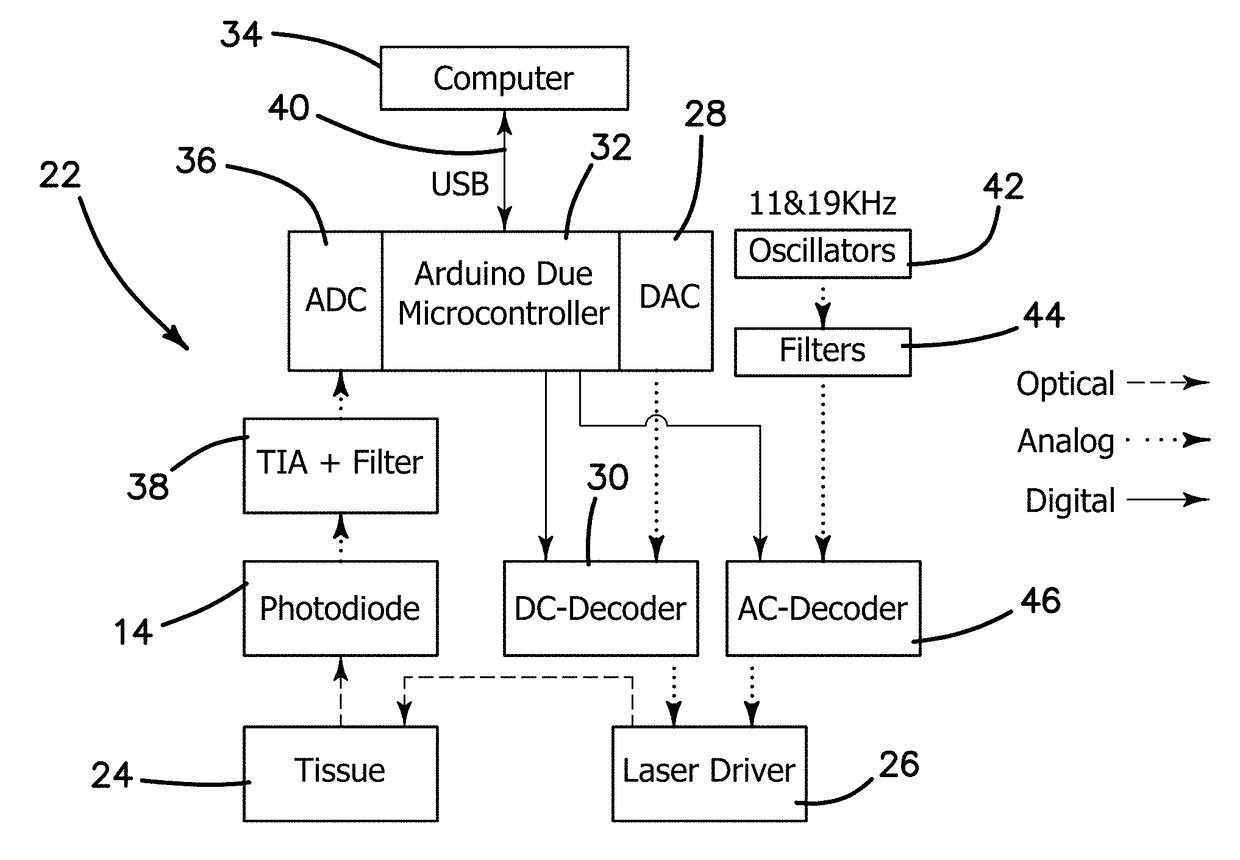
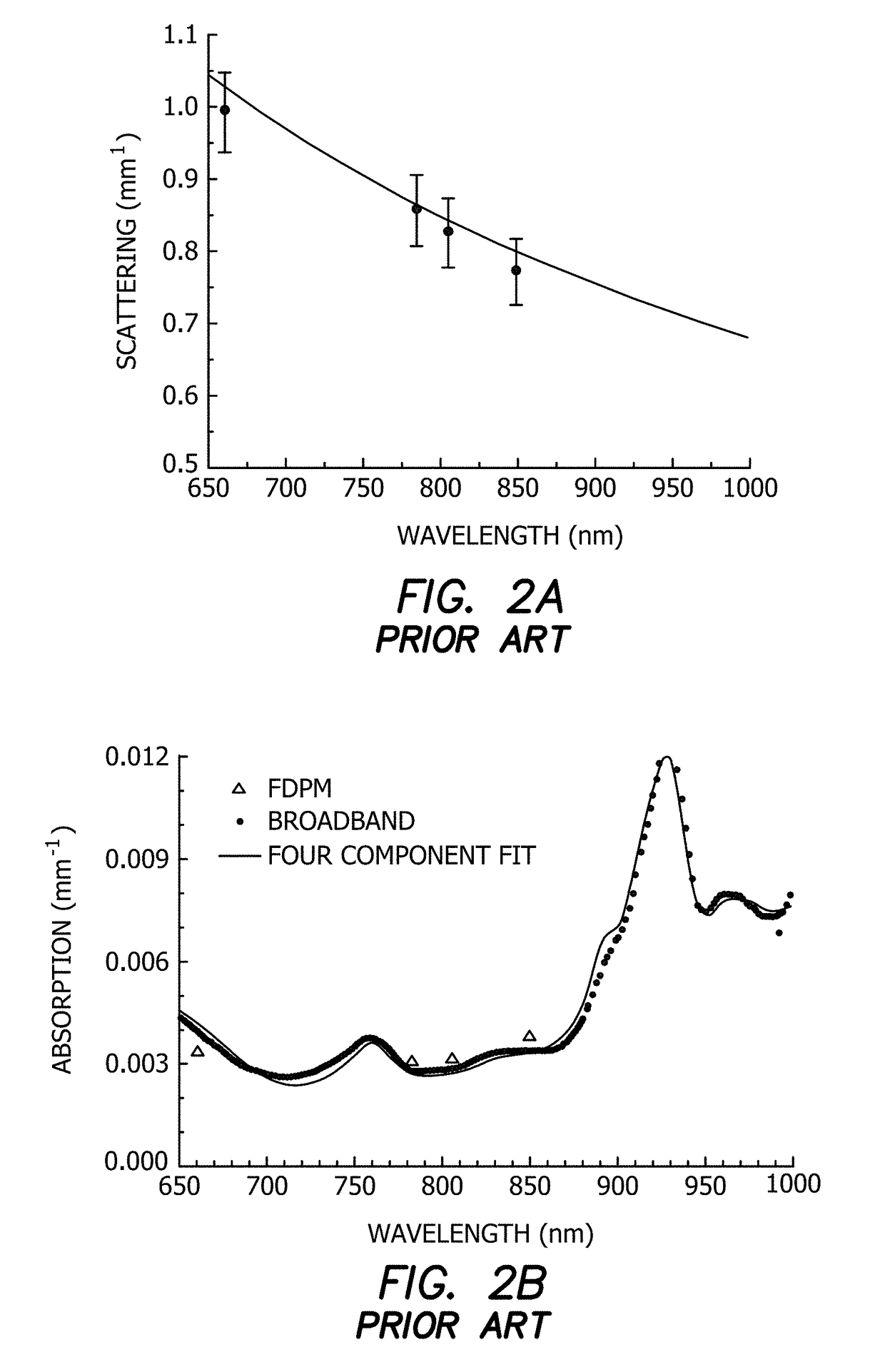
ActiveUS20170209083A1High-resolution characterizationFaster data acquisitionRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsLipid formationOptical scanners
A low cost portable high speed quantitative system for diffuse optical spectroscopic imaging of human tissue. The hybrid system (CWFD) can measure absolute optical properties from 660 nm to 980 nm and recover all tissue chromophore concentrations. The standalone FD module can be utilized to measure scattering at every measurement and recover deoxygenated and oxygenated hemoglobin concentrations. The CW module can operate concurrently with the FD module to also measure water and lipid. The high temporal resolution and large signal-to-noise ratio of the CWFD system may be used to explore tissue oximetry, vascular occlusion, and paced breathing models to measure and analyze tissue hemodynamics response to changes in blood flow. Continuous monitoring of vasculature response to various modified blood perfusion conditions can provide information about local tissue metabolism and physiological state (dysfunction).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for characterizing optical systems using holographic reticles
InactiveUS7242464B2Faster data acquisitionEasy accessUsing optical meansPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOptical radiationHolographic screen
Characterization of an optical system is quickly and easily obtained in a single acquisition step by obtaining image data within a volume of image space. A reticle and image plane are positioned obliquely with respect to each other such that a reticle having a plurality of feature sets thereon, including periodic patterns or gratings, is imaged in a volume of space, including the depth of focus. Metrology tools are used to analyze the detected or recorded image in the volume of space through the depth of focus in a single step or exposure to determine the imaging characteristics of an optical system. Focus, field curvature, astigmatism, spherical, coma, and / or focal plane deviations can be determined. The present invention is particularly applicable to semiconductor manufacturing and photolithographic techniques used therein, and is able to quickly characterize an optical system in a single exposure with dramatically increased data quality and continuous coverage of the full parameter space. In embodiments, the test reticle is holographically generated by interfering two or more beams of optical radiation. The resulting interference pattern is recorded on a reticle and used for testing the optical system. The geometry of the holographic interference pattern is tightly controlled by the properties of the interfering beams and is therefore more accurate than conventional reticle writing techniques.
Owner:ASML US LLC +1
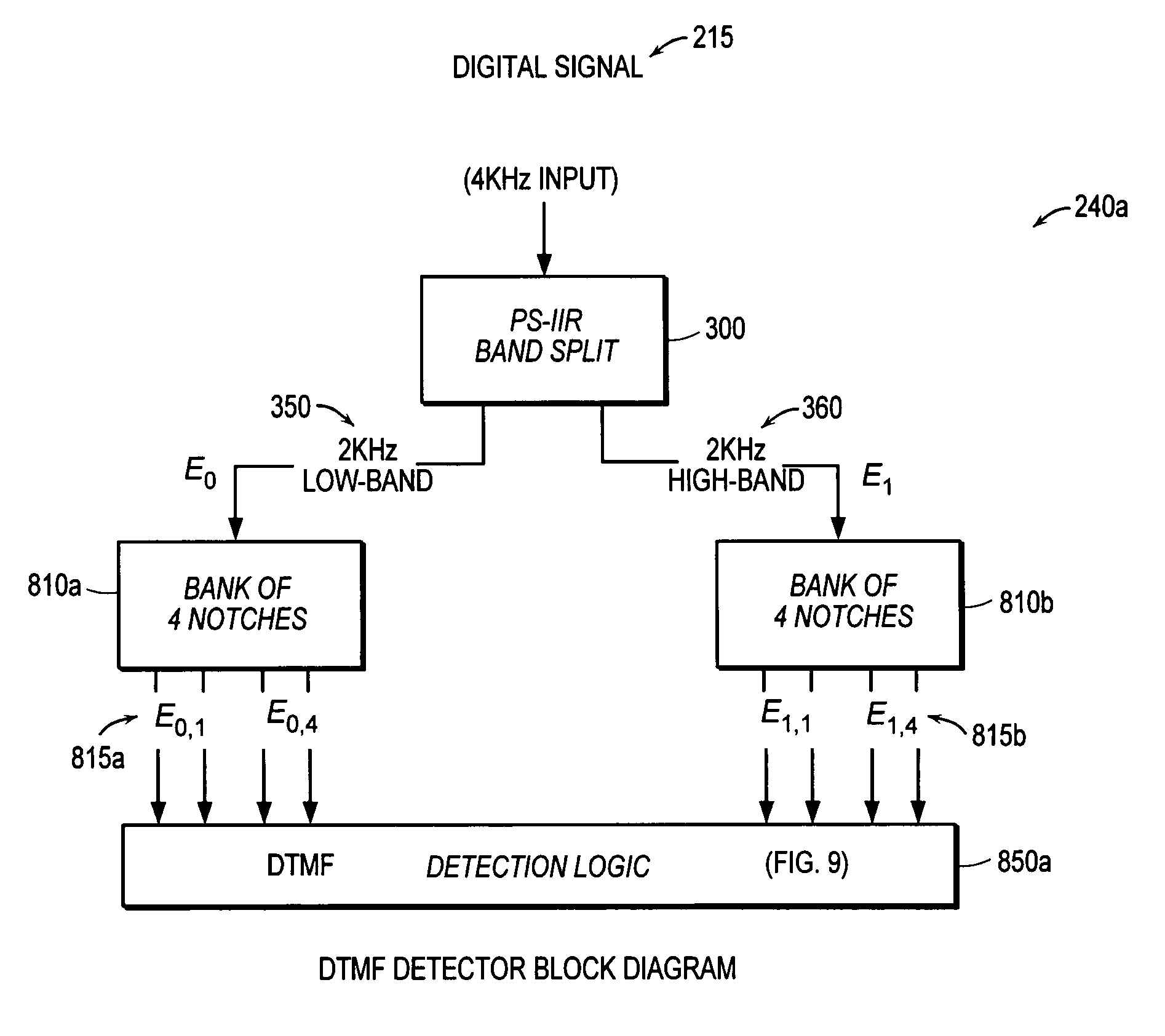
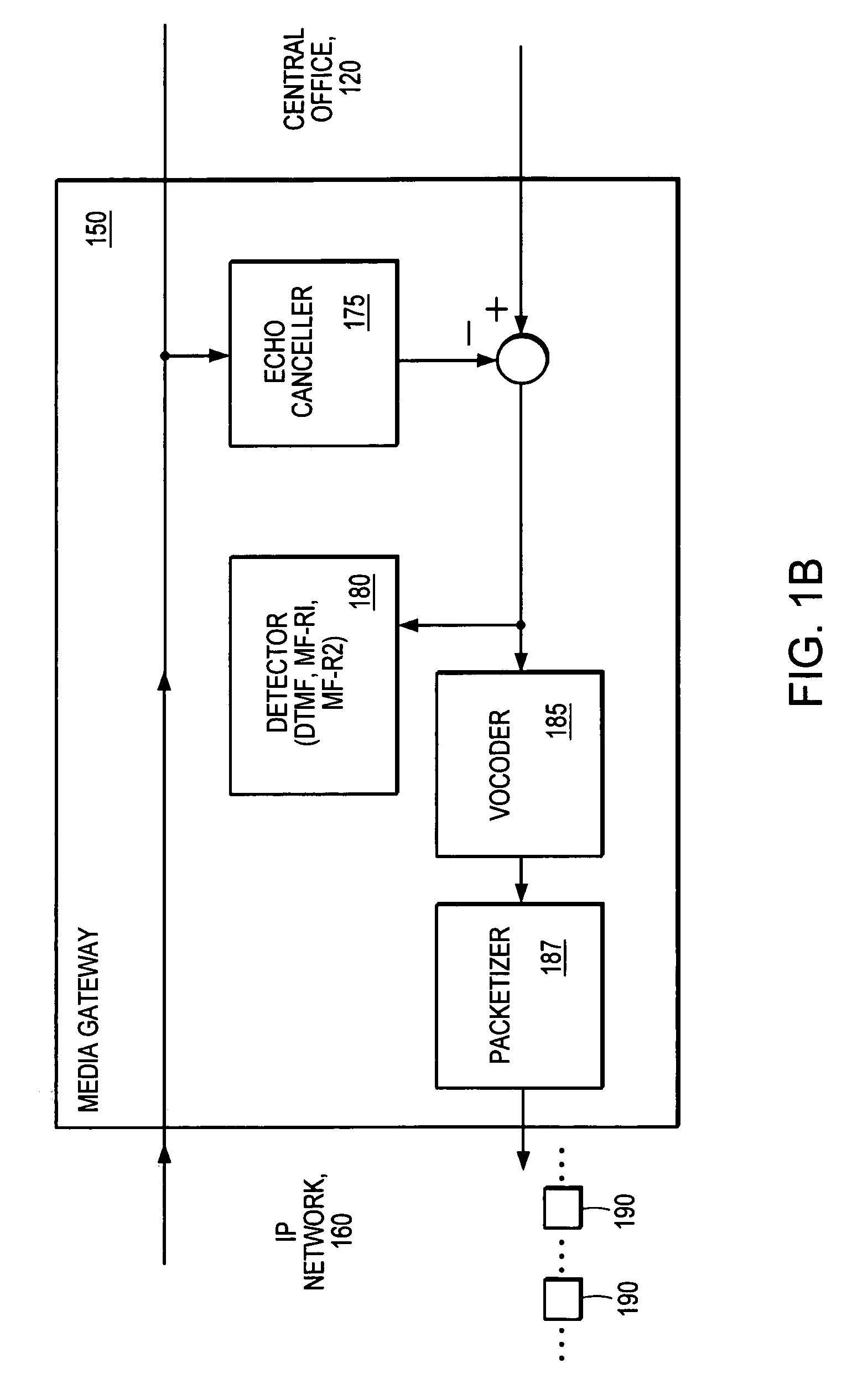
Method and apparatus for performing high-density DTMF, MF-R1, MF-R2 detection
InactiveUS7088817B1Significant computational overheadFast data acquisitionInterconnection arrangementsSubstation equipmentIir filteringHigh density
Detectors determine the presence of valid sinusoids for DTMF, MF-R1 and MF-R2 protocols for encoding dialed digits. The detectors split electrical signals into subbands. Energies within the subbands are analyzed to determine a presence of sinusoids corresponding to frequencies of dialed digits. In one embodiment, the detectors comprise a PS-IIR filter to split the electrical signal into the subbands. The detectors further comprise at least one bank of filters, such as notch filters, corresponding to the number of possible relevant frequencies within the respective subbands. The detectors further comprise detection logic comprising tests, which may include analyzing the output(s) from the bank of filters. Optionally, a preclassifier is employed to predetermine which filters in the banks of filters are to be executed. The detectors, typically deployed in digital signal processors, allow for an increase in the density of detectors and provide robust performance in talk-off situations.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
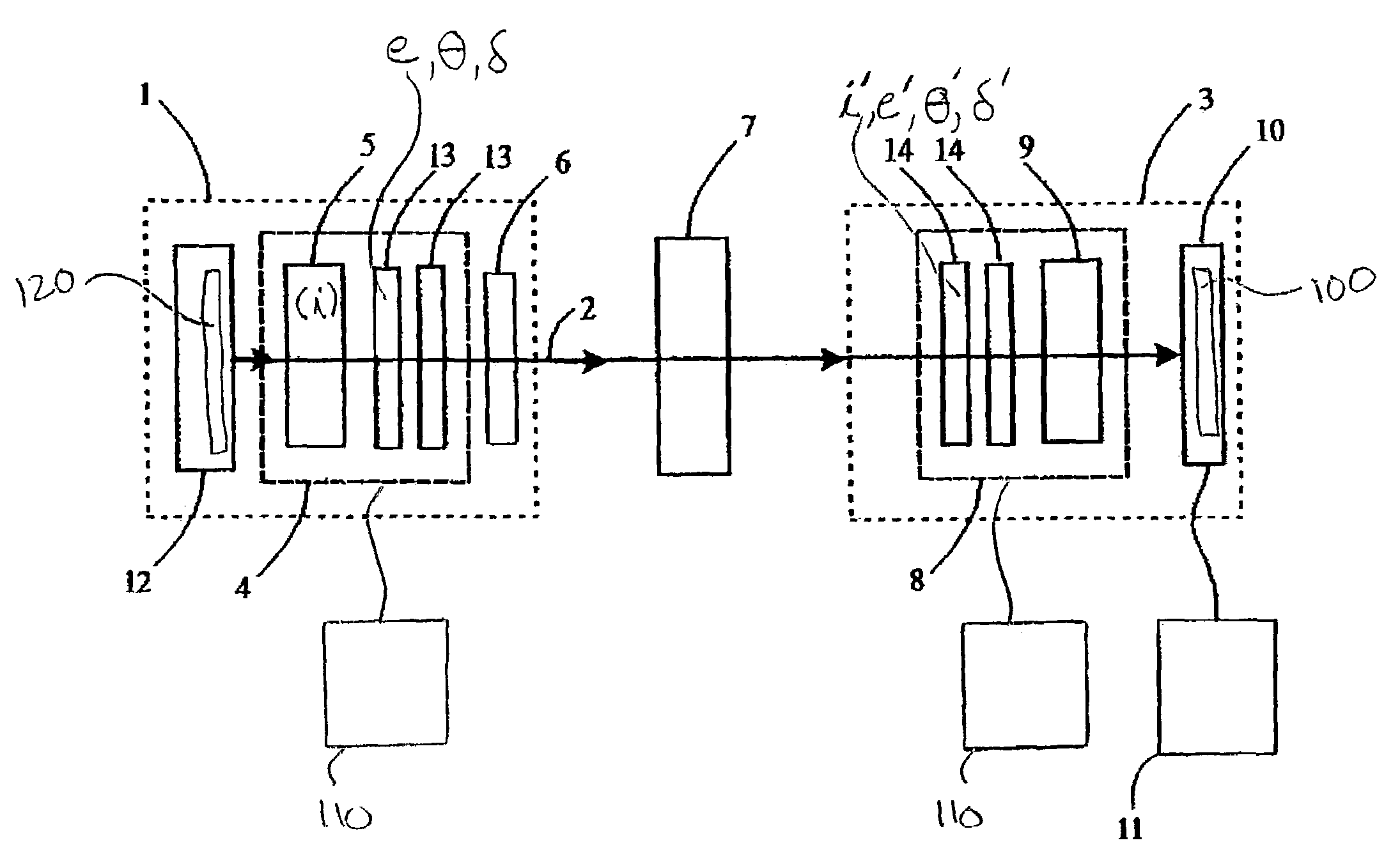
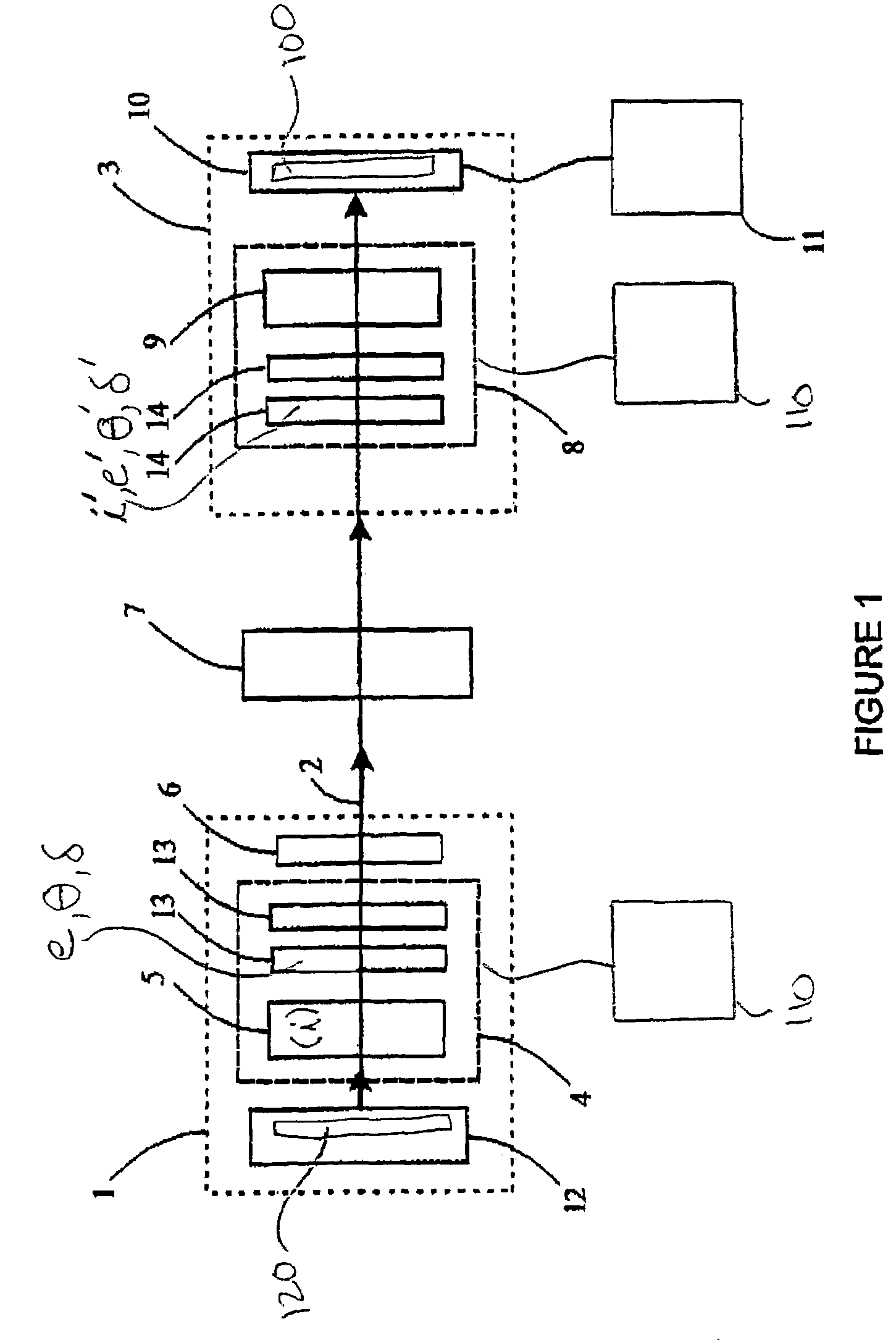
Liquid crystal based polarimetric system, a process for the calibration of this polarimetric system, and a polarimetric measurement process
ActiveUS7196792B2Wide enough acceptance angleFast data acquisitionPolarisation-affecting propertiesLight polarisation measurementReverse orderLight beam
A liquid crystal based polarimetric system, a process for the calibration of this polarimetric system, and a polarimetric measurement process intended for measuring the representative parameters of a sample in which the polarimetric system contains an excitation section emitting a light beam that passes through a polarization state generator (PSG) and onto a sample. After reflection or transmission by the sample, the beam goes through an analysis section with a polarization state detector (PSD). The PSG and PSD each have a first and a second liquid crystal elements LCj (j=1,2) having, for each LCj element of the PSG (respectively for each LCj element of the PSD), an extraordinary axis making an angle θj (resp. θ′j) with respect to the polarization direction (i), and a retardation δj (resp (δ′j) between its ordinary and extraordinary axes, the liquid crystals LCj elements being positioned in reverse order in the PSD with respect to the LCj elements of the PSG.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com