Patents
Literature
1305results about "Relay systems monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
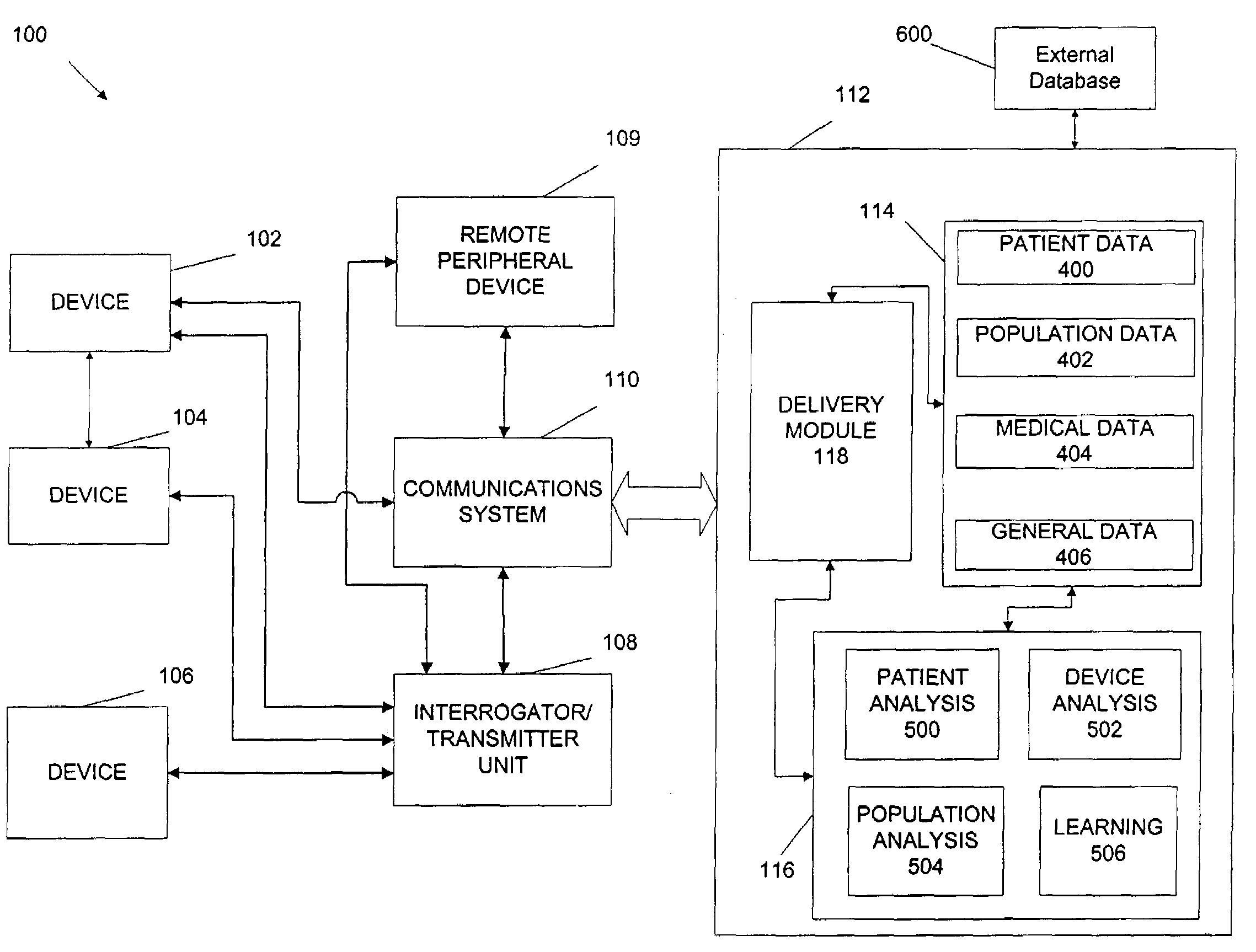
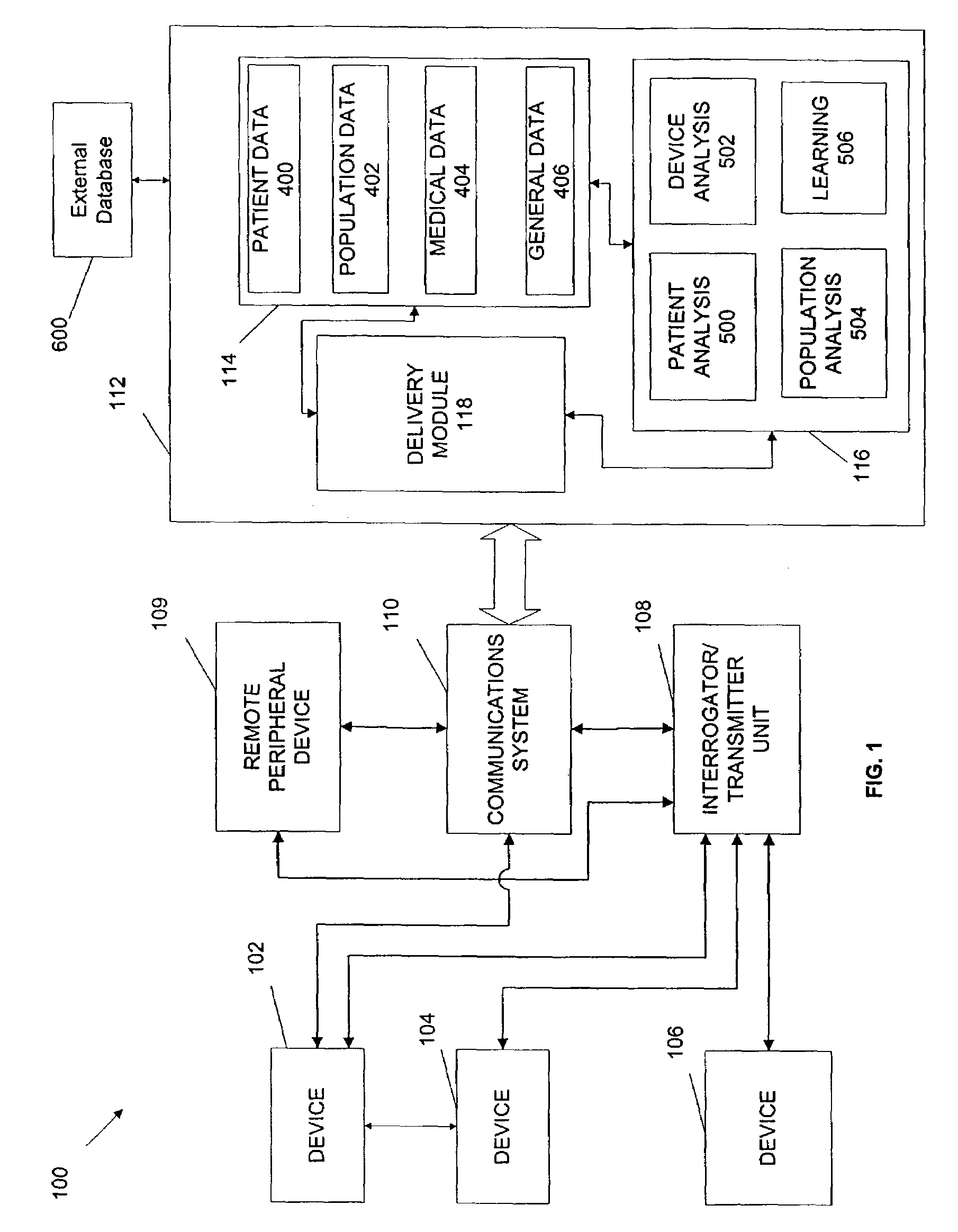
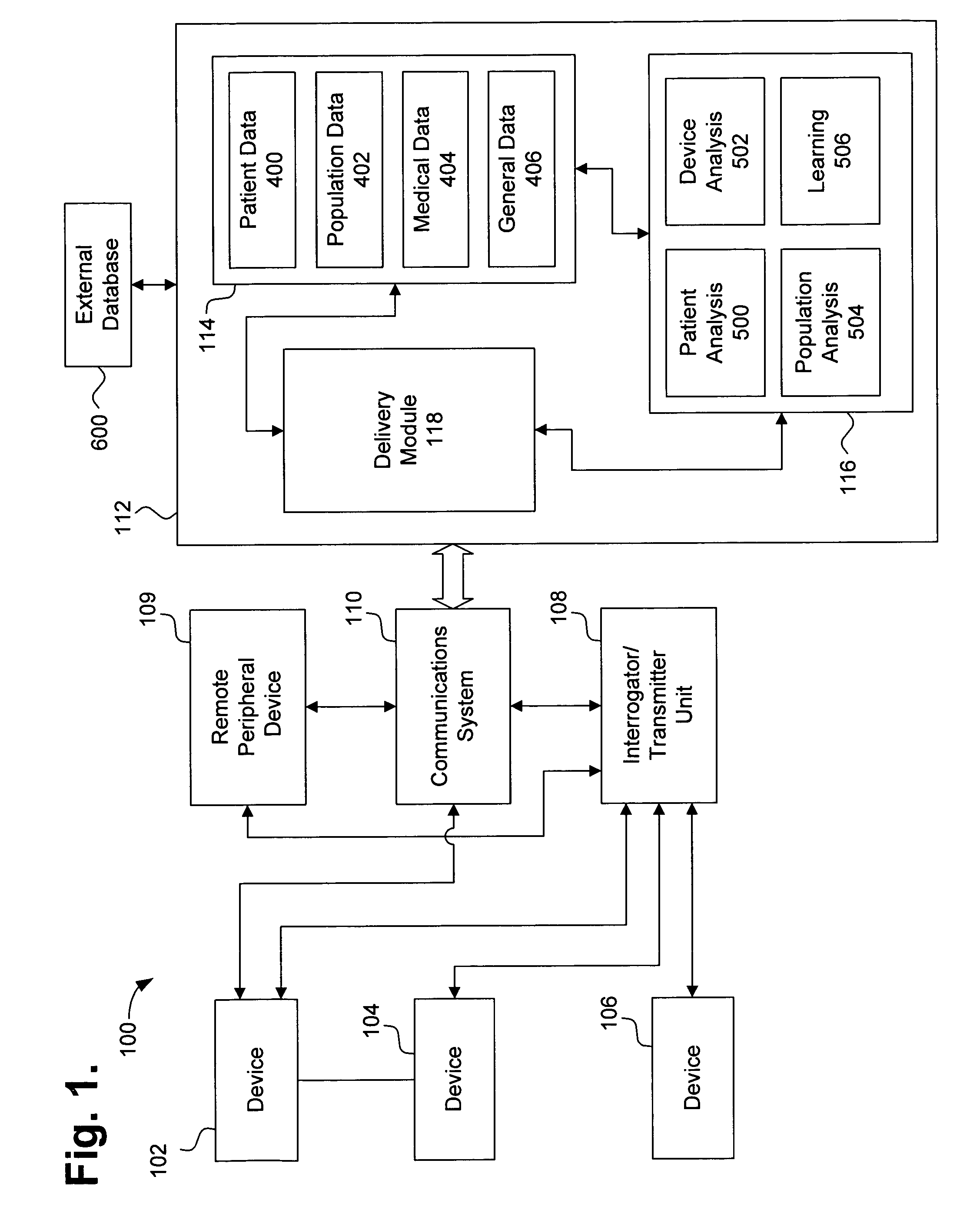
Repeater device for communications with an implantable medical device
A repeater device for an advanced patient management system communicates with a medical device coupled to a patient to obtain data about the medical device and / or patient's condition. The repeater device maintains the data while if considers various factors when coordinating transfer of the data to a repository of the advanced patient management system. The repeater device may be configured to analyze the data to determine a degree of urgency, such as whether an emergency exists, and then determine when to transfer the data based on the degree of urgency. The repeater device may also be configured to test the condition of the communication medium being used to transfer the data to the repository, such as determining whether a telephone line is in use, and then determine when to transfer the data based on the condition of the of the communication medium.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
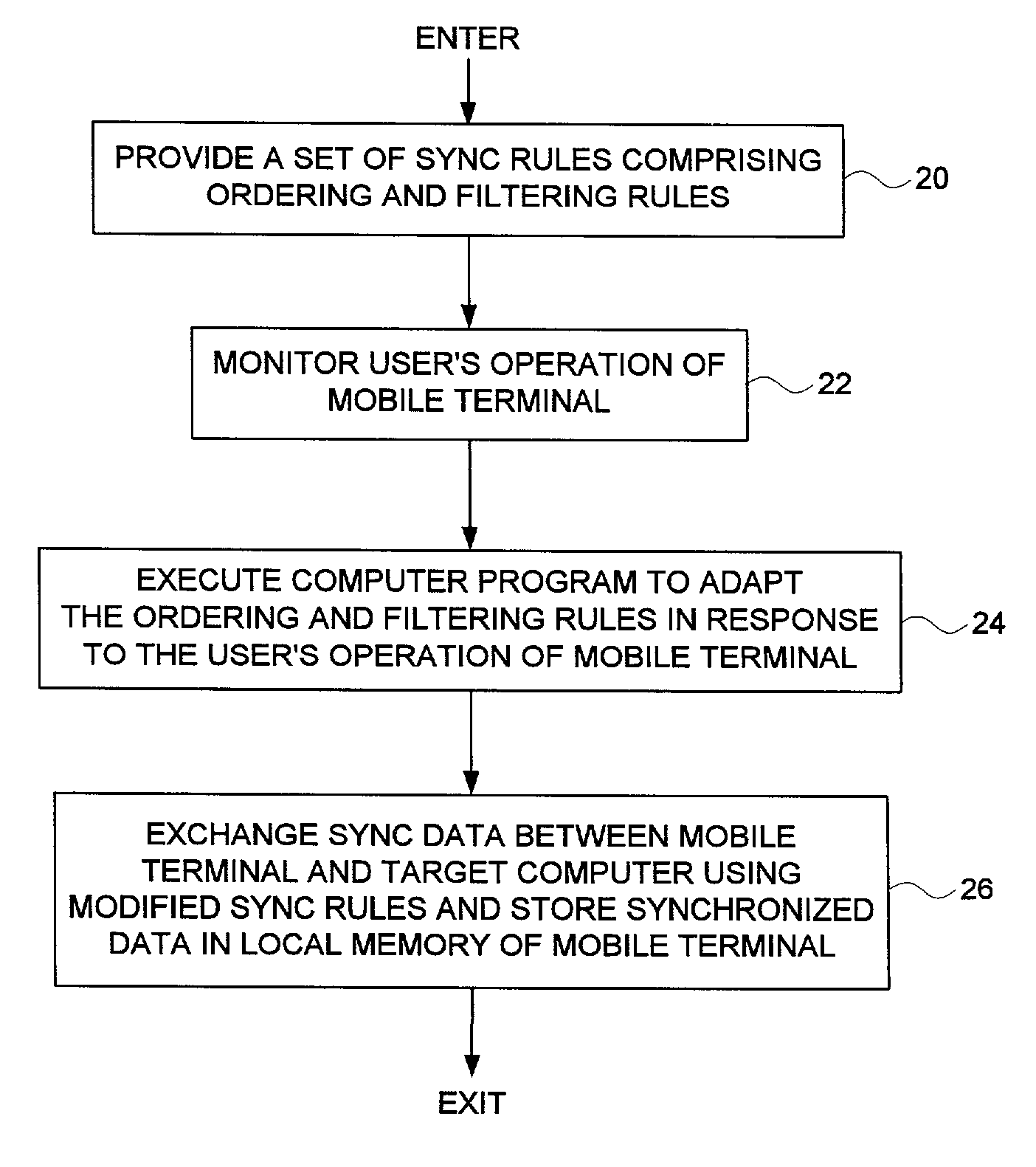
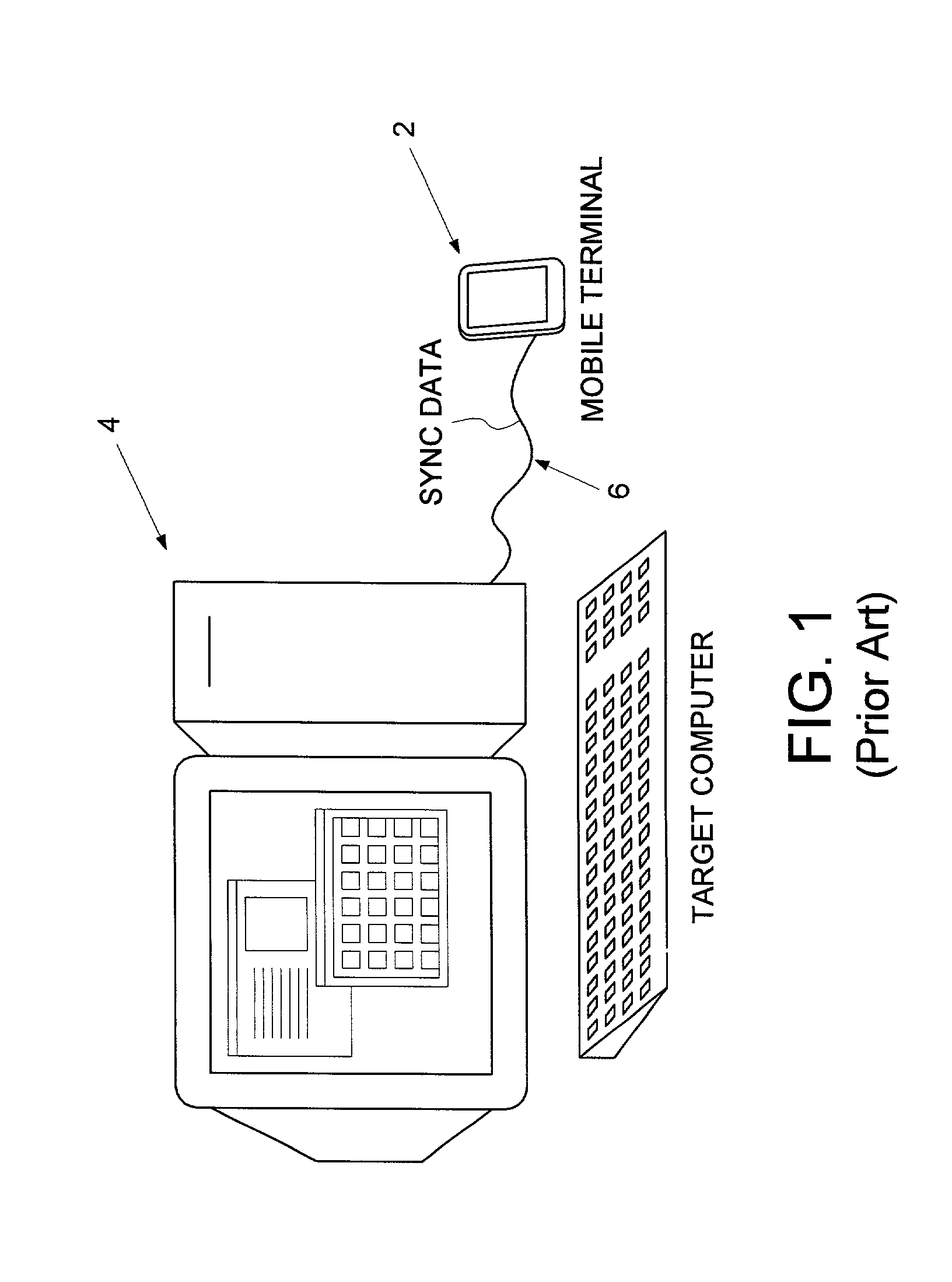
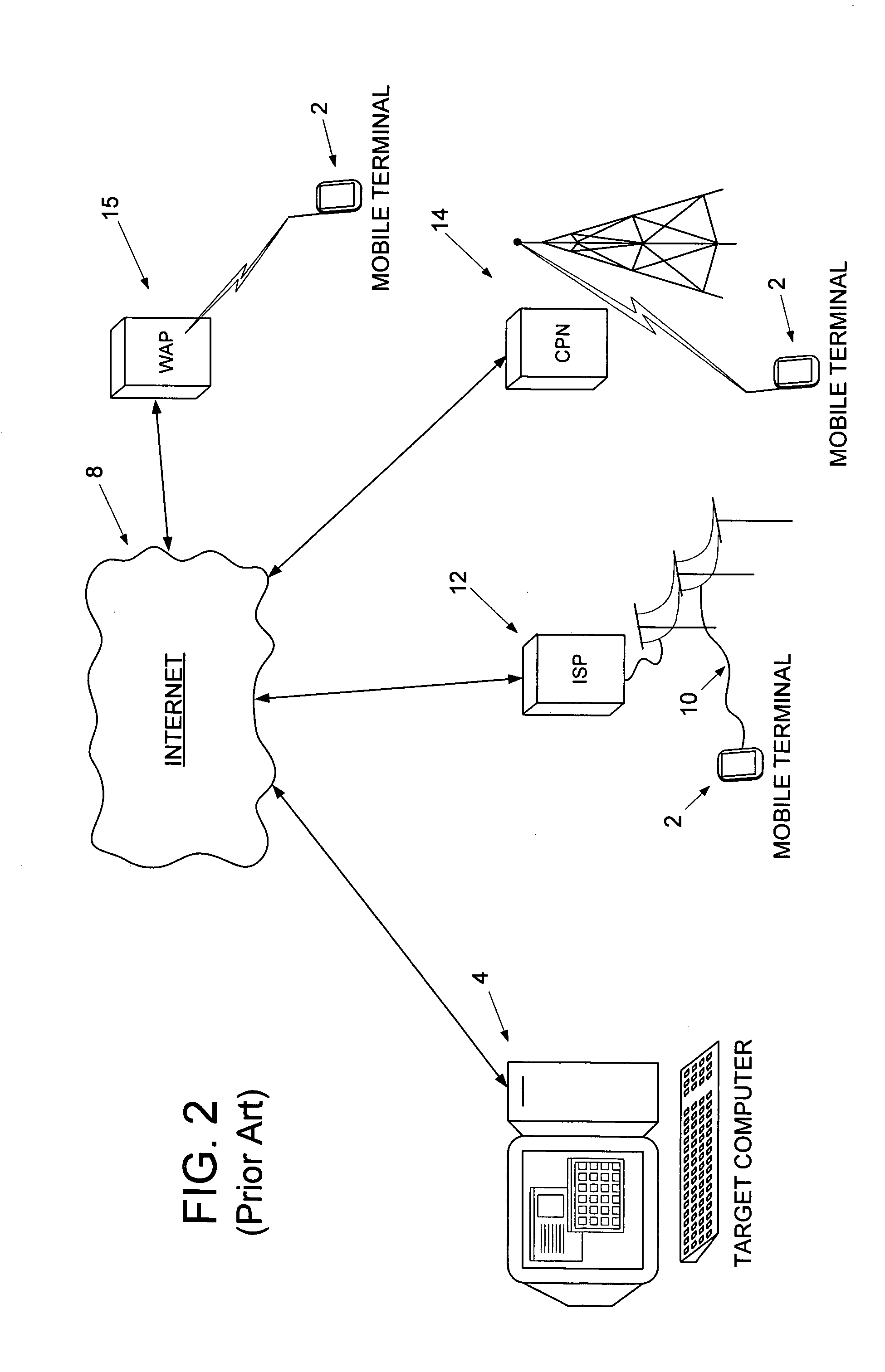
Remotely synchronizing a mobile terminal by adapting ordering and filtering synchronization rules based on a user's operation of the mobile terminal
InactiveUS7024491B1Database distribution/replicationMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer terminalDistributed computing
A method and apparatus for remotely synchronizing a mobile terminal to a target computer is disclosed. A user's operation of the mobile terminal is monitored and a computer program is executed for adapting ordering and filtering synchronization rules in response to the user's operation of the mobile terminal to generate a modified set of synchronization rules. Synchronization data is exchanged between the target computer and the mobile terminal using the modified set of synchronization rules.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
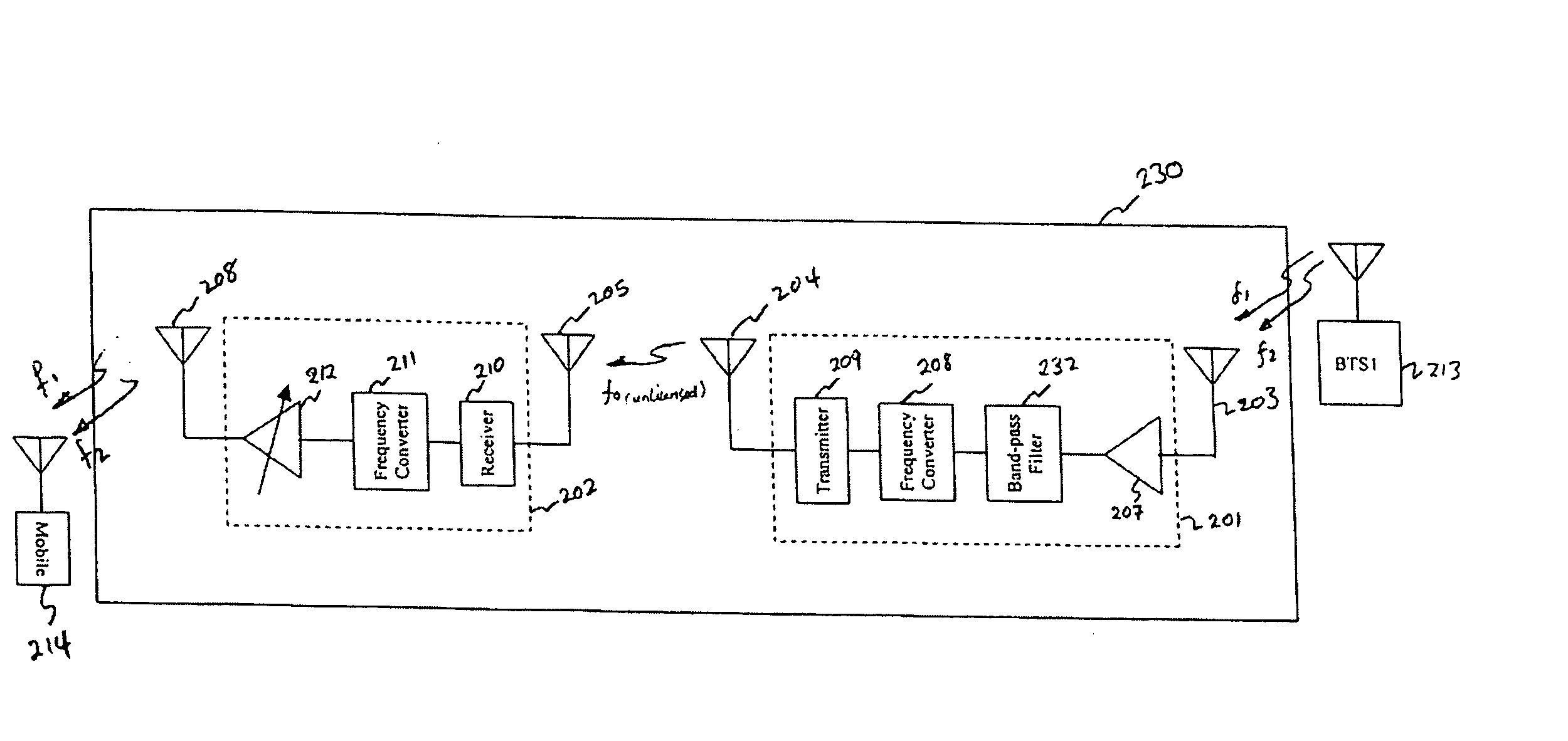
Short-range cellular booster
ActiveUS20060172781A1Facilitate signaling communicationFacilitate communicationActive radio relay systemsSubstation equipmentCommunications systemTransceiver
A repeater mediates traffic between a network transceiver and a user transceiver in a wireless communication system. The repeater comprises a network unit that maintains a network link with the network transceiver, a user unit that maintains a user link with the user transceiver, a two-way communication pathway between the network unit and the user unit; that facilitate the communication of signals between the network transceiver and the user transceiver in autonomous repeater hops between the network transceiver and the network unit, between the user transceiver and the user unit, and between the network unit and the user unit, and a gain controller that compensates for propagation losses between the network unit and user unit alone.
Owner:NEXTIVITY INC
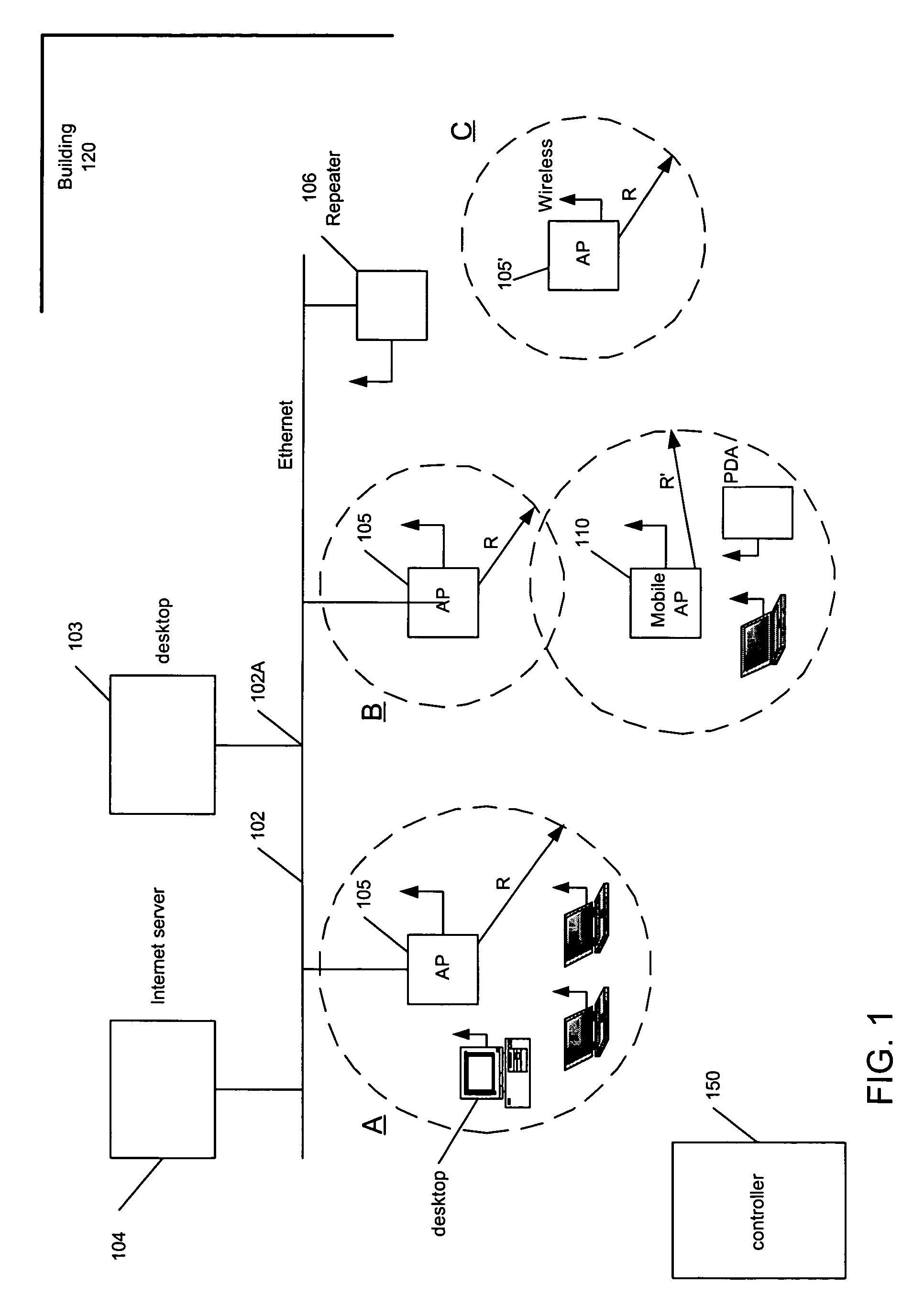
Reconfigureable arrays of wireless access points
ActiveUS20060002326A1Meet real-timeBroadcast with distributionNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceGeographic distribution
A wireless communications network includes a reconfigurable array of access points for linking wireless devices in an infrastructure mode. One or more of the access points are mobile. The mobile access points in the network can be repositioned to change the geographic distribution of the bandwidth coverage provided by the wireless network. The mobile access points may be repositioned to redistribute available network bandwidth heterogeneously according to the demand for bandwidth in local areas and to meet quality of service standards.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
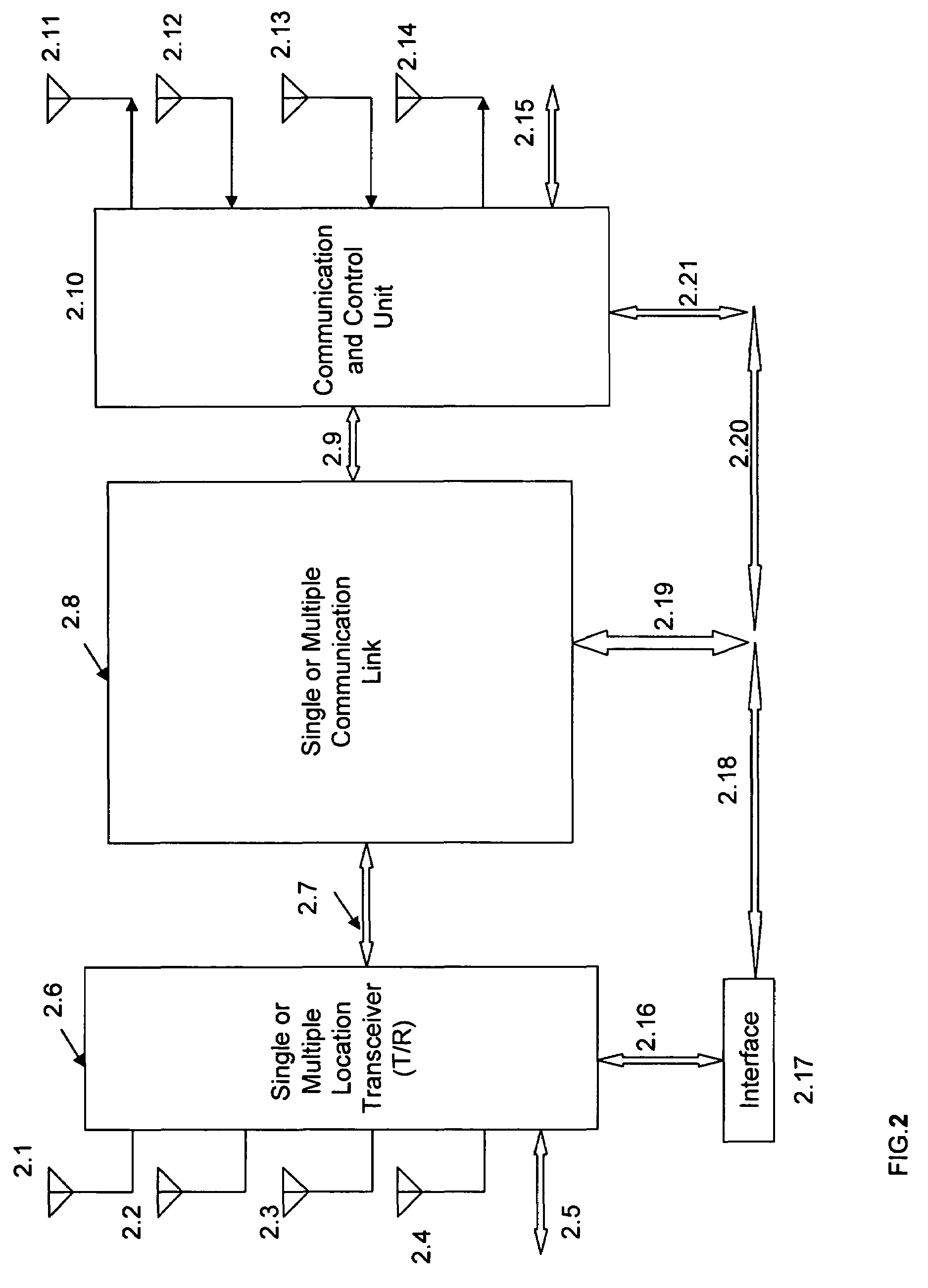
Location finder, tracker, communication and remote control system
ActiveUS7260369B2Expand coverageImprove performanceTelevision system detailsMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsRemote controlControl system
A radio frequency identification (RFID) device, locator, wired and / or wireless communicator system comprising one or more than one antennas for receiving Radio Frequency (RF) signals from one or more RFID and or location determining and / or communication transmitters. The system has one or more receivers and demodulators for reception and demodulation of signals to baseband signals. A processor circuit processes the baseband signals and provides them to a cross-correlator circuit for cross-correlating the processed baseband signals and for generation of cross-correlated baseband signals. One or more modulators modulate the baseband signals and provide them to one or more transmitters. circuitry.
Owner:FEHER KAMILO
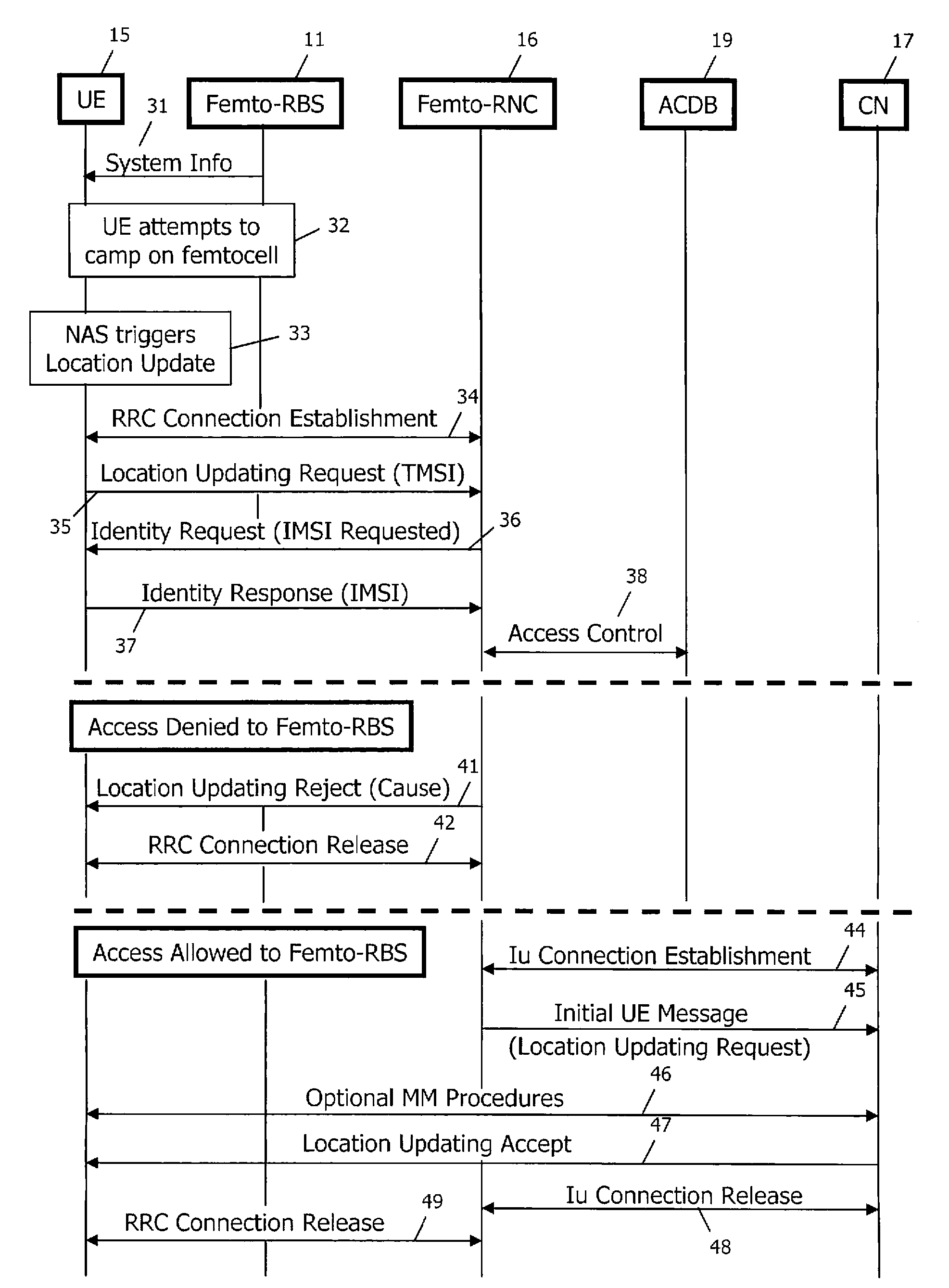
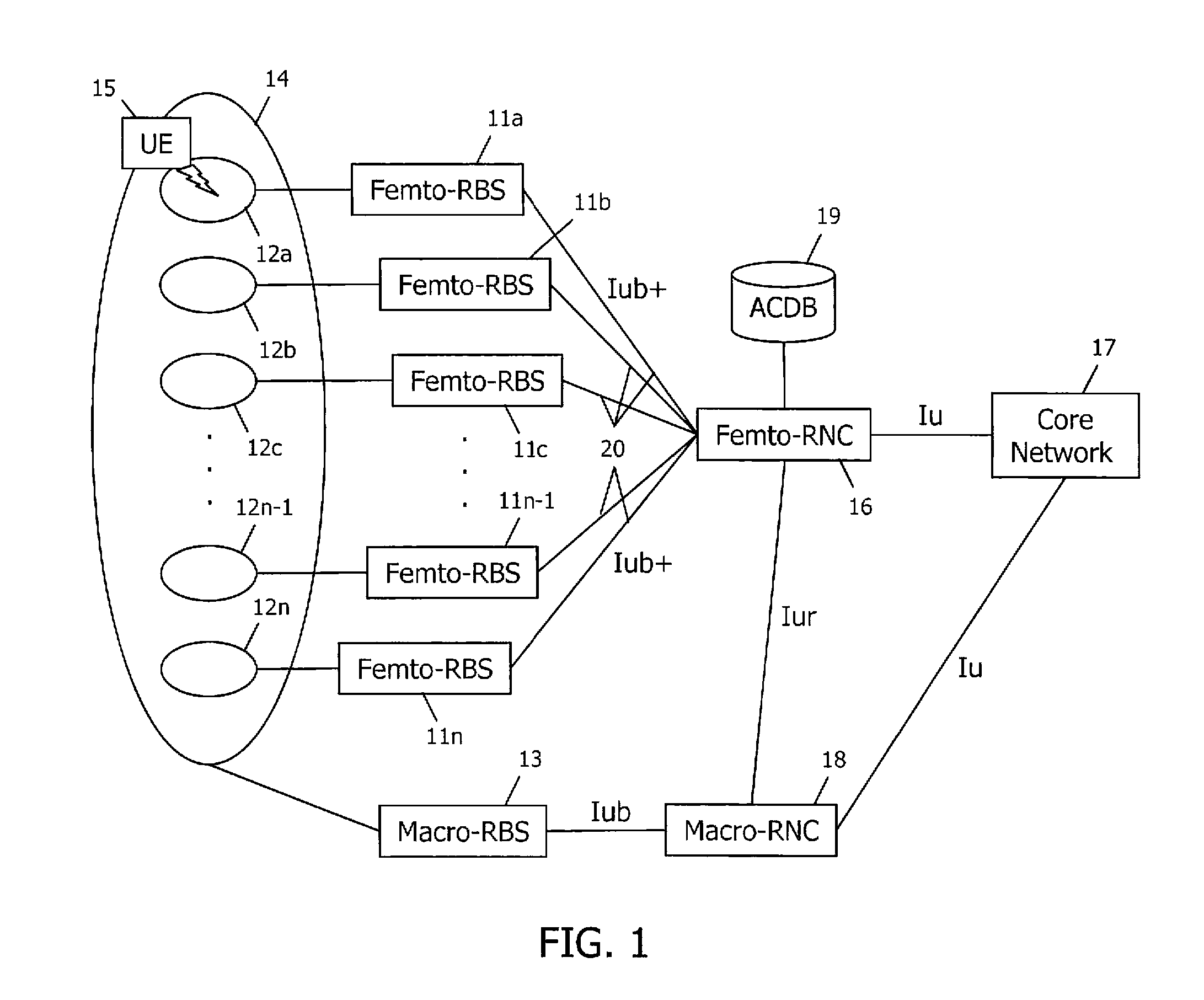
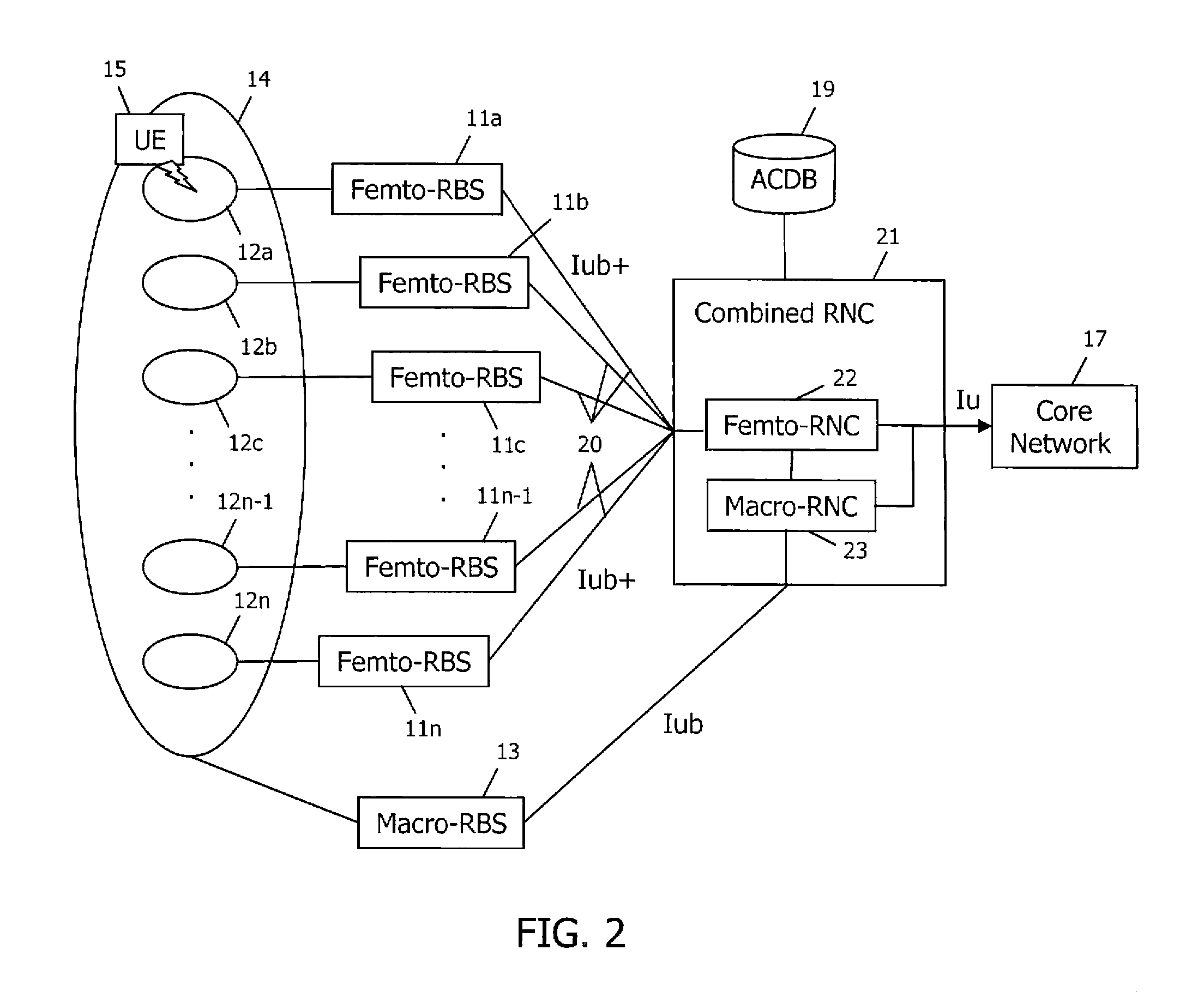
Access control in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20070270152A1Reduce loadRisk minimizationAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesAccess networkRadio networks
A method and radio network controller (RNC) in a radio access network (RAN) for controlling access to a cellular telecommunication system. Upon receiving an access request from a given user equipment (UE) through a given radio base station (RBS), the RNC retrieves authorization information from an access control database within the RAN. The authorization information indicates whether the given UE is authorized to access the system through the given RBS. The RNC alternatively grants access or denies access to the UE based on the retrieved authorization information. The RBS is particularly useful for controlling access through small cells with limited capacity.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Short-range cellular booster
ActiveUS9130641B2Facilitate communicationActive radio relay systemsSubstation equipmentTransceiverNetwork link
A repeater mediates traffic between a network transceiver and a user transceiver in a wireless communication system. The repeater comprises a network unit that maintains a network link with the network transceiver, a user unit that maintains a user link with the user transceiver, a two-way communication pathway between the network unit and the user unit; that facilitate the communication of signals between the network transceiver and the user transceiver in autonomous repeater hops between the network transceiver and the network unit, between the user transceiver and the user unit, and between the network unit and the user unit, and a gain controller that compensates for propagation losses between the network unit and user unit alone.
Owner:NEXTIVITY INC
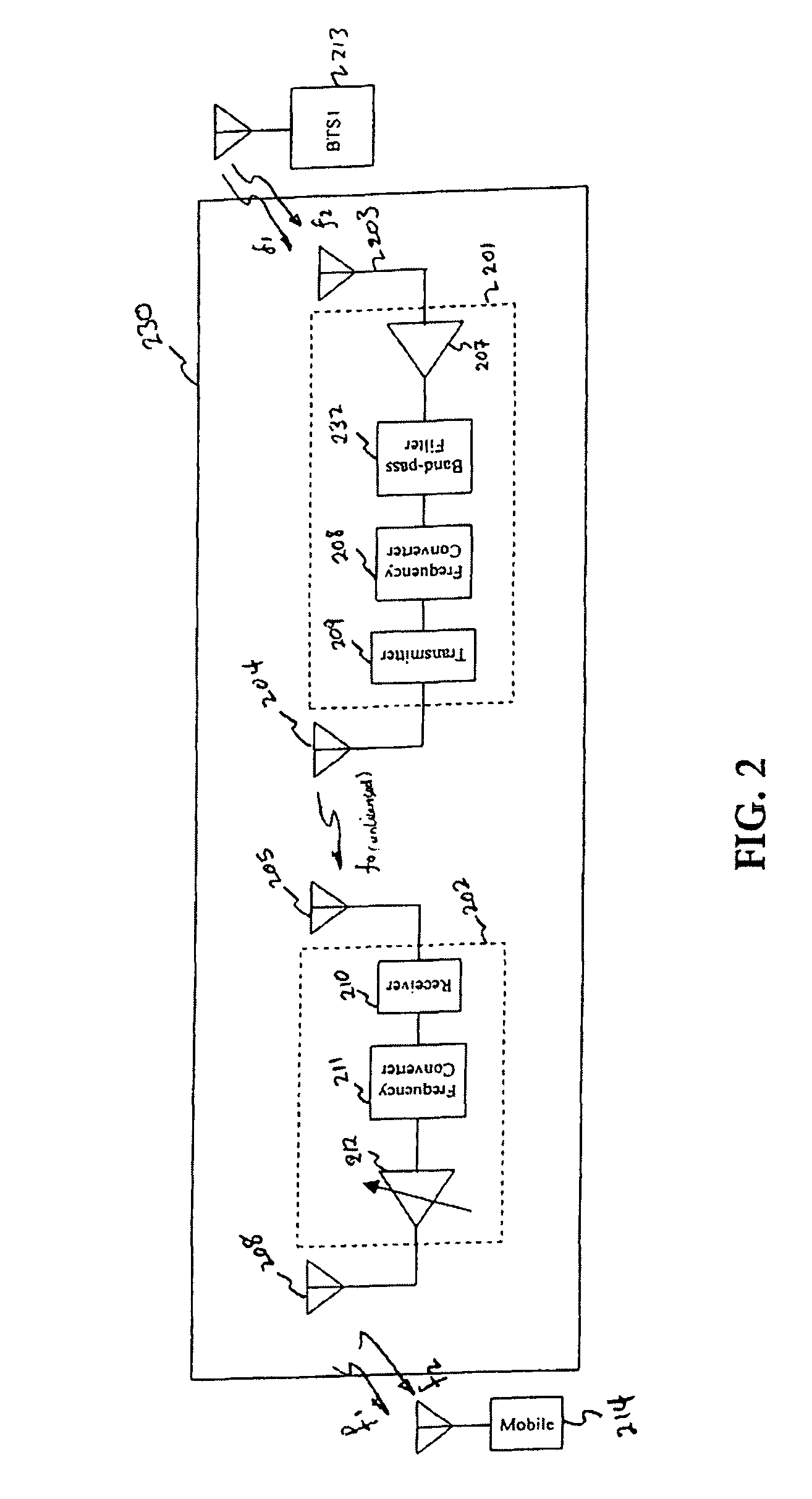
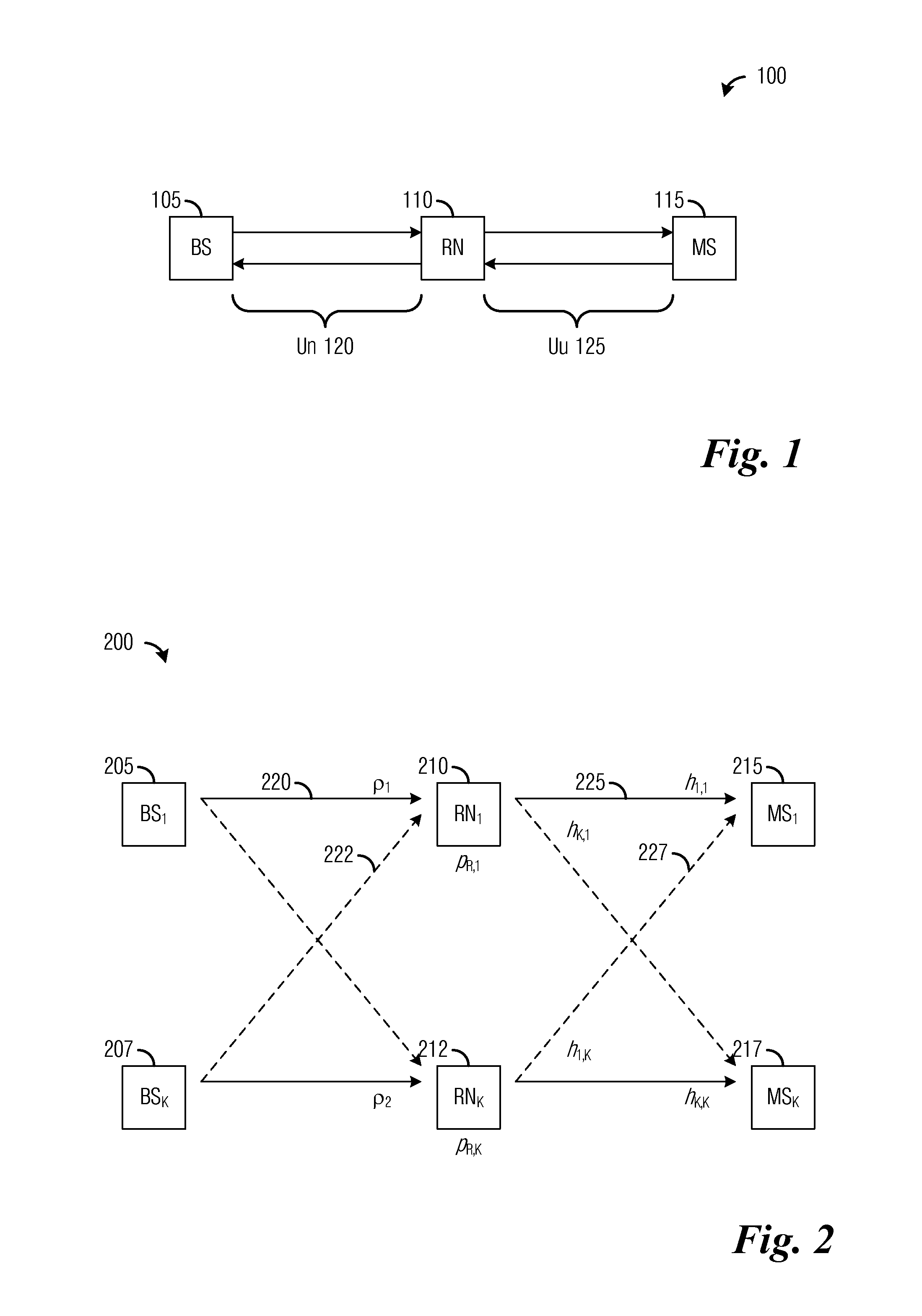
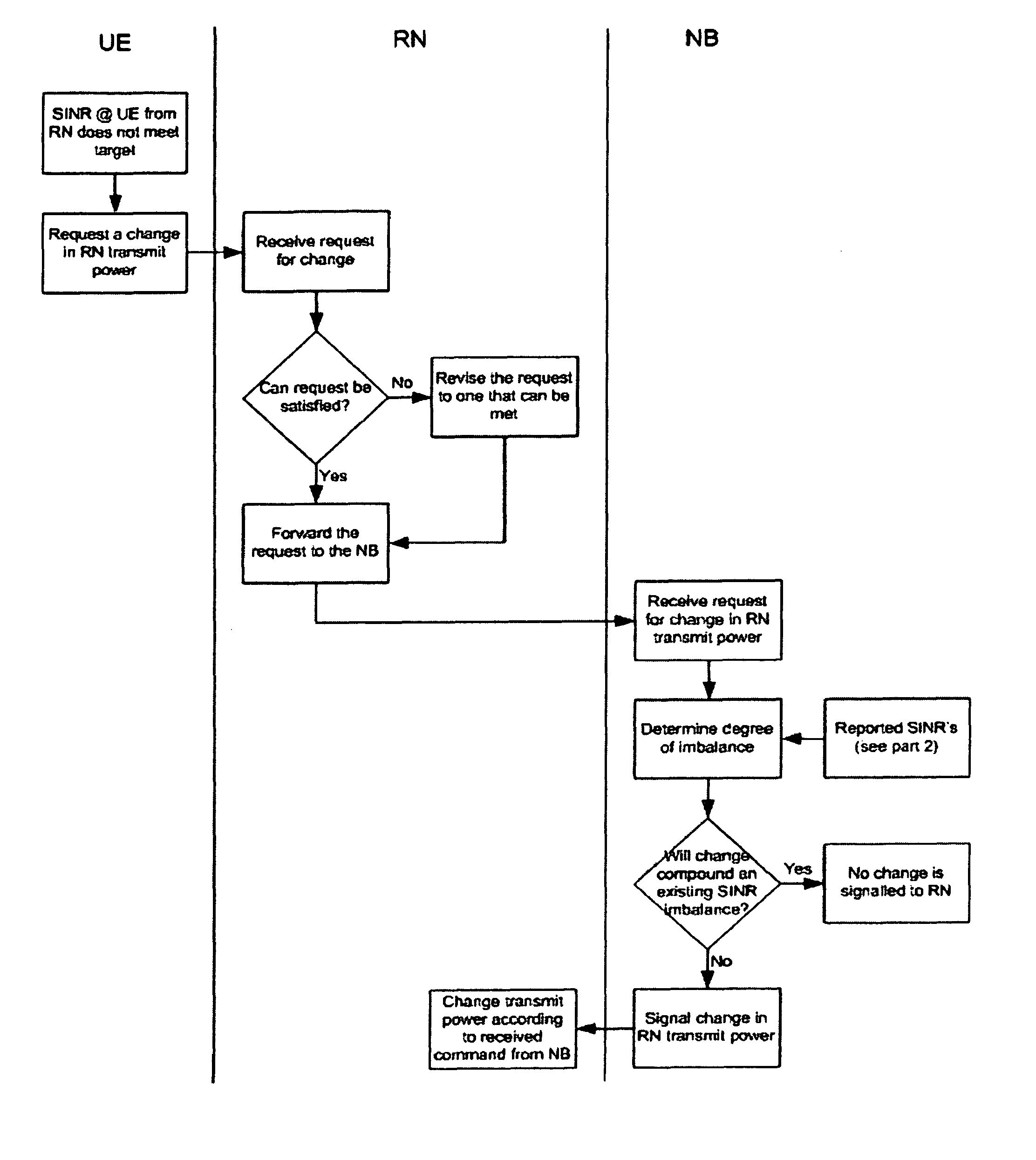
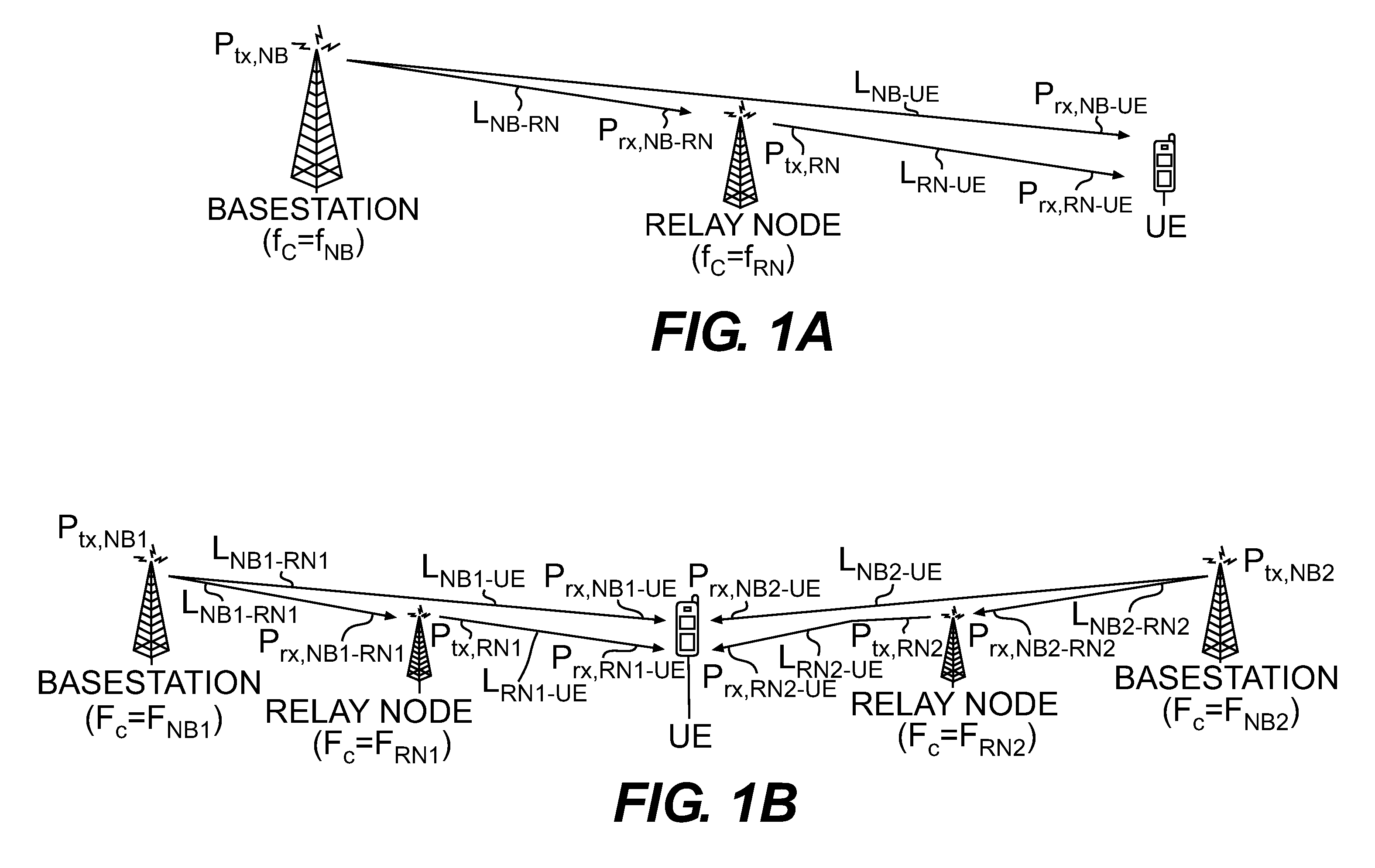
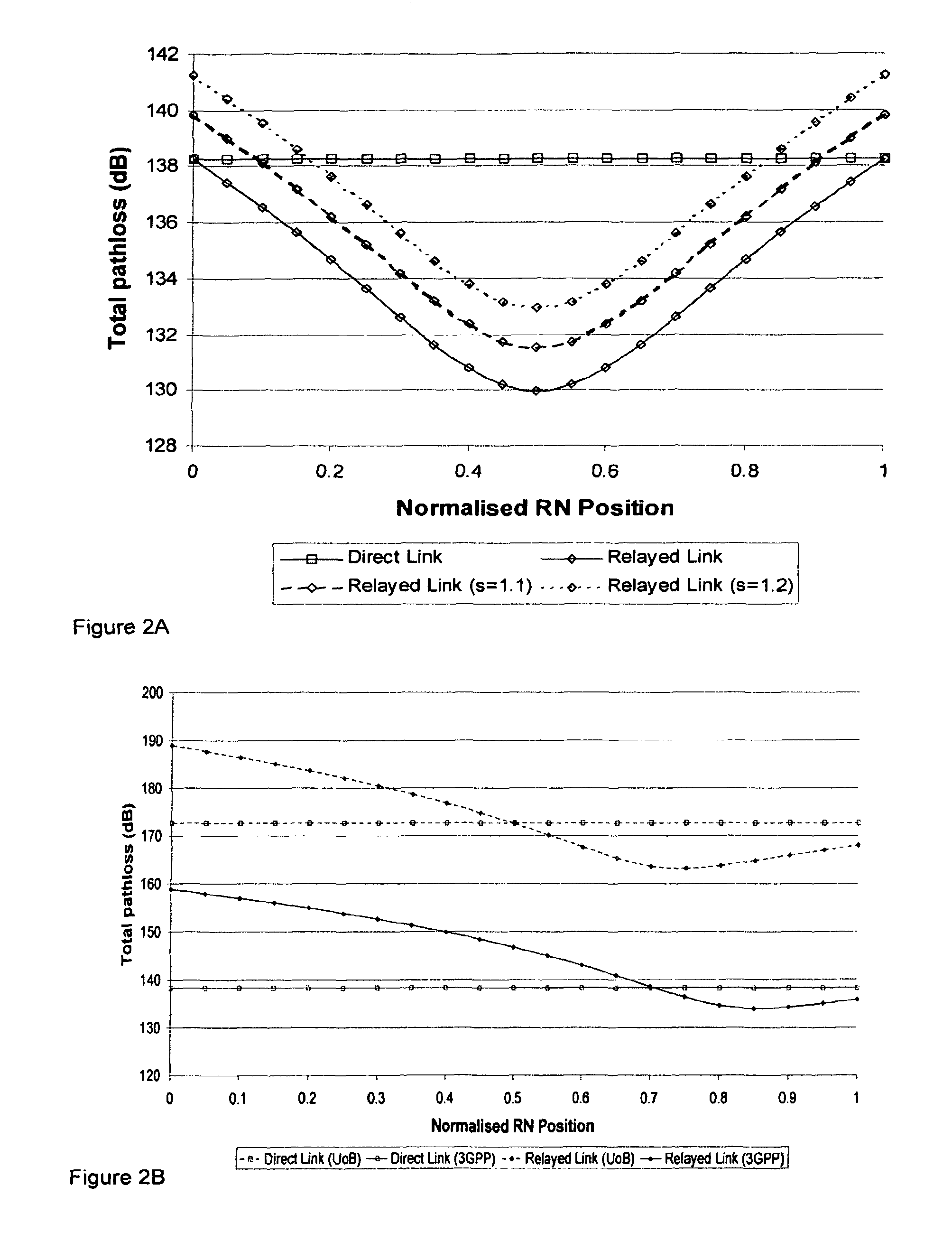
System and method for distributed power control in a communications system
InactiveUS8588840B2Improve system performanceHigh implementation costPower managementResonant long antennasCommunications systemTransmitted power
A system and method for distributed power control in a communications system are provided. A method for relay node operations includes transmitting a signal at a transmit power level on a first channel from a relay node to a user equipment, receiving a message comprising a first indication of channel quality of the first channel at the transmit power level, and determining a second indication of channel quality of a second channel between a communications controller and the relay node, where the first channel and the second channel are in a same multi-hop communication path. The method also includes altering the transmit power level of the first channel based on the first indication of channel quality and the second indication of channel quality to converge the channel quality of the first channel to a convergence value.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Communication system
ActiveUS8150311B2Reduce or prevent substantial imbalanceMaintain qualityEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTelecommunicationsCommunications system
The present application relates to a wireless communication system and related methods and apparatuses for transmitting a signal from a source apparatus to a destination apparatus, via at least one intermediate apparatus. In particular, the present invention relates to techniques which seek to improve the throughput of data in multi-hop communication systems.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Repeater device for communications with an implantable medical device
InactiveUS7292139B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsRespiratory organ evaluationPatient managementAnalysis data
A repeater device for an advanced patient management system communicates with a medical device coupled to a patient to obtain data about the medical device and / or patient's condition. The repeater device maintains the data while if considers various factors when coordinating transfer of the data to a repository of the advanced patient management system. The repeater device may be configured to analyze the data to determine a degree of urgency, such as whether an emergency exists, and then determine when to transfer the data based on the degree of urgency. The repeater device may also be configured to test the condition of the communication medium being used to transfer the data to the repository, such as determining whether a telephone line is in use, and then determine when to transfer the data based on the condition of the of the communication medium.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
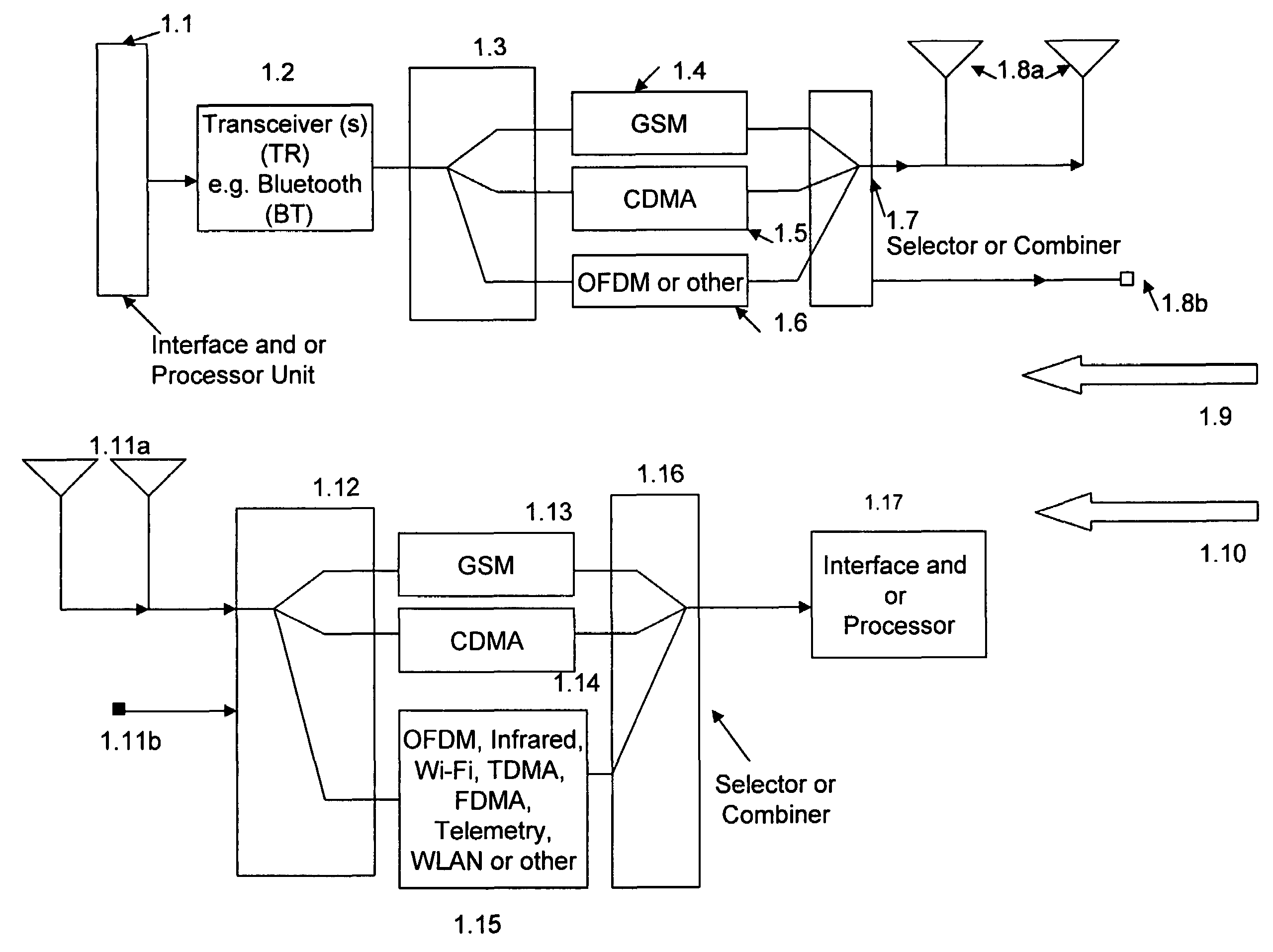
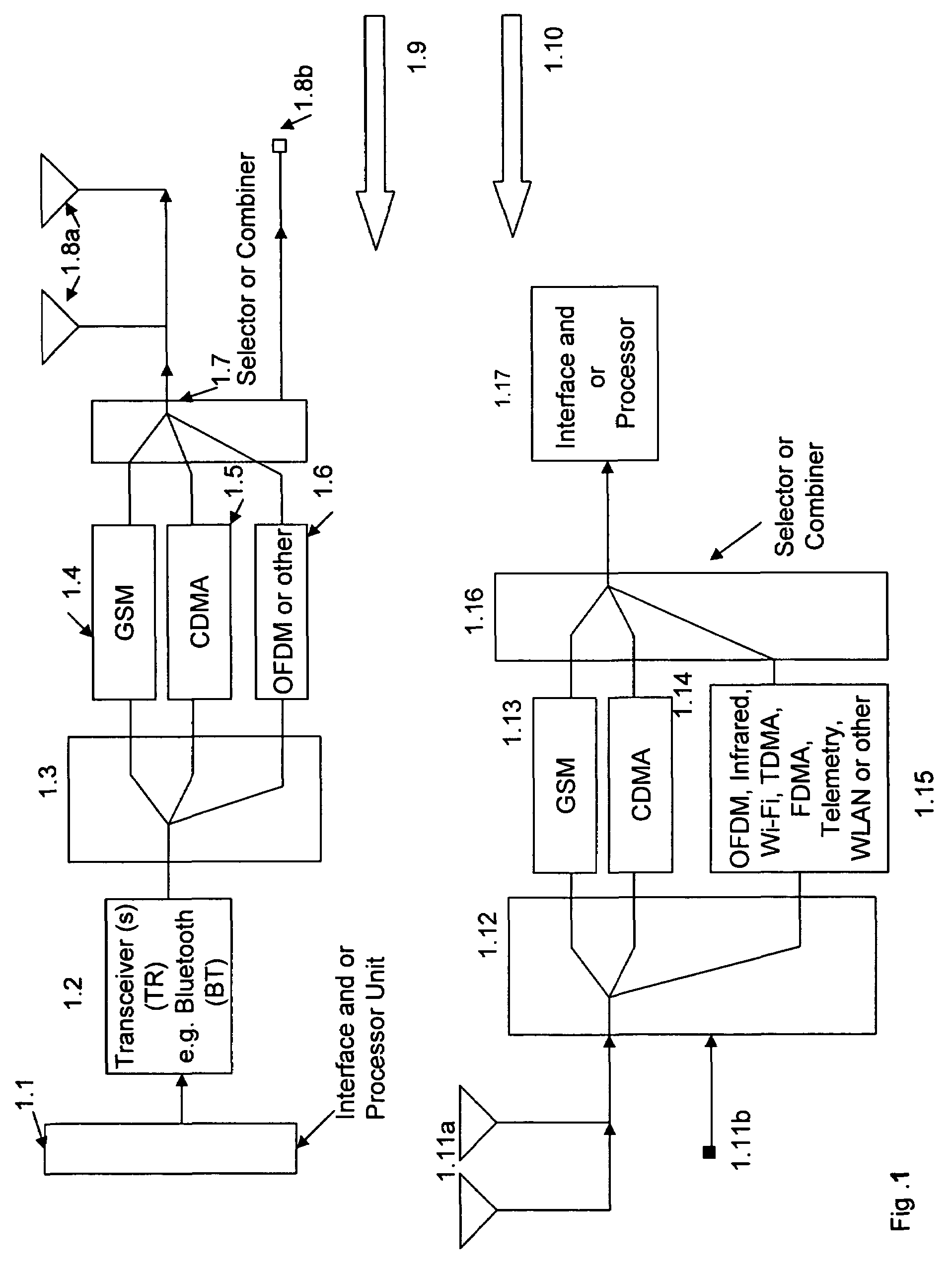
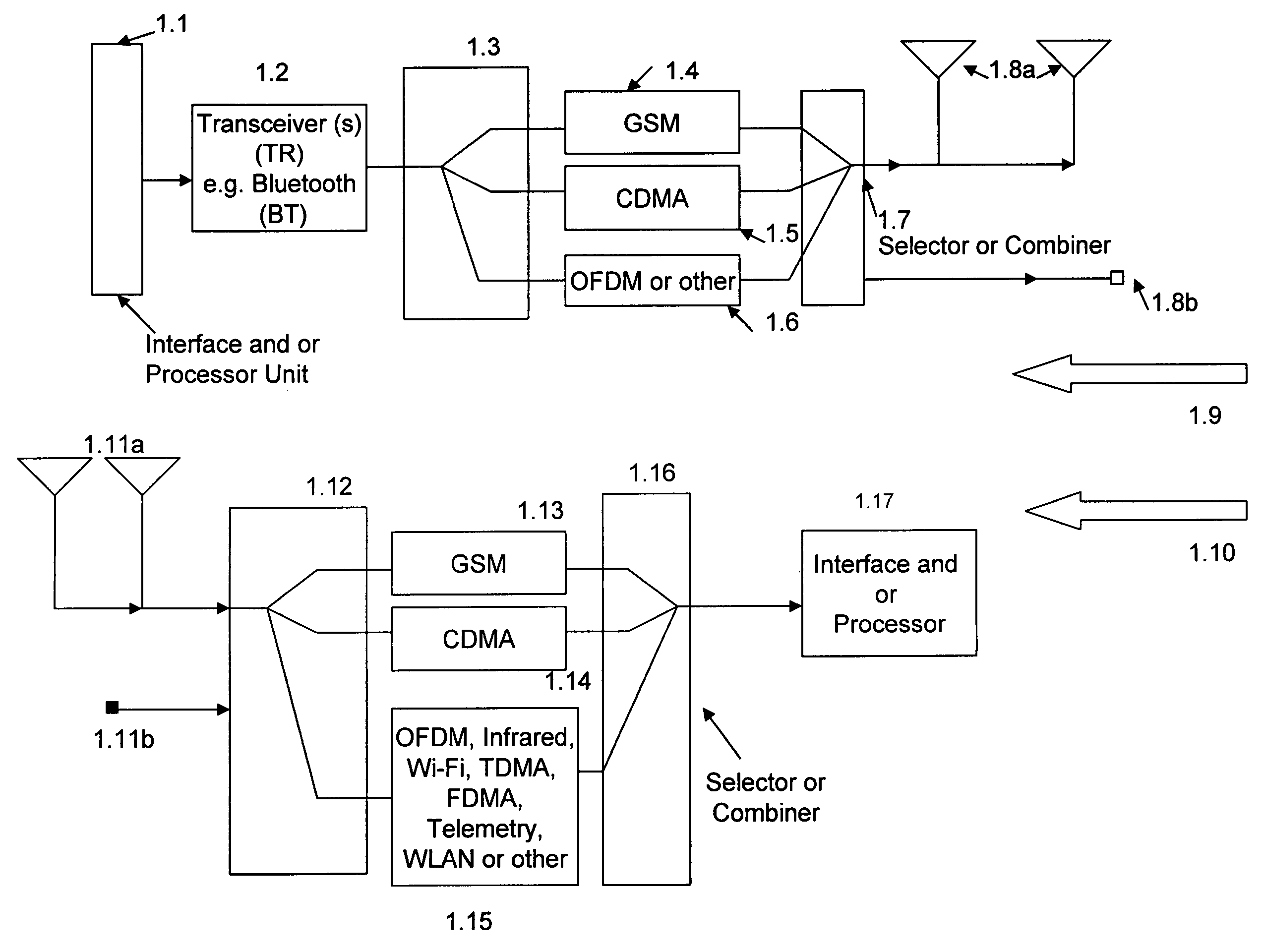
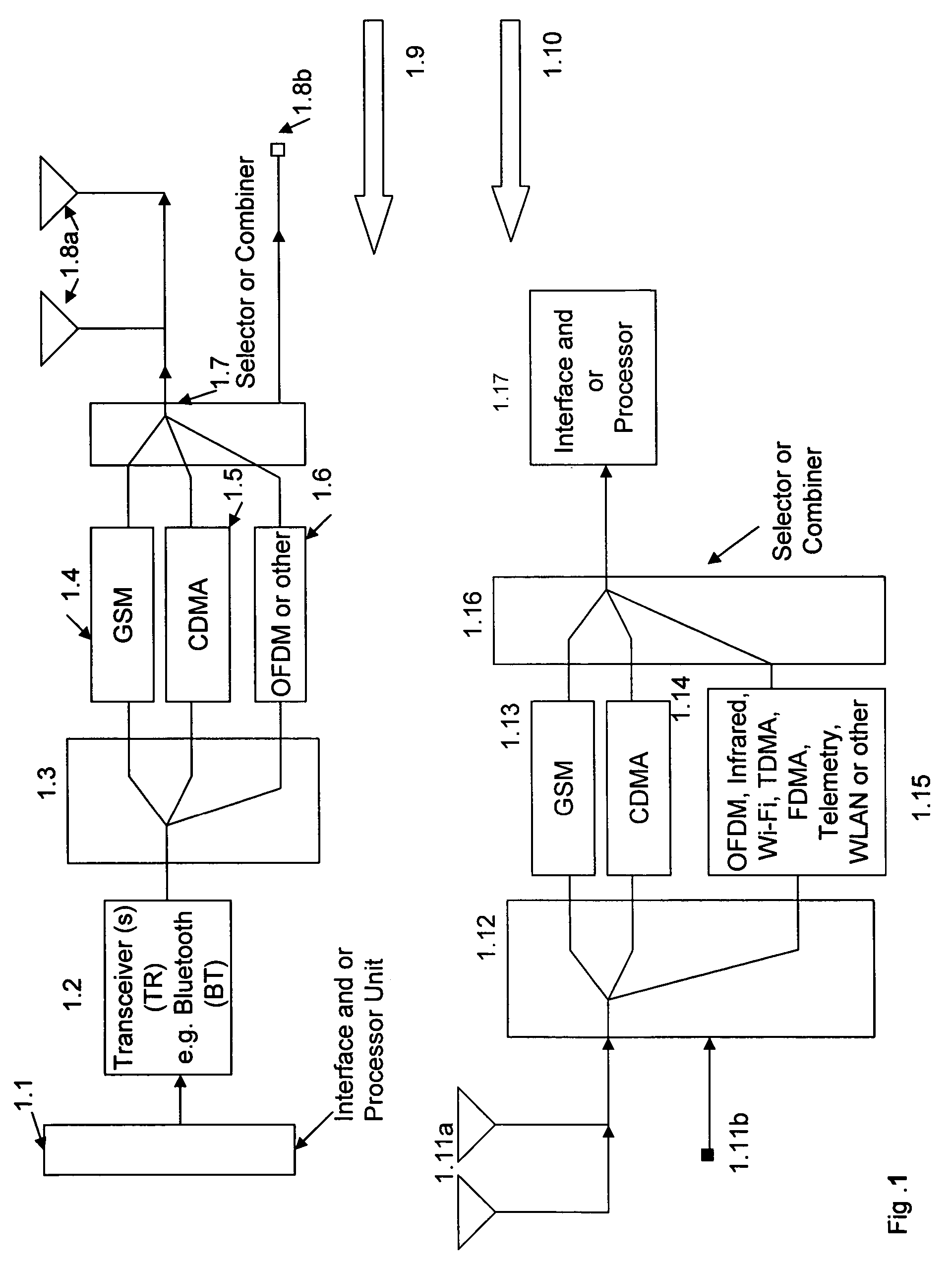
Multimode communication system
ActiveUS7280810B2Expand coverageImprove performanceElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisModem deviceCommunications system
Multimode, multi-function, multiple modulator-demodulator (modem) system containing a fingerprint sensor, detection, identification, authentication, and processing device for one or multiple fingerprint information to activate one or multiple modulators for signal transmission and generation of authentication information signals. A location information receiver and a processor device for processing and combining the location information and fingerprint information activated signals with one or more additional user generated signals. Processed, combined signals are provided for filtering and / or spread spectrum encoding and / or cross-correlating and connection to one or more modulators and transmitters.
Owner:FEHER KAMILO
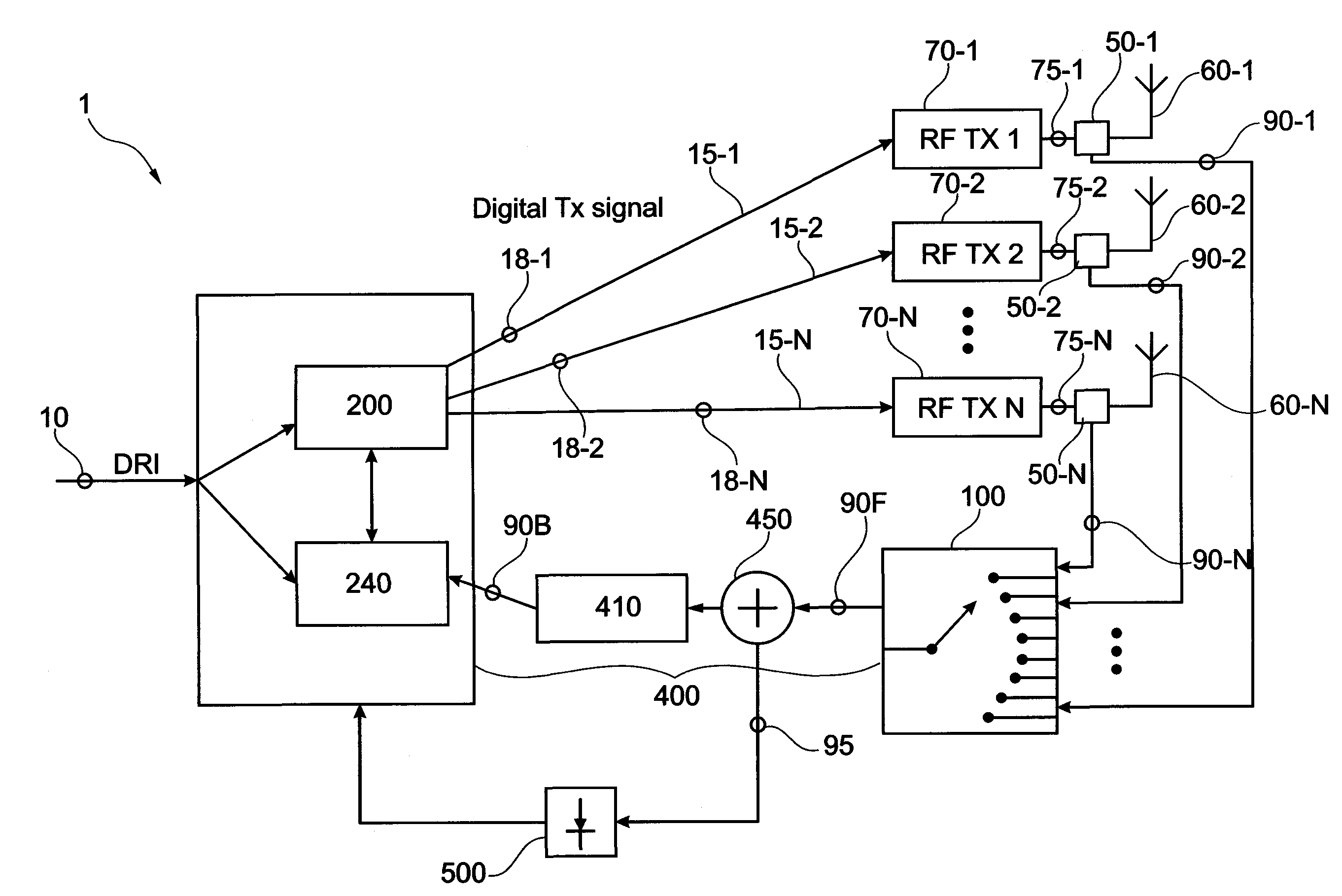
Software configurable distributed antenna system and method for reducing uplink noise
ActiveUS20140072064A1Enhance cost-effectiveness and flexibility and system performanceReduce noiseSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityDistributed antenna systemEngineering
A distributed antenna system includes a master unit including a downlink RF input operable to receive an RF input signal from a downlink port of a base station, a first optical port, and a second optical port. The distributed antenna system also includes a first remote unit coupled to the first optical port. The first remote unit comprises a downlink antenna port and a first uplink antenna port and a second remote unit coupled to the second optical port of the master unit. The second remote unit comprises a downlink antenna port and a second uplink antenna port. The master unit is operable to transmit a first RF signal associated with the first RF uplink signal to a first uplink port of the base station and transmit a second RF signal associated with the second RF uplink signal to a second uplink port of the base station.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
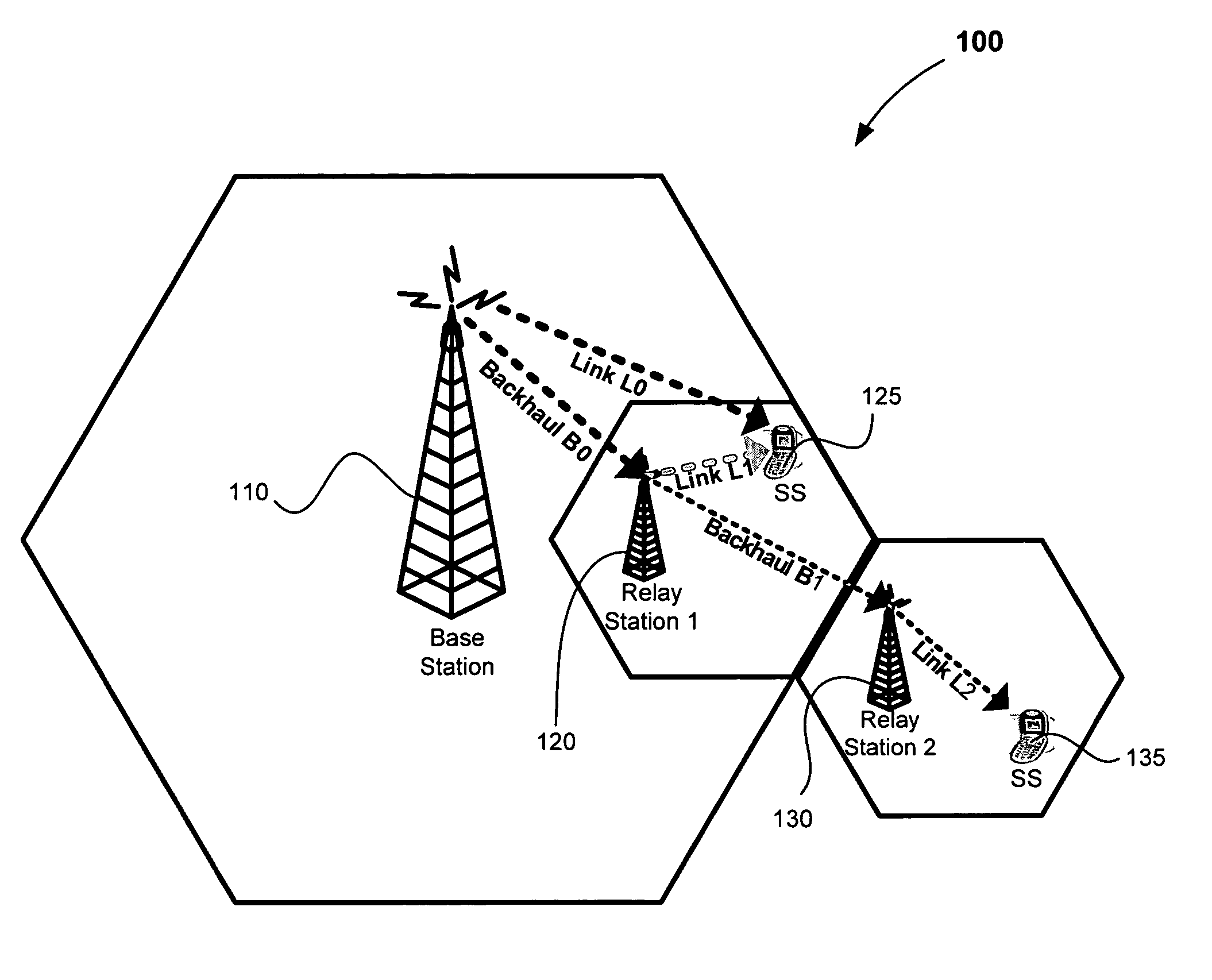
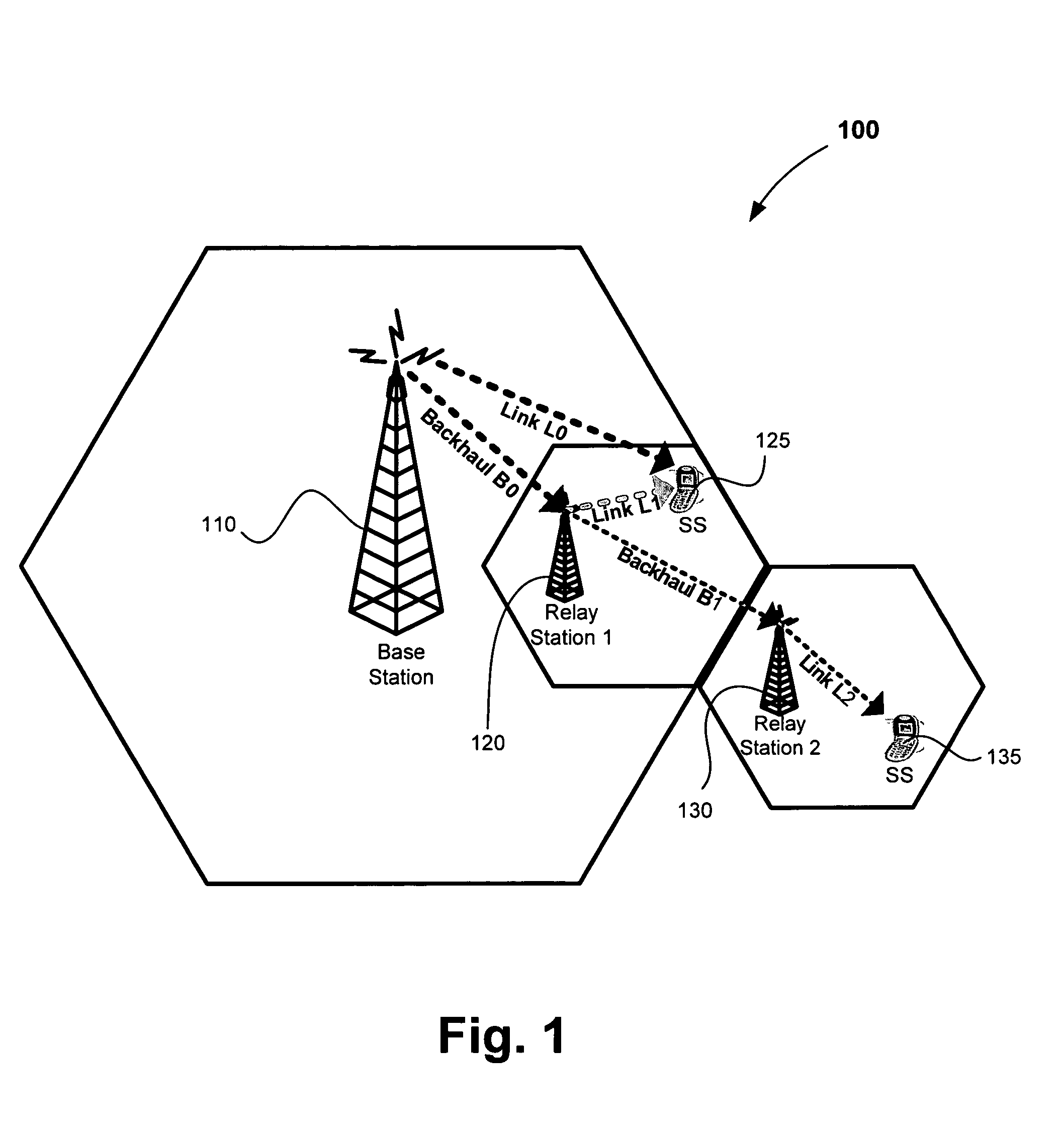
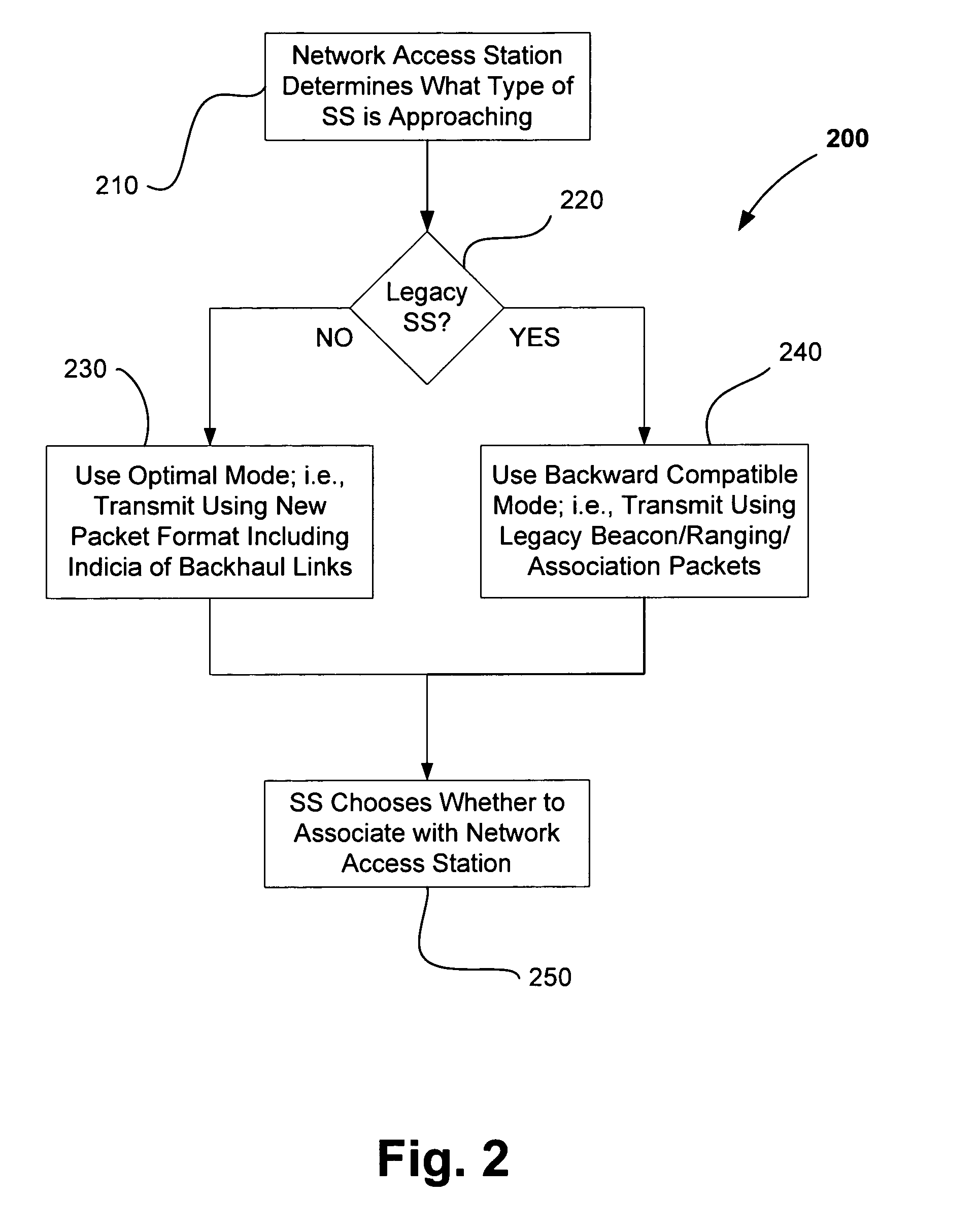
Architecture, protocols and frame formats for wireless multi-hop relay networks
InactiveUS20080080436A1Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsMulti hop relay
Methods, protocols and systems for communicating in a multi-hop wireless mesh network may include explicitly providing information relating to backhaul wireless link qualities in multi-hop wireless mesh network to next generation subscriber stations in a first mode. In a second mode, embodiments are configured to implicitly provide indicia of multi-hop wireless link qualities to legacy subscriber stations by adjusting a transmit power of frames sent to the legacy subscriber stations. Other embodiments and variations are described in the detailed description.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Radio system and method for relaying radio signals with a power calibration of transmit radio signals
ActiveUS20100255774A1Easy to measureReduce manufacturing costTransmitters monitoringRadio transmissionPower sensorTransmitted power
The present invention provides a radio system and a method for relaying radio signals, providing a power calibration of transmit radio signals. With the radio system and the method no dedicated calibration signal generator is required for providing the power calibration of the transmit radio signals. The radio system comprises at least one transmit path, a calibration unit at the least one link and a power sensor. A selected one of coupled transmit signals is forwarded to a power sensor for measuring a power level of a portion of the selected one of the coupled transmit signals, wherein the calibration unit is adapted to update a power rating of the at least one transmit path in response to the transmit power level of the selected one of the coupled transmit signals.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Emergency location transceivers (ELT)
InactiveUS20070032220A1Improve the quality of lifeEliminate and reduce cable caused potentially harmful currentTelevision system detailsMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTransceiverEngineering
Emergency Location Transceivers (ELT) and communication transceivers (transmitters and receivers) for reception and demodulation of location finder signals, Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite signals and non GPS satellite location finder and other location finder signals. The received location finder signals are demodulated to location finder baseband signals. Baseband signal processors for processing single or a plurality of input signals for providing Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex (OFDM) baseband signals, filtered signals, cross-correlated shaped in-phase and quadrature-phase baseband signals and spread spectrum signals. Signal modulators for modulating the processed signals and for providing the modulated signals to the signal transmitter for transmission of the modulated signals. Emergency receiver systems for reception, demodulation and processing of the modulated transmitted signals. Certain emergency receiver embodiments, such as receivers of calls made to emergency call number 911 contain two or more receive antennas for reception and processing of the transmitted modulated signal. In certain embodiments emergency receiver systems have two or more receive antennas operated in a diversity mode, for reception and processing of the transmitted modulated signal.
Owner:FEHER KAMILO
Gain measurement and monitoring for wireless communication systems
A method of monitoring an element in wireless communication system is provided. An operational noise measurement is obtained by measuring a noise value outside of a bandwidth of a first device, but within a bandwidth of a second, subsequent device. The operational noise measurement is alternatively obtained by tuning an input band of the element to shift the input band partially or completely outside of a bandwidth of a first device to create an open band or by suppressing an input of the antenna and measuring noise within the open bandwidth of the element of the wireless communication network. A stored parameter is retrieved and compared to the measured operational noise. Alternatively, a leakage signal of the element may be received at a signal receiver and compared to a reference. The reference is a function of components of the wireless communication system in a leakage path of the leakage signal.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Method and system for communication with an ingestible imaging device
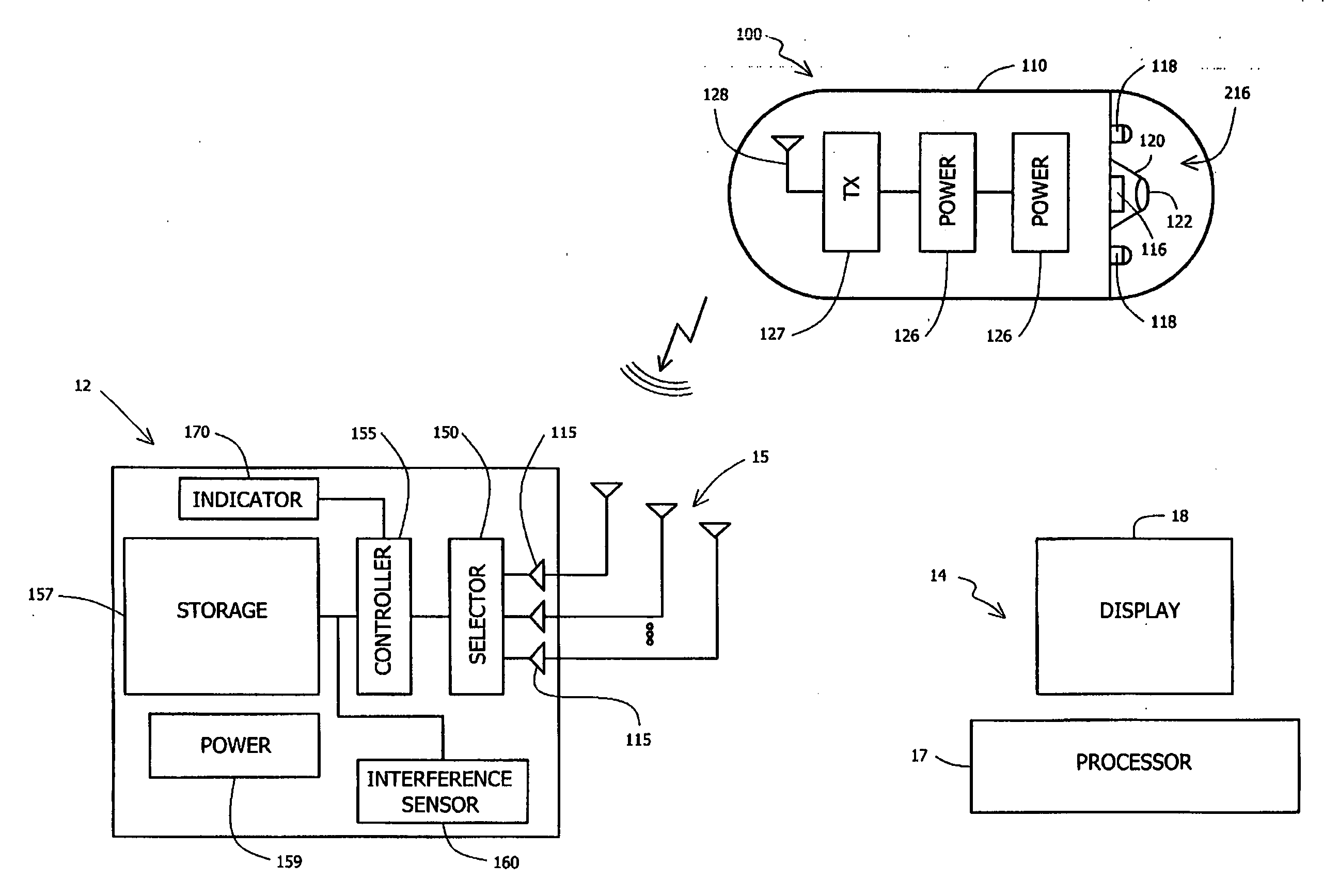
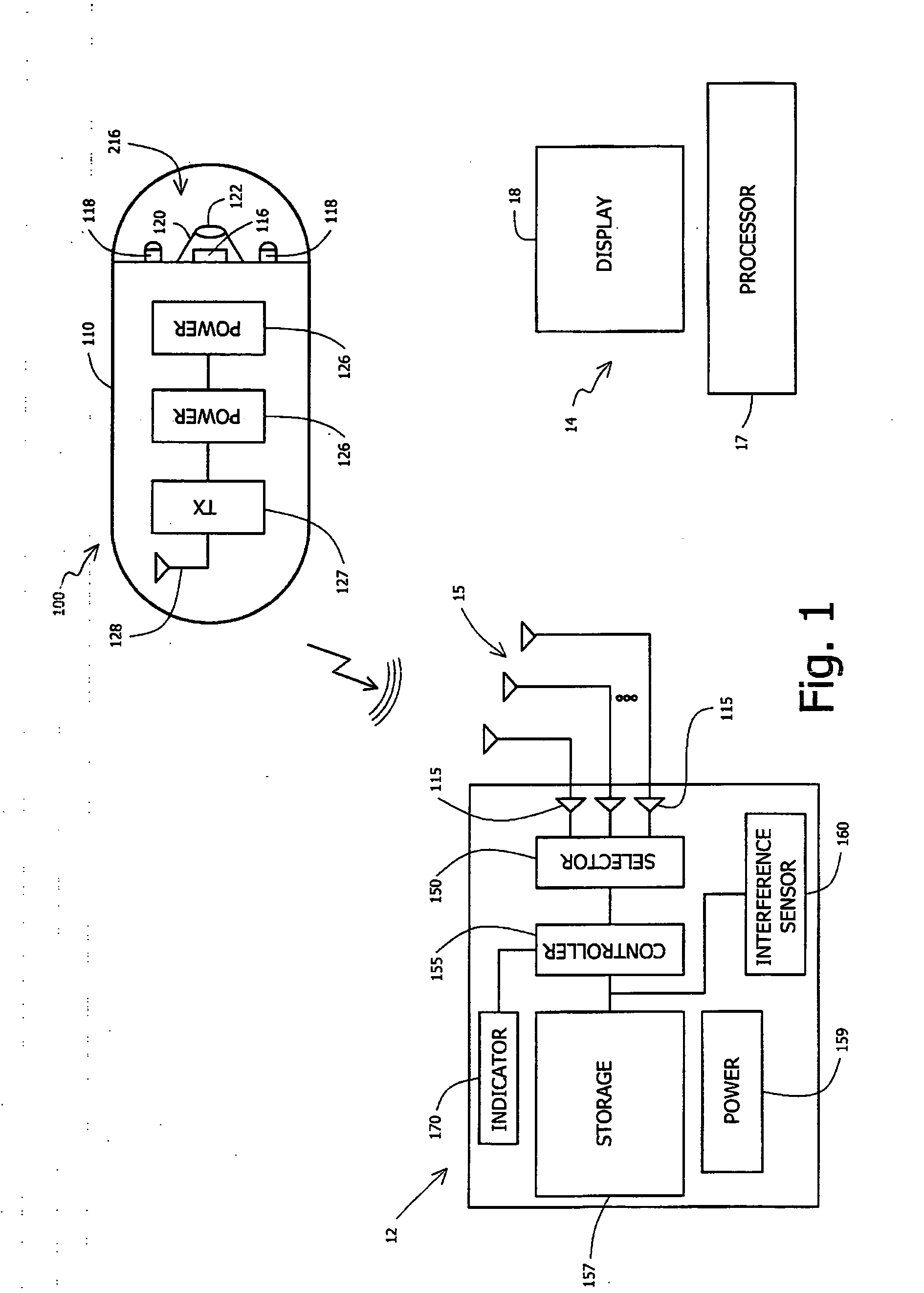
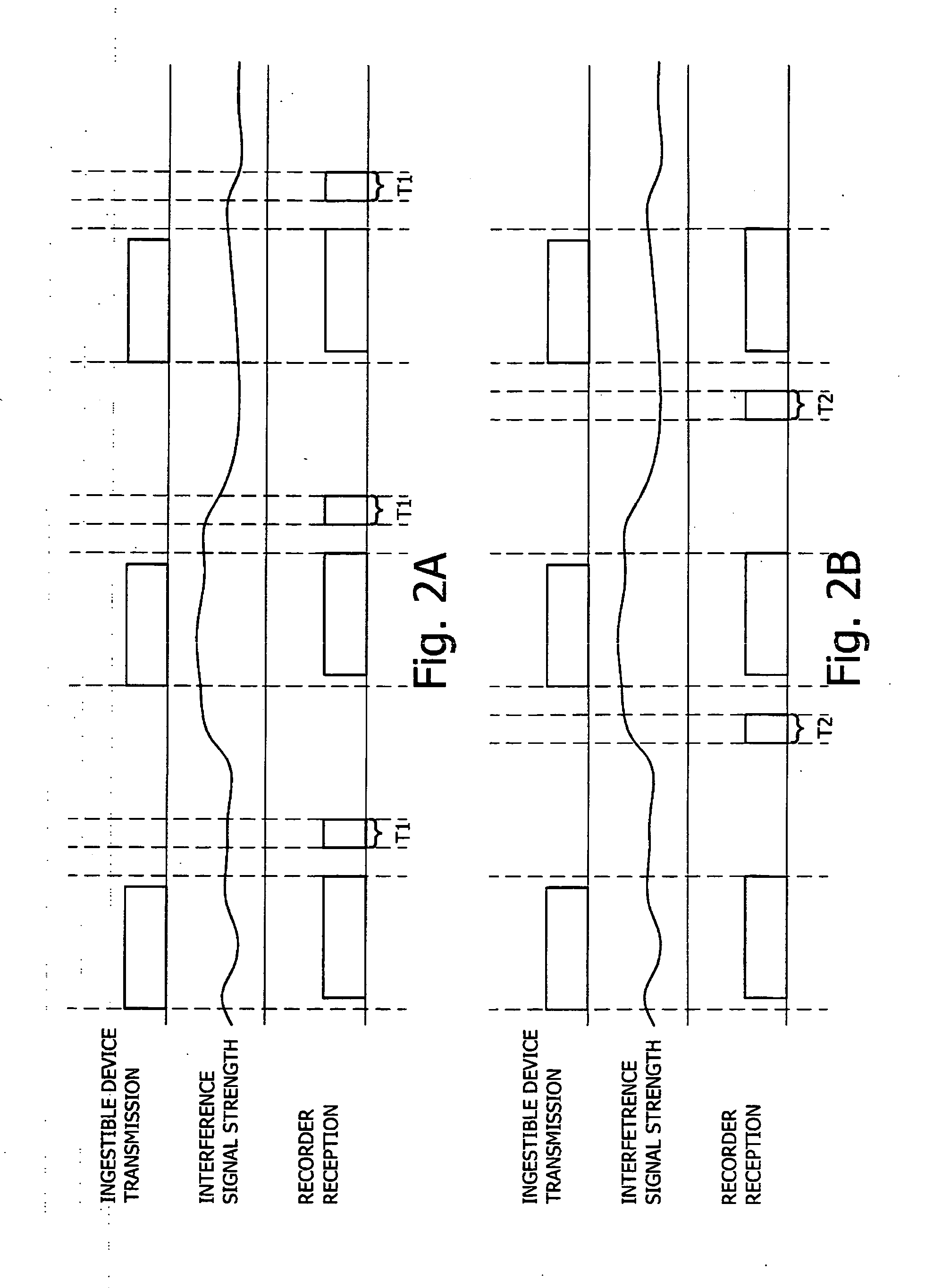
InactiveUS20070156016A1Accurate receptionReceivers monitoringFrequency-division multiplex detailsElectrical and Electronics engineeringRf communication
A system and method for detecting and recording interference in an RF communication channel for an ingestible imaging device is provided. During a period when transmission in a communication channel may be idle, interference levels may be detected and recorded. Changes in transmission levels may be altered based on the detected interference level. Transmission may be delayed due to detected levels of interfering signals.
Owner:BETESH IDO +2
Method and apparatus for channel state feedback using arithmetic coding
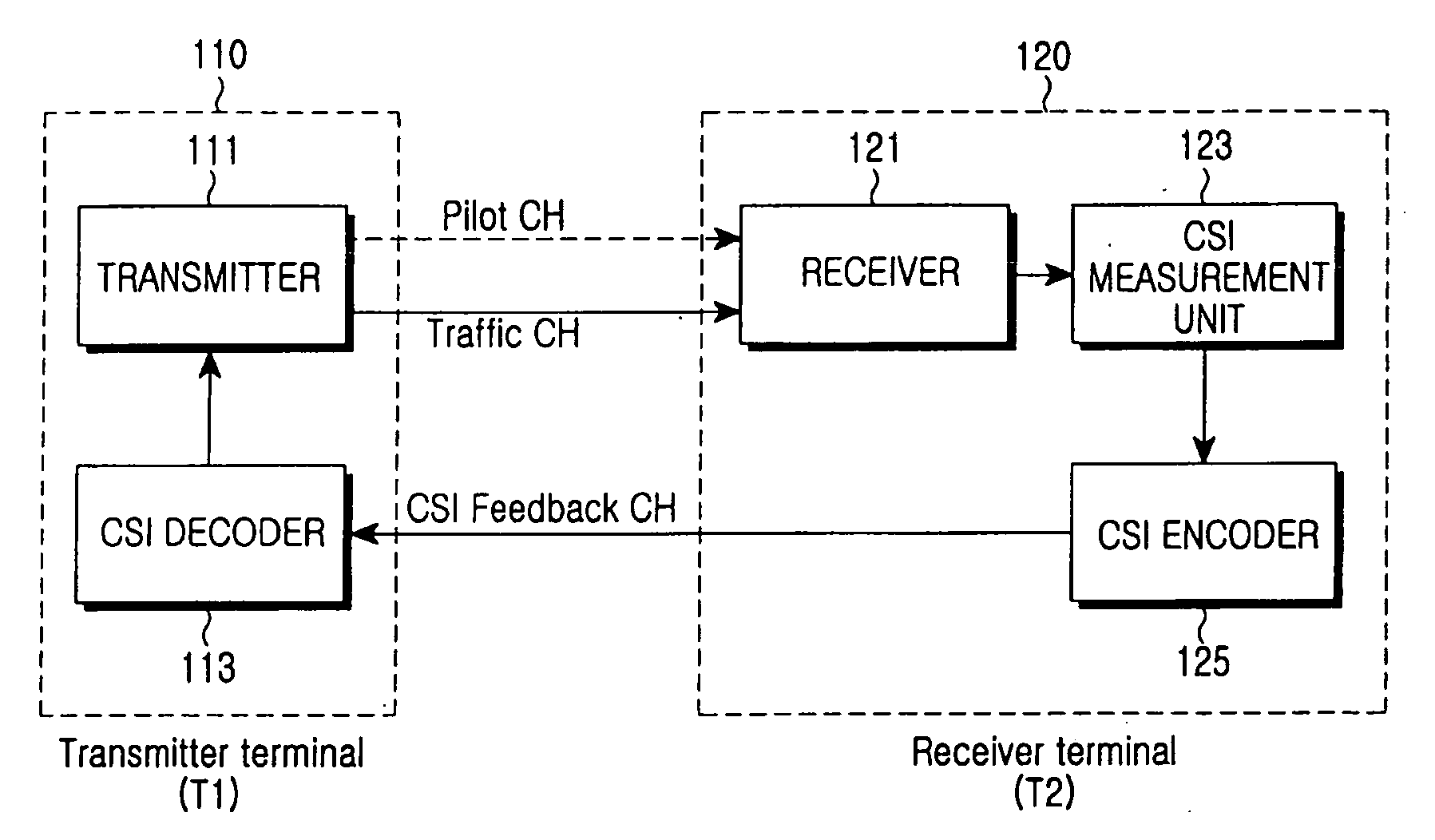
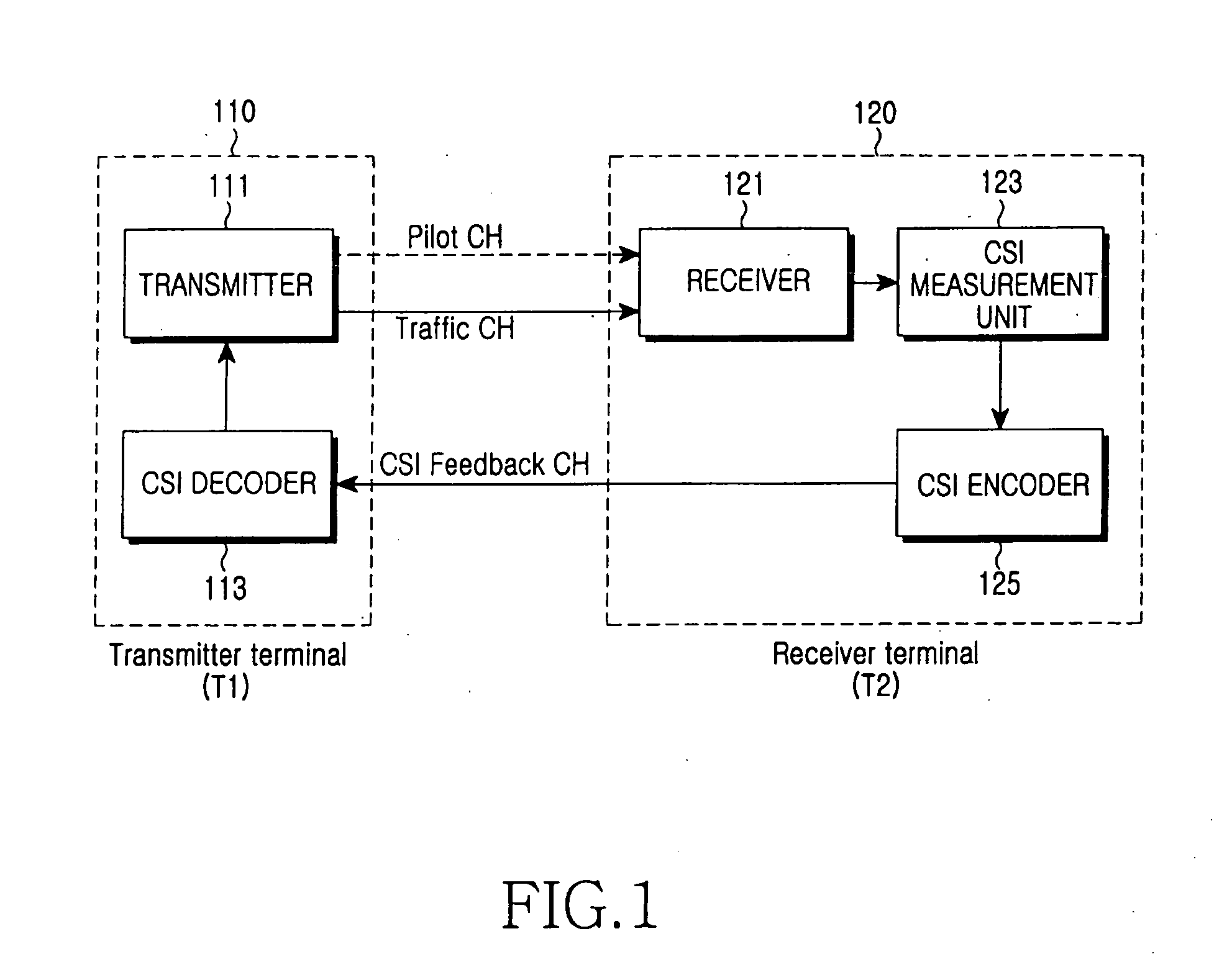
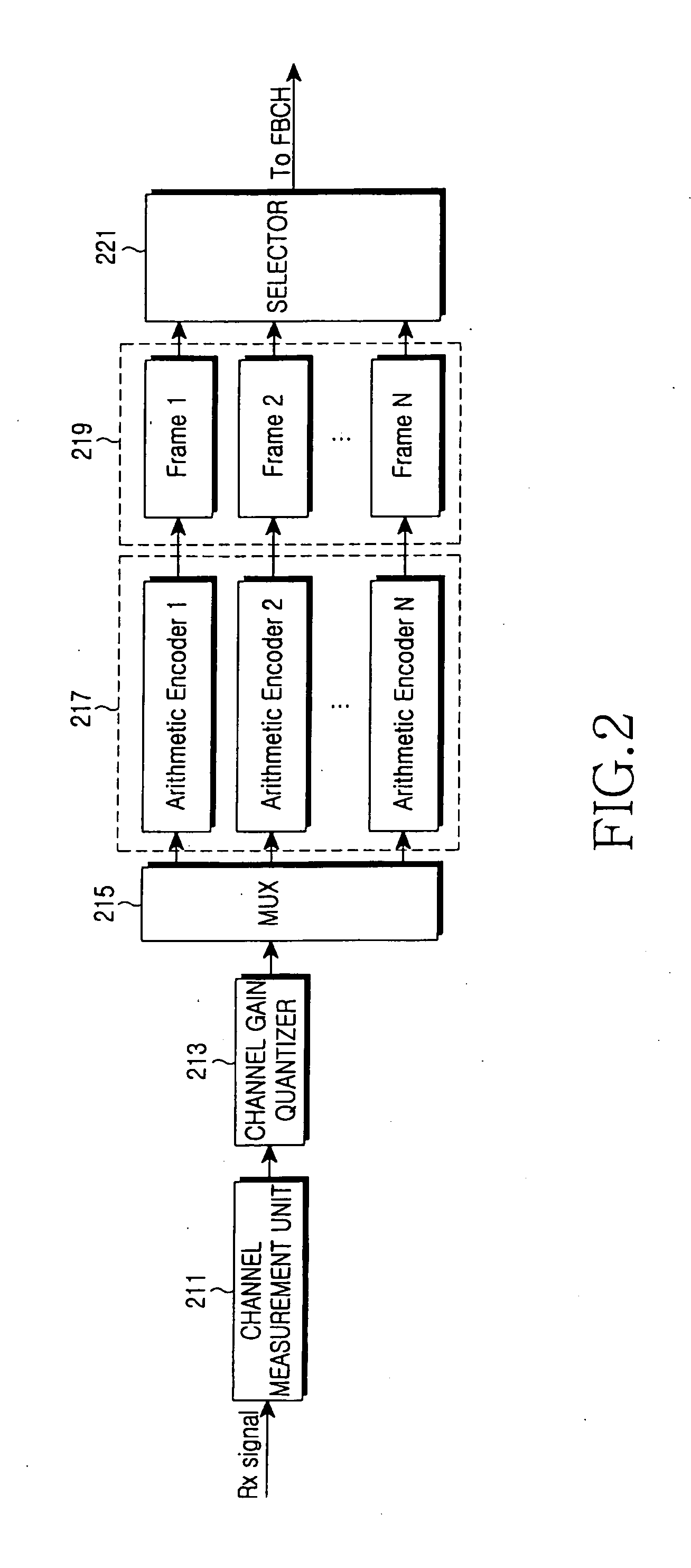
ActiveUS20050265436A1Reduce the impactImprove system performanceModulated-carrier systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemArithmetic coding
Disclosed are the design and implementation of a CSI feedback channel in a multi-carrier wireless communication system. An apparatus and a method for channel state feedback using arithmetic coding are provided to ensure efficiency and reliability of a system by transmitting the CSI while compressing the CSI with a predetermined compression rate selected depending on a channel state. The apparatus for CSI feedback in a wireless communication system performing channel estimation at a transmitter or a receiver by using a communication channel includes a transmitter terminal transmitting a signal for CSI measurement by using the communication channel, and a receiver terminal receiving the signal from the transmitter terminal, checking a channel state based on the received signal, and transmitting the signal to the transmitter terminal after compressing the signal according to the channel state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Apparatus and method for digital image correction in a receiver
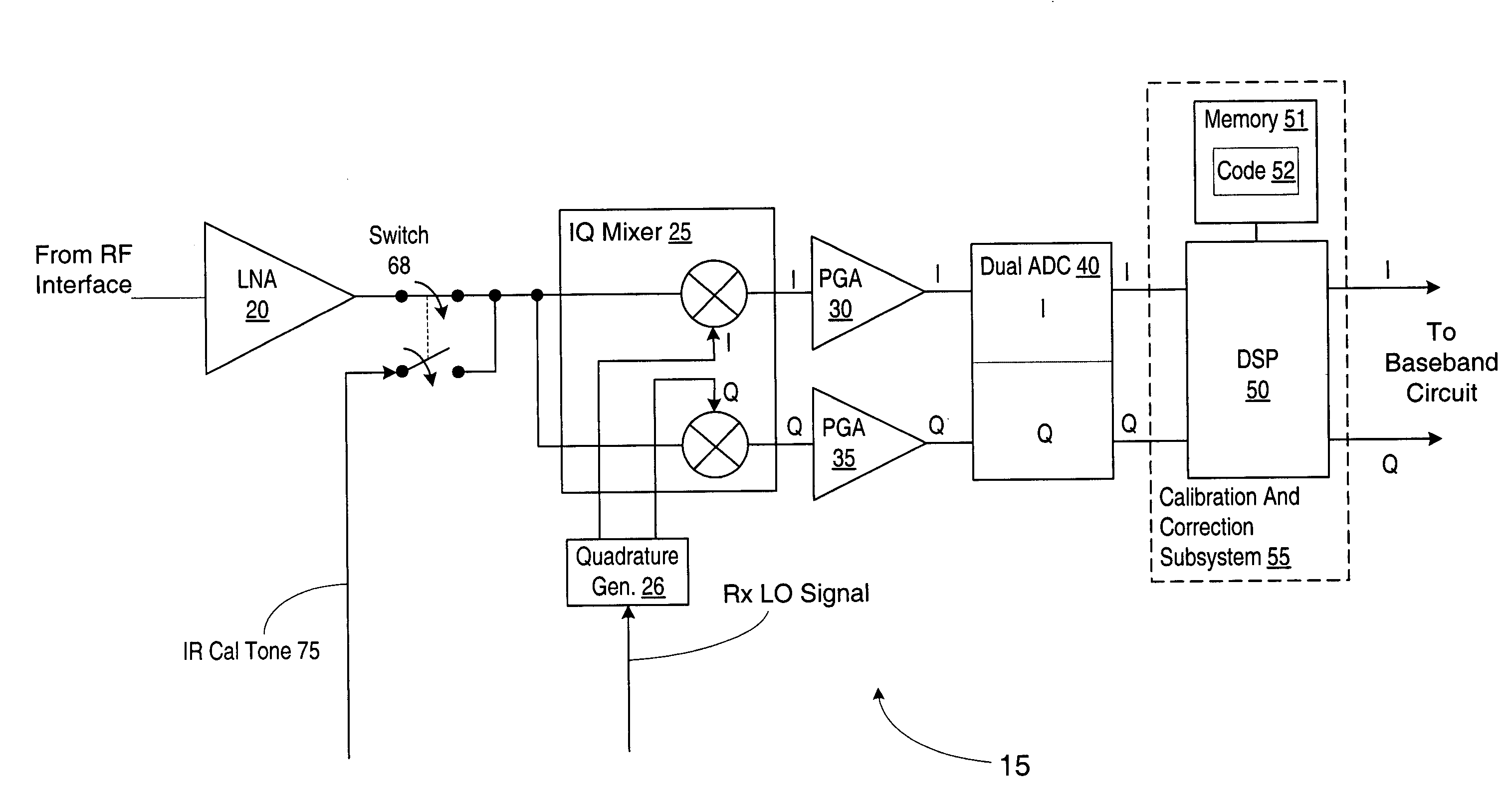
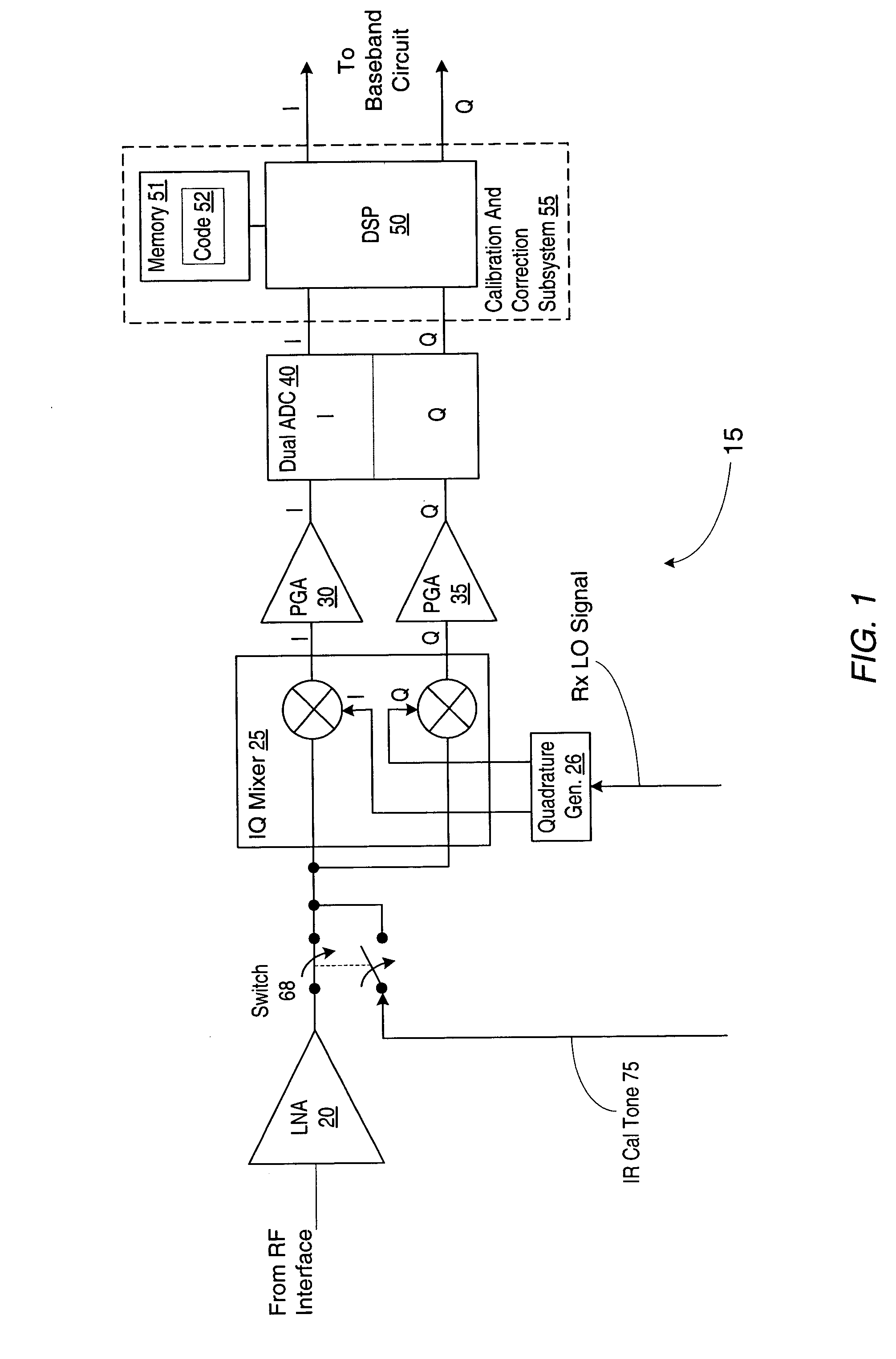
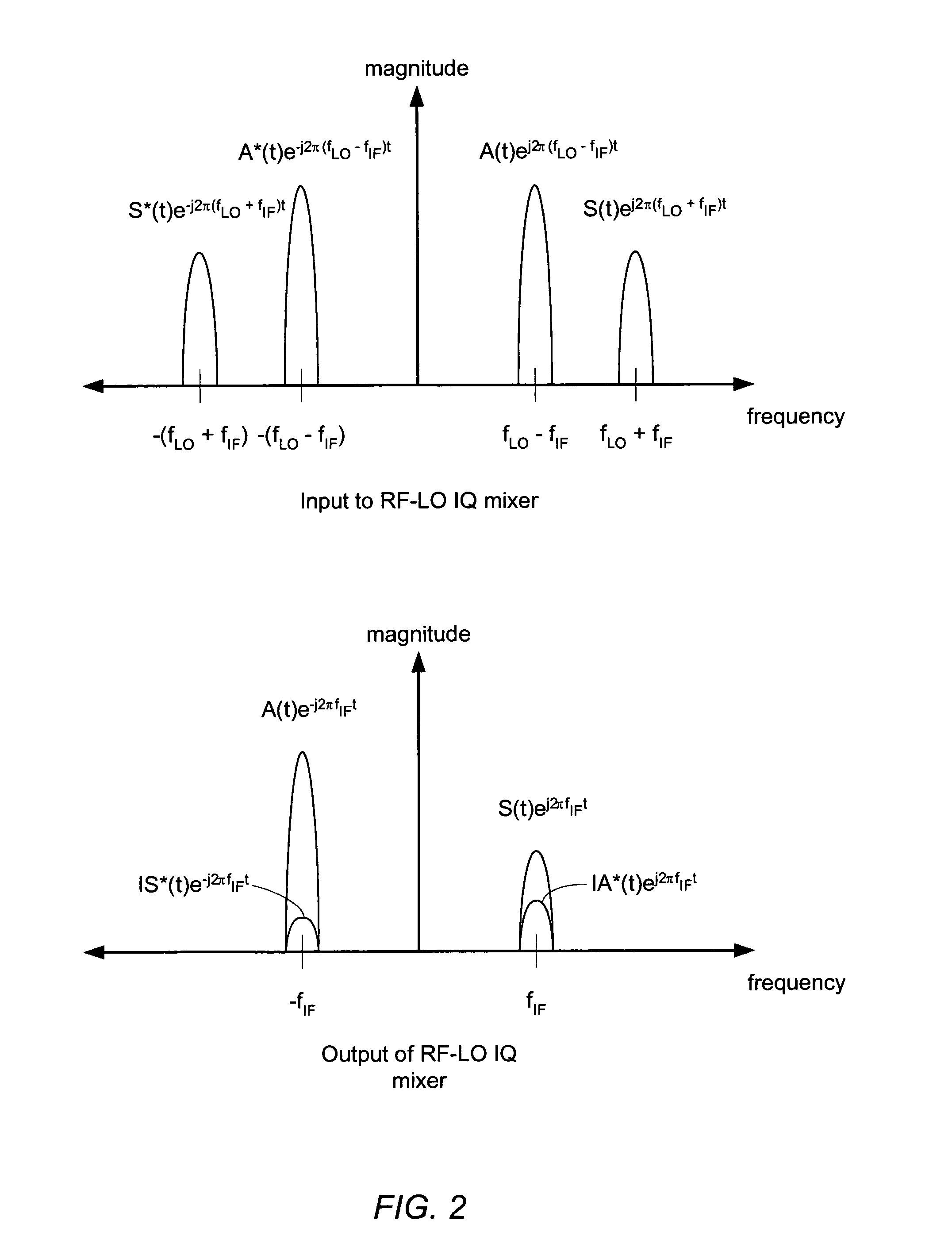
ActiveUS7142835B2Angle demodulation by oscillations conversionRelay systems monitoringProgram instructionImage correction
An apparatus and method for performing digital image correction in a receiver. In one embodiment, a receiver circuit may include an IQ signal source configured to provide a digital signal comprising in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components, such as an IQ mixer in combination with an analog to digital converter, for example. The receiver circuit may also include an image correction unit coupled to the IQ signal source and configured to combine the digital signal with a complex image correction factor. The image correction unit may be implemented using a digital signal processor under the control of associated program instructions, for example. In one specific implementation of the receiver circuit, the image correction unit may be configured to combine the digital signal with the complex image correction factor using a cross-accumulation operation.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
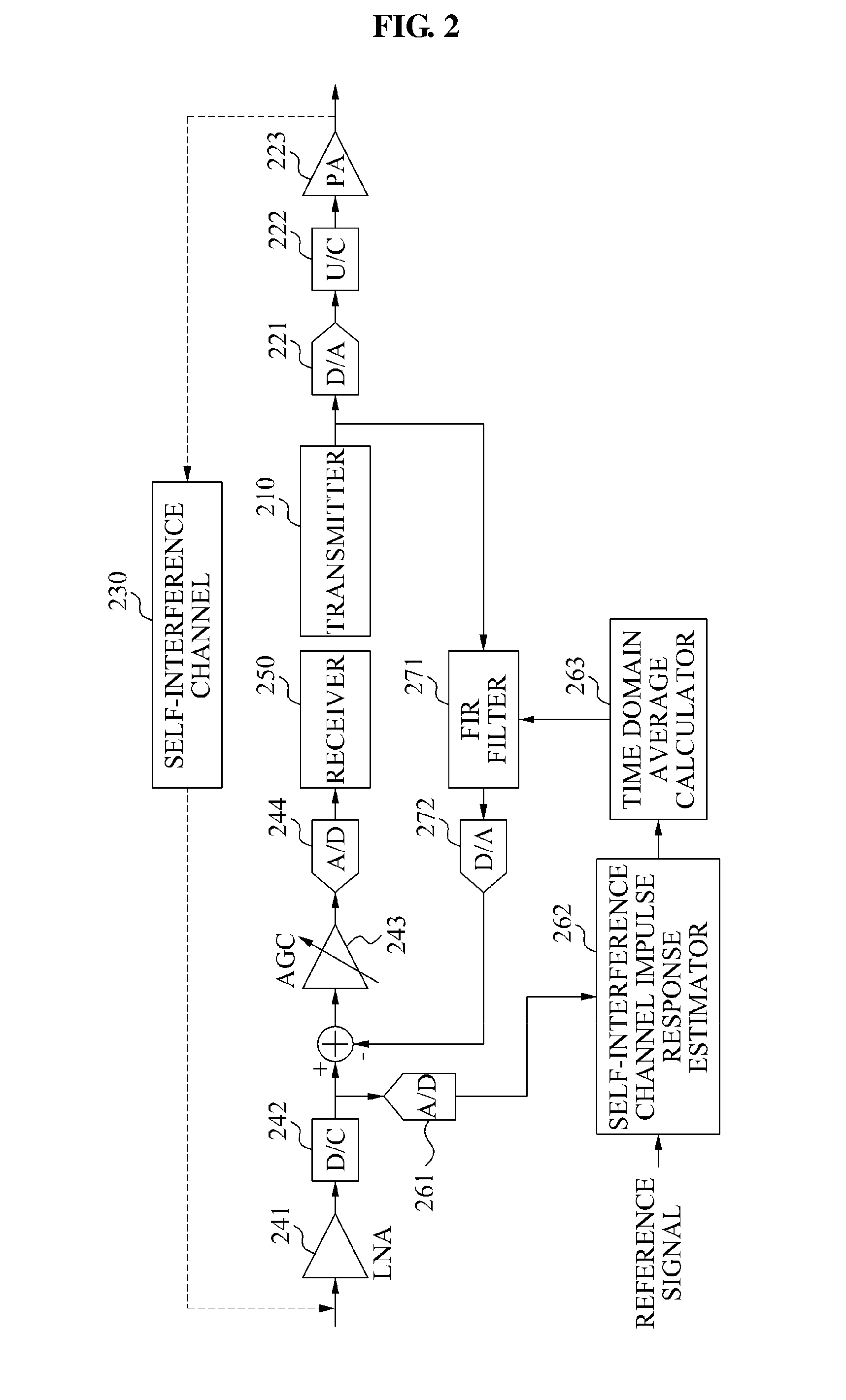
Self-interference cancellation method and apparatus of relay using the same frequency band in ofdm-based radio communication system
InactiveUS20110143655A1Modulated-carrier systemsRepeater circuitsSelf interferenceCommunications system
Provided is a self-interference cancellation method and apparatus that may remove self-interference occurring when a transmission signal of a transmit antenna is received, directly or via a reflector, by a receive antenna in a relay using the same frequency band in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM)-based radio communication system.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Radio communication system
ActiveUS20050181814A1Switch accuratelyAccurate procedureNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemSubcarrier
A TDMA radio communication system using a multiple subcarrier modulation method and comprising at least a first and a second radio station. The first radio station carries out communications by selectively modulating a subcarrier with which a desired transmission rate can be obtained in the second radio station, thereby providing a radio communication system that does not require the monitoring of each time slot by a terminal.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
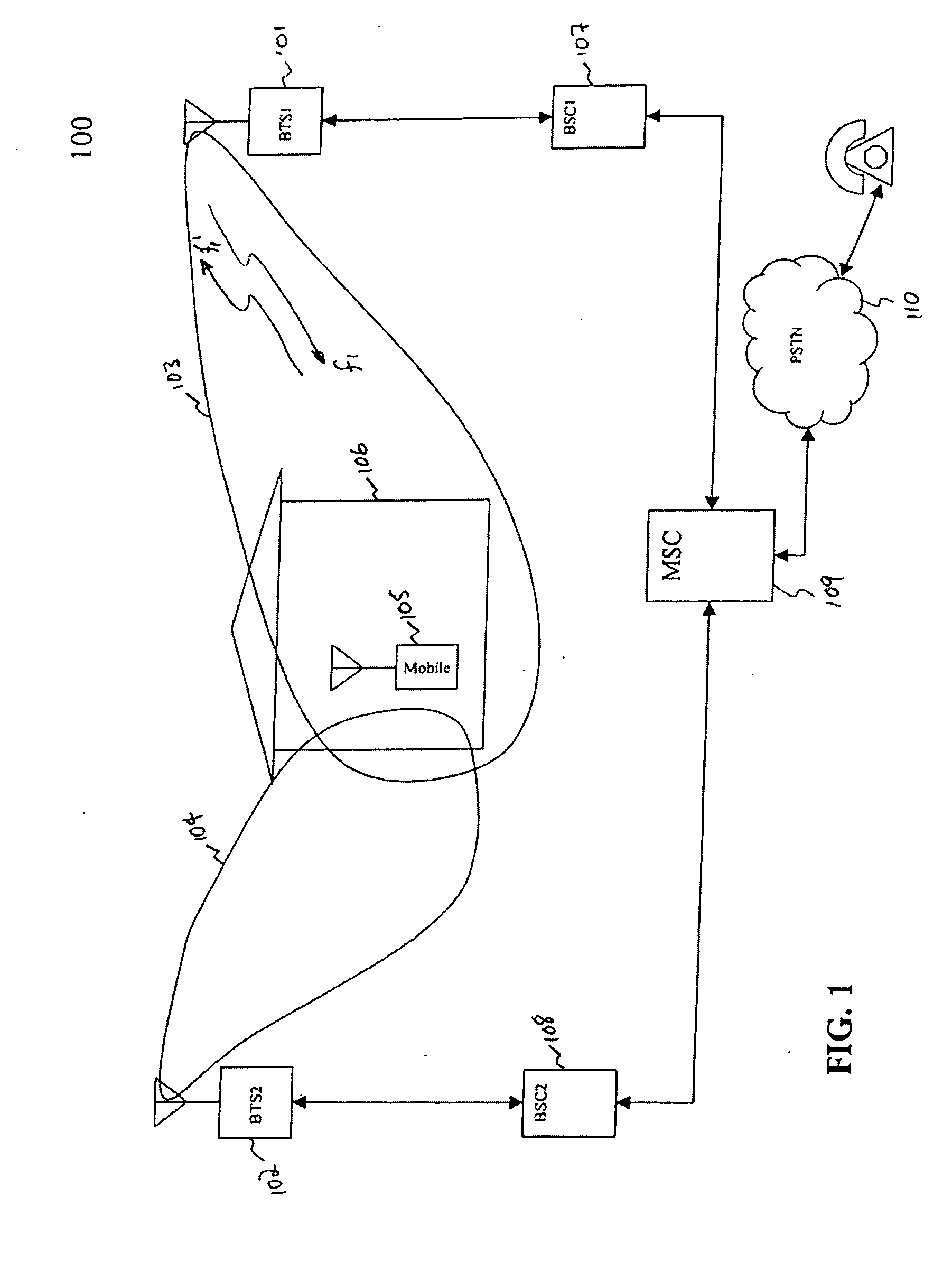
Intersystem base station handover
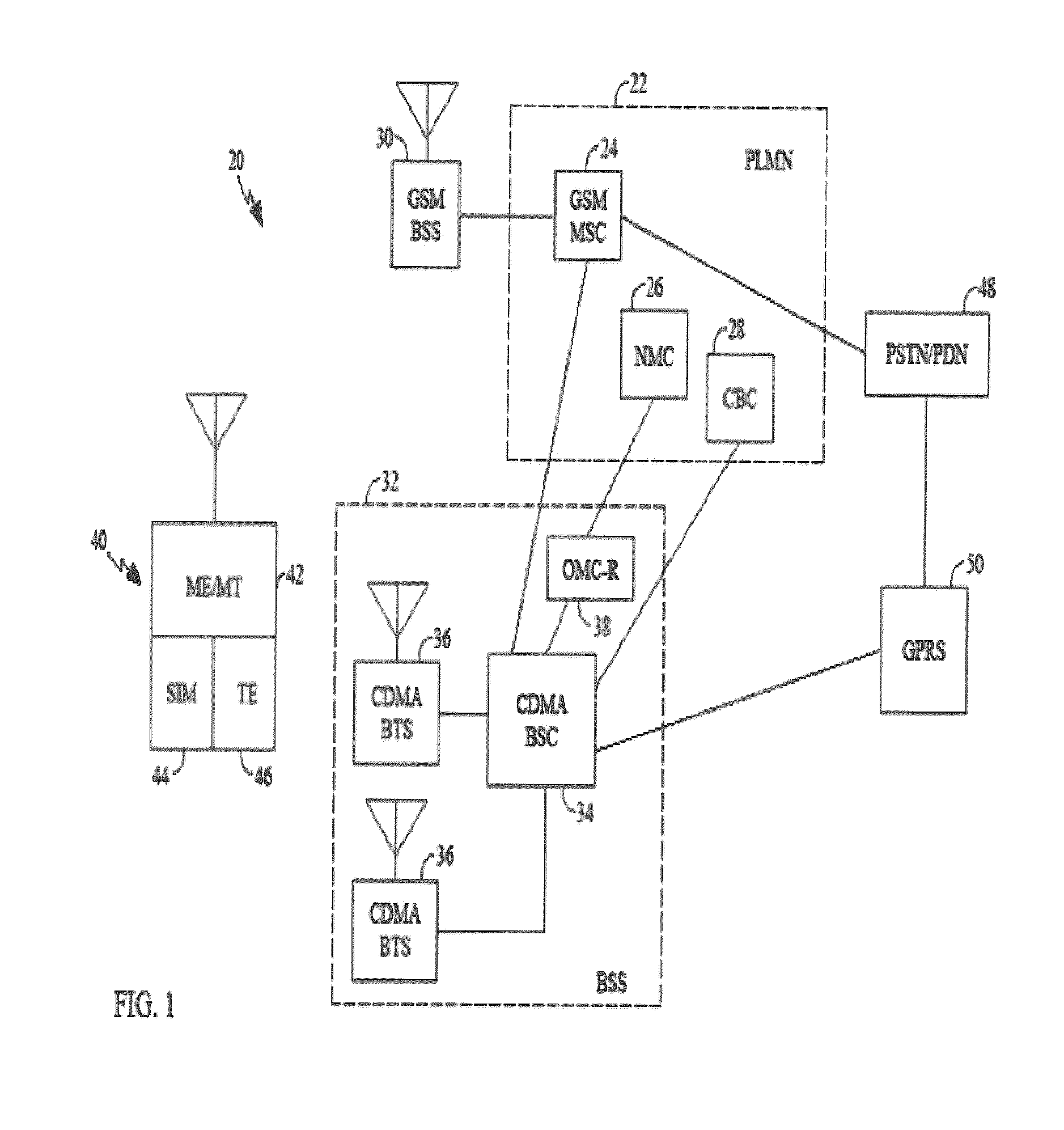
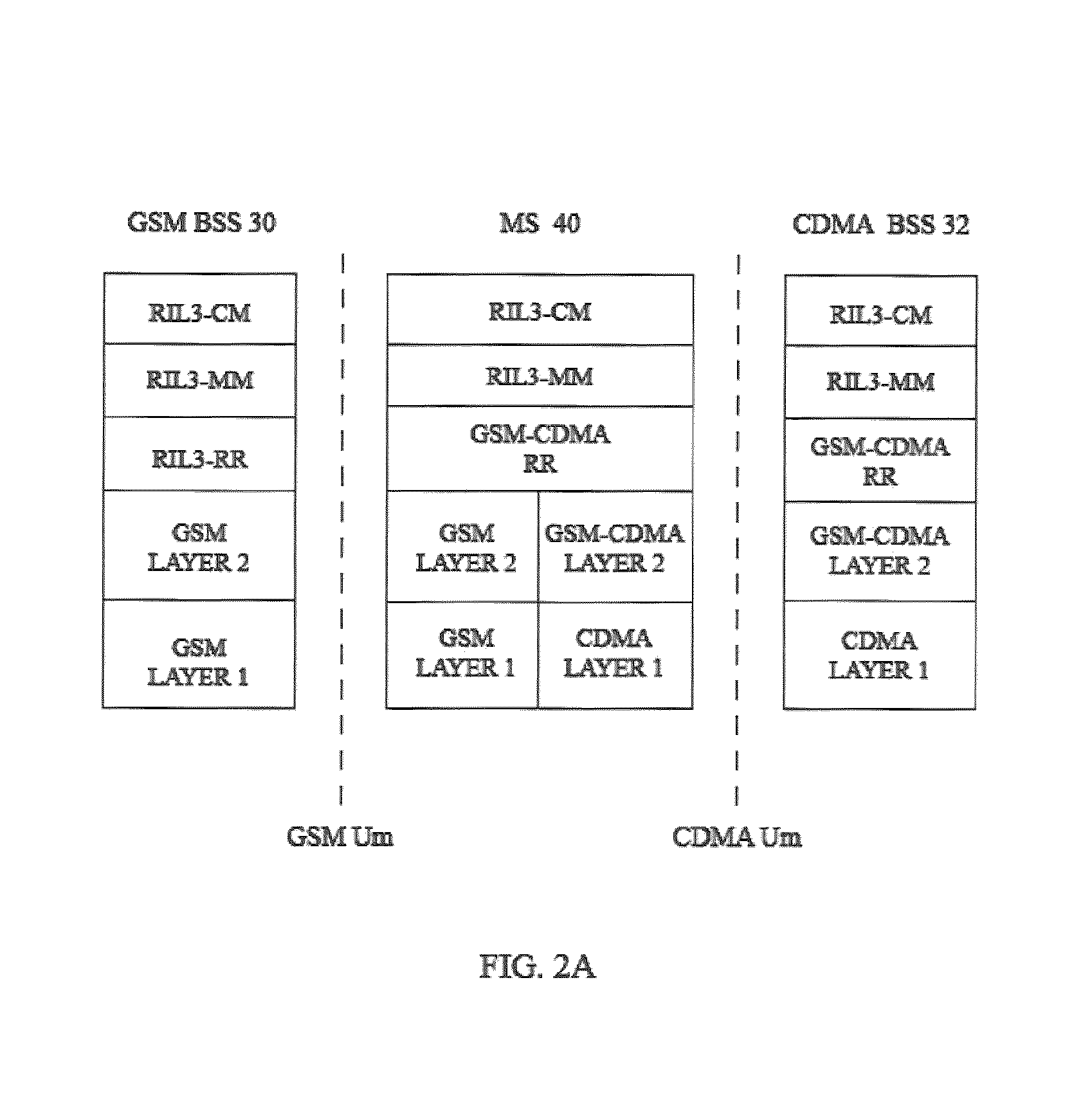
InactiveUS7876729B1Minimizing interruptionNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkAir interface
A mobile wireless telecommunications system includes base stations of a first type operating according to a first air interface, and base stations of a second type operating according to a second air interface. Methods and apparatus are provided for handing over a mobile station in the system from a first base station, which is of the first type, to a second base station, which is of the second type. A communications link is established over the first air interface between the mobile station and the first base station. Data are received from the mobile station responsive to a signal received by the mobile station over the second air interface from the second base station, substantially without breaking the communications link with the first base station. The mobile station is handed over from the first to the second base station responsive to the data received therefrom. In particular, a method of conducting intersystem handover from a multicarrier system to a direct spread system is provided. Timing synchronization is also advantageously made available through the mobile station.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Reconfigureable arrays of wireless access points
ActiveUS7496070B2Meet real-timeBroadcast with distributionNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceWireless mesh network
A wireless communications network includes a reconfigurable array of access points for linking wireless devices in an infrastructure mode. One or more of the access points are mobile. The mobile access points in the network can be repositioned to change the geographic distribution of the bandwidth coverage provided by the wireless network. The mobile access points may be repositioned to redistribute available network bandwidth heterogeneously according to the demand for bandwidth in local areas and to meet quality of service standards.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
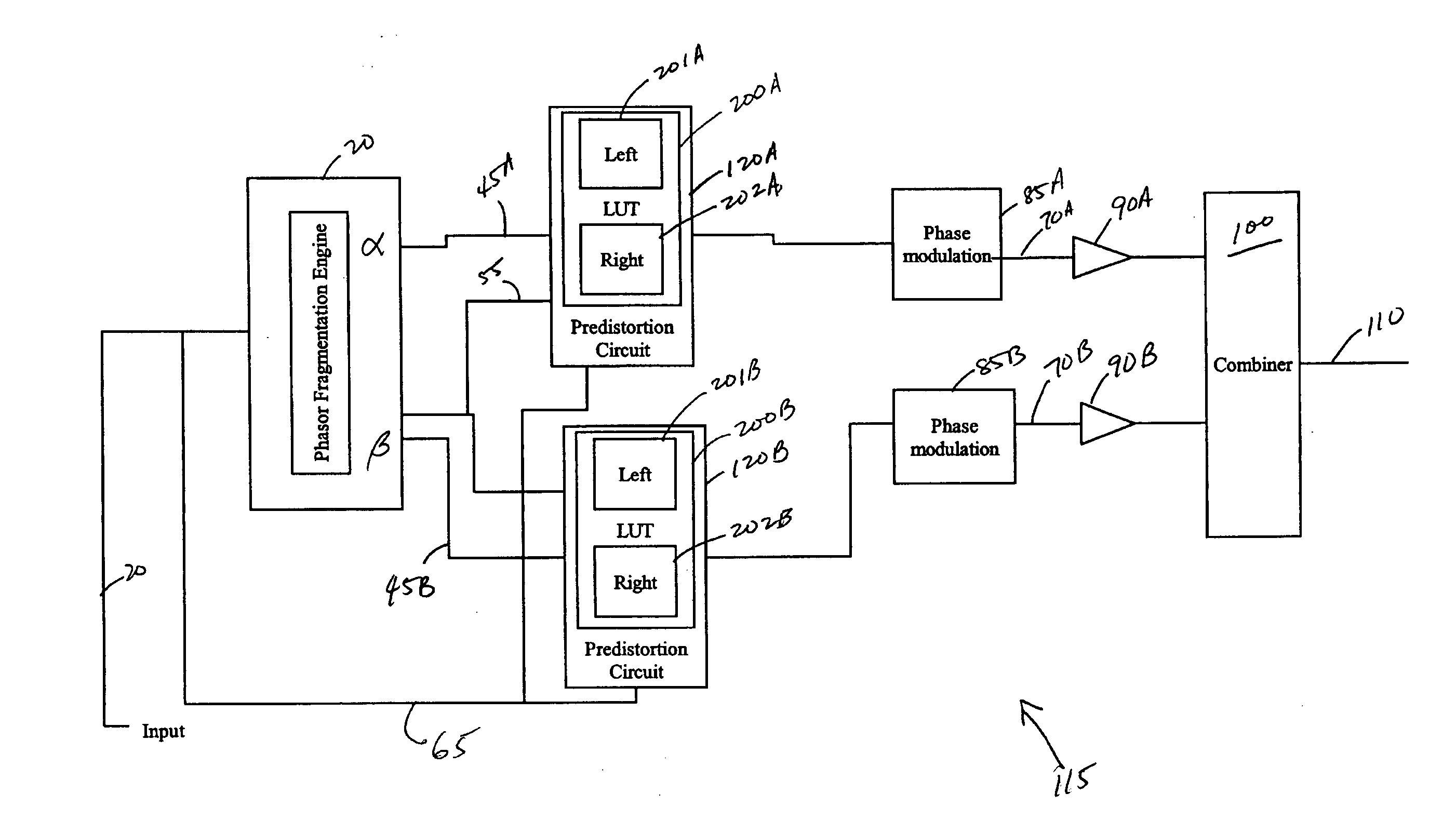
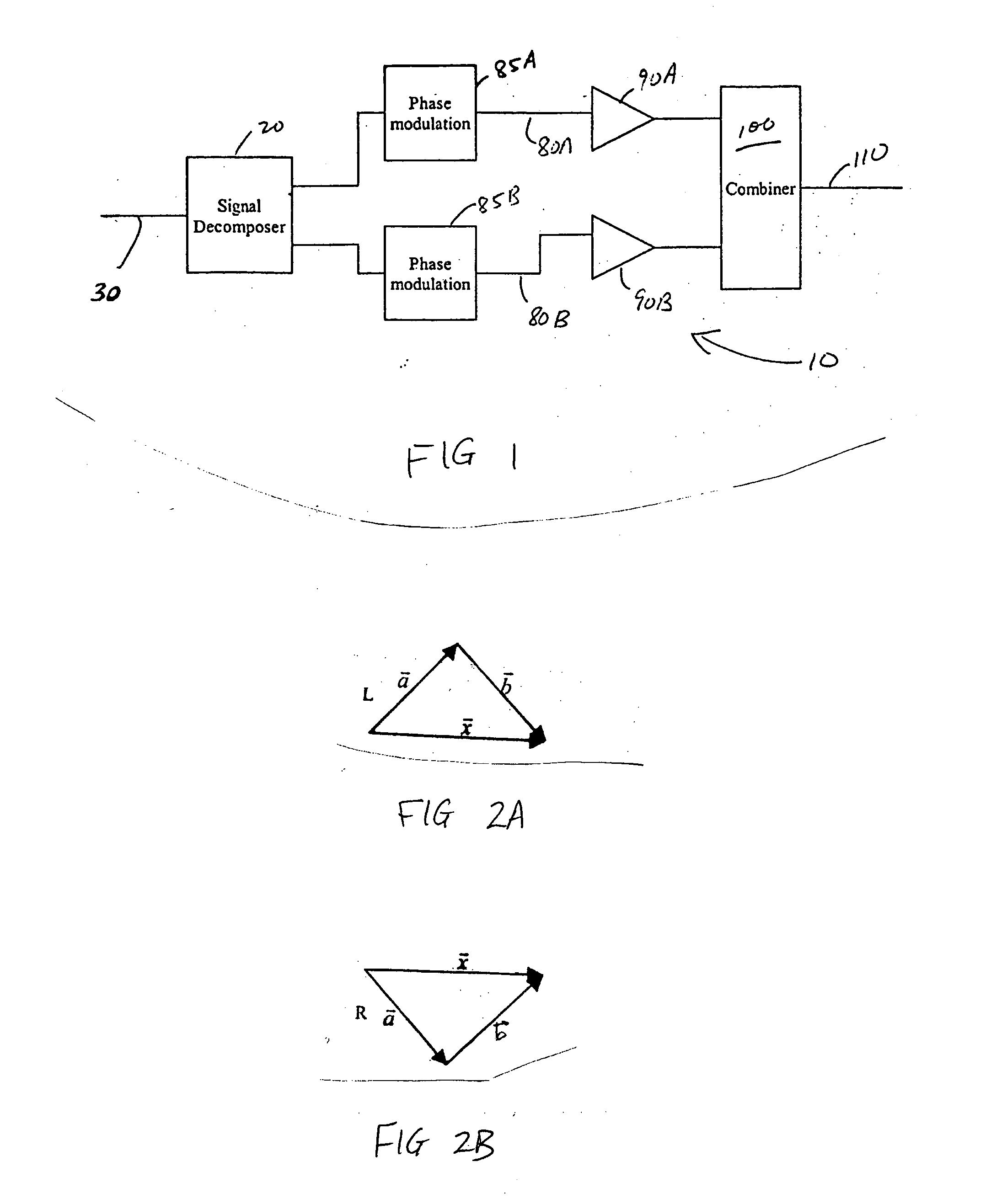
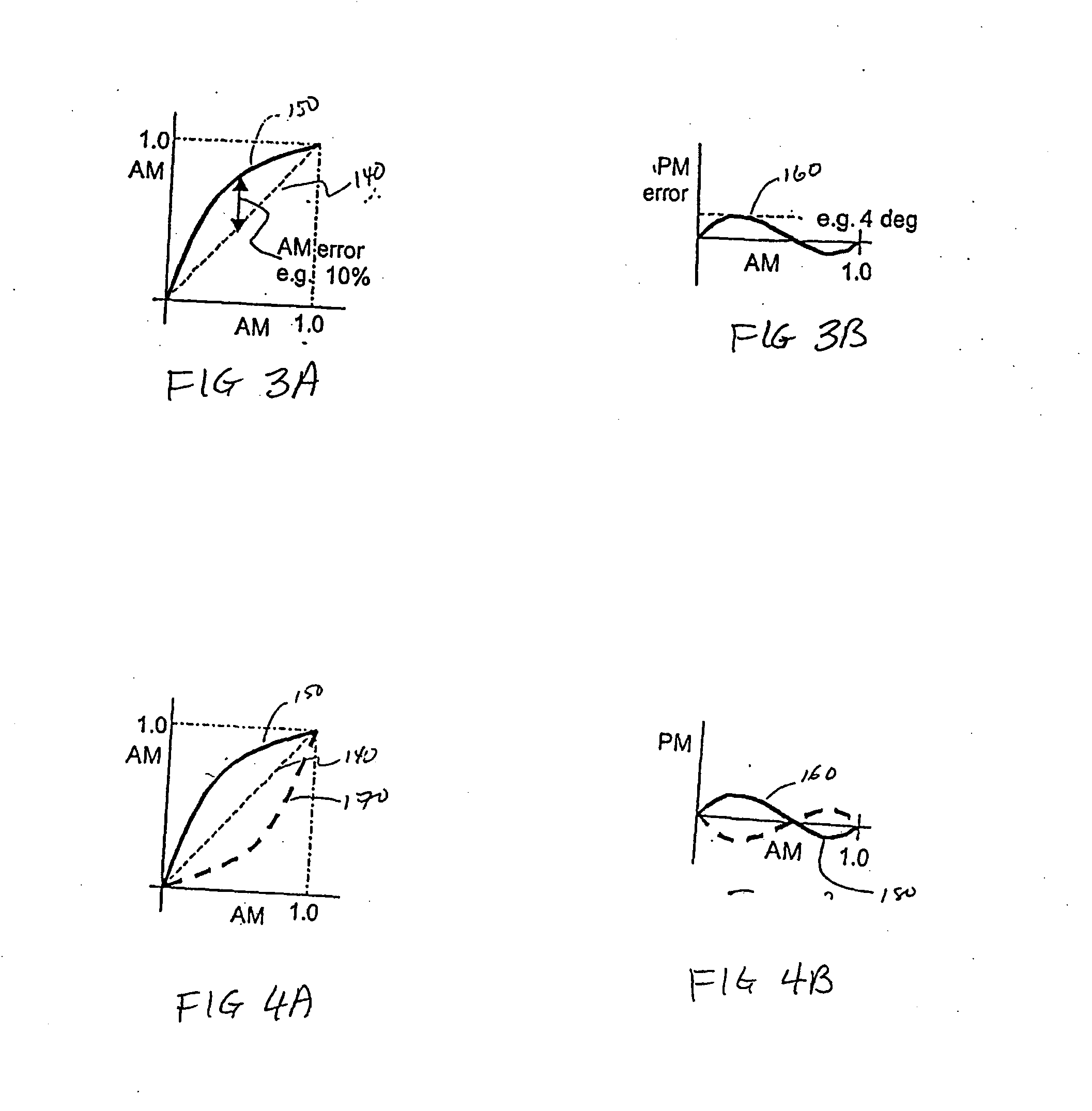
Predistortion circuit for a transmit system
Systems and methods related to amplifier systems which use a predistortion subsystem to compensate for expected distortions in the system output signal. A signal processing subsystem receives an input signal and decomposes the input signal into multiple components. Each signal component is received by a predistortion subsystem which applies a predistortion modification to the component. The predistortion modification may be a phase modification, a magnitude modification, or a combination of both and is applied by adjusting the phase of the fragment. The predistorted component is then separately processed by the signal processing subsystem. The processing may take the form of phase modulation and amplification. The phase modulated and amplified components are then recombined to arrive at an amplitude and phase modulated and amplified output signal. The predistortion modification is applied to the components to compensate for distortions introduced in the signal by the signal processing subsystem.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Signal conditioning circuit between an optical device and a processing unit
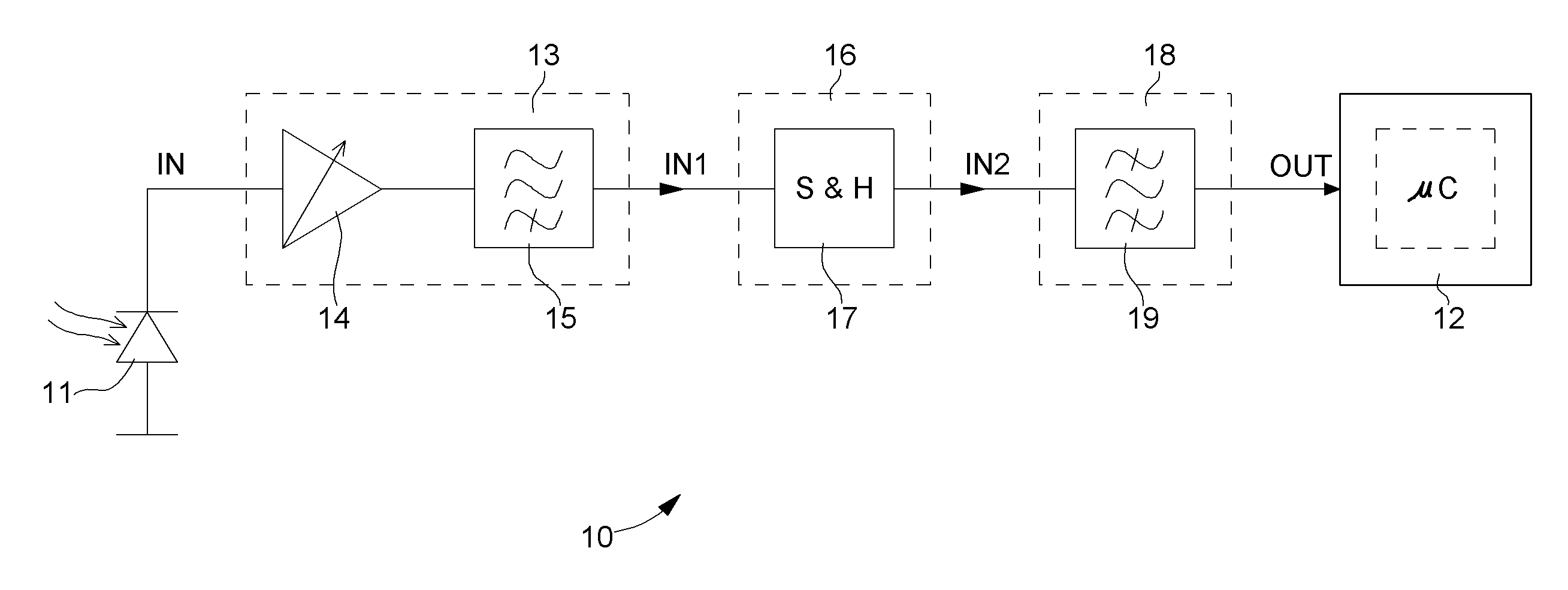
ActiveUS20070213020A1CatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal conditioning circuitsBandpass filtering
The invention concerns a conditioning circuit (10) for an external signal (IN) representative of a physiological quantity, arranged between an optical sensor (11) and a processing unit (12), the received external signal (IN) being broken down into a useful component and an ambient component, characterized in that the conditioning circuit includes a first stage (13) including a transimpedance amplifier with an incorporated high pass filter (15) using a feedback loop to subtract the ambient signal component from the received external signal, and to deliver at output an amplified useful signal (IN1), a second stage (16) including a blocker sampler circuit (17) for demodulating the amplified useful signal and delivering at output a demodulated useful signal (IN2), and a third stage (18) including a bandpass filter (19) for filtering the demodulated useful signal in the frequency band of the physiological quantity to be detected and for transmitting a conditioned signal (OUT) to the processing unit.
Owner:EM MICROELECTRONIC-MARIN
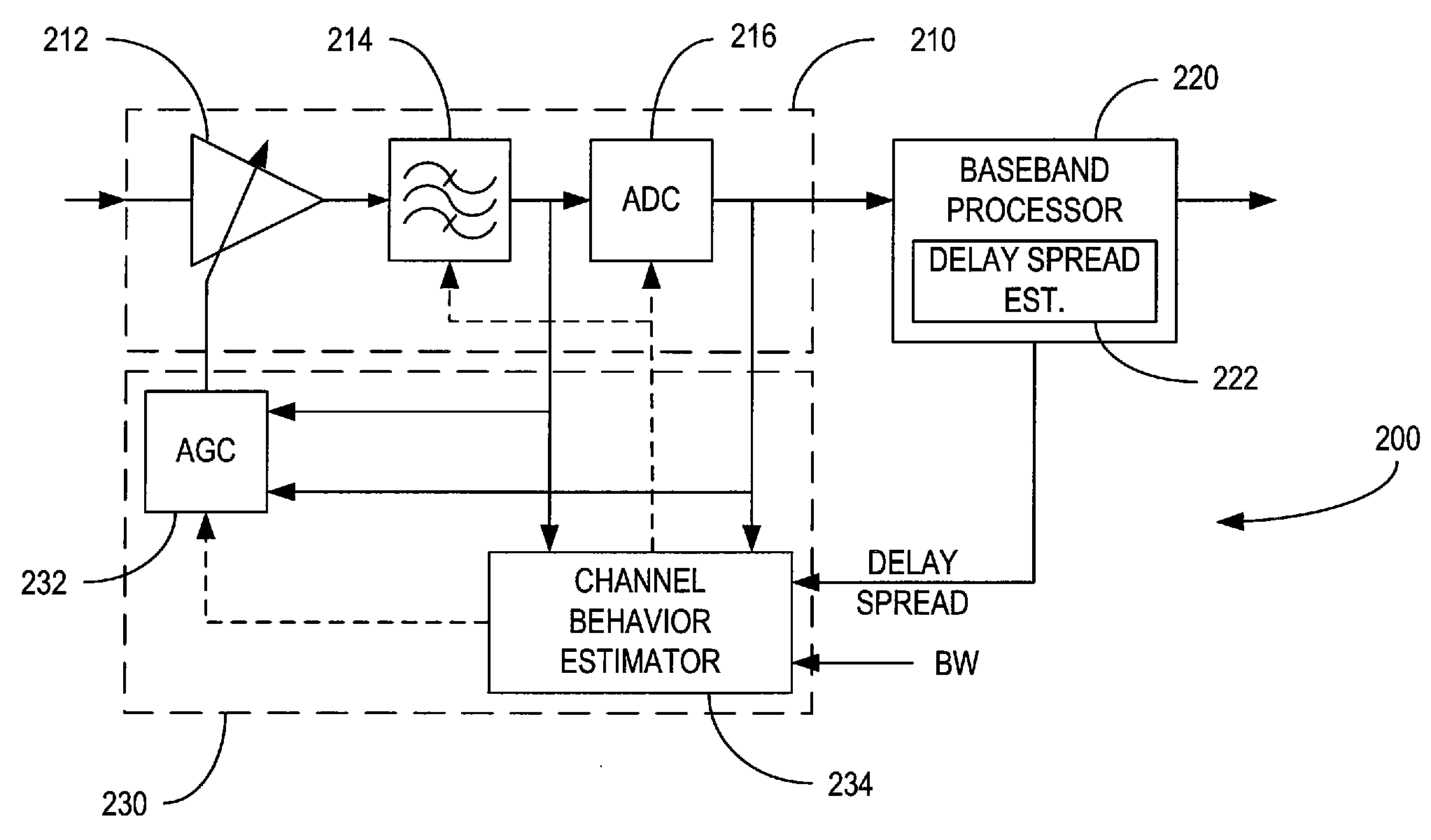
Automatic Gain Control Based on Bandwidth and Delay Spread
ActiveUS20100189203A1Dynamic range is efficientlyAmount of signal variationGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDelay spreadEngineering
A gain control circuit adjusts the signal level of a received signal responsive to the bandwidth a received signal and / or the delay spread of the channel in which the signal has propagated. The bandwidth and delay spread are evaluated to estimate the amount of signal variation that is expected due to fast fading. Adjustments to the signal level are then made to avoid clipping while at the same time ensuring that the dynamic range of a receiver component is efficiently utilized.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and apparatus for adaptively controlling signals
ActiveUS20070254592A1Enhance peak reductionReduce peakModulated-carrier systemsGain controlSignal qualityFrequency spectrum
A signal processing system according to various aspects of the present invention includes an excursion signal generator, a scaling system and a filter system. The excursion signal generator identifies a peak portion of a signal that exceeds a threshold and generates a corresponding excursion signal. The scaling system applies a real scale factor to contiguous sets of excursion samples in order to optimize peak-reduction performance. The filter system filters the excursion signal to remove unwanted frequency components from the excursion signal. The filtered excursion signal may then be subtracted from a delayed version of the original signal to reduce the peak. The signal processing system may also control power consumption by adjusting the threshold. The signal processing system may additionally adjust the scale of the excursion signal and / or individual channel signals, such as to meet constraints on channel noise and output spectrum, or to optimize peak reduction. The magnitude threshold, excursion signal and / or individual channel signals may also be adaptively adjusted based on, for example, a channel signal quality such as a noise level specification.
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Transceiver with Receive Path Performance Diversity and Combiner with Jammer Detect Feedback
Methods and apparatus for implementing a wireless communication transceiver having receive path performance diversity. The transceiver implements a plurality of signal paths that can be configured as diversity receive paths. Each of the plurality of signal paths includes a distinct RF filter. Each RF filter can be configured to provide a distinct jammer rejection profile. Each receive path also includes a jammer detector, that can be a multiple level jammer detector. Each jammer detector operates to control a level of processing gain applied to the signals in its receive path. The multiple gain scaled receive signals can be combined in a coherent combiner before being routed for further processing.PATENT
Owner:MONUMENT BANK OF INTPROP LLC
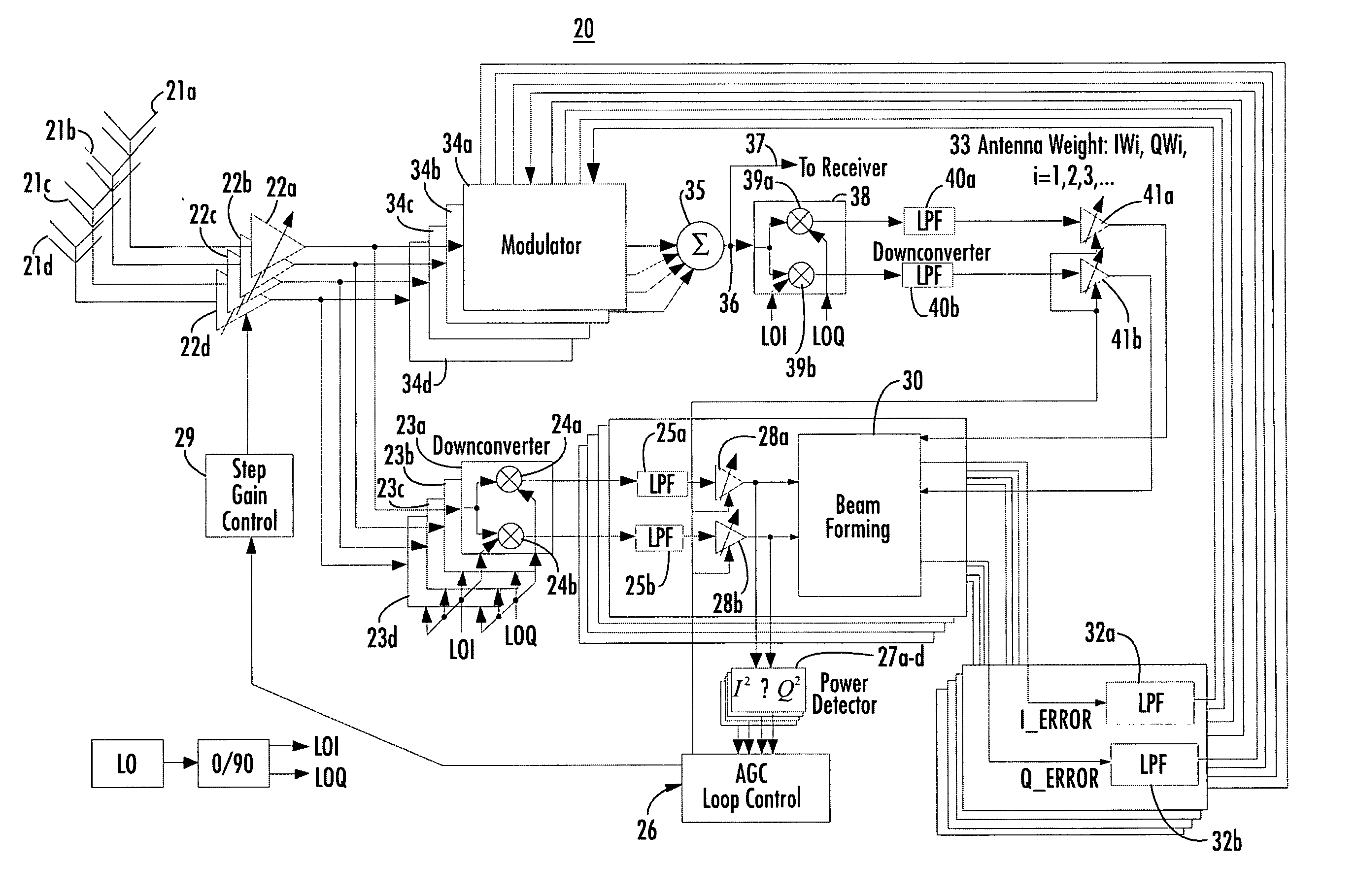
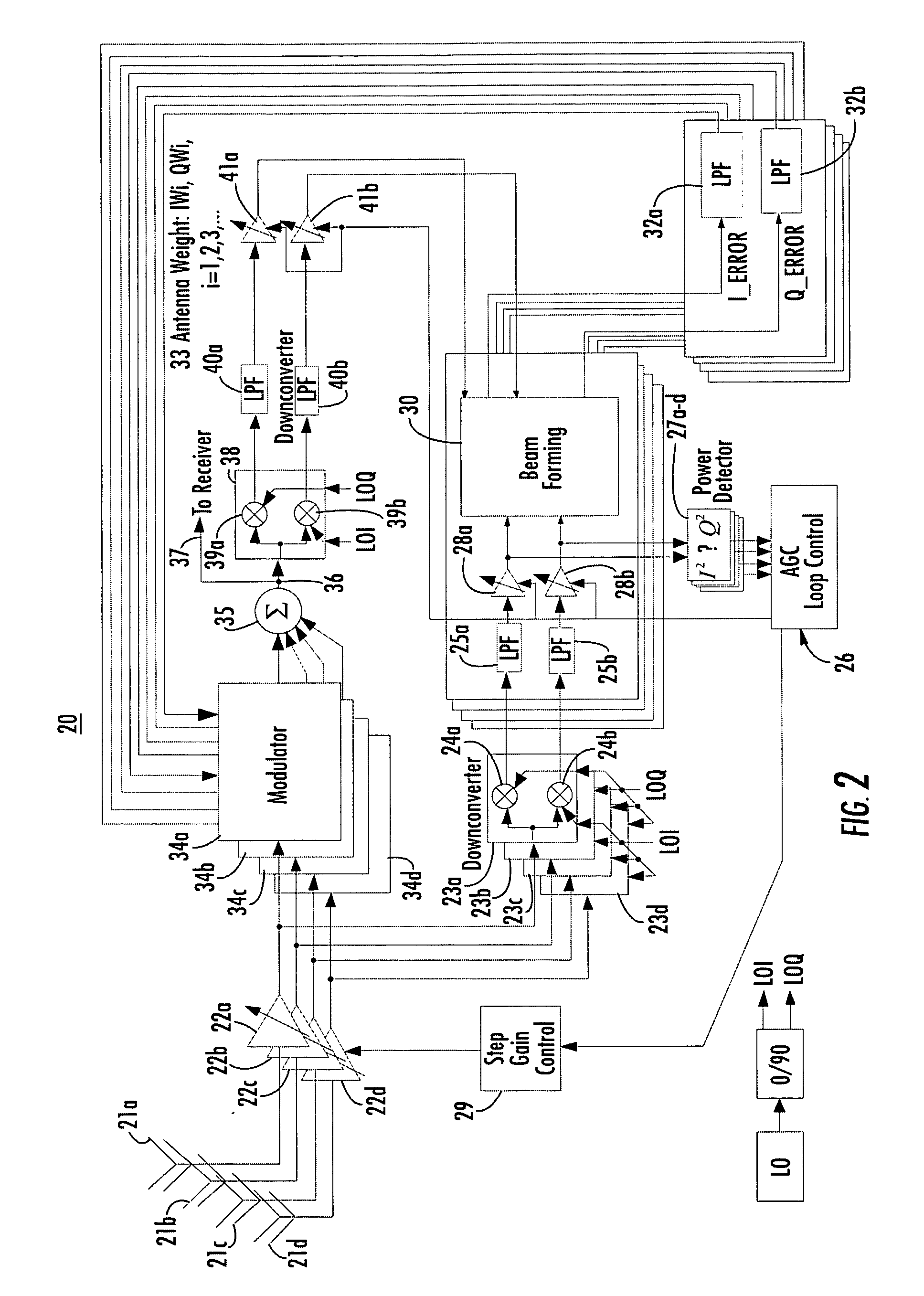
Wireless communication system using a plurality of antenna elements with adaptive weighting and combining techniques
InactiveUS20060135097A1Simple interfaceMaintain sensitivityEnergy efficient ICTSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemAdaptive weighting
The present invention provides a method and system for operating a wireless communication system in which received signals from a plurality of antennas are weighted and combined with a beam forming operation to form an output signal. The beam forming operation determines weights adjusted to increase a desired signal power in the output signal while reducing the power in the output signal of out-of-band components. In an embodiment of the present invention, beam forming operations are performed with maximal ratio combining (MRC). Alternatively, a constant modulus algorithm (CMA) can be used for beam forming operations. In an alternate embodiment, improved interference suppression is performed with a novel algorithm referred to as an interference nulling algorithm (INA). The INA receives an error signal which is 180° out of phase with a combination of the channels for individual antennas, referred to as the SUM channel. The error signal is determined by complex conjugate multiplication of the individual signals and a reference complex signal. It is desirable to simultaneously achieve diversity and combining gain and suppress the adjacent channel by combining the weight generation for MRC and that for INA, as described above, to generate antenna weights similar to those of MMSE combining.
Owner:RENDA TRUST
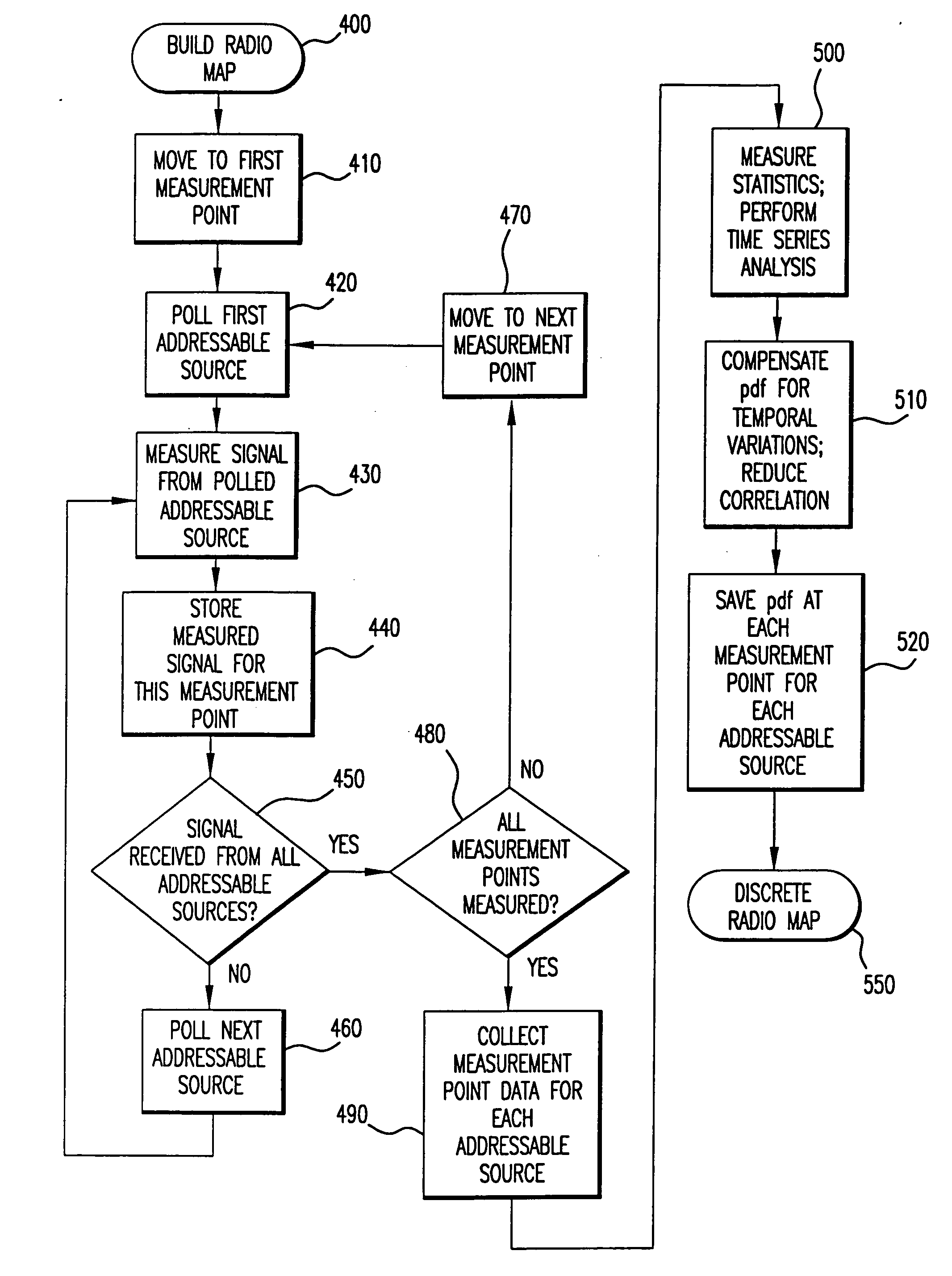
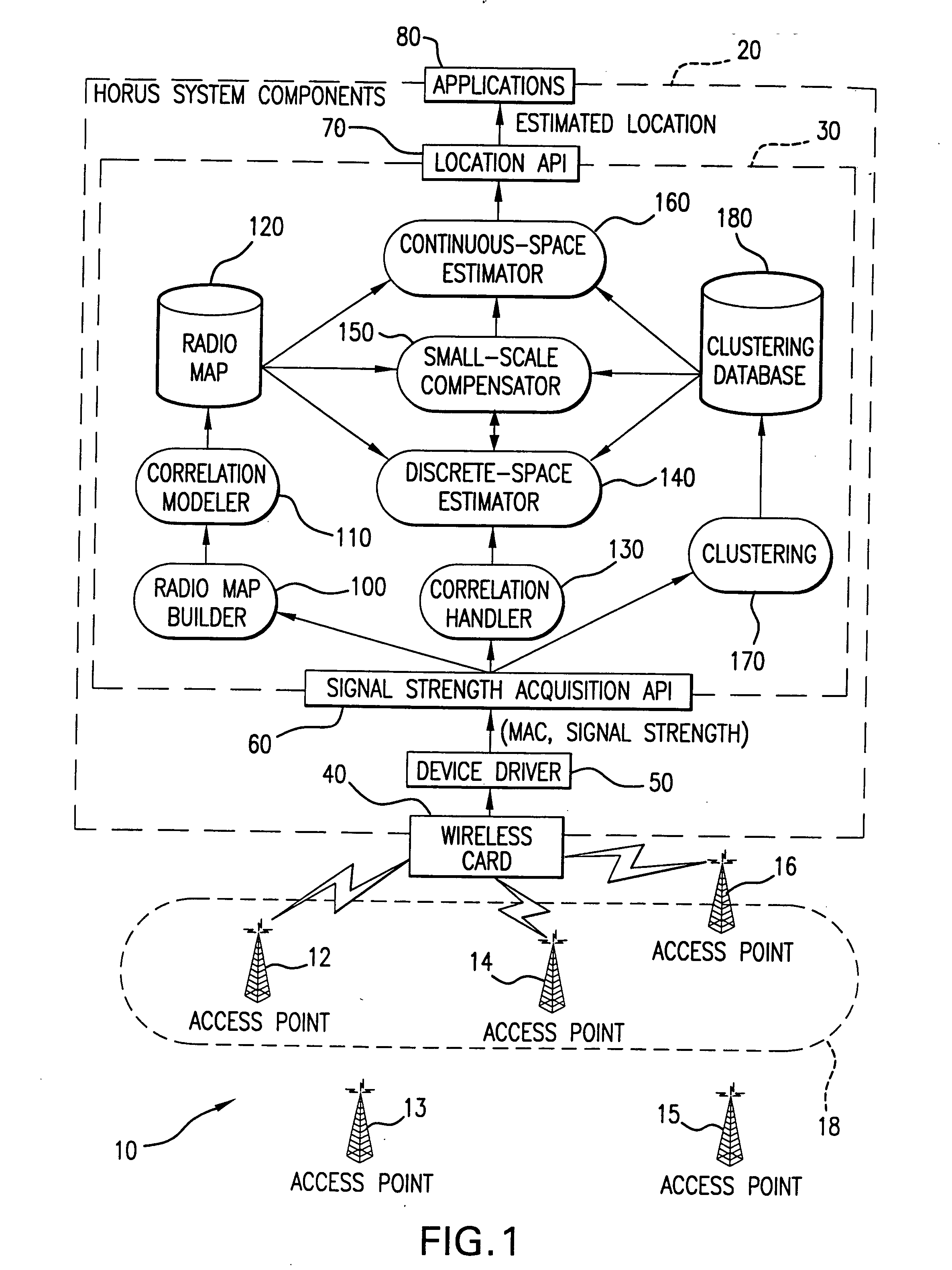
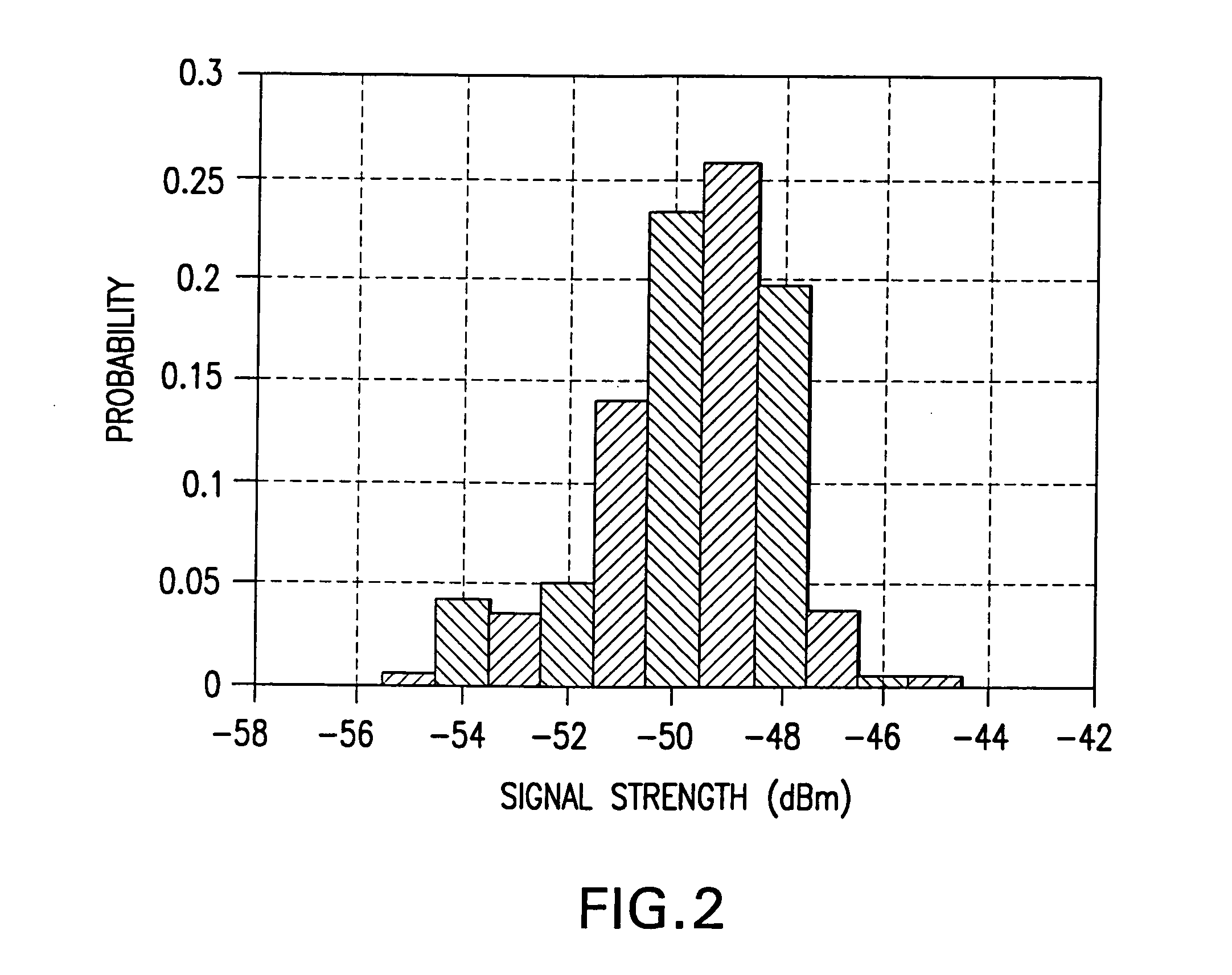
Method and system for determining user location in a wireless communication network
InactiveUS20050243936A1Maximize probabilityAccurate measurementData switching by path configurationSatellite radio beaconingProbit modelRadio map
In a wireless communication network, the location of an addressable receiver relative to the locations of a plurality of addressable sources of electromagnetic radiation is found using probabilistic models of the signal strength measured at the addressable receiver. The inventive method provides location determination on a finer spatial scale than was heretofore available. A region of interest is calibrated via a discrete-space radio map storing probability distributions of received signal strength at the measurement locations. The stored probability distributions are compensated for temporal variability and biases, such as through temporal correlations of the sampled received signal strength. A measurement of the signal strength at the addressable receiver from each of the plurality of addressable sources is used in conjunction with the discrete-space radio map to identify one of the coordinates thereof that maximizes the conditional probability P(x|s), where x is the radio map location and s is a vector of measured signal strengths. Small spatial scale variability can be compensated for using a perturbation technique. The method further implements a continuous-space estimator to return an estimated user location that falls between discrete-space radio map locations.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com