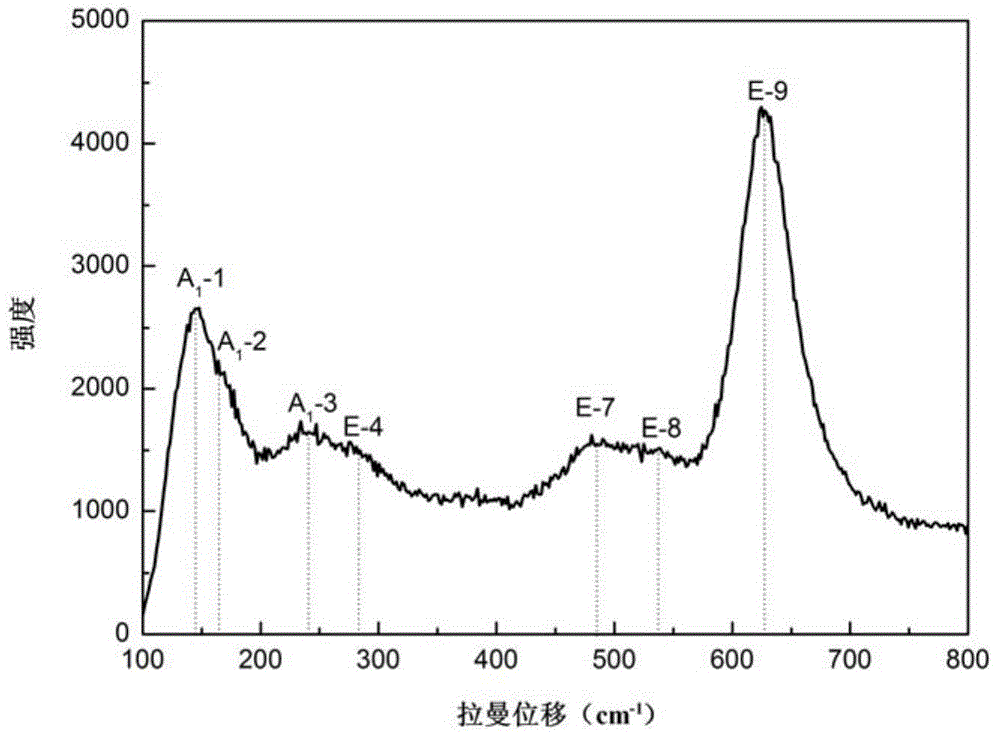
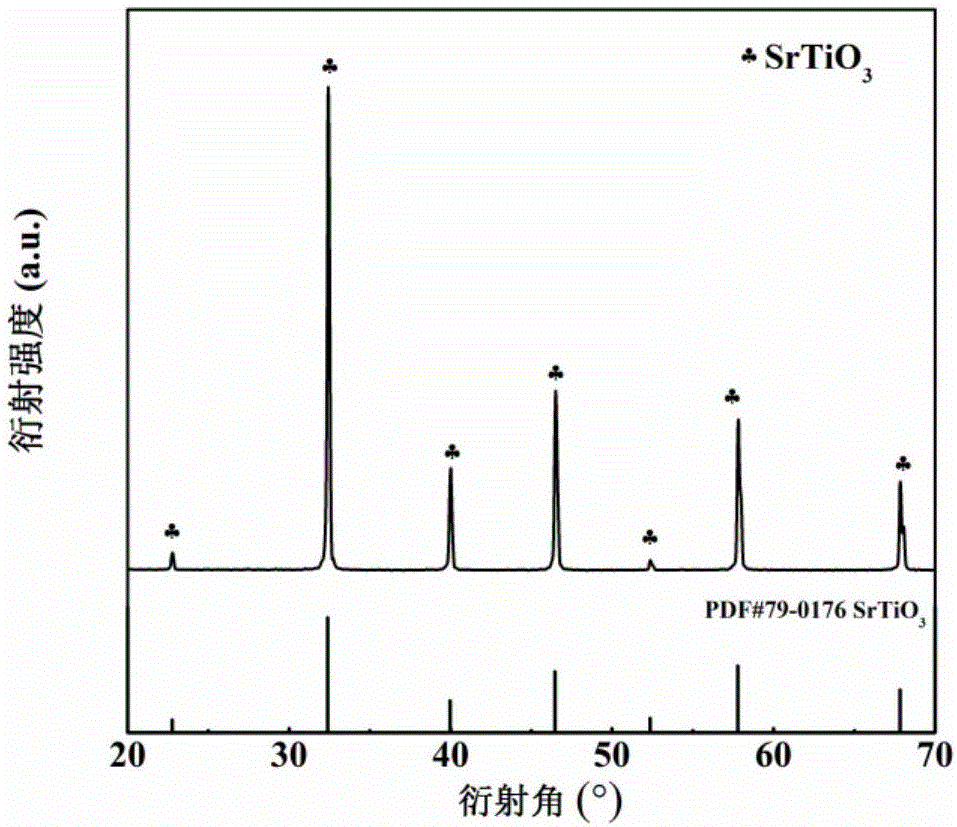
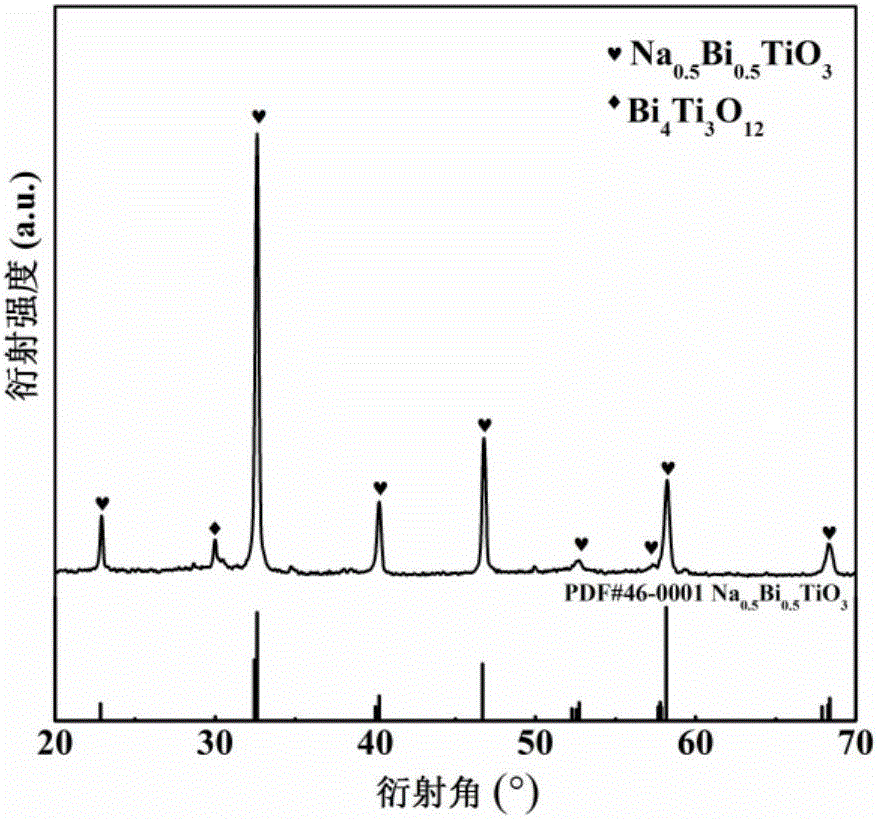
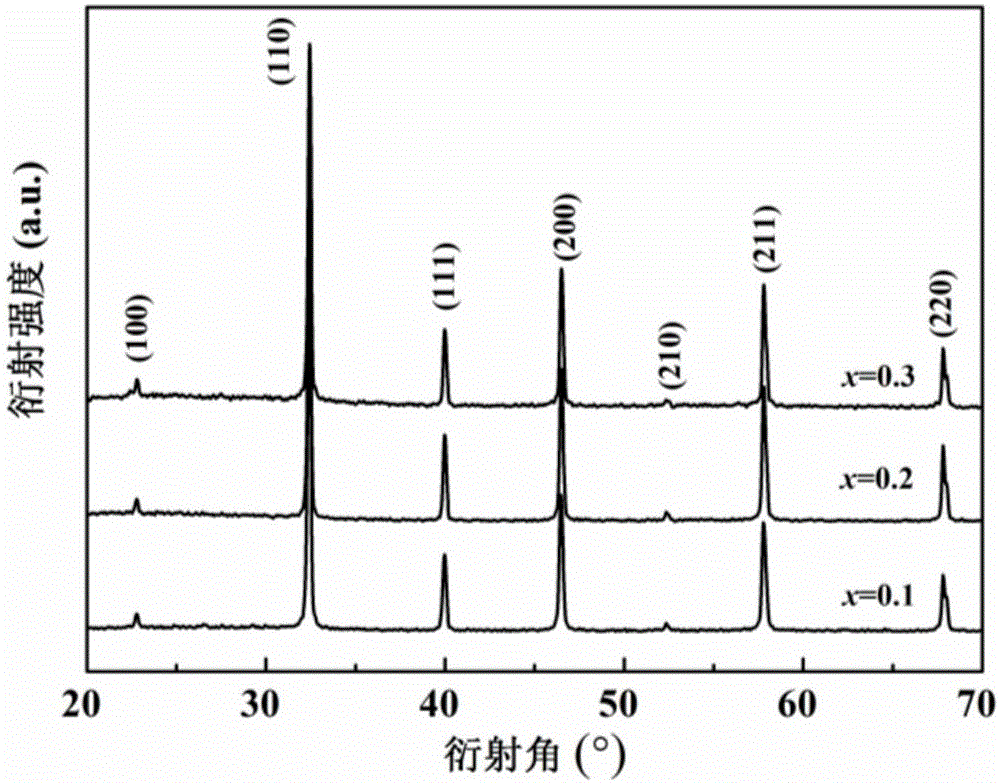
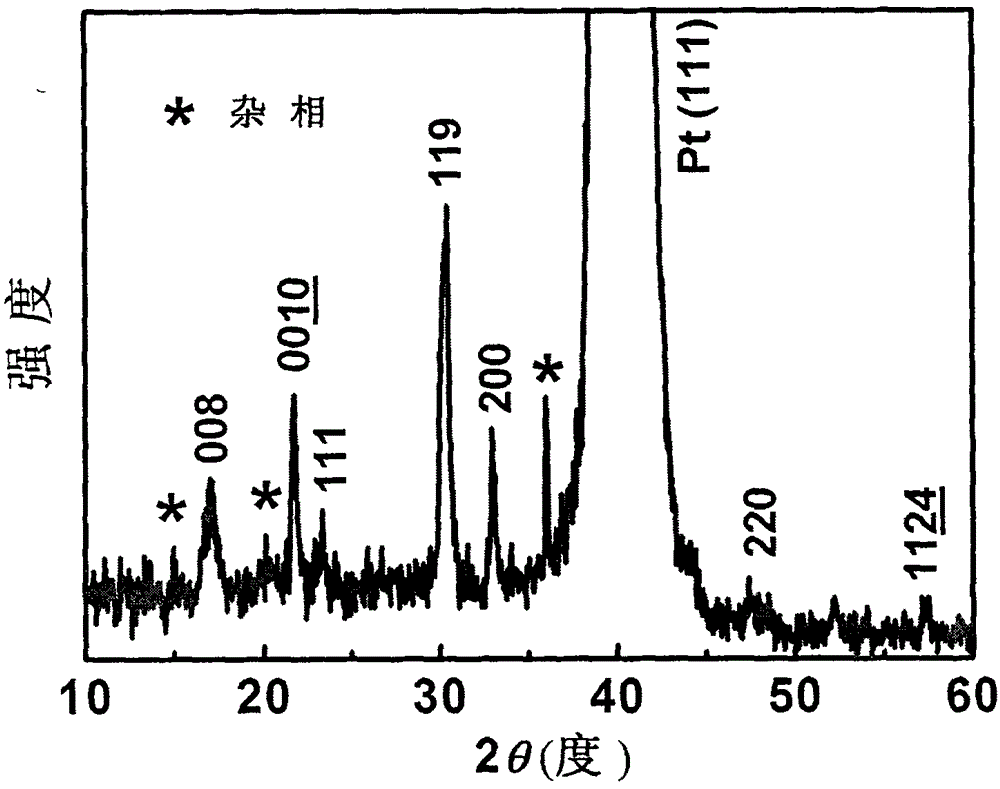
Patents
Literature
95results about How to "High polarization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
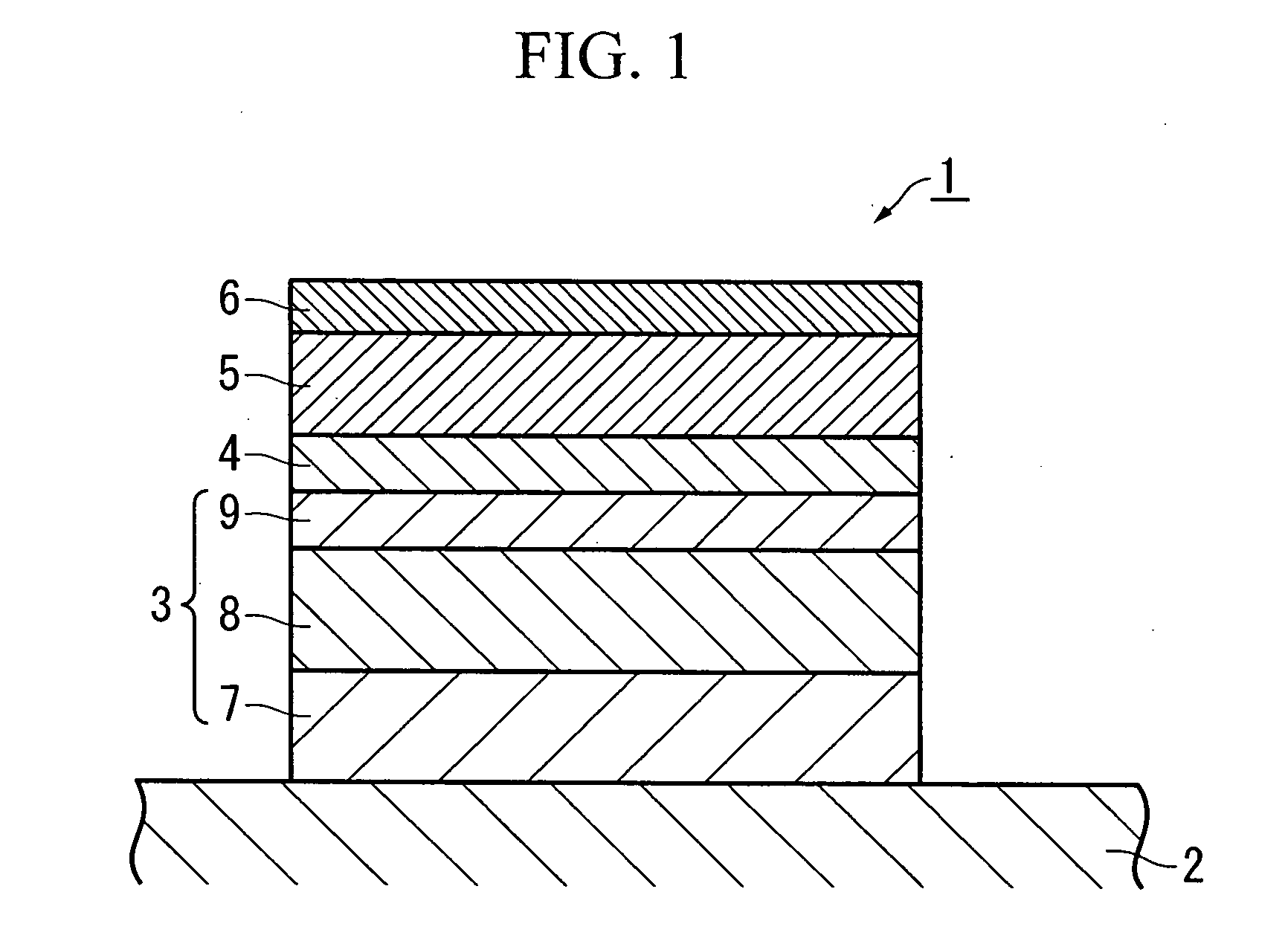
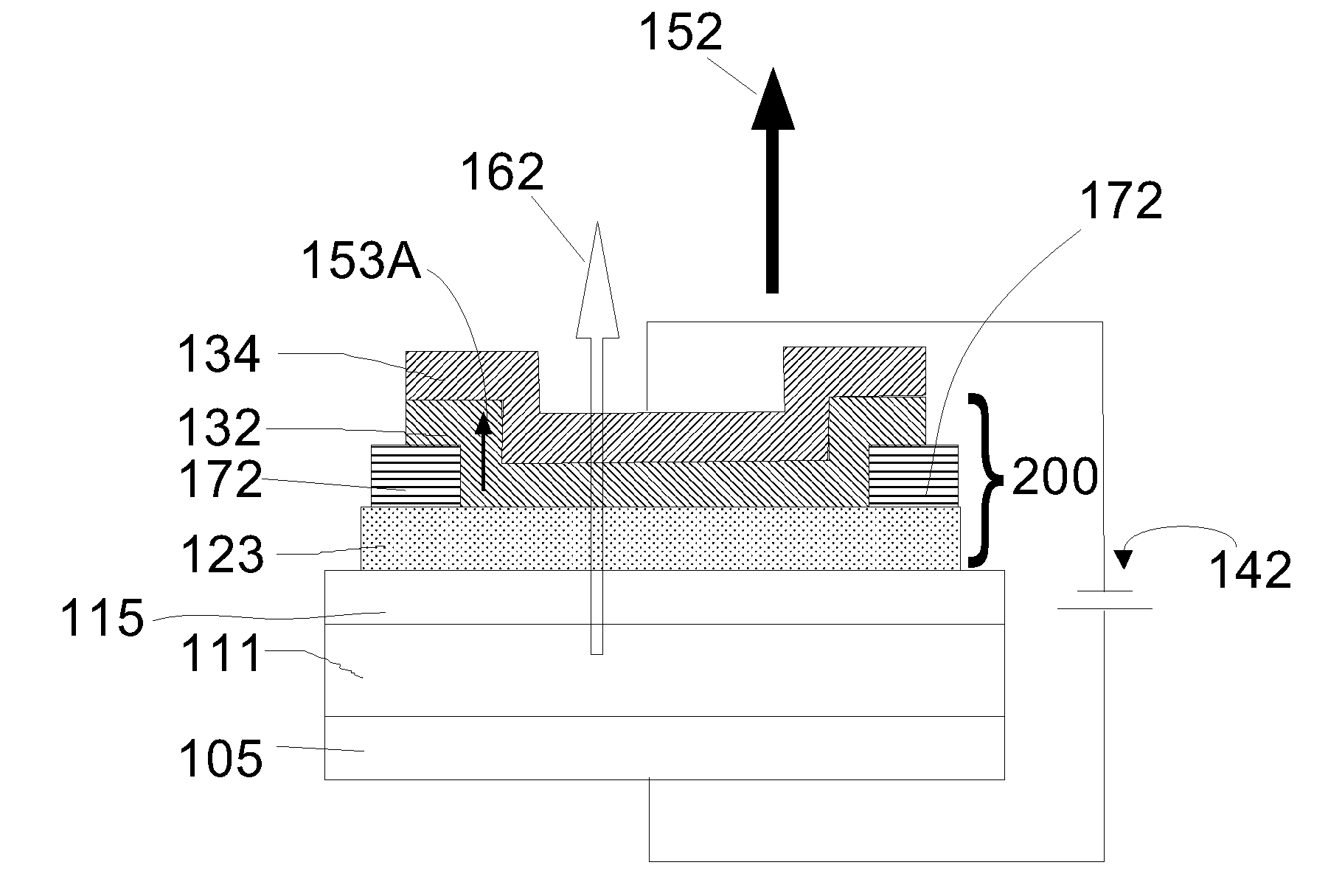
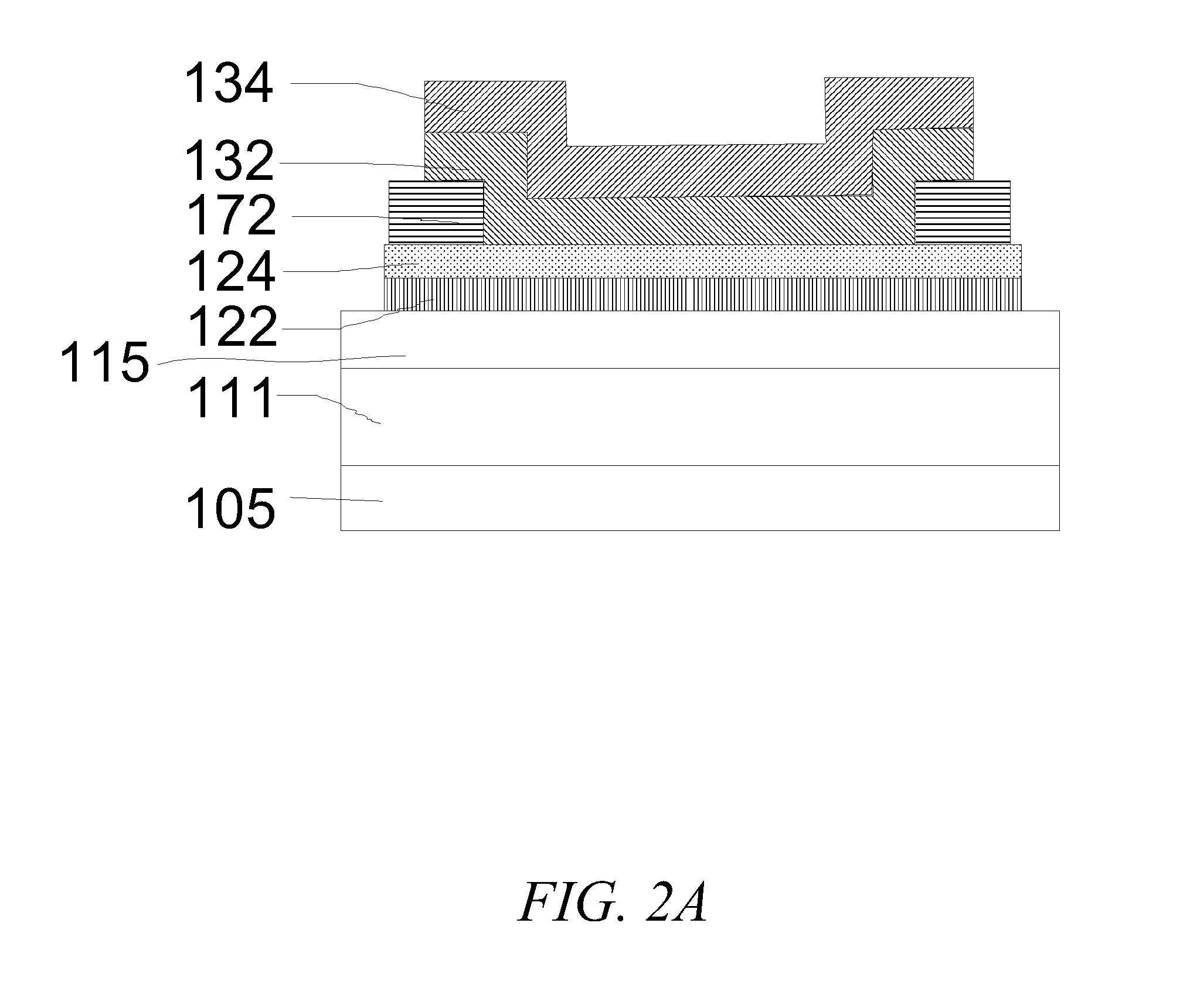
MTJ incorporating CoFe/Ni multilayer film with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for MRAM application
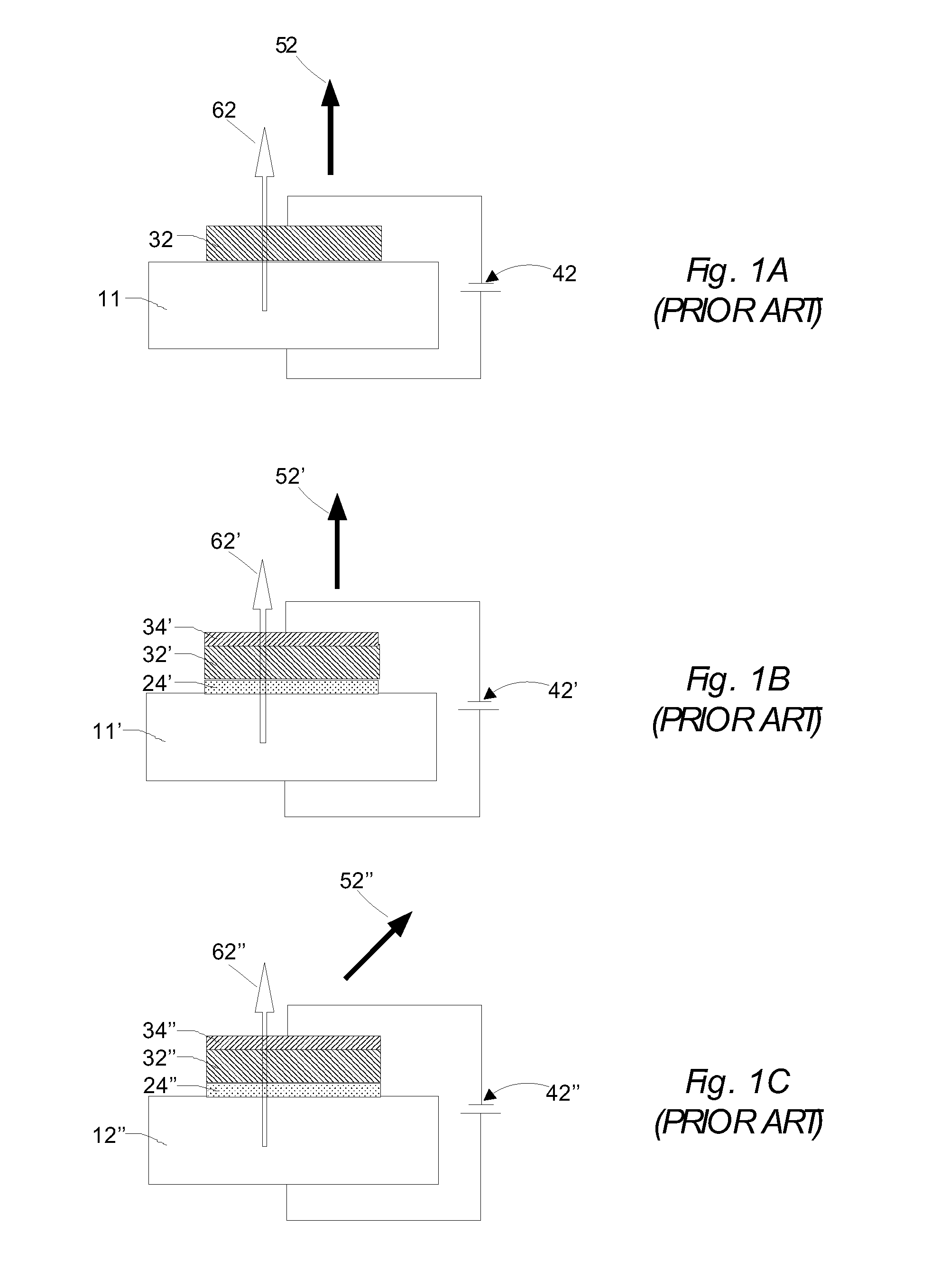
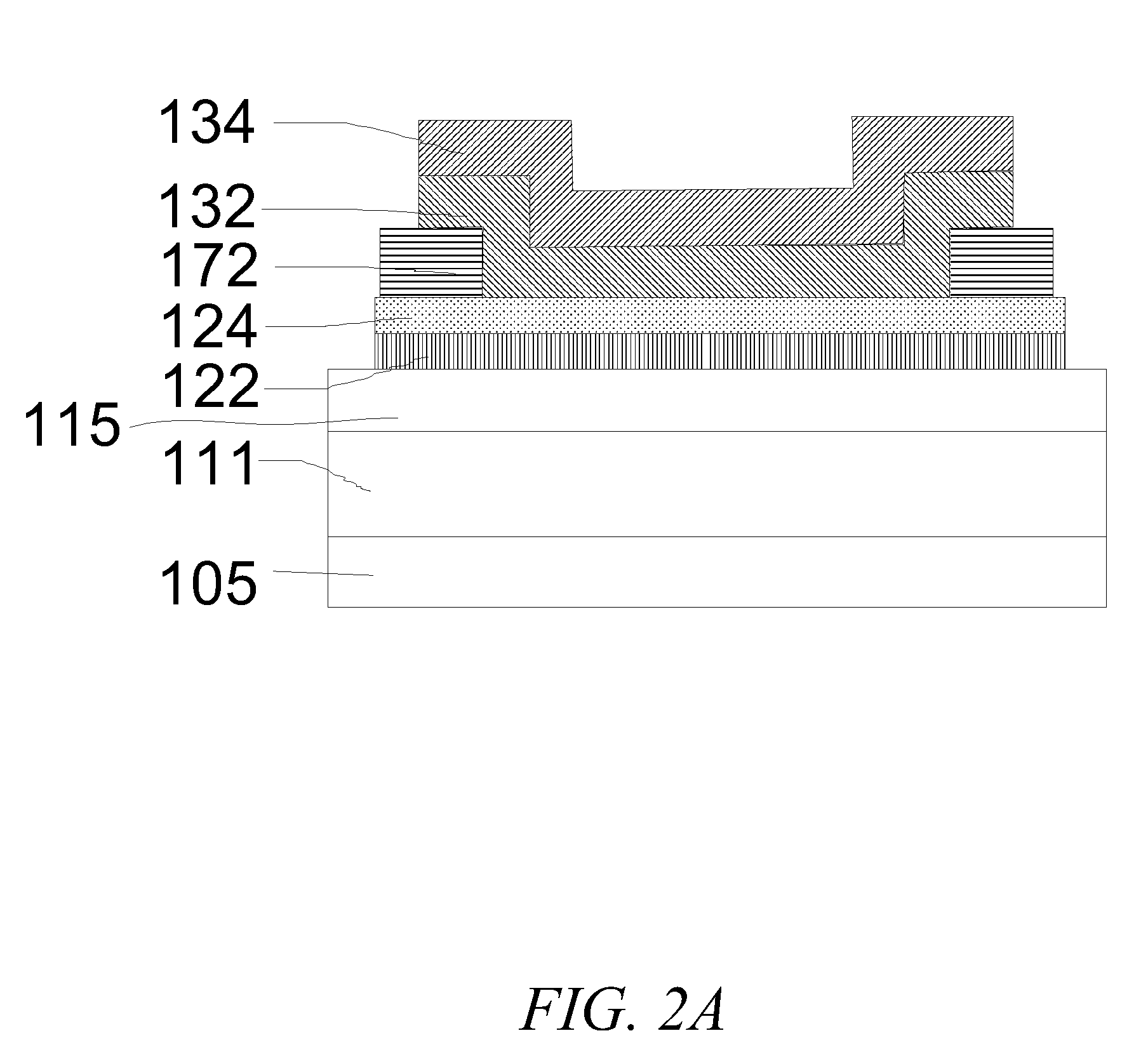
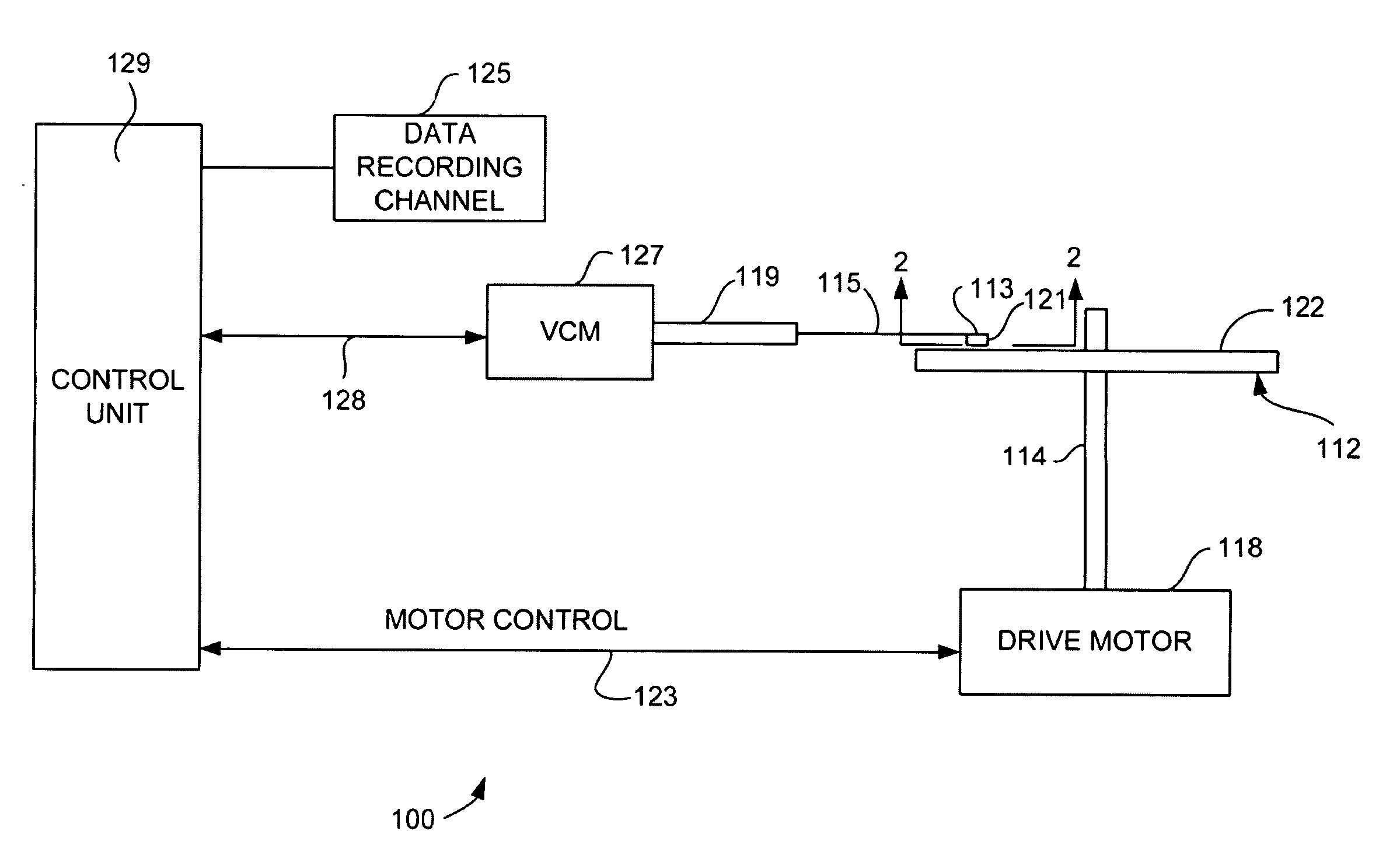
ActiveUS20110096443A1Minimize impinging ion energyMaximize PMA propertyMagnetic measurementsVacuum evaporation coatingSpin transferSpin valve
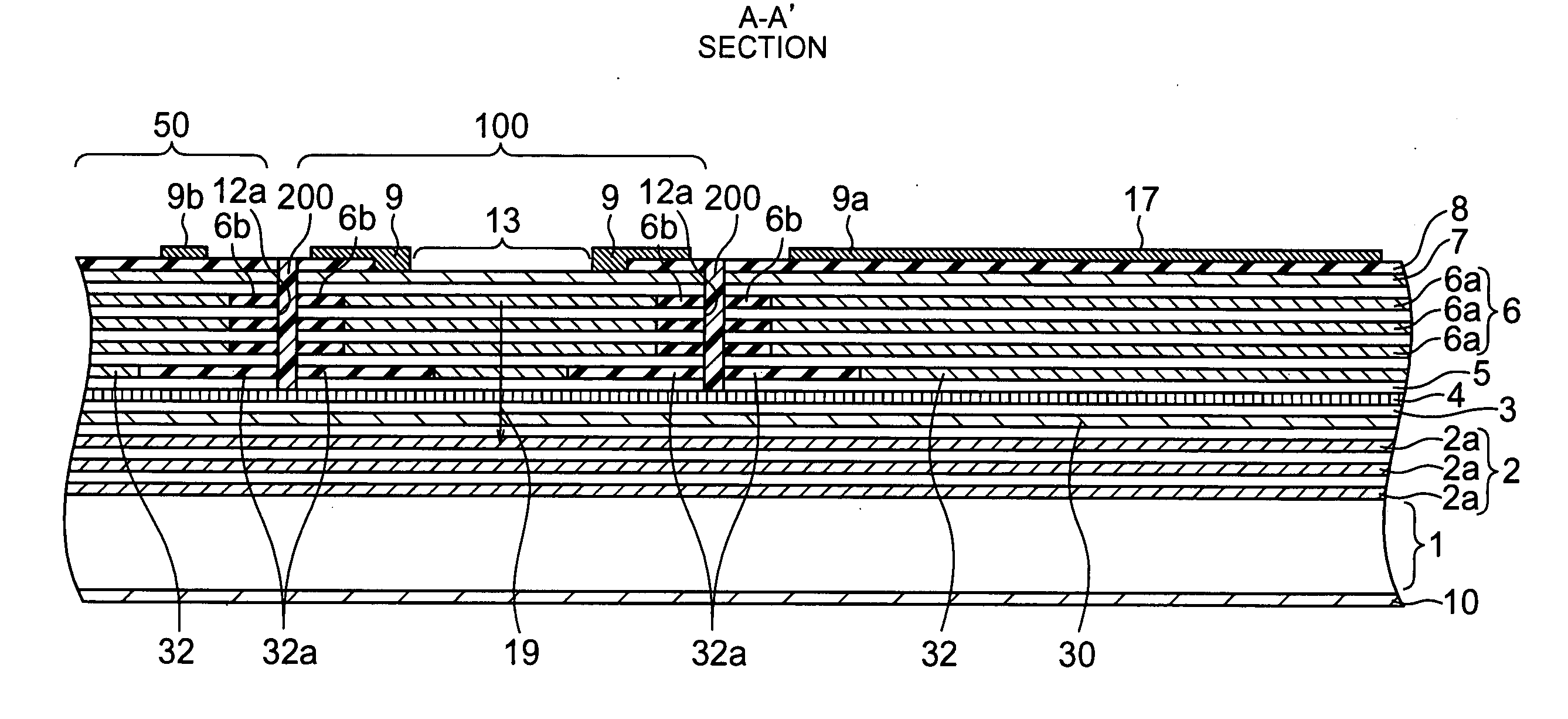
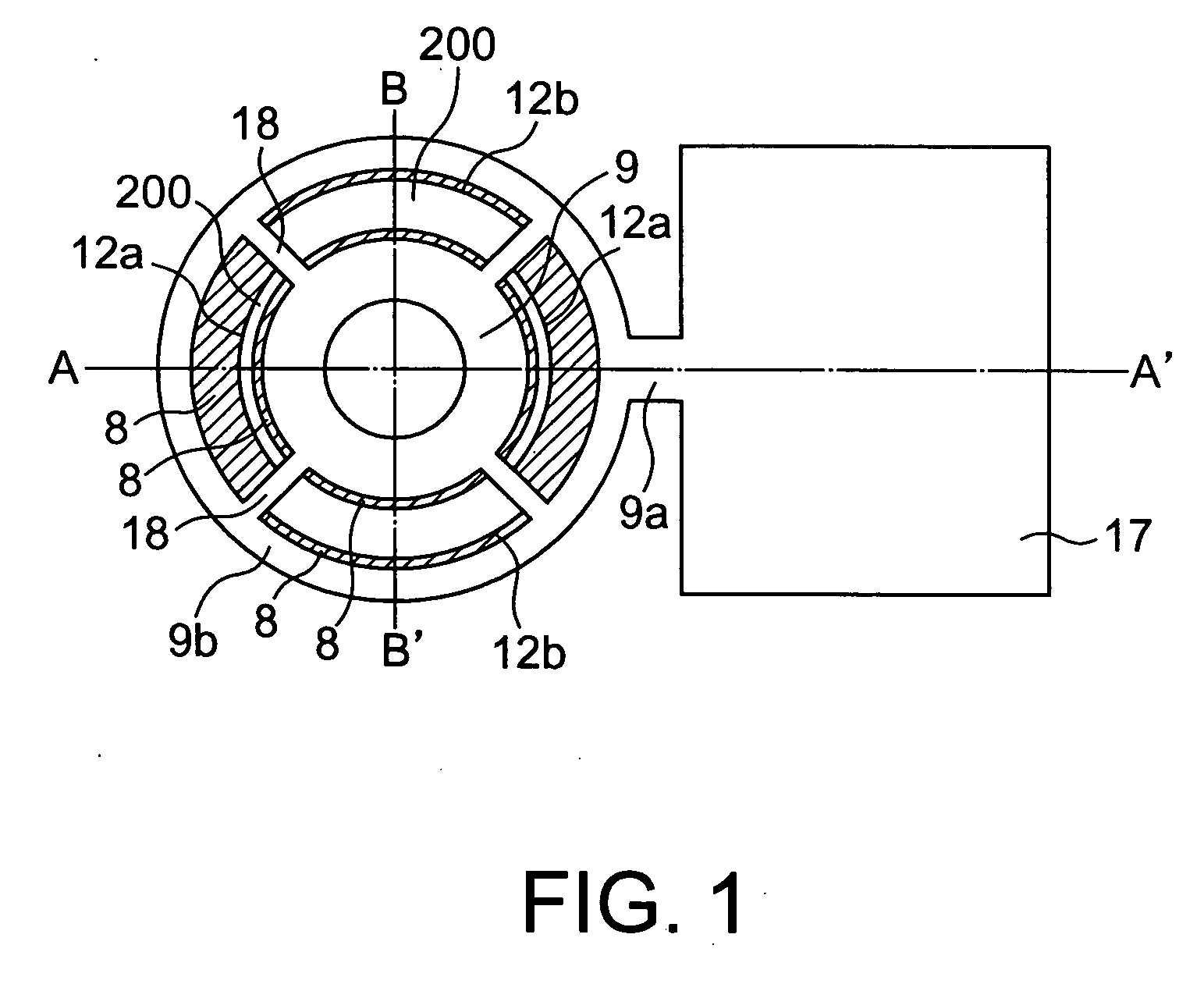
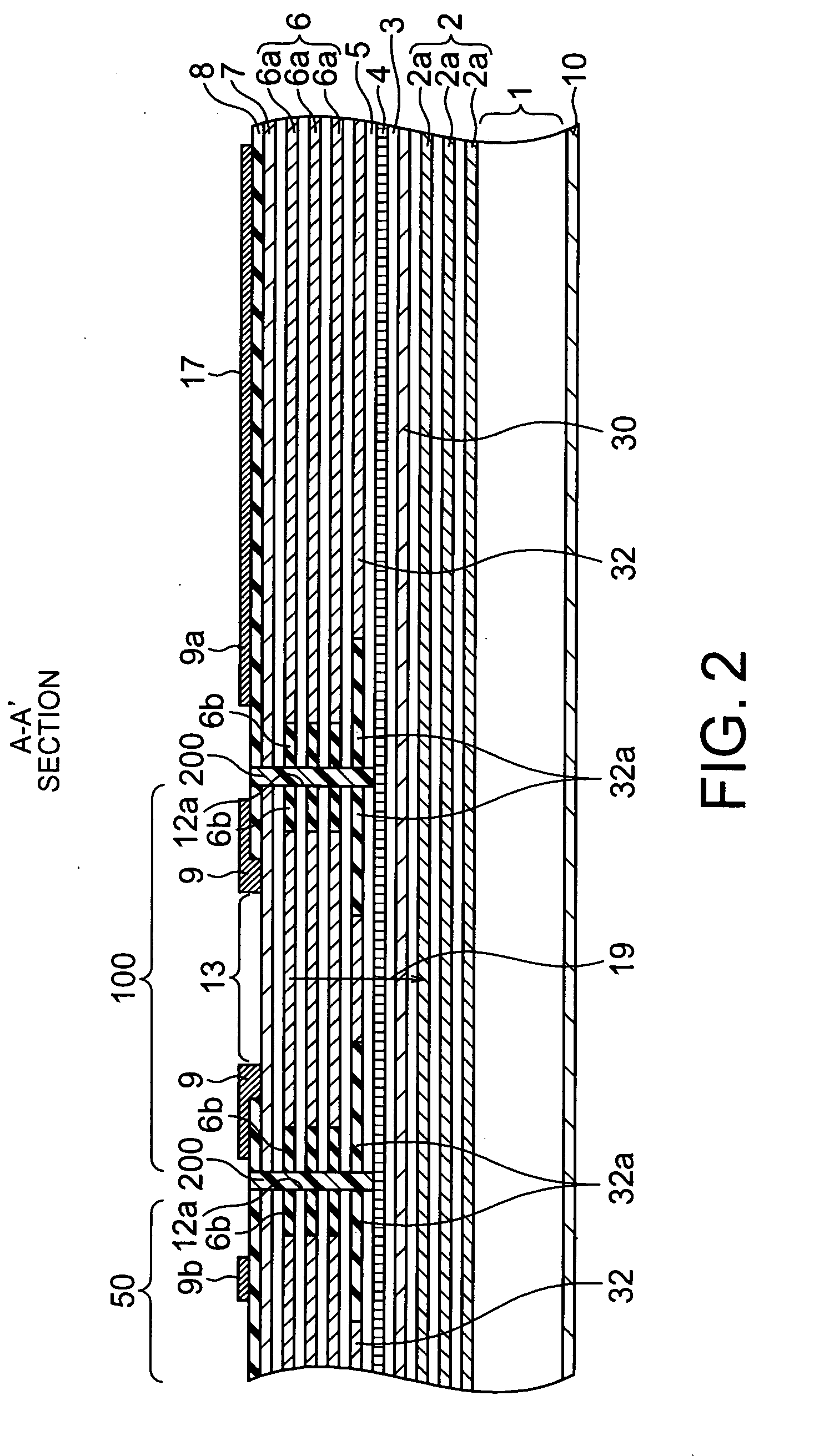
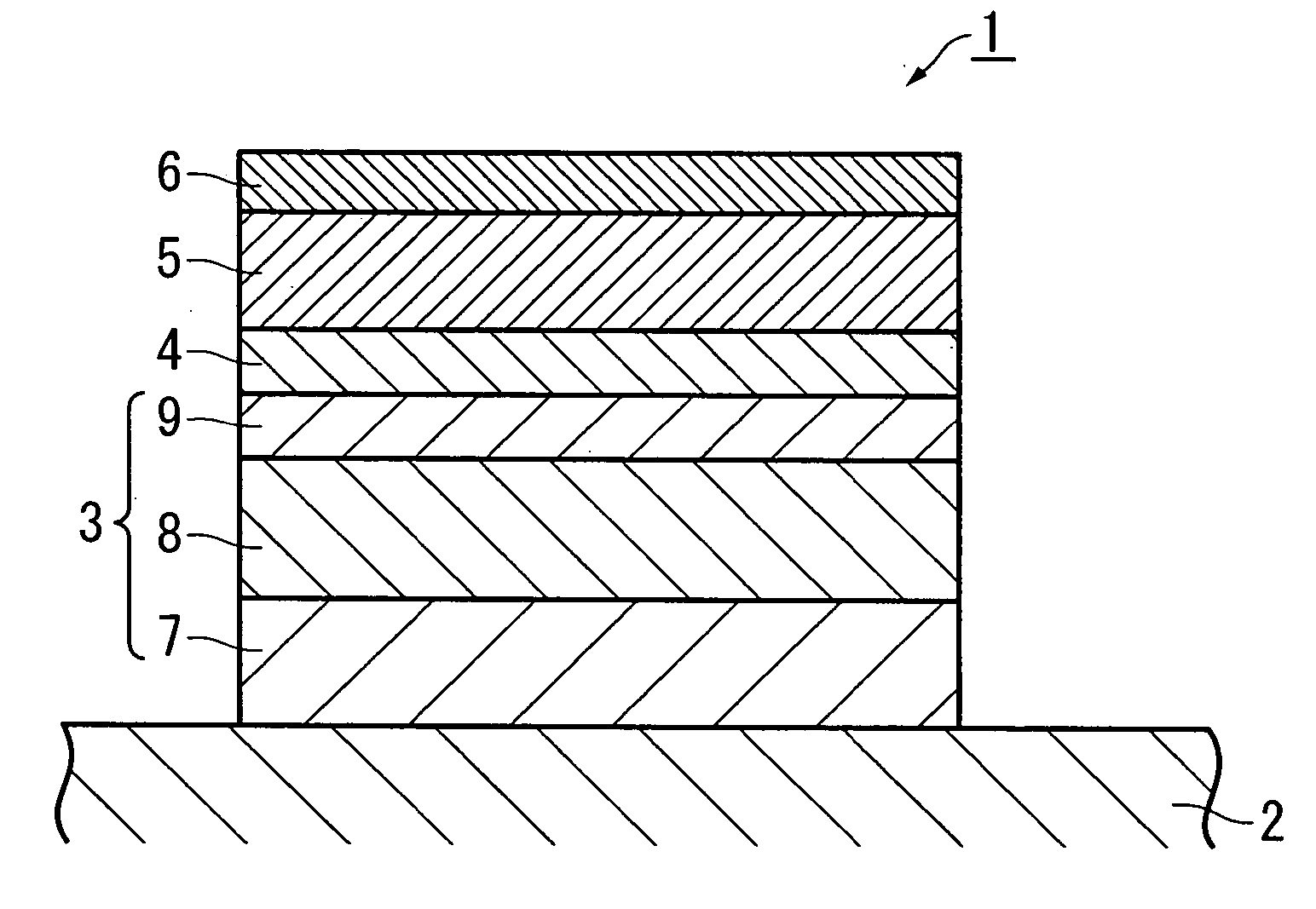
A MTJ for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a thin composite seed layer made of at least Ta and a metal layer having fcc(111) or hcp(001) texture as in Ta / Ti / Cu to enhance perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying laminated layer with a (CoFe / Ni)X, (Co / NiFe)X, (Co / NiCo)X, (CoFe / NiFe)X, or (CoFe / NiCo)X composition where x is from 5 to 30. In one embodiment, a CPP-TMR spin valve has one or both of a laminated free layer and laminated reference layer with the aforementioned compositions. The MTJ includes an interfacial layer made of CoFeB, CoFeB / CoFe, or CoFe / CoFeB between each laminated structure and the tunnel barrier. The laminated layers are deposited by a low power and high Ar pressure process to avoid damaging interfaces between adjoining layers. Annealing occurs at 220° C. to 400° C. A laminated layer with high PMA may also be included in one or more layers of a spin transfer oscillator.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
MgO-based tunnel spin injectors
InactiveUS7274080B1High polarizationImprove thermal stabilityNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsCharge carrier
A MgO tunnel barrier is sandwiched between semiconductor material on one side and a ferri- and / or ferromagnetic material on the other side to form a spintronic element. The semiconductor material may include GaAs, for example. The spintronic element may be used as a spin injection device by injecting charge carriers from the magnetic material into the MgO tunnel barrier and then into the semiconductor. Similarly, the spintronic element may be used as a detector or analyzer of spin-polarized charge carriers by flowing charge carriers from the surface of the semiconducting layer through the MgO tunnel barrier and into the (ferri- or ferro-) magnetic material, which then acts as a detector. The MgO tunnel barrier is preferably formed by forming a Mg layer on an underlayer (e.g., a ferromagnetic layer), and then directing additional Mg, in the presence of oxygen, towards the underlayer.
Owner:IBM CORP
MTJ incorporating CoFe/Ni multilayer film with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for MRAM application
ActiveUS8184411B2High perpendicular magnetic anisotropyHigh MstMagnetic measurementsVacuum evaporation coatingSpin transferSpin valve
A MTJ for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a thin composite seed layer made of at least Ta and a metal layer having fcc(111) or hcp(001) texture as in Ta / Ti / Cu to enhance perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying laminated layer with a (CoFe / Ni)x, (Co / NiFe)x, (Co / NiCo)x, (CoFe / NiFe)x, or (CoFe / NiCo)x composition where x is from 5 to 30. In one embodiment, a CPP-TMR spin valve has one or both of a laminated free layer and laminated reference layer with the aforementioned compositions. The MTJ includes an interfacial layer made of CoFeB, CoFeB / CoFe, or CoFe / CoFeB between each laminated structure and the tunnel barrier. The laminated layers are deposited by a low power and high Ar pressure process to avoid damaging interfaces between adjoining layers. Annealing occurs at 220° C. to 400° C. A laminated layer with high PMA may also be included in one or more layers of a spin transfer oscillator.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
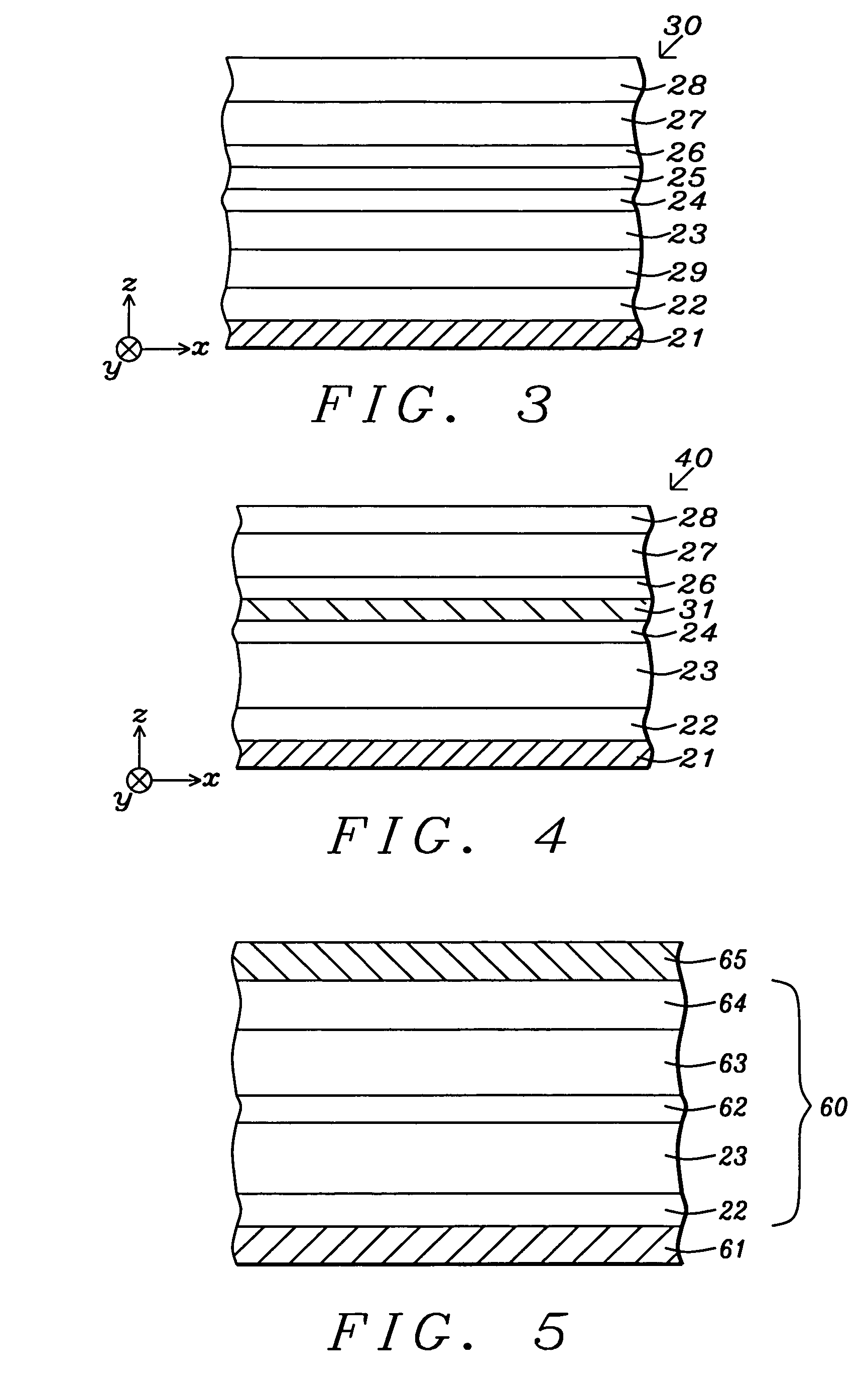
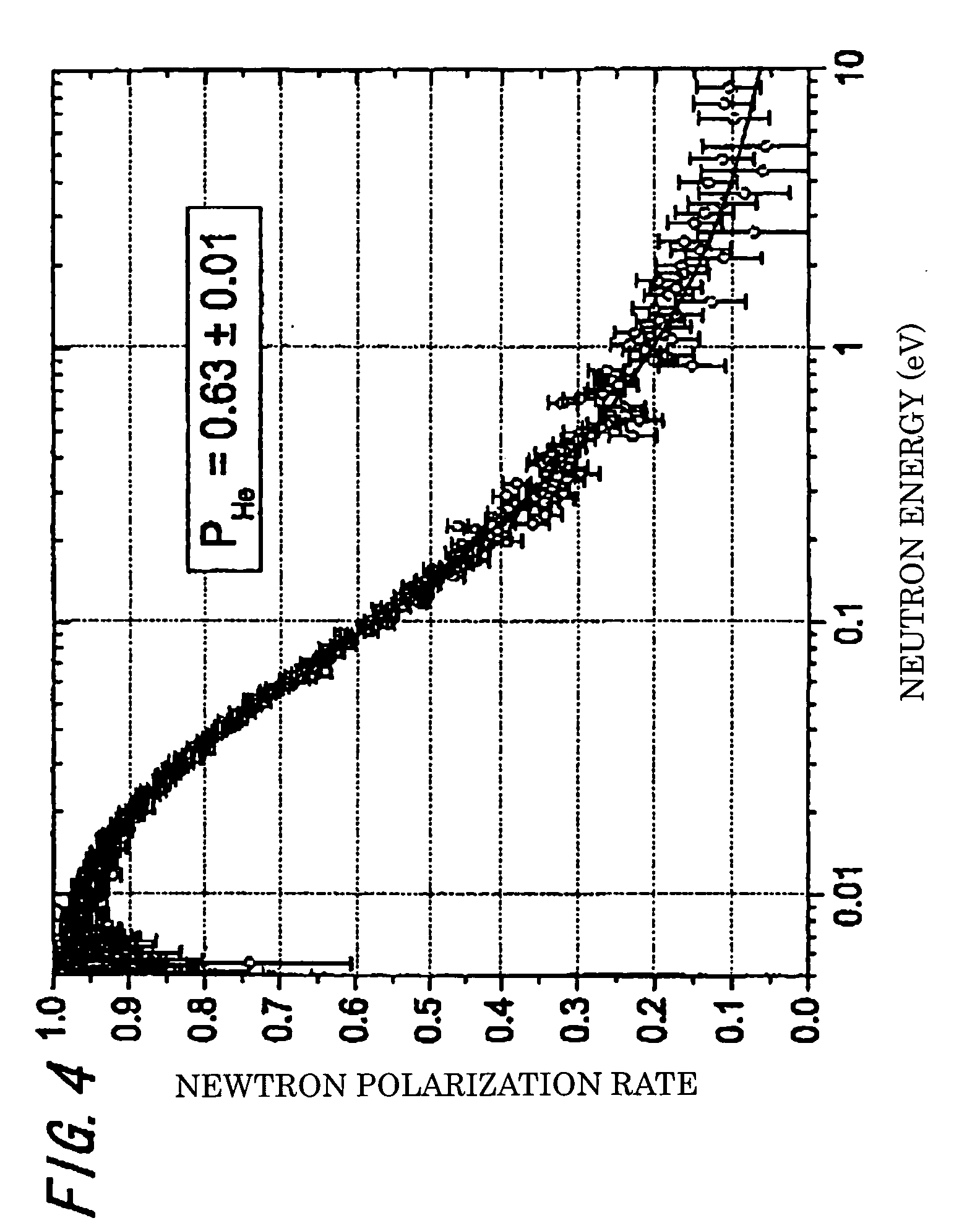
Vessel for Rare Gas Filling, and Method for Polarization of Rare Gas Atomic Nucleus Using Said Vessel
InactiveUS20090101806A1Accurate thicknessImprove polarizationOther accessoriesMasersNoble gasNeutron scattering
A vessel for rare-gas filling is provided, where almost complete light circular polarization is realized, which has a light incident window of a single crystal material whose thickness and crystal axis orientation are optimized, and a polarization method of rare gas nuclei in the vessel is also provided. In addition, embodiments of the vessel is provided, which is impervious to alkali metal, and sustains high pressure, and shows no permeability for 3He gas, and has negligibly small neutron absorption so as to be suitable for application to basic science, for example, neutron scattering, and the polarization method in the vessel is also provided.The vessel for rare-gas filling of the present invention comprises a vessel body 3, and a pipe 4, which is connected to the vessel body 3 and introduces a rare-gas containing gas and an alkali metal into the vessel body 3. A light incident window 2 made of a single-crystal material, which has proper thickness and proper crystal axis orientation, is attached to the vessel body 3. The vessel for rare-gas filling is preferably made of sapphire or the like.
Owner:HIGH ENERGY ACCELERATOR RESEARCH ORGANIZATION
Vertical cavity surface emitting laser diode
InactiveUS20060187997A1Improve performanceHigh polarizationOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPlane orientation
It is made possible to obtain high performance having high controllability in polarization mode even when a vertical cavity surface emitting laser diode is fabricated on an ordinary substrate with a plane orientation (100) plane or the like. A vertical cavity surface emitting laser diode includes: a substrate; a semiconductor active layer which is formed on the substrate and has a light emitting region; a first reflecting mirror and a second reflecting mirror sandwiching the semiconductor active layer; a first recess which has a first groove depth penetrating at least the semiconductor active layer from the outermost layer of the first reflecting mirror; a second recess having a second groove depth shallower than the first groove depth; a mesa portion which is surrounded by the first and second recesses; and an insulating film which is buried in the first recess.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Ferroelectric memory device
InactiveUS20050017269A1Improve featuresHigh dielectric polarizationSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingIon beamAtomic physics
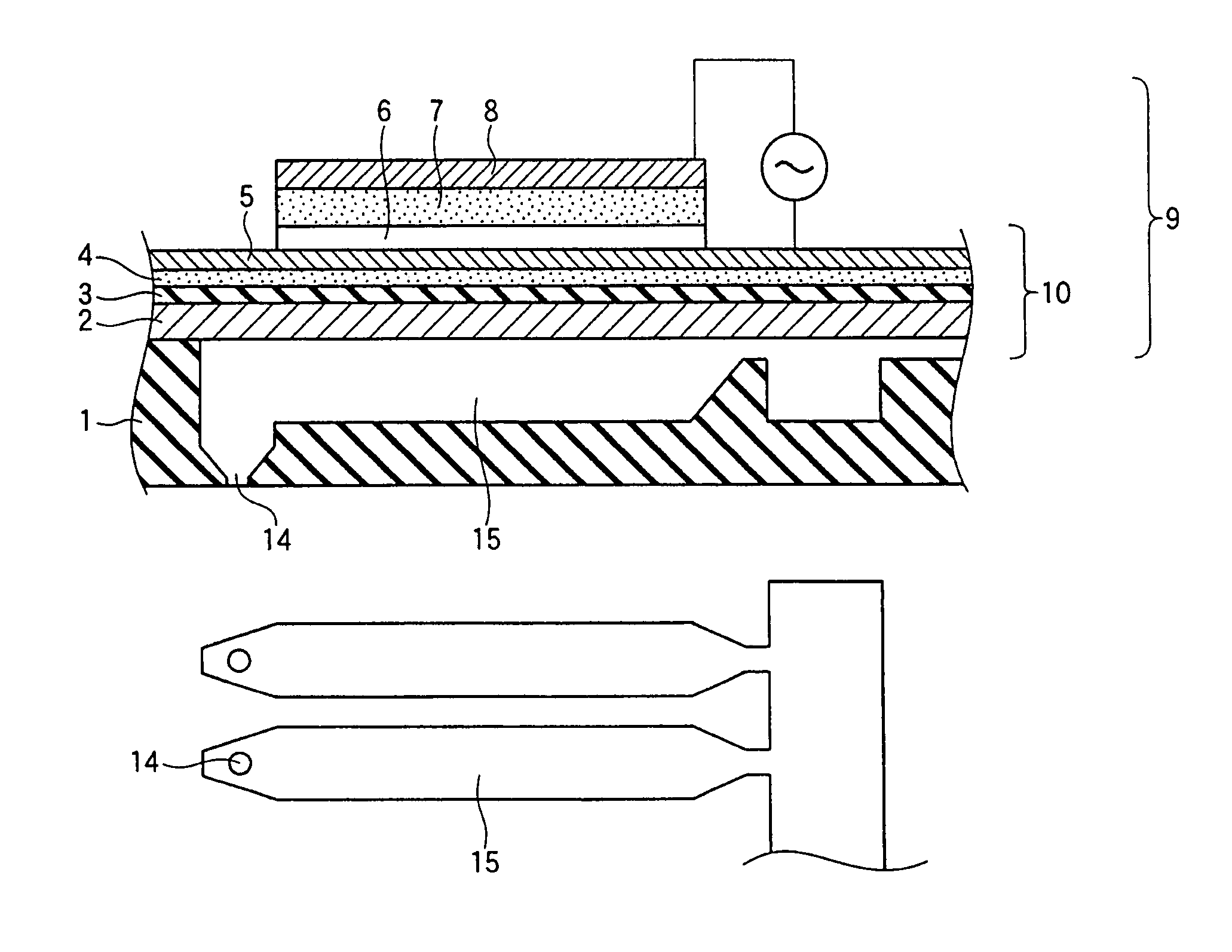
A ferroelectric memory device has a high performance, includes no Pb, and can be directly mounted onto an Si substrate. The ferroelectric memory device includes a (001)-oriented BiFeO3 ferroelectric layer 5 with a tetragonal structure, which is formed on an electrode 4 made of a perovskite material formed on an Si oxide film. The electrode 4 with a perovskite structure is formed by an ion beam assist method.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
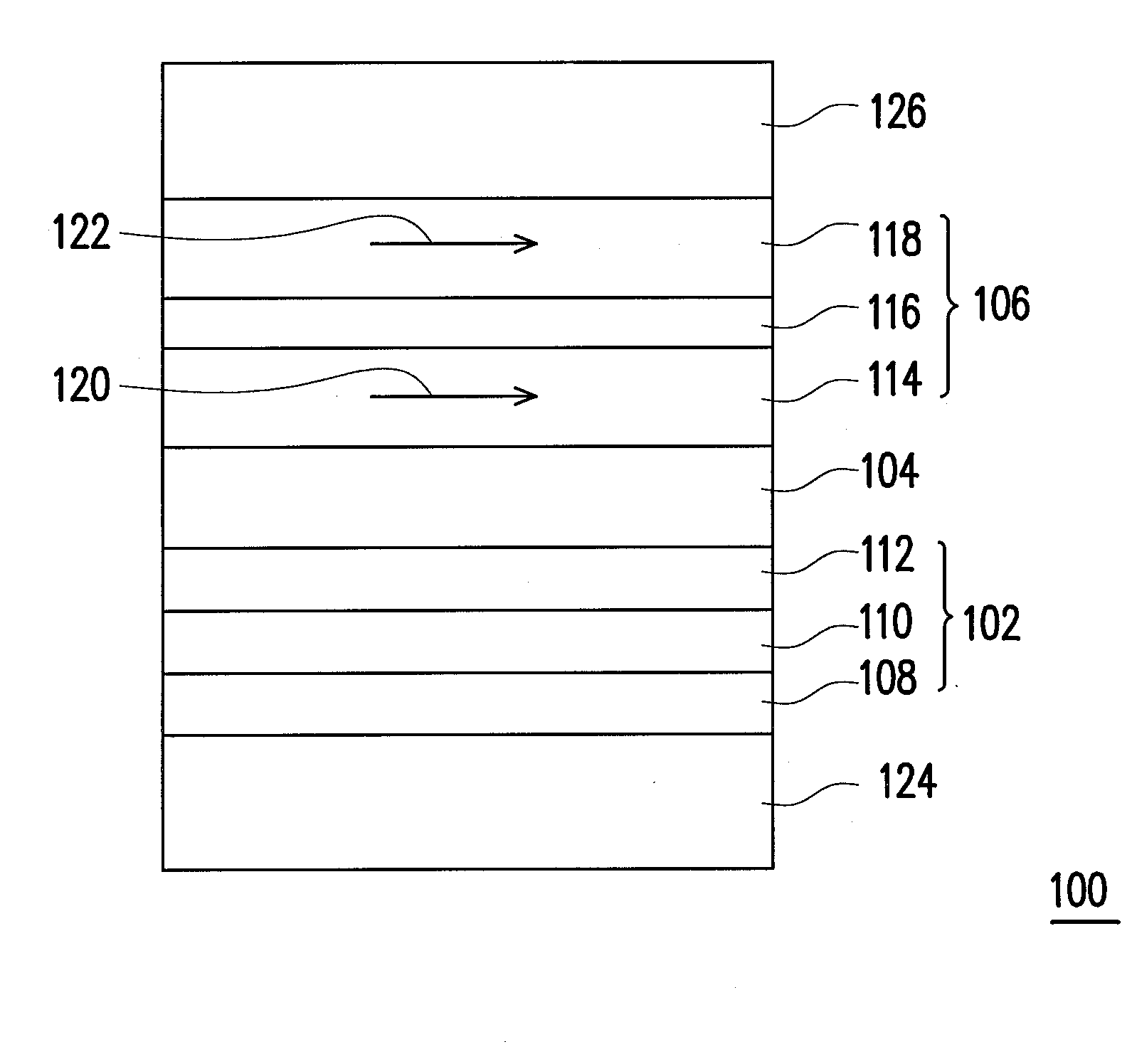
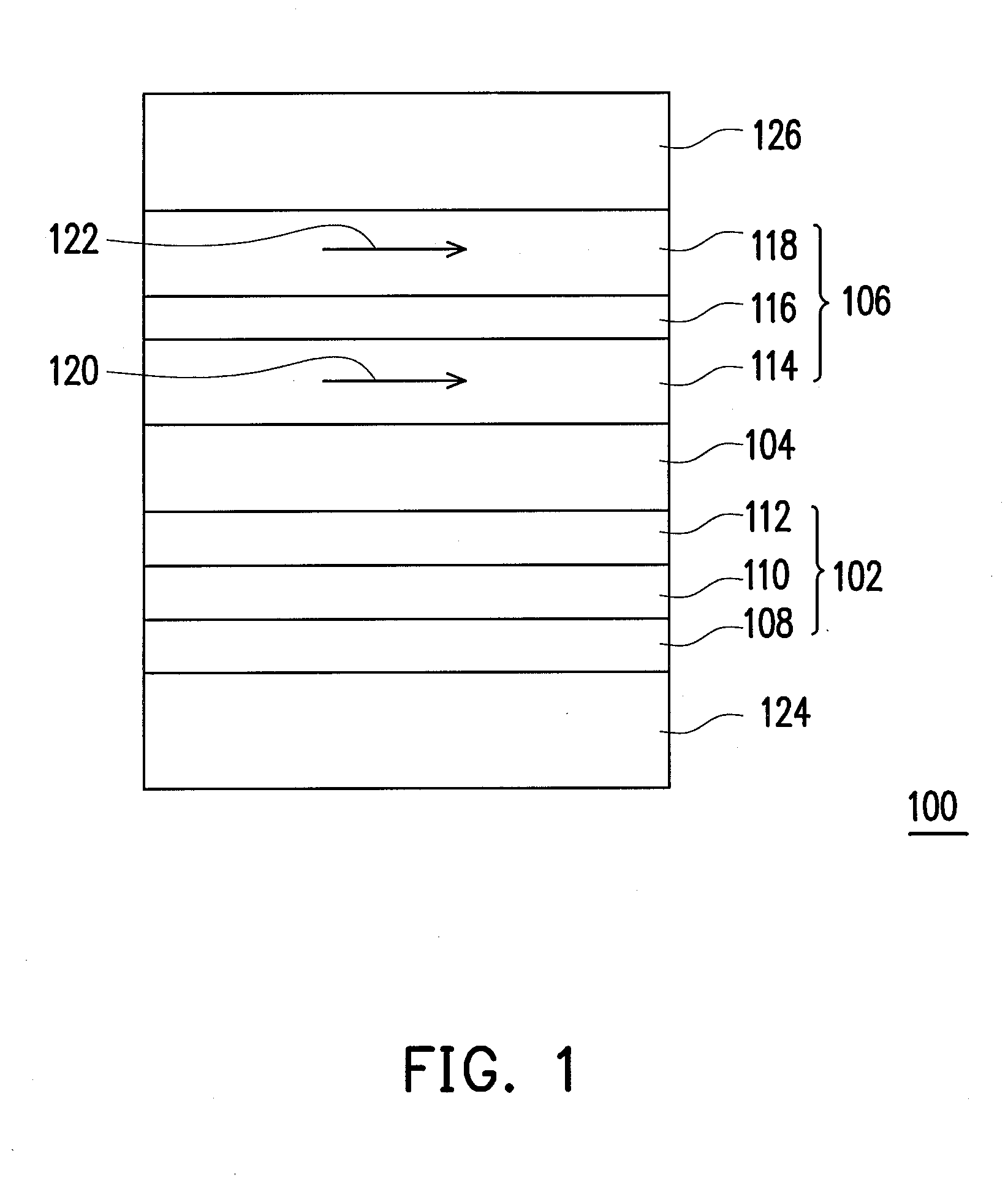
Magnetic memory element utilizing spin transfer switching
ActiveUS20100109109A1Low densityEfficient reductionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storageMagnetic memorySpin transfer
A magnetic memory element utilizing spin transfer switching includes a pinned layer, a tunneling barrier layer and a free layer structure. The tunneling barrier layer is disposed on the pinned layer. The free layer structure includes a composite free layer. The composite free layer includes a first free layer, an insert layer and a second free layer. The first free layer is disposed on the tunneling barrier layer and has a first spin polarization factor and a first saturation magnetization. The insert layer is disposed on the first free layer. The second free layer is disposed on the insert layer and has a second spin polarization factor smaller than the first spin polarization factor and a second saturation magnetization smaller than the first saturation magnetization. Magnetization vectors of the first free layer and the second free layer are arranged as parallel-coupled.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Low thermal budget fabrication of ferroelectric memory using RTP
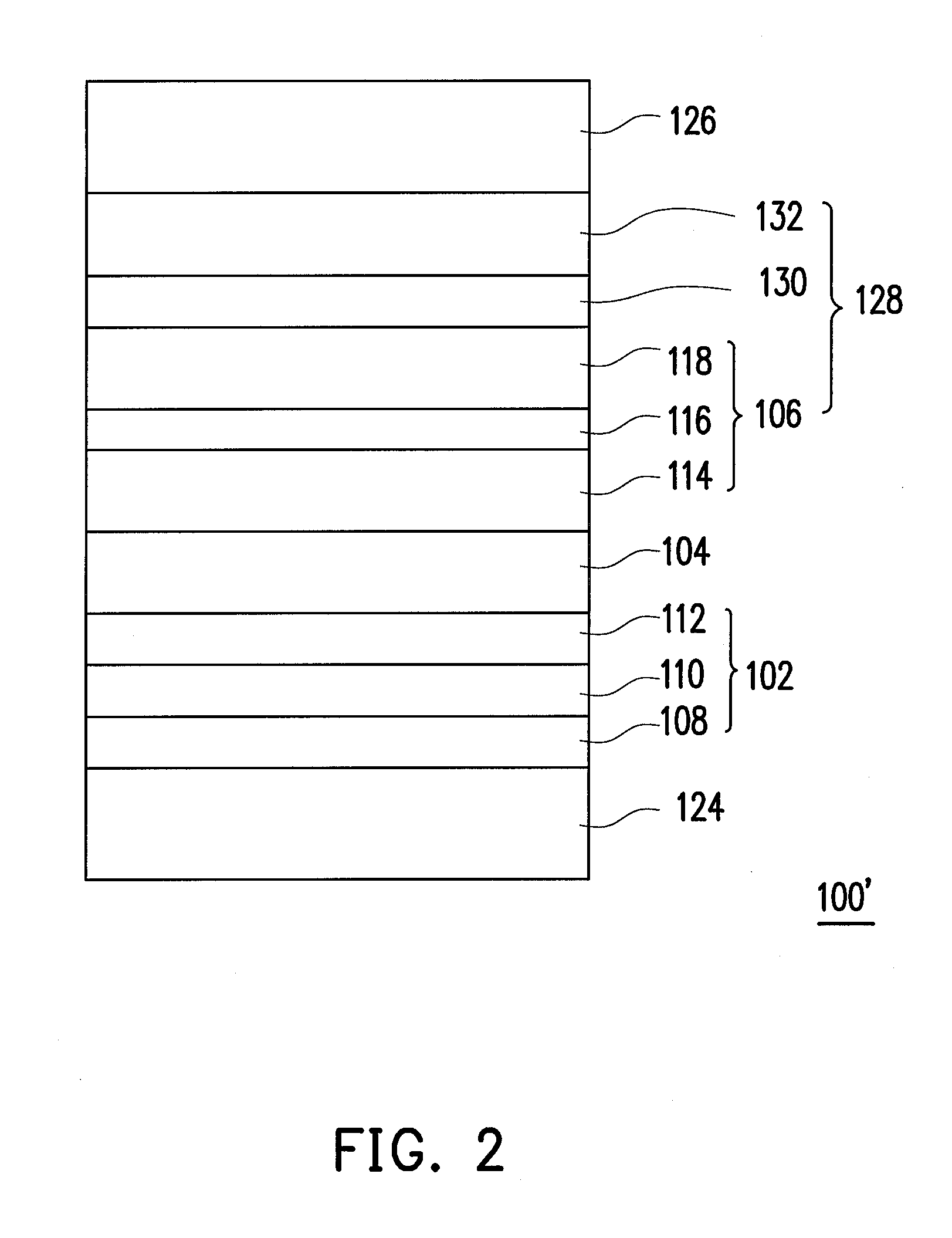
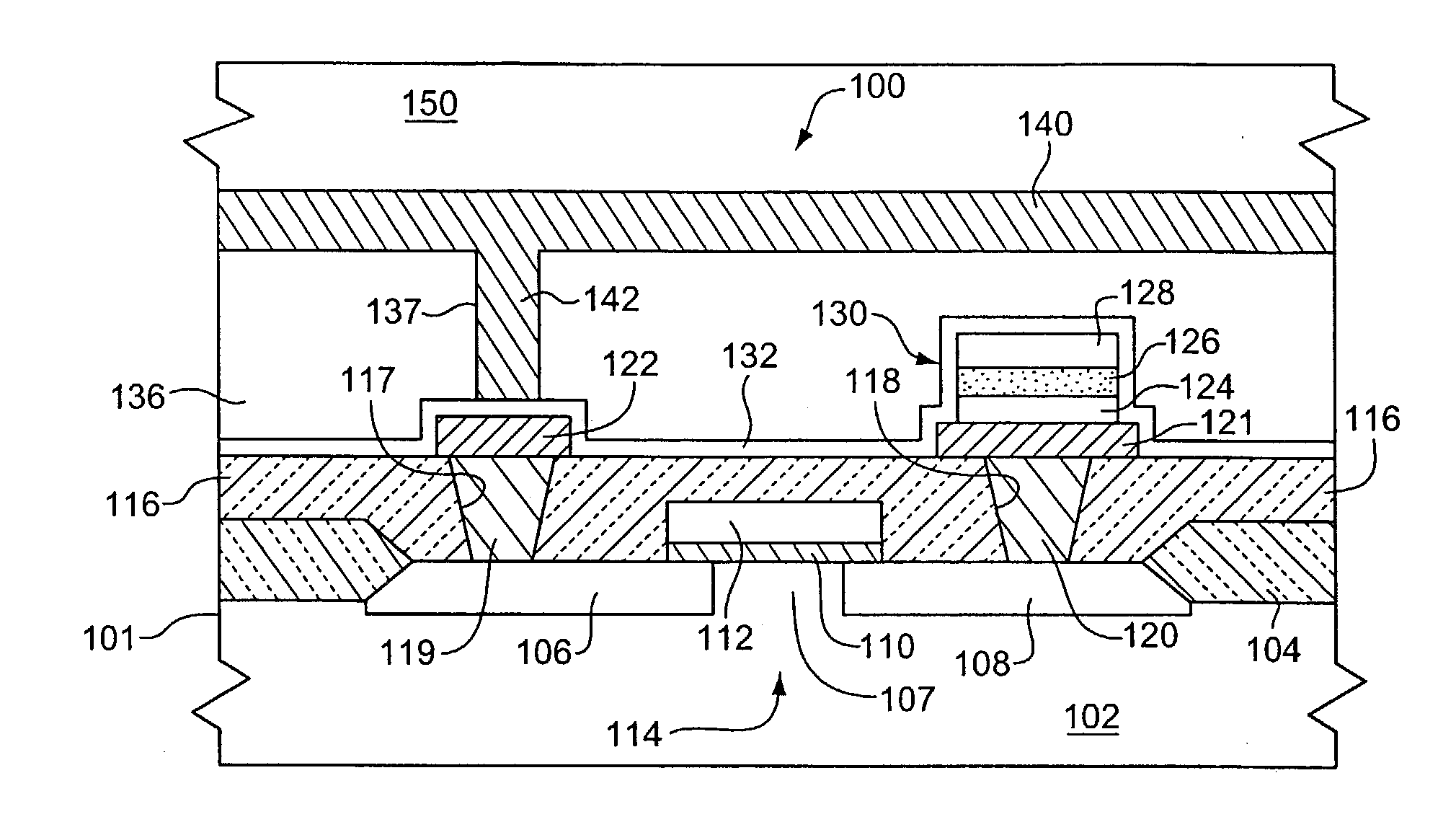
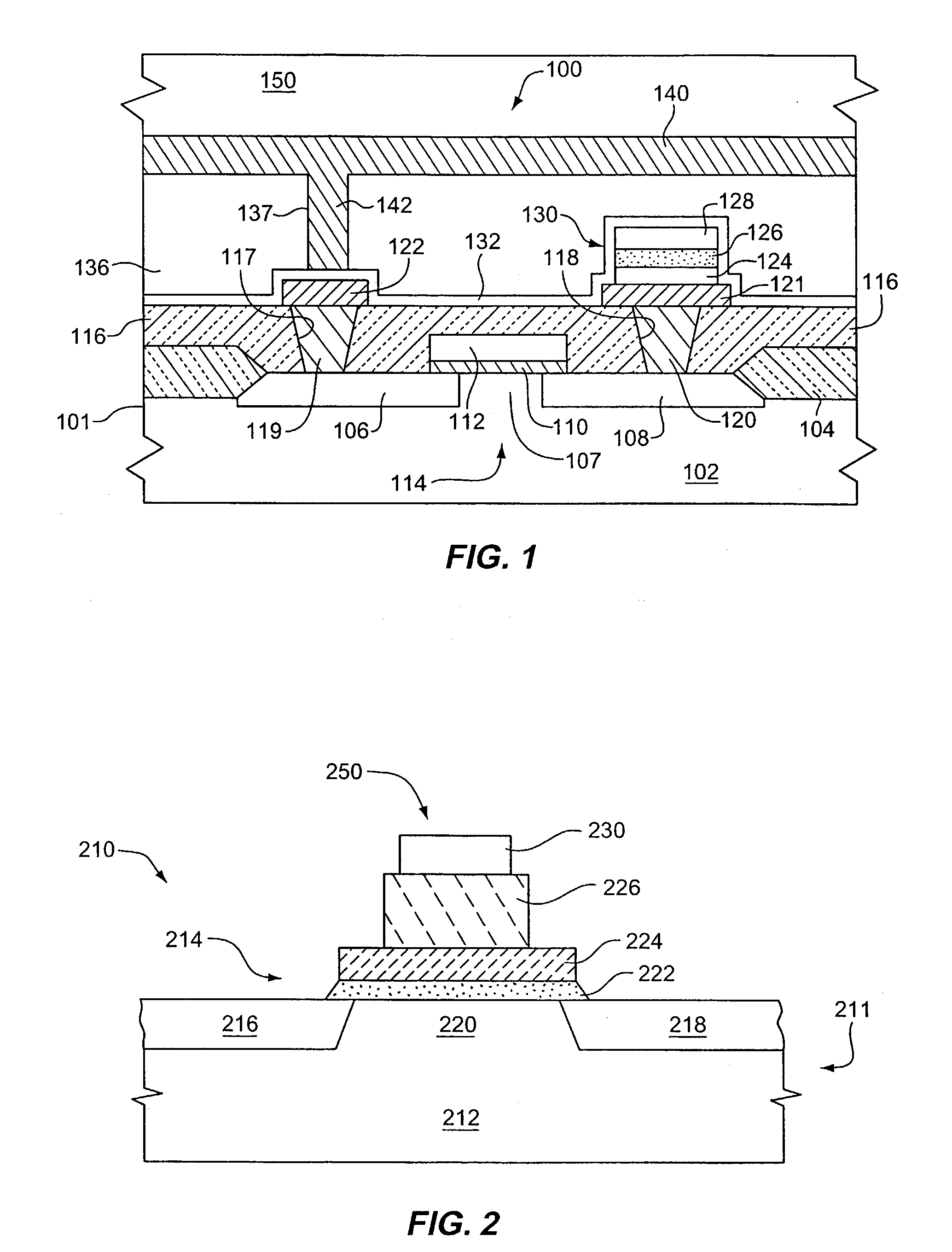
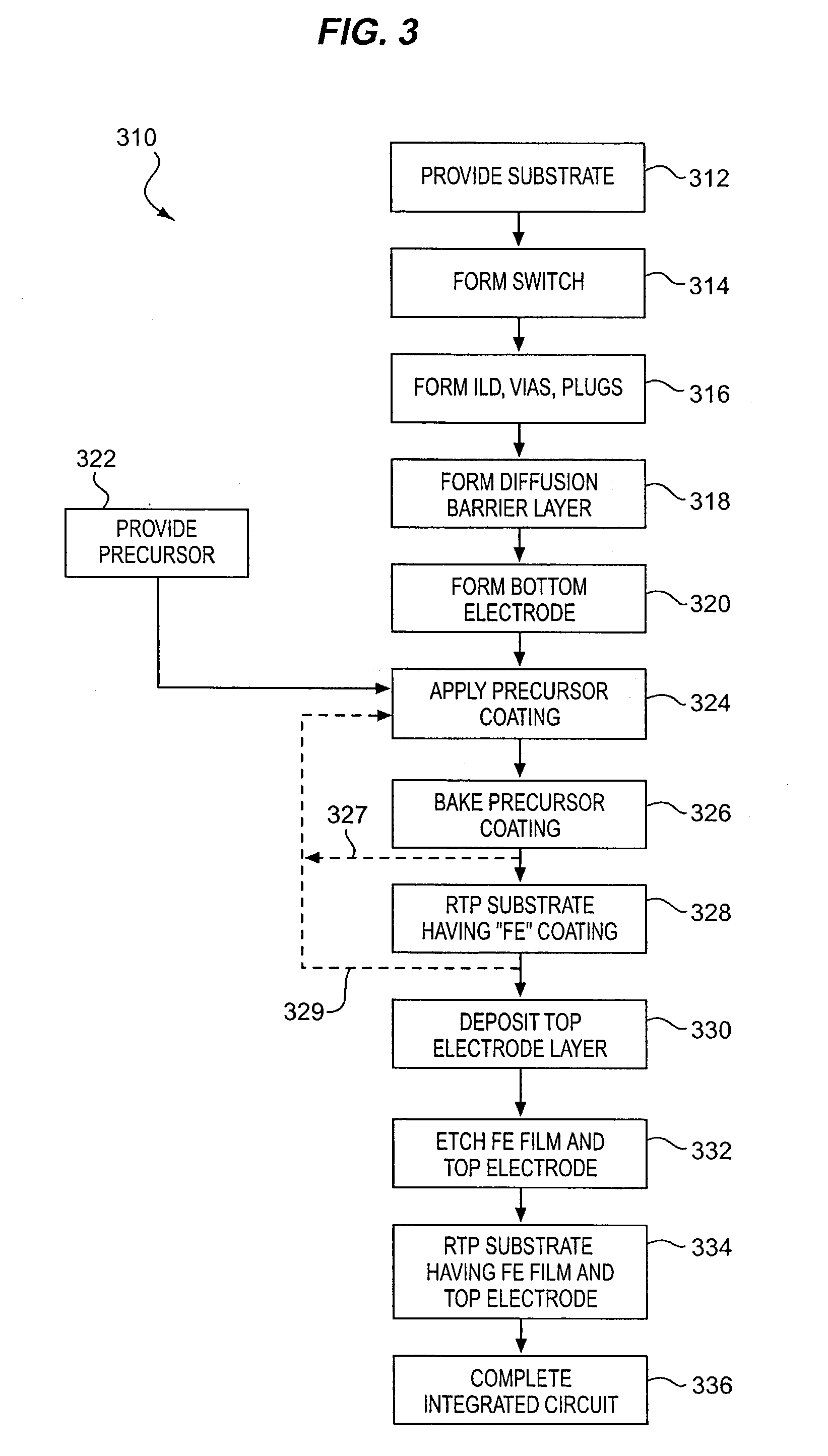
InactiveUS20040101977A1Budget is reducedReduce the temperaturePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenHeat treated
A precursor for forming a thin film of layered superlattice material is applied to an integrated circuit substrate. The precursor coating is heated using rapid thermal processing (RTP) with a ramping rate of 100° C. / second at a hold temperature in a range of from 500° C. to 900° C. for a cumulative heating time not exceeding 30 minutes, and preferably less than 5 minutes. In fabricating a ferroelectric memory cell, the coating is heated in oxygen using RTP, then a top electrode layer is formed, and then the substrate including the coating is heated using RTP in oxygen or in nonreactive gas after forming the top electrode layer. The thin film of layered superlattice material preferably comprises strontium bismuth tantalate or strontium bismuth tantalum niobate, and preferably has a thickness in a range of from 25 nm to 120 nm. The process of fabricating a thin film of layered superlattice material typically has a thermal budget value not exceeding 960,000° C.-sec, preferably less than 50,000° C.-sec.
Owner:SYMETRIX
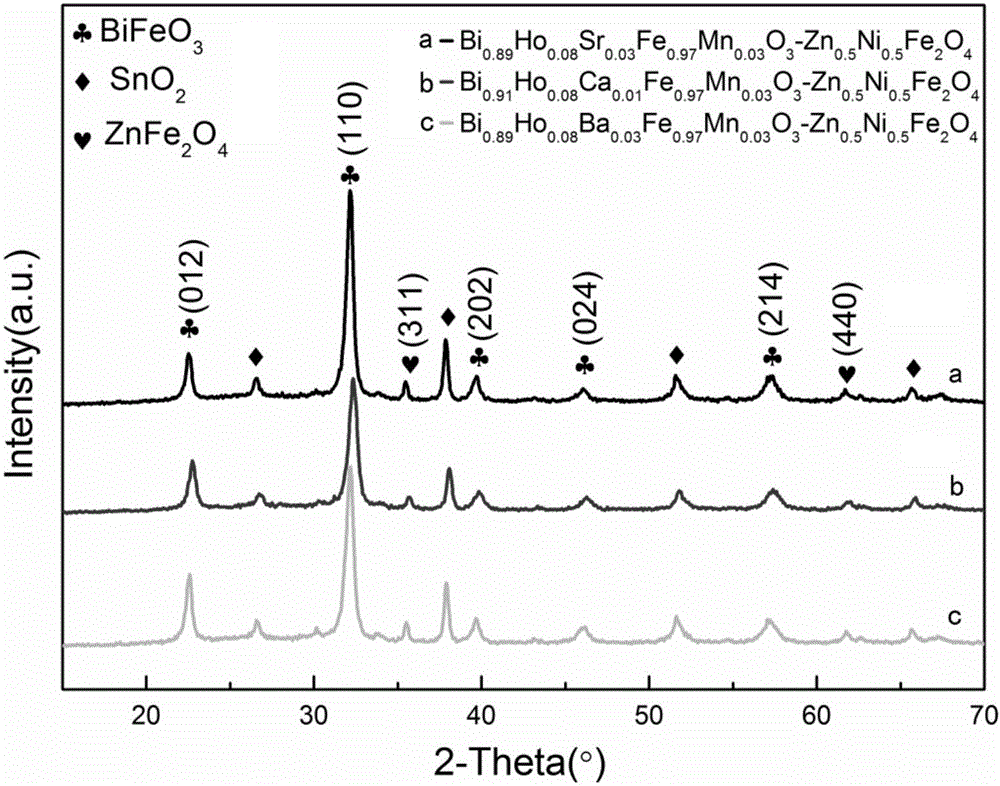
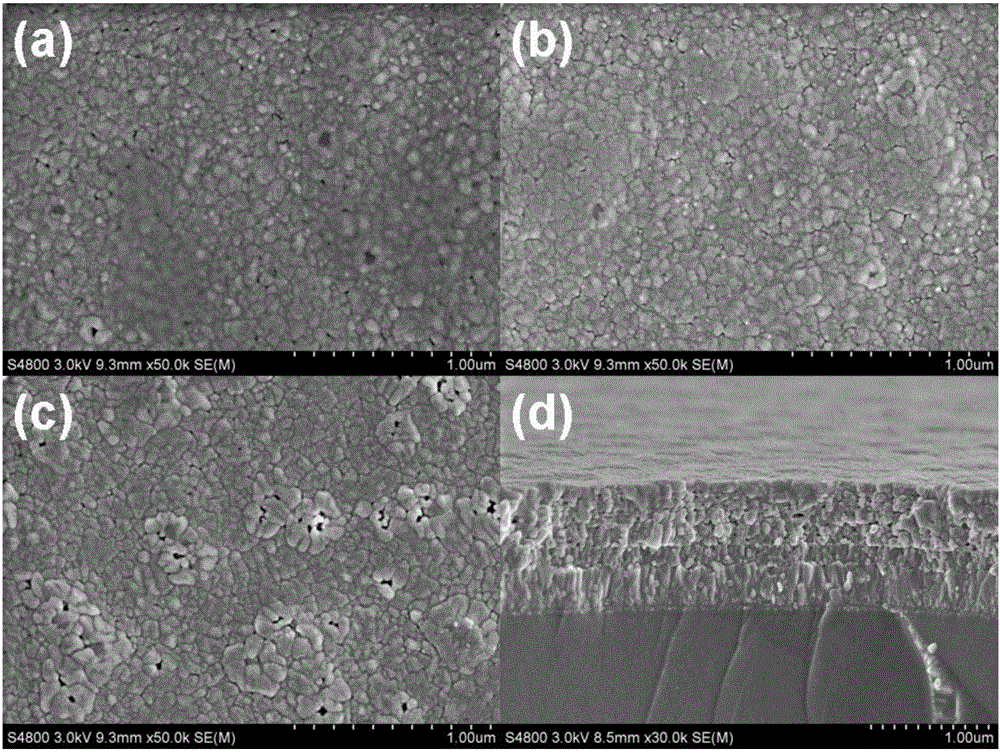
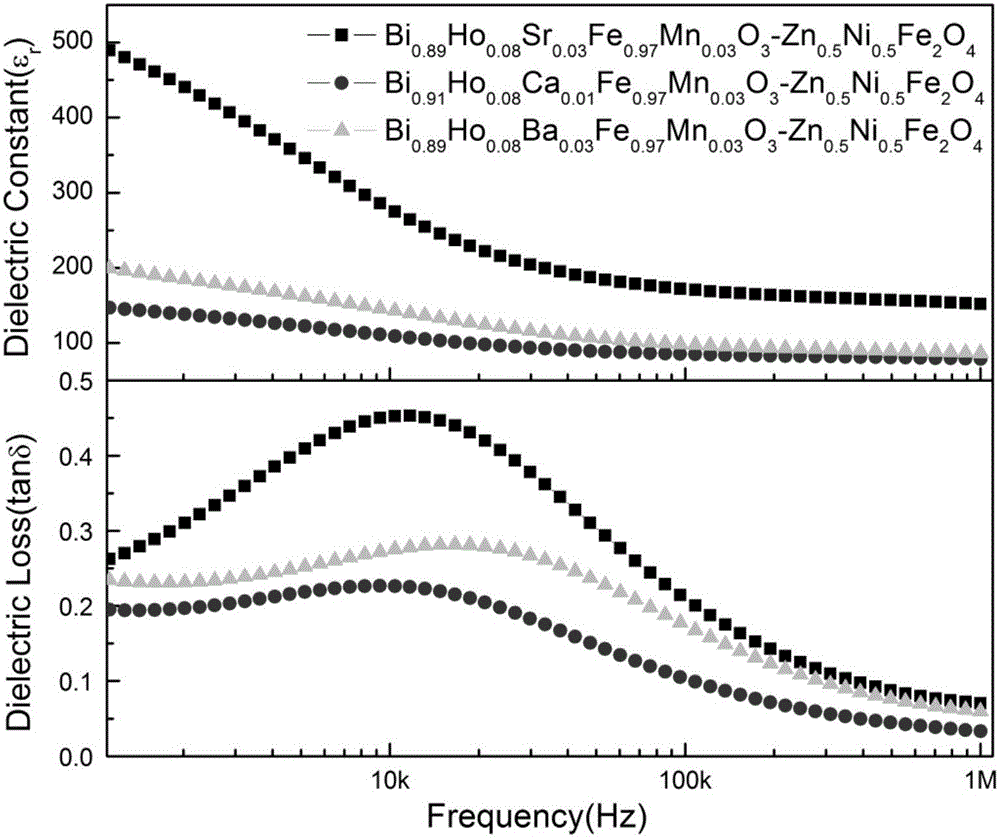
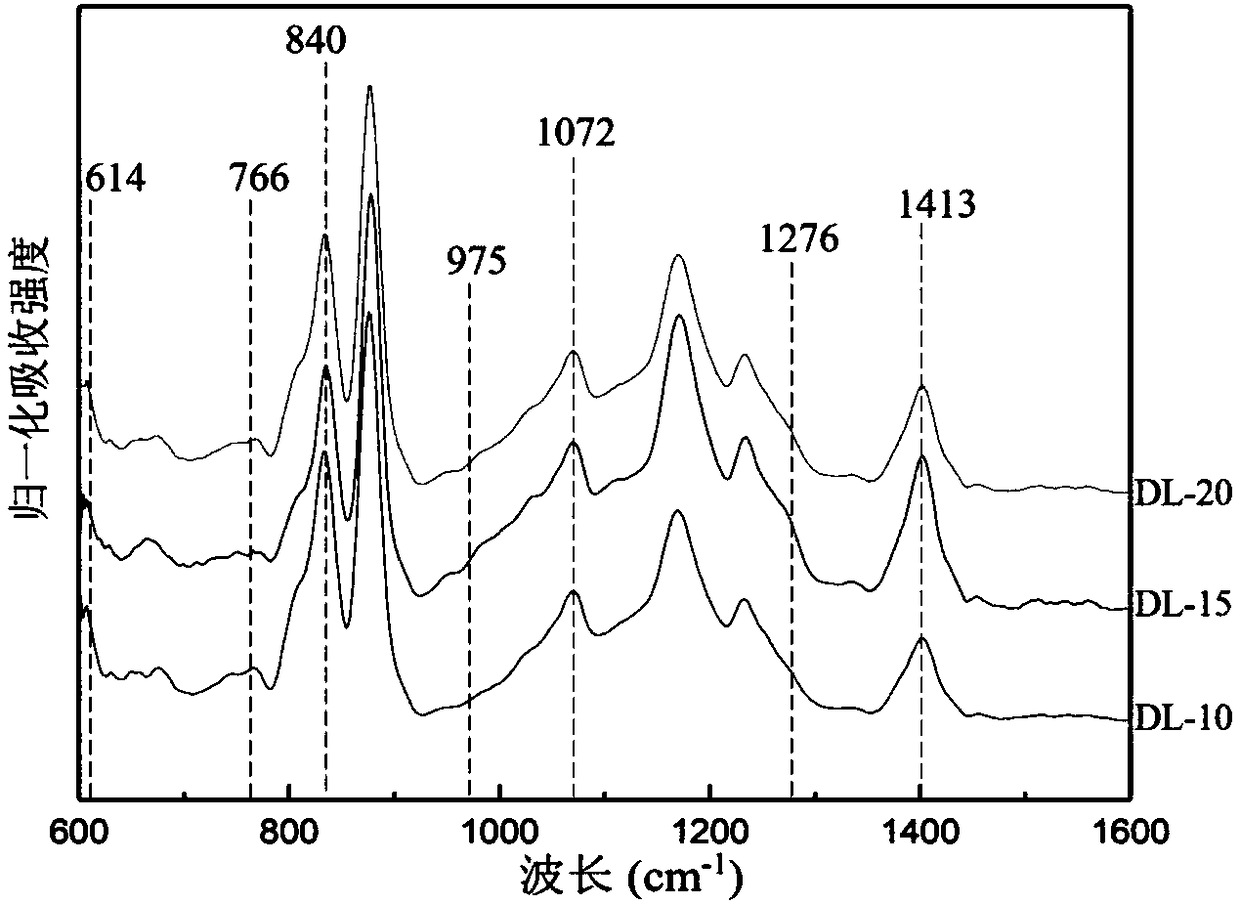
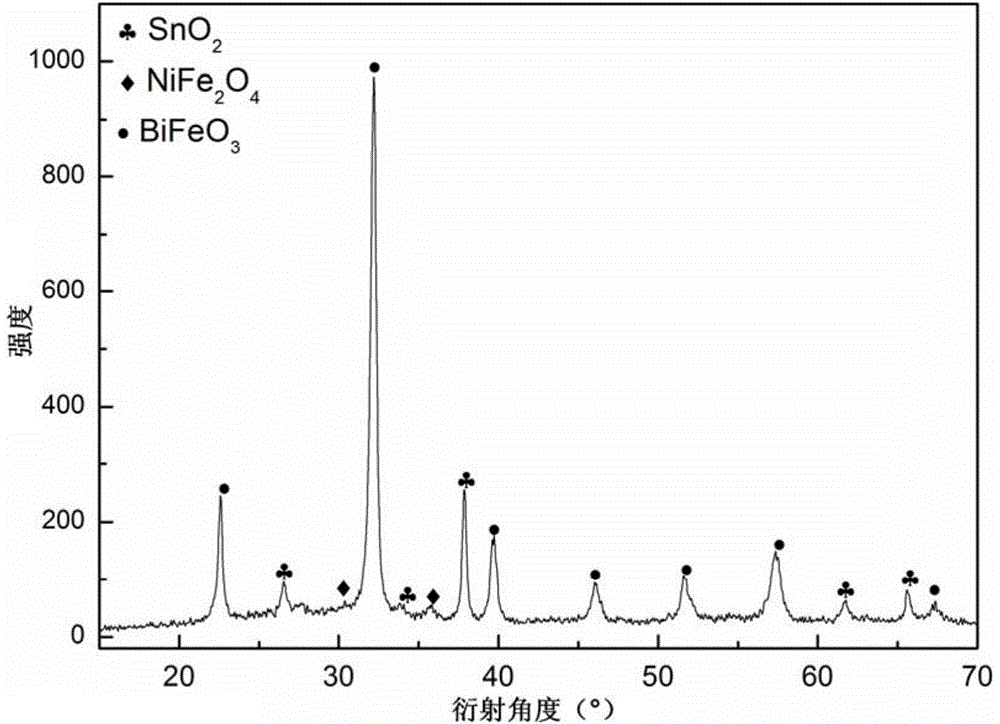
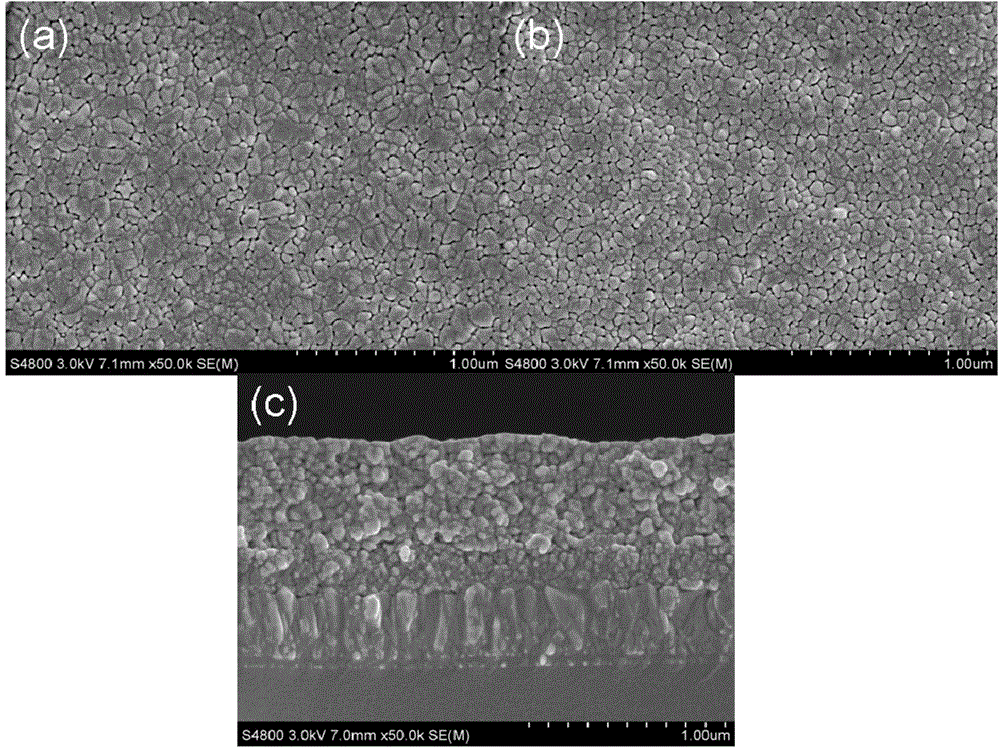
Bi0.92-xHo0.08AExFe0.97Mn0.03O3-Zn1-yNiyFe2O4 ferromagnetic composite film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105837196AReduce contentHigh polarizationCeramic layered productsMagnetic layerMagnetic composite
The invention provides a Bi0.92-xHo0.08AExFe0.97Mn0.03O3-Zn1-yNiyFe2O4 ferromagnetic composite film and a preparation method thereof. The ferromagnetic composite film comprises a Bi0.92-xHo0.08AExFe0.97Mn0.03O3 crystalline film and a Zn1-yNiyFe2O4 crystalline film, which are compounded together. The preparation method is as below: first respectively preparing a Zn1-yNiyFe2O4 precursor solution and a Bi0.92-xHo0.08AExFe0.97Mn0.03O3 precursor solution, wherein AE is Sr, Ca, Ba or Pb, x equals to 0.01-0.04, and y equals to 0.1-0.9; preparing a plurality of Zn1-yNiyFe2O4 films on a substrate by spin coating; and then preparing plurality of Bi0.92-xHo0.08AExFe0.97Mn0.03O3 films on the Zn1-yNiyFe2O4 films by spin coating, so as to obtain the ferromagnetic composite film. The method regulates the crystal structure of BiFeO3 by doping, and uses ferromagnetic Zn1-yNiyFe2O4 as the magnetic layer, so as to substantially increase the ferroelectric and ferromagnetic properties of the film, and effectively reduce the leakage current density of the film.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Double-layer structure flexible piezoelectric film with high output, preparation and application method thereof
ActiveCN108530806AHigh dielectric constantHigh polarizationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionPolyvinylidene fluorideMagnesium
Belonging to the field of electronic composite materials and nano-functional materials, the invention provides a double-layer structure flexible piezoelectric film with high output, a preparation andapplication method thereof. A layer-by-layer solution spin coating-heat treatment process is adopted, an inorganic piezoelectric material is used as the filler to enhance the piezoelectric output of the composite film, and the double-layer structure is utilized to acquire high output and good mechanical properties at the same time. The inorganic filler is nanoparticles or nanofiber of barium titanate, barium strontium titanate, lead zirconate titanate and other piezoelectric ceramics, or nanoparticles or nanofiber of magnesium oxide, zinc oxide and other metal oxides, or multiwalled carbon nanotube. The polymer matrix can be polyvinylidene fluoride, polyvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene, polyvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene-hexafluoropropylene and other materials. By adjusting thefiller content and the filler distribution in the double layers, the filler efficiency can be improved. The composite material has the characteristics of good flexibility, high piezoelectric output,high sensitivity and light weight, and can be used as a power supply of wearable equipment, as a flexible sensor to detect human activities and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
MgO-Based Tunnel Spin Injectors
InactiveUS20080145952A1High polarizationImprove thermal stabilityNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsCharge carrier
A MgO tunnel barrier is sandwiched between semiconductor material on one side and a ferri- and / or ferromagnetic material on the other side to form a spintronic element. The semiconductor material may include GaAs, for example. The spintronic element may be used as a spin injection device by injecting charge carriers from the magnetic material into the MgO tunnel barrier and then into the semiconductor. Similarly, the spintronic element may be used as a detector or analyzer of spin-polarized charge carriers by flowing charge carriers from the surface of the semiconducting layer through the MgO tunnel barrier and into the (ferri- or ferro-) magnetic material, which then acts as a detector. The MgO tunnel barrier is preferably formed by forming a Mg layer on an underlayer (e.g., a ferromagnetic layer), and then directing additional Mg, in the presence of oxygen, towards the underlayer.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Current perpendicular to plane spin valve with high-polarization material in ap1 layer for reduced spin torque
InactiveUS20090168269A1Improved resistance amplitude changeReduced spin torque noiseNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsSpinsSpin polarization
A current perpendicular to plane magnetoresistive sensor having improved resistance amplitude change and reduced spin torque noise. The sensor has an antiparallel coupled pinned layer structure with at least one of the layers of the pinned layer structure includes a high spin polarization material such as Co2FeGe. The sensor can also include an antiparallel coupled free layer.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Multiferroic Bi0.96-xSr0.04RExFe0.94Mn0.04Cr0.02O3-NiFe2O4 composite film and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a multiferroic Bi0.96-xSr0.04RExFe0.94Mn0.04Cr0.02O3-NiFe2O4 composite film and a preparation method thereof. The composite film comprises a Bi0.96-xSr0.04RExFe0.94Mn0.04Cr0.02O3 crystalline state film and a NiFe2O4 crystalline state film which are compounded together. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively preparing a Bi0.96-xSr0.04RExFe0.94Mn0.04Cr0.02O3 precursor solution and a NiFe2O4 precursor solution; and spinning on a substrate to prepare a multilayer NiFe2O4 film, and spinning on the NiFe2O4 film to prepare a multilayer Bi0.96-xSr0.04RExFe0.94Mn0.04Cr0.02O3 film, thereby obtaining the target product. The equipment requirement is simple, the prepared film is high in uniformity, the doping amount is easy to control, and the ferroelectric properties and ferromagnetic properties of the film are greatly improved. Meanwhile, the leakage current density of the film is effectively reduced.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Layered heusler alloys and methods for the fabrication and use thereof
ActiveUS9643385B1High spin polarizationLow dampingSpin-exchange-coupled multilayersElectrical equipmentMetallurgyCrystal structure
Disclosed herein are layered Heusler alloys. The layered Heusler alloys can comprise a first layer comprising a first Heusler alloy with a face-centered cubic (fcc) crystal structure and a second layer comprising a second Heusler alloy with a fcc crystal structure, the second Heusler alloy being different than the first Heusler alloy, wherein the first layer and the second layer are layered along a layering direction, the layering direction being the [110] or [111] direction of the fcc crystal structure, thereby forming the layered Heusler alloy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
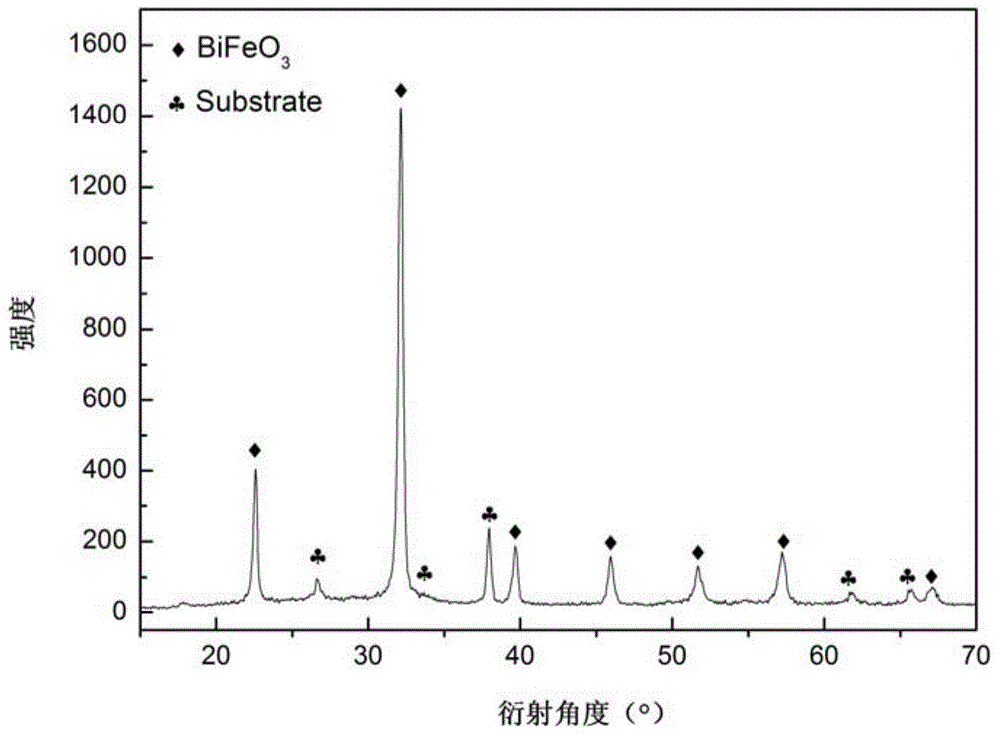
High-voltage-withstanding, low-electric-leakage and high-polarization strength bismuth ferrite thin film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103839928AHigh rectangularityHigh polarizationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMagnetizationSingle crystal
The invention relates to a high-voltage-withstanding, low-electric-leakage and high-polarization strength bismuth ferrite thin film and a preparation method thereof. The high-voltage-withstanding, low-electric-leakage and high-polarization strength bismuth ferrite thin film comprises a base body, a bottom electrode, a bismuth ferrite dielectric layer and a top electrode, a mono-crystal oxide semiconductor substrate with lattice constant close to that of the bismuth ferrite is used as the base body, the bottom electrode is a conductive oxide thin film, and the top electrode is a metal thin film point electrode. The bottom electrode is deposited on the base body in a coaxial sputtering mode, then the bismuth ferrite dielectric layer is deposited on the bottom electrode in an off-axis sputtering mode, and at last the top electrode is deposited on the bismuth ferrite dielectric layer so that the thin film can be prepared. The prepared BiFeO3 thin film is in a rhombohedral shape and achieves height orientation, a ferroelectric hysteresis loop with good rectangularity is achieved under the room temperature, the intensity of polarization is high, the intensity of magnetization can reach 100 -110 micro coulombs / cm<2>, the voltage withstanding performance is good, and the maximum withstand voltage can achieve 50 v.
Owner:欧阳俊
Bismuth-based lead-free high energy storage density ceramic material and preparation method thereof
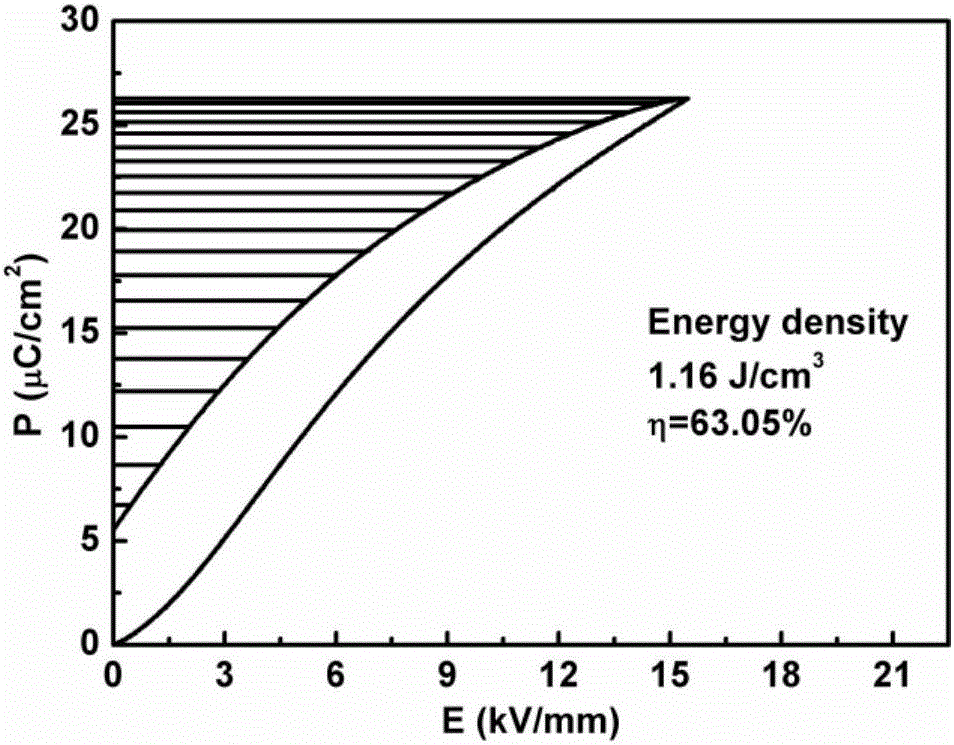
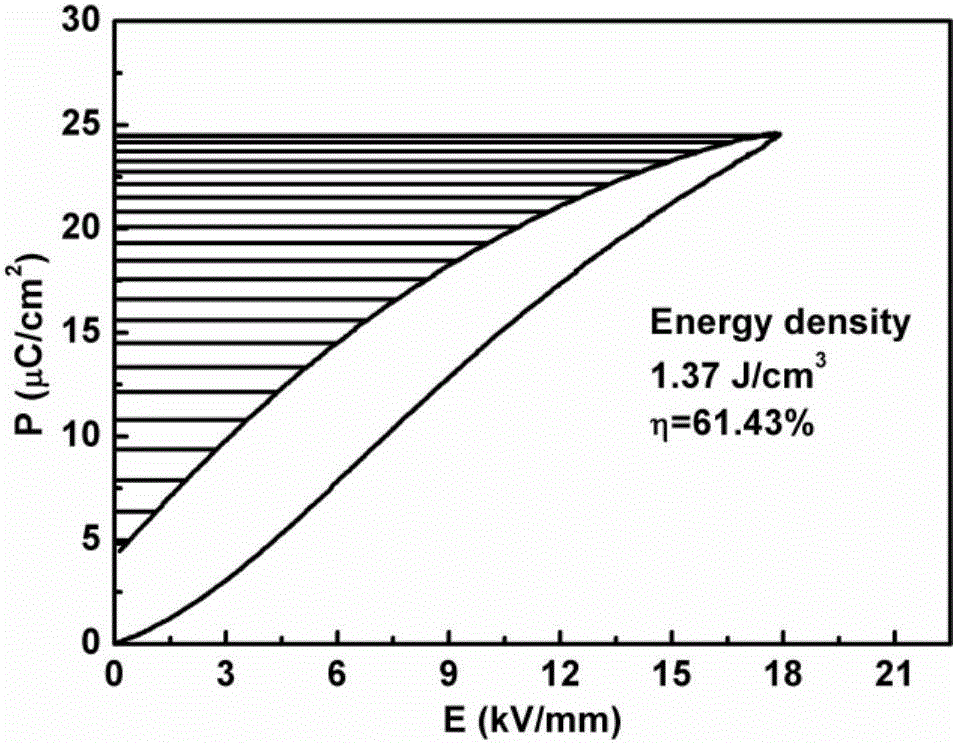
The invention discloses a bismuth-based lead-free high energy storage density ceramic material and a preparation method thereof, the material and the preparation method relate to the technical field of electronic ceramics and components, and are used in related fields of energy storage capacitor application. The chemical composition of the material conforms to the general formula: (1-x)Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3+x SrTiO3+ywt%Nb2O5, which is synthesized by traditional ceramic preparation process. Through the addition of Nb, the grain size of ceramics is refined, and the breakdown field strength is increased. The ceramic components can obtain Wrec-1.8J / cm3 energy storage density under a direct current field of E = 13kV / mm, and the energy efficiency eta can reach 80 %; and meanwhile, the material has good temperature stability of energy storage performance.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ferroelectric memory device
InactiveUS20070111335A1Improve featuresHigh polarizationVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesIon beamSilicon
A ferroelectric memory device has a high performance, includes no Pb, and can be directly mounted onto an Si substrate. The ferroelectric memory device includes a (001)-oriented BiFeO3 ferroelectric layer 5 with a tetragonal structure, which is formed on an electrode 4 made of a perovskite material formed on an Si oxide film. The electrode 4 with a perovskite structure is formed by an ion beam assist method.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
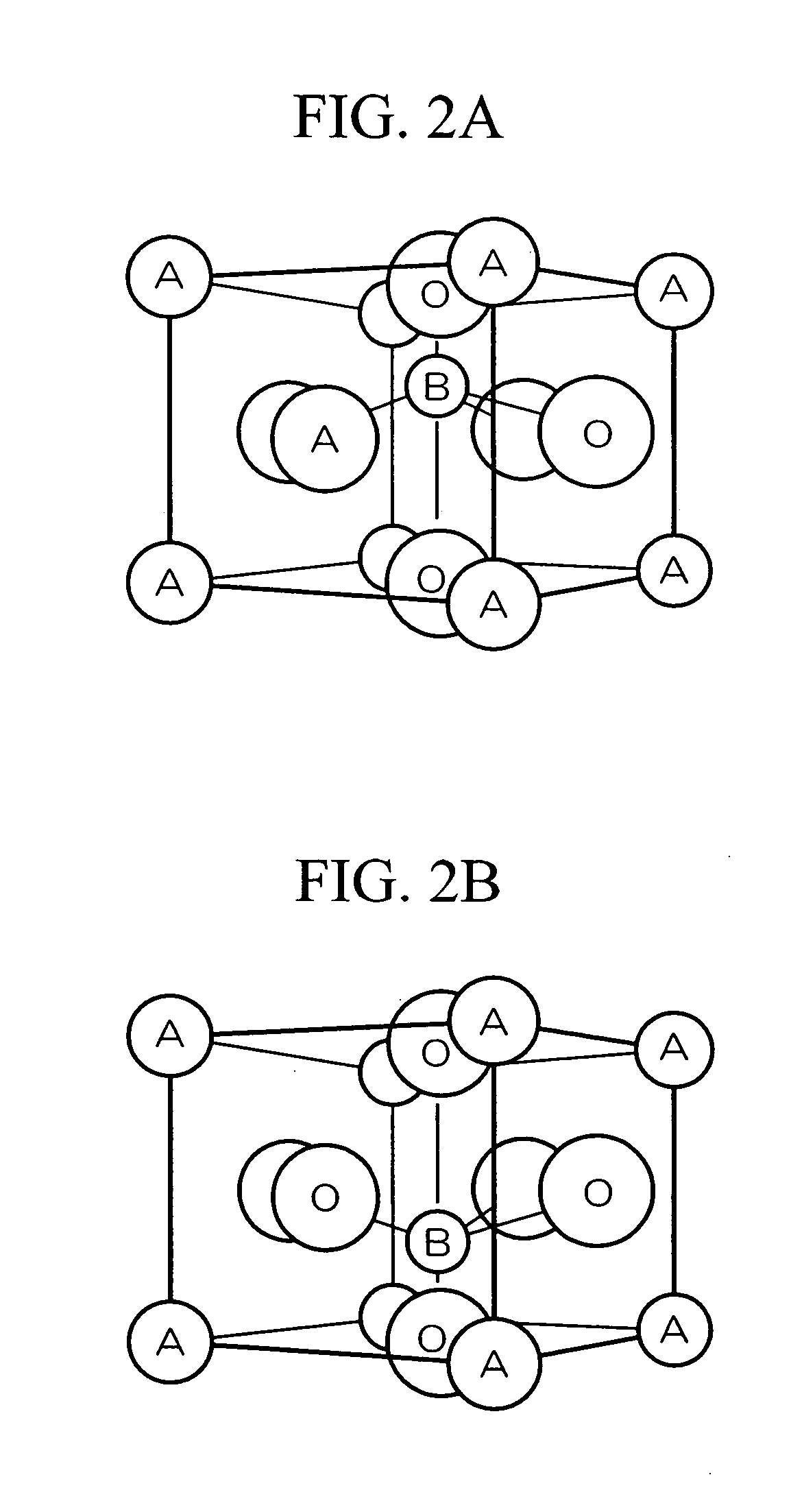
Ferroelectric thin film element, piezoelectric actuator and liquid discharge head
InactiveUS7215067B2High spontaneous polarizationImprove featuresPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesFerroelectric thin filmsPiezoelectric actuators
A ferroelectric thin film element comprises a substrate and an epitaxial ferroelectric thin film provided on the substrate. The thin film satisfies z / z0>1.003 and 0.997≦x / x0≦1.003, where a crystal face of said thin film parallel to a crystal face of a surface of the substrate is taken as a Z crystal face, a face spacing of the Z crystal face is taken as z, a face spacing of the Z crystal face of a material constituting the thin film in a bulk state is taken as z0, a crystal face of the thin film perpendicular to the Z crystal face is taken as an X crystal face, a face spacing of the X crystal face is taken as x and a face spacing of the X crystal face of the material constituting the thin film in a bulk state is taken as x0.
Owner:CANON KK
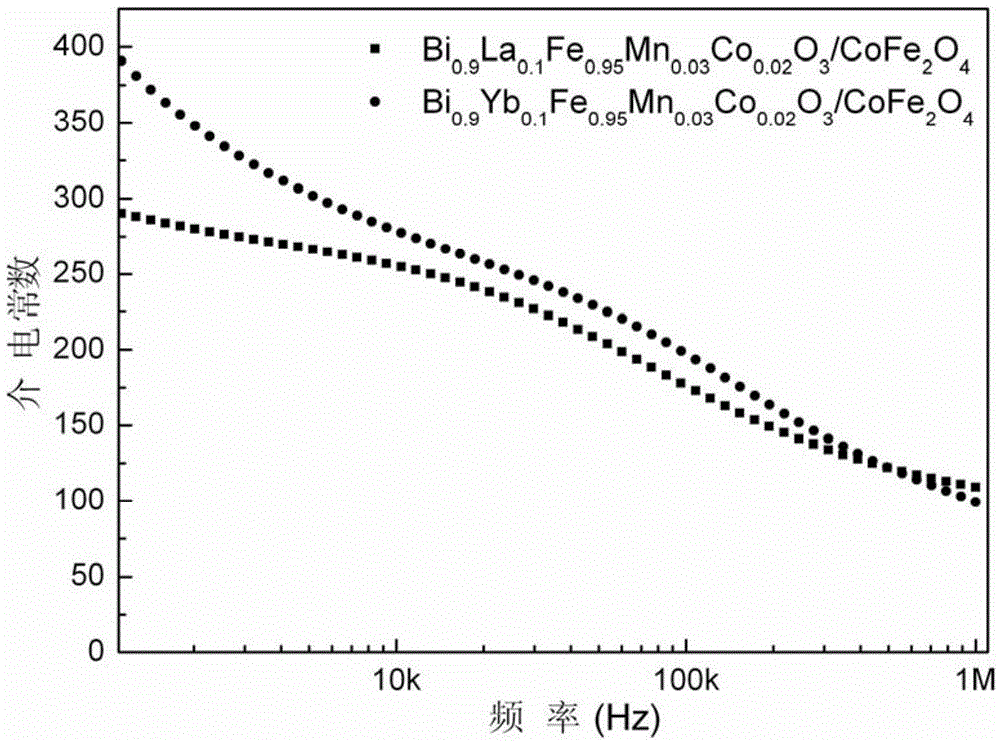
Multiferroic Bi1-xRExFe0.97-yMn0.03TMyO3/CoFe2O4 composite film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104538140AImprove multiferroic propertiesImprove ferroelectric propertiesInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureComposite filmMultiferroics
The invention provides a multiferroic Bi1-xRExFe0.97-yMn0.03TMyO3 / CoFe2O4 composite film and a preparation method thereof. The composite film comprises a Bi1-xRExFe0.97-yMn0.03TMyO3 crystalline state film and a CoFe2O4 crystalline state film. The preparation method comprises the following steps of respectively preparing Bi1-xRExFe0.97-yMn0.03TMyO3 precursor solution and CoFe2O4 precursor solution; spin coating on a substrate to prepare a plurality of layers of CoFe2O4 films, spin coating on the CoFe2O4 films to prepare a plurality of layers of Bi1-xRExFe0.97-yMn0.03TMyO3 films and accordingly obtaining a target product. According to the multiferroic Bi1-xRExFe0.97-yMn0.03TMyO3 / CoFe2O4 composite film and the preparation method thereof, the device requirement is simple, the prepared film is good in homogeneity, the doping content is easy to control, the ferroelectric property and the ferromagnetic property of the film are improved to a large extent, and the film is high in residual polarization value and residual polarization value.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System for selective irradiation with circularly polarized light
ActiveUS20150075069A1Improve energy efficiencyHigh polarizationSeed and root treatmentPoint-like light sourceOptoelectronicsIrradiation
According to the present invention, provided is a system for irradiating a target object selectively with specific circularly polarized light, comprising a polarization-state control member that controls the polarization state of light to thereby generate circularly polarized light; and a circularly polarized light-reflecting member, wherein the circularly polarized light-reflecting member is disposed at a position on which the circularly polarized light emitted from the polarization-state control member can be incident; the circularly polarized light-reflecting member generates reflected light that selectively comprises circularly polarized light of the same sense as the incident circularly polarized light from the polarization-state control member; and the circularly polarized light-reflecting member is disposed such that the target object can be irradiated with at least a part of the reflected light.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Brightness-enhancing integral polarizer and optical film structure and a manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060176422A1Reduce light transmittancePoor match of opticalNon-linear opticsOptical elementsPolarizerLightness
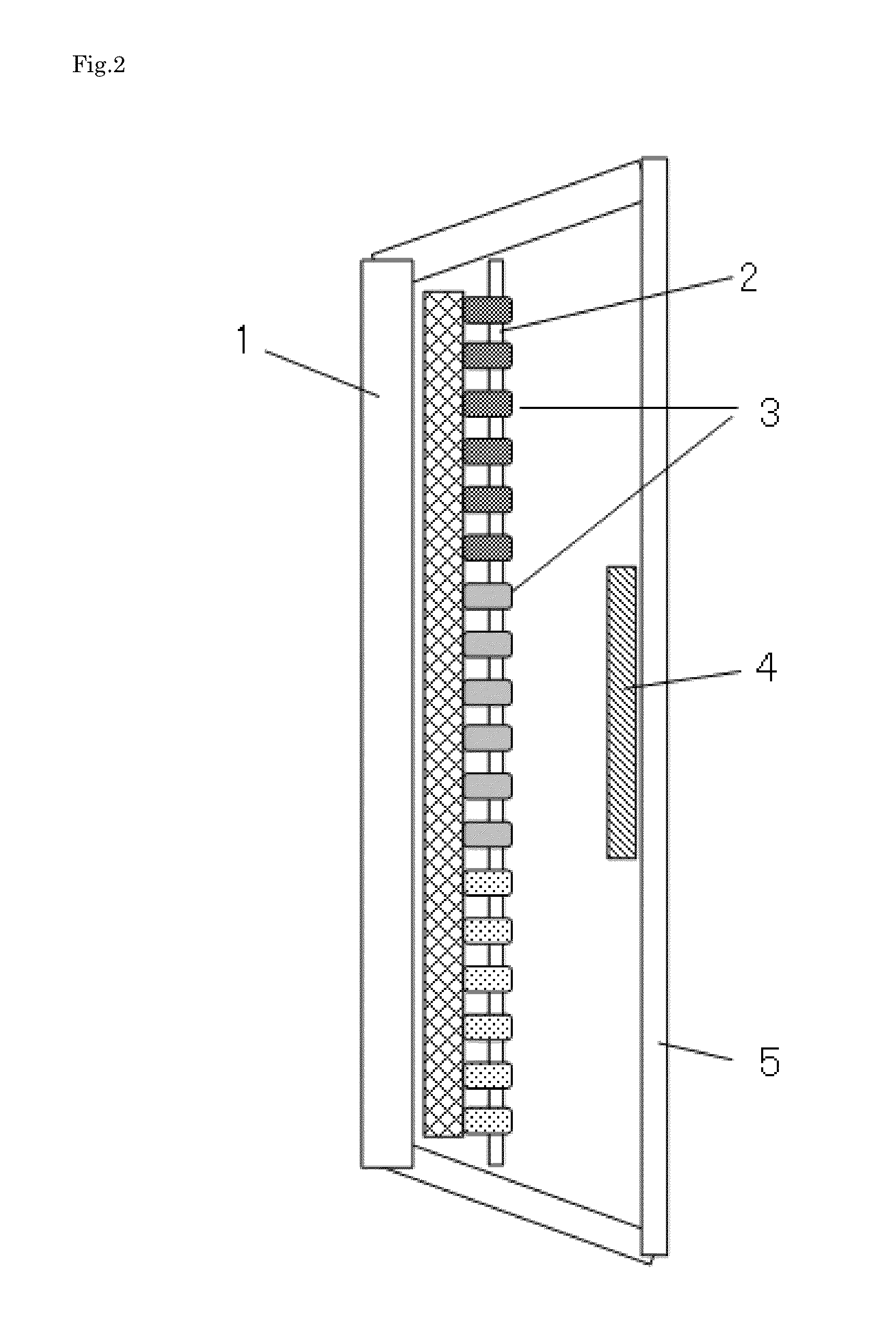
A brightness-enhancing integral polarizer and optical film structure and manufacture are described. The brightness-enhancing integral polarizer and optical film have an absorptive polarizer and a reflective polarizer. The reflective polarizer generates a reflective light source effect, and uses a nonlinear optic design to coat a brightness-enhancing integral polarizer and optical film with a different dye on at least one substrate and produce the effects of brightness enhancement, high polarization, high transmittance, wide viewing angle and high contrast for the brightness-enhancing integral polarizer and optical film structure and manufacturing method.
Owner:TAIWAN TFT LCD ASSOC +7
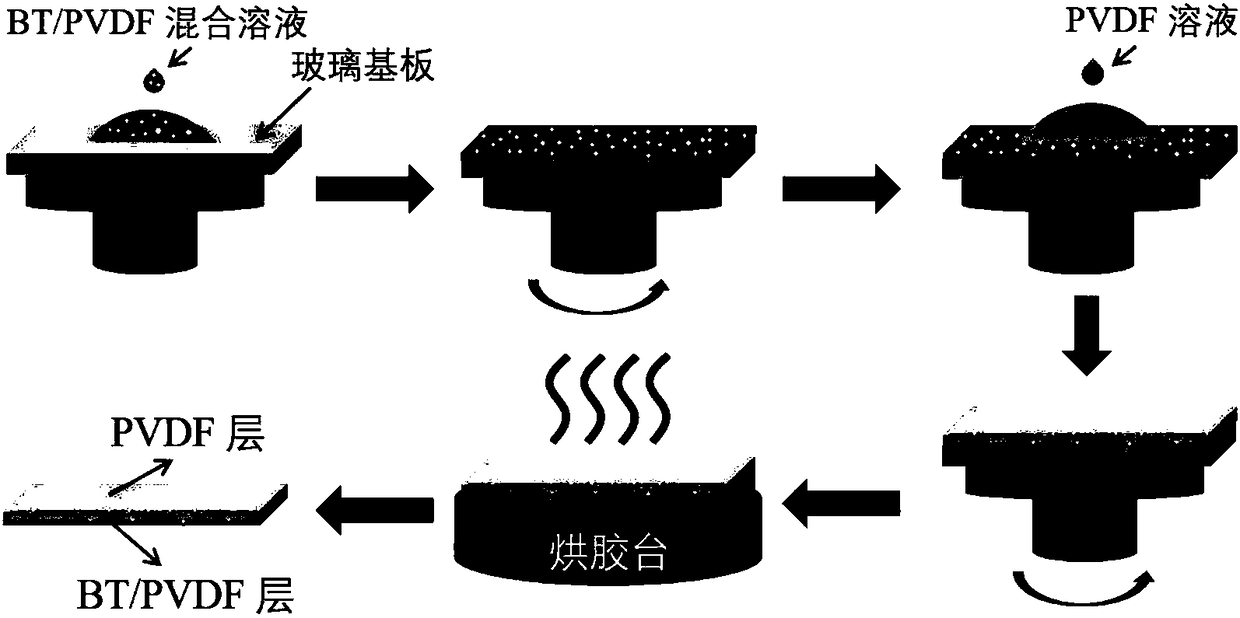
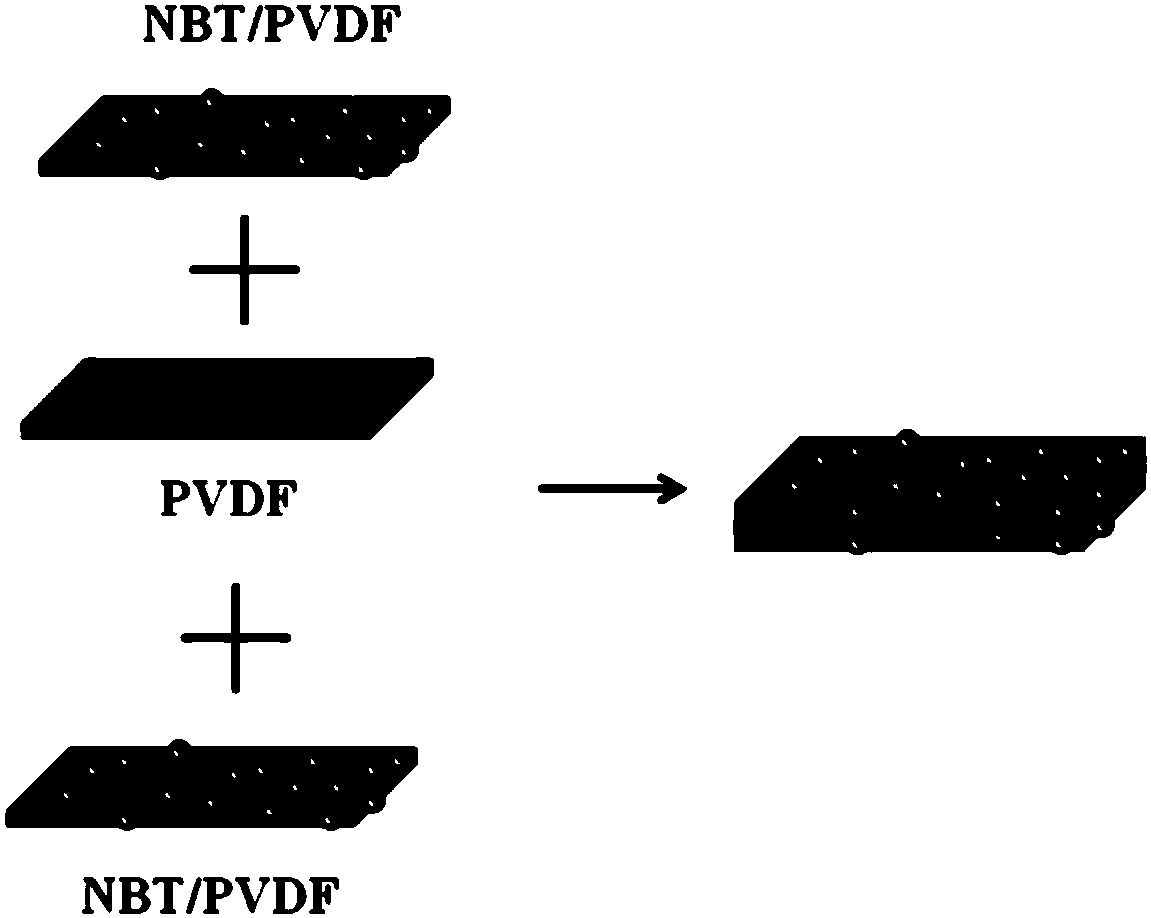
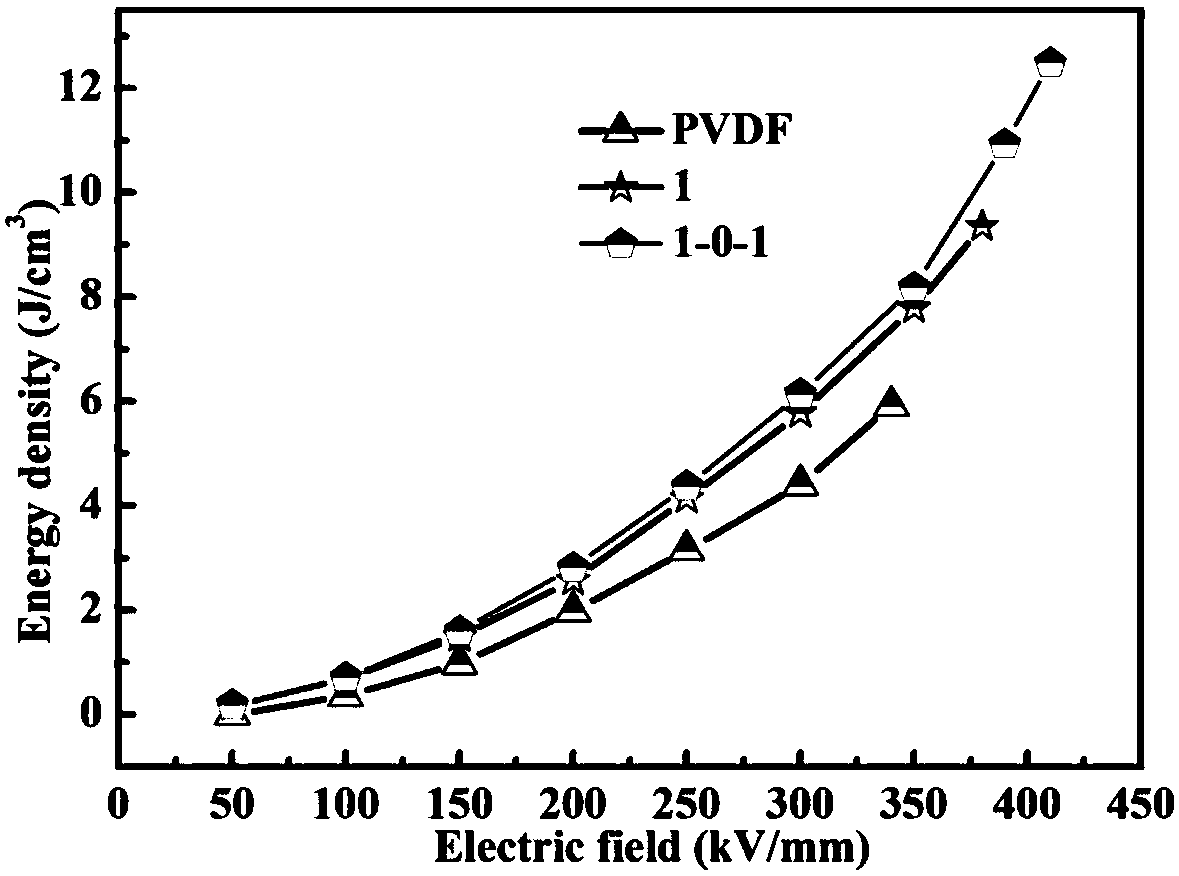
NBT/PVDF three-layer structured composite material for energy storage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108101384AHigh polarizationHigh energy storage densityCoatingsPolyvinylidene difluorideSolvent
The invention discloses an NBT / PVDF three-layer structured composite material for energy storage and a preparation method of the NBT / PVDF three-layer structured composite material for the energy storage. NBT particle powder is prepared through a ball-milling method; PVDF is divided into three parts which are respectively dissolved in a solvent to obtain three PVDF solutions; the NBT particle powder is divided into two parts and respectively added to two PVDF solutions to obtain two NBT / PVDF stock solutions; the NBT / PVDF stock solutions, the PVDF solutions and the NBT / PVDF stock solutions are laminated and subjected to tape casting on a glass substrate sequentially by using a multi-layer tape casting process. A middle layer of the composite material is a pure PVDF polymer, and the two layers of the upper and lower layers are NBT / PVDF composite layers, dielectric ceramic particles are added in an upper-lower two-layer structure, the polarization intensity and energy storage density are used, and the middle layer uses the pure PVDF polymer to obtain high breakdown field strength.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multiferroic Bi(0.98-x)Sr0.02RExFe0.97Mn0.03O3-CuFe2O4 composite film and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a multiferroic Bi(0.98-x)Sr0.02RExFe0.97Mn0.03O3-CuFe2O4 composite film and a preparation method thereof. The composite film comprises Bi(0.98-x)Sr0.02RExFe0.97Mn0.03O3 crystal films and CuFe2O4 crystal films which are composited together. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a Bi(0.98-x)Sr0.02RExFe0.97Mn0.03O3 precursor solution and a CuFe2O4 precursor solution respectively; secondly, preparing multiple layers of CuFe2O4 films on a substrate by spin coating, and preparing multiple layers of Bi(0.98-x)Sr0.02RExFe0.97Mn0.03O3 films on the CuFe2O4 films by spin coating to obtain a target product. The equipment requirement is simple, the uniformity of the prepared film is high, the doping amount is easy to control, the ferroelectric and ferromagnetic properties of the film are improved, and the leakage current density of the film is effectively reduced.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
SrTiO<3>-based lead-free high-energy-density ceramic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106587997AHigh polarizationHigh energy storage densityFixed capacitor dielectricMaterials preparationSilver electrode
The invention discloses an SrTiO<3>-based lead-free high-energy-density ceramic material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of material preparation. According to the method, firstly, 10 to 30 mol percent of Na<0.5>Bi<0.5>TiO<3> powder is added into SrTiO<3> powder to form a mixture; the mixture is subjected to ball milling and drying to obtain dried materials; then, the dried materials are sequentially granulated and sieved to form granulation materials; the granulation materials are made into test specimens; then, sintering is performed to obtain sintering test specimens; grinding and cleaning are performed on the obtained sintering test specimens; the front side and the back side of the ground and cleaned sintering test specimens are uniformly coated with silver electrode slurry; then, sintering is performed; and (1-x)SrTiO<3>-xNa<0.5>Bi<0.5>TiO<3> ceramics are obtained. The high-energy-density ceramic material obtained by using the method provided by the invention has the advantages that the preparation process is simple; the material cost is low; and the mass production can be realized, so that an effective path is provided for the application of the high-energy-density ceramic material.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Spin transfer torque (STT) device with template layer for heusler alloy magnetic layers
ActiveUS20190279667A1High spin polarizationReduce critical currentConstruction of head windingsRecord information storageSpin-transfer torqueRandom access memory
A spin transfer torque (STT) device has a free ferromagnetic layer that includes a Heusler alloy layer and a template layer beneath and in contact with the Heusler alloy layer. The template layer may be a ferromagnetic alloy comprising one or more of Co, Ni and Fe and the element X, where X is selected from one or more of Ta, B, Hf, Zr, W, Nb and Mo. A CoFe nanolayer may be formed below and in contact with the template layer. The STT device may be a spin-torque oscillator (STO), like a STO incorporated into the write head of a magnetic recording disk drive. The STT device may also be a STT in-plane or perpendicular magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) cell for magnetic random access memory (MRAM). The template layer reduces the critical current density of the STT device.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
LaSrMnCo codoped bismuth ferrite multiferroic film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107117830AGood dielectricImprove ferroelectric propertiesCoatingsMANGANESE ACETATEAcetic anhydride
The invention provides a LaSrMnCo codoped bismuth ferrite multiferroic film and a preparation method thereof. A Bi(0.97-x)LaxSr0.03Fe0.94Mn0.04Co0.02O3 multiferroic film, namely the LaSrMnCo codoped bismuth ferrite multiferroic film, is prepared by taking bismuth nitrate, lanthanum nitrate, strontium nitrate, ferric nitrate, manganese acetate and cobalt nitrate as raw materials (bismuth nitrate of excessive 5 percent), taking ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and acetic anhydride as solvents and using a spin-coating method and a layer-by-layer annealing process. A sol-gel process is adopted, spin-coating and layer-by-layer annealing methods are adopted, equipment requirements are simple, experimental conditions are easy to realize, the film is suitably prepared on a large surface and an irregularly shaped surface, chemical components are accurately controllable, the multiferroic property of the BiFeO3 film can be improved, the prepared the LaSrMnCo codoped bismuth ferrite multiferroic film has high uniformity and is a multiferroic film with high residual polarization value and low coercive field, and the ferroelectric and dielectric properties of the film are effectively enhanced.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chemical preparation method of Bi4LaTi3FeO15 multiferroic film
InactiveCN103951404AImproved ferroelectricityImprove ferroelectric propertiesIron compoundsMaterials preparationRapid thermal processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of physico-chemical material preparation, and relates to a chemical preparation method of a Bi4LaTi3FeO15 multiferroic film. The method is characterized in that single-layer magnetic octahedral group LaFeO3 is inserted into three-layer of layered perovskite-type ferroelectric Bi4Ti3O12 to form a novel four-layer layered perovskite-type Bi4LaTi3FeO15 multiferroic film. According to the method of the invention, a Bi4LaTi3FeO15 precursor sol is firstly prepared by a chemical preparation method, and then is deposited on a clean substrate of (111)Pt / Ti / SiO2 / Si(100) directly to form a wet film; and annealing treatment in O2 atmosphere is carried out in a rapid heat treatment furnace. The method is simple in required equipment, low in cost, compatible with microelectronic technology and process, and suitable for industrial production. The prepared Bi4LaTi3FeO15 multiferroic film is pure in phase, good in ferroelectric properties, and quite beneficial to application and popularization of Bi4LaTi3FeO15 multiferroic films.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Functionalized active-nucleus complex sensor
InactiveUS20020037253A1Improve bindingFast exchangeBiocideNanotechNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceChemistry
A functionalized active-nucleus complex sensor that selectively associates with one or more target species, and a method for assaying and screening for one or a plurality of target species utilizing one or a plurality of functionalized active-nucleus complexes with at least two of the functionalized active-nucleus complexes having an attraction affinity to different corresponding target species. The functionalized active-nucleus complex has an active-nucleus and a targeting carrier. The method involves functionalizing an active-nucleus, for each functionalized active-nucleus complex, by incorporating the active-nucleus into a macromolucular or molecular complex that is capable of binding one of the target species and then bringing the macromolecular or molecular complexes into contact with the target species and detecting the occurrence of or change in a nuclear magnetic resonance signal from each of the active-nuclei in each of the functionalized active-nucleus complexes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Lead-free BiFeO3-based ferroelectric ceramic material with high energy storage density and high energy storage efficiency and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109293353AHigh energy storage densityImprove energy storage efficiencyFixed capacitor dielectricChemical compositionHigh energy
The invention relates to a lead-free BiFeO3-based ferroelectric ceramic material with high energy storage density and high energy storage efficiency and a preparation method thereof. The lead-free BiFeO3-based energy-storage ceramic material is a ferroelectric phase at the room temperature, and the chemical composition is (1-z-x)BiFeO3-zBaTiO3-xBa(Zn1 / 3Ta2 / 3)O3+yMnCO3, wherein x is greater than orequal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.10, z is greater than or equal to 0.32 and less than or equal to 0.36, y is greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0. 15wt%, and y is a mass percent ratio of MnCO3 to (1-z-x)BiFeO3-zBaTiO3-xBa(Zn1 / 3Ta2 / 3)O3.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
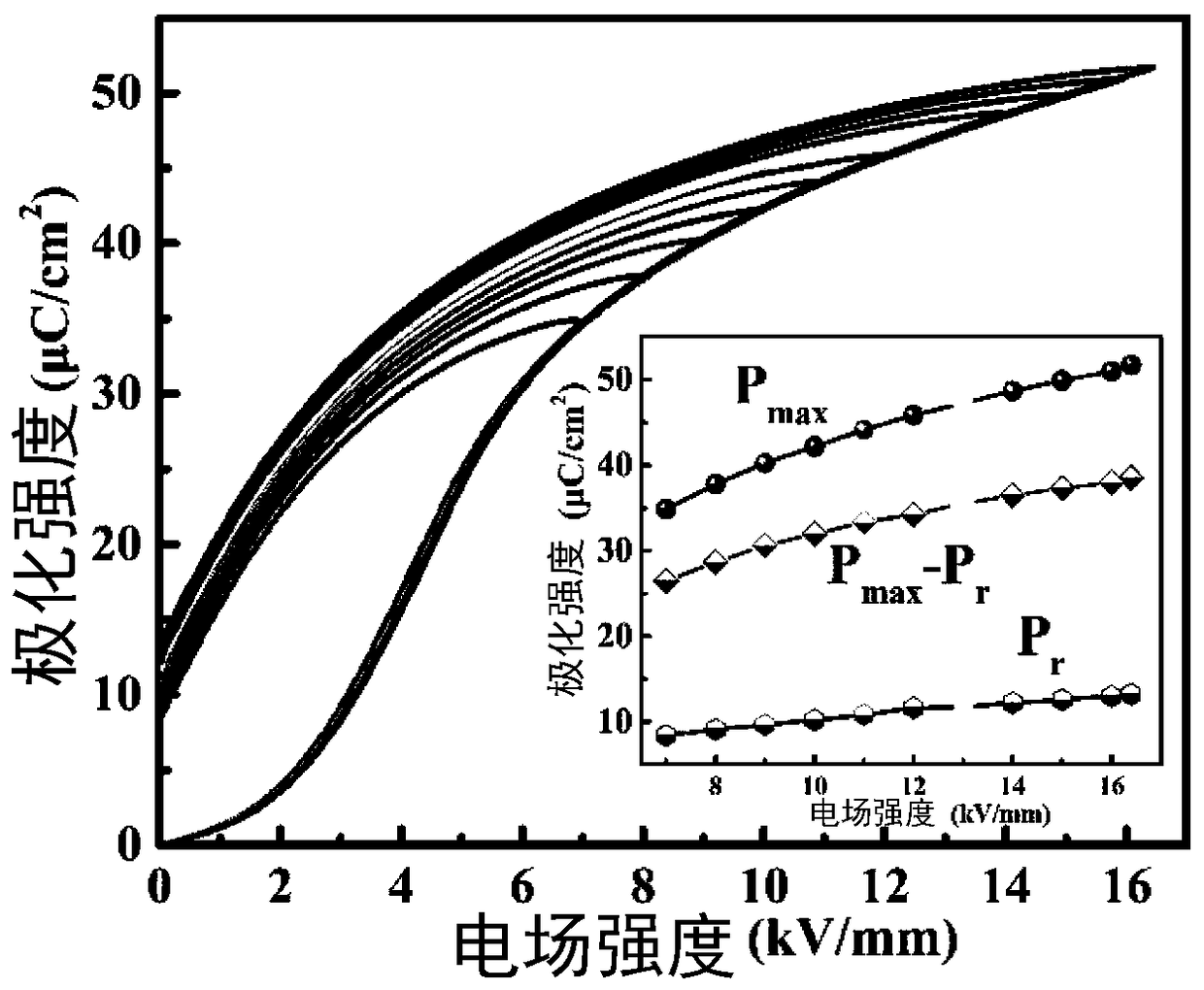
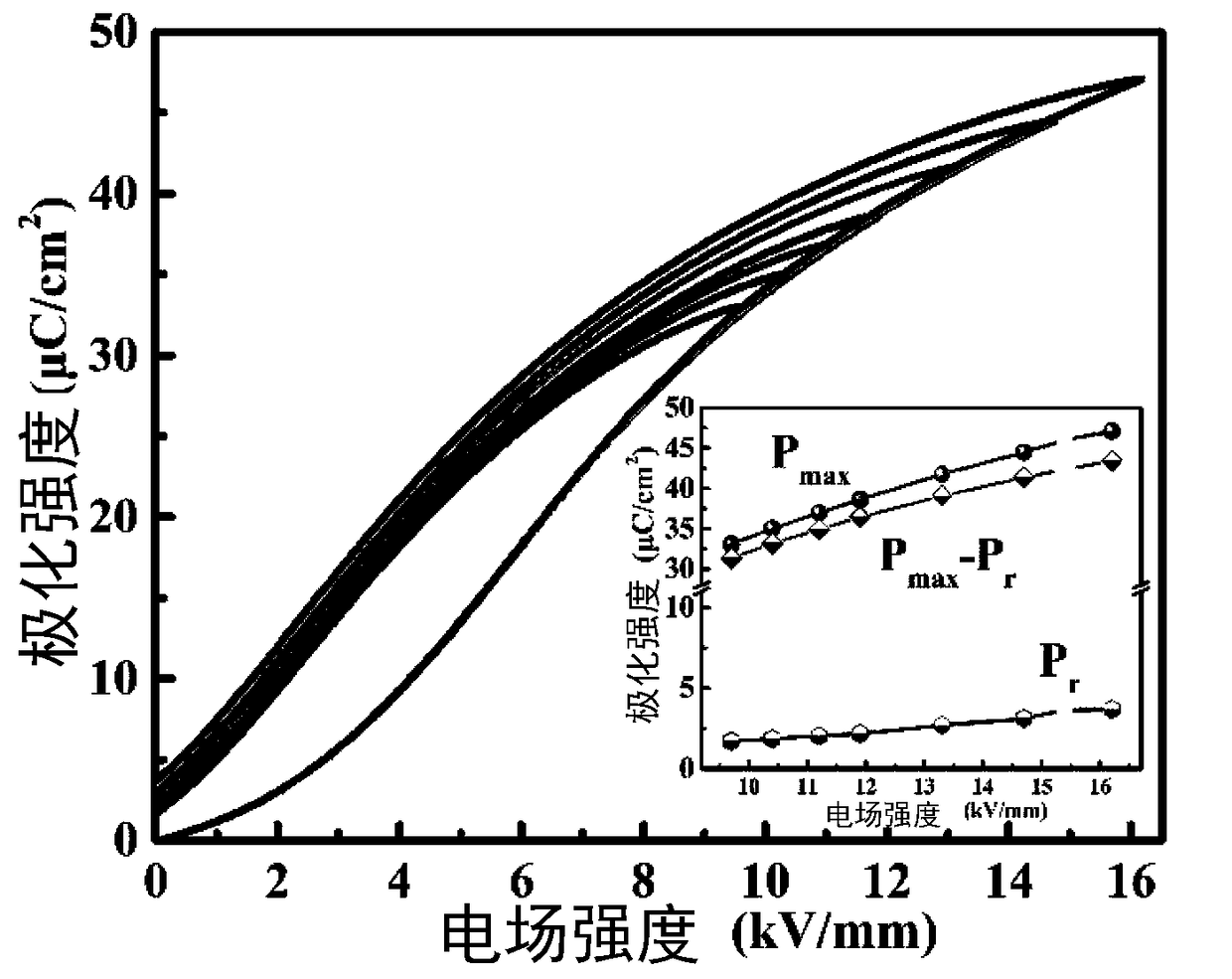
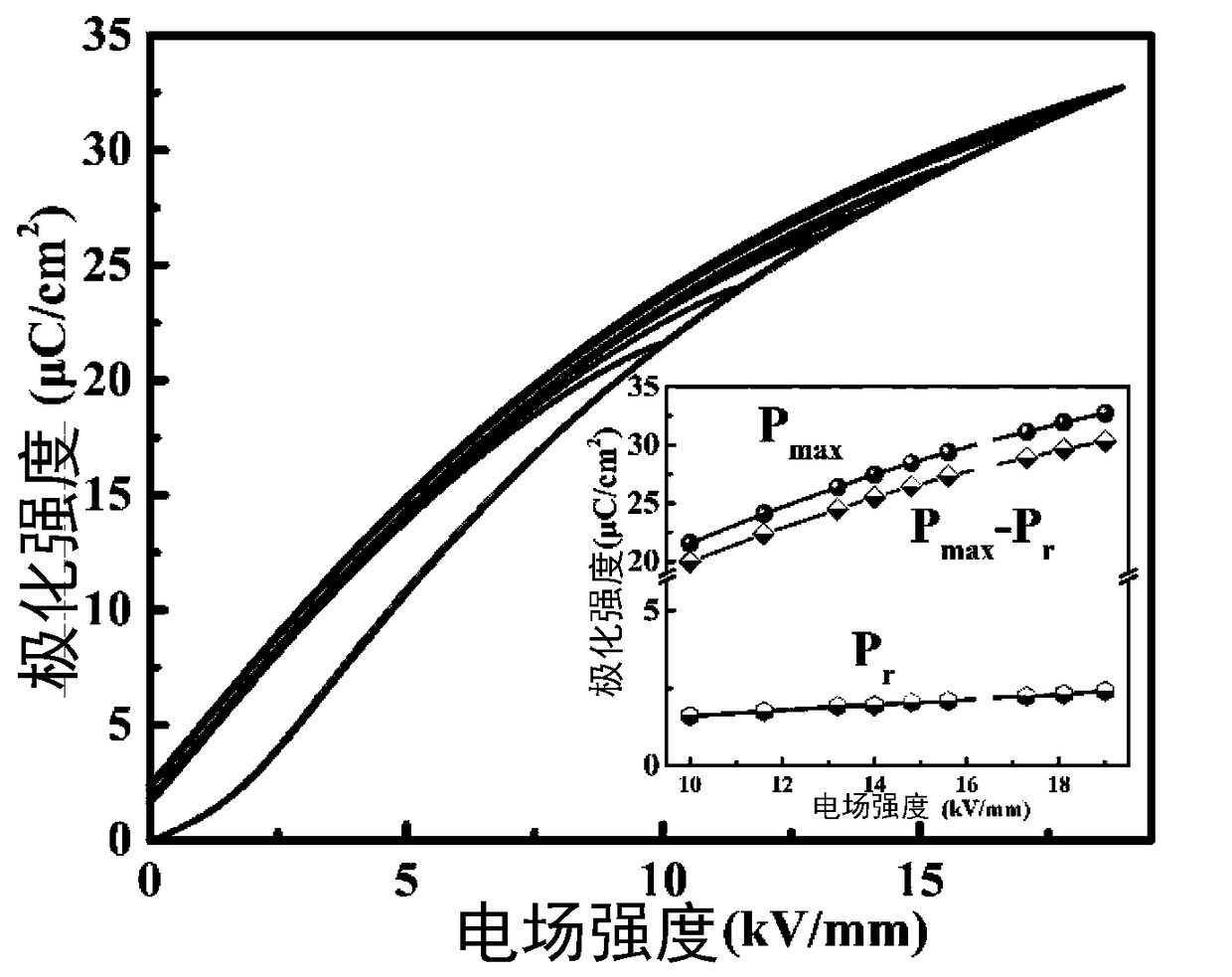
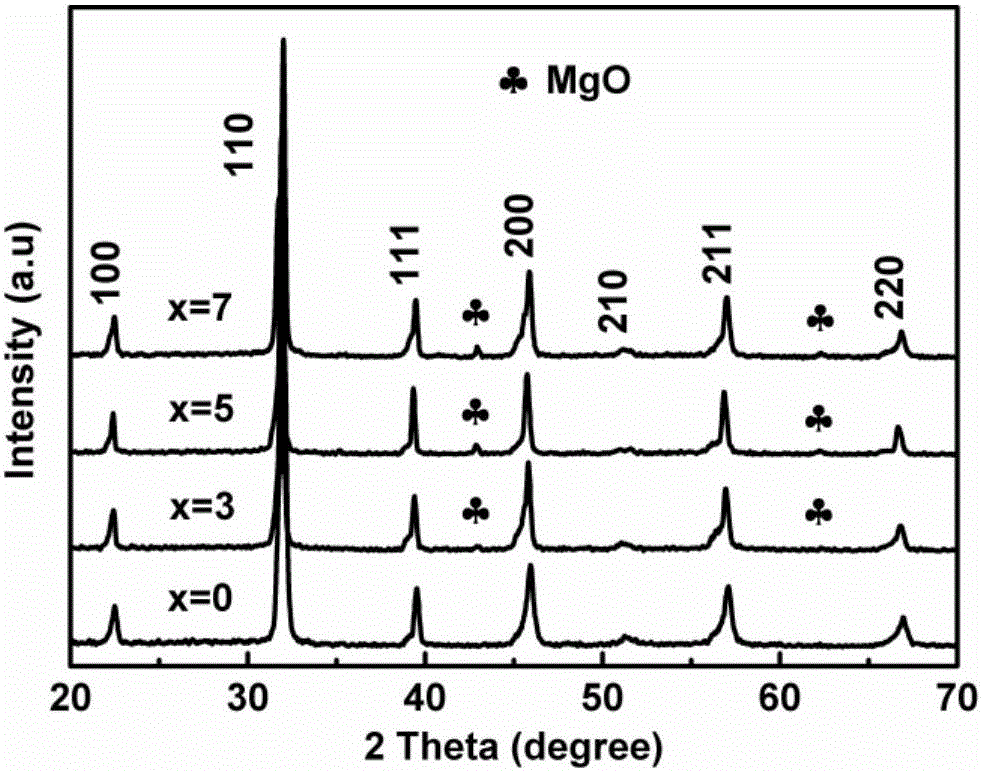
0.5NBT-0.5BCTZ-xwt%MgO high-storage-energy-density ceramic material prepared by microwave sintering and method
The invention relates to a 0.5NBT-0.5BCTZ-xwt%MgO high-storage-energy-density ceramic material prepared by microwave sintering and a method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, proportioning BCTZ ceramic powder, NBT ceramic powder and magnesium oxide powder according to a stoichiometric ratio of a chemical formula 0.5NBT-0.5BCTZ-xwt%MgO, uniformly mixing, pelletizing and forming; and sintering and forming ceramics by preserving heat for 4 to 20 minutes at a temperature ranging from 900 DEG C to 1100 DEG C in a microwave sintering mode, thereby obtaining the high-storage-energy-density ceramic material, wherein x ranges from 3 to 7. Through microwave sintering, the method has the advantages of high heating speed, uniform heating and the like; reaction of MgO and a matrix material can be effectively restrained at a relatively low sintering temperature within relatively short sintering time, and the microstructure of the material can be optimized to improve the compactness of the material, so that breakdown strength of the material is effectively improved, and the high-storage-energy-density ceramic material is prepared.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com