Patents
Literature
80 results about "If filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
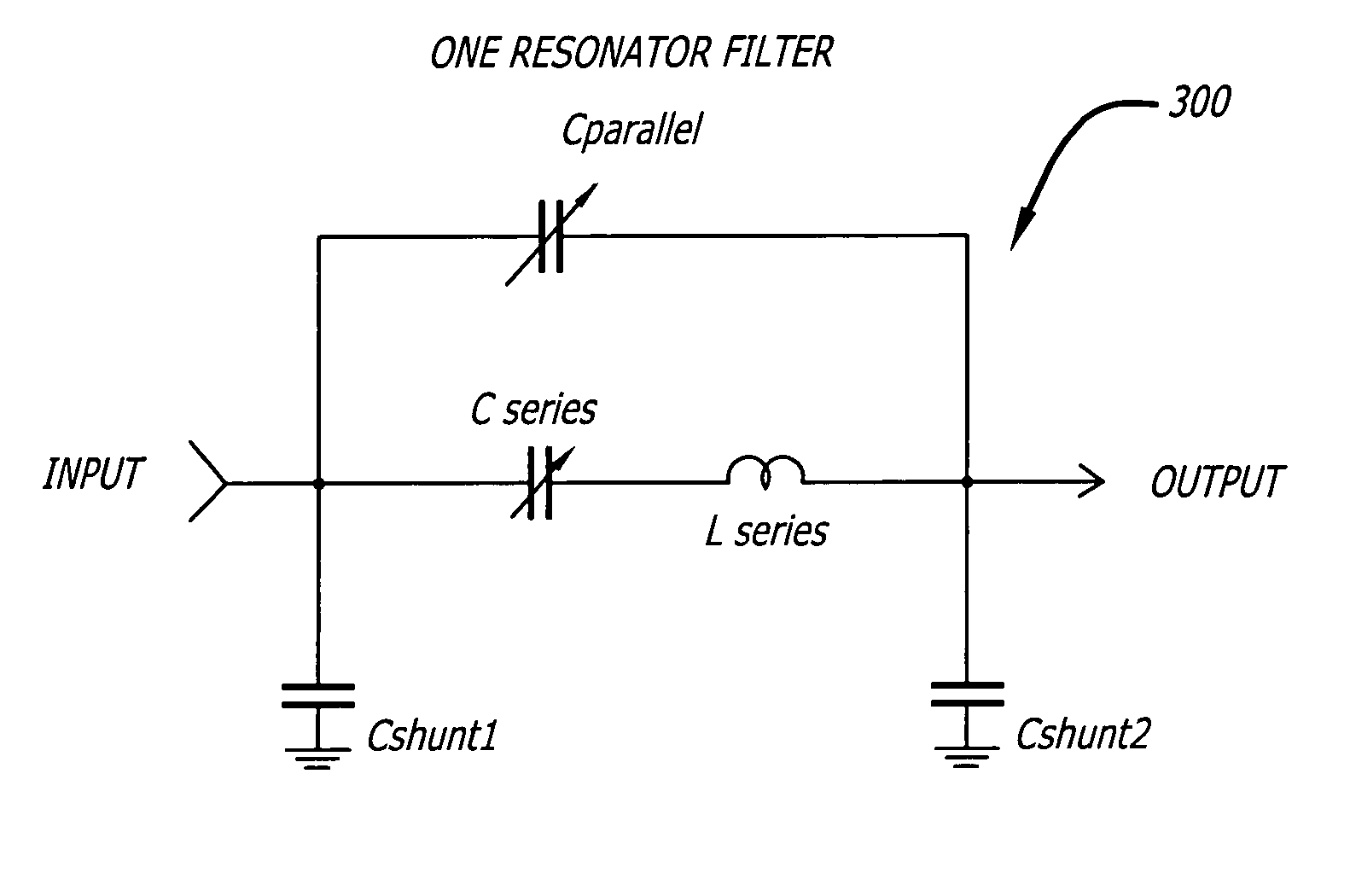
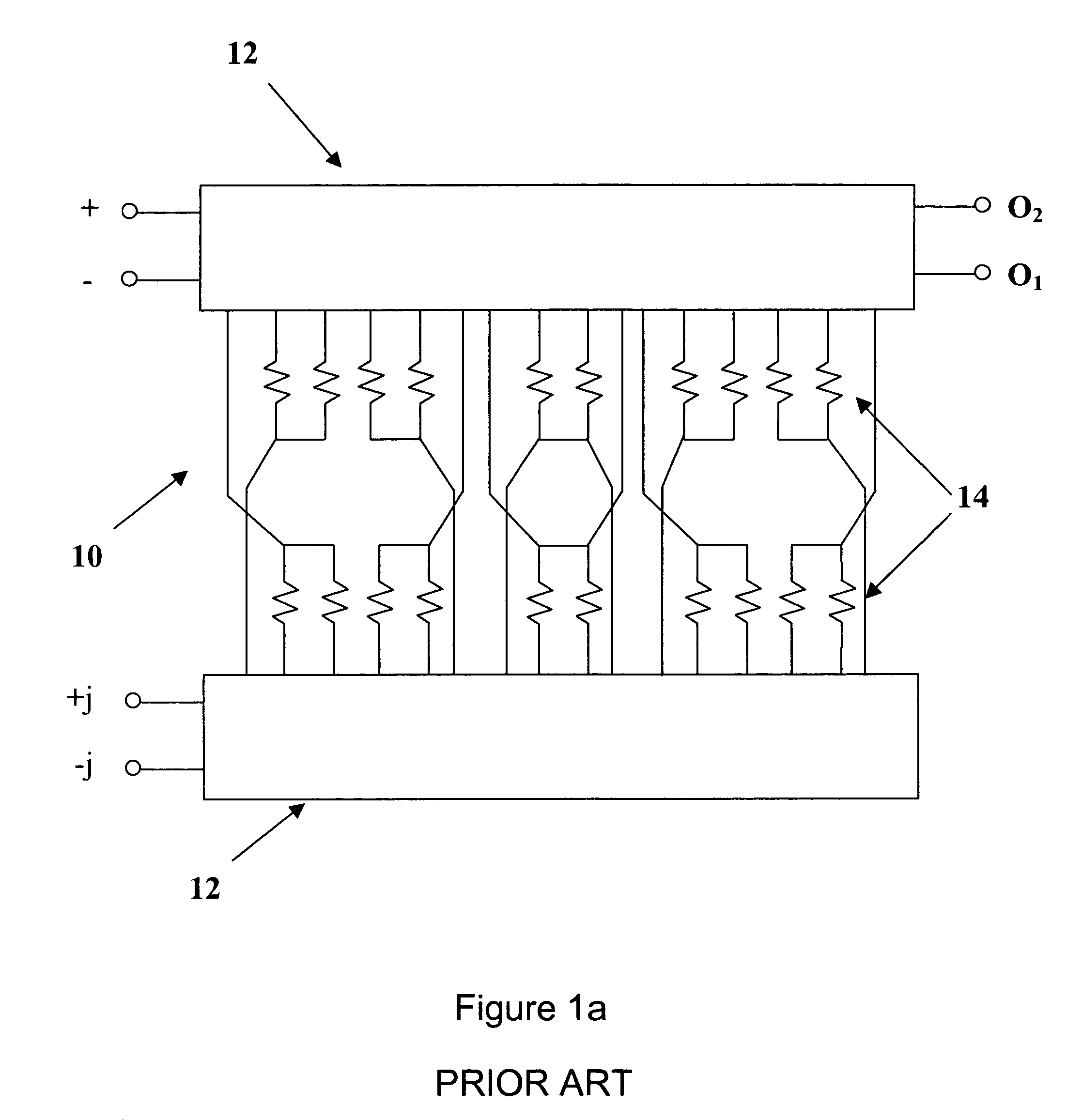
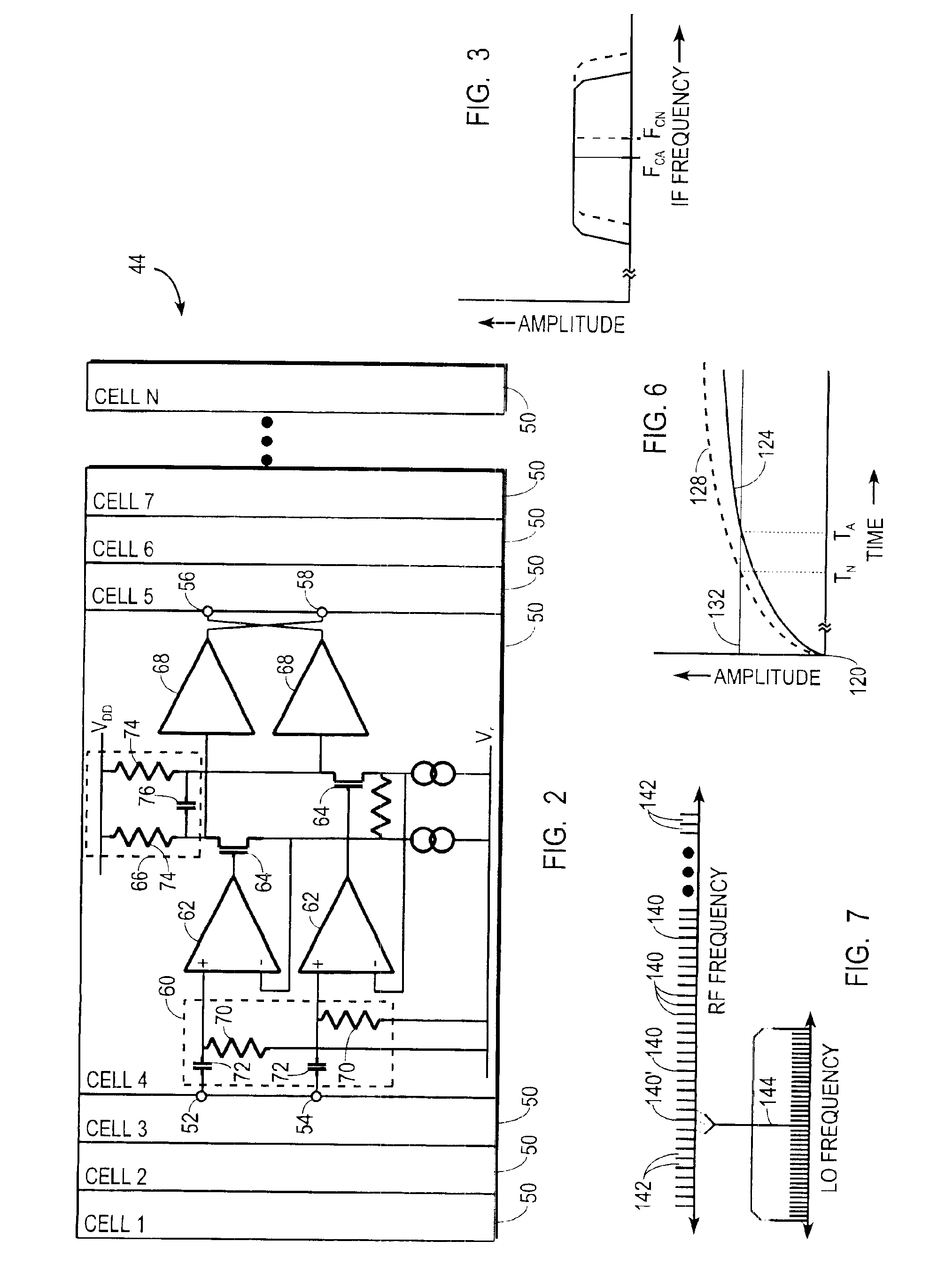
Broadband integrated digitally tunable filters
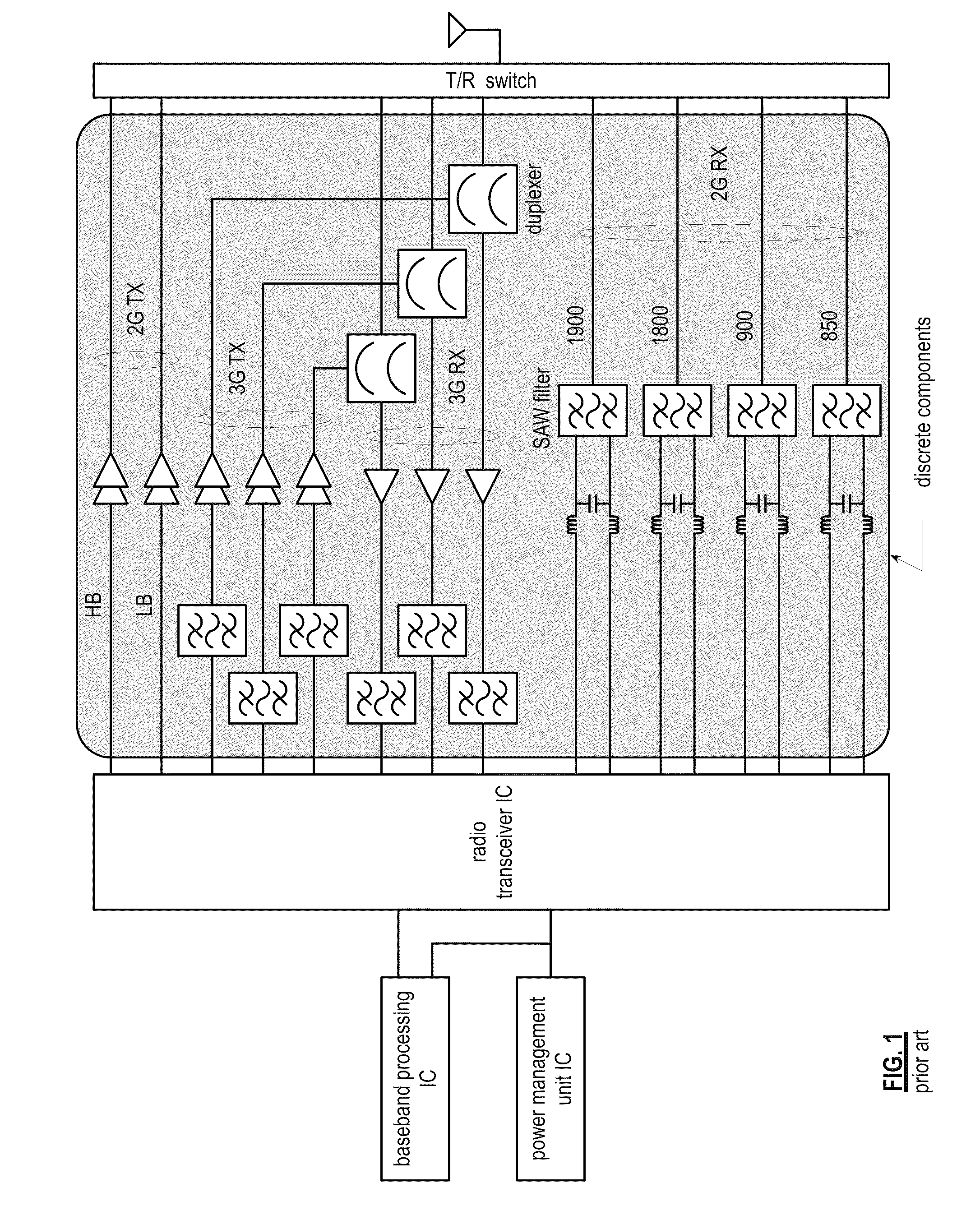
InactiveUS20050040909A1Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationAudio power amplifierBroadband
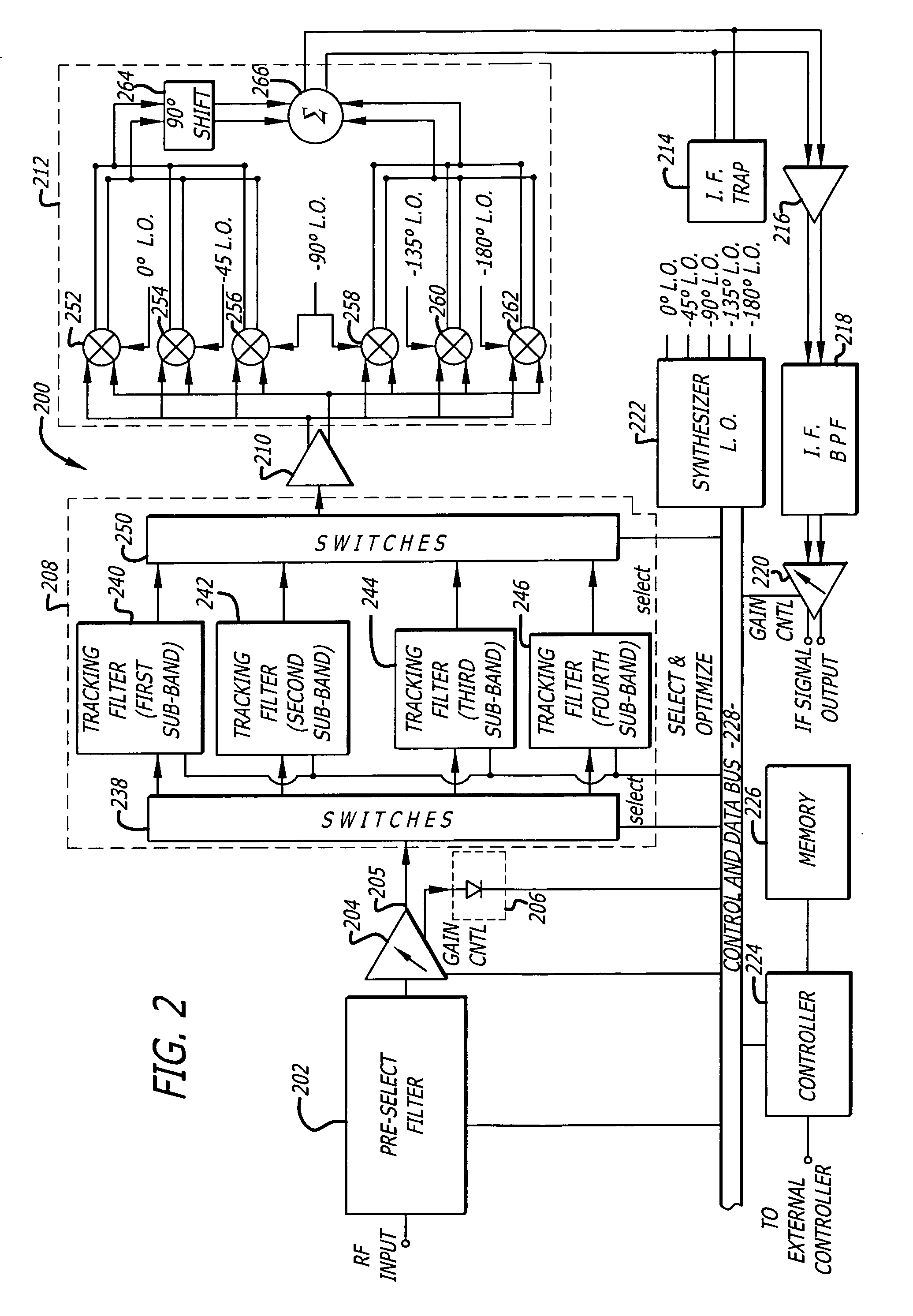
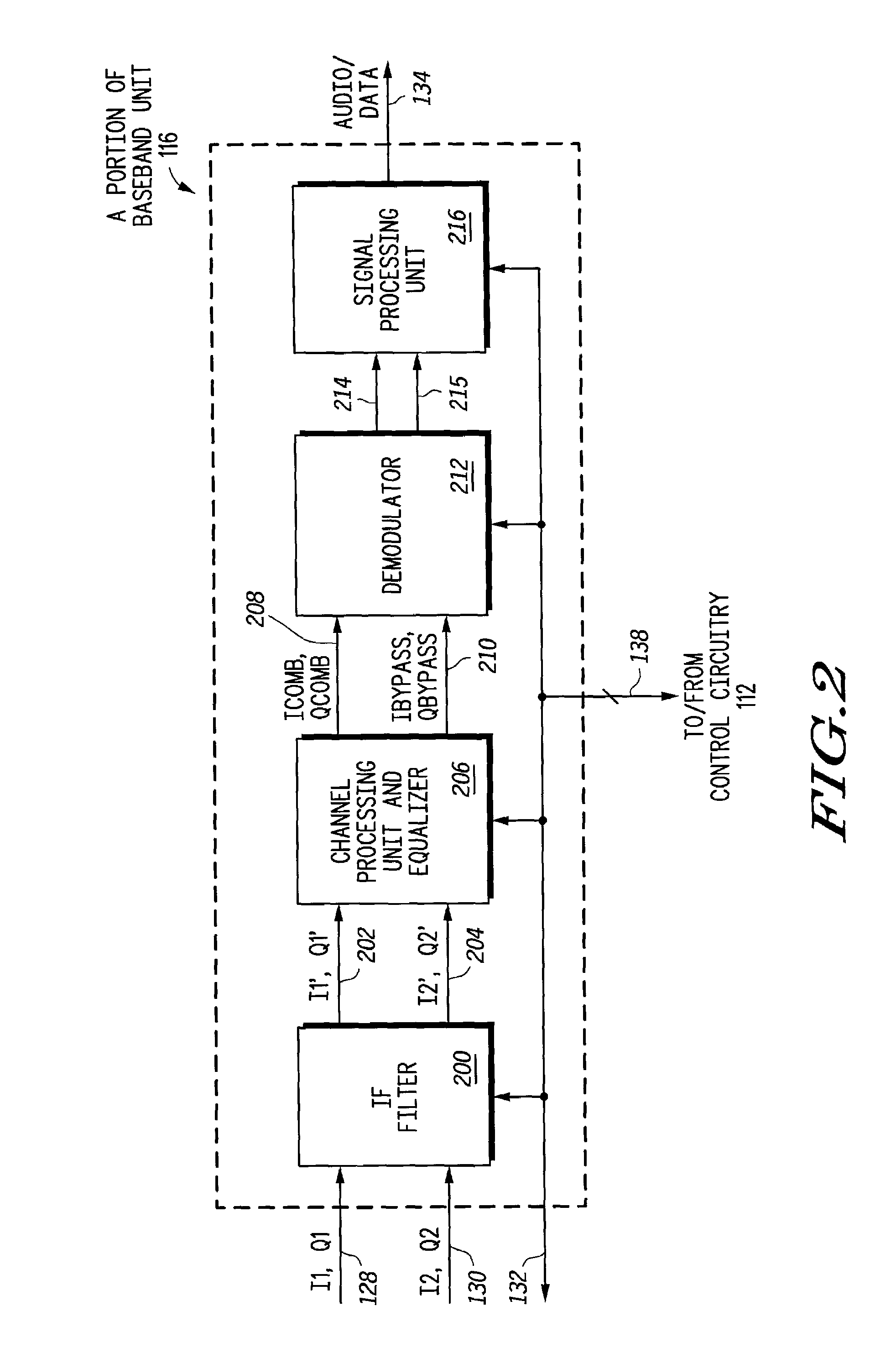
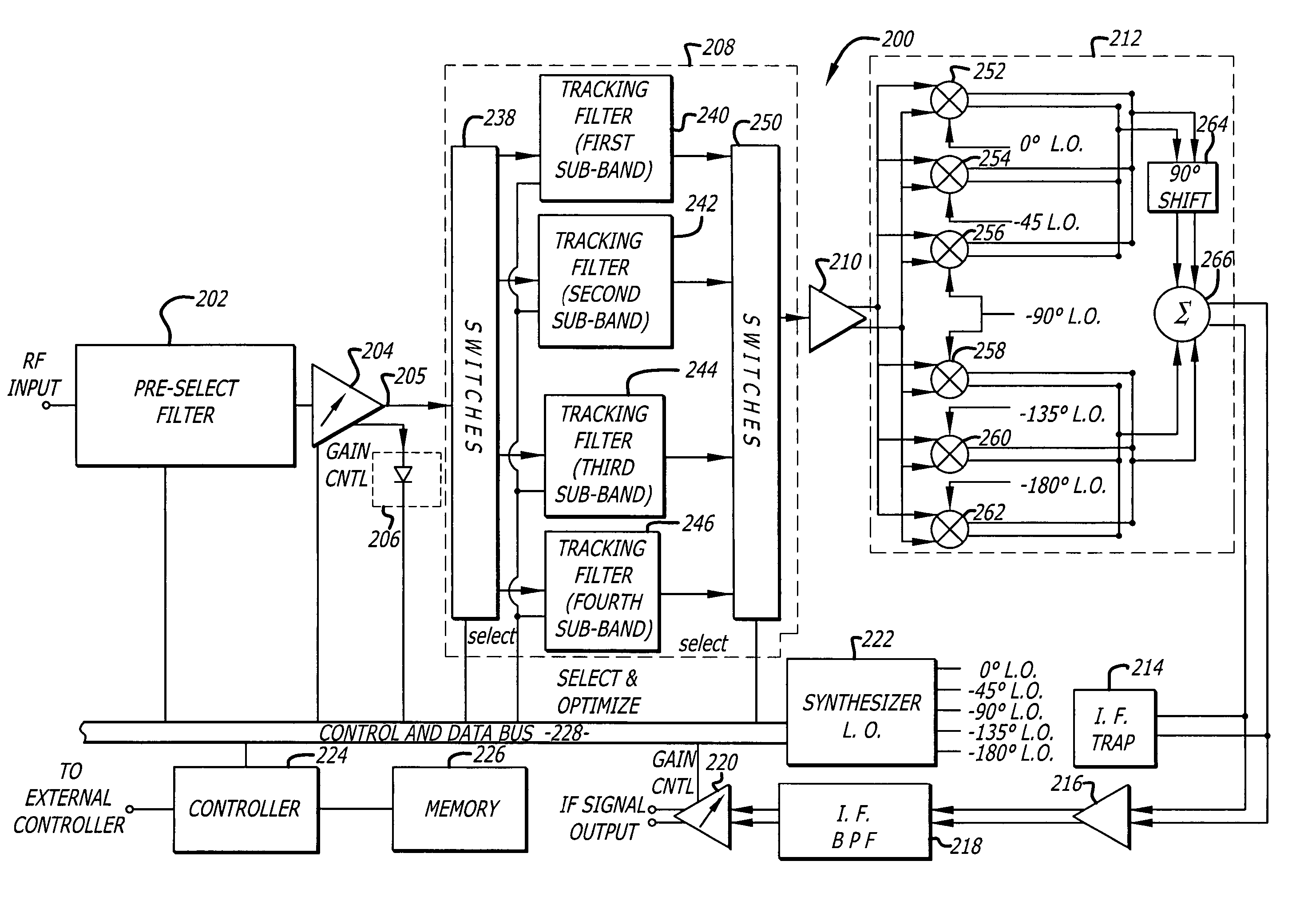
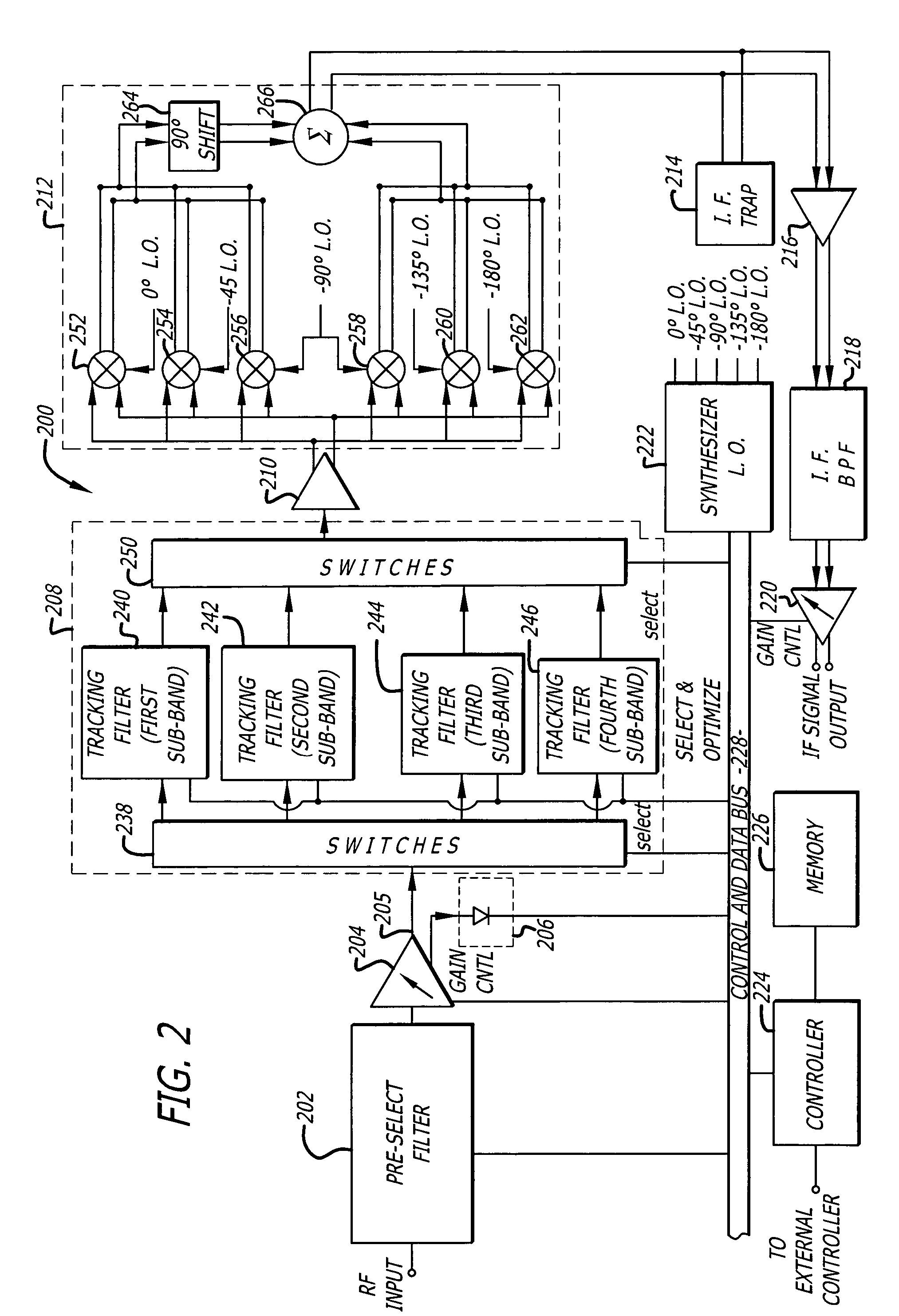
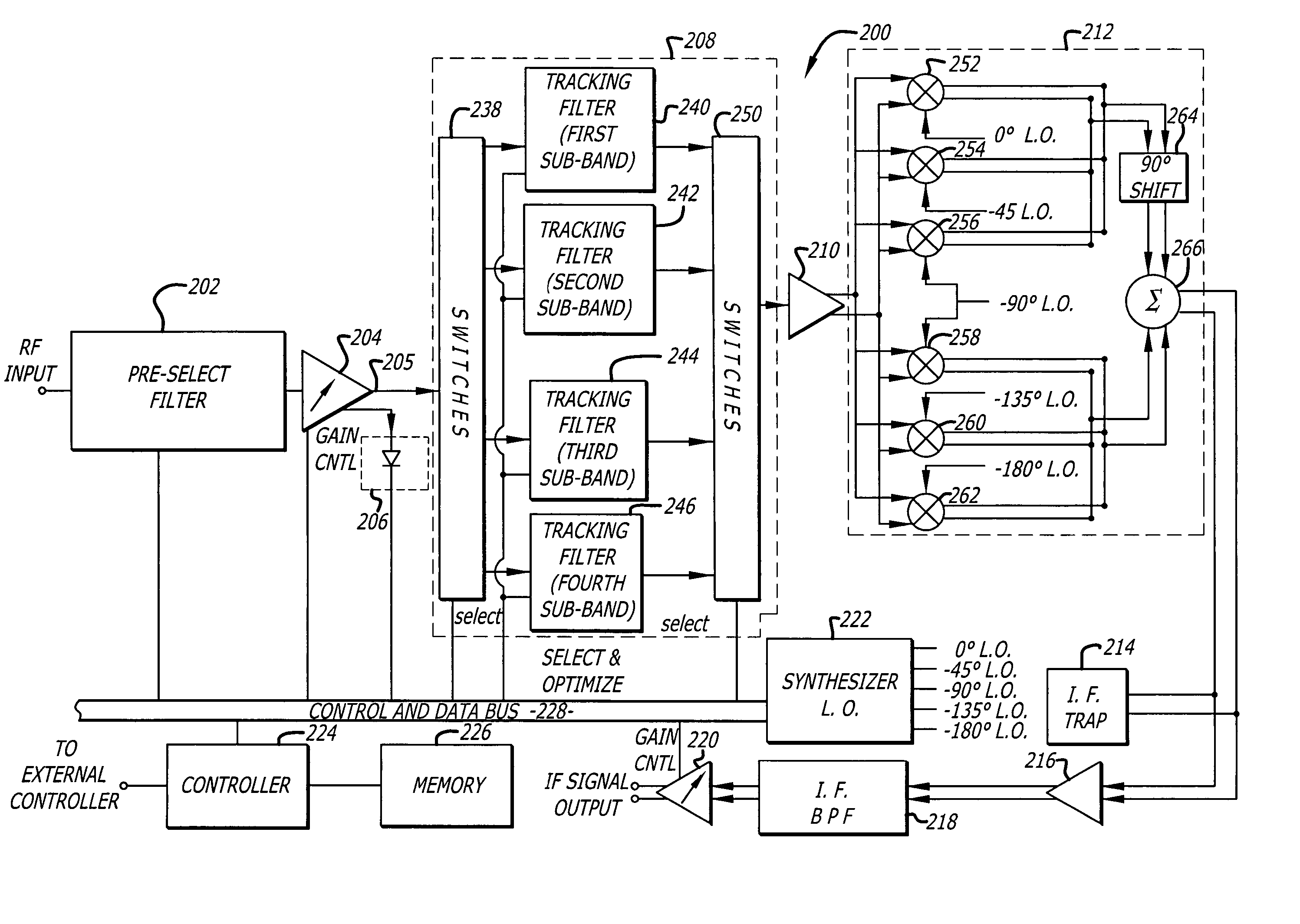
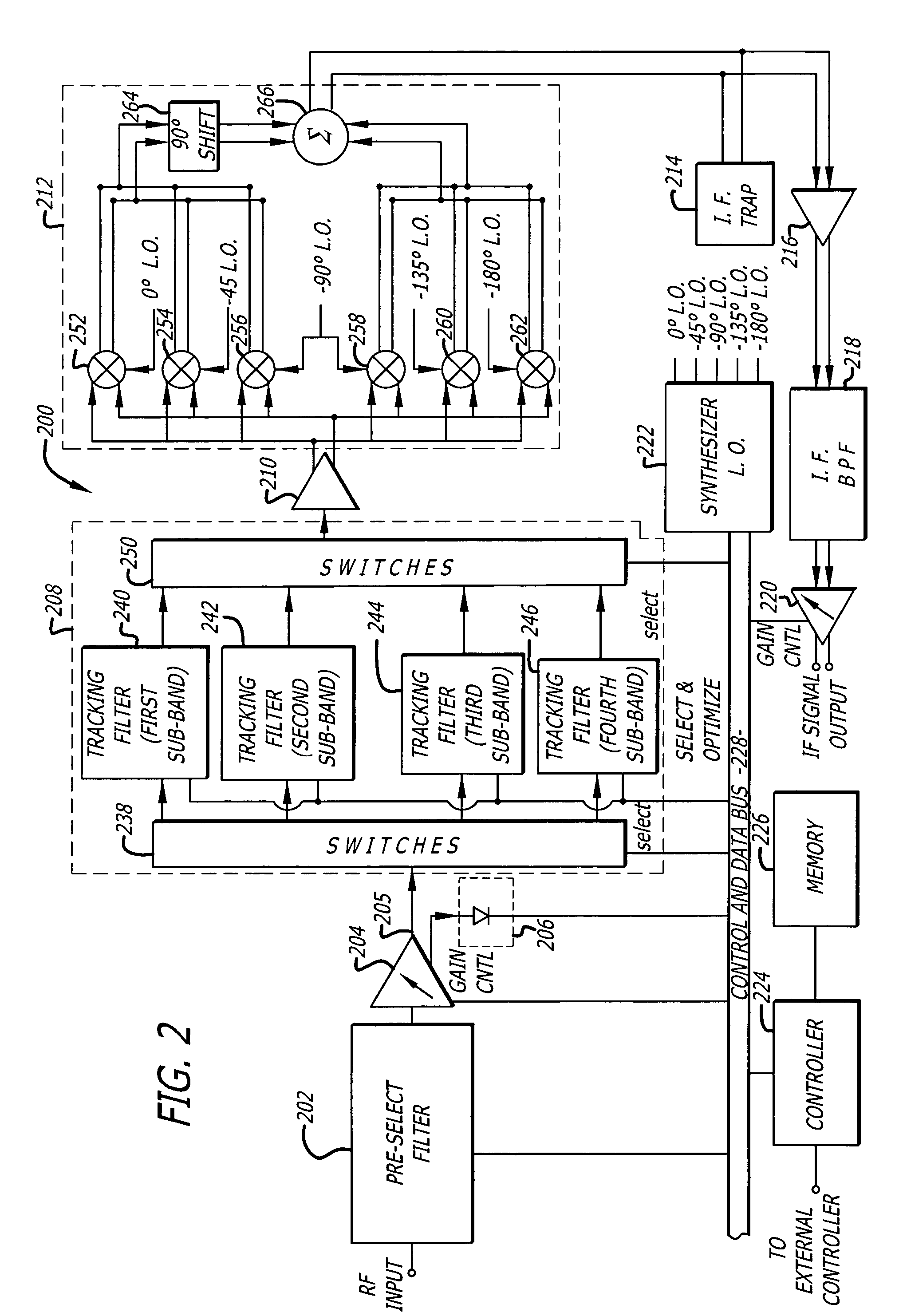
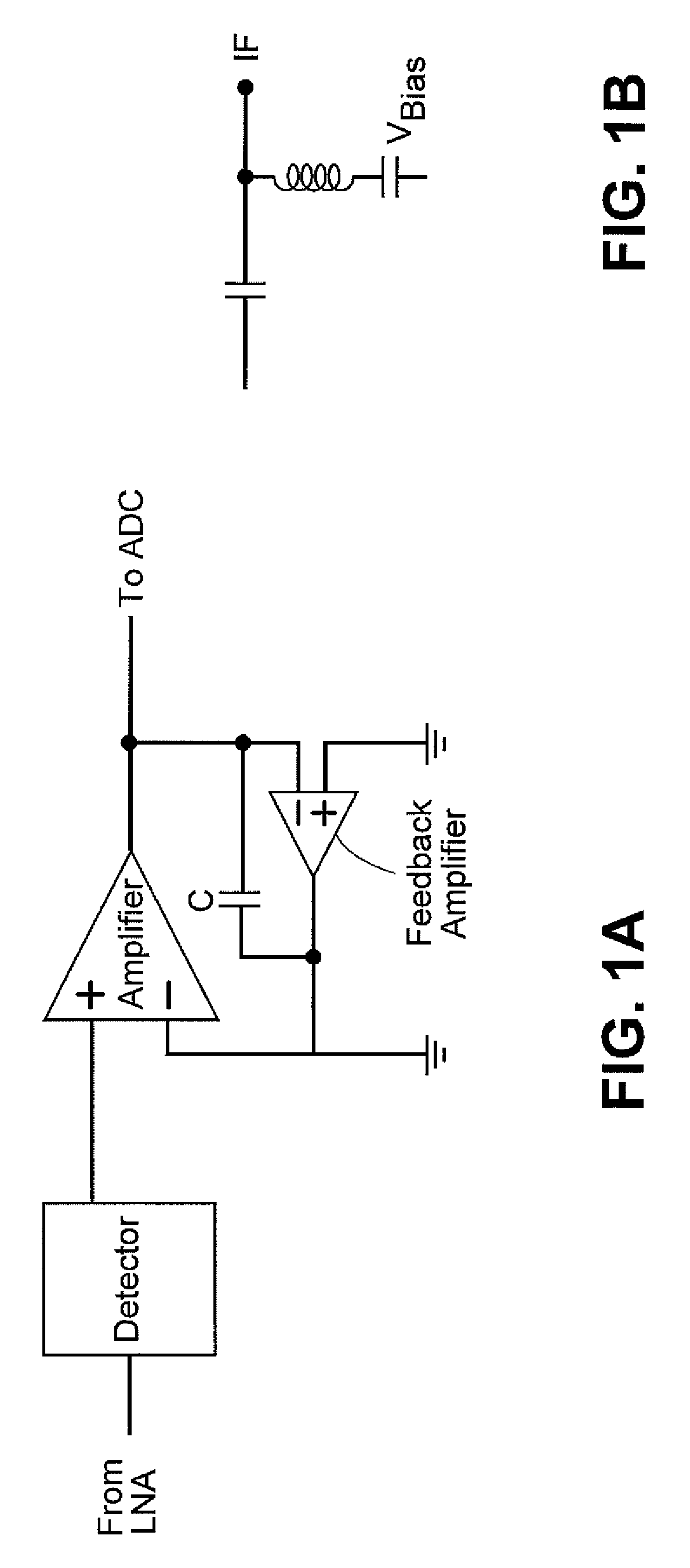
A tunable receiver is disclosed including a plurality of select filters to perform an initial band selection, a variable-gain low noise amplifier (LNA) whose gain is controlled to prevent its output power level to exceed a predetermined power threshold, a plurality of digitally-tunable tracking filters to pass signals within a selected channel and to reject signals in a corresponding image band, a second LNA to further amplify the received RF signal and to generate differential signal outputs, a down converting stage which converts the received RF signal to an IF signal while rejecting signals in the image band, an IF trap to further reject undesired signals present at the output of the down converting stage, an IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal to compensate for losses, an IF filter to provide channel select and reject undesirable signals, and a variable-gain IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal and maintain its power level within specification.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
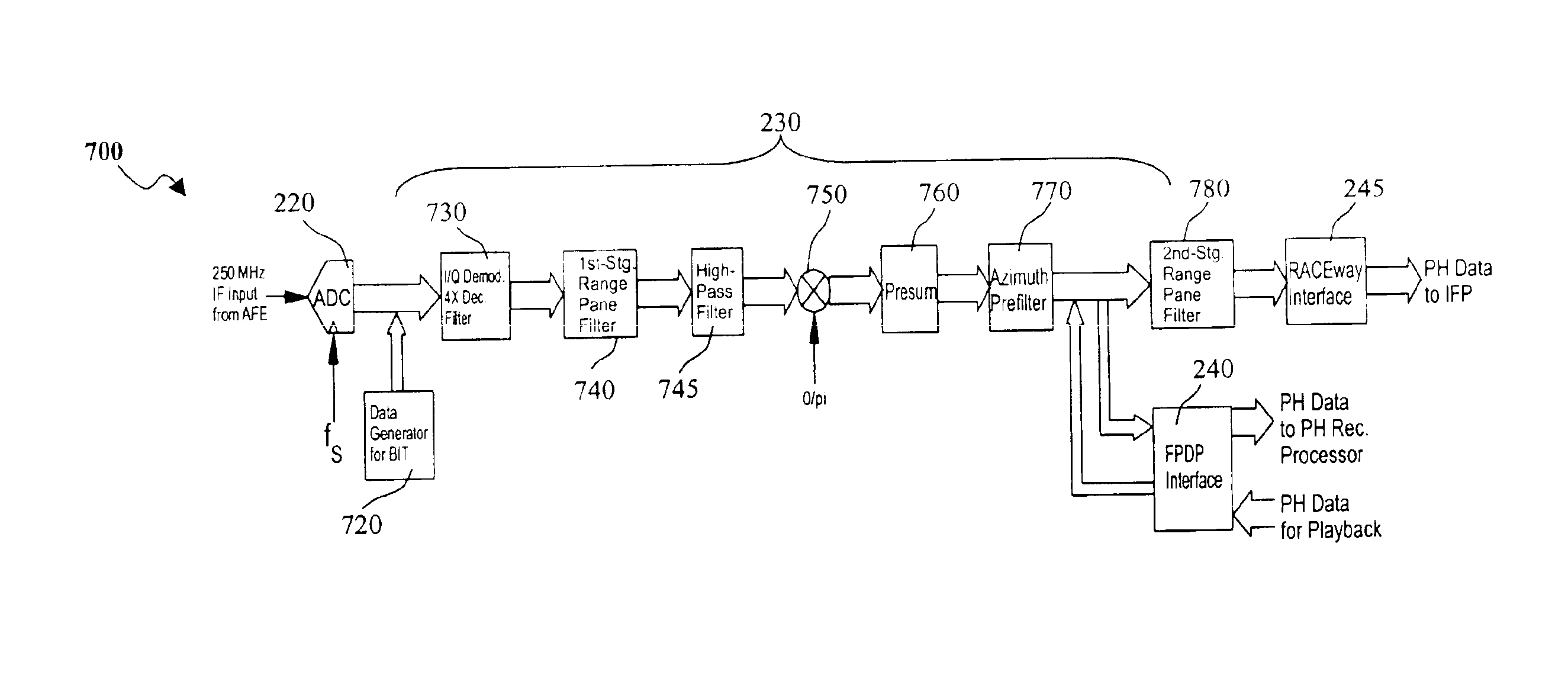
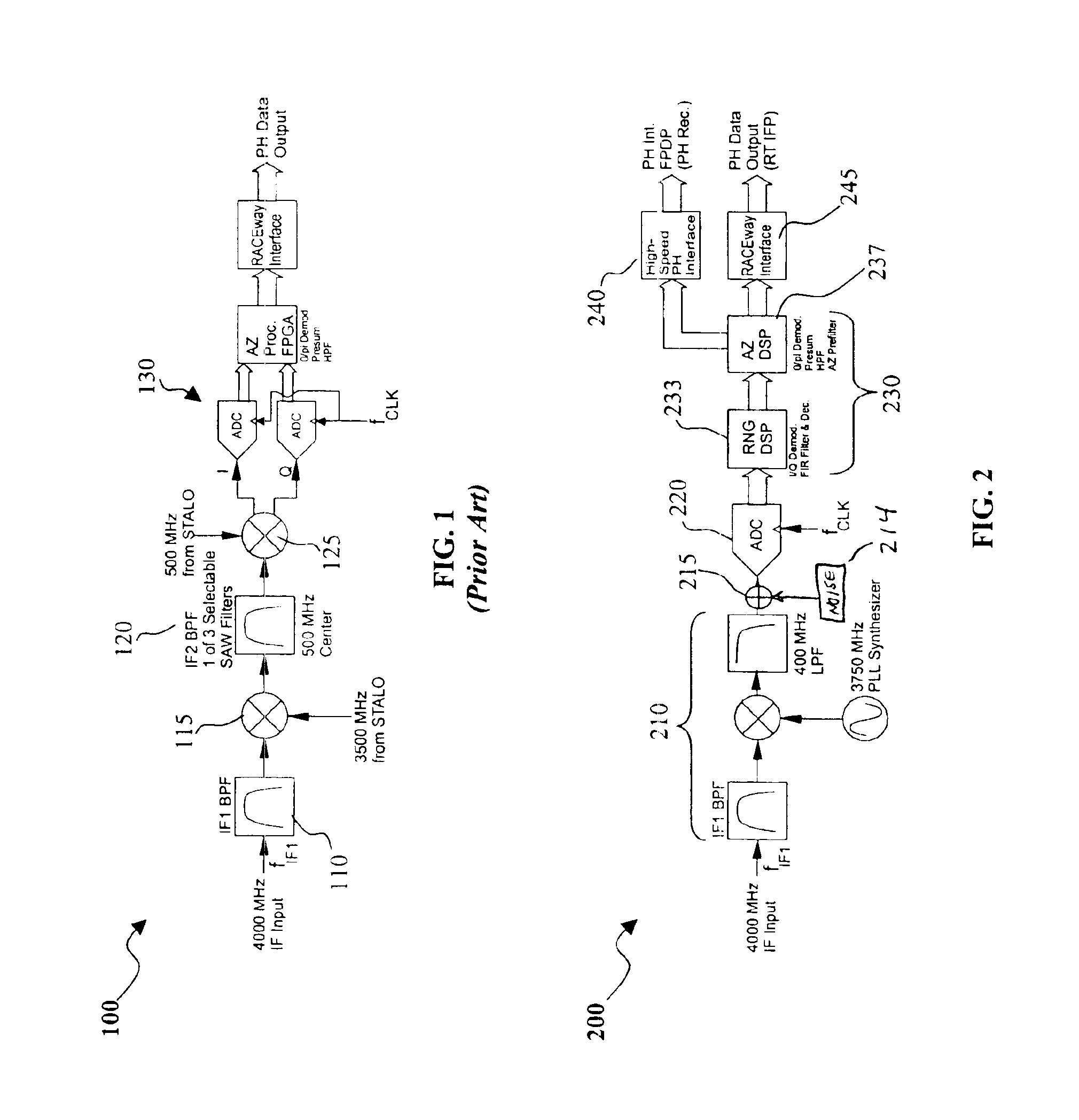
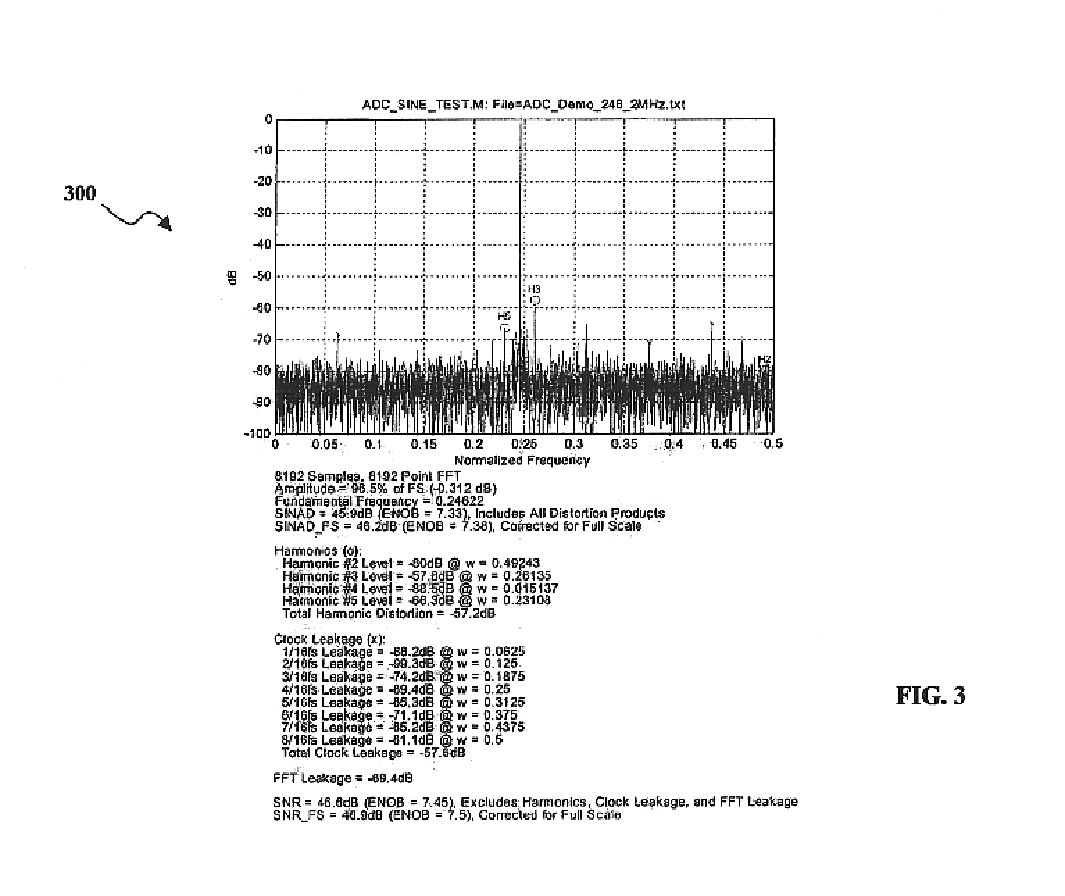
Digital intermediate frequency receiver module for use in airborne SAR applications
ActiveUS6864827B1Increase flexibilityIncrease spacingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingRadar systems
A digital IF receiver (DRX) module directly compatible with advanced radar systems such as synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems. The DRX can combine a 1 G-Sample / sec 8-bit ADC with high-speed digital signal processor, such as high gate-count FPGA technology or ASICs to realize a wideband IF receiver. DSP operations implemented in the DRX can include quadrature demodulation and multi-rate, variable-bandwidth IF filtering. Pulse-to-pulse (Doppler domain) filtering can also be implemented in the form of a presummer (accumulator) and an azimuth prefilter. An out of band noise source can be employed to provide a dither signal to the ADC, and later be removed by digital signal processing. Both the range and Doppler domain filtering operations can be implemented using a unique pane architecture which allows on-the-fly selection of the filter decimation factor, and hence, the filter bandwidth. The DRX module can include a standard VME-64 interface for control, status, and programming. An interface can provide phase history data to the real-time image formation processors. A third front-panel data port (FPDP) interface can send wide bandwidth, raw phase histories to a real-time phase history recorder for ground processing.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
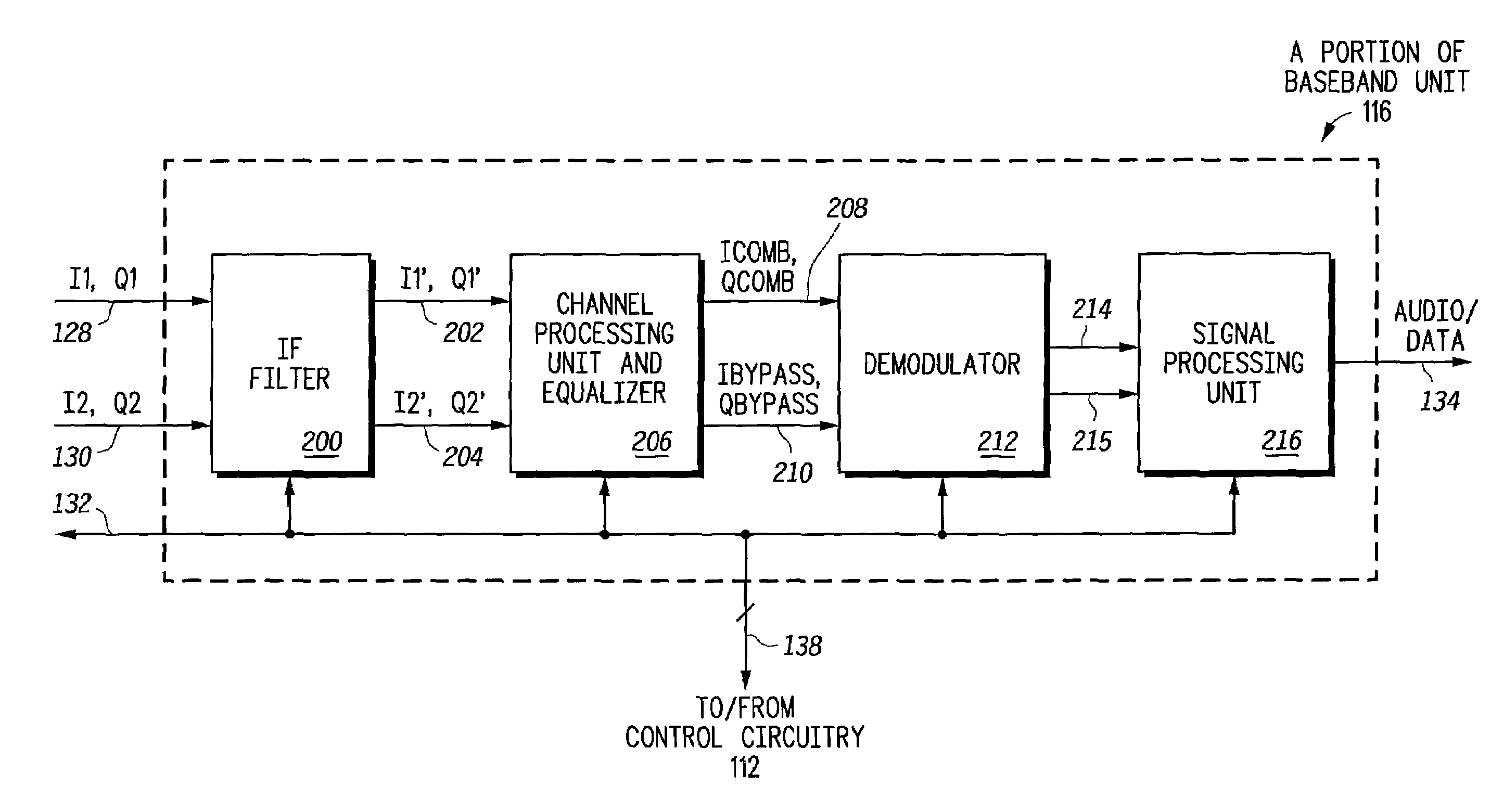
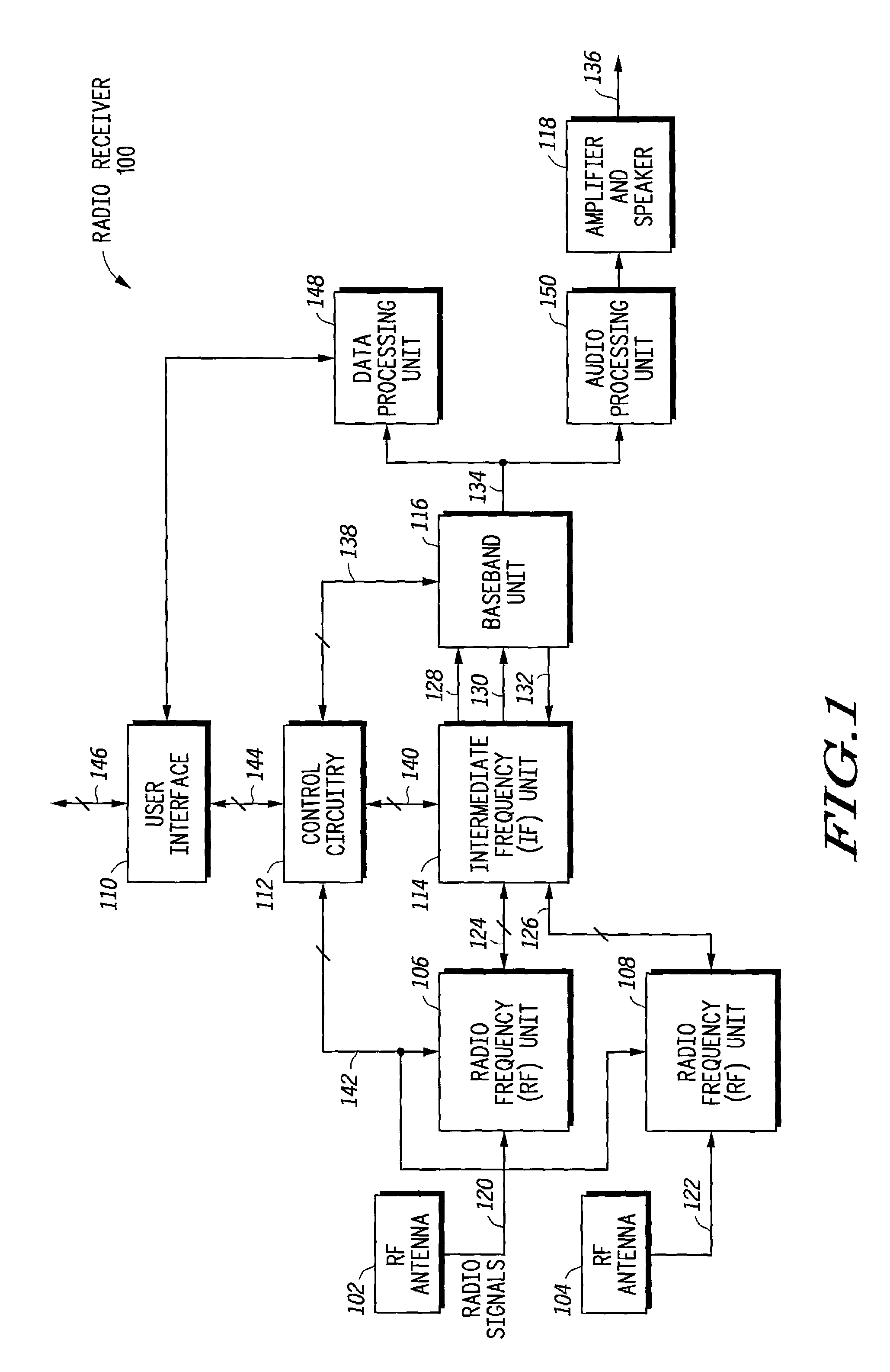
Radio receiver having an adaptive equalizer and method therefor
A radio receiver (100) has an equalizer (500) that operates in the time domain to remove residual interference that is not removed by an IF filter (200) operating in the frequency domain that is caused by an adjacent interfering FM station. The equalizer (500) includes a modified constant modulus algorithm (CMA) to generate a tap update signal from the output of the equalizer (500). The equalizer (500) uses the modified CMA to reduce an amplitude fluctuation of the received signal caused by the adjacent interfering station. The CMA is modified to use an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter (540) to generate the tap update. The IIR filter (540) also speeds up a convergence of the modified CMA to provide better performance.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
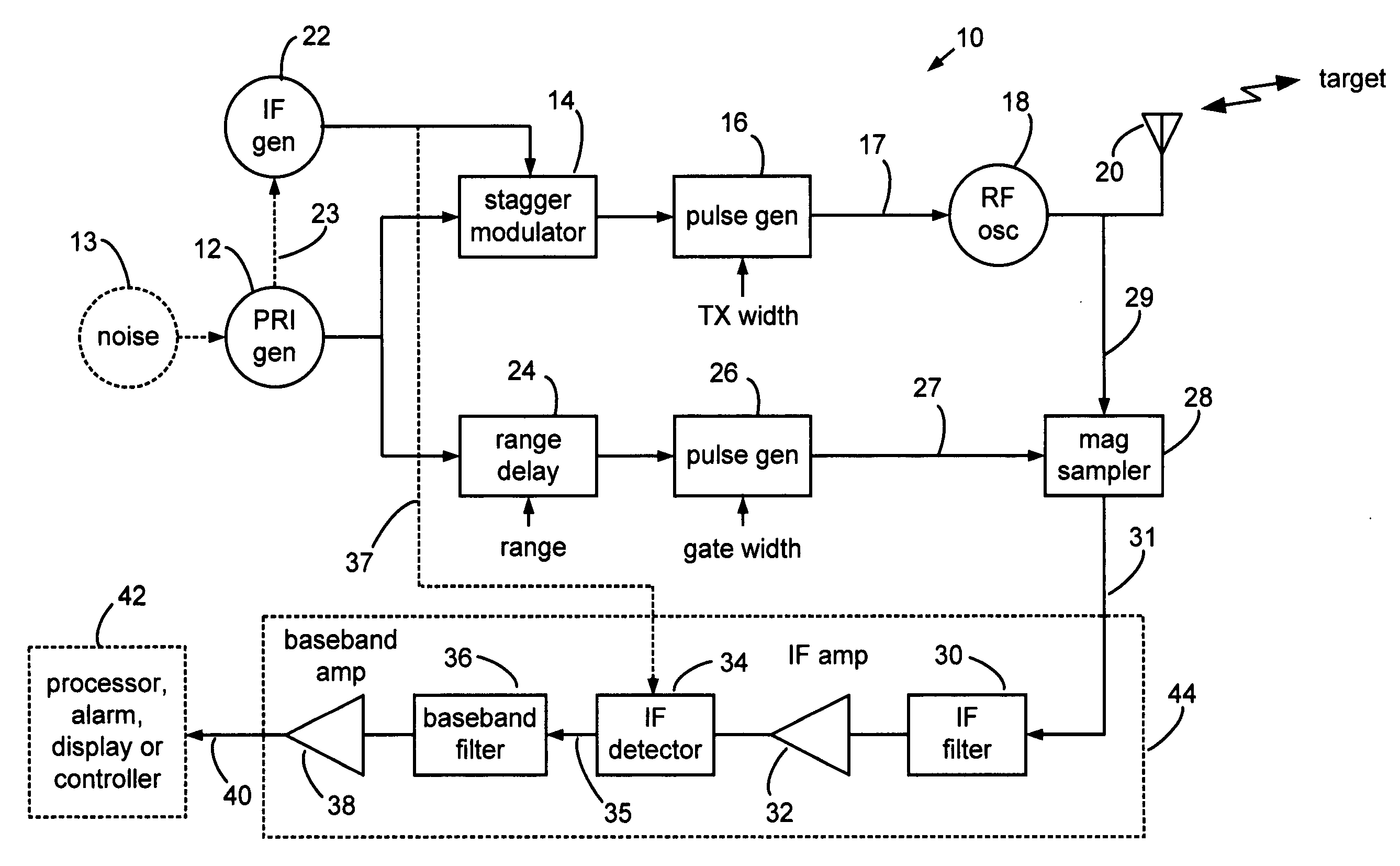
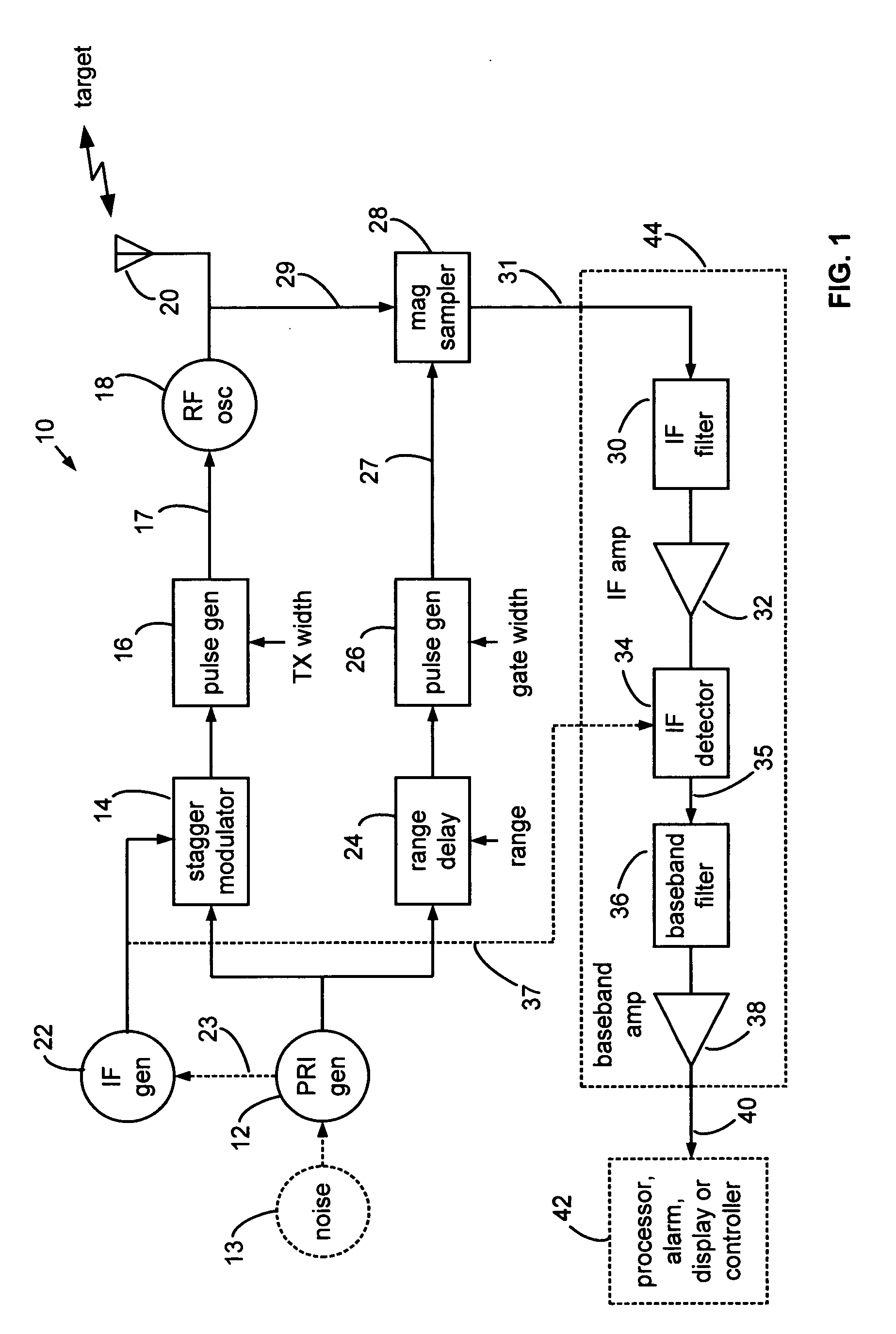
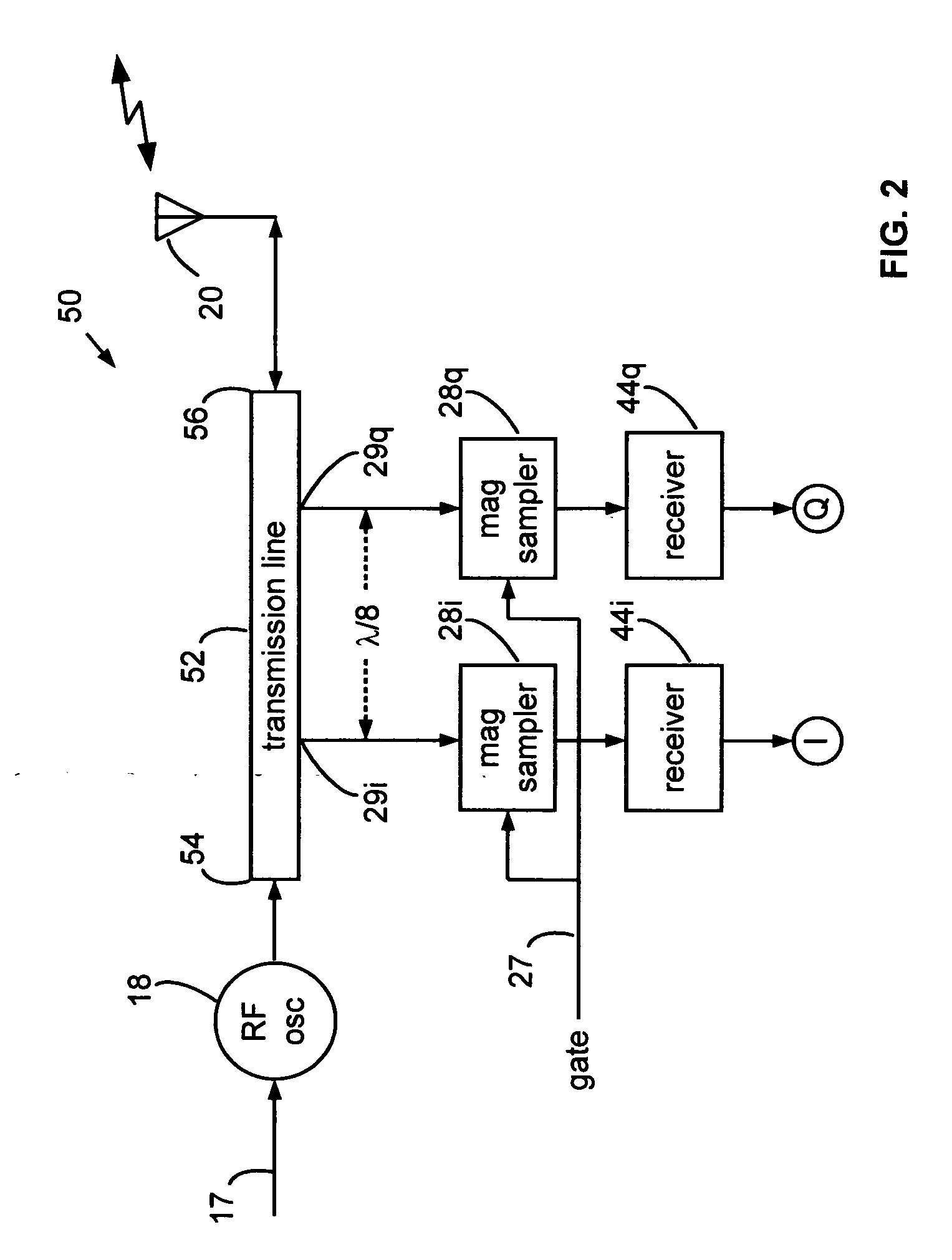
Range gated holographic radar
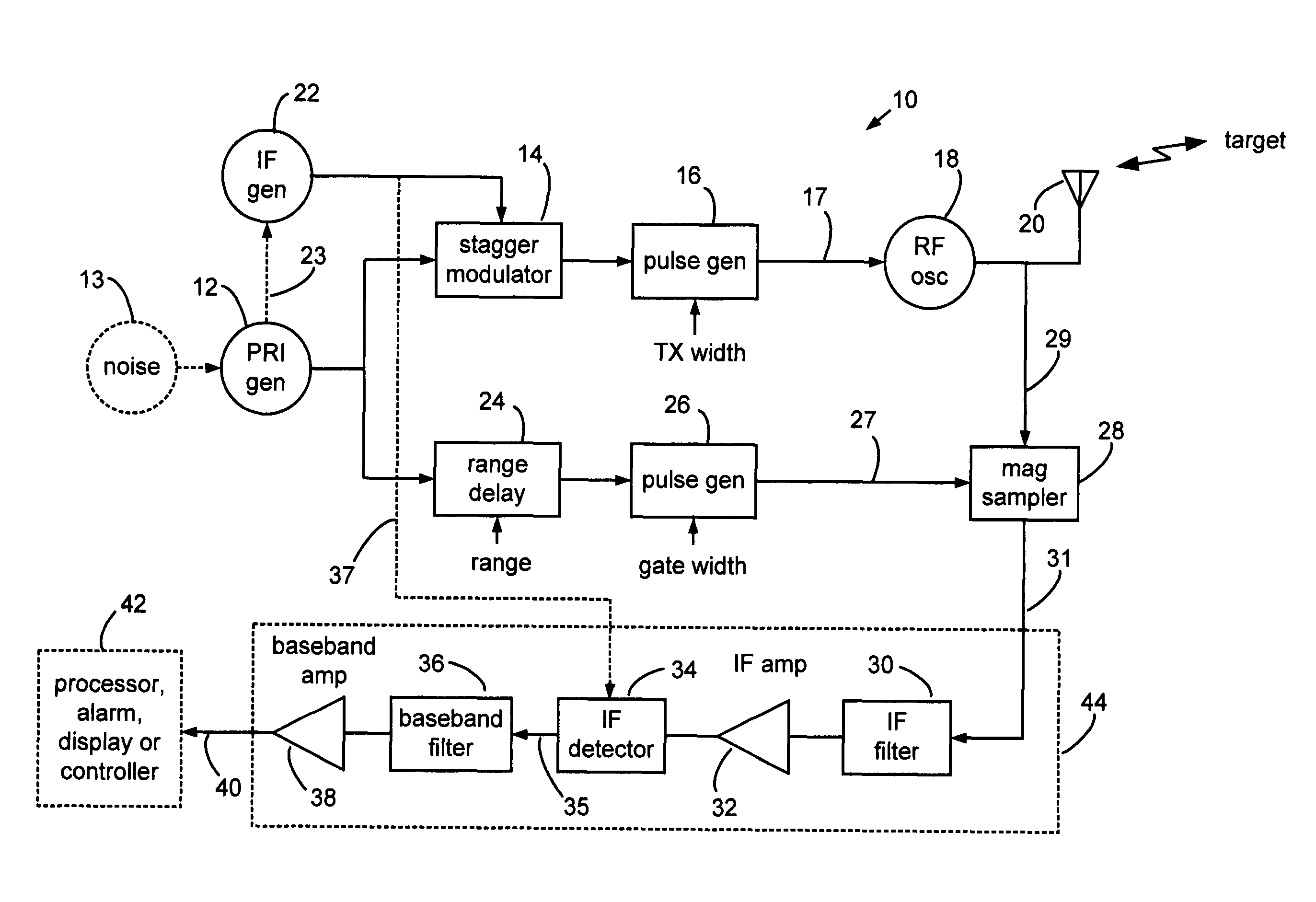
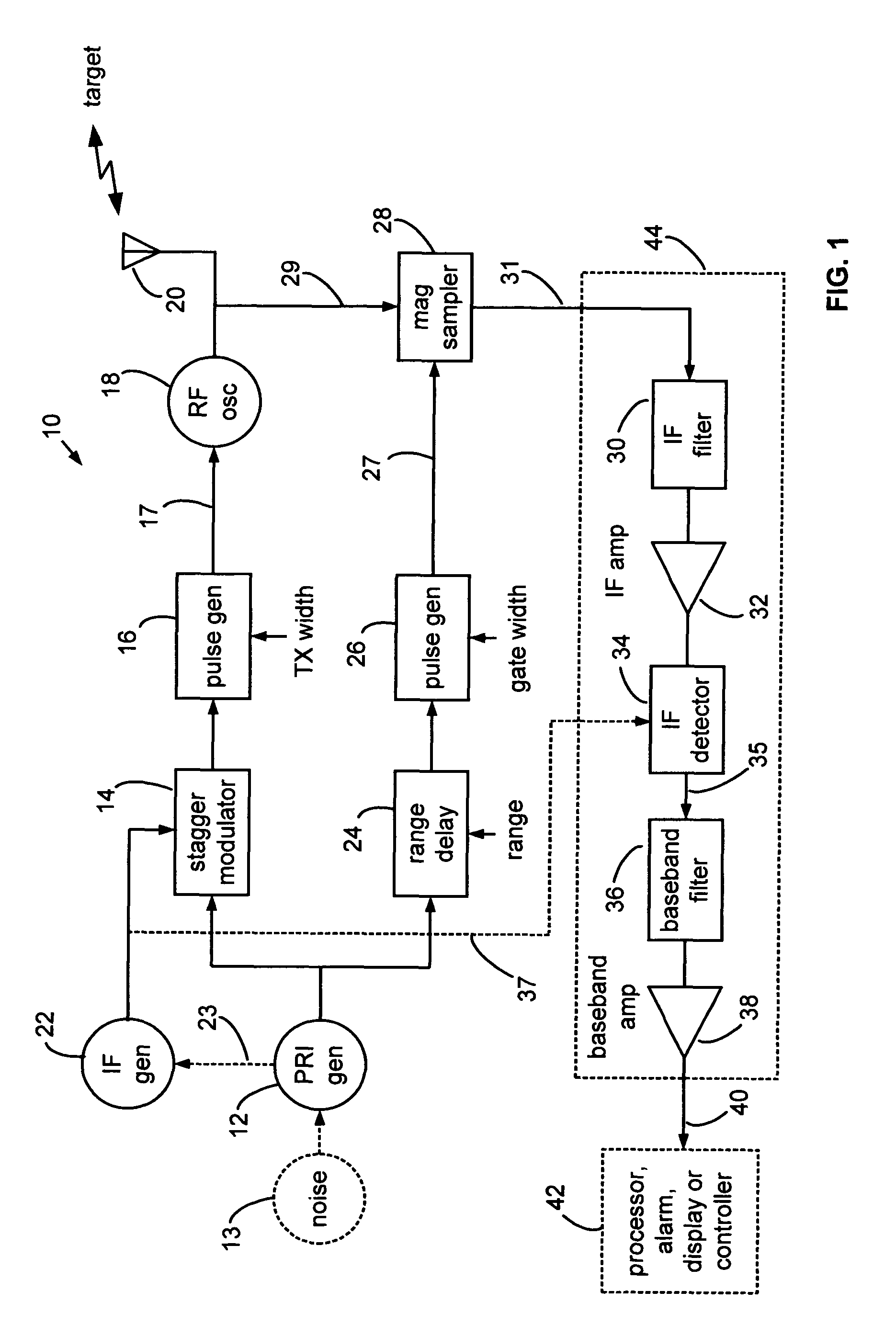
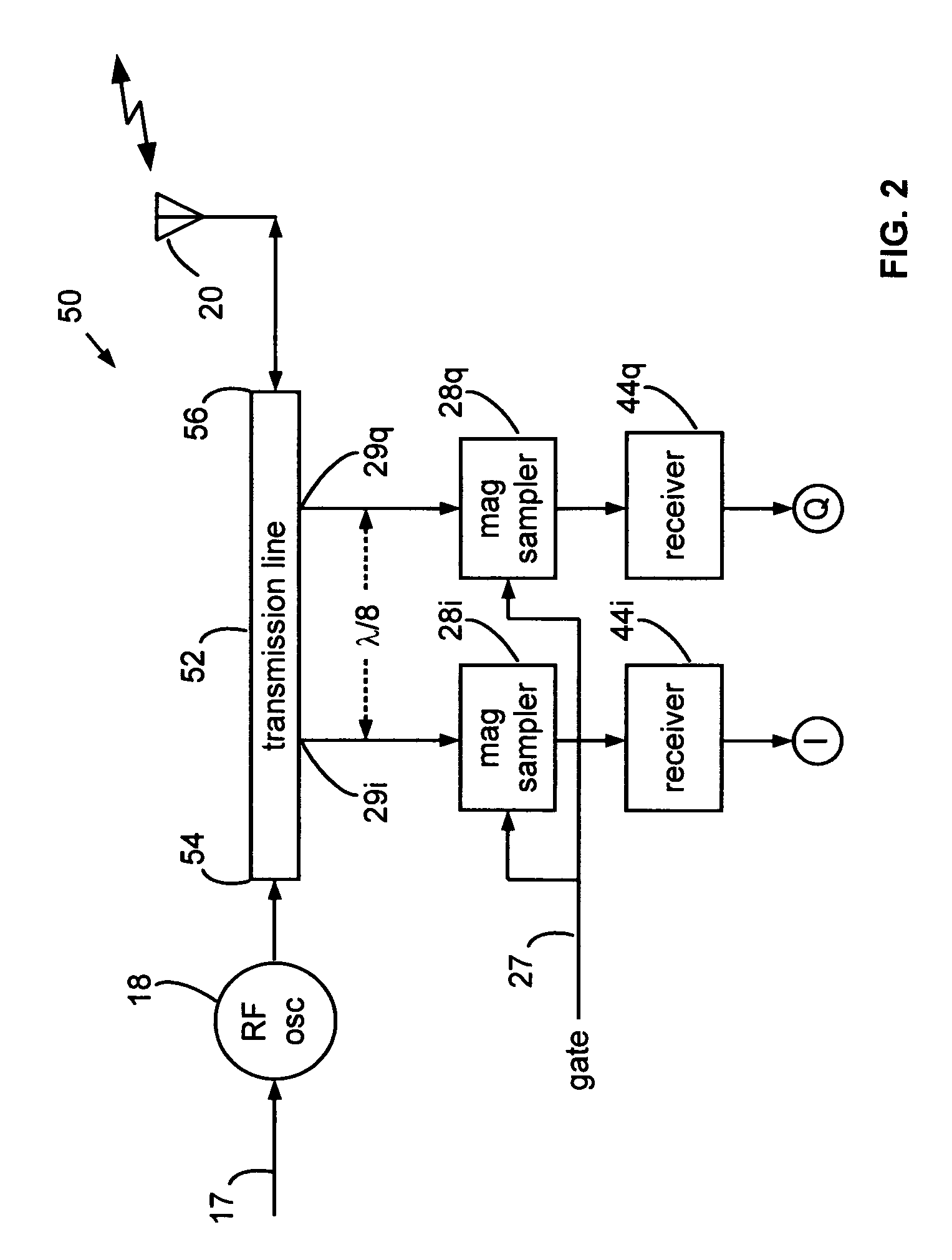
Narrow virtual transmit pulses are synthesized by differencing long-duration, staggered pulse repetition interval (PRI) transmit pulses. PRI is staggered at an intermediate frequency IF. Echoes from virtual pulses form IF-modulated interference patterns with a reference wave. Samples of interference patterns are IF-filtered to produce high spatial resolution holographic data. PRI stagger can be very small, e.g., 1-ns, to produce a 1-ns virtual pulse from very long, staggered transmit pulses. Occupied Bandwidth (OBW) can be less than 10 MHz due to long RF pulses needed for holography, while spatial resolution can be very high, corresponding to ultra-wideband (UWB) operation, due to short virtual pulses. X-Y antenna scanning can produce range-gated surface holograms from quadrature data. Multiple range gates can produce stacked-in-range holograms. Motion and vibration can be detected by changes in interference patterns within a range-gated zone.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
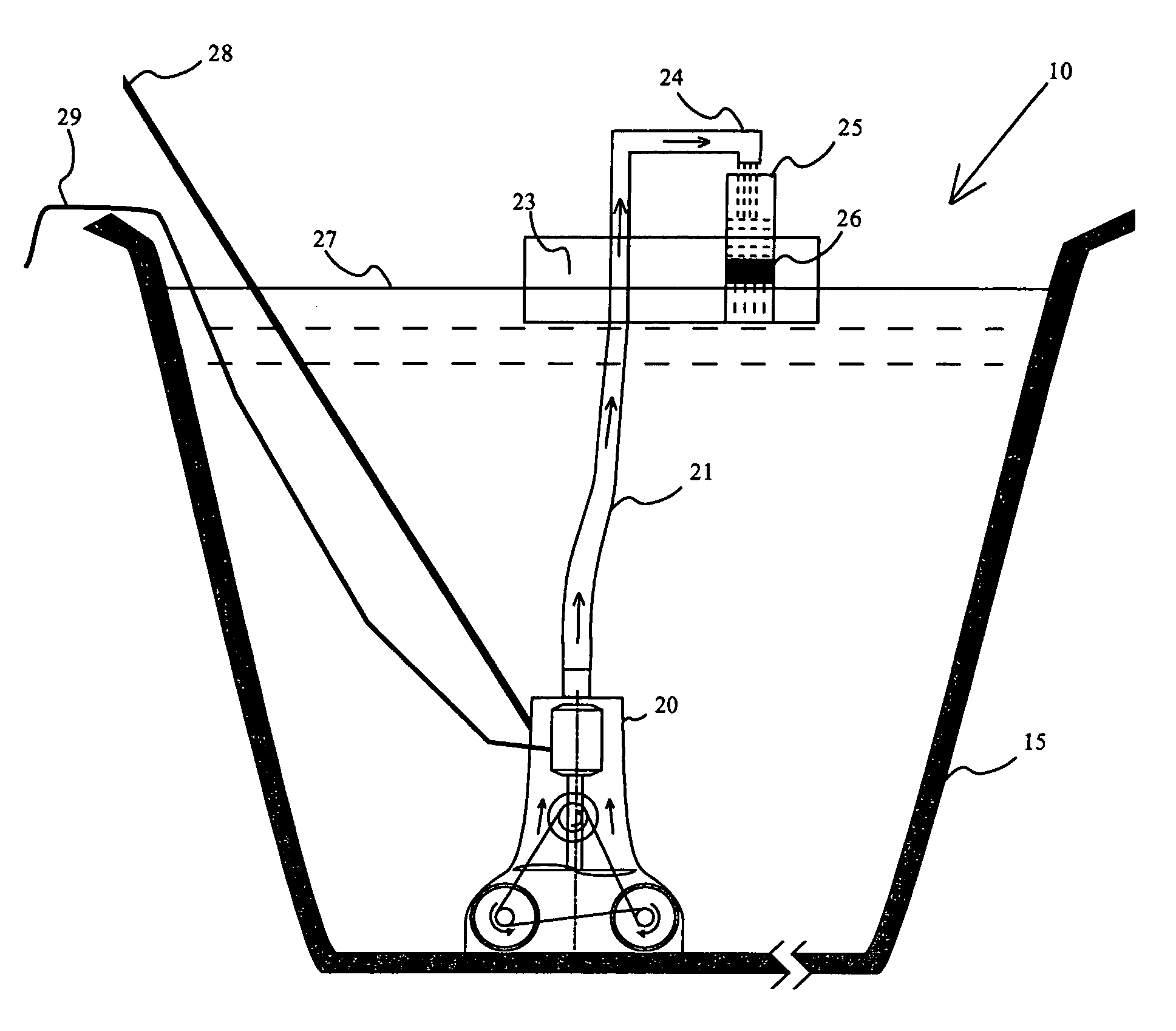
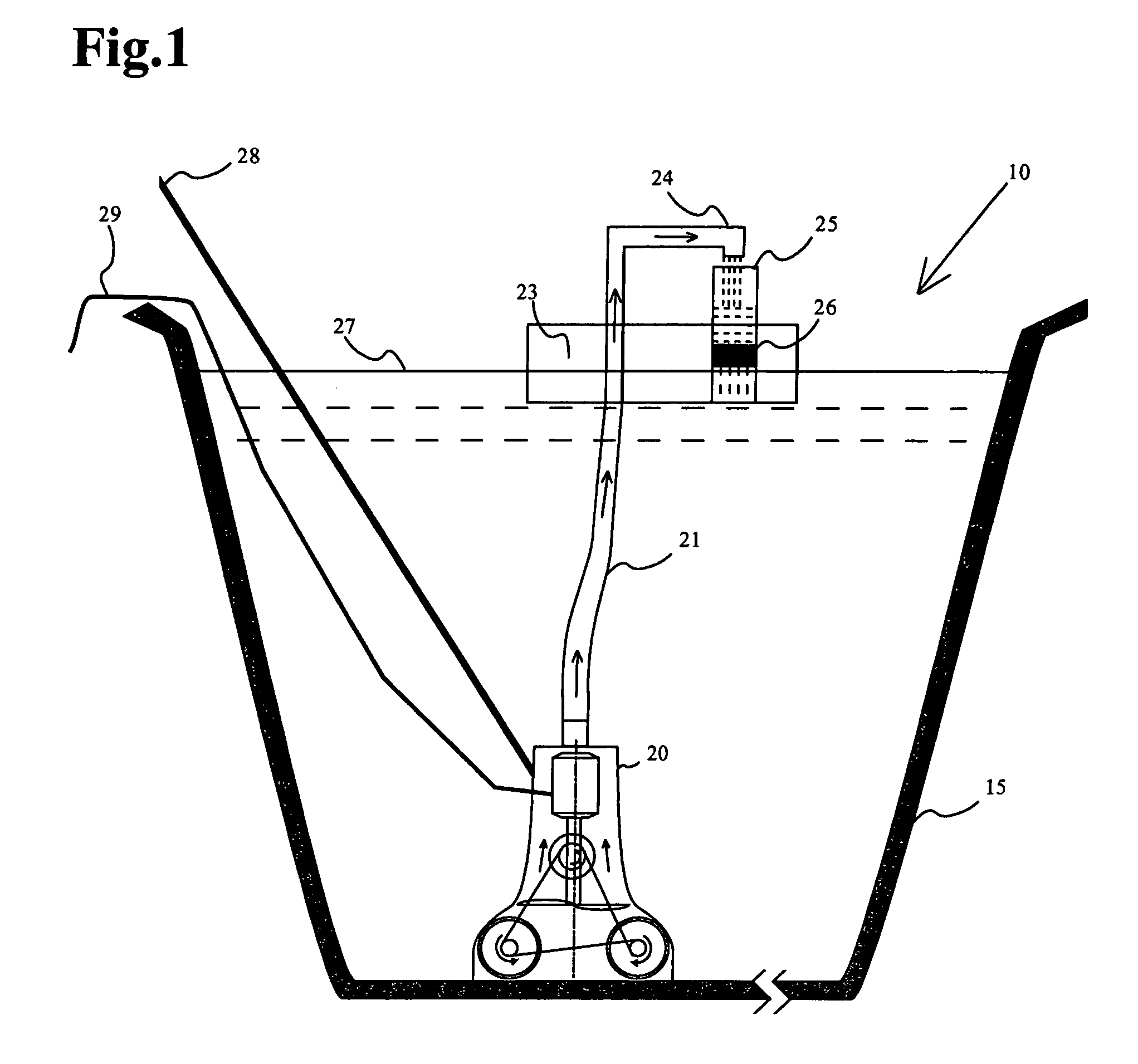
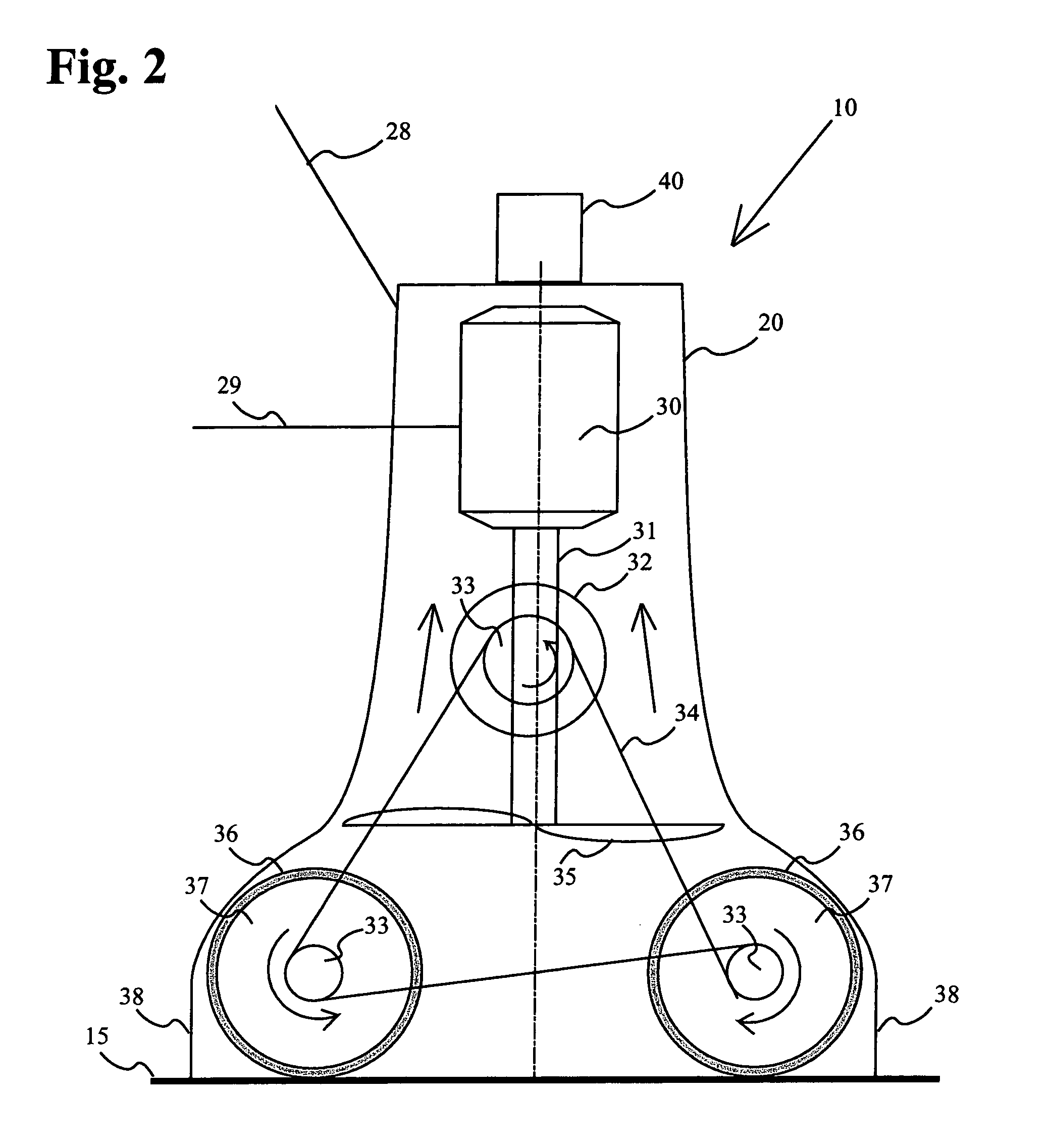
Open-air filtration cleaning device for pools and hot tubs
InactiveUS6942790B1Guaranteed uptimeLow costWater cleaningHollow article cleaningImpellerMotor drive
An open-air filtration device cleans swimming pools and hot tubs in an efficient, reliable manner. An open-air filter with a suction chamber unit comprises two scrubbing brushes and an impeller powered by a motor drive. Water containing debris is pumped to a level above the swimming pool or hot tub surface. The debris containing water is discharged through a spout into a filter tube. A filter element associated with the filter tube, and open to atmosphere filters the debris containing water by gravitational forces solely. The spout and filter tube are, optionally, attached to a pole that manually propels the suction unit. They may alternatively be attached to a floating platform that floats on the water surface of the pool or hot tub. If filter efficiency decreases, the water level in the filter tube rises, indicating that the filter element must be replaced. A rise in water level is visually observed or detected automatically and communicated using a visible or audible alarm.
Owner:DOLTON EDWARD
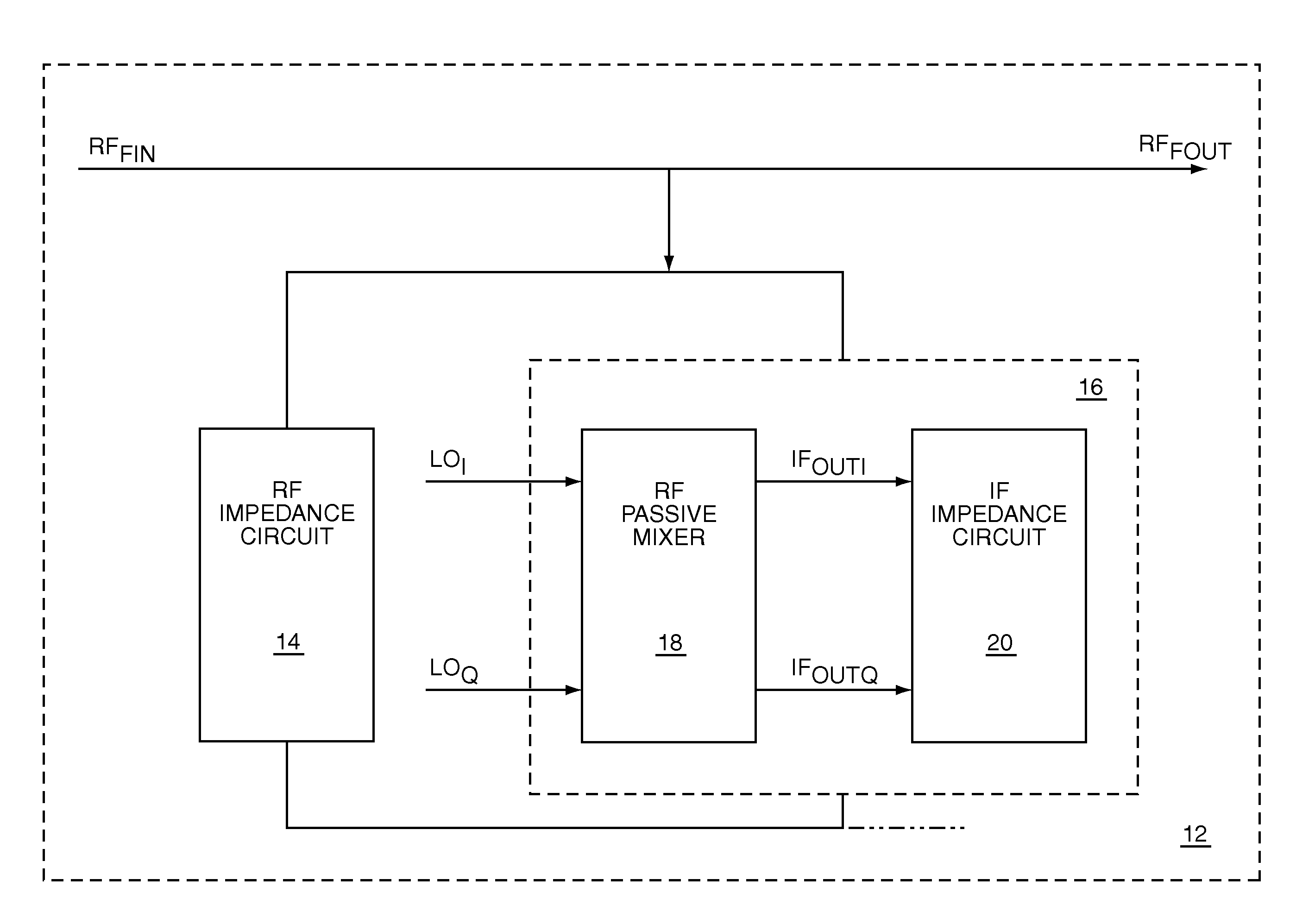
Radio frequency filter using intermediate frequency impedance translation
The present invention is an RF filter that translates impedances of an IF circuit to create a filter with an RF center frequency having the high Q roll-off characteristics of an IF filter. The RF filter is self-aligned with the frequency of an RF local oscillator. The RF filter has an impedance divider, which is formed by coupling an RF impedance circuit to a translated IF impedance circuit. The translated IF impedance circuit includes an RF passive mixer and an IF impedance circuit. The mixer translates the impedance of the IF impedance circuit by mixing an RF input signal with an RF local oscillator signal, which determines the RF center frequency. Filtered RF signals may be provided by the impedance divider. Filtered IF signals may be provided by the IF impedance circuit. To effectively translate and preserve the IF impedance characteristics, the IF impedance circuit presents a high impedance at harmonics of the RF local oscillator signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Broadband single conversion tuner integrated circuits
ActiveUS20050024544A1Television system detailsGHz frequency transmissionEngineeringSignal transition
A tunable receiver is disclosed including a plurality of select filters to perform an initial band selection, a variable-gain low noise amplifier (LNA) whose gain is controlled to prevent its output power level to exceed a pre-determined power threshold, a plurality of digitally-tunable tracking filters to pass signals within a selected channel and to reject signals in a corresponding image band, a second LNA to further amplify the received RF signal and to generate differential signal outputs, a down converting stage which converts the received RF signal to an IF signal while rejecting signals in the image band, an IF trap to further reject undesired signals present at the output of the down converting stage, an IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal to compensate for losses, an IF filter to provide channel select and reject undesirable signals, and a variable-gain IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal and maintain its power level within specification.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Broadband single conversion tuner integrated circuits
ActiveUS7095454B2Television system detailsGHz frequency transmissionAudio power amplifierDifferential signaling
A tunable receiver is disclosed including a plurality of select filters to perform an initial band selection, a variable-gain low noise amplifier (LNA) whose gain is controlled to prevent its output power level to exceed a pre-determined power threshold, a plurality of digitally-tunable tracking filters to pass signals within a selected channel and to reject signals in a corresponding image band, a second LNA to further amplify the received RF signal and to generate differential signal outputs, a down converting stage which converts the received RF signal to an IF signal while rejecting signals in the image band, an IF trap to further reject undesired signals present at the output of the down converting stage, an IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal to compensate for losses, an IF filter to provide channel select and reject undesirable signals, and a variable-gain IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal and maintain its power level within specification.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Enhanced emission from pc-LEDs using IF filters
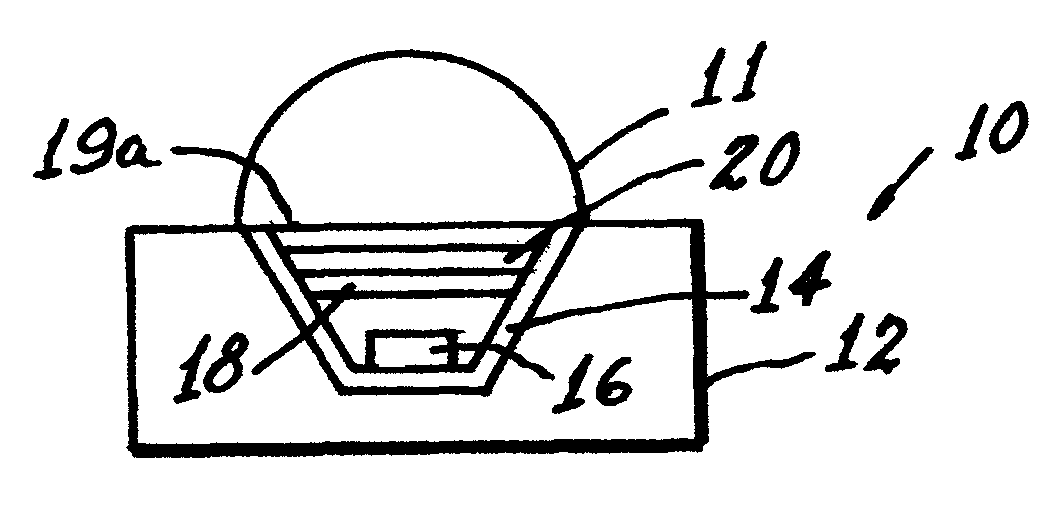
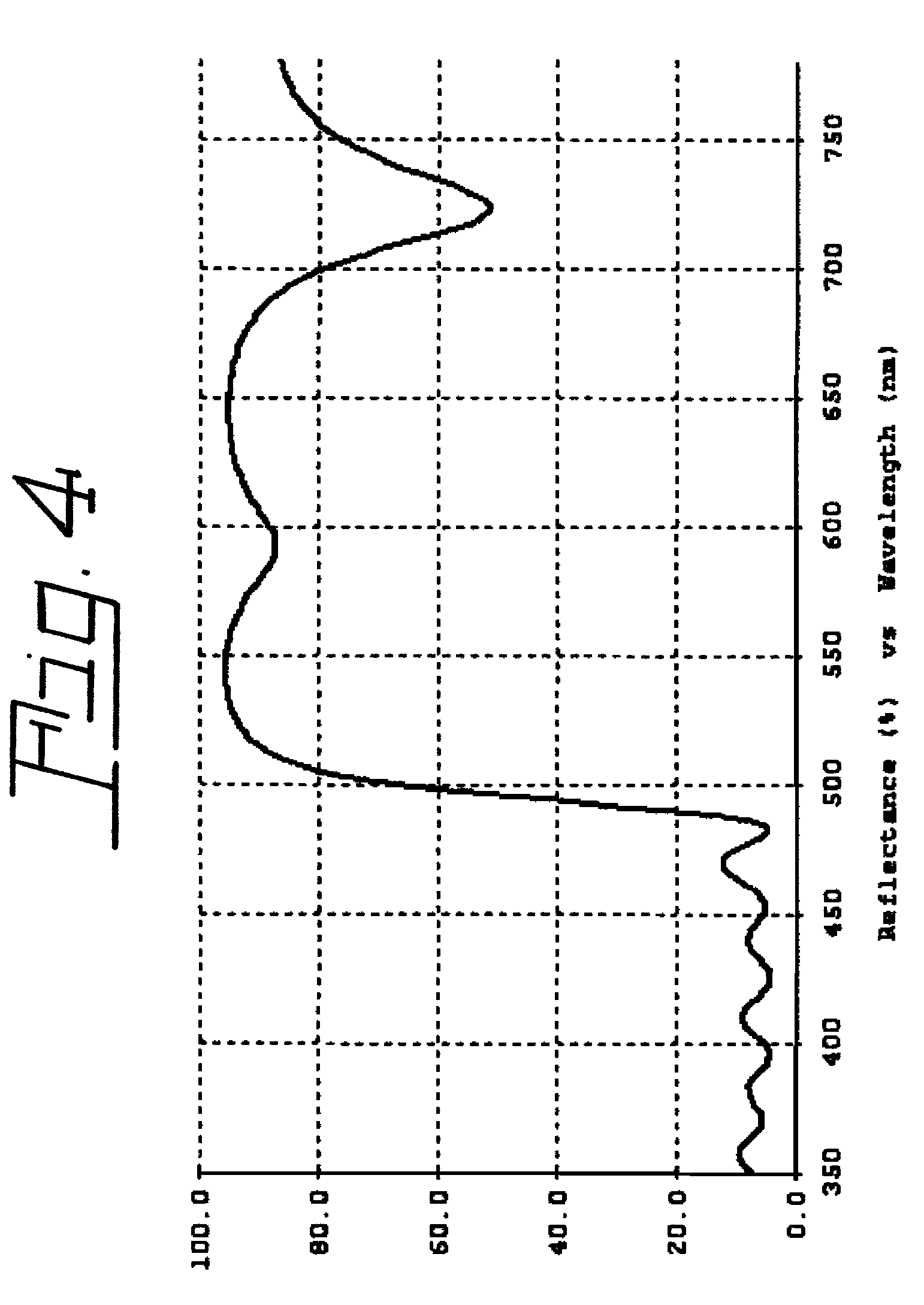
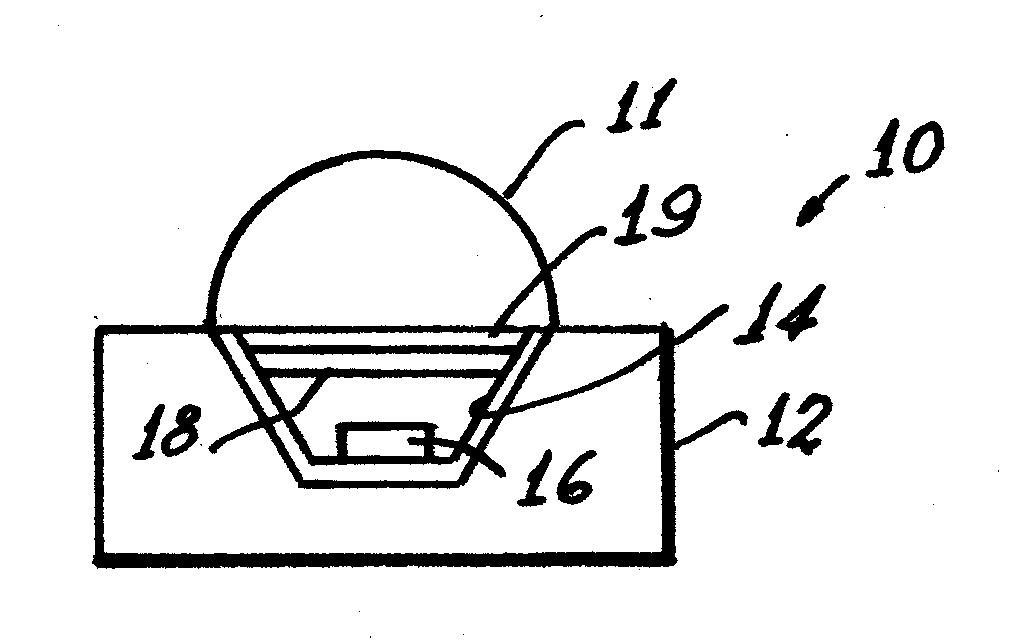
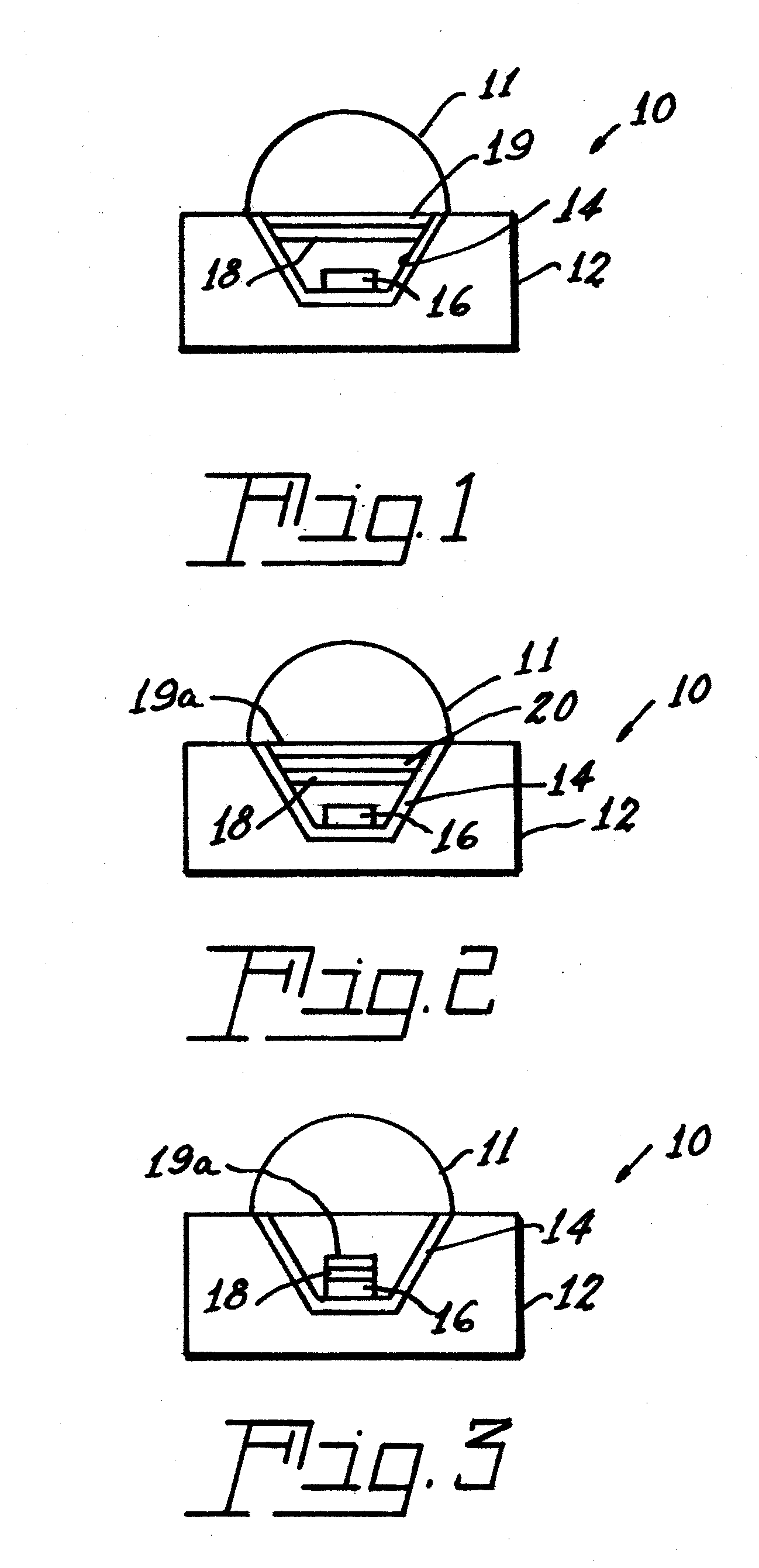
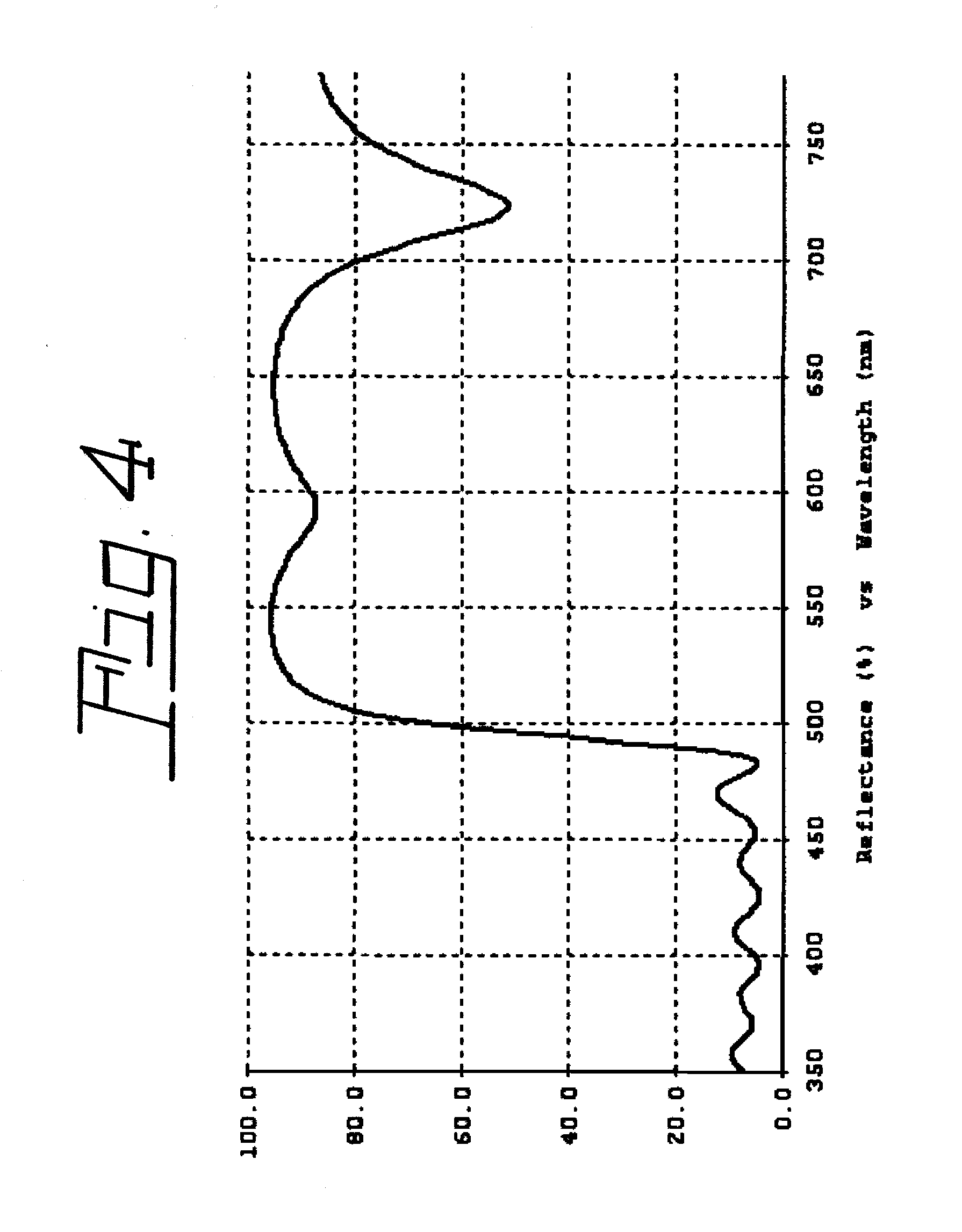
InactiveUS7800287B2Easy to operateImprove light outputIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensPhosphorFluorescence
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
Enhanced Emission from pc-LEDs Using IF Filters
InactiveUS20080054803A1Easy to operateImprove light outputIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensFluorescencePhosphor
White-light efficiency from a light emitting diode is enhanced by recycling inwardly penetrating light outwardly by application of a multi-layer, thin film filter between the LED die and the phosphor layer. This procedure increases the package extraction efficiency.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
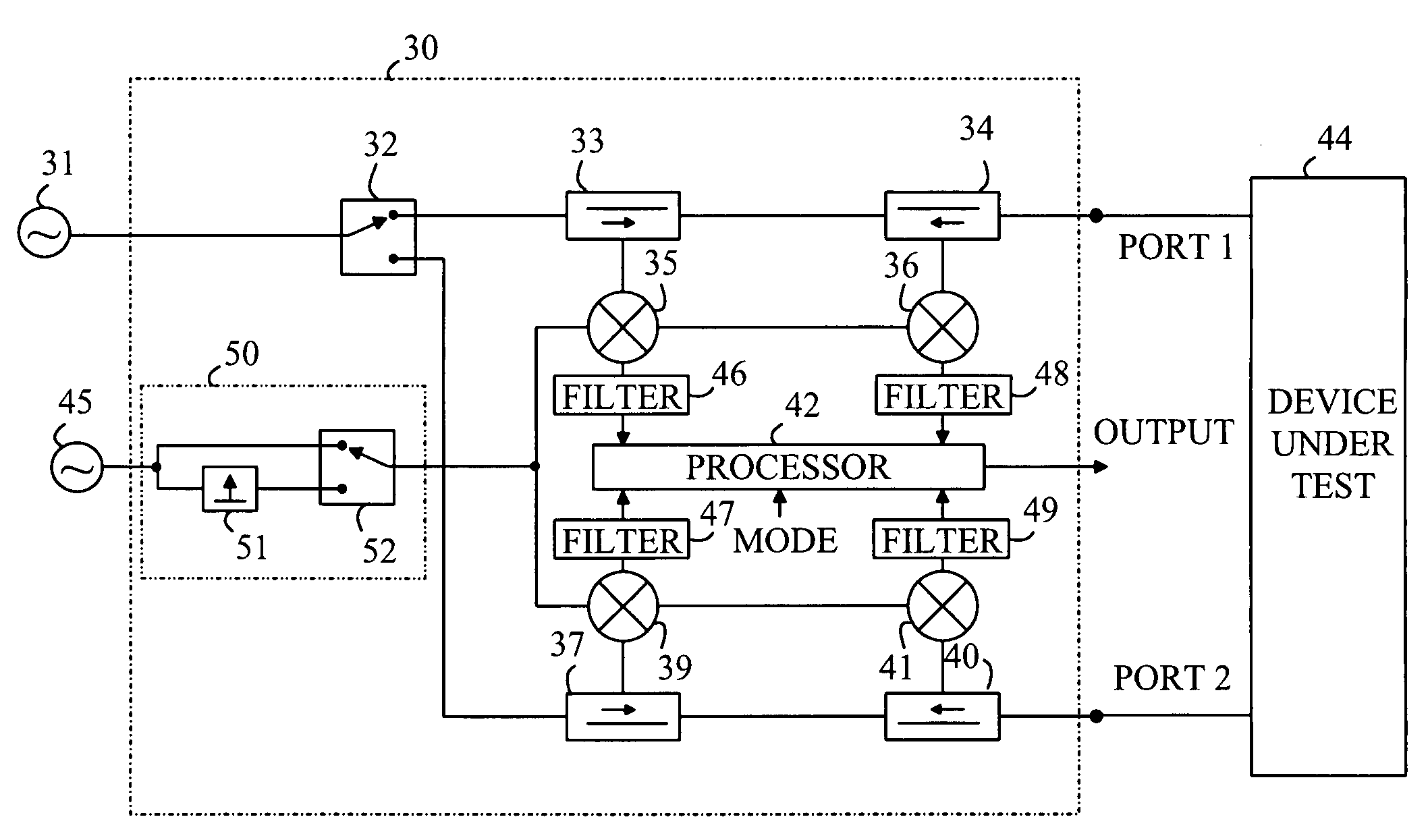
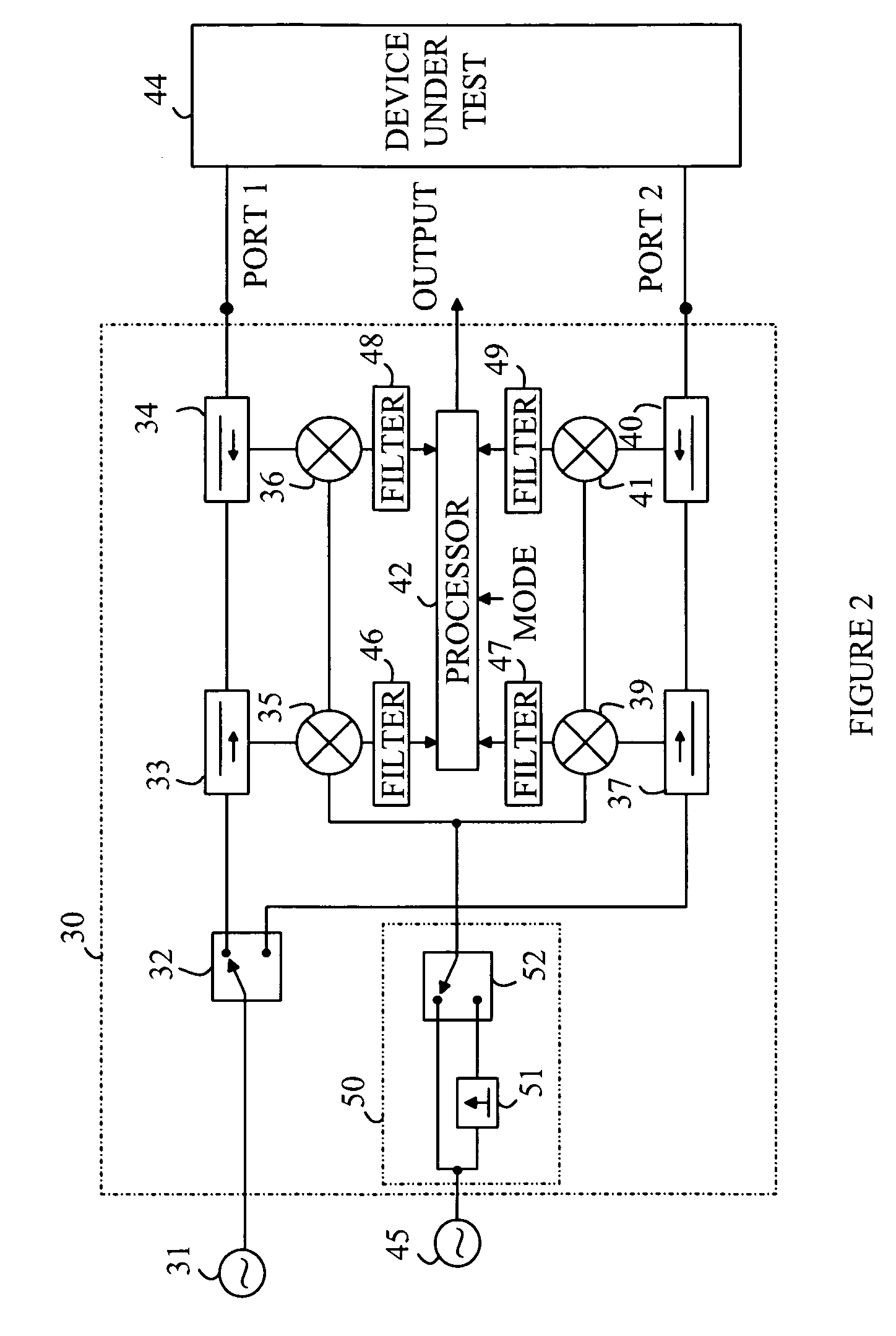
Dual Mode Vector Network Analyzer
A multimode network analyzer (VNA) and the method of using the same are disclosed. The VNA includes a signal input port that receives a test signal, an LO signal generator, a mixer, an IF filter and a processor. The LO signal generator generates a mixer LO signal from a mixer input test signal, the LO signal generator having first and second modes. The mixer LO signal is substantially a first periodic signal in the first mode and a second periodic signal having a plurality of harmonically related tones in the second mode. The mode that is currently operative is determined by a mixer control signal. The mixer is driven by the LO signal and has an output that is filtered by the IF filter to generate an IF signal. The processor analyzes the IF signal to determine a parameter characterizing the test signal and outputs that parameter.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
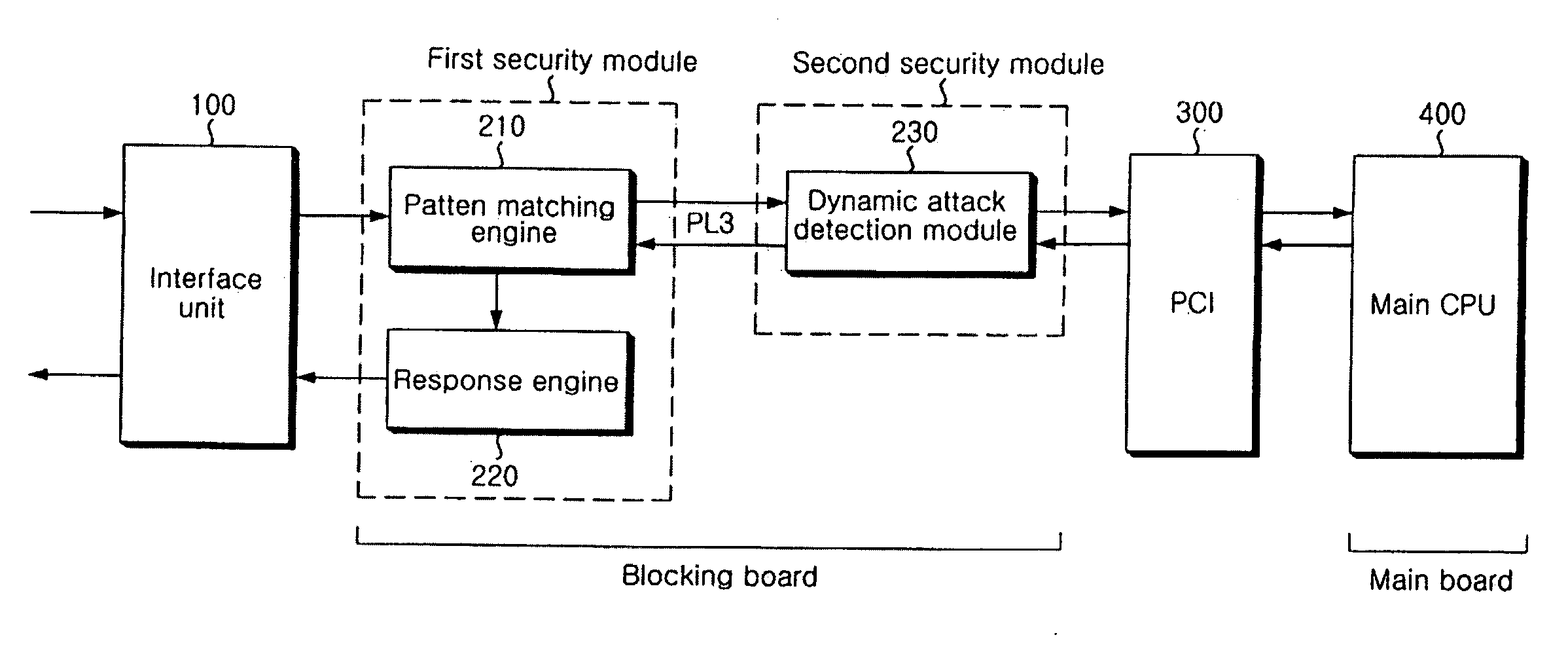
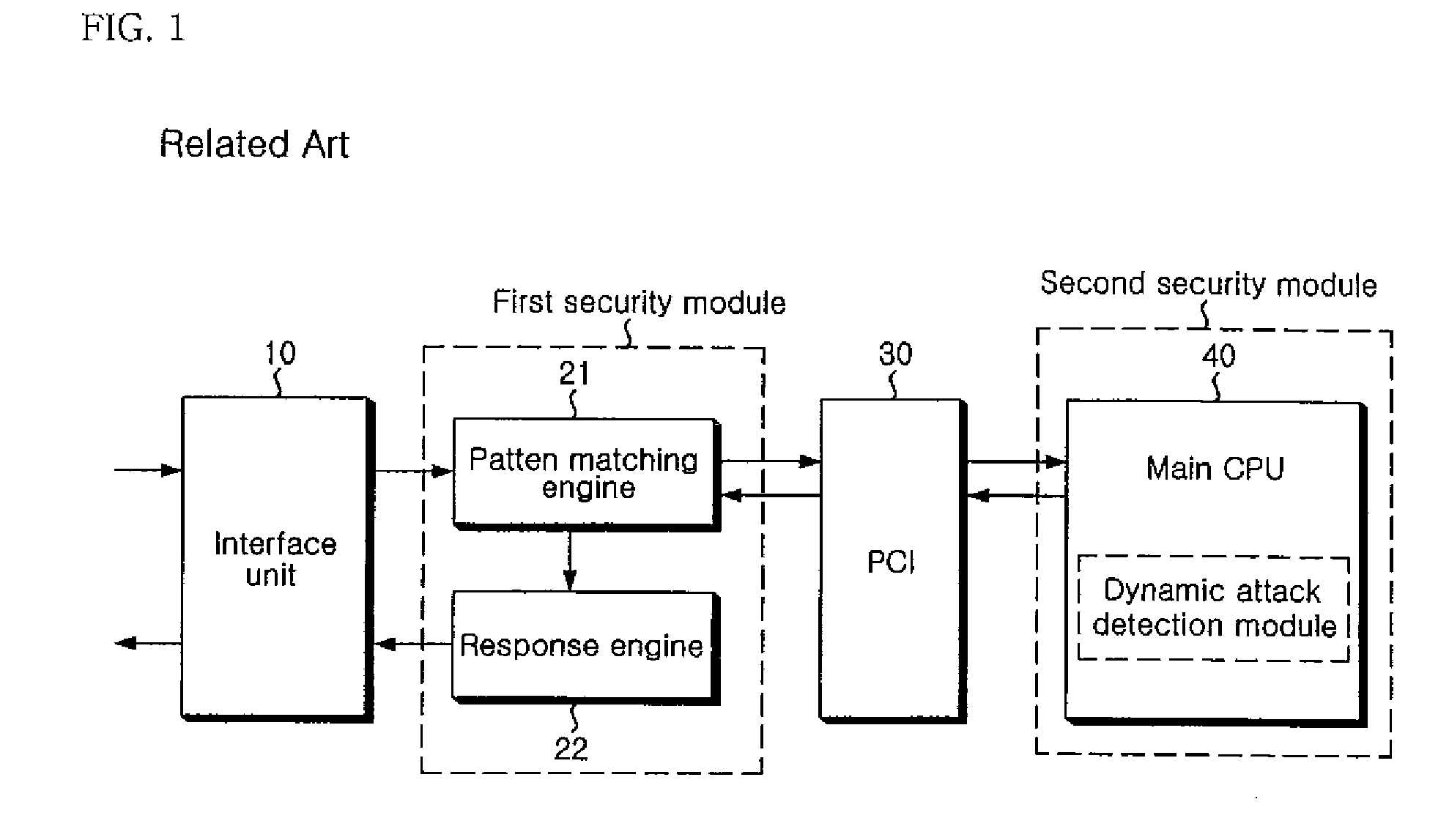
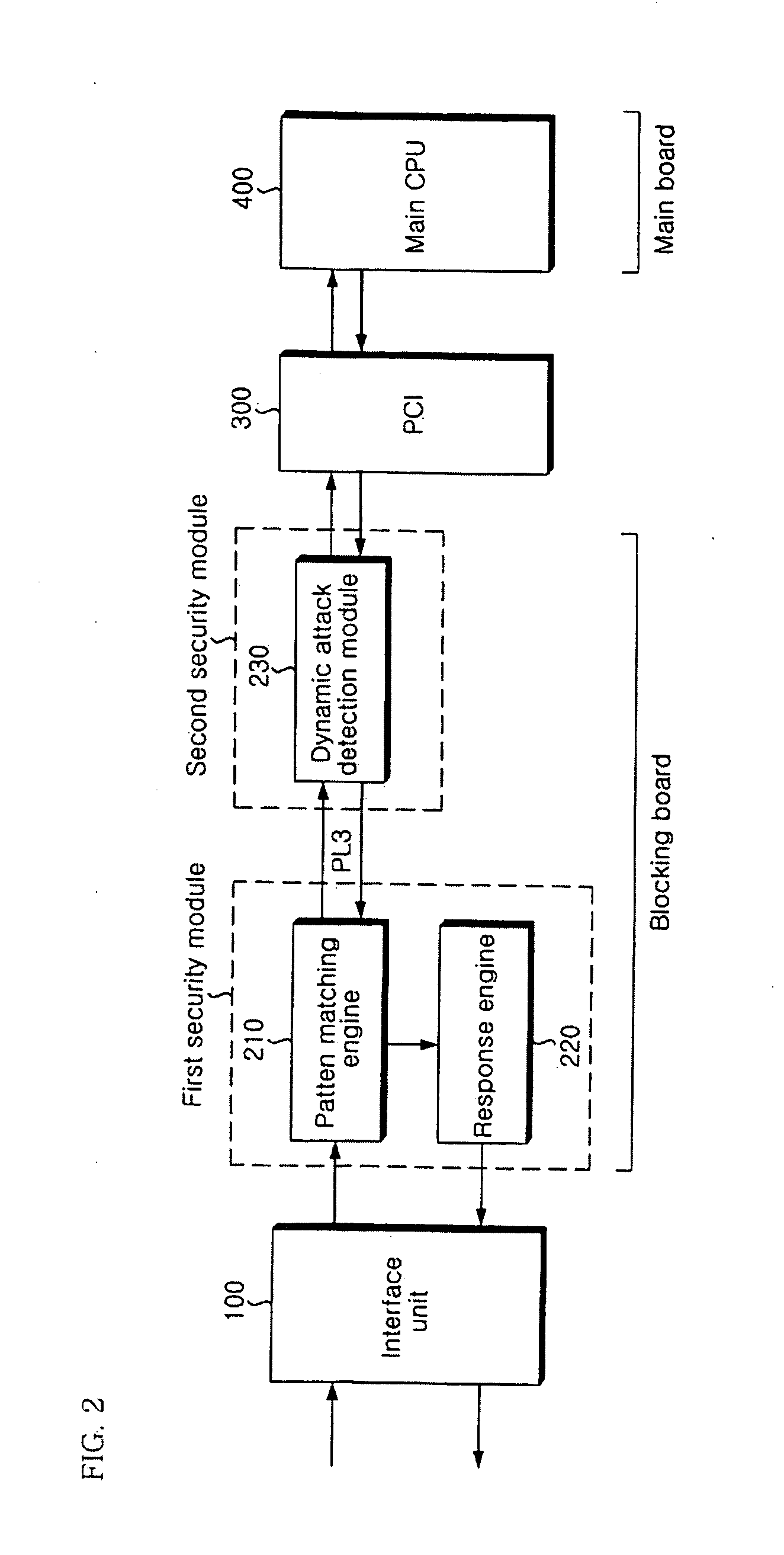
Apparatus and method of securing network
ActiveUS20080163356A1Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsSecurity solutionPattern matching
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method of securing a network. In the present invention, a pattern matching engine 210 corresponding to a first security module initially performs a hardware-based filtering process for a static attack of an input network packet and transmits a normal packet determined to be normal as a result of the filtering to a dynamic attack detection module 230 corresponding to a second security module through a PL3 interface. The dynamic attack detection module230 performs a hardware-based filtering process for a dynamic attack of the normal packet transmitted from the pattern matching engine 210. The dynamic attack detection module 230 transmits the filtering result to a main CPU 400 through a PCI 300 if filtering the dynamic attack is completed. Then, a main CPU 400 transmits a response policy based on the transmitted filtering result to a response engine 220 through the PCI 300 and the dynamic attack detection module 230 to block an abnormal packet. Therefore, the present invention is very effective in that accuracy of detection is enhanced, and weakness in processing speed and performance of a network security solution can be compensated to meet requirements on real-time.
Owner:LG CNS
Range gated holographic radar
InactiveUS20100214157A1Improve spatial resolutionLow noise rangeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra-widebandImage resolution
Narrow virtual transmit pulses are synthesized by differencing long-duration, staggered pulse repetition interval (PRI) transmit pulses. PRI is staggered at an intermediate frequency IF. Echoes from virtual pulses form IF-modulated interference patterns with a reference wave. Samples of interference patterns are IF-filtered to produce high spatial resolution holographic data. PRI stagger can be very small, e.g., 1-ns, to produce a 1-ns virtual pulse from very long, staggered transmit pulses. Occupied Bandwidth (OBW) can be less than 10 MHz due to long RF pulses needed for holography, while spatial resolution can be very high, corresponding to ultra-wideband (UWB) operation, due to short virtual pulses. X-Y antenna scanning can produce range-gated surface holograms from quadrature data. Multiple range gates can produce stacked-in-range holograms. Motion and vibration can be detected by changes in interference patterns within a range-gated zone.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
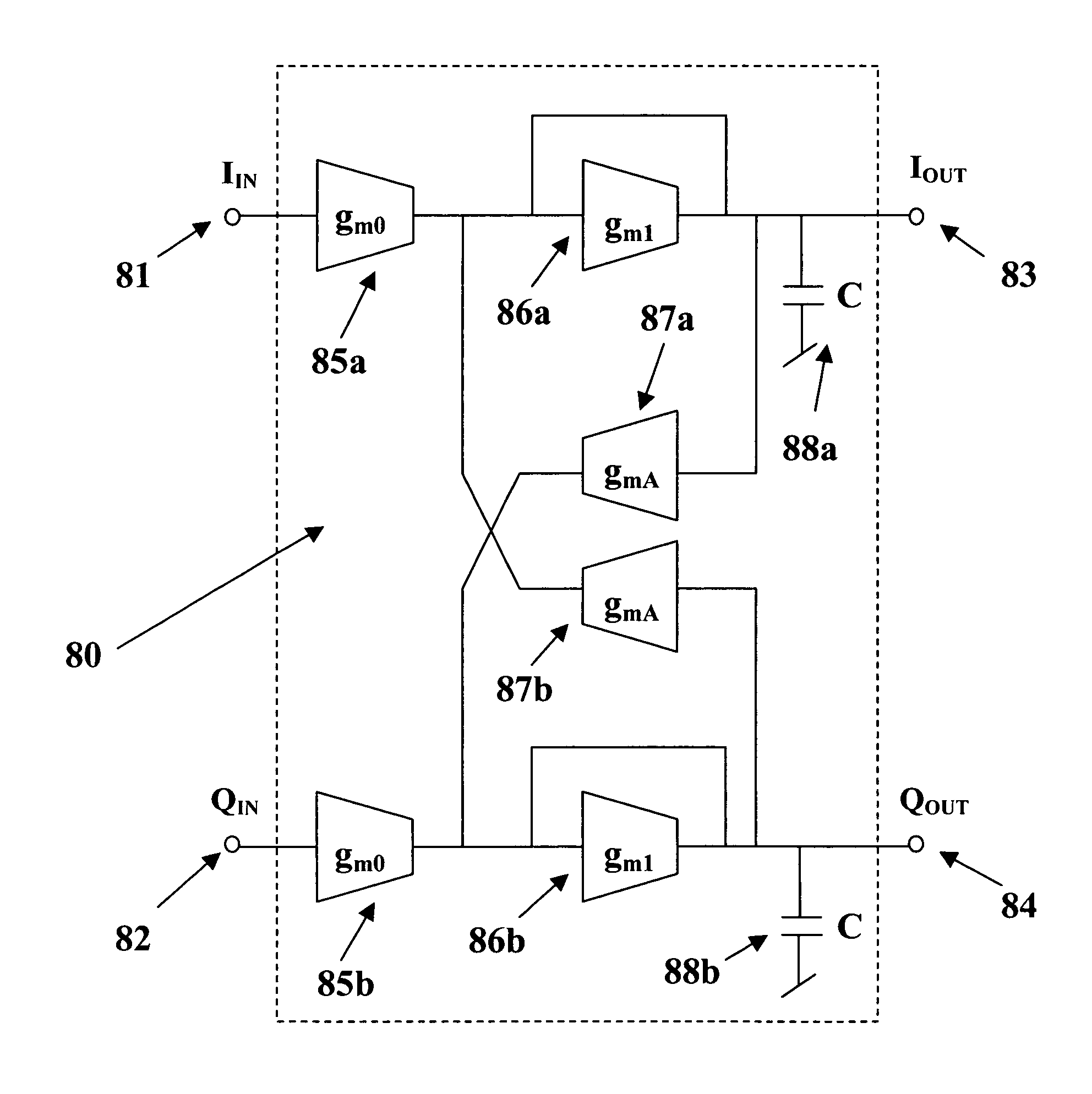
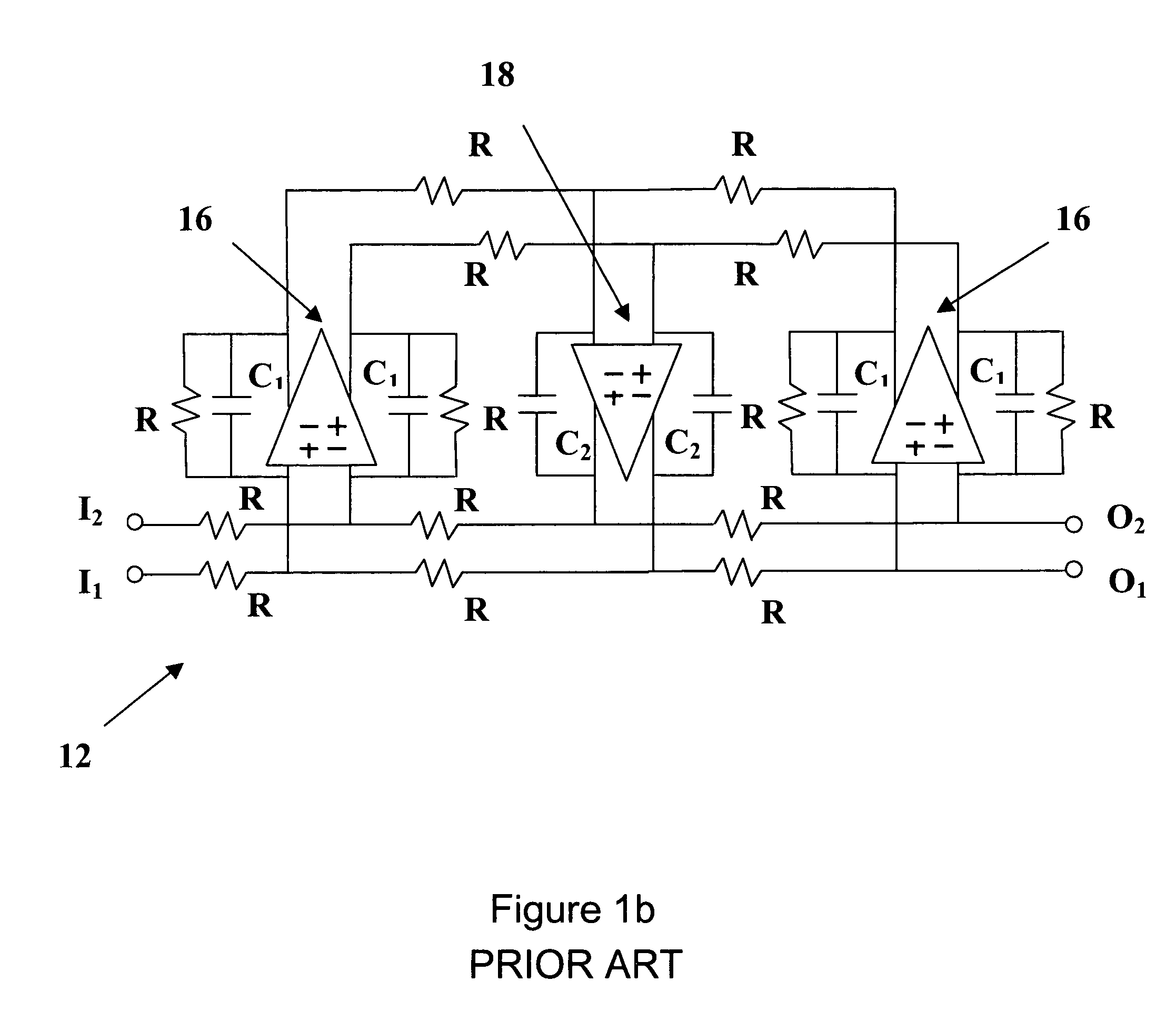
Synthesis method for an active polyphase filter
InactiveUS7098731B1Improve the level ofOscillations generatorsTransmissionElectrical conductorSynthesis methods
A fully-integrated continuous-time active complex bandpass IF filter that may contain transmission zeros yielding much sharper roll-off than that of an all-pole filter is implemented using transconductors and capacitors only. Each of the filter second-Order sections realizes a pair of complex poles and a may realize a double imaginary axis zero. Since the transconductors are electronically tunable the positions of filter zeros and poles are adjustable using an automatic tuning system. In each filter section the value of different transconductors are modified to separately change the pole frequency, its Q-factor and the zero frequency. Each pole and zero are separately tuned, which achieves a higher level of tuning accuracy than in case where all poles and zeros were adjusted simultaneously.
Owner:WYSZYNSKI ADAM S
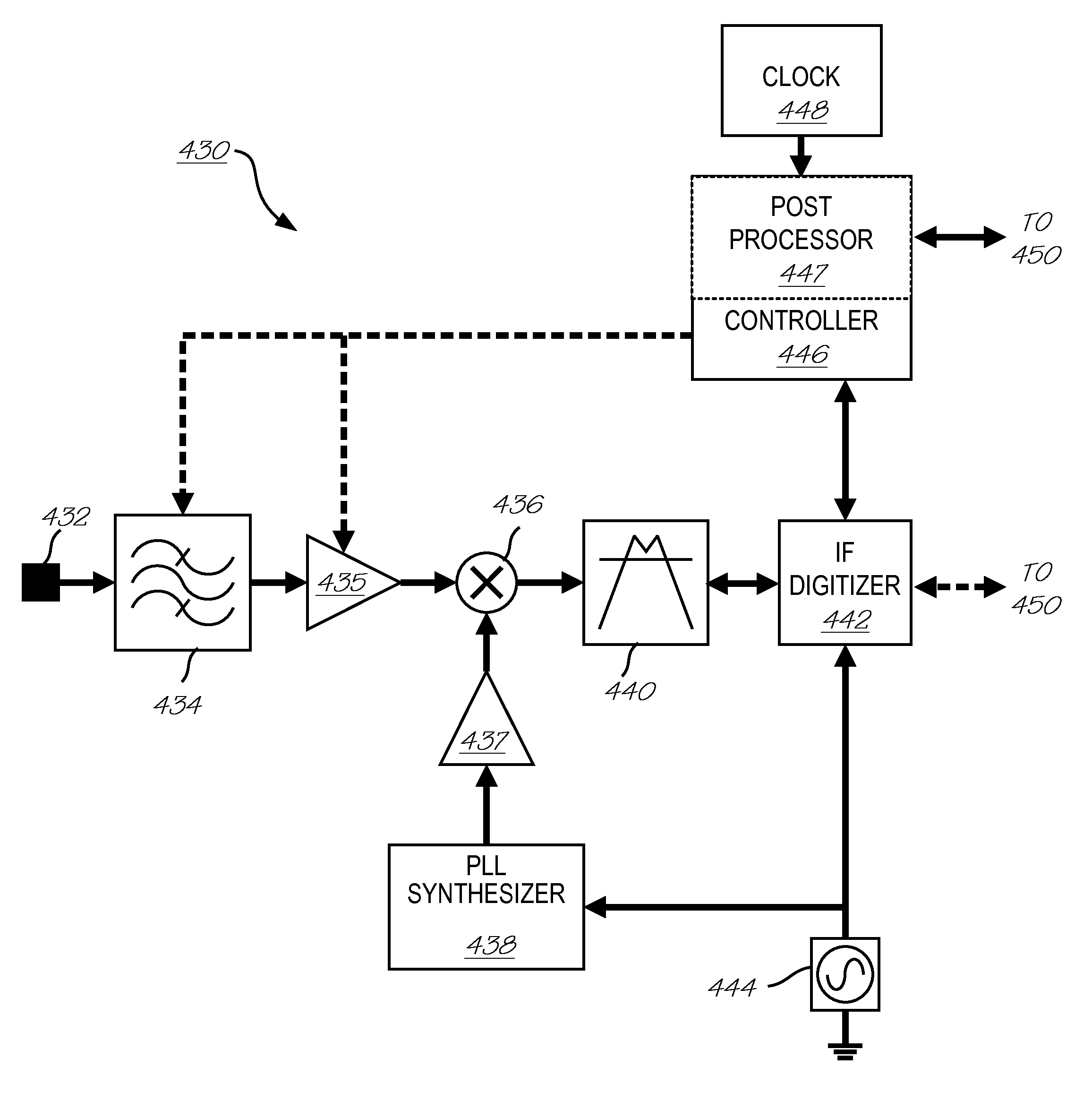
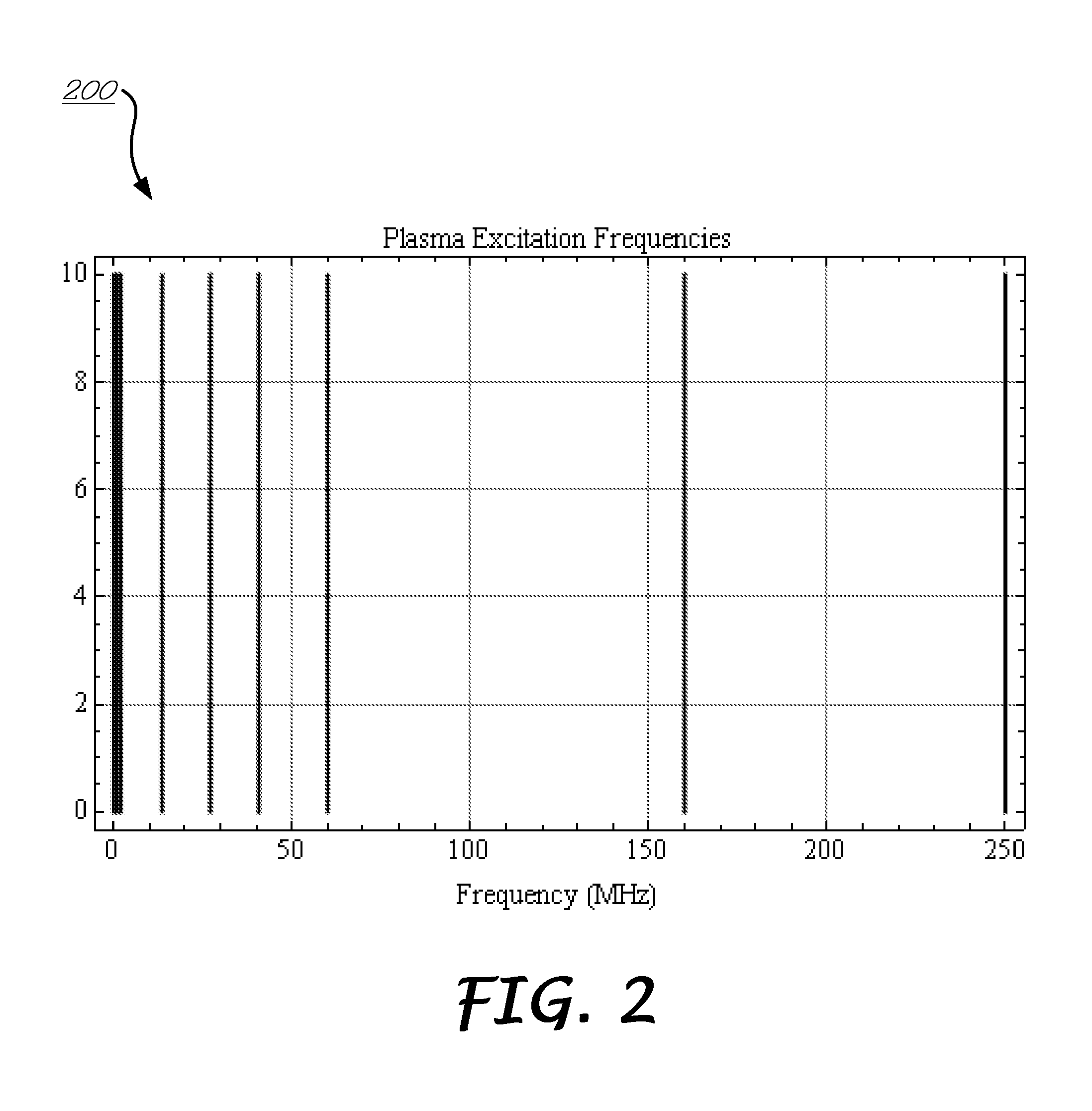
Method and Apparatus for Measuring Process Parameters of a Plasma Etch Process
InactiveUS20130016344A1Easy to processImprove conveniencePhotometry using reference valueSpectrum investigationFrequency spectrumSignal Conditioner
A configurable hybrid superheterodyne spectrum analyzer for deriving process state parameters from detected modulated light emitted by a plasma receives and conditions the electric signals converted from the modulated light for subsequent superheterodyne mixing at a specific intermediate frequency (IF) that is lower than the frequency of the modulated light. Signal conditioning includes filtering noise, aliasing and DC and / or amplifying or de-amplifying the signal. Once mixed, the superheterodyne signal is further filtered by an IF filter to define the signal bandwidth characteristics relevant to the process state parameters. The IF filter may configurably employ multiple filter functions such as Gaussian filtering of increasing widths and / or comb filtering for multiple passbands in the frequency spectrum. Finally, the IF mixed and filtered signal is digitized with respect to the specific intermediate frequency using an IF digitizer. The processed signal is then passed to a signal analyzer for derivation of process state parameters. The system may further include a controller for receiving information from the signal analyzer regarding signal processing requirements and then actively configuring one or all of the signal conditioner filter, signal conditioner amplifier, IF filter and IF digitizer to meet those requirements.
Owner:BULLOCK LARRY +2
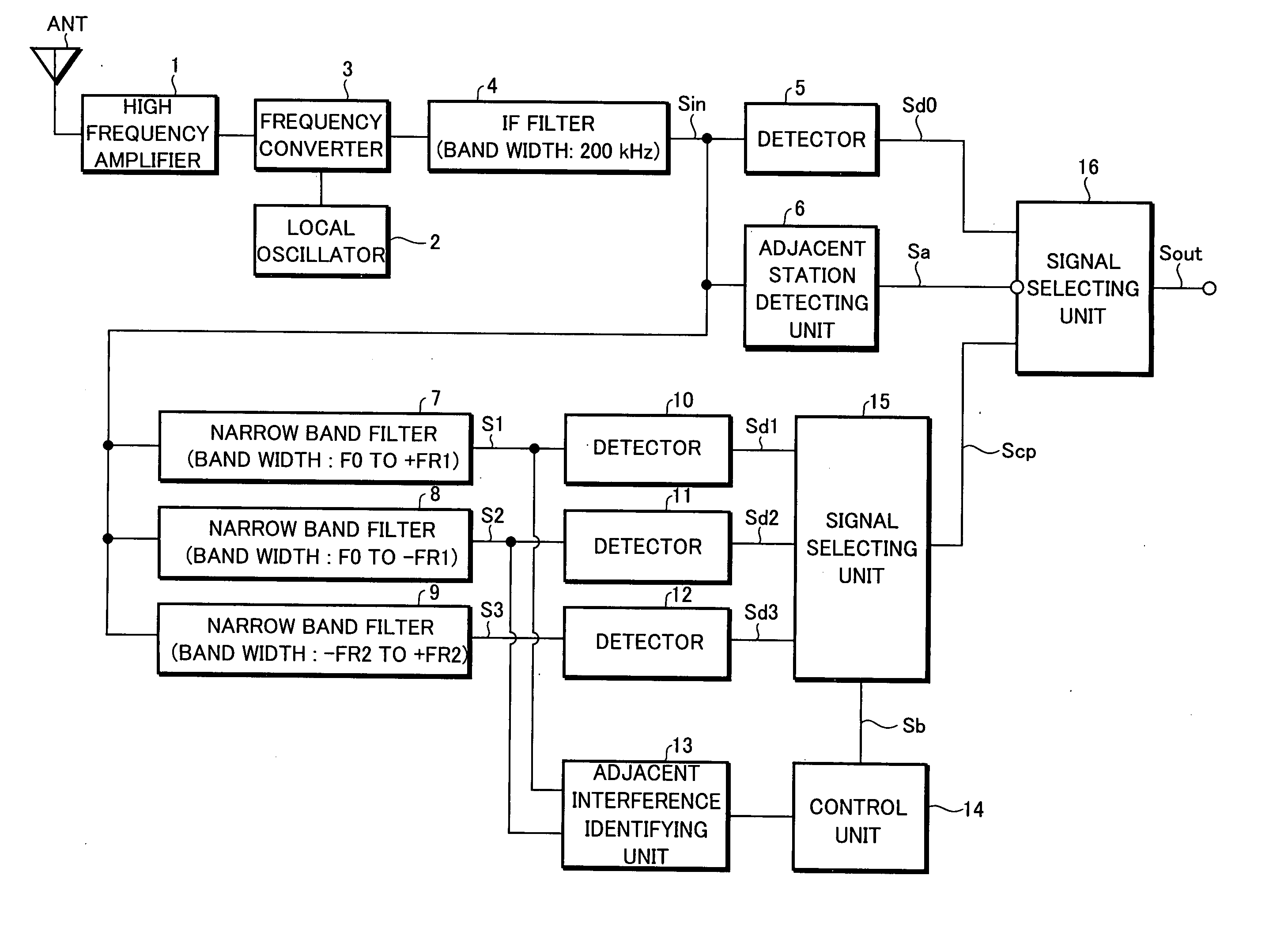
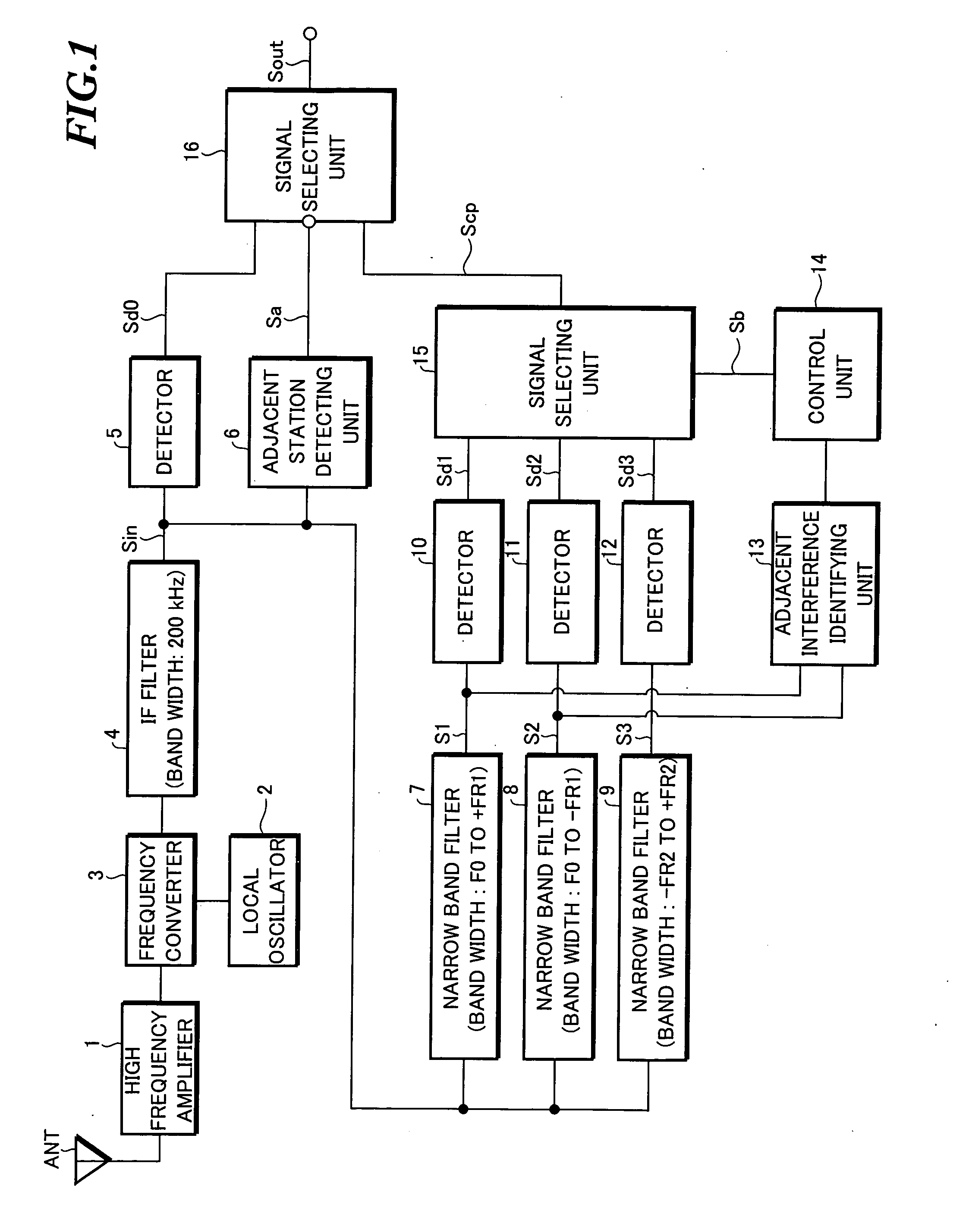
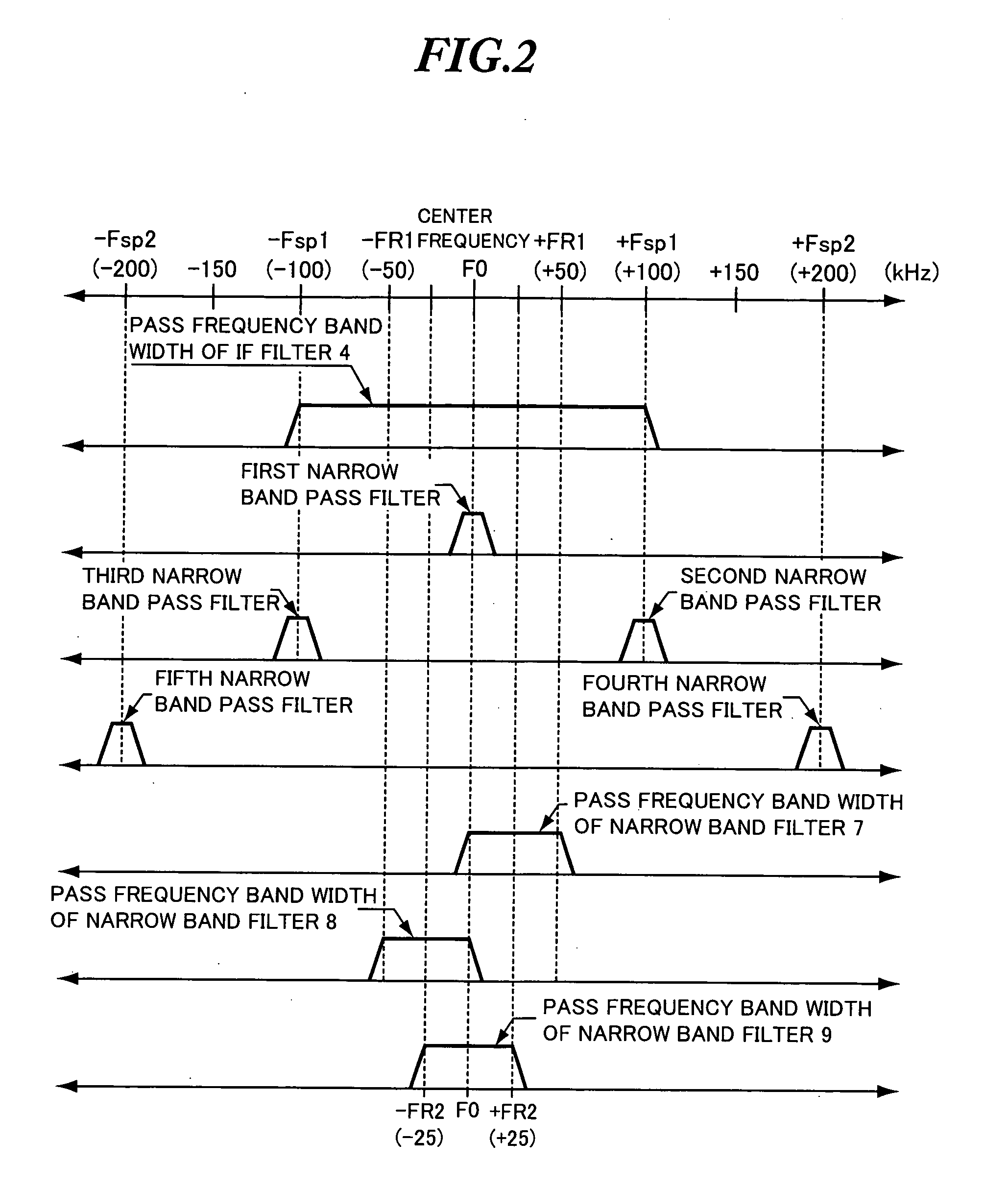
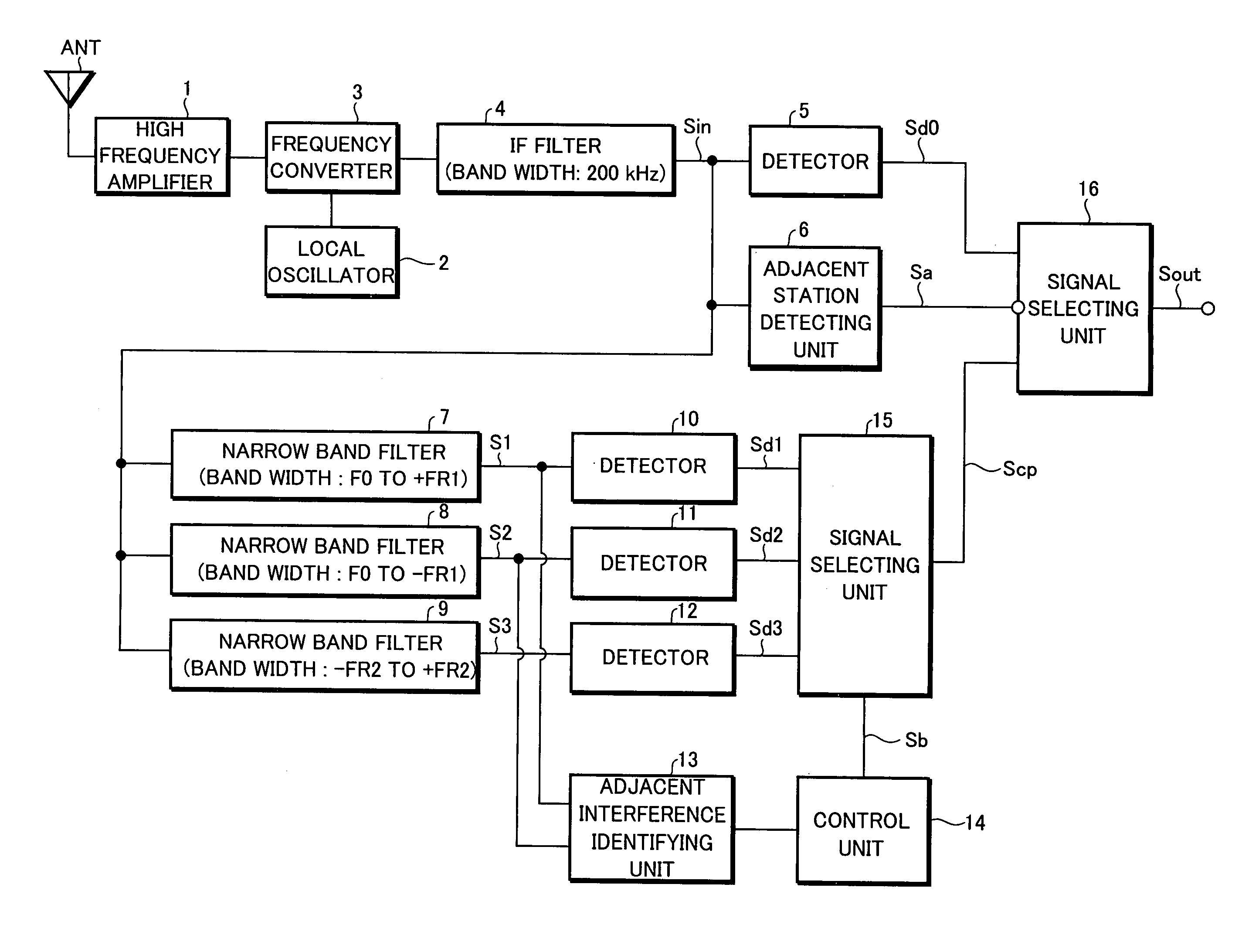
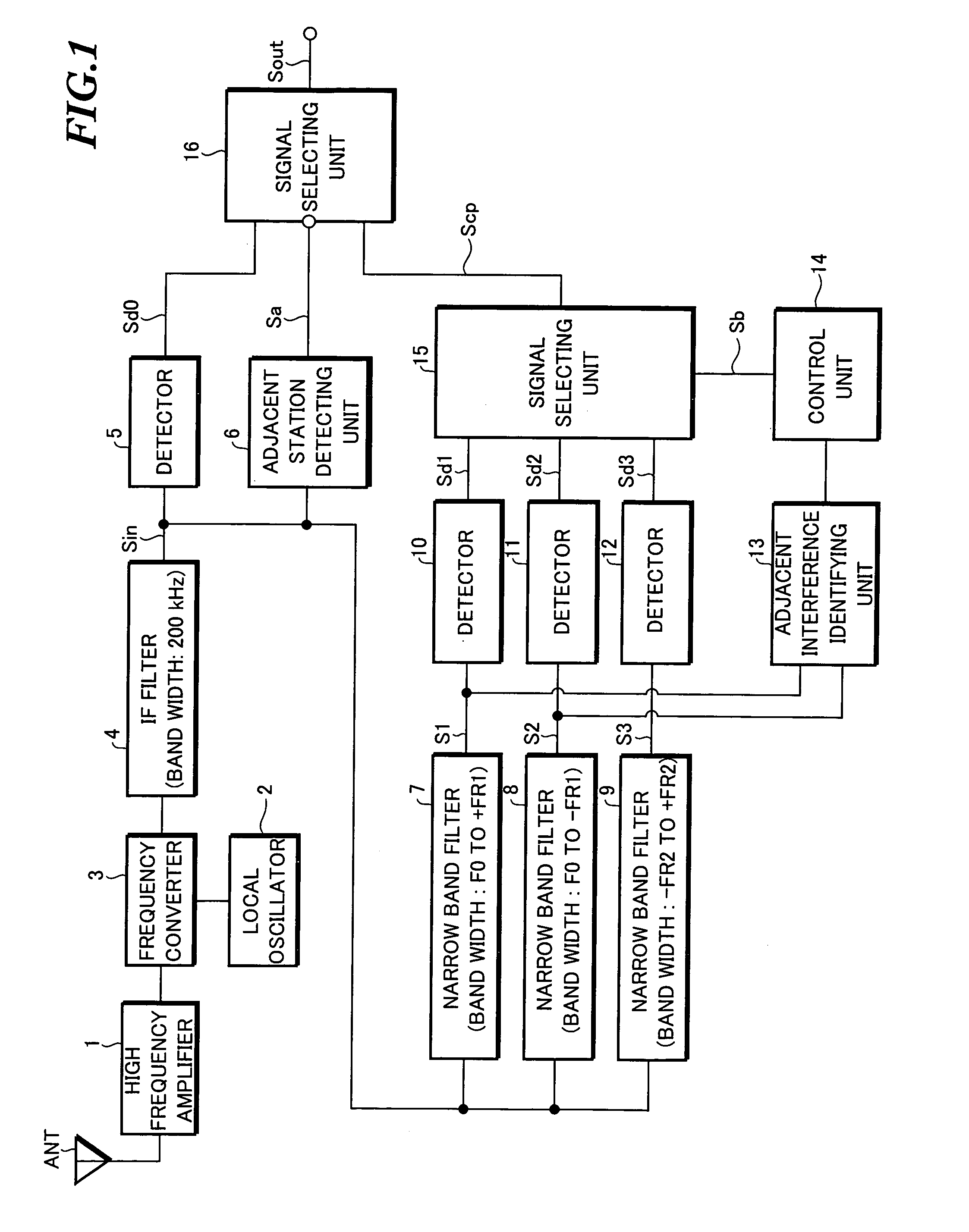
Adjacent interference removal device
InactiveUS20050164665A1Improve reception qualityRadio transmissionTransmission monitoringCenter frequencyPhysics
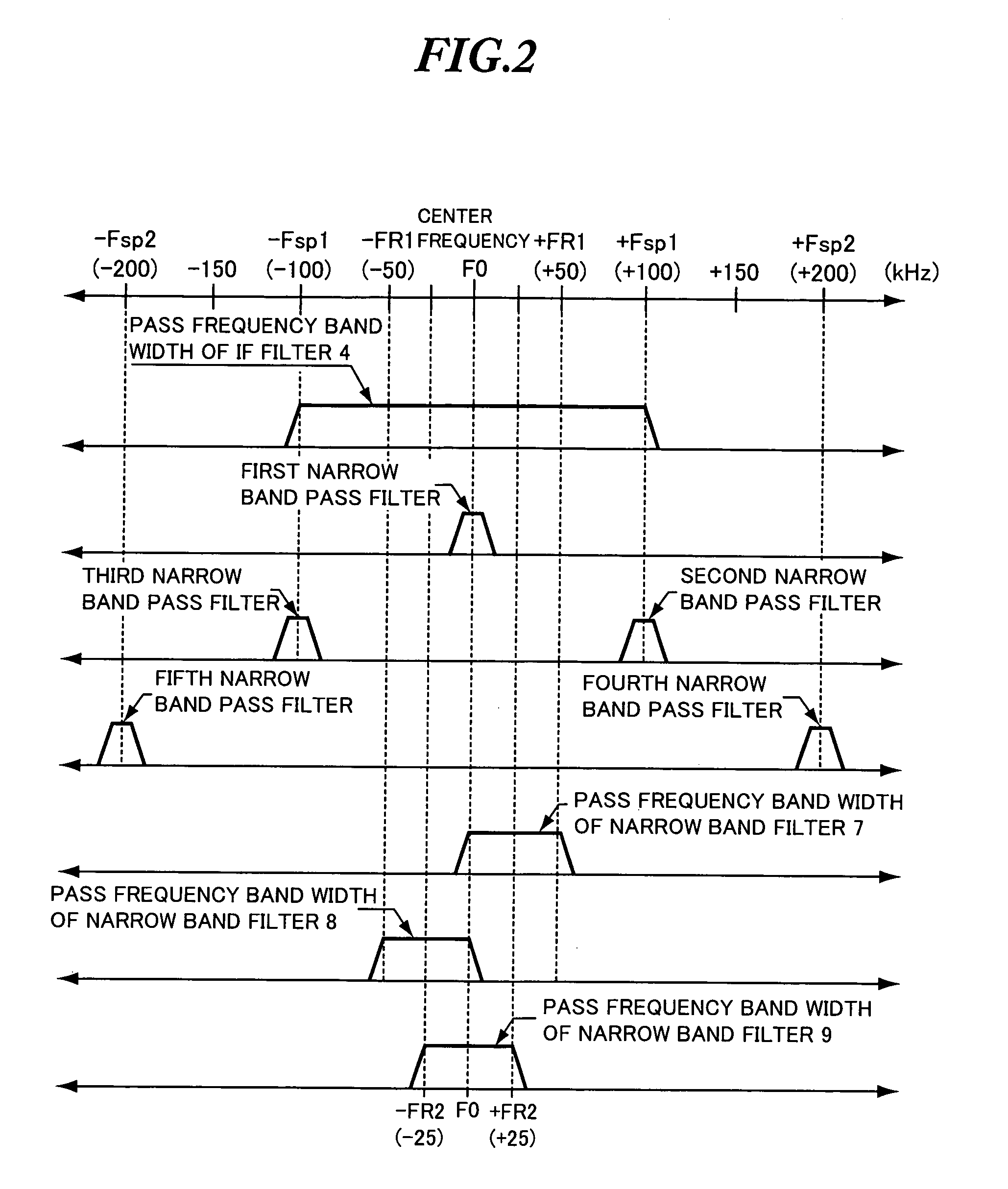
An adjacent interference removal device capable of providing an improved reception quality. An IF signal Sin having passed through an IF filter having a pass frequency band width of 200 kHz is supplied to a first narrow band filter having a pass frequency band width extending from a center frequency (carrier frequency) of the IF filter to +50 kHz, as well as to a second narrow band filter having a pass frequency band width extending from a center frequency (carrier frequency) of the IF filter to −50 kHz. When an interference signal is contained in a first signal S1 outputted from the first narrow band filter but not in a second signal S2 outputted from the second narrow band filter, and when an interference signal is contained in a detection signal Sd2 generated by detecting the second signal S2 in a detector and contained in the second signal S2 itself but not-contained in the first signal S1, the detection signal Sd1 generated by detecting the first signal S1 in another detector is outputted by performing a switchover in a signal selecting unit.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Method and apparatus for on-demand interference rejection in multi-band GNSS receivers
ActiveUS20140369452A1Increase resistanceReserved functionActive element networkCommunication jammingTransceiverAnti jamming
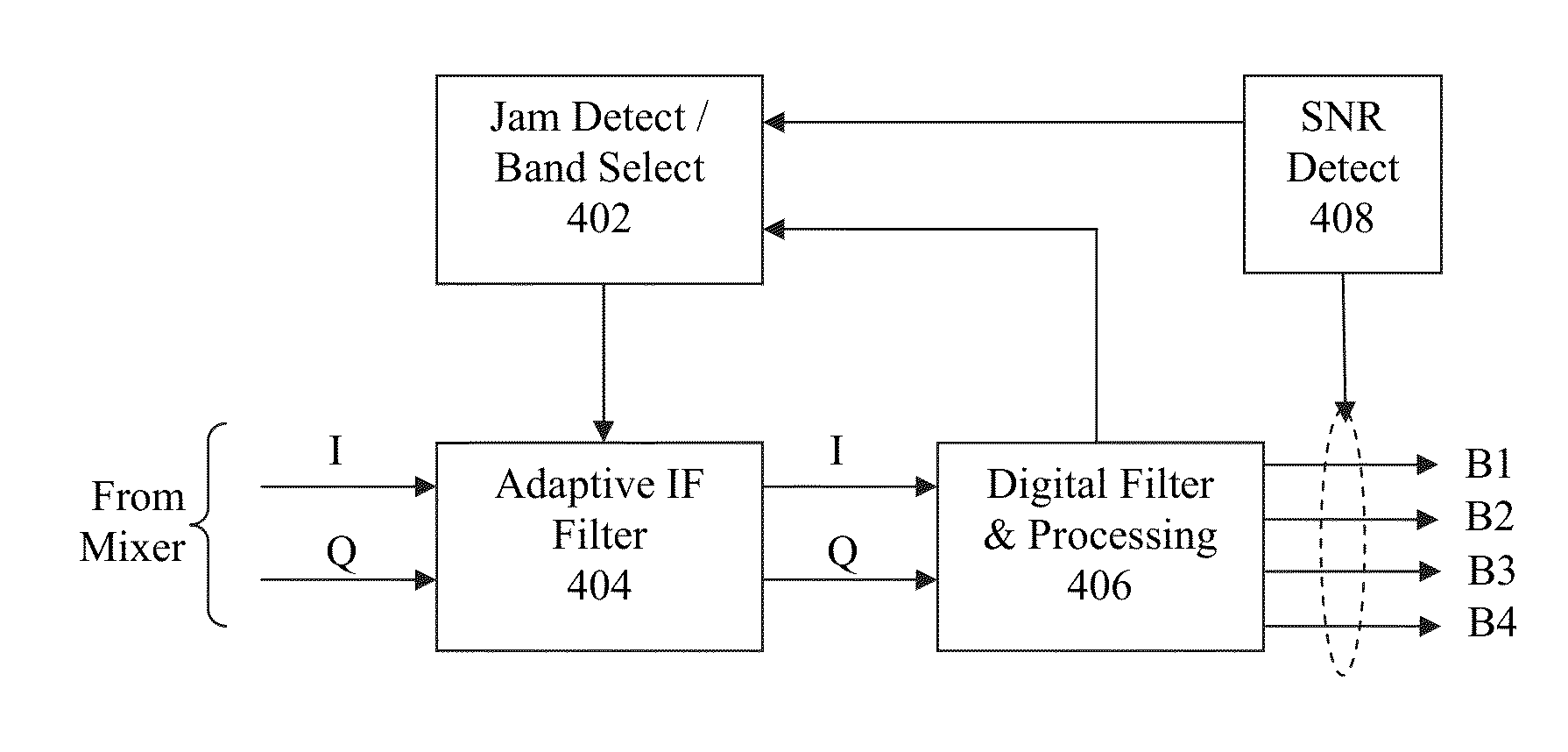
In general, the present invention relates to an adaptive IF filter for a multiband receiver. According to certain aspects, the adaptive IF filter can be dynamically configured as a low-pass architecture or a complex band-pass architecture. According to further aspects, the adaptive IF filter enables a wideband receiver which can simultaneously receive multiple frequency bands, but still protect itself from close-in or in-band jammers by selecting a single frequency band or subset of frequency bands. This retains the multiband functionality of the receiver under nominal conditions, which is traded off dynamically for a single-frequency-band with high jammer resistance under severe jamming conditions. According to still further aspects, the approach of the invention is particularly useful for GNSS receivers, since unlike a cellular transceiver, a temporary loss of signal is not catastrophic to GNSS receivers due to the long integration times.
Owner:QUALCOMM TECH INT
Bias signal generator in radio receiver
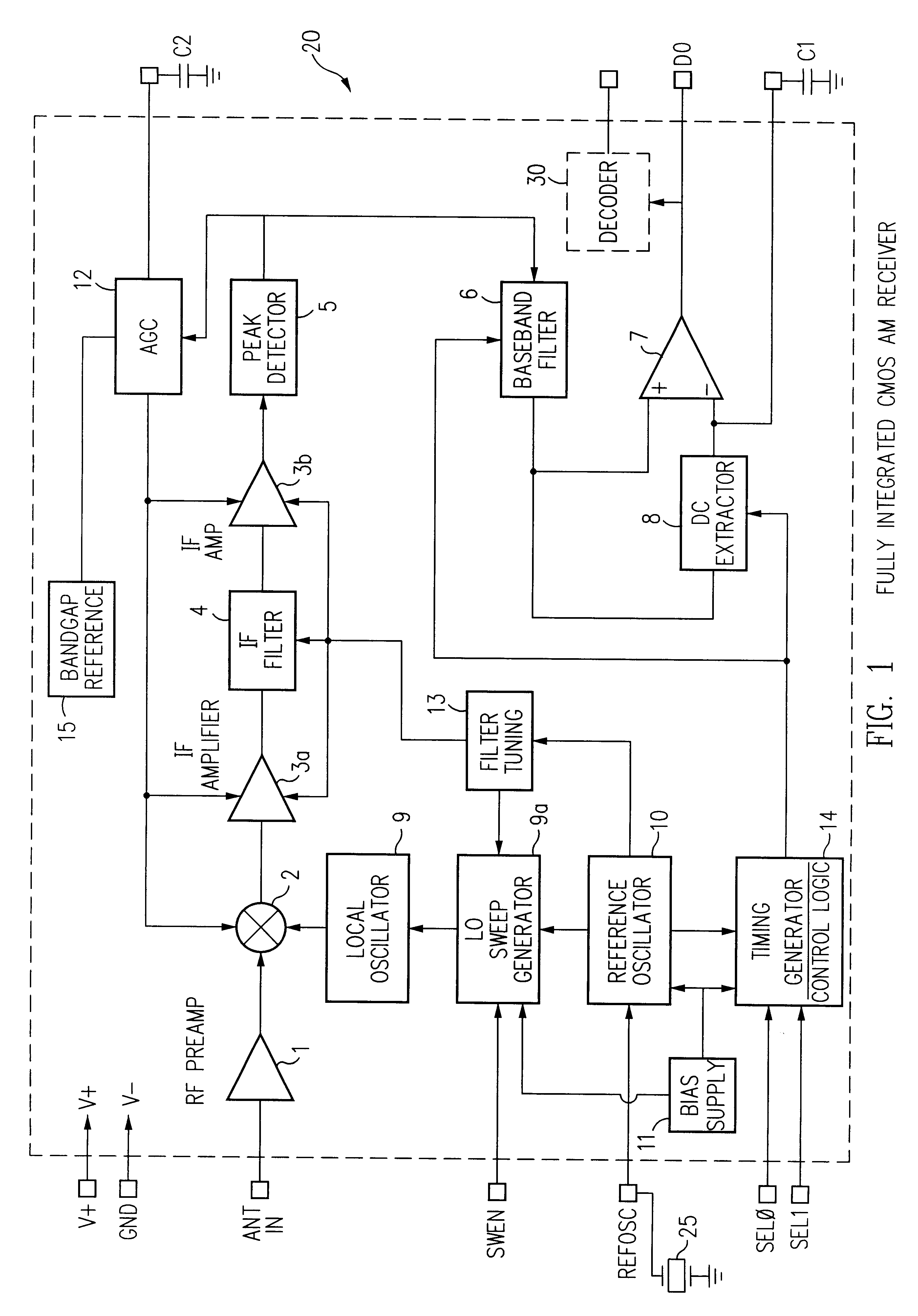
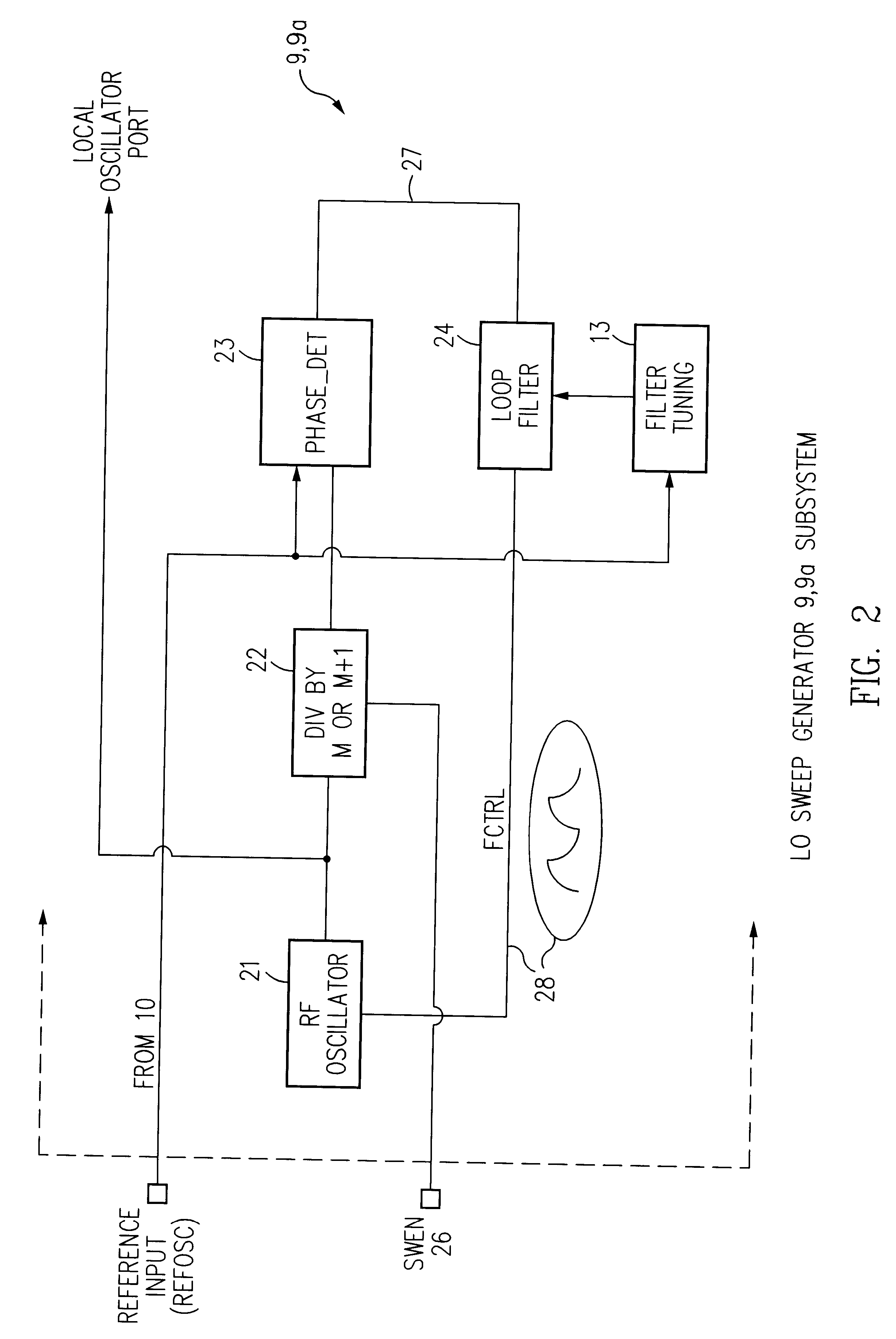
InactiveUS6278866B1Easy to controlLower requirementPulse automatic controlRadio transmissionDigital dataRadio receiver
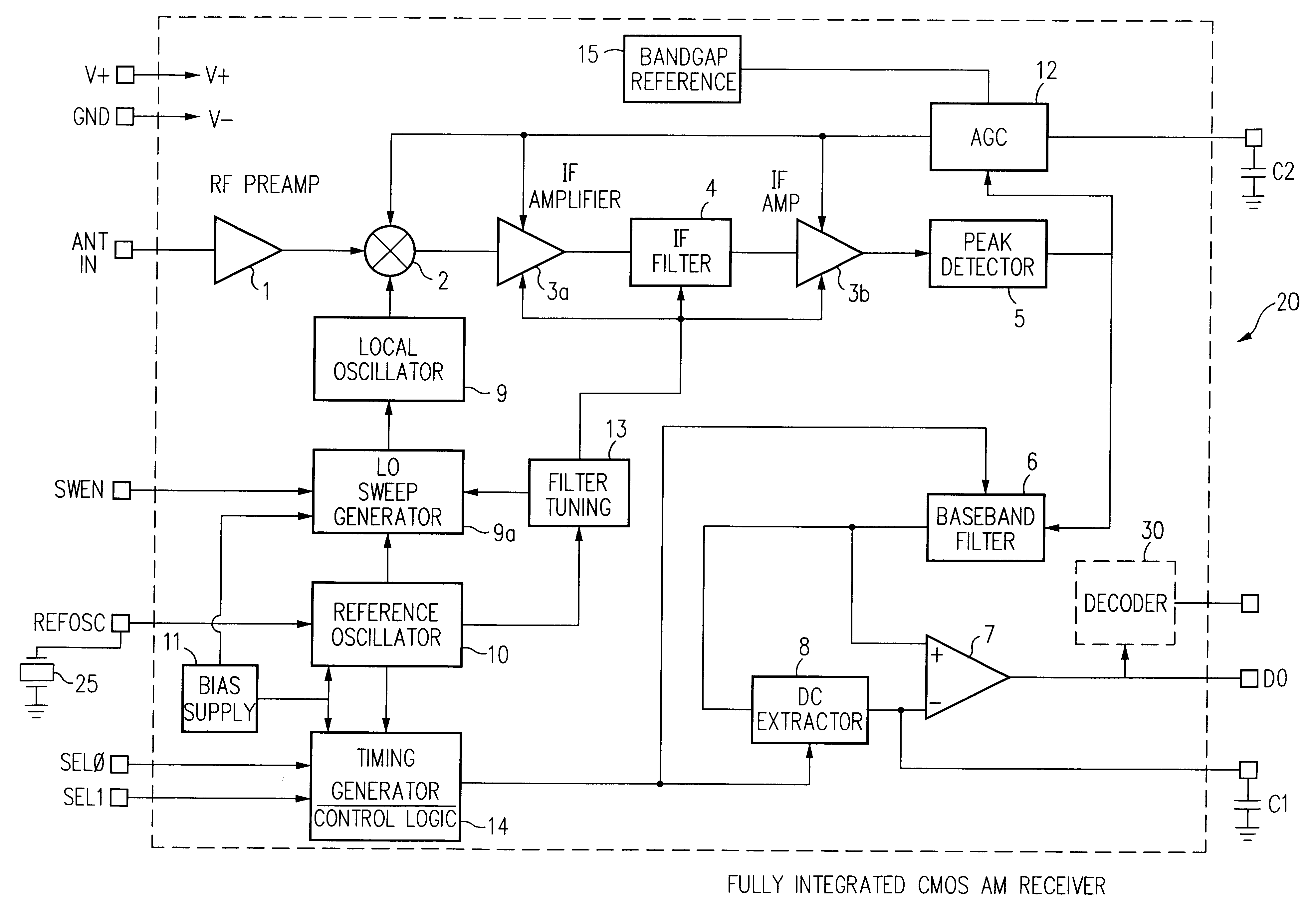
A single chip superhetrodyne AM receiver is disclosed herein. To compensate for process variations in the implementation of the IC, bias currents setting the operating conditions for various amplifiers and other components in the system are adjusted based on frequency control signals in a PLL circuit in the local oscillator. Since the magnitude of the control signal reflects the process variations, the bias currents are adjusted based on the control signal to offset these variations in other portions of the receiver. To further improve the signal to noise ratio of the receiver, the IF filter is tuned within a range so as not to include any integer multiple or integer divisor of the timing reference frequency. Various techniques are described for enabling a complete superhetrodyne AM receiver to be implemented on a single chip which receives an antenna input signal and outputs a digital data signal.
Owner:MICREL
Adjacent interference removal device
An adjacent interference removal device capable of providing an improved reception quality. An IF signal Sin having passed through an IF filter having a pass frequency band width of 200 kHz is supplied to a first narrow band filter having a pass frequency band width extending from a center frequency (carrier frequency) of the IF filter to +50 kHz, as well as to a second narrow band filter having a pass frequency band width extending from a center frequency (carrier frequency) of the IF filter to −50 kHz. When an interference signal is contained in a first signal S1 outputted from the first narrow band filter but not in a second signal S2 outputted from the second narrow band filter, and when an interference signal is contained in a detection signal Sd2 generated by detecting the second signal S2 in a detector and contained in the second signal S2 itself but not contained in the first signal S1, the detection signal Sd1 generated by detecting the first signal S1 in another detector is outputted by performing a switchover in a signal selecting unit.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Wireless communication receiver with i/q imbalance estimation and correction techniques
ActiveUS20150117577A1Improve the correction effectImprove accuracyError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTransceiverPower efficient
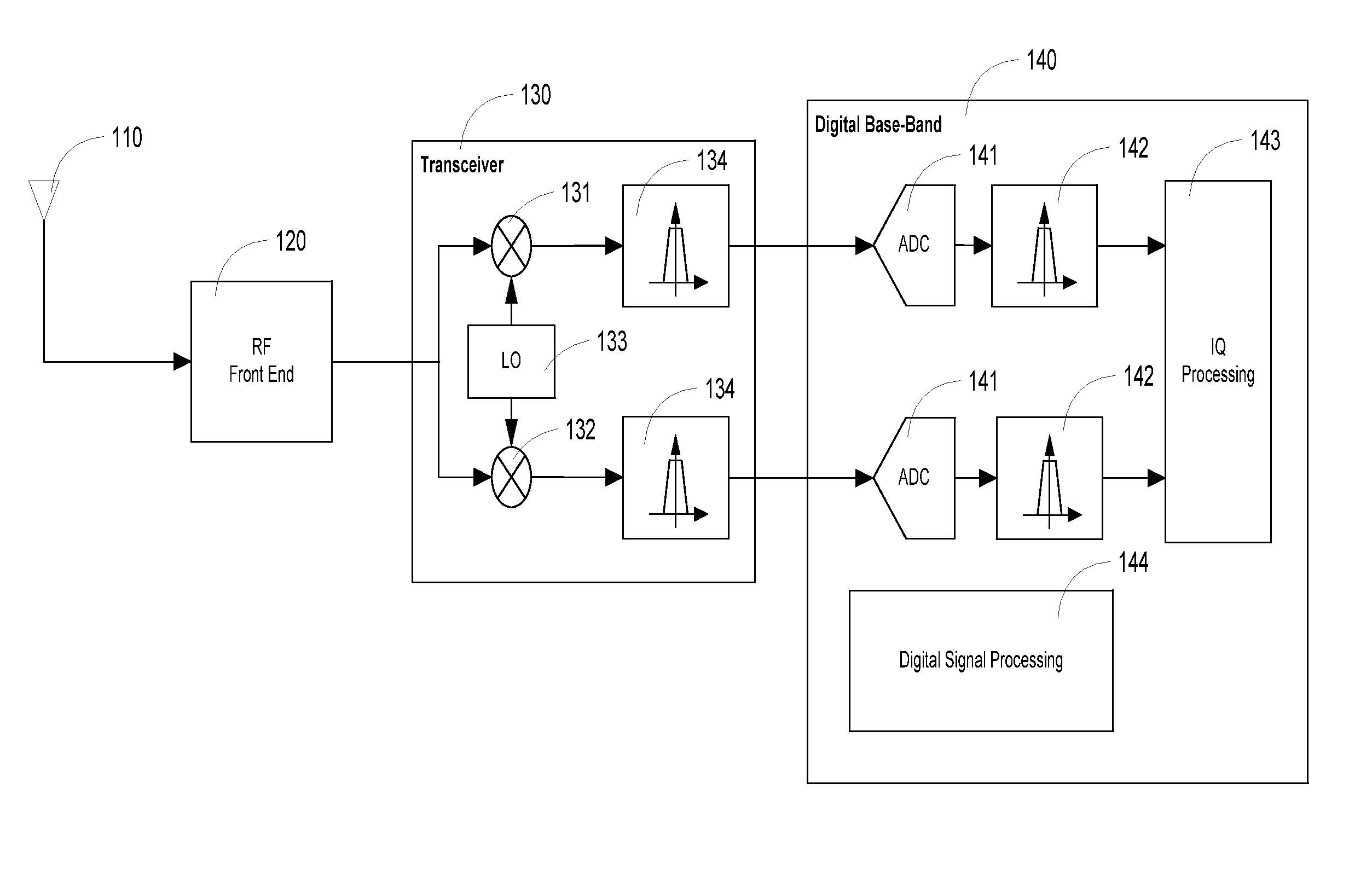
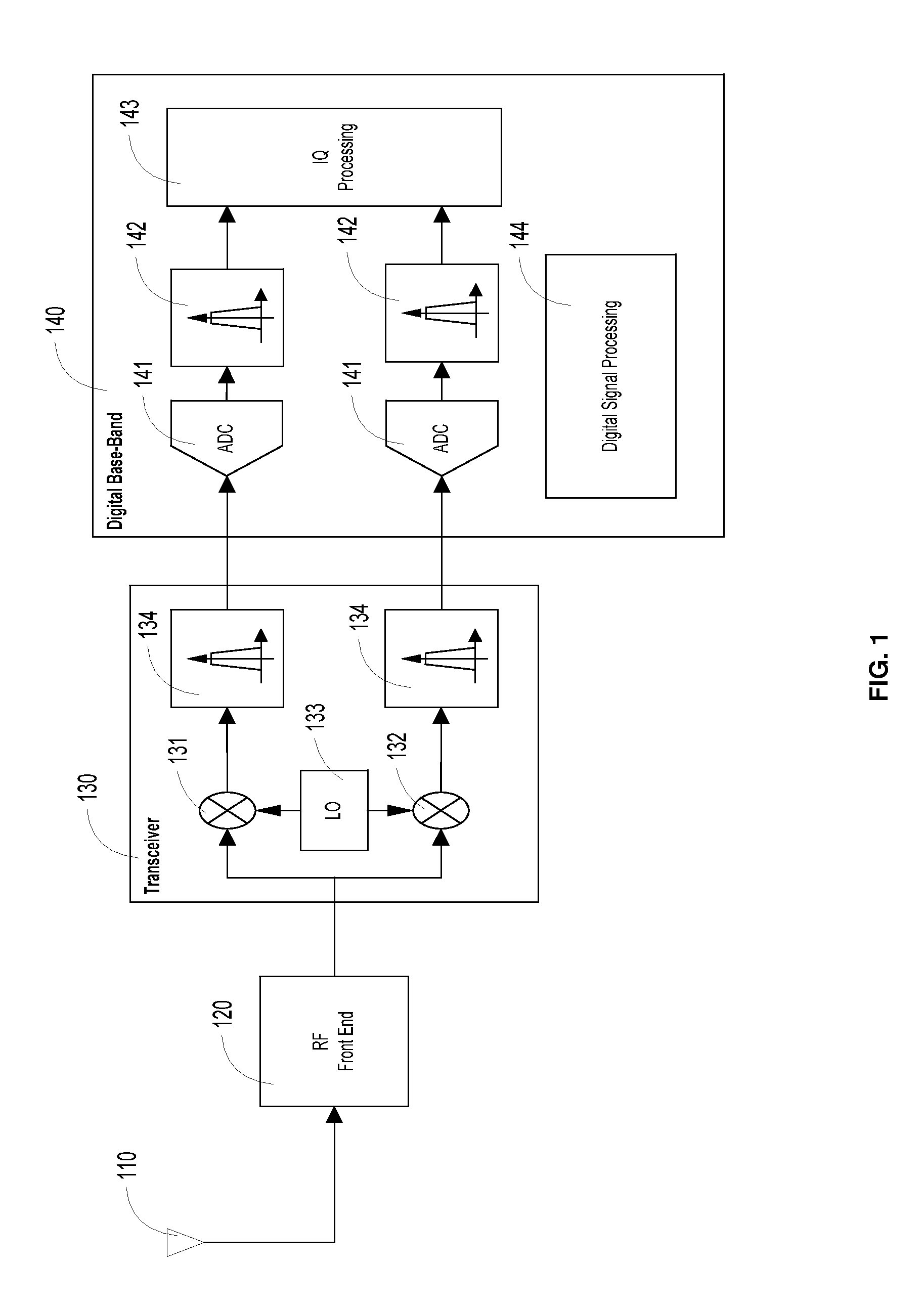
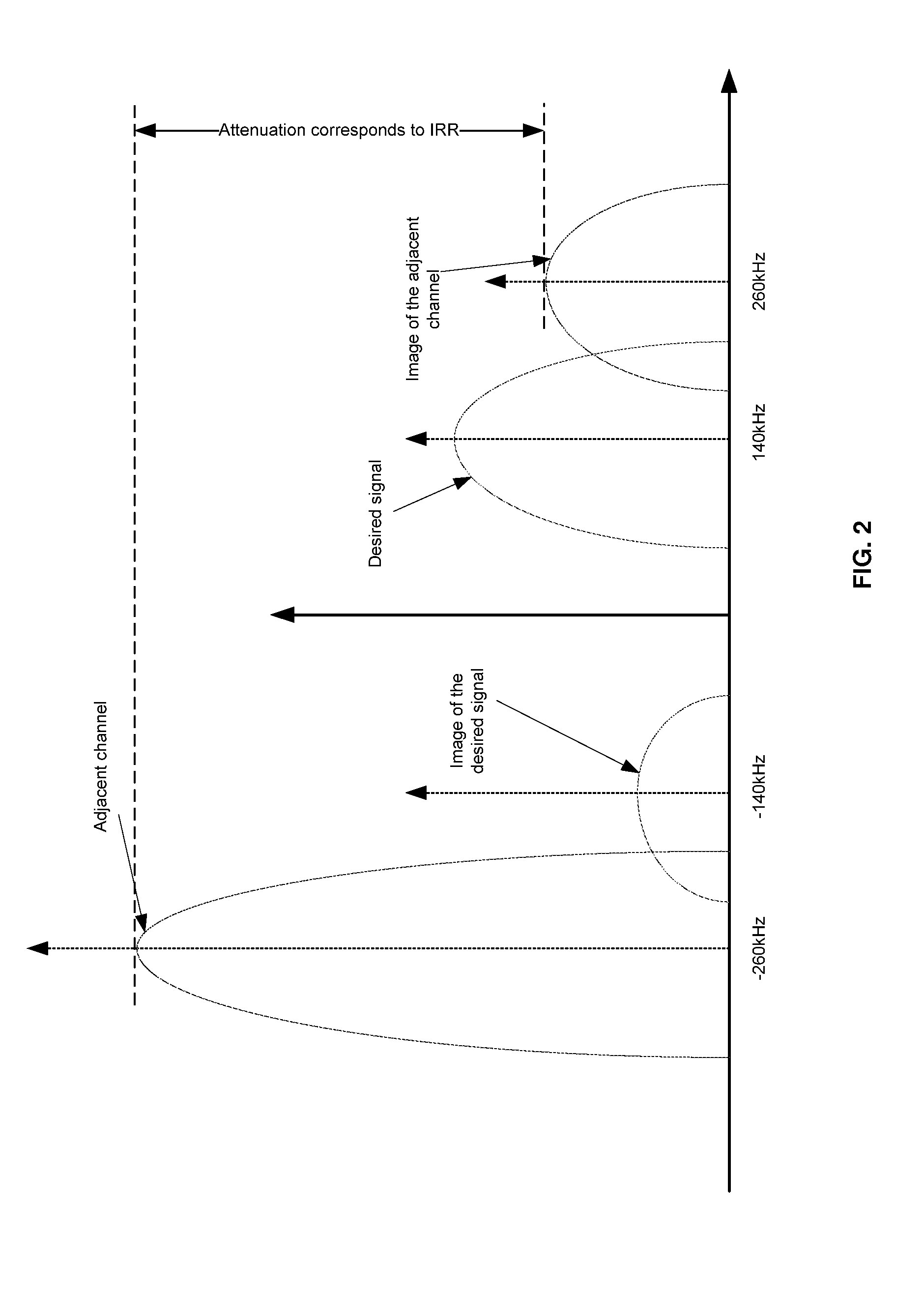
Techniques are provided that utilize information on the characteristics of the transmitted signal to improve the accuracy of the I / Q imbalance estimation and correction. These techniques can be used to achieve improved image rejection performance over existing solutions, through the use of signal conditioning, windowing and the use of statistical information on the received signal. A number of techniques aimed at improving the accuracy of the I / Q imbalance estimation / correction are presented, including different modes of I / Q imbalance estimation and I / Q imbalance correction in the presence of a complex IF filter in the transceiver. The processing is performed mostly in the DBB in order to be area / power efficient.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
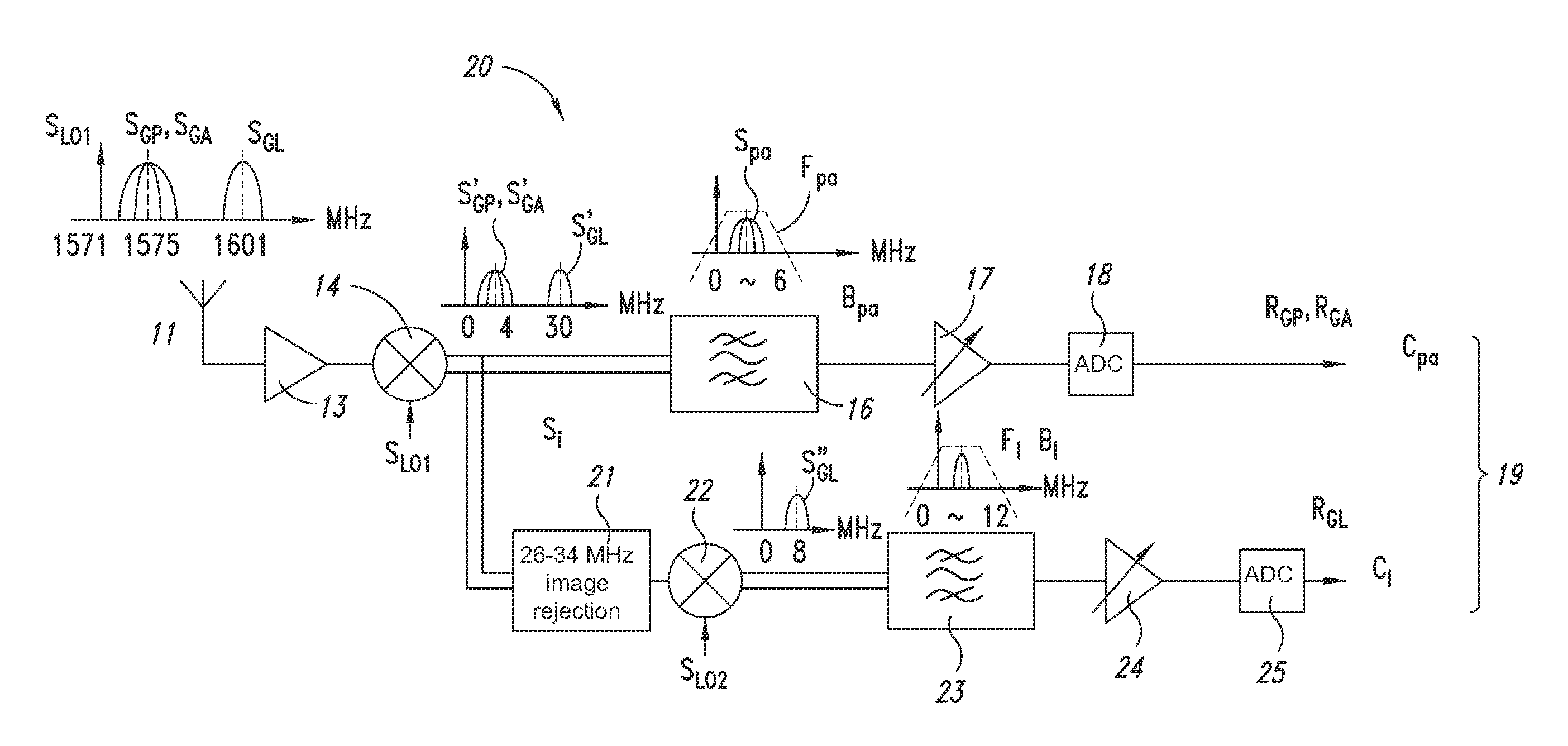
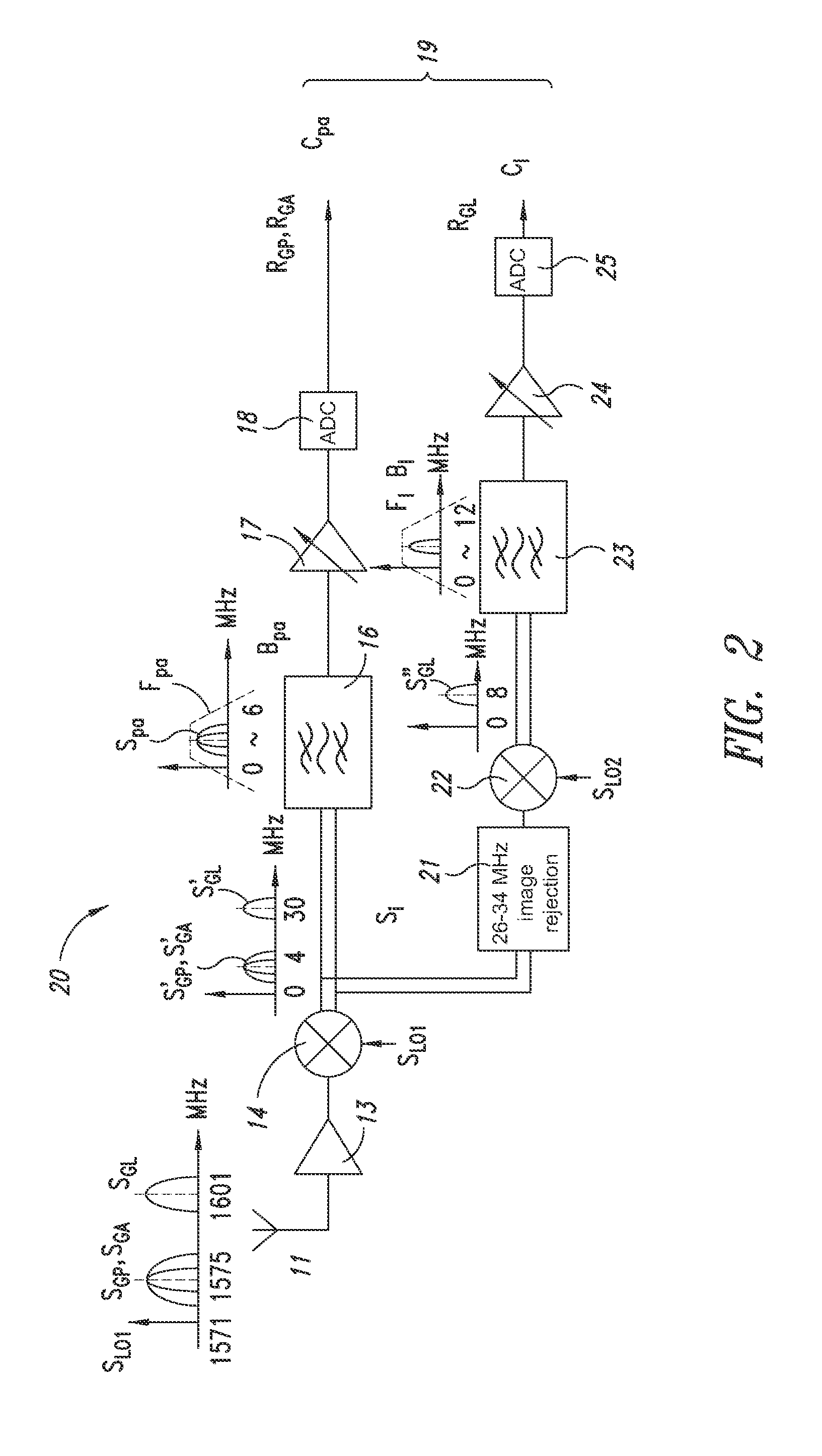
Receiver for receiving a plurality of GNSS (global navigation satellite system) signals
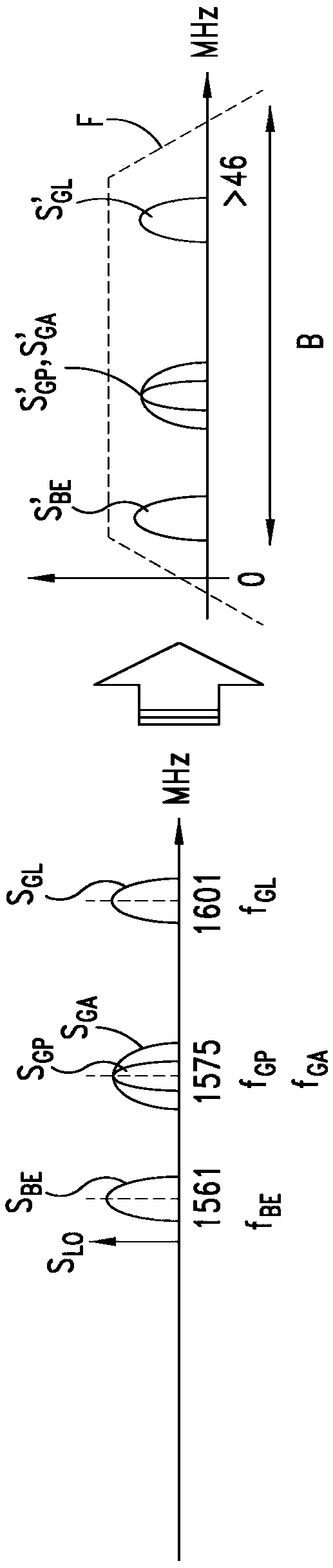
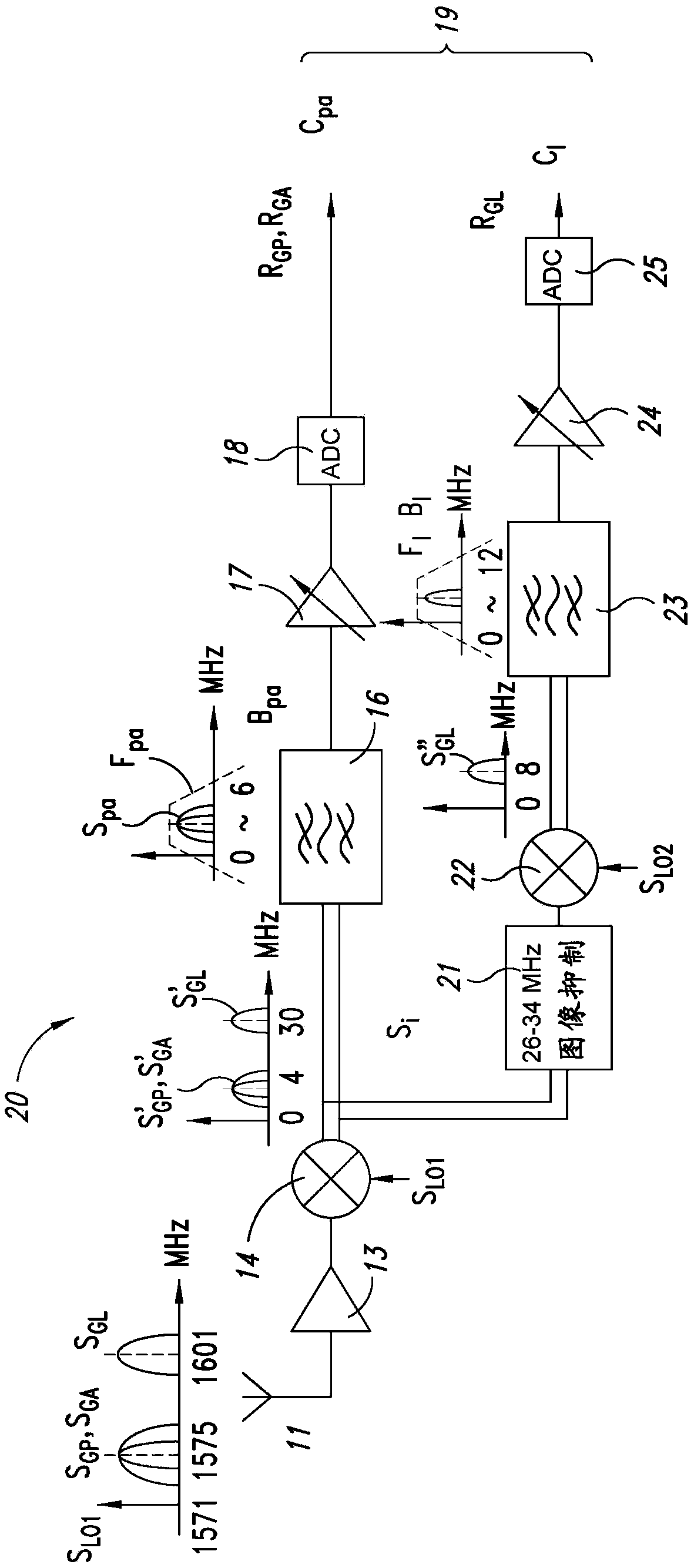
ActiveUS20160103225A1Save area consumptionSave power consumptionSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteBandpass filtering
A receiver is arranged to receive a plurality of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signals from up to four different satellite navigation systems including a GLONASS system, a BeiDou system, a GPS system, and a Galileo system. Received GNSS signals are mixed with a first local frequency signal to generate a plurality of mixed signals. The mixed signals are processed in up to three parallel branches. In a first branch, a first portion of the mixed signals are transformed by passing the first portion through a band-pass filter having a bandwidth between about 0 MHz and 46 MHz and by amplifying the filtered signals with an AGC circuit. In a second branch, a second portion of the mixed signals are transformed by rejecting image signals of the second portion with an image rejection filter and mixing image rejection filter output signals with a second local frequency signal to derive first remixed signals. In a third branch, a third portion of the mixed signals are transformed by adjusting a phase of the third portion to overlap a band of the first remixed signals. The adjusted third portion of the mixed signals and the first remixed signals are concurrently band pass filtered with a low IF filter.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
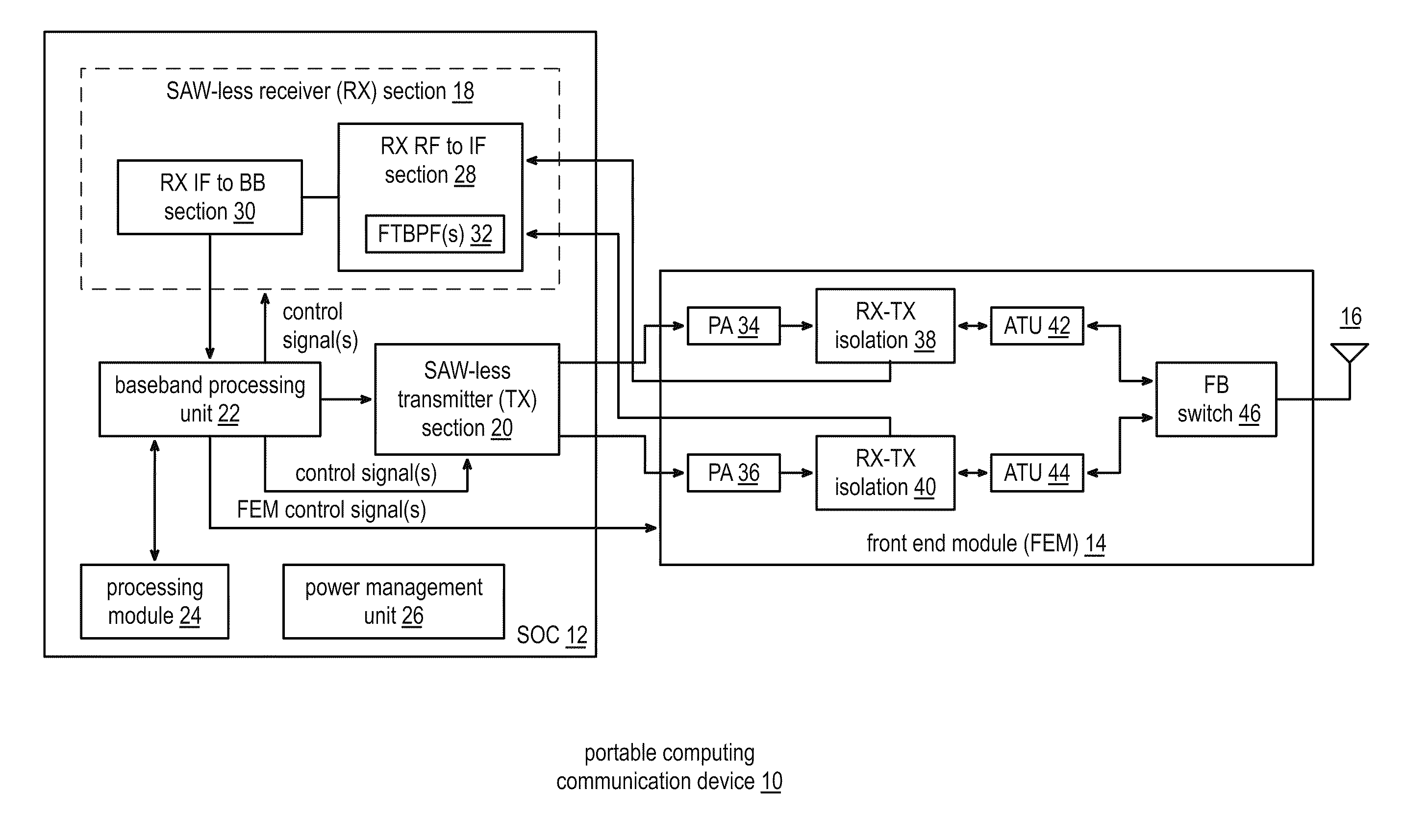
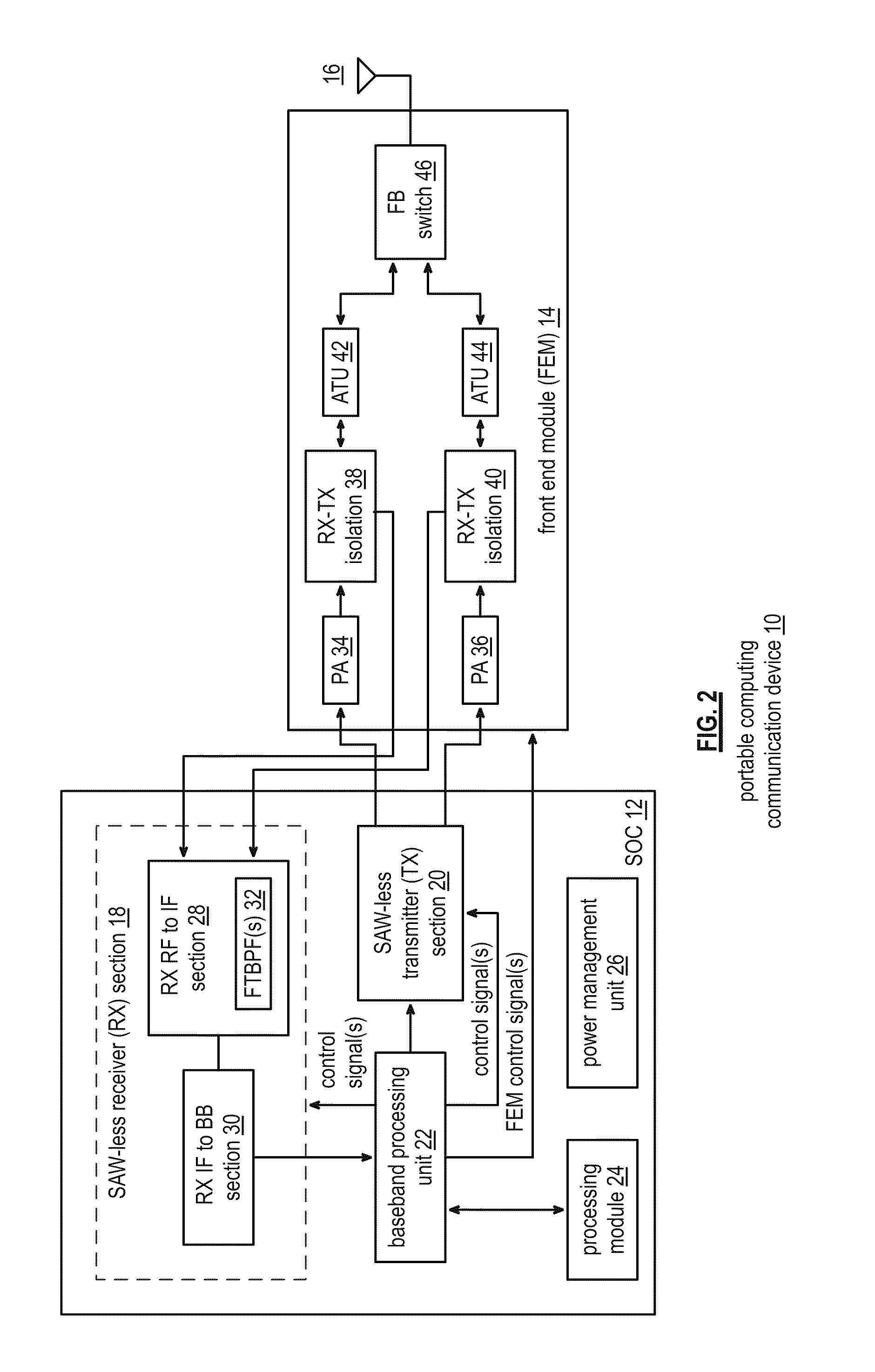
Portable computing device with a saw-less transceiver
A portable computing device includes an FEM, a SAW-less receiver, a SAW-less transmitter, and a baseband processing unit. The FEM isolates one or more outbound RF signals from one or more inbound RF signals. The SAW-less receiver converts the one or more inbound RF signals into one or more inbound intermediate frequency (IF) signals by frequency translating a baseband filter response to an IF filter response and / or an RF filter response. The SAW-less receiver filters the inbound RF signal(s) in accordance with the RF filter response and / or filters the inbound IF signal(s) in accordance with the IF filter response. The SAW-less receiver then converts the inbound IF signal(s) into inbound symbol stream(s). The SAW-less transmitter converts outbound symbol stream(s) into the outbound RF signal(s). The baseband processing unit converts outbound data into the outbound symbol stream(s) and convert the inbound symbol stream(s) into inbound data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
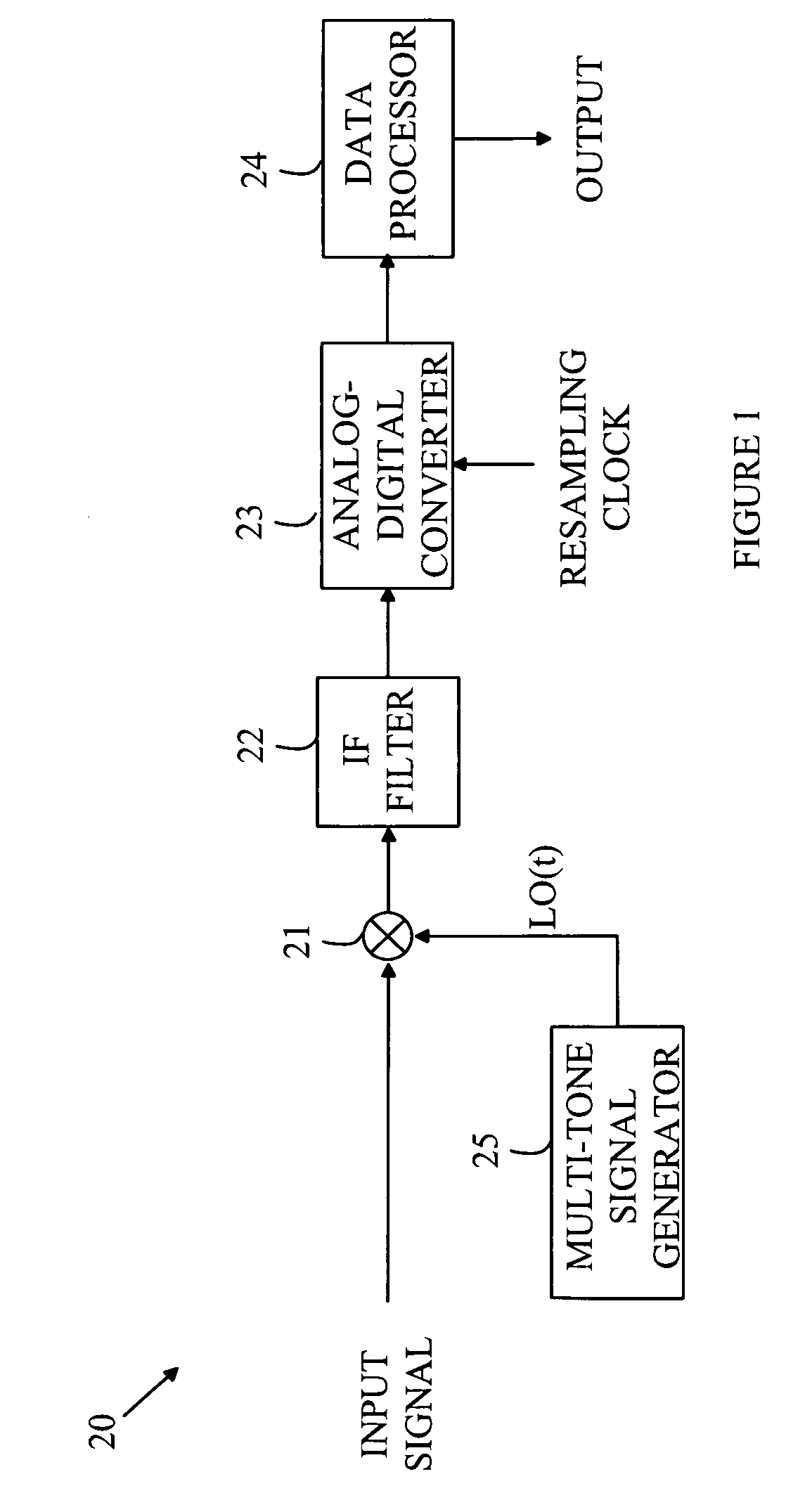
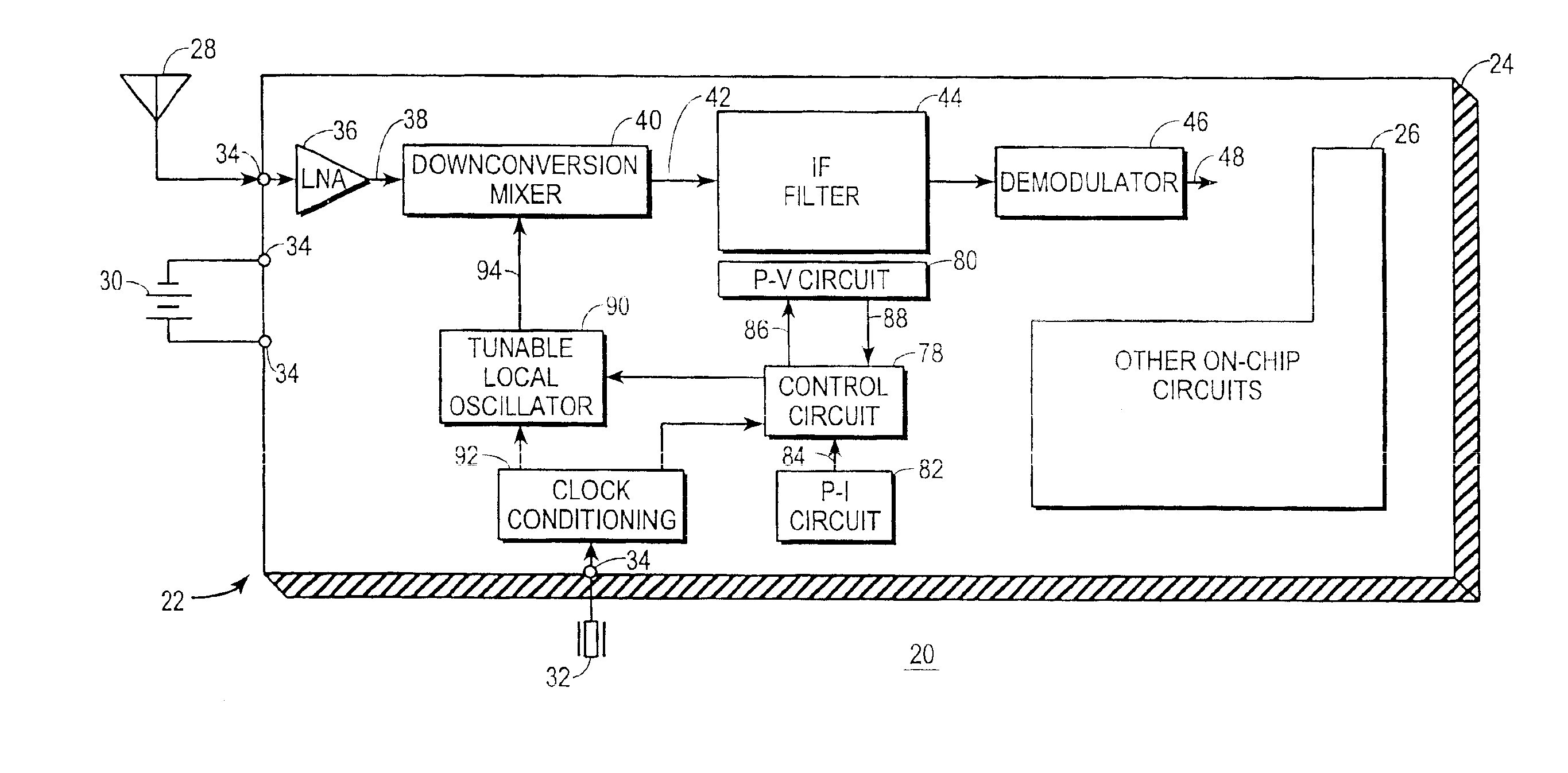
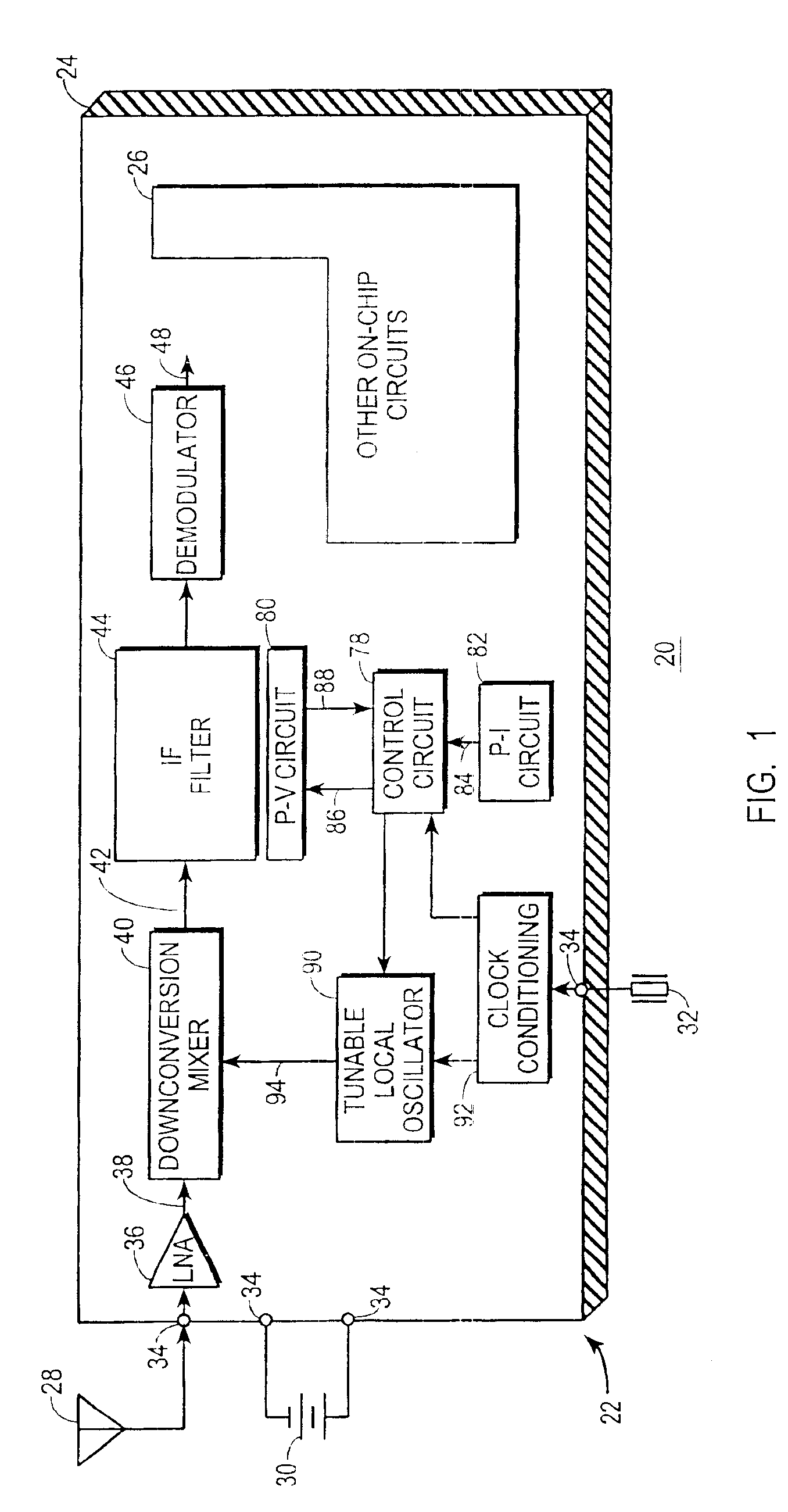
Communications receiver with integrated IF filter and method therefor
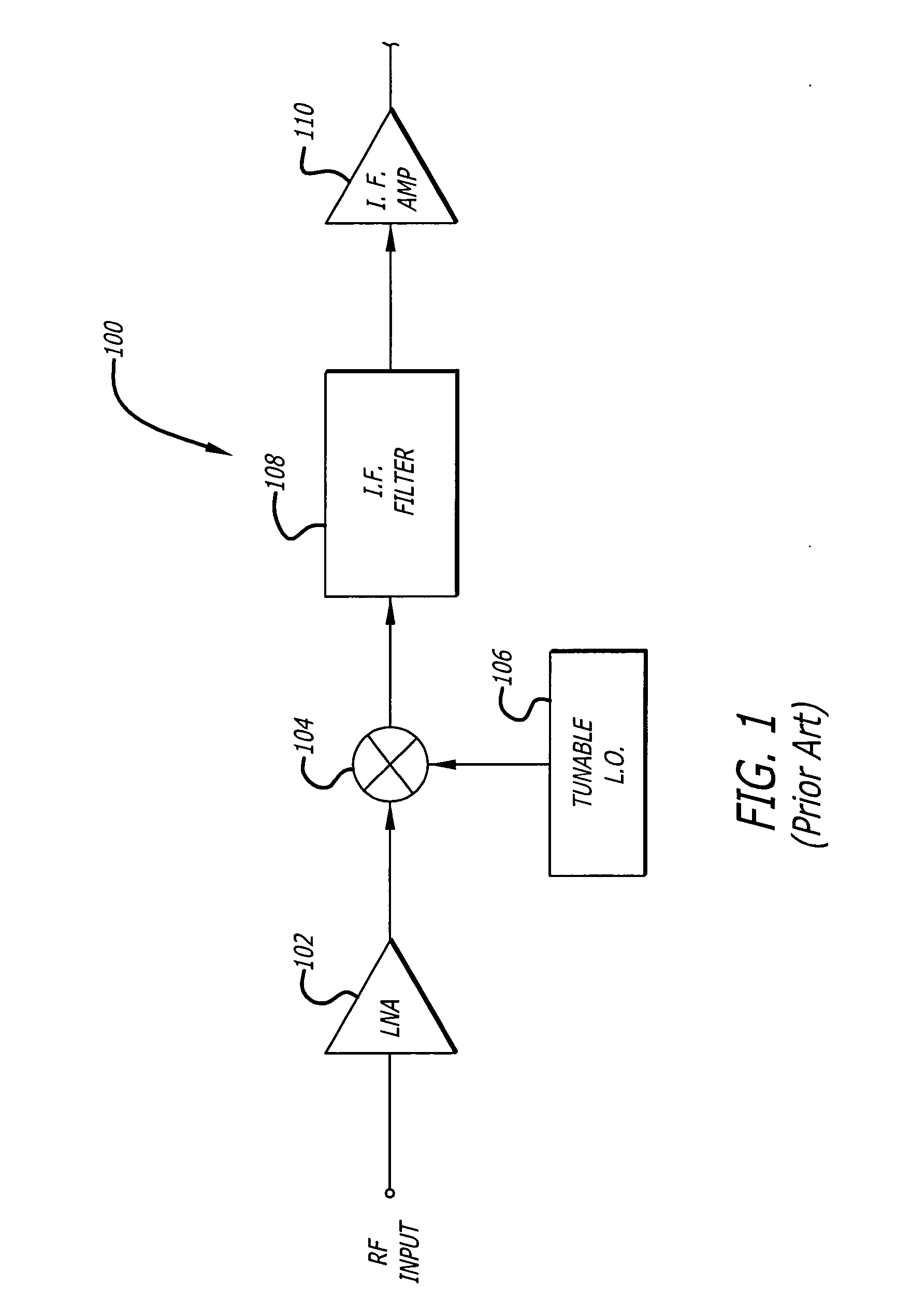
InactiveUS6885853B2Low powerSimple methodContinuous tuning detailsRadio transmissionLocal oscillatorEngineering
A receiver (22) includes an IF filter (44) and a nearby process-variant circuit (80) formed on a common semiconductor substrate (24). The actual center frequency of the IF filter (44) is determined by resistors (70, 74) and capacitors (72, 76) exhibiting imprecise values and is unlikely to equal a nominal center frequency. The process-variant circuit (80) includes a test resistor (102) and test capacitor (104) formed using the same resistor-forming and capacitor-forming processes used to form the IF filter resistors (70, 74) and capacitors (72, 76). In response a test signal (88) from the process-variant circuit (80) and a reference signal (84) from a process-invariant circuit (82), a tuning parameter for a tunable local oscillator (90) is determined so that a local oscillation signal (94) will exhibit a frequency which, when mixed with an RF signal (38) yields an IF signal (42) at the actual center frequency of the IF filter (44).
Owner:NAT SCI
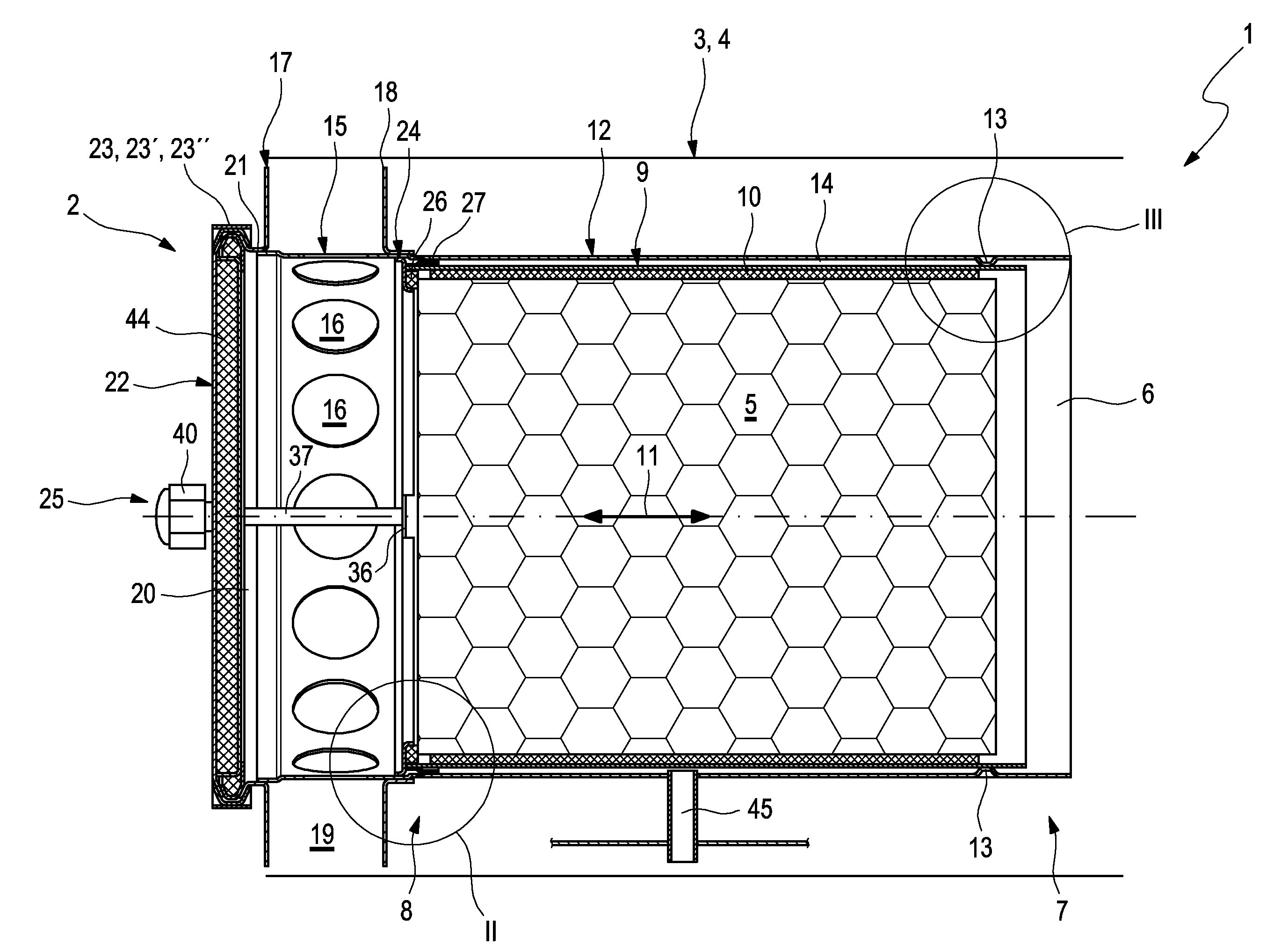
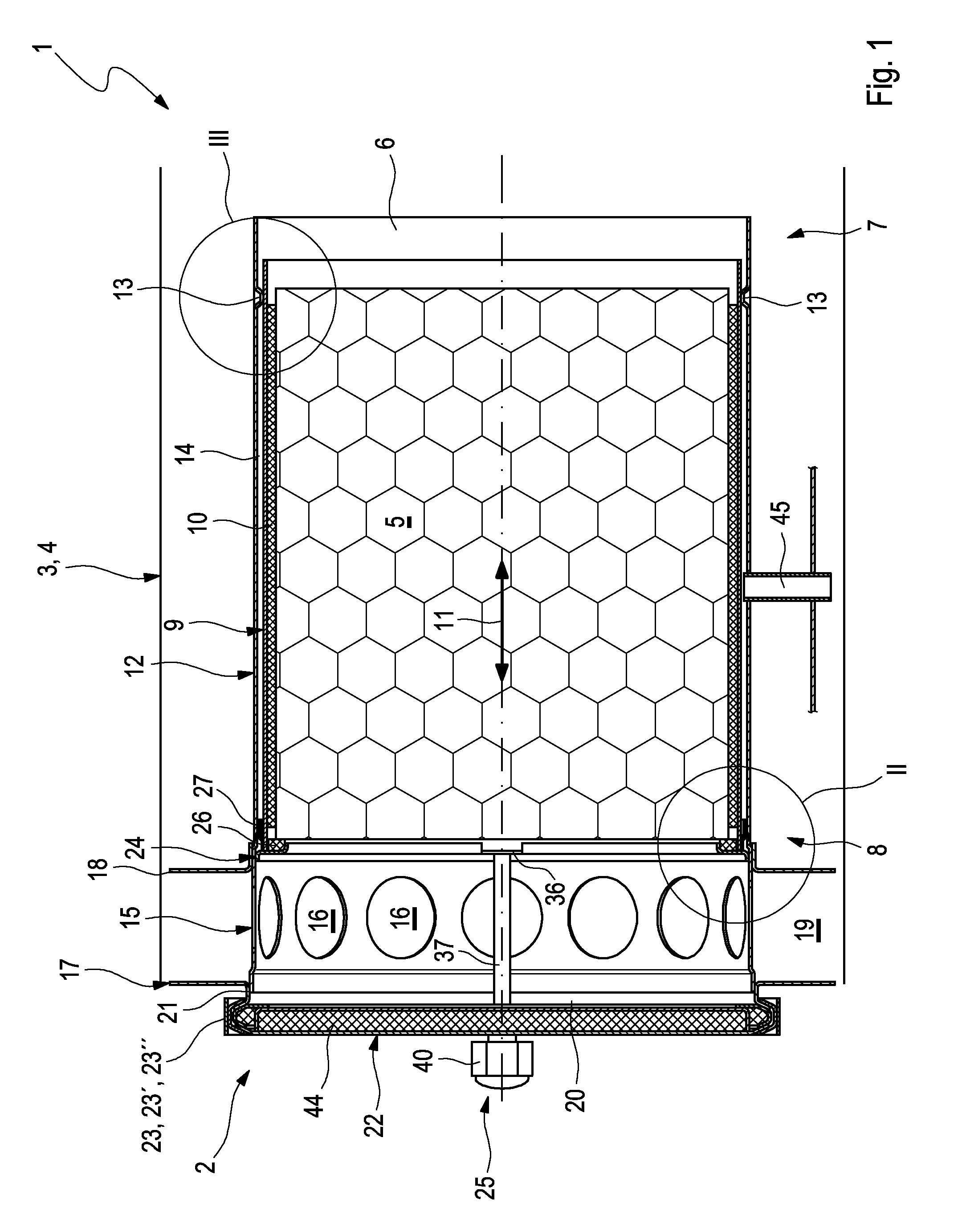
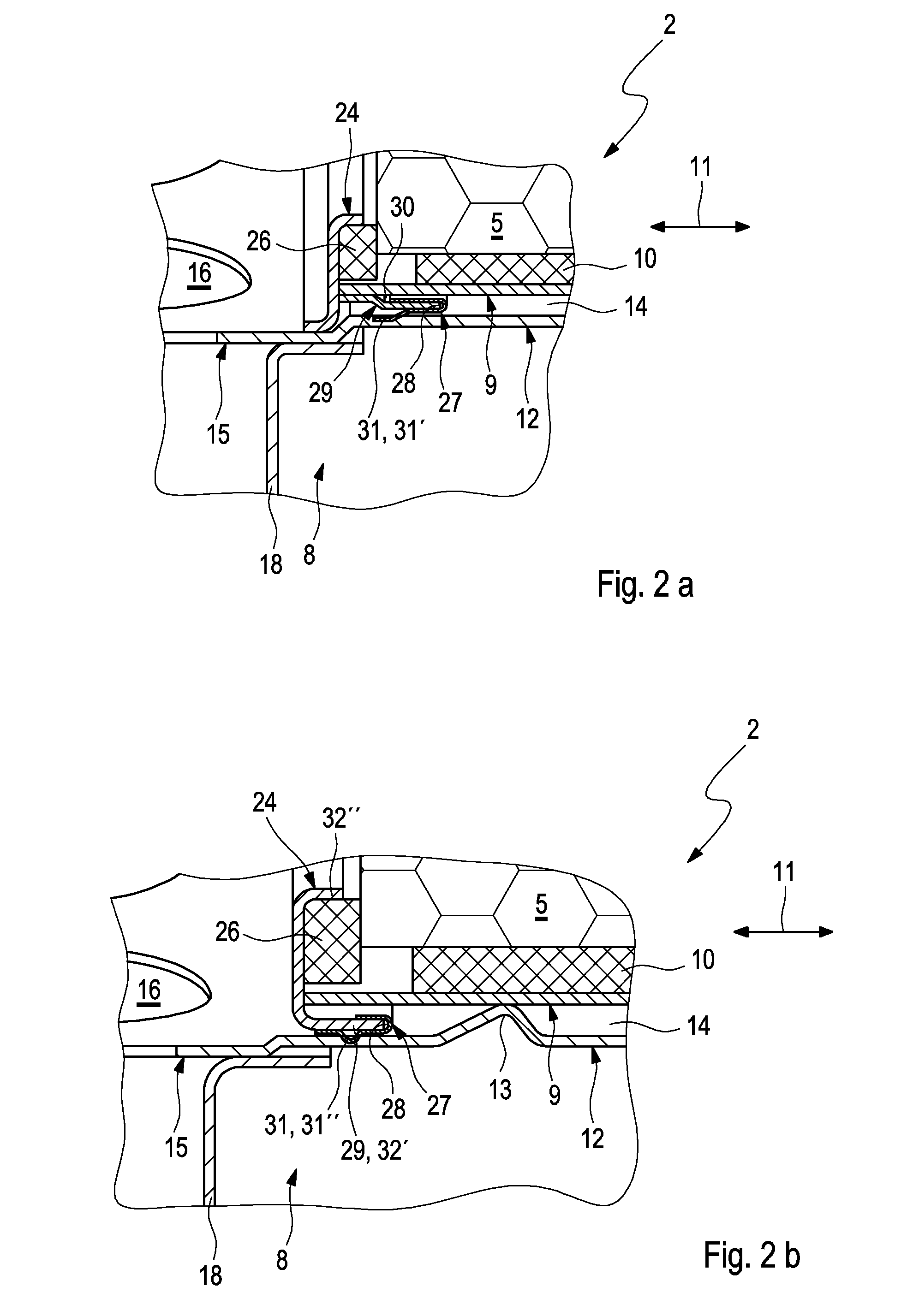
Particle filter
ActiveUS20150107458A1Easy to installEasy to replaceCombination devicesGas treatmentInternal combustion engineMuffler
A particle filter (2) for filtering exhaust gas in an internal combustion engine includes a housing and a filter element. A simplified installation and / or simplified replacement of the filter element (5) and / or improved sealing of the housing (4) results if the filter element (5) is supported in an inner jacket (9), which is supported radially in an outer jacket (12) and is arranged so as to be axially movable in the outer jacket (12). The inner jacket (9) is axially supported on a ring (24), which is supported axially on a cover (22) that closes an installation opening (20) of the housing (4) via at least one supporting element (25) in order to transmit pressure forces. A muffler (1) is provided having such a particle filter (2), wherein a section of a muffler housing (3) of the muffler (1) forms the housing (4) of the particle filter (2).
Owner:PUREM GMBH
Radio receiver having a variable bandwidth IF filter and method therefor
InactiveUS6957054B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsRadio transmissionLow-pass filterRadio receiver
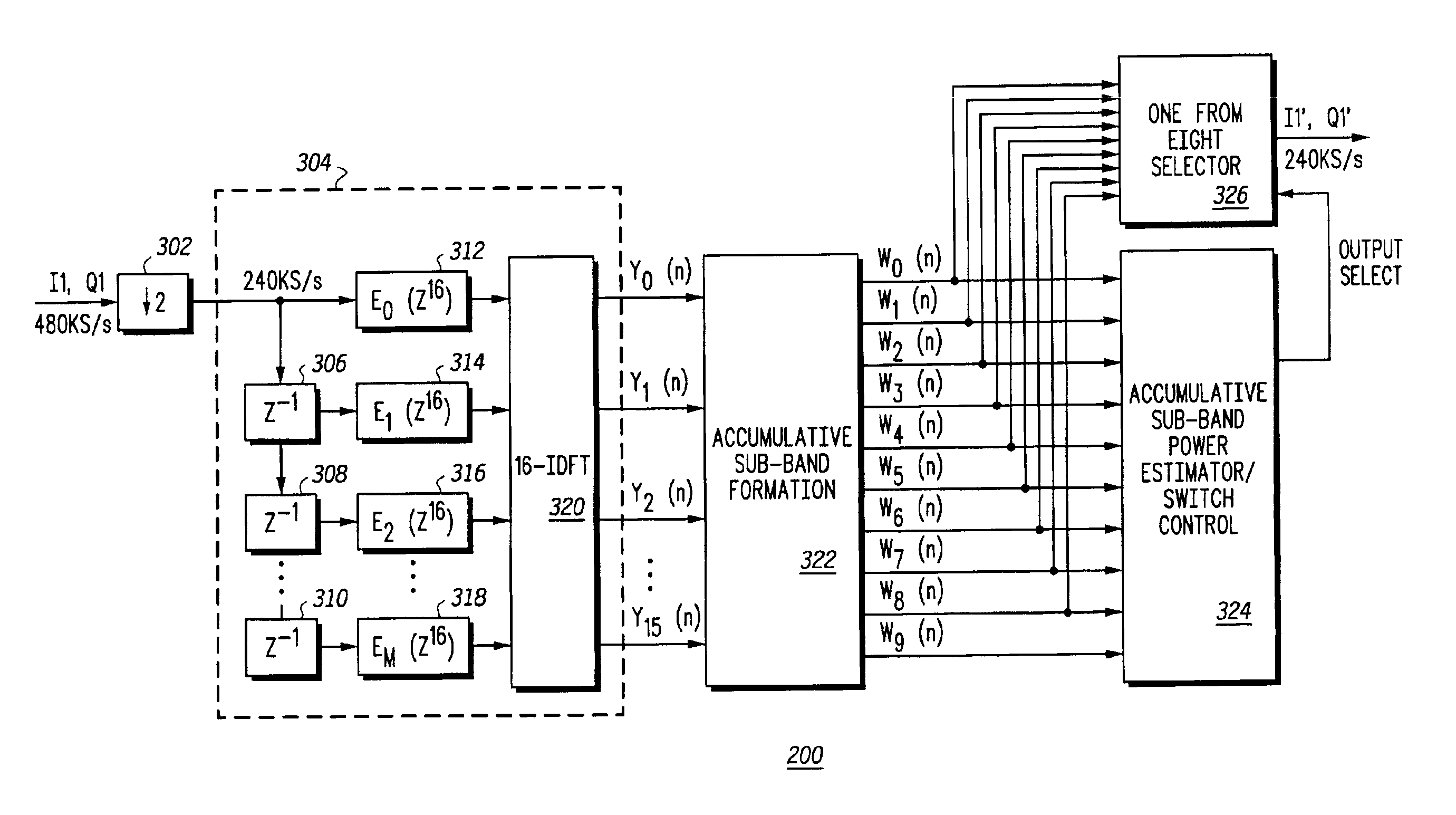
A radio receiver (100) has an IF (intermediate frequency) filter (200) for automatically adjusting its intermediate frequency. The filter (200) includes a filter bank (304), an accumulative sub-band formation (322) and an accumulative sub-band power estimator / switch control (324). The filter bank (304) generates sub-bands, each sub-band having a predetermined frequency range. The accumulative sub-band formation (322) selectively sums the sub-bands to provide lowpass filters having incrementally increasing bandwidth. Power estimates of the lowpass filters are used to determine which lowpass filter output is appropriate for adjacent station interference. Also, if there is no adjacent station interference, the IF filter (200) selects the appropriate filter output depending on the signal strength of the desired station.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
A receiver for receiving a plurality of GNSS (global navigation satellite system) signals
A receiver for receiving a plurality of GNSS (global navigation satellite system) signals is arranged to receive a plurality of global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals from up to four different satellite navigation systems including a GLONASS system, a BeiDou system, a GPS system, and a Galileo system. Received GNSS signals are mixed with a first local frequency signal to generate a plurality of mixed signals. The mixed signals are processed in up to three parallel branches. In a first branch, a first portion of the mixed signals are transformed by passing the first portion through a band-pass filter having a bandwidth between about 0 MHz and 46 MHz and by amplifying the filtered signals with an AGC circuit. In a second branch, a second portion of the mixed signals are transformed by rejecting image signals of the second portion with an image rejection filter and mixing image rejection filter output signals with a second local frequency signal to derive first remixed signals. In a third branch, a third portion of the mixed signals are transformed by adjusting a phase of the third portion to overlap a band of the first remixed signals. The adjusted third portion of the mixed signals and the first remixed signals are concurrently band pass filtered with a low IF filter.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
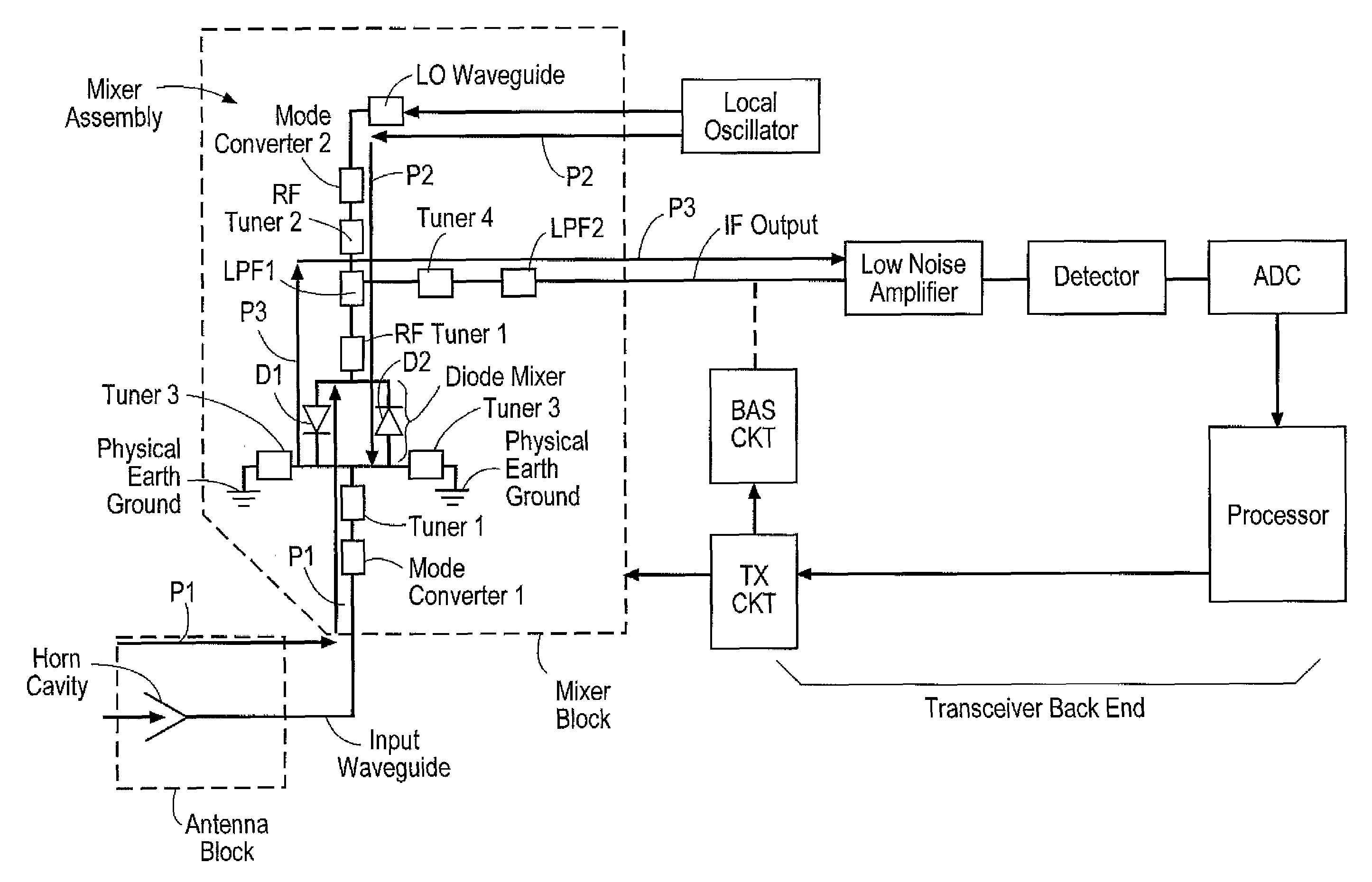
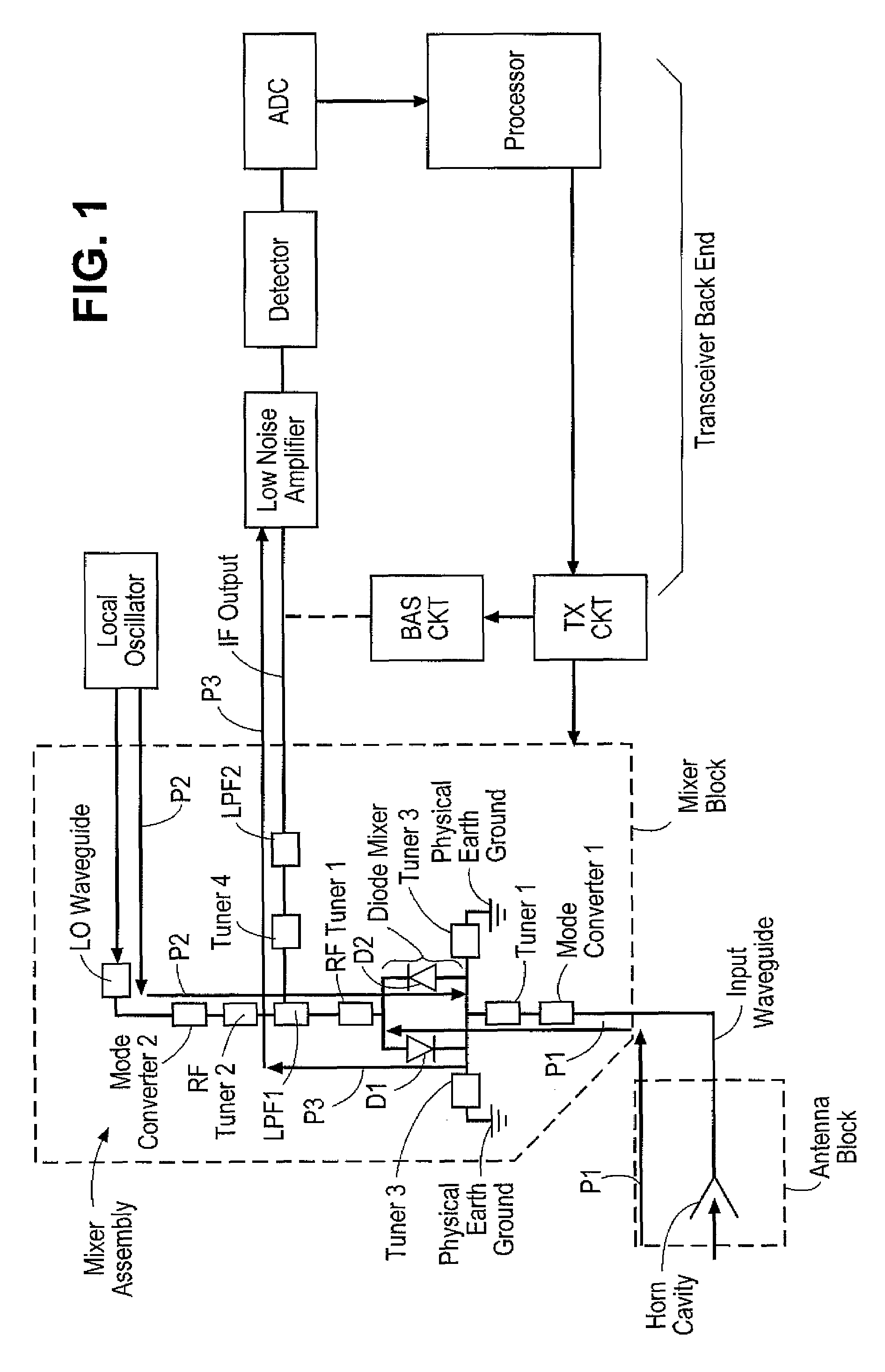
Transceiver
A transceiver capable of processing signals having wavelengths of less than 1 millimeter and / or more than 1 millimeter comprising a mixer / filter circuit coupled to an IF filter where said mixer / filter circuit is positioned within a mixer block to receive incoming signals guided into one or more feed horn openings of the mixer block by an optical arrangement. The IF filter is also disposed within the mixer block, but is positioned substantially orthogonal with respect to the mixer / filter circuit for efficient use of space.
Owner:THRUVISION LTD +1
FMCW radar distance resolution and distance measurement range dynamic adjusting method
ActiveCN109283517ARealize dynamic adjustmentExcellent distance resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFar distanceRadar systems
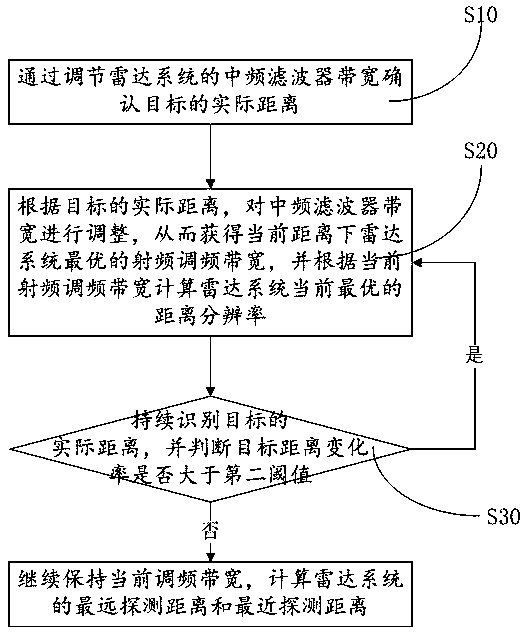
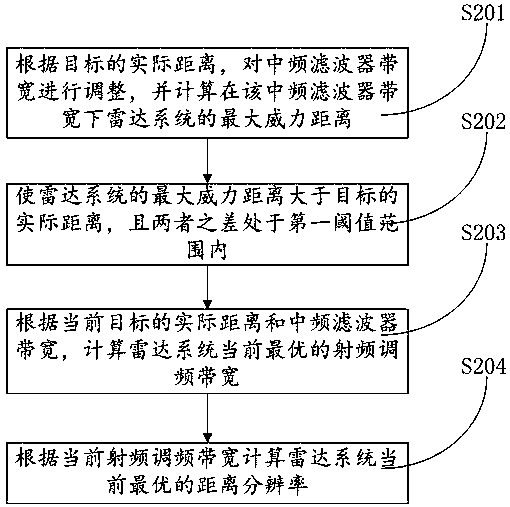
The invention relates to an FMCW radar distance resolution and distance measurement range dynamic adjusting method. The method includes: confirming an actual distance of a target by adjusting an IF filter bandwidth of a radar system; adjusting an IF filter bandwidth according to the actual distance of the target, and then obtaining the optimal RF frequency modulation bandwidth and the optimal distance resolution of the radar system at the current distance; continuously identifying the actual distance of the target, and determining whether the target distance change rate is greater than a second threshold, and returning to the previous step if so, otherwise continuing to maintain the current IF filter bandwidth and the current RF frequency modulation bandwidth, and calculating the distancemeasurement range of the radar system. The method dynamically adjusts the bandwidth of the IF filter to achieve dynamic adjustment of target parameters at different distances, so that a better distance resolution can be obtained when a close range target is measured, and a far distance measurement distance can be obtained when a distant target is measured, and the dynamic adjustment of the invention can make the radar system performance better according to the actual distance of the target.
Owner:HUIZHOU DESAY SV AUTOMOTIVE
Network system with shared filtering information
InactiveUS20050204059A1Network can be lightenedImprove securityTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer hardwareInformation sharing
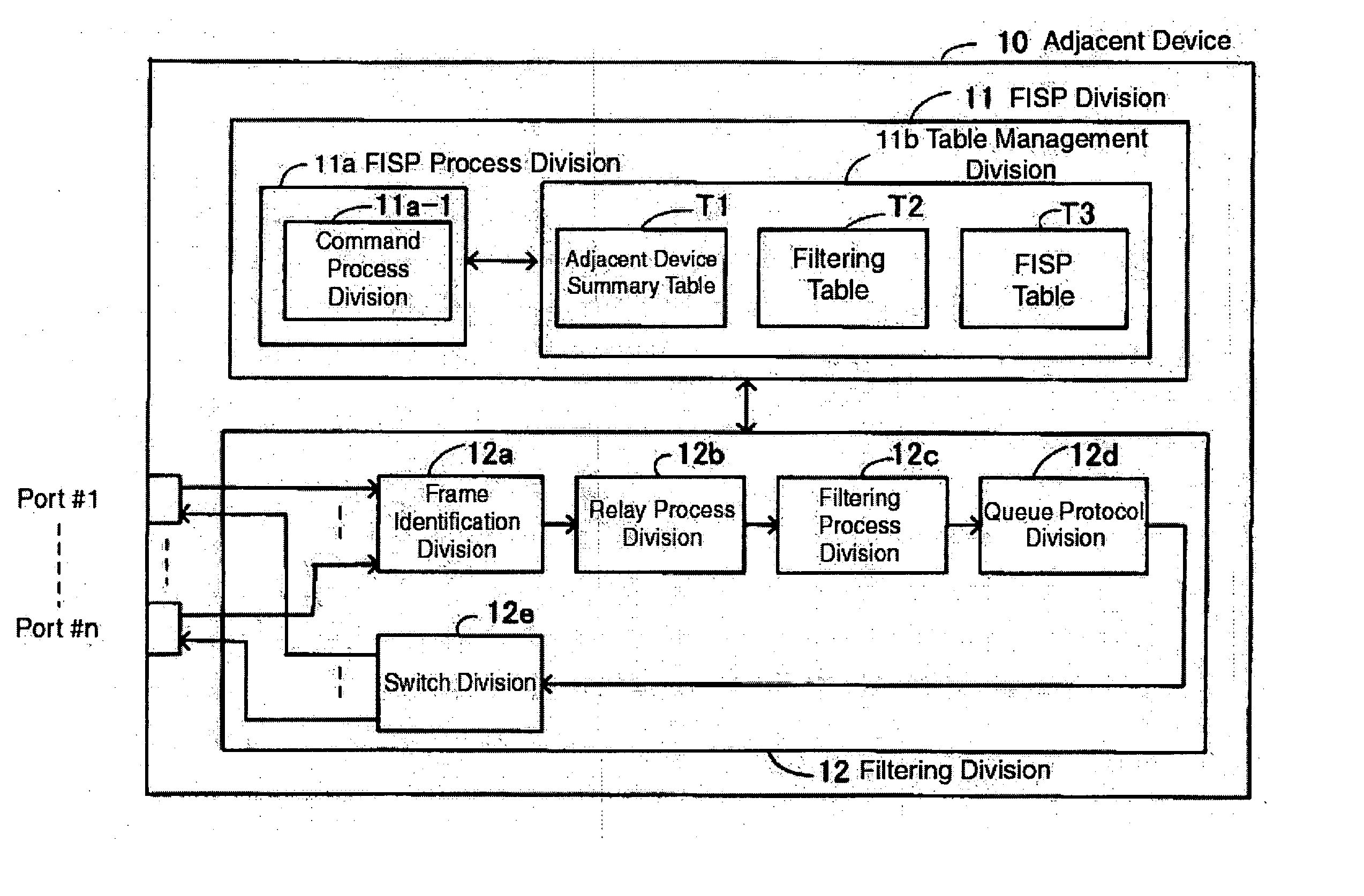
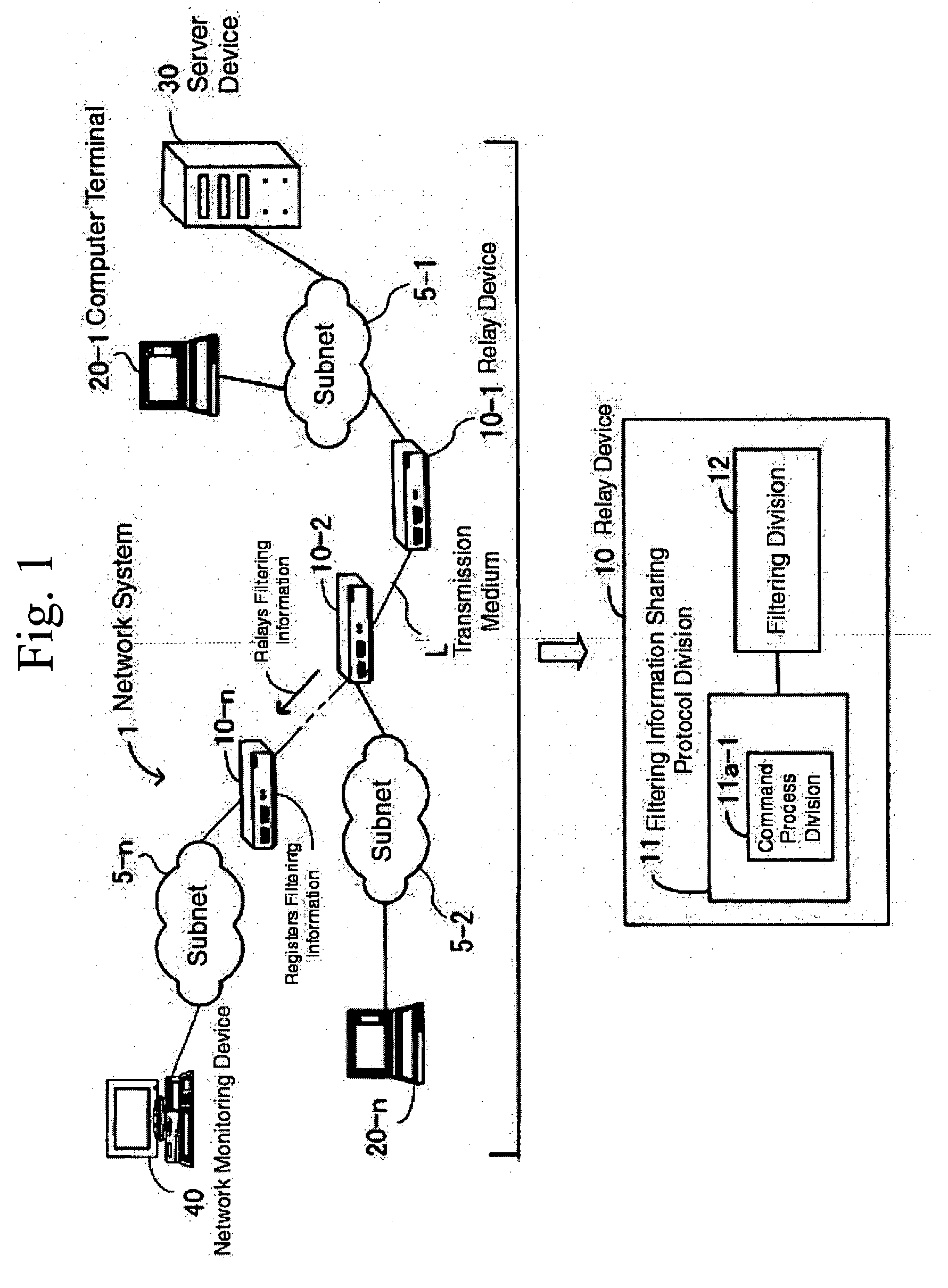
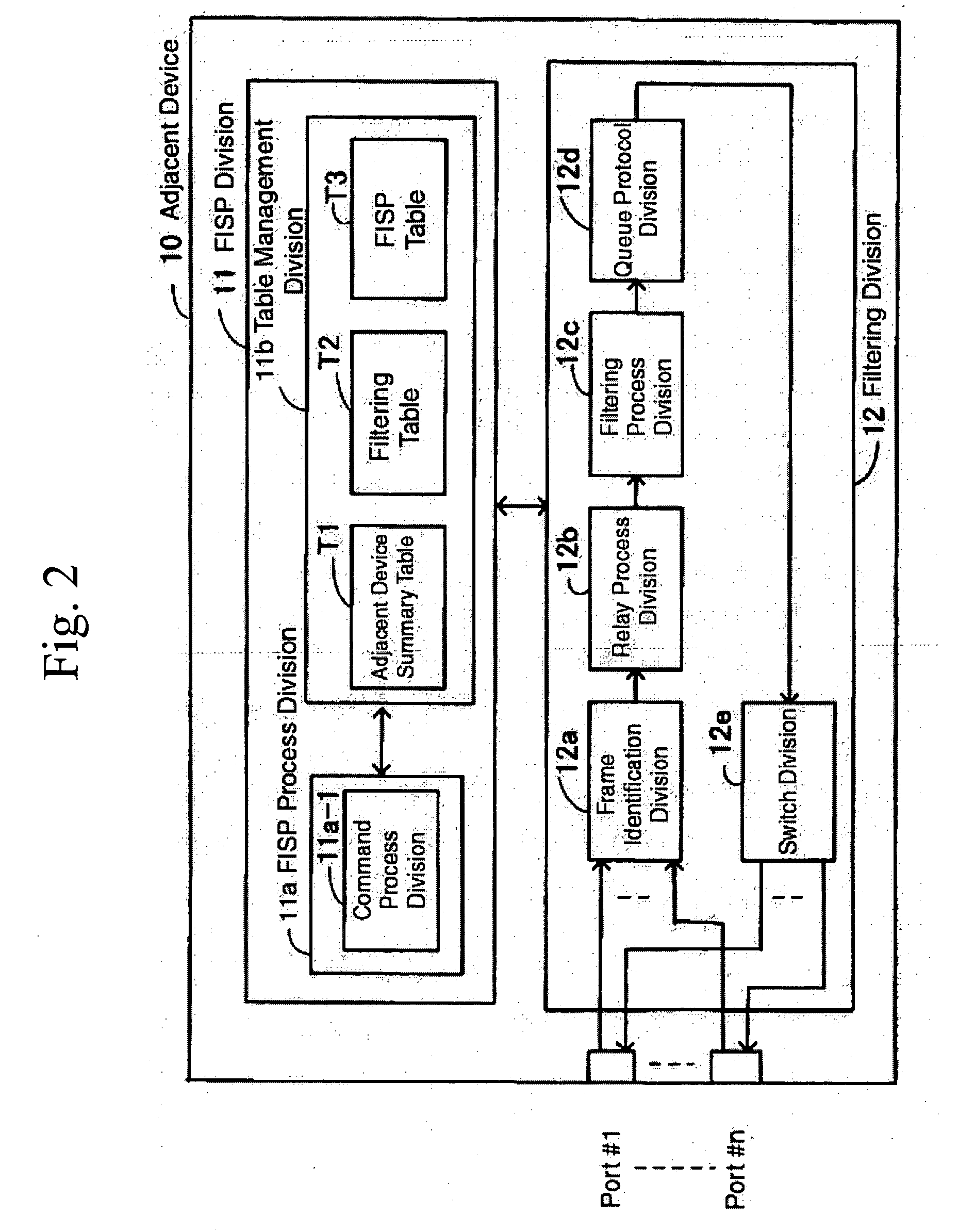
A network system comprising a transmission medium coupling a plurality of devices on the network, a plurality of relay devices connected to the transmission medium, each relay device operable to apply filtering on data from the network and transmits frames, each relay device comprising command process division operable to generate and parse commands that include filtering information relating the sharing of filtering information on the network, and when filtering sharing conditions are applied, register filtering information on its own device and apply a protocol to relay to an adjacent device if filtering information sent from an adjacent device through the filtering sharing conditions has a destination address, if a port that received the filtering information from the adjacent matches a relay destination port of the destination address, and if there is only one relay destination port for the destination address, register a receiving port of the filtering information as a destination port, if there is no destination address information in the filtering information sent from the adjacent device through the filtering sharing conditions, and a filtering information sharing protocol division operable to apply a protocol so that filtering information is not relayed to an adjacent device, and a filtering division operable to relay filtering information and frames, or filters discarded information, based on instruction from the filtering information sharing protocol division.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
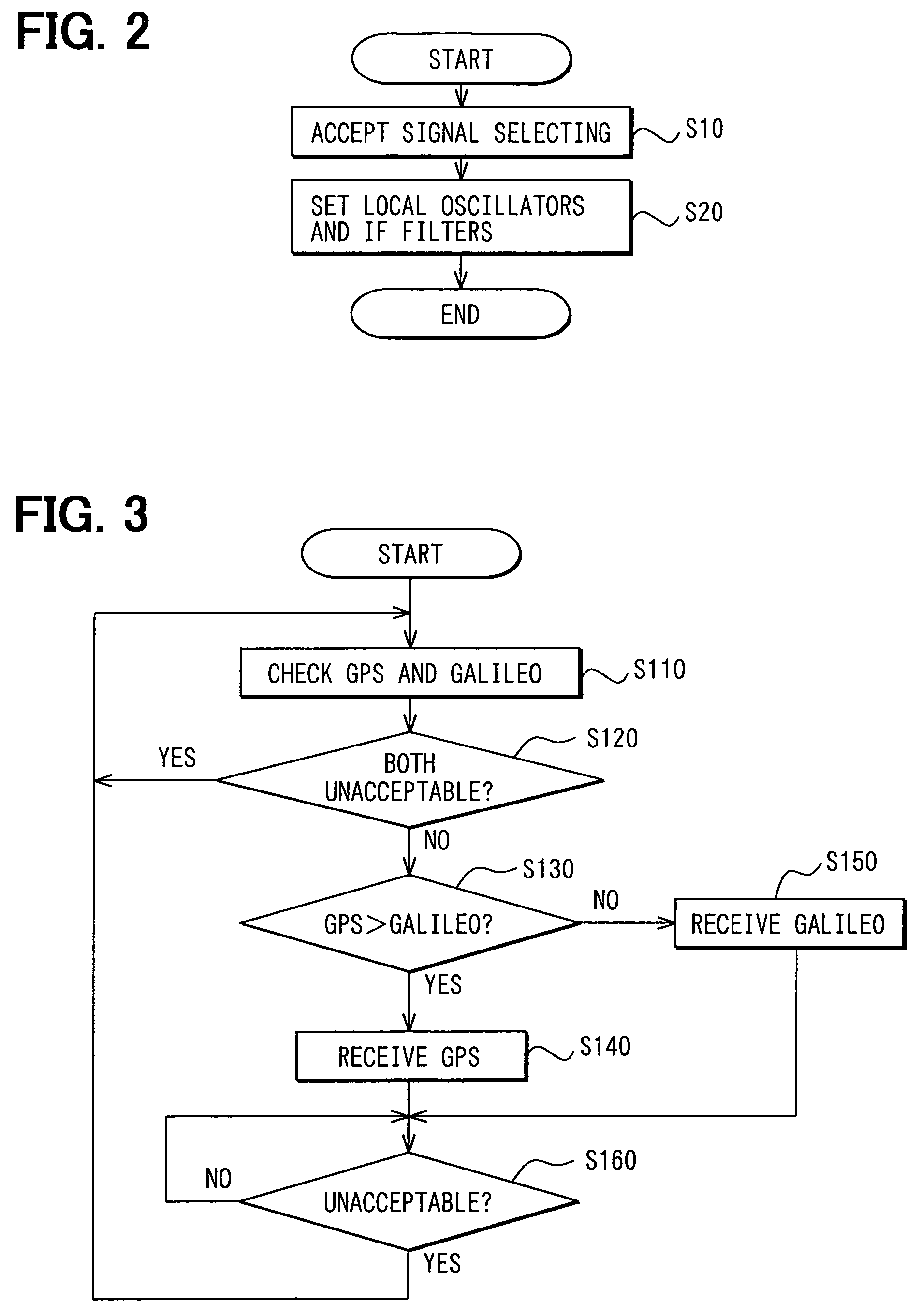
Satellite-positioning signal receiving device
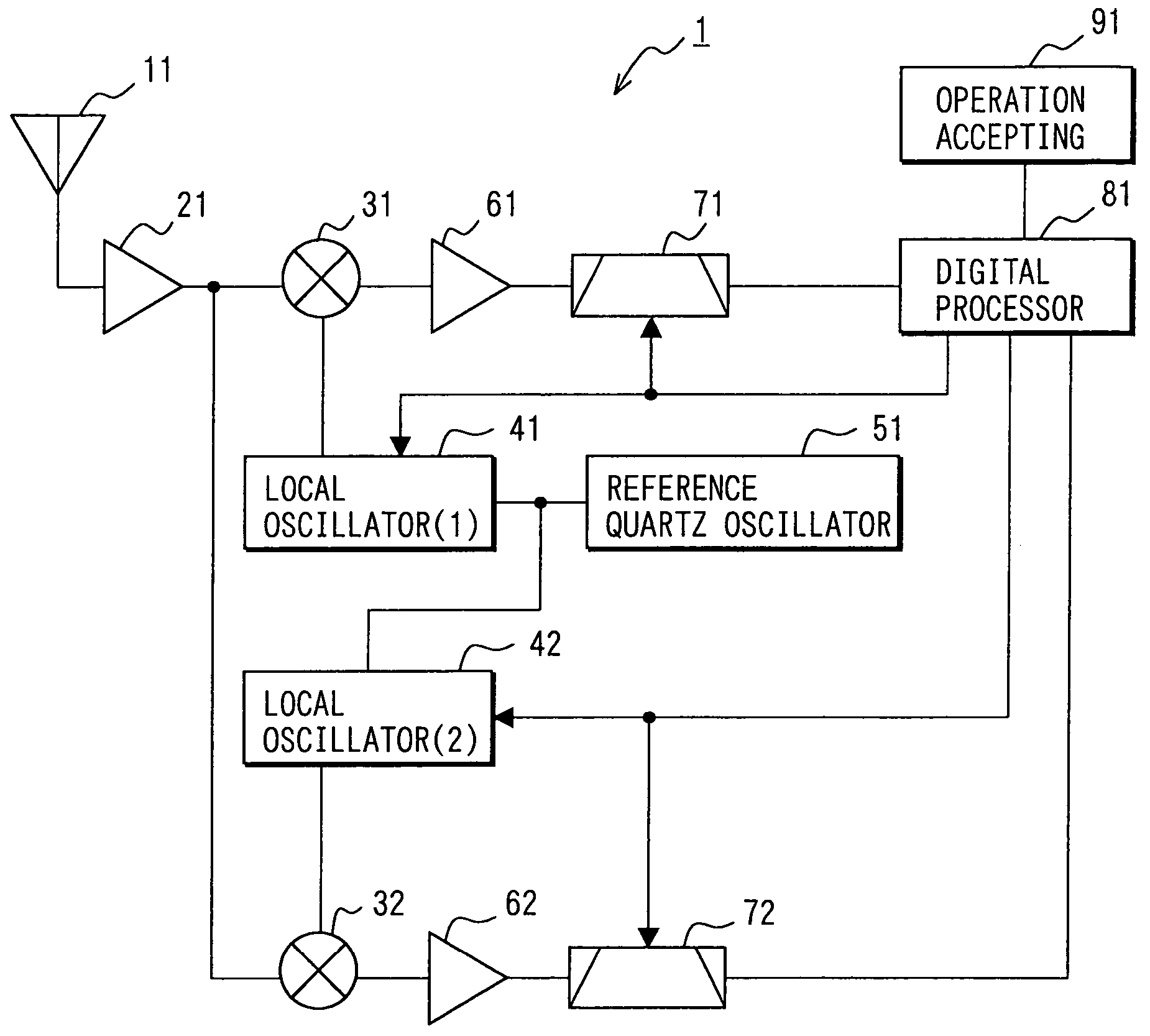
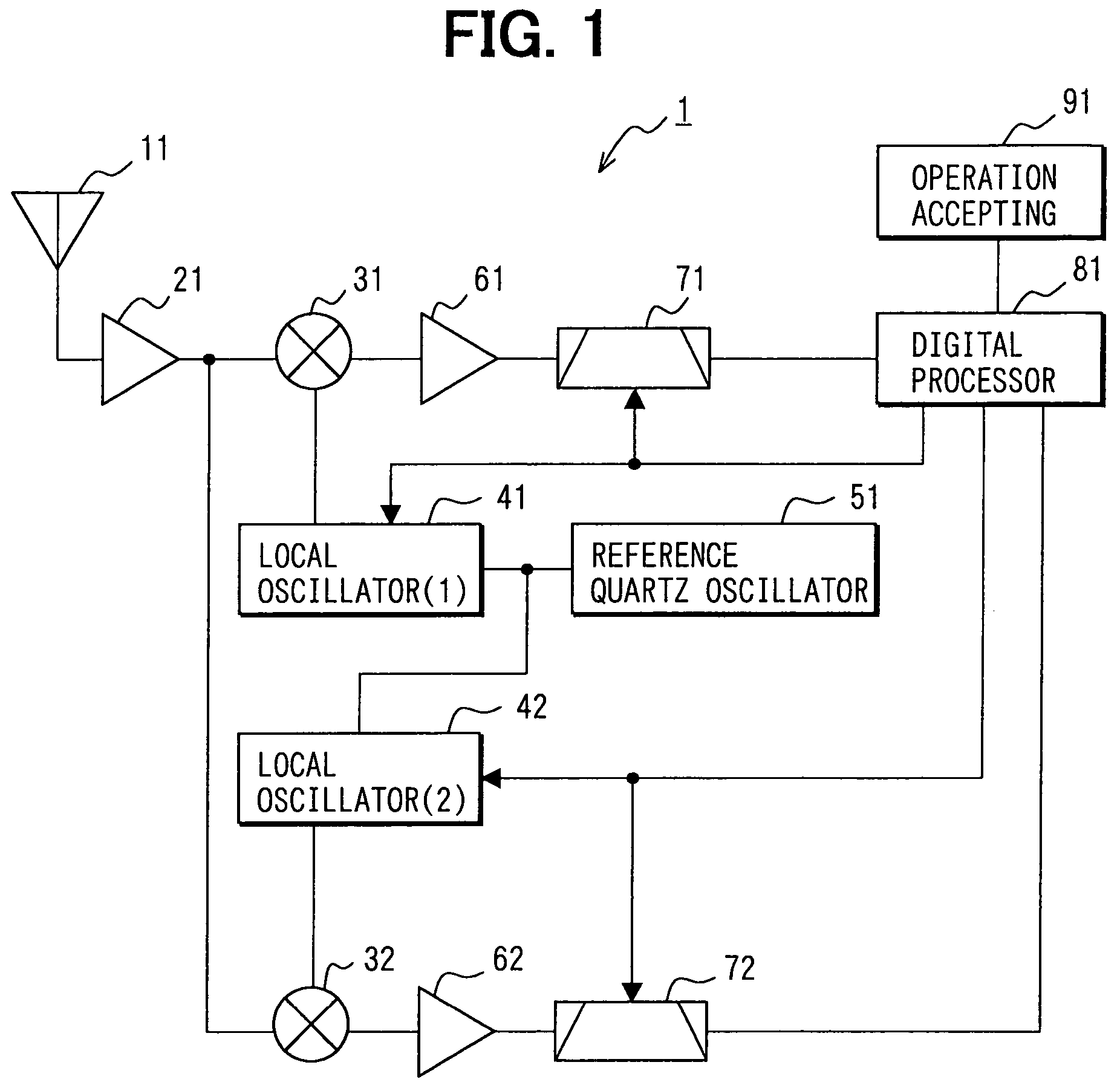
A satellite-positioning receiving device includes: an antenna which receives a signal from a satellite; an RF amplifier unit which amplifies the signal received by the antenna; a reference quartz oscillator; a digital processor unit which performs signal processing; an operation accepting unit; and two reception processing systems, that is, a first reception processing system including a first mixer unit, a first local oscillator, a first IF amplifier unit, and a first IF filter unit and a second reception processing system including a second mixer unit, a second local oscillator, a second IF amplifier unit, and a second IF filter unit. The digital processor unit is connected to the local oscillators and the IF filter units, and is so constituted that it is capable of individually changing and setting their characteristics.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com