Patents
Literature
570 results about "Probit model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistics, a probit model is a type of regression where the dependent variable can take only two values, for example married or not married. The word is a portmanteau, coming from probability + unit. The purpose of the model is to estimate the probability that an observation with particular characteristics will fall into a specific one of the categories; moreover, classifying observations based on their predicted probabilities is a type of binary classification model.
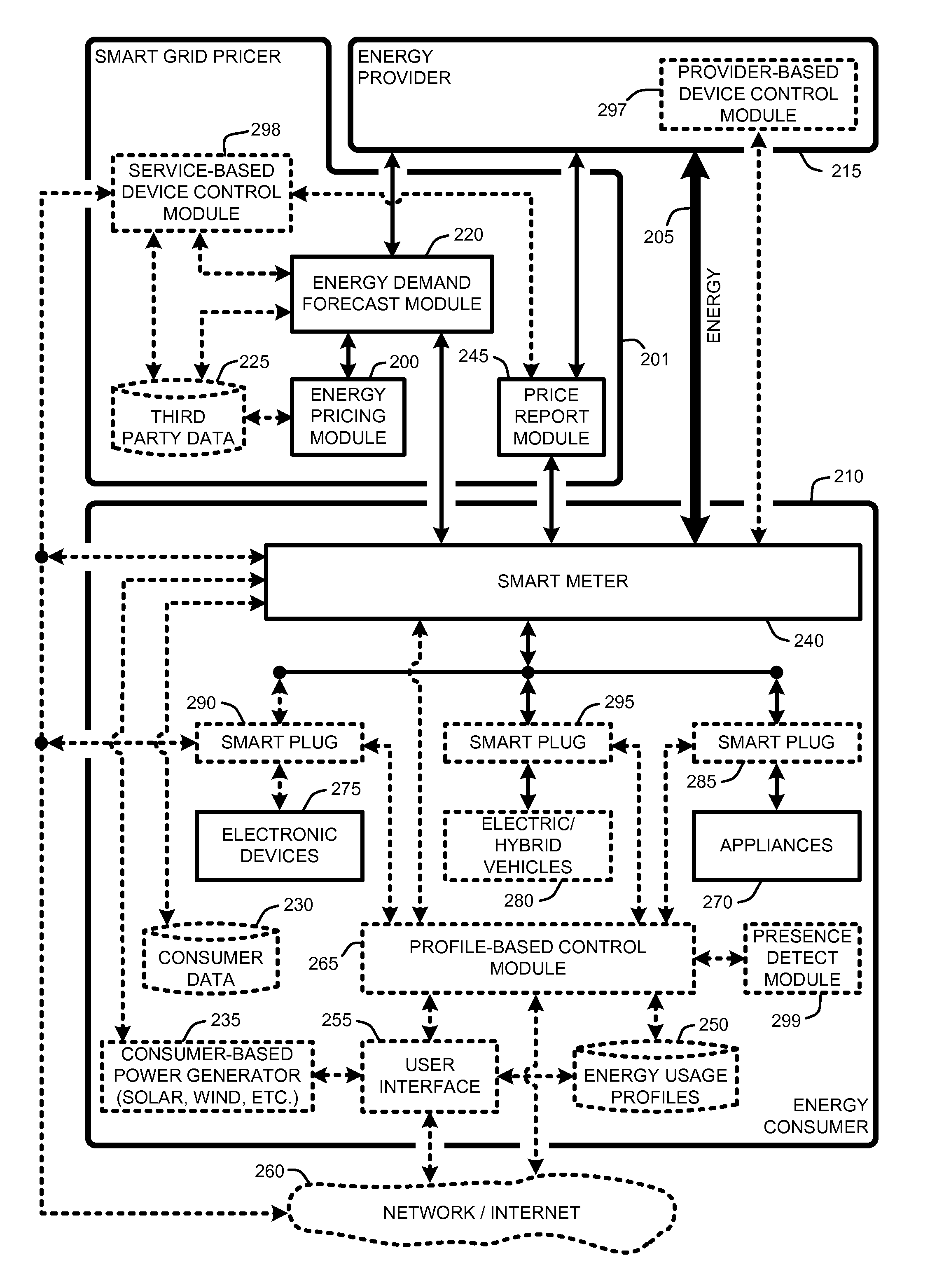
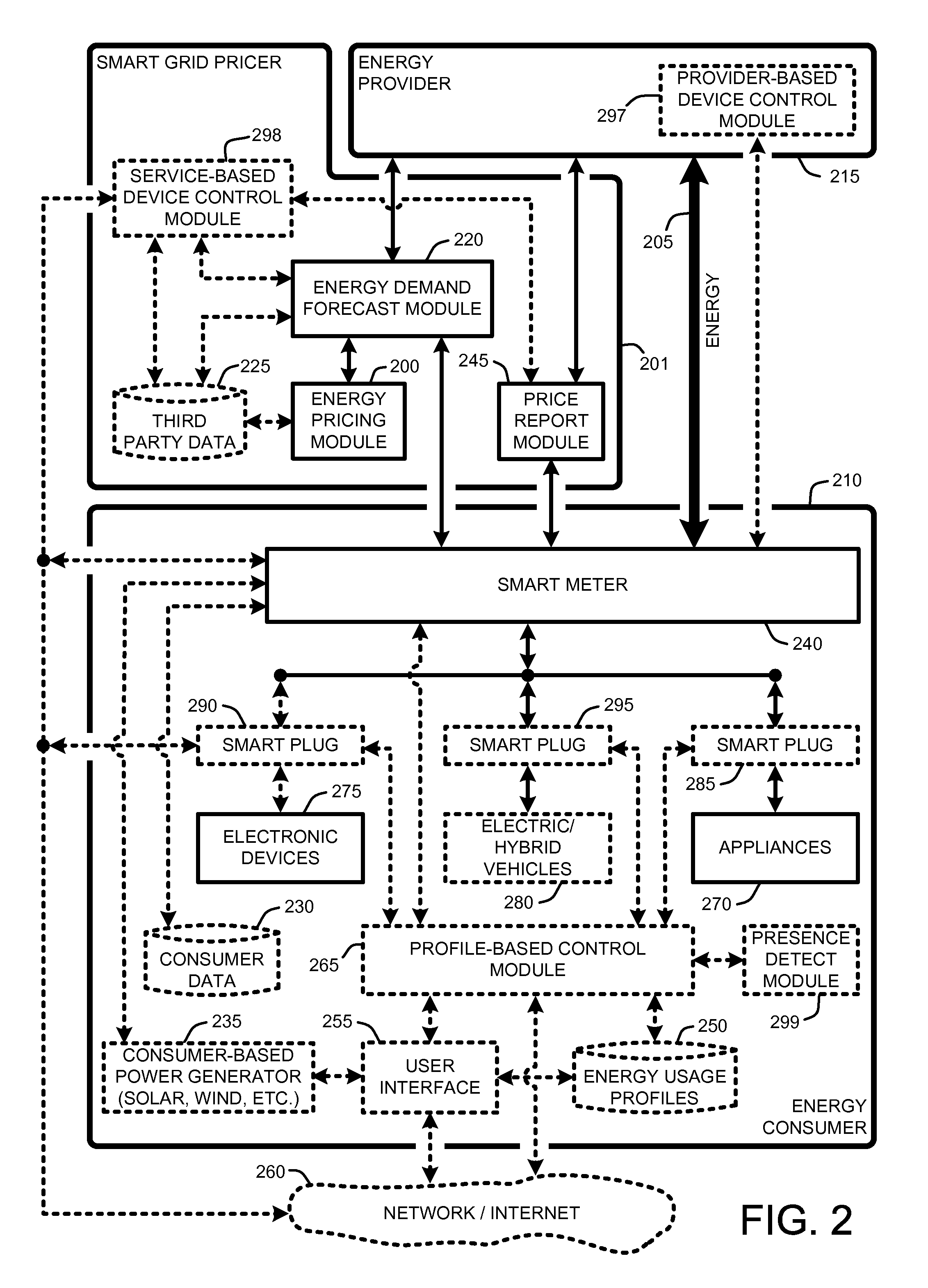
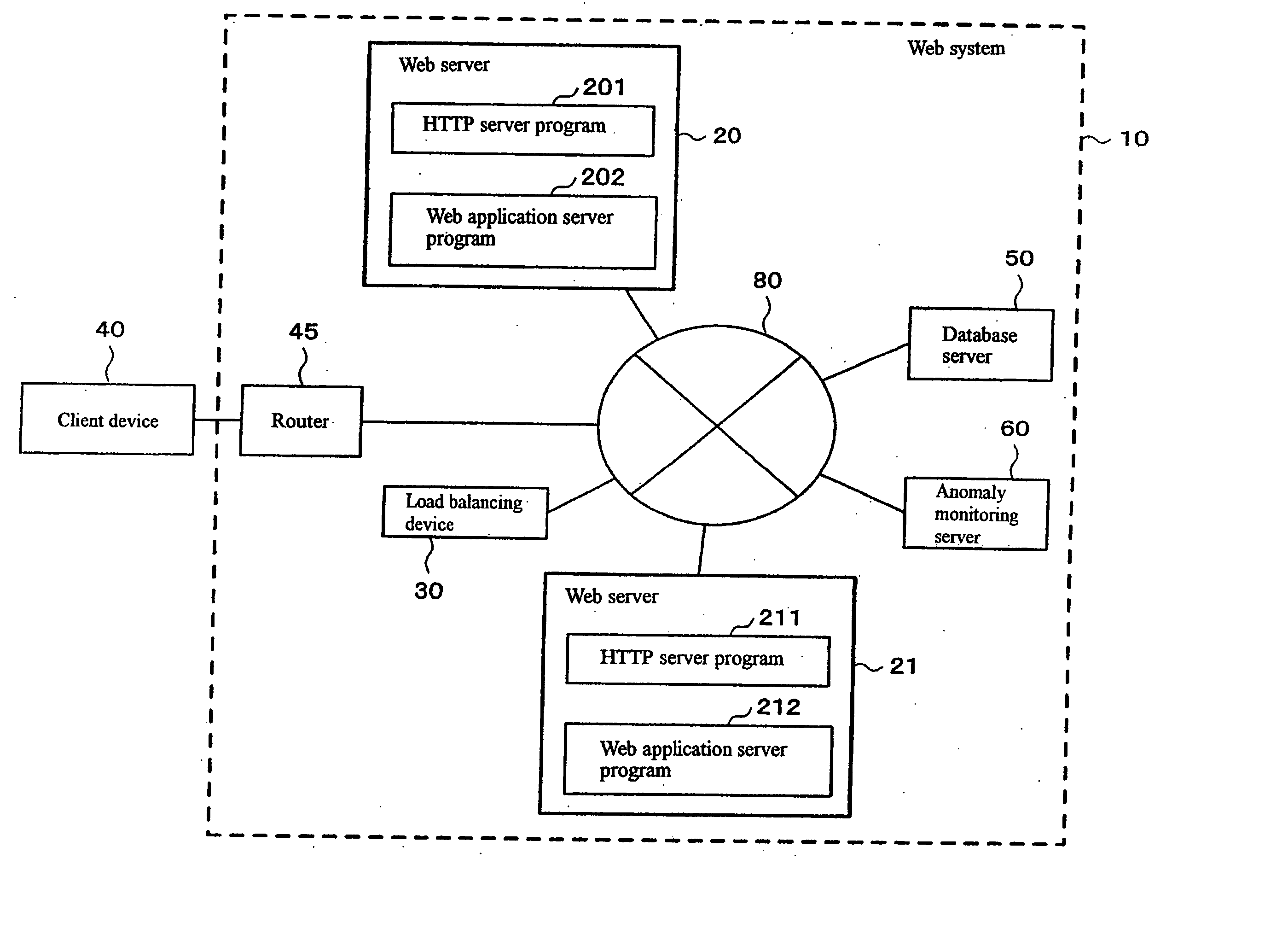
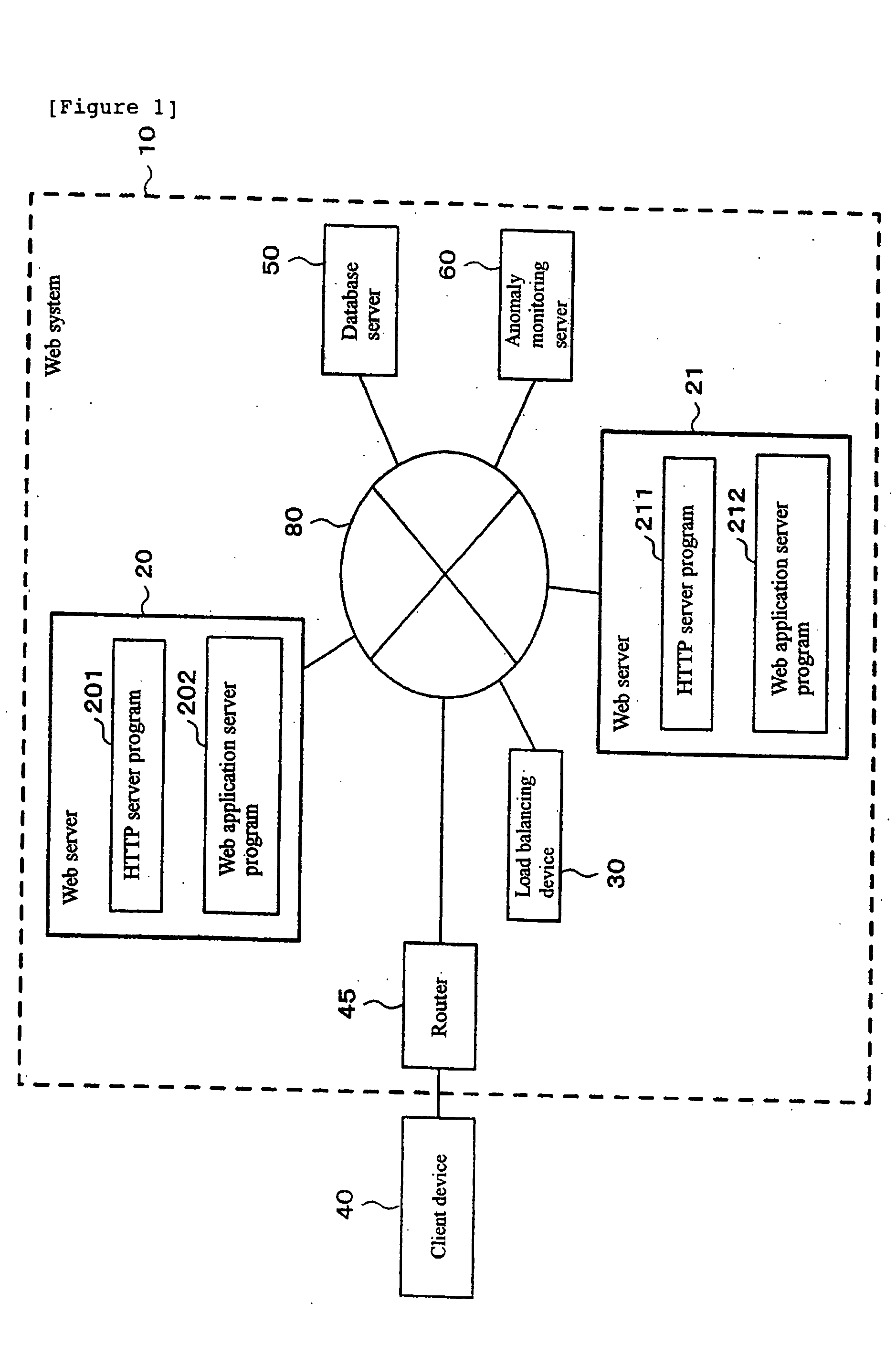
Smart grid price response service for dynamically balancing energy supply and demand
InactiveUS20100138363A1Energy consumptionReduce energy useLevel controlSpecial tariff metersProbit modelSmart grid
A “Smart Grid Pricer” enables automated balancing of the supply and demand of energy supply and consumption, such as the generation and consumption of electricity between electricity providers and electricity consumers. The Smart Grid Pricer automatically computes and delivers real-time energy pricing information to consumers on behalf of energy retailers (e.g., electricity utilities) to help drive the balance of demand with supply. In various embodiments, real-time pricing is determined by using various probabilistic models to estimate overall consumer demand as a function of factors such as energy price, time of day, region, weather, etc. to compute a price that will result in an energy demand that is closely balanced to the available supply. On the consumer side, various components of the Smart Grid Pricer automatically respond to such pricing information to optimize energy consumption in accordance with a variety of automated and / or user defined rules and preferences.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
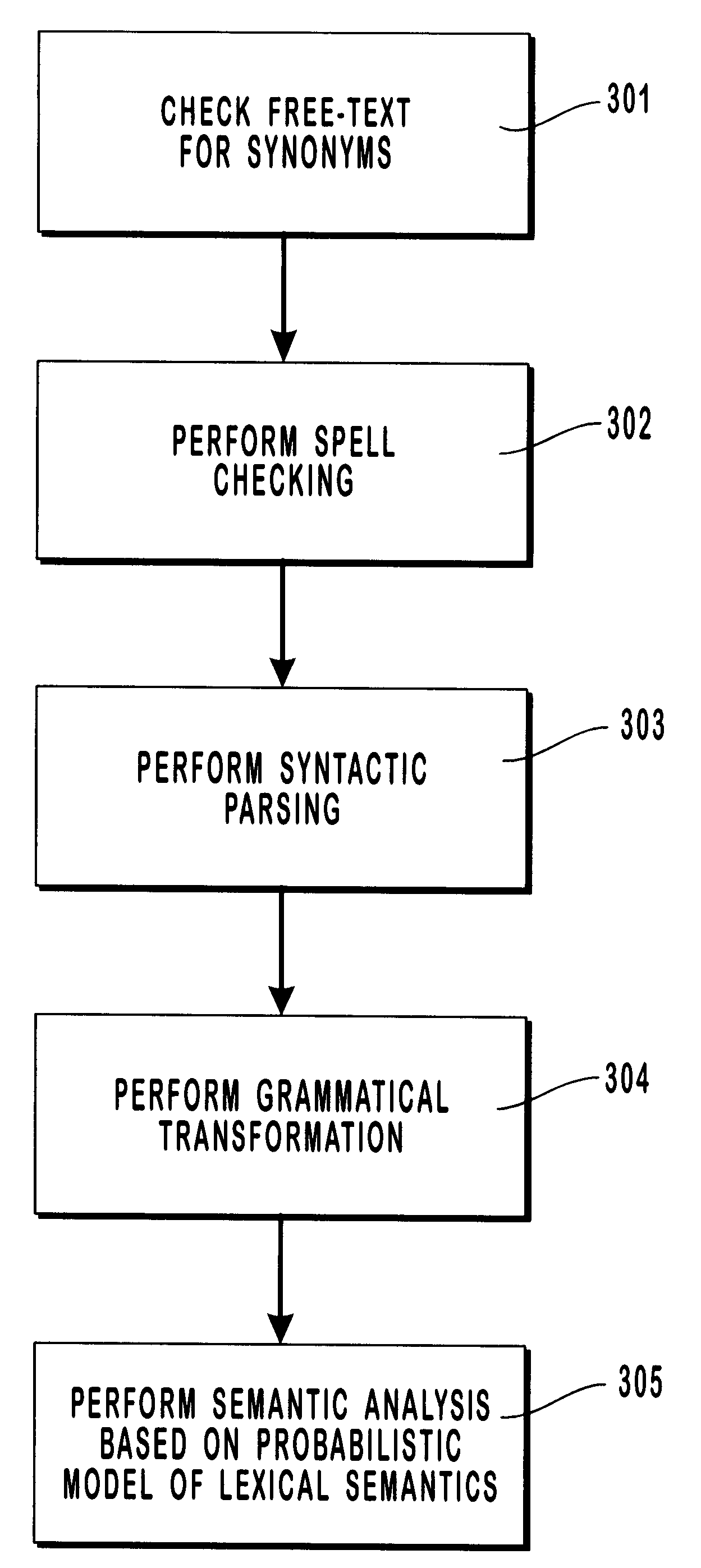
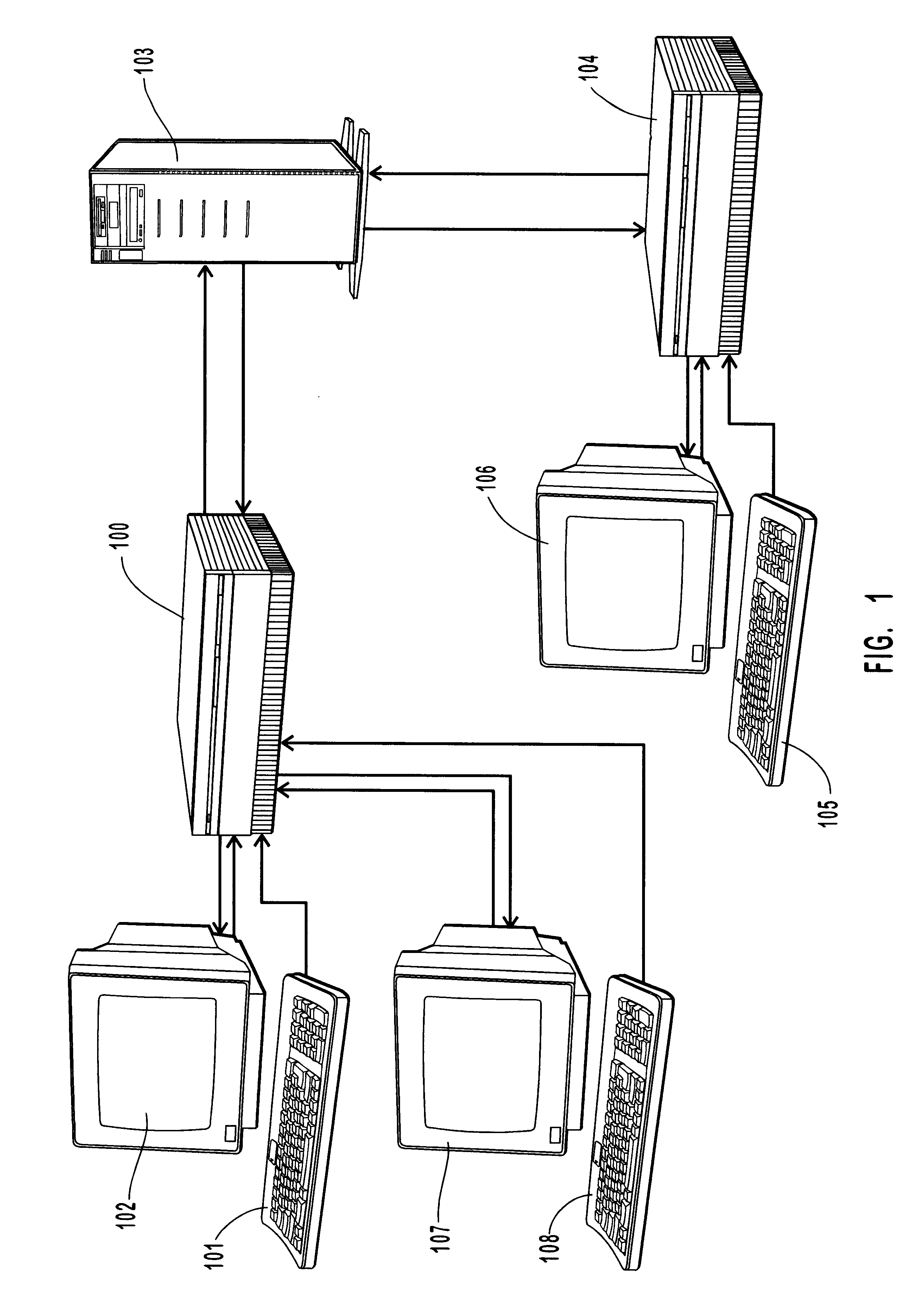
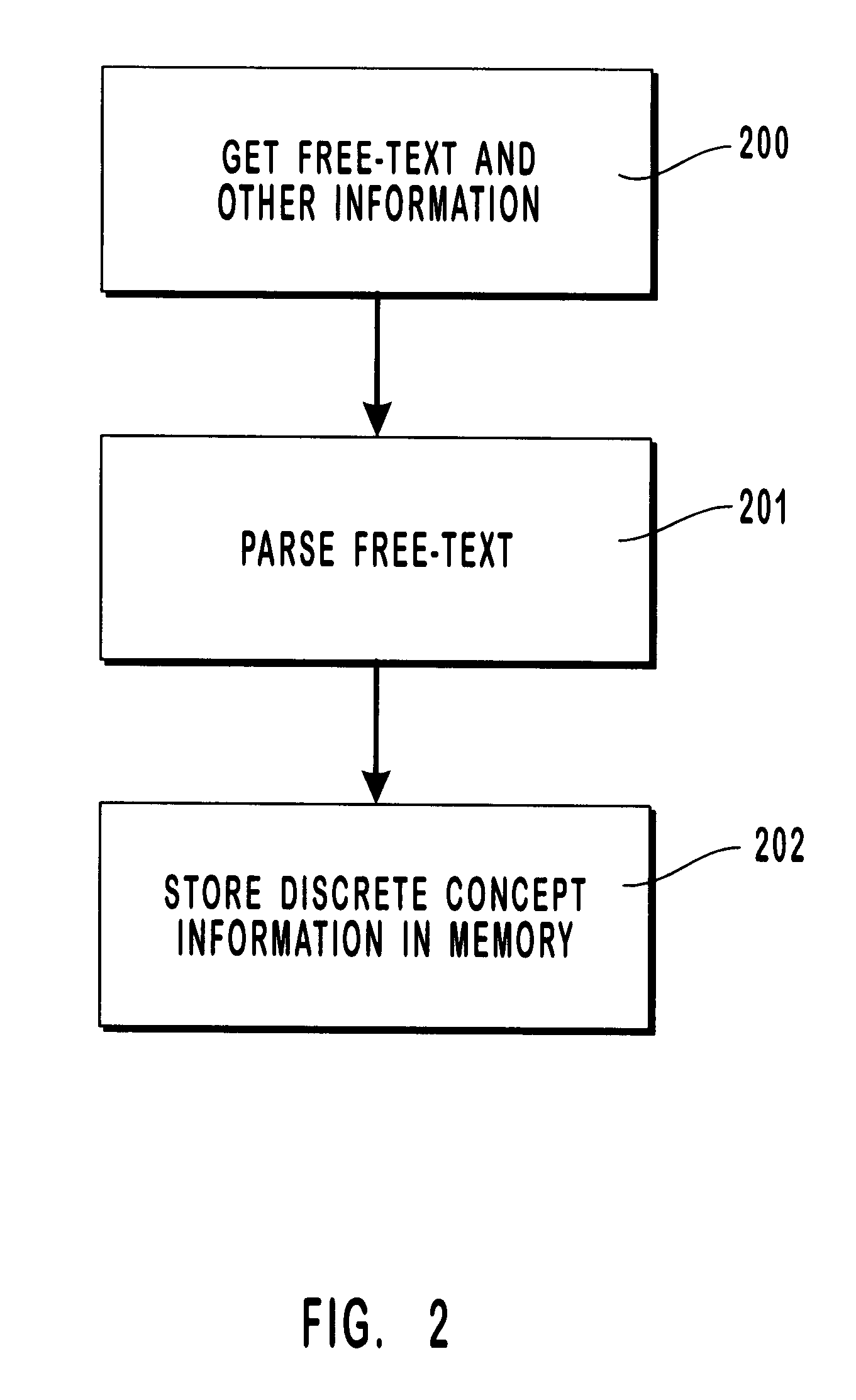
Probabilistic method for natural language processing and for encoding free-text data into a medical database by utilizing a Bayesian network to perform spell checking of words
InactiveUS6292771B1Improve accuracyAccurate identificationSemantic analysisText processingProbit modelProbabilistic method
A natural language understanding system is described which provides for the generation of concept codes from free-text medical data. A probabilistic model of lexical semantics, in the preferred embodiment of the invention implemented by means of a Bayesian network, is used to determine the most probable concept or meaning associated with a sentence or phrase. The inventive method and system includes the steps of checking for synonyms, checking spelling, performing syntactic parsing, transforming text to its "deep" or semantic form, and performing a semantic analysis based on a probabilistic model of lexical semantics. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, spell checking and transformational processing as well as semantic analysis make use of semantic probabilistic determinations.
Owner:INTERMOUNTAIN INTELLECTUAL ASSET MANAGEMENT LLC
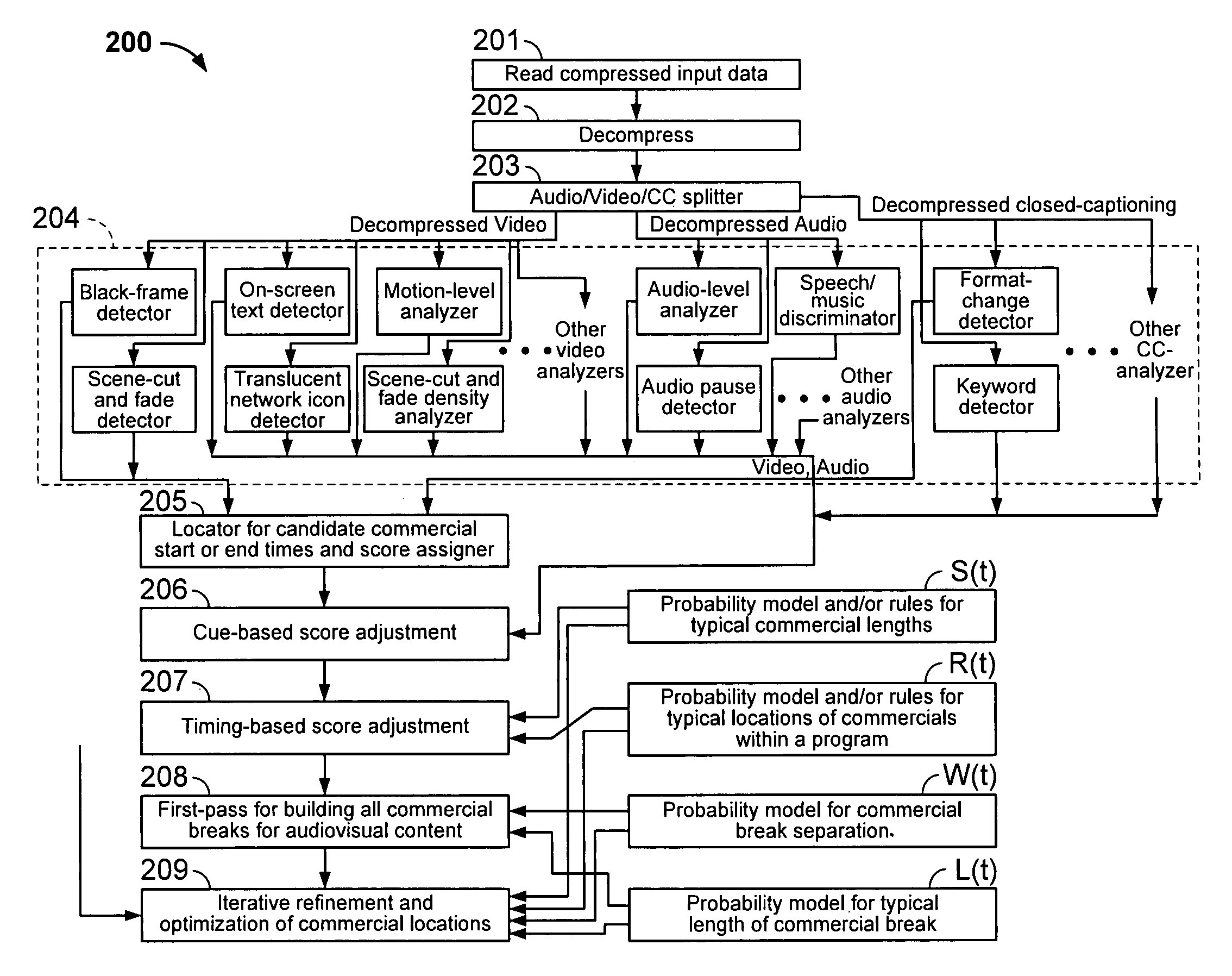
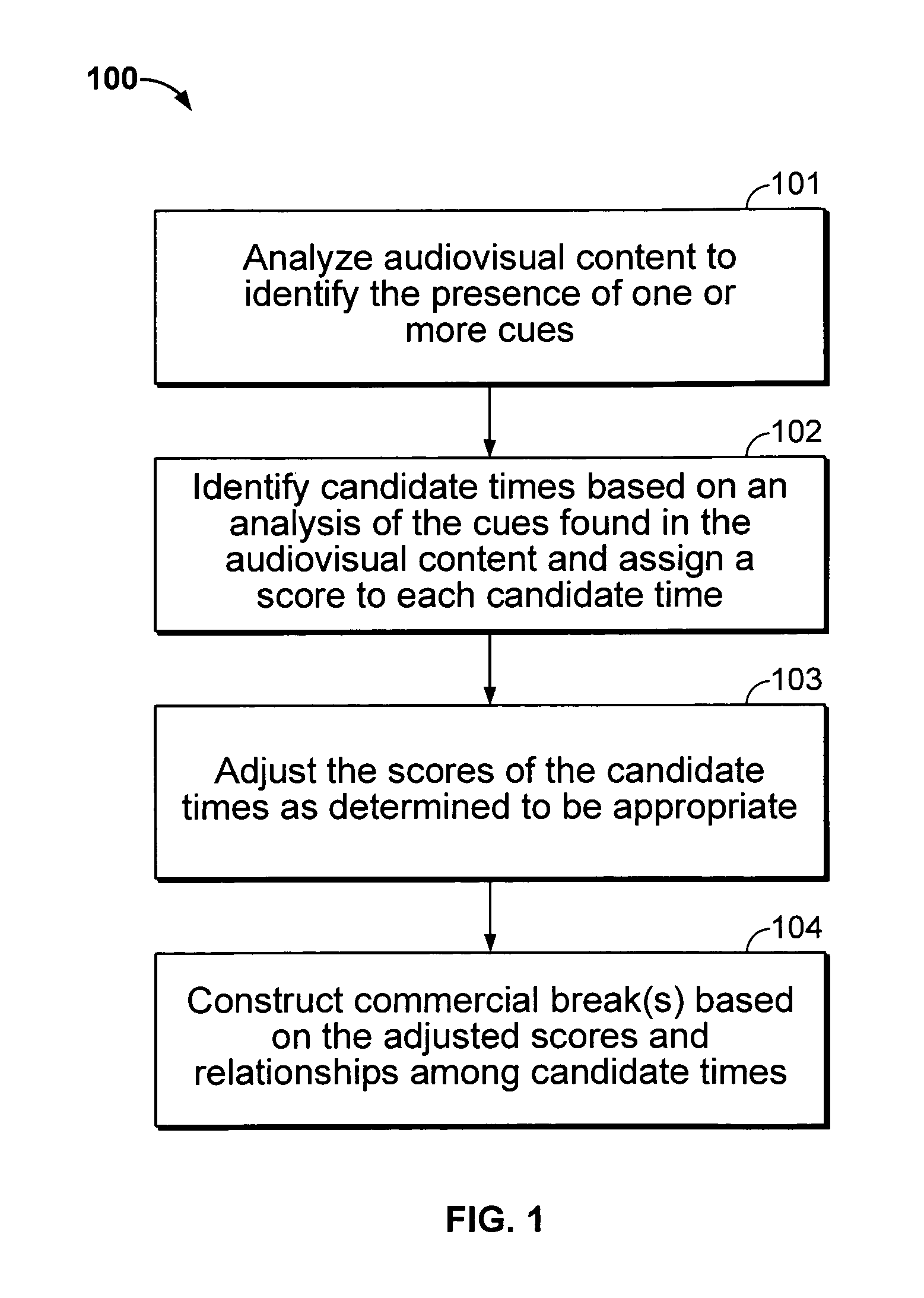
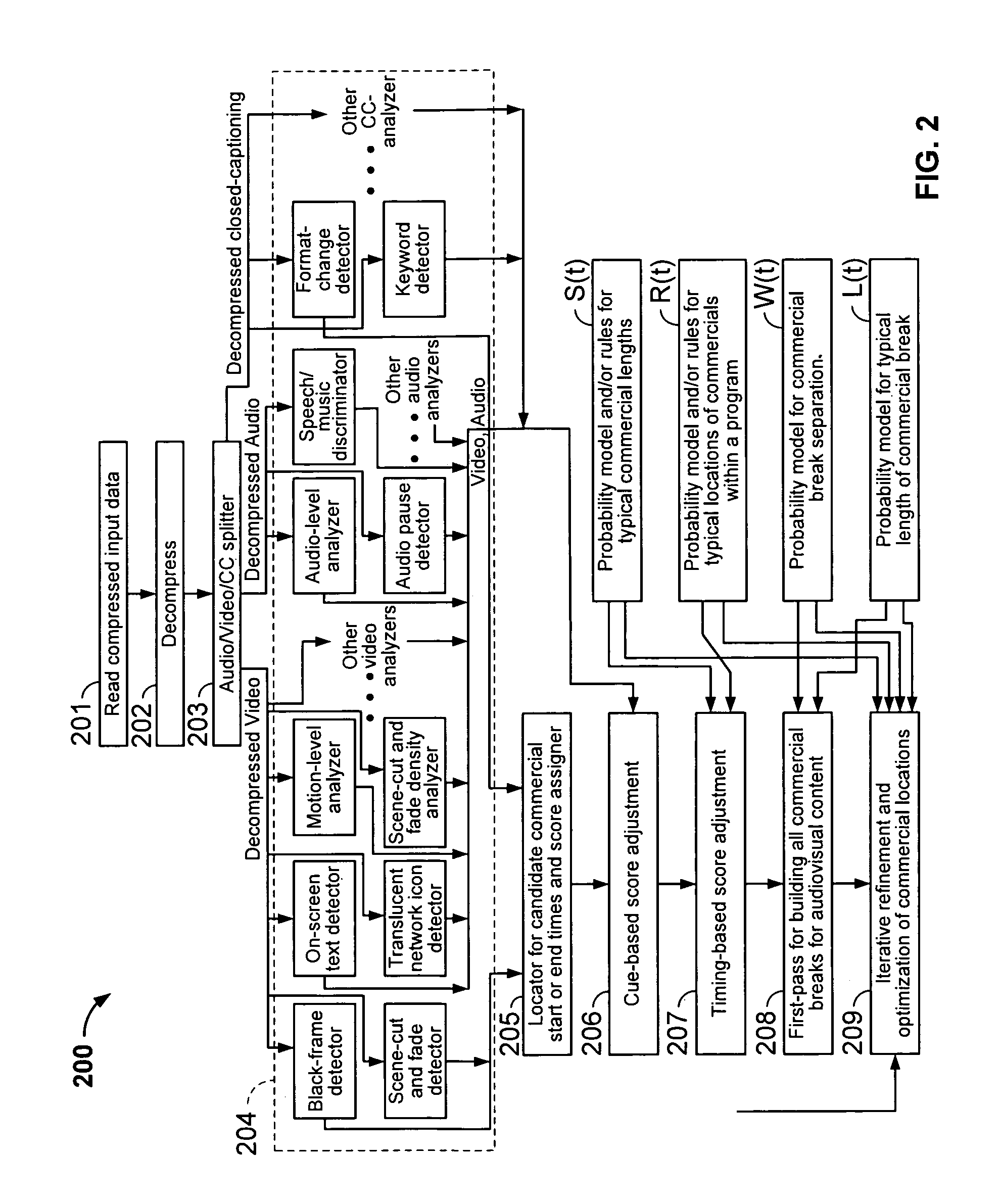
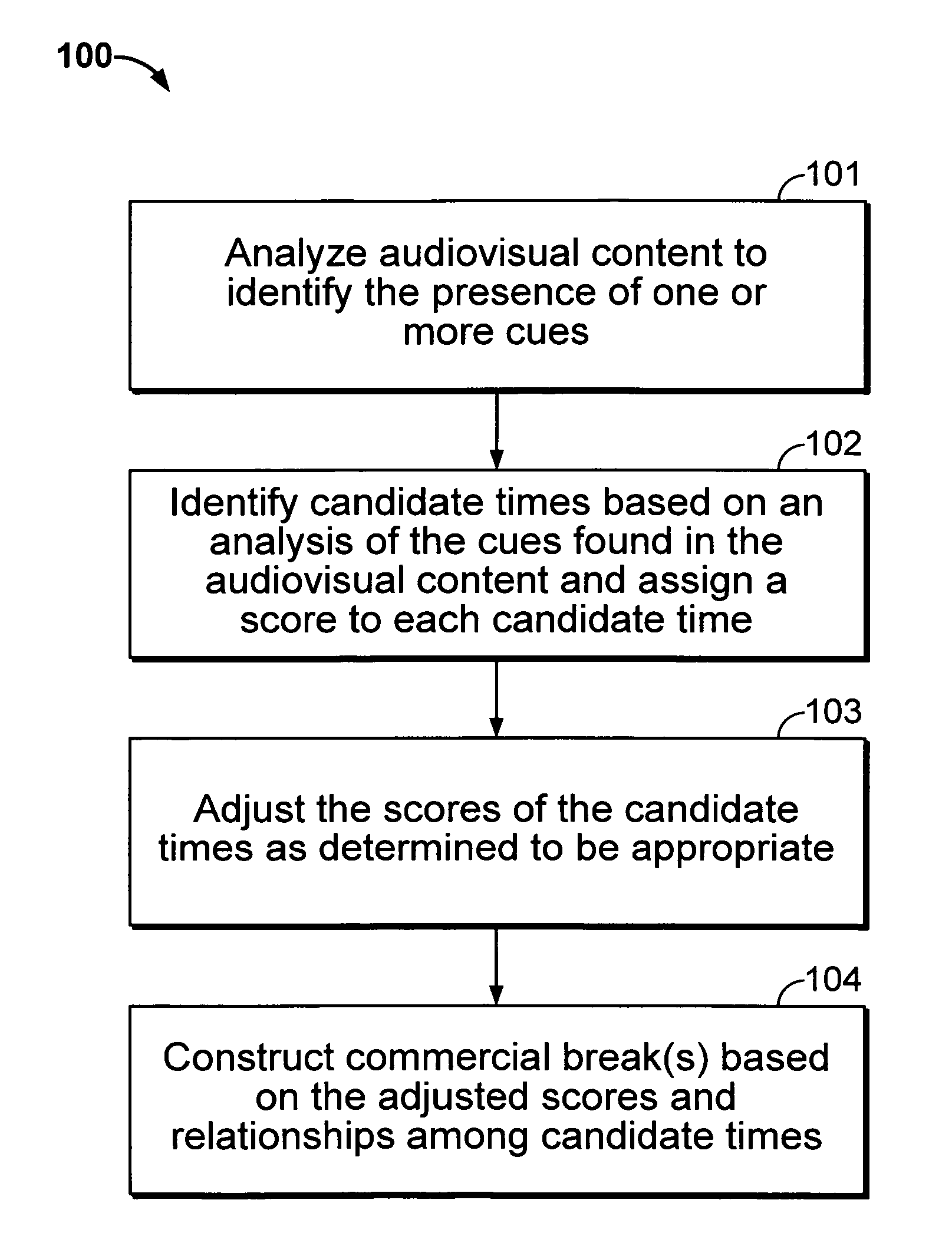
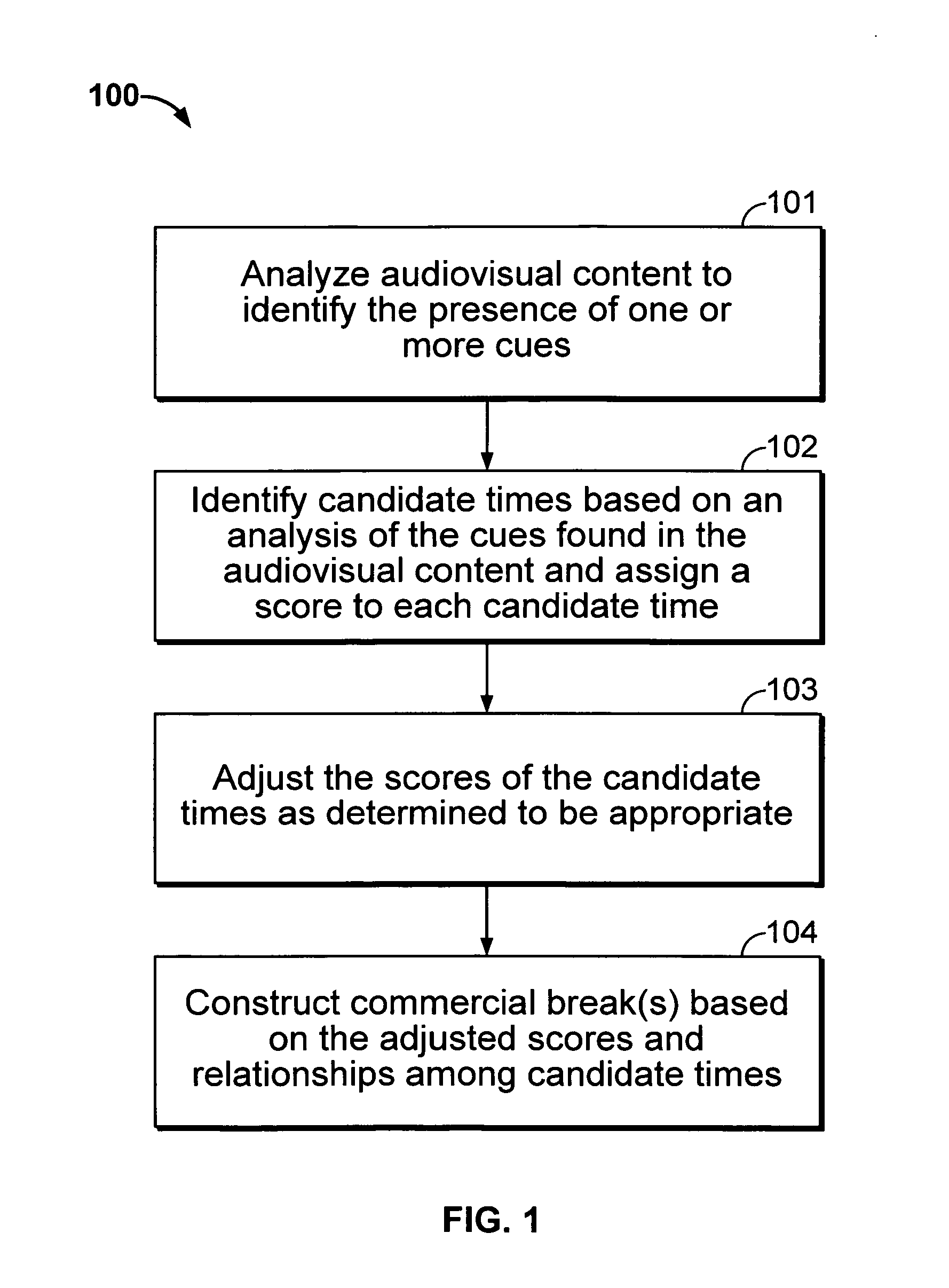
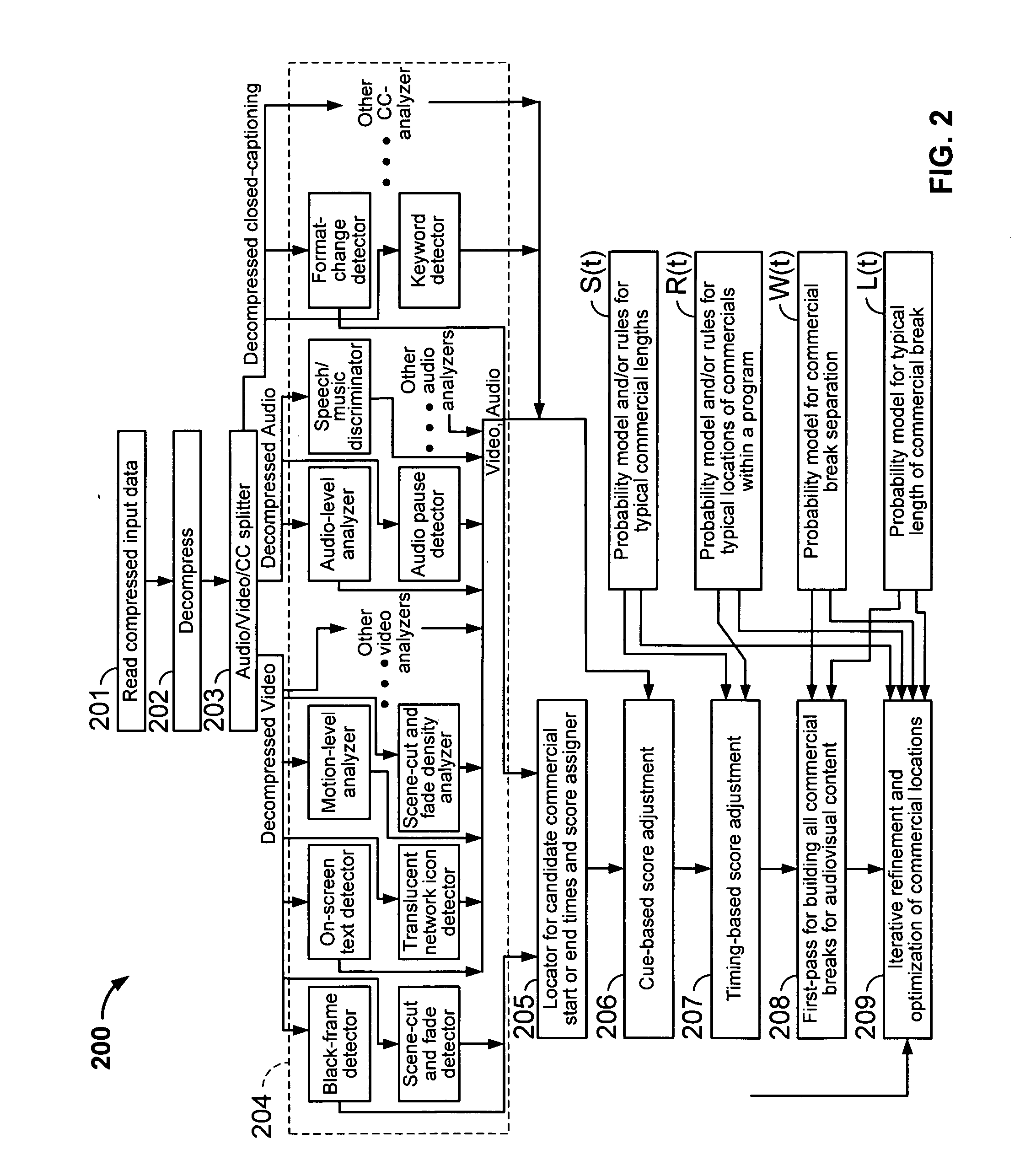
Iterative, maximally probable, batch-mode commercial detection for audiovisual content
InactiveUS6993245B1Improve accuracyPromote resultsTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsProbit modelLocation detection
Owner:INTERVAL RESEARCH CORPORATION
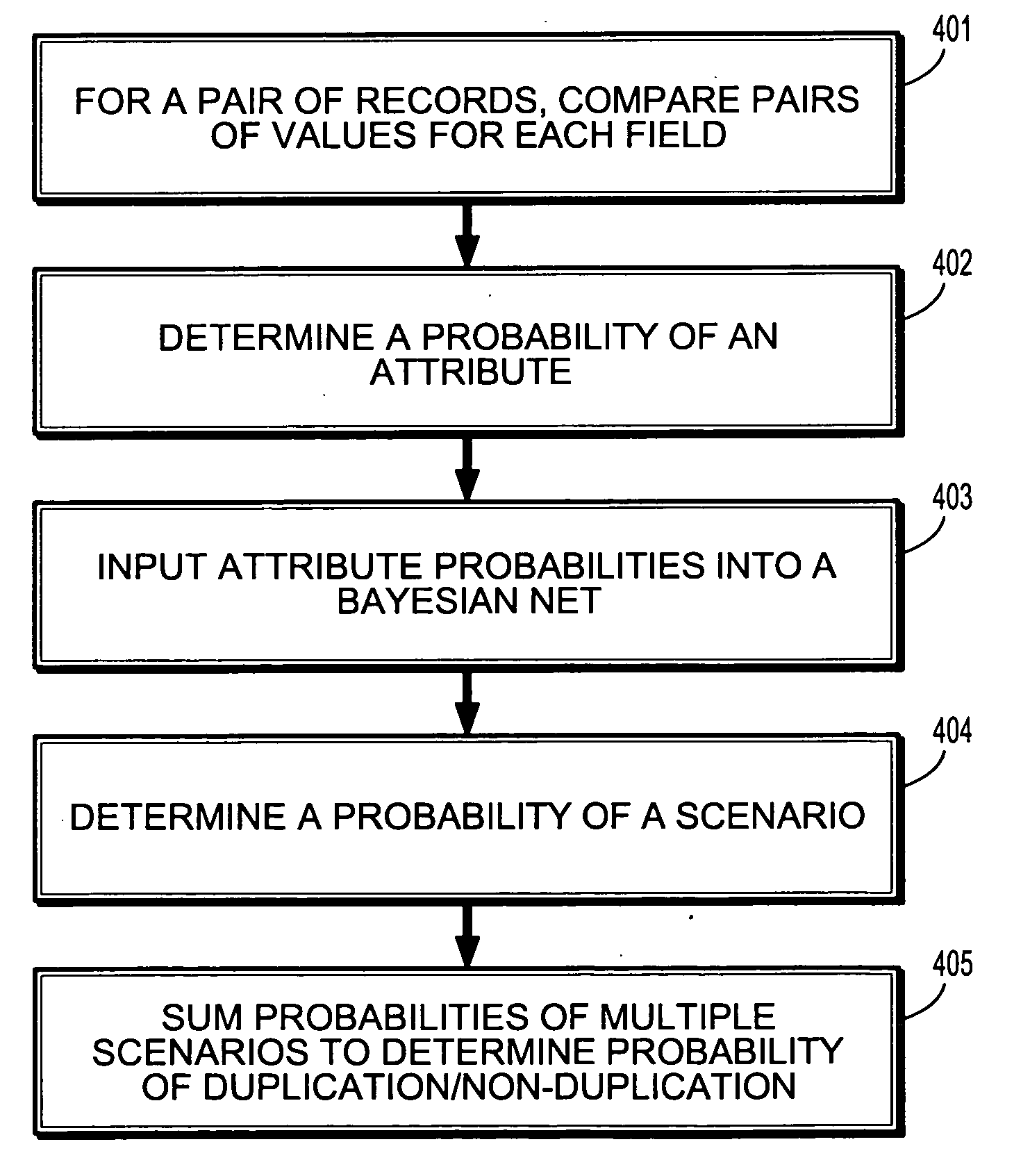
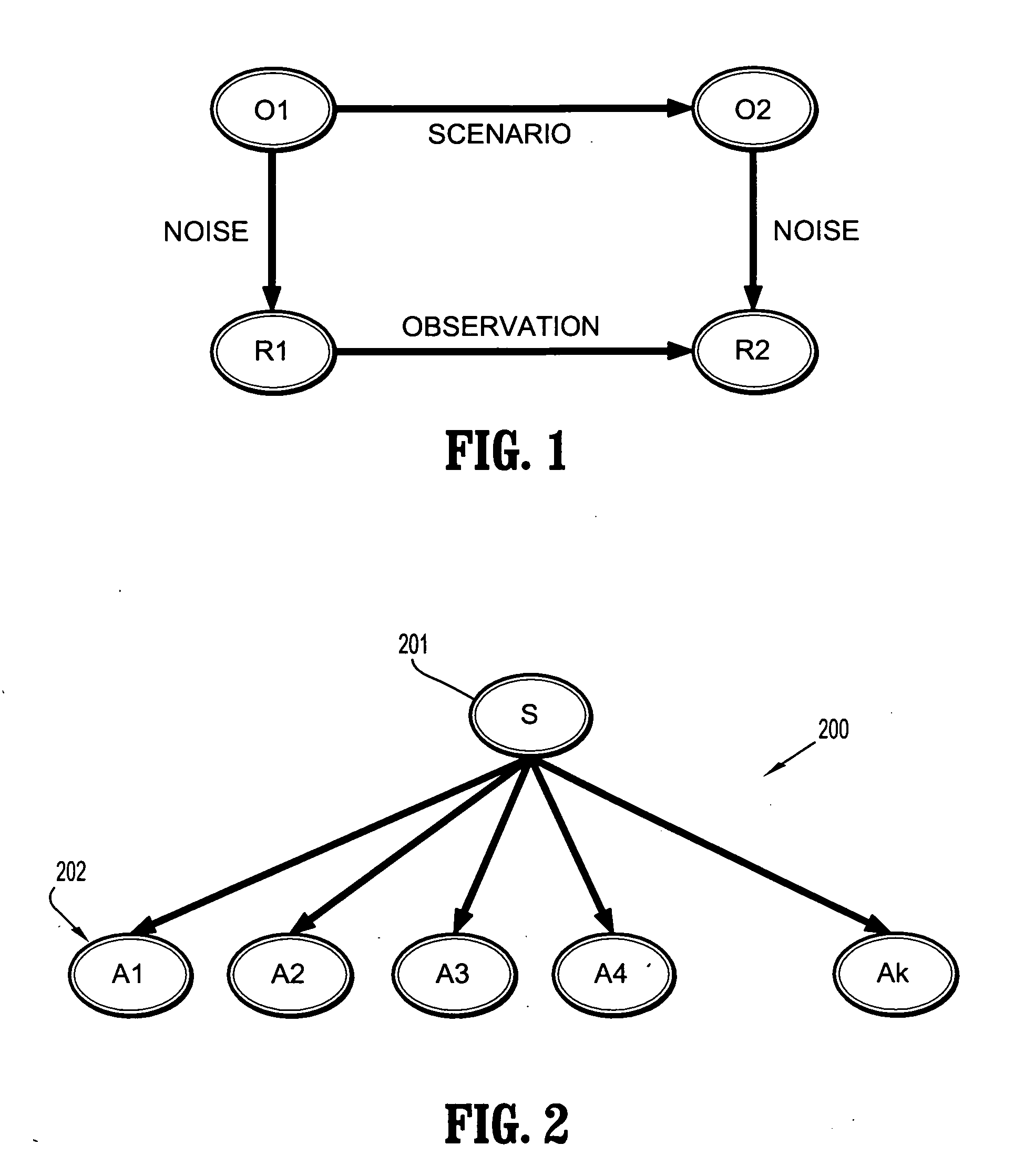
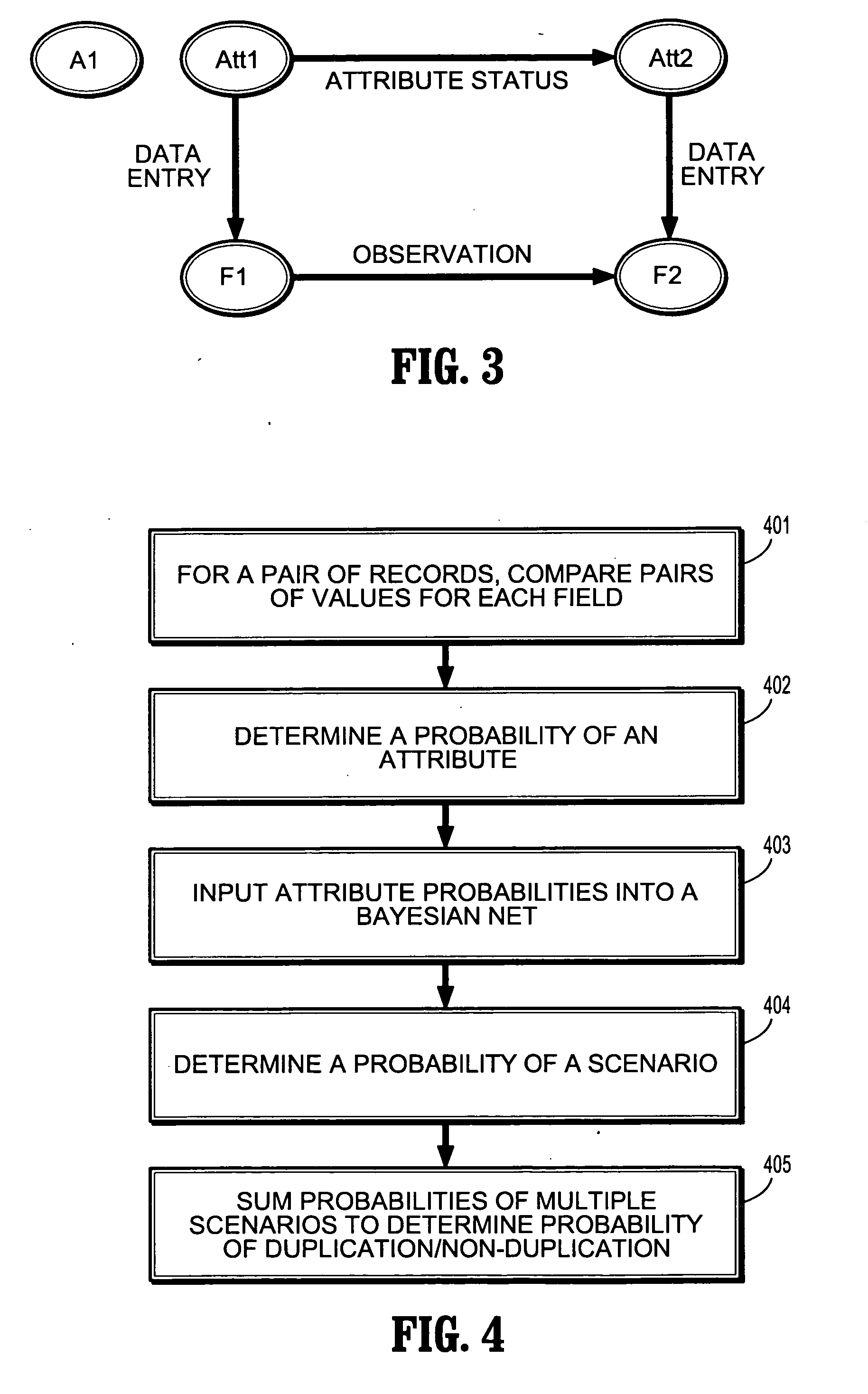
Probabilistic model for record linkage
InactiveUS20060179050A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsProbit modelRecord linkage
A method for probabilistic record linkage includes providing a record pair comprising a plurality of fields, providing a plurality of scenarios, each scenario relating to a distribution of patterns among a plurality of attribute statuses, and comparing the record pair to determine a record difference. The method includes determining a probability of a status for each of a plurality of attributes based on the distance metric of the plurality of fields, wherein each field corresponds to a respective attribute, wherein the field is observable and the attribute is hidden, determining a probability of each scenario based on the probability of the status for each attribute and the Bayesian net representing the probabilistic model on the relationship between scenarios and attributes, and outputting a probability of duplication or non-duplication of the record pair determined from the probabilities of the plurality of scenarios.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
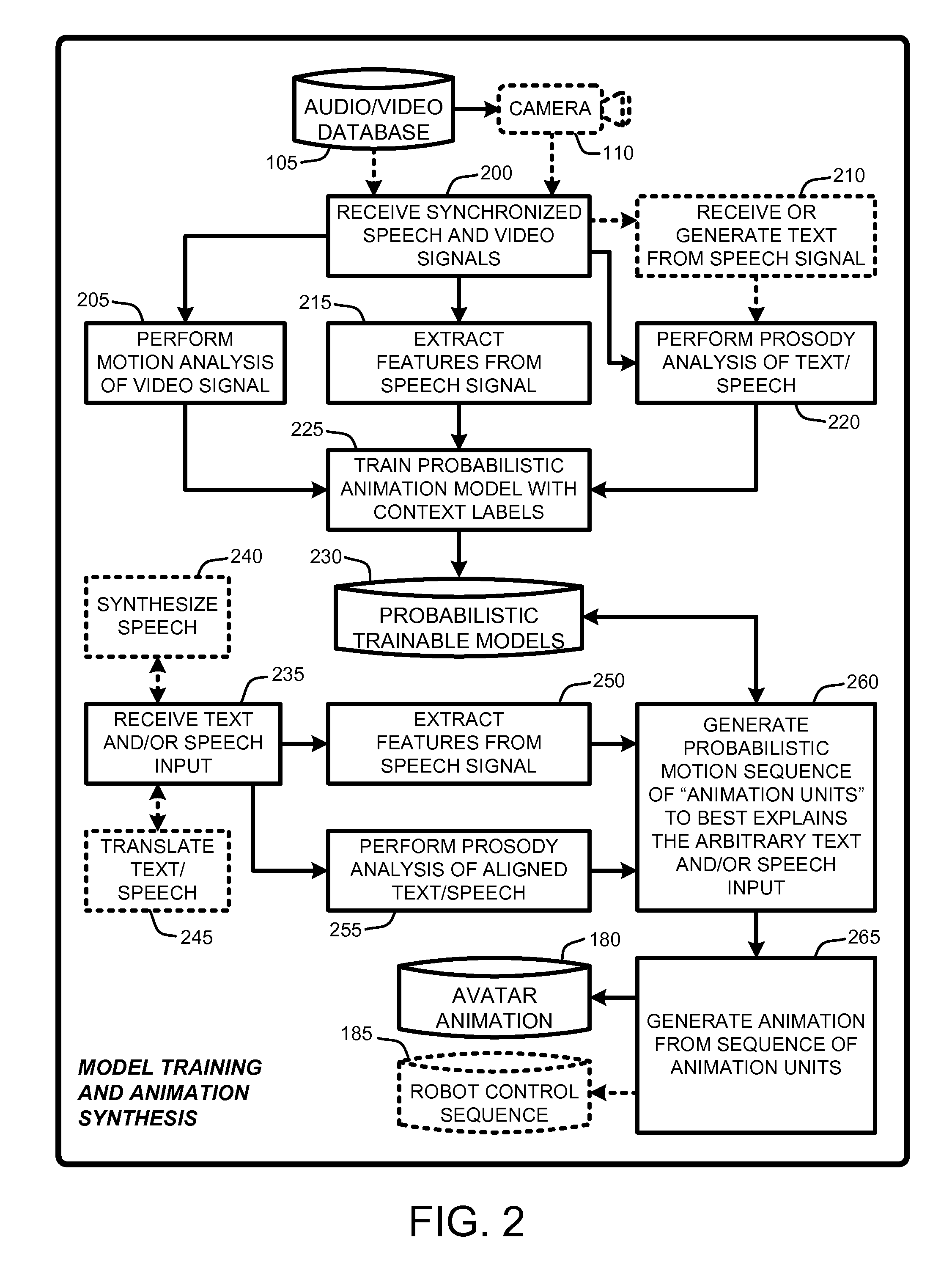
Speech and text driven hmm-based body animation synthesis
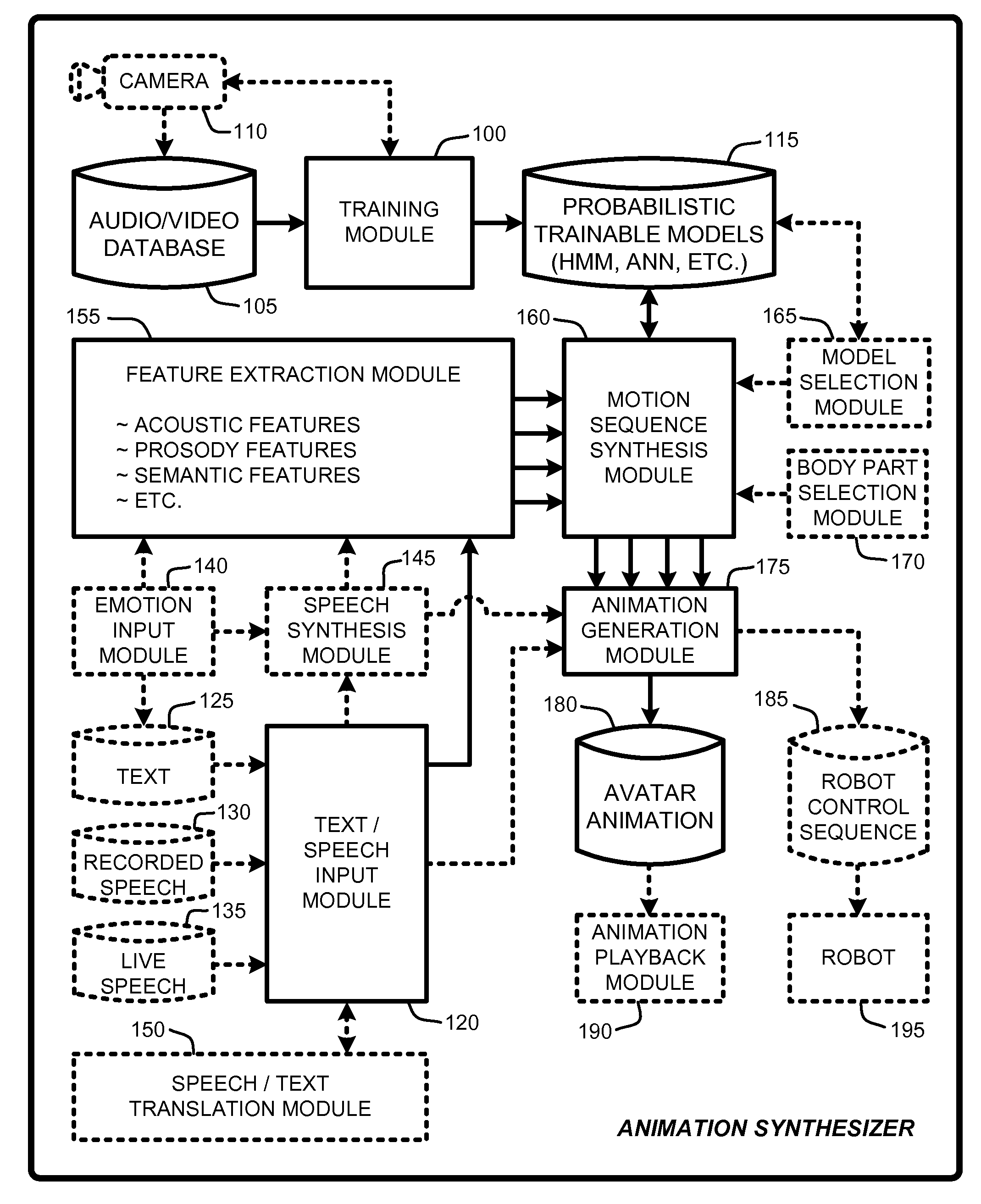
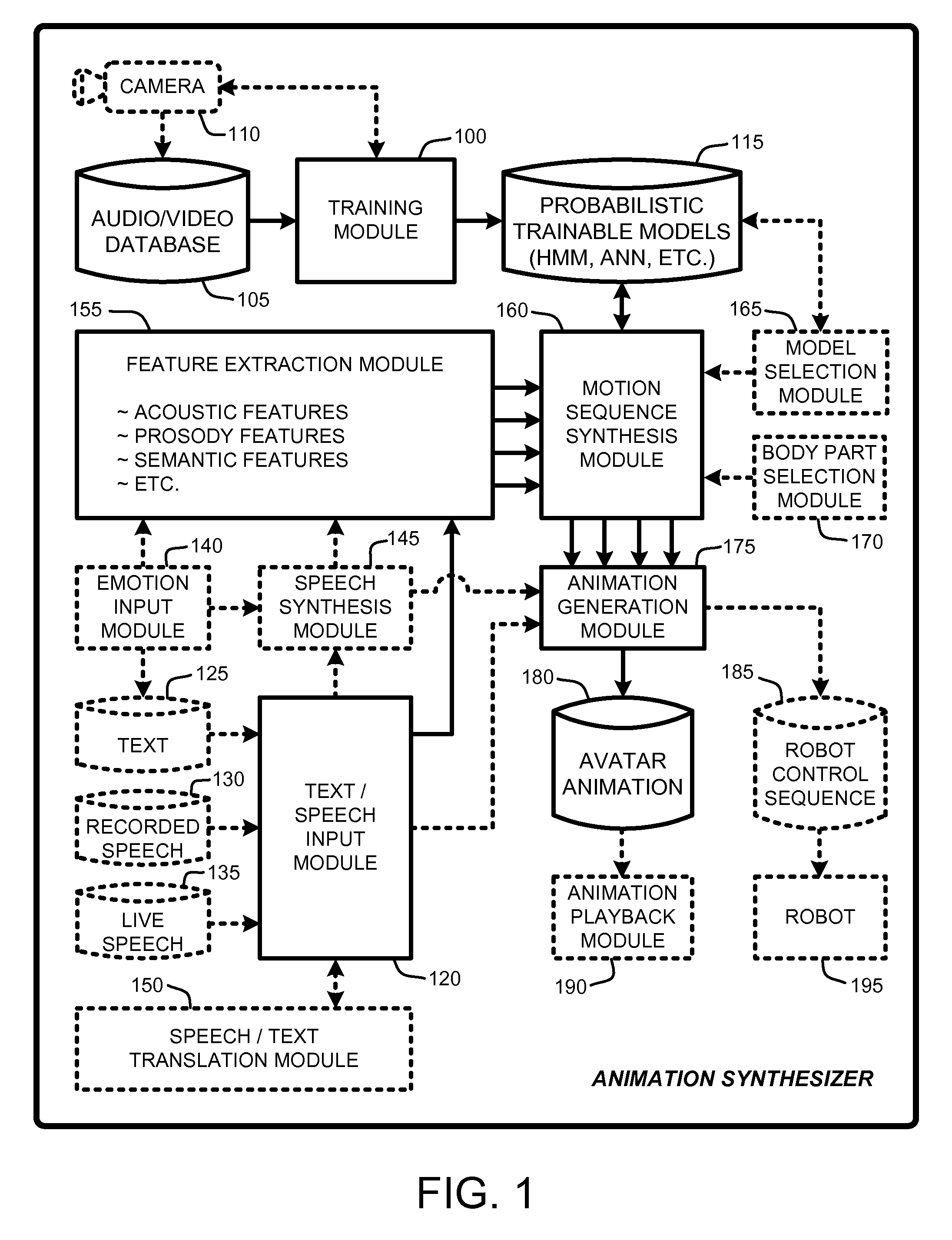
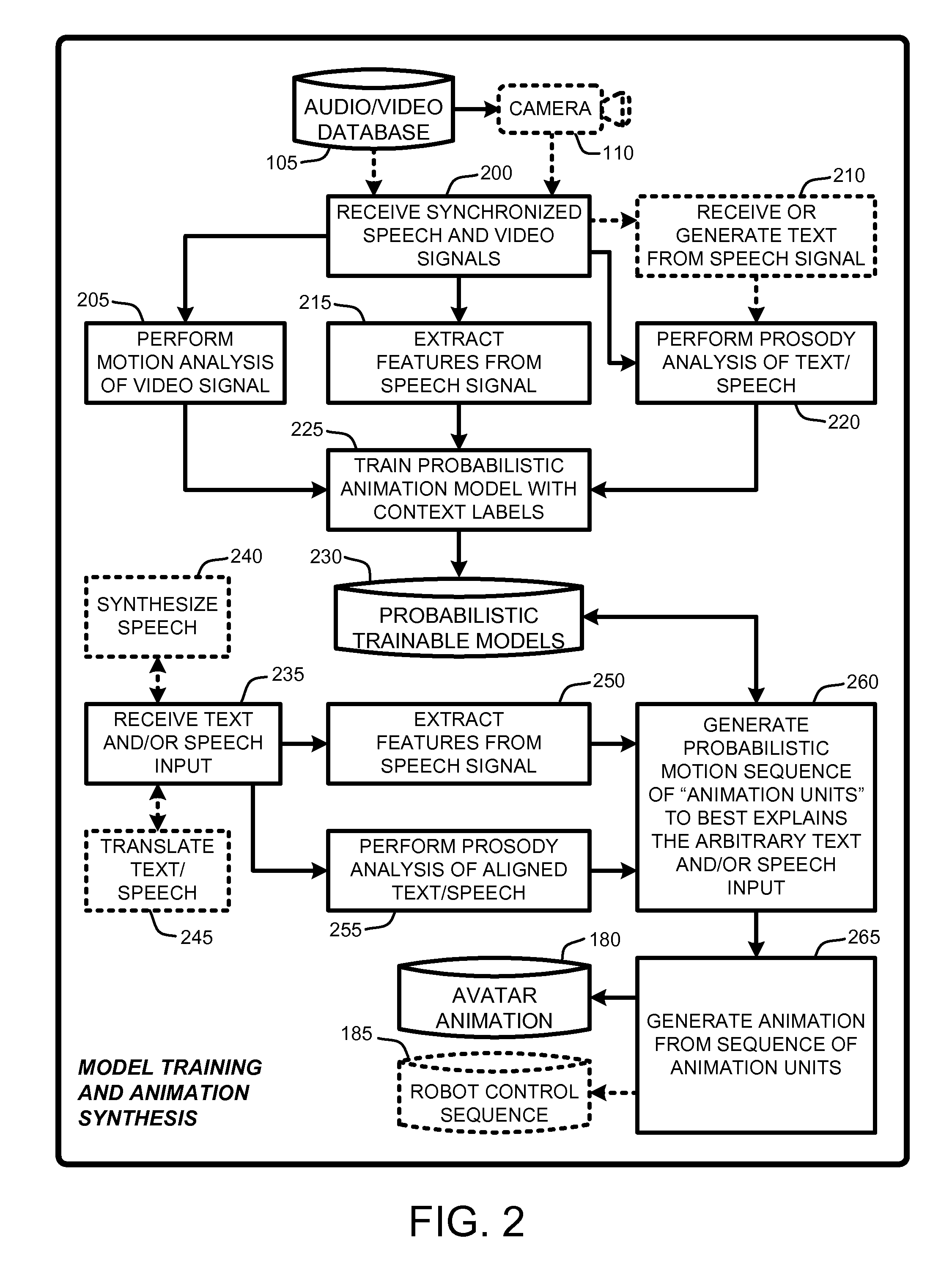
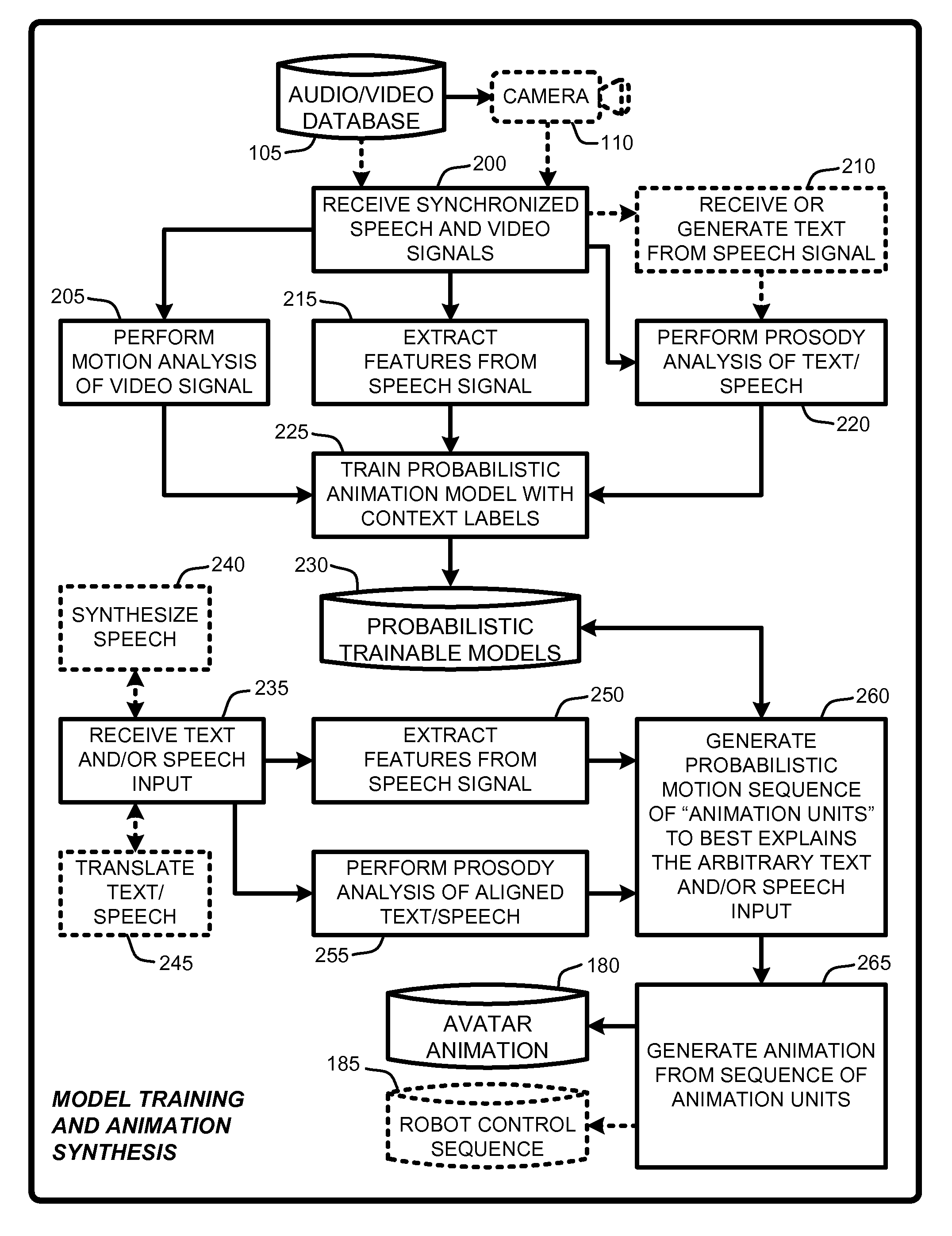
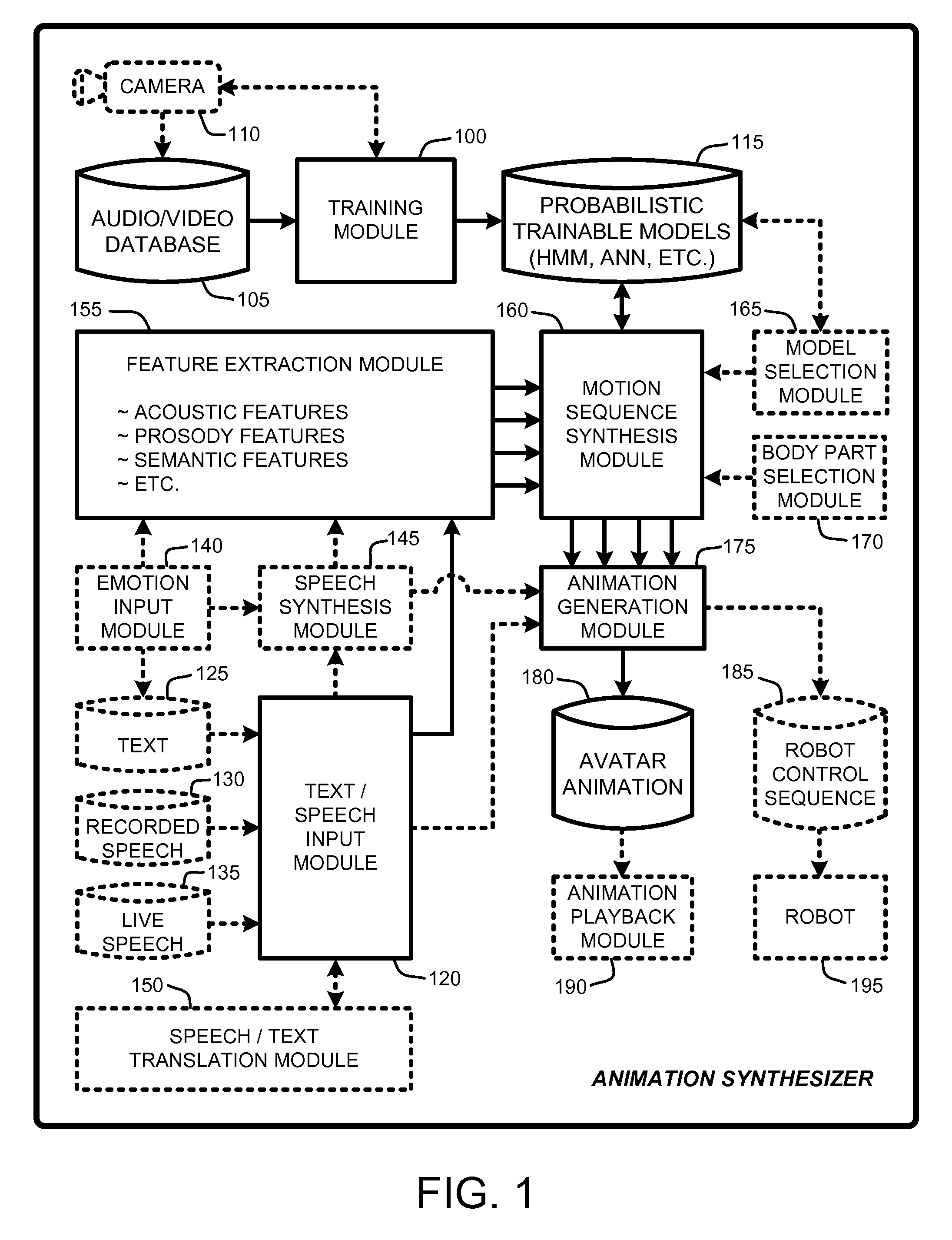
An “Animation Synthesizer” uses trainable probabilistic models, such as Hidden Markov Models (HMM), Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), etc., to provide speech and text driven body animation synthesis. Probabilistic models are trained using synchronized motion and speech inputs (e.g., live or recorded audio / video feeds) at various speech levels, such as sentences, phrases, words, phonemes, sub-phonemes, etc., depending upon the available data, and the motion type or body part being modeled. The Animation Synthesizer then uses the trainable probabilistic model for selecting animation trajectories for one or more different body parts (e.g., face, head, hands, arms, etc.) based on an arbitrary text and / or speech input. These animation trajectories are then used to synthesize a sequence of animations for digital avatars, cartoon characters, computer generated anthropomorphic persons or creatures, actual motions for physical robots, etc., that are synchronized with a speech output corresponding to the text and / or speech input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
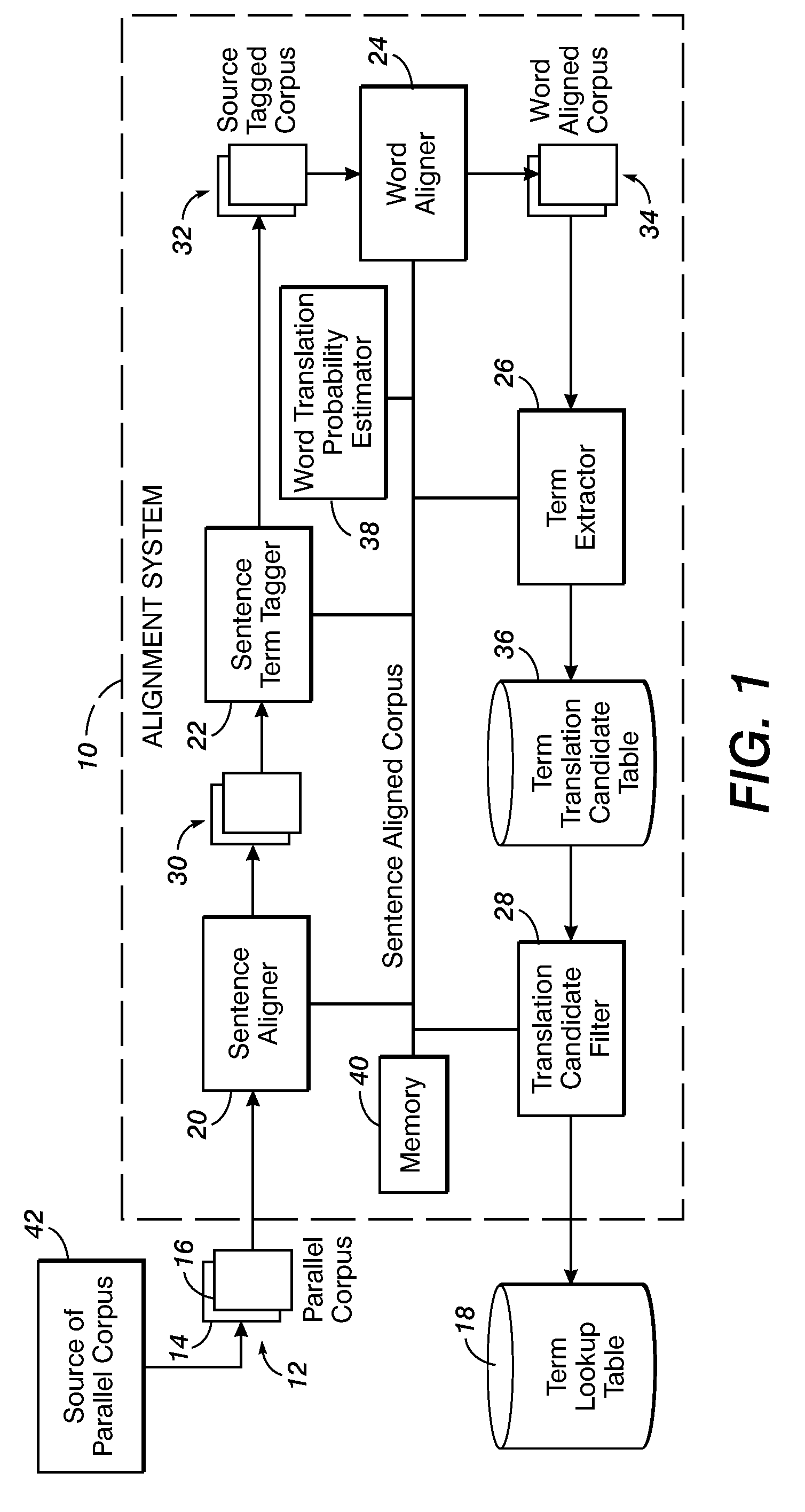
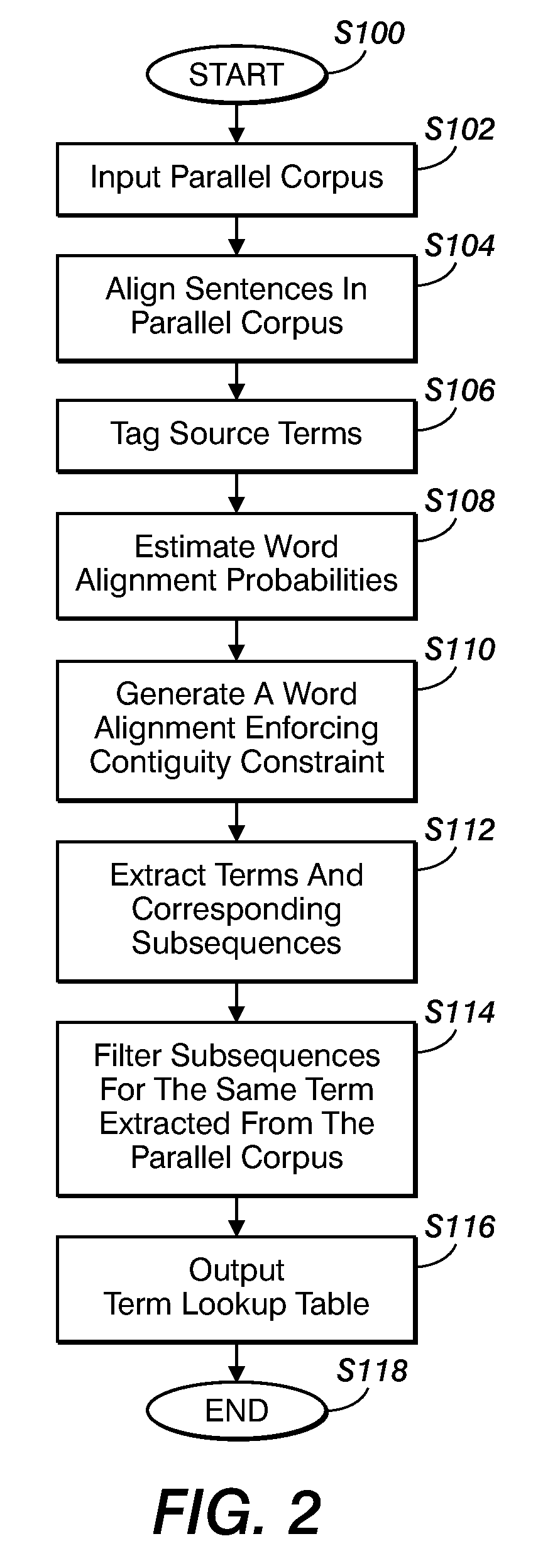
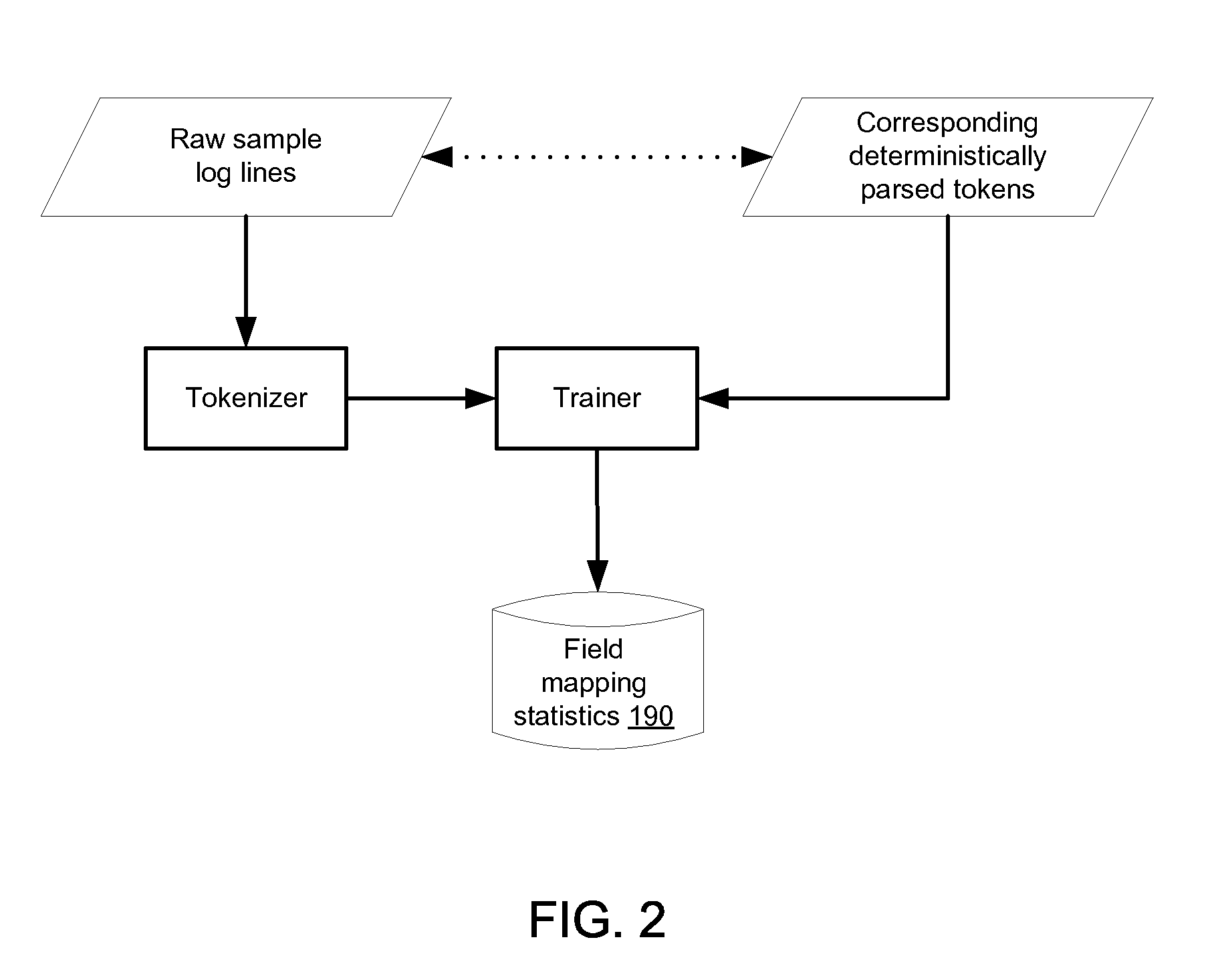
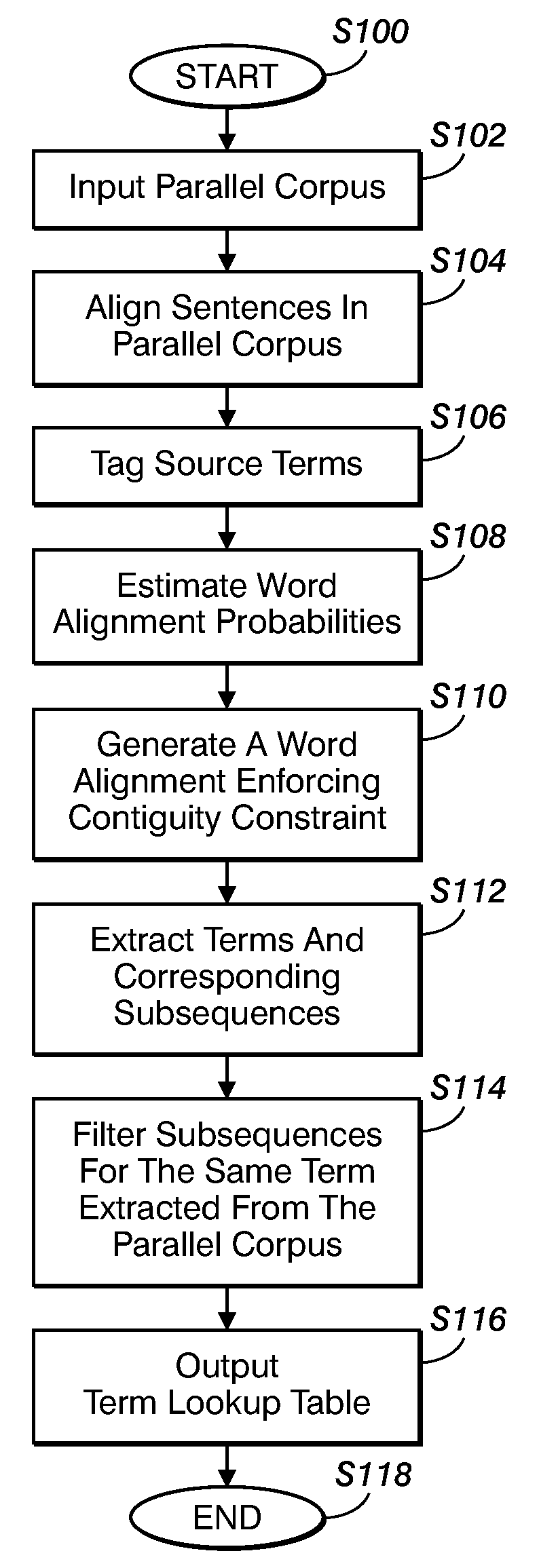
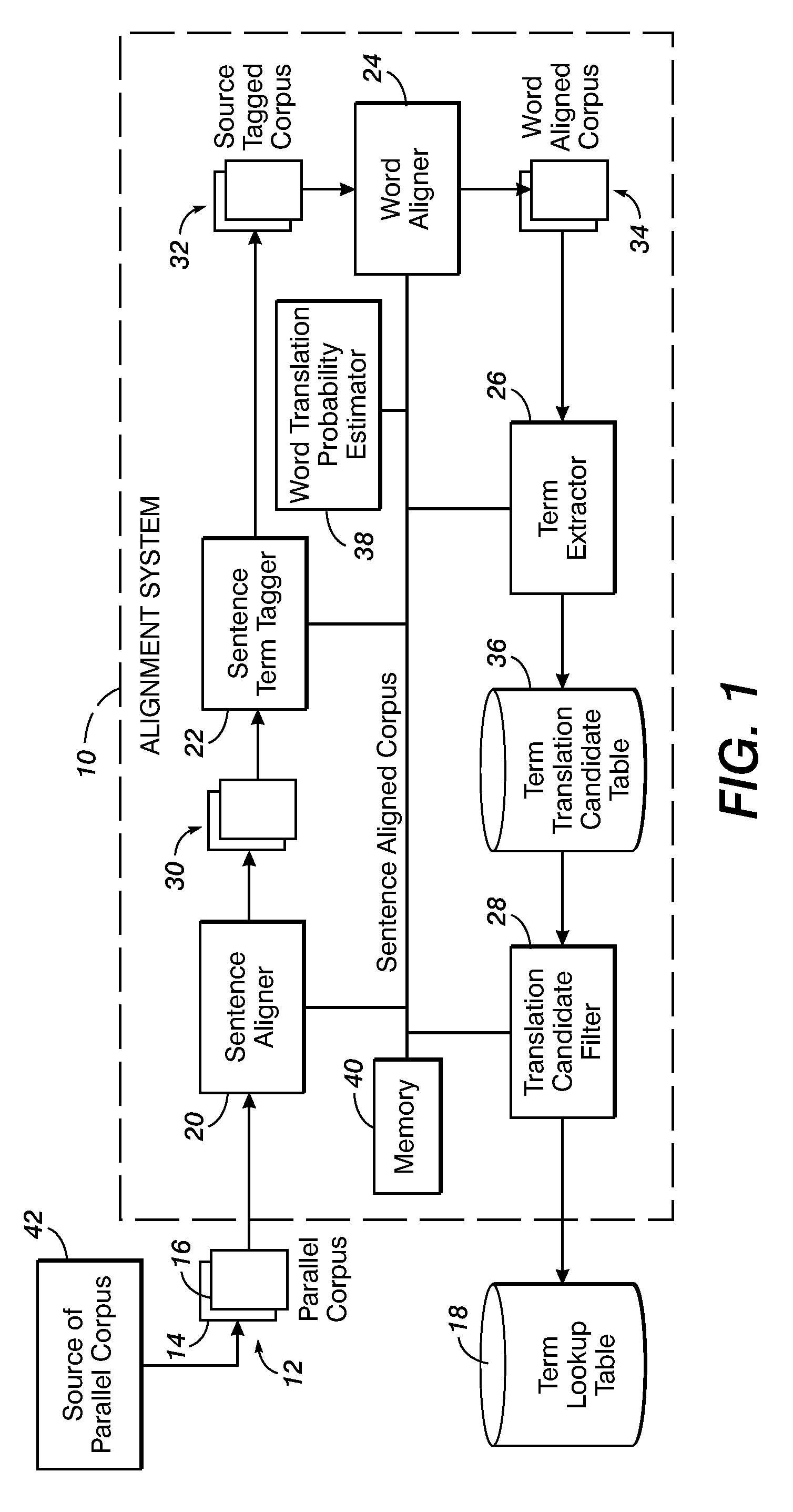
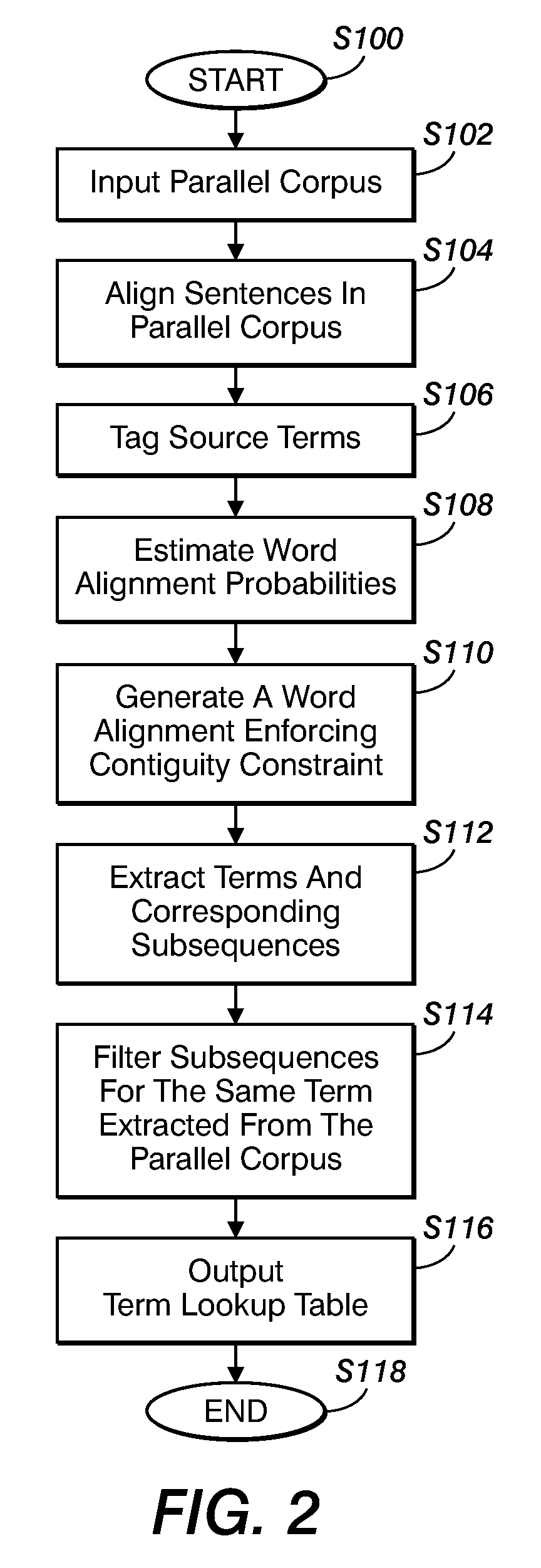
Method for aligning sentences at the word level enforcing selective contiguity constraints
InactiveUS9020804B2Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsProbit modelConditional probability
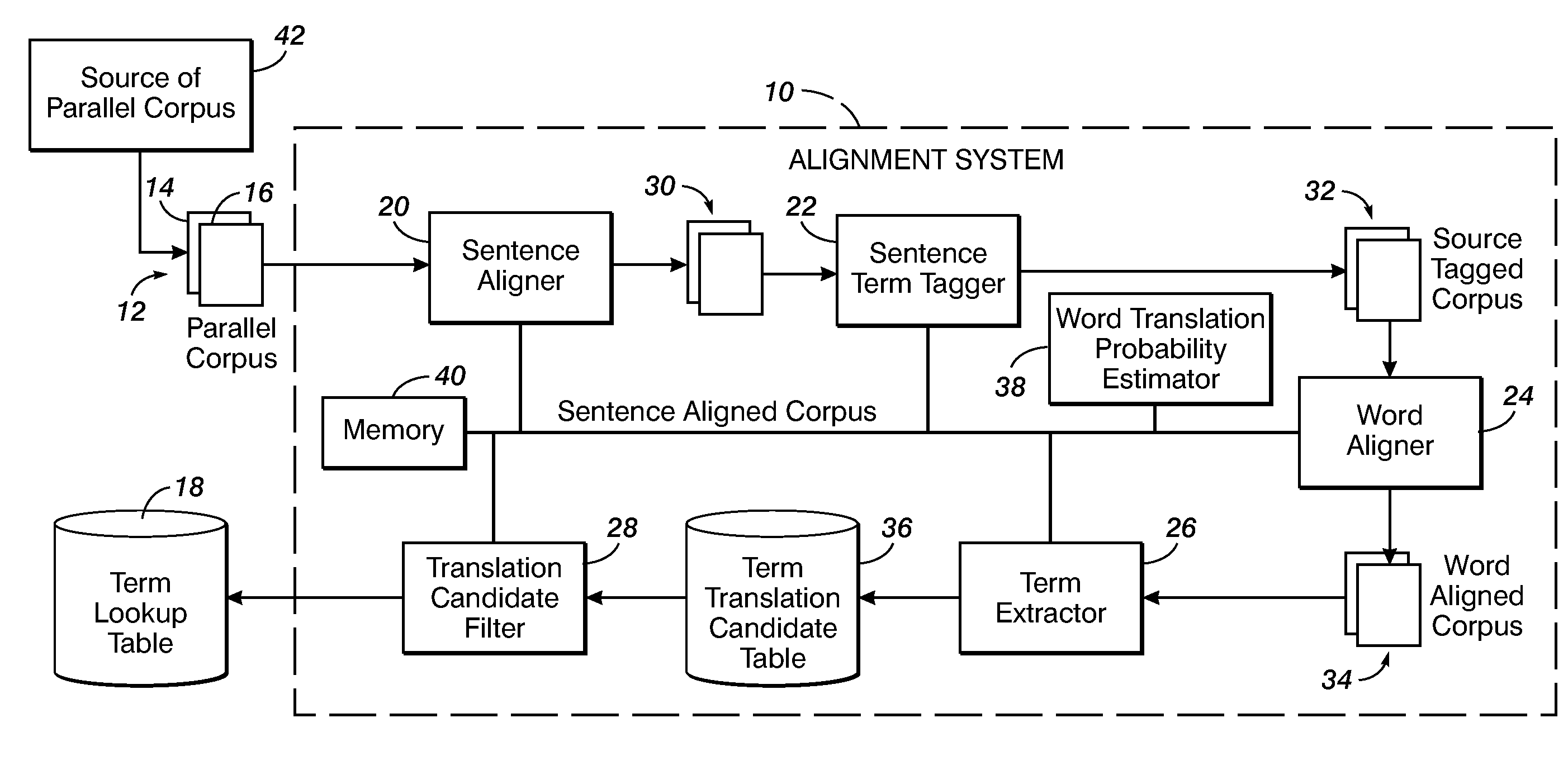
An alignment method includes, for a source sentence in a source language, identifying whether the sentence includes at least one candidate term comprising a contiguous subsequence of words of the source sentence. A target sentence in a target language is aligned with the source sentence. This includes developing a probabilistic model which models conditional probability distributions for alignments between words of the source sentence and words of the target sentence and generating an optimal alignment based on the probabilistic model, including, where the source sentence includes the at least one candidate term, enforcing a contiguity constraint which requires that all the words of the target sentence which are aligned with an identified candidate term form a contiguous subsequence of the target sentence.
Owner:XEROX CORP
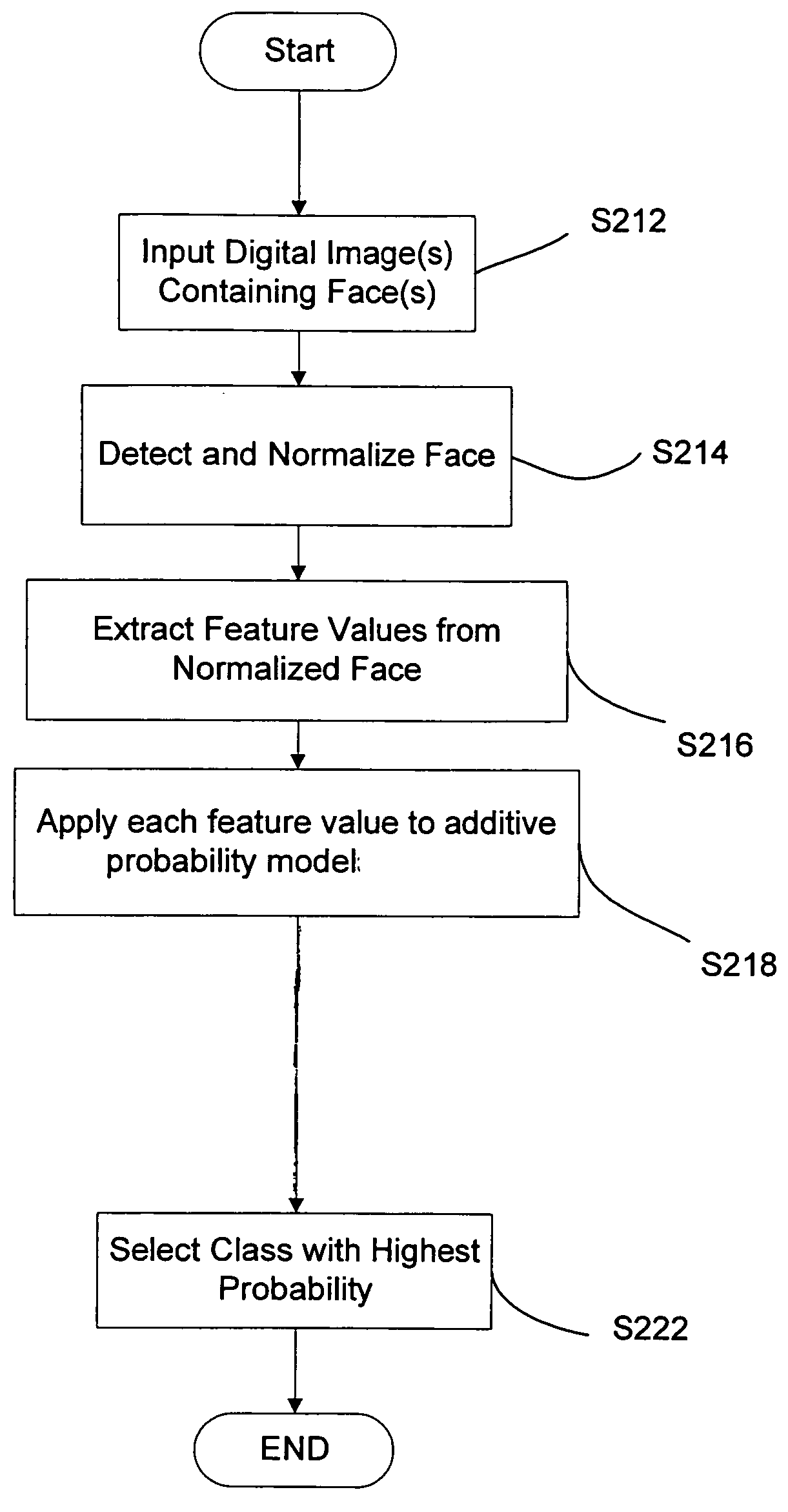
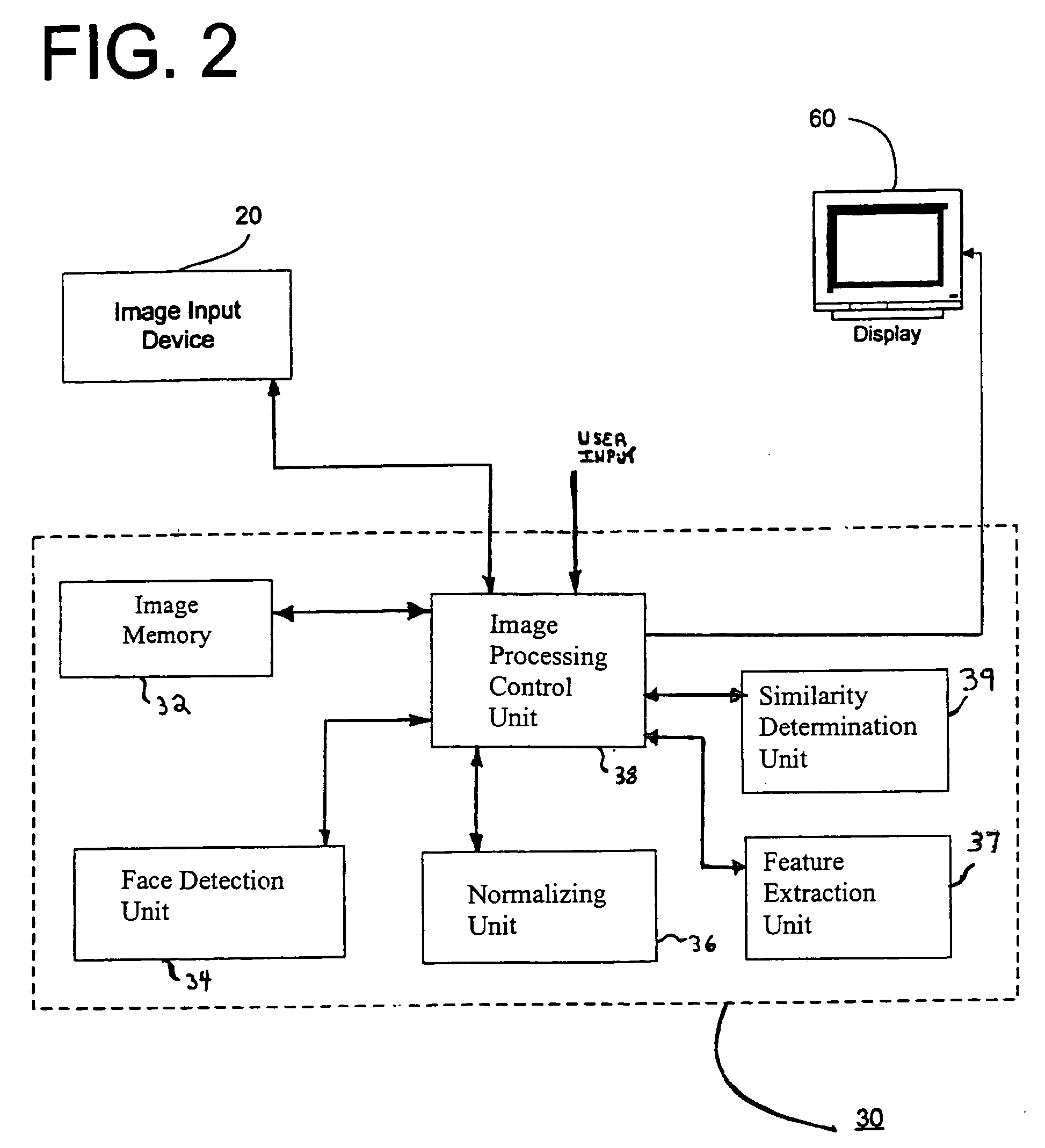
Method and apparatus for object recognition using probability models
InactiveUS20050105780A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionProbit model
A method and an apparatus automatically recognize or verify objects in a digital image using probability models. According to a first aspect, a method and apparatus automatically recognize or verify objects in a digital image by: accessing digital image data including an object of interest therein; detecting an object of interest in the image; normalizing the object to generate a normalized object representation; extracting a plurality of features from the normalized object representation; and applying each feature to a previously-determined additive probability model to determine the likelihood that the object of interest belongs to an existing class. In one embodiment, the previously-determined additive probability model is an Additive Gaussian Model.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
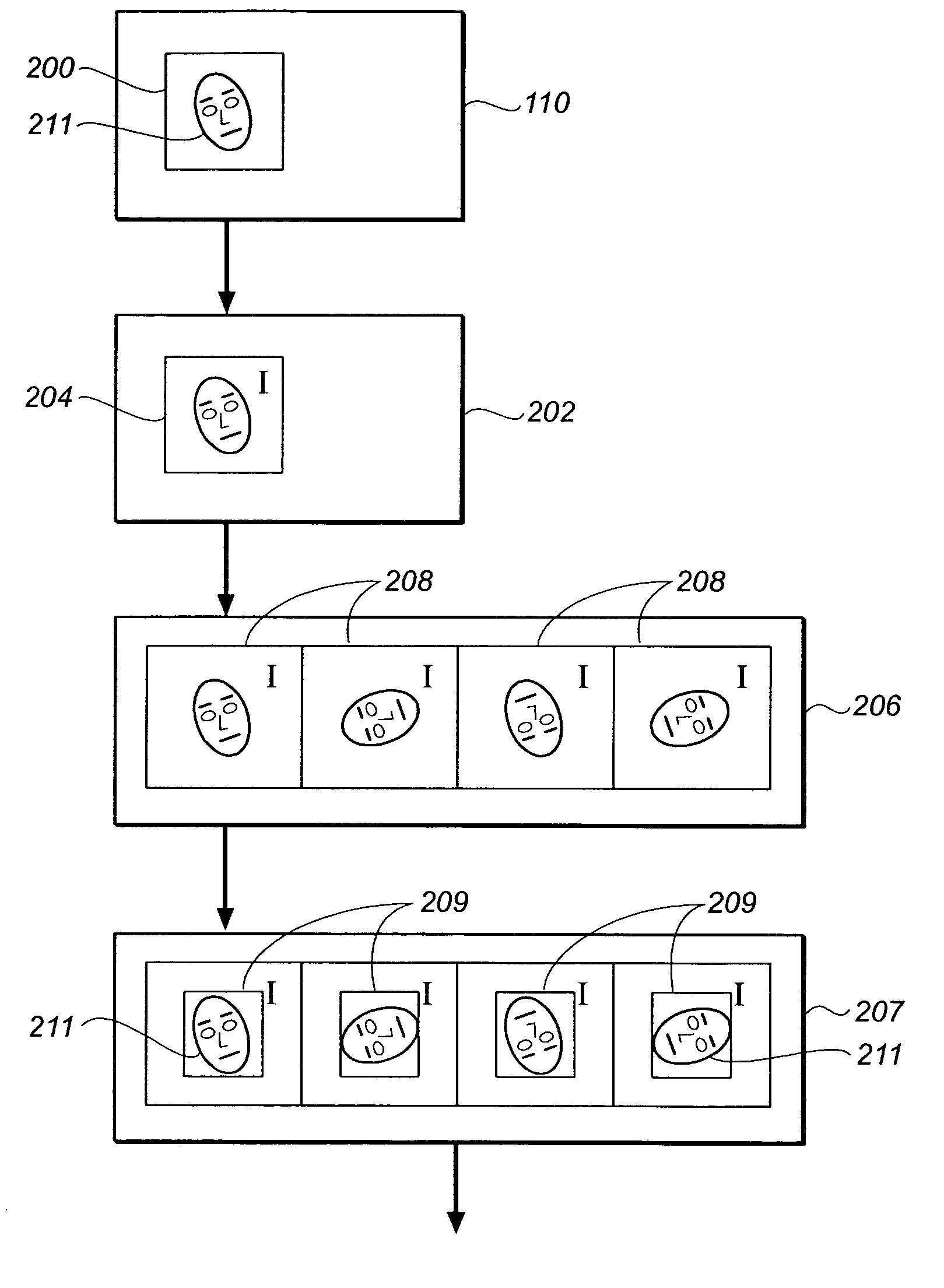
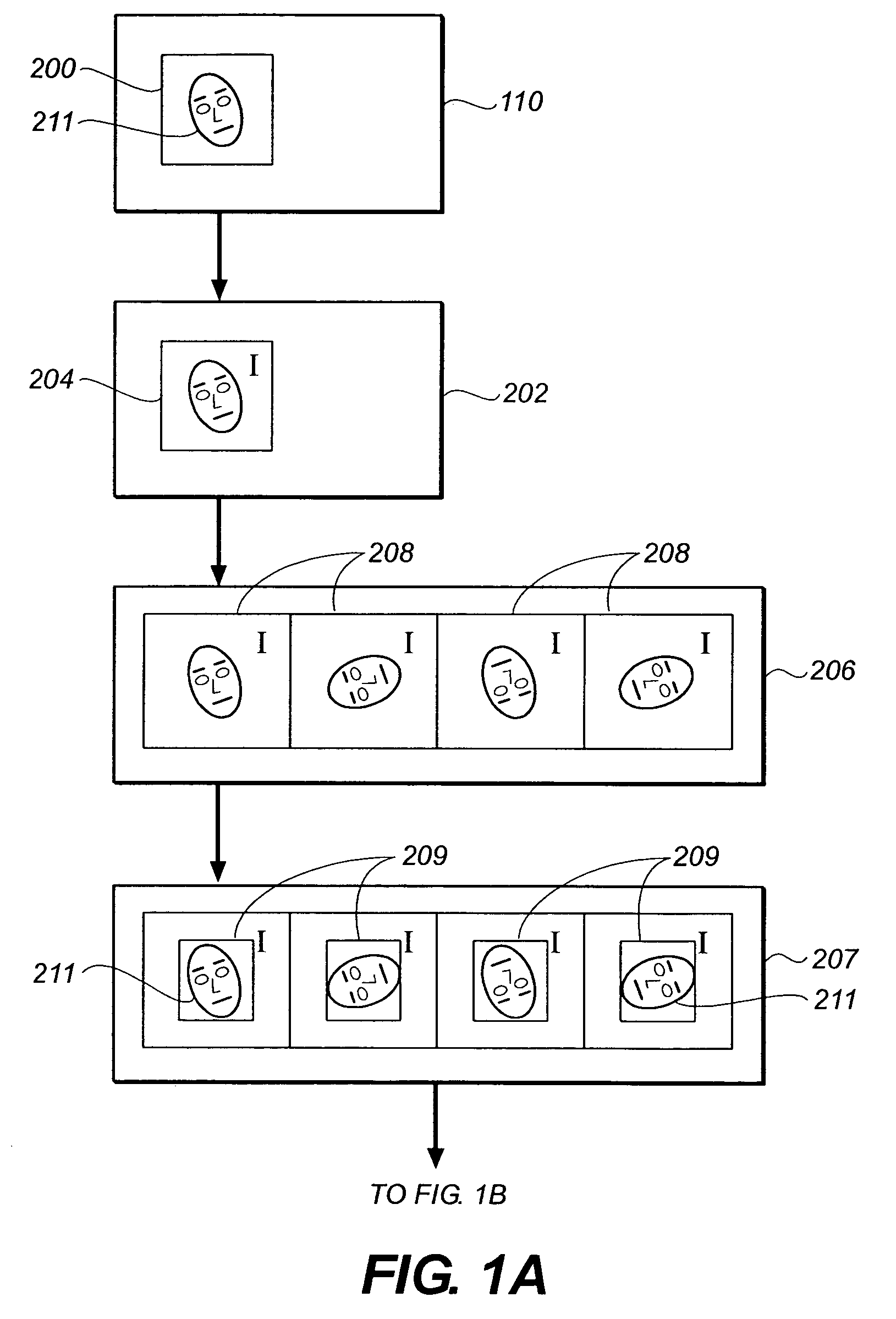
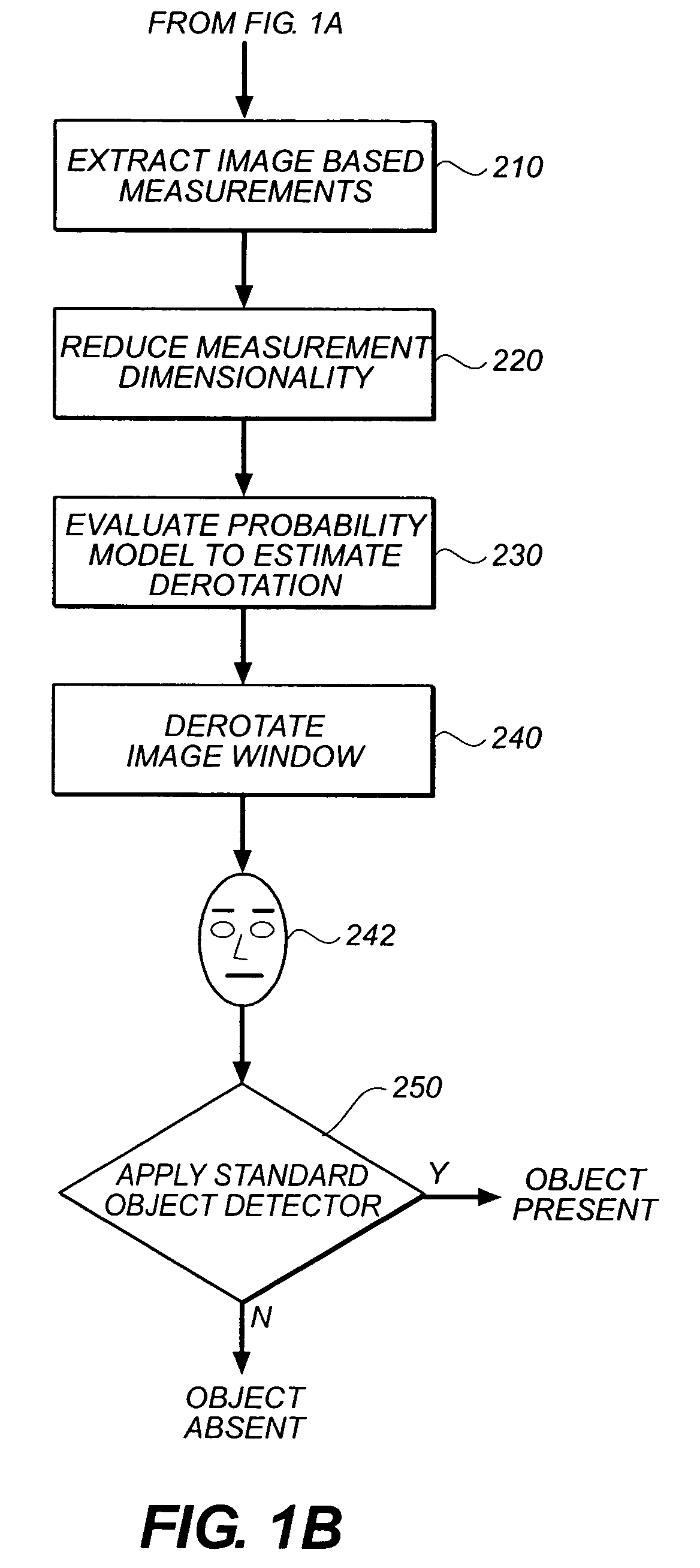
In-plane rotation invariant object detection in digitized images
In methods, systems, and computer program products for locating a regularly configured object within a digital image, a plurality of primary rotated integral images of the digital image are computed. Each primary rotated integral image has a different in-plane rotation. A set of secondary rotated integral images are derived from each of the primary rotated integral images. The secondary rotated integral images have further in-plane rotations relative to the respective primary rotated integral image. A window is defined within the digital image and corresponding windows of the rotated integral images. The values of convolution sums of a predetermined set of feature boxes within the window, in each of the rotated integral images are extracted. The dimensionality of the convolution sums is reduced to provide a set of reduced sums. A probability model is applied to the reduced sums to provide a best estimated derotated image of the window.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
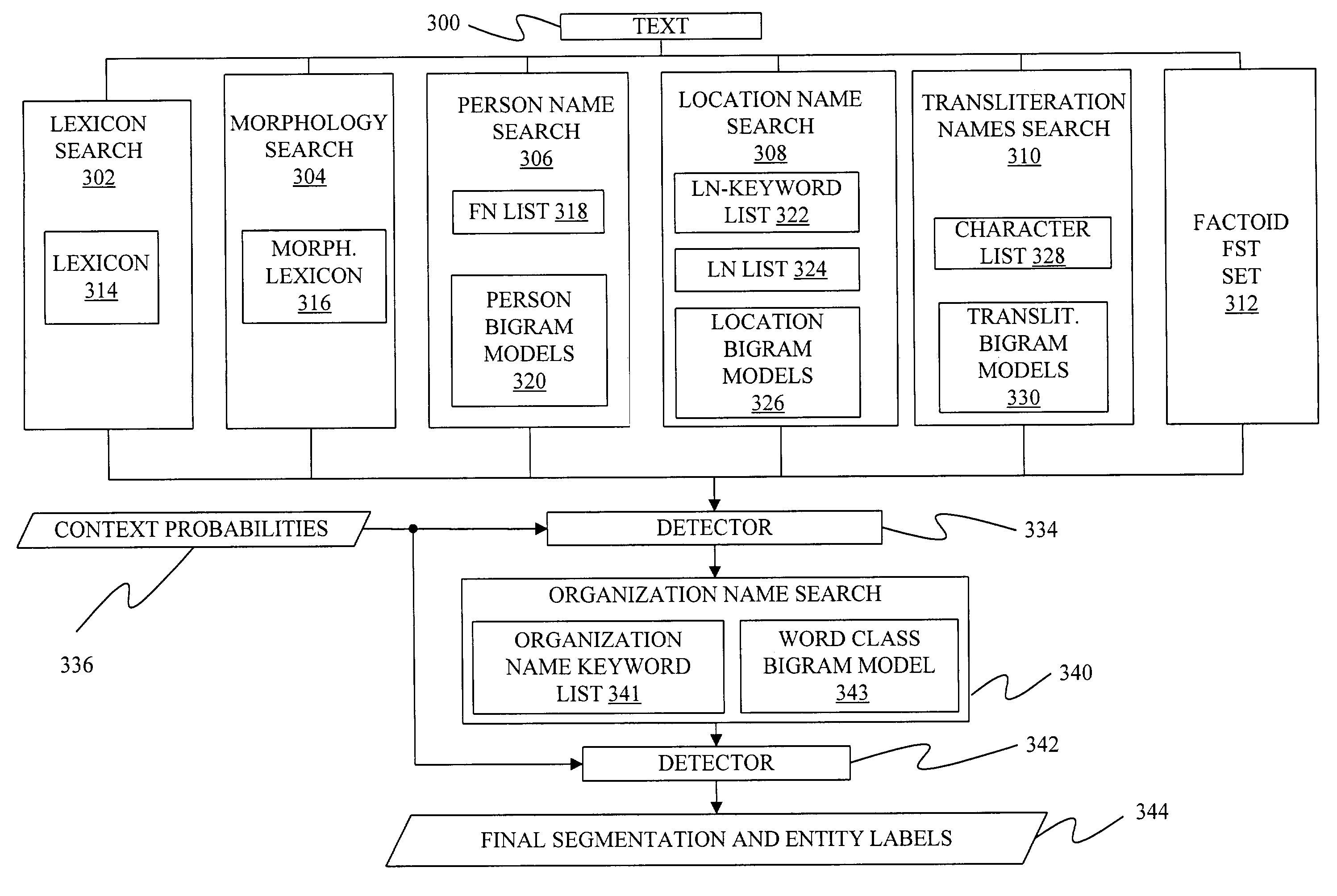
Using source-channel models for word segmentation
A method and apparatus for segmenting text is provided that identifies a sequence of entity types from a sequence of characters and thereby identifies a segmentation for the sequence of characters. Under the invention, the sequence of entity types is identified using probabilistic models that describe the likelihood of a sequence of entities and the likelihood of sequences of characters given particular entities. Under one aspect of the invention, organization name entities are identified from a first sequence of identified entities to form a final sequence of identified entities.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
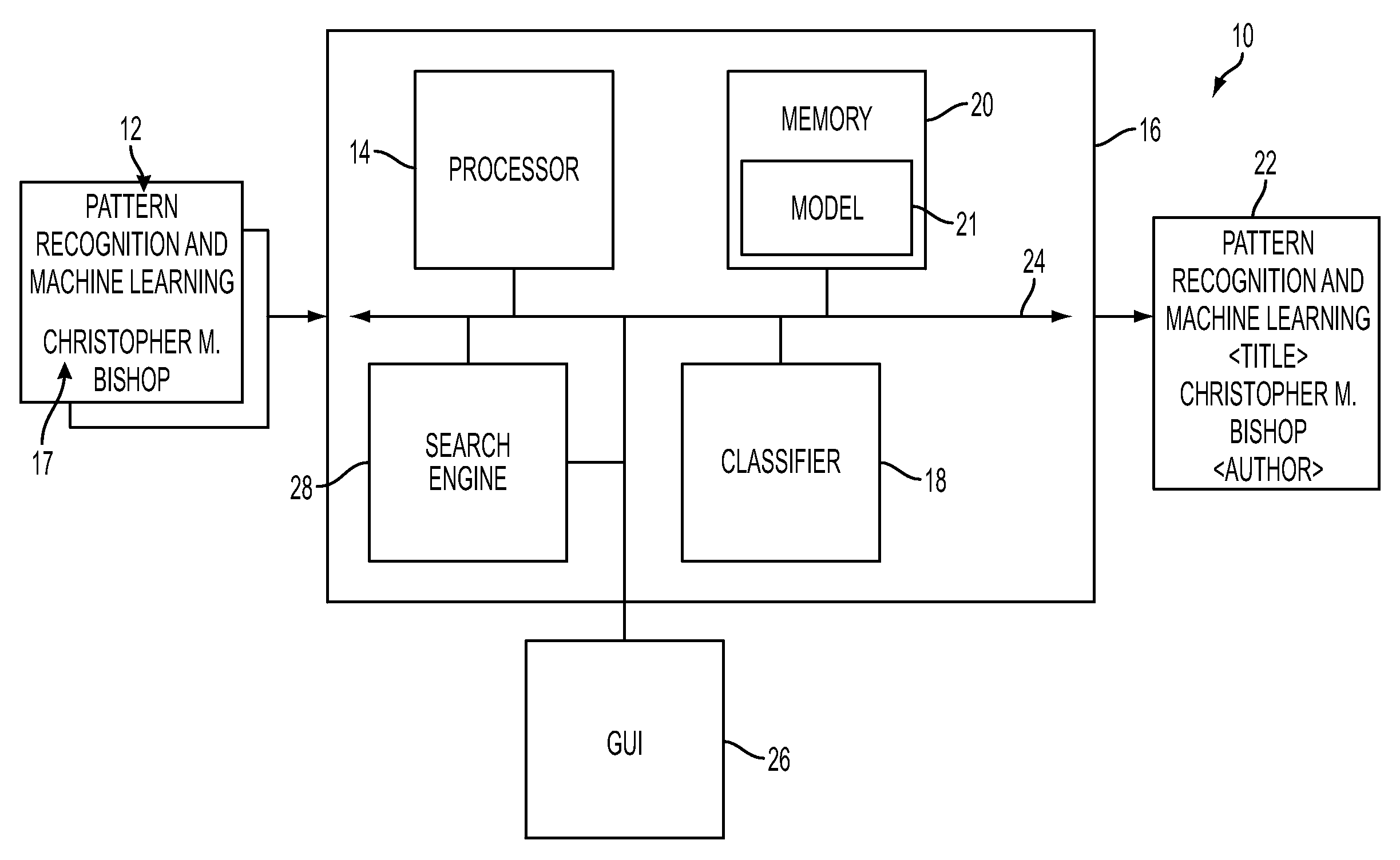
Stacked generalization learning for document annotation
A document annotation method includes modeling data elements of an input document and dependencies between the data elements as a dependency network. Static features of at least some of the data elements are defined, each expressing a relationship between a characteristic of the data element and its label. Dynamic features are defined which define links between an element and labels of the element and of a second element. Parameters of a collective probabilistic model for the document are learned, each expressing a conditional probability that a first data element should be labeled with information derived from a label of a neighbor data element linked to the first data element by a dynamic feature. The learning includes decomposing a globally trained model into a set of local learning models. The local learning models each employ static features to generate estimations of the neighbor element labels for at least one of the data elements.
Owner:XEROX CORP
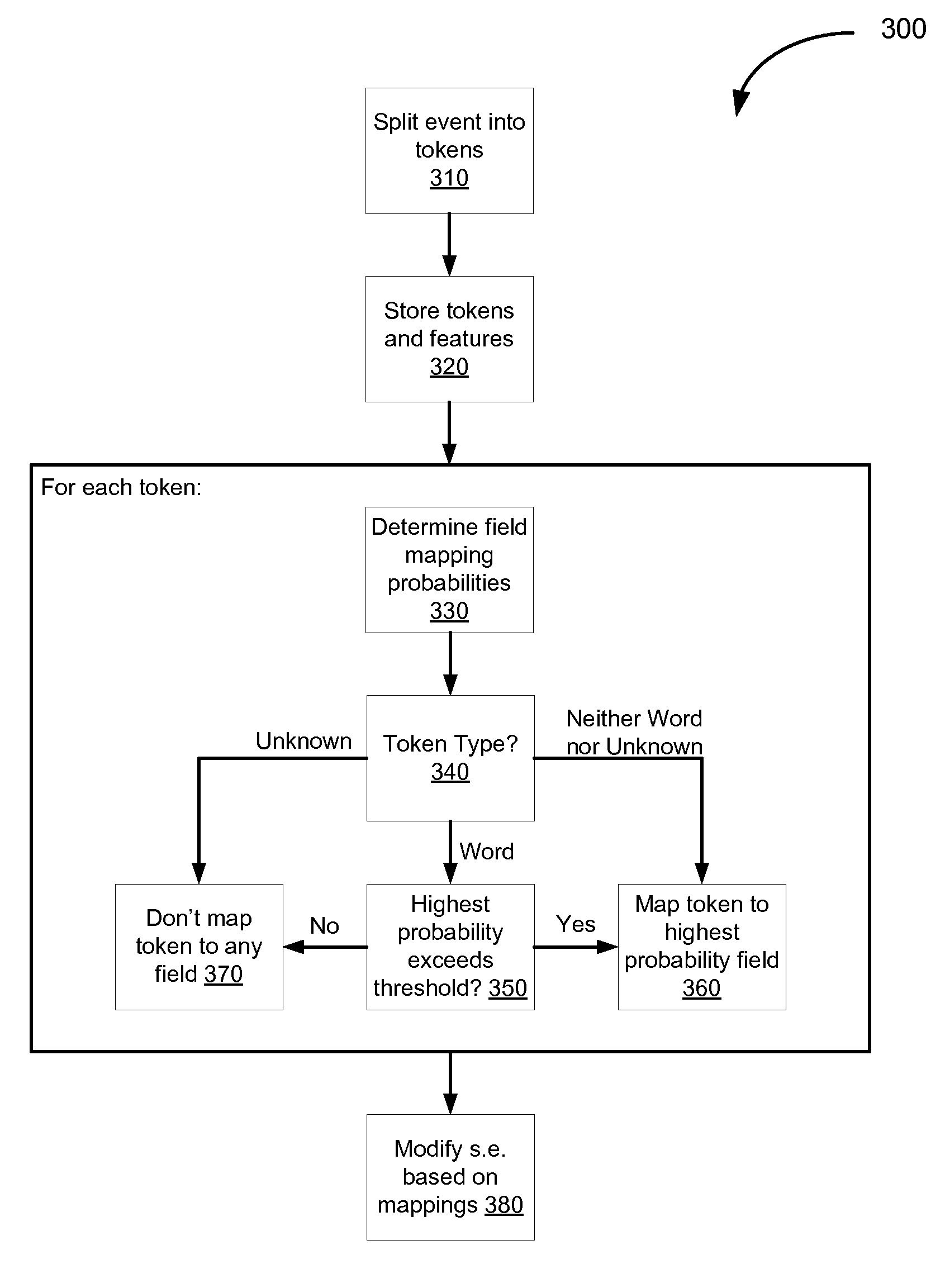
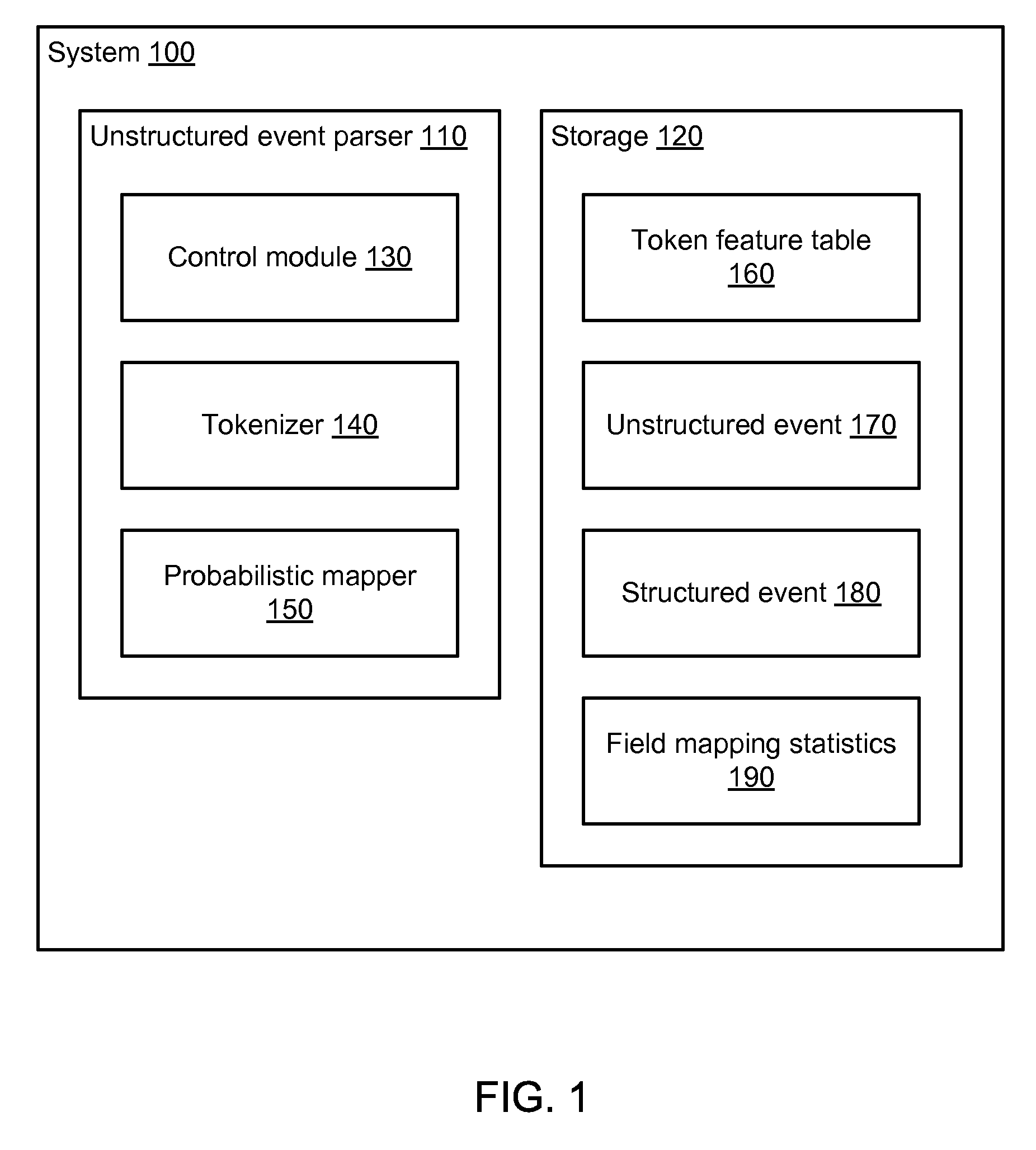
Extracting information from unstructured data and mapping the information to a structured schema using the naïve bayesian probability model
An “unstructured event parser” analyzes an event that is in unstructured form and generates an event that is in structured form. A mapping phase determines, for a given event token, possible fields of the structured event schema to which the token could be mapped and the probabilities that the token should be mapped to those fields. Particular tokens are then mapped to particular fields of the structured event schema. By using the Naïve Bayesian probability model, a “probabilistic mapper” determines, for a particular token and a particular field, the probability that that token maps to that field. The probabilistic mapper can also be used in a “regular expression creator” that generates a regex that matches an unstructured event and a “parameter file creator” that helps a user create a parameter file for use with a parameterized normalized event generator to generate a normalized event based on an unstructured event.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
Method for aligning sentences at the word level enforcing selective contiguity constraints
InactiveUS20080300857A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsProbit modelConditional probability
An alignment method includes, for a source sentence in a source language, identifying whether the sentence includes at least one candidate term comprising a contiguous subsequence of words of the source sentence. A target sentence in a target language is aligned with the source sentence. This includes developing a probabilistic model which models conditional probability distributions for alignments between words of the source sentence and words of the target sentence and generating an optimal alignment based on the probabilistic model, including, where the source sentence includes the at least one candidate term, enforcing a contiguity constraint which requires that all the words of the target sentence which are aligned with an identified candidate term form a contiguous subsequence of the target sentence.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Automated Compilation of Probabilistic Task Description into Executable Neural Network Specification
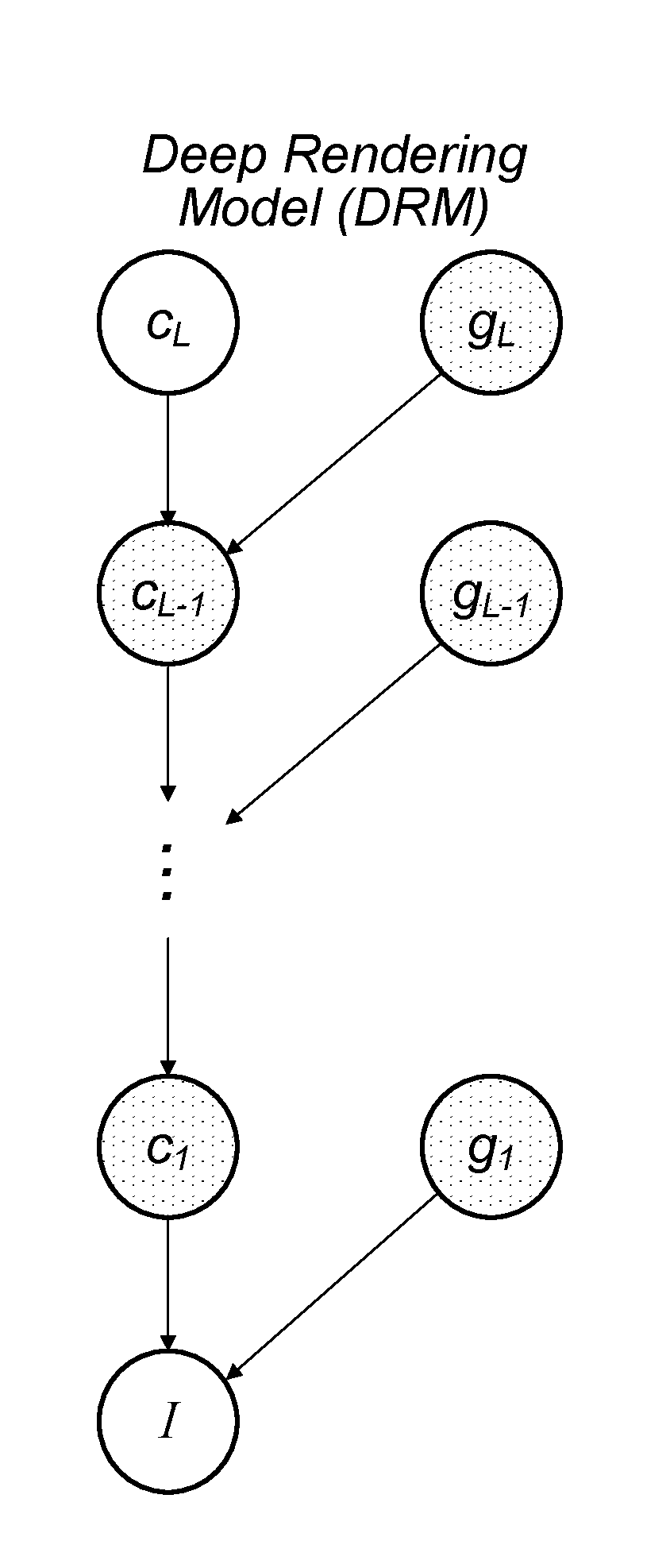
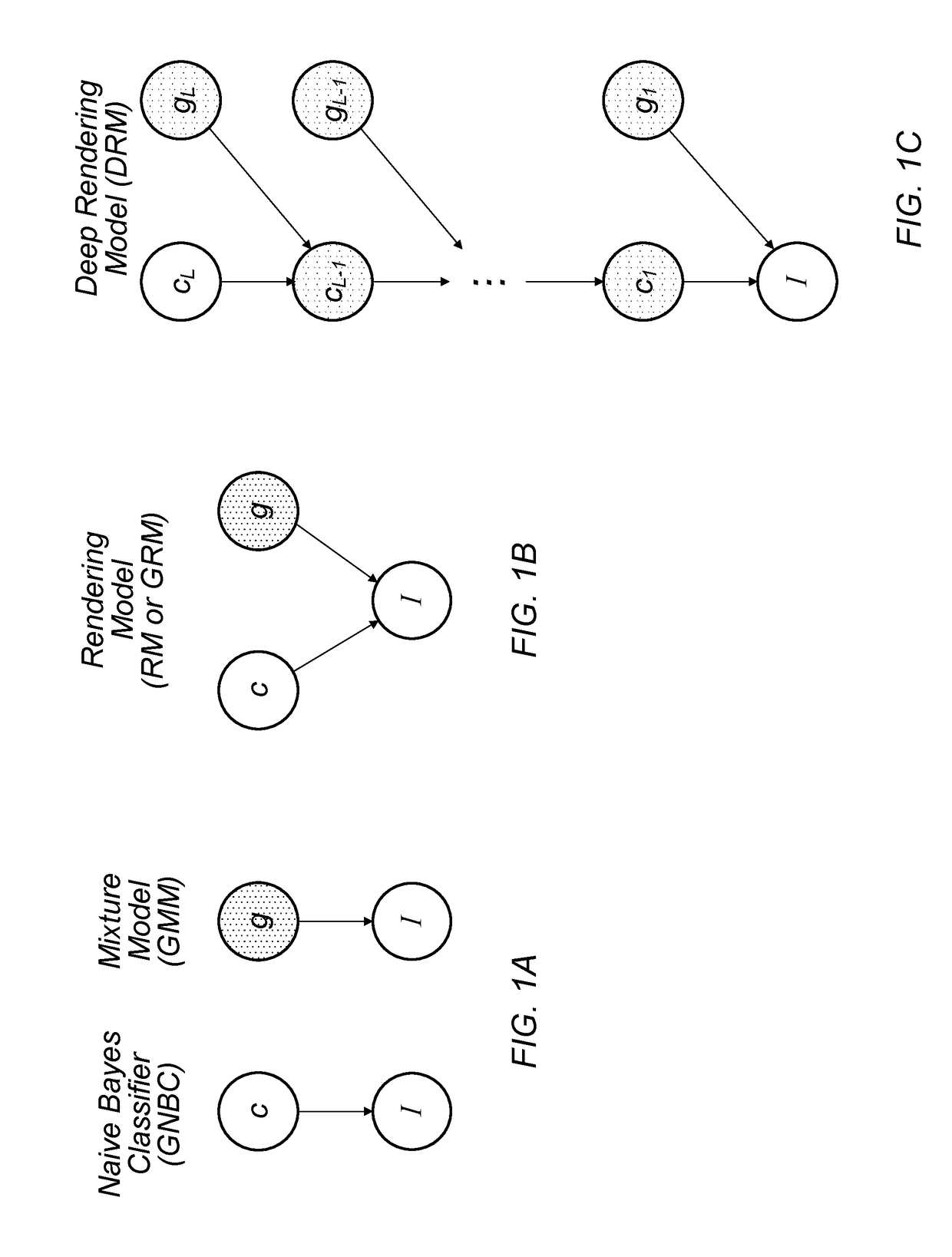
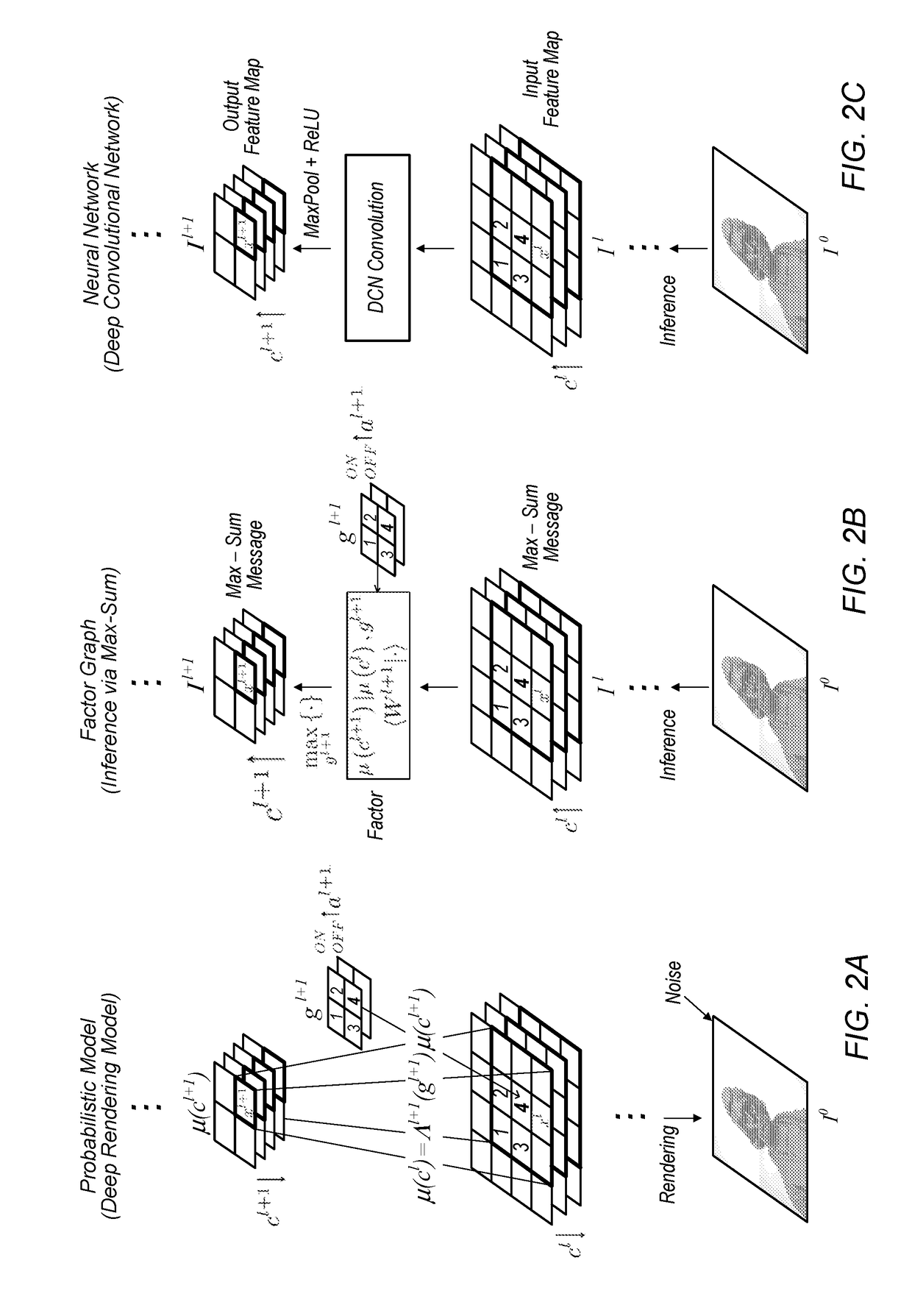
A mechanism for compiling a generative description of an inference task into a neural network. First, an arbitrary generative probabilistic model from the exponential family is specified (or received). The model characterizes a conditional probability distribution for measurement data given a set of latent variables. A factor graph is generated for the generative probabilistic model. Each factor node of the factor graph is expanded into a corresponding sequence of arithmetic operations, based on a specified inference task and a kind of message passing algorithm. The factor graph and the sequences of arithmetic operations specify the structure of a neural network for performance of the inference task. A learning algorithm is executed, to determine values of parameters of the neural network. The neural network is then ready for performing inference on operational measurements.
Owner:RICE UNIV
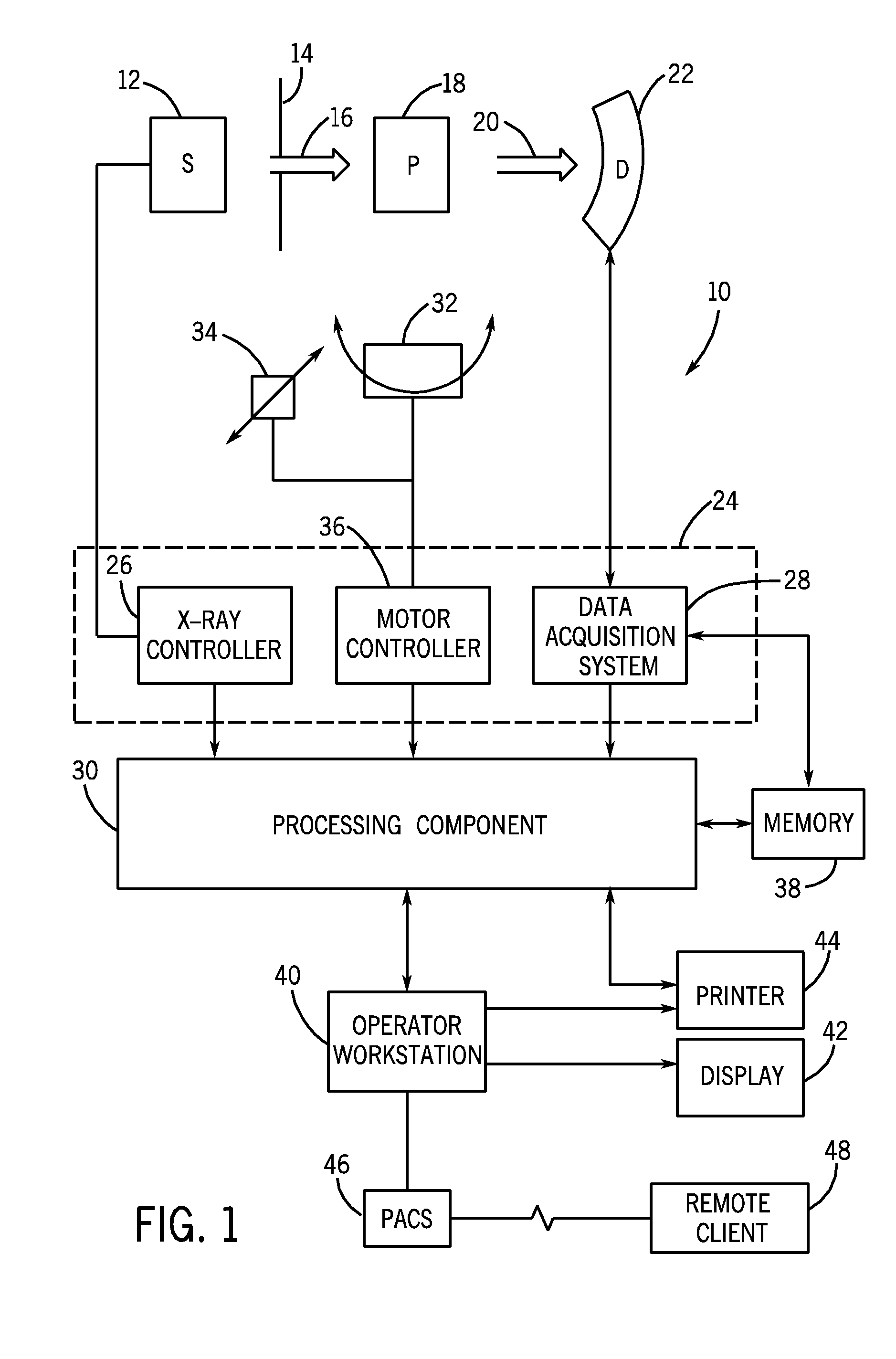
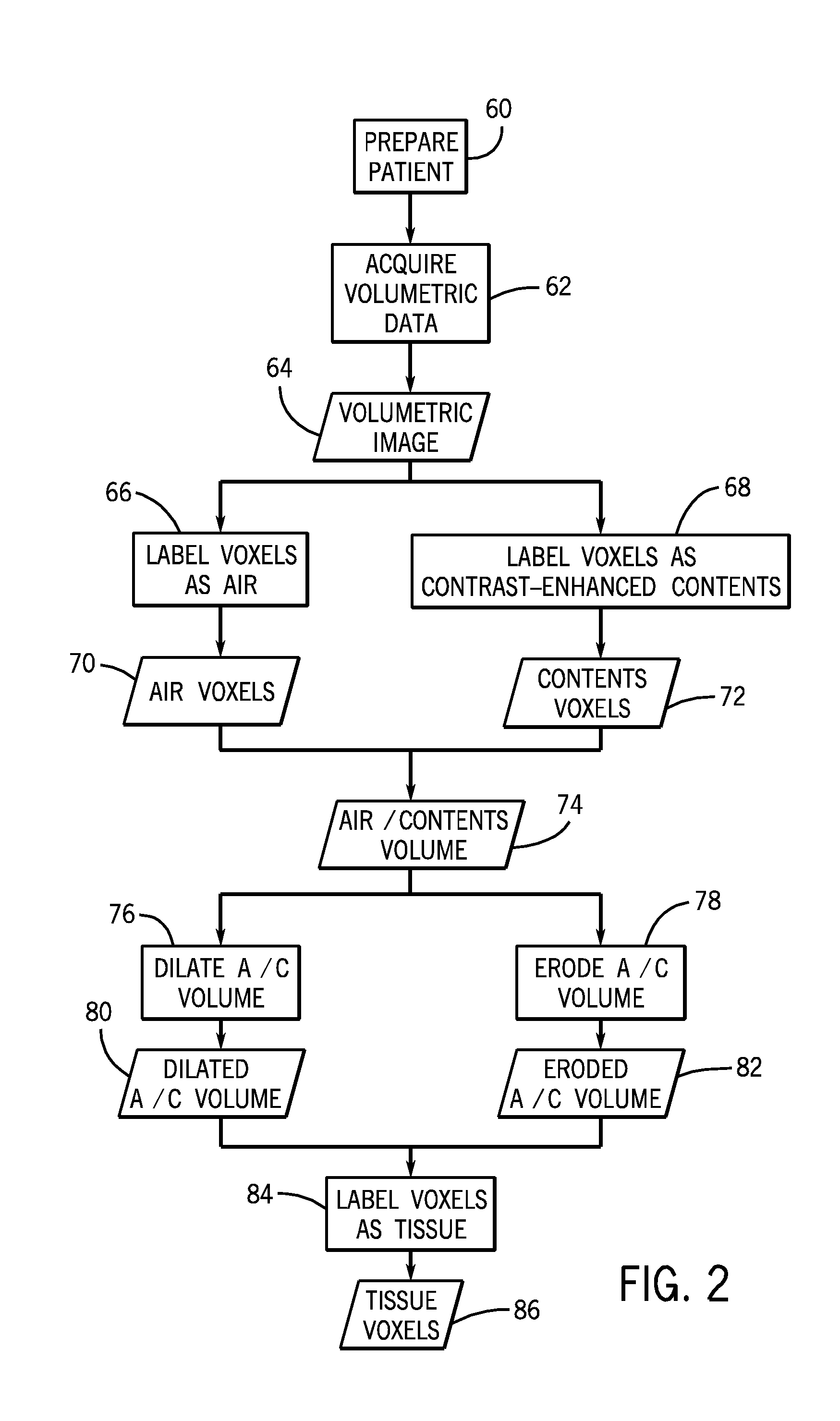
Tissue classification in medical images
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
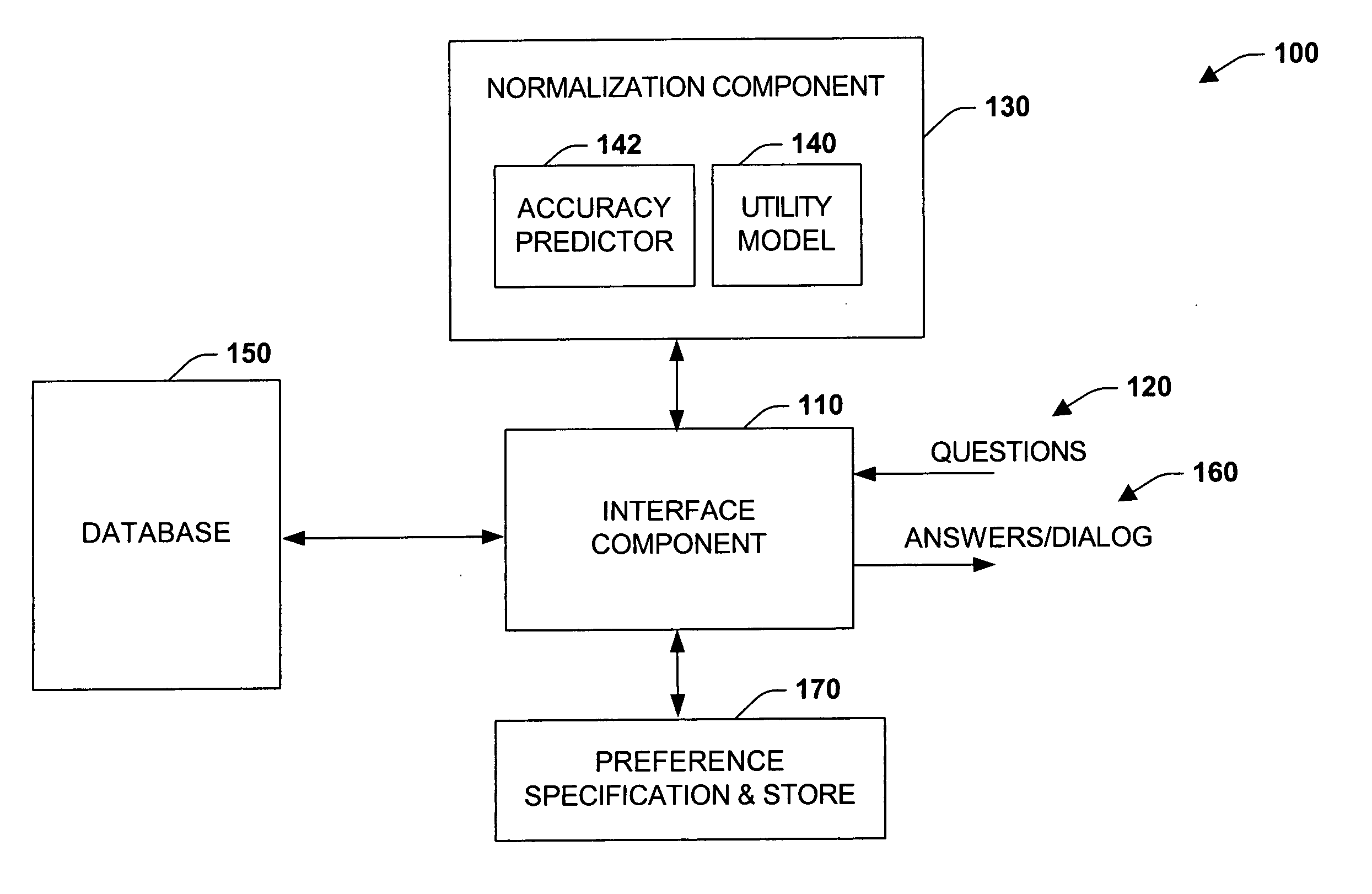
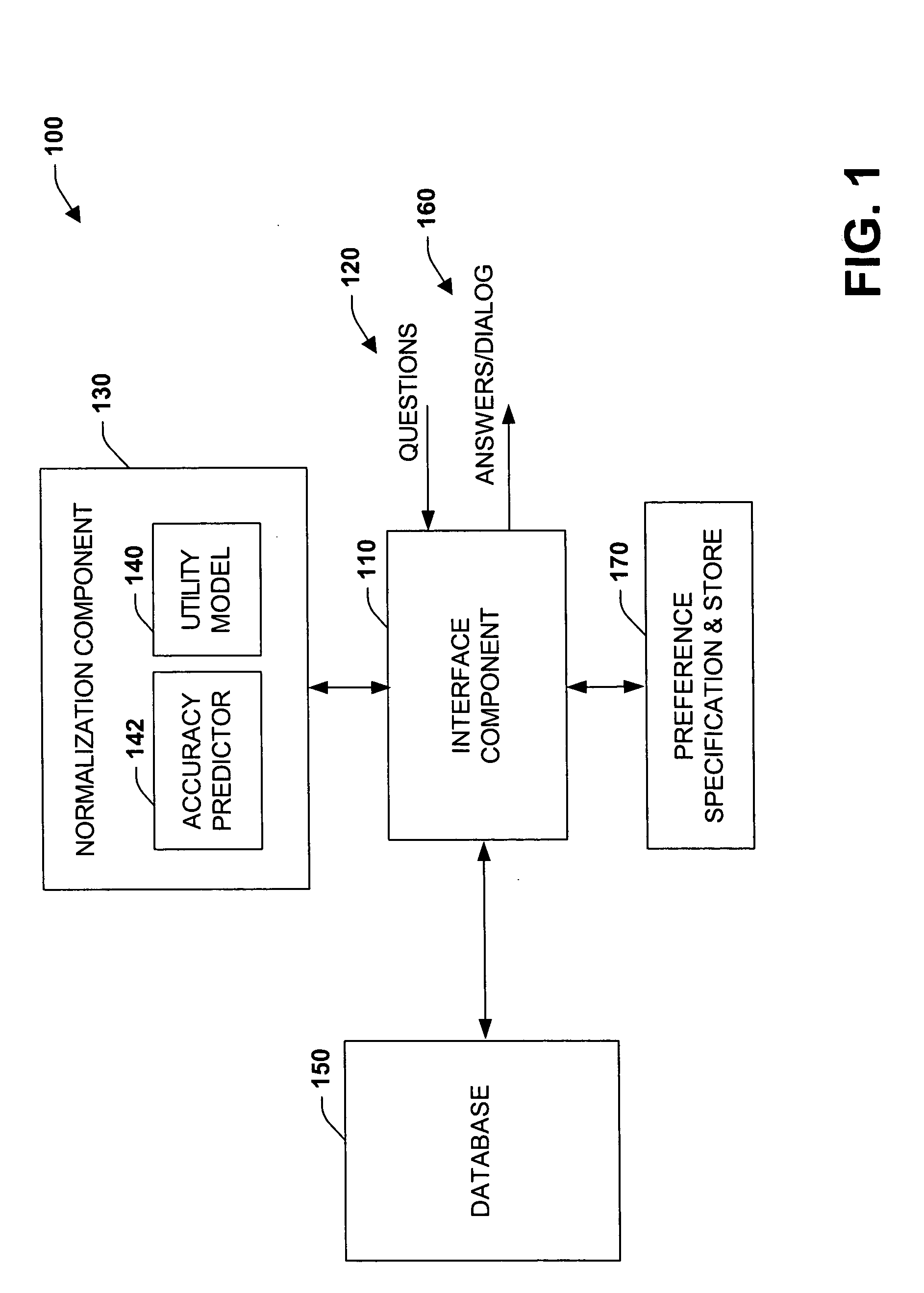
Cost-benefit approach to automatically composing answers to questions by extracting information from large unstructured corpora
InactiveUS20050033711A1Simple modelImprove predictive performanceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalProbit modelBenefit analysis
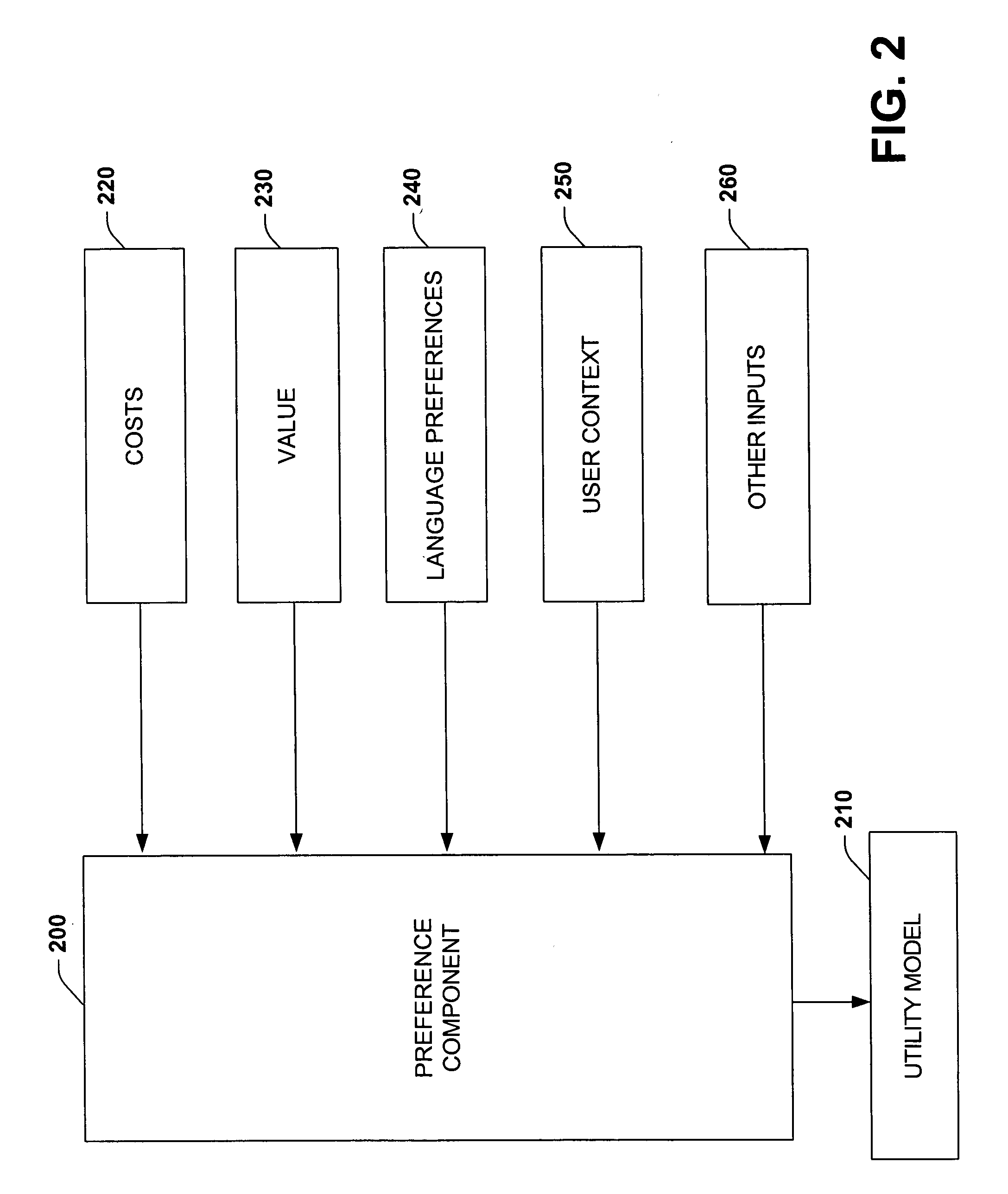
The present invention relates to a system and methodology to facilitate extraction of information from a large unstructured corpora such as from the World Wide Web and / or other unstructured sources. Information in the form of answers to questions can be automatically composed from such sources via probabilistic models and cost-benefit analyses to guide resource-intensive information-extraction procedures employed by a knowledge-based question answering system. The analyses can leverage predictions of the ultimate quality of answers generated by the system provided by Bayesian or other statistical models. Such predictions, when coupled with a utility model can provide the system with the ability to make decisions about the number of queries issued to a search engine (or engines), given the cost of queries and the expected value of query results in refining an ultimate answer. Given a preference model, information extraction actions can be taken with the highest expected utility. In this manner, the accuracy of answers to questions can be balanced with the cost of information extraction and analysis to compose the answers.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
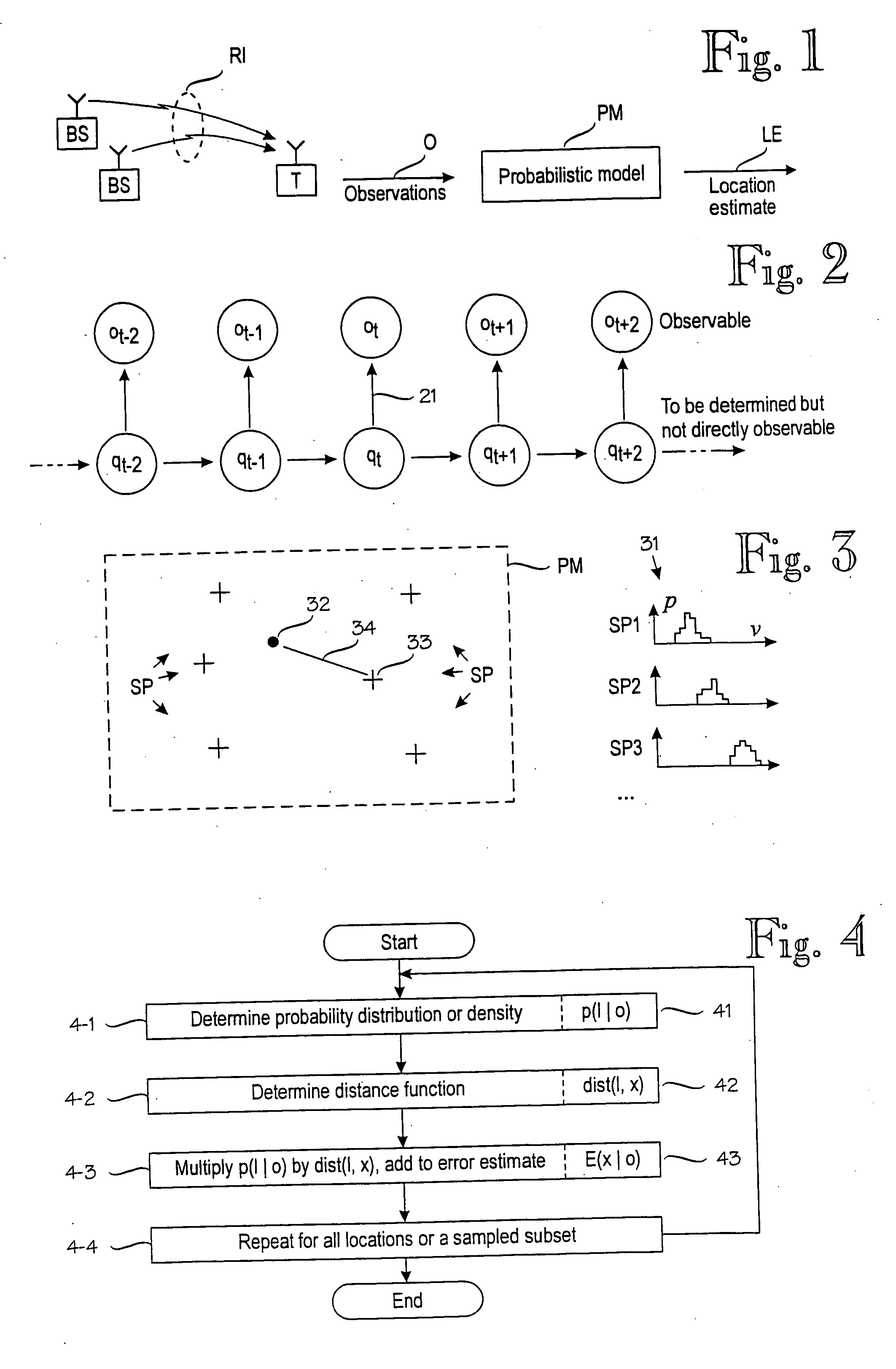
Error estimate concerning a target device's location operable to move in a wireless environment
ActiveUS20050131635A1Improve efficiencyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlProbit modelPosition error
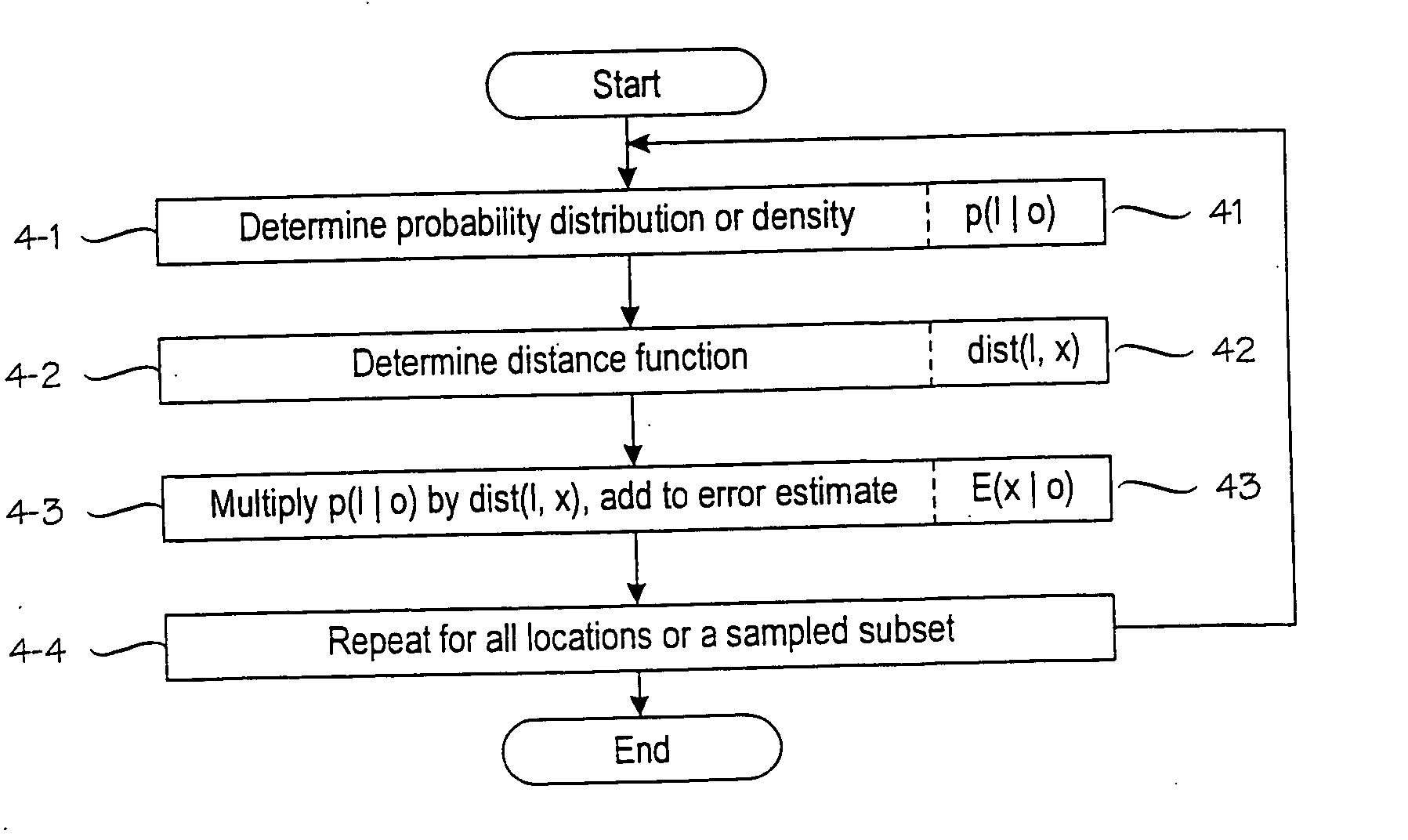
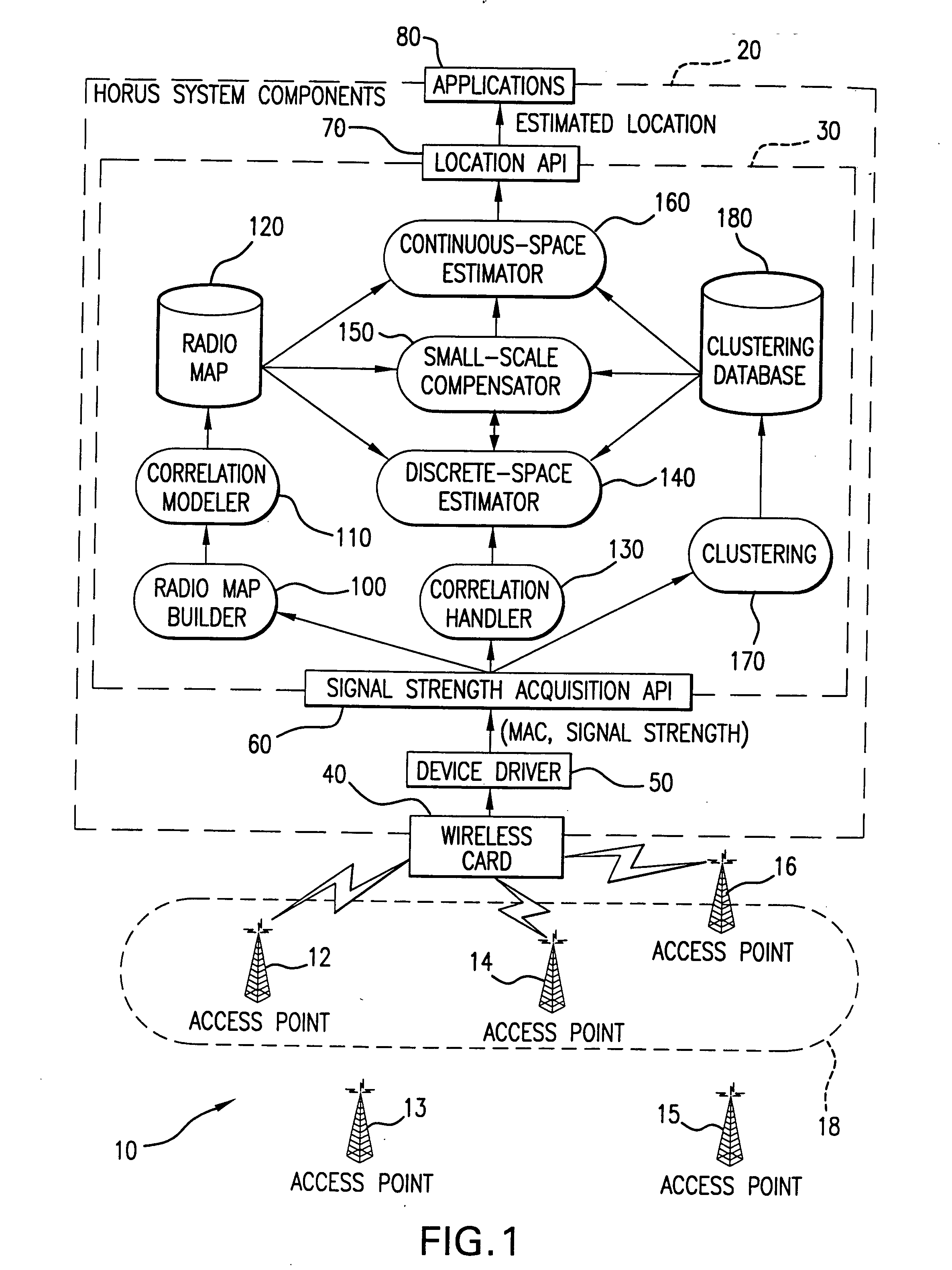
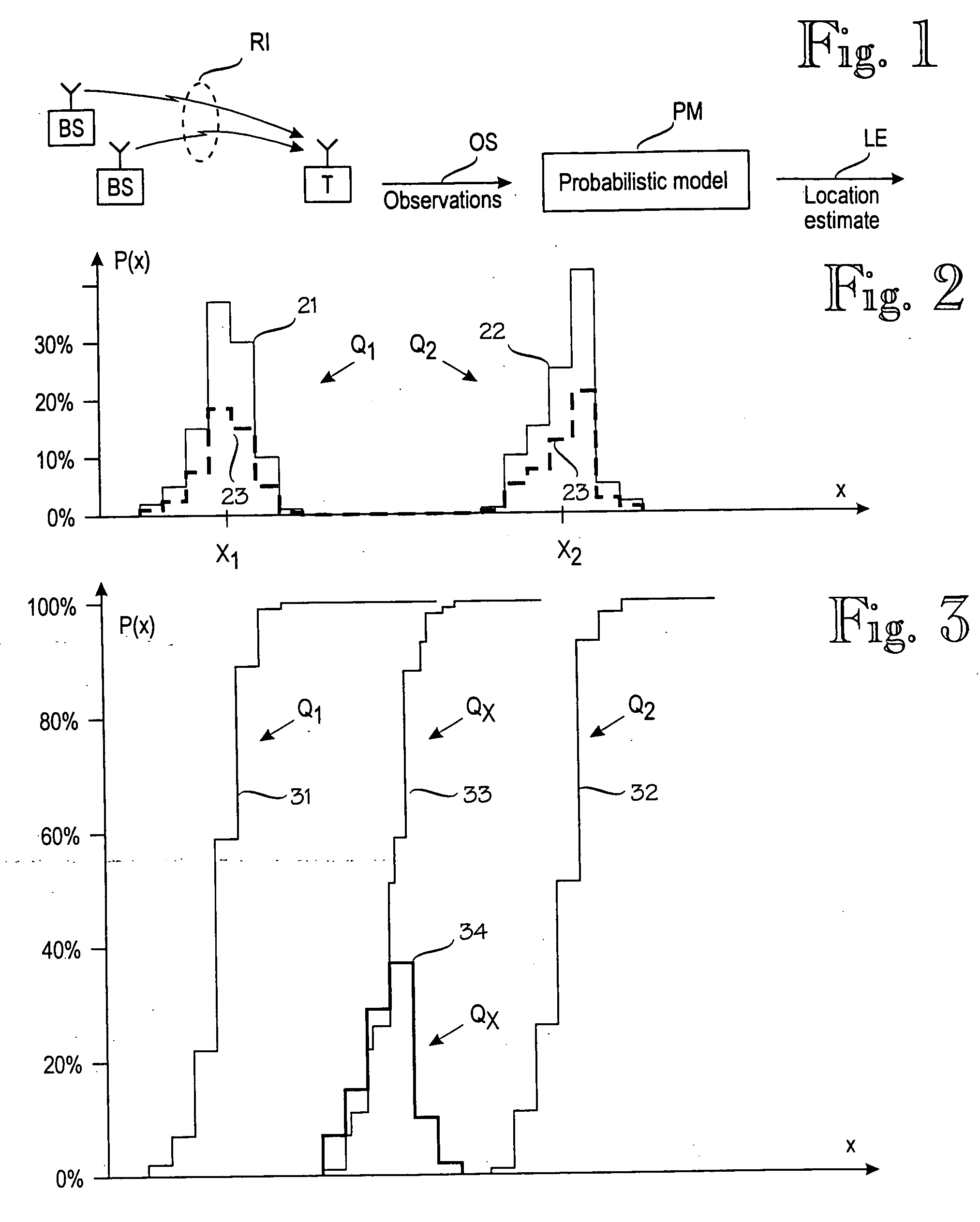
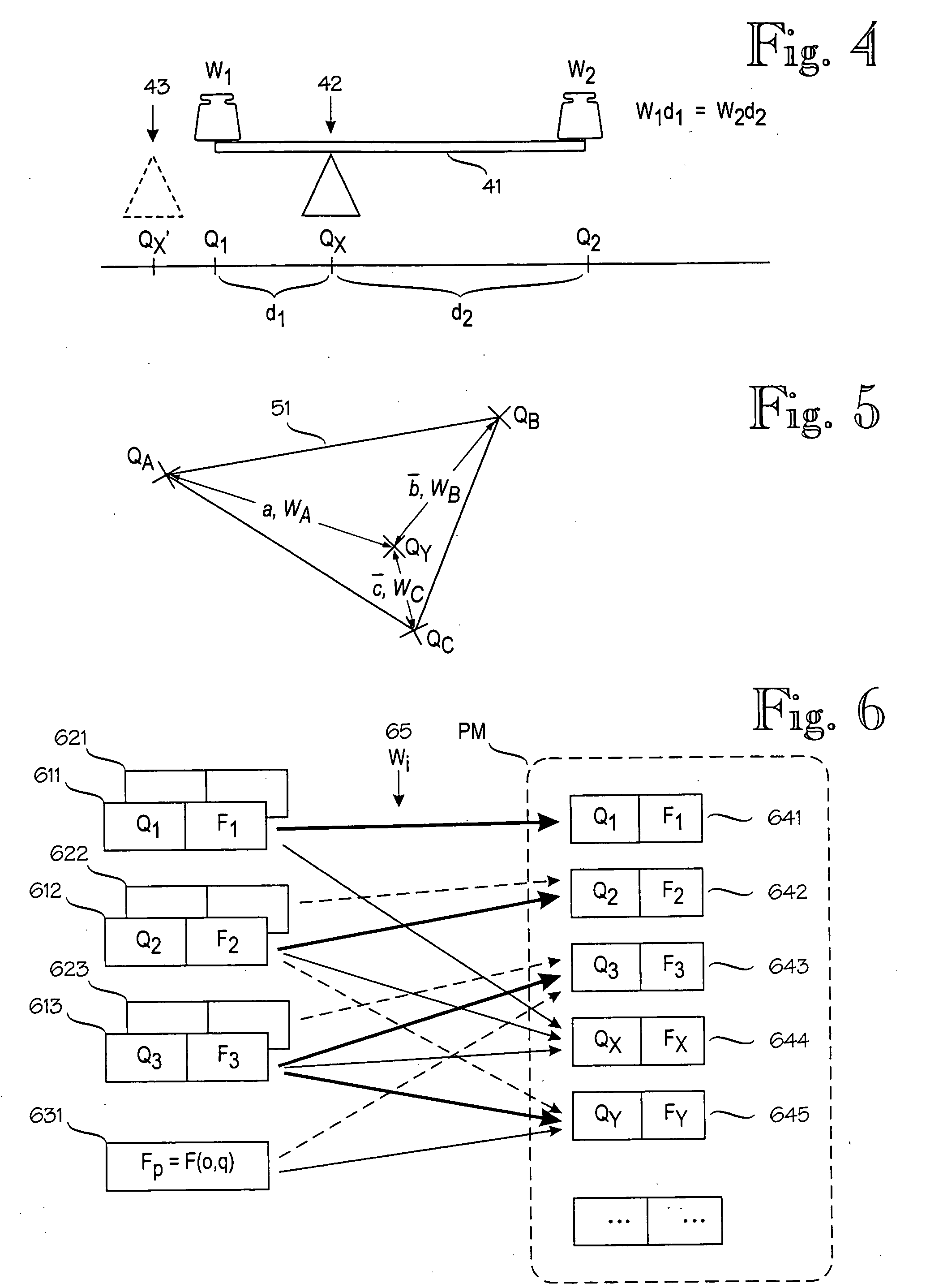
A method for determining an error estimate concerning a target device's location. The target device moves and communicates in a wireless environment using signals having at least one measurable signal value. A probabilistic model of the wireless environment indicates a probability distribution for signal values at several sample points in the wireless environment. A set of observations of signal values is made and the target device's location is estimated based on the probabilistic model and the set of observations. The error estimate (43) is determined as a combination of products over several sample points (SP). Each product comprises a probability distribution (41) for the sample point in question being the target device's location and a distance function (43) between the sample point in question and the target device's estimated location.
Owner:AIRISTA FLOW INC +1
Method and apparatus for tracking a number of objects or object parts in image sequences
ActiveUS20080031492A1Reduce computational complexityReduce complexityImage enhancementImage analysisProbit modelVisual perception
Owner:FOND BRUNO KESSLER
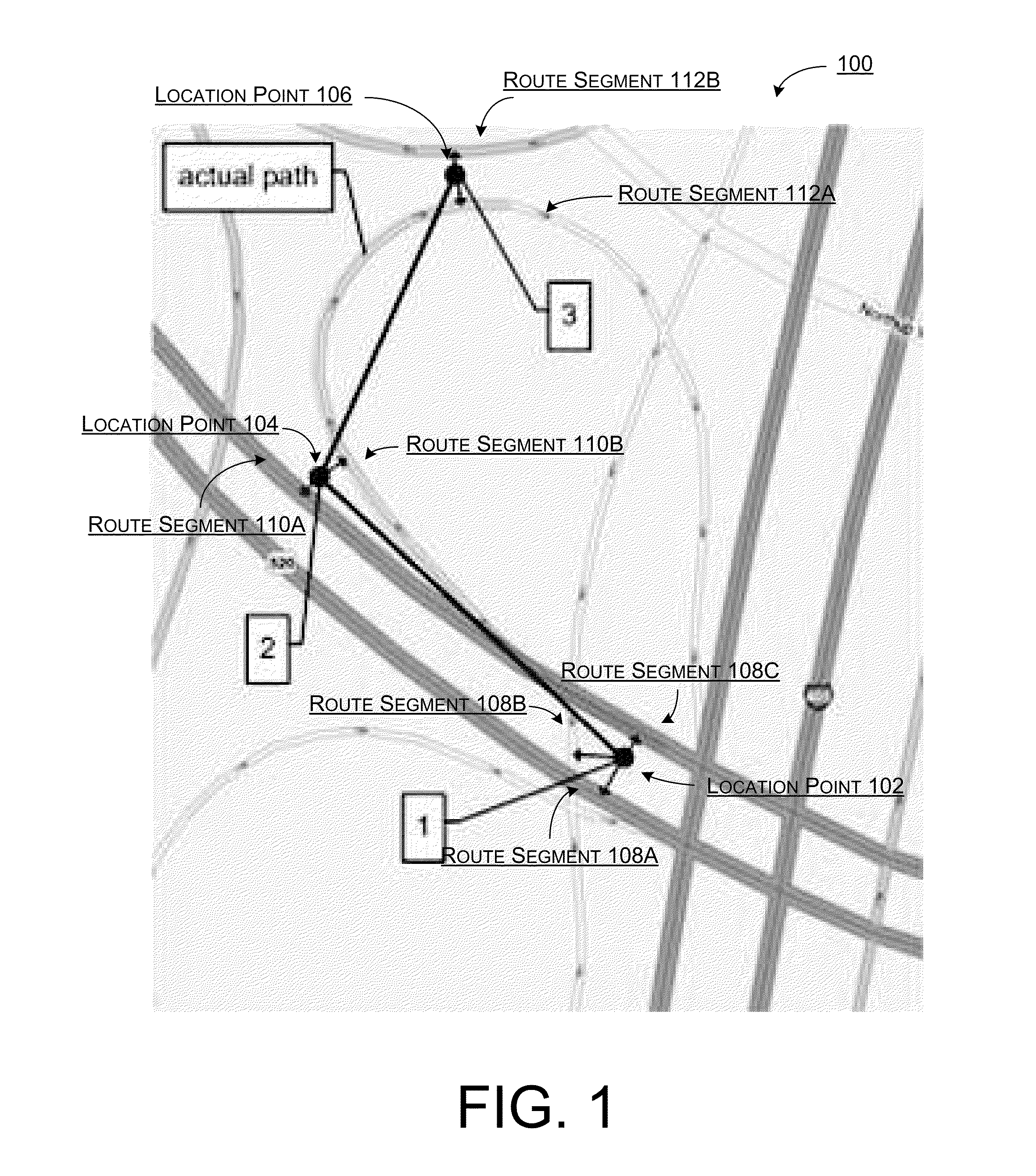
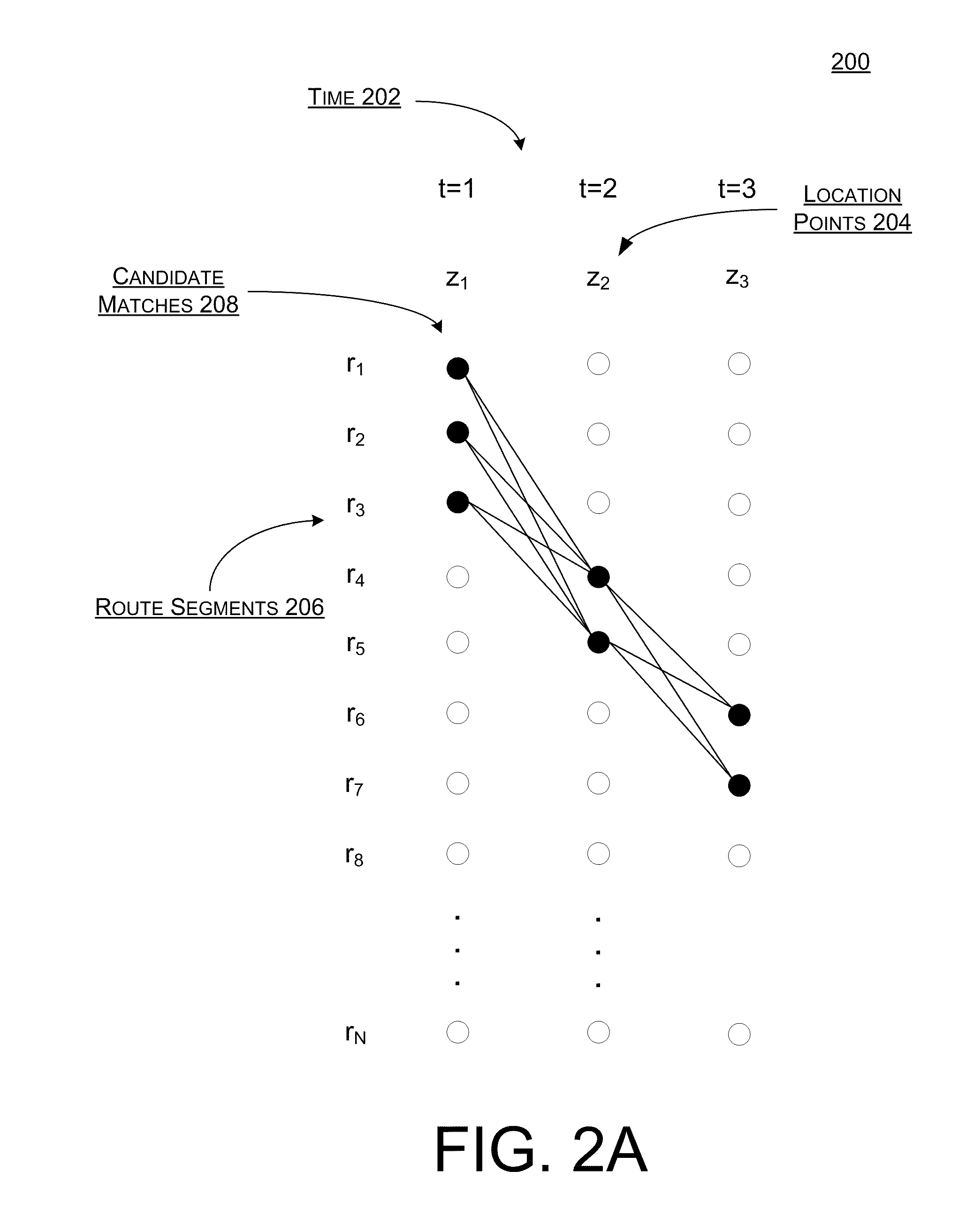
Probabilistic Map Matching From A Plurality Of Observational And Contextual Factors
ActiveUS20110313648A1Well formedInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlProbit modelHide markov model
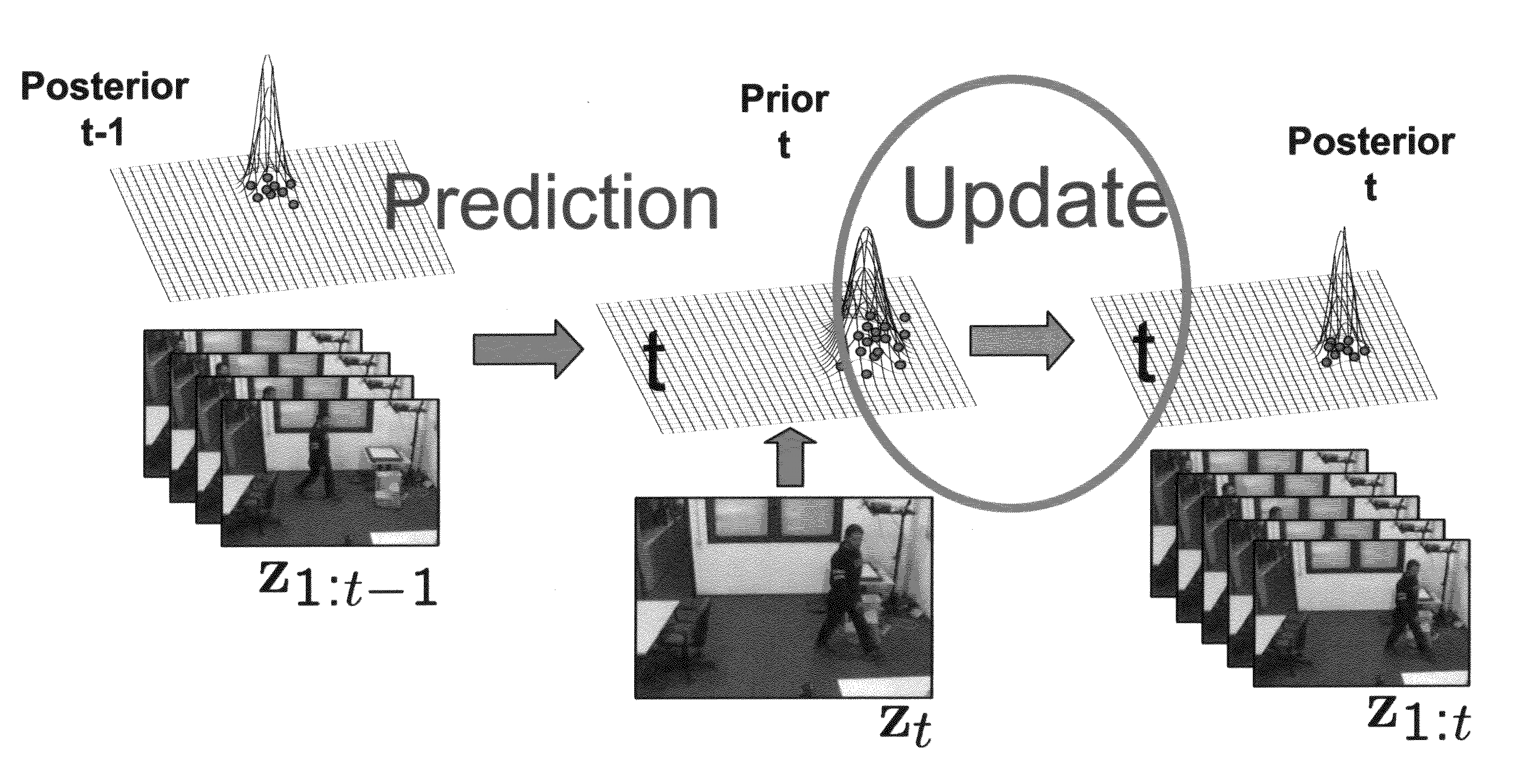
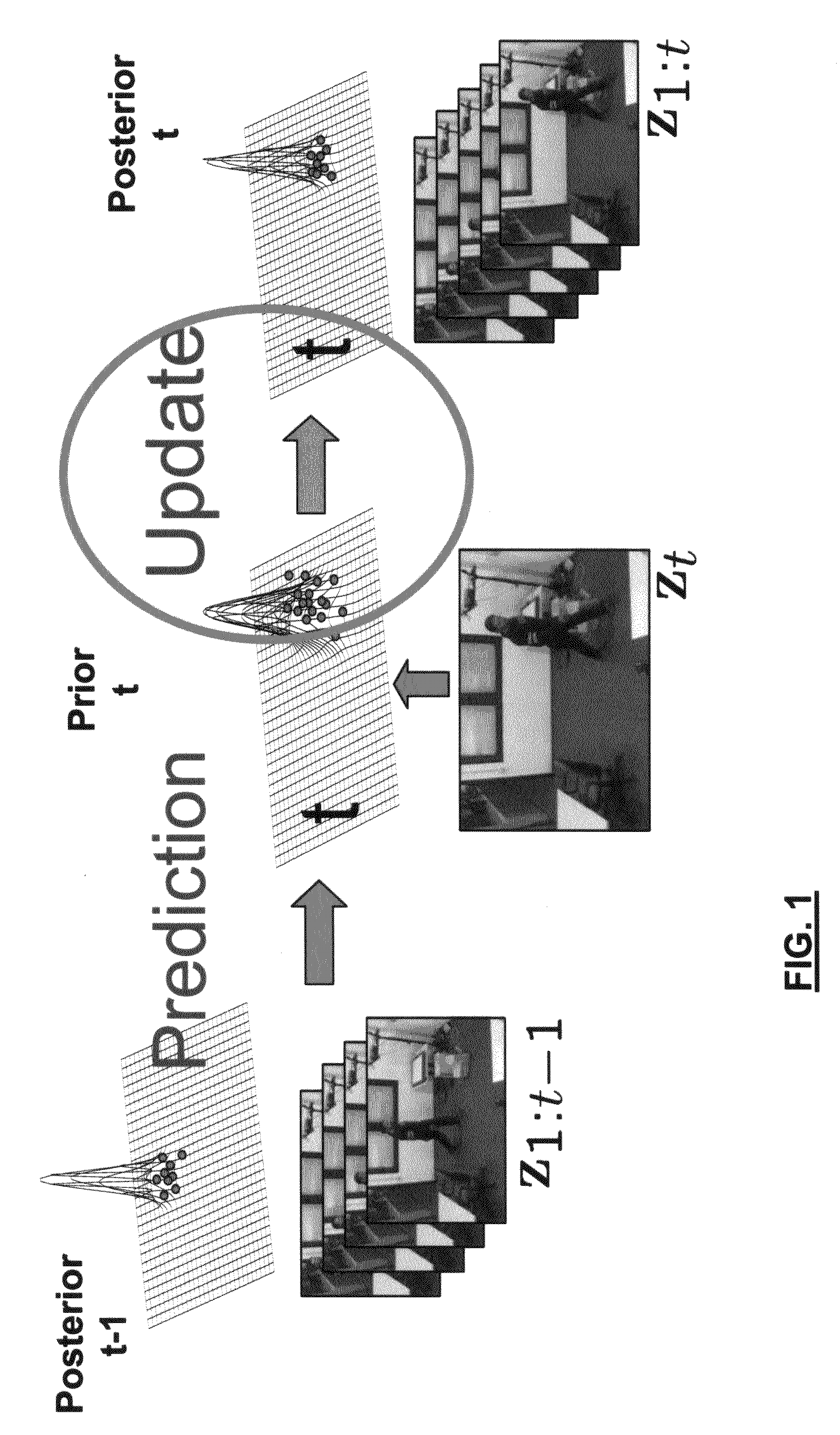
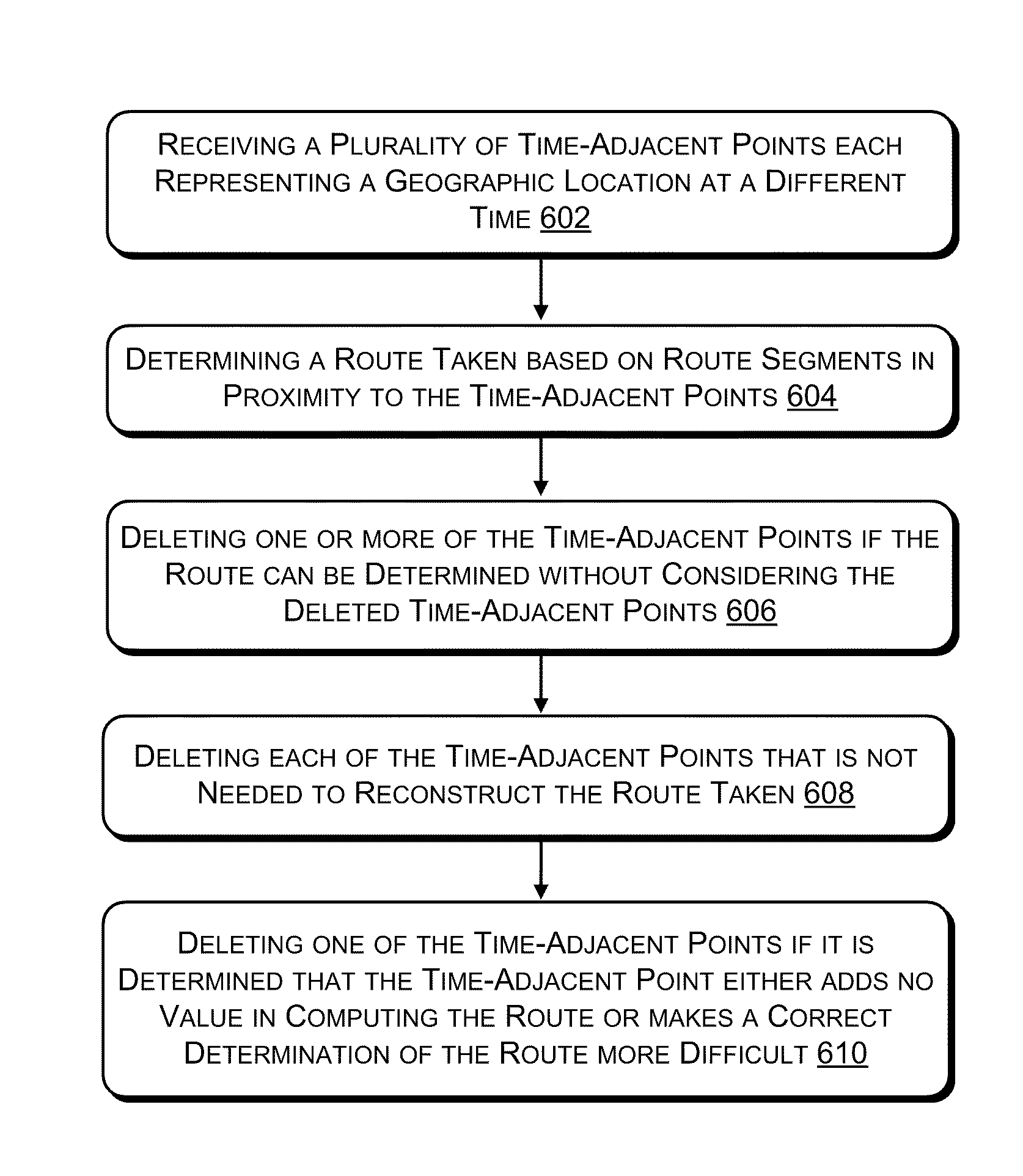
Systems, methods, and devices are described for implementing map matching techniques relating to measured location data. Probabilistic models, including temporal Bayesian network models and Hidden Markov Models, may be used for combining multiple classes of evidence relating to potential locations of points traversed on routes over time. Multiple route segments and overall routes may be maintained under relative uncertainty as candidates. The candidate route segments and overall routes may then be reduced into a smaller number of candidates or a single most likely route as a trip progresses. As the trip progresses, route segments in proximity to each location point are identified and candidate matches are determined. A probability of an entity traversing a candidate match at a given time and a probability of an entity traversing between a first candidate match at a first time and a second candidate match at a second time are determined based on a plurality of factors. Different modalities may be used to measure and transmit the location data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
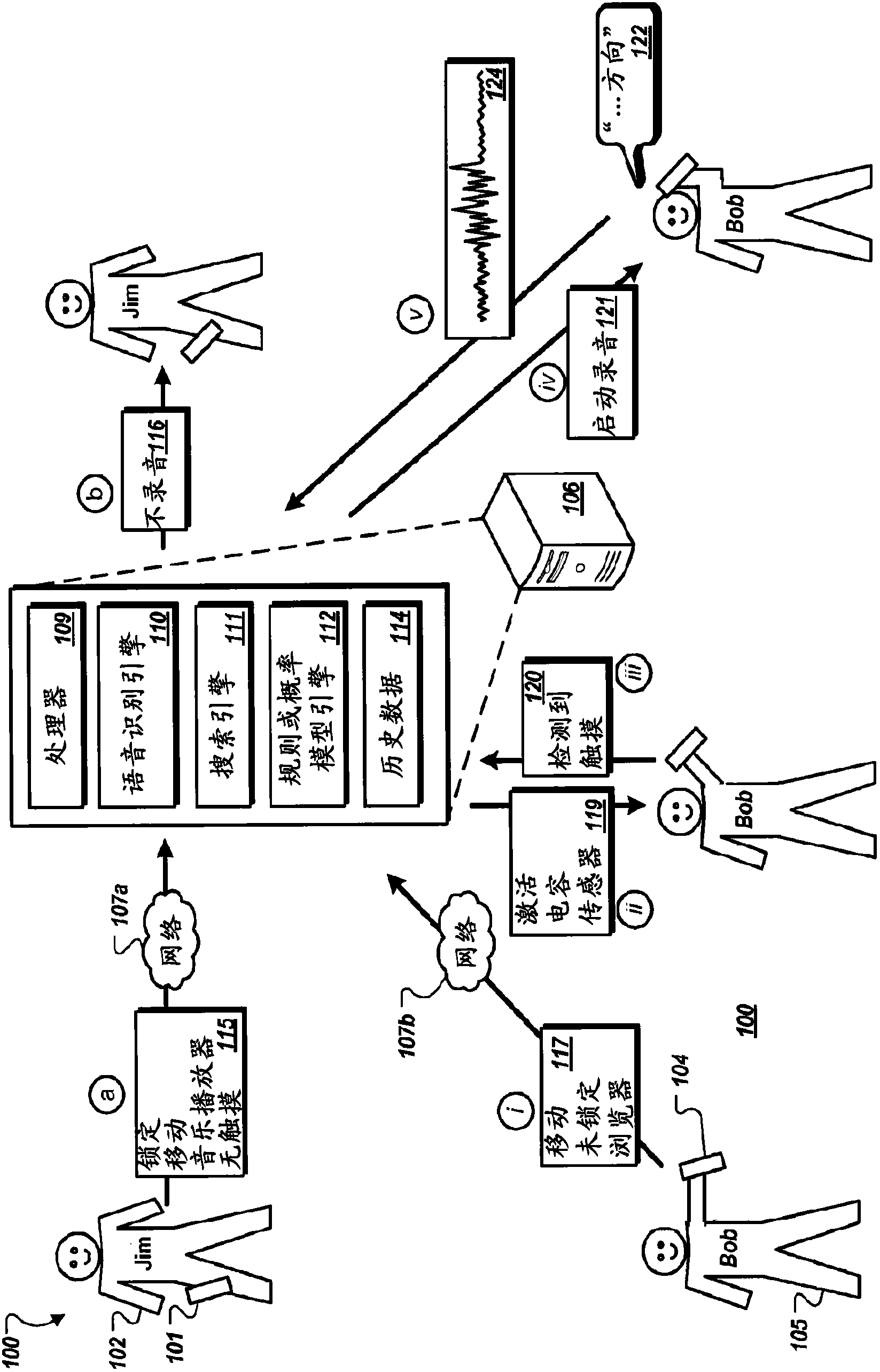
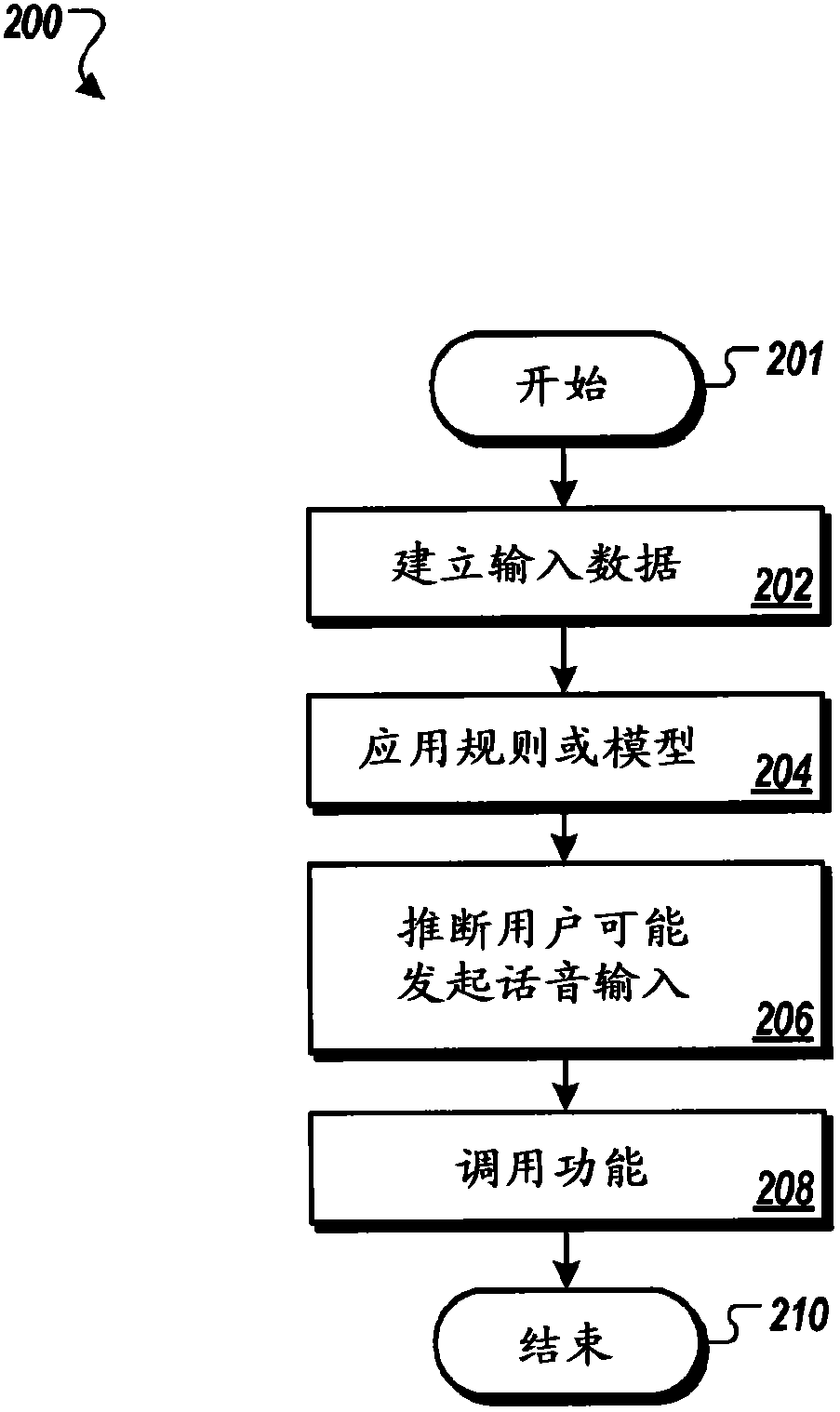
Predictive pre-recording of audio for voice input
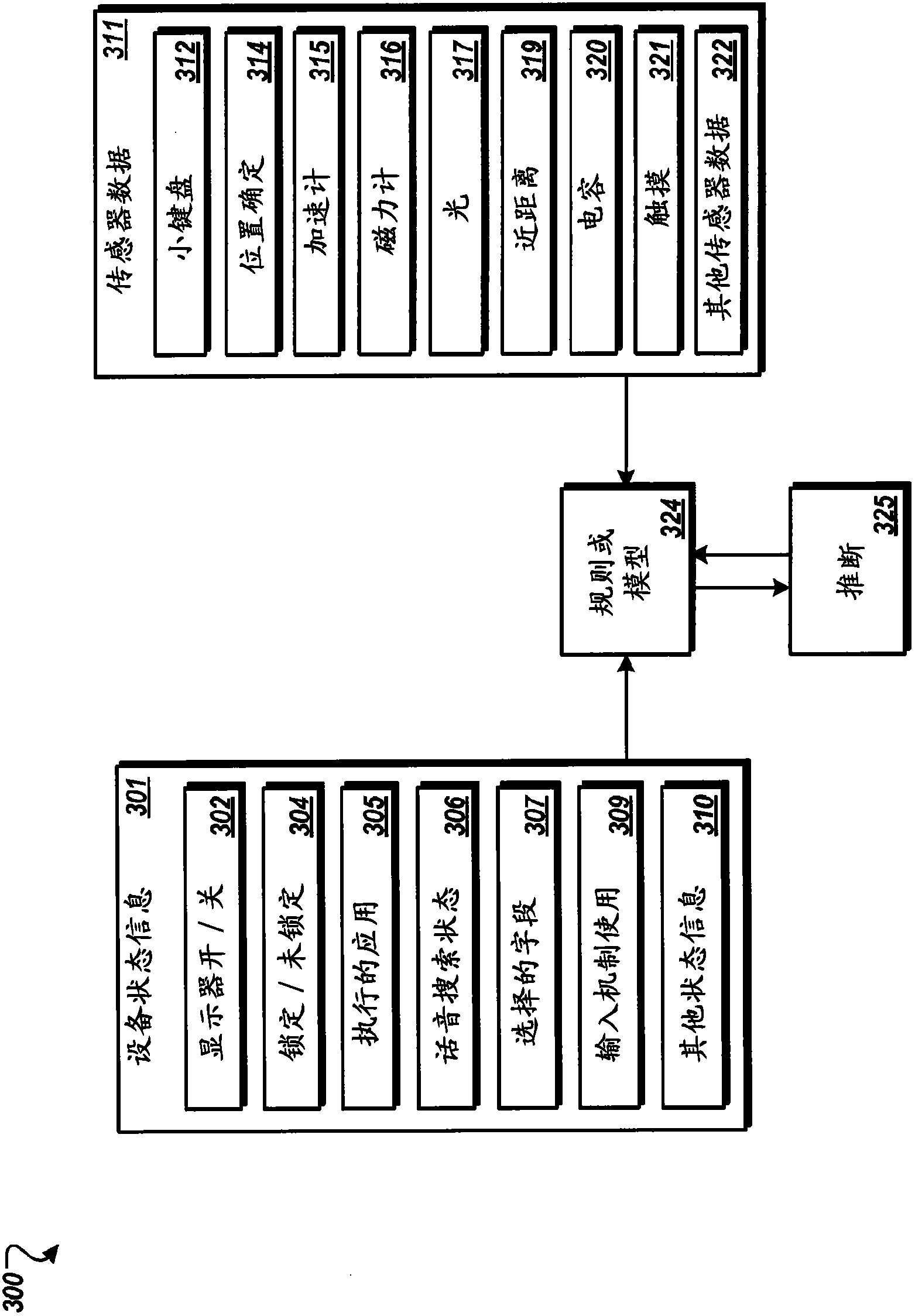
ActiveCN102918493AAvoid front truncationShortened battery lifeDigital data processing detailsNatural language data processingProbit modelDevice status
Methods, systems, and apparatus, including computer programs encoded on a computer storage medium, for providing predictive pre-recording of audio for voice input. In one aspect, a method includes establishing, as input data, state data that references a state of a mobile device and sensor data that is sensed by one or more sensors of the mobile device, applying a rule or a probabilistic model to the input data, inferring, based on applying the rule or the probabilistic model to the input data, that a user of the mobile device is likely to initiate voice input, and invoking one or more functionalities of the mobile device in response to inferring that the user is likely to initiate voice input.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for predicting the failure of a component
ActiveUS7016825B1Plug gaugesComputation using non-contact making devicesProbit modelComputer science
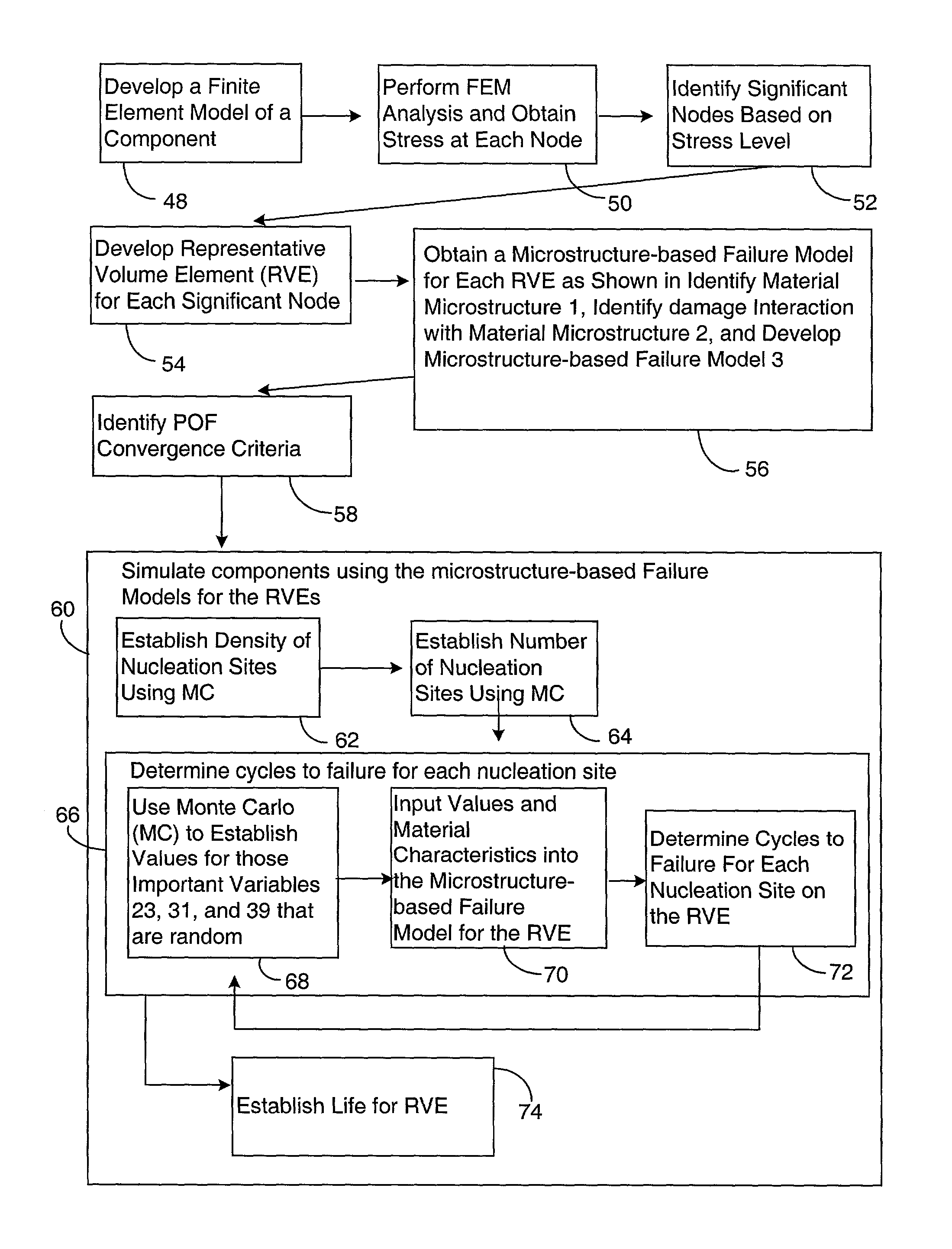
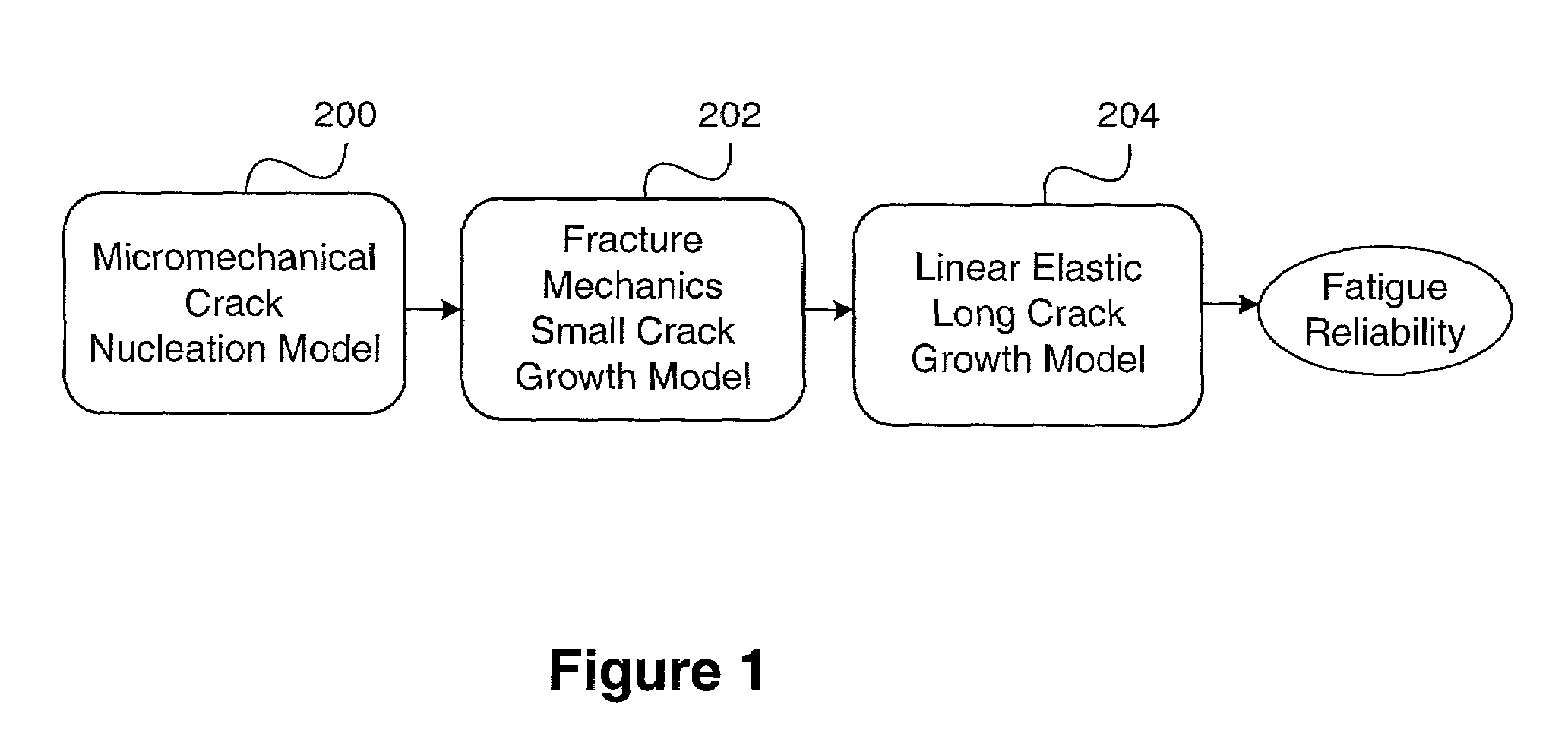
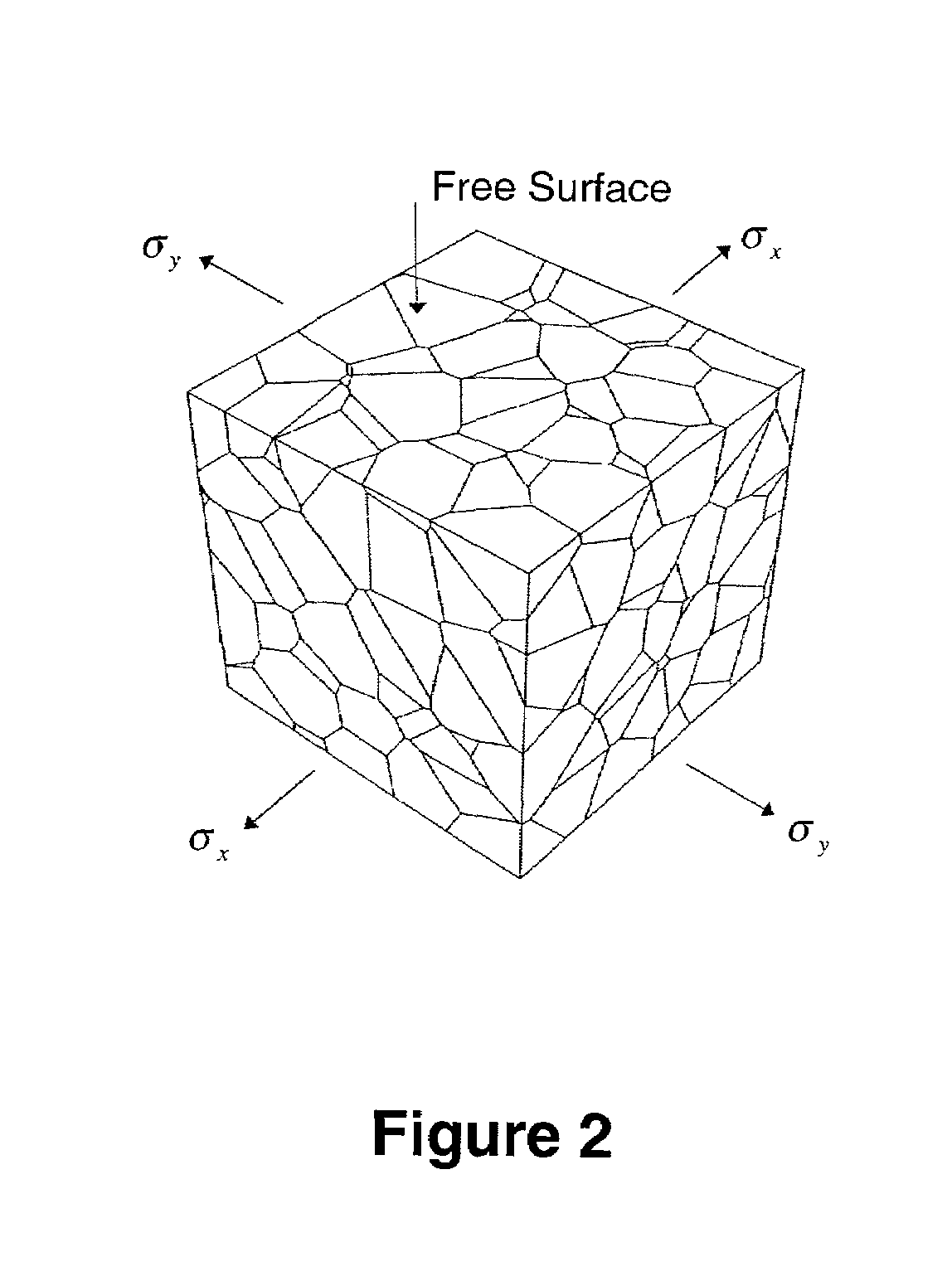
The invention provides a method and apparatus for predicting the failure of a component using a probabilistic model of a material's microstructural-based response to fatigue. The method predicts the component failure by a computer simulation of multiple incarnations of real material behavior, or virtual prototyping. The virtual prototyping simulates the effects of characteristics that include grain size, grain orientation, micro-applied stress and micro-yield strength that are difficult to simulate with real specimens. The invention provides an apparatus for predicting the response of a component to fatigue using the method.
Owner:VEXTEC CORP
Anomaly detection
InactiveUS20050193281A1Not easy to detectDigital computer detailsHardware monitoringProbit modelFeature vector
A system such as a Web-based system in which a plurality of computers interact with each other is monitored to detect online an anomaly. Transactions of a service provided by each of a plurality of computers to another computer are collected, a matrix of correlations between nodes in the system is calculated from the transactions, and a feature vector representing anode activity balance is obtained from the matrix. The feature vector is monitored using a probability model to detect a transition to an anomalous state.
Owner:IBM CORP
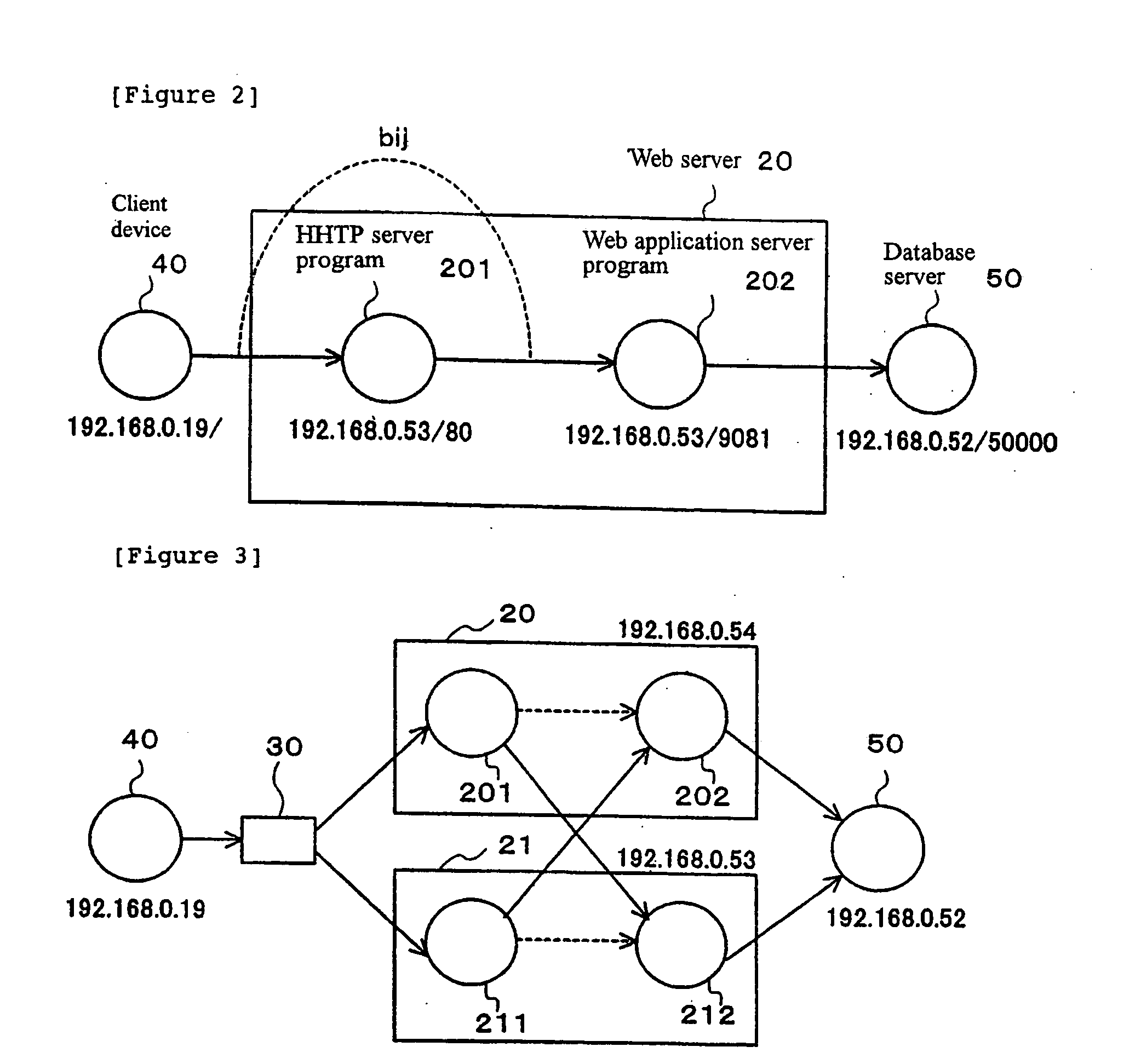
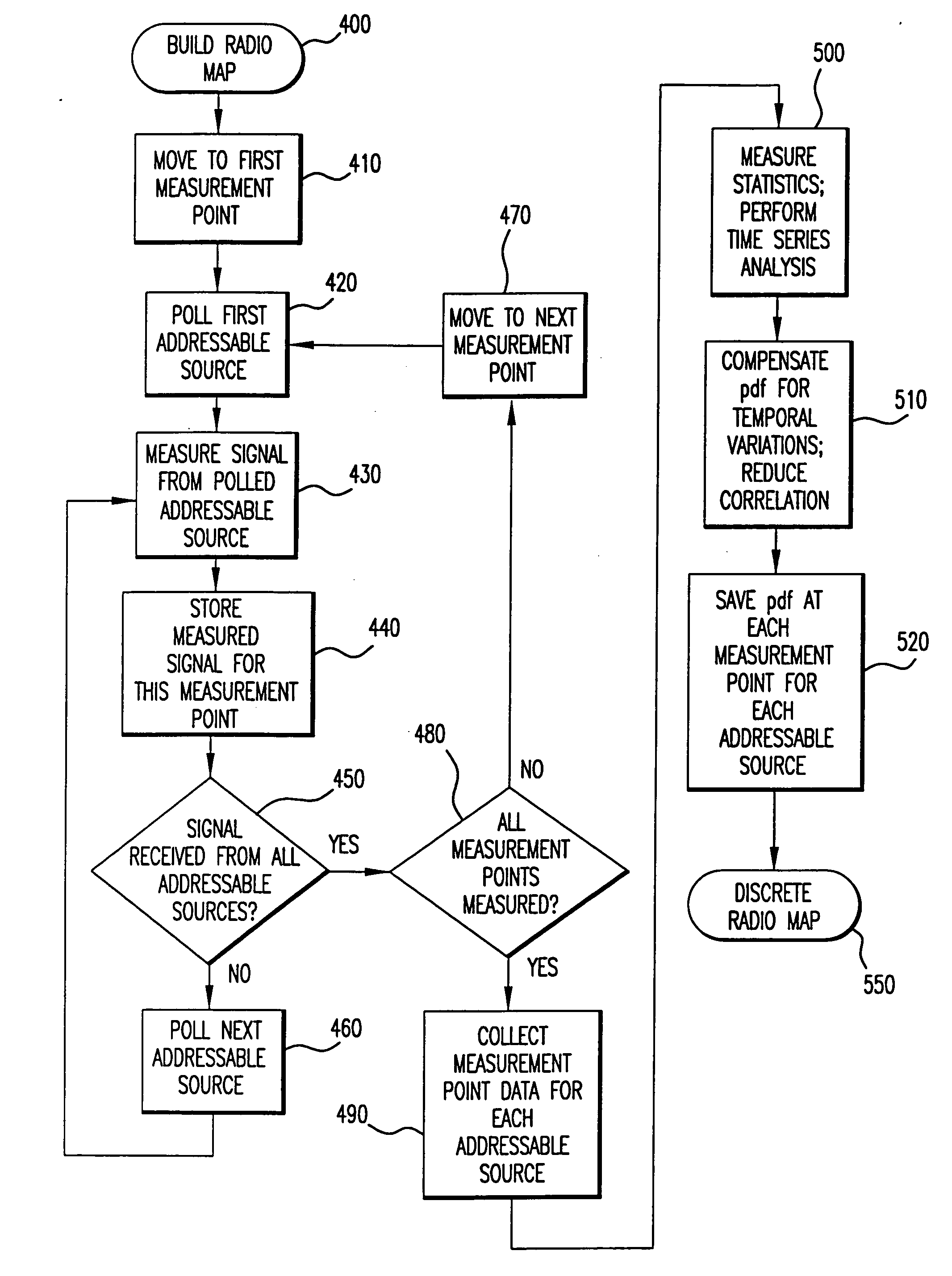
Method and system for determining user location in a wireless communication network
InactiveUS20050243936A1Maximize probabilityAccurate measurementData switching by path configurationSatellite radio beaconingProbit modelRadio map
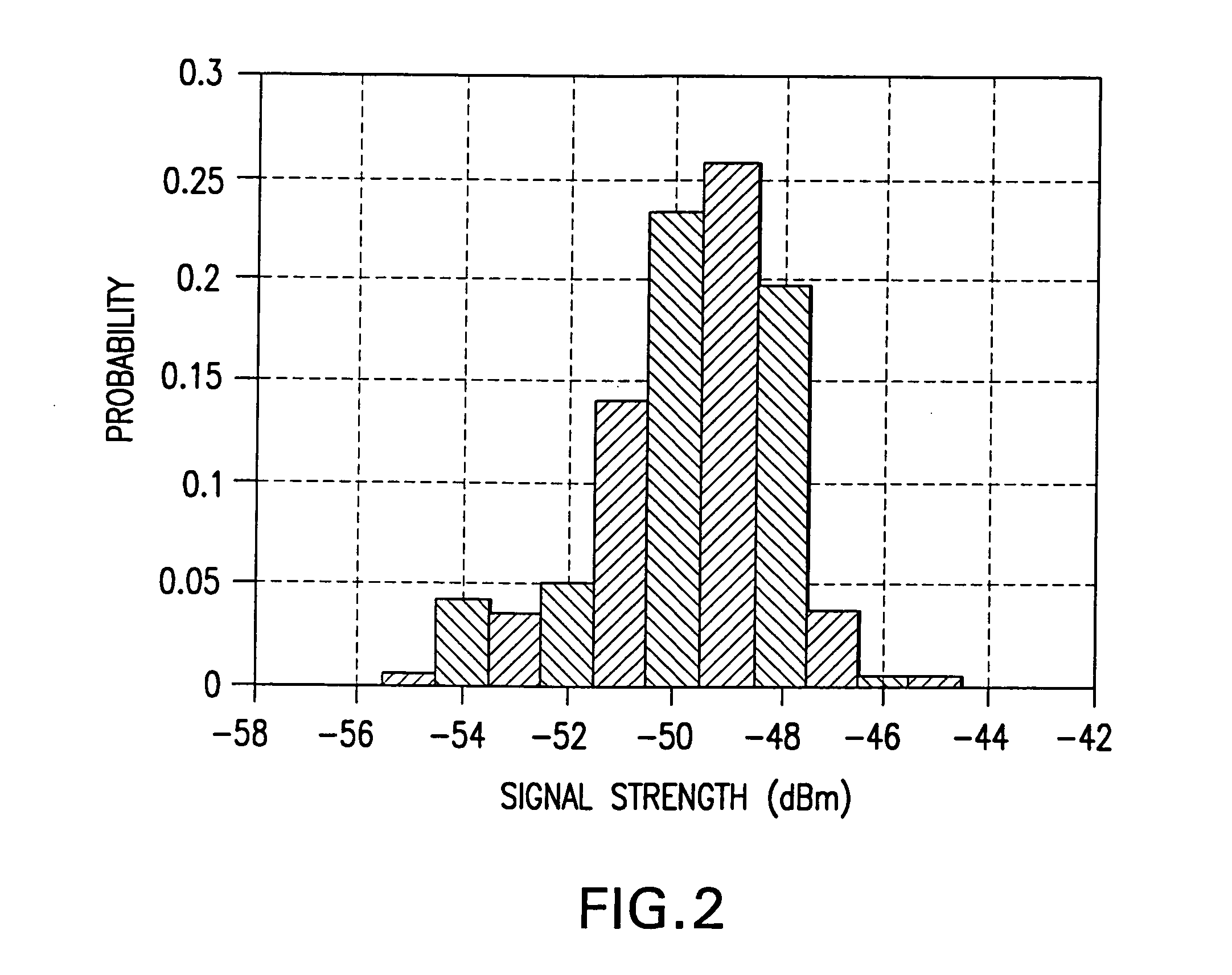
In a wireless communication network, the location of an addressable receiver relative to the locations of a plurality of addressable sources of electromagnetic radiation is found using probabilistic models of the signal strength measured at the addressable receiver. The inventive method provides location determination on a finer spatial scale than was heretofore available. A region of interest is calibrated via a discrete-space radio map storing probability distributions of received signal strength at the measurement locations. The stored probability distributions are compensated for temporal variability and biases, such as through temporal correlations of the sampled received signal strength. A measurement of the signal strength at the addressable receiver from each of the plurality of addressable sources is used in conjunction with the discrete-space radio map to identify one of the coordinates thereof that maximizes the conditional probability P(x|s), where x is the radio map location and s is a vector of measured signal strengths. Small spatial scale variability can be compensated for using a perturbation technique. The method further implements a continuous-space estimator to return an estimated user location that falls between discrete-space radio map locations.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Speech and text driven HMM-based body animation synthesis
An “Animation Synthesizer” uses trainable probabilistic models, such as Hidden Markov Models (HMM), Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), etc., to provide speech and text driven body animation synthesis. Probabilistic models are trained using synchronized motion and speech inputs (e.g., live or recorded audio / video feeds) at various speech levels, such as sentences, phrases, words, phonemes, sub-phonemes, etc., depending upon the available data, and the motion type or body part being modeled. The Animation Synthesizer then uses the trainable probabilistic model for selecting animation trajectories for one or more different body parts (e.g., face, head, hands, arms, etc.) based on an arbitrary text and / or speech input. These animation trajectories are then used to synthesize a sequence of animations for digital avatars, cartoon characters, computer generated anthropomorphic persons or creatures, actual motions for physical robots, etc., that are synchronized with a speech output corresponding to the text and / or speech input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Extensible bayesian network editor with inferencing capabilities
A system for the representation, editing, evaluation, and inference of graphical models is disclosed which can be used to construct and evaluate a graphical model or graphical network and to calculate inference values. An efficient method of updating graphical models is demonstrated, and provides the basis for an improved system for manipulation and evaluation of probabilistic models. The graphical network editor is useful in the construction of graphical modes such as Bayesian Networks. The graphical network and network graphical user interface (GUI) are used in conjunction with each other to model a system wherein failure probabilities and the current state of components are taken into account to monitor the health and progress of a system for an engineer or engineering software to evaluate and monitor. The evaluation is useful in the monitoring of assets and other real systems having multiple, dependent, and independently operating components such as a pump, a manufacturing plant, a production line, an assembly line, where asset health and quality control is a concern. The asset components each influencing some overall outcome of a system or situation. Success or failure or probability of success, probability of failure and health of the system can be monitored and manipulated by altering the values of prior probability and posterior probability values. Failure correlation between components can be evaluated wherein failure rates of asset is unknown. Production and quality can be monitored and altered.
Owner:QUANTUM LEAP RES
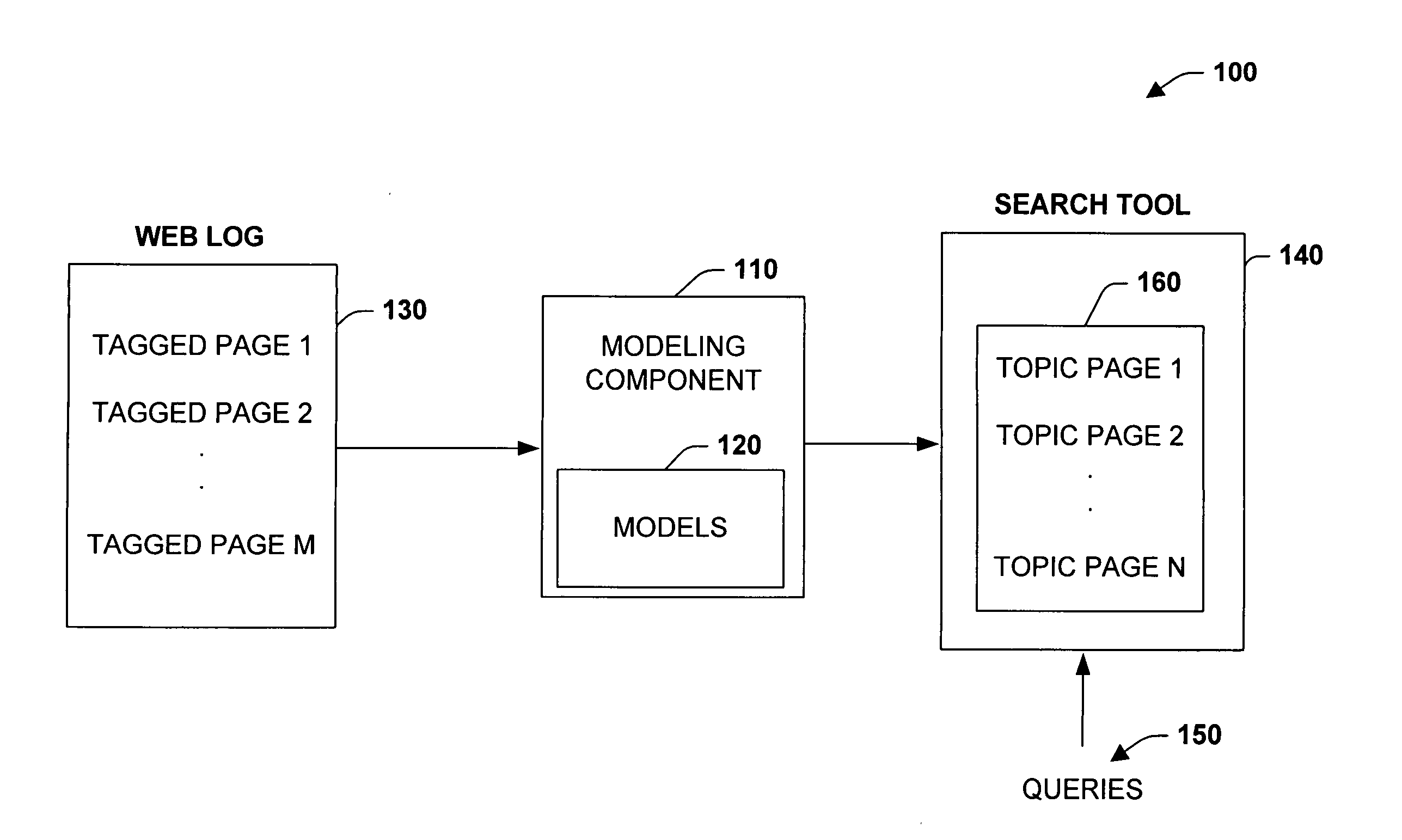
Analysis of topic dynamics of web search
The subject invention relates to probabilistic models that are trained from transitions among various topics of pages visited by a sample population of search users. In one aspect, probabilistic models of topic transitions are learned for individual users and groups of users. Topic transitions for individuals versus larger groups are analyzed, wherein the relative accuracies of personal models of topic dynamics with models constructed from sets of pages drawn from similar groups and from a larger population of users are compared. To exploit temporal dynamics, the accuracy of these models are tested for predicting transitions in topics of visits at increasingly more distant times in the future. The models can be applied to search topic dynamics of tagged pages, and then utilized to predict topics of subsequent pages visited by users.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
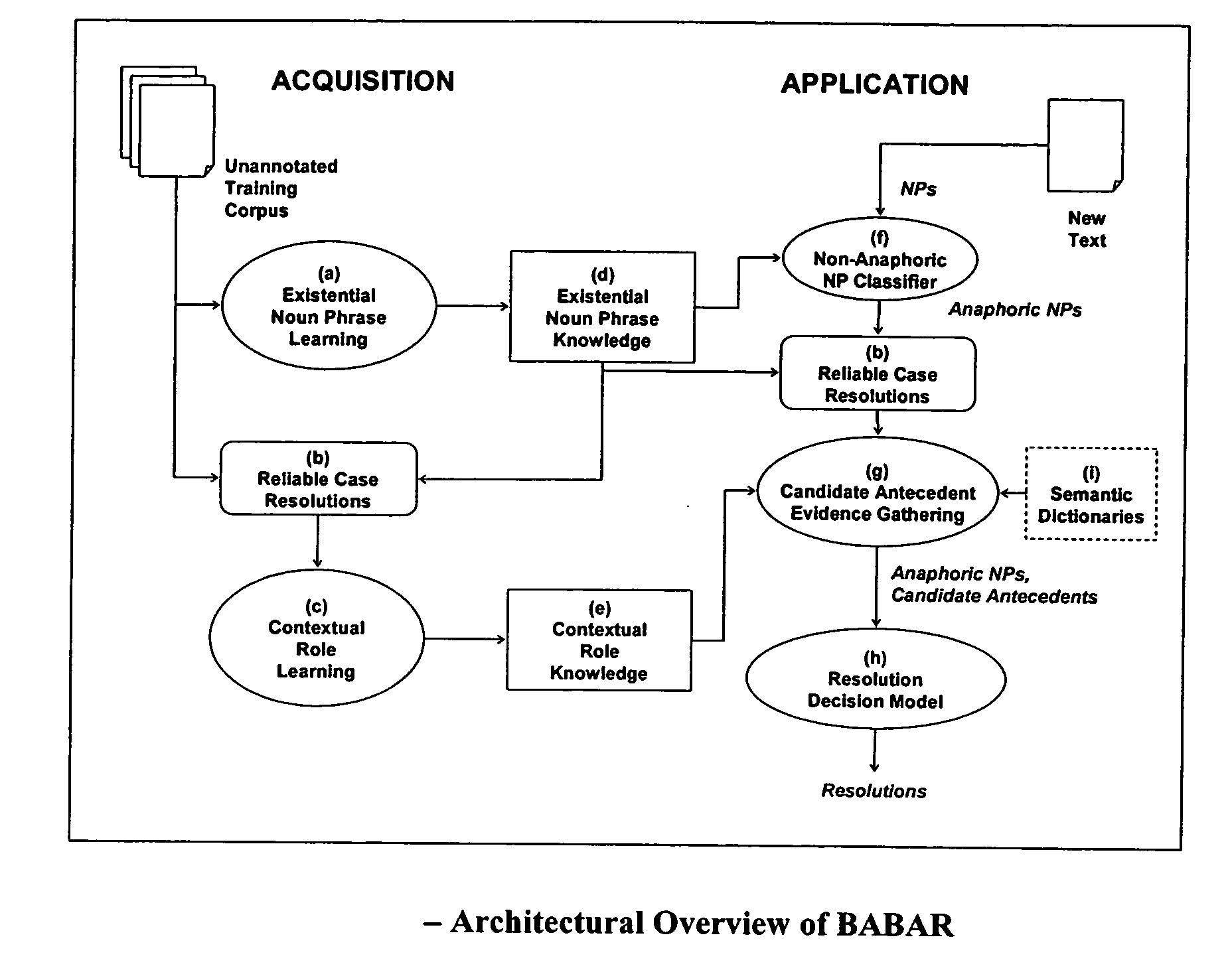
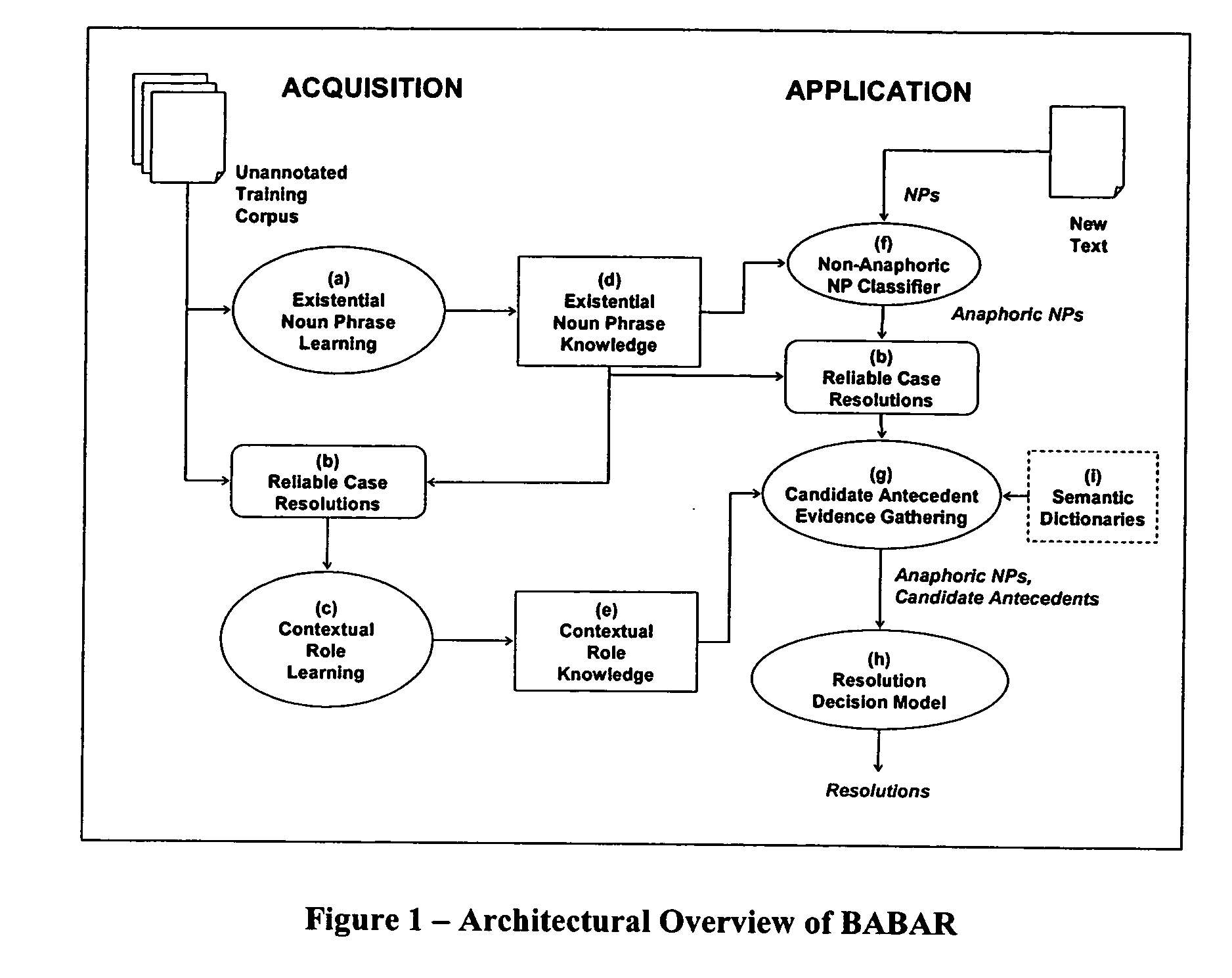
Acquisition and application of contextual role knowledge for coreference resolution
ActiveUS20090326919A1Reduce precisionImprove performanceNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsProbit modelImage resolution
Coreference resolution is the process of identifying when two noun phrases (NP) refer to the same entity. Two main contributions to computational coreference resolution are made. First, this work contributes a new method for recognizing when an NP is anaphoric. Second, traditional approaches to coreference resolution typically select the most appropriate antecedent by recognizing word similarity, proximity, and agreement in number, gender, and semantic class. This work contributes a new source of evidence that focuses on the roles that an anaphor and antecedent play in particular events or relationships. I show that using contextual role knowledge as part of the coreference resolution process increases the number of anaphors that can be resolved, and I demonstrate an unsupervised method for acquiring contextual role knowledge that does not require an annotated training corpus. A probabilistic model based on the Dempster-Shafer model of evidence is used to incorporate contextual role knowledge with traditional evidence sources.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Iterative, maximally probable, batch-mode commercial detection for audiovisual content
InactiveUS20060029368A1Improve accuracyPromote resultsTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsLocation detectionProbit model
Owner:INTERVAL RESEARCH CORPORATION
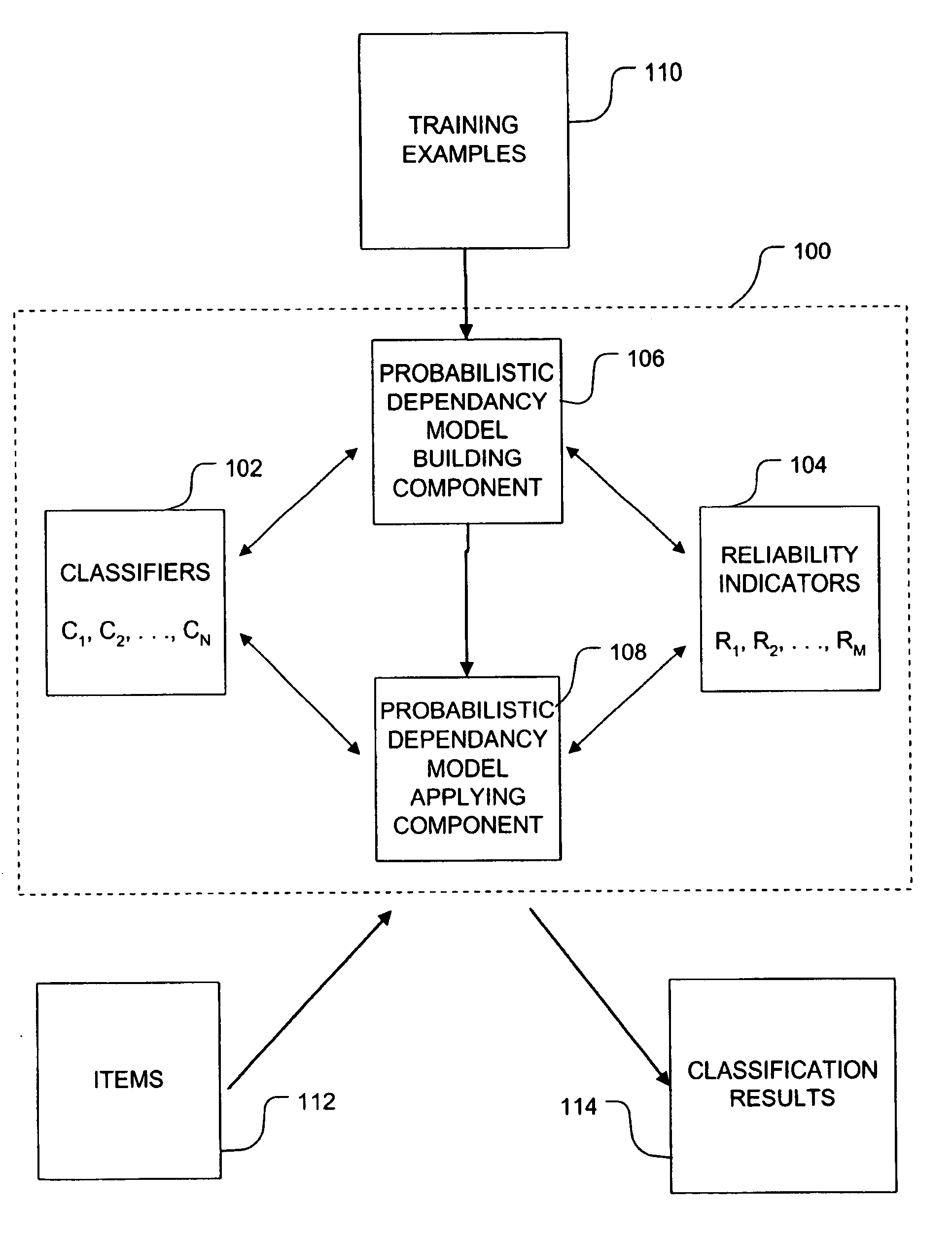
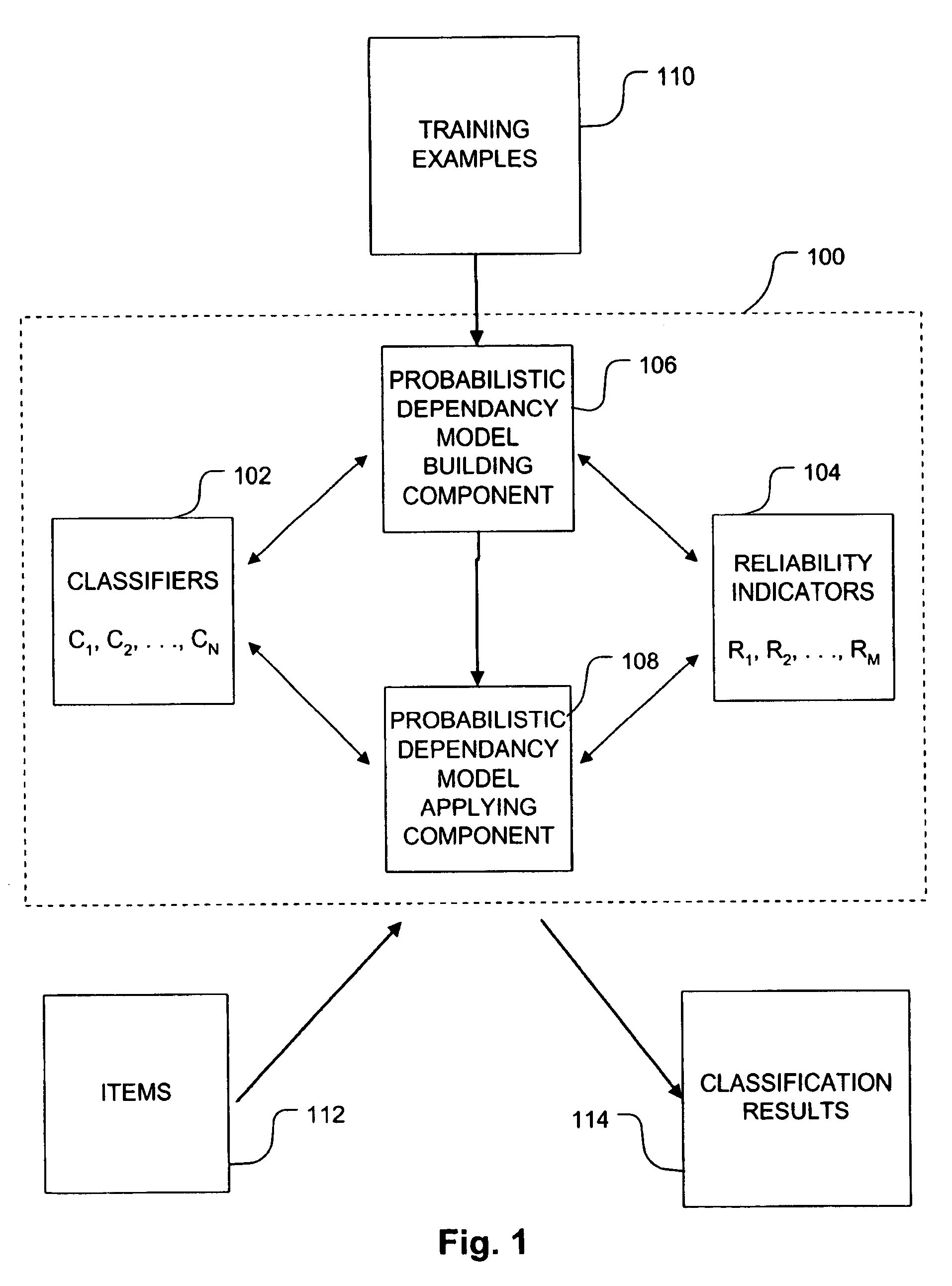
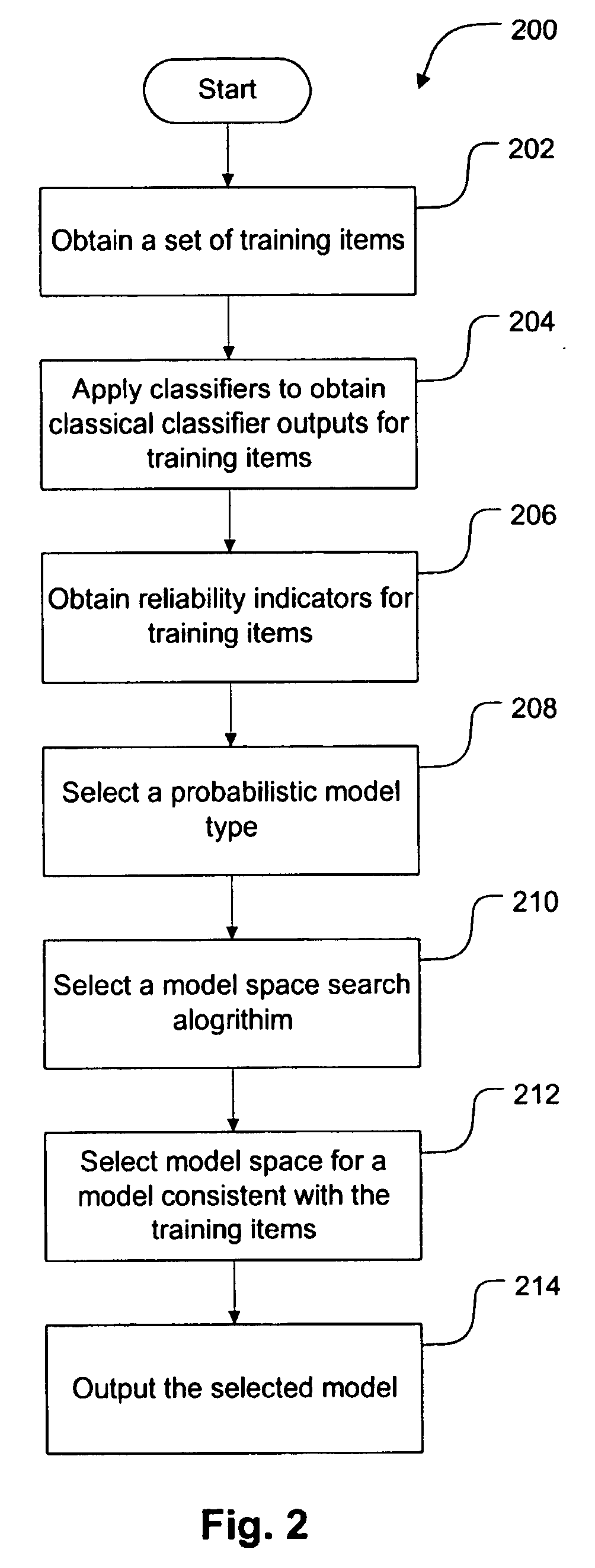
Probablistic models and methods for combining multiple content classifiers
InactiveUS7107254B1Substantial computational savingSubstantial computational savingsDigital computer detailsProbabilistic networksProbit modelProbabilistic method
The invention applies a probabilistic approach to combining evidence regarding the correct classification of items. Training data and machine learning techniques are used to construct probabilistic dependency models that effectively utilize evidence. The evidence includes the outputs of one or more classifiers and optionally one or more reliability indicators. The reliability indicators are, in a broad sense, attributes of the items being classified. These attributes can include characteristics of an item, source of an item, and meta-level outputs of classifiers applied to the item. The resulting models include meta-classifiers, which combine evidence from two or more classifiers, and tuned classifiers, which use reliability indicators to inform the interpretation of classical classifier outputs. The invention also provides systems and methods for identifying new reliability indicators.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
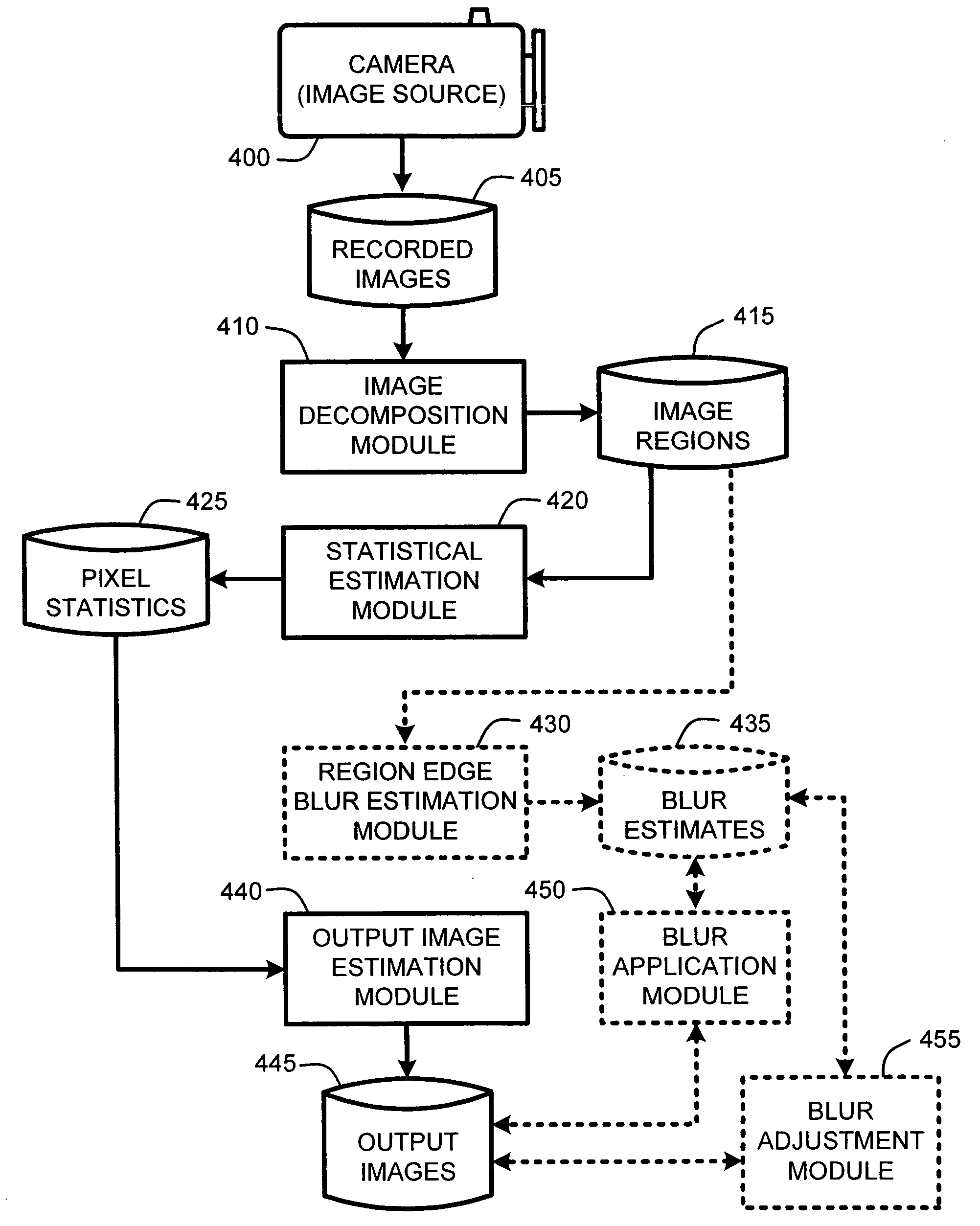
Region-based image denoising
ActiveUS20070177817A1Well formedImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionImage denoising
An “Image Denoiser” provides a probabilistic process for denoising color images by segmenting an input image into regions, estimating statistics within each region, and then estimating a clean (or denoised) image using a probabilistic model of image formation. In one embodiment, estimated blur between each region is used to reduce artificial sharpening of region boundaries resulting from denoising the input image. In further embodiments, the estimated blur is used for additional purposes, including sharpening edges between one or more regions, and selectively blurring or sharpening one or more specific regions of the image (i.e., “selective focus”) while maintaining the original blurring between the various regions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
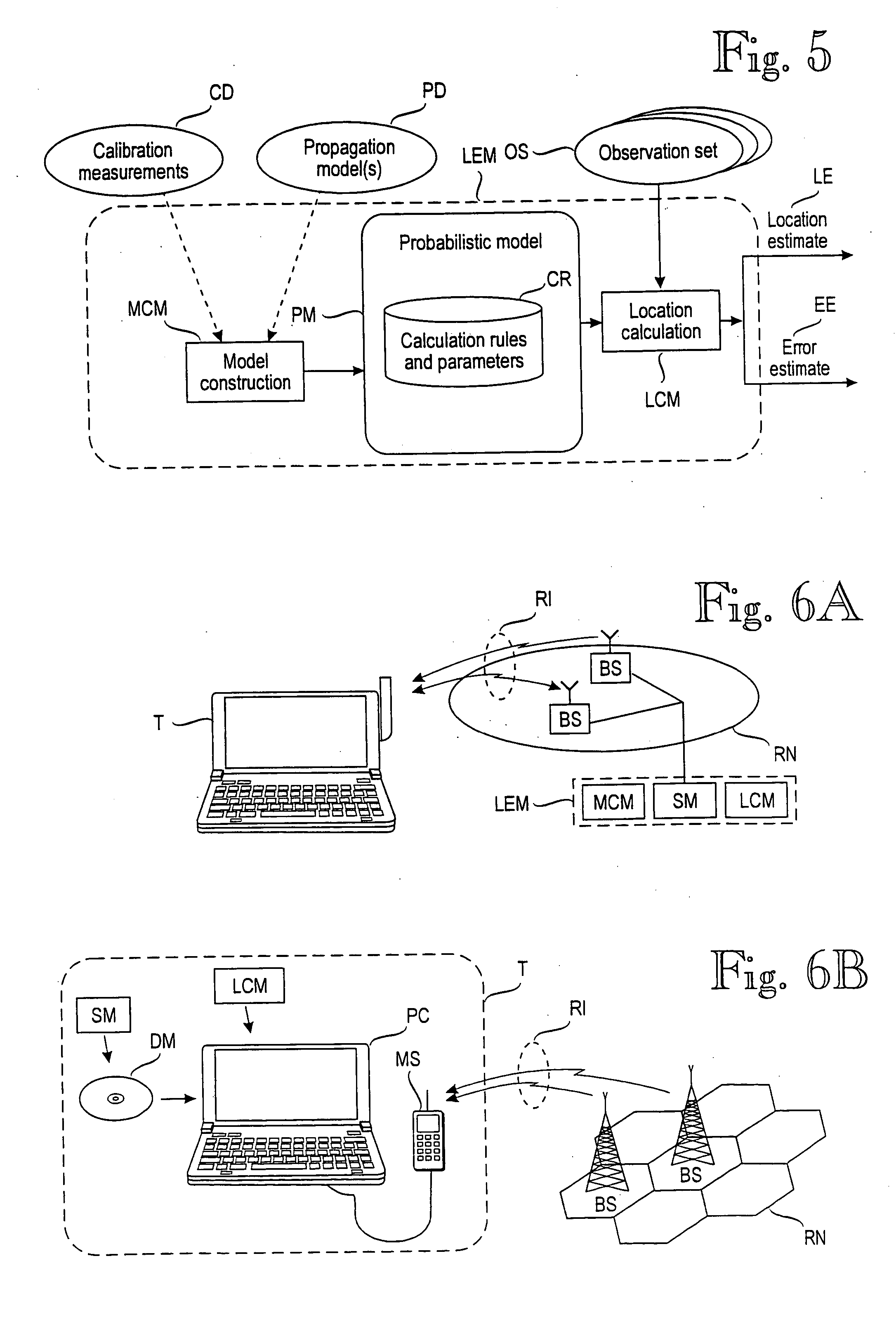
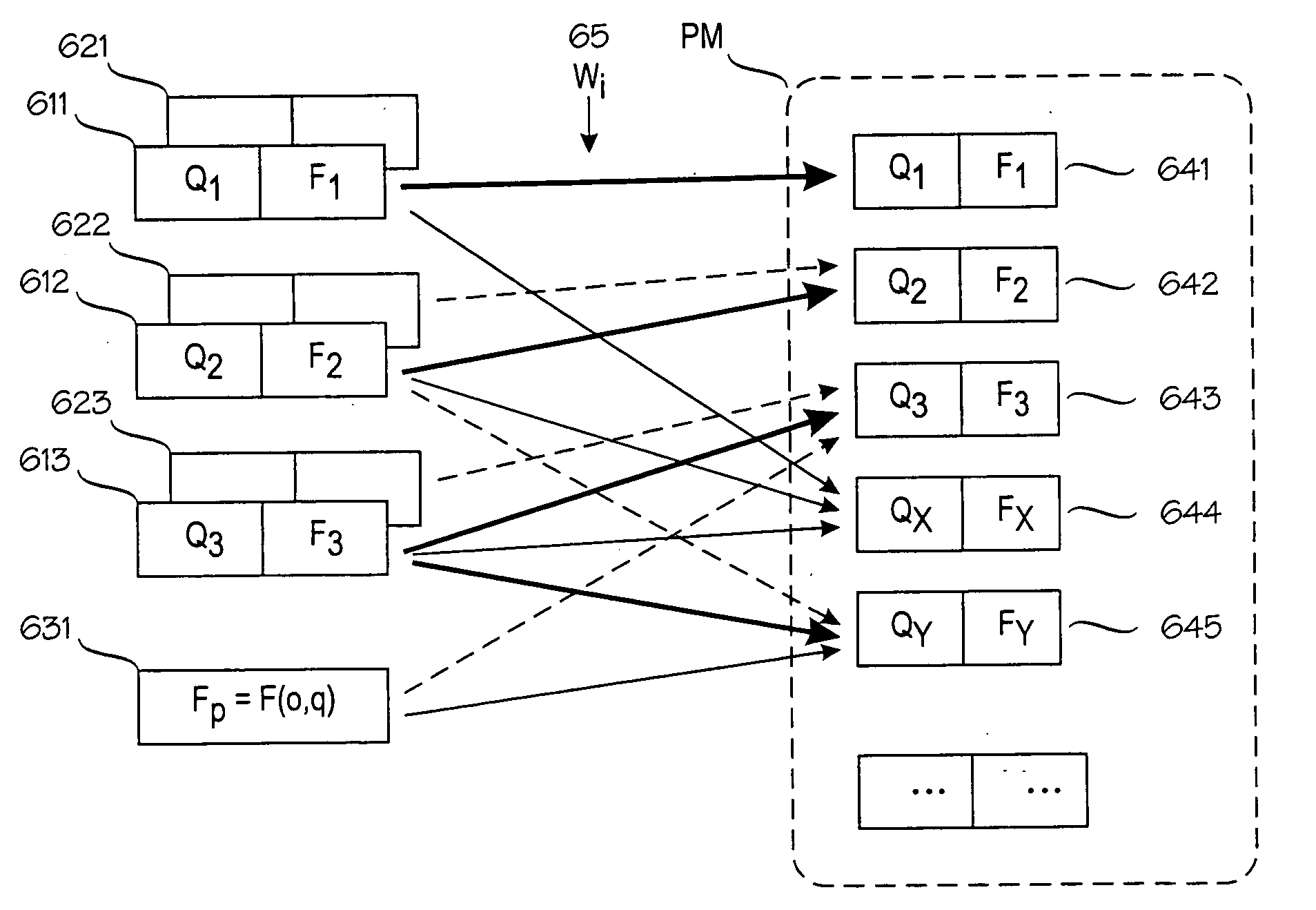
Probabilistic model for a positioning technique
A model construction module (MCM) for constructing a probabilistic model (PM) of a wireless environment (RN) in which a target device (T) communicates using signals that have a measurable signal value (x), such as signal strength. The model construction module forms several submodels (611-631) of the wireless environment (RN). Each submodel indicates a probability distribution (F1-F3) for signal values at one or more locations (Q1-QY) in the wireless environment. The module combines the submodels to a probabilistic model (PM) of the wireless environment (RN), such that the probabilistic model indicates a probability distribution for signal values at several locations in the wireless environment. Alternatively, the model may insert new locations to a single model based on a combination of existing locations. The combination of submodels or existing locations comprises combining the inverse cumulative distribution functions of the submodels or existing locations.
Owner:AIRISTA FLOW INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com