Patents
Literature
684 results about "Linear region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
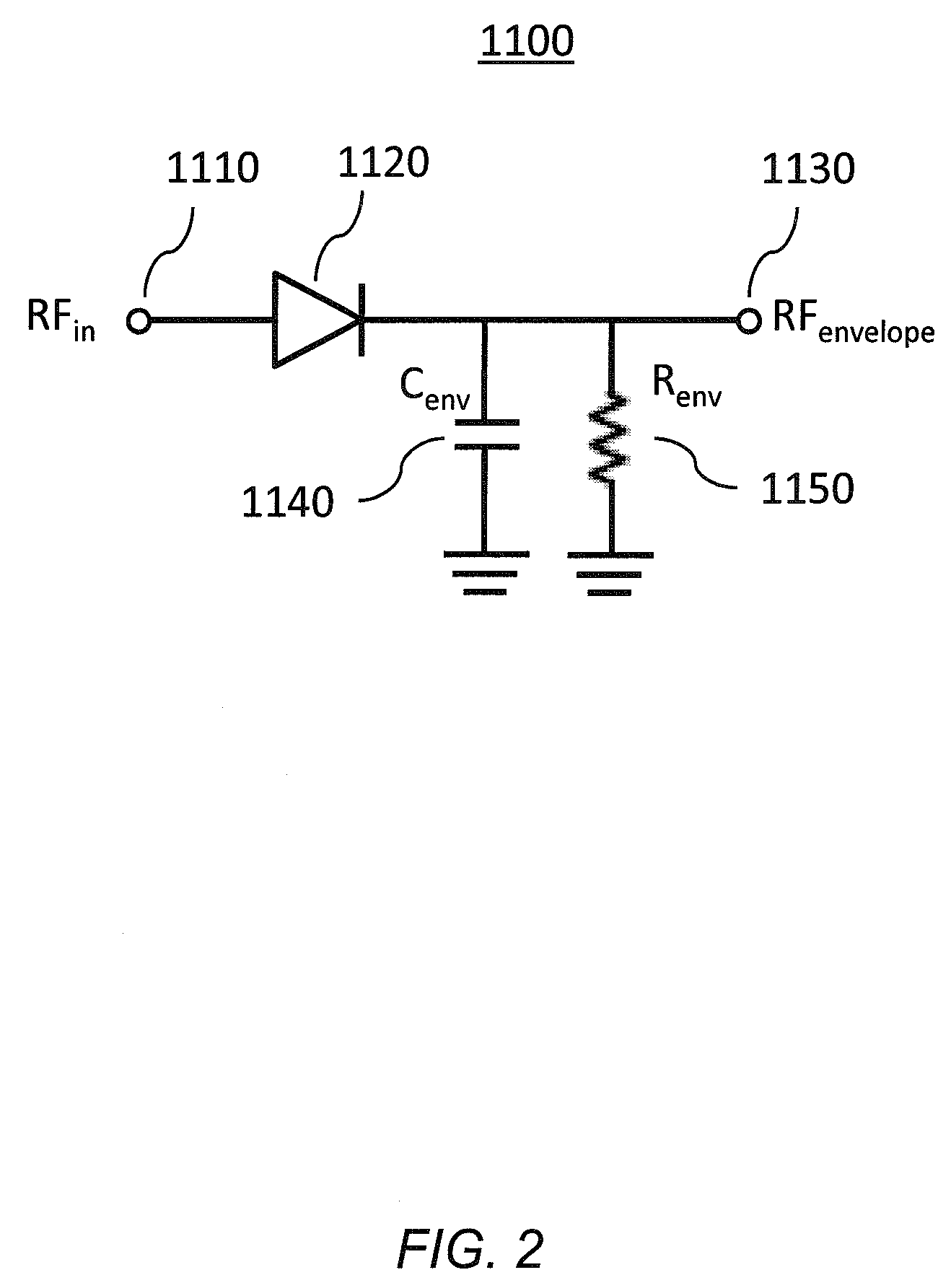
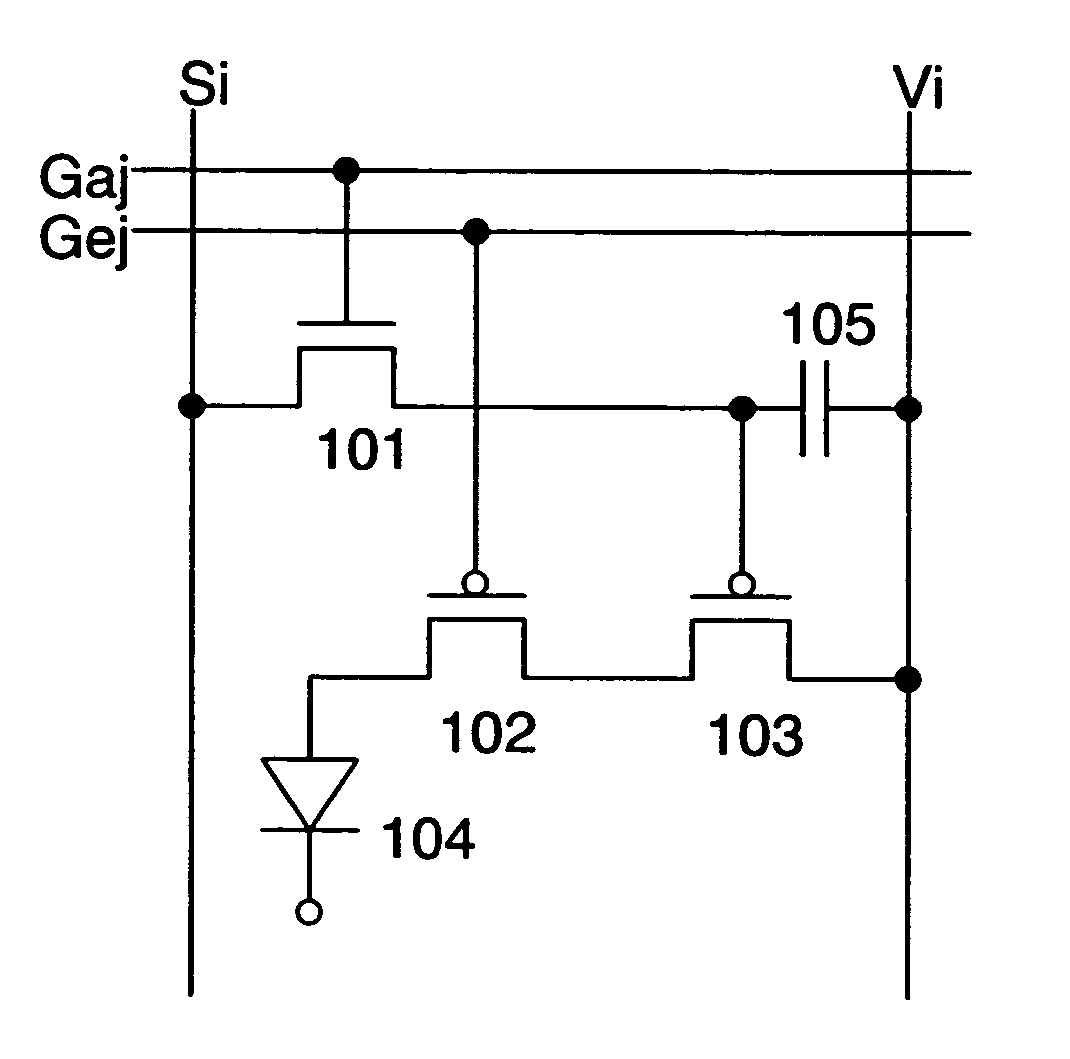
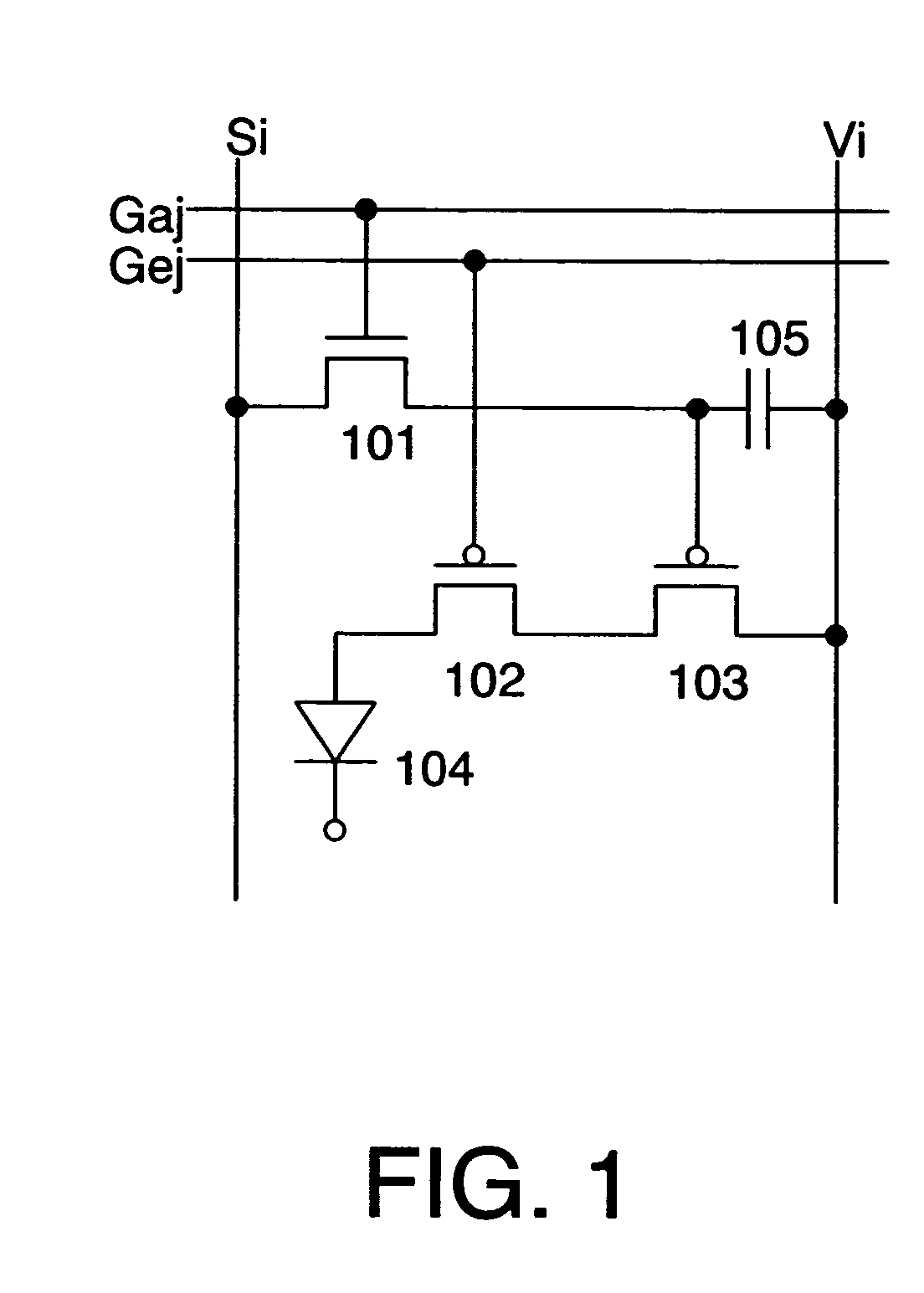
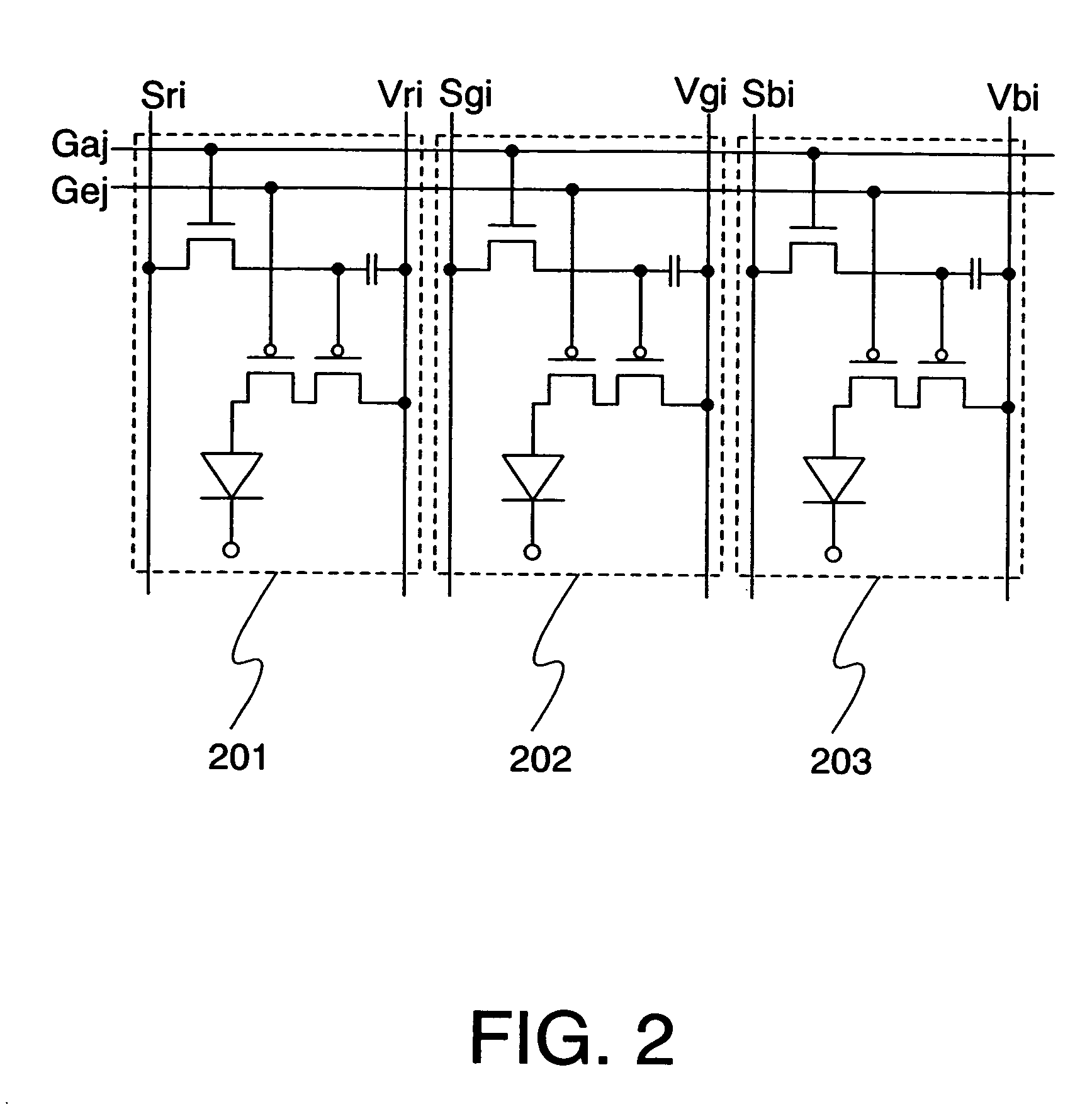
The linear region is supposed to be that part of the active region in the transfer curve of transistor (Vout vs Vin) where the output voltage Vout is linearly dependent on the input voltage Vin. Consider the following circuit:
Color printer characterization using optimization theory and neural networks
InactiveUS6480299B1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionICC profile
A color management method / apparatus generates image color matching and International Color Consortium (ICC) color printer profiles using a reduced number of color patch measurements. Color printer characterization, and the generation of ICC profiles usually require a large number of measured data points or color patches and complex interpolation techniques. This invention provides an optimization method / apparatus for performing LAB to CMYK color space conversion, gamut mapping, and gray component replacement. A gamut trained network architecture performs LAB to CMYK color space conversion to generate a color profile lookup table for a color printer, or alternatively, to directly control the color printer in accordance with the a plurality of color patches that accurately. represent the gamut of the color printer. More specifically, a feed forward neural network is trained using an ANSI / IT-8 basic data set consisting of 182 data points or color patches, or using a lesser number of data points such as 150 or 101 data points when redundant data points within linear regions of the 182 data point set are removed. A 5-to-7 neuron neural network architecture is preferred to perform the LAB to CMYK color space conversion as the profile lookup table is built, or as the printer is directly controlled. For each CMYK signal, an ink optimization criteria is applied, to thereby control ink parameters such as the total quantity of ink in each CMYK ink printed pixel, and / or to control the total quantity of black ink in each CMYK ink printed pixel.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
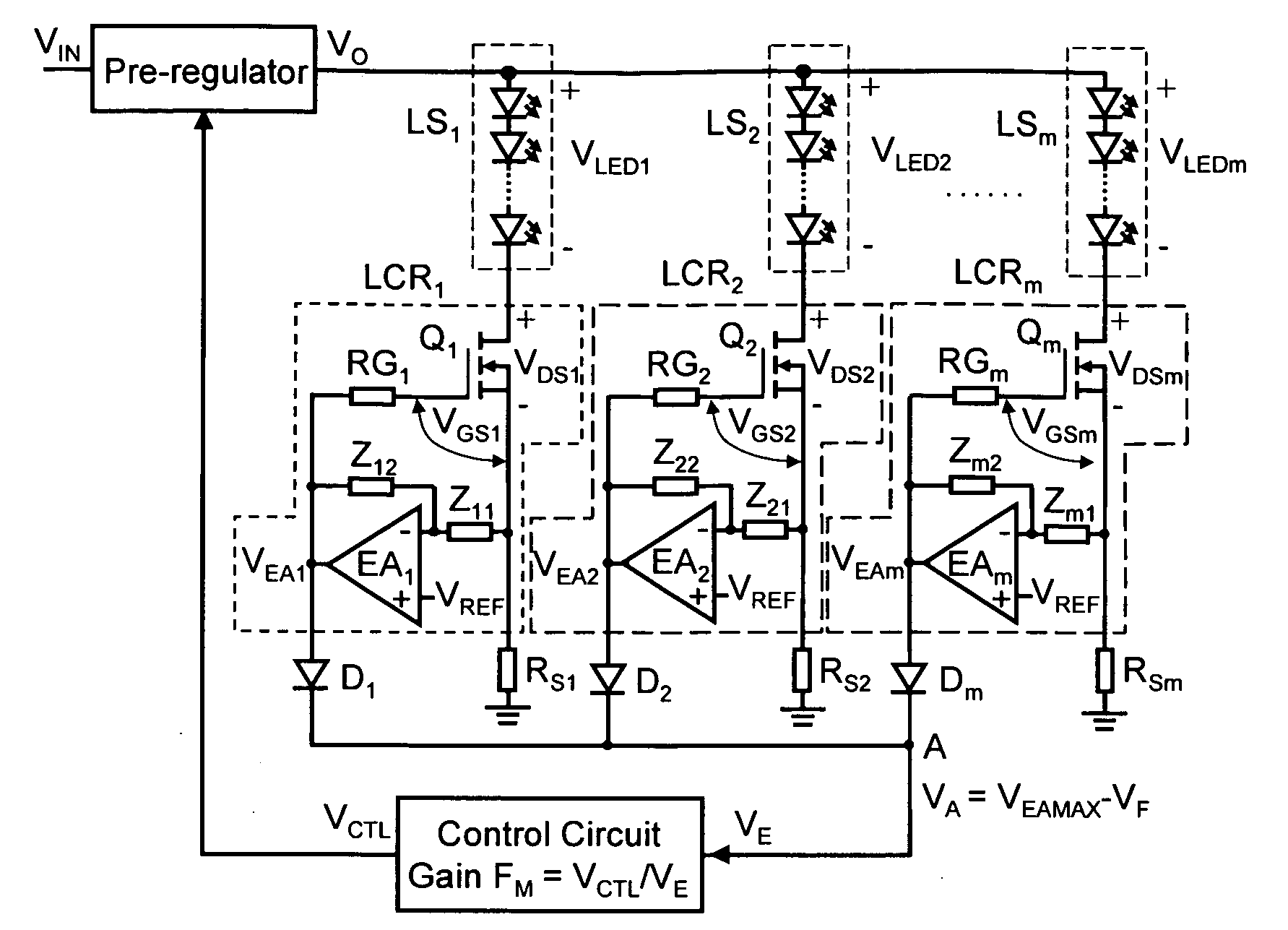
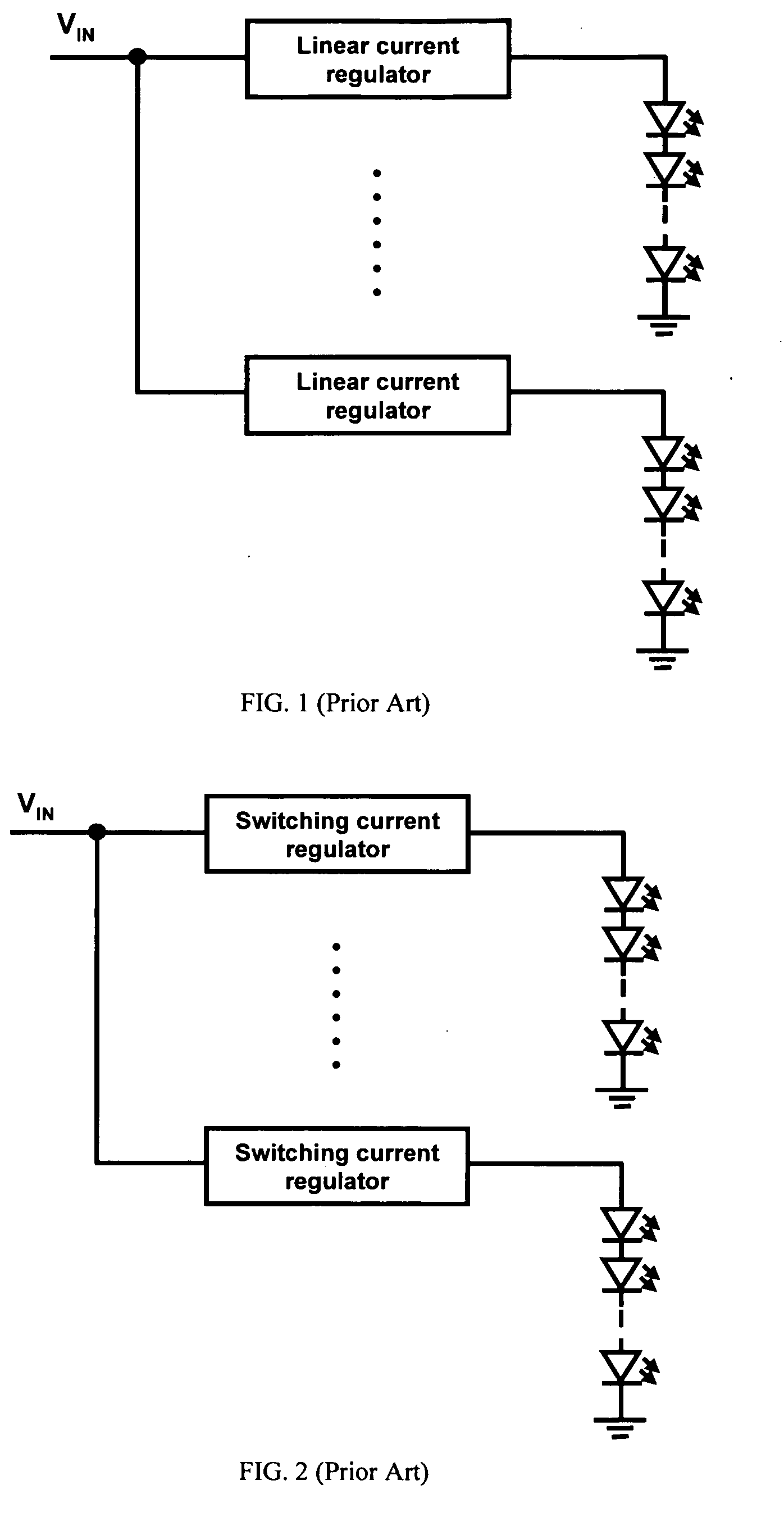
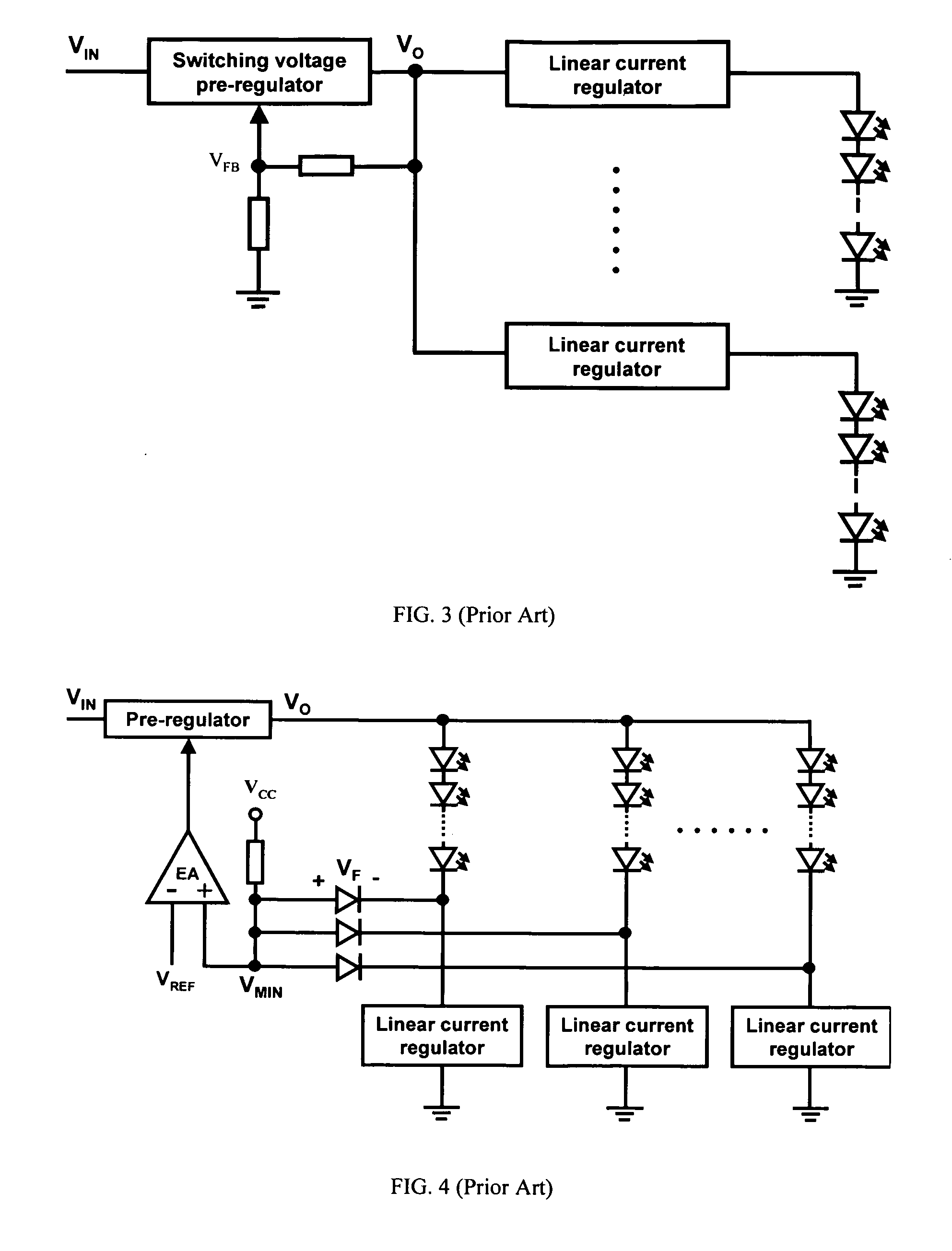
Driver that efficiently regulates current in a plurality of LED strings
InactiveUS20090187925A1Minimize output voltageImprove performanceElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesLinear regulatorMOSFET
A light-emitting diode (LED) driver according to the present invention consists of a voltage pre-regulator and multiple linear current regulators with an adaptively-controlled drive voltage. In this LED driver, the efficiency maximization is achieved by eliminating the sensing of the voltage drops across the linear regulators, i.e., by removing the external voltage feedback for the adjustment of the output voltage of the pre-regulator. In the LED driver of the present invention, the self-adjustment of drive voltage is achieved by relying on a relatively strong dependence between the gate-to-source and drain-to-source voltages of a current-regulating transistor, e.g., a MOSFET, operating in the linear region. The driver powers all LEDs in a string with a constant current and provides consistent illumination and optimum operating efficiency at low cost over a wide range of input / output voltage and temperature.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
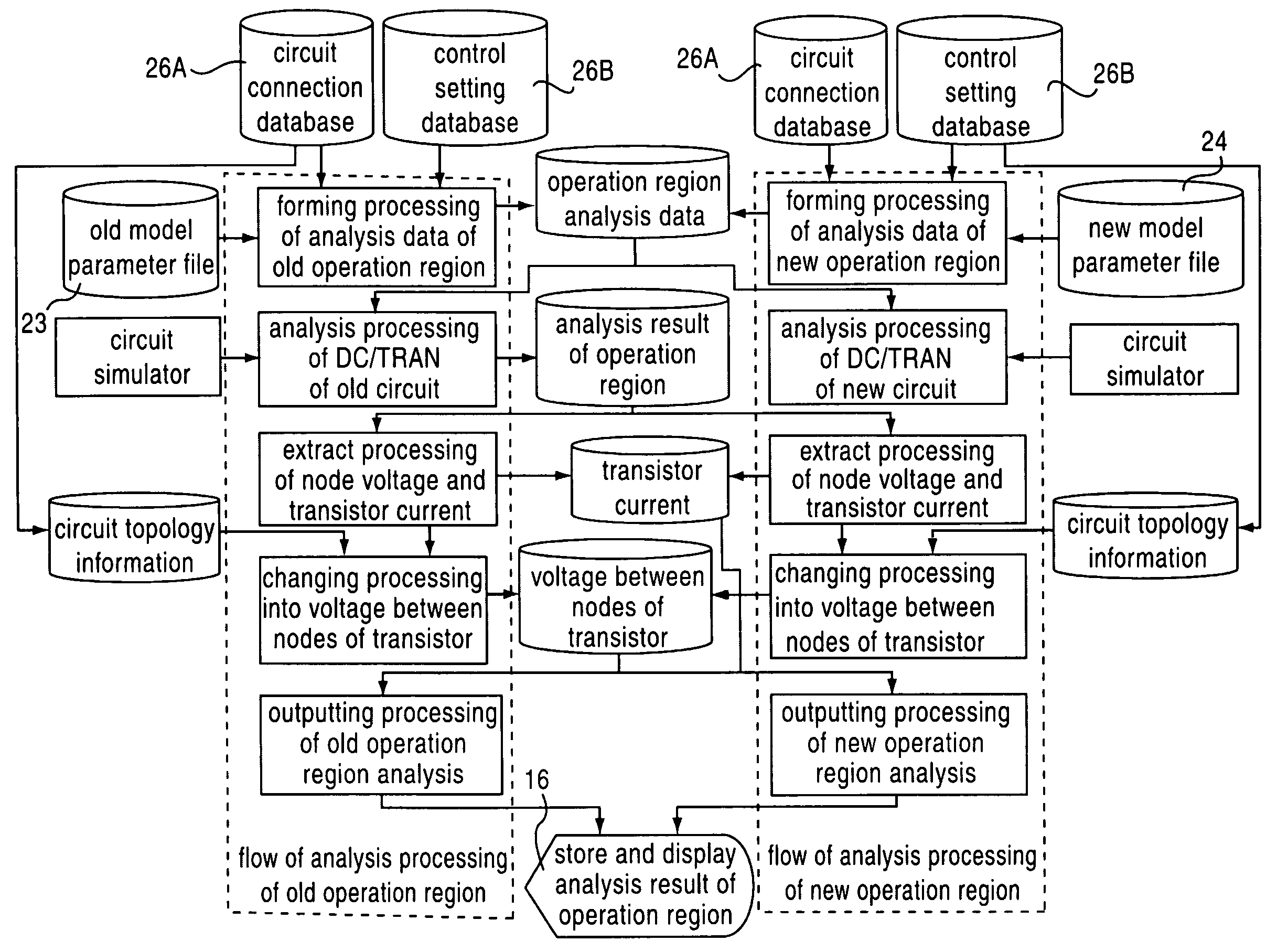
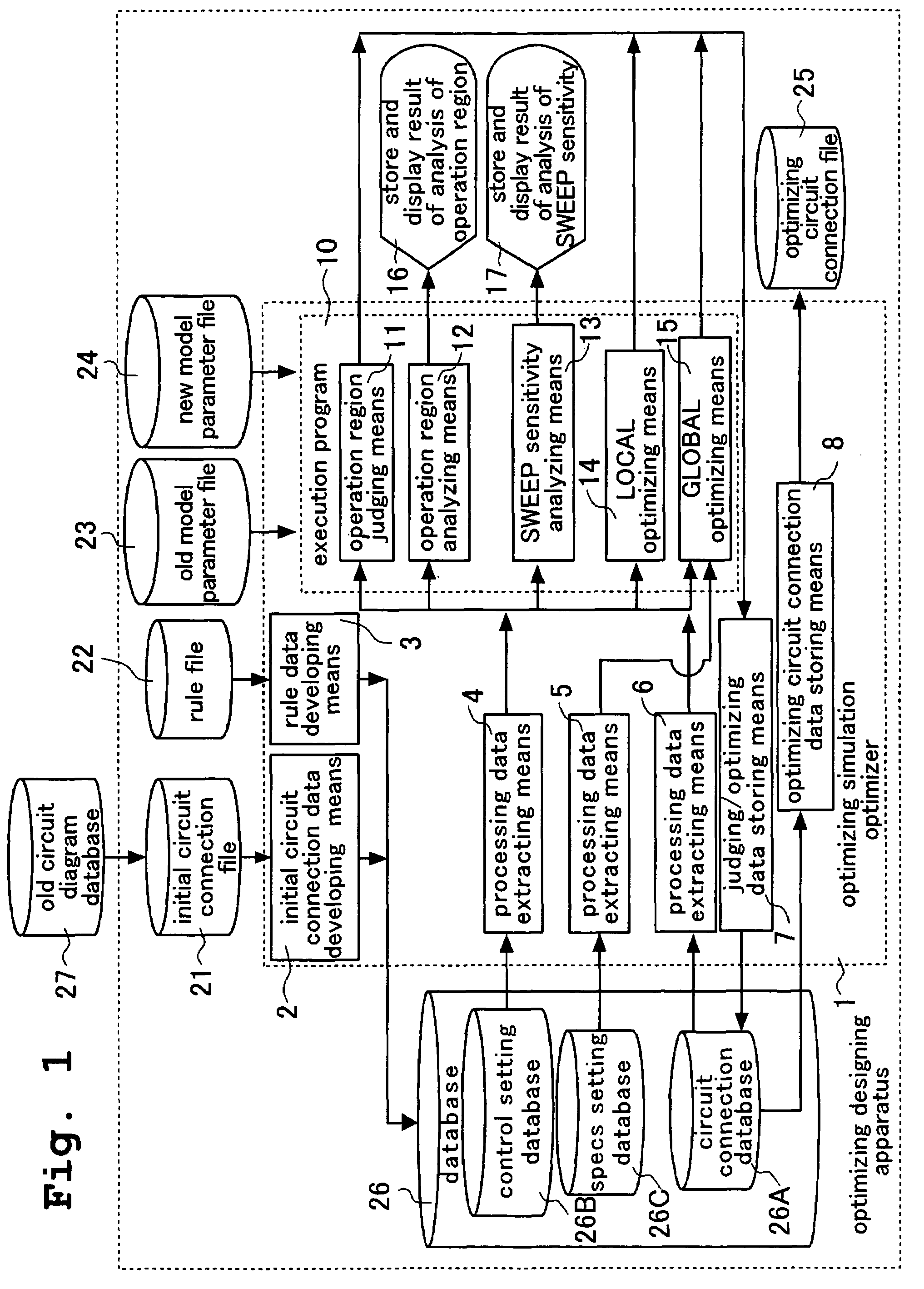
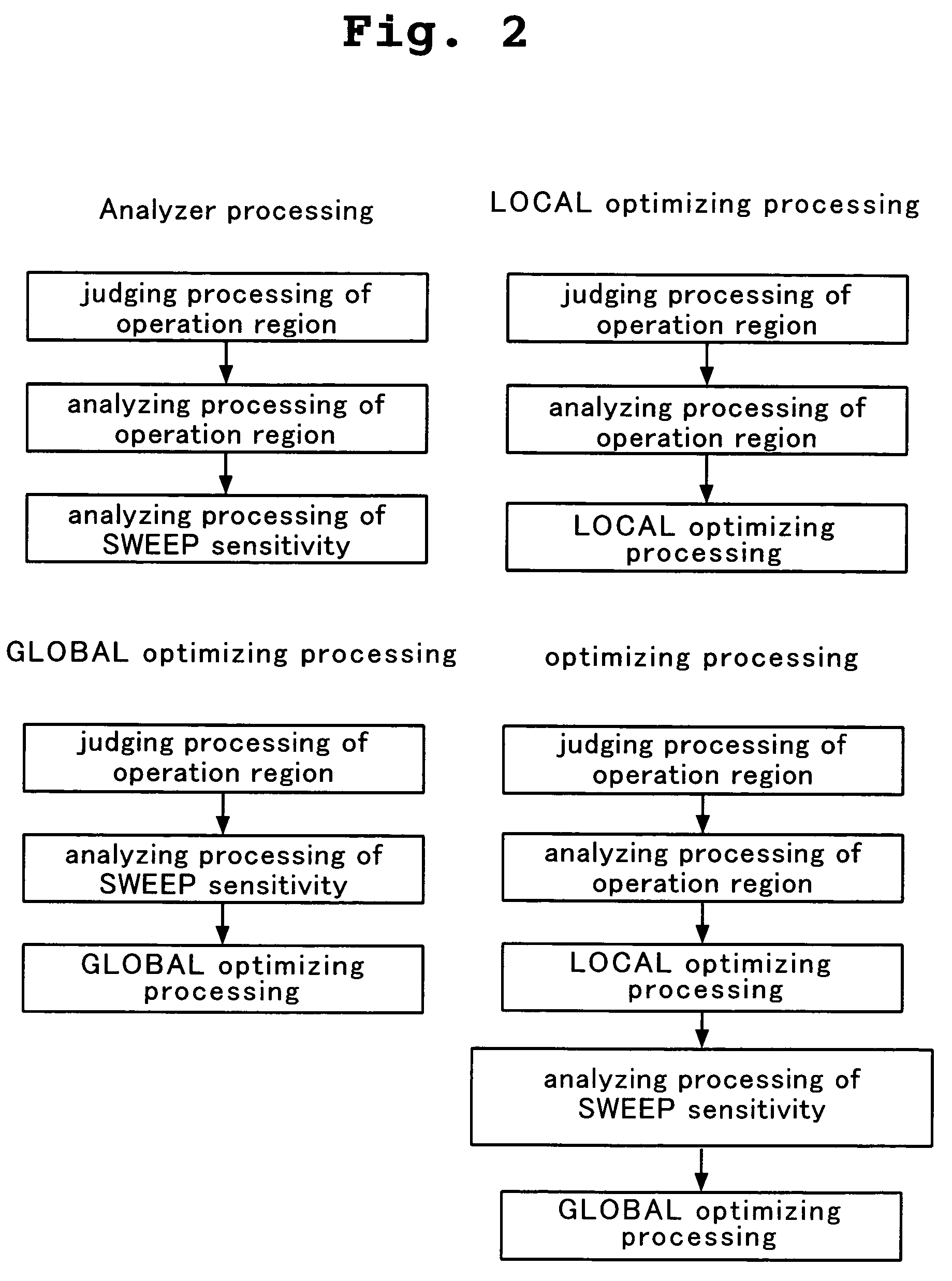
Optimizing designing apparatus of integrated circuit, optimizing designing method of integrated circuit, and storing medium in which program for carrying out optimizing designing method of integrated circuit is stored
ActiveUS7155685B2Easy to carryAnalogue computers for electric apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLinear regionRegion analysis
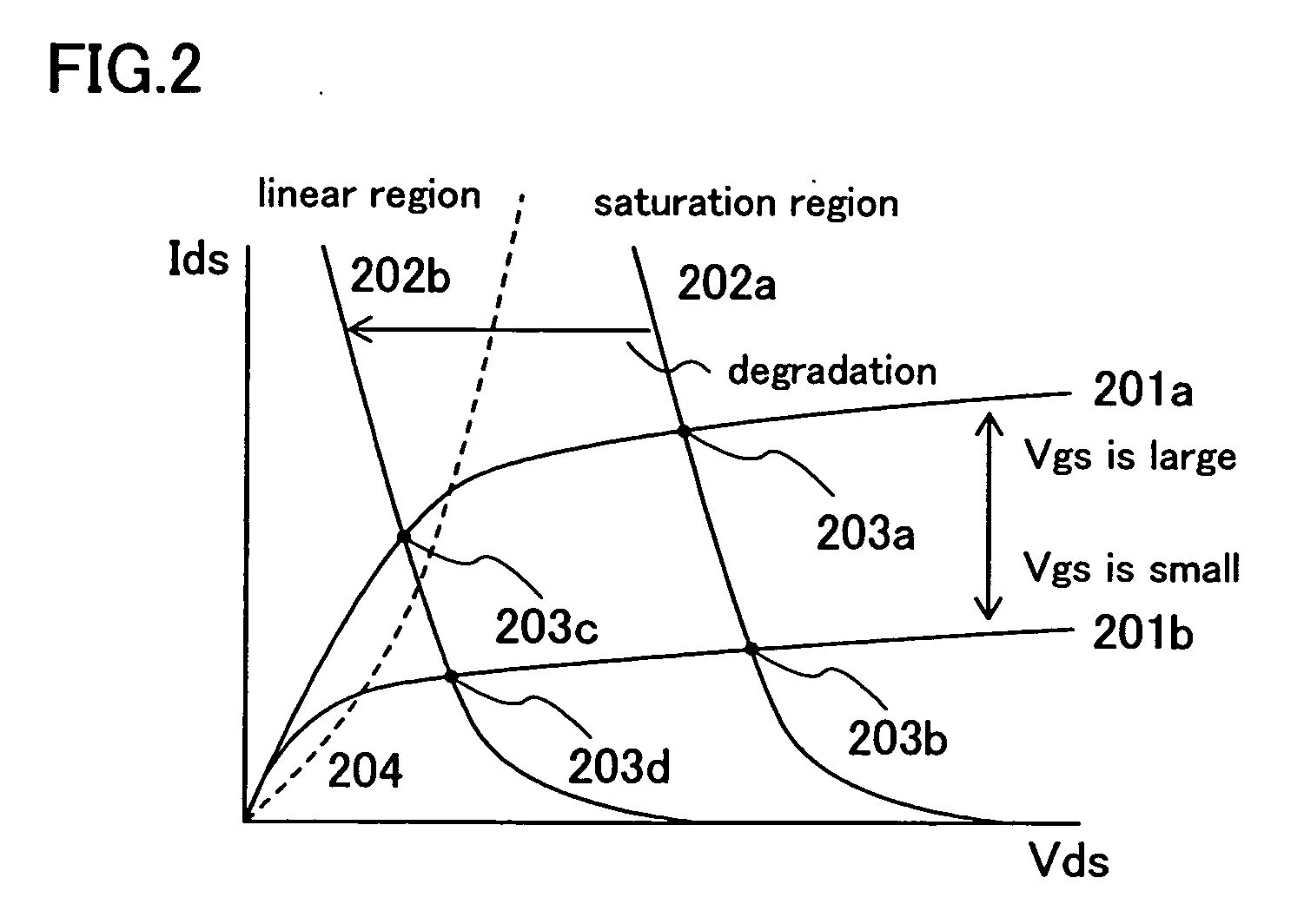
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method, an apparatus and a program having high optimization precision and capable of obtaining an answer required by a designer in a short time by combining optimization between individual transistors and optimization as the entire circuit, or by appropriately combining judgment of an operation region, an analysis of the operation region and a SWEEP sensitivity analysis when the optimization is carried out. An optimizing designing apparatus of an integrated circuit for designing a circuit, comprises operation region judging means for adjusting an operation region (linear region, saturation region) of the circuit, operation region analysis means for displaying liner characteristics (Ids-Vgs characteristics) of the circuit and saturation characteristics (Ids-Vds characteristics) of the circuit, and SWEEP sensitivity analysis means for displaying variation in output characteristics of the circuit.
Owner:ABLIC INC
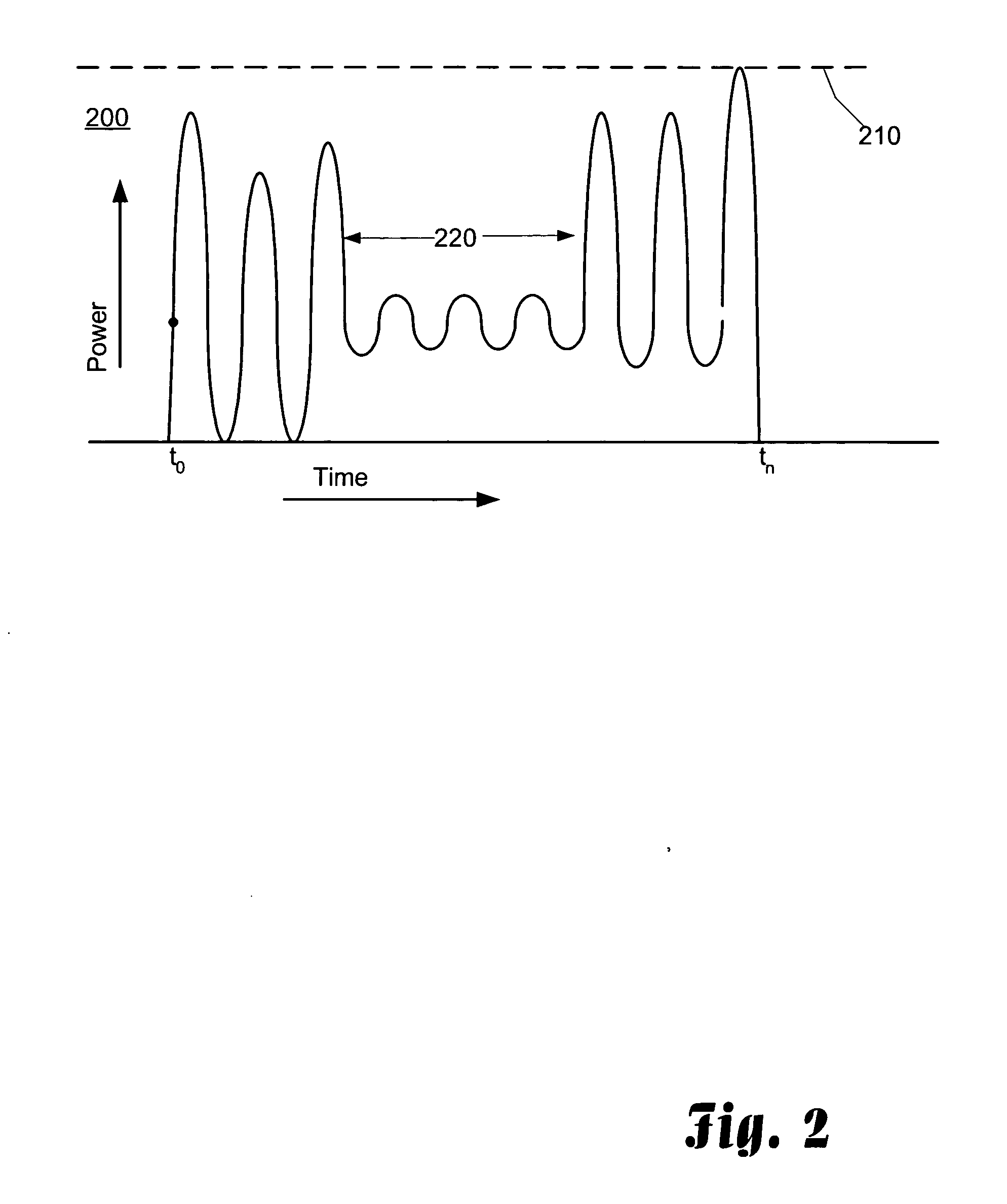
Detecting and maintaining linearity in a power amplifier system through comparing peak and RMS power levels
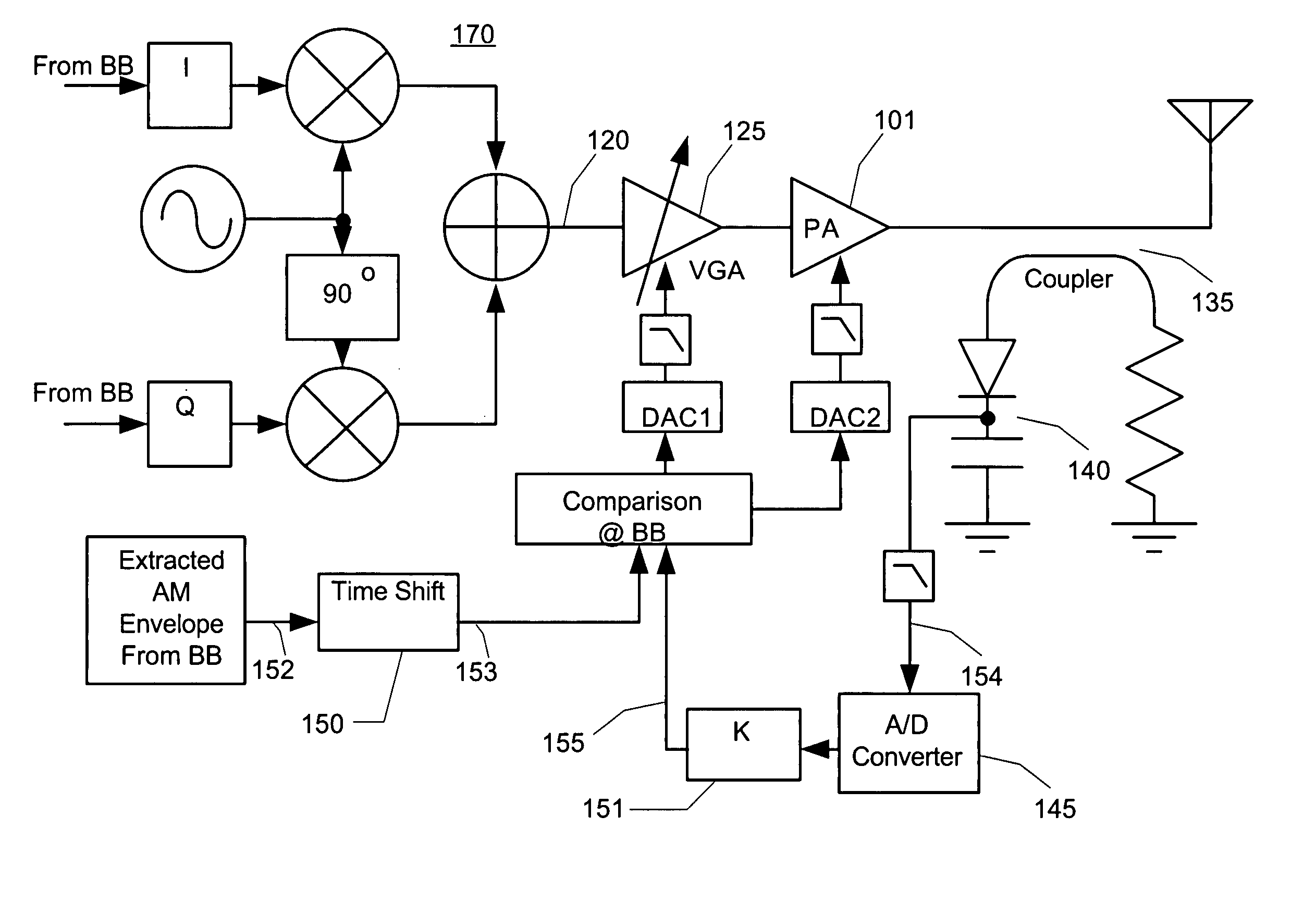
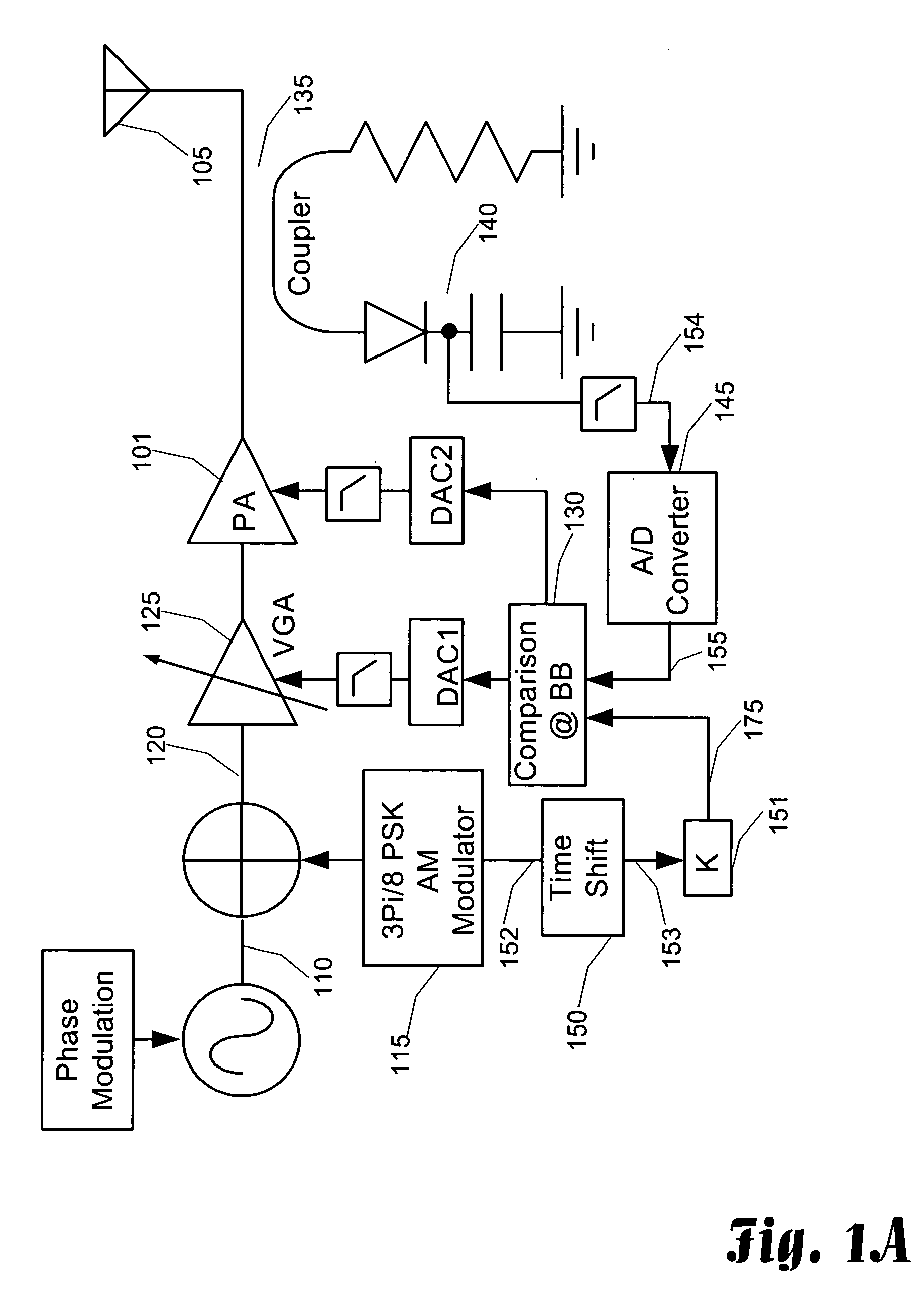
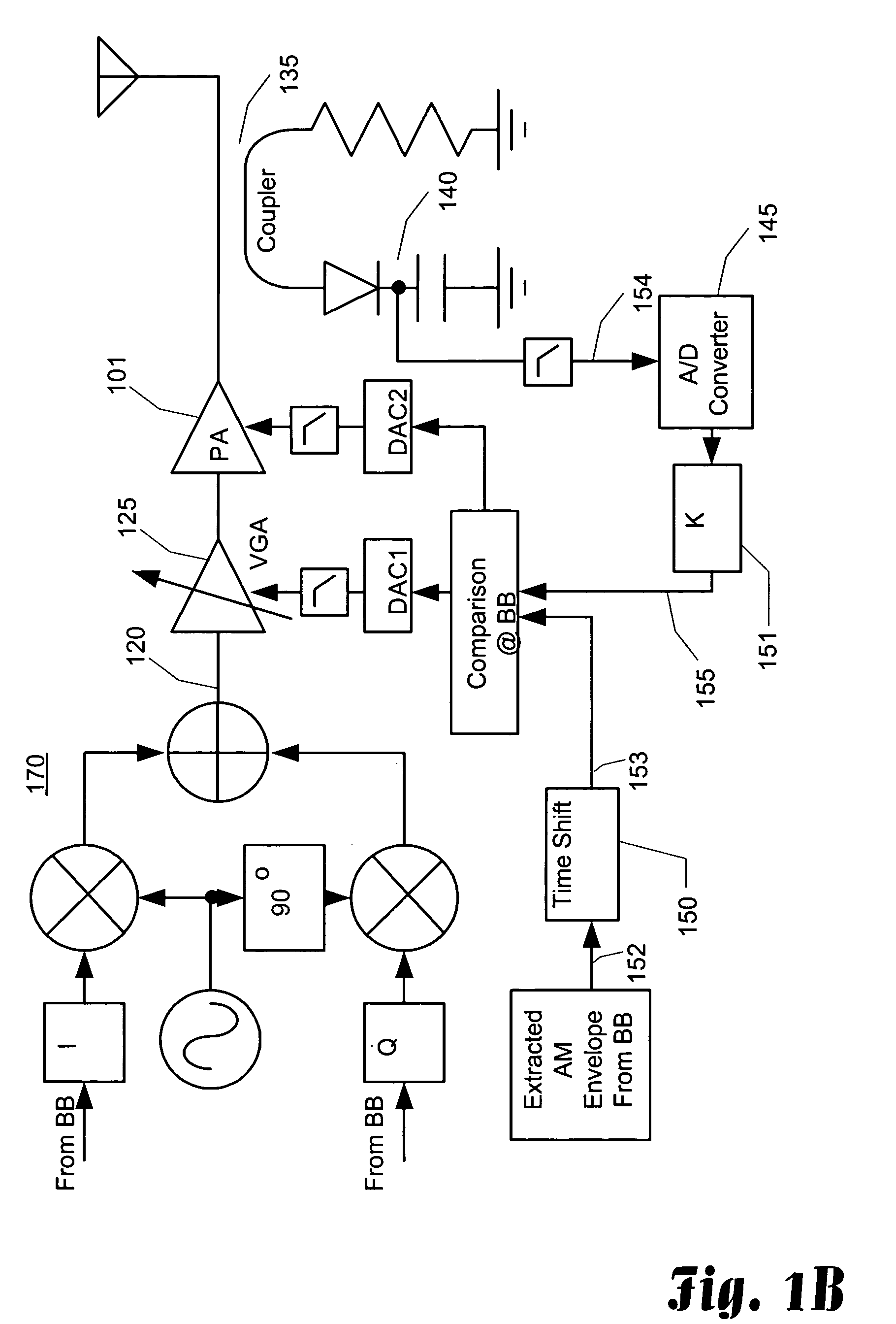
InactiveUS20050227646A1Raise the ratioRestore linearityResonant long antennasSupply voltage varying controlAudio power amplifierLinear region
Small portable communication devices that support multiple modulation techniques cannot gain the benefits of using an isolator at the output of a power amplifier to provide stability in the load impedance. However, for communication devices that include amplitude modulation schemes, maintaining linear operation of the power amplifier is still required. In the presence of unstable load impedance, this can be a difficult task. As a solution, the linearity of the power amplifier is detected by determining the peak power of the output signal and the average or root-mean-square of a portion of the output signal, such as a mid-amble). The ratio of the peak power and the average power of the output signal are used to determine if the power amplifier is operating in the linear region. If the ratio is too high, then the power amplifier may be operating in the linear region. By adjusting the power level of the input signal to the power amplifier when the ratio increases, linearity of the power amplifier is maintained.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electroluminescent display compensated drive signal
ActiveUS20100225634A1Increase the aperture ratioIncrease productionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingChannel length modulationDriving current
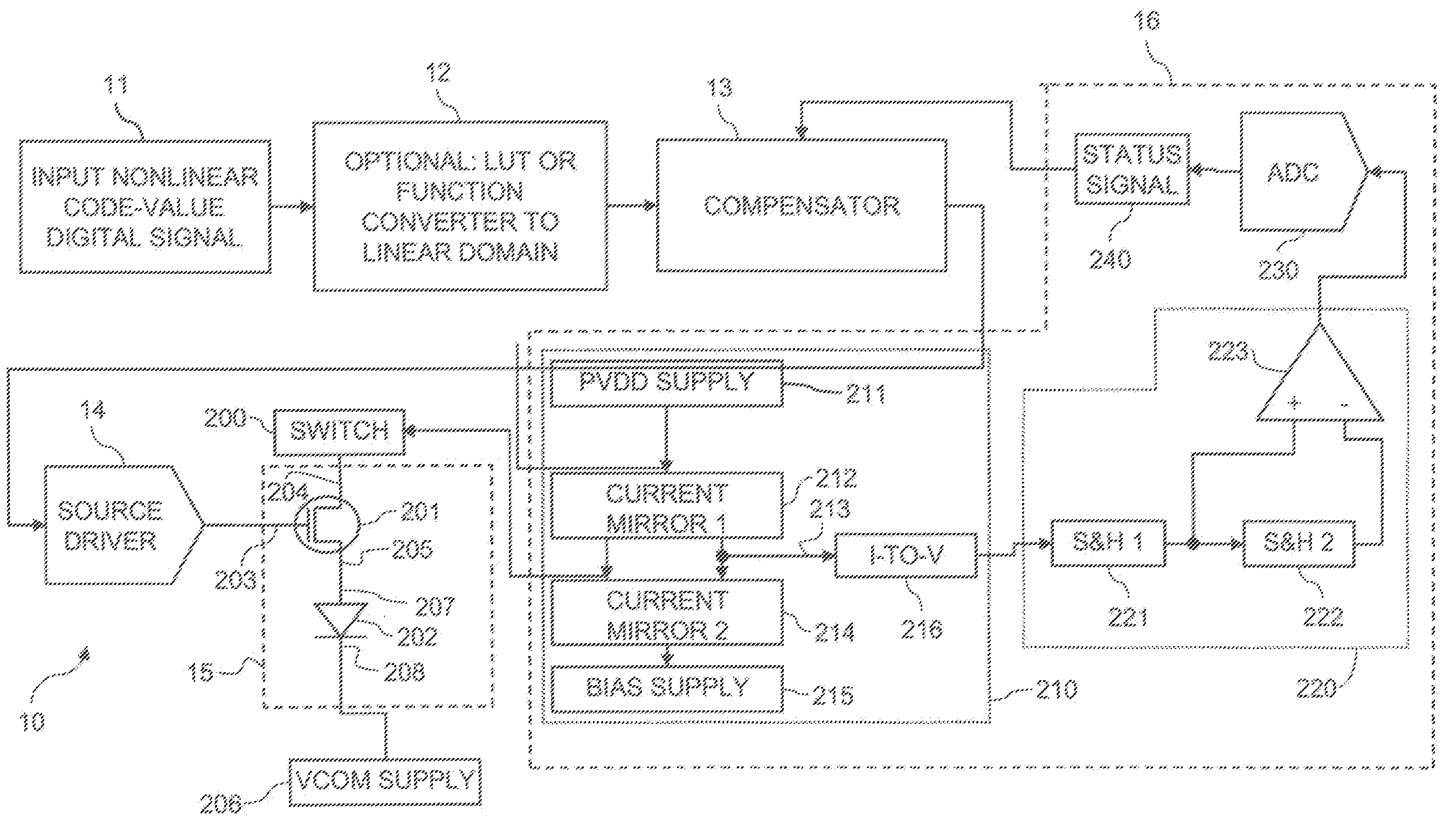
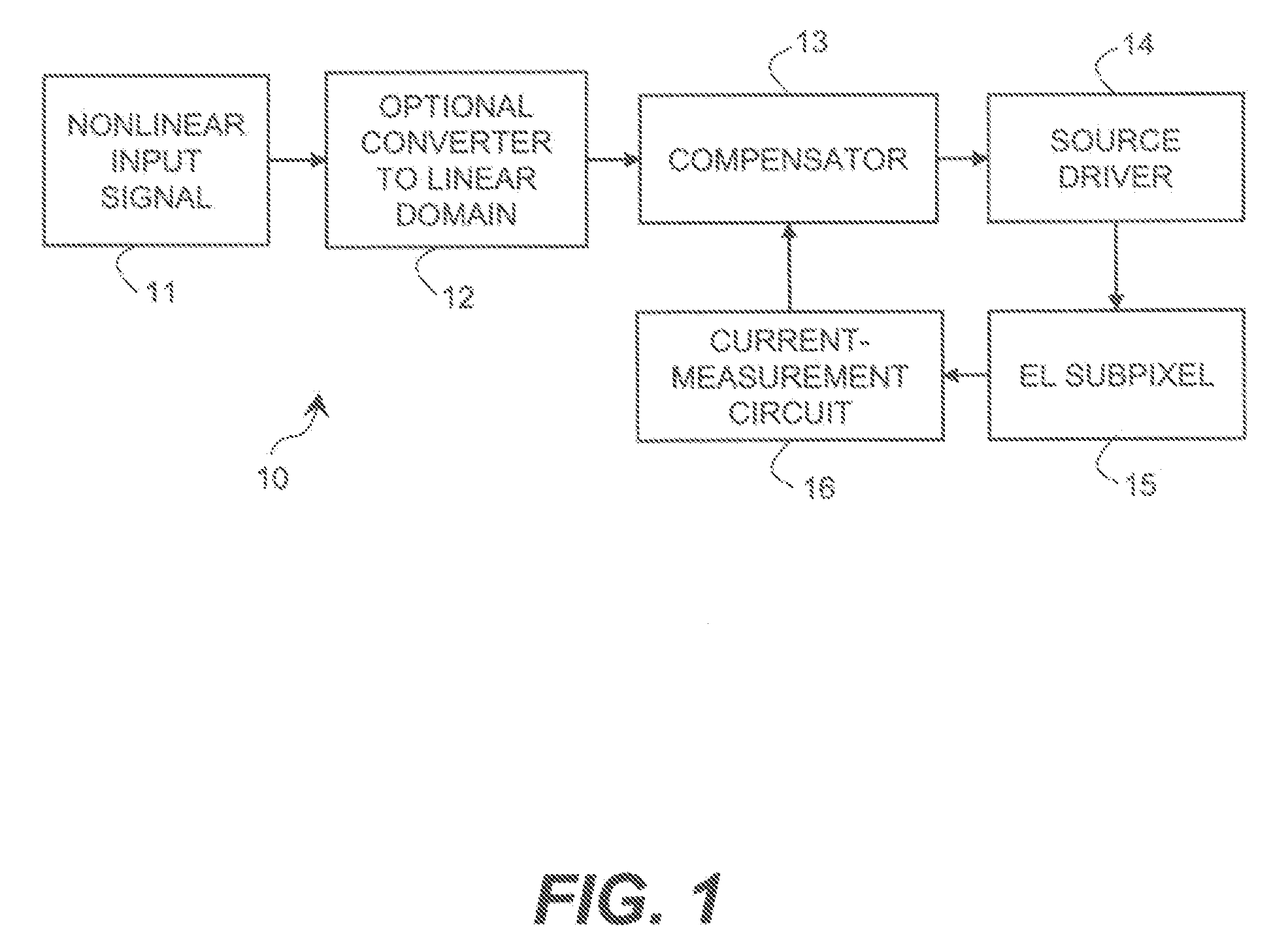
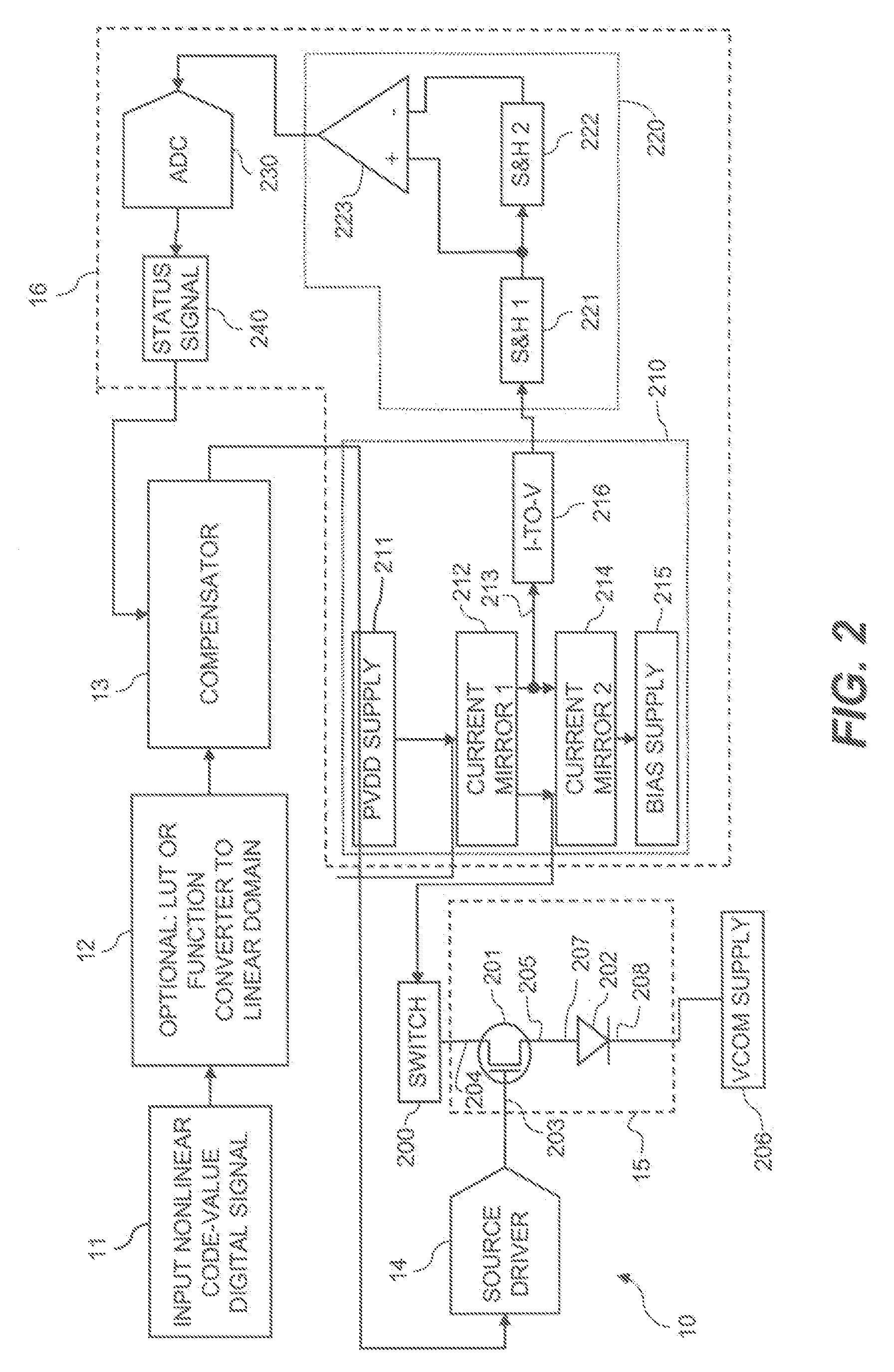
Subpixels on an electroluminescent (EL) display panel, such as an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) panel, are compensated for initial nonuniformity (“mura”) and for aging effects such as threshold voltage Vth shift, EL voltage Voled shift, and OLED efficiency loss. The drive current of each subpixel is measured at one or more measurement reference gate voltages to form status signals representing the characteristics of the drive transistor and EL emitter of those subpixels. Current measurements are taken in the linear region of drive transistor operation to improve signal-to-noise ratio in systems such as modern LTPS PMOS OLED displays, which have relatively small Voled shift over their lifetimes and thus relatively small current change due to channel-length modulation. Various sources of noise are also suppressed to further increase signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Optimization Methods for Amplifier with Variable Supply Power
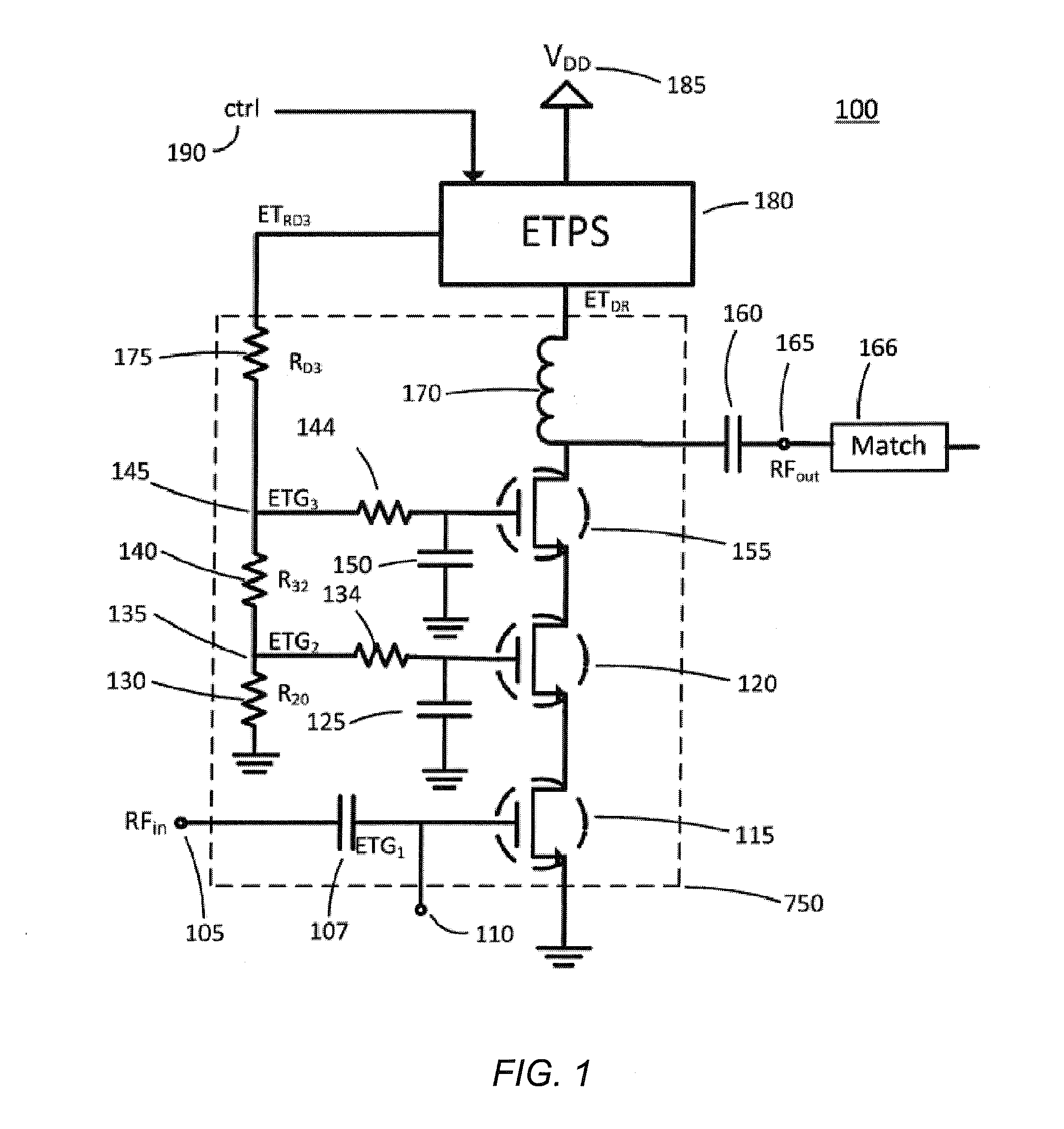
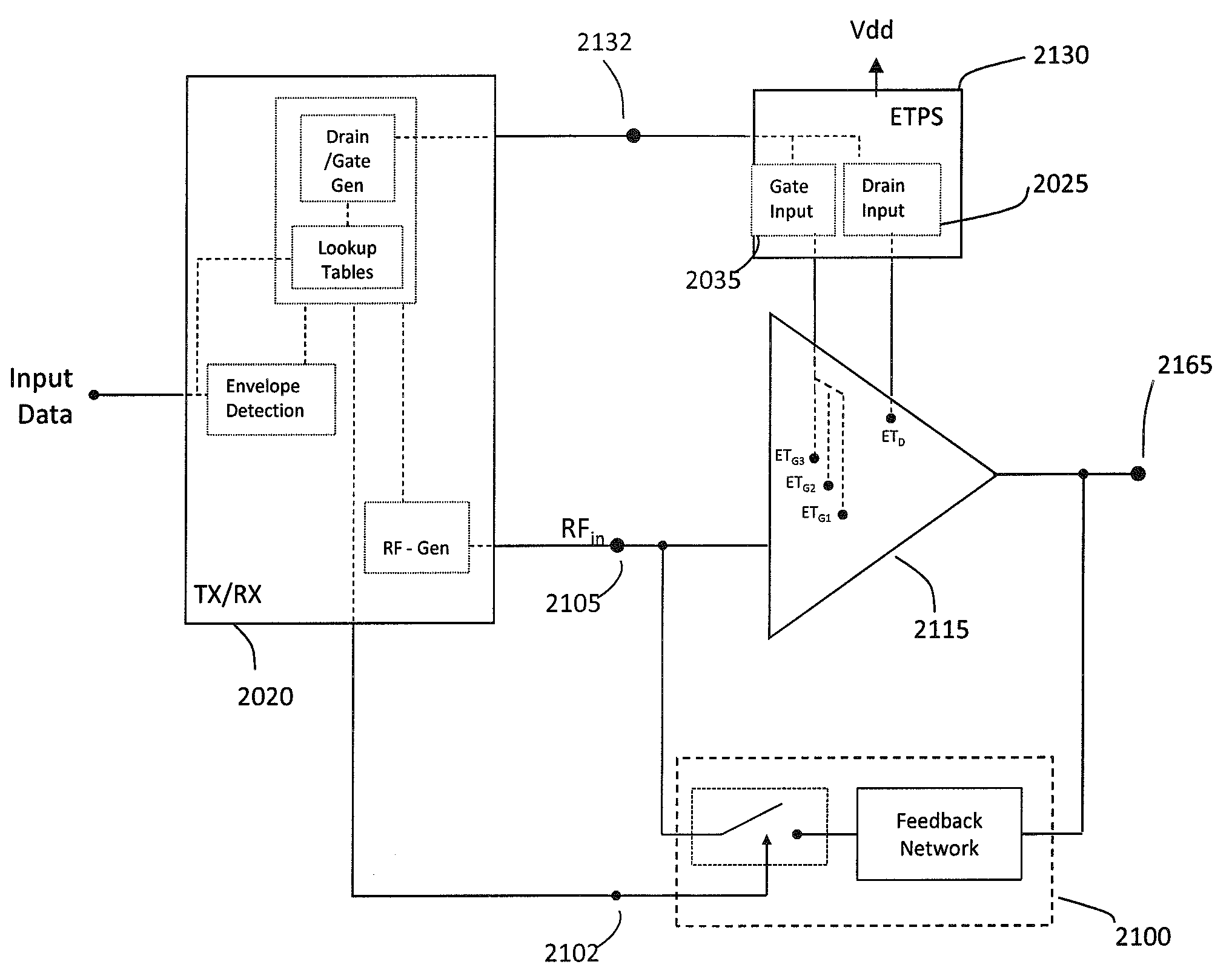
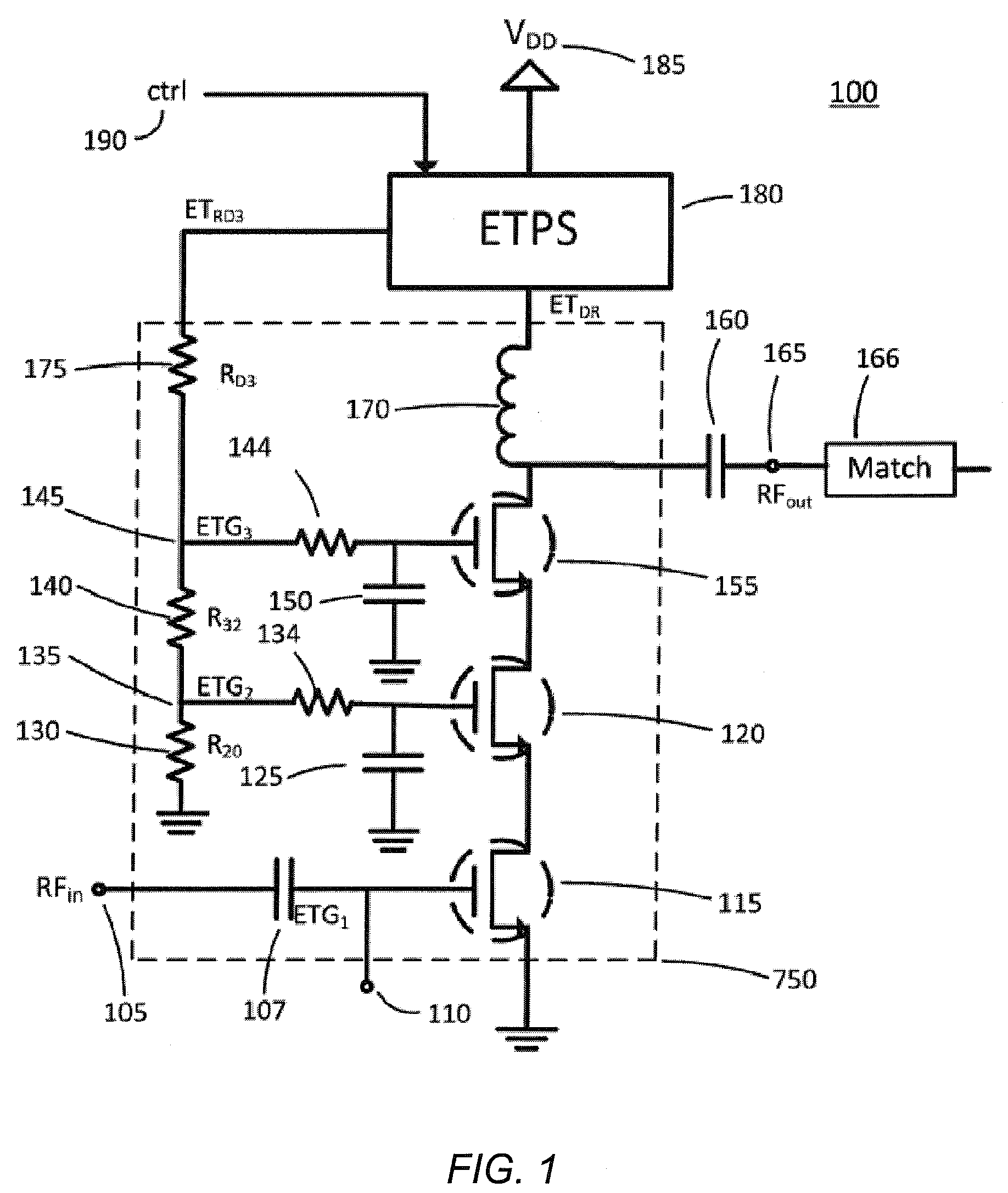
ActiveUS20140184334A1Affecting responseAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierLinear region
Optimization methods via various circuital arrangements for amplifier with variable supply power are presented. In one embodiment, a switch can be controlled to include or exclude a feedback network in a feedback path to the amplifier to adjust a response of the amplifier dependent on a region of operation of the amplifier arrangement (e.g. linear region or compression region).
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Optimization methods for amplifier with variable supply power
ActiveUS9219445B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlLinear regionAudio power amplifier
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Display device
ActiveUS20040252085A1Little changeReduce voltageStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesLinear regionLow voltage
By operating a driving TFT in a saturation region, luminance is not easily reduced when an EL element is degraded. However, such problems occur as a high voltage, high power consumption, and heat generation. In the case of operating a driving TFT in a saturation region, luminance varies due to a variation of driving TFTs. In view of the aforementioned problems, a high current capacity TFT is used in the high gray-scale and a low current capacity TFT is used in the low gray-scale. The high current capacity TFT can supply a large current with a lower Vgs, therefore, it does not easily operate in a linear region even when Vds is lowered. Thus, a luminance is not reduced easily even when an EL element is degraded, and an operation at a low voltage is realized. The low current capacity TFT supplies current when high Vgs is applied. With high Vgs, an effect of variation in characteristics of TFTs, especially in Vth can be ameliorated.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Detecting and maintaining linearity in a power amplifier system through envelope power comparisons
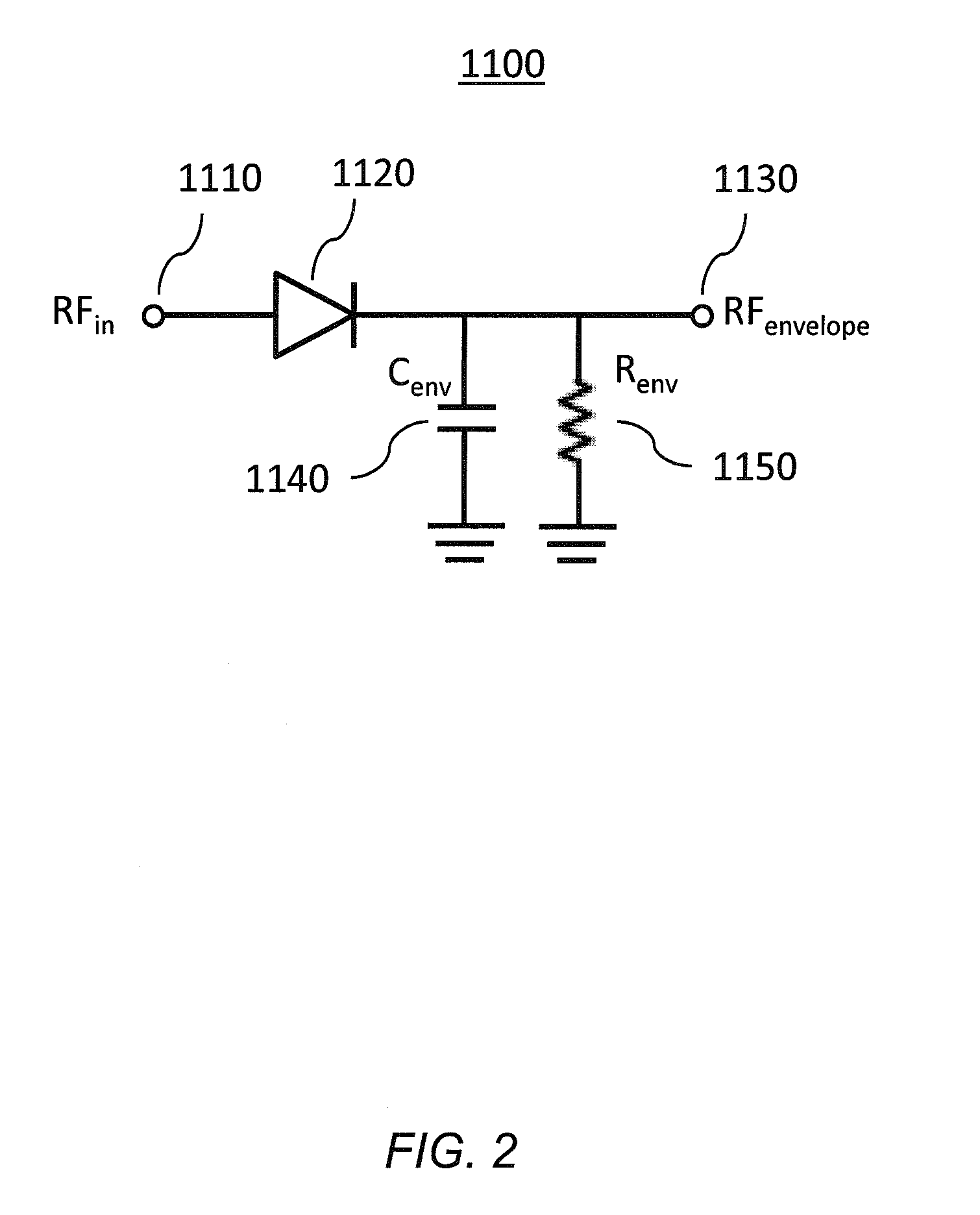
InactiveUS20050208907A1Keep linearImprove efficiencyResonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierLinear region
Small portable communication devices that support multiple modulation techniques cannot gain the benefits of using an isolator at the output of a power amplifier to provide stability in the load impedance. However, for communication devices that include amplitude modulation schemes, maintaining linear operation of the power amplifier is still required. In the presence of unstable load impedance, this can be a difficult task. As a solution, the linearity of the power amplifier is detected by comparing the envelope of the output signal with the base band signal used to modulate the output signal. If the envelopes are similar, then the power amplifier may be operating in the linear region. When the linearity of the power amplifier degrades, there is an increase in the difference between the envelopes. By adjusting the power level of the input signal to the power amplifier when the envelope difference appears, linearity of the power amplifier is maintained.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Closure device
InactiveUS20060135989A1Improve performance consistencyTrend downDiagnostic markersStaplesLinear regionAxis of symmetry
A clip for engaging tissue includes a generally annular-shaped body defining a plane and disposed about a central axis extending normal to the plane. The body includes alternating inner and outer curved regions, defining a zigzag pattern about a periphery of the clip. The body is biased towards a planar configuration lying in the plane and deflectable towards a transverse configuration extending out of the plane. Tines extend from the inner curved regions, the tines being oriented towards the central axis in the planar configuration, and parallel to the central axis in the transverse configuration. The tines include primary tines and secondary tines that are shorter than the primary tines. The primary tines may be disposed on opposing inner curved regions and oriented towards one another. The primary tines are configured such that they are offset from the axes of symmetry of the curved regions from which they extend and are connected to the curved regions by curved or linear regions or are connected directly to the curved regions. The primary tines may overlap the body and may be of different lengths.
Owner:INTEGRATED VASCULAR SYST
Organic el display panel and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20100181559A1Flat surfaceImprove wettabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLinear regionOrganic layer
Disclosed is an organic EL display panel which includes: a substrate; a linear first bank which is disposed over the substrate and defines a linear region; a second bank which defines two or more pixel regions arranged in the linear region; a pixel electrode disposed in the pixel region; a linear organic layer which is formed by coating method in the linear region over the pixel electrode and second bank; and a counter electrode over the organic layer, wherein the first bank is larger in height than the second bank, the first and second banks are made of resin, anisole contact angle at the top of the first bank is 30-60°, and anisole contact angle at the top of the second bank is 5-30°.
Owner:JOLED INC
Closure device
InactiveUS7806904B2Improve deformationStress minimizationDiagnostic markersStaplesLinear regionAxis of symmetry
A clip for engaging tissue includes a generally annular-shaped body defining a plane and disposed about a central axis extending normal to the plane. The body includes alternating inner and outer curved regions, defining a zigzag pattern about a periphery of the clip. The body is biased towards a planar configuration lying in the plane and deflectable towards a transverse configuration extending out of the plane. Tines extend from the inner curved regions, the tines being oriented towards the central axis in the planar configuration, and parallel to the central axis in the transverse configuration. The tines include primary tines and secondary tines that are shorter than the primary tines. The primary tines may be disposed on opposing inner curved regions and oriented towards one another. The primary tines are configured such that they are offset from the axes of symmetry of the curved regions from which they extend and are connected to the curved regions by curved or linear regions or are connected directly to the curved regions. The primary tines may overlap the body and may be of different lengths.
Owner:INTEGRATED VASCULAR SYST
Closed-loop load control circuit having a wide output range
ActiveUS20110080112A1Amount be controlElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLinear regionClosed loop
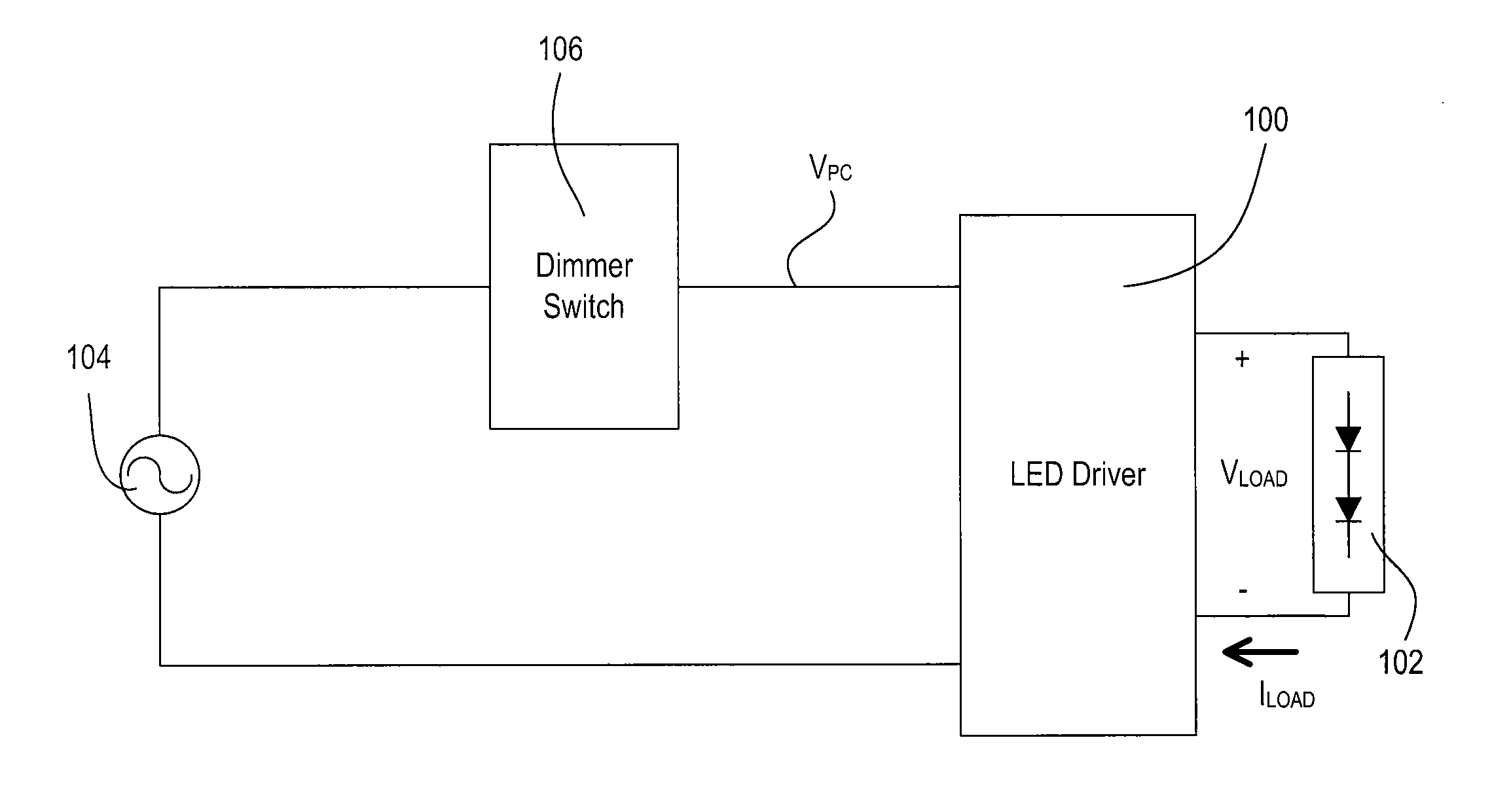
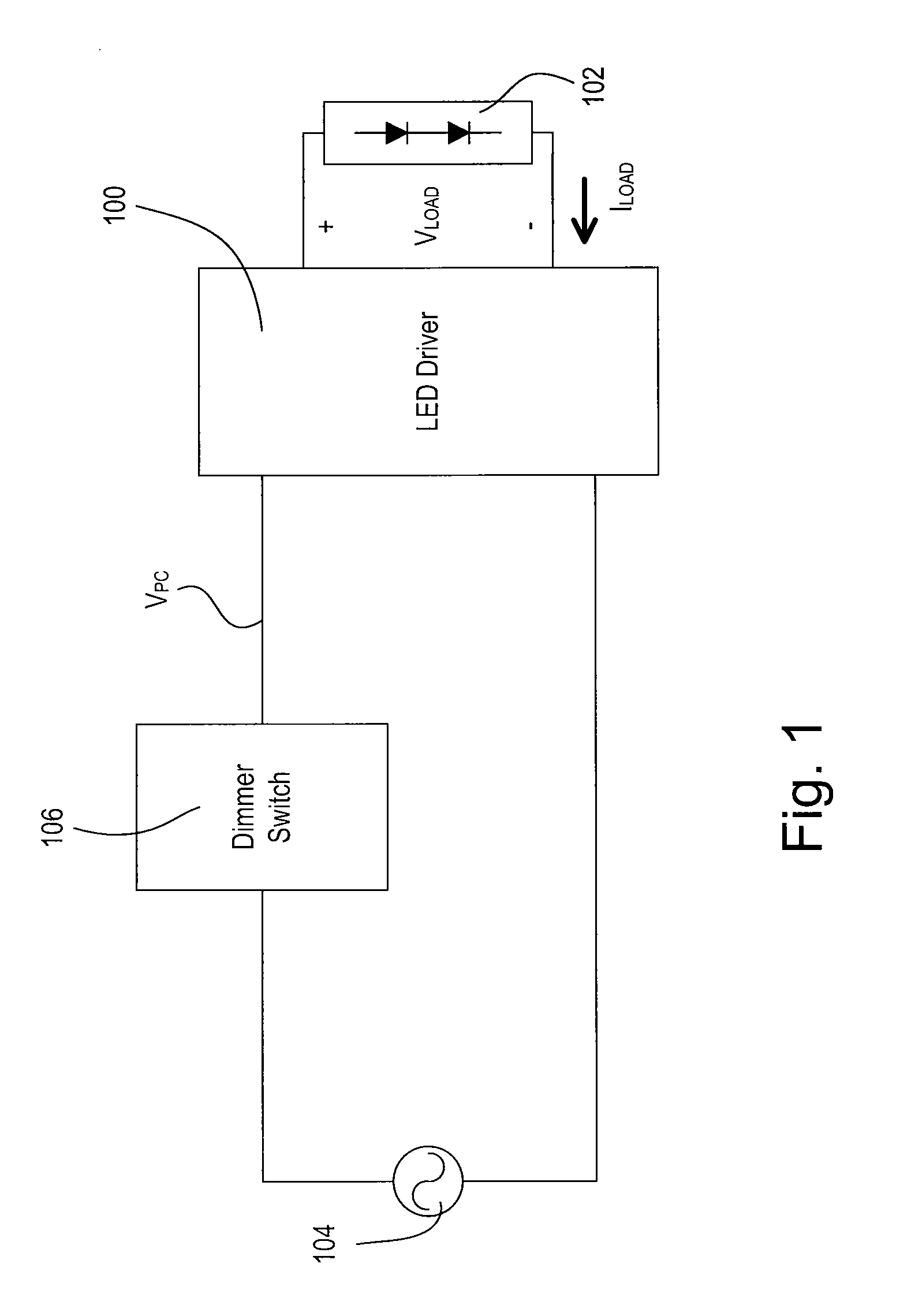
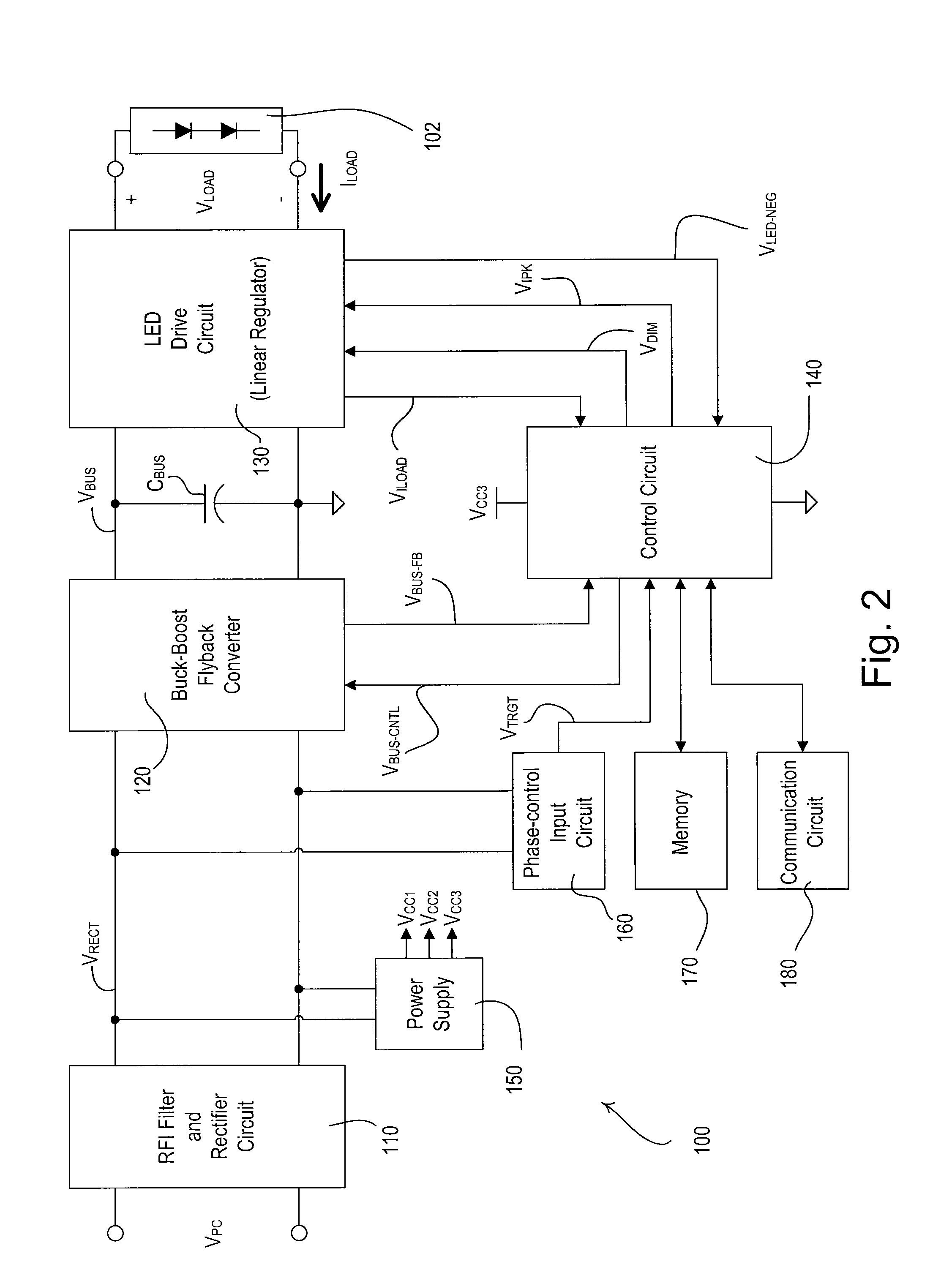
A load control circuit, such as a light-emitting diode (LED) driver, for controlling the amount of power delivered to an electrical load, such as an LED light source, comprises a regulation transistor adapted to be coupled in series with the load, and a feedback circuit coupled in series with the regulation transistor, whereby the load control circuit is able to control the magnitude of a load current conducted through the load from a minimum load current to a maximum load current, which is at least approximately one thousand times larger than the minimum load current. The feedback circuit generates at least one load current feedback signal representative of the magnitude of the load current. The regulation transistor operates in the linear region to control the magnitude of the load current conducted through the load in response to the magnitude of the load current determined from the load current feedback signal.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Automatic gain control device for electronic endoscope
InactiveUS7248296B2Accurate gainTelevision system detailsEndoscopesVariable-gain amplifierLinear region
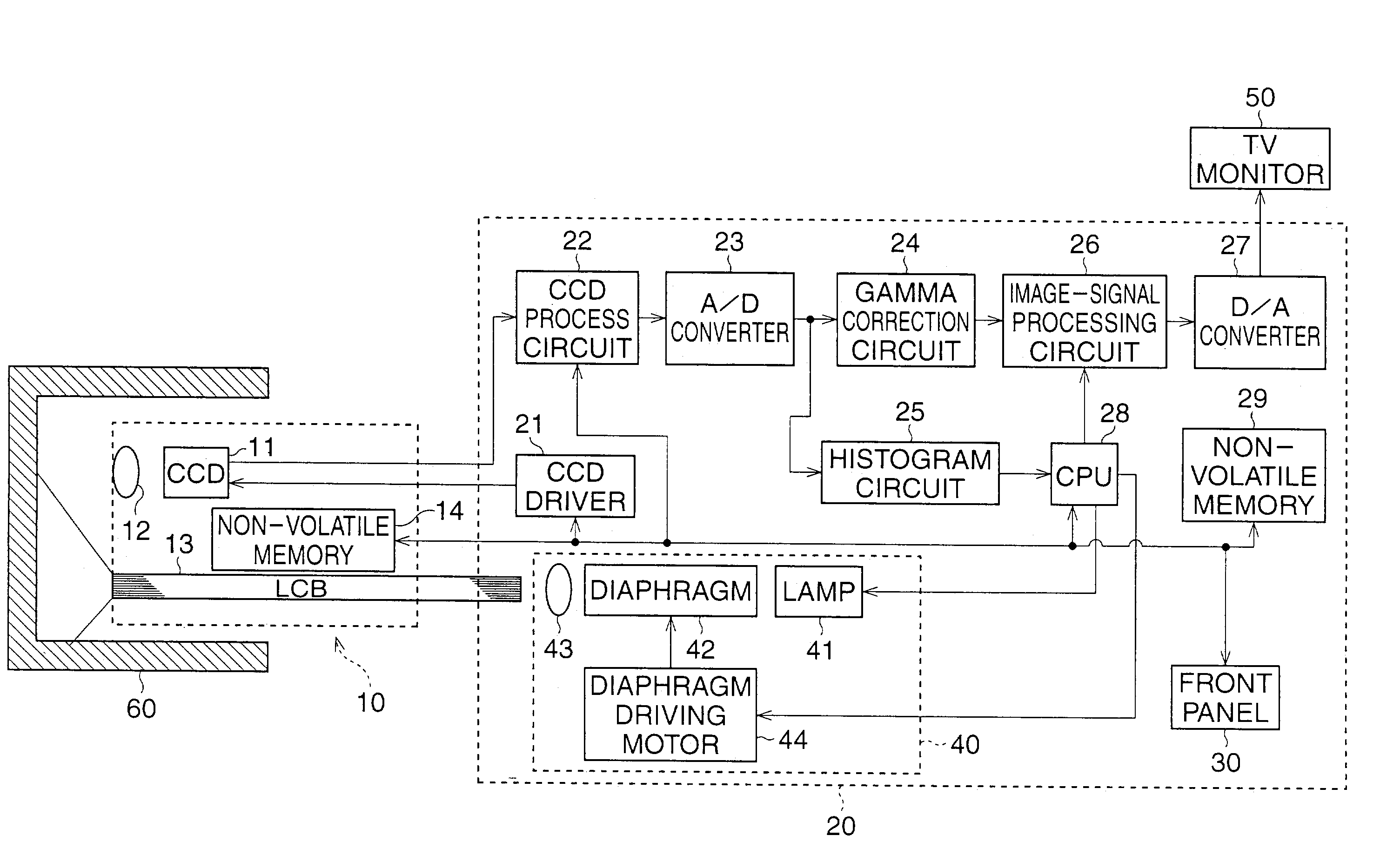
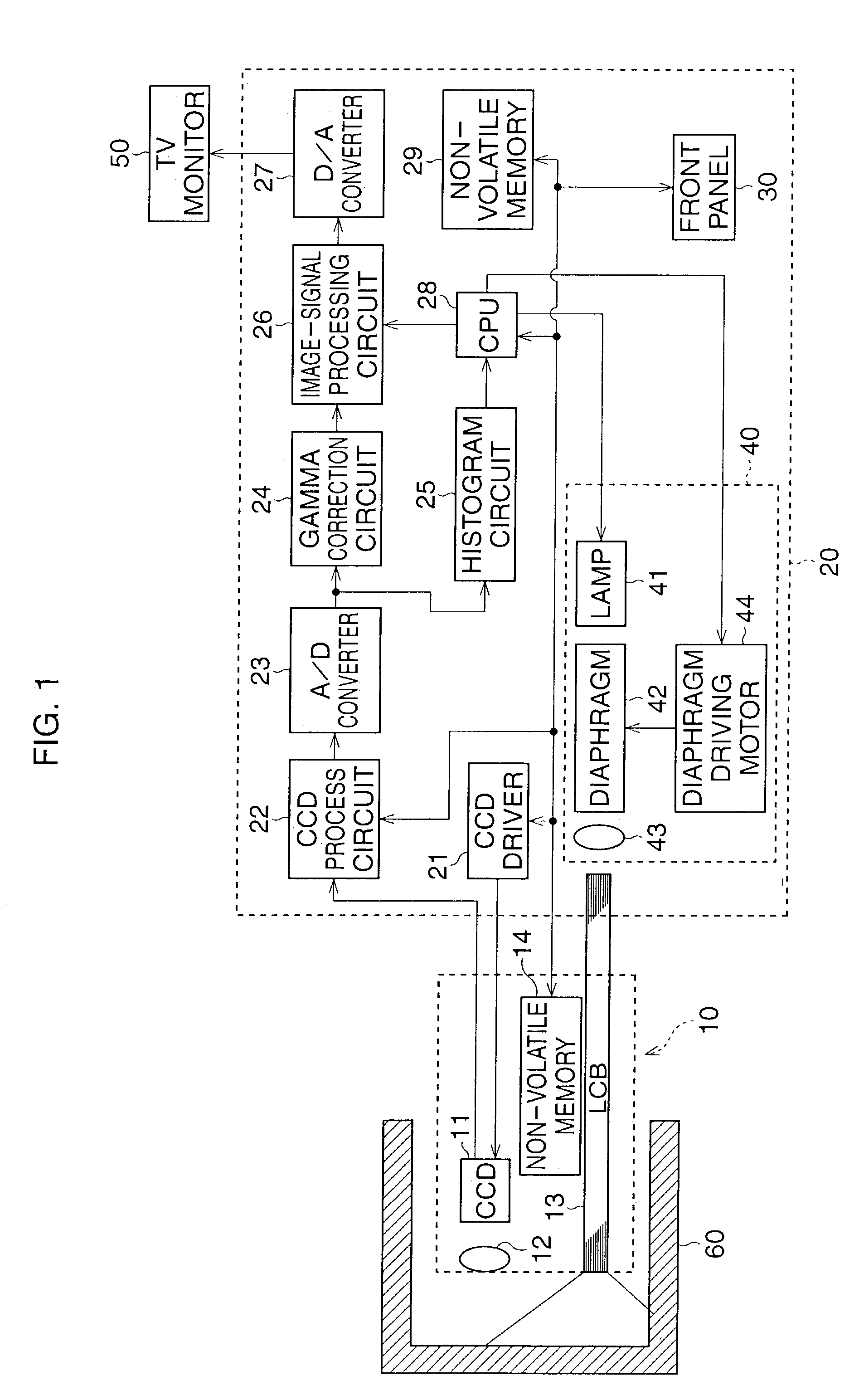
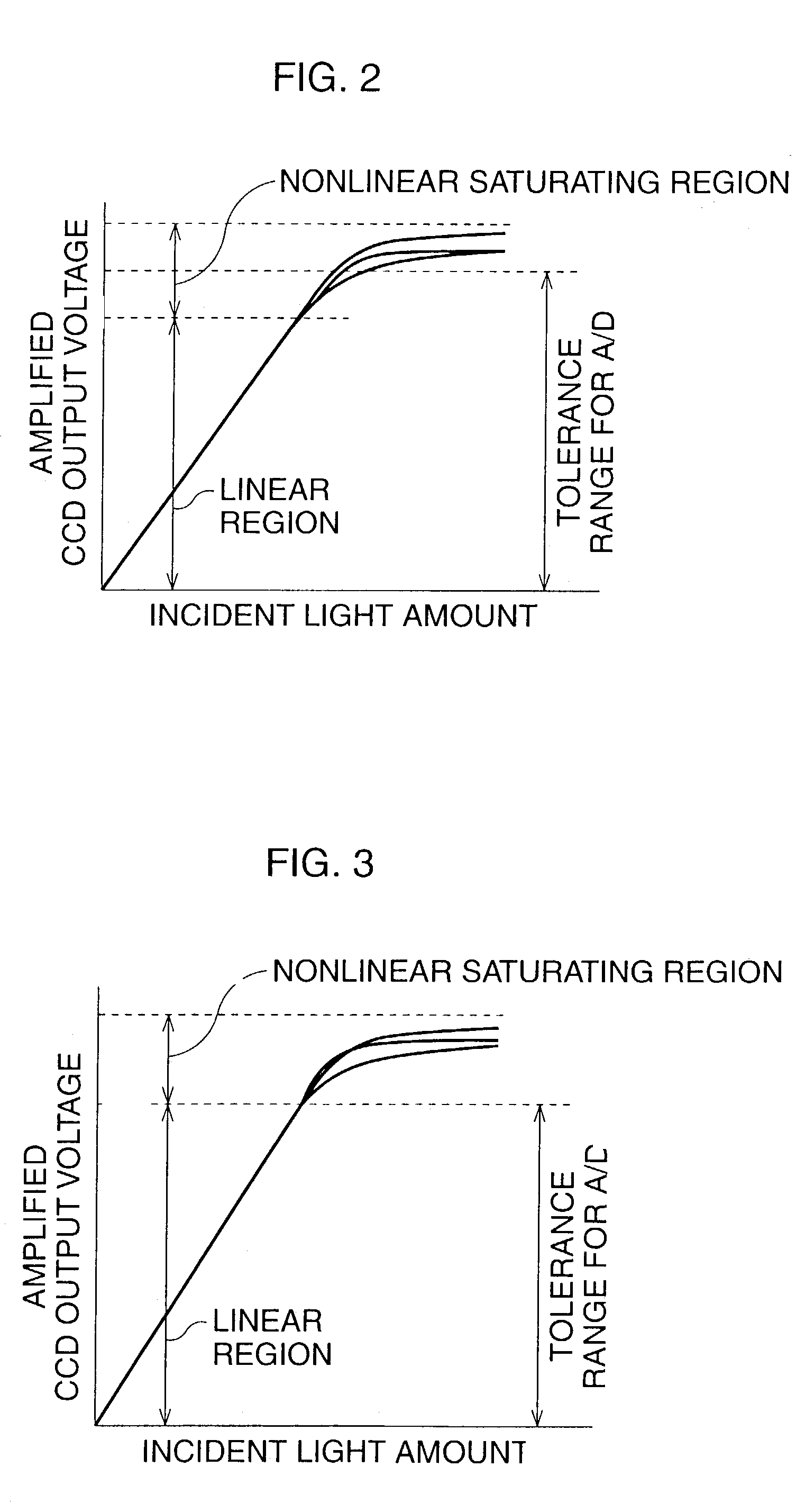
An automatic gain control device for an electronic endoscope is provided and comprises a controllable gain amplifier, an A / D converter, a histogram circuit, and a CPU. The controllable gain amplifier amplifies image signals from an imaging device. Amplified image signals from the controllable gain amplifier are input to the A / D converter. A histogram of the amplified image signals from the controllable gain amplifier is produced by the histogram circuit when an image taken in a white-balance test accessory is taken. By using the CPU, the gain of the controllable gain amplifier is adjusted in accordance with the determination of whether a saturated pixel exists for signals in the tolerance range of the A / D converter, so that a linear region of the image signals from the controllable gain amplifier substantially coincides with the tolerance range.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Security systems
InactiveUS20110057816A1Road vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionLinear region
A vehicle detection system for detecting the presence of at least part of a vehicle in image data, the system comprising: an interface configured to receive image data; an identifier module configured to identify a plurality of linear regions in an image represented by the image data; a comparator configured to compare at least one of the number, cumulative size, and density of the linear regions with a respective threshold value; and an output configured to issue a signal indicating the detection of a vehicle based on the results of the comparison.
Owner:TAGMASTER AB
Modular plastic conveyor belt with high beam strength
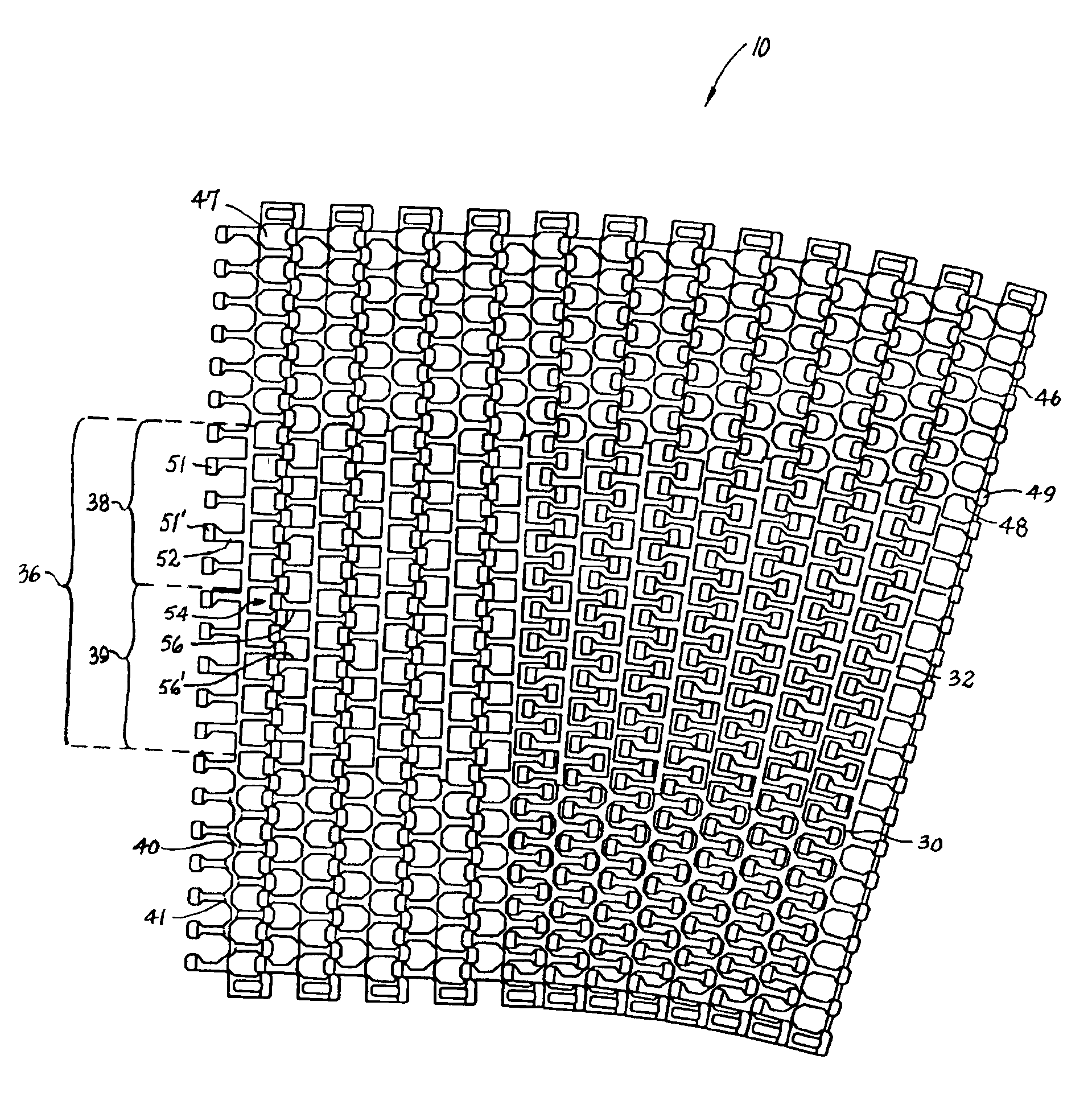
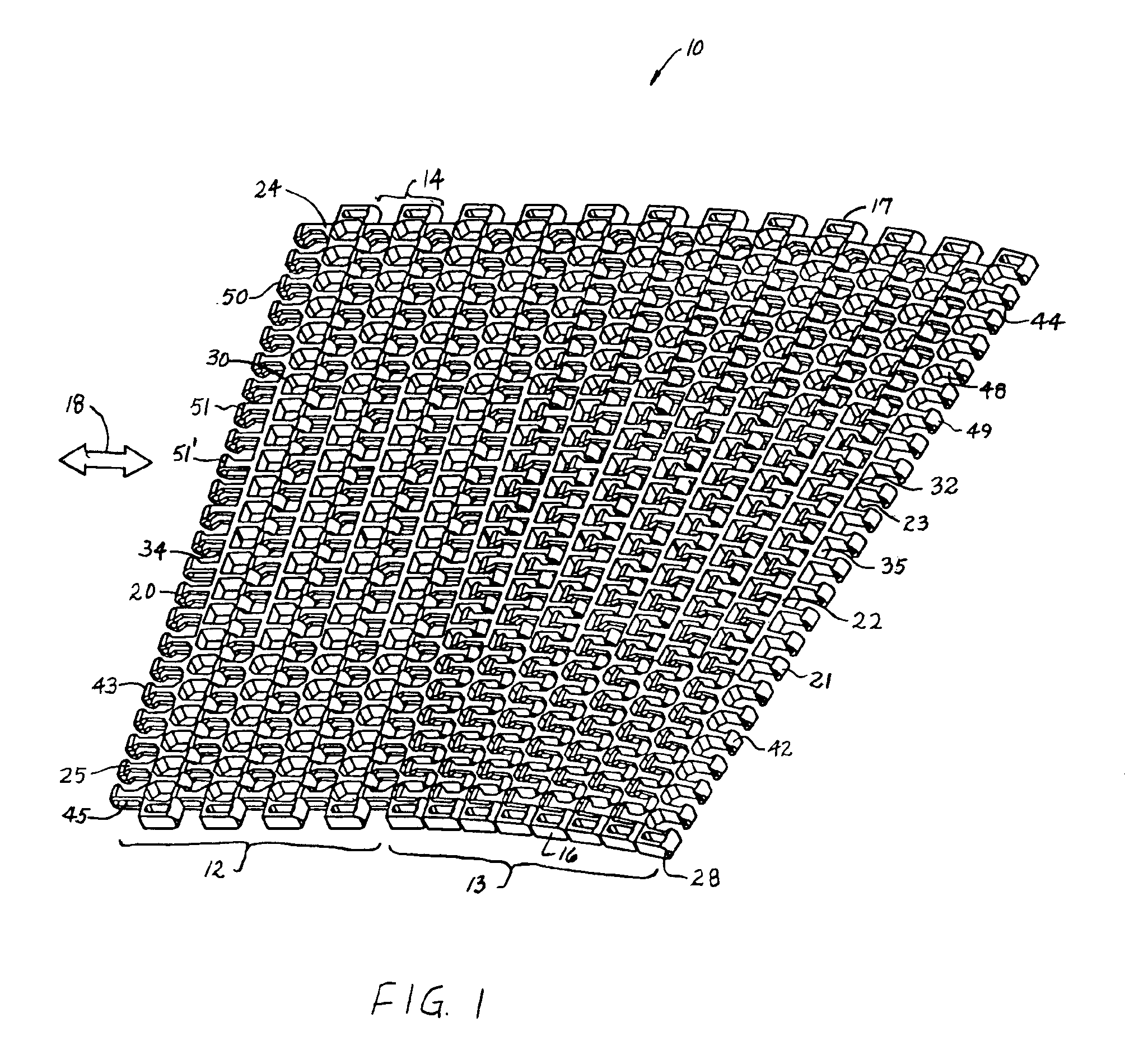
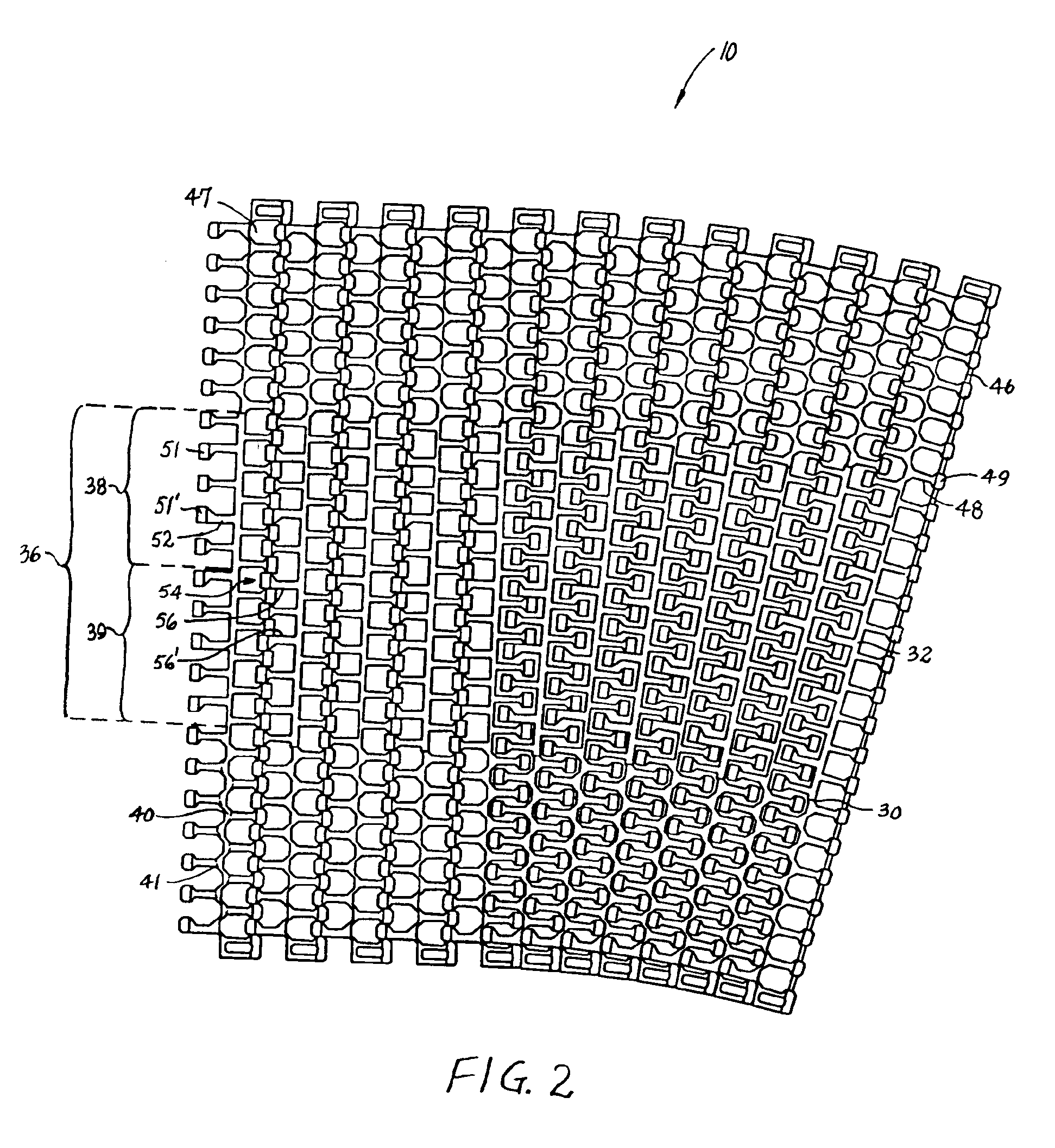
A modular plastic conveyor belt having a central beam along each belt row. The beam extends laterally across the width of a belt row and includes a linear portion in a middle region of the belt and a sinuous region near both side edges of the belt. In the linear region, the beam includes a portion of constant thickness with linearly tapering portions toward the side edges of the belt. In this way, the thicker portions of the beam in the middle of the belt provide beam strength to allow less frequent support beneath the belt and the thinner sinuous portions at the edges of the belt give it the flexibility and mobility to collapse at the inside of a turn.
Owner:LAITRAM LLC
Clamp circuit
InactiveUS6737905B1Reduce areaLow costPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesLevel shiftingLinear region
Owner:DENSO CORP
Clamp circuit
InactiveUS20040080352A1Reduce areaLow costPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceLevel shifting
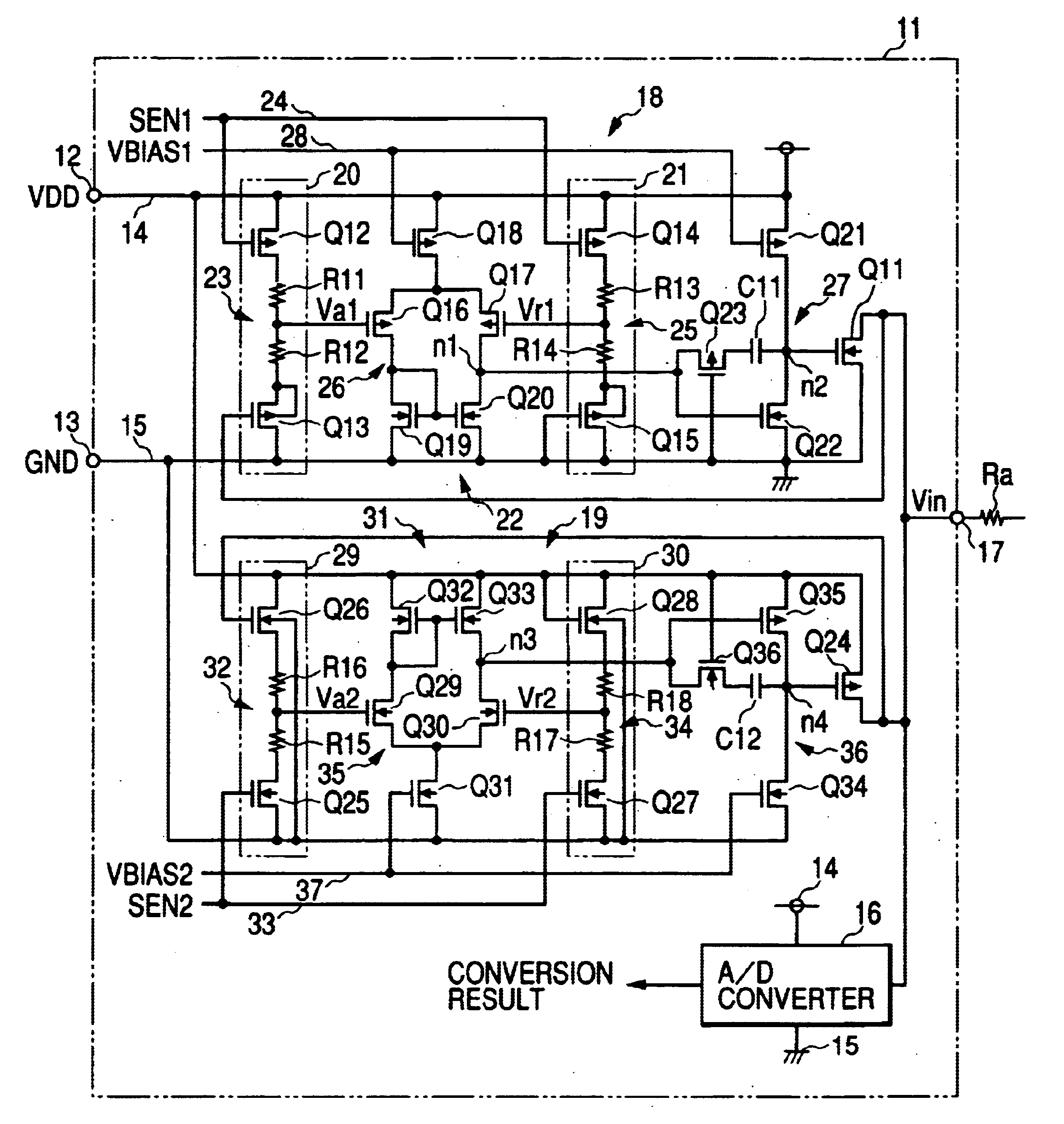
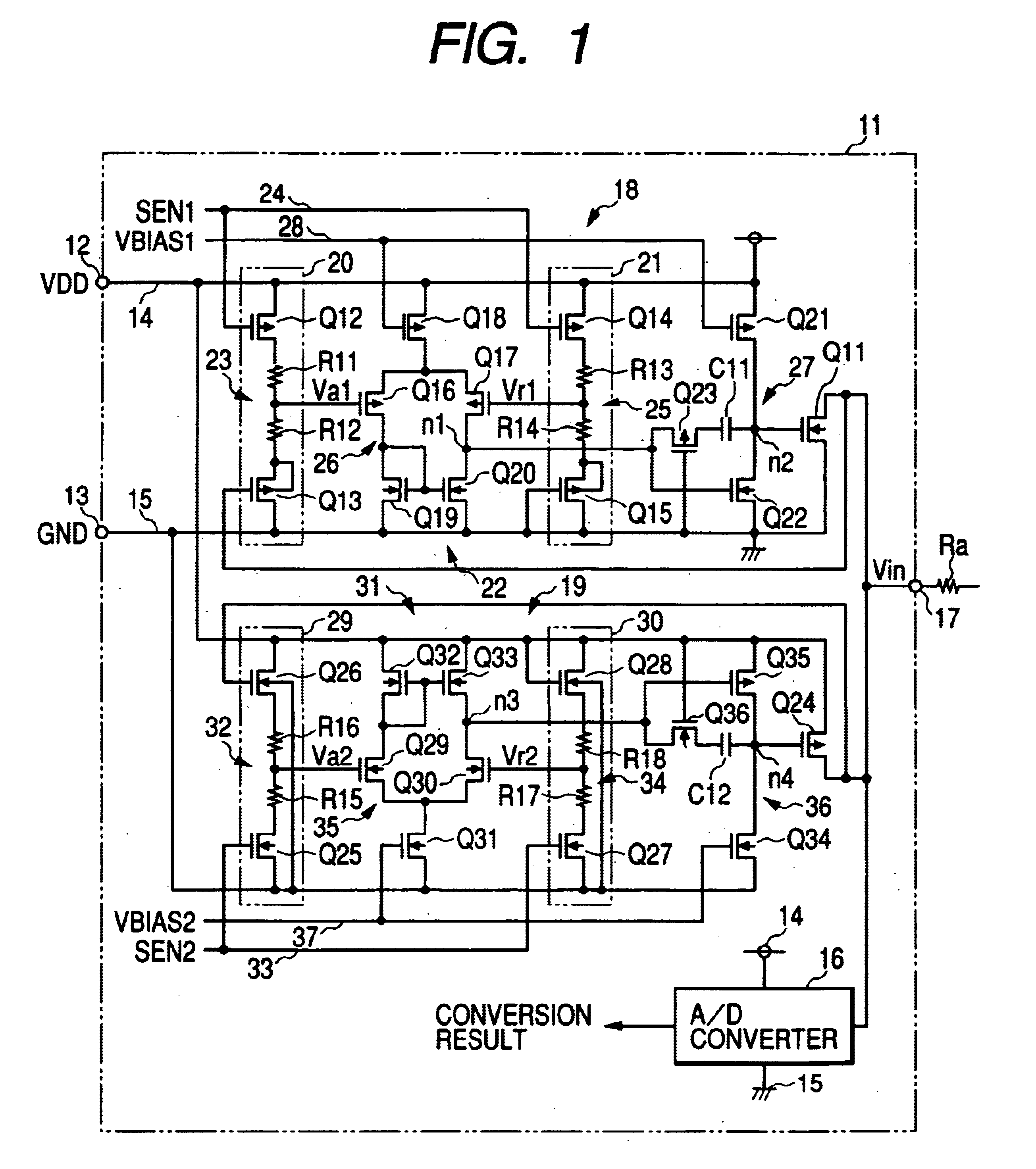
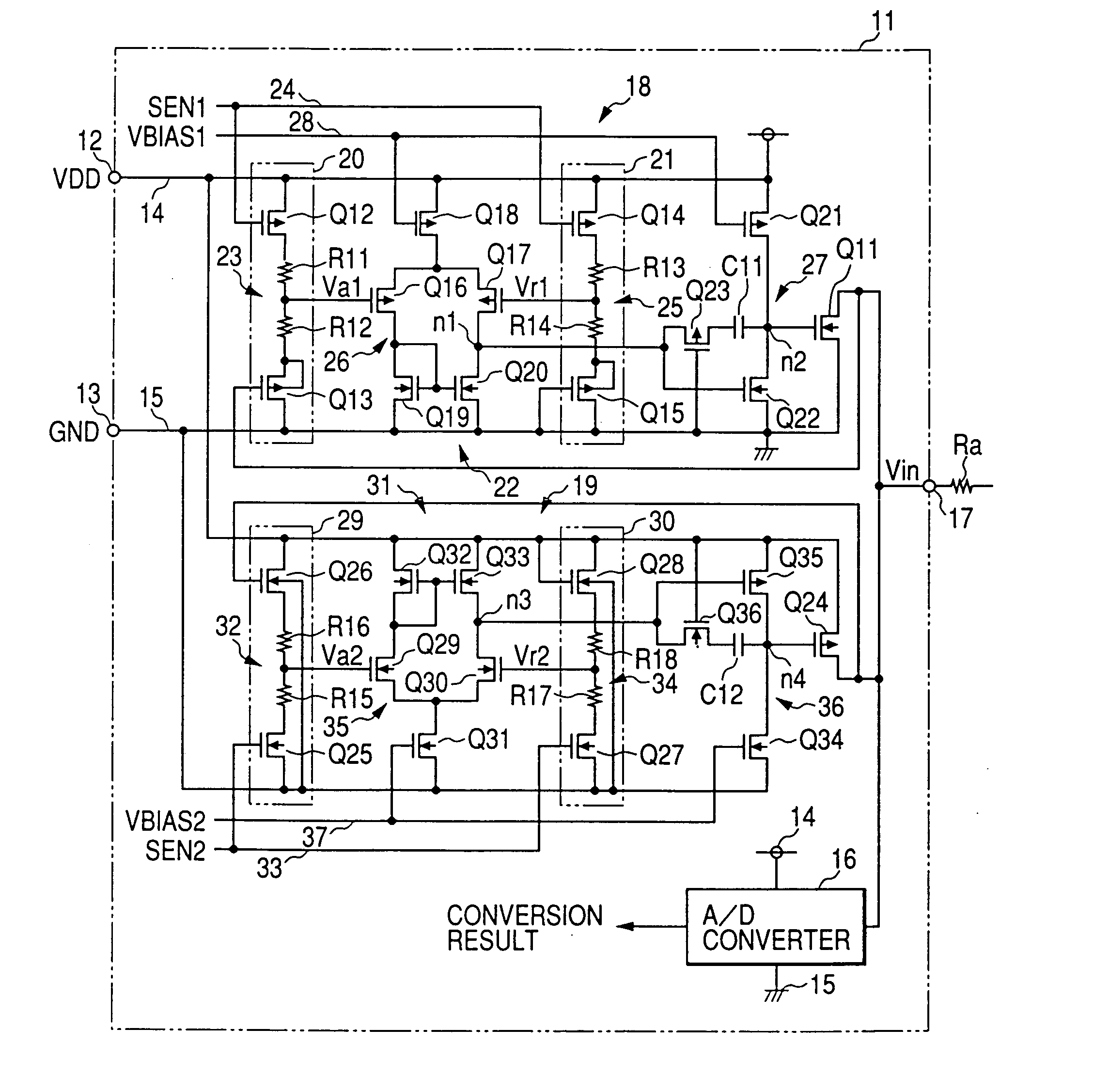
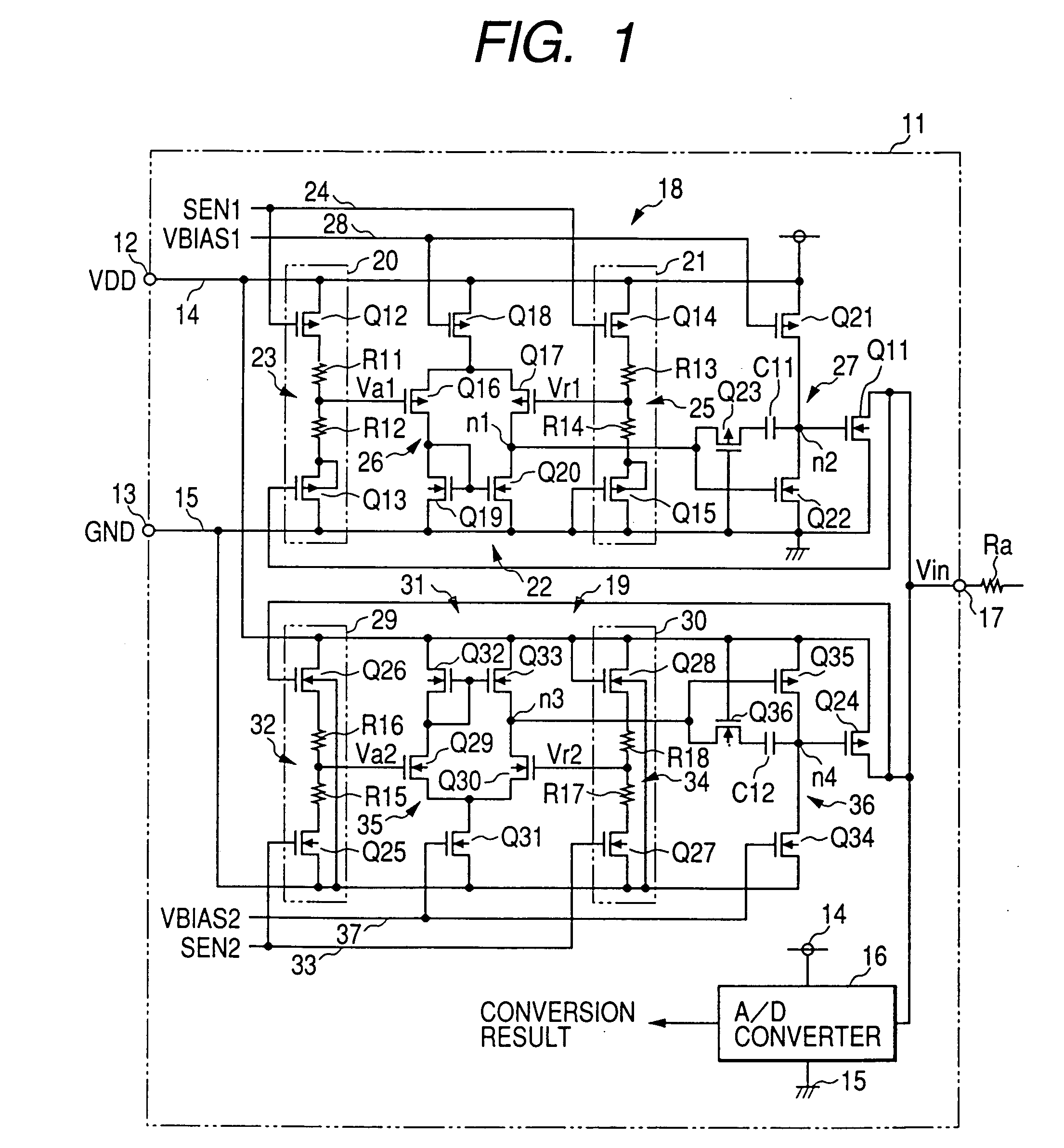
The clamp circuit clamps an input voltage at prescribed higher and lower clamp voltages which are stabilized under a temperature fluctuation. Transistors Q12 and Q14 are switched on in their linear region. In a lower voltage clamp circuit 18, an Vin detecting circuit 20 outputs Va1 by level-shifting Vin by Q13 and voltage-divides by series resistance circuit 23 the level-shifted Vin, while a reference voltage generating circuit 21 outputs Vr1 by level-shifting 0 V by Q15 and voltage-divides by series resistance circuit 25 the level-shifted voltage. Q11 is switched on, when a comparator 22 determines that Va1 descends and goes across Vr1. Here, Q12 is of the same characteristics as Q14, while Q13 is of the same characteristics as Q15. Further, the resistance of the circuits 23 is the same as that of the circuit 25. The higher voltage clamp circuit 19 is similar to the circuit 18.
Owner:DENSO CORP
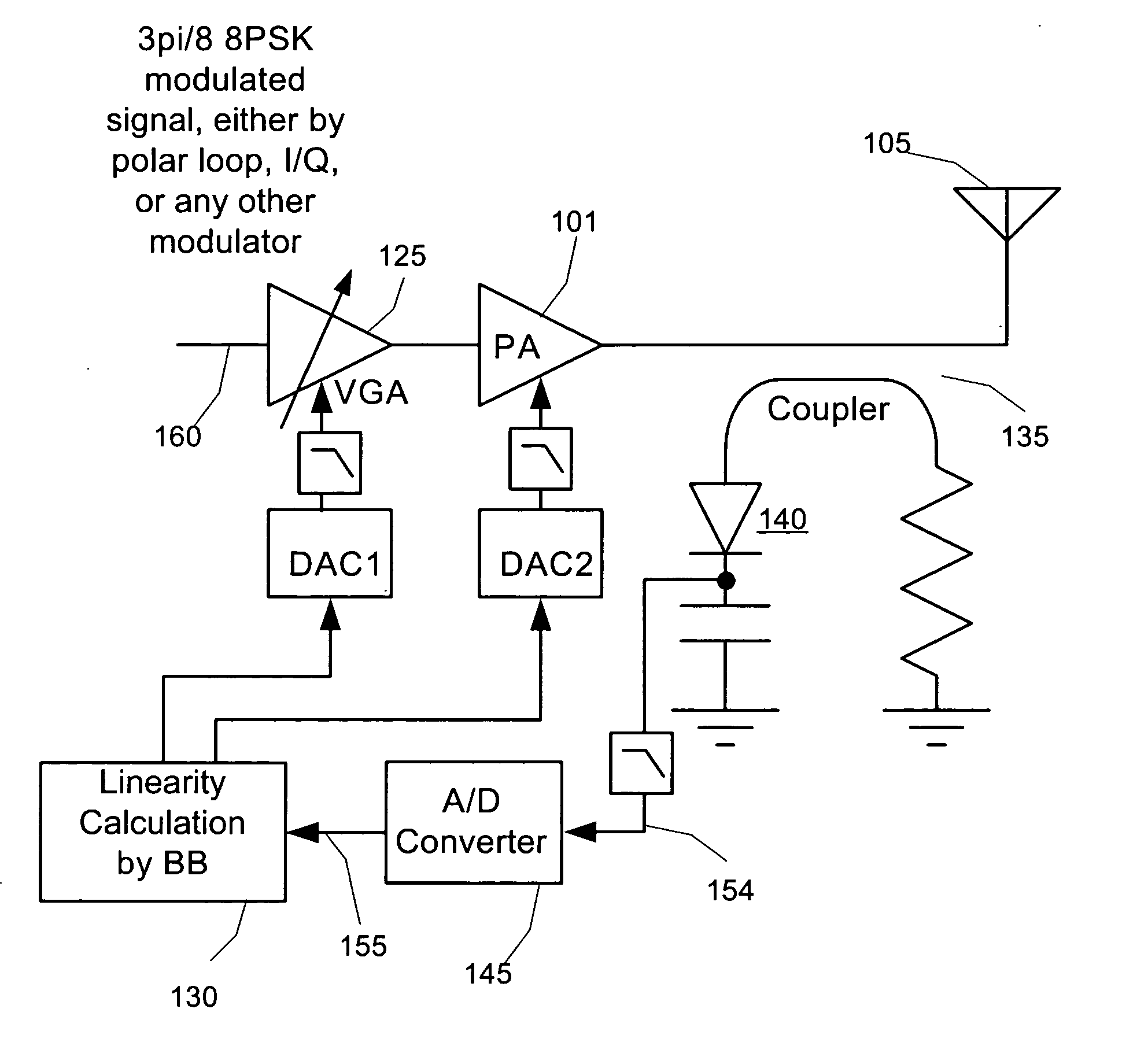
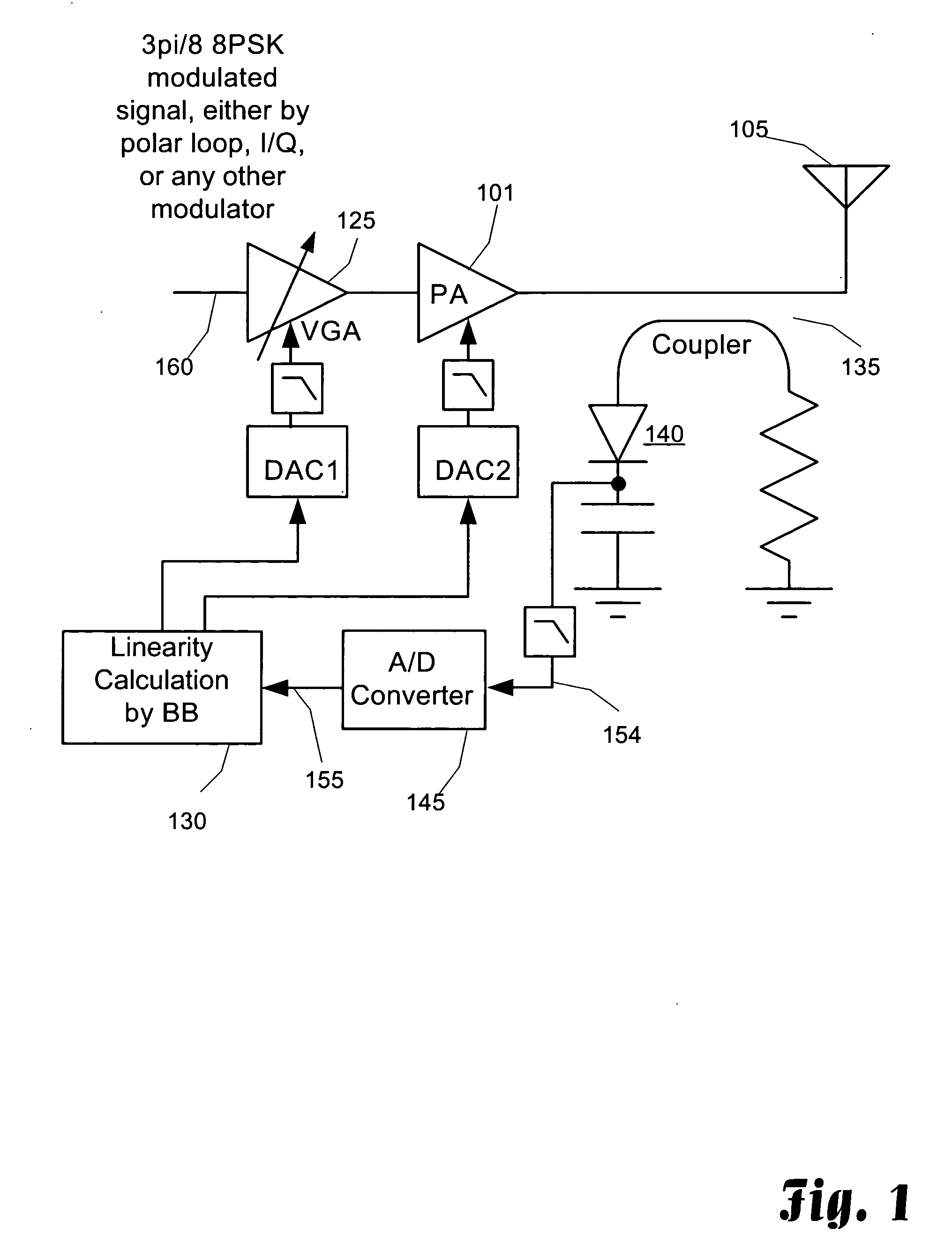
Adaptive Complex Gain Predistorter for a Transmitter
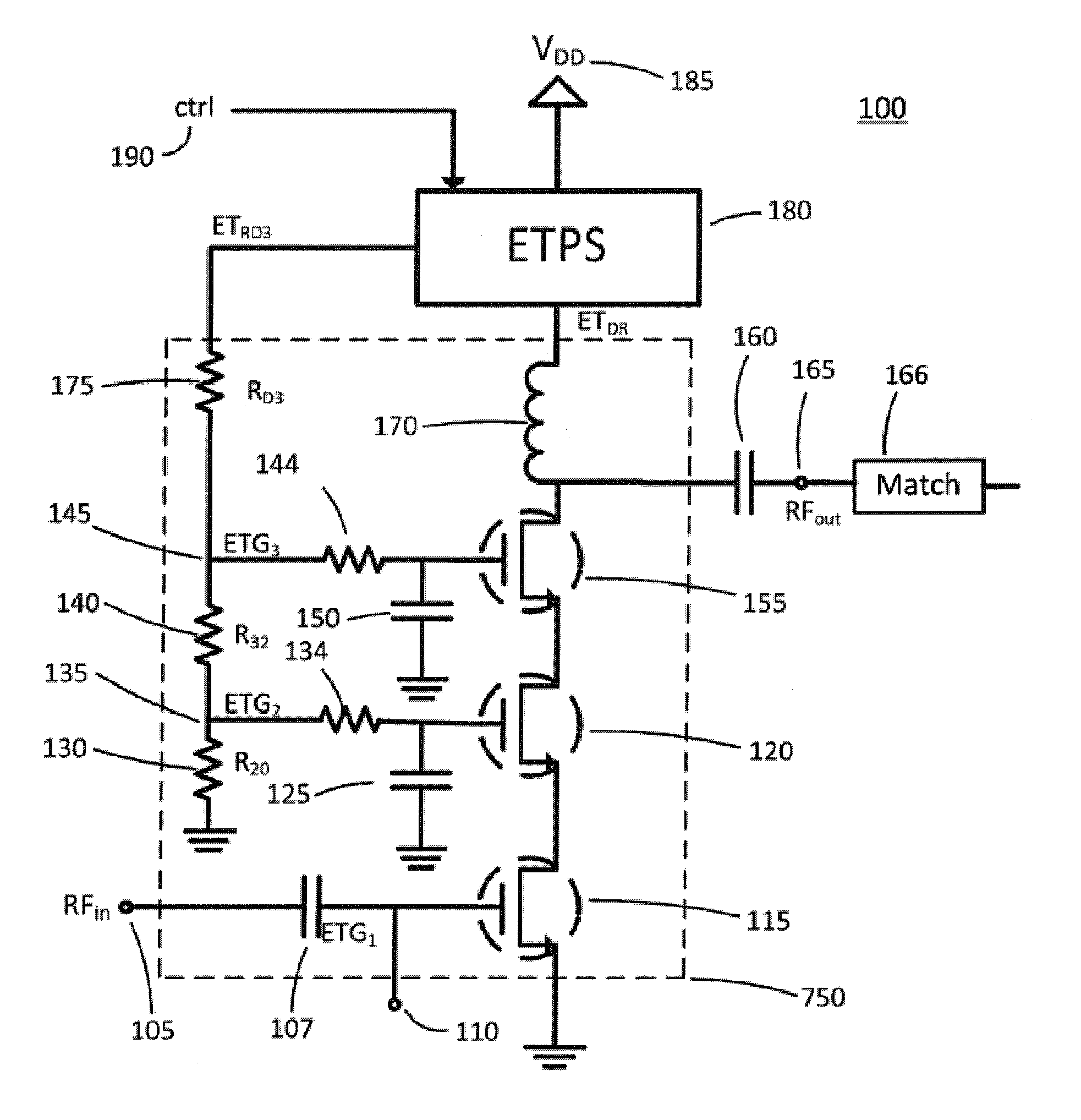
ActiveUS20100035554A1Resonant long antennasPower amplifiersLinear regionIn-phase and quadrature components
Symbols are transmitted in a Cartesian transmitter by pre-distorting an input signal X having in-phase and quadrature components using a first compensation lookup table operable to hold complex valued entries to carry out in-phase and quadrature compensation pre-distortion with respect to the input signal to form a pre-distorted signal Z. The pre-distorted signal Z is processed to form an output signal Y using a nonlinear element. A complex gain normalization parameter adaptively updated to reflect varying gain of a linear region of the nonlinear element. A normalized feed back signal {tilde over (Y)} is formed using the adaptively updated complex gain normalization parameter. The first compensation lookup table is updated based on the pre-distorted input signal Z and the adaptively normalized feedback signal {tilde over (Y)}.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Element substrate and a light emitting device
InactiveUS7173586B2High field-effect mobilityHigh currentElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesLinear regionScan line
A light emitting device and an element substrate which are capable of suppressing variations in the luminance intensity of a light emitting element among pixels due to characteristic variations of a driving transistor without suppressing off-current of a switching transistor low and increasing storage capacity of a capacitor. According to the invention, a driving transistor also serves as an erasing transistor and the driving transistor is operated in a saturation region. The gate of the driving transistor is connected to an erasing scan line and it can be selected whether or not to flow current by a potential of the erasing scan line. In addition, a current controlling transistor which operates in a linear region is connected in series to the driving transistor, thus a video signal transmitting a light emission or non-emission of a pixel is input to the gate of the current controlling transistor through a switching transistor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Magnetic-bias currency detecting magnetic head with sensitive direction parallel to detection face
ActiveCN102968845AHigh sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioPaper-money testing devicesDigital storageLinear regionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Light emitting device
InactiveUS6873116B2Manufacturing process is complicatedInfluence of a variation in characteristics of a driver transistor is suppressedStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesLinear regionLight emitting device
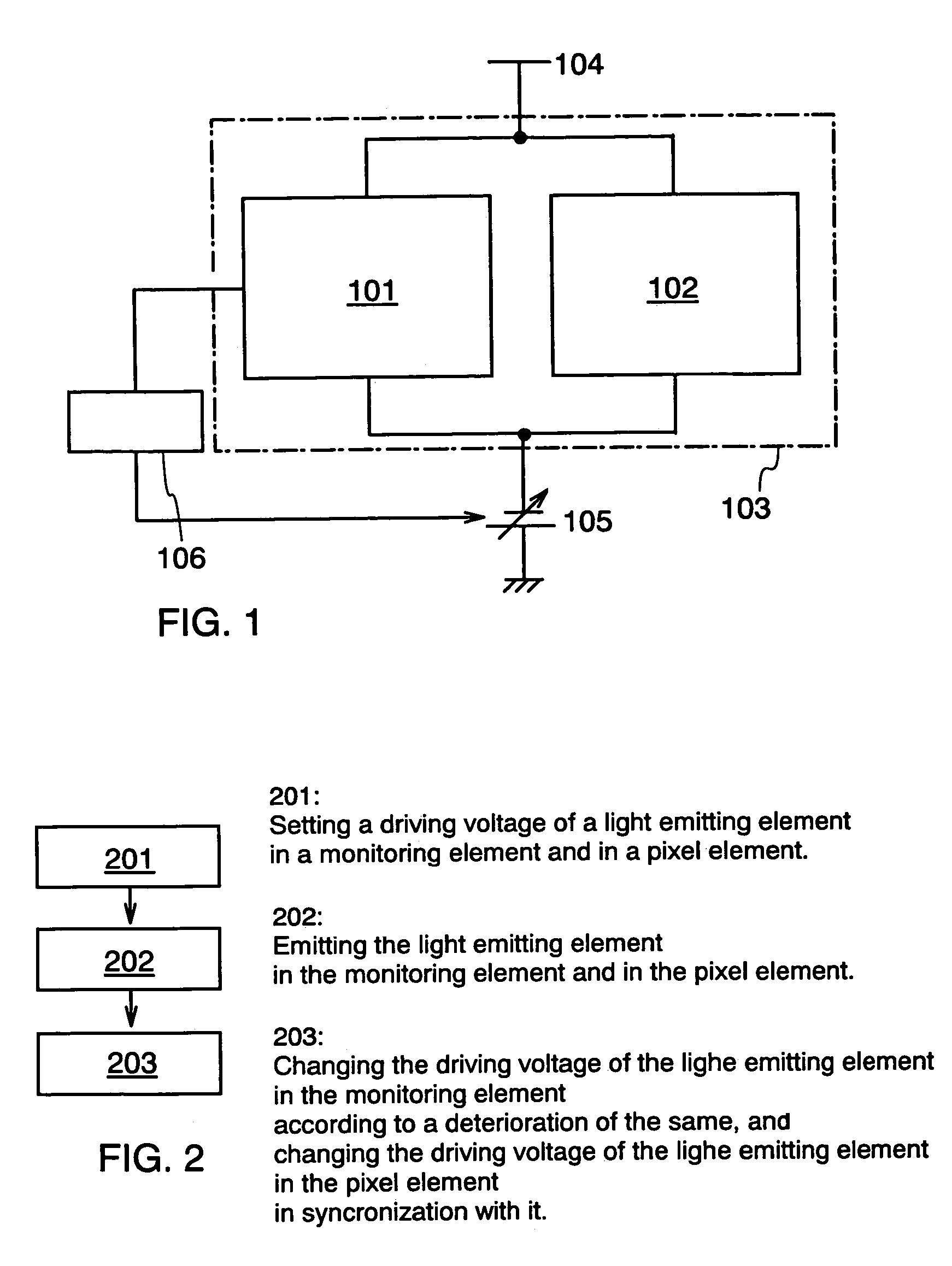
In order to suppress the influence of deterioration of a light emitting element resulting from a change over time, the present invention provides a light emitting device in which an electrical circuit for flowing a constant charge between both electrodes of the light emitting element is provided in each pixel. In addition, the present invention provides a light emitting device in which a transistor provided in each pixel is operated in a linear region and used as only a switch, so that the light emitting device is not influenced by a variation in characteristic of the transistor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
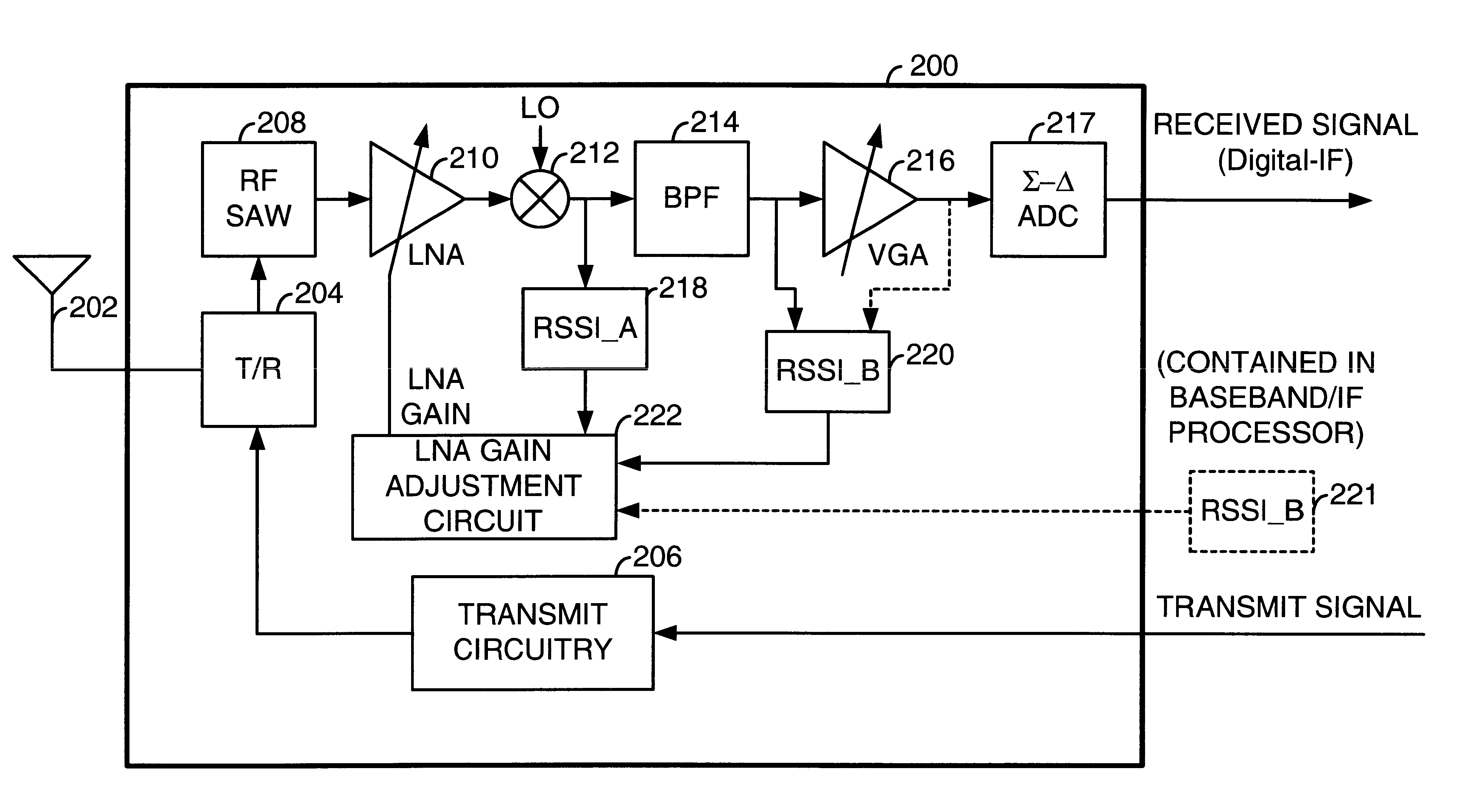
Timing based LNA gain adjustment in an RF receiver to compensate for intermodulation interference
InactiveUS6873832B2Keep linearMaximize signal to noise ratioAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlLinear regionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A Radio Frequency (RF) receiver includes a low noise amplifier (LNA) and a mixer coupled to the output of the LNA. The gain of the LNA is adjusted to maximize signal-to-noise ratio of the mixer and to force the mixer to operate well within its linear region when an intermodulation interference component is present. The RF receiver includes a first received signal strength indicator (RSSI_A) coupled to the output of the mixer that measures the strength of the wideband signal at that point. A second received signal strength indicator (RSSI_B) couples after the BPF and measures the strength of the narrowband signal. The LNA gain is set based upon these signal strengths. LNA gain is determined during a guard period preceding an intended time slot of a current frame and during a guard period following an intended time slot of a prior frame. The lesser of these two LNA gains is used for the intended time slot of the current frame.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
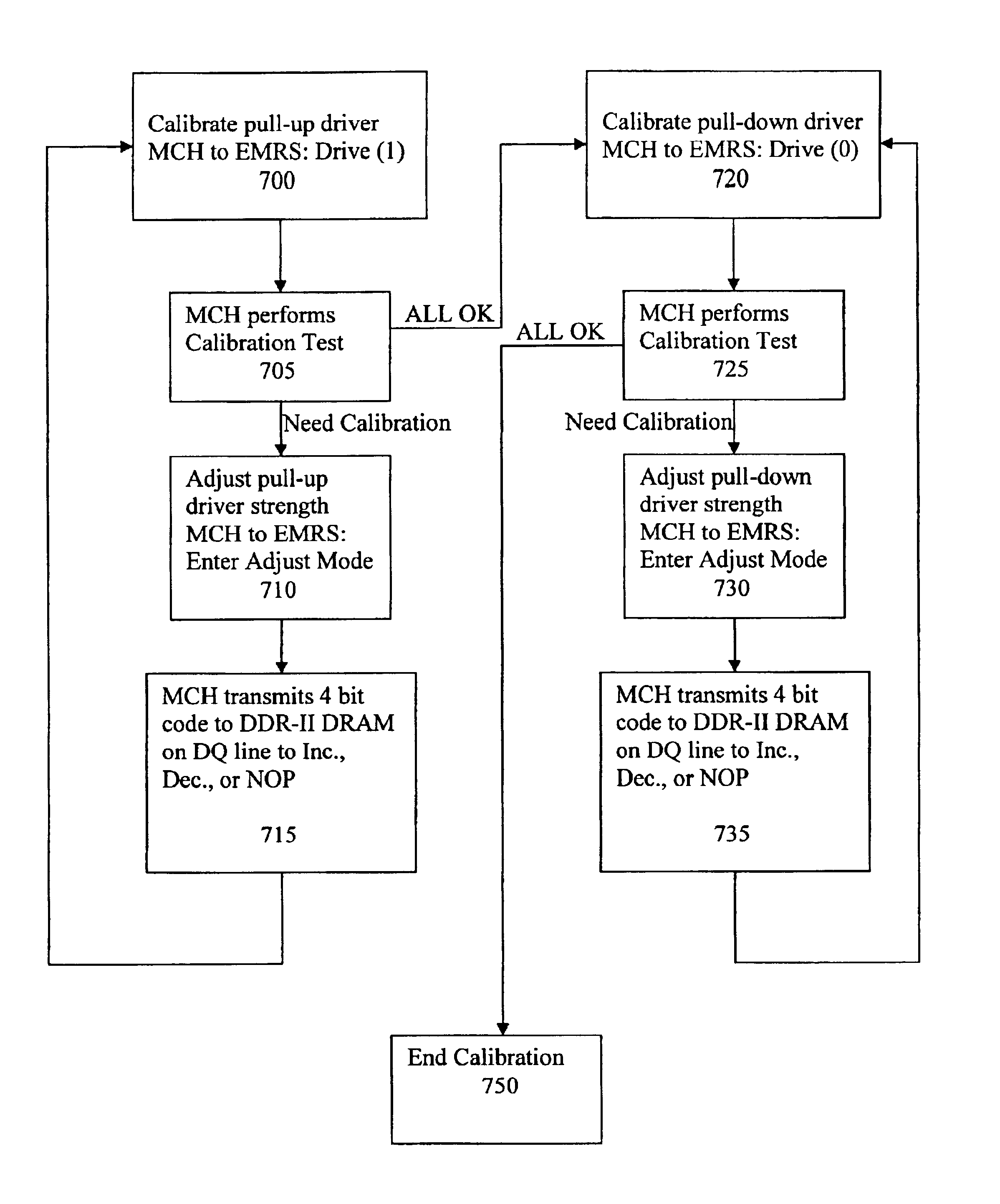
Circuit and method for calibrating DRAM pullup Ron to pulldown Ron
Embodiments of the present invention enable the matching of pull-up and pull-down driver strengths of a slave device (DDRII SDRAM), i.e., the P-channel / N-channel driver pull-up / pull-down Ron and also calibrates the P-channel / N-channel pull-up / pull-down drivers in their linear region of operation. Specifically, embodiments of the present invention may use the DDR-II Off Chip Driver (OCD) protocol for calibration, in addition to using circuit techniques to calibrate the slave driver pull-up Ron within 1 LSB of the pull-down Ron.
Owner:INTEL CORP
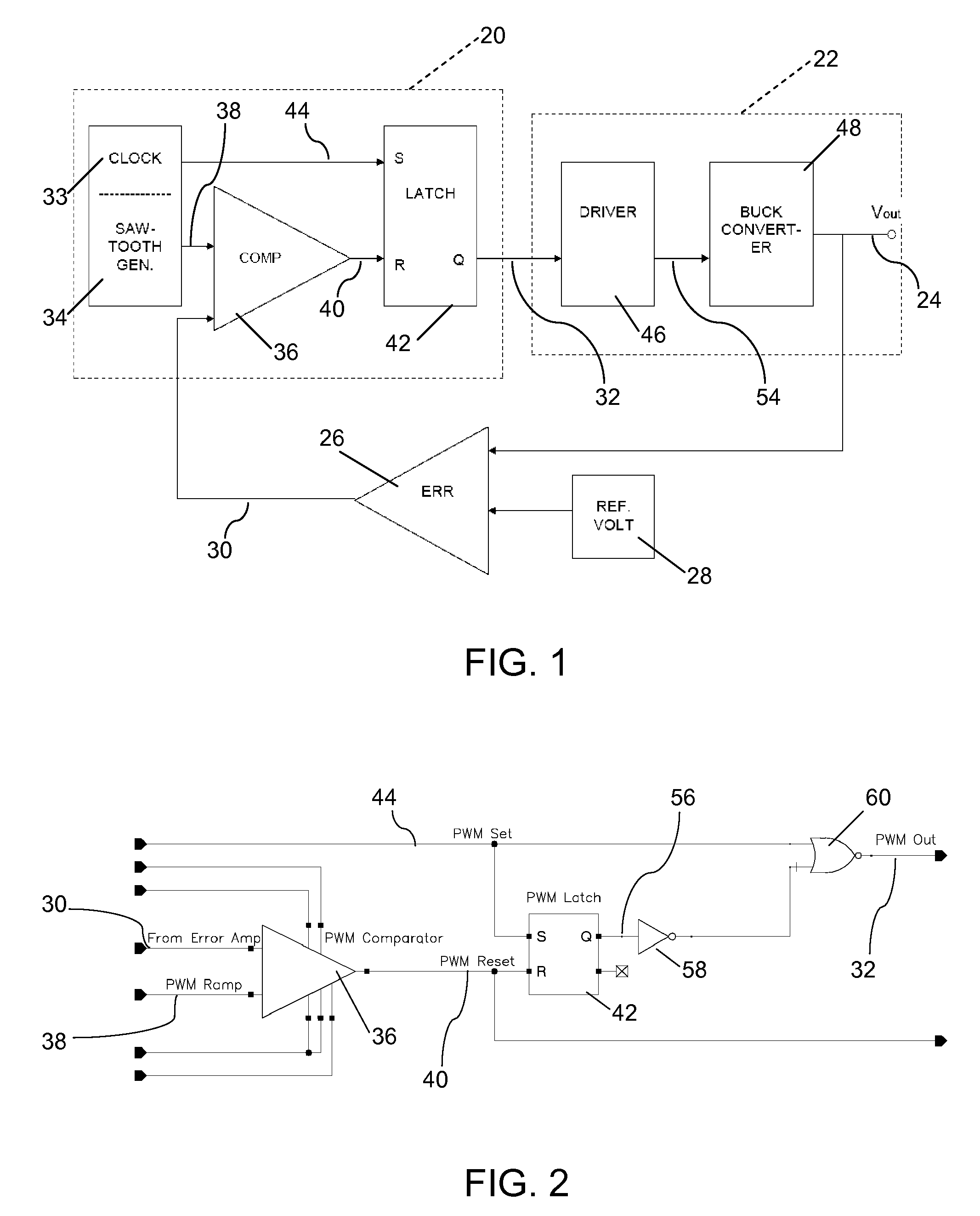
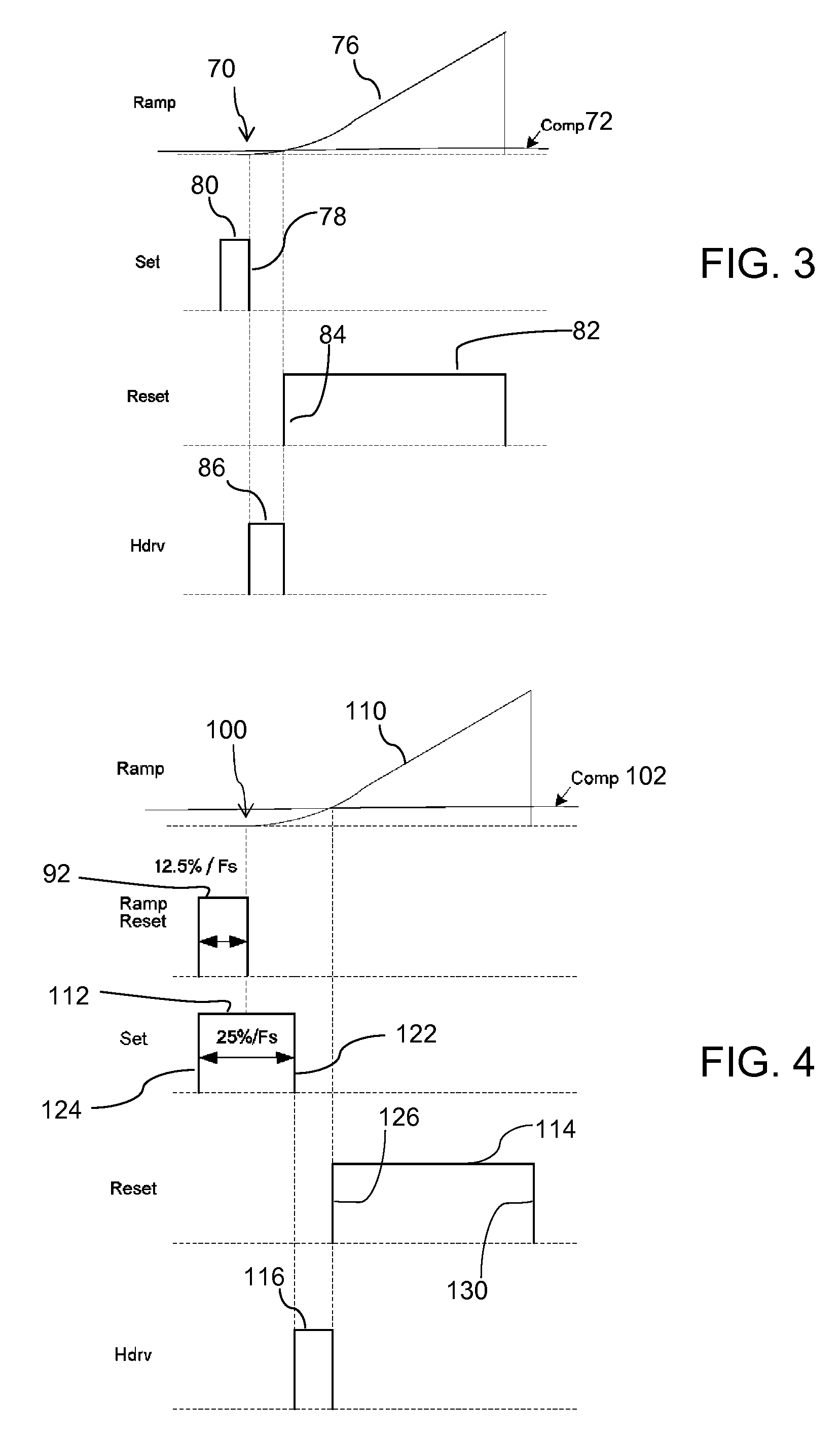
Minimum pulse width for pulse width modulation control
The rising edge of a pulse width modulated output signal occurs after an input ramp signal starts to rise. The ramp signal starts to rise after the rising edge of a periodic set signal and before the falling edge of a periodic set signal. A feedback control signal intersects a substantially linear region of the ramp signal to generate a reset signal using a PWM comparator. The periodic set signal and reset signal are input to a latching circuit to generate the pulse width modulated output signal. The minimum pulse width can approach zero while having adequate overdrive to the PWM comparator. Having the rising edge of the reset signal rise before the falling edge of the set signal can allow a zero percent duty cycle without the need for a ramp offset voltage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Low-power, low-area power headswitch
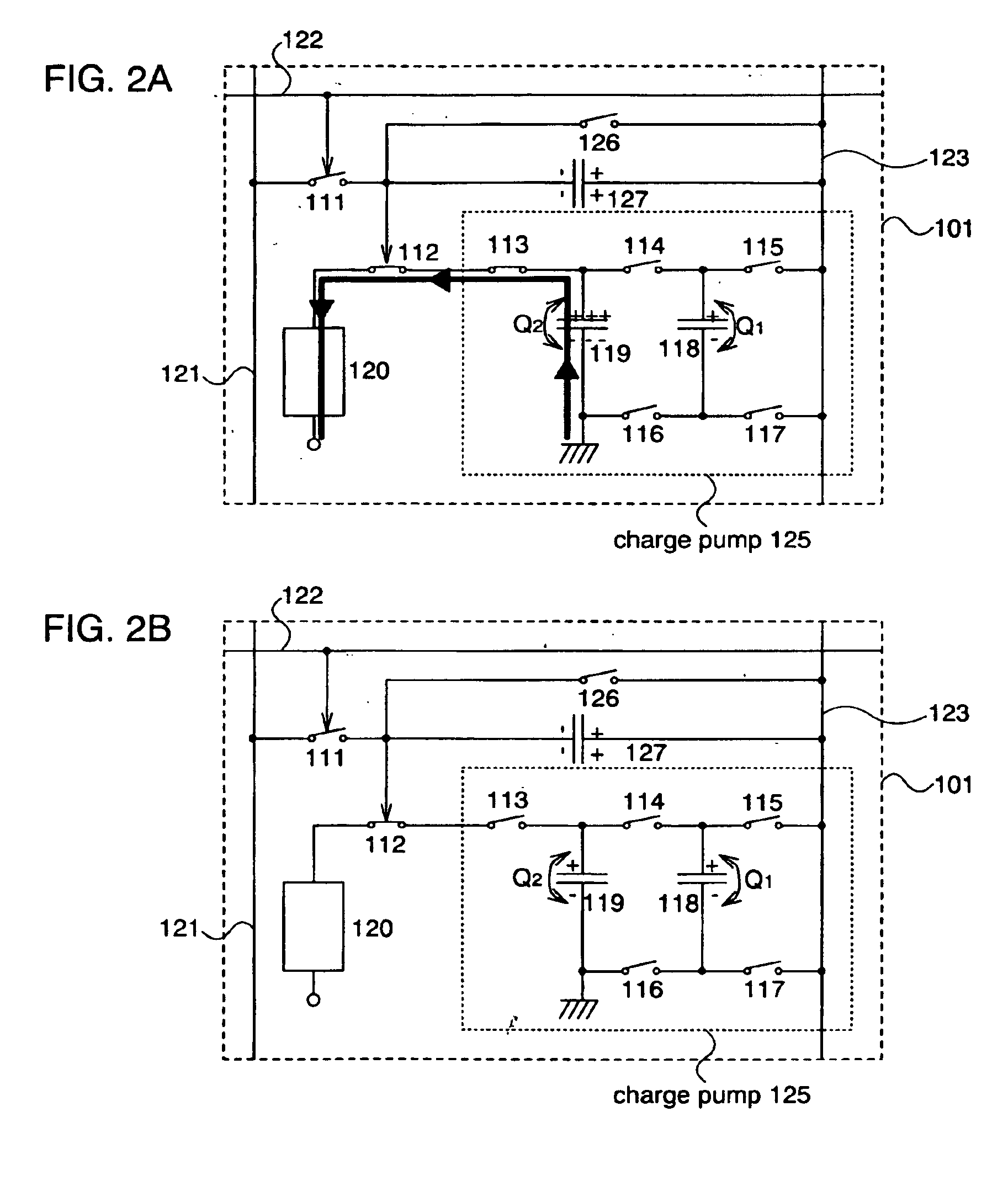
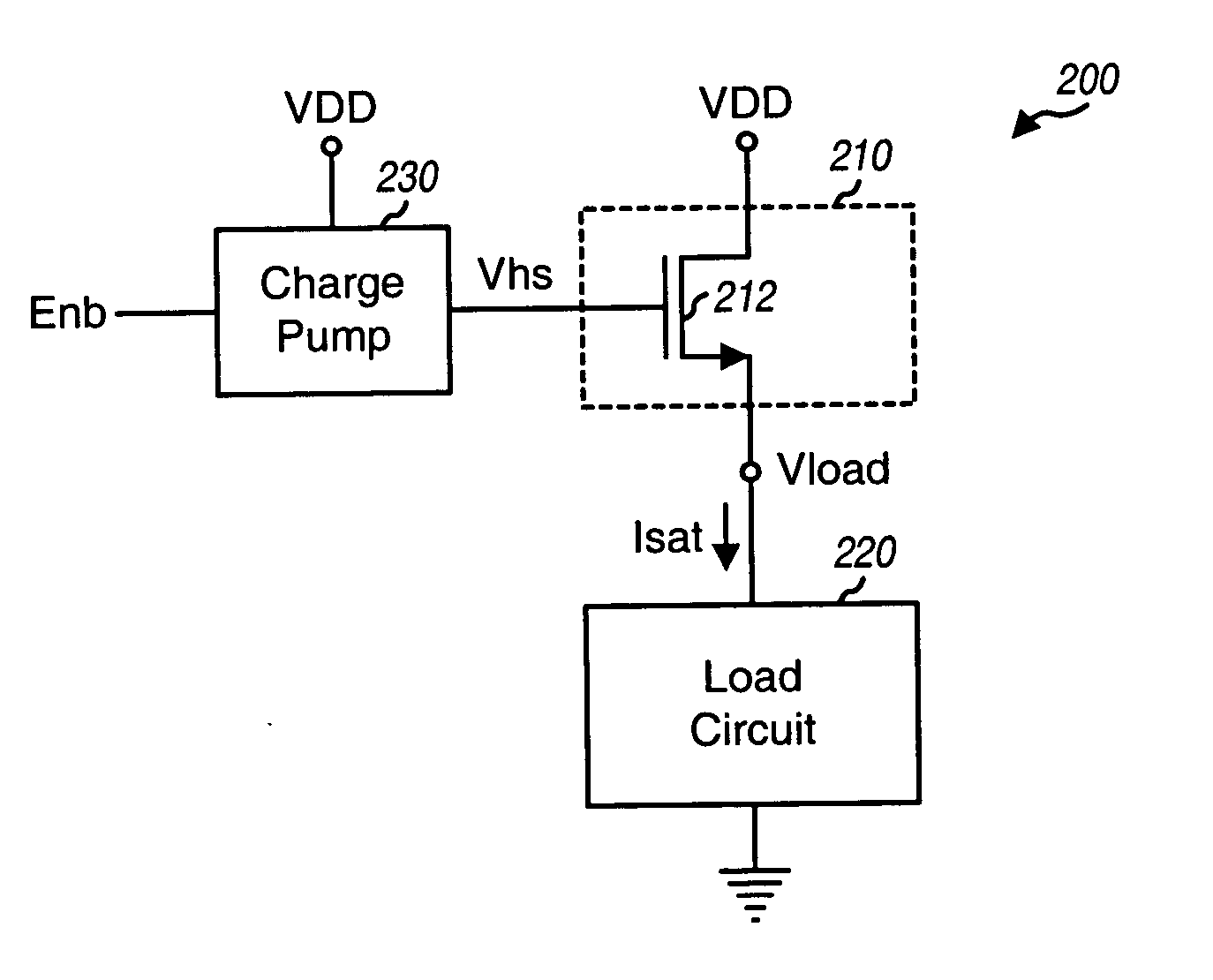
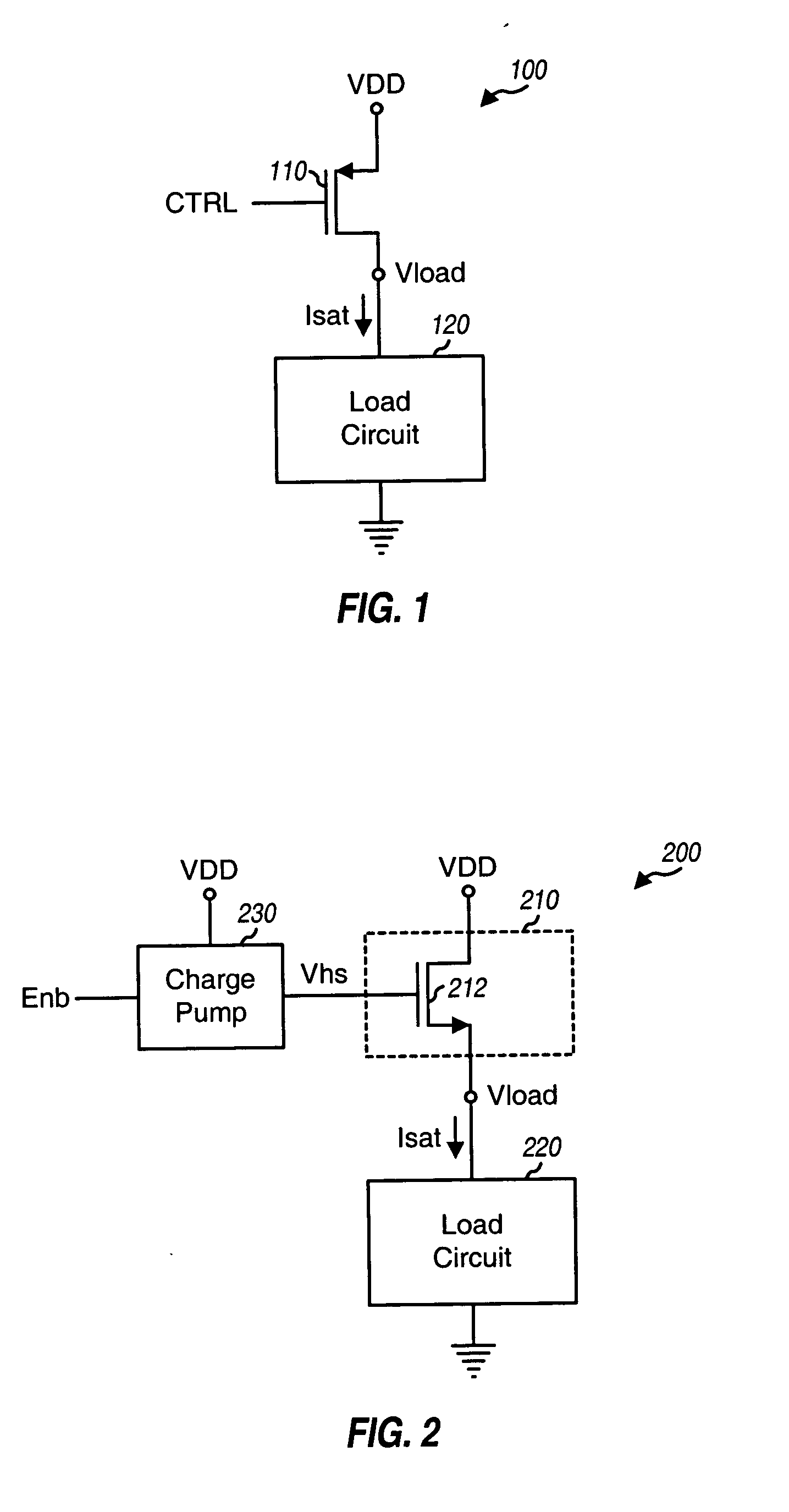
ActiveUS20050007178A1Improve performanceAvoid excessive currentTransistorElectronic switchingLoad circuitControl signal
An N-FET headswitch has improved performance (e.g., less leakage current, lower ON resistance, and smaller area) over a conventional P-FET headswitch. The N-FET headswitch includes at least one N-FET device and couples between a power supply and a load circuit, which may be, e.g., a microprocessor, a digital signal processor, or a memory unit. The headswitch couples the power supply to the load circuit when the headswitch is enabled and cuts off the power supply from the load circuit when disabled. A charge pump couples to the headswitch and provides a control signal. This control signal is sufficiently high when the headswitch is enabled to ensure that the N-FET device operates in a linear region and has a small drain to source voltage drop. The headswitch may be operated as a power switch or in a feedback configuration to implement a linear or a digital voltage regulator.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Alloy, magnetic core and process for the production of a tape from an alloy
ActiveUS20120262266A1Degradation of magnetic propertyImprove regularity of soft magnetic property of magneticNanomagnetismIndividual molecule manipulationHysteresisLinear region
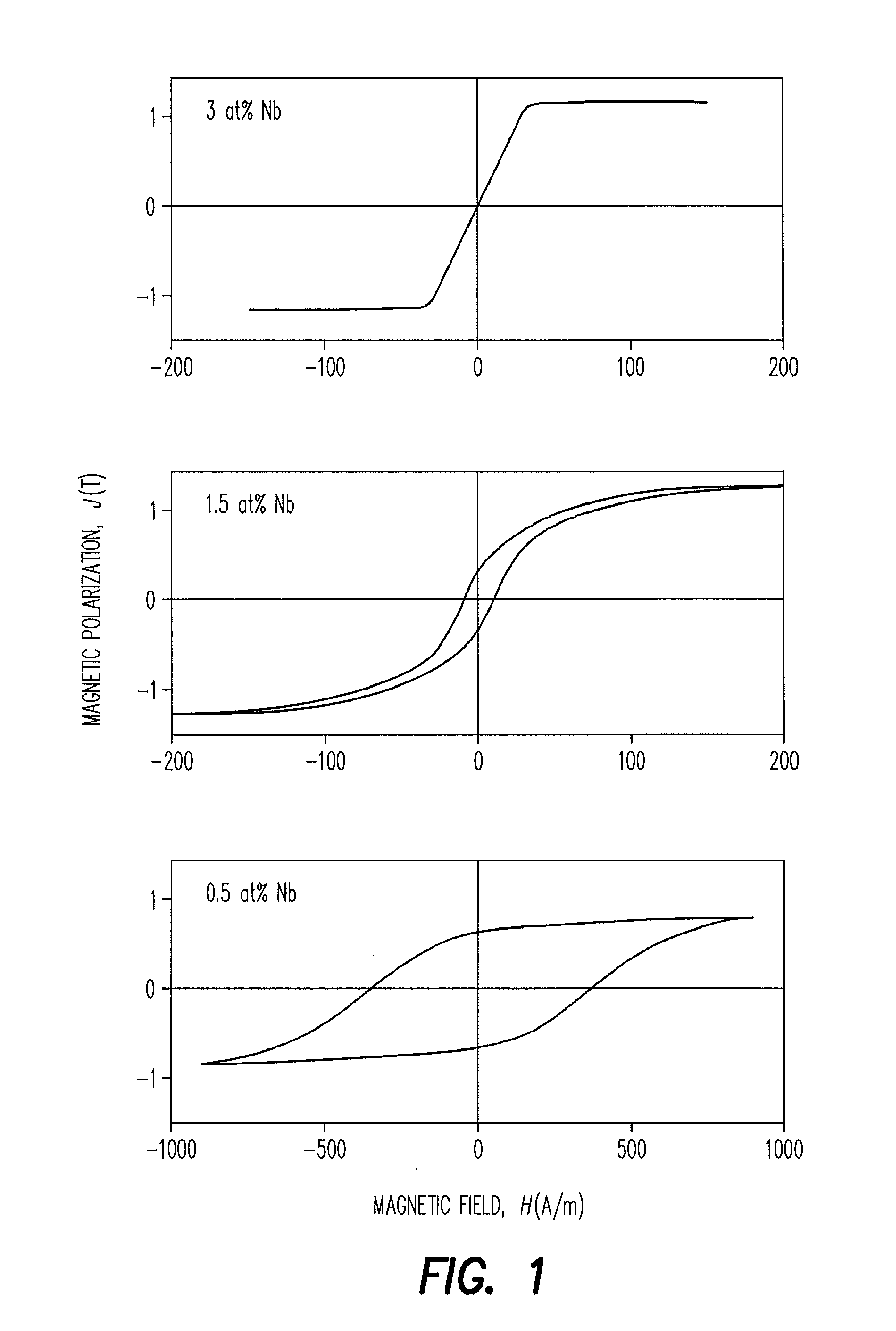
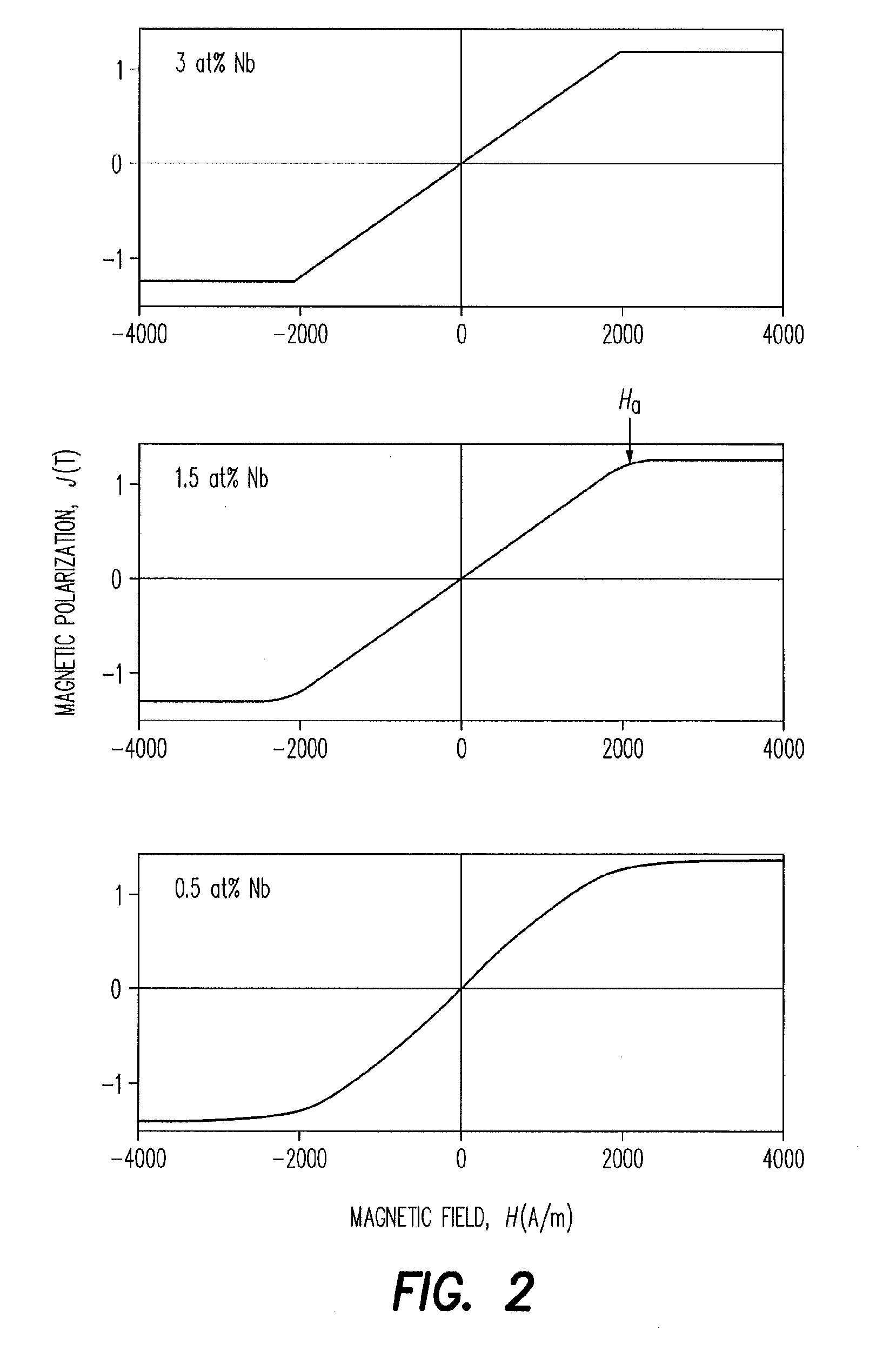
An alloy is provided which consists of Fe100-a-b-c-d-x-y-zCuaNbbMcTdSixByZz and up to 1 at % impurities, M being one or more of the elements Mo, Ta and Zr, T being one or more of the elements V, Mn, Cr, Co and Ni, Z being one or more of the elements C, P and Ge, 0 at %≦a<1.5 at %, 0 at %≦b<2 at %, 0 at %≦(b+c)<2 at %, 0 at %≦d<5 at %, 10 at %<x<18 at %, 5 at %<y<11 at % and 0 at %≦z<2 at %. The alloy is configured in tape form and has a nanocrystalline structure in which at least 50 vol % of the grains have an average size of less than 100 nm, a hysteresis loop with a central linear region, a remanence ratio Jr / Js of <0.1 and a coercive field strength Hc to anisotropic field strength Ha ratio of <10%.
Owner:VACUUMSCHMELZE GMBH & CO KG
Self-adaptation LED current ripple canceling circuit
ActiveCN104080256ATo achieve the purpose of no flickerElectric light circuit arrangementLinear regionAudio power amplifier
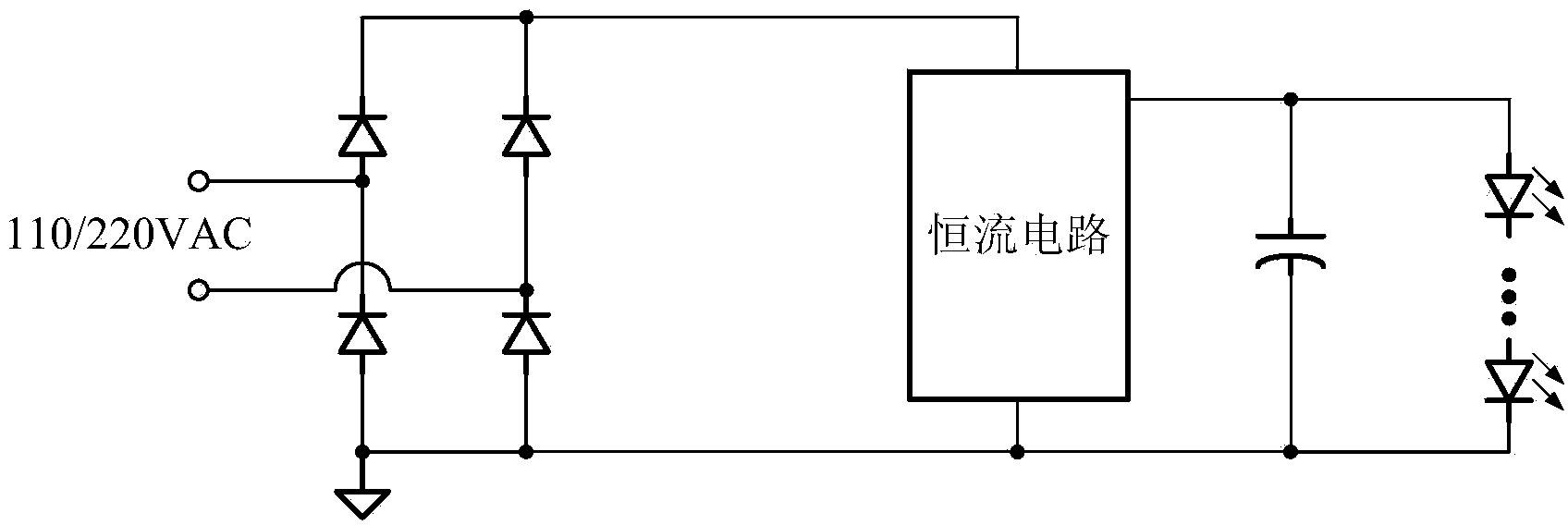
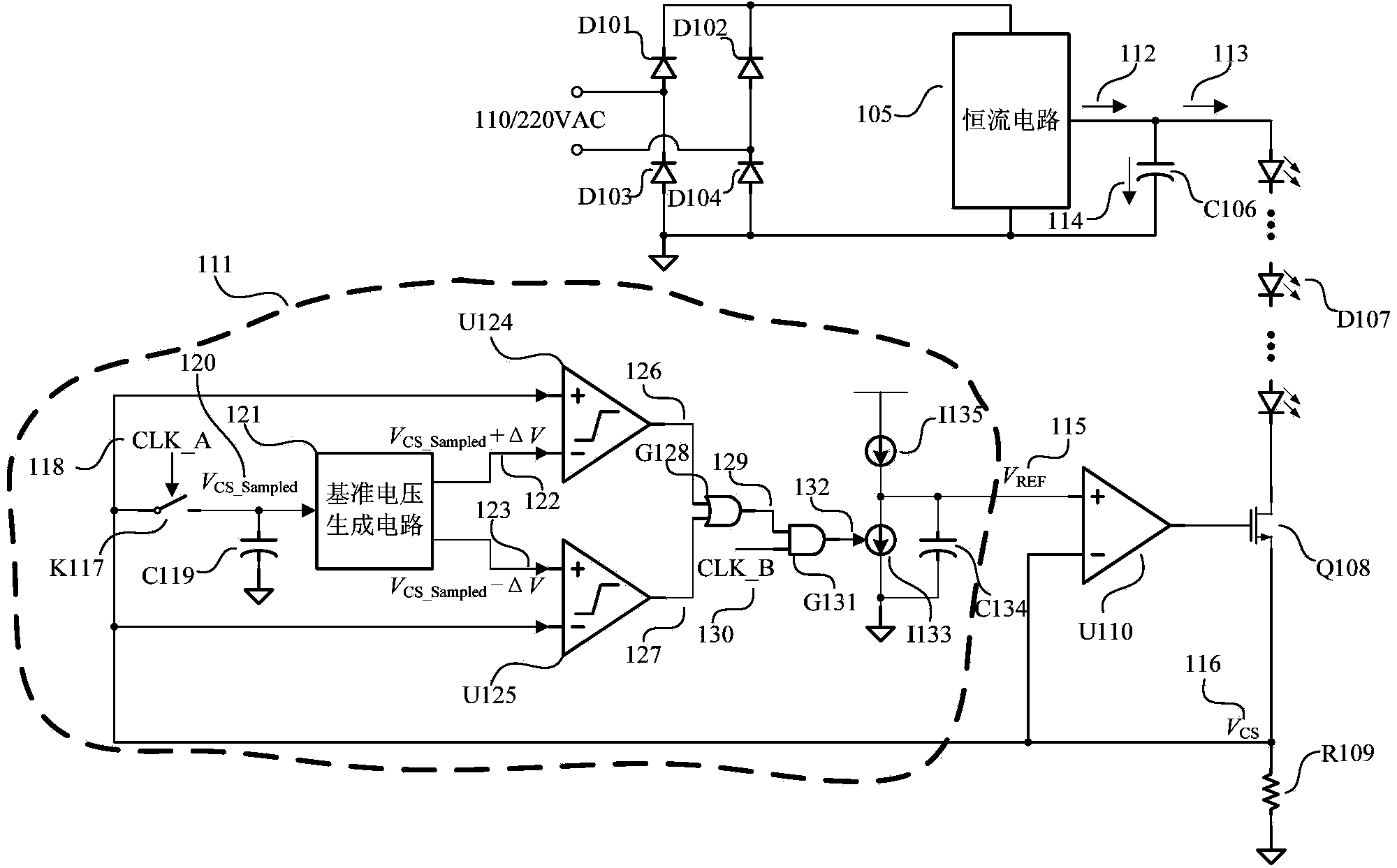
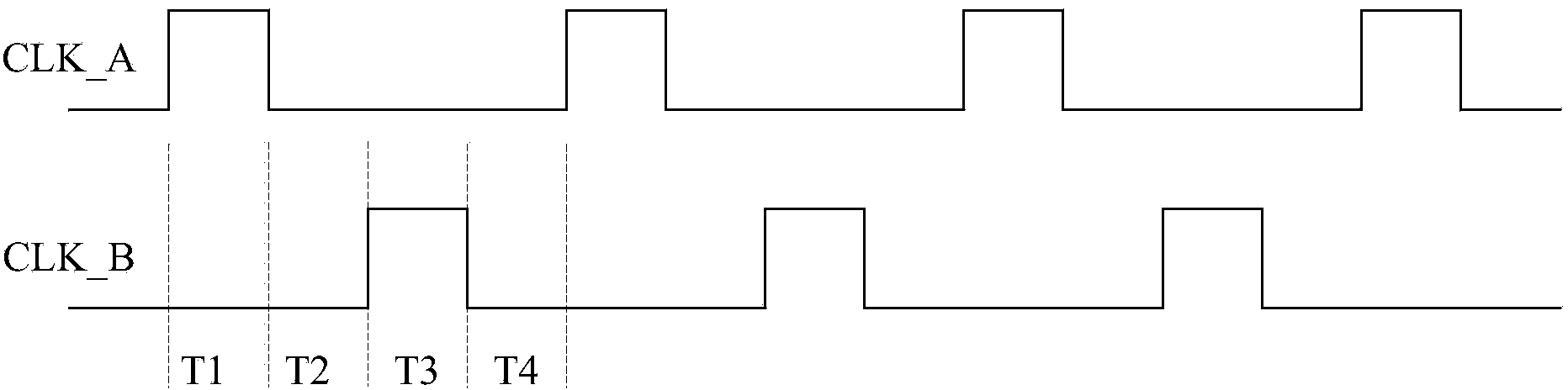
The invention provides a self-adaptation LED current ripple canceling circuit. The circuit comprises a power tube Q108, a current sampling resistor R109, an operational amplifier U110 and a self-adaptation reference voltage generating circuit. A drain electrode of the power tube Q108 is connected to a negative electrode of an LED load, and a source electrode of the power tube Q108 is connected to one end of the current sampling resistor R109, the inverting input end of the operational amplifier U110 and the input end of the self-adaptation reference voltage generation circuit; the output end of the self-adaptation reference voltage generating circuit is connected to the non-inverting input end of the operational amplifier U110. The output end of the operational amplifier U110 is connected with a grid electrode of the power tube Q108. The other end of the current sampling resistor R109 serves as the grounding end of the self-adaptation LED current ripple canceling circuit. The self-adaptation reference voltage generating circuit is used for automatically adjusting output voltage according to sampling voltage and controlling the operational amplifier U110 so as to control the working state of the power tube Q108 to transfer to a saturation region from a linear region. The circuit is used for canceling LED frequency flickering.
Owner:WUXI SI POWER MICRO ELECTRONICS
Method and system for radiated power control for short range RFID tag reading
ActiveUS20090021374A1Electric signal transmission systemsMemory record carrier reading problemsUltrasound attenuationControl power
A method and system for power control for Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tag reading is provided. The system includes a power amplifier for providing an RF transmit signal for the RFID tag reading. The RF transmit signal is provided to an antenna for radiating the transmit signal. The power of the radiated transmit signal defining a read range for the RFID tag reading. The system includes an attenuator provided between the power amplifier and the antenna for controlling the power of the radiated transmit signal to adjust the read range. A handheld RFID reader may include the system. The method includes calibrating the output power of a reader having a power amplifier and an attenuator provided between the power amplifier and an antenna. The step of calibrating includes at least one of controlling power of the power amplifier in its linear region, and controlling attenuation level of the attenuator.
Owner:PSION
Display device and controlling method thereof
InactiveUS7180515B2High heat generationHigh power consumptionSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsLinear regionDisplay device
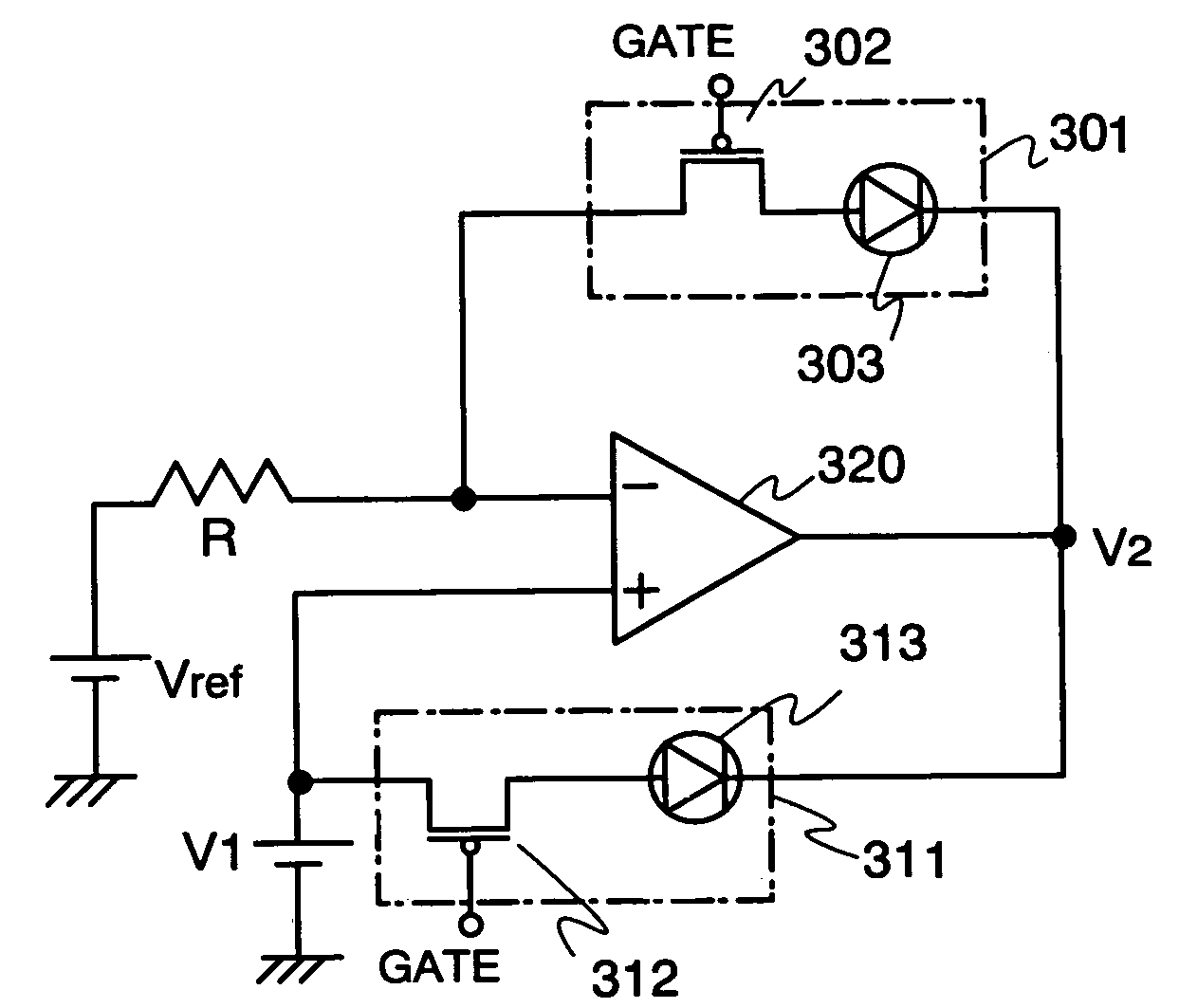
A conventional setting voltage was a value with an estimated margin of a characteristic change of a light, emitting element. Therefore, a voltage between the source and drain of a driver transistor Vds had to be set high (Vds≧Vgs−VTh+a). This caused high heat generation and power consumption, because a voltage applied to the light emitting element. The invention is characterized by, feedbacking a change in a current value in accordance with the deterioration of a light emitting element and a power source voltage controller which modifies a setting voltage. Namely, according to the invention, the setting voltage is to be set in the vicinity of the boundary (critical part) between, a saturation region and a linear region, and a voltage margin for the deterioration is not required particularly for an initial setting voltage.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com