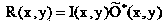Patents
Literature
85 results about "Inversion pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
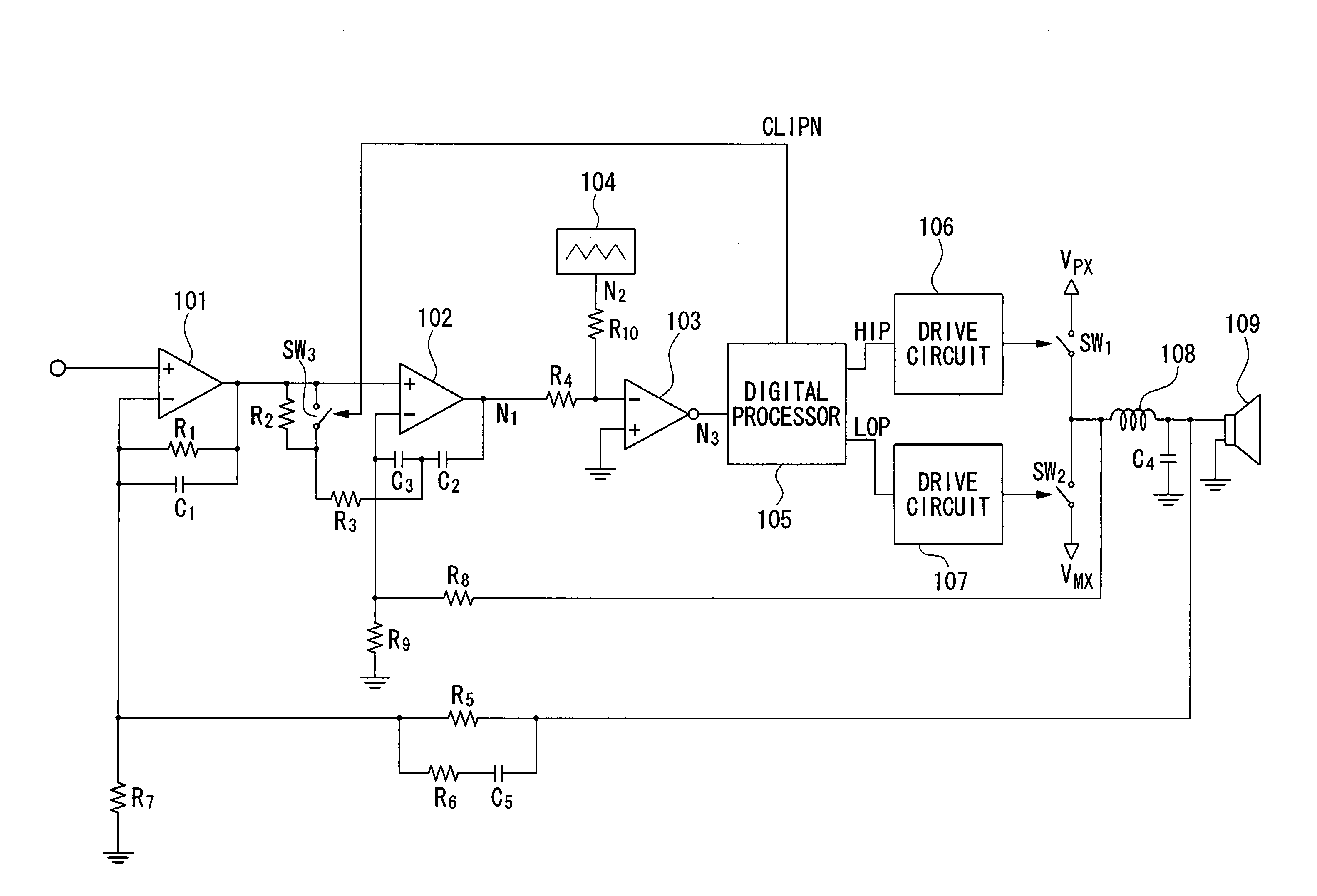
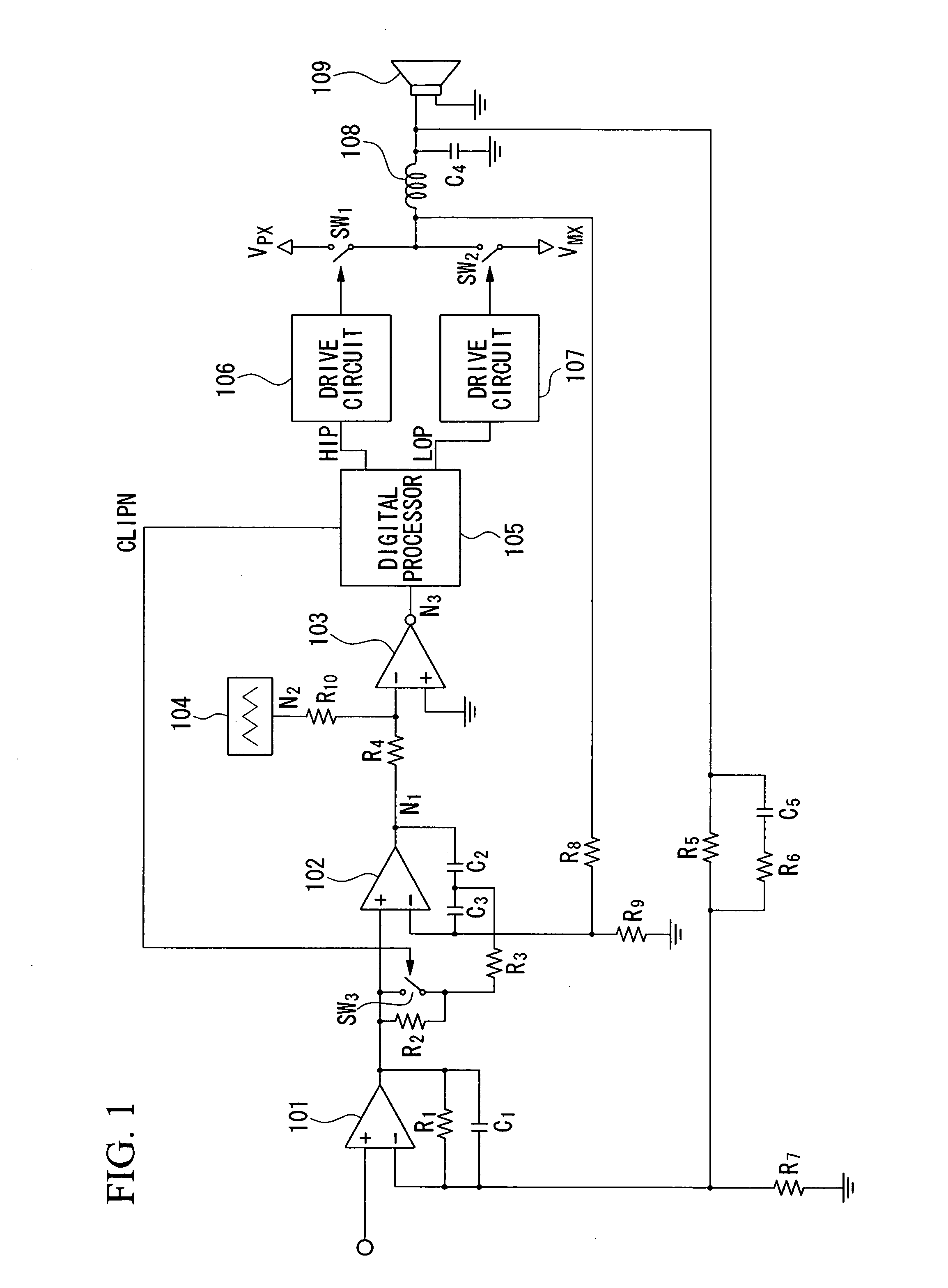
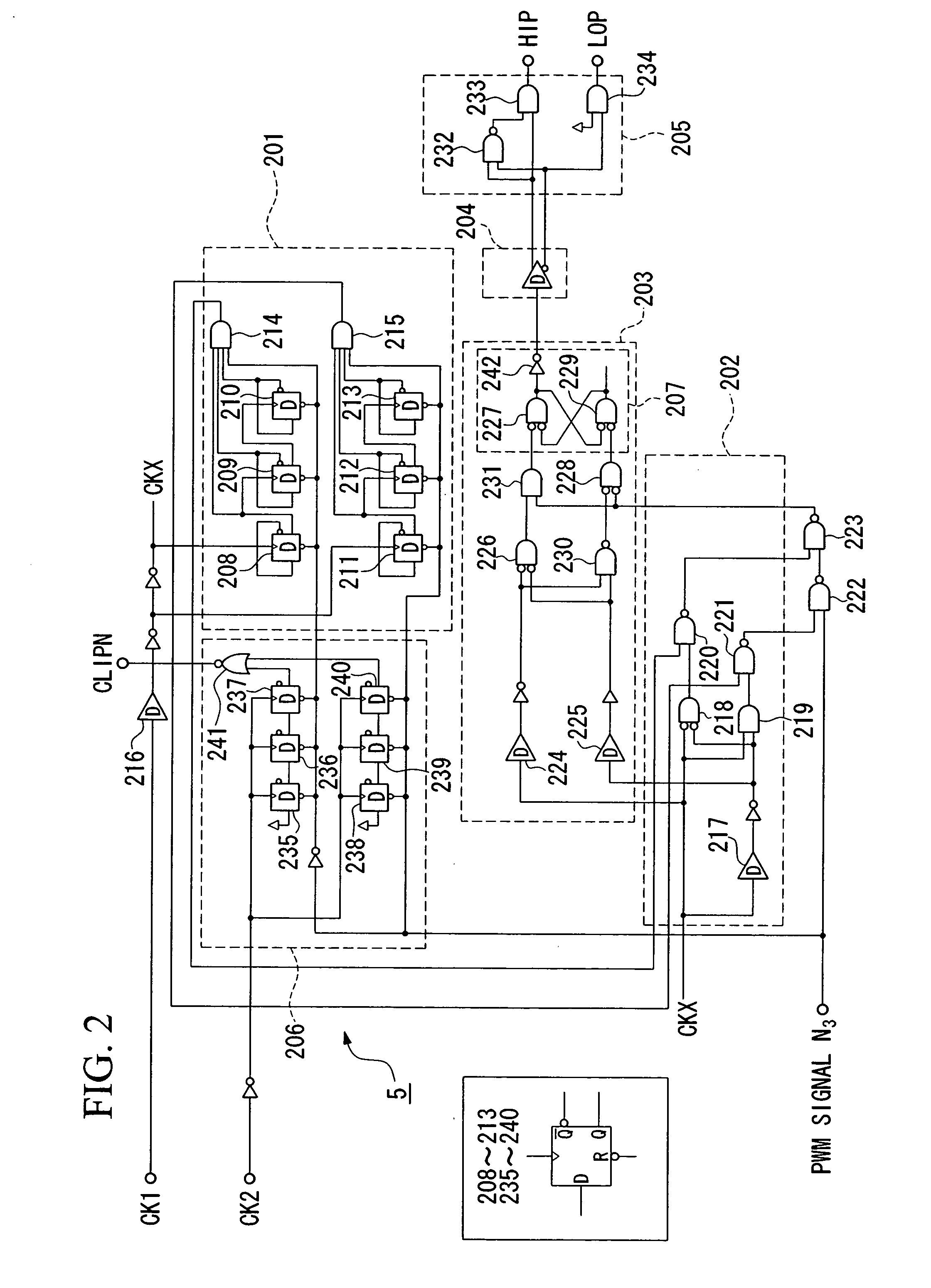
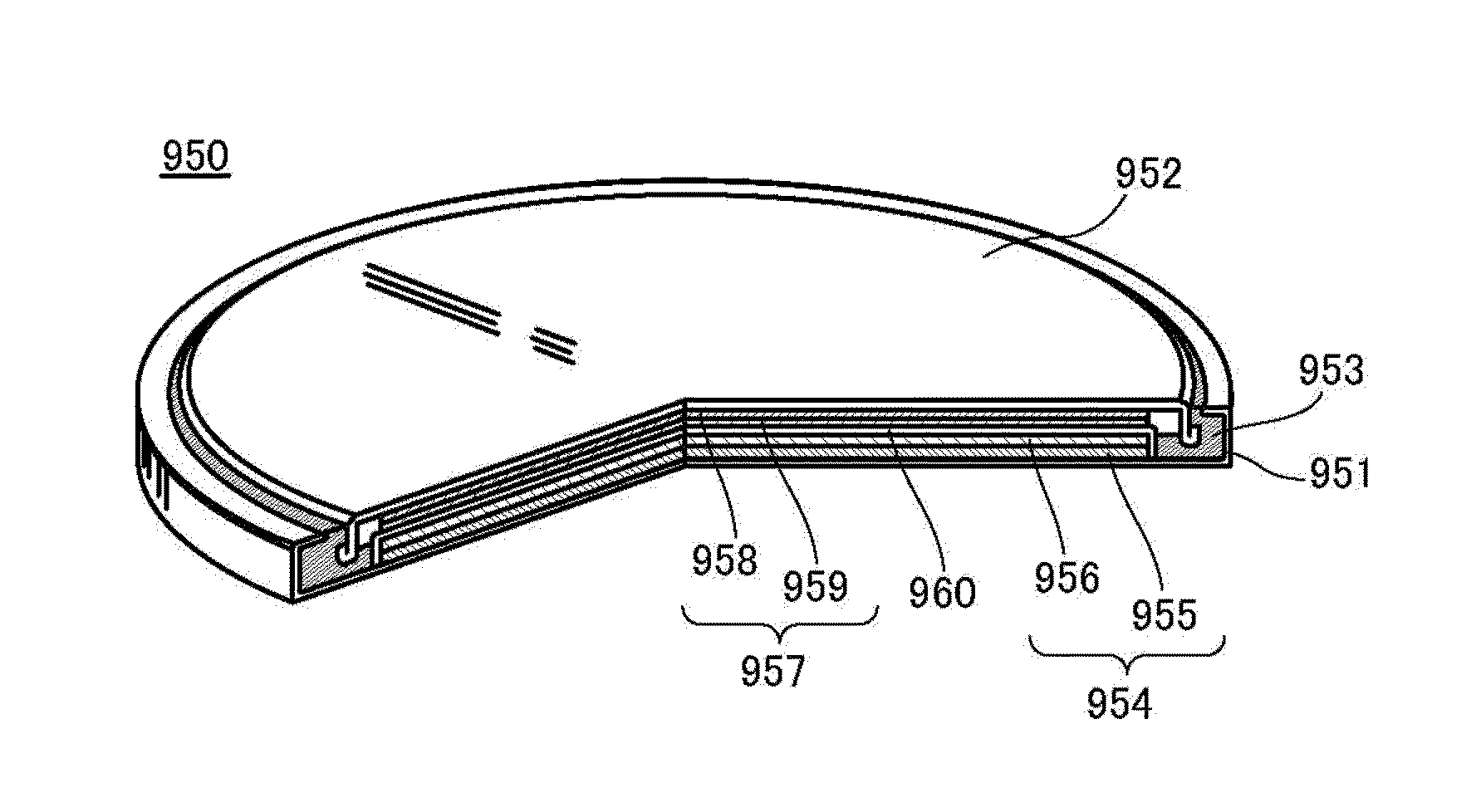
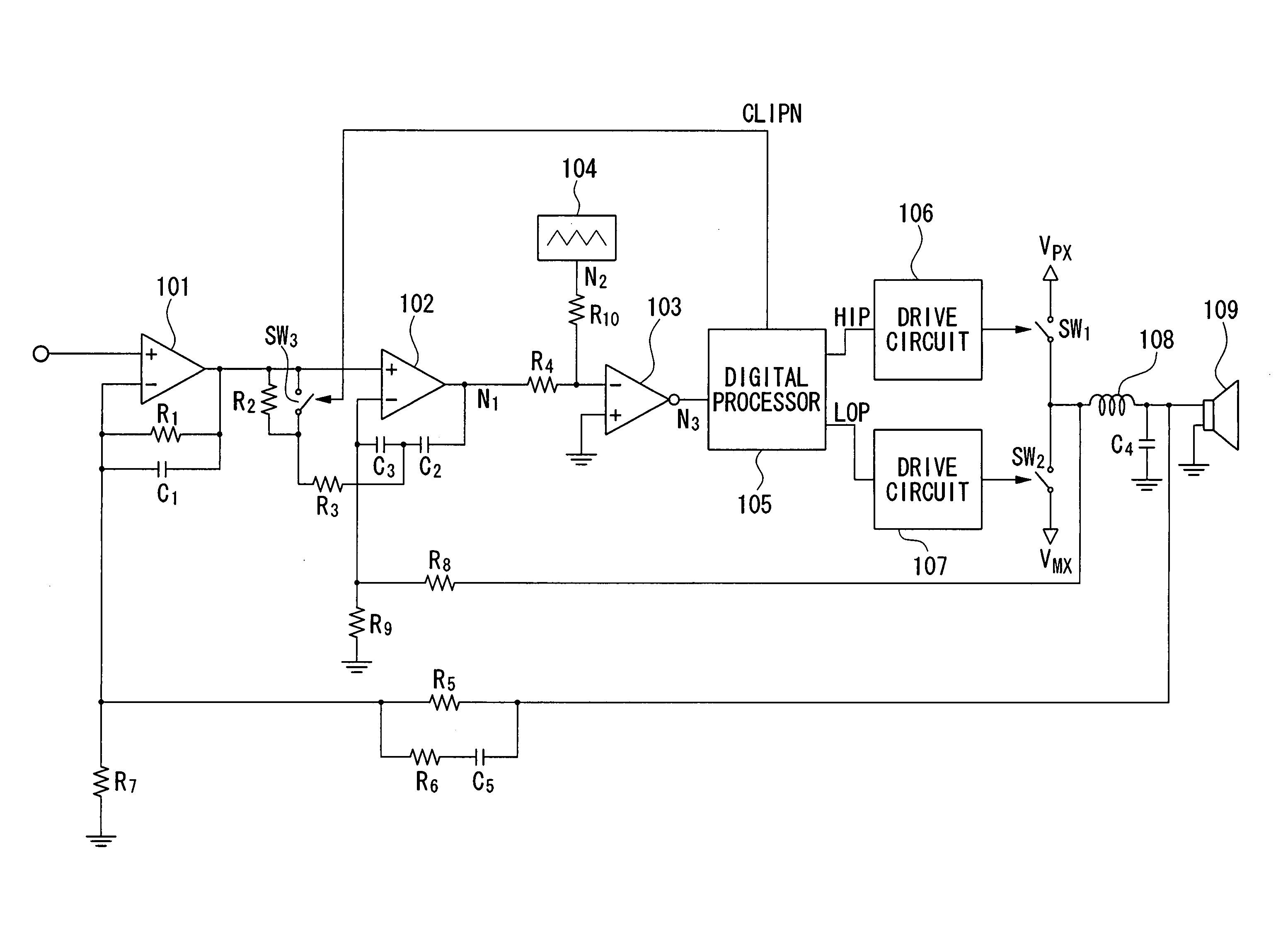
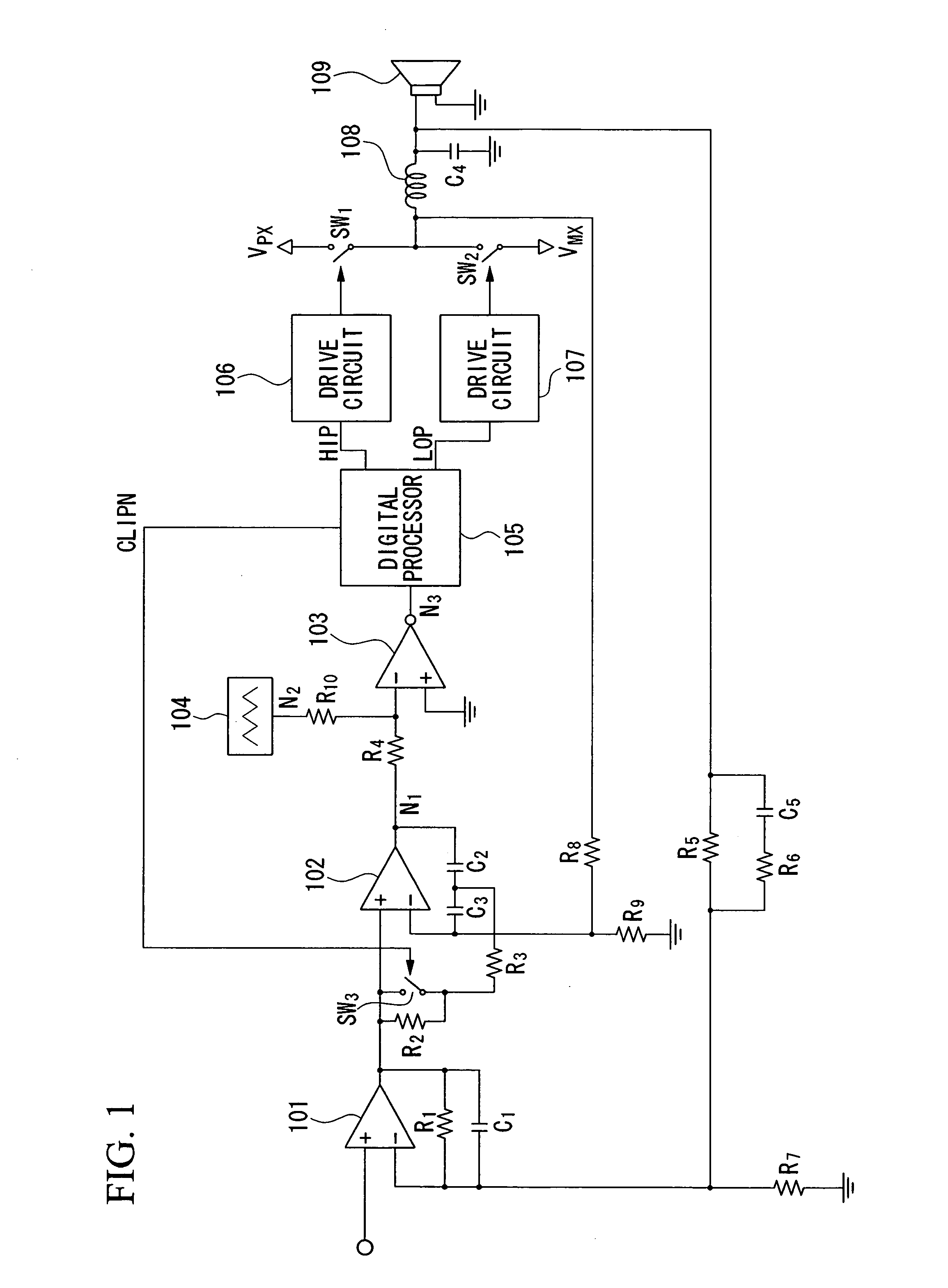
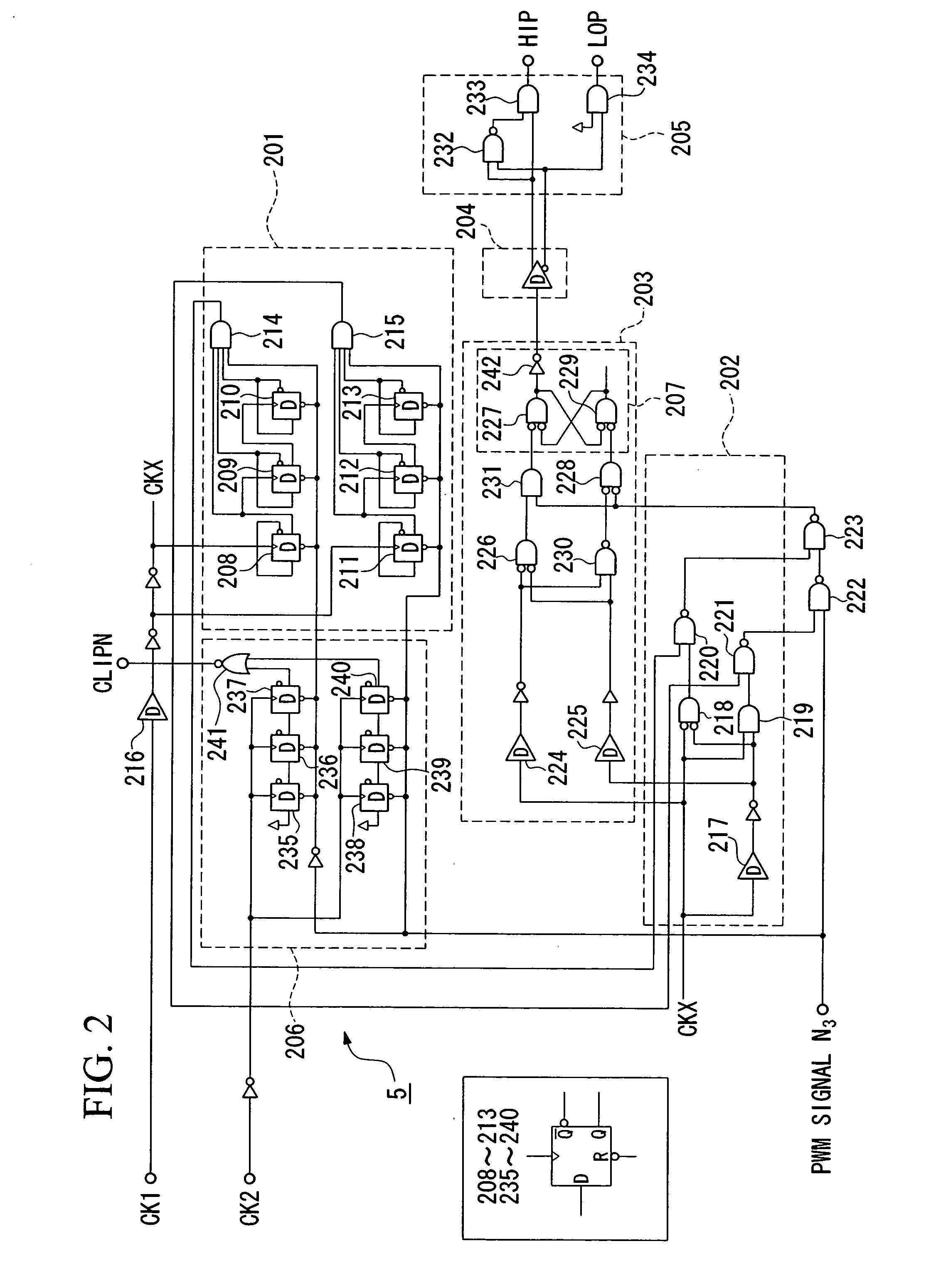
Pulse-width modulation amplifier and suppression of clipping therefor
ActiveUS20060008095A1Avoid excessive currentPower use efficiency decreaseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlLeading edgeAudio power amplifier
A pulse-width modulation (PWM) amplifier is adapted to a class-D amplifier in which an analog input signal is subjected to integration, pulse-width modulation, and switched amplification, wherein a glitch elimination circuit eliminates noise from a pulse-width modulated signal, from which a high pulse signal and a low pulse signal are isolated such that each pulse is delayed by a dead time at the leading-edge timing thereof. When both of them are simultaneously set to a high level, one of them is reduced in level. In response to the occurrence of clipping, an integration constant applied to an operational amplifier is automatically changed from a primary integration constant to a secondary integration constant. When the clipped state is sustained for a prescribed time, an inversion pulse is compulsorily introduced into the pulse-width modulated signal.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
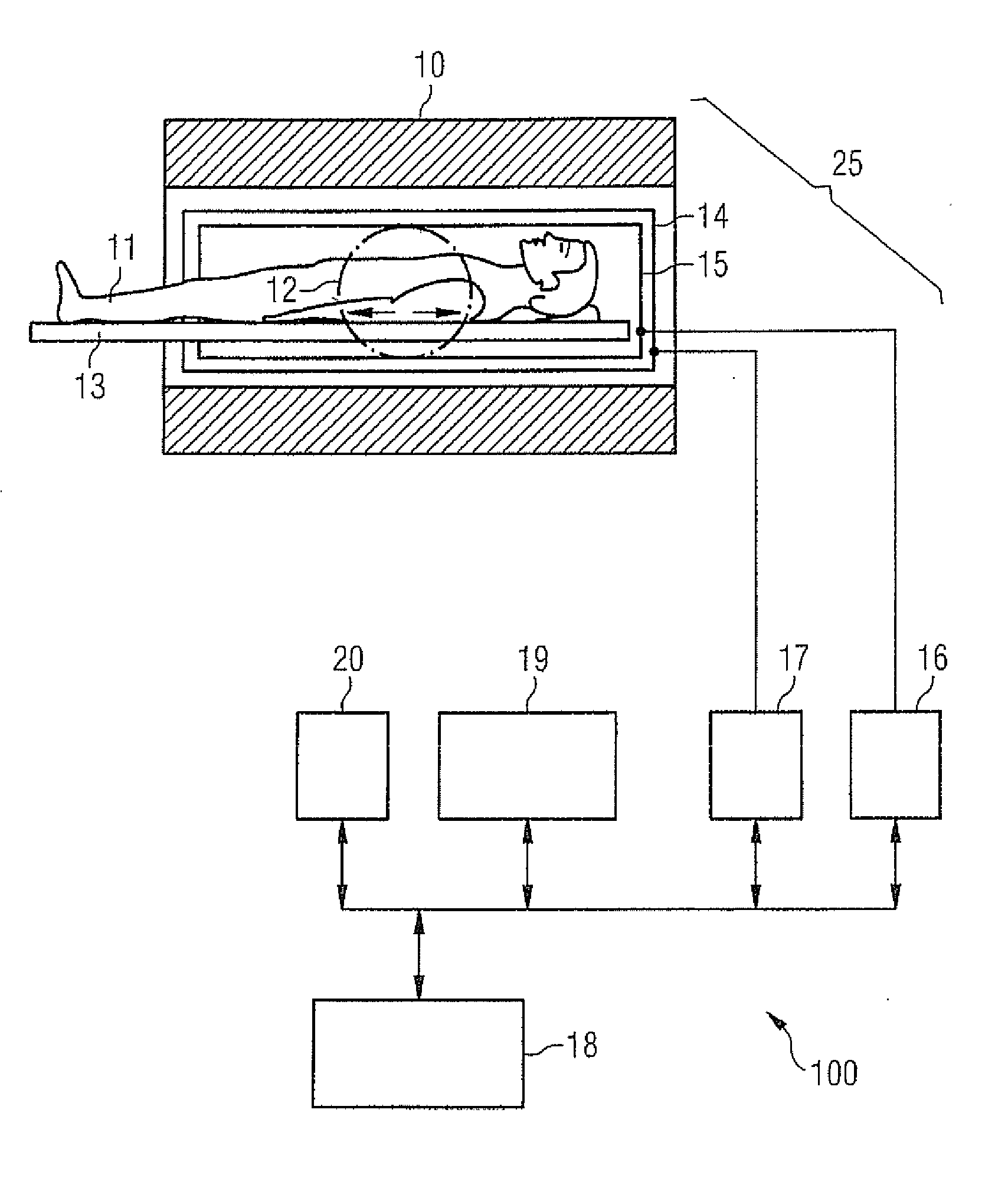
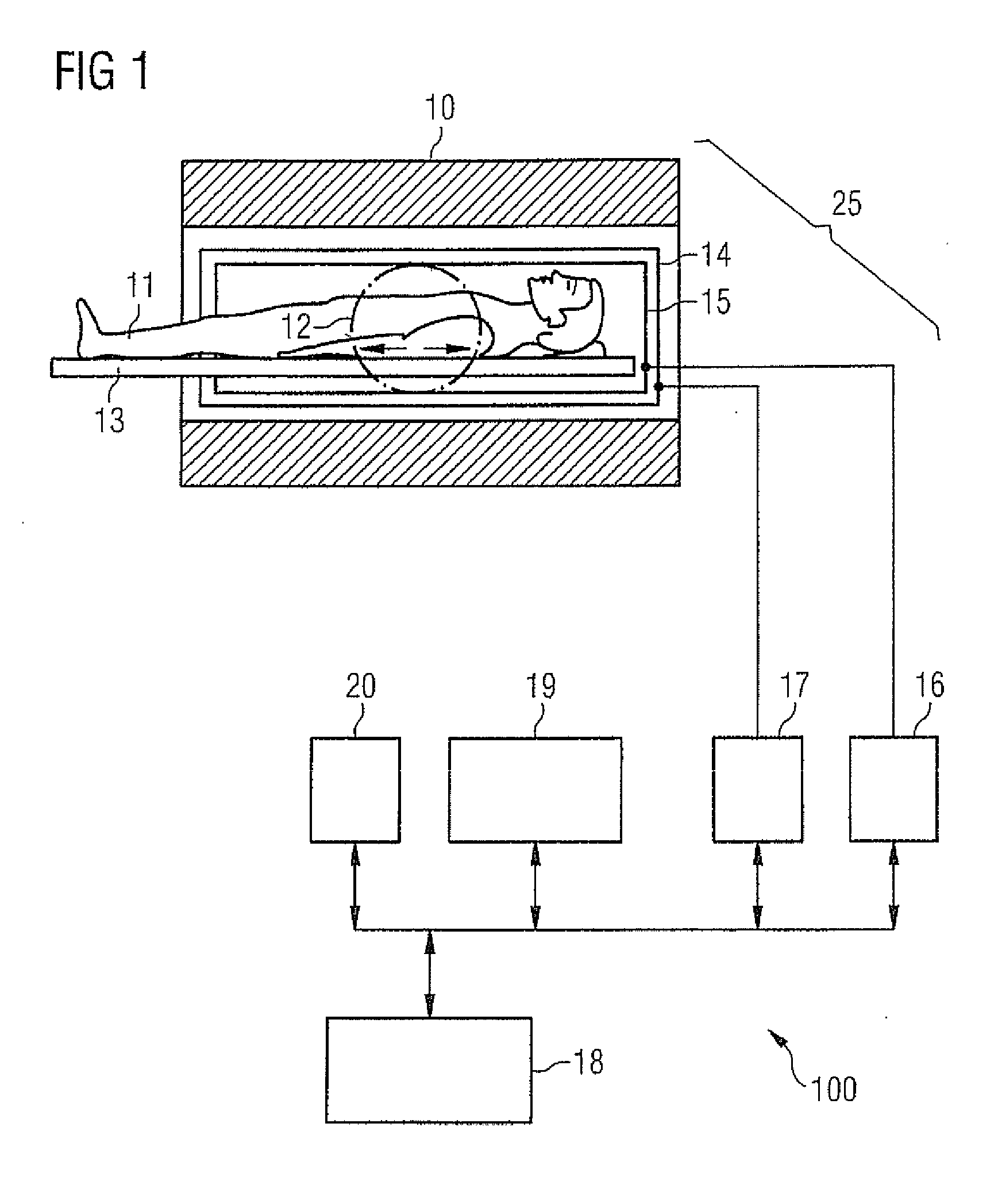
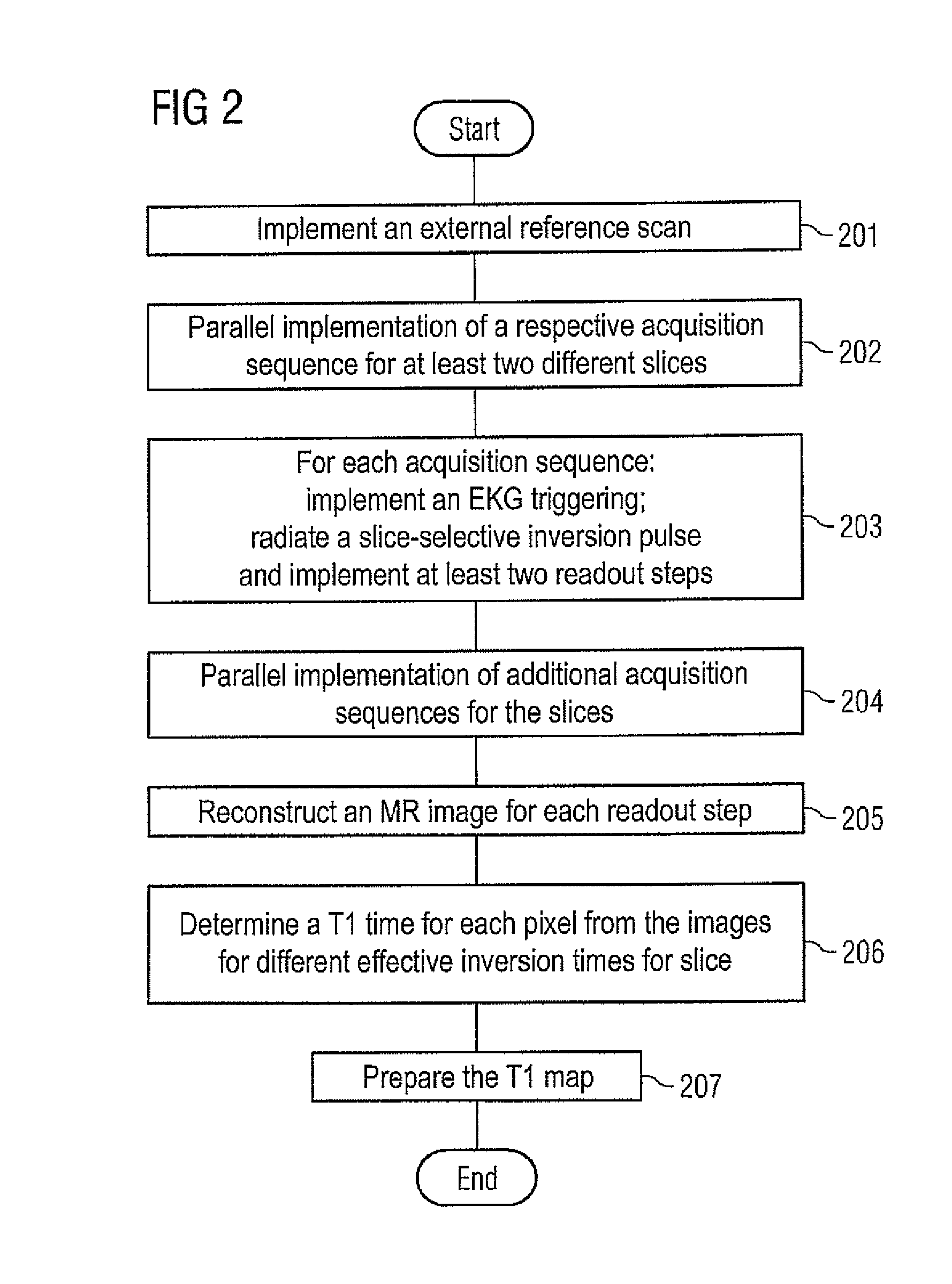
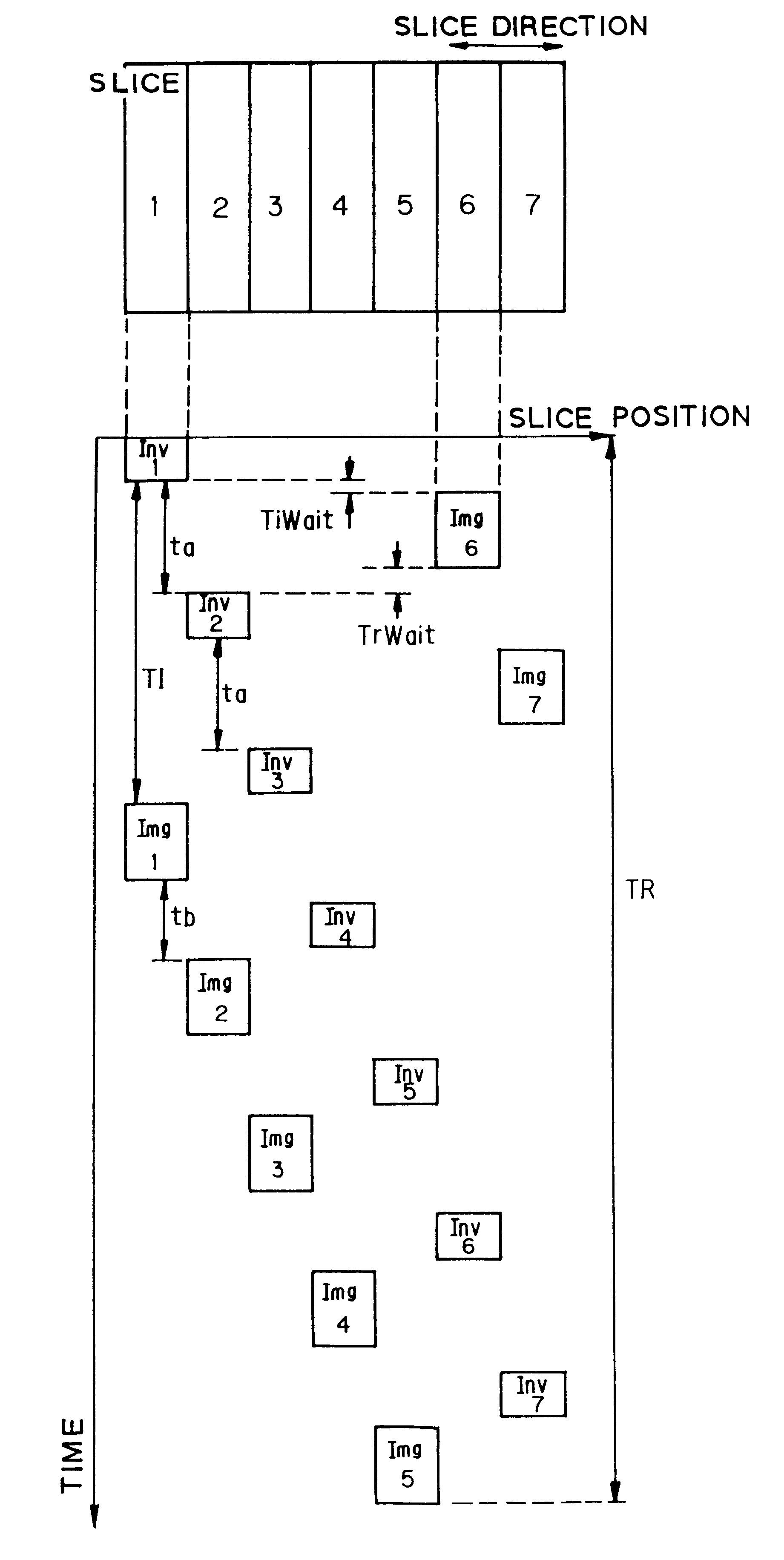
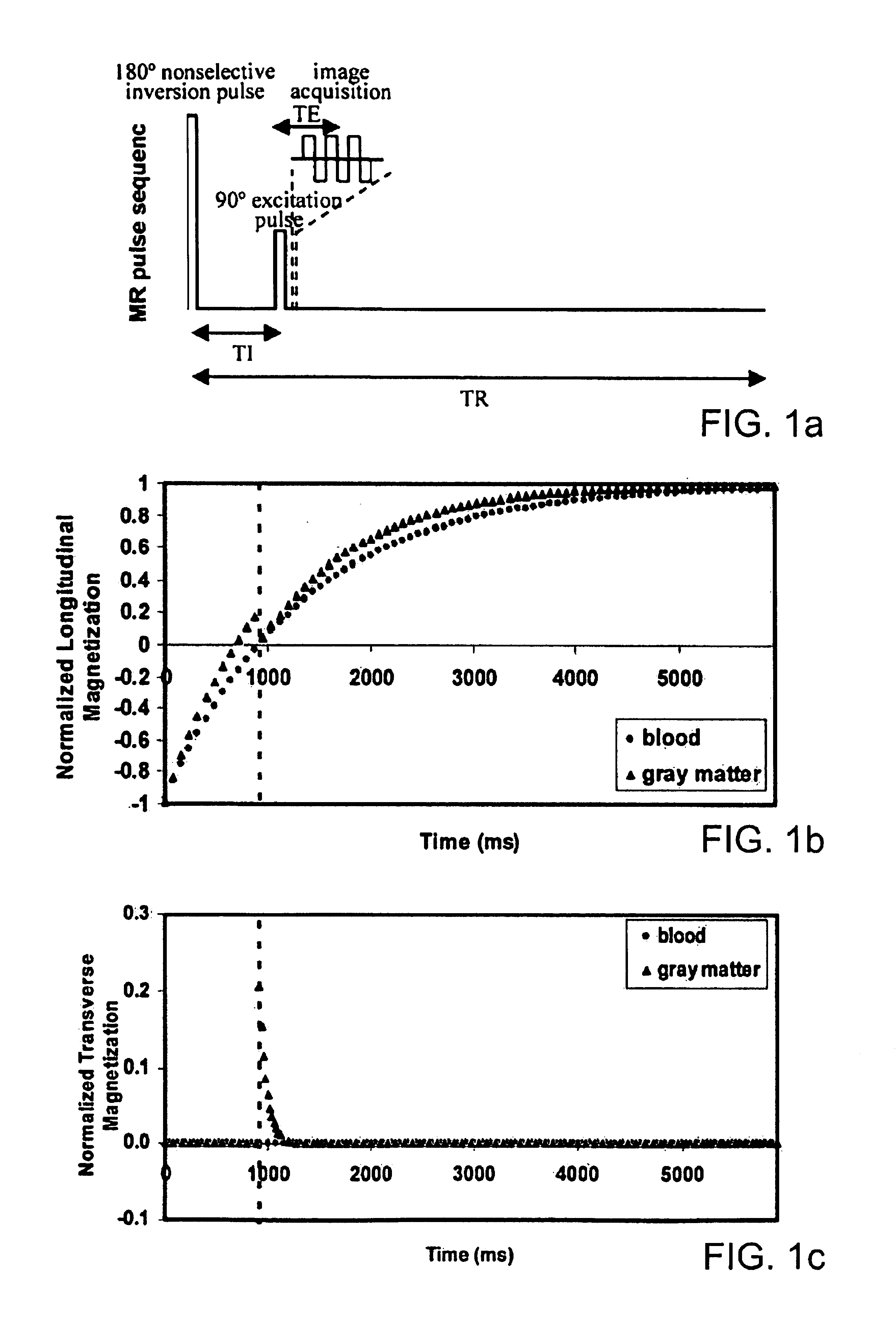
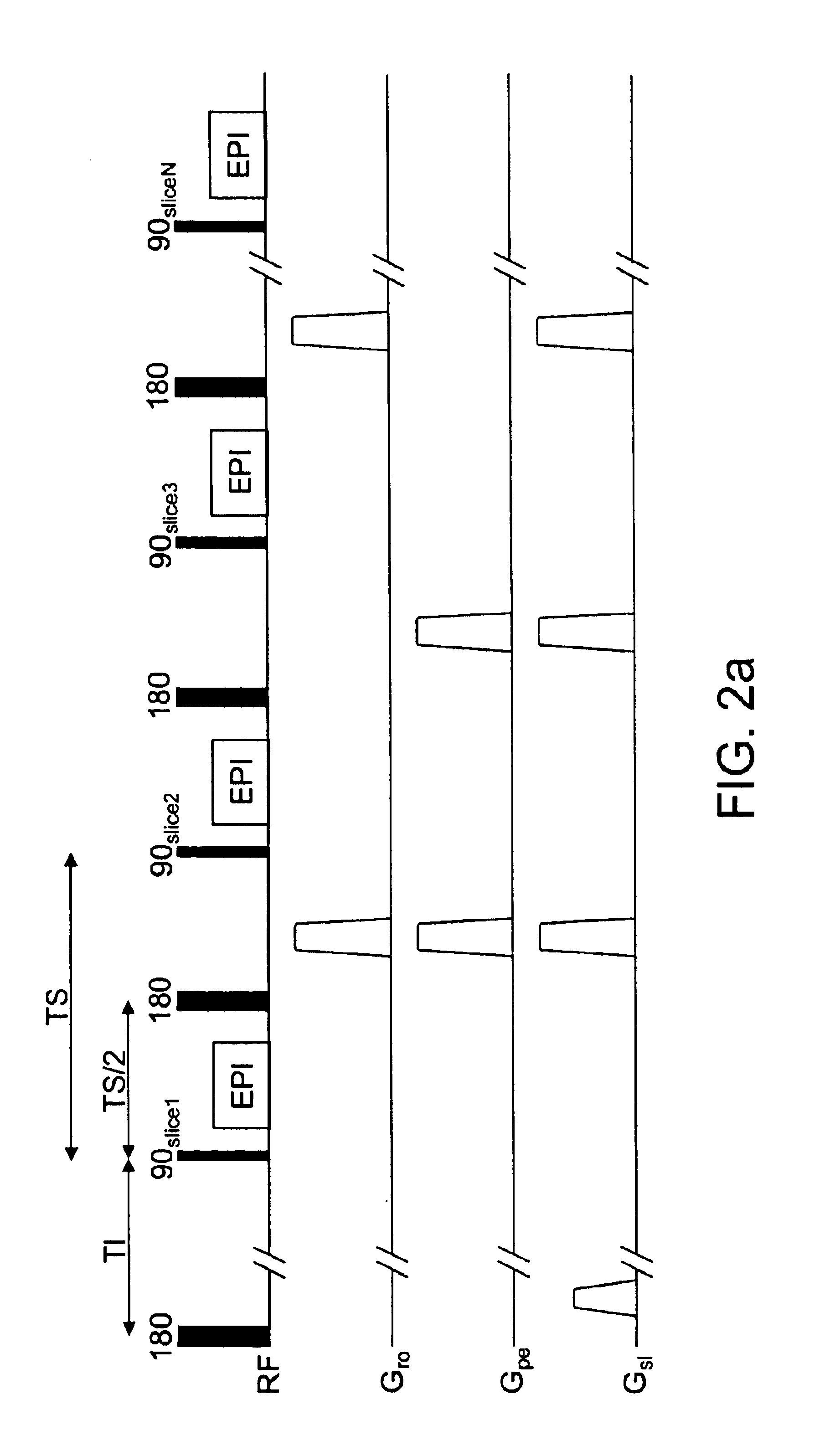
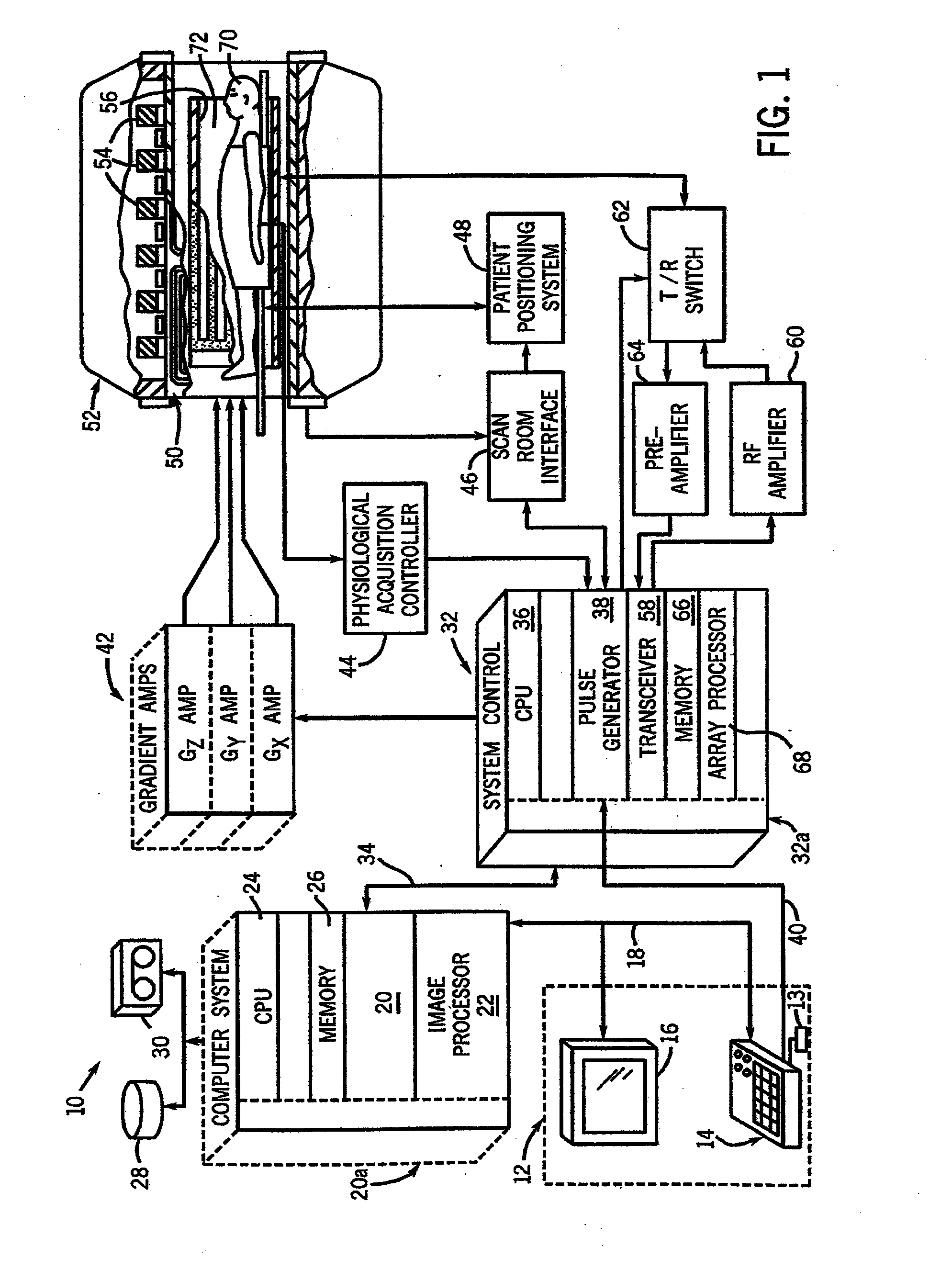
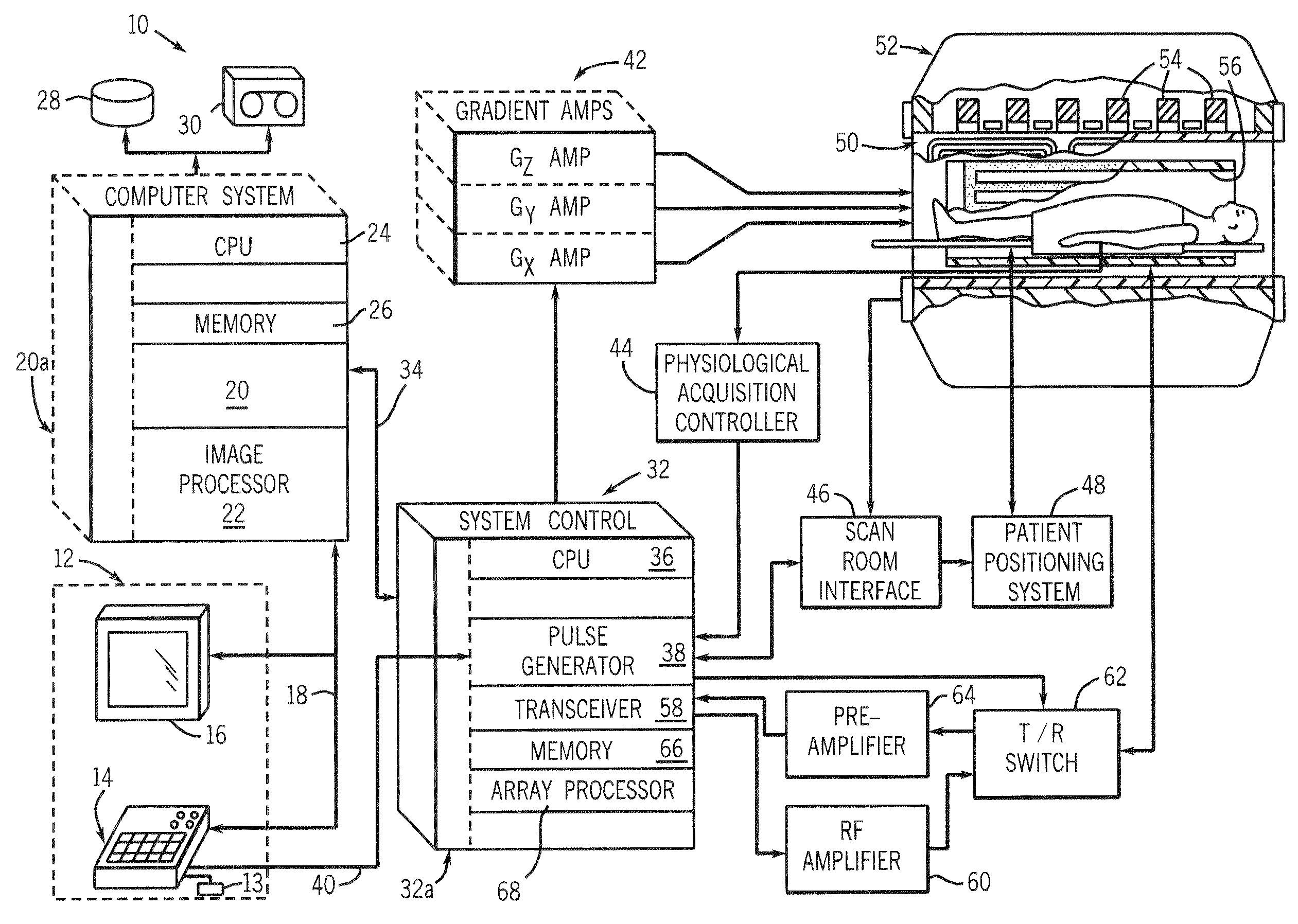
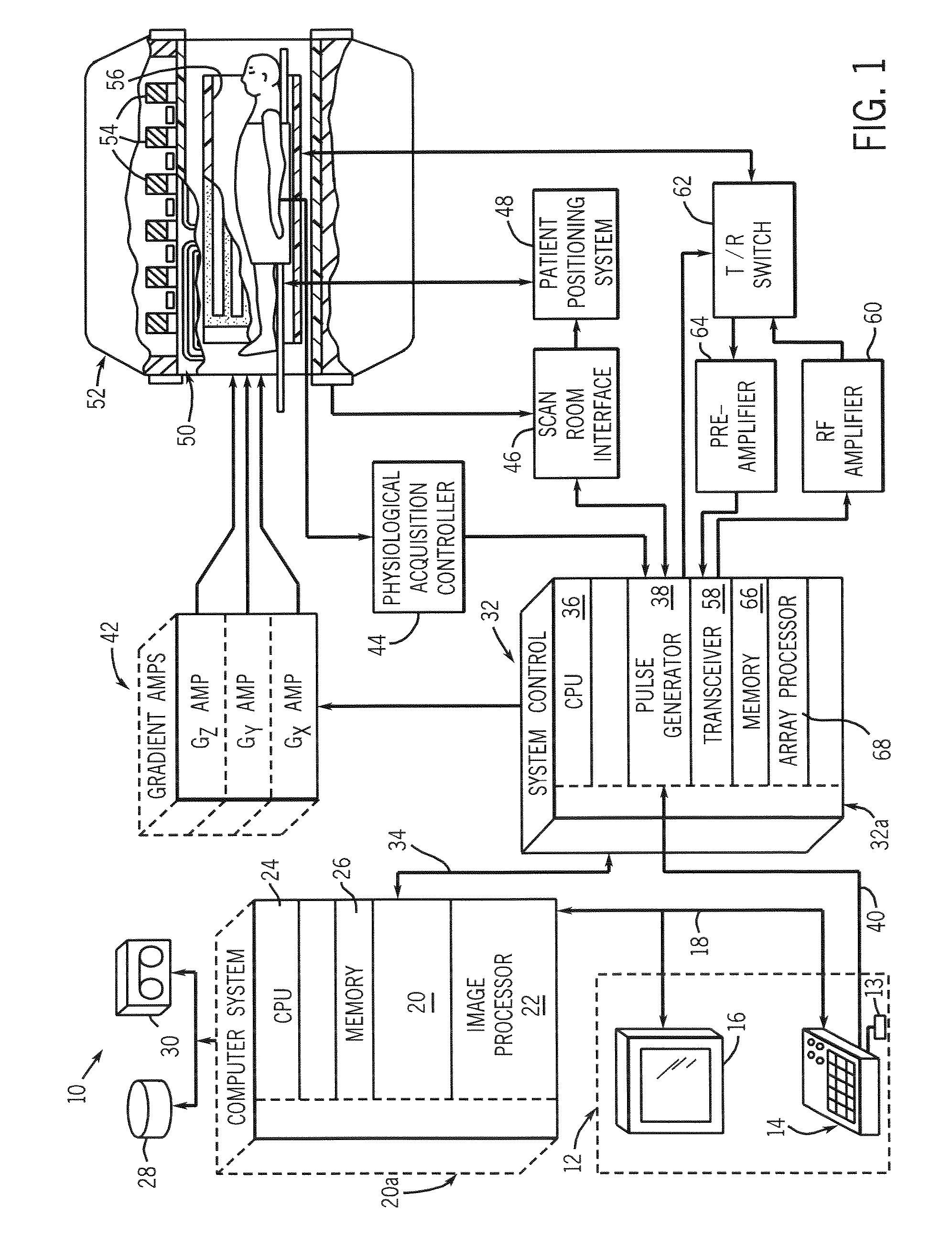
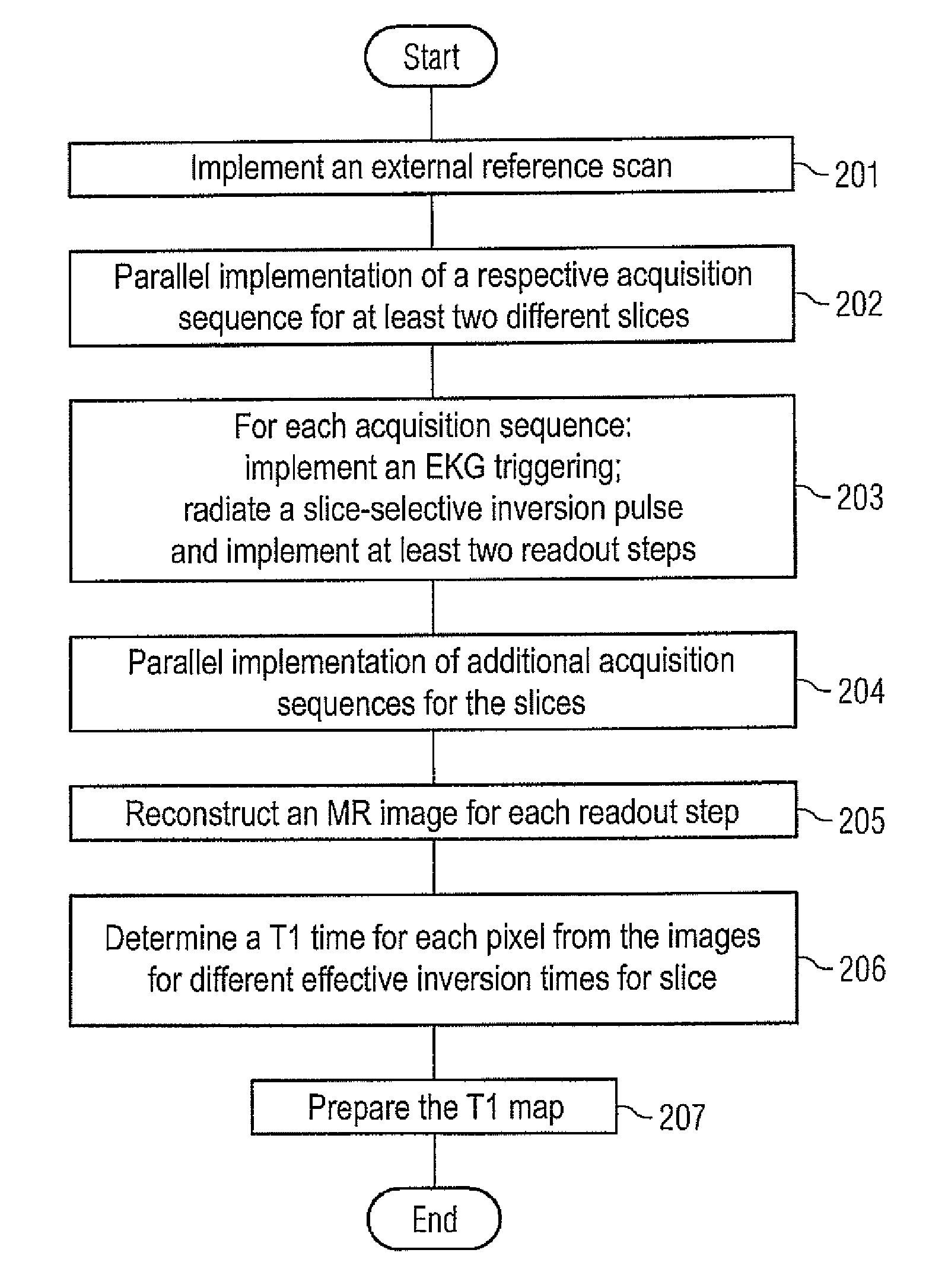
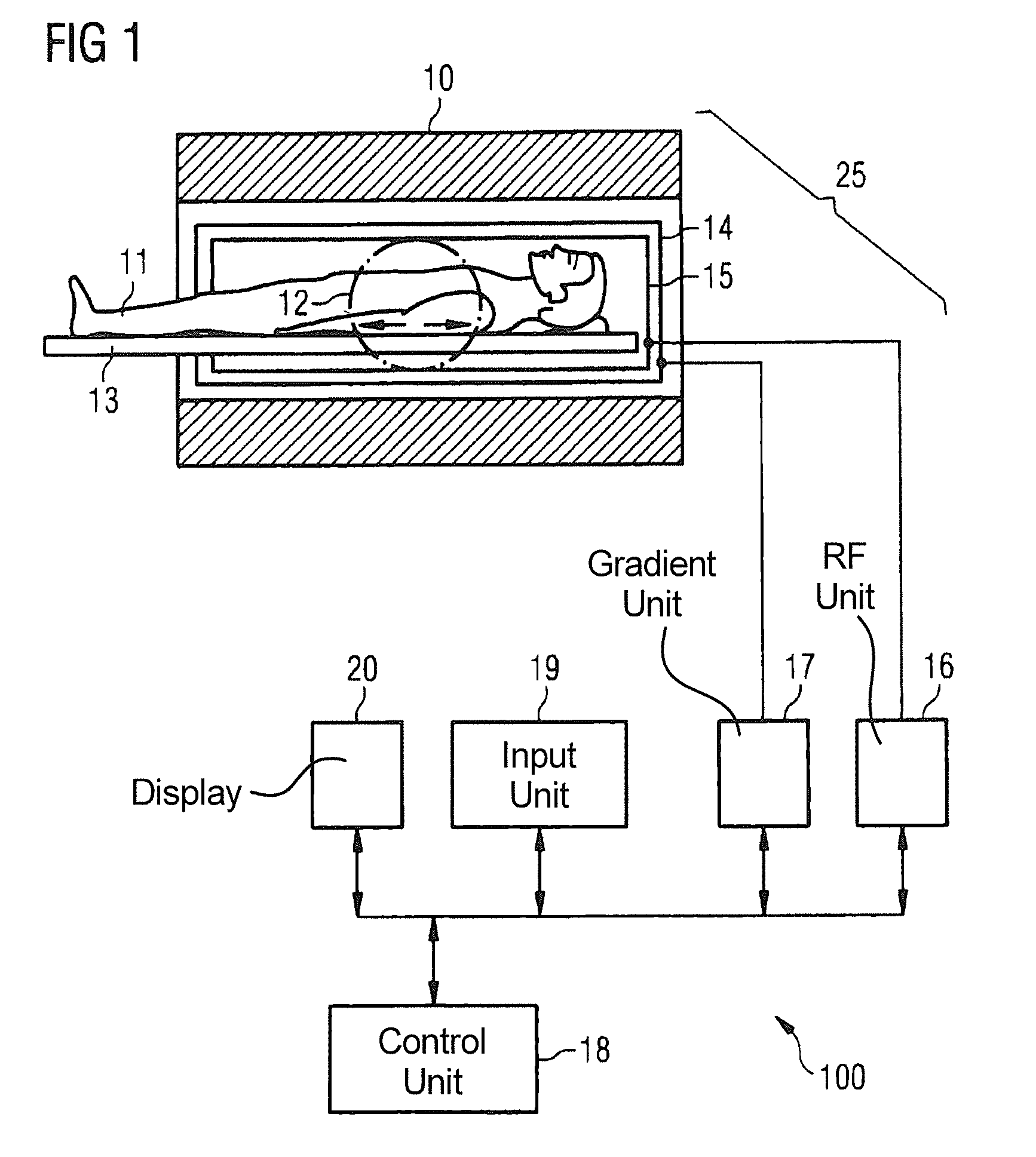
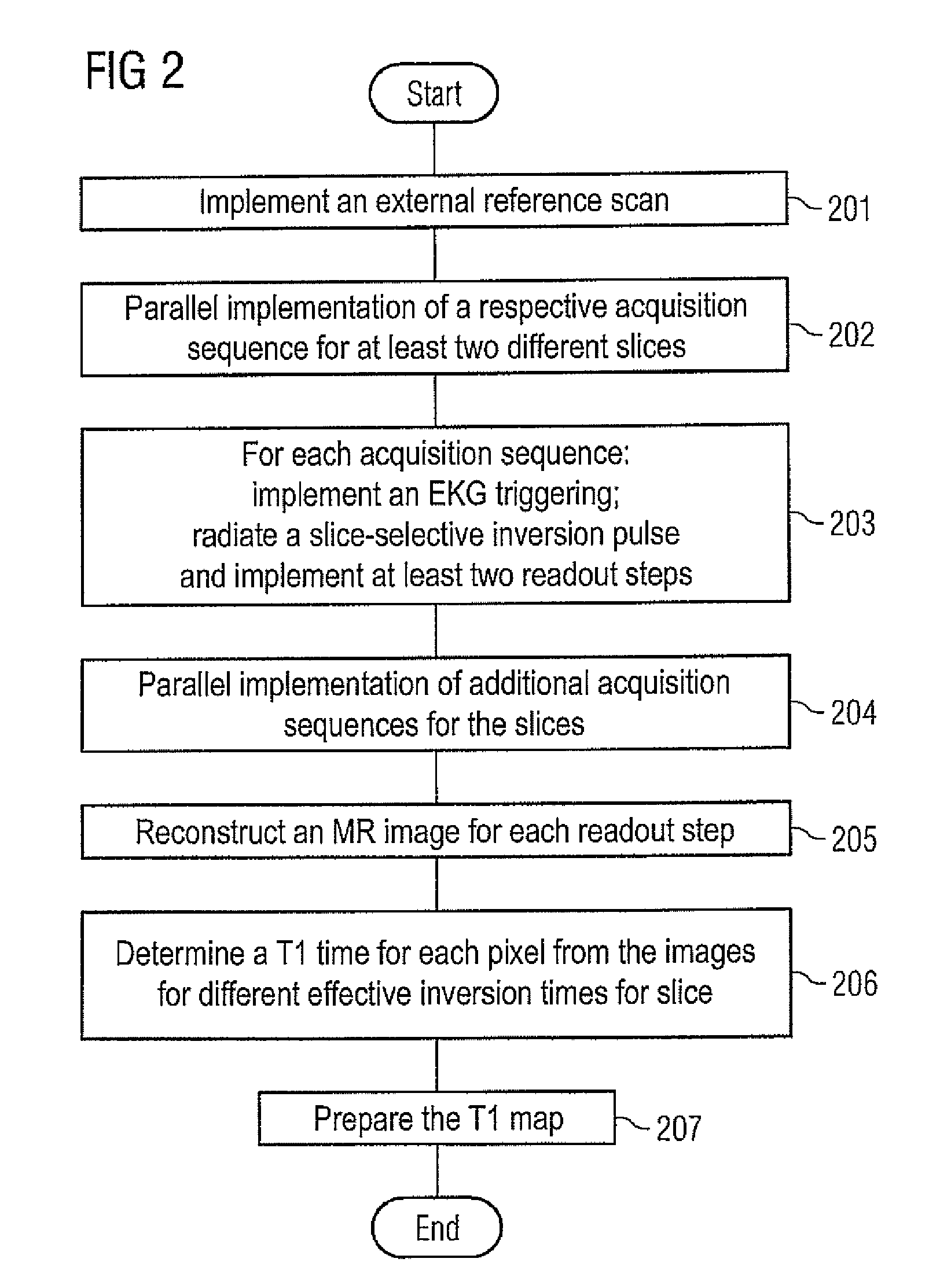
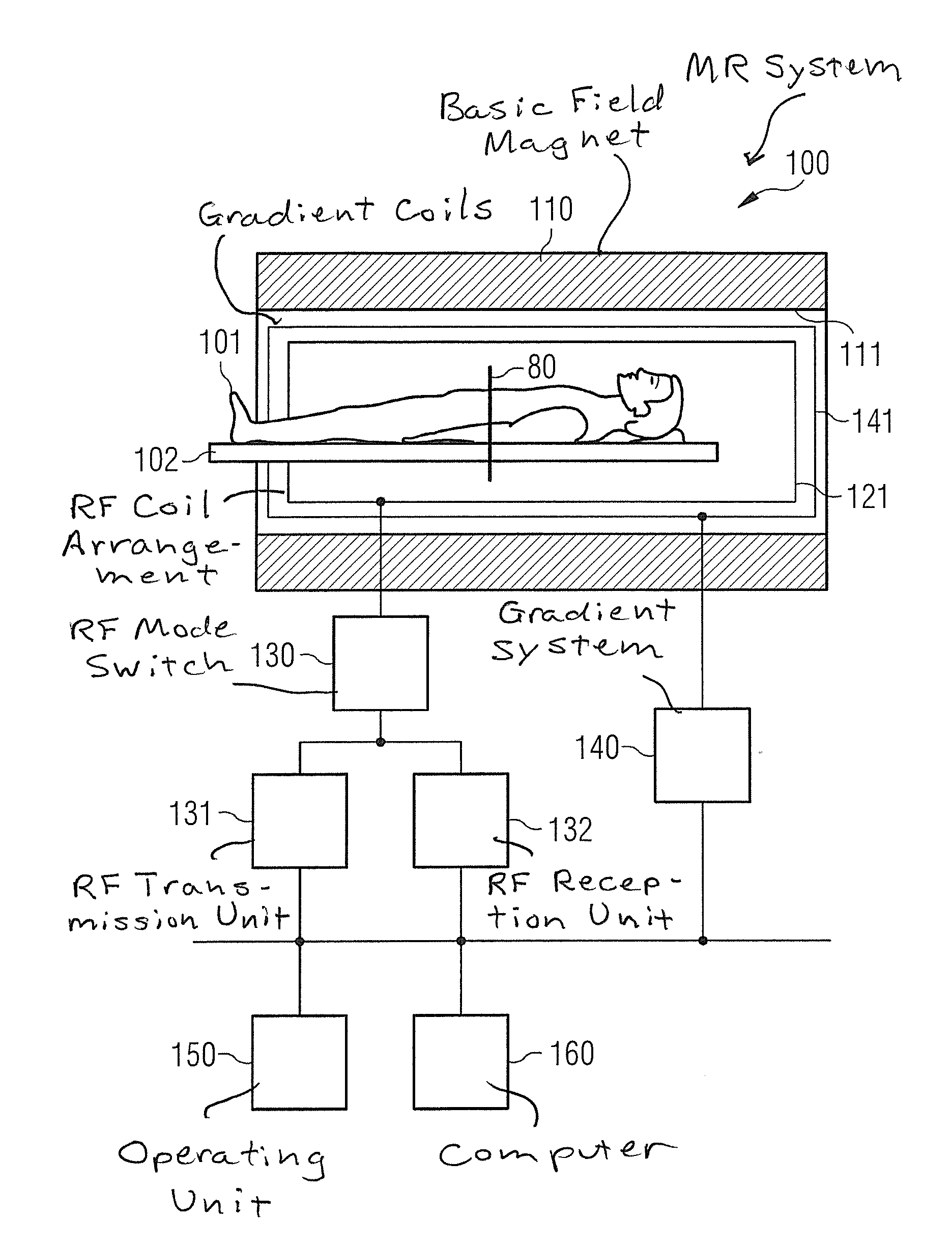
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging to create t1 maps
ActiveUS20110181285A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSpatially resolvedProton magnetic resonance
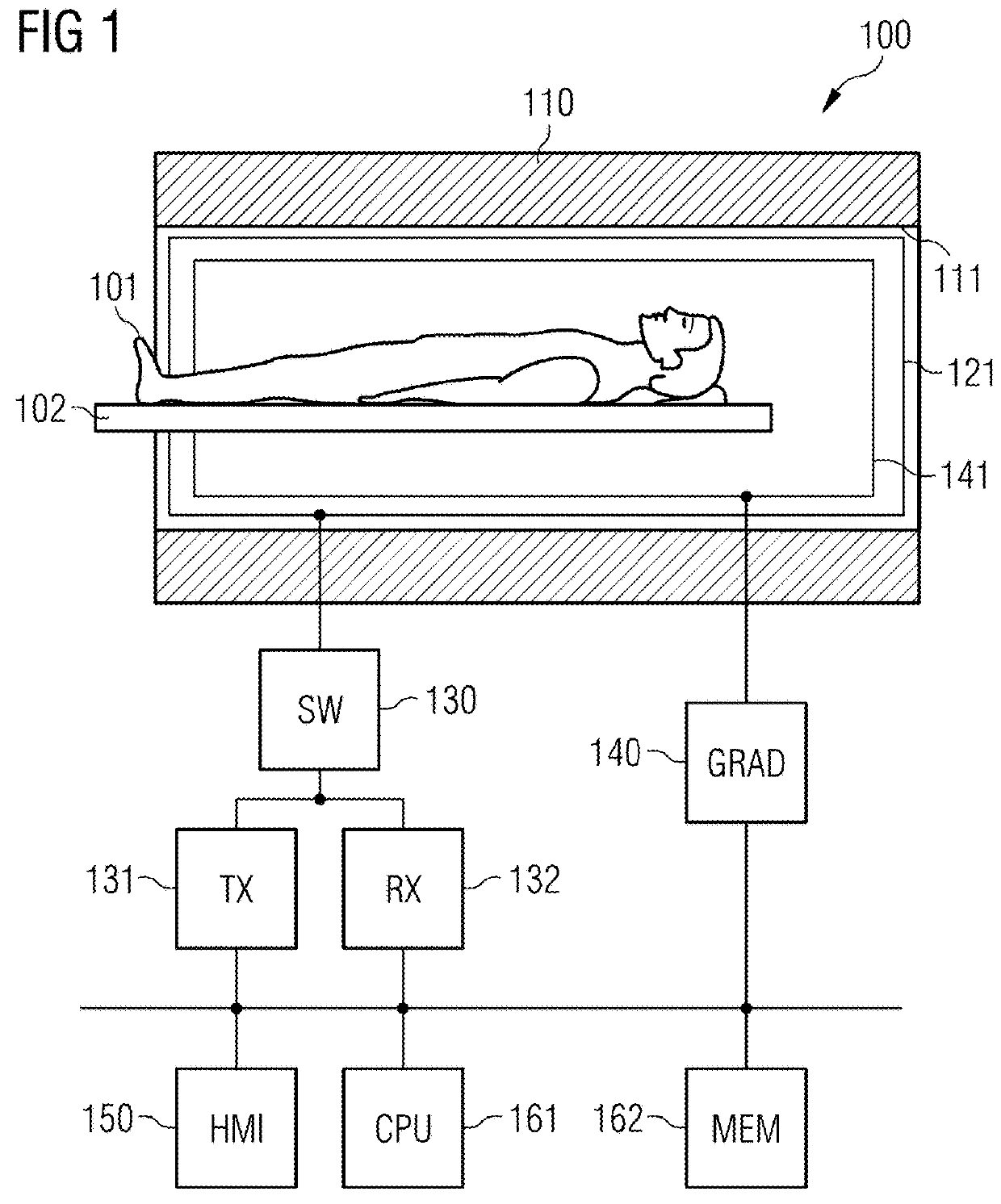
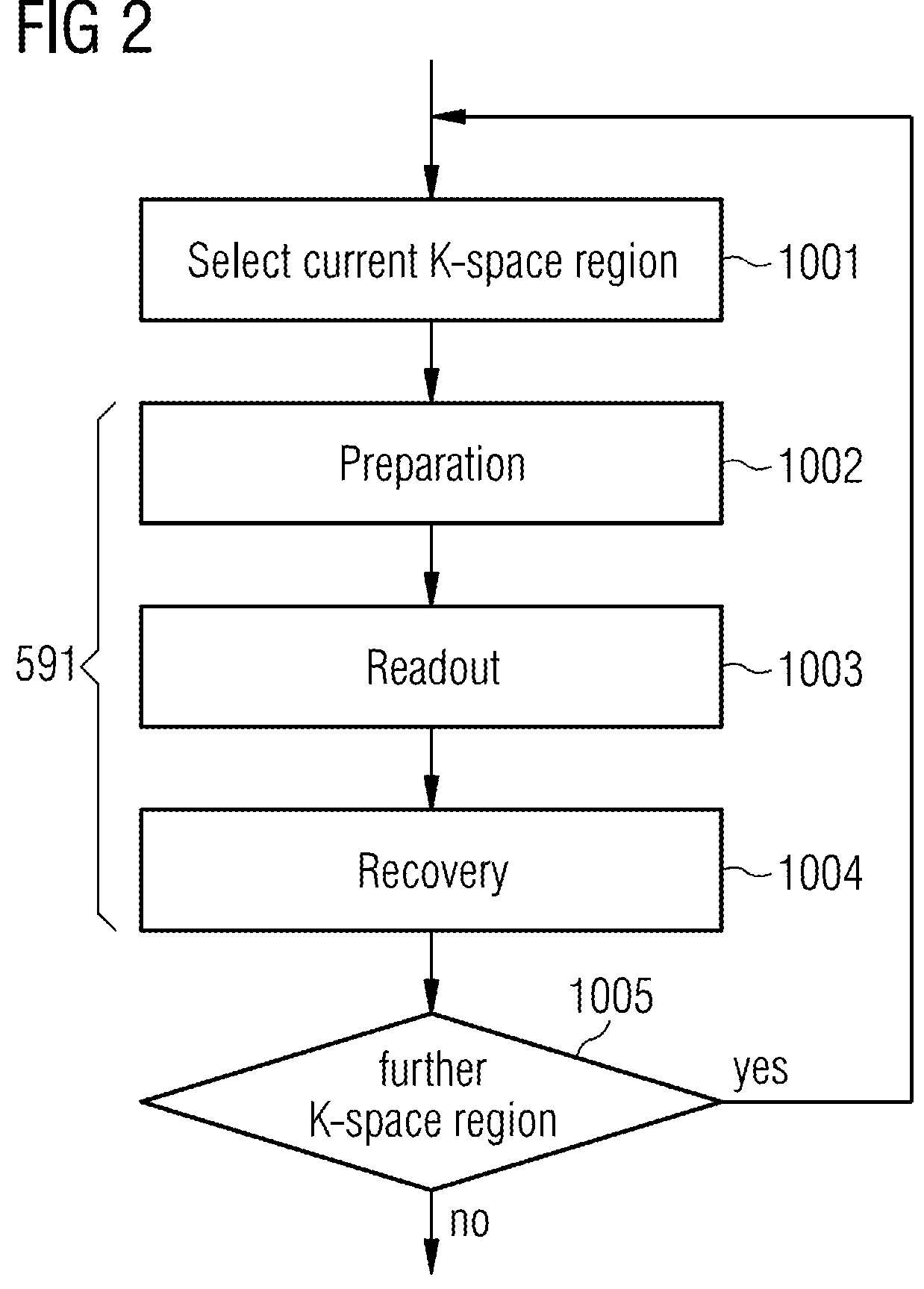
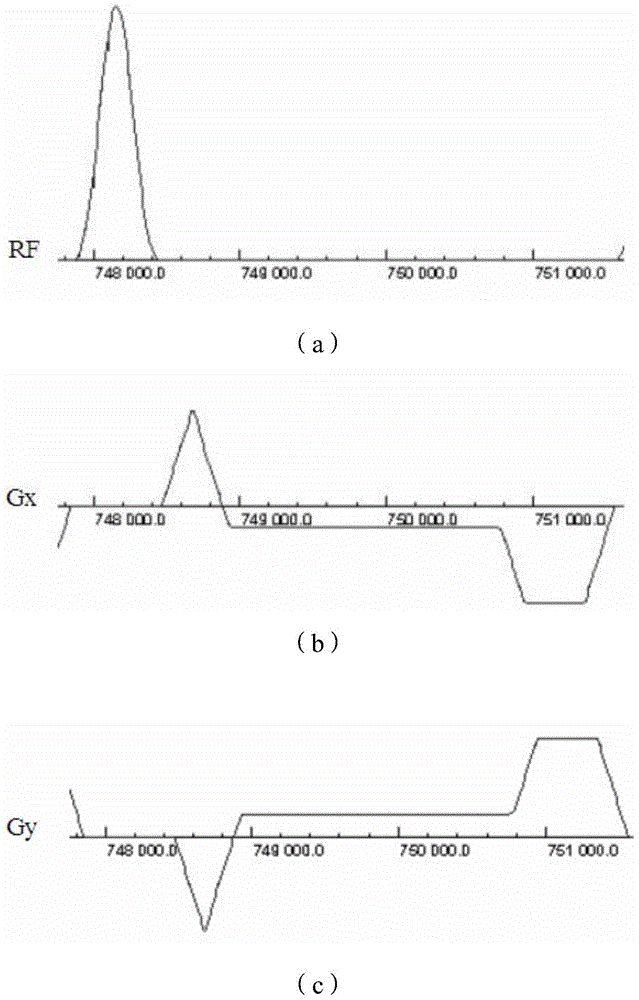
In a method and apparatus for MR imaging, a data acquisition sequence is executed wherein at least two slices of an examination subject are imaged in parallel with a gradient echo method for spatially resolved quantification of the T1 relaxation time.At least one first acquisition sequence is implemented to acquire MR data from a first slice of the examination subject and at least one second acquisition sequence is implemented to acquire MR data from a second slice of the examination subject. The acquisition sequences each include an inversion pulse and at least two successive readout steps. The first and second acquisition sequences are temporally offset from one another such that they at least partially overlap.
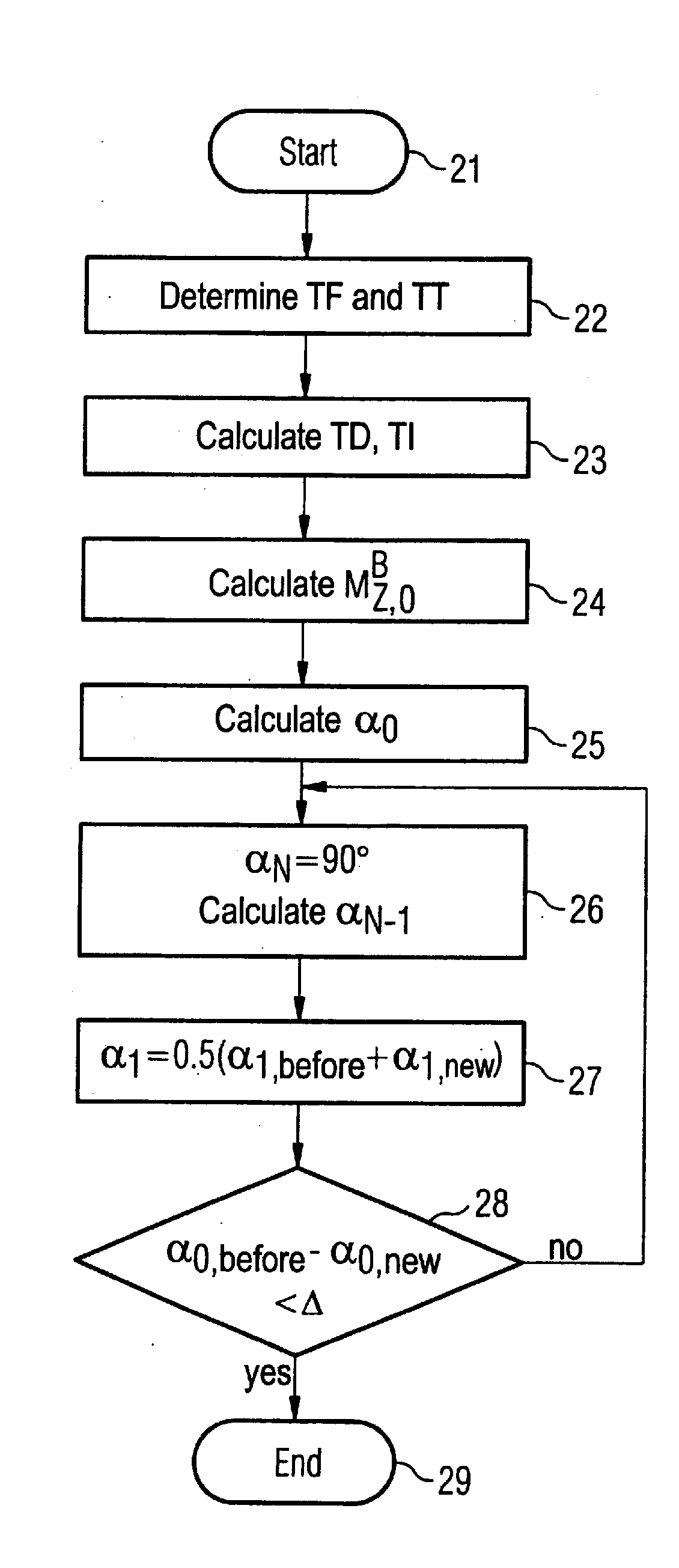
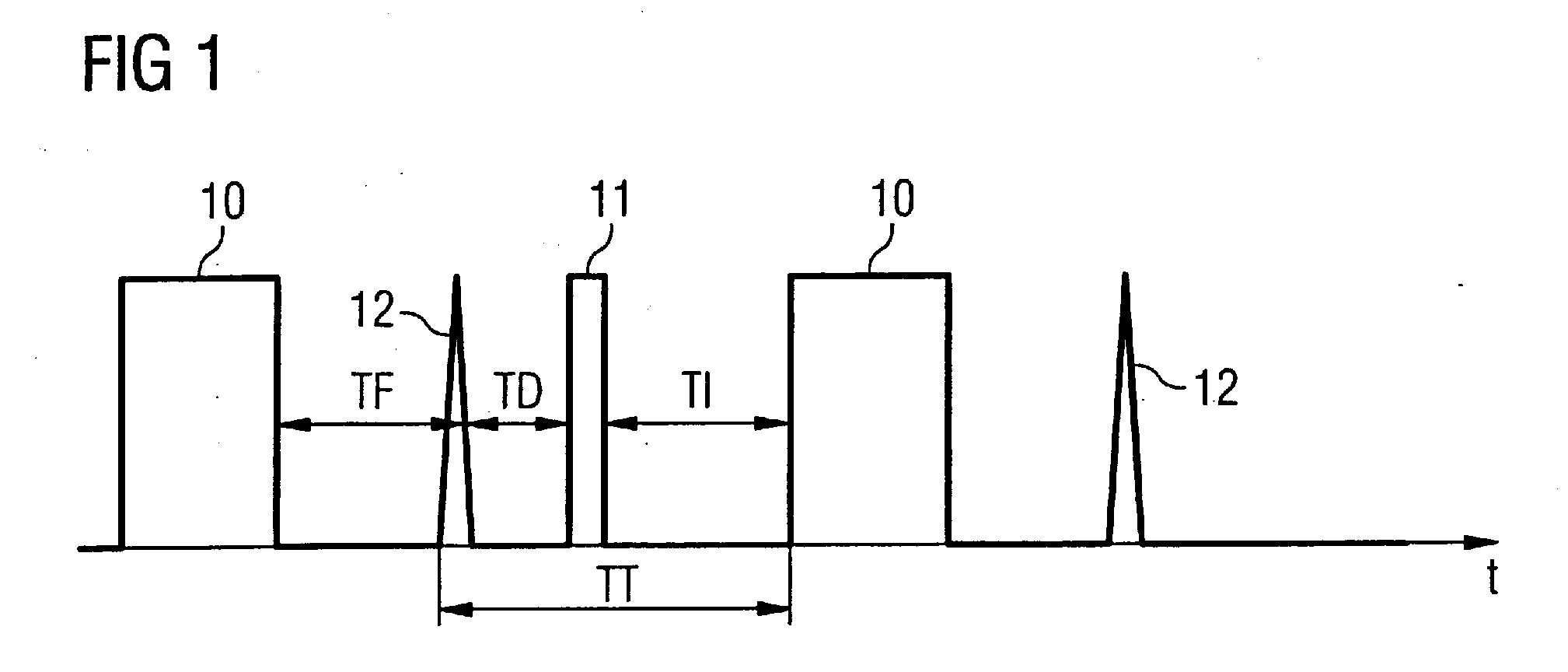
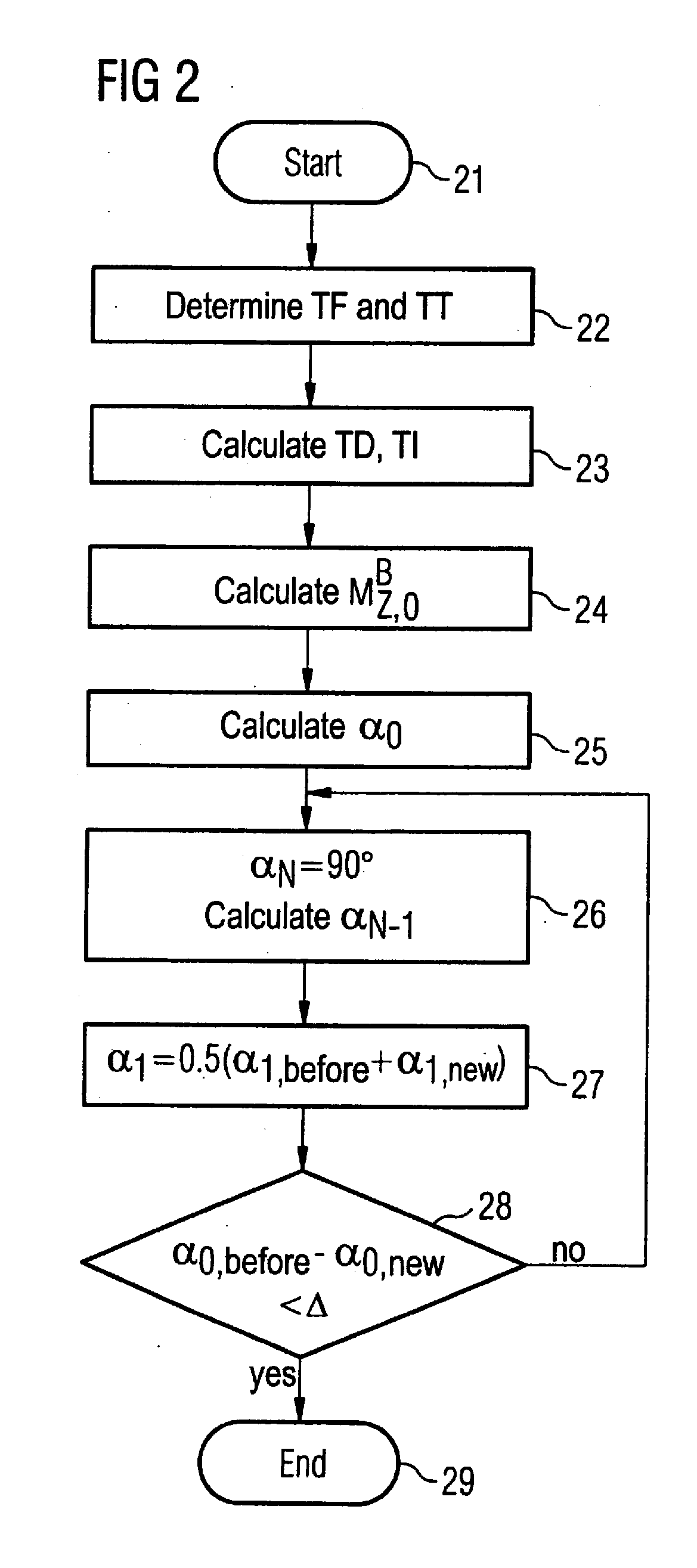
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
MR imaging using nested pulse sequence involving IR pulse
InactiveUS6850793B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSignificant positive effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCross relaxationImage contrast
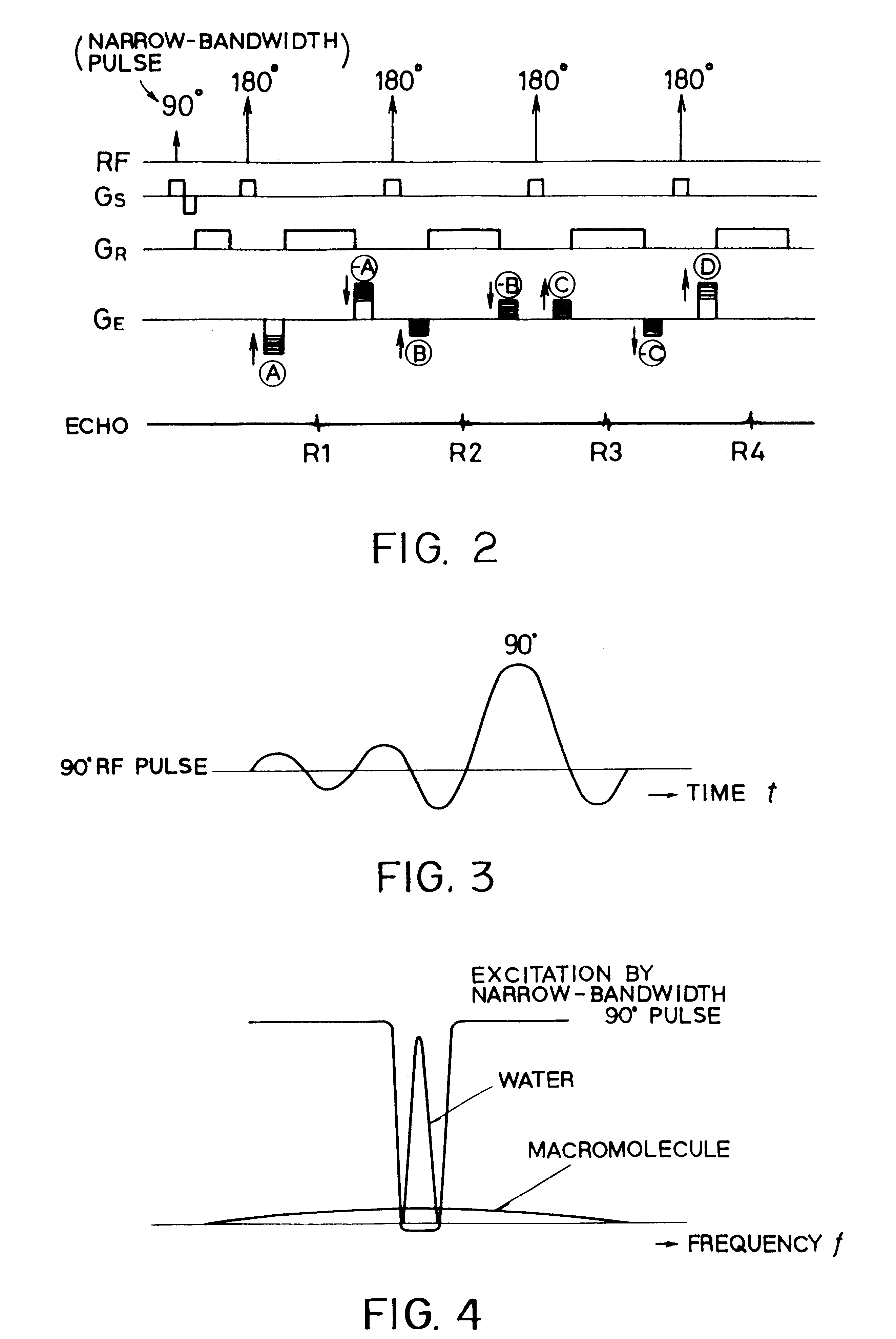
In addition to the known MT (magnetization transfer) effect, an RMT (reverse MT) is newly found, which increases a detected MR signal strength. Both the MT and RMT effects can be explained with mutual interaction, such as phenomena of chemical exchange and / or cross relaxation, acted between a pool of water proton spins and another pool of macromolecule proton spins, for example, within an object. In order to enhance the MT or RMT effect, the frequency bandwidths of RF pulses, such as a 90° RF exciting pulse in a SE or FSE method, an inversion pulse in a FLAIR or fast FLAIR method, and others, are controlled. To enhance the MT effect, the bandwidth is controlled into a wider value (approx. more than 1250 Hz) than the normally (conventionally) used bandwidth, while to obtain the RMT effect, the bandwidth is controlled into a narrower value (approx. less than 1000 Hz) than the normally used bandwidth. Actively controlling the MT or RMT effect permits changed image contrast in MR imaging.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Heart imaging with adaptive inversion time
InactiveUS20080242973A1Increase contrastLong period of timeElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsResonanceInversion Time
In a method for acquisition of magnetic resonance images of the heart, MR signals of the heart are acquired using an imaging sequence, wherein the magnetization is inverted by an RF inversion pulse before the acquisition of the MR signals; and of the heart activity is detected, and the point in time of the switching of the RF inversion pulse dependent on the detected heart activity.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
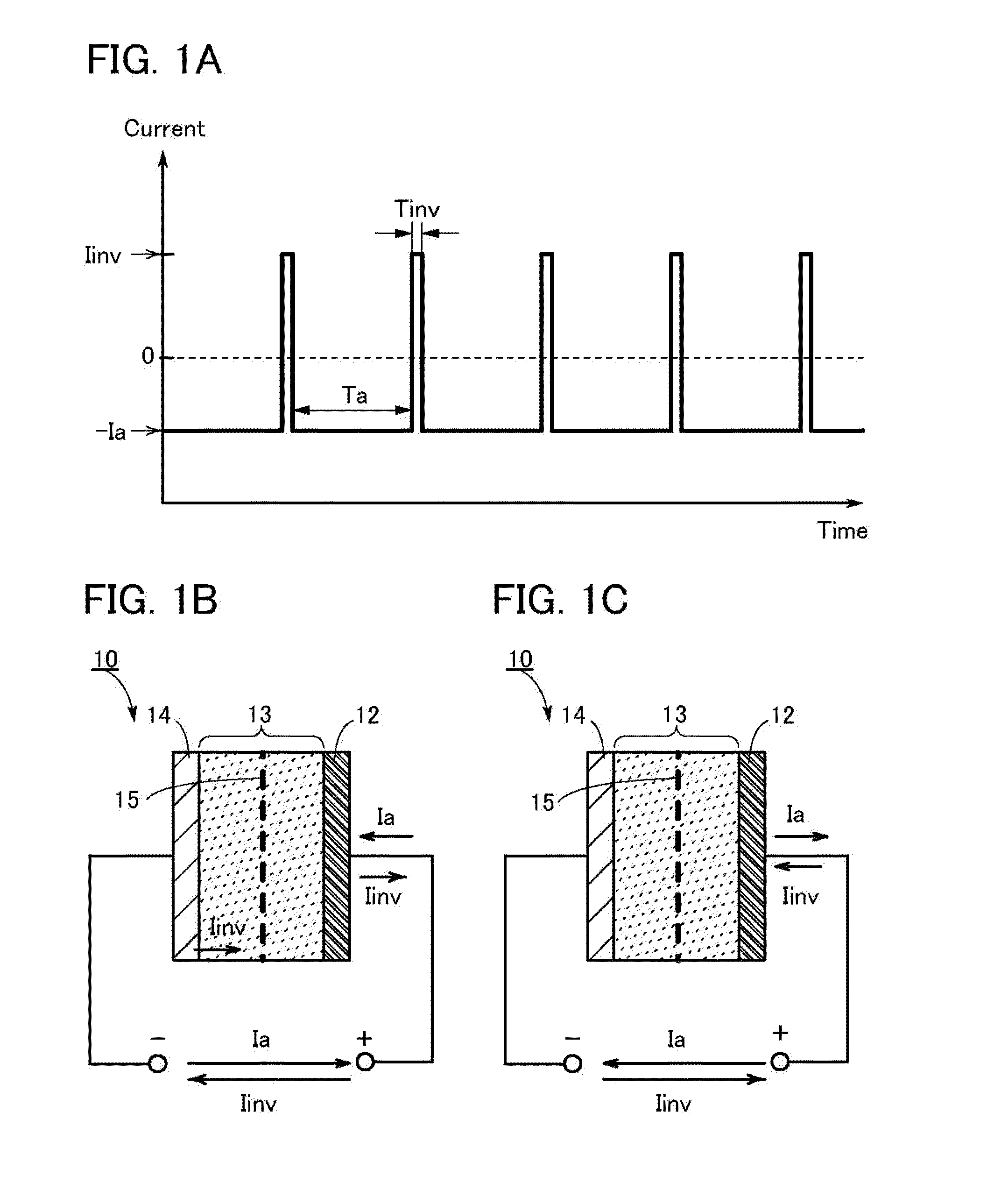
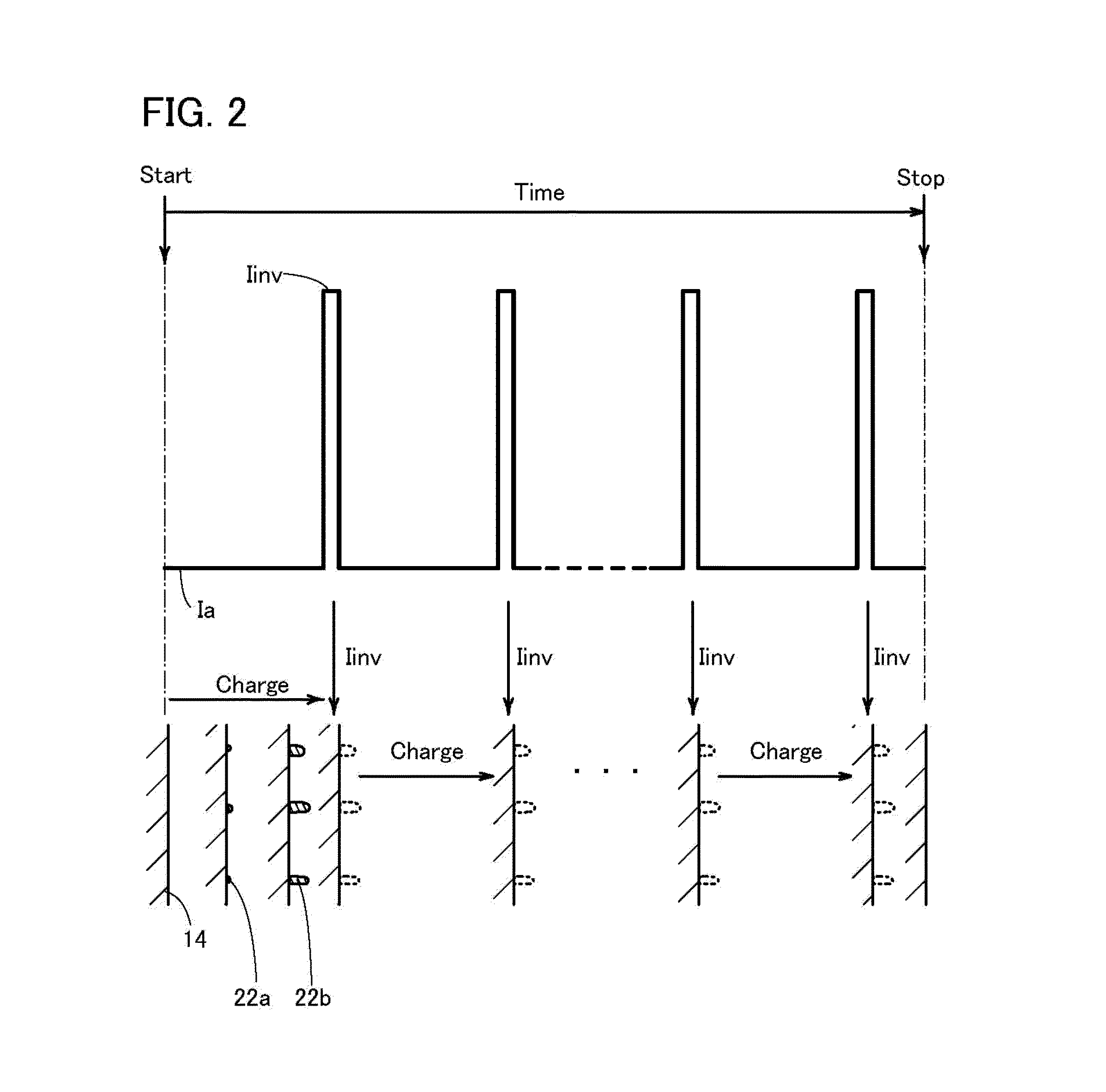
Electrochemical device
InactiveUS20140197797A1Avoid changeReduce the degree of deteriorationFinal product manufactureActive material electrodesElectrochemical responseElectricity
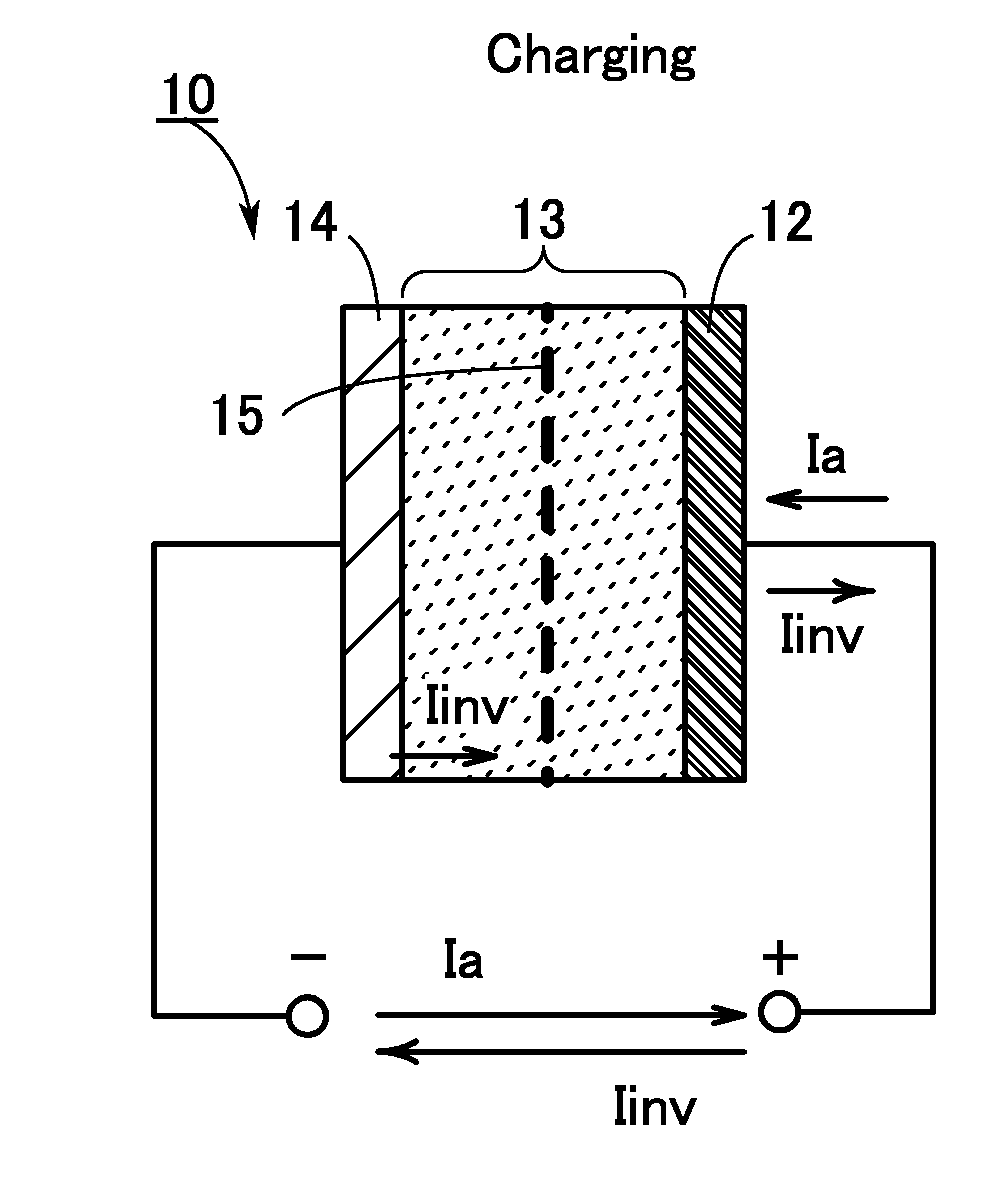
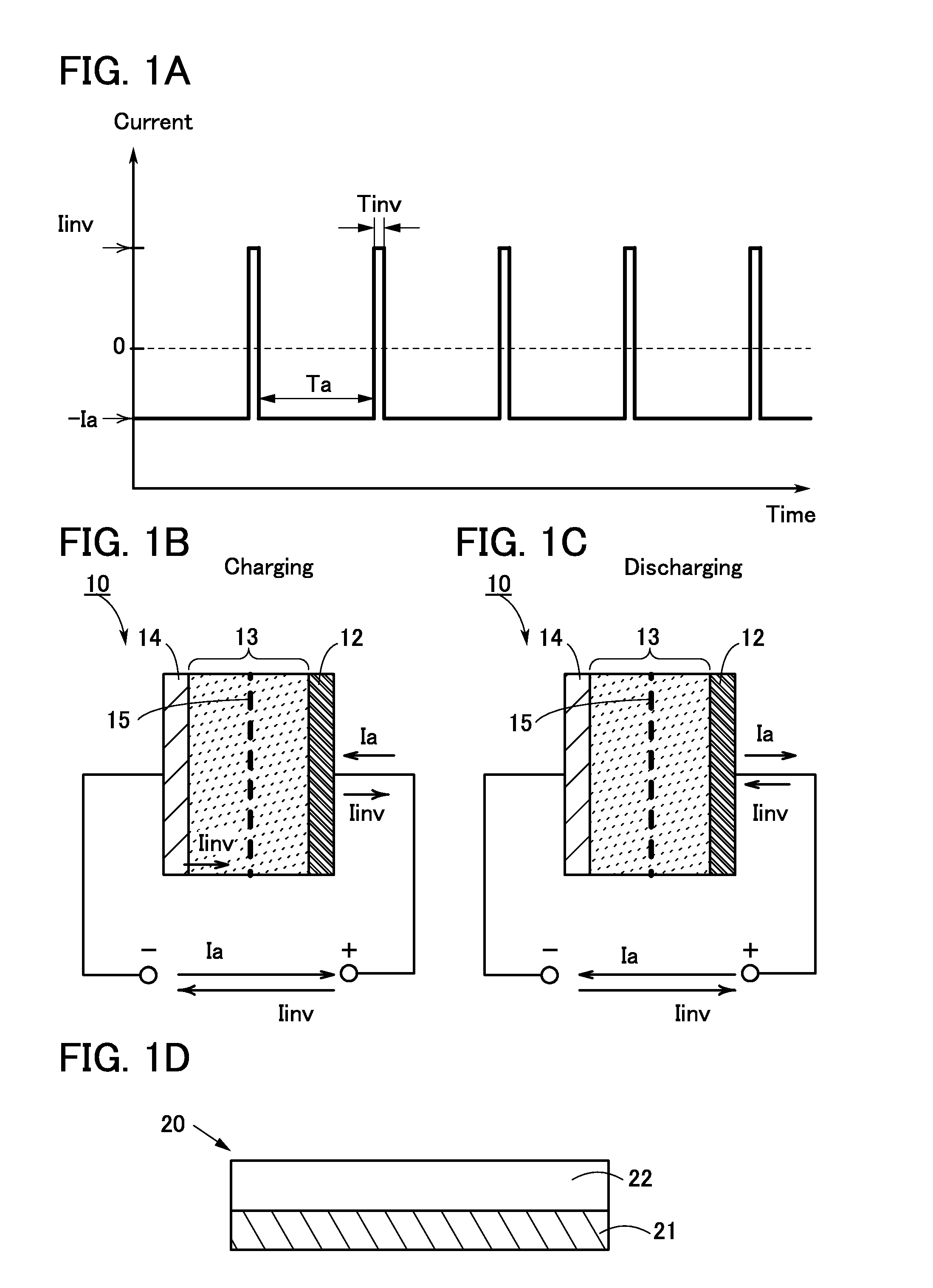
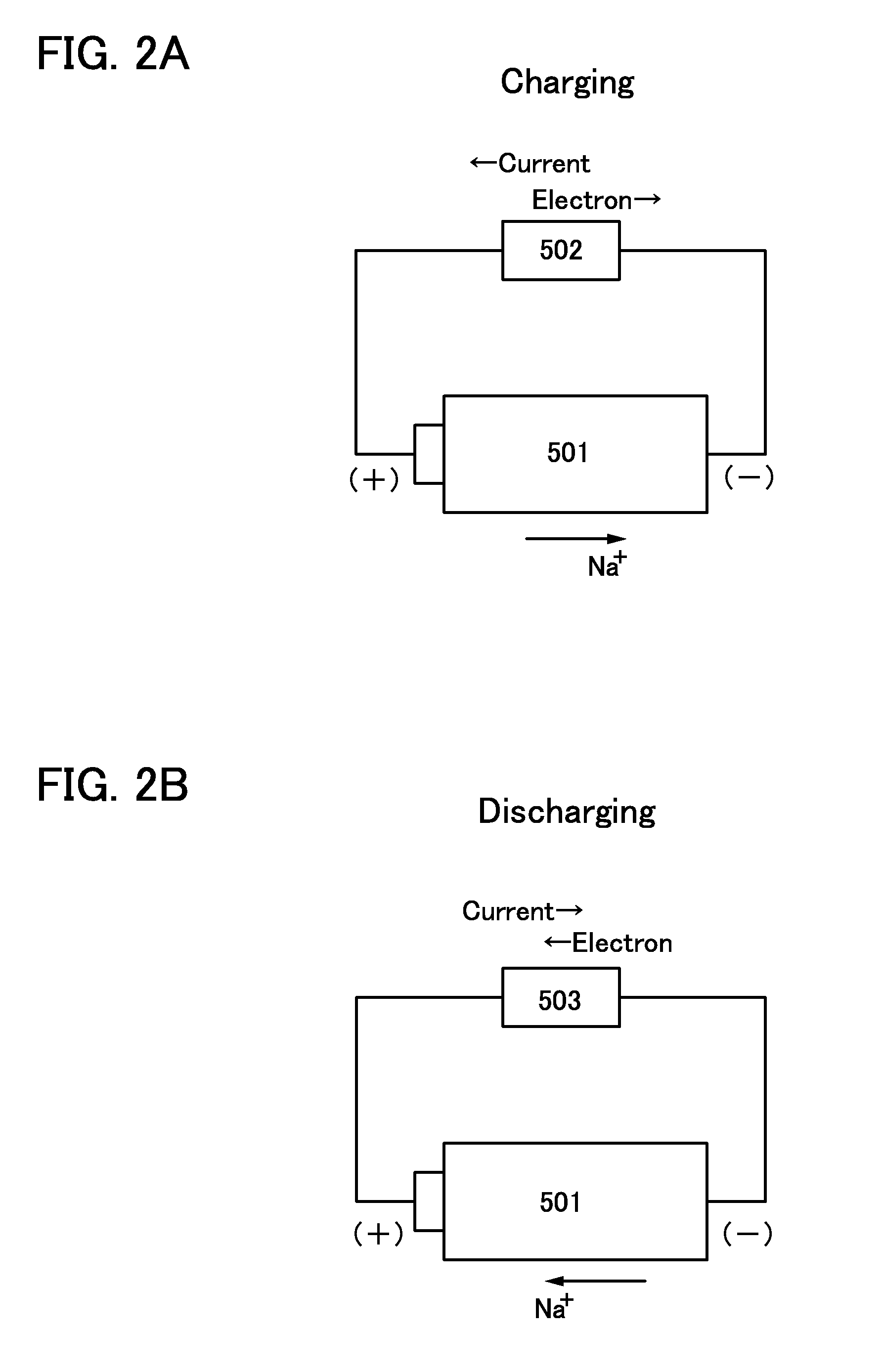
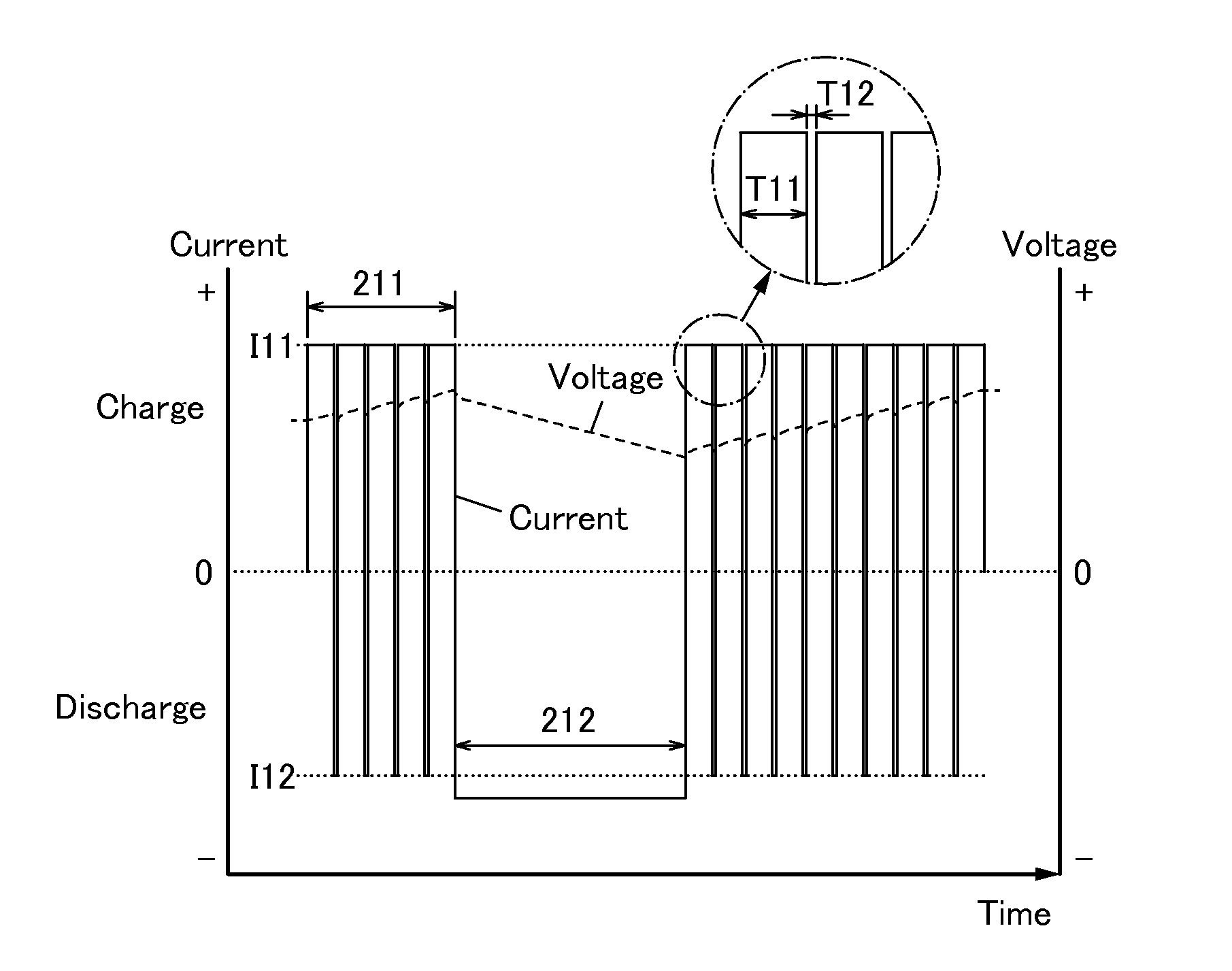
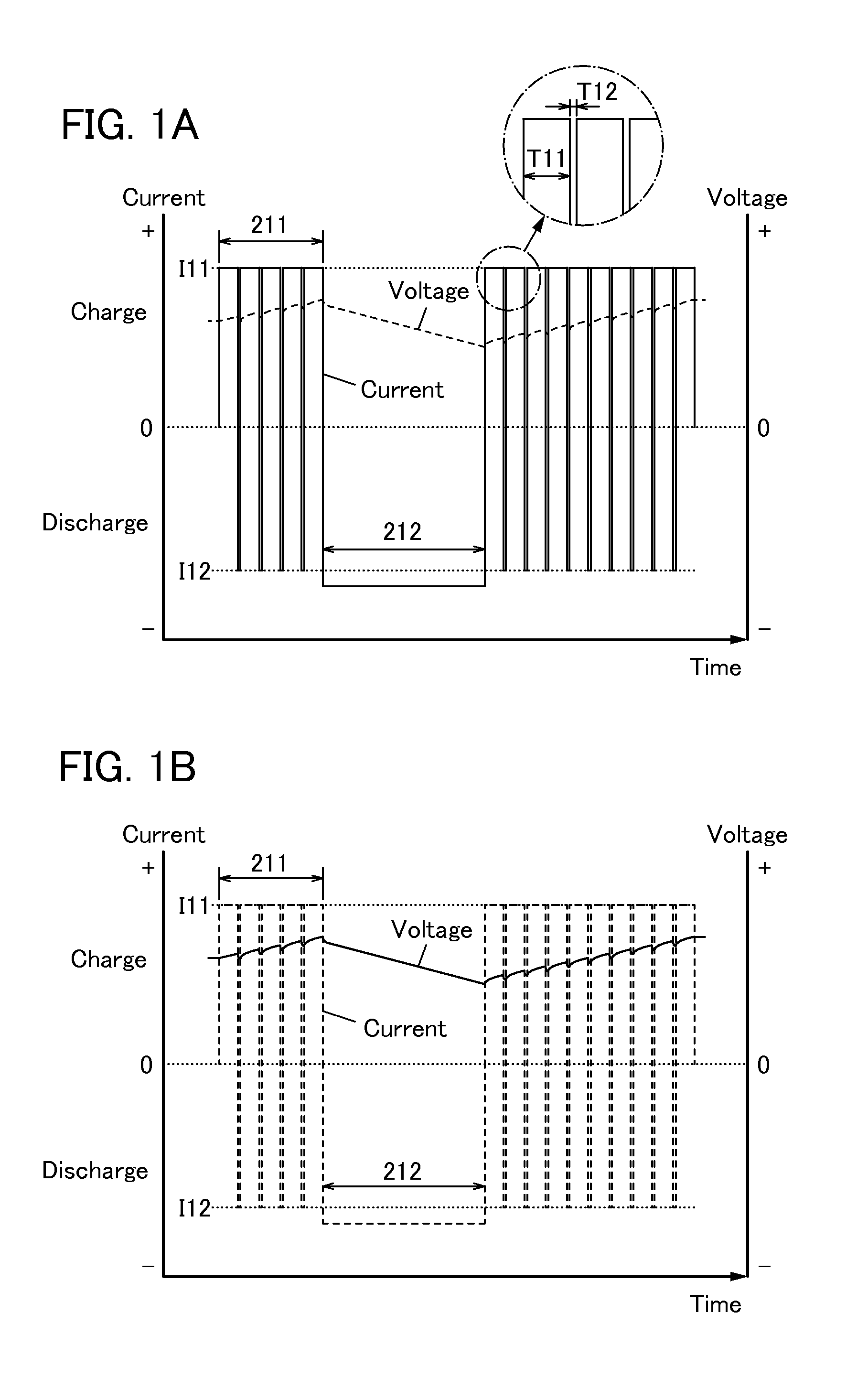
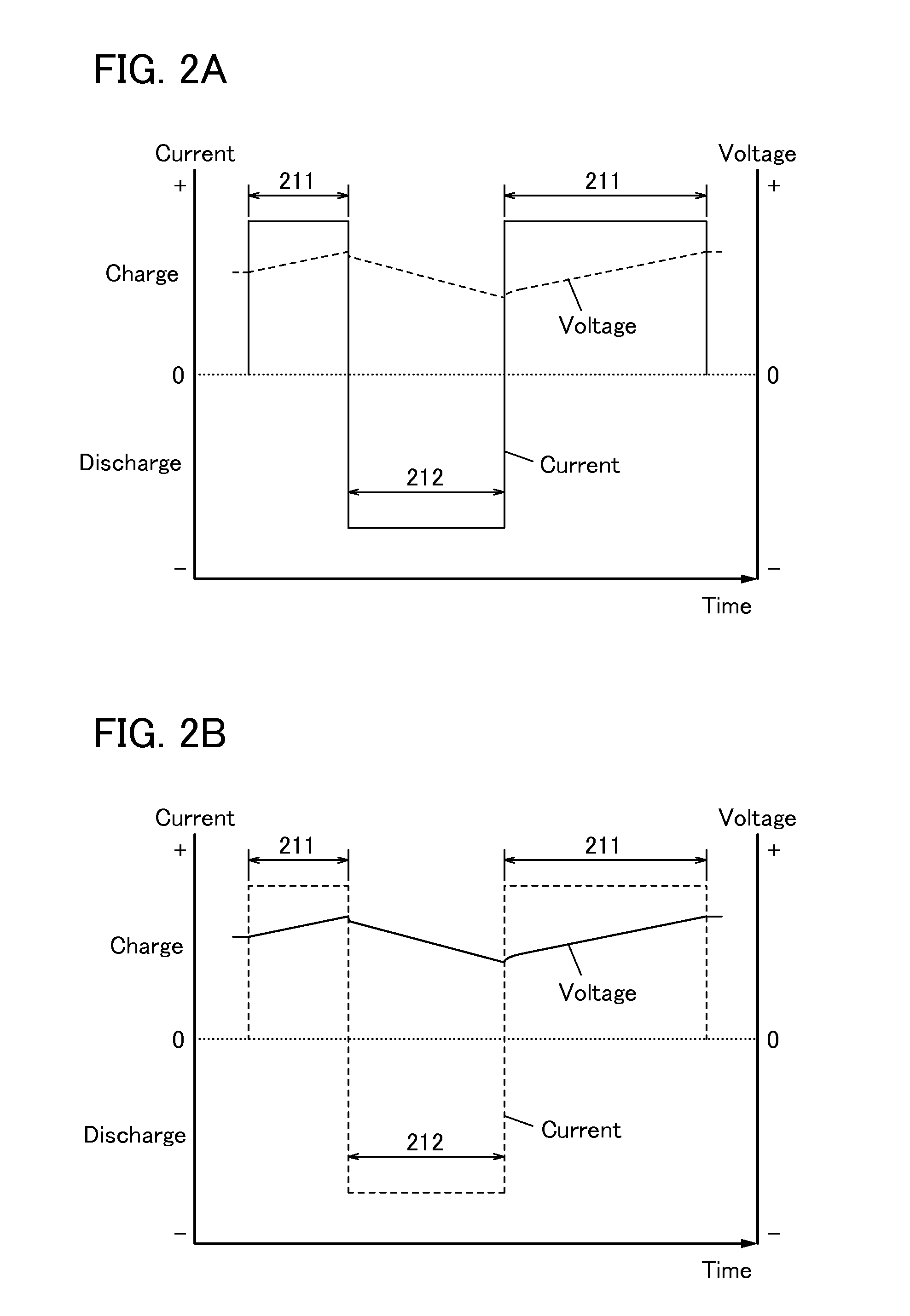
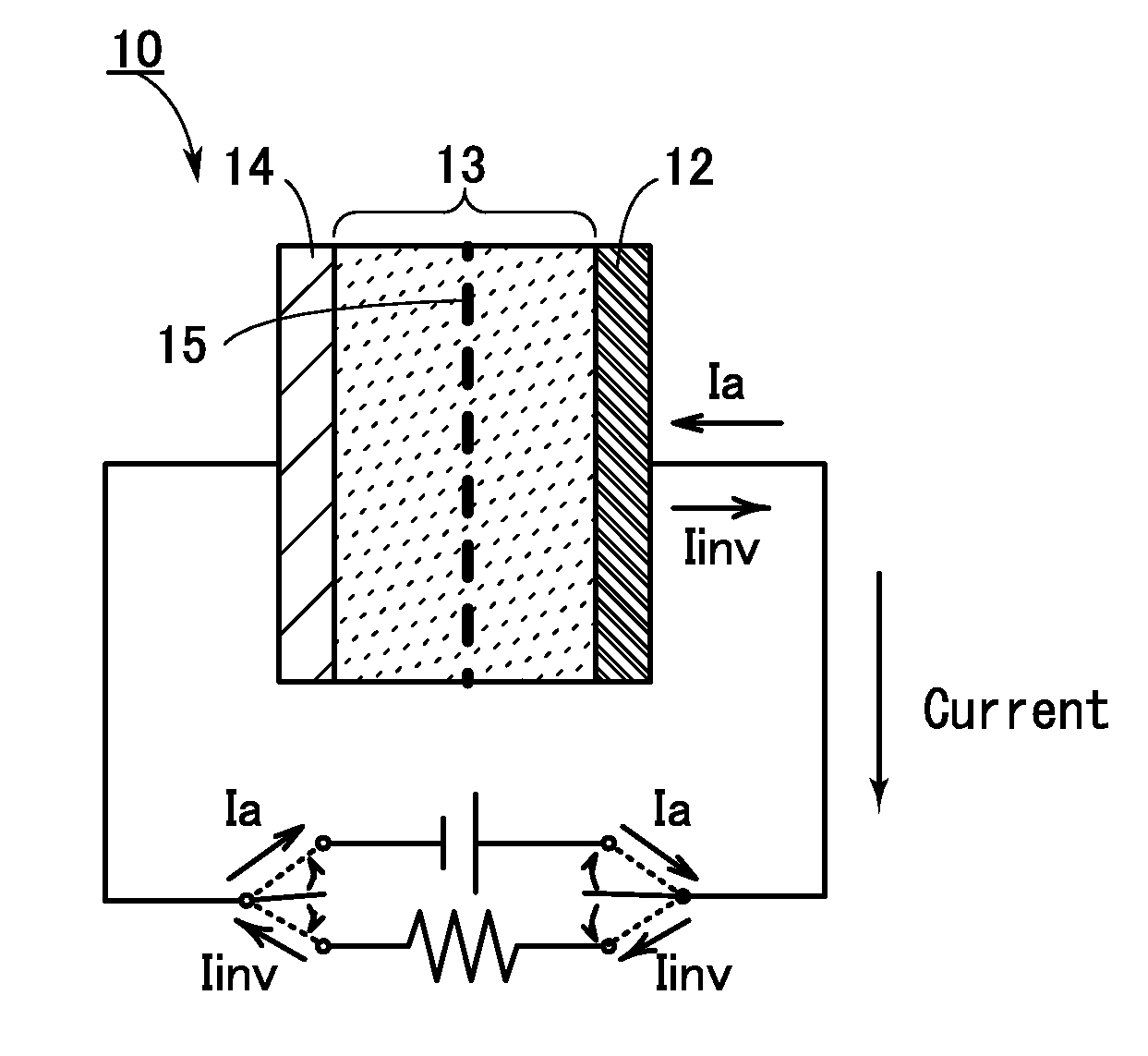
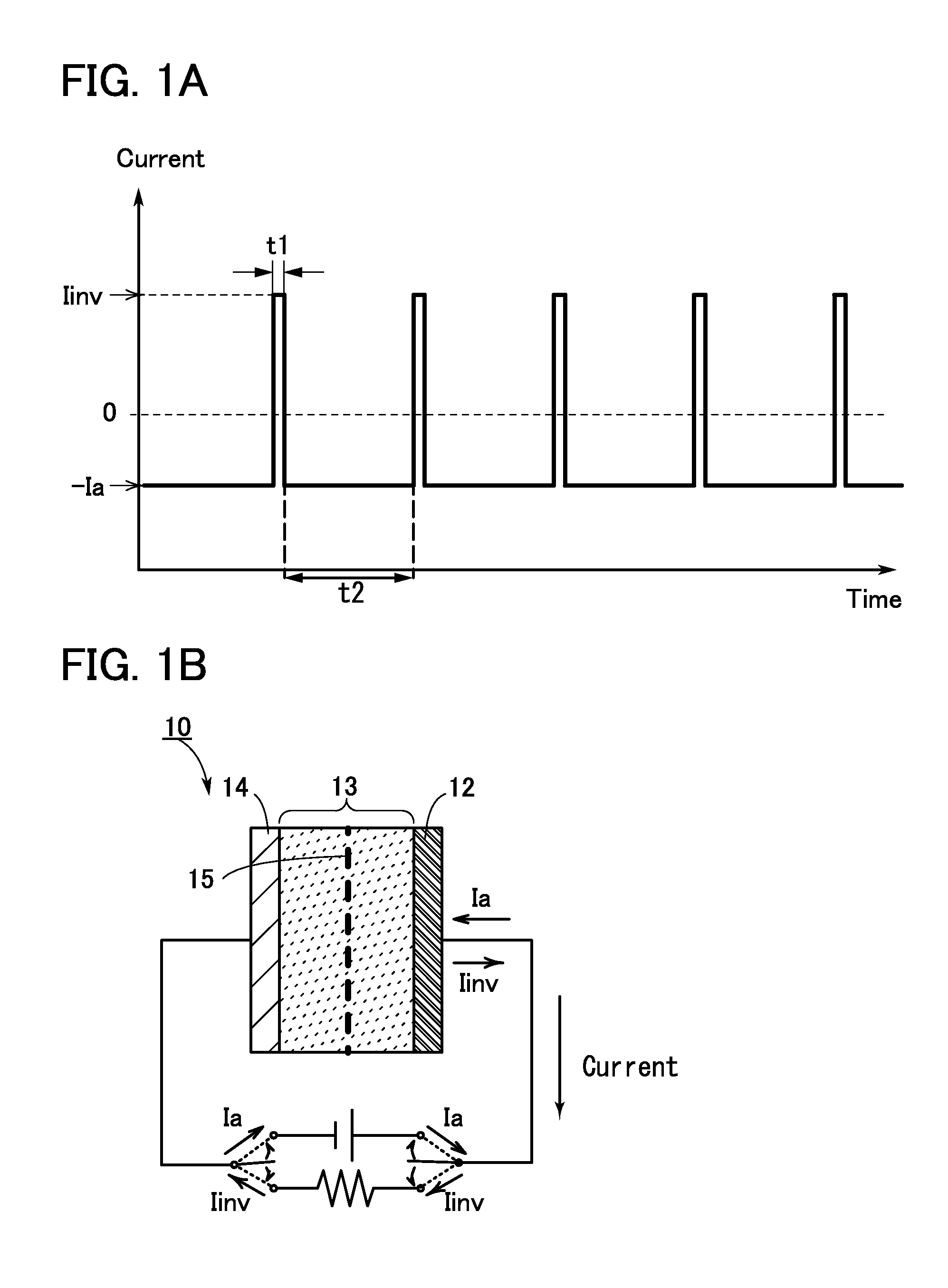
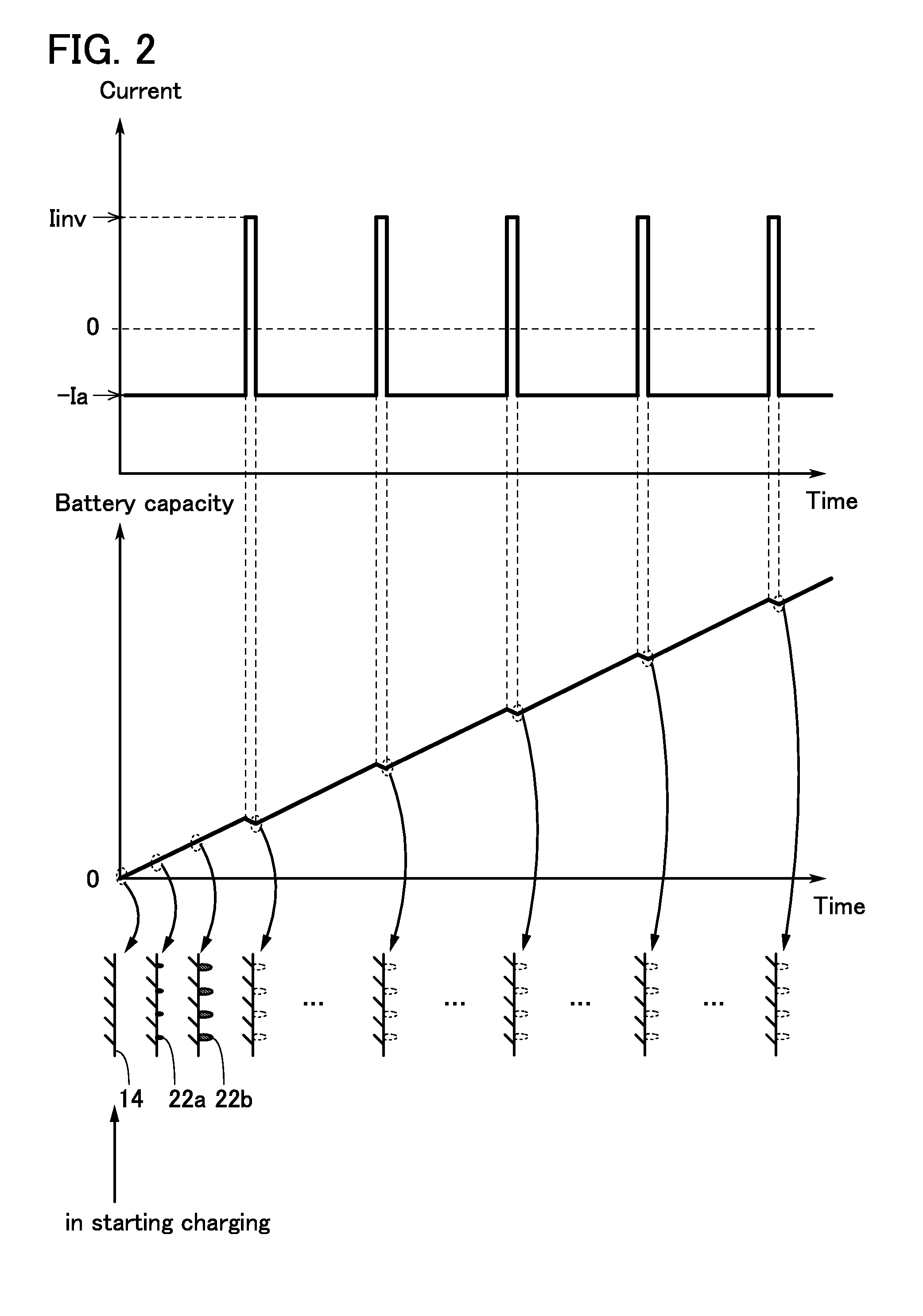
To prevent deterioration of a battery or reduce the degree of deterioration of a battery and to maximize charge and discharge performance of the battery and maintain charge and discharge performance of the battery for a long time. A reaction product formed on an electrode surface causes various malfunctions and deterioration of a battery typified by a lithium-ion secondary battery. The present inventors have found a breakthrough technological idea that a reaction product is prevented from being deposited on an electrode in charging or discharging or a formed reaction product is dissolved by application of an electrical stimulus to an electrochemical device that operates utilizing an electrochemical reaction, typified by a lithium-ion secondary battery. Specifically, the reaction product is dissolved by supplying a signal (inversion pulse current) with which a current flows in the reverse direction of a current with which a reaction product is formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
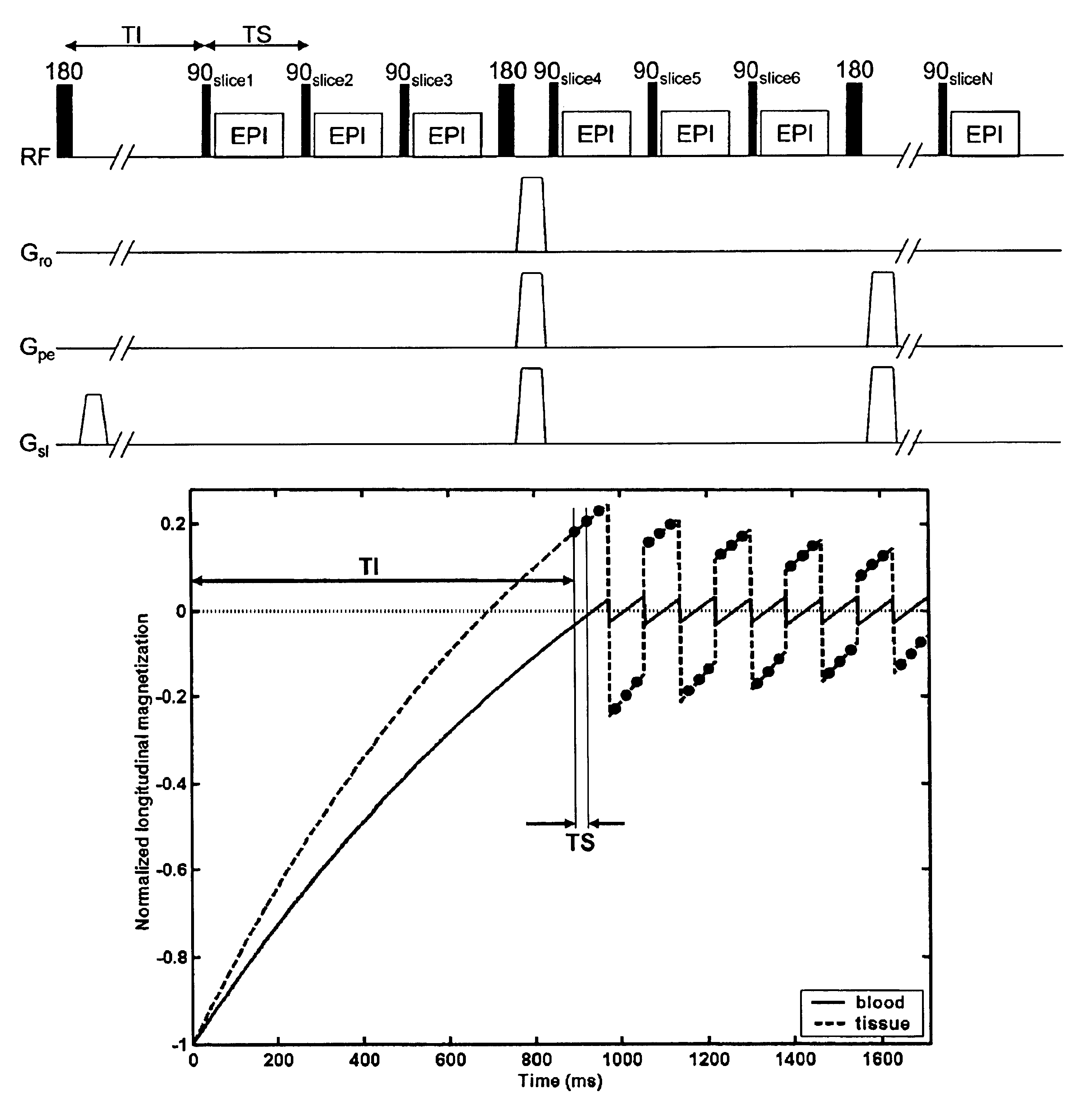
Methods for multiple acquisitions with global inversion cycling for vascular-space-occupancy dependant and apparatuses and devices related thereto
ActiveUS7071689B2Minimize signalingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetizationInversion pulse
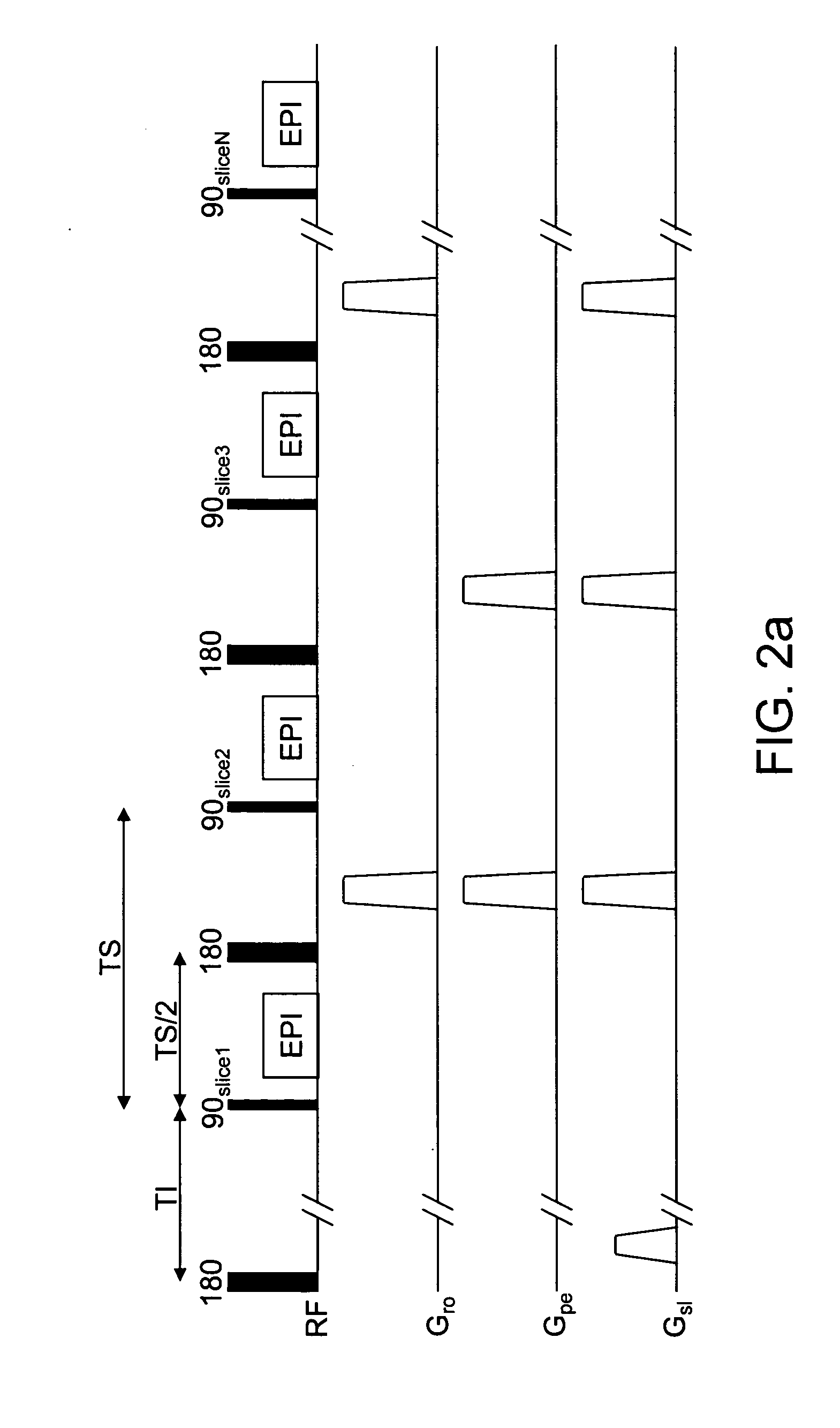
Featured are methods for magnetic resonance imaging in which MR signals of selected tissues, fluid or body components in a target area are desired to be essentially eliminated, which method includes applying an initial RF inversion pulse to invert the magnetization of the selected tissues or to apply any other T1 preparation aimed at nulling one or more tissue species and successively applying one or more RF inversions pulses thereafter. More particularly, the successively applied RF inversion pulses are applied so as to essentially maintain the magnetization of the selected tissues at or about the zero-crossing point of the longitudinal magnetization. Such methods further include interleaving a plurality of excitation pulses for acquiring image data and the RF inversion pulses so that at least one of the plurality of excitation pulses follows in a time sequence the application of one of the applied RF inversion pulses such that the image data is acquired following an inversion pulse.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Pulse-width modulation amplifier and suppression of clipping therefor
ActiveUS7315202B2Avoid excessive currentAvoid it happening againAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlLeading edgeAudio power amplifier
A pulse-width modulation (PWM) amplifier is adapted to a class-D amplifier in which an analog input signal is subjected to integration, pulse-width modulation, and switched amplification, wherein a glitch elimination circuit eliminates noise from a pulse-width modulated signal, from which a high pulse signal and a low pulse signal are isolated such that each pulse is delayed by a dead time at the leading-edge timing thereof. When both of them are simultaneously set to a high level, one of them is reduced in level. In response to the occurrence of clipping, an integration constant applied to an operational amplifier is automatically changed from a primary integration constant to a secondary integration constant. When the clipped state is sustained for a prescribed time, an inversion pulse is compulsorily introduced into the pulse-width modulated signal.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
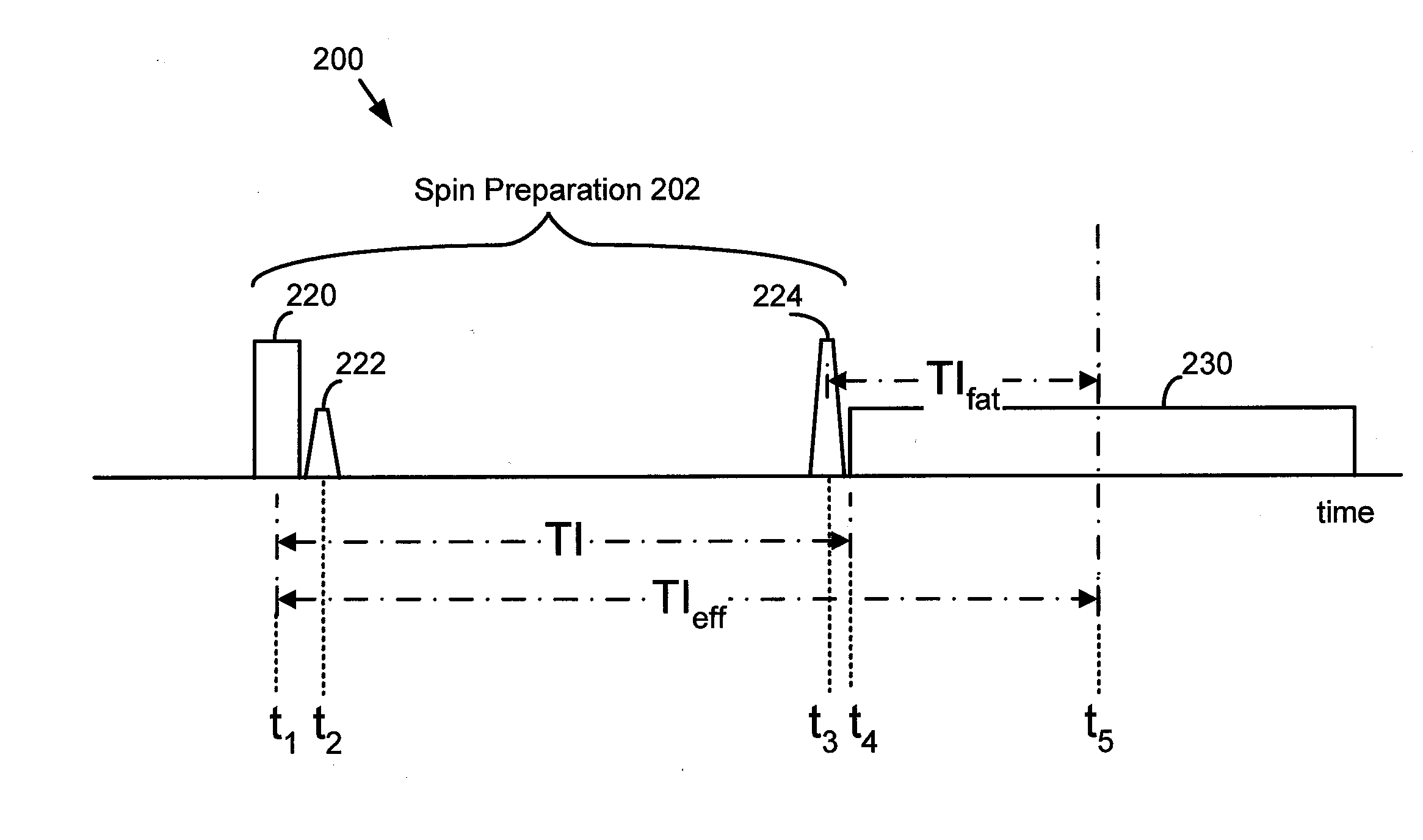
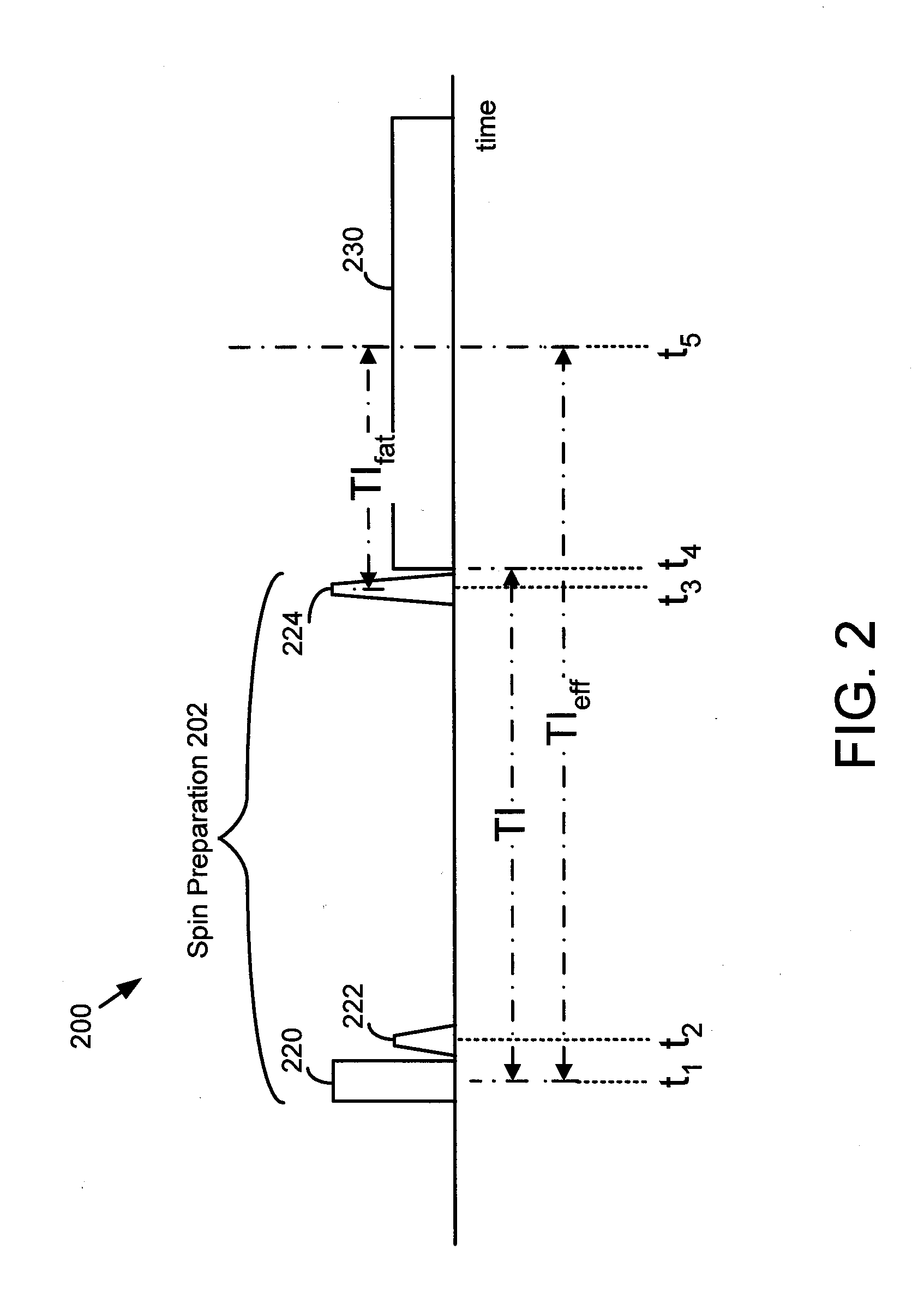
Method and apparatus for generating a magnetic resonance image
A method for generating a magnetic resonance image includes a series of inversion and saturation pulses, in which the pulses null the MRI signal from both fat and a second tissue for a single MRI acquisition. An inversion pulse is used to provide a null point for the second tissue. A pair of fat-selective saturation and inversion pulses are used to null the MRI signal from fat at approximately the same time as the second tissue reaches its null point. The saturation pulse is used to create a known state for the fat magnetization, allowing the flip angle of the fat-selective inversion pulse to be determined such that the null point of fat approximately coincides with the null point of the second tissue.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus of gradient echo imaging with on-the-fly optimization of tissue suppression
InactiveUS20050070785A1Minimize timeSuppress signalDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData acquisitionMagnetization
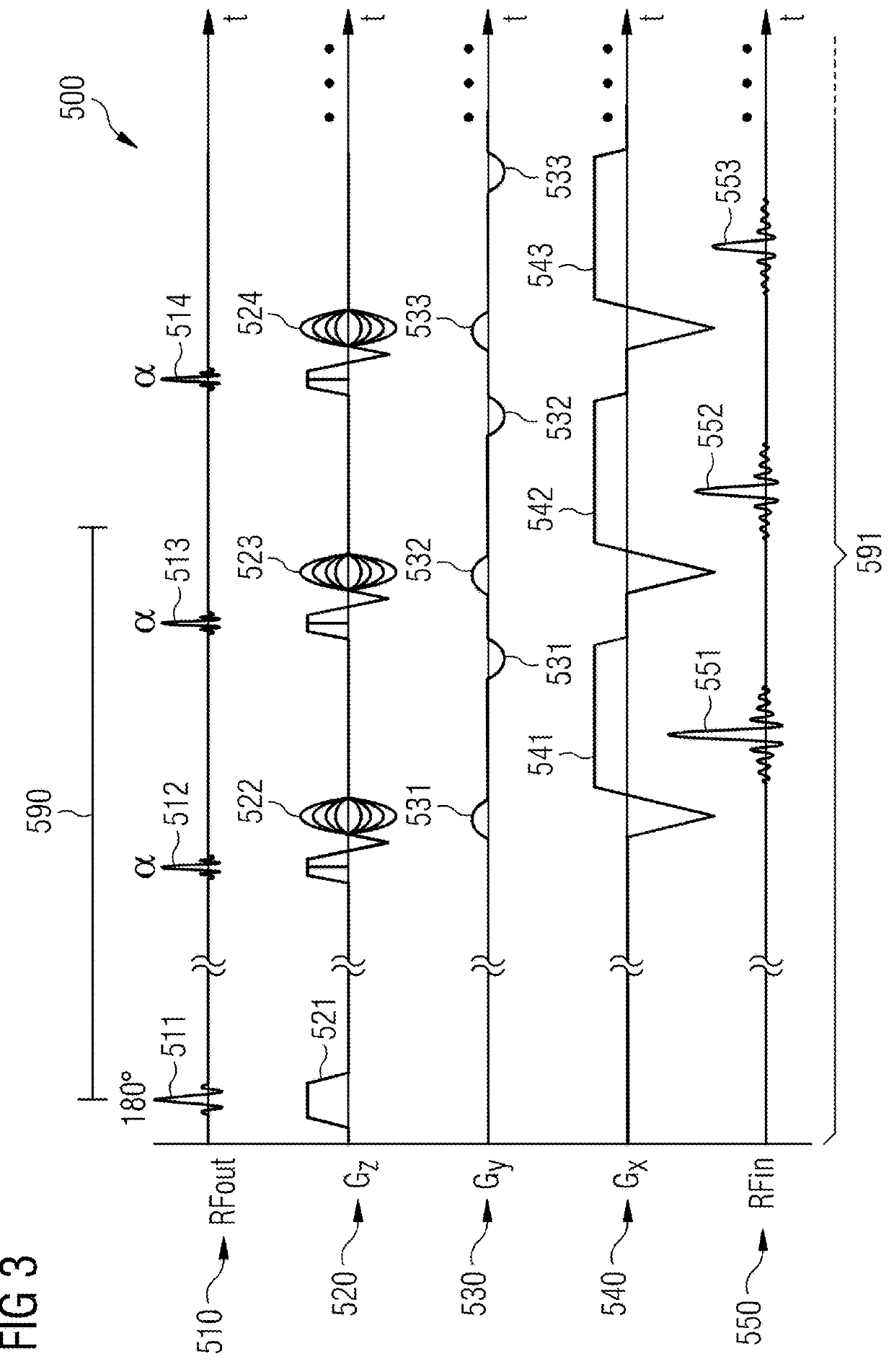
The present invention provides a system and method for on-the-fly optimization of the timing of suppression pulses and a k-space filling scheme for user-prescribed imaging parameters. The invention also minimizes total data acquisition time for the sequence tailored to the particular user-prescribed imaging parameters. A pulse sequence uses a 180° pulse to invert the magnetization corresponding to the suppressed tissue so that a maximum amount of time is provided to play out alpha or imaging pulses after each inversion. The pulse sequence optimizes the number of alpha pulses played out after each inversion pulse based on a specific protocol or imaging parameters selected by the user. This pulse sequence allows for a modified k-space filling scheme that places, at the center of k-space, the echo that most closely corresponds to the null point of the suppressed tissue. For the first inversion pulse, a flip angle less than 180° is used to drive the suppressed tissue magnetization into a steady-state condition immediately.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
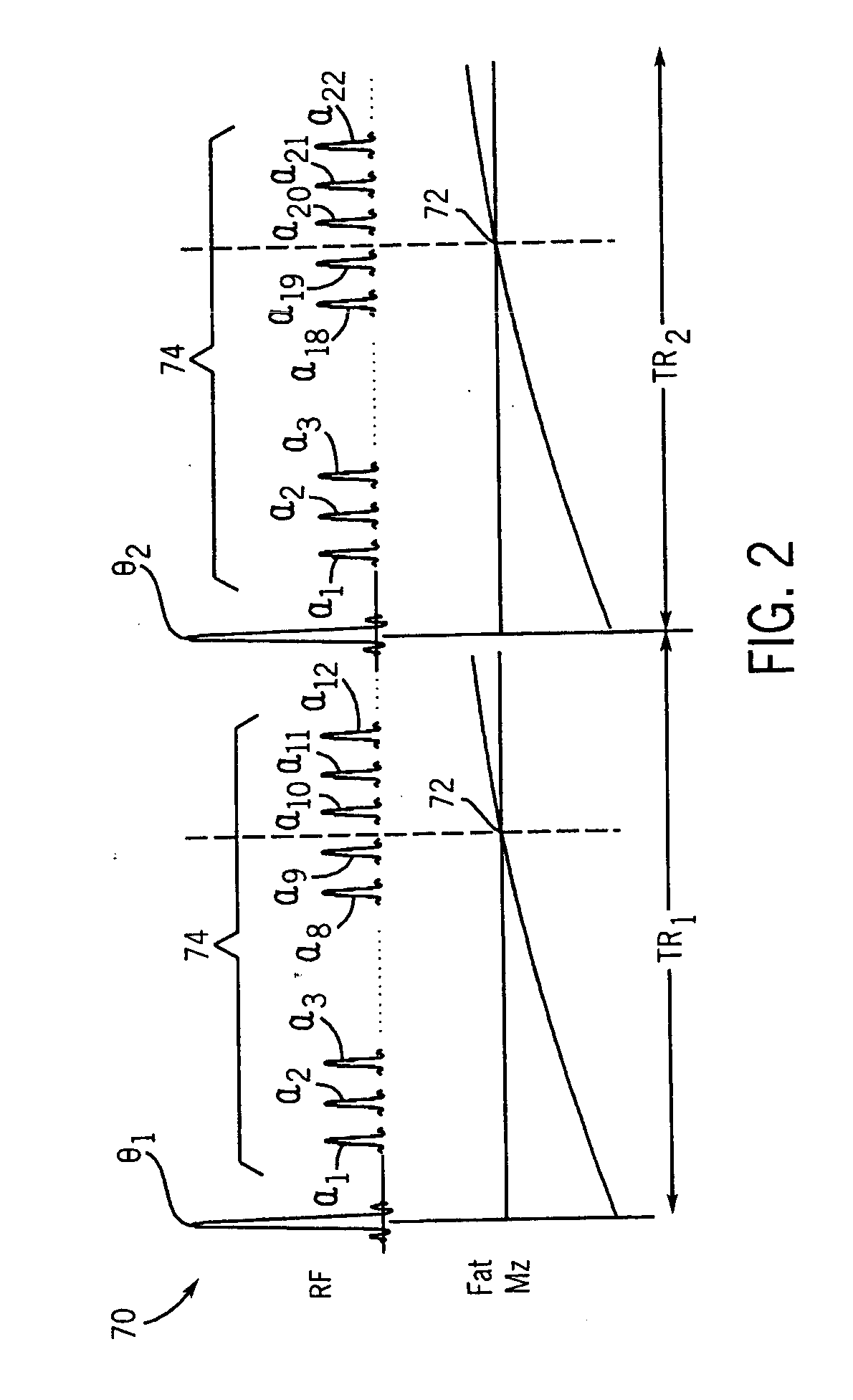
Microvascular blood volume magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20050215881A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientRed blood cell
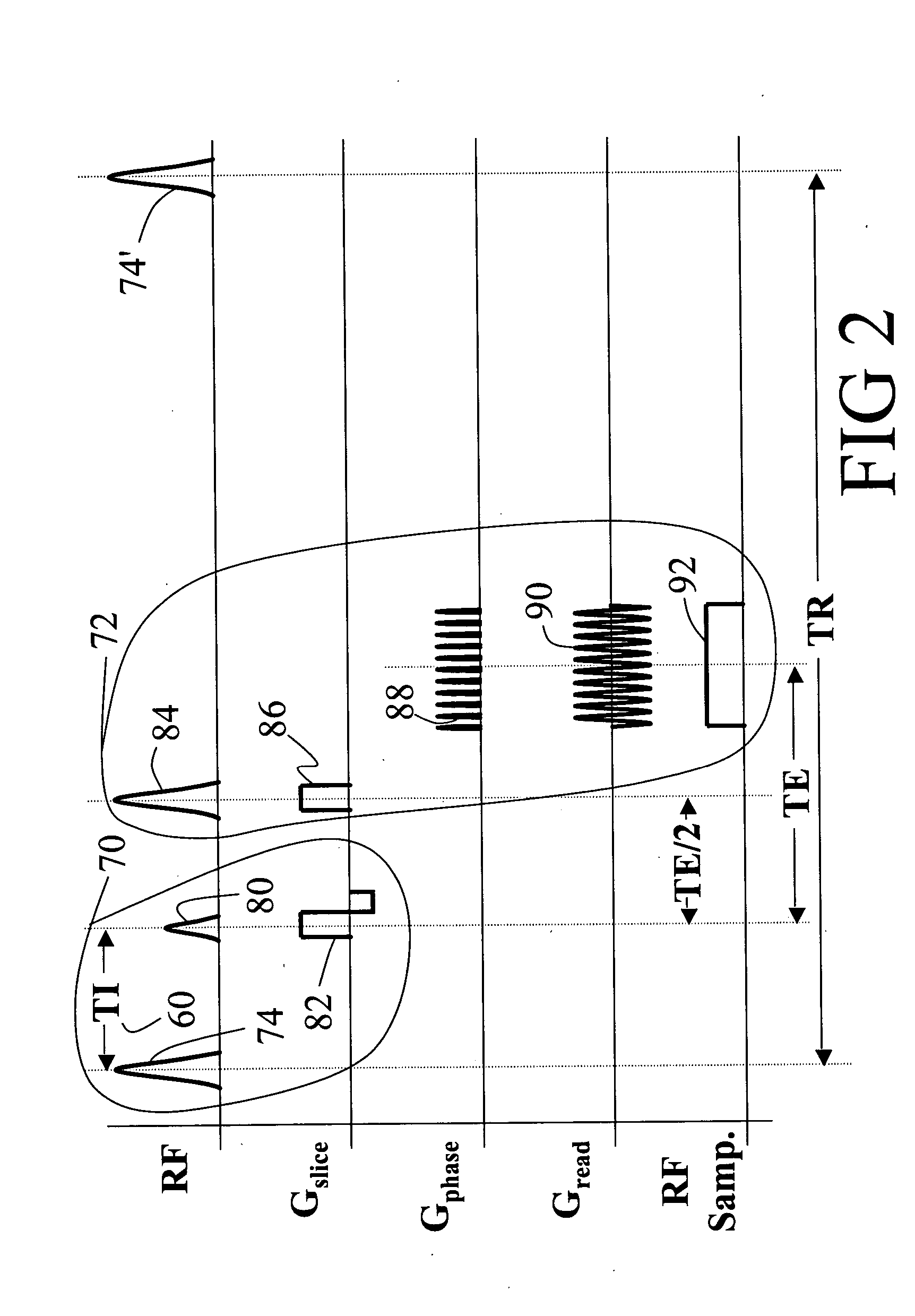
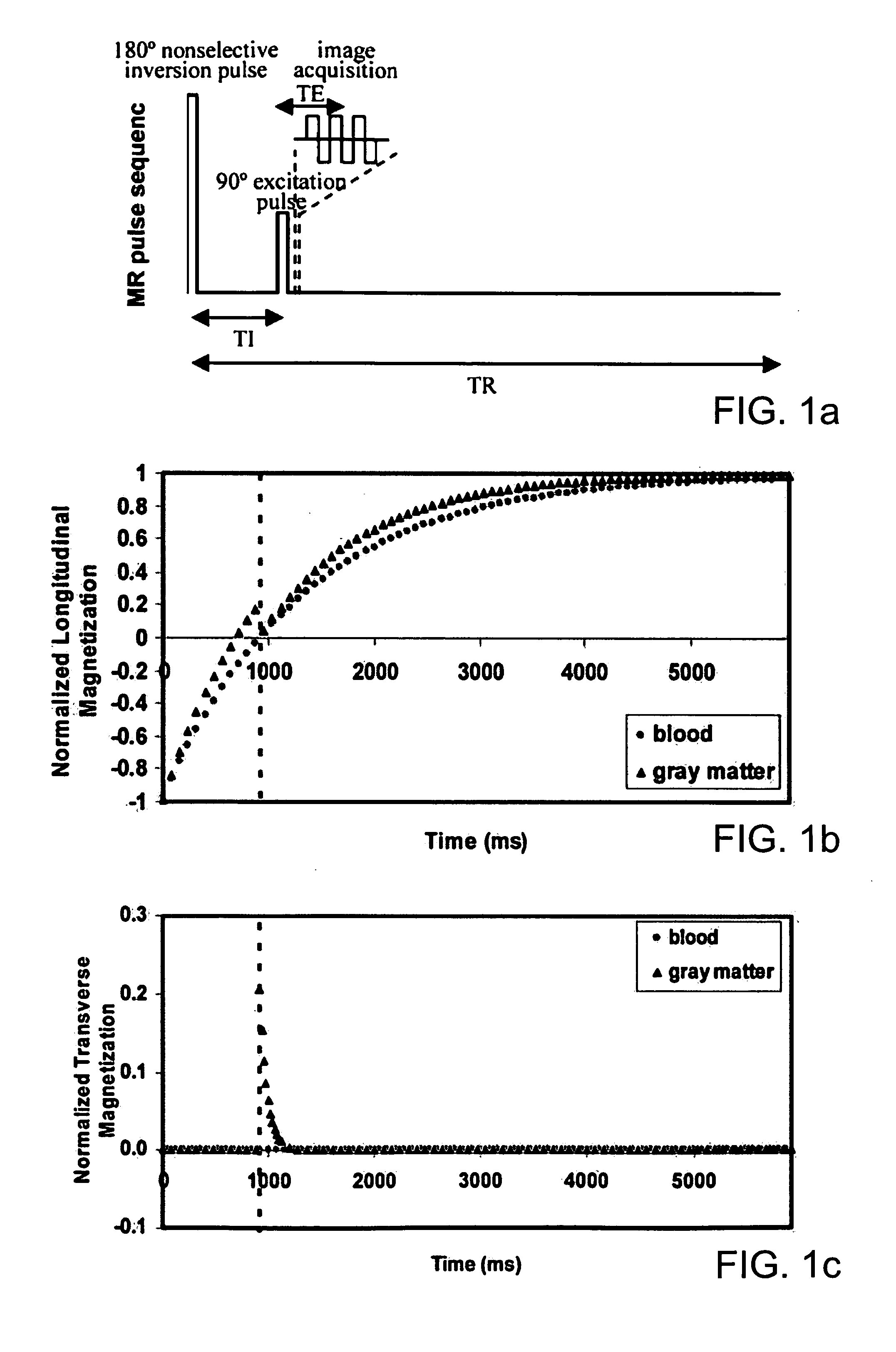
A magnetic resonance imaging system includes a magnetic resonance imaging scanner (10) that performs an inversion recovery magnetic resonance excitation sequence (70) having a blood-nulling inversion time (60) determined based on a blood T1 value appropriate for a selected magnetic field and blood hematocrit, whereby magnetic resonance of blood is substantially nulled. The inversion recovery excitation sequence (70) includes an inversion radio frequency pulse (74) applied with a small or zero slice-selective magnetic field gradient pulse to avoid inflow effects, and an excitation radio frequency pulse (80). The inversion pulse (74) and excitation pulse (80) are separated by the inversion time (60). The magnetic resonance imaging scanner (10) subsequently performs a readout magnetic resonance sequence (72) or spectroscopy sequence to acquire a magnetic resonance signal from tissue other than the nulled blood. A reconstruction processor (44) generates a reconstructed image from the acquired magnetic resonance signal.
Owner:KENNEDY KRIEGER INST
Electrochemical device
InactiveUS20140239905A1Secure and improve long-term reliabilityConsiderable costPrimary cellsSecondary cells charging/dischargingEngineeringElectrochemistry
Deterioration of a battery is prevented or the degree of deterioration of a battery is reduced, and charge and discharge performance of the battery is maximized and the charge and discharge performance of the battery is maintained for a long time. In a battery such as a sodium-ion secondary battery, various malfunctions or deterioration is caused by a reaction product deposited on an electrode surface. The reaction product is dissolved by applying a signal (inversion pulse current) to make a current flow in a direction opposite to a direction in which the reaction product is formed more than once in charging or discharging.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Methods for multiple acquisitions with global inversion cycling for vascular-space-occupancy dependant and apparatuses and devices related thereto
ActiveUS20050030024A1Minimize signalingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetizationInversion pulse
Featured are methods for magnetic resonance imaging in which MR signals of selected tissues, fluid or body components in a target area are desired to be essentially eliminated, which method includes applying an initial RF inversion pulse to invert the magnetization of the selected tissues or to apply any other T1 preparation aimed at nulling one or more tissue species and successively applying one or more RF inversions pulses thereafter. More particularly, the successively applied RF inversion pulses are applied so as to essentially maintain the magnetization of the selected tissues at or about the zero-crossing point of the longitudinal magnetization. Such methods further include interleaving a plurality of excitation pulses for acquiring image data and the RF inversion pulses so that at least one of the plurality of excitation pulses follows in a time sequence the application of one of the applied RF inversion pulses such that the image data is acquired following an inversion pulse.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Imaging method for MRI contrast enhancement
ActiveCN104161517ASolve the scan time is too longReduce usageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInversion recoveryPhase sensitive
The invention discloses an imaging method for MRI contrast enhancement. Optimized inversion pulses are utilized to replace inversion pulses of a conventional inversion recovery sequence in MRI and to restore delay time, under the precise control of the optimized pluses, spin of different tissue will be evolved towards the trend of maximization of longitudinal magnetic moment differences, and the maximum longitudinal magnetic moment difference is obtained at the end moment of the pluses; on that basis, 90-degree excitation read pluses are applied to enable the maximized magnetic moment difference among the tissue to be turned over to a transverse plane, gradient echo signals are collected to form k spatial data, and the purpose of contrast enhancement among the tissue can be finally achieved through improvement on a phase sensitive image reconstruction method. According to the imaging method, the problem of too long scanning time of the conventional inversion recovery sequence is solved, the advantages of flexibility of optimized pulse waveforms and flexibility of the phase sensitive image reconstruction method are fully utilized, use of expensive magnetic resonance contrast media can be avoided, and the imaging method is superior to an existing MRI contrast enhancement method both in performance and in cost.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
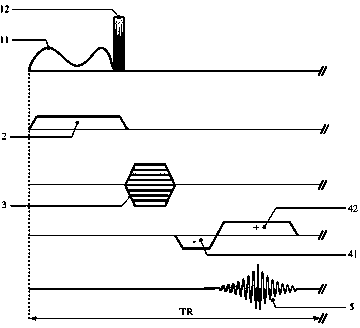
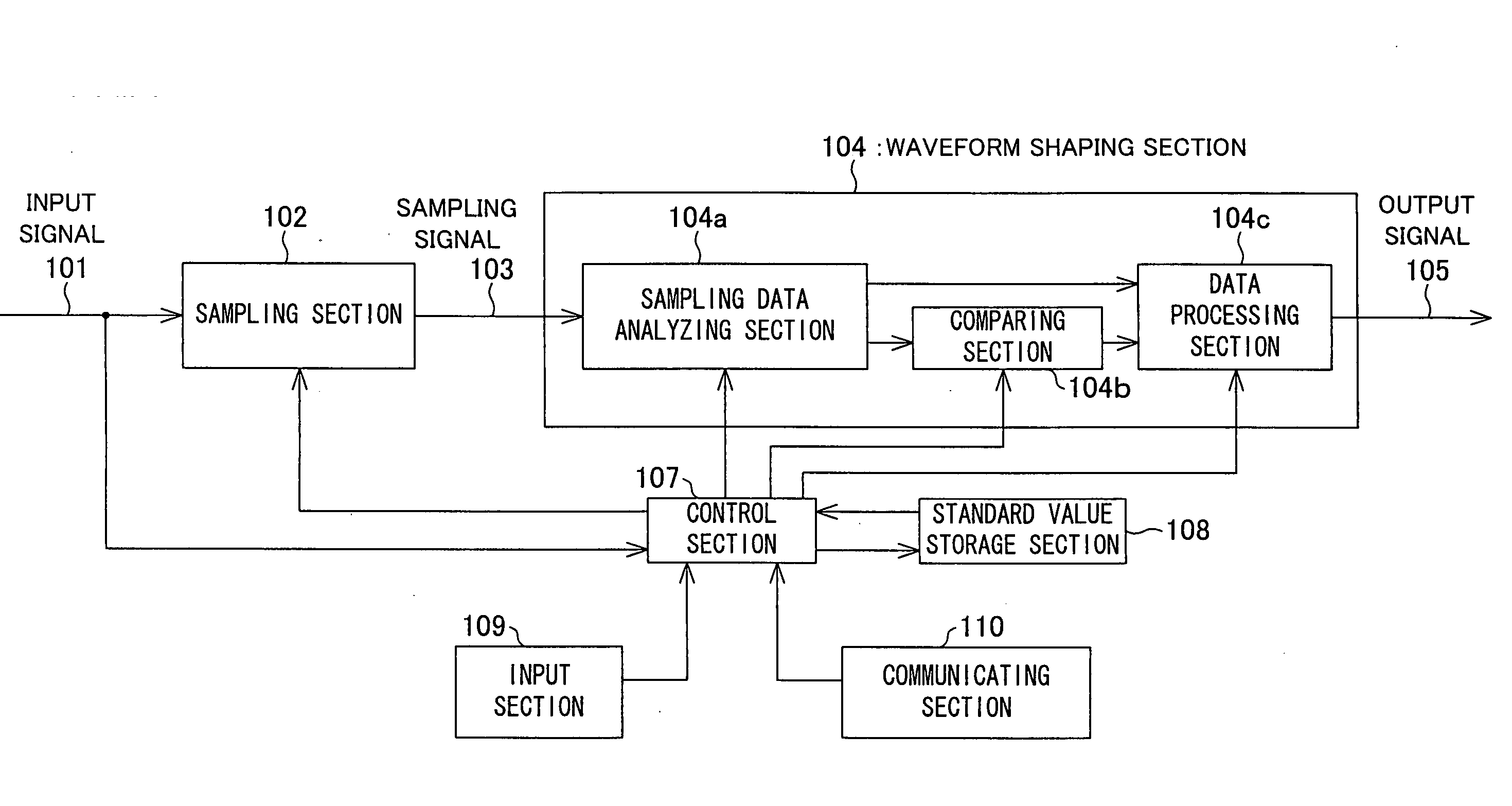
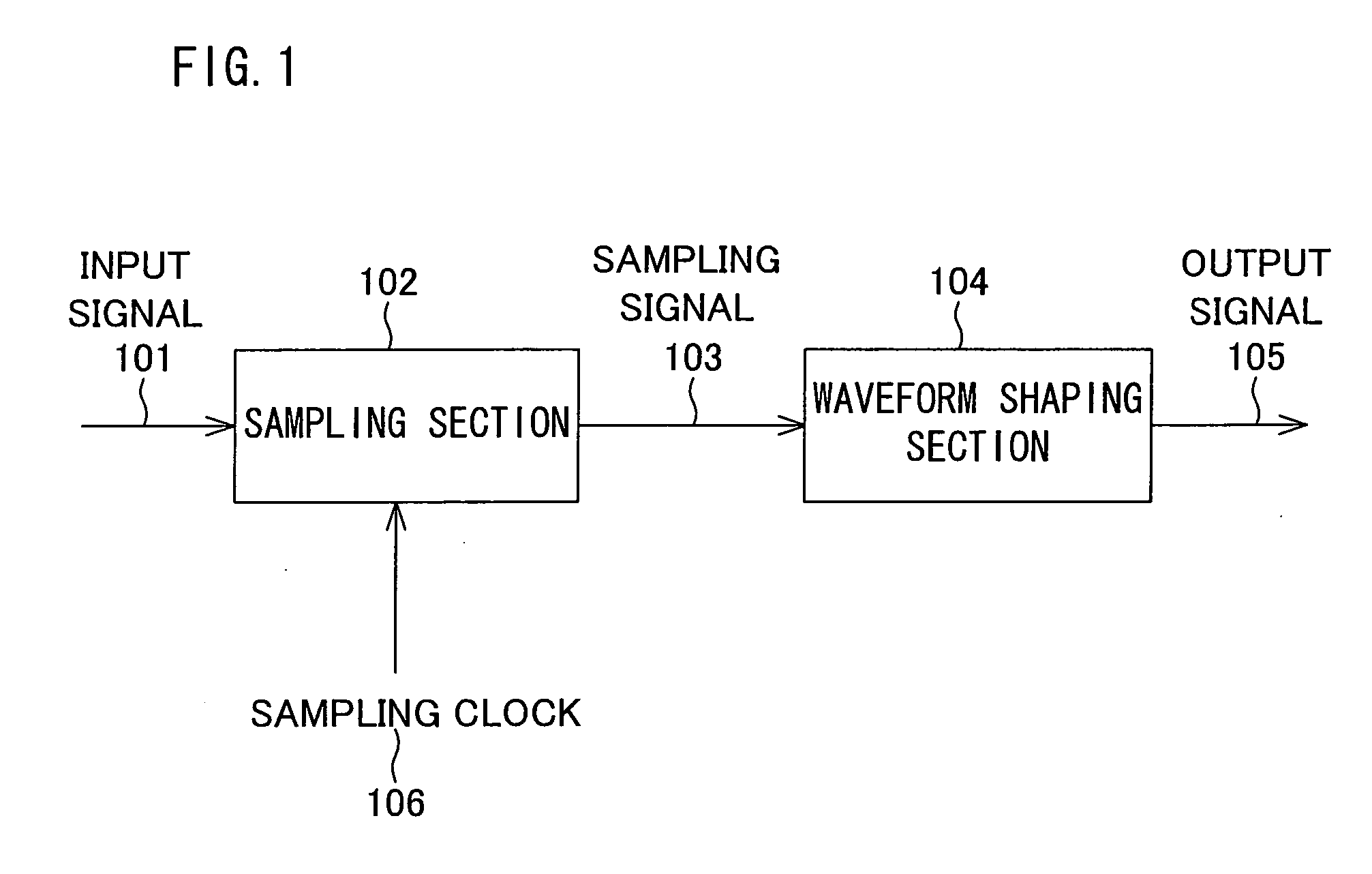
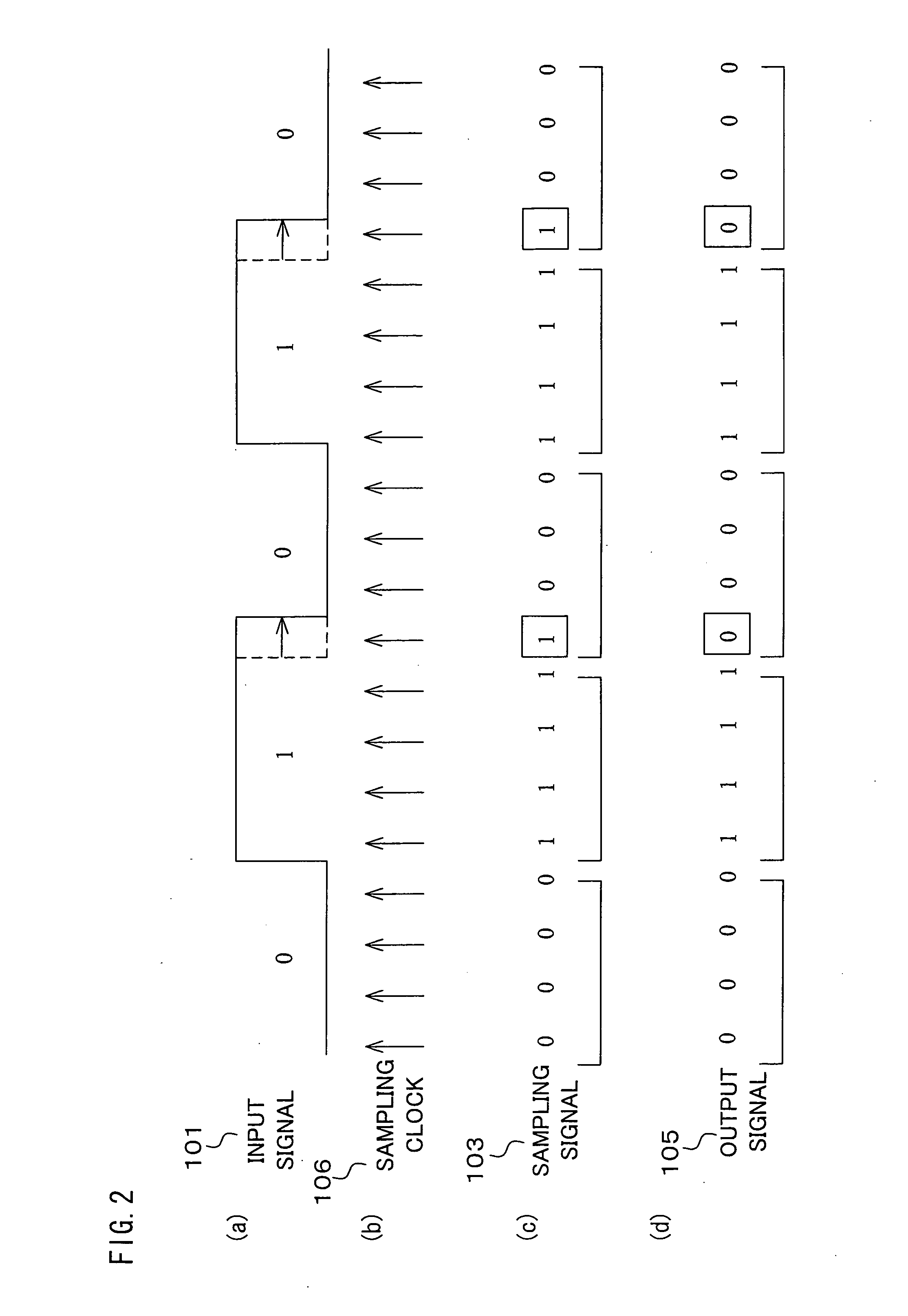
Waveform shaping method, waveform shaping device, electronic device, waveform shaping program and recording medium
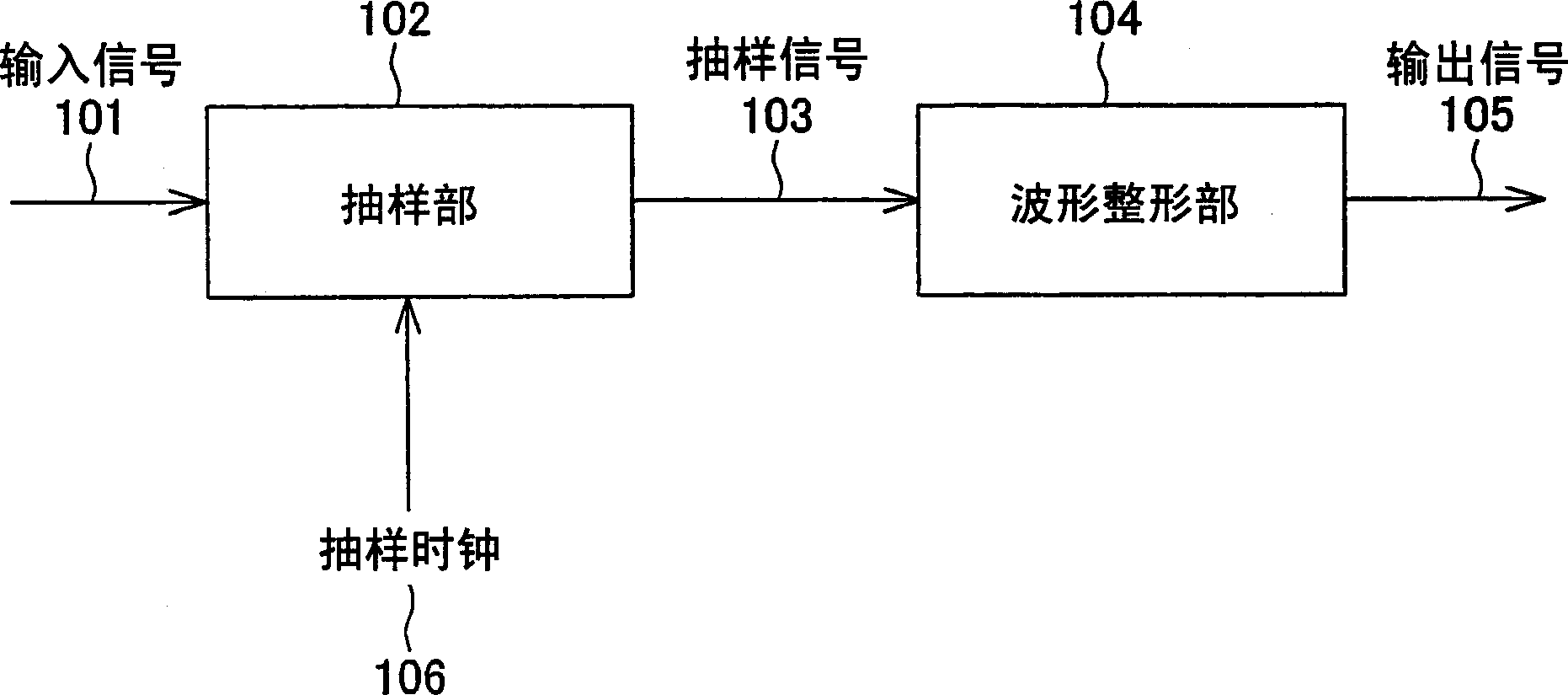
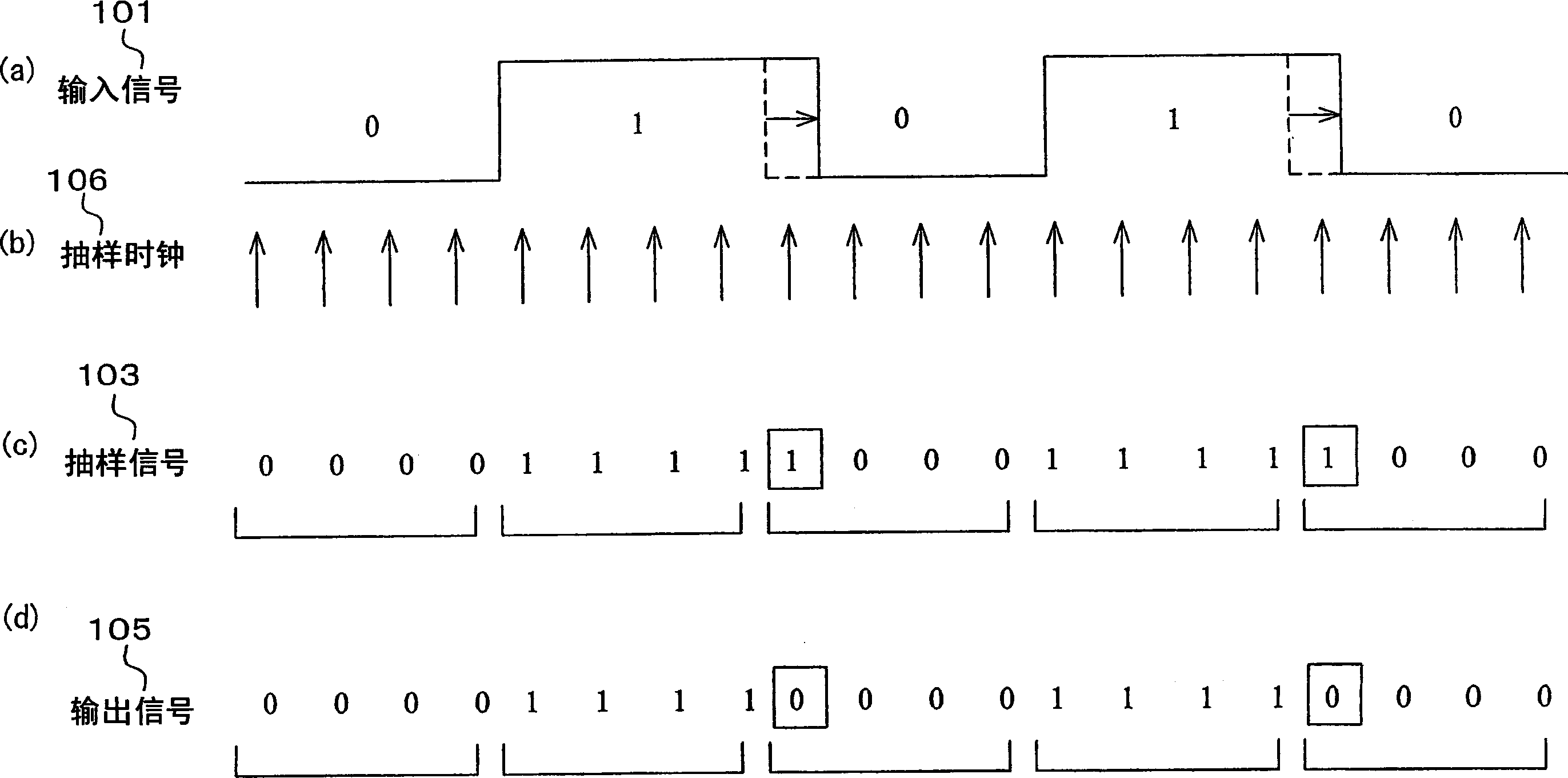
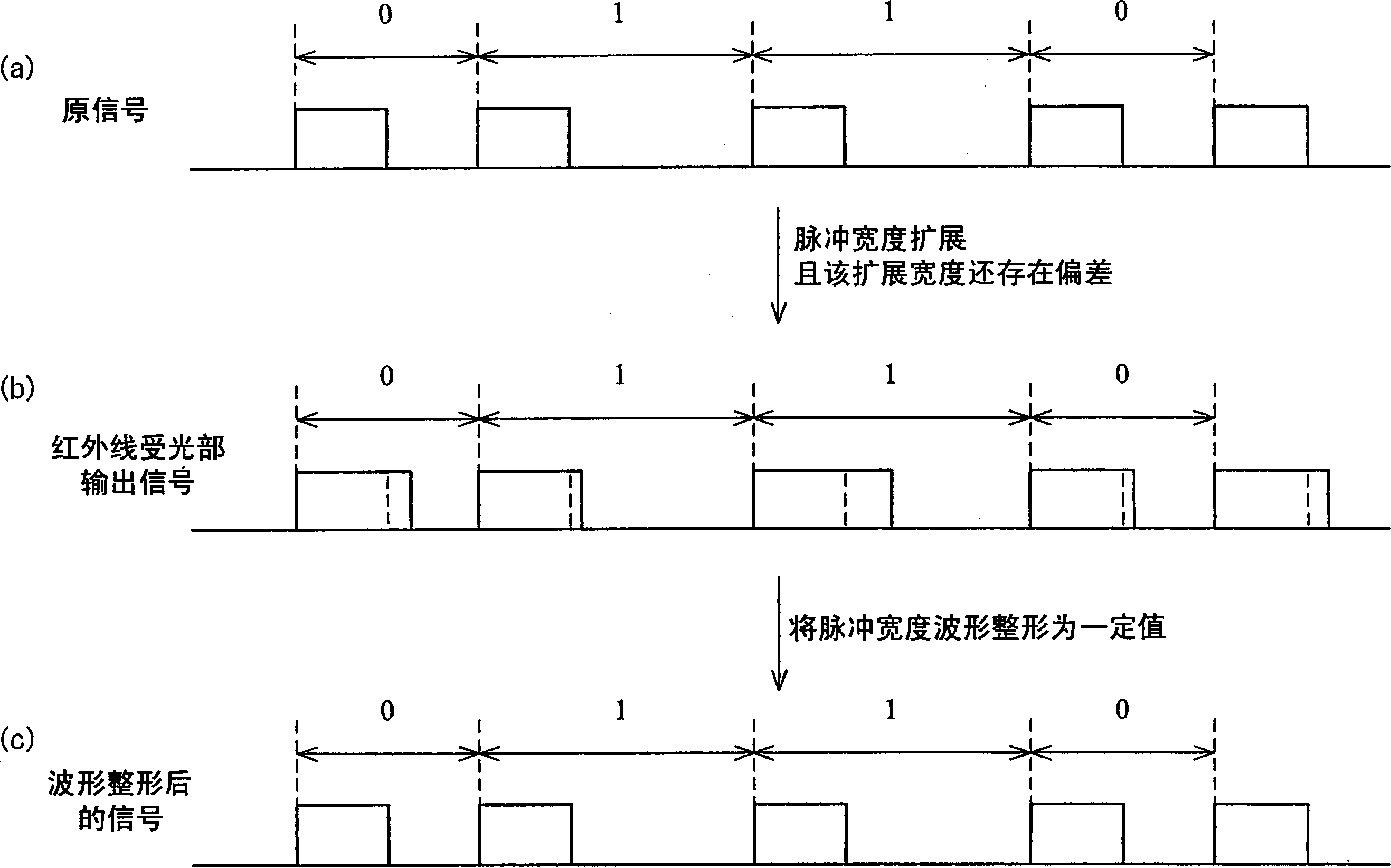
InactiveUS20060274872A1Prevent information contained in input signalAccurate informationModification of read/write signalsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsWaveform shapingEngineering
A sampling section (102) is provided for generating a sampling signal (103) by sampling an input signal (101) using a sampling clock (106) which is faster than a data speed of the input signal (101). A waveform shaping section (104) is provided for I) processing (e.g. inverting a pulse) the sampling signal (103), so as to shape a restored digital signal obtained from a pulse of the input signal (101), and II) outputting the restored digital signal as an output signal (105). In this way, it becomes possible to provide: A) a waveform shaping method and a waveform shaping device, each of which is capable of correcting distortion in an input signal by means of a simple method or configuration; B) a waveform shaping program that realizes the waveform shaping method or the waveform shaping device; and C) a recording medium storing therein the waveform shaping program.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging to create T1 maps
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging on the basis of a gradient echo sequence
ActiveUS8165657B2Sharp contrastMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringImage contrastResonance
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging on the basis of a gradient echo sequence by excitation of nuclear spins and measurement of radio-frequency signals arising from the excited nuclear spins:(a) the magnetization of the spins is prepared by an inversion pulse;(b) a number of steps for spin excitation are implemented as well as acquisition of an RF response signal for a first image contrast, with the measurement data being acquired along a first two-dimensional slice, and this first two-dimensional slice being parallel to a plane spanned by two coordinate axes x, y standing orthogonal to one another;(c) implementation of a number of steps for spin excitation as well as acquisition of an RF response signal for a second image contrast, with the measurement data being acquired along the first two-dimensional slice that exist in (b); and(d) repetition of steps (a) through (c) for further two-dimensional slices that are offset parallel to the first two-dimensional slice along a third coordinate axis z that is orthogonal to the first two coordinate axes x and y.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Vehicle including power storage unit
ActiveUS20140203738A1Inhibit deteriorationEasy to solidifyHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsLithiumEngineering
Deterioration of a power storage unit included in a vehicle is prevented or the power storage unit that has deteriorated is repaired, and the charge and discharge performance of the power storage unit is maximized to be maintained for a long time. Attention has focused on a reaction product formed on an electrode surface which causes malfunction or deterioration of a power storage unit such as a lithium-ion secondary battery. In the power storage unit used for a vehicle that runs on the power of an electric motor, rapid discharge occurring in the acceleration of the vehicle or the like tends to promote the solidification of the reaction product. The reaction product is removed by application of an electrical stimulus, specifically, an inversion pulse voltage.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
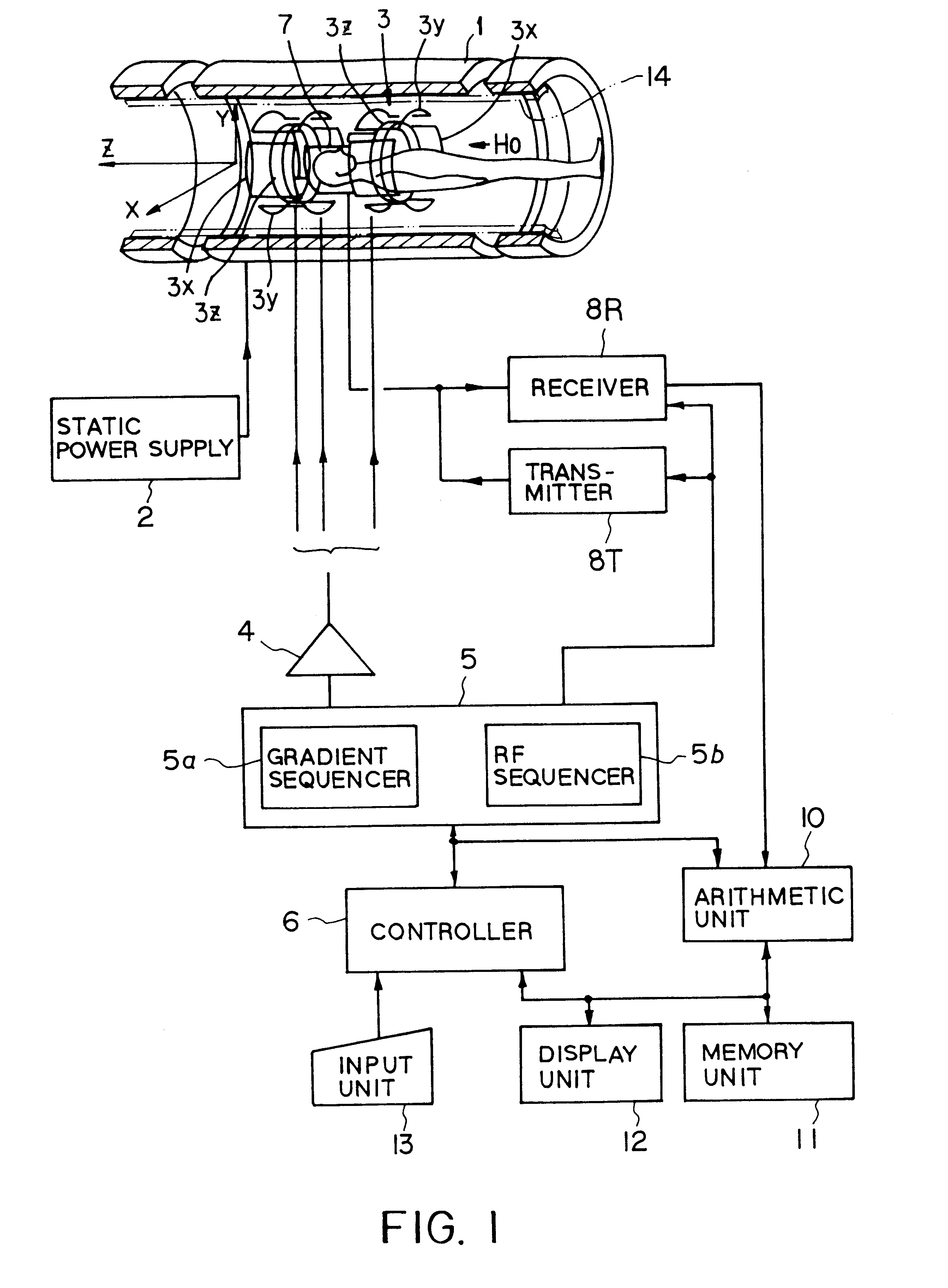
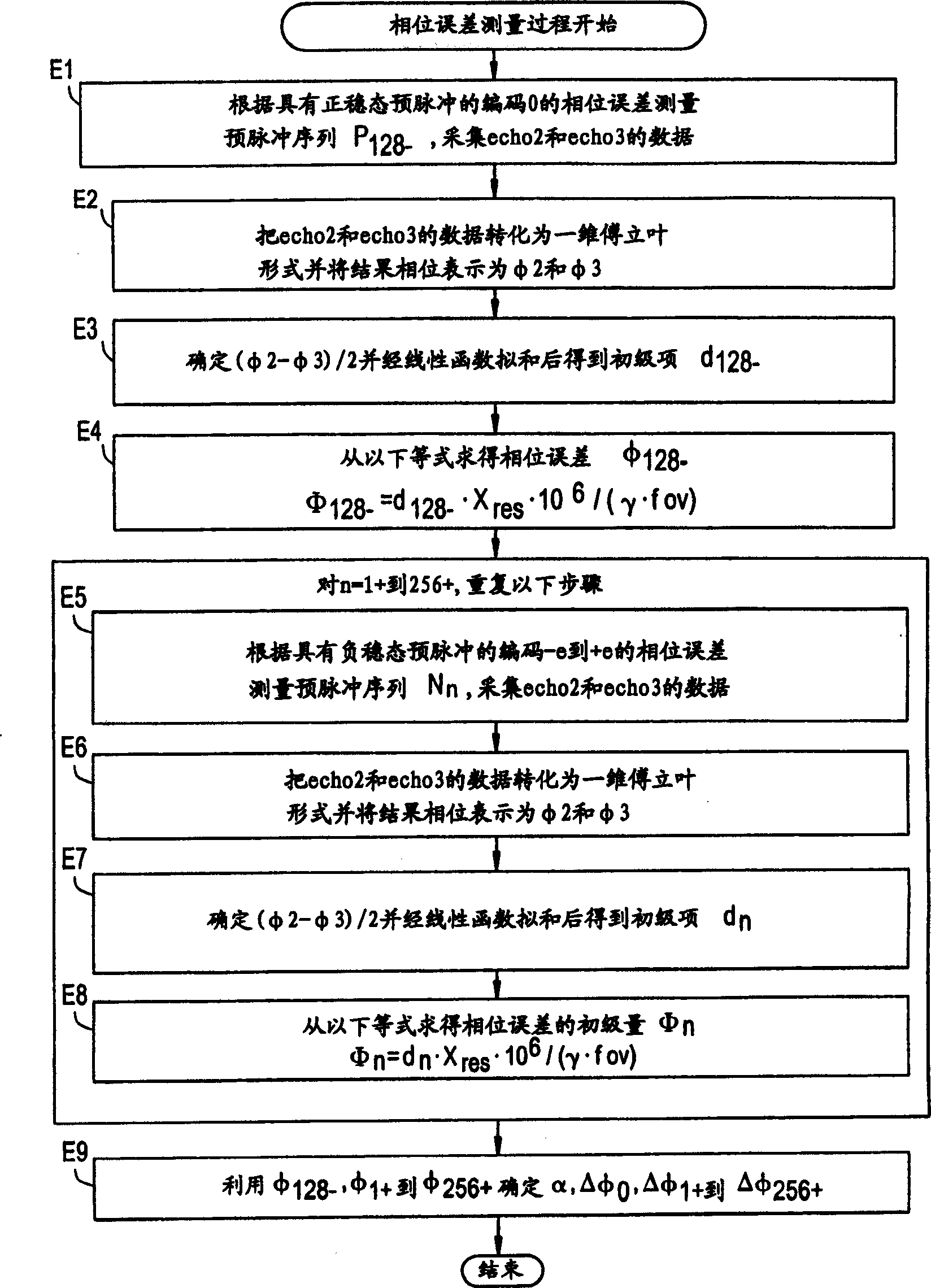
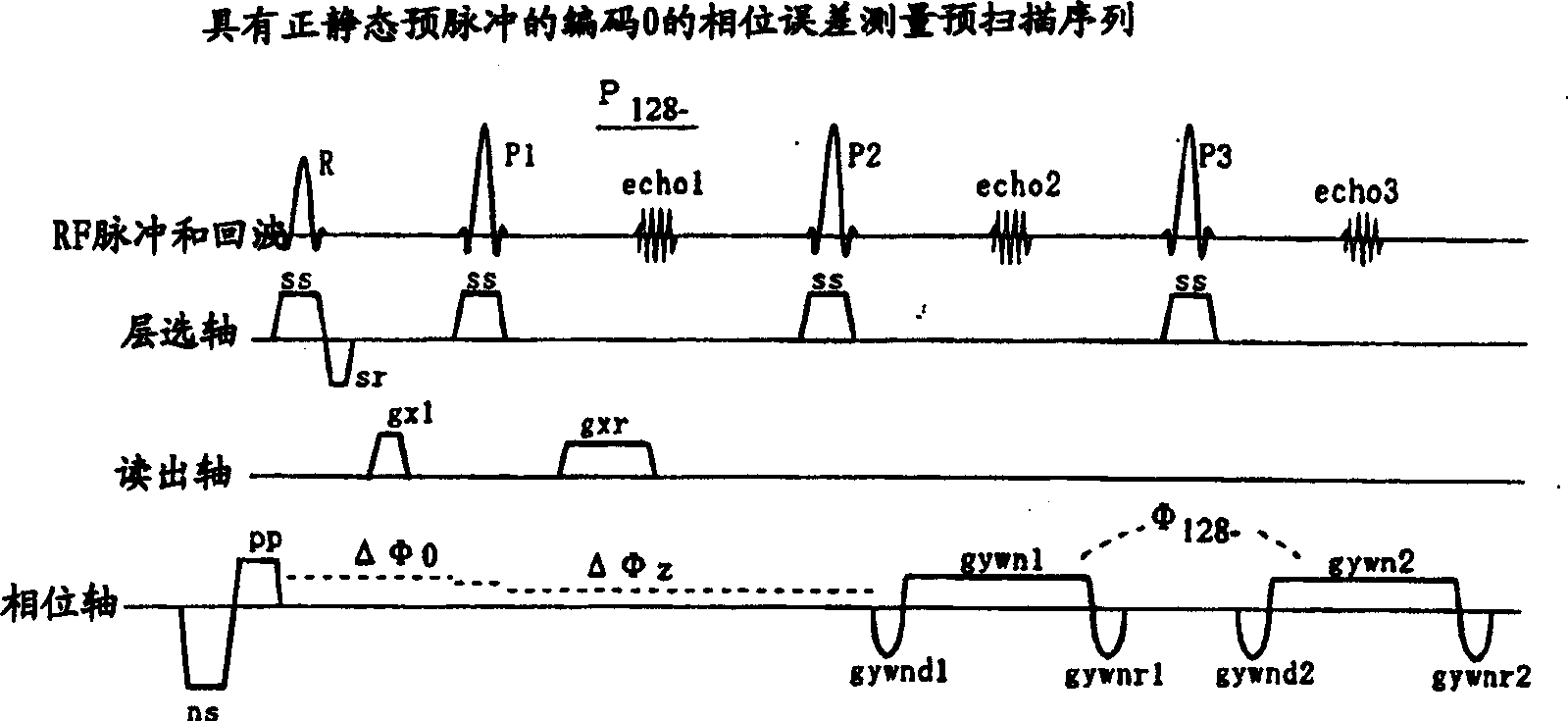
MR imaging method, phase error measuring method and MRI system
InactiveCN1363044ASuppresses the influence of residual magnetismReduce image quality degradationMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringFast spin echoImaging quality
The present invention aims to reduce degradation in image quality due to residual magnetization. In a pulse sequence of a high-speed spin echo process, a pre-pulse is applied before an excitation pulse, and a correction pulse for correcting a phase error caused by the pre-pulse is applied before an initial inversion pulse.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Electrochemical device and method for suppressing deterioration of the electrochemical device
InactiveUS20140295261A1Inhibit deteriorationHigh viscosityFinal product manufactureCell electrodesLithiumEngineering
An object is to provide an electrochemical device in which lithium deposition and reduction in battery capacity can be inhibited even when the concentration of a lithium salt in an electrolytic solution is lower than 1.0 M. Lithium deposition can be inhibited and lithium whiskers can be dissolved by applying an inversion pulse current for a short time more than once in a charging period of a secondary battery which deteriorates. By applying the inversion pulse current more than once, deterioration of a lithium-ion secondary battery due to repeated charging can be suppressed even when it is a secondary battery in which the concentration of a lithium salt in an electrolytic solution is lower than 1.0 M and therefore lithium is easily deposited.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method and apparatus for accelerated magnetic resonance imaging
PendingUS20180164395A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceMagnetization
In a method for controlling a radio-frequency transmitter of a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus to apply an inversion pulse to a sample magnetization, in a multi-shot readout phase, a gradient system of the magnetic resonance imaging apparatus is controlled to apply a steady-state gradient echo readout sequence having at least one first phase-encoding gradient along a first direction, at least one second phase-encoding gradient along a second direction, and a sequence of readout gradients along a readout direction. In the multi-shot readout phase, the gradient system is controlled to apply first AC gradients along the first direction and at least partly contemporaneously with readout gradients of the sequence of readout gradients, and the gradient system is controlled to apply second AC gradients along the second direction and at least partly contemporaneously with the readout gradients of the sequence of readout gradients.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
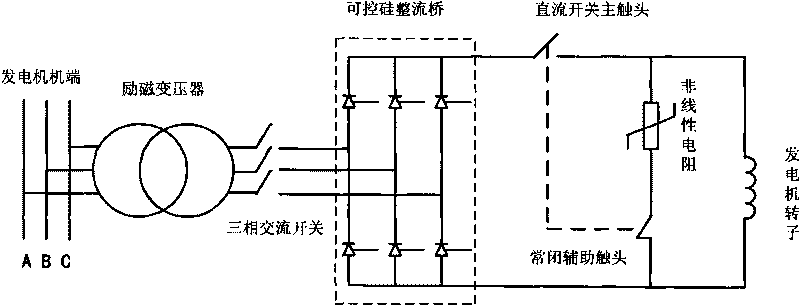
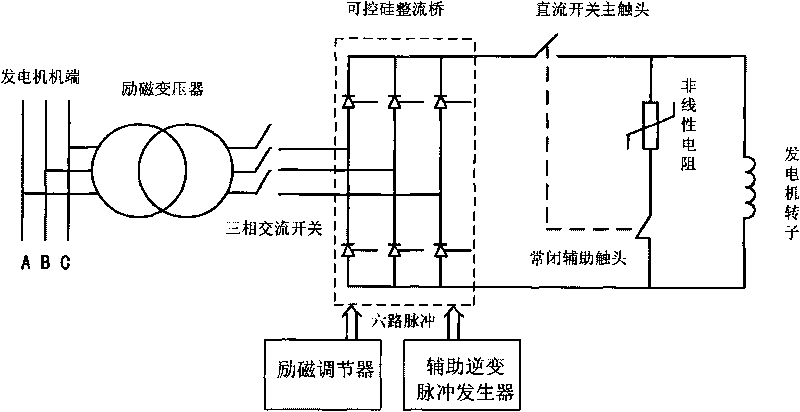
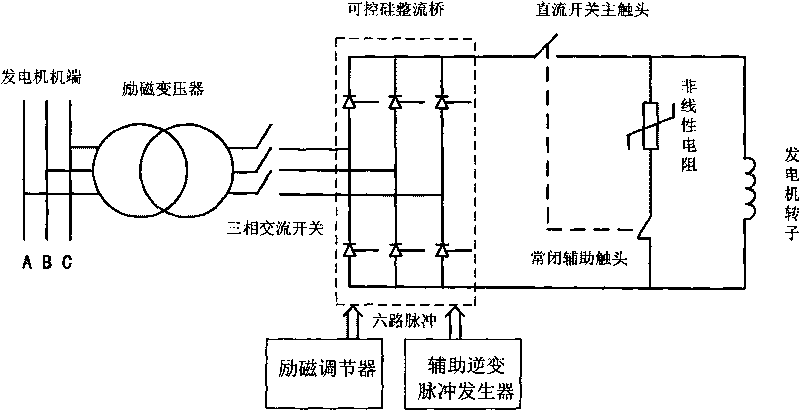
Generator de-excitation method by utilizing auxiliary inversion pulse generator to participate in de-excitation
ActiveCN101702609ALower requirementImprove the reliability of demagnetizationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectric generator controlInversion pulseSilicon
The invention relates to a generator de-excitation method by utilizing an auxiliary inversion pulse generator to participate in de-excitation, which is realized on the basis of an excitation circuit with the auxiliary inversion pulse generator and takes an independent auxiliary inversion pulse controller as a core; in normal shutdown, the auxiliary inversion pulse generator is used for stand-by; in accidental shutdown, when an excitation jump switch needs to be protected, especially force excitation by mistake or regulator out of control happens, control pulse of an excitation regulator is cut off, and the auxiliary inversion pulse controller is adopted to achieve the inversion function so as to ensure that the inversion does not rely on whether the regulator is normal or not, and a direct-current side voltage of a silicon controlled rectification bridge can be changed into a negative value, therefore, the requirements to the de-excitation switch is greatly lowered, and the de-excitation reliability is greatly improved.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +1
Magnetic resonance imaging needing a long waiting time between pre-pulses and imaging pulse train
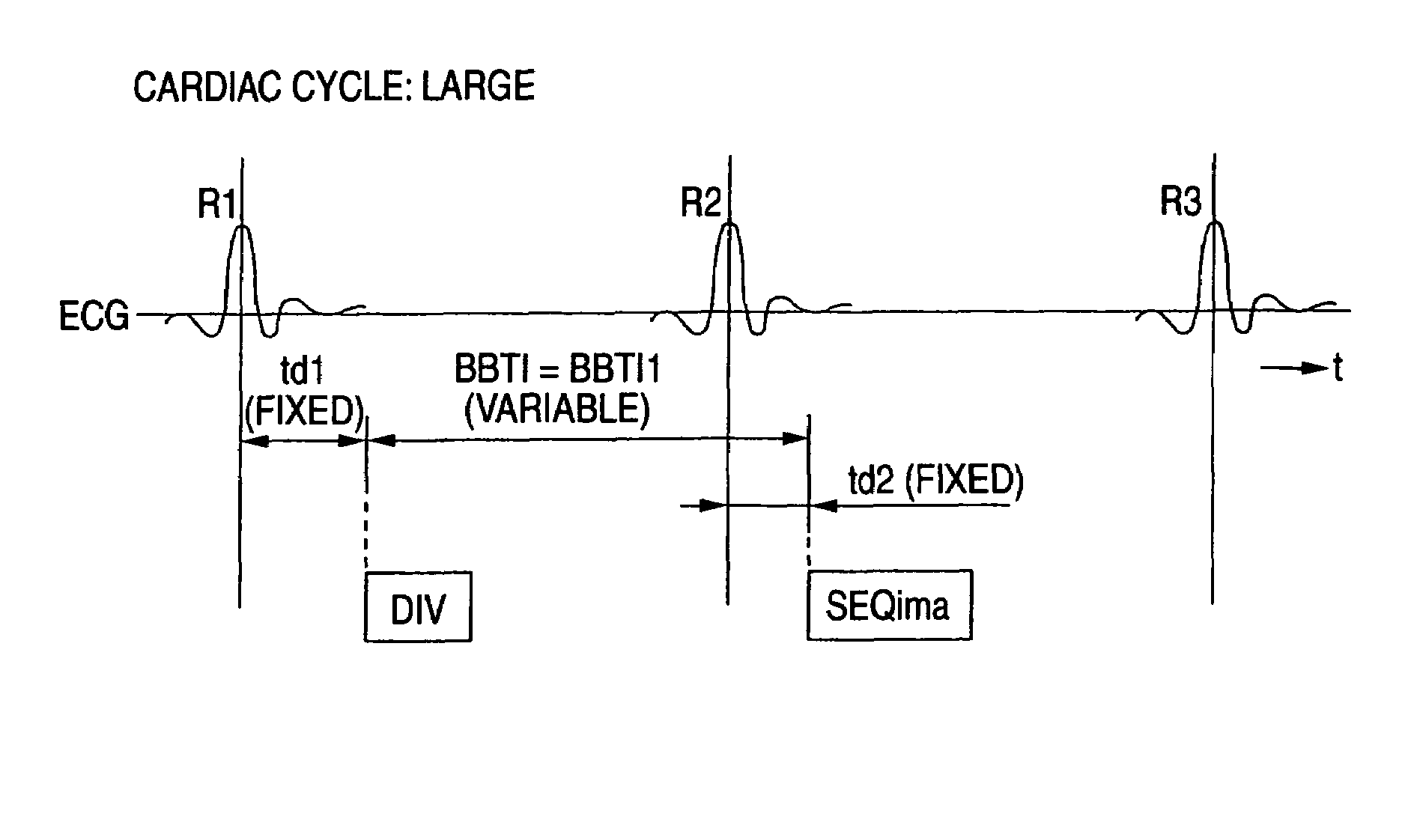
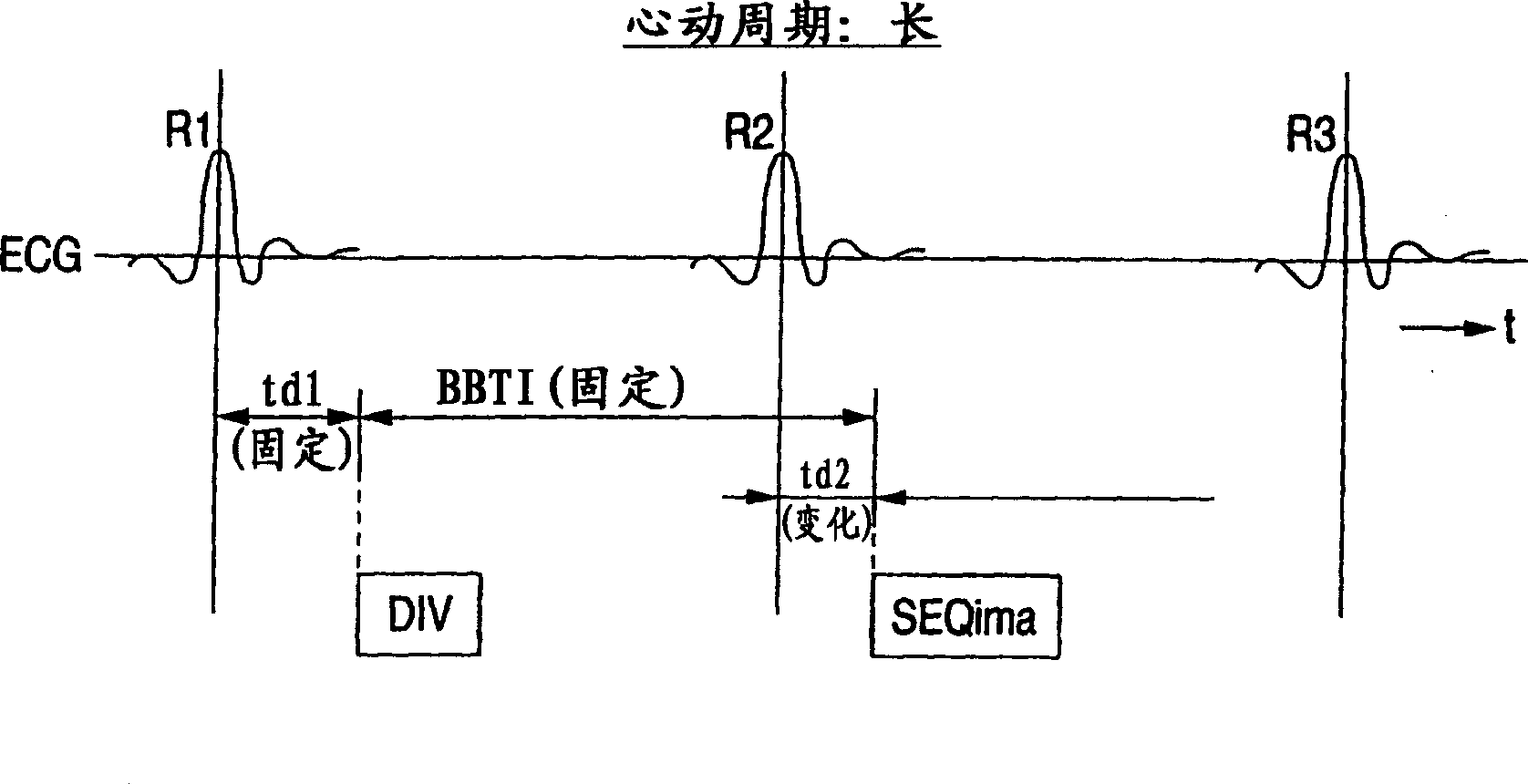
InactiveUS7623901B2Improve image qualityReduce artifactsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalSystole
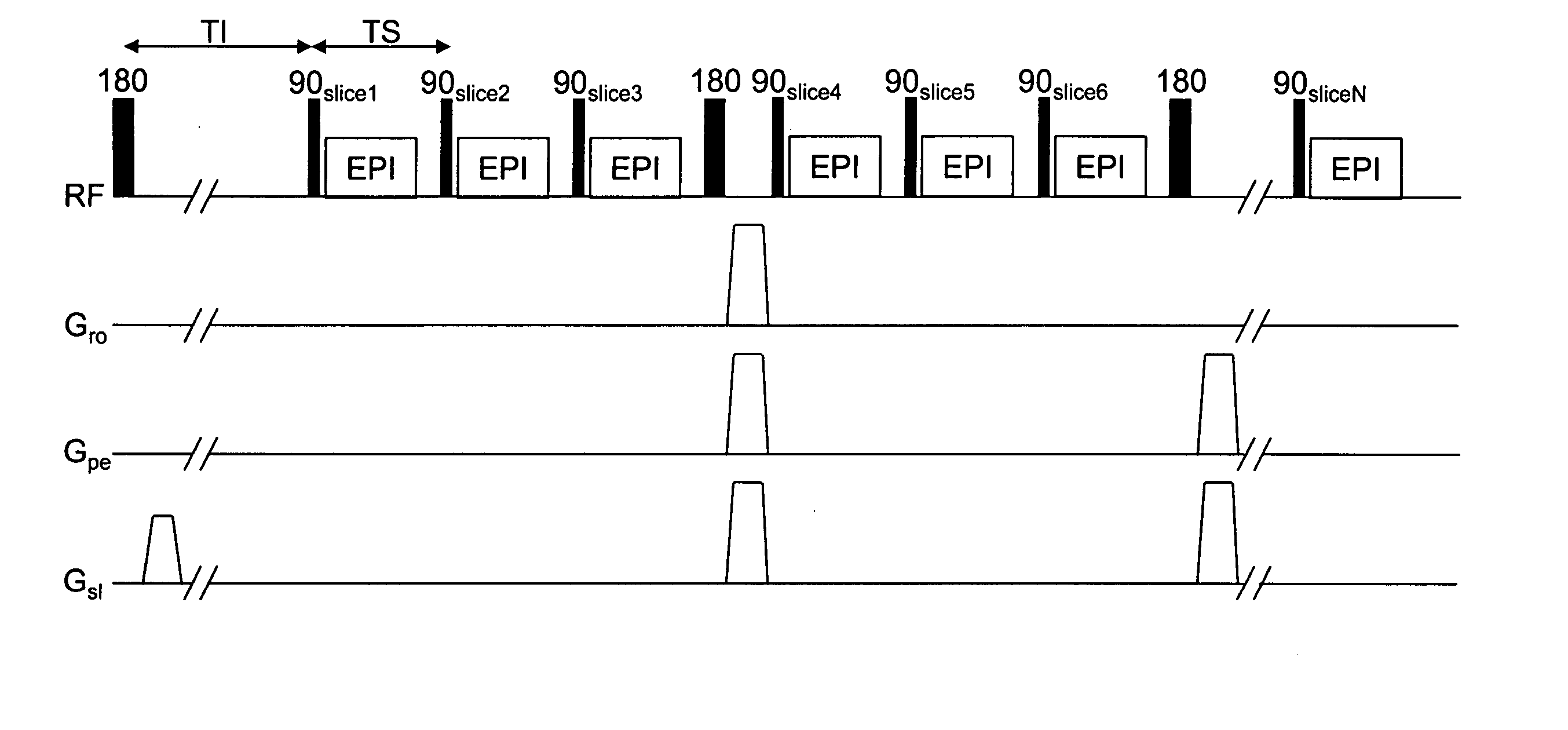
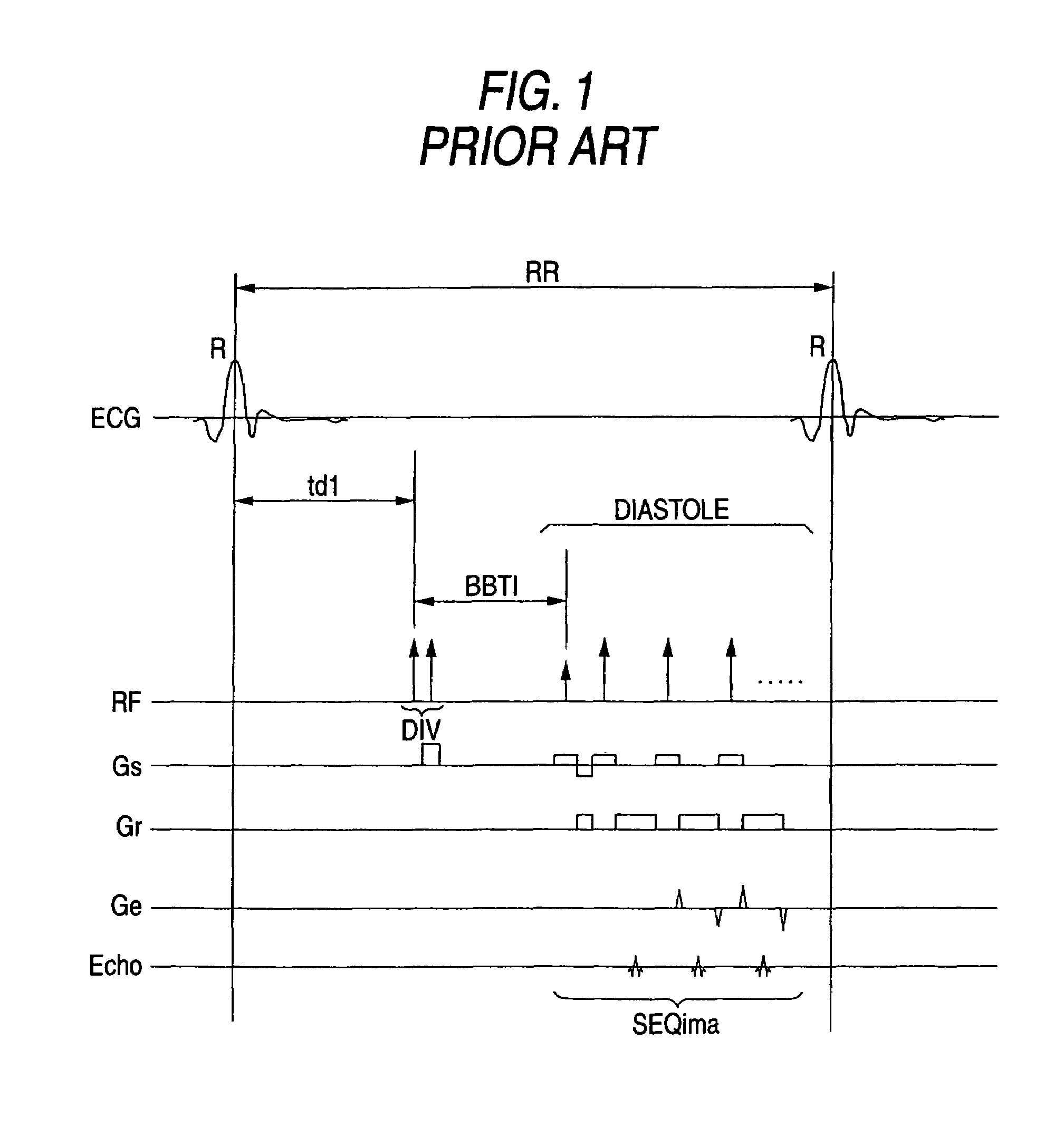
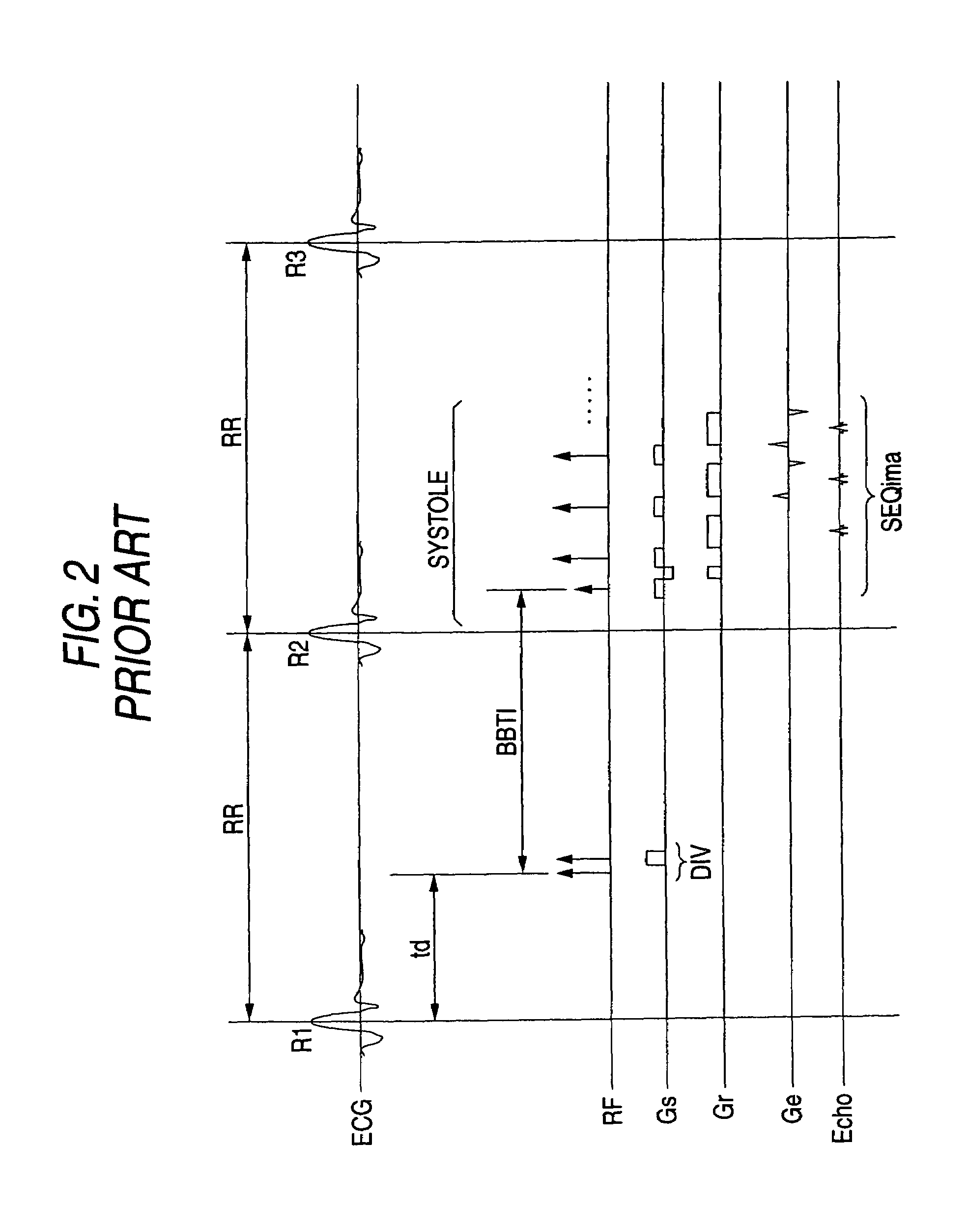
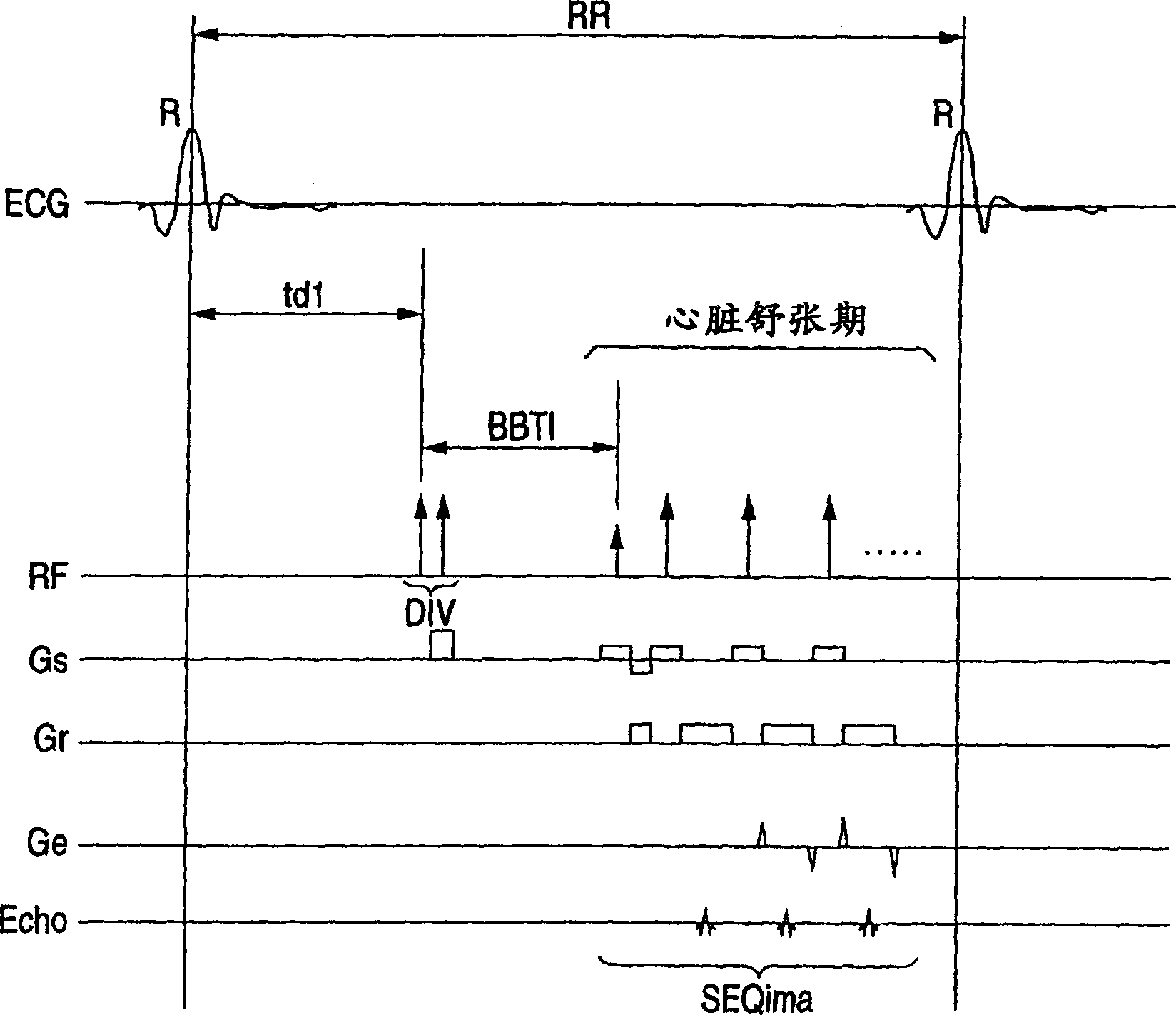
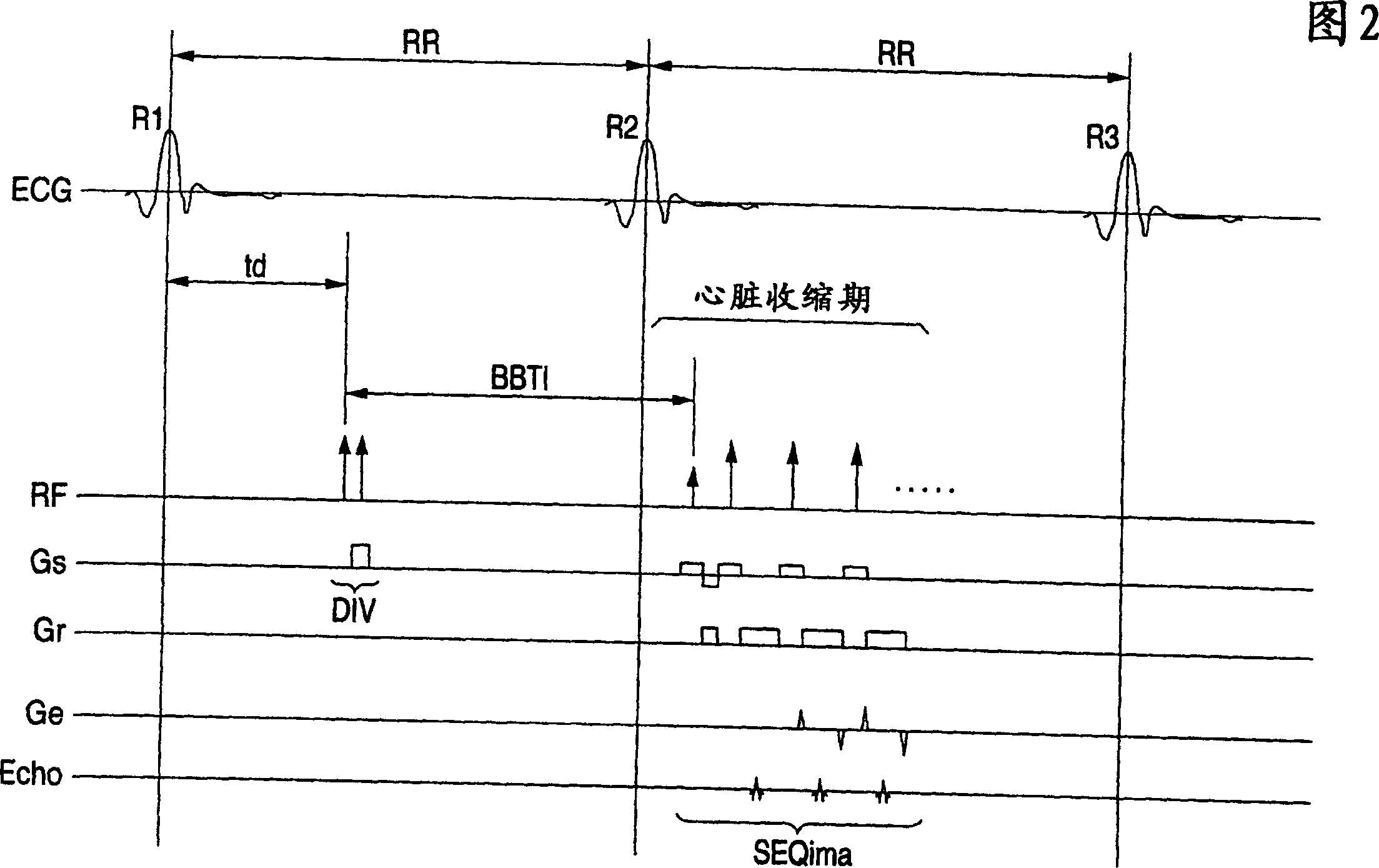
In the black blood method using a double inversion pulse, images in the systole of the cardiac cycle can be captured in a reliable manner even in the presence of a cycle-to-cycle variance in the heart beat cycle. A pulse sequence of the black blood method composed of a double inversion pulse DIV and an imaging pulse train SEQima is used. This sequence is applied in sync with an ECG signal of a subject to be imaged, and magnetic resonance imaging is thereby performed. The double inversion DIV is applied in sync with an R-wave:R1 appearing on the ECG signal at a given timing, with a first delay time td1 (fixed value), and the imaging pulse train SEQima is applied in sync with the following R-wave:R2 with a second delay time td2 (fixed value: set in accordance with the systole). A variance of the cardiac cycle is absorbed in an inversion time BBTI.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Nuclear magnetic resonance machine requiring long waiting time between pre-pulses and imaging pulse train
InactiveCN1543326AReliable captureImprove image qualityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalBlack blood
In the black blood method using a double inversion pulse, images in the systole of the cardiac cycle can be captured in a reliable manner even in the presence of a cycle-to-cycle variance in the heart beat cycle. A pulse sequence of the black blood method composed of a double inversion pulse DIV and an imaging pulse train SEQima is used. This sequence is applied in sync with an ECG signal of a subject to be imaged, and magnetic resonance imaging is thereby performed. The double inversion DIV is applied in sync with an R-wave:R1 appearing on the ECG signal at a given timing, with a first delay time td1 (fixed value), and the imaging pulse train SEQima is applied in sync with the following R-wave:R2 with a second delay time td2 (fixed value: set in accordance with the systole). A variance of the cardiac cycle is absorbed in an inversion time BBTI.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
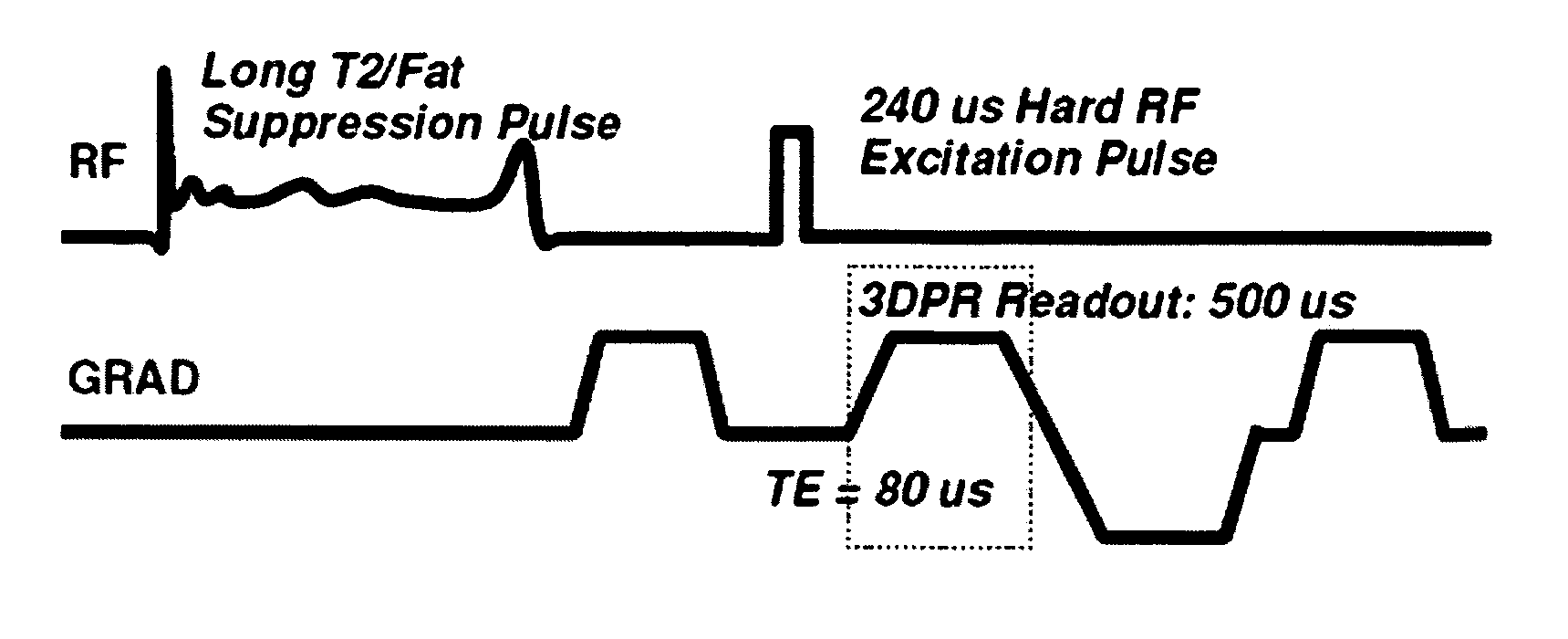
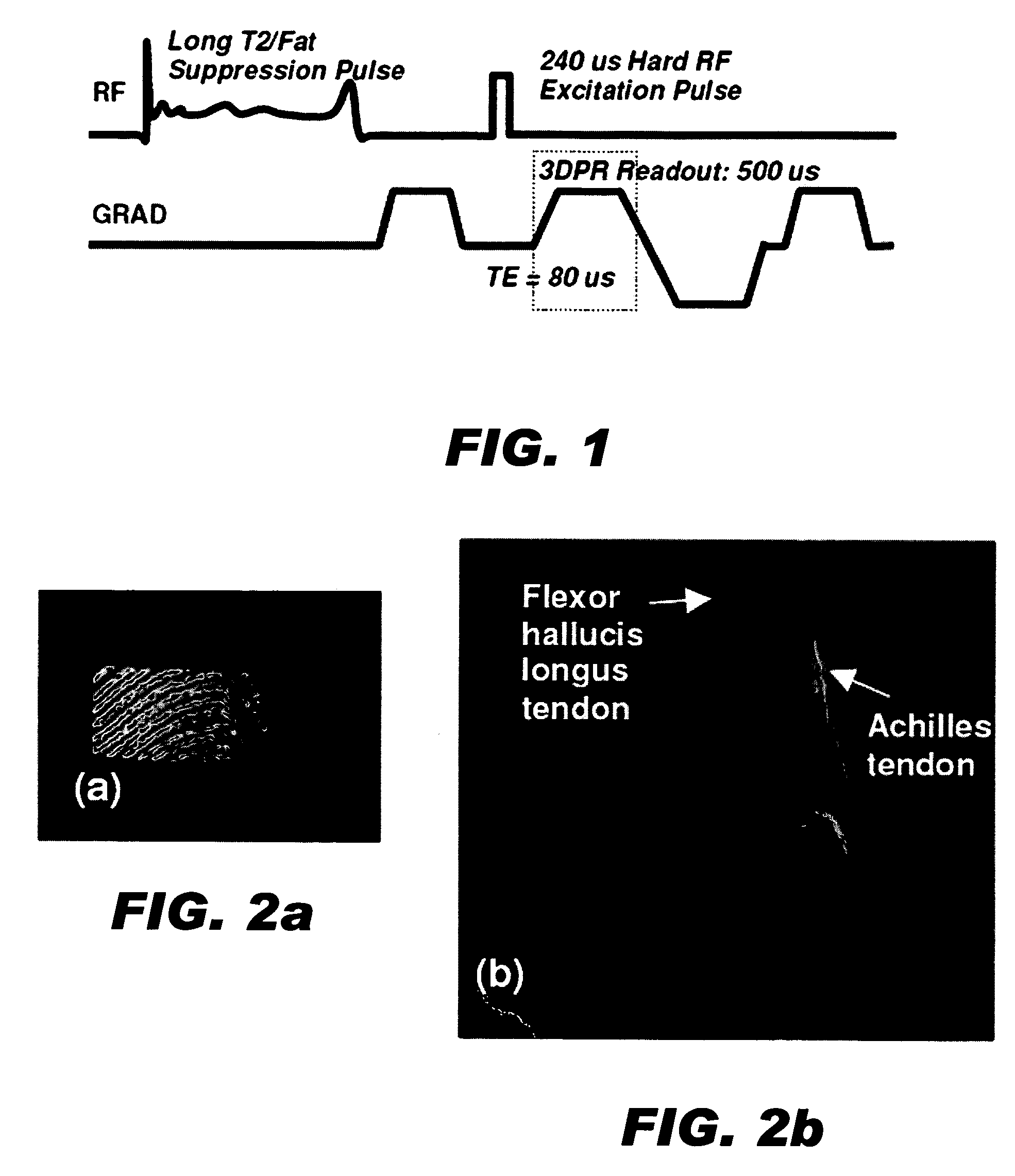
RF pulses for long T2 suppression in MRI
ActiveUS7288936B2Minimal interferenceMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse planePulse sequence
In imaging a first species having a short T2 magnetic resonance parameter in the presence of a second and third species having longer T2 parameters, a method of suppressing signals from the longer T2 species comprises the steps of: a) applying a RF saturation pulse with multiple suppression bands for the second and third species to excite nuclei spins of the longer T2 species with the magnitude of the RF pulse being sufficiently low so as not to excite nuclei spins of the short T2 species, the RF saturation pulse being sufficiently long to rotate the longer T2 species nuclei spins into a transverse plane, and b) dephasing the longer T2 species nuclei spins in the transverse plane. An imaging pulse sequence is then applied to image the short T2 species. Alternatively, the method can comprise the steps of a) applying a first inversion pulse for selective inverting species of the second longer T2 species, b) obtaining first image signals after step a, c) applying a second inversion pulse for selectively inverting species of the third longer T2 species, d) obtaining second image signals after step c), and e) combining the first image signals and the second image signal to image the first short T2 species with the longer second and third species cancelling in the combination. In each of these methods, either the second or third longer T2 species can be suppressed without suppressing the other by applying the RF saturation or inversion pulse only to the species to be suppressed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
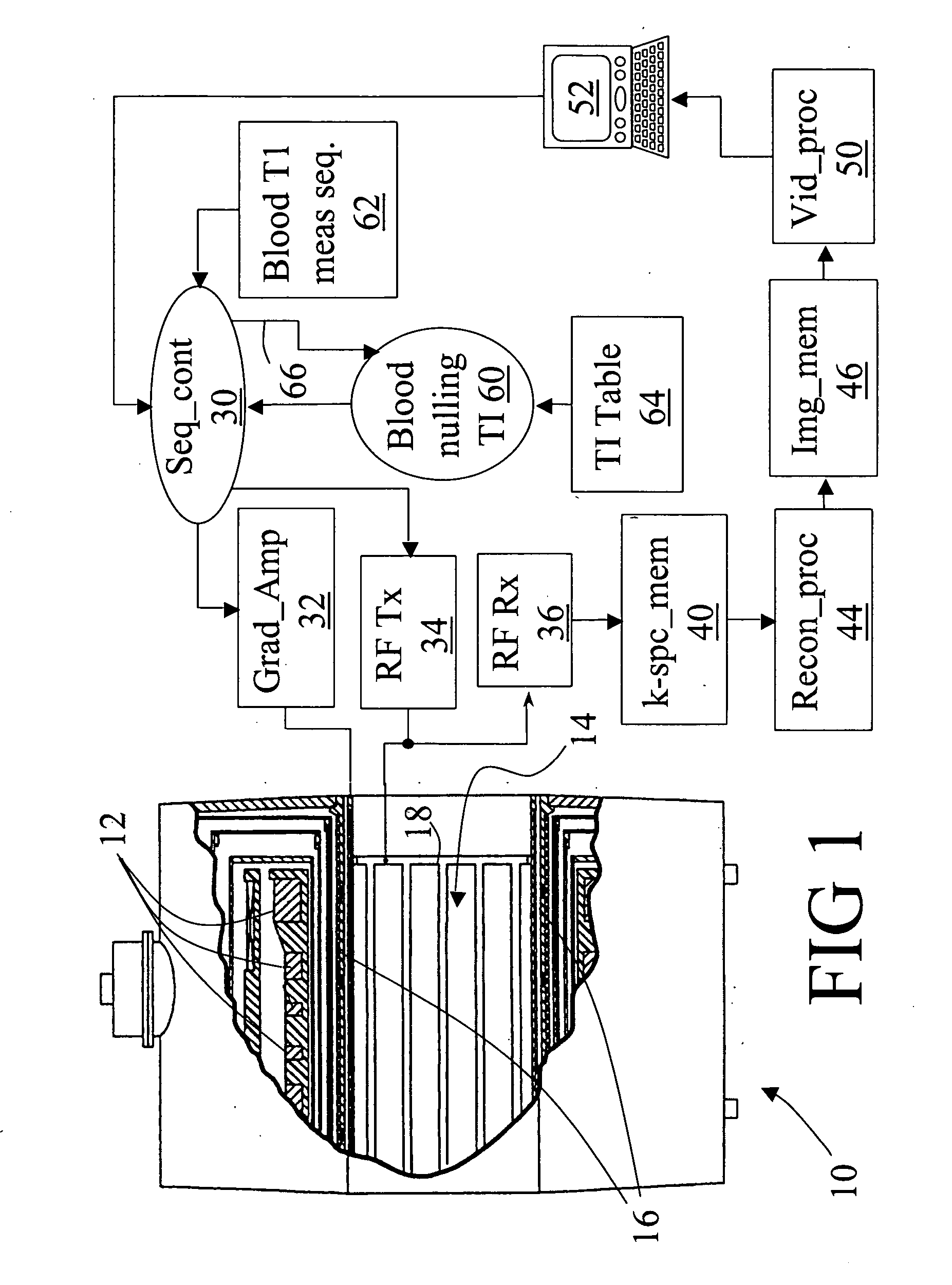
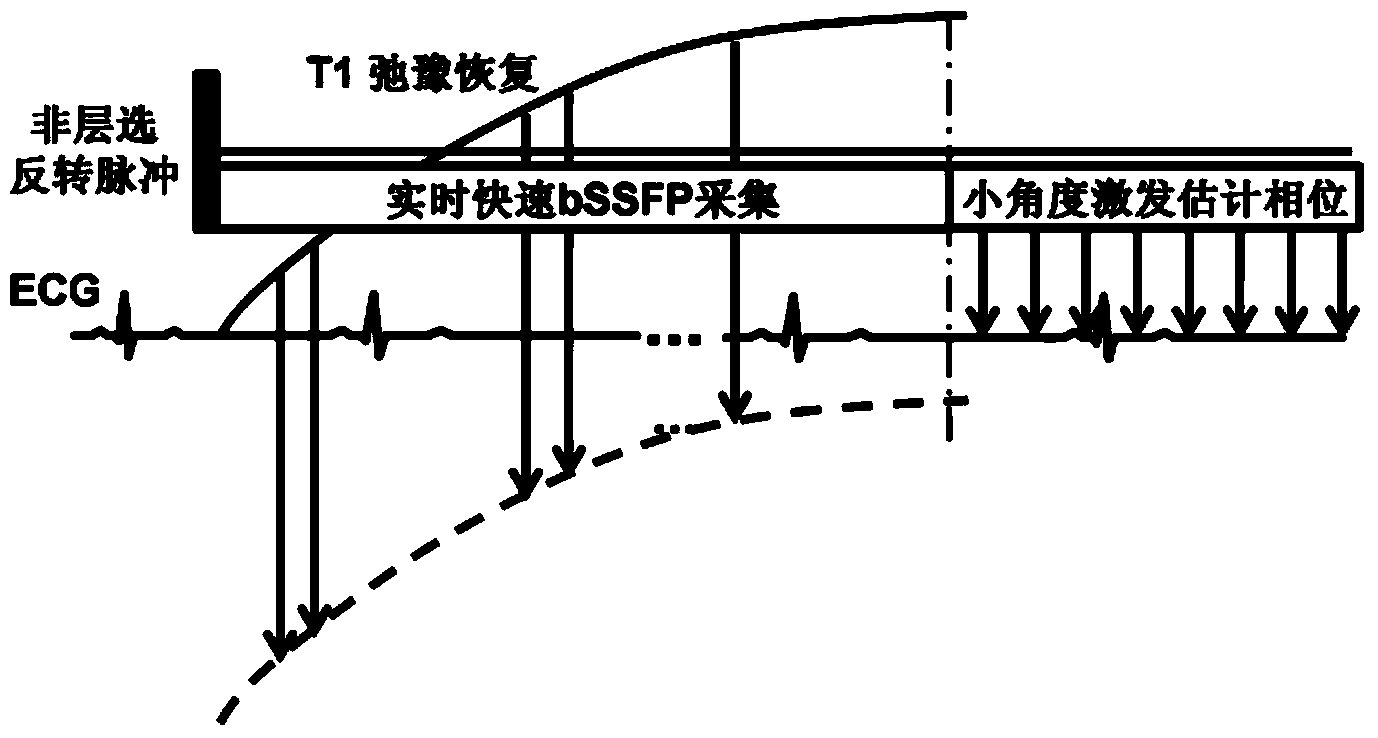
Myocardium T1 value measuring method and system
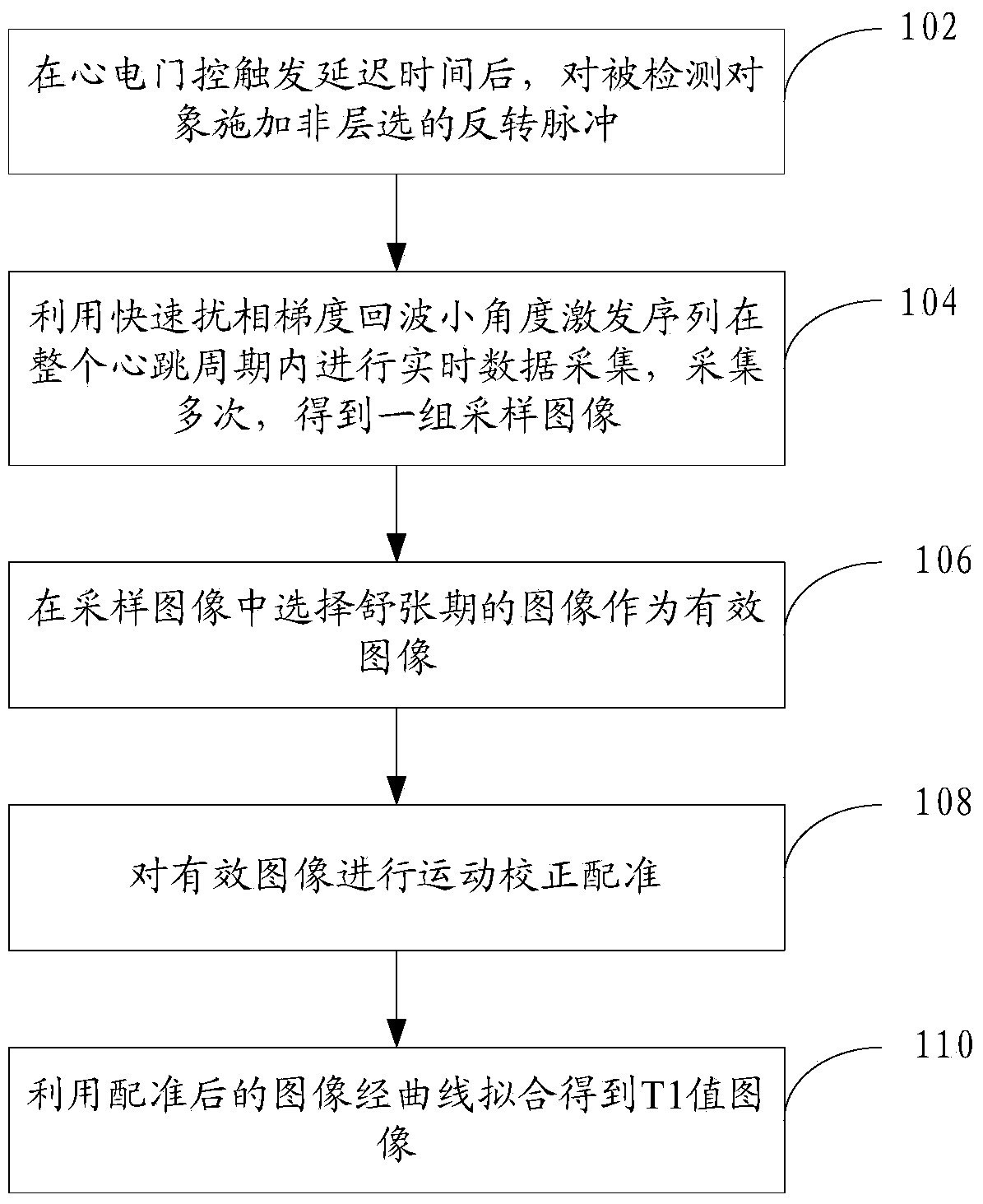
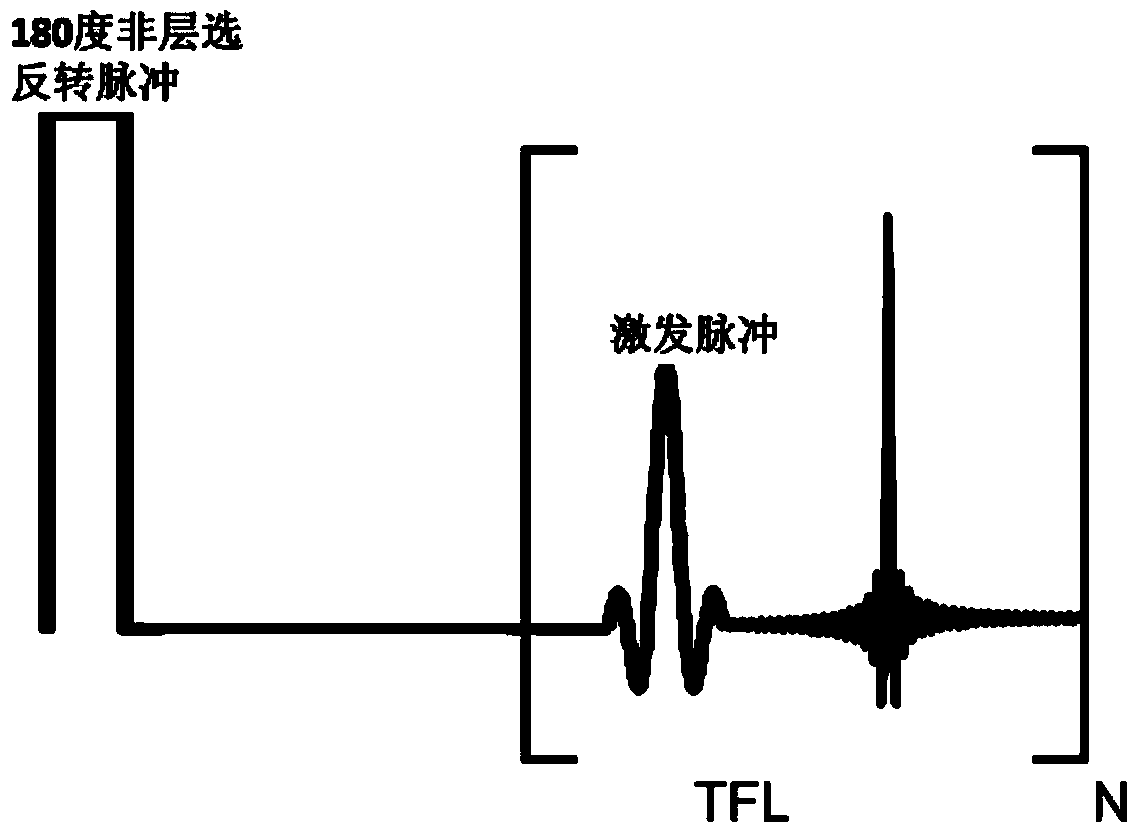
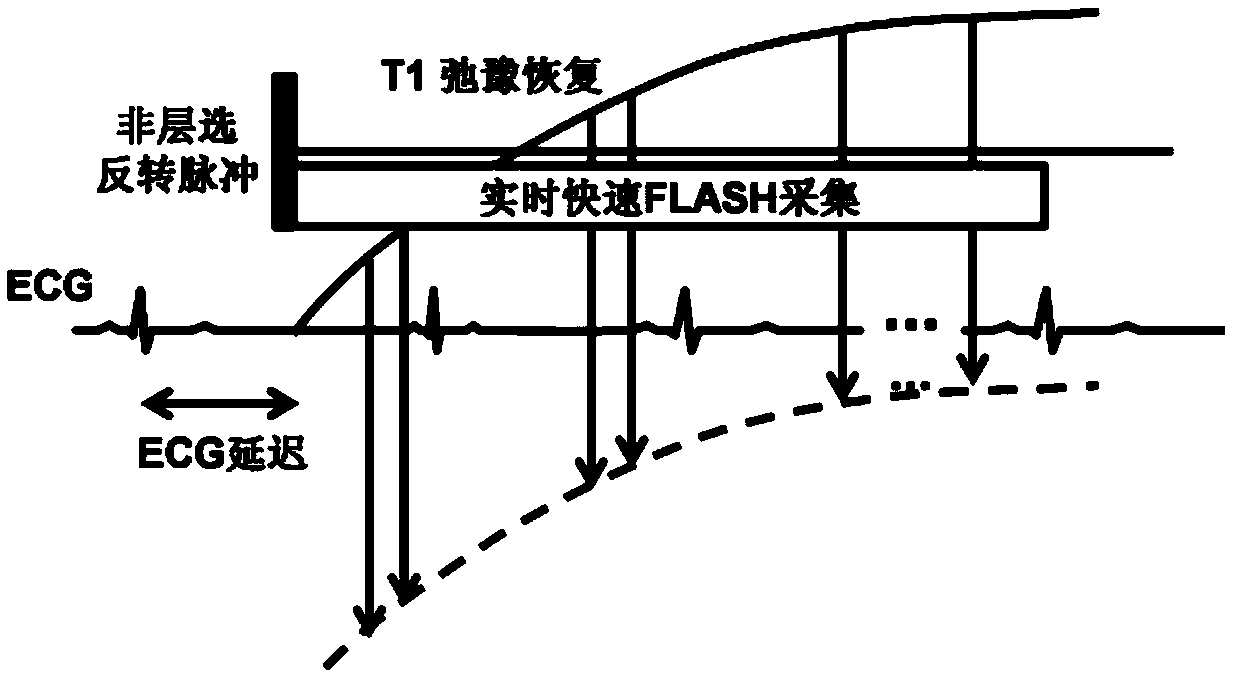
ActiveCN104013404AAvoid errorsImprove collection efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsReal-time dataCardiac cycle
A myocardium T1 value measuring method includes the steps that after when delay time is triggered through electrocardiograph gating, non-layer-selection inversion pulses are applied to a detected object; real-time data are acquired in the whole cardiac cycle many times through a fast spoiled gradient echo small-angle excitation sequence, and a set of sampling images are obtained; the images in the diastole period are selected from the sampling images to serve as effective images, and motion correction and registration are performed on the effective images; curve fitting is performed on the registered images, and a Ti value image is obtained. Through the method, the acquisition efficiency is improved, and the T1 value can be effectively measured. The invention further provides a myocardium T1 value measuring system.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Myocardium T1 quantifying method and device
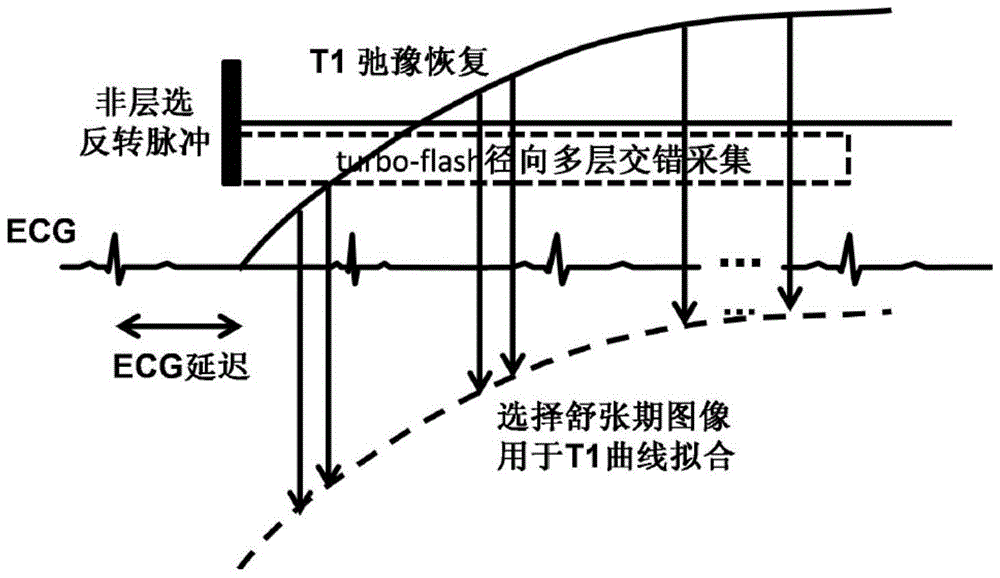
ActiveCN105662413AWaste less timeClear timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInversion recoveryCardiac muscle
The invention discloses a myocardium T1 quantifying method. The method includes the steps that after electrocardiograph gating trigger delay, non-layer-selection inversion pulses are applied; real-time interlaced collection of at least two layers of images is carried out with a fast spoiled gradient echo low-angle shot sequence of a radial sampling trajectory, and the inversion recovery process of signals is captured; a sampling line in diastole is selected to serve as a K space center line; with the selected sampling line as the center, the sampling line is symmetrically selected to carry out image reconstruction according to the size of a reconstruction window; a T1 quantifying graph is fitted with restructured images. The invention further discloses a device based on the method. By means of the method and the device, multiple layers of T1 quantifying images can be collected in one time of breathholding, the whole heart can be covered in two or three times of breathholding, and thus time waste and patient discomfort caused by breathholding are reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Look-locker IR-SSFP for cardiac MR imaging with simultaneous generation of cardiac T1 maps, cine images and IR-prepared images
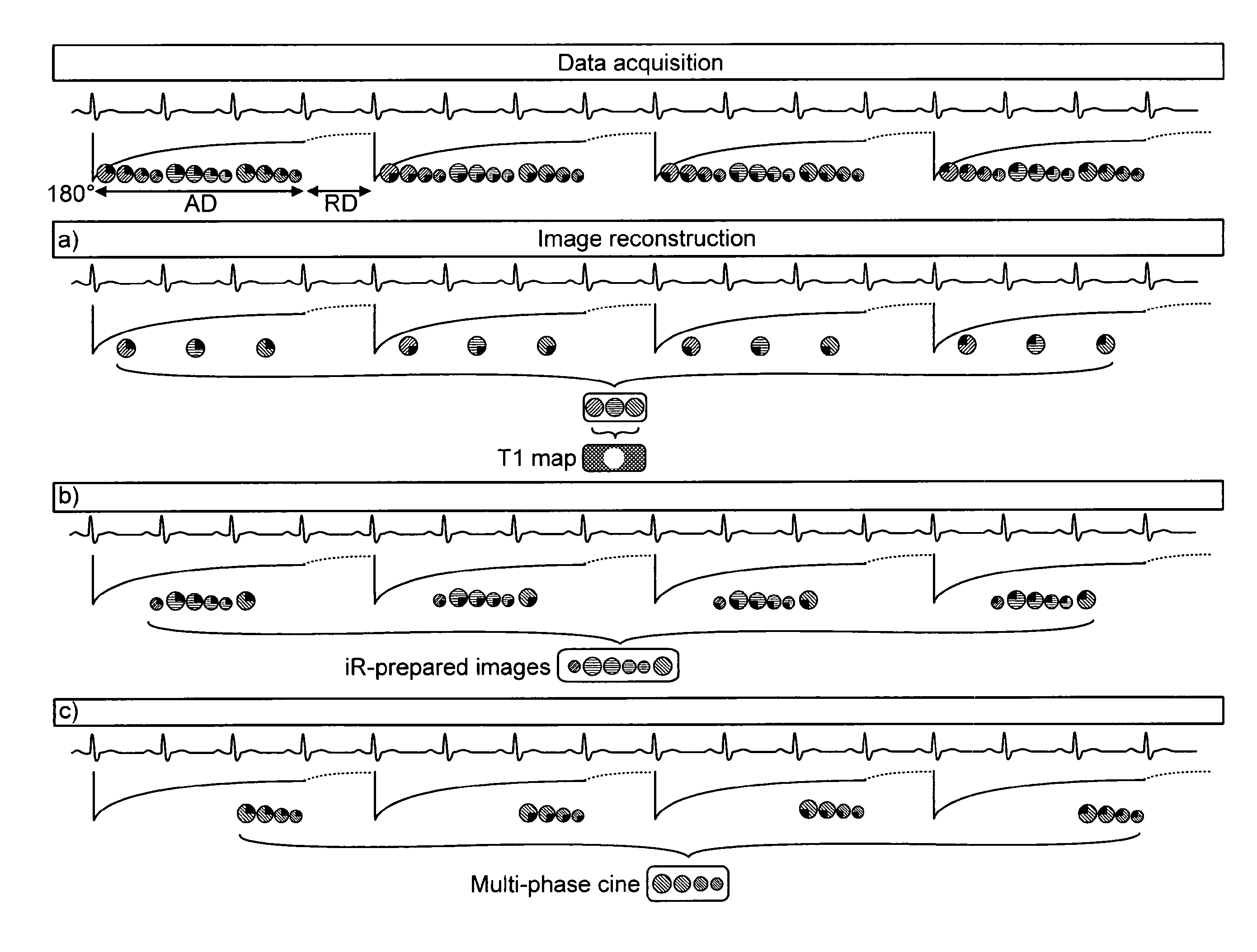
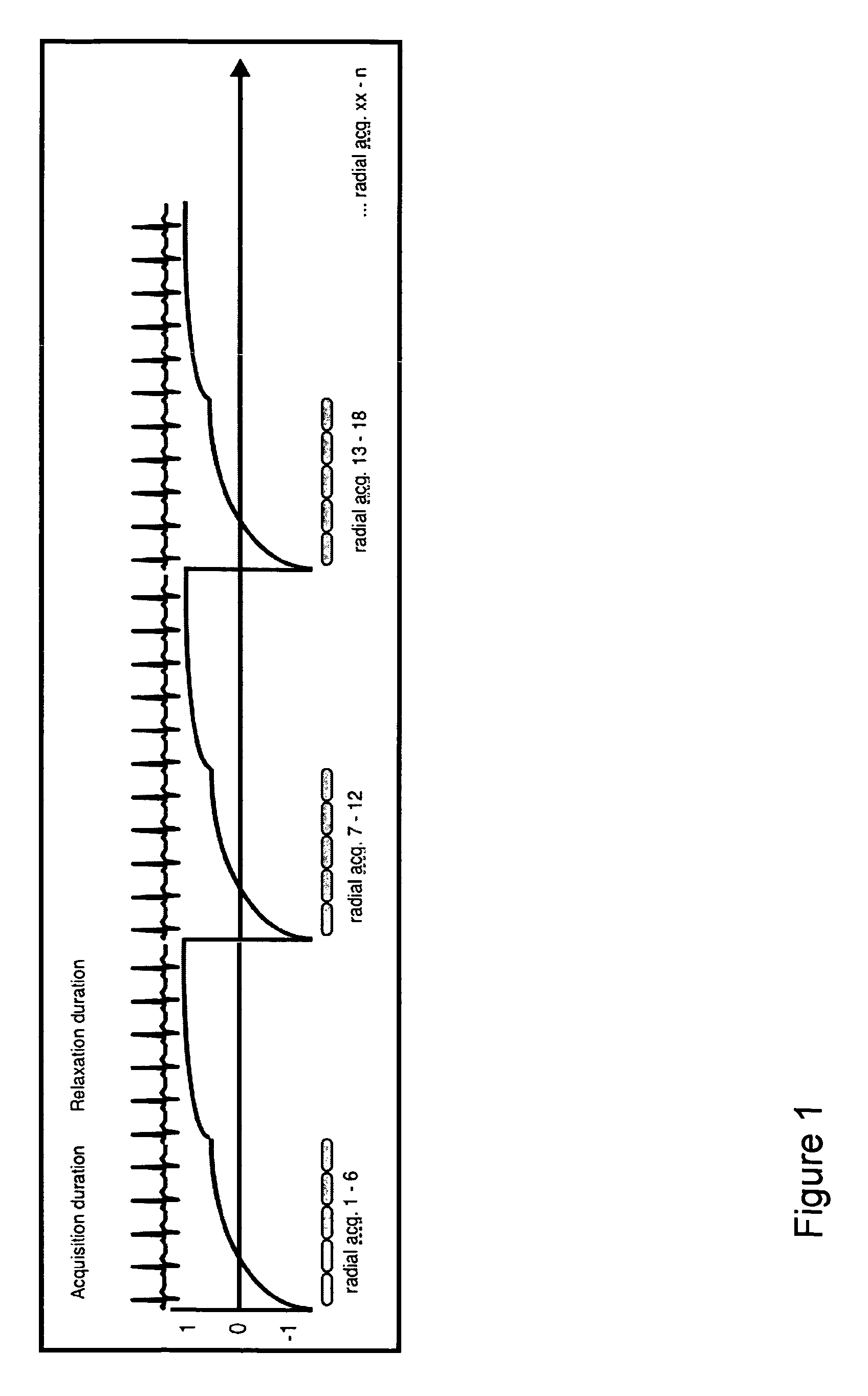
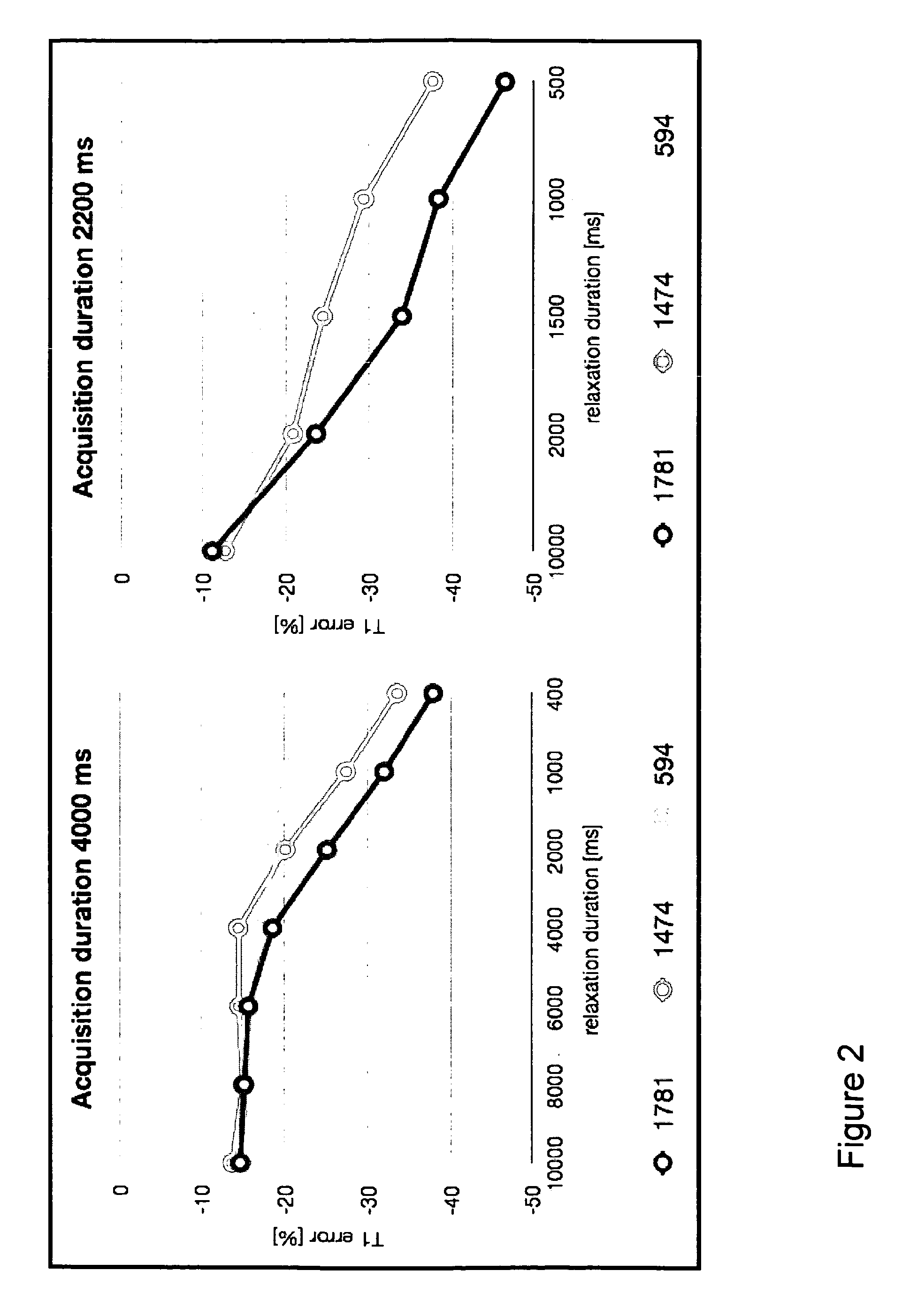
InactiveUS9008753B2Increase heart rateExtended collection timeDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAcquisition DurationData acquisition
The present invention is directed to a method for use in conducting cardiac MR imaging which allows for reconstruction of T1 maps, cine images and IR-prepared images from one raw data set, wherein the method comprises the following steps: a) acquisition of raw data by use of an ECG-triggered, segmented, inversion recovery (IR) -prepared Look-Locker type pulse sequence for data acquisition, wherein the pulse sequence encompasses more than one shot, wherein each shot comprises: i) an ECG-triggered inversion pulse; ii) SSFP cine data acquisition of radial segmented profiles over more than one RR-interval for a predefined acquisition duration AD; and iii) a relaxation duration RD, during which no data is acquired; b) retrospective gating of raw data by sorting acquired raw data for each RR-interval into a pre-determined number of heart phases by definition of specific time windows within the RR-intervals and sampling of raw data acquired during the time windows respectively; c) image reconstruction, wherein the retrospectively gated raw data is used for reconstruction of T1 maps, cine images and / or IR-prepared images.
Owner:DEUTES HERZZENT BERLIN
Mr imaging with signal suppression of a spin series
ActiveUS20150042336A1High sensitivityLarge amplitudeDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonance measurementSignal Repression
In a magnetic resonance measurement sequence, an inversion pulse is applied that acts on a longitudinal magnetization of a first spin species and a second spin species, for example on a water portion and a fat portion. An excitation pulse is applied after a predetermined time period. At least one manipulation pulse is subsequently applied, respectively with associated gradient pulse.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Dynamic myocardium activity detection method and system
ActiveCN104013405AEfficient determinationImprove collection efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInversion recoveryCine mri
The invention discloses a dynamic myocardium activity detection method. The dynamic myocardium activity detection method comprises the steps that a non-layer-selection inversion pulse is applied on a detected object; a balanced steady-state free procession is used for carrying out real-time sampling on the inversion recovery process of signals in the whole cardiac cycle including a diastole period and a systole period, and a set of heart cine-MRI images; a small-angle excitation balanced steady-state free procession within a preset range is used for collecting a reference image; phase sensitivity inversion recovery reconstruction is carried out on the collected heart cine-MRI images through the reference image. By the adoption of the dynamic myocardium activity detection method, the collection efficiency and imaging efficiency can be improved, and the dynamic myocardium activity is effectively measured. The invention further provides a dynamic myocardium activity detection system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Waveform shaping method, waveform shaping device, electronic device, waveform shaping program, and recording medium
InactiveCN1771661AGood reproducibilitySimple compositionTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsPulse shapingData signalWaveform shaping
A sampling unit (102) is provided for sampling the input signal (101) by a sampling clock (106) faster than the data rate of the input signal (101) to generate a sampling signal (103). A waveform shaping unit (104) is provided which processes a sampling signal (103) (for example, an inverted pulse) and outputs an output signal (105) obtained by shaping a restored digital signal from the pulse of the input signal (101). In this way, it is possible to provide a waveform shaping method, a waveform shaping device, a waveform shaping program for them, and a storage medium having the program capable of shaping distortion generated in an input signal with a simple method or structure.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com