Patents
Literature
327results about How to "Avoid excessive current" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
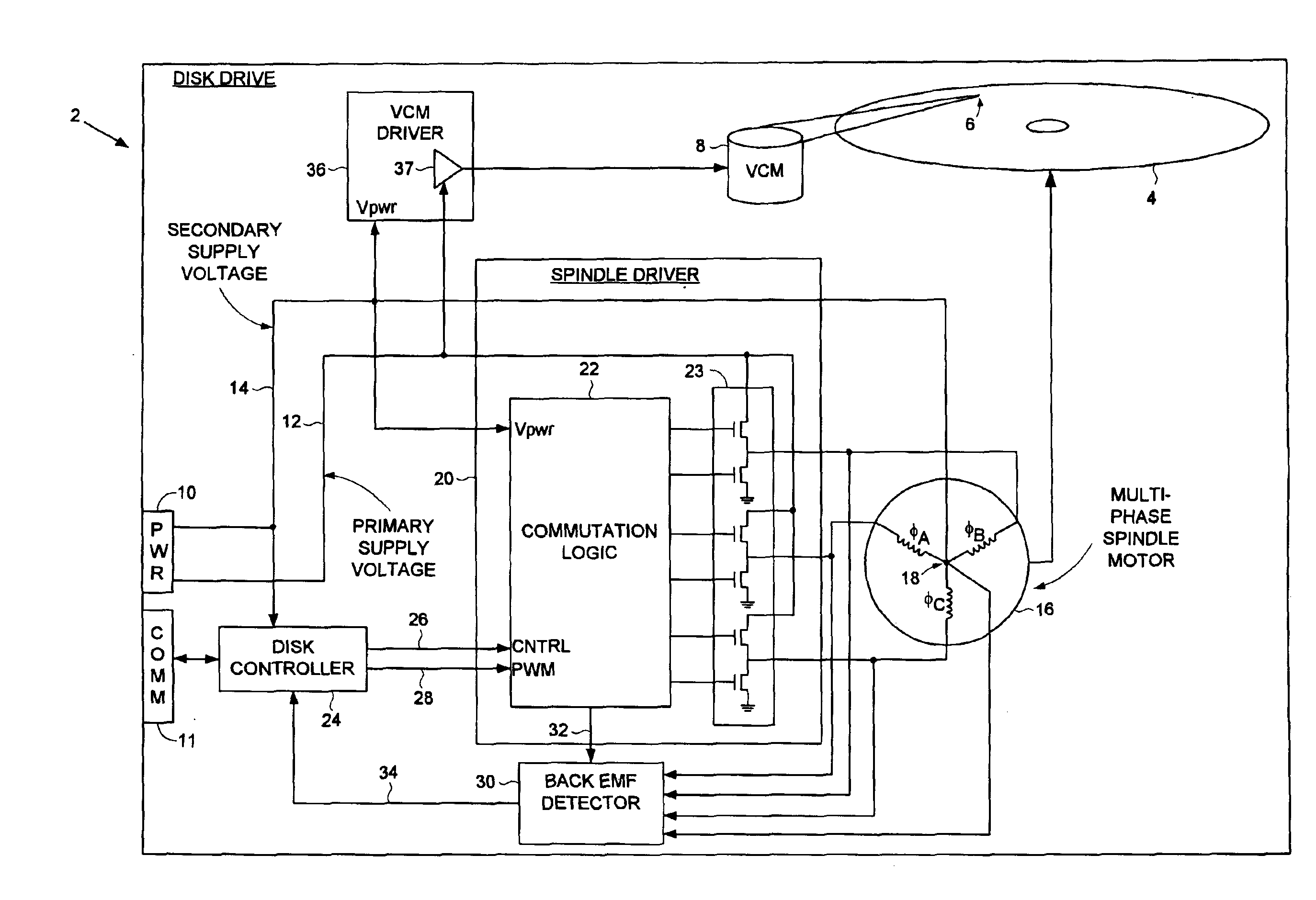
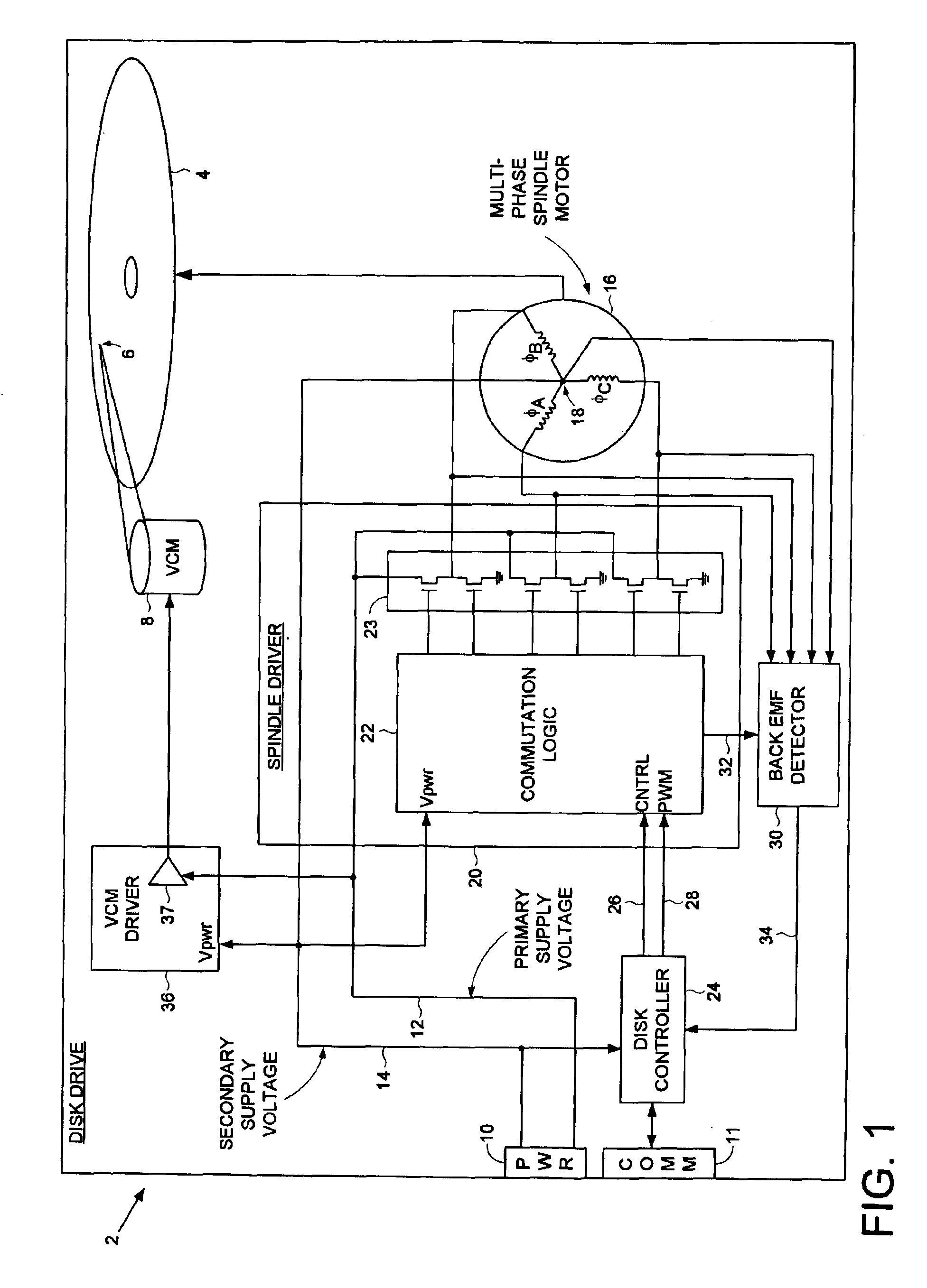
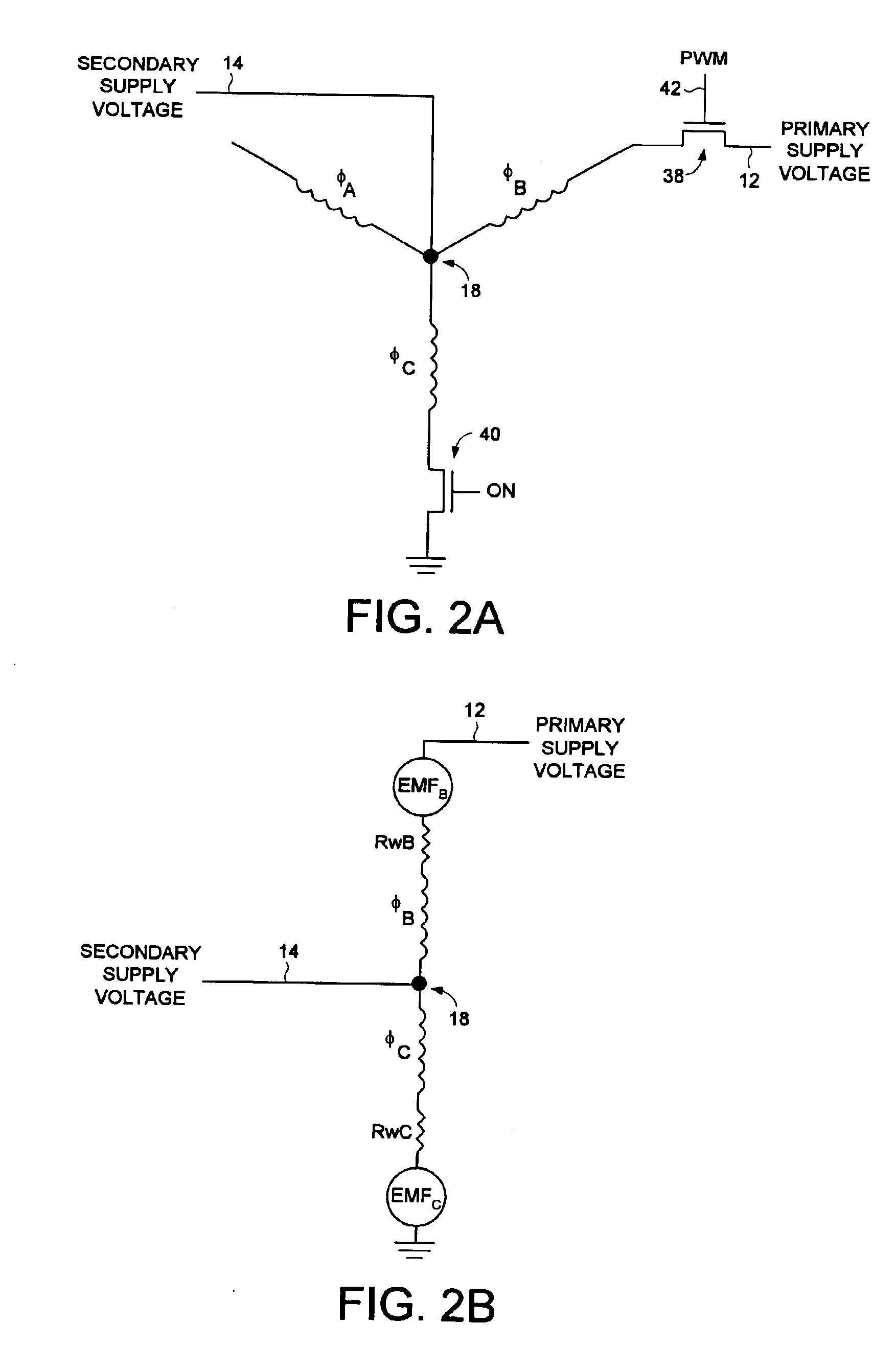
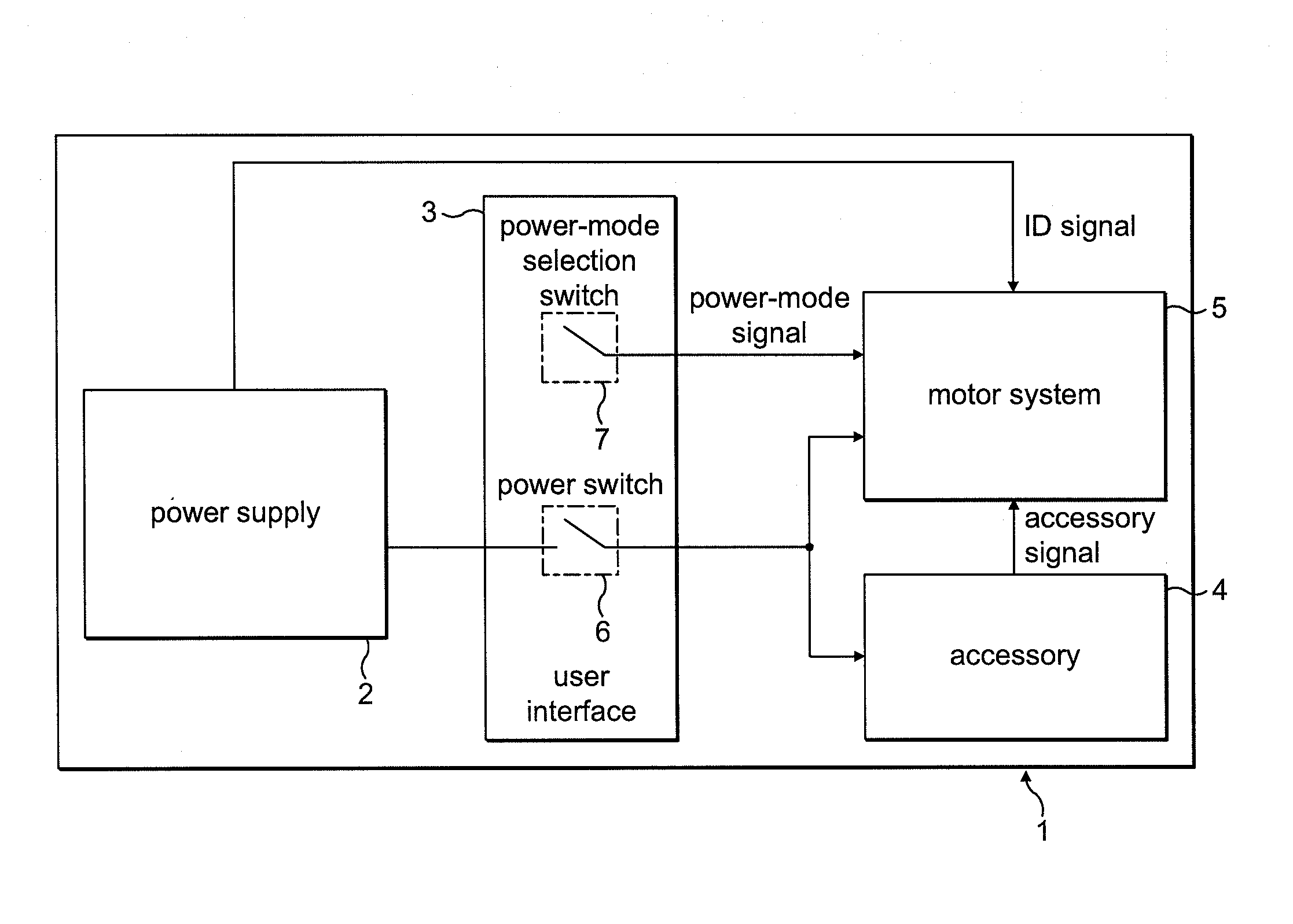
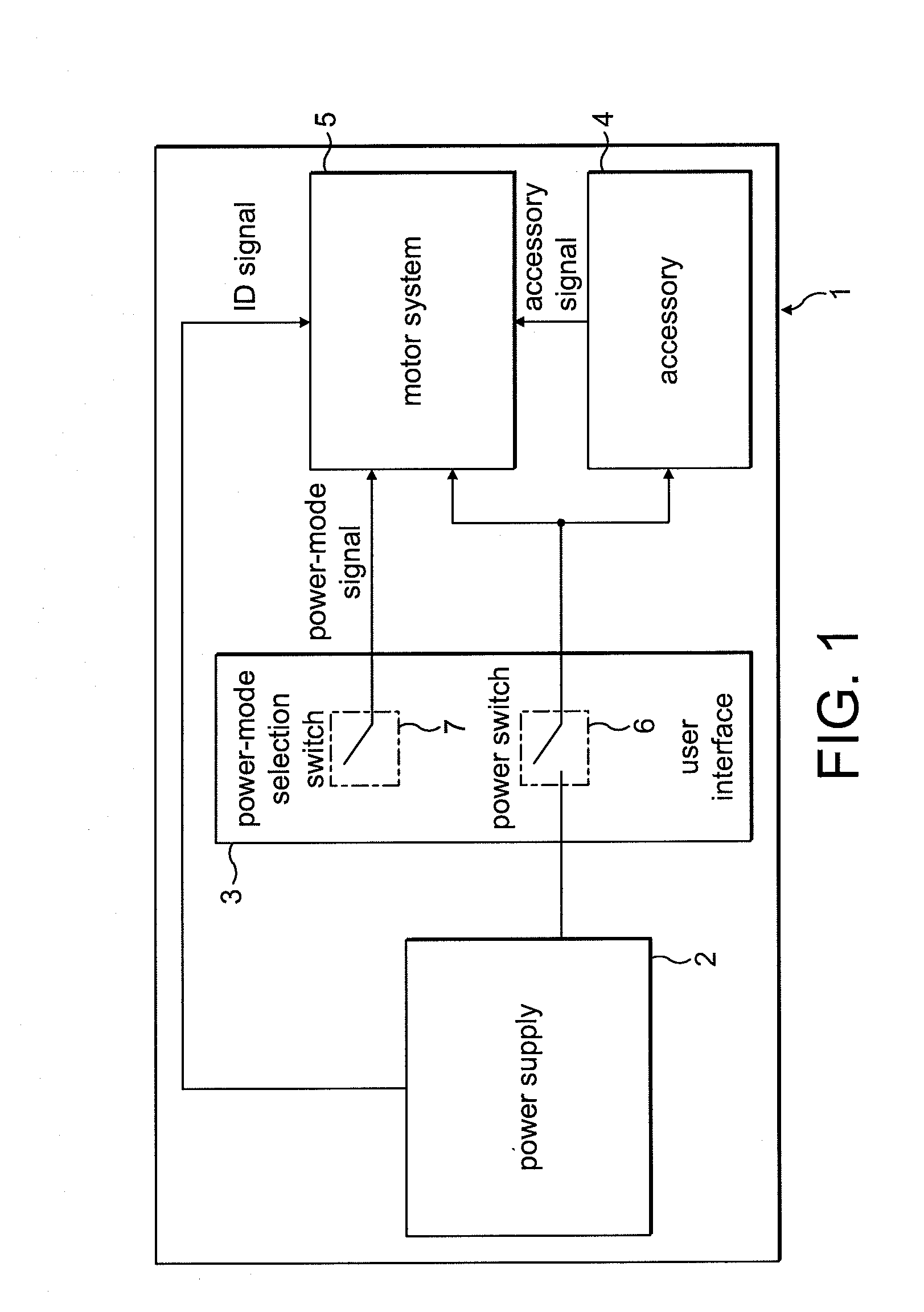
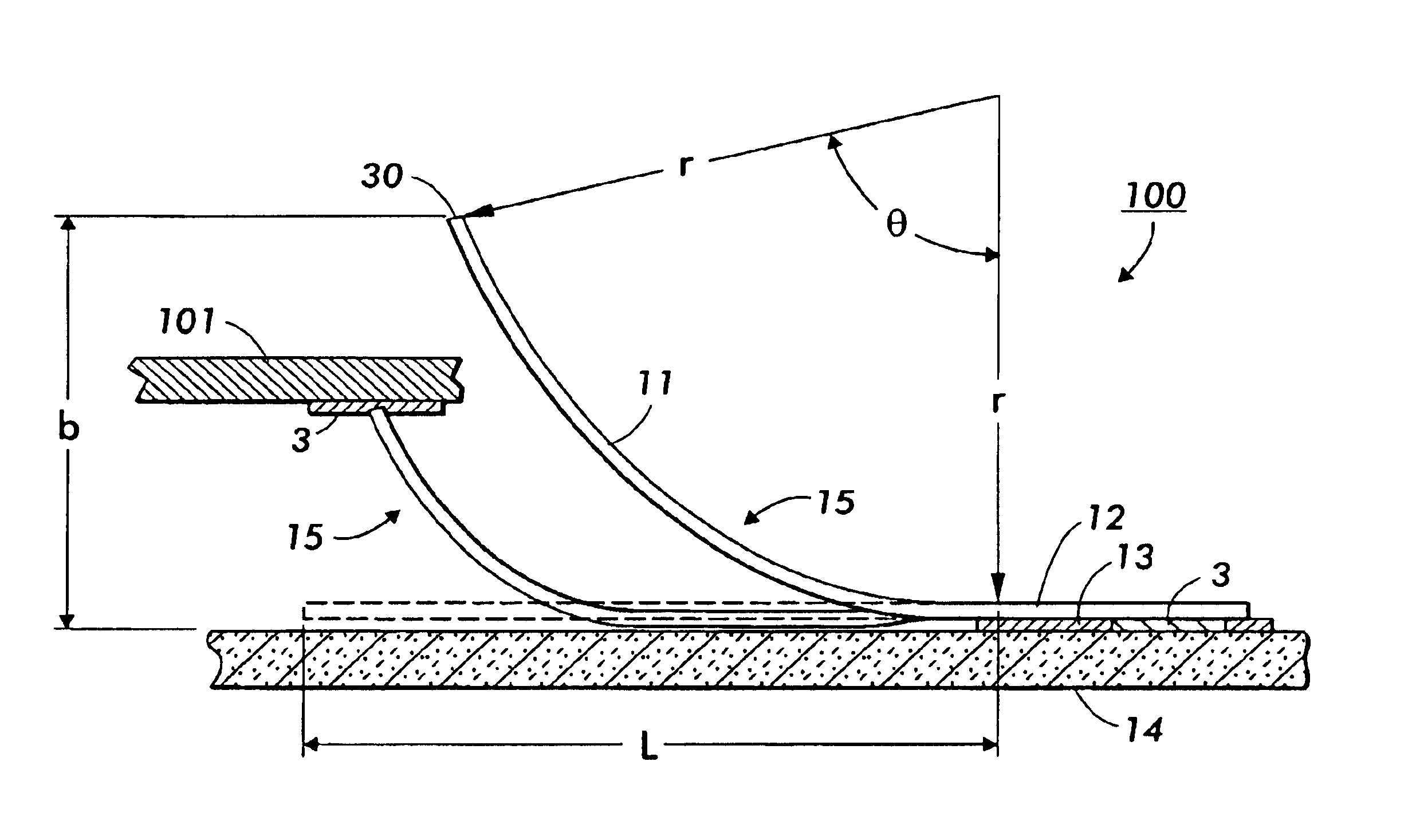
Disk drive comprising a multi-phase spindle motor having a center tap connectable to a secondary supply voltage
InactiveUS7006320B1Avoid excessive currentMore currentDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageElectric machineEngineering
A disk drive is disclosed comprising an interface for receiving a primary supply voltage and a secondary supply voltage from a host computer. The primary supply voltage is applied to the windings of a multi-phase spindle motor in a commutation sequence, and the secondary supply voltage is connectable to a center tap of the windings.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
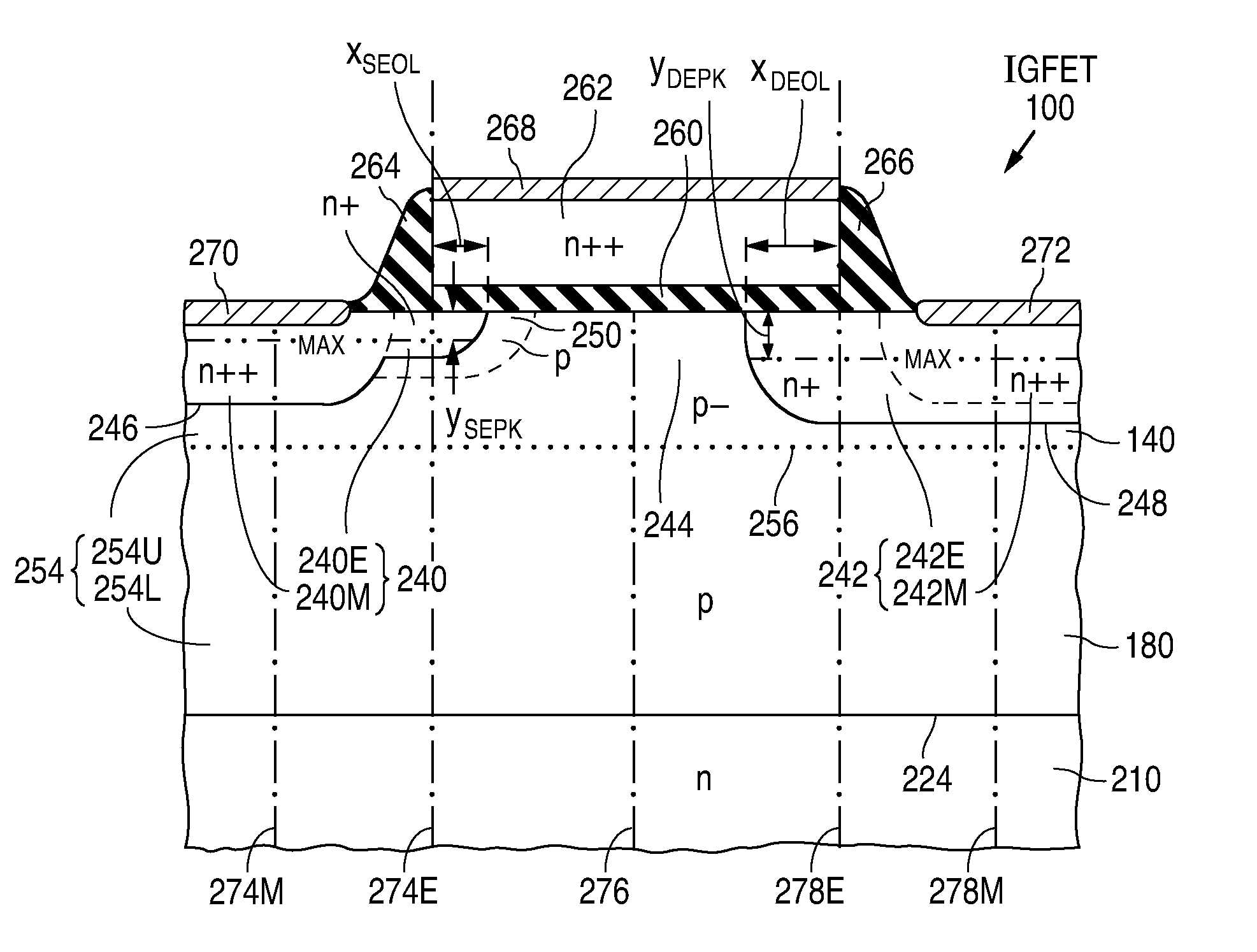
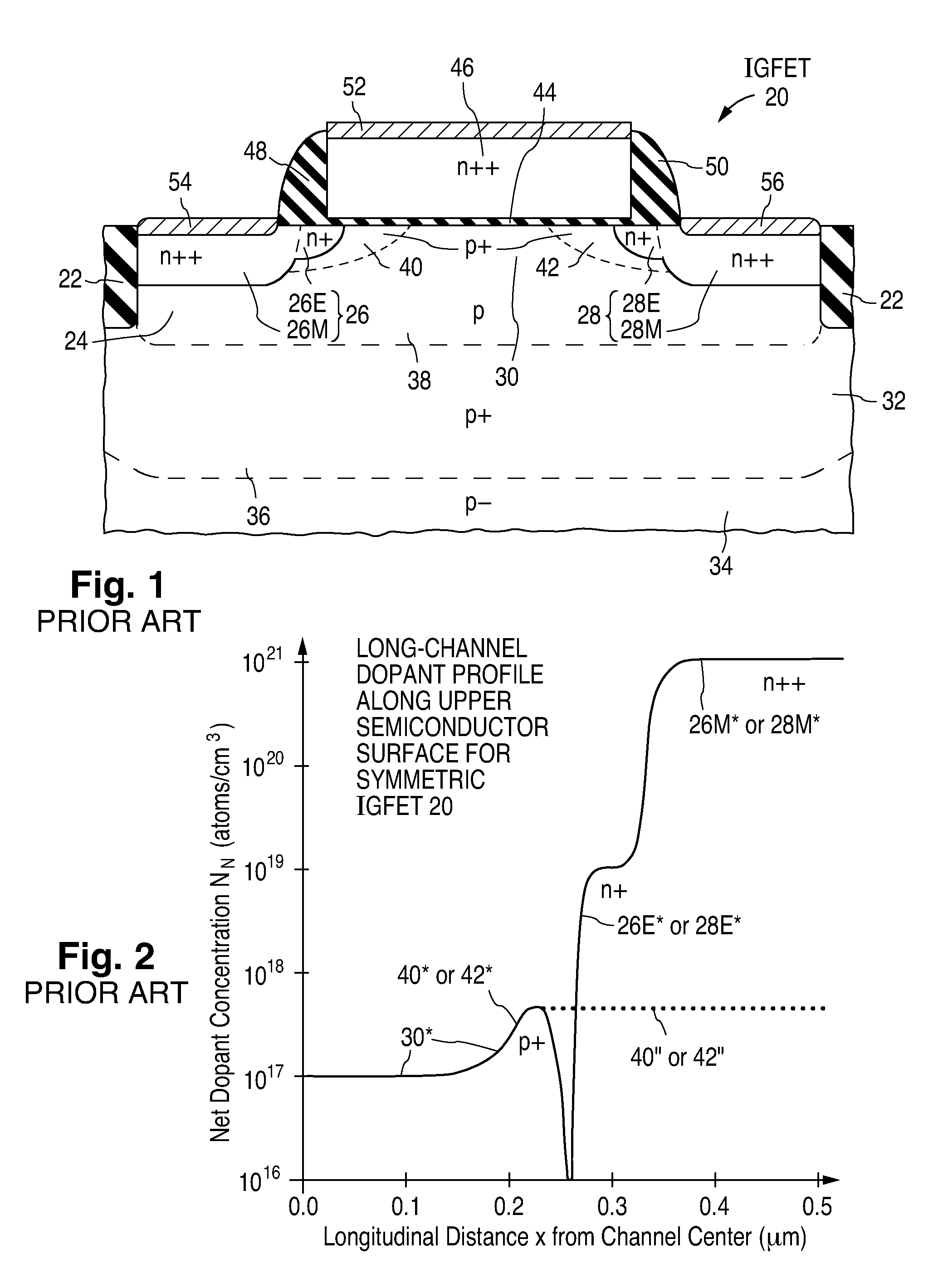
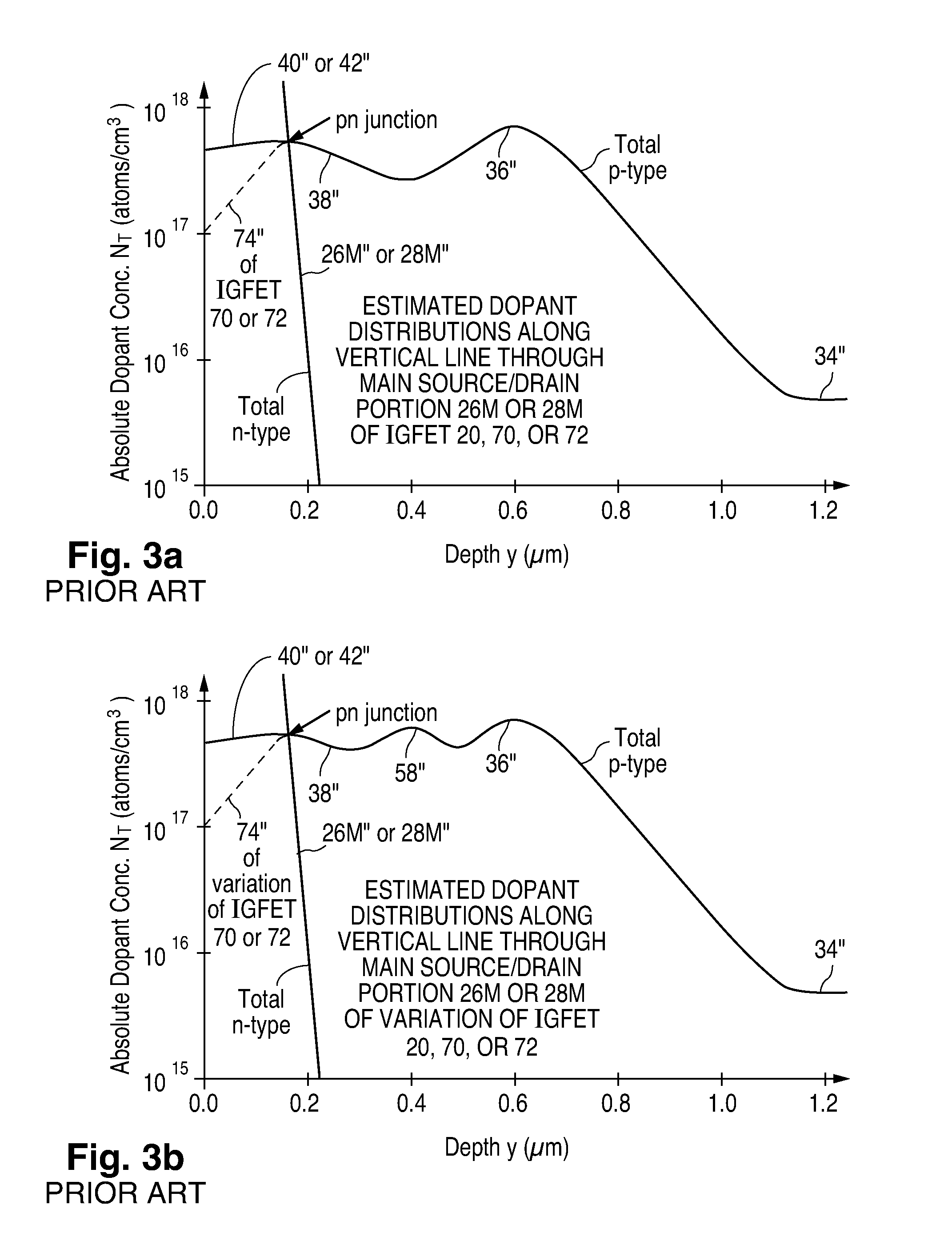
Fabrication of semiconductor structure having asymmetric field-effect transistor with tailored pocket portion along source/drain zone
ActiveUS8163619B2Good analog characteristicReduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantGate dielectric
An asymmetric insulated-gate field effect transistor (100U or 102U) is provided along an upper surface of a semiconductor body so as to have first and second source / drain zones (240 and 242 or 280 and 282) laterally separated by a channel zone (244 or 284) of the transistor's body material. A gate electrode (262 or 302) overlies a gate dielectric layer (260 or 300) above the channel zone. A pocket portion (250 or 290) of the body material more heavily doped than laterally adjacent material of the body material extends along largely only the first of the S / D zones and into the channel zone. The vertical dopant profile of the pocket portion is tailored to reach a plurality of local maxima at respective locations (PH-1-PH-3-NH-3) spaced apart from one another. This typically enables the transistor to have reduced current leakage.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
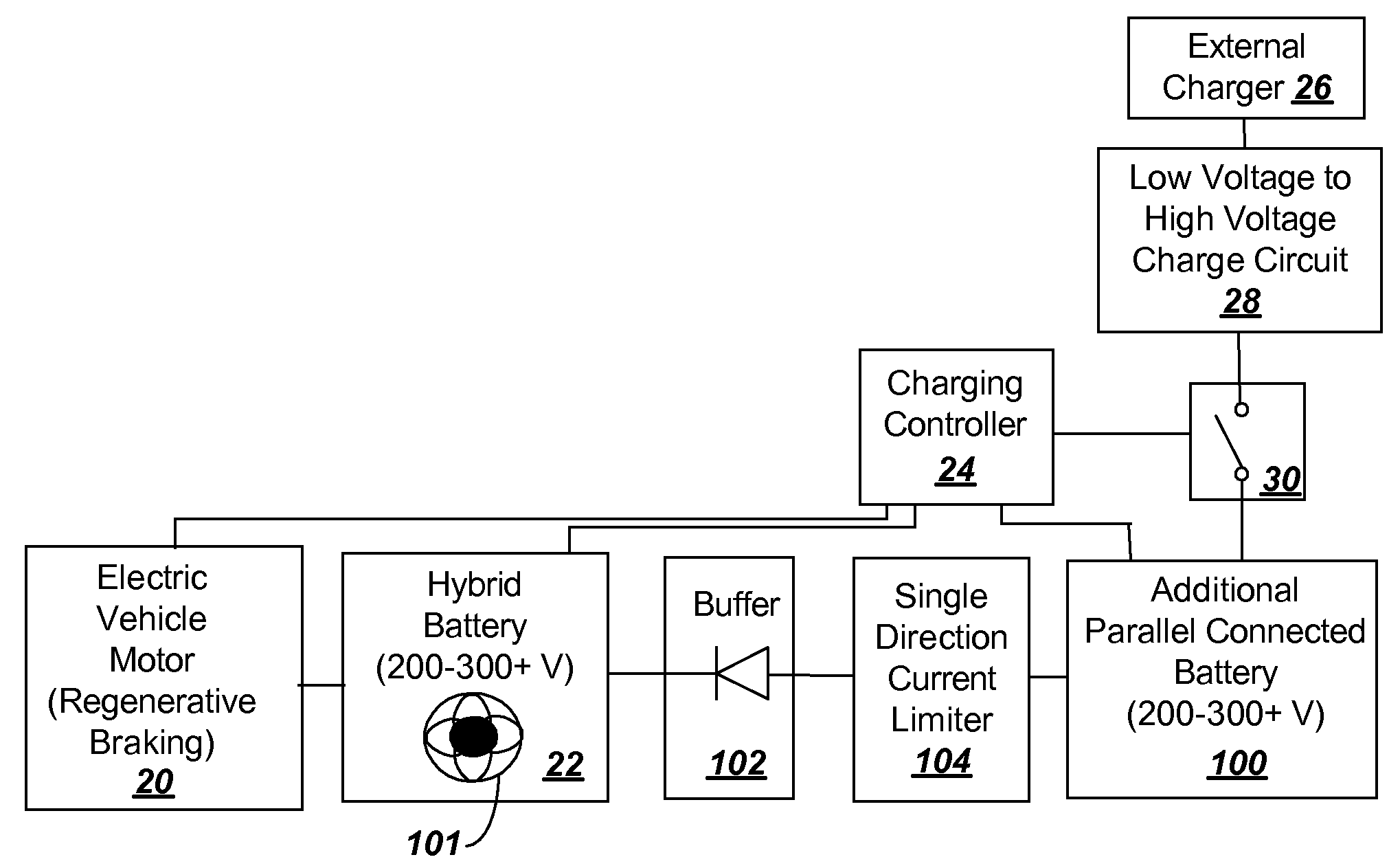
Current limiting parallel battery charging system to enable plug-in or solar power to supplement regenerative braking in hybrid or electric vehicle
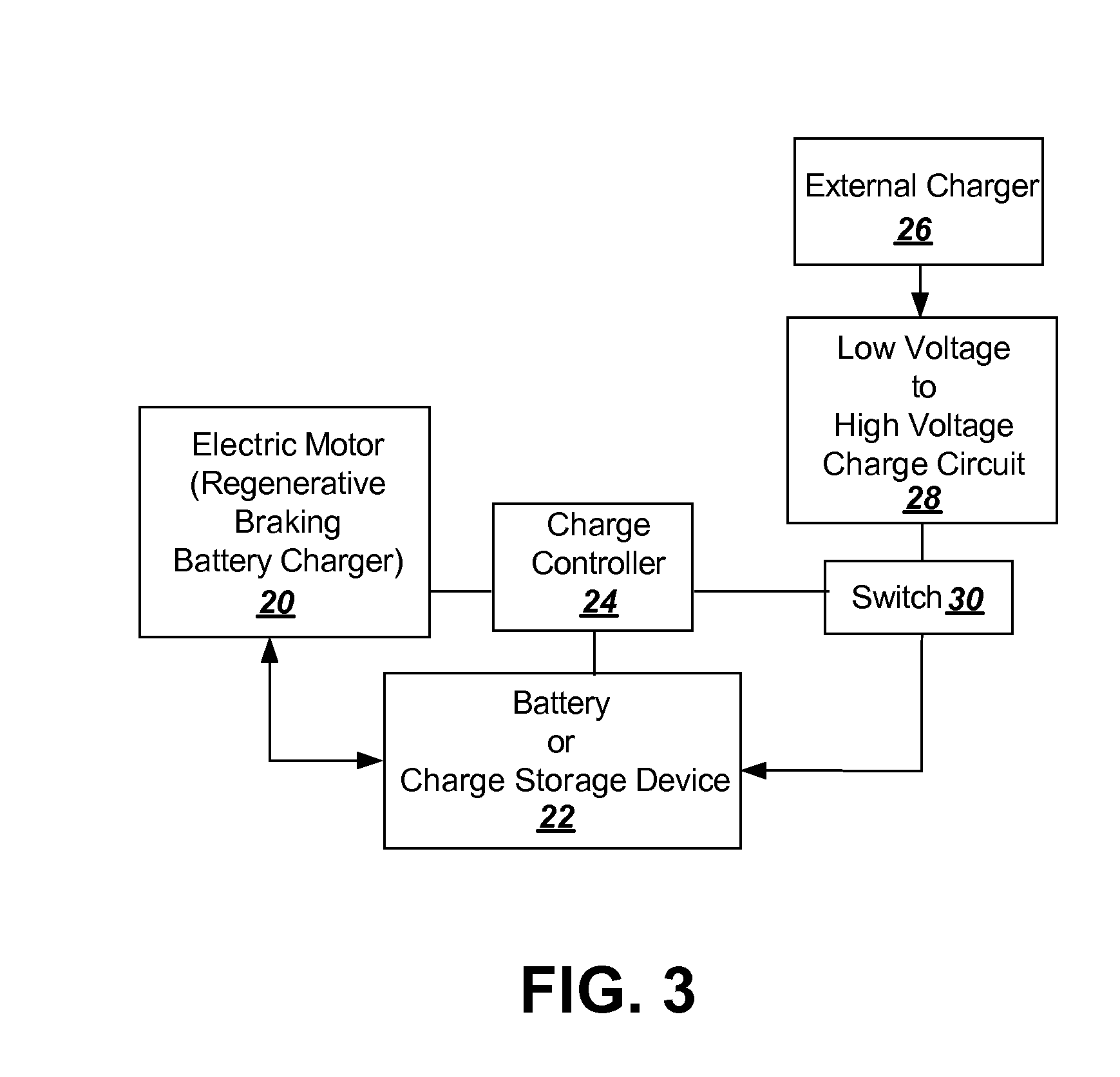
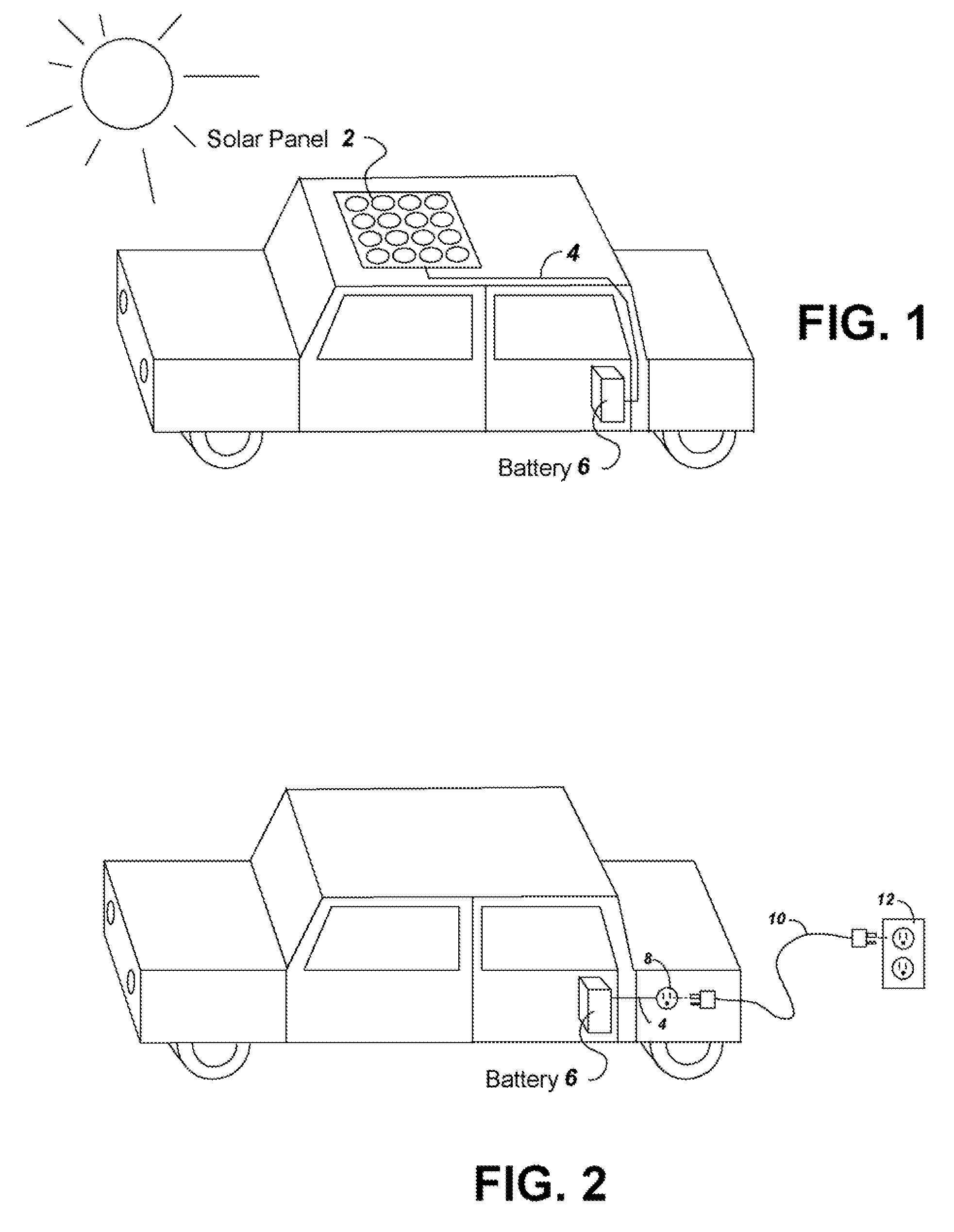
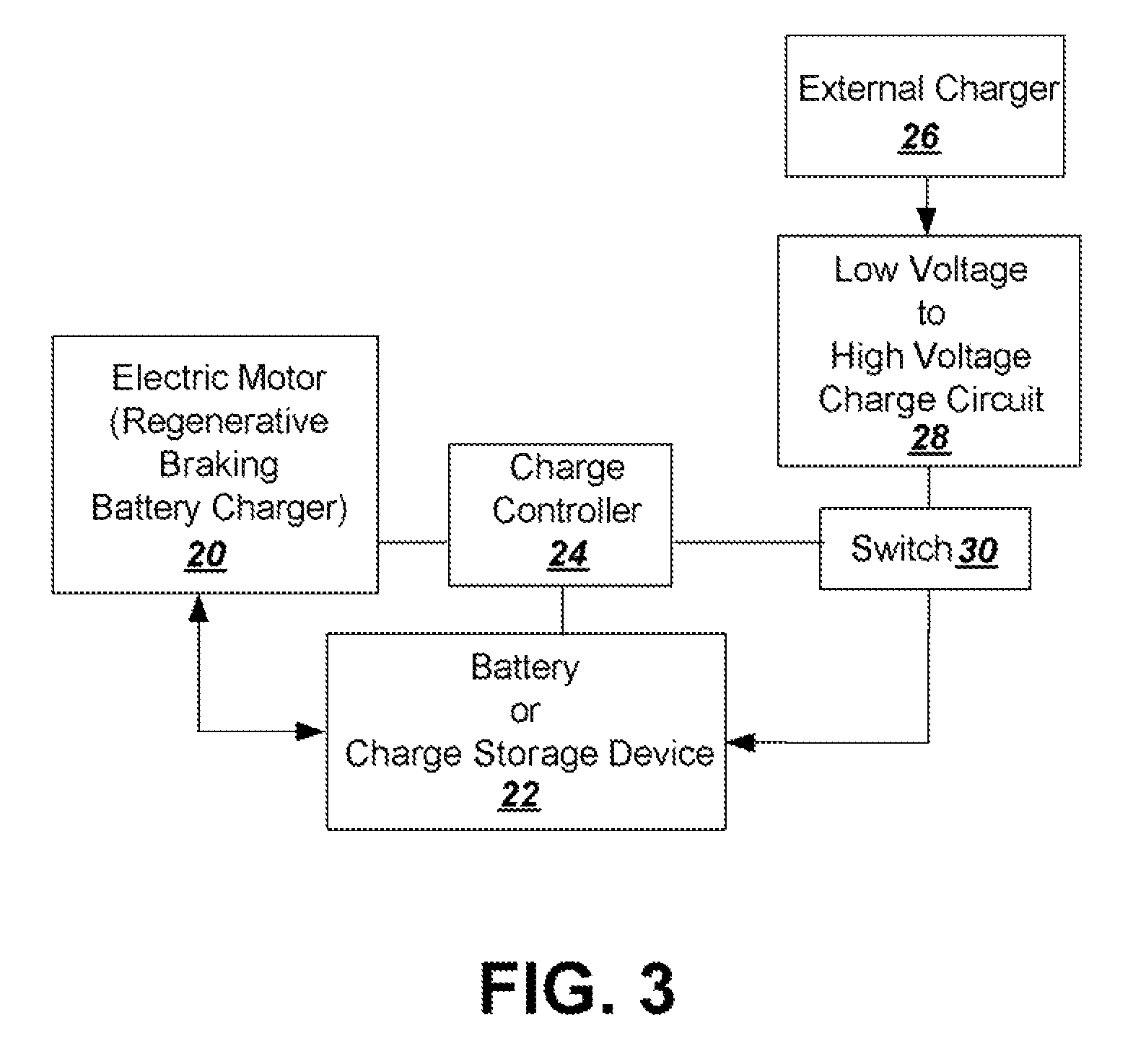
InactiveUS20080203966A1Simple processBattery system is simplifiedHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsEngineeringSolar power
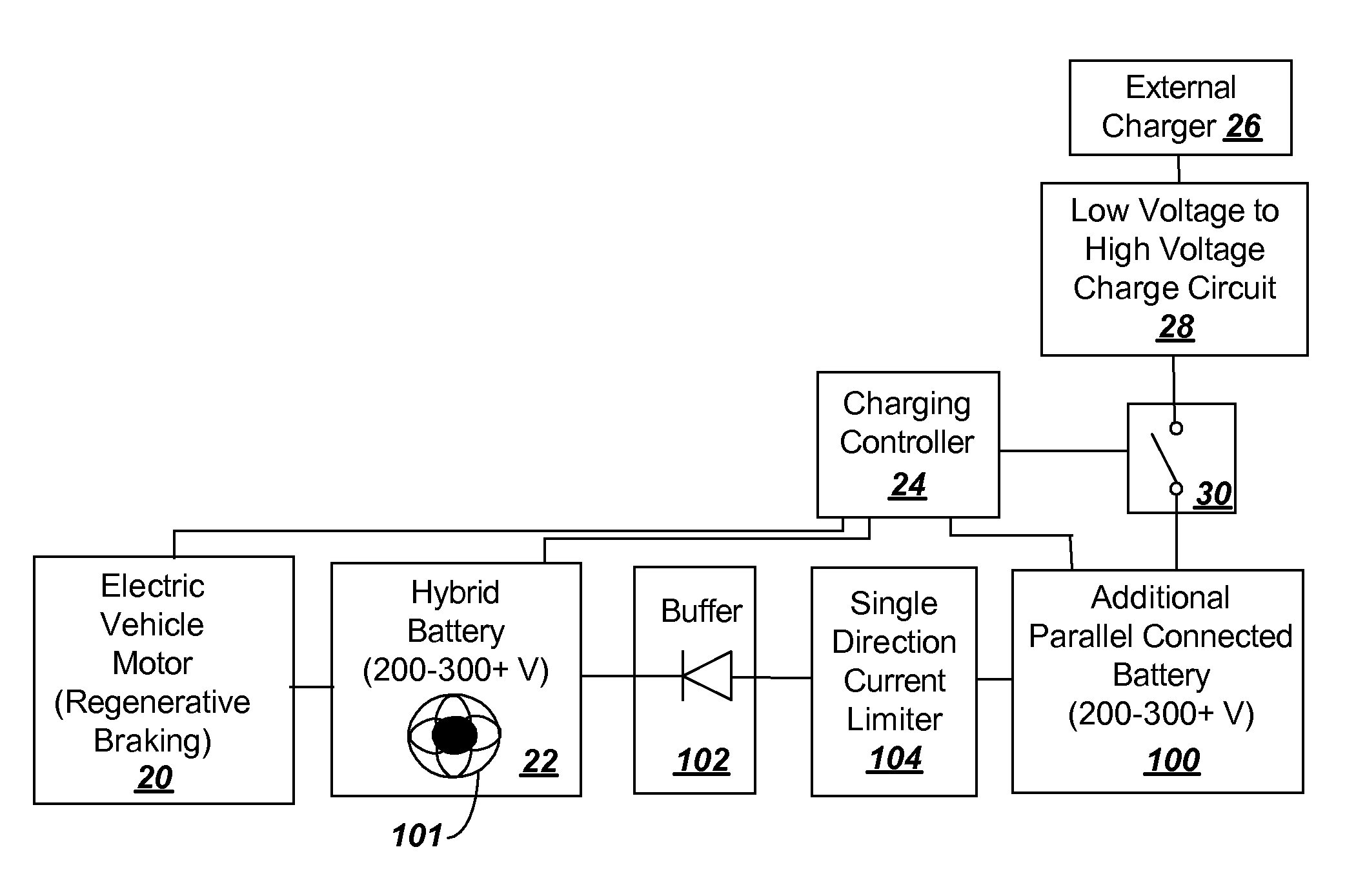
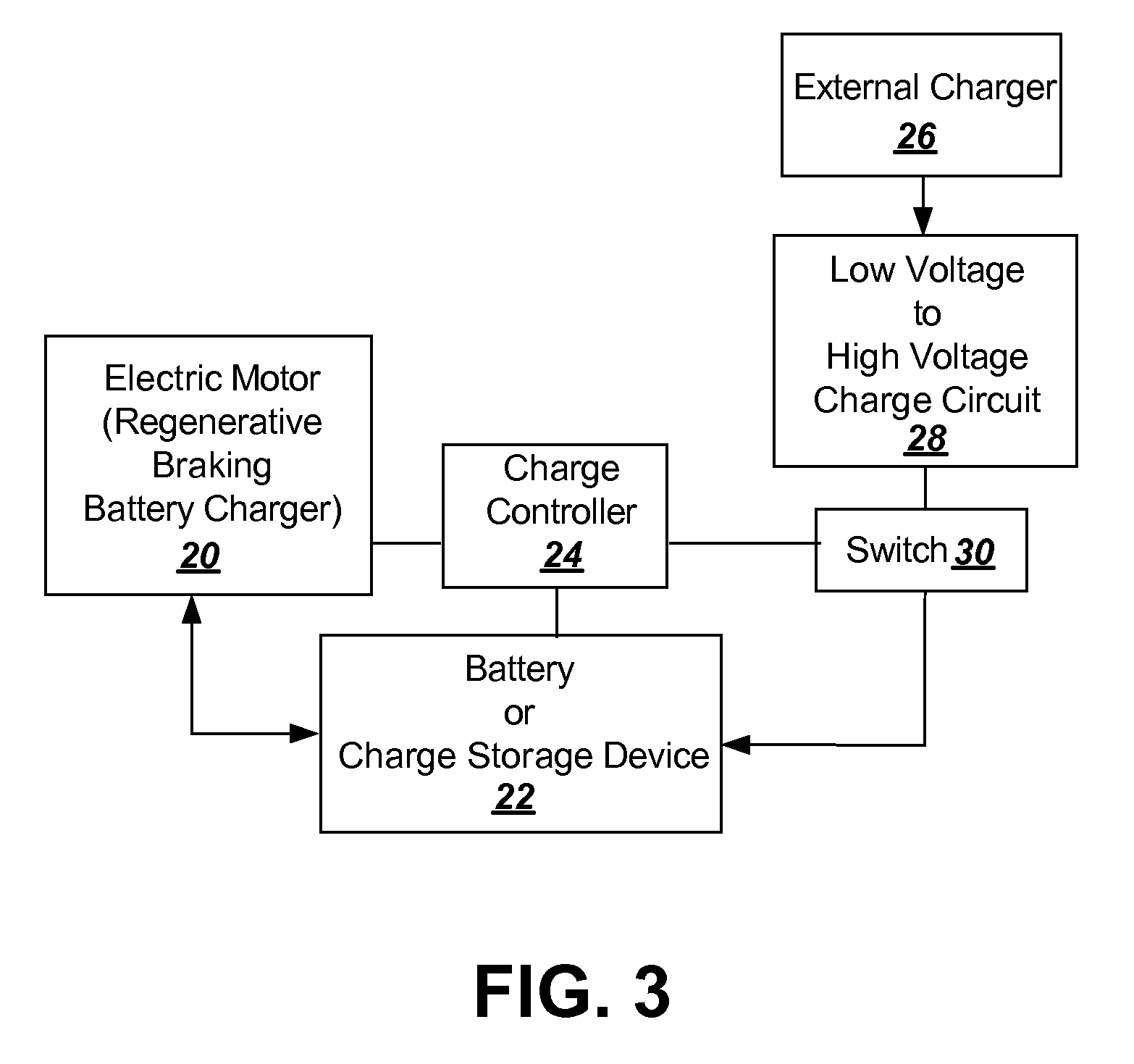
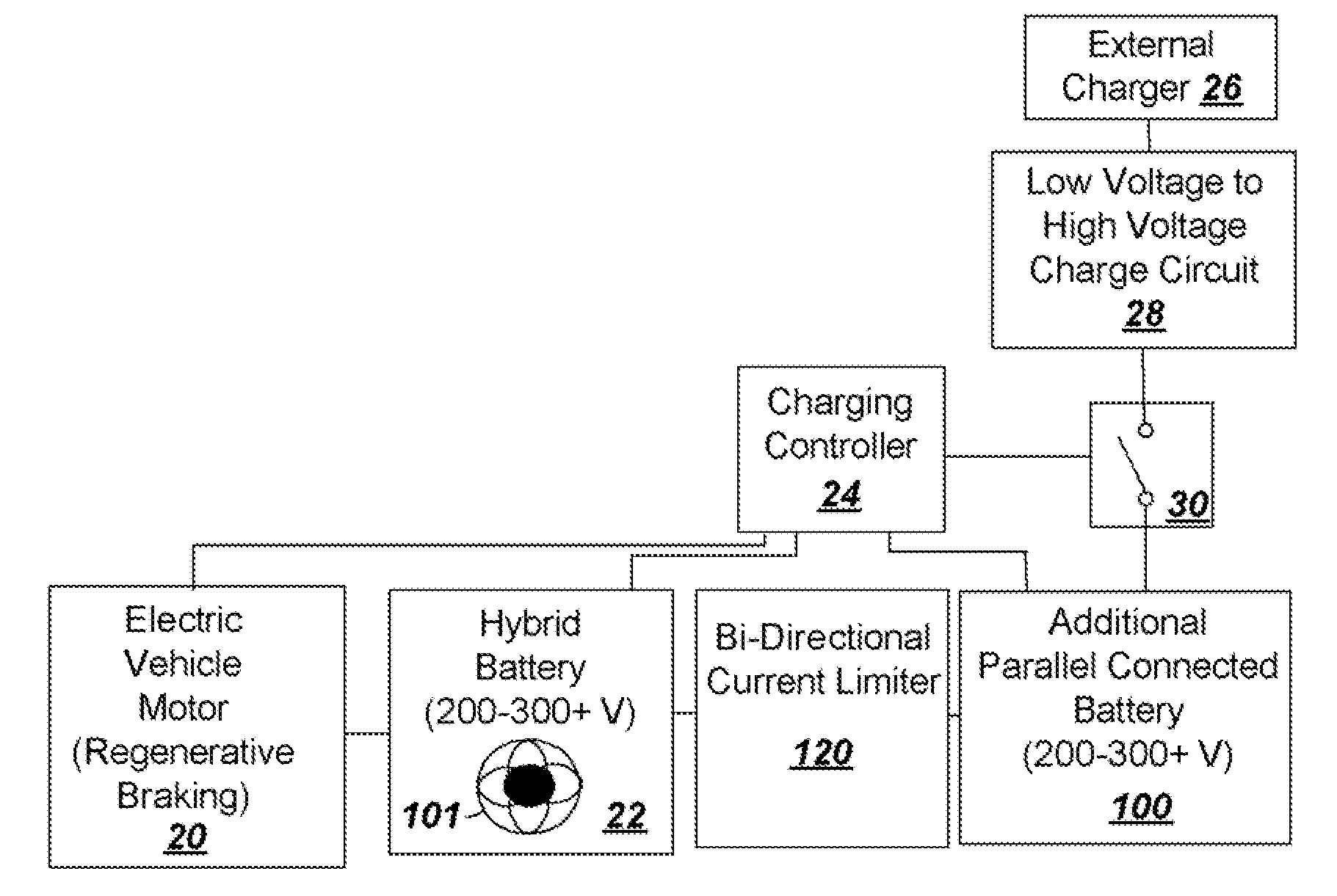
To provide additional charge storage for an electric vehicle, an additional battery (100) is connected in parallel with a regenerative braking direct charged battery (22) through a current limiting circuit (104 or 120). The additional battery (100) is charged by an external charger such as a plug-in charger or a solar panel that supply minimal current to prevent generation of battery heat. Current flows from the additional battery (100) to the regenerative braking charged batteries (22) so that both batteries can be charged. However, when excessive charge is drawn to drive the vehicle electric motor (20), the current limiter circuit (104 or 120) serves to prevent the discharge of additional battery (100) from creating excessive heat in the additional battery (100). Further, when regenerative braking is applied the current limiter circuit (120), or a diode buffer (102) in combination with current limiter (104), serves to prevent charging from creating excessive heat in the additional battery (100) and eliminates the need for a cooling structure in the additional battery (100).
Owner:WARD THOMAS A
Scan method and topology for capacitive sensing
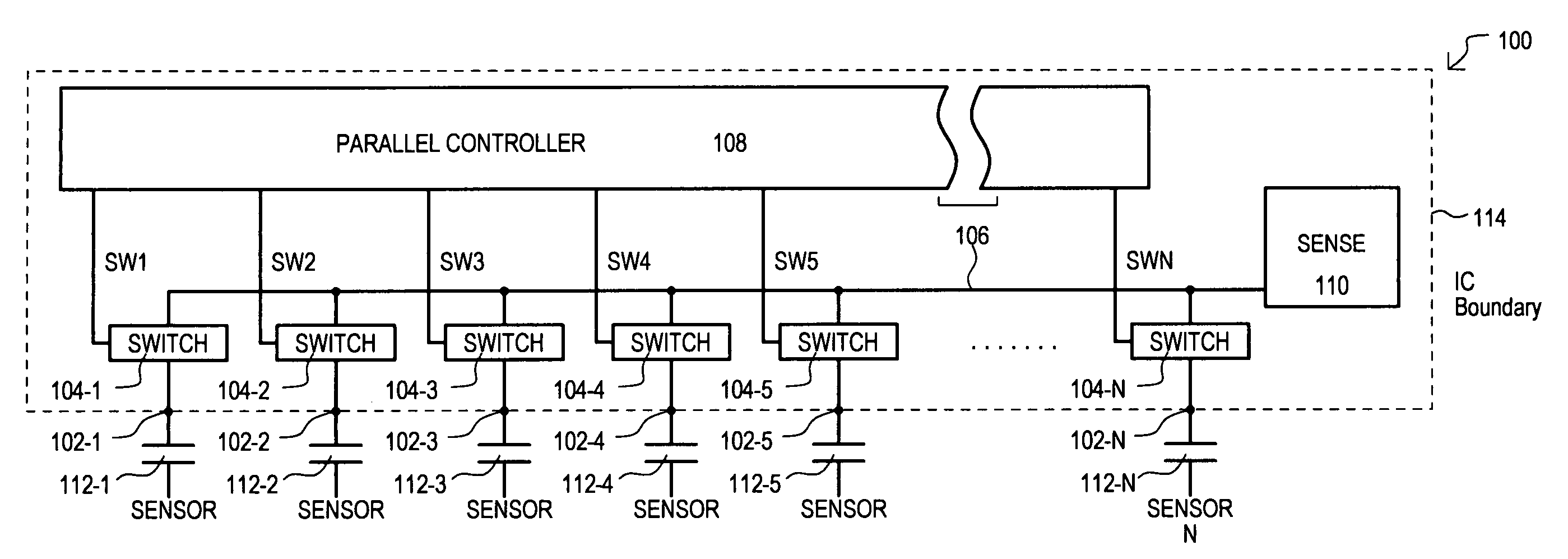
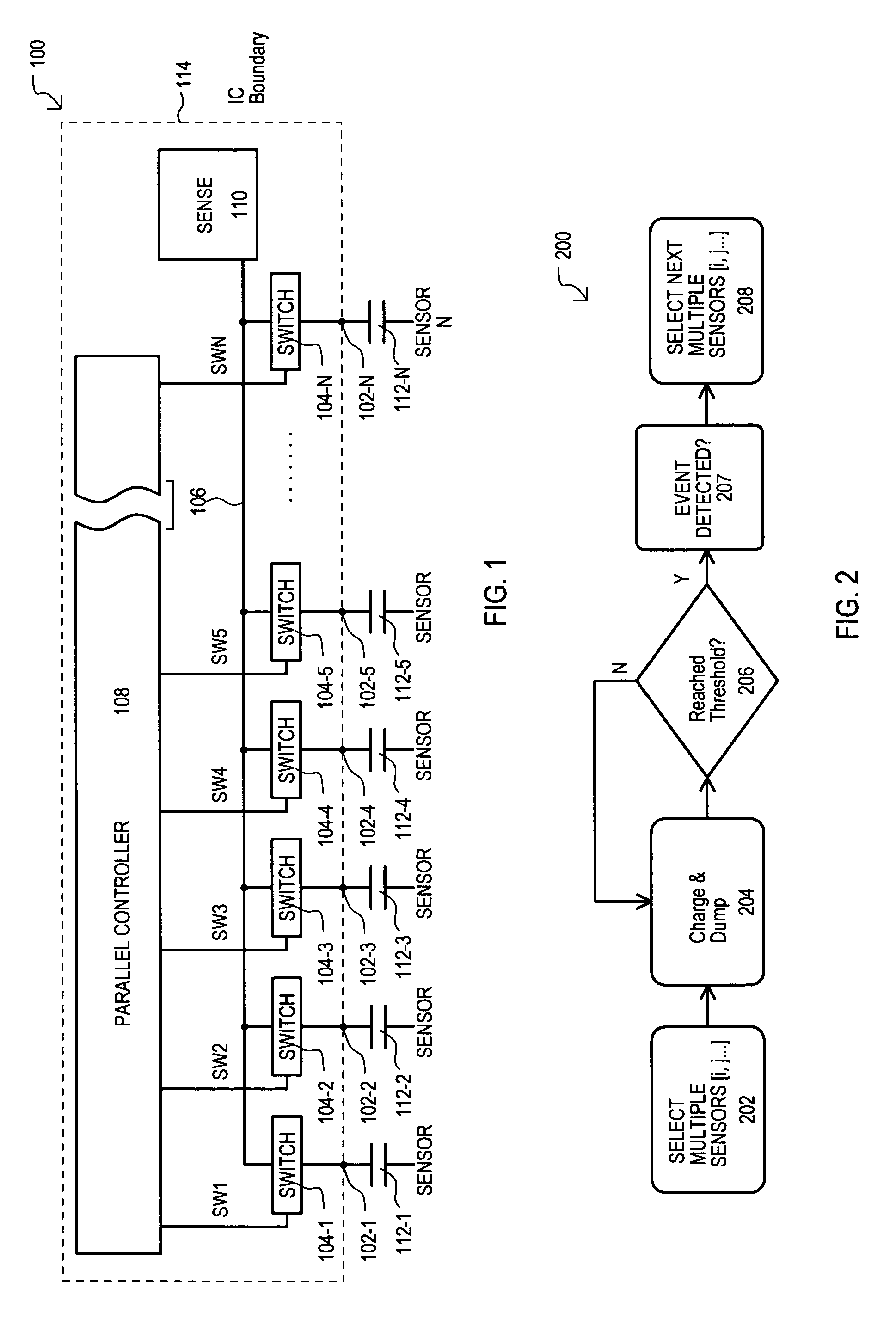
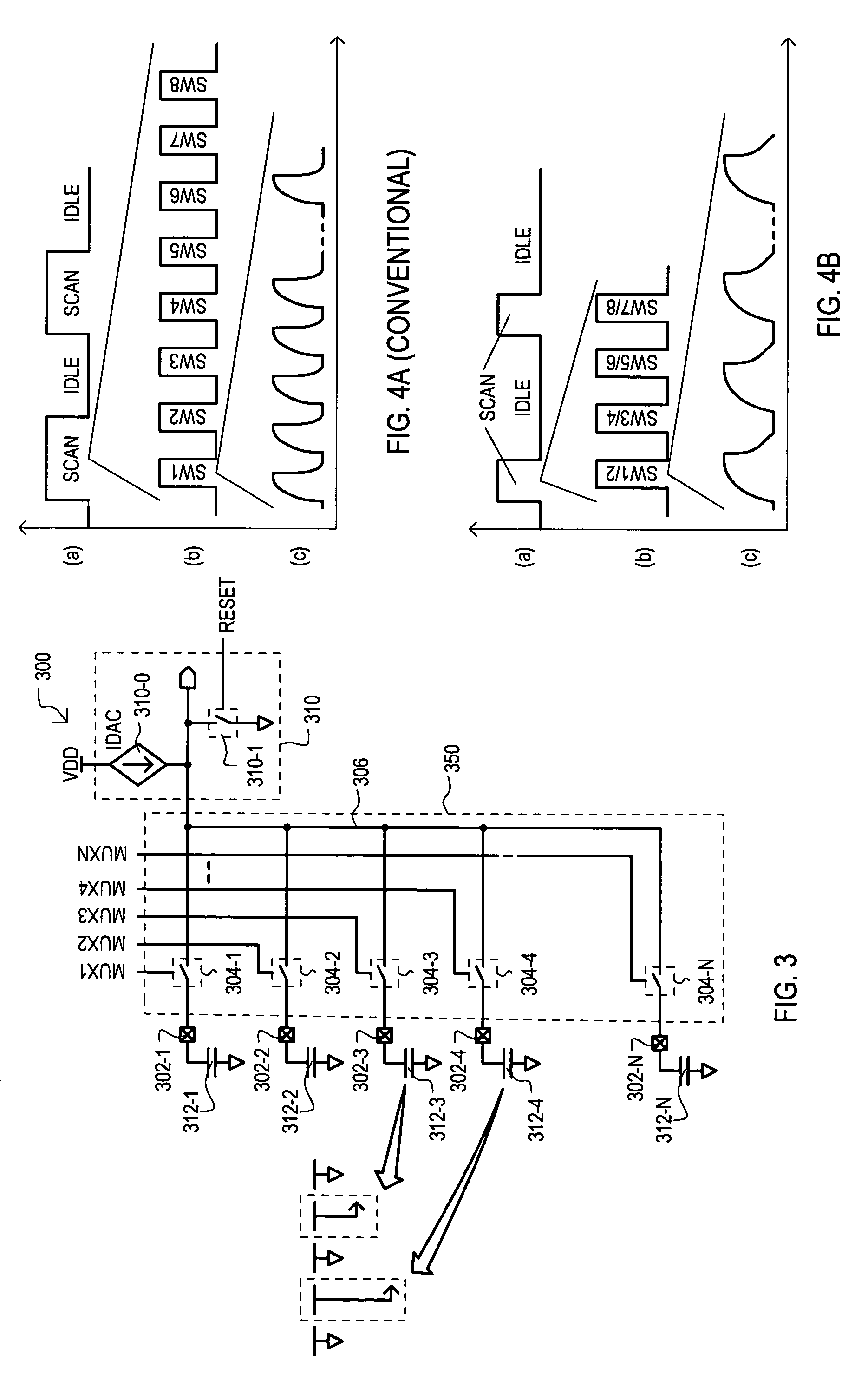
InactiveUS7375535B1Faster completion timeAvoid excessive currentResistance/reactance/impedenceConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyEngineeringCapacitive sensing
A capacitive sensing system (100) can connect groups of capacitive sensors (112-1 to 112-N) to a common node (106) to detect change in capacitance. States of a set of capacitive sensors (112-1 to 112-N) can thus be scanned faster than approaches that scan such sensors one-by-one. Faster scanning can allow for reduced power consumption in applications that only periodically scan the set of capacitive sensors (112-1 to 112-N).
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Optical communication device, method and system
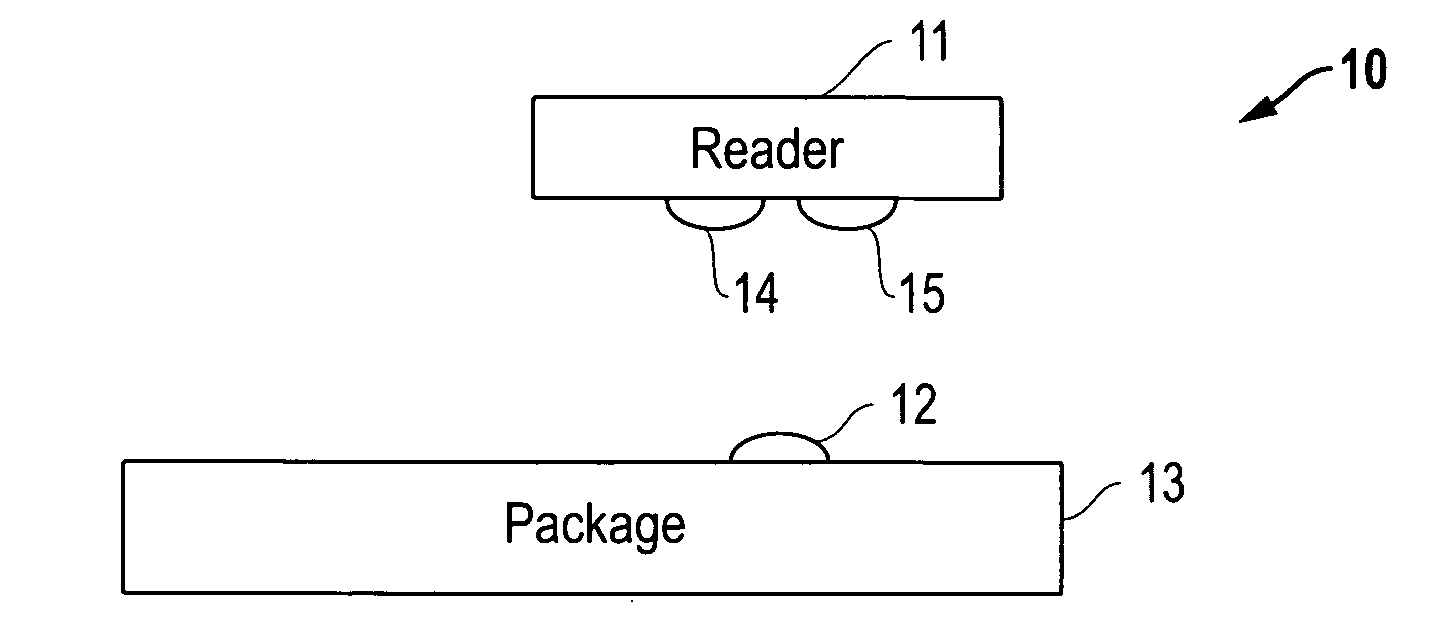
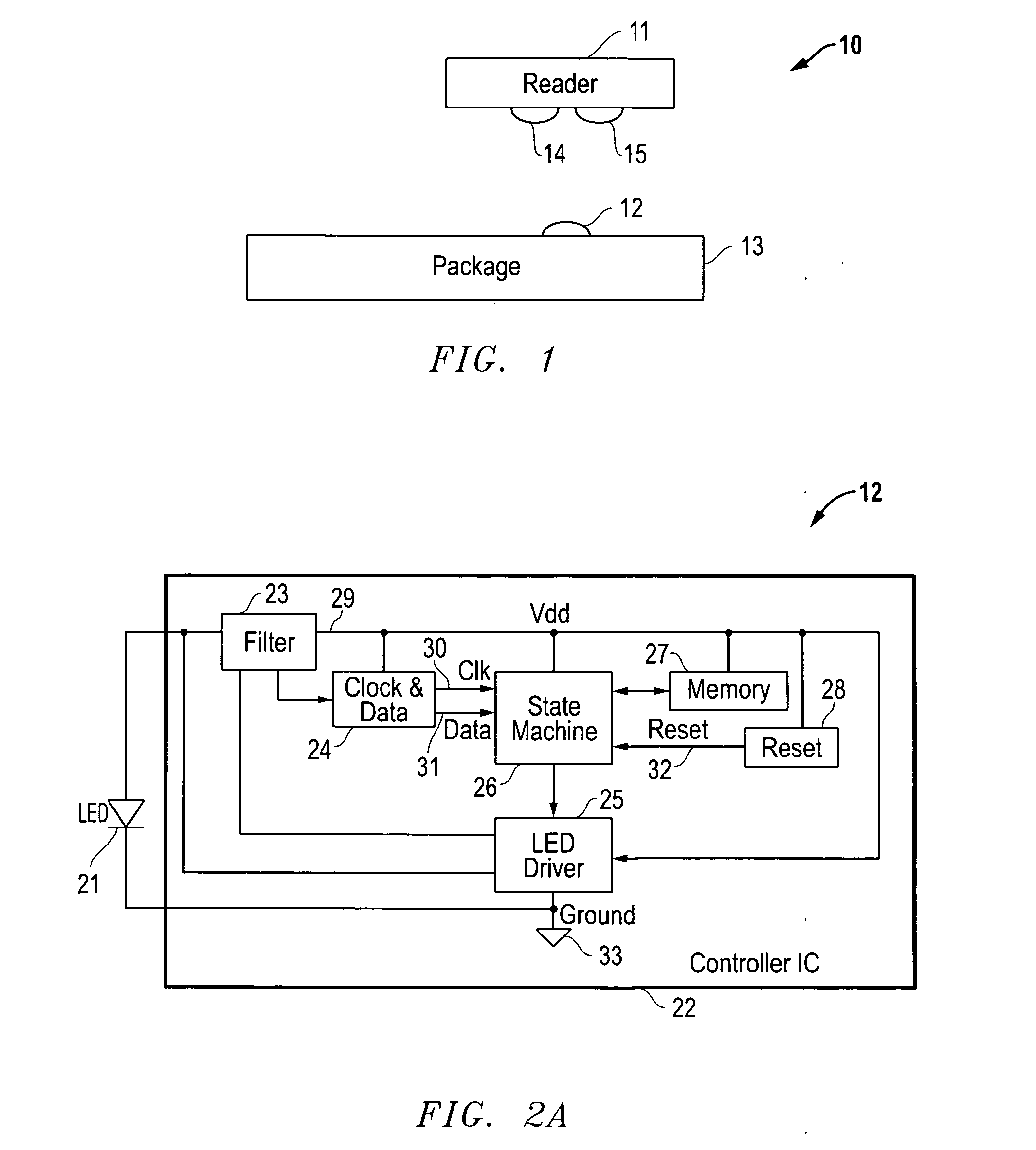
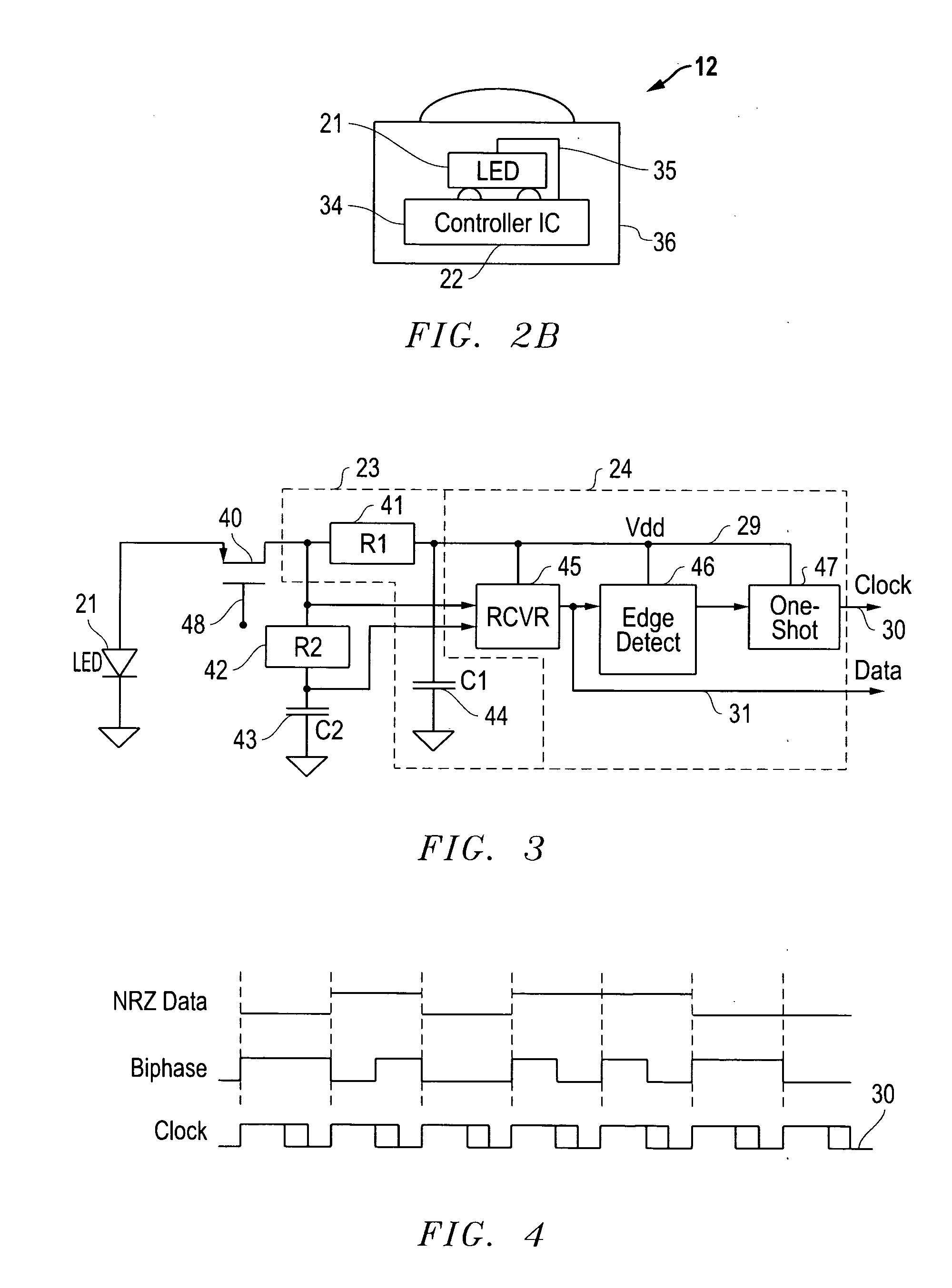
ActiveUS20100061734A1Avoid excessive currentHigh voltageElectromagnetic transceiversComputer hardwareTelecommunications link
Exemplary optical communication devices are described which, in certain embodiments, derive power optically from and communicate optically to a reading device. The communication devices may also receive data from modulated light from the reading device to achieve a bi-directional optical communication link between the self-powered optical communication device and the reading device. In some embodiments, the communication device is powered by ambient light, such as sunlight, captures data from a sensor, and communicates the stored data some time later to a reading device. In some embodiments, the communication device is powered locally and communicates through air, optical fiber, or other medium with another communication device.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
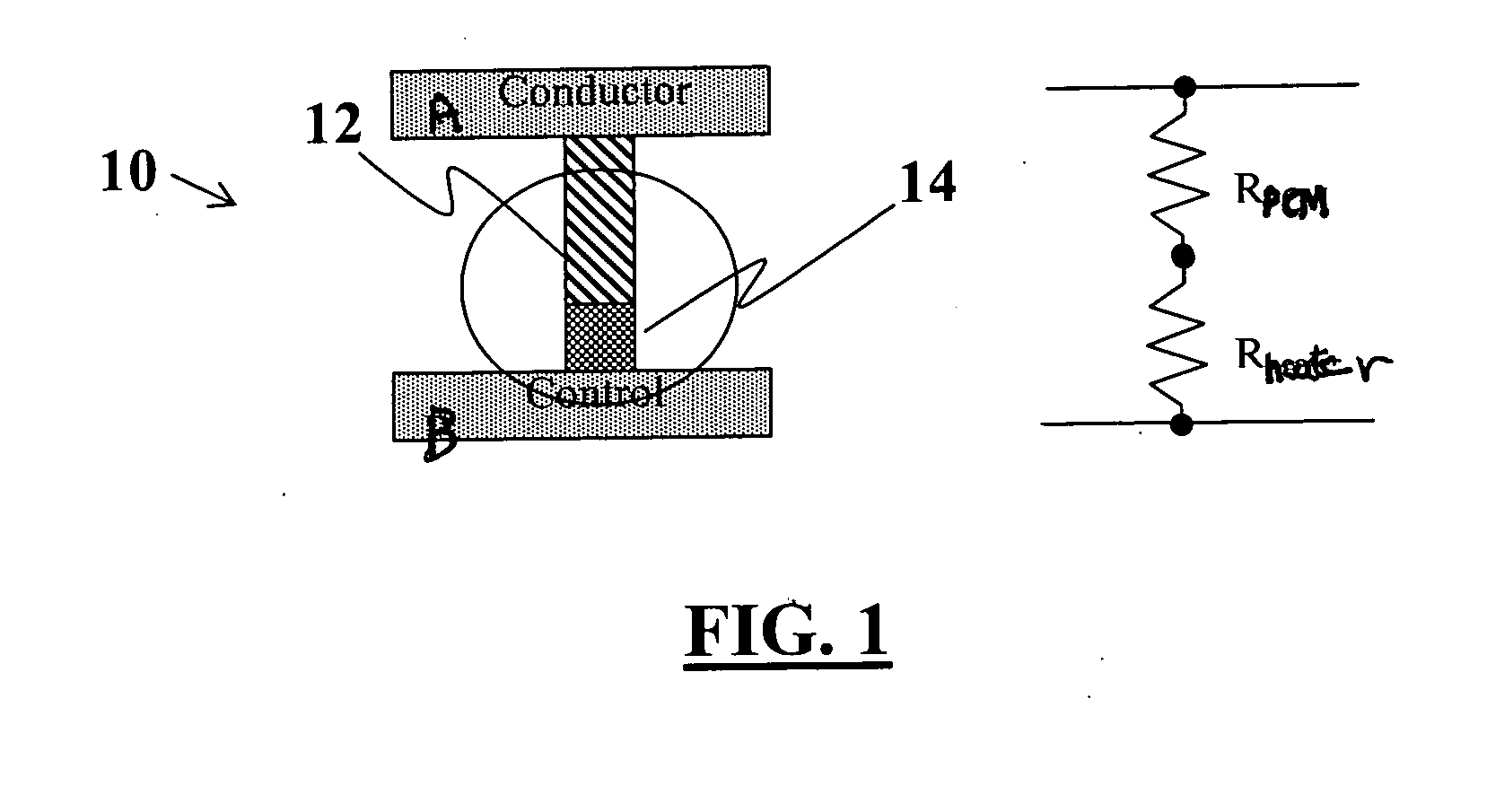
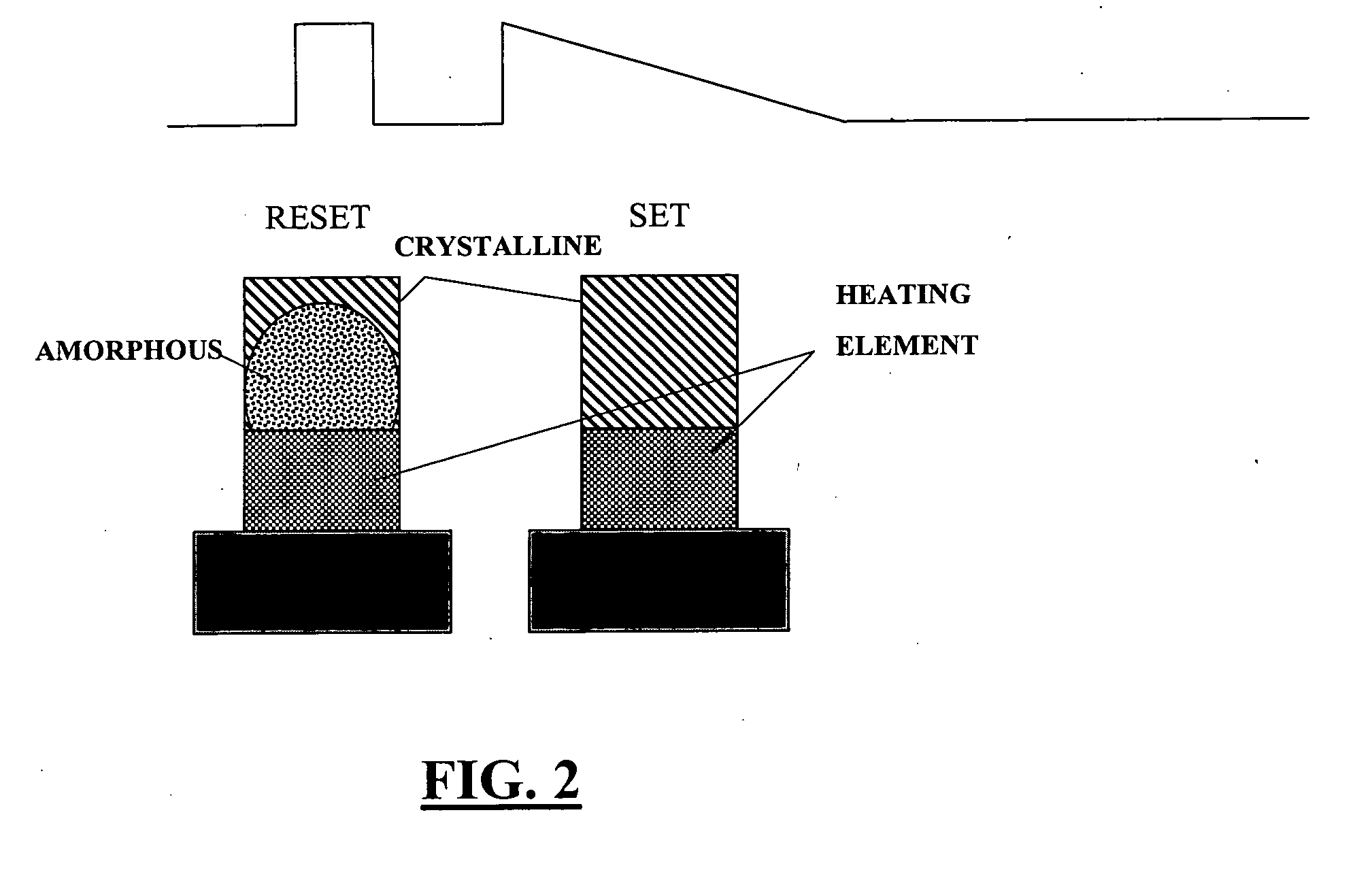
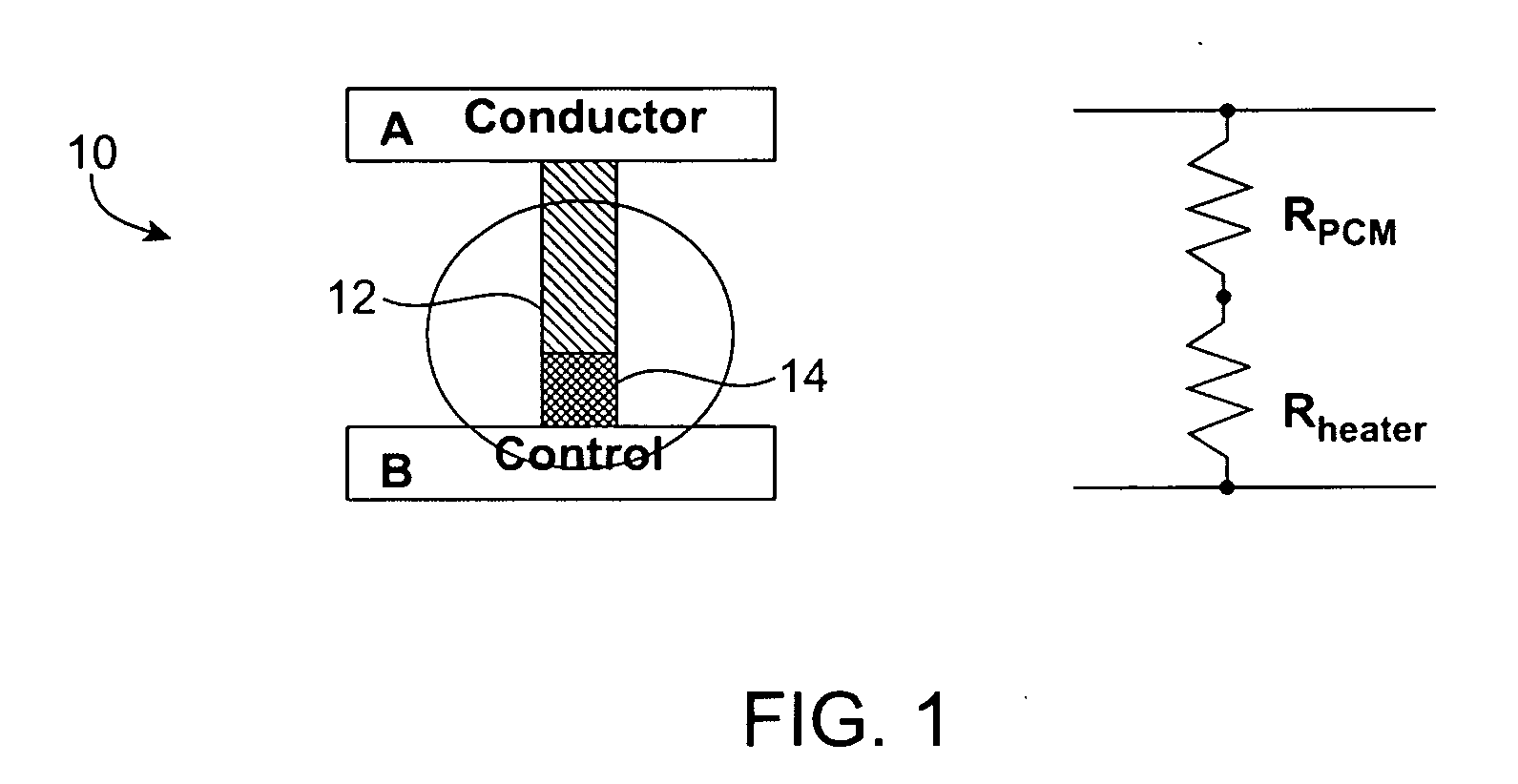
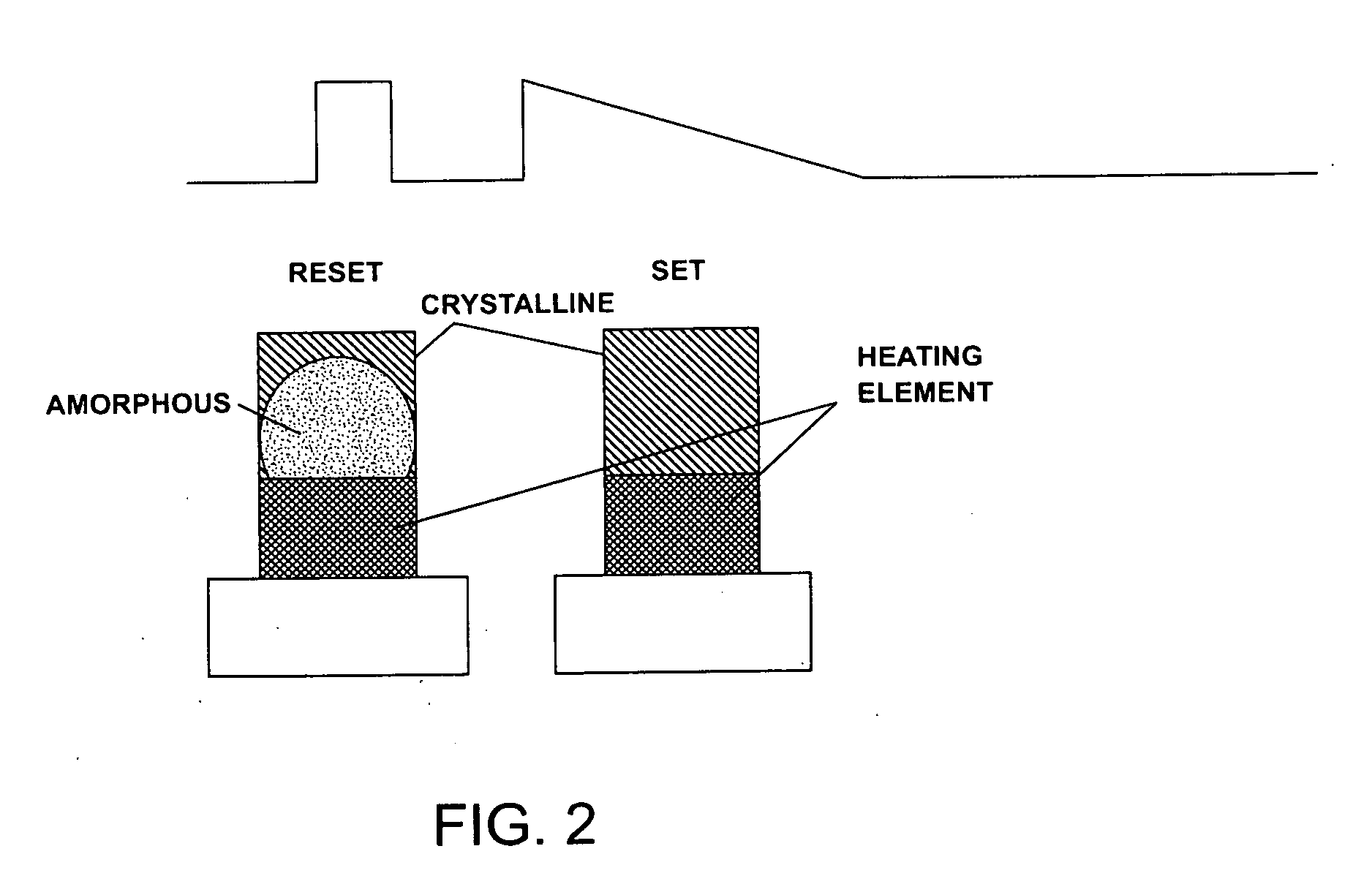
Methods for fabricating multi-terminal phase change devices
InactiveUS20070099405A1Reduce capacitanceReduce resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceControl signal
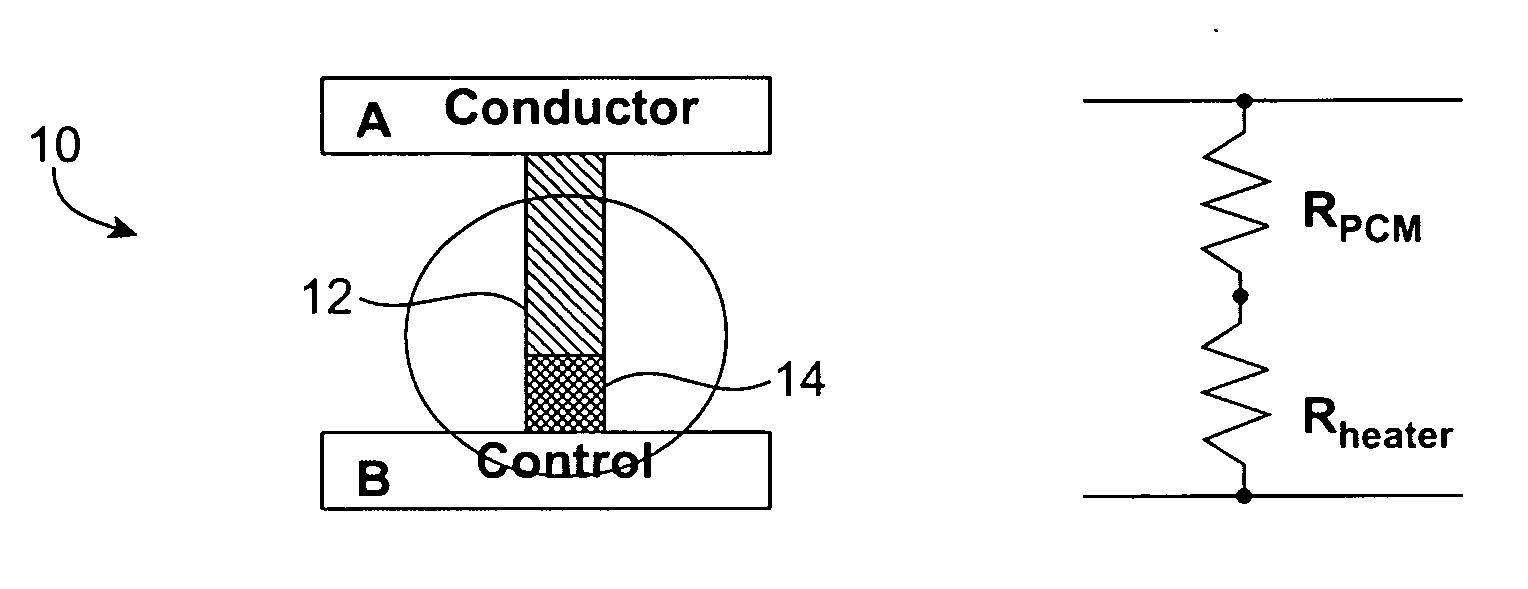
Phase change devices, and particularly multi-terminal phase change devices, include first and second active terminals bridged together by a phase-change material whose conductivity can be modified in accordance with a control signal applied to a control electrode. This structure allows an application in which an electrical connection can be created between the two active terminals, with the control of the connection being effected using a separate terminal or terminals. Accordingly, the resistance of the heater element can be increased independently from the resistance of the path between the two active terminals. This allows the use of smaller heater elements thus requiring less current to create the same amount of Joule heating per unit area. The resistance of the heating element does not impact the total resistance of the phase change device. The programming control can be placed outside of the main signal path through the phase change device, reducing the impact of the associated capacitance and resistance of the device.
Owner:AGATE LOGIC BEIJING
System and Methods for Determination of Analyte Concentration Using Time Resolved Amperometry
ActiveUS20090194432A1Improved determinationEasy to monitorImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteCurrent decay
A method for determining a concentration of an analyte is disclosed. The method includes applying a potential excitation to a fluid sample containing an analyte and determining if a current decay curve associated with the fluid sample has entered an analyte depletion stage. The method also includes measuring a plurality of current values associated with the fluid sample during the analyte depletion stage and calculating an analyte concentration based on at least one of the plurality of current values.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
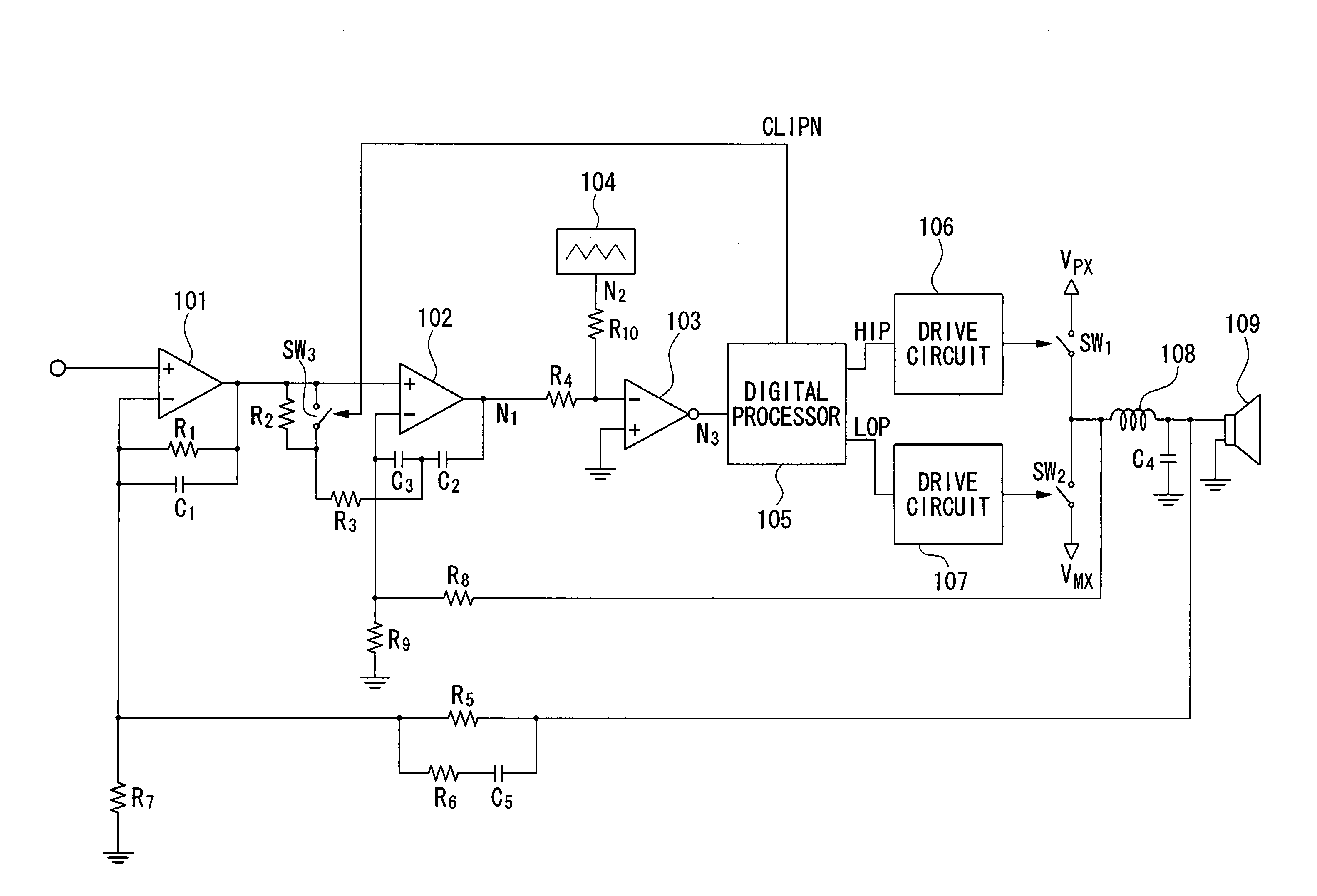
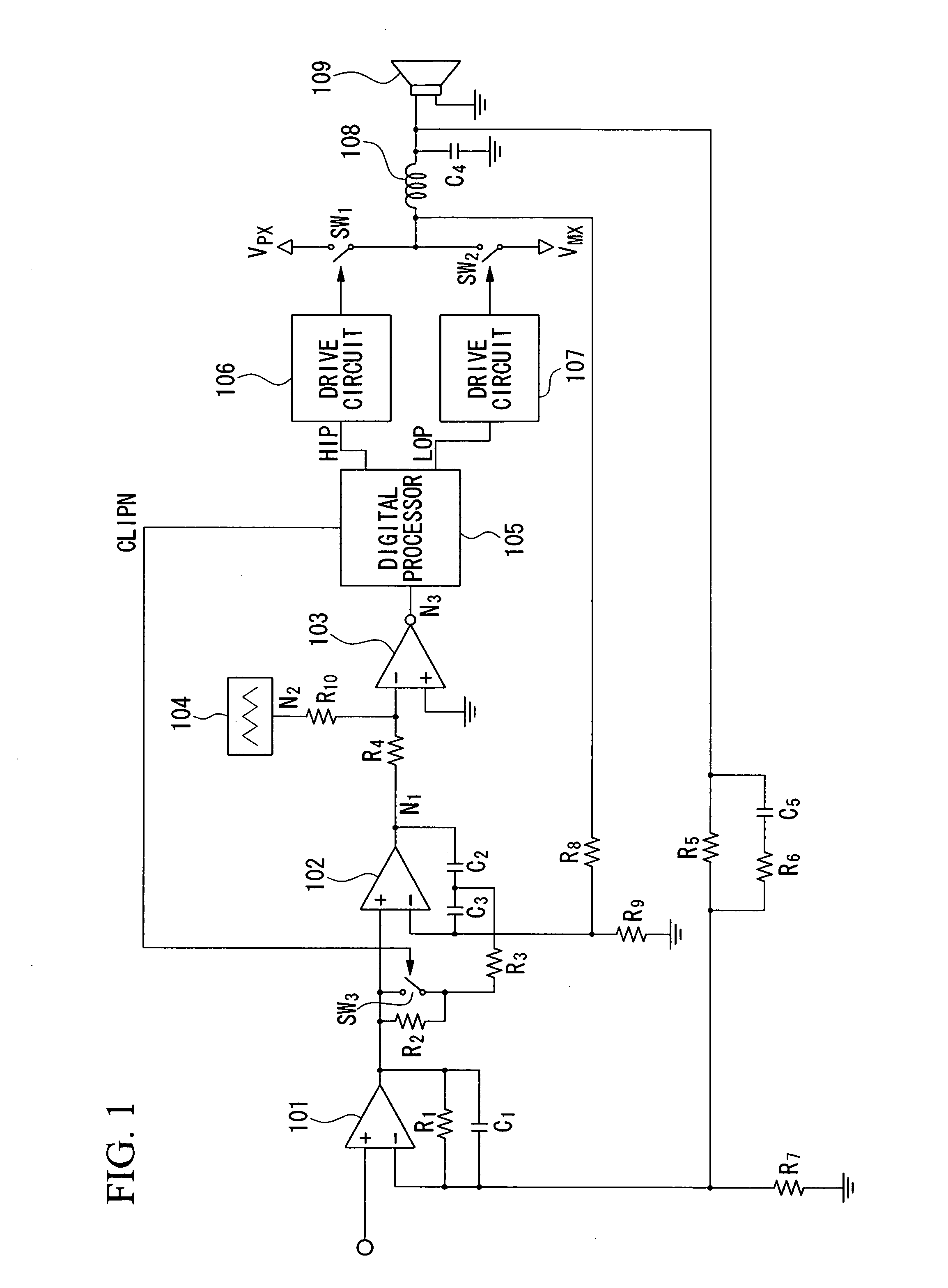
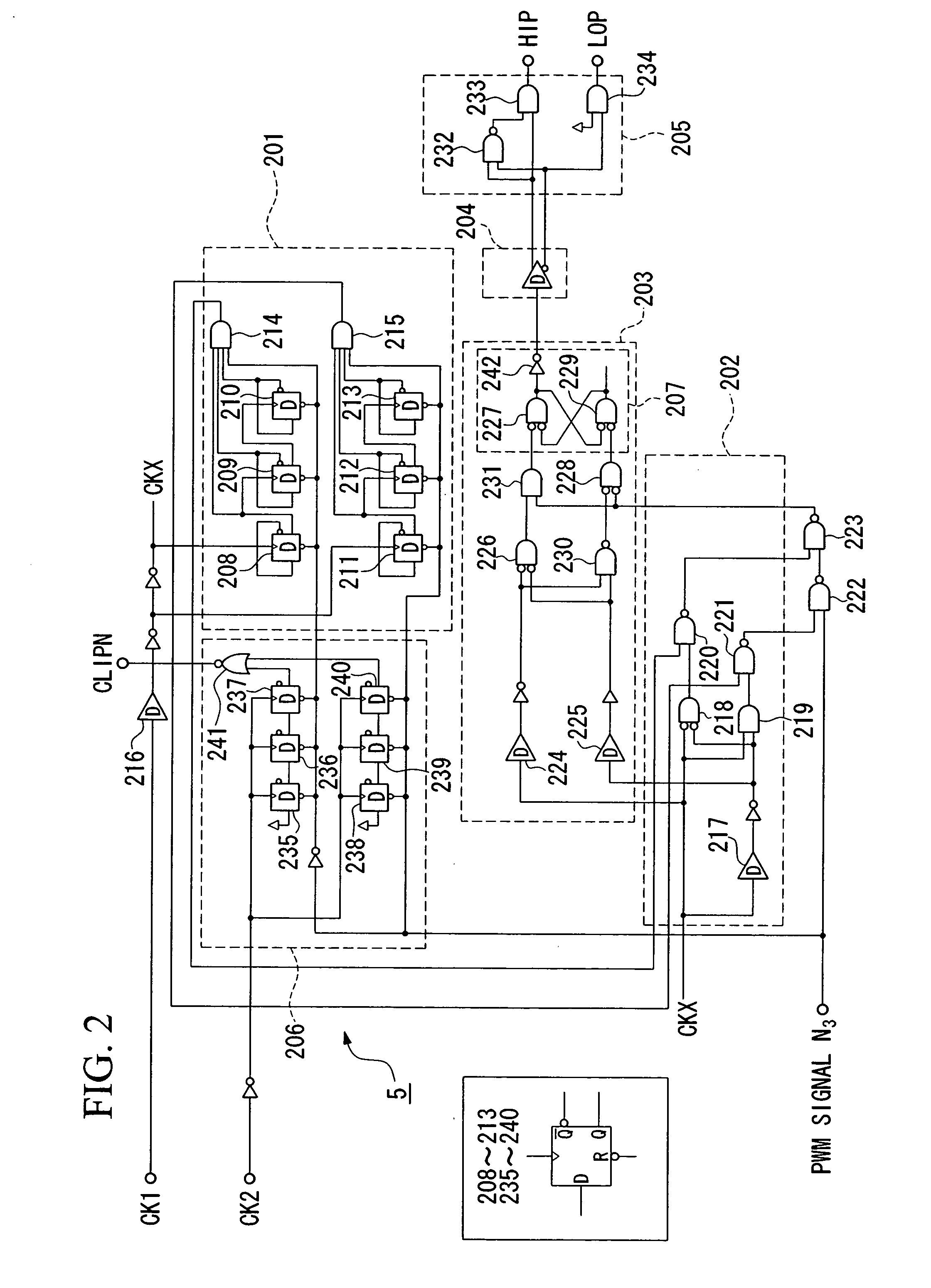
Pulse-width modulation amplifier and suppression of clipping therefor
ActiveUS20060008095A1Avoid excessive currentPower use efficiency decreaseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlLeading edgeAudio power amplifier
A pulse-width modulation (PWM) amplifier is adapted to a class-D amplifier in which an analog input signal is subjected to integration, pulse-width modulation, and switched amplification, wherein a glitch elimination circuit eliminates noise from a pulse-width modulated signal, from which a high pulse signal and a low pulse signal are isolated such that each pulse is delayed by a dead time at the leading-edge timing thereof. When both of them are simultaneously set to a high level, one of them is reduced in level. In response to the occurrence of clipping, an integration constant applied to an operational amplifier is automatically changed from a primary integration constant to a secondary integration constant. When the clipped state is sustained for a prescribed time, an inversion pulse is compulsorily introduced into the pulse-width modulated signal.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Lens assembly with actuating means and auto-focus controlling apparatus having the same
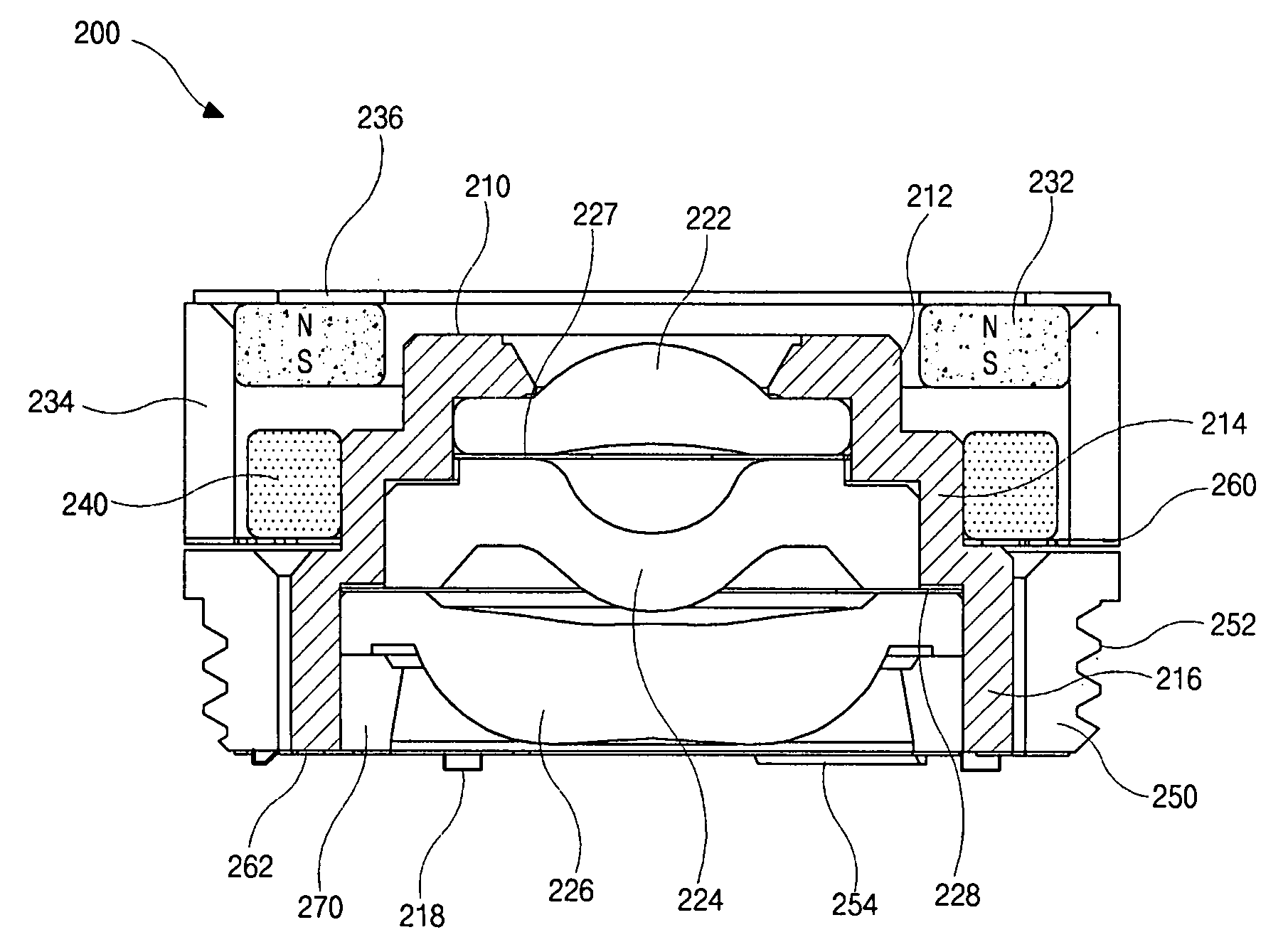
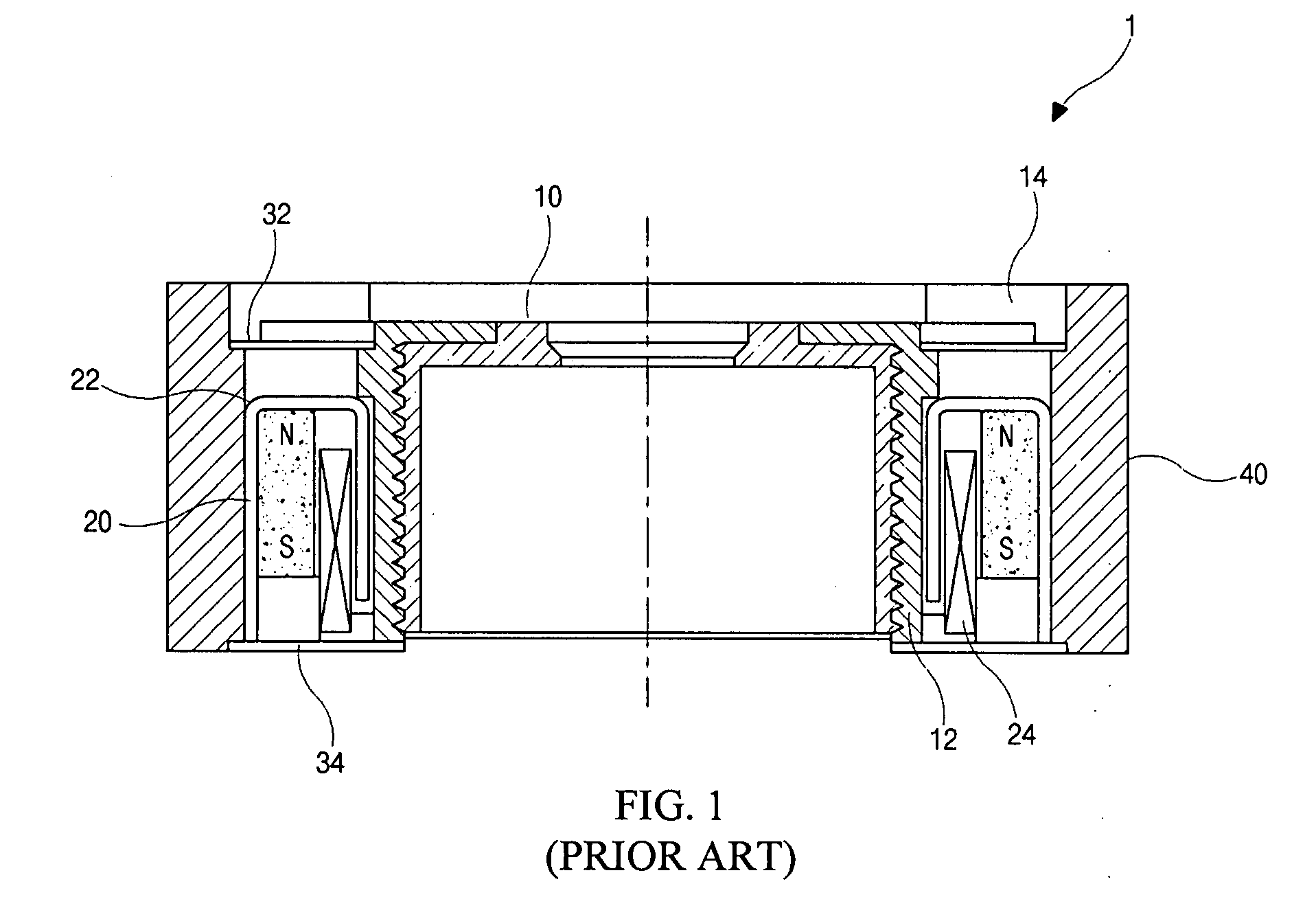
InactiveUS20080037143A1Avoid excessive currentSmall sizeMountingsFocusing aidsSmall lensCamera module
A lens assembly has a driving actuator which includes a magnet, a yoke and a coil and is formed along a lens barrel that accommodates a lens unit for focusing and an auto-focus controlling apparatus comprises the lens assembly for camera module. The magnet or the coil has an internal diameter smaller than a maximal diameter of the lens barrel. Therefore, it is possible to manufacture much smaller lens assembly according to the present invention compared to the conventional ones and to reduce the possibility of component damages in the lens assembly in operating the camera module.
Owner:DIOSTECH
Multi-terminal phase change devices
InactiveUS20070096071A1Reduce capacitanceReduce resistanceDigital storageBulk negative resistance effect devicesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
Phase change devices, and particularly multi-terminal phase change devices, include first and second active terminals bridged together by a phase-change material whose conductivity can be modified in accordance with a control signal applied to a control electrode. This structure allows an application in which an electrical connection can be created between the two active terminals, with the control of the connection being effected using a separate terminal or terminals. Accordingly, the resistance of the heater element can be increased independently from the resistance of the path between the two active terminals. This allows the use of smaller heater elements thus requiring less current to create the same amount of Joule heating per unit area. The resistance of the heating element does not impact the total resistance of the phase change device. The programming control can be placed outside of the main signal path through the phase change device, reducing the impact of the associated capacitance and resistance of the device.
Owner:AGATE LOGIC BEIJING
Rechargeable battery assembly
ActiveUS20070273327A1Avoid excessive currentMore currentSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsSecondary cellsCharge controlRechargeable cell
A rechargeable battery assembly comprises a built in connector, circuitry to provide charge control, at least one rechargeable battery unit, and circuitry providing a further function. The battery assembly is mechanically reversible between a deployed configuration having a general form and functions of a conventional battery format and a charge configuration in which the connector is made accessible. In the deployed configuration the battery assembly is capable of providing a discharge to at least one voltage level and can be charged by means of a suitable external charger device. In the charge configuration the battery assembly can be charged by means of the integral charge control circuitry when the connector is connected to a suitable powered receptacle on a computing or peripheral device.
Owner:MOIXA ENERGY HLDG
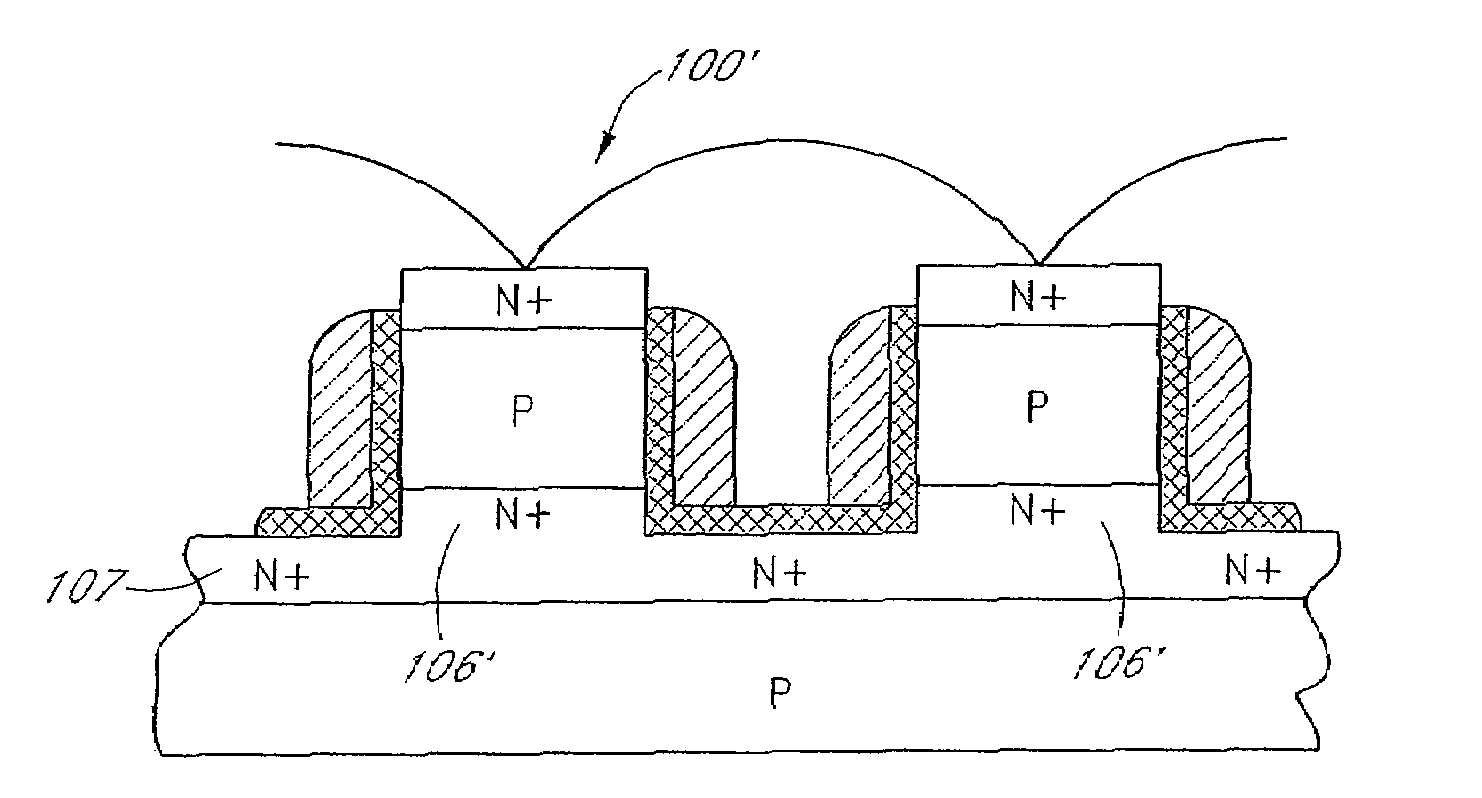
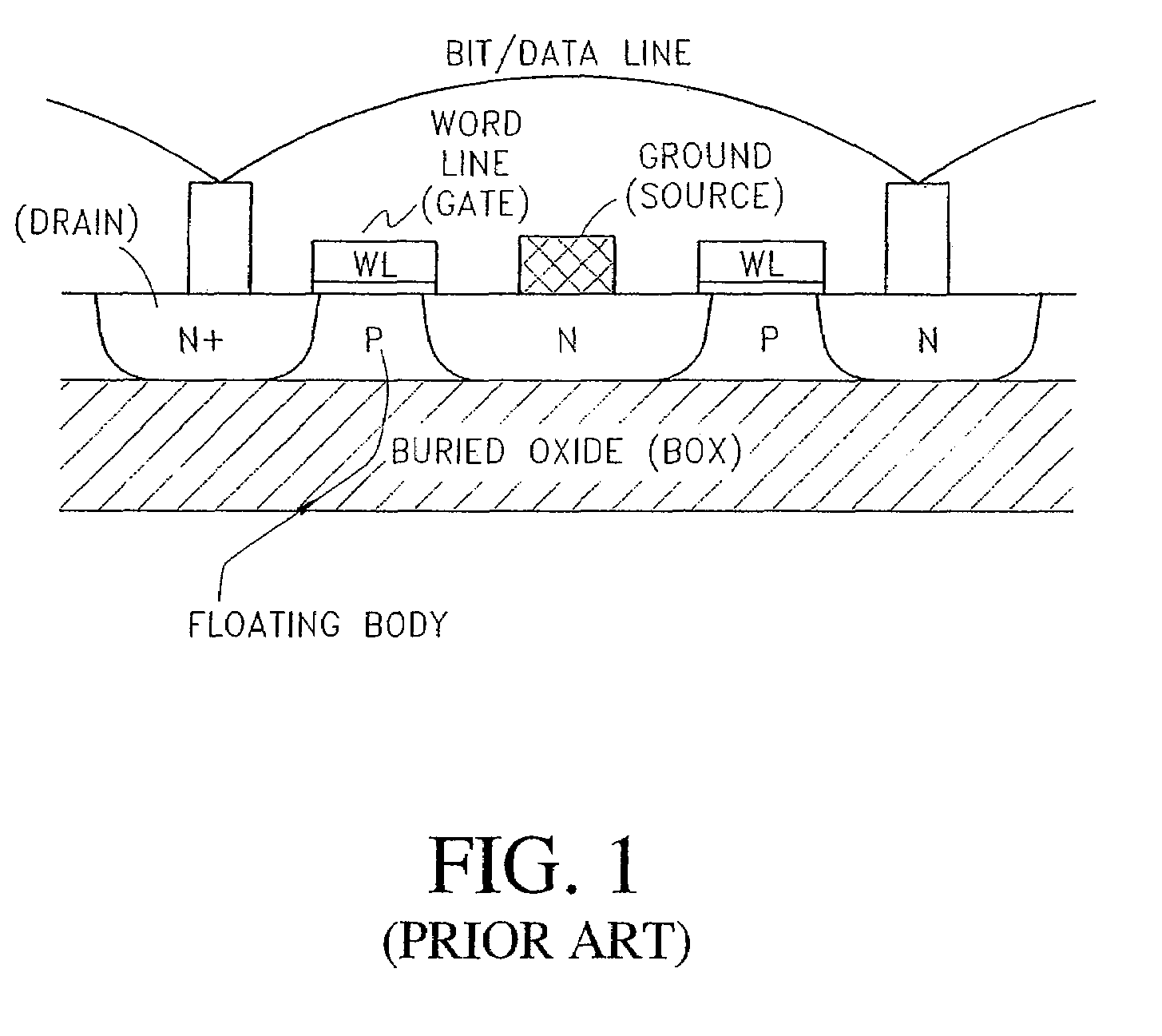
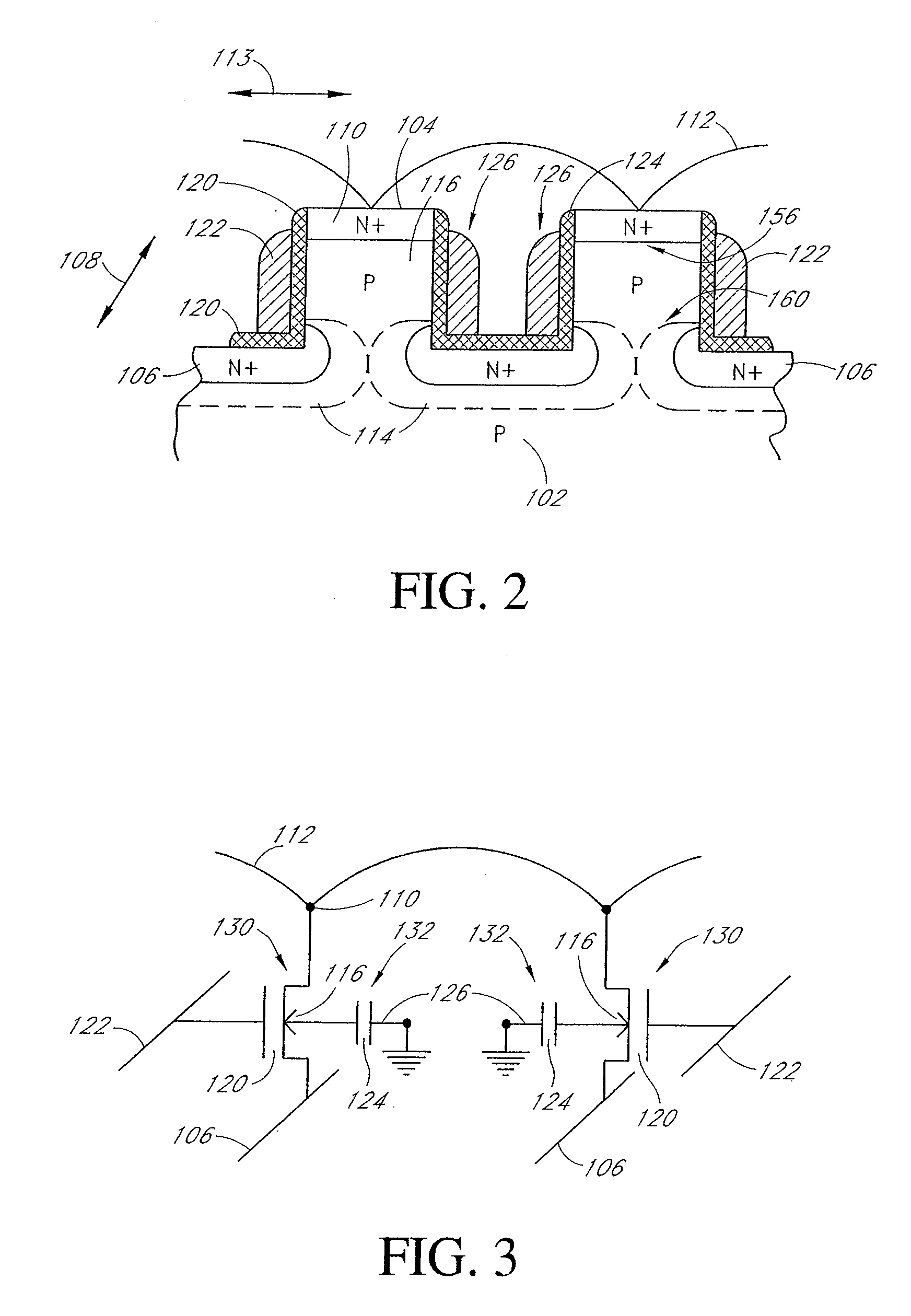
Long retention time single transistor vertical memory gain cell
ActiveUS7271052B1High band gap energyAvoid excessive leakage currentTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh cellRetention time
A single transistor vertical memory gain cell with long data retention times. The memory cell is formed from a silicon carbide substrate to take advantage of the higher band gap energy of silicon carbide as compared to silicon. The silicon carbide provides much lower thermally dependent leakage currents which enables significantly longer refresh intervals. In certain applications, the cell is effectively non-volatile provided appropriate gate bias is maintained. N-type source and drain regions are provided along with a pillar vertically extending from a substrate, which are both p-type doped. A floating body region is defined in the pillar which serves as the body of an access transistor as well as a body storage capacitor. The cell provides high volumetric efficiency with corresponding high cell density as well as relatively fast read times.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Lens driver for variable-optic electronic ophthalmic lens
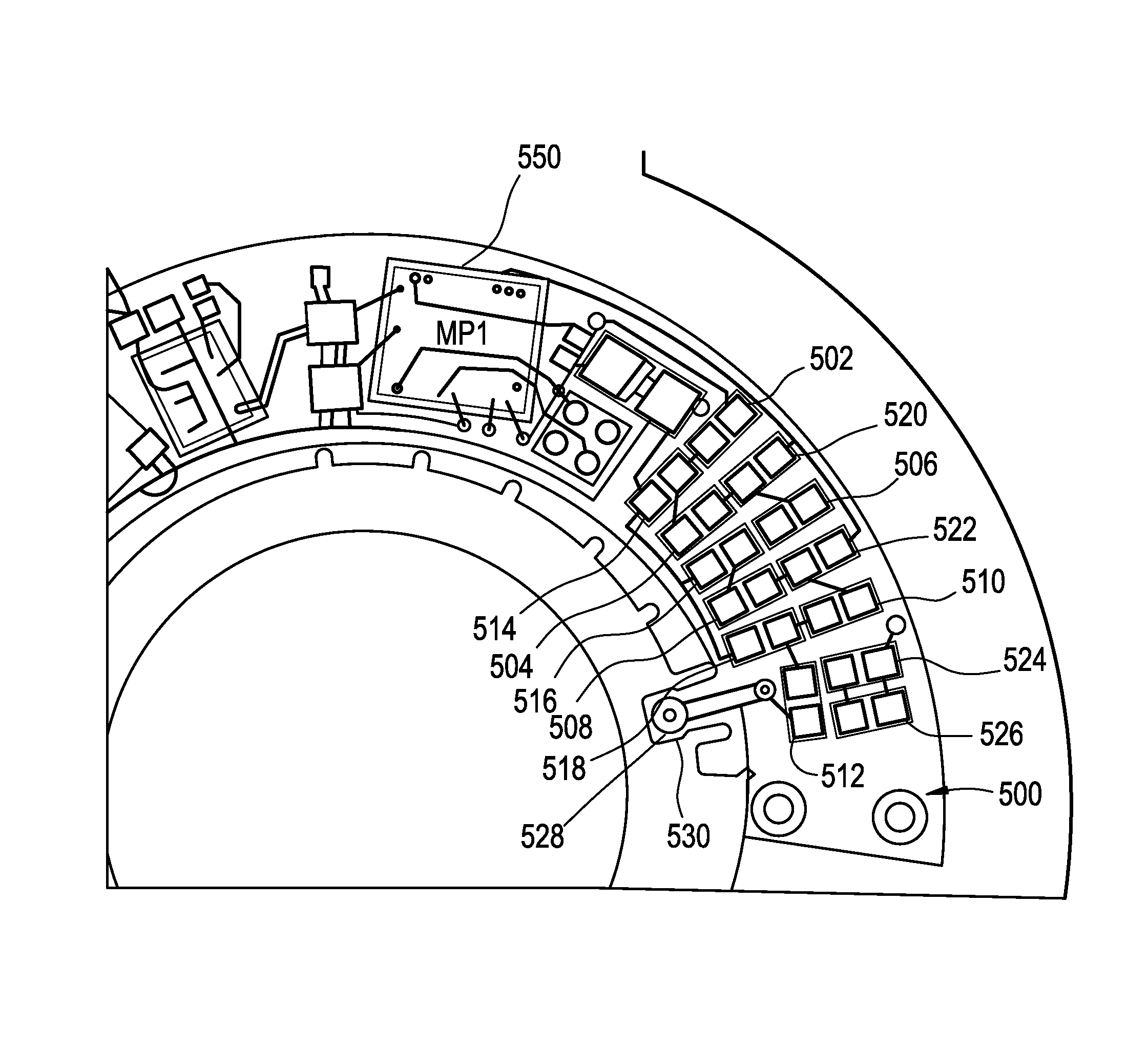
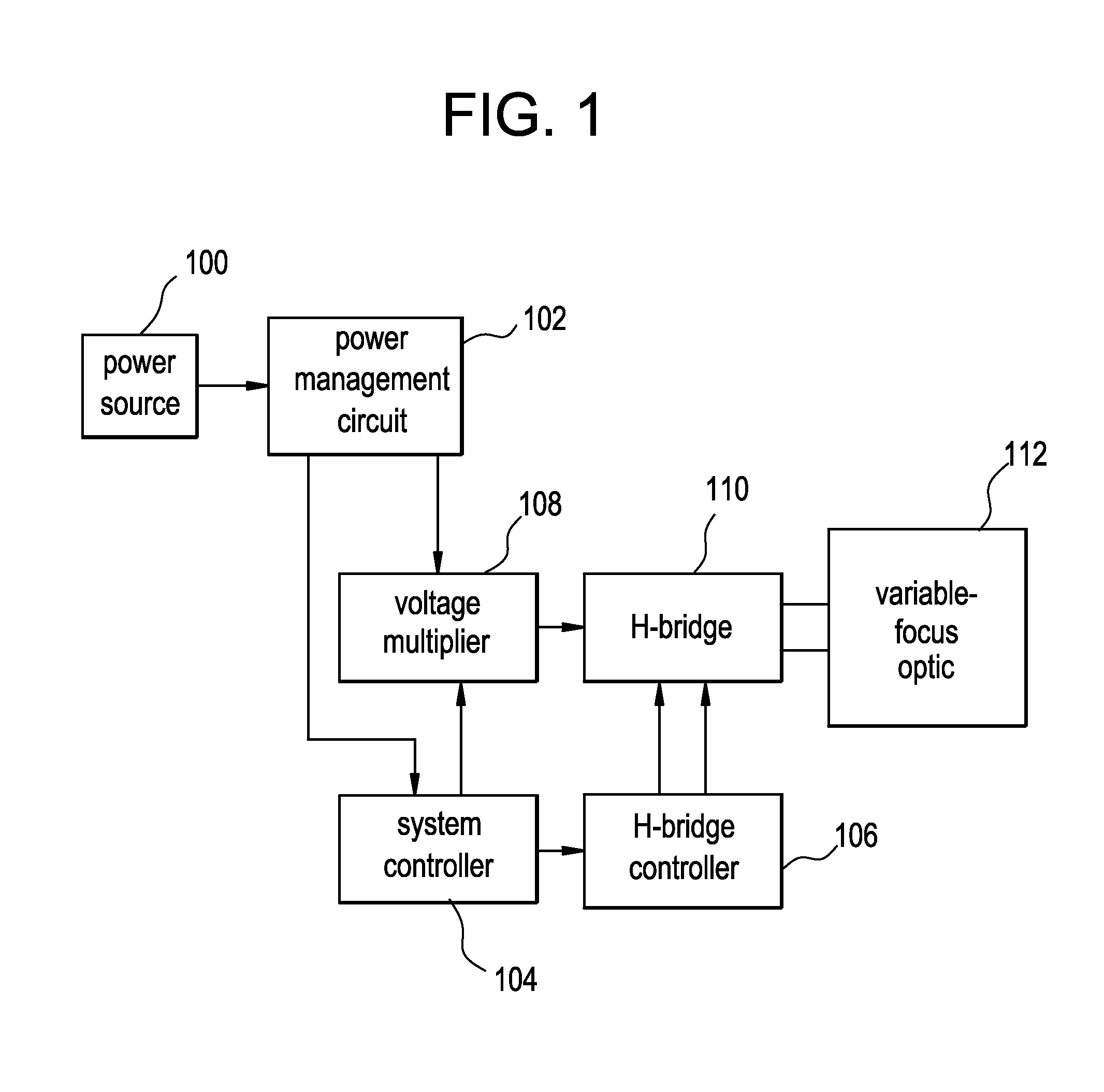
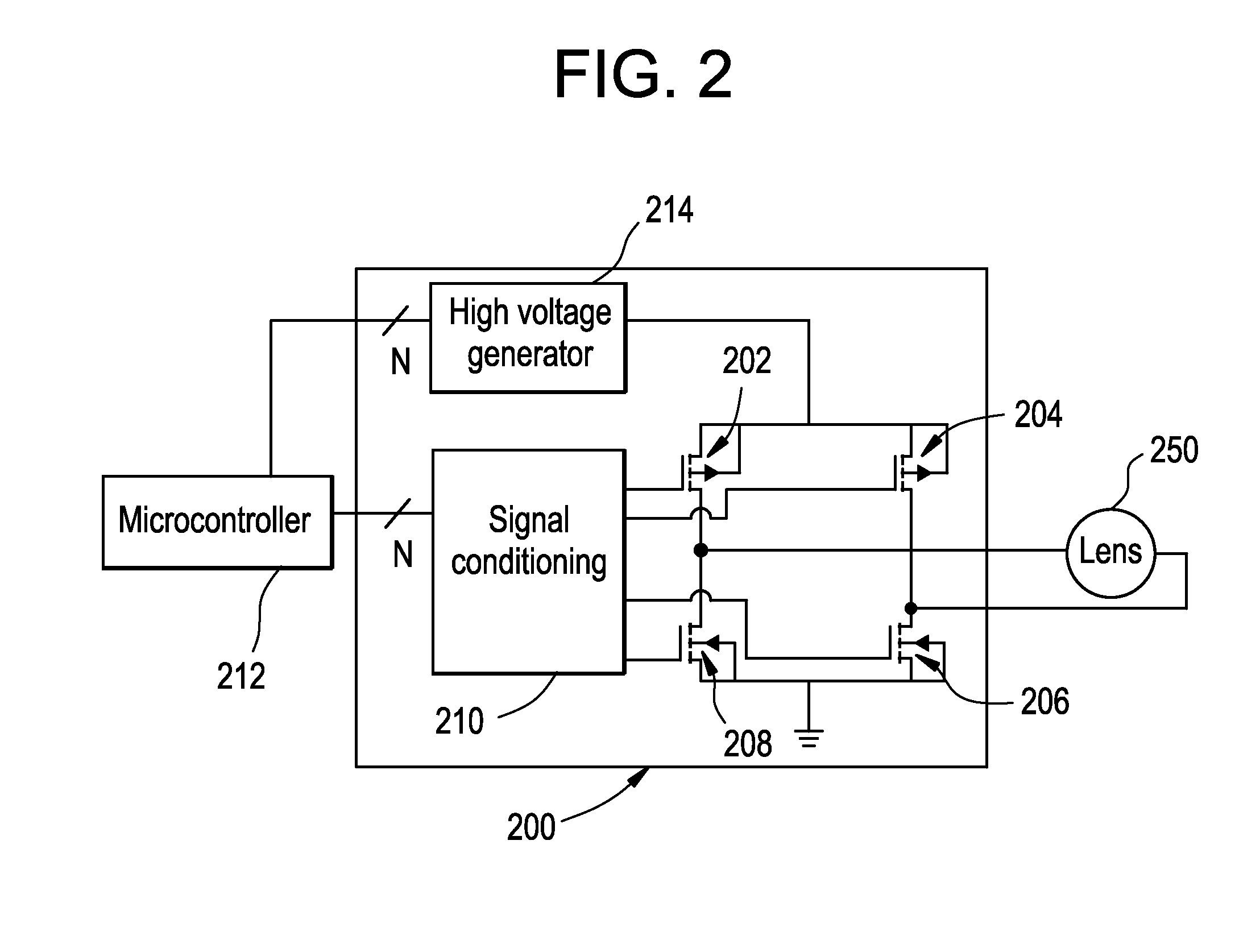
ActiveUS20130258275A1Avoid excessive currentLow voltage requirementIntraocular lensOptical partsOphthalmological deviceCamera lens
A lens driver or lens driver circuitry for an ophthalmic apparatus comprising an electronic system which actuates a variable-focus optic is disclosed herein. The lens driver is part of an electronic system incorporated into the ophthalmic apparatus. The electronic system includes one or more batteries or other power sources, power management circuitry, one or more sensors, clock generation circuitry, control algorithms and circuitry, and lens driver circuitry. The lens driver circuitry includes one or more power sources, one or more high voltage generators and one or more switching circuits.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
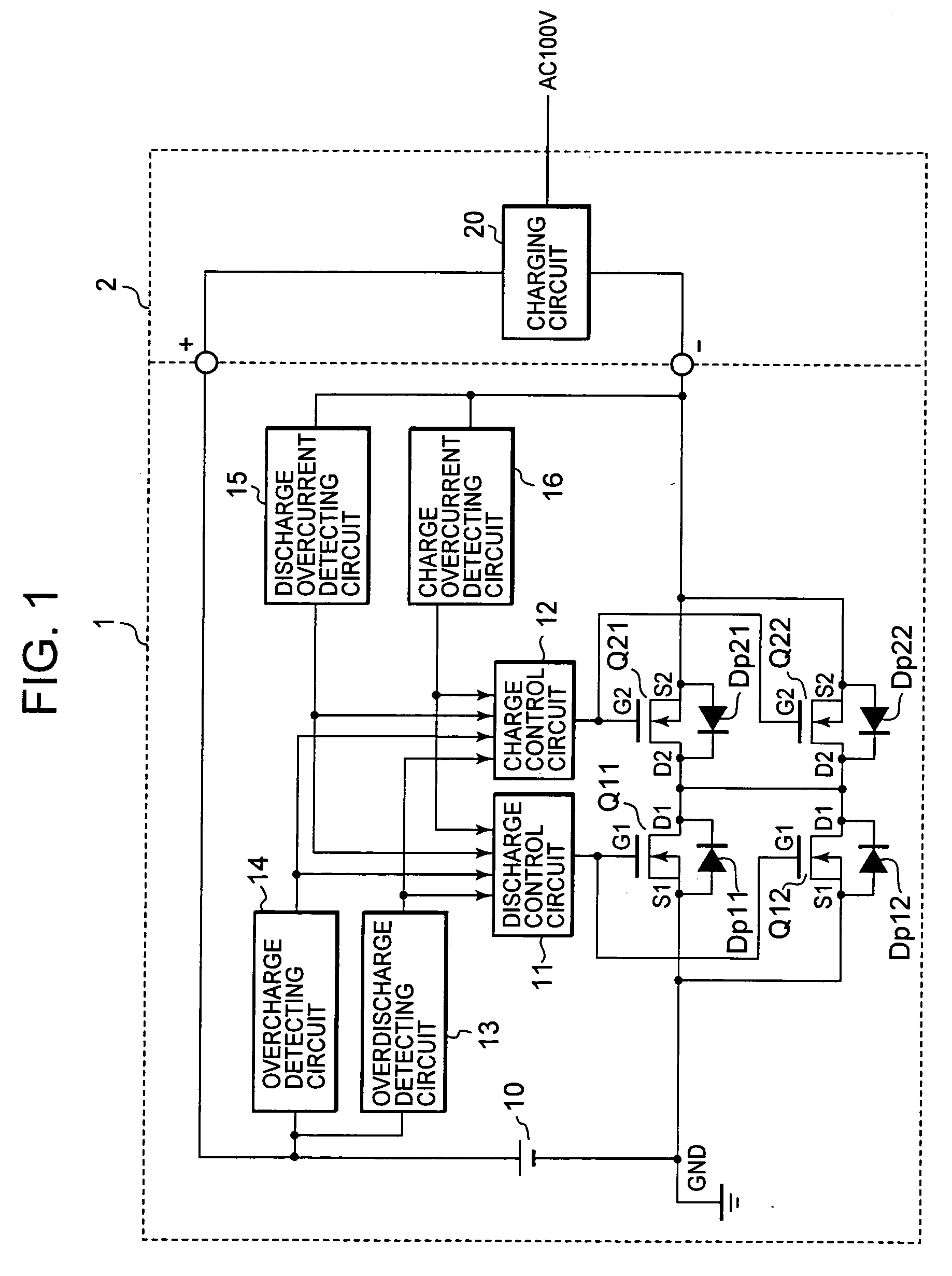
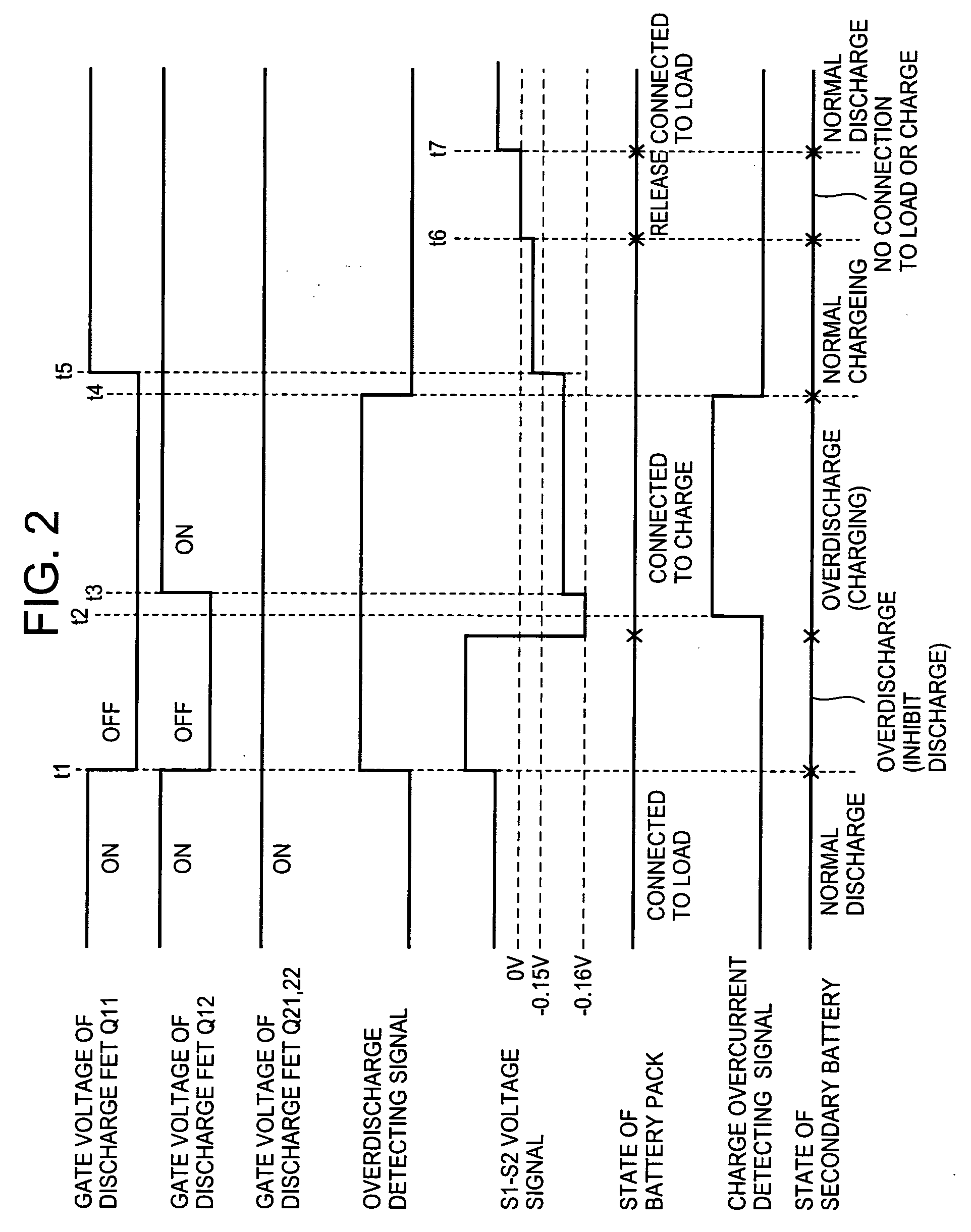
Battery protective device and semiconductor integrated circuit device
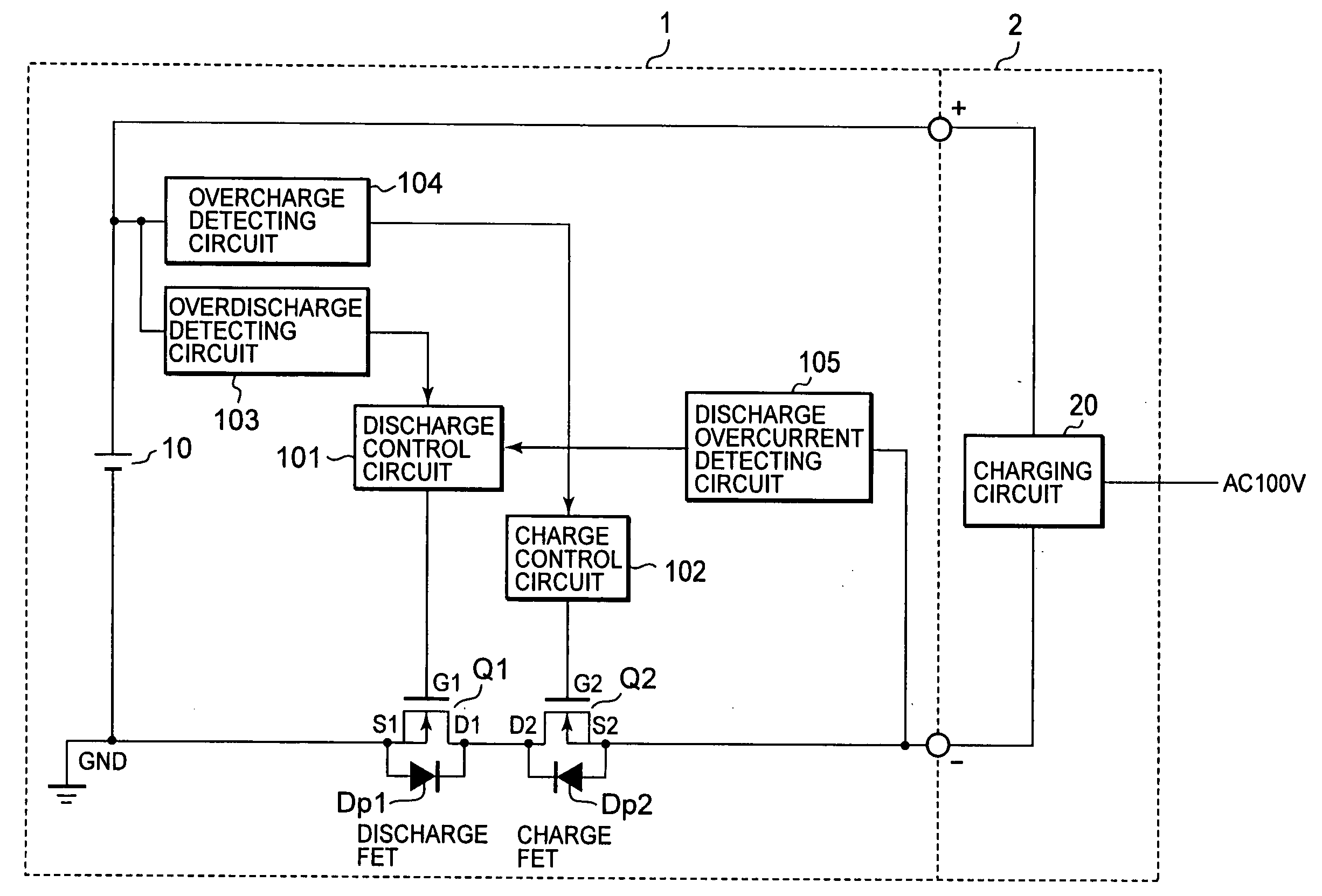
InactiveUS20080278116A1Avoid thermal damageEasy to detect chargeTransistorElectronic switchingElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A battery protective device that protects against battery damage and semiconductor destruction from overdischarge and overcharge of the battery. Resistance across switching elements is controllable to prevent current leakage through parasitic dipole elements in the integrated circuit. Current is detected with an overdischarge detecting circuit and an overcharge detecting circuit. Direction of the current to / from the battery is detected by discharge overcurrent and charge overcurrent detecting circuits. Switching discharge FETs and charge FETs are enabled as independently controlled, ON-OFF parallel switching elements, interposed in series in the charge / discharge current path of the battery. Only a part of the discharge or charge switching FETs can be turned ON and OFF for accurate current control in accordance with the detected current and its direction.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
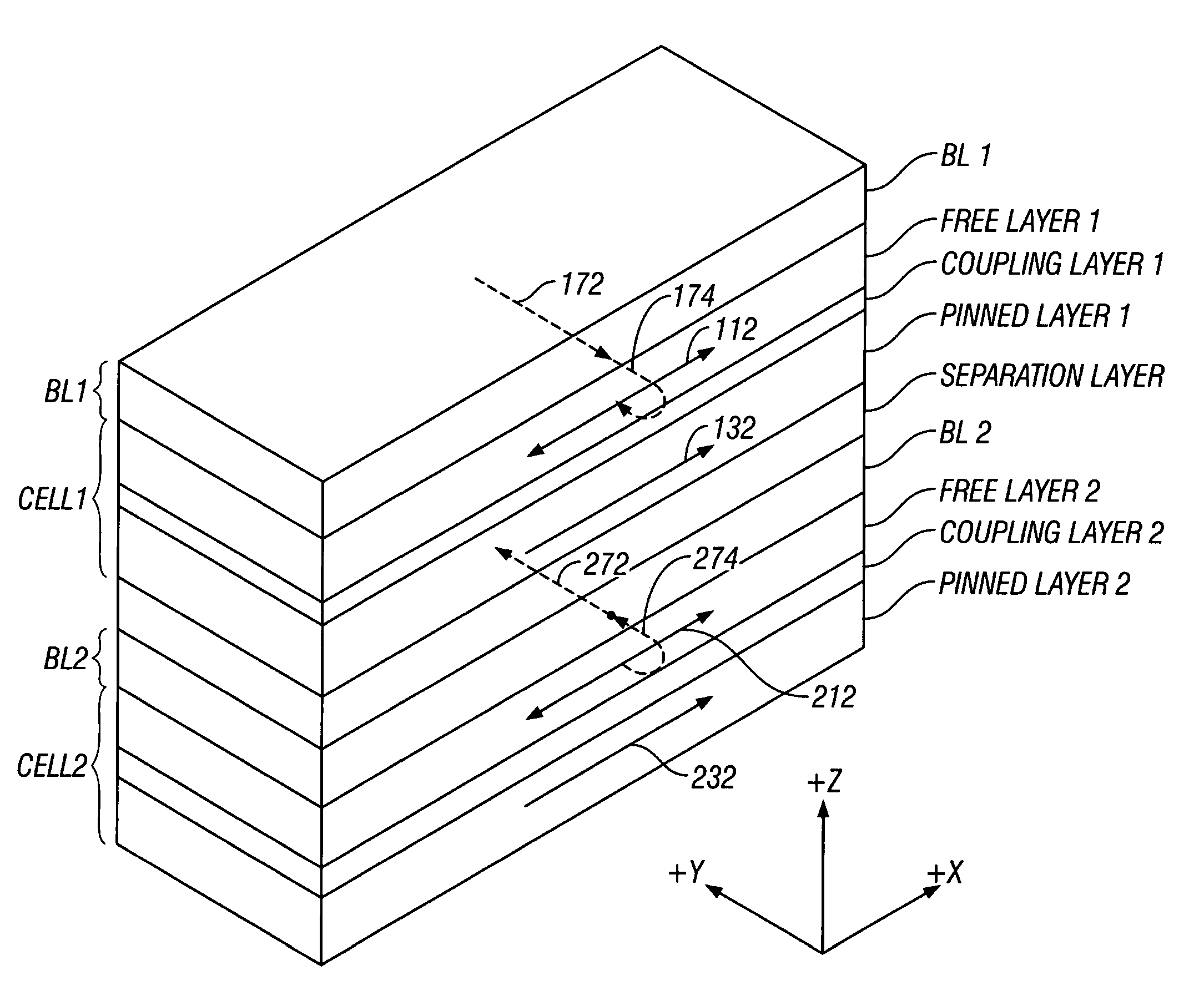
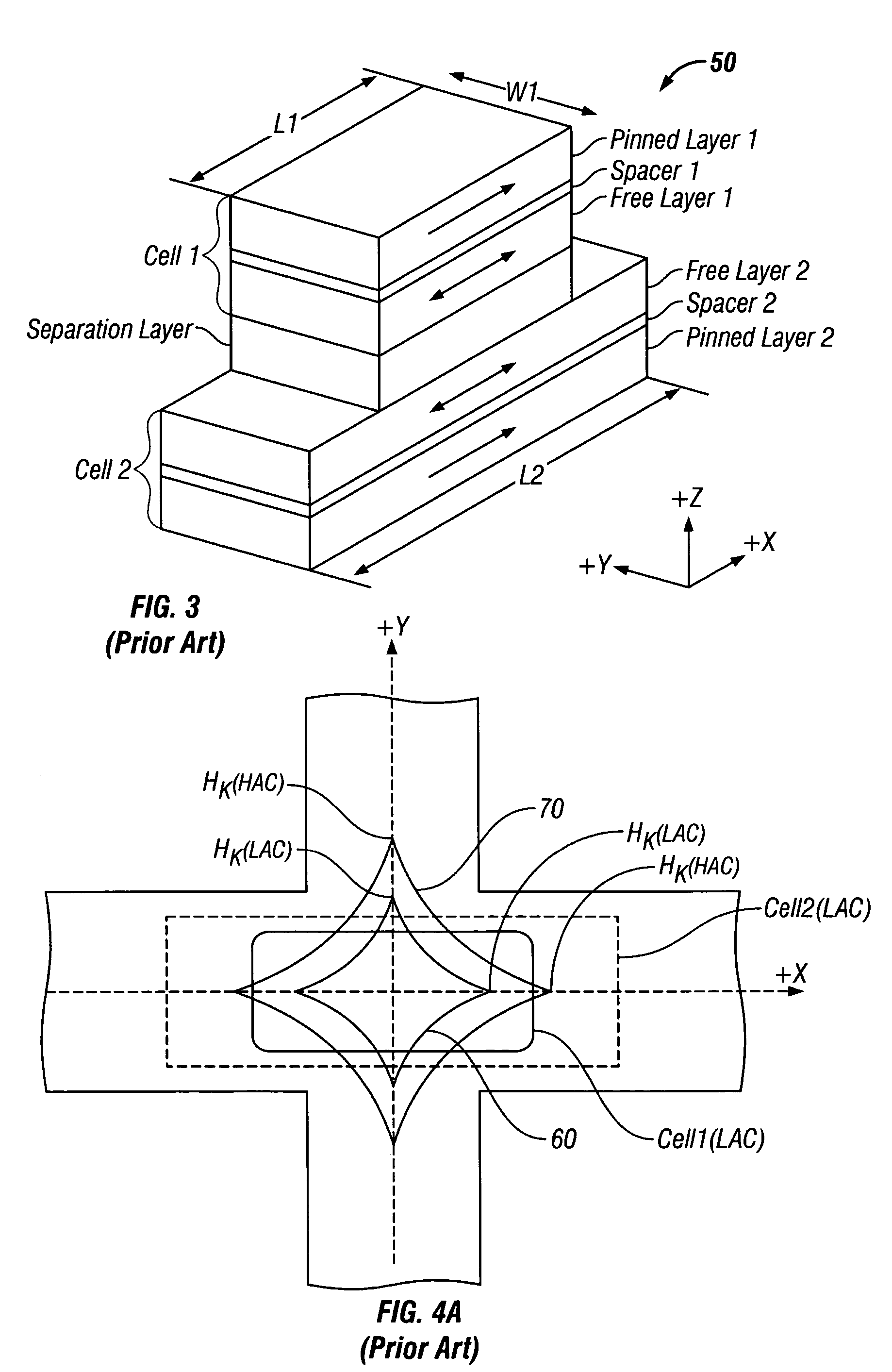
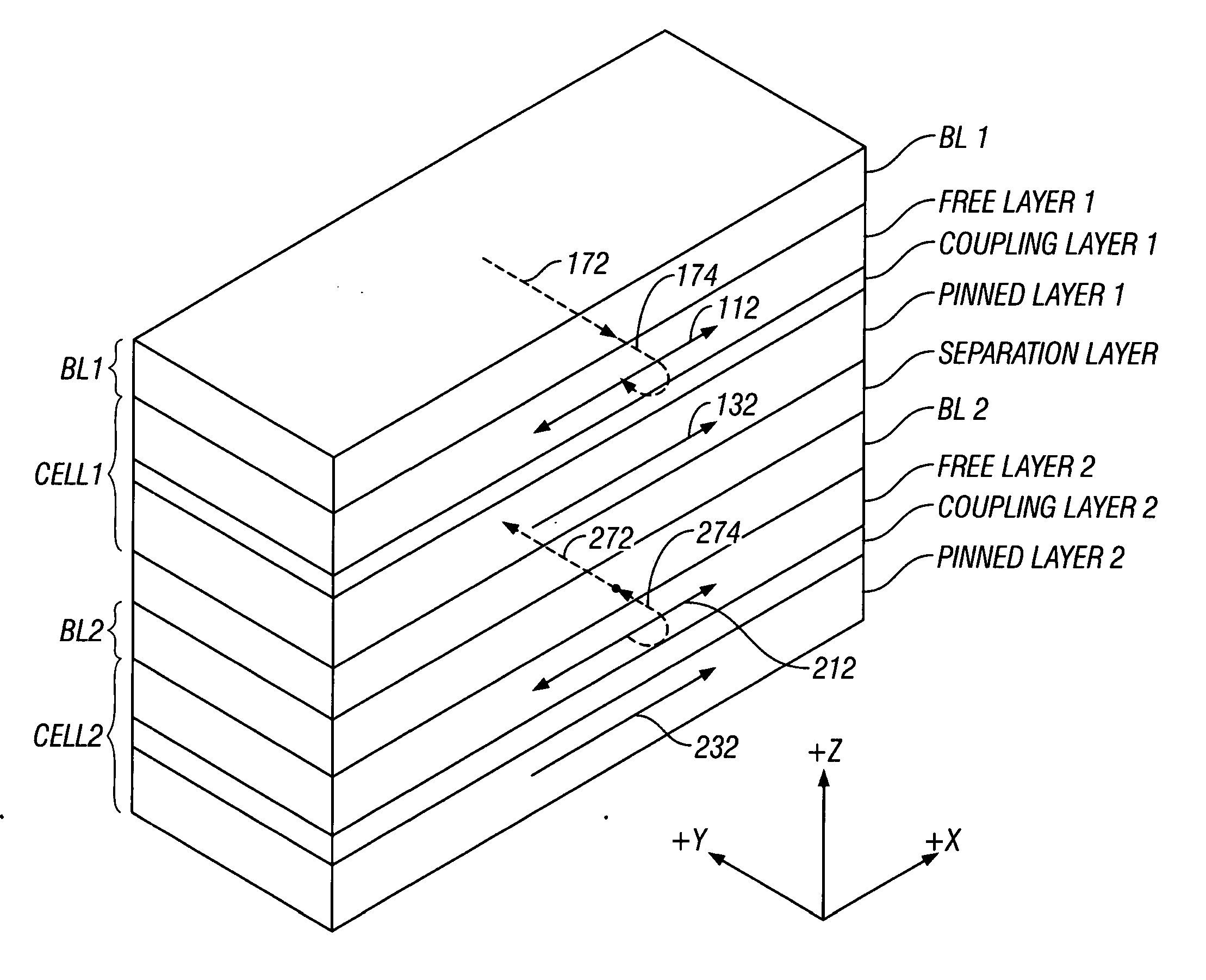
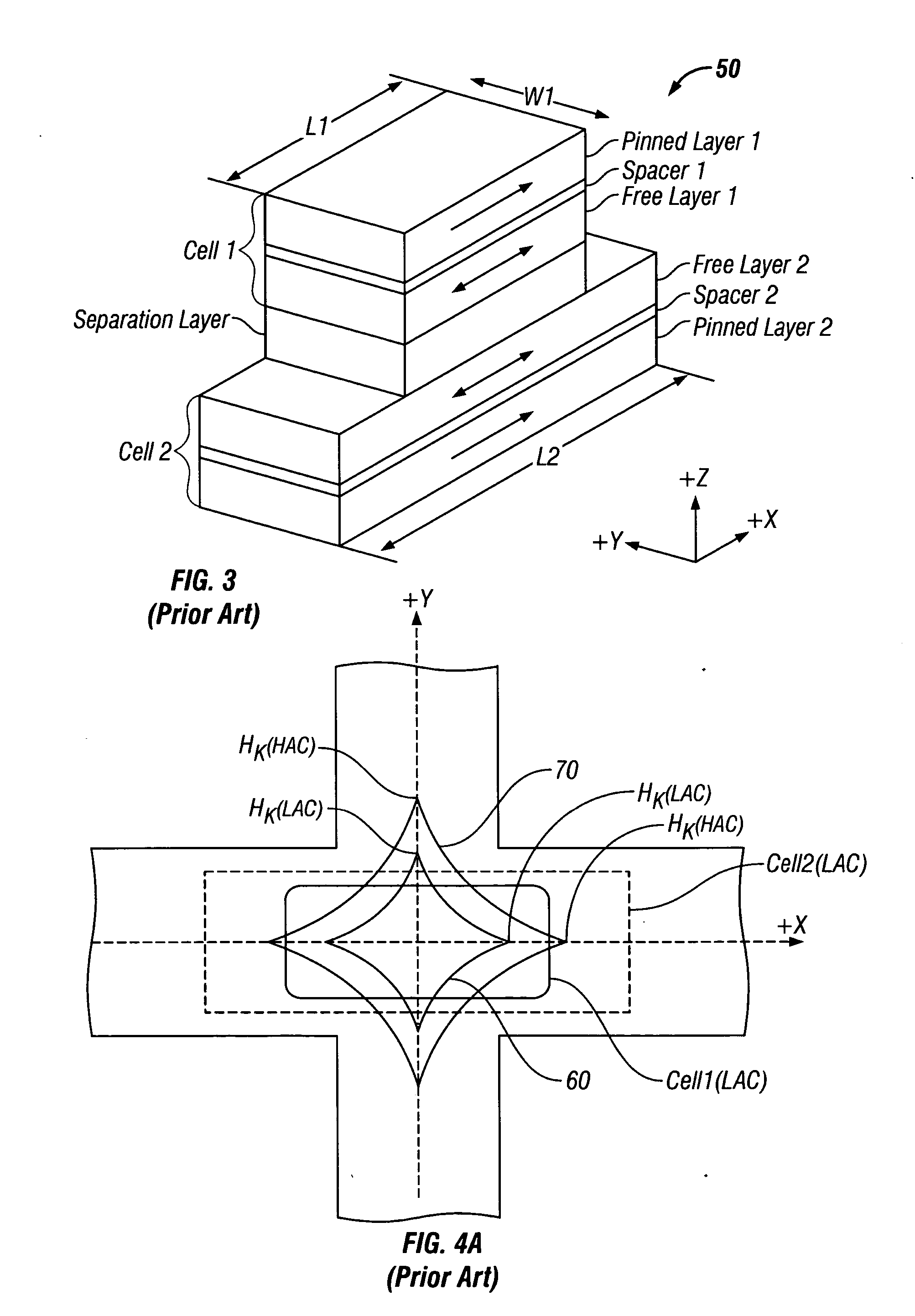
Magnetic random access memory with stacked memory cells having oppositely-directed hard-axis biasing
ActiveUS7285836B2Reduce switchingReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn planeStatic random-access memory
A magnetic random access memory (MRAM) has memory stacks arranged in the X-Y plane on the MRAM substrate, with each memory stack having two memory cells stacked along the Z axis and each memory cell having an associated biasing layer. Each biasing layer reduces the switching field of its associated cell by applying a biasing field along the hard-axis of magnetization of the free layer of its associated cell. The free layers in the two cells in each stack have their in-plane easy axes of magnetization aligned parallel to one another. Each biasing layer has its in-plane magnetization direction oriented perpendicular to the easy axis of magnetization (and thus parallel to the hard axis) of the free layer in its associated cell. The hard-axis biasing fields generated by the two biasing layers are in opposite directions.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
Magnetic random access memory with stacked memory cells having oppositely-directed hard-axis biasing
ActiveUS20060202244A1Lower switching fieldReduce switchingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn planeRandom access memory
A magnetic random access memory (MRAM) has memory stacks arranged in the X-Y plane on the MRAM substrate, with each memory stack having two memory cells stacked along the Z axis and each memory cell having an associated biasing layer. Each biasing layer reduces the switching field of its associated cell by applying a biasing field along the hard-axis of magnetization of the free layer of its associated cell. The free layers in the two cells in each stack have their in-plane easy axes of magnetization aligned parallel to one another. Each biasing layer has its in-plane magnetization direction oriented perpendicular to the easy axis of magnetization (and thus parallel to the hard axis) of the free layer in its associated cell. The hard-axis biasing fields generated by the two biasing layers are in opposite directions.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
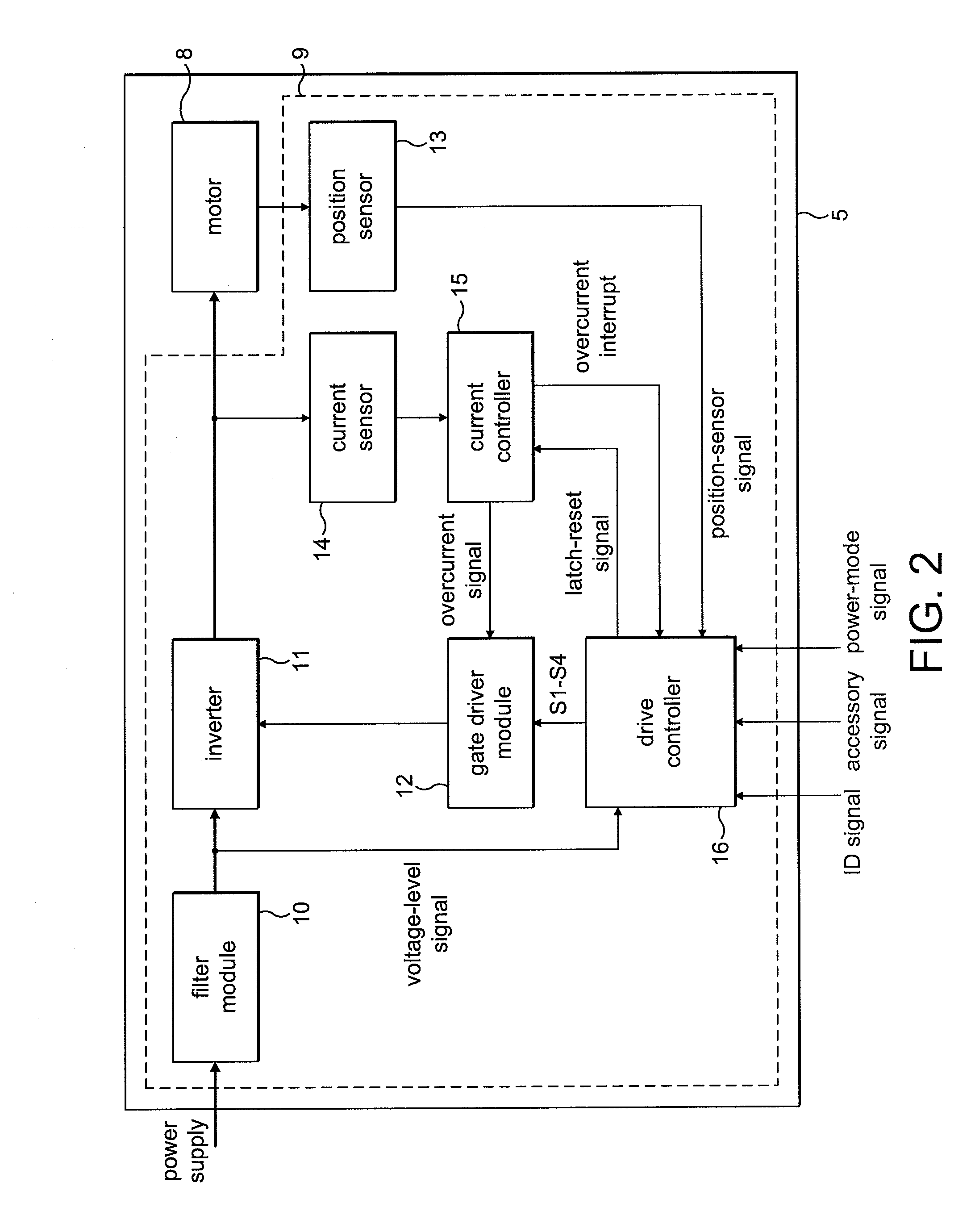
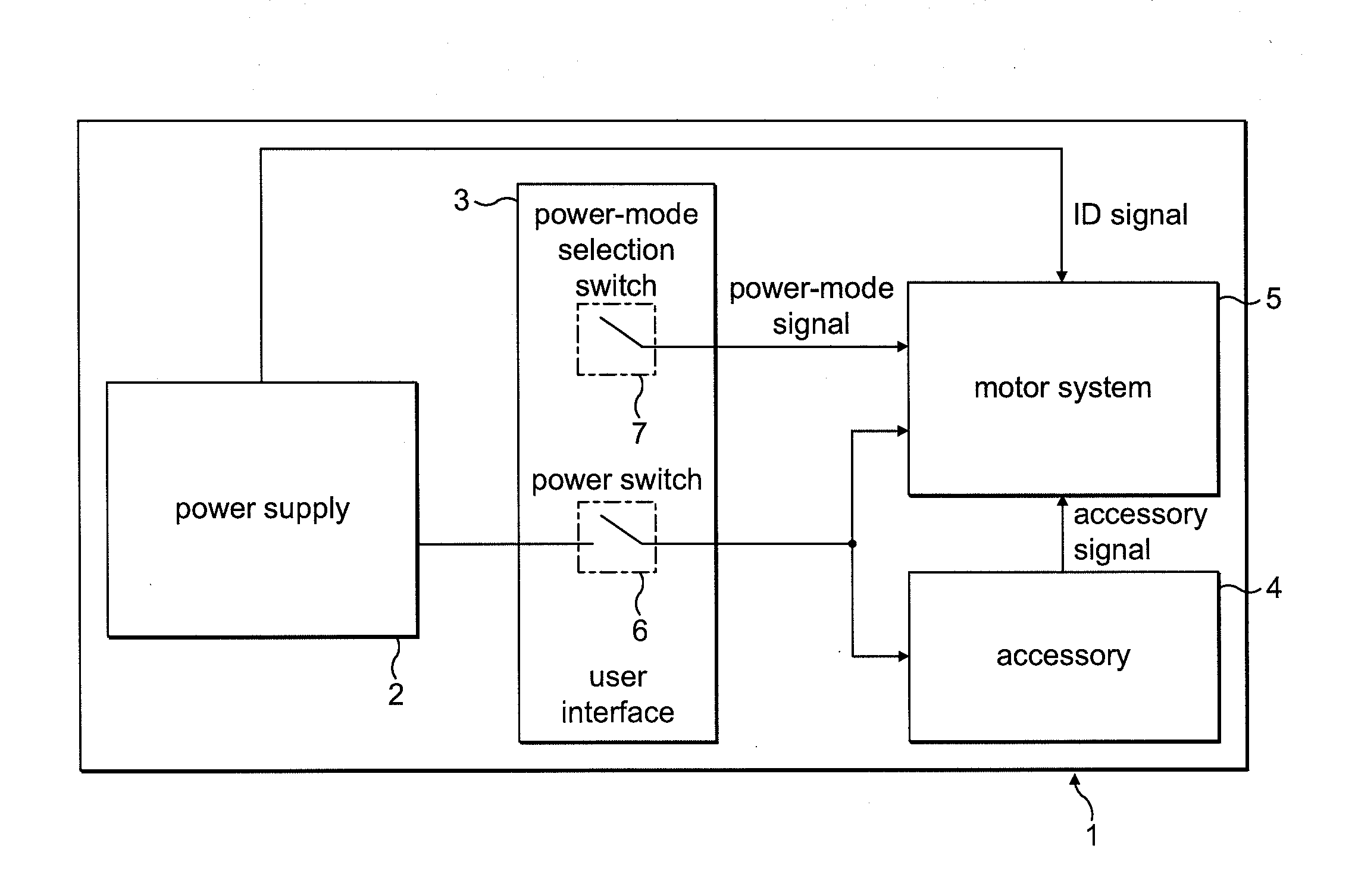
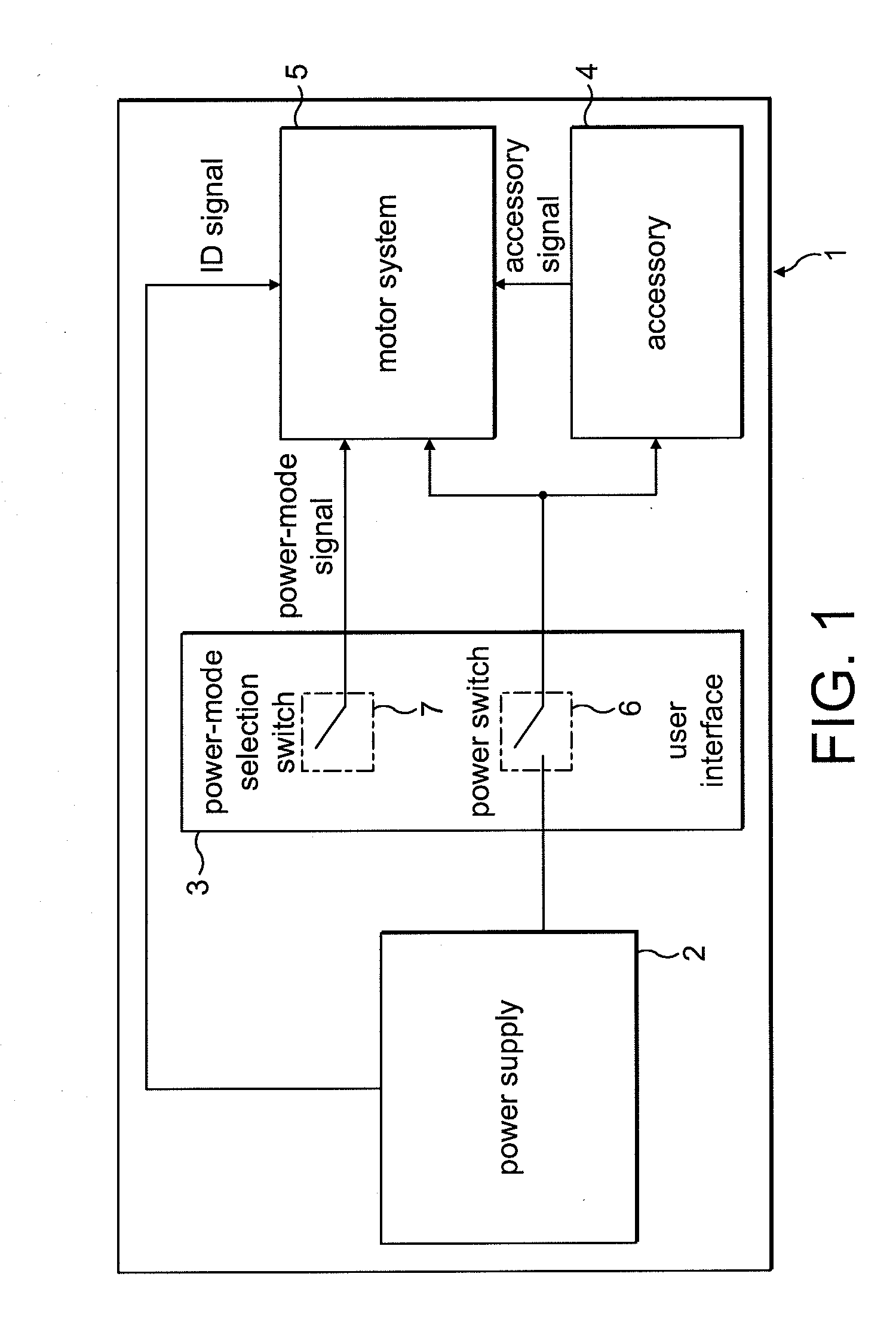
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS20100253257A1Reduce the impactLimited powerMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersSignal selectionControl system
A method of controlling an electric machine, the method comprising storing a plurality of power maps, each power map comprising control values for driving the electric machine at different power, and selecting a power map in response to an input signal. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
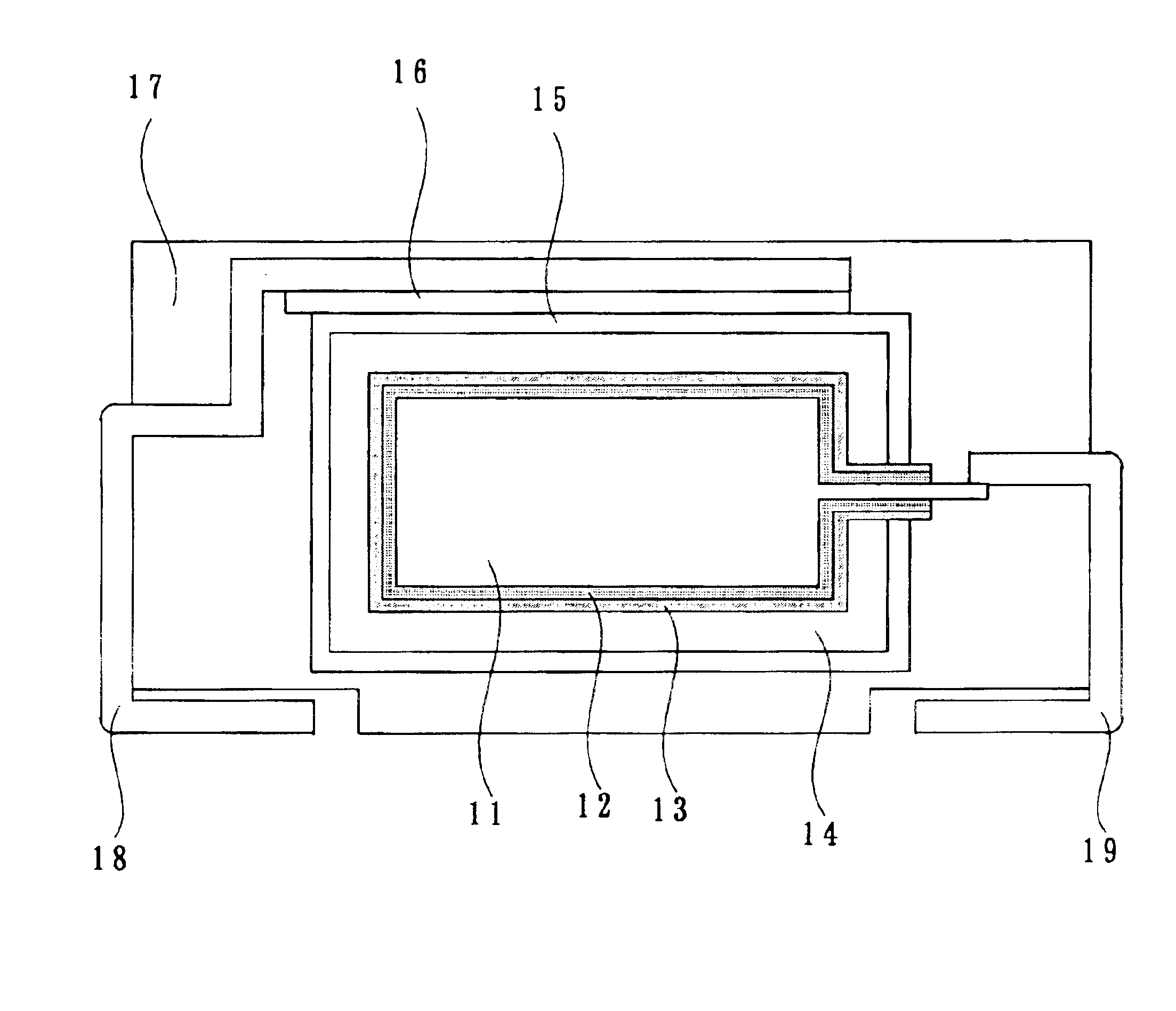
Electrolytic capacitor and a fabrication method therefor
InactiveUS6876083B2Avoid excessive leakage currentAvoid excessive currentTransistorSolid electrolytic capacitorsElectrolytic capacitorNiobium alloy
An electrolytic capacitor including one type of electrode selected from a group consisting of an electrode of at least one type of alloy selected from a group consisting of niobium alloy, titanium alloy, and tungsten alloy, an electrode of mixed sinter of niobium and aluminum, or a fluorine-doped electrode of niobium or niobium alloy and on a surface of each electrode a dielectric layer is formed by anodizing the electrode.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Photolithographically-patterned variable capacitor structures and method of making
InactiveUS6922327B2Speed and easeEliminate needAnti-noise capacitorsMechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitanceDielectric layer
A new type of high-Q variable capacitor includes a substrate, a first electrically conductive layer fixed to the substrate, a dielectric layer fixed to a portion of the electrically conductive layer, and a second electrically conductive layer having an anchor portion and a free portion. The anchor portion is fixed to the dielectric layer and the free portion is initially fixed to the dielectric layer, but is released from the dielectric layer to become separated from the dielectric layer, and wherein an inherent stress profile in the second electrically conductive layer biases the free portion away from the dielectric layer. When a bias voltage is applied between the first electrically conductive layer and the second electrically conductive layer, electrostatic forces in the free portion bend the free portion towards the first electrically conductive layer, thereby increasing the capacitance of the capacitor.
Owner:XEROX CORP
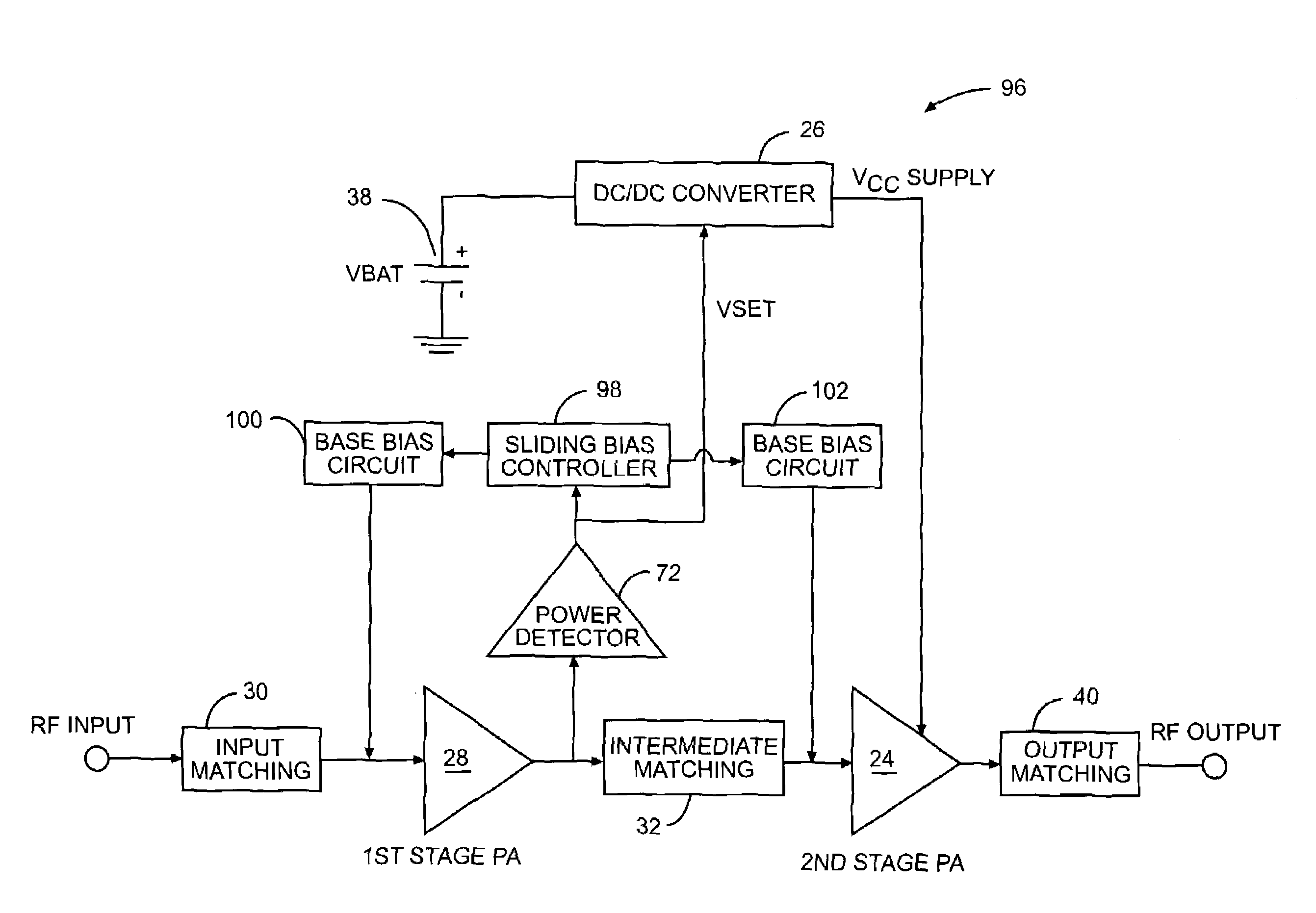
Sliding bias controller for use with radio frequency power amplifiers
ActiveUS7315211B1Reducing quiescent currentImprove power amplifier efficiencyGain controlRF amplifierAudio power amplifierControl signal
A two stage power amplifier circuit that employs both a DC to DC converter and sliding bias controller to improve power amplifier efficiency. The control signal that is generated by the power detector circuit to control the input voltage to the DC to DC converter is also used to provide the reference voltage that controls the sliding bias controller. The sliding bias controller reduces the quiescent current of the power amplifiers by reducing the bias currents, and thus the DC voltage at lower power output levels driving the power amplifiers. This causes the power amplifiers to operate at or near higher efficiency Class B operation at lower power output levels. As the power level increases, the sliding bias controller reduces its control on the bias currents so that the power amplifier can be driven at necessary higher power output levels.
Owner:QORVO US INC +1
Photolithographically-patterned out-of-plane coil structures and method of making
InactiveUS6856225B1Reduce speedEliminate needSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsMicro structureTransformer
An out-of-plane micro-structure which can be used for on-chip integration of high-Q inductors and transformers places the magnetic field direction parallel to the substrate plane without requiring high aspect ratio processing. The photolithographically patterned coil structure includes an elastic member having an intrinsic stress profile. The intrinsic stress profile biases a free portion away from the substrate forming a loop winding. An anchor portion remains fixed to the substrate. The free portion end becomes a second anchor portion which may be connected to the substrate via soldering or plating. A series of individual coil structures can be joined via their anchor portions to form inductors and transformers.
Owner:XEROX CORP
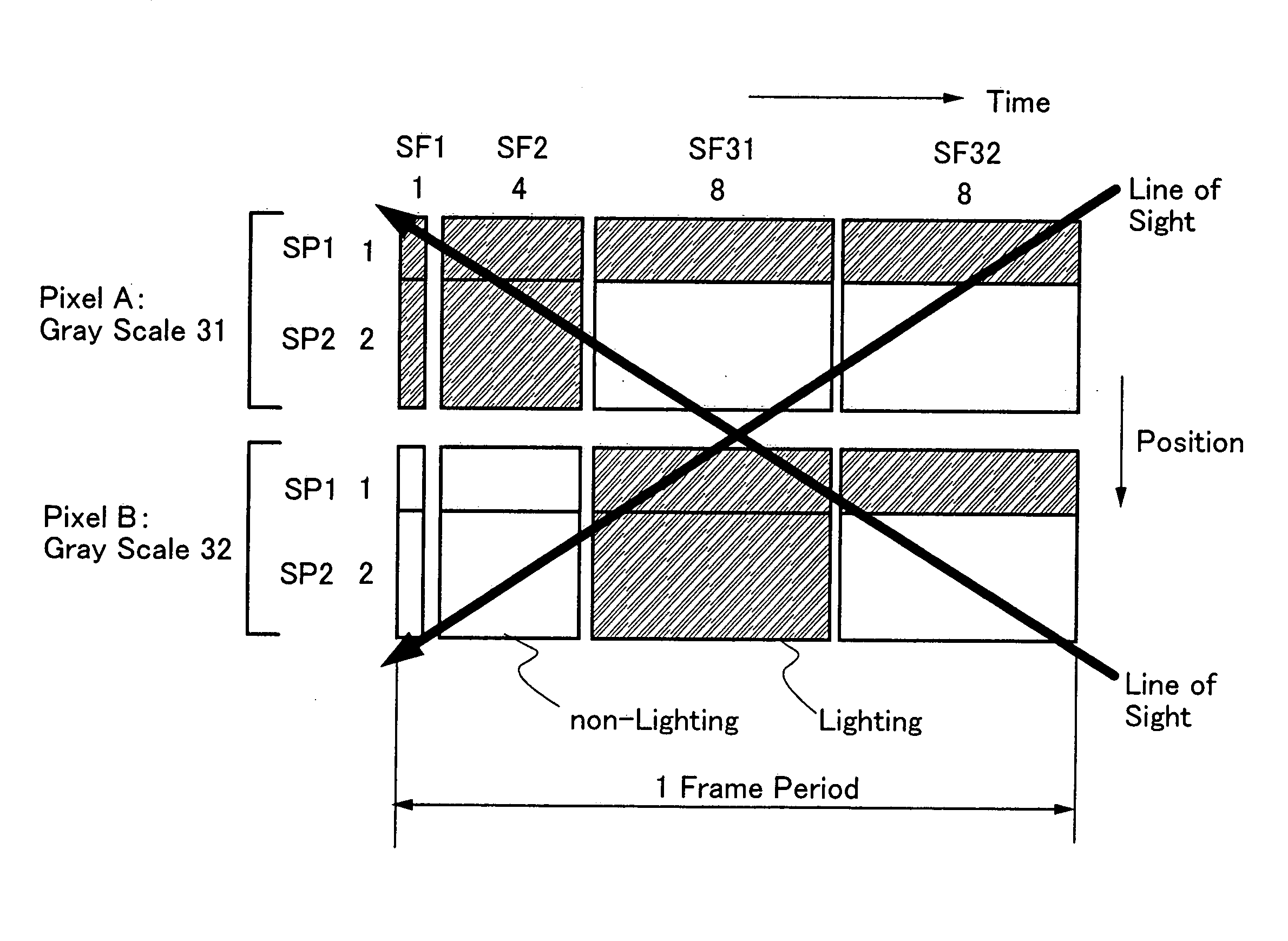
Display device, driving method of display device, and electronic appliance
InactiveUS20070279344A1Clear imagingImprove display qualitySolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceComputer science
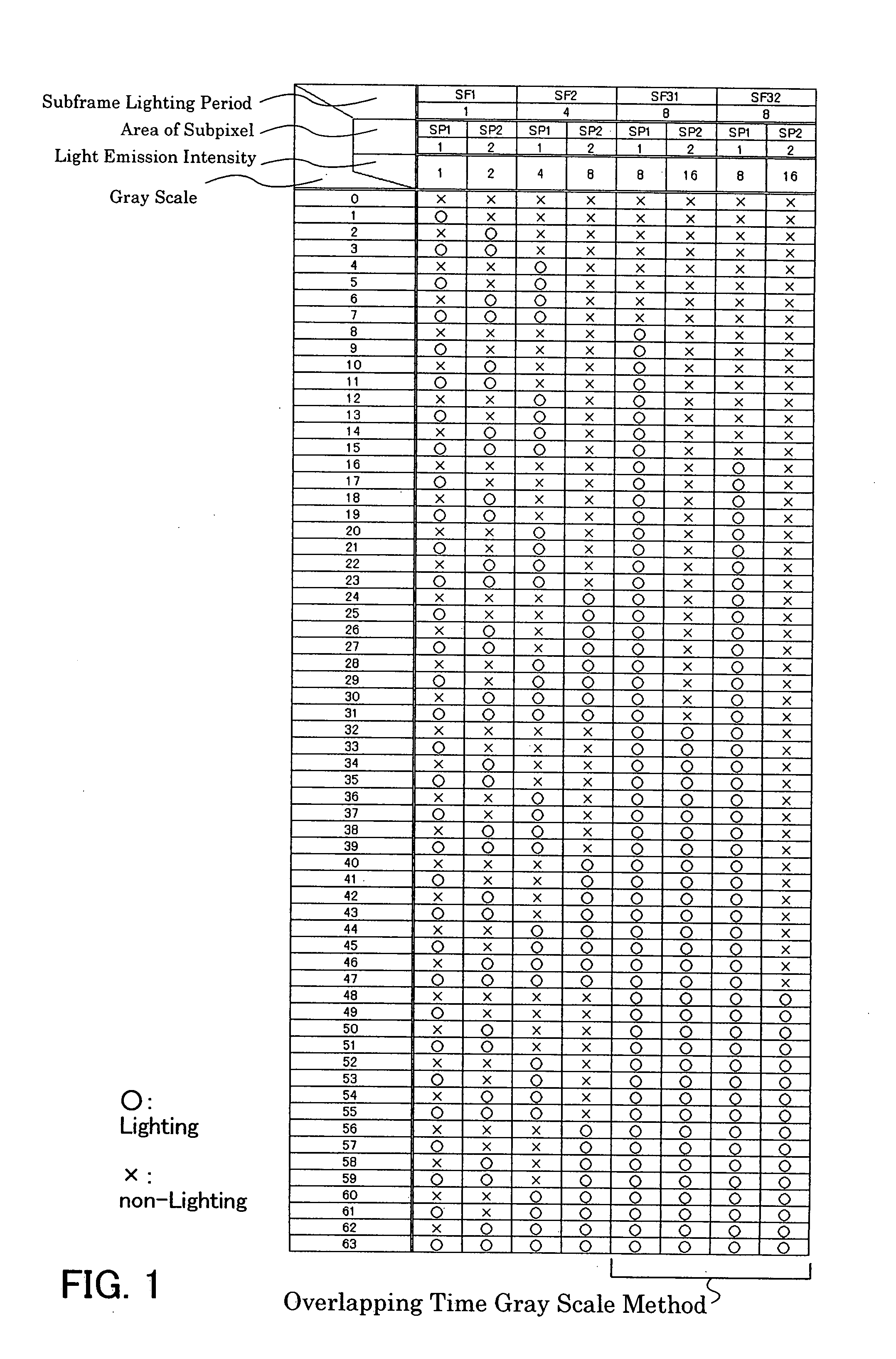
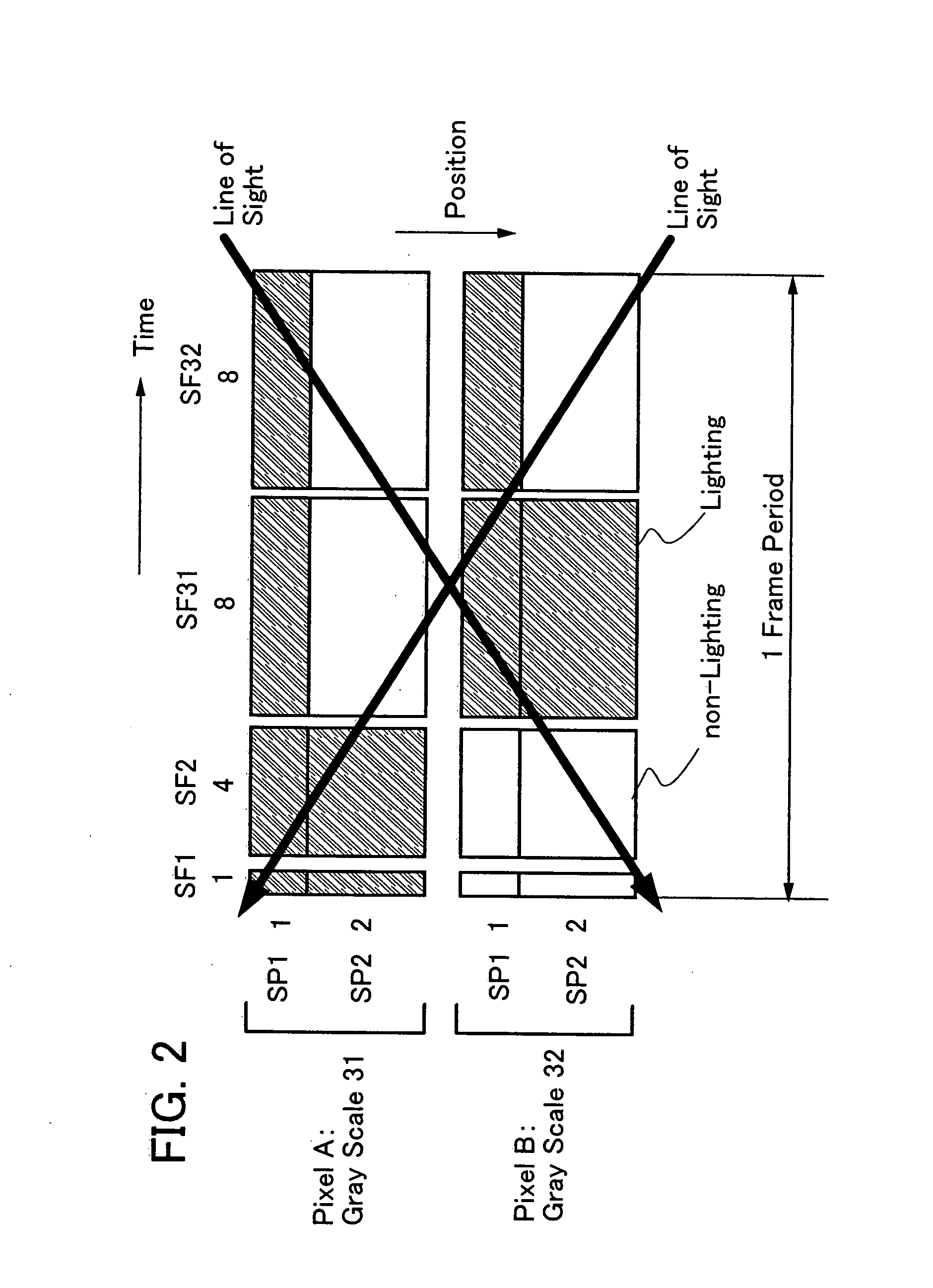
An object is to reduce a pseudo contour occurring in time gray scale method display. One pixel is divided into m subpixels (m is an integer of m≧2), and the area of the (s+1)th subpixel (1≦s≦m−1) is twice the area of the s-th subpixel. Further, one frame is divided into n subframes (n is an integer of n≧2), and a lighting period of the (p+1)th subframe (1≦p≦n−1) is 2m times longer than a lighting period of a p-th subframe. Then, at least one subframe of the n subframes is divided into a plurality of subpixels each having a lighting period shorter than that of the subframe so that the n subframes are increased to t subframes (t>n). In at least one subframe of the t subframes, lighting periods of the subframes in a lighting state are sequentially added by the m subpixels, so that a gray scale of the pixel is expressed. (174 words)
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Apparatus, method and program to optimize battery life in a wireless device
ActiveUS7003331B2Shortened battery lifeExtend battery lifePower managementEnergy efficient ICTSymbol rateMobile device
The battery life of batteries of a mobile device operating in a wireless network is optimized by dynamically changing symbol rates and bits per symbol and selecting one for communicating based upon the source providing power to the mobile device.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
Nitride semiconductor device and power conversion apparatus including the same
InactiveUS20090206371A1Avoid excessive leakage currentImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWide bandNitride semiconductors
A nitride semiconductor device includes a first, a second, and a third nitride semiconductor layers that are laminated on a foundation semiconductor layer in stated order, the third nitride semiconductor layer having a wider band gap as compared with the second nitride semiconductor layer, a recess area that is dug from an upper surface of the third nitride semiconductor layer down to a middle of the second nitride semiconductor layer, a first electrode and a second electrode respectively formed on one side and the other side of the recess area so as to be in contact with one of the third nitride semiconductor layer and the second nitride semiconductor layer, a dielectric film formed on the third nitride semiconductor layer and an inner surface of the recess area, and a control electrode formed on the dielectric film in the recess area.
Owner:SHARP KK
Current limiting parallel battery charging system to enable plug-in or solar power to supplement regenerative braking in hybrid or electric vehicle
InactiveUS7872443B2Battery system is simplifiedAvoid excessive currentHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsSolar powerElectric vehicle
To provide additional charge storage for an electric vehicle, an additional battery (100) is connected in parallel with a regenerative braking direct charged battery (22) through a current limiting circuit (104 or 120). The additional battery (100) is charged by an external charger such as a plug-in charger or a solar panel that supply minimal current to prevent generation of battery heat. Current flows from the additional battery (100) to the regenerative braking charged batteries (22) so that both batteries can be charged. However, when excessive charge is drawn to drive the vehicle electric motor (20), the current limiter circuit (104 or 120) serves to prevent the discharge of additional battery (100) from creating excessive heat in the additional battery (100). Further, when regenerative braking is applied the current limiter circuit (120), or a diode buffer (102) in combination with current limiter (104), serves to prevent charging from creating excessive heat in the additional battery (100) and eliminates the need for a cooling structure in the additional battery (100).
Owner:WARD THOMAS A
Current clamping parallel battery charging system to supplement regenerative braking in electric vehicle
InactiveUS20110089904A1Simple processBattery system is simplifiedCircuit monitoring/indicationCharging stationsElectrical batteryEngineering
To provide additional charge storage for an electric vehicle, an additional battery (100) is connected in parallel with a regenerative braking direct charged battery (22) through a current limiting or clamping circuit (104 or 120). The additional battery (100) is charged by an external charger such as a plug-in charger or a solar panel that supply minimal current to prevent generation of battery heat. Current flows from the additional battery (100) to the regenerative braking charged batteries (22) so that both batteries can be charged. However, when excessive charge is drawn to drive the vehicle electric motor (20), the current limiting or clamping circuit (104 or 120) serves to prevent the discharge of additional battery (100) from creating excessive heat in the additional battery (100). Further, when regenerative braking is applied the current clamping circuit (120), or a diode buffer (102) in combination with current limiter (104), serves to prevent charging from creating excessive heat in the additional battery (100) and eliminates the need for a cooling structure in the additional battery (100).
Owner:WARD THOMAS ALLAN
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS20100251512A1Less torqueSmoother currentSynchronous motors startersSingle motor speed/torque controlZero crossingConductor Coil
A method of controlling an electric machine that includes exciting a winding of the electric machine in synchrony with zero-crossings of back emf when operating over a first speed range. The method then includes exciting the winding in advance of the zero-crossings by a fixed period of time when operating over a second speed range, and exciting the winding in advance of the zero-crossings by a period of time that varies with speed when operating over a third speed range. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
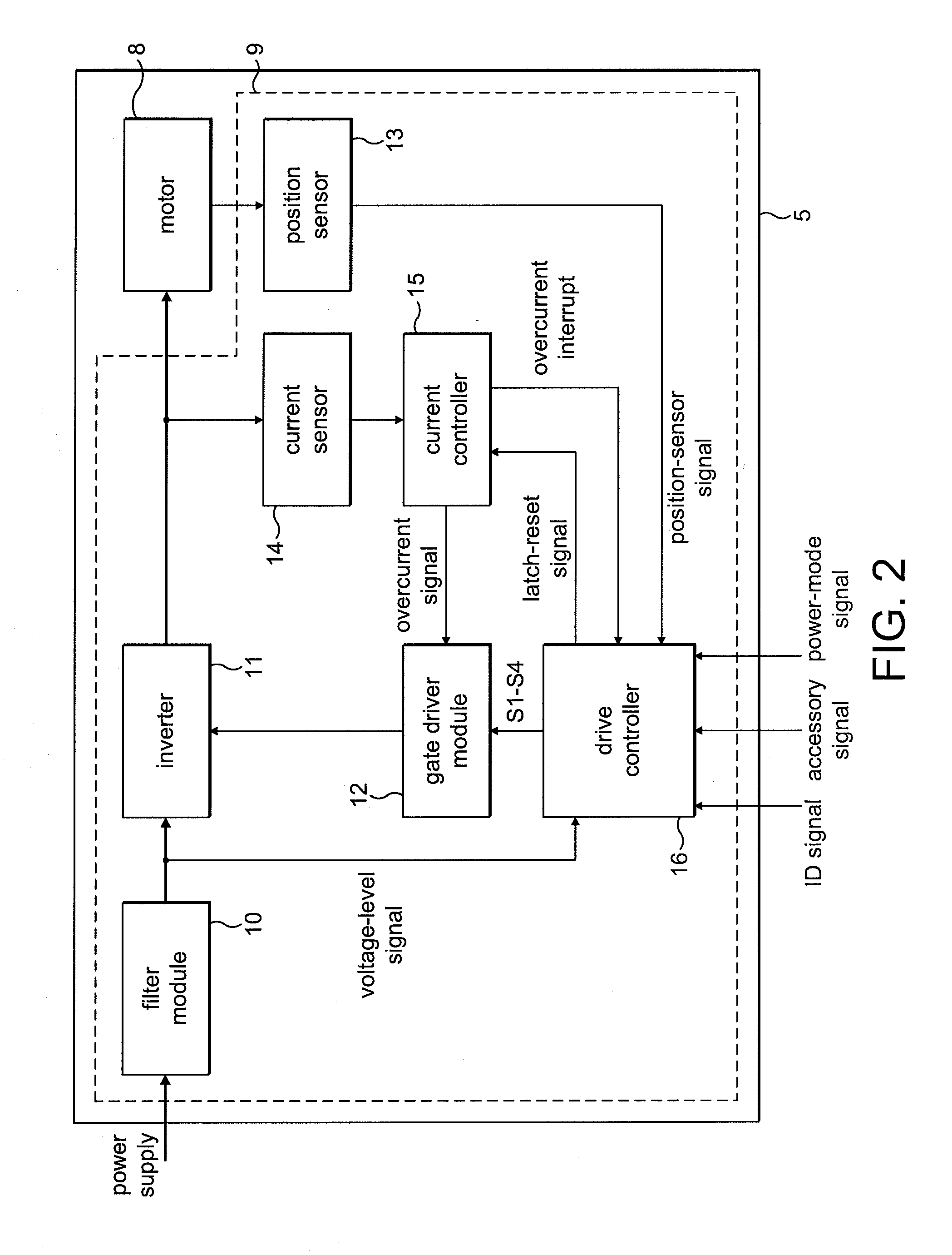
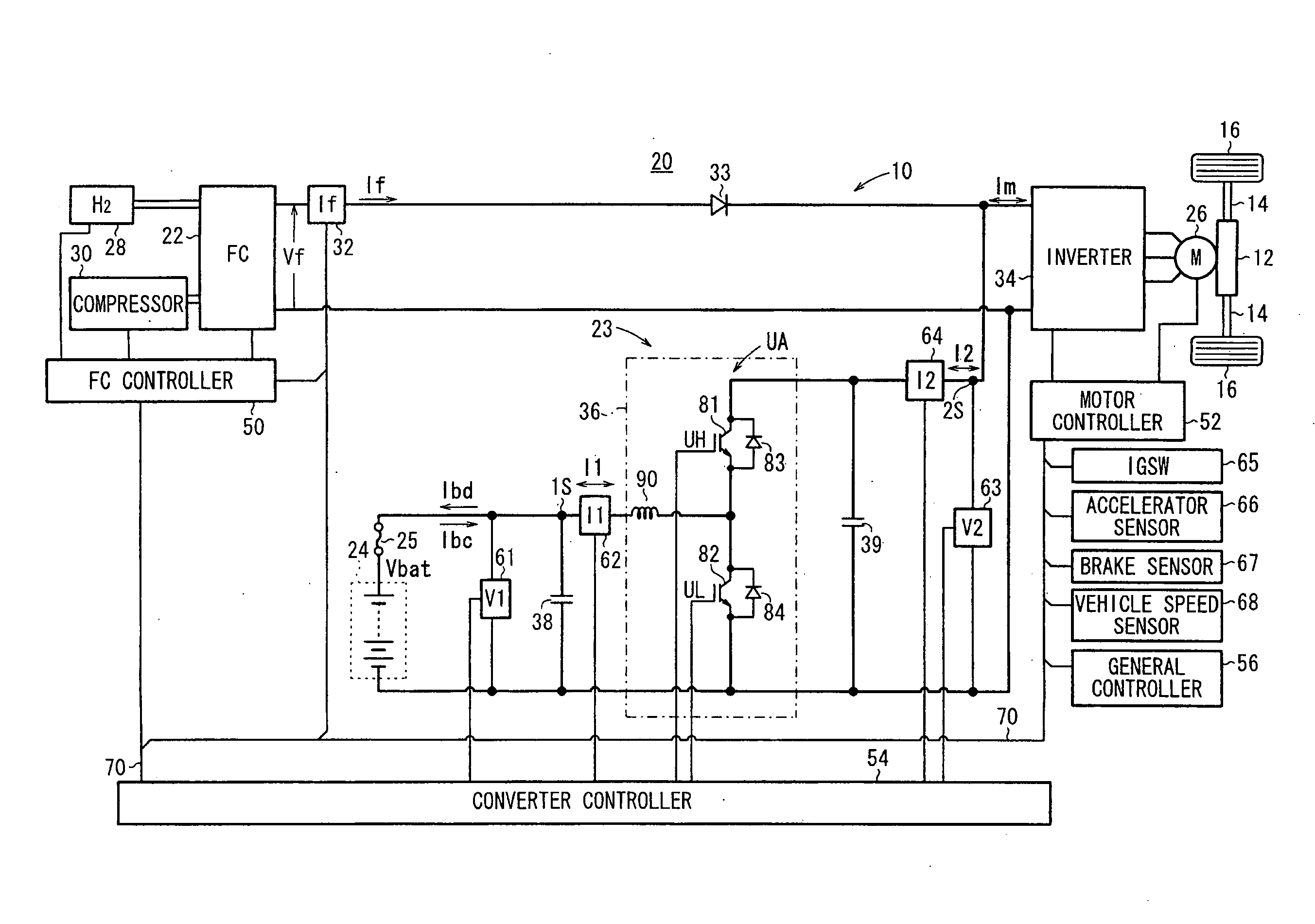
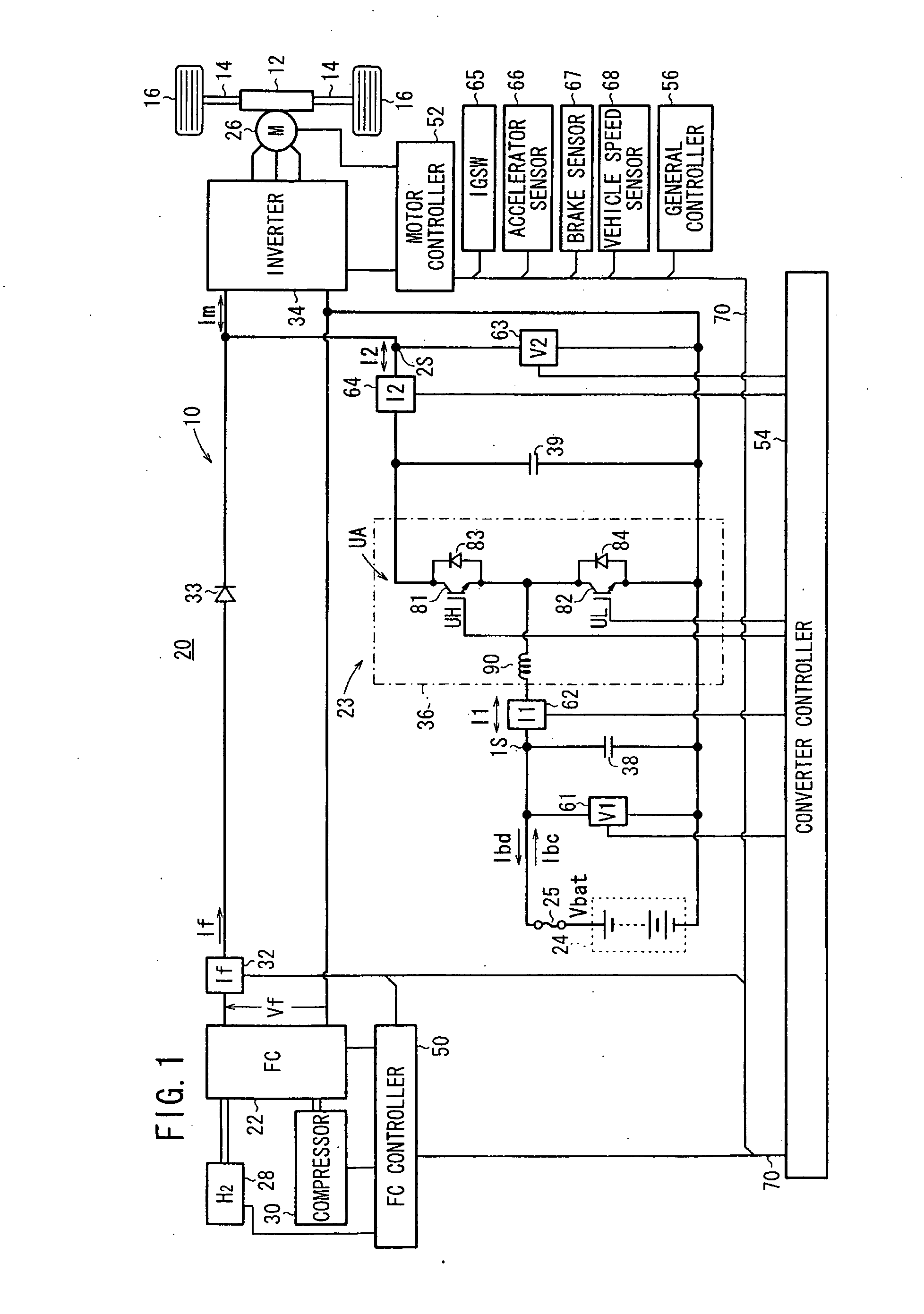
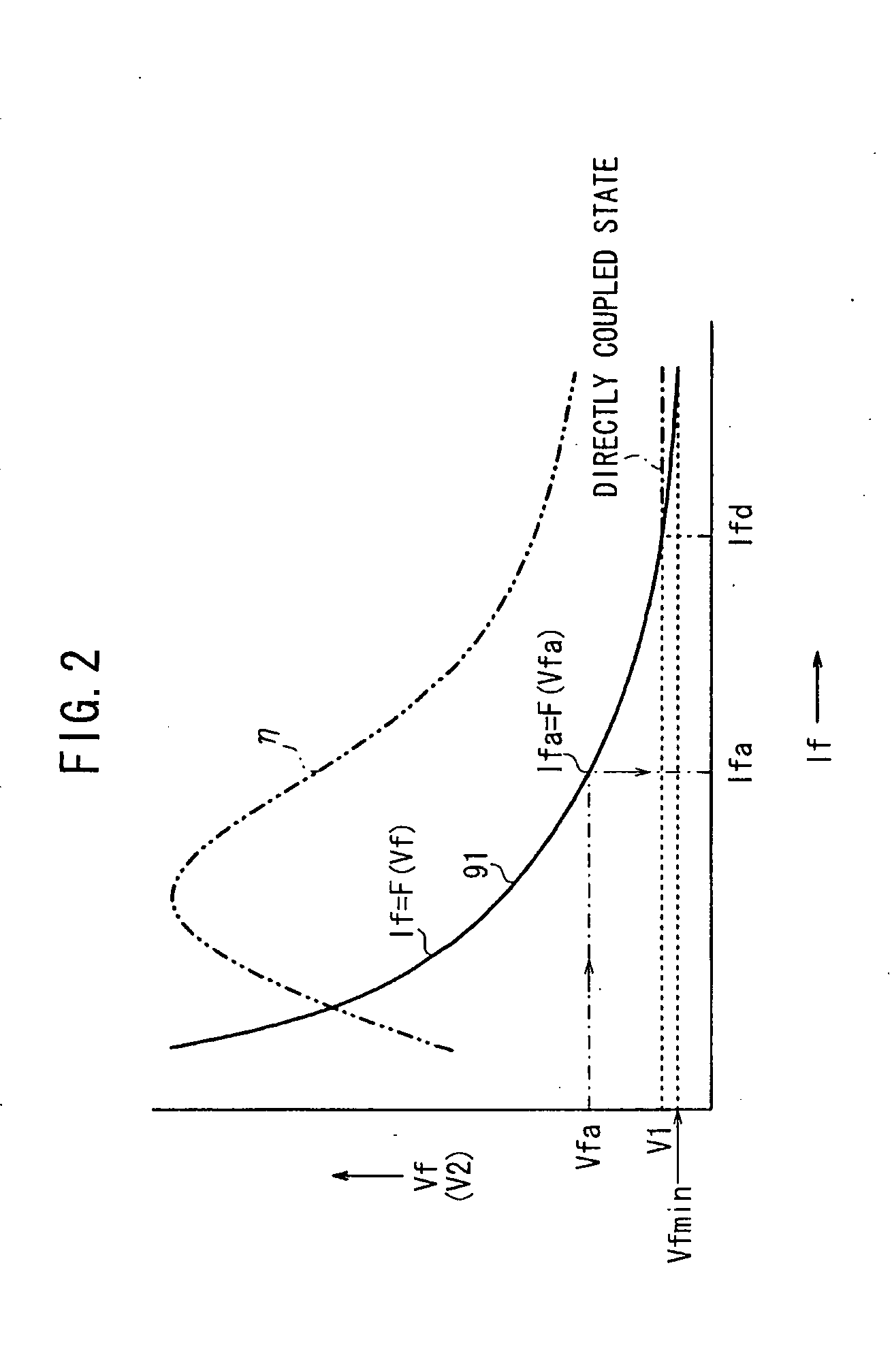
Method of protecting electricity storage device in hybrid DC power supply system
ActiveUS20090230917A1Excessive currentAvoid excessive currentConverter typesSecondary cells charging/dischargingDrive motorElectricity
A method protects a battery in a fuel cell vehicle, in which an inverter-driven motor is supplied with electric power from the battery and a fuel cell. If a battery voltage of the battery falls outside of a prescribed range, a primary current and a secondary current that flow through the DC / DC converter, or currents in branch paths that correspond to the primary current and the secondary current, are reduced in order to limit a charging current flowing into the battery or a discharging current flowing from the battery.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
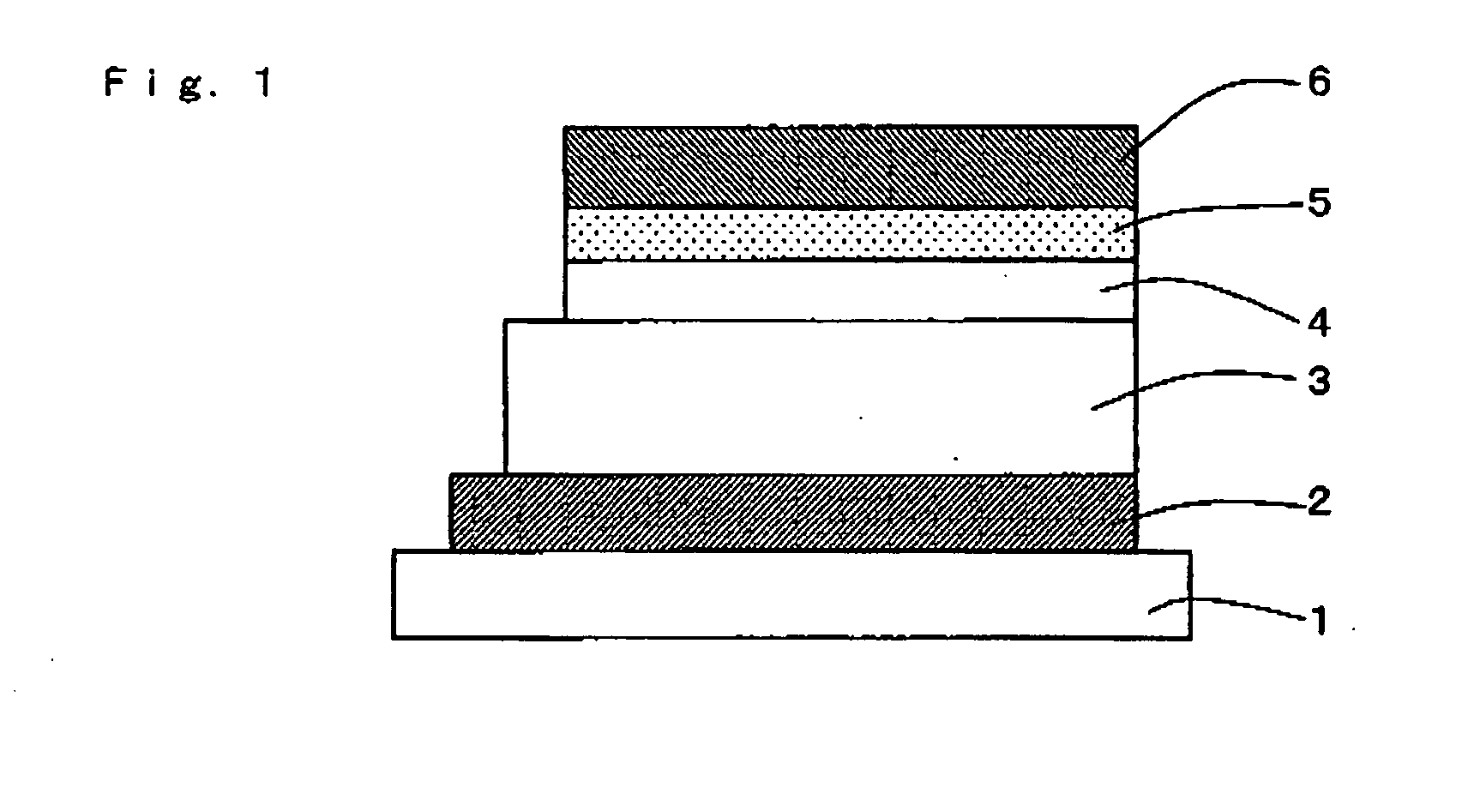
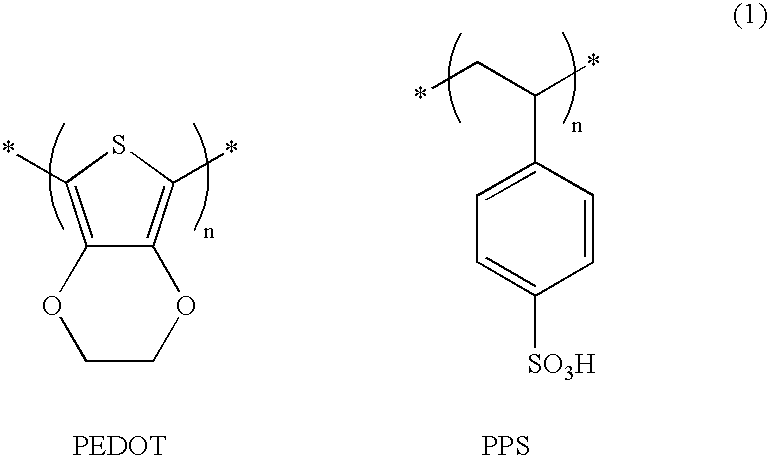
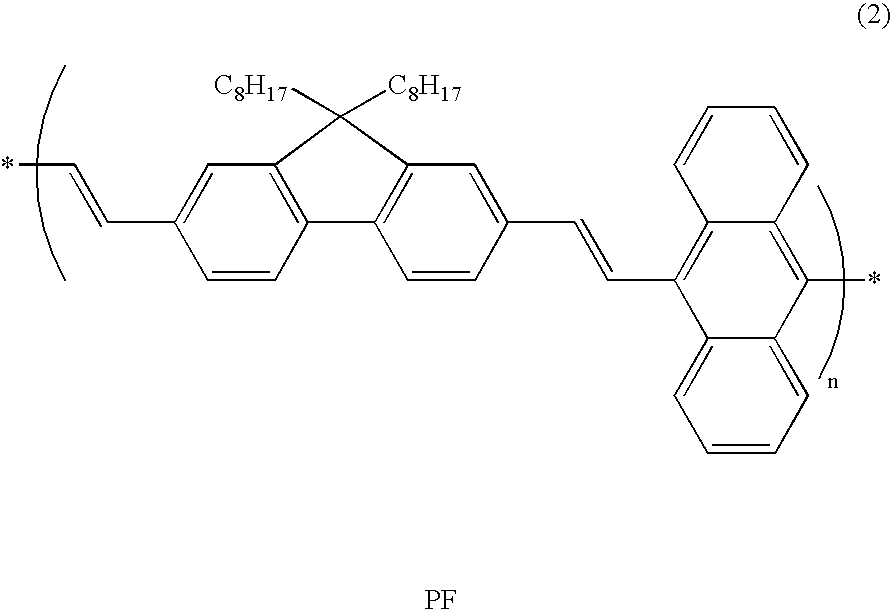
Organic electroluminescent element
InactiveUS20050007016A1Less in characteristic deteriorationImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSputteringOptical transparency
In an organic electro luminescent element, an organic layer and an electron injecting layer are inhibited from being oxidized, and alleviated in damage caused by the sputtering during manufacture. Thereby, an organic electroluminescent element that takes out light with high efficiency from a cathode of a top side and is capable of displaying a high quality image can be provided. An organic electroluminescent element according to the present invention includes at least a base material, an anode, an organic electroluminescent layer, a conductive protection layer having the optical transparency and a cathode having the optical transparency all of which are formed sequentially on the base material, wherein the conductive protection layer is made of a metal or a metal and a metal oxide thereof.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
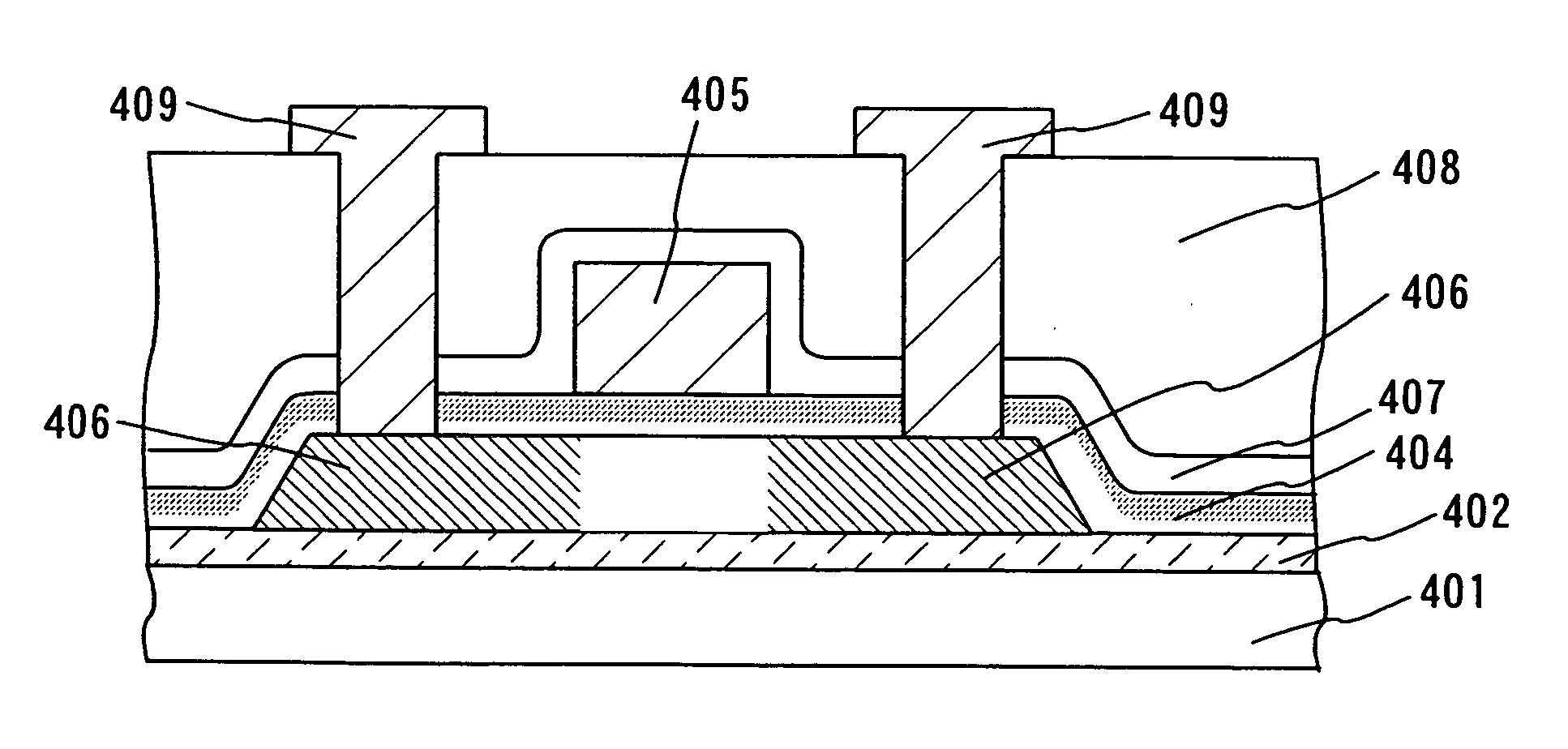
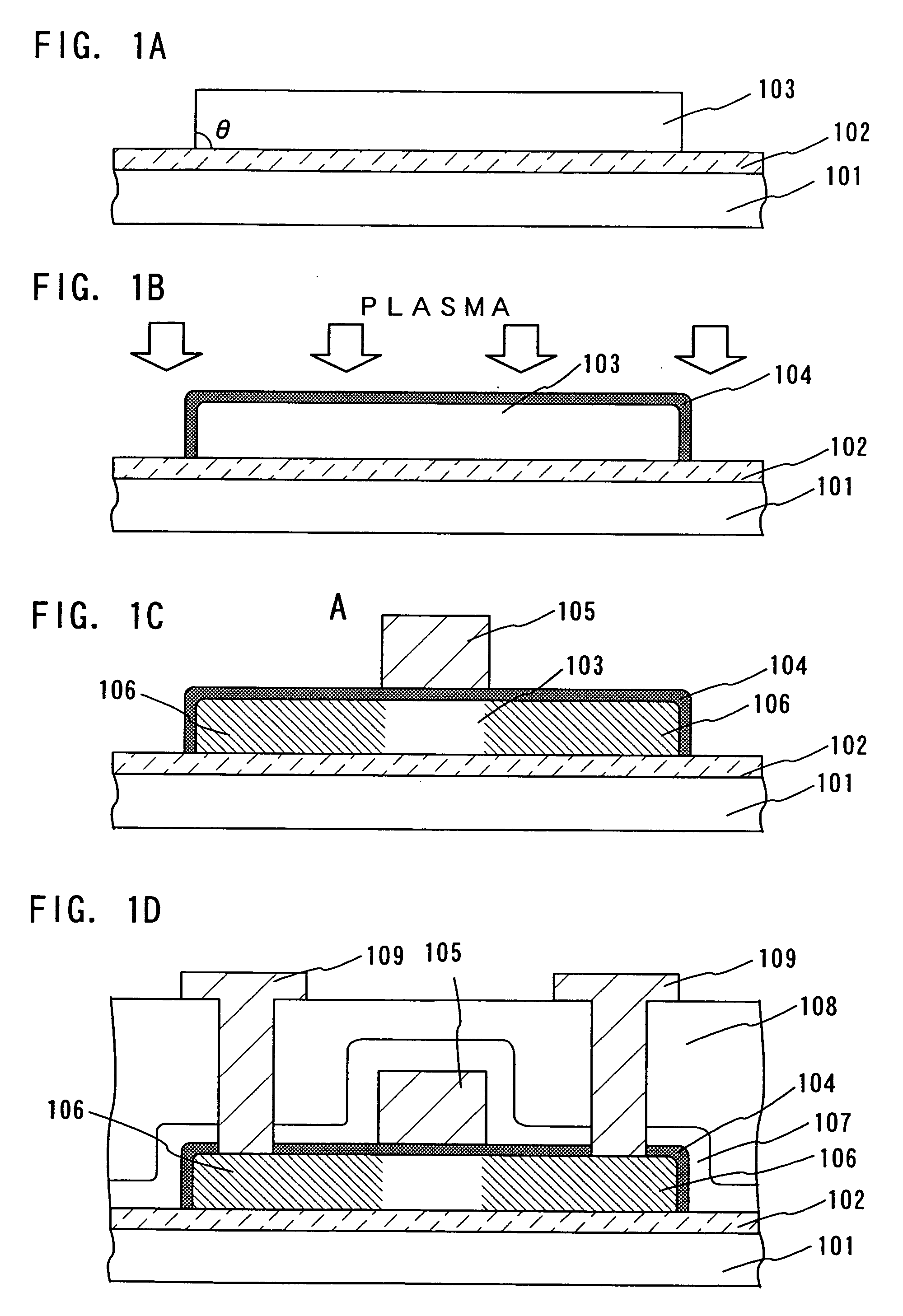
Manufacturing method of thin film transistor, display device using thin film transistor, and electronic device incorporating display device
ActiveUS20060246633A1Less leakage currentEasily removeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPlasma nitridationElectron temperature
In forming a thin film transistor, to form a film superior in quality to a film formed by a conventional CVD method and to form a film equal or superior in quality to a film formed by a thermal oxidation method at a temperature which does not affect a substrate. Plasma oxidation or plasma nitridation with a low electron temperature and a high electron density is performed to at least one of a glass substrate, a semiconductor film containing amorphous silicon formed into a predetermined pattern, a gate electrode and a wire pulled from the gate electrode, an insulating film to be a gate insulating film, and a protective film with a temperature of the glass substrate set at a temperature 100° C. or more lower than a strain point of the glass substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com