Patents
Literature
3108 results about "Automatic gain control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Automatic gain control (AGC), is a closed-loop feedback regulating circuit in an amplifier or chain of amplifiers, the purpose of which is to maintain a suitable signal amplitude at its output, despite variation of the signal amplitude at the input. The average or peak output signal level is used to dynamically adjust the gain of the amplifiers, enabling the circuit to work satisfactorily with a greater range of input signal levels. It is used in most radio receivers to equalize the average volume (loudness) of different radio stations due to differences in received signal strength, as well as variations in a single station's radio signal due to fading. Without AGC the sound emitted from an AM radio receiver would vary to an extreme extent from a weak to a strong signal; the AGC effectively reduces the volume if the signal is strong and raises it when it is weaker. In a typical receiver the AGC feedback control signal is usually taken from the detector stage and applied to control the gain of the IF or RF amplifier stages.
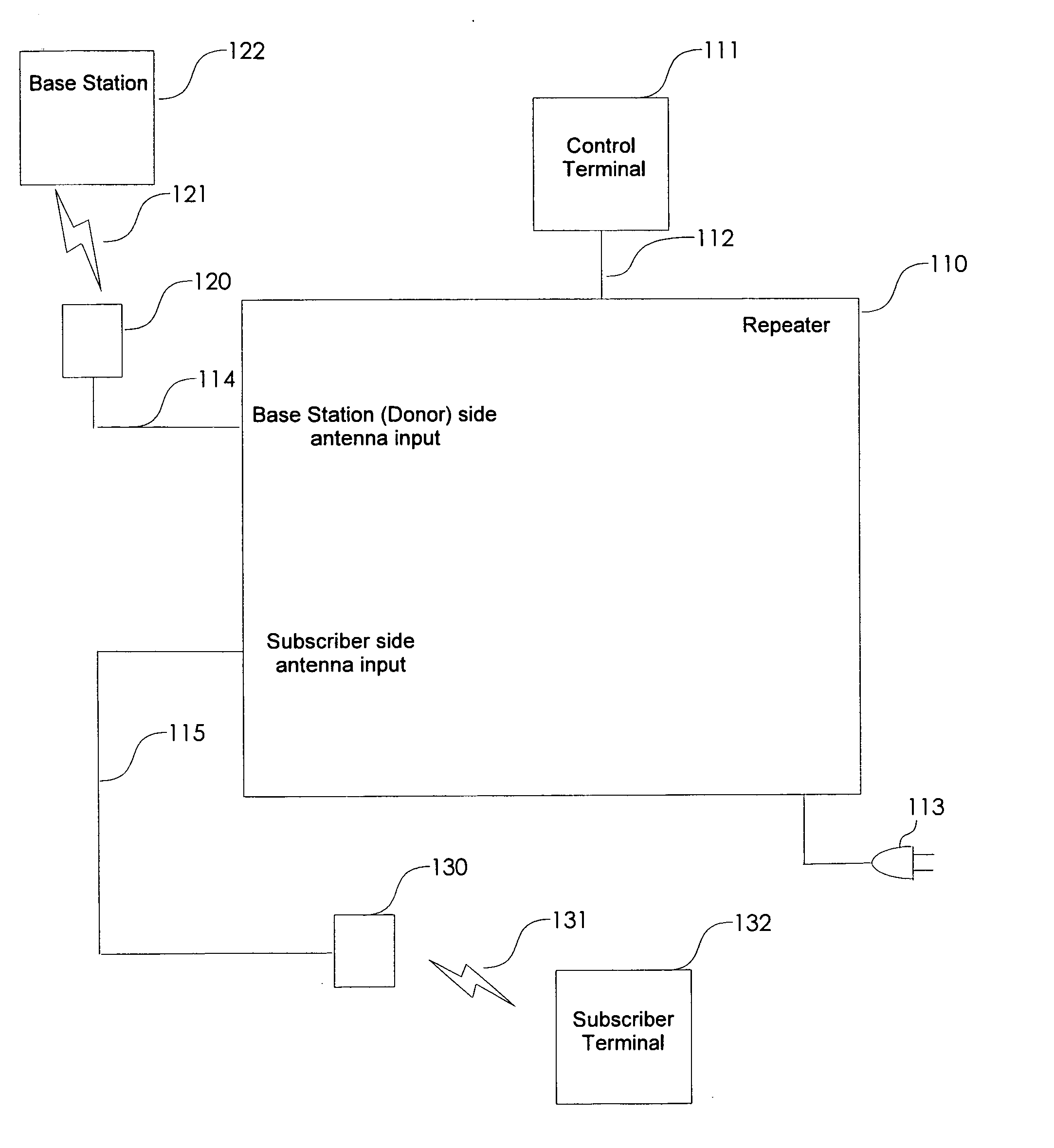
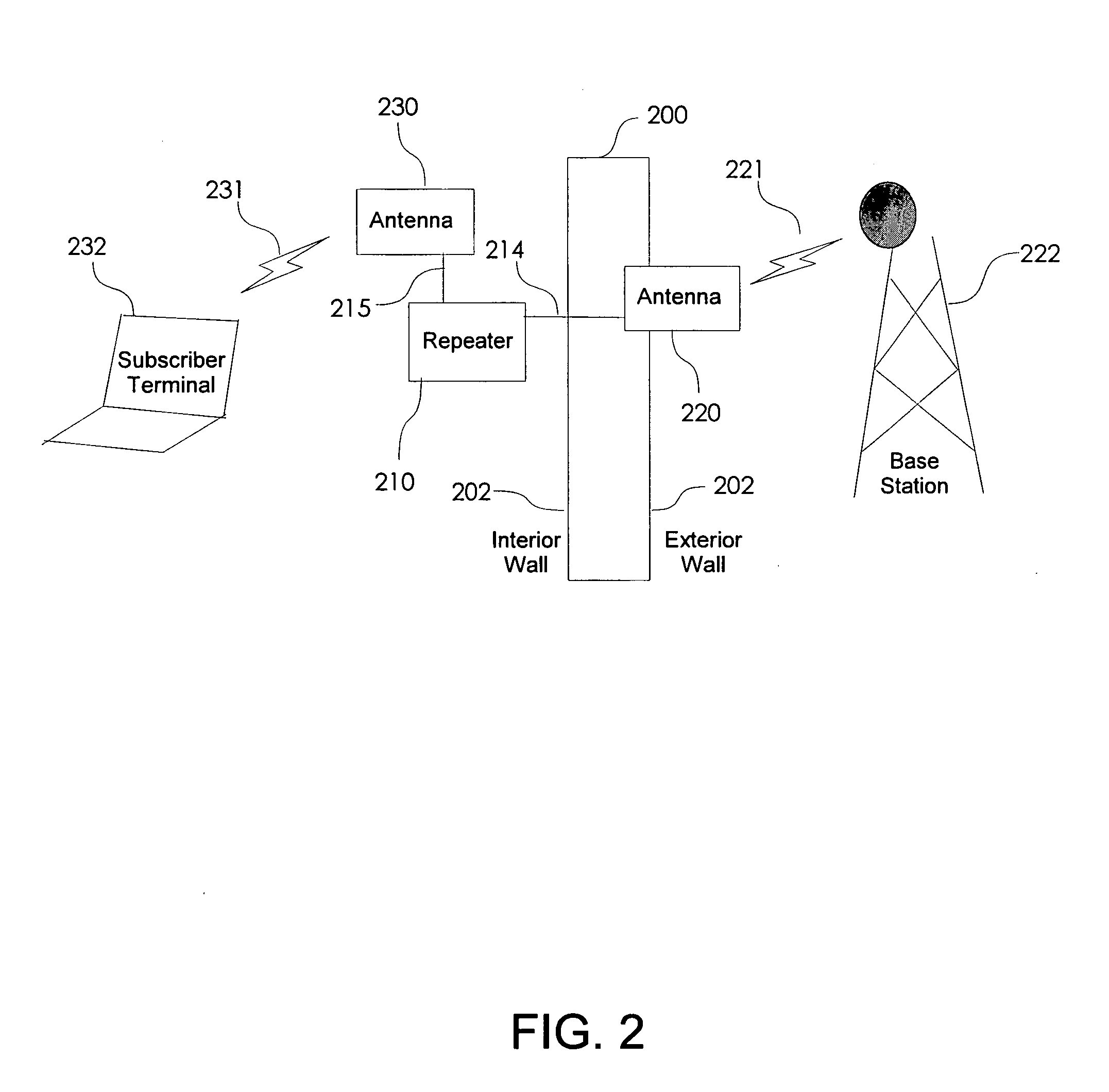
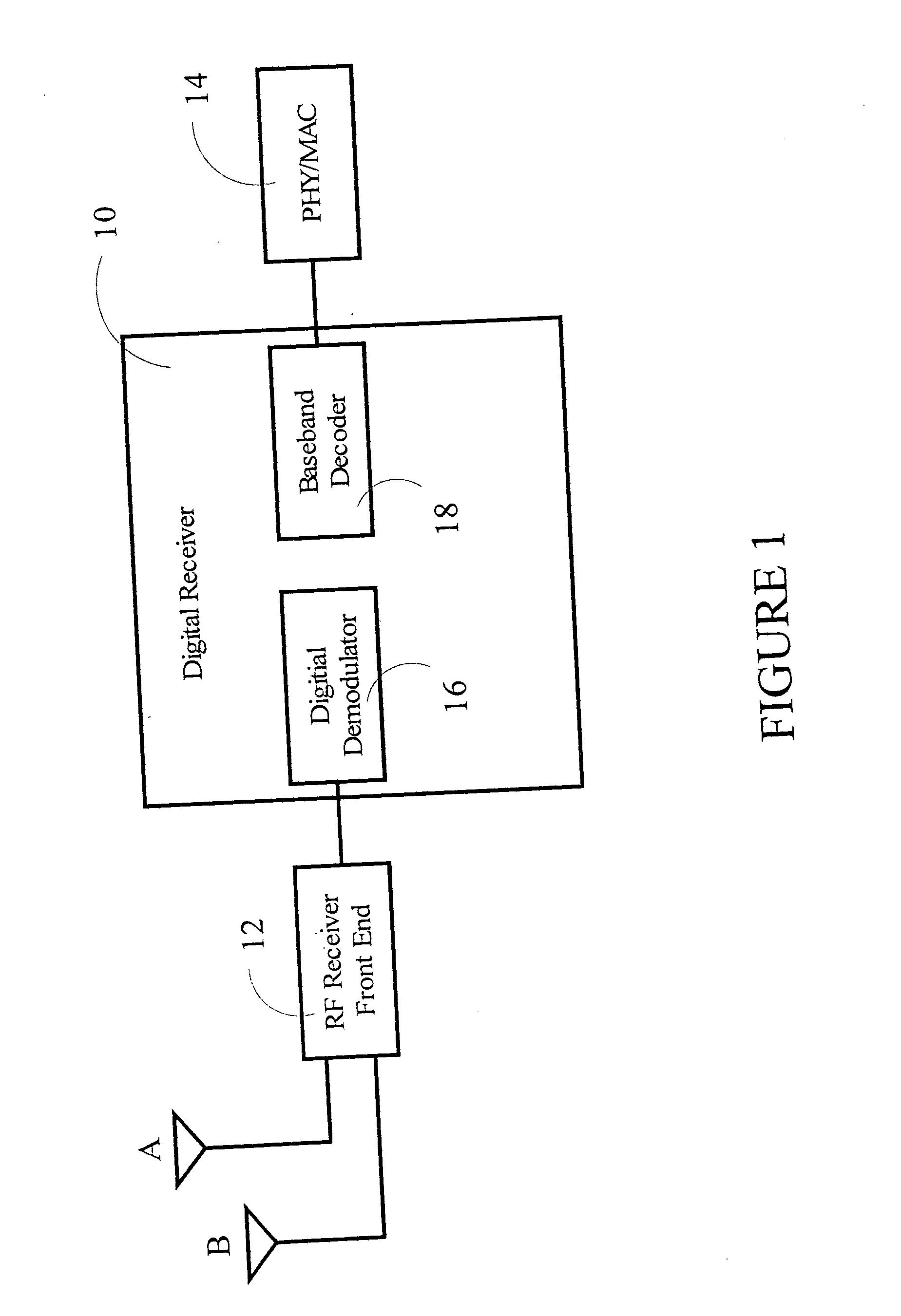
Non-frequency translating repeater with detection and media access control
A non-frequency translating repeater (110, 210, 300) for use in a time division duplex (TDD) radio protocol communications system includes detection retransmission and automatic gain control. Detection is performed by detectors (309, 310) and a processor (313). Detection can be overridden by processor (313) using logic elements (314). Antennae (220, 230) having various form factors can be used to couple a base station (222) to a subscriber terminal (232) which can be located in a sub-optimal location such as deep inside a building or the like.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
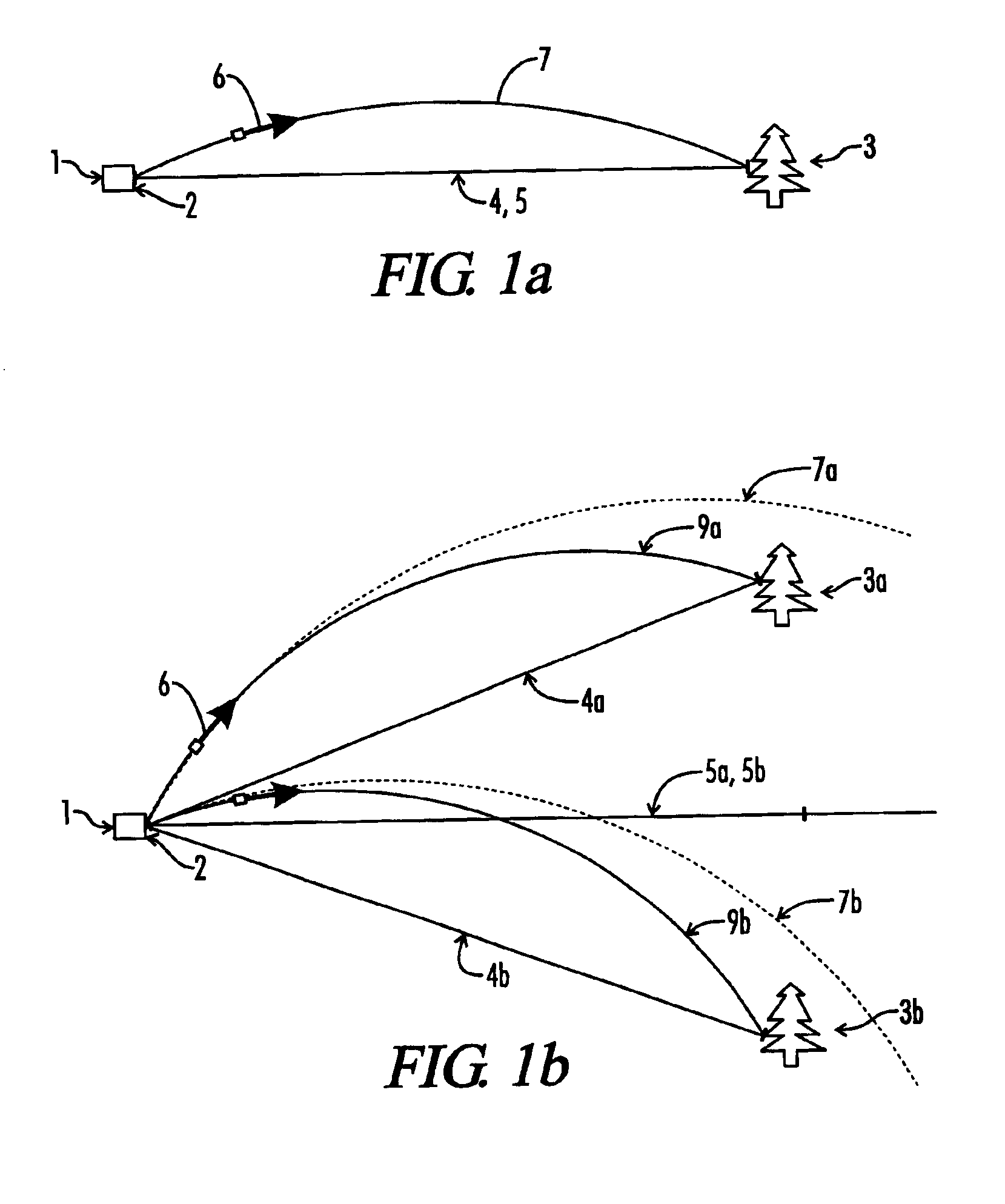
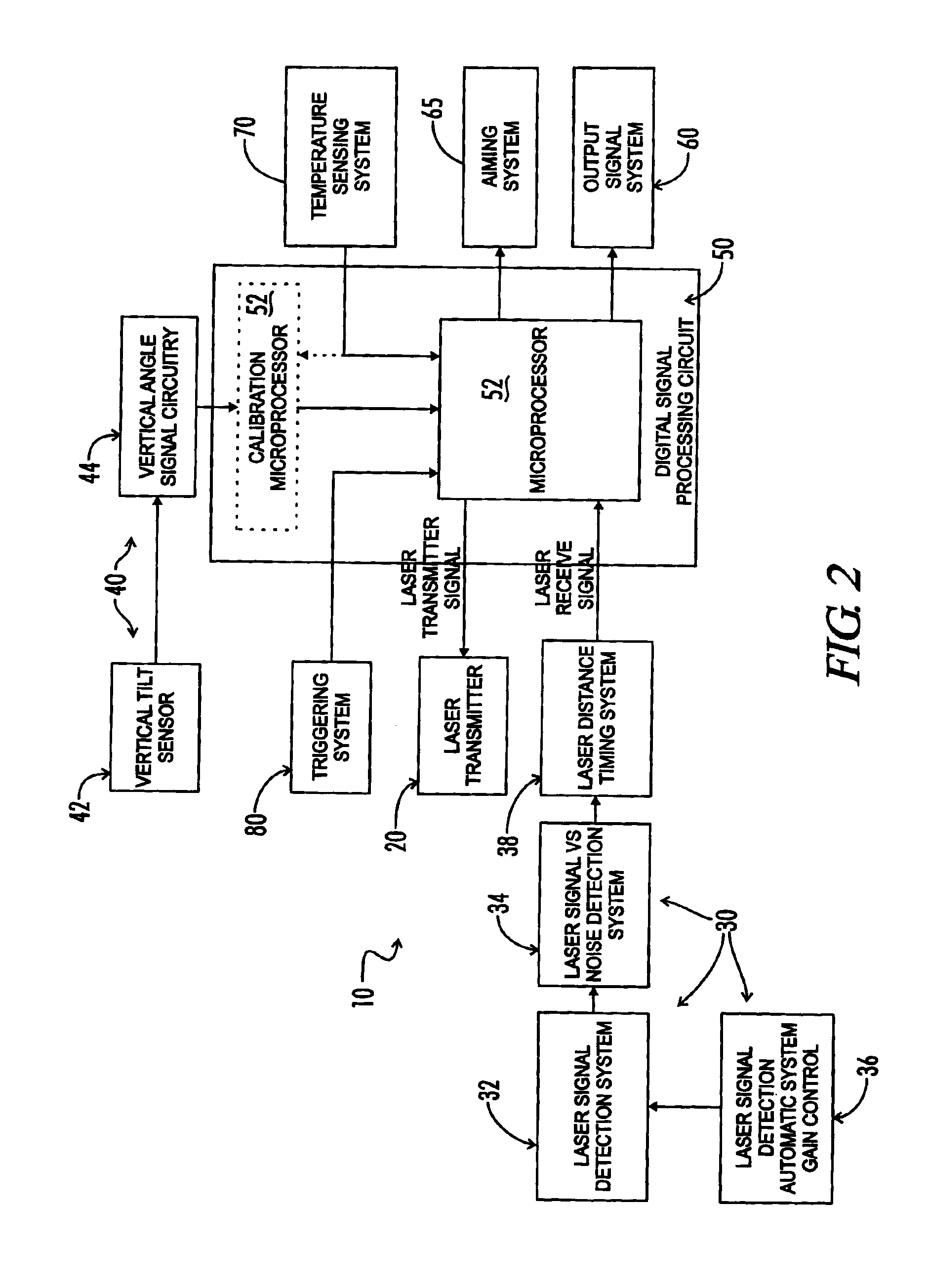
Tilt-compensated laser rangefinder
InactiveUS6873406B1Minimize impactError minimizationAngle measurementOptical rangefindersDigital signal processingInternal temperature
The present invention is a laser ranging device that incorporates an internal tilt sensor, an internal temperature sensor, and an internal pressure sensor. The tilt sensor is used to measure the target's vertical angle relative to the horizontal reference plane. Digital signal processing circuitry controls the firing of the laser pulse, calculation of time-of-flight range, measurement of the vertical angle of the tilt sensor, measurement of ambient temperature and storage of tilt sensor and temperature sensor calibration data. The digital signal processing circuitry then provides the user temperature corrected ballistic ranging information, including horizontal range. Additionally, an automatic gain control system minimizes the effects of target to target variance in reflectivity and its associated errors. It is also an object of this invention to electronically minimize errors in the measurement of a vertical angle caused by housing vibration and by temperature variance errors.
Owner:OPTI LOGIC CORP
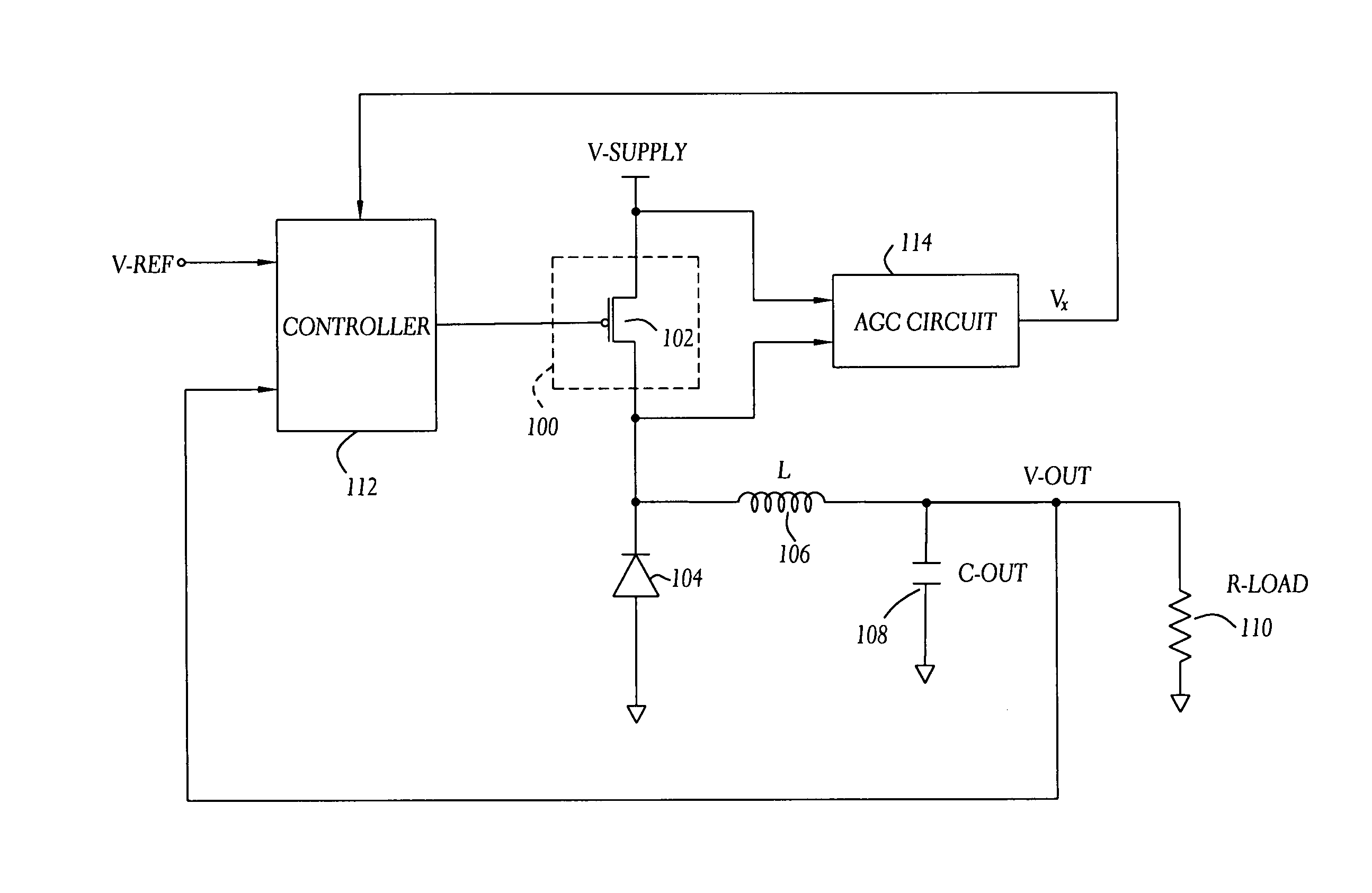
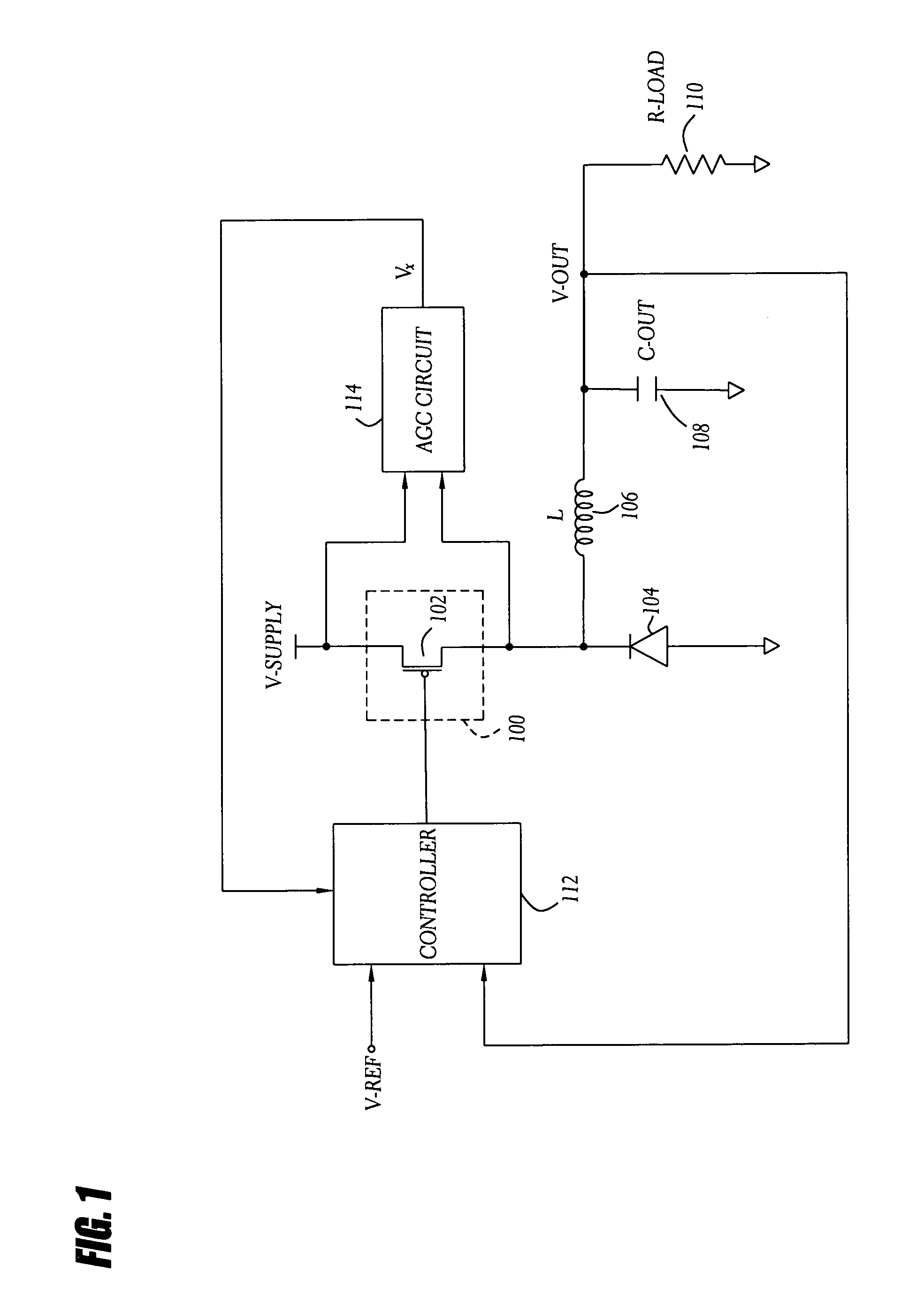
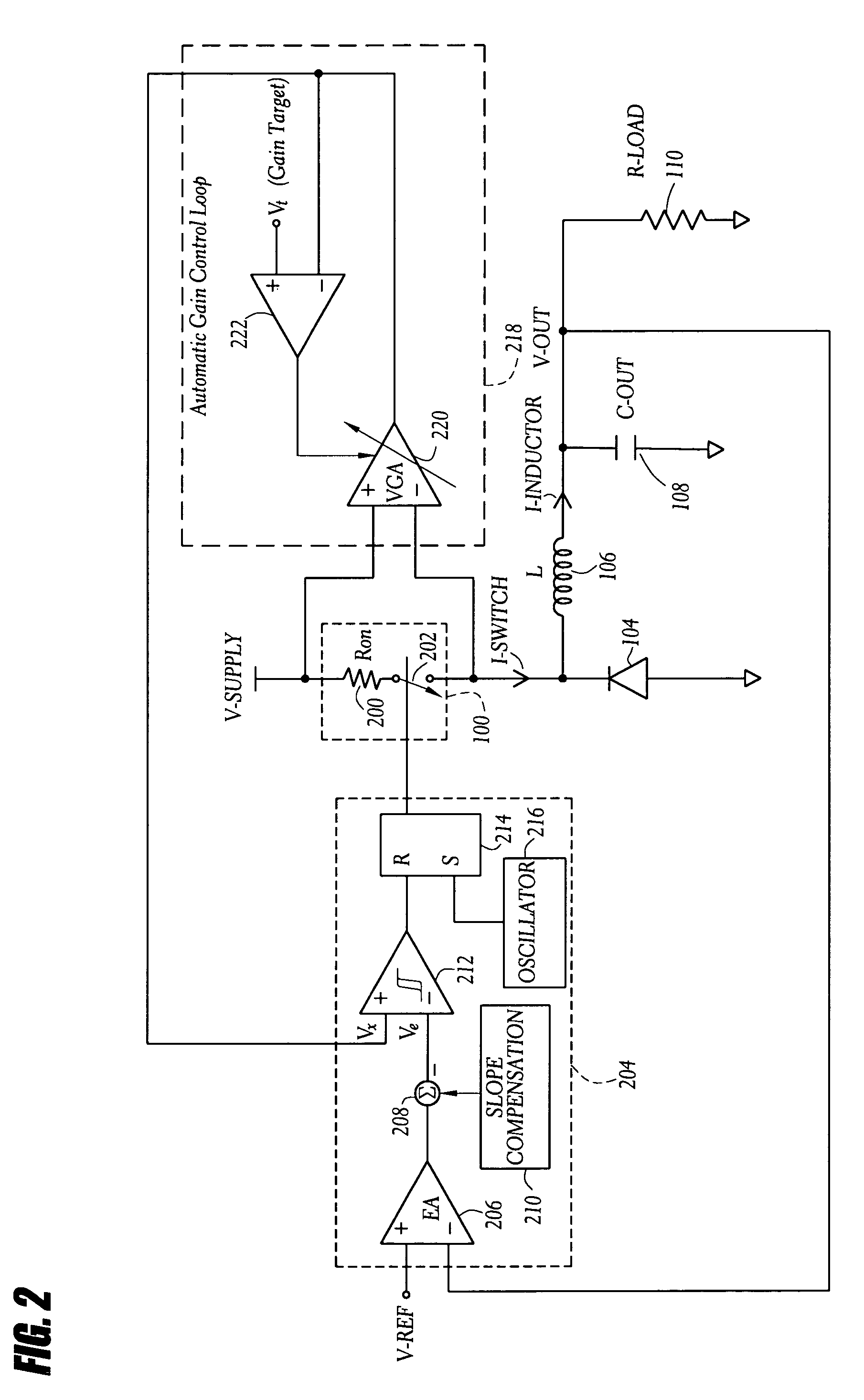
Automatic gain control technique for current monitoring in current-mode switching regulators
InactiveUS7919952B1Reduce component count and circuit board sizeFacilitates efficient and reliable monitoringDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringCurrent mode
A current-mode switching regulator uses adaptive current sensing to reliably monitor an inductor current in a cost-efficient and power-efficient manner. A semiconductor switch periodically turns on to conduct the inductor current. A voltage drop across the semiconductor switch is monitored when the semiconductor switch is on. A variable gain amplifier with an automatic gain control loop generates a feedback signal from the voltage drop of the semiconductor switch when conducting to provide an indication of the inductor current to a controller. The automatic gain control loop compensates for any variations in the on-resistance of the semiconductor switch.
Owner:MICROSEMI
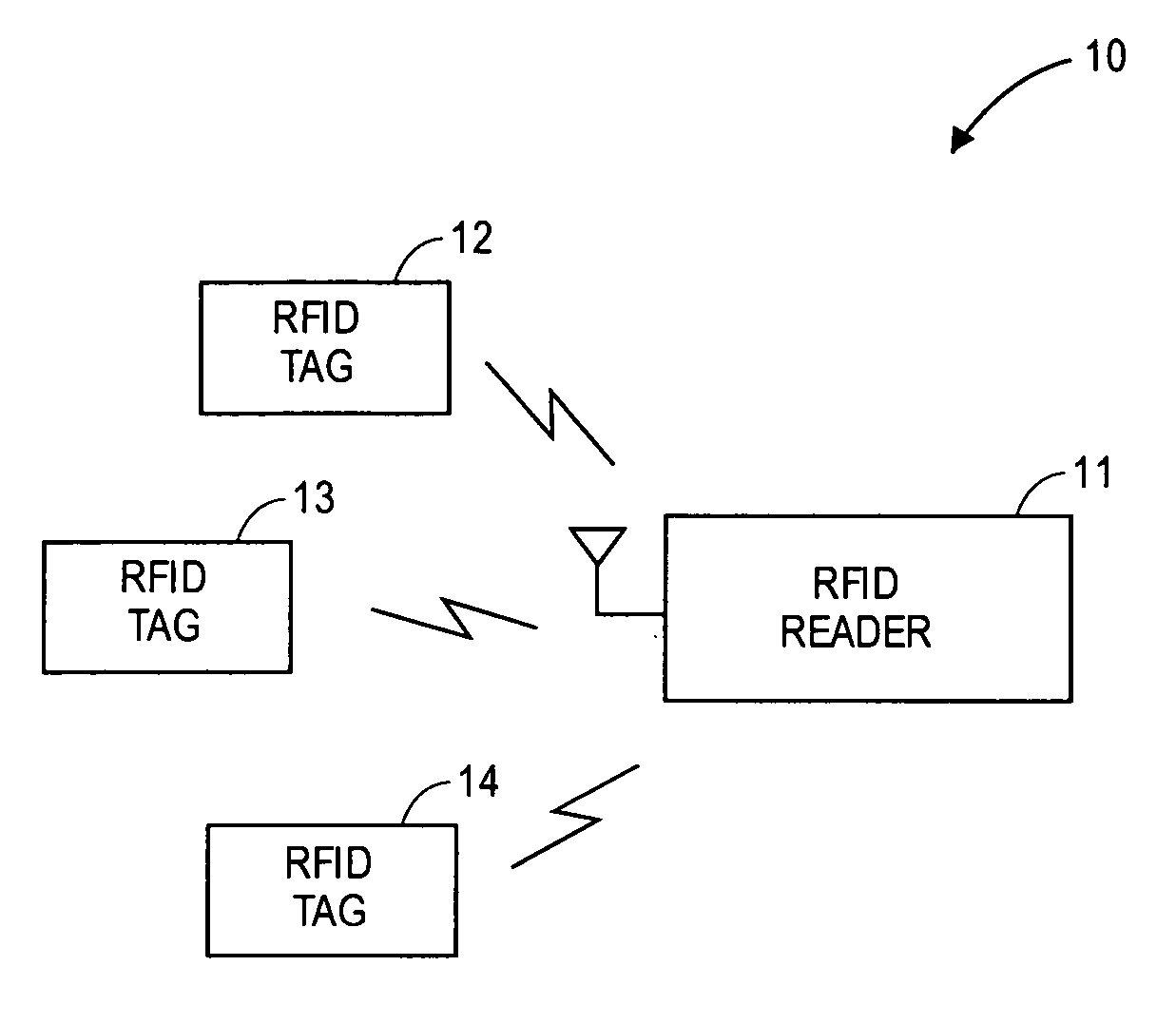
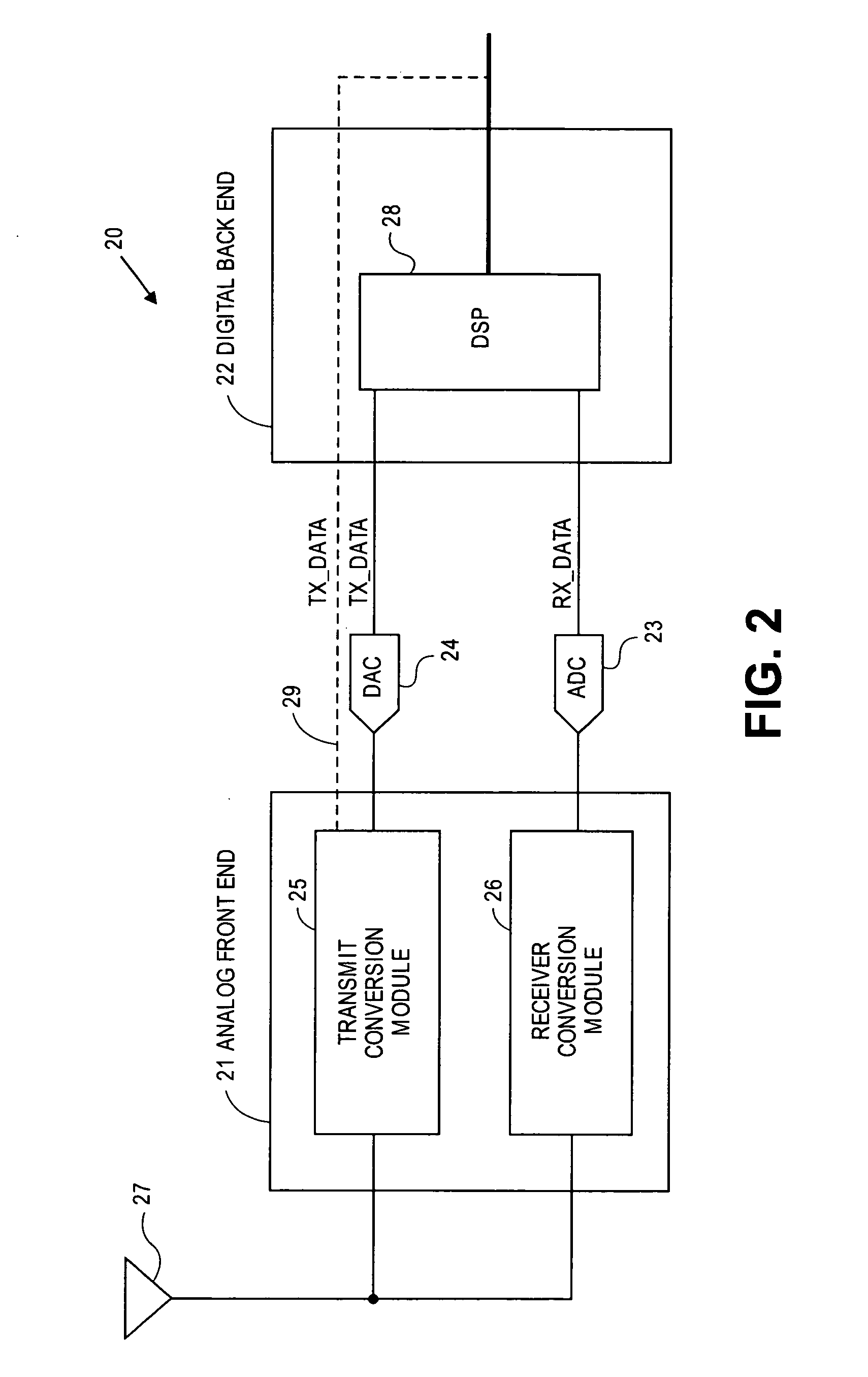
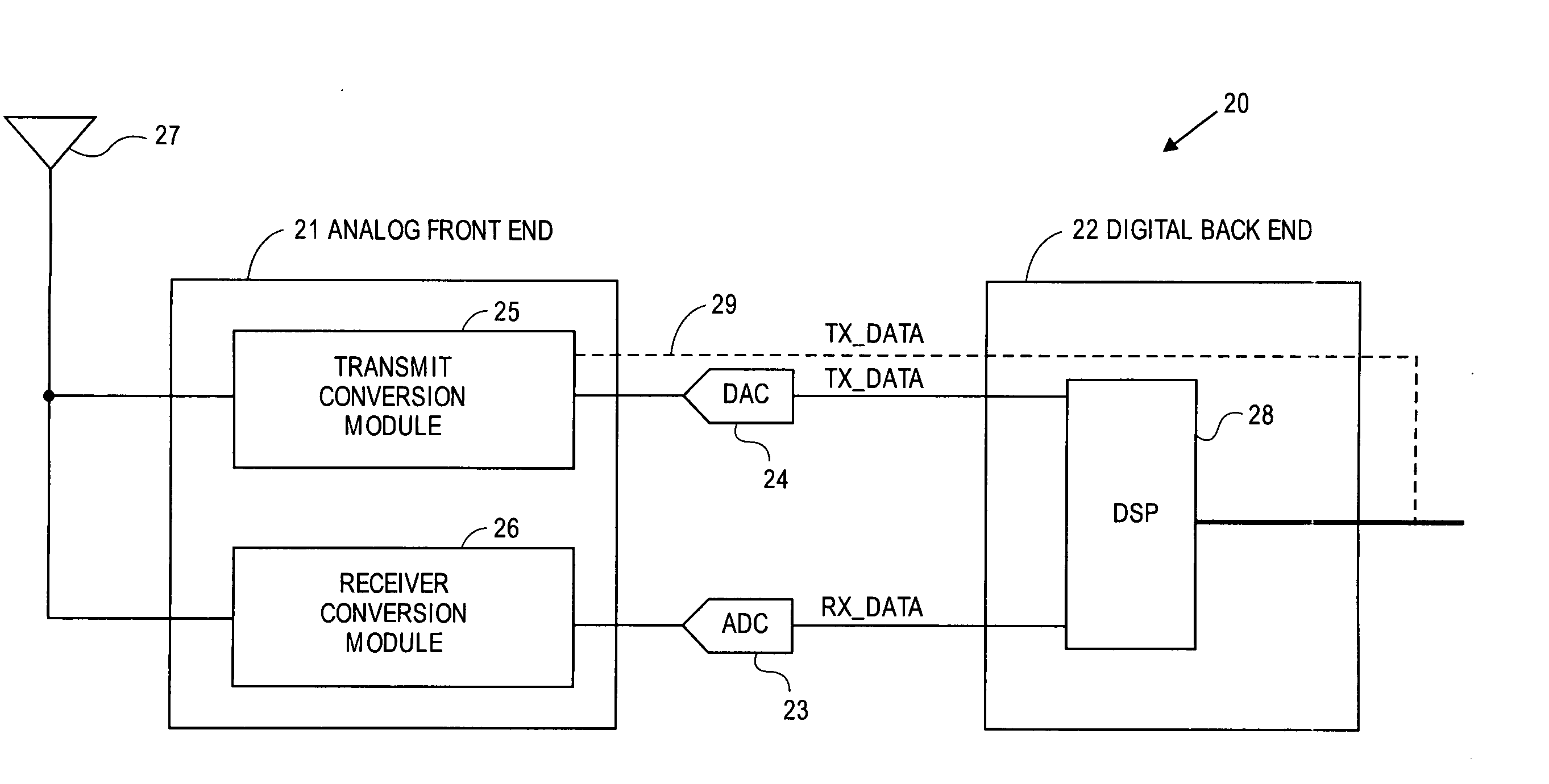
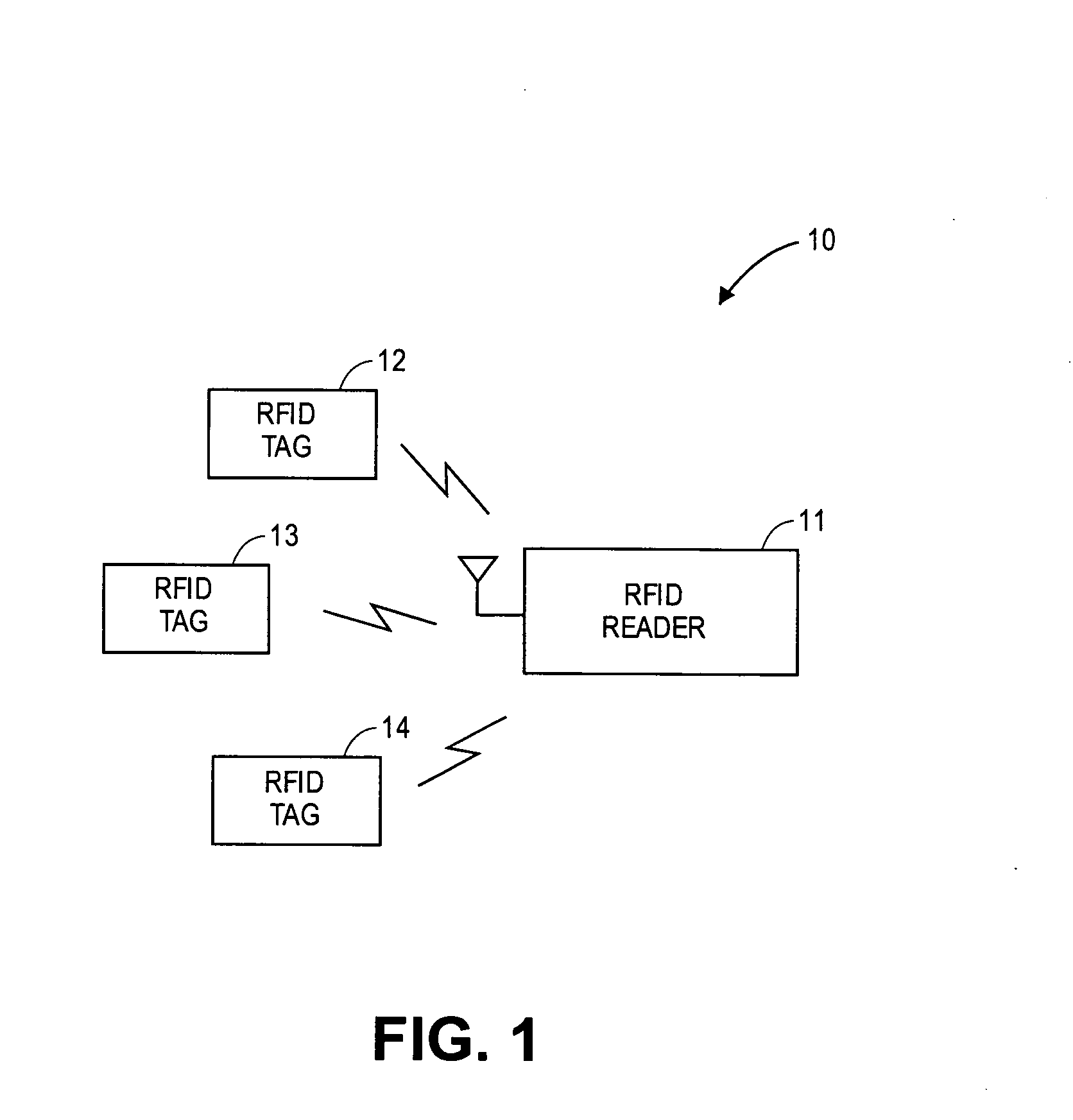
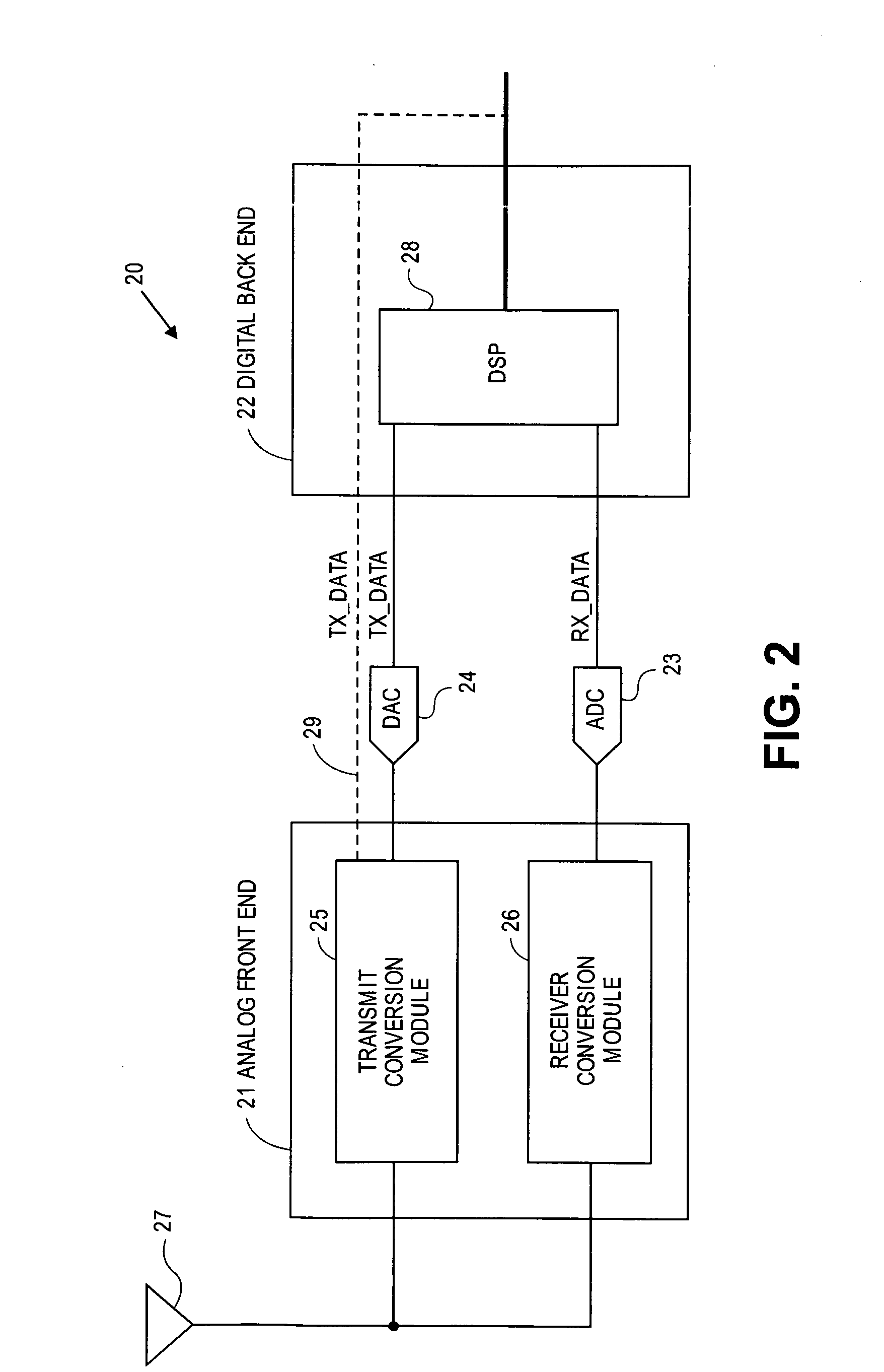
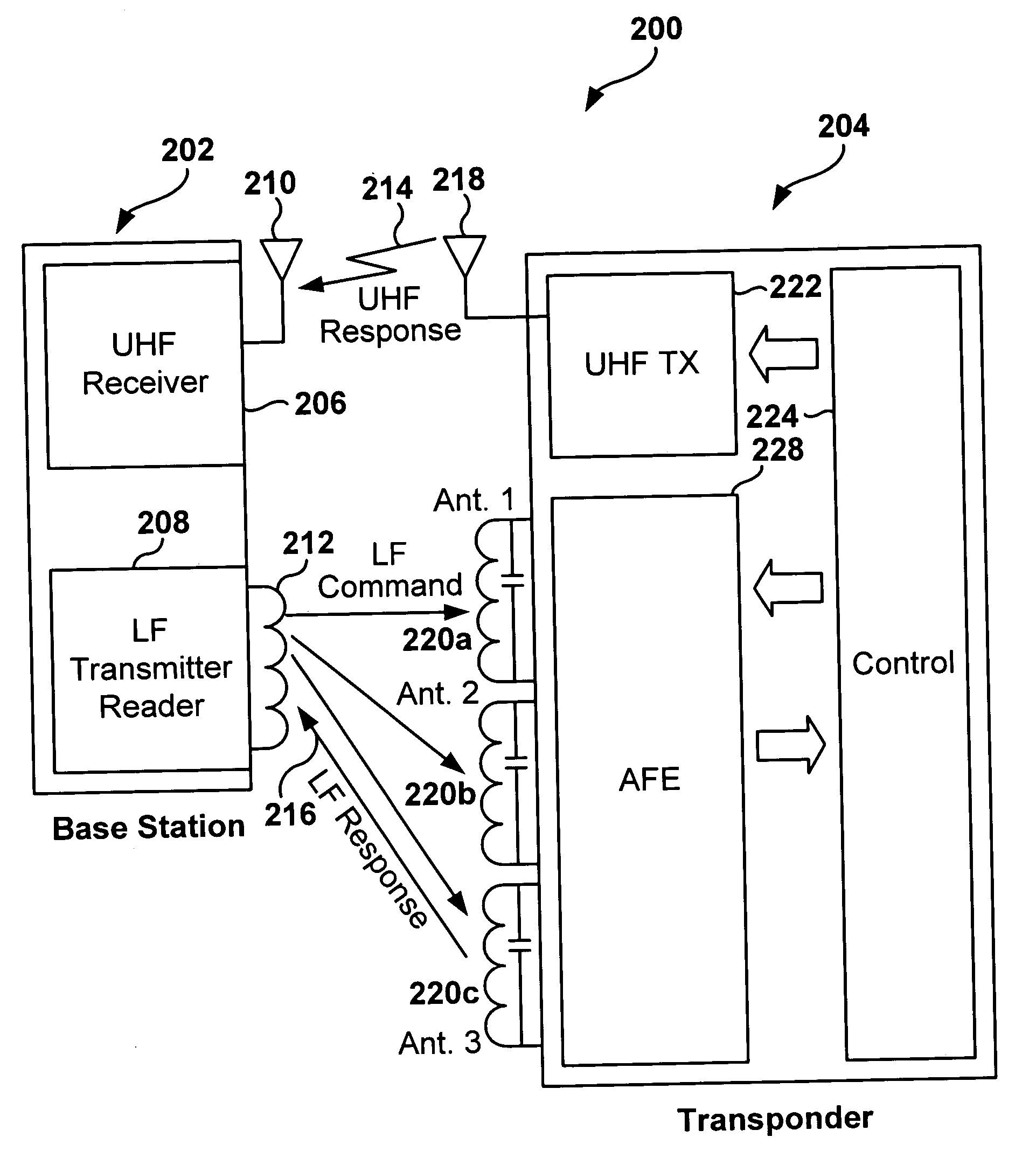
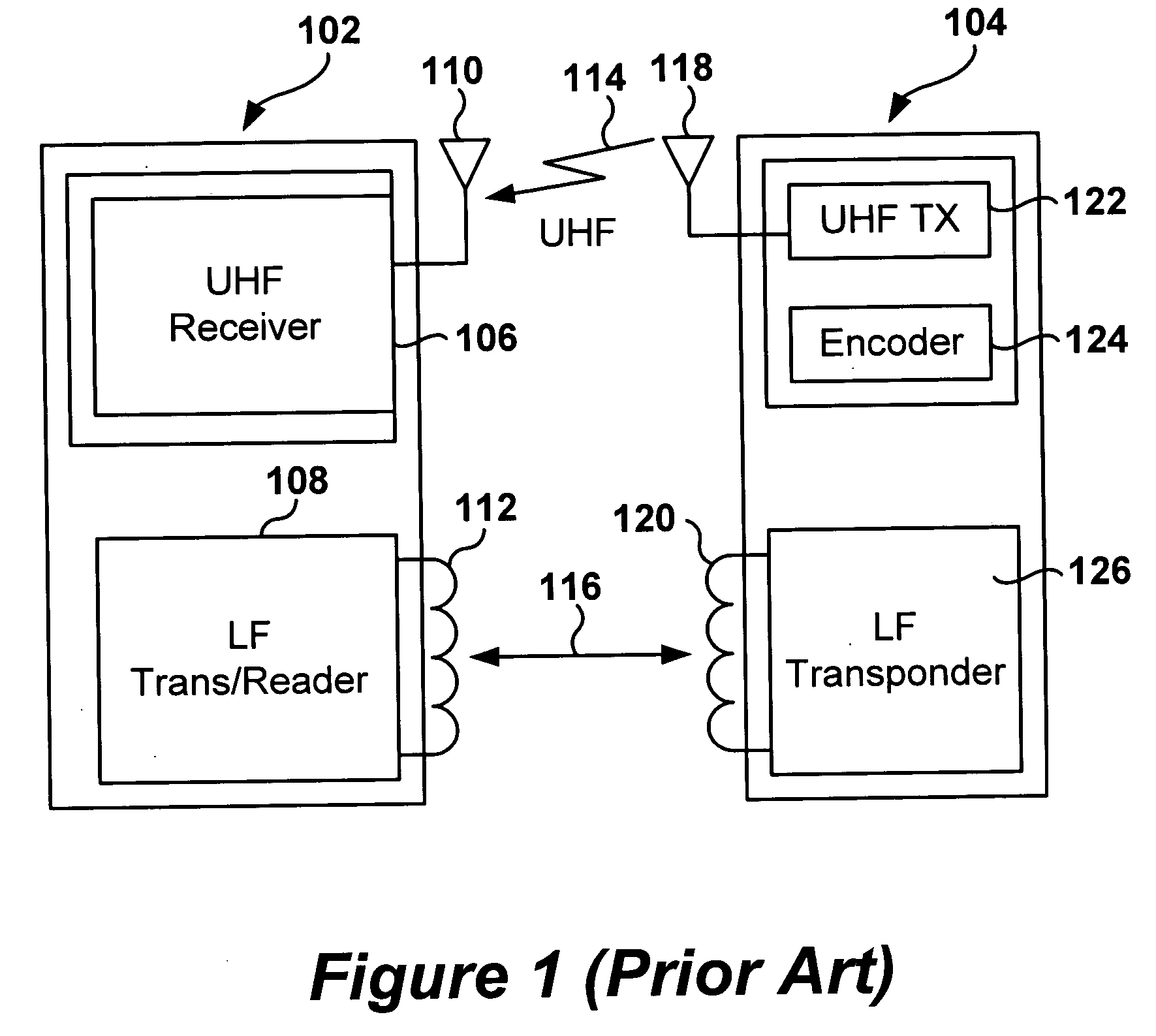
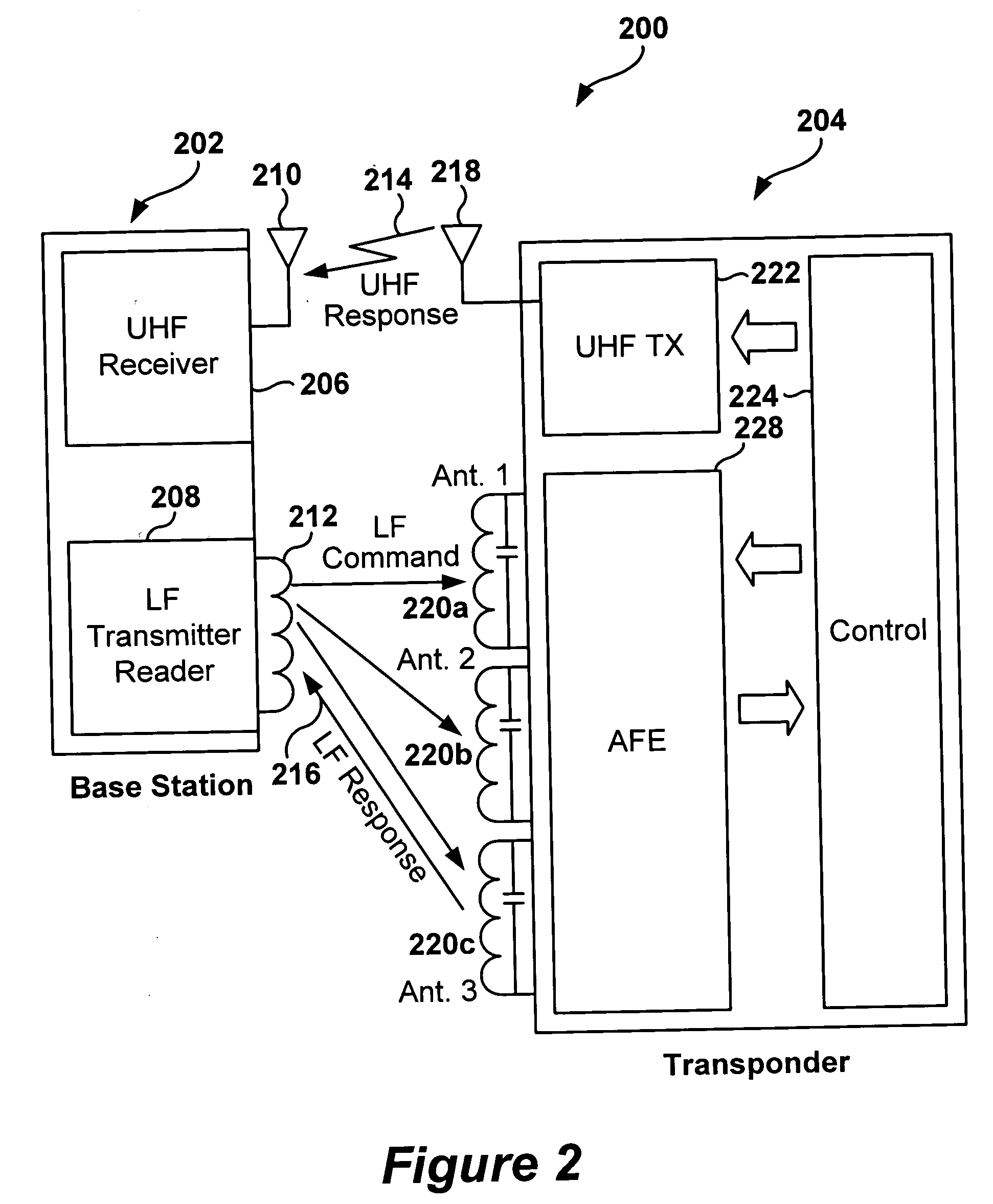
Multi-protocol radio frequency identification transponder transceiver
ActiveUS20060238301A1Memory record carrier reading problemsNear-field in RFIDTransceiverIn-phase and quadrature components
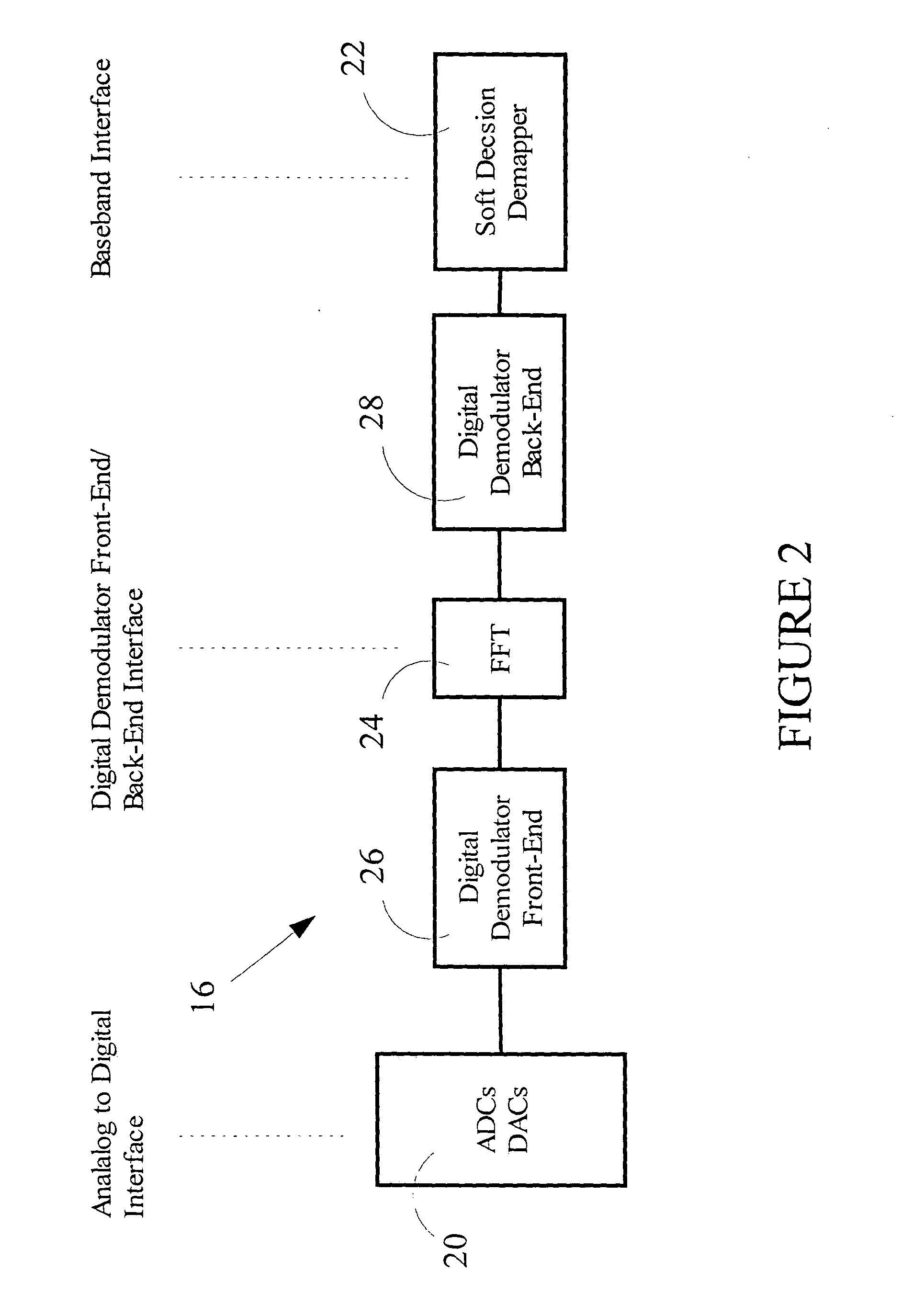
A transceiver for a RFID reader and a transceiver for a RFID transponder (tag) allow communication between the two devices. The RFID reader utilizes an analog front end and a digital backend. In the receiver portion of the transceiver, the front end of the RFID reader uses a pair of down-conversion mixers to demodulate a received signal into in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components and analog-to-digital converters (ADC) digitize the signal. A digital signal processor (DSP) in the back end processes the digital signal and uses a matched filter for data detection. The RFID tag receives an inductively coupled signal from the reader and the receiver portion of the tag uses a pulse / level detector that employs an analog comparator and a sample and hold circuit to detect the received signal. A digital decoder / controller is used to decode the incoming data and to establish a sampling clock for the pulse / level detector. An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit adjusts a receiver gain according to the received signal strength and controls tuning of magnetic coupling circuitry.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Integrated beamformer/modem architecture
ActiveUS7260141B2High computational complexityDecreasing computational rateSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityTransceiverModem device
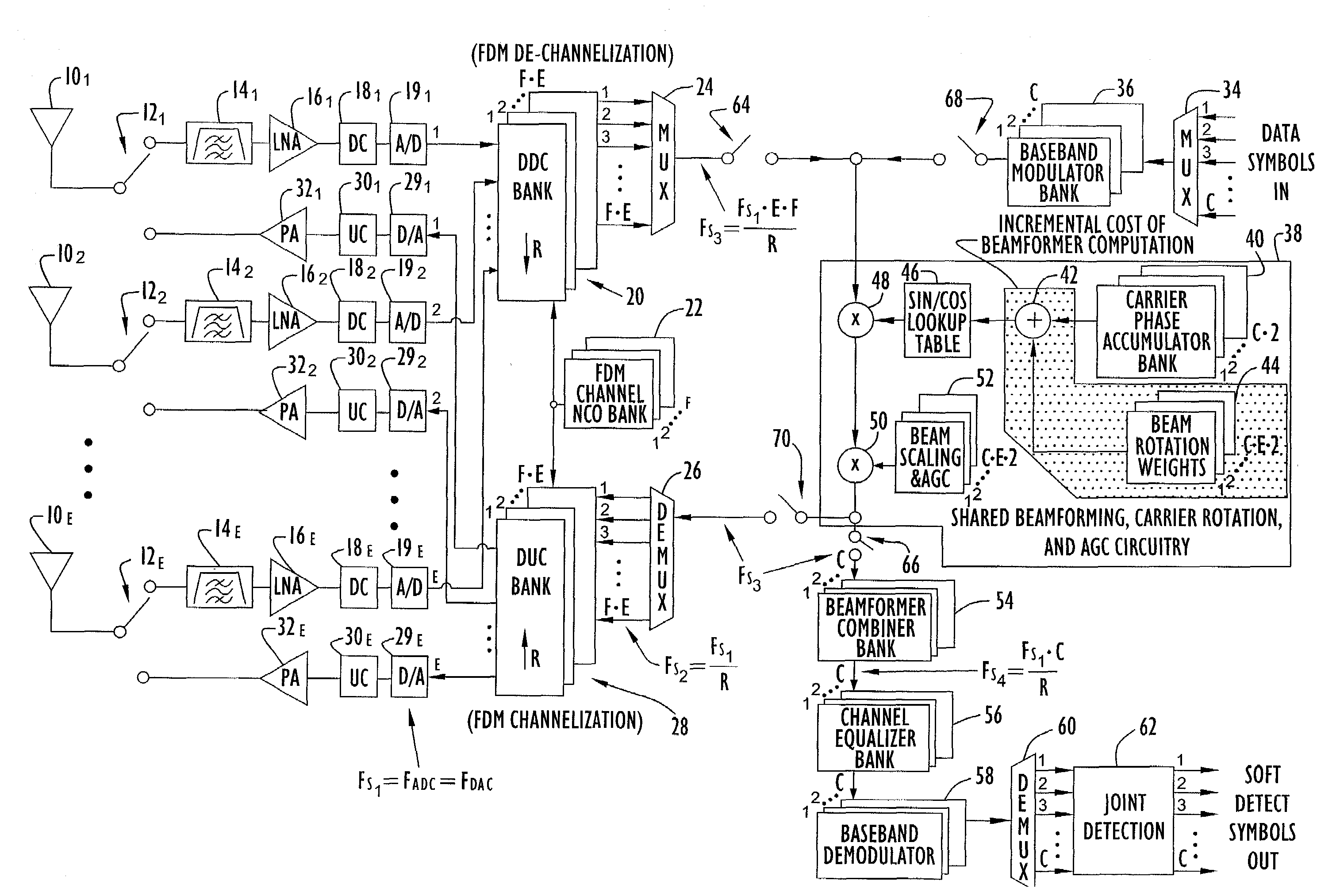
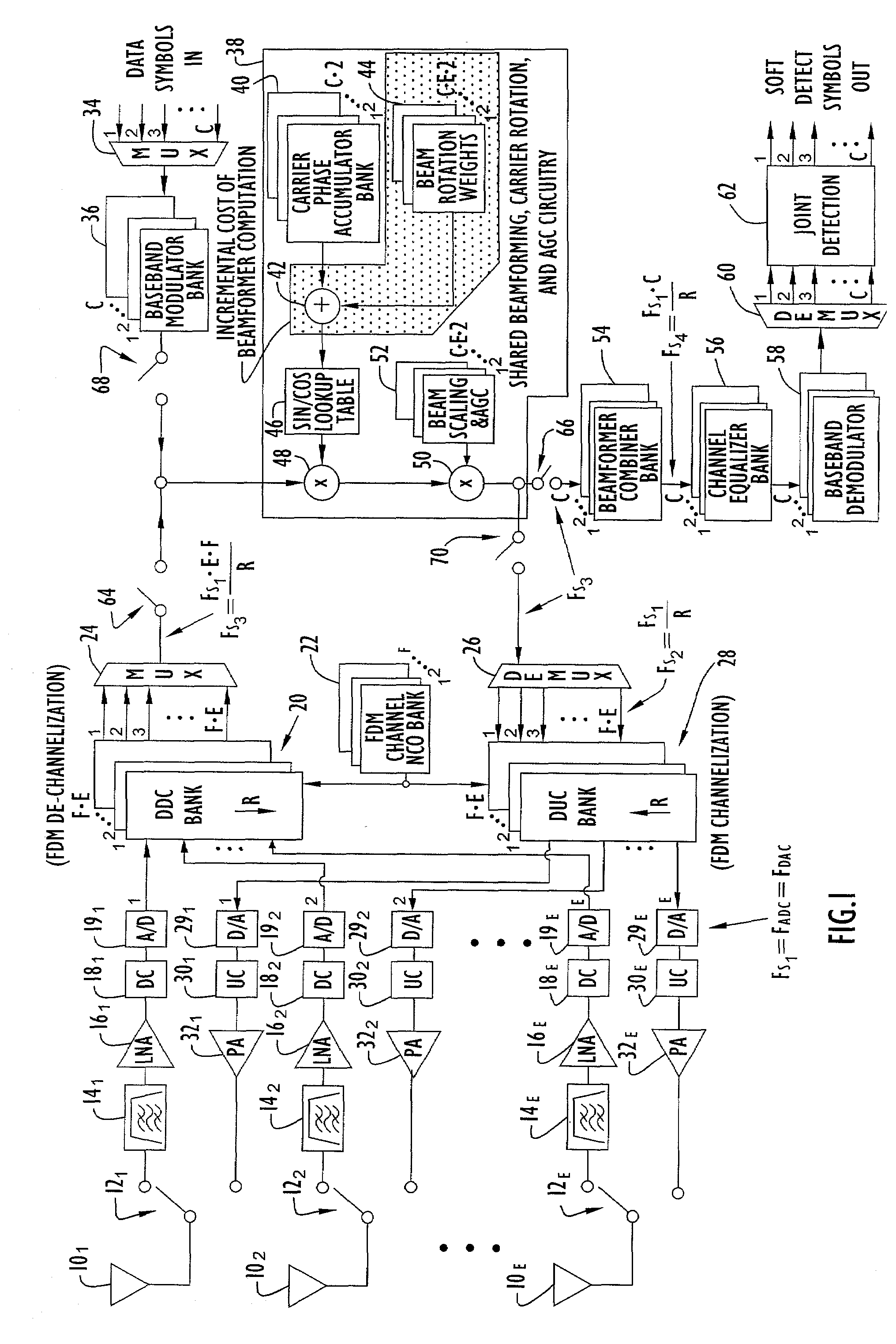
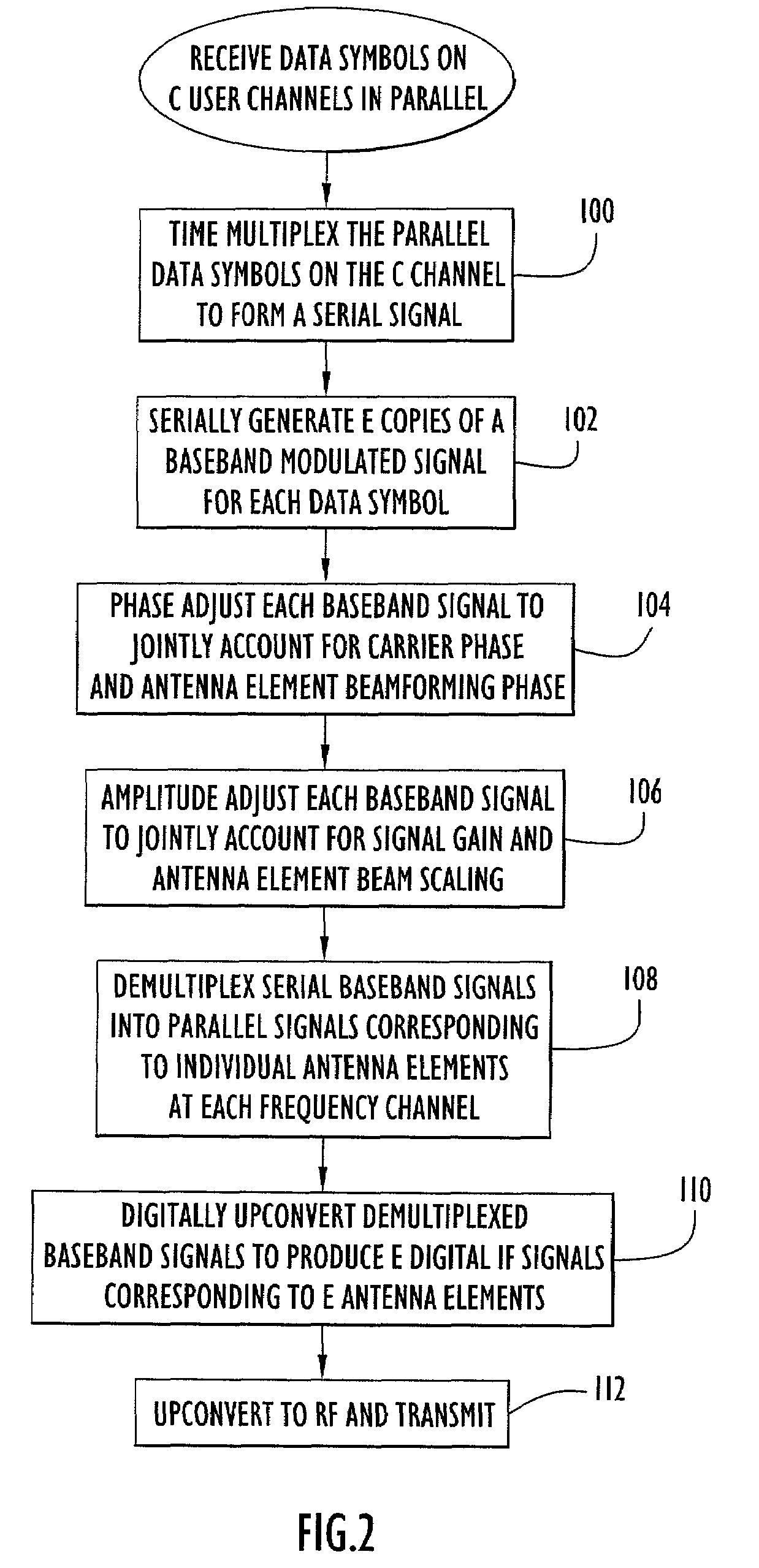
A transceiver employing a steerable phased-array antenna includes a modem architecture in which signals from each antenna element in the array are independently processed down to the individual baseband channel level, and digital beamforming is performed at baseband. The data rate reduction from IF to baseband permits parallel signal data from multiple antenna elements to be time multiplexed and serially processed at acceptable data rates at baseband with minimal modem hardware requirements. Both for transmit signal modulation and received signal demodulation, the computation of carrier tracking, automatic gain control (AGC) / power-control, and beamforming are shared by the same processing circuitry for all channels when performed at baseband. The resulting baseband circuitry is only incrementally larger than that required for carrier tracking and AGC alone, yet accomplishes independent beamforming for each antenna element on each user channel.
Owner:LIONRA TECH LTD
Methods and apparatus for magnetic article detection
ActiveUS7362094B2Reduce errorsUsing electrical meansDevices using electric/magnetic meansControl signalAutomatic gain control
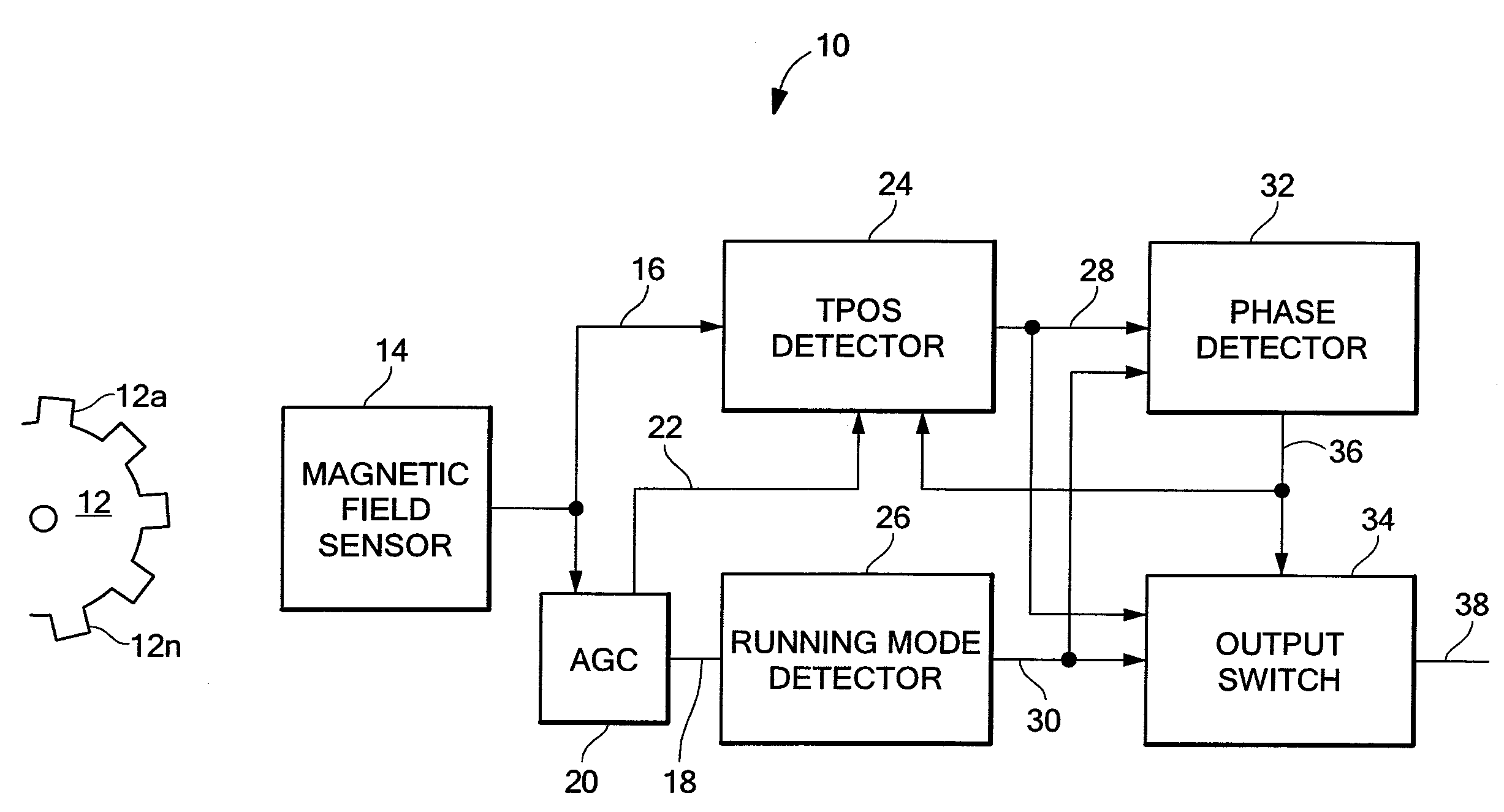
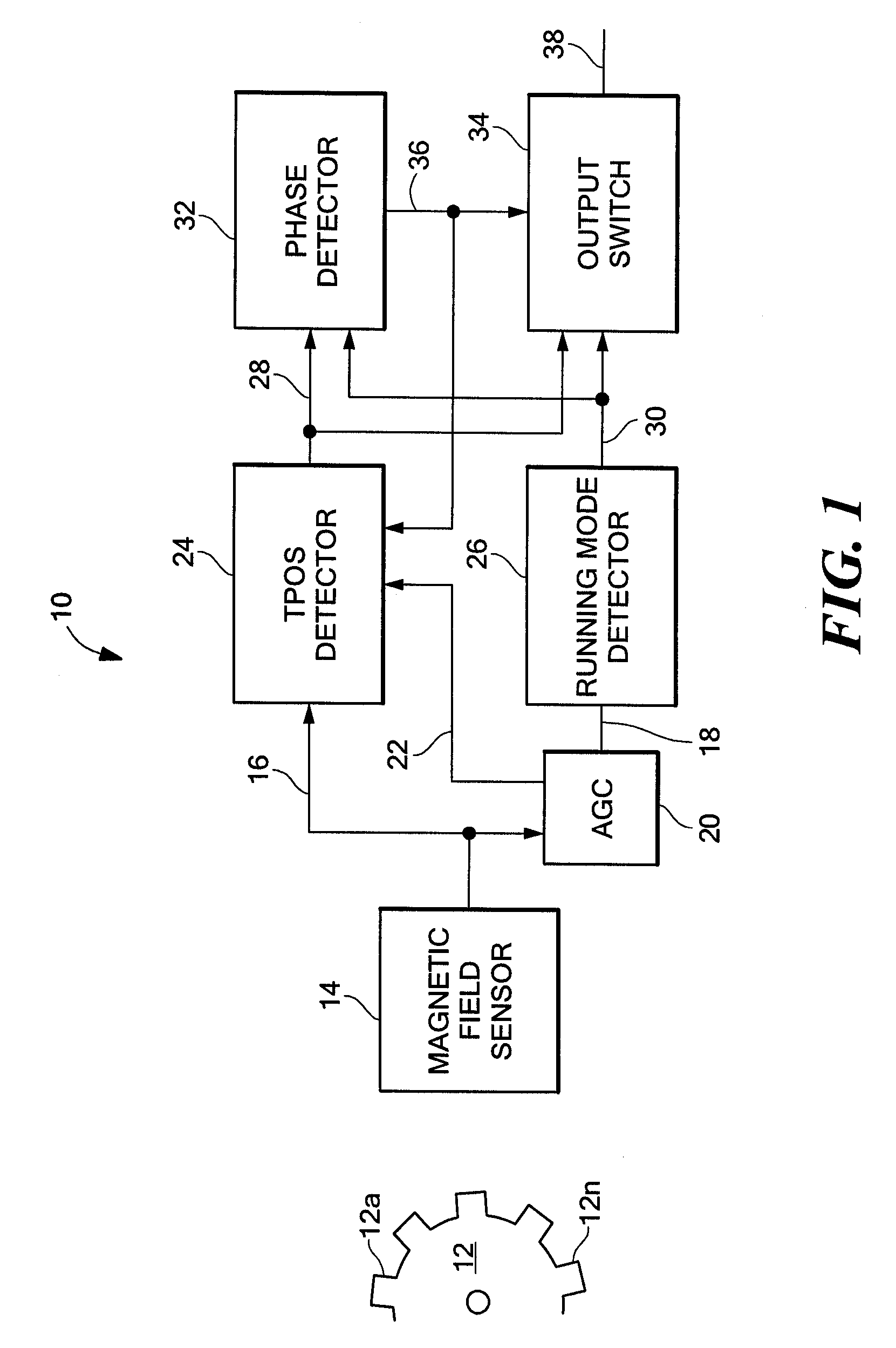
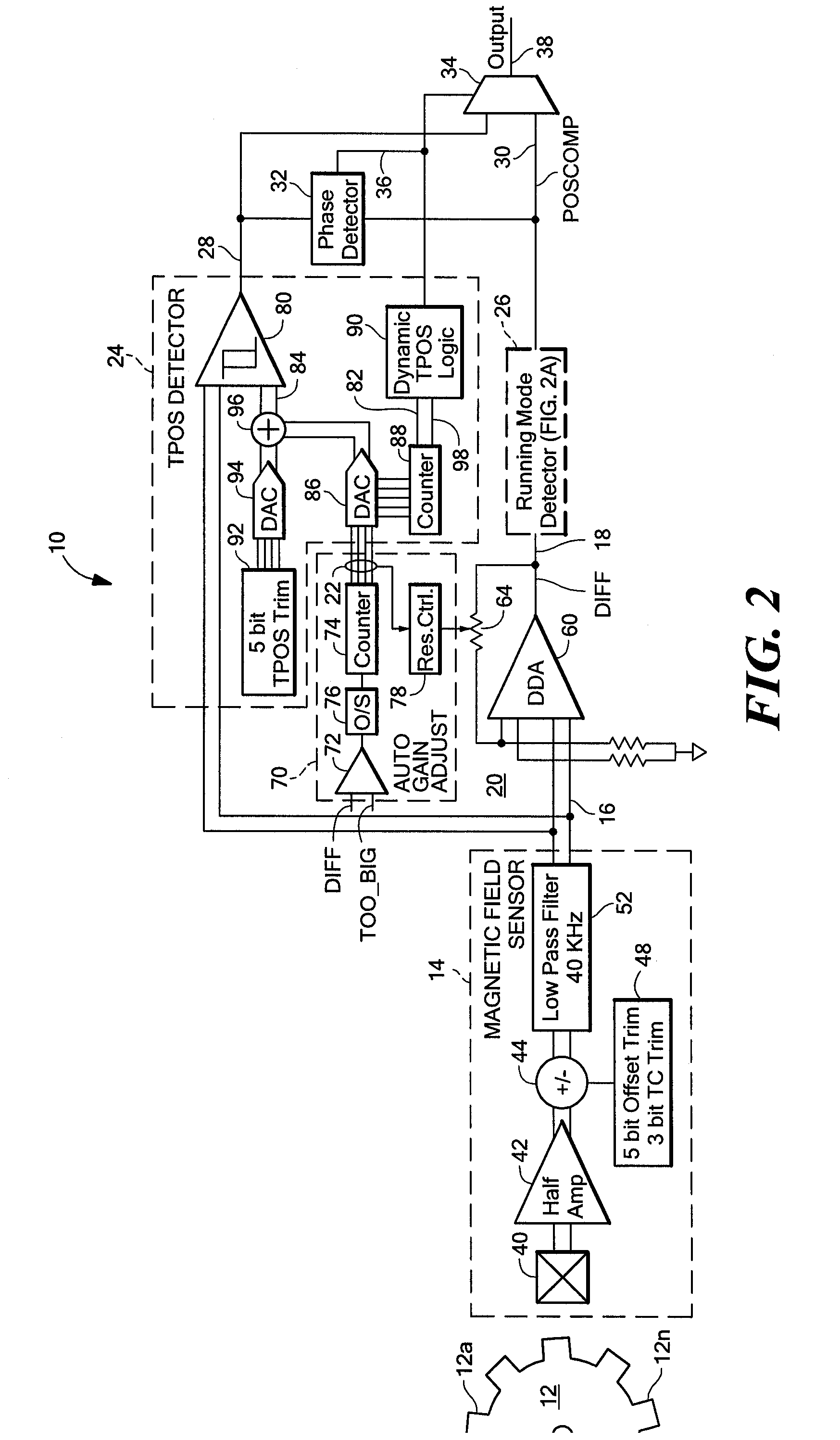
Apparatus and methods for detecting passing magnetic articles using a first, True Power On State (TPOS) detector during a first time interval and transitioning to a second, running mode detector after the first time interval, when the output of the second detector is accurate. A phase comparator is responsive to the output signal of the first and second detectors and provides a control signal indicative of a change in the phase relationship between the two output signals. An output switch controlled by the phase comparator provides, as the detector output signal, the first detector output signal during the first time interval and the second detector output signal thereafter. A threshold signal associated with the TPOS detector is at a fixed level during a first portion of the first time interval and is adjusted during a second portion of the first time interval in response to an automatic gain control circuit in order to reduce the phase error associated with transitioning from the TPOS detector to the running mode detector. Also described are apparatus and methods for updating a running mode threshold signal that is a percentage of the peak-to-peak magnetic field sensor signal, so that unnecessary update events are reduced.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
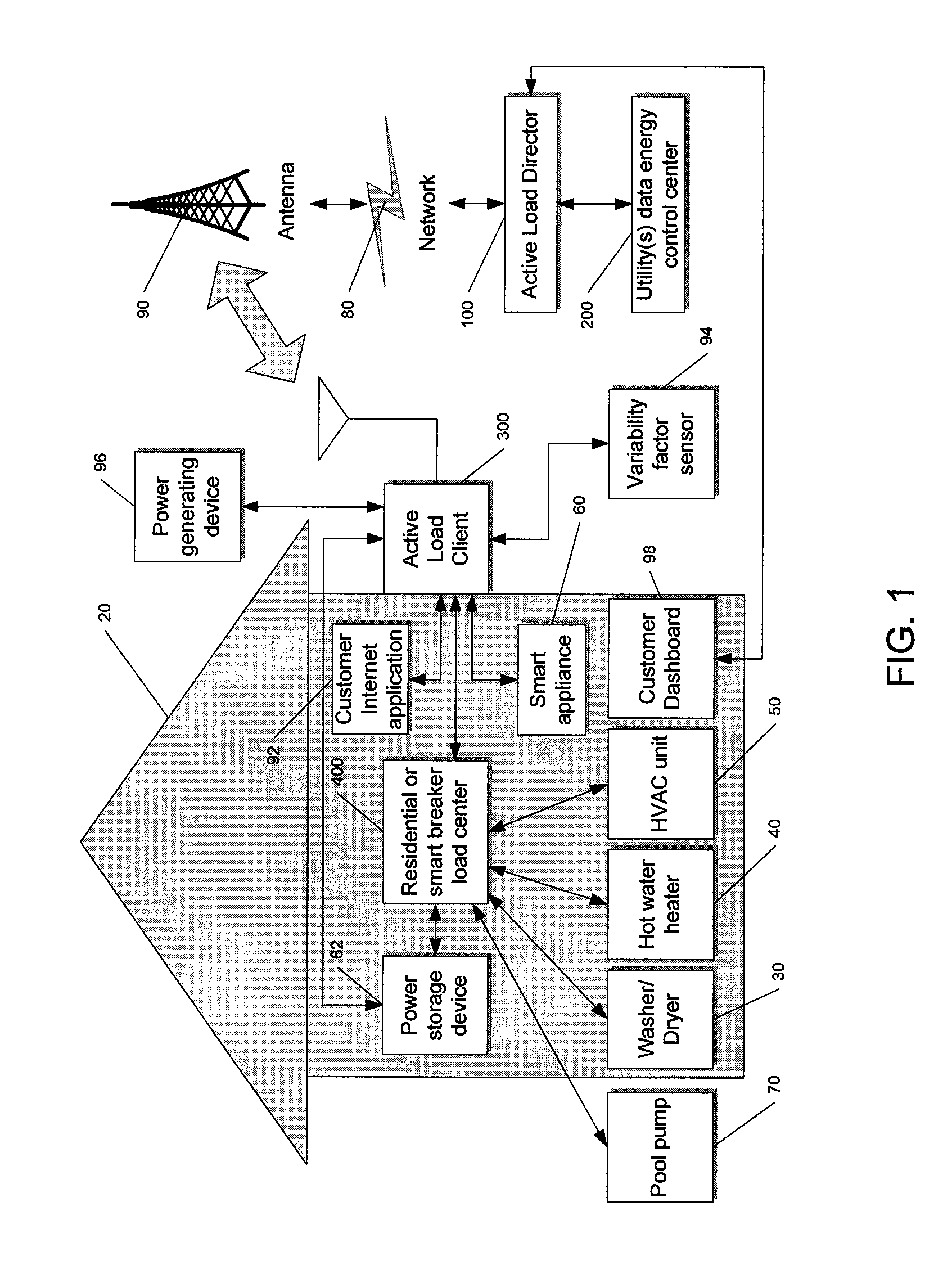
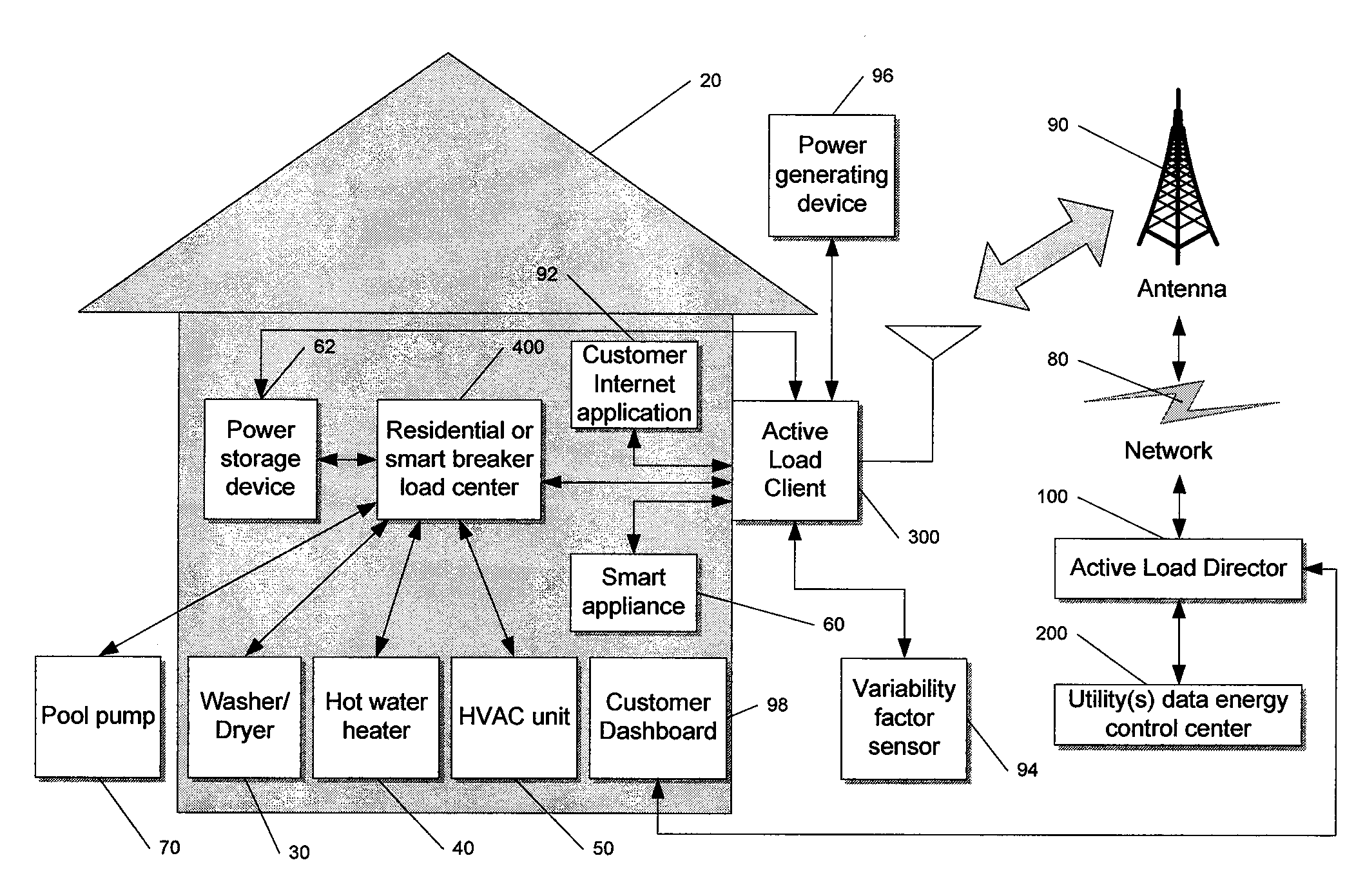
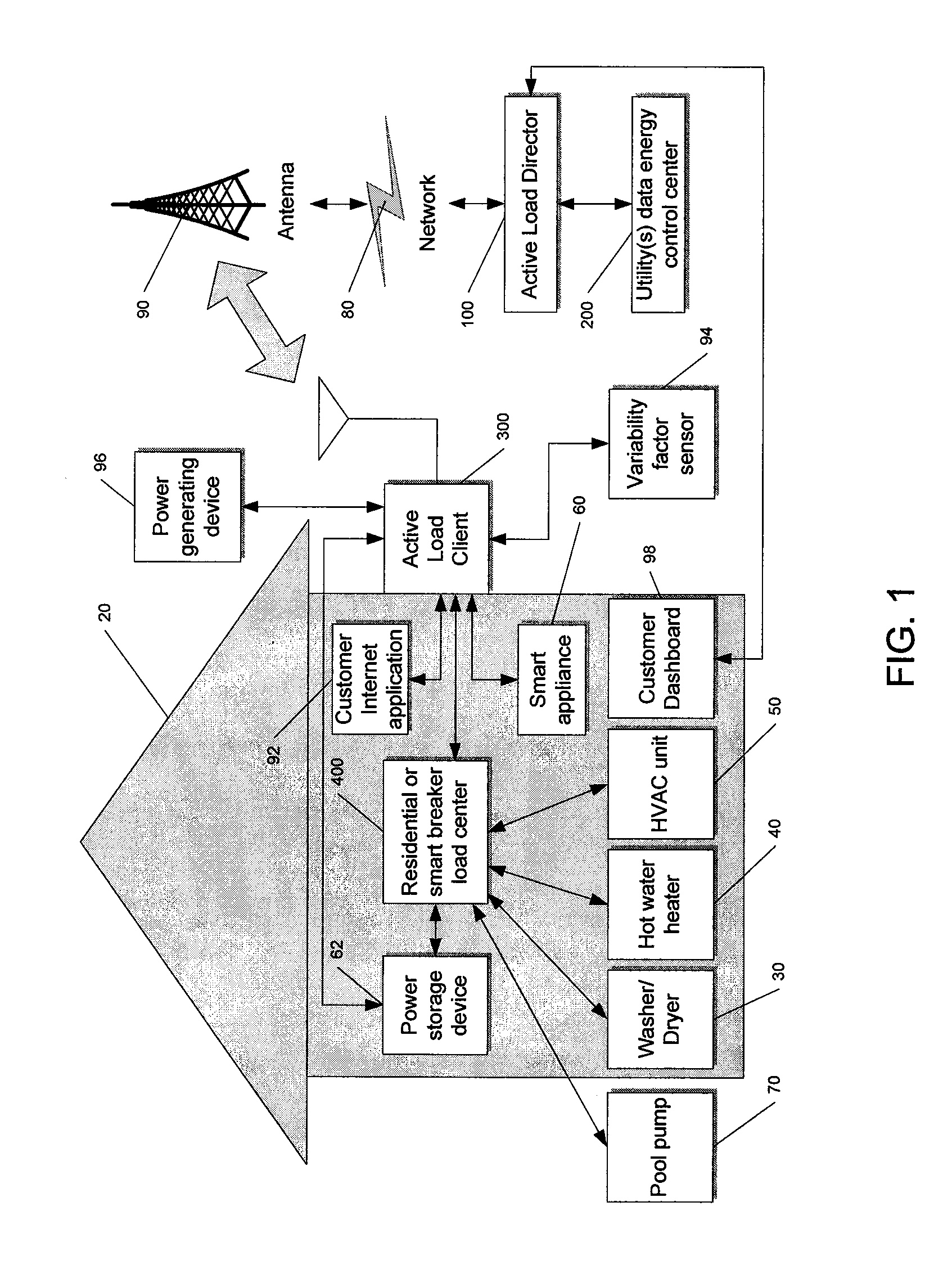
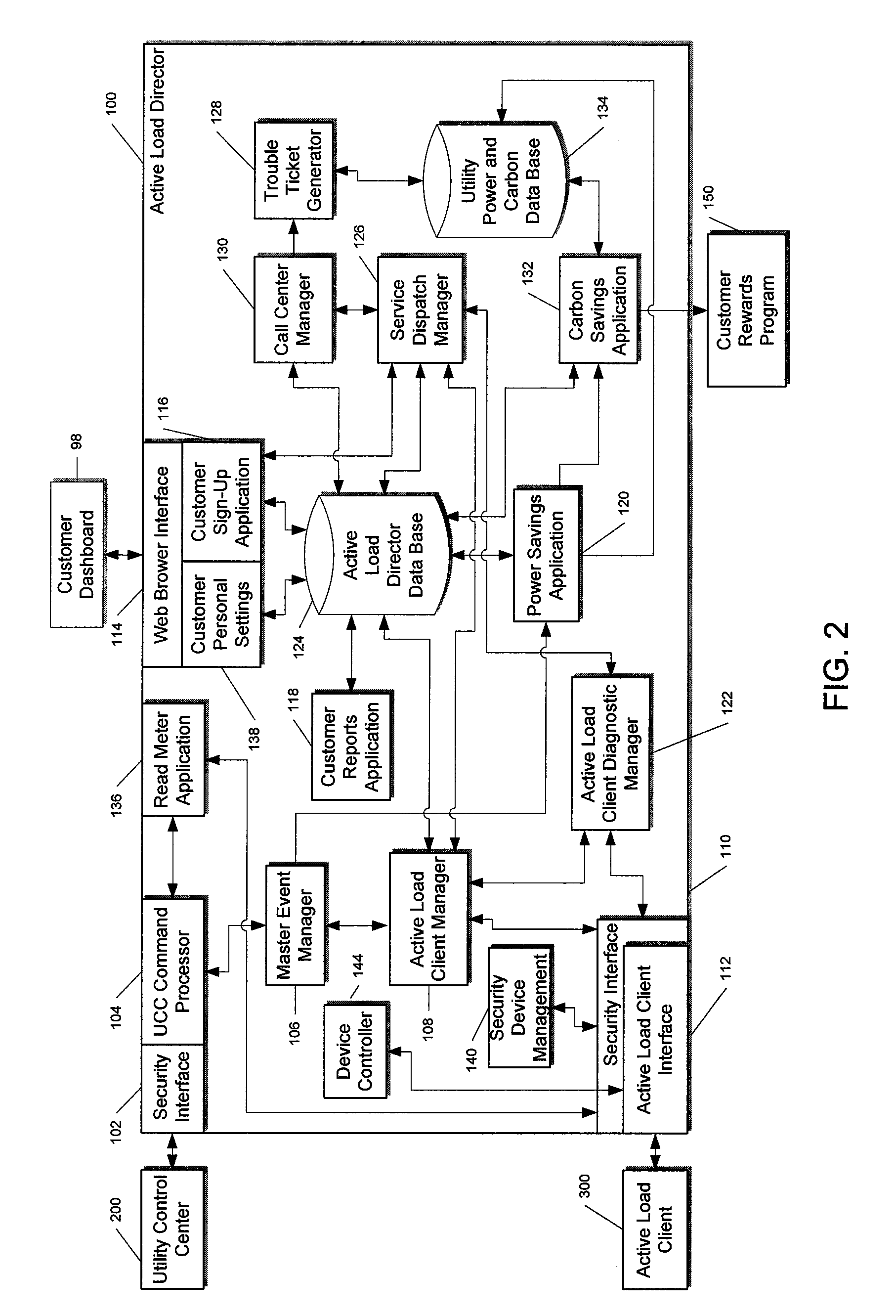
System and method for manipulating controlled energy using devices to manage customer bills
Owner:JOSEPH W FORBES JR +1
Hearing compensation system incorporating signal processing techniques
InactiveUS20050111683A1Signal processingCombination control in untuned amplifierBandpass filteringEngineering
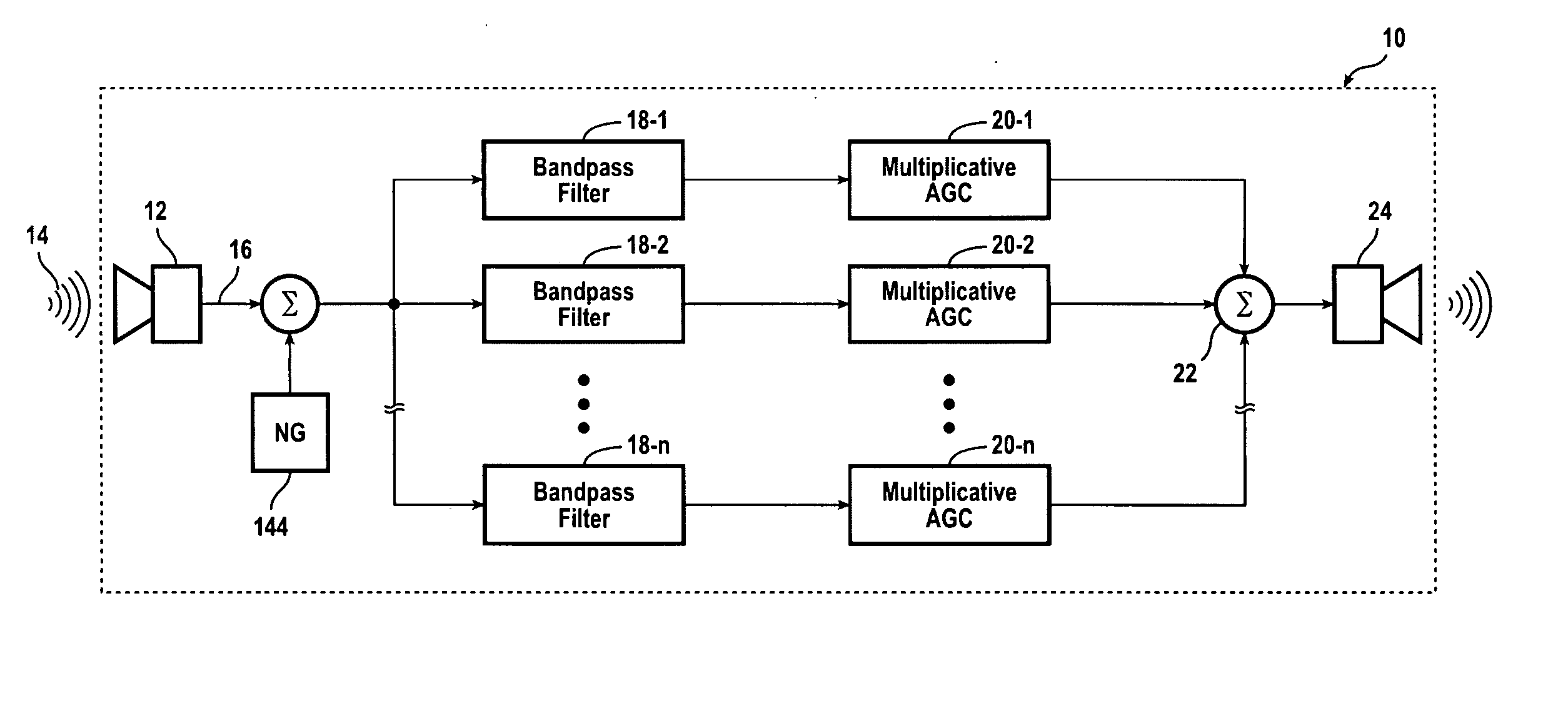
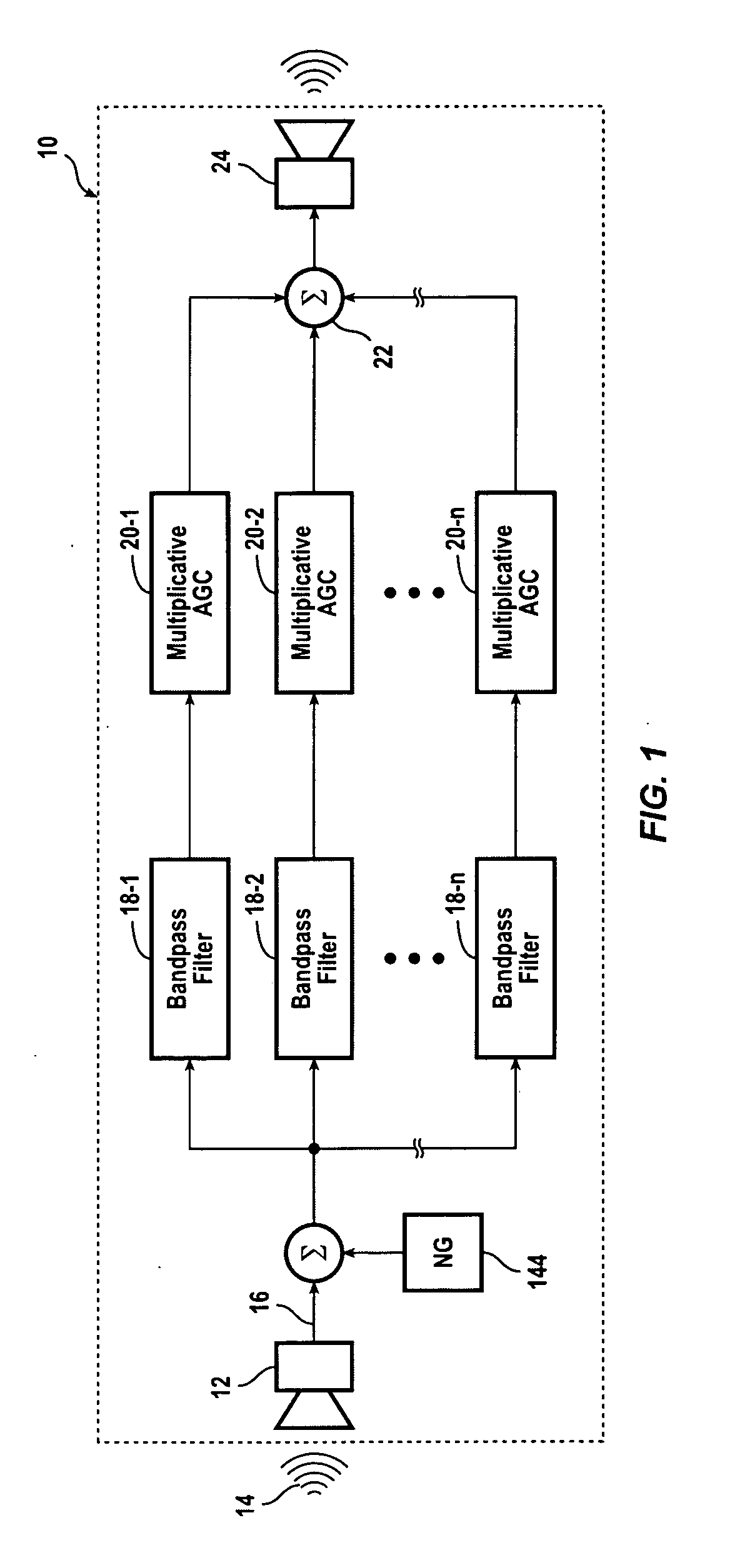
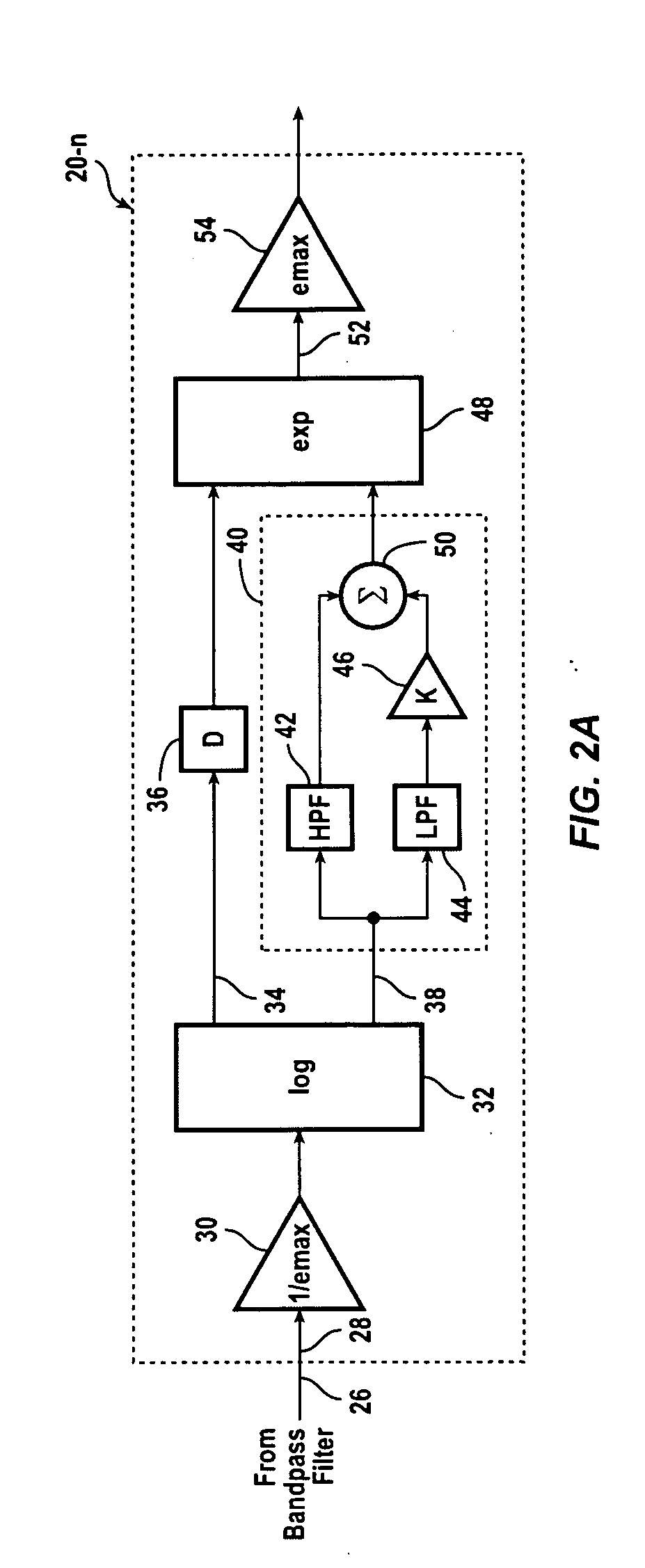
A hearing compensation system comprises a plurality of bandpass filters having an input connected to an input transducer and each bandpass filter having an output connected to the input of one of a plurality of multiplicative automatic gain control (MAGC) circuits whose outputs are summed together and connected to the input of an output transducer. The MAGC circuits attenuate acoustic signals having a constant background level without the loss of speech intelligibility. The identification of the background noise portion of the acoustic signal is made by the constancy of the envelope of the input signal in each of the several frequency bands. The background noise that will be suppressed includes multi-talker speech babble, fan noise, feedback whistle, florescent light hum, and white noise. For use in the consumer electronics field background acoustic noise may be sensed and used to adjust gain in the various MAGC circuits so as to improve a user's listening experience, whether the user is hearing impaired or not.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
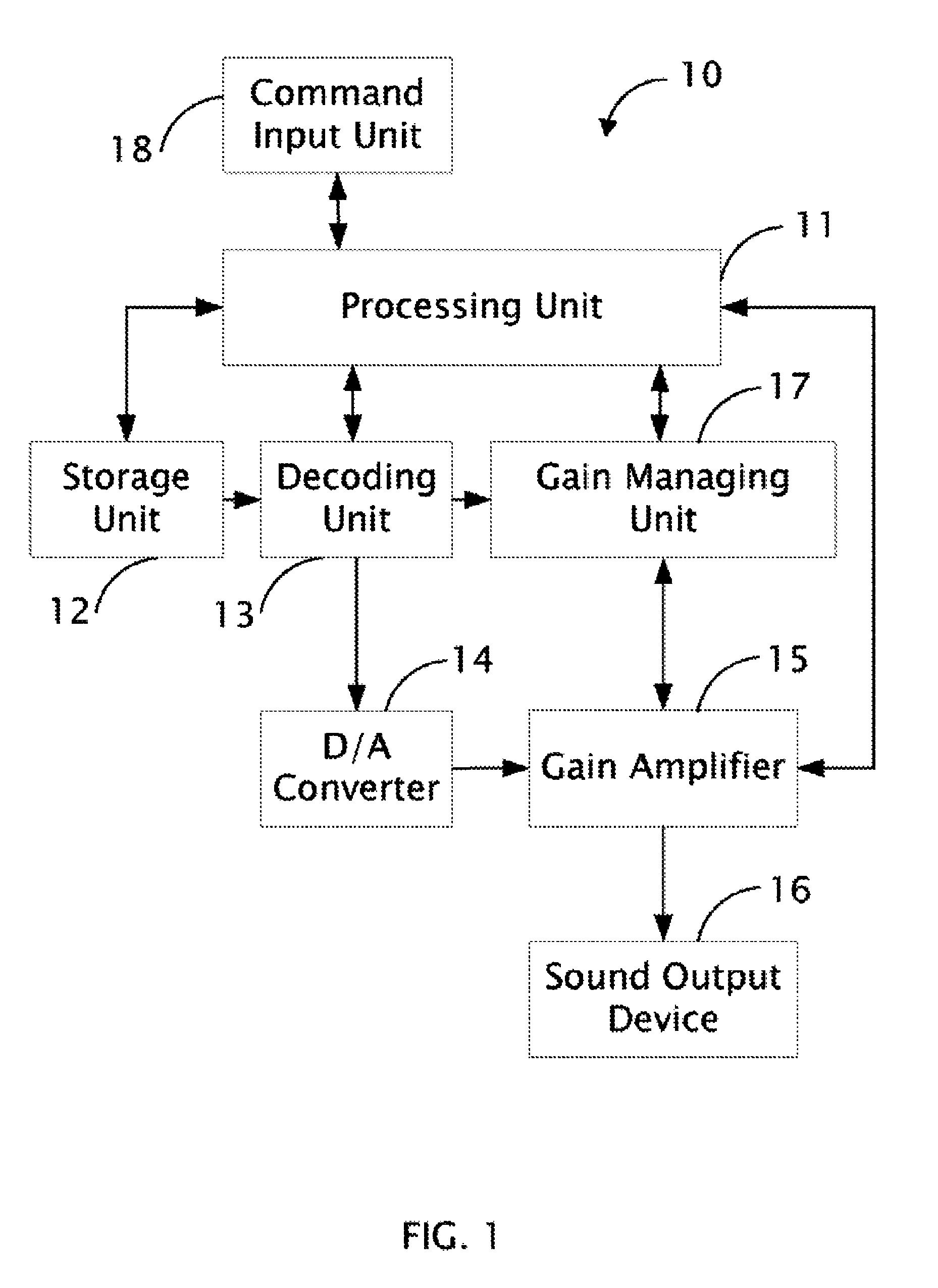
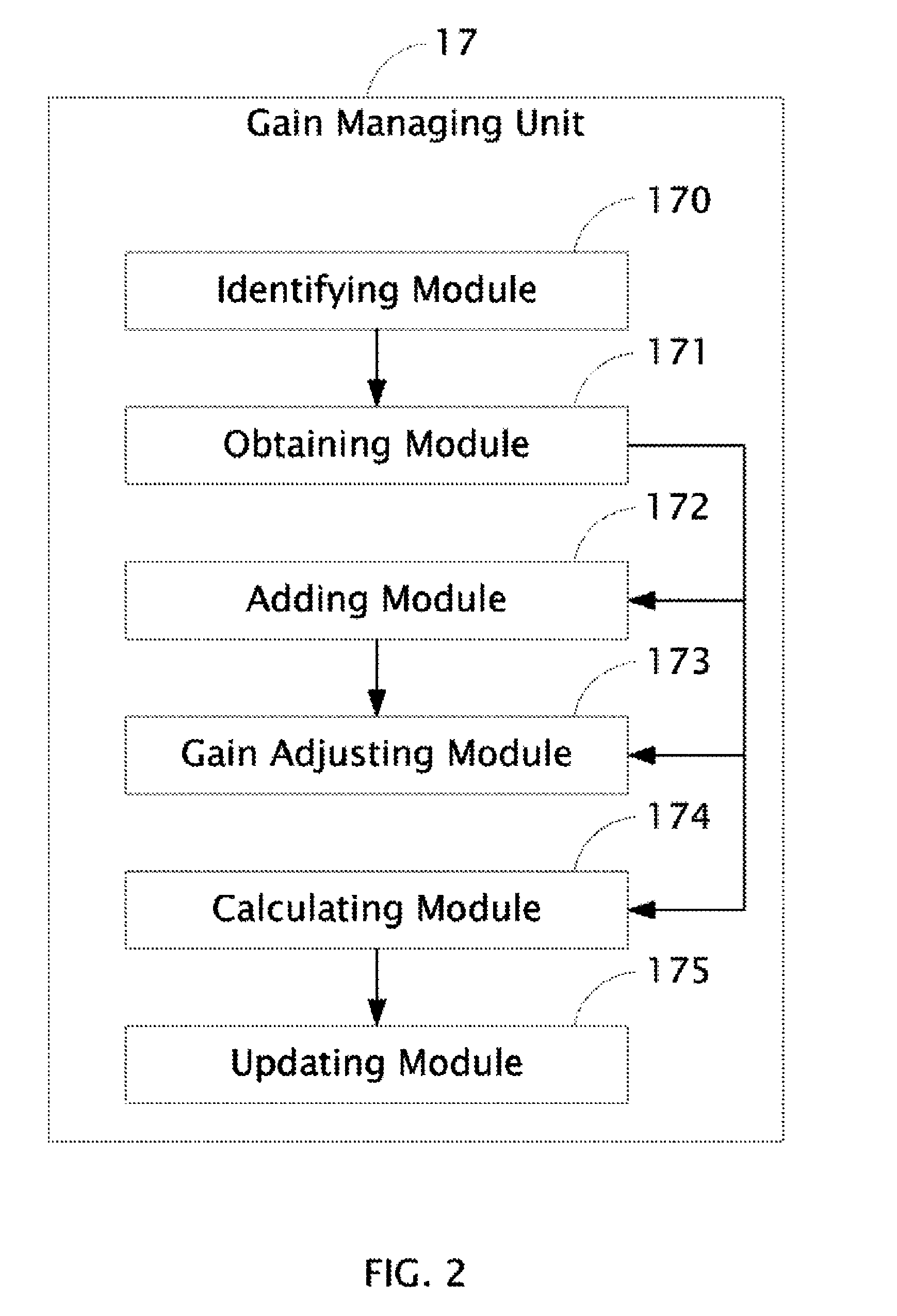
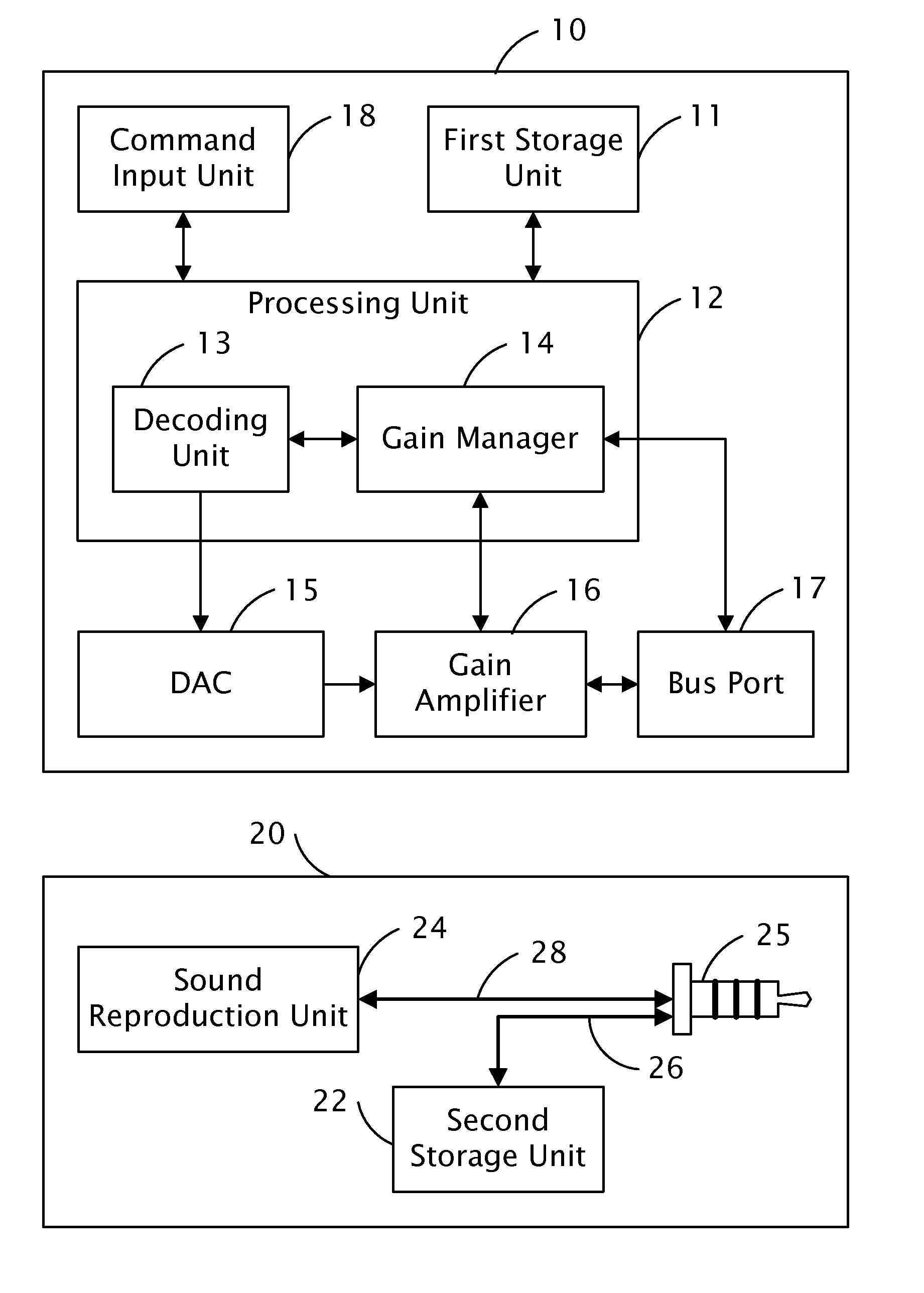
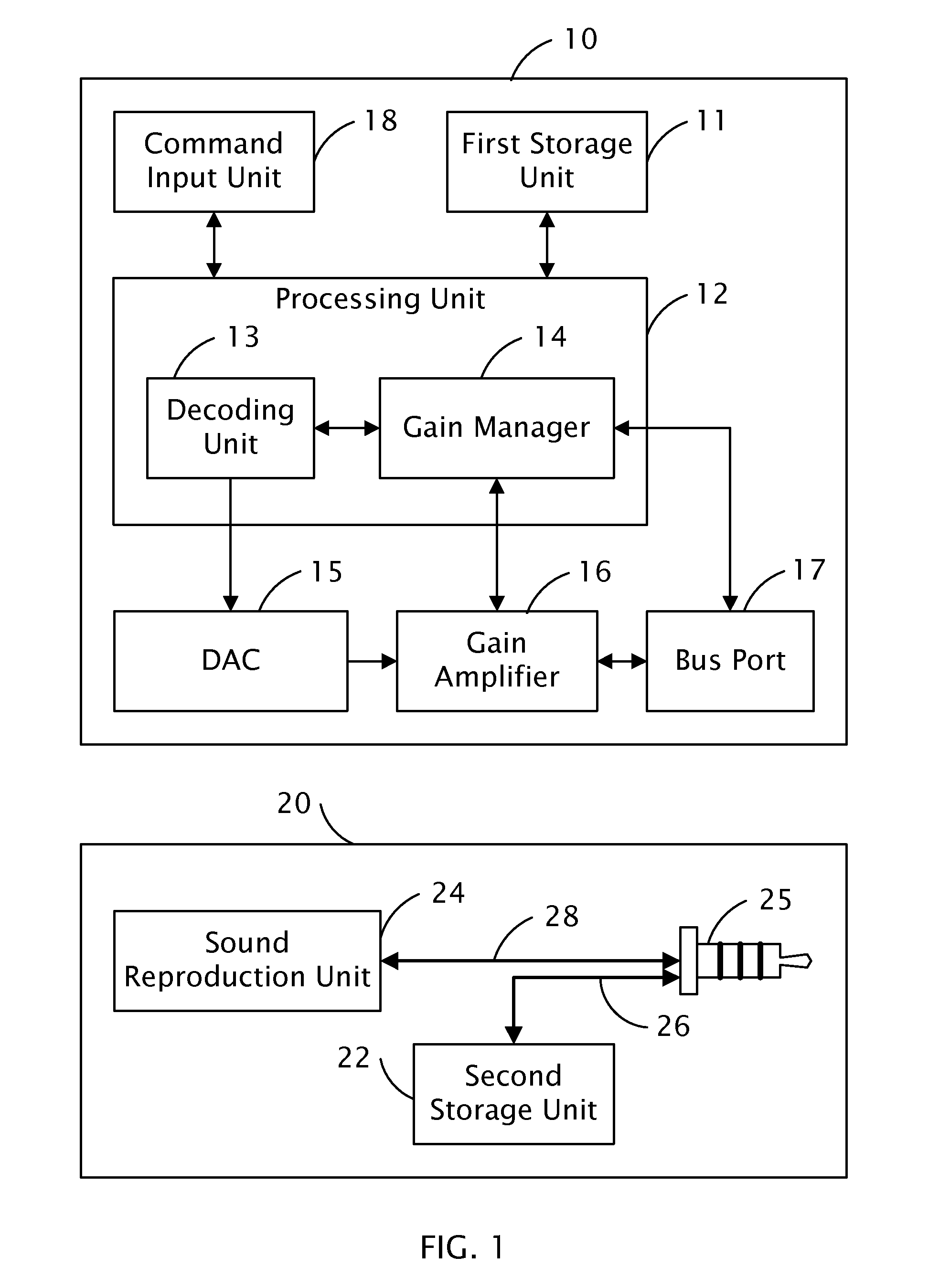
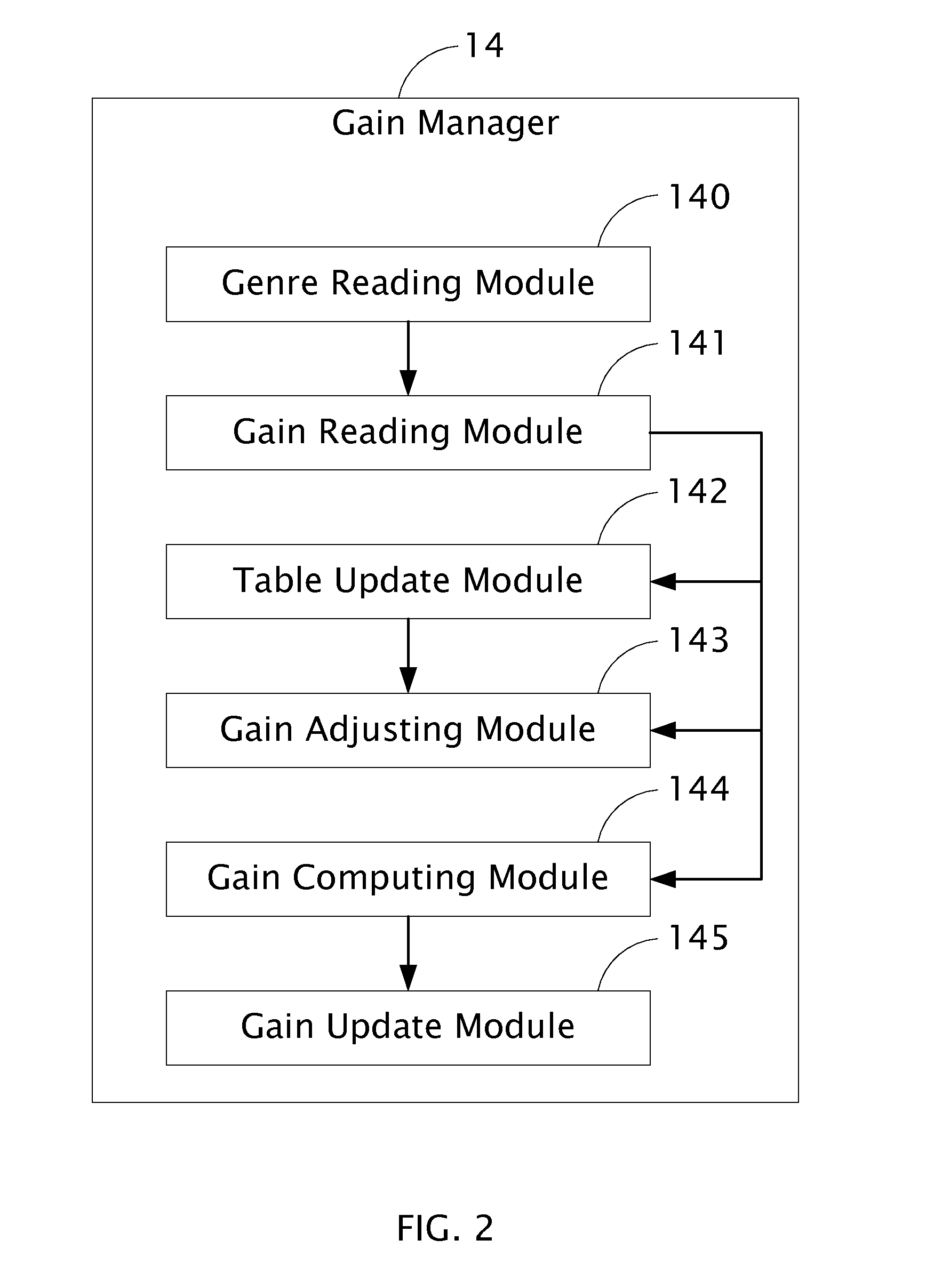
Audio processing system with function of automatic gain control and method thereof
ActiveUS8019094B2Analog signal digital controlSpecial data processing applicationsAudio power amplifierAutomatic control
The present invention relates to an audio processing system with function of automatic gain control and method thereof. The method includes steps of: receiving a playing command to play an audio file; reading a genre type of the audio file from a tag of the audio file; reading a genre gain value of the genre type from a gain setting table stored in a storage unit; decoding the audio file and generating digital audio signals; converting the digital audio signals to analog audio signals; and signaling a gain amplifier to amplify the analog audio signals by the genre gain value, thereby sounds corresponding to the analog audio signals amplified is proper to a listener's hearing.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
System and method for manipulating controlled energy using devices to manage customer bills
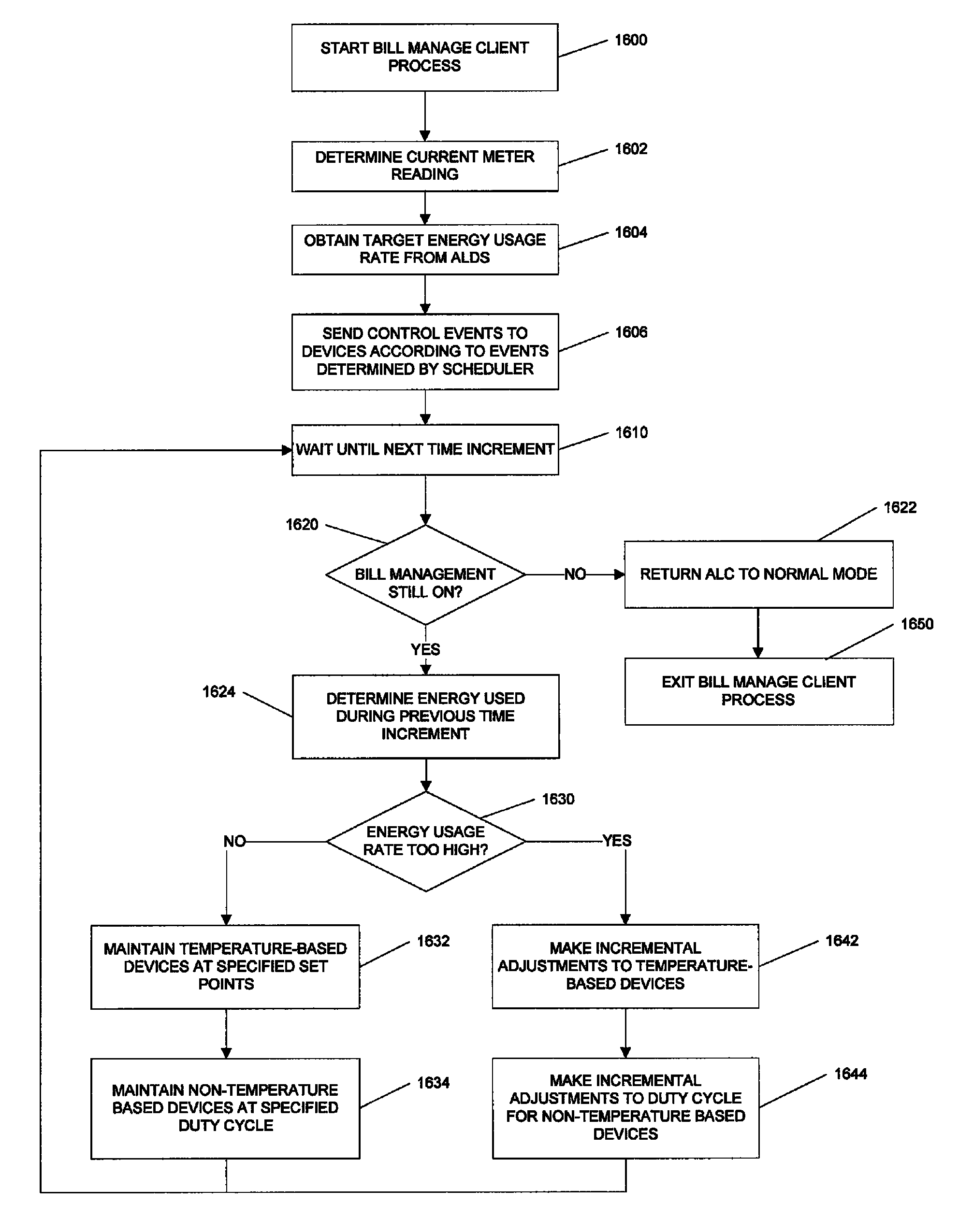
A control system and method to create an Internet Protocol (IP) enabled automatic gain control loop for encasing a desired cost value in a utility derived consumer controlled pricing envelope. A customer uses a web browser to view billing estimates for the current month as well as related months. The customer can set limits on the actual billing amount for the upcoming month and make adjustments to this amount if it seems unrealistic in the coming month. Control event actions are carried out to limit power usage within preferences set by the customer.
Owner:LANDISGYR INNOVATIONS INC +1
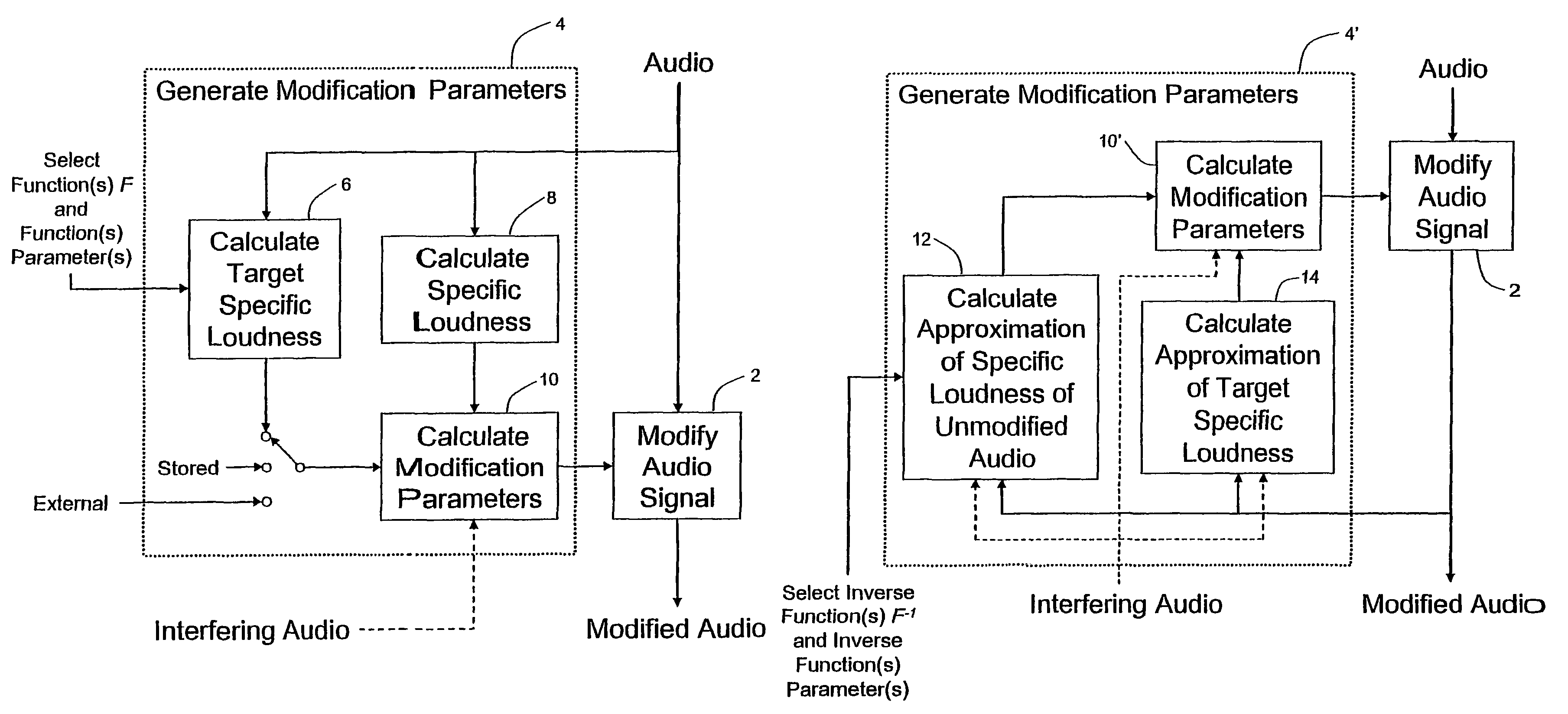
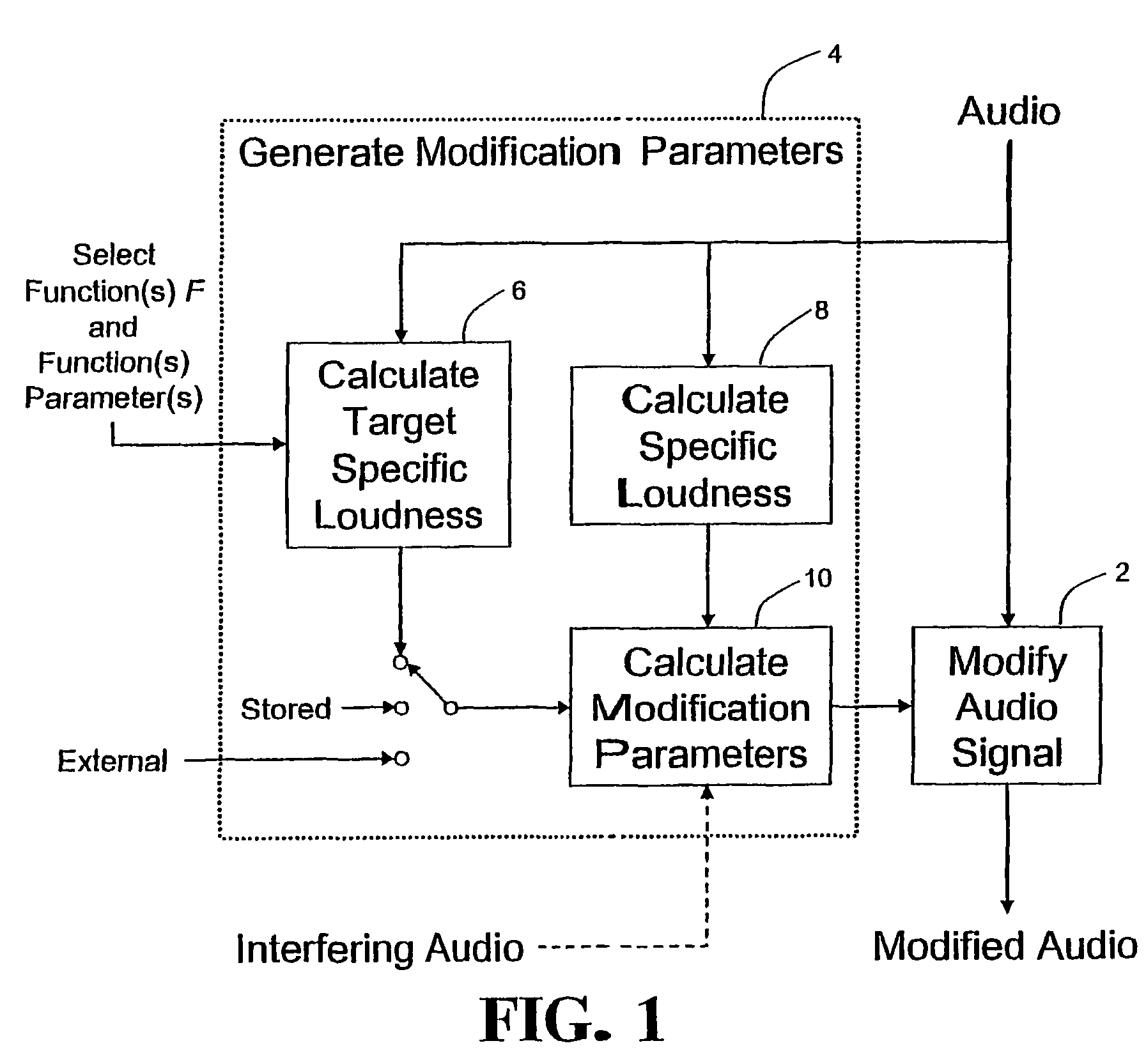
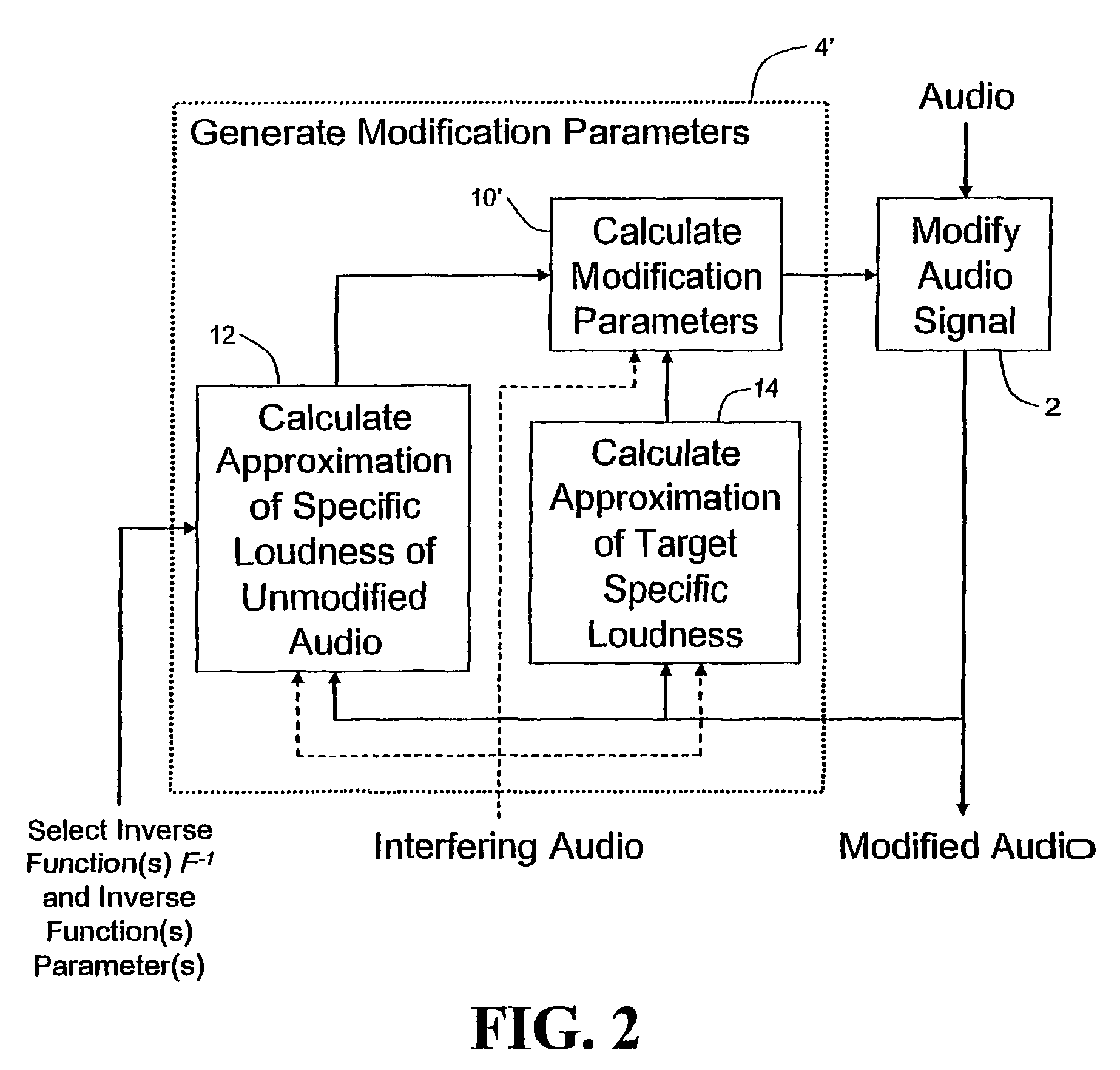
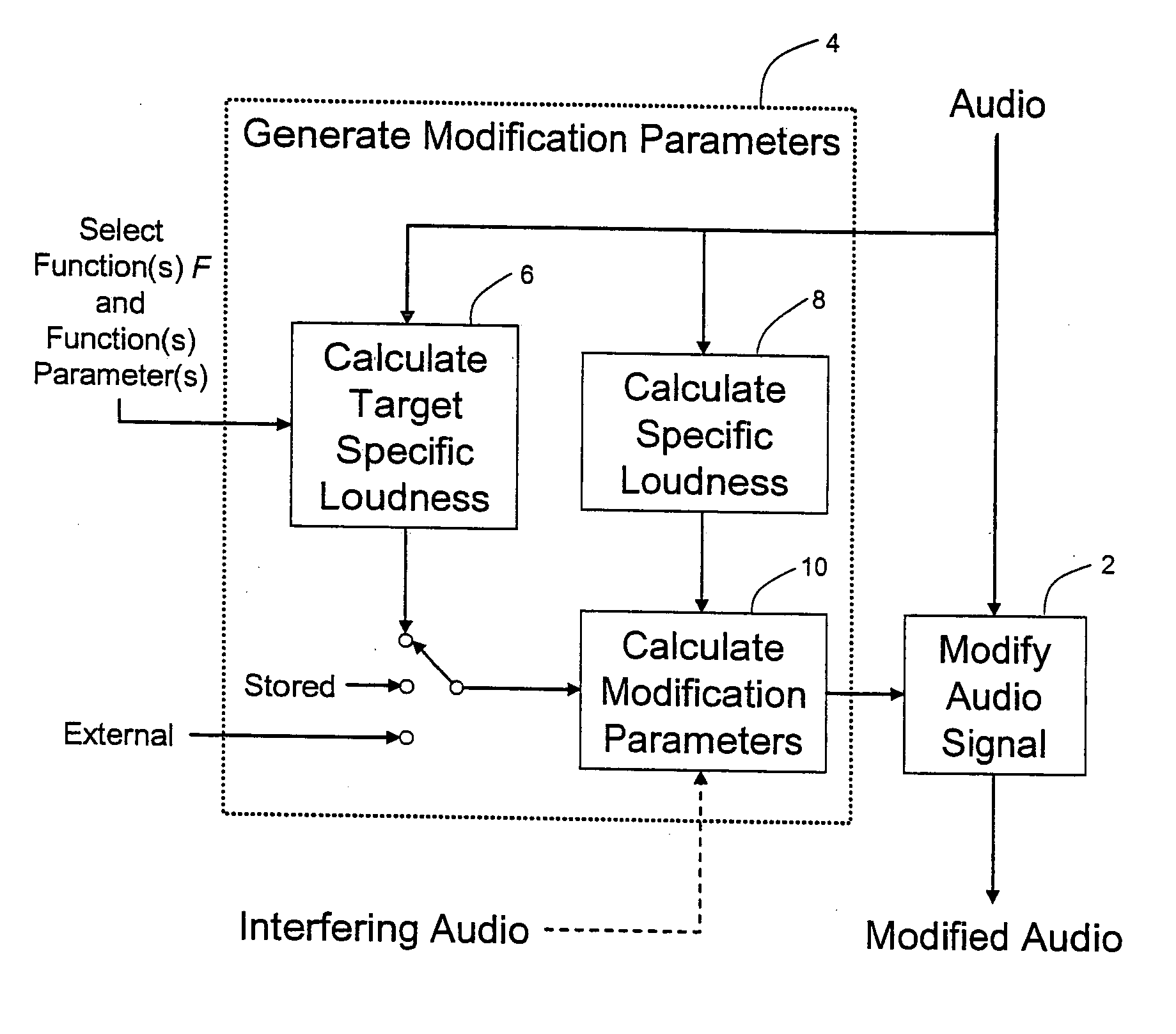
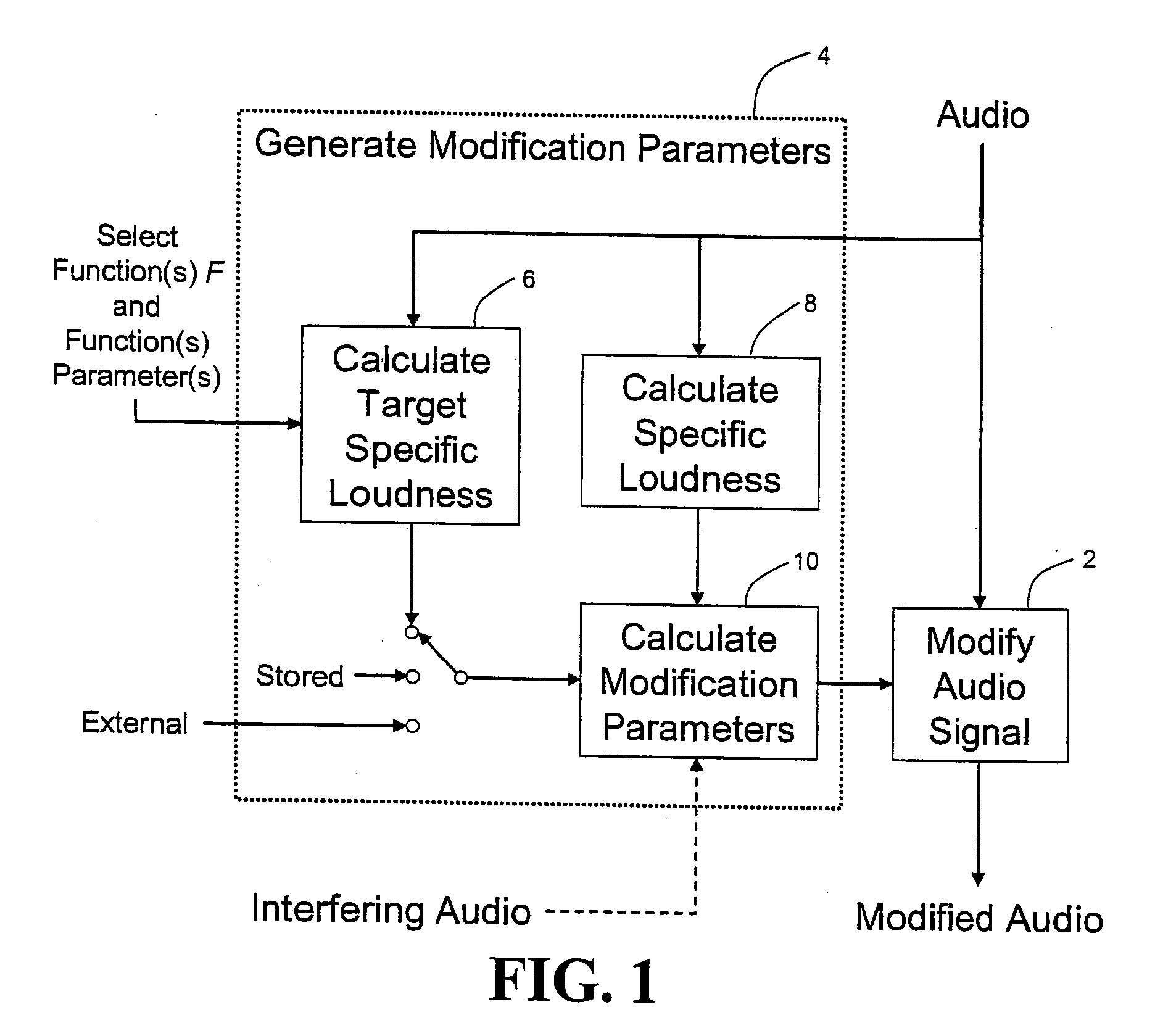
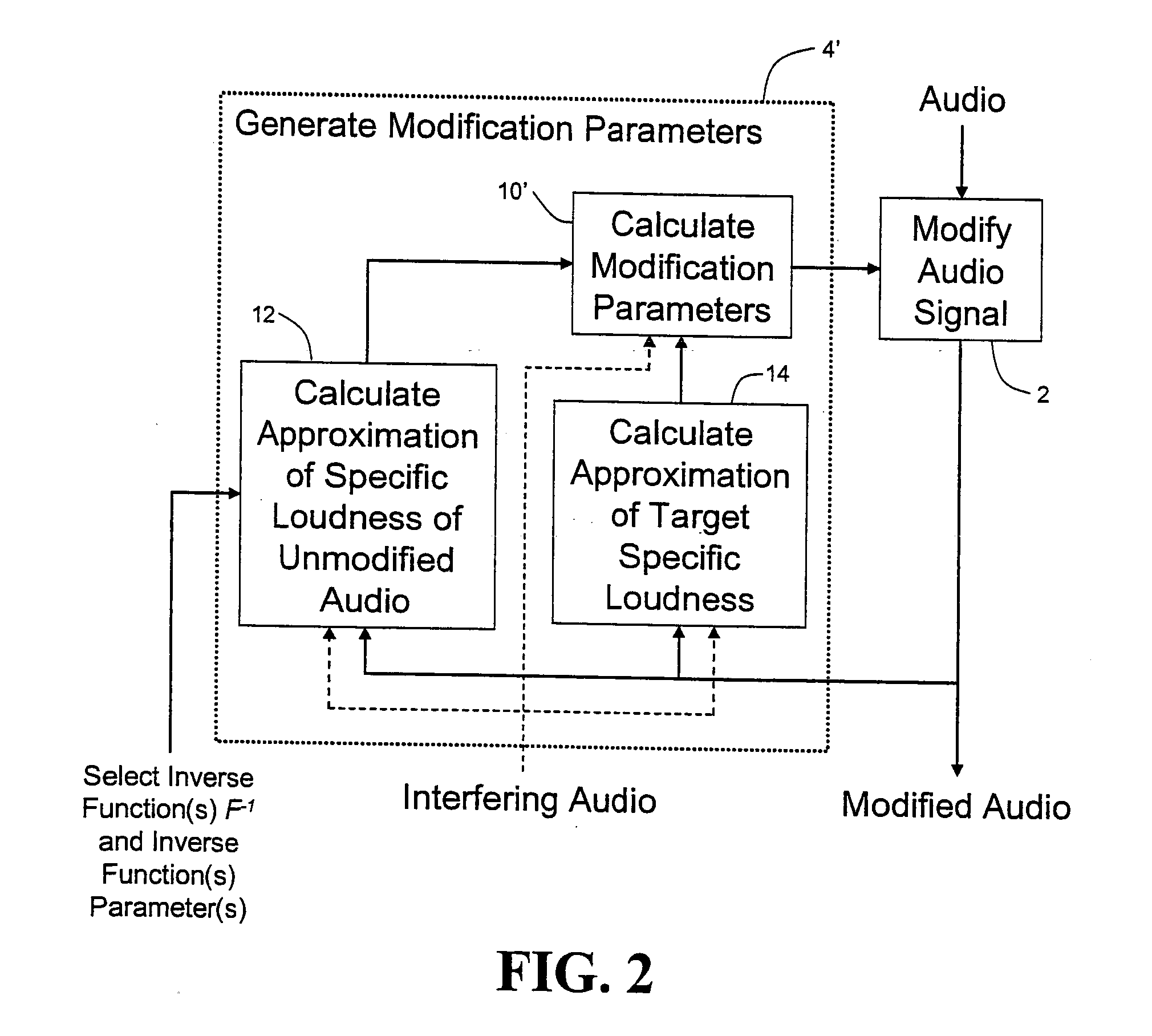
Calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness and/or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal
ActiveUS8090120B2Reduce the differenceReduce impactGain controlSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumEqualization
The invention relates to the measurement and control of the perceived sound loudness and / or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal. An audio signal is modified in response to calculations performed at least in part in the perceptual (psychoacoustic) loudness domain. The invention is useful, for example, in one or more of: loudness-compensating volume control, automatic gain control, dynamic range control (including, for example, limiters, compressors, expanders, etc.), dynamic equalization, and compensating for background noise interference in an audio playback environment. The invention includes not only methods but also corresponding computer programs and apparatus.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Multi-protocol radio frequency identification reader transceiver
ActiveUS20060186995A1Electric signal transmission systemsError preventionTransceiverDown conversion mixer
A transceiver for a RFID reader and a transceiver for a RFID transponder (tag) allow communication between the two devices. The RFID reader utilizes an analog front end and a digital backend. In the receiver portion of the transceiver, the front end of the RFID reader uses a pair of down-conversion mixers to demodulate a received signal into in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components and analog-to-digital converters (ADC) digitize the signal. A digital signal processor (DSP) in the back end processes the digital signal and uses a matched filter for data detection. The RFID tag receives an inductively coupled signal from the reader and the receiver portion of the tag uses a pulse / level detector that employs an analog comparator and a sample and hold circuit to detect the received signal. A digital decoder / controller is used to decode the incoming data and to establish a sampling clock for the pulse / level detector. An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit adjusts a receiver gain according to the received signal strength and controls tuning of magnetic coupling circuitry.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Audio processing apparatus for automatic gain control
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
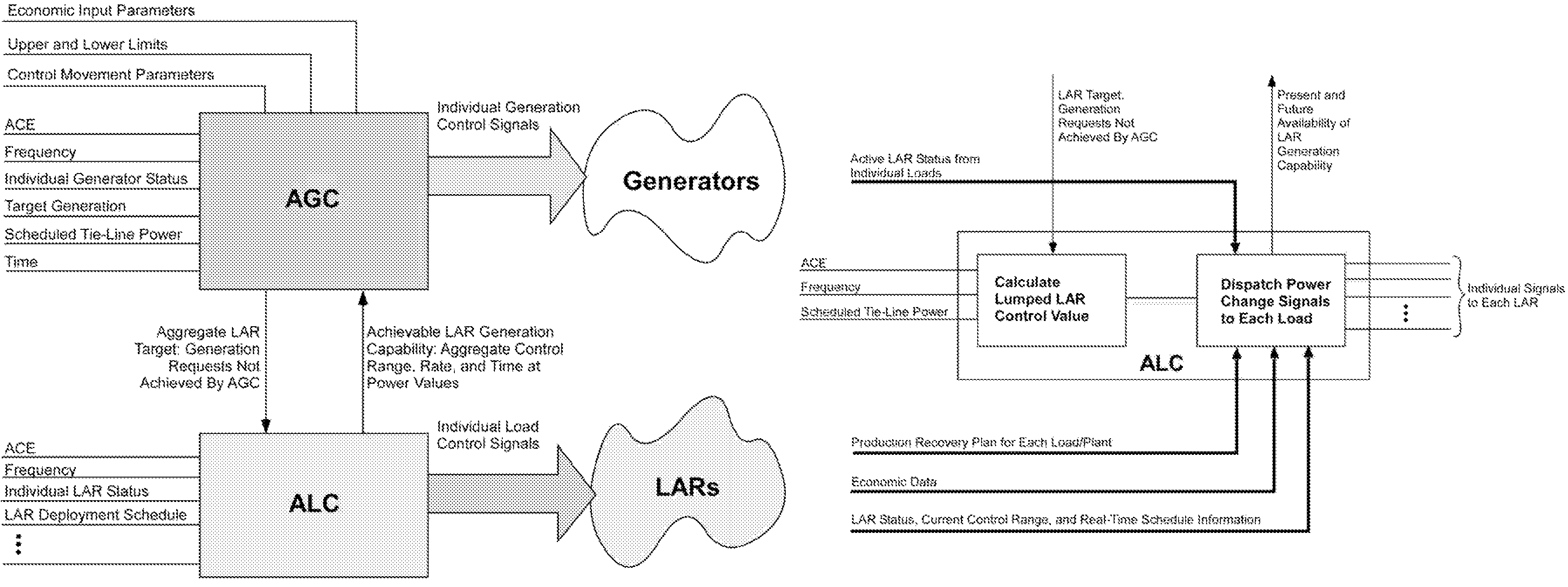
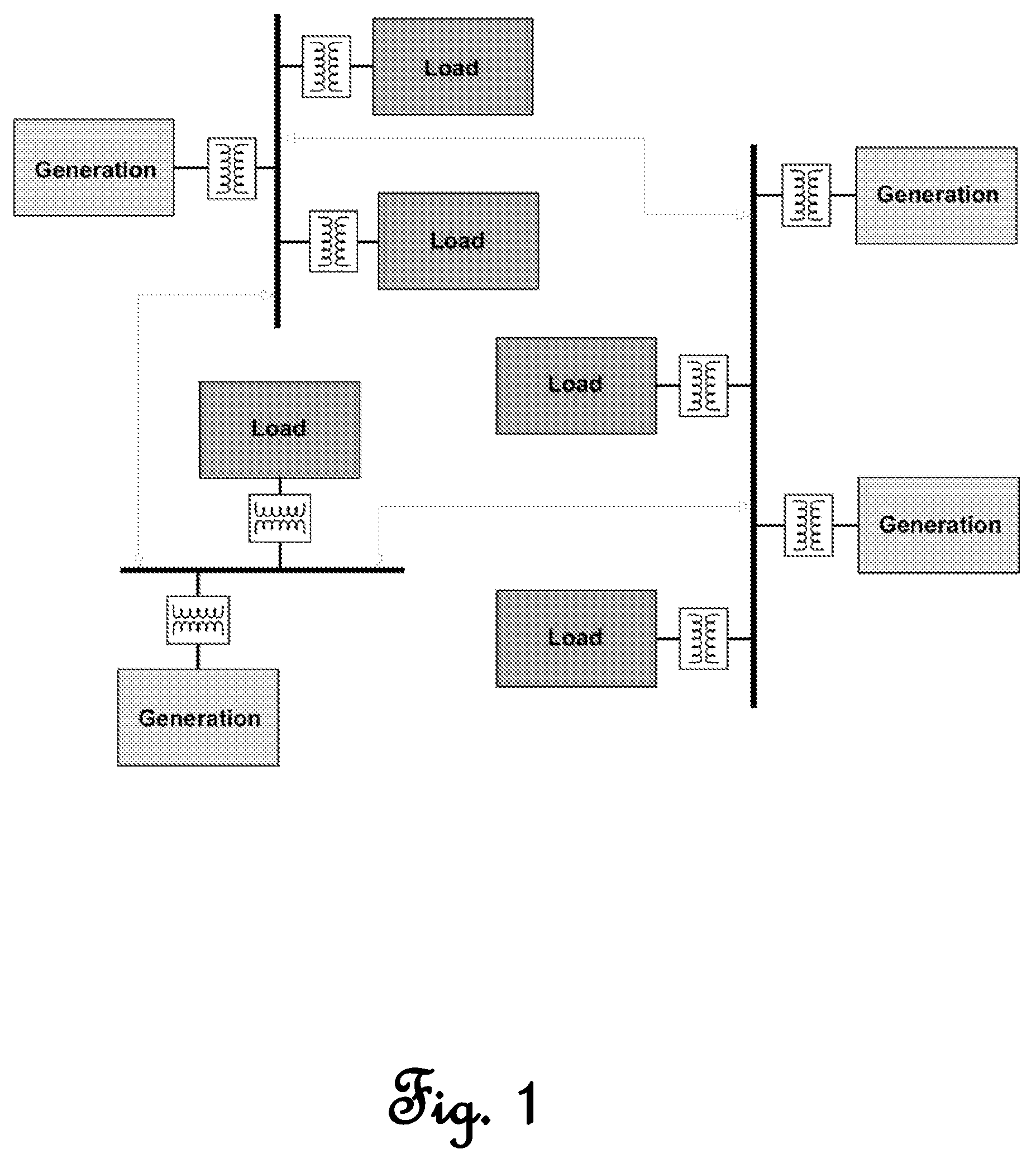
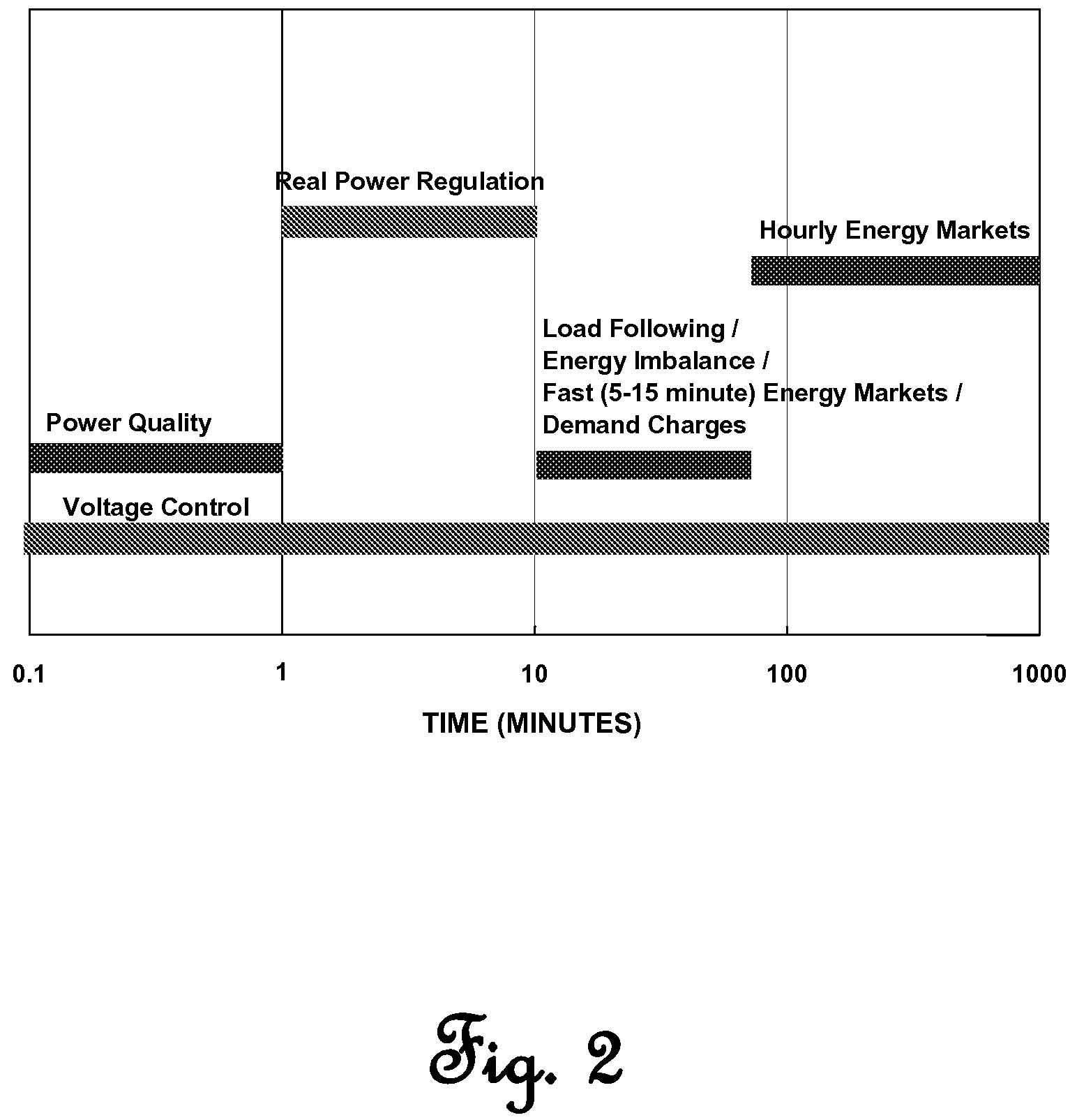
Real power regulation for the utility power grid via responsive loads
ActiveUS7536240B2Quick responseAccurate responseMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlAutomatic Generation ControlAutomatic control
A system for dynamically managing an electrical power system that determines measures of performance and control criteria for the electric power system, collects at least one automatic generation control (AGC) input parameter to at least one AGC module and at least one automatic load control (ALC) input parameter to at least one ALC module, calculates AGC control signals and loads as resources (LAR) control signals in response to said measures of performance and control criteria, propagates AGC control signals to power generating units in response to control logic in AGC modules, and propagates LAR control signals to at least one LAR in response to control logic in ALC modules.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
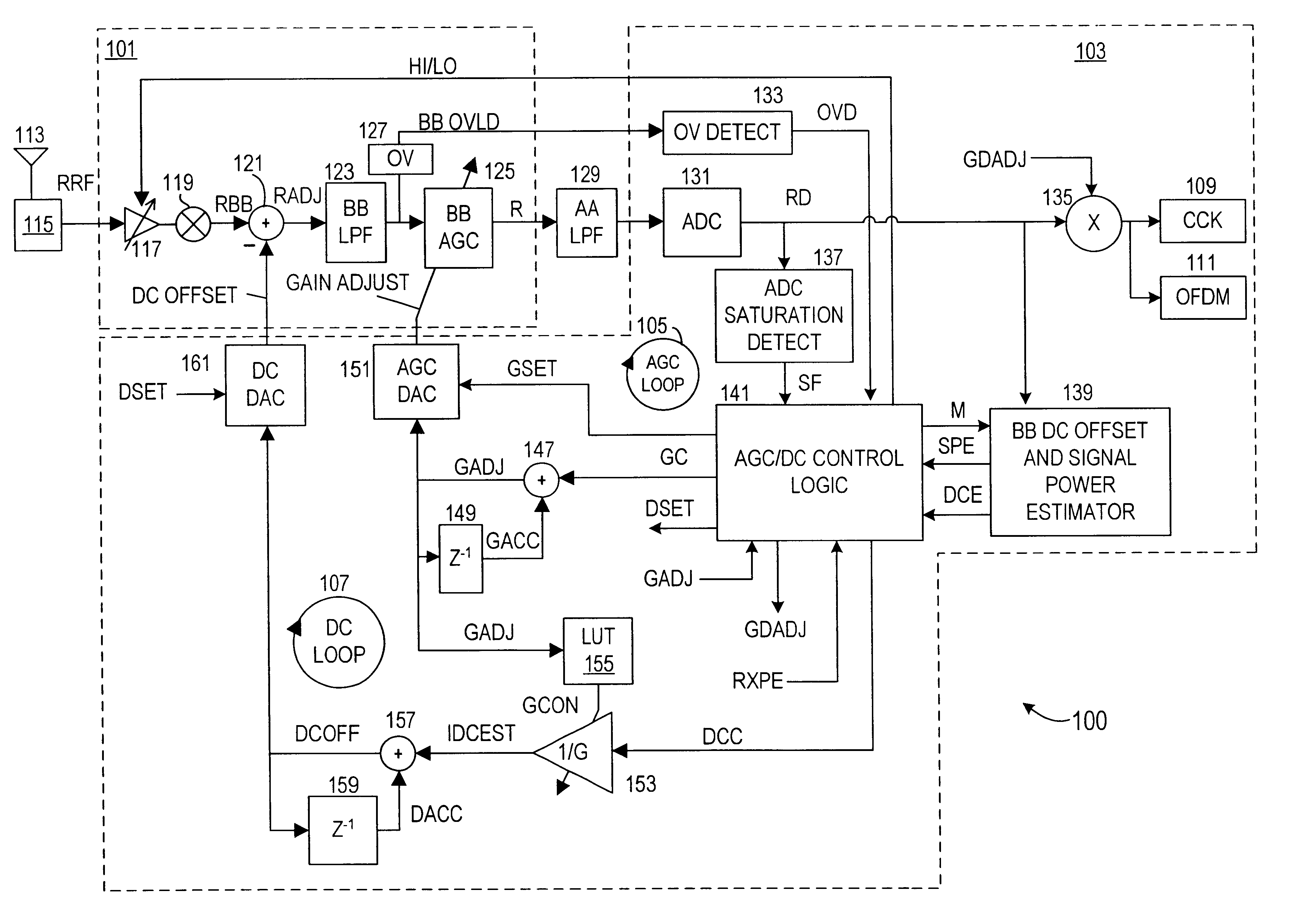
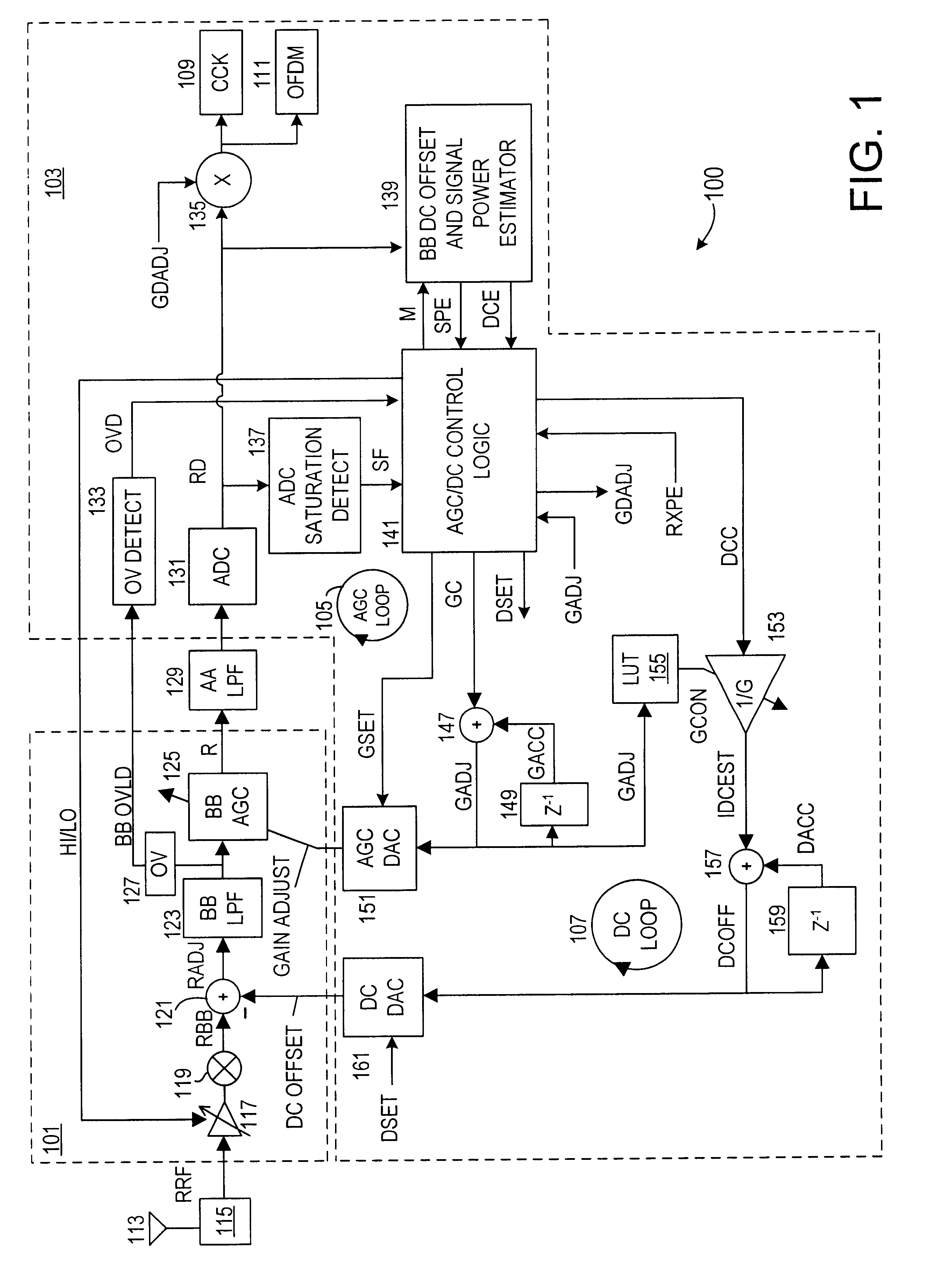
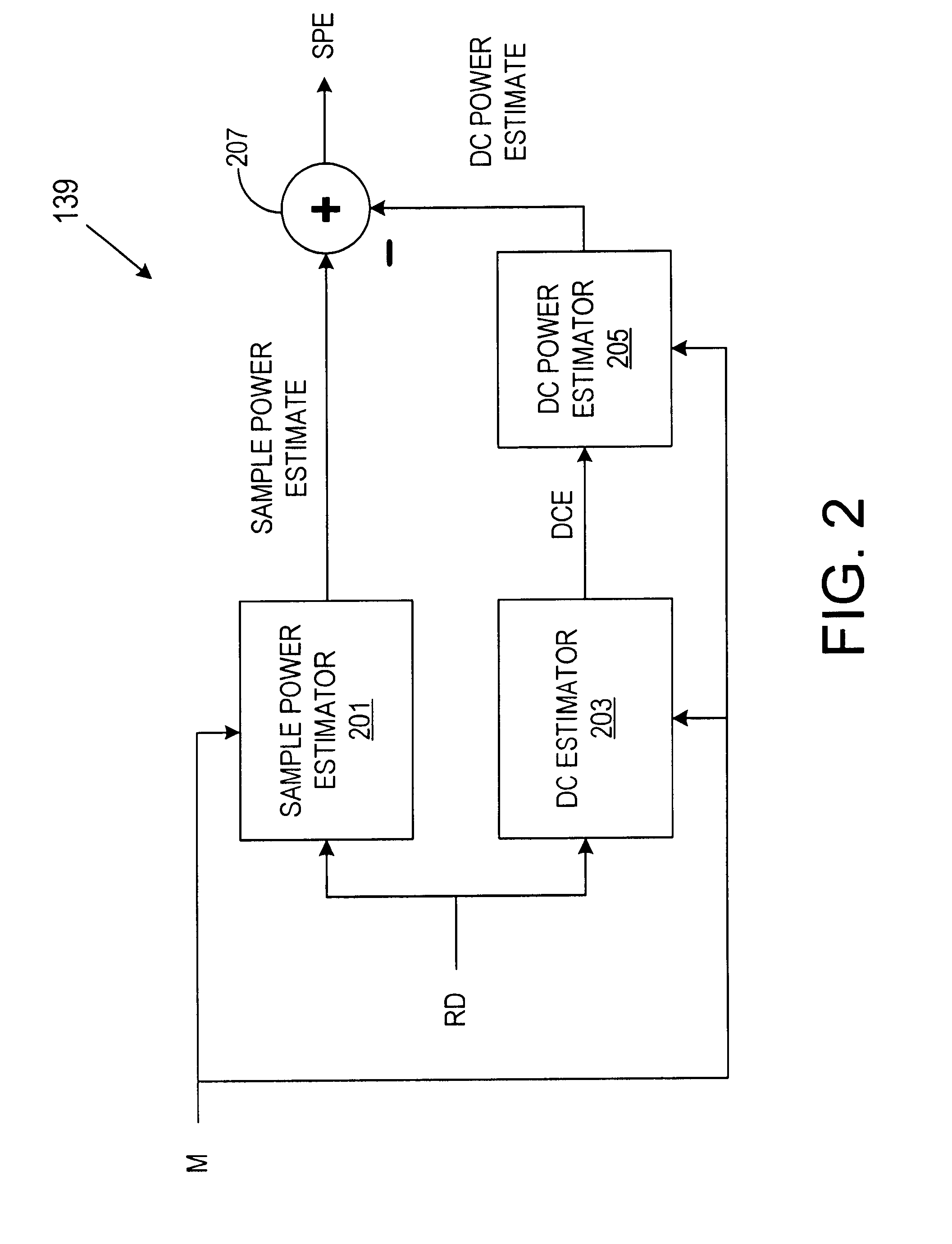
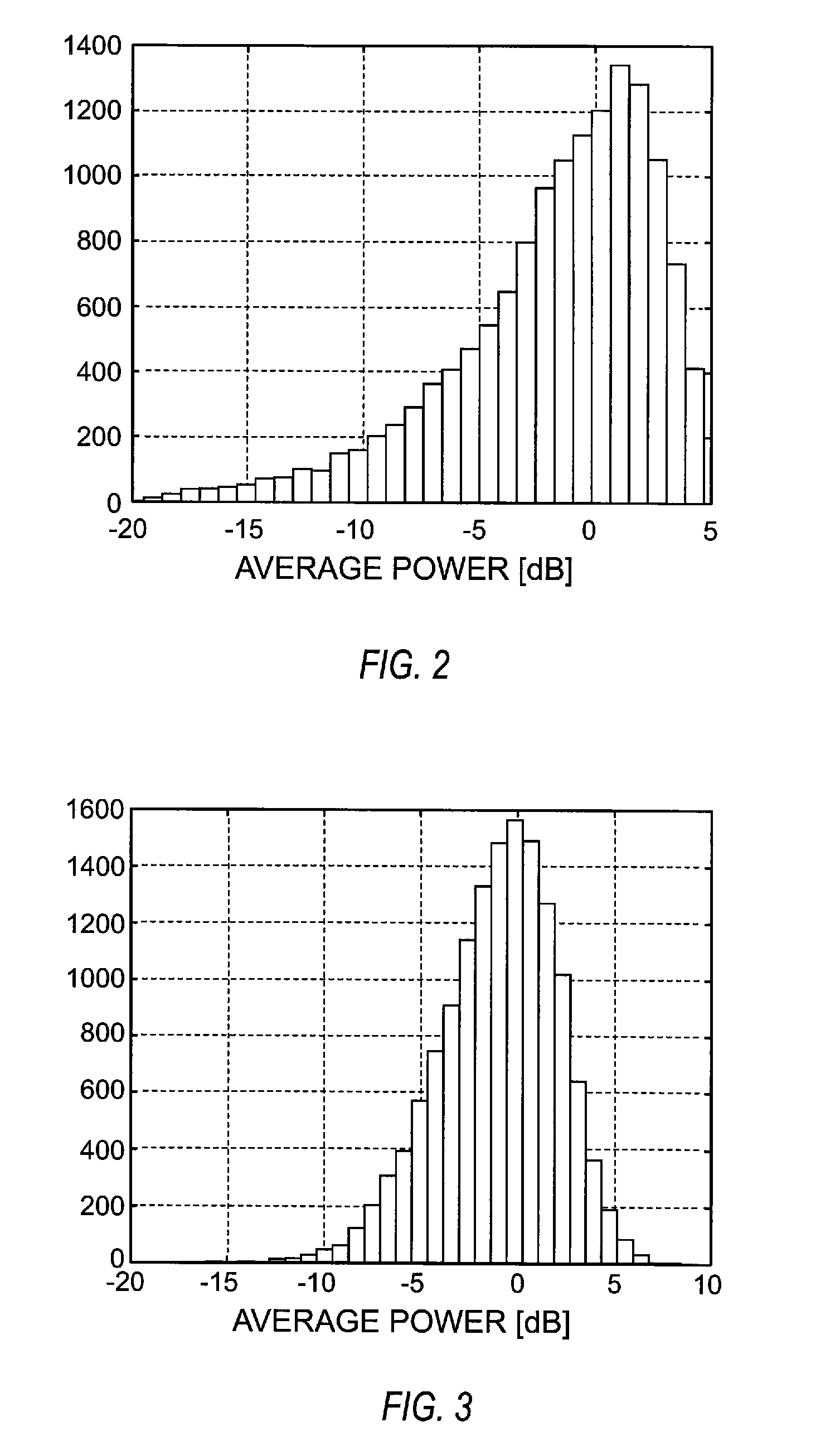
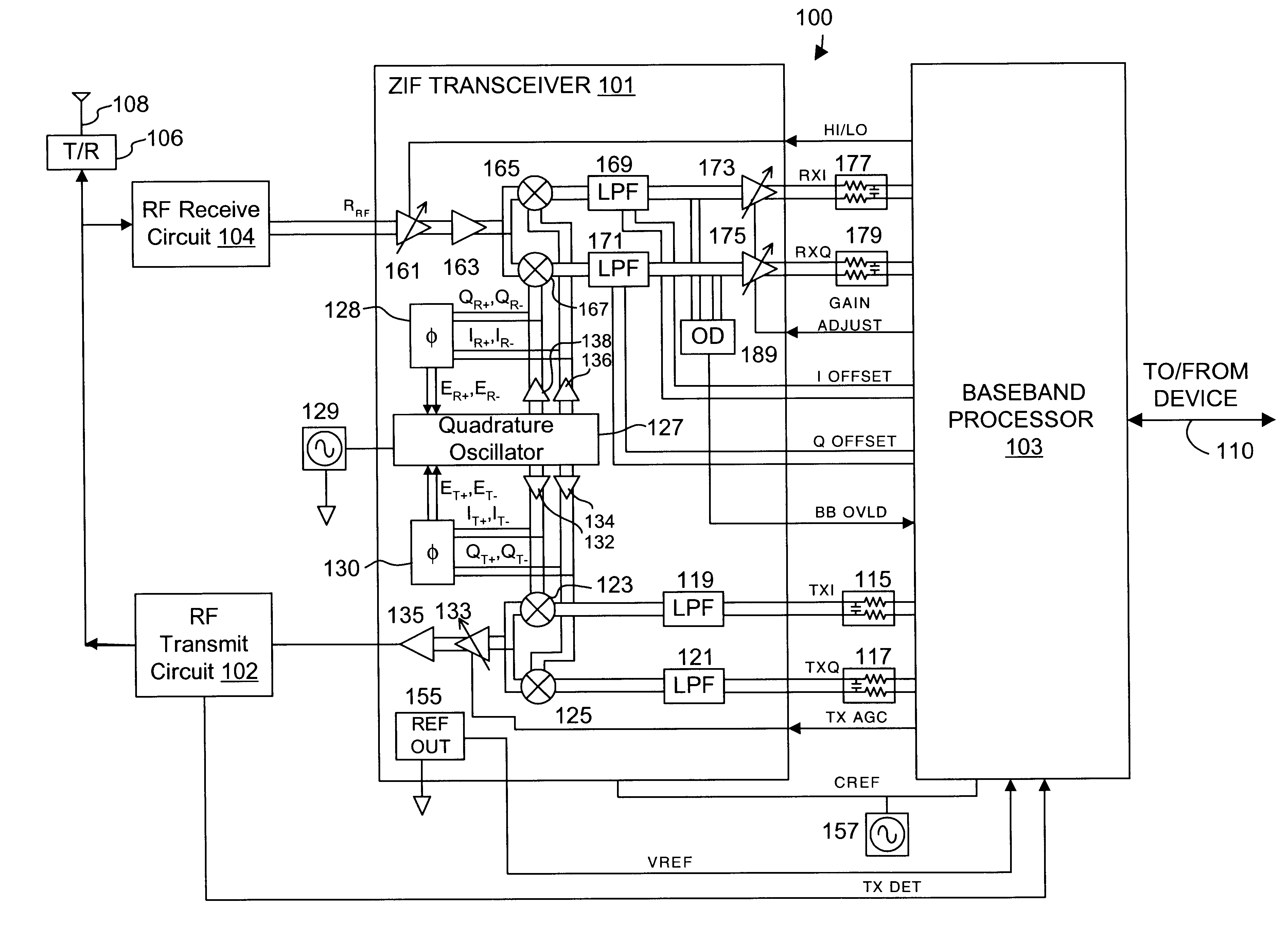
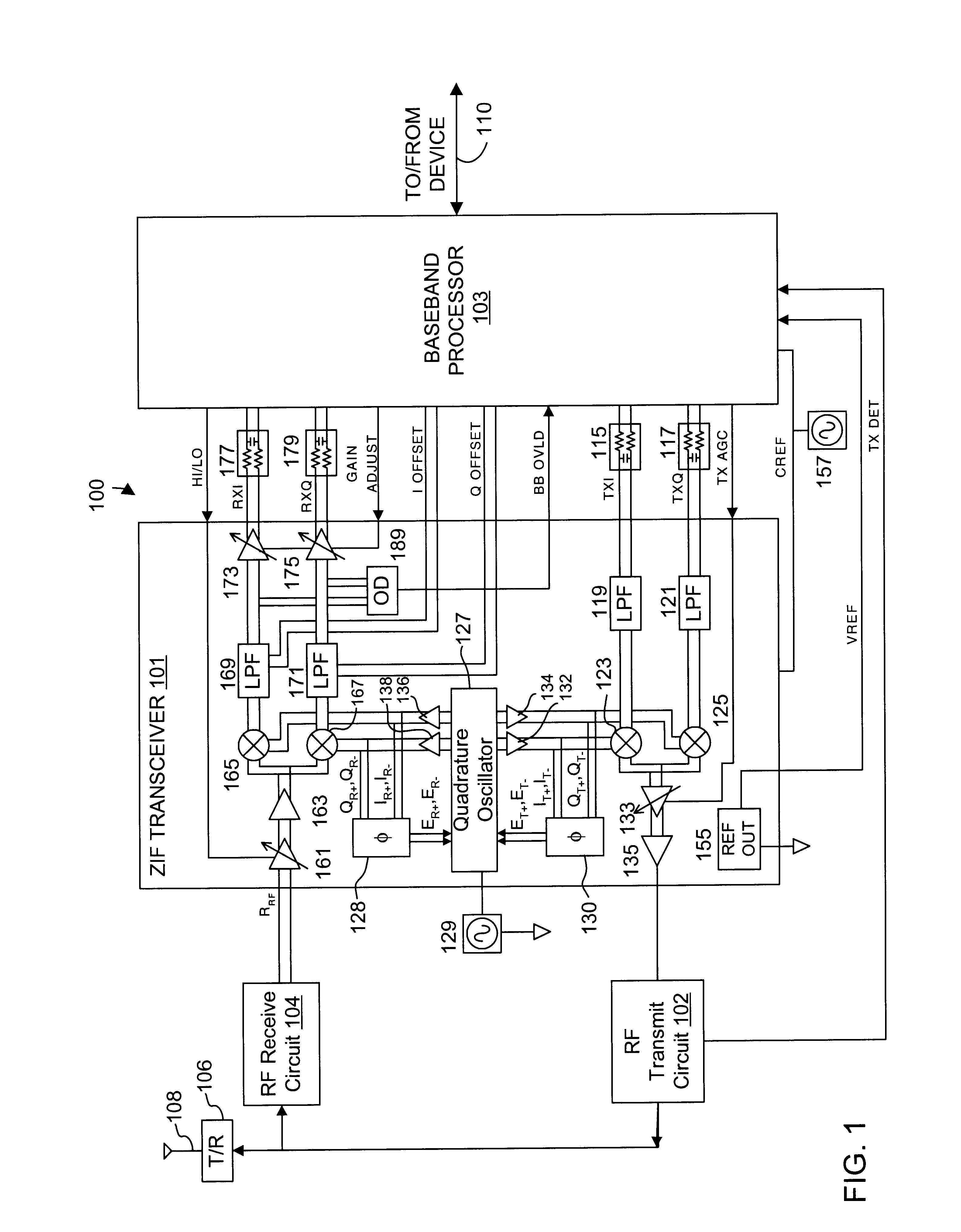
Automatic gain control system and method for a ZIF architecture
A system and method for controlling amplification of a signal received by a ZIF radio having a power level within a full power range relative to a minimum noise floor. The ZIF radio includes a ZIF receiver front end, an overload detector, an ADC, a saturation detector, a DC and power estimator, and control logic. The control logic utilized full visibility of the ADC to limit gain of the baseband amplifier to a maximum gain setting sufficient to view the minimum noise floor and to view a received signal having a power level within any of several segments of the power spectrum. The segmentation of the power spectrum is based on an overload condition of the ZIF receiver front end and a saturation condition of the ADC. The control logic further employs limited gain stepping of the baseband amplifier to avoid exceeding a DC budget of the ADC.
Owner:M RED INC
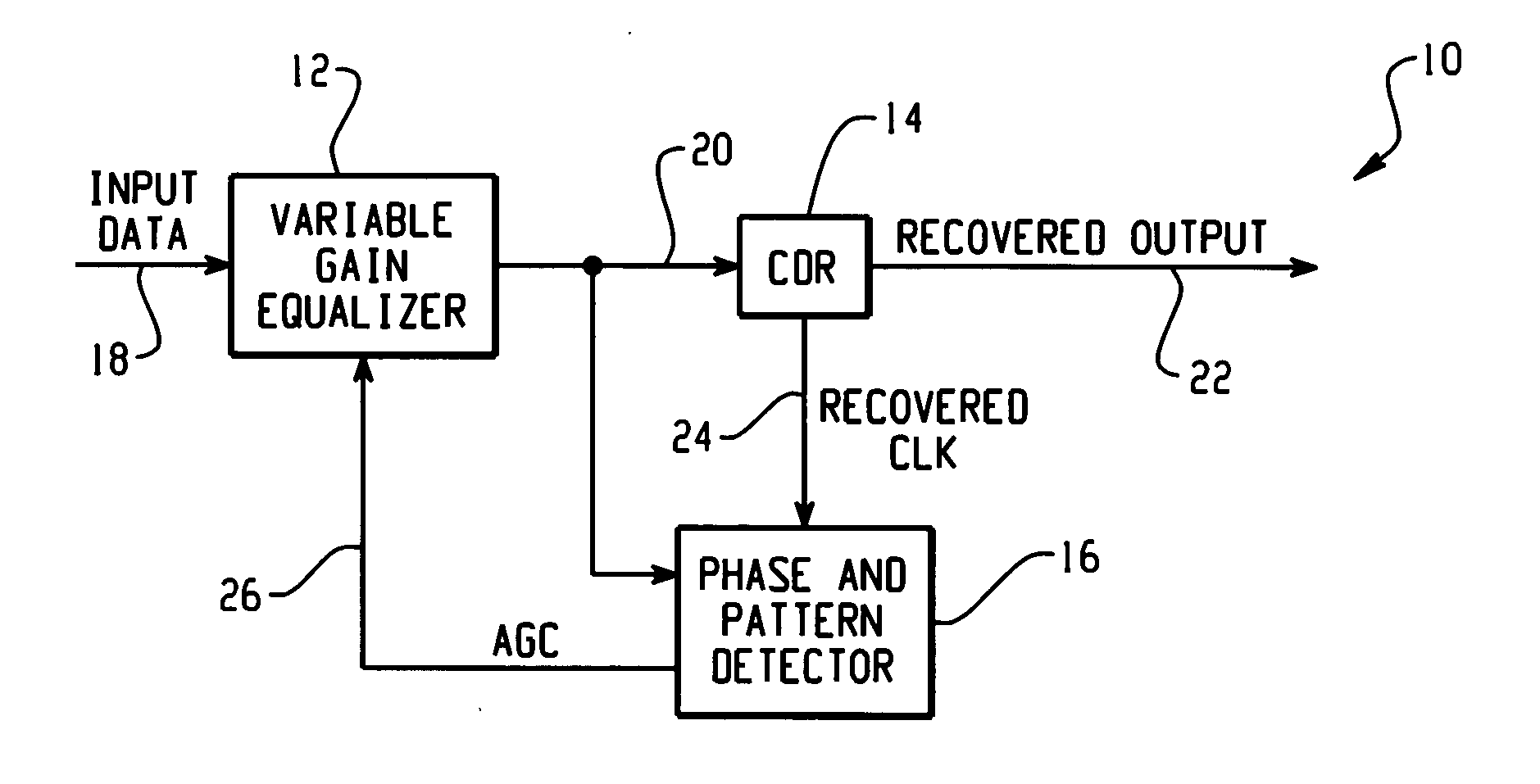
Precision adaptive equalizer
InactiveUS20050047500A1Multiple-port networksAdaptive networkDetector circuitsAutomatic gain control
In accordance with the teachings described herein, systems and methods are provided for a precision adaptive equalizer. A variable gain equalizer may be used to apply a variable gain to an input signal to generate an equalized output signal. A phase and pattern detector circuit may be coupled in a feedback loop with the variable gain equalizer. The phase and pattern detector circuit may be used to identify a high frequency data pattern in the equalized output signal and compare the high frequency data pattern with a clock signal to detect a high frequency phase error. The phase and pattern detector circuit may be further operable to generate an automatic gain control signal as a function of the high frequency phase error, the automatic gain control signal being fed back to the variable gain equalizer to control the variable gain applied to the input signal.
Owner:SEMTECH CANADA
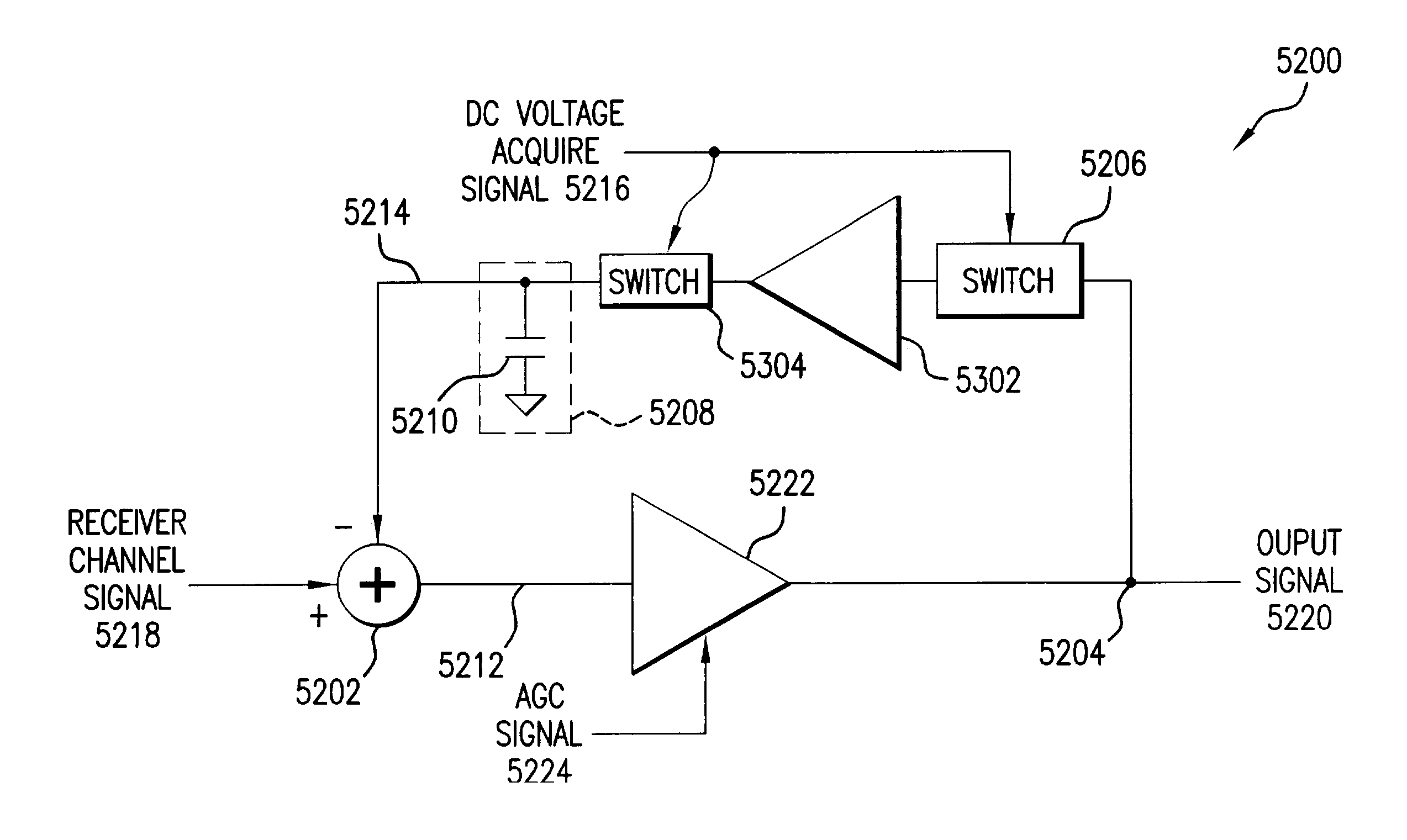
Method and apparatus for reducing DC offsets in a communication system
InactiveUS7072427B2Reduce DC offsetError preventionGain controlCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
Methods and apparatuses for reducing DC offsets in a communication system are described. In a first aspect, a feedback loop circuit reduces DC offset in a wireless local area network (WLAN) receiver channel. The frequency response of the feedback loop circuit can be variable. In a second aspect, a circuit provides gain control in a WLAN receiver channel. The stored DC offset is subtracted from the receiver channel. First and second automatic gain control (AGC) amplifiers are coupled in respective portions of the receiver channel. In a third aspect, a feedback loop circuit reduces DC offset in a WLAN receiver channel. The feedback loop circuit includes a storage element that samples and stores receiver channel DC offset. The loop is opened, and the DC offset stored in the storage element is subtracted from the receiver channel. Circuits for monitoring DC offset, and for providing control signals for controlling the frequency response of the DC offset reducing circuits are also provided.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
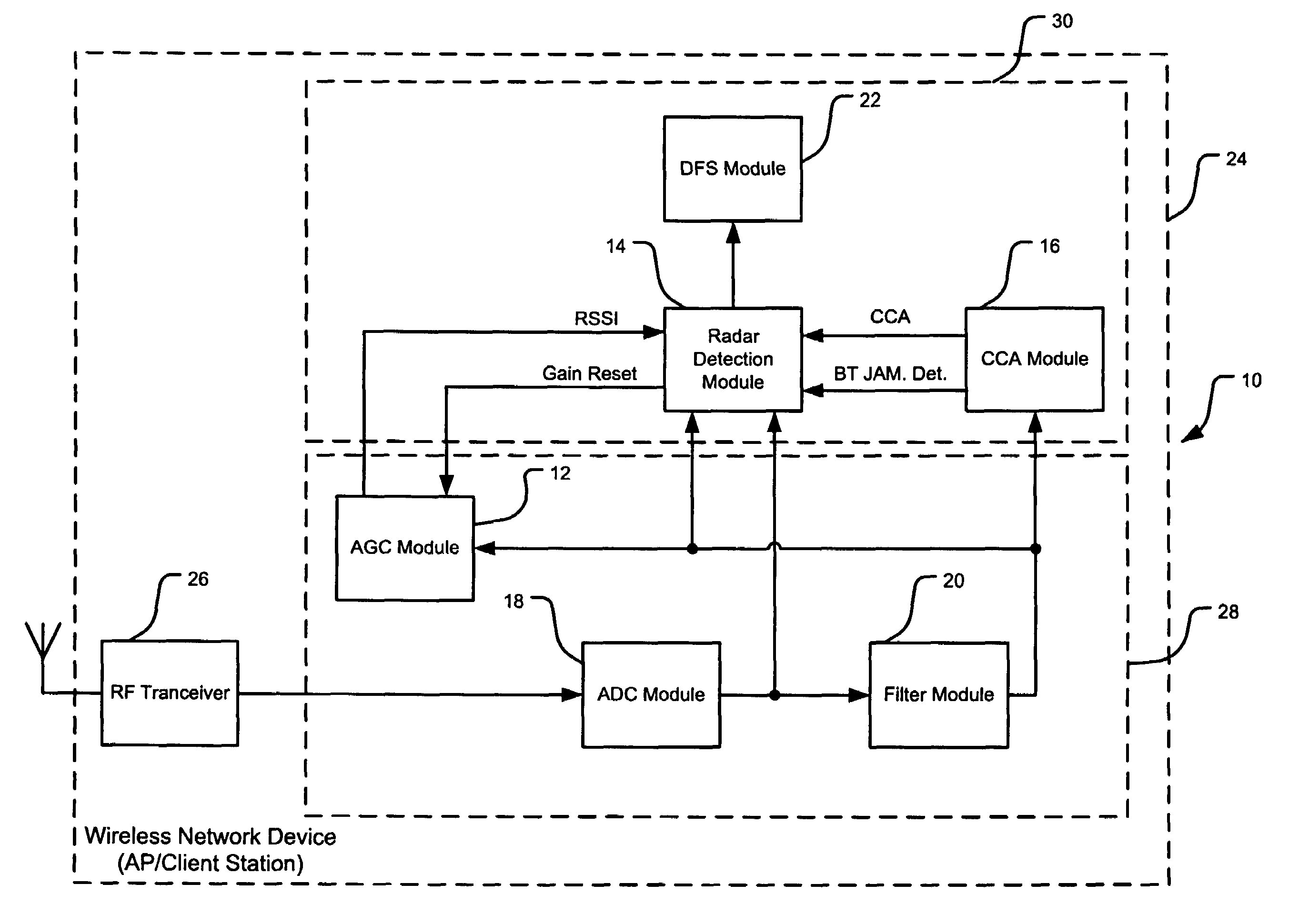
Radar detection and dynamic frequency selection
ActiveUS7702044B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunication jammingAutomatic controlControl signal
A wireless network device includes a correlation module, an automatic gain control module, and a control module. The correlation module correlates a predetermined portion of a radio frequency (RF) signal and generates a correlation signal based thereon. The automatic gain control (AGC) module generates a gain control signal based on said RF signal. The control module selectively determines whether said RF signal is a radar signal based on said correlation signal and said gain control signal.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Calculating and adjusting the perceived loudness and/or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal
ActiveUS20090097676A1Easy to controlReduce the differenceGain controlVolume compression/expansionFrequency spectrumEqualization
Audio signal processing relating to the measurement and control of the perceived sound loudness and / or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal is useful, for example, in one or more of: loudness-compensating volume control, automatic gain control, dynamic range control (including, for example, limiters, compressors, expanders, etc.), dynamic equalization, and compensating for background noise interference in an audio playback environment. In various embodiments, modification parameters are derived for modifying the audio signal in order to reduce the difference between its specific loudness and a target specific loudness.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
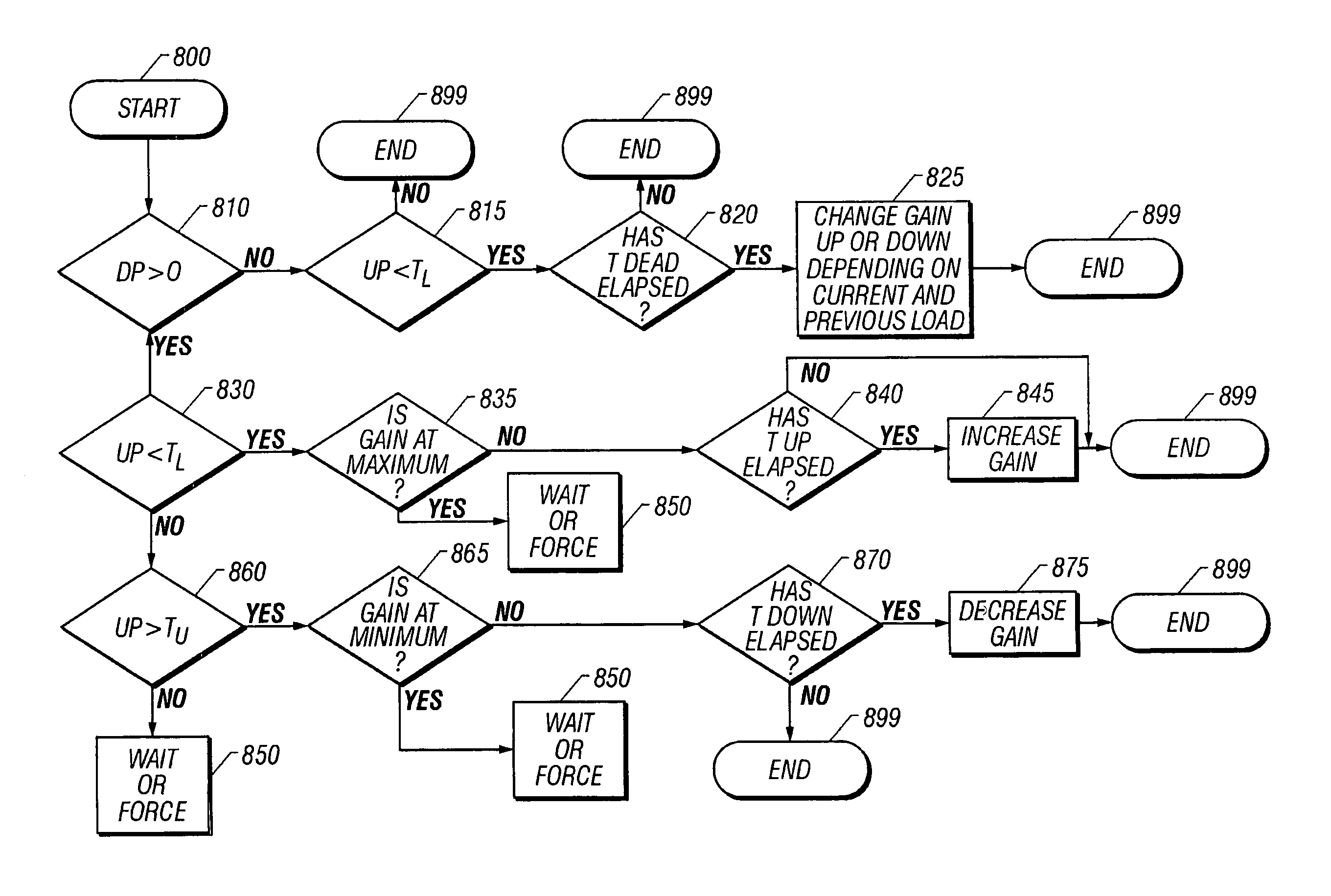
Long subscriber loops using automatic gain control mid-span extender unit
InactiveUS7142619B2Transmission control/equlisationRepeater/relay circuitsVariable-gain amplifierAudio power amplifier
Systems and methods are described for long subscriber loops using automatic gain control. A method includes extending a digital subscriber loop including: producing an output signal in a first direction from a variable gain amplifier at a mid-span extender unit responsive to an input signal in the first direction from the digital subscriber loop; monitoring a signal strength of said output signal in the first direction at the mid-span extender unit; generating a gain control signal responsive to the signal strength at the mid-span extender unit; controlling a gain of the variable gain amplifier at the mid-span extender unit responsive to the gain control signal; and controlling a second gain of a second variable gain amplifier at said mid-span extender unit responsive to said gain control signal to produce an output signal in a second direction from said second variable gain amplifier at said mid-span extender unit responsive to a second input signal in said second direction from said digital subscriber loop.
Owner:SYMMETRICOM
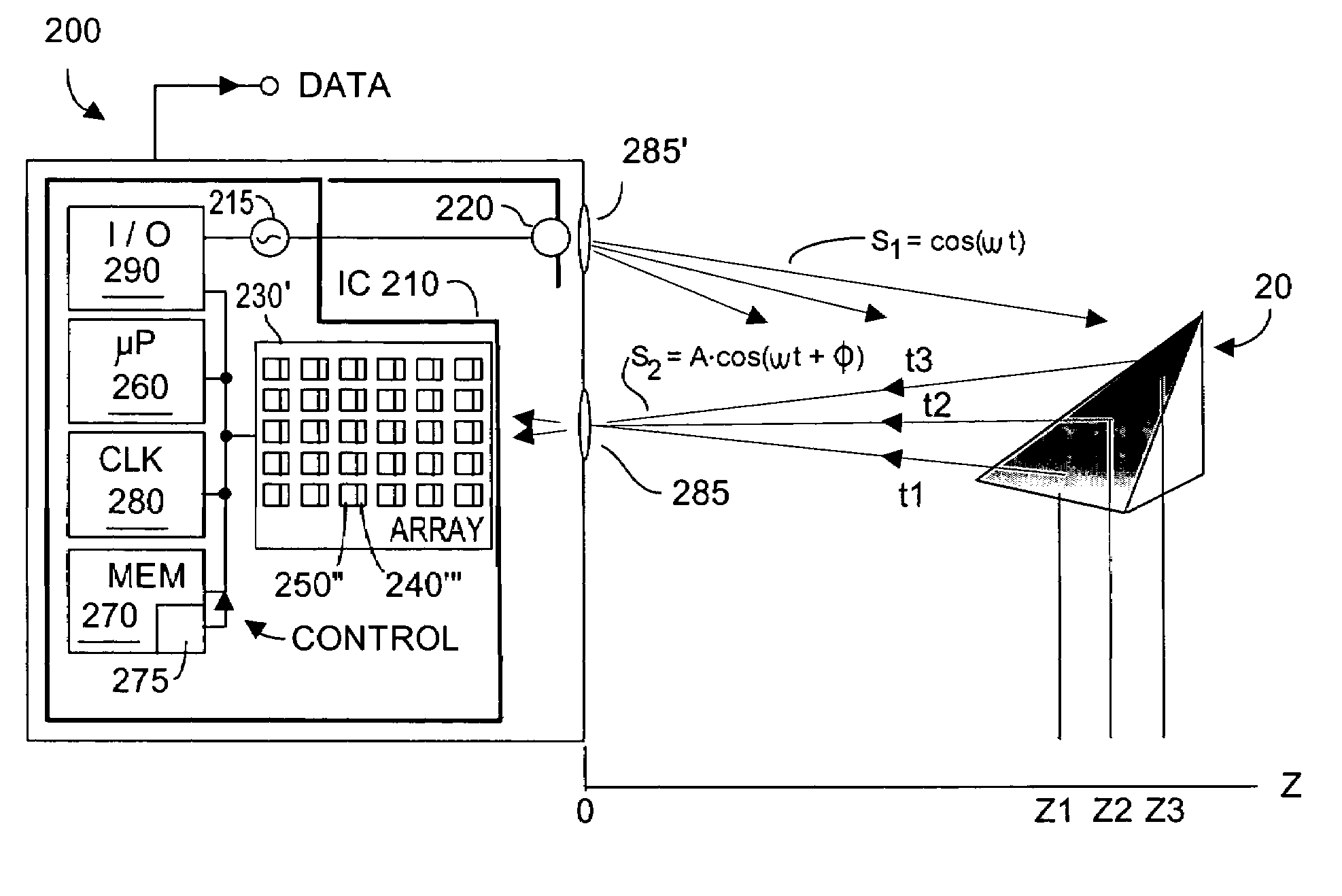
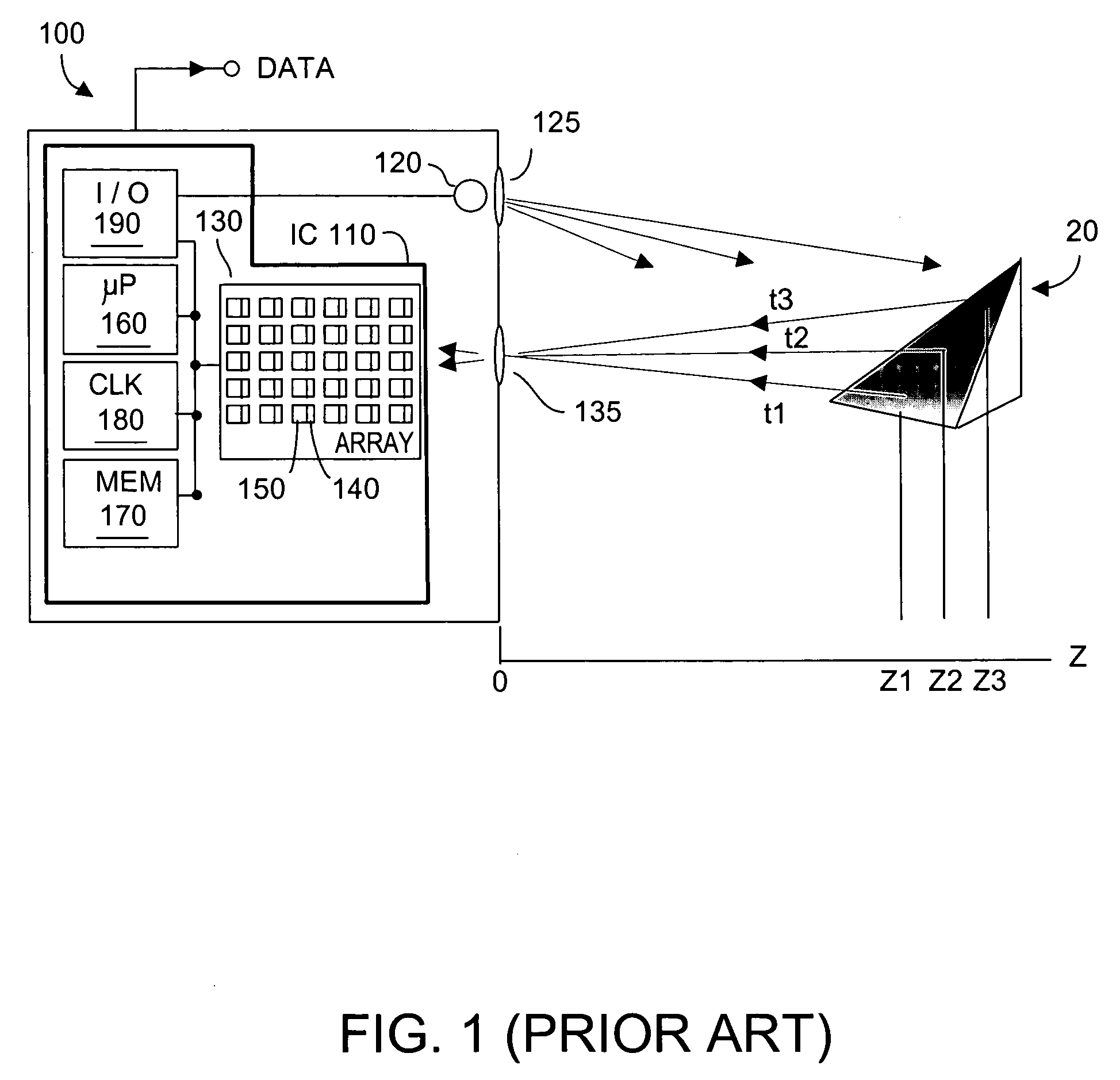
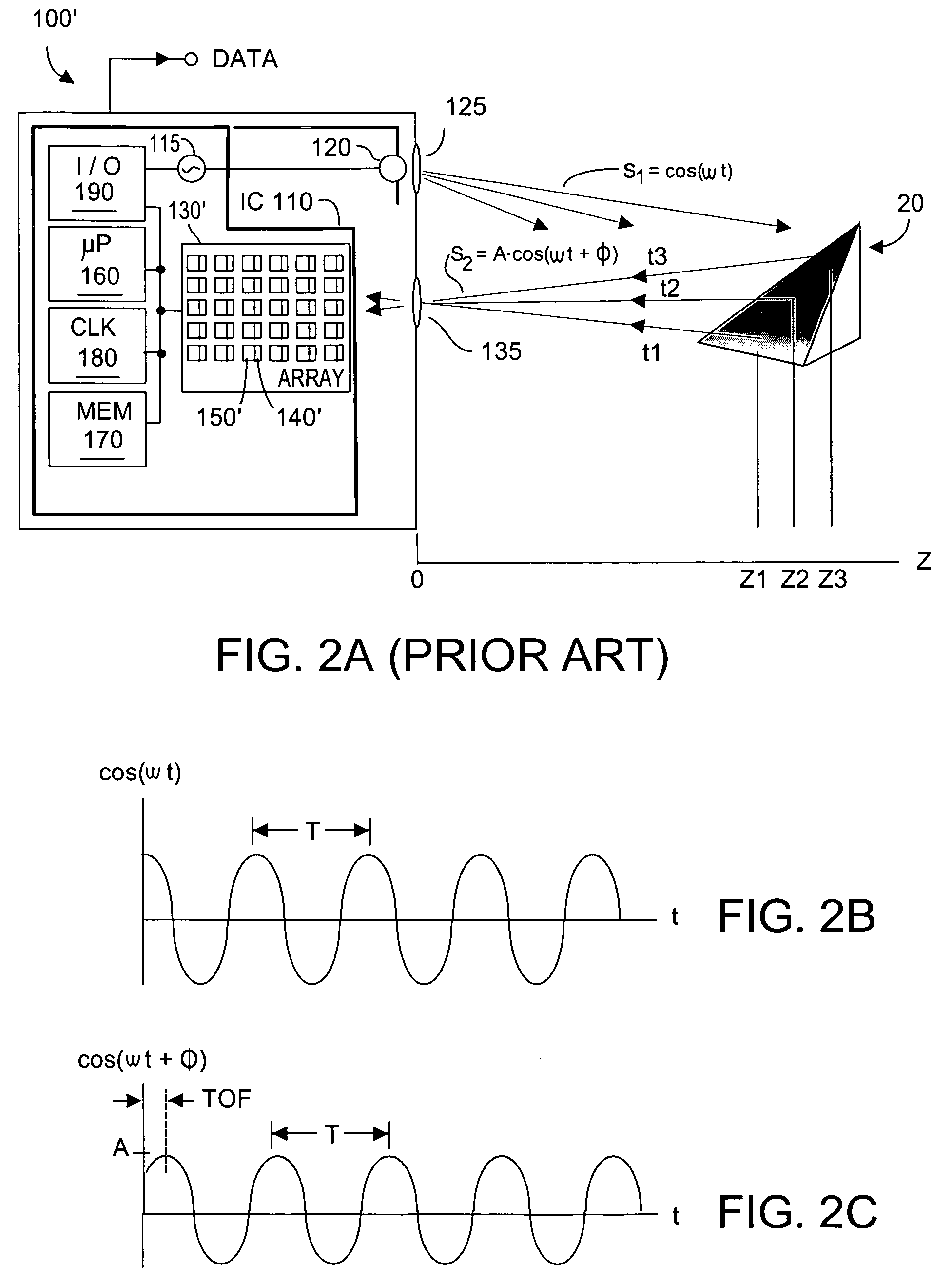
Method and system for automatic gain control of sensors in time-of-flight systems
InactiveUS7379163B2Maximizing numberMaximize number of pixelOptical rangefindersAutomatic controlExposure Elapsed Time
Performance of pixel detectors in a TOF imaging system is dynamically adjusted to improve dynamic range to maximize the number of pixel detectors that output valid data. The invention traverses the system-acquired z depth, the brightness, and the active brightness images, and assigns each pixel a quantized value. Quantization values encompass pixels receiving too little light, normal light, to too much light. Pixels are grouped into quantized category groups, whose populations are represented by a histogram. If the number of pixels in the normal category exceeds a threshold, no immediate corrective action is taken. If the number of pixel receiving too little (or too much) light exceeds those receiving too much (or too little) light, the invention commands at least one system parameter change to increase (or decrease) light reaching the pixels. Controllable TOF system parameters can include exposure time, common mode resets, video gain, among others.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
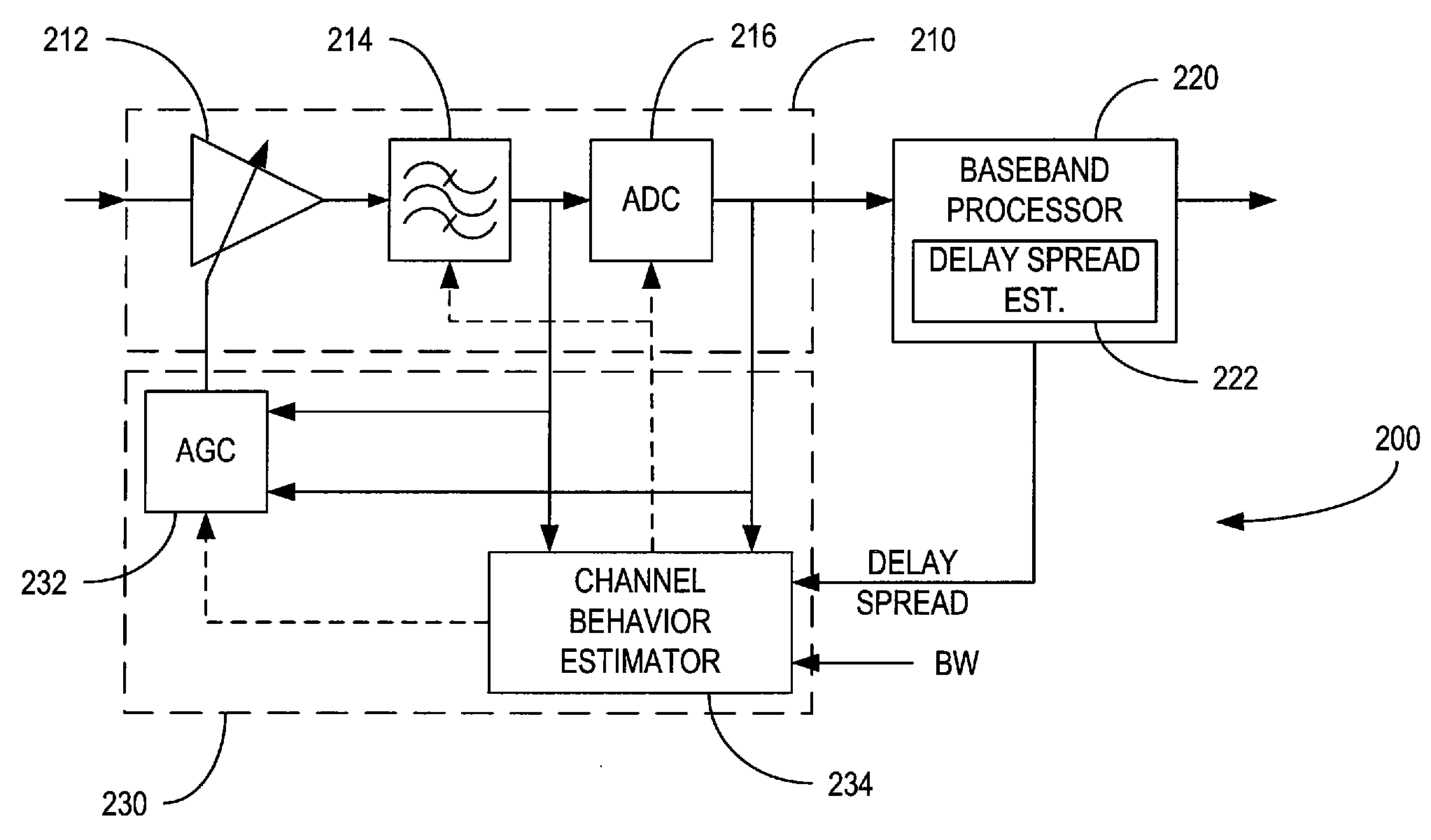
Automatic Gain Control Based on Bandwidth and Delay Spread
ActiveUS20100189203A1Dynamic range is efficientlyAmount of signal variationGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDelay spreadEngineering
A gain control circuit adjusts the signal level of a received signal responsive to the bandwidth a received signal and / or the delay spread of the channel in which the signal has propagated. The bandwidth and delay spread are evaluated to estimate the amount of signal variation that is expected due to fast fading. Adjustments to the signal level are then made to avoid clipping while at the same time ensuring that the dynamic range of a receiver component is efficiently utilized.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
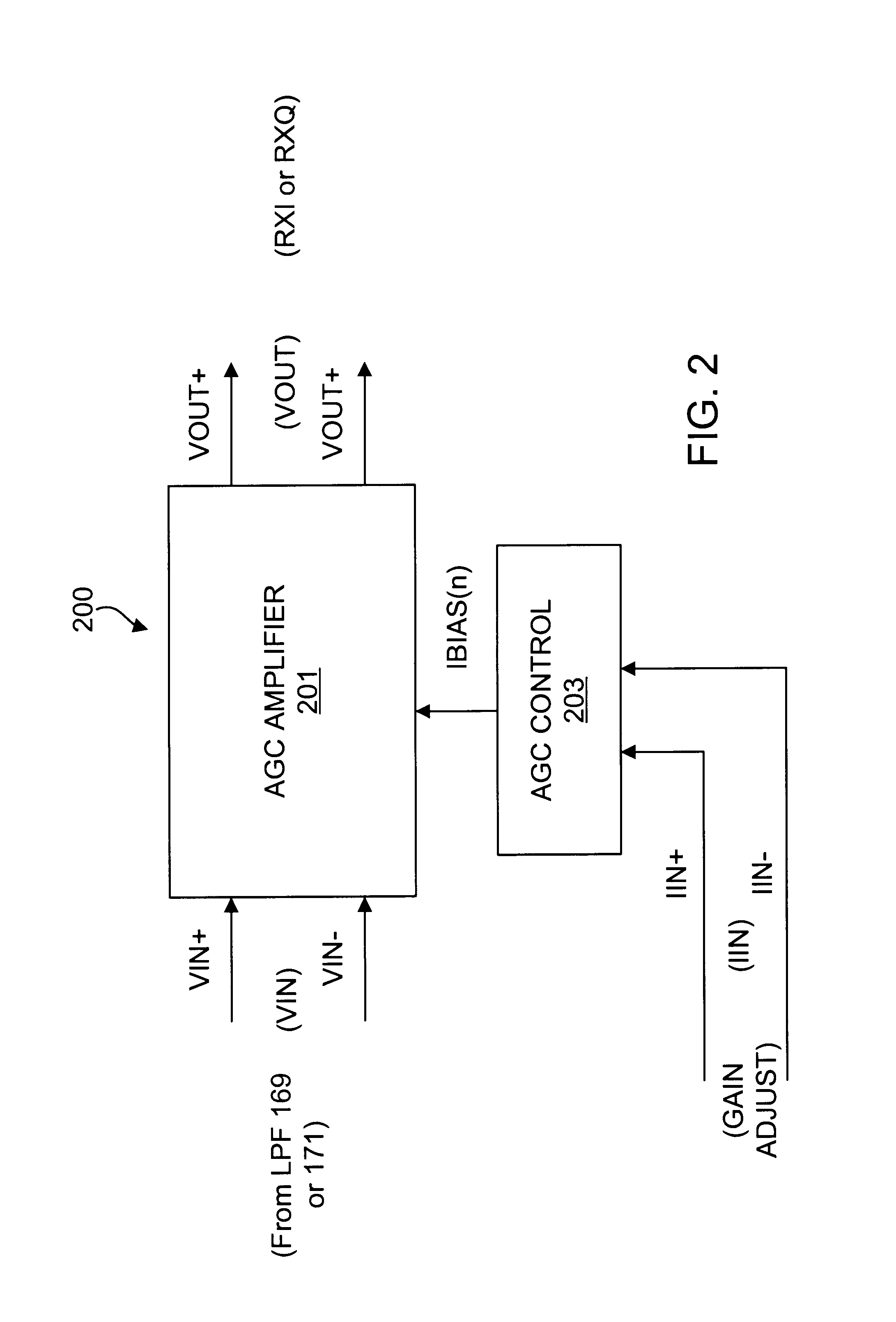
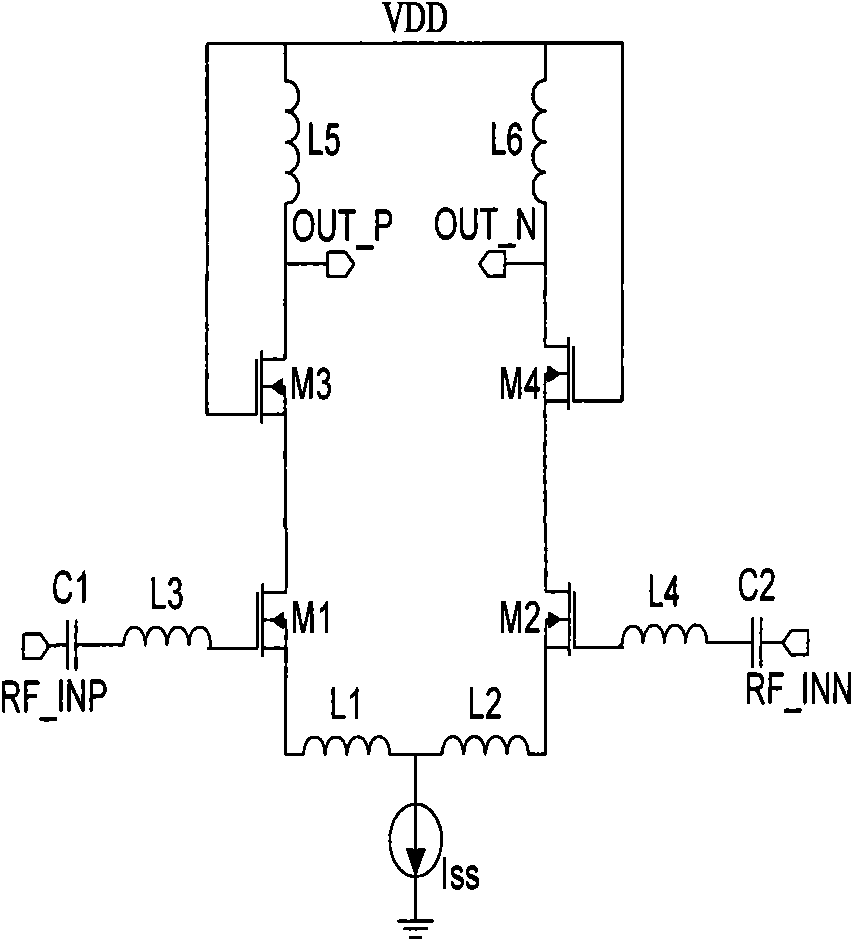
Precision automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS6763228B2Low absolute gain toleranceImprove matchResonant long antennasVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierClosed loop
An automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier including a high gain transimpedance amplifier, a resistive feedback network and multiple transconductance stages coupled in the feedback path of the AGC amplifier. The feedback network receives an input signal and is coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and has multiple intermediate nodes. Each transconductance stage has an input coupled to an intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. Each transconductance stage is independently controllable to position a virtual ground within the feedback network to control closed loop gain. Each transconductance stage may have a bias current input coupled to a bias current control circuit. The control circuit controls each bias current to vary the gain of the AGC amplifier. The bias currents may be linearly controlled employing a ramp function to achieve a linear in dB gain response.
Owner:M RED INC
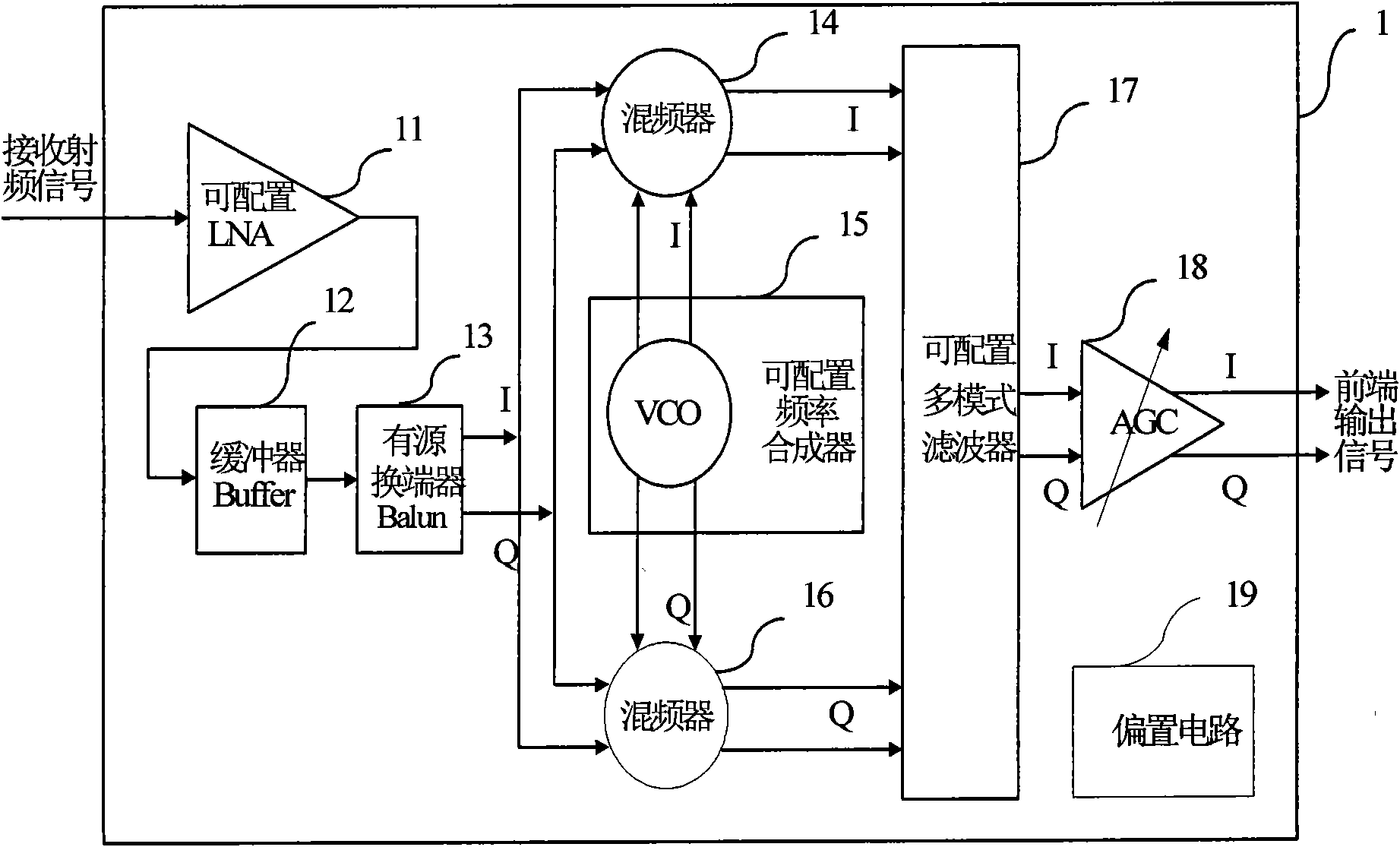
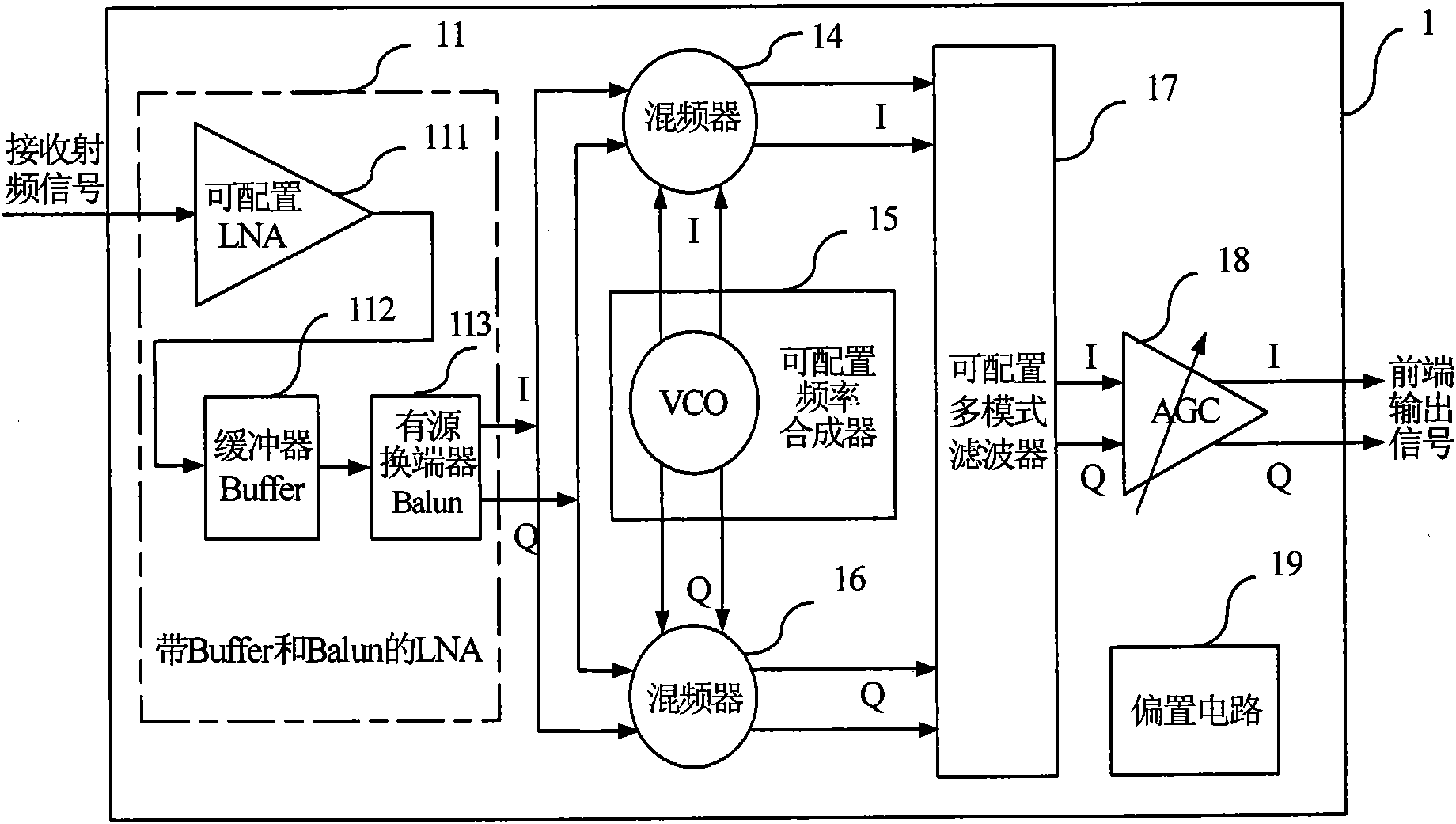
Method for constructing radio frequency front end of multi-mode multi-band satellite navigation receiver and module thereof
InactiveCN102096079ASimple and reliable compositionReduce common mode noiseBeacon systems using radio wavesSatellite radio beaconingMulti bandDifferential signaling
The invention discloses a configurable multi-mode multi-band satellite navigation receiving method and a radio frequency front end module constructed by the method. The front end module can receive signals of satellite navigation and positioning systems such as a global positioning system (GPS), the Big Dipper, a Galileo positioning system and a global navigation satellite system (Glonass), and comprises a configurable low-noise amplifier (LNA) with a buffer and an active balun, a folding passive mixer with a configurable frequency synthesizer, a configurable multi-mode filter, an automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier, a direct-current bias circuit, and a multi-mode multi-band program controlled and coded on-off control word from a receiving system. The radio frequency front end module can meet the requirement of multi-band multi-mode work through the control word programmed by the receiving system, has a simple and reliable structure, does not need complicated time division multiplexing control system and off-chip module, has low cost and high flexibility, and improves the noise performance of the radio frequency front end of the whole receiver and multi-mode multi-band signal processing capacity; and a one-channel signal is input into the module, and the module outputs a two-channel differential signal. The receiver can be used for receiving and processing multi-mode satellite navigation signals asynchronously, and receiving and processing satellite navigation signals with the required mode in different time intervals according to the requirement.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
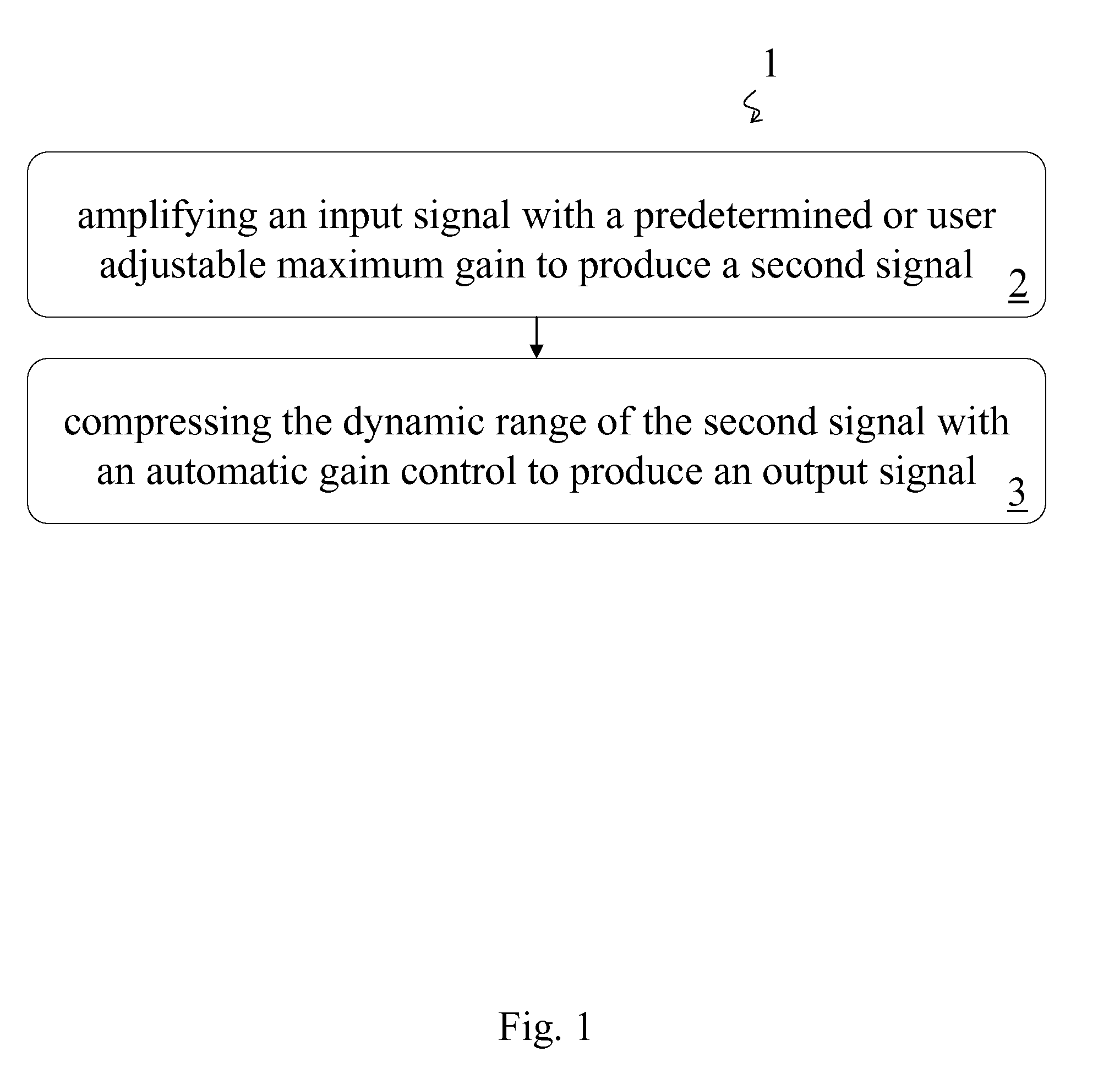
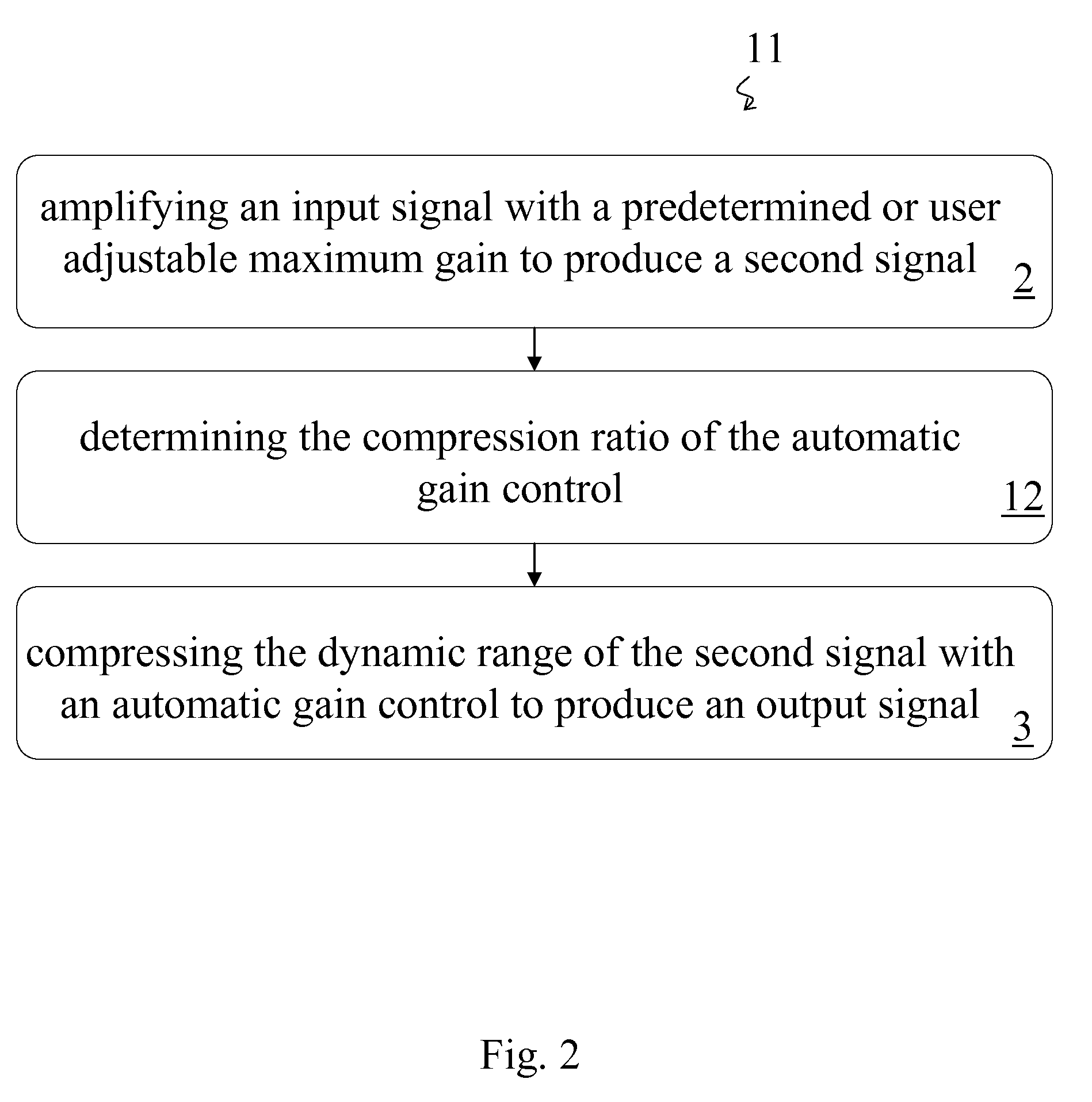
Amplifier and Method of Amplification
InactiveUS20080069385A1Cancel noiseVolume compression/expansion in untuned/low-frequency amplifiersFrequency response correctionAudio power amplifierEngineering
A method of amplification includes amplifying an input signal with a predetermined or user adjustable maximum gain to produce a second signal and compressing the dynamic range of the second signal with an automatic gain control to produce an output signal. The compression ratio of the automatic gain control is greater than one for output signals below a predetermined threshold output signal level and is essentially one for output signals above the predetermined threshold output signal level. The compression ratio may be predetermined or the method may include determining the compression ratio of the automatic gain control. The compression ratio may be determined according to the amplitude of the output signal or according to an input-output curve. The input-output curve my be predetermined and may be selected according to the auditory needs of a listener. Preferably the input-output curve is determined according to the predetermined or user adjustable maximum gain.
Owner:REVITRONIX
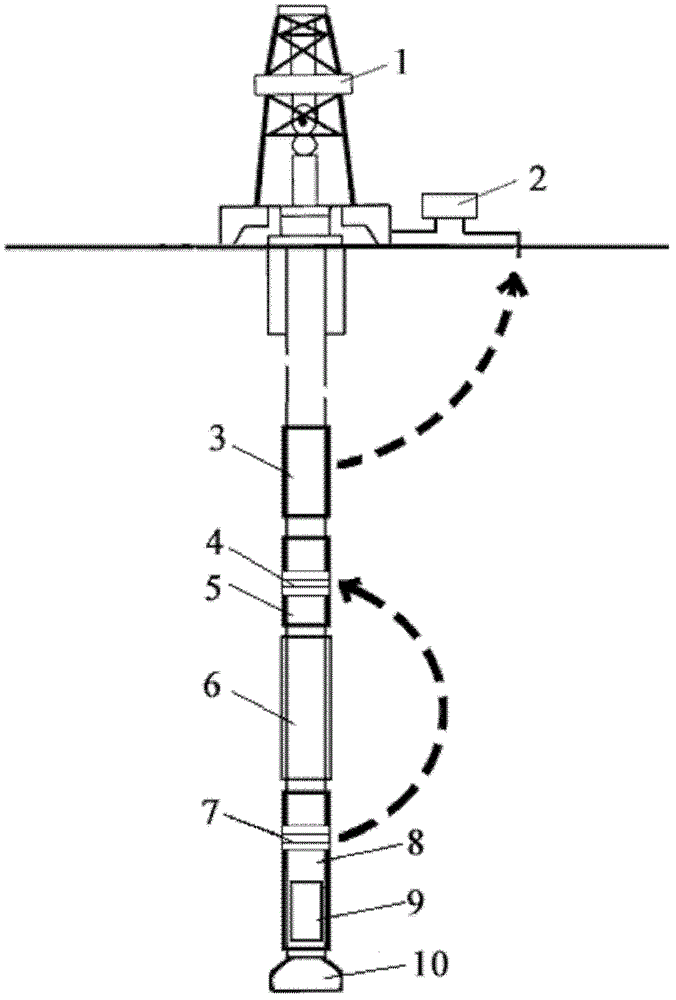
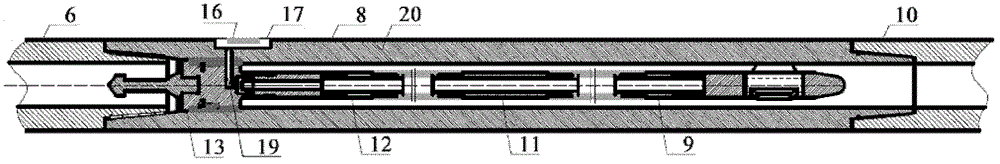
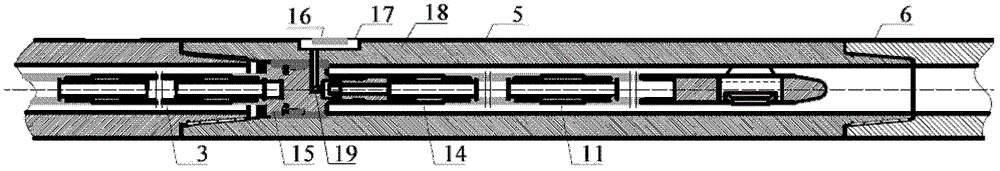
Short distance transmission system for wireless electromagnetic wave signals of downhole near bit and short distance transmission method
The invention provides a short distance transmission system for wireless electromagnetic wave signals of a downhole near bit and a short distance transmission method, and belongs to the field of geosteering systems and measurement while drilling instruments in industries such as petroleum, mines and geological prospecting. The automatic gain control technology is adopted in the short distance transmission system for realizing the automatic adjustment of enlargement factors of downhole weak signals. The short distance transmission system comprises a short section receiving assembly and a short section transmitting assembly, wherein the short section receiving assembly and the short section transmitting assembly are respectively provided with a receiving antenna and a transmitting antenna. Due to the fact that radial coupled antennas are adopted, the short distance transmission system is relatively simple in structure. Meanwhile, the short distance transmission system is high in arithmetic speed and can meet demands for real-time transmission of a large number of signals. Moreover, a front end processing module special for the downhole weak signals is utilized for carrying out the automatic gain adjustment to the collected signals, maintaining stable output of the signals and lowering processing difficulty of subsequent signals, and therefore the signal transmission quality is greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Dynamic configuration of a radio frequency transponder
ActiveUS20050237163A1Increased power consumptionShortened battery lifeElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsCapacitanceRadio frequency
A multi-channel remote keyless entry (RKE) transponder having dynamically re-configurable input channel selection, channel disable, settable sensitivity for each channel, wake-up filter timing parameters, automatic gain control hold, internal tuning capacitor selection for each channel's antenna, minimum modulation depth requirement for input signal and bi-directional talk-back. Programmable minimum modulation depth requirement reduces false wake-up of the RKE transponder. An antenna for each channel of the RKE transponder may be tuned with internal tuning capacitors for improved range and receiver sensitivity. The internal tuning capacitor parameters may be stored in a configuration register. Gain of the channel may be fixed while the antenna is tuned. The antennas may be de-queued for talk-back to a base station for low frequency bi-directional communications. An external control device may dynamically read from and write to the configuration registers via a serial communications interface.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
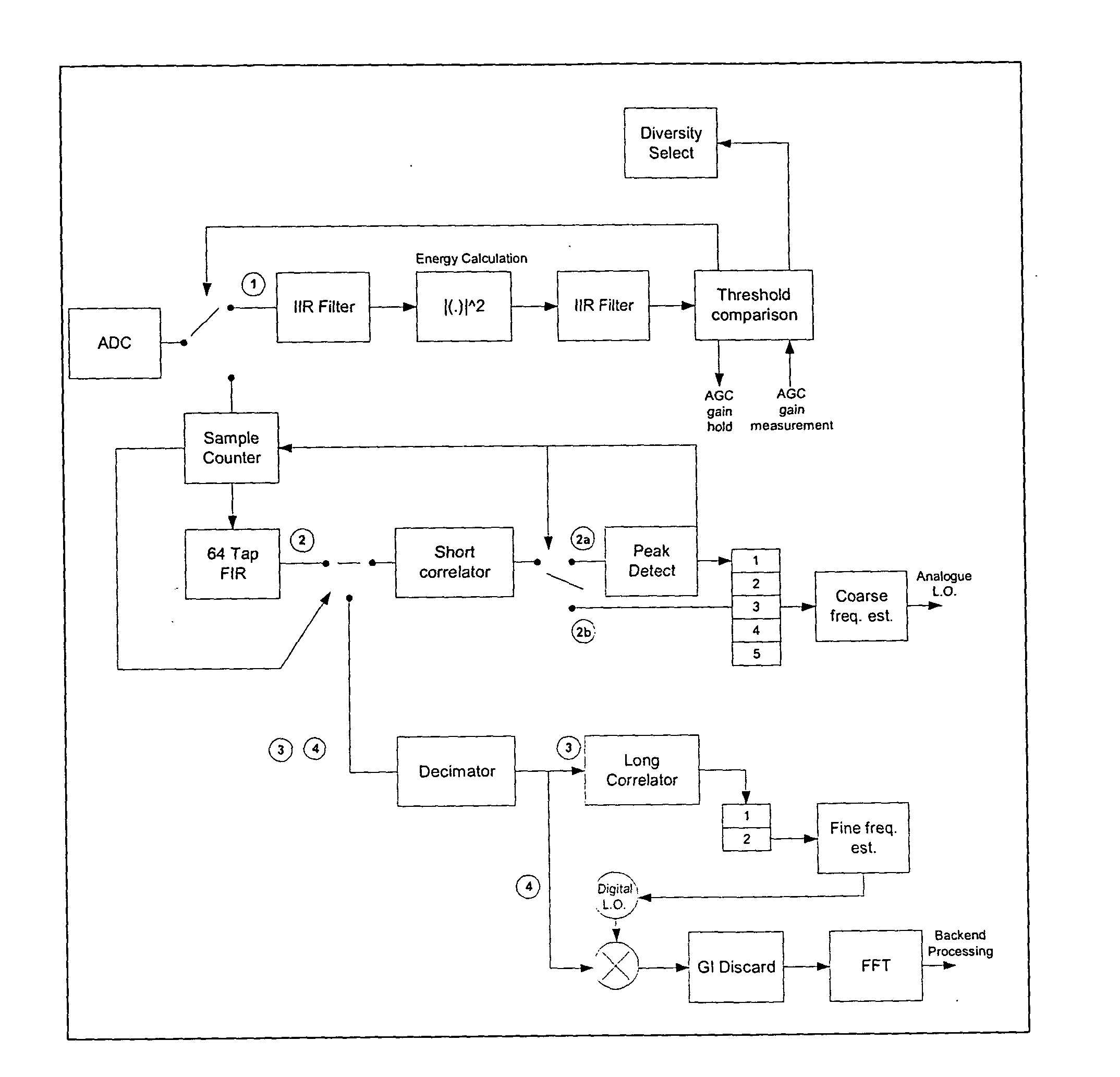
Method for amplitude insensitive packet detection
ActiveUS20050058227A1High outputEasy to detectAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPhase correlationComputer science
The invention relates generally to the field of wireless communications and more particularly to a method of and device for detecting the presence of a received data packet in a digital receiver. The present invention proposes a simplified method of correlation by removing dependency on the amplitude fluctuations while at the same time maintaining phase relevancy. The key advancement involves mapping the complex quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) preamble to a quantized phase shift keying (PSK) constellation before application to a matched complex correlator. The proposed process essentially “amplitude normalizes” the input signal without the use or complexity associated with a divider. This simplified normalization scheme makes the packet detection algorithm robust against amplitude variations in the input signal, while still allowing for good correlation output. In applications where interference is superimposed on the I / Q input signals, the invention improves the detection capability over automatic gain control (AGC) normalization methods.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
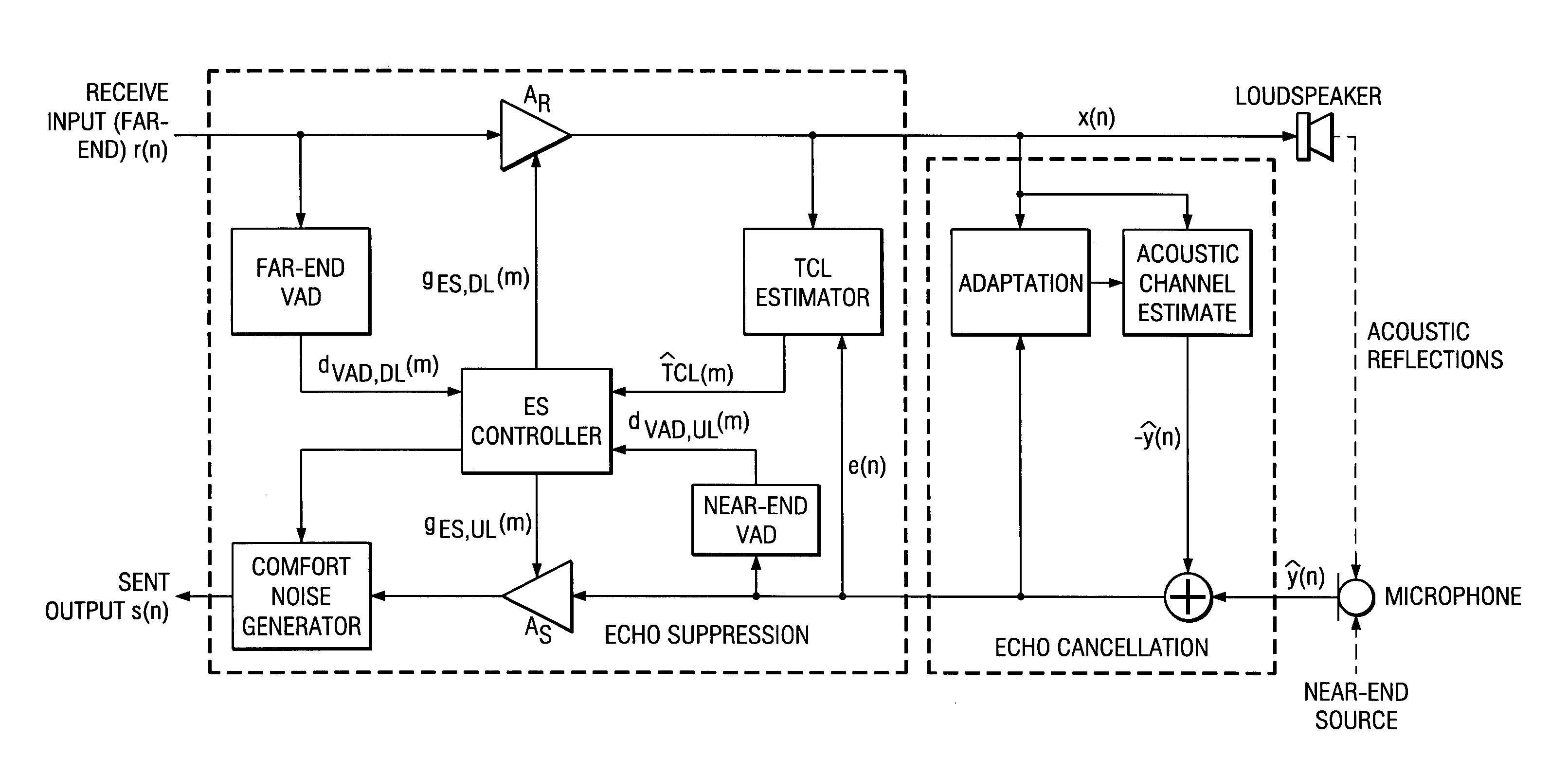
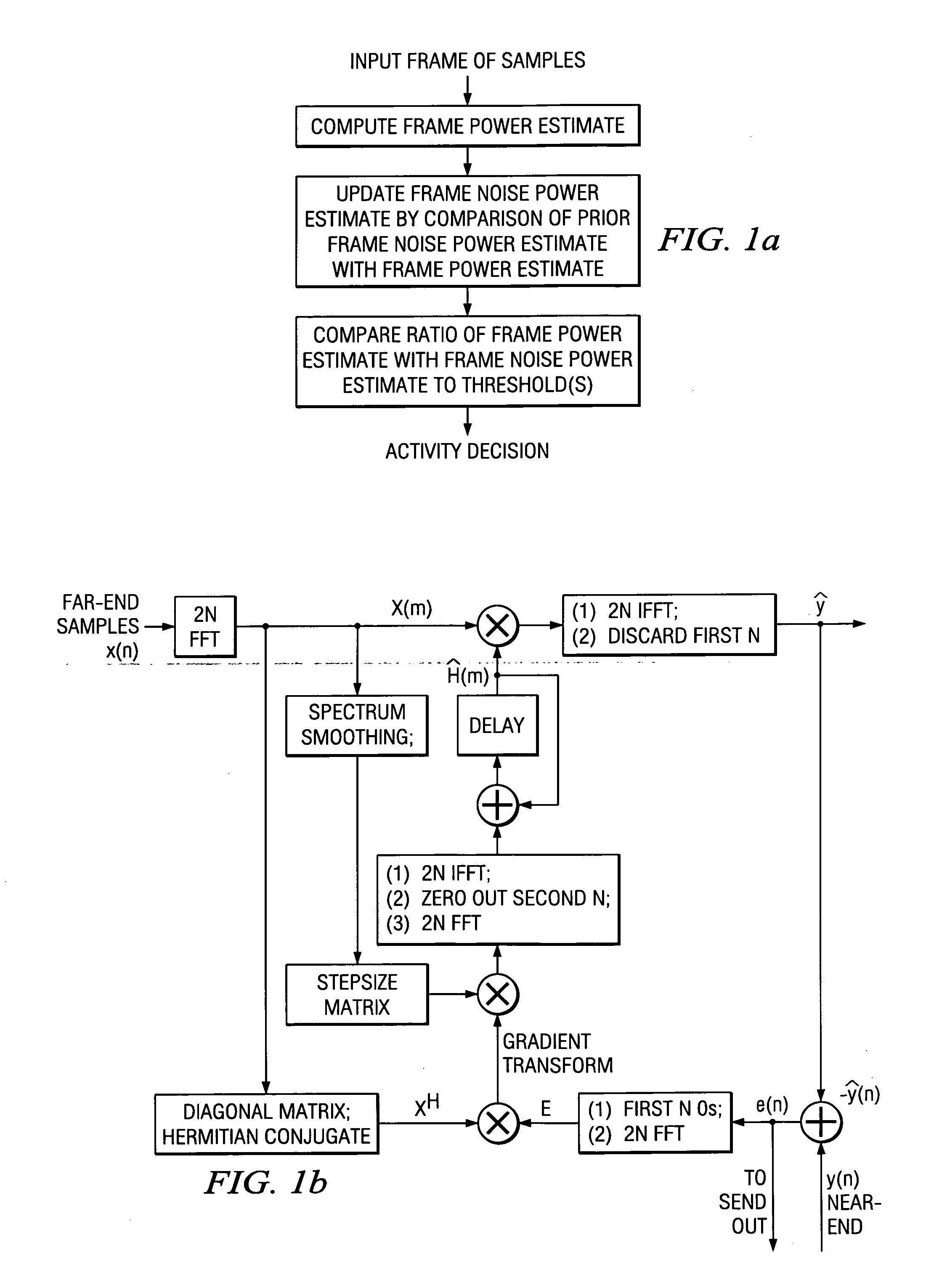
Acoustic echo devices and methods
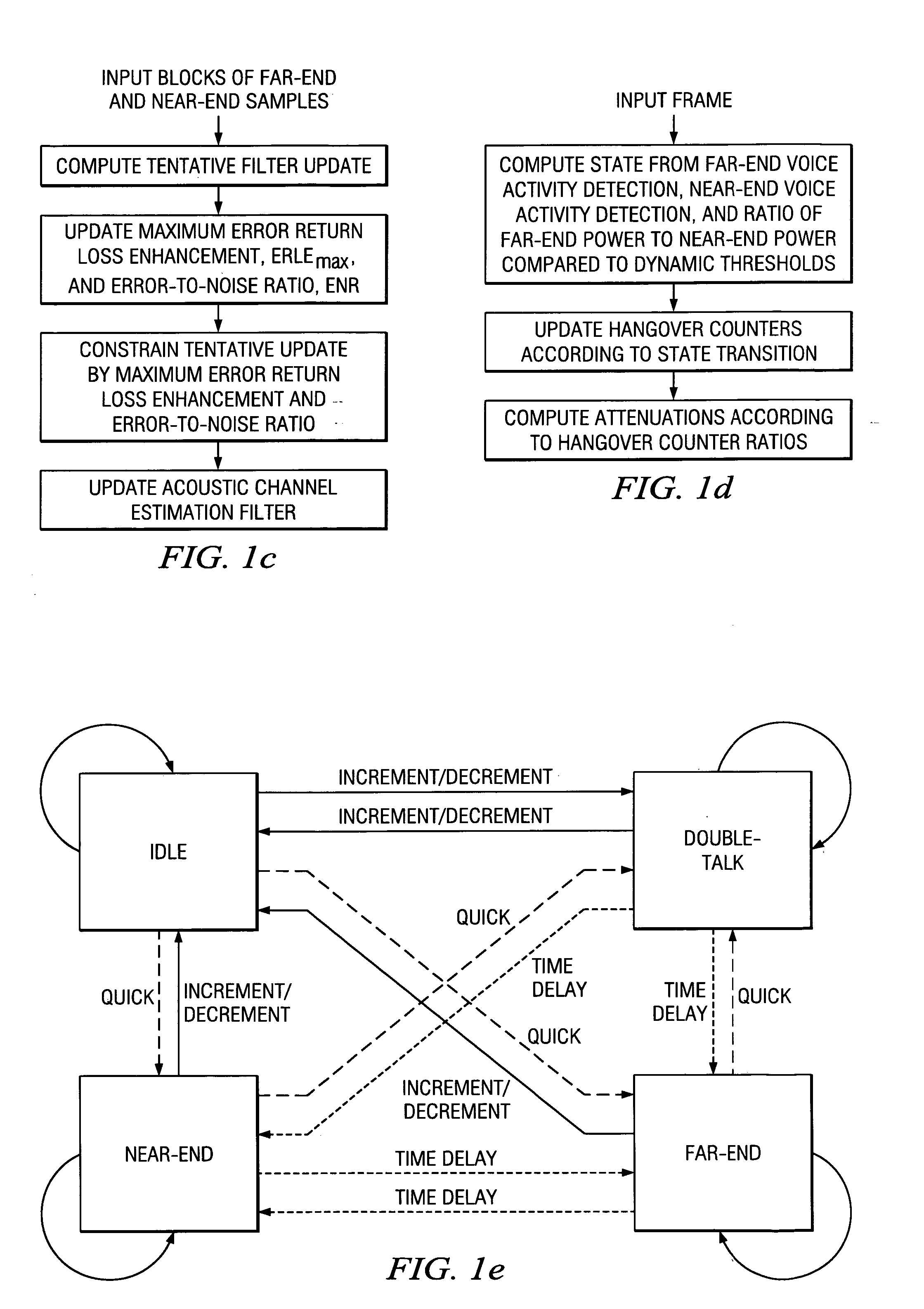
Hands-free phones with voice activity detection using a comparison of frame power estimate with an adaptive frame noise power estimate, automatic gain control with fast adaptation and minimal speech distortion, echo cancellation updated in the frequency domain with stepsize optimization and smoothed spectral whitening, and echo suppression with adaptive talking-state transitions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Audio gain control using specific-loudness-based auditory event detection
ActiveUS8144881B2Change damageSlow down the rate of change of gainSignal processingGain controlLoudnessComputer science
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com