Patents
Literature
2277results about "Superconductor devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phase-change memory cell and method of fabricating the phase-change memory cell
InactiveUS6936840B2Improve reliabilityHigh yieldTransistorSolid-state devicesPhase-change memoryEngineering
A memory cell and method of fabricating the memory cell includes an insulating layer formed on a first electrode layer, the insulating layer having a first opening, a stencil layer formed on the insulating layer, and having a second opening formed in an area of the first opening, a phase-change material layer formed on a surface of the first electrode layer in the first opening, and an electrically conductive layer including a first portion formed on the stencil layer and defining a second electrode layer and a second portion formed on the phase-change material layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Terahertz interconnect system and applications
InactiveUS6967347B2Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsElectromagnetic signal
An assembly includes a first electrical circuitry for providing a first electrical signal containing data and a transmitting arrangement, connected with the first electrical circuitry, for receiving the first electrical signal and for converting the first electrical signal into an electromagnetic signal containing at least a portion of the data. The electromagnetic signal has a carrier frequency greater than 300 GHz. The assembly also includes a receiving arrangement for receiving the electromagnetic signal and for converting the electromagnetic signal into a second electrical signal containing at least some of the portion of the data, and a second electrical circuitry connected with the receiving arrangement and configured for receiving the second electrical signal.
Owner:RGT UNIVERSITTY OF COLORADO THE
RRAM memory cell electrodes
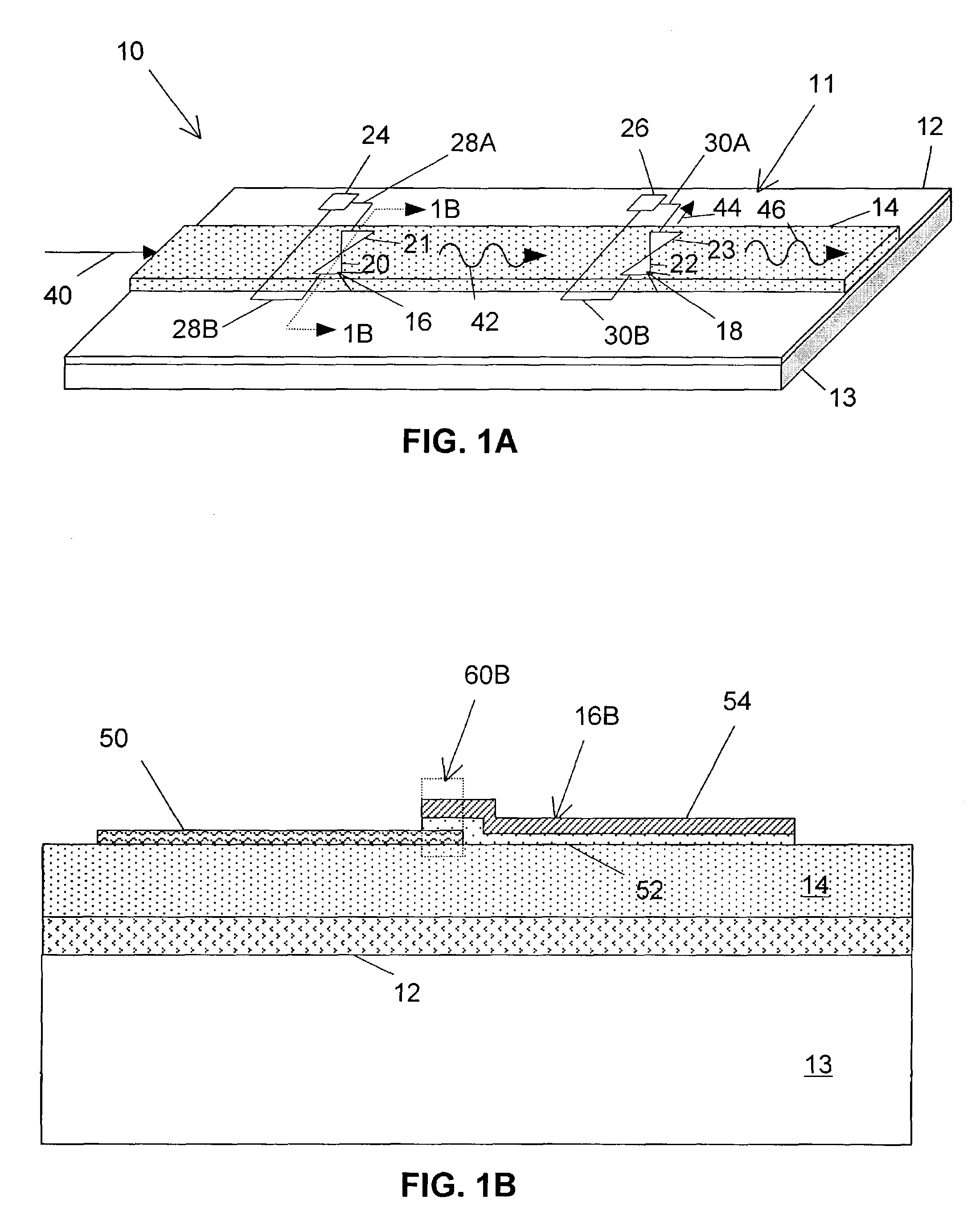
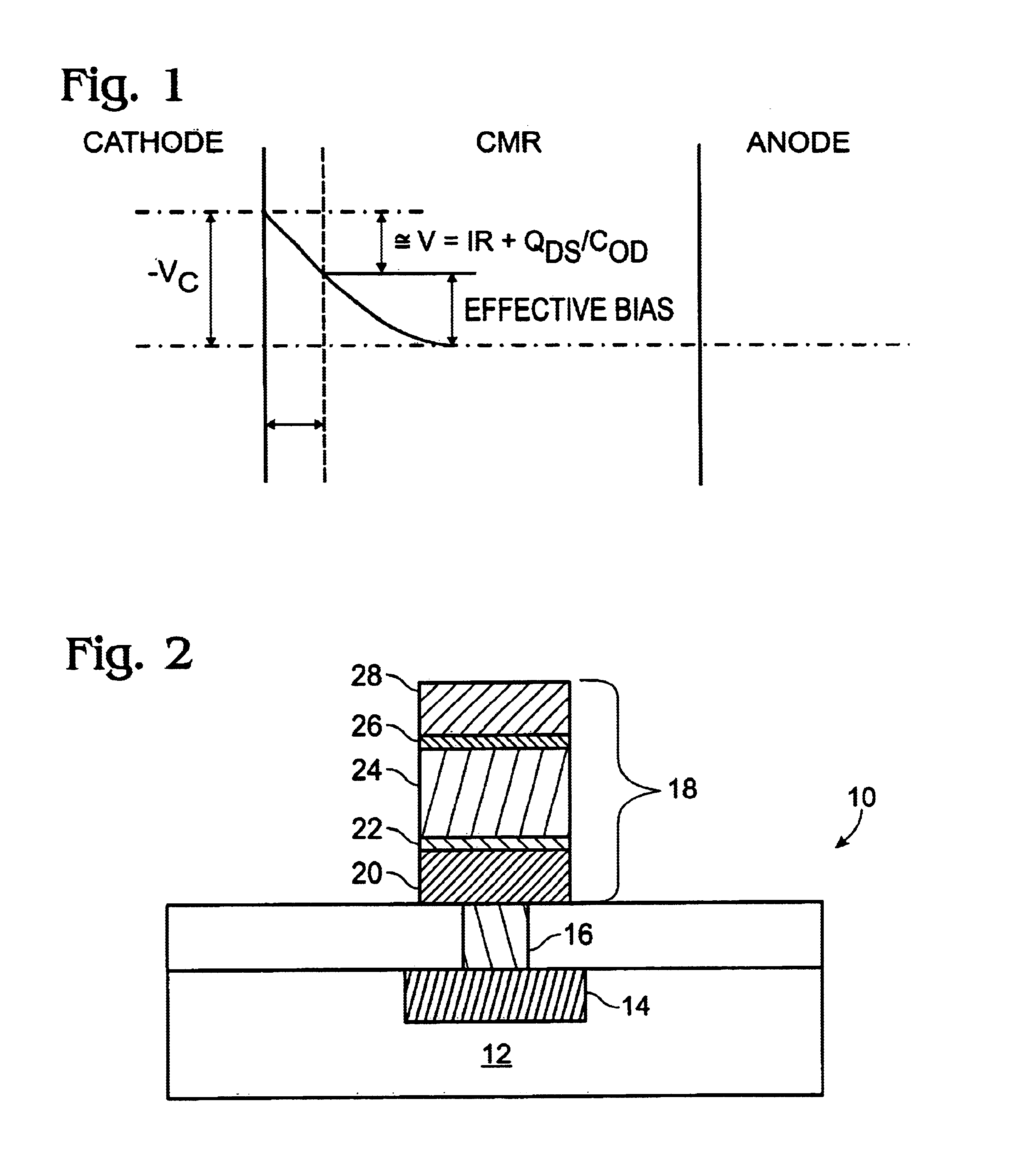
ActiveUS6849891B1Improve device reliabilityImprove device device enduranceTransistorMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsOxidation resistantSilicon
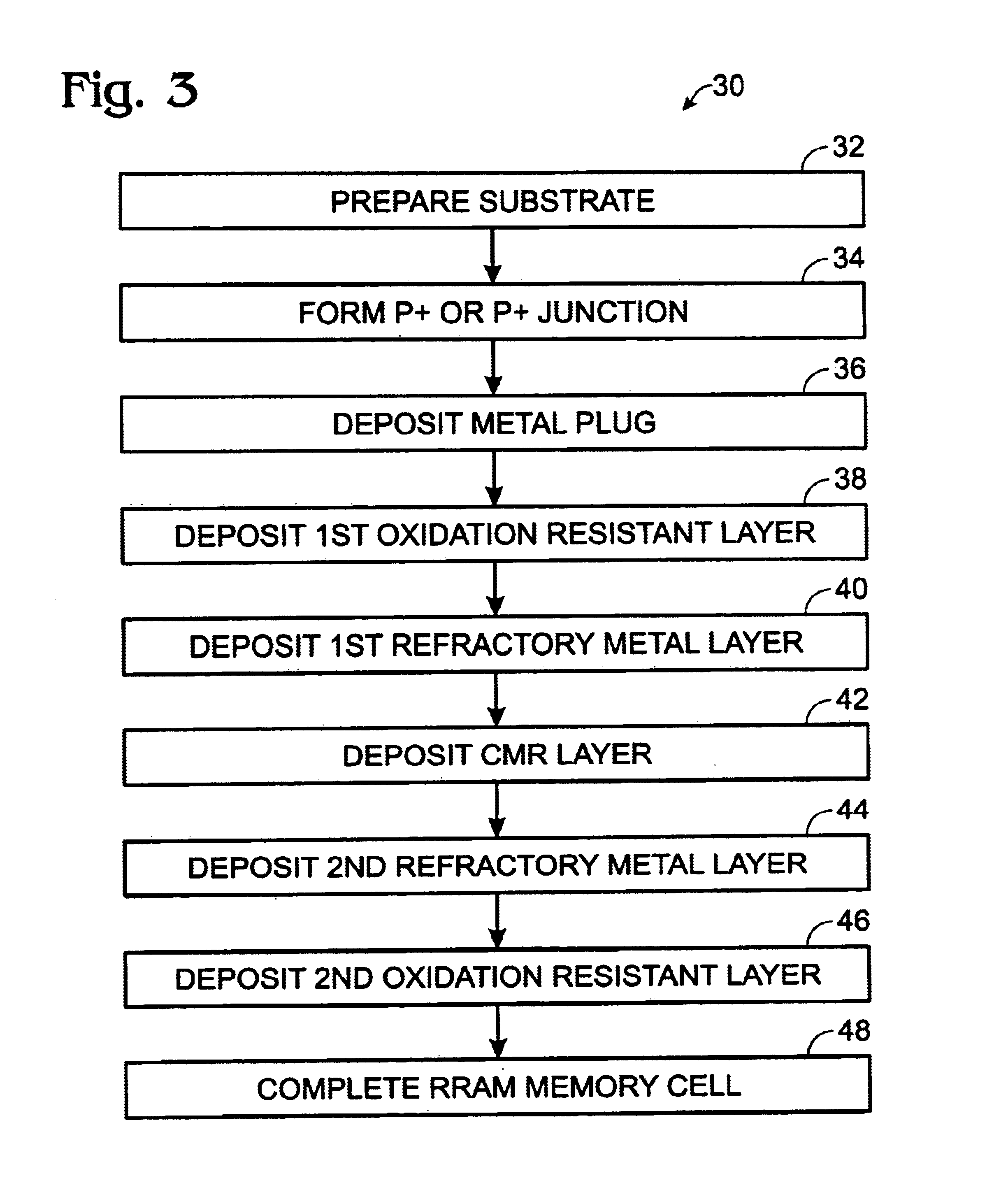
A RRAM memory cell is formed on a silicon substrate having a operative junction therein and a metal plug formed thereon, includes a first oxidation resistive layer; a first refractory metal layer; a CMR layer; a second refractory metal layer; and a second oxidation resistive layer. A method of fabricating a multi-layer electrode RRAM memory cell includes preparing a silicon substrate; forming a junction in the substrate taken from the group of junctions consisting of N+ junctions and P+ junctions; depositing a metal plug on the junction; depositing a first oxidation resistant layer on the metal plug; depositing a first refractory metal layer on the first oxidation resistant layer; depositing a CMR layer on the first refractory metal layer; depositing a second refractory metal layer on the CMR layer; depositing a second oxidation resistant layer on the second refractory metal layer; and completing the RRAM memory cell.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Tunable ferroelectric resonator arrangement
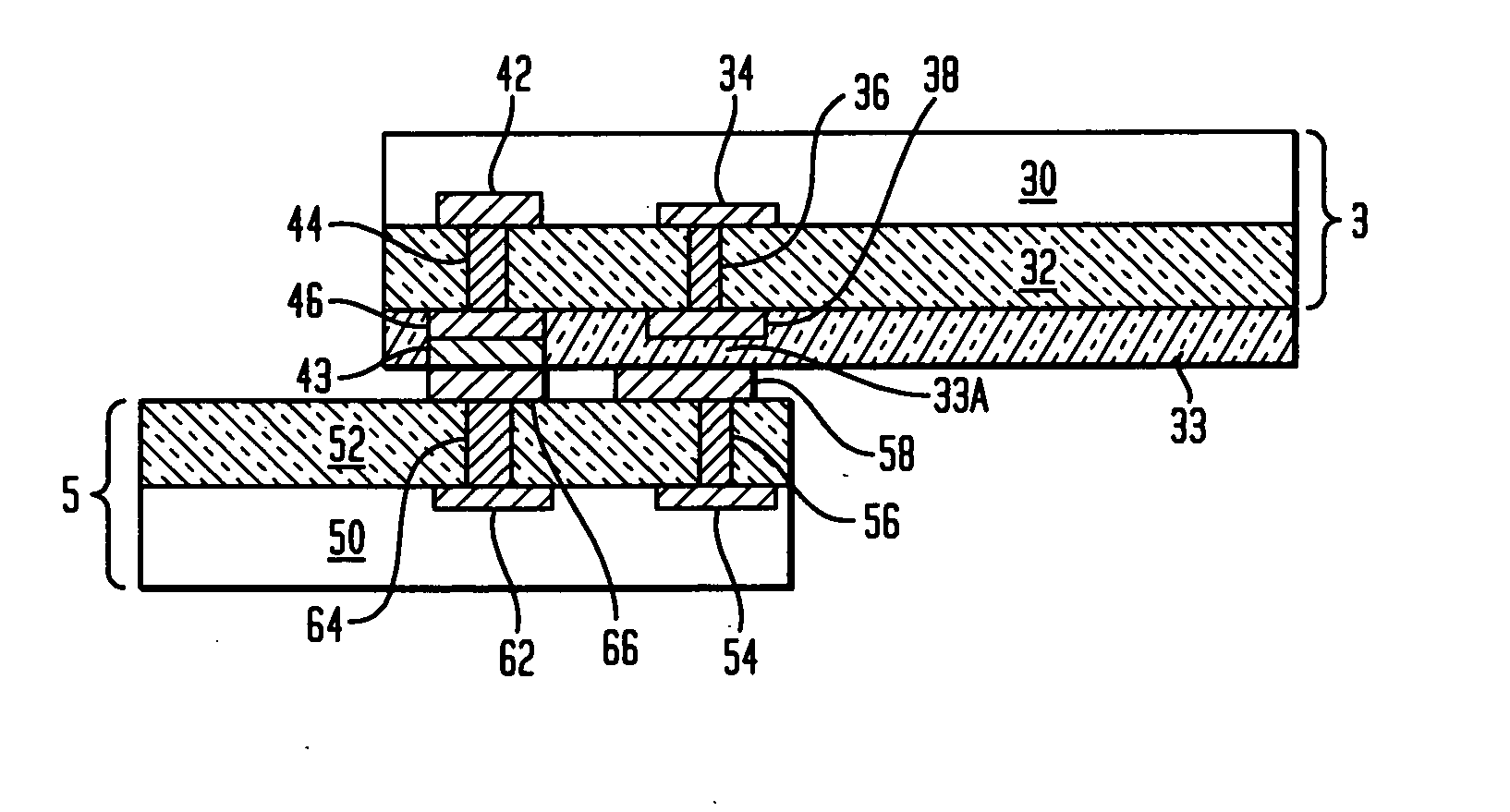
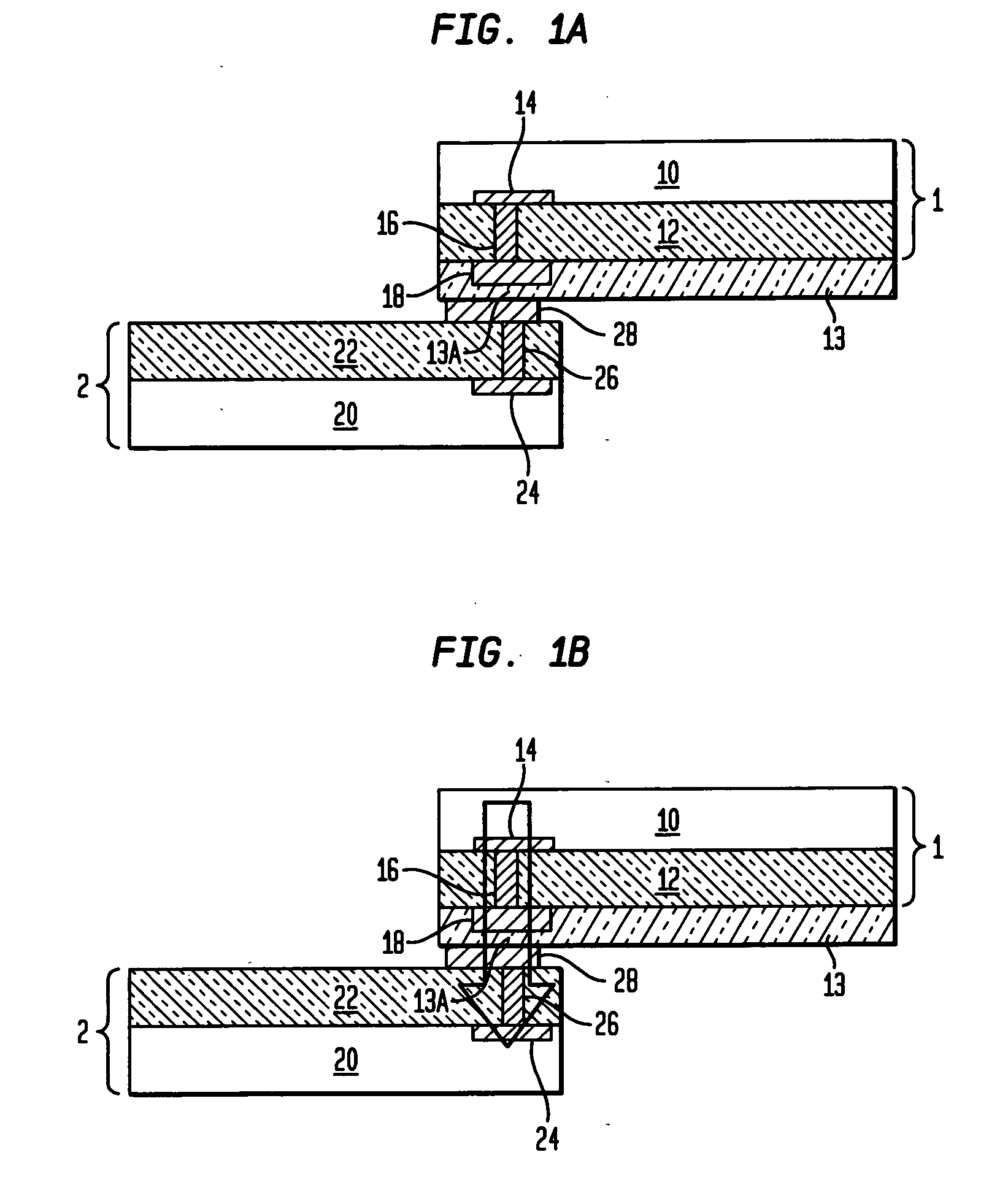
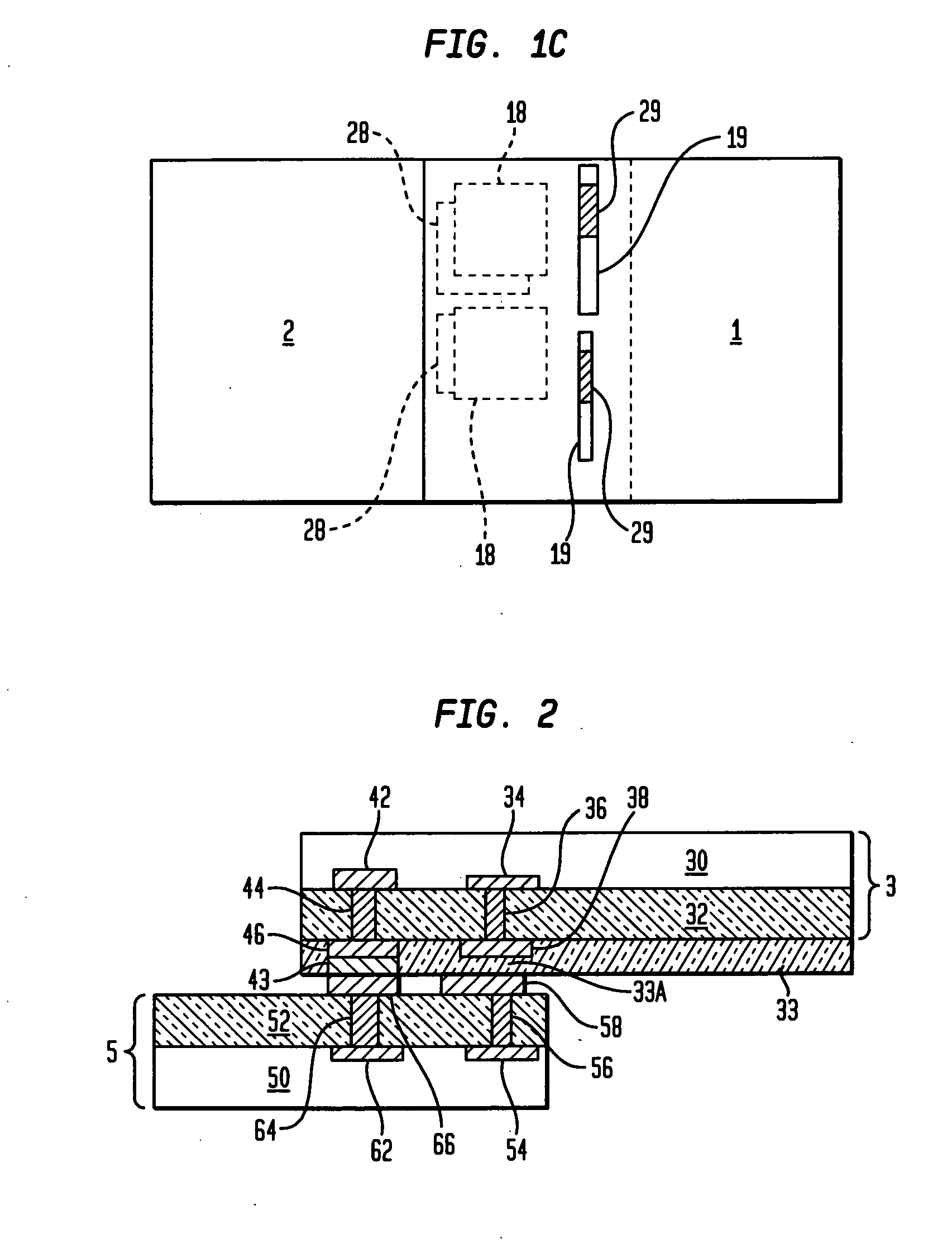
InactiveUS7069064B2Efficiency tuningGuaranteed uptimeSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesCouplingEnergy coupling
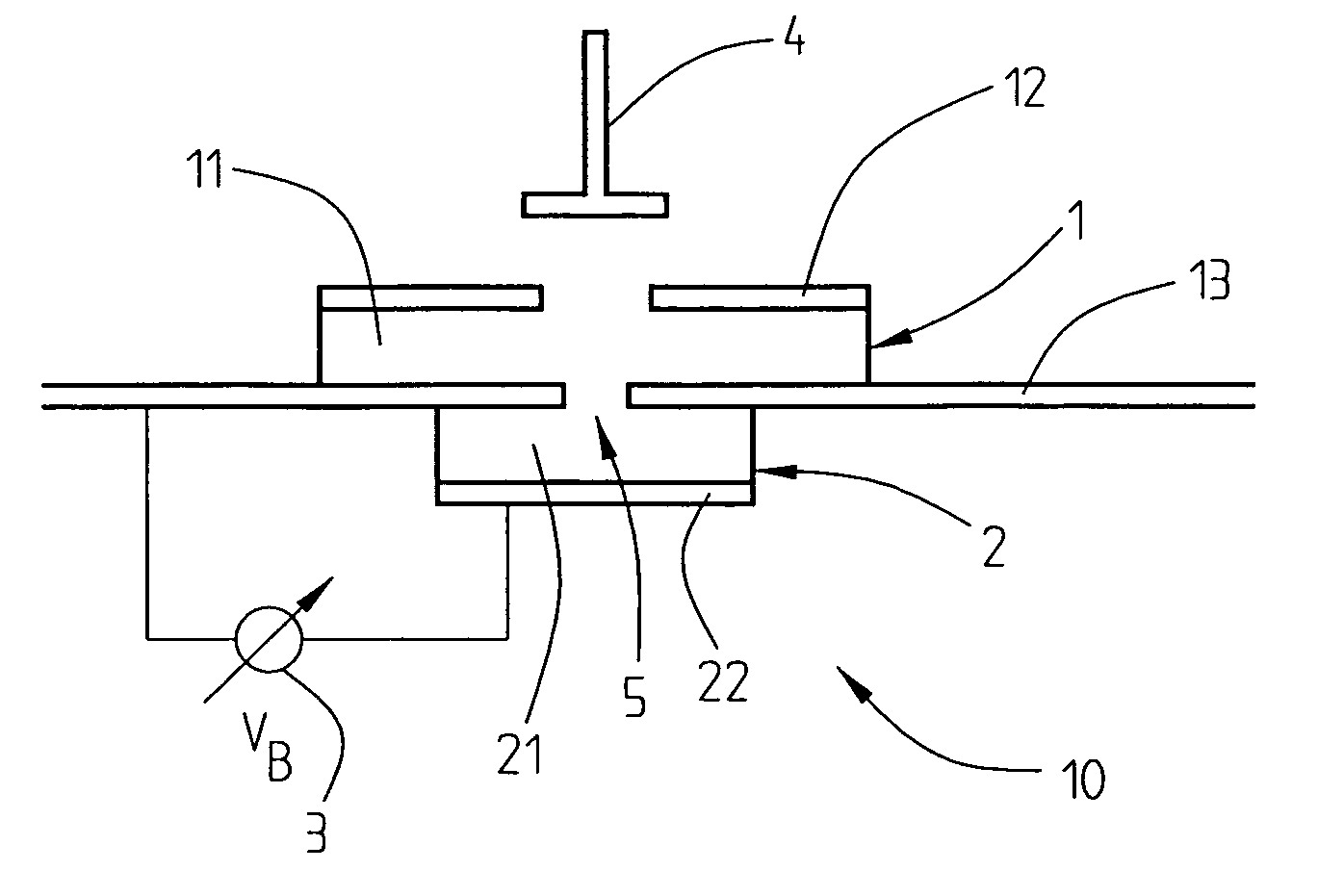
The present invention relates to a tunable resonating arrangement comprising a resonator apparatus (10), input / output coupling (4) means for coupling electromagnetic energy into / out of the resonator apparatus, and a tuning device (3) for application of a biasing voltage / electric field to the resonator apparatus. The resonator apparatus comprises a first resonator (1) and a second resonator (2). Said first resonator is non-tunable and said second resonator is tunable and comprises a ferroelectric substrate (21). Said first and second resonators are separated by a ground plane (13) which is common for said first and second resonators, and coupling means (5) are provided for providing coupling between said first and second resonators. For tuning of the resonator apparatus, the biasing voltage / electric field is applied to the second resonator (2).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
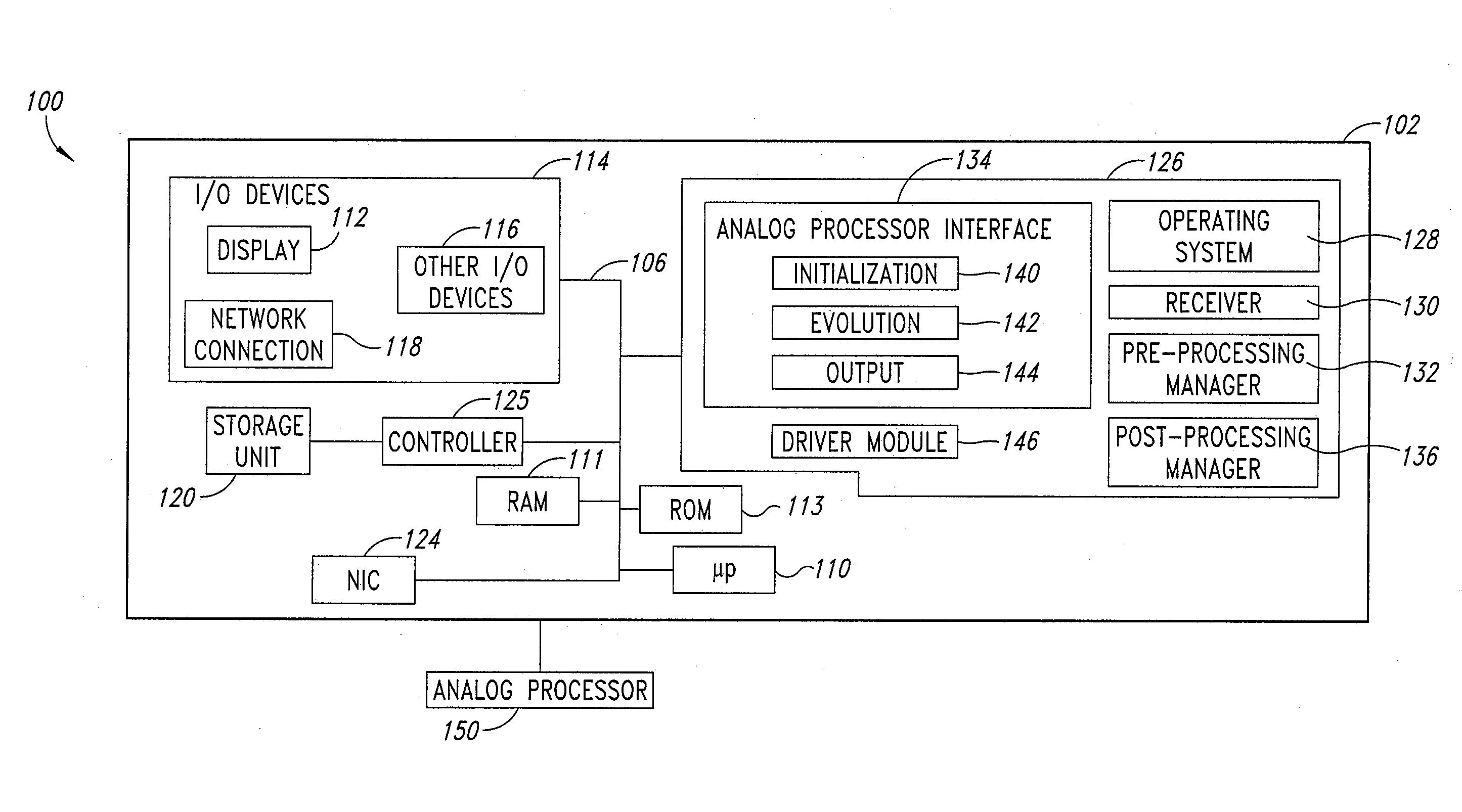
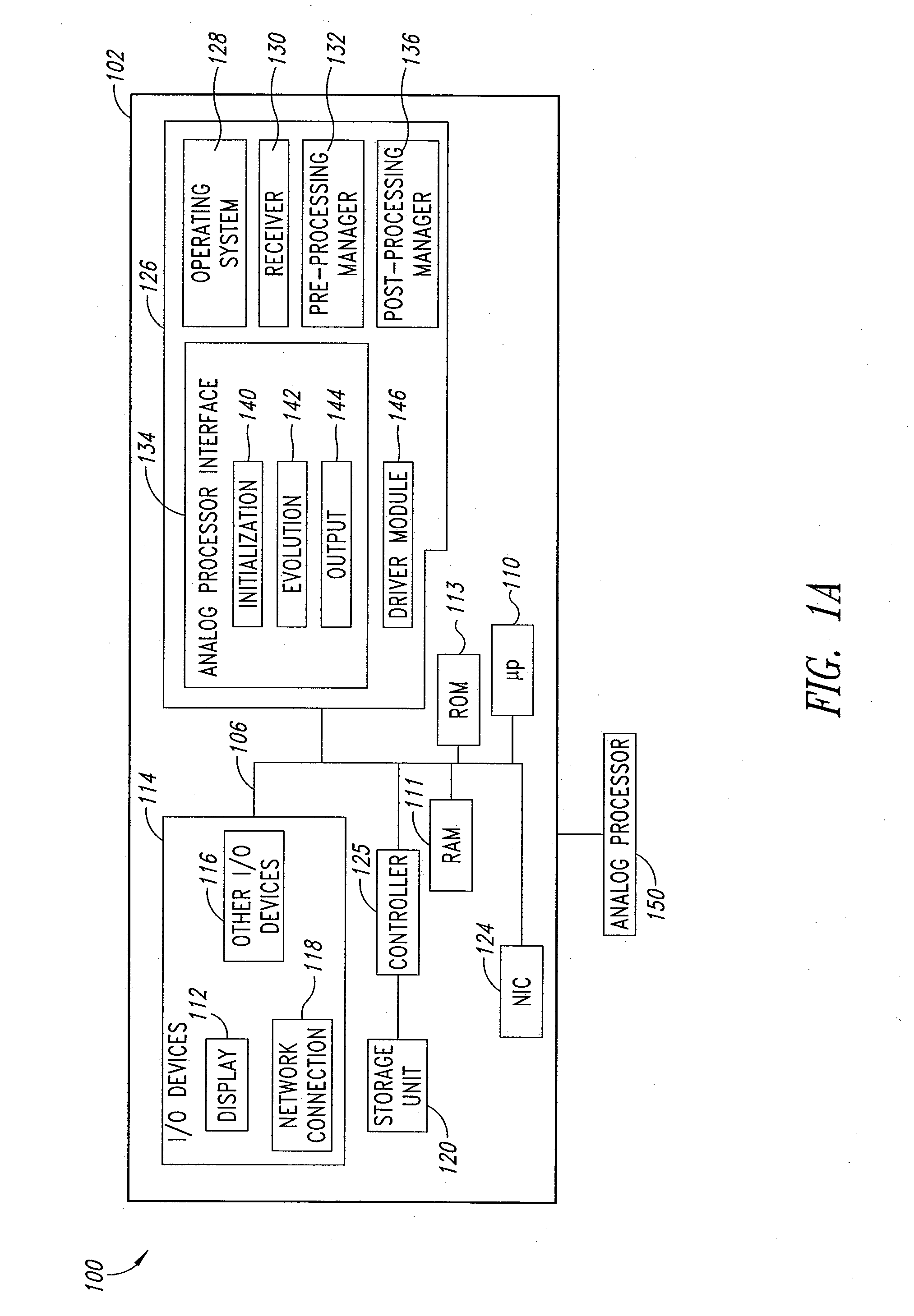
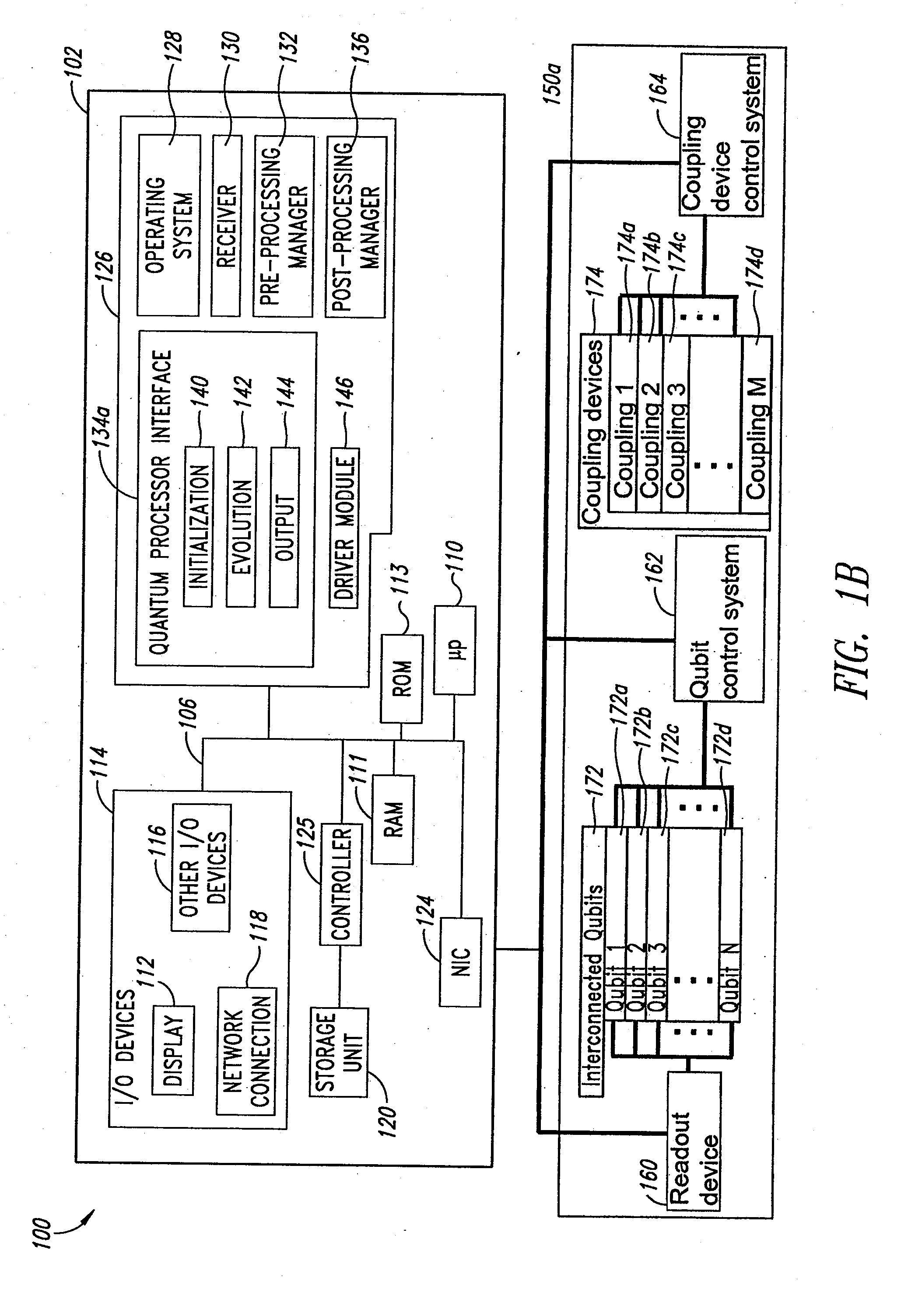
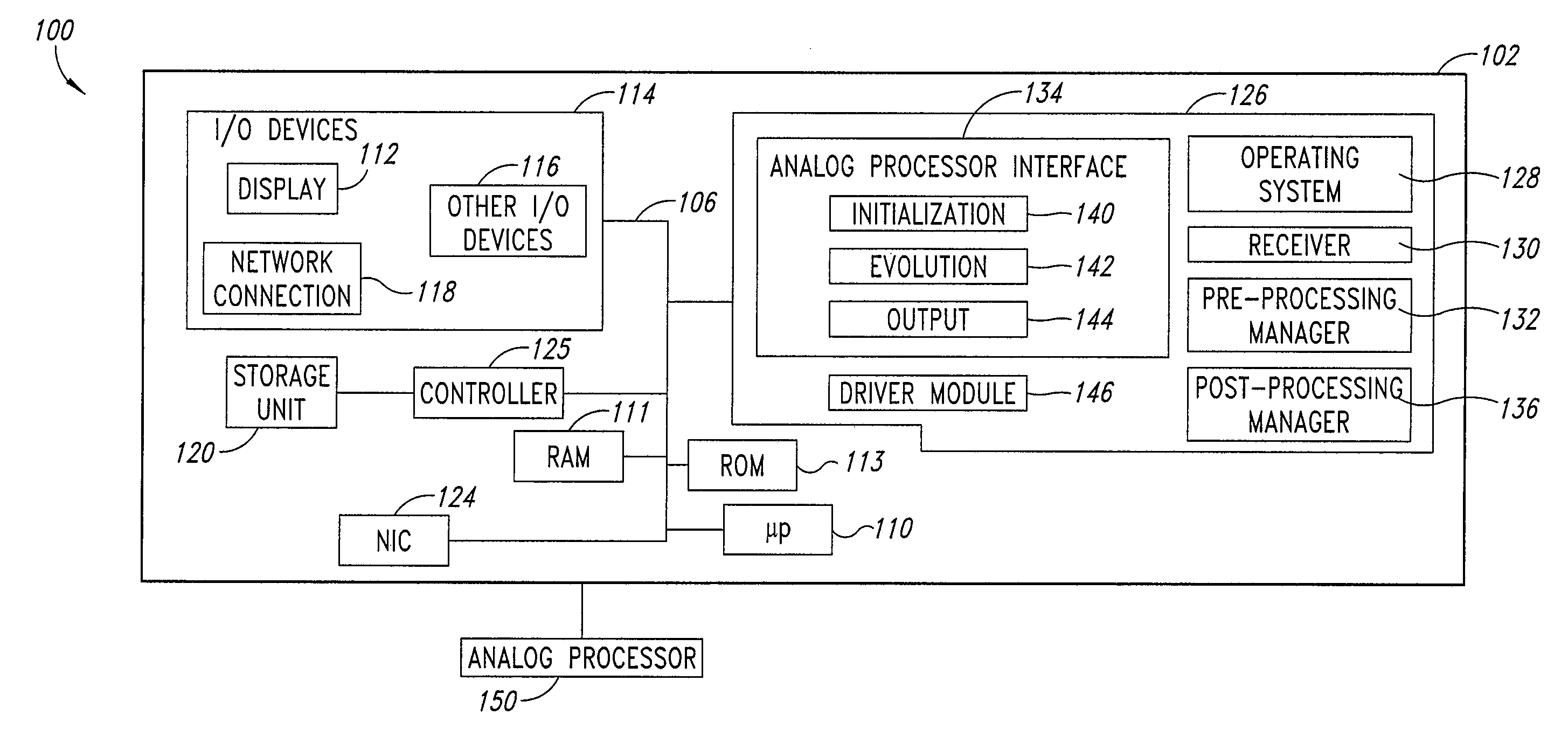
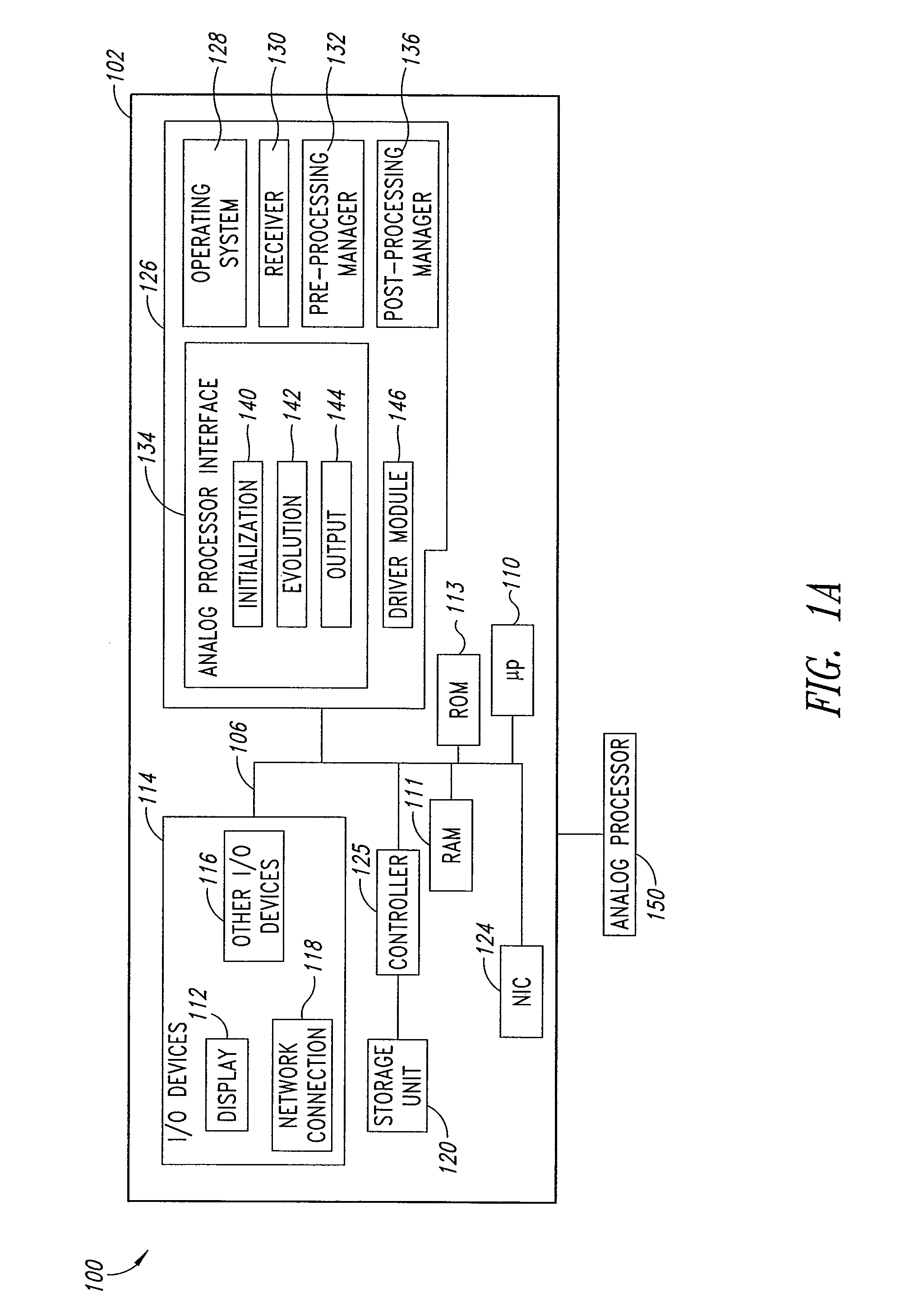
Systems, devices, and methods for interconnected processor topology
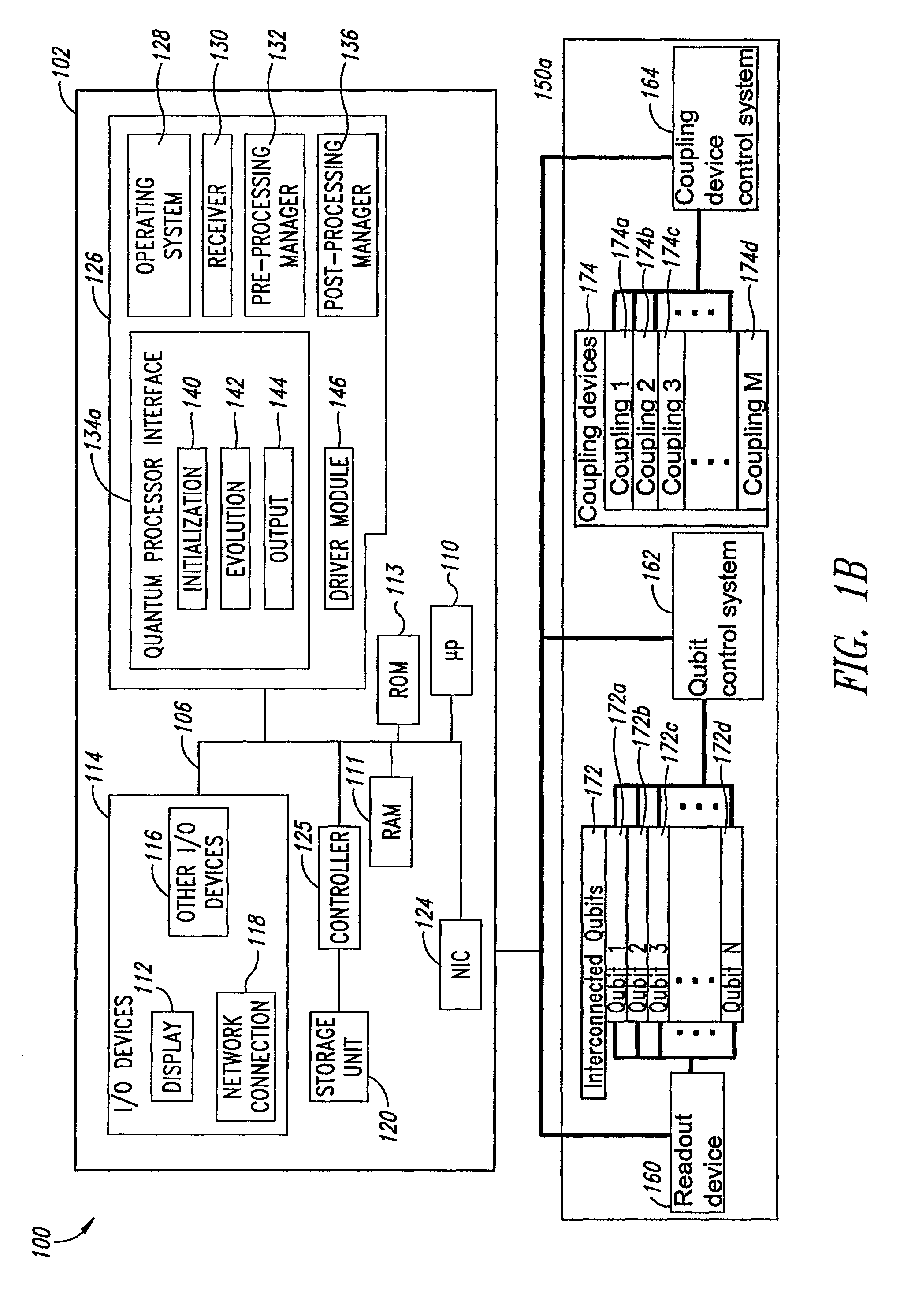
ActiveUS20080176750A1Improve legibilityQuantum computersProgram control using wired connectionsAnalog processorCoupling
An analog processor, for example a quantum processor may include a plurality of elongated qubits that are disposed with respect to one another such that each qubit may selectively be directly coupled to each of the other qubits via a single coupling device. Such may provide a fully interconnected topology.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
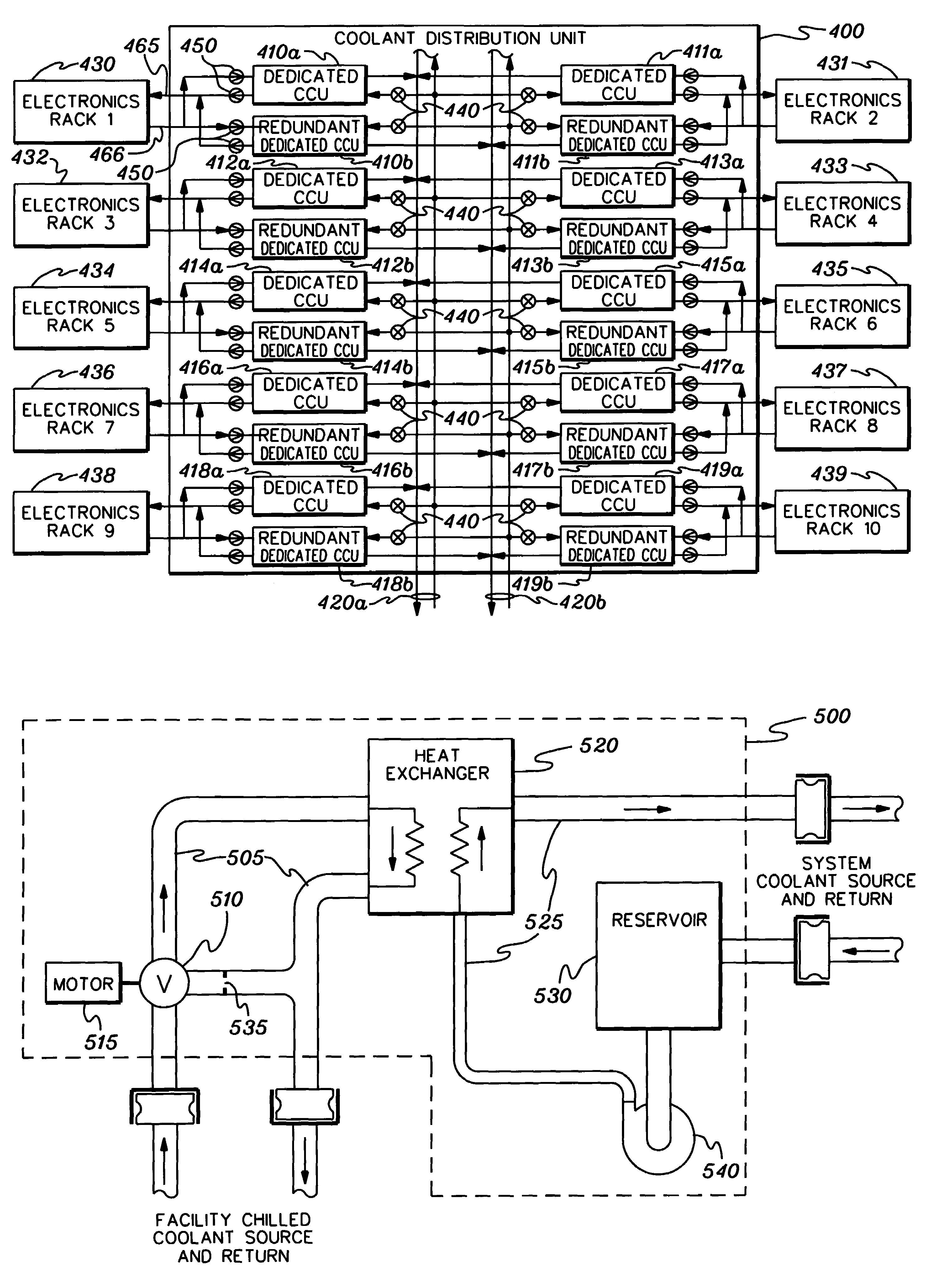
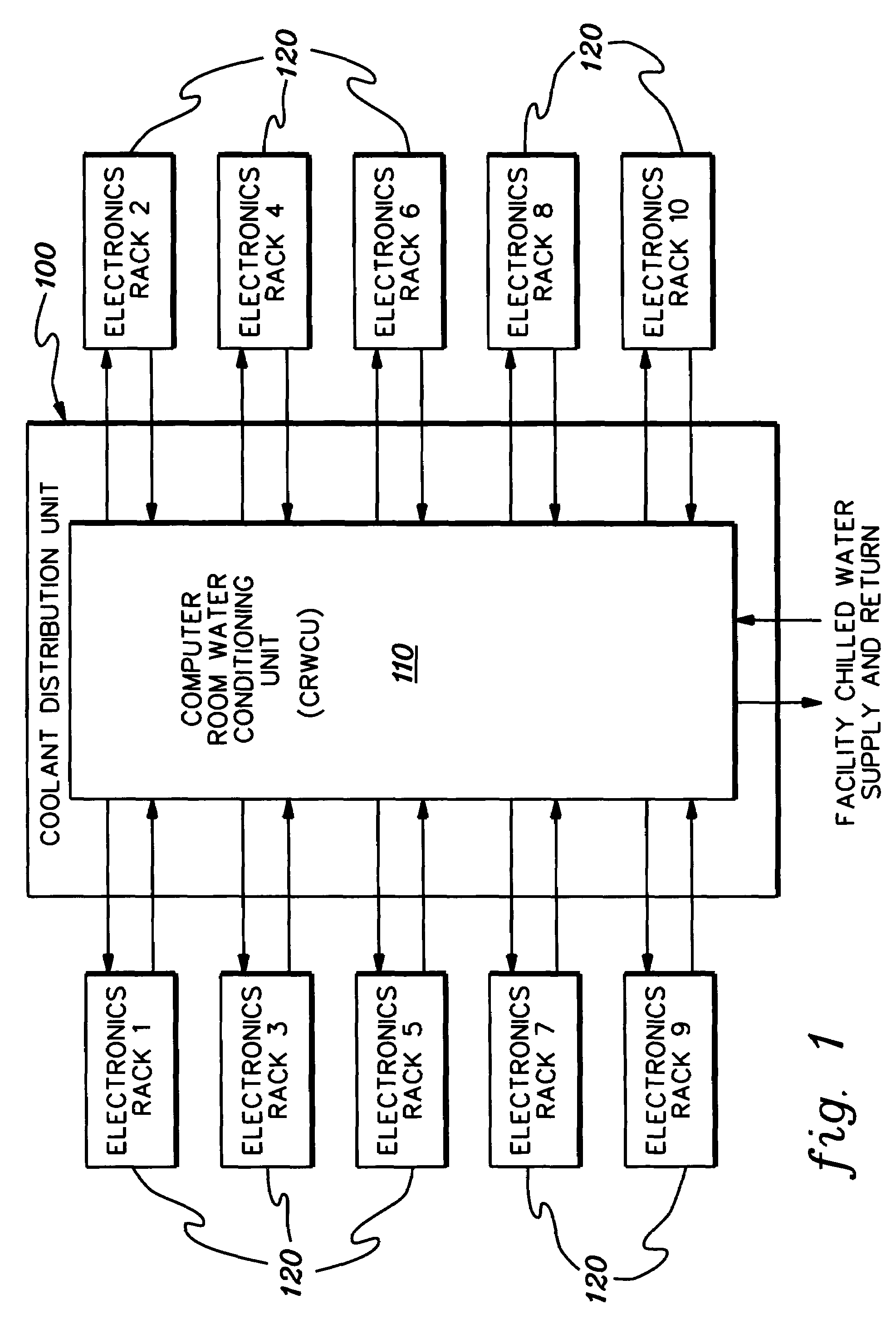
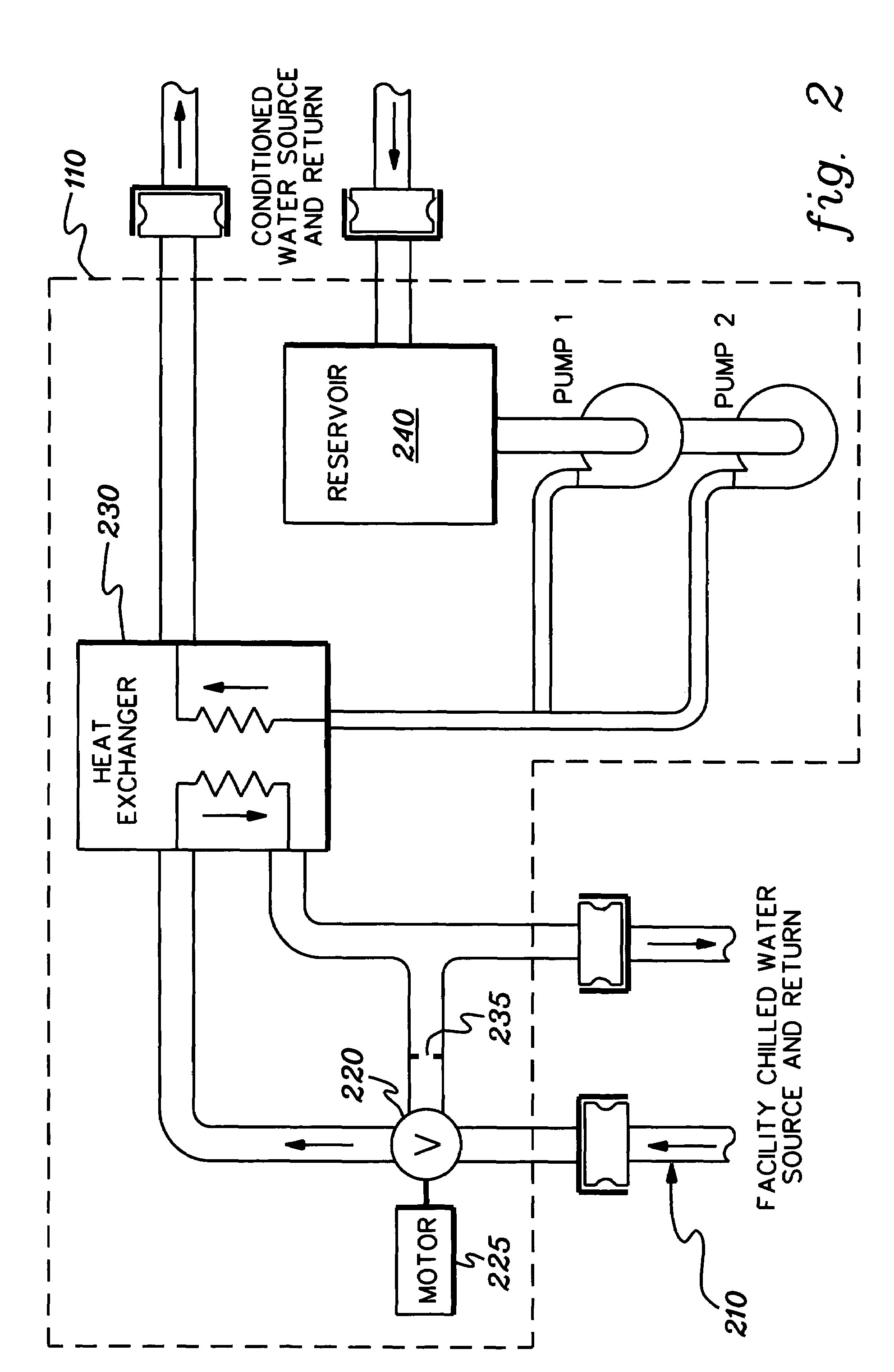
Cooling system and method employing multiple dedicated coolant conditioning units for cooling multiple electronics subsystems
InactiveUS7106590B2Superconductors/hyperconductorsDomestic cooling apparatusCoolant flowNuclear engineering
A cooling system is provided employing multiple coolant conditioning units (CCUs). Each CCU, which is coupled to a different, associated electronics rack of multiple electronics racks to be cooled, includes a heat exchanger, a first cooling loop with a control valve, and a second cooling loop. The first cooling loop receives chilled facility coolant from a source and passes at least a portion thereof via the control valve through the heat exchanger. The second cooling loop provides cooled system coolant to the associated electronics rack, and expels heat in the heat exchanger from the electronics rack to the chilled facility coolant in the first cooling loop. The control valve allows regulation of the facility coolant flow through the heat exchanger, thereby allowing independent control of temperature of the system coolant in the second cooling loop. Various CCU and associated component redundancies of the cooling system are also provided.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Systems, devices, and methods for interconnected processor topology
An analog processor, for example a quantum processor may include a plurality of elongated qubits that are disposed with respect to one another such that each qubit may selectively be directly coupled to each of the other qubits via a single coupling device. Such may provide a fully interconnected topology.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
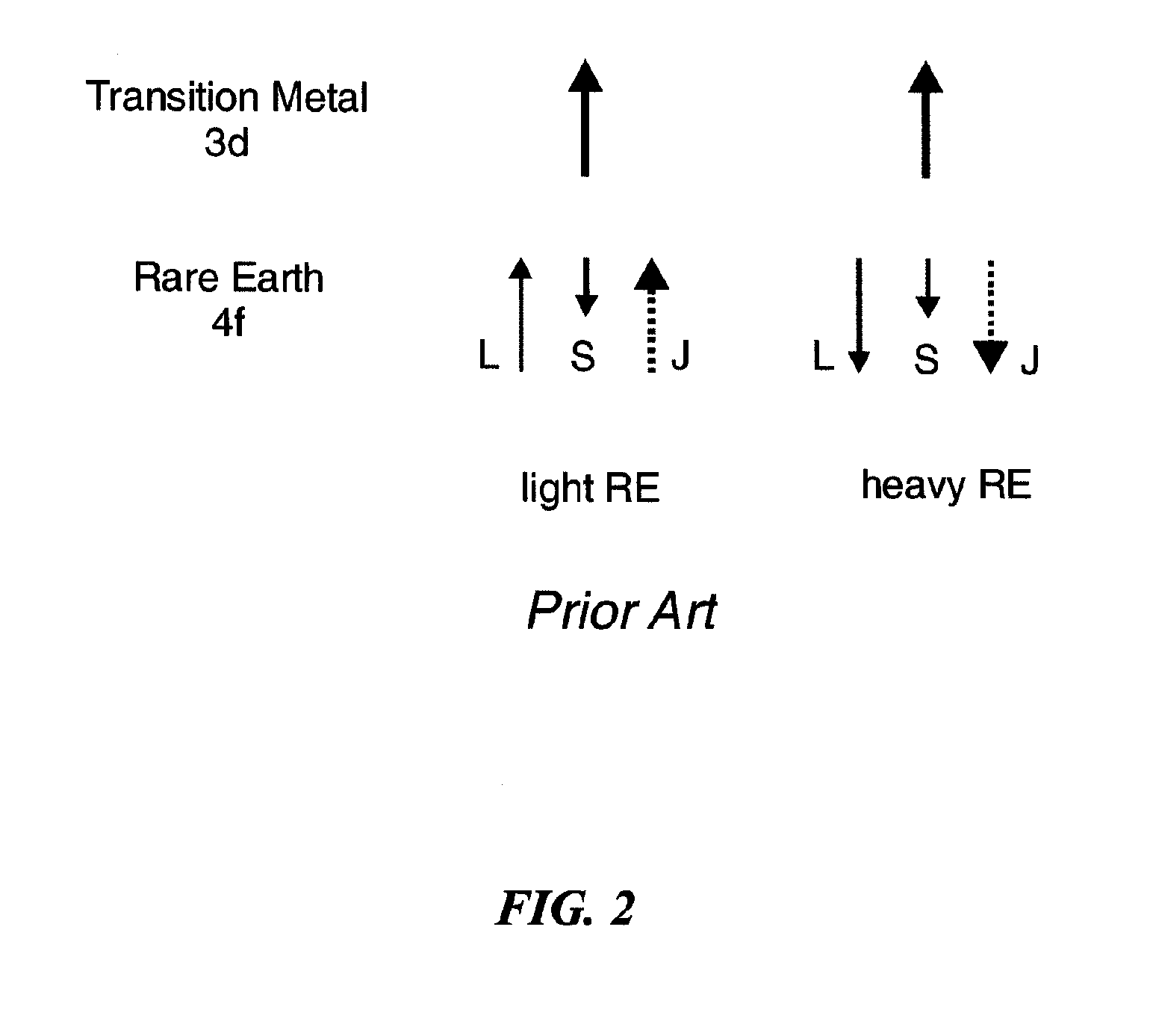
Spin-polarization devices using rare earth-transition metal alloys
ActiveUS7230265B2Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionRare-earth elementMetal alloy
A tunnel barrier in proximity with a layer of a rare earth element-transition metal (RE—TM) alloy forms a device that passes negatively spin-polarized current. The rare earth element includes at least one element selected from the group consisting of Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, and Yb. The RE and TM have respective sub-network moments such that the absolute magnitude of the RE sub-network moment is greater than the absolute magnitude of the TM sub-network moment. An additional layer of magnetic material may be used in combination with the tunnel barrier and the RE—TM alloy layer to form a magnetic tunnel junction. Still other layers of tunnel barrier and magnetic material may be used in combination with the foregoing to form a flux-closed double tunnel junction device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Magnetic field measurement system and optical pumping magnetometer
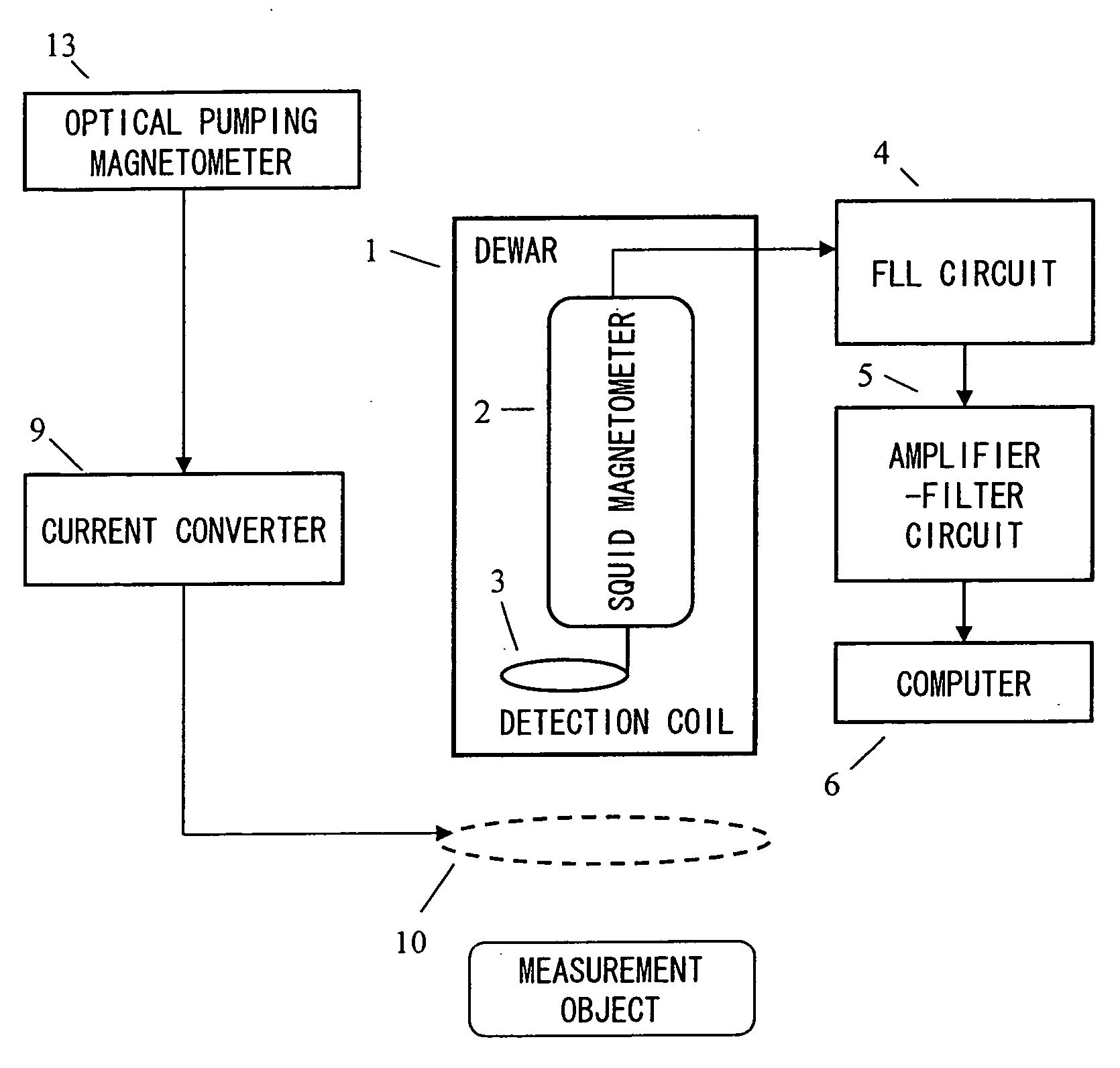
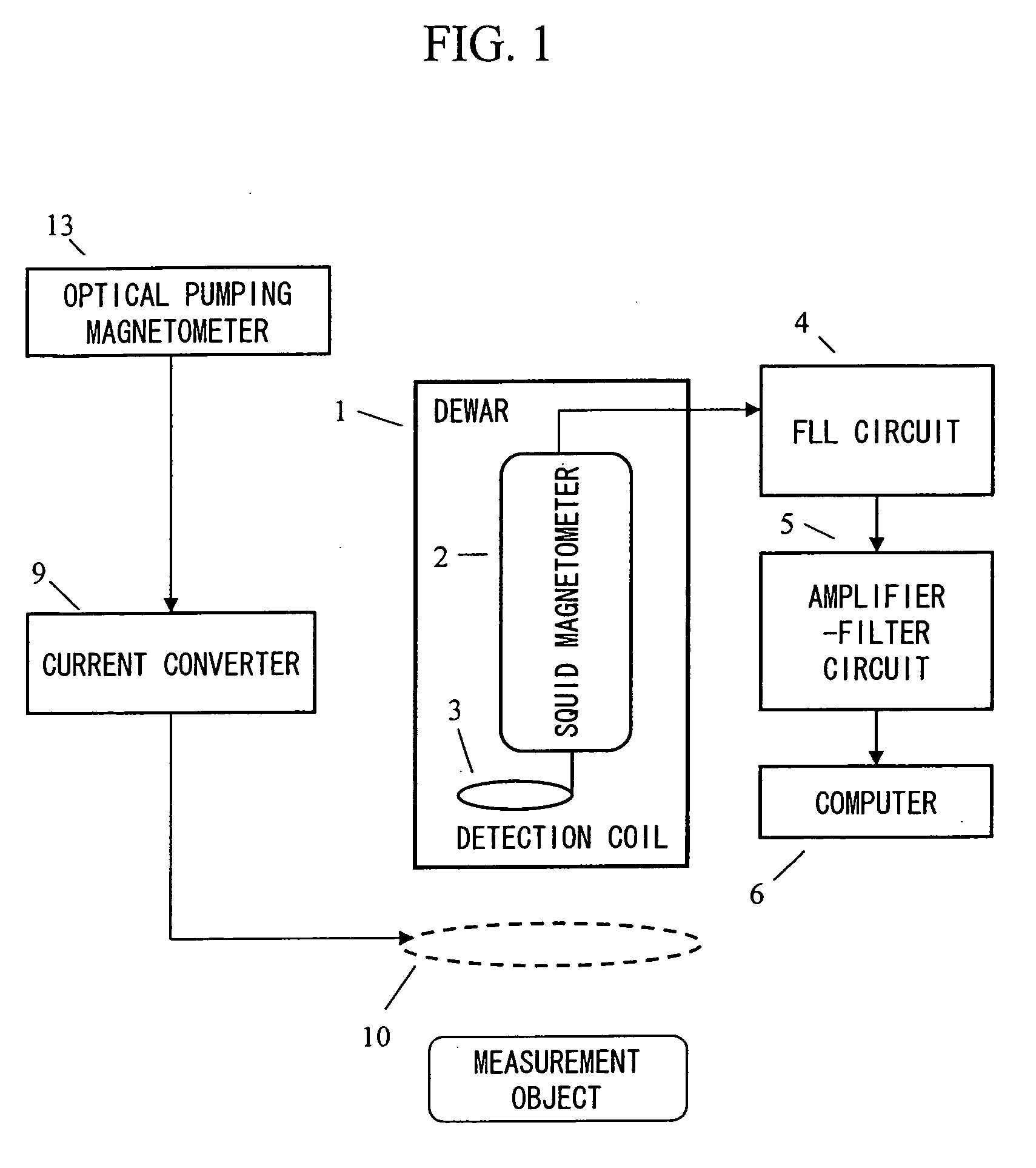
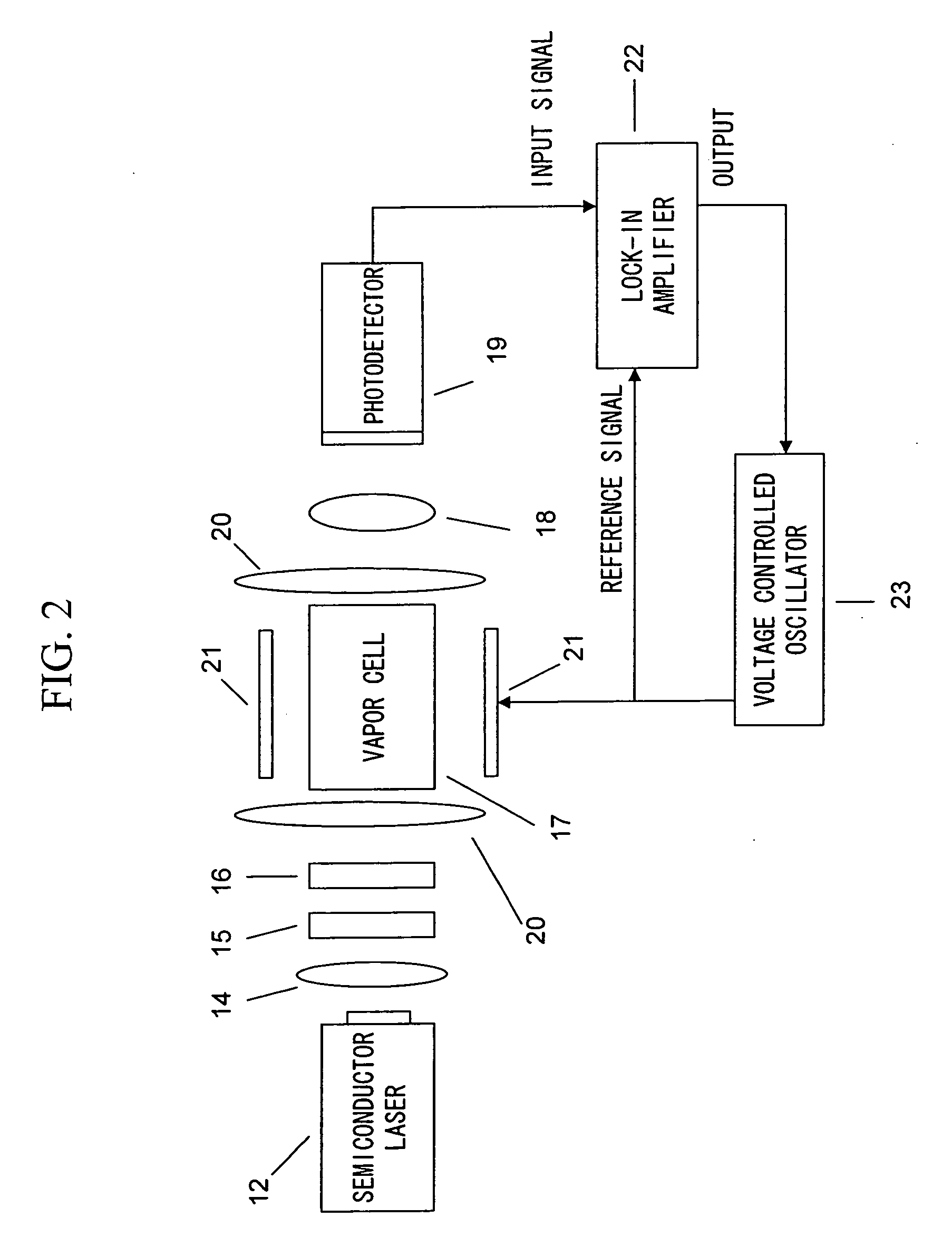
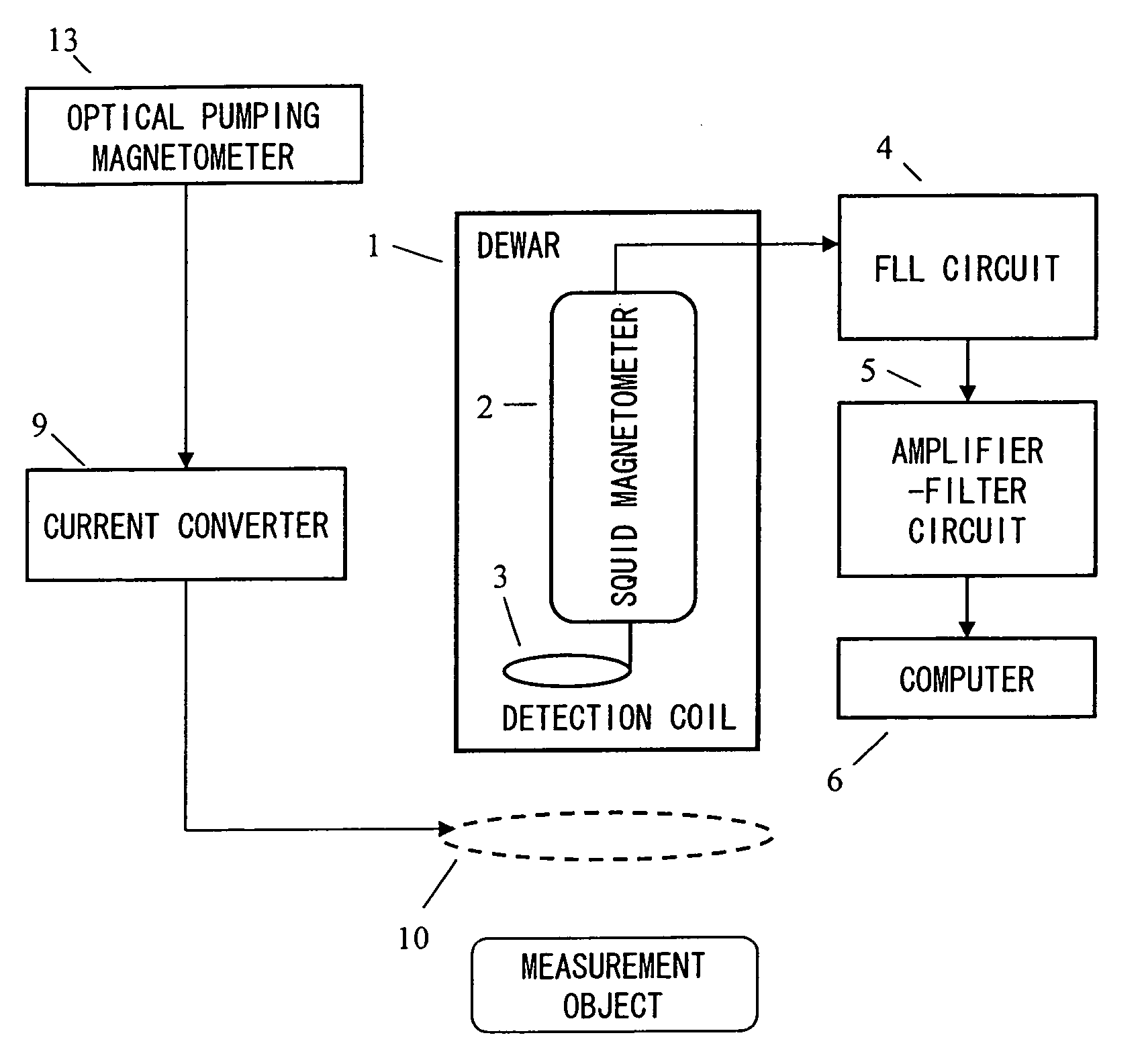
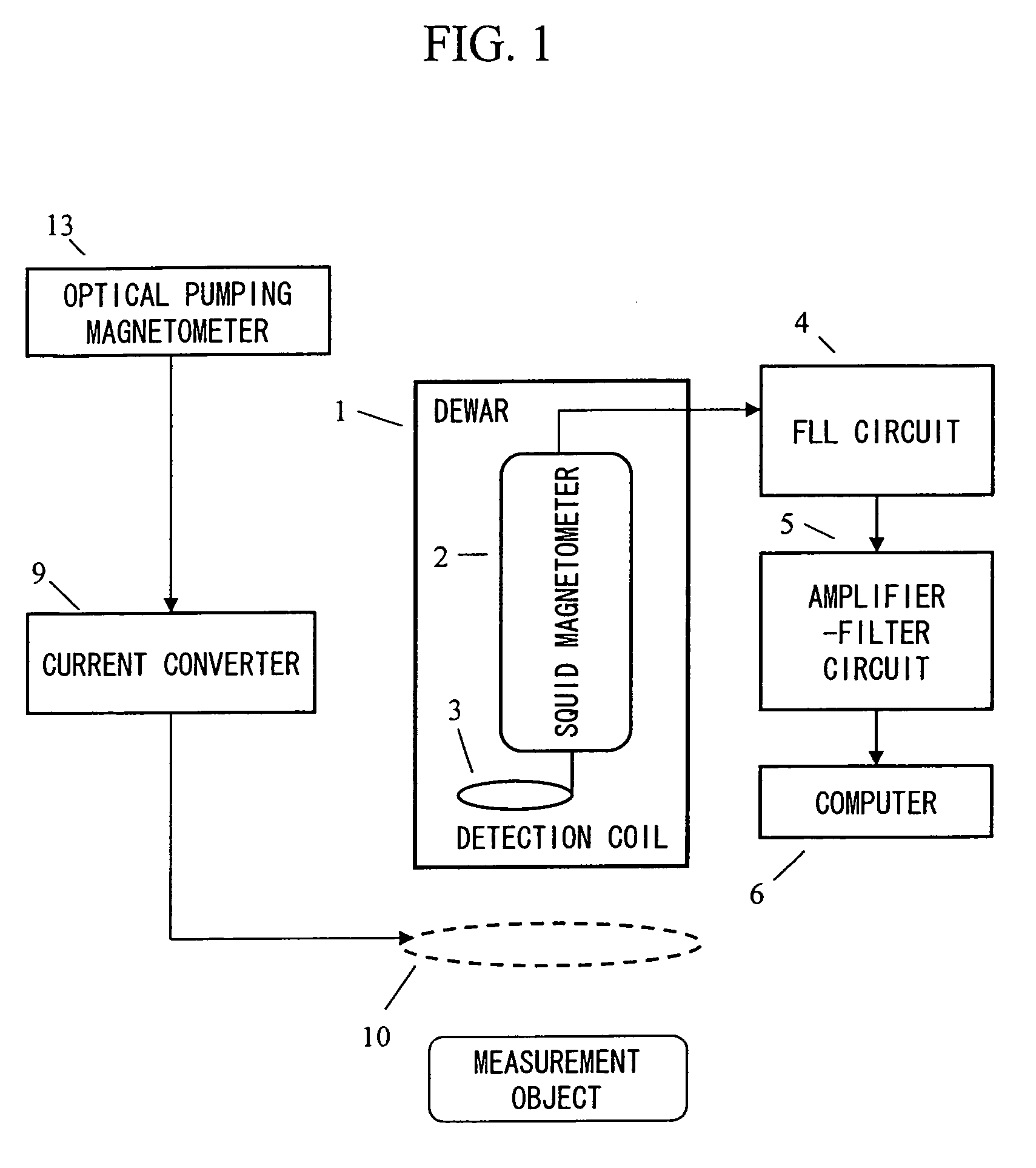
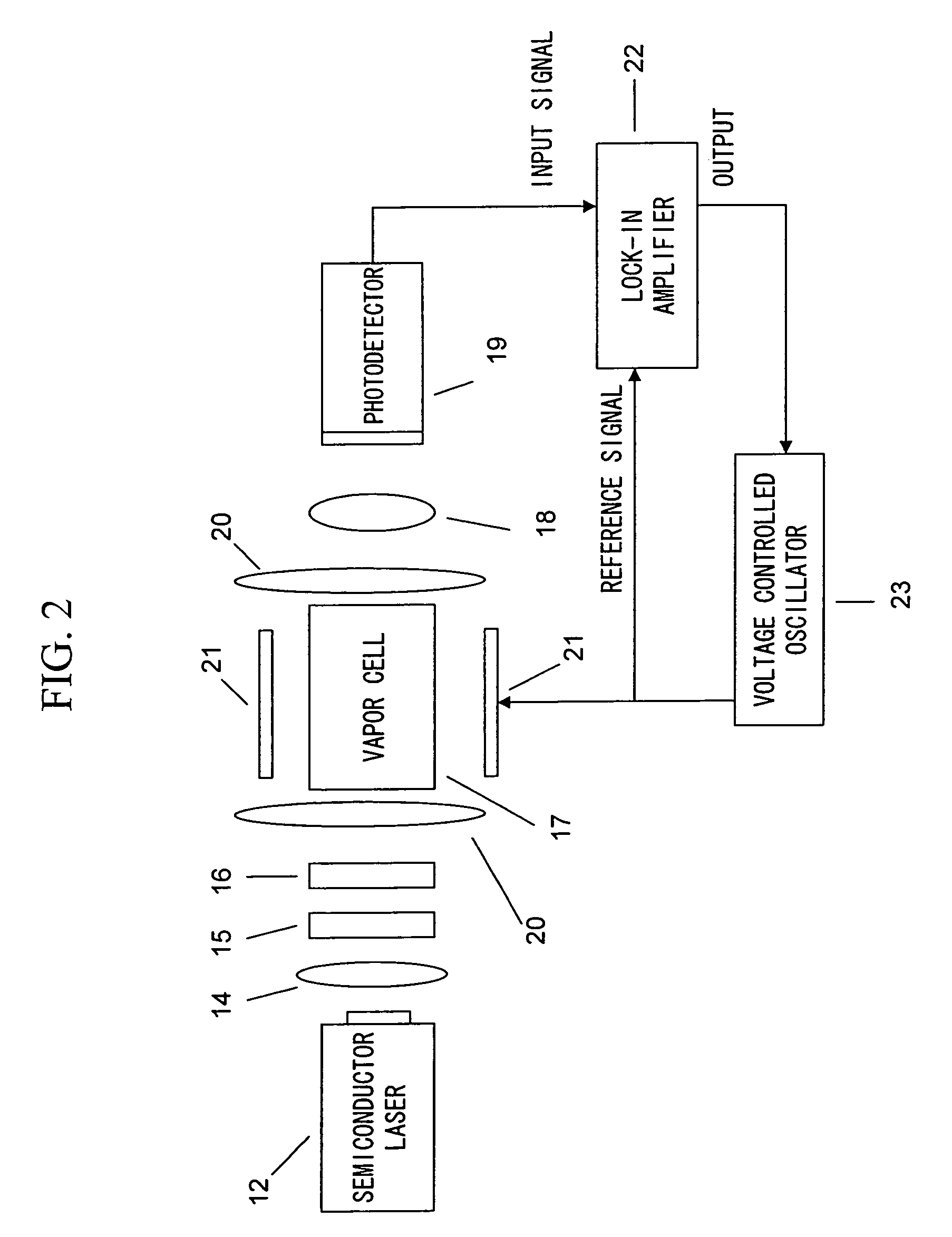
ActiveUS20070120563A1Reduce magnetic noiseAffect operationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectricityComing out
Provided is a highly accurate optical pumping magnetometer, in which a static magnetic field and an oscillating field to be applied to a vapor cell are stabilized. To this end, the optical pumping magnetometer includes: Helmholtz coils for applying a constant static magnetic field to a vapor cell serving as a magnetic field detector; fluxgate magnetometers for detecting environmental magnetic noise in two directions of X-axis direction and Y-axis direction other than Z-axis direction which is a direction for detecting a magnetic field coming out of a measurement object while locating the vapor cell in the center thereof; magnetometer drive circuits for driving the fluxgate magneotometers; current converters for converting outputs of the magnetometer drive circuits into amount of currents; and magnetic field generating coils for generating a magnetic field in a phase opposite to the environmental magnetic noise in the two directions.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
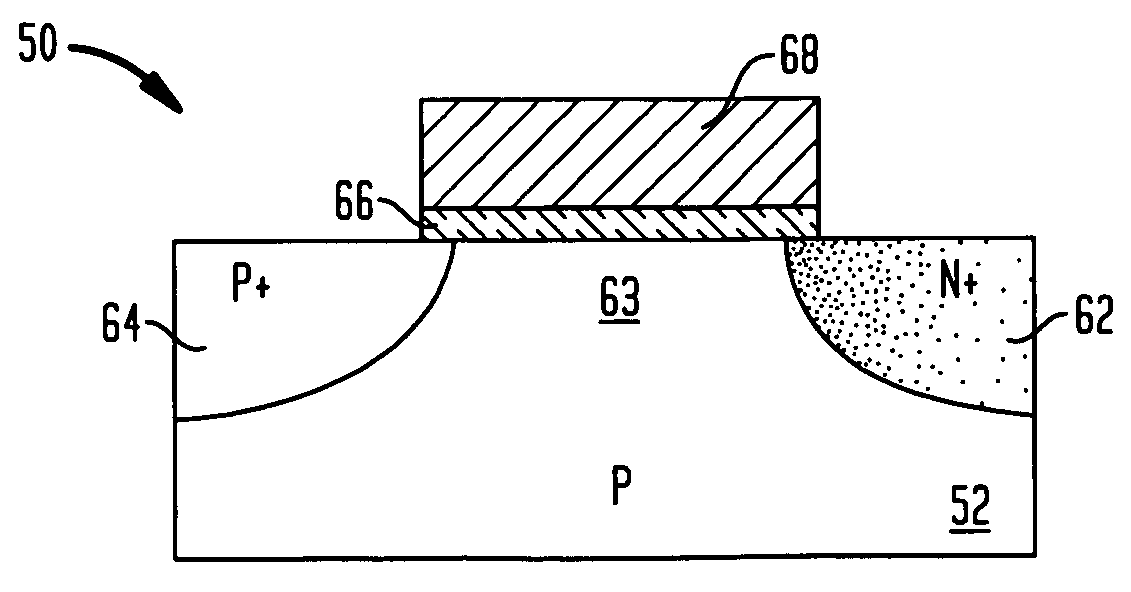
Phase-change memory cell and method of fabricating the phase-change memory cell
InactiveUS20050167656A1Improve reliabilityHigh yieldTransistorDigital storagePhase-change memoryEngineering
A memory cell and method of fabricating the memory cell includes an insulating layer formed on a first electrode layer, the insulating layer having a first opening, a stencil layer formed on the insulating layer, and having a second opening formed in an area of the first opening, a phase-change material layer formed on a surface of the first electrode layer in the first opening, and an electrically conductive layer including a first portion formed on the stencil layer and defining a second electrode layer and a second portion formed on the phase-change material layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
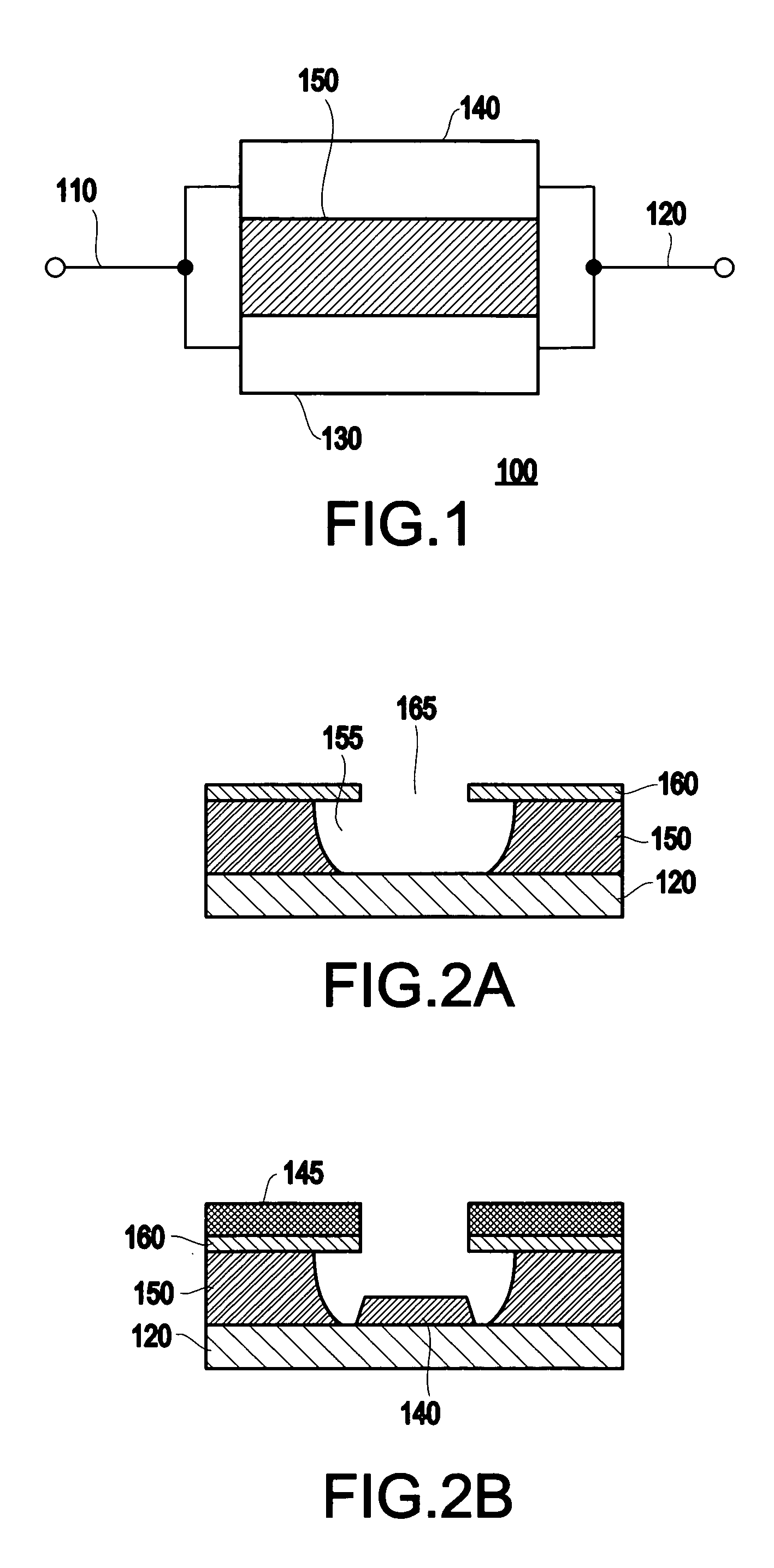
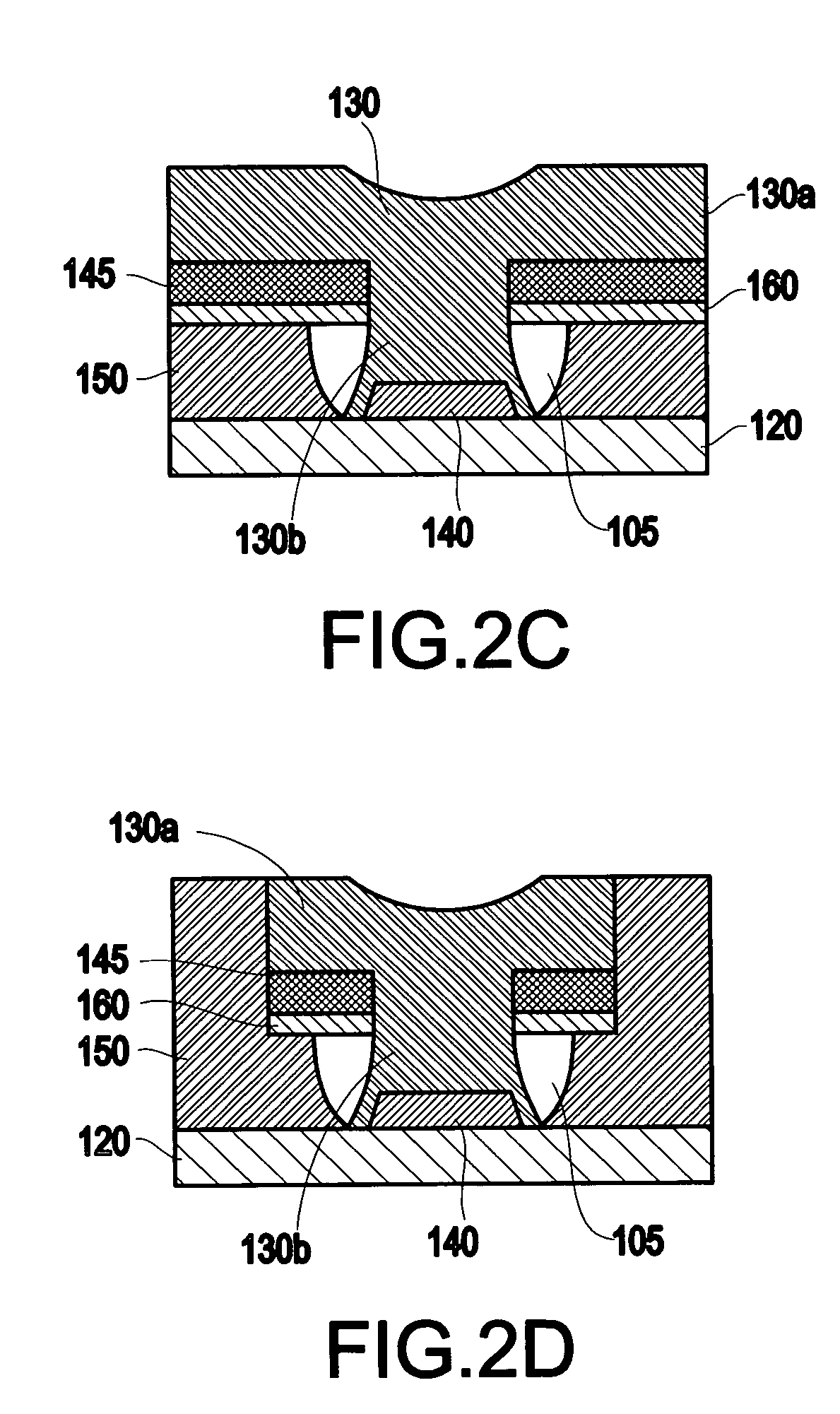
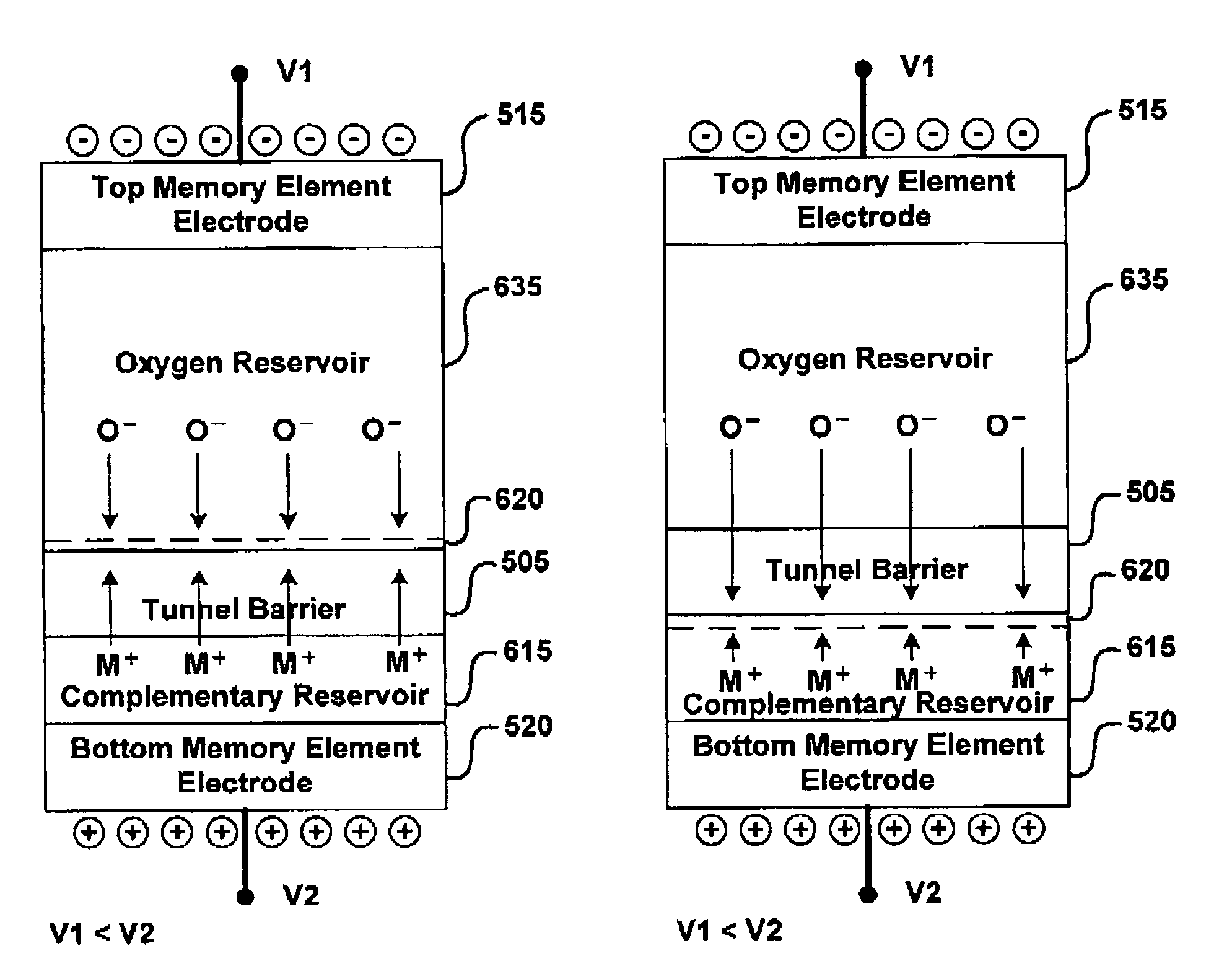
Memory using variable tunnel barrier widths
A memory using a tunnel barrier is disclosed. A memory element includes a tunneling barrier and two conductive materials. The conductive material typically has mobile ions that either move towards or away from the tunneling barrier in response to a voltage across the memory element. A low conductivity region is irreversibly formed for one time programmable memory. The tunneling barrier can be formed by mobile ions combining with complementary ions. The low conductivity region increases the effective width of the tunnel barrier, making electrons tunnel a greater distance, which reduces the memory element's conductivity. By varying conductivity, multiple states can be created in the memory cell.
Owner:HEFEI RELIANCE MEMORY LTD
Magnetic tunnel junction with improved tunneling magneto-resistance
InactiveUS20050110004A1Improve featuresNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismInterface layerMagnetic memory
A magnetic tunnel element that can be used, for example, as part of a read head or a magnetic memory cell, includes a first layer formed from an amorphous material, an amorphous tunnel barrier layer, and an interface layer between the first layer and the tunnel barrier layer. The interface layer is formed from a material that is crystalline when the material is in isolation from both the first layer and the tunnel barrier layer. Alternatively, the thickness of the interface layer is selected so that the interface layer is not crystalline. The first layer is formed from at least one material selected from the group consisting of amorphous ferromagnetic material, amorphous ferrimagnetic materials, and amorphous non-magnetic materials. The interface layer is formed from a material selected from the group consisting of a ferromagnetic material and a ferrimagnetic material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Oxide films with nanodot flux pinning centers
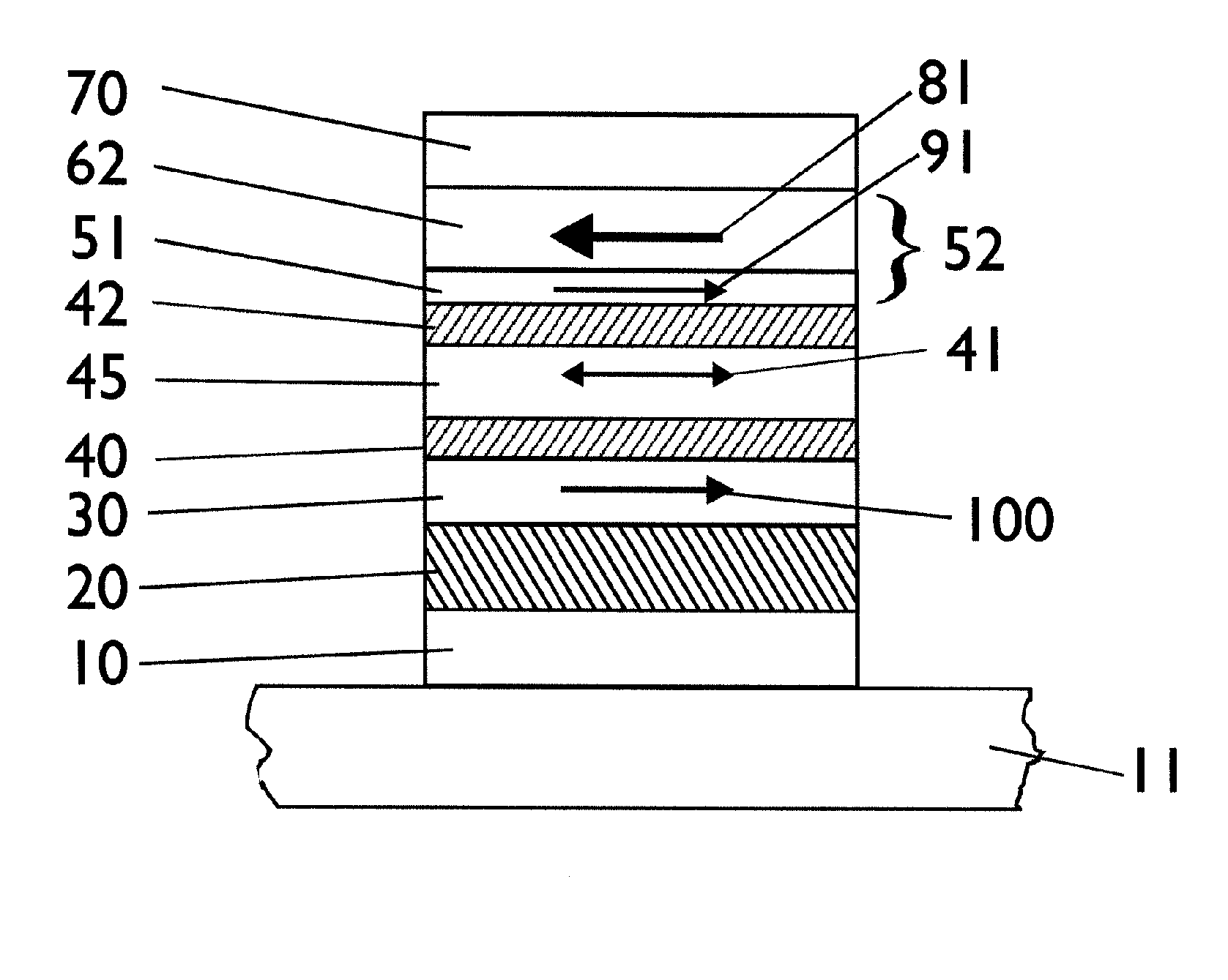
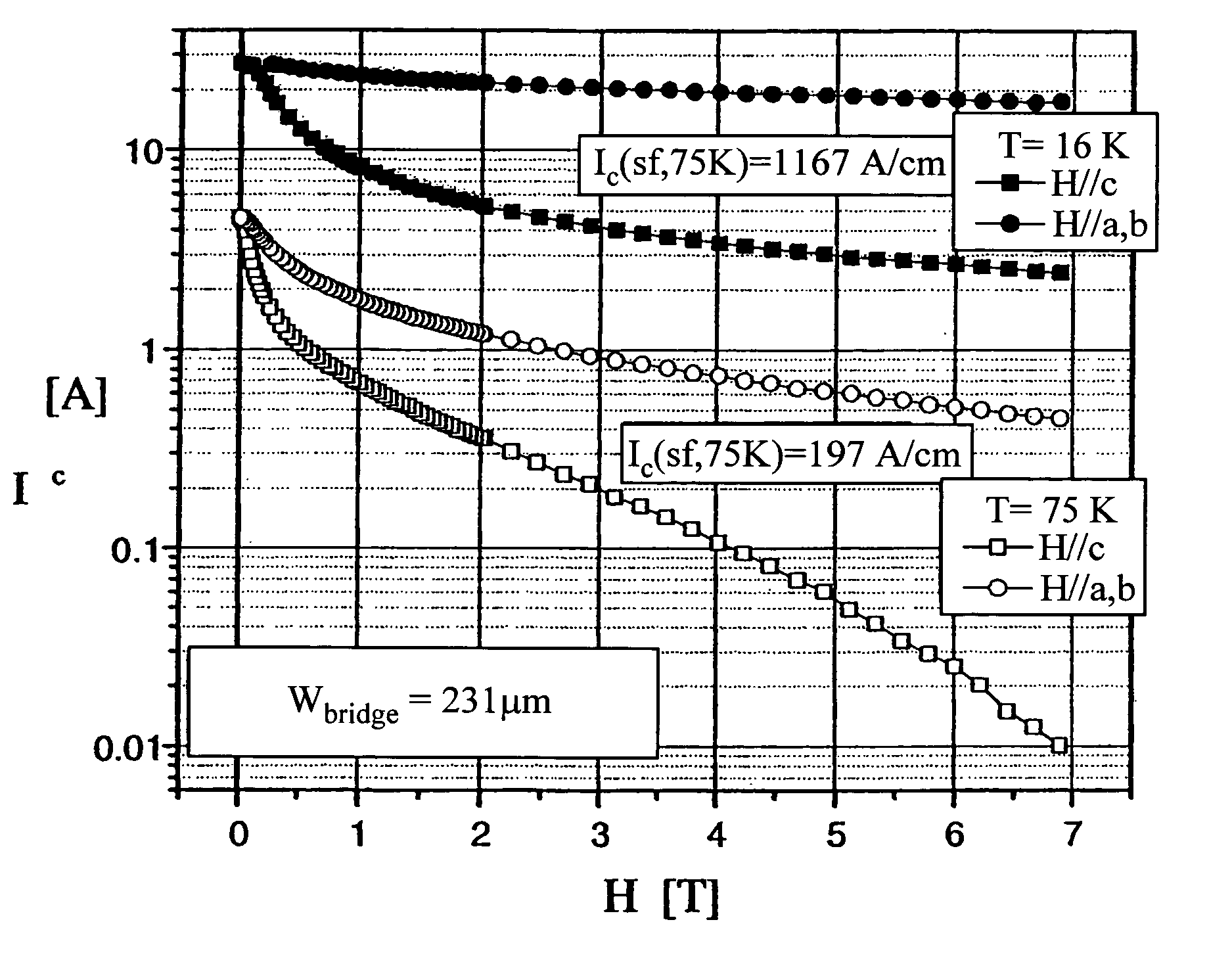
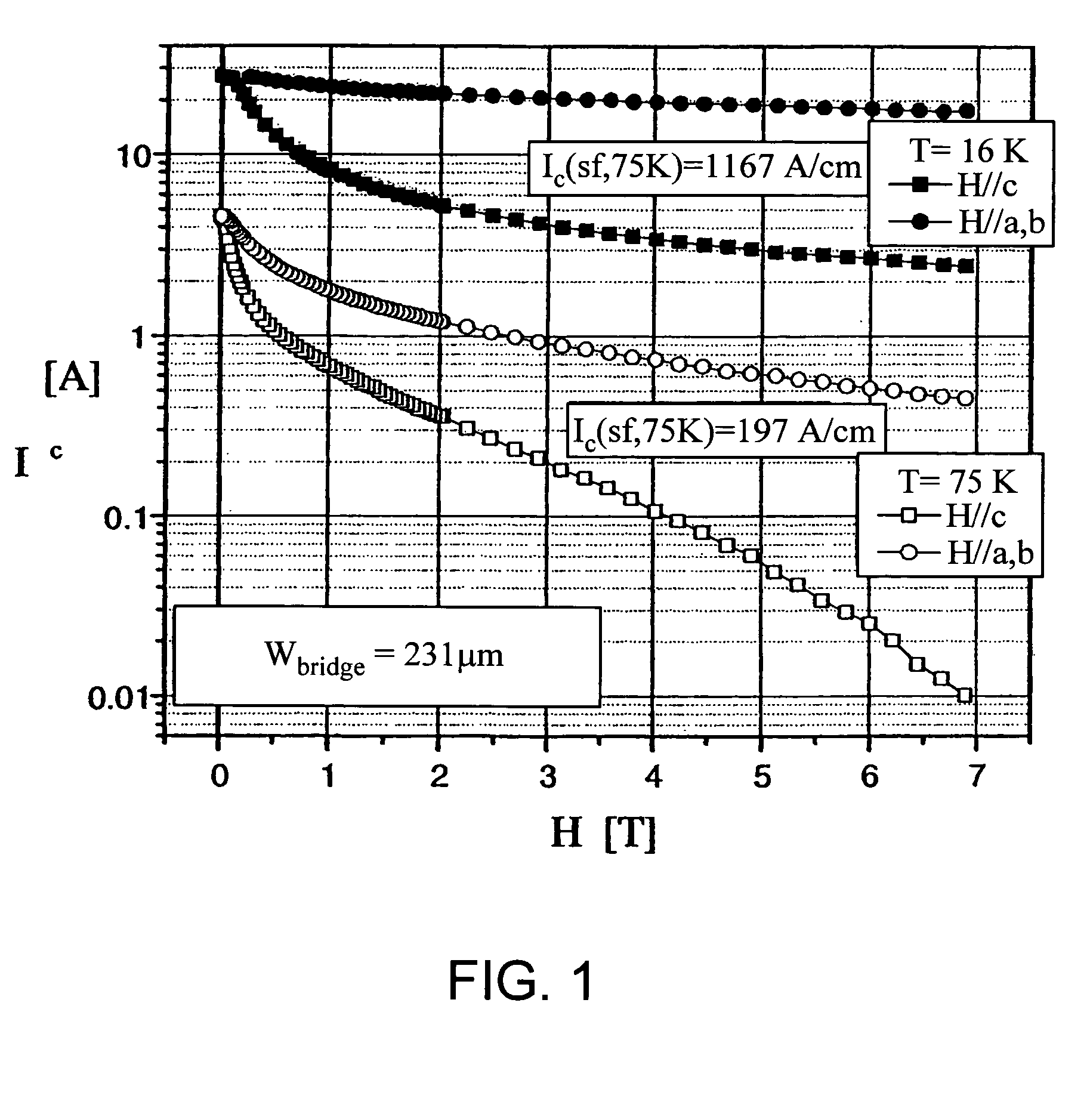
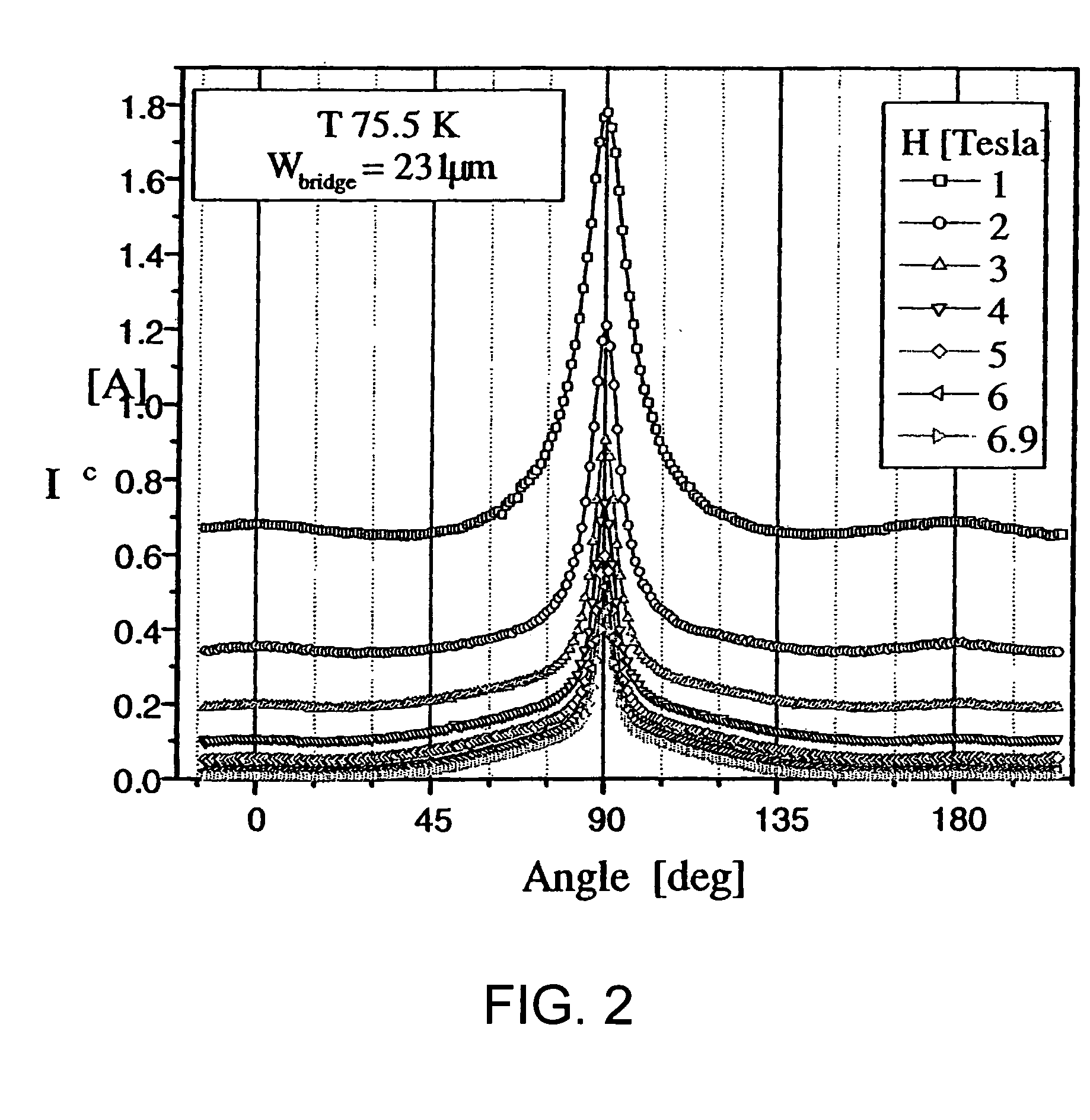
InactiveUS20050159298A1Increasing critical current densitySimple and versatileMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular sieve catalystsNanodotRare-earth element
A method for producing a thin film includes disposing a precursor solution onto a substrate to form a precursor film. The precursor solution contains precursor components to a rare-earth / alkaline-earth-metal / transition-metal oxide including a salt of a rare earth element, a salt of an alkaline earth metal, and a salt of a transition metal in one or more solvents, wherein at least one of the salts is a fluoride-containing salt. The precursor solution also contains an additive component comprising one or more metal compounds capable of forming a second phase nanoparticle, either alone or in combination with one or more of the precursor components of the precursor solution or a dopant component comprising one or more metal compounds capable of substituting for an element of the rare-earth / alkaline-earth-metal / transition-metal oxide, and treating the precursor film to form an intermediate metal oxyfluoride including the rare earth, the alkaline earth metal, the transition metal and the additive metal or dopant metal of the precursor solution.
Owner:AMERICAN SUPERCONDUCTOR
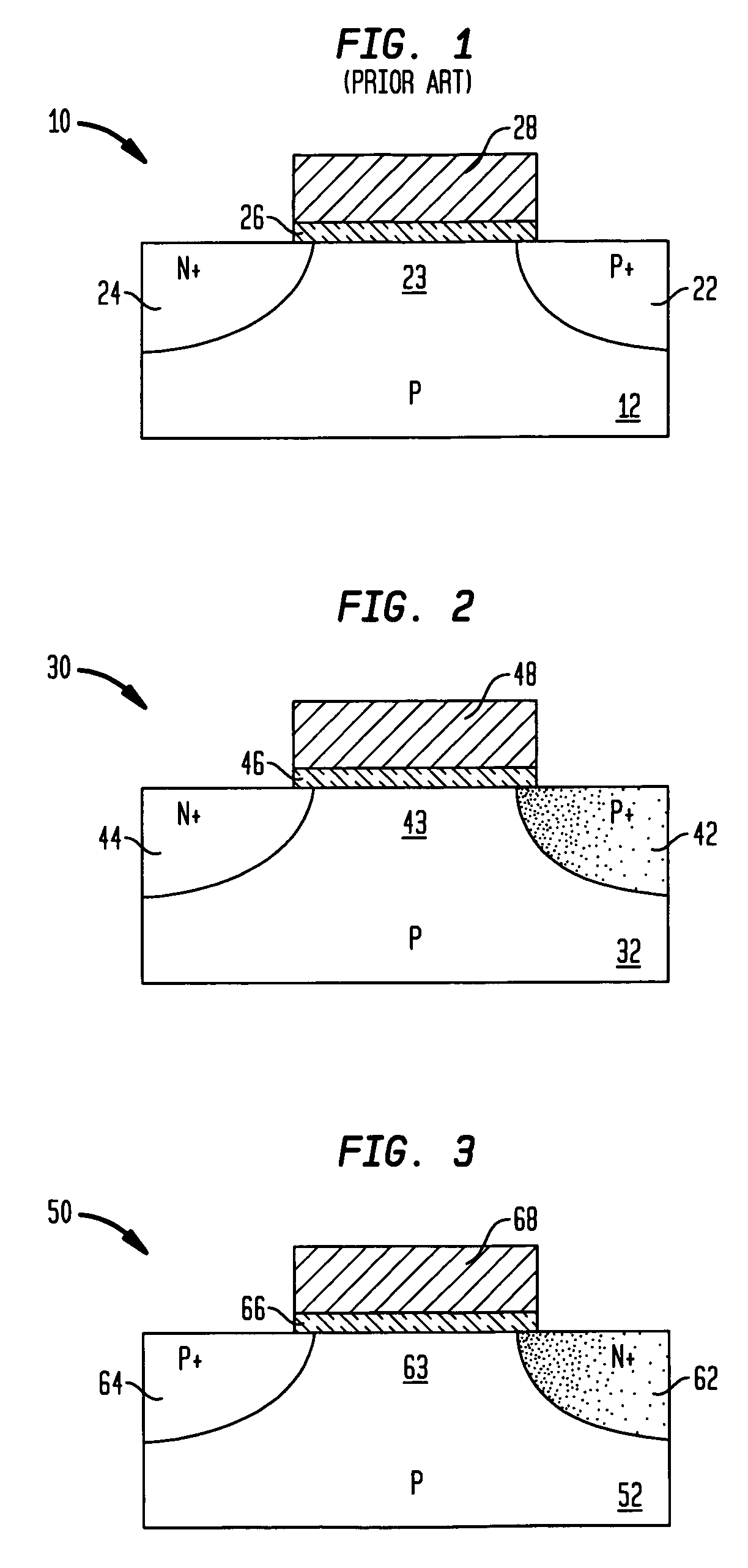
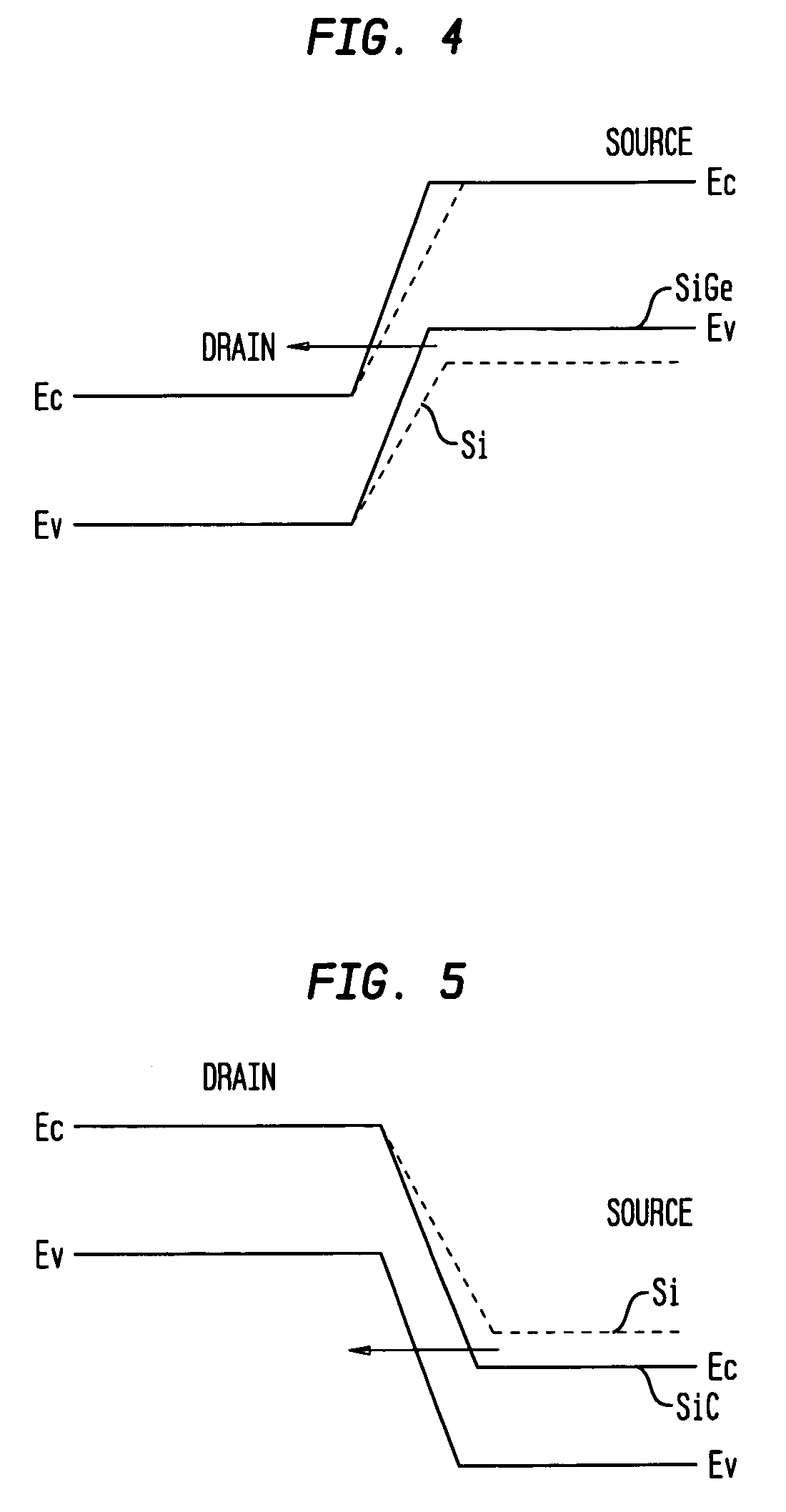
Heterojunction tunneling field effect transistors, and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070178650A1Increase currentEnhance junction currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeHeterojunctionDopant
The present invention relates to a heterojunction tunneling effect transistor (TFET), which comprises spaced apart source and drain regions with a channel region located therebetween and a gate stack located over the channel region. The drain region comprises a first semiconductor material and is doped with a first dopant species of a first conductivity type. The source region comprises a second, different semiconductor material and is doped with a second dopant species of a second, different conductivity type. The gate stack comprises at least a gate dielectric and a gate conductor. When the heterojunction TFET is an n-channel TFET, the drain region comprises n-doped silicon, while the source region comprises p-doped silicon germanium. When the heterojunction TFET is a p-channel TFET, the drain region comprises p-doped silicon, while the source region comprises n-doped silicon carbide.
Owner:IBM CORP
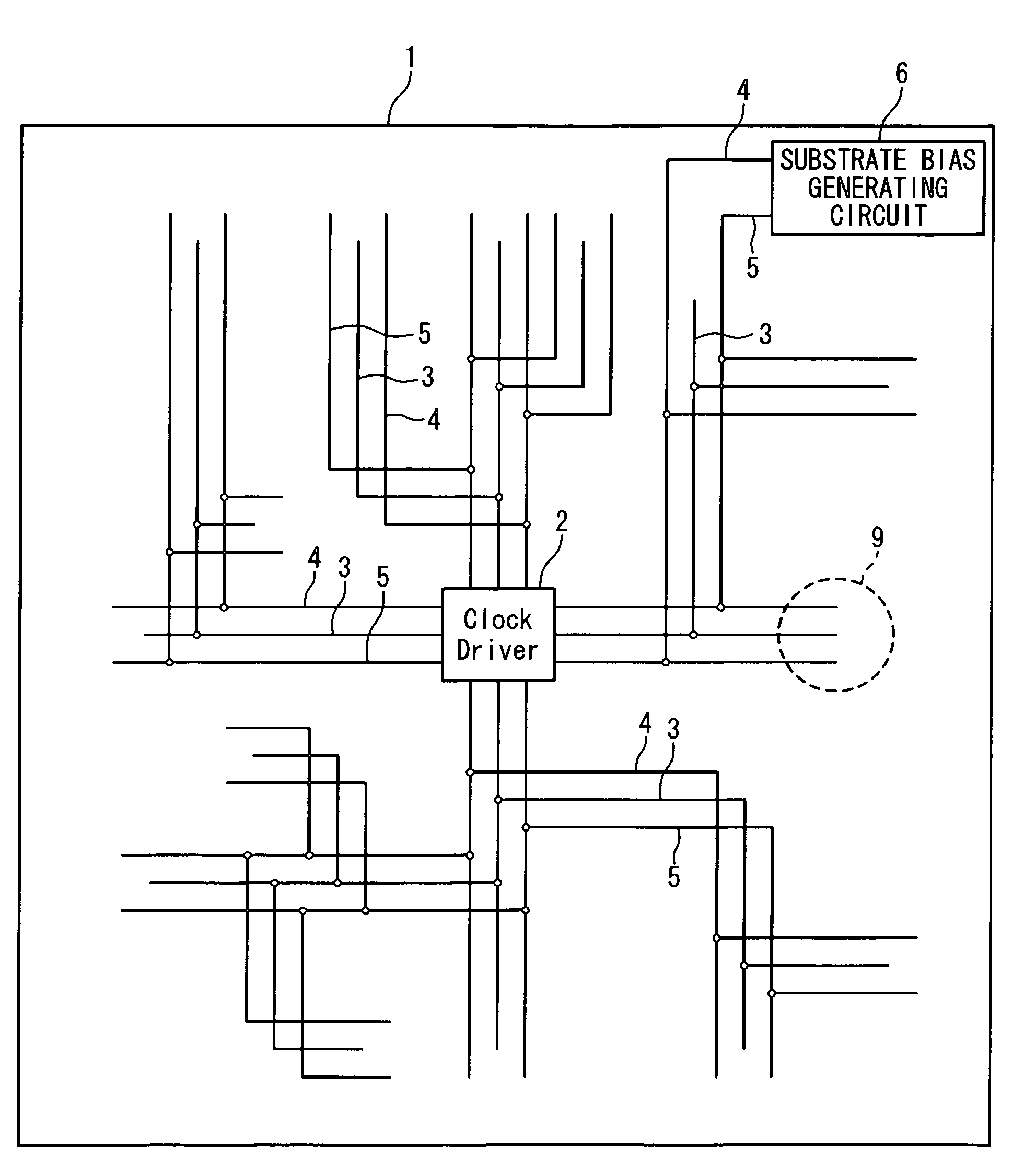
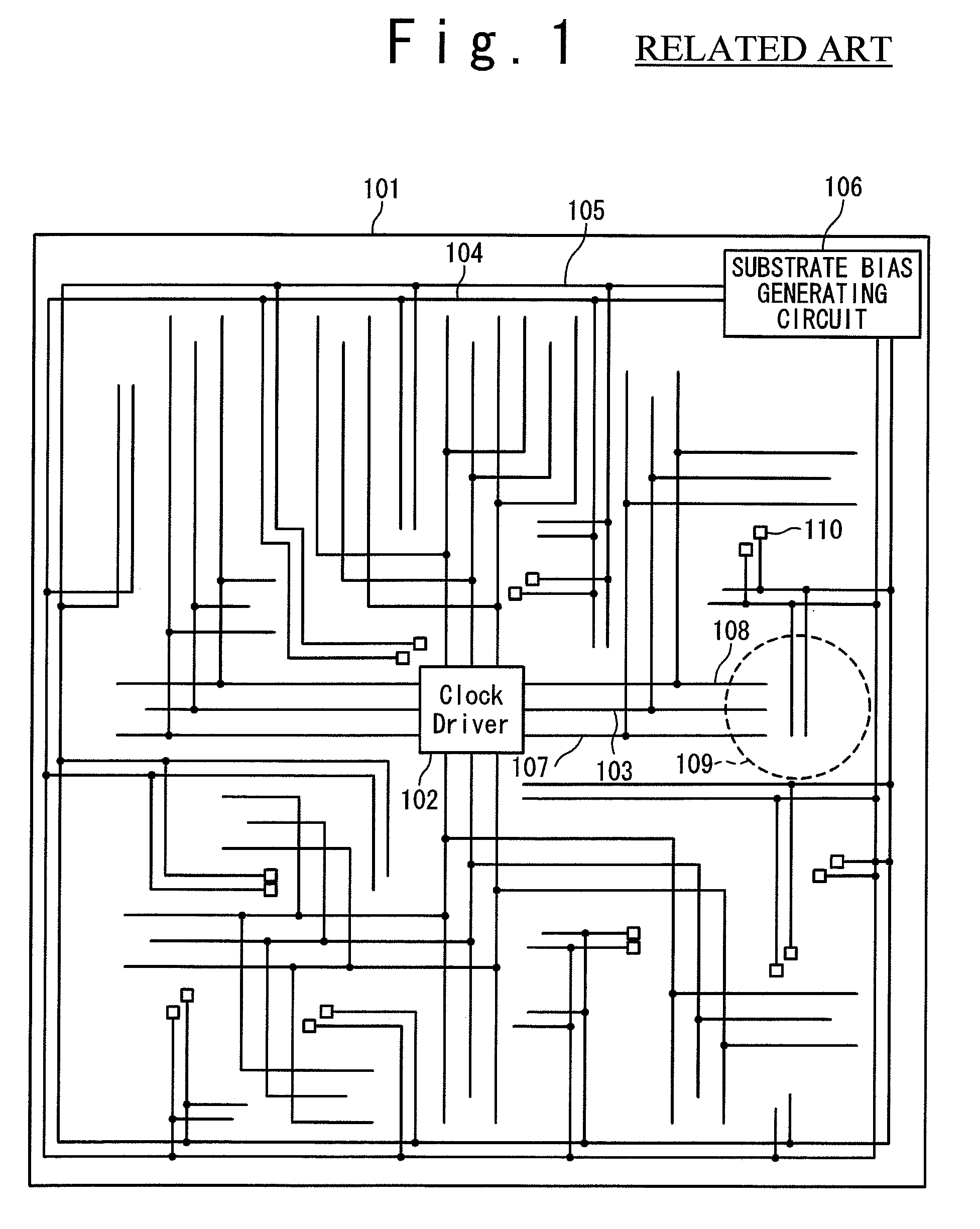
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7514766B2Advancement of hyperfine structureAvoid response delaysSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInterconnectionSemiconductor
A semiconductor device in which the threshold voltage of transistors is controlled through the applied substrate bias and having relatively small size. The semiconductor device includes: a clock signal line; a shield wiring for shielding the clock signal line from another interconnection; and a substrate bias generating circuit. The substrate bias is applied through the shield wiring to a region on which a transistor is formed. The threshold voltage of the transistor depends to the substrate bias applied to the transistor.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
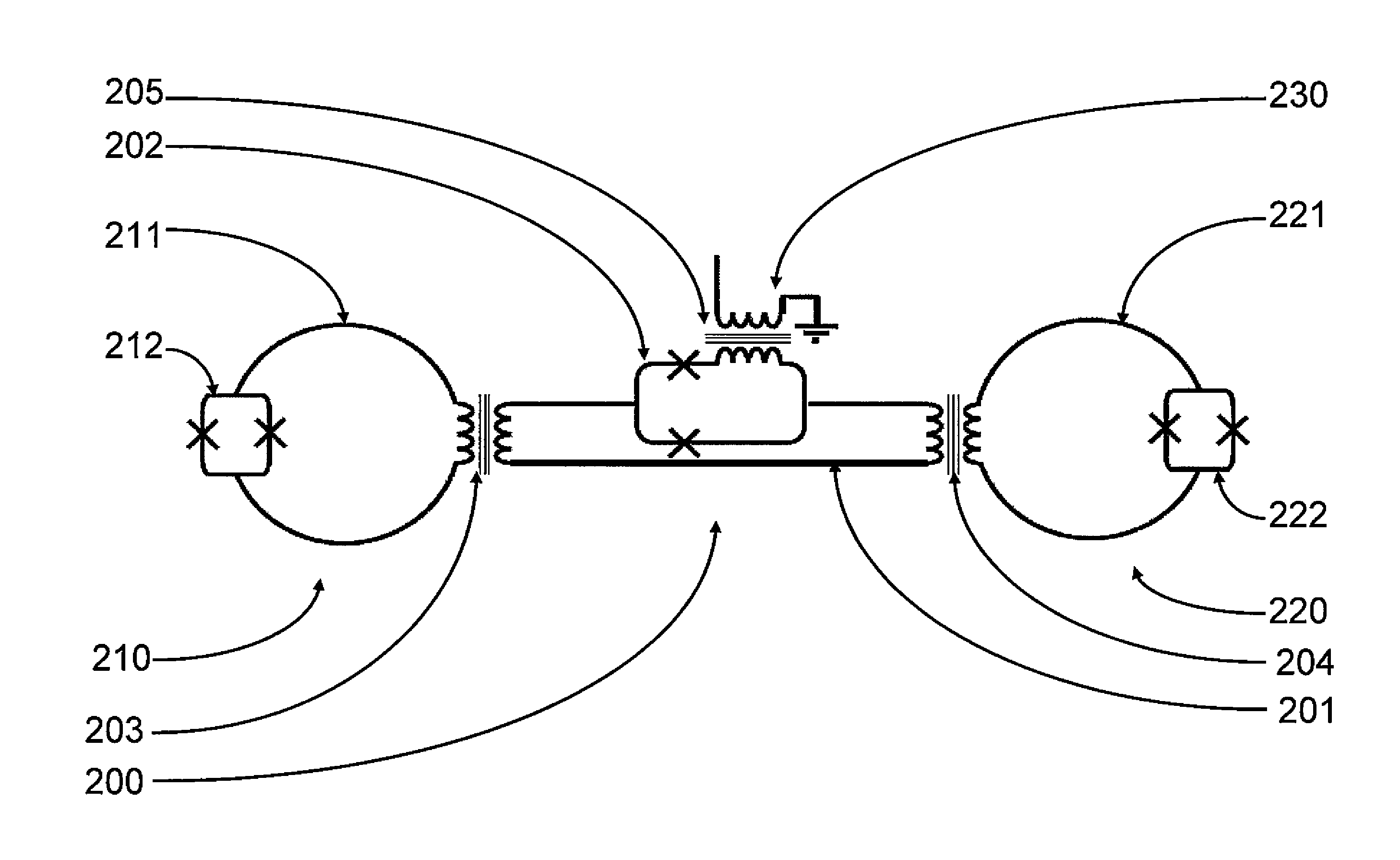
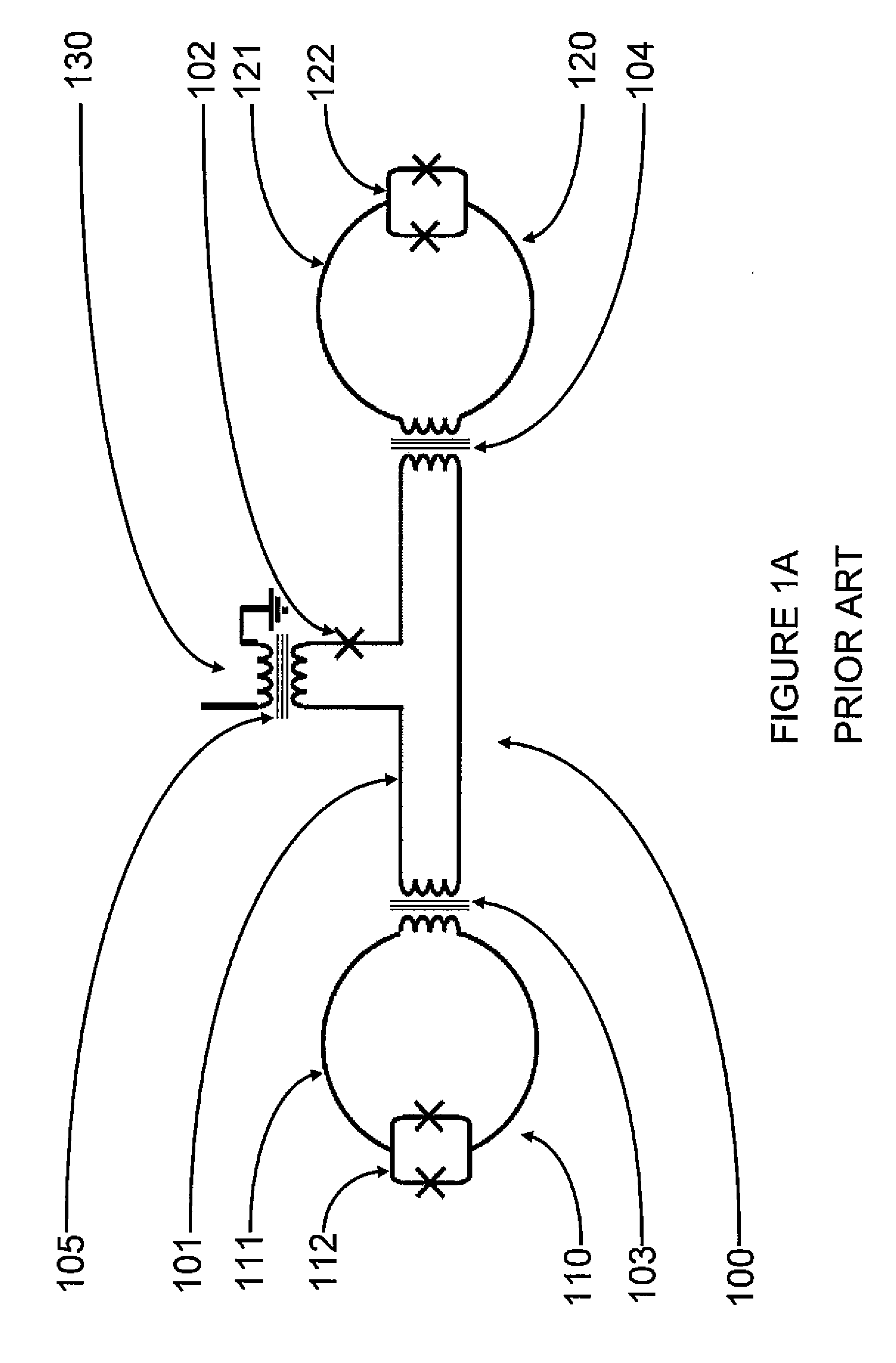
Coupling methods and architectures for information processing
A structure comprising (i) a first information device, (ii) a second information device, (iii) a first coupling element and (iv) a second coupling element is provided. The first information device has at least a first lobe and a second lobe that are in electrical communication with each other. The second information device and has at least a first lobe and a second lobe that are in electrical communication with each other. The first coupling element inductively couples the first lobe of the first information device to the first lobe of the second information device. The second coupling element inductively couples the first lobe of the first information device to the second lobe of the second information device.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Systems, devices, and methods for controllably coupling qubits
InactiveUS20080238531A1Improve drawing legibilityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsCoupling systemInductor
A coupling system may include an rf-SQUID having a loop of superconducting material interrupted by a compound Josephson junction; and a first magnetic flux inductor configured to selectively provide a mutual inductance coupling the first magnetic flux inductor to the compound Josephson junction, wherein the loop of superconducting material positioned with respect to a first and second qubits to provide respective mutual inductance coupling therebetween. The coupling system may further include a second magnetic flux inductor configured to selectively provide a second magnetic flux inductor mutual inductance coupling the second magnetic flux inductor to the compound Josephson junction. A superconducting processor may include the coupling system and two or more qubits. A method may include providing the first, the second and the third mutual inductances.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Vacuum jacket for phase change memory element
ActiveUS7449710B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBit linePhase-change memory
A memory device including a phase change element and a vacuum jacket. The device includes a first electrode element; a phase change element in contact with the first electrode element; an upper electrode element in contact with the phase change element; a bit line electrode in contact with the upper electrode element; and a dielectric fill layer surrounding the phase change element and the upper electrode element, spaced from the same and sealed by the bit line electrode to define a vacuum jacket around the phase change element and upper electrode element.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
MgO-based tunnel spin injectors
InactiveUS7274080B1High polarizationImprove thermal stabilityNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsCharge carrier
A MgO tunnel barrier is sandwiched between semiconductor material on one side and a ferri- and / or ferromagnetic material on the other side to form a spintronic element. The semiconductor material may include GaAs, for example. The spintronic element may be used as a spin injection device by injecting charge carriers from the magnetic material into the MgO tunnel barrier and then into the semiconductor. Similarly, the spintronic element may be used as a detector or analyzer of spin-polarized charge carriers by flowing charge carriers from the surface of the semiconducting layer through the MgO tunnel barrier and into the (ferri- or ferro-) magnetic material, which then acts as a detector. The MgO tunnel barrier is preferably formed by forming a Mg layer on an underlayer (e.g., a ferromagnetic layer), and then directing additional Mg, in the presence of oxygen, towards the underlayer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Quantum processor based systems and methods that minimize an objective function
ActiveUS20140187427A1Accurate solutionQuick mergeQuantum computersMathematical modelsAlgorithmHigh probability
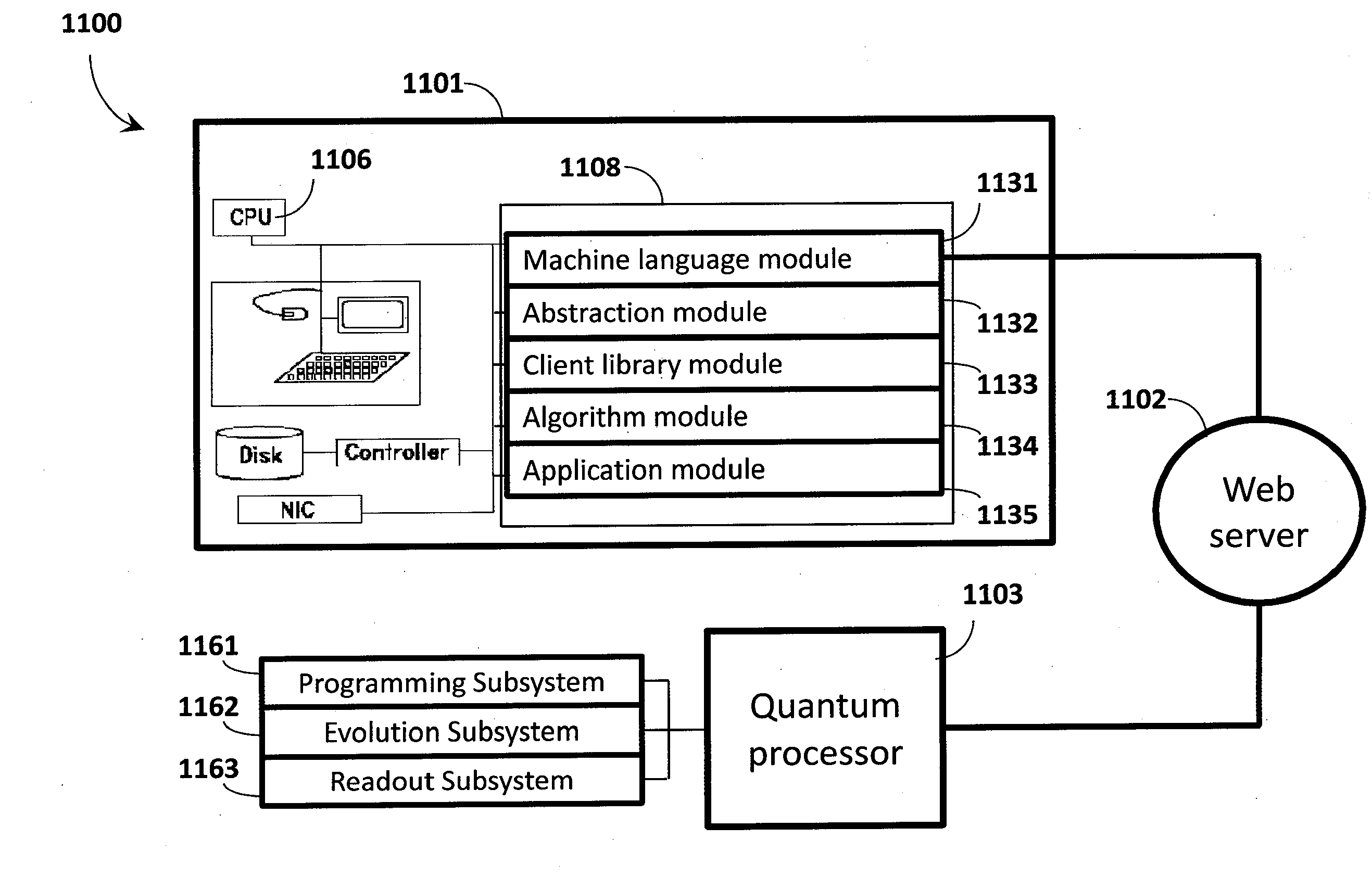
Quantum processor based techniques minimize an objective function for example by operating the quantum processor as a sample generator providing low-energy samples from a probability distribution with high probability. The probability distribution is shaped to assign relative probabilities to samples based on their corresponding objective function values until the samples converge on a minimum for the objective function. Problems having a number of variables and / or a connectivity between variables that does not match that of the quantum processor may be solved. Interaction with the quantum processor may be via a digital computer. The digital computer stores a hierarchical stack of software modules to facilitate interacting with the quantum processor via various levels of programming environment, from a machine language level up to an end-use applications level.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Chemically synthesized and assembled electronic devices
InactiveUS20010054709A1Simple and inexpensive implementationMaterial nanotechnologyElectronic circuit testingSignal routingChemical synthesis
A route to the fabrication of electronic devices is provided, in which the devices consist of two crossed wires sandwiching an electrically addressable molecular species. The approach is extremely simple and inexpensive to implement, and scales from wire dimensions of several micrometers down to nanometer-scale dimensions. The device of the present invention can be used to produce crossbar switch arrays, logic devices, memory devices, and communication and signal routing devices. The present invention enables construction of molecular electronic devices on a length scale than can range from micrometers to nanometers via a straightforward and inexpensive chemical assembly procedure. The device is either partially or completely chemically assembled, and the key to the scaling is that the location of the devices on the substrate are defined once the devices have been assembled, not prior to assembly.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO +1
High speed multi-stage switching network formed from stacked switching layers
InactiveUS6829237B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsImage analysisExchange networkHigh velocity
A compact multi-stage switching network (100), and a router (510) incorporating such multi-stage switching network, adapted for simultaneously routing a plurality of data packets from a first plurality of input ports (110) to selected ones of a second plurality of output ports (190) comprising: a first stack (140) of IC switching layers (113) that are stacked in physical contact with one another, each IC switching layer containing at least one switching element circuit (142); a second stack (160) of IC switching layers (113) that are stacked in physical contact with one another, each IC switching layer (113) containing at least one switching element circuit (162); and interconnecting circuitry (150) that connects the first stack (140) of IC layers to the second stack (160) of IC layers to form the compact multi-stage switching network. The stacks (140, 160) are preferably mated to one another in a transverse fashion in order to achieve a natural full-mesh connection. Also contemplated are the use of superconducting IC switching circuits (142) and a suitable superconducting cooling housing (730), as permitted by the compact nature of the multi-stage switching network (100), in order to operate at high speed and low power.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
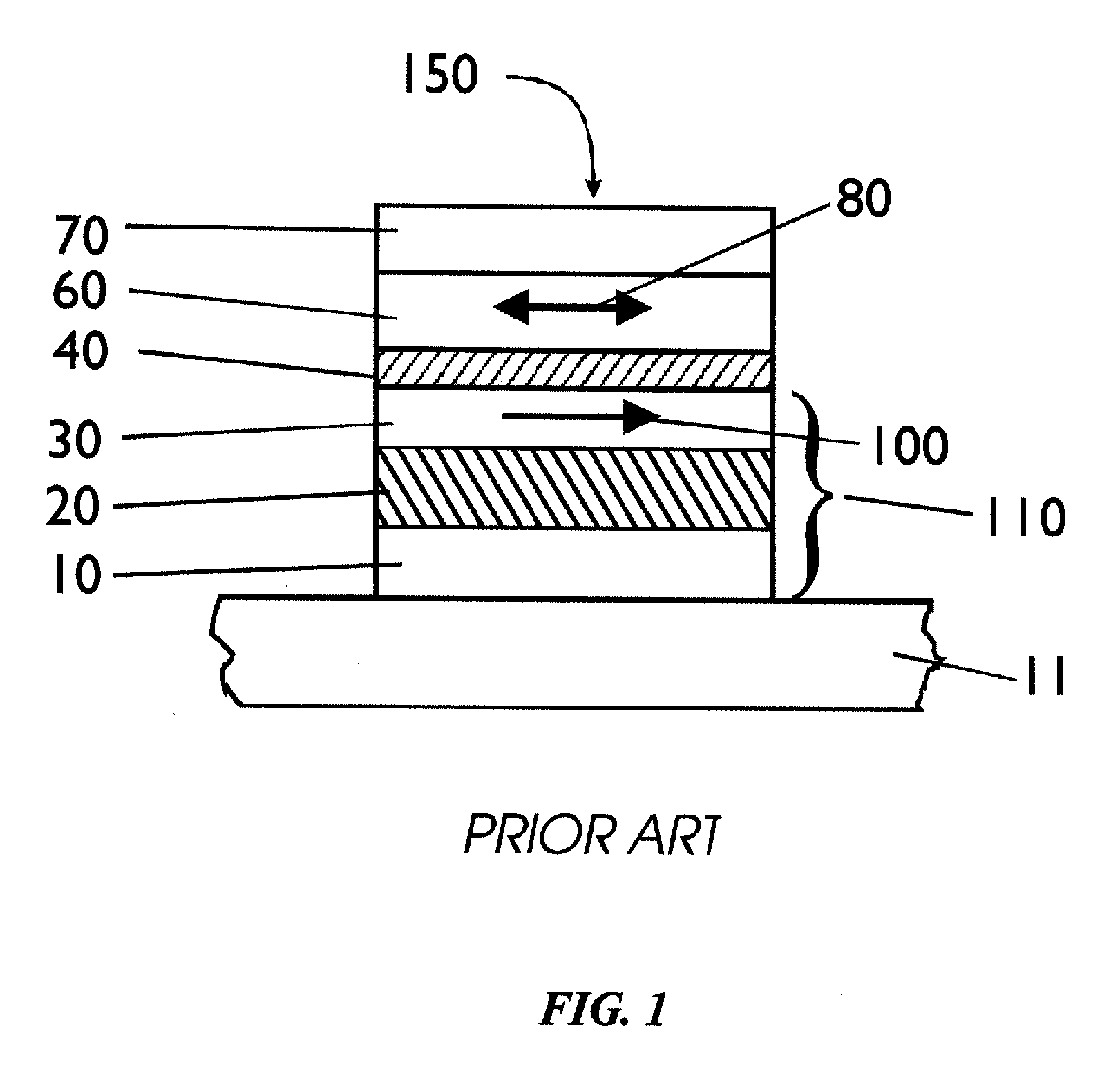
Multilayer thin film
InactiveUS6258459B1High crystallinityIncrease the buffer functionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCrystallinityMaterials science
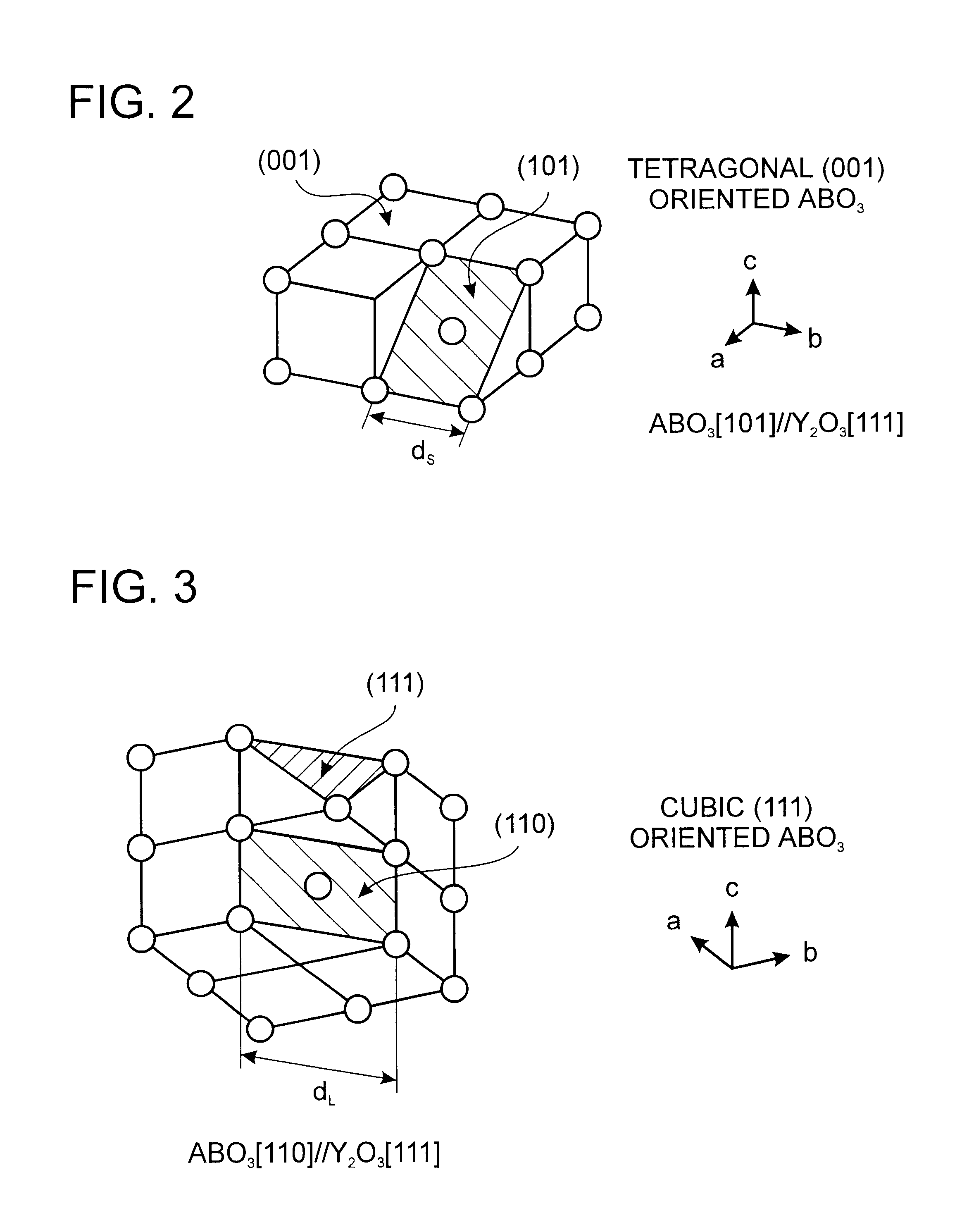
The first object of the invention is to provide means that enables a perovskite oxide thin film having (100) orientation, (001) orientation or (111) orientation to be easily obtained, and the second object of the invention is to provide a multilayer thin film comprising a unidirectionally oriented metal thin film of good crystallinity. The multilayer thin film according to the first embodiment of the invention comprises a buffer layer and a perovskite oxide thin film present thereon. The interface between the buffer layer and the perovskite oxide thin film is made up of a {111} facet plane. Substantially parallel to the facet plane there is present a {110} face of a cubic, rhombohedral, tetragonal or orthorhombic crystal of the perovskite oxide thin film, a {101} face of the tetragonal or orthorhombic crystal or a {011} face of the orthorhombic crystal. The multilayer thin film according to the second embodiment of the invention comprises a metal thin film that is a cubic (100) unidirectionally oriented epitaxial film, and a buffer layer where a {111} facet plane is present on the interface of the buffer layer in contact with the metal thin film.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Tunneling transistor suitable for low voltage operation
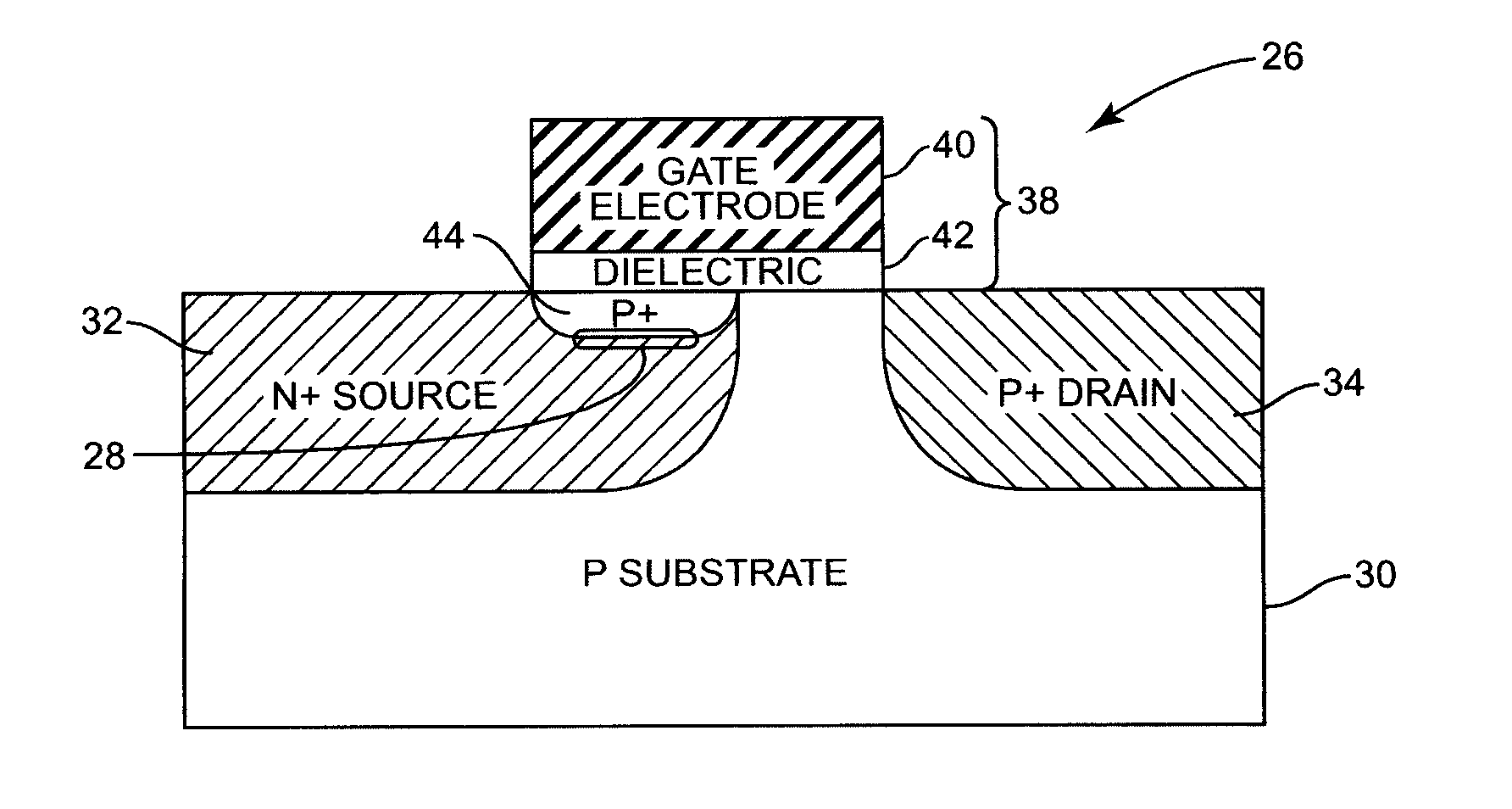
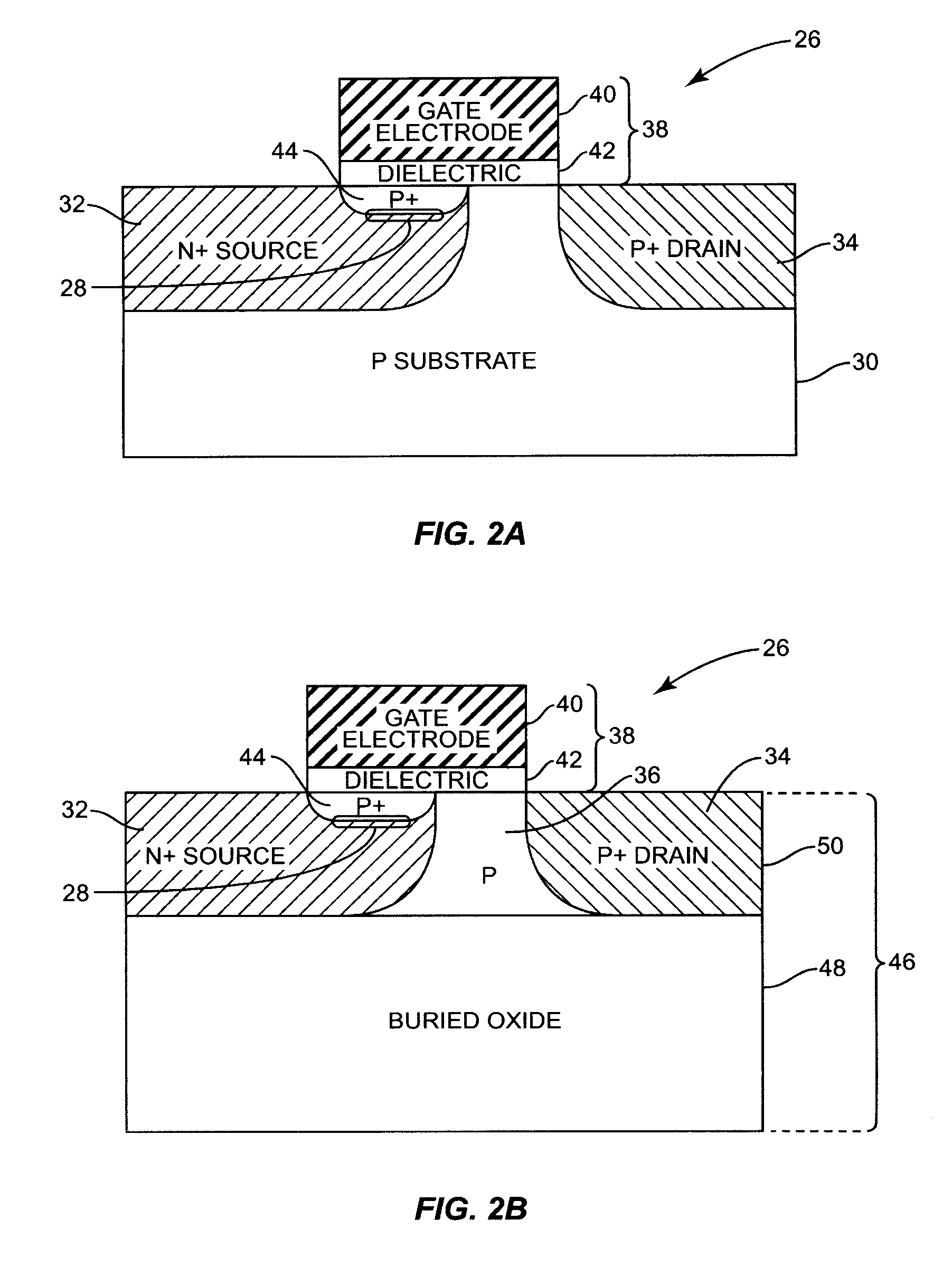
InactiveUS8384122B1Increase the on-currentOn-current of the tunneling transistor is substantially improvedNanotechnologySuperconductor devicesLow voltageEngineering
Several embodiments of a tunneling transistor are disclosed. In one embodiment, a tunneling transistor includes a semiconductor substrate, a source region formed in the semiconductor substrate, a drain region formed in the semiconductor substrate, a gate stack including a metallic gate electrode and a gate dielectric, and a tunneling junction that is substantially parallel to an interface between the metallic gate electrode and the gate dielectric. As a result of the tunneling junction that is substantially parallel with the interface between the metallic gate electrode and the gate dielectric, an on-current of the tunneling transistor is substantially improved as compared to that of a conventional tunneling transistor. In another embodiment, a tunneling transistor includes a heterostructure that reduces a turn-on voltage of the tunneling transistor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Inter-chip ESD protection structure for high speed and high frequency devices
ActiveUS20070029646A1Reduce load capacitanceImprove system performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringHigh velocity
The present invention relates to inter-chip electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection structures for high speed, and high frequency devices that contain one or more direct, inter-chip signal transmission paths. Specifically, the present invention relates to a structure that contains: (1) a first chip including a first circuit, (2) a second chip including a second circuit, (3) an intermediate insulator layer located between the first and second chips, wherein the first and second circuits form a signal transmission path for transmitting signals through the intermediate insulator layer. An electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection path is provided in the structure between the first and the second chip through the intermediate insulator layer, to protect the signal transmission path from ESD damages.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Magnetic field measurement system and optical pumping magnetometer
ActiveUS7656154B2Reduce magnetic noiseAffect operationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectricityComing out
Provided is a highly accurate optical pumping magnetometer, in which a static magnetic field and an oscillating field to be applied to a vapor cell are stabilized. To this end, the optical pumping magnetometer includes: Helmholtz coils for applying a constant static magnetic field to a vapor cell serving as a magnetic field detector; fluxgate magnetometers for detecting environmental magnetic noise in two directions of X-axis direction and Y-axis direction other than Z-axis direction which is a direction for detecting a magnetic field coming out of a measurement object while locating the vapor cell in the center thereof; magnetometer drive circuits for driving the fluxgate magneotometers; current converters for converting outputs of the magnetometer drive circuits into amount of currents; and magnetic field generating coils for generating a magnetic field in a phase opposite to the environmental magnetic noise in the two directions.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Multiple SQUID magnetometer
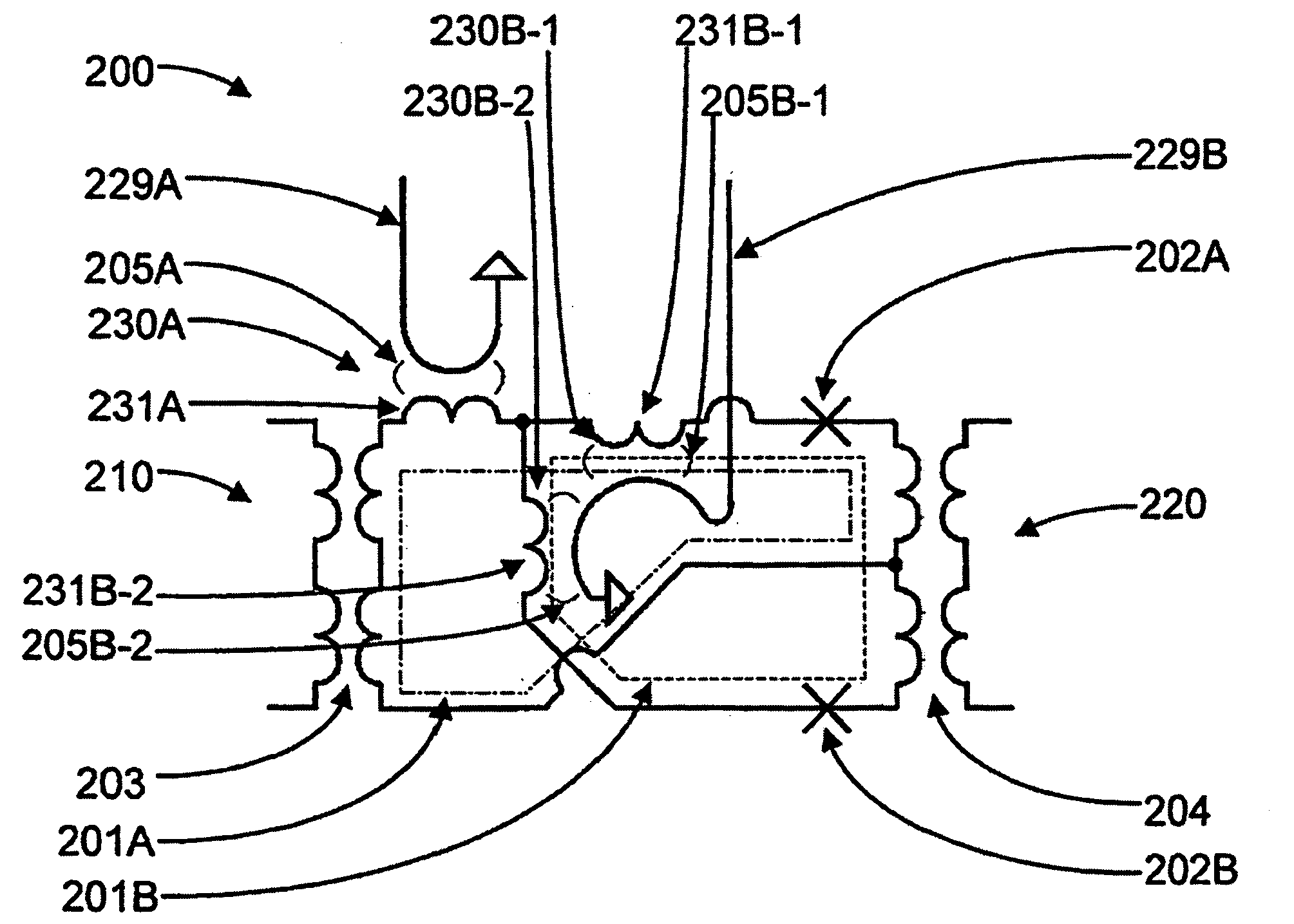
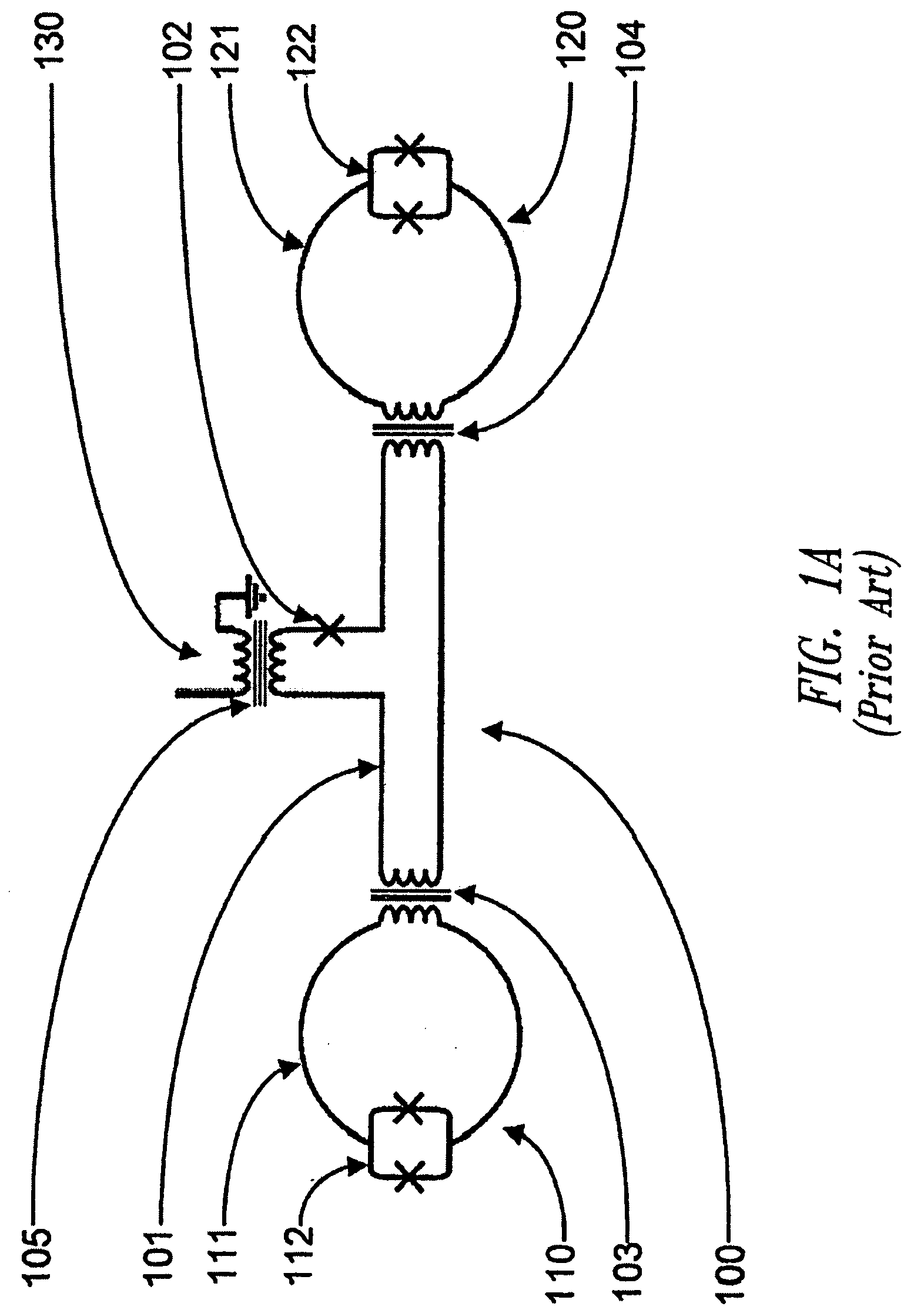
InactiveUS20070241747A1Avoid complicationsHigh sensitivitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesCondensed matter physicsSQUID
Multiple SQUID magnetometers that include at least two SQUID loops, each of which is composed of at least two Josephson Junctions connected in parallel with superconducting wires, are provided. The SQUID loops are fabricated such that they share a common Josephson Junction. Devices and application that employ the multiple SQUID magnetometers are also provided.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Cooling system and method for cooling superconducting magnet devices
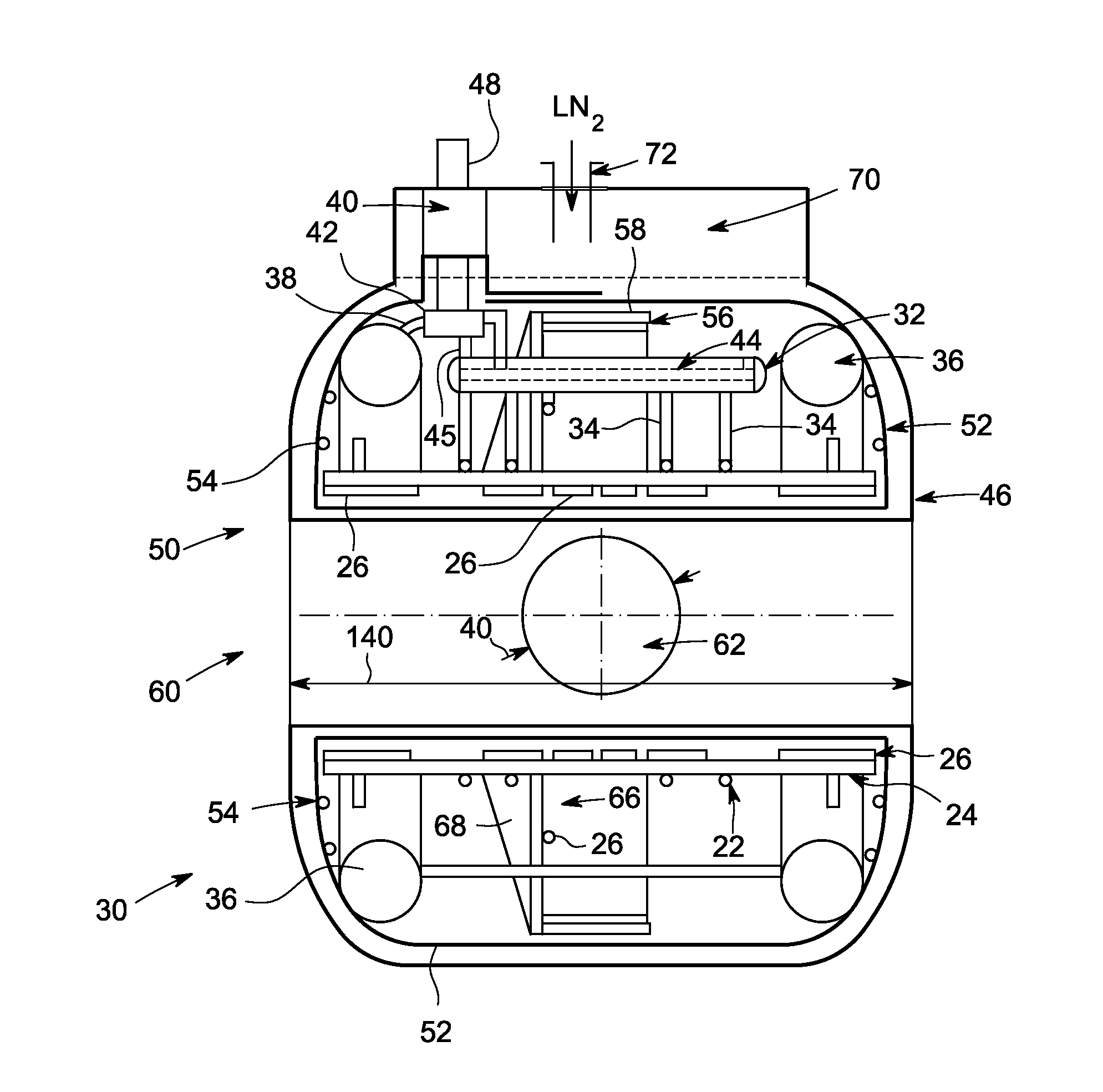
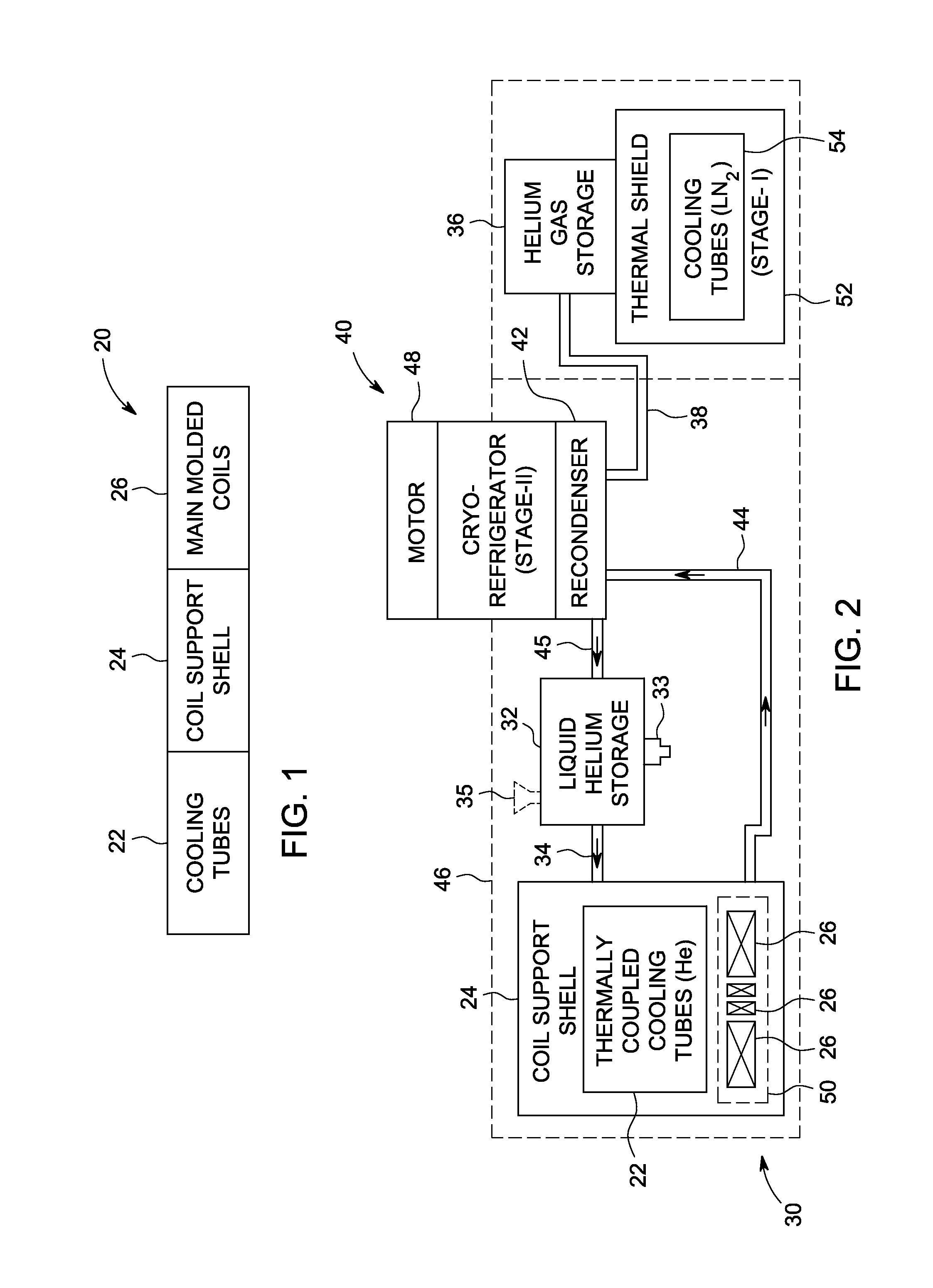
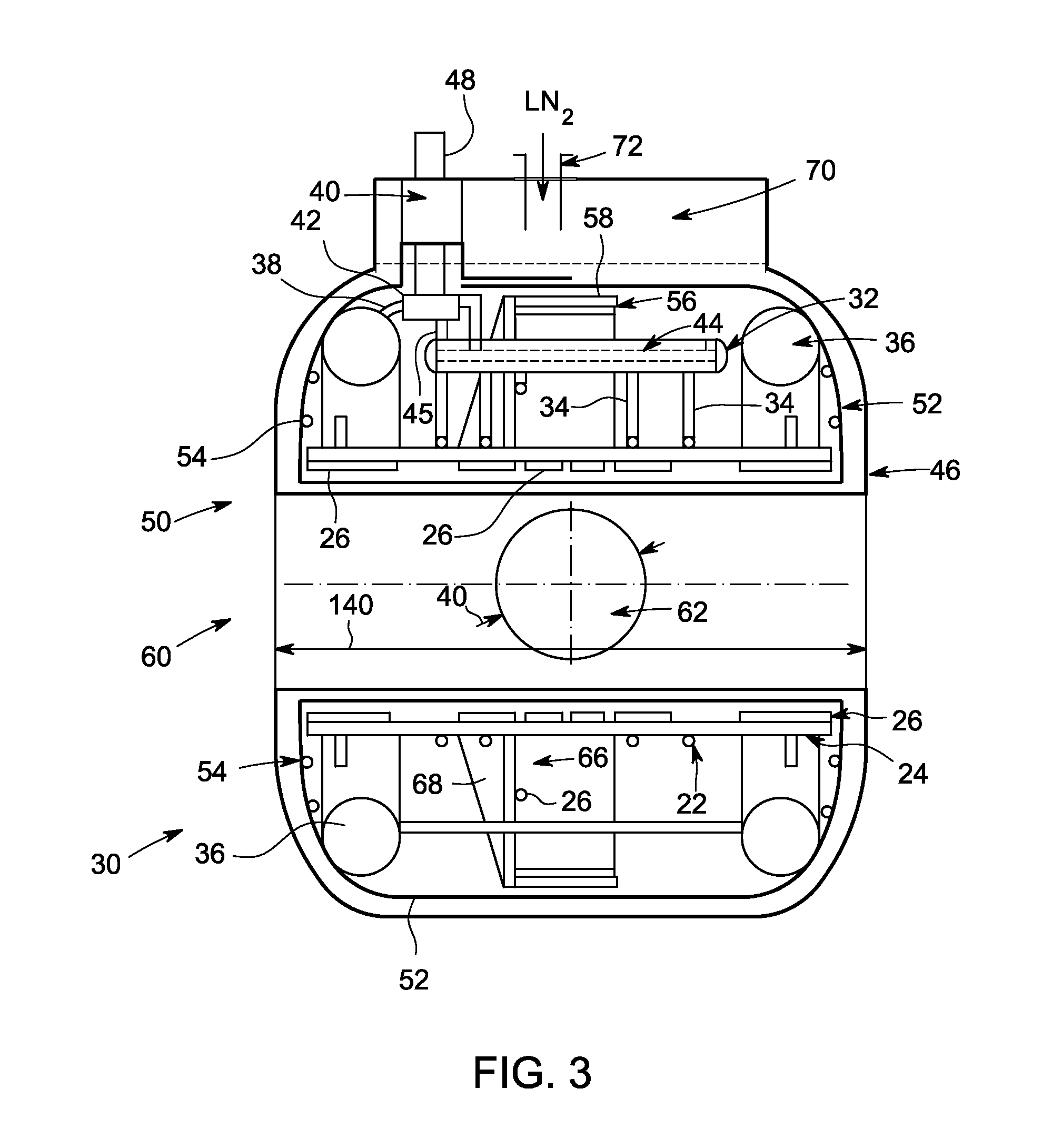
A cooling system and method for cooling superconducting magnet coils are provided. One magnet system for a superconducting magnet device includes a cooling system having at least one coil support shell, a plurality of superconducting magnet coils supported by the at least one coil support shell and a plurality of cooling tubes thermally coupled to the at least one coil support shell. The magnet system also includes a cryorefrigerator system fluidly coupled with the plurality of cooling tubes forming a closed circulation cooling system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
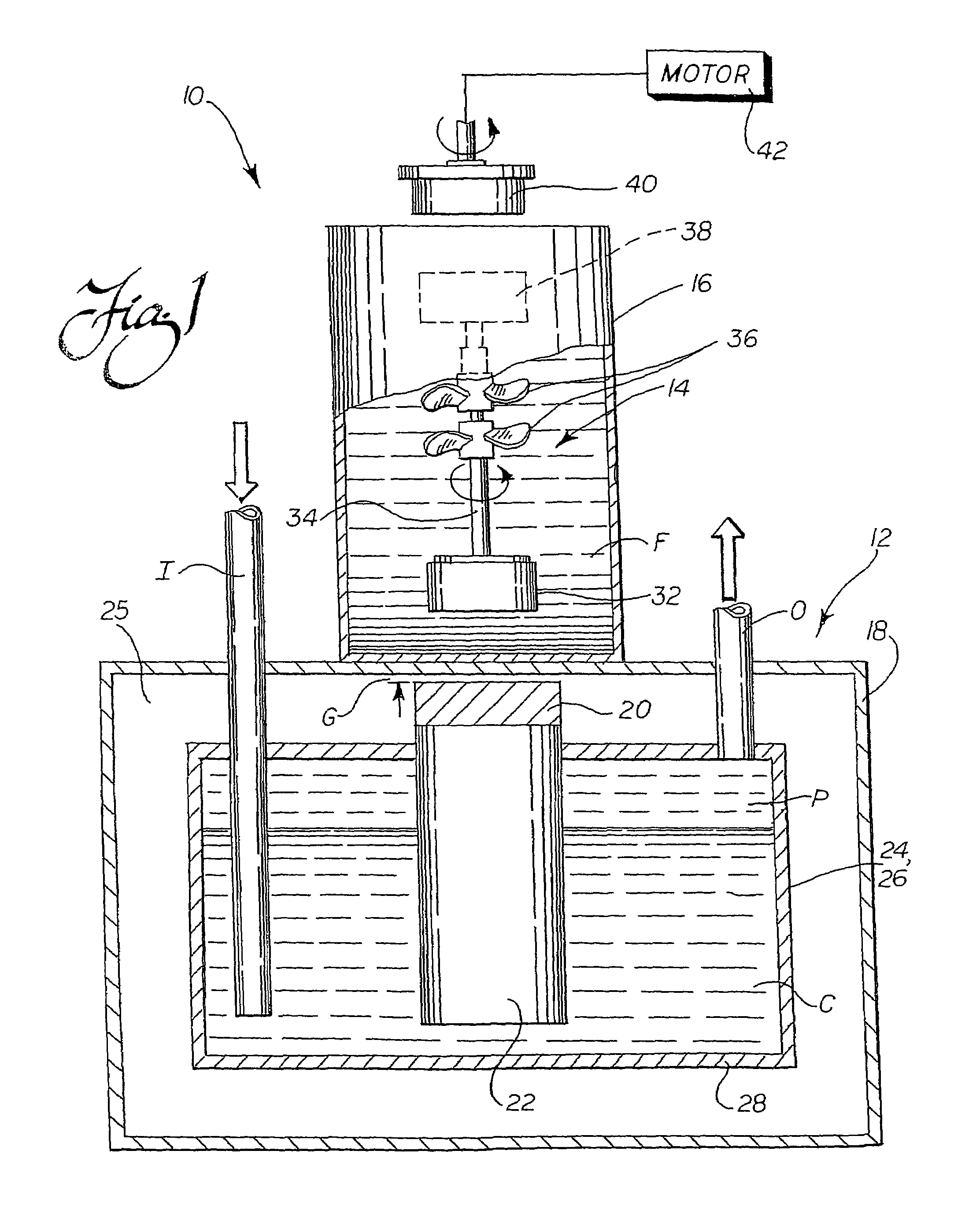
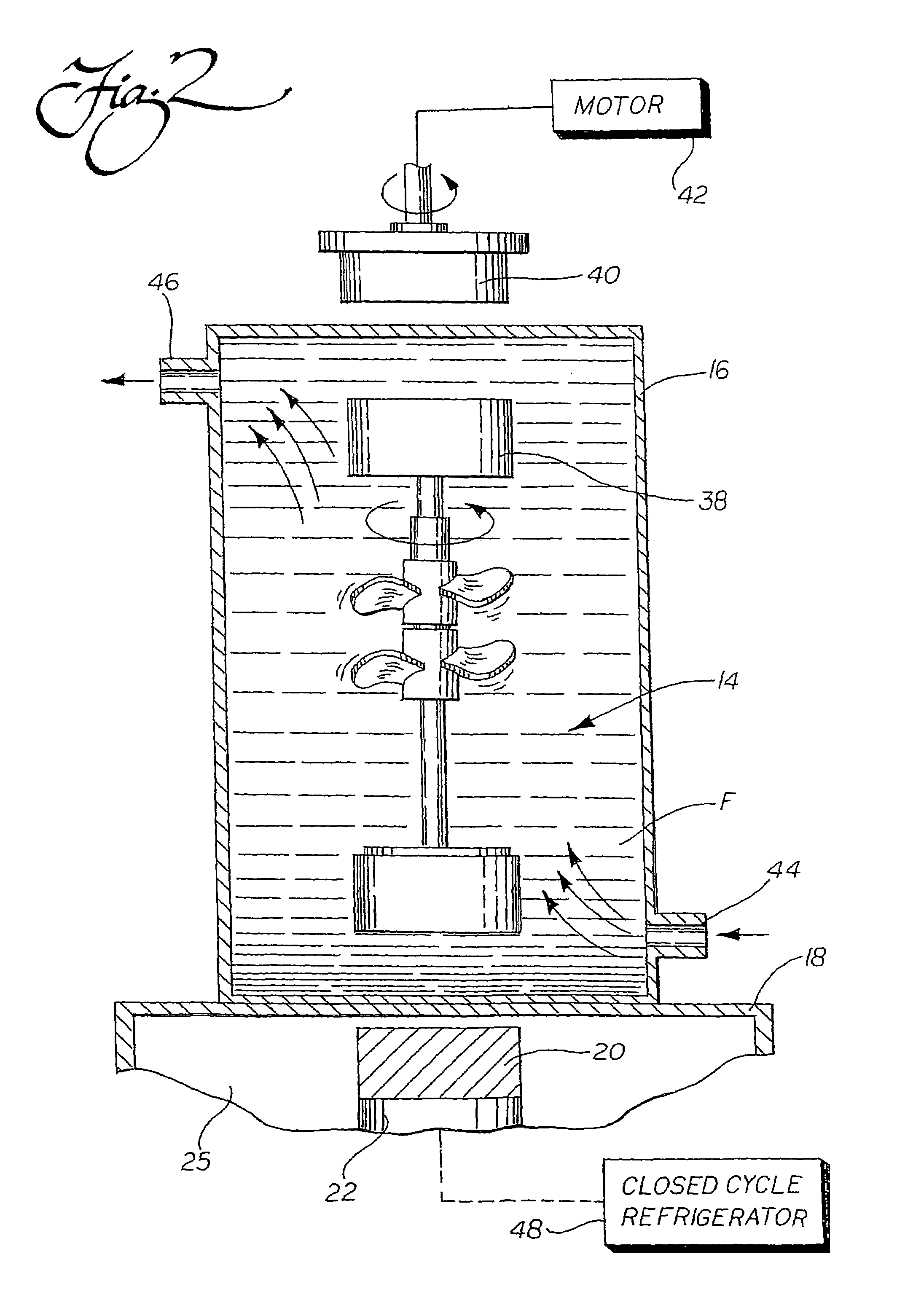
System using a levitating, rotating pumping or mixing element and related methods
InactiveUS7086778B2Eliminate deleterious thermal transferPrecise positioningShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersFlow mixersLevitationEngineering
A system for pumping or mixing a fluid using a levitating, rotating pumping or mixing element and various other components for use in a pumping or mixing system are disclosed. The pumping or mixing element is placed in a fluid-containing vessel in close proximity to a superconducting element. A cooling source thermally linked to the superconducting element provides the necessary cooling to induce levitation in the pumping or mixing element. The superconducting element may be thermally isolated, such that the pumping or mixing element, the vessel, and any fluid contained therein are not exposed to the cold temperatures required to produce the desired superconductive effects and the resulting levitation. By using means external to the vessel to rotate and / or stabilize the pumping or mixing element levitating in the fluid, including possibly rotating the superconducting element itself or moving it relative to the vessel, the desired effective pumping or mixing action may be provided.
Owner:PALL TECH UK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com