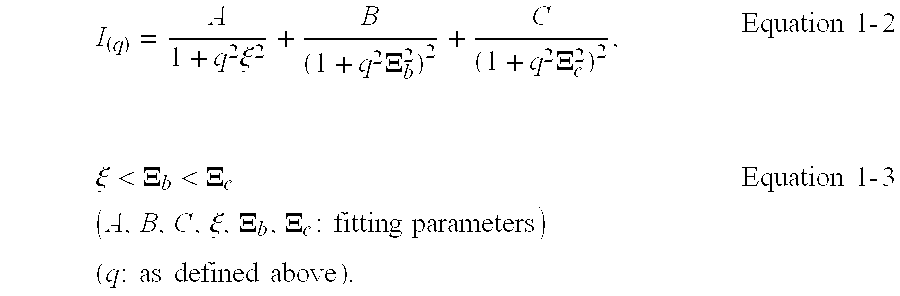Patents
Literature
126 results about "Neutron scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neutron scattering, the irregular dispersal of free neutrons by matter, can refer to either the naturally occurring physical process itself or to the man-made experimental techniques that use the natural process for investigating materials. The natural/physical phenomenon is of elemental importance in nuclear engineering and the nuclear sciences. Regarding the experimental technique, understanding and manipulating neutron scattering is fundamental to the applications used in crystallography, physics, physical chemistry, biophysics, and materials research.
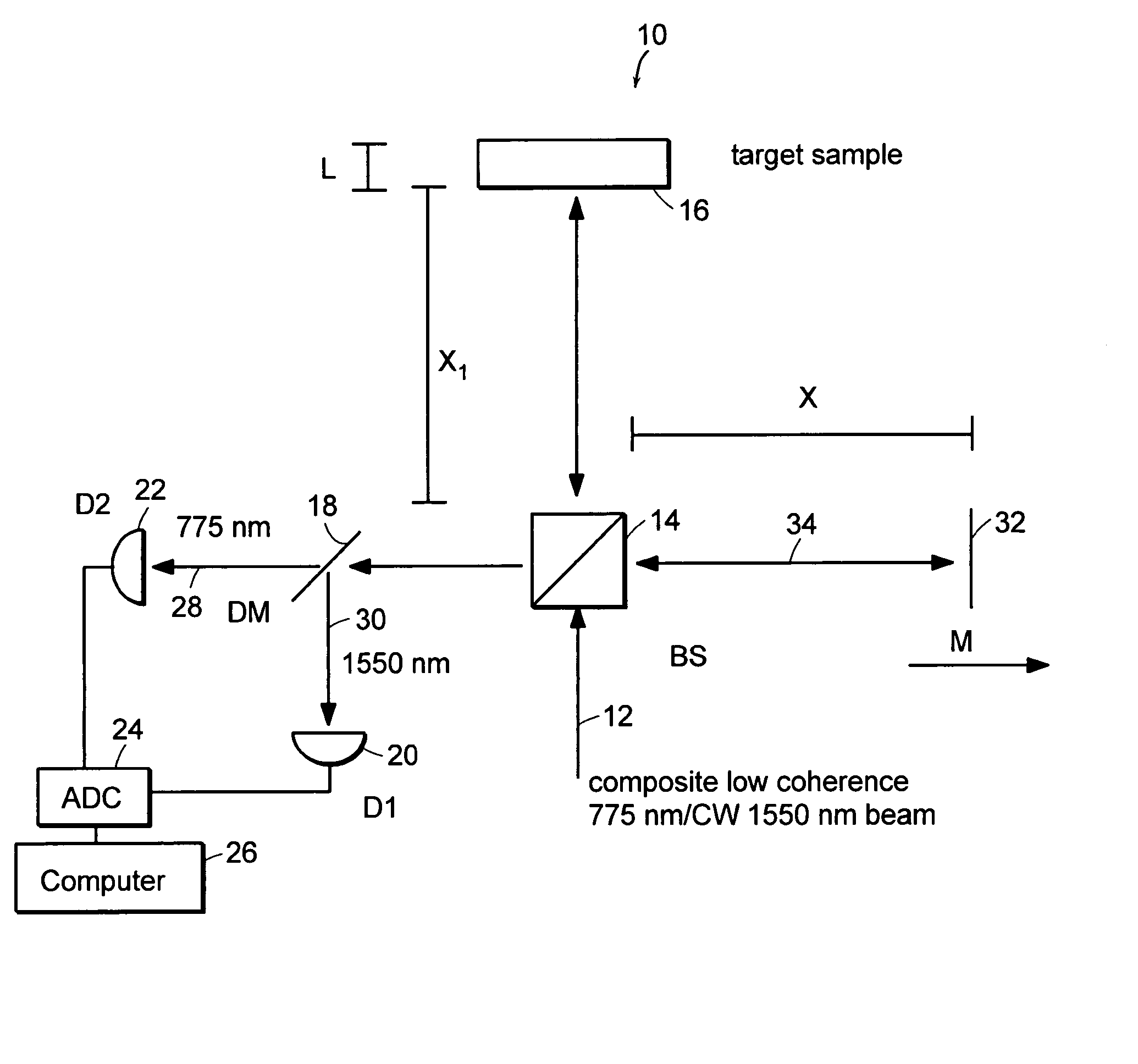
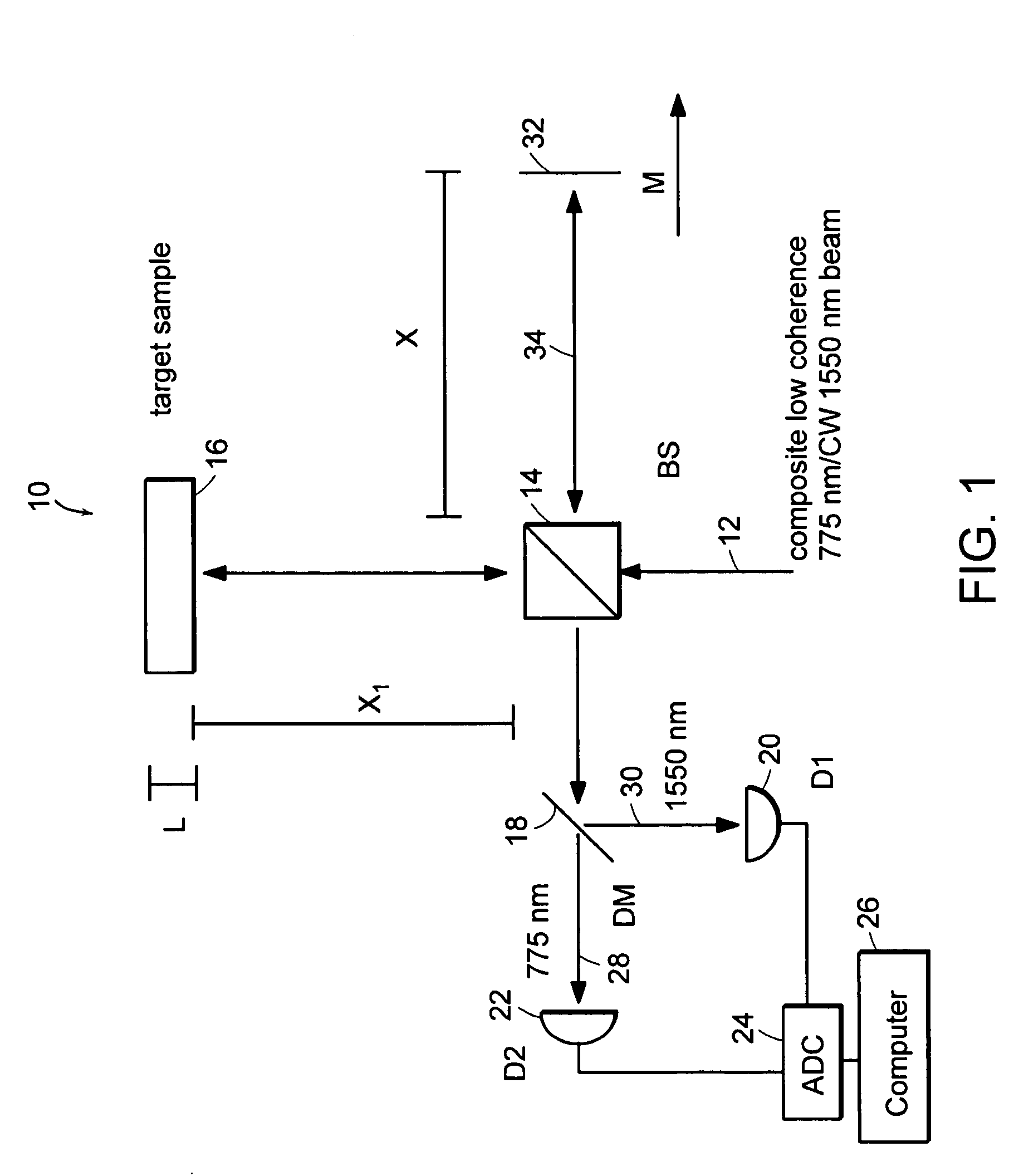
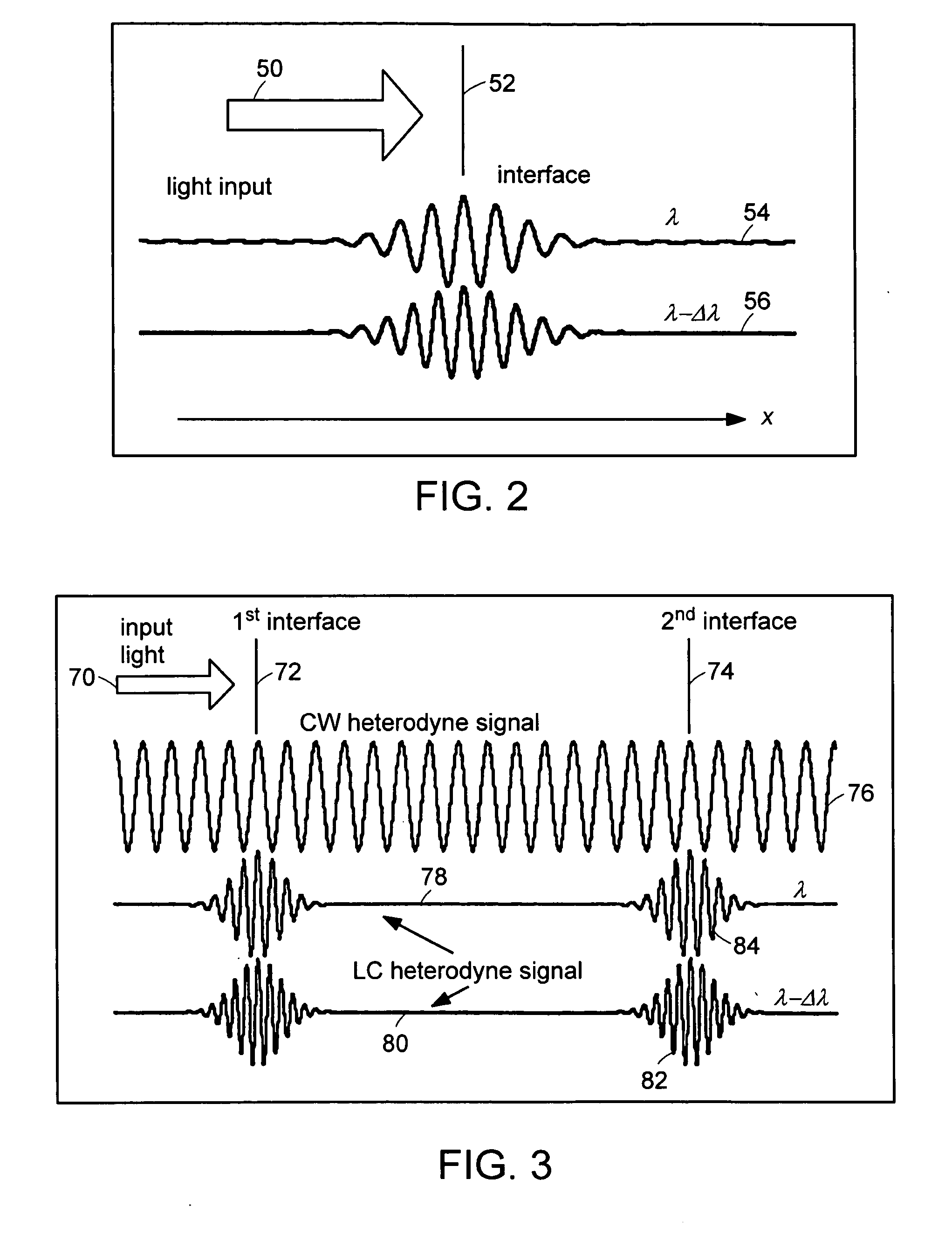
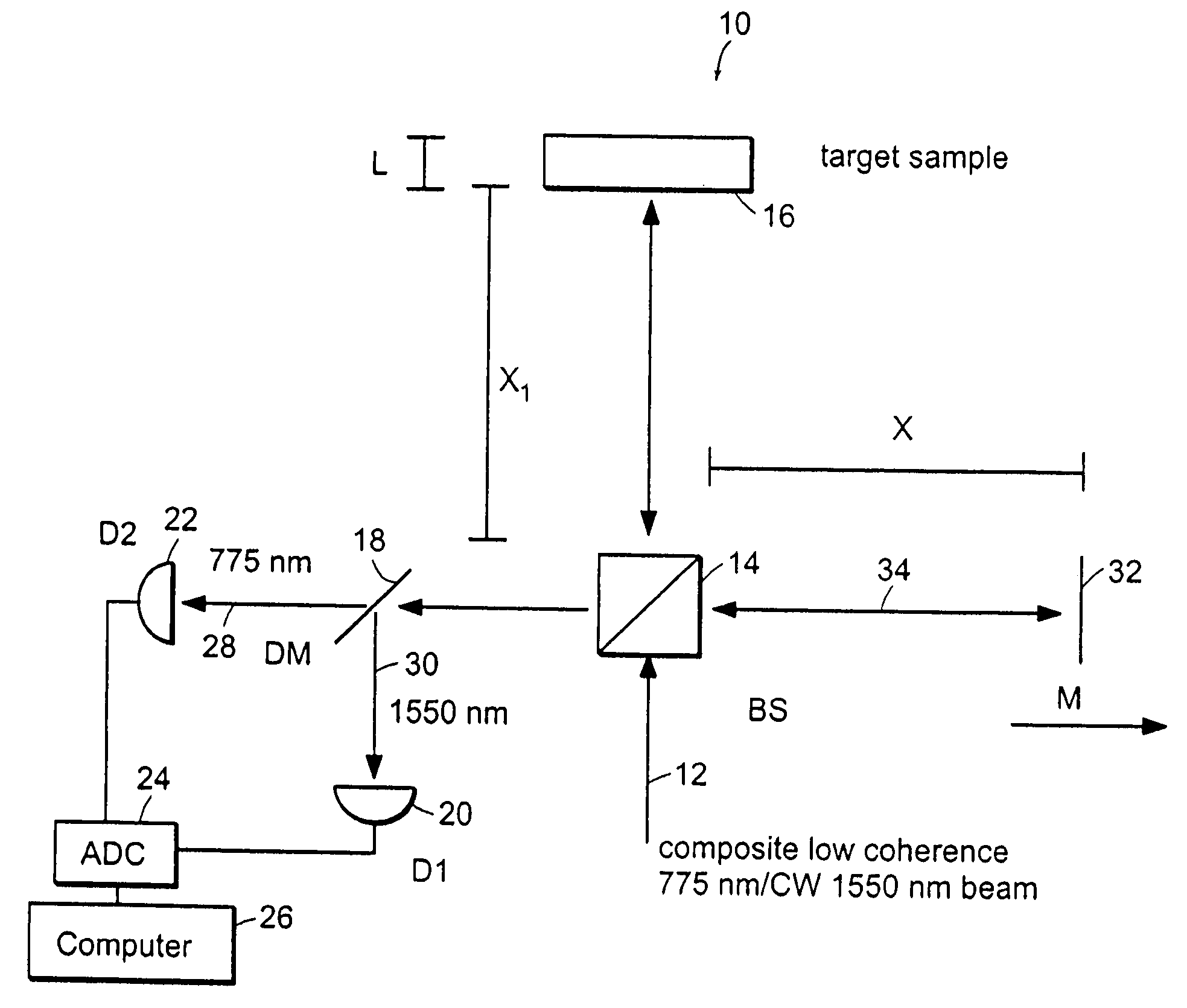
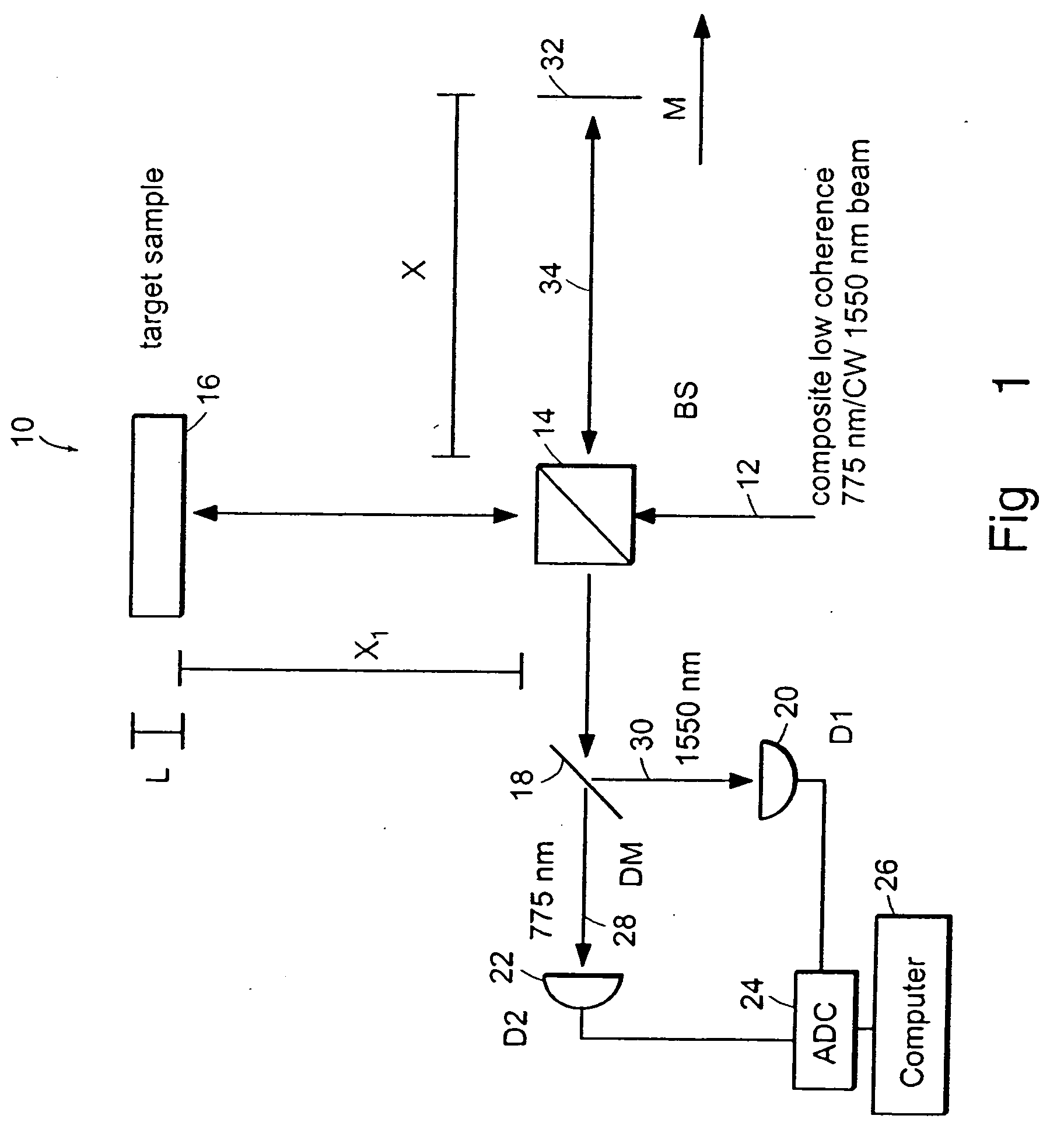
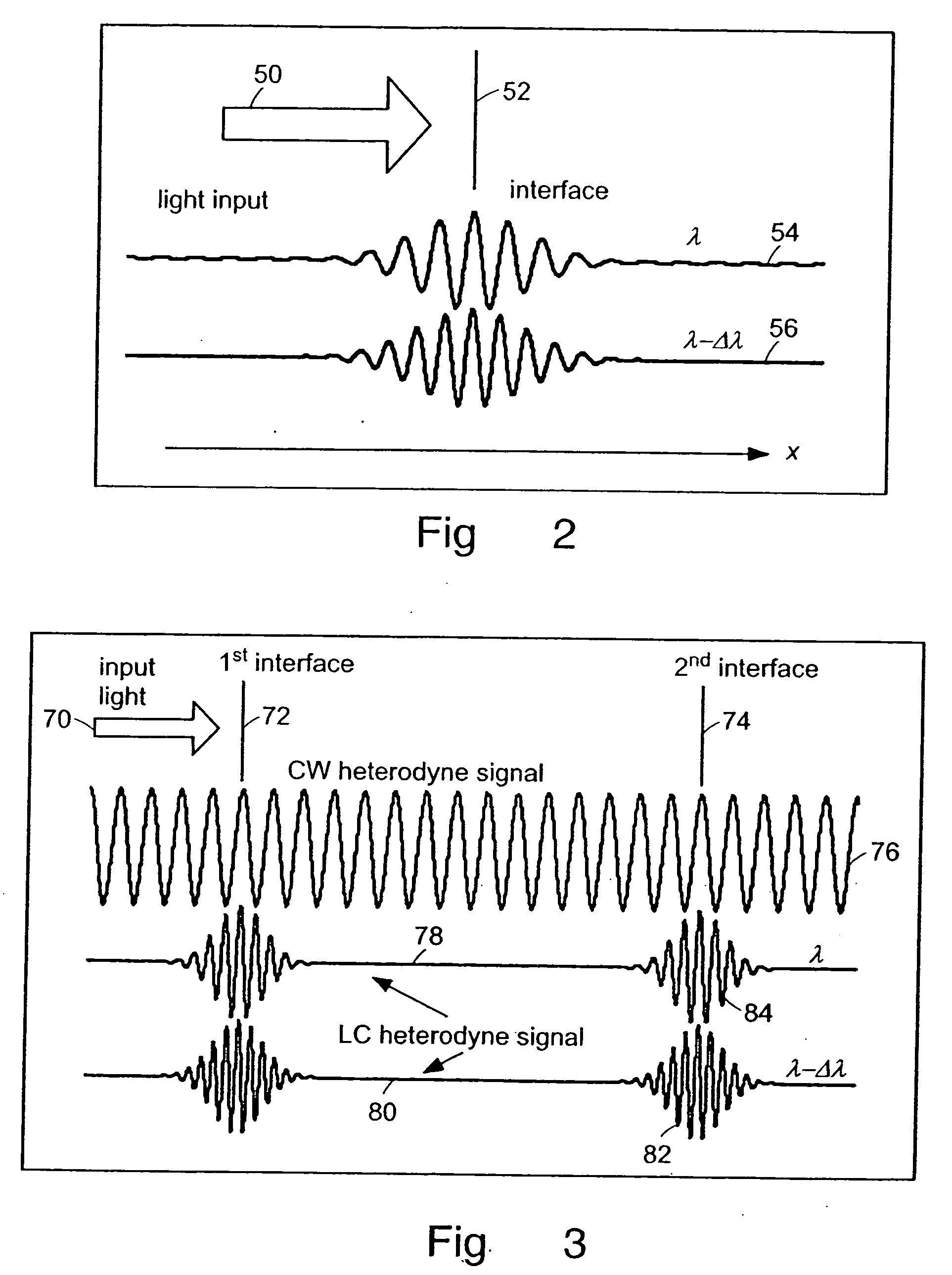
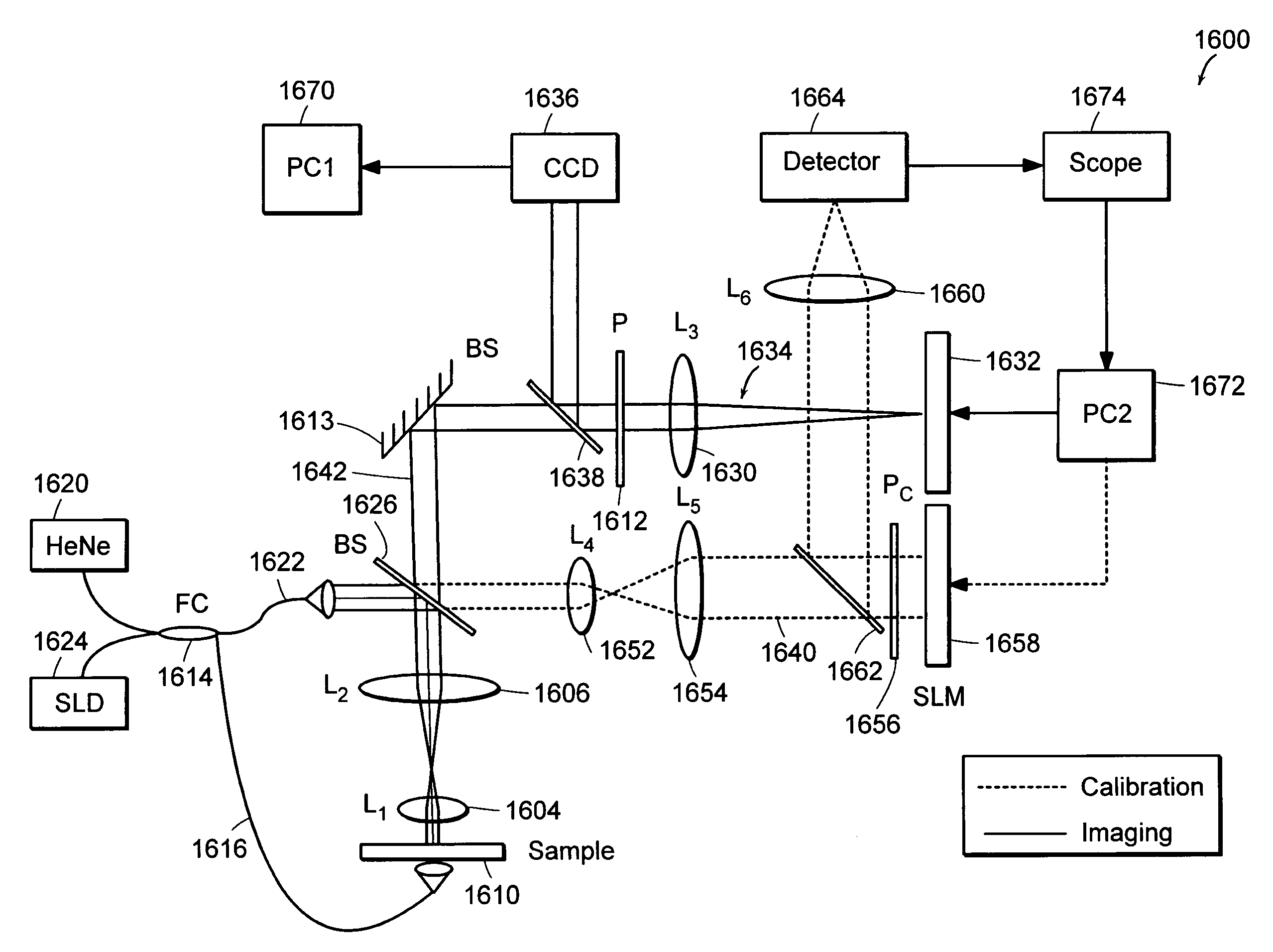
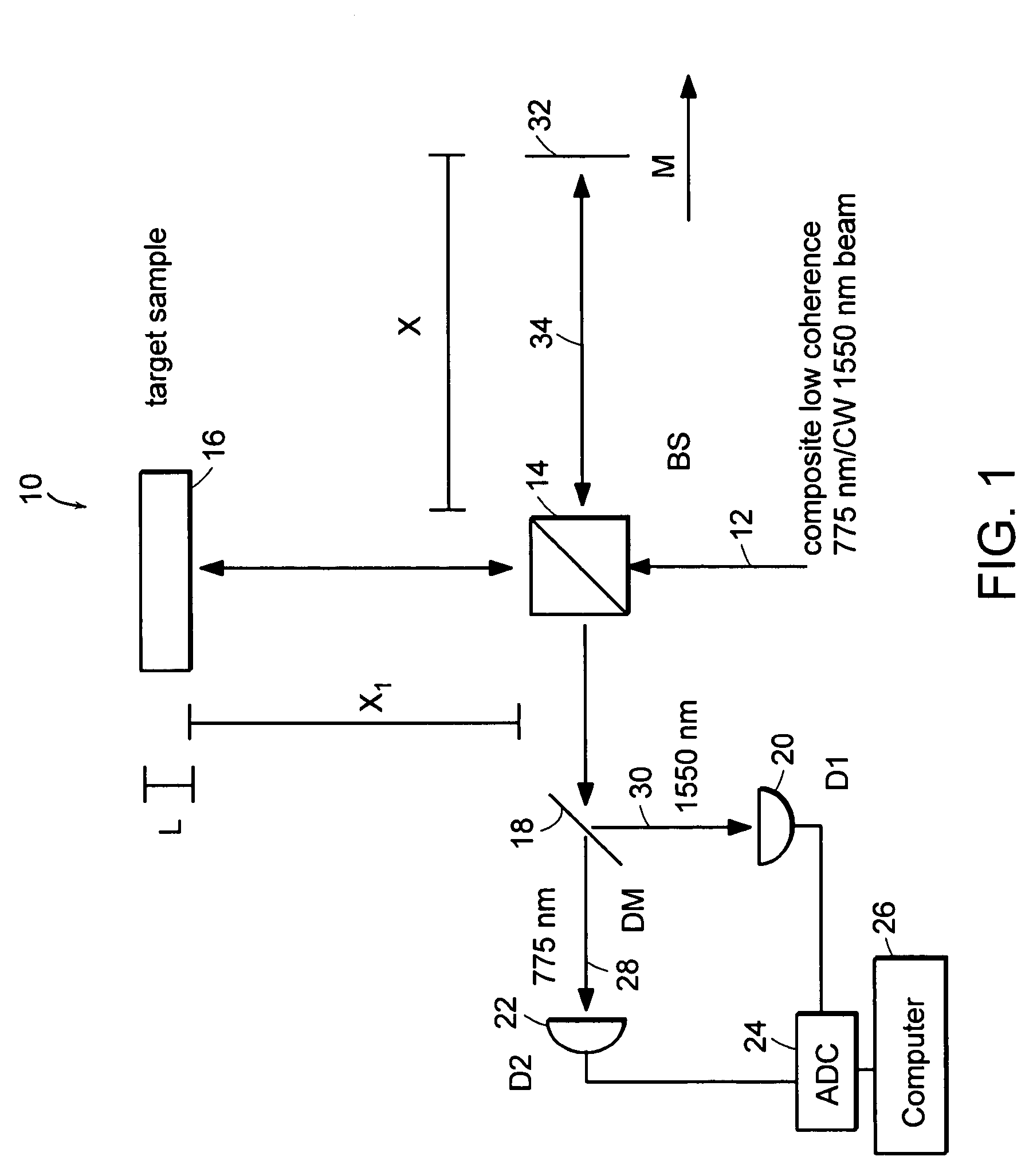
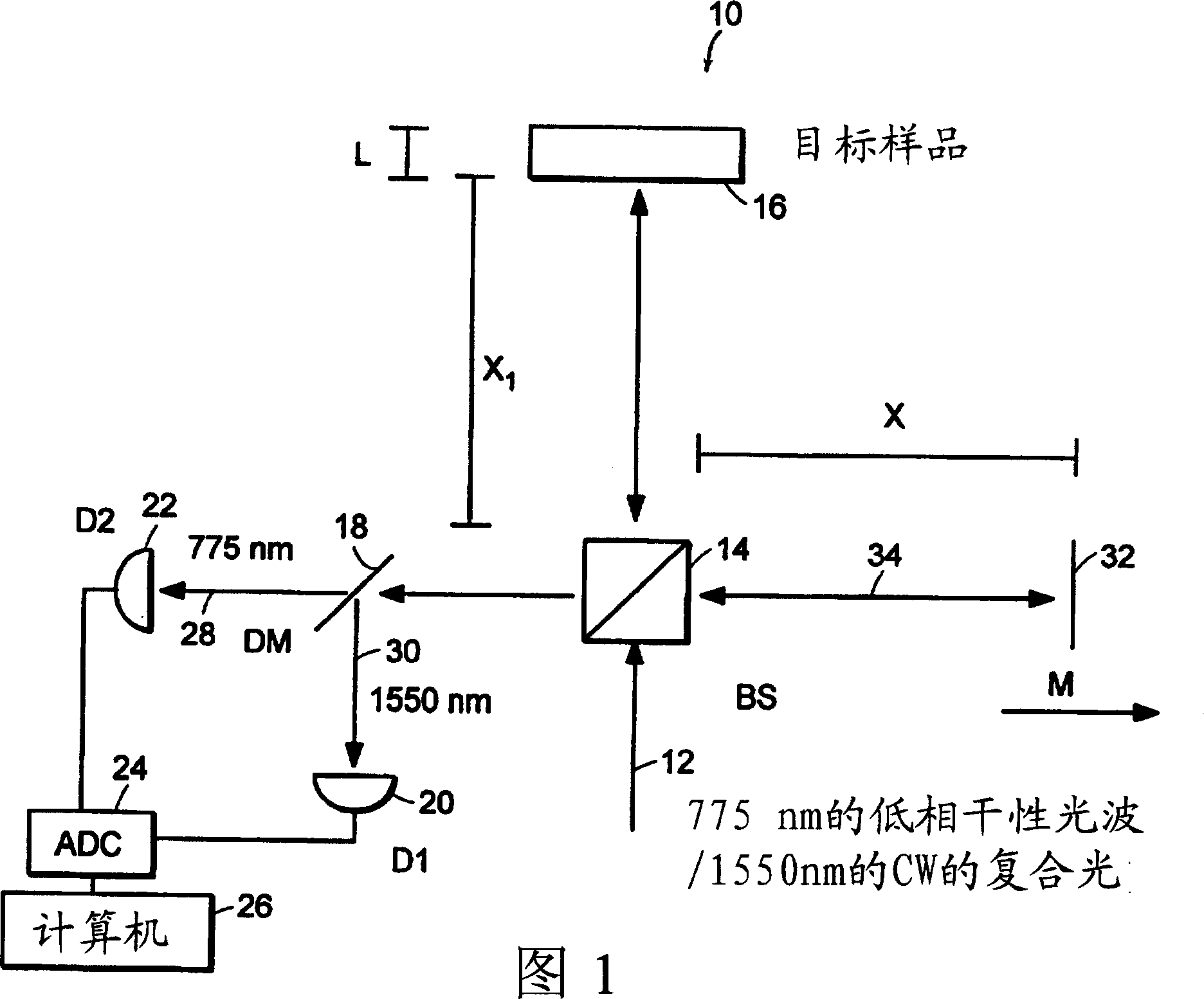
Systems and methods for phase measurements
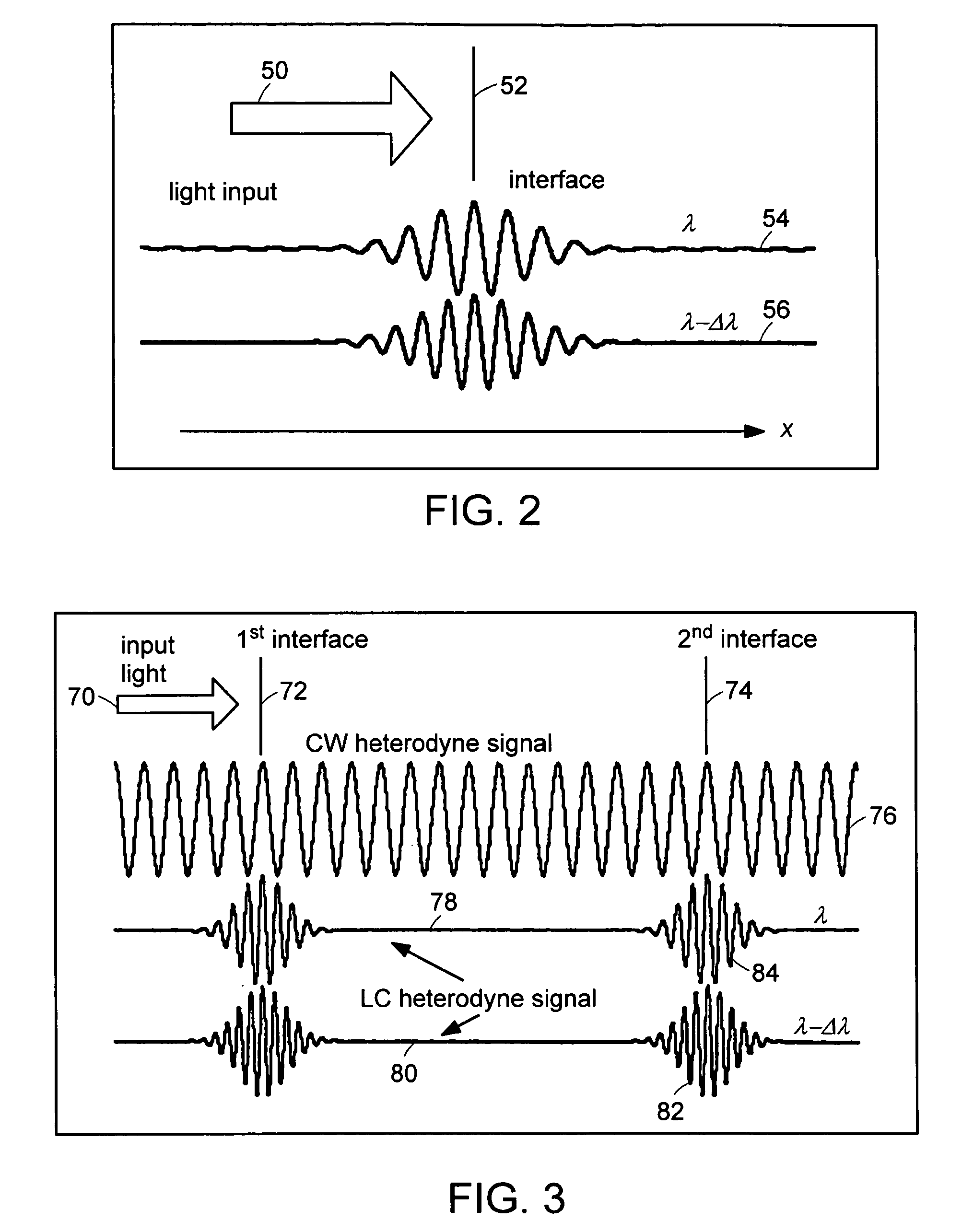
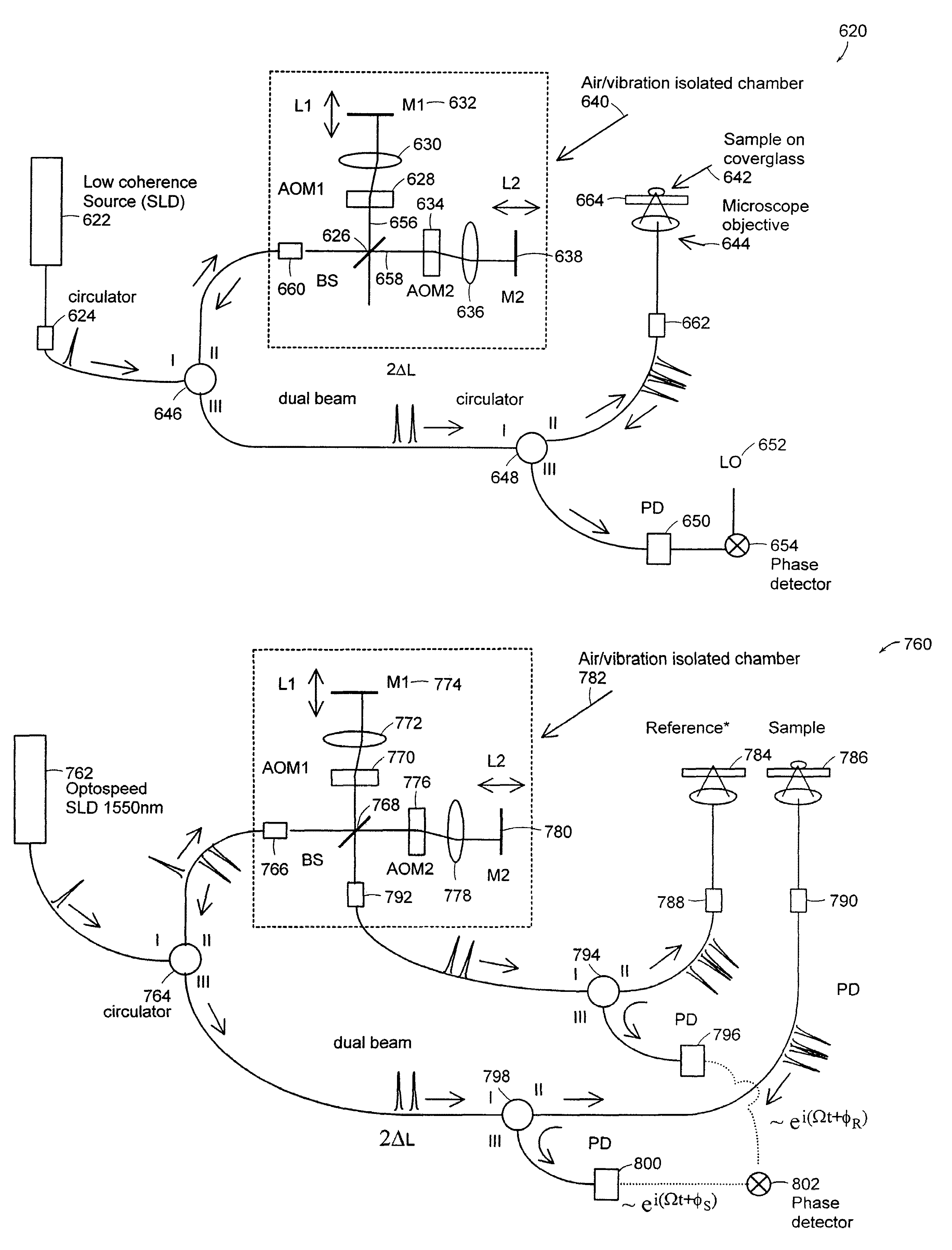
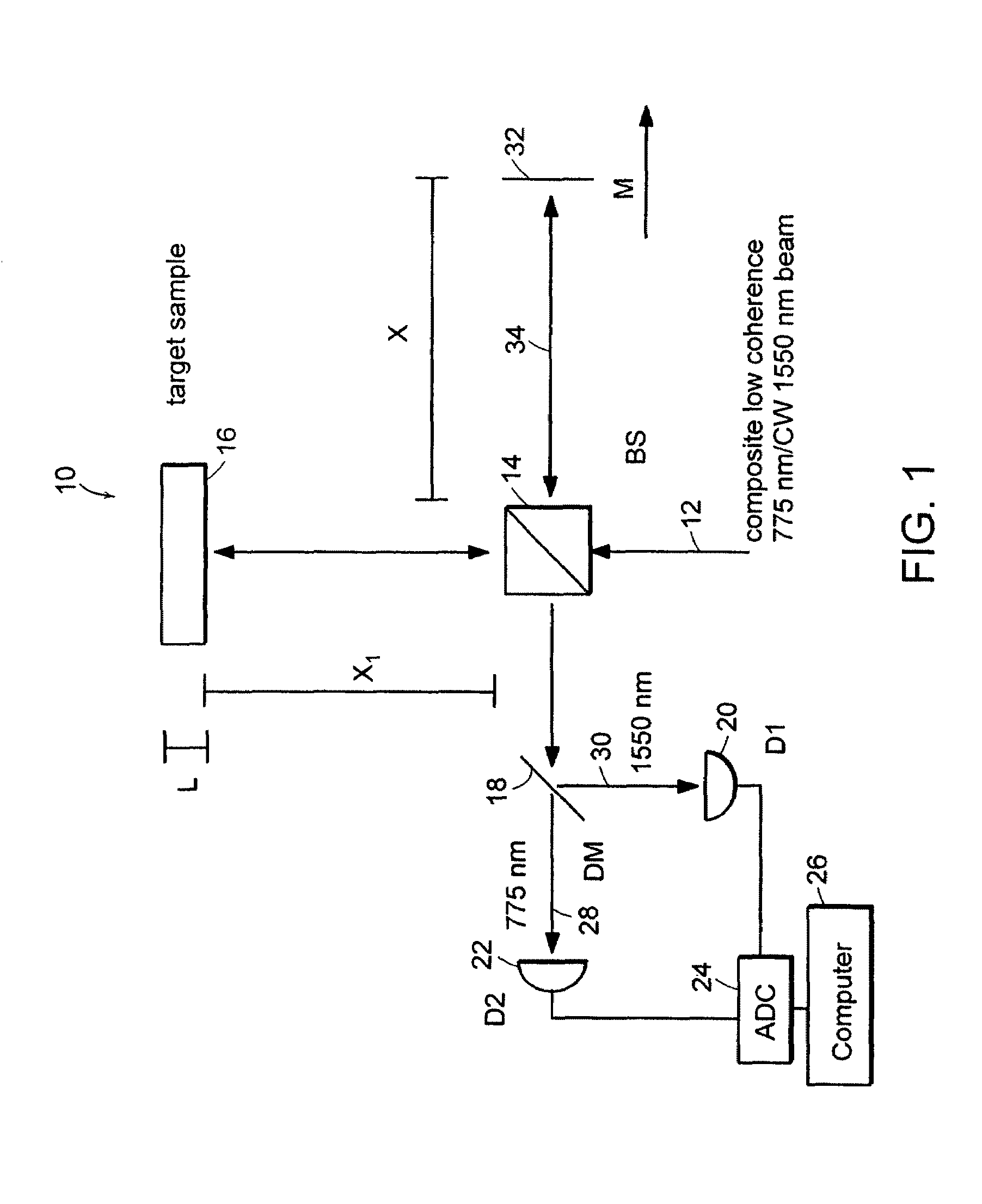
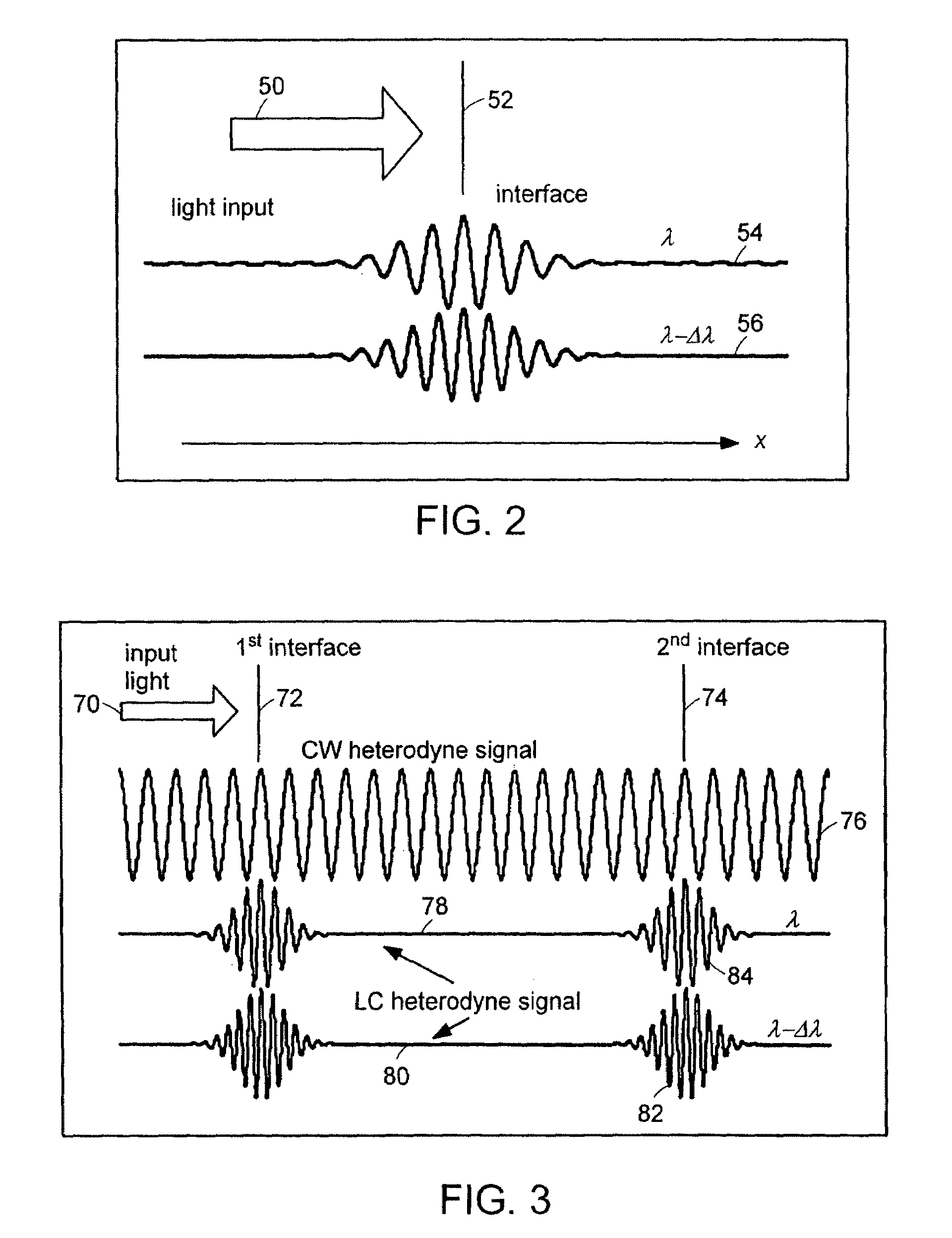
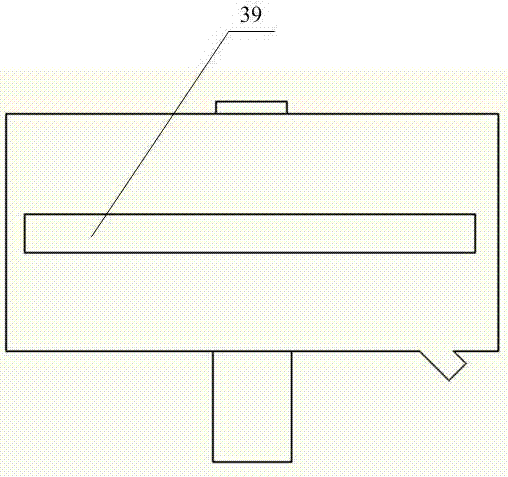
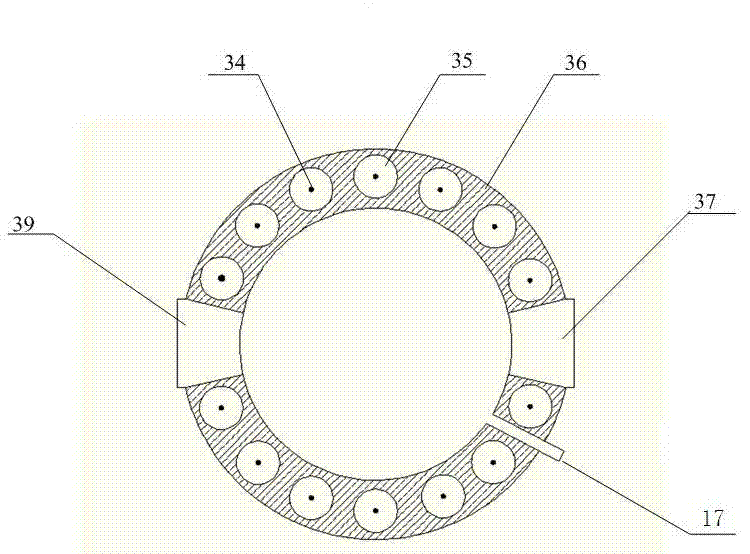
InactiveUS20050057756A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsCellular componentPhase noise
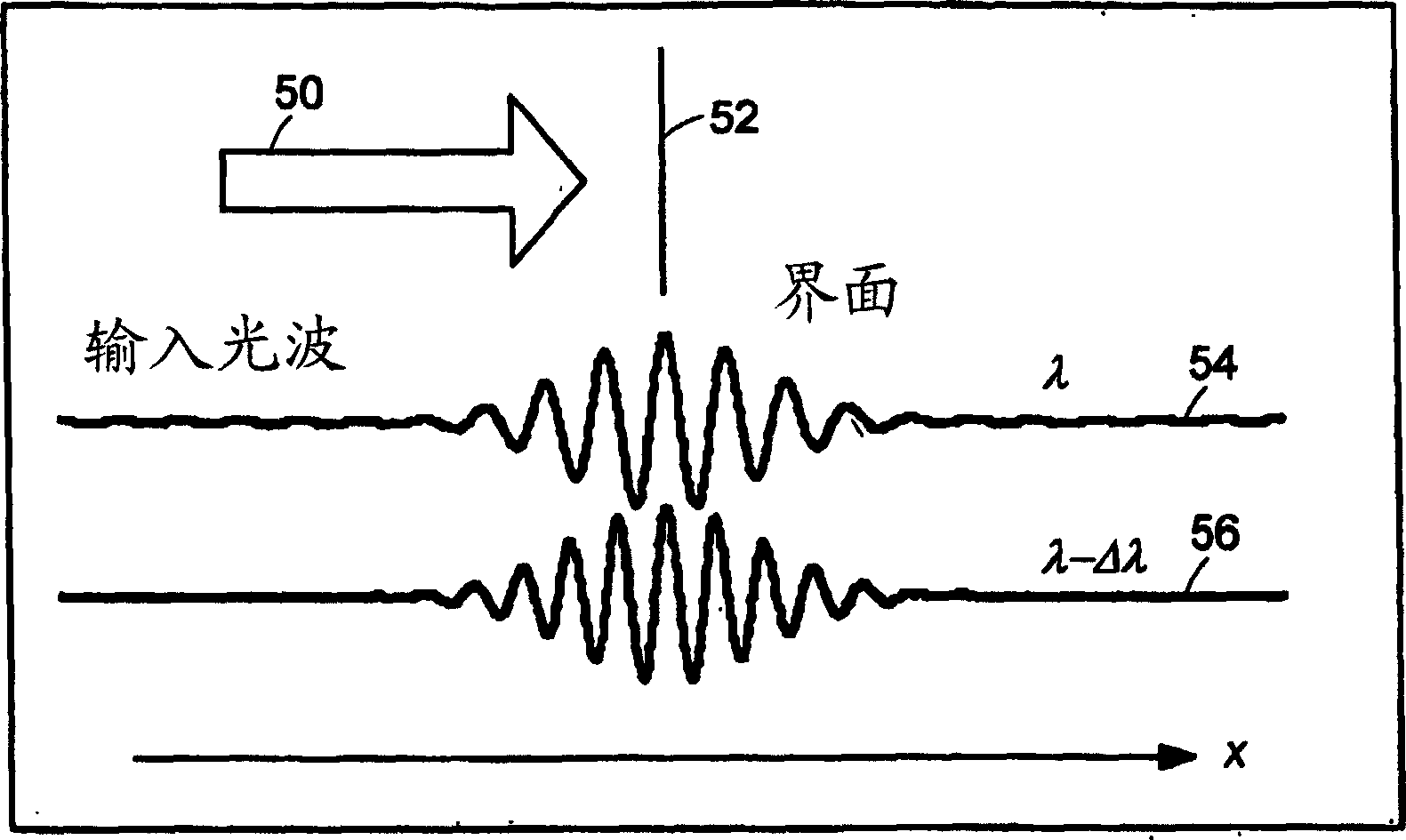
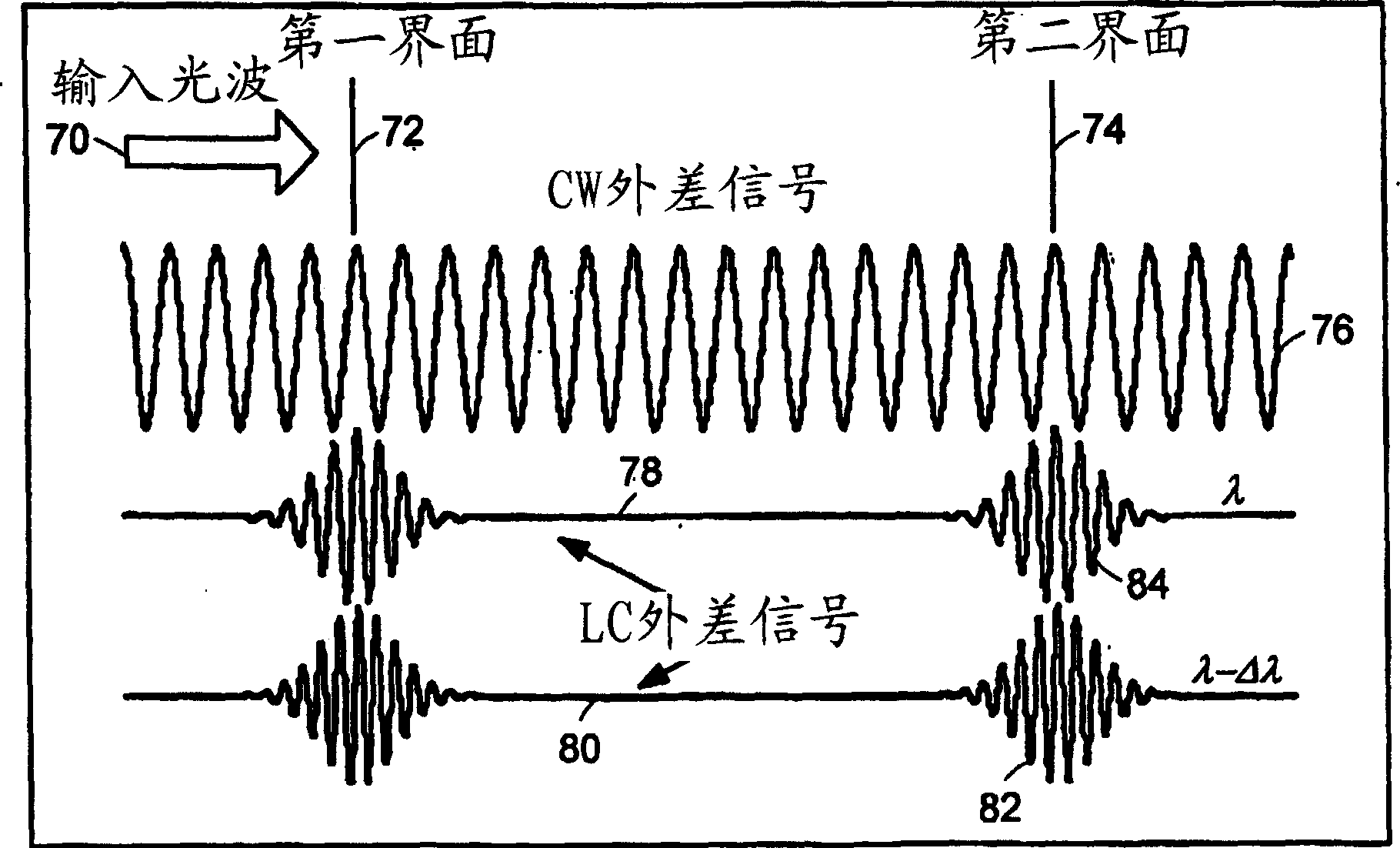
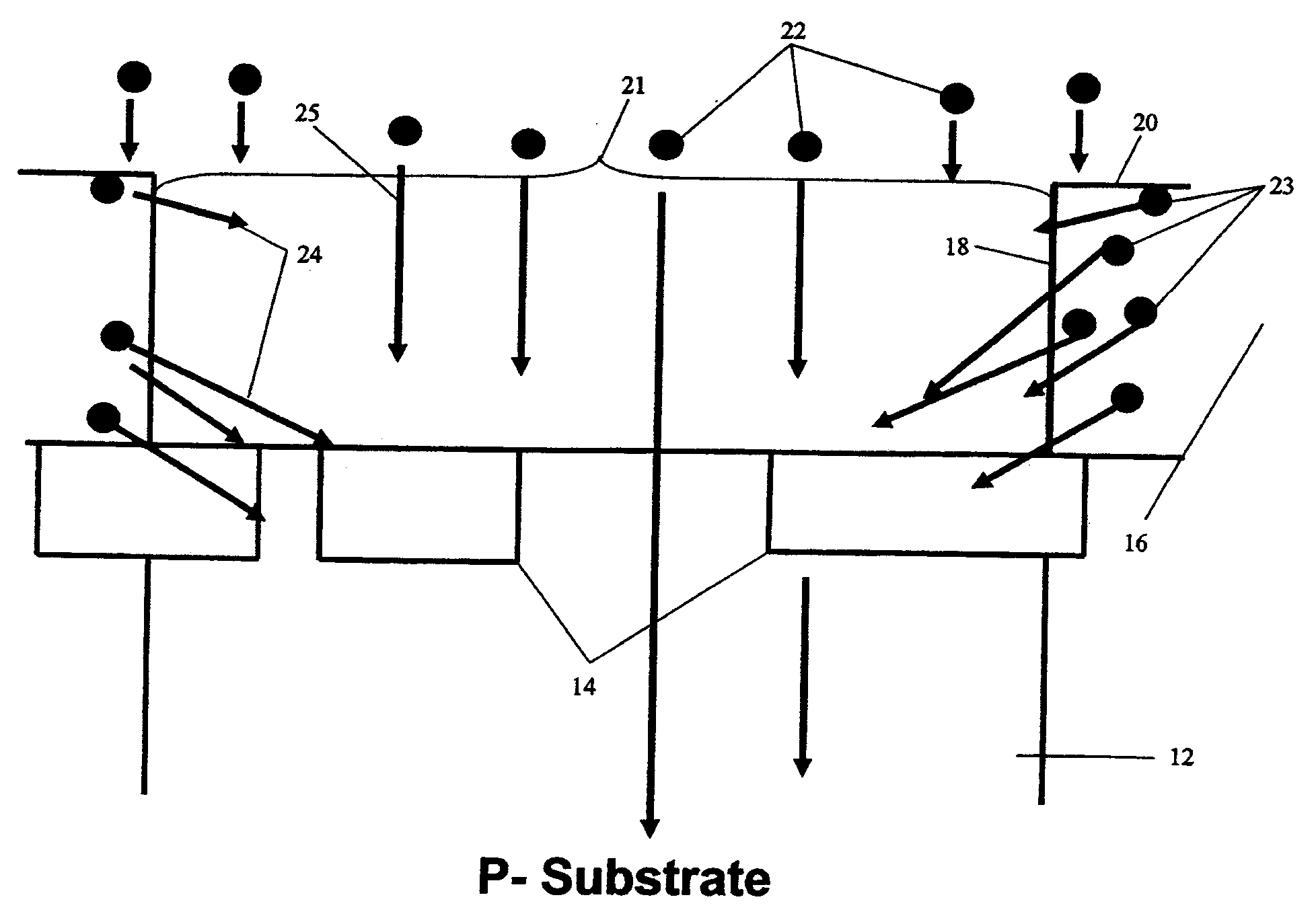
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7365858B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7557929B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for measuring phase
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
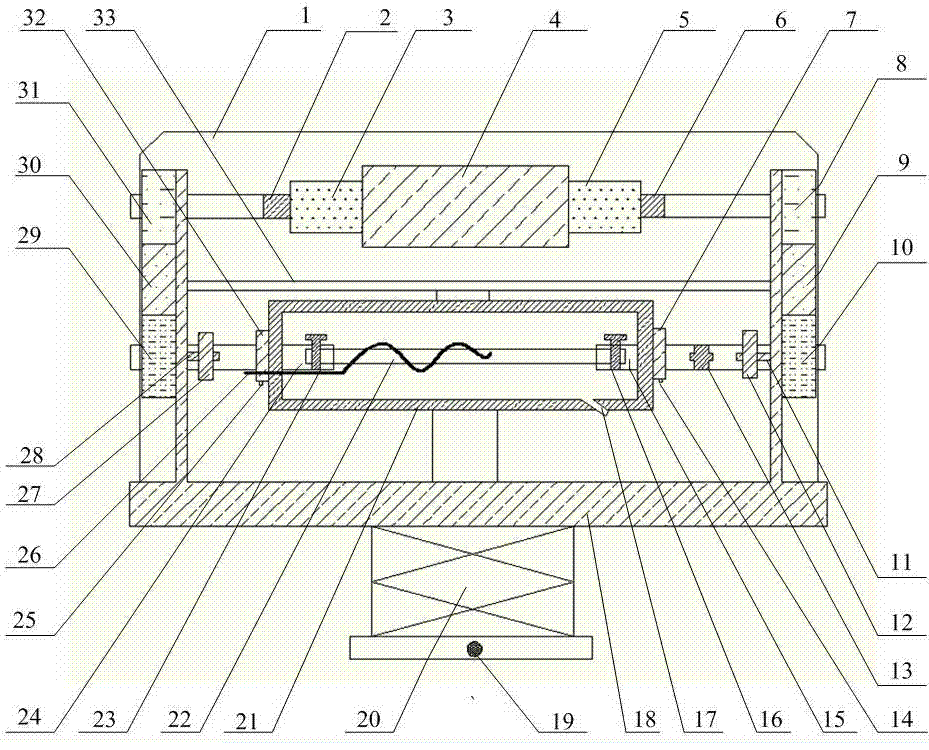
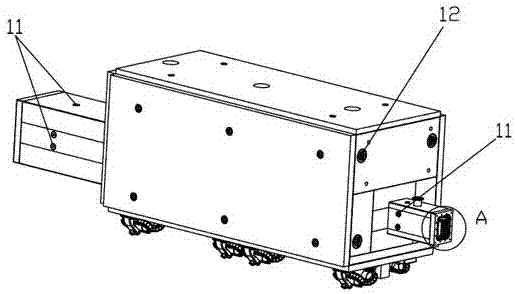
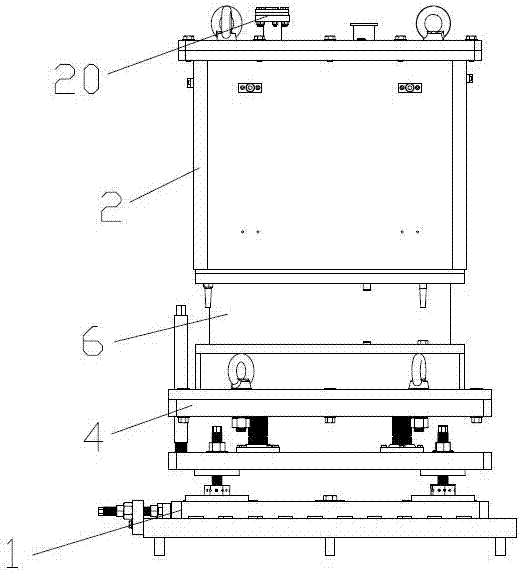
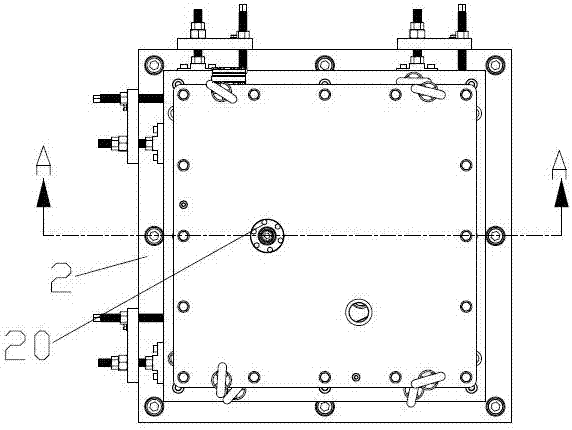
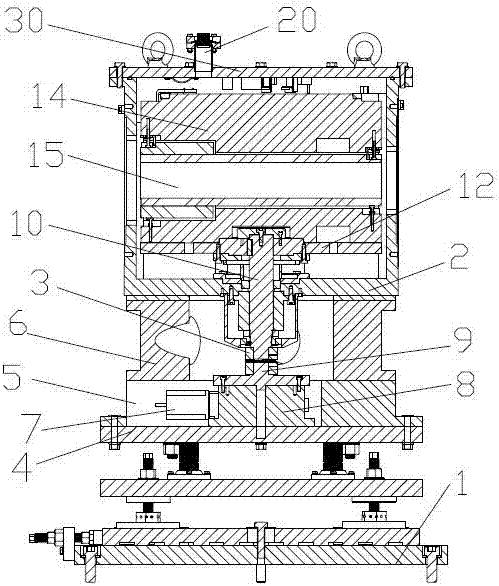
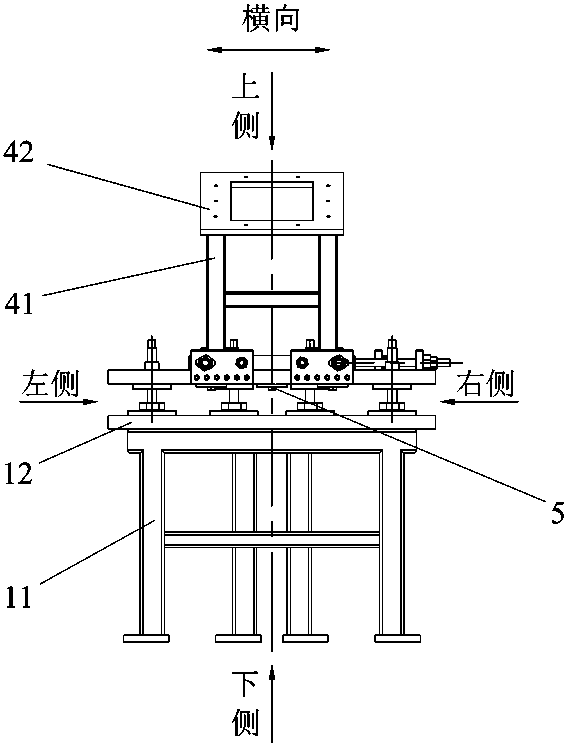
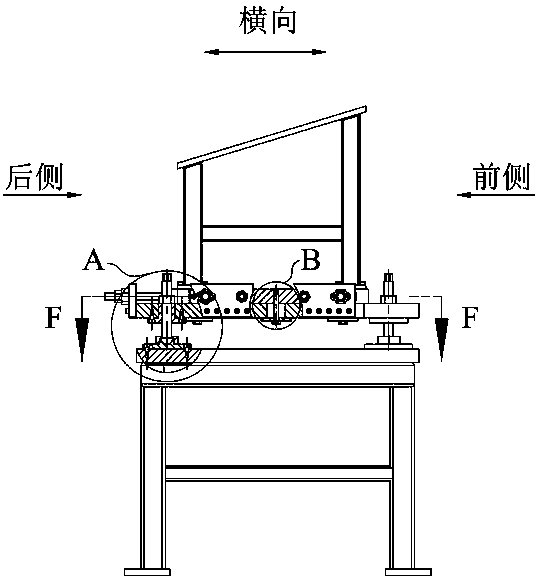
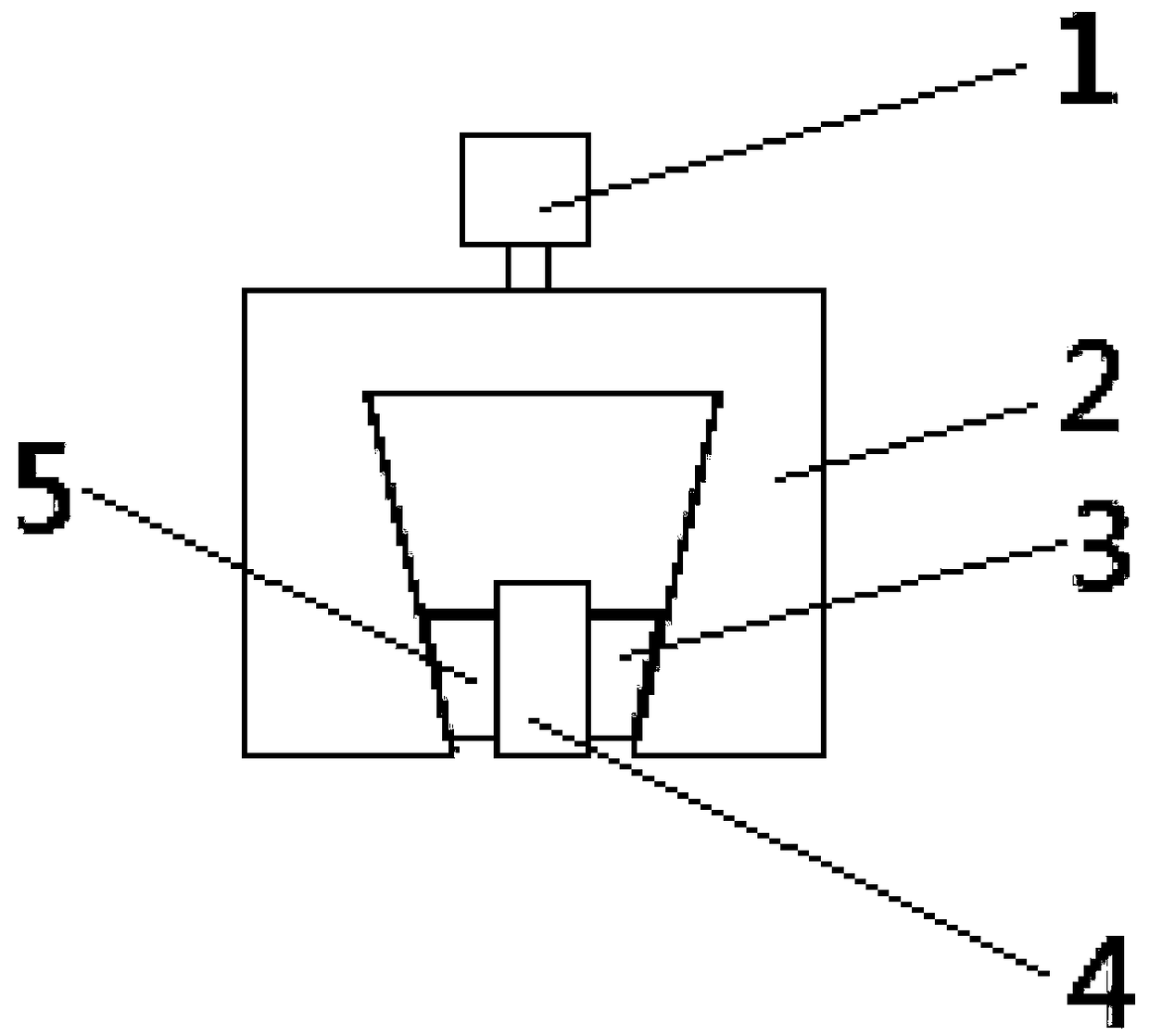
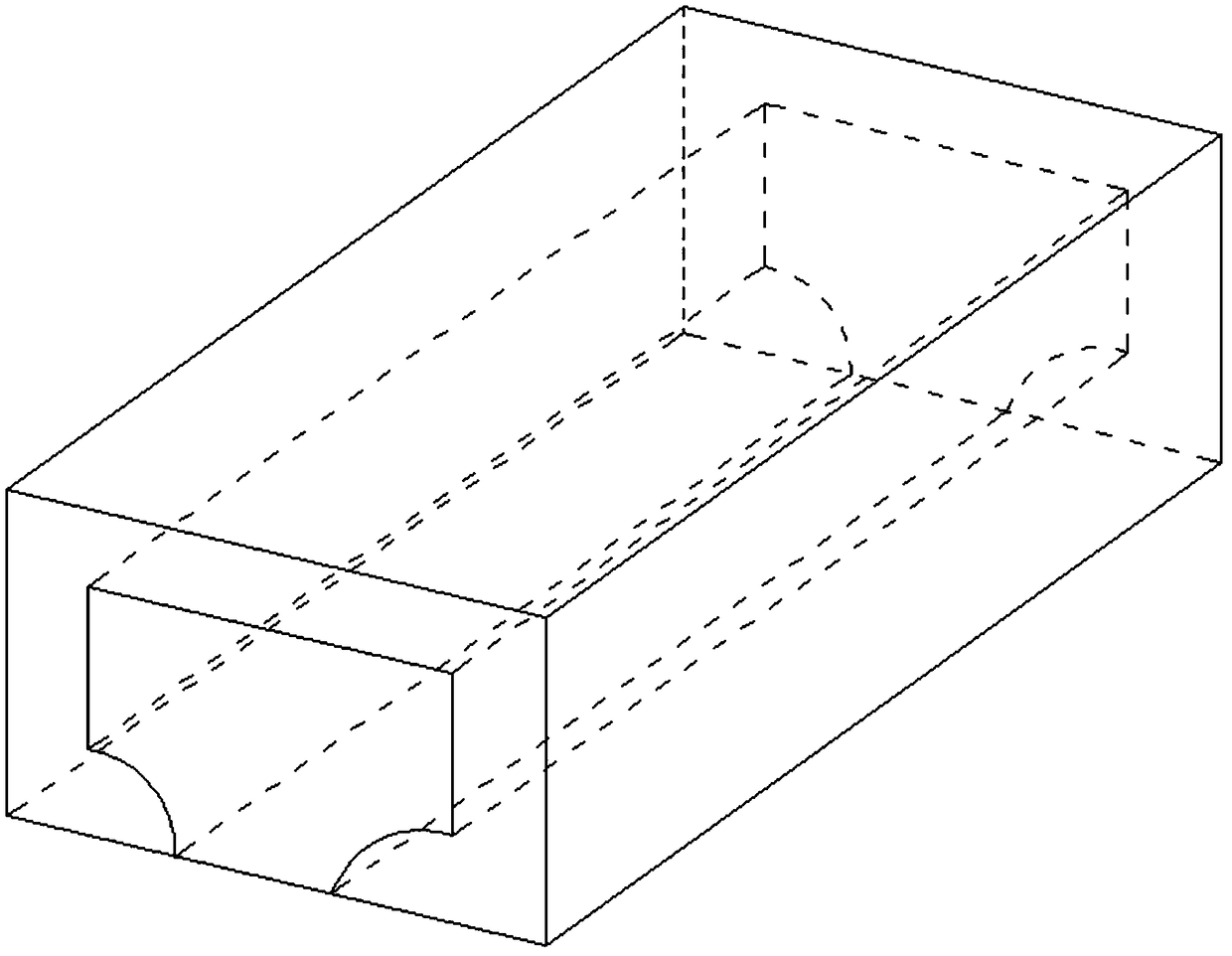
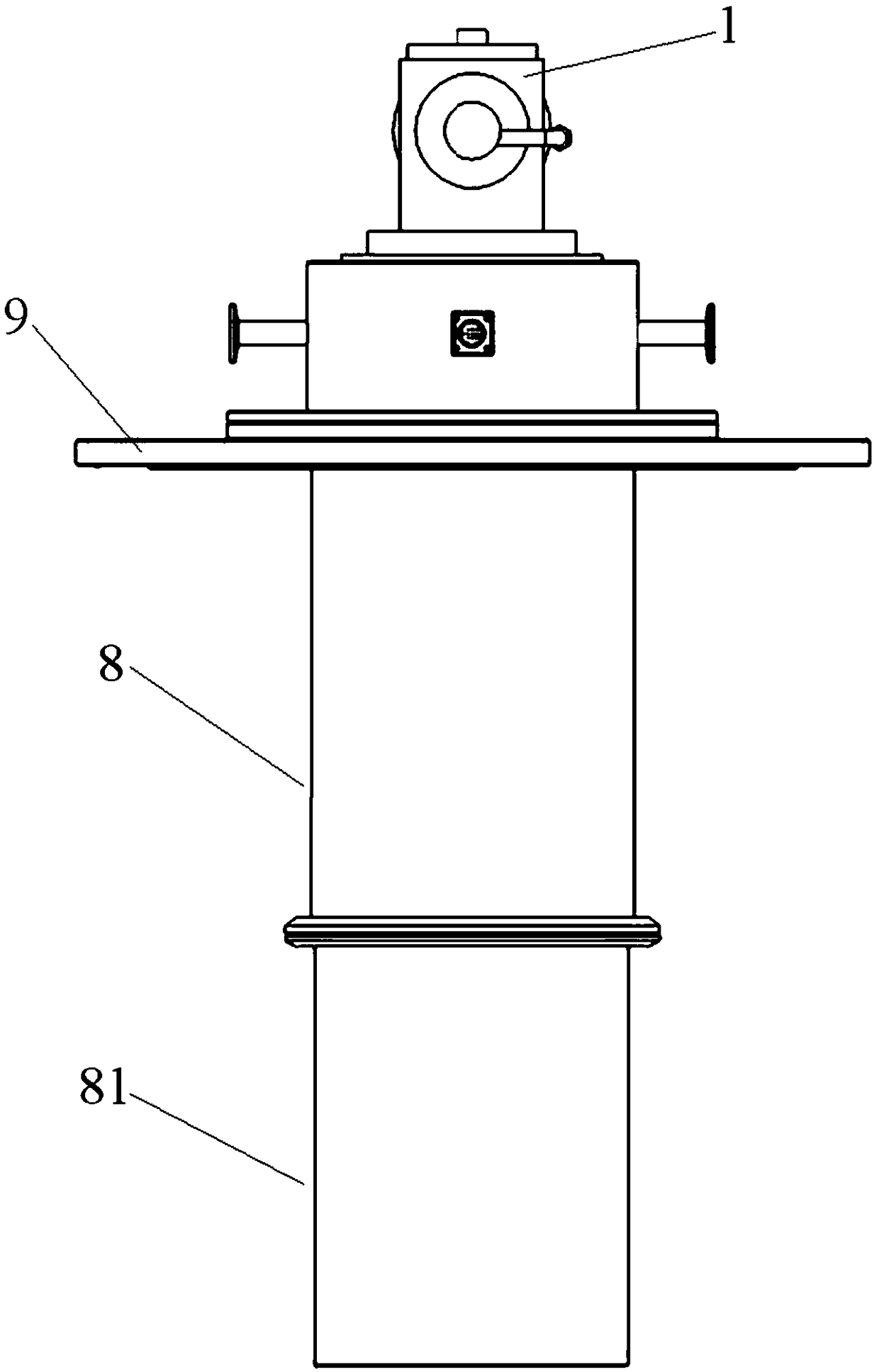
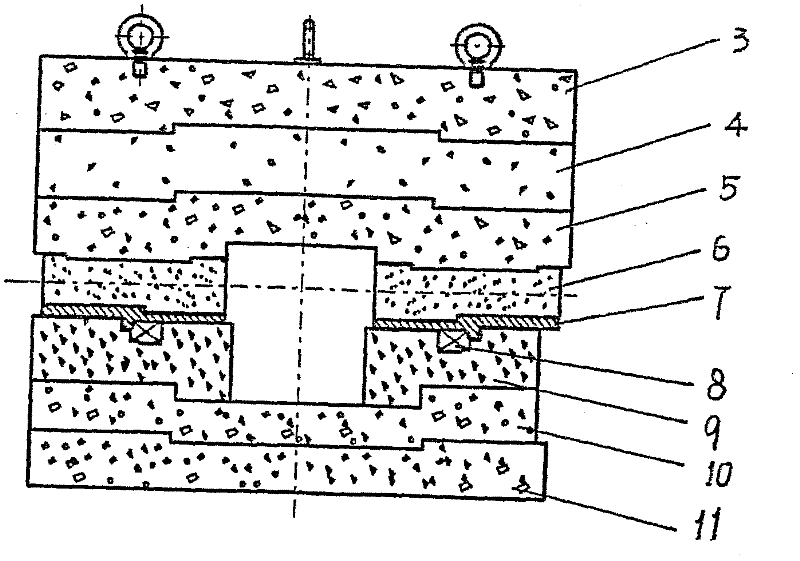
In-situ stress-temperature loading device for neutron diffraction technology
The invention discloses an in-situ stress-temperature loading device for a neutron diffraction technology. A frame in the device is designed into a door frame type structure, a hollow-shaft servomotor is utilized for driving multiple stages of gears with the same specification and the size to rotate via a speed reducer, and the horizontal motion operation of a test sample can be further realized through a guide component and a clamp. By controlling the forward rotation (reverse rotation) of the hollow-shaft servomotor, bidirectional synchronous drawing (compression) of the test sample is realized; and by controlling the rotational speed of the hollow-shaft servomotor, the speed regulation of drawing (compression) of the test sample is realized. A cavity type high-temperature furnace with the design based on a resistance heat radiation structure is matched with the frame to use, a temperature control instrument is used for controlling the temperature in a body cavity of the high-temperature furnace, fan-shaped through holes are respectively formed in the neutron incidence direction and the scattering direction, and quartz glass is further used for sealing. The in-situ stress-temperature loading device for the neutron diffraction technology, disclosed by the invention, can be used on a variety of neutron scattering (diffraction) spectrometers for realizing the neutron scattering (diffraction) in-situ stress-temperature loading testing technology.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
Vessel for Rare Gas Filling, and Method for Polarization of Rare Gas Atomic Nucleus Using Said Vessel
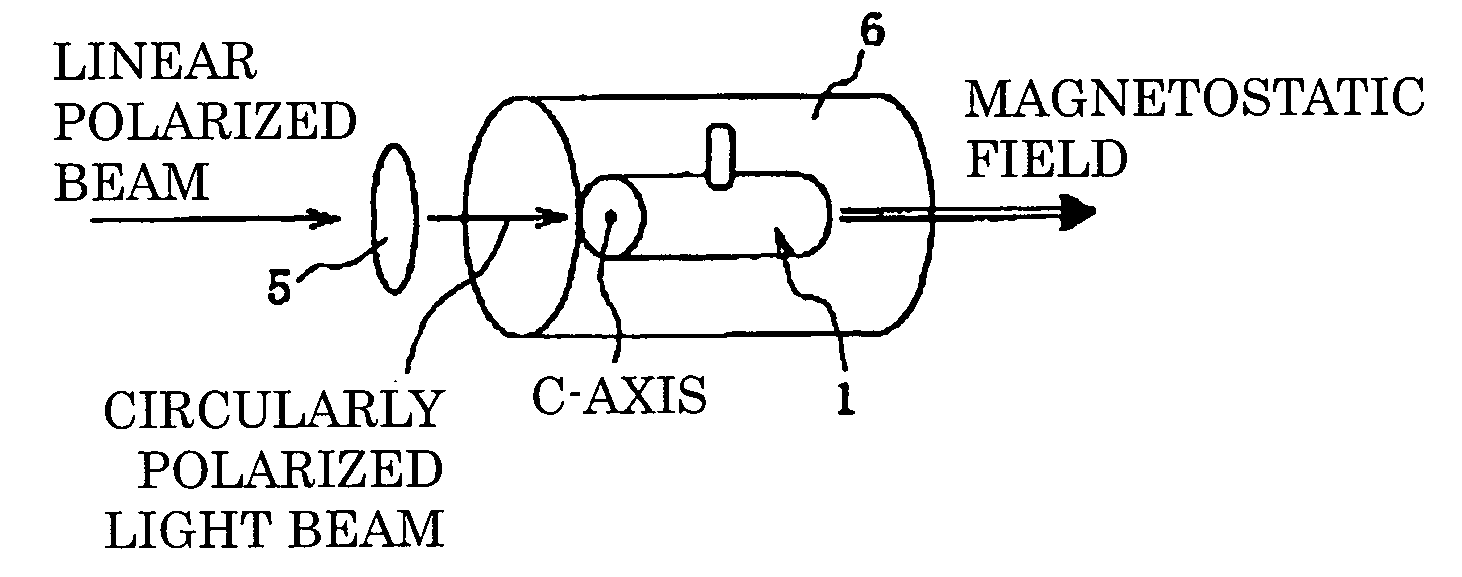
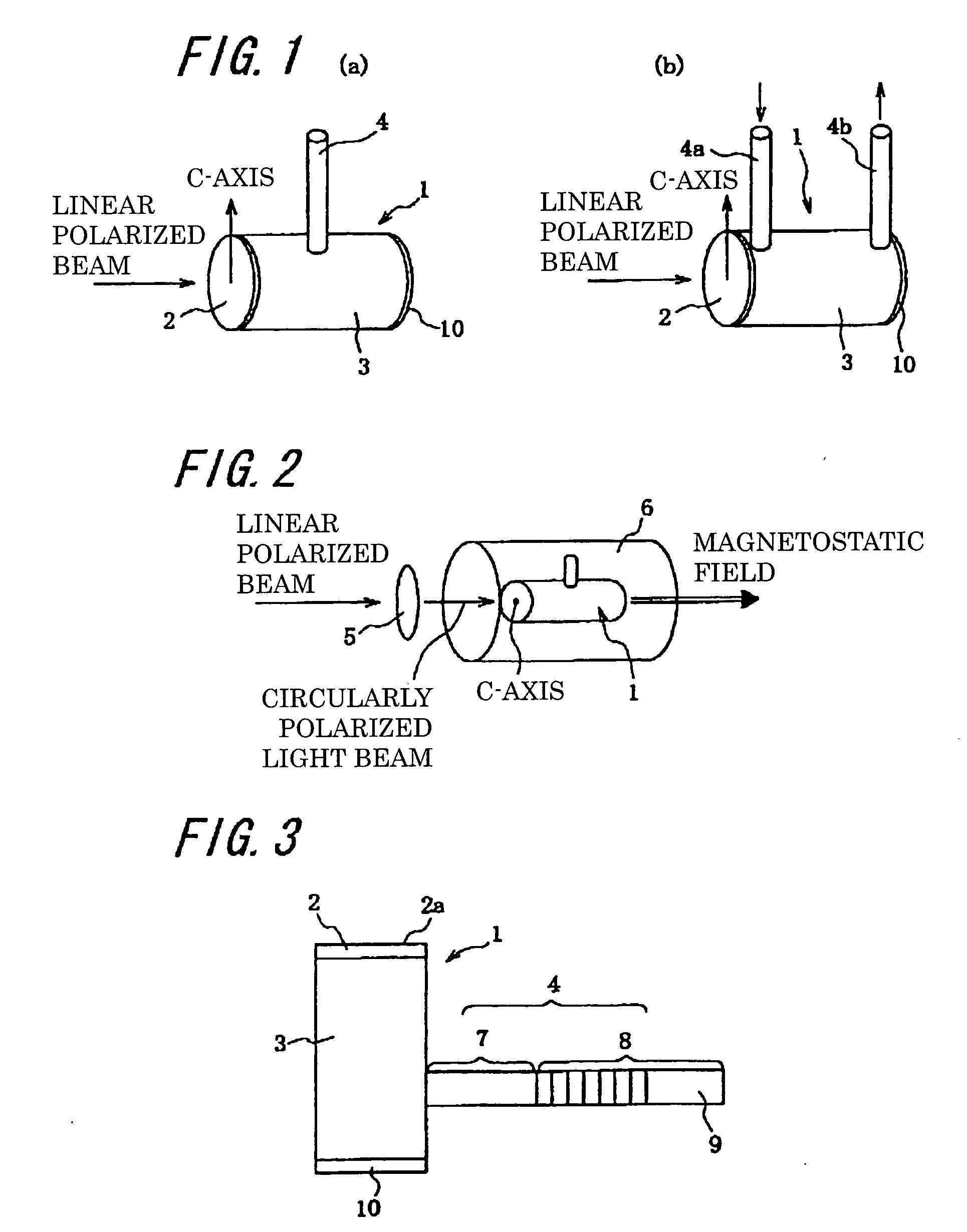
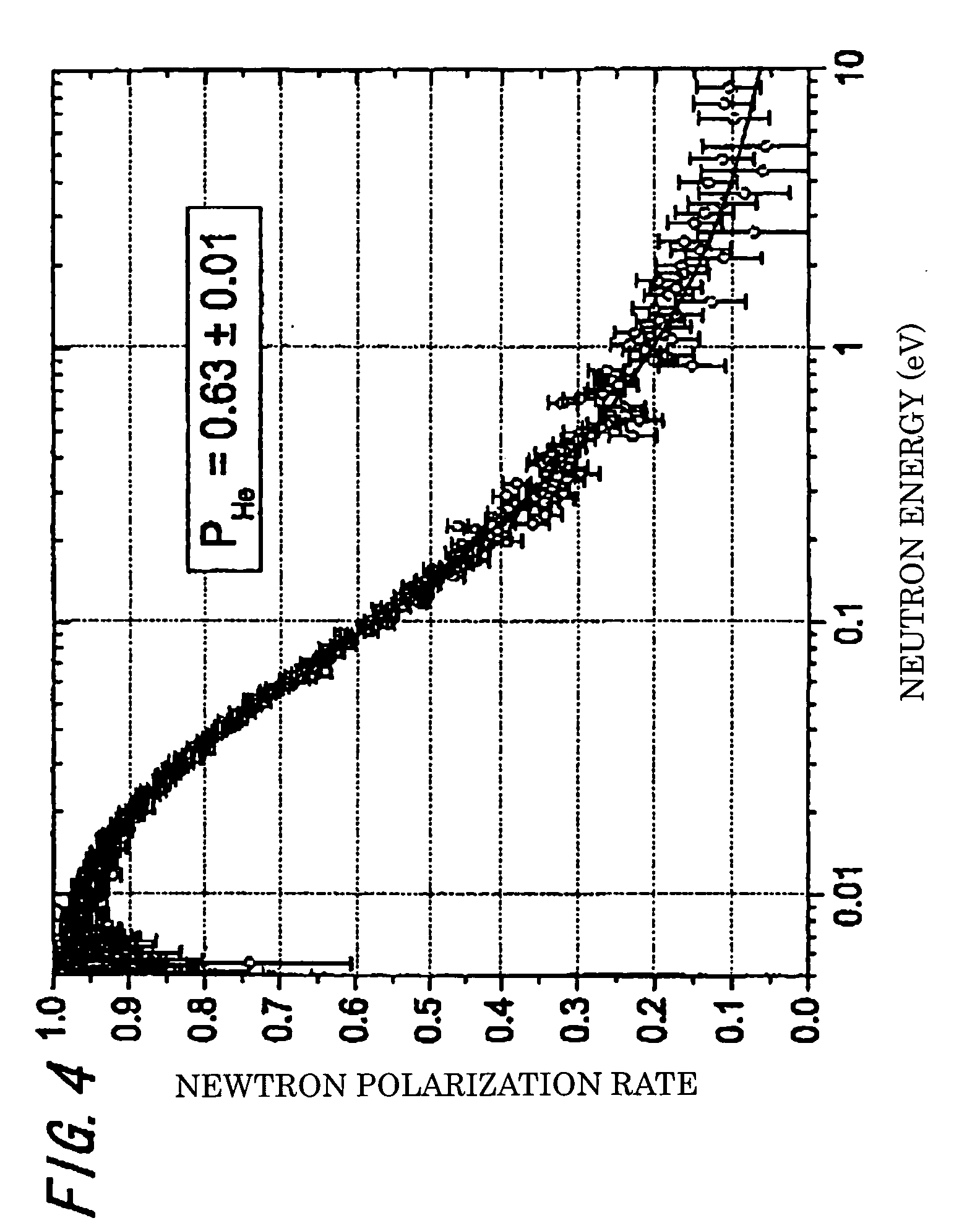
InactiveUS20090101806A1Accurate thicknessImprove polarizationOther accessoriesMasersNoble gasNeutron scattering
A vessel for rare-gas filling is provided, where almost complete light circular polarization is realized, which has a light incident window of a single crystal material whose thickness and crystal axis orientation are optimized, and a polarization method of rare gas nuclei in the vessel is also provided. In addition, embodiments of the vessel is provided, which is impervious to alkali metal, and sustains high pressure, and shows no permeability for 3He gas, and has negligibly small neutron absorption so as to be suitable for application to basic science, for example, neutron scattering, and the polarization method in the vessel is also provided.The vessel for rare-gas filling of the present invention comprises a vessel body 3, and a pipe 4, which is connected to the vessel body 3 and introduces a rare-gas containing gas and an alkali metal into the vessel body 3. A light incident window 2 made of a single-crystal material, which has proper thickness and proper crystal axis orientation, is attached to the vessel body 3. The vessel for rare-gas filling is preferably made of sapphire or the like.
Owner:HIGH ENERGY ACCELERATOR RESEARCH ORGANIZATION
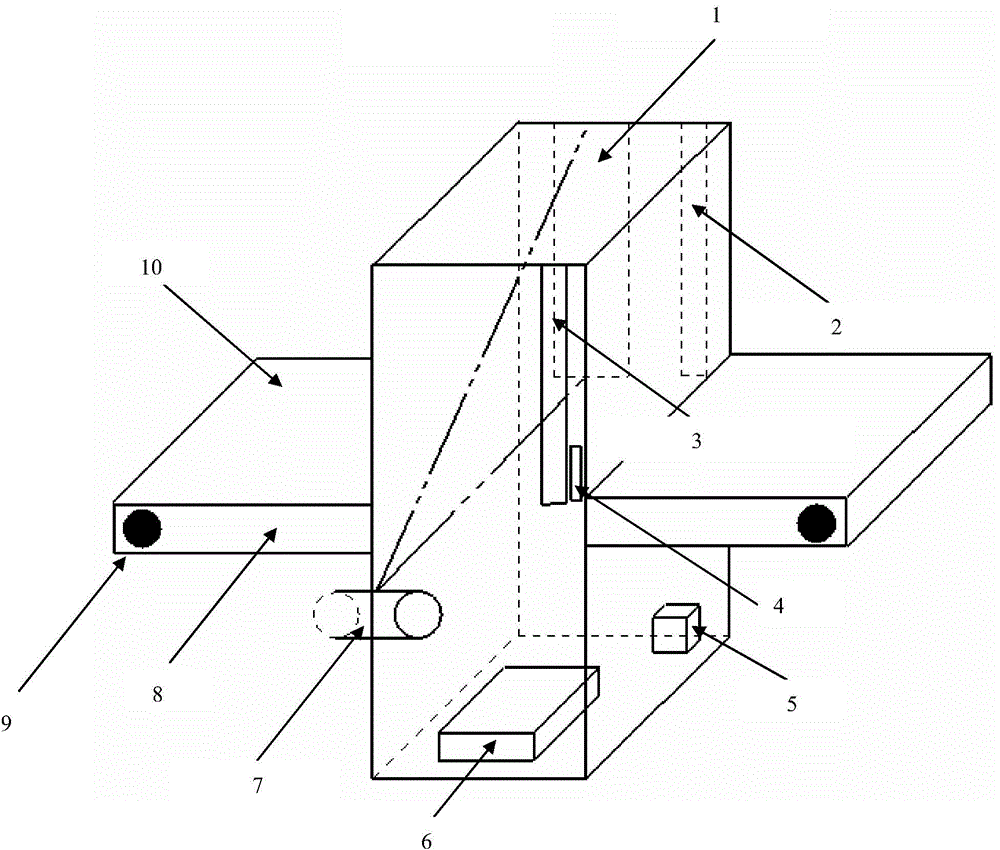
Device and method for carrying out substance identification by double-energy transmission and low-energy scattering
The invention provides a device and a method for carrying out substance identification by double-energy transmission and low-energy scattering. The device comprises a rack, a conveyor belt, a roller shaft motor, a main control cabinet, an X-ray generator, a collimator, a double-energy transmission detector, a low-energy front scattering detector, a low-energy back scattering detector, an industrial personal computer, a light barrier and a display, wherein an output end of the light barrier is connected with an input end of the main control cabinet; a control output end of the main control cabinet is respectively connected with a control input end of the X-ray generator, the control input end of the roller shaft motor and the industrial personal computer; the input end of the industrial personal computer is connected with the output end of the double-energy transmission detector, the output end of the low-energy front scattering detector and the output end of the low-energy back scattering detector; the output end of the industrial personal computer is connected with the display. The device and the method focuses on feature extraction and identification of radiation image data and combines a double-energy X-ray transmission image with a low-energy scattering image to solve a real object grey level so as to identify substances by classes, aiming at the situation that packages shield mutually and cannot be detected accurately in a security check field.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
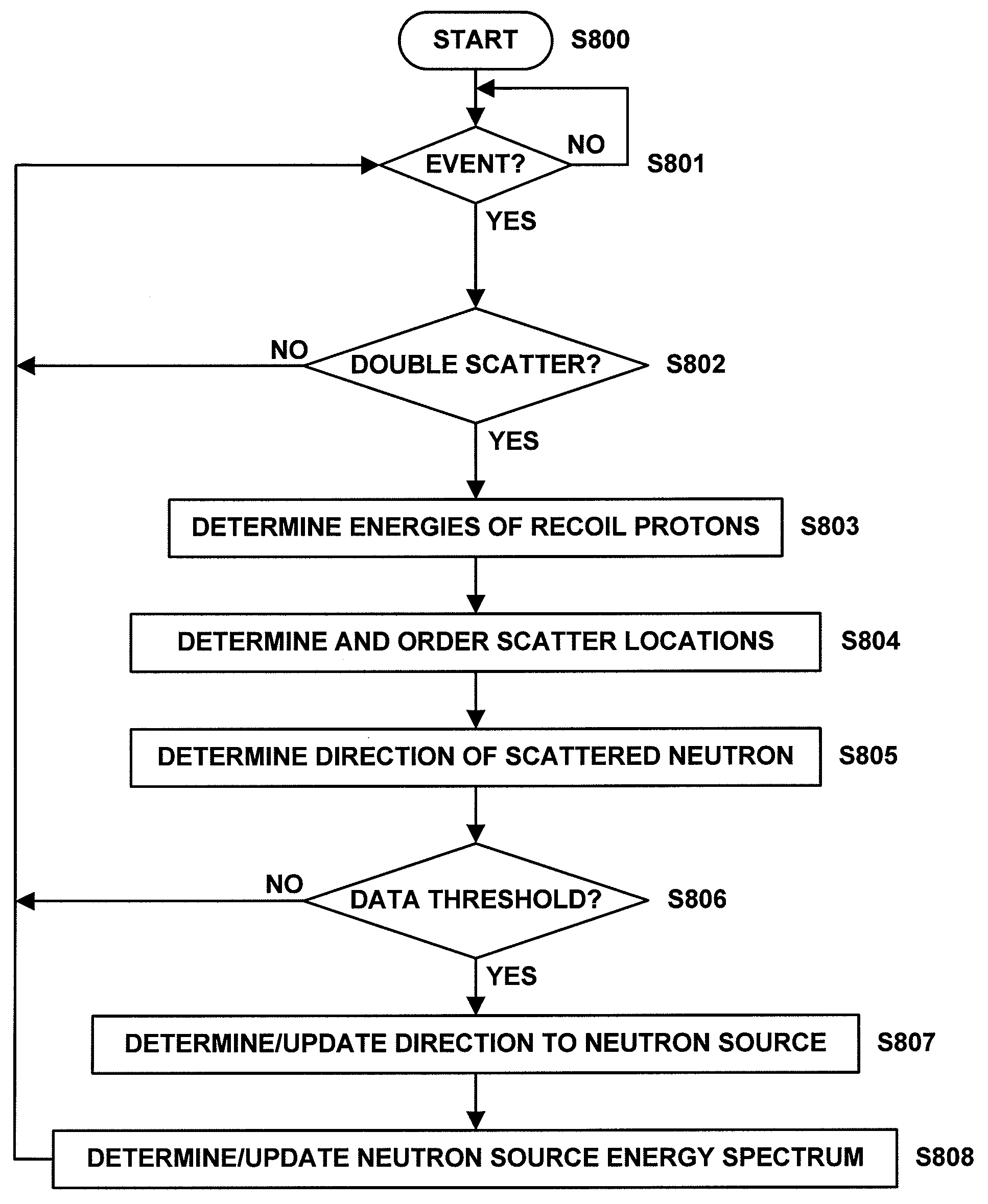
Neutron source detector
ActiveUS7667206B1Measurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron scatteringEnergy spectrum
A neutron source detector is provided for detecting and determining an energy spectrum of a neutron source and a direction to the neutron source. The neutron source detector includes a detection system configured to detect and record the location and energy of interaction between a detector and a recoil proton produced by a scattering of a neutron emitted by the neutron source. A processor is configured to determine the energy of each of a plurality of recoil protons produced by respective scatterings of a neutron based on the recorded locations and energies of interactions of the recoil protons and determine and order scatter locations of the scattered neutron based on the determined energies of the recoil protons. A direction of the scattered neutron is determined based on the order of the scatter locations. The direction to the neutron source is determined based on the determined directions of a plurality of scattered neutrons, and the energy spectrum of the neutron source is determined based on the determined direction to the neutron source, the determined directions of the plurality of scattered neutrons, and the determined energies of the plurality of recoil protons produced by the respective plurality of scattered neutrons.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Multiaxial neutron monochromator attitude adjustment device
ActiveCN102253405AGuaranteed uptimeAchieve integrationNeutron radiation measurementControl systemNeutron scattering
The invention belongs to the neutron scattering technology and in particular relates to a multiaxial neutron monochromator attitude adjustment device. The adjustment device comprises a mechanical stage body and a control system connected with the mechanical stage body by a cable. The adjustment device is characterized in that the mechanical stage body comprises a revolving stage arranged on a chassis; translation adjusters are arranged on the revolving stage; an oblique adjuster is arranged above the translation adjusters; a monochromator transposition revolving stage is arranged on the oblique adjuster; each movement mechanism of the mechanical stage body drives a monochromator to carry out multiple-degree-of-freedom position combination adjustment; and the control system comprises an industrial control computer provided with control software and a motor control unit realizing control of a stepping motor via a driver. The adjustment device integrates optics, mechanics, electronics and the computer control technology and can carry out five-degree-of-freedom movement adjustment on the neutron monochromator.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Method for obtaining intermediate resonance factor in reactor multigroup nuclear database
ActiveCN106202868AAccurate multi-group absorption cross sectionAccurate Intermediate Resonance FactorInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsResonanceMatrix expression
The invention relates to a method for obtaining an intermediate resonance factor in a reactor multigroup nuclear database. On the basis of a free gas model, a continuum energy neutron scattering matrix expression Sigma<r, s, T> (E->E') of the resonance absorption nuclide relevant to the temperature TK is obtained through formula derivation; a neutron slowing down equation is solved on the basis of the continuum energy neutron scattering matrix at the temperature TK to obtain the neutron-flux density at the temperature TK; the multigroup adsorption cross section of the resonance absorption nuclide at the temperature TK is further worked out through group merging calculation; the intermediate resonance factor is finally obtained through the intermediate resonance factor calculation; and an intermediate resonance factor multinomial coefficient using the temperature and the background cross section as independent variables is obtained by a least squares fitting method. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the intermediate resonance factor after the intermediate resonance factor calculation is more accurate; the calculation precision and the calculation efficiency of the intermediate resonance factor are improved; and finally, in the reactor physical calculation, the resonance calculation precision is improved, and the resonance calculation speed is accelerated.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and structure for ion implantation by ion scattering
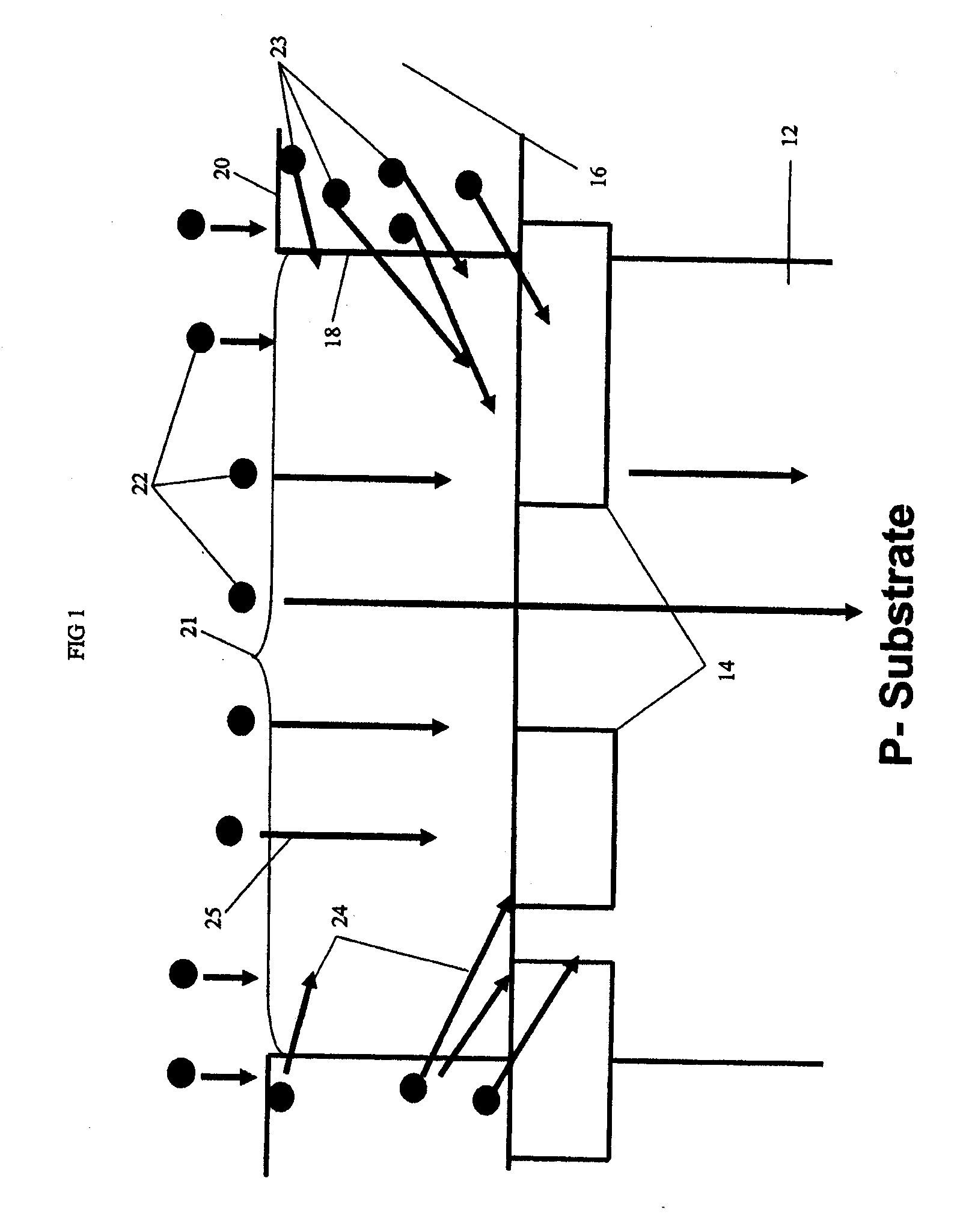
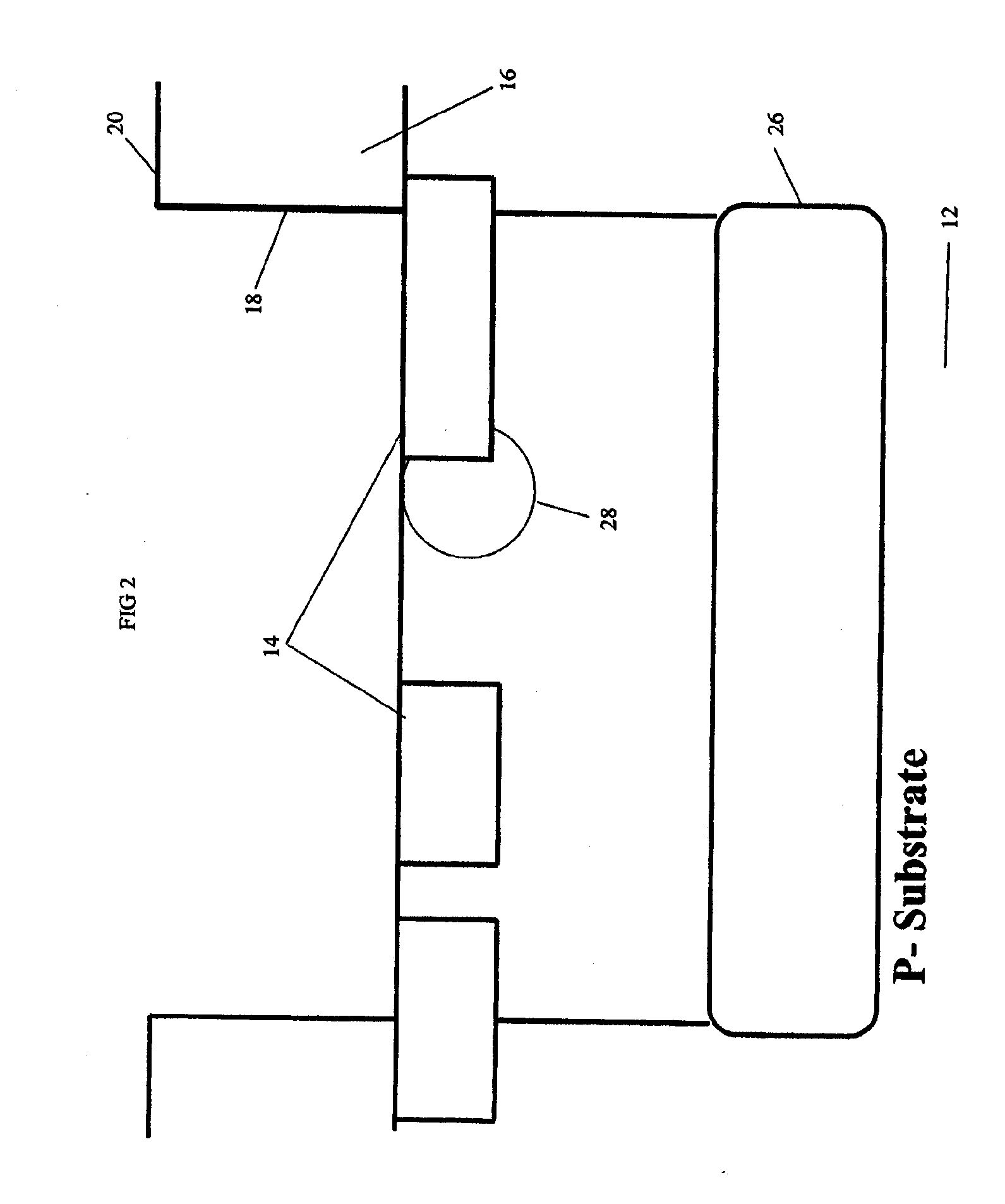
InactiveUS20060234484A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle implantNeutron scattering
A scatter-implant process and device is provided where a bi-level doping pattern is achieved in a single doping step. Additionally, devices having different breakdown voltages can be produced in a single implant process. The scatter-implant is fabricated by scattering implant ions off the edge of a mask, thereby reducing the ion energy causing the ions to doping shallower regions than the non-scattered ions which dope a lower region. By adjusting various parameters of the doping process such as, for example, ion type, ion energy, mask type and geometry, in a position of scattering edge relative to other structure of the device, the scatter-implant can be tuned to achieve certain properties of the semiconductor device. Additionally, circuits can be made using the scatter-implant process where pre-selected portion of the circuit incorporate the scatter-implant region and other portions of the circuit do not rely on the scatter region.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Neutron insertion piece system and collimation mounting method thereof
ActiveCN107358988ASimple structureImprove machinabilityHandling using diaphragms/collimetersNeutron scatteringEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of a neutron scattering spectrometer and particularly relates to a neutron insertion piece system and a collimation mounting method thereof. The system comprises a neutron insertion piece, an inner adjusting mechanism in a shielding cylinder, and an outer adjusting mechanism outside the shielding cylinder, wherein the neutron insertion piece is mounted in the shielding cylinder, the inner adjusting mechanism is mounted at a bottom portion of the neutron insertion piece, the outer adjusting mechanism is arranged on a transition steel plate, the transition steel plate is pre-embedded in a concrete base station, and the neutron insertion piece is conveyed in and out of the shielding cylinder through the outer adjusting mechanism. The neutron insertion piece system is advantaged in that the structure is relatively simple, strong machinability and adjustability are realized, the deviation relationship of an actual value and a theoretical value of a target set can be acquired, update and maintenance of the neutron insertion piece are facilitated, a collimation mounting apparatus is a laser tracker and a measurement arm, collimation and mounting of the neutron insertion piece can be rapidly and conveniently realized, and replacement of the neutron insertion piece can be realized in minutes.
Owner:DONGGUAN NEUTRON SCI CENT
High-precision second neutron bunch switch
ActiveCN107064192AAchieve openAchieve closureMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionDrive shaftElectric machine
The invention relates to the technical field of a neutron bunch switch, and particularly relates to a high-precision second neutron bunch switch applied to a neutron scattering spectrometer for realizing the switching of turning on and off the neutron bunch switch; through an operation system starting switch, a rotating system drives a transmission system to rotate, and a driving shaft of the transmission system transmits torque to a rotating circular cone system; a rotating circular cone and a neutron guide pipe at the inner part are rotated together at 90 degrees, thus a boron carbide baffle intercepts a neutron bunch flow; the rotating circular cone is reversely rotated at 90 degrees so that the neutron guide pipe is conducted; through the reciprocating motion at 90 degrees, the switching of opening and closing the neutron guide pipe is realized. The parts are rigidly connected and coaxially treated by a step or a pin structure; the parts apply driving of a motor, feedback control of an encoder, and minor control of a limiting switch; an optical grid ruler can feedback and position a terminal position; the high-precision second neutron bunch switch is simple in operation, short in movement time, high in repeat positioning precision in a conducting state, and capable of rapidly and conveniently opening and closing the neutron guide pipe.
Owner:DONGGUAN NEUTRON SCI CENT
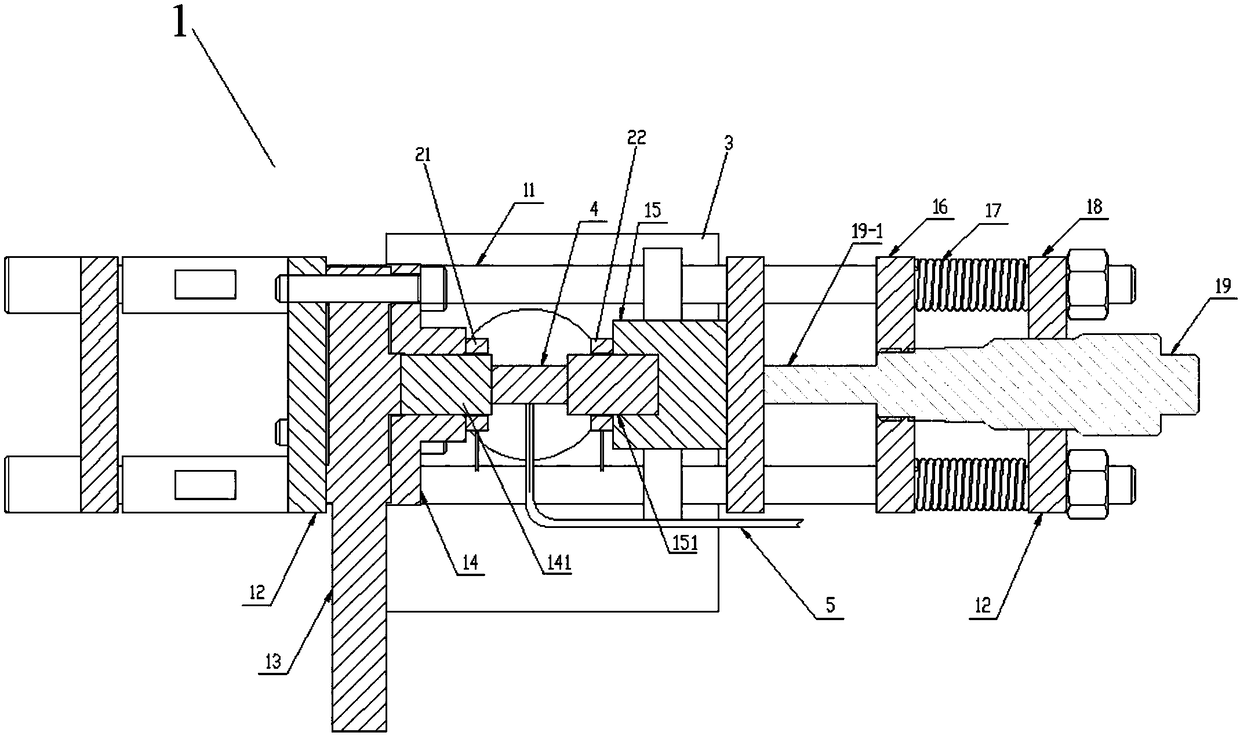
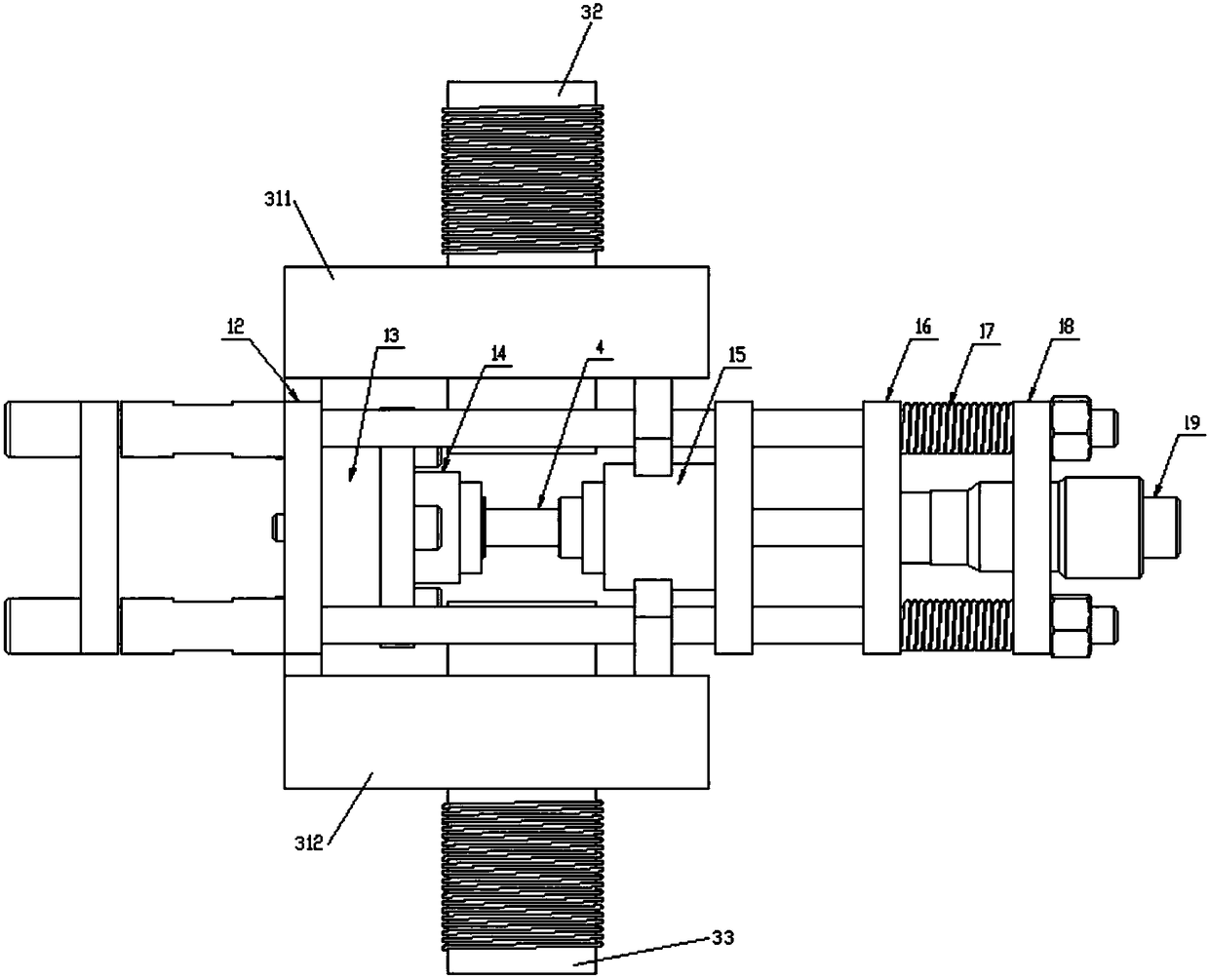
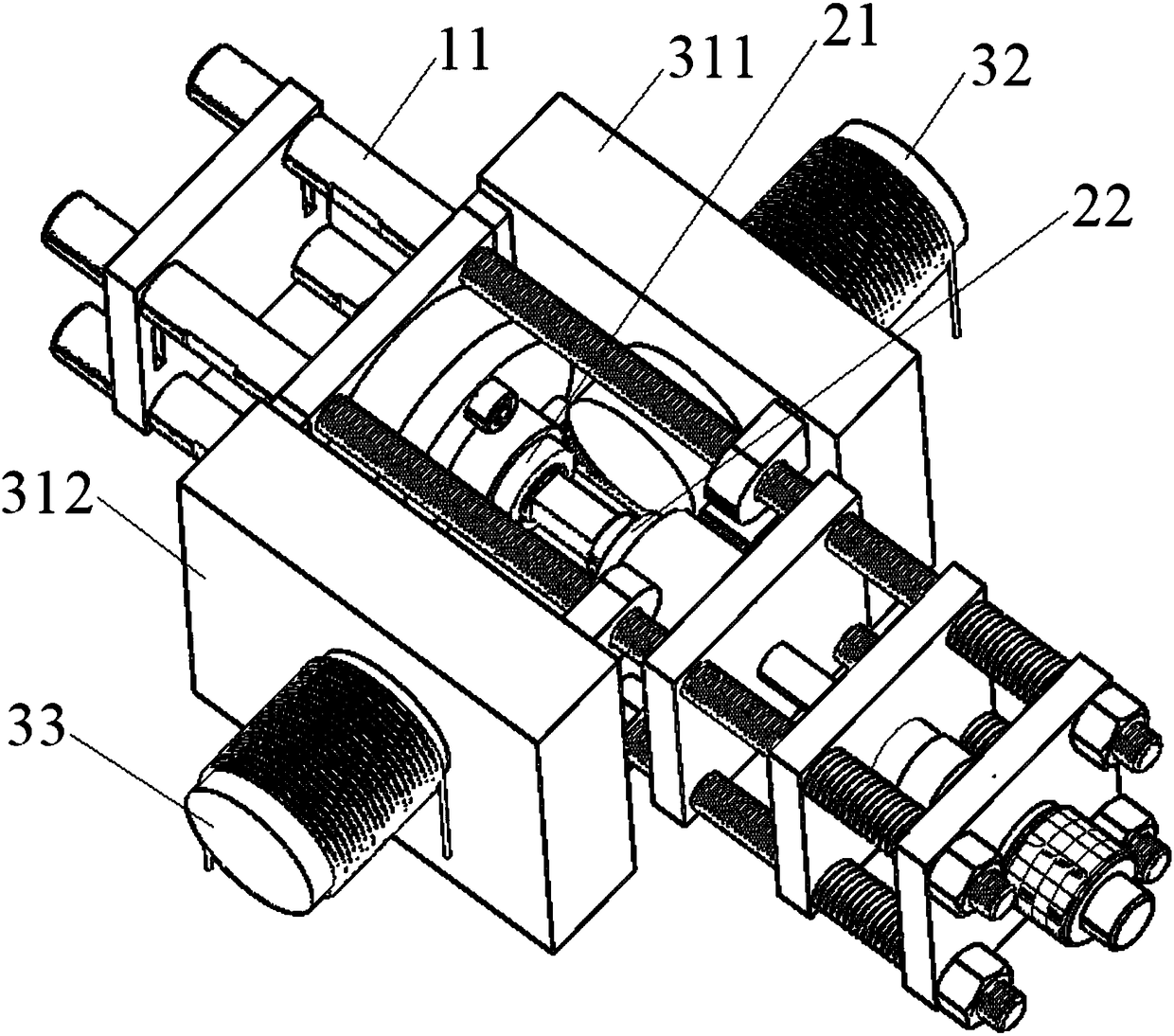
Portable in-situ multi-field coupling loading device for neutron scattering
ActiveCN108459035ACompact structureMeet the needs of complex usage environmentsMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionMulti siteMulti field
The invention discloses a portable in-situ multi-field coupling loading device for neutron scattering. The device comprises a stress loading and testing assembly, a temperature loading assembly and amagnetic field loading assembly, wherein the stress loading and testing assembly comprises four parallel guide rods for supporting; a first fixing plate, a force sensor, a left clamp, a right clamp, aspring moving plate, a spring set, a second fixing plate and a stress loader are sequentially mounted on each guide rod from left to right; the temperature loading assembly comprises a left heating ring and a right heating ring which are correspondingly arranged on clamp heads of the left clamp and the right clamp; the magnetic field loading assembly comprises a support which his provided with two vertical arms, and the two vertical arms are correspondingly arranged at the front and back of a guide rod set. According to the device, the stress, temperature and magnetic field multi-field coupling loading is developed and achieved for the first time, and a foundation is provided to multi-site in-situ research of magnetic material type magnetic structures in evolving micromechanisms; and thedevice is applicable to different neutron source neutron scattering spectrometers.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Rear-end rough collimator support for neutron scattering and installation and debugging method
ActiveCN108303438ASimple structureEasy to adjustMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNeutron scatteringCollimator
The invention relates to the field of science and technology of neutron scattering, in particular to a rear-end rough collimator support for neutron scattering and an installation and debugging method. The rear-end rough collimator support mainly comprises a fixing base, a vertical moving plate, a horizontal moving plate and an upper-end support which are installed sequentially from bottom to top,wherein the upper-end support is installed on the upper end surface of the horizontal moving plate through screws, the vertical moving plate and the horizontal moving plate are fastened through a vertical pull plate assembly, the fixing base and the vertical moving plate are connected through vertical adjusting mechanisms, and horizontal adjusting mechanisms are installed on the vertical moving plate and the horizontal moving plate. The three-dimensional independent adjustment capability is obtained through the independent horizontal adjusting mechanisms and vertical adjusting mechanisms, andthe installation verticality can be adjusted through the vertical pull plate assembly. The rear-end rough collimator support is simple in structure and convenient to manufacture and install and has the shape identical to the vertical projection of a rear-end rough collimator, all that is required for installation adjustment is the space under the rough collimator of the support, and small space is occupied on the whole.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
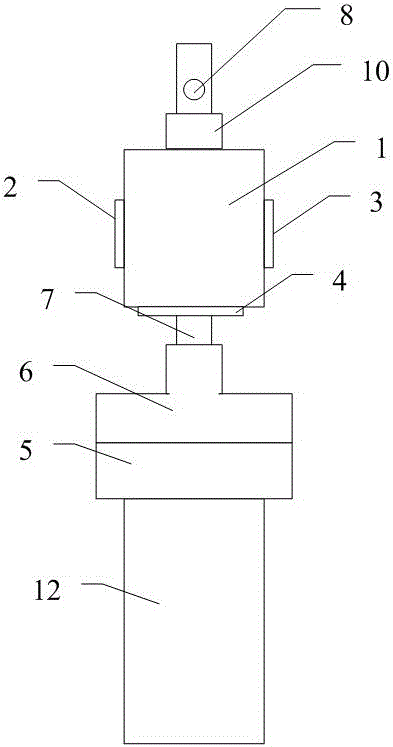
Dedicated clamp for neutron small-angle scattering high-temperature in-site tensile test
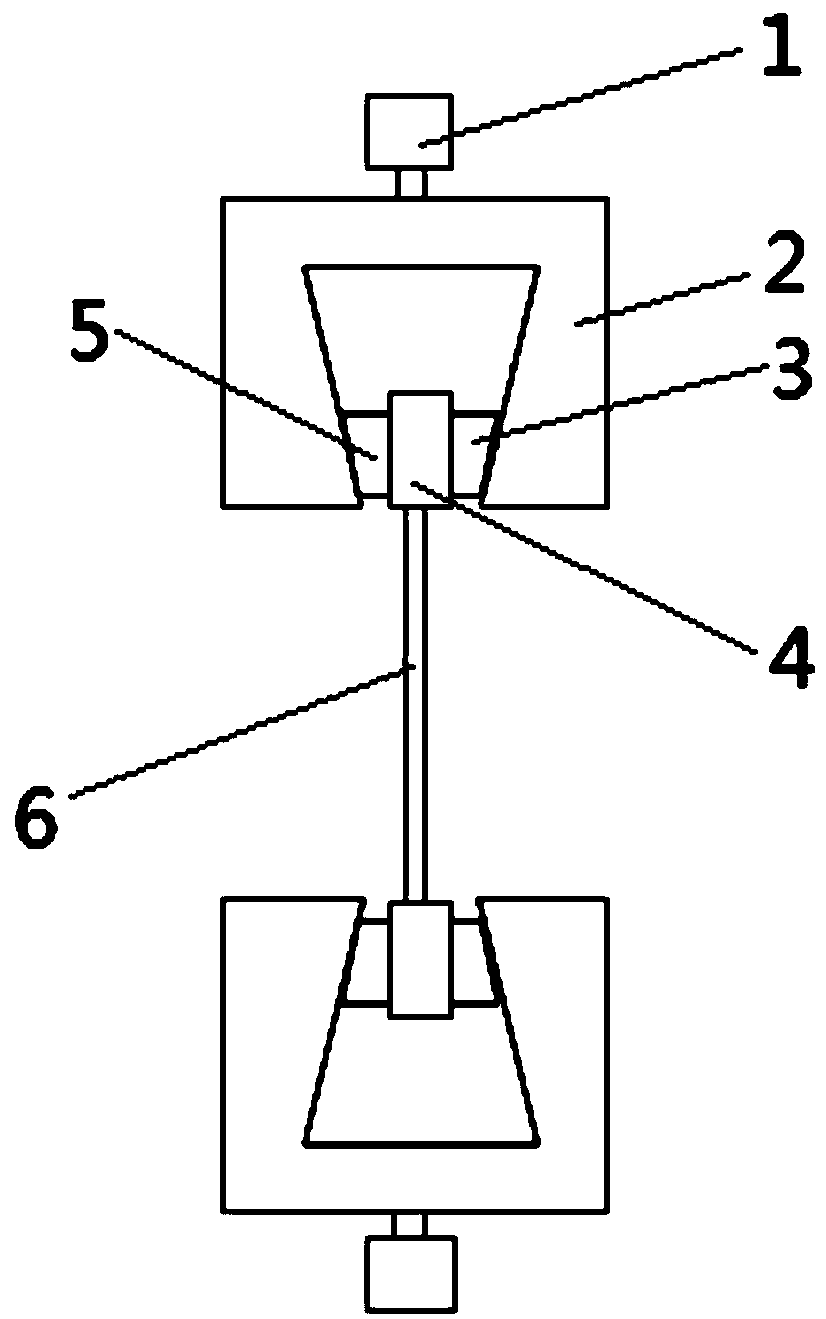
PendingCN108760483AInhibit sheddingThe thickness can be adjusted at willMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesNeutron scatteringTensile testing
The invention belongs to the field of neutron scattering experiments and especially relates to a dedicated clamp for a neutron small-angle scattering high-temperature in-site tensile test. The clamp comprises a clamp head bolt, a clamp head body and a sample fixing assembly, wherein the clamping head bolt is connected with a tensile testing machine pull rod, the clamping head bolt is fixedly connected to the clamping head body, and the clamping head body can provide axial tension for the sample fixing assembly. Therefore, the dedicated clamp for the neutron small-angle scattering high-temperature in-site tensile test disclosed by the invention has the advantages of convenience in assembling and disassembling and firmness in clamping.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
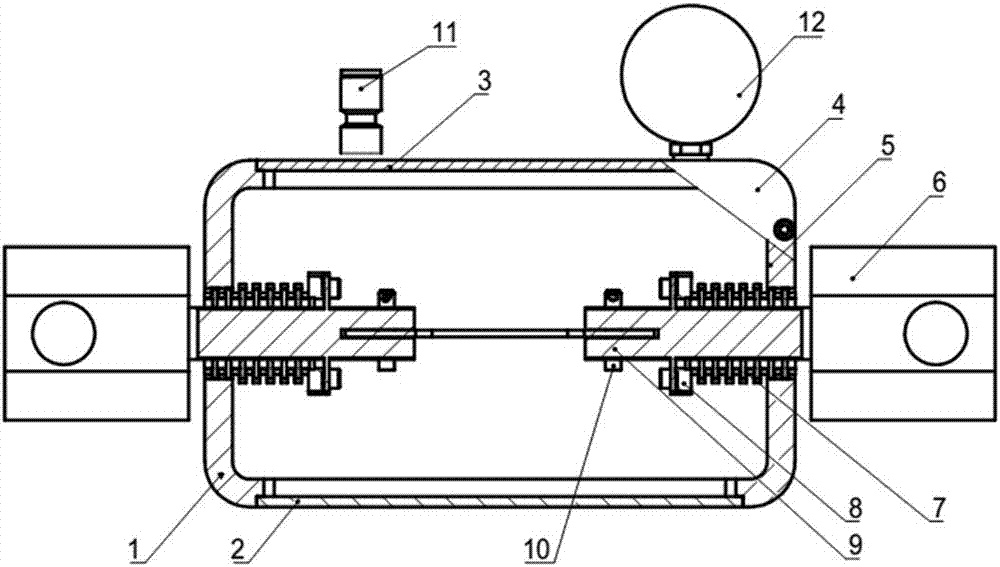
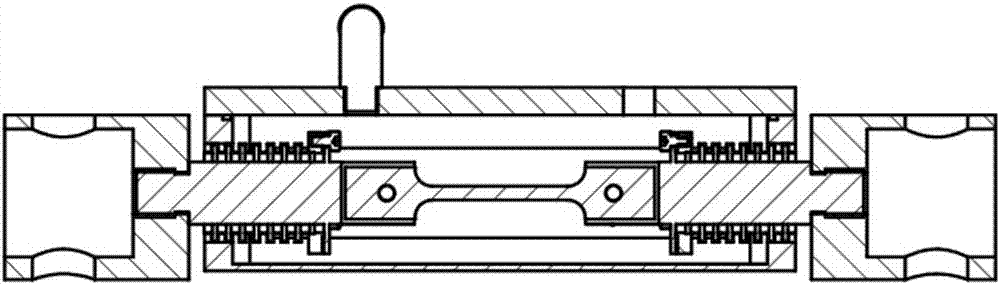
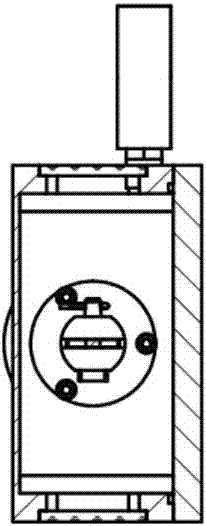
Room-temperature mechanical loading device for metal beryllium in neutron scattering experiment
PendingCN107063872AWon't leakRisk of Hazard PreventionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesNeutron scatteringBeryllium Powder
The invention discloses a room-temperature mechanical loading device for metal beryllium in a neutron scattering experiment. The loading device comprises a sealed cavity, an incident window plate, an emergent window plate, a sealing cover, a sealing ring, a loading rod, a corrugated pipe, a sealing flange, a sample fixture, a dowel, a vacuumization crossover coupling and a vacuum manometer. A sample feeding hole is formed in the sealed cavity of the room-temperature mechanical loading device for metal beryllium in the neutron scattering experiment and matched with the sample fixture to complete loading and unloading of a sample, the cavity is sealed through the sealing cover, mechanical loading of the sample by certain displacement can be ensured to be realized by means of the telescopic characteristic of the corrugated pipe in a telescopic connection assembly when the inside of the sealed cavity is in a negative pressure state, so that metal beryllium powder produced after the sample is broken cannot leak to the outside of the sealing cavity, the device has the advantages of being simple in structure, easy to establish and safe and reliable in performance, and the risk that an experimenter is harmed by metal beryllium powder can be prevented effectively.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
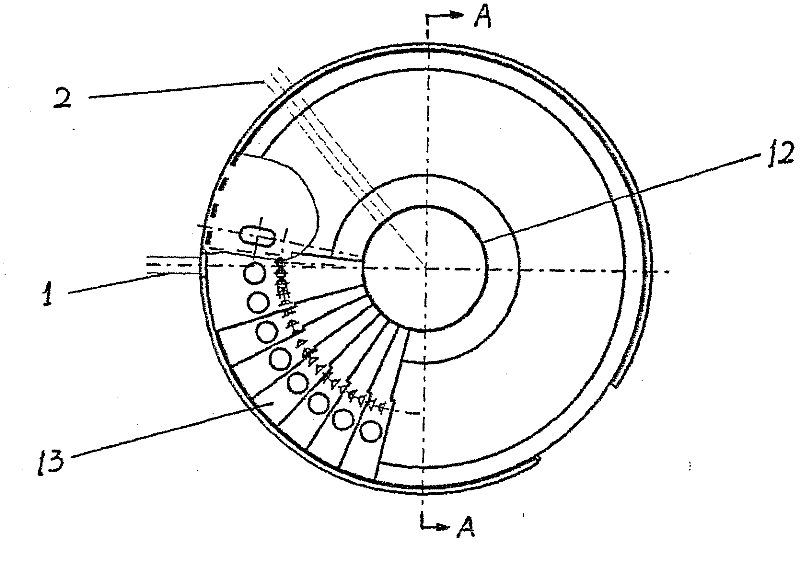
Adjusting device for first collimator of neutron texture diffractometer
ActiveCN102332318ALow costSmall footprintHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionNeutron scatteringPhysics
The invention, which relates to the neutron scattering technology field, discloses an adjusting device for a first collimator of a neutron texture diffractometer. In the prior art, when position adjustment is carried out on a plurality of first collimators, the plurality of first collimators are moved integrally, an occupied space volume is too large, and costs on an external shield are increased substantially; however, the above-mentioned problems can be solved according to the invention. A scheme provided in the embodiment of the invention is as follows: the invention provides an adjusting device for a first collimator of a neutron texture diffractometer; the neutron texture diffractometer comprises a plurality of first collimators and a translation guide rail; a translation units, which are used for installing the plurality of first collimators and enable each the first collimator to make translational motions independently, are arranged on the translation guide rail. The embodiment of the invention is suitable for application to a neutron texture diffractometer and the like.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
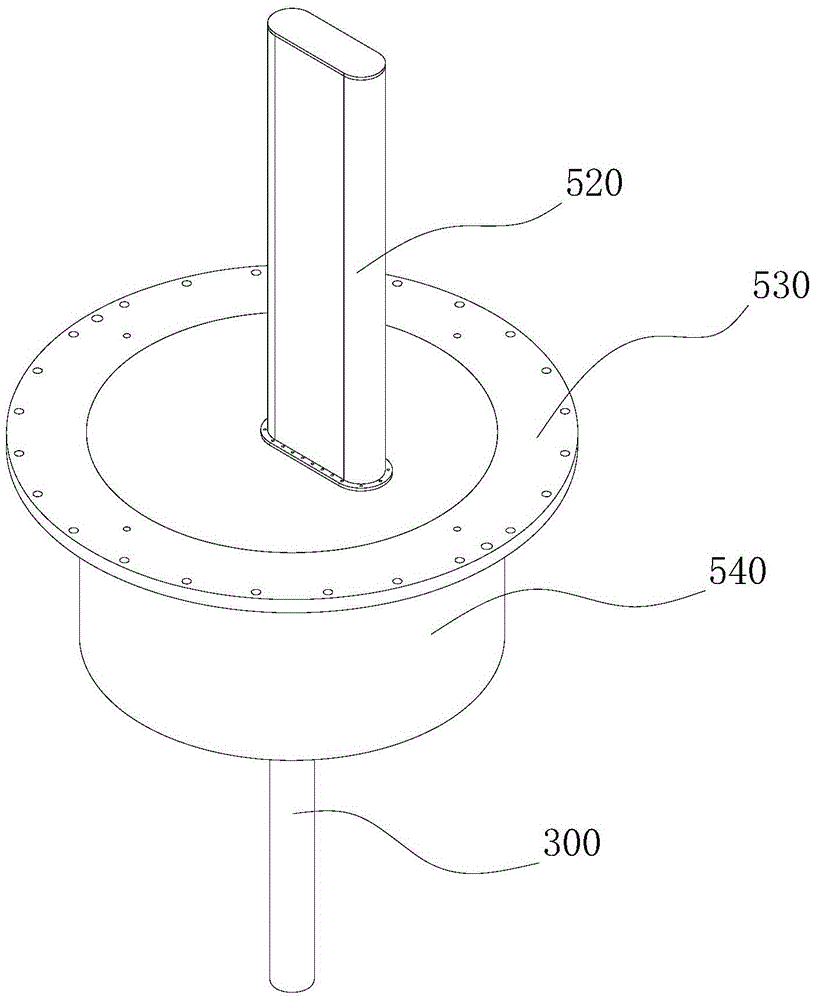
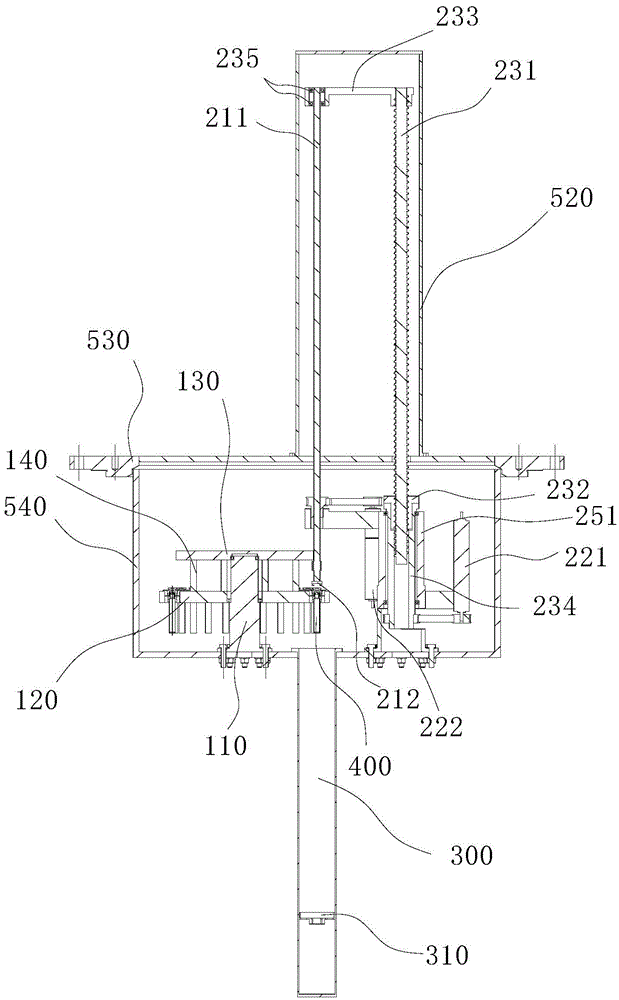
Sample replacing device for neutron scattering experiment
ActiveCN105548226ARealize automatic replacementImprove experimental efficiencyMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionNeutron scatteringAtomic physics
The application discloses a sample replacing device for a neutron scattering experiment. The device comprises a sample-box-storing device, a neutron scattered beam window, and a sample-box-moving device. A sample-box-storing disc comprises at least two sample-box-storing places for storing sample boxes containing samples. The neutron scattered beam window is used for carrying out the neutron scattering experiment on the samples placed in the window and is provided with sample-box-arranging places for arranging the sample boxes. The sample-box-moving device comprises a drive unit and a chuck assembly, wherein the drive unit drives the chuck assembly to pick the sample boxes up and to transfer the sample boxes between the sample-box-storing device and the neutron scattered beam window. When the neutron scattering experiment is carried out, through the device, the sample boxes can be moved through the sample-box-moving device, thereby enabling at least two samples to be subjected to the neutron scattering experiment. Compared with the prior art, the experiment efficiency is improved, and the experiment cost is saved.
Owner:DONGGUAN NEUTRON SCI CENT
Neutron monochromator shielding device
ActiveCN101599307ALow powerLess power; moment of inertia generated by simultaneous rotationShielded cellsNeutron scatteringMonochromator
The invention belongs to the technical filed of neutron scattering and discloses a shielding device of a neutron monochromator. The device has a closed cylindrical drum-shaped structure; a middle rotating part consists of a rotating tray which is provided with a gear ring and N+1 rotating preventing electromagnets, a large wedge block arranged on the rotating tray, N small division wedge blocks and a lower rotating tray bearing; the large wedge block and the rotating tray are mutually fixed together; and the N small division wedge blocks are sequentially arranged on the gap position of the large wedge block. A fixed electromagnet is arranged above the small wedge block, and the rotating preventing electromagnets and the fixed electromagnet attract the small wedge blocks when being electrified. The technical proposal provided by the invention finishes the complicated movement by the matching of software and hardware, and the structure is simple and the processing is convenient.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Neutron howitzer and neutron scattering spectrometer
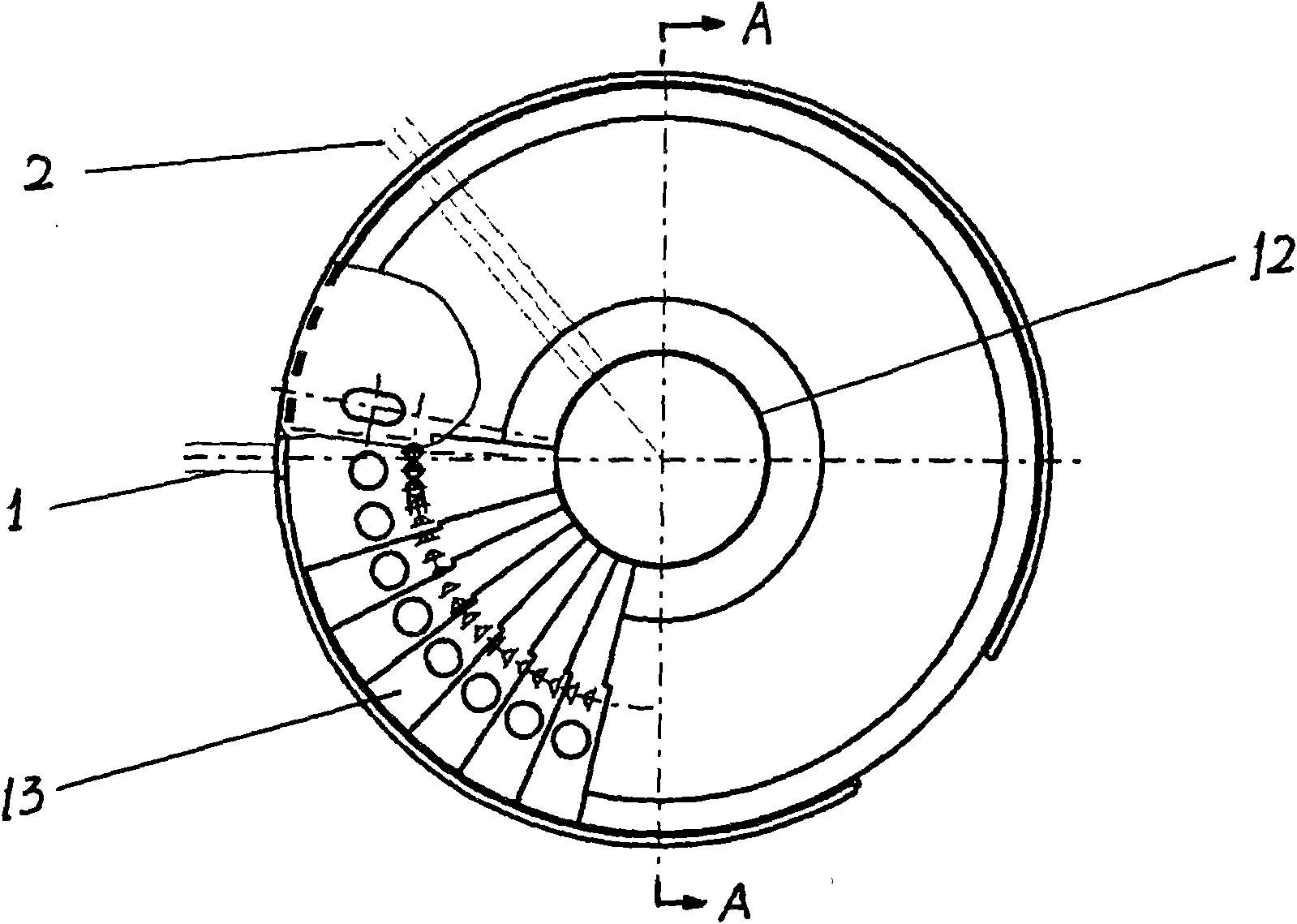
InactiveCN102324259AImprove transmittanceExtended service lifeHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionMetal foilNeutron scattering
The invention discloses a neutron howitzer and a neutron scattering spectrometer. The invention relates to the technical field of neutron scattering, and solves the problem that while increasing the neutron transmissivity, the prior art has poor radiation aging-resistant capability. In the scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the neutron howitzer comprises partitions, and is characterized in that: each partition consists of a carrier layer and a neutron-absorbing layer, the carrier layer is a metal foil, and the neutron-absorbing layer is attached on the carrier layer. The embodiment of the invention is applicable to neutron measurement instruments and the like.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Method for evaluating energy loss, chipping resistance and abrasion resistance of polymeric material
InactiveUS20140140483A1Highly accurate evaluationReduce measurement errorMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayNeutron scattering
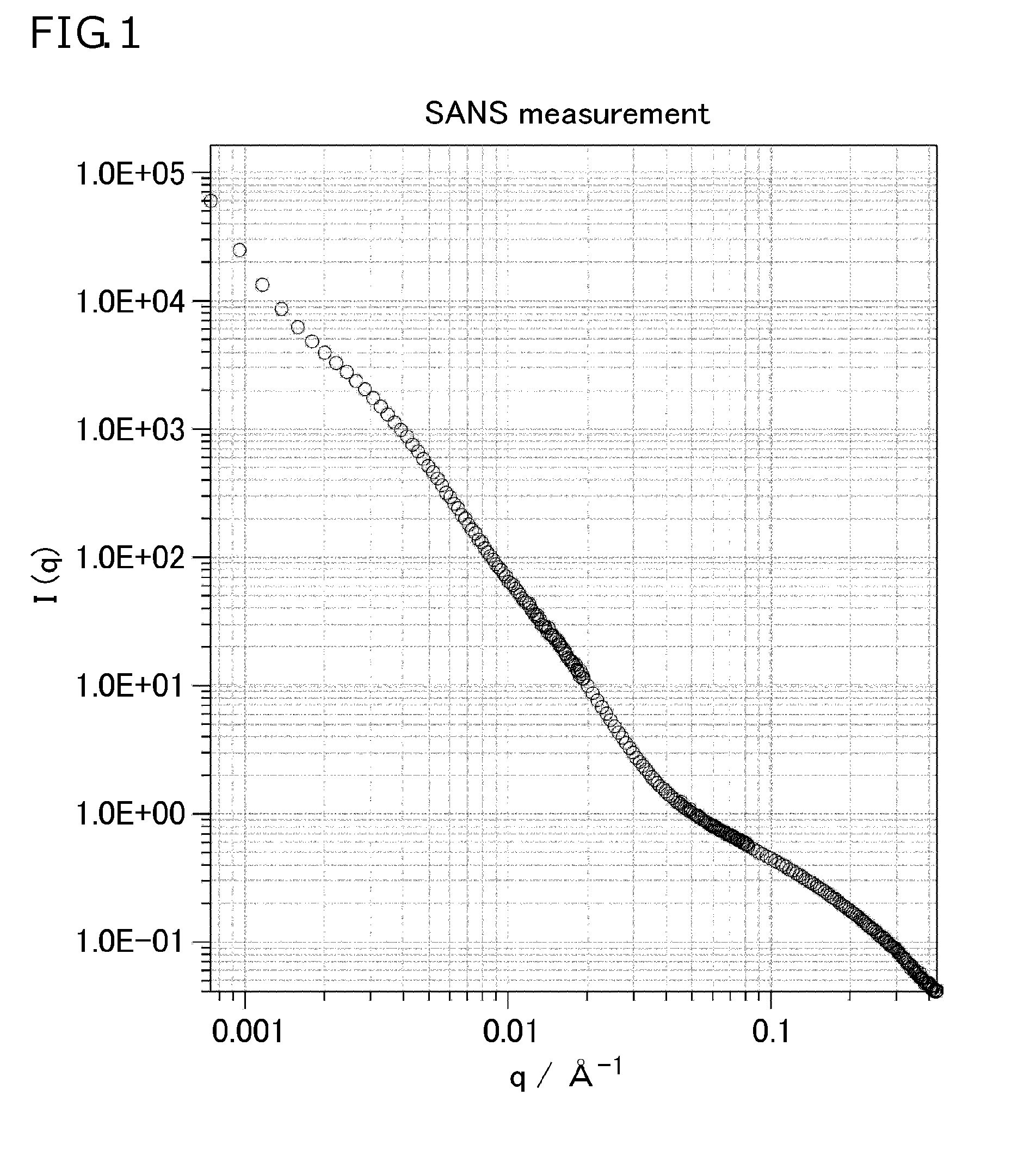
The present invention provides a method for evaluating energy loss in a polymeric material, wherein the method provides sufficient evaluation of the difference in performance between samples with excellent measurement accuracy; a method for evaluating chipping resistance of a polymeric material, wherein the method provides evaluation in a short period of time and at low cost with excellent measurement accuracy; and a method for evaluating abrasion resistance of a polymeric material, wherein the method provides sufficient evaluation of the difference in performance between samples with excellent measurement accuracy. The present invention relates to methods for evaluating energy loss, chipping resistance, and abrasion resistance of a polymeric material, and the methods include irradiating the polymeric material with X-rays or neutrons to perform X-ray scattering measurement or neutron scattering measurement.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Sample environment coupling loading device for neutron scattering
ActiveCN108663276AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesInterference fitNeutron scattering
The invention discloses a sample environment coupling loading device for neutron scattering. The device comprises a G-M refrigerator, a high pressure sample chamber, a sample tube and a piston; the high pressure sample chamber comprises an outer cylinder and an inner cylinder, two ends of the outer cylinder are open, and internal threads are arranged at positions, at the openings, of the inner wall of the outer cylinder; two ends of the inner cylinder are open, and the inner cylinder is interference fit with the outer cylinder; one end of the sample tube is open, the open end of the sample tube is downward inserted into the inner chamber of the inner cylinder to be in close fit with the inner cylinder; a plug is inserted into the cavity of the sampling tube from the opening of the sample tube, and is in close fit with the structure of the piston; the piston is inserted into the inner cylinder from the top end, and is in sliding fit with the inner cylinder, and the piston is in contactwith the bottom of the sample tube; the top opening of the outer cylinder is sealed by an upper locking nut, a central hole is arranged on the central axis of the upper locking nut, and is used for accommodating a pressurizing rod; and one end of a heat conduction cylinder column is connected with the cold head of the G-M refrigerator, and the other end of the heat conduction cylinder column is connected with the upper locking nut. The device can realize dual loading of high pressure and low temperature, and is great significance to study the change of the structure and the properties of a substance under the co-action of multi-dimensional factors in neutron scattering.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
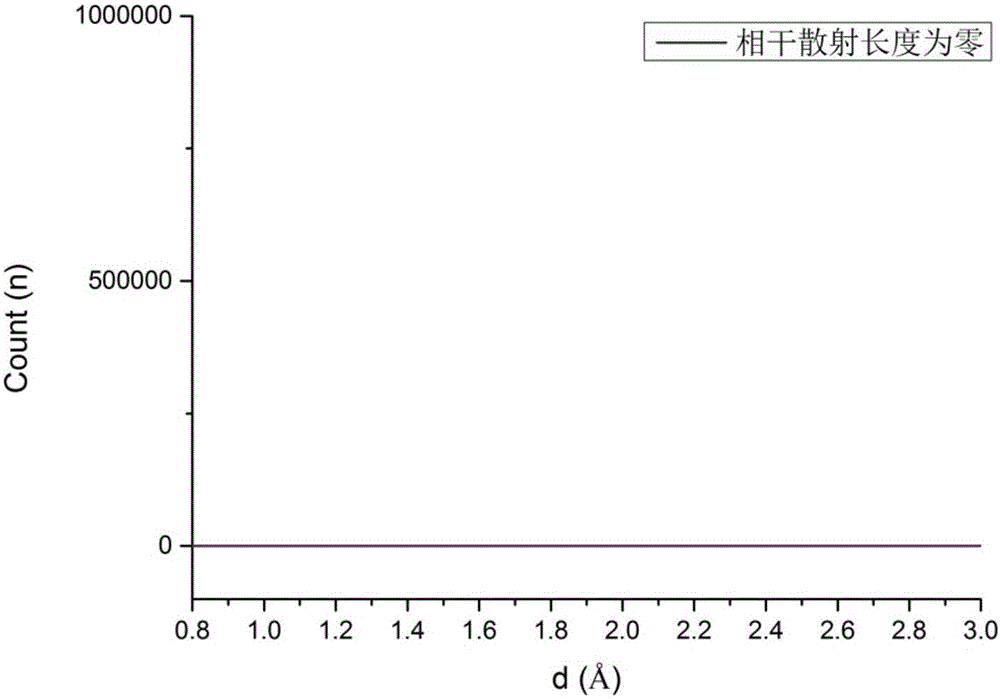
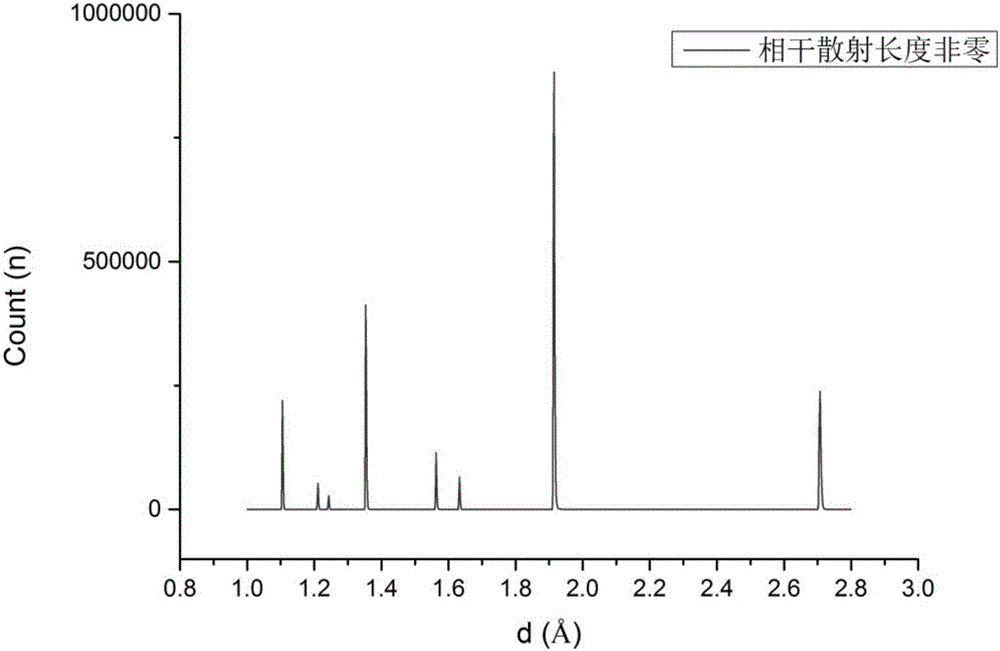
Zirconium-titanium alloy for preparing non-magnetic sample box for neutron scattering experiments and application of zirconium-titanium alloy
InactiveCN106198584AHigh strengthImprove data qualityMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionTest sampleNeutron scattering
The invention discloses a zirconium-titanium alloy for preparing a non-magnetic sample box for neutron scattering experiments and application of the zirconium-titanium alloy. The general formula of the zirconium-titanium alloy for preparing the non-magnetic sample box for neutron scattering experiments is TixZry, wherein the atomicity ratio of titanium to zirconium, namely, x:y is (2.08+ / -0.1):1. According to the zirconium-titanium alloy material, the zirconium-titanium alloy with the atomicity ratio of titanium to zirconium being (2.08+ / -0.1):1, especially, the zirconium-titanium alloy Ti2.083Zr is adopted, so that the prepared sample box hardly generates interference signal peaks in detected test sample data, and thus the data quality of neutron scattering experiments is more reliable and more credible. Meanwhile, the material is high in strength, nonmagnetic and capable of being produced in batches and widely applied to neutron scattering experiments, especially, experiments with a high magnetism control requirement, and a foundation is laid for application and popularization of the neutron scattering technology.
Owner:DONGGUAN NEUTRON SCI CENT
Neutron monochromator shielding device
ActiveCN101599307BLow powerRealize continuously adjustableShielded cellsNeutron scatteringMonochromator
The invention belongs to the technical filed of neutron scattering and discloses a shielding device of a neutron monochromator. The device has a closed cylindrical drum-shaped structure; a middle rotating part consists of a rotating tray which is provided with a gear ring and N+1 rotating preventing electromagnets, a large wedge block arranged on the rotating tray, N small division wedge blocks and a lower rotating tray bearing; the large wedge block and the rotating tray are mutually fixed together; and the N small division wedge blocks are sequentially arranged on the gap position of the large wedge block. A fixed electromagnet is arranged above the small wedge block, and the rotating preventing electromagnets and the fixed electromagnet attract the small wedge blocks when being electrified. The technical proposal provided by the invention finishes the complicated movement by the matching of software and hardware, and the structure is simple and the processing is convenient.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
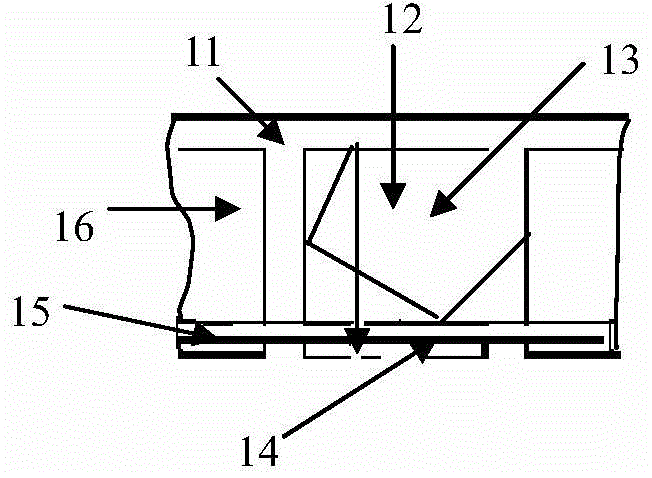
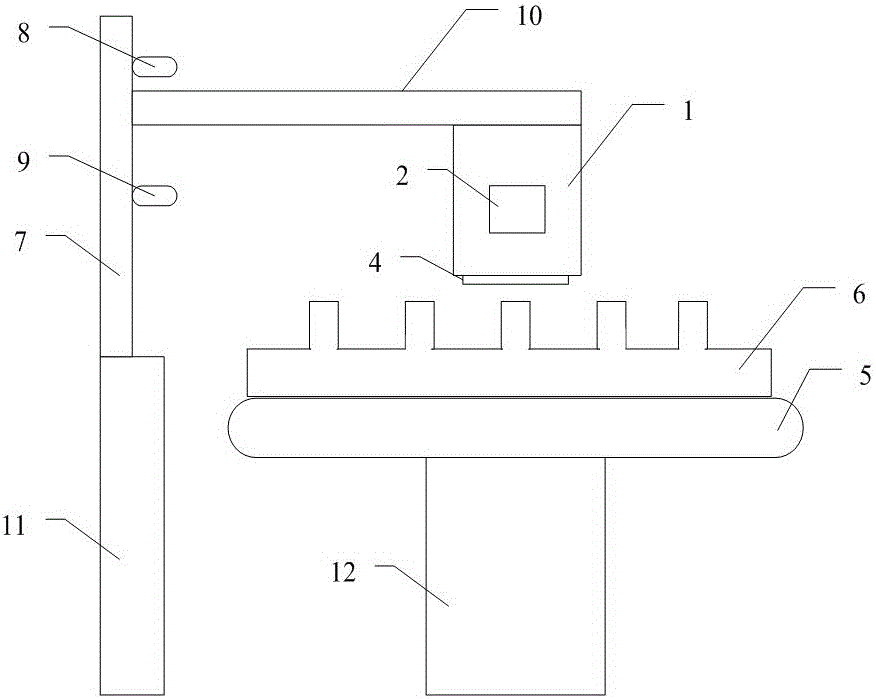
Temperature loading device for neutron scattering experiment
PendingCN106841254AAvoid burnsReduce labor intensityMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionNeutron scatteringEngineering
The invention provides a temperature loading device for a neutron scattering experiment. The device comprises a heating furnace assembly, a translation sample stage assembly and a pneumatic lifting bracket assembly, wherein the heating furnace assembly comprises a furnace body cavity, an incident window plate, an emergent window plate and a water cooling pipe; the translation sample stage assembly comprises a servo electric cylinder, a sample stage surface and a sample stage base; the pneumatic lifting bracket assembly comprises a lifting air cylinder, a high position limit switch, a low position limit switch, a movable bracket and a lifting base. A sample loading hole is formed in the heating furnace in the temperature loading device for the neutron scattering experiment, is matched with the pneumatic lifting bracket assembly to complete automatic loading and unloading of the heating furnace of samples, and is coordinated with a blocking state of the translation sample stage assembly, so that in-situ temperature environment loading of multiple samples and automatic switching of the samples in the neutron scattering (diffraction) experiment can be achieved, the labor intensity of an experimenter and the ray irradiation risk are reduced, and the sample switching time is shortened.
Owner:INST OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS & CHEM CHINA ACADEMY OF
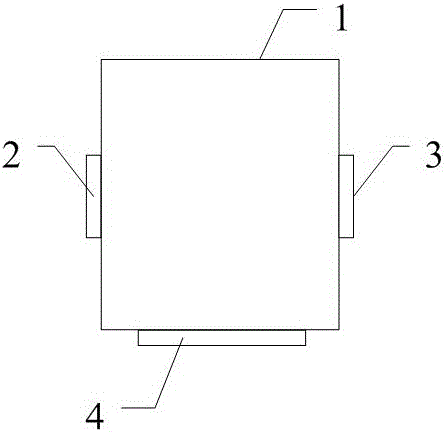
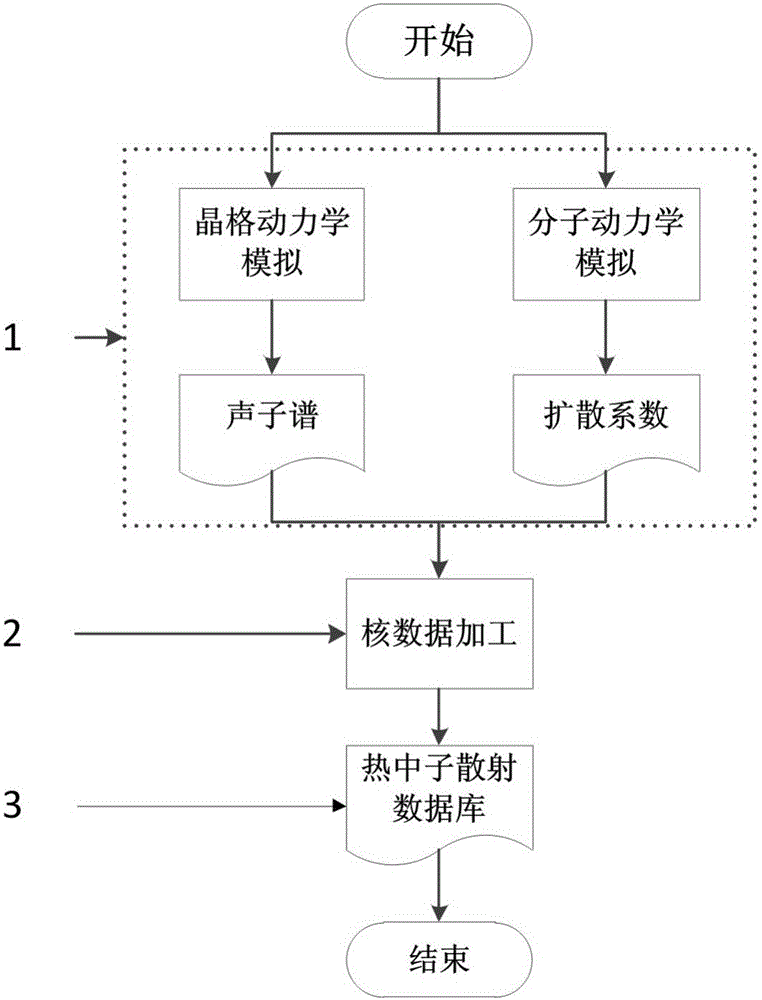
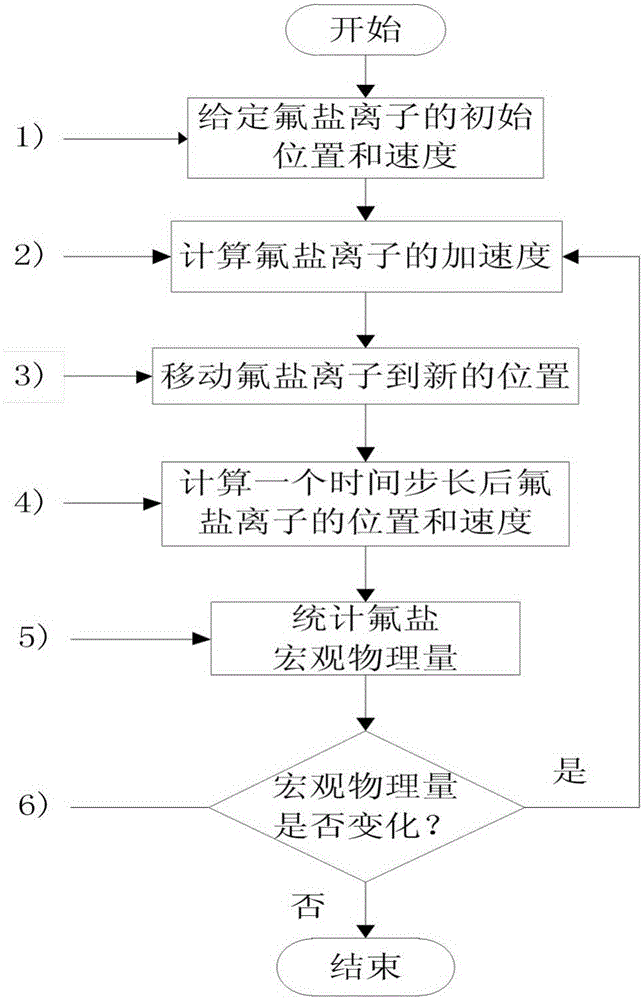
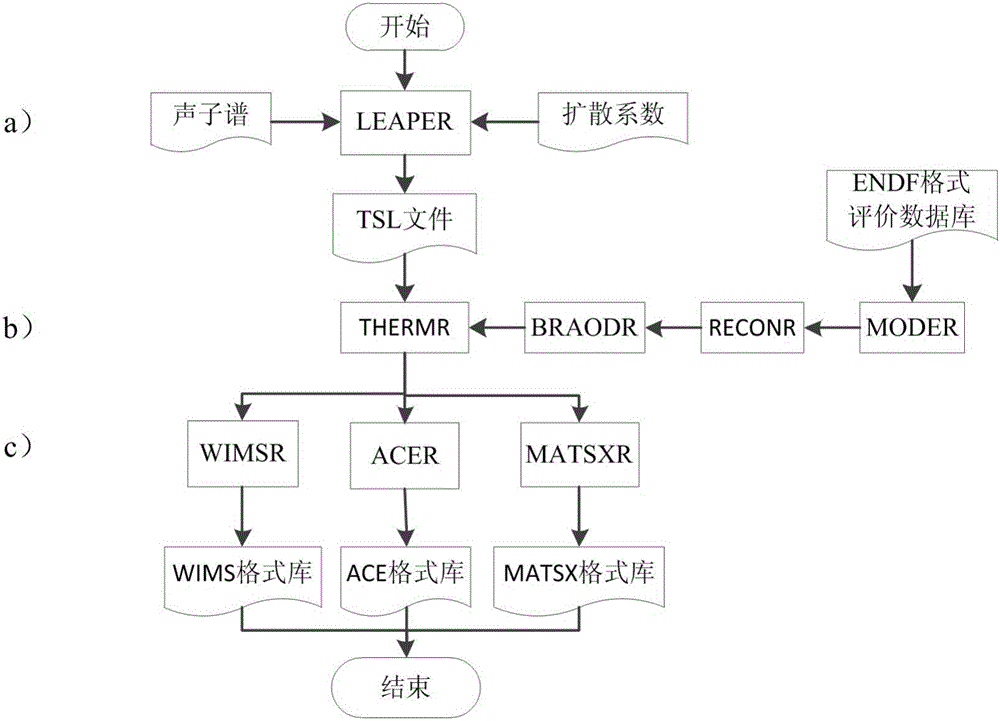
Solid state and liquid state villiaumite thermal neutron scattering database obtaining method and database
ActiveCN106126928AEfficient and accurate processingCapable of coherent elastic scatteringSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsMolecular dynamicsIon
The invention relates to a solid state and liquid state villiaumite thermal neutron scattering database obtaining method and a database; the method comprises the following steps: 1, using a crystal lattice dynamics program based on the primary quantum mechanics principle to calculate phonon spectrum distribution of solid state villiaumite crystal and liquid state villiaumite solution; in addition, using a statistics physical method based on the molecule dynamics to calculate the diffusion coefficient of each villiaumite ion of the liquid state villiaumite solution; 2, supplying the phonon spectrum distribution and diffusion coefficients obtained in the step1 to a data processing program NJOY, thus obtaining solid state and liquid state villiaumite thermal neutron scattering data; 3, matching corresponding nucleus database index files according to different application purposes, and the index files and the thermal neutron scattering data obtained in step2 can form a complete thermal neutron scattering database. The invention also discloses the database obtained by the method, thus filling the blanks in the thermal neutron scattering database making field in international solid state villiaumite crystal and liquid villiaumite solution multi-group transport and subgroup resonance calculation.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Flat panel X-ray detector with reduced internal scattering for improved attenuation accuracy and dynamic range
InactiveUS7812314B1Substantial transparencyEasy to assembleSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansX-rayDynamic range
An x-ray detector is disclosed that has had all unnecessary material removed from the x-ray beam path, and all of the remaining material in the beam path made as light and as low in atomic number as possible. The resulting detector is essentially transparent to x-rays and, thus, has greatly reduced internal scatter. The result of this is that x-ray attenuation data measured for the object under examination are much more accurate and have an increased dynamic range. The benefits of this improvement are that beam hardening corrections can be made accurately, that computed tomography reconstructions can be used for quantitative determination of material properties including density and atomic number, and that lower exposures may be possible as a result of the increased dynamic range.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Buckle-type warning lamp preventing internal scattering
ActiveCN105546455ABlock astigmatismAvoid influenceElectric circuit arrangementsOptical signallingNeutron scatteringEngineering
The invention discloses a buckle-type warning lamp preventing internal scattering, which comprises a base (1), an end cap (2), a lamp bank (6) and a control circuit board (7), wherein an end cap buckle (12) and an end cap neck (13) are arranged at the lower part of the end cap, and an end cap positioning block (14) is further arranged in the end cap neck; a light barrier support (4) is mounted at the lower part of the end cap through the end cap buckle and an end cap neck, and a light barrier (3) is mounted on the light barrier support. A front inner neck (8) is formed on the inner side of an opening of the base, an outer neck (9) is formed on the lower outer side of the opening, and a rear inner neck (11) is formed in the rear part of the base. In the warning lamp, the plurality of necks different in positions are formed in both of the end cap and the base, a plurality of screws for assembly are not required any more, and the efficiencies of production and dismounting maintenance are improved; the light barrier support and the light barrier are used for effectively block light scattering of the lamp body, so as to avoid the influence on people in a car and meet the high technical requirement of warning lamps.
Owner:WENZHOU HUNDAR POLICE EQUIP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com