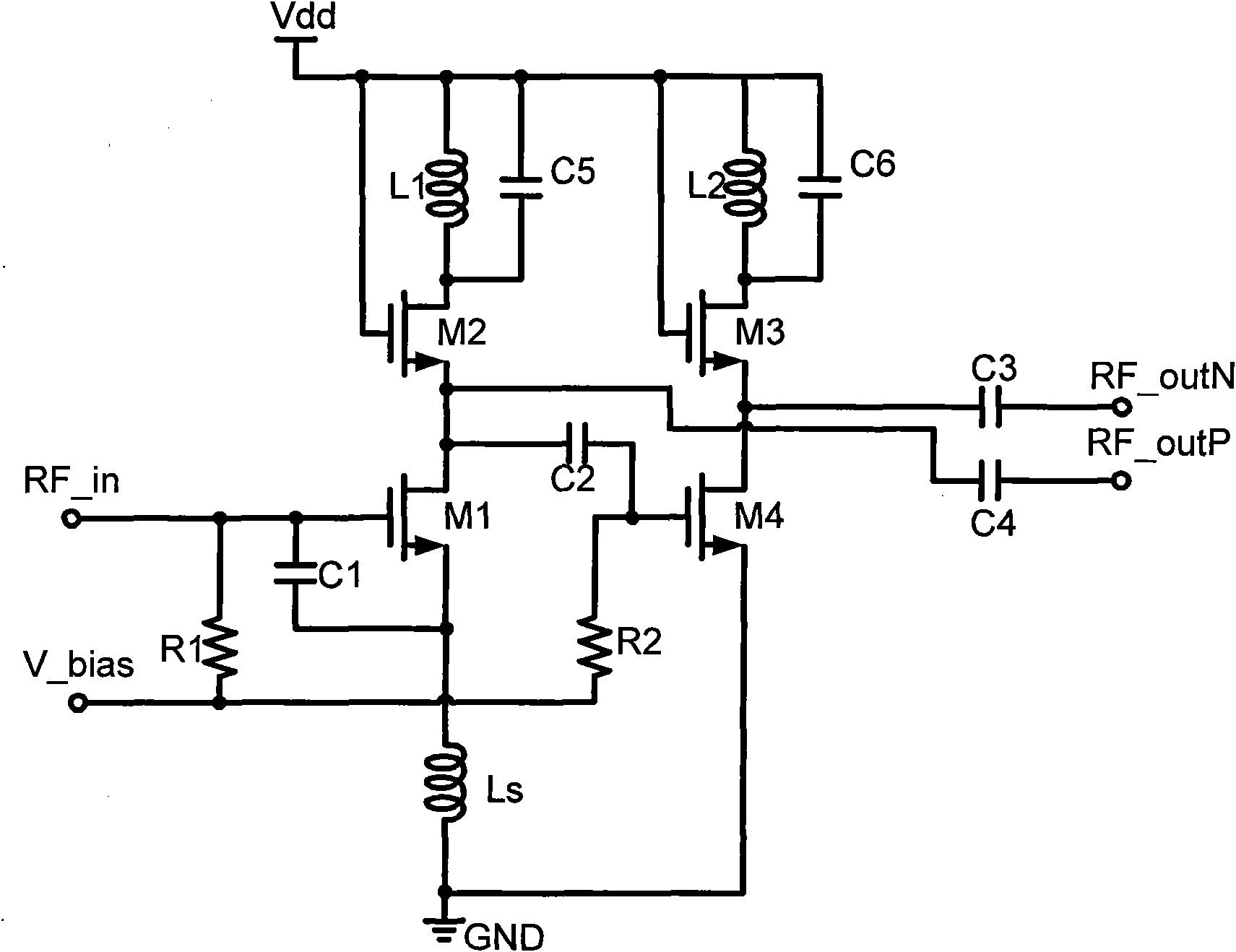
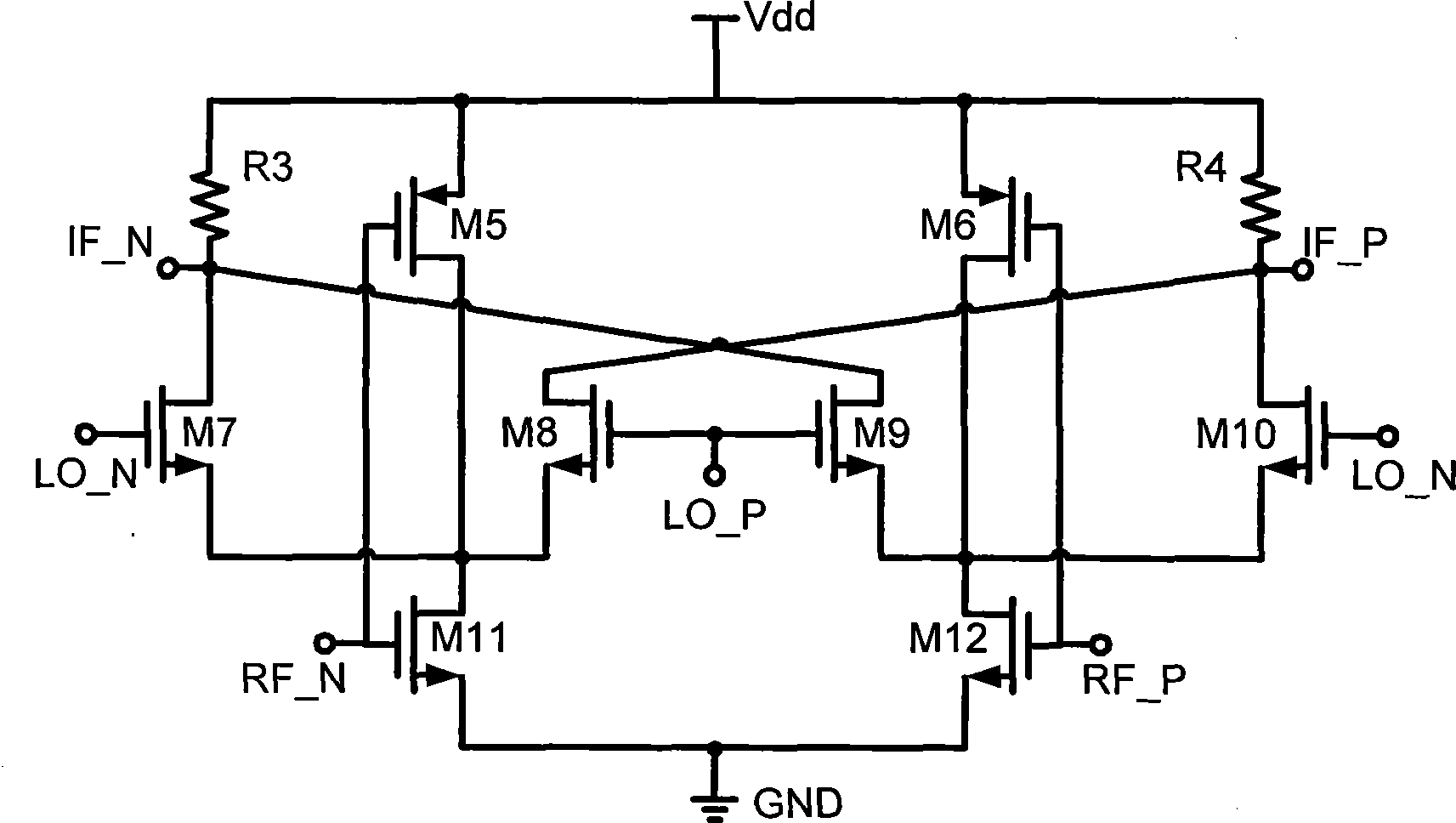
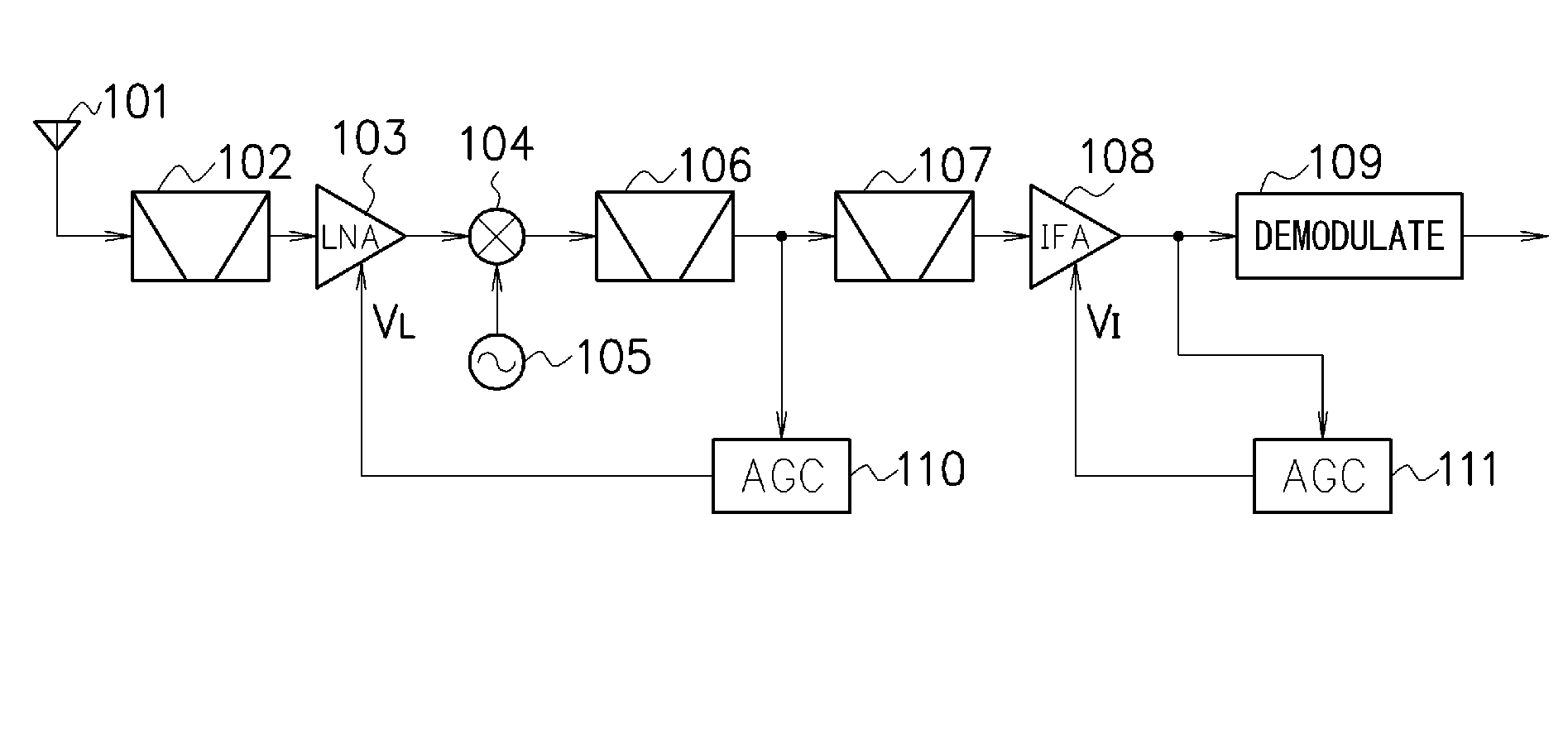
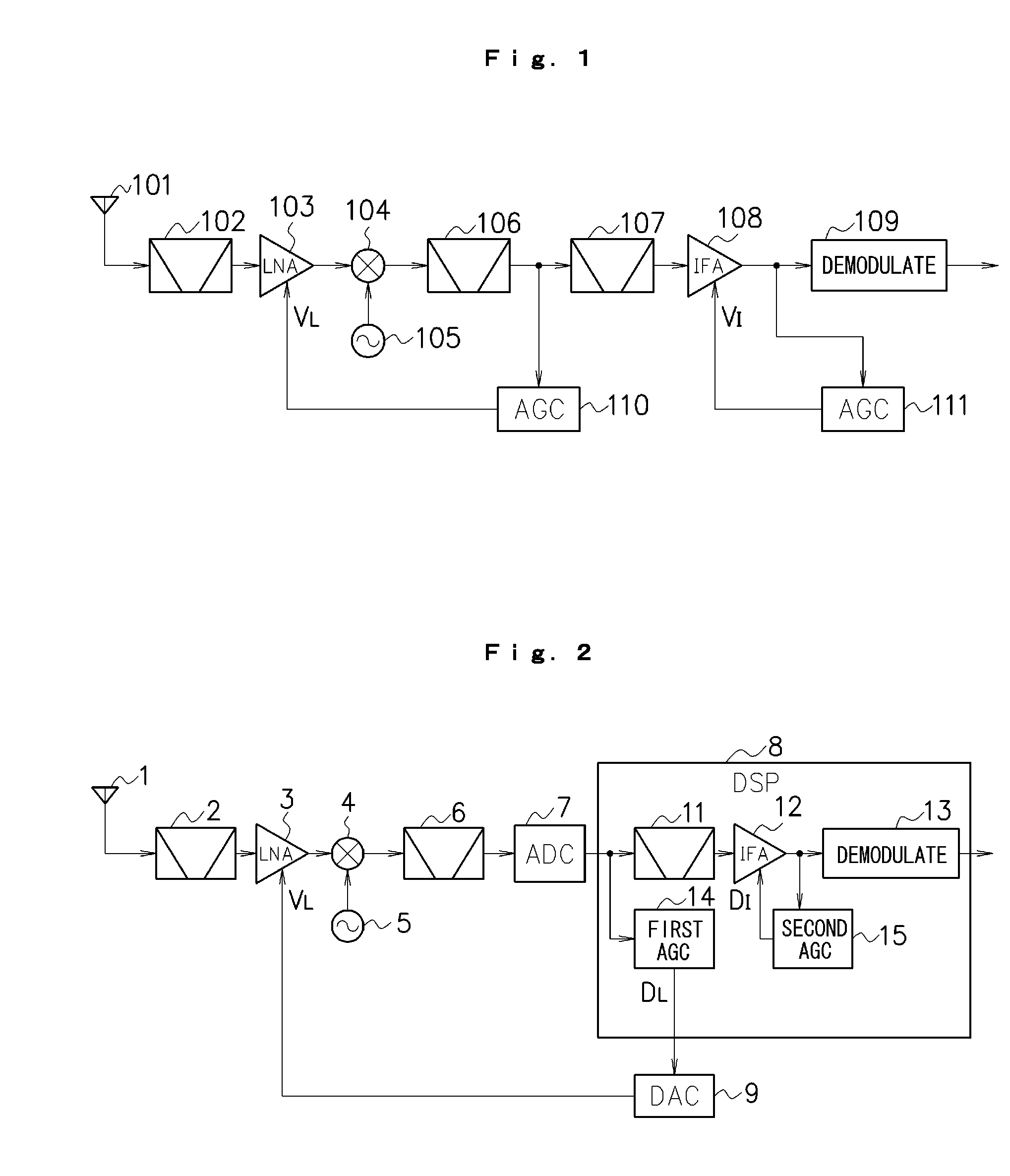
Patents
Literature
105 results about "If amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
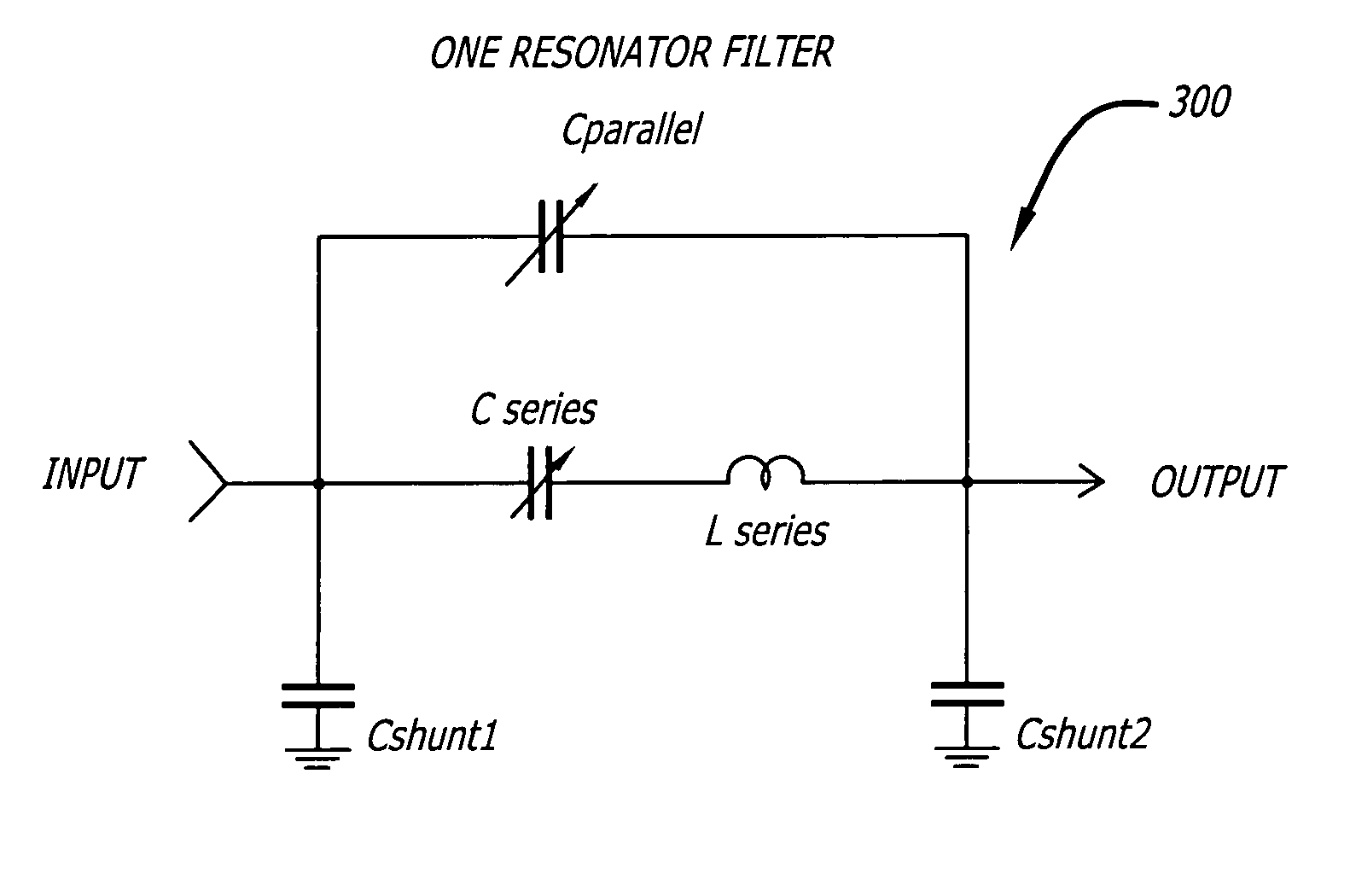
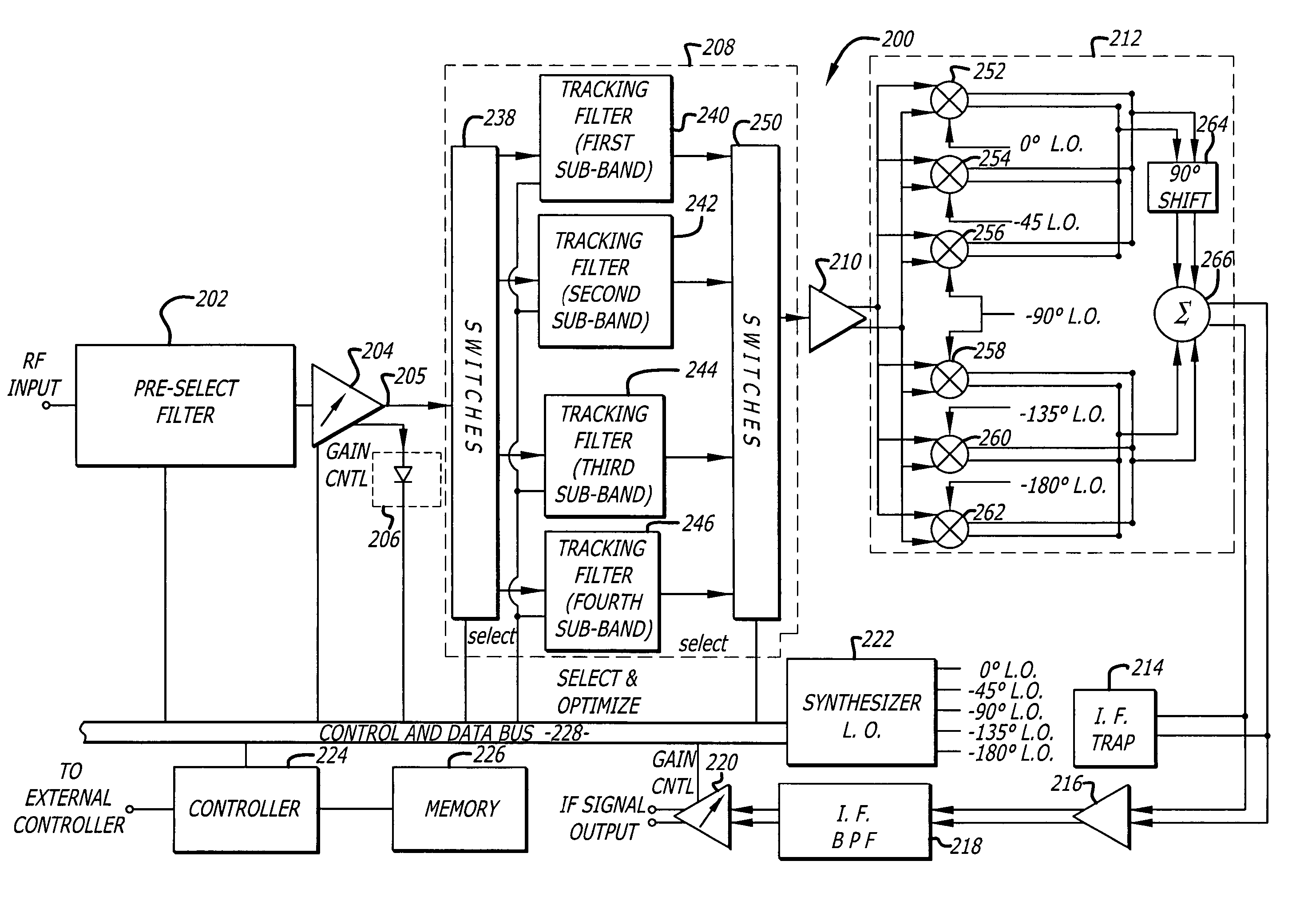
Broadband integrated digitally tunable filters
InactiveUS20050040909A1Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationAudio power amplifierBroadband
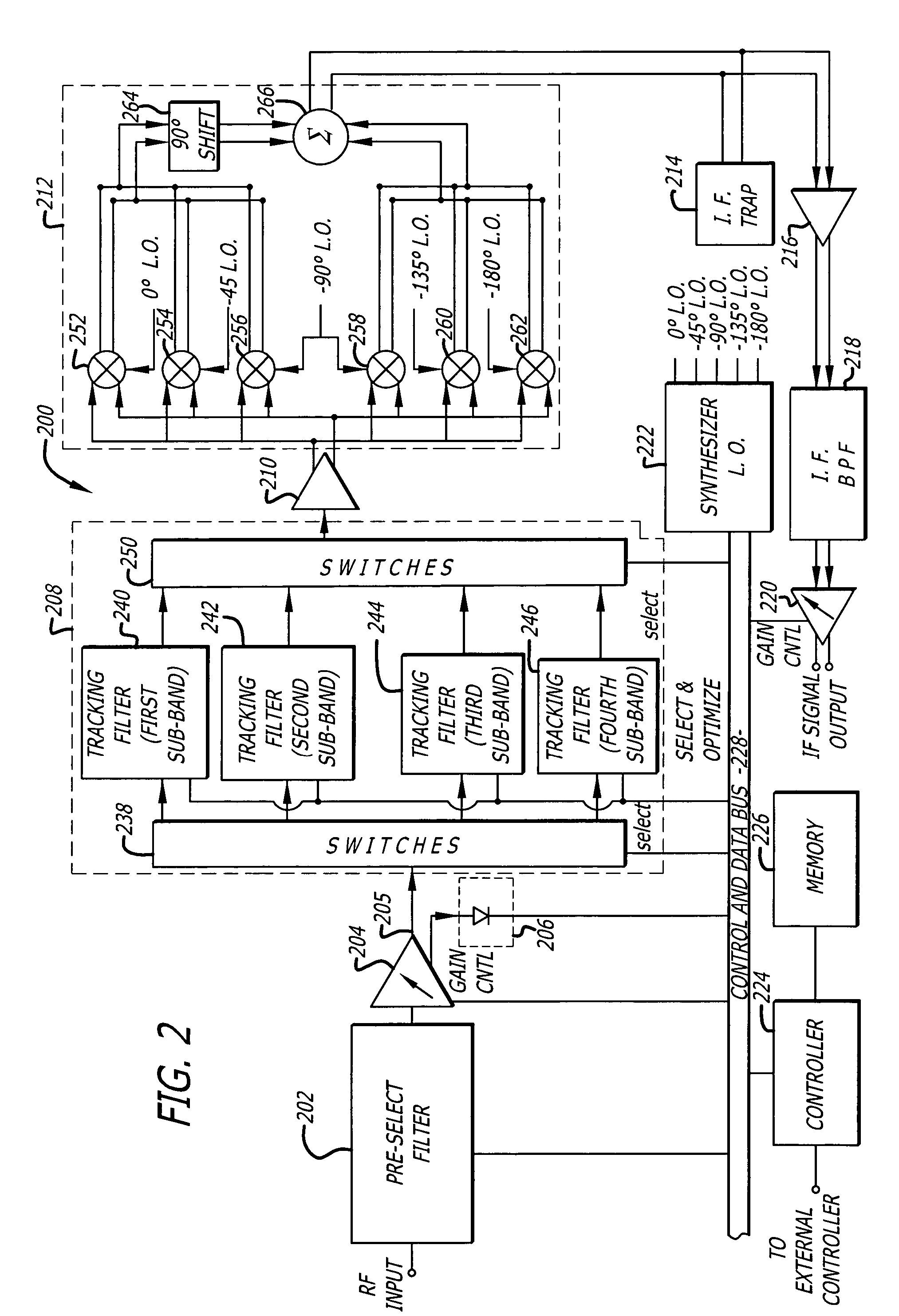
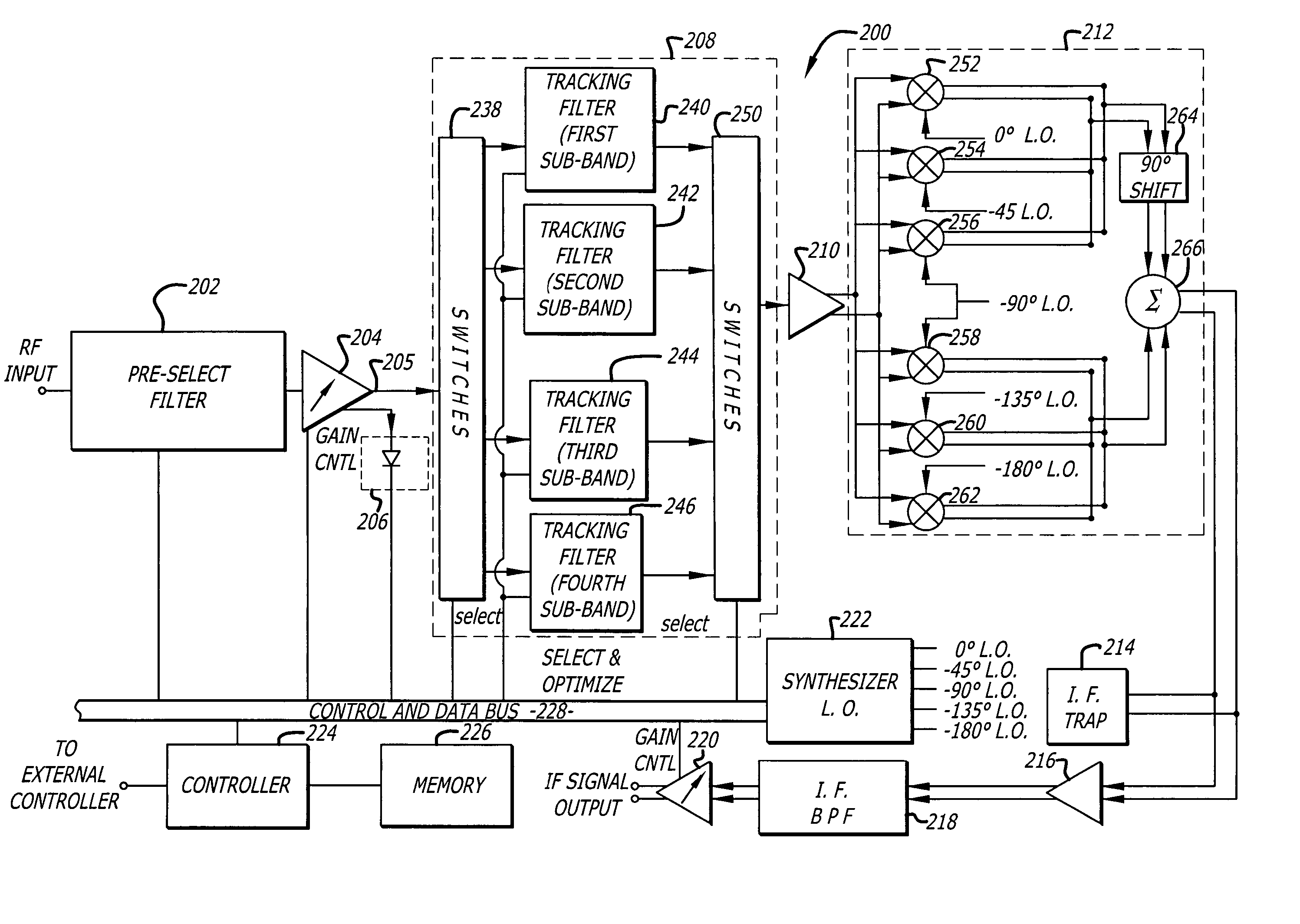
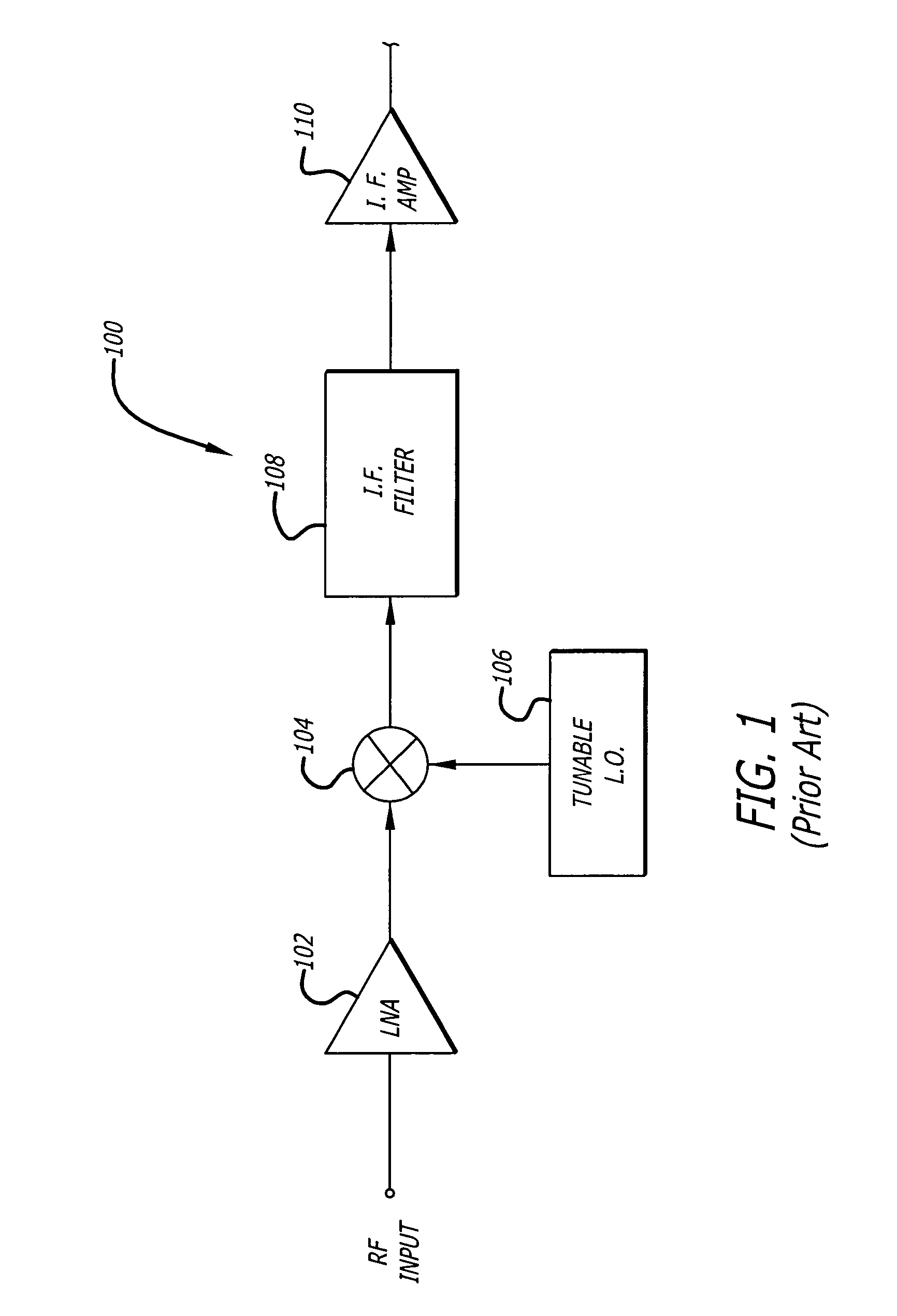
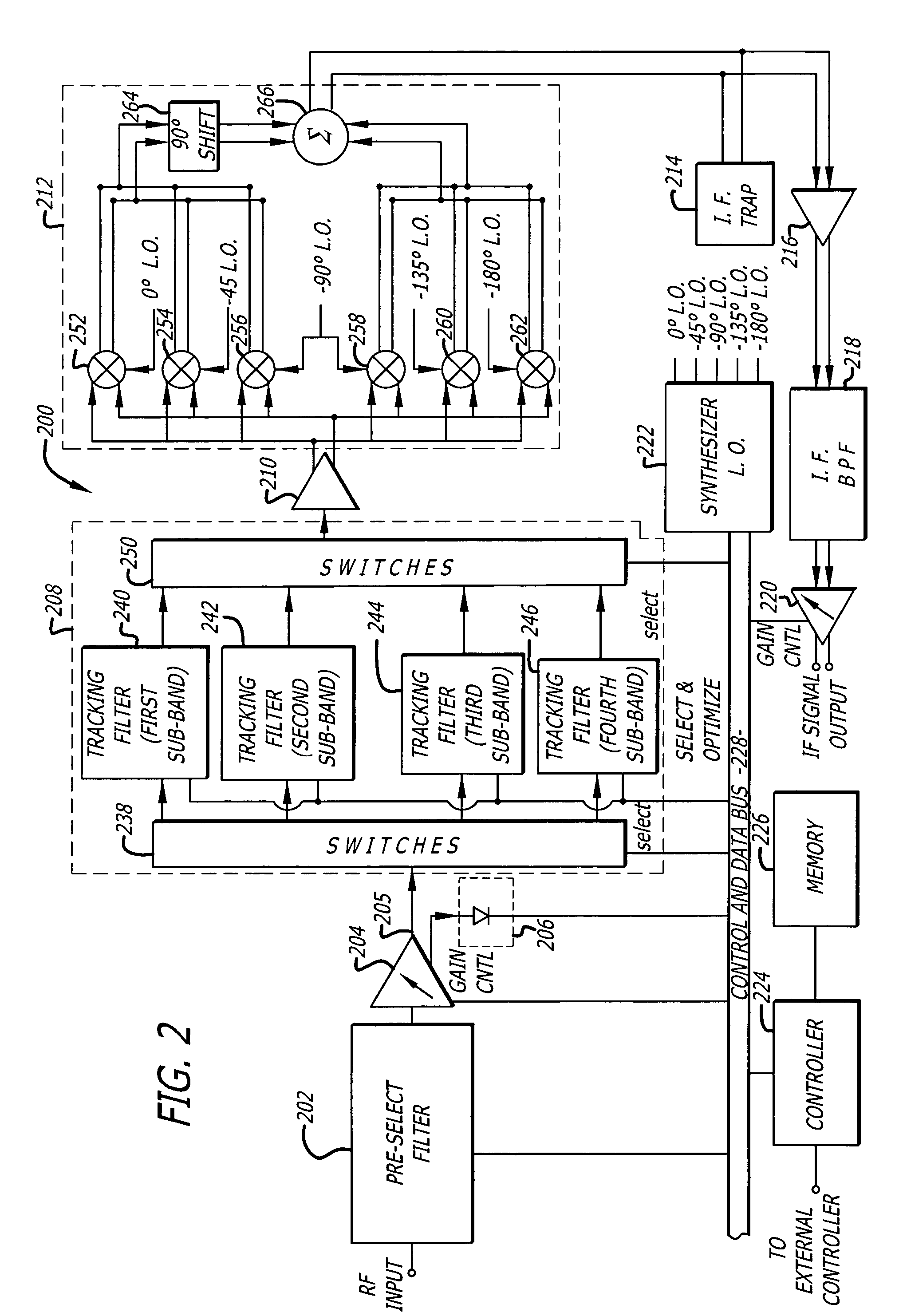
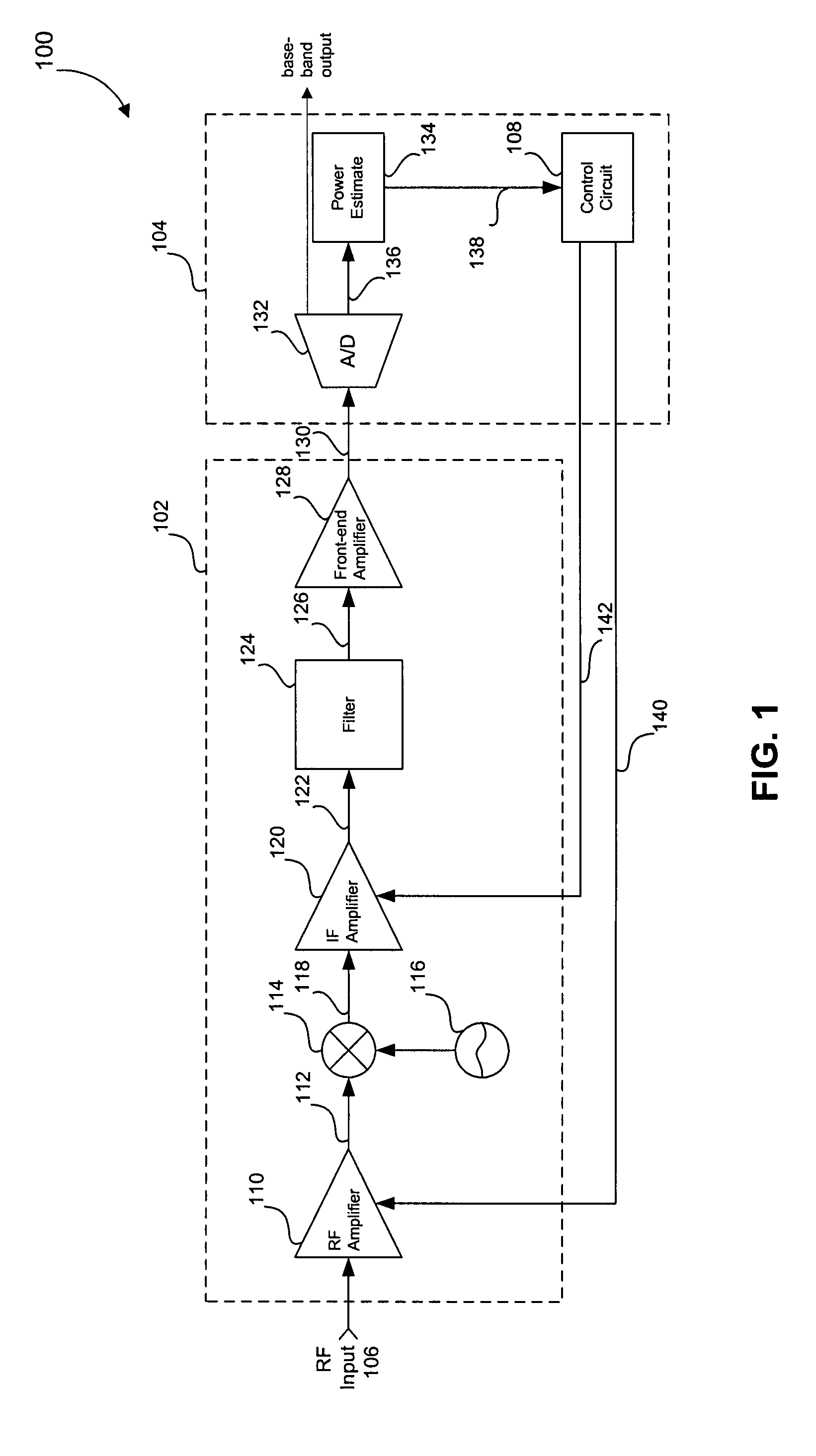
A tunable receiver is disclosed including a plurality of select filters to perform an initial band selection, a variable-gain low noise amplifier (LNA) whose gain is controlled to prevent its output power level to exceed a predetermined power threshold, a plurality of digitally-tunable tracking filters to pass signals within a selected channel and to reject signals in a corresponding image band, a second LNA to further amplify the received RF signal and to generate differential signal outputs, a down converting stage which converts the received RF signal to an IF signal while rejecting signals in the image band, an IF trap to further reject undesired signals present at the output of the down converting stage, an IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal to compensate for losses, an IF filter to provide channel select and reject undesirable signals, and a variable-gain IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal and maintain its power level within specification.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
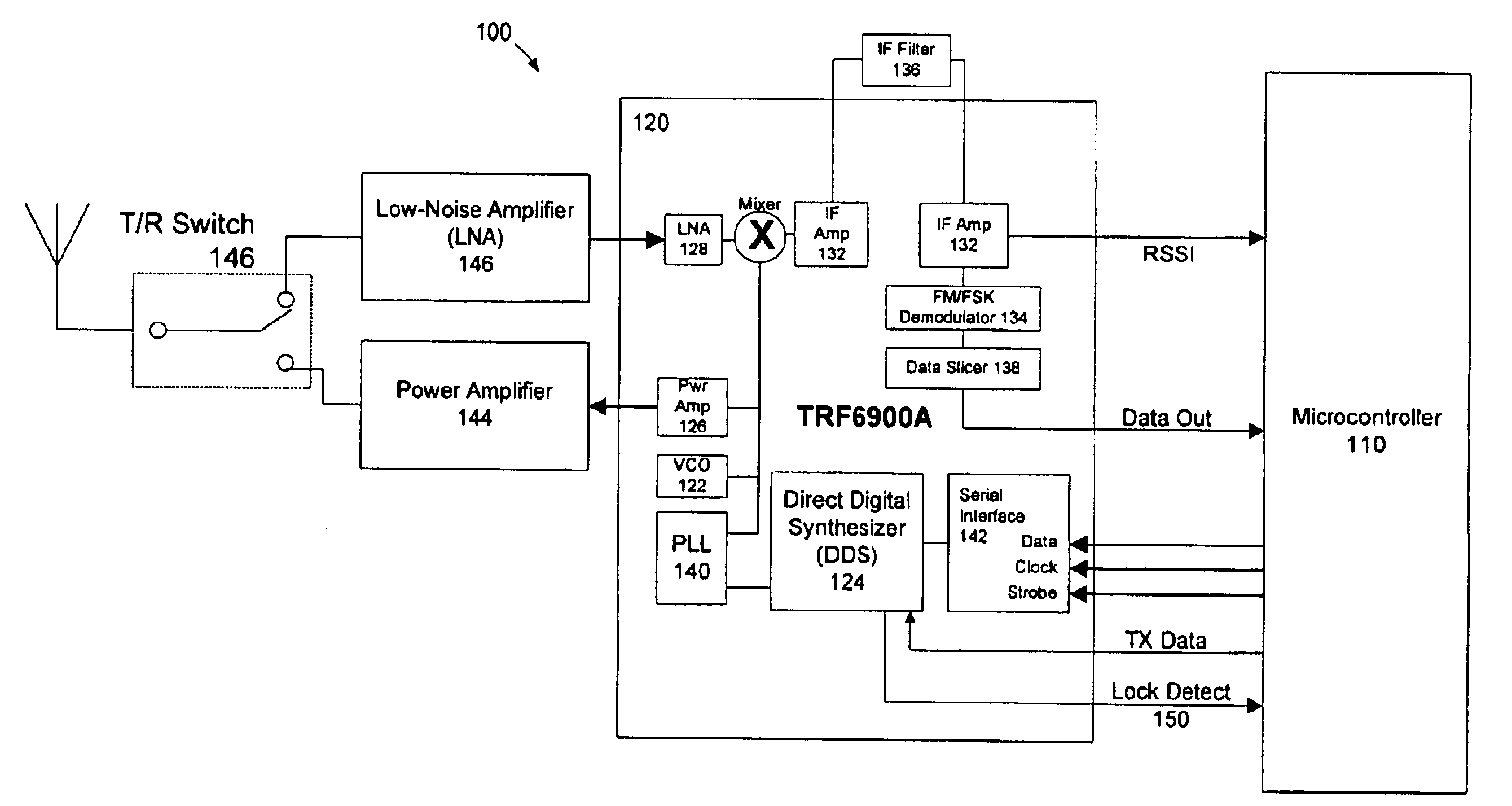
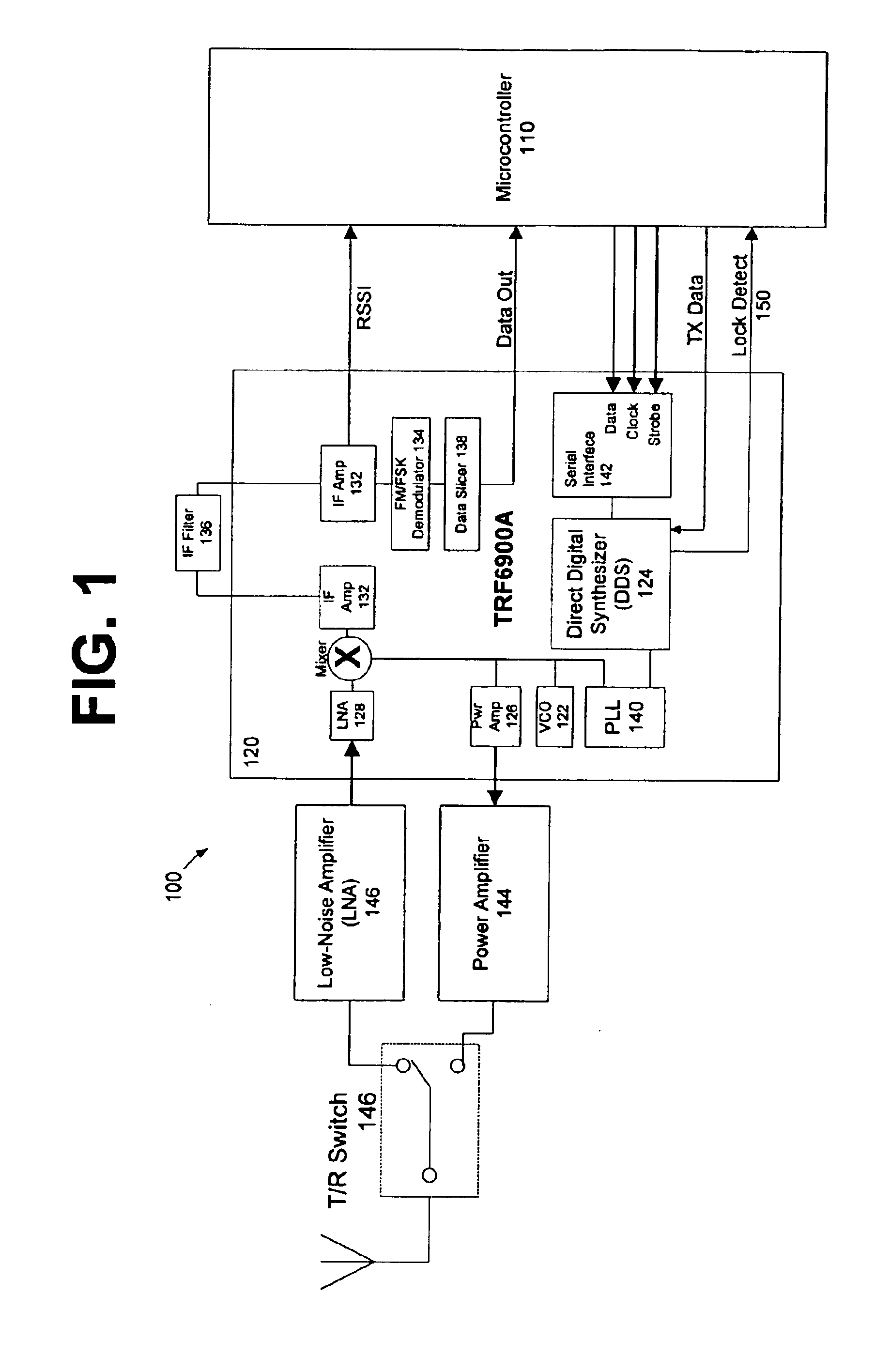
Frequency hopping spread spectrum communications system
InactiveUS6888876B1Modulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMicrocontrollerTransceiver
The present invention is directed to a frequency hopping spread spectrum transceiver. The transceiver includes a microcontroller; a transmitter having a voltage controlled oscillator, a direct digital synthesizer, and a power amplifier; and a receiver having an amplifier, a mixer, an IF amplifier, a demodulator, and a data slicer. When transmitting, the transmitter communicates a preamble over a predetermined number of preamble channels, and thereafter communicate groups of data bytes that each comprise a subset of the data message over a predetermined sequence of data channels. When receiving, the receiver investigates the predetermined number of preamble channels to search for the preamble, each of the predetermined number of preamble channels being associated with a predetermined number of data channels in each sequence of data channels. A number of bytes that comprises each group of data bytes is determined in accordance with a number of channels in the sequence of data channels and the predetermined number of times each byte of the data message is to be transmitted.
Owner:ELSTER ELECTRICTY LLC
Broadband single conversion tuner integrated circuits
ActiveUS20050024544A1Television system detailsGHz frequency transmissionEngineeringSignal transition
A tunable receiver is disclosed including a plurality of select filters to perform an initial band selection, a variable-gain low noise amplifier (LNA) whose gain is controlled to prevent its output power level to exceed a pre-determined power threshold, a plurality of digitally-tunable tracking filters to pass signals within a selected channel and to reject signals in a corresponding image band, a second LNA to further amplify the received RF signal and to generate differential signal outputs, a down converting stage which converts the received RF signal to an IF signal while rejecting signals in the image band, an IF trap to further reject undesired signals present at the output of the down converting stage, an IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal to compensate for losses, an IF filter to provide channel select and reject undesirable signals, and a variable-gain IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal and maintain its power level within specification.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Broadband single conversion tuner integrated circuits
ActiveUS7095454B2Television system detailsGHz frequency transmissionAudio power amplifierDifferential signaling
A tunable receiver is disclosed including a plurality of select filters to perform an initial band selection, a variable-gain low noise amplifier (LNA) whose gain is controlled to prevent its output power level to exceed a pre-determined power threshold, a plurality of digitally-tunable tracking filters to pass signals within a selected channel and to reject signals in a corresponding image band, a second LNA to further amplify the received RF signal and to generate differential signal outputs, a down converting stage which converts the received RF signal to an IF signal while rejecting signals in the image band, an IF trap to further reject undesired signals present at the output of the down converting stage, an IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal to compensate for losses, an IF filter to provide channel select and reject undesirable signals, and a variable-gain IF amplifier to amplify the IF signal and maintain its power level within specification.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
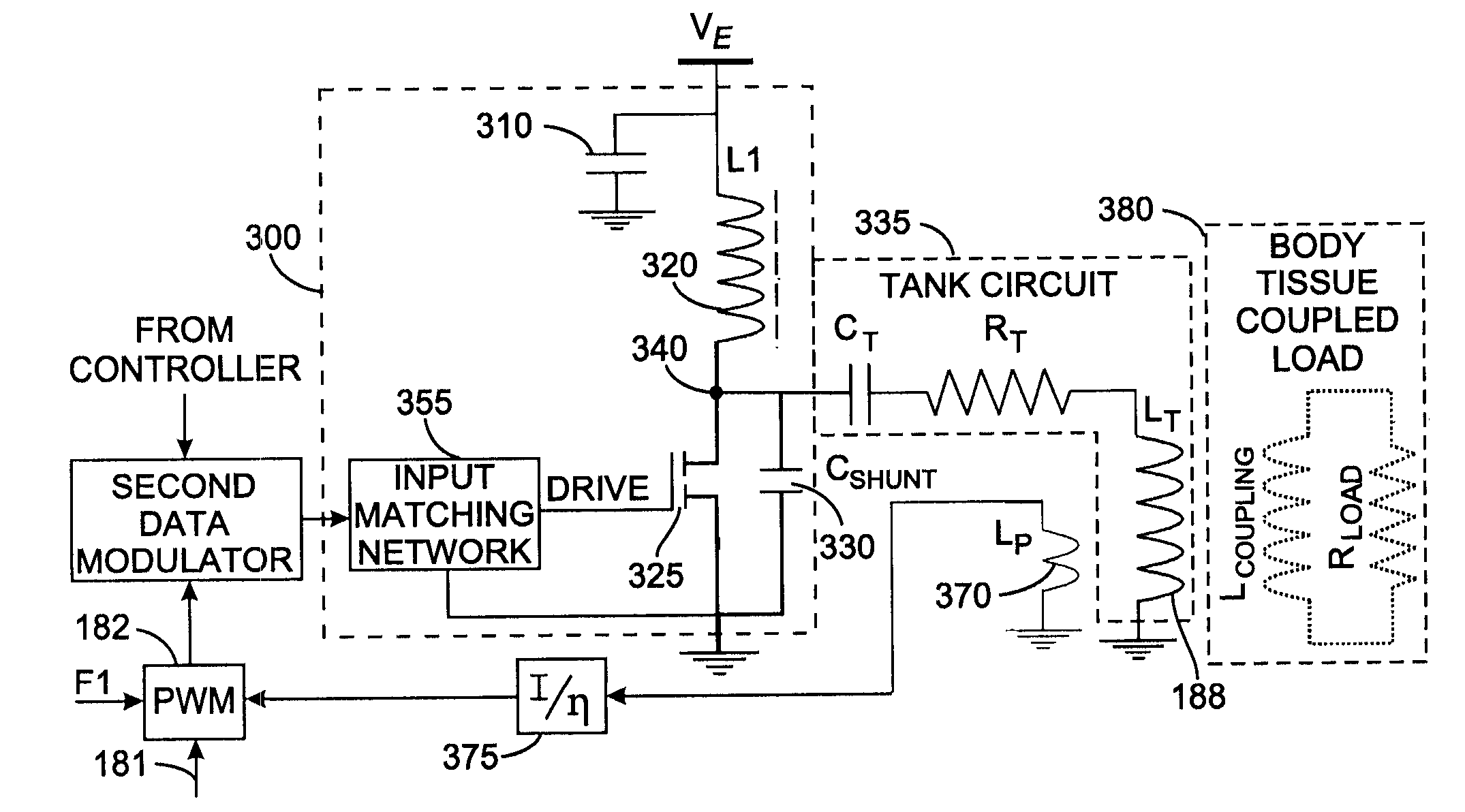
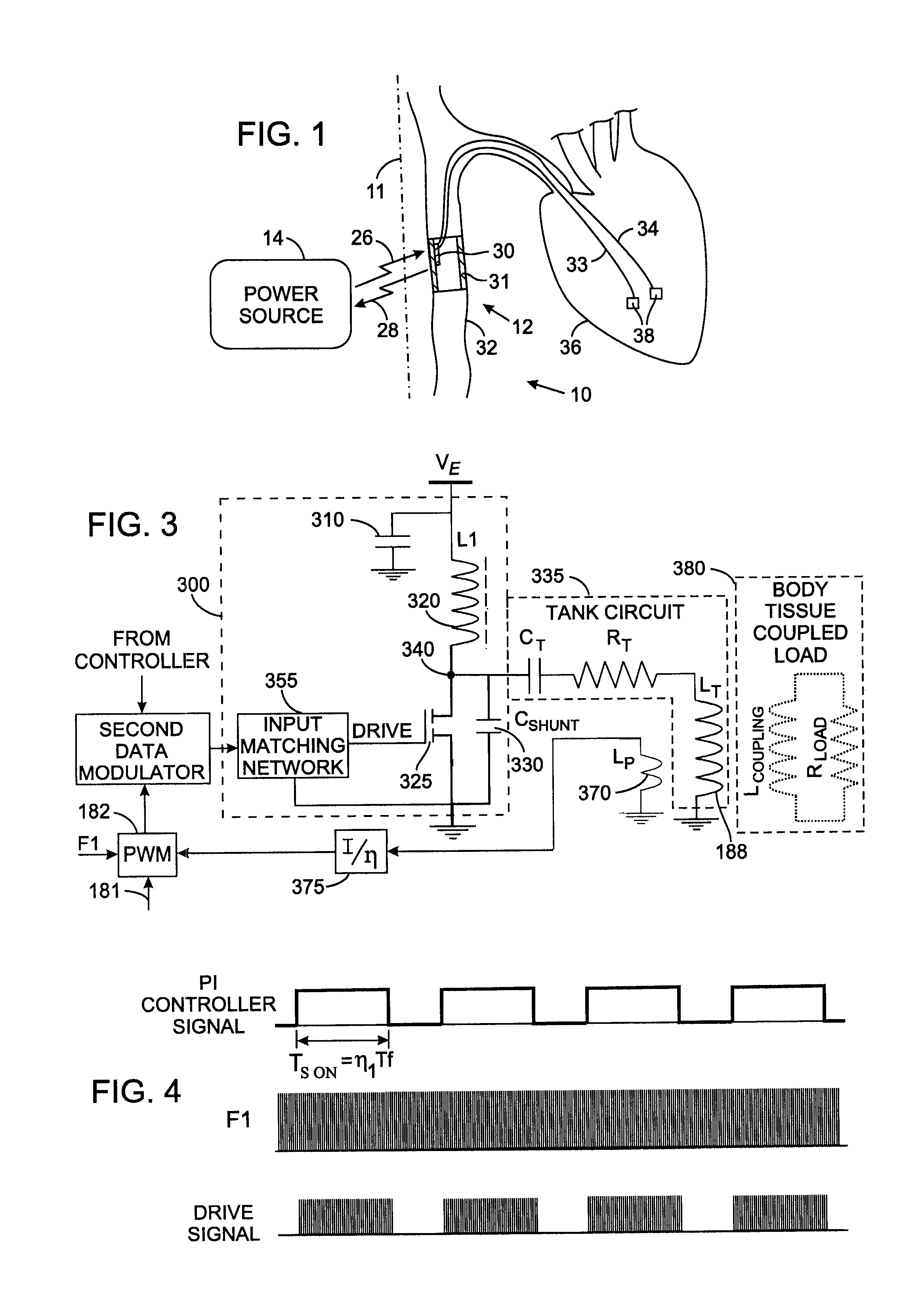
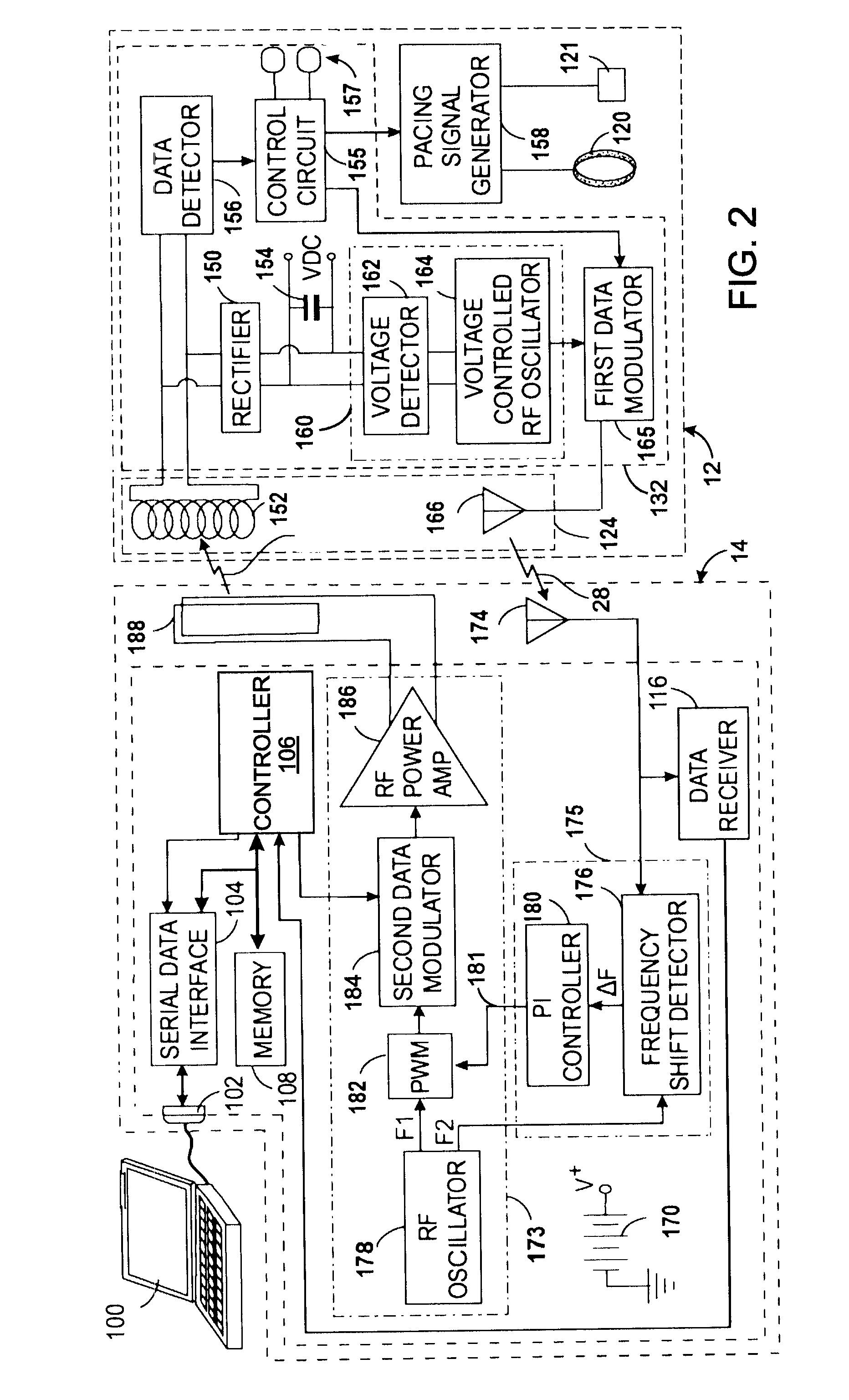
Class-E radio frequency power amplifier with feedback control
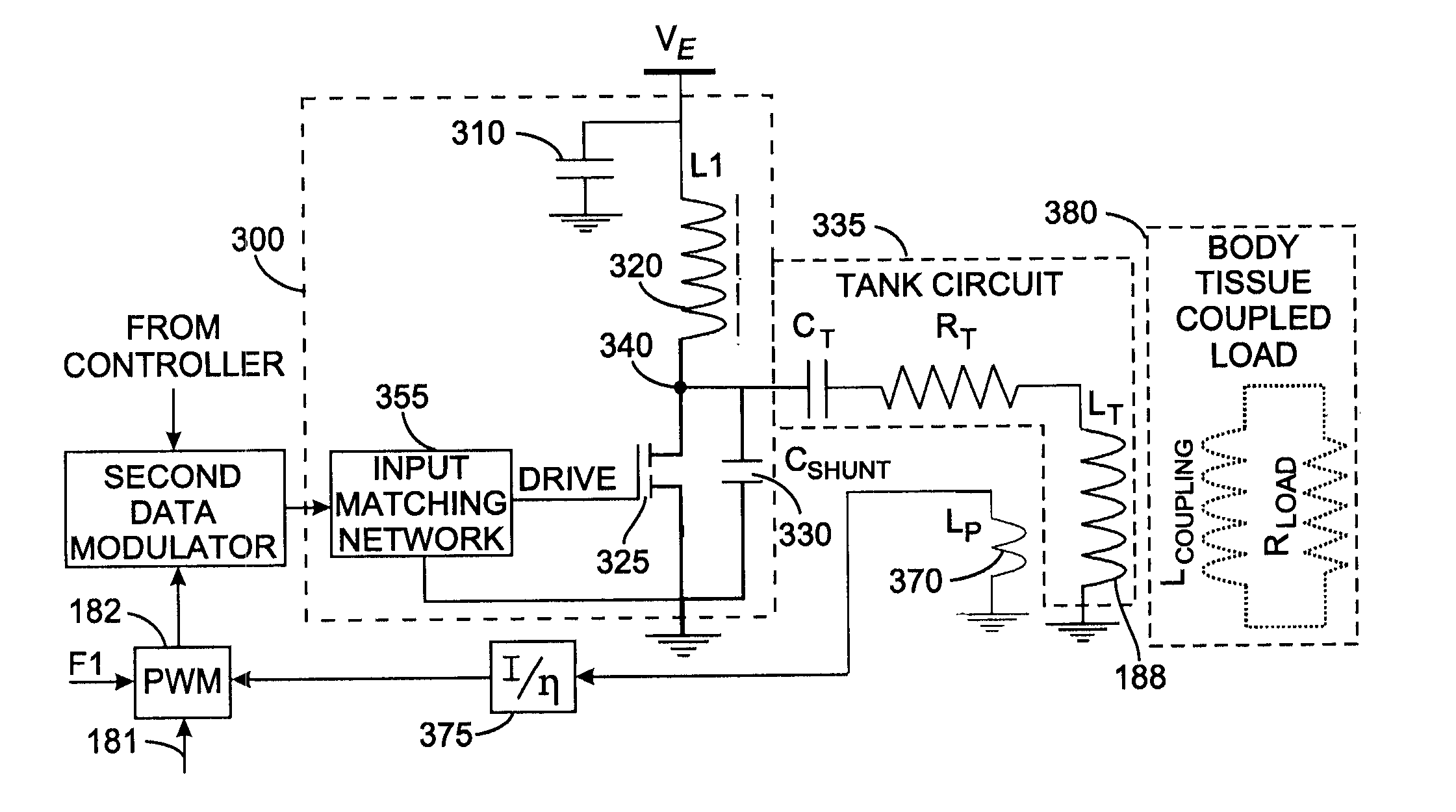
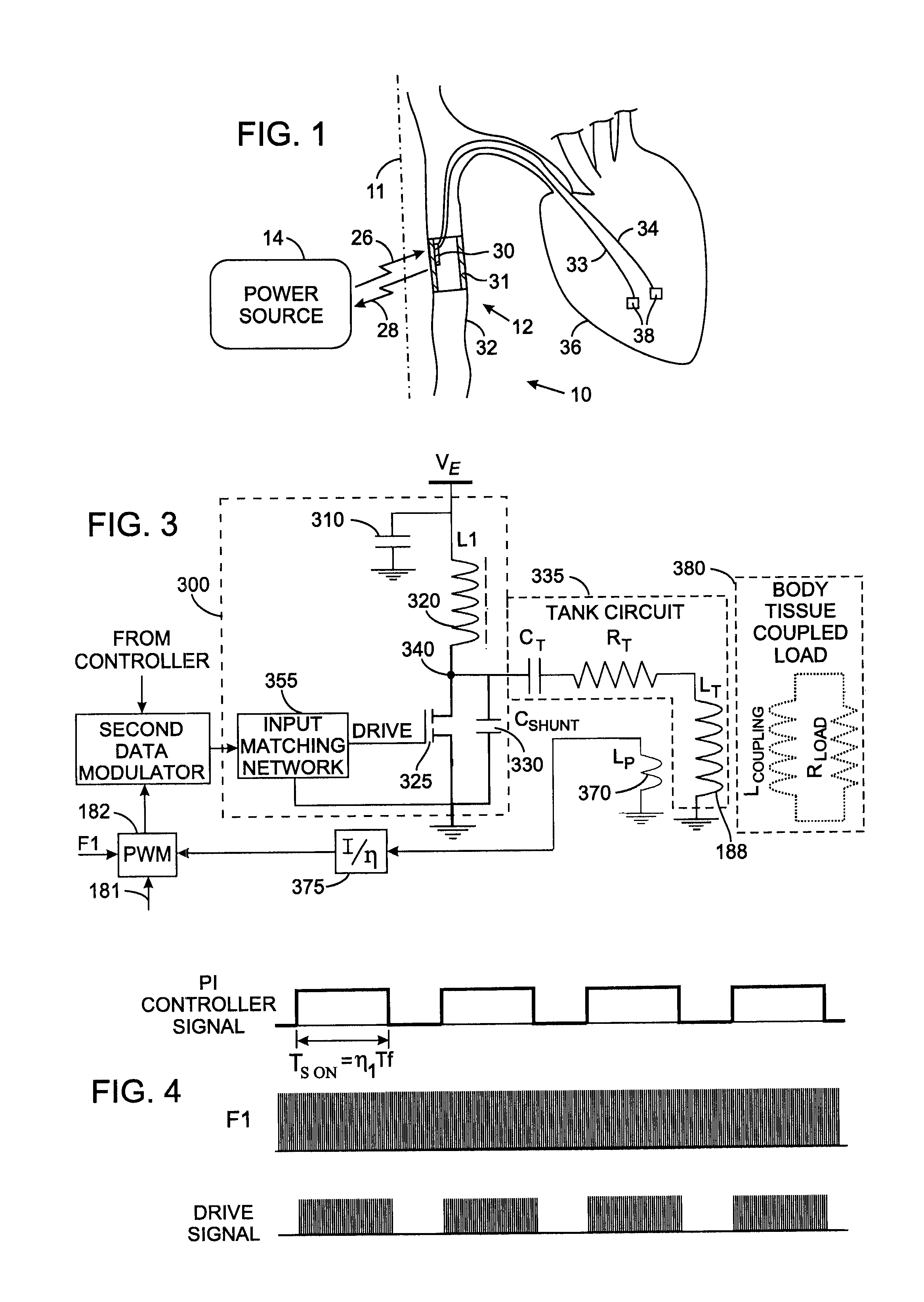
InactiveUS7535296B2ElectrotherapyNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsShunt capacitorsAudio power amplifier
A Class-E power amplifier includes a choke and a switch connected in series between a source of a supply voltage and circuit ground and connected to an inductively coupled coil. An output node of the amplifier is formed between choke and the switch and connected to a transmitter antenna. A shunt capacitor couples the amplifier's output node to the circuit ground. A feedback signal, indicating an intensity if the signal at the amplifier output node is used to vary the input signal to the Class-E power amplifier and thereby control operation of the switch.
Owner:KENERGY INC
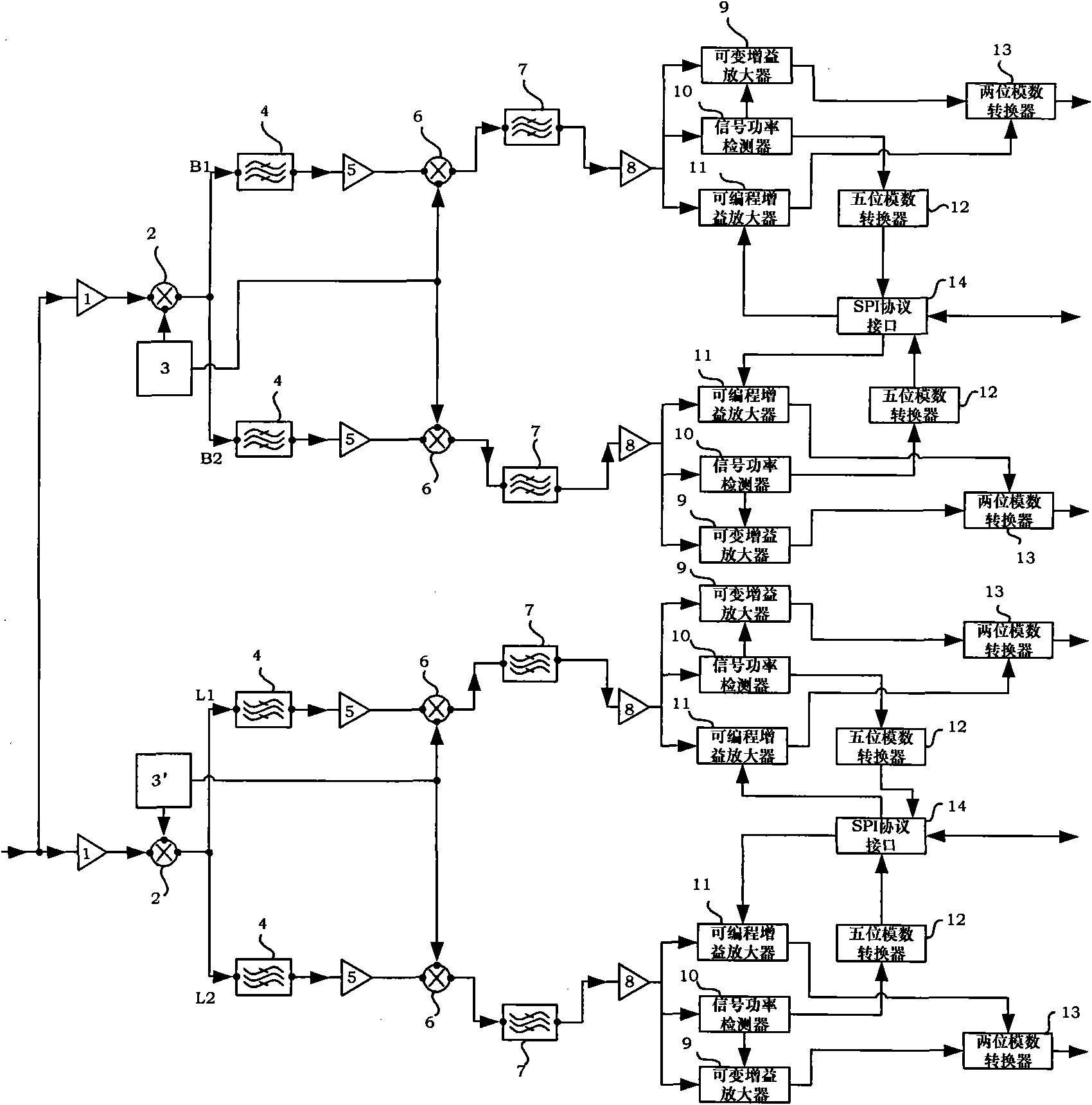
Radio frequency front-end device for dual-system and dual-frequency navigation receiver
ActiveCN101915932AReduce power consumptionReduce Power Consumption and NoiseSatellite radio beaconingProgrammable-gain amplifierPhysics
The invention discloses a radio frequency front-end device for a dual-system and dual-frequency navigation receiver. By using down-conversion structure twice, a low-noise amplifier, a first-stage frequency mixer, a second-stage frequency mixer, a frequency synthesizer, a first-stage medium frequency amplifier, a second-stage medium frequency amplifier, a variable gain amplifier, a signal power detector, a programmable gain amplifier, a five-bit analog-to-digital converter, an SPI protocol interface and a two-bit analog-to-digital converter are integrated on the same radio frequency front-end chip; and the radio frequency front-end device for the navigation receiver is formed by the chip, a first-stage filter and a second-stage filter. The device can simultaneously receive radio frequency signals of L1 and L2 wave bands of a global positioning system (GPS) and B1 and B2 wave bands of a big dipper second-generation navigation system (BD2) with high accuracy; the device reduces the power consumption and noise by using a design method of low power consumption and multi-layer isolating ring and deep N well technology; and because the device is implemented by using an up-to-date CMOS integrated circuit process, the device has the characteristics of low power consumption, low noise, small size and the like and can be widely applied to the fields of traffic, navigation, transportation and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Receiver
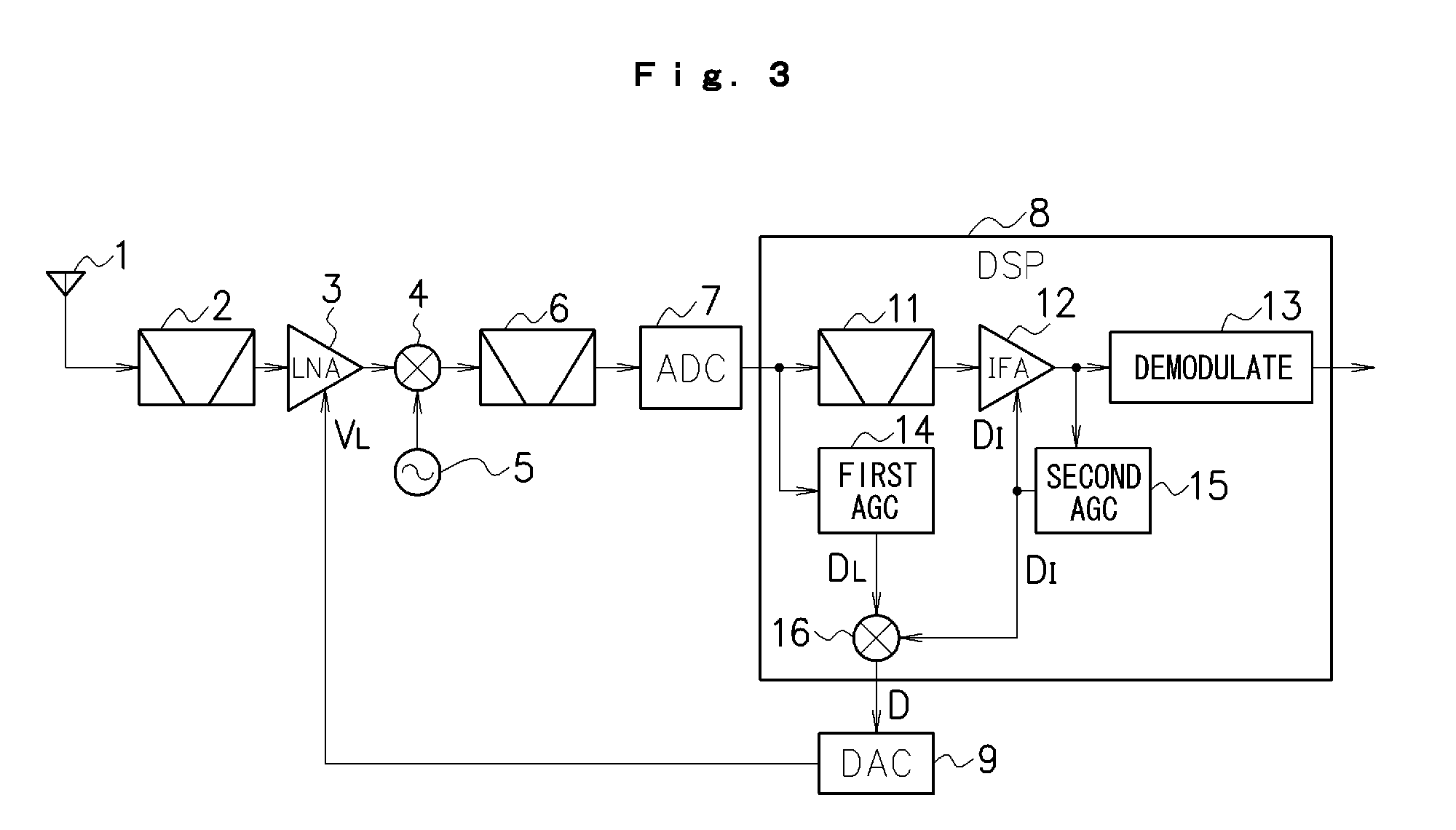
InactiveUS20090298454A1Ensure correct executionEasy to controlGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAudio power amplifierControl data
By A / D converting a signal output from a mixer (4) and inputting the A / D converted signal to a DSP (8), and generating AGC control data (DL) corresponding to a level of the signal to control a gain of an LNA (3) in such a manner that a voltage input to an A / D converting circuit (7) is lower than a full scale voltage of the A / D converting circuit (7), it is possible to prevent a signal having an excessively high level beyond a dynamic range of the A / D converting circuit (7) from being input to the A / D converting circuit (7). By controlling the gain of the LNA (3) corresponding to a level of a broad band signal before passing through a BPF (11) and controlling a gain of an IF amplifier (12) corresponding to a level of a narrow band signal after passing through the BPF (11), moreover, it is possible to properly control a gain of an AGC as a whole in consideration of signal levels of both a desirable wave and a disturbing wave.
Owner:NIIGATA SEIMITSU +1
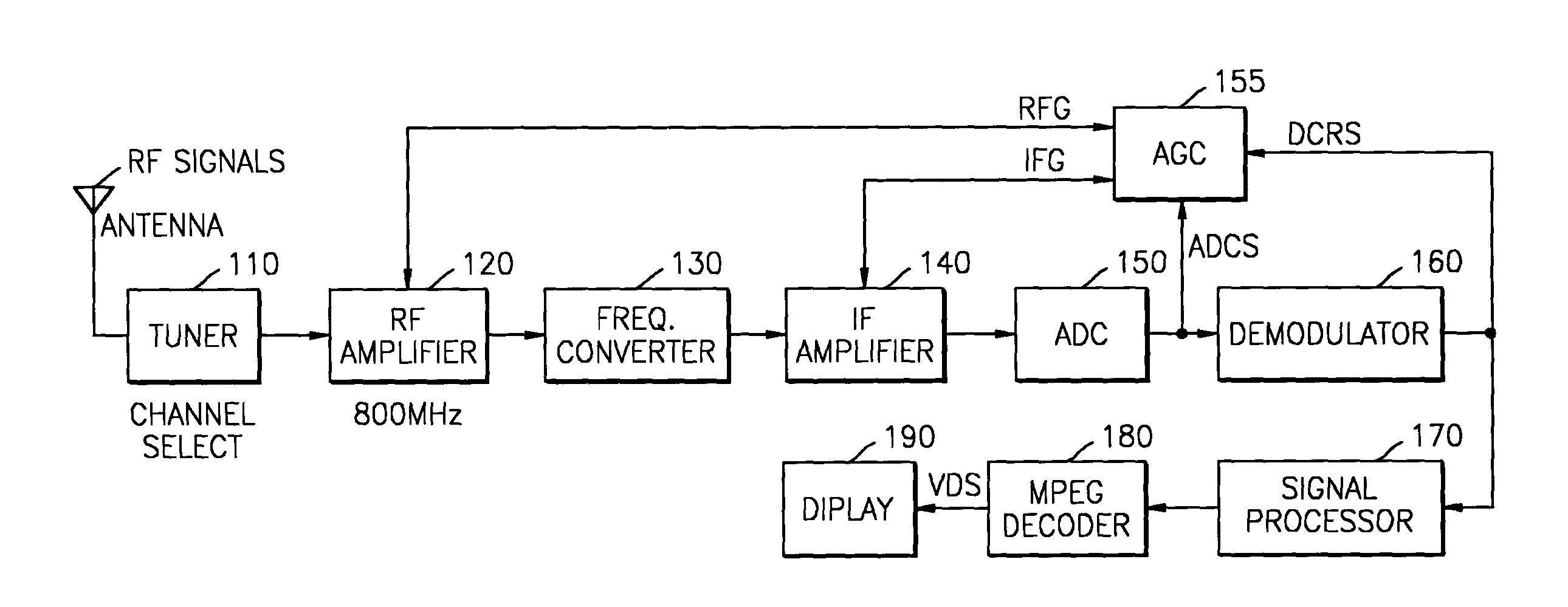
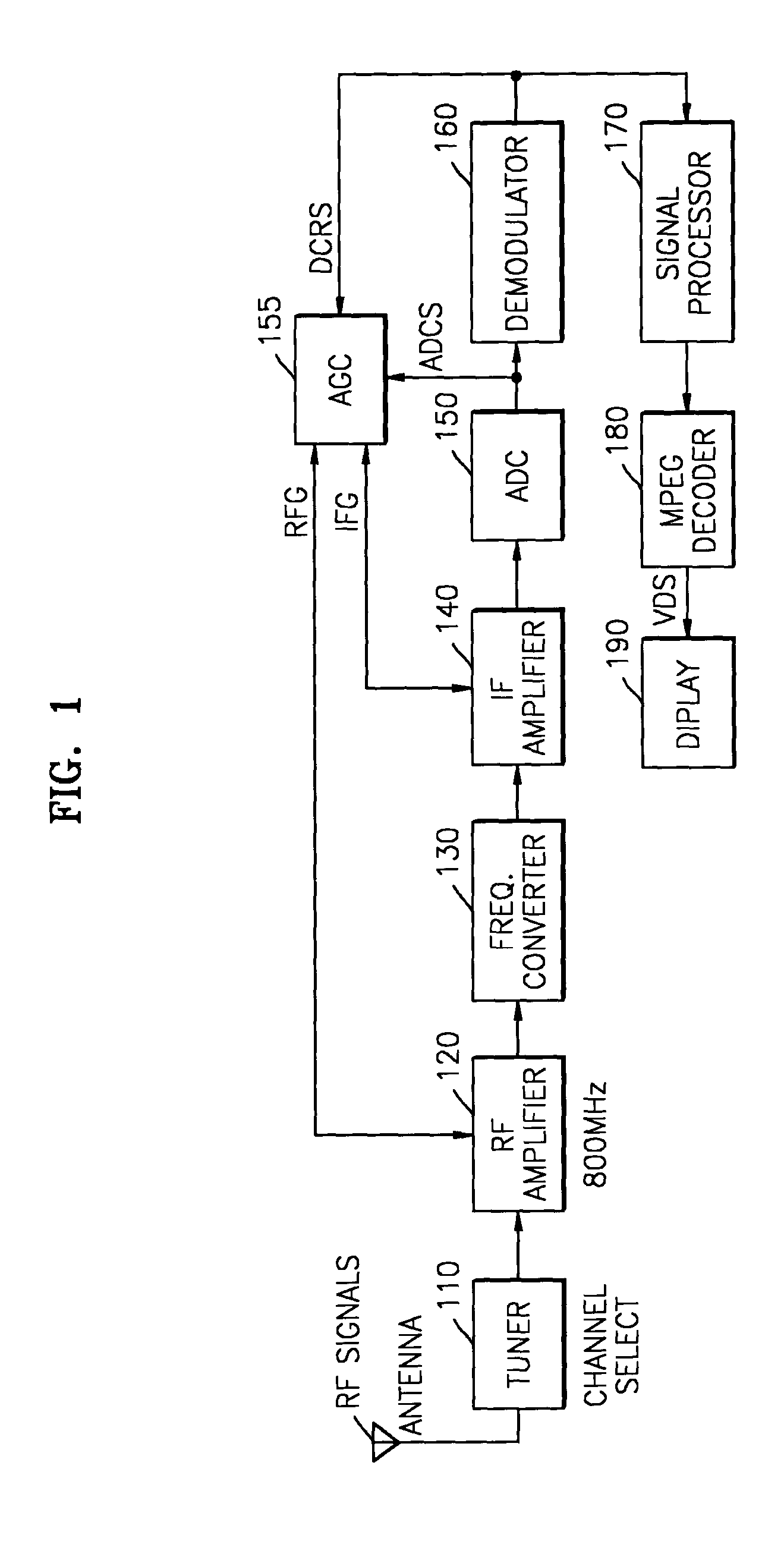
Digital television receiver with automatic gain control unit and method
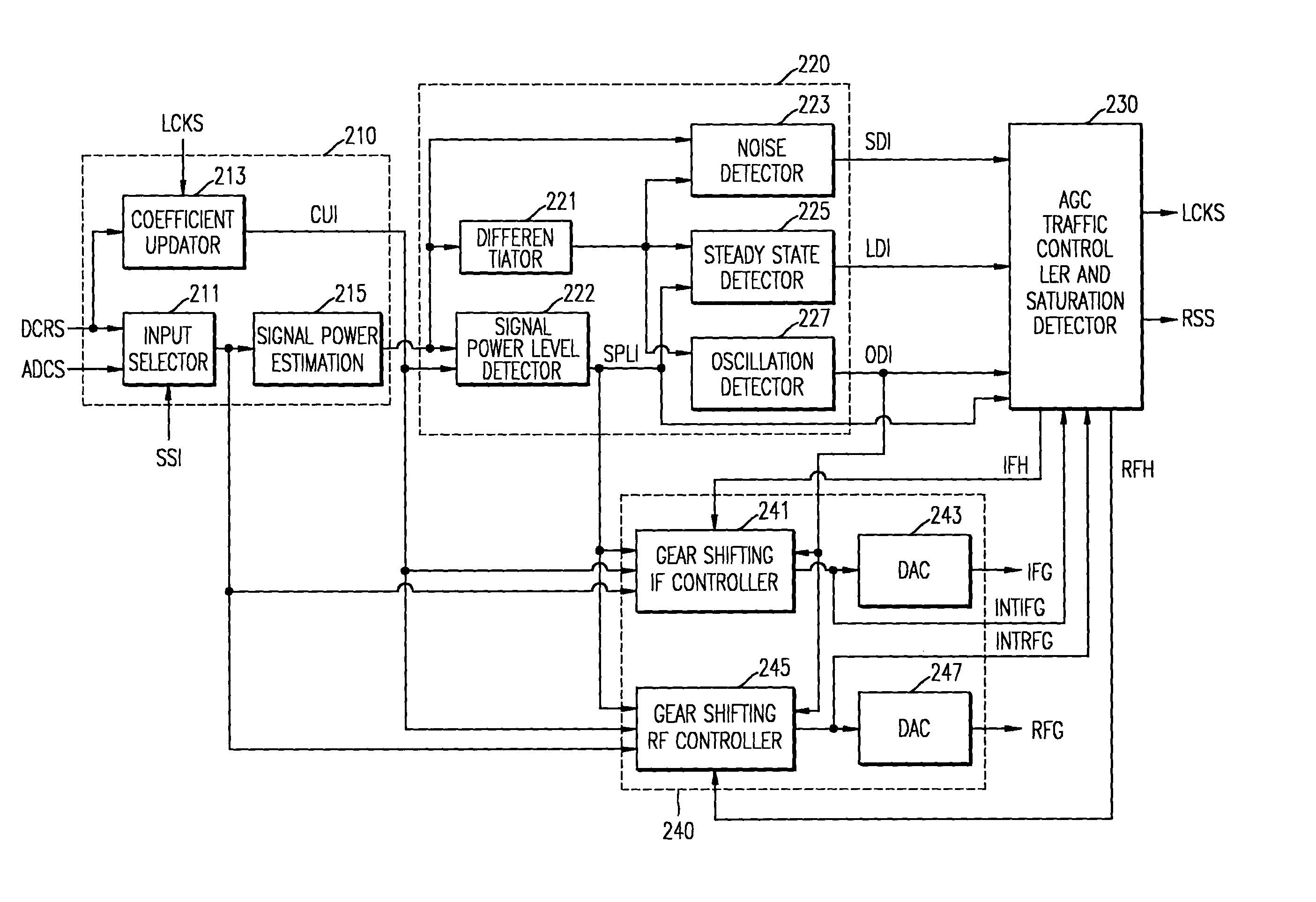
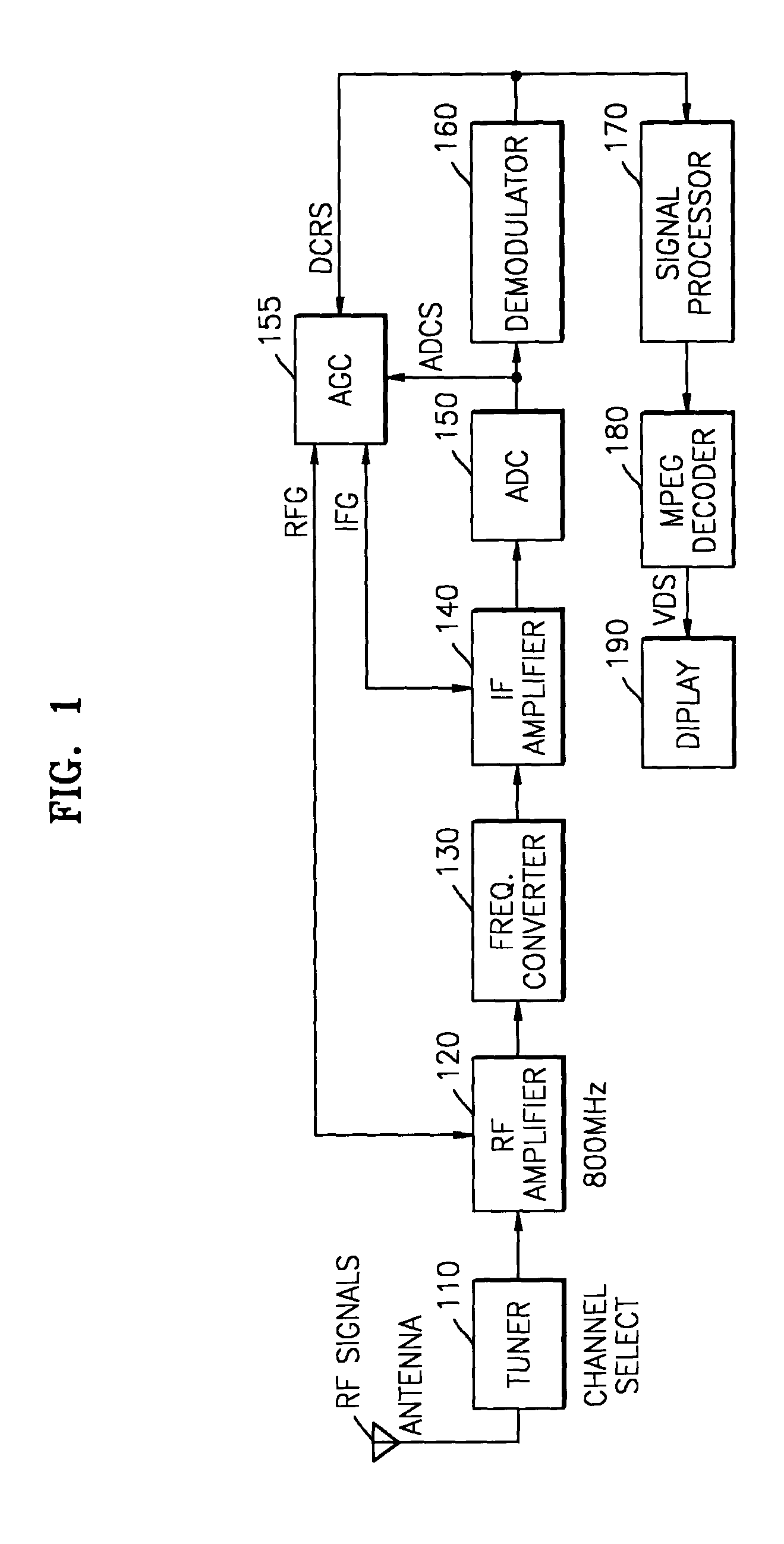
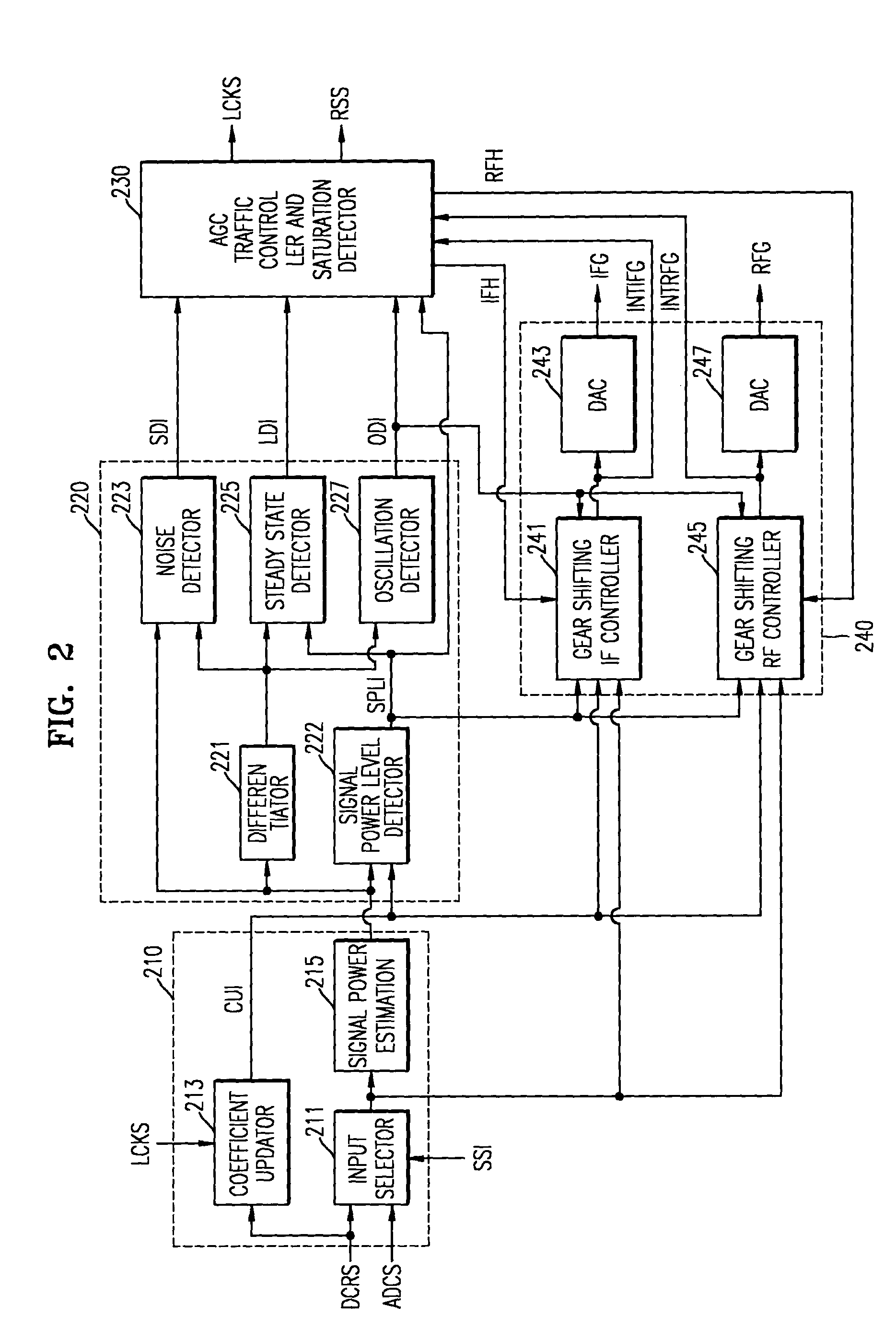
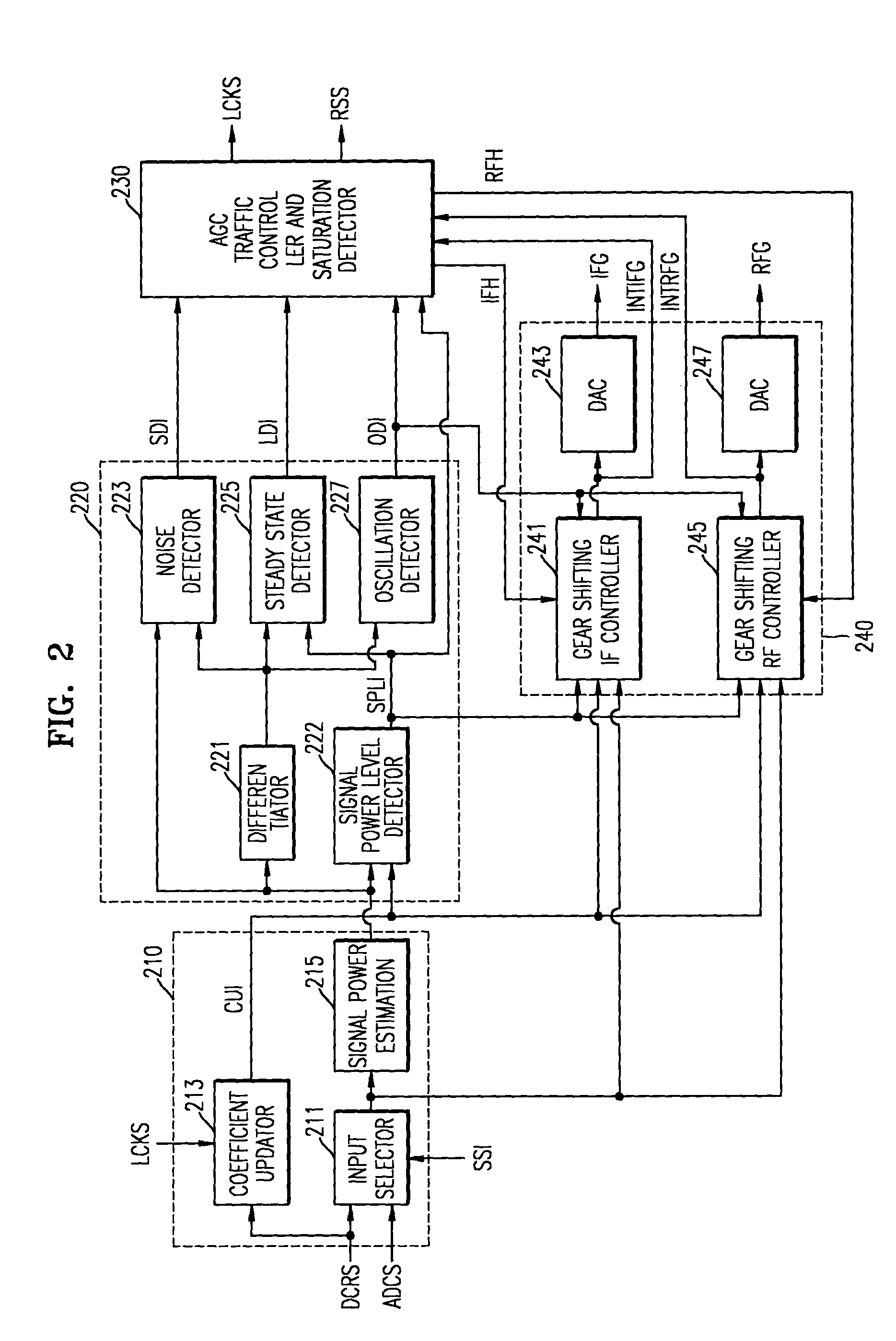
ActiveUS20040207761A1Reduce distortion problemsEnhance the imageTelevision system detailsGain controlHysteresisAudio power amplifier
An automatic gain controller (AGC) and method for use in a digital TV receiver having an IF amplifier, an RF amplifier, an analog to digital converter (ADC) connected to the IF amplifier, and a demodulator connected to the ADC, the AGC comprising: an input selector for selecting as feedback signal one of a digitized IF signal output of the ADC and a demodulated signal output of the demodulator; a signal detection unit for detecting the conditions of the feedback signal and outputting status signals; and a traffic controller for receiving the status signals and outputting control signals based on the status signals to an IF gain controller and an RF gain controller for independent gain control of the RF amplifier and the IF amplifier. The AGC and method further including hysteresis-curve-based switching for alternatively halting adjustments to IF gain while adjusting RF gain or halting adjustments to RF gain while adjusting IF gain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
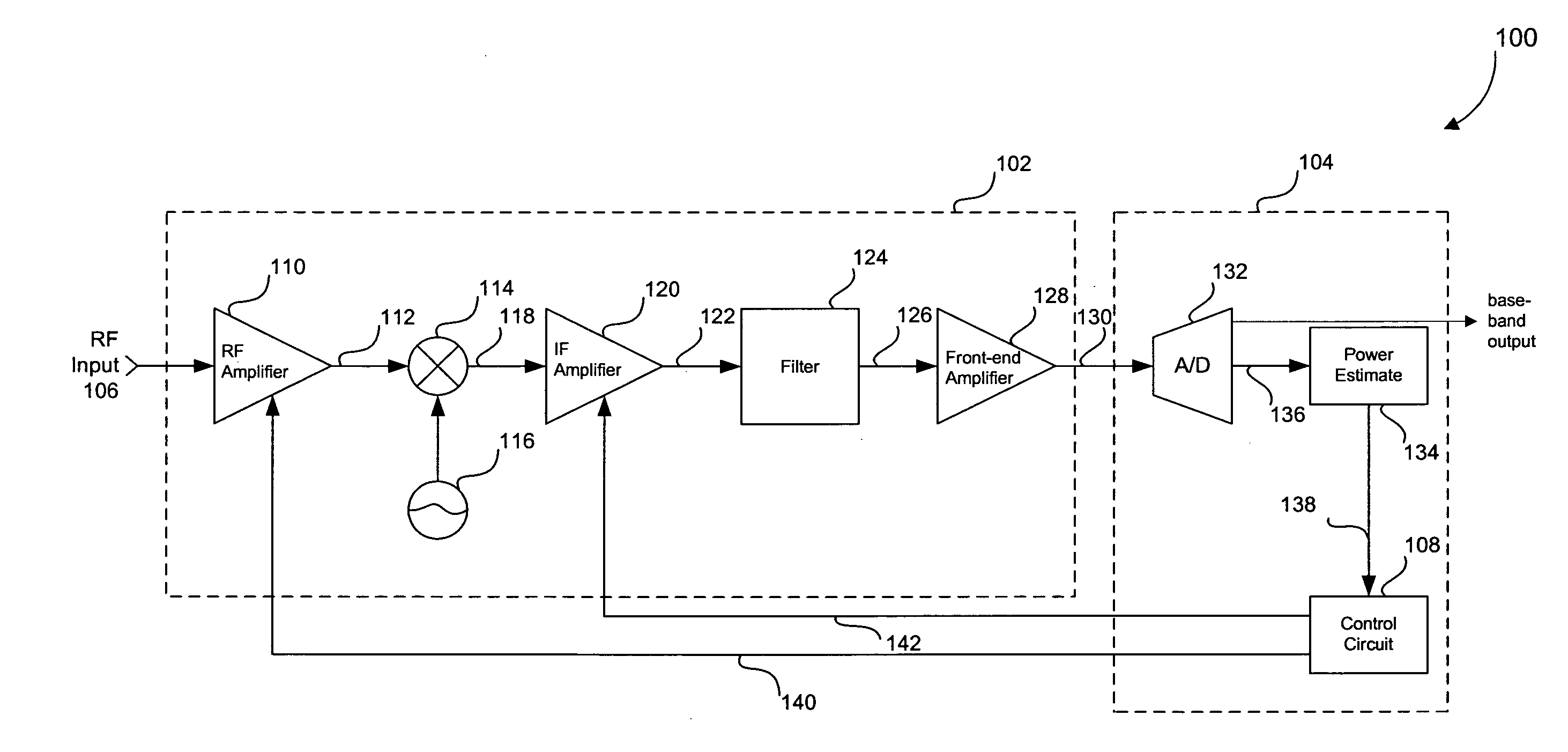
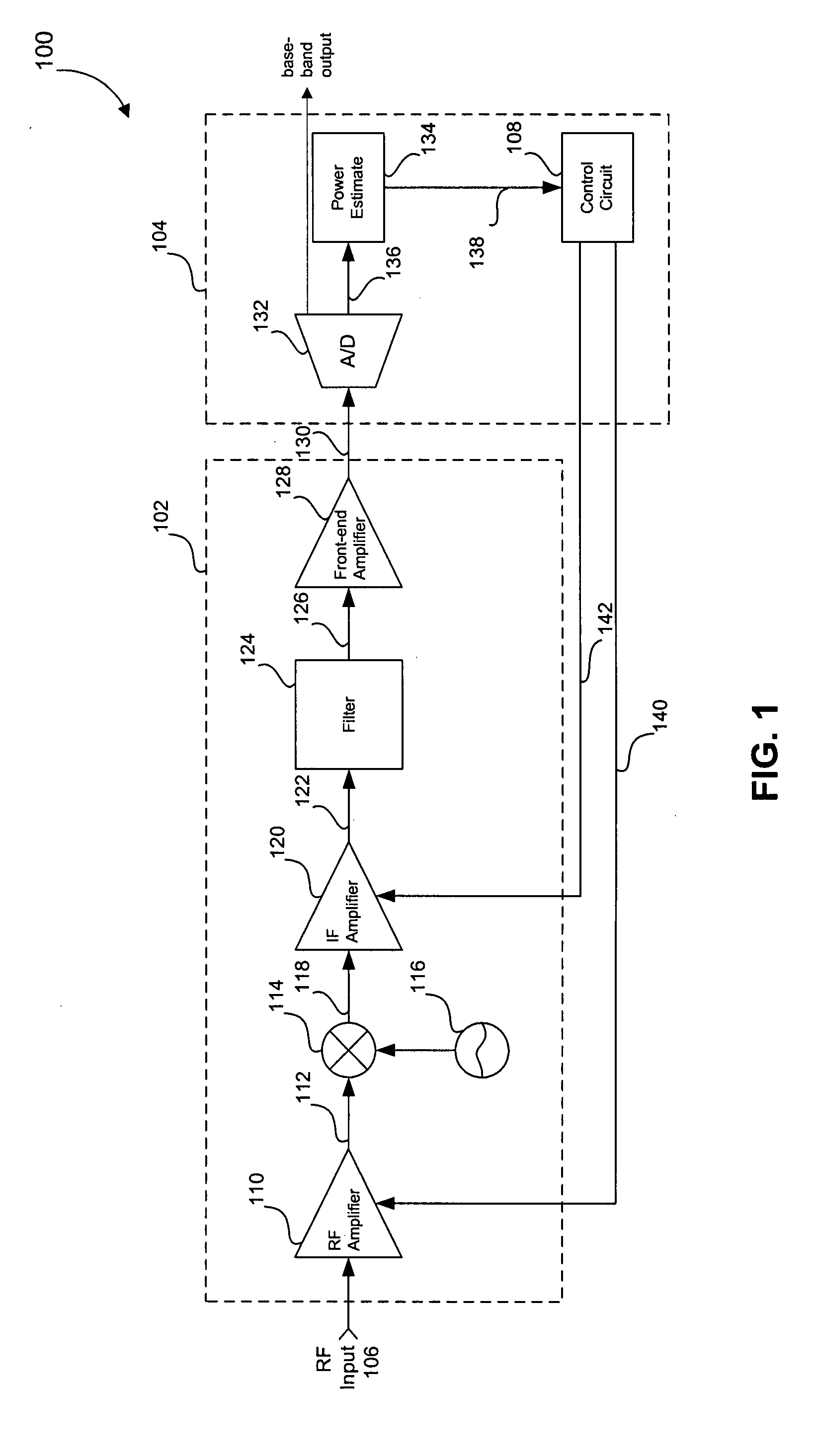
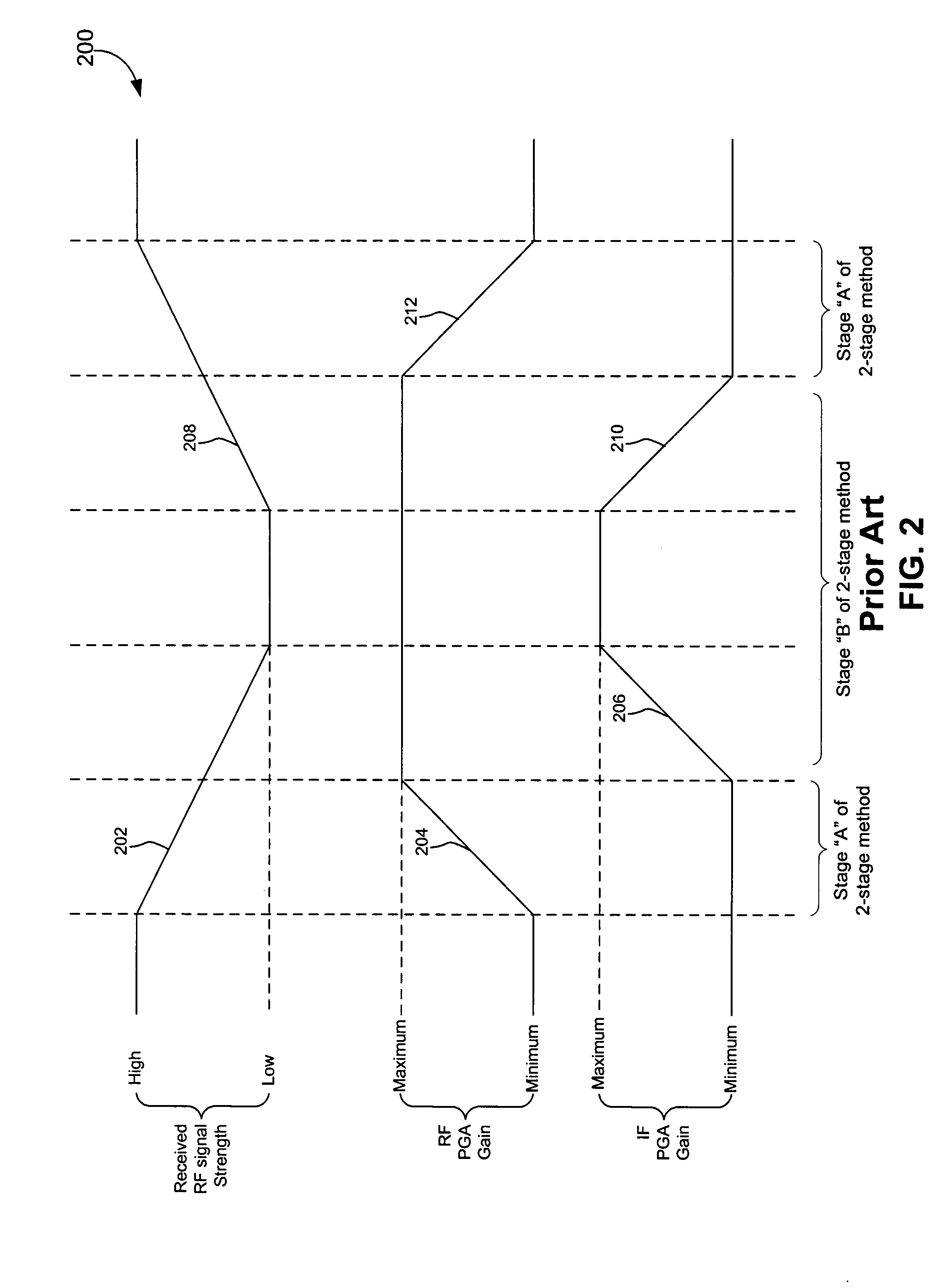
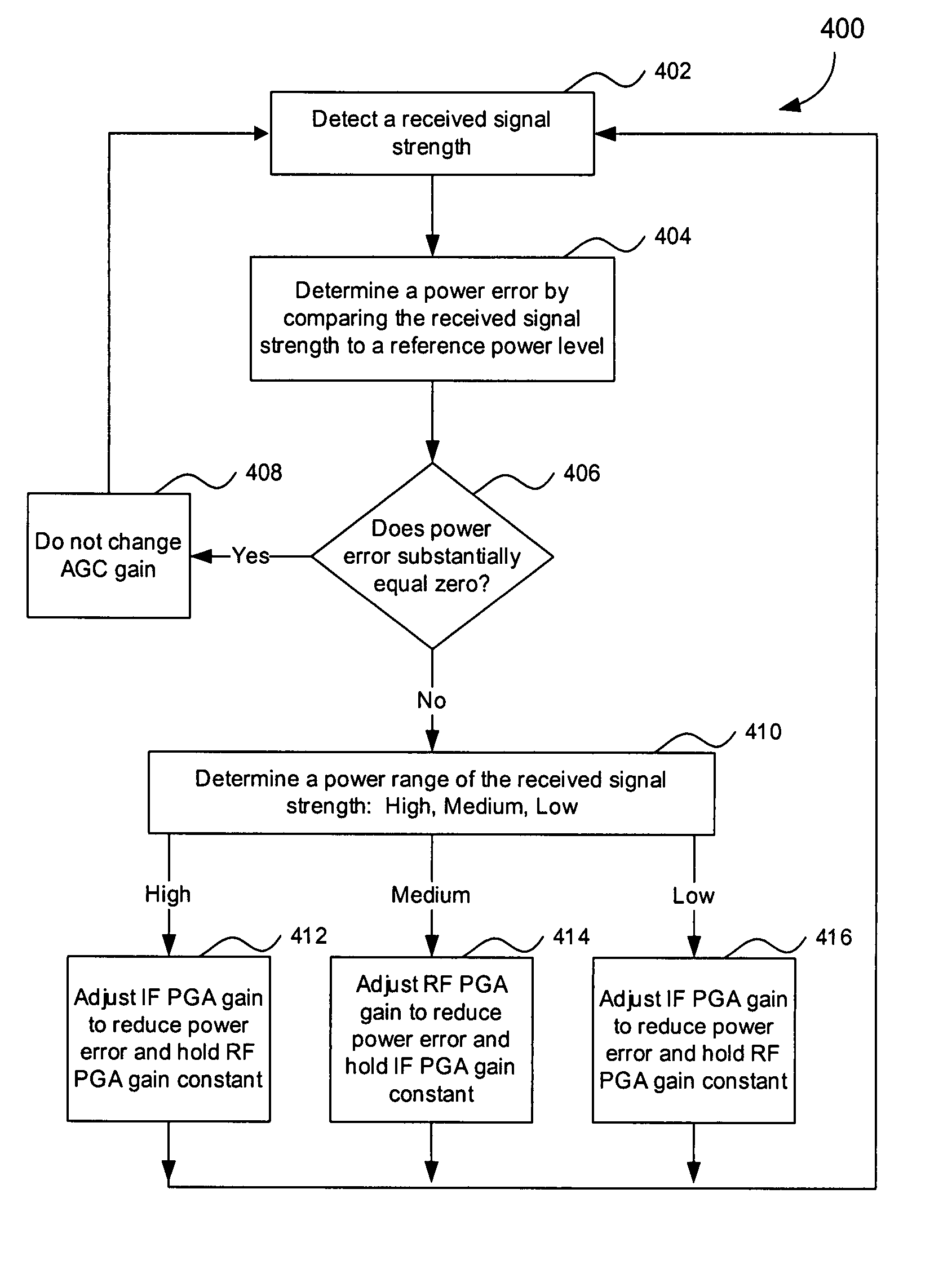
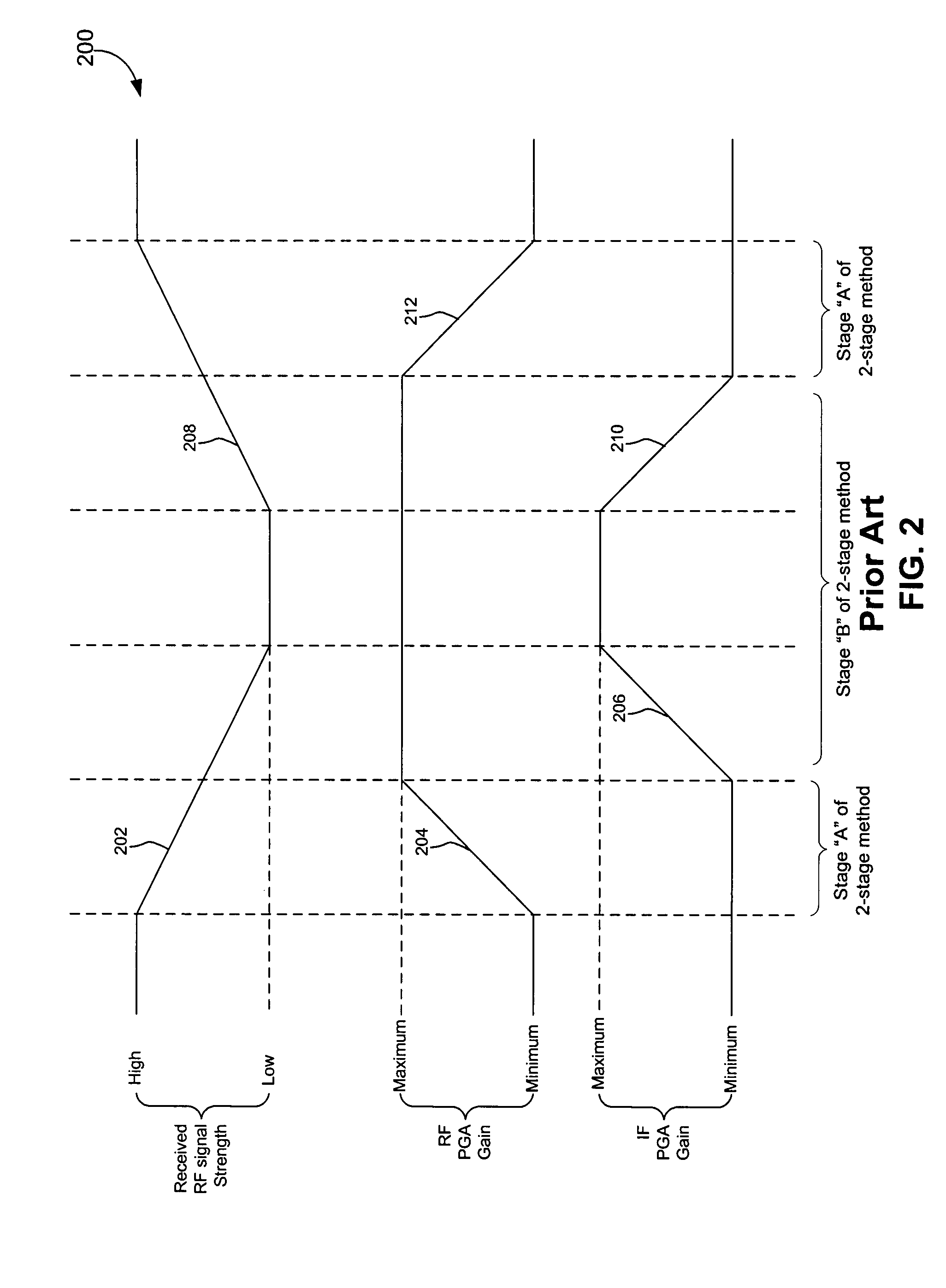
Three stage algorithm for automatic gain control in a receiver system
In an embodiment, a receiver for processing a RF input signal having a variable signal strength includes an RF amplifier, an IF amplifier, and a controller. The RF amplifier is configured to receive and amplify the RF input signal. The IF amplifier is coupled to an output of the RF amplifier. The controller controls gains of the RF amplifier and the IF amplifier during times of falling signal strength. A gain of the IF amplifier is increased as the signal strength falls until a first amplitude threshold is reached for the falling signal strength. If the signal strength falls beyond the first threshold, a gain of the RF amplifier is increased until a second amplitude threshold is reached. The second amplitude threshold is lower than the first amplitude threshold. If the signal strength falls below the second amplitude threshold, the gain of the IF amplifier is further increased.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
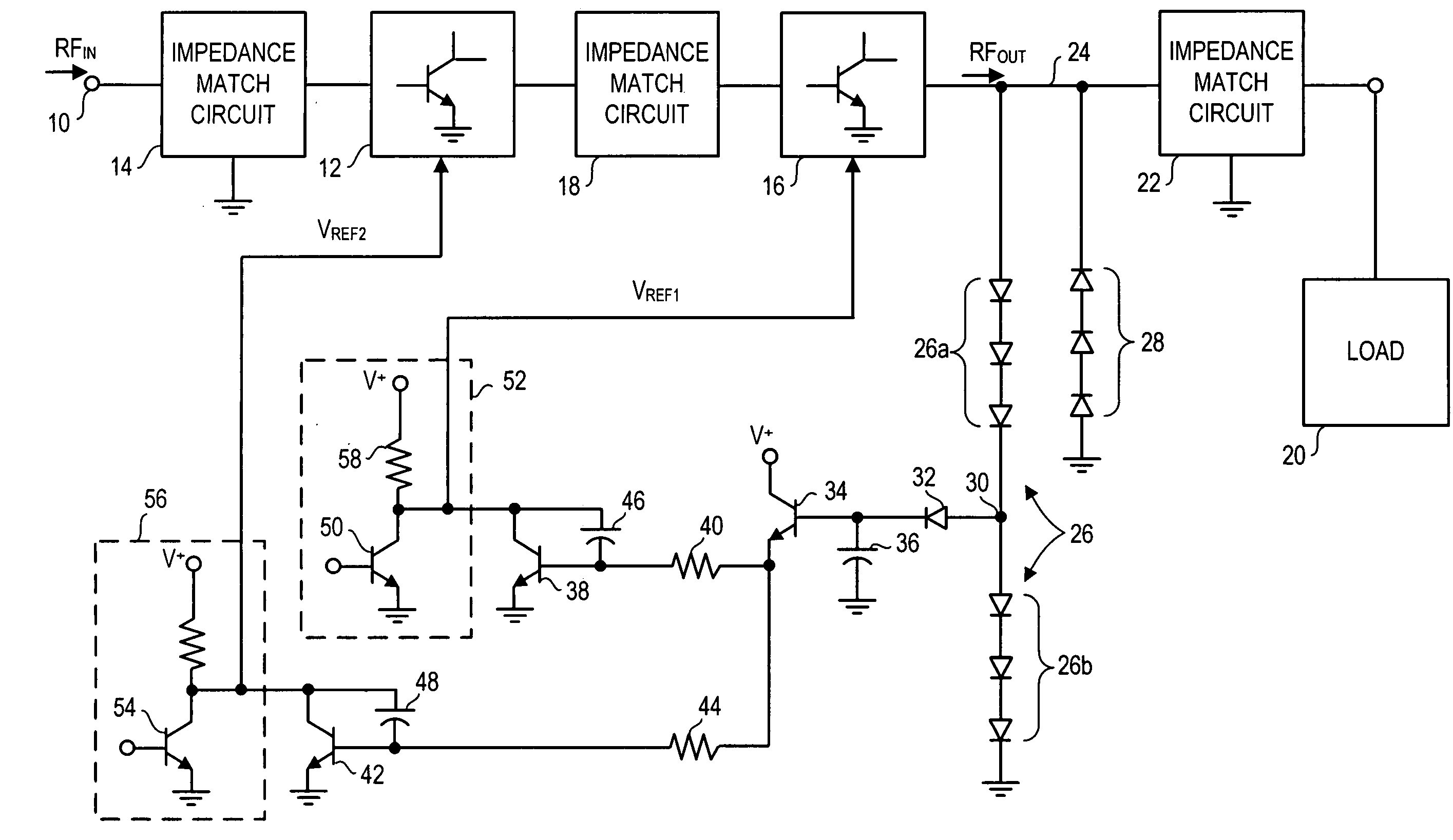
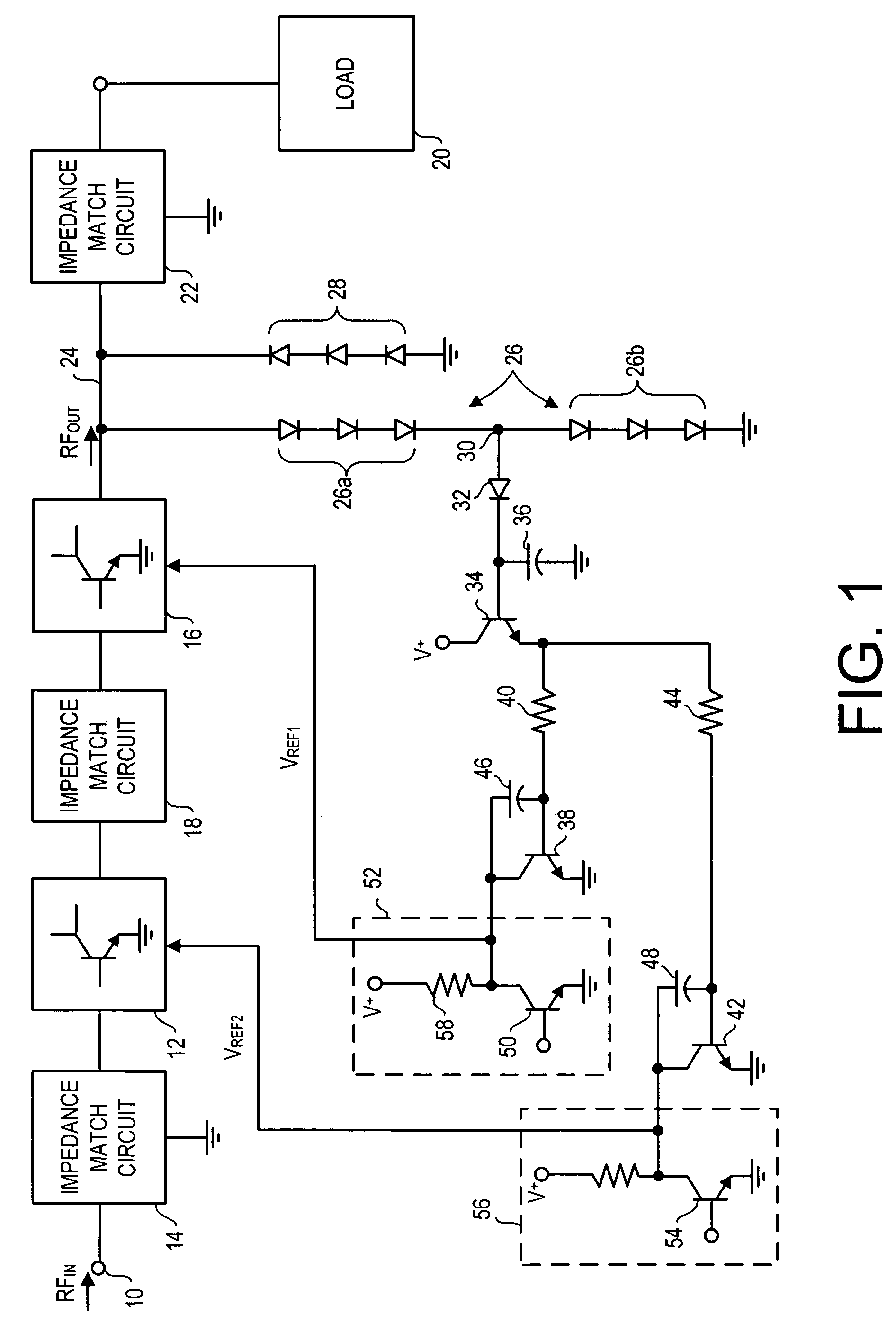
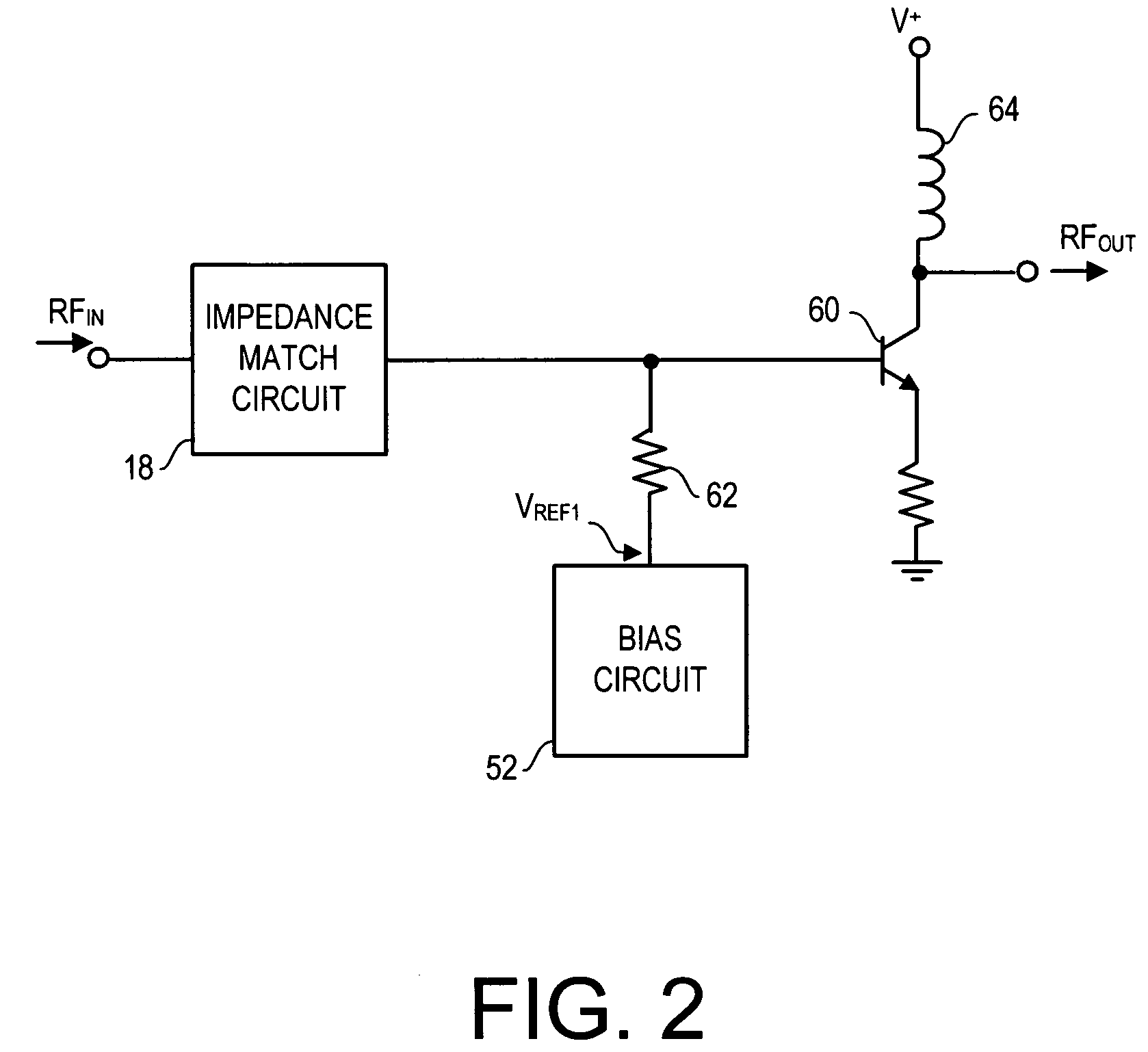
Active protection circuit for load mismatched power amplifier
InactiveUS7148748B2Reduce output powerVoltage output is limitedGain controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesOvervoltageAudio power amplifier
A peak detector detects an amplifier output overvoltage condition if the amplifier drives a mismatched load impedance. In response to the detected overvoltage condition, a clamping transistor lowers a reference DC bias voltage supplied by a bias circuit to the amplifier. The lowered reference DC bias voltage lowers amplifier gain and output power, thus protecting the amplifier.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Digital television receiver with automatic gain control unit and method
An automatic gain controller (AGC) and method for use in a digital TV receiver having an IF amplifier, an RF amplifier, an analog to digital converter (ADC) connected to the IF amplifier, and a demodulator connected to the ADC, the AGC comprising: an input selector for selecting as feedback signal one of a digitized IF signal output of the ADC and a demodulated signal output of the demodulator; a signal detection unit for detecting the conditions of the feedback signal and outputting status signals; and a traffic controller for receiving the status signals and outputting control signals based on the status signals to an IF gain controller and an RF gain controller for independent gain control of the RF amplifier and the IF amplifier. The AGC and method further including hysteresis-curve-based switching for alternatively halting adjustments to IF gain while adjusting RF gain or halting adjustments to RF gain while adjusting IF gain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Load overcurrent protection circuit and load overcurrent protection method
ActiveCN106451341ASolve the problem that the delay time is short and it is easy to burn out the MOS tubeChange off timeEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionStart timeAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a load overcurrent protection circuit. The load overcurrent protection circuit comprises a current sampling resistor, an amplifier, a comparator I, a timer, a self-locking control circuit and an electronic switch, wherein the current sampling resistor is connected with the electronic switch; the comparator I is connected with a reference source I; the amplifier amplifies the voltage of the current sampling resistor and transmits the voltage to the comparator I; the comparator I compares a voltage signal output by the amplifier with the reference source I; and the timer starts time delay timing if the voltage signal output by the amplifier is higher than the reference source I, the timer stops timing and the electronic switch normally switches on if the voltage signal output by the amplifier is lower than the reference source I in the time delay timing process, otherwise, the timer performs time delay timing to reach a set value, and the self-locking control circuit switches off the electronic switch and locks the off state of the electronic switch. The load overcurrent protection circuit solves the problems that the delayed time of overcurrent protection is short and an MOS tube is susceptible to burnout.
Owner:YIJIAHE TECH CO LTD
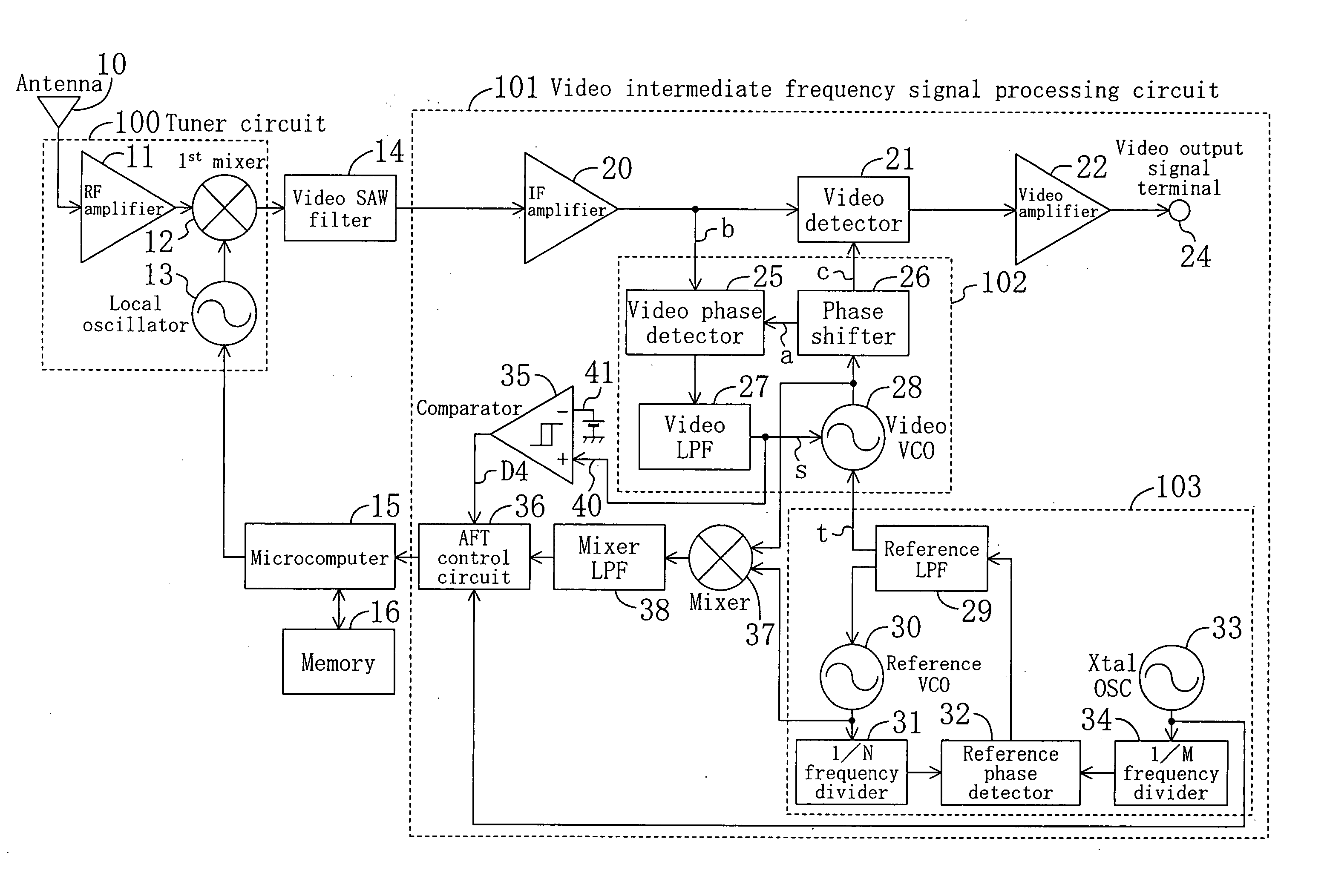
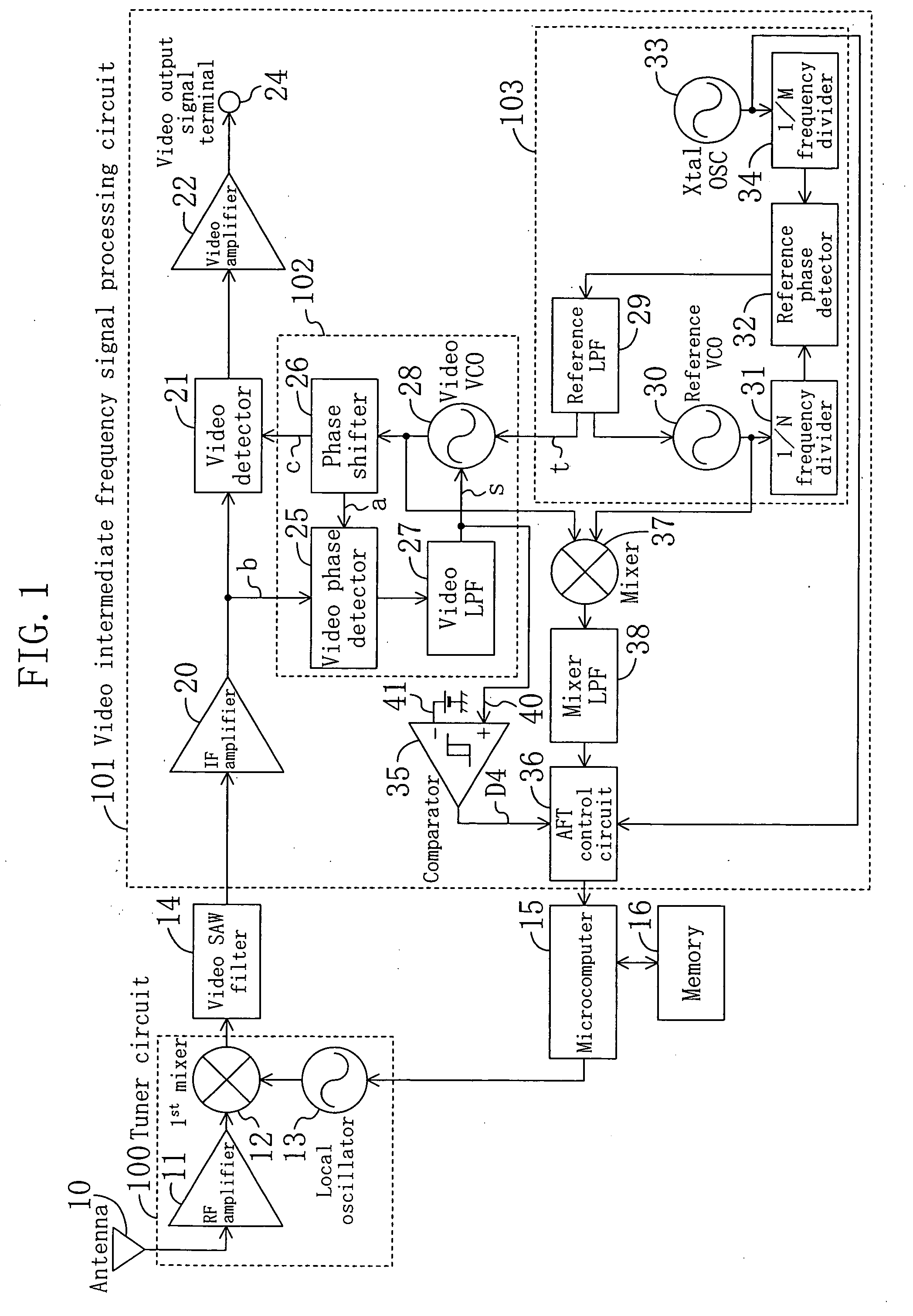
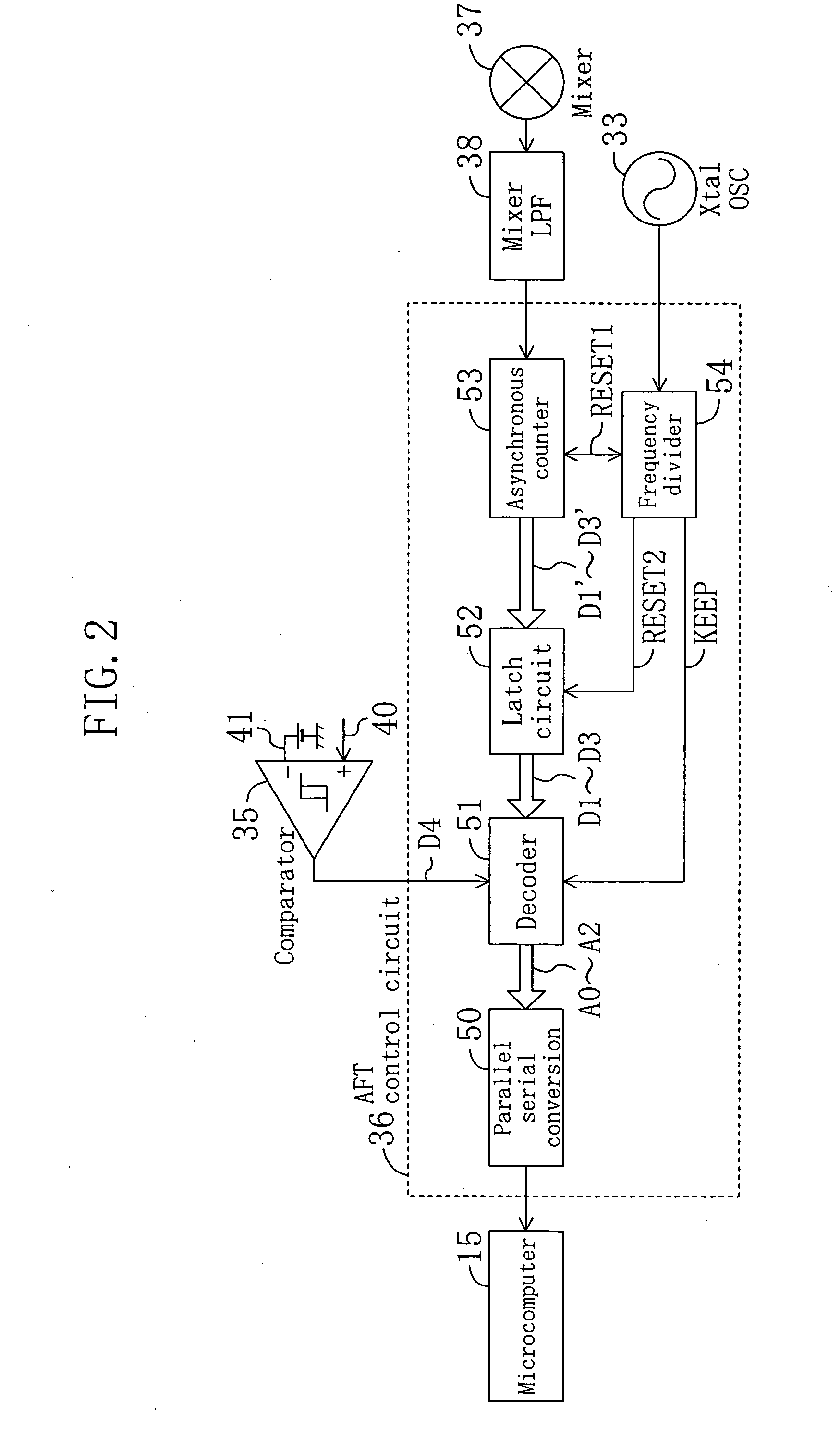
Automatic frequency tuning system
InactiveUS20060066759A1Improve performanceReduce circuit sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMicrocomputerLow-pass filter
An automatic frequency tuning system according to the present invention includes an antenna, a tuner circuit, a video SAW filter, a video intermediate frequency amplifier, a video detector, a video amplifier, a video PLL circuit, an AFT control circuit, a microcomputer and a memory. In addition to the above members, the automatic frequency tuning system further includes a reference PLL circuit for reducing variation in a free running frequency of a video voltage controlled oscillator, a comparator for determining a magnitude relationship between a received video frequency and a standard video frequency, a mixer for mixing an output signal of the video control frequency and an output signal of a reference voltage controlled oscillator and retrieving sum and difference signals for frequencies of the outputs, and a mixer low pass filter for supplying only a frequency difference signal to a subsequent stage.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
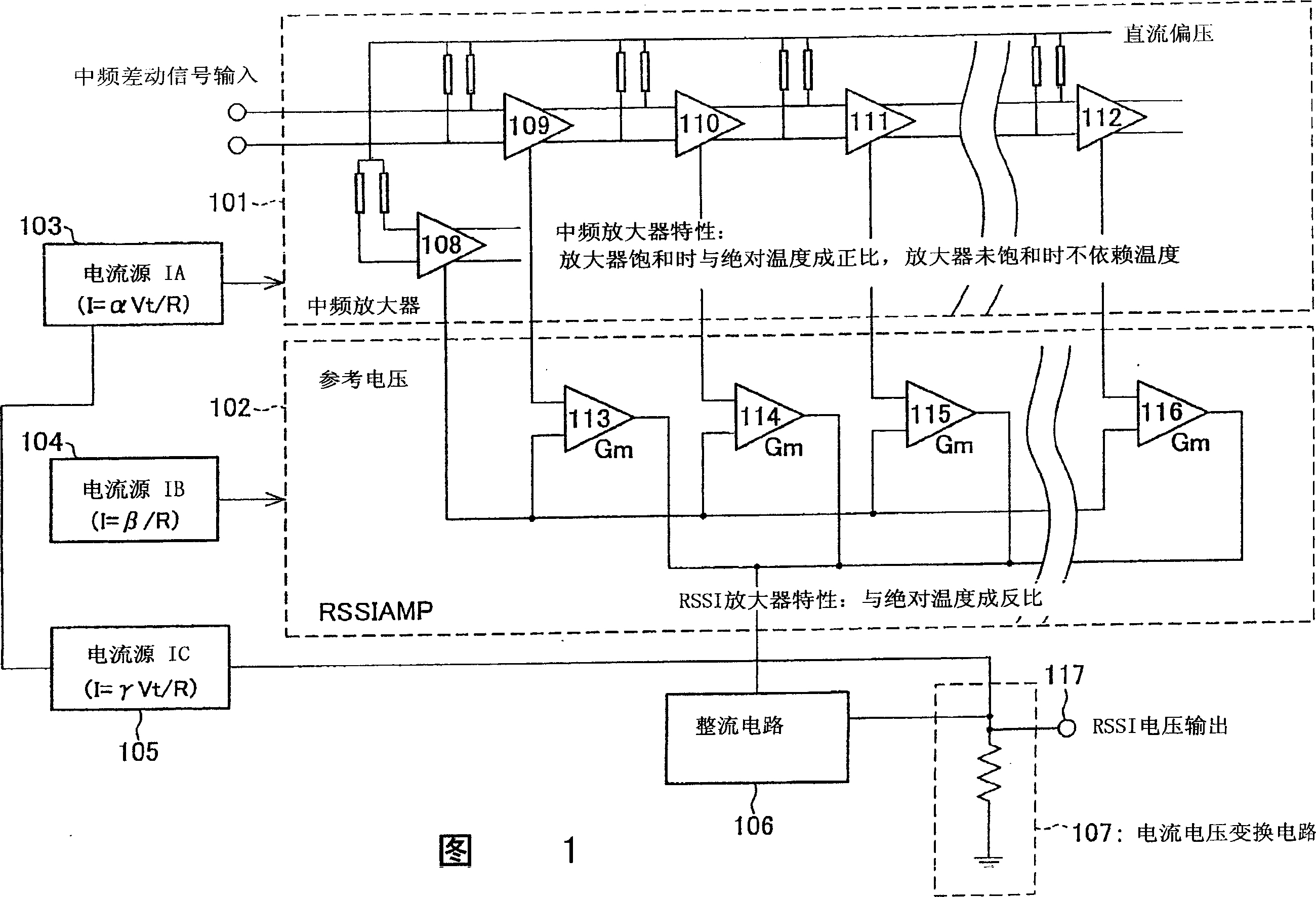
Received signal strength measurement circuit, received signal strength detection circuit and wireless receiver
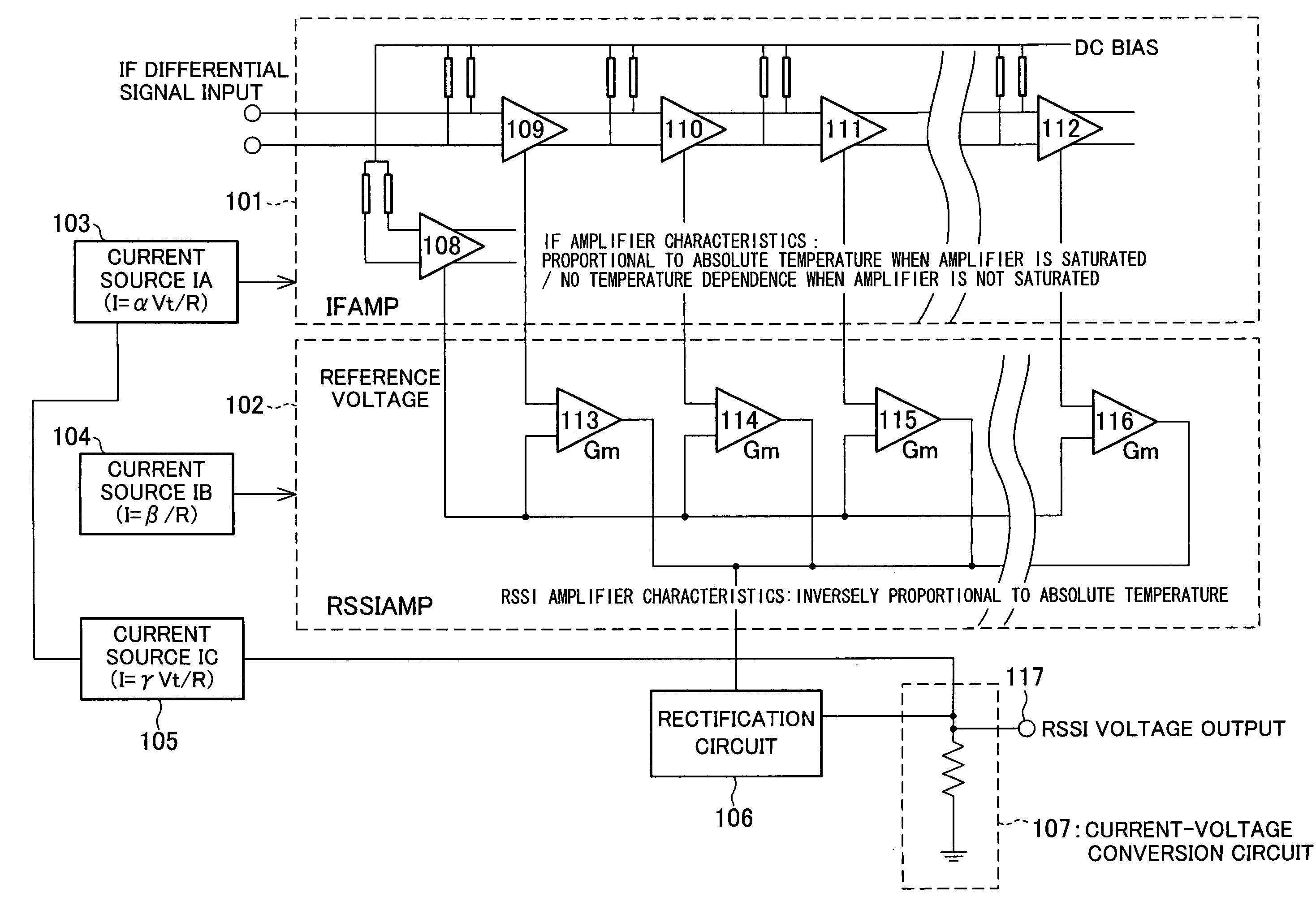
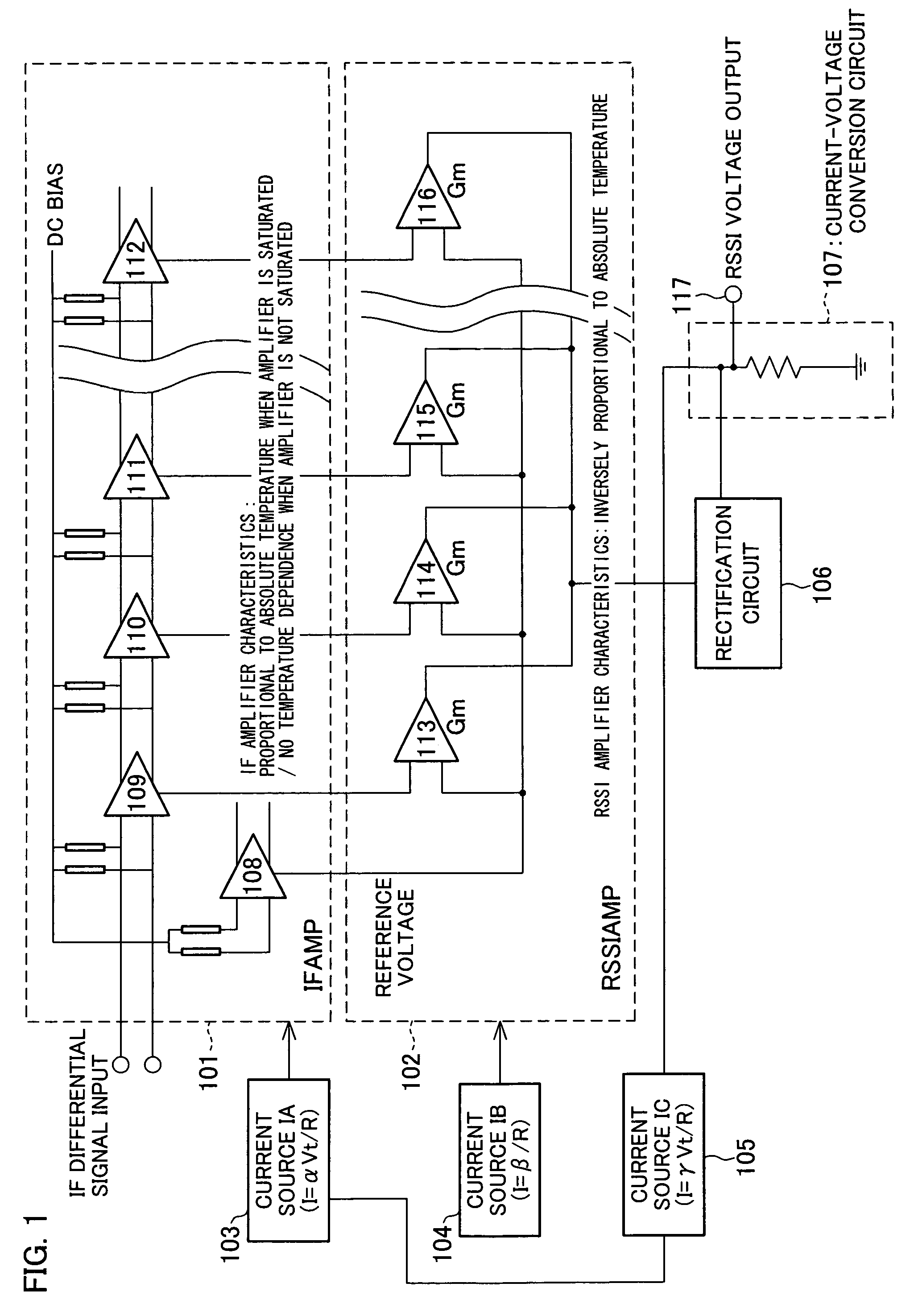
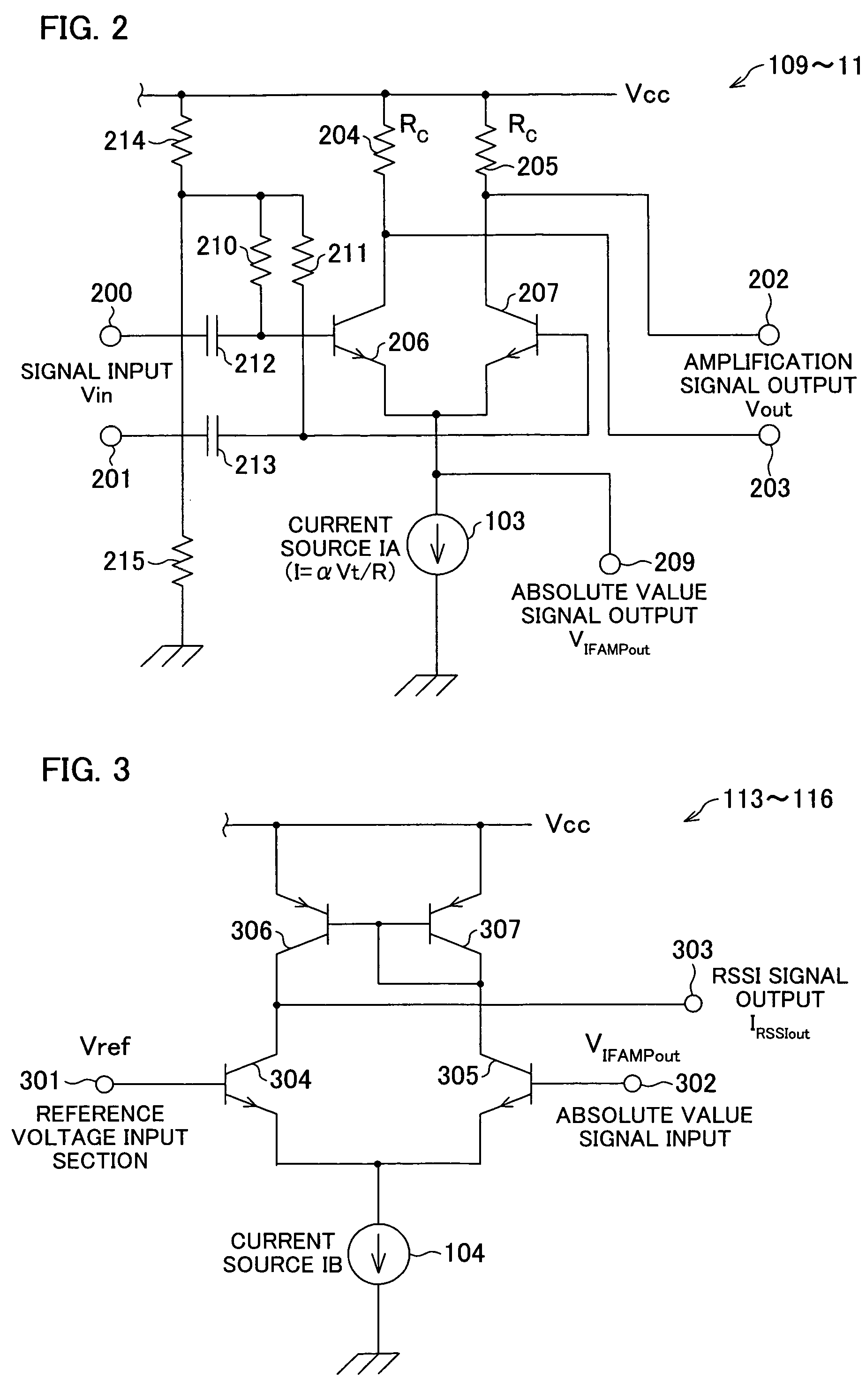
InactiveCN1747367AControl temperature dependenceTemperature-dependent inhibition or eliminationAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplifier combinationsVoltage amplitudeCurrent voltage
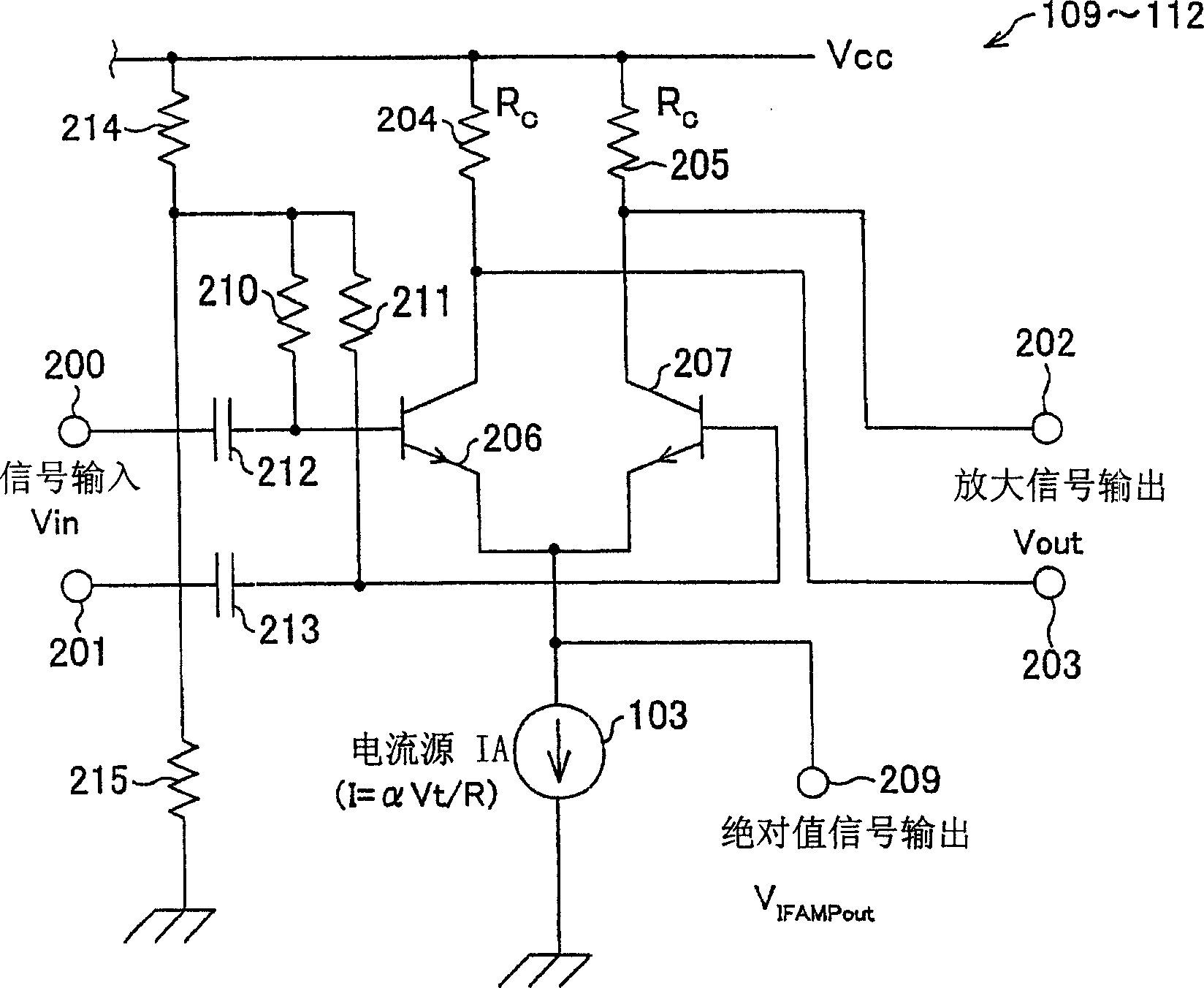
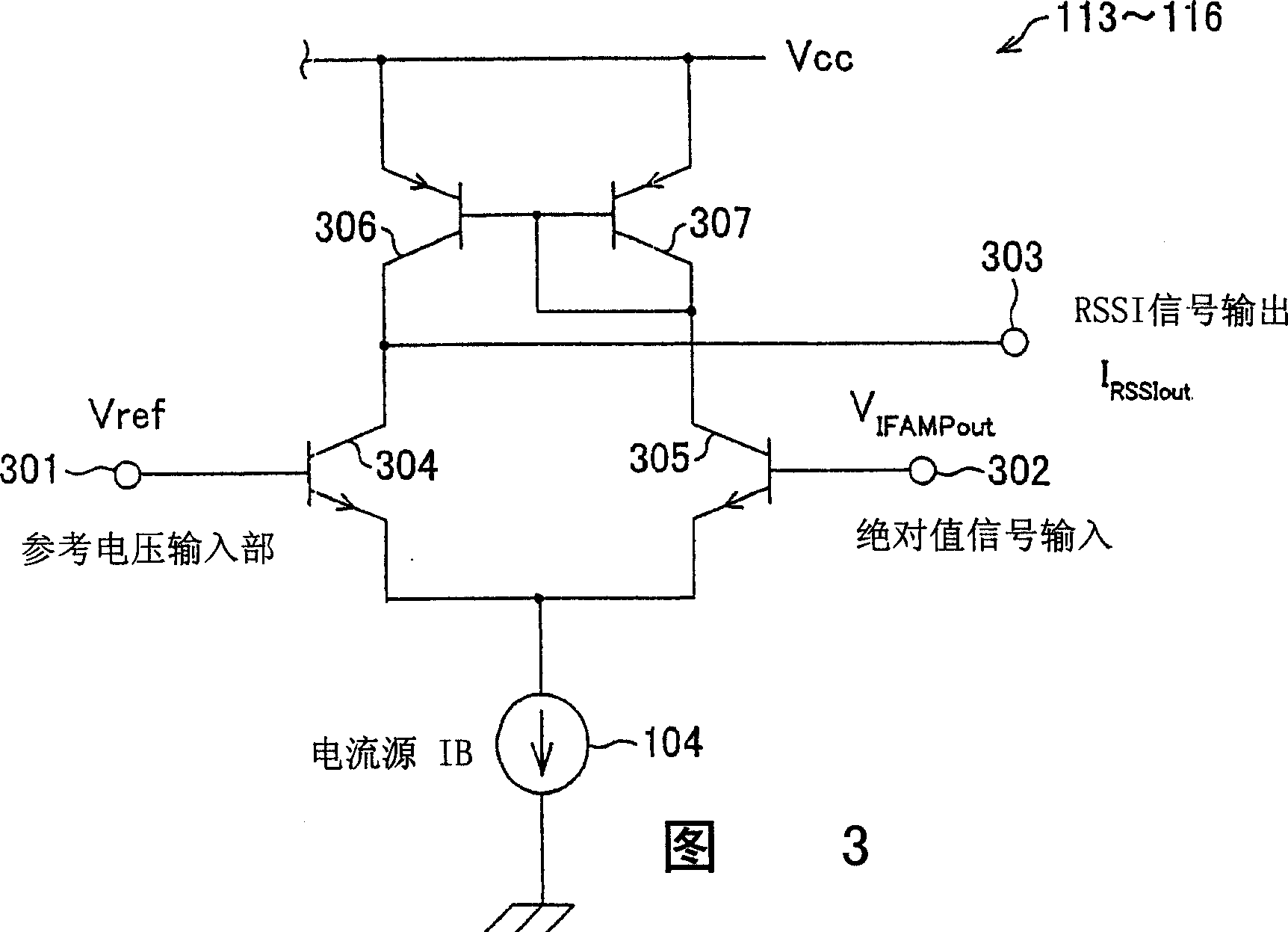
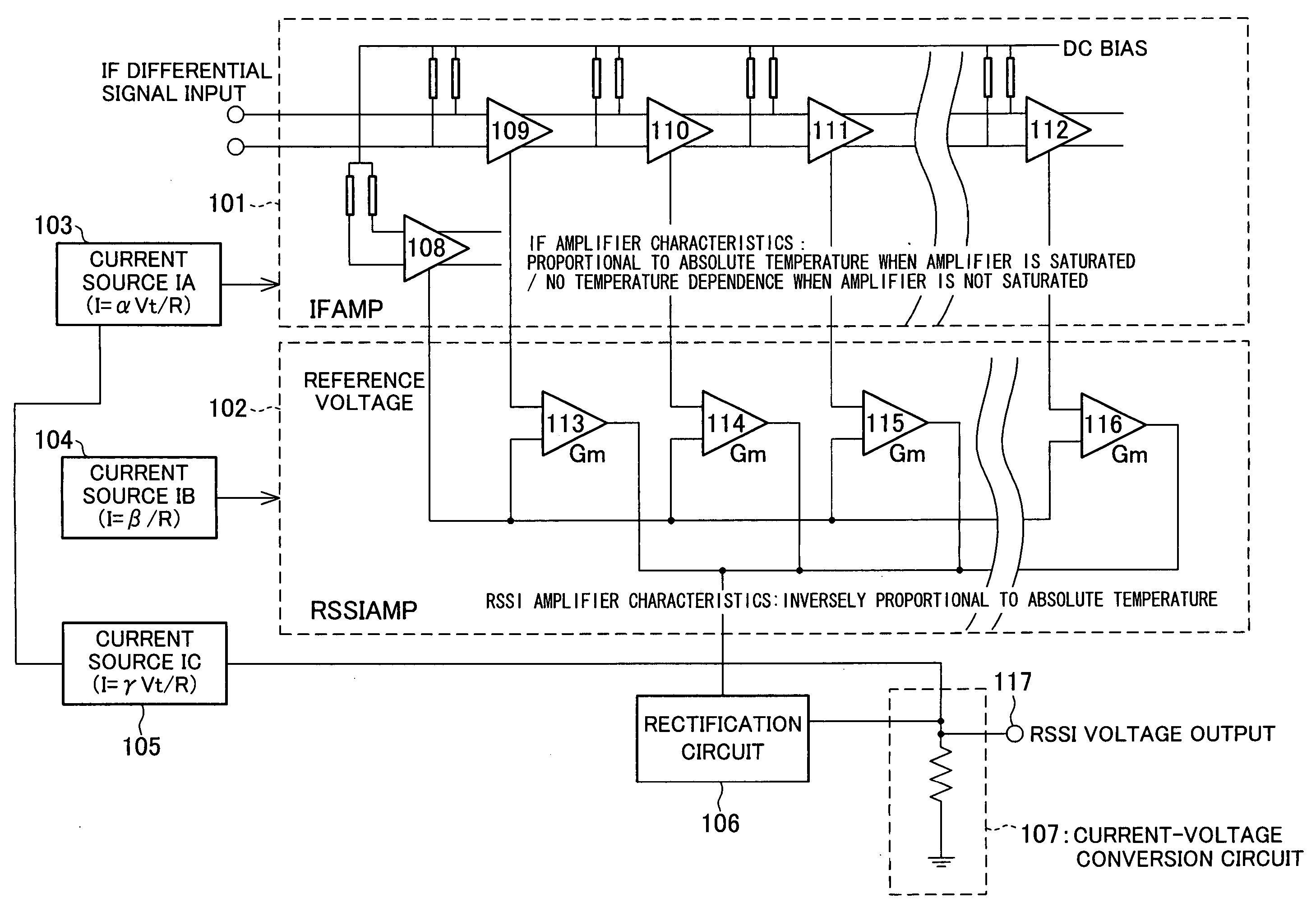
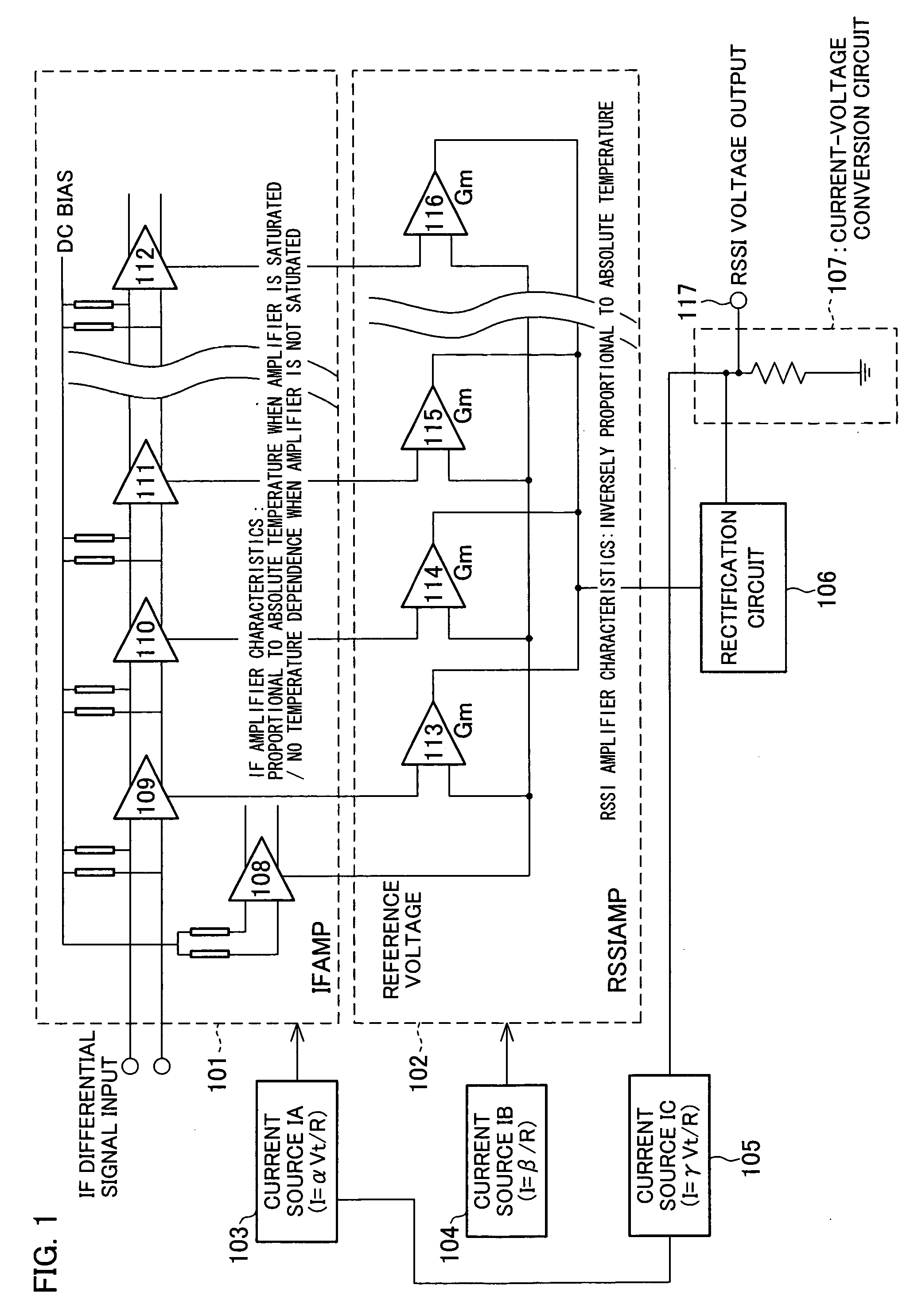
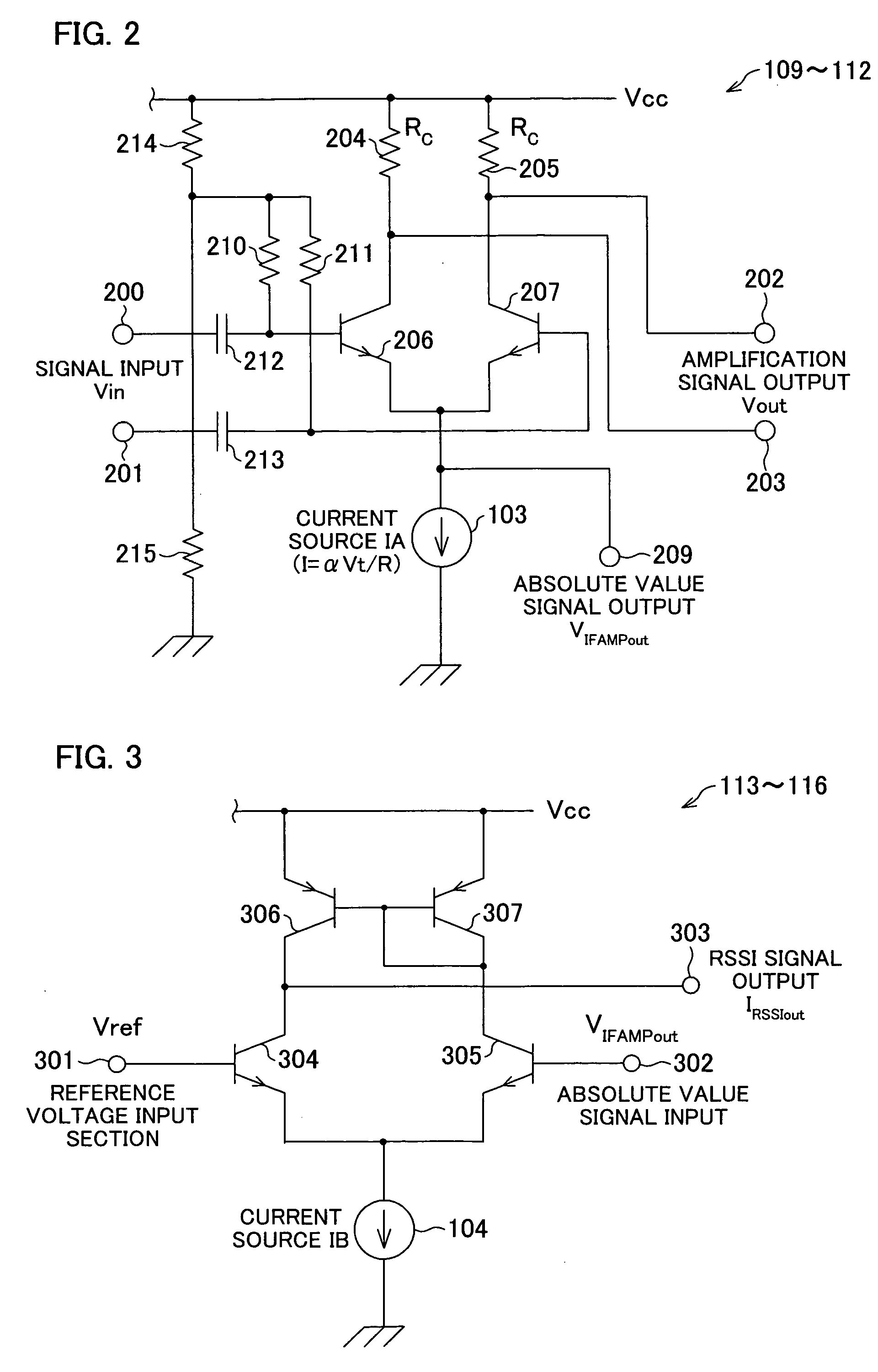
The RSSI circuit of the present invention includes: an IF amplifier section, which includes multiple stages of serially connected differential amplifiers for amplifying, with use of a current source IA provided as a power source for amplification, an IF signal corresponding to a received signal; an RSSI amplifier section for converting into current a voltage amplitude of an absolute value signal outputted from the differential amplifiers of the IF amplifier section, using a current source IB provided as a power source for conversion, and adding and outputting the converted current; and a current voltage conversion circuit for converting into voltage the output current from the RSSI amplifier section, and outputting the converted voltage as a measurement voltage value. The RSSI amplifier section is set so that a current value of the RSSI amplifier section is inversely proportional to absolute temperature. With the configuration, it is possible to realize an RSSI circuit, a received signal strength detection circuit and a wireless receiver, which are able to stabilize a strength measurement of a received signal relative to a change in temperature and to increase communication characteristics.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and apparatus for adjusting the gain of an if amplifier in a communication system
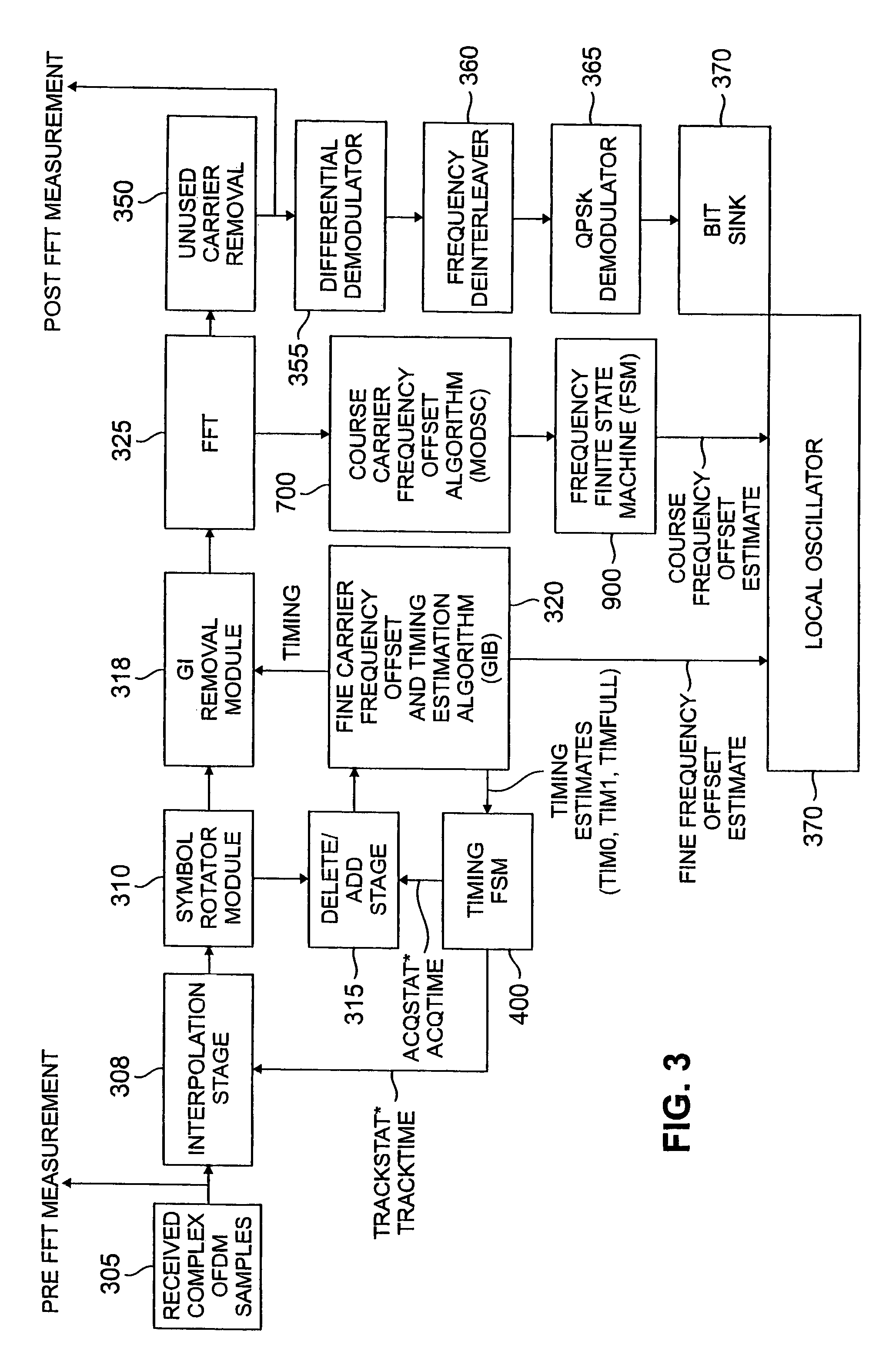
ActiveUS7499508B2Maximizing numberAvoid clippingResonant long antennasGain controlFast Fourier transformCommunications system
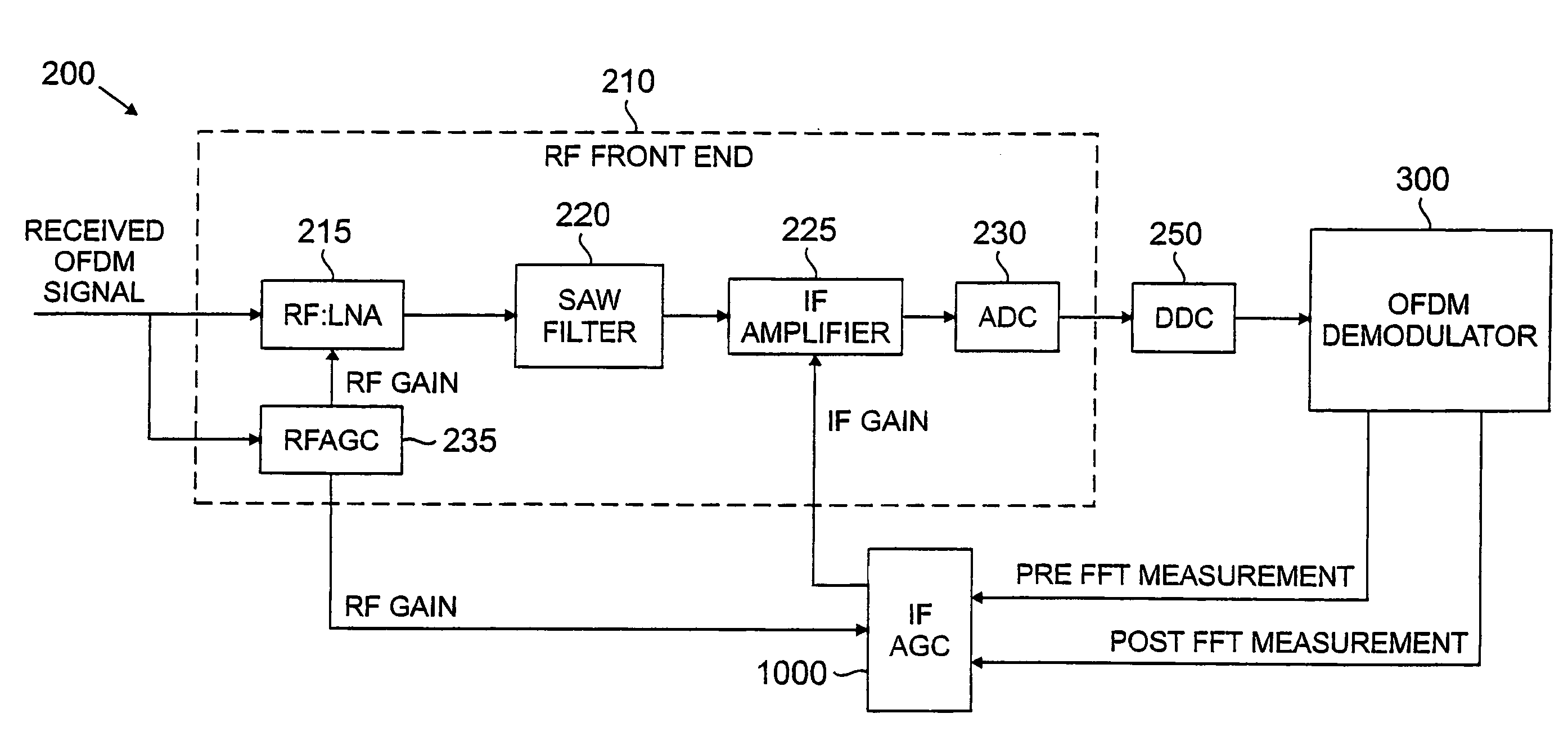
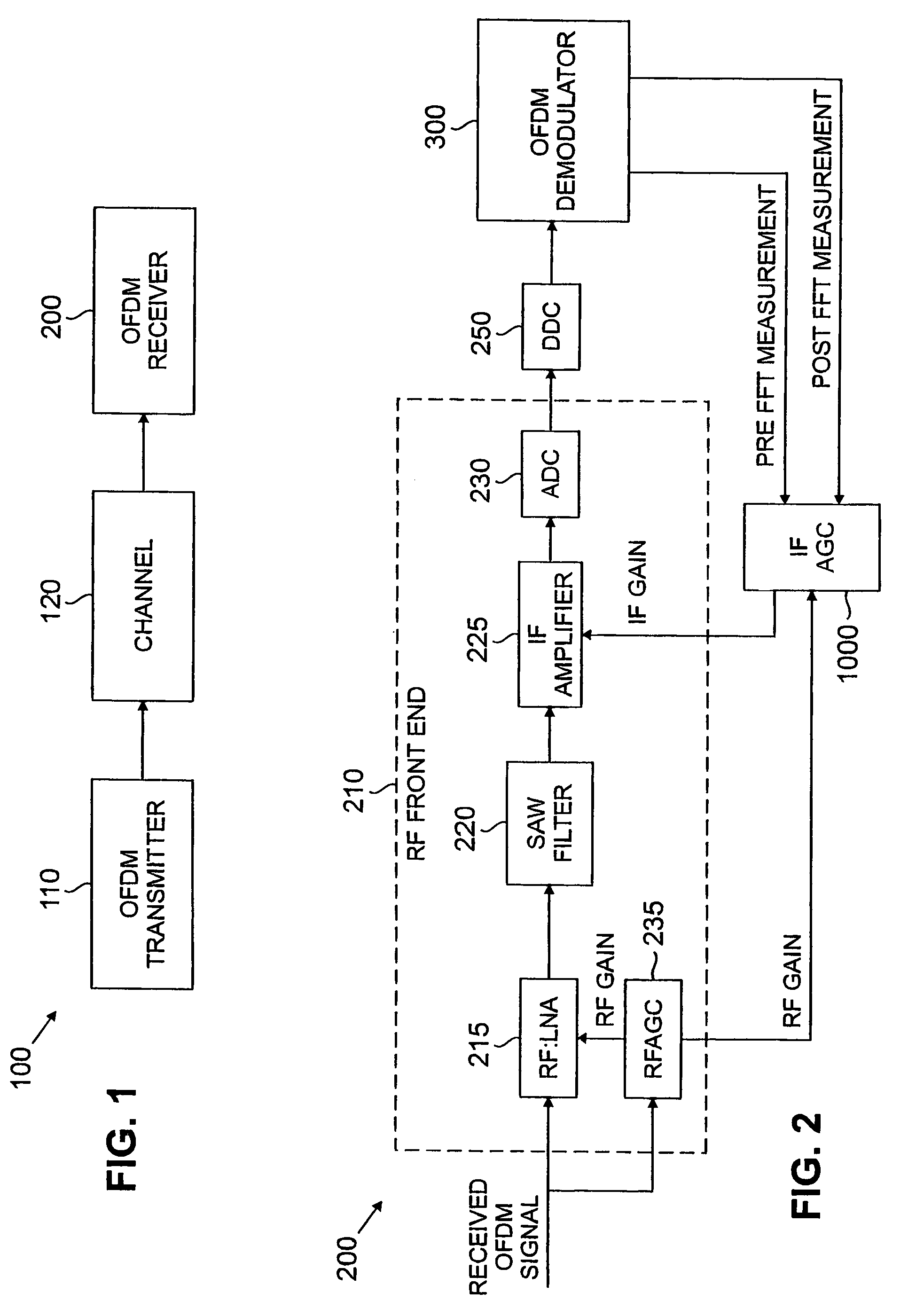
An automatic gain control technique is disclosed for adjusting the gain of an IF amplifier in a communication system, such as an OFDM or DMT communication system. The gain of an RF amplifier is controlled by a known RF automatic gain control circuit that generates an RF gain value. The disclosed IF automatic gain control (AGC) circuit controls the gain of an IF amplifier in the receiver. The disclosed IF AGC monitors the RF gain value, as well as pre-FFT and post-FFT signal energy measurements performed before and after a fast Fourier transform (FFT) stage, respectively, to maintain a desired set point. The IF AGC adjusts the previous IF gain value by an amount opposite to the adjusted RF gain value, if any. If there is no RF gain adjustment, then the IF AGC will adjust the IF gain based on thresholds established for the pre-FFT and post-FFT measurements. If the pre-FFT measurement is within a desired tolerance of the pre-FFT threshold, then the IF gain will be lowered in stepped increments. Otherwise, the IF gain adjustment is the minimum of the difference between (i) the pre-FFT measurement and its threshold, or (ii) the post-FFT measurement and its threshold, multiplied by a loop gain constant.
Owner:AGERE SYST GUARDIAN
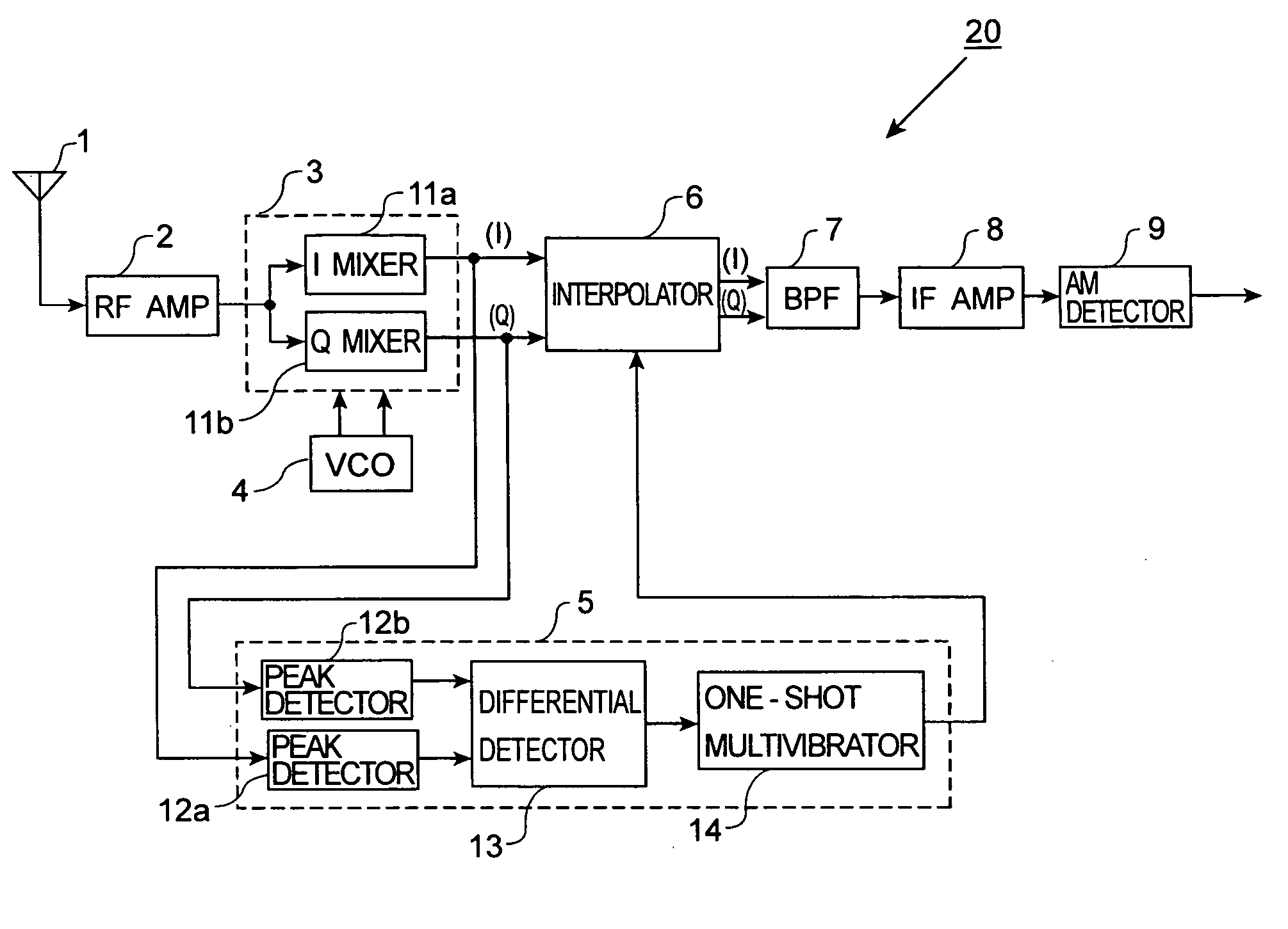
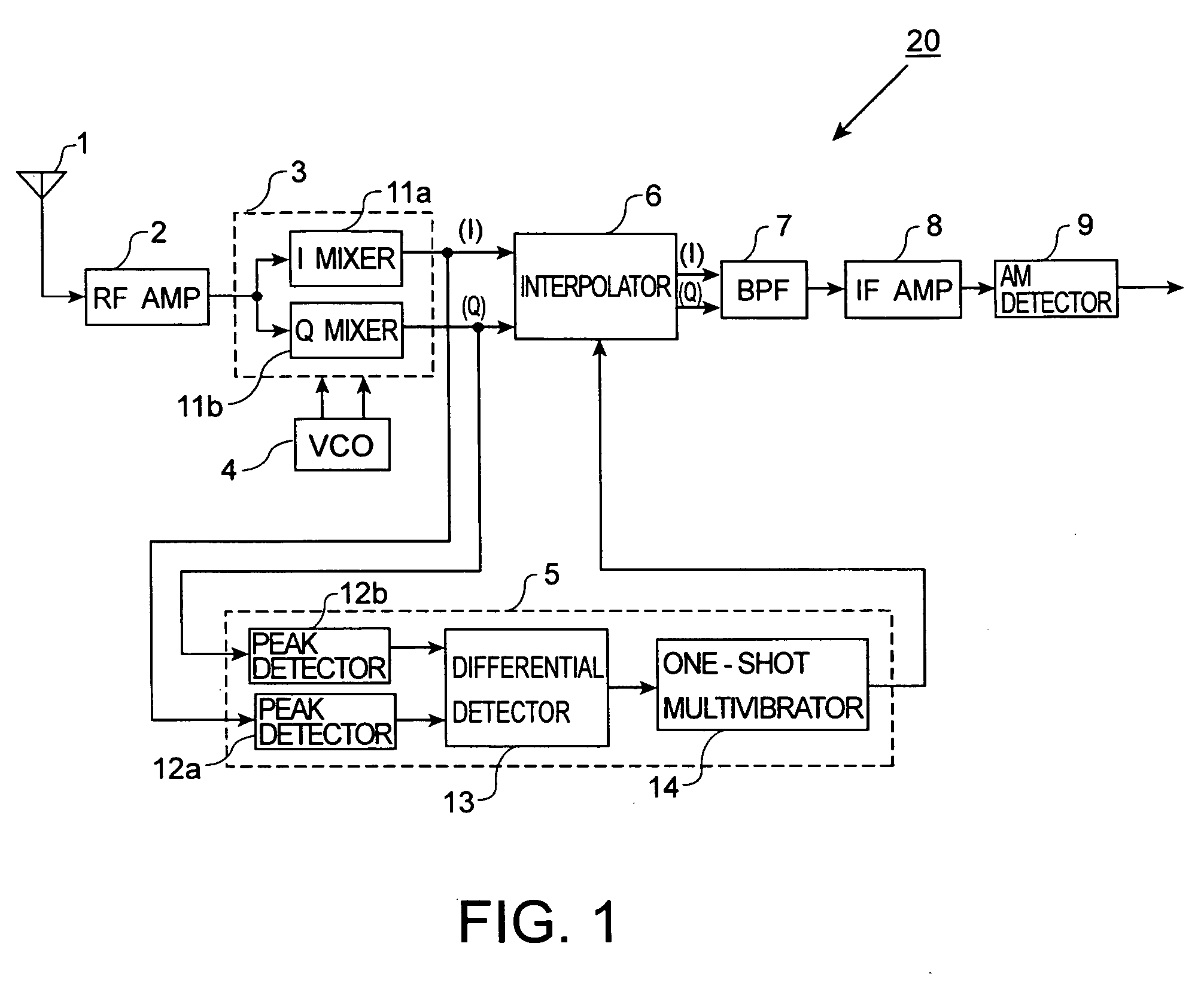
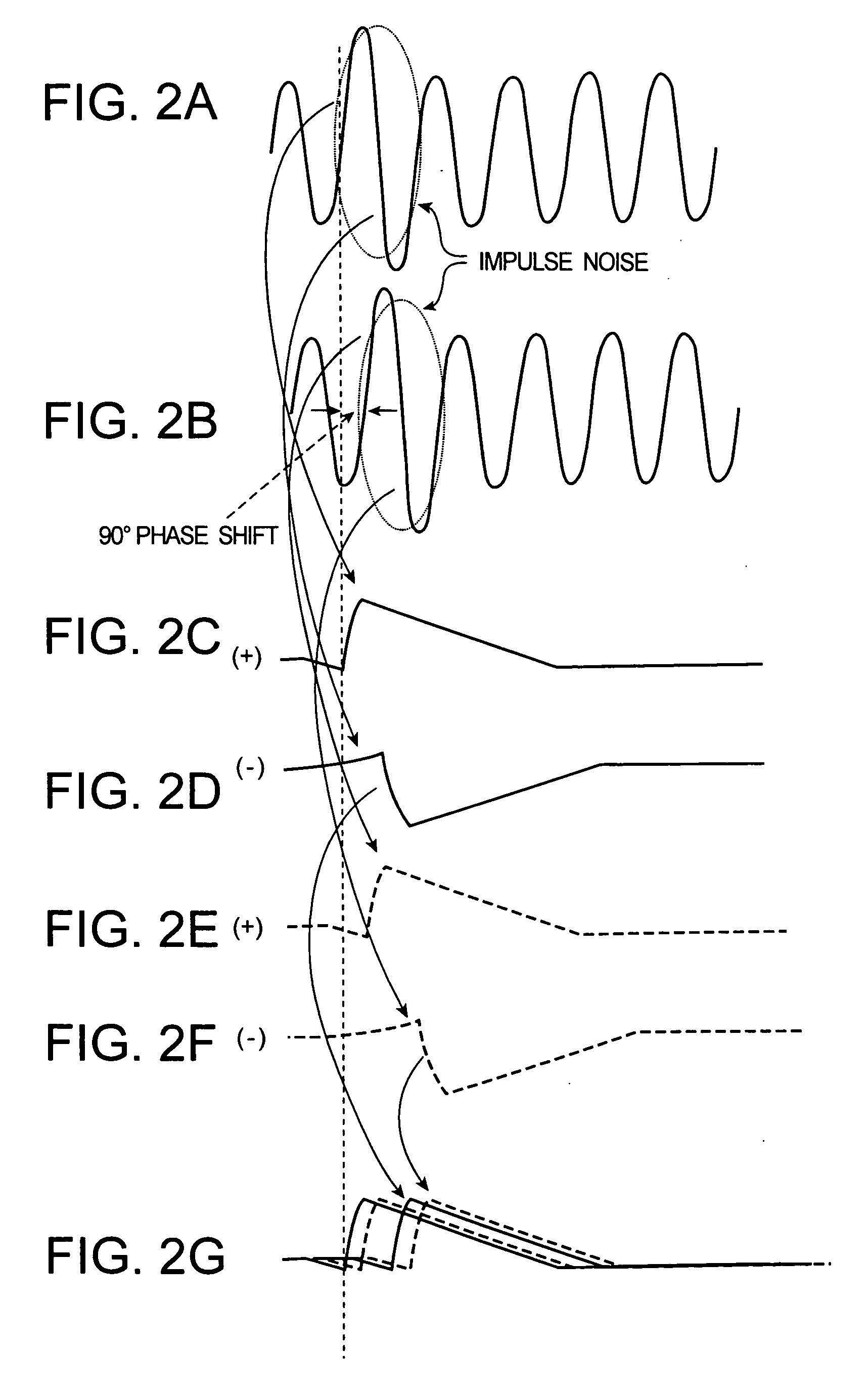
Receiver
AM receiver 20 is provided with antenna 1, RF amplifier 2, I / Q mixer 3, VCO 4, impulse noise detector 5, interpolator 6, BPF 7, IF amplifier 8 and AM detector 9. I / Q mixer 3 is composed of I mixer 11a as an in-phase mixer and Q mixer 11b as an orthogonal mixer. Impulse noise detector 5 generates an interpolation signal from in-phase and orthogonal output signals from I / Q mixer 3. Interpolator 6 carries out shaping of waveforms of the output signals from I / Q mixer 3 in response to the interpolation signal and eliminates impulse noises from the output signals from I / Q mixer 3.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Class-e radio frequency power amplifier with feedback control
InactiveUS20070210867A1ElectrotherapyNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsShunt capacitorsAudio power amplifier
A Class-E power amplifier includes a choke and a switch connected in series between a source of a supply voltage and circuit ground and connected to an inductively coupled coil. An output node of the amplifier is formed between choke and the switch and connected to a transmitter antenna. A shunt capacitor couples the amplifier's output node to the circuit ground. A feedback signal, indicating an intensity if the signal at the amplifier output node is used to vary the input signal to the Class-E power amplifier and thereby control operation of the switch.
Owner:KENERGY INC
Radar for detecting the distance to a target
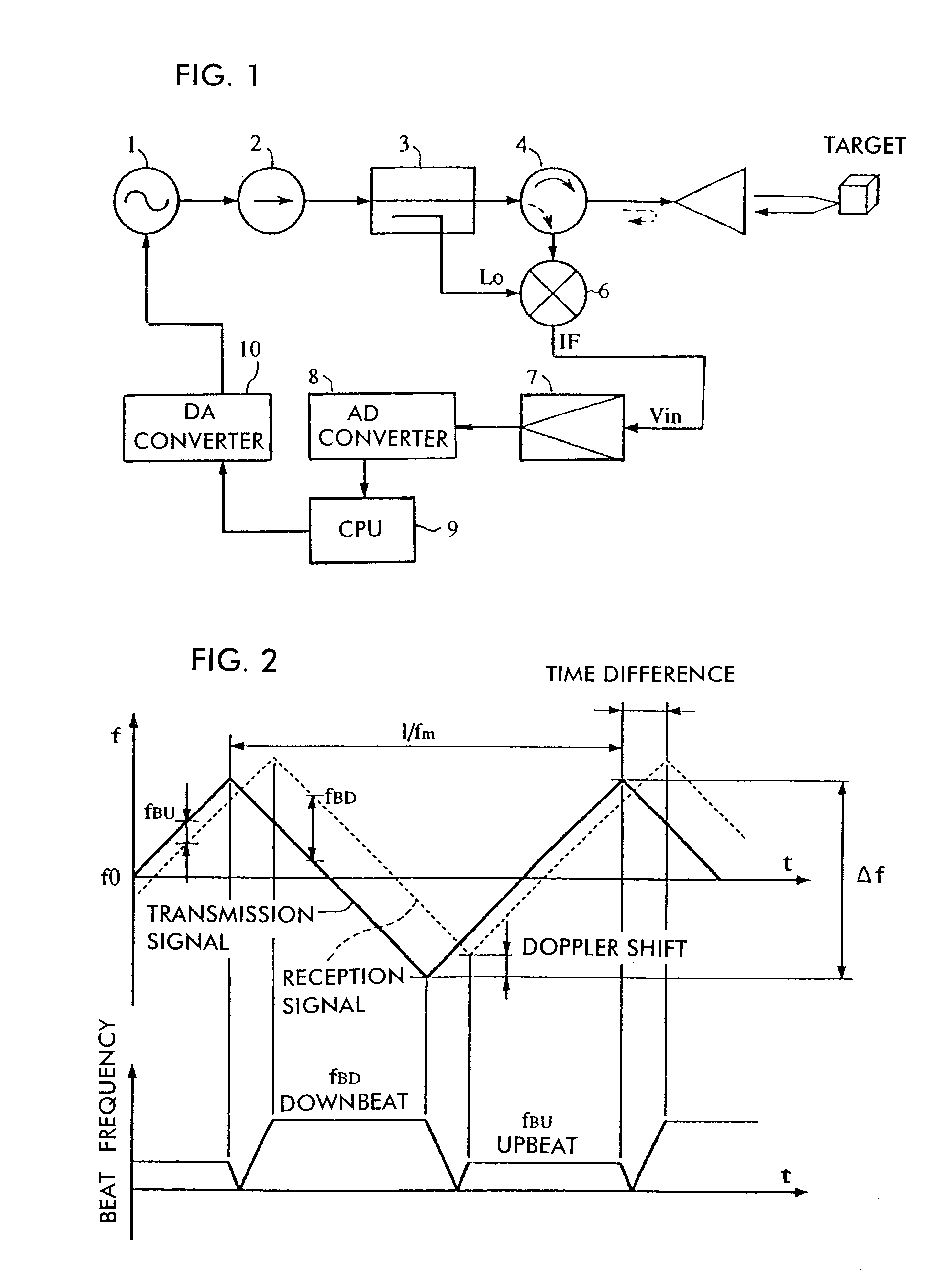
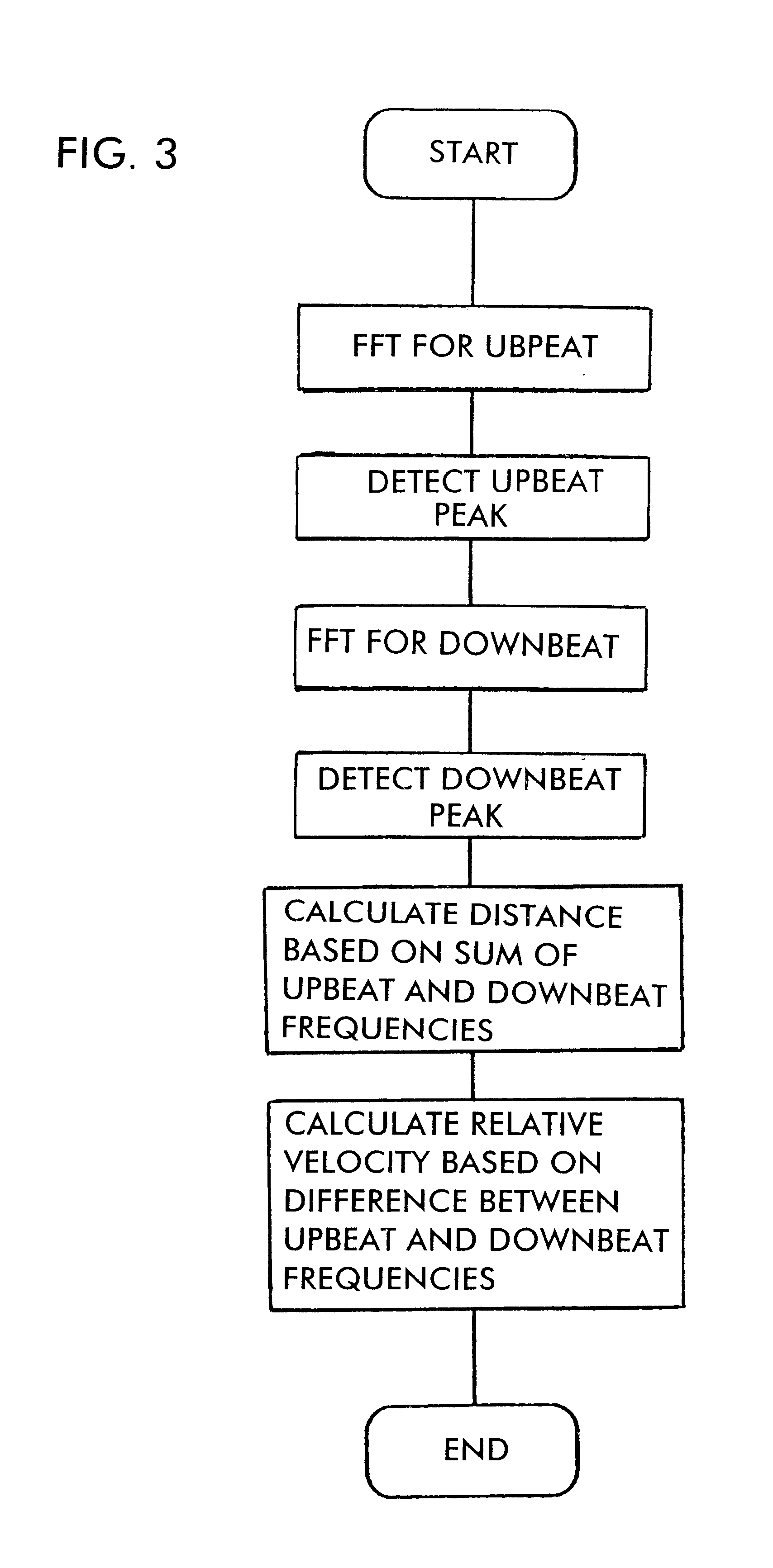
InactiveUS6593874B2Raise the ratioReduction in degradationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarShortest distance
In a radar, a frequency-modulated transmission signal whose frequency varies in time is generated. The gain-frequency characteristics of an IF signal which represents a beat signal between the transmission signal and a reception signal has its peak at or below one half of the sampling frequency of an AD converter. The gain-frequency characteristics of an IF amplifier circuit is determined so that the gain increases as the frequency increases at or below the frequency corresponding to the peak, the ratio of change in the gain relative to change in the frequency becomes smaller at short distances for which a saturation of a mixer is caused, and the gain is reduced at DC and in the vicinity of DC.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
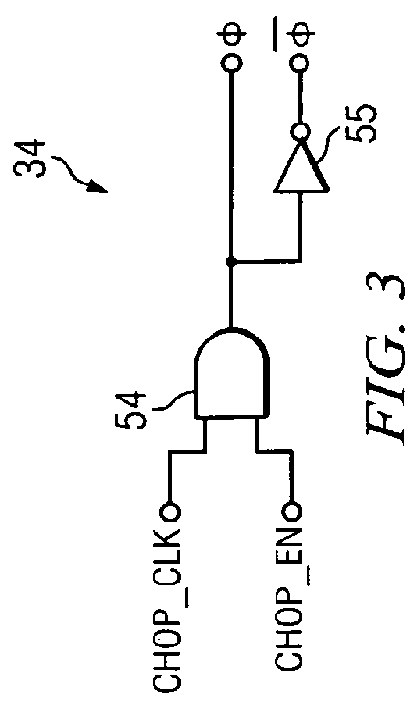
Circuit and method for reducing input leakage in chopped amplifier during overload conditions
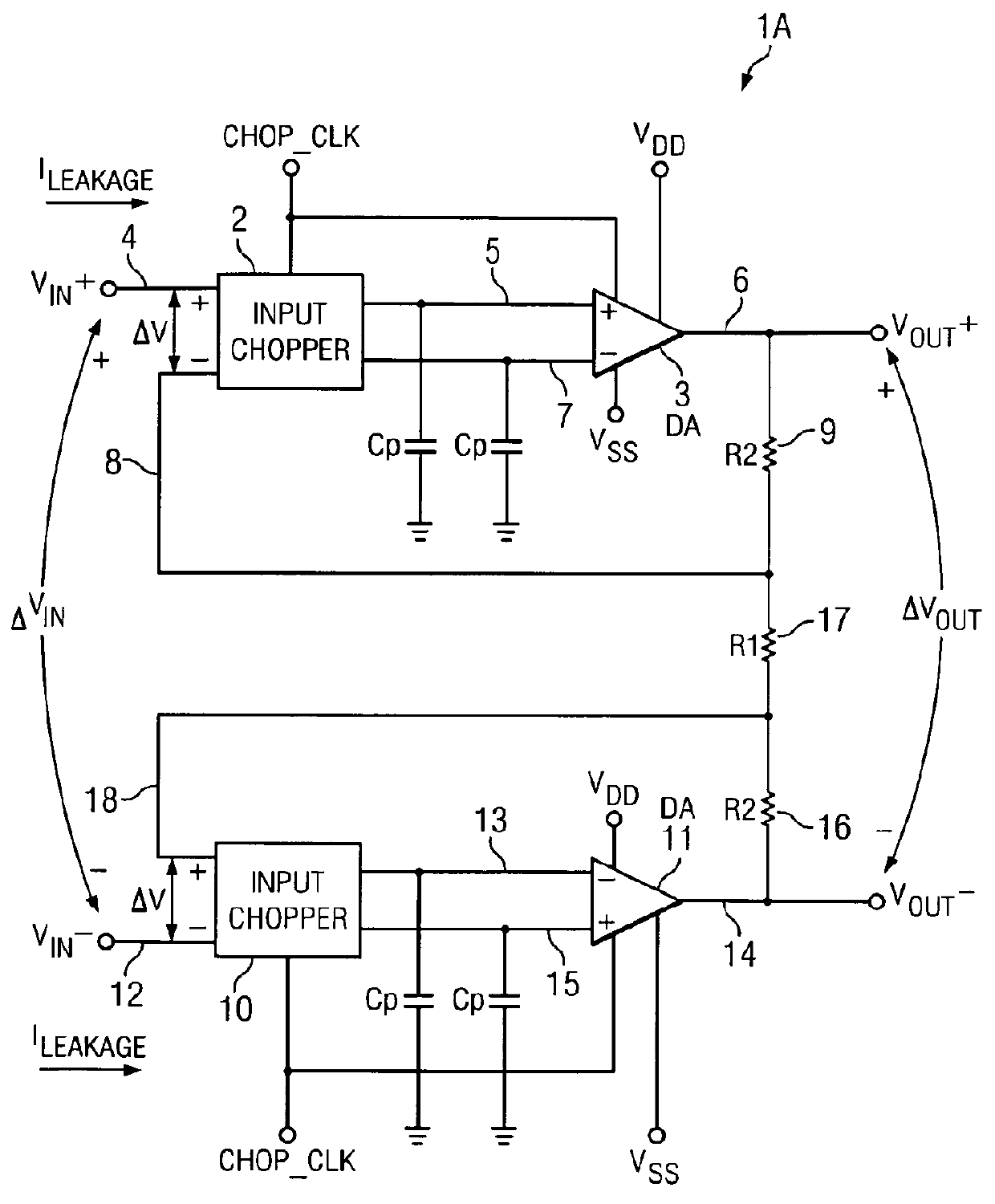
ActiveUS8258863B2Low input leakage currentHigh input impedanceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierChopper amplifier
A chopper-stabilized amplifier (20A) includes an amplifier (3), an input chopper (2A) having a first input (4) receiving an input signal (VIN+), an output (5) coupled to a first input of the amplifier, and a feedback resistor (9) coupled to an output (6) of the amplifier to couple a feedback signal (VFB+) to a second input of the amplifier (3). The input chopper operates in response to a chopping clock (CHOP_CLK). If the amplifier (3) is unacceptably close to a saturation condition, the chopping clock (CHOP_CLK) is disabled to reduce input leakage current (ILEAKAGE) of the chopper-stabilized amplifier.
Owner:DURACELL U S OPERATIONS +1
Received signal strength measurement circuit, received signal strength detection circuit and wireless receiver
InactiveUS20060046677A1Measurement stabilityImprove reception accuracyAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplifier combinationsVoltage amplitudeCurrent voltage
The RSSI circuit of the present invention includes: an IF amplifier section, which includes multiple stages of serially connected differential amplifiers for amplifying, with use of a current source IA provided as a power source for amplification, an IF signal corresponding to a received signal; an RSSI amplifier section for converting into current a voltage amplitude of an absolute value signal outputted from the differential amplifiers of the IF amplifier section, using a current source IB provided as a power source for conversion, and adding and outputting the converted current; and a current voltage conversion circuit for converting into voltage the output current from the RSSI amplifier section, and outputting the converted voltage as a measurement voltage value. The RSSI amplifier section is set so that a current value of the RSSI amplifier section is inversely proportional to absolute temperature. With the configuration, it is possible to realize an RSSI circuit, a received signal strength detection circuit and a wireless receiver, which are able to stabilize a strength measurement of a received signal relative to a change in temperature and to increase communication characteristics.
Owner:SHARP KK
Received signal strength measurement circuit, received signal strength detection circuit and wireless receiver
InactiveUS7415256B2Stably measure strengthImprove reception accuracyAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAmplifier combinationsVoltage amplitudeCurrent voltage
The RSSI circuit of the present invention includes: an IF amplifier section, which includes multiple stages of serially connected differential amplifiers for amplifying, with use of a current source IA provided as a power source for amplification, an IF signal corresponding to a received signal; an RSSI amplifier section for converting into current a voltage amplitude of an absolute value signal outputted from the differential amplifiers of the IF amplifier section, using a current source IB provided as a power source for conversion, and adding and outputting the converted current; and a current voltage conversion circuit for converting into voltage the output current from the RSSI amplifier section, and outputting the converted voltage as a measurement voltage value. The RSSI amplifier section is set so that a current value of the RSSI amplifier section is inversely proportional to absolute temperature. With the configuration, it is possible to realize an RSSI circuit, a received signal strength detection circuit and a wireless receiver, which are able to stabilize a strength measurement of a received signal relative to a change in temperature and to increase communication characteristics.
Owner:SHARP KK
Television broadcast receiving apparatus
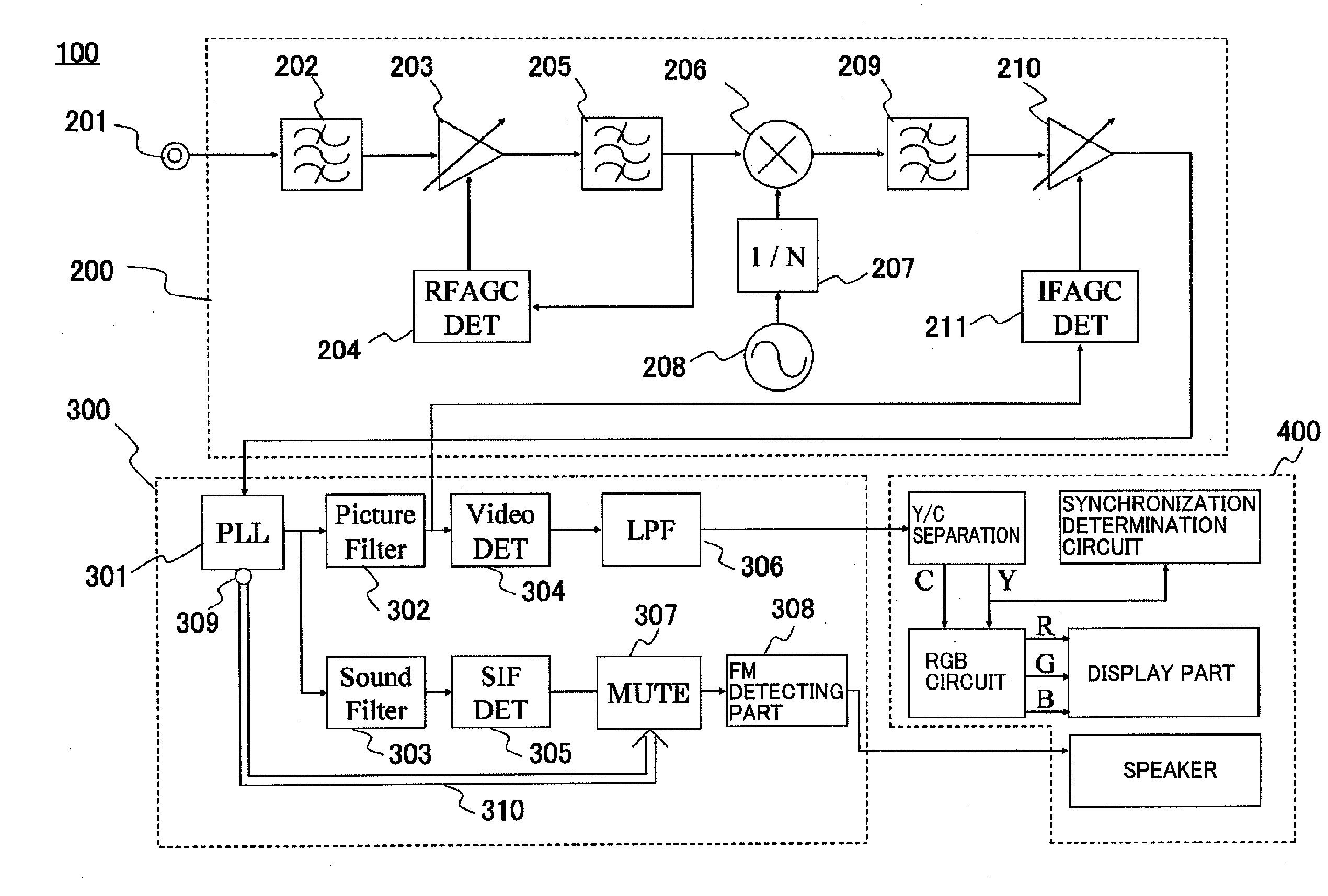
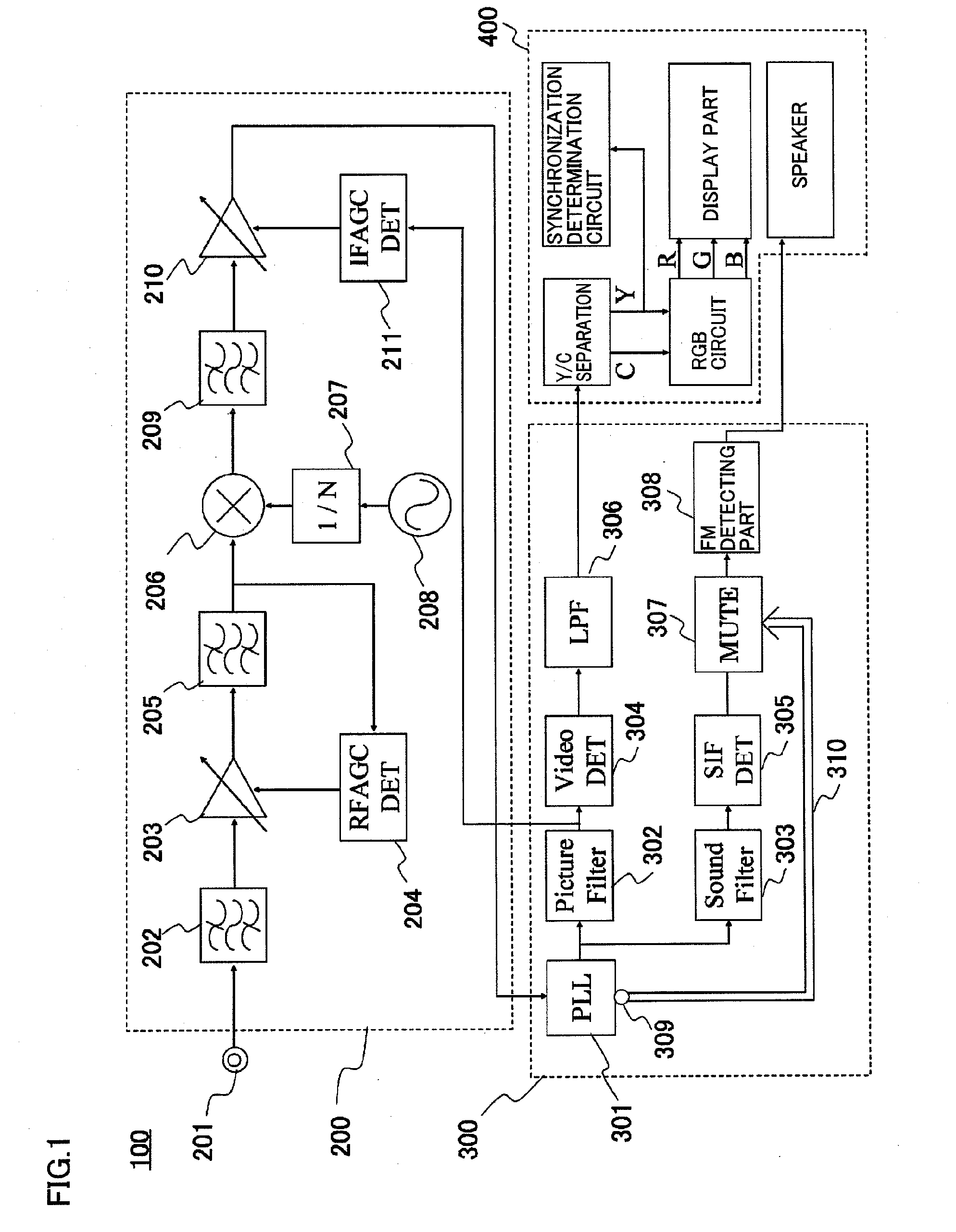
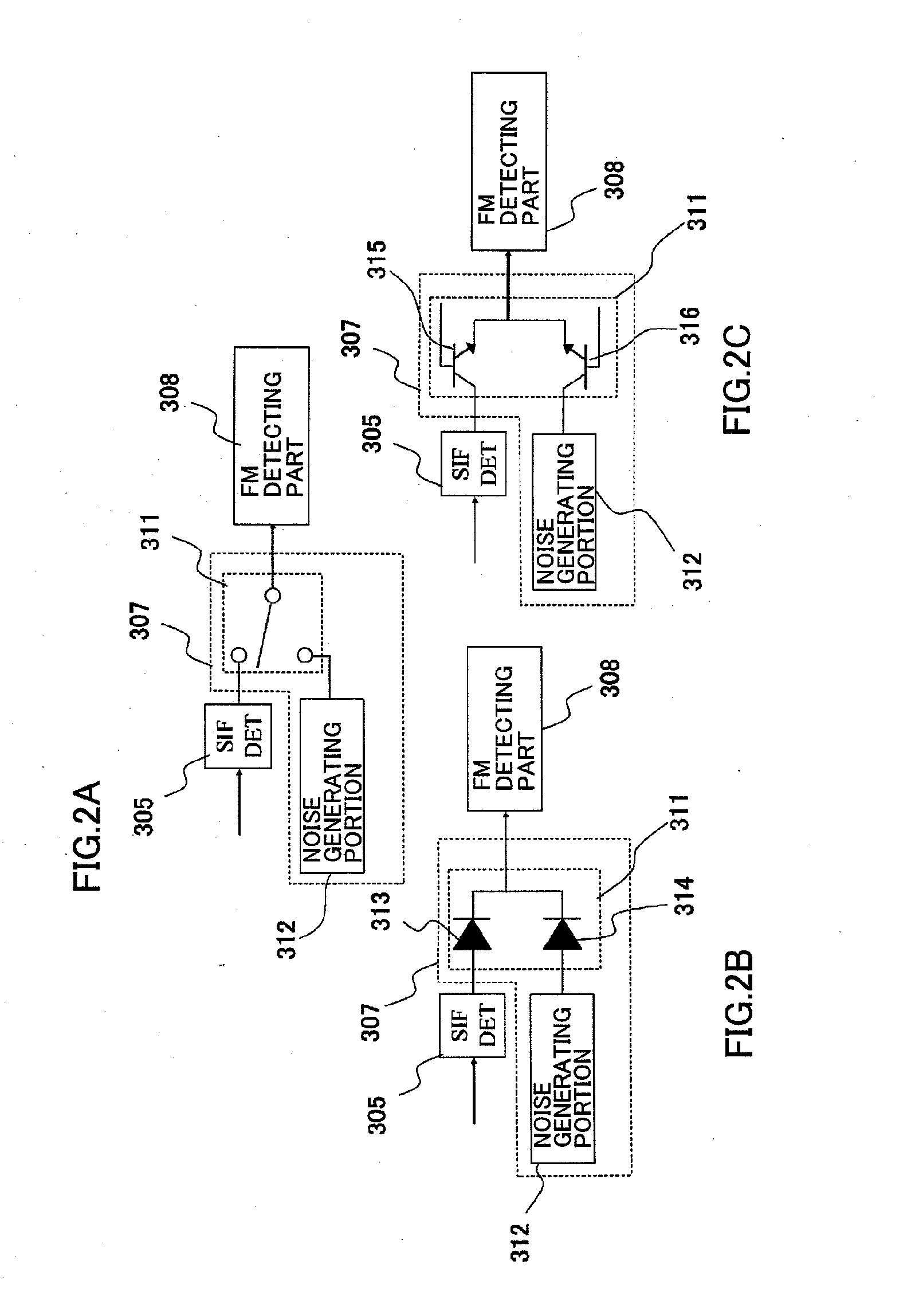
InactiveUS20110285907A1Abrupt break in a sound can be avoidedHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCarrier signalEngineering
A television broadcast receiving apparatus has a demodulating unit including a PLL part synchronizing a phase of an IF signal with a phase of an internally generated carrier signal and outputting an out-of-synchronization flag signal when the IF signal and the carrier signal are in an unsynchronized state, and a muting part muting a sound intermediate frequency signal and outputting a noise signal of a predetermined level when the out-of-synchronization flag signal is outputted from the PLL part. Therefore, even when an IF amplifier of a tuning unit amplifies a noise at the maximum gain when there is no signal, an abnormal sound can be prevented from being outputted from a speaker of a decode and output unit.
Owner:SHARP KK
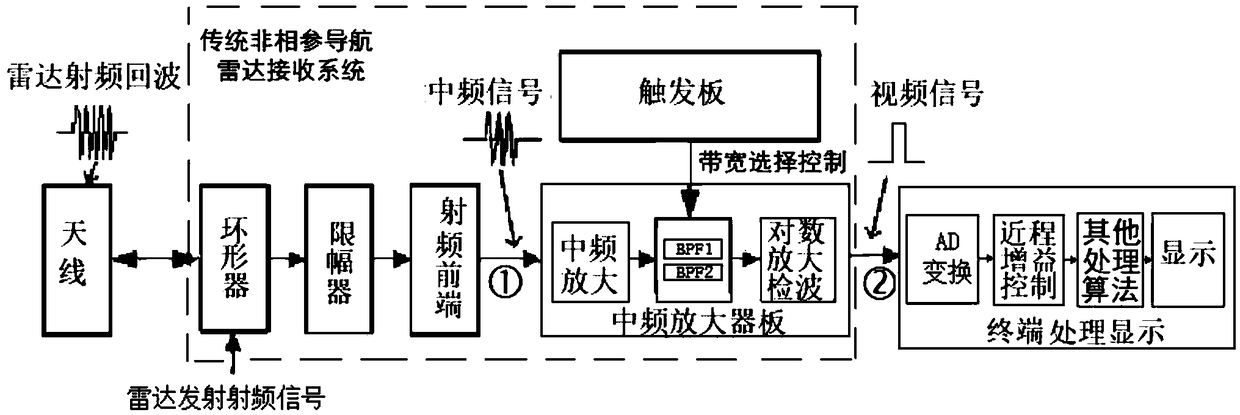
Large dynamic range radar receiving system based on intermediate frequency shrot-range gain control
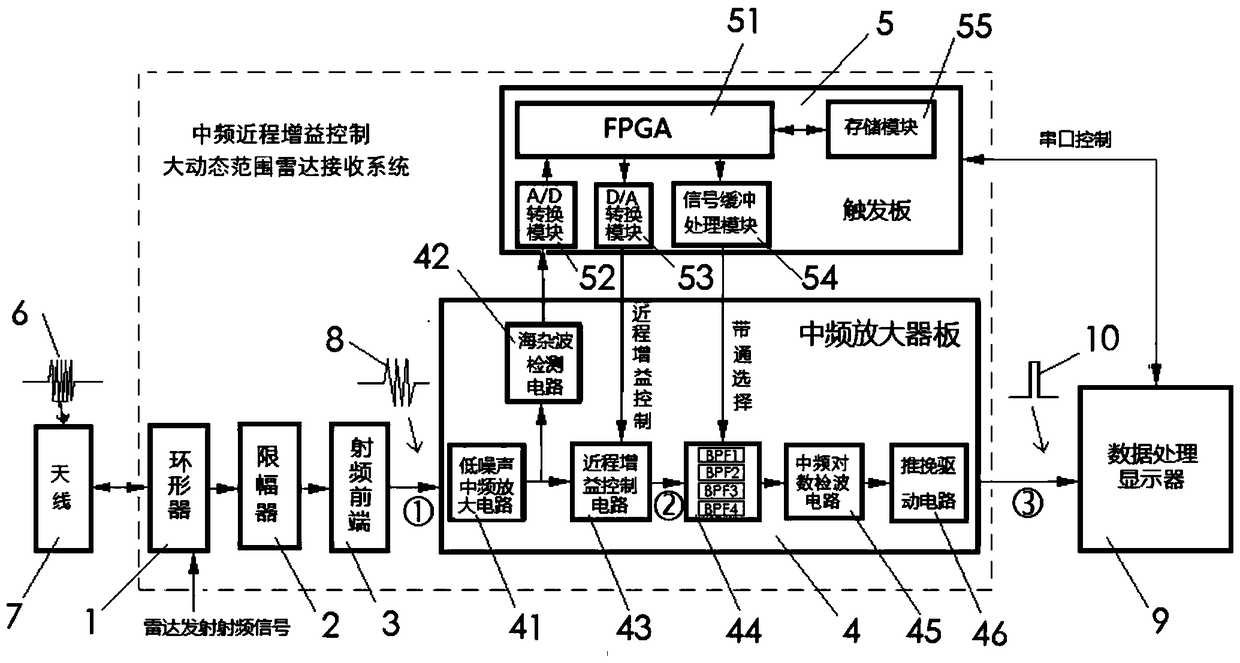
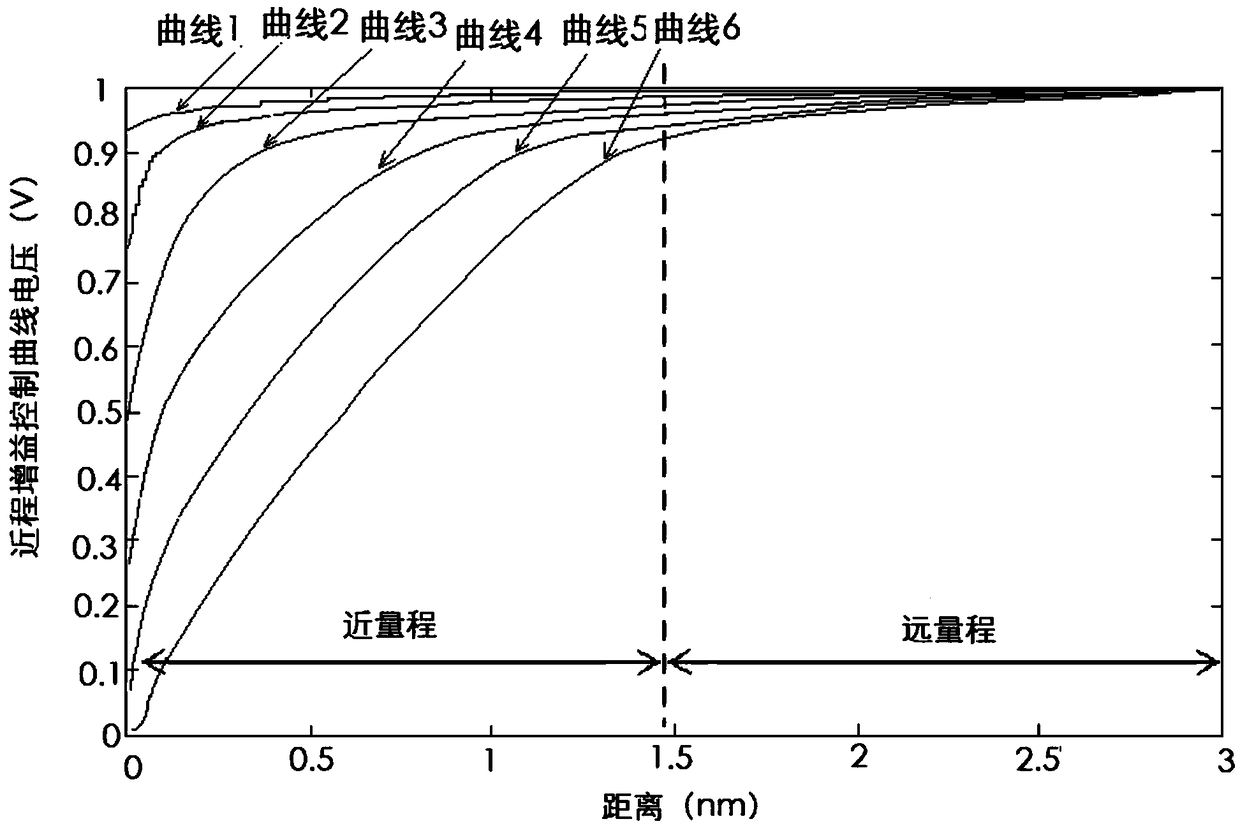
PendingCN109298399AMaximize dynamic rangeAvoid saturationWave based measurement systemsLow noiseIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a large dynamic range radar receiving system based on an intermediate frequency short-range gain control. The system comprises a circulator, a limiter, a radio frequency frontend, an intermediate frequency amplifier board and a trigger board. Radio frequency echo signals enter each member in sequence after being received by an antenna. The intermediate frequency amplifierboard comprises a low-noise intermediate frequency amplification circuit, a sea clutter detection circuit, a short-range gain control circuit, a band-pass selection circuit, an intermediate frequencylogarithm detecting circuit and a push-pull driving circuit. The trigger board comprises an FPGA, an A / D conversion module, a D / A conversion module, a signal buffer processing module and a storage module. The system performs short-range gain control on a radar intermediate frequency echo signal, transmits the intermediate frequency signal to the intermediate frequency logarithm detecting circuit to perform amplification, and then transmits the intermediate frequency signal to a data processing display through the push-pull driving circuit. According to the large dynamic range radar receiving system based on the intermediate frequency short-range gain control, the saturation problem of the close-range echo is overcome, and the dynamic range of the receiving system is maximized, so that theshort-range small target is clear. The data processing display is connected with the trigger board by serial port control.
Owner:上海广电通信技术有限公司
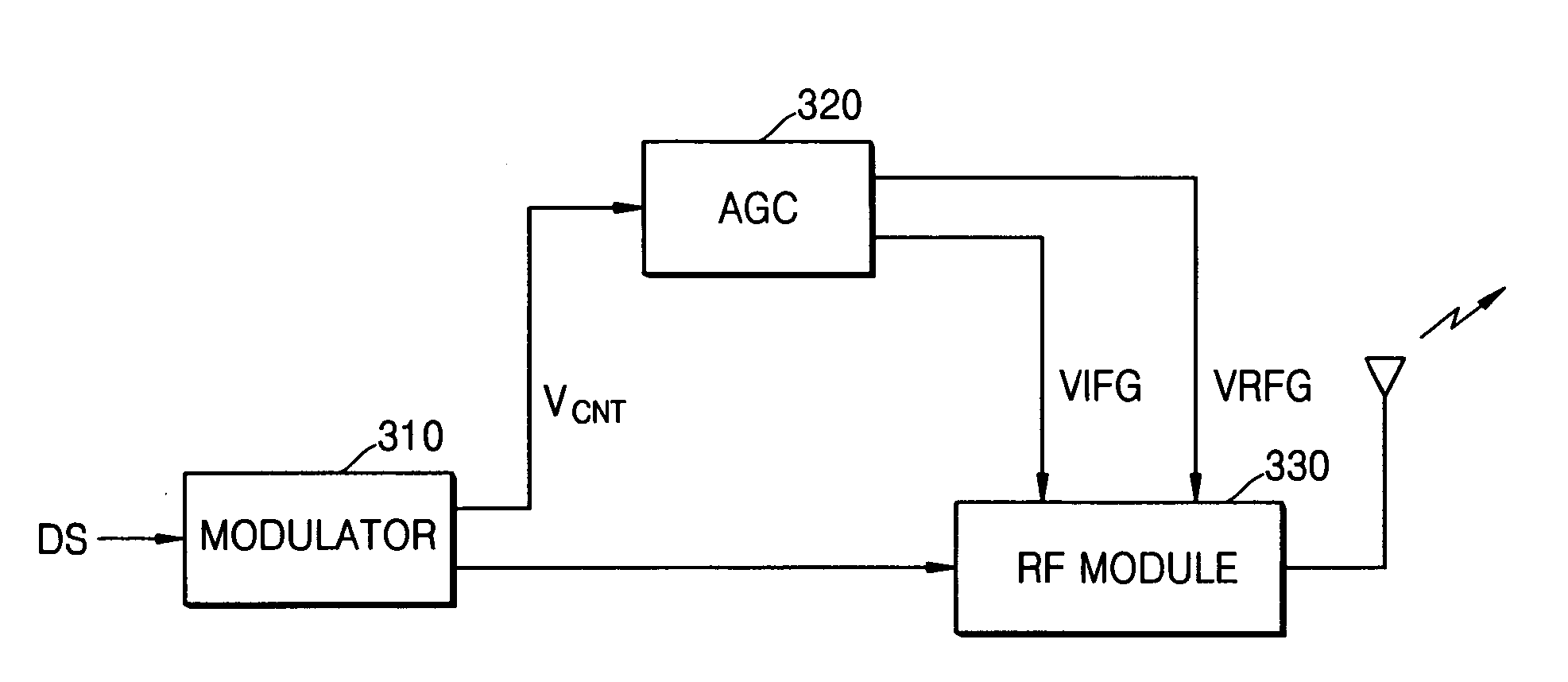
Automatic gain controller for achieving high signal-to-noise ratio and low power loss, and a transmitting apparatus and method for use with a mobile communication terminal having the automatic gain controller
InactiveUS7333782B2Energy efficient ICTPower managementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Radio frequency
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Three stage algorithm for automatic gain control in a receiver system
In an embodiment, a receiver for processing a RF input signal having a variable signal strength includes an RF amplifier, an IF amplifier, and a controller. The RF amplifier is configured to receive and amplify the RF input signal. The IF amplifier is coupled to an output of the RF amplifier. The controller controls gains of the RF amplifier and the IF amplifier during times of falling signal strength. A gain of the IF amplifier is increased as the signal strength falls until a first amplitude threshold is reached for the falling signal strength. If the signal strength falls beyond the first threshold, a gain of the RF amplifier is increased until a second amplitude threshold is reached. The second amplitude threshold is lower than the first amplitude threshold. If the signal strength falls below the second amplitude threshold, the gain of the IF amplifier is further increased.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
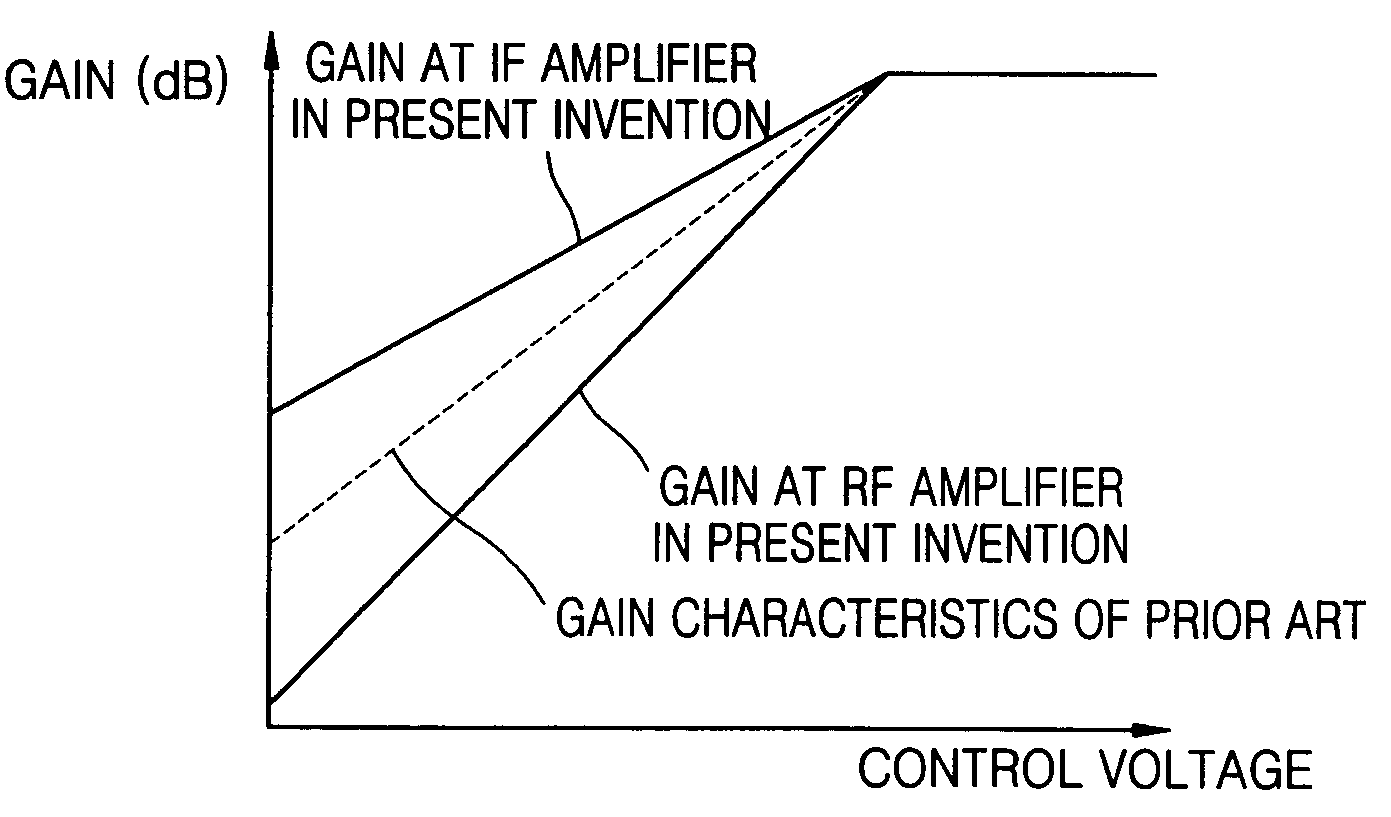
Automatic gain controller for achieving high signal-to-noise ratio and low power loss, and a transmitting apparatus and method for use with a mobile communication terminal having the automatic gain controller
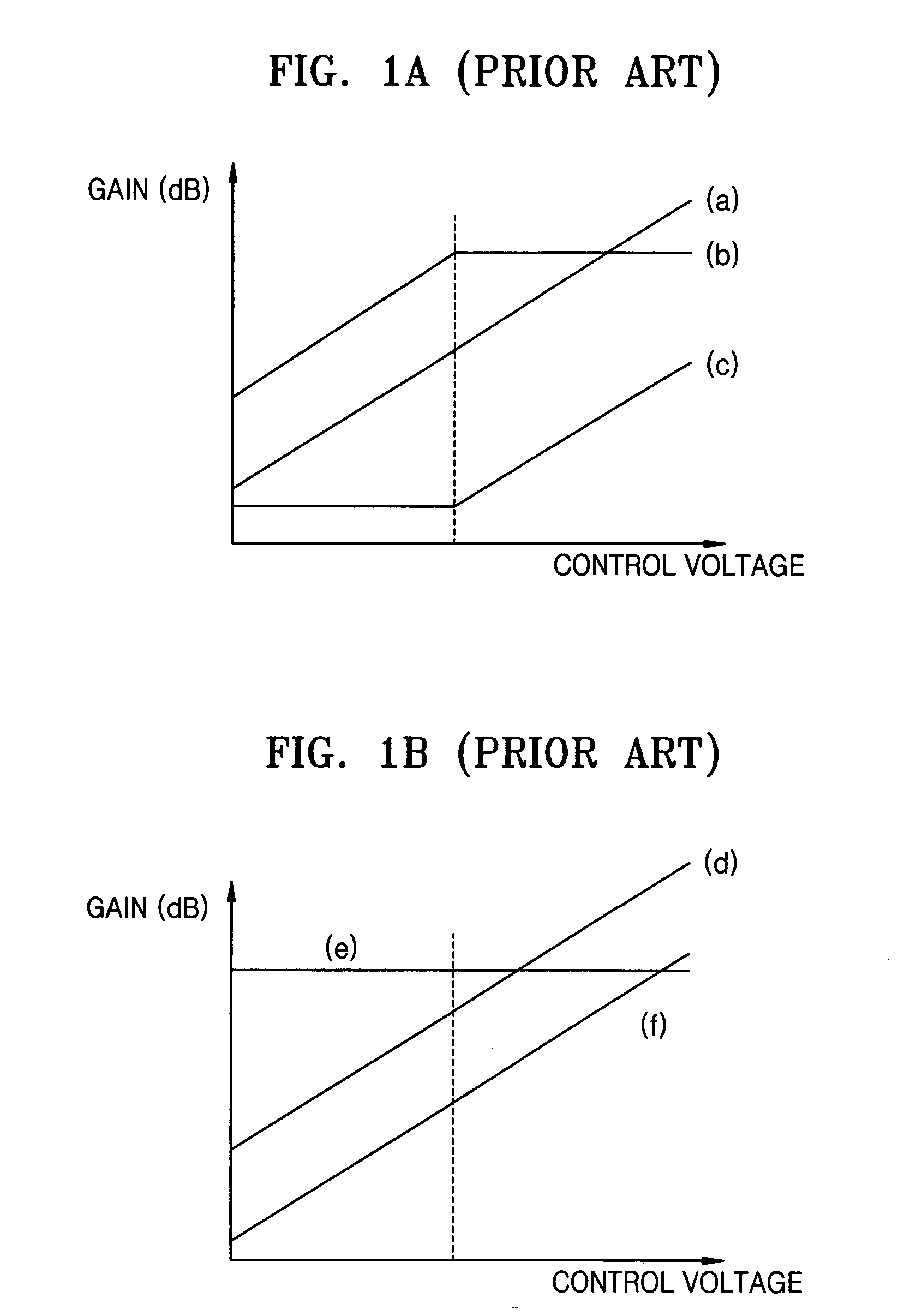
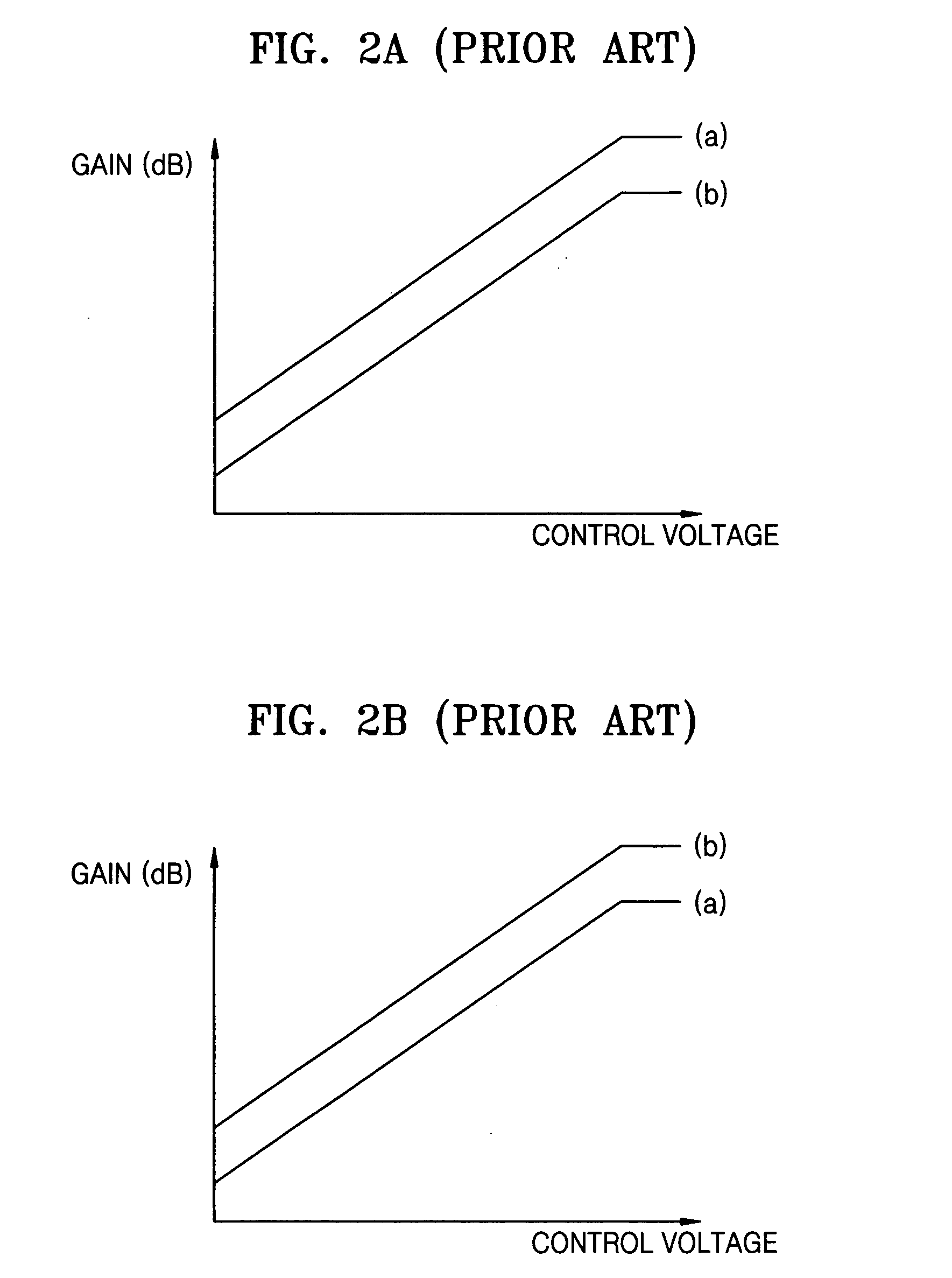
Provided is an automatic gain controller for obtaining a high a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and for reducing power loss by controlling a gain until the gain reaches a maximum value, and a transmitting apparatus and method for use with a mobile communication terminal having the automatic gain controller. The automatic gain controller causes a variation of a gain at a radio frequency (RF) amplifier with respect to the variation of a control voltage to have a larger gradient than a variation of gain at an intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier with respect to the variation of the control voltage, and causes a total gain to have a decreasing gradient in accordance with the control voltage until the total gain reaches its maximum. Therefore, a high SNR can be obtained by adjusting the gain at the IF amplifier to be larger than the gain at the RF amplifier at a power of, for example, -13 dBm, to obtain improved adjacent channel power rejection (ACPR) characteristics at a high power, and to reduce power loss by controlling gain so that the total gain has a decreasing gradient in accordance with the control voltage until the total gain reaches its maximum.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus for regulating automatic gain control voltage in diversity reception switch
InactiveCN101369838AImproved strength impactImprove working conditionSpatial transmit diversityAudio power amplifierSignal quality
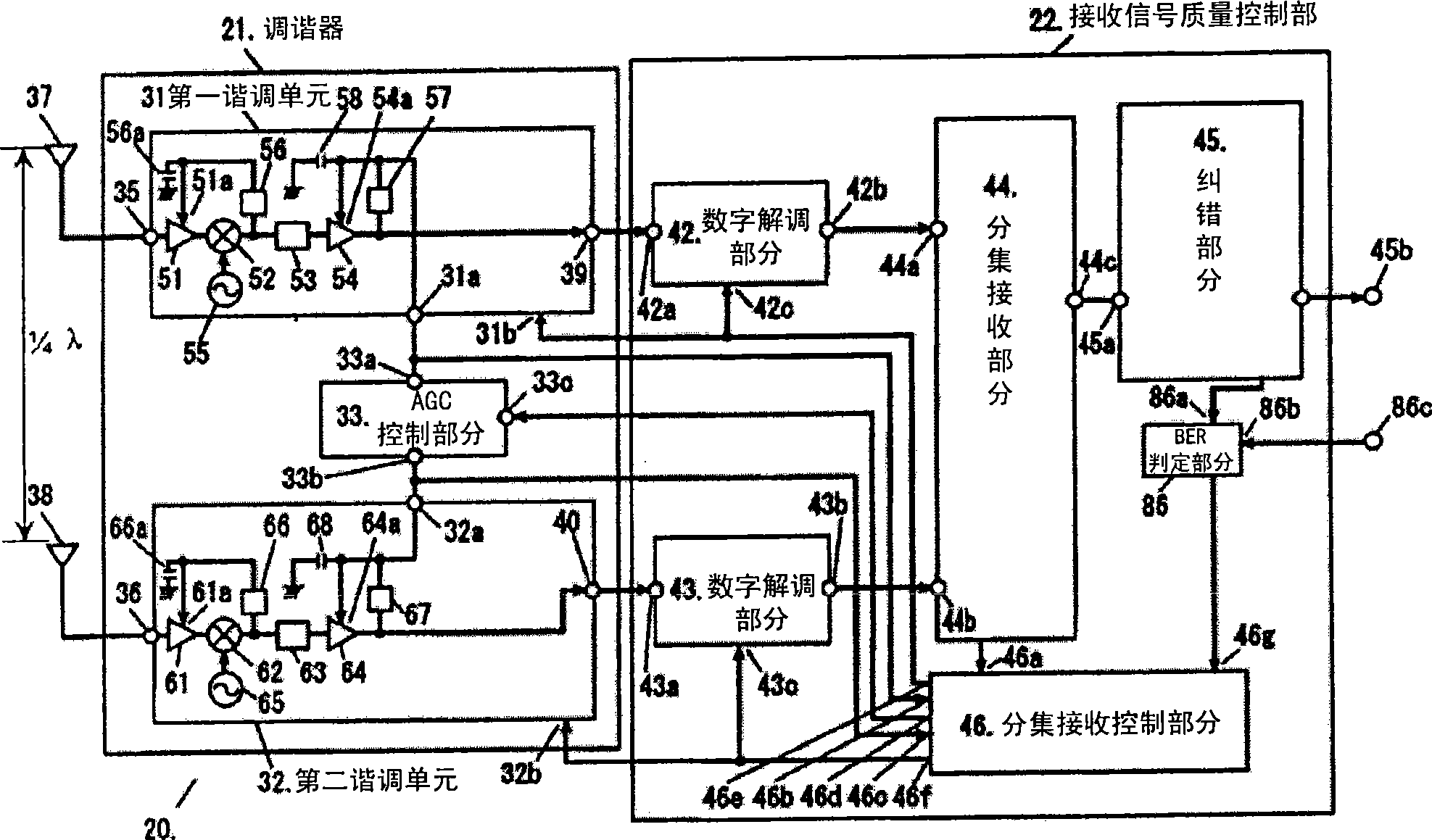
A diversity reception apparatus comprises a first tune unit for down-conversion of a received communication signal to an if signal and amplification of the if signal; a second tune unit for down-conversion of a received communication signal to an if signal and amplification of the if signal; a diversity reception control part for switching between a single reception mode and the diversity reception mode according to the received signal quality; and an automatic grain control part for controlling the control voltage supplied for if amplifiers in the first tune unit and the second tune unit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
RFID frequency conversion card reader and frequency sweeping and label reading method thereof
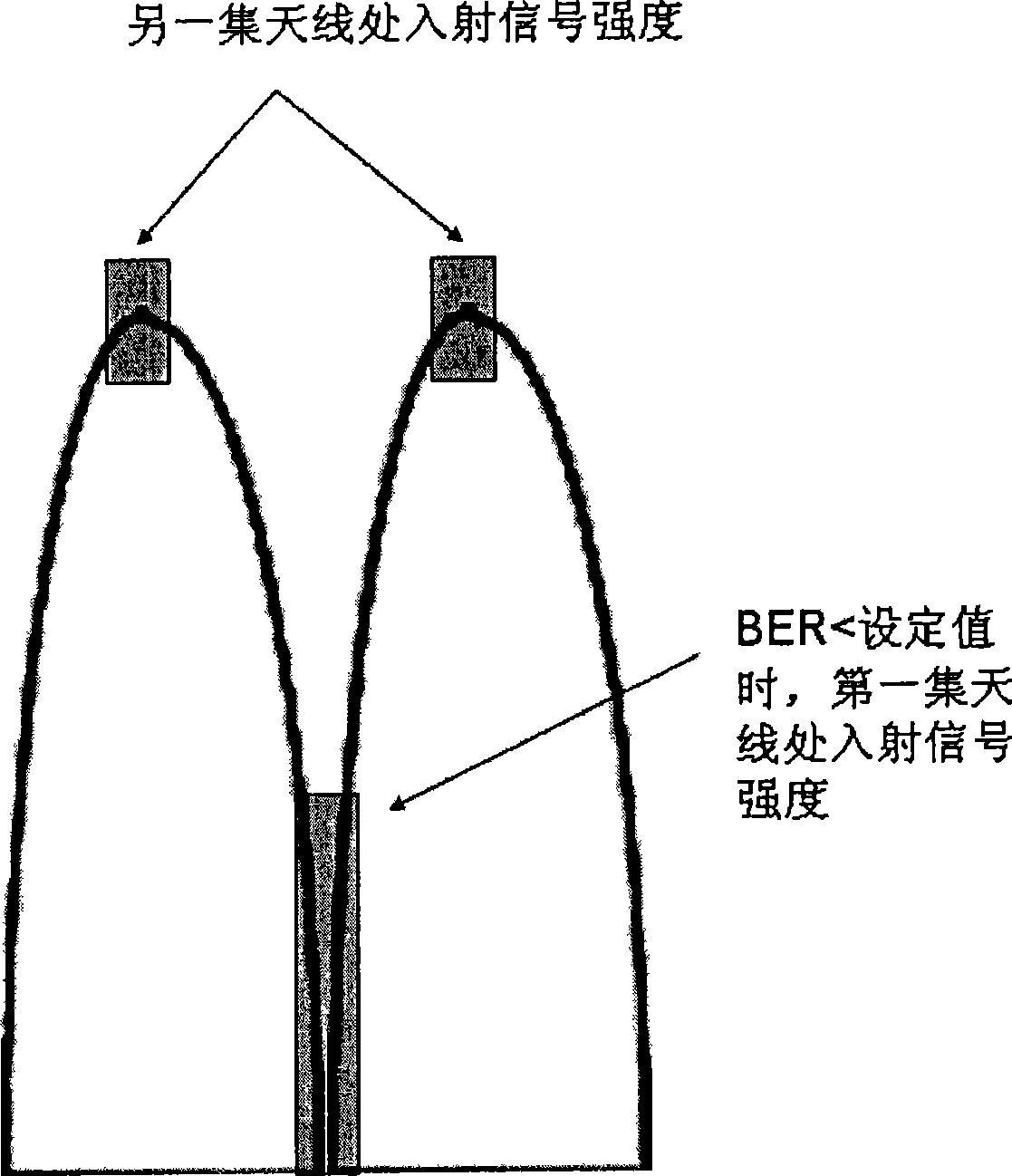
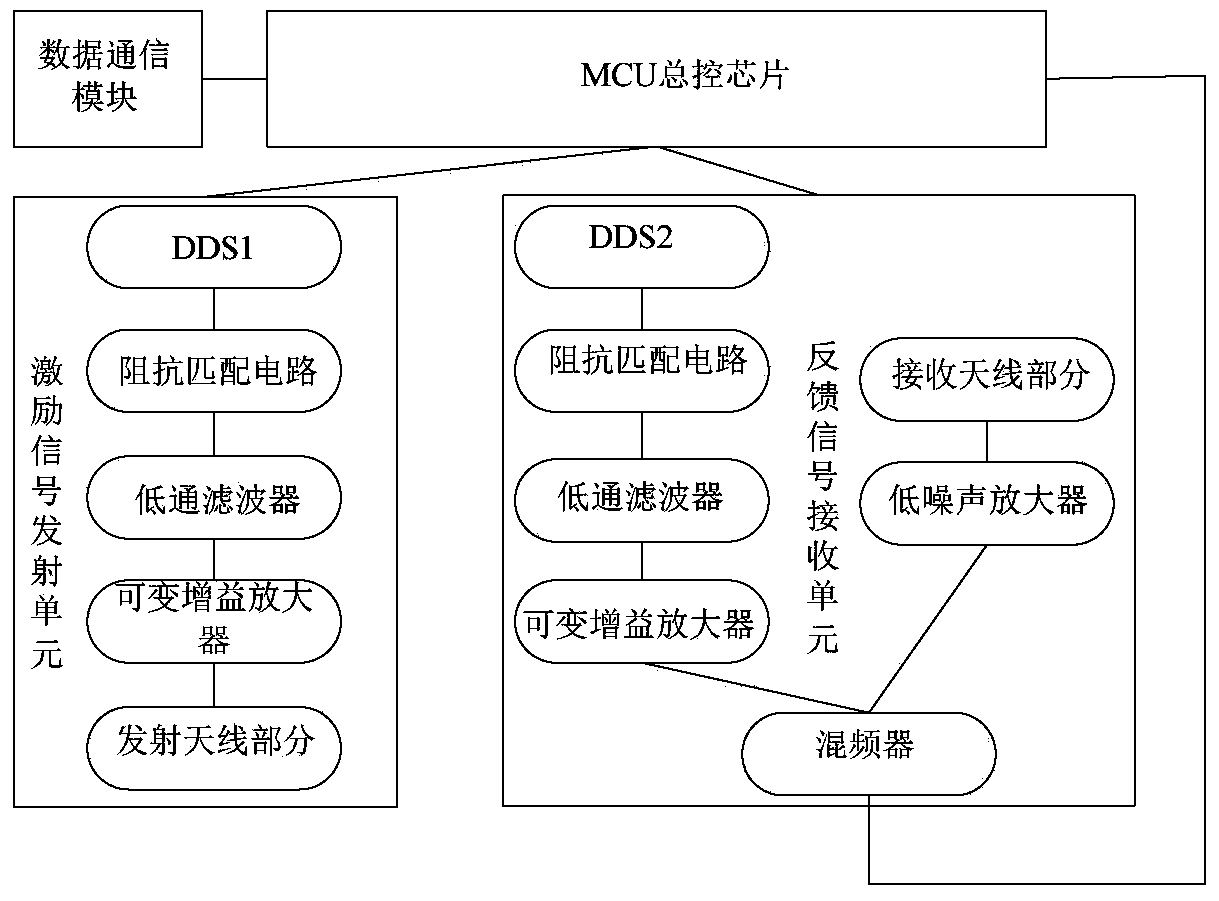
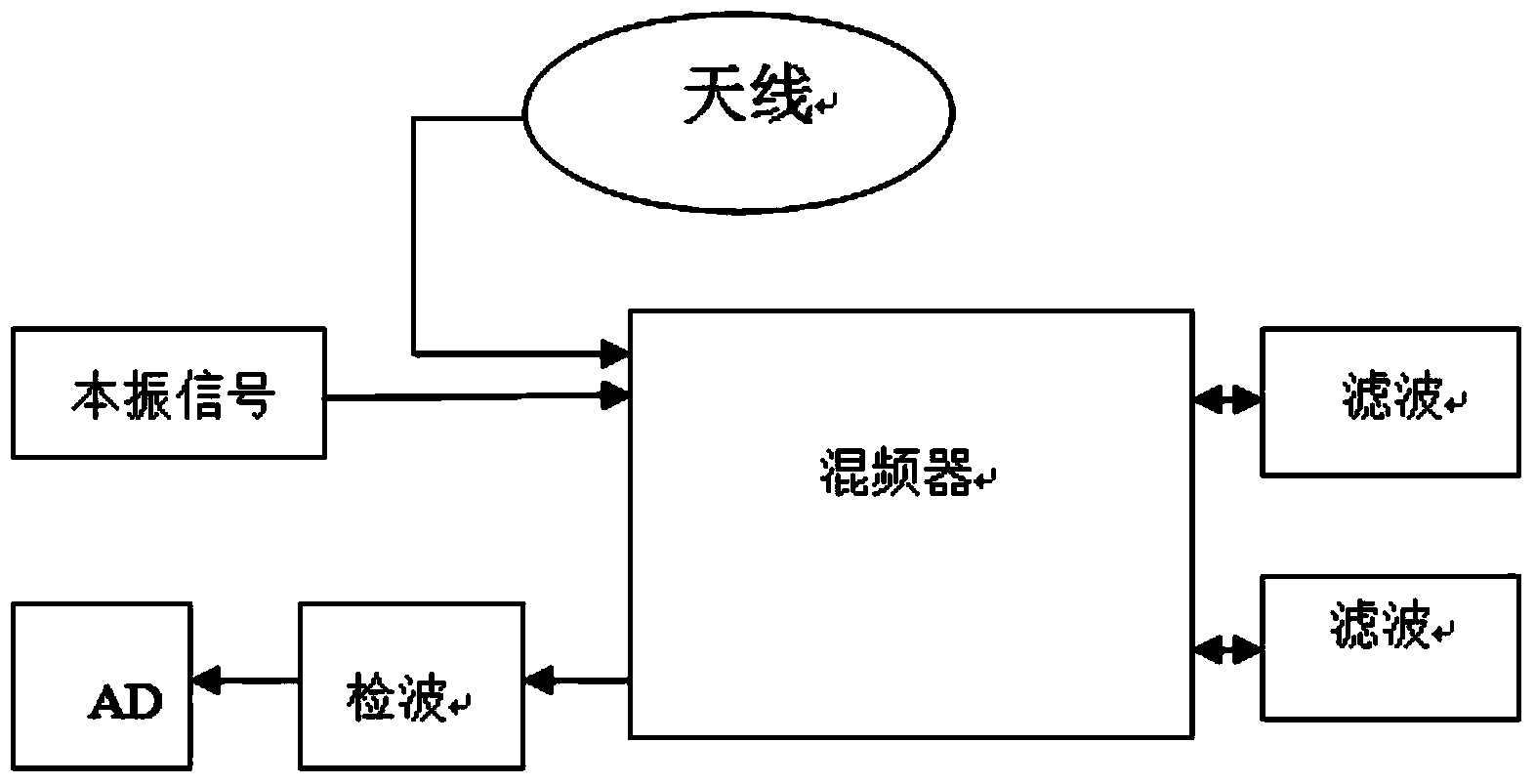
The invention discloses a RFID frequency conversion card reader and a frequency sweeping and label reading method of the RFID frequency conversion card reader. The card reader comprises an MCU master control chip, an excitation signal emission unit and a feedback signal receiving unit. The excitation signal emission unit comprises a direct digital synthesizer 1 (DDS1) connected with the MCU master control chip, an impedance matching circuit connected with the DDS1, a low-pass filter connected with the impedance matching circuit, a gain amplifier connected with the low-pass filter and a transmitting antenna part. The feedback signal receiving unit comprises a receiving antenna part, a differential signal source part, a mixer for receiving input signals and an intermediate frequency amplifier, wherein the differential signal source part is used for generating another path of mixer input signals, and the circuit structure generated by the input signals is the same as the circuit structure generated by signals of the excitation signal emission unit. By means of the novel RFID frequency conversion card reader, the labels of a VHF frequency band can be read, the information can be sent to a mobile terminal as well, and thus product information is stored and displayed.
Owner:睿芯(大连)股份有限公司
Wireless diversity receiving method
InactiveCN103647593AQuality improvementImprove signal qualitySpatial transmit diversityLow noisePacket loss
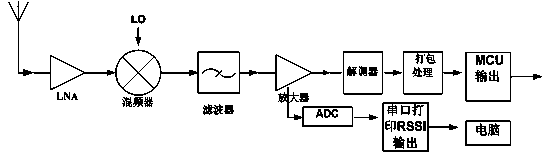
The invention discloses a wireless diversity receiving method. A receiving end uses two or more antennas to simultaneously receive signals of different paths. The signals of all the paths are respectively amplified by a low-noise amplifier, input to a frequency mixer, converted into intermediate-frequency signals through the frequency mixer and input to an intermediate-frequency amplifier, and the intermediate-frequency amplifier amplifies the intermediate-frequency signals and outputs the intermediate-frequency signals through two paths; one path of signals is input to a demodulator, data demodulated by the demodulator is packed and sent to a MCU selector; the other path of signals is input to an ADC to be converted into RSSI parameters; and RSSI data output through a plurality of paths is sent to a MCU comparator, the MCU comparator determines a path of signals with the best RSSI parameters through comparison, and the MCU selector selects packed data of the path of signals with the best RSSI parameters as signal output. The effect of signal fading is mitigated, the quality of signal transmission is improved, and the undesirable phenomena such as off-and-on voice and video and data packet loss in wireless communication are overcome.
Owner:SYSU HUADU IND SCI & TECH INST
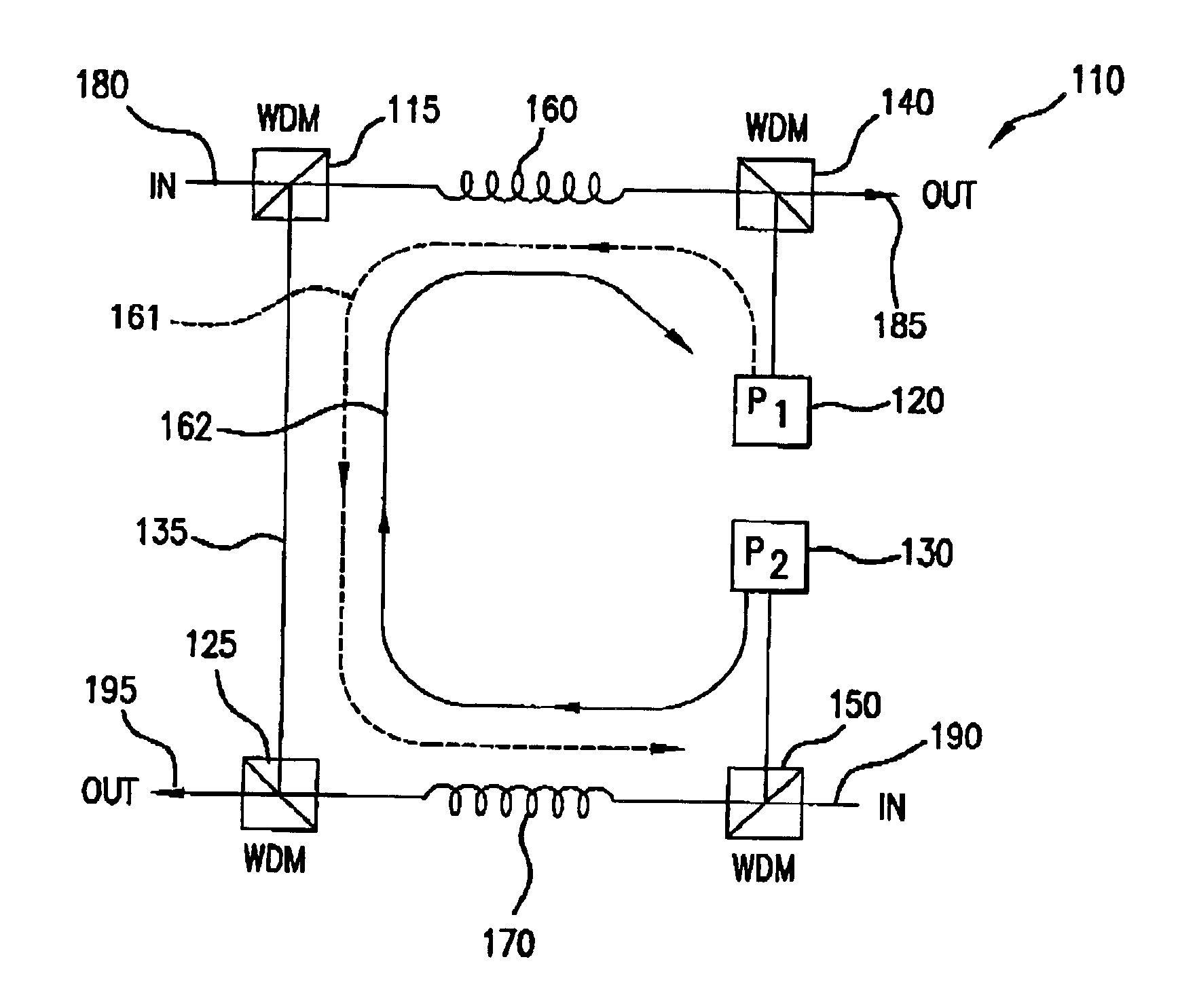
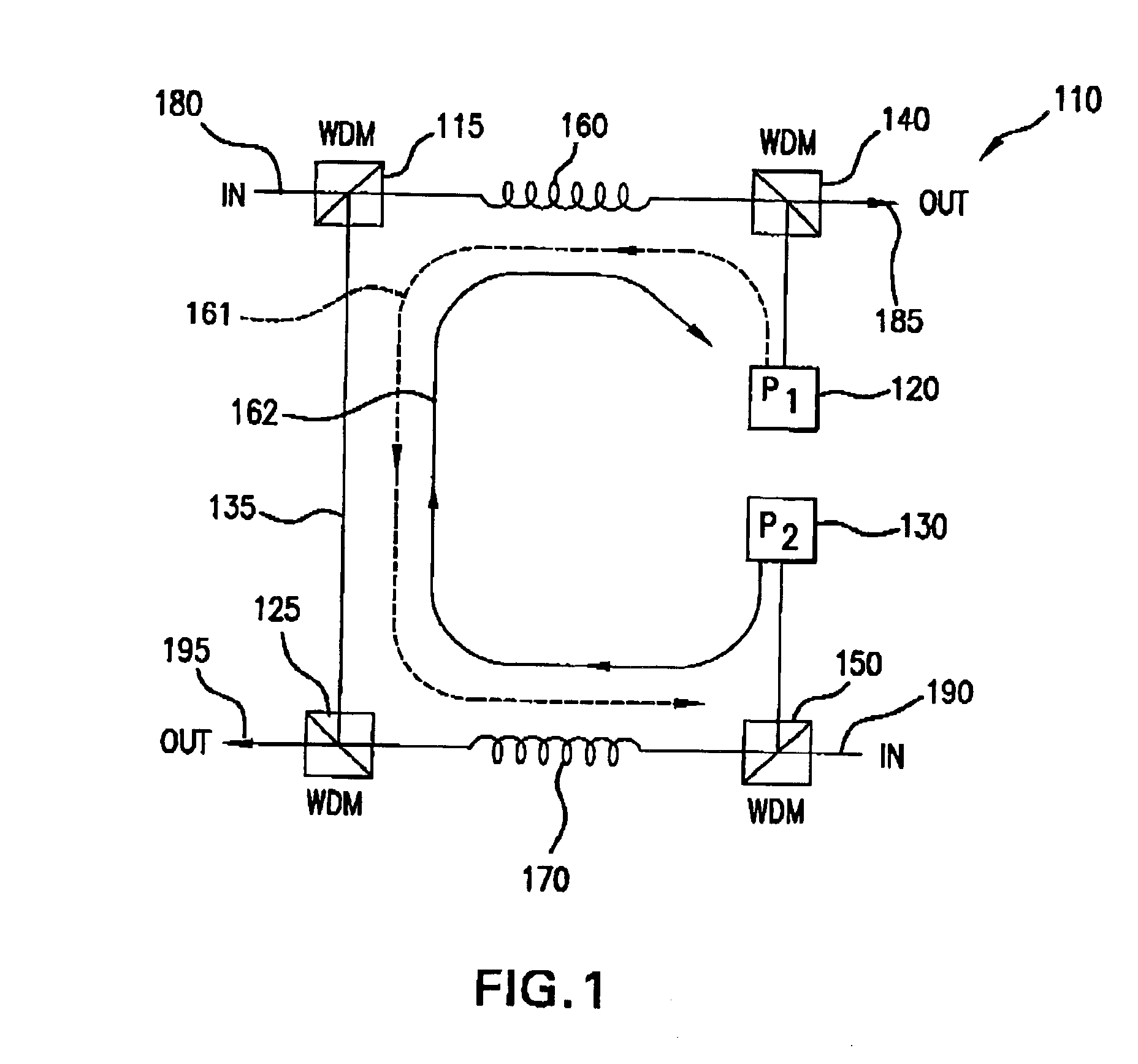
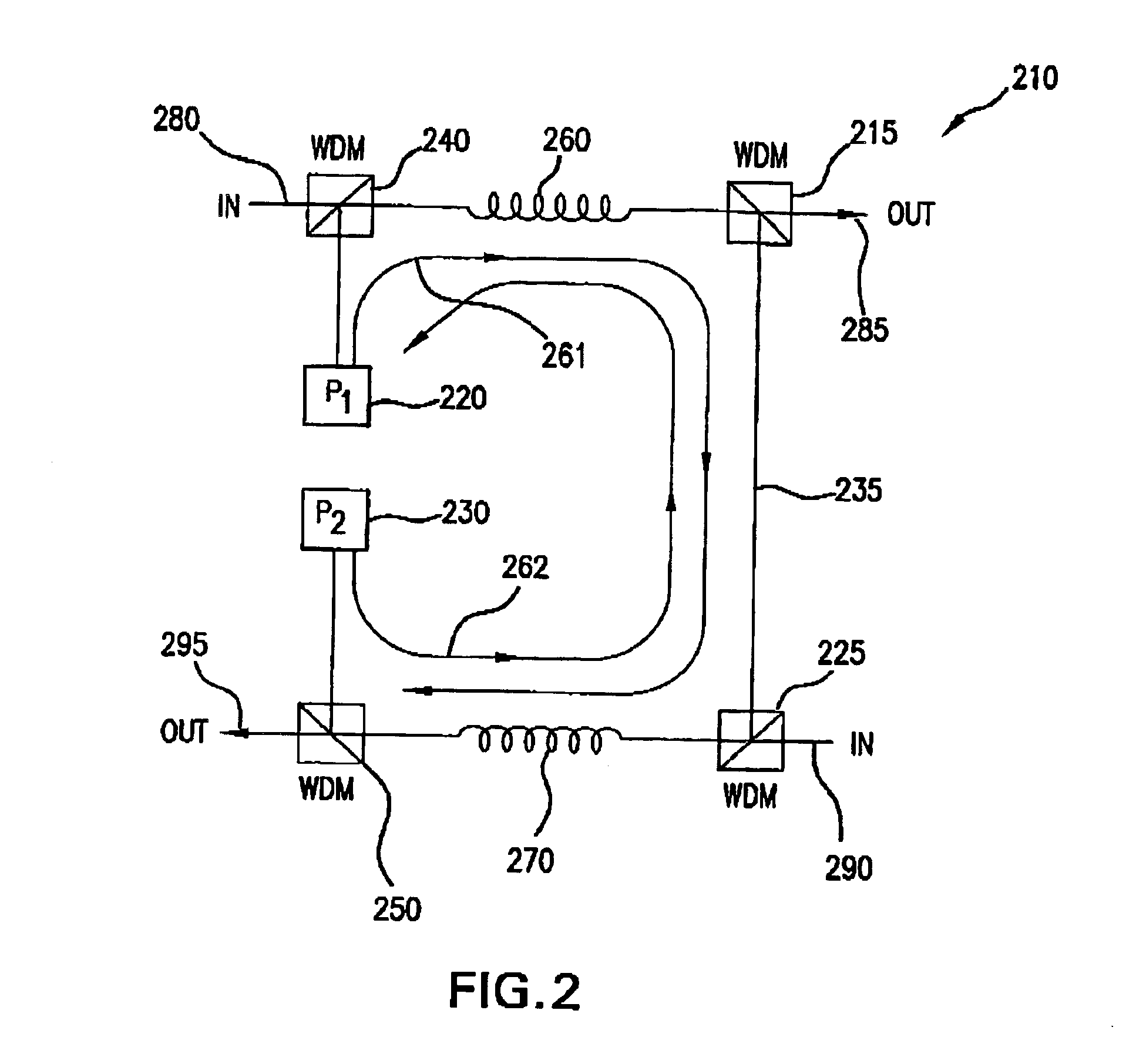
Fault tolerant optical amplifier configuration using pump feedthrough
A method and apparatus for amplifying optical transmission signals is described. A bi-directional amplifier utilizes a pump feed-through signal from one of the optical pumps used to pump a first amplifying fiber to provide pump power to a second amplifying fiber. If an optical pump within the amplifier fails, this feed-through signal is used to pump the amplifying fiber directly pumped by the failed pump source.
Owner:TYCO TELECOMM US
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com