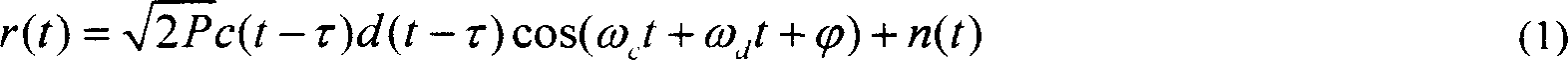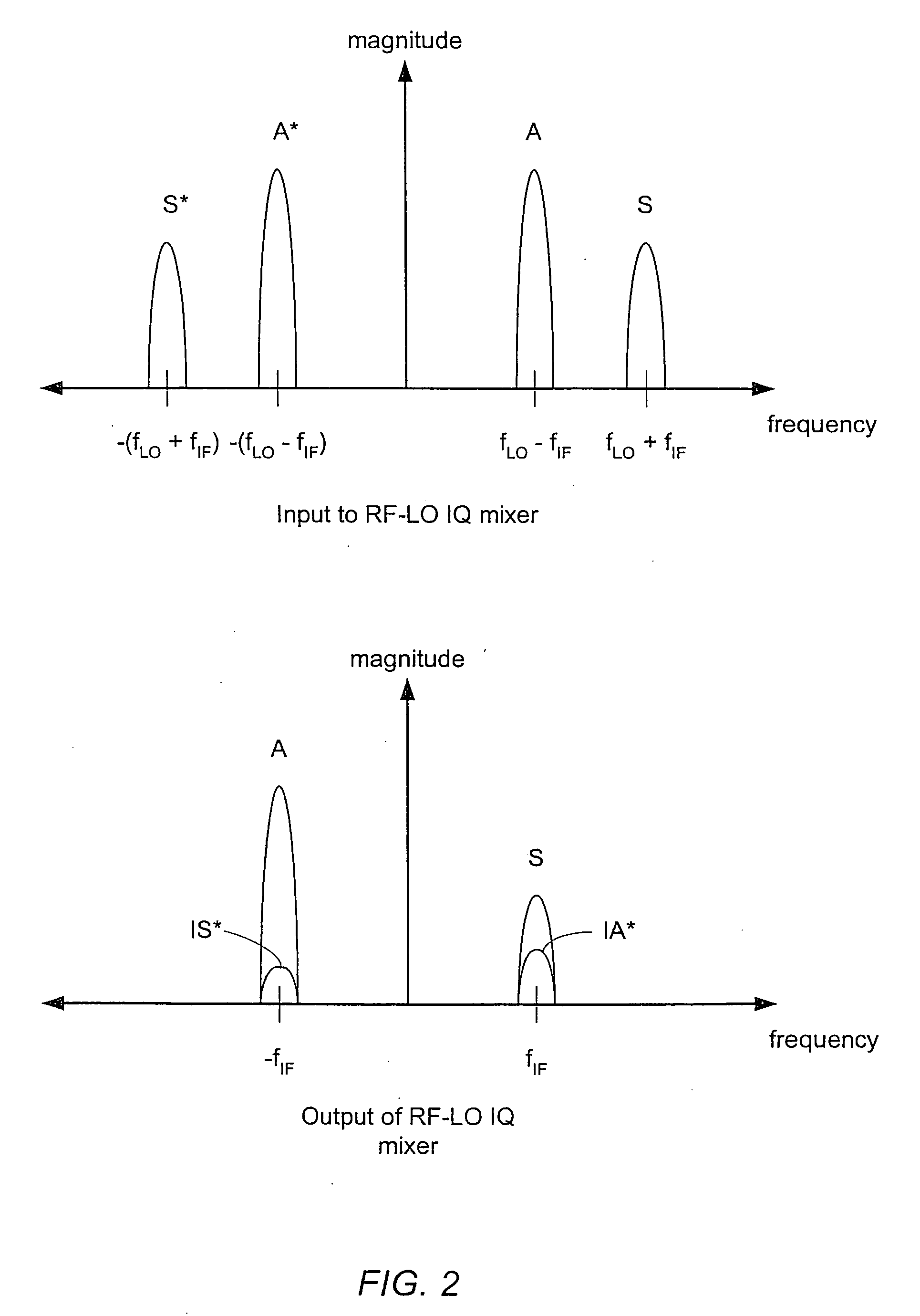Patents
Literature
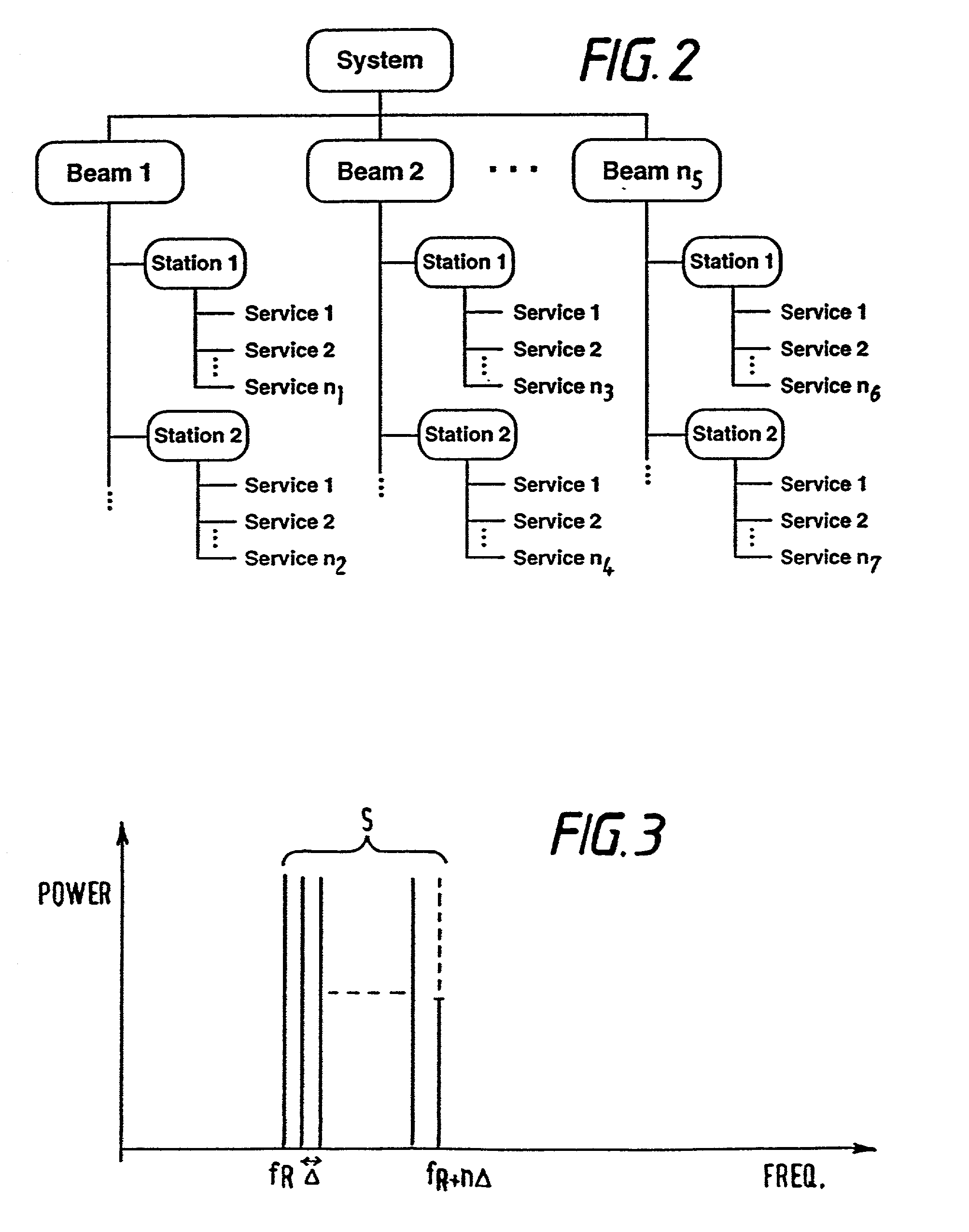
184 results about "In-phase and quadrature components" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electrical engineering, a sinusoid with angle modulation can be decomposed into, or synthesized from, two amplitude-modulated sinusoids that are offset in phase by one-quarter cycle (π/2 radians). All three functions have the same frequency. The amplitude modulated sinusoids are known as in-phase and quadrature components. In some contexts it is more convenient to refer to only the amplitude modulation (baseband) itself by those terms.
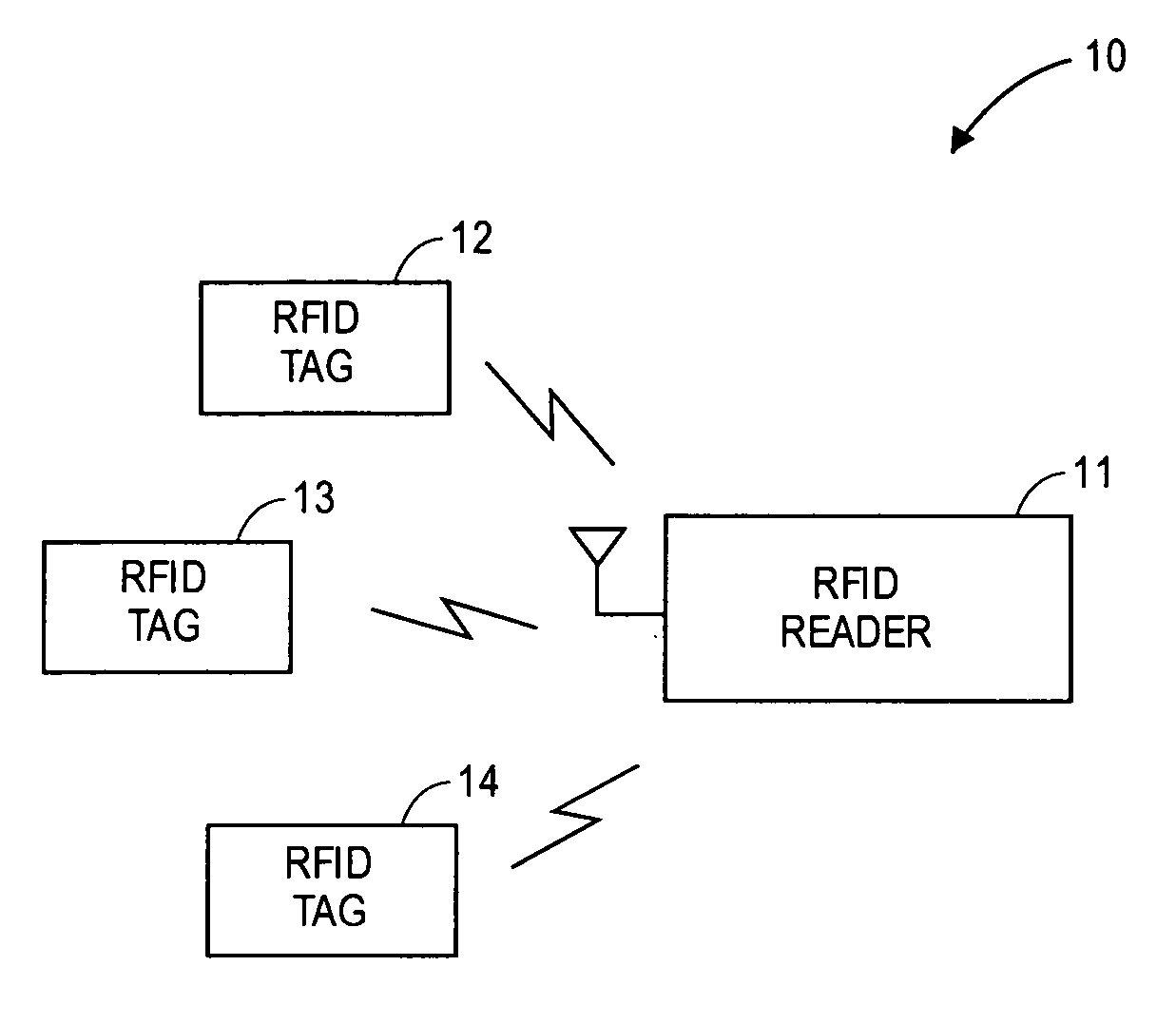
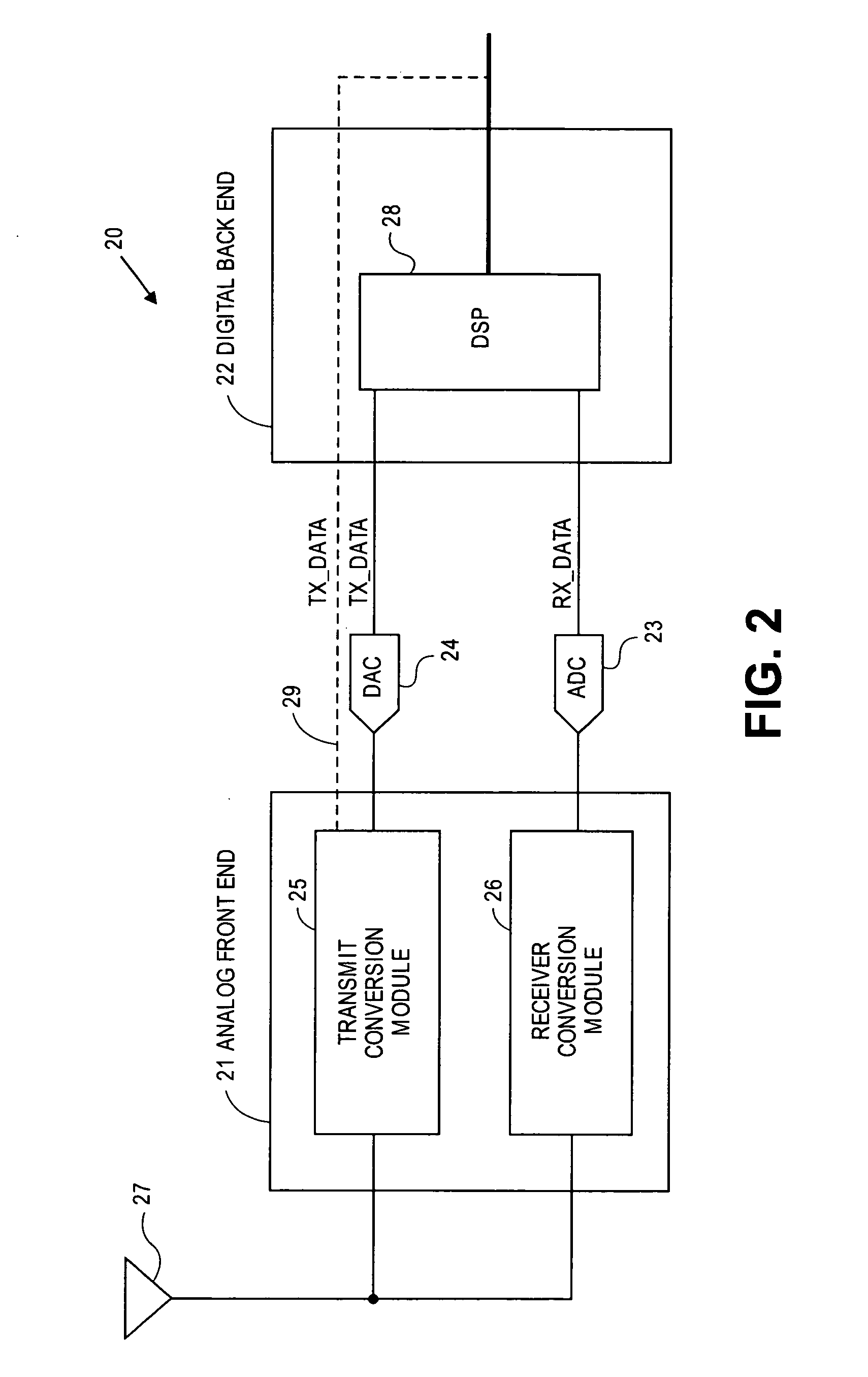
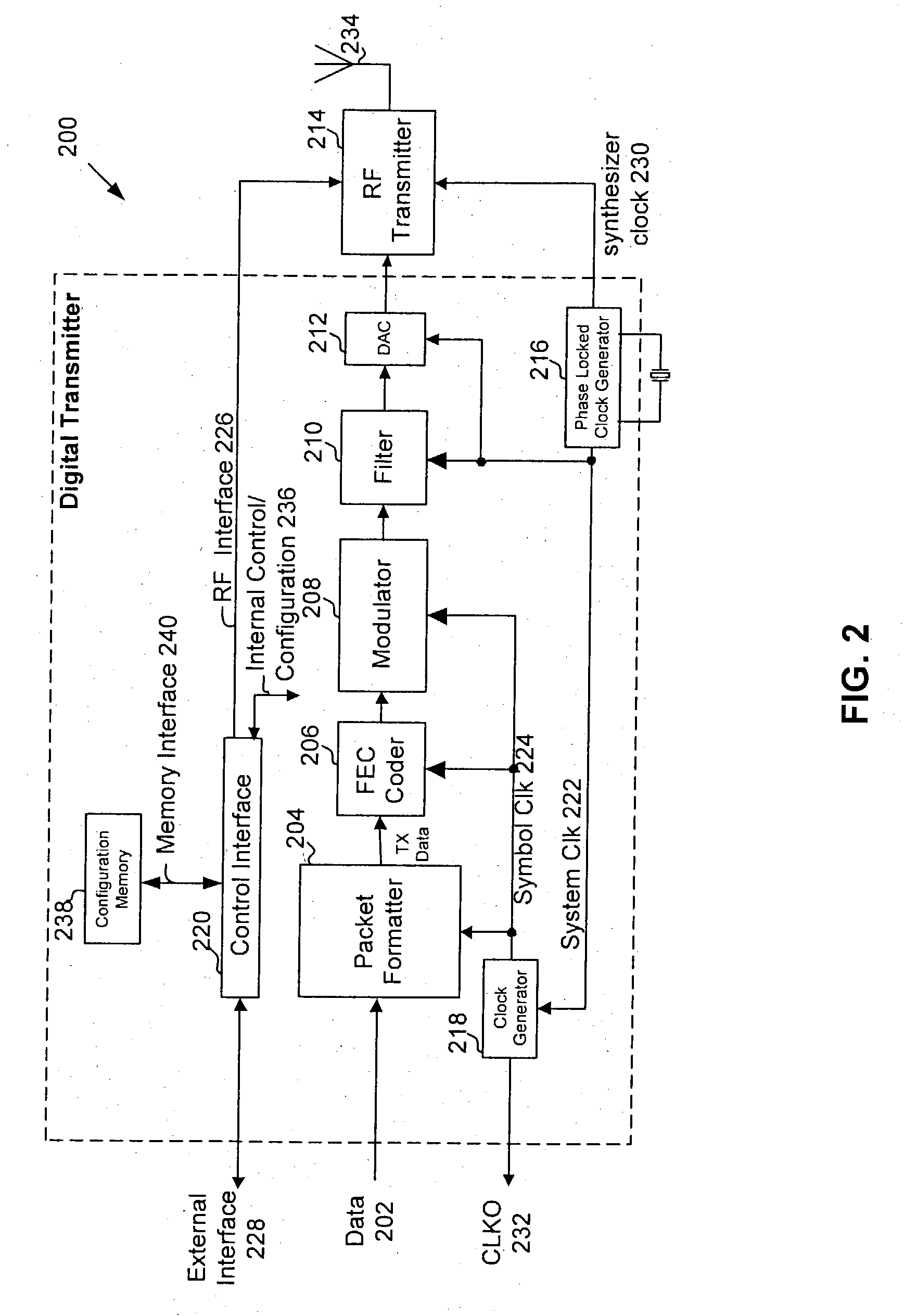
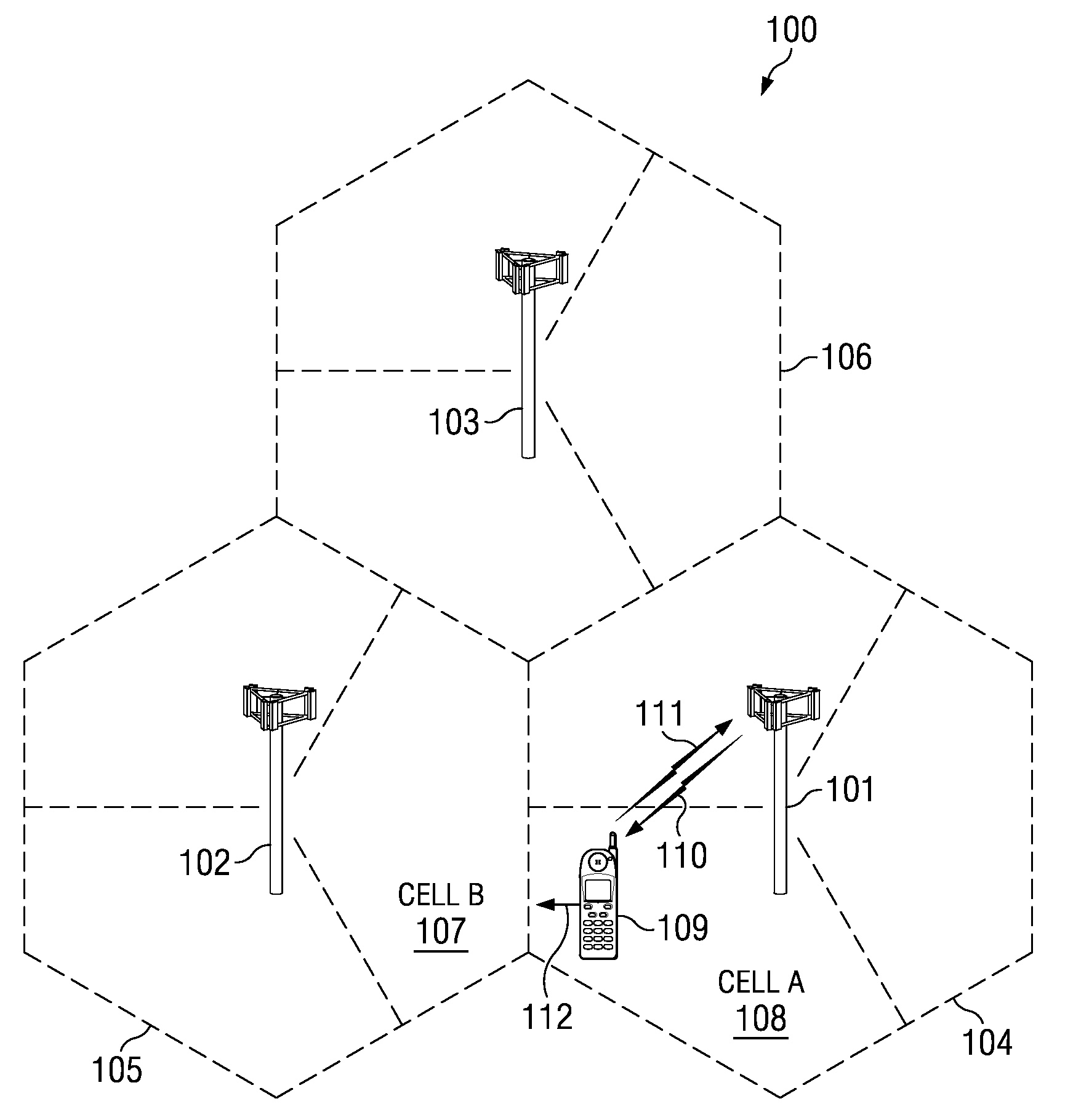
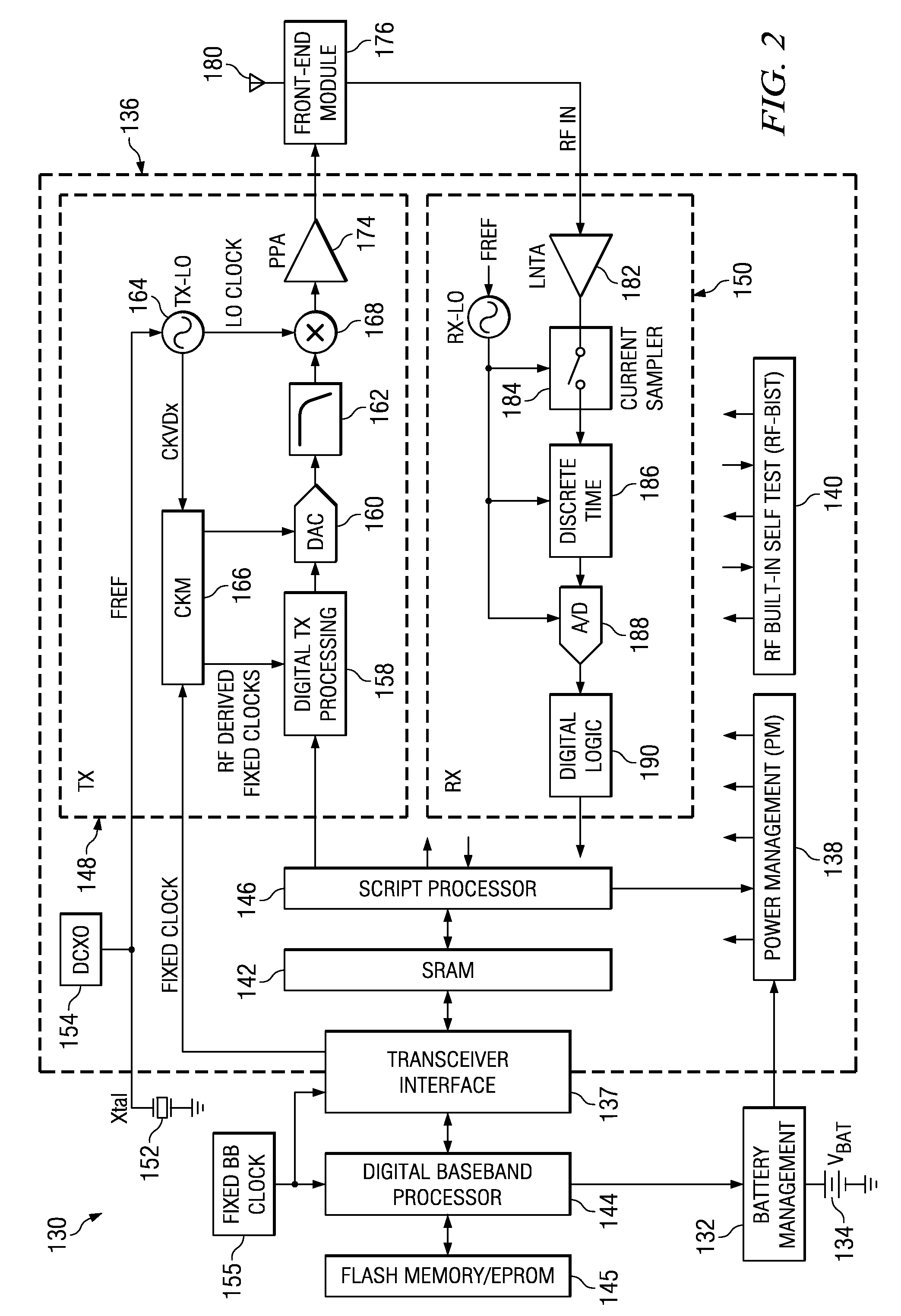
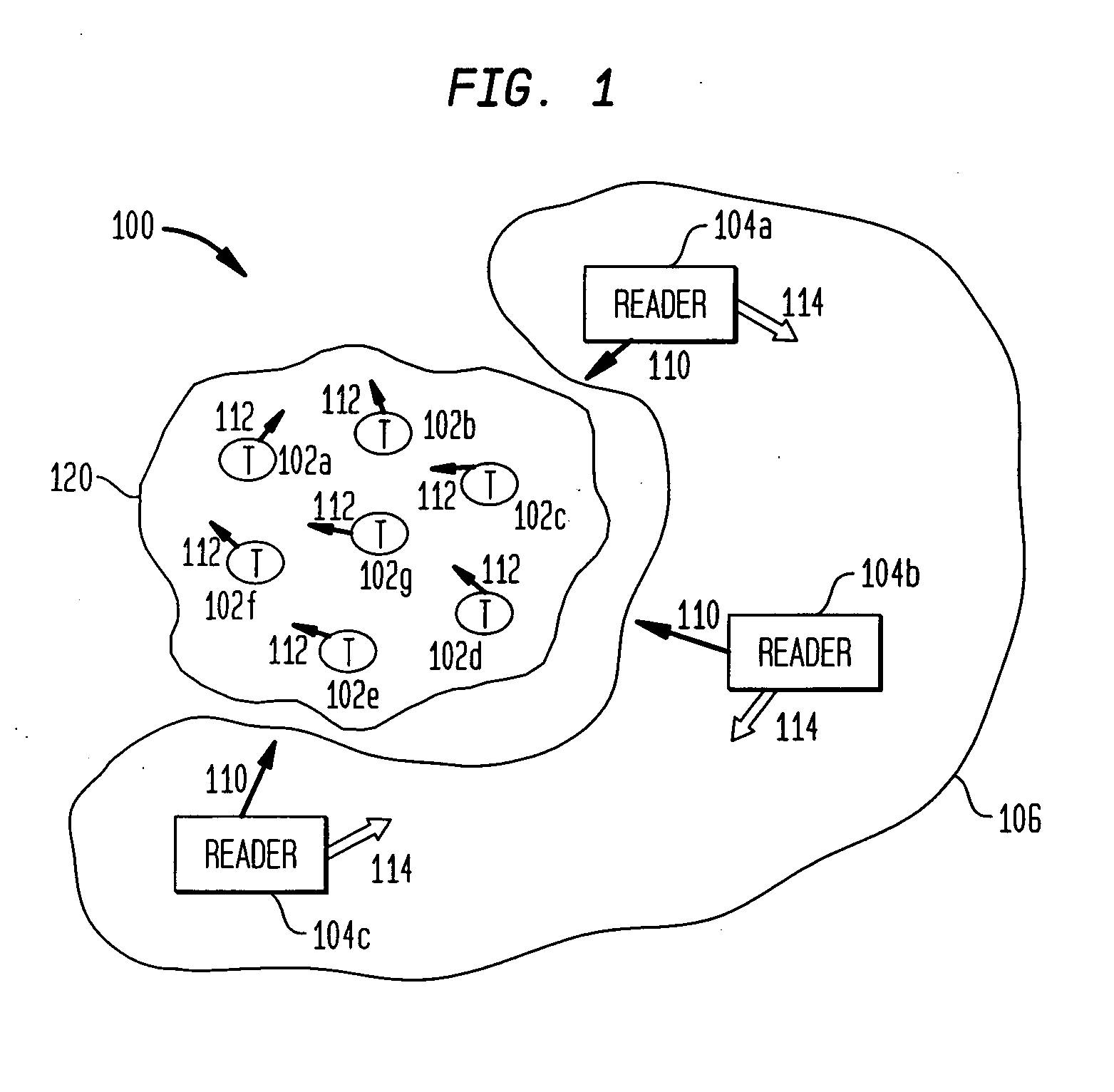
Multi-protocol radio frequency identification transponder transceiver
ActiveUS20060238301A1Memory record carrier reading problemsNear-field in RFIDTransceiverIn-phase and quadrature components
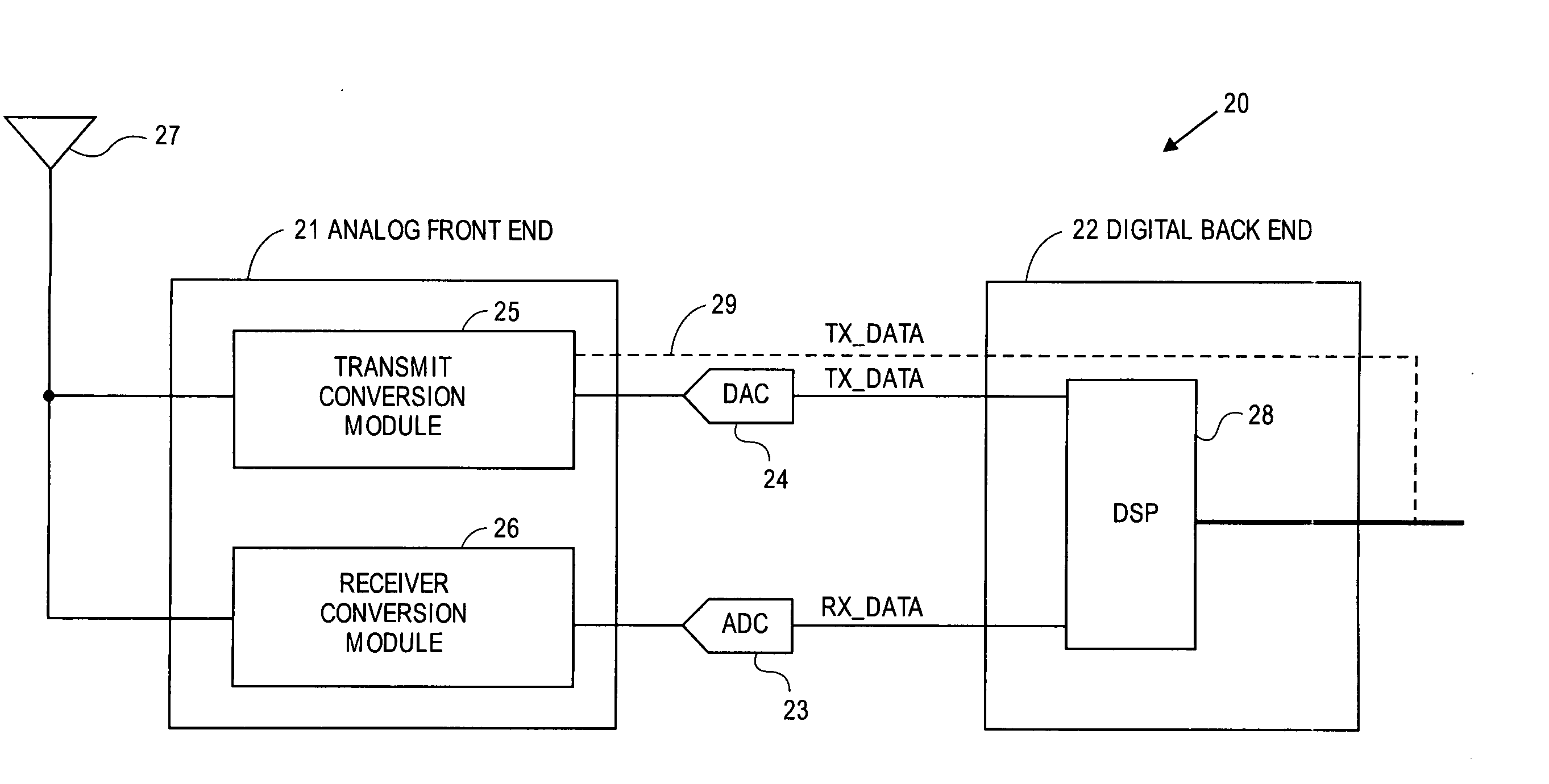
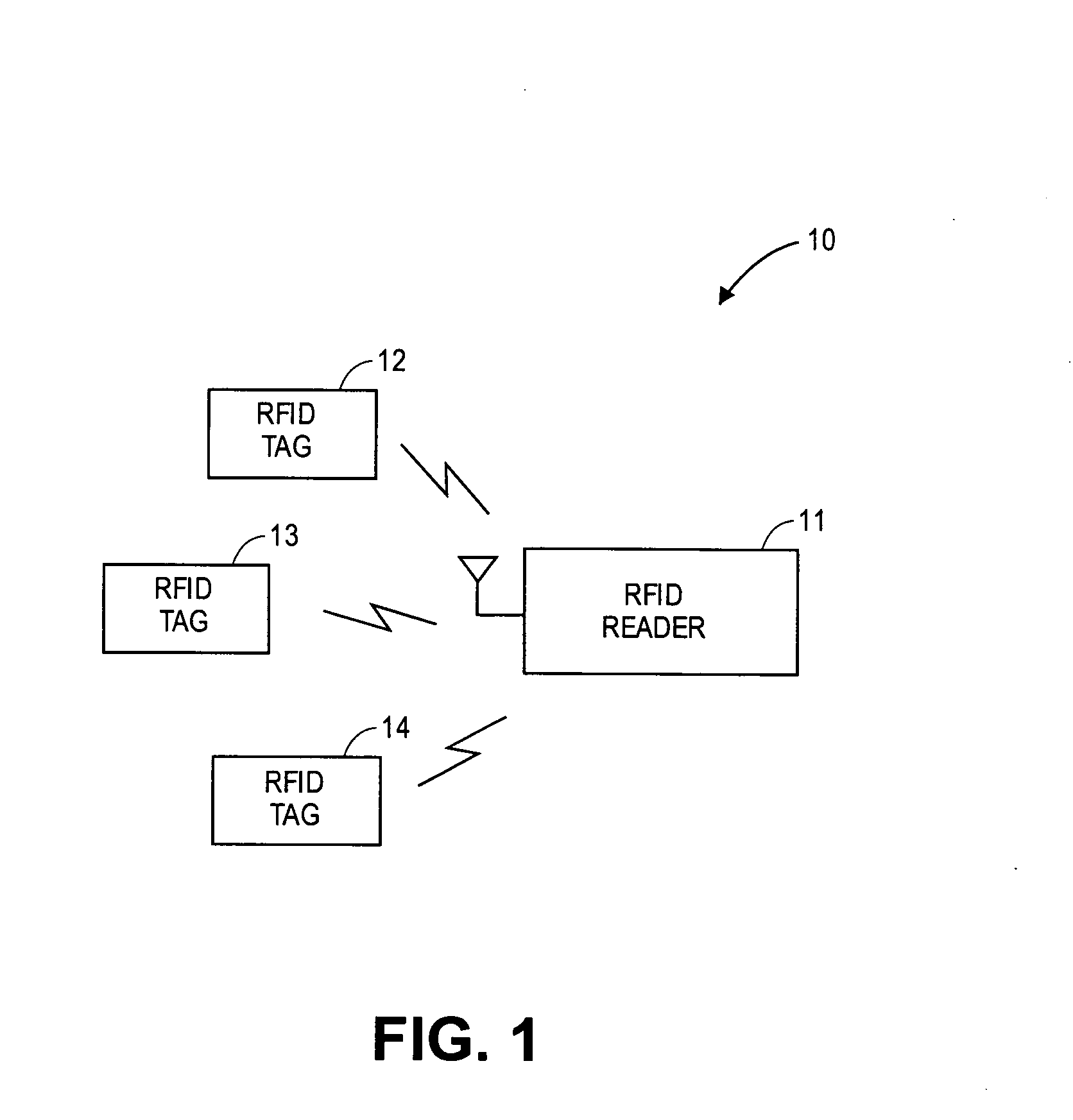
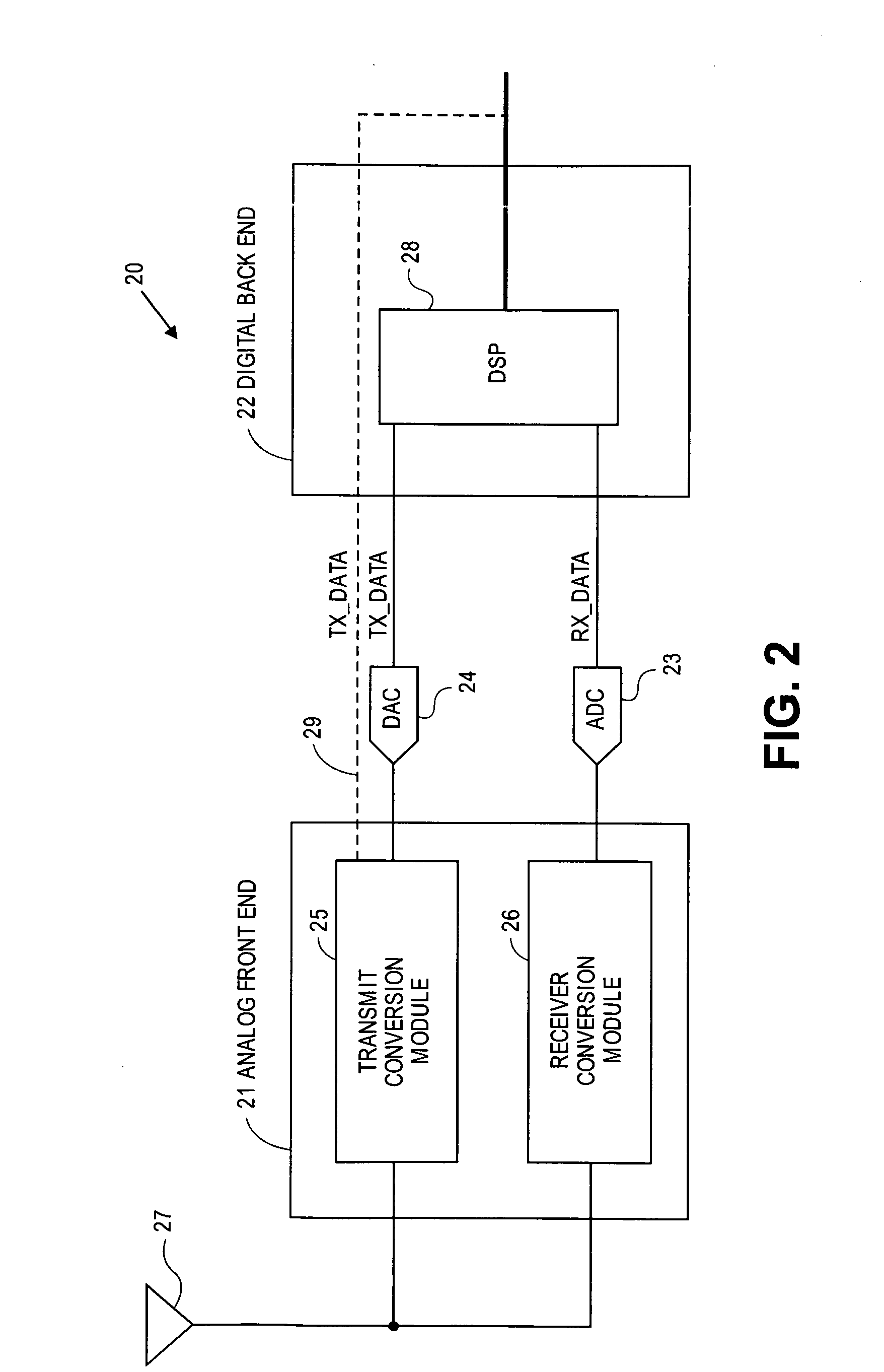
A transceiver for a RFID reader and a transceiver for a RFID transponder (tag) allow communication between the two devices. The RFID reader utilizes an analog front end and a digital backend. In the receiver portion of the transceiver, the front end of the RFID reader uses a pair of down-conversion mixers to demodulate a received signal into in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components and analog-to-digital converters (ADC) digitize the signal. A digital signal processor (DSP) in the back end processes the digital signal and uses a matched filter for data detection. The RFID tag receives an inductively coupled signal from the reader and the receiver portion of the tag uses a pulse / level detector that employs an analog comparator and a sample and hold circuit to detect the received signal. A digital decoder / controller is used to decode the incoming data and to establish a sampling clock for the pulse / level detector. An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit adjusts a receiver gain according to the received signal strength and controls tuning of magnetic coupling circuitry.
Owner:NXP USA INC
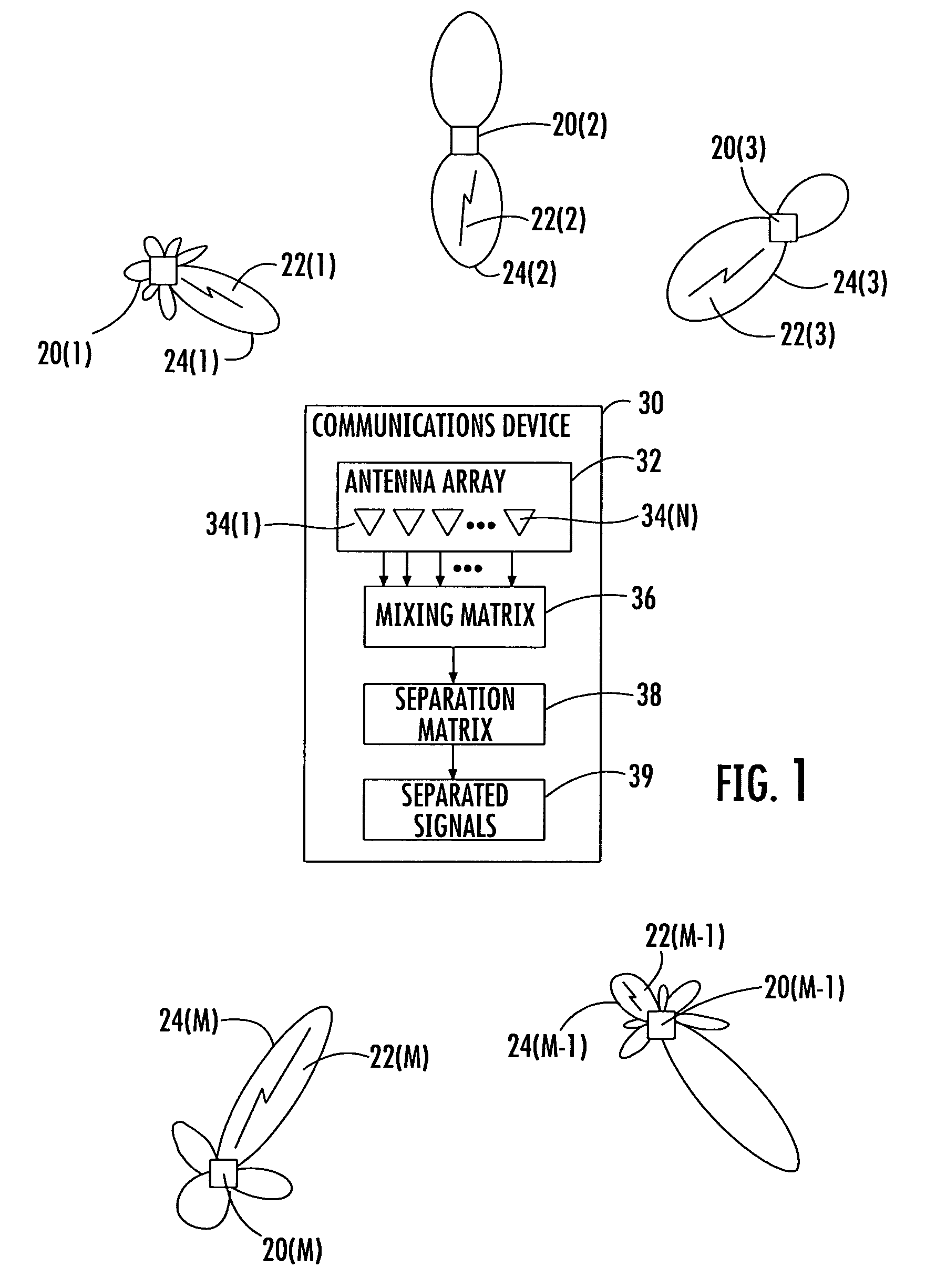
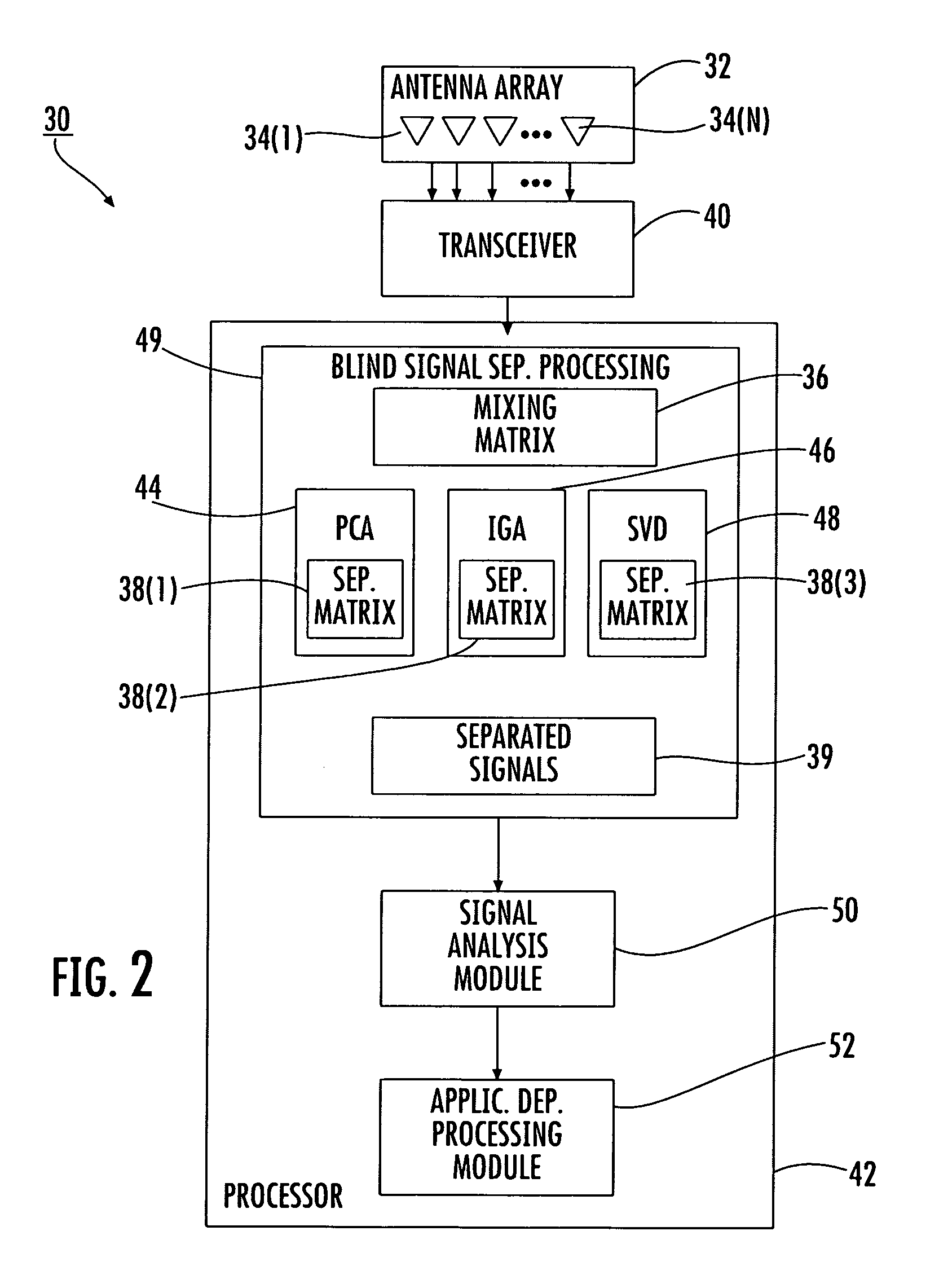
Blind signal separation using I and Q components
InactiveUS7123191B2Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSpatial transmit diversityBlind signal separationIn-phase and quadrature components
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Multiplex communication
InactiveUS20020114270A1Improve noiseImprove protectionResource management arrangementsCode conversionMultiplexingCommunications system
Owner:INMARSAT
Multi-protocol radio frequency identification reader transceiver
ActiveUS20060186995A1Electric signal transmission systemsError preventionTransceiverDown conversion mixer
A transceiver for a RFID reader and a transceiver for a RFID transponder (tag) allow communication between the two devices. The RFID reader utilizes an analog front end and a digital backend. In the receiver portion of the transceiver, the front end of the RFID reader uses a pair of down-conversion mixers to demodulate a received signal into in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components and analog-to-digital converters (ADC) digitize the signal. A digital signal processor (DSP) in the back end processes the digital signal and uses a matched filter for data detection. The RFID tag receives an inductively coupled signal from the reader and the receiver portion of the tag uses a pulse / level detector that employs an analog comparator and a sample and hold circuit to detect the received signal. A digital decoder / controller is used to decode the incoming data and to establish a sampling clock for the pulse / level detector. An automatic gain control (AGC) circuit adjusts a receiver gain according to the received signal strength and controls tuning of magnetic coupling circuitry.
Owner:NXP USA INC
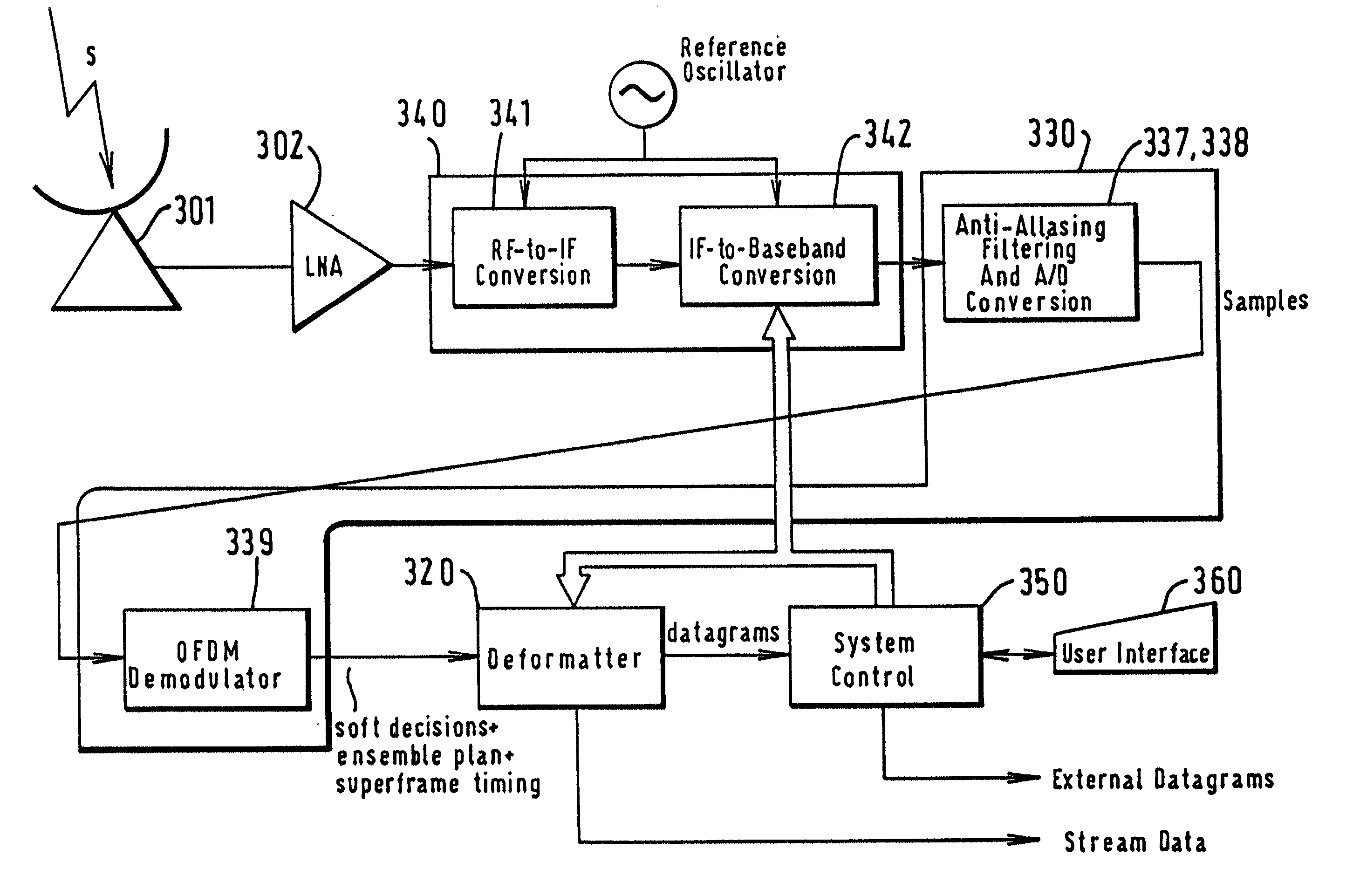
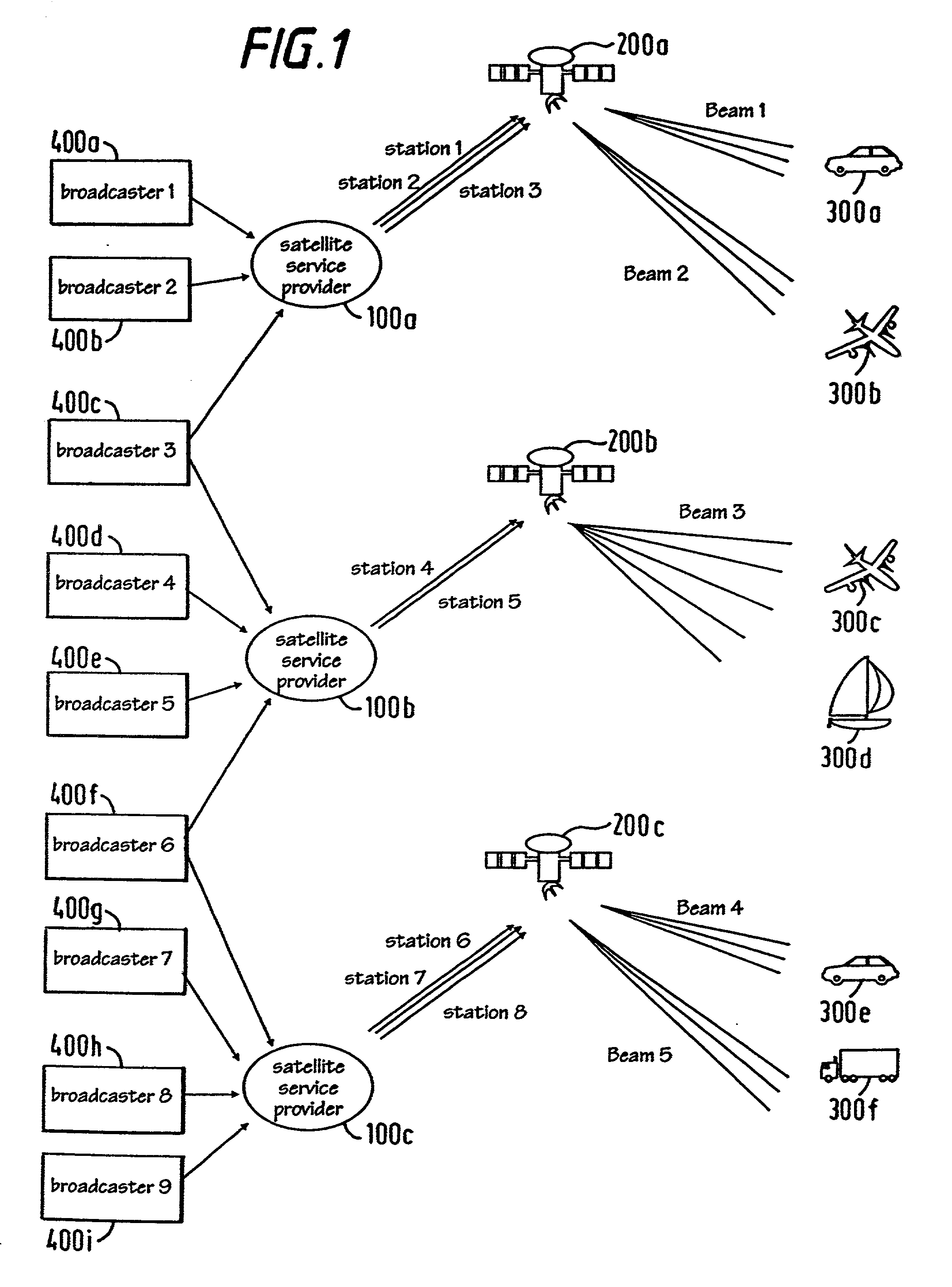
Multiplex communication
InactiveUS20010055320A1Improve noiseImprove protectionResource management arrangementsBroadcast transmission systemsMultiplexingCommunications system
An OFDM communications system comprises broadcast providers 400, earth stations 100, repeater satellites 200, and receivers 300 (for example mobile receivers). The size of the multiplex can be increased by adding extra channels. Two channels are provided, on the in phase and quadrature components of each subcarrier.
Owner:PIERZGA WAYNE FRANCIS +4
Simultaneous tuning of multiple channels using intermediate frequency sub-sampling
ActiveUS6888888B1Improve cooling effectImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesAudio power amplifierIntermediate frequency
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Linear RF power amplifier and transmitter
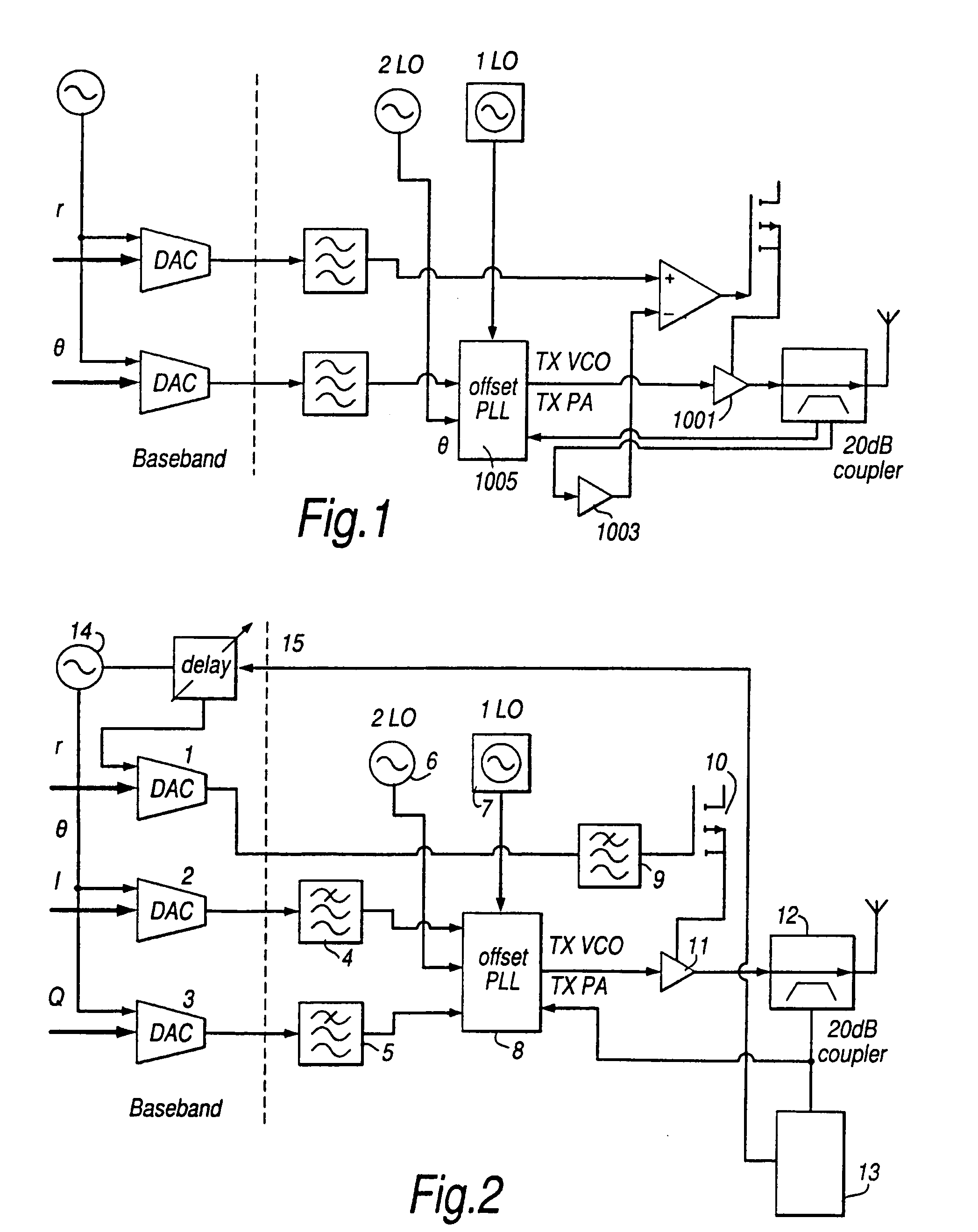
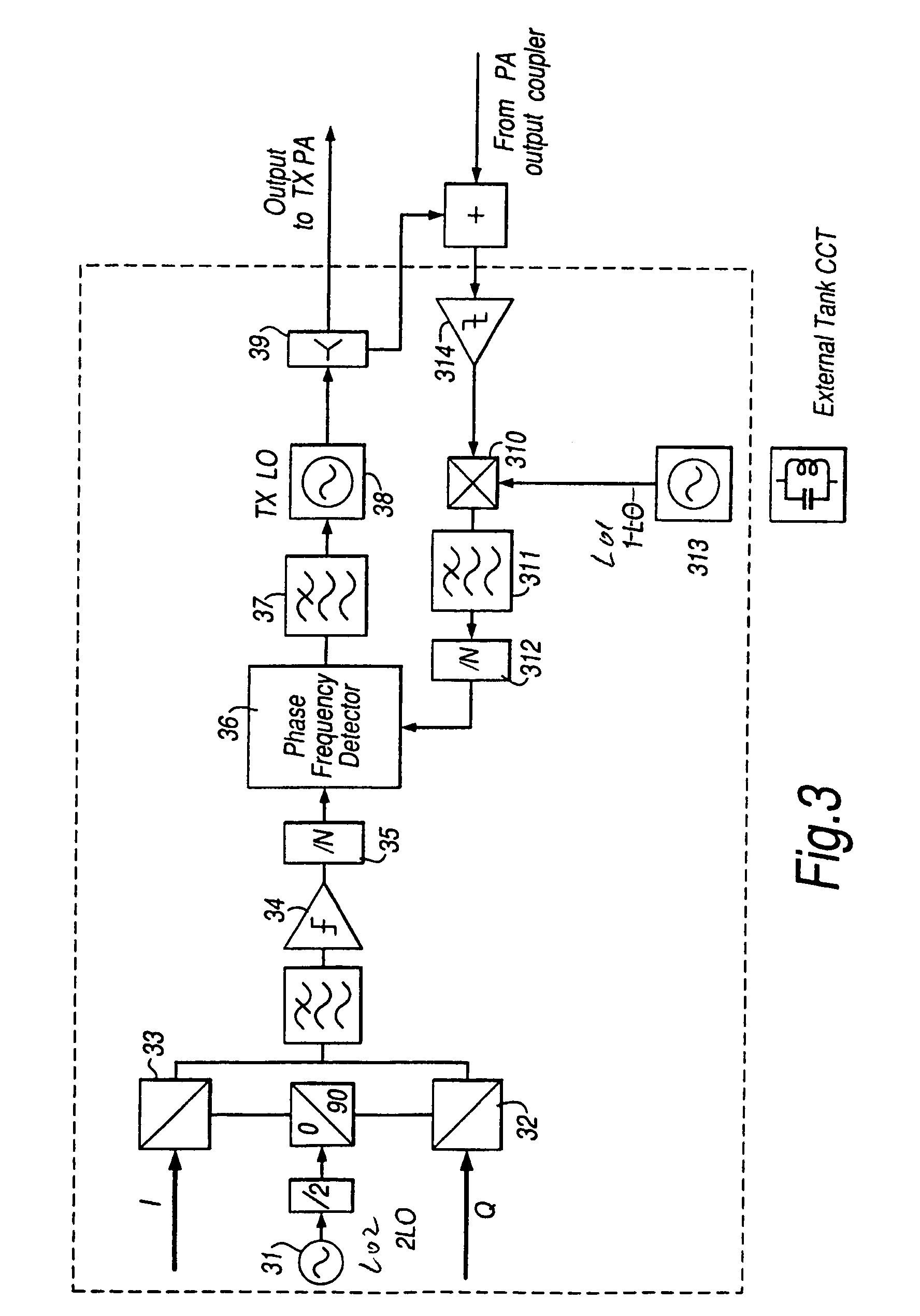
InactiveUS7010280B1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierIn-phase and quadrature components
A transmitter circuit means is arranged to provide linear amplification of non-constant envelope modulated RF signals by directly amplitude modulating the transmitter power amplifier with the amplitude component of the baseband signal. In addition, the signal to be transmitted is phase modulated by the In-phase and quadrature components of the baseband signal, and synchronization means arc provided in order to correct any time slippage between the directly applied amplitude modulation and the phase modulation. The modulation synchronisation correction contributes significantly to the linearity of the transmitter.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Low complexity synchronization for wireless transmission
ActiveUS20040196926A1Eliminate needInexpensive and low-complexity synchronization for communication systemsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlDigital dataCommunications system
A receiver, system and method for providing symbol timing recovery that allows for inexpensive and low-complexity synchronization for communication systems. A receiver receives a signal including digital data in the form of packets that is transmitted from a transmitter. The receiver uses information contained in each of the packets to align a phase of the receiver clock with a phase of the transmitter clock. The receiver further controls a sampling device such that the in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components are sampled at an optimum sample rate and at an optimum instance of time without requiring a numerically controlled oscillator or voltage controlled oscillator.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
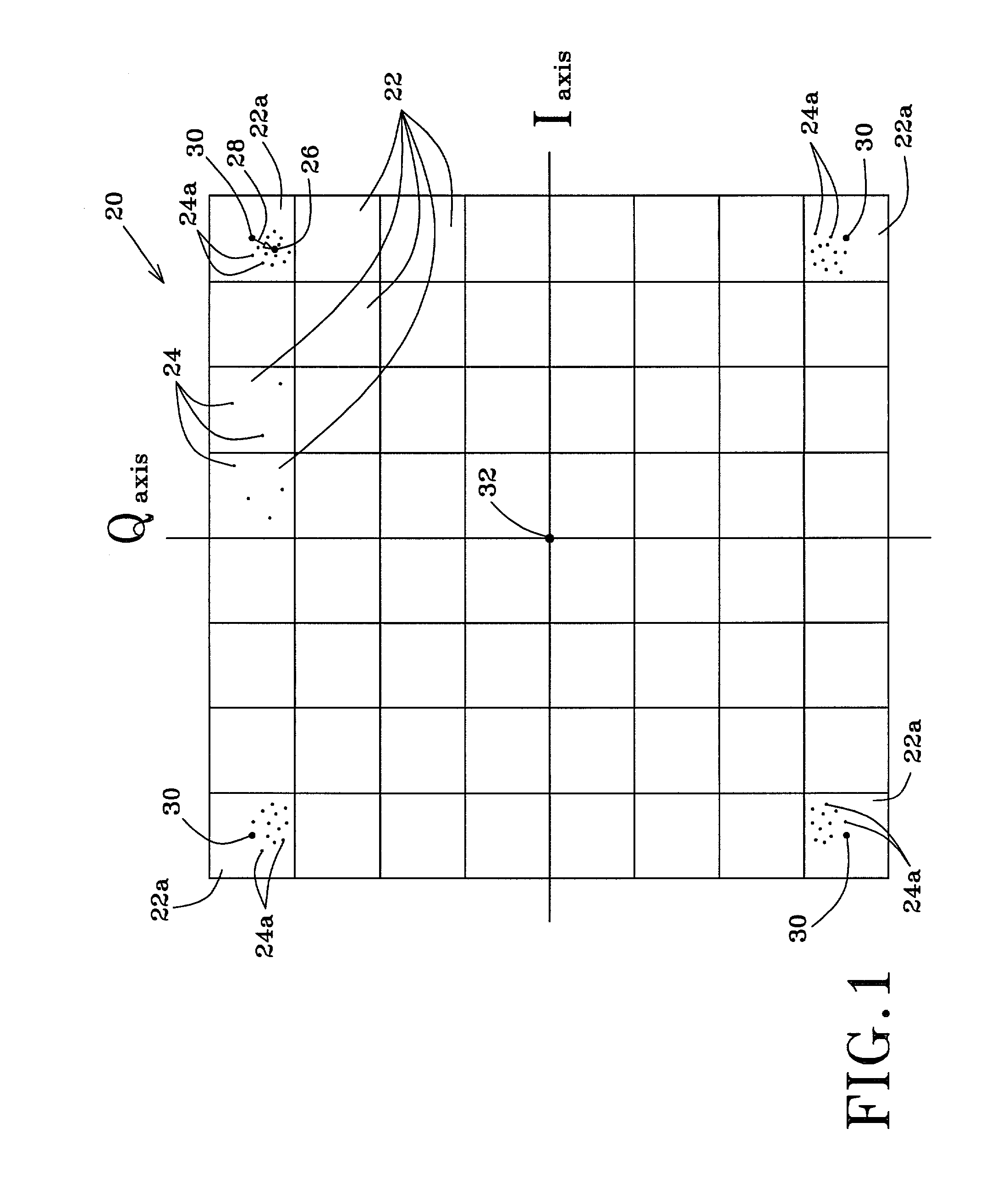
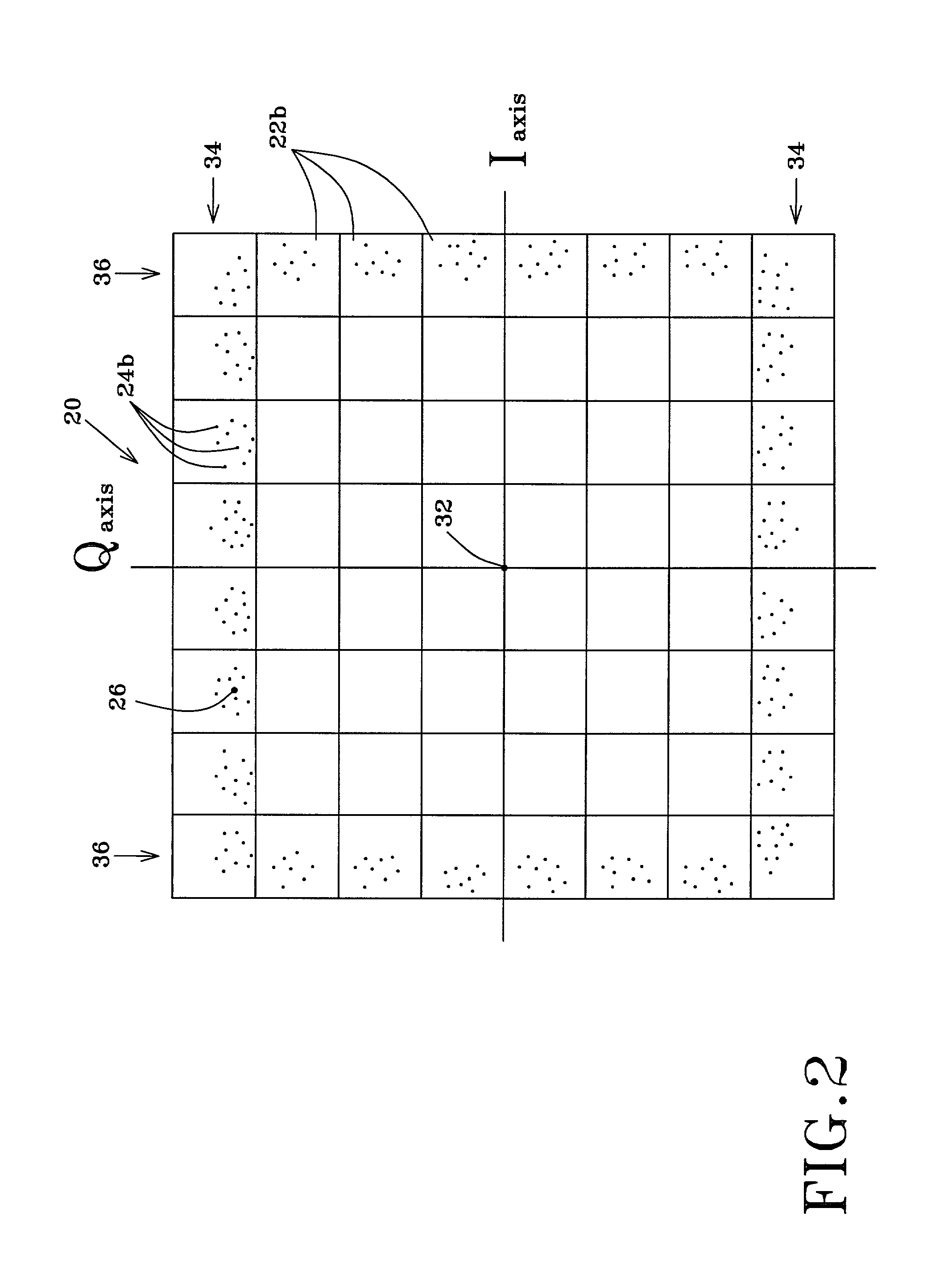
Method and apparatus for detecting and quantifying impairments in QAM signals
InactiveUS7142609B2The result is accurateSimple principleSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemIn-phase and quadrature components
A method for detecting and quantifying impairments of a received communication signal of a QAM data communication system represented by a plurality of ideal values. The method includes storing a statistically significant number of a plurality of received points of the signal for each ideal value corresponding to a plurality of groups of said plurality of ideal values. The received points are defined by an in-phase and a quadrature components in a coordinate system in which a first axis is the in-phase axis and a second axis is a quadrature axis. The components have corresponding ideal components from their respective ideal value. Each group corresponds to respective impairments and is specific to the same.
Owner:VEEX
Method and system for multi-band direct conversion CMOS mobile television tuner
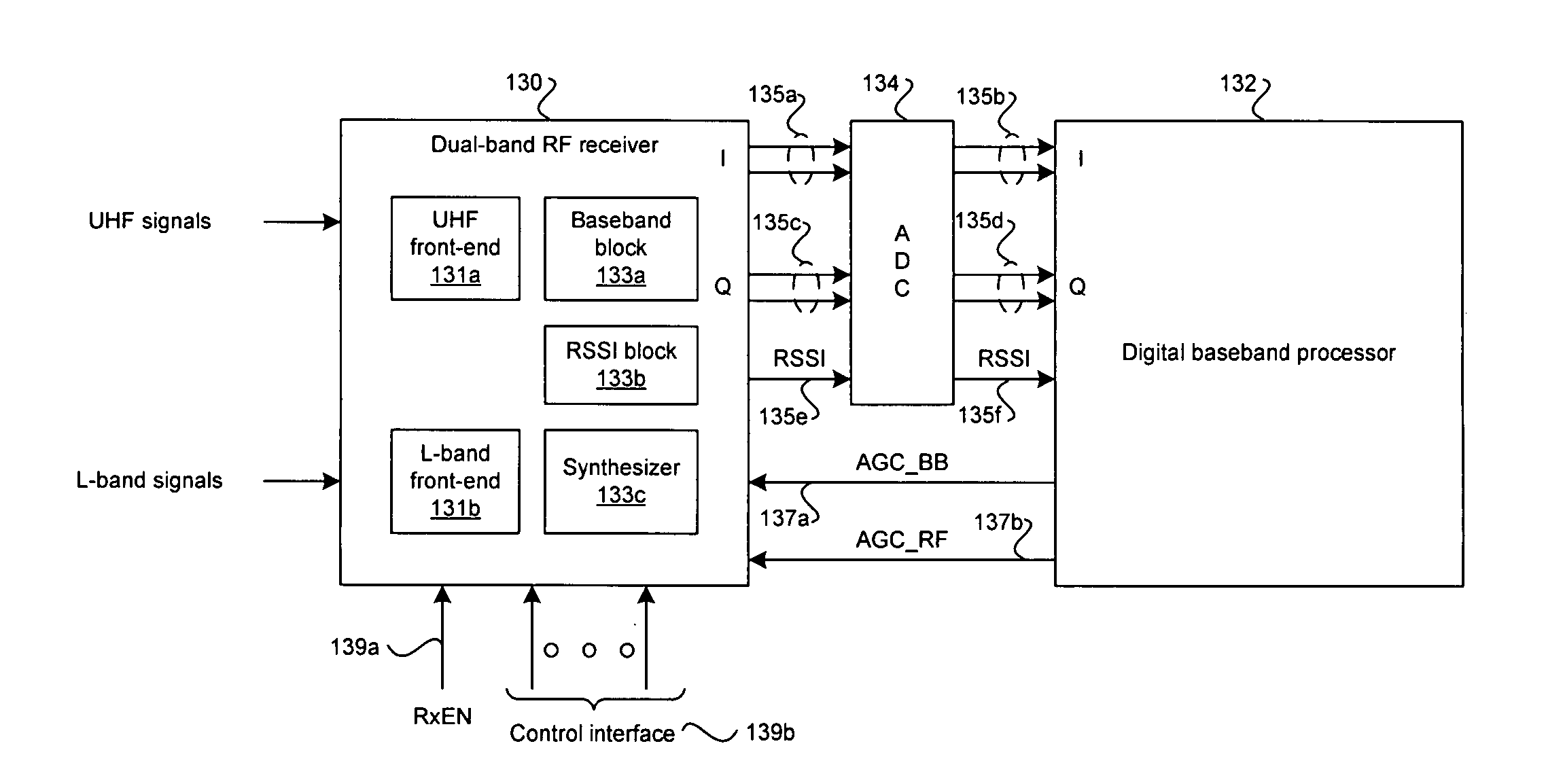
Aspects of a method and system for a multi-band direct conversion CMOS mobile television tuner are provided. A single-chip multi-band RF receiver in a mobile terminal comprising UHF and L-band front-ends receives and amplifies an RF signal utilizing an LNA integrated into the front-end that corresponds to the type of signal received. A received signal strength indicator (RSSI) value may be determined for the amplified signal within the single-chip receiver and may be utilized to adjust a gain of the LNA. The adjustment may be made via on-chip or off-chip processing of the RSSI value. The single-chip receiver may directly convert the amplified signal to a baseband frequency signal and generate in-phase and quadrature components. The components of the baseband frequency signal may be filtered and / or amplified via programmable devices within the single-chip receiver. Circuitry within the single-chip receiver may be controller via an on-chip digital interface.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
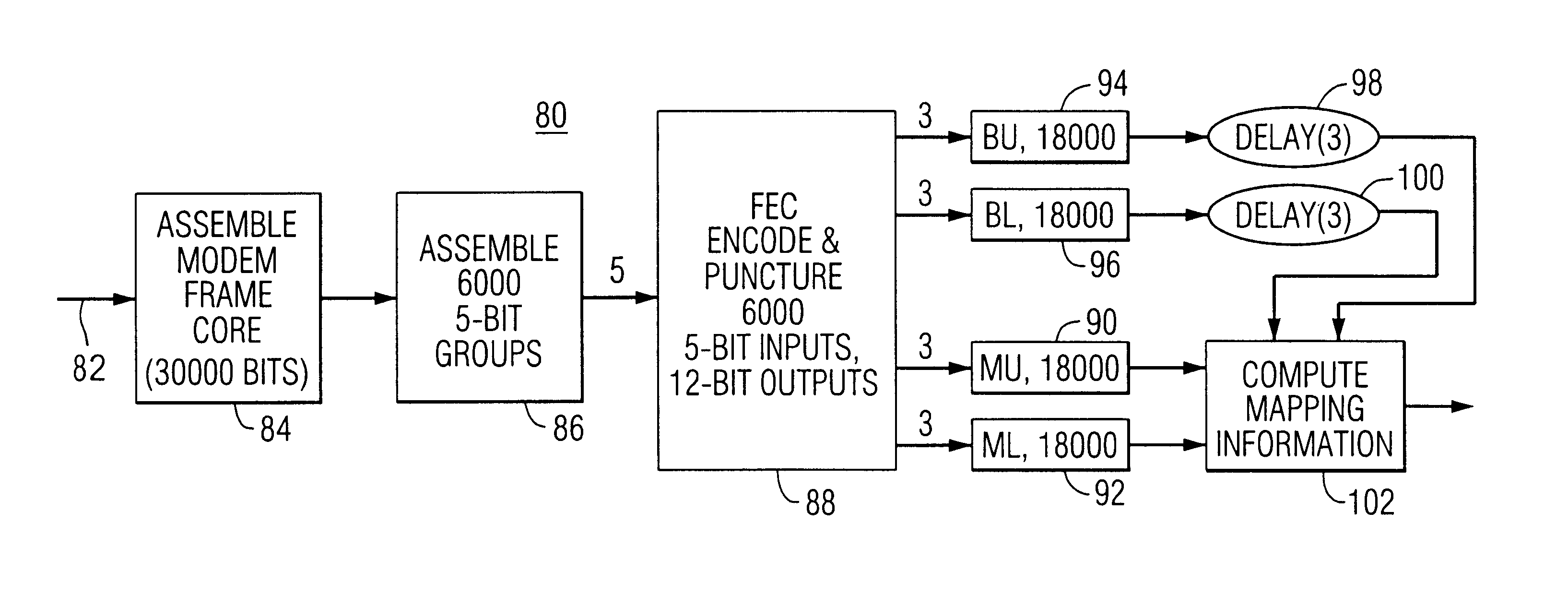
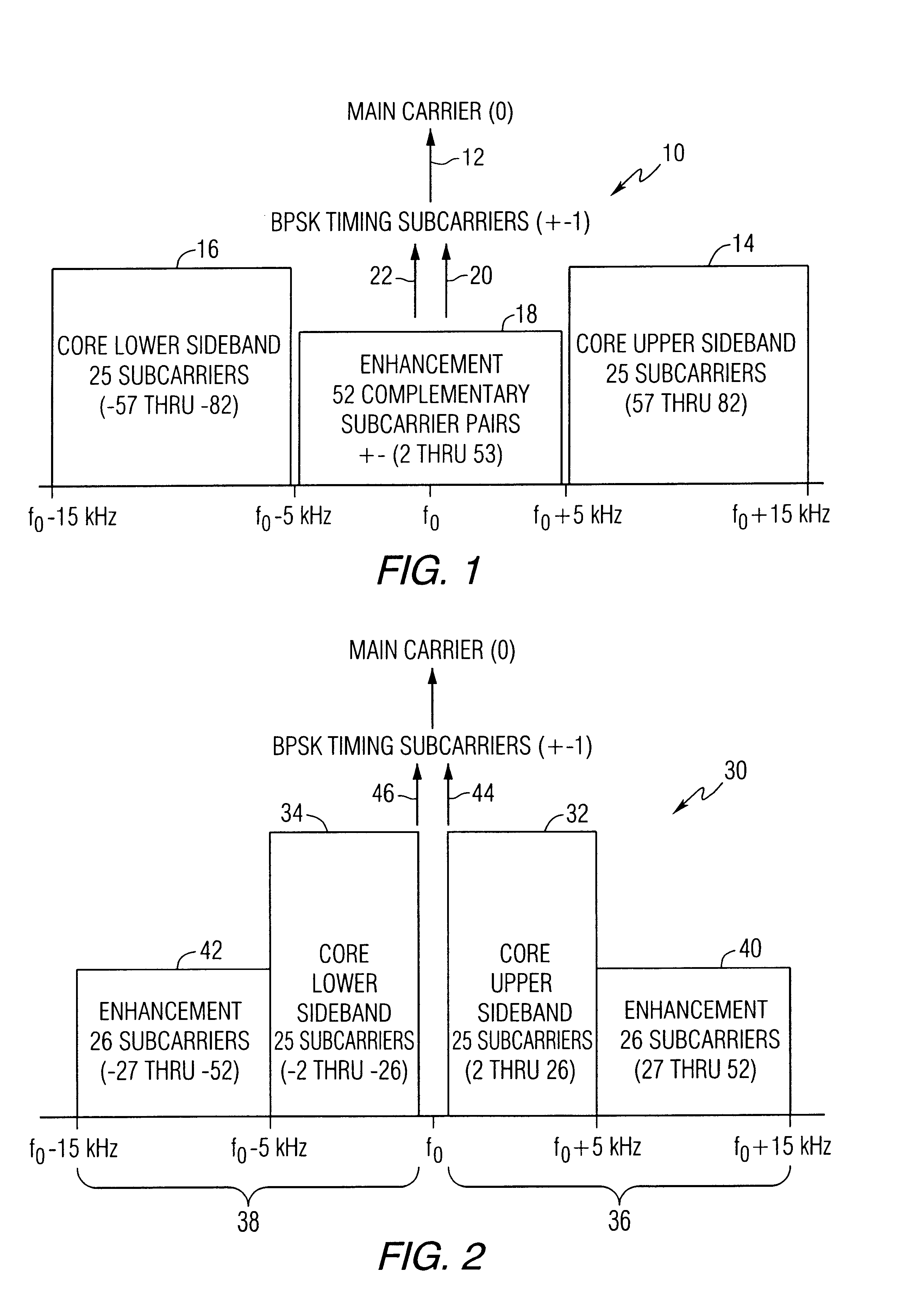
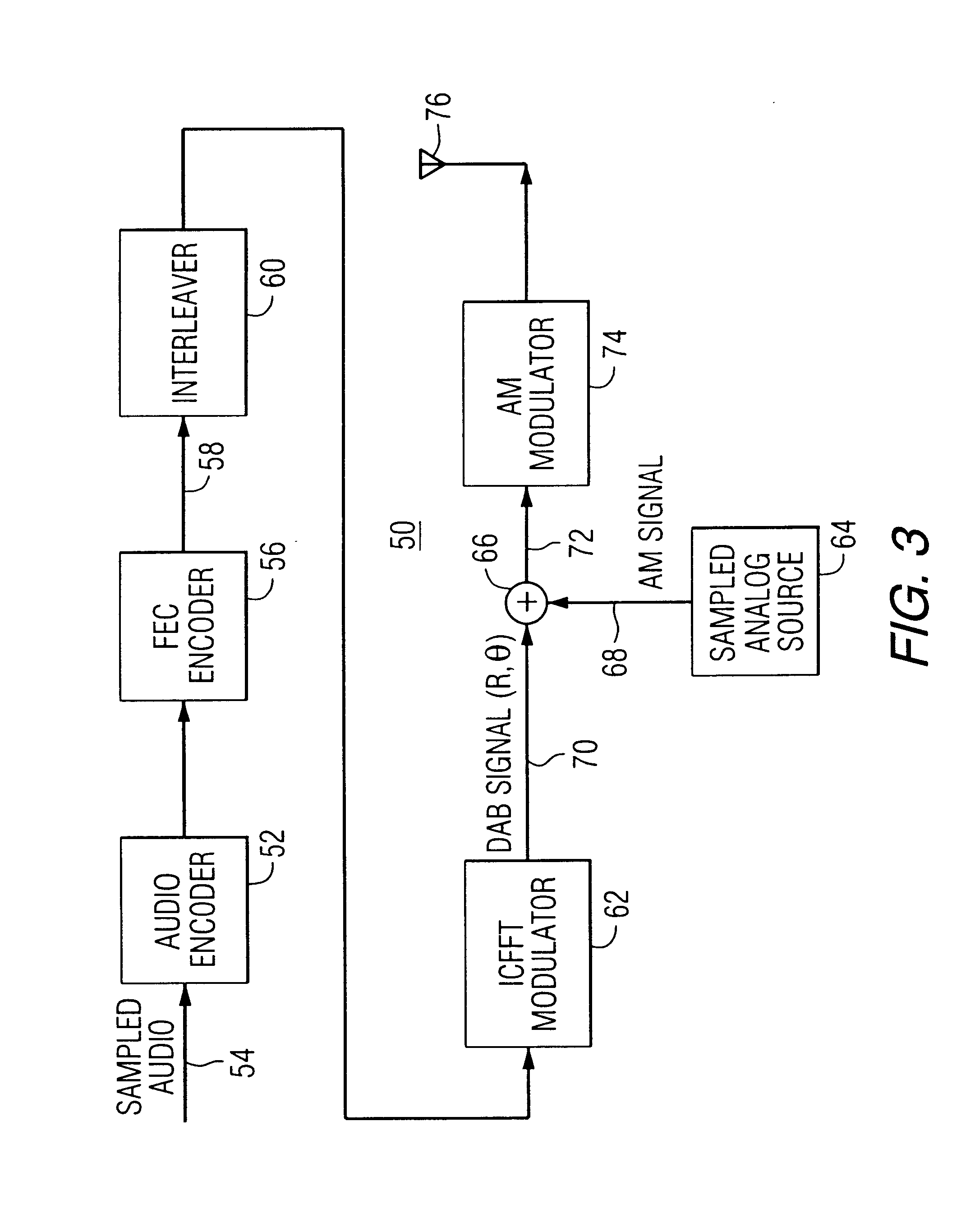
Digital audio broadcasting method and apparatus using complementary pattern-mapped convolutional codes
ActiveUS7043681B2Overcome limitationsError correction/detection using convolutional codesTransmission path divisionIn-phase and quadrature componentsCarrier signal
A method of transmitting digital information comprises the steps of forward error correction encoding a plurality of bits of digital information using complementary pattern-mapped convolutional codes, modulating a plurality of carrier signals with the forward error corrected bits, and transmitting the carrier signals. The modulation can include the step of independently amplitude shift keying in-phase and quadrature components of the QAM constellation using Gray code constellation points corresponding to amplitude levels. Transmitters that transmit signals in accordance with the method and receivers that receive such signals are also included.
Owner:IBIQUITY DIGITAL CORP
Radio system for long-range high-speed wireless communication
Devices and systems, and methods of using them, for point-to-point transmission / communication of high bandwidth signals. Radio devices and systems may include a pair of reflectors (e.g., parabolic reflectors) that are adjacent to each other and configured so that one of the reflectors is dedicated for sending / transmitting information, and the adjacent reflector is dedicated for receiving information. Both reflectors may be in a fixed configuration relative to each other so that they are aligned to send / receive in parallel. In many variations the two reflectors are formed of a single housing, so that the parallel alignment is fixed, and reflectors cannot lose alignment. The device / systems may be configured to allow switching between duplexing modes. These devices / systems may be configured as wide bandwidth zero intermediate frequency radios including alignment modules for automatic alignment of in-phase and quadrature components of transmitted signals.
Owner:UBIQUITI INC
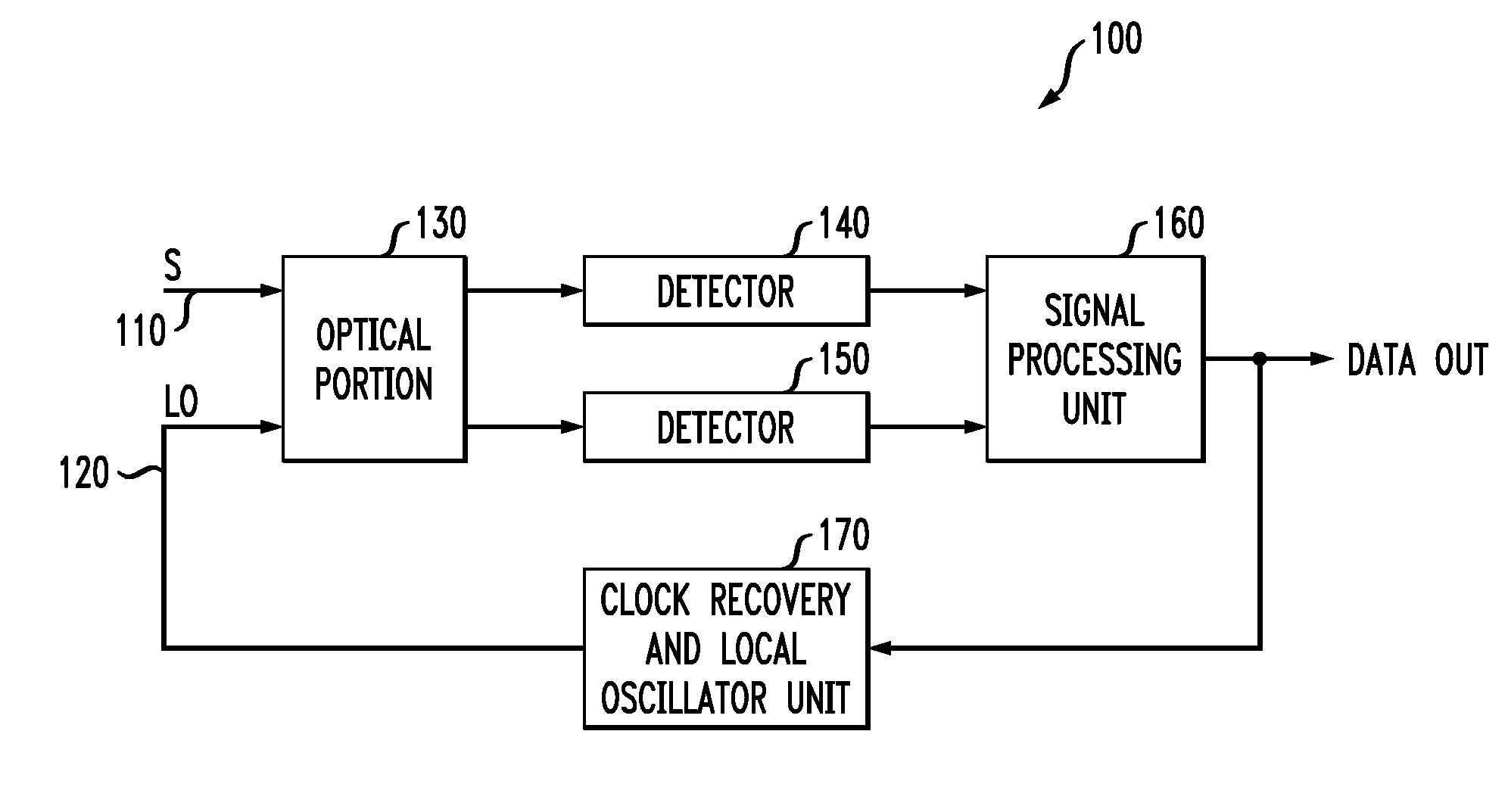
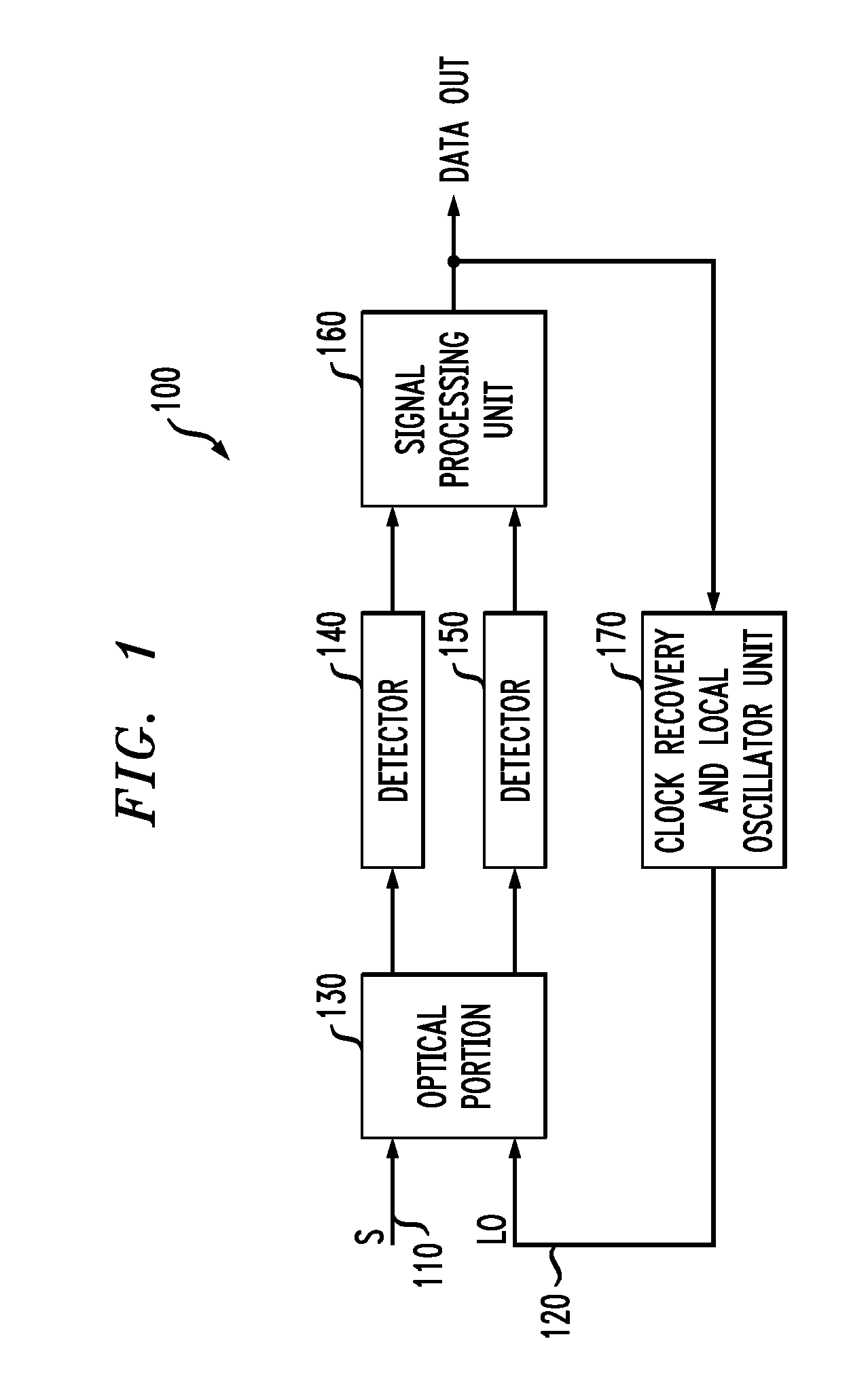
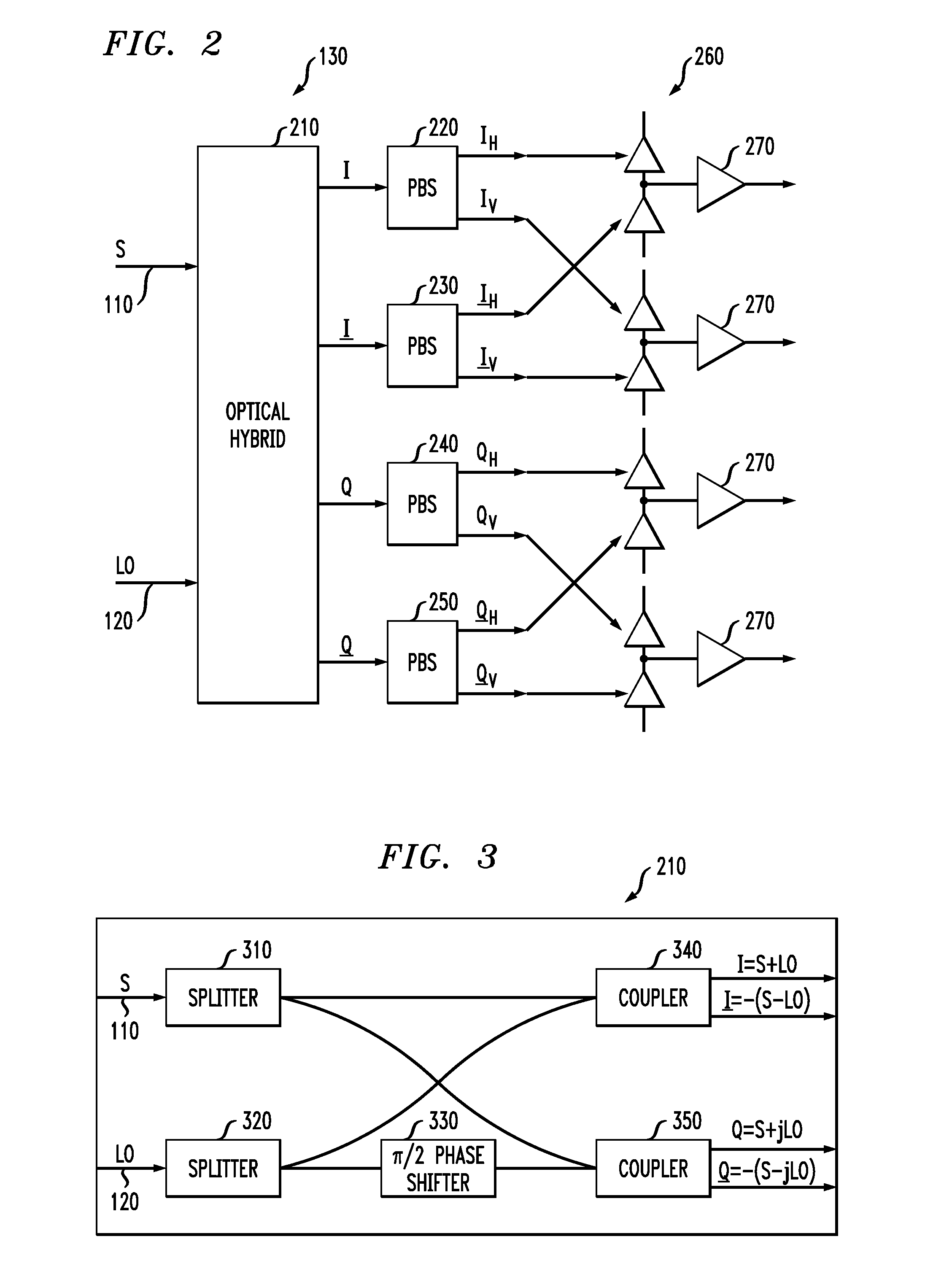
System and method for receiving coherent, polarizaztion-multiplexed optical signals
ActiveUS20070297806A1Easy to useElectromagnetic receiversPolarization diversityIn-phase and quadrature components
An apparatus, a polarization diversity receiver and a method of receiving a received optical signal. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes: (1) an optical device configured to separate in-phase and quadrature components of a received optical signal, to transmit the in-phase components to a first optical output thereof and to transmit the quadrature components to a second optical output thereof, (2) a first polarization splitter coupled to receive light at the first optical output and (3) a second polarization splitter coupled to receive light at the second optical output.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
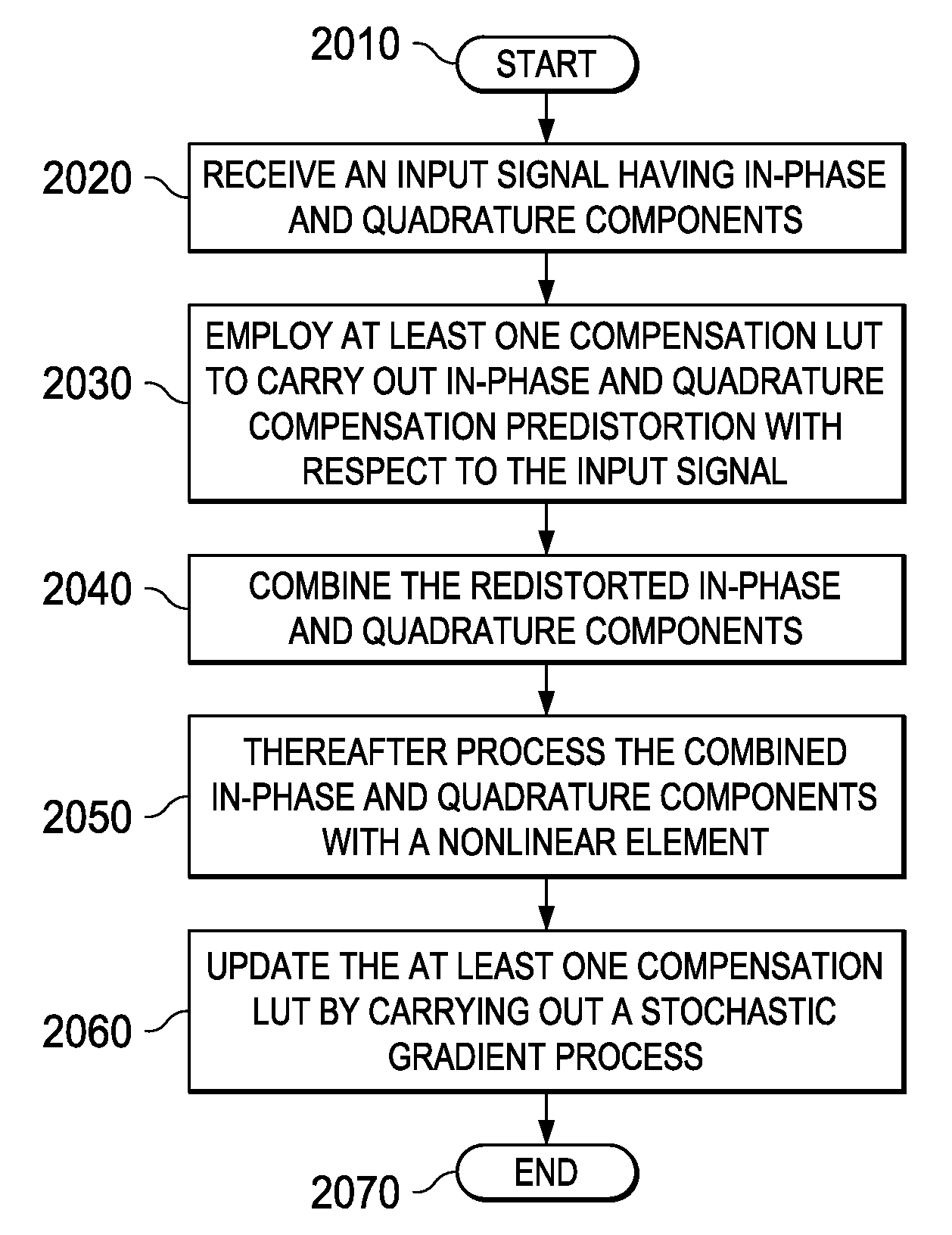
Adaptive Complex Gain Predistorter for a Transmitter
ActiveUS20100035554A1Resonant long antennasPower amplifiersLinear regionIn-phase and quadrature components
Symbols are transmitted in a Cartesian transmitter by pre-distorting an input signal X having in-phase and quadrature components using a first compensation lookup table operable to hold complex valued entries to carry out in-phase and quadrature compensation pre-distortion with respect to the input signal to form a pre-distorted signal Z. The pre-distorted signal Z is processed to form an output signal Y using a nonlinear element. A complex gain normalization parameter adaptively updated to reflect varying gain of a linear region of the nonlinear element. A normalized feed back signal {tilde over (Y)} is formed using the adaptively updated complex gain normalization parameter. The first compensation lookup table is updated based on the pre-distorted input signal Z and the adaptively normalized feedback signal {tilde over (Y)}.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
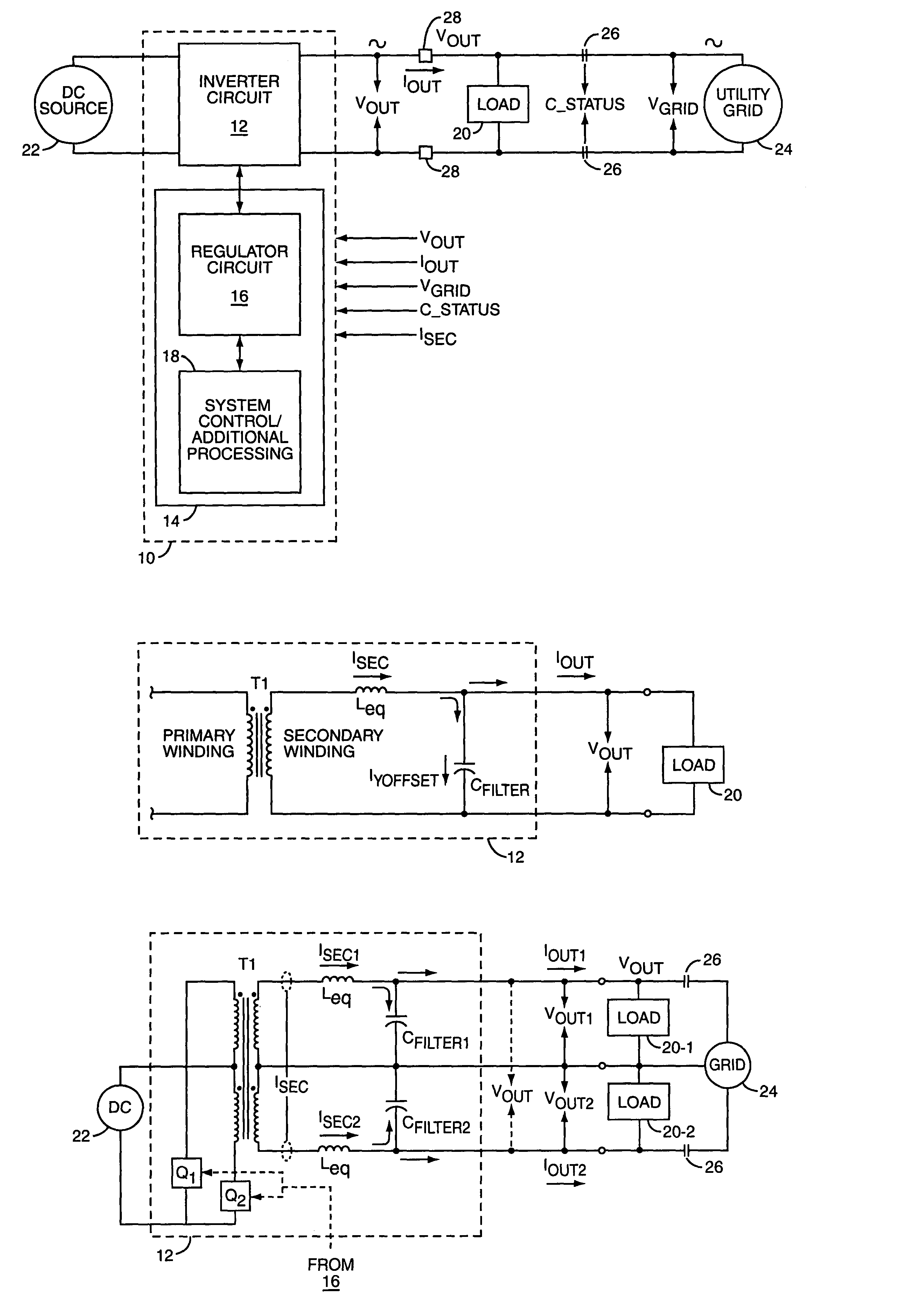
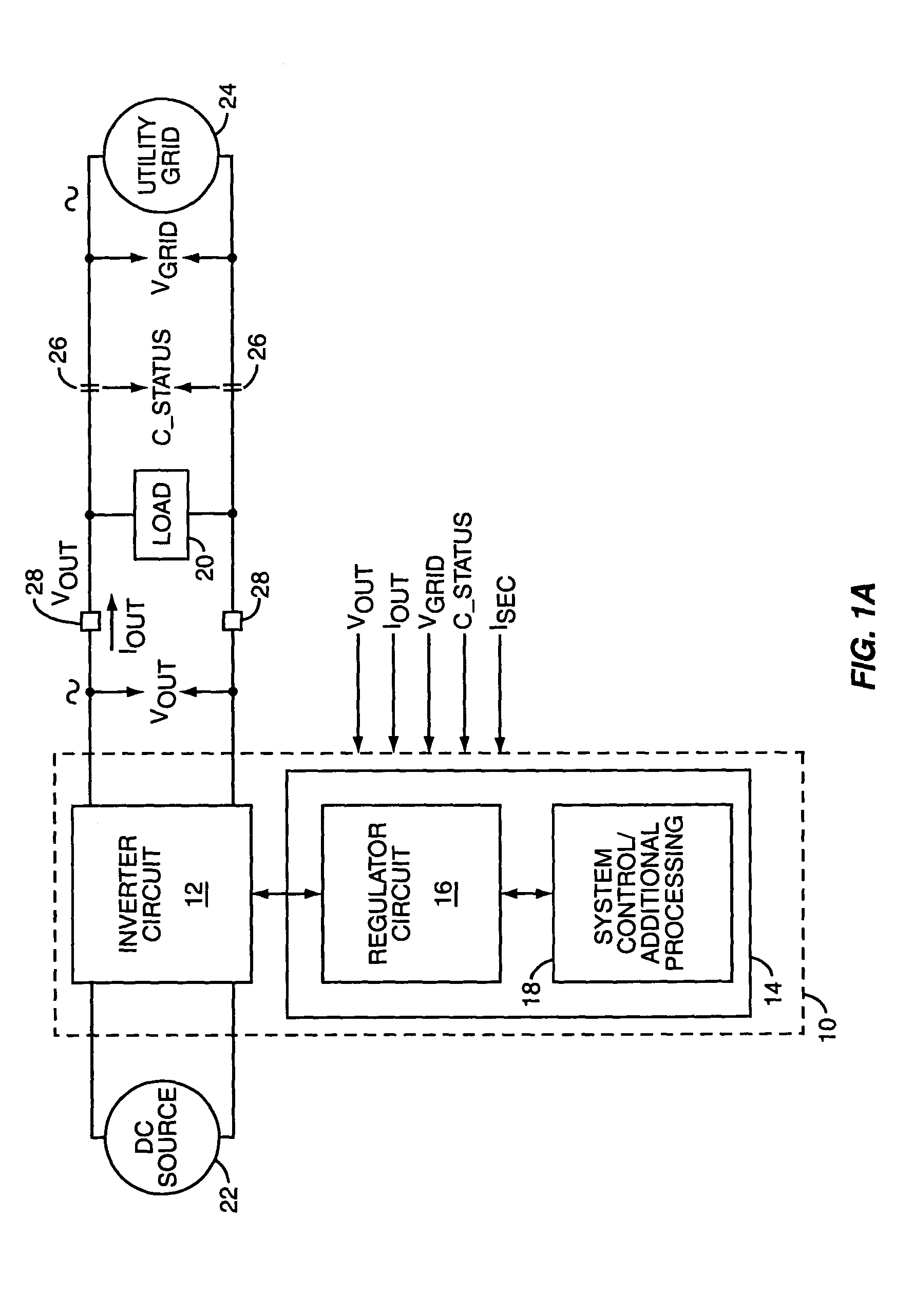
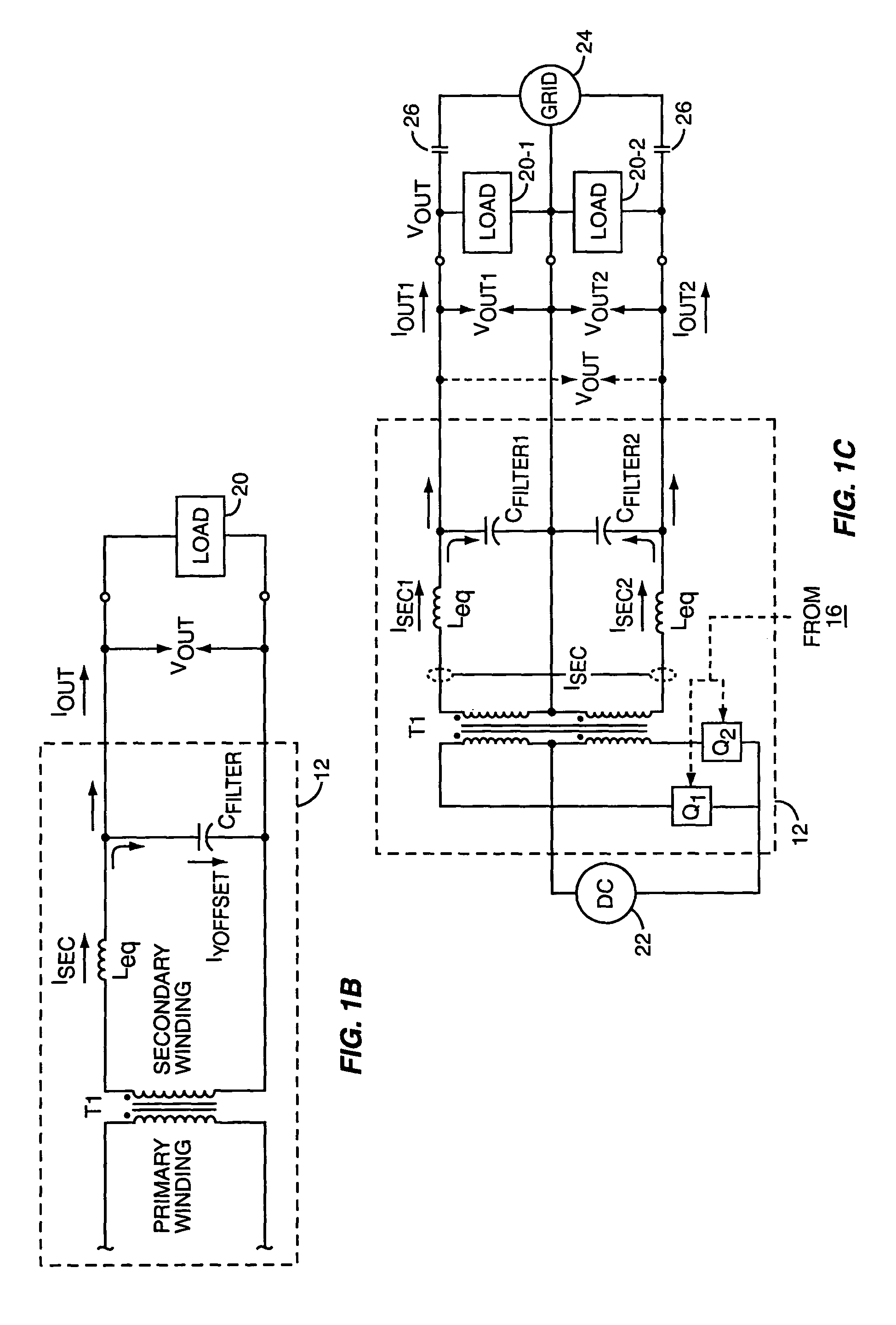
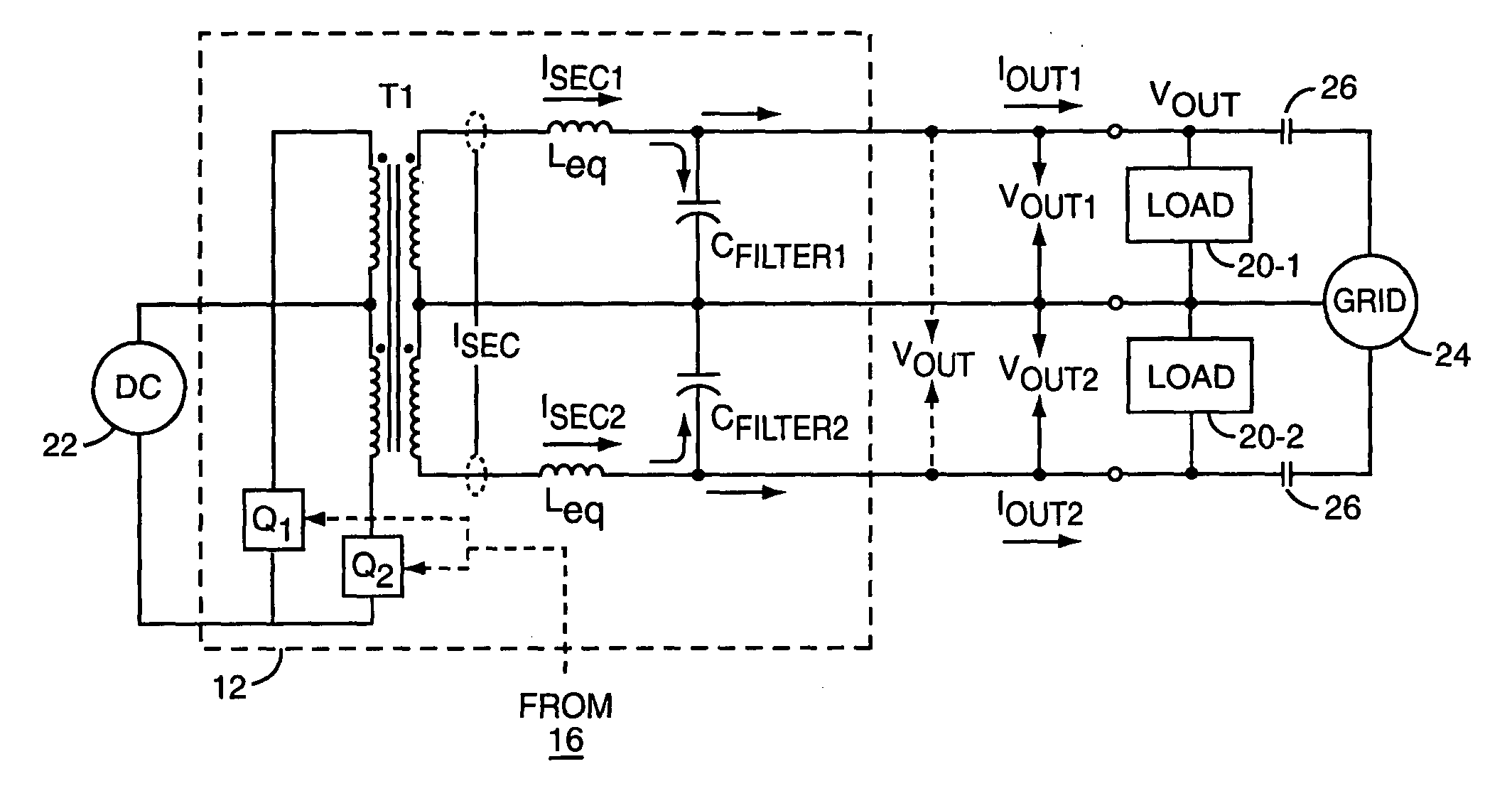
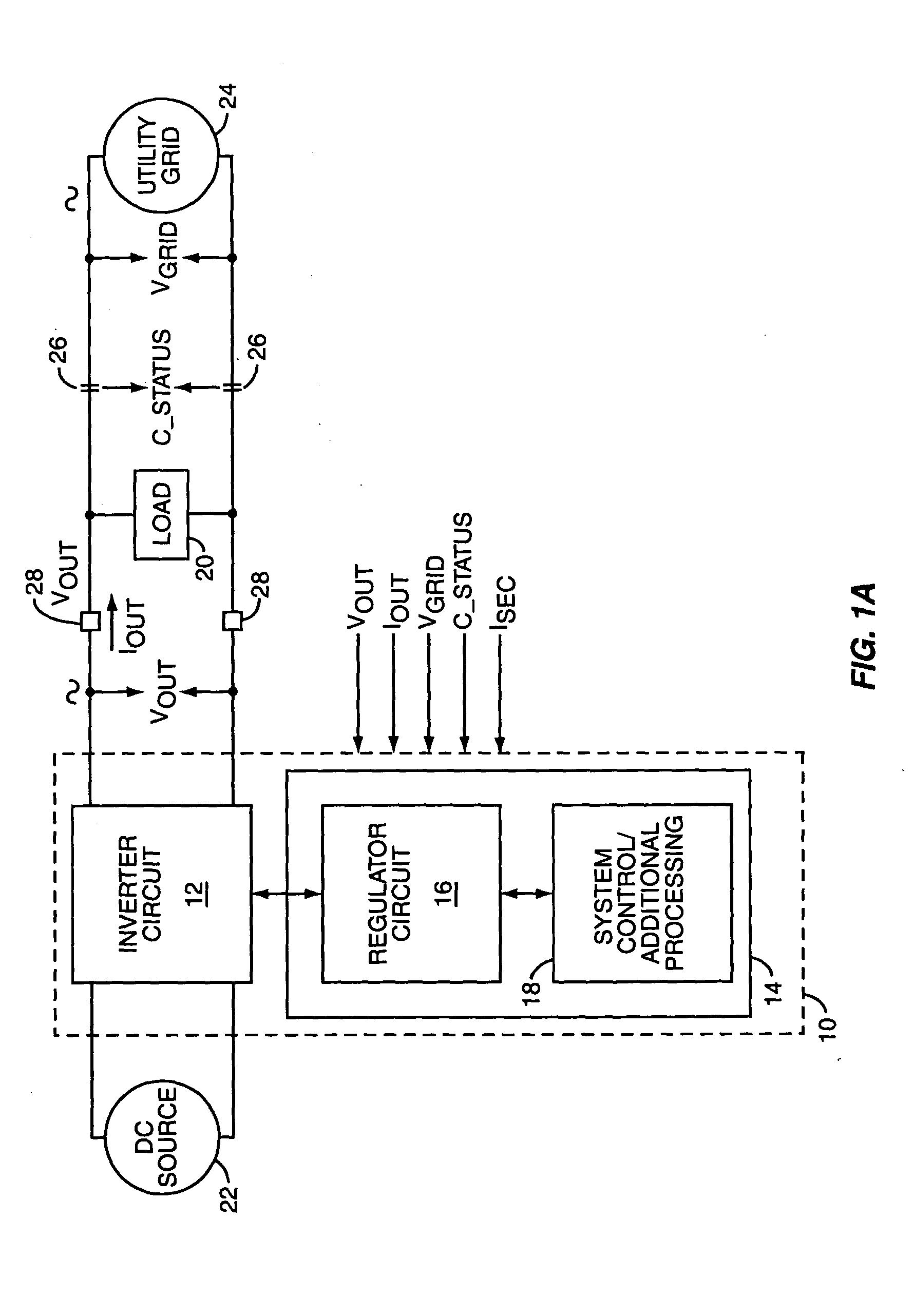
Power regulator for power inverter
ActiveUS7015597B2Reduce the differenceBatteries circuit arrangementsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower inverterPower conditioner
A power inverter includes a regulator circuit that controls real and reactive power output by the inverter. The regulator measures real and reactive output power by calculating x-phasor components of the inverter's voltage and current output waveforms. Phasor calculation can be adapted for one or more pairs of single-phase voltages and currents. Determining the fundamental in-phase and quadrature components of output voltage and current reduces computational complexity by permitting the regulator to perform its power control processing largely in a dc signal domain, and enables separate real and reactive power control. The power inverter can include islanding detection logic, which exploits the ability to separately control reactive power. Exemplary islanding detection logic is based on determining whether changing the amount of reactive power output by the inverter induces an output frequency shift.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
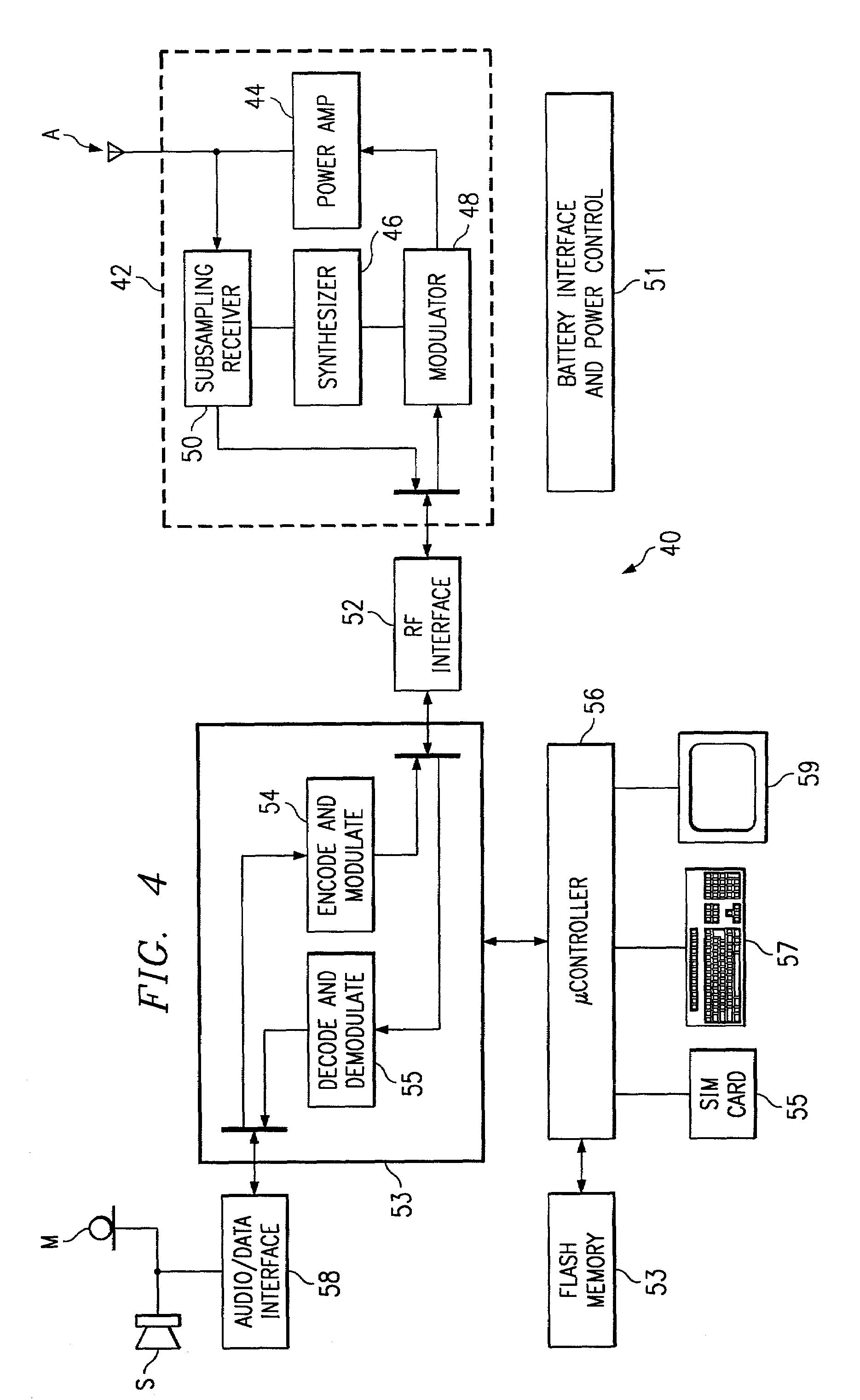
Subsampling RF receiver architecture
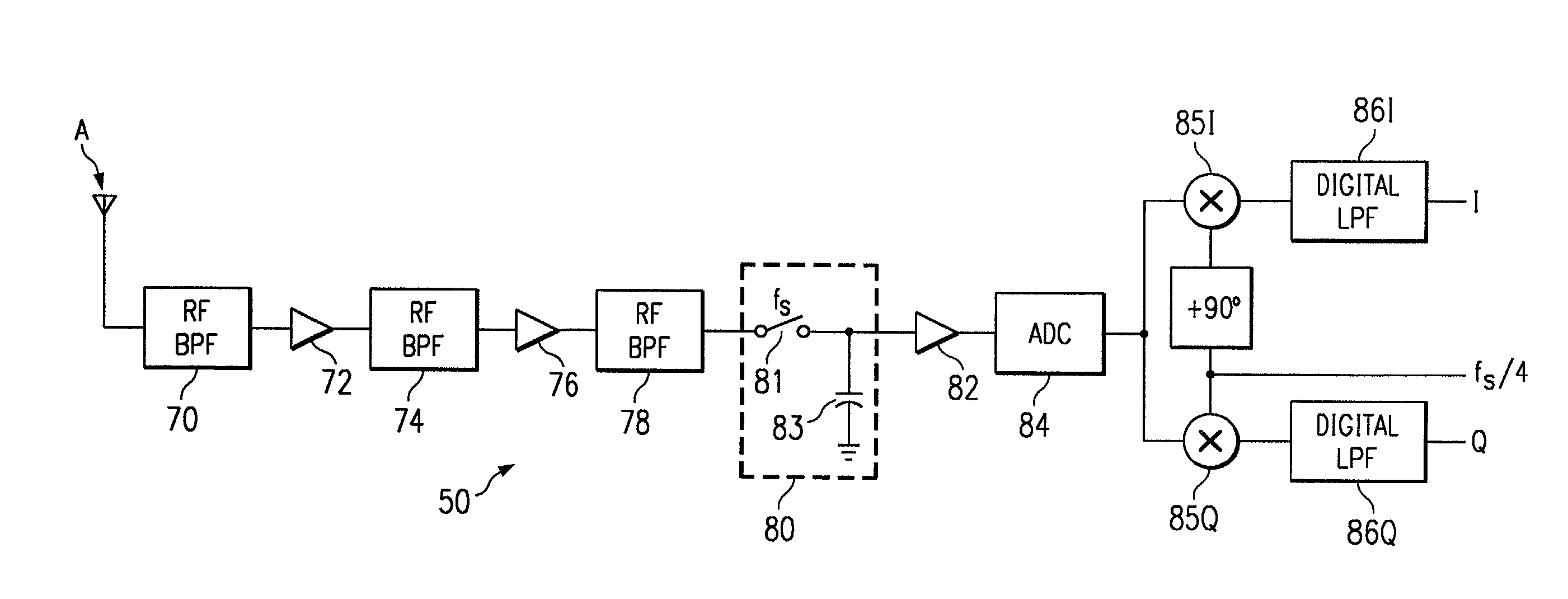
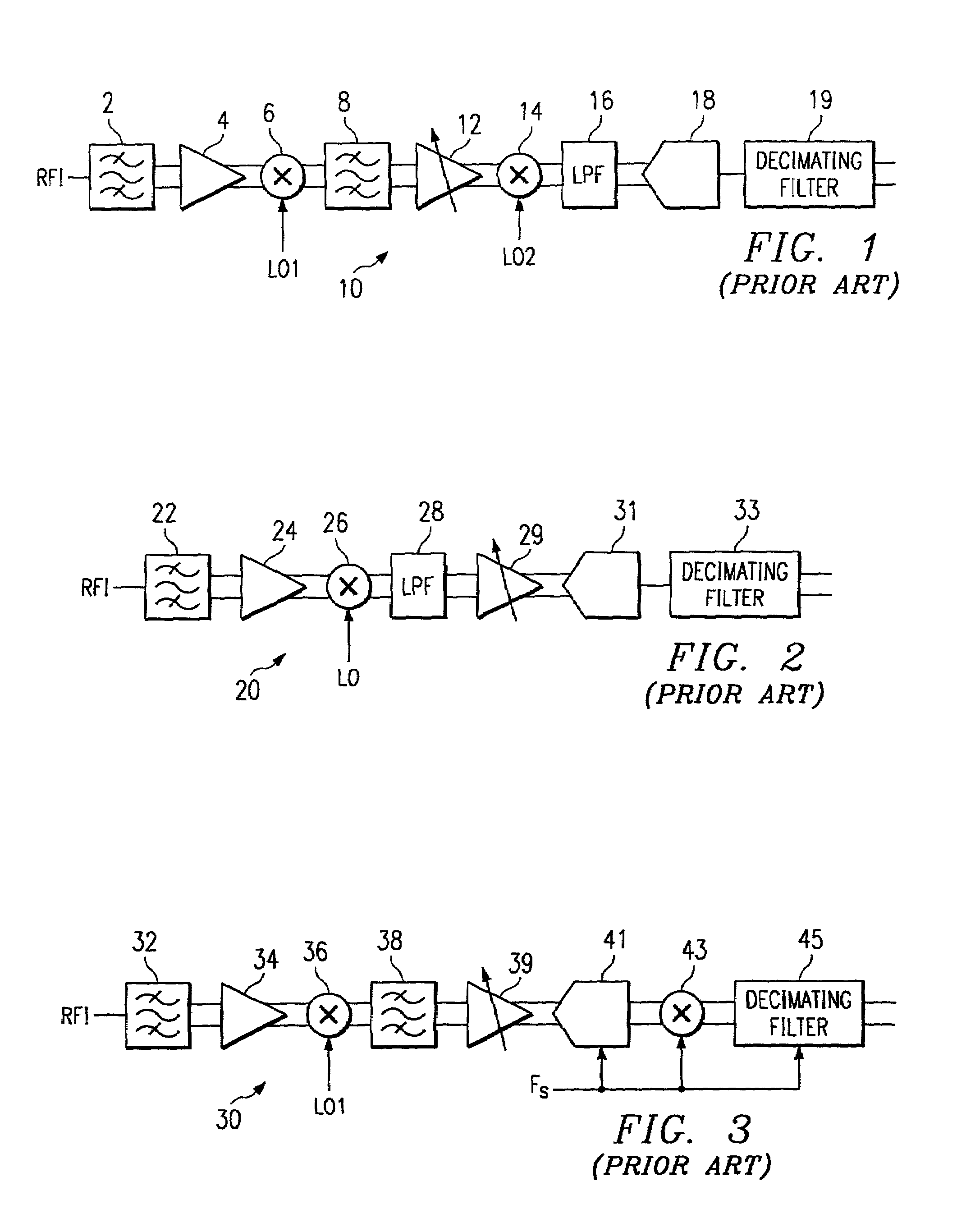
InactiveUS7110732B2Improve performanceLow costModulated-carrier systemsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesBandpass filteringIntermediate frequency
A subsampling receiver (50, 50′, 50″) for converting an RF signal to baseband is disclosed. The subsampling receiver (50, 50′, 50″) may be implemented into a wireless communications device (40), such as a wireless telephone handset. In one disclosed embodiment, the receiver (50) includes a sample and hold circuit (80) that samples a bandpass filtered input modulated signal at the subsampling frequency (fs) that is well below the RF carrier frequency but twice the bandwidth (BW) of the payload; the sampled signal is digitized, and applied to two digital mixers (85I, 85Q) to produce in-phase and quadrature components (I,Q) of the payload. In another embodiment, the receiver (50′) includes two sample and hold circuits (96I, 96Q) to sample the filtered signal at different phases of the sampling frequency, to produce the in-phase and quadrature digital components. In a third embodiment, the receiver (50″) includes an analog mixer (116) to downconvert the RF input to an intermediate frequency, prior to digitization and digital mixing at quadrature phase.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
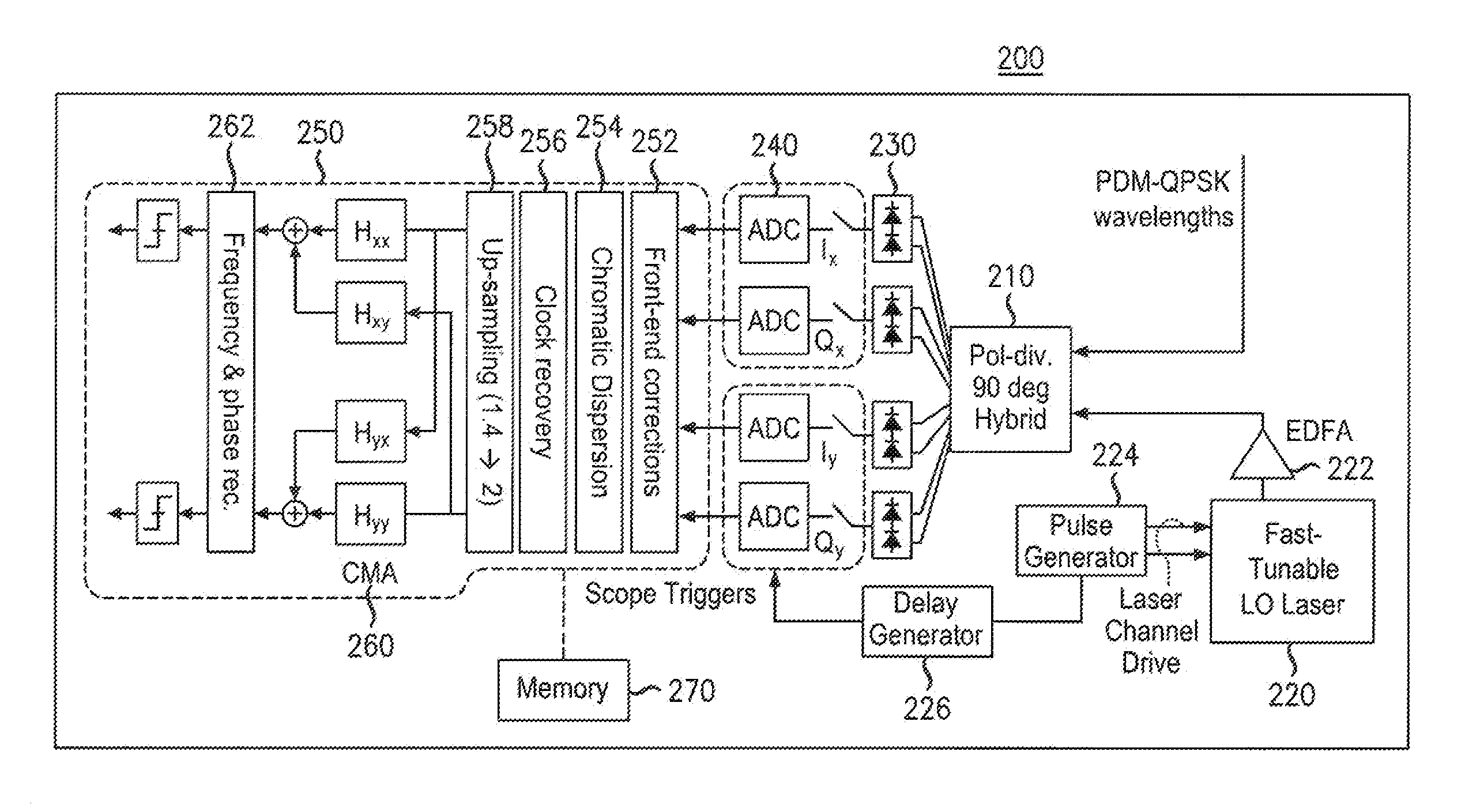
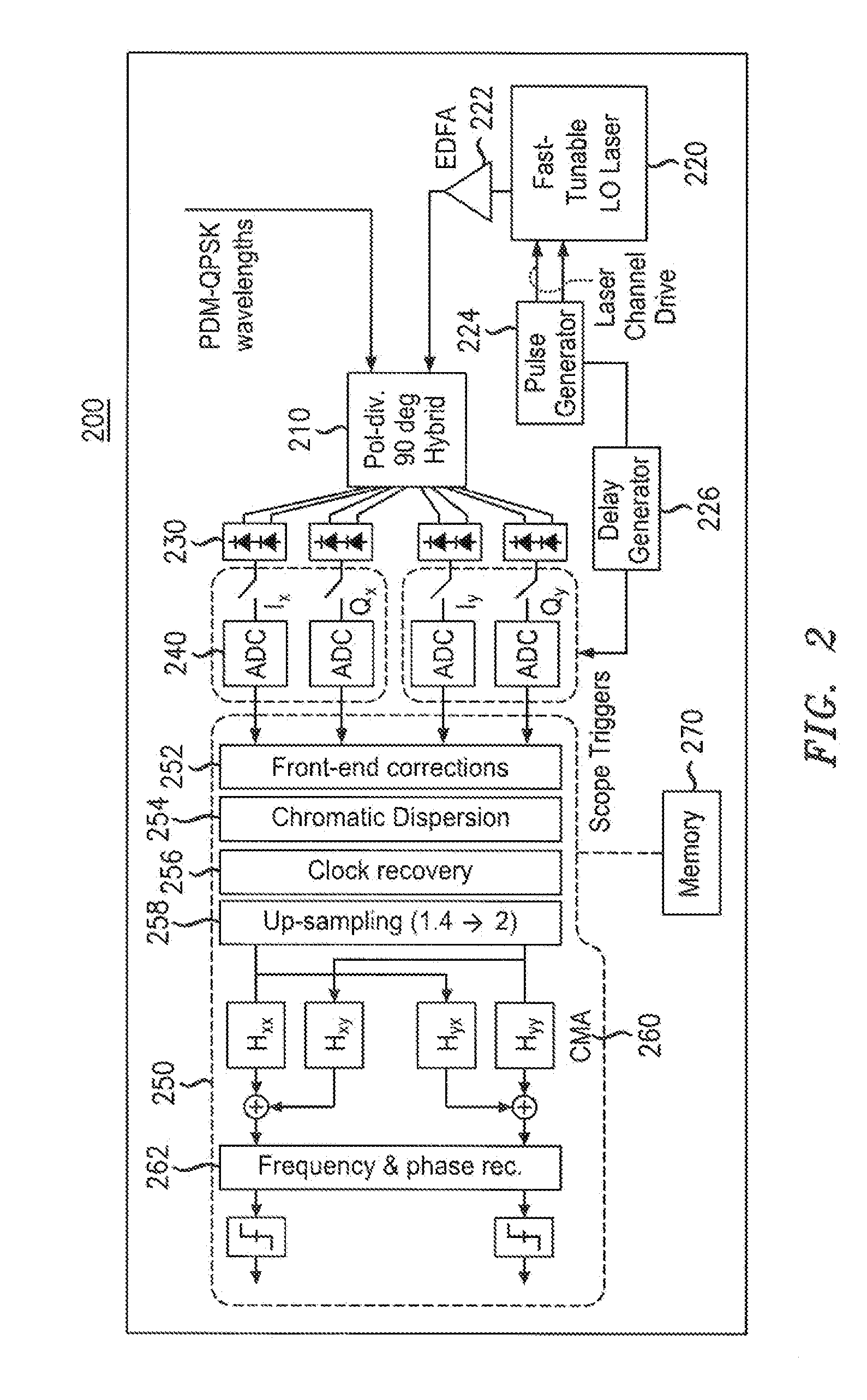
Tunable Receiver
ActiveUS20110229137A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsDigital signal processingLocal oscillator signal
Embodiments for optical communication are provided in which tunable receiver selects and demodulates a first channel of a WDM signal. An example receiver includes a tunable local oscillator for generating a local oscillator signal approximately centered at a first channel wavelength. An optical hybrid of the receiver receives at a first input a wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) signal with a M-ary modulation scheme, wherein M is an integer greater than 2, and at a second input the local oscillator signal. A plurality of detectors detect in-phase and quadrature components of the first channel wavelength output of the optical hybrid, which are digitizing by a plurality of analog-to-digital converters. A digital signal processor processes the digitized in-phase and quadrature components in order to recover data carried by the first channel of the WDM signal.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and apparatus for interference cancellation in communication signal processing
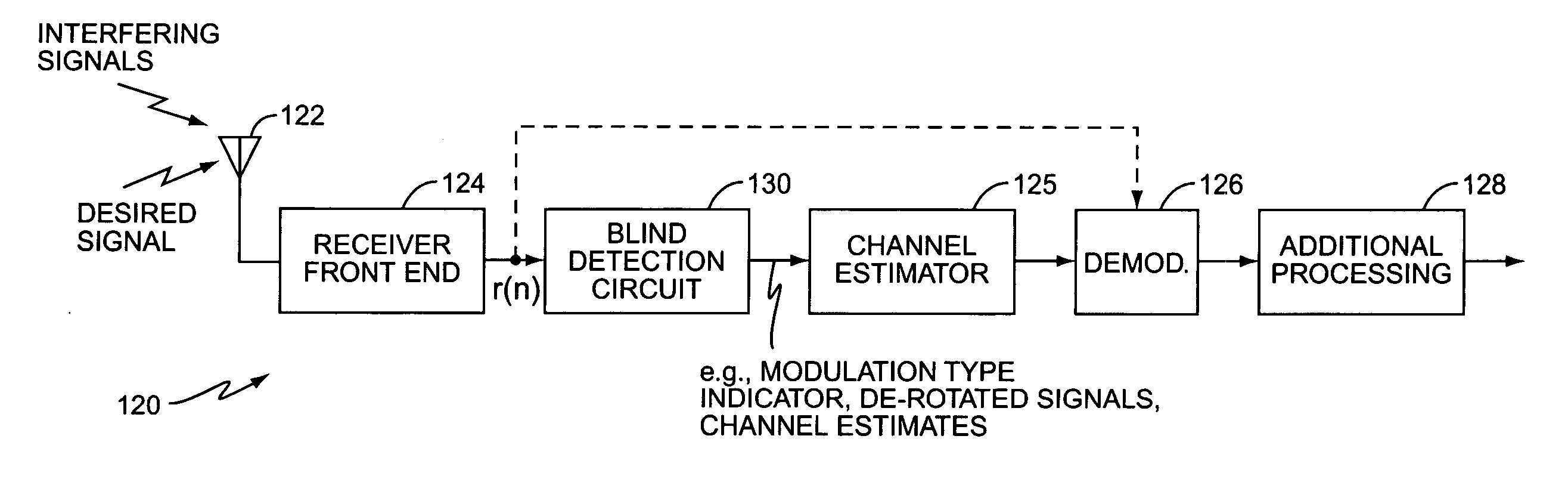
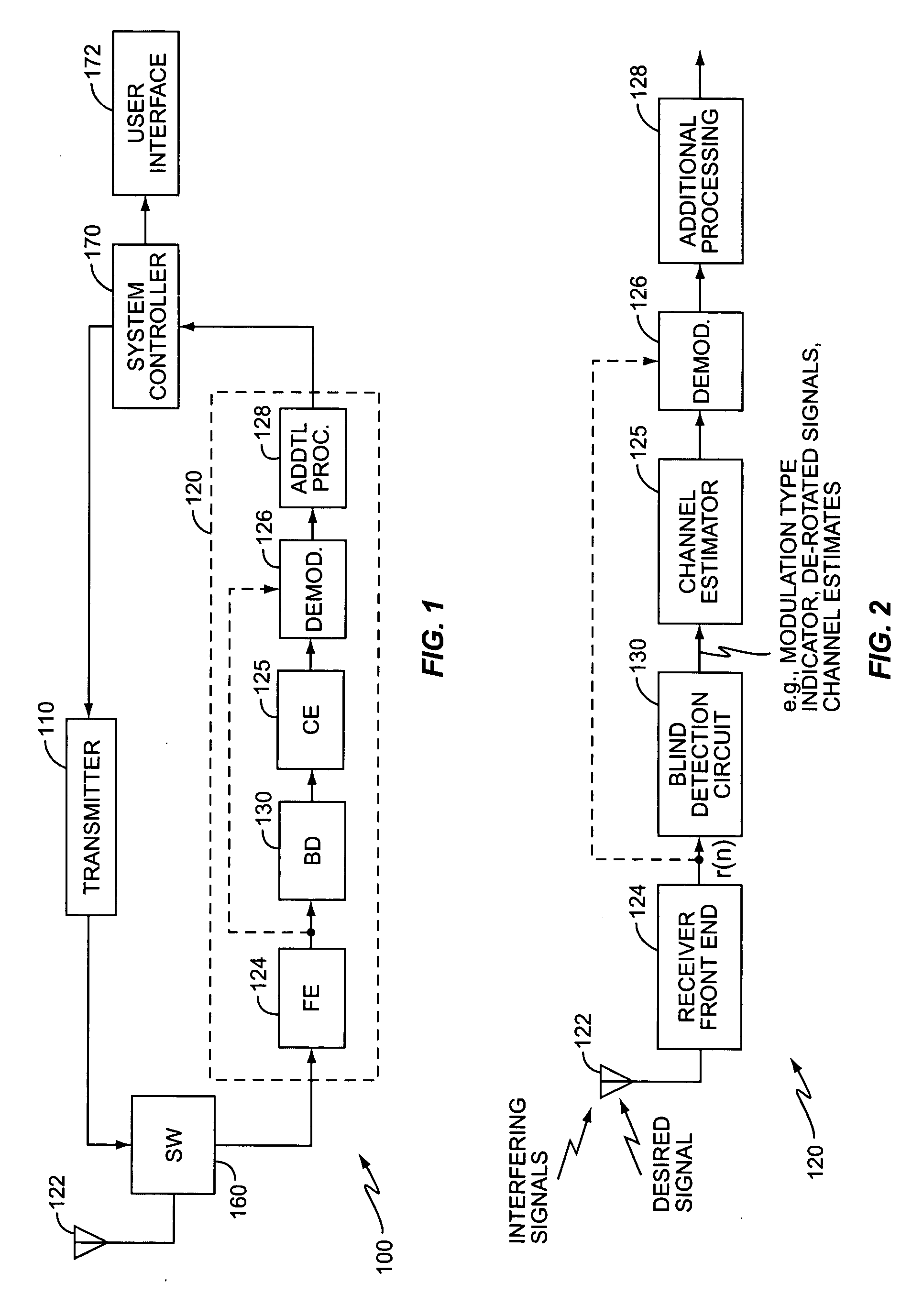
ActiveUS20050254600A1Reduce distractionsPolarisation/directional diversityModulation type identificationSpatial correlationIn-phase and quadrature components
A method and apparatus blindly detects a received signal's modulation type characterizing an impairment component of the received signal for each postulated modulation type by determining spatial correlations between In-phase and Quadrature components of the received signal. The blind detection circuit then detects the modulation type based on the characterized impairment component. A metric generator generates a postulation metric for each postulated modulation type based on the characterized impairment component. After evaluating the postulation metrics, an evaluation circuit identifies the postulated modulation type having the best postulation metric as the modulation type of the received signal. According to an exemplary embodiment, the blind detection circuit determines a whitened noise estimate for each postulated modulation type and generates the postulation metrics based on the whitened noise estimate to reduce interference effects in the postulation metrics.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
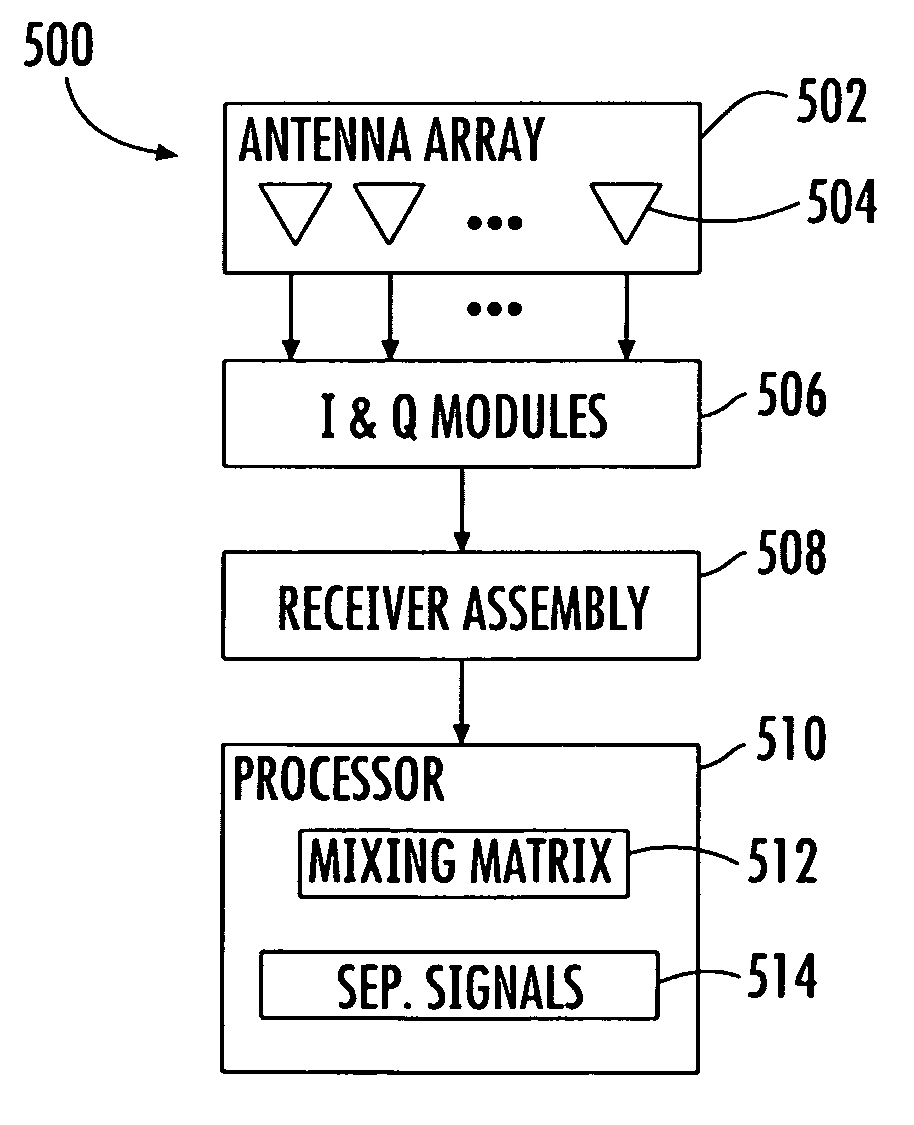
Distributed conformal adaptive antenna array for SATCOM using decision direction
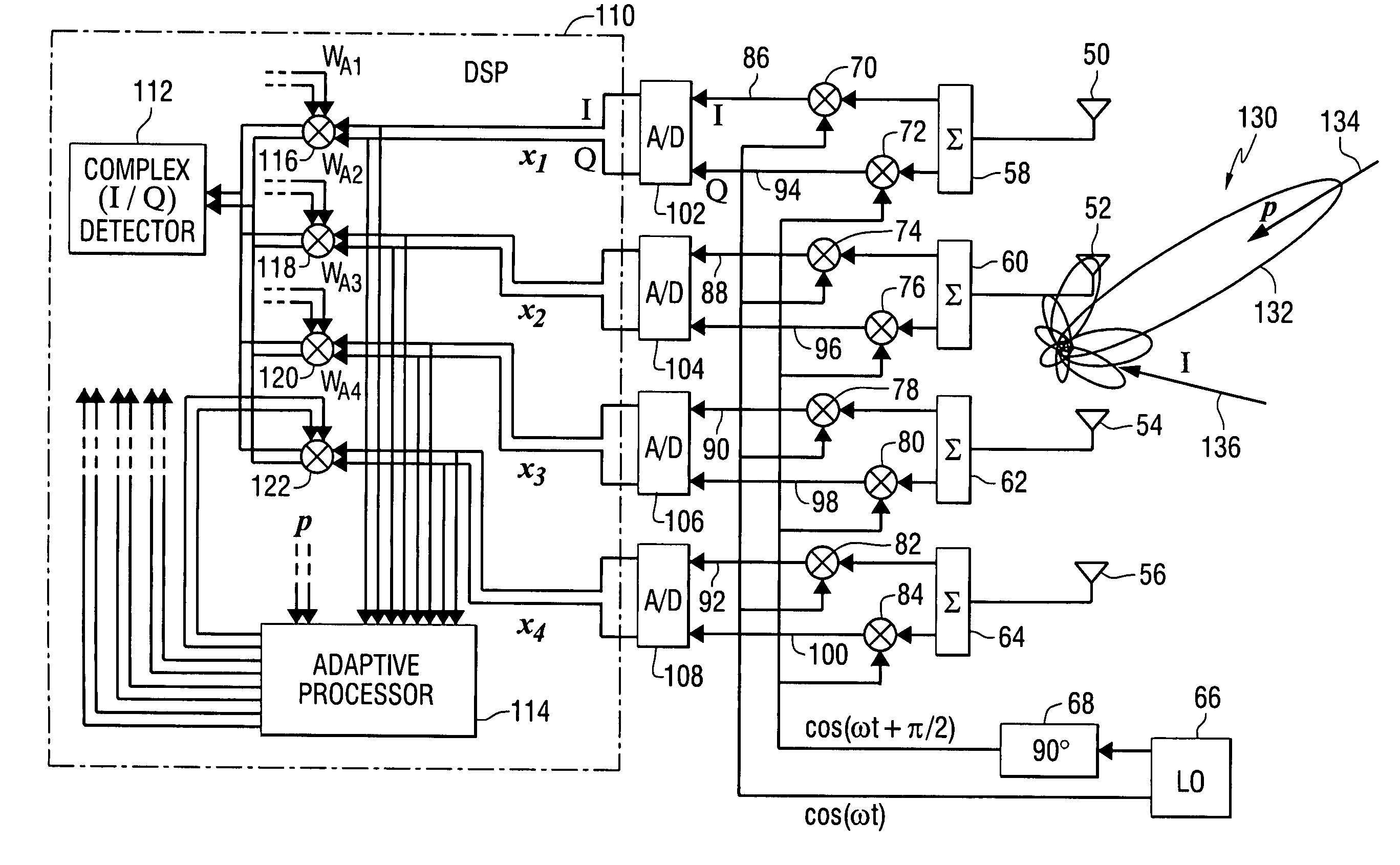
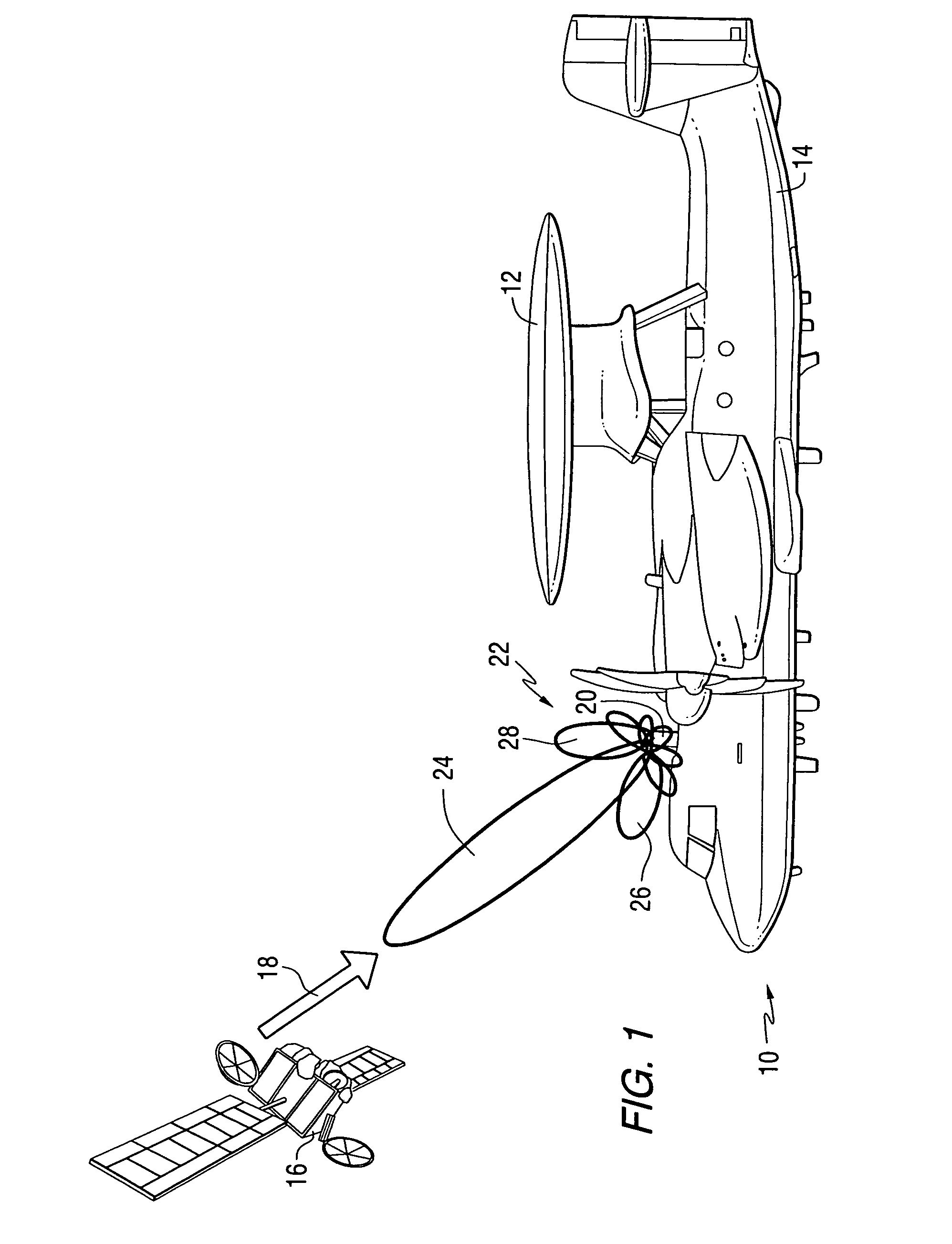
ActiveUS7606528B2Antenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesDirect feedbackIn-phase and quadrature components
An apparatus comprises a distributed array of antenna elements for receiving a radio frequency signal on a satellite communications link, wherein the radio frequency signal includes a known preamble; a plurality of mixers for translating the radio frequency signal to a plurality of baseband signals having in-phase and quadrature components; a processor for applying weights to the baseband signals, wherein the weights are found adaptively in response to the preamble in combination with decision-directed feedback when the preamble is not present; and a receiver for processing the weighted baseband signals. A pre-processor can be used to create sub-arrays of the antenna elements using maximal-ratio weighting. A method performed by the apparatus is also provided.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
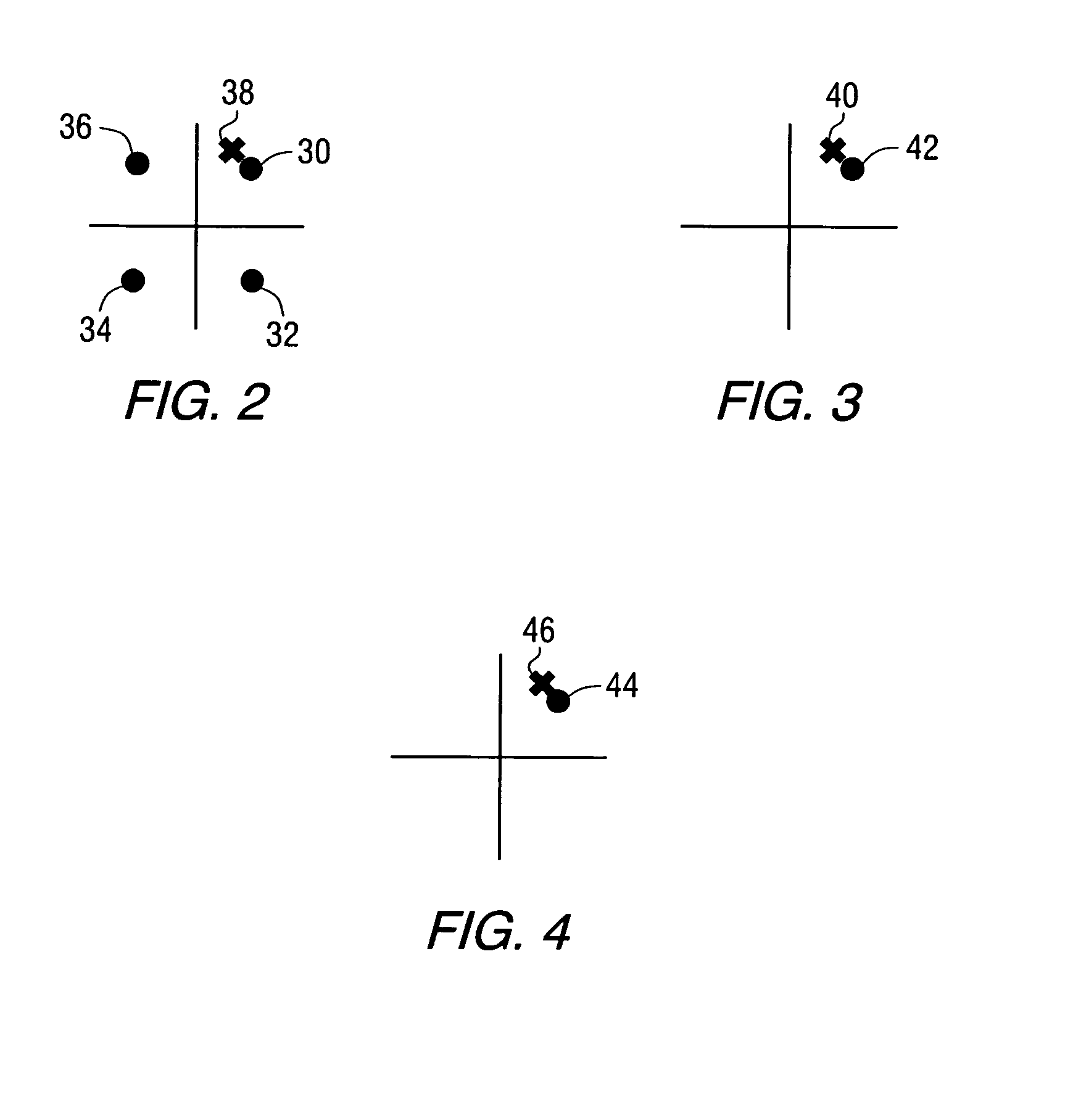
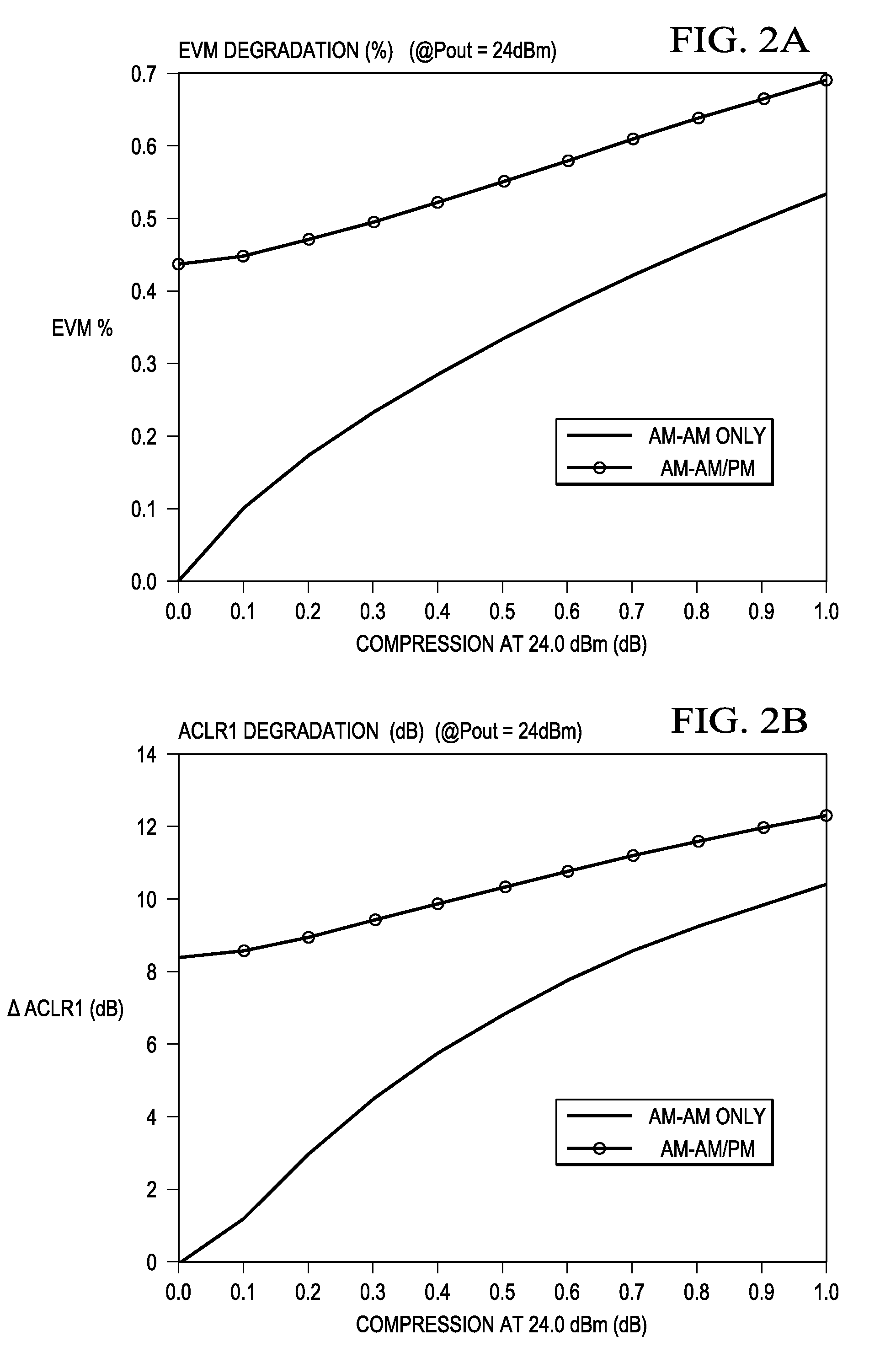
Apparatus and Method for Adaptive Cartesian Transmitter Linearization and Wireless Transmitter Employing the Same
ActiveUS20090054016A1Power amplifiersSecret communicationIn-phase and quadrature componentsNonlinear element
A Cartesian transmitter and a method of linearizing a Cartesian transmitter. In one embodiment, the transmitter includes: (1) a transmit chain configured to receive an input signal having in-phase and quadrature components and having a predistorter configured to employ at least one compensation lookup table to carry out in-phase and quadrature compensation predistortion with respect to the input signal, a combiner configured to combine outputs of the predistorter and a nonlinear element configured to process an output of the combiner, (2) a receiver coupled to the transmit chain and (3) predistortion compensation circuitry associated with the receiver and configured to update the at least one compensation lookup table based on the input signal and a signal from the receiver.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and system for single weight (SW) antenna system for spatial multiplexing (SM) MIMO system for WCDMA/HSDPA
ActiveUS20060072514A1Low delay link adaptationSpatial transmit diversitySimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationData streamIn-phase and quadrature components
Methods and systems for processing signals in a receiver are disclosed herein and may comprise receiving spatially multiplexed signals via M receive antennas. A plurality of multiple data streams may be separated in the received spatially multiplexed signals to detect MIMO data streams. Each of the MIMO data streams may correspond to a spatially multiplexed input signal. Complex phase and / or amplitude may be estimated for each detected MIMO data streams utilizing (M-1) phase shifters. Complex waveforms, comprising in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components for the MIMO data streams within the received spatially multiplexed signals may be processed and the processed complex waveforms may be filtered to generate baseband bandwidth limited signals. Phase and / or amplitude for one or more received spatially multiplexed signals may be adjusted utilizing the estimated complex phase and amplitude. Phase and / or amplitude may be adjusted continuously and / or at discrete intervals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
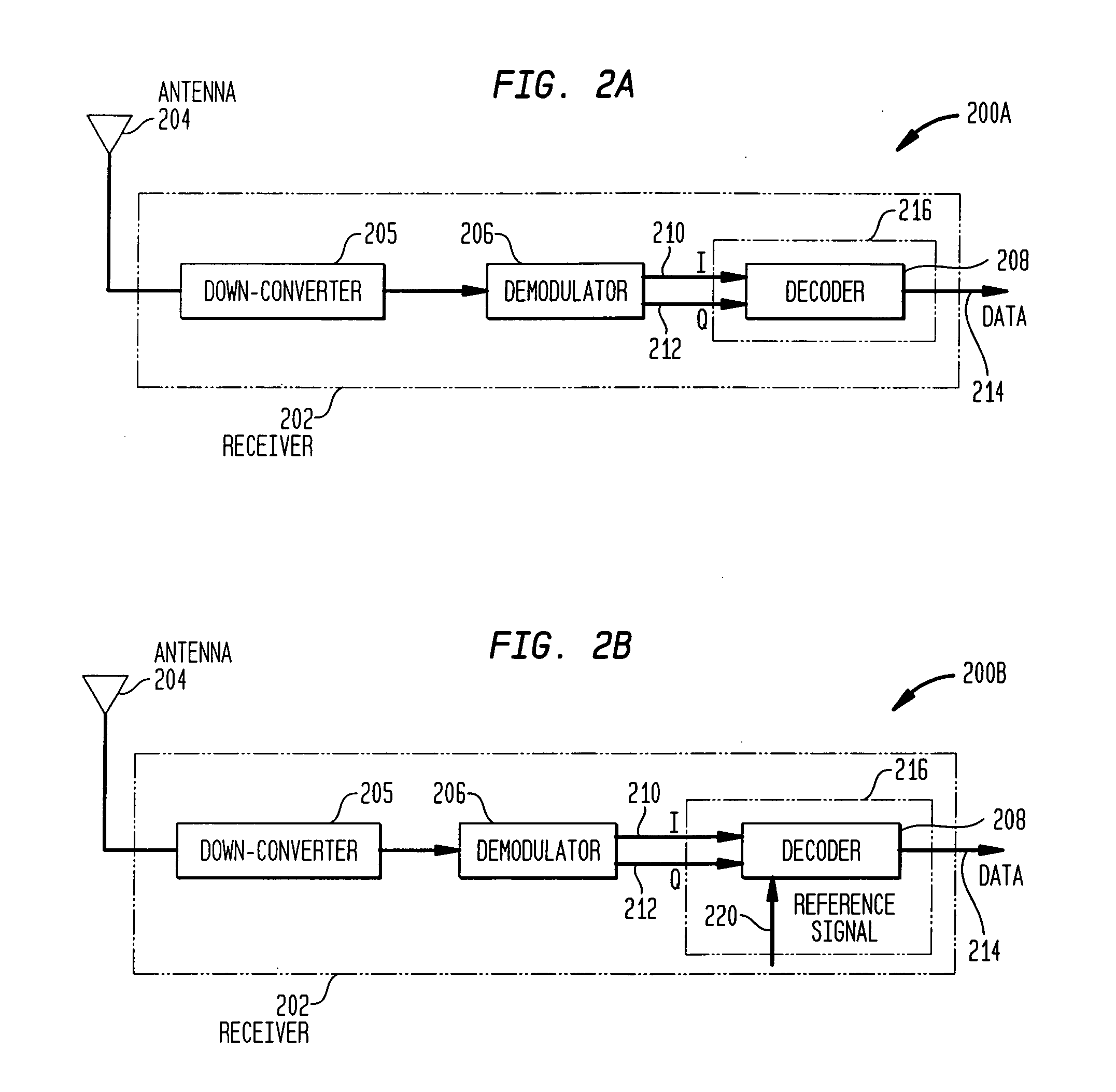
Method and apparatus for data signal processing in wireless RFID systems
InactiveUS20070025475A1Memory record carrier reading problemsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsIn-phase and quadrature componentsData signal
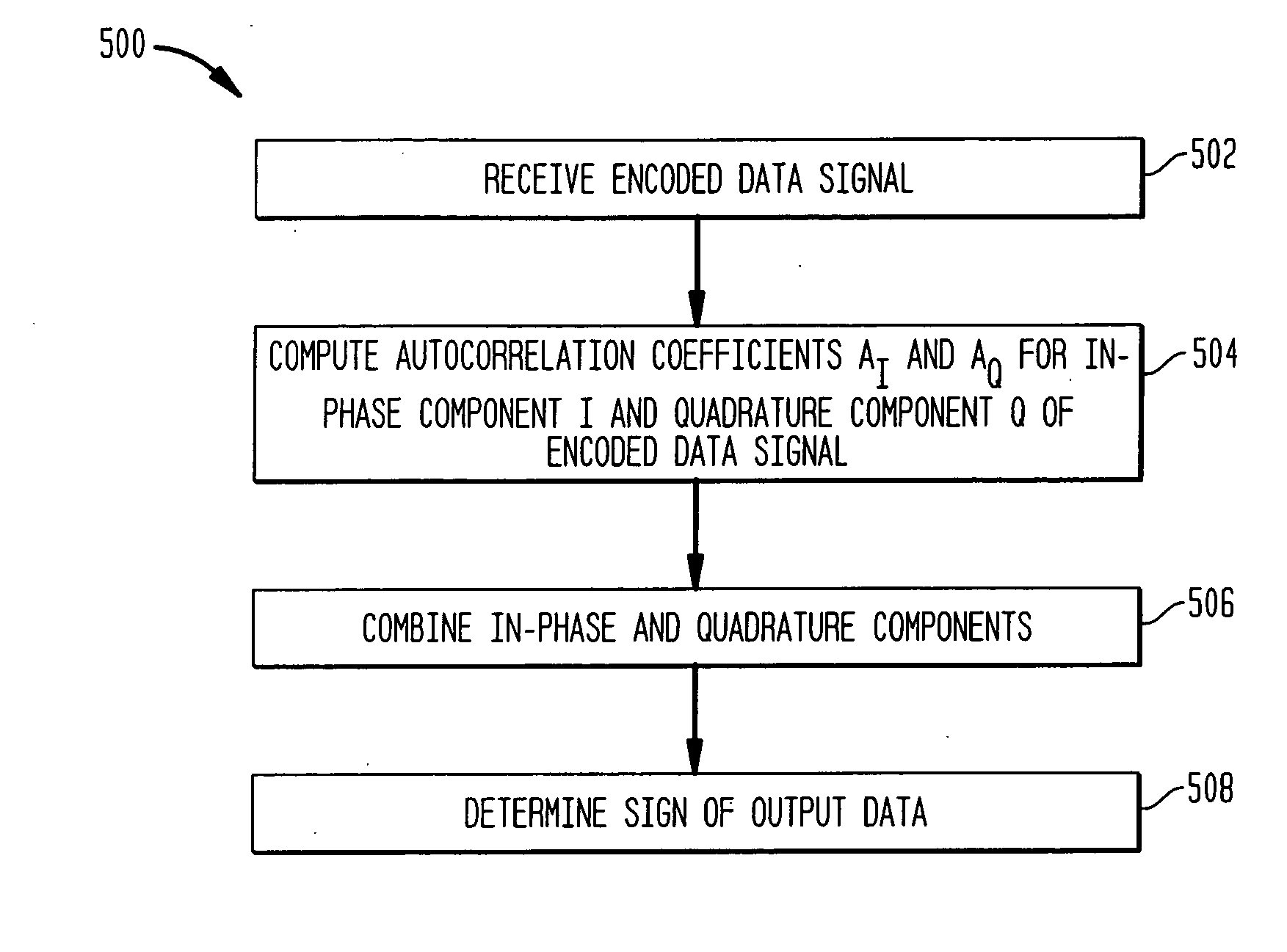
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for demodulation and decoding of backscattered RFID tag signals, represented by their in-phase and quadrature components at the output of the demodulator in the receiver portion of a reader interrogator. Autocorrelation coefficients for the in-phase and quadrature components of the received signal are calculated. The in-phase and quadrature coefficients are combined. The sign of output data is determined. Embodiments of the present invention are applicable to Gen 2 RFID systems as well as any wireless telecommunications system with the corresponding data modulation and / or encoding technique.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
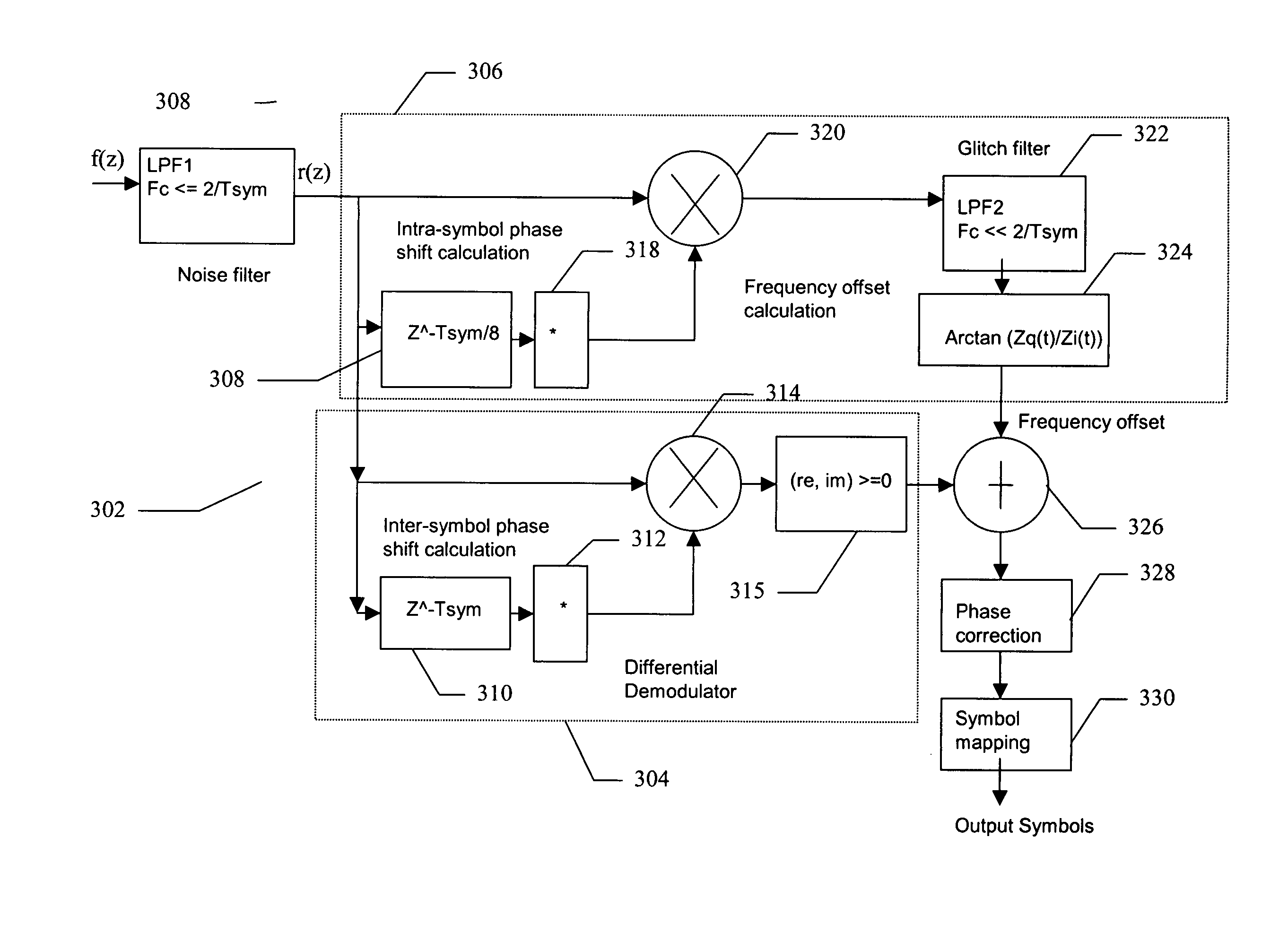
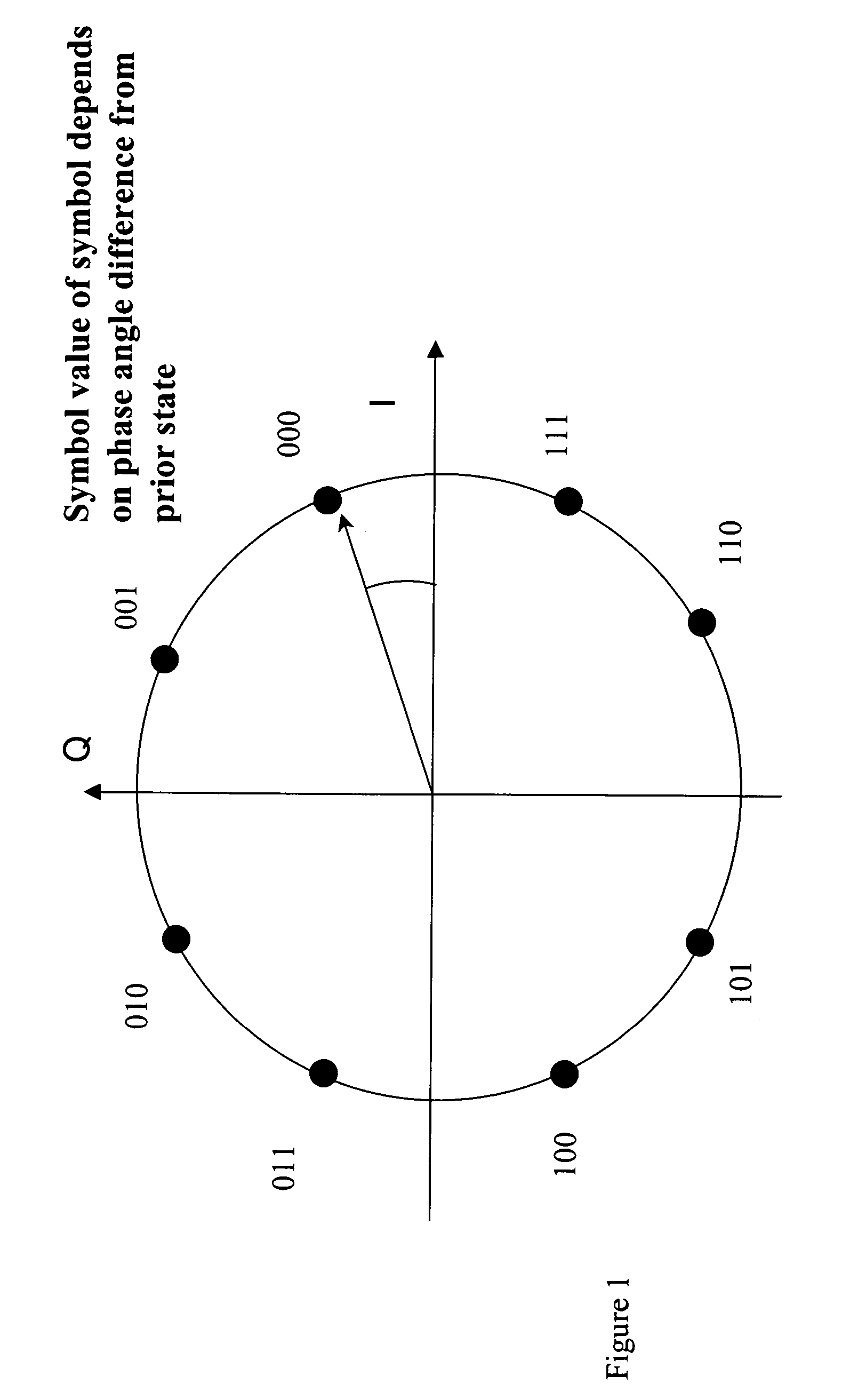
Computationally efficient demodulation for differential phase shift keying
InactiveUS20050008101A1Reduce power consumptionSignificant computational efficiencyCarrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDigital transformationPhase conversion
A DPSK demodulator demodulates DPSK signals in a computationally efficient manner to reduce the power requirements of the DPSK demodulator. A DPSK signal is received, digitized, converted to its in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components and filtered to remove noise. The I and Q components are processed to determine a relative phase and frequency offset. The phase is adjusted using the frequency offset. The adjusted phase is converted to an absolute phase, which is then mapped to a symbol representative of one or more bits of data.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and apparatus for estimating signal noise ratio of frequency-amplifying signal
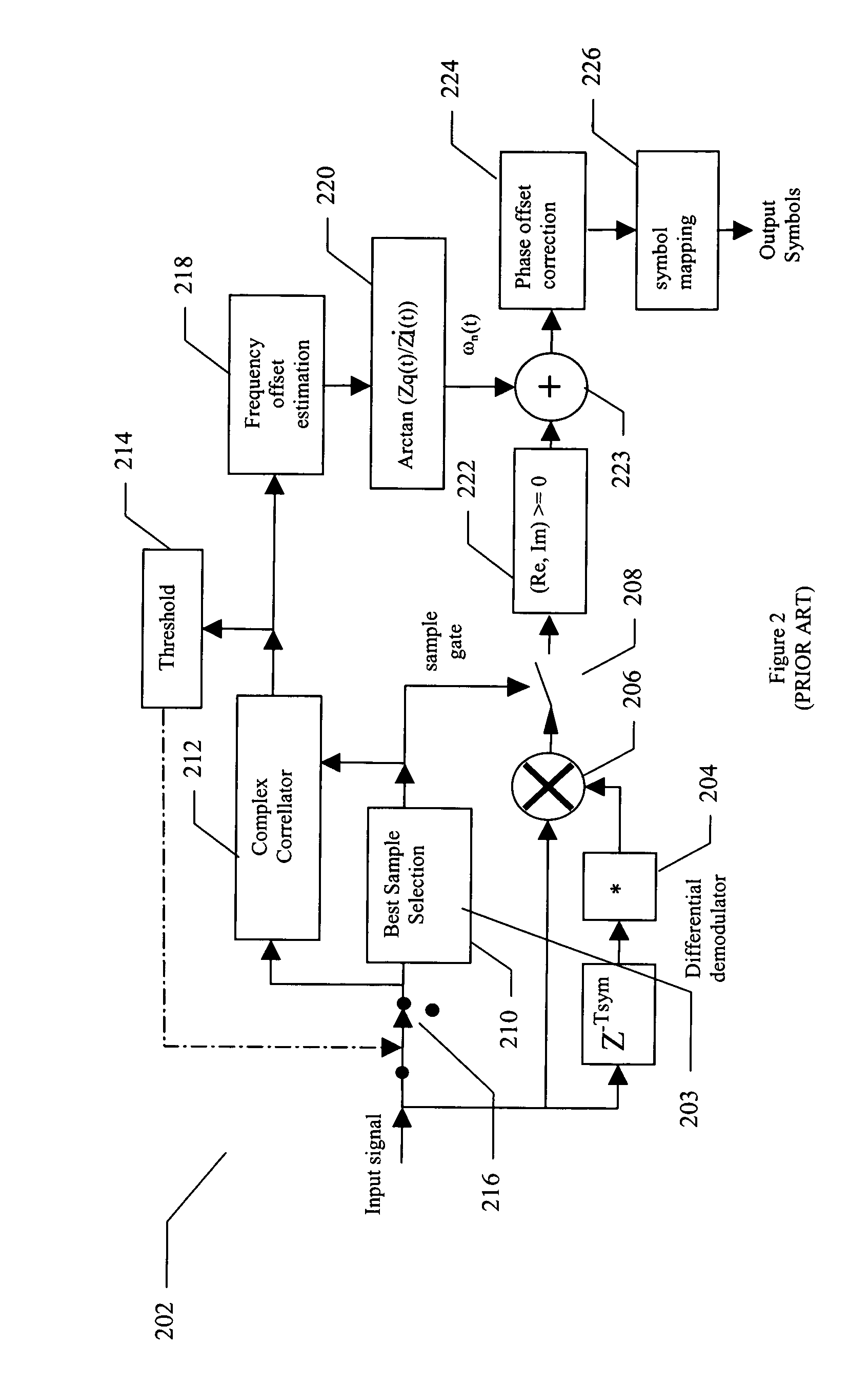
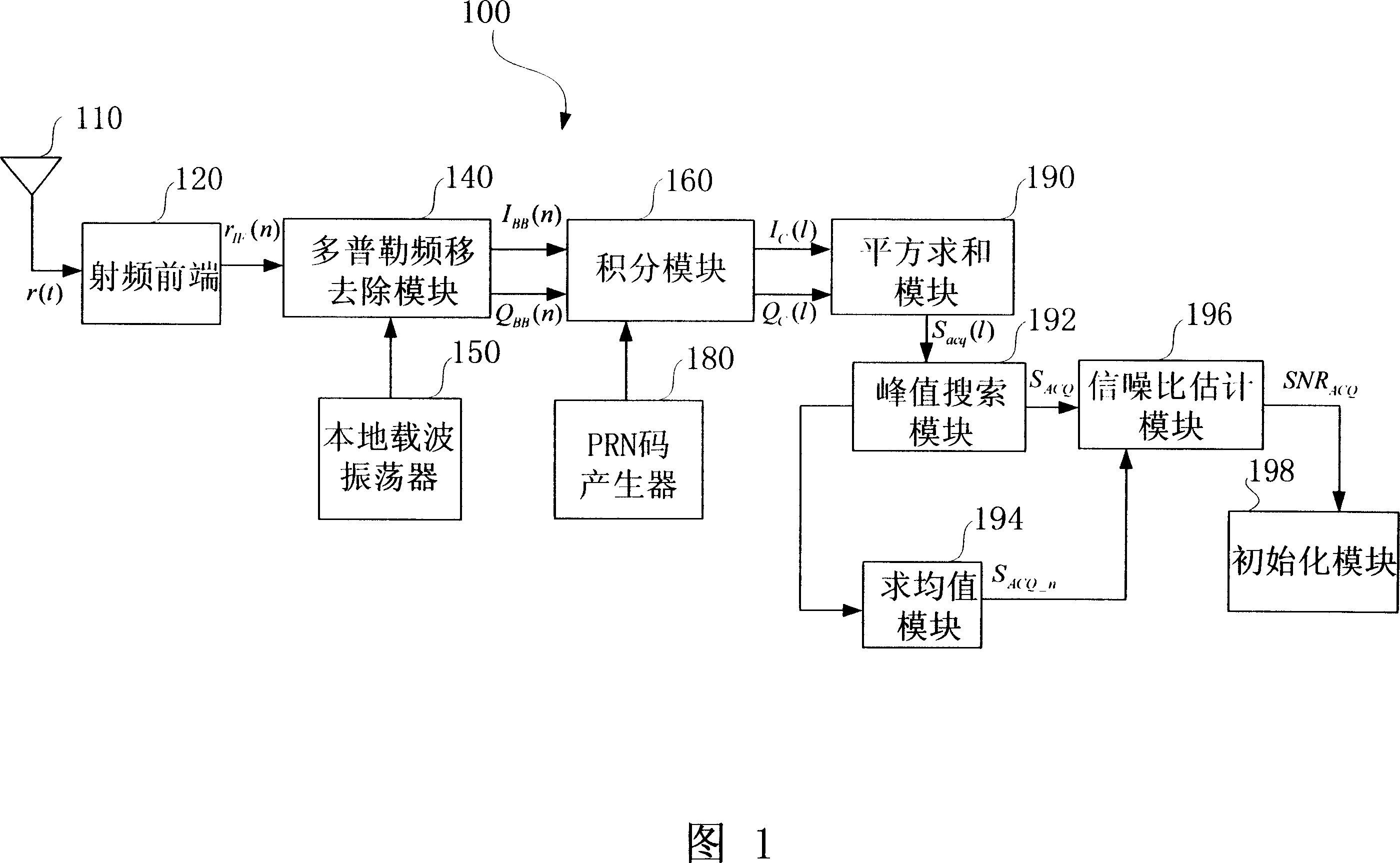
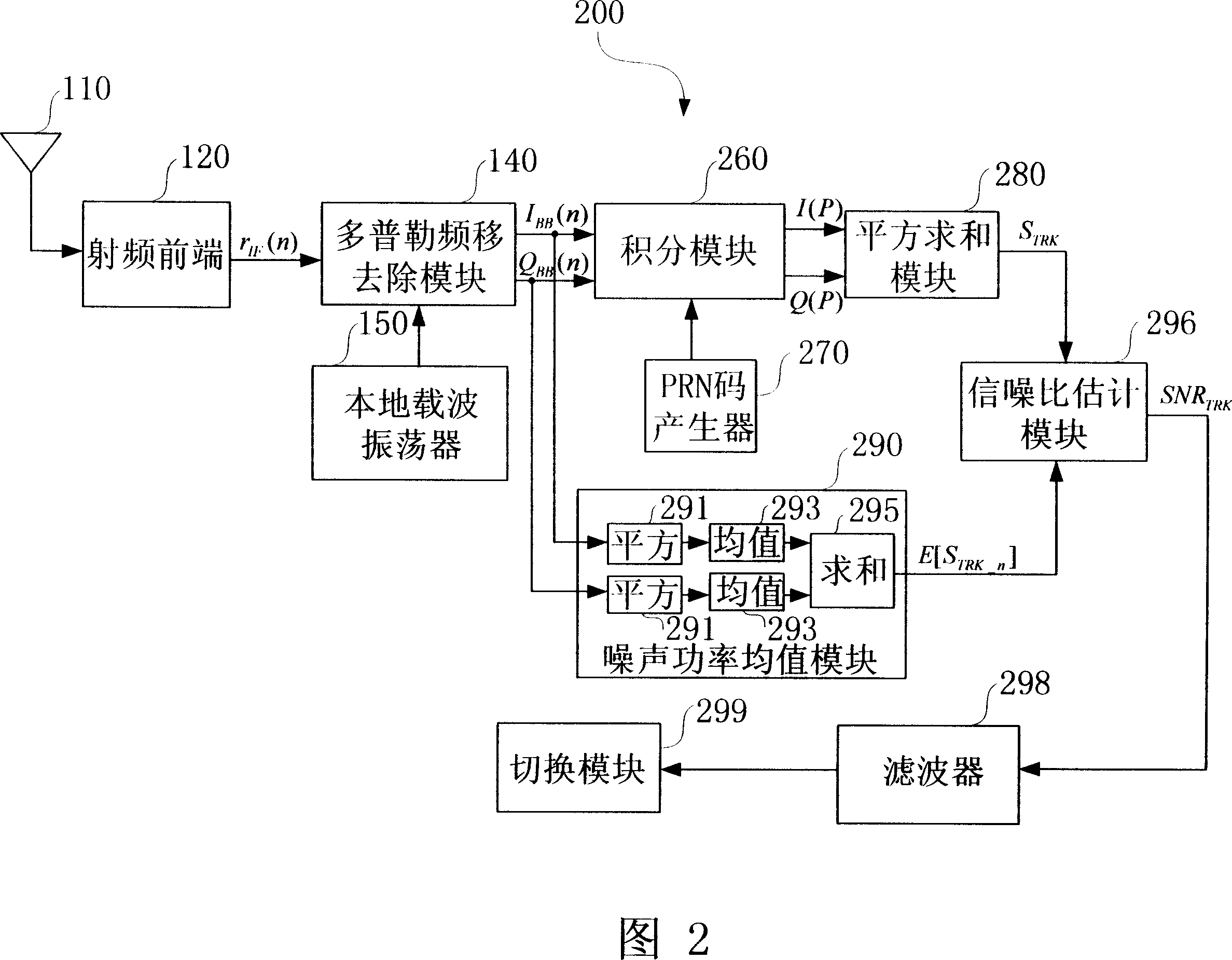
ActiveCN101030787AThe estimation method is simple and reliableEffective trackingTransmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)In-phase and quadrature components
The method comprises: converting the received spread spectrum signals to the digital signals, and dividing the digital signals into the in-phase and quadrature signal components. In the capturing stage, the in-phase and quadrature signal components and the local pseudo random noise code are executed with relevant calculation to get the output of several in-phase and quadrature signal components; making summation for the square of each in-phase and quadrature signal components output to get the signal power and noise power in order to figured out the signal / noise ratio of the spread spectrum signals. In the tracing stage, the in-phase and quadrature signal components and the local pseudo random noise code are executed with relevant calculation; making the summation for the square of output result; based on the in-phase and quadrature signal components, figuring out the average power of noise; based on the signal power and the average power of noise, figuring out the signal / noise ration of spread spectrum signals.
Owner:凹凸科技平潭有限公司
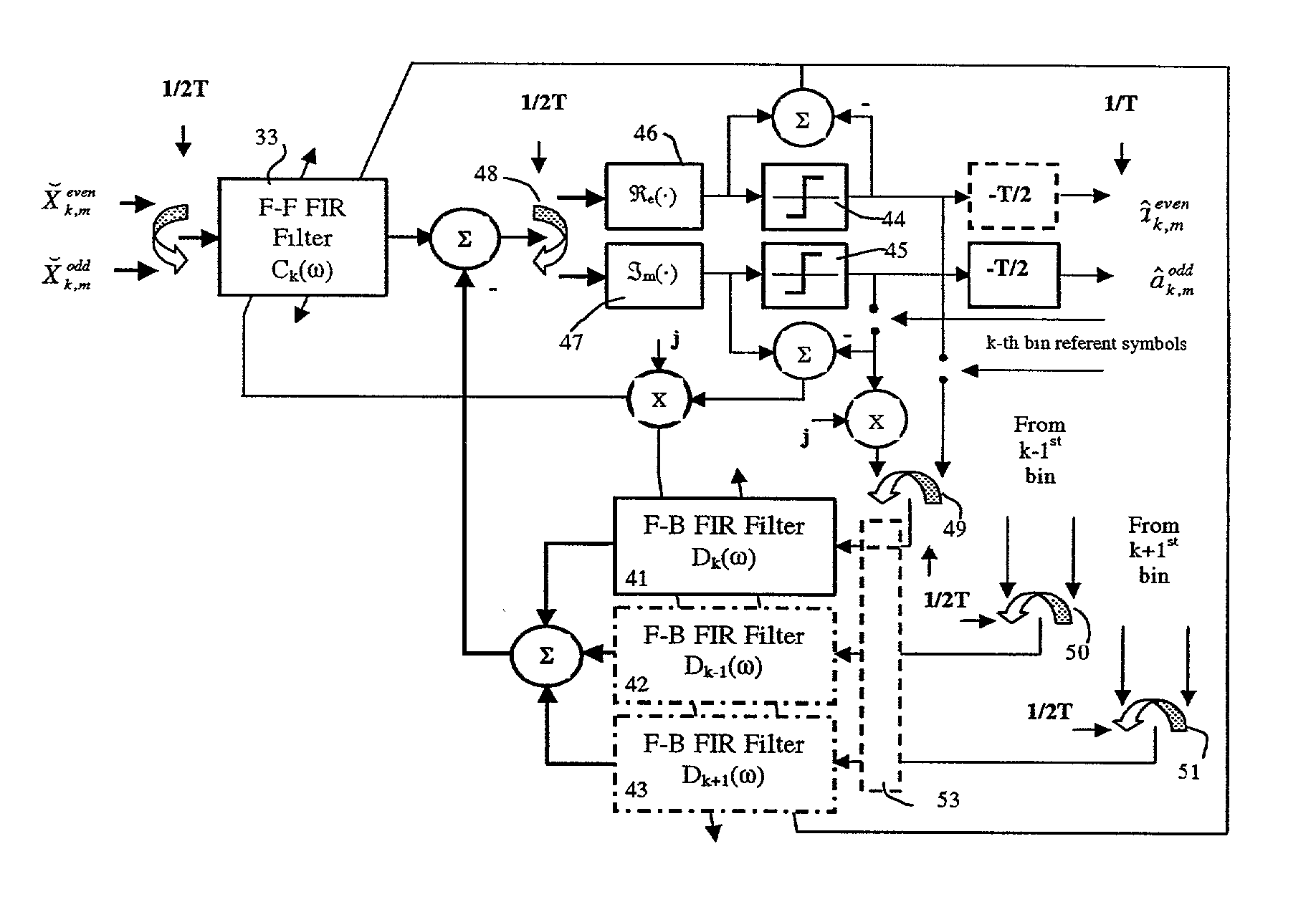
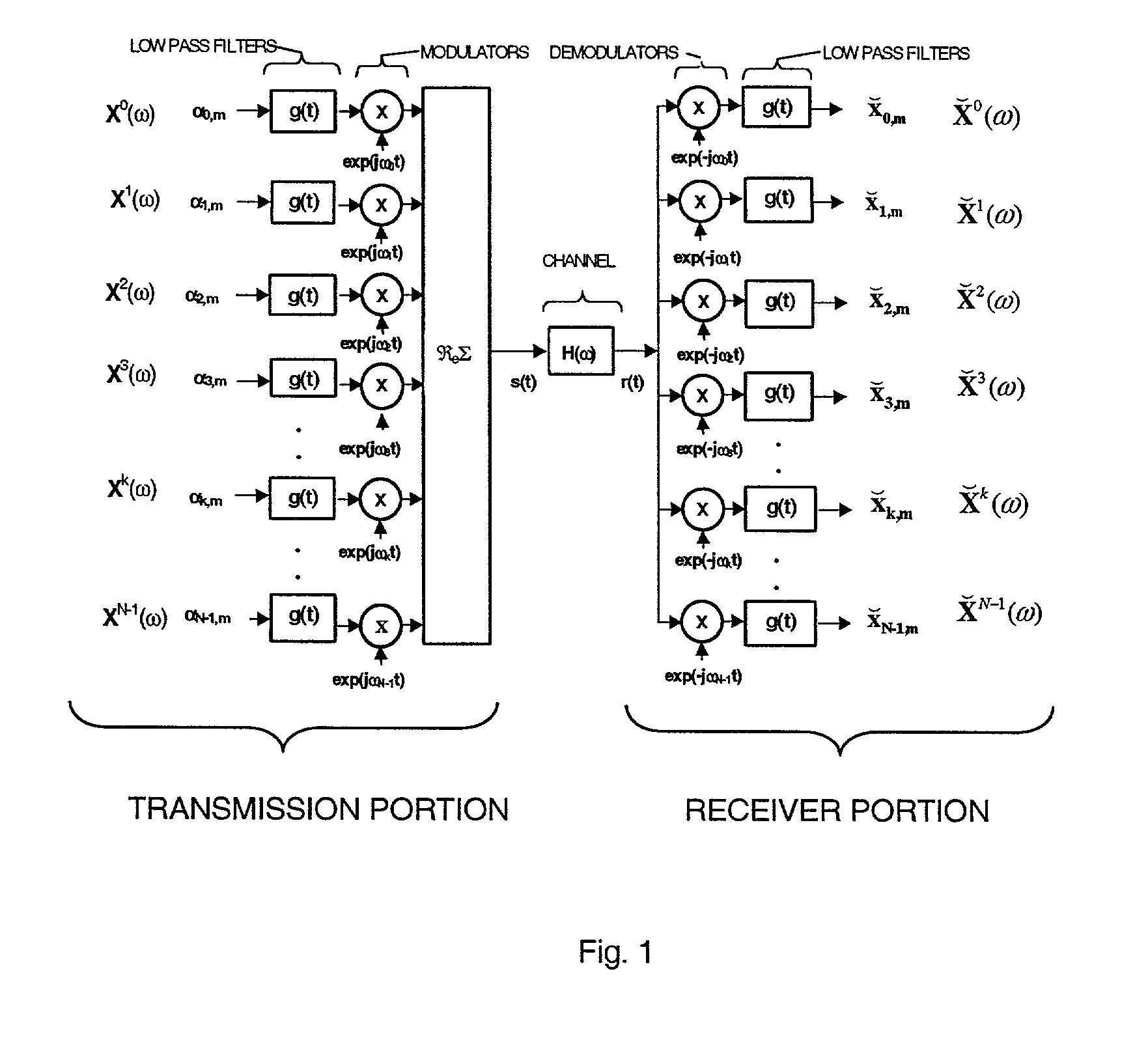
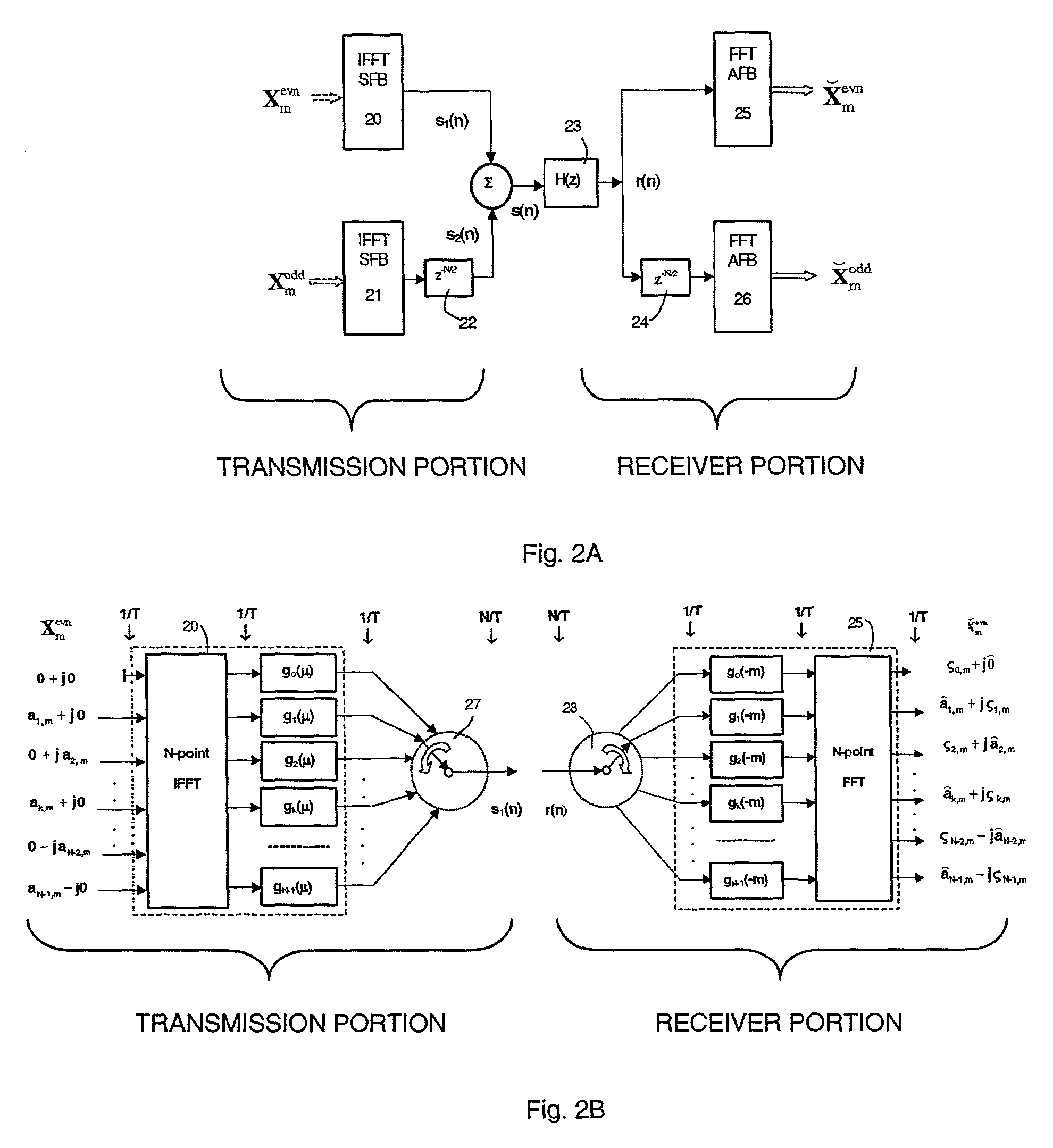
Per-bin DFE for advanced OQAM-based multi-carrier wireless data transmission systems
An Apparatus for non-linear per-bin adaptive equalization in orthogonal multi-carrier data transmission systems with the Nyquist sub-channel spectral shaping and T / 2 staggering of in-phase and quadrature components is disclosed. A previously introduced linear equalization embodiments are augmented by up to three, or more decision feed-back filters, to improve performance in presence of narrow-band interference (NBI) in wire-line and wire-less data transmission systems, and to enable exploitation of implicit diversity of multi-path fading channels, both with and without transmitter-end pre-coding. Adaptation properties of per-bin DFE equalization are analyzed by computer simulation for an intermediate number of constituent sub-channels. BER performance comparison between the conventional Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplication-(OFDM) and (Orthogonal Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (OQAM)-based multi-carrier systems of similar modulation / demodulation complexity and transmission latency is provided and the potential advantage of using spectrally well shaped orthogonal sub-channels in wireless applications is demonstrated.
Owner:NEC CORP
Apparatus and method for digital image correction in a receiver
ActiveUS20060252399A1Angle demodulation by oscillations conversionRelay systems monitoringProgram instructionImage correction
An apparatus and method for performing digital image correction in a receiver. In one embodiment, a receiver circuit may include an IQ signal source configured to provide a digital signal comprising in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components, such as an IQ mixer in combination with an analog to digital converter, for example. The receiver circuit may also include an image correction unit coupled to the IQ signal source and configured to combine the digital signal with a complex image correction factor. The image correction unit may be implemented using a digital signal processor under the control of associated program instructions, for example. In one specific implementation of the receiver circuit, the image correction unit may be configured to combine the digital signal with the complex image correction factor using a cross-accumulation operation.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Power regulator for power inverter
ActiveUS20050057950A1Reduce the differenceBatteries circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionPower inverterIslanding
A power inverter includes a regulator circuit that controls real and reactive power output by the inverter. The regulator measures real and reactive output power by calculating x-phasor components of the inverter's voltage and current output waveforms. Phasor calculation can be adapted for one or more pairs of single-phase voltages and currents. Determining the fundamental in-phase and quadrature components of output voltage and current reduces computational complexity by permitting the regulator to perform its power control processing largely in a dc signal domain, and enables separate real and reactive power control. The power inverter can include islanding detection logic, which exploits the ability to separately control reactive power. Exemplary islanding detection logic is based on determining whether changing the amount of reactive power output by the inverter induces an output frequency shift.
Owner:SQUARE D CO
Transmitter of a System for Detecting a Buried Conductor
ActiveUS20100001731A1Pulse automatic controlCurrent/voltage measurementAudio power amplifierElectrical conductor
A system for detecting a buried conductor comprises a transmitter for generating a test signal in the buried conductor and a detector for detecting an electromagnetic signal resulting from the test signal flowing in the buried conductor. The transmitter comprises a waveform generator for generating a drive waveform signal, a power supply, an amplifier, connected to the power supply and the waveform generator for producing an output drive signal based on the drive waveform signal and an output circuit for acting on the output drive signal to generate an output signal having a current and a voltage. In-phase and quadrature components of the current and voltage of the output signal are fed back for controlling the amplifier.
Owner:RADIODETECTION
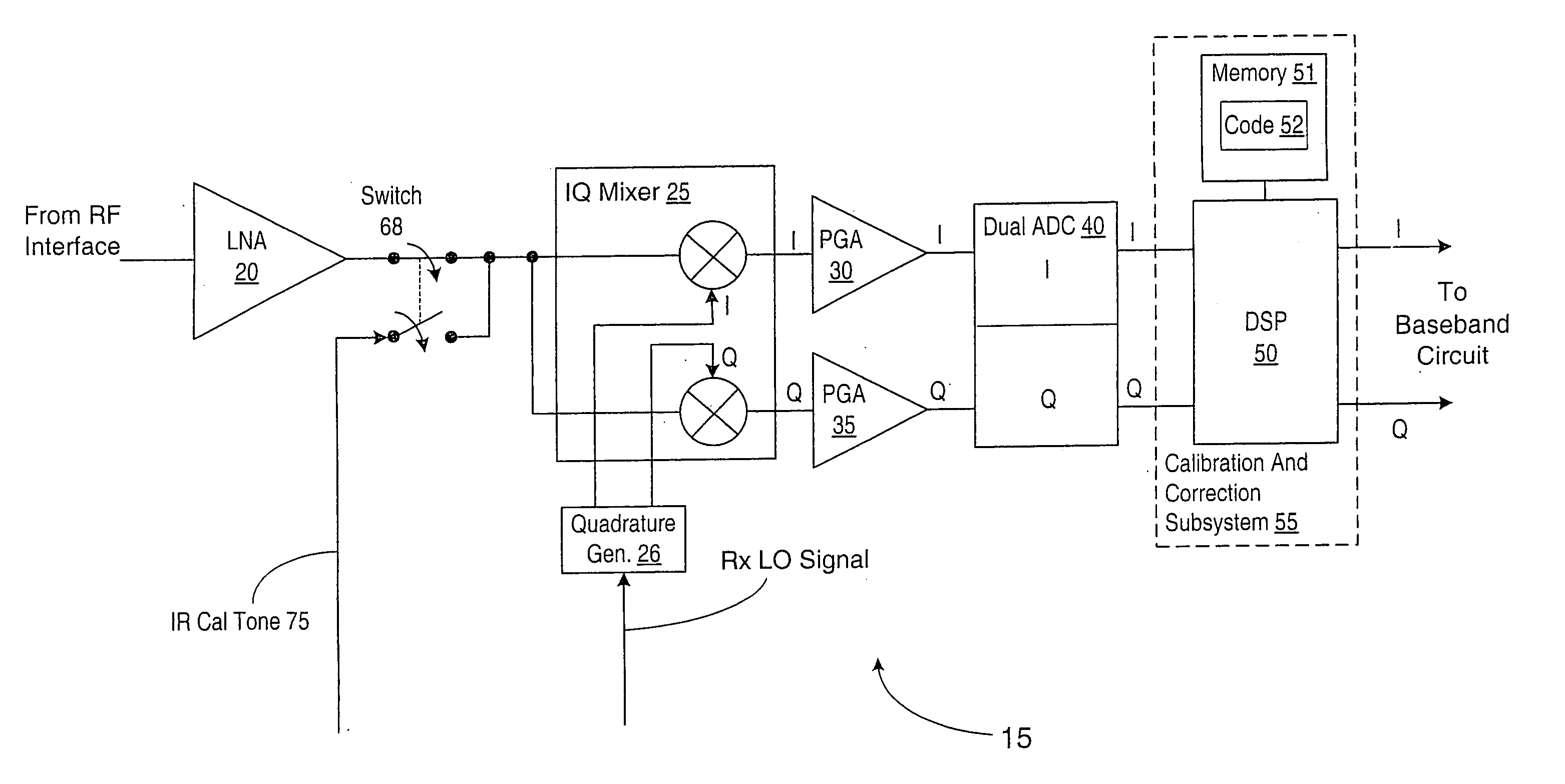
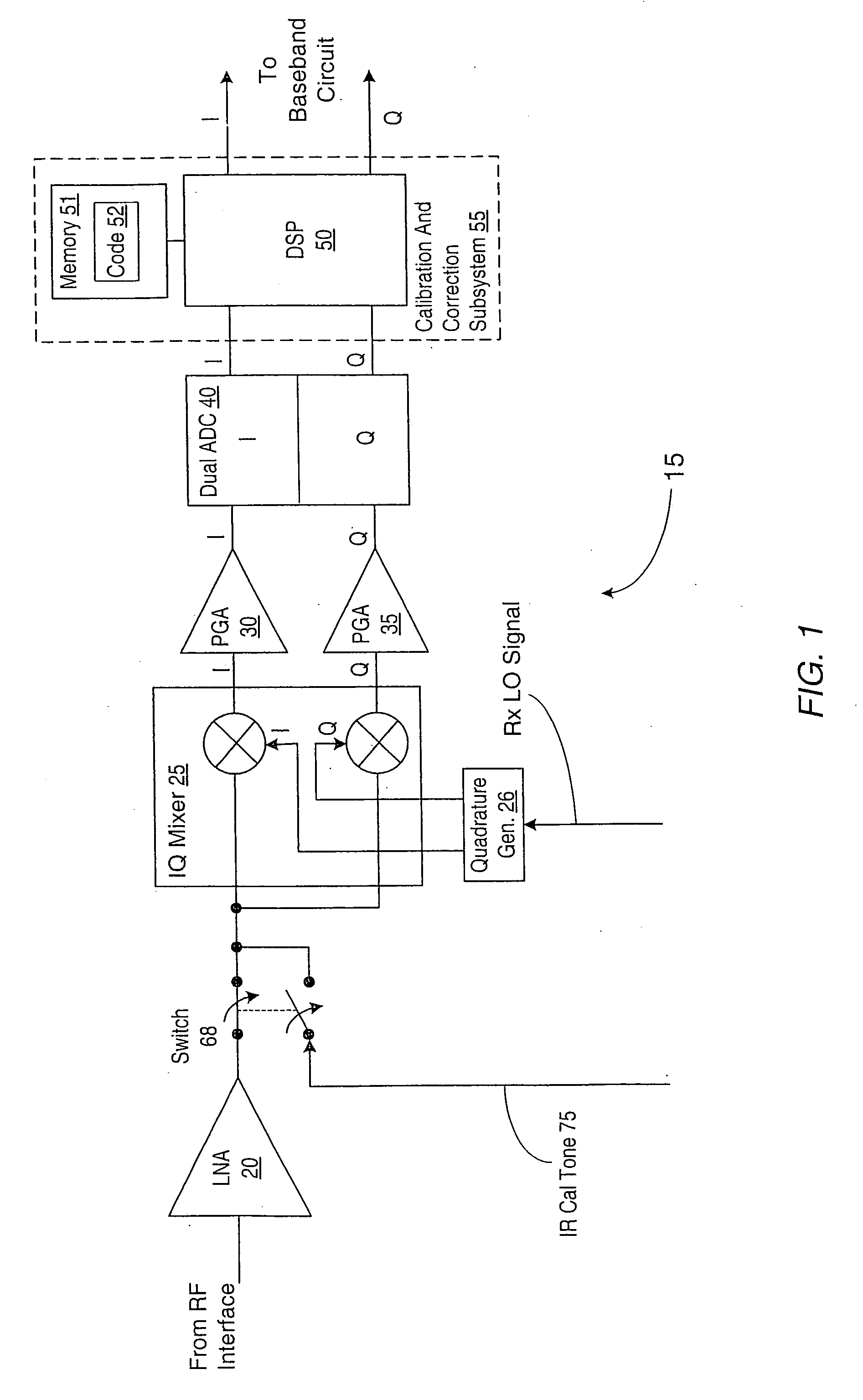
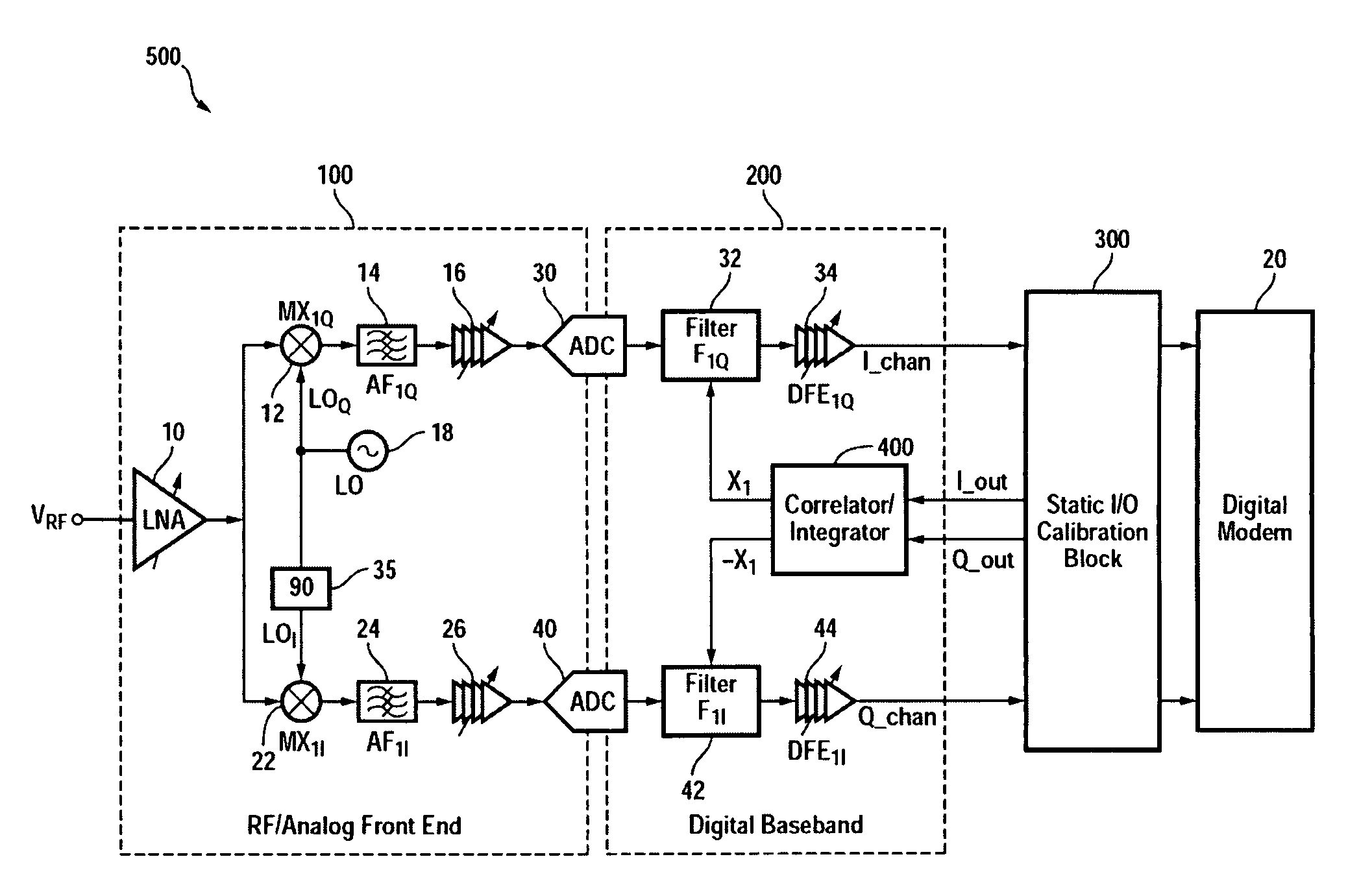
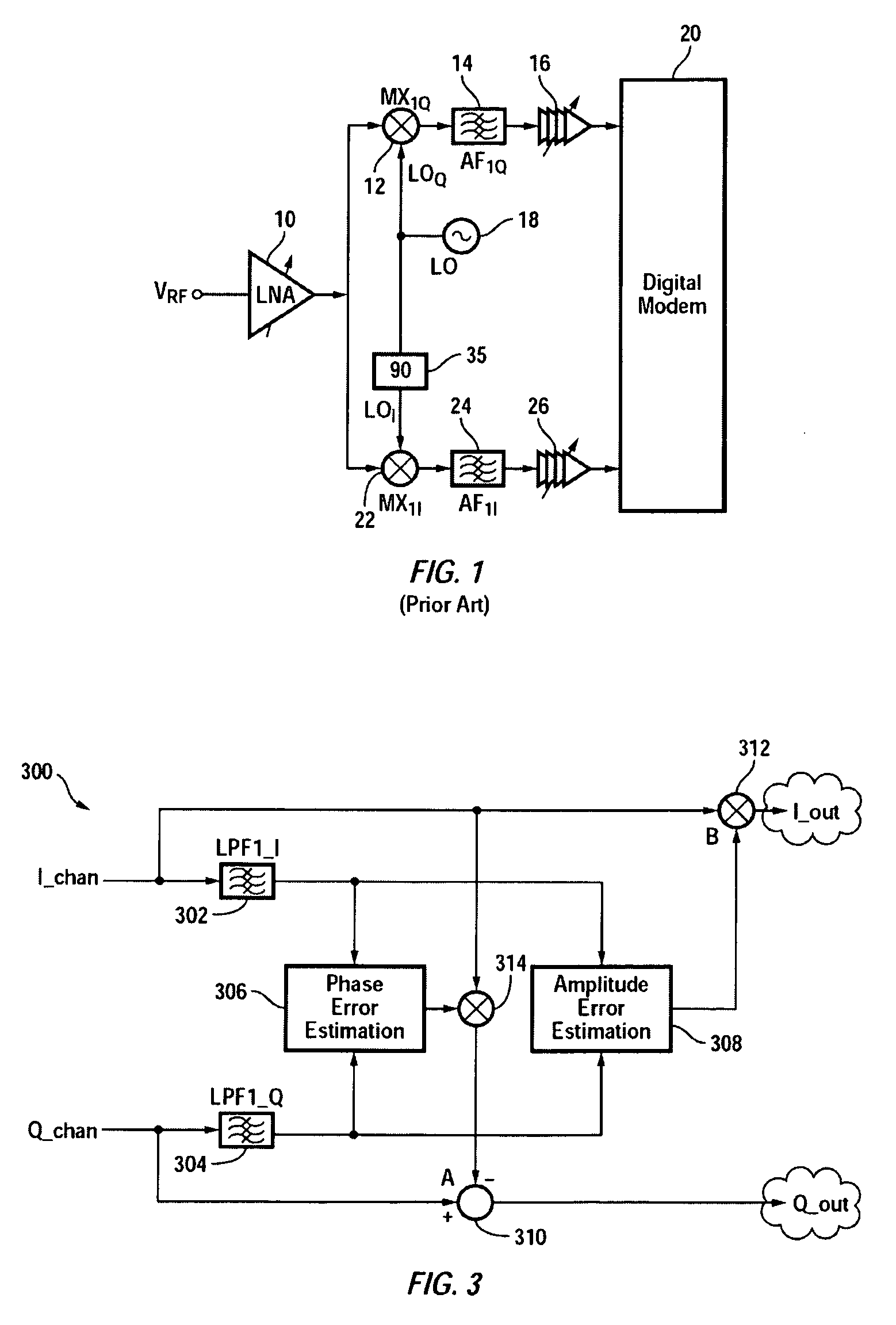
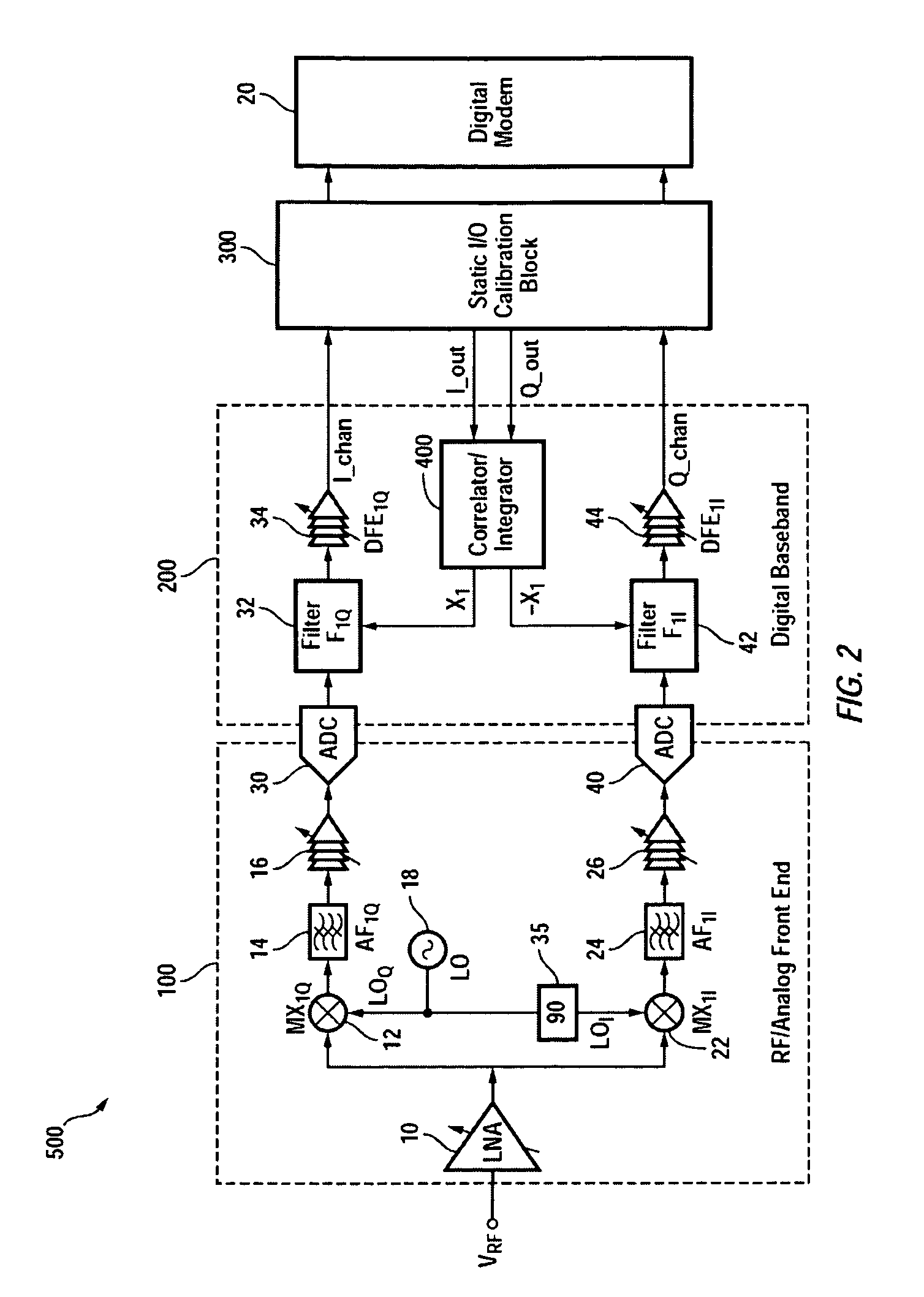
I/Q Calibration Techniques
ActiveUS20090088120A1Carrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumIn-phase and quadrature components
A receiver includes a static I / Q calibration block and a correlation / integration block. The static I / Q calibration block is configured to substantially eliminate mismatches between in-phase and quadrature components of a portion of the spectrum having associated I / Q mismatches that are relatively frequency-independent. The correlation / integration block is configured to substantially eliminate mismatches between the in-phase and quadrature components of portions of the spectrum having associated I / Q mismatches that are relatively frequency-dependent in accordance with a pair of signals generated by the static I / C calibration block.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
Spread spectrum communication system
A spread spectrum communication system wherein spreading codes for in-phase and quadrature components are composed by addition and subtraction and the received signal is multiplied by these composed codes for despreading. The communication system comprises a transmitter generating in-phase and quadrature components. The transmitter includes a spreading circuit for spreading the in-phase and quadrature components. The system further includes a receiver, a phase correction circuit for correcting the phase of despreaded components, a rake combiner for combining the components corrected by the phase correction circuit and a circuit for outputting a combined signal and a delay detection circuit for delaying detection of the combined signal. The receiver also comprises a provisional judgment portion for judging the phase of a pair of the in-phase and quadrature phase components. The phase correction circuit corrects the phase according to the phase judged by the provisional judgment portion.
Owner:YOZAN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com