Patents
Literature
314 results about "Iir filtering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An IIR filter is a particular type of filter; typical uses of an IIR filter would be to simplify cyclical data that includes random noise over a steadily increasing or decreasing trend. The IIR filter you cretae with this module defines a set of constants (or coefficients) that alter the signal that is passed through.
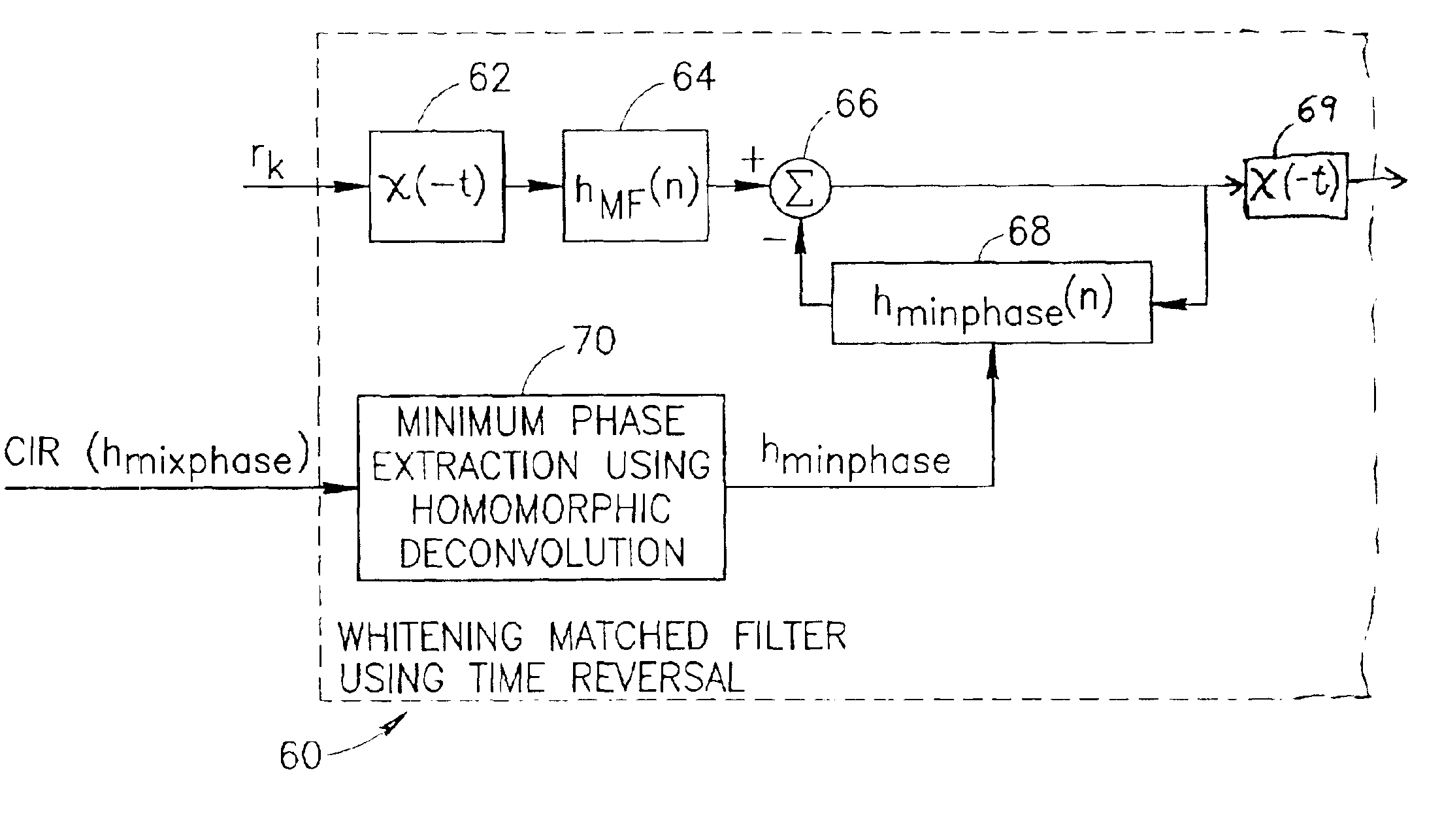
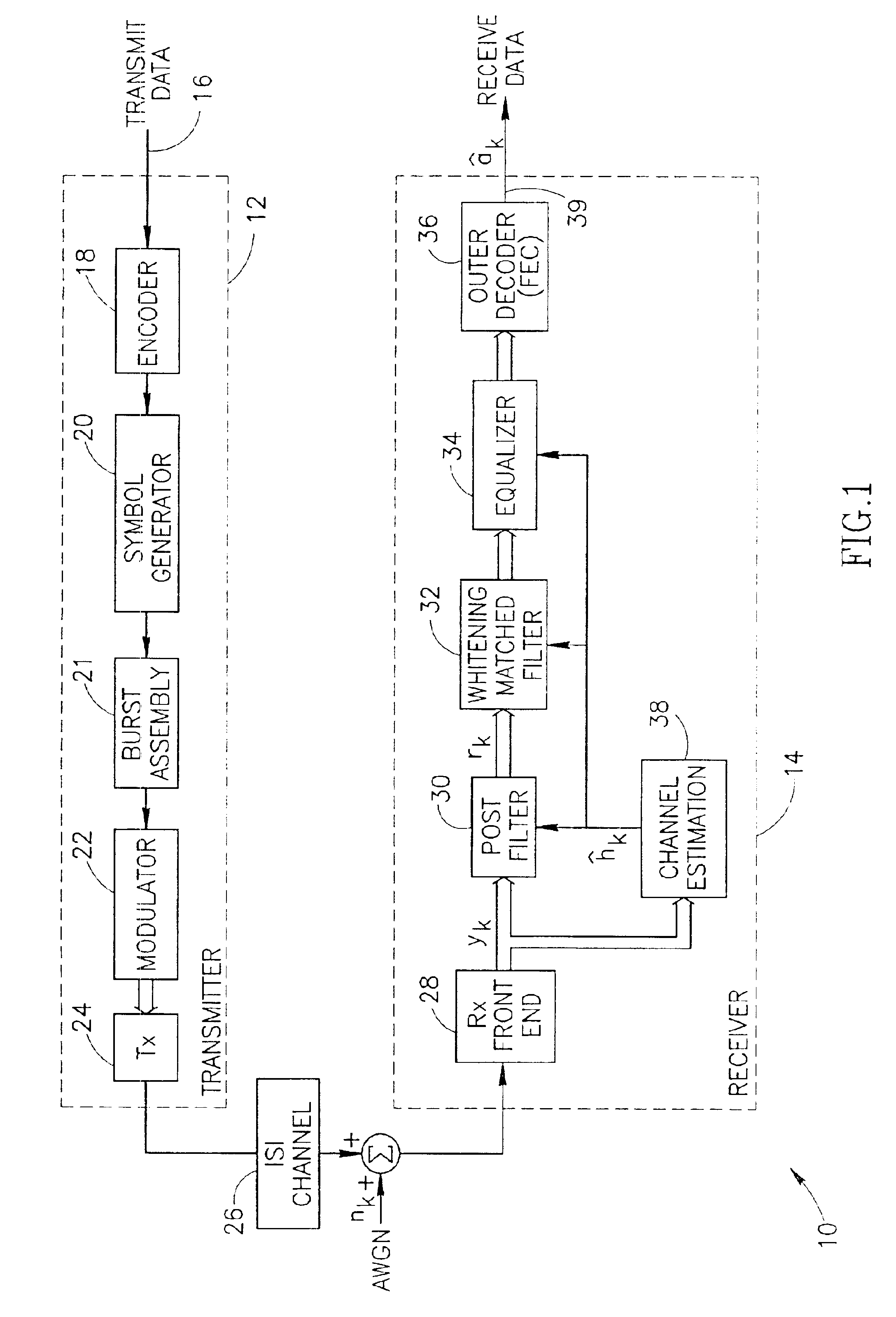
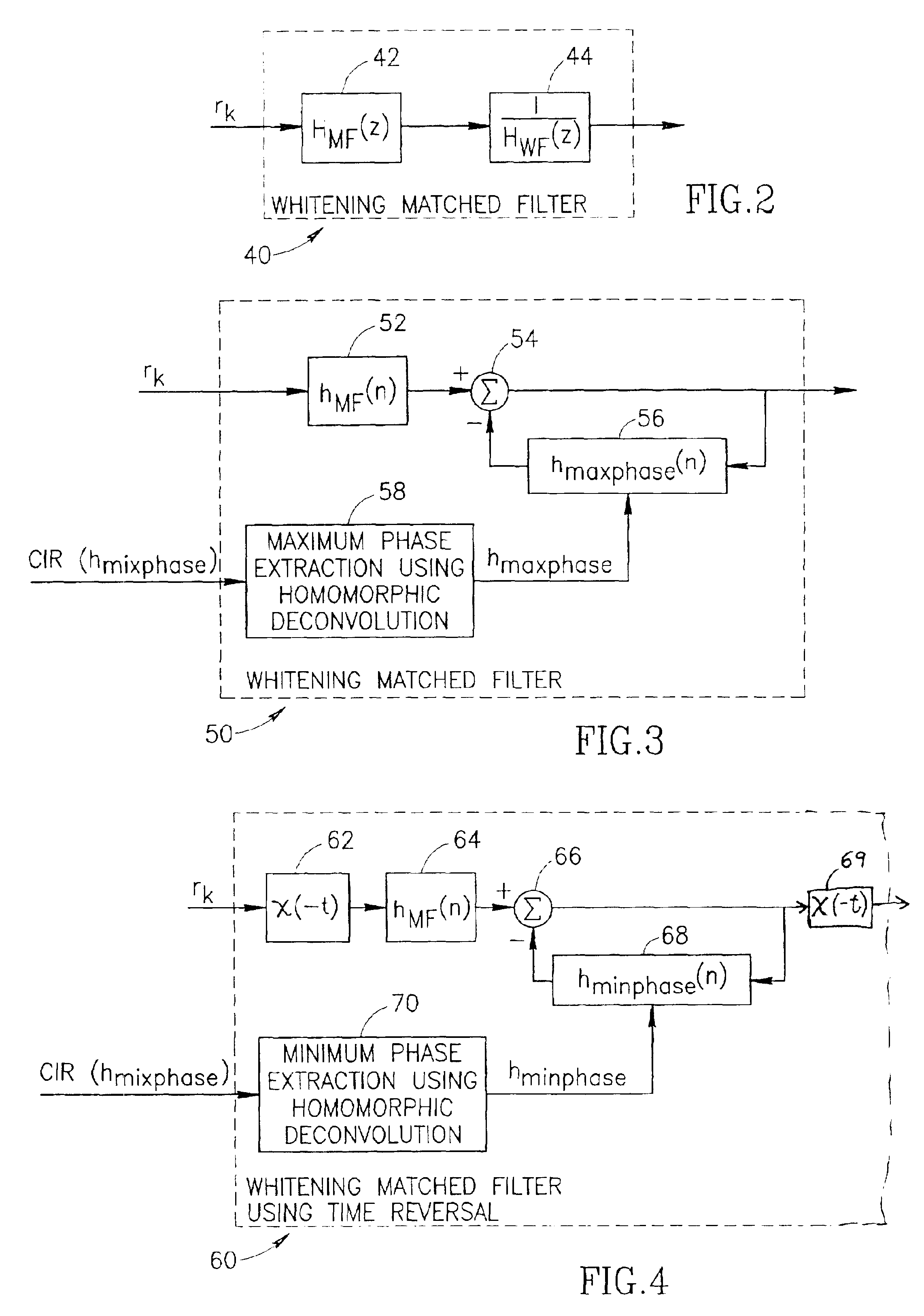
Whitening matched filter for use in a communications receiver
InactiveUS6862326B1Improve performanceMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkIir filteringChannel impulse response
A novel and useful whitening matched filter (WMF) for use in a communications receiver. The WMF is constructed by cascading a matched filter and a noise-whitening filter. The response of the matched filter is derived from the time reversed complex conjugate of the channel impulse response. The whitening filter is derived by extracting the minimum phase portion of the mixed phase channel impulse response using homomorphic deconvolution. The whitening filter is implemented using either an FIR or IIR filter adapted to process the data received before and after the training sequence using a minimum phase system in a direction in time opposite to that of the direction of corresponding data sample processing performed by the equalizer.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
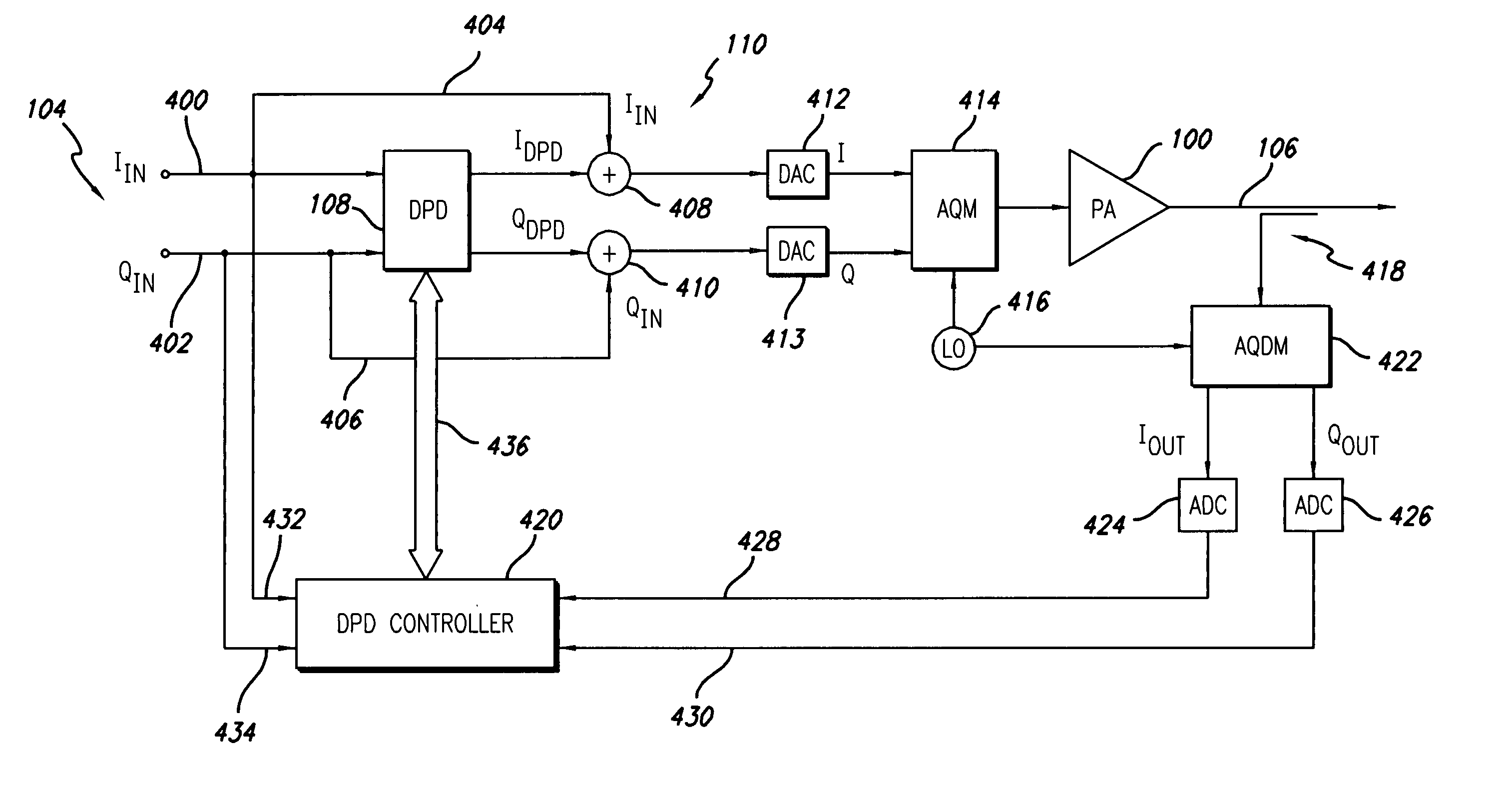
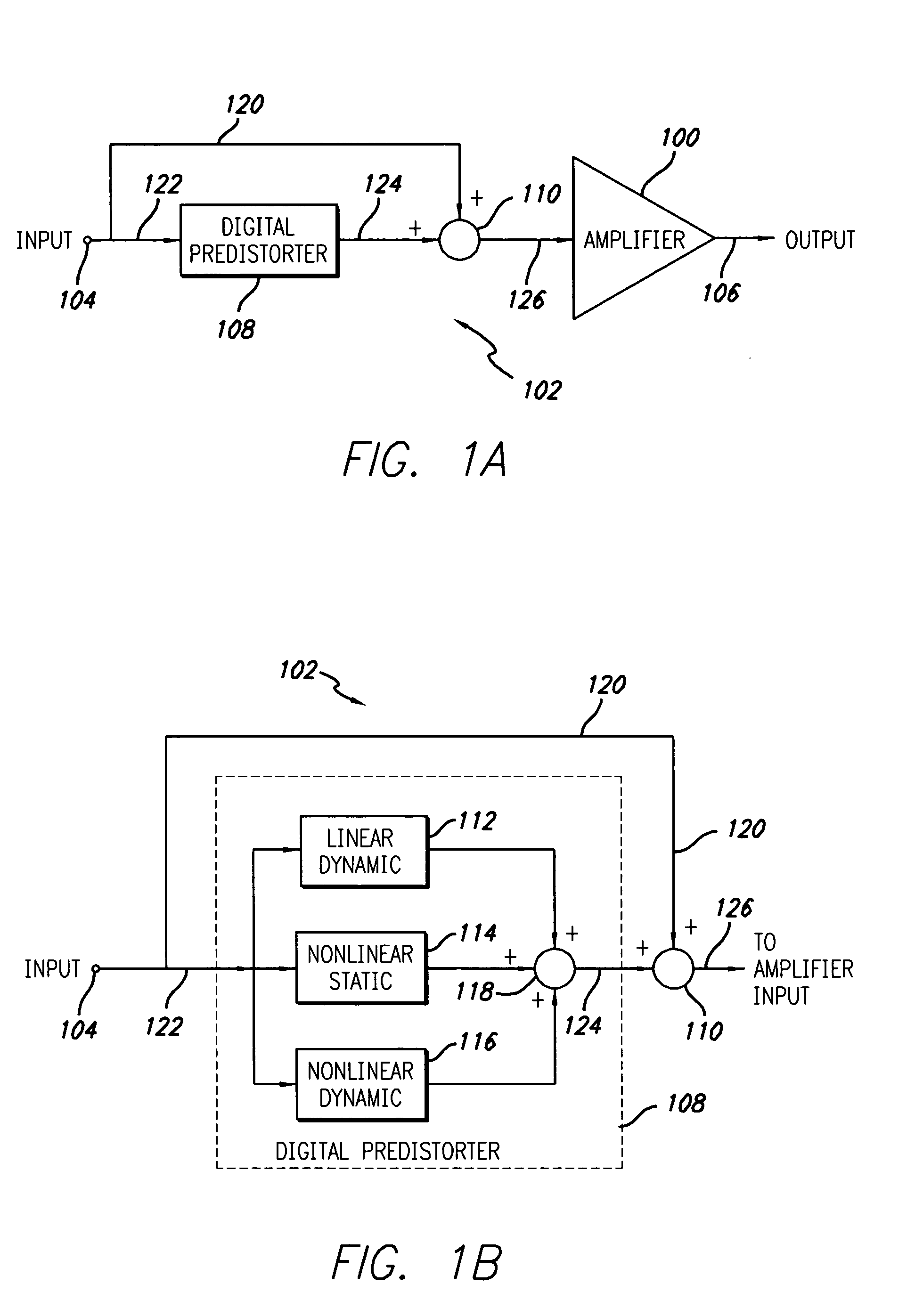
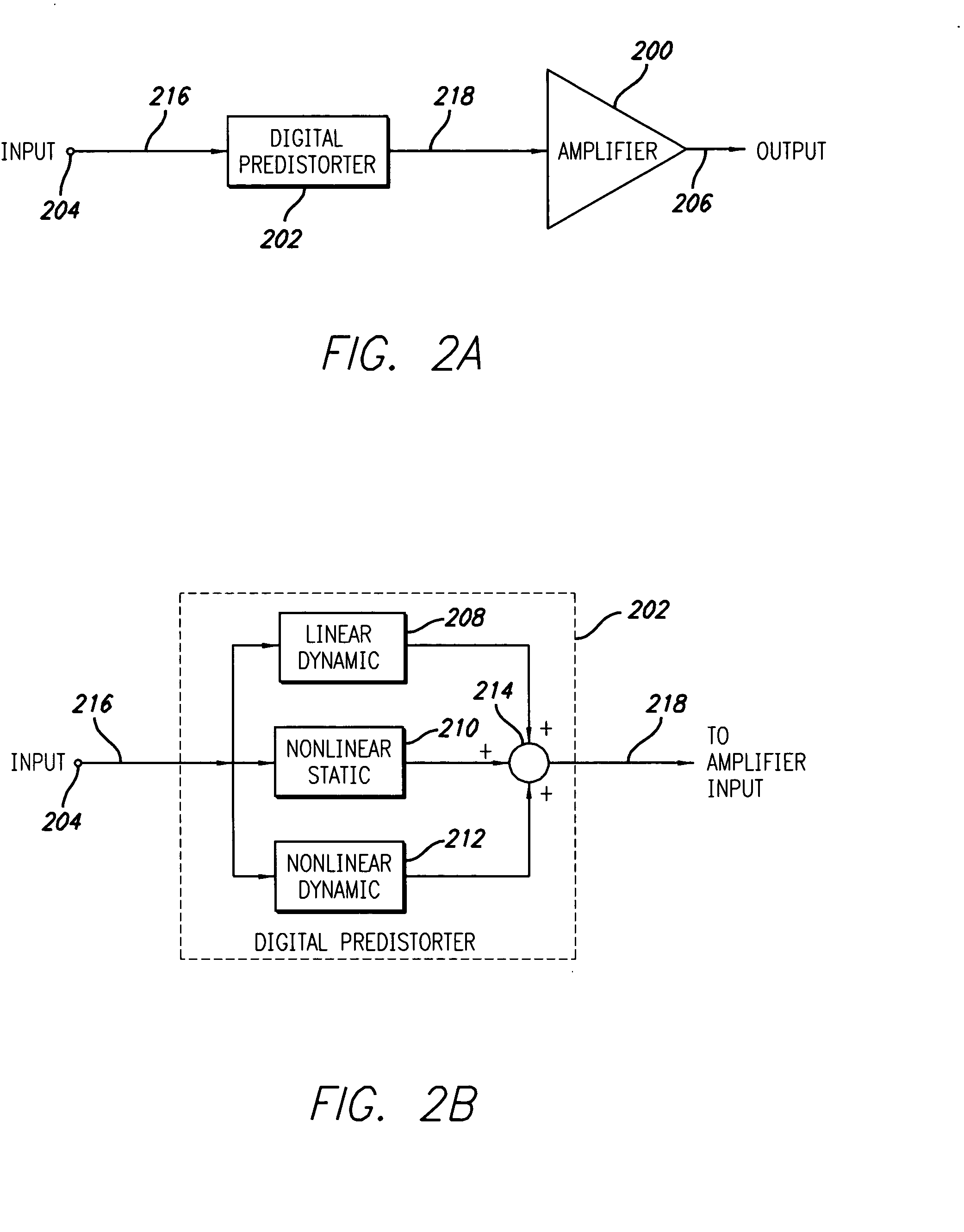
Digital predistortion system and method for high efficiency transmitters
ActiveUS20050195919A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifiers with memory effect compensationNon linear dynamicEngineering
A system for digitally linearizing the nonlinear behaviour of RF high efficiency amplifiers employing baseband predistortion techniques is disclosed. The system provides additive or multiplicative predistortion of the digital quadrature (I / Q) input signal in order to minimize distortion at the output of the amplifier. The predistorter uses a discrete-time polynomial kernel to model the inverse transfer characteristic of the amplifier, providing separate and simultaneous compensation for nonlinear static distortion, linear dynamic distortion and nonlinear dynamic effects including reactive electrical memory effects. Compensation for higher order reactive and thermal memory effects is embedded in the nonlinear dynamic compensation operation of the predistorter in an IIR filter bank. A predistortion controller periodically monitors the output of the amplifier and compares it to the quadrature input signal to compute estimates of the residual output distortion of the amplifier. Output distortion estimates are used to adaptively compute the values of the parameters of the predistorter in response to changes in the amplifier's operating conditions (temperature drifts, changes in modulation input bandwidth, variations in drive level, aging, etc). The predistortion parameter values computed by the predistortion controller are stored in non-volatile memory and used in the polynomial digital predistorter. The digital predistortion system of the invention may provide broadband linearization of highly nonlinear and highly efficient RF amplification circuits including, but not limited to, dynamic load modulation amplifiers.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
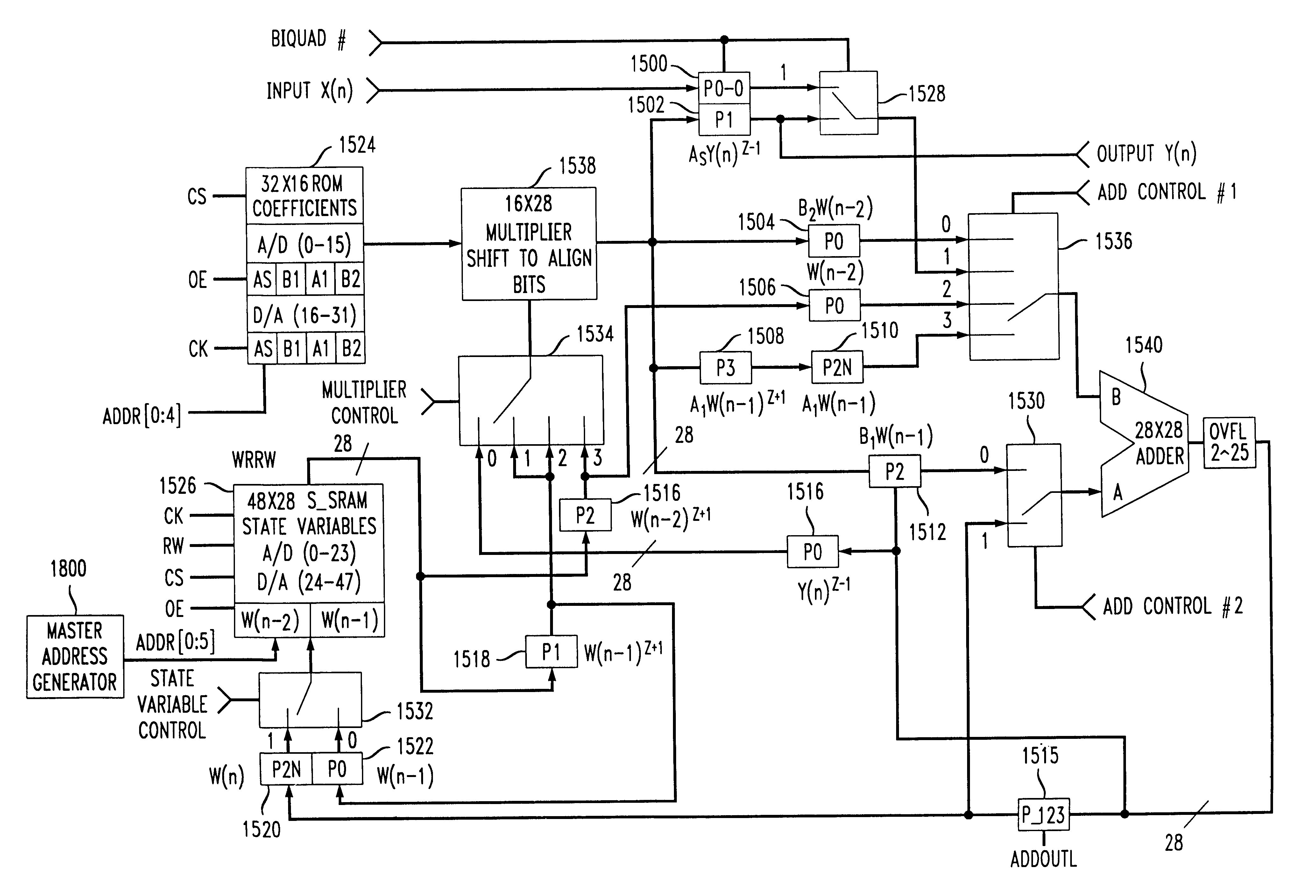
System for digital filtering in a fixed number of clock cycles
InactiveUS6175849B1Digital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsIir filteringState variable
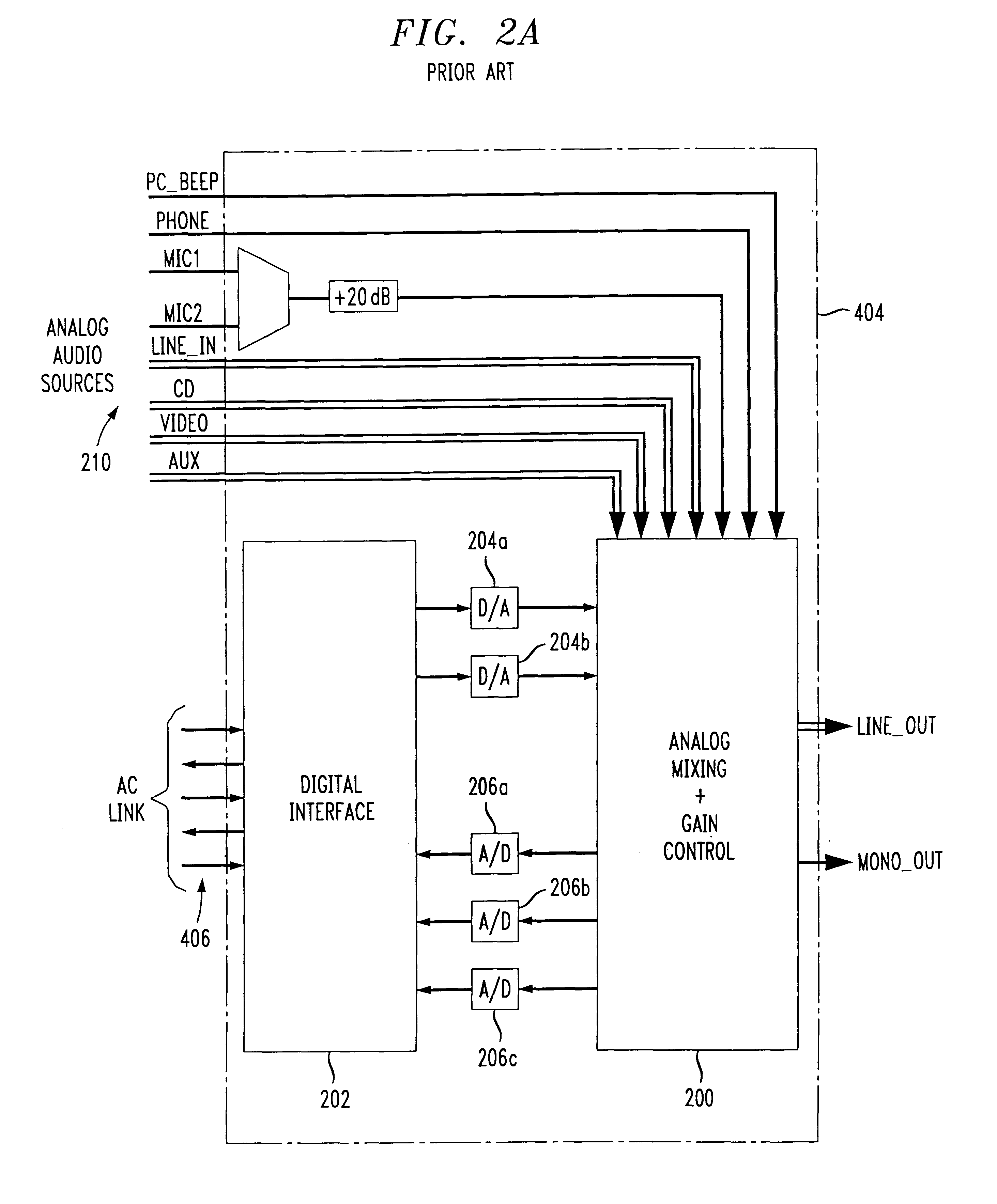
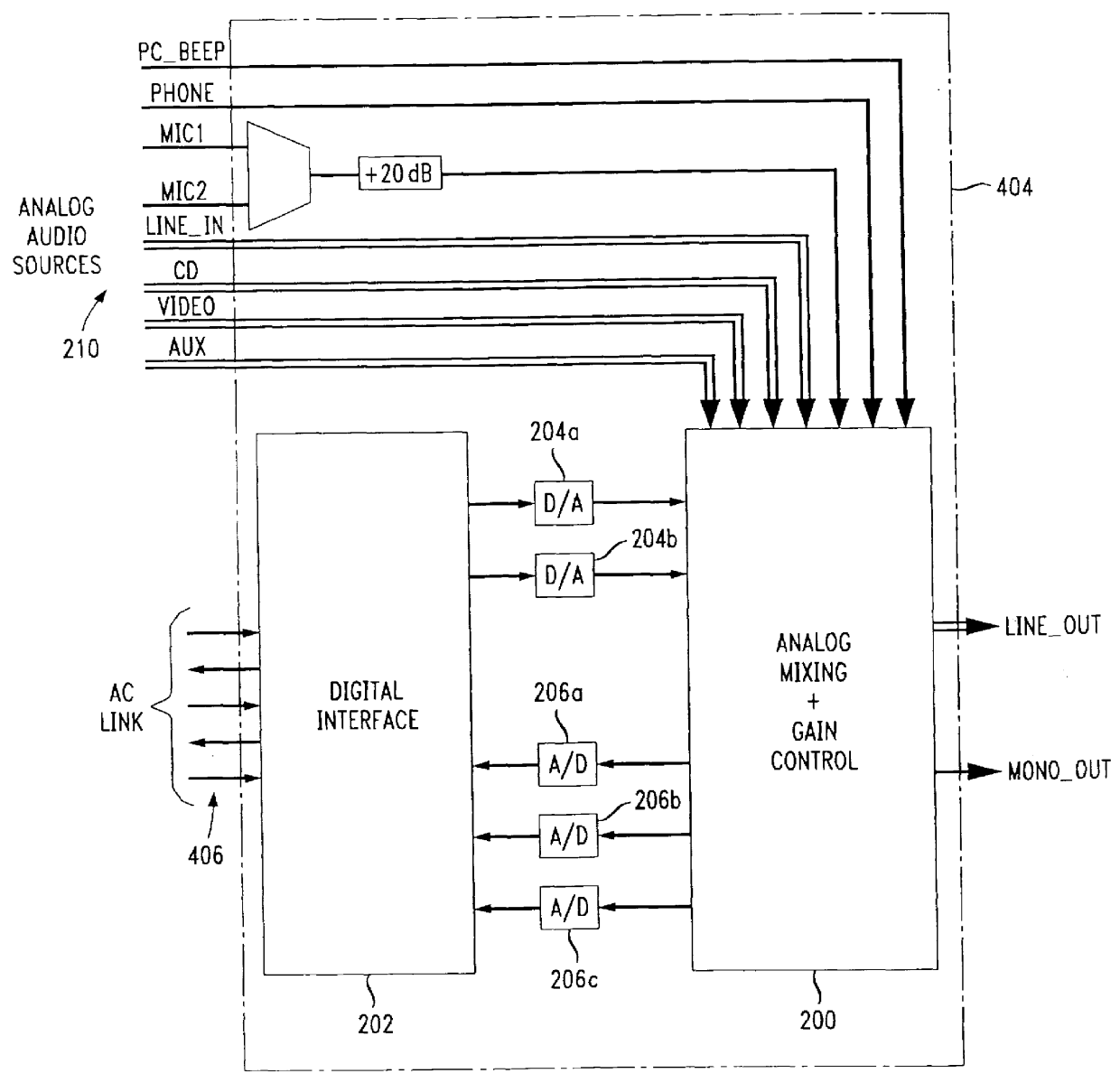
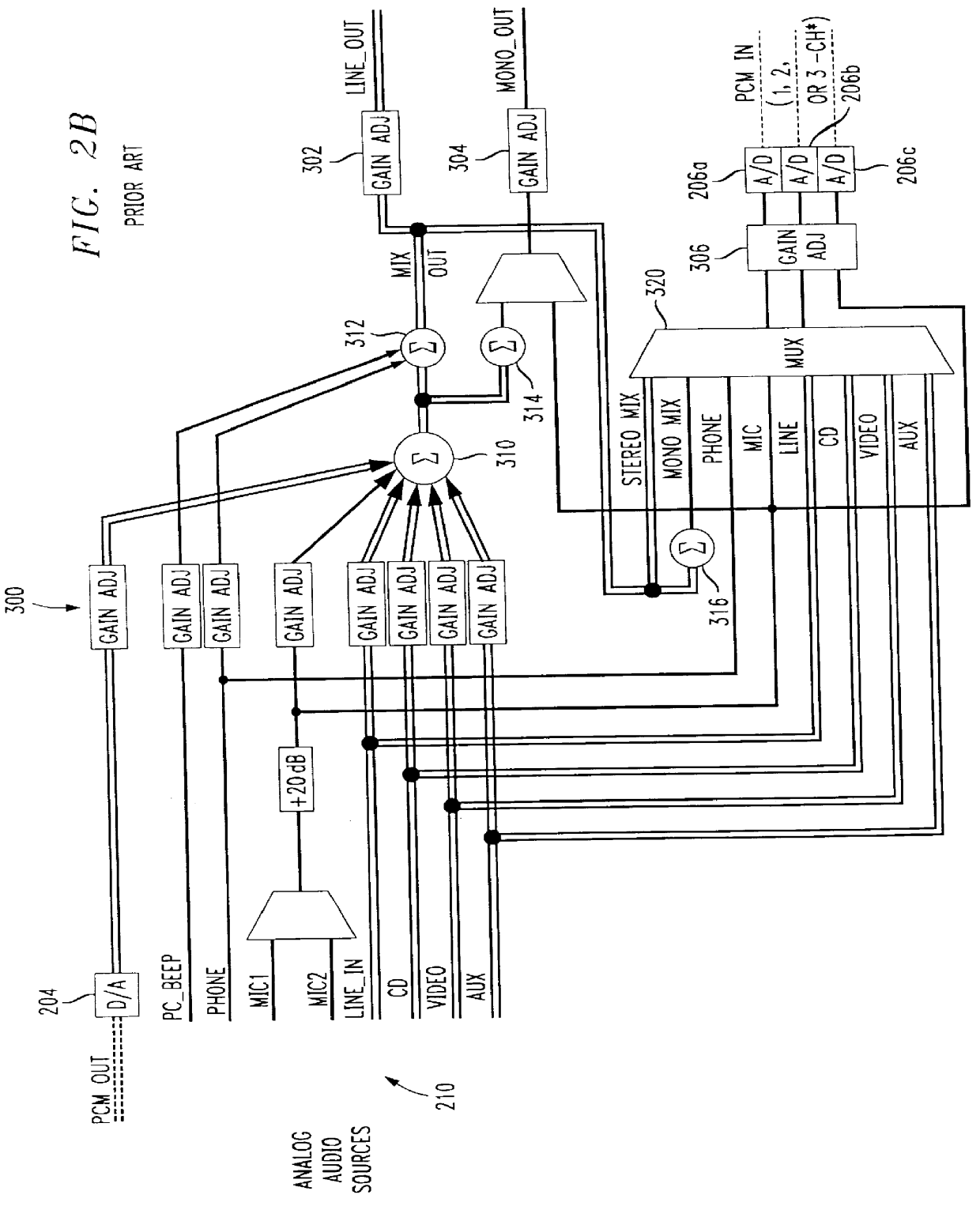
An integrated circuit, e.g. an AC '97 conforming audio codec, includes a digital filter and gain module including multiple channels of gain control and multiple channels of digital filtering. A gain control module includes an overflow check of data samples requiring differing lengths of clamping. Each channel of the digital filter includes a finite impulse response (FIR) filter, and an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter. The digital filtering is implemented largely in hardware independent of the number of channels required and / or independent of the required order of the filtering. Thus, filter channels can be added or additional filtering implemented merely by increasing the clock speed without changing the digital filter design. The FIR filter is capable of being reset each frame to prevent a DC buildup at internal nodes. The IIR filter performs a plurality of 2nd order biquadratic equations in an overall average of as few as four clock cycles per 2nd order biquad. A RAM is used to store the state variables for the 2nd order biquadratic equations. The state variable RAM is reset by controlling the clear input of latches at an input and / or the output of the state variable RAM, and the state variable RAM is addressed by a delta counter which is independent of the particular number of filter channels or filter orders implemented. Test patterns may be inserted between functional modules of an integrated circuit such as the disclosed audio codec by appropriate control of the preset and clear inputs to output latches of the functional modules.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Recursive digital filter with reset
InactiveUS6167415ADigital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsIir filteringState variable
An integrated circuit, e.g. an Audio Codec (AC) '97 conforming audio codec, includes a digital filter and gain module including multiple channels of gain control and multiple channels of digital filtering. A gain control module includes an overflow check of data samples requiring differing lengths of clamping. Each channel of the digital filter includes a finite impulse response (FIR) filter, and an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter. The digital filtering is implemented largely in hardware independent of the number of channels required and / or independent of the required order of the filtering. Thus, filter channels can be added or additional filtering implemented merely by increasing the clock speed without changing the digital filter design. The FIR filter is capable of being reset each frame to prevent a direct current (DC) buildup at internal nodes. The IIR filter performs a plurality of 2nd order biquadratic equations in an overall average of as few as four clock cycles per 2nd order biquad. A random access memory (RAM) is used to store the state variables for the 2nd order biquadratic equations. The state variable RAM is reset by controlling the clear input of latches at an input and / or the output of the state variable RAM, and the state variable RAM is addressed by a delta counter which is independent of the particular number of filter channels or filter orders implemented. Test patterns may be inserted between functional blocks of an integrated circuit such as the disclosed audio codec by appropriate control of the preset and clear inputs to output latches of the functional blocks.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
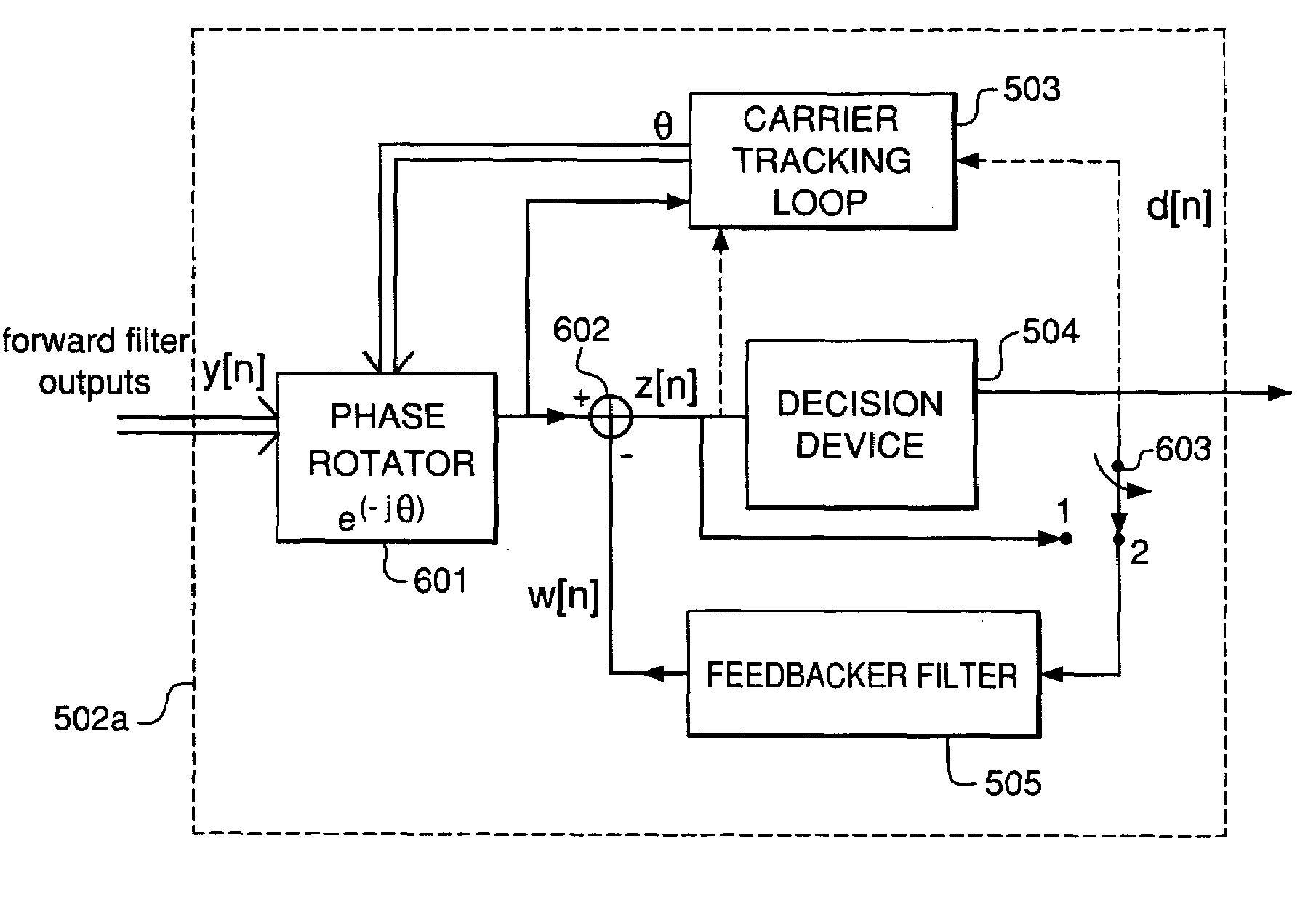
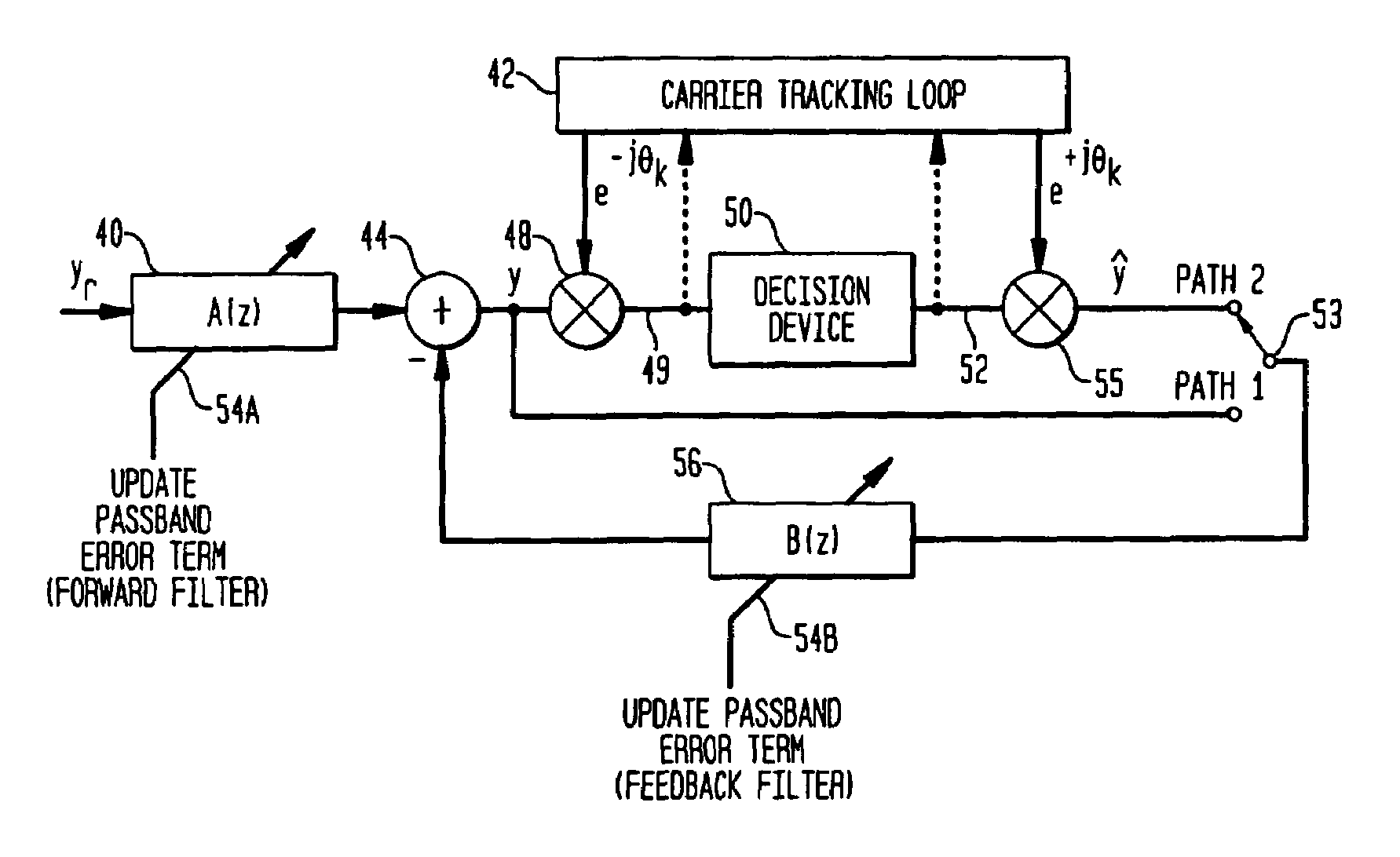
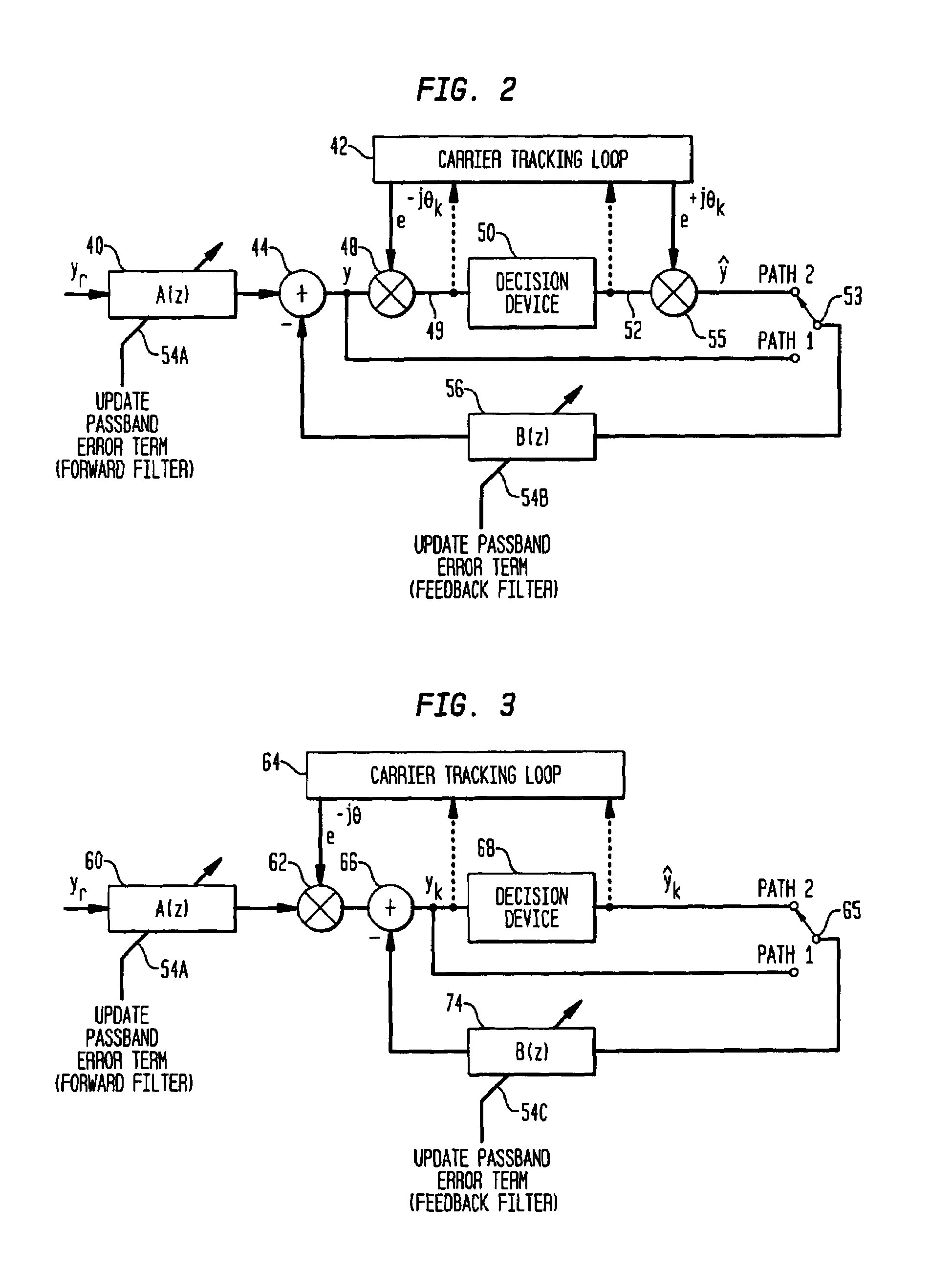
Carrier phase estimation based on single-axis constant modulus cost criterion and Bussgang criteria
Carrier phase recovery employs a single-axis blind cost criterion from the Bussgang class of functions, and its stochastic gradient, to generate a carrier phase error used to adjust a received and demodulated signal to near baseband. For one implementation, the estimate is derived in accordance with a Single-Axis Constant Modulus (SA-CM) criterion and its stochastic gradient via a SA-CM algorithm (SA-CMA). The carrier phase error is then used to adjust the carrier frequency and phase of the received and demodulated signal toward the frequency and phase of the carrier used to modulate the transmitted symbols, driving the carrier phase error to zero. The values used for the phase recovery may be either i) an IIR filtered signal, ii) a processed signal (e.g., decisions for the signal symbols), or iii) an equalized and processed signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
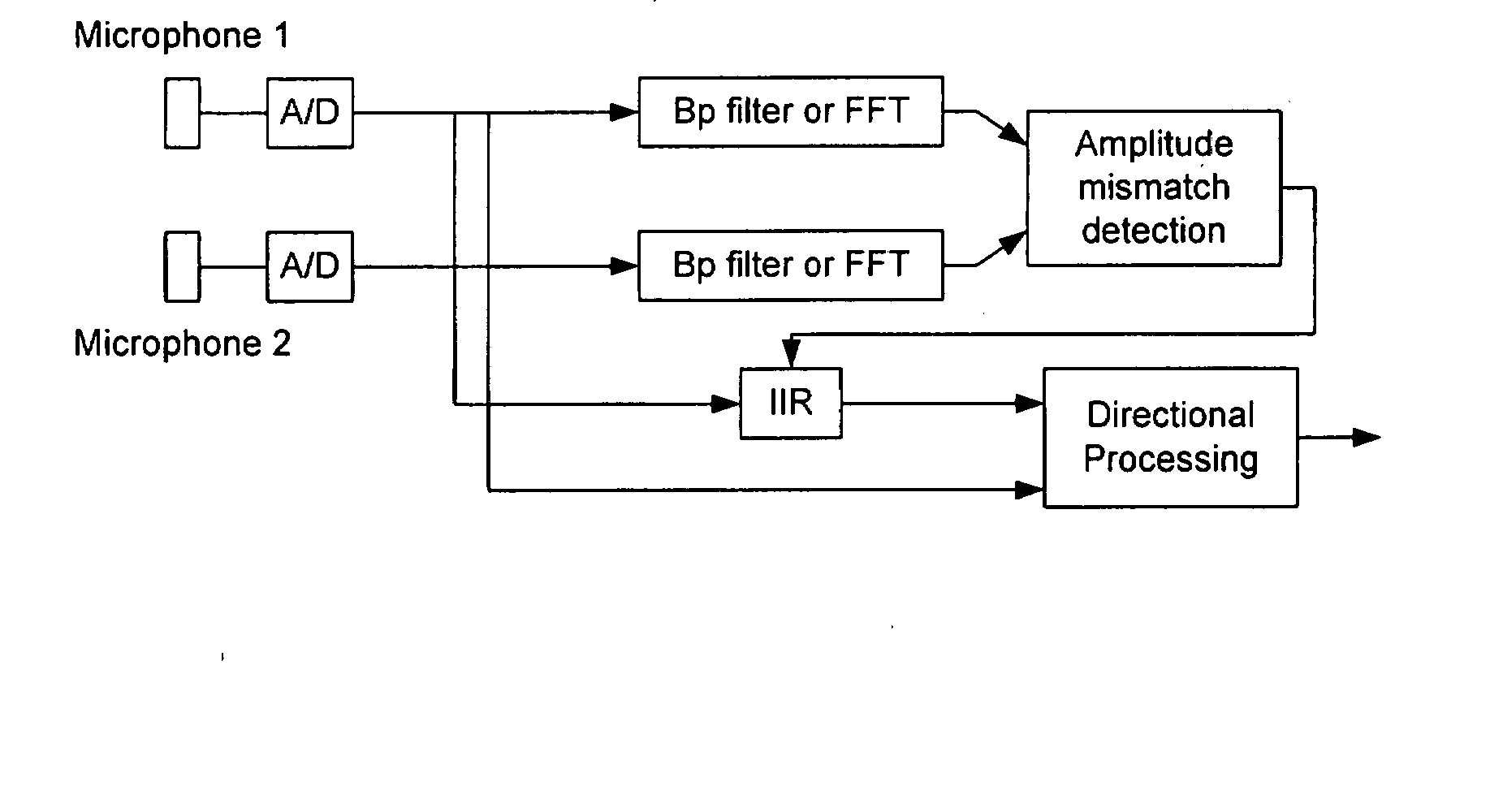
Low Frequency Phase Matching for Microphones
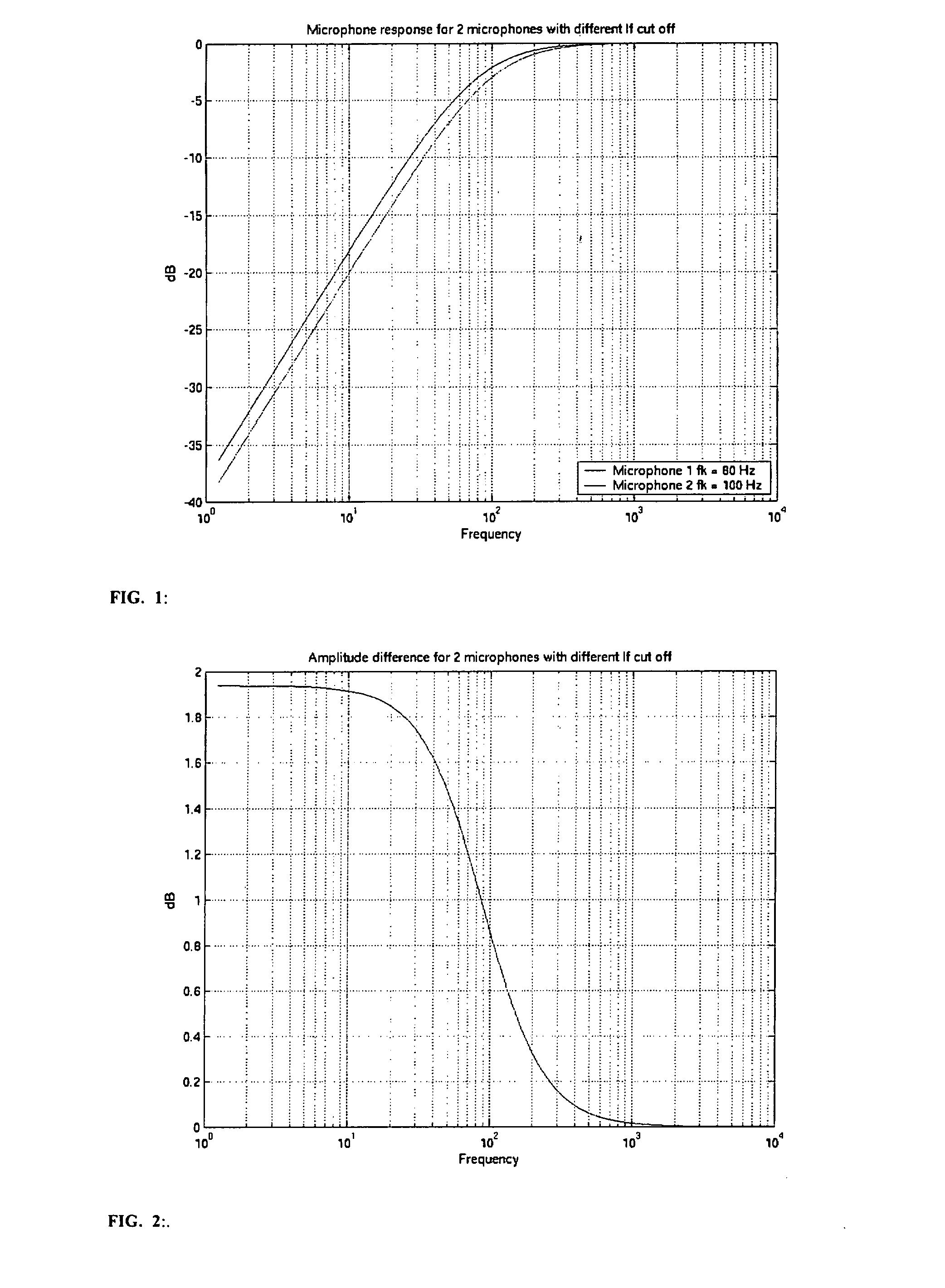
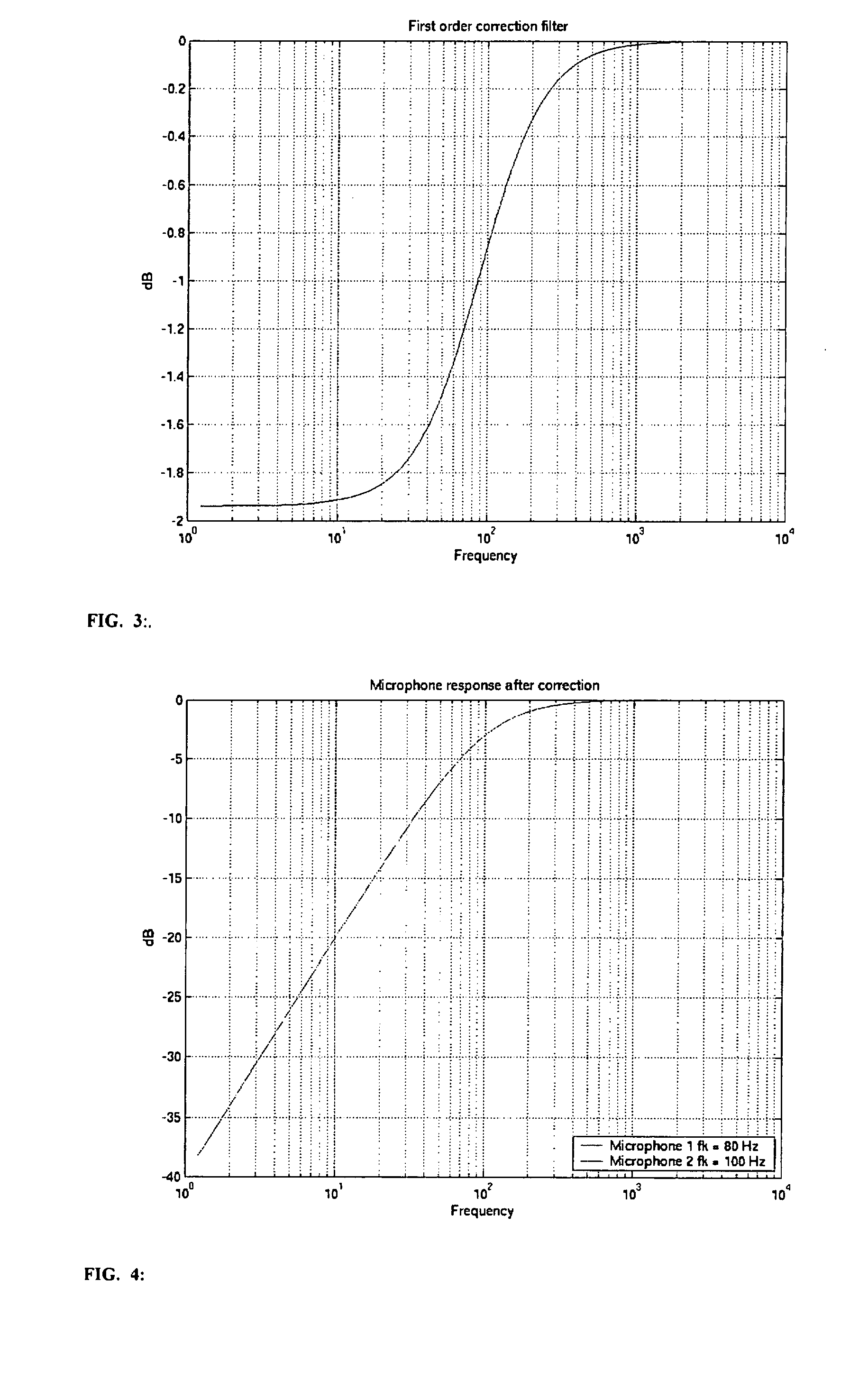
InactiveUS20070258597A1Reliable and adequate correctionStereophonic arrangmentsIir filteringPhase response
The invention relates to a communication device having at least two microphones, where in order to match the microphone performance in respect of the phase response a correction filter in the form of a IIR filter is implemented and where the amplitude of the transfer function for the correction filter is the inverse of the difference between the two microphone amplitudes.
Owner:OTICON
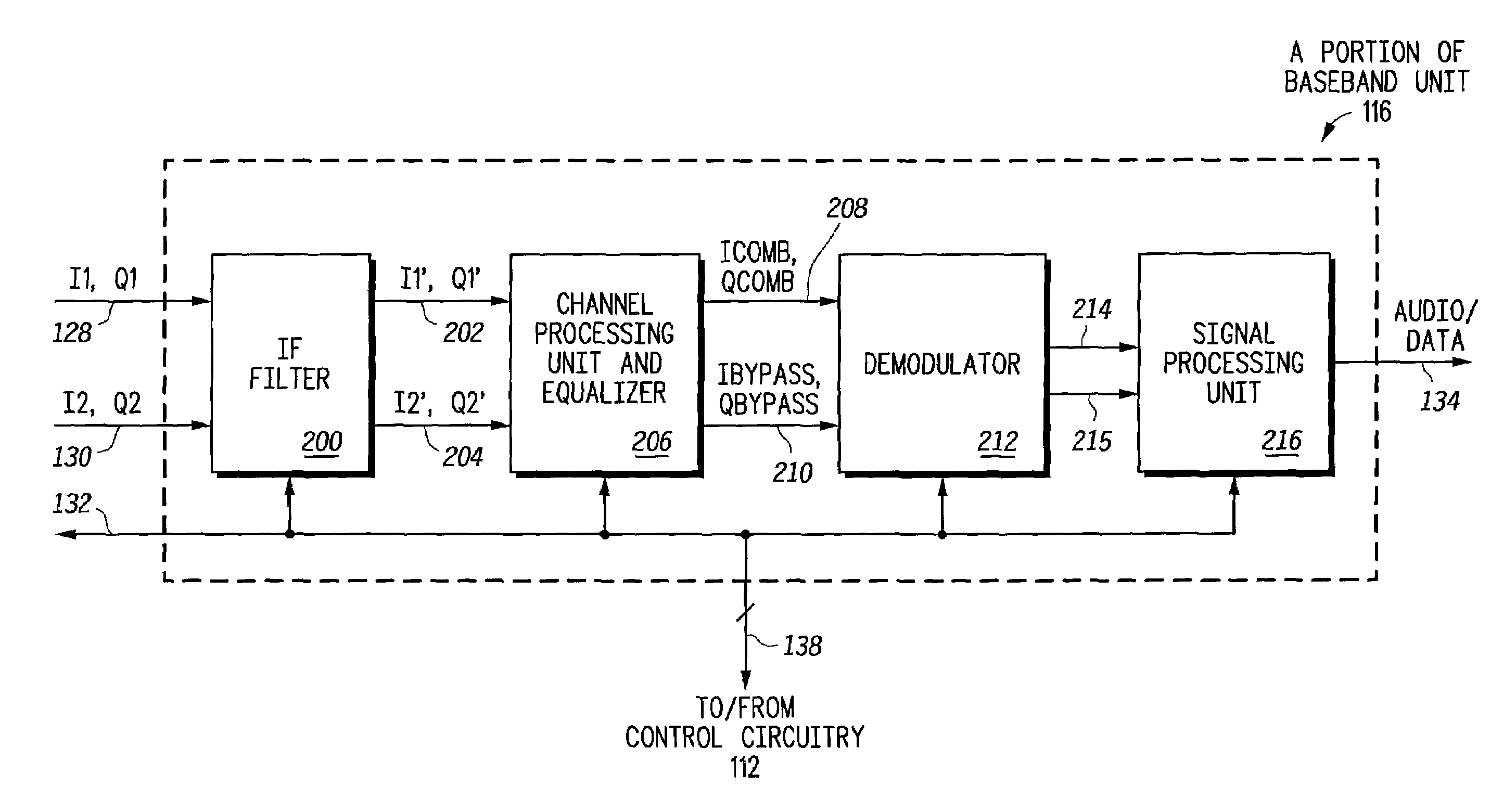
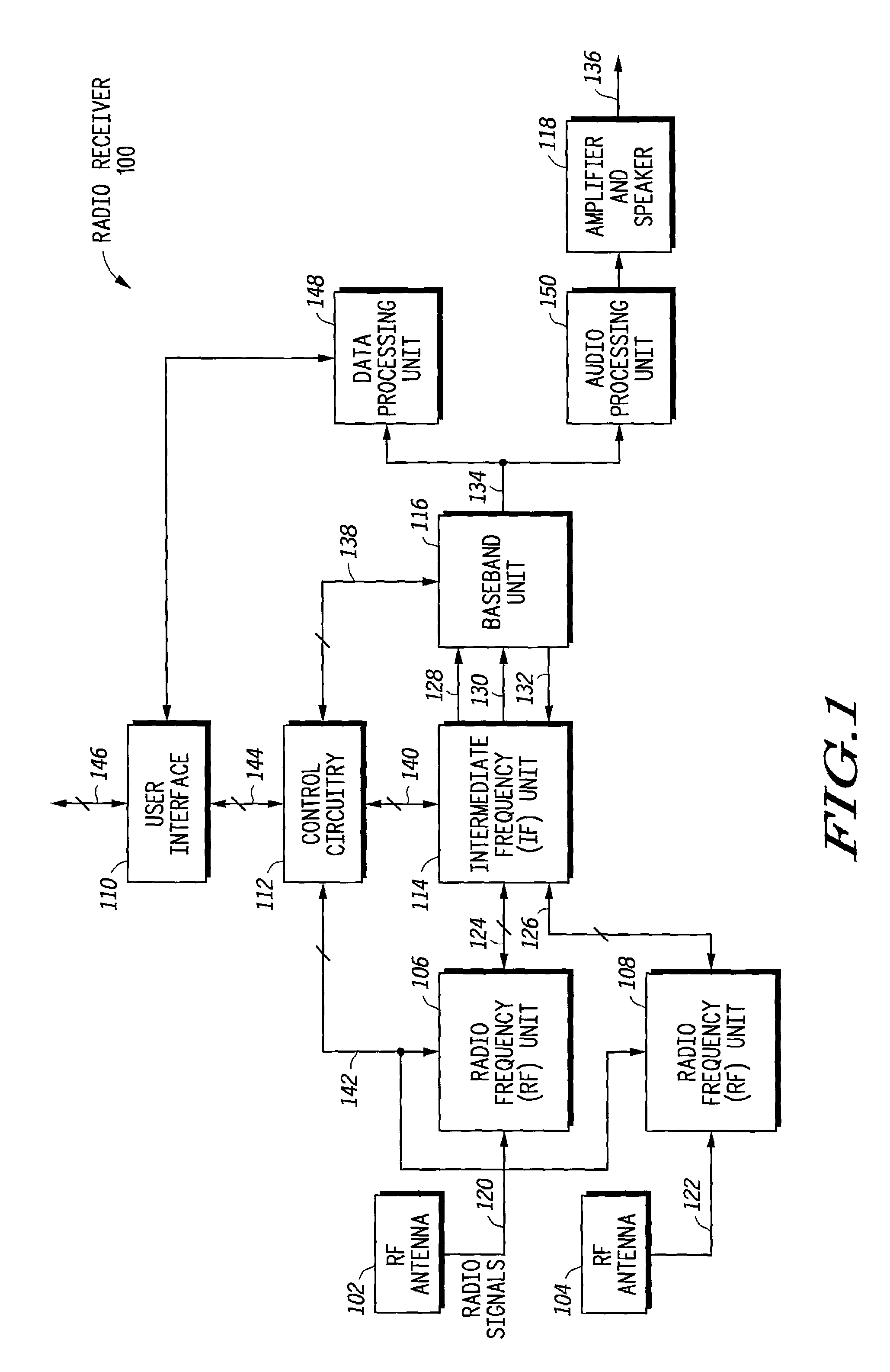
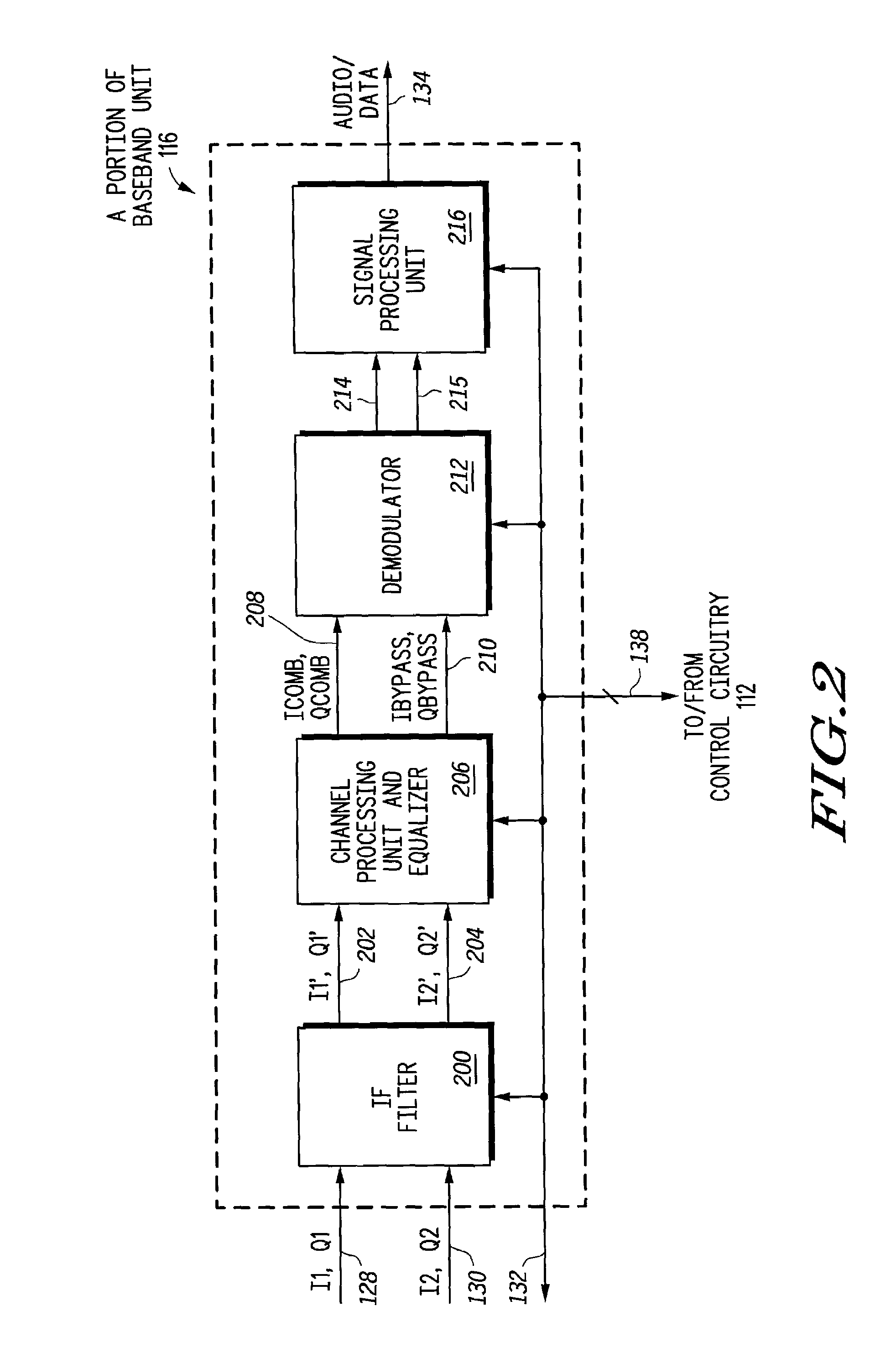
Radio receiver having an adaptive equalizer and method therefor
A radio receiver (100) has an equalizer (500) that operates in the time domain to remove residual interference that is not removed by an IF filter (200) operating in the frequency domain that is caused by an adjacent interfering FM station. The equalizer (500) includes a modified constant modulus algorithm (CMA) to generate a tap update signal from the output of the equalizer (500). The equalizer (500) uses the modified CMA to reduce an amplitude fluctuation of the received signal caused by the adjacent interfering station. The CMA is modified to use an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter (540) to generate the tap update. The IIR filter (540) also speeds up a convergence of the modified CMA to provide better performance.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
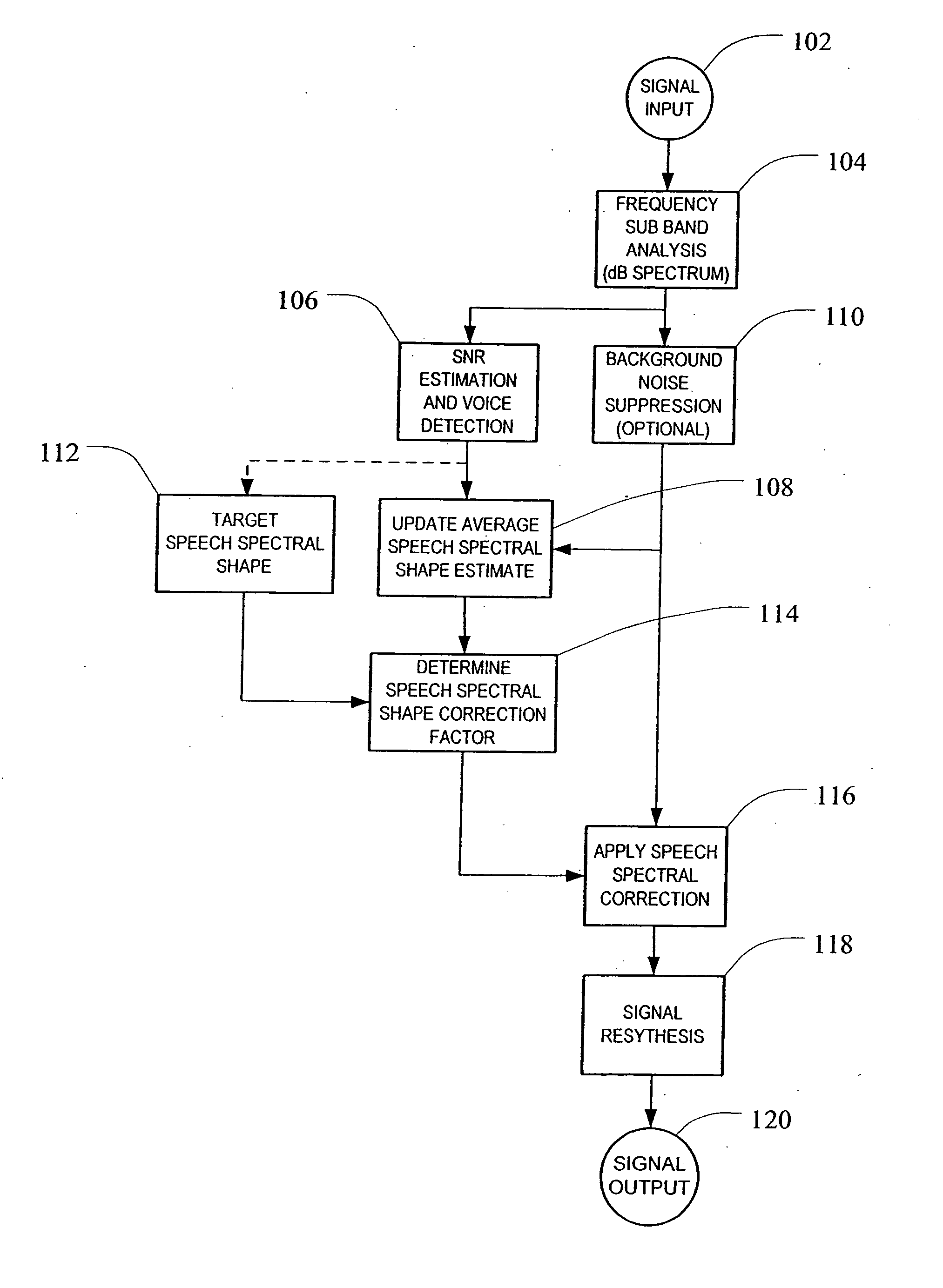
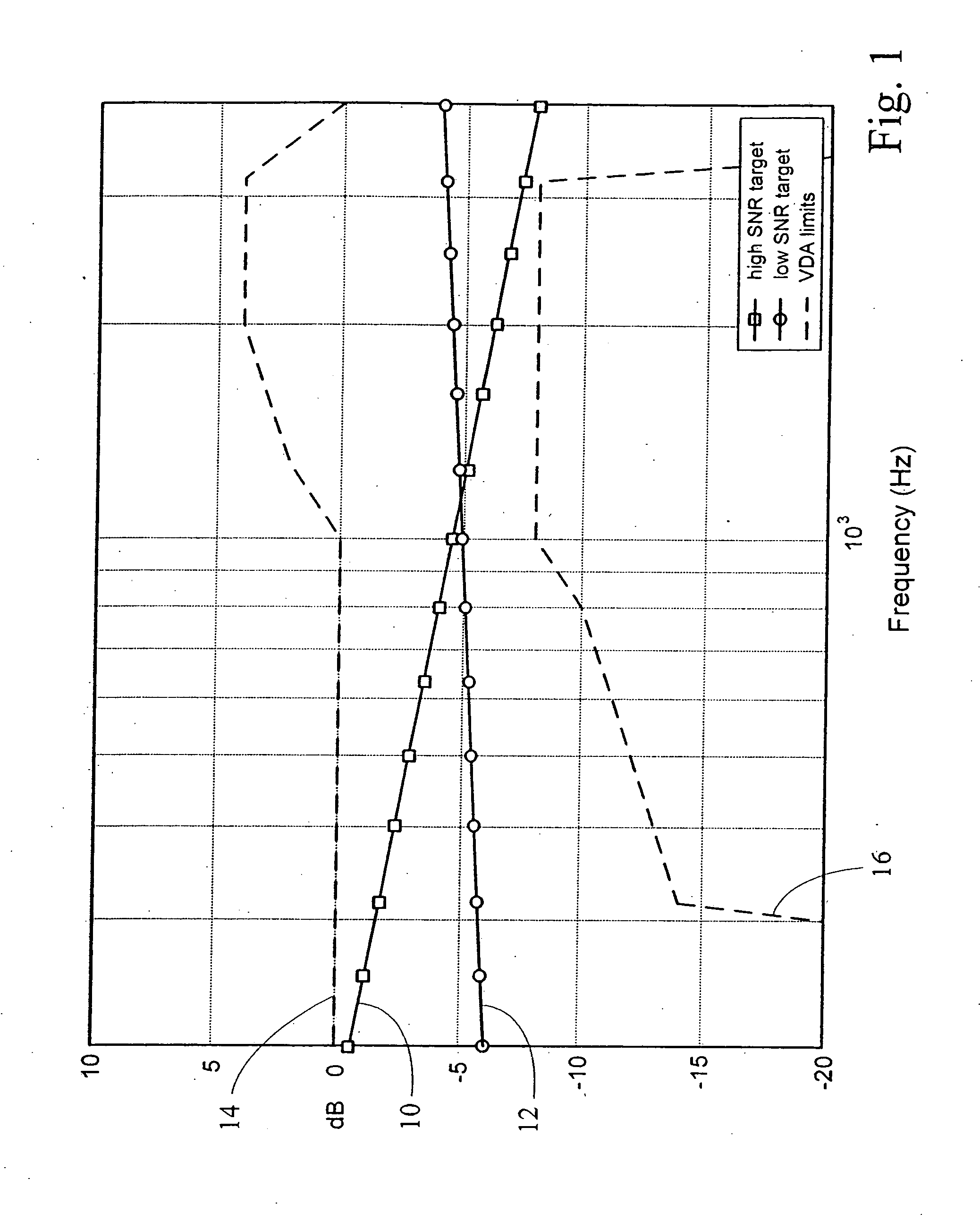
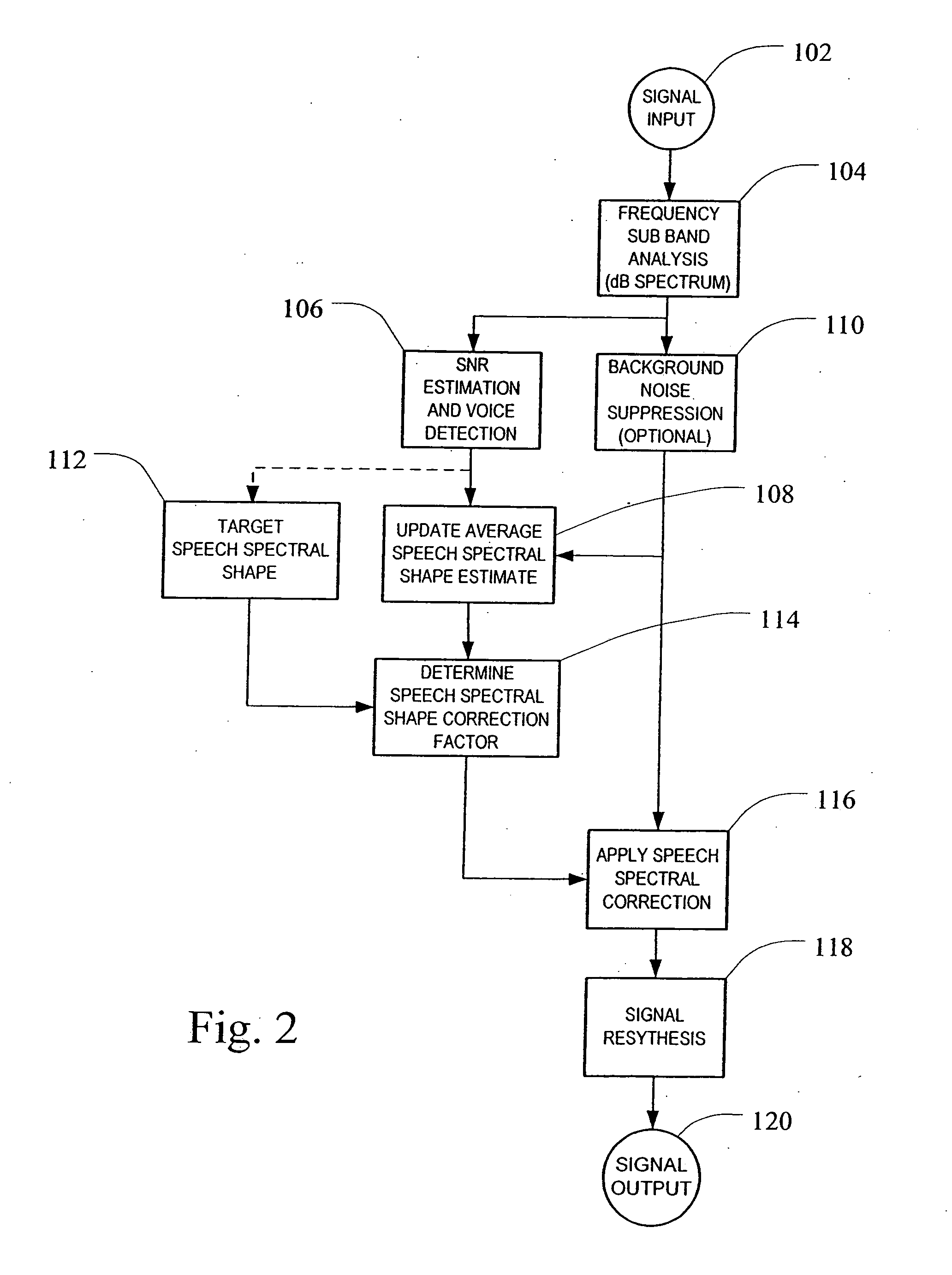
System and method for adaptive enhancement of speech signals
ActiveUS20060293882A1High frequency responseQuality improvementEar treatmentSpeech recognitionIir filteringFrequency spectrum
A method and system for enhancing the frequency response of speech signals are provided. An average speech spectral shape estimate is calculated over time based on the input speech signal. The average speech spectral shape estimate may be calculated in the frequency domain using a first order IIR filtering or “leaky integrators.” Thus, the average speech spectral shape estimate adapts over time to changes in the acoustic characteristics of the voice path or any changes in the electrical audio path that may affect the frequency response of the system. A spectral correction factor may be determined by comparing the average speech spectral shape estimate to a desired target spectral shape. The spectral correction factor may be added (in units of dB) to the spectrum of the input speech signal in order to enhance or adjust the spectrum of the input speech signal toward the desired spectral shape, and an enhanced speech signal re-synthesized from the corrected spectrum.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
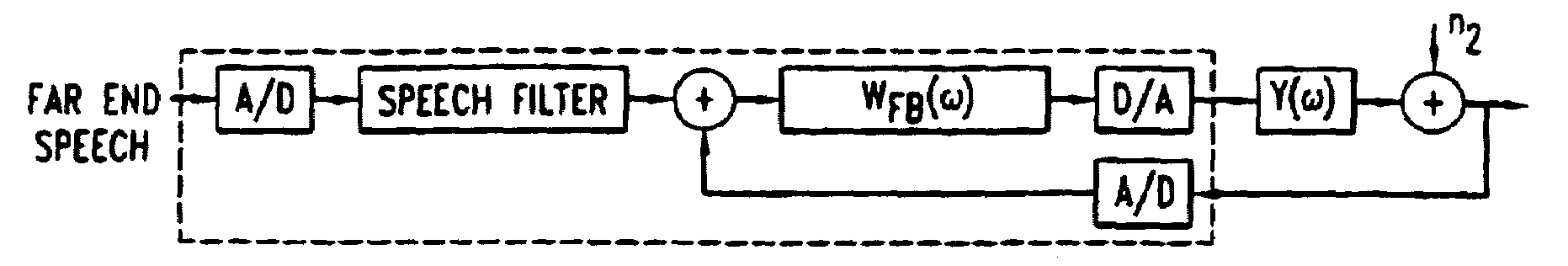
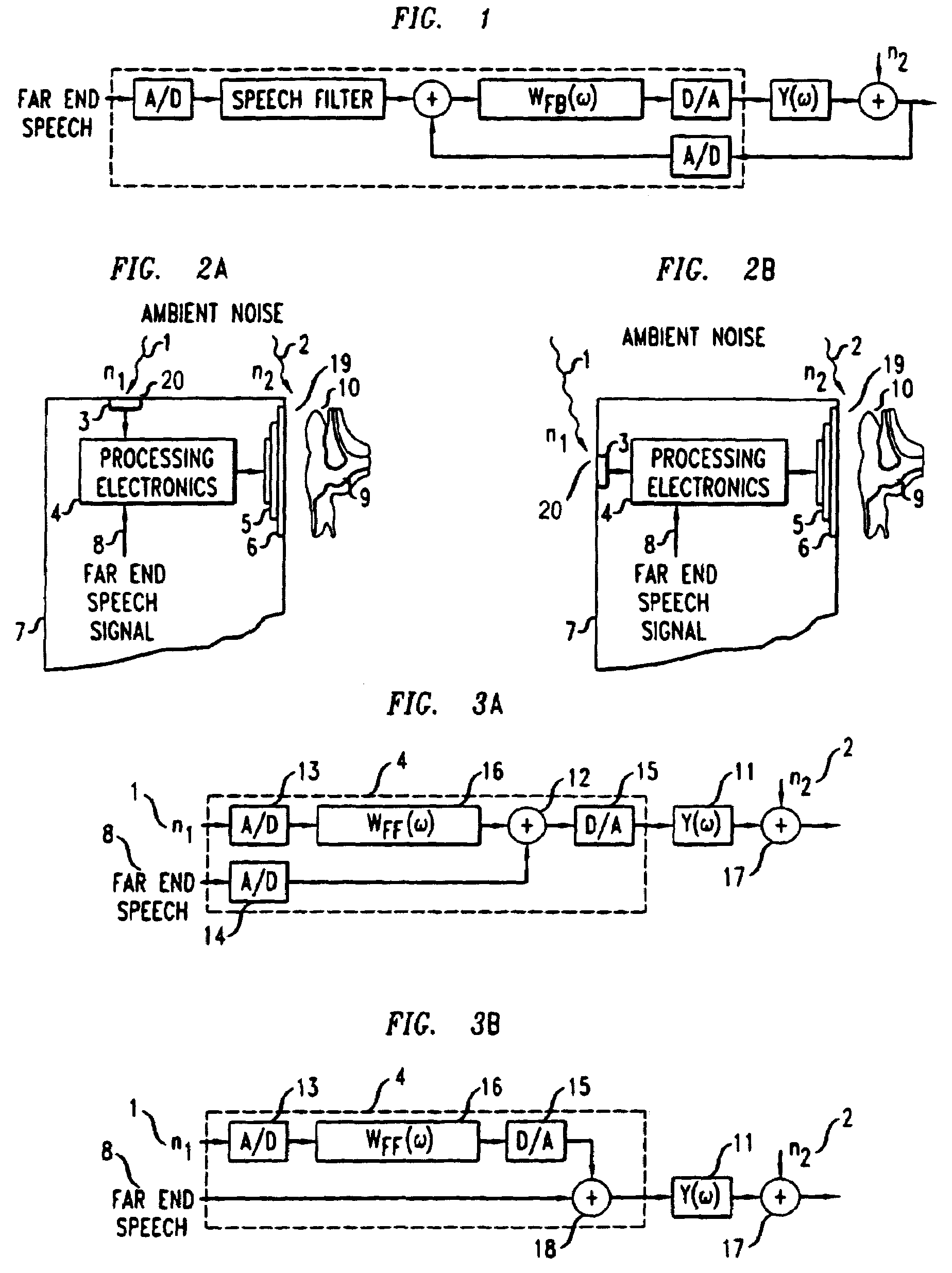
Telephonic handset employing feed-forward noise cancellation
InactiveUS7031460B1Effective noise cancellationRobust against inter-user variabilityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsEar treatmentNoise fieldIir filtering
A telephonic handset comprises an active noise reduction (ANR) system. The ANR system comprises a reference microphone and an IIR filter. The IIR filter is receivingly coupled to the reference microphone with respect to noise reference signals, and it is transmittingly coupled to the receiver transducing element of the handset. The ANR system is configured as a fixed feed-forward noise cancellation system. Preferably, the IIR filter has a transfer function derived, in part, from the open-loop gain of a feedback noise cancellation system.In specific embodiments of the invention, the noise reference microphone is situated so as to sample the ambient noise field near the front face of the receiver, but without directly sampling the noise field on the front face.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
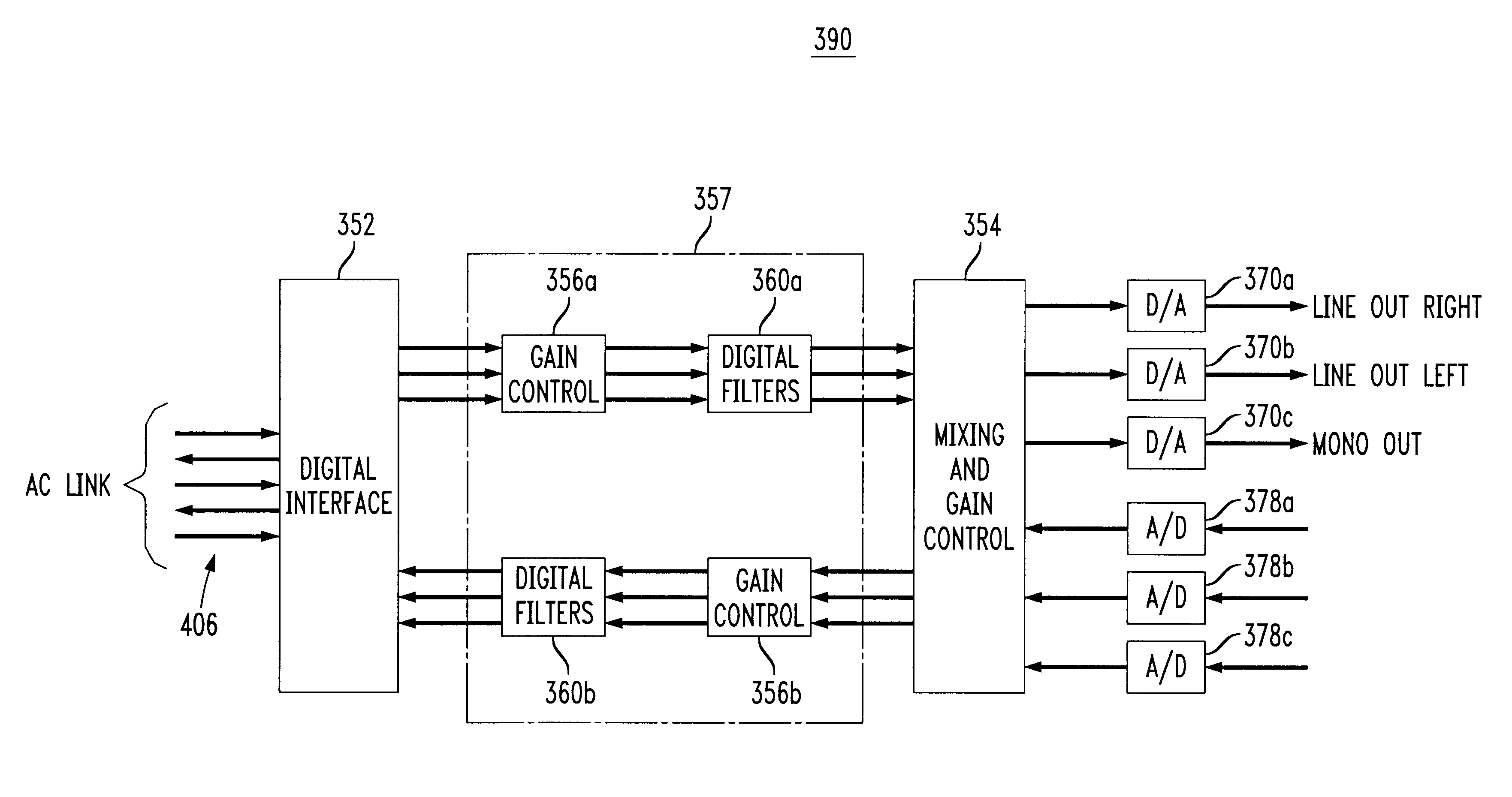
Distributed gain for audio codec
InactiveUS6215429B1Electric signal transmission systemsDigital technique networkIir filteringState variable
An integrated circuit, e.g. an AC '97 conforming audio codec, includes a digital filter and gain module including multiple channels of gain control and multiple channels of digital filtering. A gain control module includes an overflow check of data samples requiring differing lengths of clamping. Each channel of the digital filter includes a finite impulse response (FIR) filter, and an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter. The digital filtering is implemented largely in hardware independent of the number of channels required and / or independent of the required order of the filtering. Thus, filter channels can be added or additional filtering implemented merely by increasing the clock speed without changing the digital filter design. The FIR filter is capable of being reset each frame to prevent a DC buildup at internal nodes. The IIR filter performs a plurality of 2nd order biquadratic equations in an overall average of as few as four clock cycles per 2nd order biquad. A RAM is used to store the state variables for the 2nd order biquadratic equations. The state variable RAM is reset by controlling the clear input of latches at an input and / or the output of the state variable RAM, and the state variable RAM is addressed by a delta counter which is independent of the particular number of filter channels or filter orders implemented. Test patterns may be inserted between functional blocks of an integrated circuit such as the disclosed audio codec by appropriate control of the preset and clear inputs to output latches of the functional blocks.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
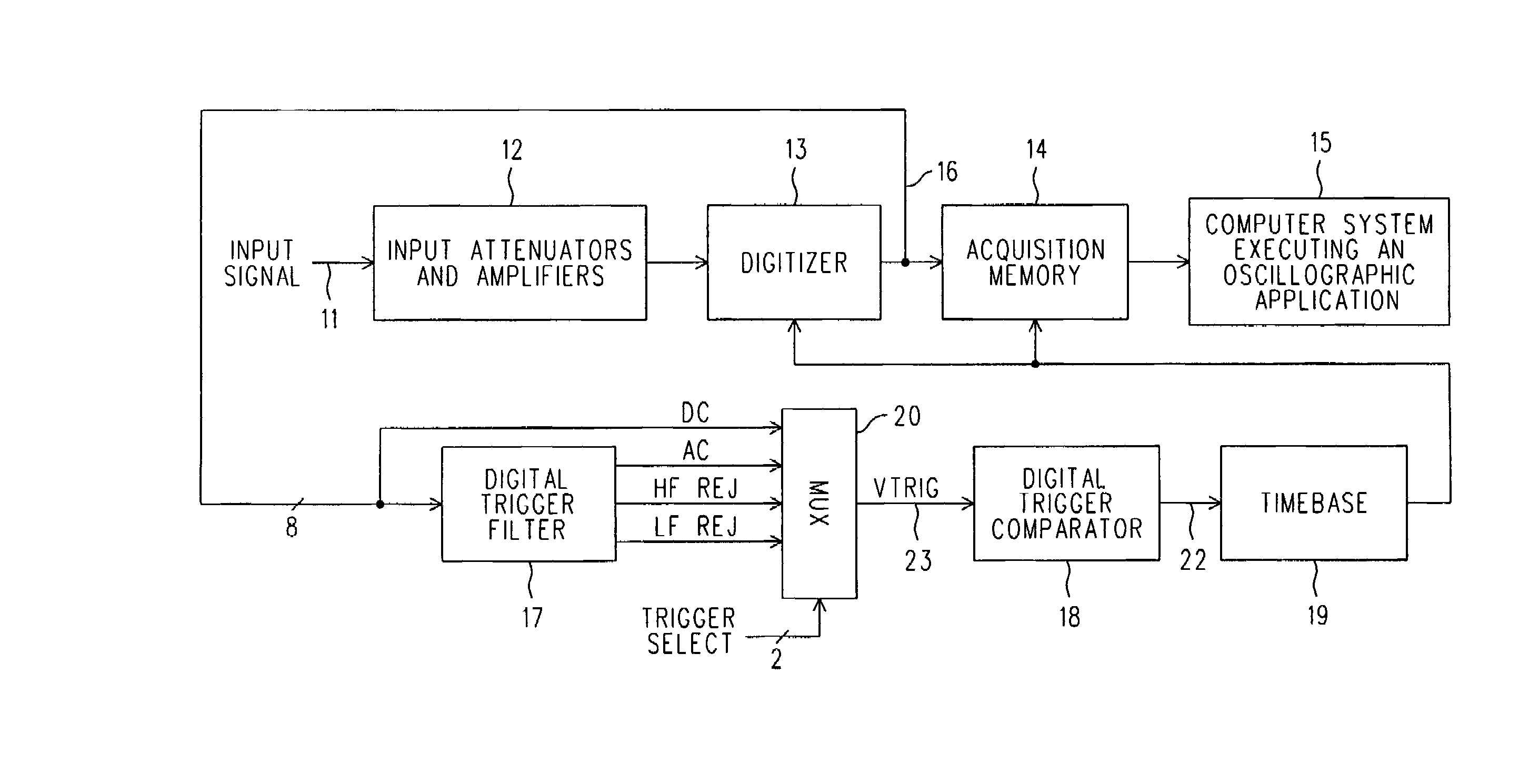
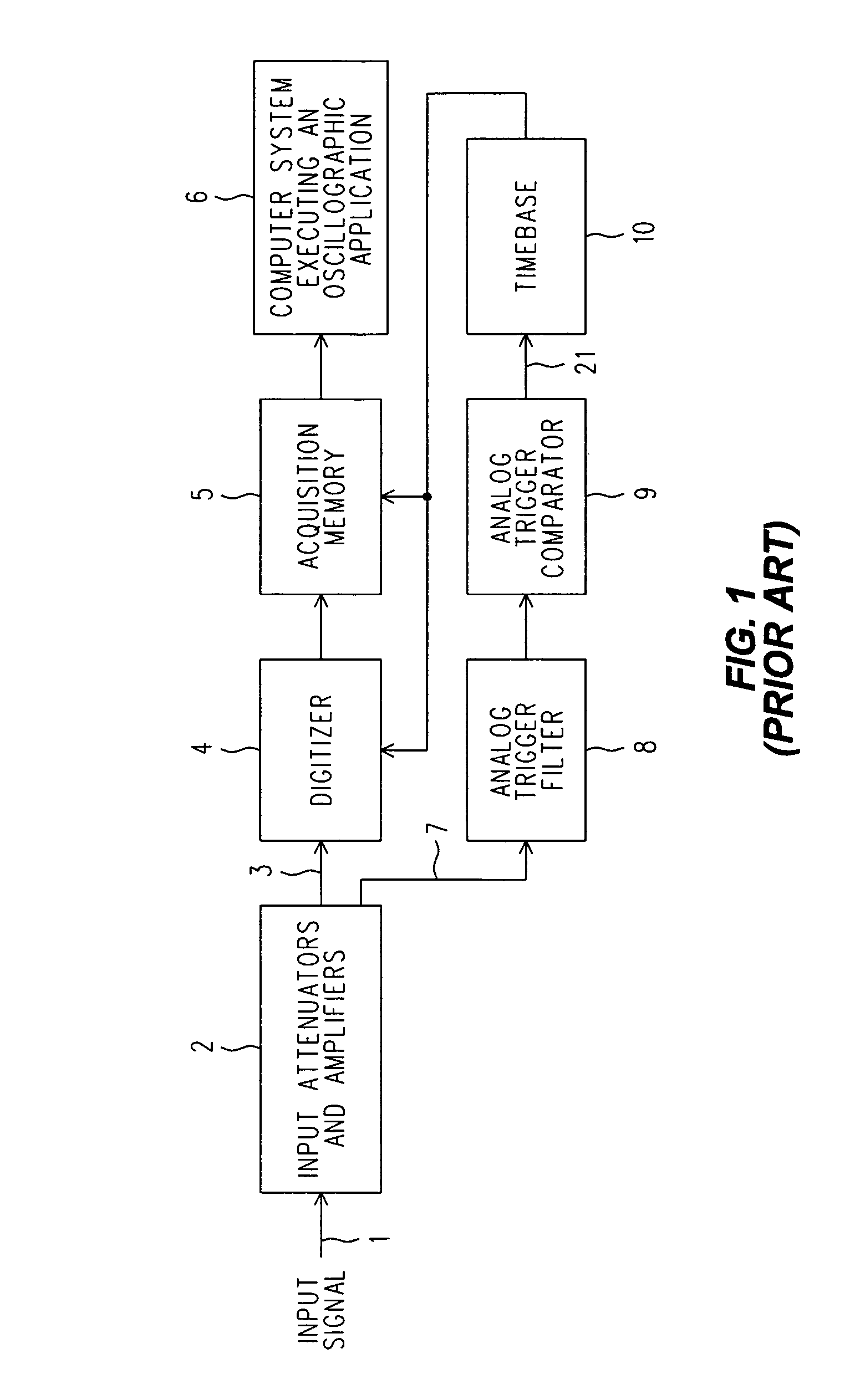
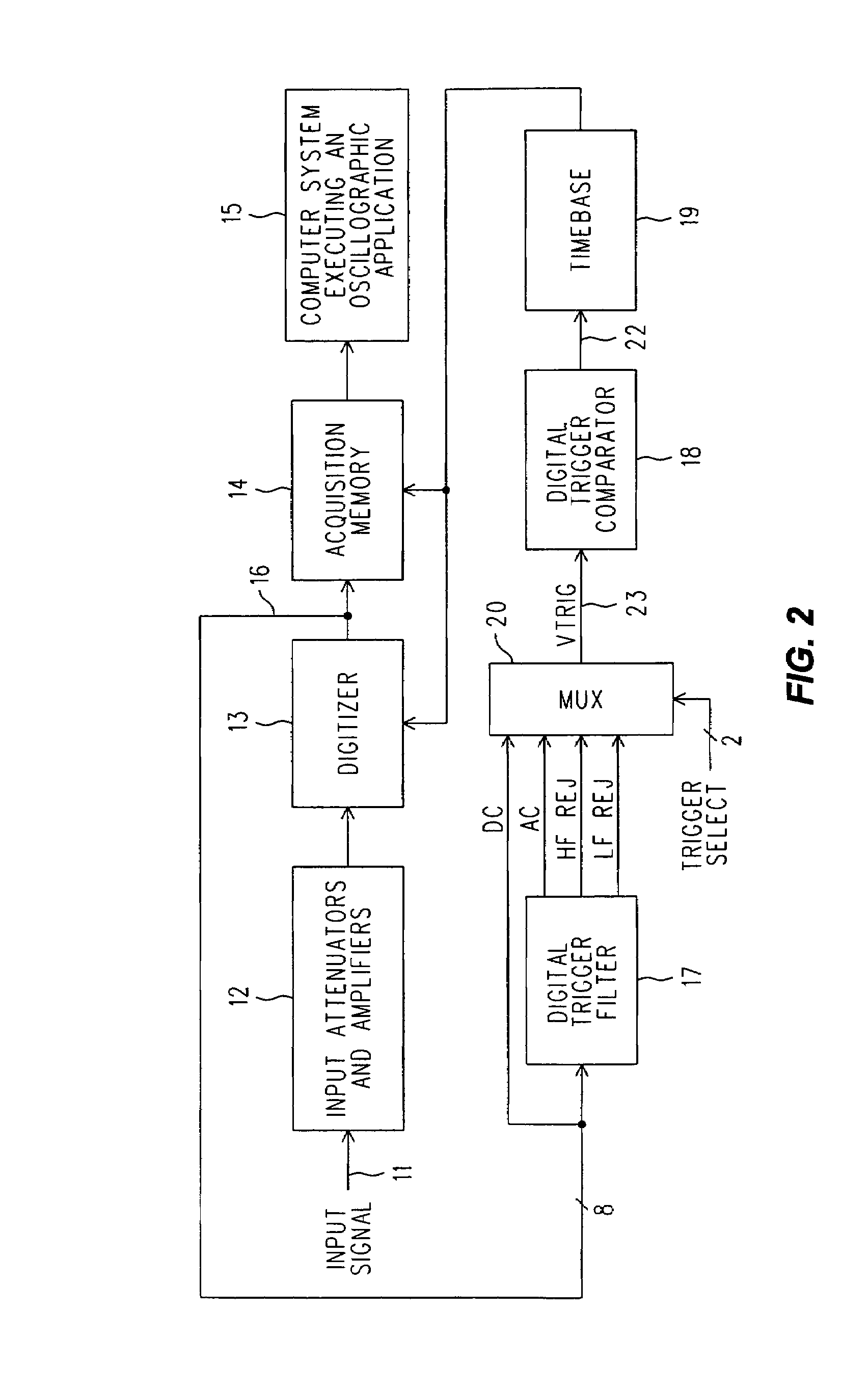
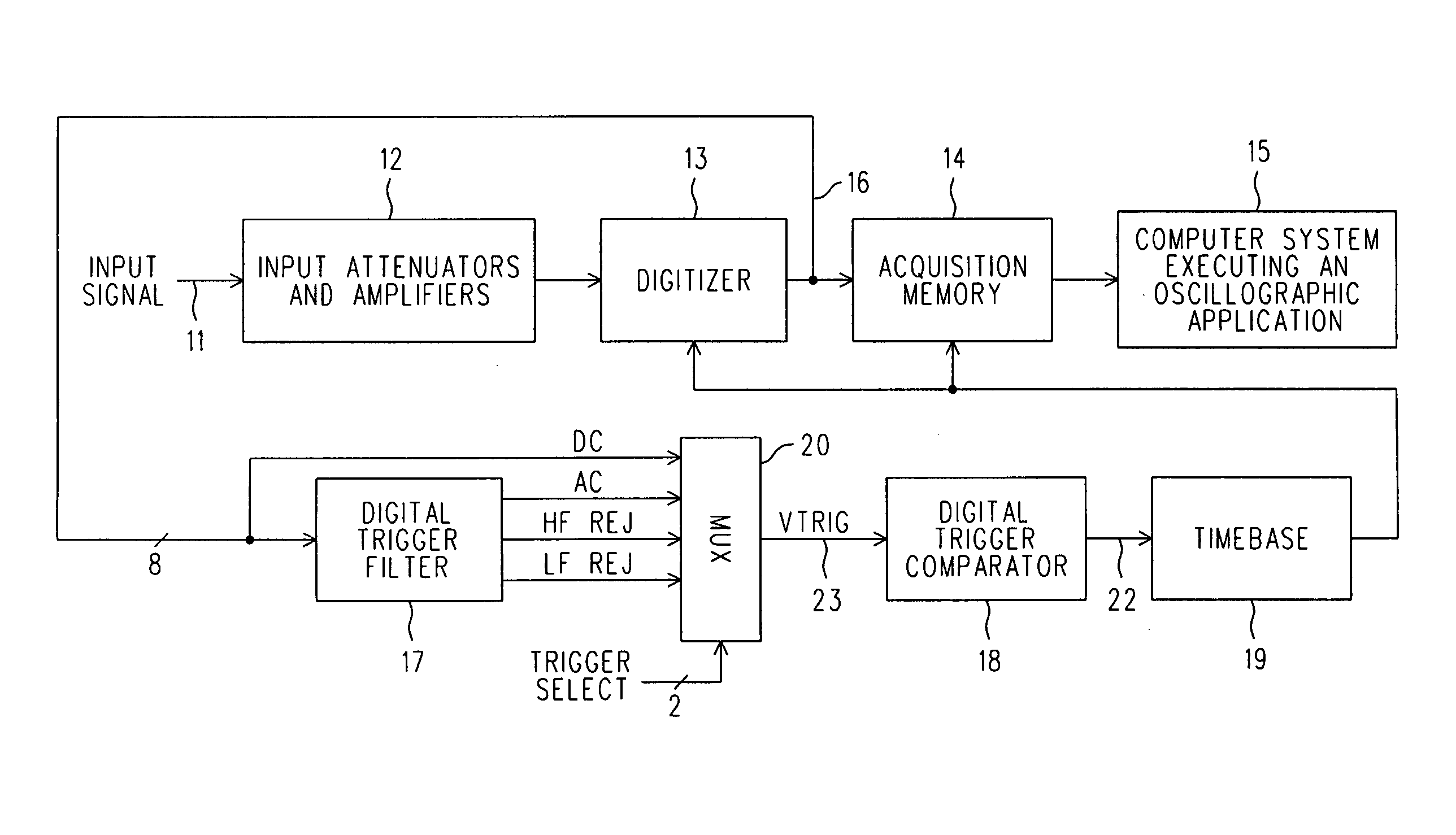
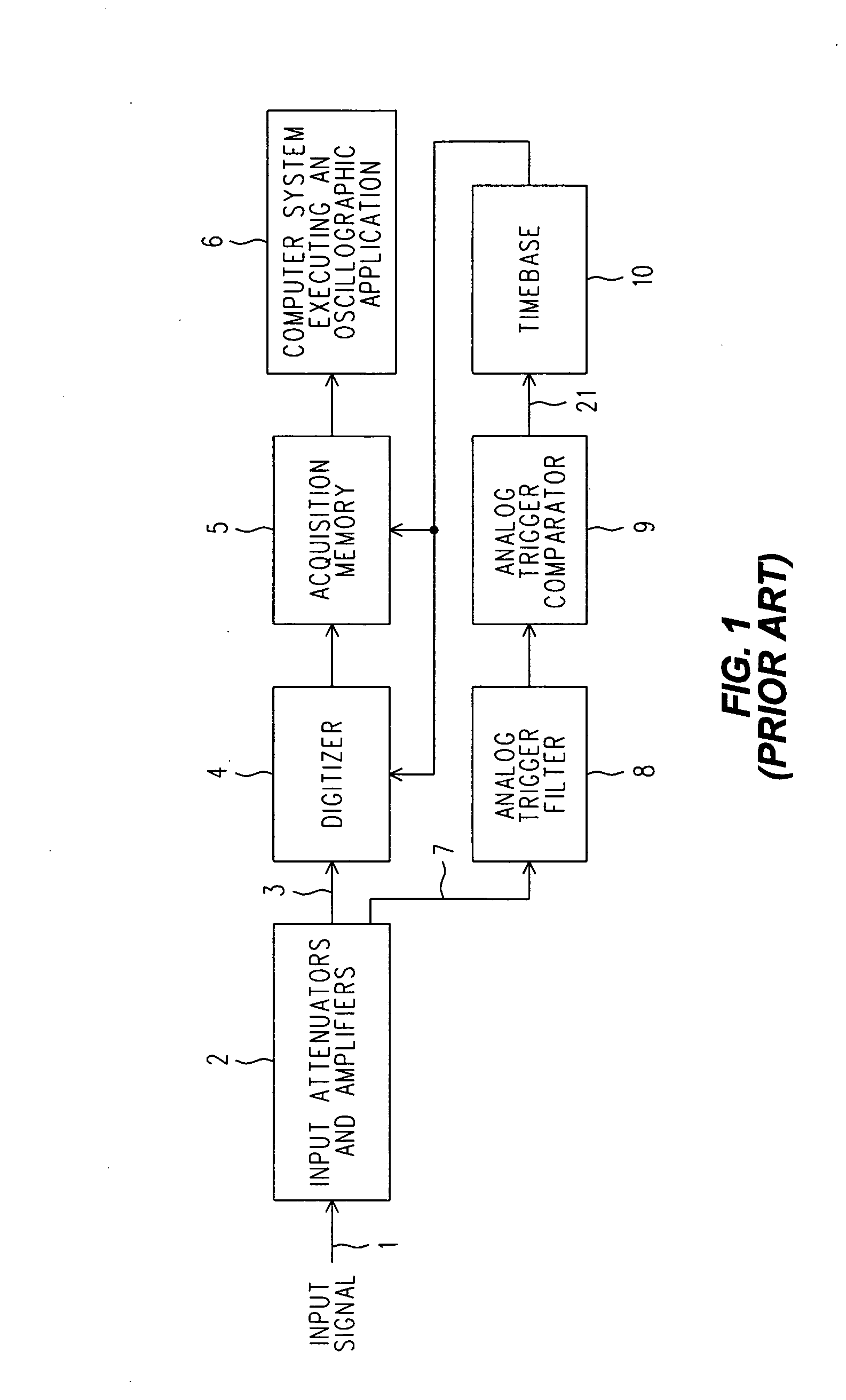
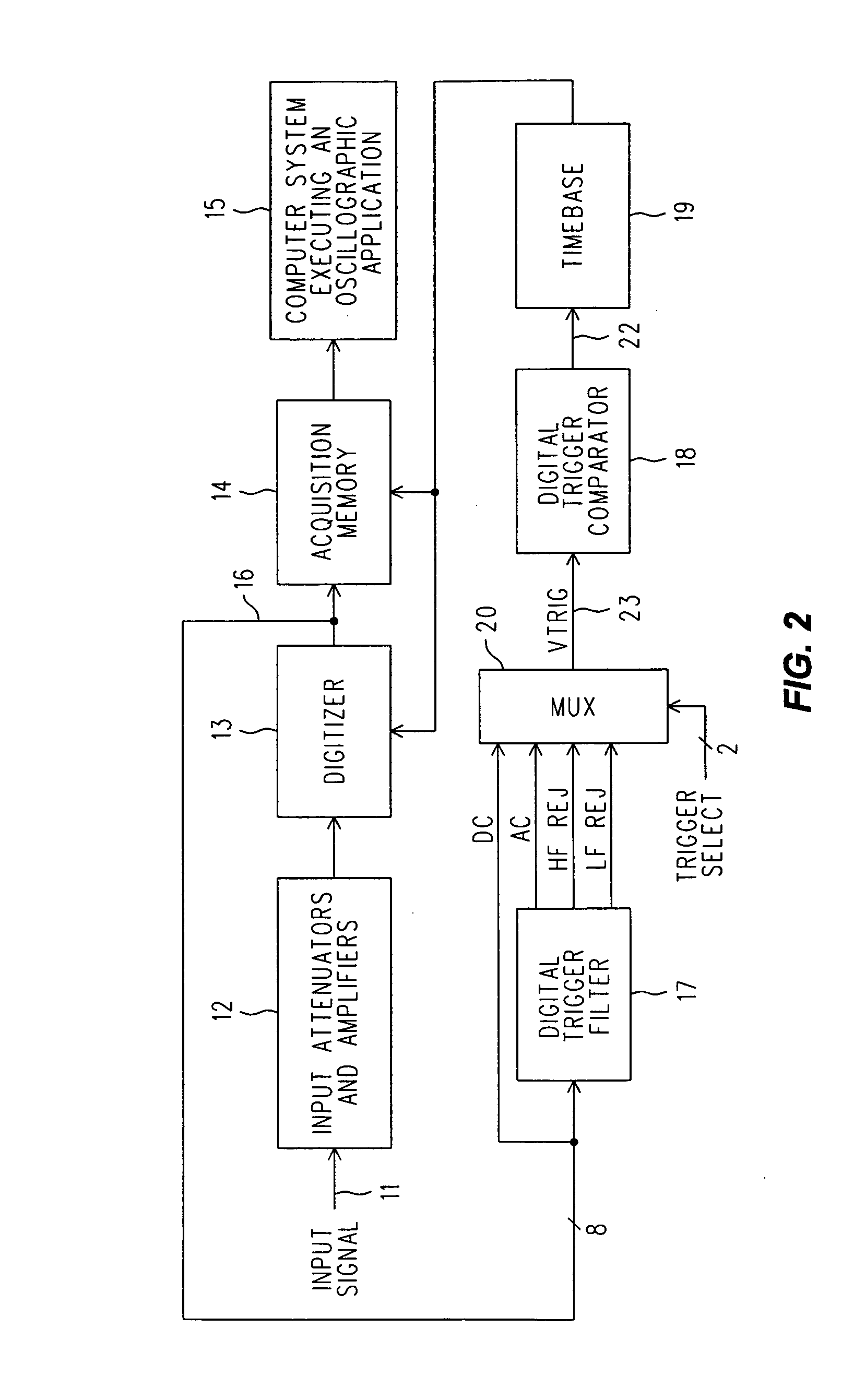
Digital trigger filter for a real time digital oscilloscope
ActiveUS7072804B2Spectral/fourier analysisNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementIir filteringEngineering
A real time DSO is equipped with a Digital Trigger Filter that performs high frequency rejection, low frequency rejection, AC and DC triggering. The Digital Trigger Filter includes first and second digitally implemented IIR (Infinite Input Response) Filters. A digitized Conditioned Input Signal is applied to the first IIR Filter. It has taps that provide the Trigger Signal outputs needed for high and low frequency rejection. The high frequency rejection output of the first ER Filter is essentially a low pass output (3 dB down at 50 KHz) and is also used as the digital input to the second IIR Filter, whose output is a much more aggressive suppression of high frequencies (3 dB down at 50 Hz). The AC Trigger Signal output is produced by subtracting the output of the second IIR filter from the original input to the entire Digital Trigger Filter, and the DC Trigger Signal output is simply the same as that original input. A MUX selects which Trigger Signal is applied to a Digital Trigger Comparator.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
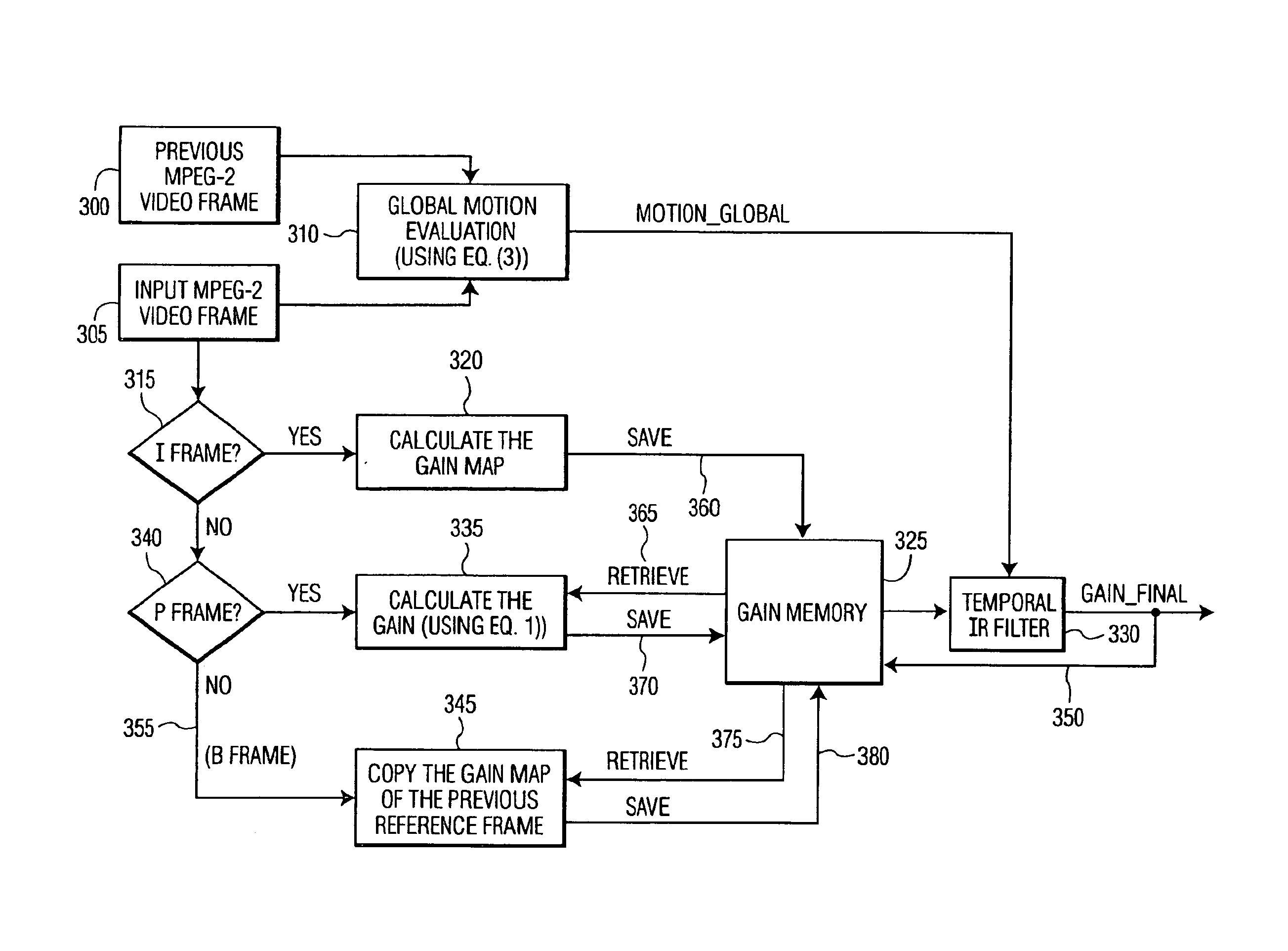
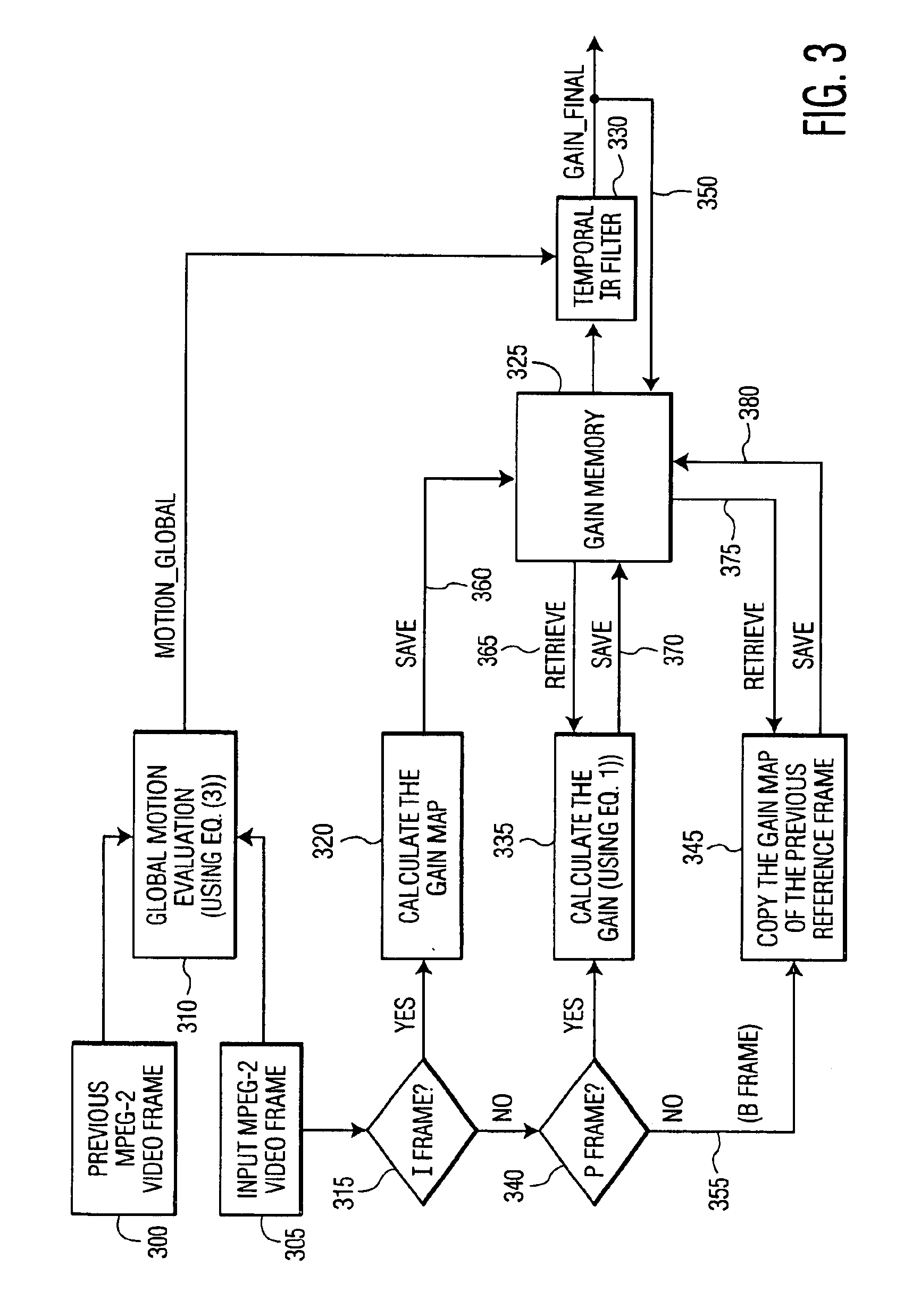
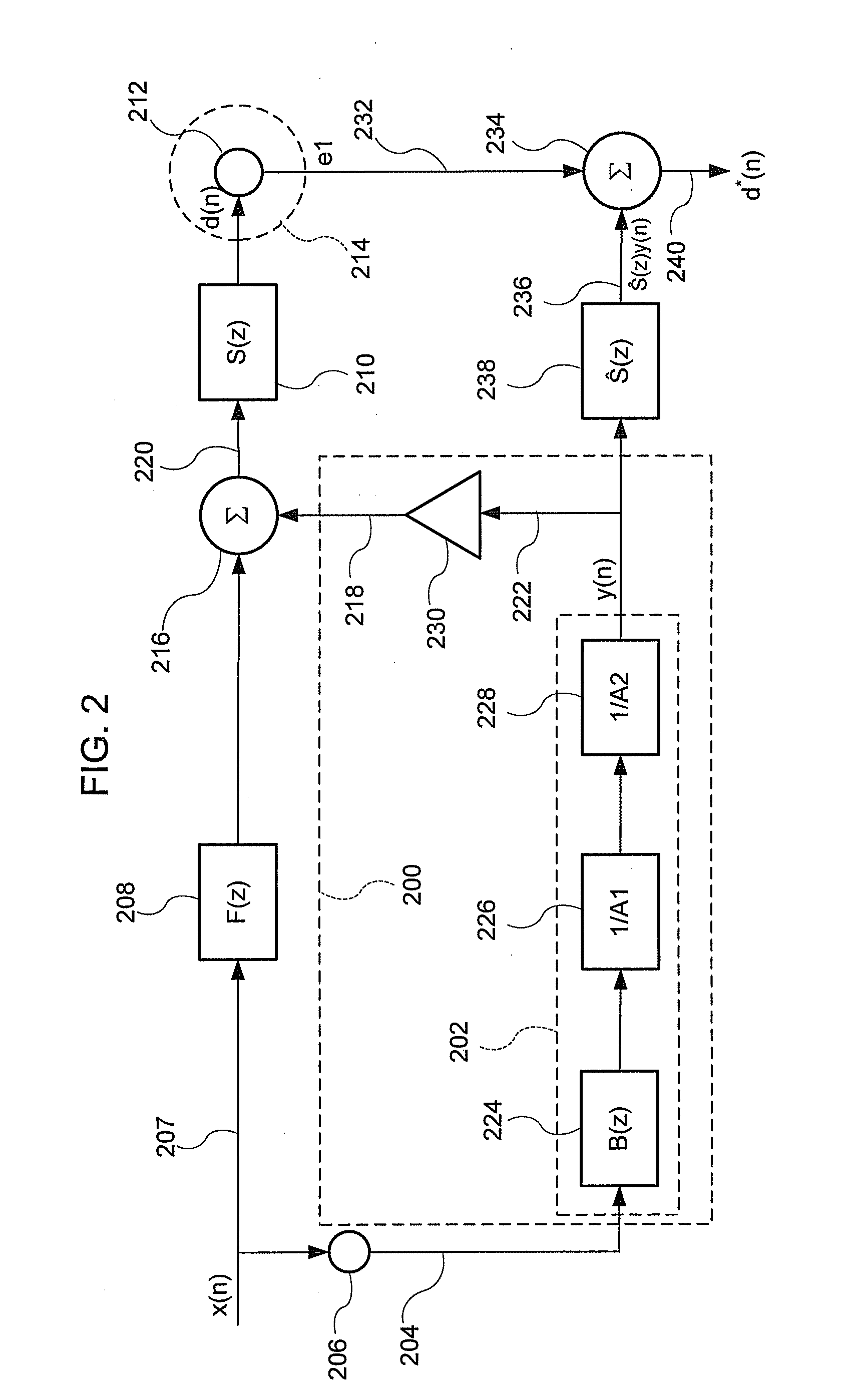
Method of and system for improving temporal consistency in sharpness enhancement for a video signal
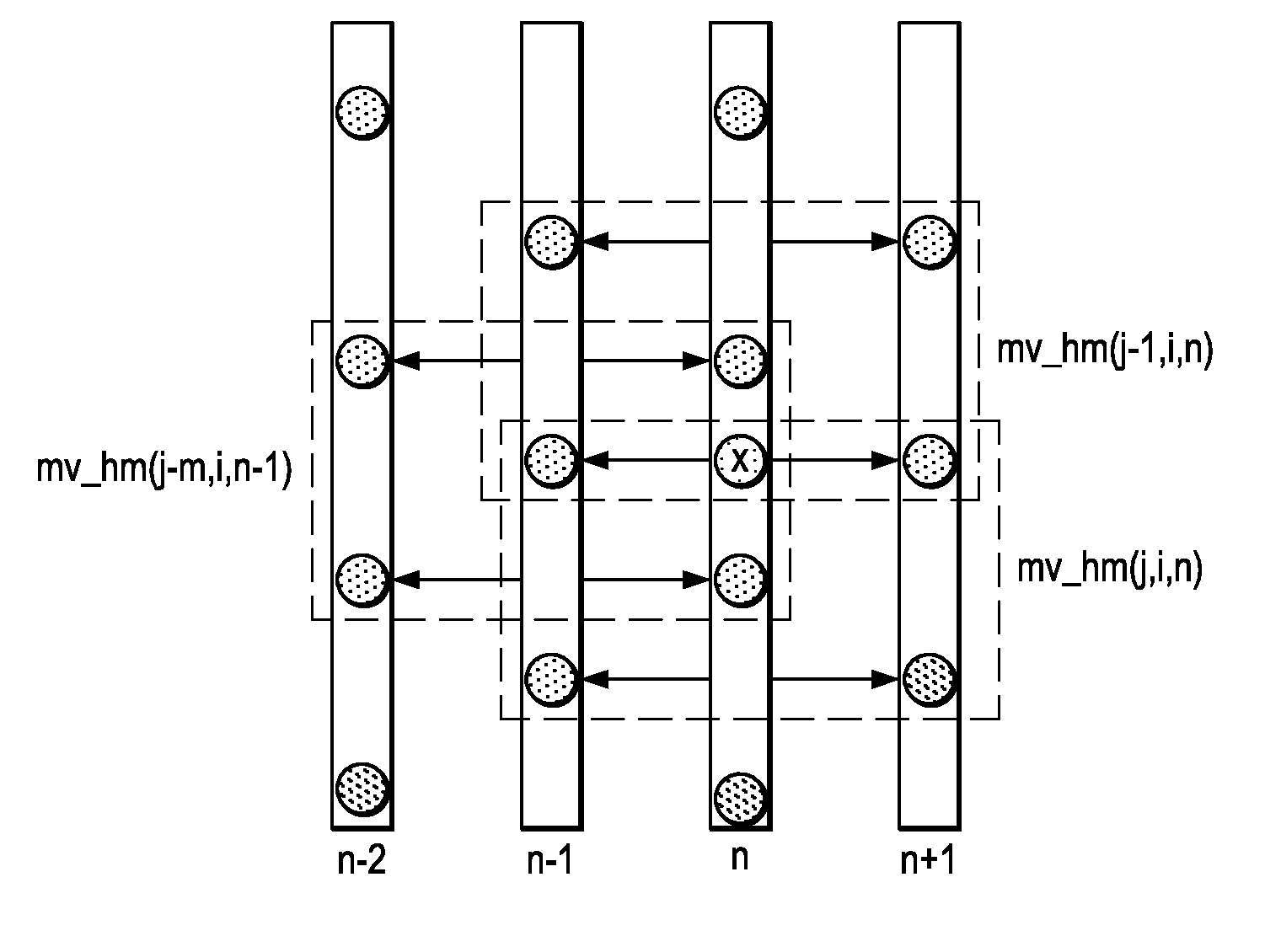
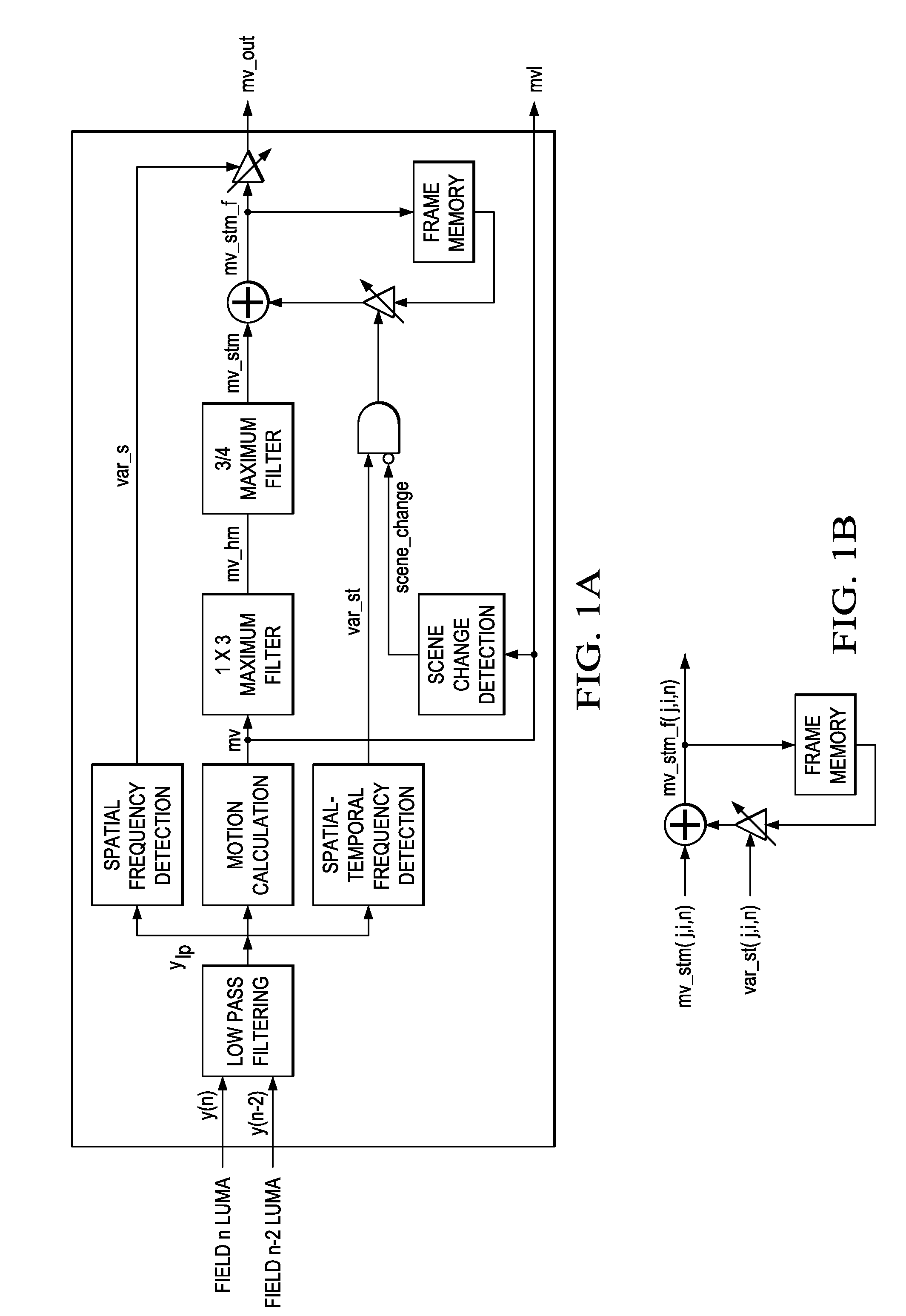
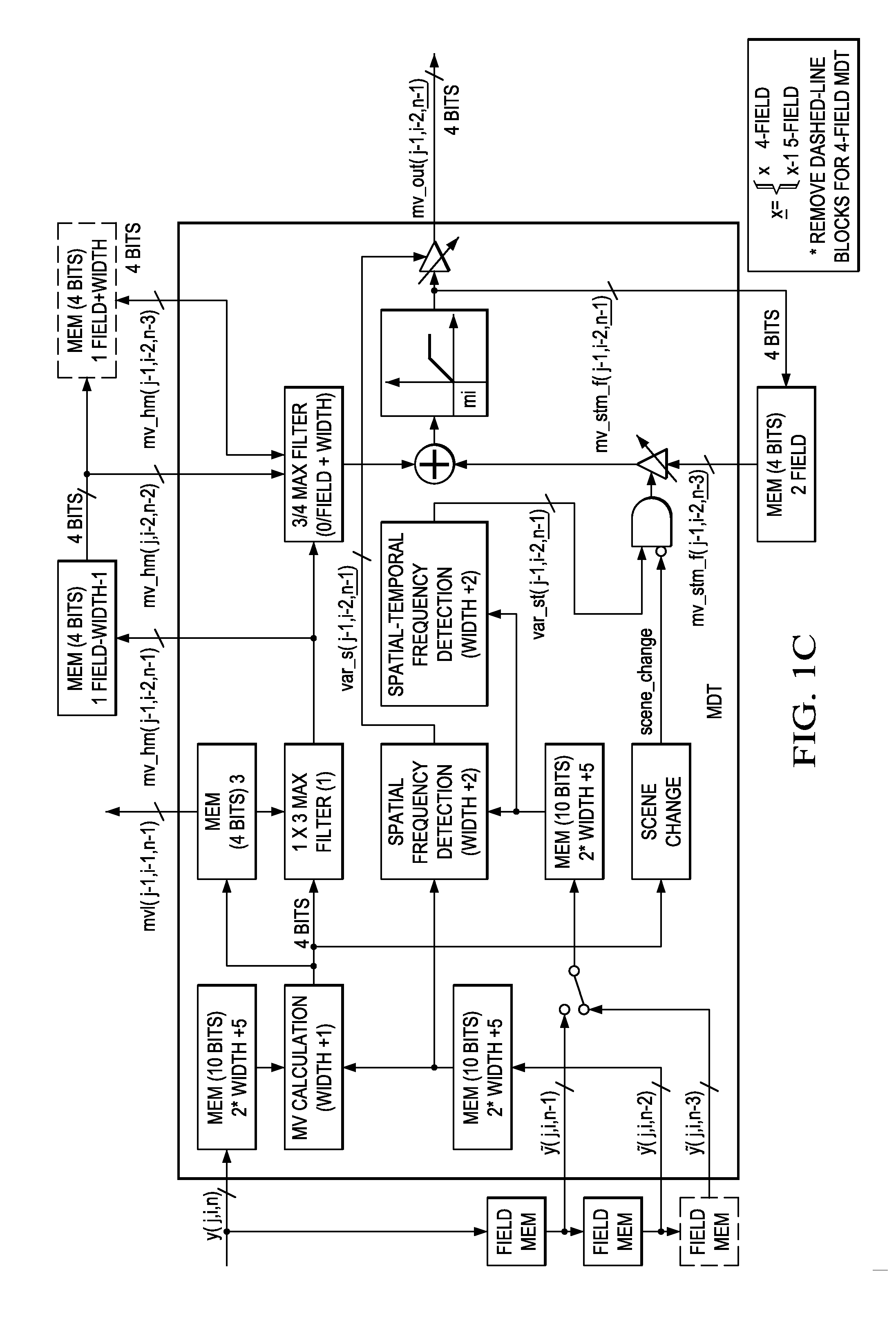
ActiveUS6873657B2Improving temporal consistencyHigh gainTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesIir filteringMotion vector
In accordance with the preferred embodiment of the present invention, a method of and system for improving temporal consistency of an enhanced signal representative of at least one frame using a sharpness enhancement algorithm with an enhancement gain are provided. The method comprises the steps of: receiving the enhanced signal comprising at least one frame, obtaining an enhancement gain for each pixel in the frame, retrieving an enhancement gain value of each pixel in a reference frame from a gain memory using motion vectors, identifying if the frame is an I, P or B frame type and determining an updated enhancement gain for an I frame type by calculating a gain map for use in the sharpness enhancement algorithm. The updated enhancement gain of each pixel is equal to enhancement gain previously determined for use in the sharpness enhancement algorithm. In addition, the method includes storing the updated enhancement gain to gain memory, and applying the updated enhancement gain to the sharpness enhancement algorithm to improve temporal consistency of the enhanced signal. The method may further comprise the step of further improving the updated enhancement gain by applying a motion adaptive temporal IIR filter on the updated enhancement gain.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Hybrid soft and hard decision feedback equalizer
InactiveUS7006565B1Improve signal qualityImprove current qualityMultiple-port networksAdaptive networkIir filteringEngineering
An equalizer for use in a communication receiver includes an infinite impulse response (IIR) feedback filter operated in acquisition and tracking feedback modes on a sample by sample basis to form a hybrid Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) architecture. In acquisition mode, soft decision samples from the filtered received signal are input to the IIR filter. In the tracking mode, hard decision samples from a slicer are input to the IIR filter. Acquisition and tracking operating modes are selected in accordance with a set of decision rules on a sample by sample basis based on the quality of the current hard decision. If the current hard decision is low quality, then the soft decision sample (acquisition mode) is used. If the current hard decision is high quality, then the hard decision sample (tracking mode) is used. In such manner, the DFE is operated in a hybrid mode, i.e., using both soft and hard decisions on a sample by sample basis. Furthermore, the decision rules that are responsive to signal reliability to select acquisition and tracking modes are adaptive.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
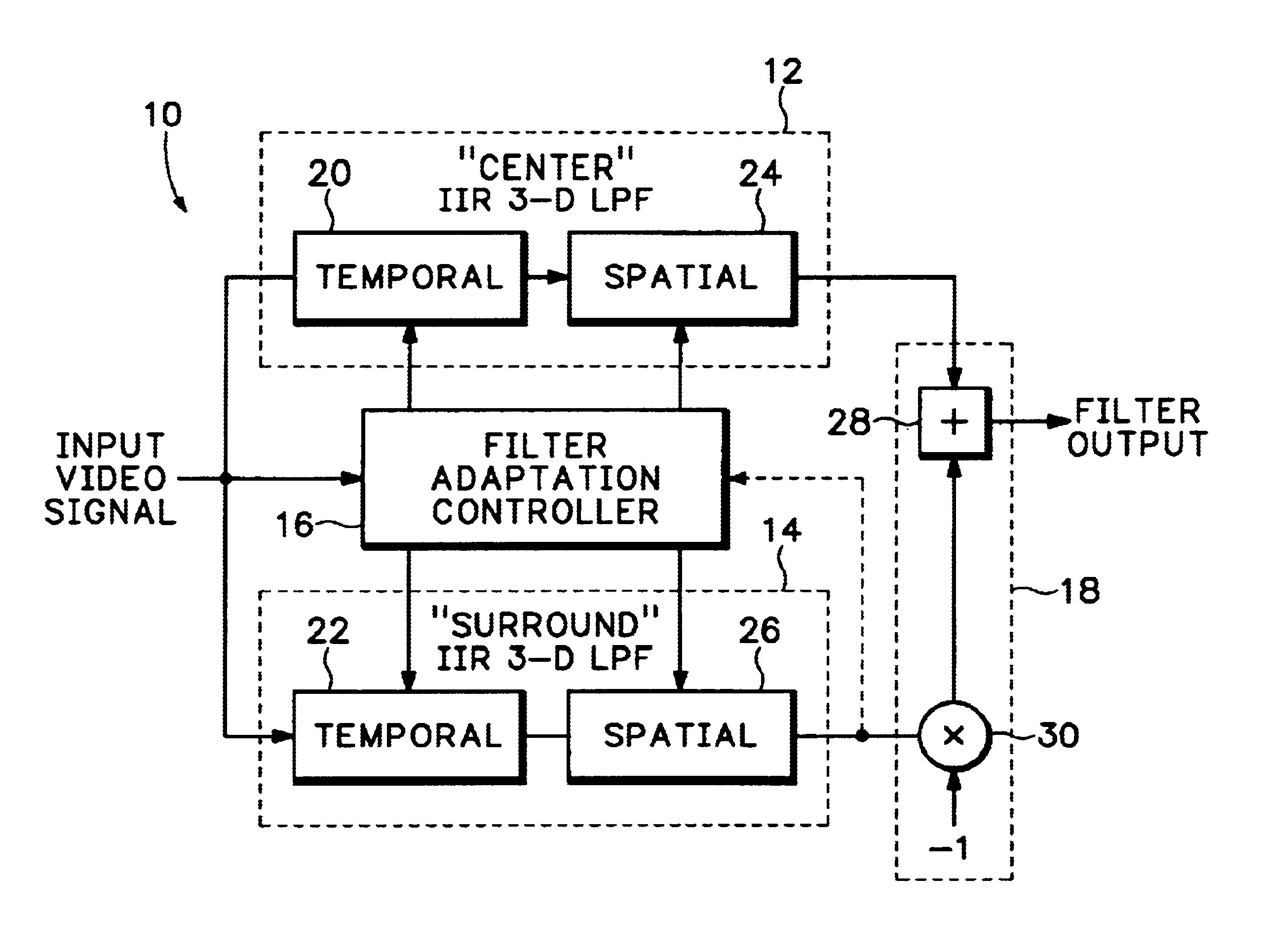
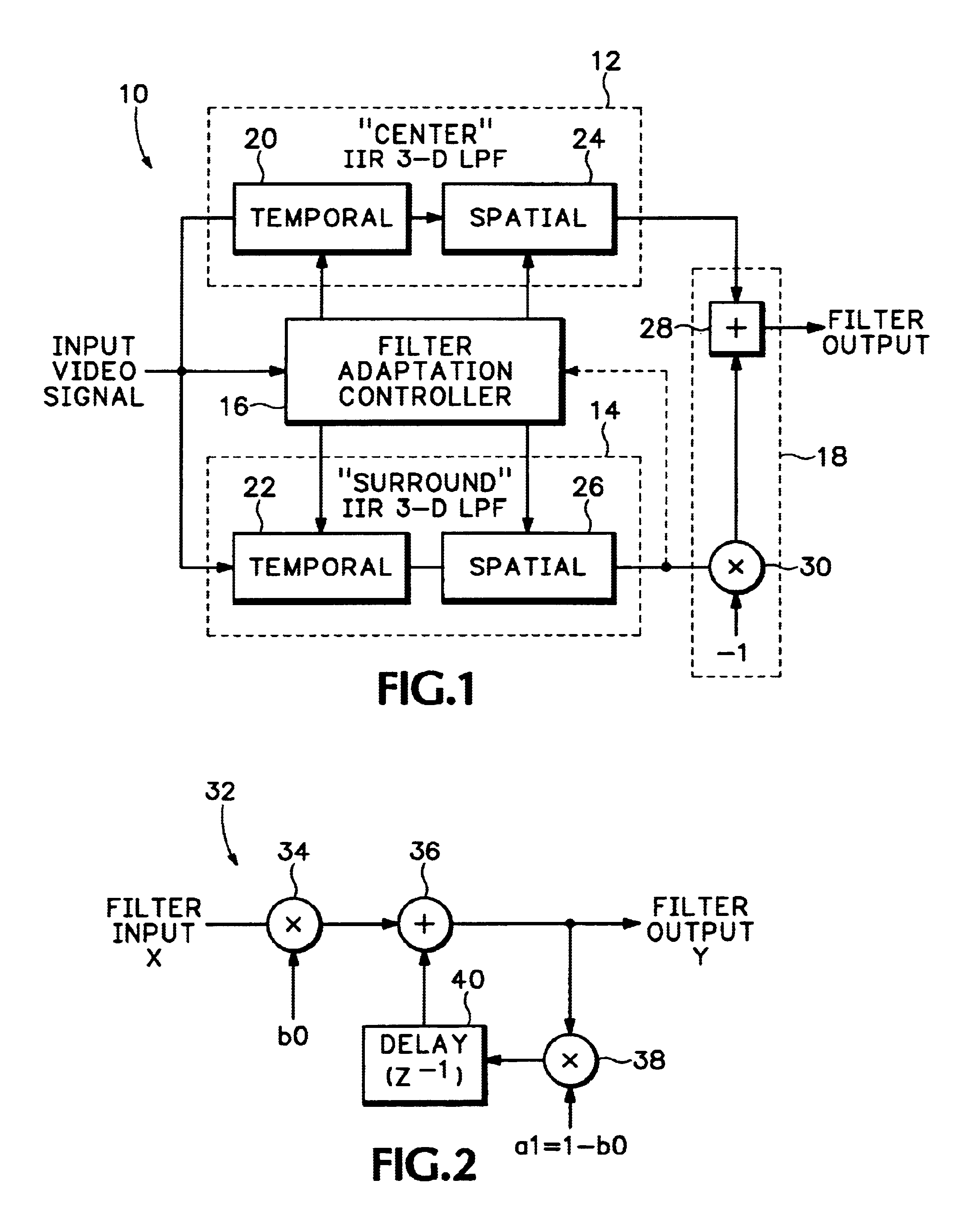
Adaptive spatio-temporal filter for human vision system models
InactiveUS6907143B2Image enhancementTelevision system detailsHuman visual system modelLow-pass filter
An adaptive spatio-temporal filter for use in video quality of service instruments based on human vision system models has a pair of parallel, lowpass, spatio-temporal filters receiving a common video input signal. The outputs from the pair of lowpass spatio-temporal filters are differenced to produce the output of the adaptive spatio-temporal filter, with the bandwidths of the pair being such as to produce an overall bandpass response. A filter adaptation controller generates adaptive filter coefficients for each pixel processed based on a perceptual parameter, such as the local average luminance, contrast, etc., of either the input video signal or the output of one of the pair of lowpass spatio-temporal filters. Each of the pair of lowpass spatio-temporal filters has a temporal IIR filter in cascade with a 2-D spatial IIR filter, and each individual filter is composed of a common building block,5 i.e., a first order, unity DC gain, tunable lowpass filter having a topology suitable for IC implementation. At least two of the building blocks make up each filter with the overall adaptive spatio-temporal filter response having a linear portion and a non-linear portion, the linear portion being dominant at low luminance levels and the non-linear portion being consistent with enhanced perceived brightness as the luminance level increases.
Owner:PROJECT GIANTS LLC
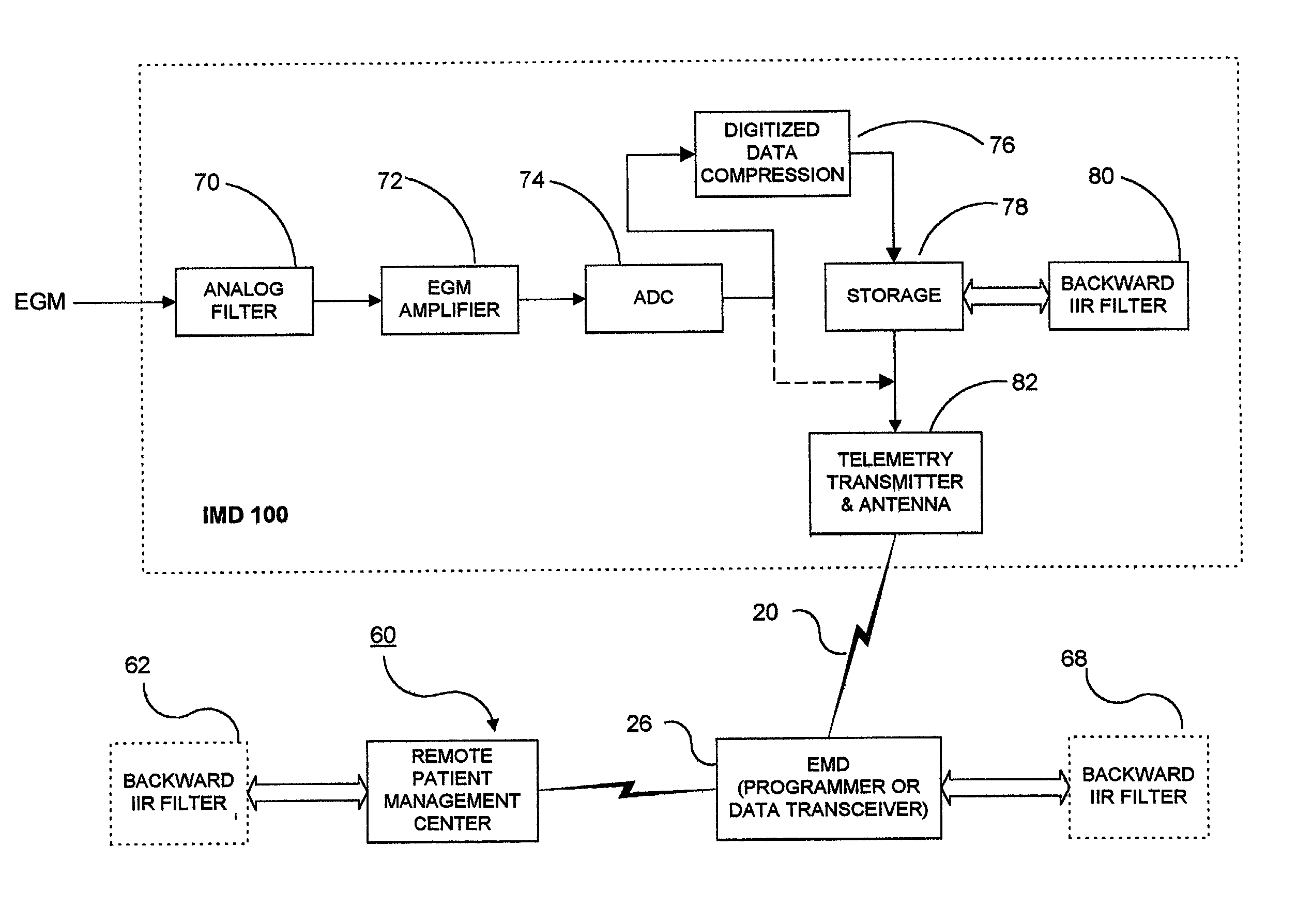
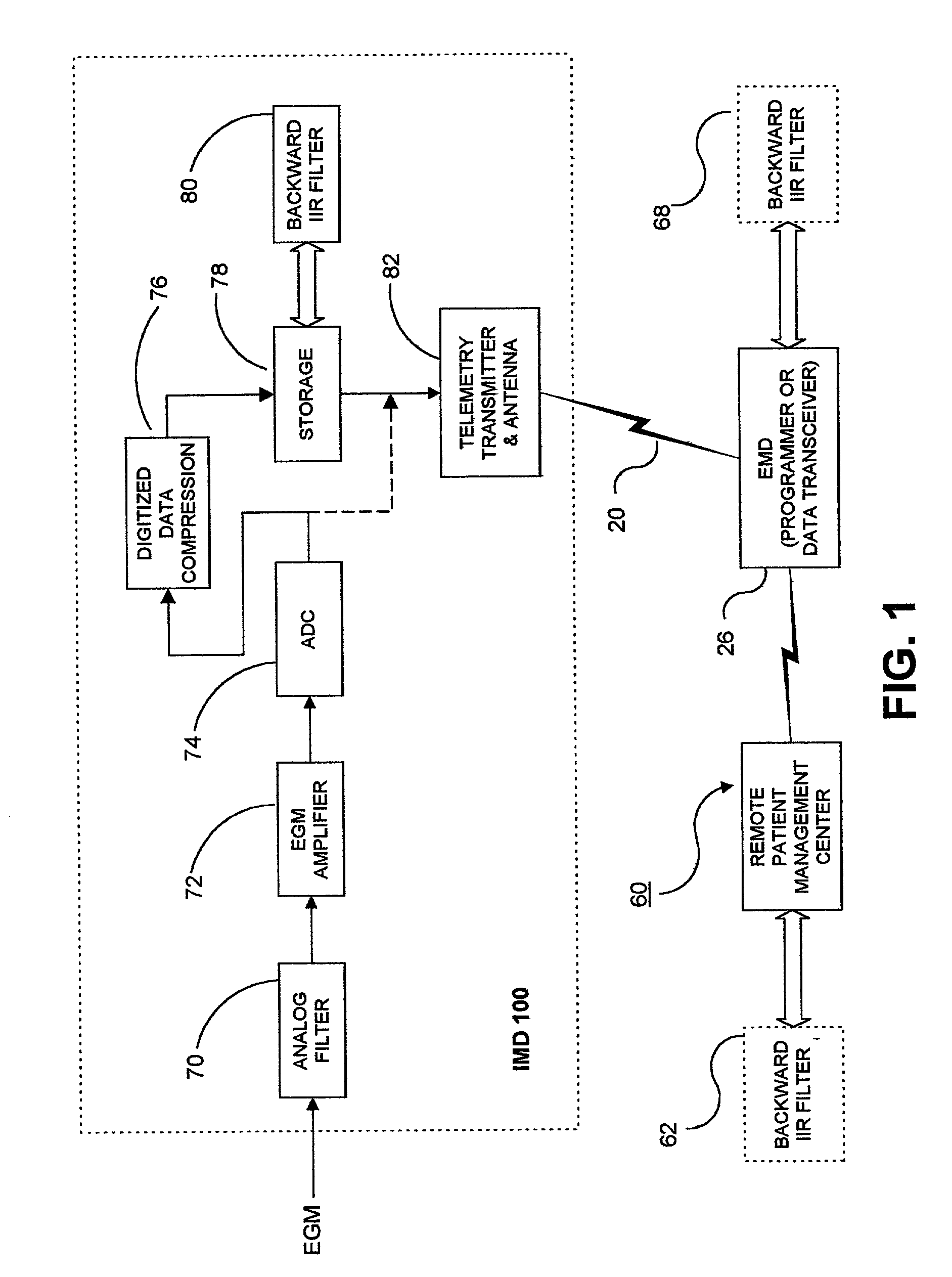
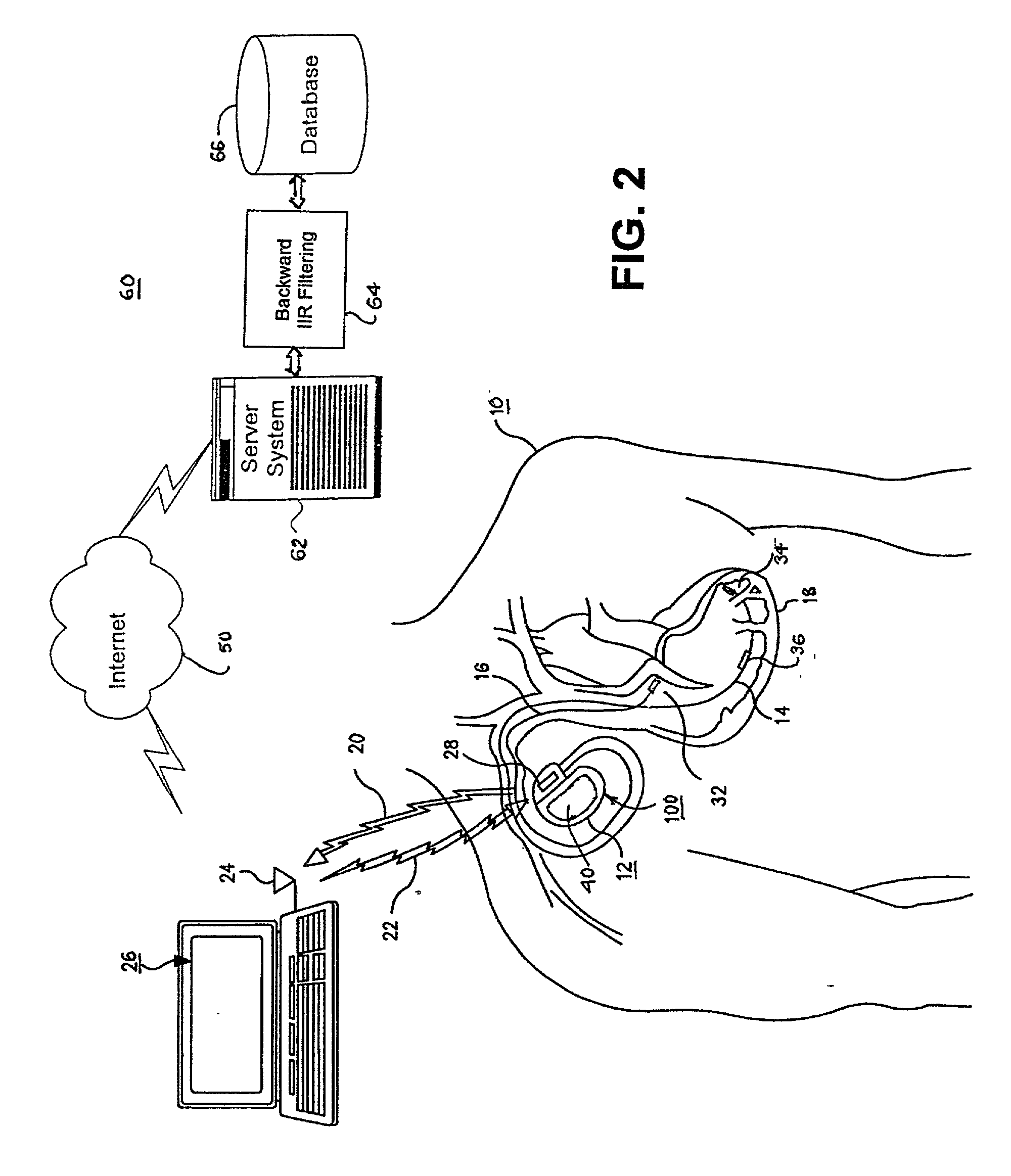
Methods and apparatus for filtering EGM signals detected by an implantable medical device
An analog physiologic signal, e.g., the cardiac EGM, sensed by an IMD is filtered with a high pass filter (HPF), the cut-off frequency of the HPF being within a predetermined frequency bandwidth, wherein a low-band portion of the predetermined frequency bandwidth is attenuated in the filtered physiologic signal. The filtered physiologic signal is digitized in real time order, and the digital data set is filtered in reverse time order employing a digital IIR filter having characteristics substantially matching the cut-off frequency and filter characteristics of the HPF. When the system is implemented within an IMD, the filtered digital data set is compressed by lossy compression algorithm, and the compressed data set is filtered in reverse time order. In certain embodiments, the filtered digital data set is uplink telemetry transmitted to an external medical device, and the uplink telemetered data set is filtered in reverse time order employing a digital backward IIR filter resident in the external medical device.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
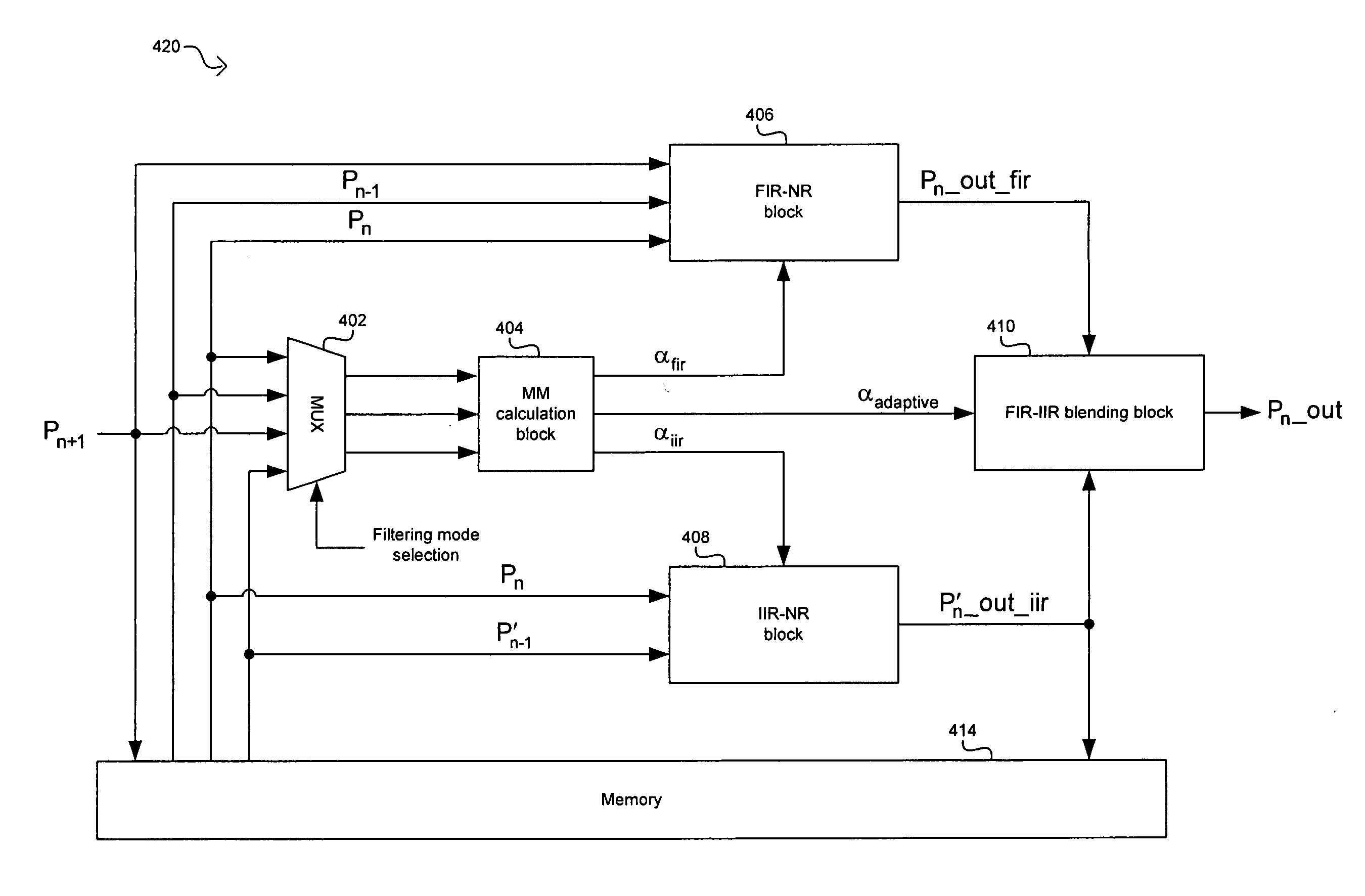
Method and system for analog video noise reduction by blending FIR and IIR filtering
InactiveUS20070139563A1Reduce noiseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionIir filtering
A method and system for analog video noise reduction by blending finite impulse response (FIR) and infinite impulse response (IIR) filtering are provided. A filtering mode may be selected to generate noise-reduced pixels using FIR, IIR, or a blend of FIR / IIR filtering. Blending a current pixel and an FlR-filtered current pixel may generate a first blended current pixel. The FIR filtering may be based on the current pixel, a previous collocated pixel, and a next collocated pixel. Blending the current pixel and an IIR-filtered current pixel may generate a second blended current pixel. Blending the first blended current pixel and the second blended current pixel using an adaptive blending factor may dynamically generate a filtered output pixel. The IIR filtering may be based on the current pixel and a collocated pixel of the previous second blended video image or of the previous filtered output video image.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
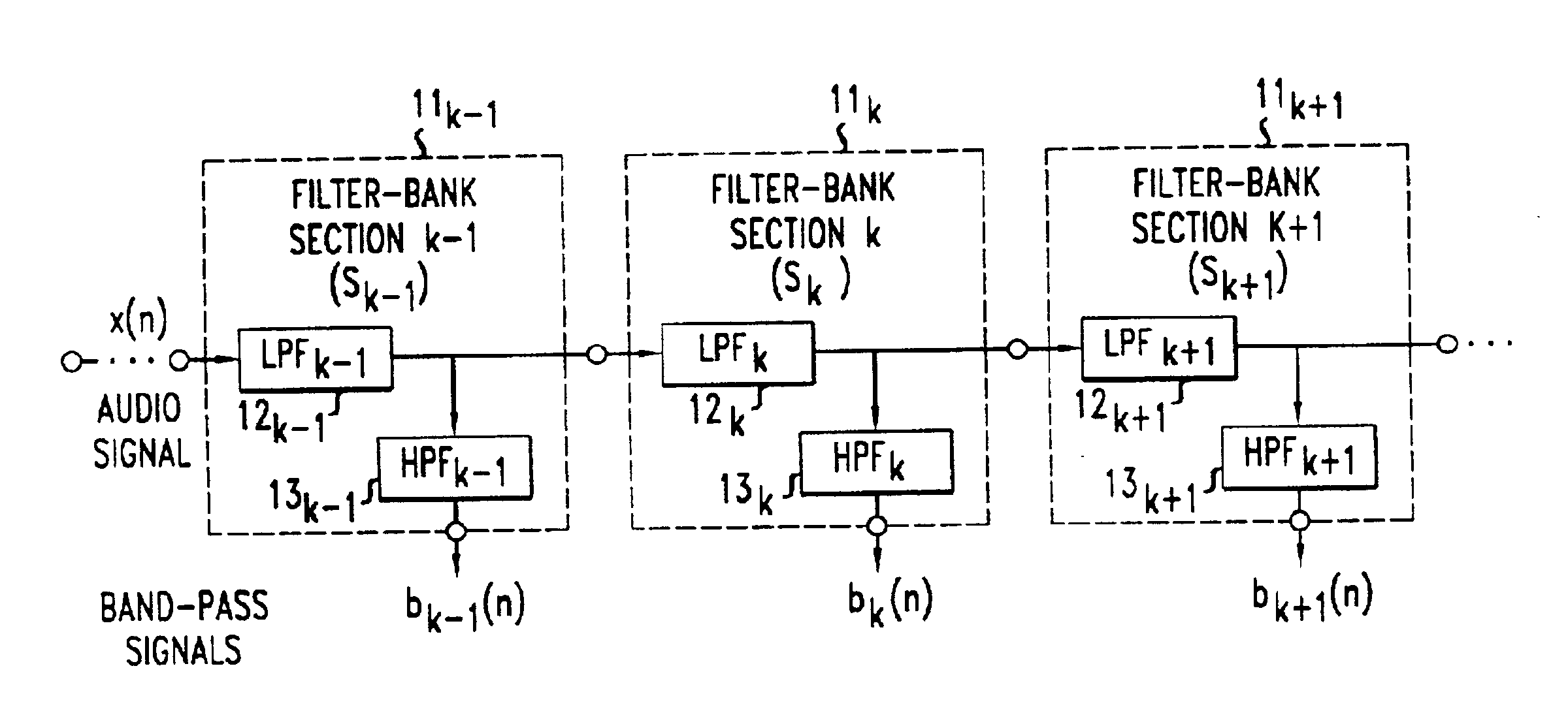
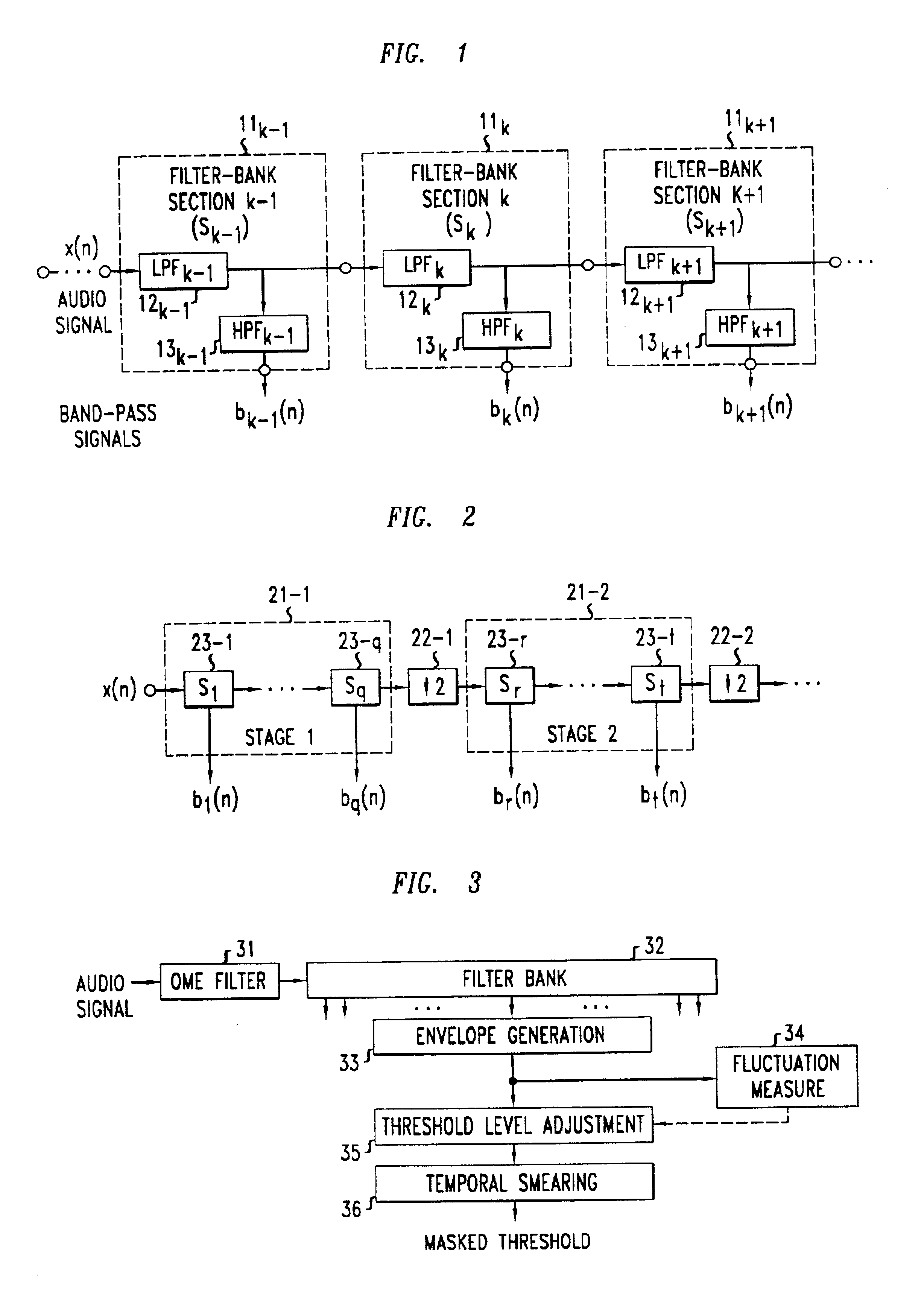
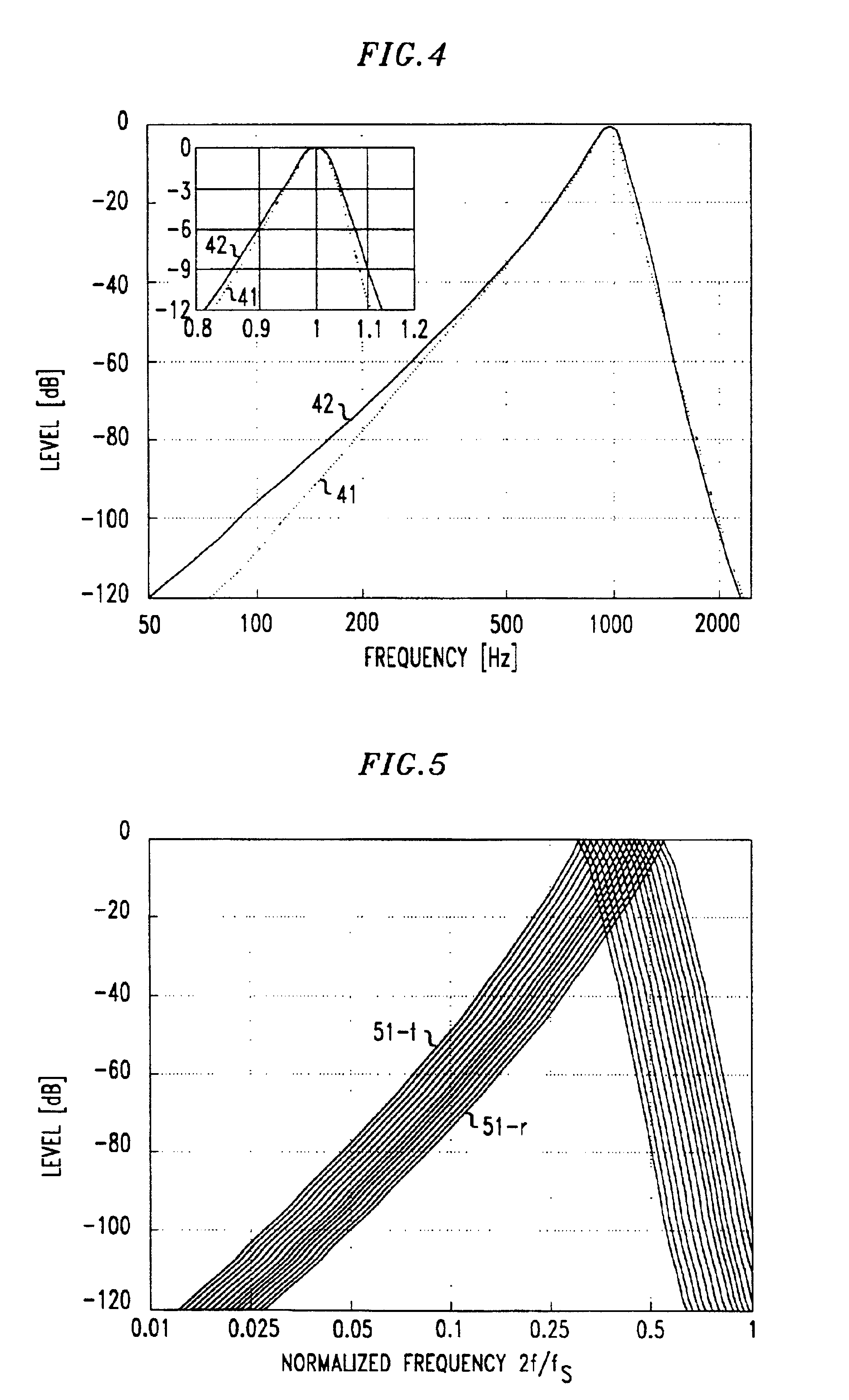
Cochlear filter bank structure for determining masked thresholds for use in perceptual audio coding
InactiveUS6915264B2Reduced sampling rate requirementsSimple modelSpeech analysisComplex mathematical operationsIir filteringEngineering
A method and apparatus for determining masked thresholds for a perceptual auditory model used, for example, in a perceptual audio coder, which makes use of a filter bank structure comprising a plurality of filter bank stages which are connected in series, wherein each filter bank stage comprises a plurality of low-pass filters connected in series and a corresponding plurality of high-pass filters applied to the outputs of each of the low-pass filters, and wherein downsampling is advantageously applied between each successive pair of filter bank stages. In accordance with one illustrative embodiment, the filter bank comprises low order IIR filters. The cascade structure advantageously supports sampling rate reduction due to the continuously decreasing cutoff frequency in the cascade. The filter bank coefficients may advantageously be optimized for modeling of masked threshold patterns of narrow-band maskers, and the generated thresholds may be advantageously applied in a perceptual audio coder.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Digital trigger filter for a real time digital oscilloscope
ActiveUS20060074607A1Reduce frequencySpectral/fourier analysisNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementIir filteringEngineering
A real time DSO is equipped with a Digital Trigger Filter that performs high frequency rejection, low frequency rejection, AC and DC triggering. The Digital Trigger Filter includes first and second digitally implemented IIR (Infinite Input Response) Filters. A digitized Conditioned Input Signal is applied to the first IIR Filter. It has taps that provide the Trigger Signal outputs needed for high and low frequency rejection. The high frequency rejection output of the first ER Filter is essentially a low pass output (3 dB down at 50 KHz) and is also used as the digital input to the second IIR Filter, whose output is a much more aggressive suppression of high frequencies (3 dB down at 50 Hz). The AC Trigger Signal output is produced by subtracting the output of the second IIR filter from the original input to the entire Digital Trigger Filter, and the DC Trigger Signal output is simply the same as that original input. A MUX selects which Trigger Signal is applied to a Digital Trigger Comparator.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
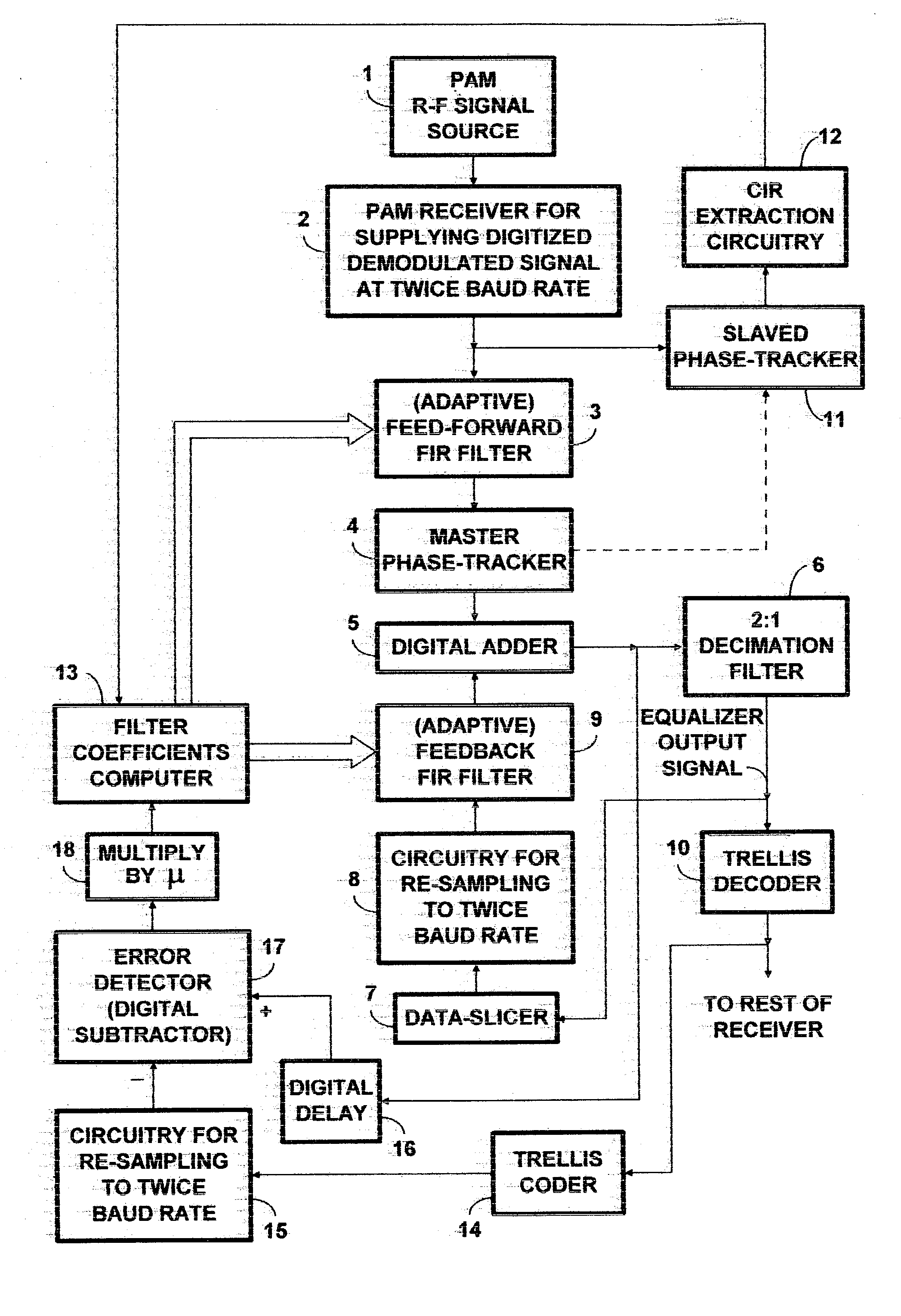
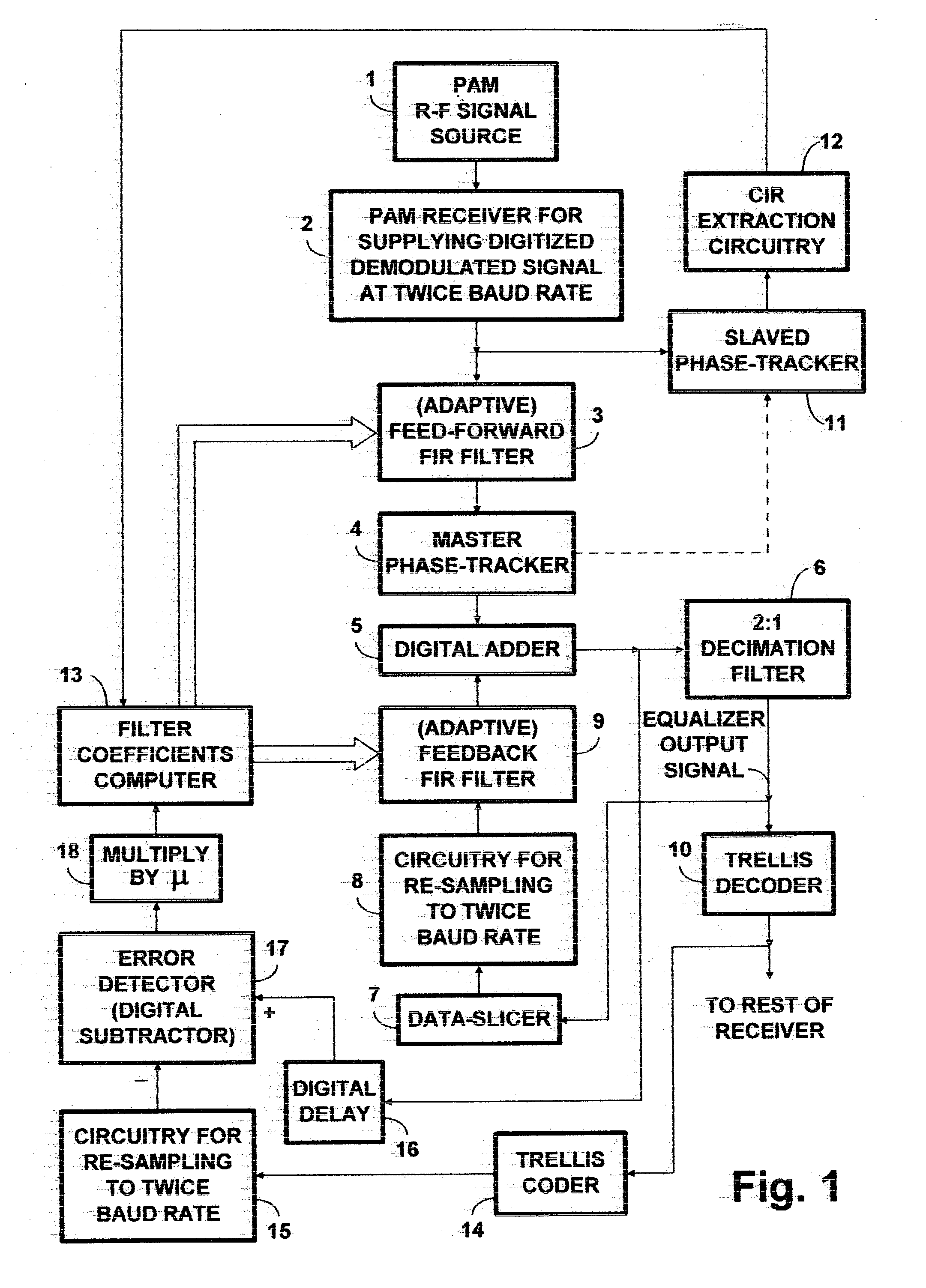
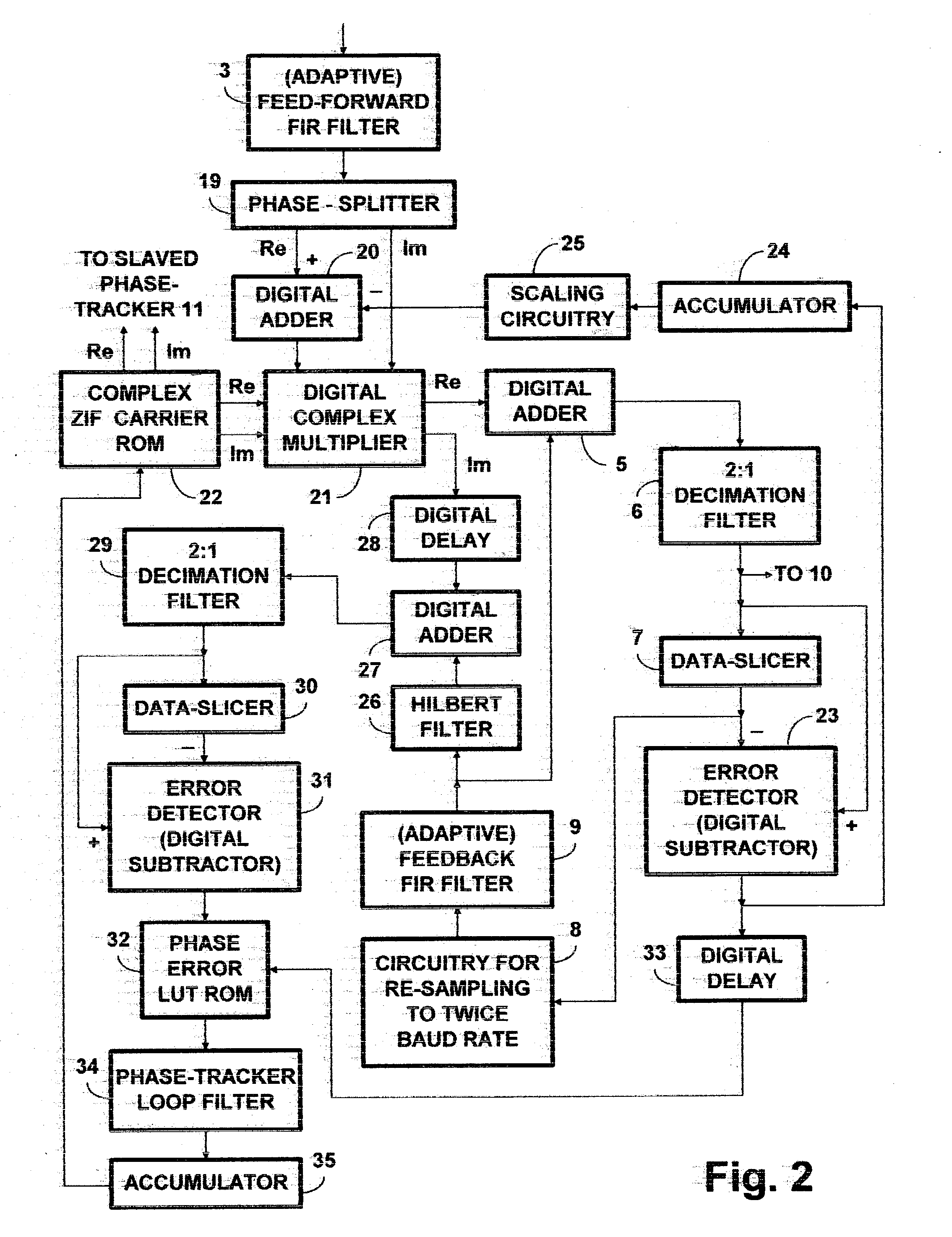
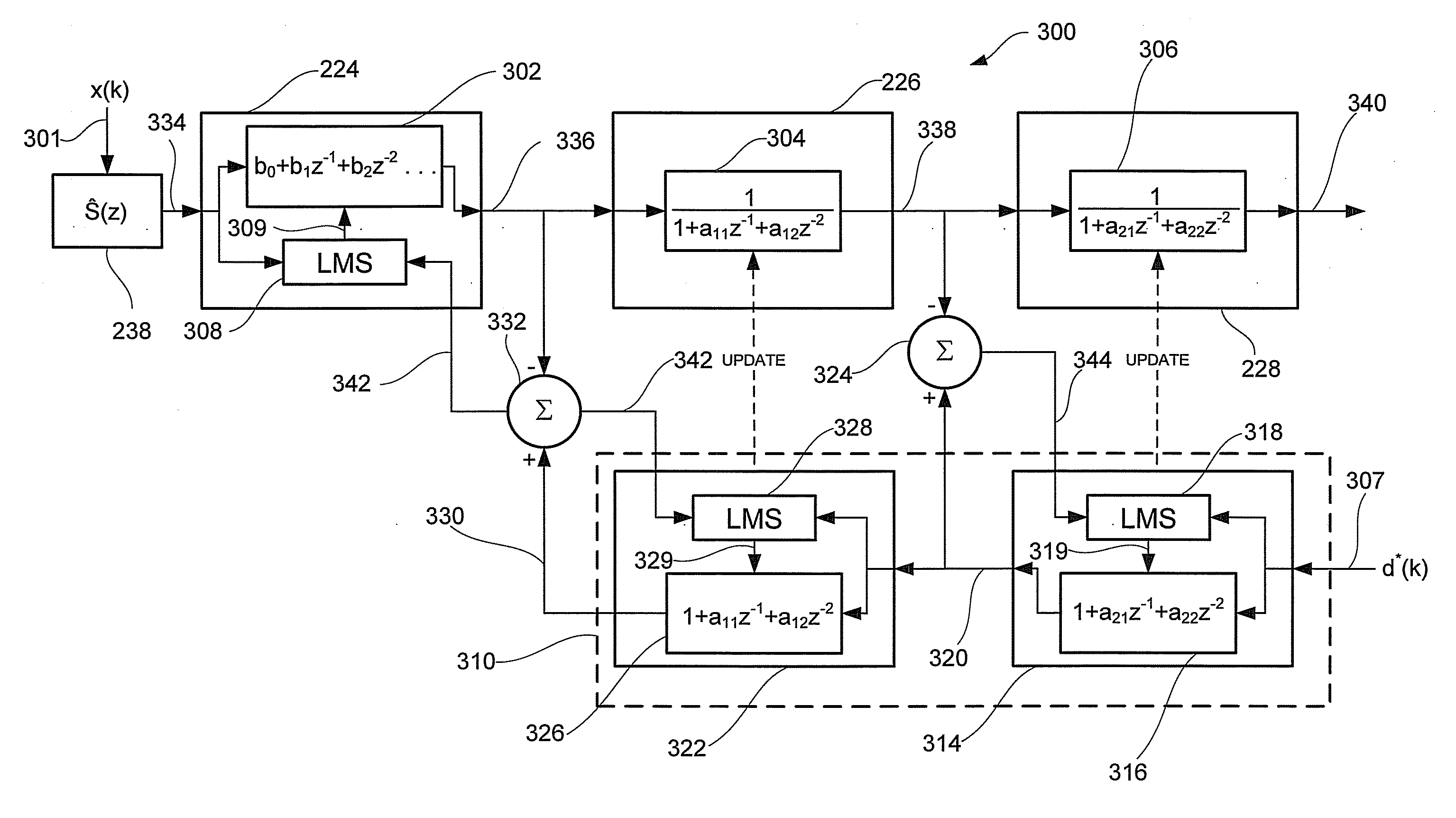
PAM radio signal receiver with phase-tracker succeeding adaptive FIR filtering and preceding adaptive IIR filtering
InactiveUS20050002474A1Reduce Intersymbol InterferenceReduce phase noiseMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsDigital dataIir filtering
A PAM receiver for reproducing a baseband signal that symbol codes digital data is combined with an decision-feedback equalizer (DFE) incorporating first adaptive digital filtering as a feed-forward element and second adaptive digital filtering as a feedback element. The DFE response is supplied to symbol decoding circuitry for reproducing the digital data. A de-rotator re-samples the first adaptive digital filtering response before it is combined with the second adaptive digital filtering response to generate an equalizer response. The resulting baud-rate equalizer response is sampled at baud rate and quantized to generate baud-rate decisions that applied to the second adaptive digital filtering as input signal, for completing the decision-feedback loop. The re-sampling of the first adaptive digital filtering response by the de-rotator is controlled, so as to provide a phase-tracker that reduces phase noise and intersymbol interference, prior to the making of decisions for decision feedback.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
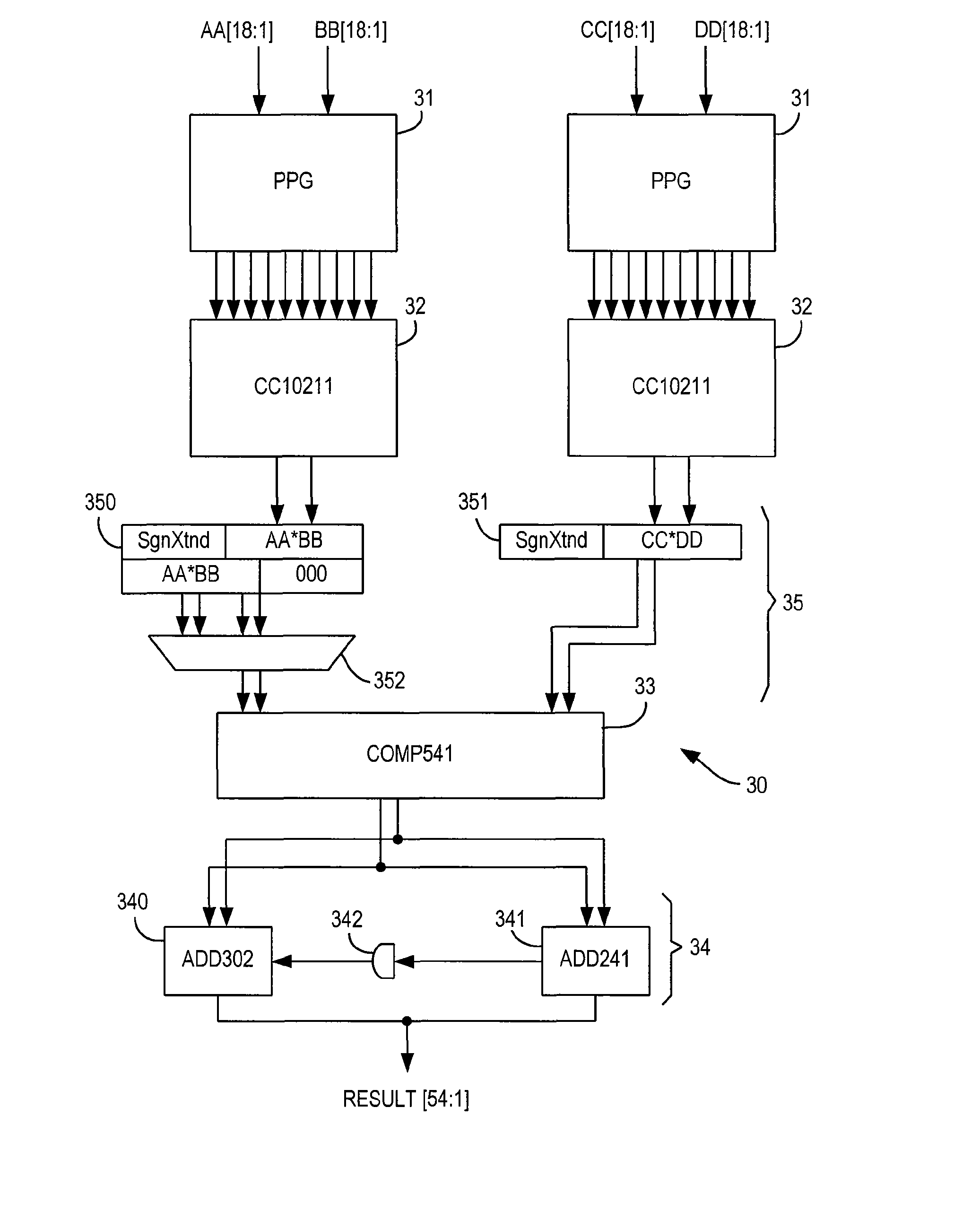
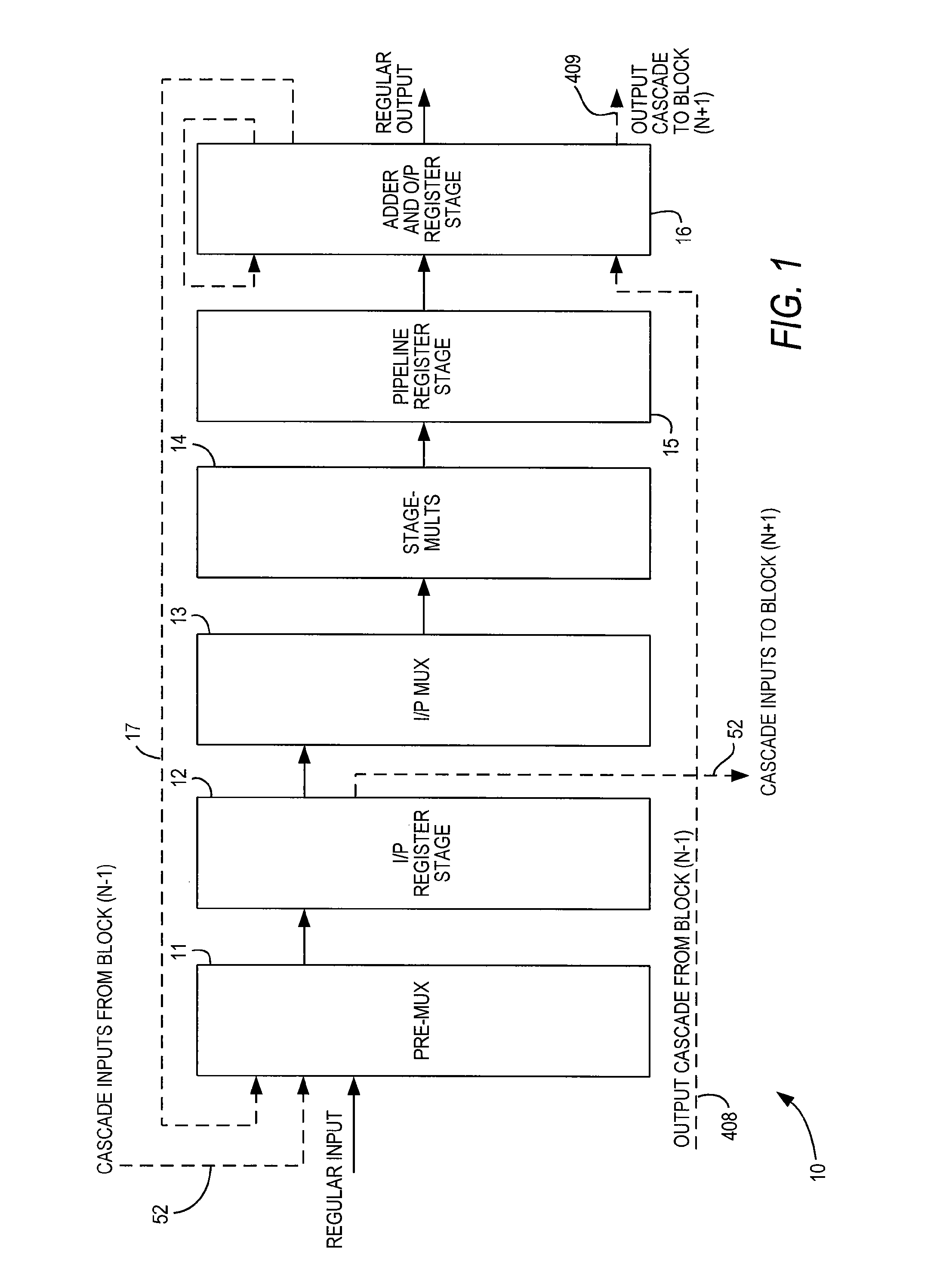
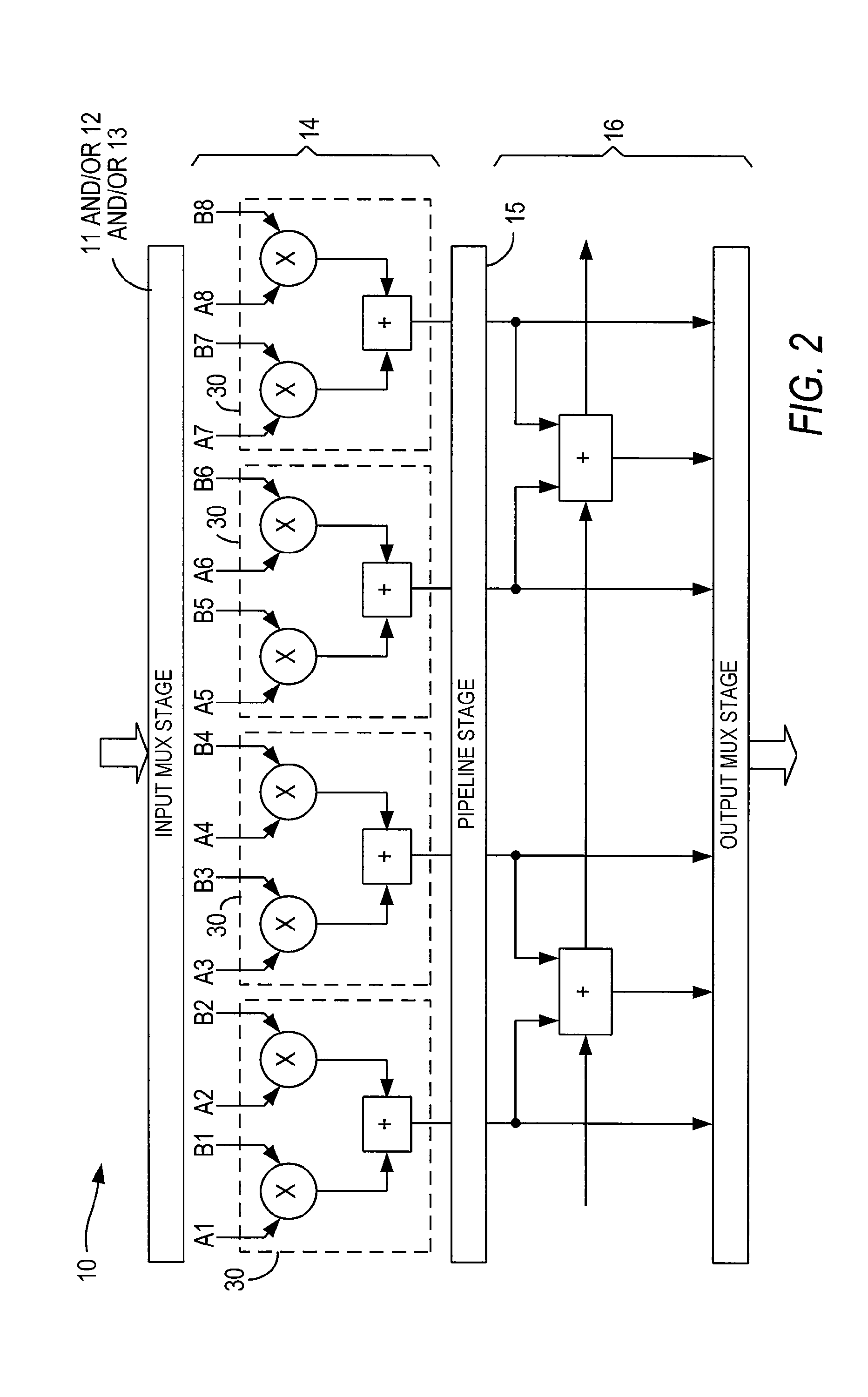
Specialized processing block for programmable logic device
ActiveUS8041759B1Reduce areaImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsDigital signal processingIir filtering
A specialized processing block for a programmable logic device incorporates a fundamental processing unit that performs a sum of two multiplications, adding the partial products of both multiplications without computing the individual multiplications. Such fundamental processing units consume less area than conventional separate multipliers and adders. The specialized processing block further has input and output stages, as well as a loopback function, to allow the block to be configured for various digital signal processing operations, including finite impulse response (FIR) filters and infinite impulse response (IIR) filters. By using the programmable connections, and in some cases the programmable resources of the programmable logic device, and by running portions of the specialized processing block at higher clock speeds than the remainder of the programmable logic device, more complex FIR and IIR filters can be implemented.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
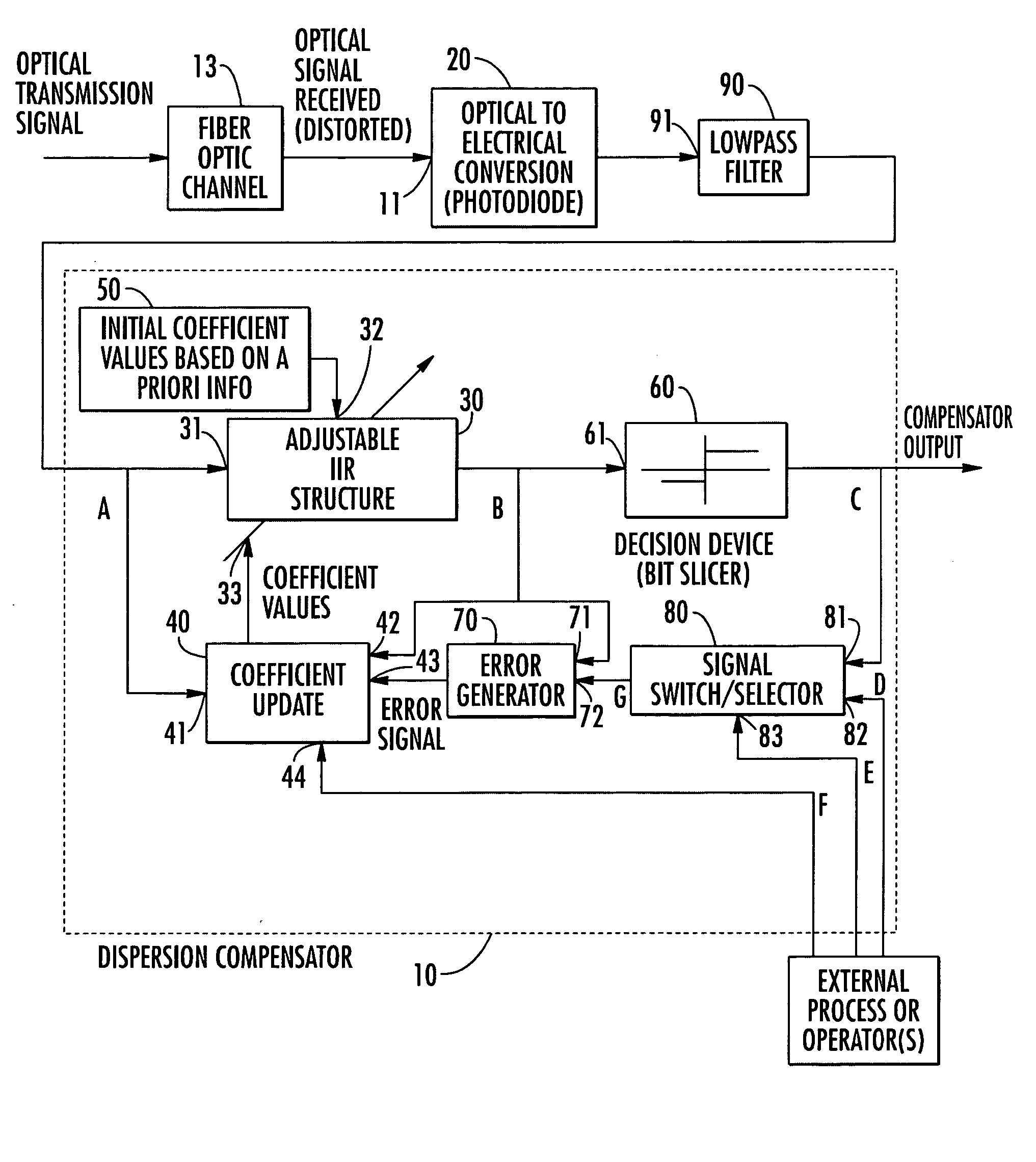
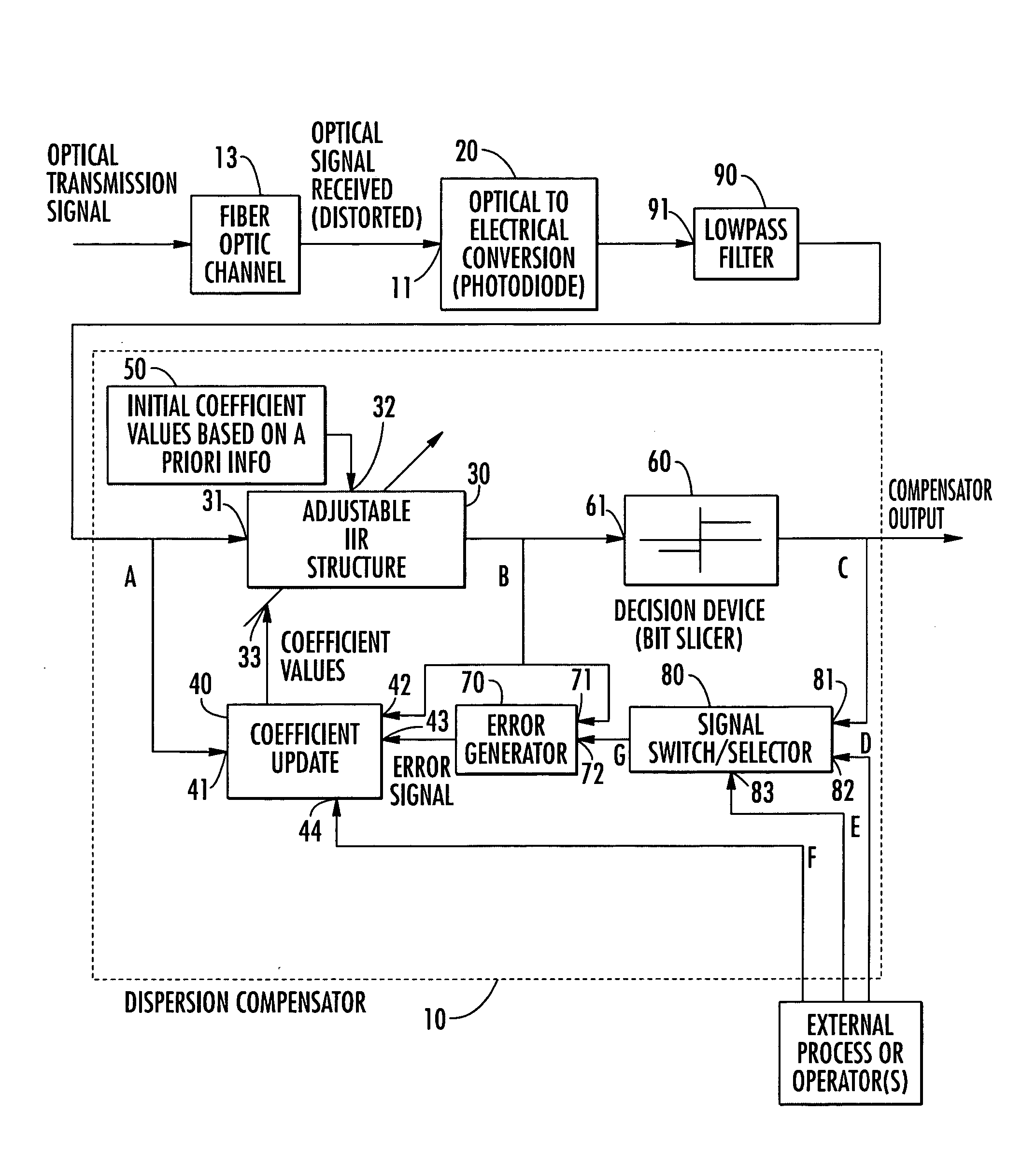
Post-detection, fiber optic dispersion compensation using adjustable infinite impulse response filter employing trained or decision-directed adaptation
InactiveUS20050047802A1Distortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic receiversIir filteringFiber chromatic dispersion
An adaptive infinite impulse response (IIR) filter compensates for dispersive distortion in a fiber optic channel. The weighting coefficients of the IIR filter are updated in accordance with an error signal obtained by differentially combining the output of the IIR filter with downstream decision values or with an undistorted training signal. Undistorted training signals may be derived from training patterns (e.g., preamble) expressly transmitted for the purpose by the upstream transmitter, or from non-training, but known or predictable patterns transmitted by the upstream transmitter.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
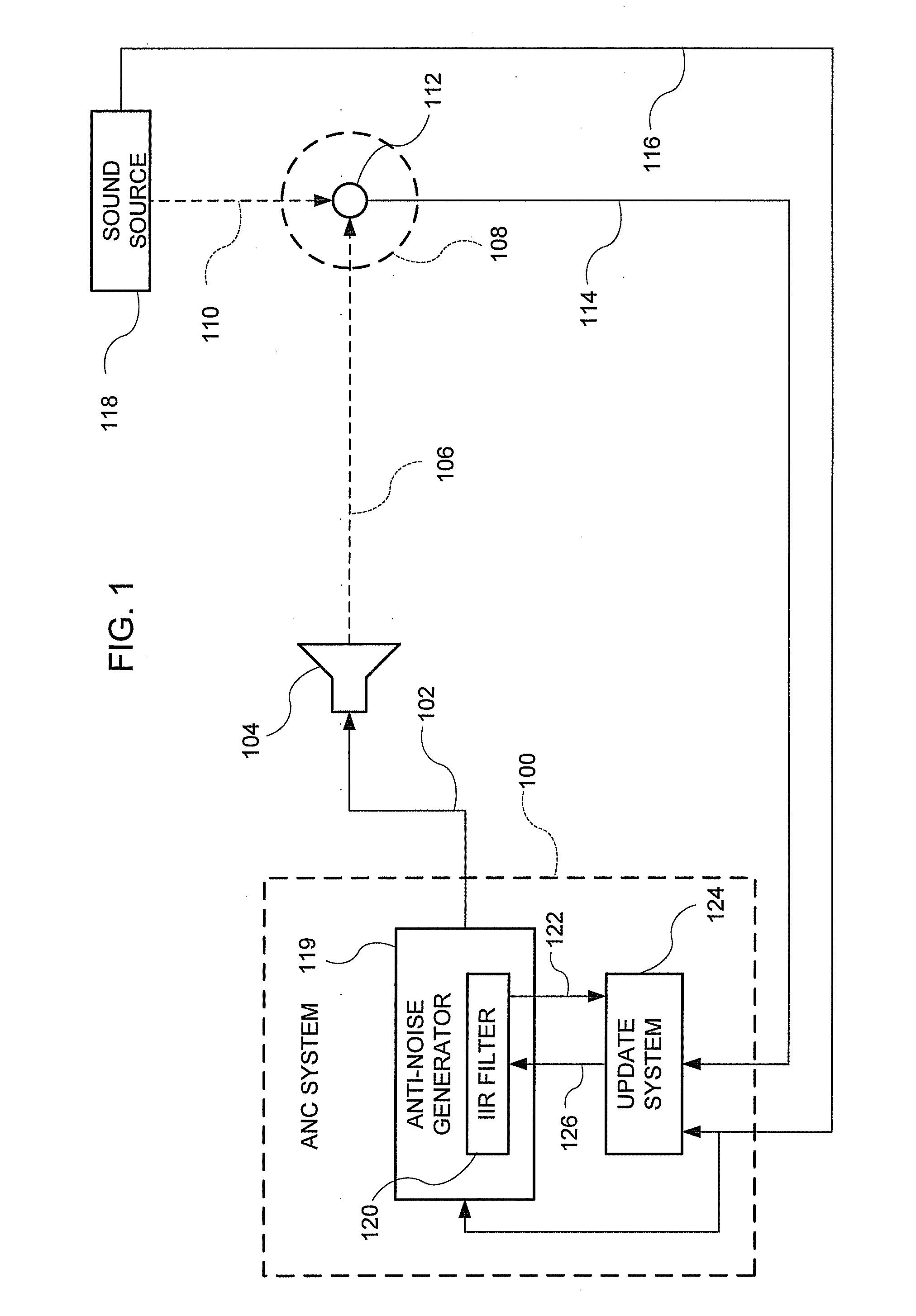
System for active noise control with an infinite impulse response filter
An active noise control (ANC) system includes at least one infinite impulse response filter (IIR). The IIR filter generates an output signal based on an input signal representative of an undesired sound. The ANC system generates an anti-noise signal based on the output signal of the IIR filter. The anti-noise signal is used to drive a speaker to generate sound waves to destructively interfere with the undesired sound. The ANC system includes an update system to generate update coefficients. The update system determines the stability of the update coefficients. Coefficients of the IIR filter are replaced with the update coefficients. The update system generates a set of update coefficients for each sample of the input signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
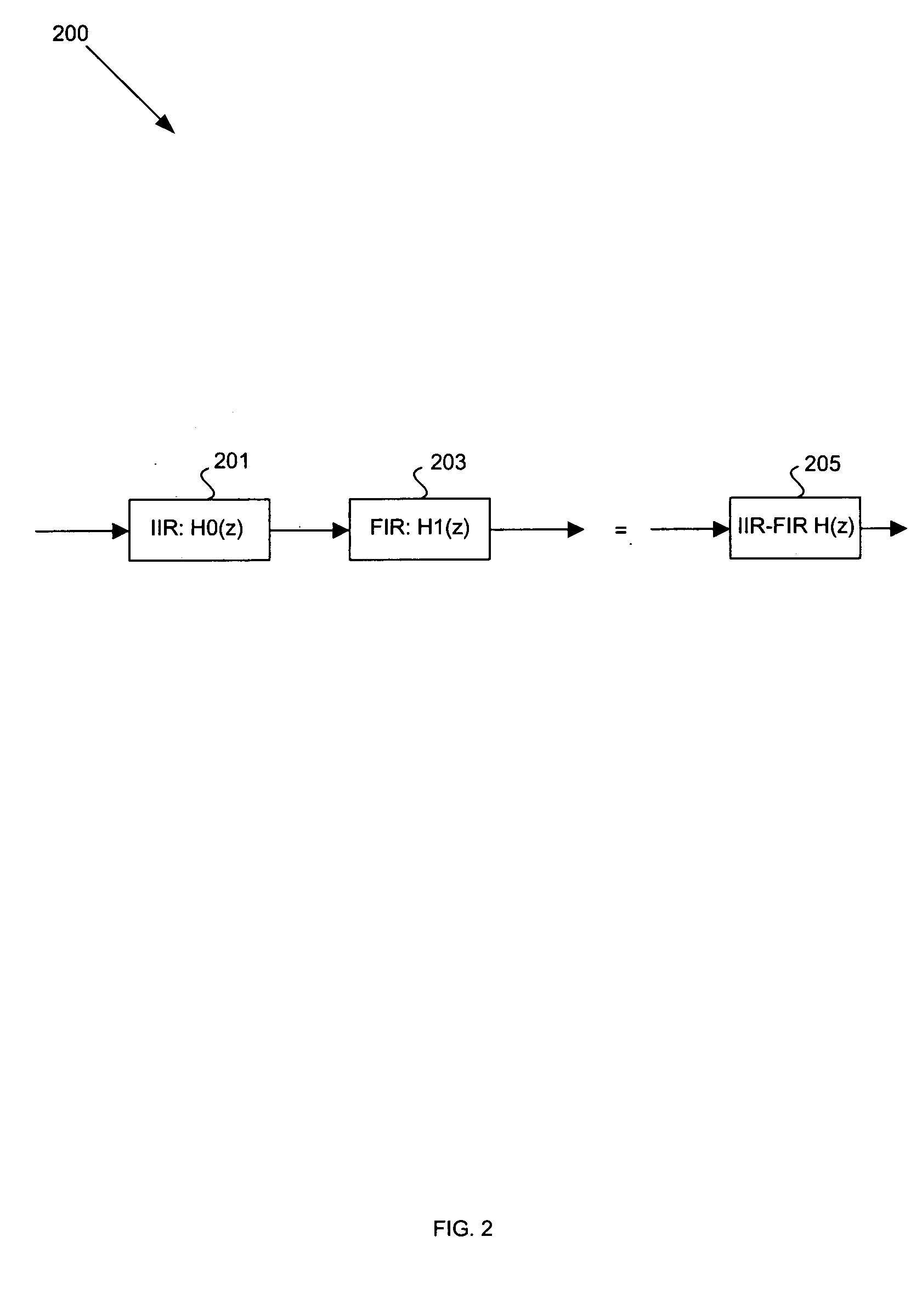
Method and system for polyphase filtering by combining IIR and FIR filters and its applications in video scaling
ActiveUS20050196072A1High sub-pixel precisionImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPhase shiftedIir filtering
Methods and systems for achieving high sub-pixel precision while processing a video signal are provided. Aspects of the method may include selecting IIR filter coefficients for implementing an IIR filter for filtering a video signal during scaling. Polyphase filter coefficients may be selected for implementing a polyphase filter for filtering the video signal during the scaling. The video signal may be filtered using a combination of the IIR filter having the selected IIR filter coefficients and the polyphase filter having the selected polyphase filter coefficients. The polyphase filter coefficients may implement a finite impulse response (FIR) filter for filtering the video signal. The video signal may be phase-shifted. The scaling of the video signal may comprise upscaling or downscaling the video signal. The video signal may be converted from a first format to a second format by combined IIR-filtering and polyphase filtering.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Biquad digital filter operating at maximum efficiency
ActiveUS20050076073A1Increase initiativeEasily incorporated into audio processing circuitryDigital technique networkDigital data processing detailsIir filteringOrder of operations
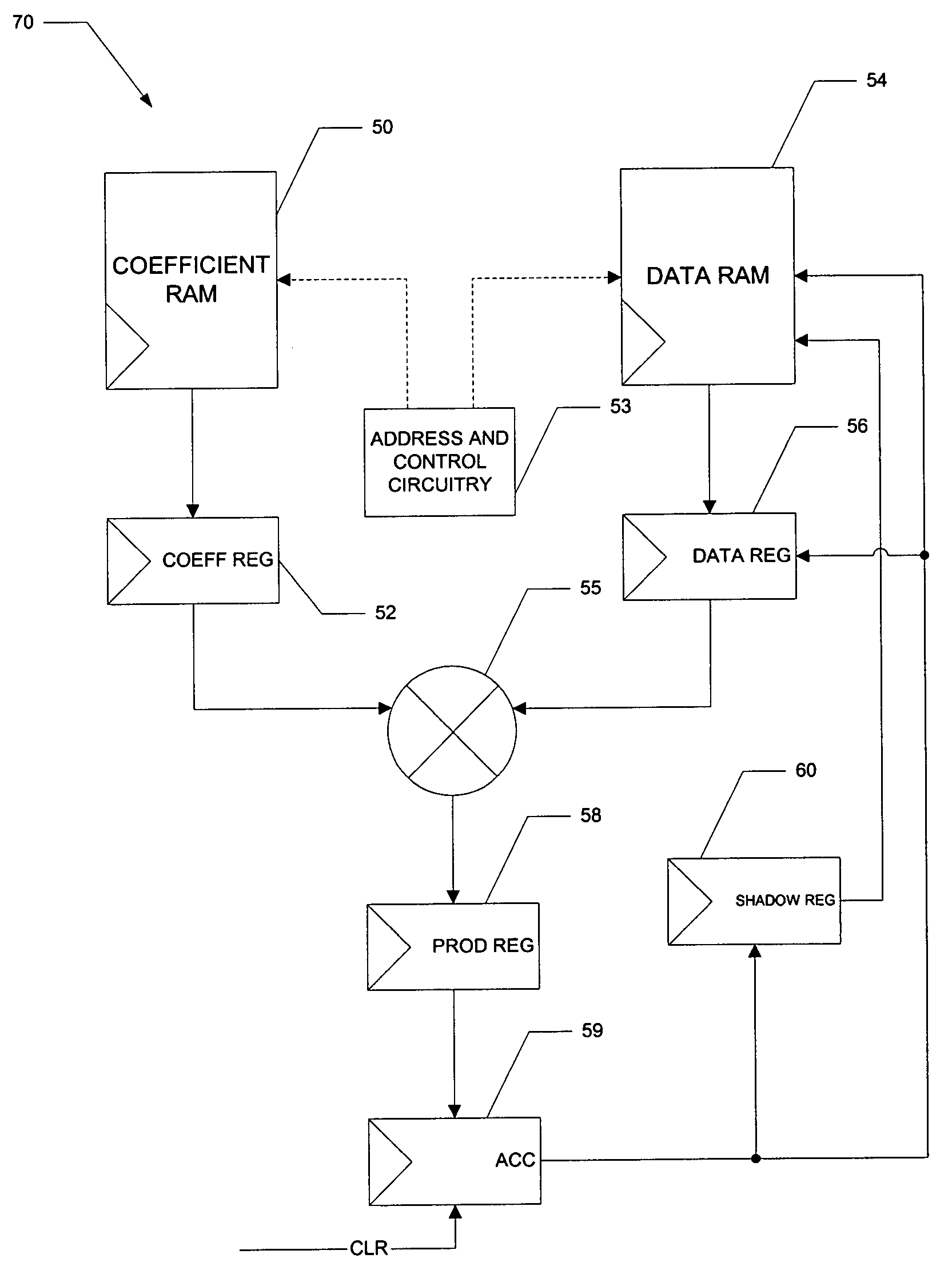
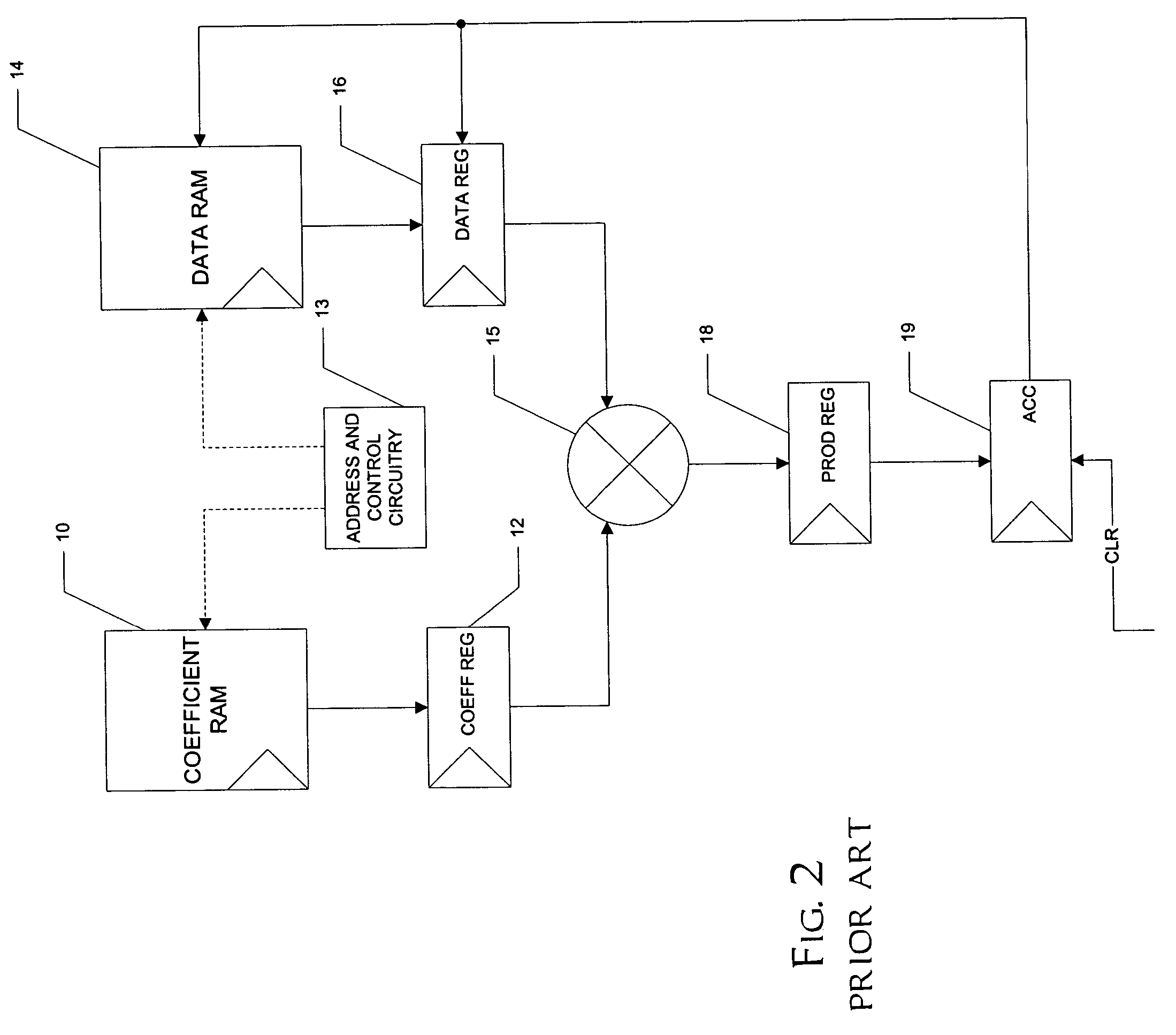
An architecture for a biquad (70), second-order infinite impulse response (IIR) digital filter, that is capable of operating at maximum efficiency, is disclosed. The biquad (70) includes coefficient memory (50) and data memory (52), along with control circuitry (53) that loads values from these memories (50, 52) into a coefficient register (52) and a data register (54), respectively. A multiplier (55) multiplies the values in the coefficient register (52) and data register (54), with the resulting product being stored in a product register (58). An accumulator (59) adds successive product results to derive a new output value in each instance of the IIR filter. A shadow register (60) temporarily stores the output of the accumulator (59) from a previous instance, permitting this output to be stored in the data memory (52) at a later time in the sequence. This permits the order of operations in the second and successive biquads to be altered so that each successive biquad instance can start well before the previous result is derived; as a result, the multiplier (55) is fed with values each cycle, enabling maximum efficiency operation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Noise reduction with integrated tonal noise reduction
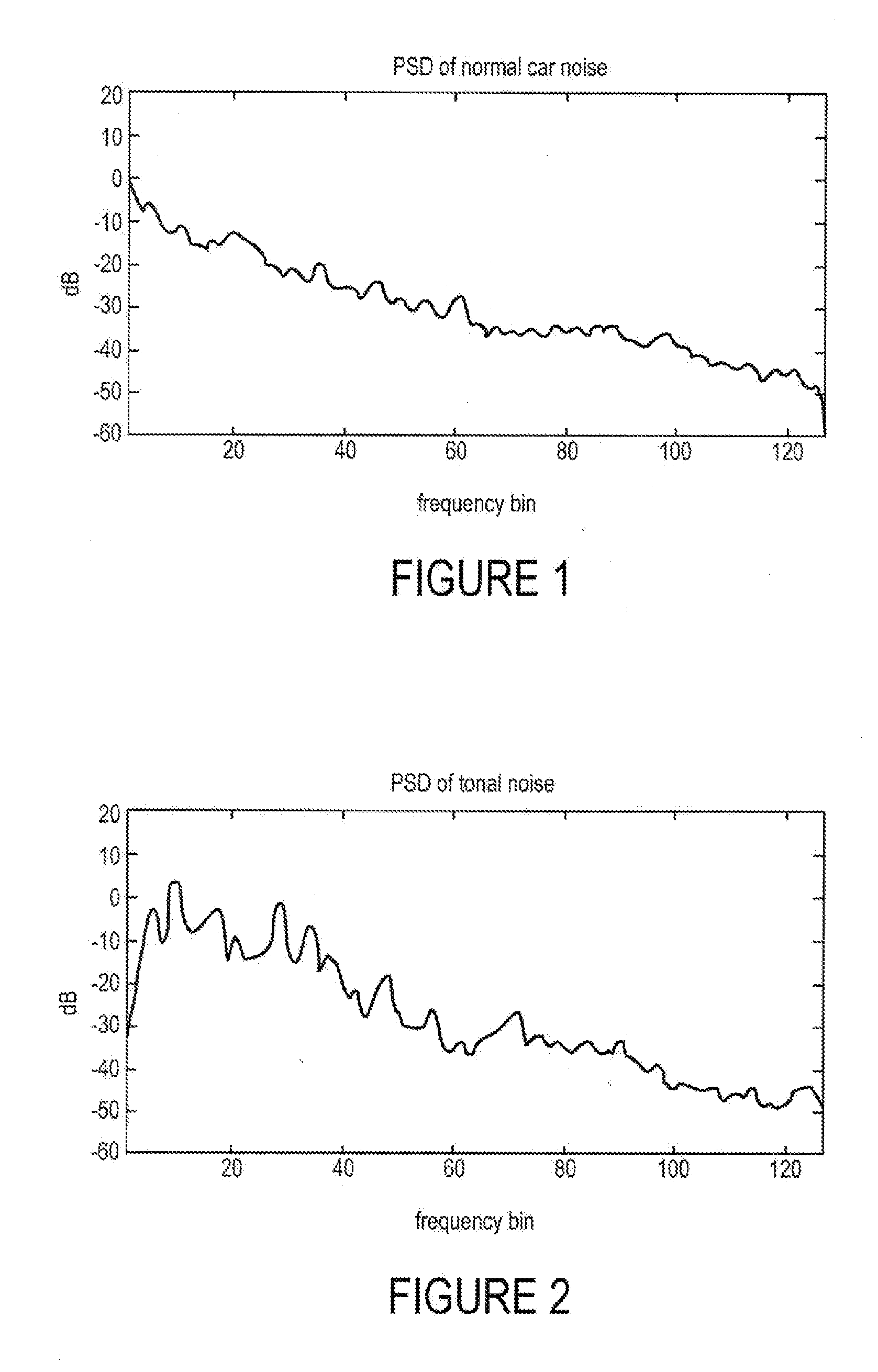
ActiveUS20080167870A1Improve the attenuation effectSpeech recognitionTransmission noise suppressionIir filteringAcoustic noise reduction
The system provides a technique for suppressing or eliminating tonal noise in and input signal. The system operates on the input signal at a plurality of frequency bins and uses information generated at a prior bin to assist in calculating values at subsequent bins. The system first identifies peaks in a signal and then determines if the peaks are from tonal effects. This can be done by comparing the estimated background noise of a current bin to the smoothed background noise of the same bin. The smoothed background noise can be calculated using an asymmetric IIR filter. When the ratio of the current background noise estimate to the currently calculated smoothed background noise is far greater than 1, tonal noise is assumed. When tonal noise is found, a number of suppression techniques can be applied to reduce the tonal noise, including gain suppression with fixed floor factor, an adaptive floor factor gain suppression technique, and a random phase technique.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
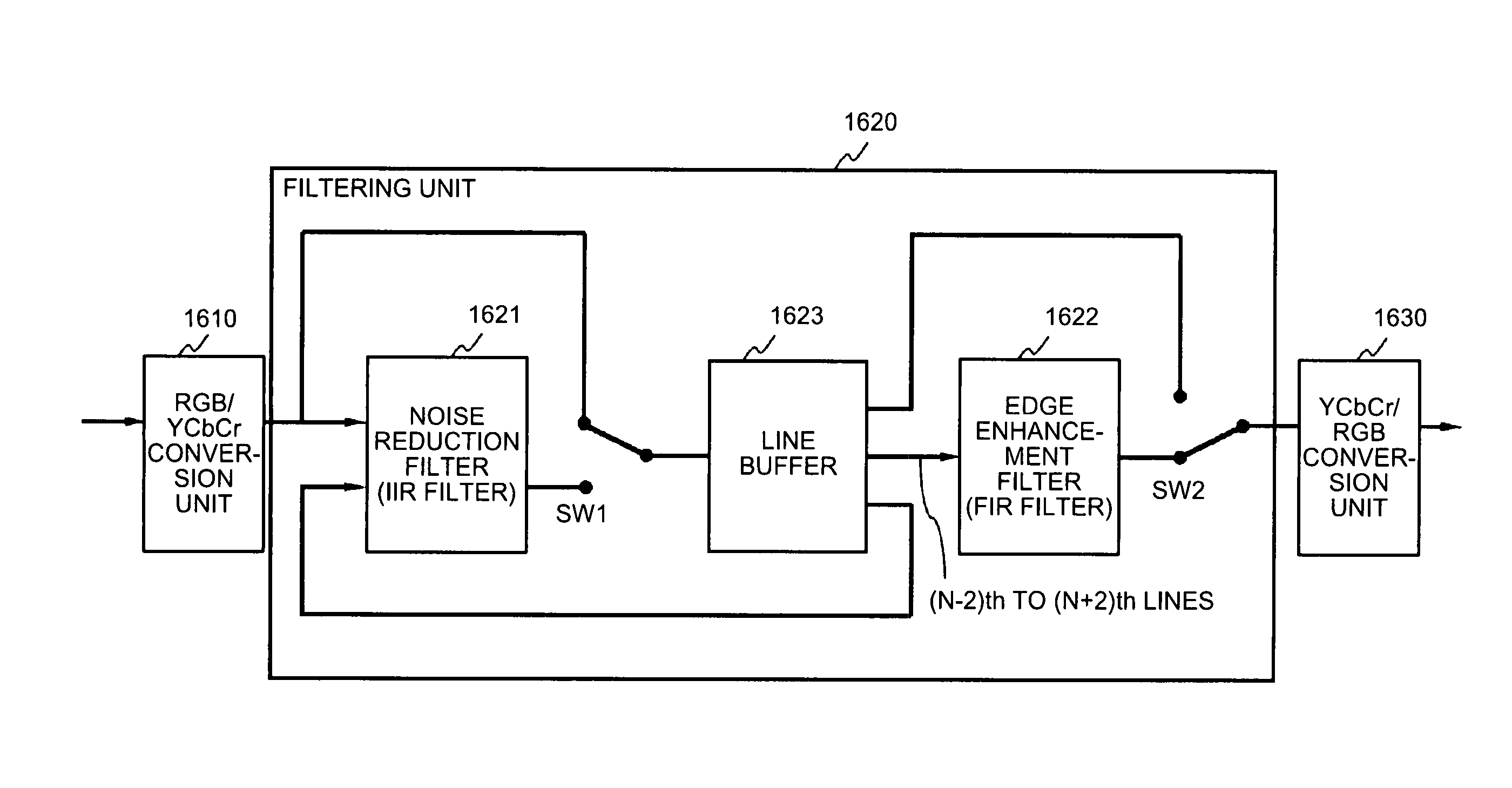
Image processing apparatus and on-vehicle camera apparatus
InactiveUS8854421B2Reduce circuit sizeEnhancing high-frequency componentImage enhancementTelevision system detailsLow noiseIir filtering
An image processing apparatus includes a line buffer, an FIR filter serving as an edge enhancement filter that enhances high-frequency components of an image, and an IIR filter serving as a low-pass filter that reduces noise. The same line buffer is used by both the FIR filter and the IIR filter. According to a switching signal, switches enable the FIR filter and disable the IIR filter for a relatively low noise level while the switches enable IIR filter and disable the FIR filter for a relatively high noise level.
Owner:RICOH KK
Single lead electroencephalogram sleep automatic staging method based on Stacking
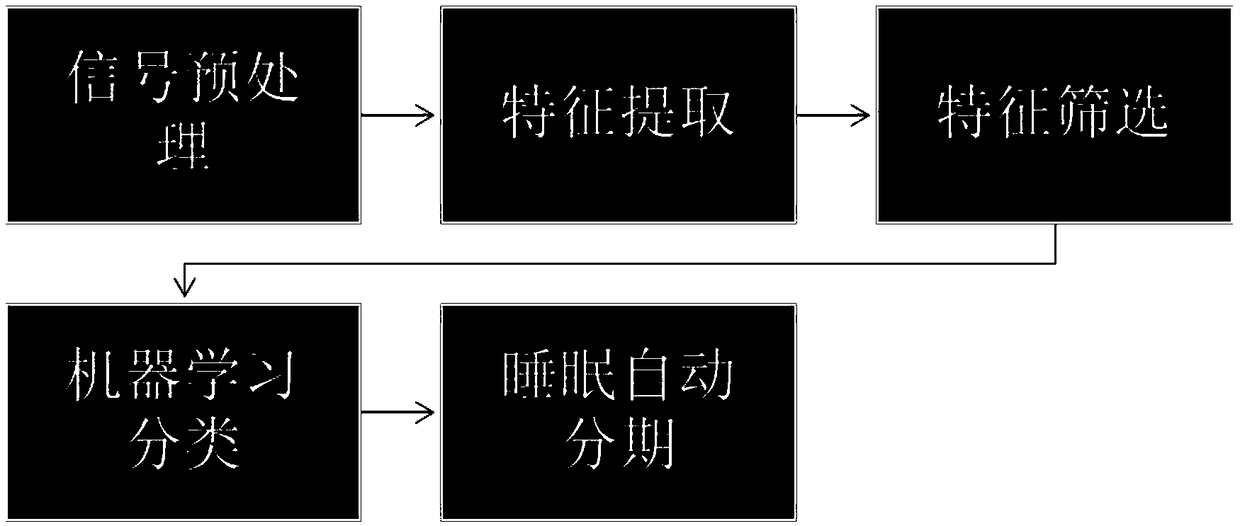
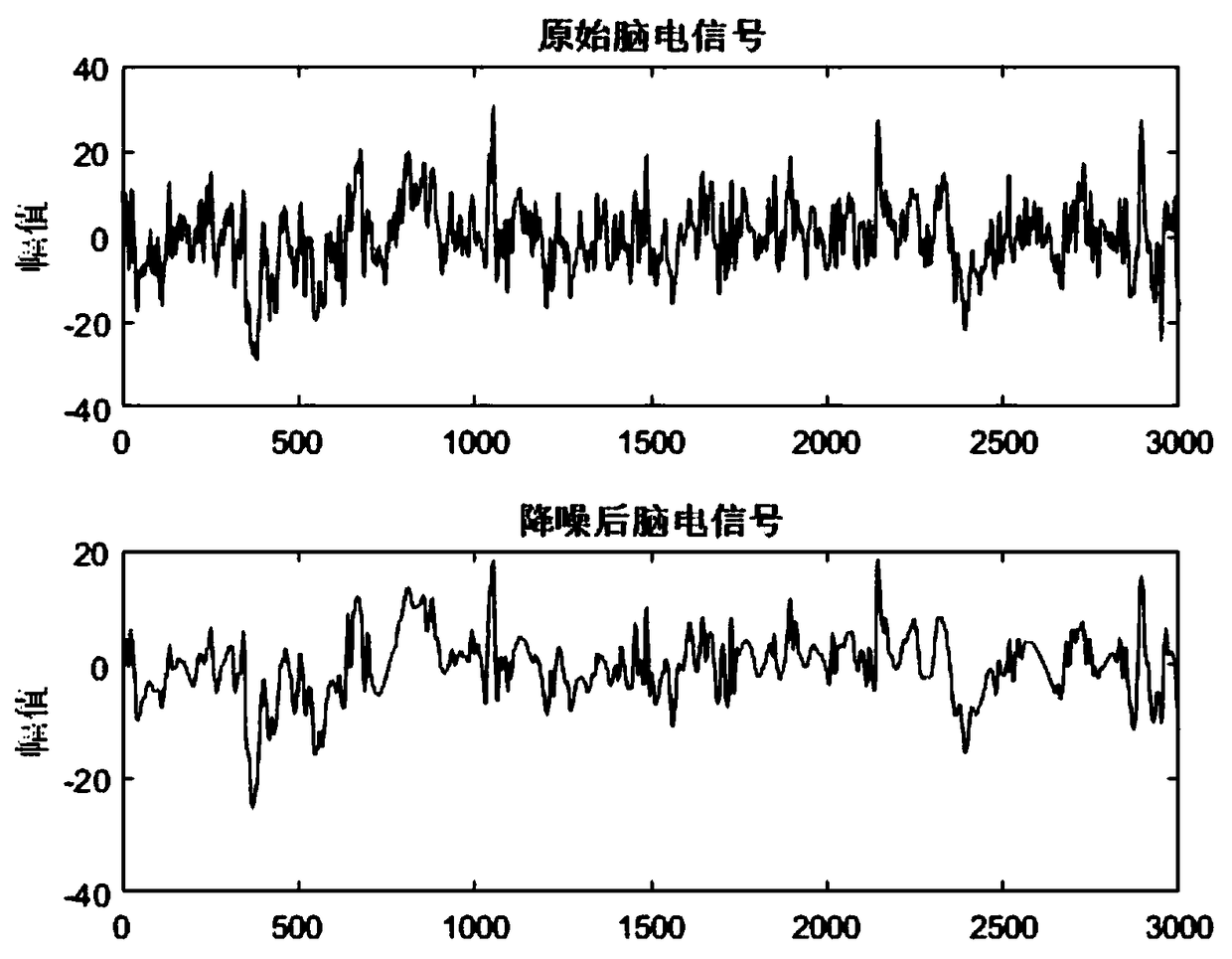
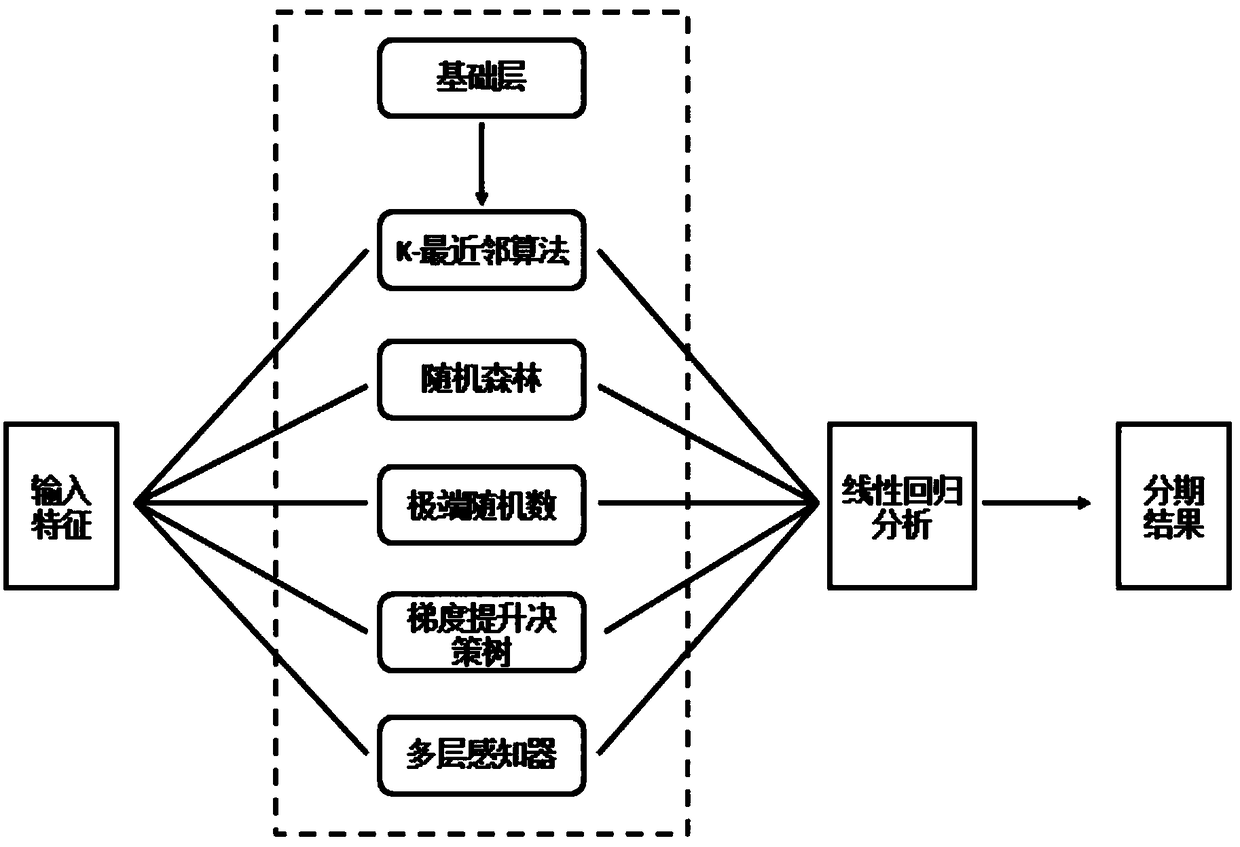
PendingCN108742517AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNoise reductionFeature parameter
The invention relates to a single lead electroencephalogram sleep automatic staging method based on Stacking, and belongs to the field of machine learning algorithms. The method comprises the steps that S1: sleep electroencephalograms are preprocessed; S2: multi-feature extraction and screening are carried out on the sleep electroencephalograms; S3: machine learning classification is carried out;S4: sleep automatic staging is carried out. The method can acquire a filtering method combining a wavelet function of a self-adaption threshold value and an IIR filtering function to conduct noise reduction processing on the electroencephalograms and effectively improve the signal to noise ratio of the electroencephalograms; a feature algorithm can be optimized and screened to acquire a new feature parameter set so as to take the new feature parameter set as a feature of sleep staging; a new multi-feature and integrated learning algorithm composition with high accuracy can be acquired and taken as the sleep staging method.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Motion detection for interlaced video
Motion detection in interlaced video fields, as useful in de-interlacing, includes spatial-temporal maximum filtering, temporal IIR filtering dependent upon spatial-temporal variance, and spatial variance dependent moving-still interpolation blending factor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Mixer having frequency selection function
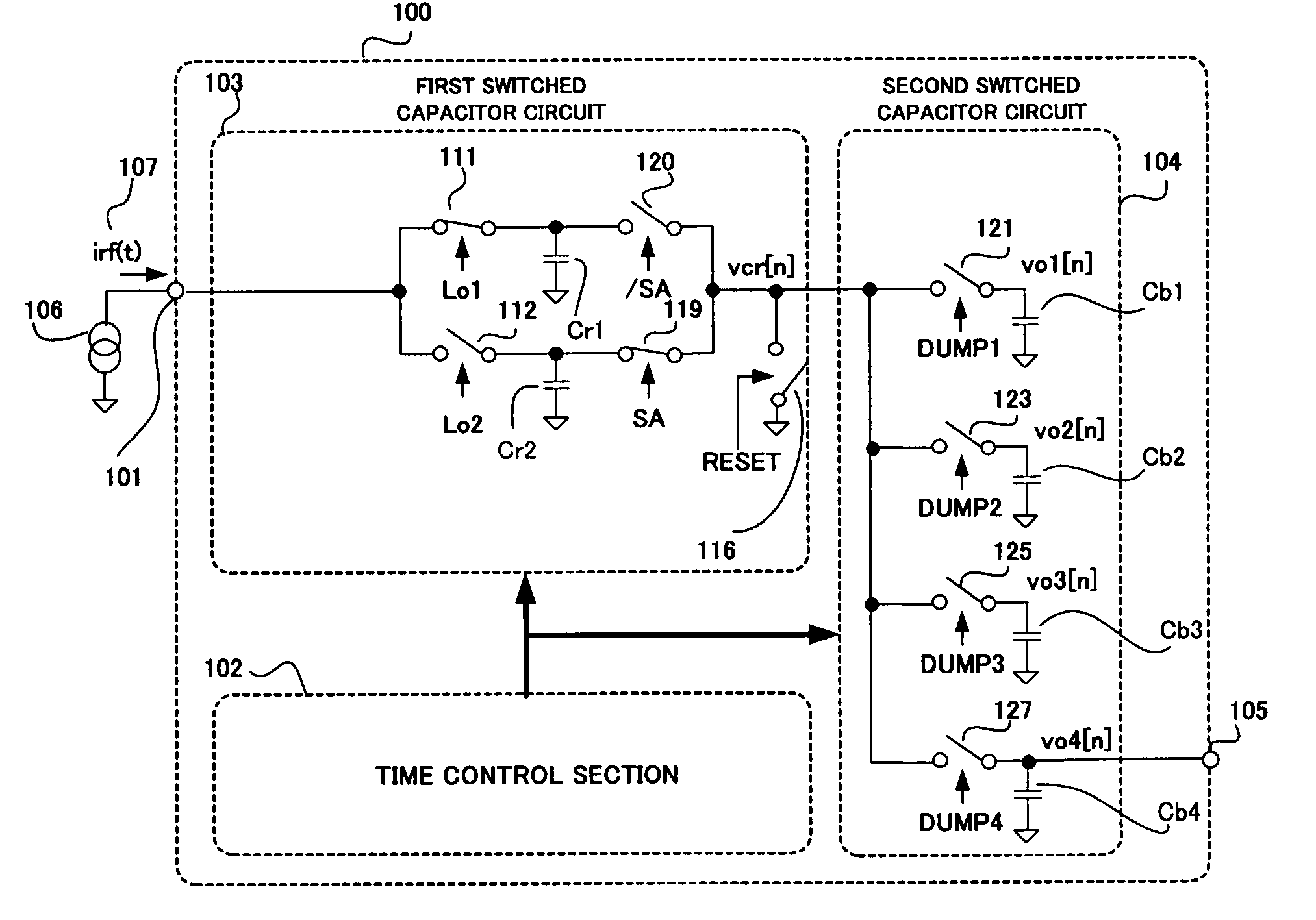
InactiveUS20070275684A1Enhanced frequency selection functionPass loss reducedModulation transference balanced arrangementsElectric analogue storesIir filteringCapacitance
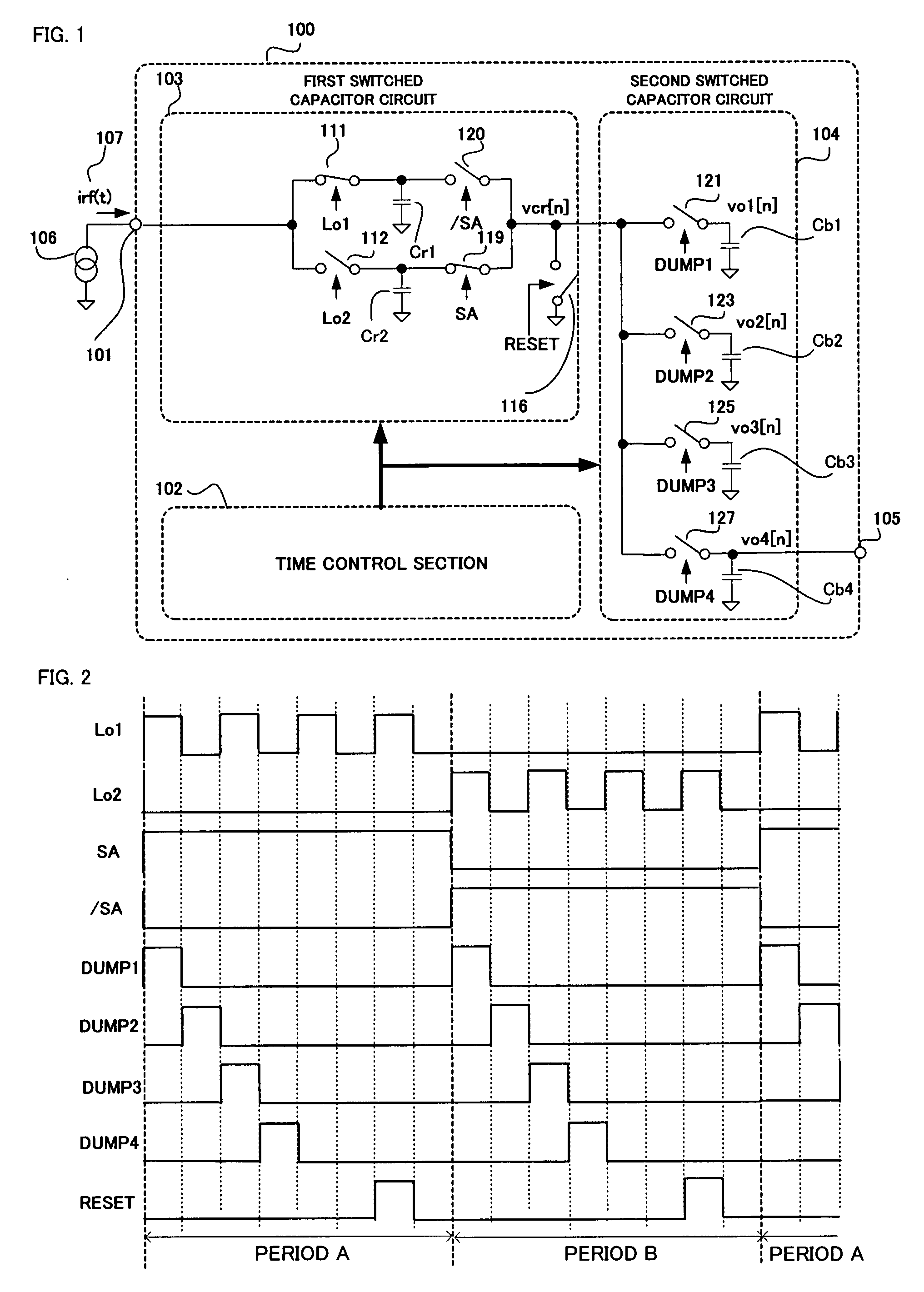
A mixer which has an enhanced frequency selection characteristic and generates no pass loss is realized without using an operation control signal having a frequency higher than a sampling frequency. Provided are a time control section 102 for supplying control signals, a first switched capacitor circuit 100 for outputting a discrete time sample stream of the input signal 107 in accordance with integration operation control signals Lo1 and Lo2, and a second switched capacitor circuit 104 functioning as a high-order IIR filter by sharing a charge, and a frequency of each of the integration operation control signals Lo1 and Lo2 is higher than frequencies of other control signals.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Digital adaptive equalizer for T1/E1 long haul transceiver
InactiveUS6980592B1Exact matchMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFinite impulse responseIir filtering
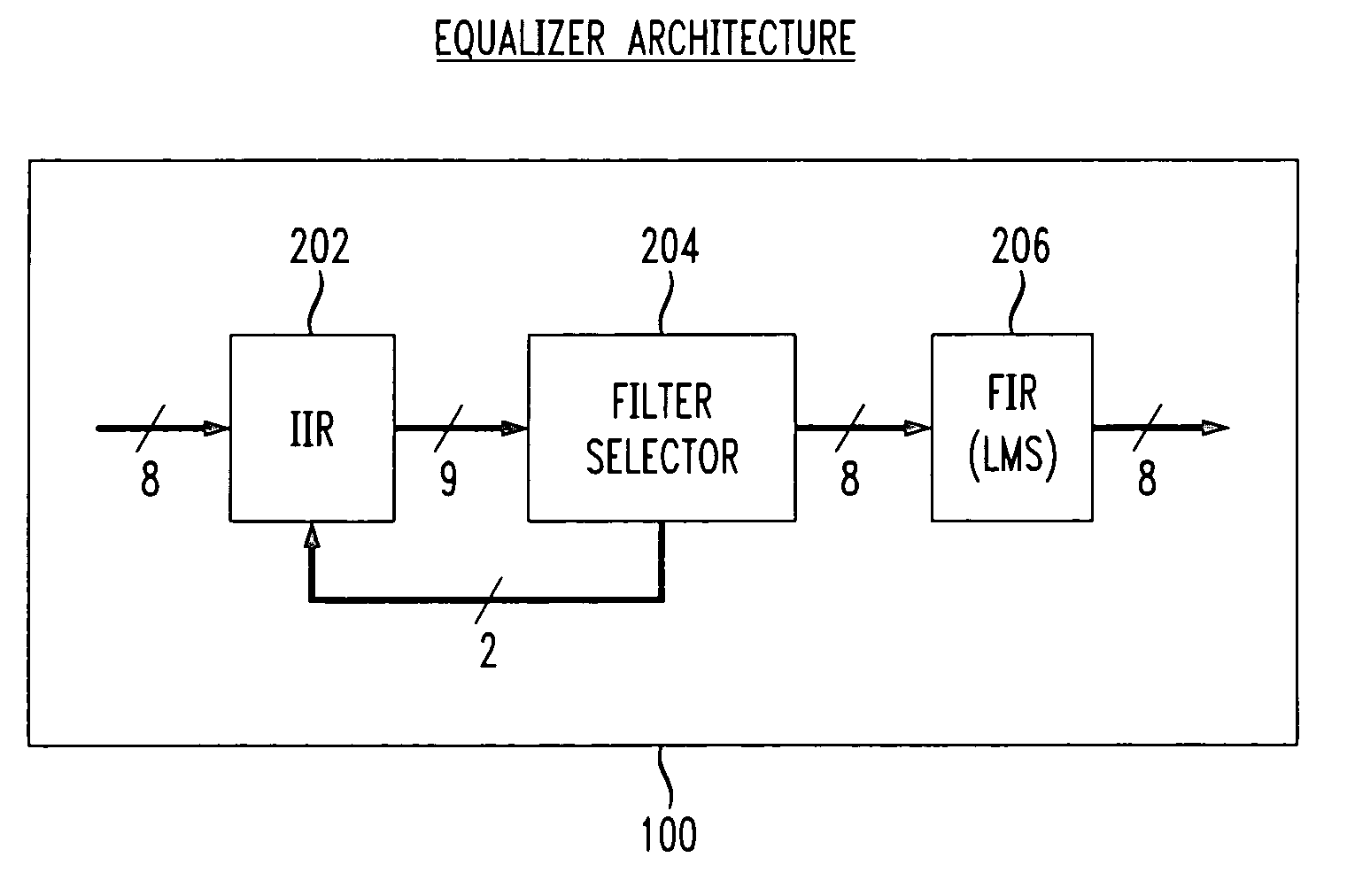
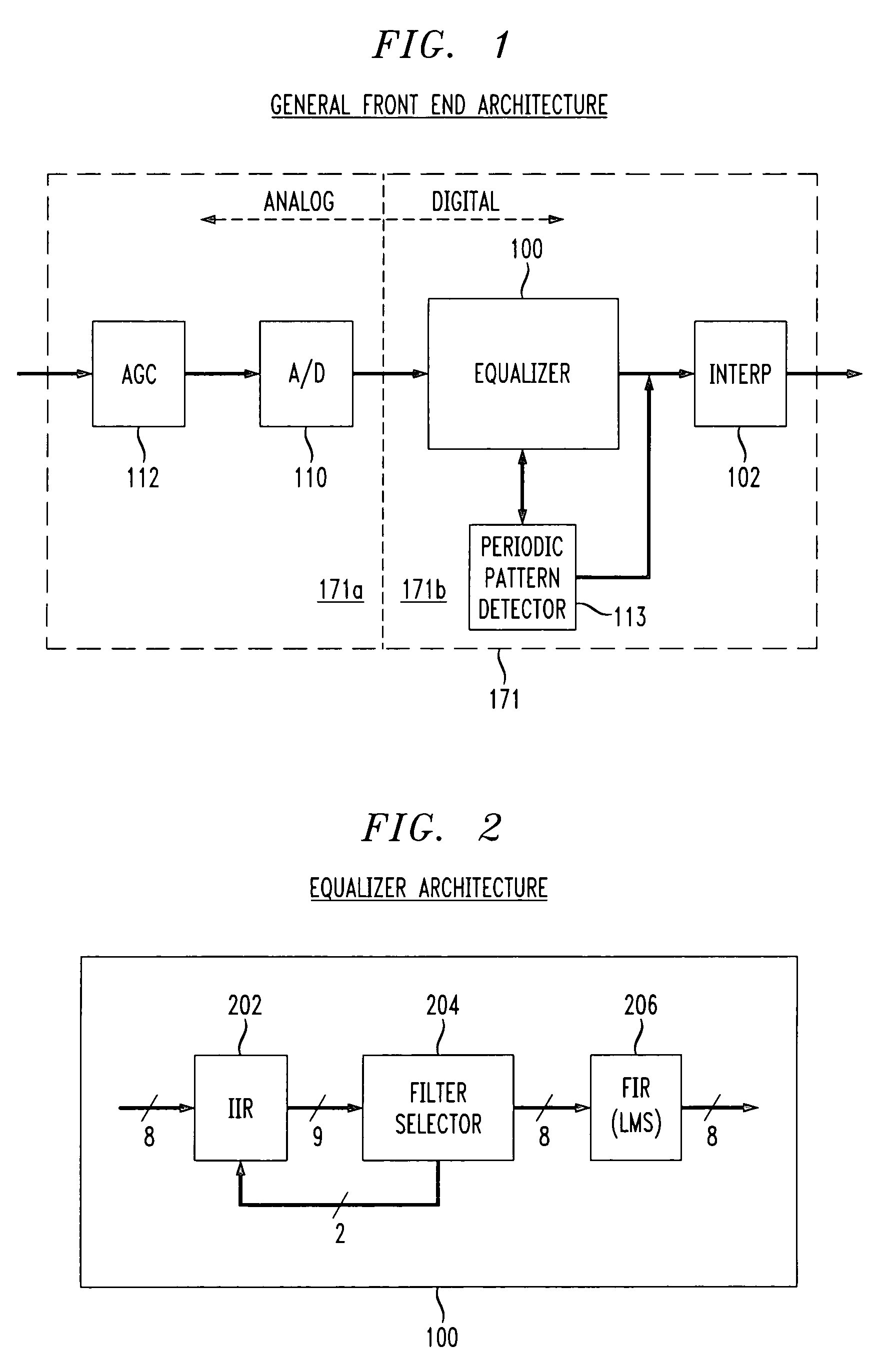
The present invention relates to the implementation of a digital adaptive equalizer for a T1 / E1 long haul transceiver which is capable of adapting to a wide range of cable types, cable lengths, and / or other data transmission impairments, particularly when the transmission path type and / or length are unknown. The digital adaptive equalizer contains two filter blocks, i.e., an IIR filter and a FIR filter, together with a filter selector block to select a best IIR filter based on an error estimation of the received data. Only a few sets of coefficients are found to be necessary to allow proper digital equalization of a large number of cable types and / or lengths. A filter selector block selects a desired set of coefficients corresponding to the optimum IIR filter. The coefficients may be programmed into volatile memory (e.g., RAM) or non-volatile memory (e.g., Flash). Alternatively, the coefficients may be hardwired into the IIR filter. The back end of the digital adaptive equalizer contains an adaptive finite impulse response (FIR) filter. In the disclosed embodiment, the FIR filter uses a least mean square (LMS) algorithm for adaptation to the unknown or changed T1 or E1 transmission channel or medium. The adaptive FIR filter adjusts the output from the IIR filter to accurately match the inverse response of the unknown channel used to transmit the received T1 / E1 signal. Equalization may be temporarily frozen if periodic patterns are detected in the received T1 / E1 signal. A restored T1 or E1 signal is output from the FIR filter, and thus from the digital adaptive equalizer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com