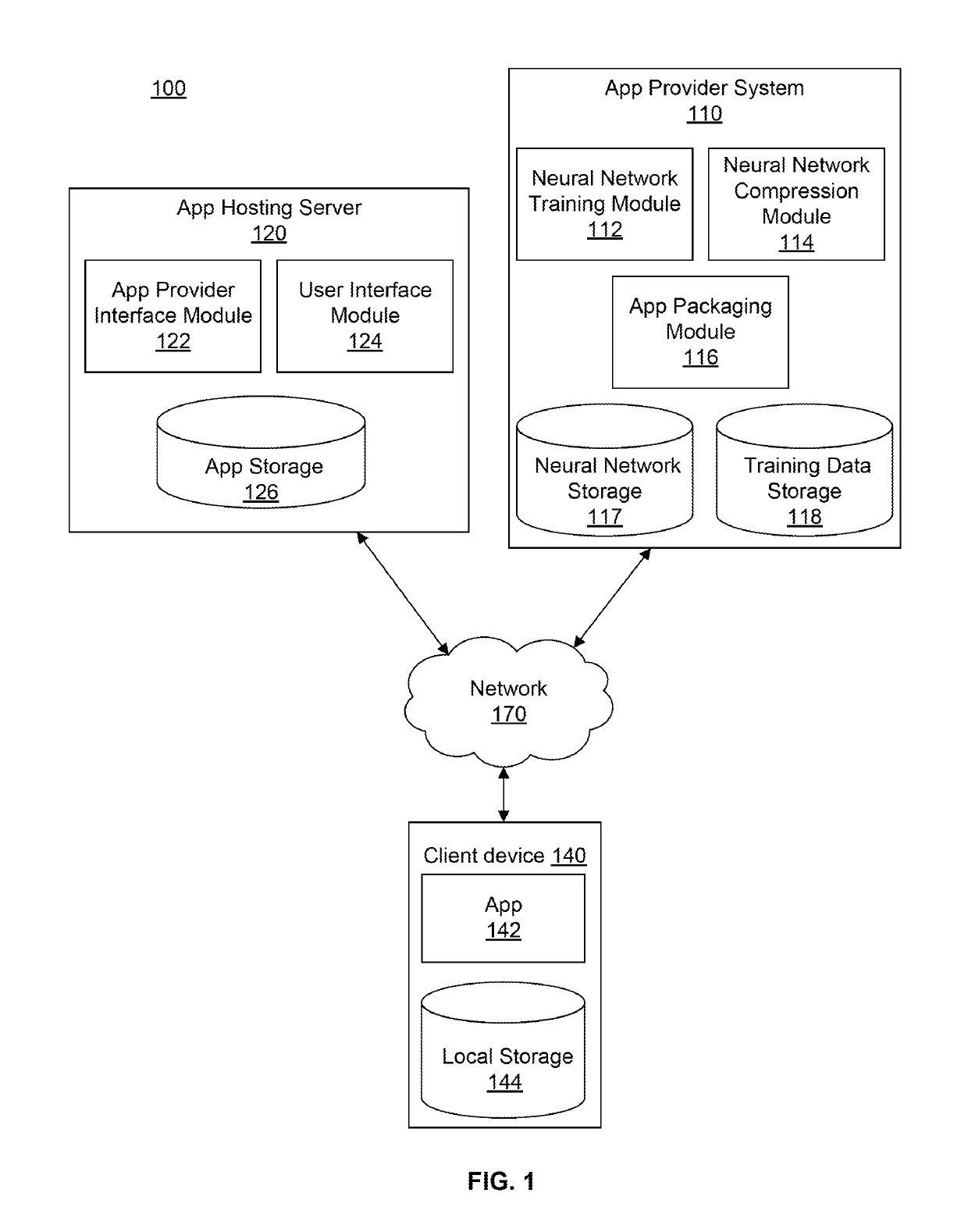
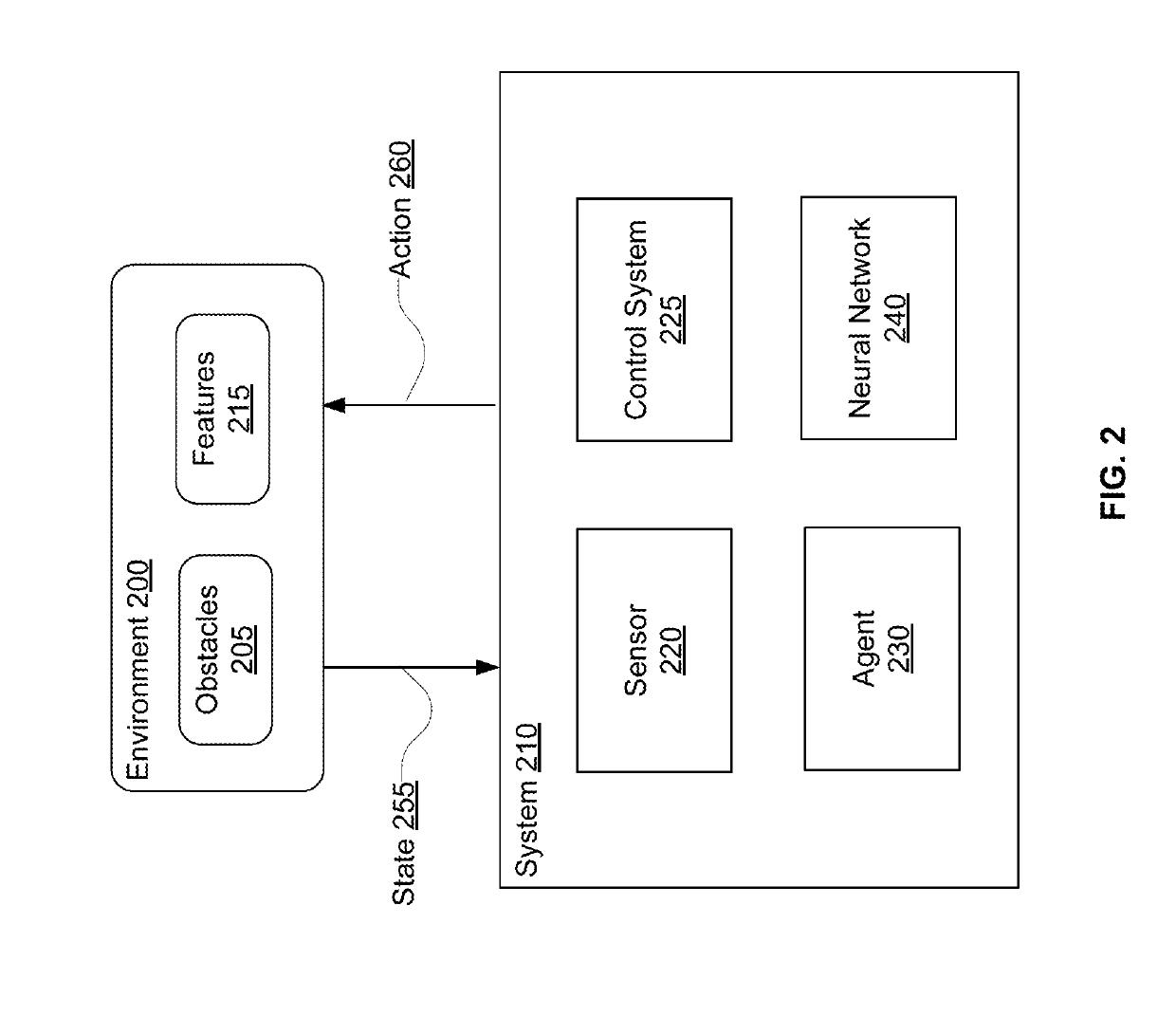
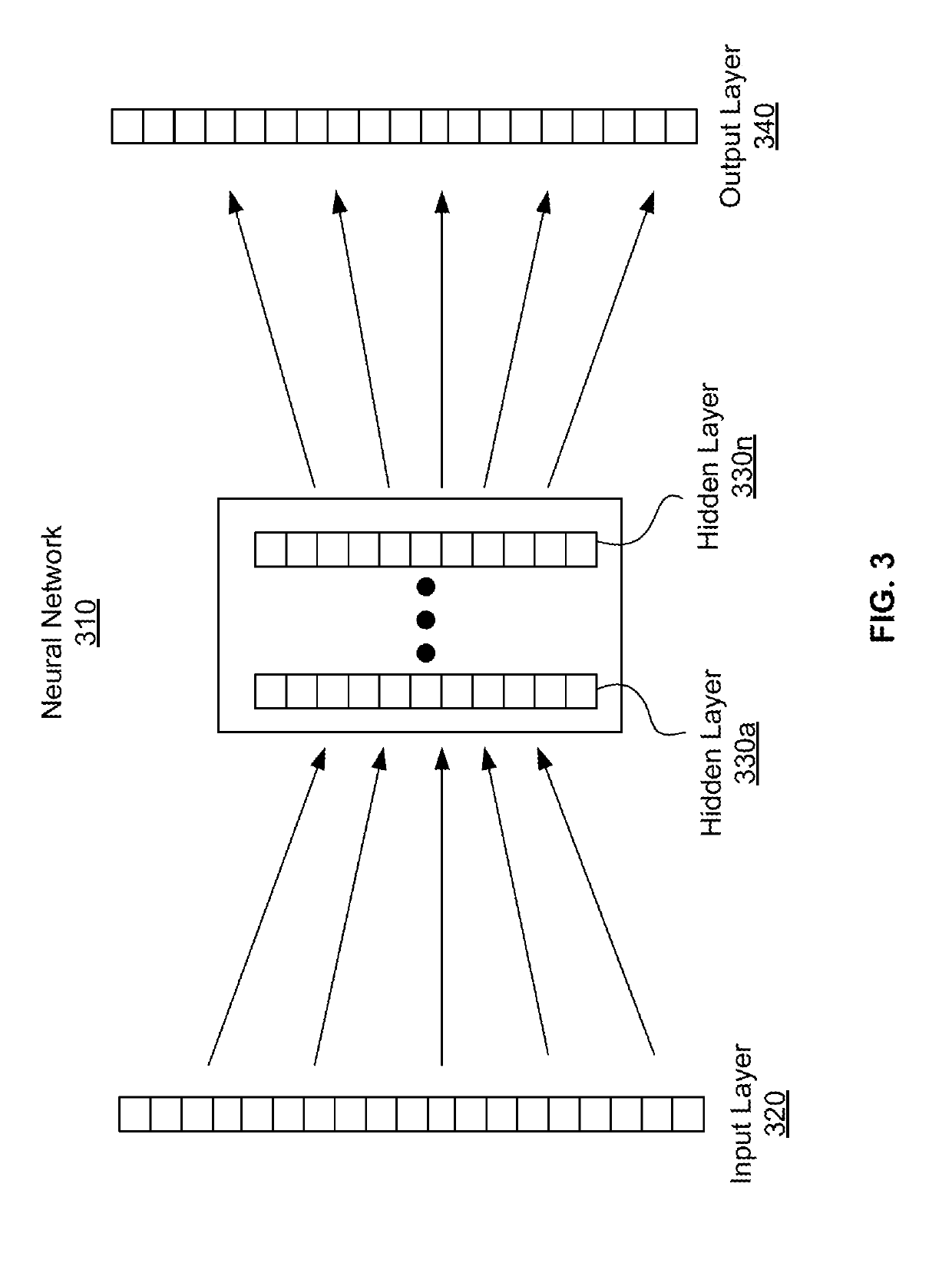
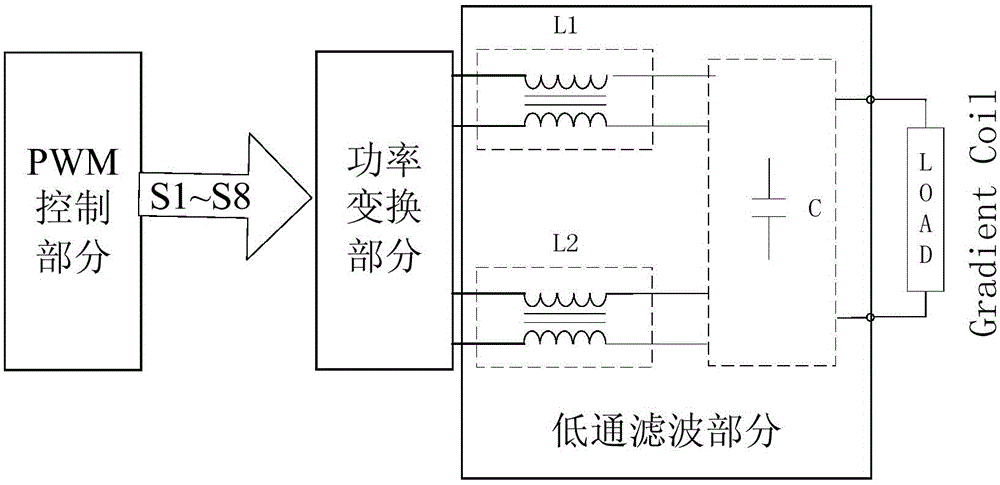
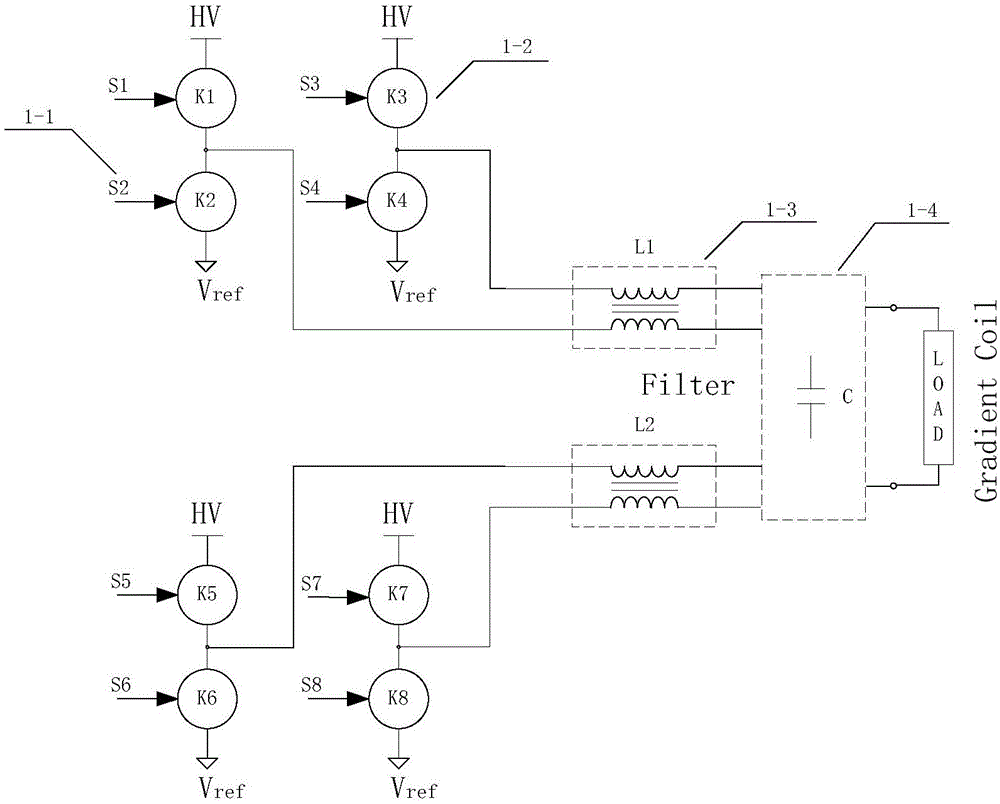
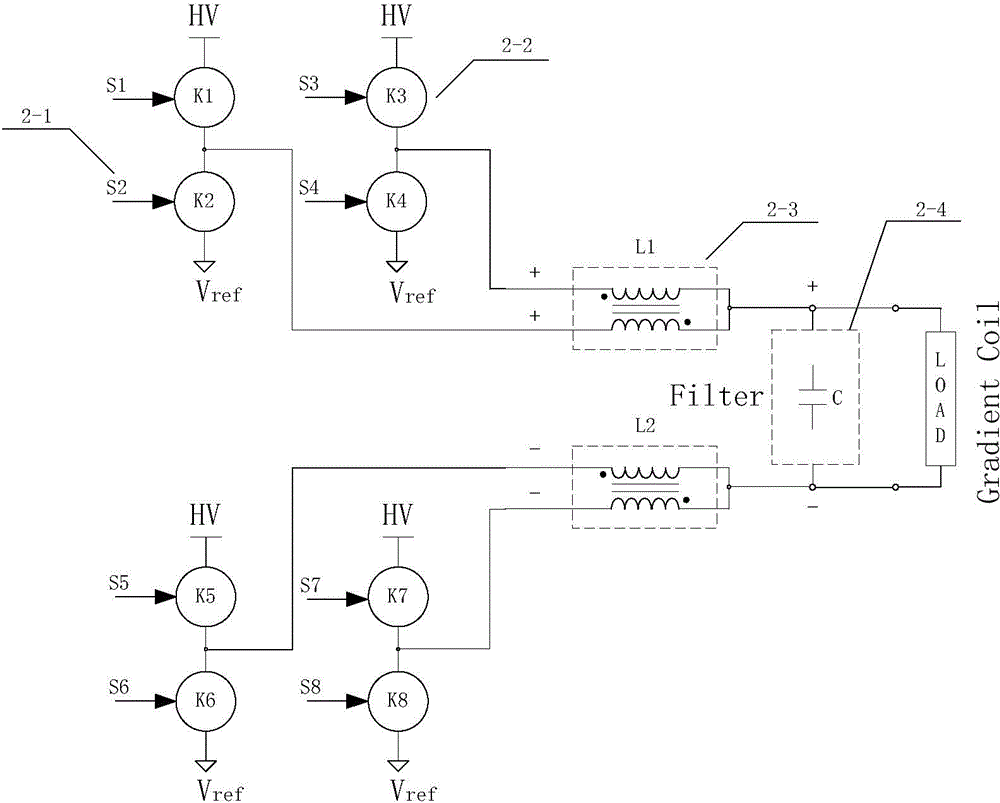
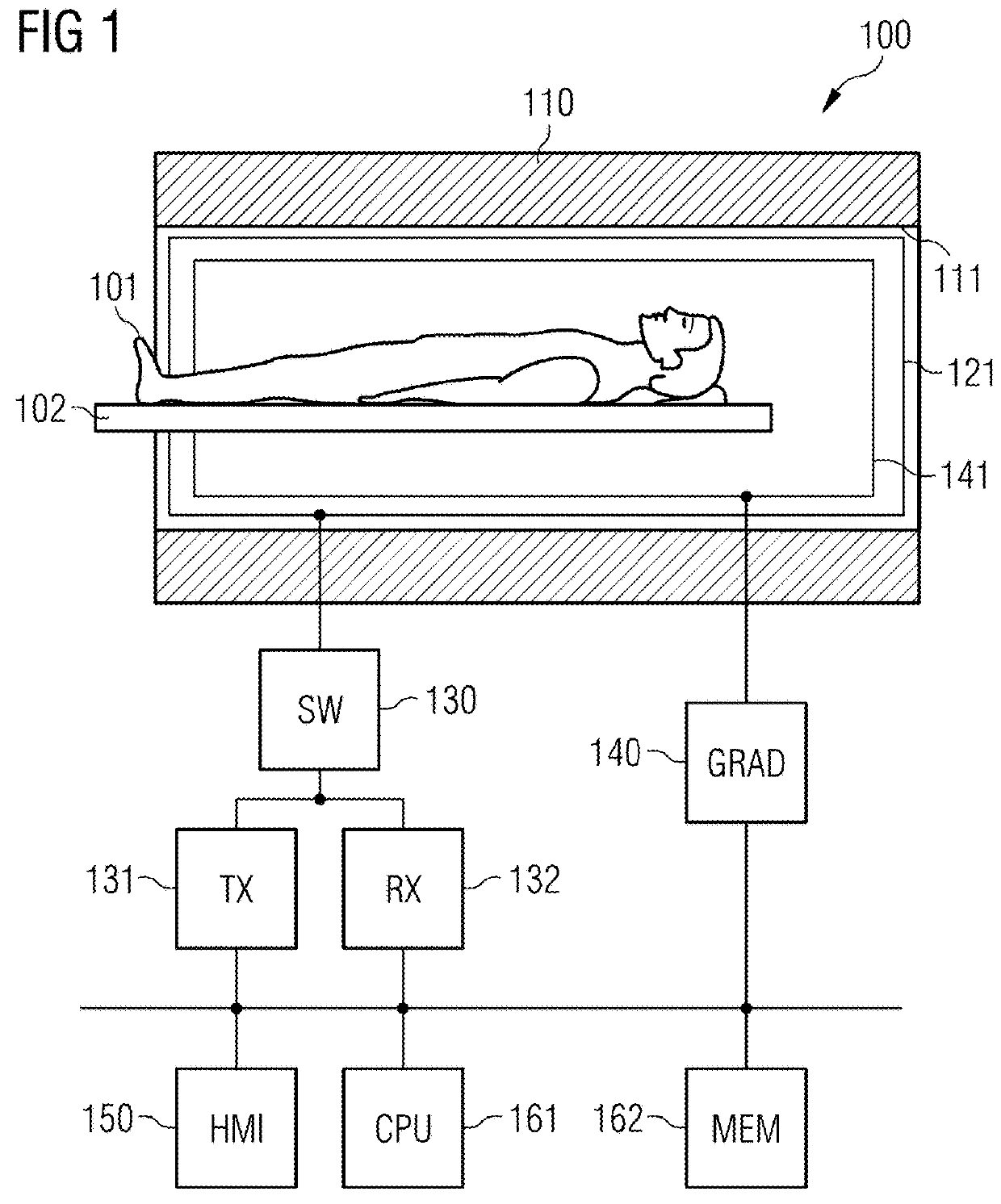
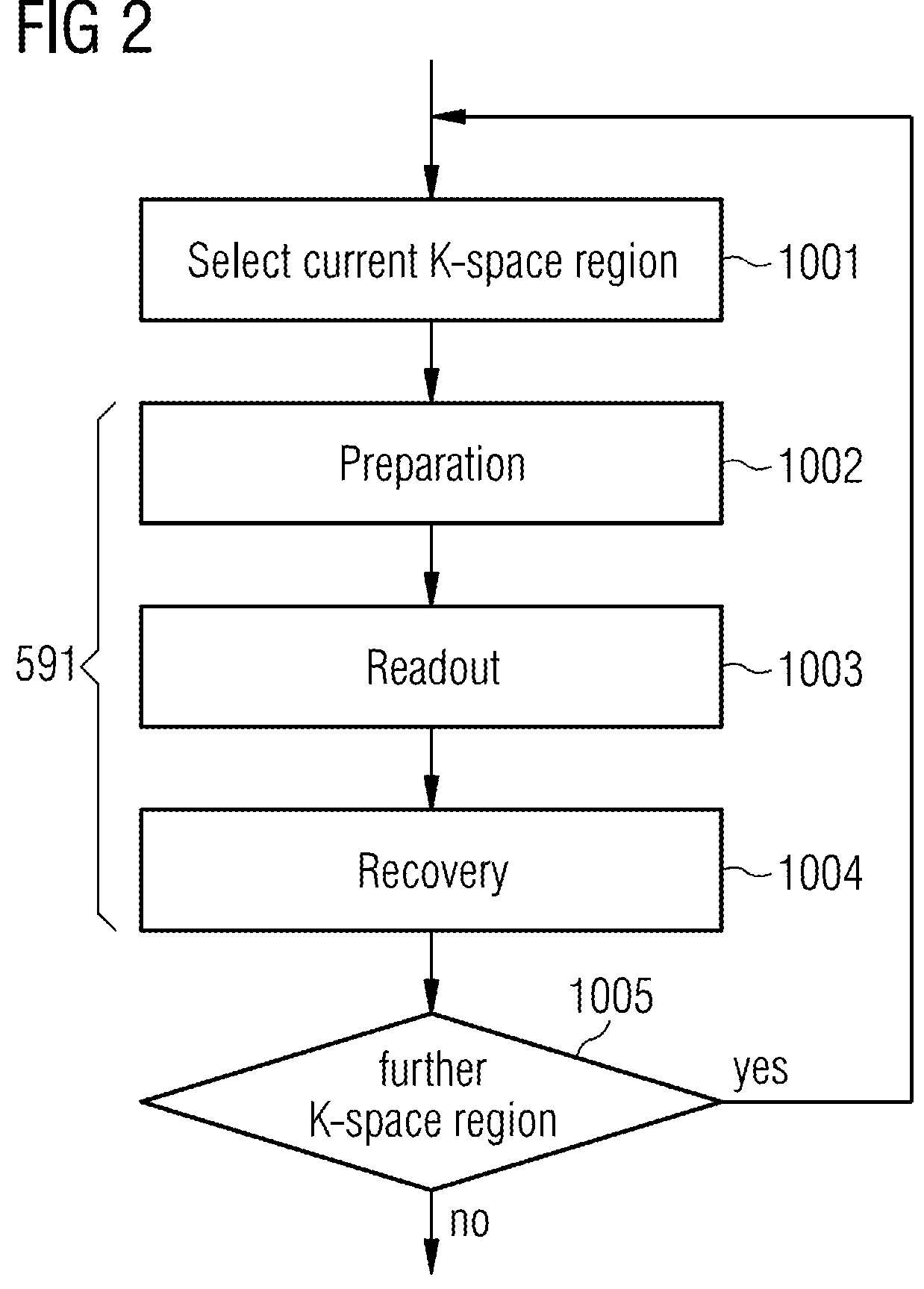
Patents
Literature
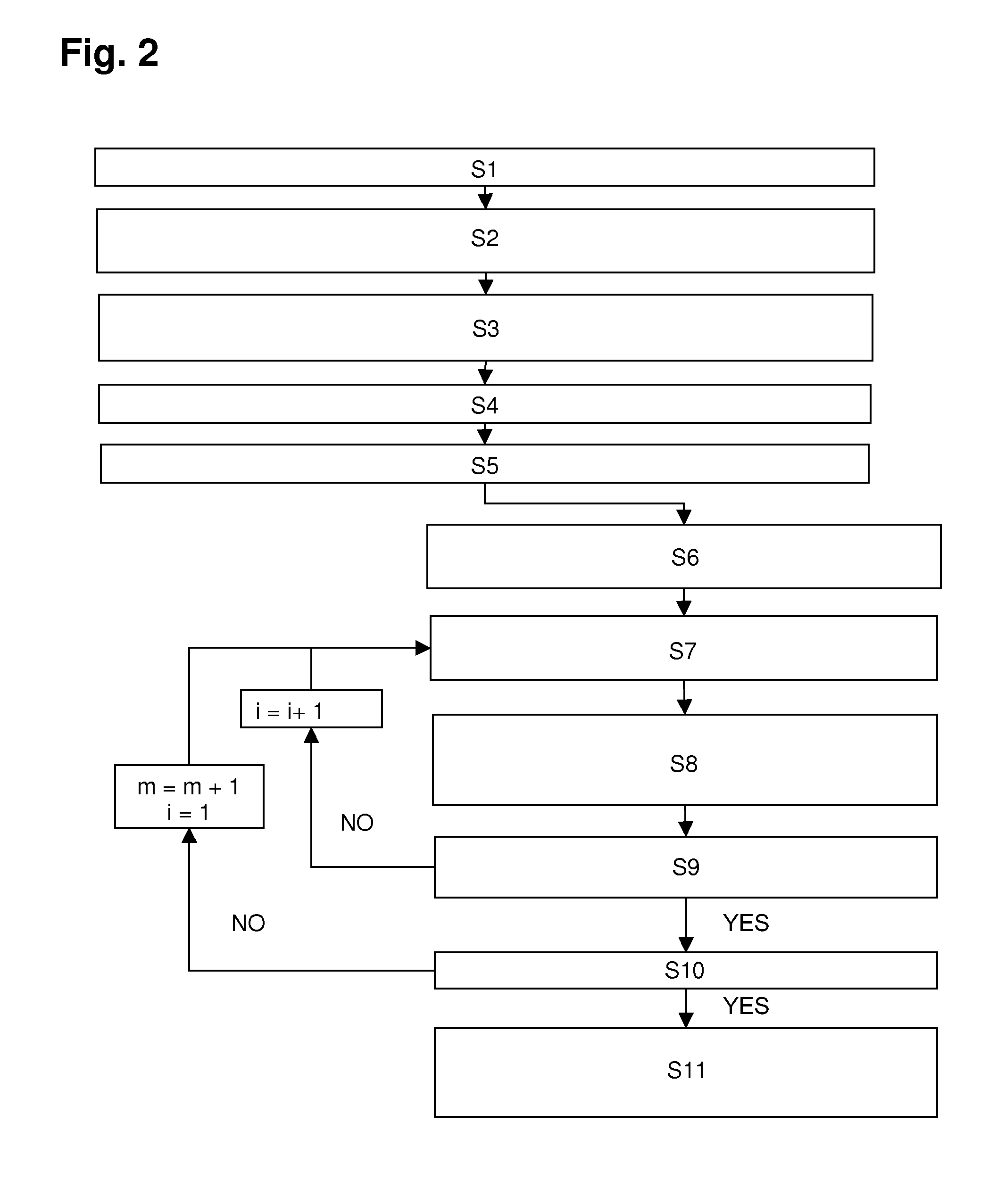
92 results about "Gradient system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any slope can be called a gradient. In the interstate highway system, the maximum gradient is 6 percent; in other words, the highway may never ascend more than 6 vertical feet over a distance of 100 feet. Any rate of change that's shown on a graph may have a sloped gradient.
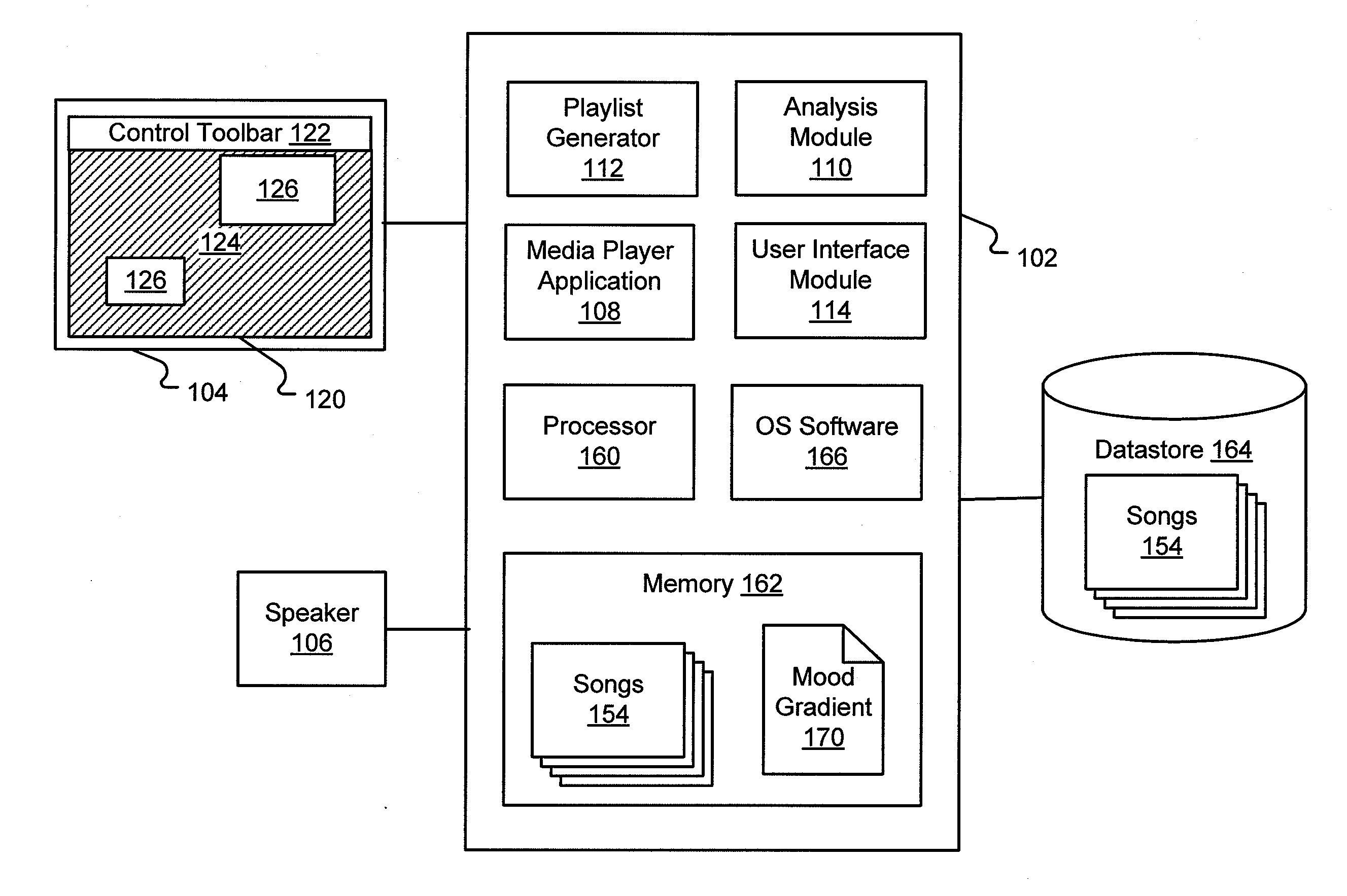
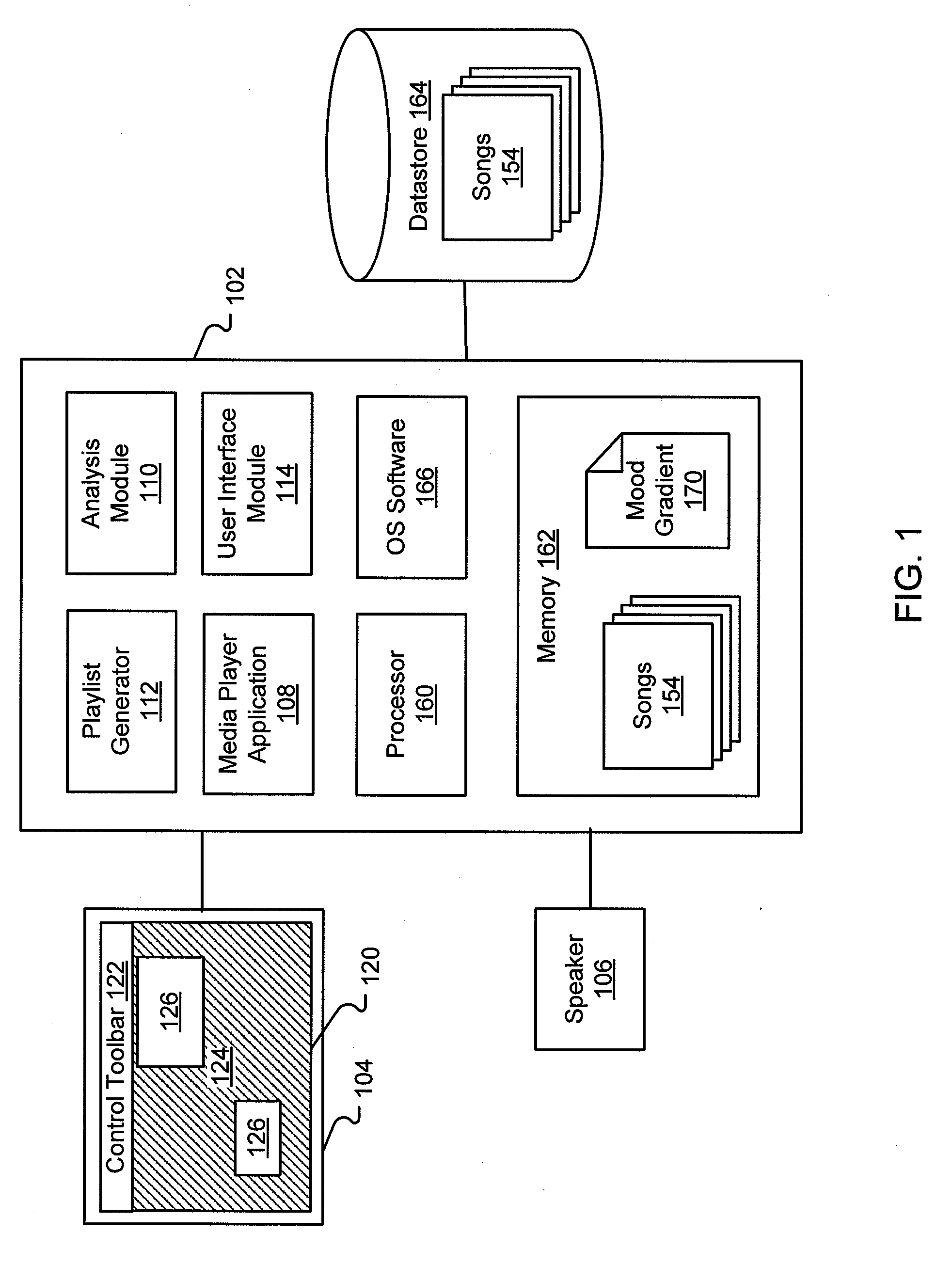
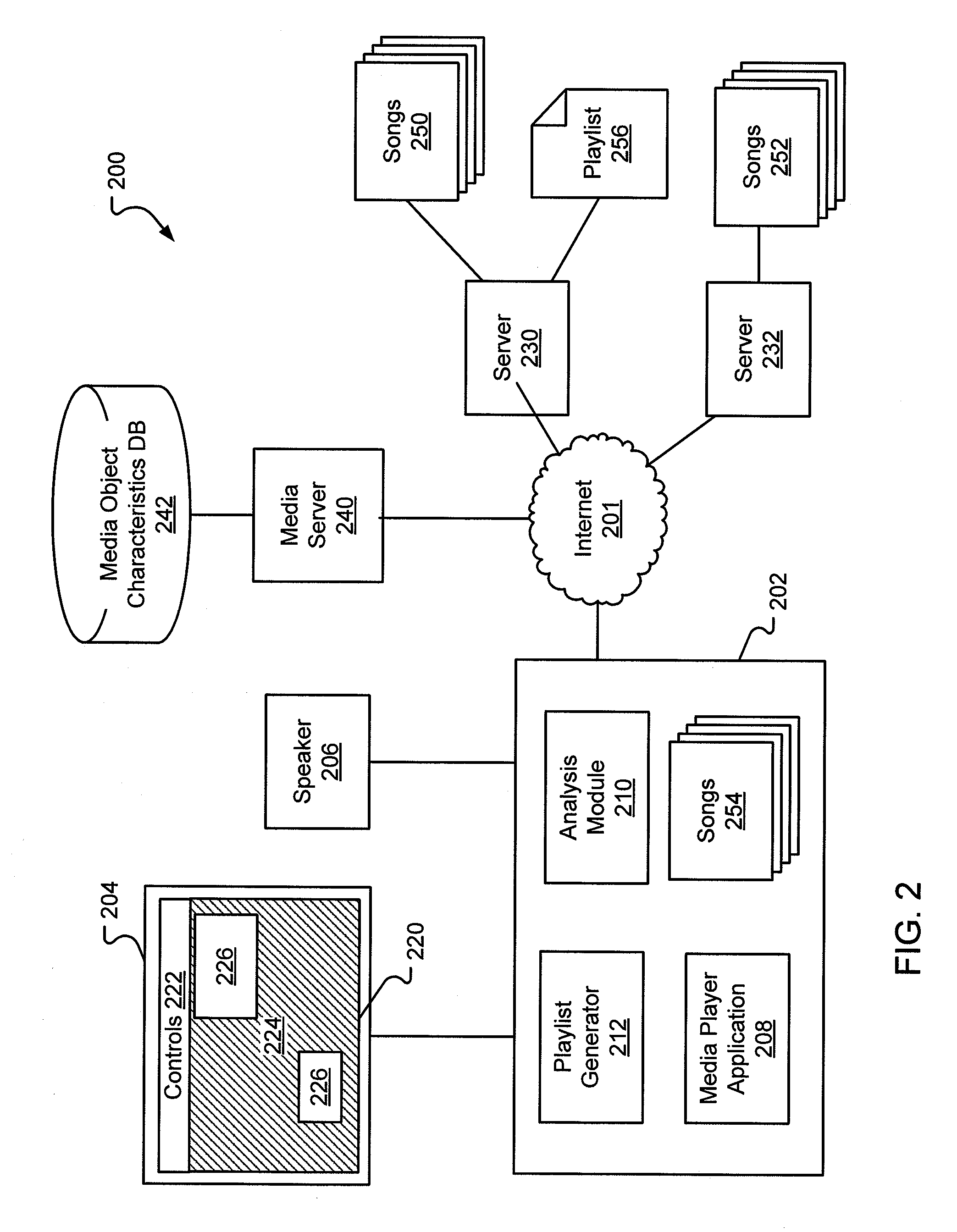
System and method for generating a playlist from a mood gradient
ActiveUS20090063414A1More experienceSmoother and more enjoyable music playback experienceMetadata audio data retrievalRecording carrier detailsObject basedThree-dimensional space
Systems and methods for generating and playing a sequence of media objects based on a mood gradient are also disclosed. A mood gradient is a sequence of items, in which each item is media object having known characteristics or a representative set of characteristics of a media object, that is created or used by a user for a specific purpose. Given a mood gradient, one or more new media objects are selected for each item in the mood gradient based on the characteristics associated with that item. In this way, a sequence of new media objects is created but the sequence exhibits a similar variation in media object characteristics. The mood gradient may be presented to a user or created via a display illustrating a three-dimensional space in which each dimension corresponds to a different characteristic. The mood gradient may be represented as a path through the three-dimensional space and icons representing media objects are located within the three-dimensional space based on their characteristics.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
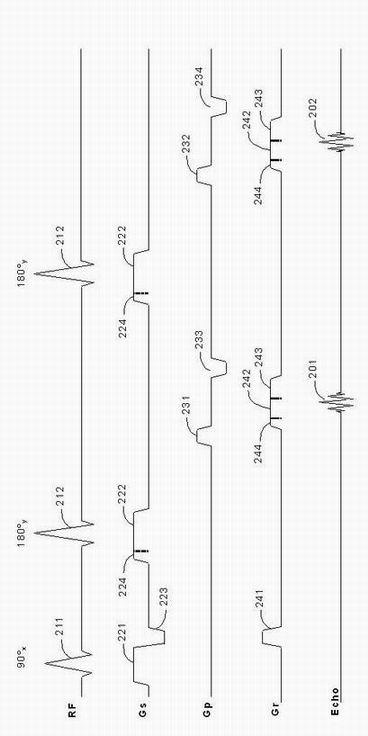
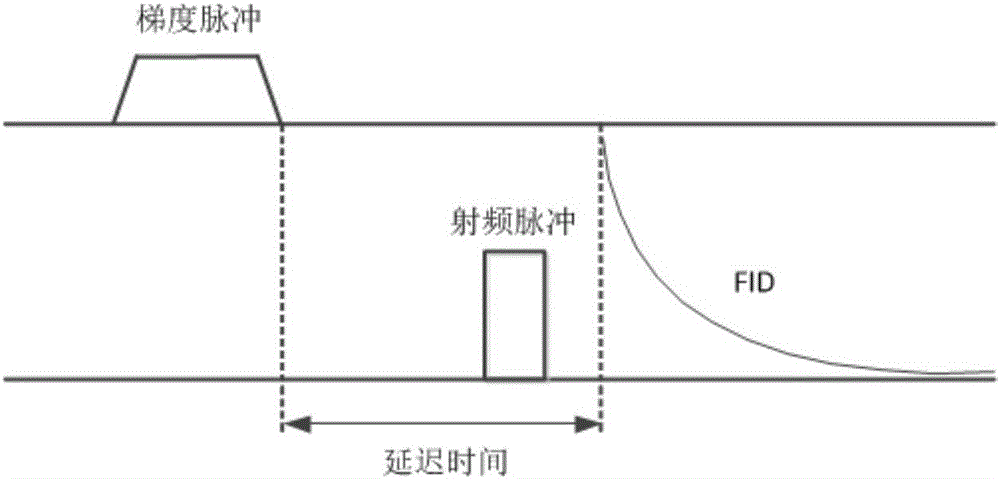
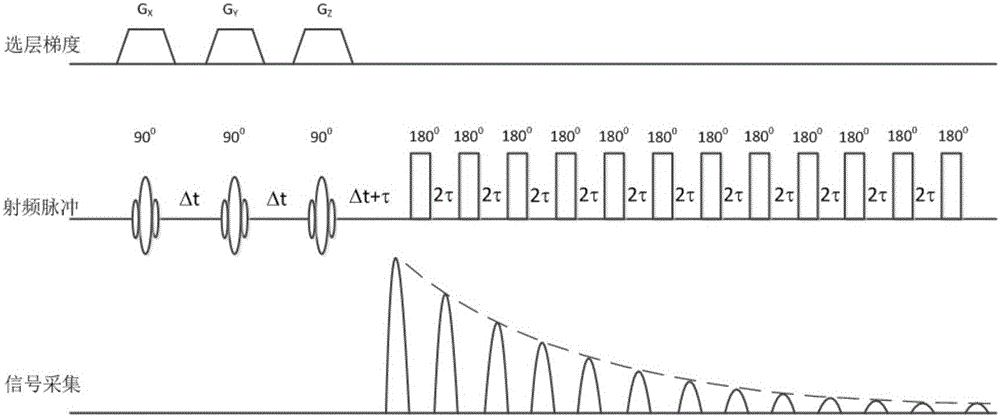
Gradient system time delay correction method for fast spin echo pulse sequence
InactiveCN102096054AReduce hardware costsReduce system complexityMagnetic measurementsFast spin echoCoronal plane
The invention provides a gradient system time delay correction method for a fast spin echo pulse sequence. In the method, a gradient system time delay is corrected by correcting a gradient pulse, and an amplitude synthetic matrix for correcting the gradient pulse is calculated by using the normalized gradient system time delay. By the method, the influence of the gradient system time delay on thefast spin echo pulse sequence is overcome, and the hardware cost and the system complexity of a magnetic resonance imaging system are not increased; and even if the gradient system time delays in x, y and z directions are unequal, the power of a gradient power amplifier is not enough to provide overshooting impulse with larger amplitude in a gradient waveform. By the method, the gradient system time delay can still be corrected so as to enhance the image quality of a sagittal plane, a coronal plane, a cross section and various diagonal planes in a fast spin echo image.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
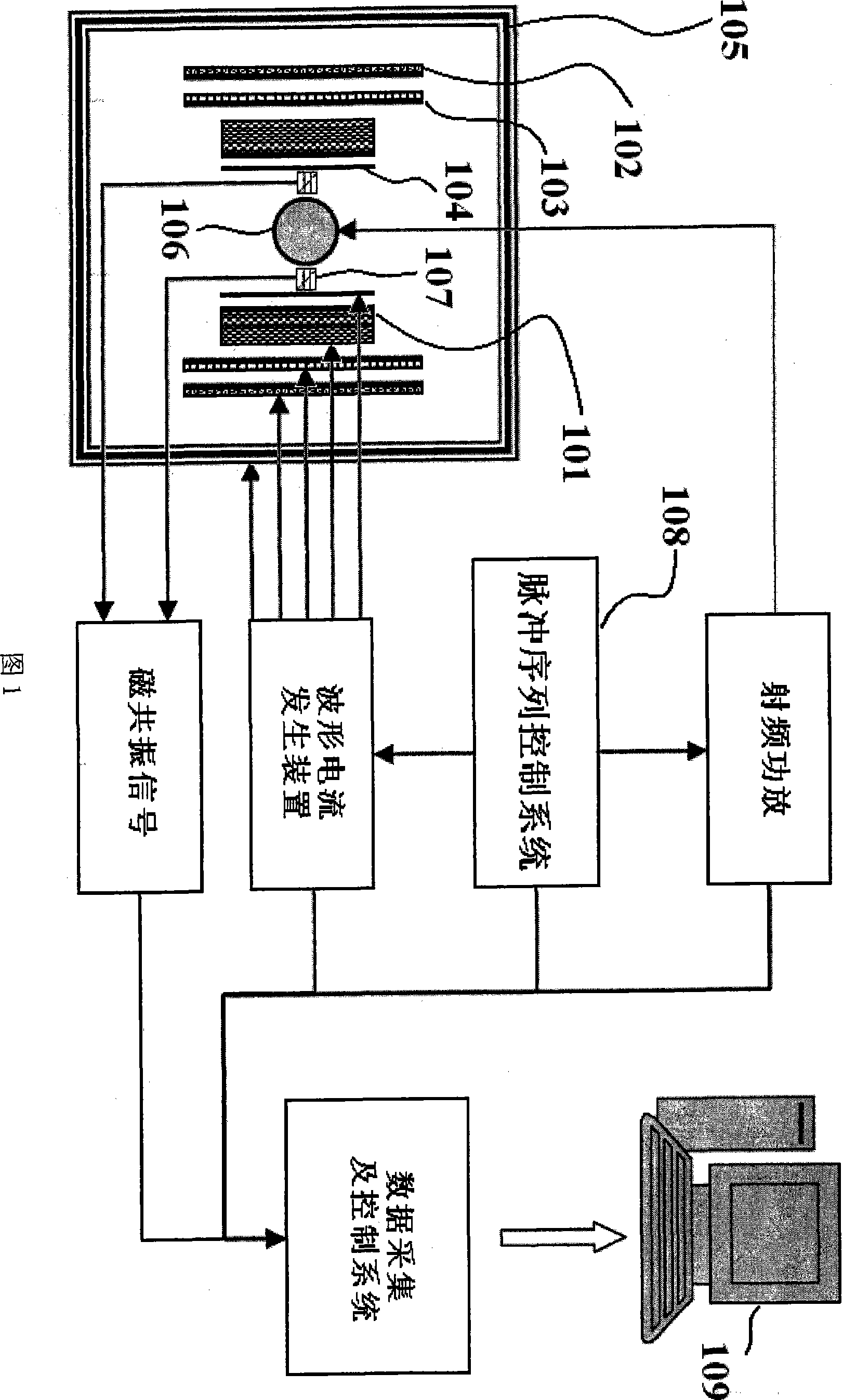
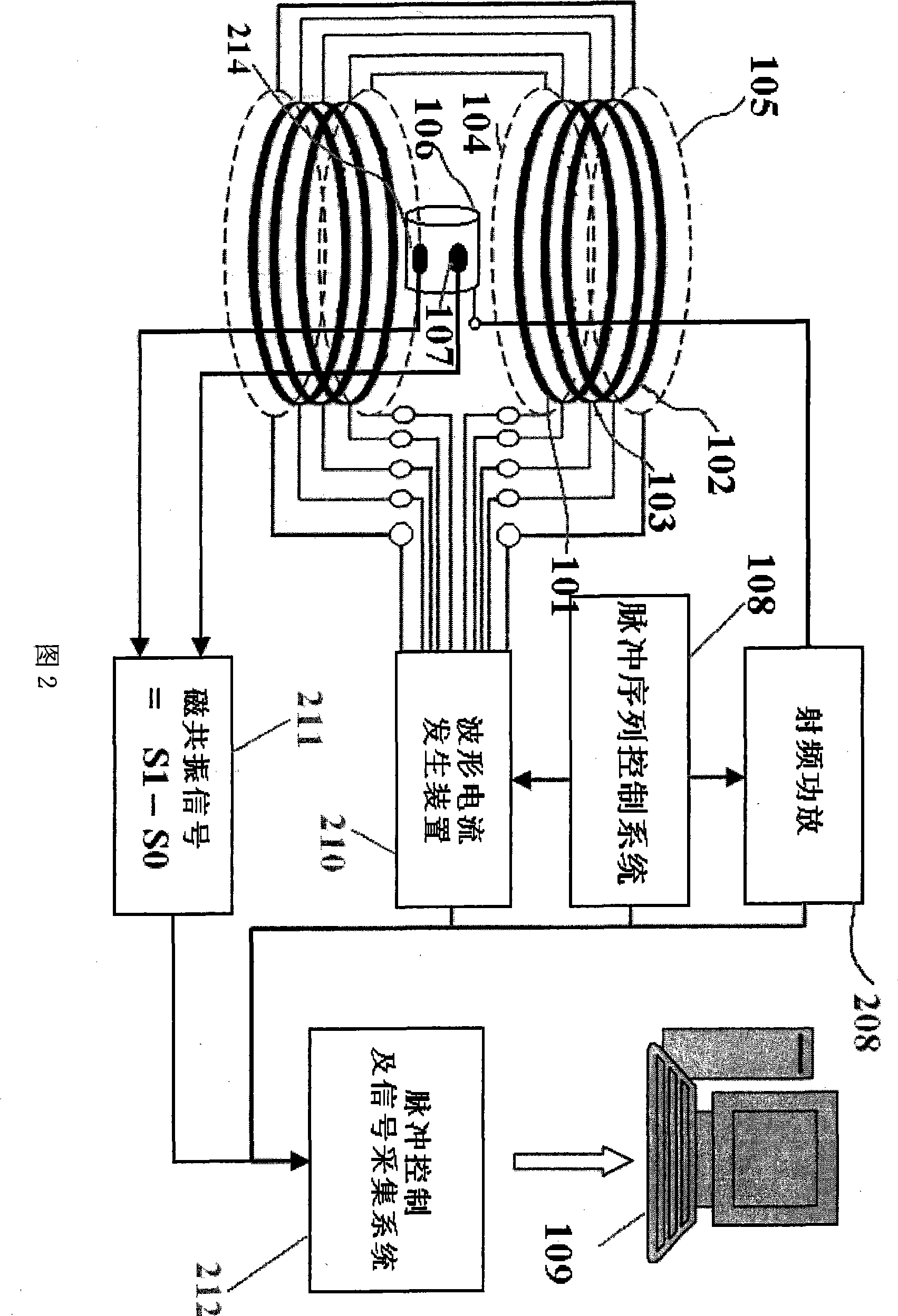
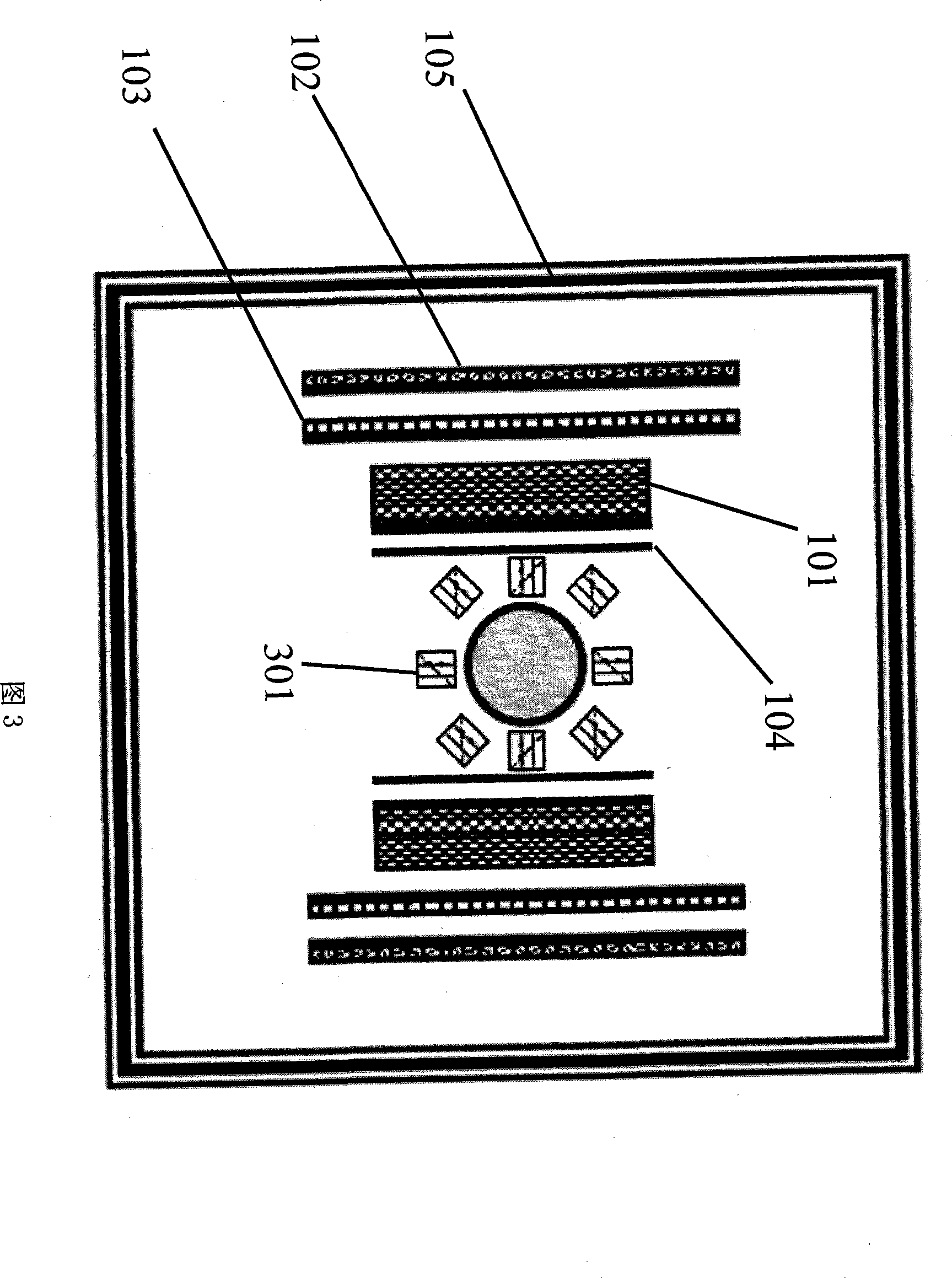
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus thereof
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance imaging method. The method comprises the following steps: applying a strong polarizing magnetic field to an imaging object, closing the polarizing magnetic field, applying a low-polar encoding magnetic field to the sample, applying a gradient magnetic field to the sample for space coding in this magnetic field, closing the encoding magnetic field, reading magnetic resonance signals by an optomagnetic resonance method in an nT-level magnetic field environment, and rebuilding images. The device comprises a polarizing magnet (101) for generating the polarizing magnetic field with controllable magnetic field, an encoding magnet (102) for generating the encoding magnetic field with the controllable magnetic field, a 3D gradient system (103) for generating the gradient magnetic field, an nT coil (104) for generating the nT-level magnetic field, a magnetic shielding system (105), a radio frequency coil (106), an optomagnetic probe (107), a pulse sequence control system (108) and an image processing computer (109). The imaging object and the optomagnetic probe (107) are arranged in the encoding magnet (102) and the polarizing magnet (101).
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
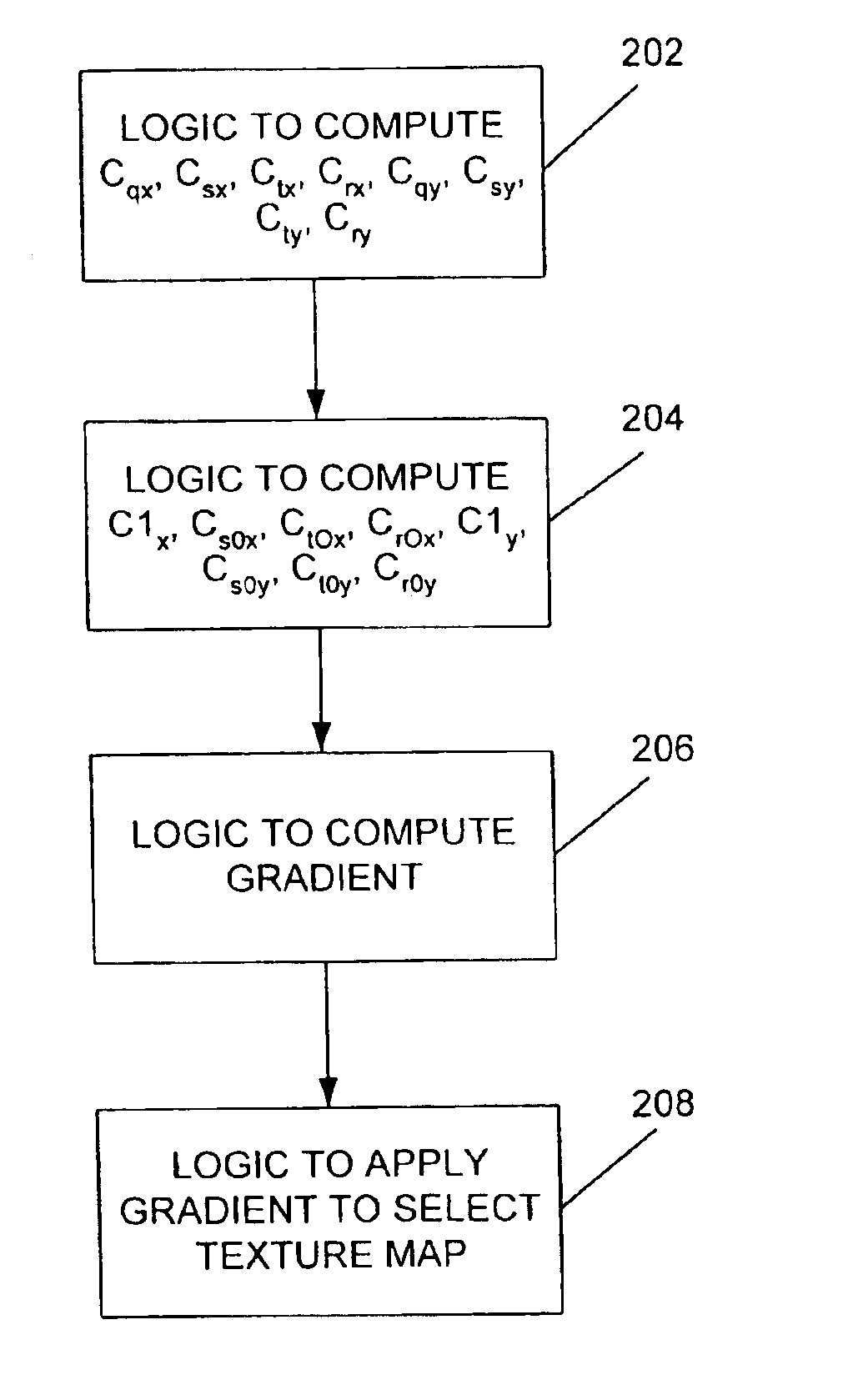
System and method for calculating a texture-mapping gradient
Systems and methods provide a more efficient and effective gradient computation. Specifically, in one embodiment, a method is provided for calculating a texture-mapping gradient, which comprises calculating constant values for use in a gradient-calculating equation, passing the constant values to logic configured to calculate the gradient, and computing the gradient using barycentric coordinates and the calculated constant values. In accordance with another embodiment, an apparatus is provided for calculating a texture-mapping gradient, which comprises logic for calculating constant values for use in a gradient-calculating equation, and logic for computing the gradient-calculating equation using barycentric coordinates and the calculated constant values. In accordance with another embodiment, a computer-readable medium is also provided that contains code (e.g., RTL logic) for generating the computational logic mentioned above.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
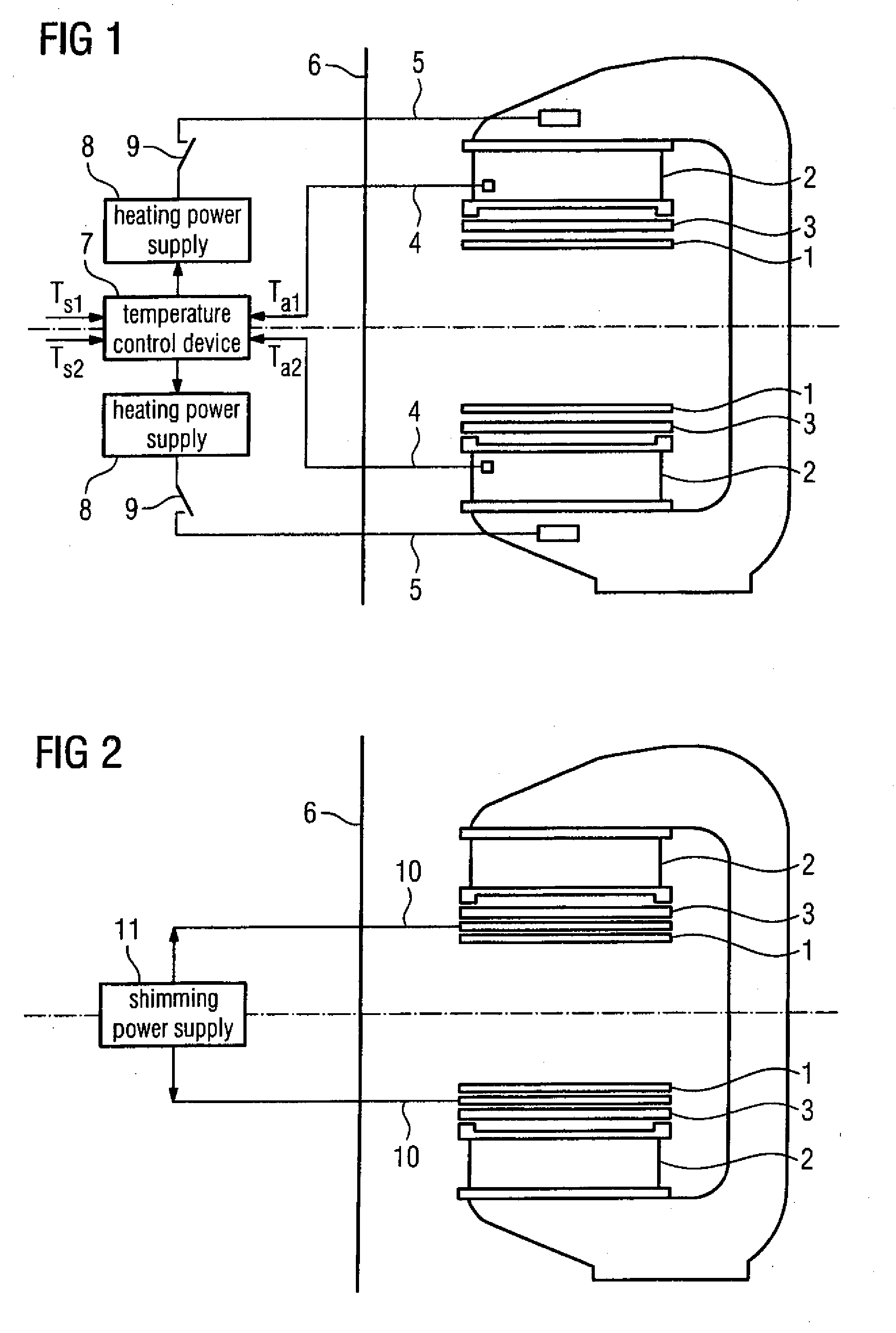
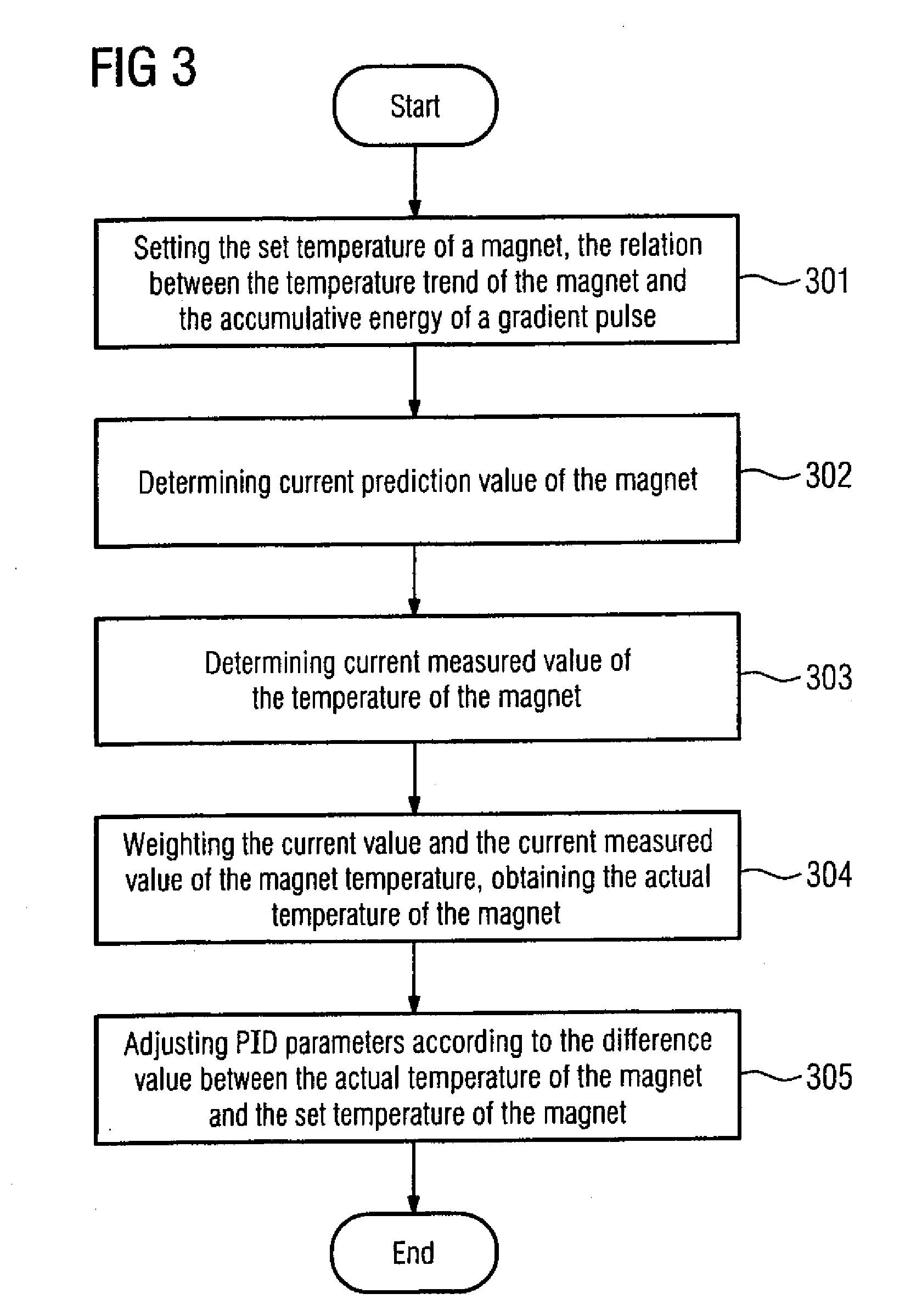
Temperature-controlled magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus
InactiveUS20090140735A1Improve image qualityEnhanced magnetic resonance imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTemperature controlImaging quality
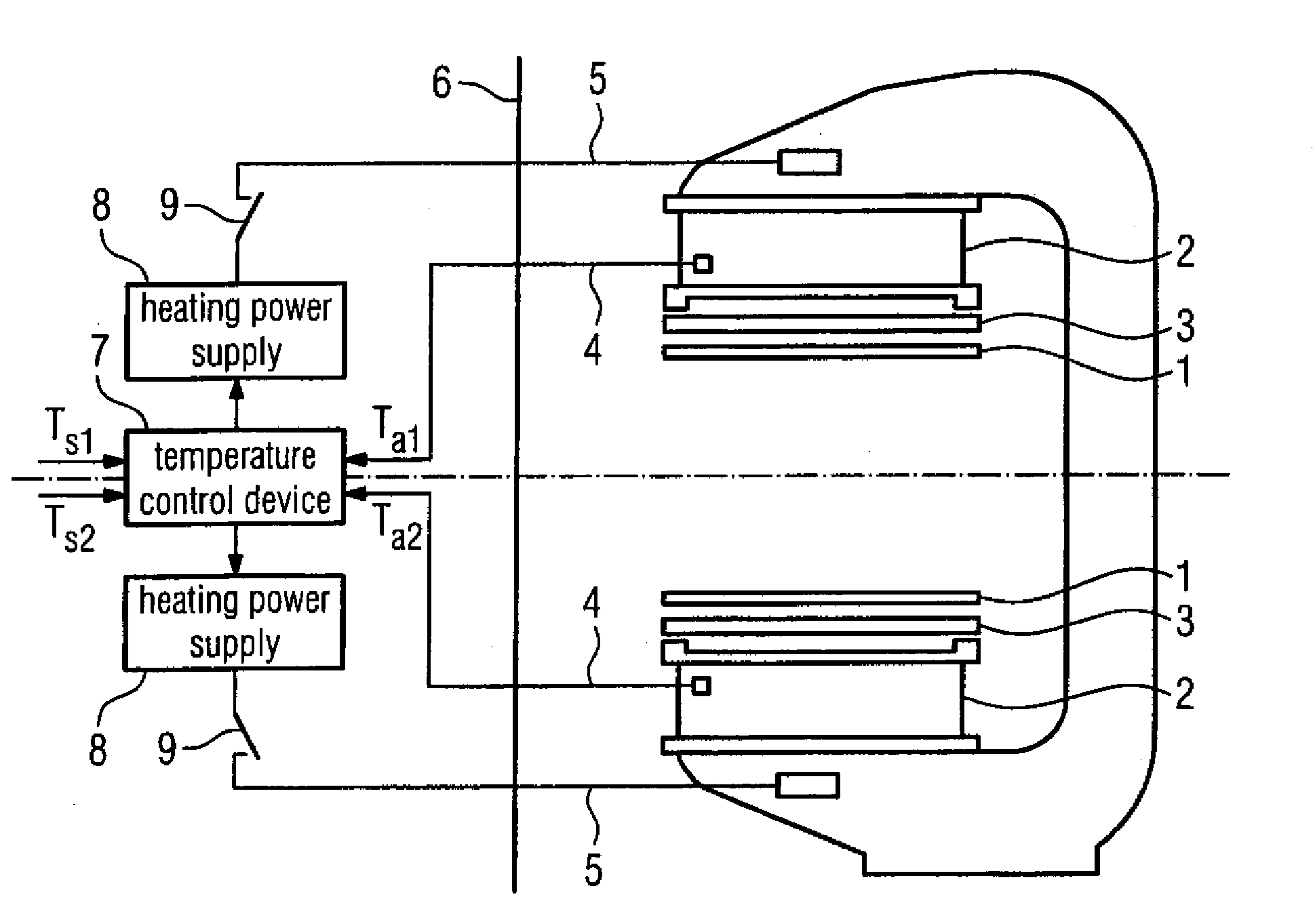
A method for improving the imaging quality of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment and MRI equipment, include obtaining a corresponding relationship between a deterioration factor of imaging quality and the cumulative energy of gradient pulses applied by successive scanning MRI sequences, then determining a predicted value of a current deterioration factor of imaging quality according to the currently applied cumulative energy of the gradient pulses and said corresponding relationship, adopting a corresponding method to carry out dynamic regulation or compensation using the predicted value of said deterioration factor of imaging quality as a reference, so as to cancel the influence produced by the heating effect of the gradient system to the imaging quality, thereby effectively improving the imaging quality of the MRI equipment.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
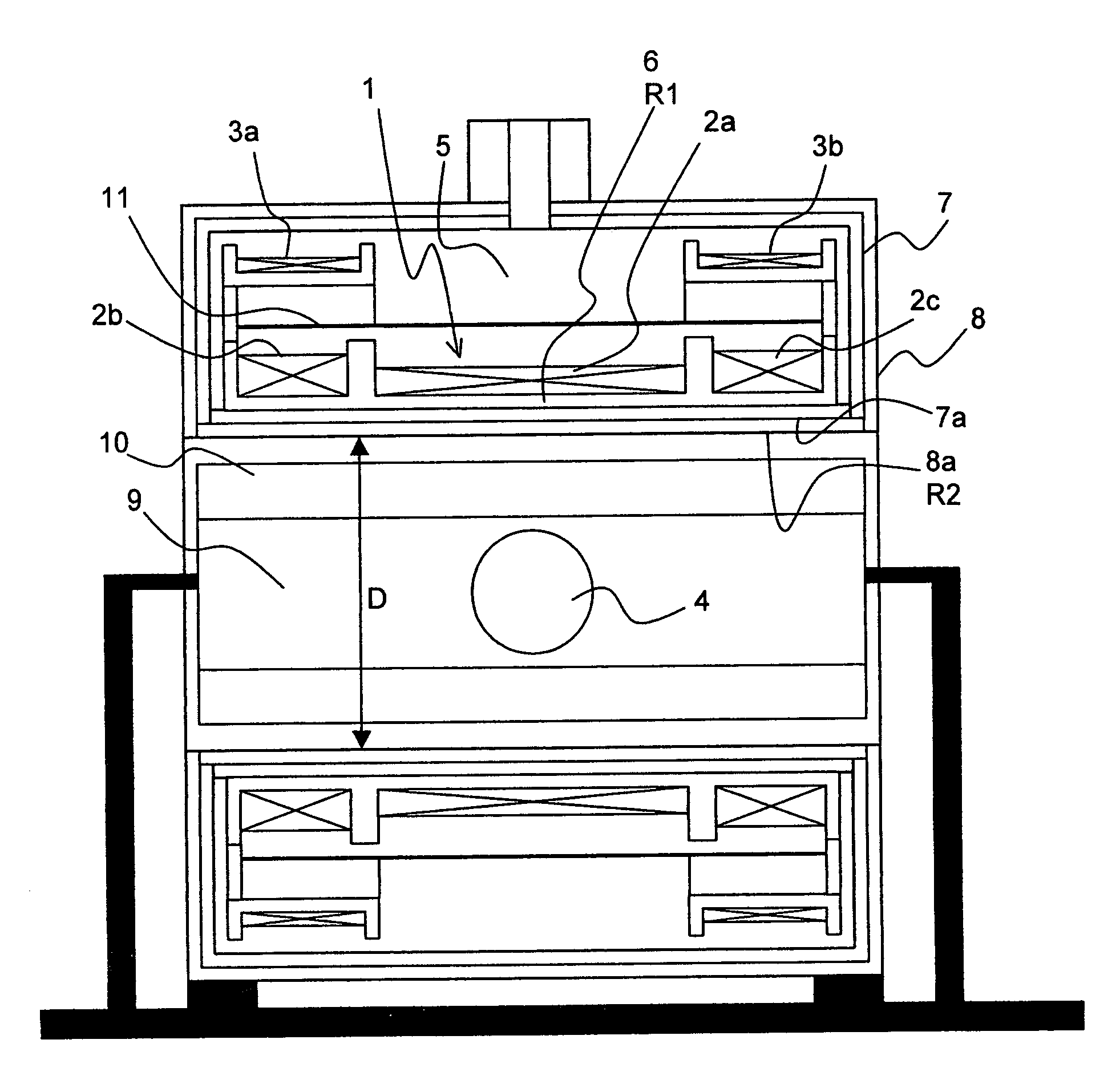
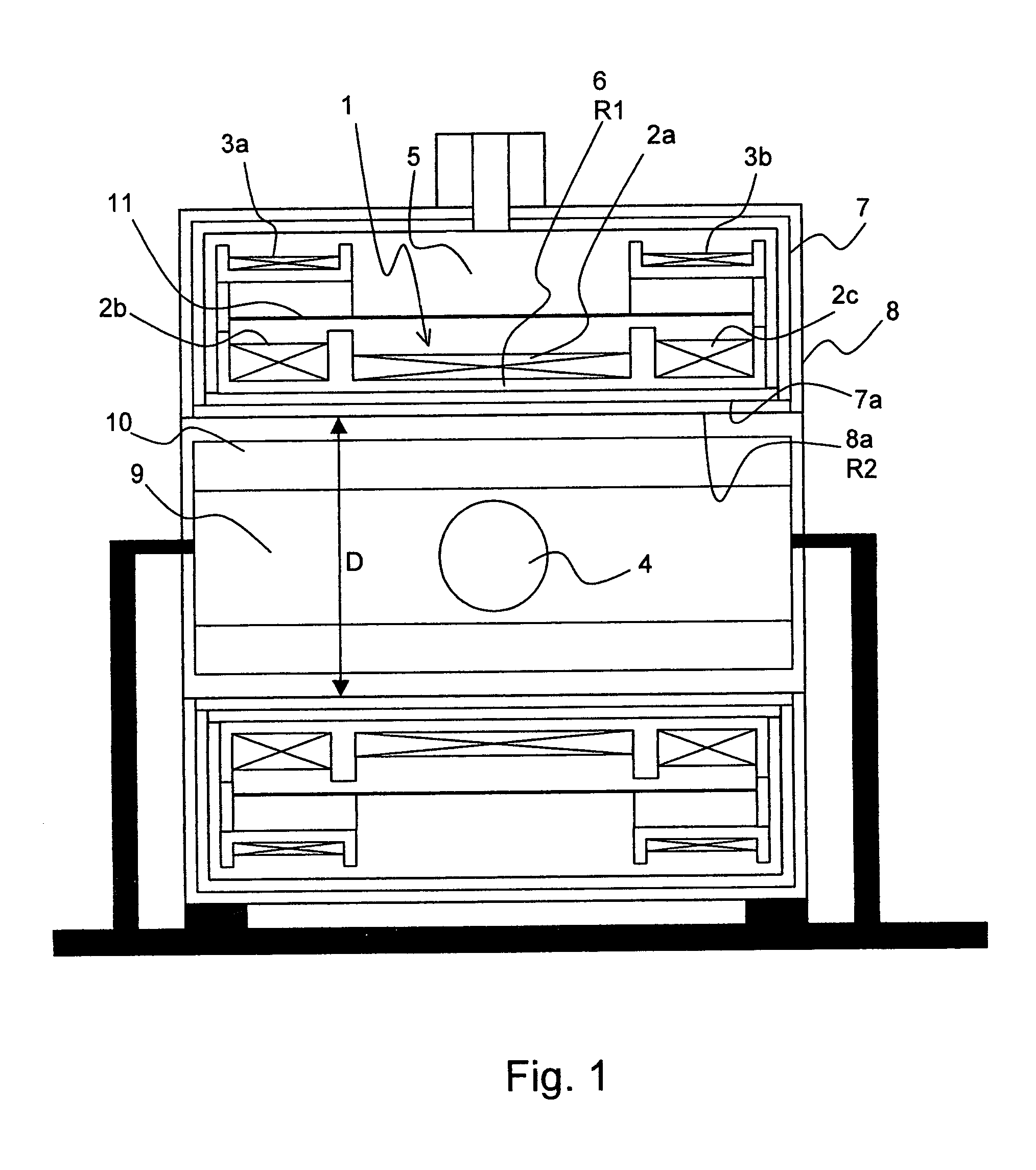
Superconducting magnet configuration with reduced heat input in the low temperature regions
ActiveUS7514928B2Increase valueCooling is also considerably facilitated and less expensiveMagnetic measurementsSuperconducting magnets/coilsSuperconducting CoilsMechanical resonance
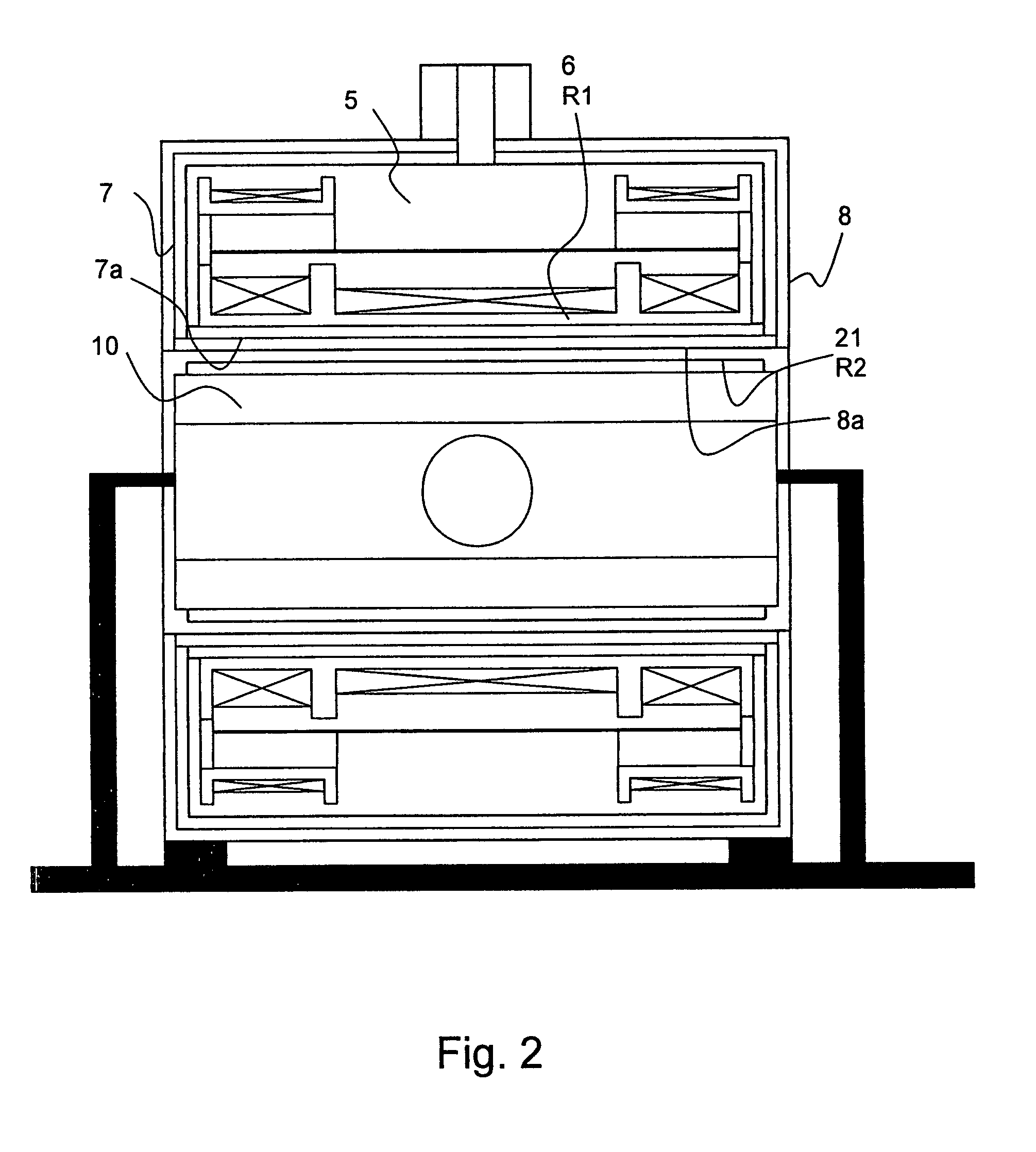
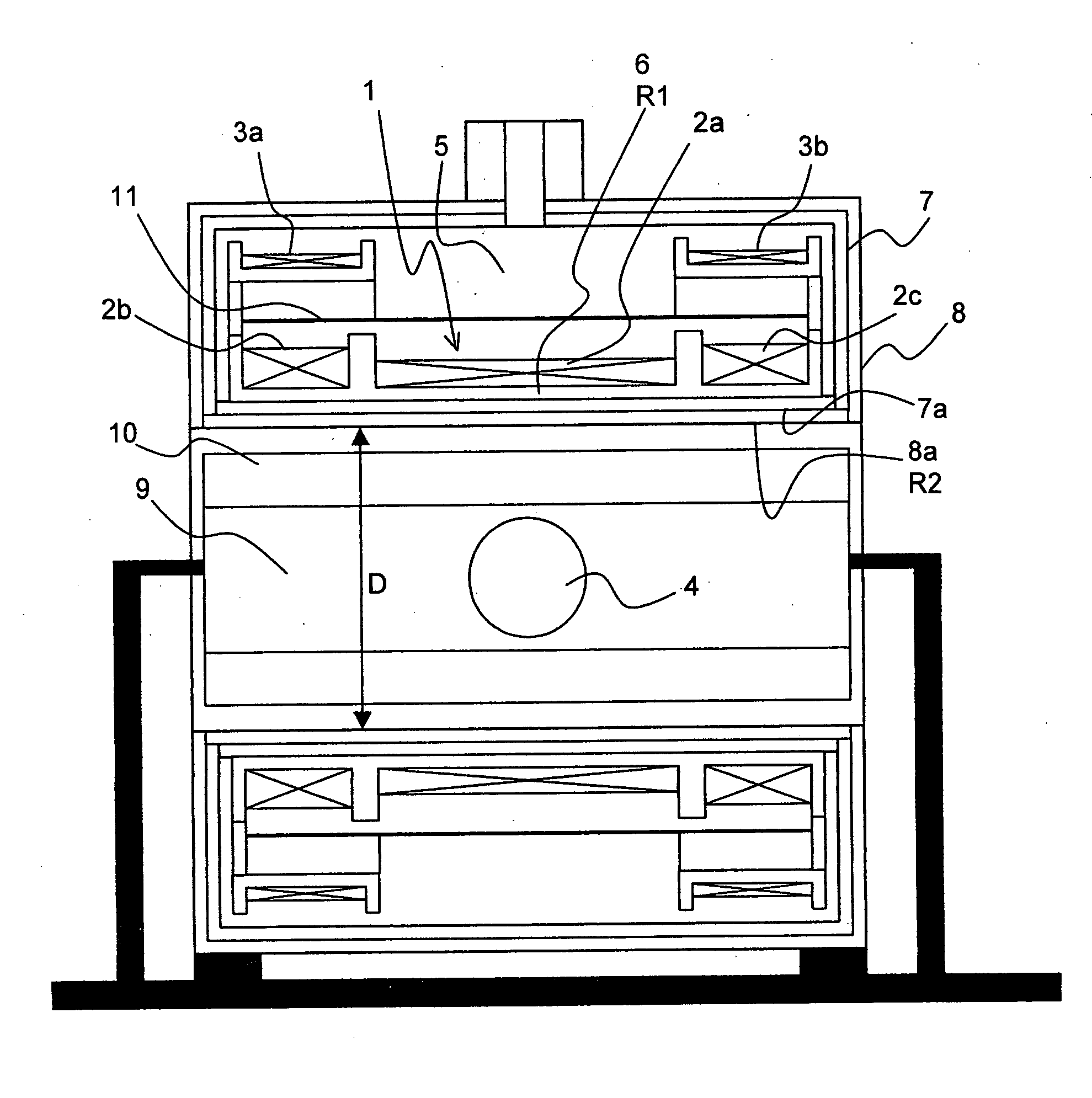
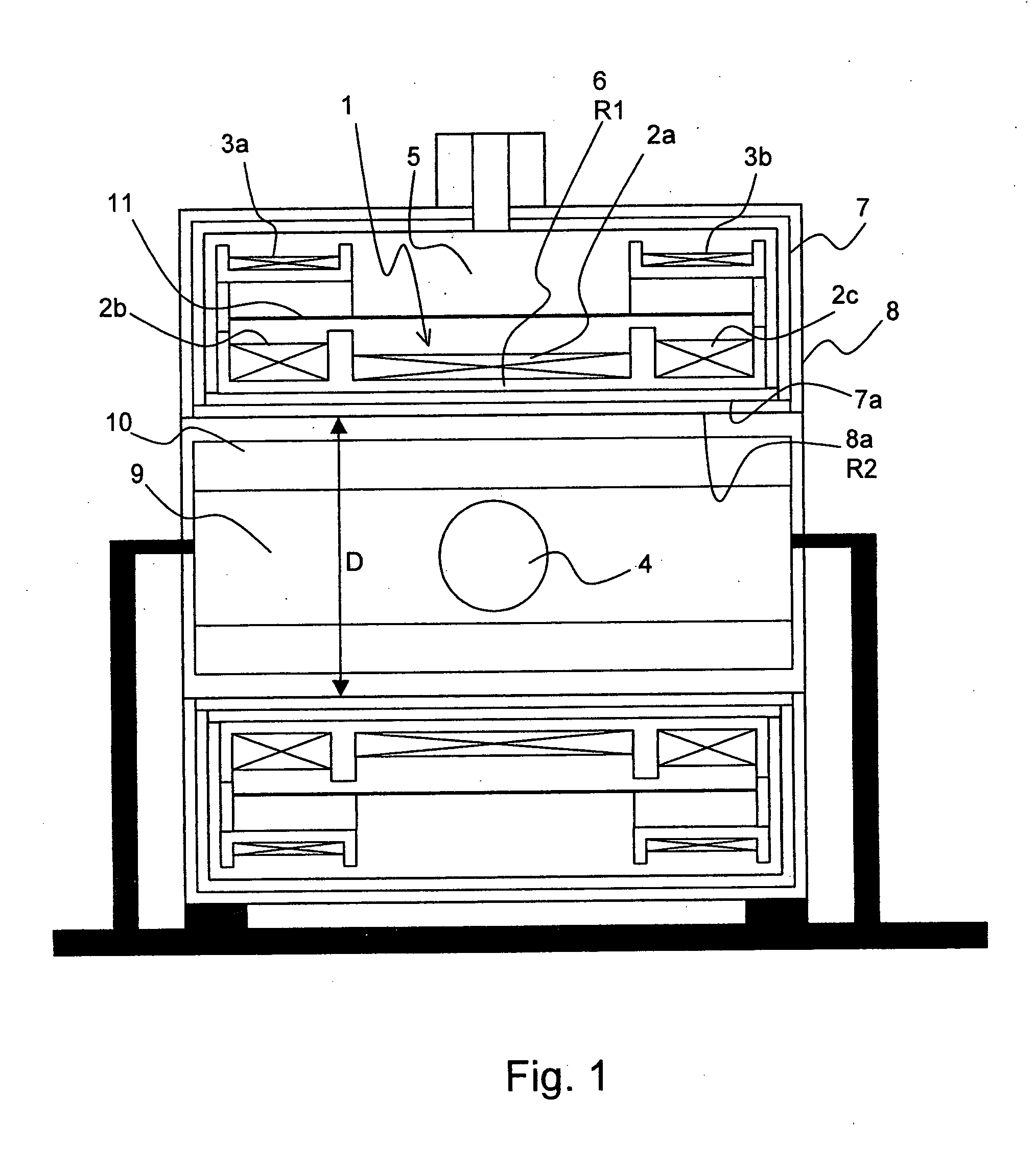
The invention concerns a magnet configuration comprising a superconducting magnet coil (1) within which a gradient system is to be switched. All low temperature oscillation systems (R1) with a temperature T1<10K within the magnet coil (1) are produced from a material having good electrical conducting properties, and at least one warm oscillation system (R2) with a temperature T2>10K within the magnet coil (1) has worse electrical conducting properties and has a considerably different mechanical resonance frequency (separation approximately 500 Hz or more) than at least one of the low temperature oscillation systems (R1). This reduces the undesired heating power supplied to the low temperature oscillation systems due to mechanical oscillations and induced eddy currents.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Method for inverting earth gravitational field by using variance-covariance diagonal tensor principle
InactiveCN103076640AImprove inversion accuracyFast inversionGravitational wave measurementNatural satelliteComputer performance
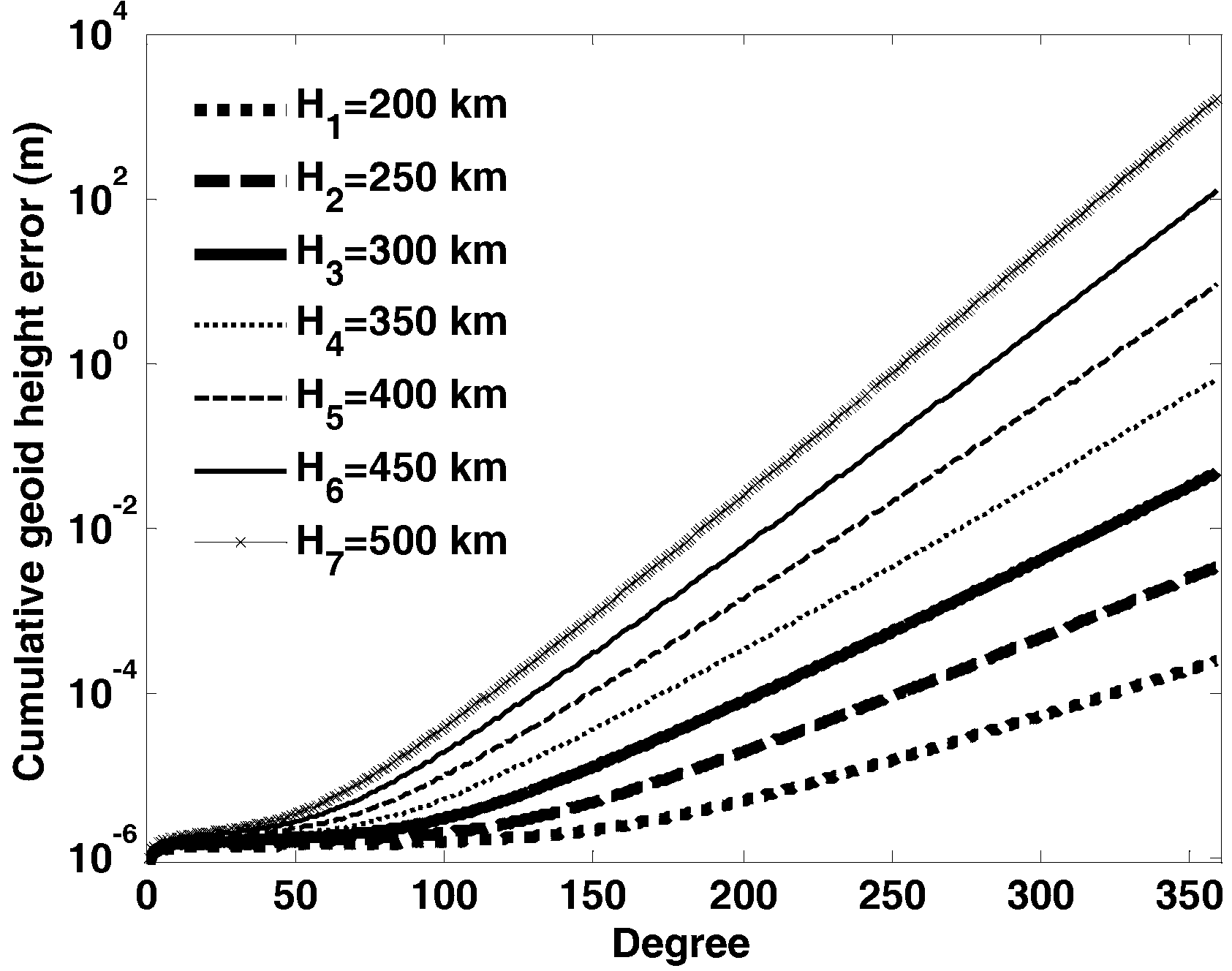
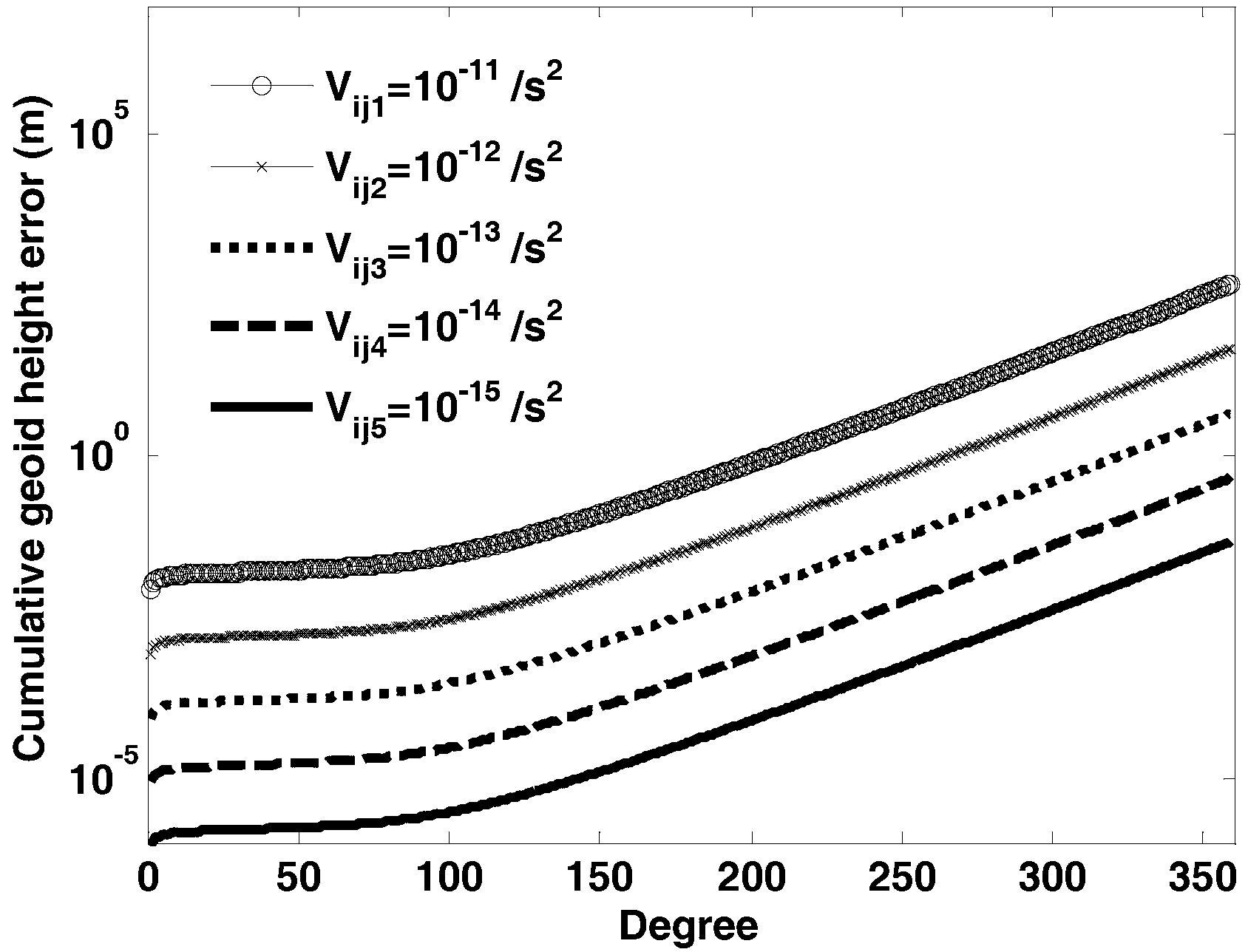
The invention relates to a method for precisely measuring the earth gravitational field, in particular to a method for inverting the earth gravitational field by using a variance-covariance diagonal tensor principle. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a cumulative geoidal surface error model on the basis of satellite gravity gradient variance-covariance diagonal tensor principle; accurately and rapidly inverting the earth gravitational field by using the satellite gravity gradient measurement data of a spaceborne gravity gradiometer; and developing requirement argumentation on a GOCE (Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer)-II satellite gravity gradient system by using the satellite orbit altitude and the precision index of the satellite gravity gradiometer. The method disclosed by the invention is high in inversion precision of the earth gravitational field, high in inversion speed of the satellite gravity gradient, explicit in physical content of a satellite observation equation, capable of easily developing the requirement analysis of the satellite gravity gradient system and low in requirement on computer performances. Therefore, the method for inverting the earth gravitational field by using the variance-covariance diagonal tensor principle is an effective method for resolving the earth gravitational field with high precision and high spatial resolution.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Apparatus and method for NMR tomography acquisition with local magnetic field gradients in connection with local receiver coils
ActiveUS7411395B2Small magnetic field differenceFast switching timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientResonance
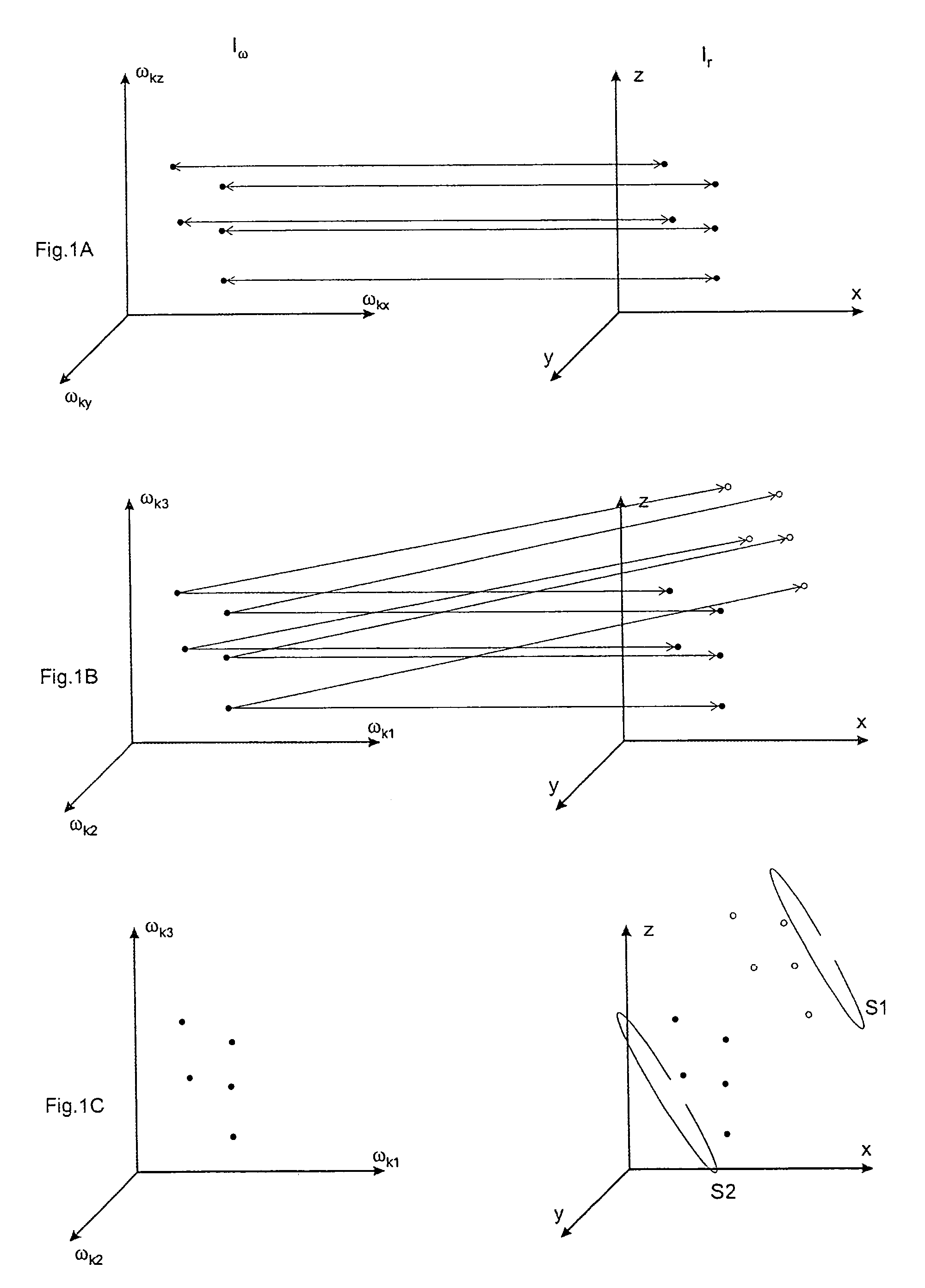
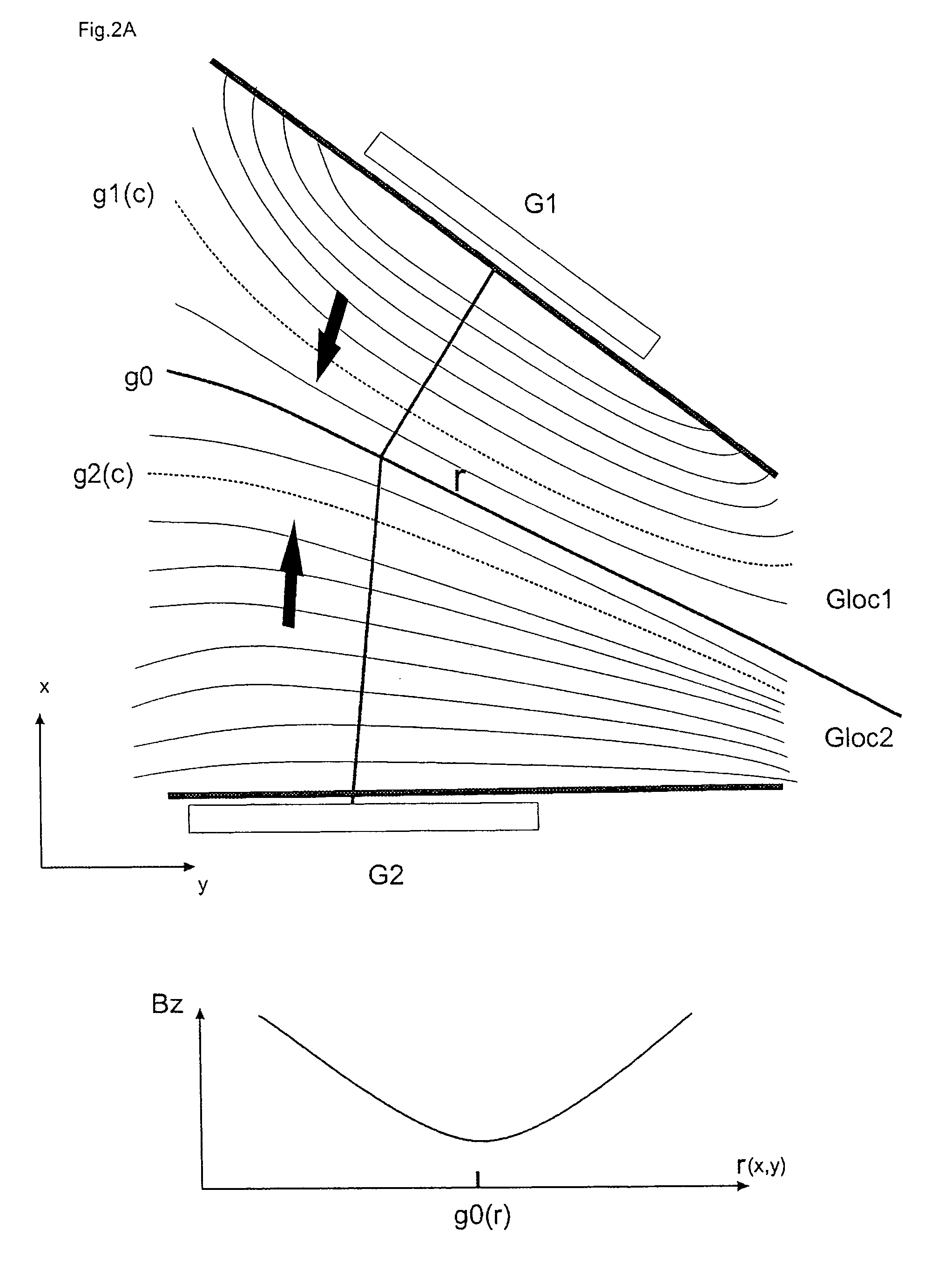
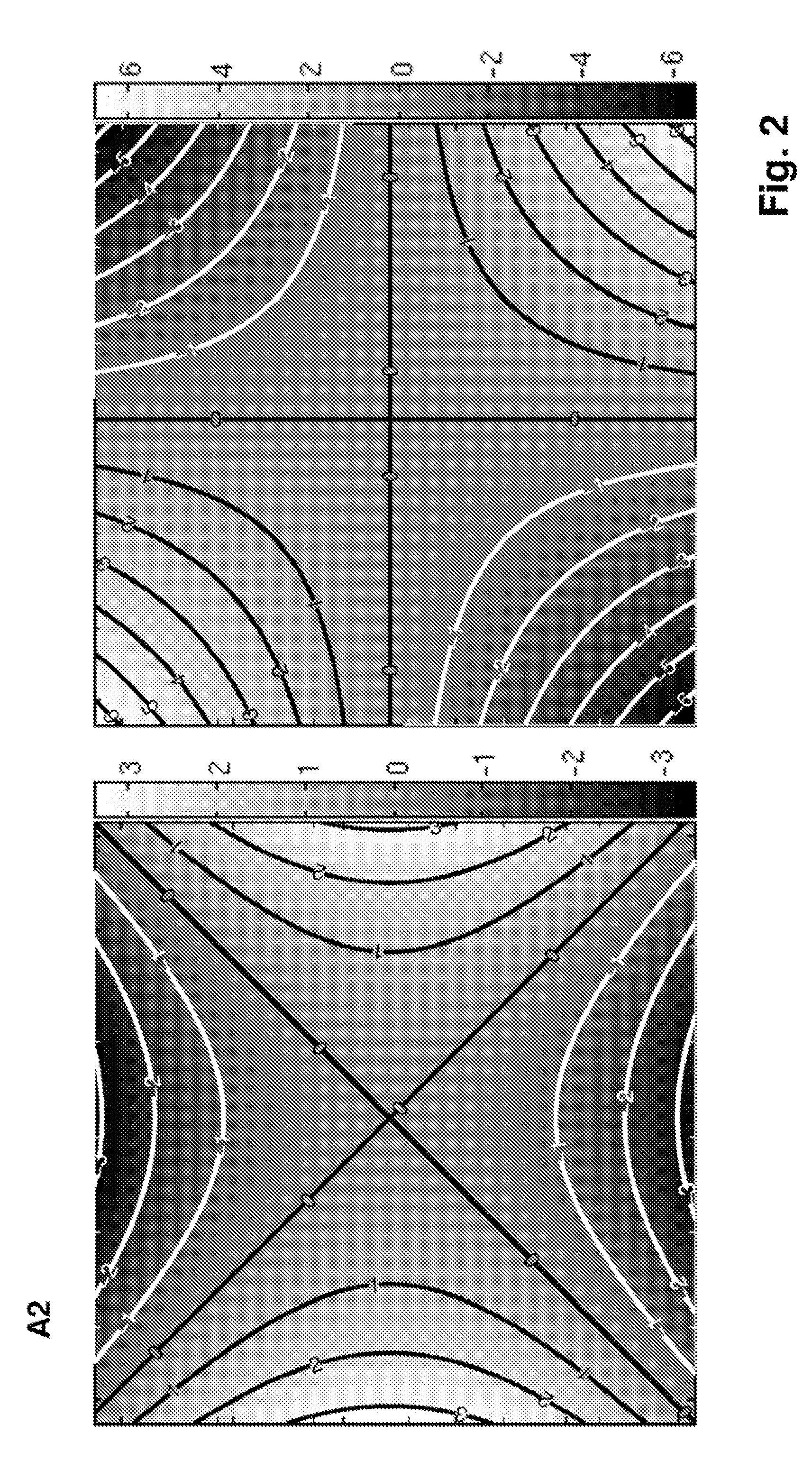
A magnetic resonance tomography apparatus, includes a gradient system that can generate at least one spatially varying and optionally time-varying magnetic field for at least one-dimensional local encoding of measuring signals in an area of a test sample to be imaged. The gradient system contains at least one subsystem which can generate a non-bijective spatially varying magnetic (NBSEM) field for local encoding, such that the function of the field strength of such an NBSEM within the area to be imaged has at least one local extreme value (maximum or minimum), such that the area to be imaged is divided along the hyper surface formed by the entirety of all local extreme values of the at least one NBSEM. The apparatus can produce images of the same quality with smaller magnetic field differences and permits easy realization.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
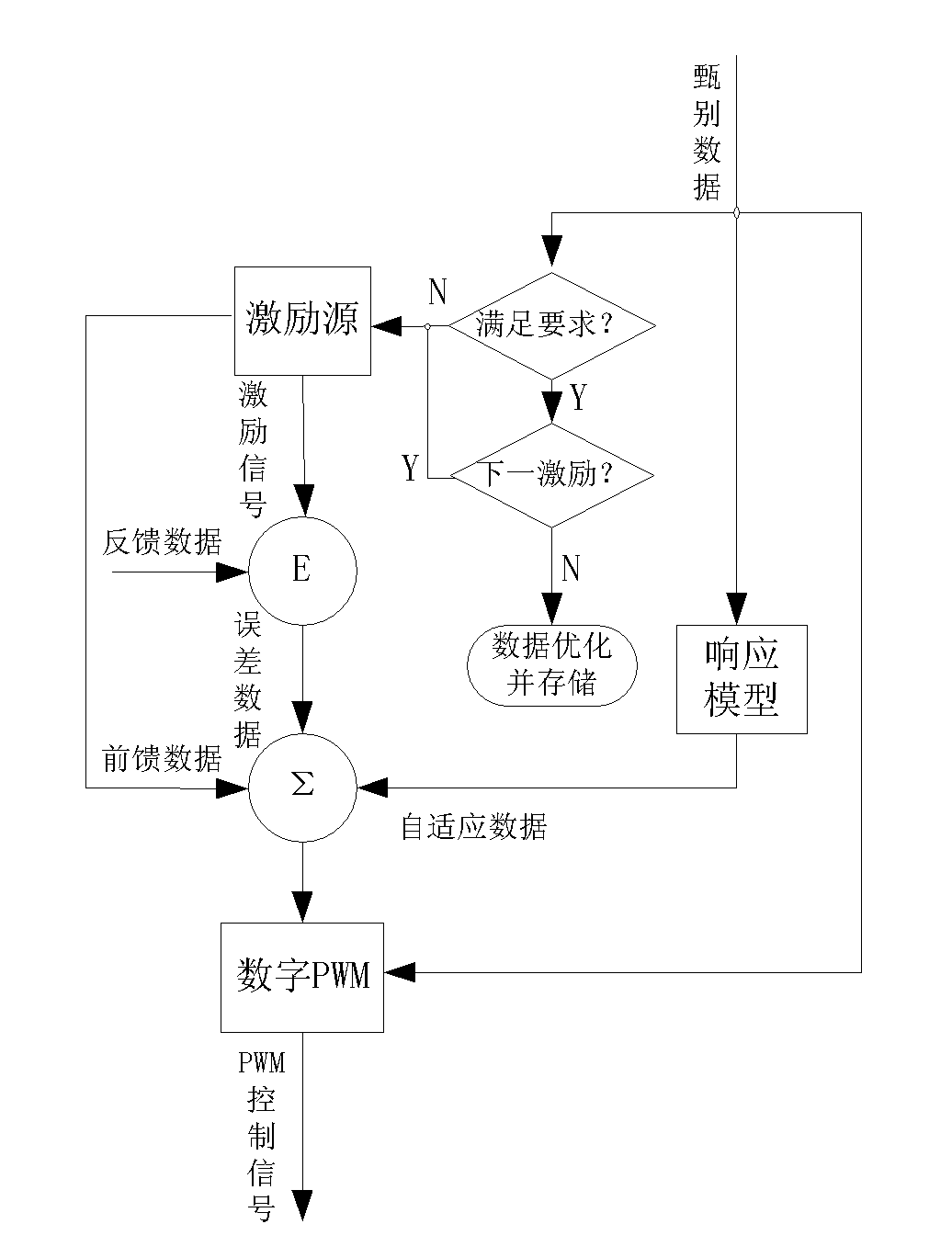
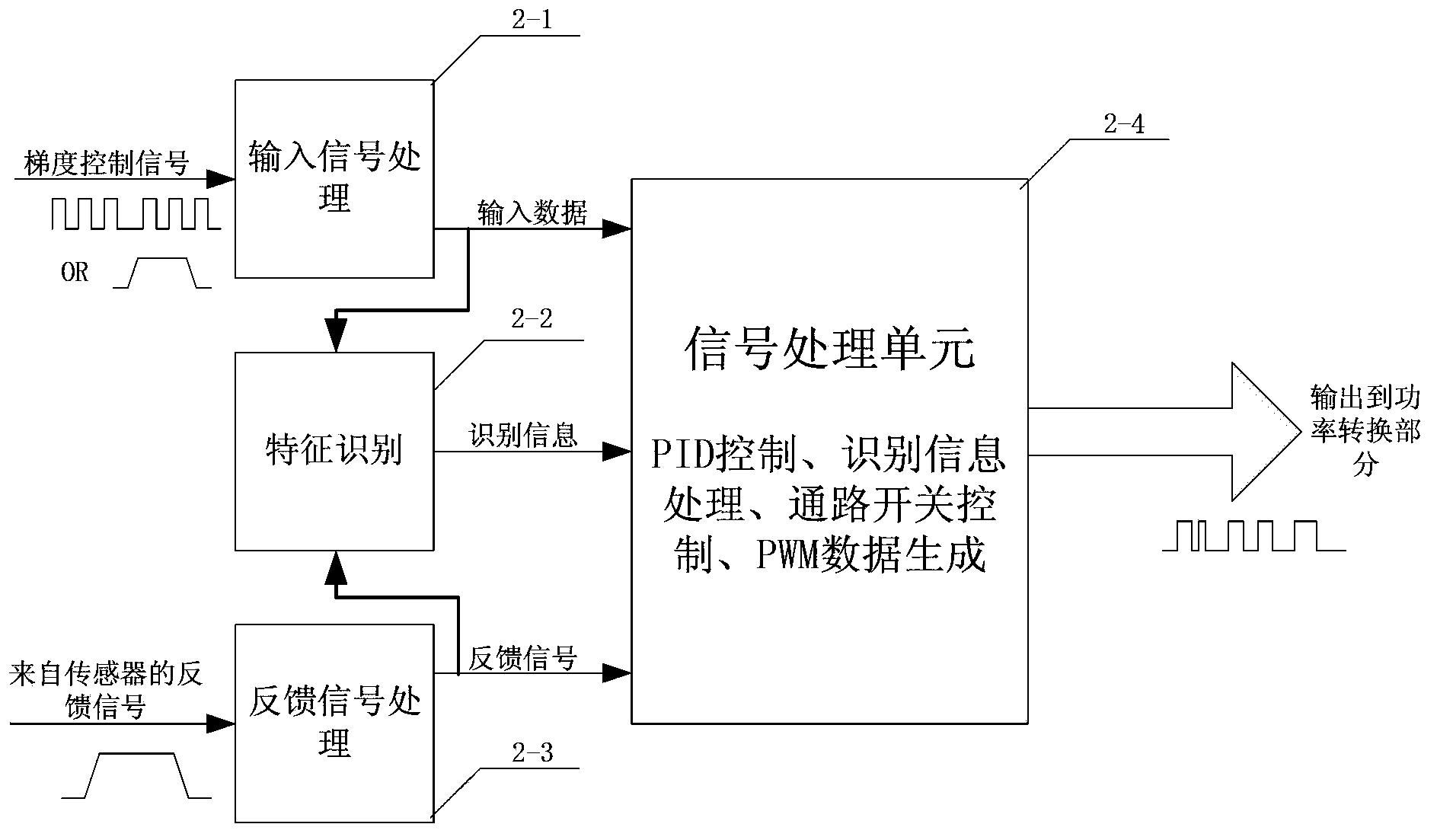
Digital variable frequency PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) gradient amplifier with adaptively-controlled load
ActiveCN102508183ALow costImprove performanceMagnetic measurementsDigital signal processingResonance
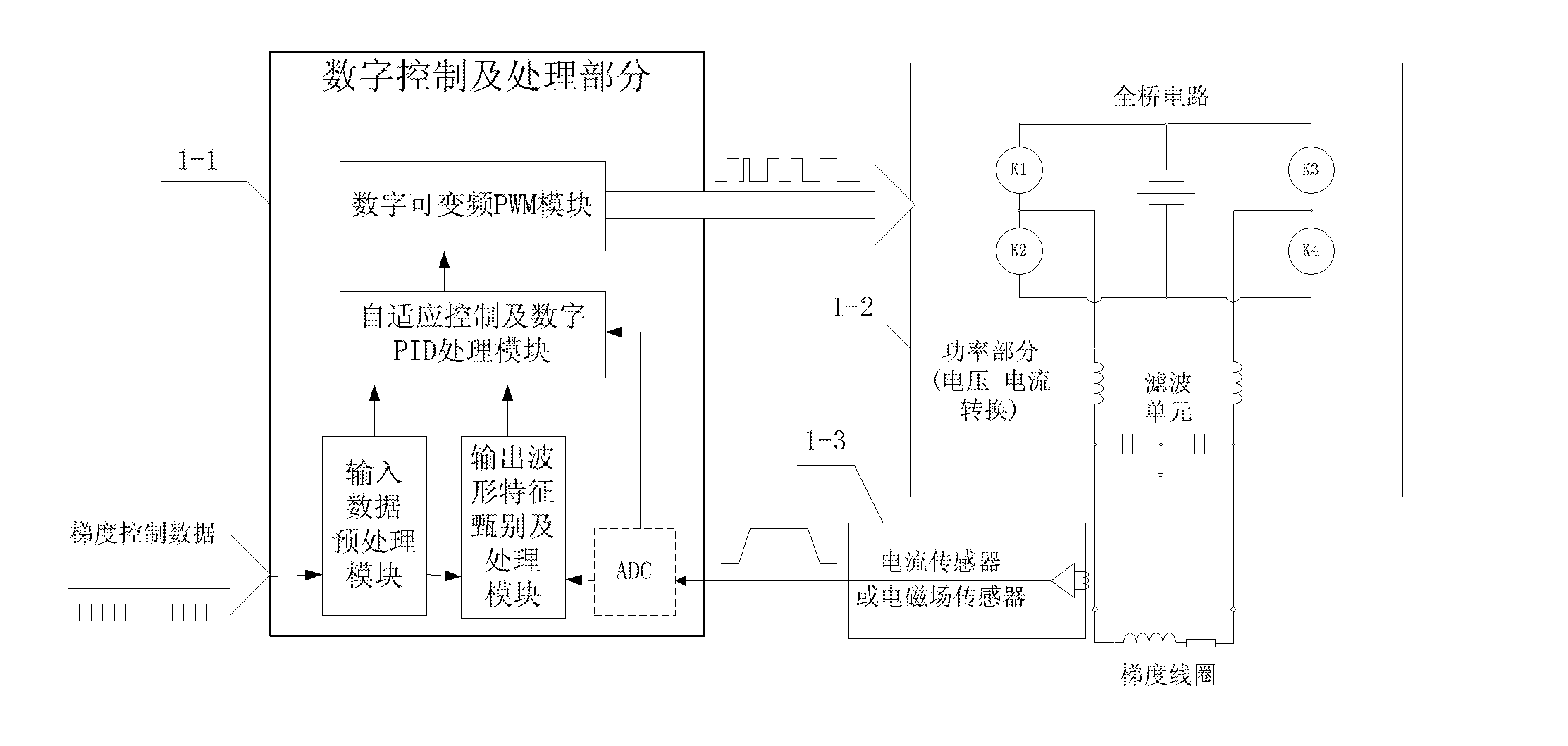
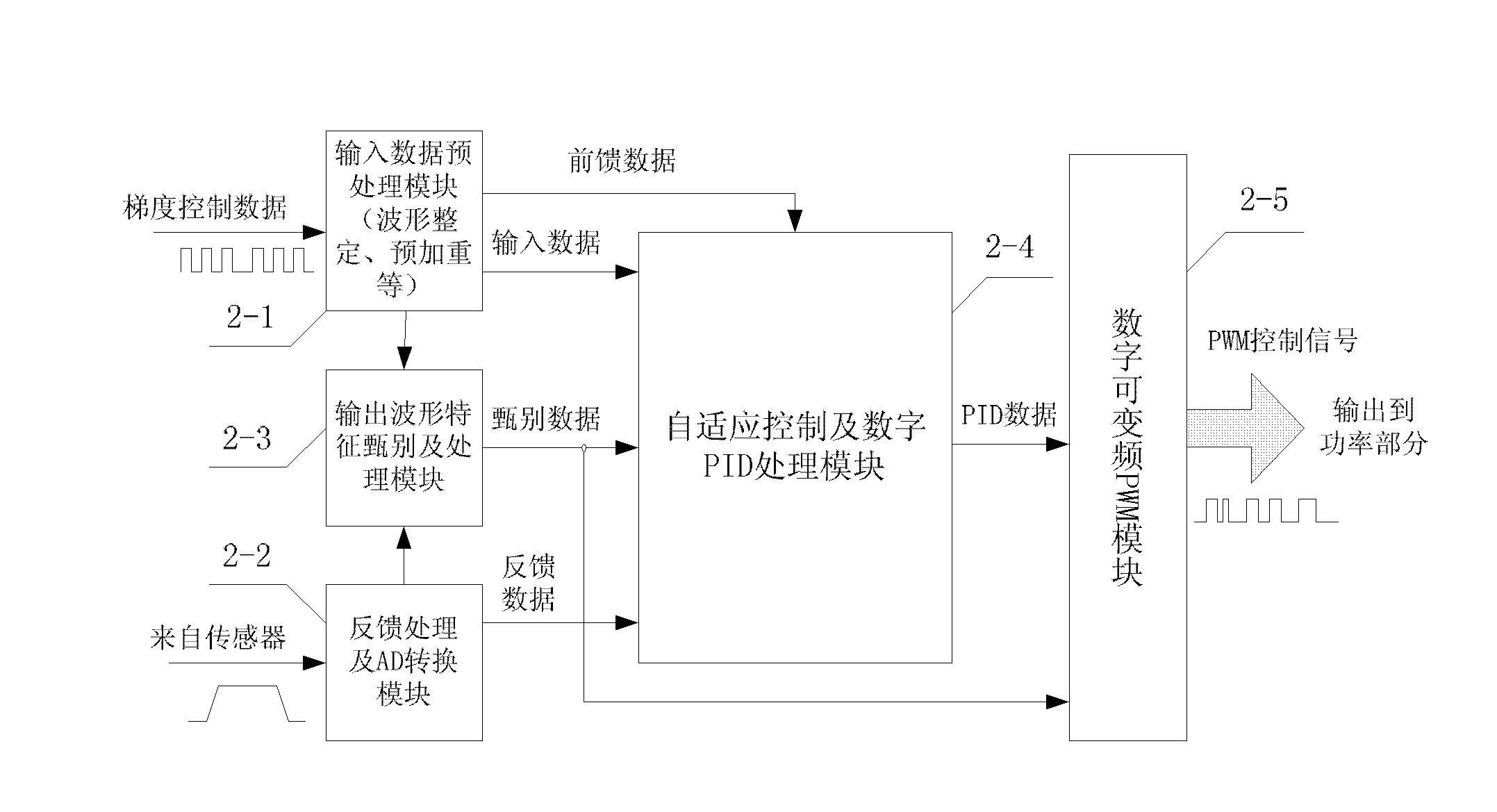
The invention relates to a digital variable frequency PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) gradient amplifier with an adaptively-controlled load. The digital variable frequency PWM gradient amplifier is used for driving a gradient coil to further generate a gradient filed required for imaging of a magnetic resonance system. The digital variable frequency PWM gradient amplifier with the adaptively-controlled load comprises a digital controlling and processing part, a power part and an output signal detecting part. The digital variable frequency PWM gradient amplifier with the adaptively-controlled load, disclosed by the invention, can be used for automatically adjusting the optimal PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) parameter according to different output loads, forming a PWM control signal ofdriving the power part through digital signal processing and digital frequency conversion and generating the required target gradient field. The gradient amplifier provided by the invention is capable of reducing hardware cost, increasing work efficiency and optimizing the gradient system performance to the maximum extent.
Owner:LIAONING KAMPO MEDICAL SYST
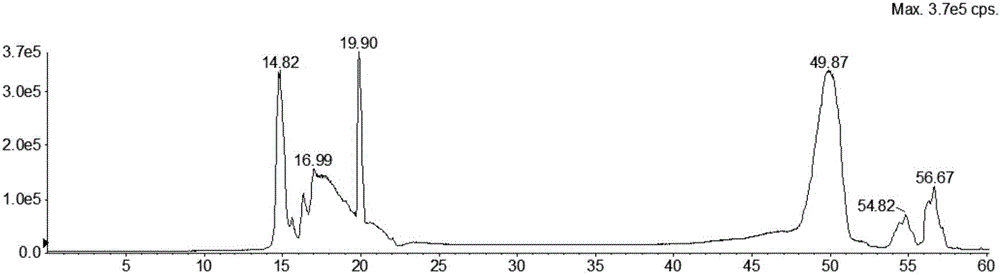
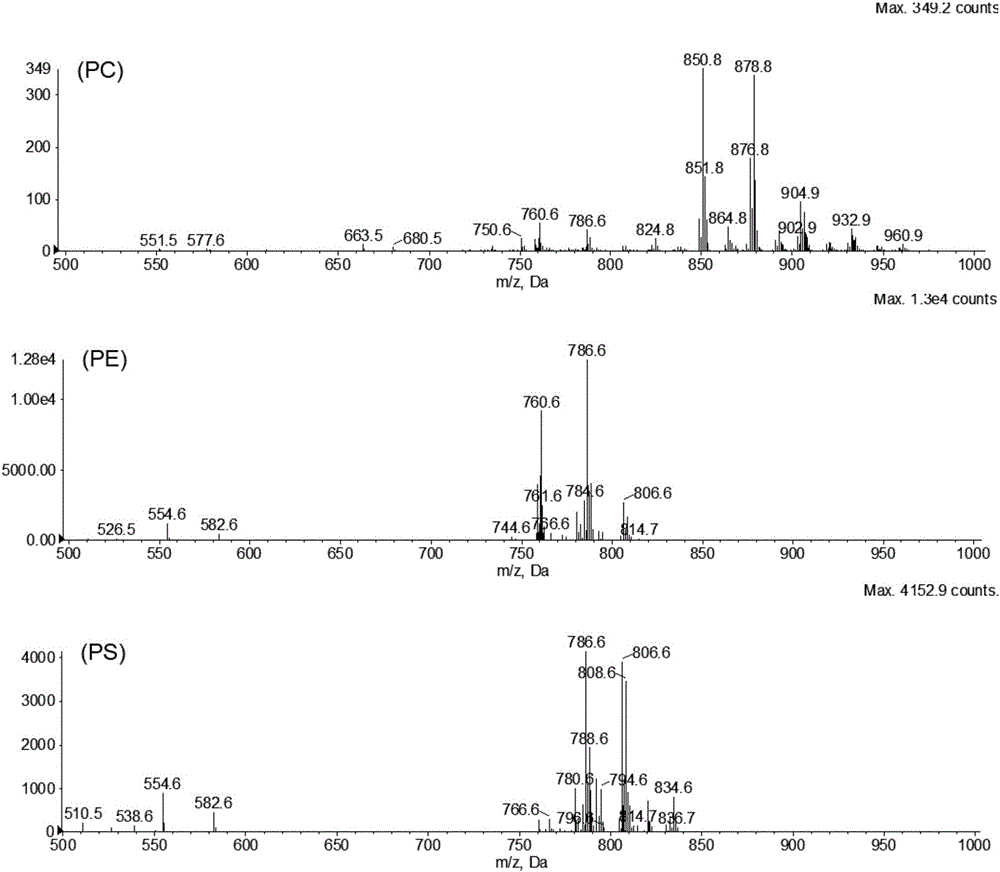
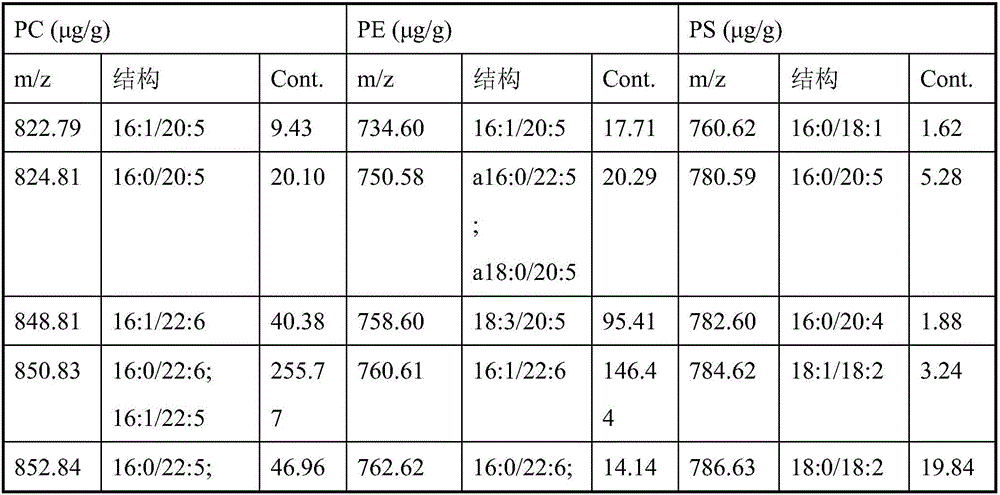
Hydrophilic interaction chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection method of phospholipids in Metapenaeus ensis
ActiveCN106153763ASimple and fast operationEasy to trainComponent separationLipid formationPhospholipid
The invention discloses a hydrophilic interaction chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry detection method of phospholipids in Metapenaeus ensis. The method includes the steps of firstly, performing corresponding preprocessing on ground Metapenaeus ensis to obtain crude lipid extract; secondly, performing liquid phase separation on the crude lipid extract, wherein a chromatographic column is a YMC Triart diol HILIC column, a gradient elution method is used, a gradient system comprises a flowing phase A and a flowing phase B, the flowing phase A is an acetonitrile solution containing 53mmol / L formic acid, and the flowing phase B is an aqueous solution containing 60mM ammonium formate and 53mM formic acid; thirdly, performing mass spectrometric detection analysis on the elution liquid obtained in the second step. By the method, the total content of PE, PS and PC in the Metapenaeus ensis can be detected accurately, and mass spectrometry identification of various molecular species in the PC, PE and PS phospholipids can be achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and method for NMR tomography acquisition with local magnetic field gradients in connection with local receiver coils
ActiveUS20070090838A1Fast switching timeSmall differenceMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientResonance
A magnetic resonance tomography apparatus, comprising a gradient system that can generate at least one spatially varying and optionally time-varying magnetic field for at least one-dimensional local encoding of measuring signals in an area of a test sample to be imaged, is characterized in that the gradient system contains at least one subsystem which can generate a non-bijective spatially varying magnetic field (=NBSEM or ambivalent / non-bijective spacially encoding magnetic field) for local encoding, such that the function of the field strength of such an NBSEM within the area to be imaged has at least one local extreme value (maximum or minimum), such that the area to be imaged is divided along the hyper surface formed by the entirety of all local extreme values of the at least one NBSEM into ng partial areas, with ng≧2, that the magnetic field profile has a non-unidirectional distribution within and / or over these partial areas, and that least ng receiver coils are provided which have a differing sensitivity in these partial areas. The apparatus can produce images of the same quality with smaller magnetic field differences and permits easy realization.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
High-precision three-dimensional chemical shift imaging method
ActiveCN105785298AOvercome errorImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsChemical shift imagingImaging quality
Disclosed in the invention is a high-precision three-dimensional chemical shift imaging method. A water image and a fat image that are separated from each other and in-phase graphs and anti-phase graphs of the water image and the fat image can be obtained by scanning once by using a three-dimensional single excited long echo string collection way, a radio frequency refocusing pulse string or frequency coding gradient technology, a pre scanning scheme having an echo amplitude and phase error precision correction feature, and a data post processing method. The method has the low requirements on magnetic field uniformity and gradient system performances; and the image quality and the diagnosis value can be improved obviously.
Owner:谱影医疗科技(苏州)有限公司
Method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals with use of local spatially encoding magnetic fields
InactiveUS7843195B2Reduce field of viewReduced measurement timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationExcitation pattern
A method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance (MR) signals from an imaging region has a preparatory step in which an encoding scheme with I phase encoding steps is defined, for each phase encoding step according to the phase encoding scheme, an excitation pattern of the transverse magnetization is defined and RF pulses to be irradiated to implement this pattern are calculated, wherein the same phase is defined at all spatial locations of the imaging region within an MSEM region and, in the execution step, according to the spatial encoding scheme each encoding step is performed I times according to the phase encoding scheme, wherein selection of the imaging region, amplitude modulation, and phase encoding are performed with the calculated RF pulses during excitation of the nuclear spin. This results in unique determination of the spatial distribution of the magnetic resonance signals with a simple RF receiver configuration using local gradient systems.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Superconducting magnet configuration with reduced heat input in the low temperature regions
ActiveUS20080157771A1Little mechanical oscillationSubstantial electrical conductivityMagnetic measurementsSuperconducting magnets/coilsSuperconducting CoilsMechanical resonance
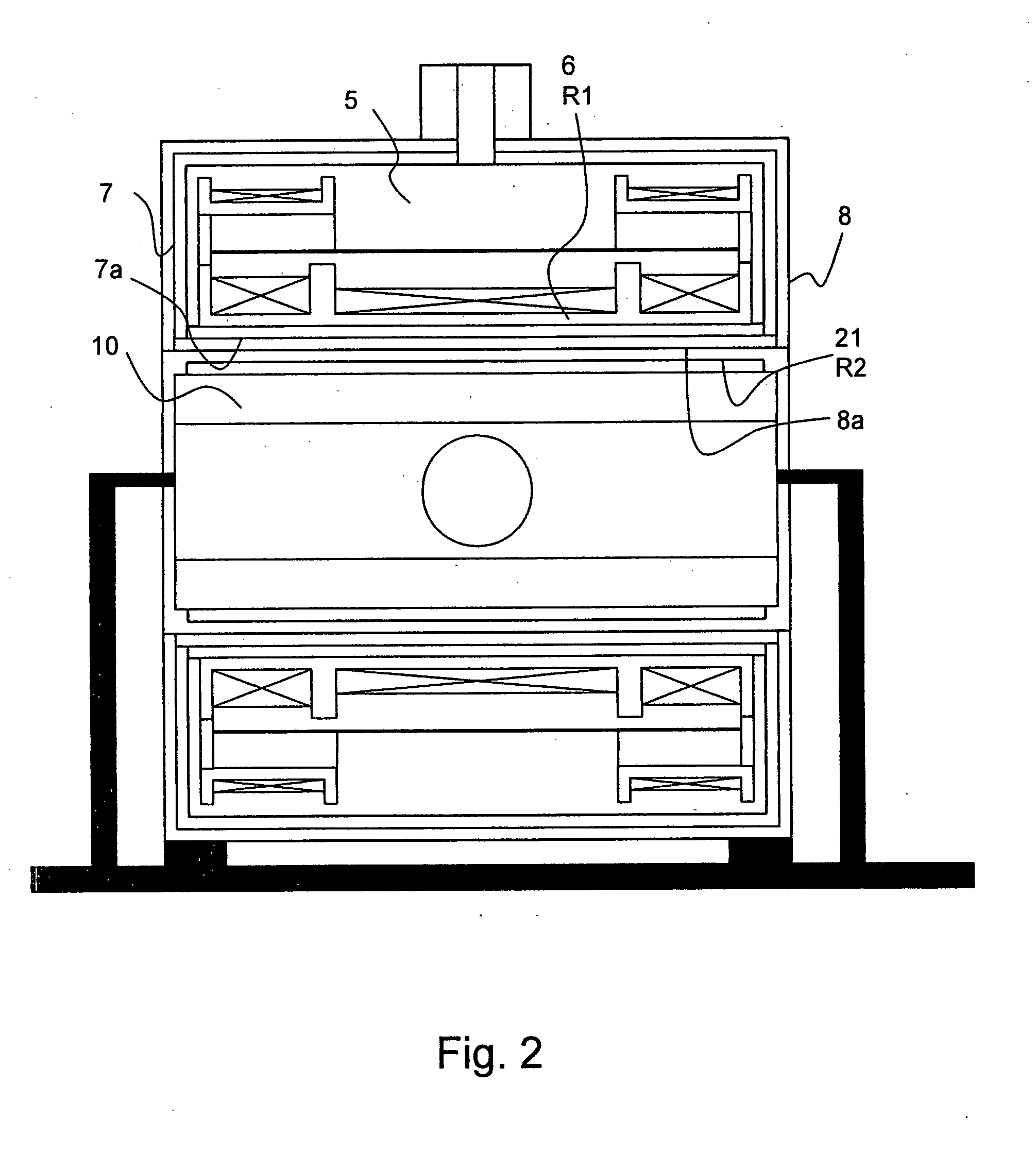
The invention concerns a magnet configuration comprising a superconducting magnet coil (1) within which a gradient system is to be switched. All low temperature oscillation systems (R1) with a temperature T1<10K within the magnet coil (1) are produced from a material having good electrical conducting properties, and at least one warm oscillation system (R2) with a temperature T2>10K within the magnet coil (1) has worse electrical conducting properties and has a considerably different mechanical resonance frequency (separation approximately 500 Hz or more) than at least one of the low temperature oscillation systems (R1). This reduces the undesired heating power supplied to the low temperature oscillation systems due to mechanical oscillations and induced eddy currents.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Single-excitation fat-water separation imaging error correction system and method
InactiveCN105929350AAchieve clinical diagnostic valueOvercome hardware imperfectionsElectrical measurementsData pre-processingSpectrometer
The invention discloses a single-excitation fat-water separation imaging error correction system and method. A pre-scanning module and a fat-water scanning module are installed on a host of a magnetic resonance imager and are loaded to a sequence generator of a spectrometer, for controlling a radio frequency system and a gradient system to realize excitation, space encoding and acquisition of human body proton signals. A matched data preprocessing module, a primary amplitude correction module, a primary phase correction module, a phase unwrapping module, a high-grade error correction module and a fat-water image separation module are installed on the host. According to the invention, the problem of imperfect hardware of MRI equipment is effectively overcome, a field nonuniform effect and a chemical displacement effect of a TE period are taken into consideration, the error correction precision of echo amplitude errors and phase errors and the efficiency of a phase unwrapping algorithm are improved, and the need of clinic image diagnosis is satisfied.
Owner:谱影医疗科技(苏州)有限公司
Surface coil arrangement for magnetic resonance tomographs
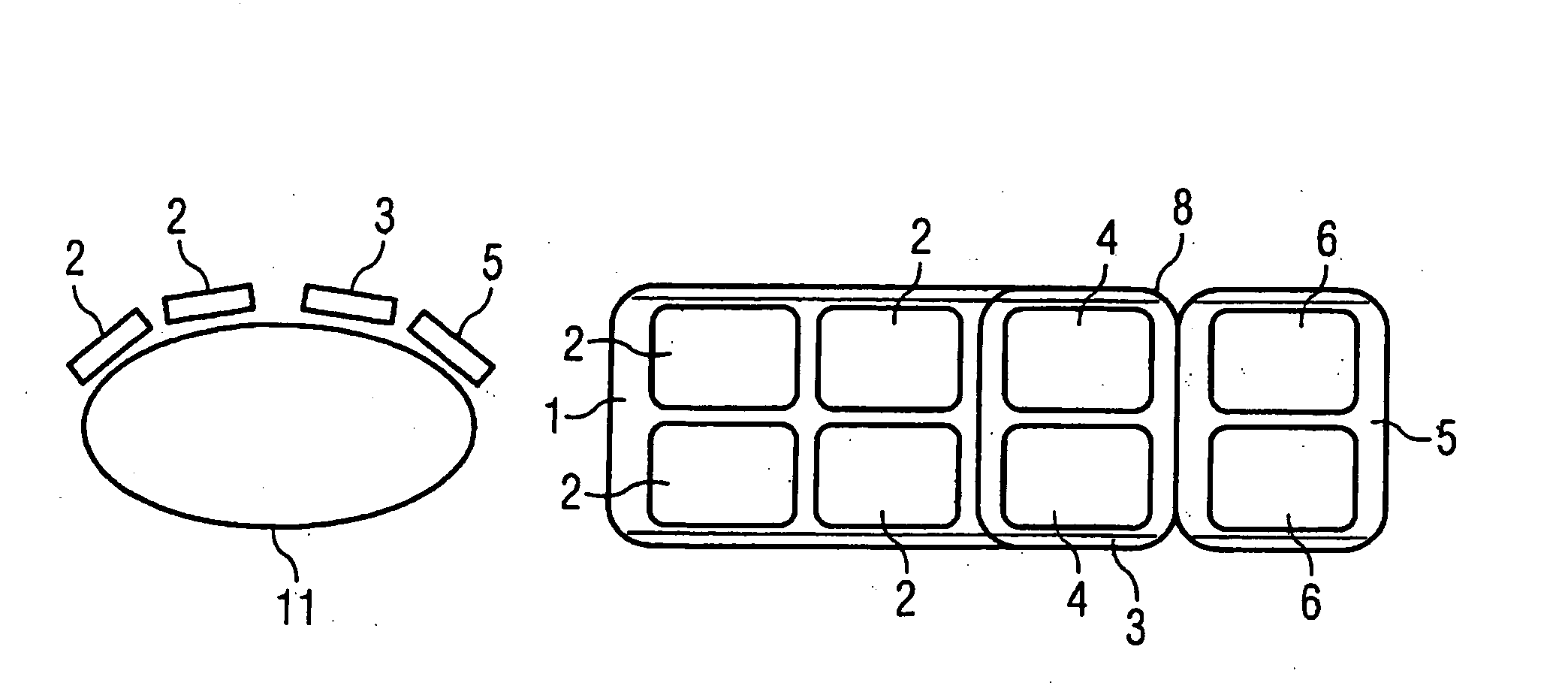
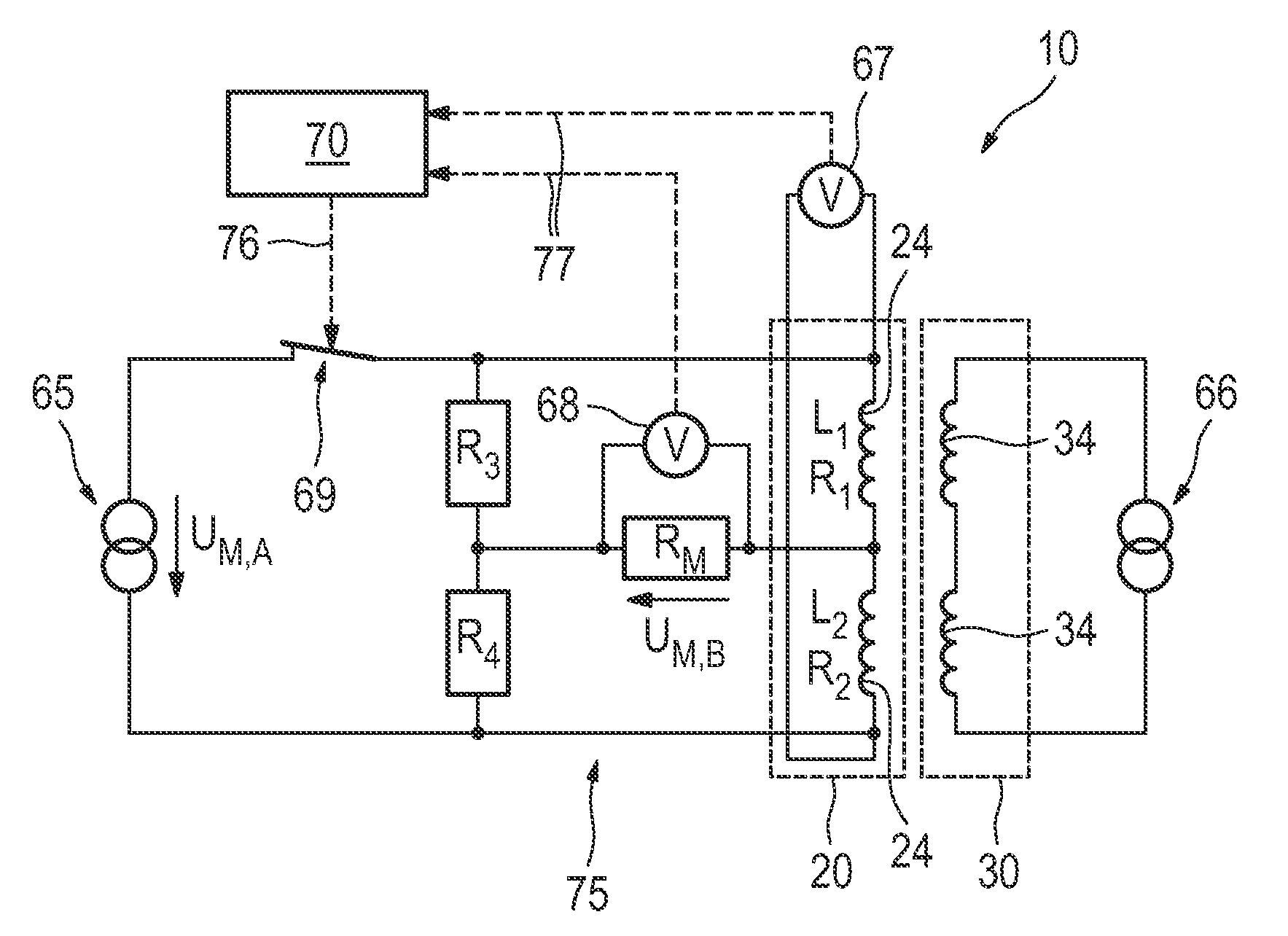
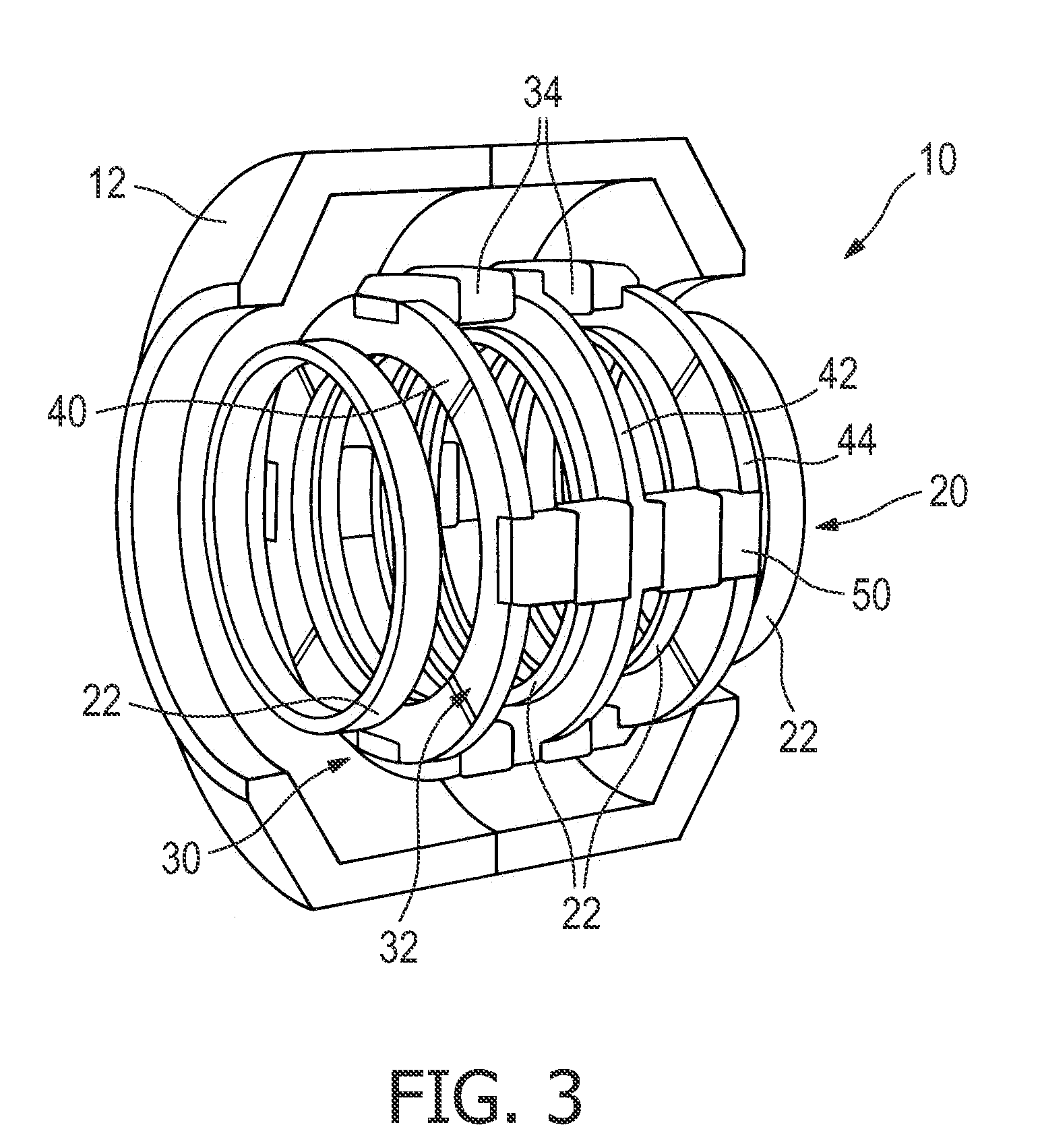
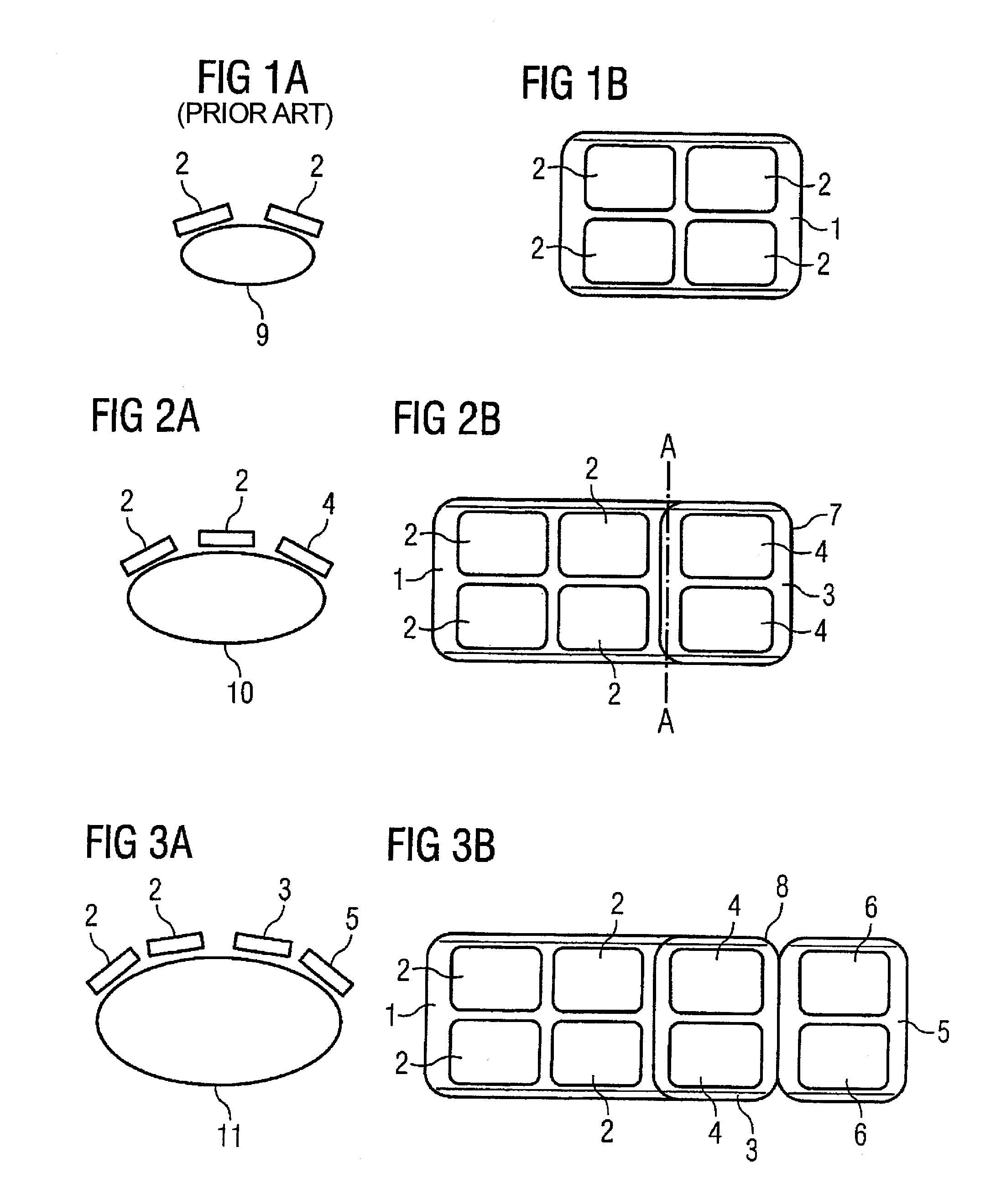
A surface coil arrangement of a gradient system for an MR tomography apparatus has coil elements mounted on a first antenna, the antenna being extendable by at least one further antenna that likewise includes an arrangement of at least one coil element, and which is detachably or movably fastened to the first antenna.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
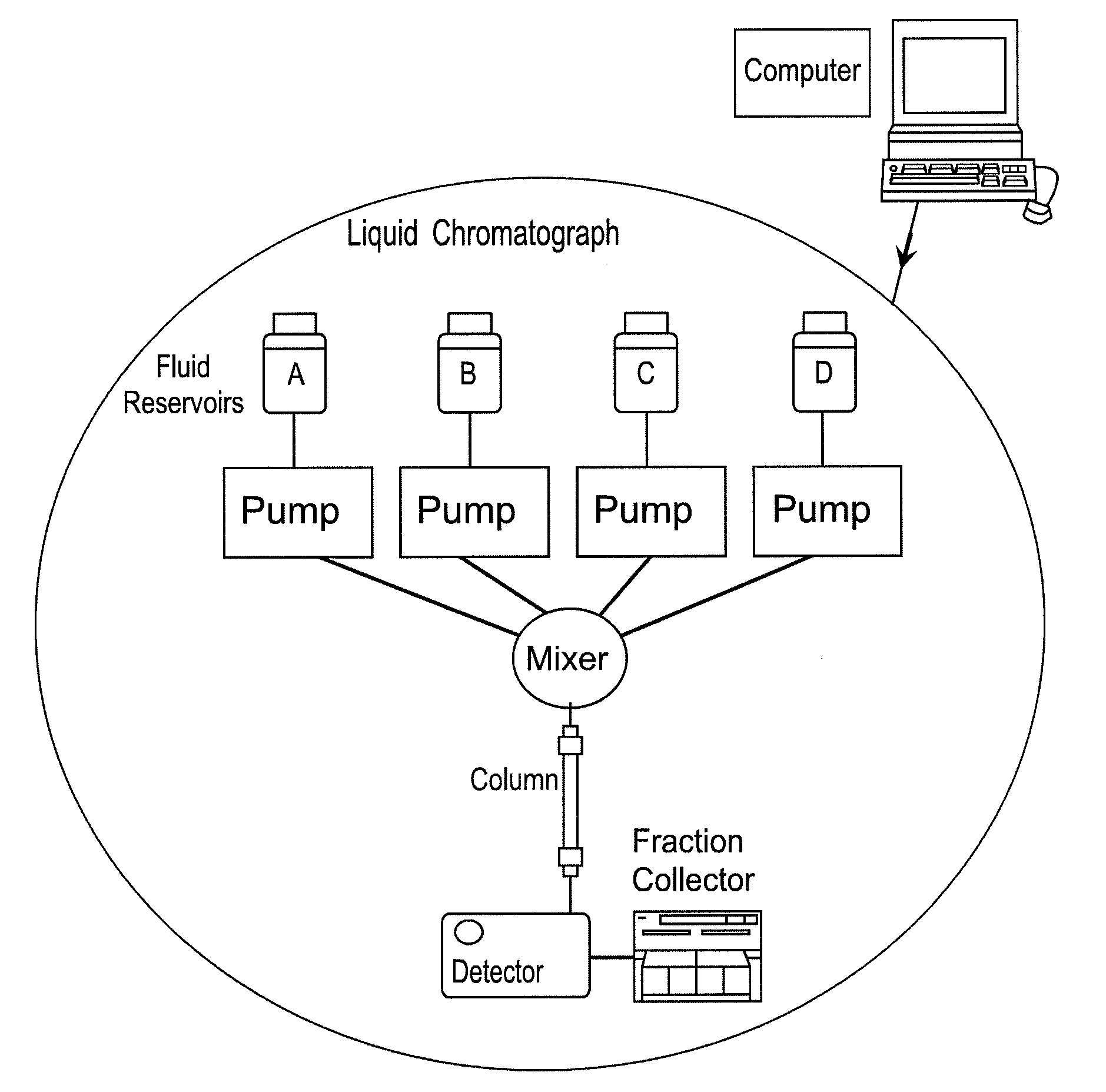
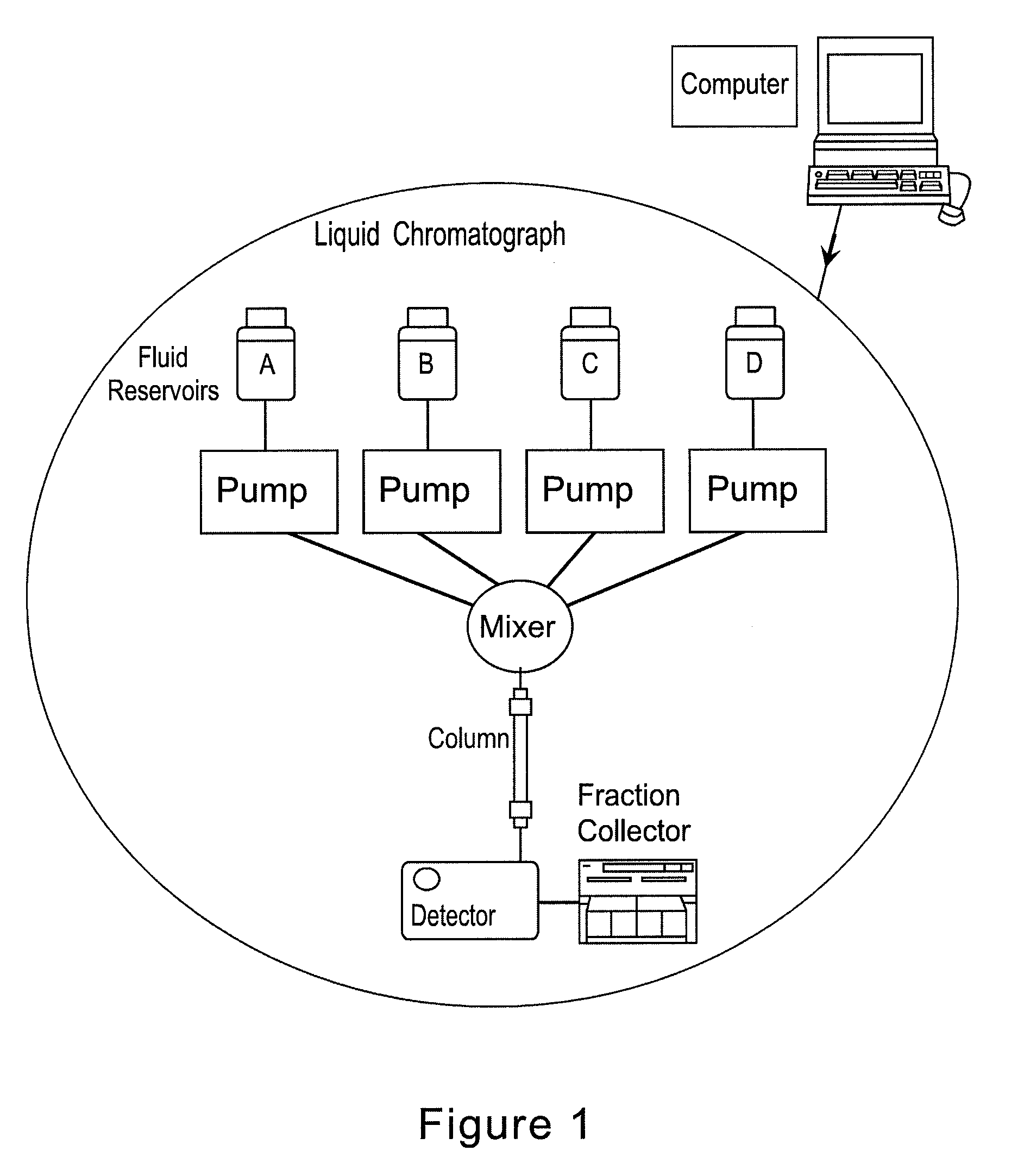
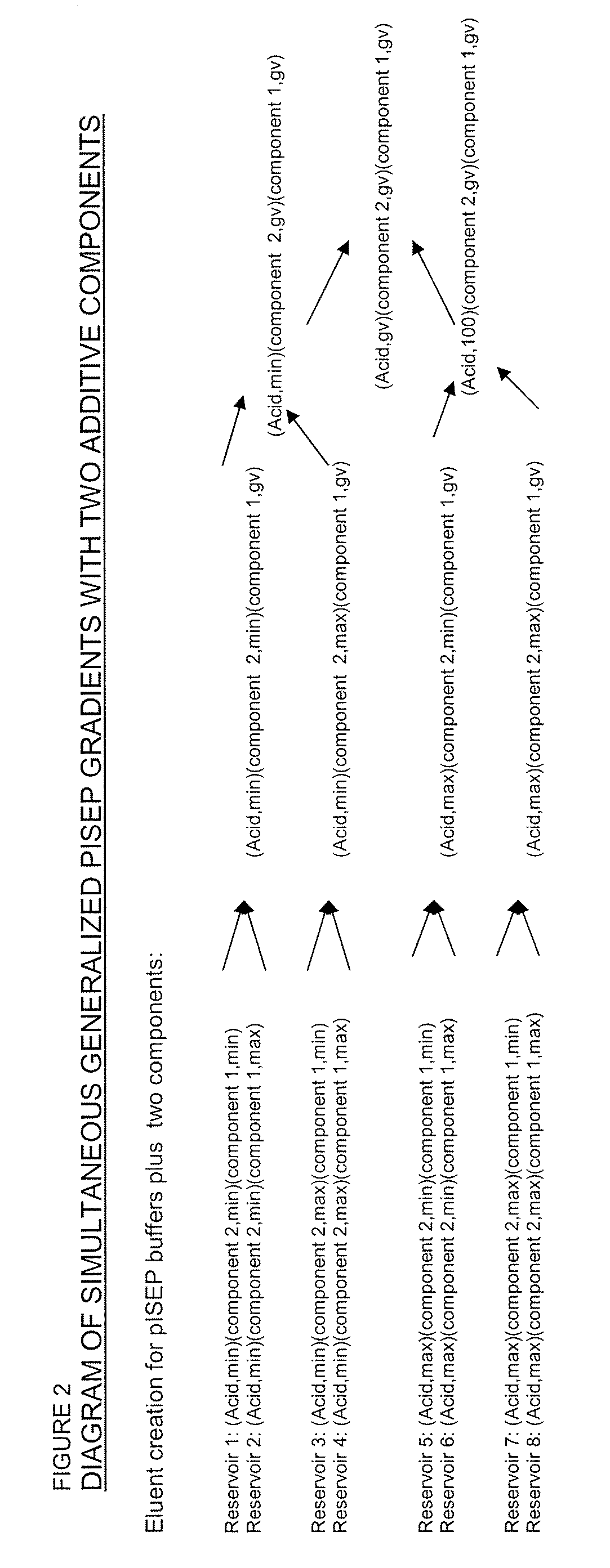
Multi-Component, Simultaneous, Independent Multi-Gradient System for Liquid Chromatography
ActiveUS20080053830A1Easy to separateEfficient separationSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsStationary phaseLiquid phase
Systems and methods for separating charged molecules on the basis of their differential electrostatic binding to a charged stationary phase comprise controlling the creation of simultaneous independent or dependent pH and additive gradients.
Owner:CRYOBIOPHYSICA
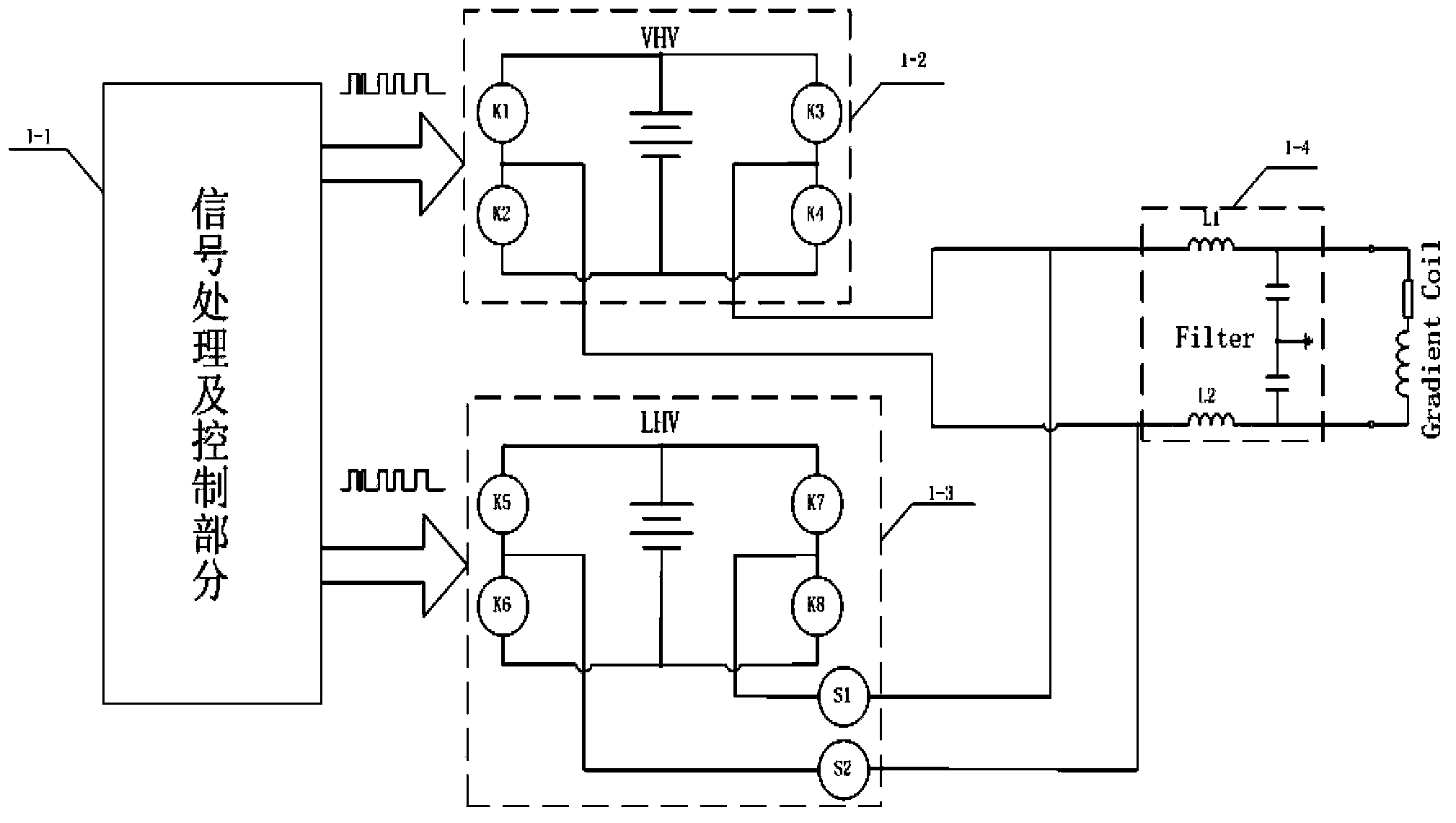
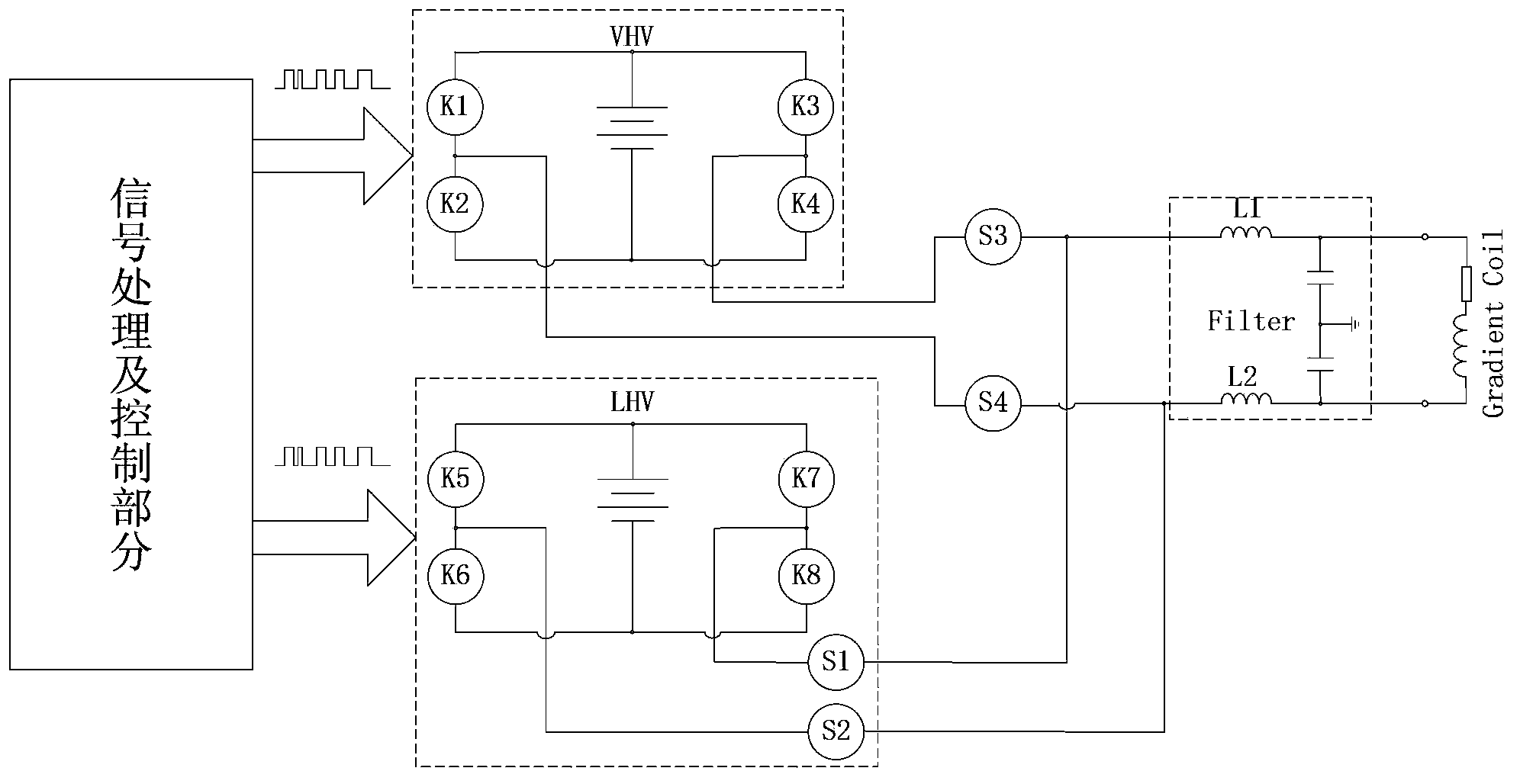
High-voltage high-current small-ripple-wave gradient amplifier
ActiveCN104142483ALow costSimplify design difficultyMagnetic measurementsAudio power amplifierLow voltage
The invention relates to a high-voltage high-current small-ripple-wave gradient amplifier which is used for driving a gradient coil and further generating a gradient field needed by imaging of a magnetic resonance system. The high-voltage high-current small-ripple-wave gradient amplifier is composed of a signal processing and controlling part, a high-voltage power conversion part, a low-voltage power conversion part and a low-pass filtering part. The high-voltage high-current small-ripple-wave gradient amplifier can use different power conversion parts according to different characteristics of input and output signals, the needed target gradient field is generated rapidly and accurately by outputting filtering waves, and output ripple-wave current is reduced as mush as possible. The gradient amplifier can simplify the design of a high-voltage high-current amplifier, reduce hardware cost, improve system efficiency and optimize the performance of a gradient system to the maximum extent.
Owner:LIAONING KAMPO MEDICAL SYST
Training of artificial neural networks using safe mutations based on output gradients
ActiveUS20190188573A1Safe modificationSmall perturbationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesAlgorithmArtificial intelligence
Systems and methods are disclosed herein for ensuring a safe mutation of a neural network. A processor determines a threshold value representing a limit on an amount of divergence of response for the neural network. The processor identifies a set of weights for the neural network, the set of weights beginning as an initial set of weights. The processor trains the neural network by repeating steps including determining a safe mutation representing a perturbation that results in a response of the neural network that is within the threshold divergence, and modifying the set of weights of the neural network in accordance with the safe mutation.
Owner:UBER TECH INC
Gradient amplifier applying coupled inductors to output filter
InactiveCN104950273ALow Output Ripple CurrentSimplify and Optimize DesignsElectric variable regulationMeasurements using magnetic resonancePower flowAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a gradient amplifier applying coupled inductors to output filter, so as to meet requirements of an imaging system with low output ripple current and quick output response. The gradient amplifier by applying the coupled inductors to output filter is composed of a PWM control part, a power conversion part and a low pass filter part. According to the gradient amplifier of the invention, design of the coupled inductors is optimized, different control logics of the PWM control signals drive power conversion and output, a low pass filter capacitor part is combined, and requirements of the imaging system with low output ripple current and quick gradient current output response can be met. According to the gradient amplifier of the invention, the coupled inductors are applied to output filter, design of the high-voltage large-current amplifier can be simplified and optimized, effectiveness and performance of the gradient system are enhanced, the hardware cost is reduced, and the cost performance of the gradient system is greatly improved.
Owner:LIAONING KAMPO MEDICAL SYST
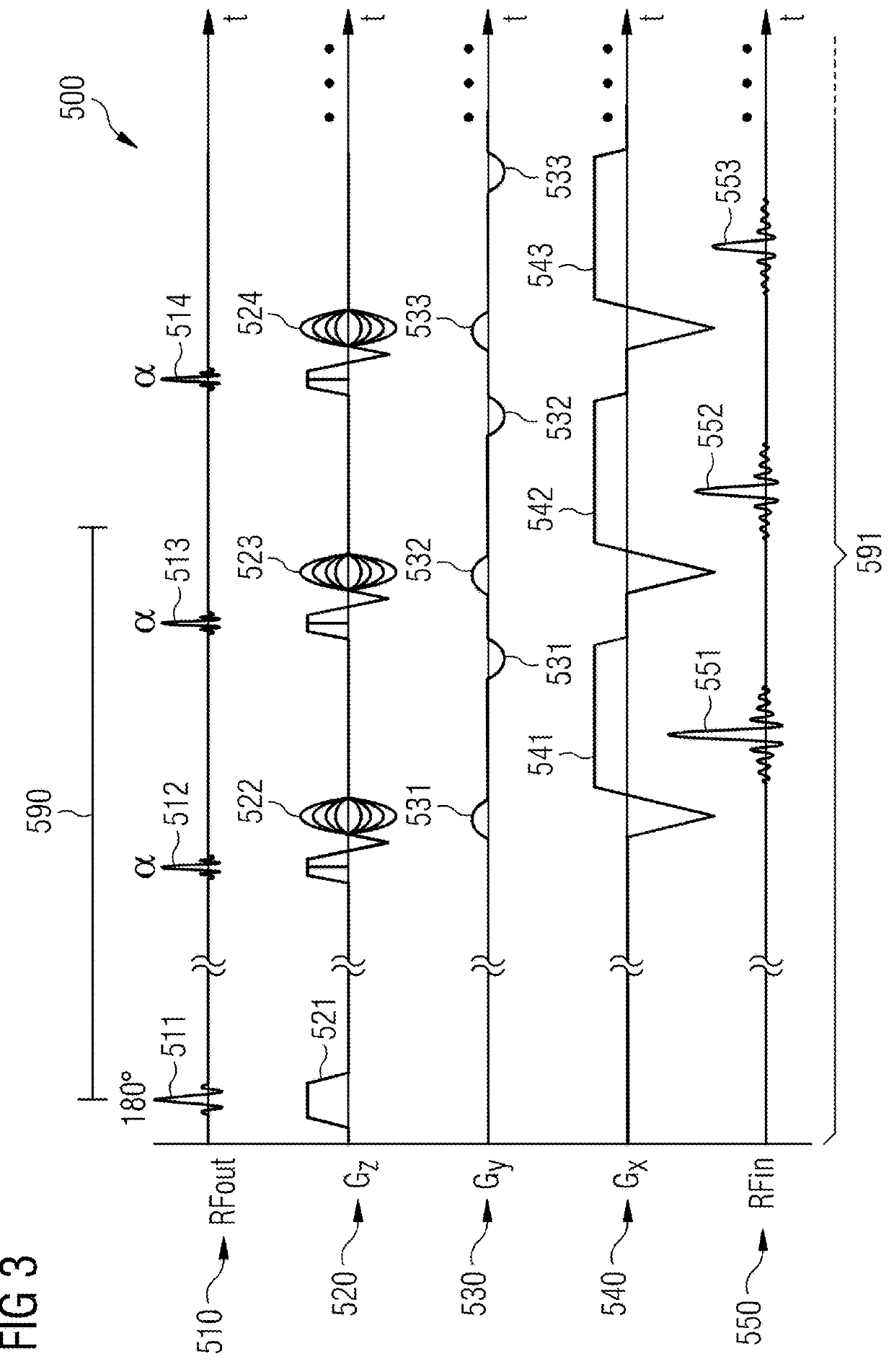
Method and apparatus for accelerated magnetic resonance imaging
PendingUS20180164395A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceMagnetization
In a method for controlling a radio-frequency transmitter of a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus to apply an inversion pulse to a sample magnetization, in a multi-shot readout phase, a gradient system of the magnetic resonance imaging apparatus is controlled to apply a steady-state gradient echo readout sequence having at least one first phase-encoding gradient along a first direction, at least one second phase-encoding gradient along a second direction, and a sequence of readout gradients along a readout direction. In the multi-shot readout phase, the gradient system is controlled to apply first AC gradients along the first direction and at least partly contemporaneously with readout gradients of the sequence of readout gradients, and the gradient system is controlled to apply second AC gradients along the second direction and at least partly contemporaneously with the readout gradients of the sequence of readout gradients.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
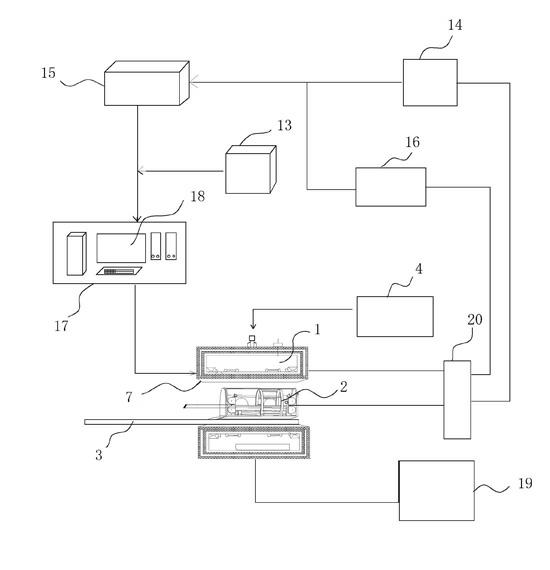
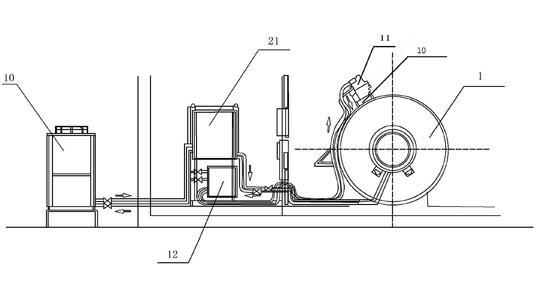
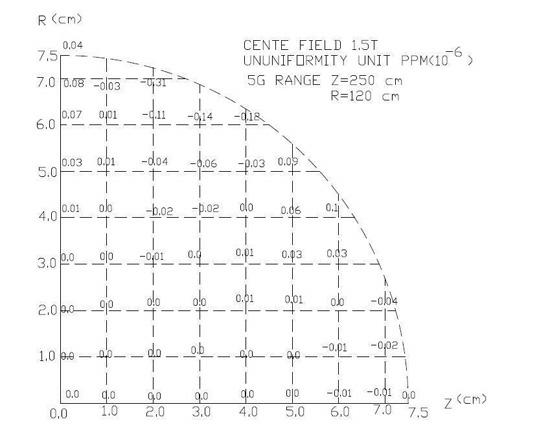
Special magnetic resonance imaging device for baby
ActiveCN102579047ASmall sizeUniform magnetic fieldDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSupporting systemSoftware system
The invention discloses a special magnetic resonance imaging device for a baby. The special magnetic resonance imaging device comprises a magnetic resonance imager, a filter board (20), a control device, a software system and a display system. The magnetic resonance imager consists of a superconducting magnet (1), a radio frequency system (2), a gradient system (7) and a patient supporting system (3). The superconducting magnet (1) comprises a superconducting magnetic field coil (5), a driving and driven shimming system (6) and a refrigerating system (4). The diameters of the inner walls of the superconducting magnetic field coil (5), the driving and driven shimming system (6) and the gradient system (7) are sequentially arranged in descending order. The refrigerating system is a classified refrigeration cycle system. By the adoption of the structure, the magnetic field is uniform; and the temperature variation is smooth and the environment is stable by the space positioning of a magnetic resonance imaging system signal and the two-stage refrigeration cycle system.
Owner:马启元
Satellite gravity gradient retrieval method based on filtering principle
InactiveCN103163562AImprove inversion accuracyCalculation speedGravitational wave measurementComputer performanceSatellite observation
The invention relates to a precision measurement method of an earth gravitational field, in particular to a satellite gravity gradient retrieval method based on the filtering principle. A novel satellite gravity gradient observation equation is set through the filtering principle, and then accurately and rapidly inverts the earth gravitational field. The satellite gravity gradient retrieval method based on the filtering principle is high in inversion accuracy, is high in calculation speed of the earth gravitational field, carries out sensitivity analysis of a satellite gravity gradient system easily, is definite in physical meanings of the satellite observation equation, and has low requirements for computer performance, thereby being an effective method for calculating the high-accuracy and high-spatial-resolution earth gravitational field.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for position dependent change in the magnetization in an object in a magnetic resonance experiment
ActiveUS20110080169A1Reduce signal lossShorten the lengthMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonance measurementMagnetization
A method for position dependent change in the magnetization in an object, according to a requirement in a magnetic resonance measurement, wherein radio-frequency pulses are irradiated in conjunction with supplementary magnetic fields that vary in space and over time and are superposed on the static and homogeneous basic field of a magnetic resonance measurement apparatus along a z-direction, is characterized in that non-linear supplementary magnetic fields are used, whose spatial gradient of the z-component is not constant at least at one instant of the irradiation, and that the radio-frequency pulses to be irradiated are calculated in advance, wherein progressions over time of the field strengths of the supplementary magnetic fields in the region of the object that are calculated and / or measured position-dependently are included in this calculation. This enables change in the magnetization with an at least locally spatially higher resolution and / or shorter irradiation duration of the RF pulses and supplementary magnetic fields than is feasible with linear supplementary magnetic fields produced by conventional gradient systems. In particular, this is possible under the technical and physiological conditions that currently constrain the performance of the known methods using linear supplementary fields.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG +1
Detecting quench in a magnetic resonance examination system
InactiveUS20100056378A1Ramped-down safelyLimit dissipationMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesSuperconductor devicesMagnetic field gradientResonance
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance examination system (10) and to a method of operating such a magnetic resonance examination system (10). In particular the present invention relates to a magnetic resonance examination system (10) comprising a superconducting main magnet (20) surrounding an examination region (18) and generating a main magnetic field in the examination region (18), and further comprising a magnetic field gradient system (30) selectively causing alternating gradient magnetic fields in the examination region (18), said magnetic field gradient system (30) being coupled to the main magnet (20). In order to provide a technique to reliably detect a quench of the superconducting main magnet (20) of such a magnetic resonance examination system (10) a detecting device (91) is suggested for detecting an emerging quench of the main magnet (20), said detecting device (91) being adapted to operate in different modes depending on the mode of operation of the magnetic resonance examination system (e.g. ramp-up, ramp-down or continuous operation).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
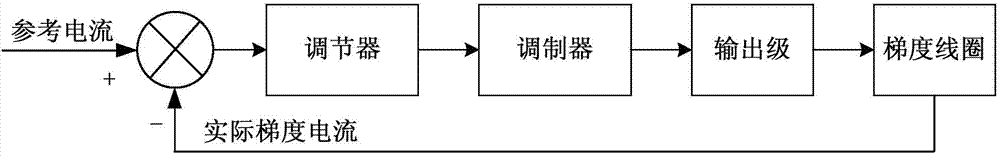
Gradient system and gradient magnetic field control method and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) system
ActiveCN104237818AEasy to controlRealize automatic compensationMagnetic measurementsClosed loopEddy current
The invention provides a gradient system and a gradient magnetic field control method and an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) system. The gradient system based on current magnetic flux double closed loop control at least comprises a detecting module, a first comparator, a first adjuster, a second comparator, a gradient coil, a sensor and a gradient amplifier, wherein the detecting module is used for detecting and feeding back corresponding induced electromotive force according to variation of magnetic flux of the gradient magnetic field, the sensor is connected with the gradient coil and used for detecting and feeding back gradient current, the gradient amplifier is connected with the second comparator, the gradient coil and the sensor and used for amplifying current error obtained after comparing control current outputted by the second comparator with the gradient current fed back by the sensor so as to drive the corresponding gradient current of the gradient coil, and accordingly, the gradient magnetic field is controlled. By the gradient system based on the current magnetic flux double closed loop control, automatic compensation of eddy current loss is realized, and control of the gradient magnetic field is more accurate.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Surface coil arrangement for magnetic resonance tomographs
A surface coil arrangement of a gradient system for an MR tomography apparatus has coil elements mounted on a first antenna, the antenna being extendable by at least one further antenna that likewise includes an arrangement of at least one coil element, and which is detachably or movably fastened to the first antenna.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Porphyrin/aluminum oxide nano-channel membrane and application thereof in energy conversion device
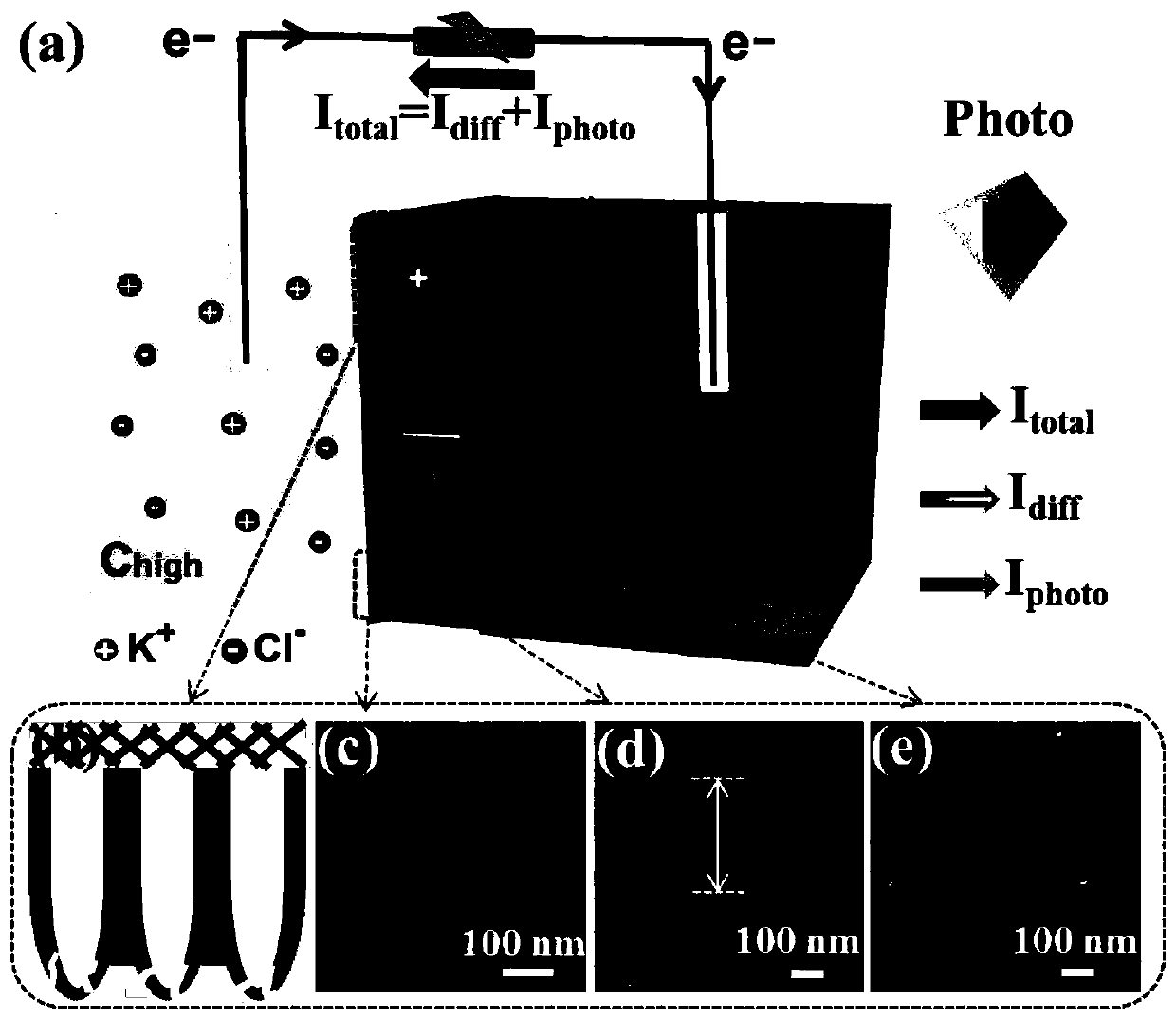
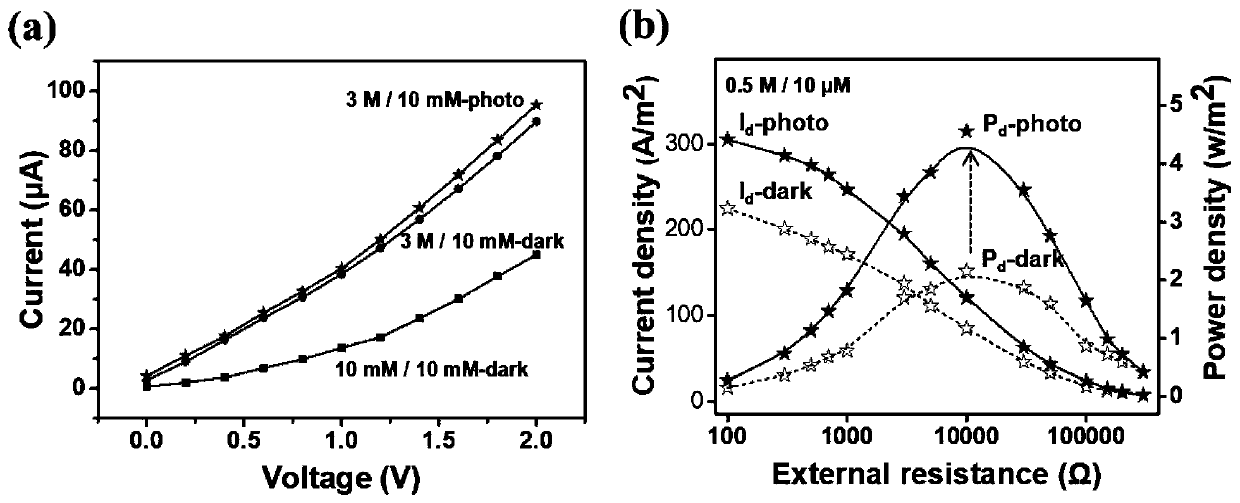
ActiveCN110417297AGood choiceGood photoresponse performanceKinetic-electric generatorPerformance enhancementLight energy
The invention discloses a porphyrin / aluminum oxide nano-channel membrane and an application thereof in an energy conversion device, and belongs to the field of energy conversion of nano materials. Theenergy conversion device takes a self-made porphyrin / aluminum oxide nano-channel membrane as a medium, and synergistically converts the clean and sustainable solar energy and salinity gradient energyinto electric energy which can be directly utilized by human beings. The porphyrin / aluminum oxide nano-channel has cation selectivity and light responsiveness at the same time, and the ionic currentflux passing through the salinity gradient system increases under the assistance of simulated sunlight, so that the power generation power is increased. According to the invention, a light-assisted enhanced salinity gradient power generation system is constructed by only relying on the porphyrin / aluminum oxide nano-channel membrane, and the light energy and the salinity gradient energy are simultaneously utilized to increase the overall electric energy output, thereby providing a brand new idea for the design and performance enhancement of other nanofluidic energy conversion devices.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Magnetic resonance system with transmission of a digitized magnetic resonance signal across an air gap
ActiveUS20100072997A1Reliable and comfortableHigh sensitivityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionCarrier signalEngineering
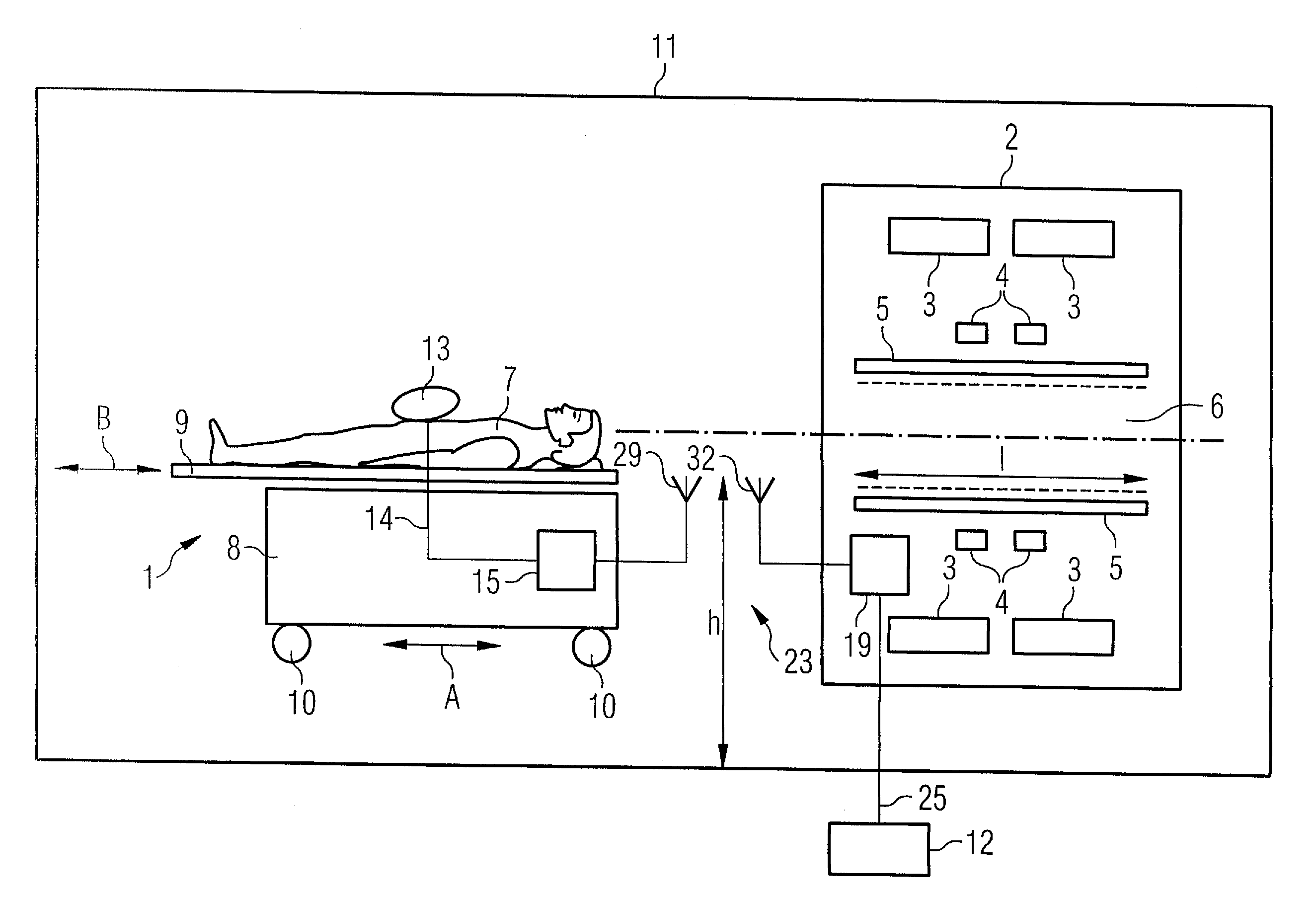
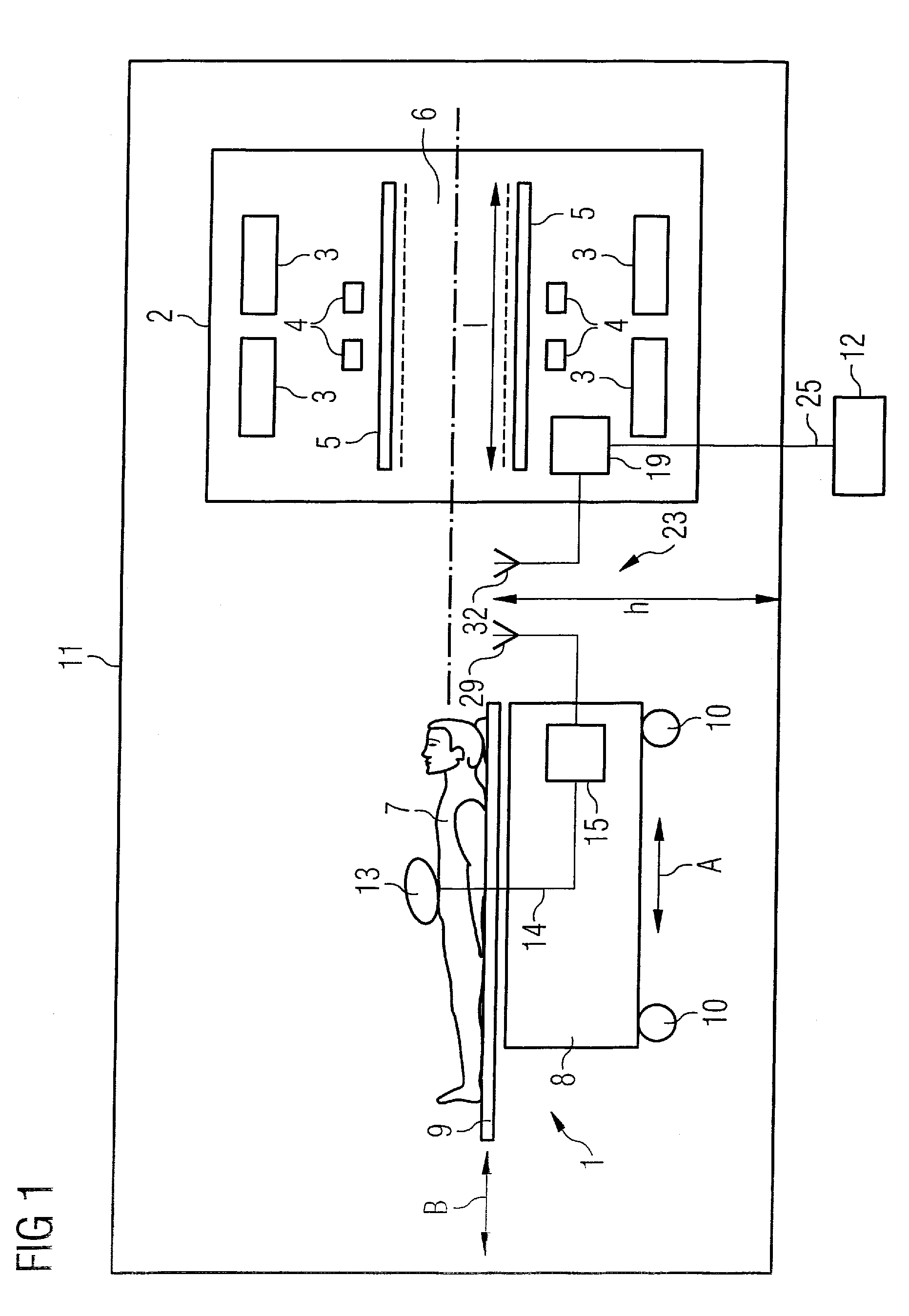
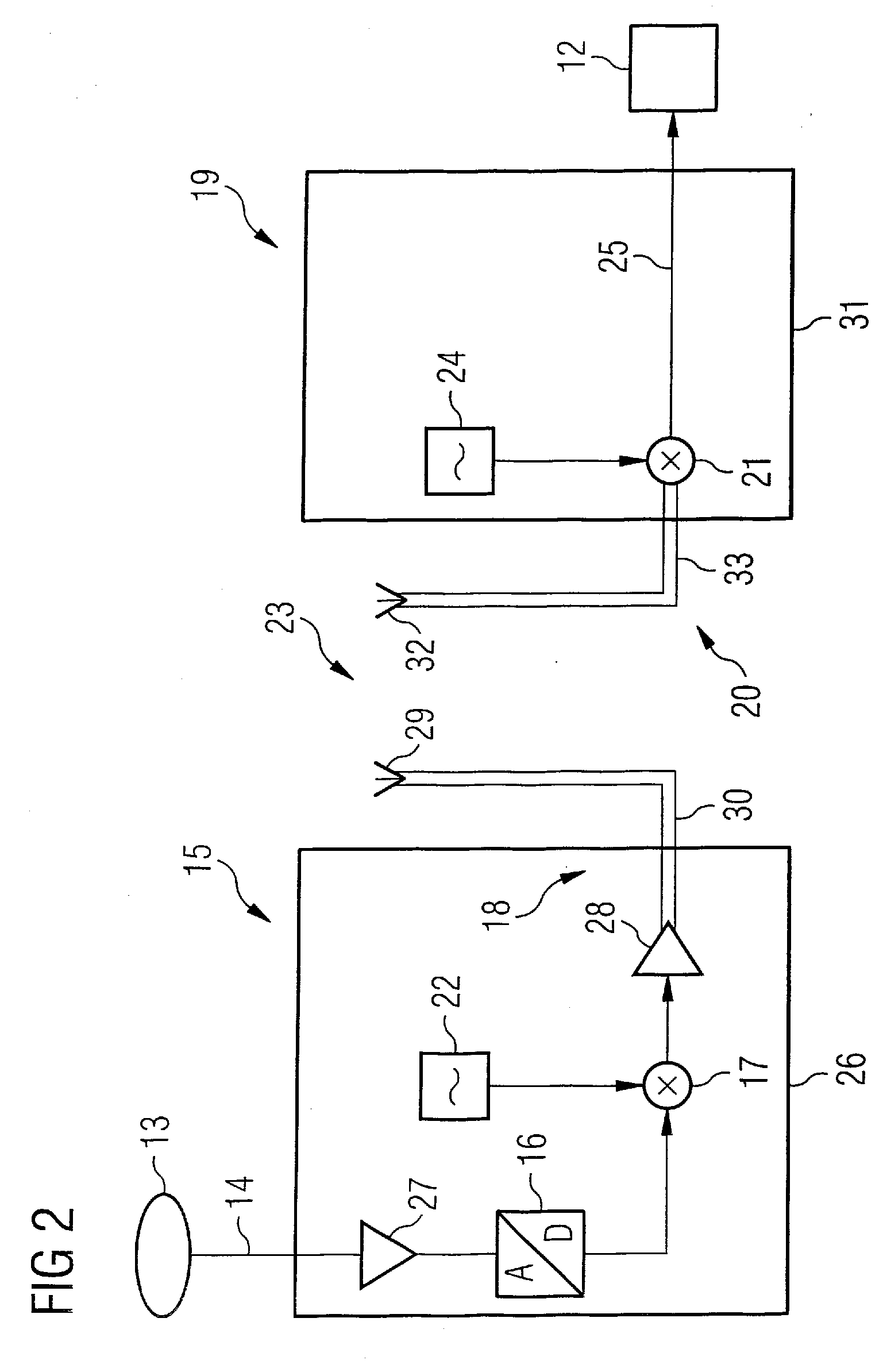
A magnetic resonance system has a patient receptacle and a base body. The patient receptacle has a subframe and a patient bed supported thereon so as to move a patient thereon through the base body. The base body has a basic field magnet system, a gradient system and an RF system that are operable to obtain an analog magnetic resonance signal from the patient. The patient receptacle has a signal conversion device composed of an A / D converter, a modulator, and a transmitter. The base body has a signal conversion device composed of a receiver and a demodulator. The A / D converter receives the magnetic resonance signal and digitizes it. The modulator modulates a carrier signal with the digitized magnetic resonance signal. The transmitter transmits the modulated carrier signal via an air gap to the receive. The receiver receives the transmitted carrier signal. The demodulator extracts the digitized magnetic resonance signal from the received carrier signal by demodulation and supplies it to an evaluation device for continuing evaluation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
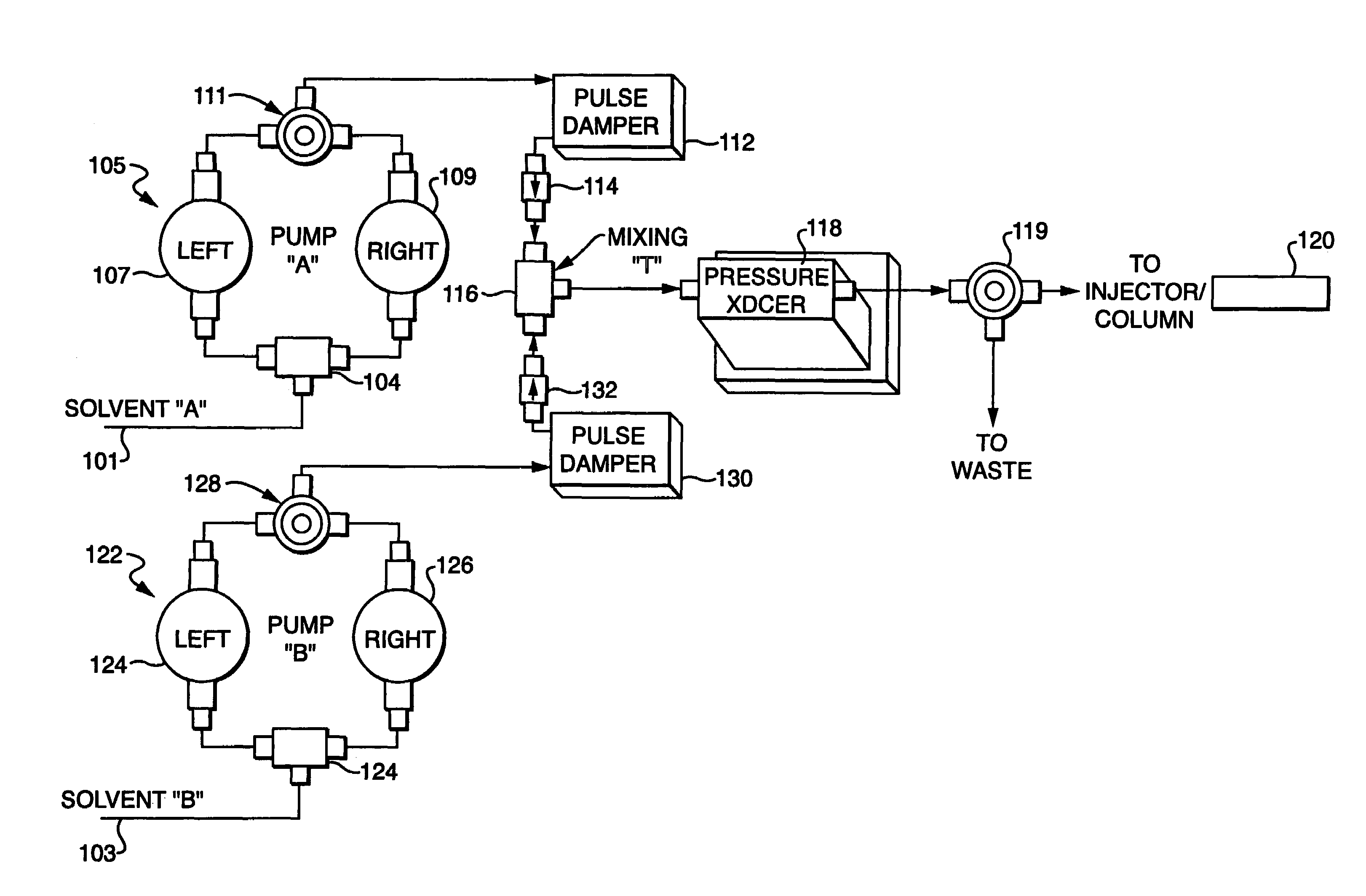
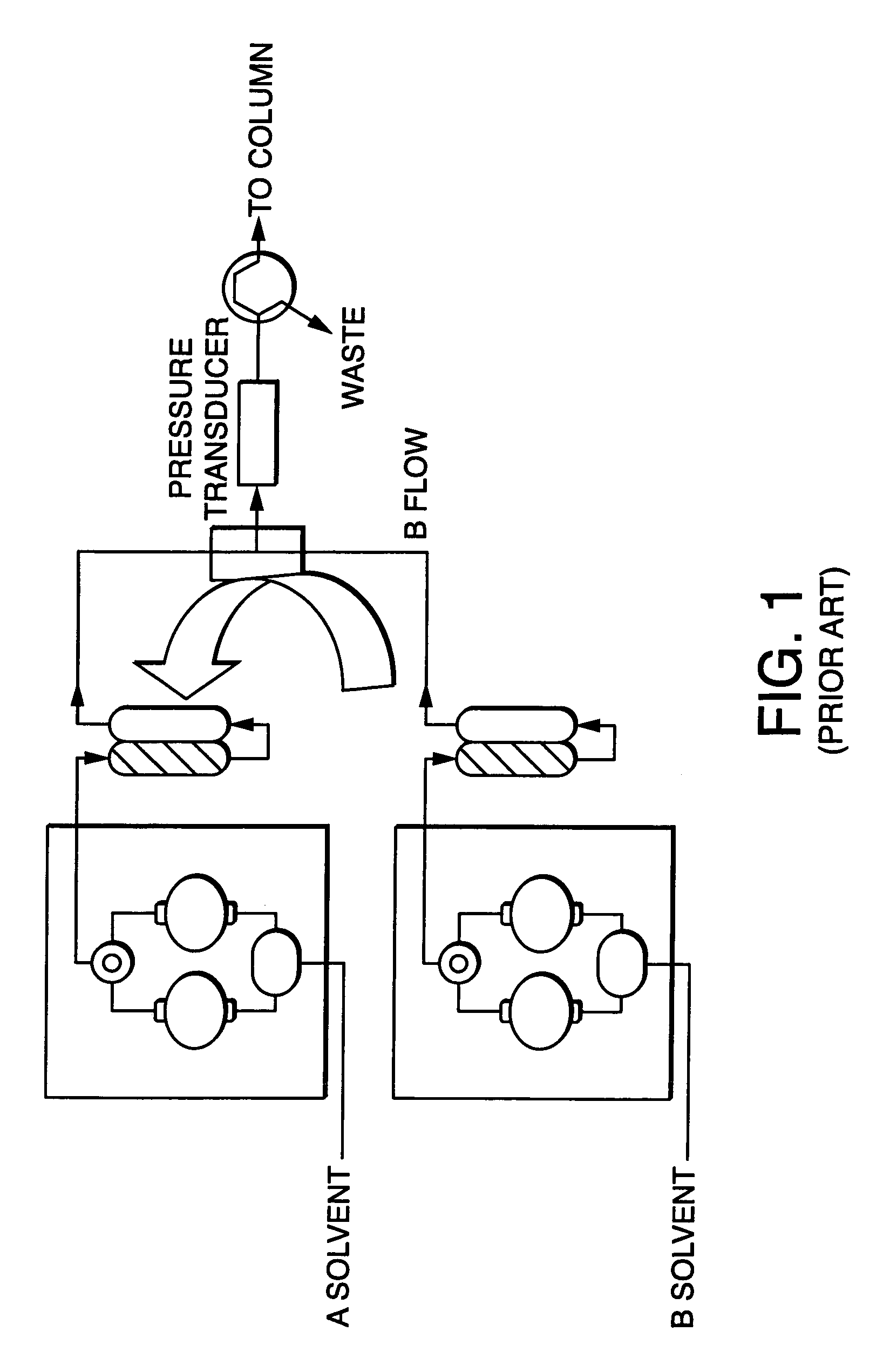
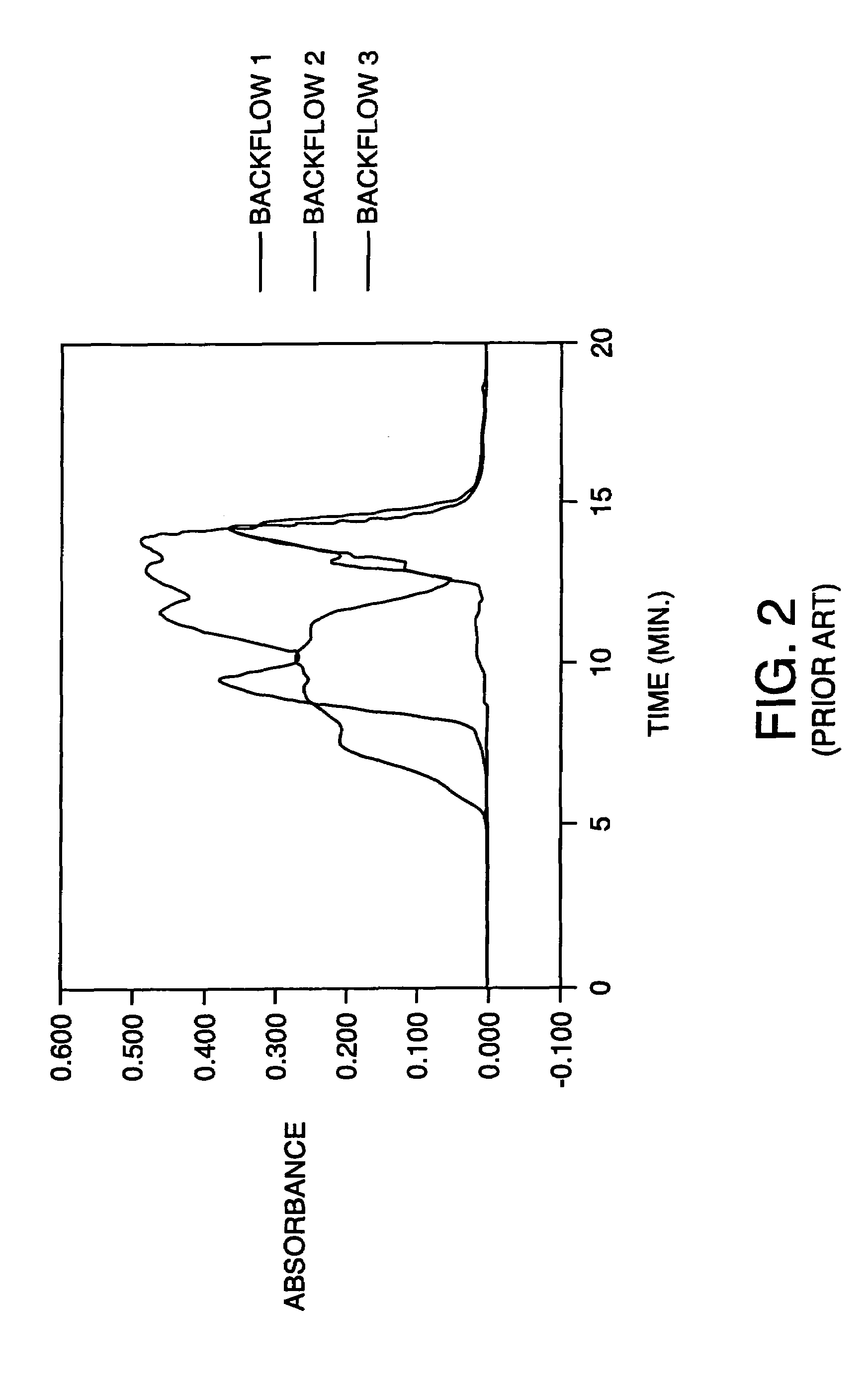
Backflow prevention for high pressure gradient systems
ActiveUS7396469B2Improving compositional accuracyImprove performanceComponent separationIon-exchanger regenerationEngineeringSolvent
Gradient performance with high pressure gradient solvent delivery system is optimized by approximation of infinite stroke volume of high pressure pumps by the addition of pulse dampening with backflow prevention to each high pressure pump. The backflow prevention adds sufficient minimum flow resistance, thereby enhancing the performance of the pulse dampening over a wider range of flow rates resulting in consistent gradient performance.
Owner:WATERS INVESTMENTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com