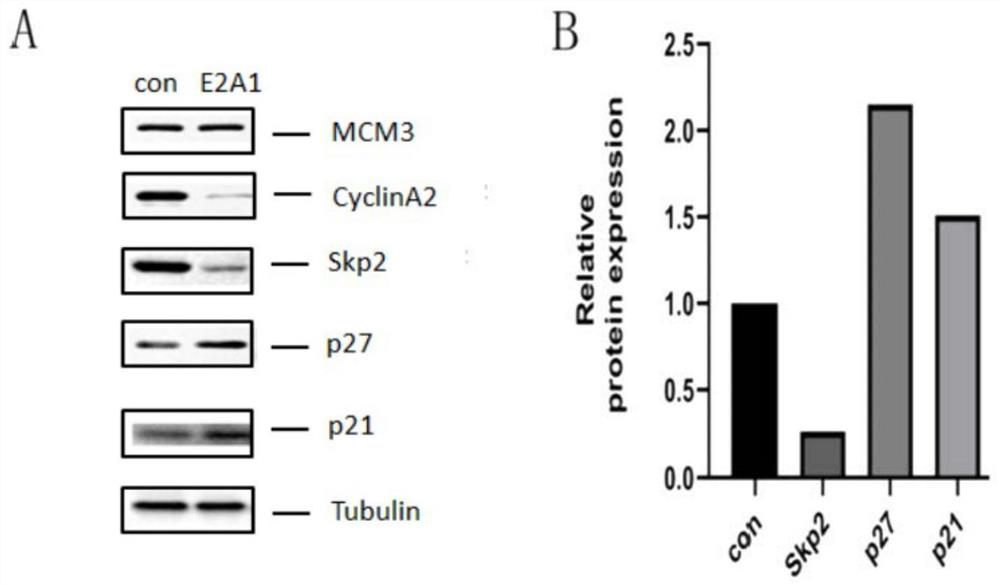
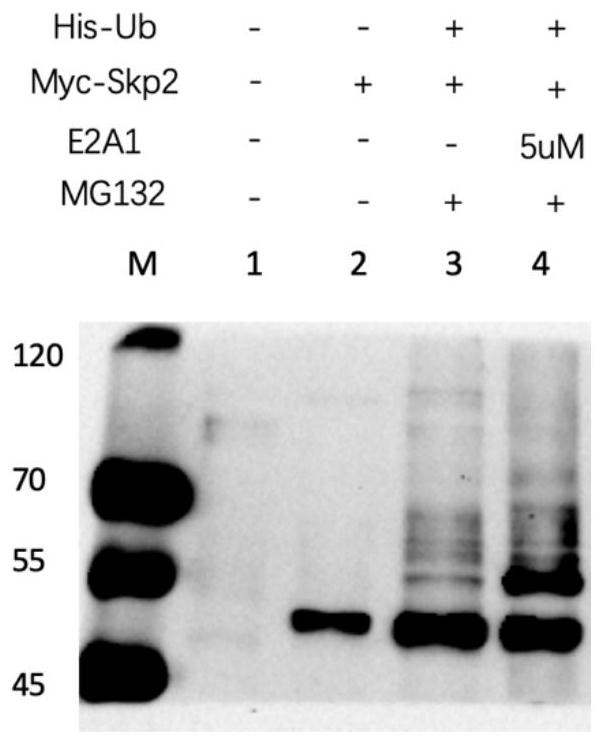
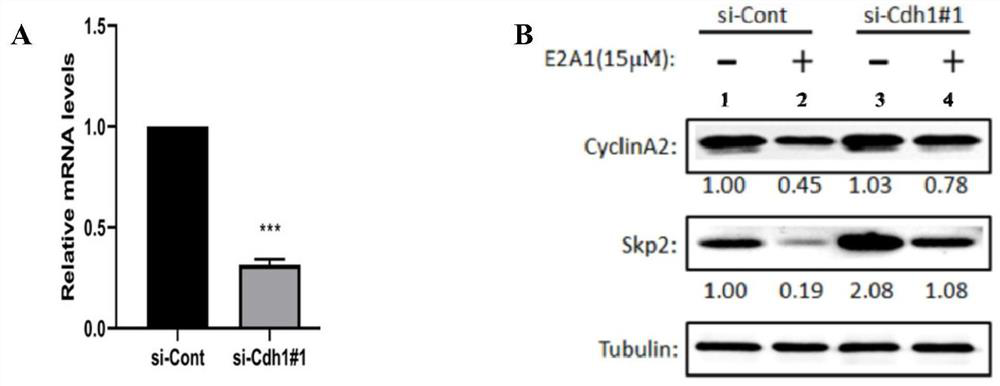
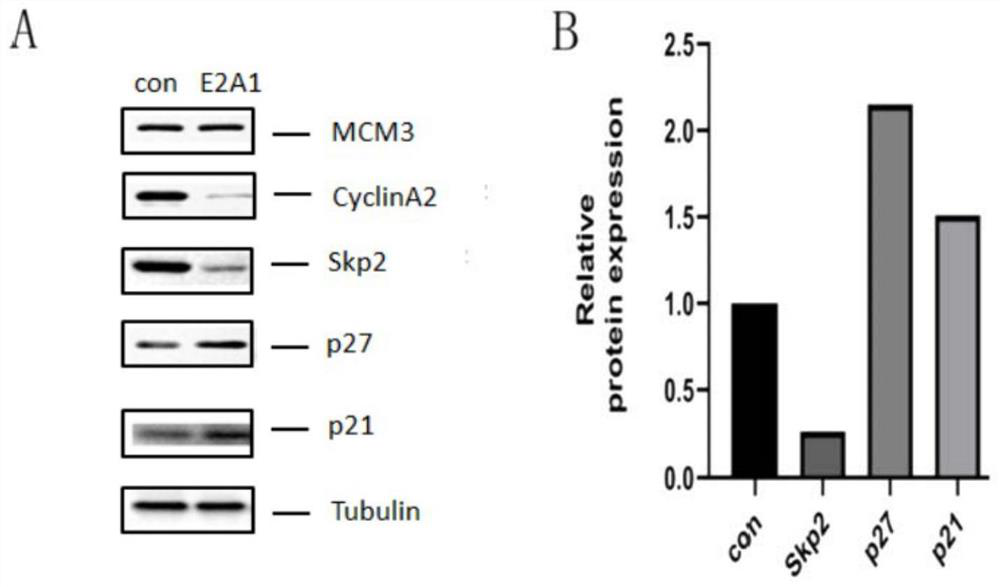
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Cell physiology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell physiology is the biological study about the activities that take place in a cell to keep it alive. This includes, among animal cells, plant cells and microorganisms. The term "physiology" refers to all the normal functions that take place in a living organism. All of these activities in the cell could be counted as following ; nutrition, environmental response, cell growth, cell division, reproduction and differentiation. The differences among the animal cell, plant cell and microorganisms shows the essential functional similarity even though those cells have different structures. Absorption of water by roots, production of food in the leaves, and growth of shoots towards light are examples of plant physiology. The heterotrophic metabolism of food derived from plants and animals and the use of movement to obtain nutrients (even if the organism itself remains in a relatively stationary position) are characteristic of animal physiology.
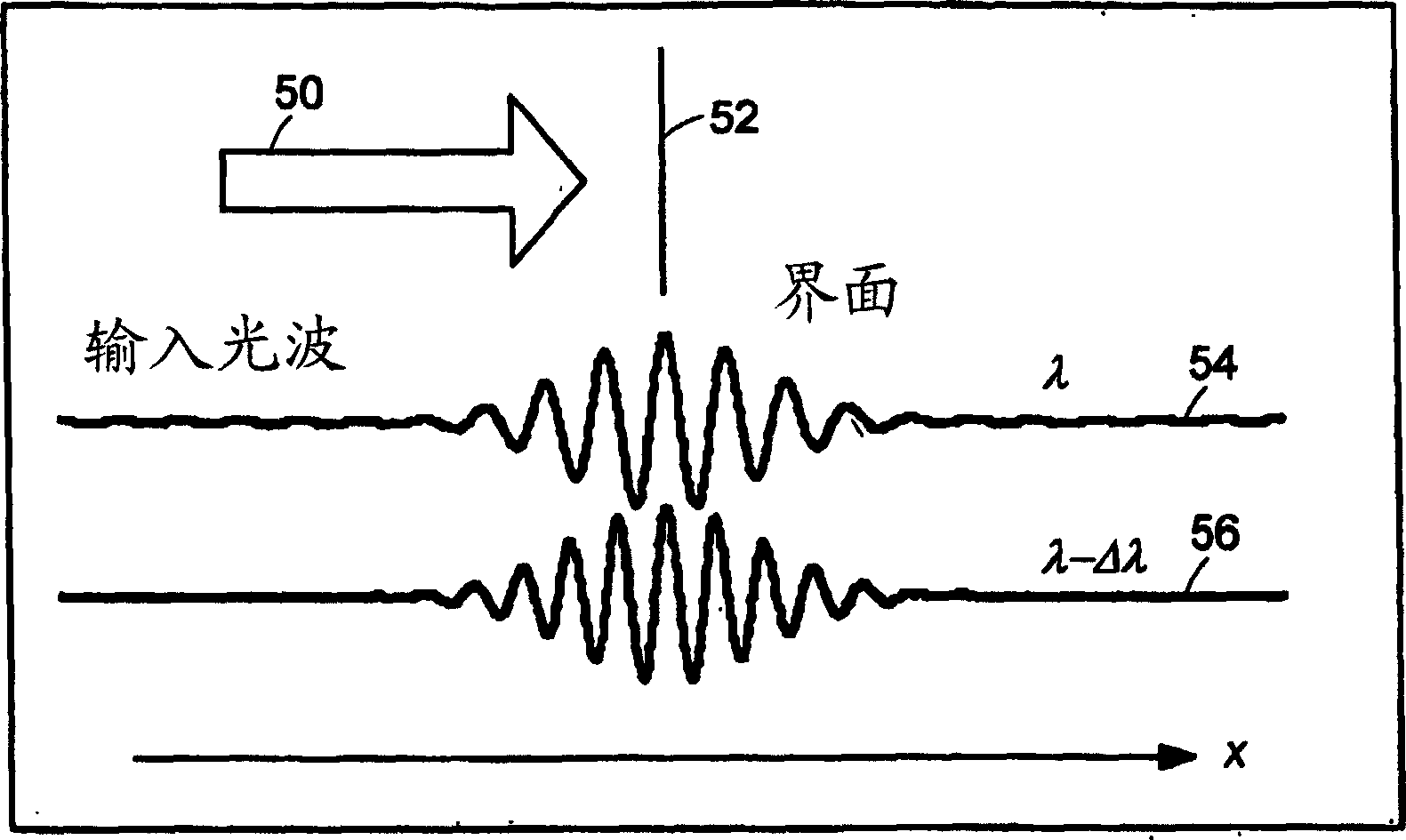
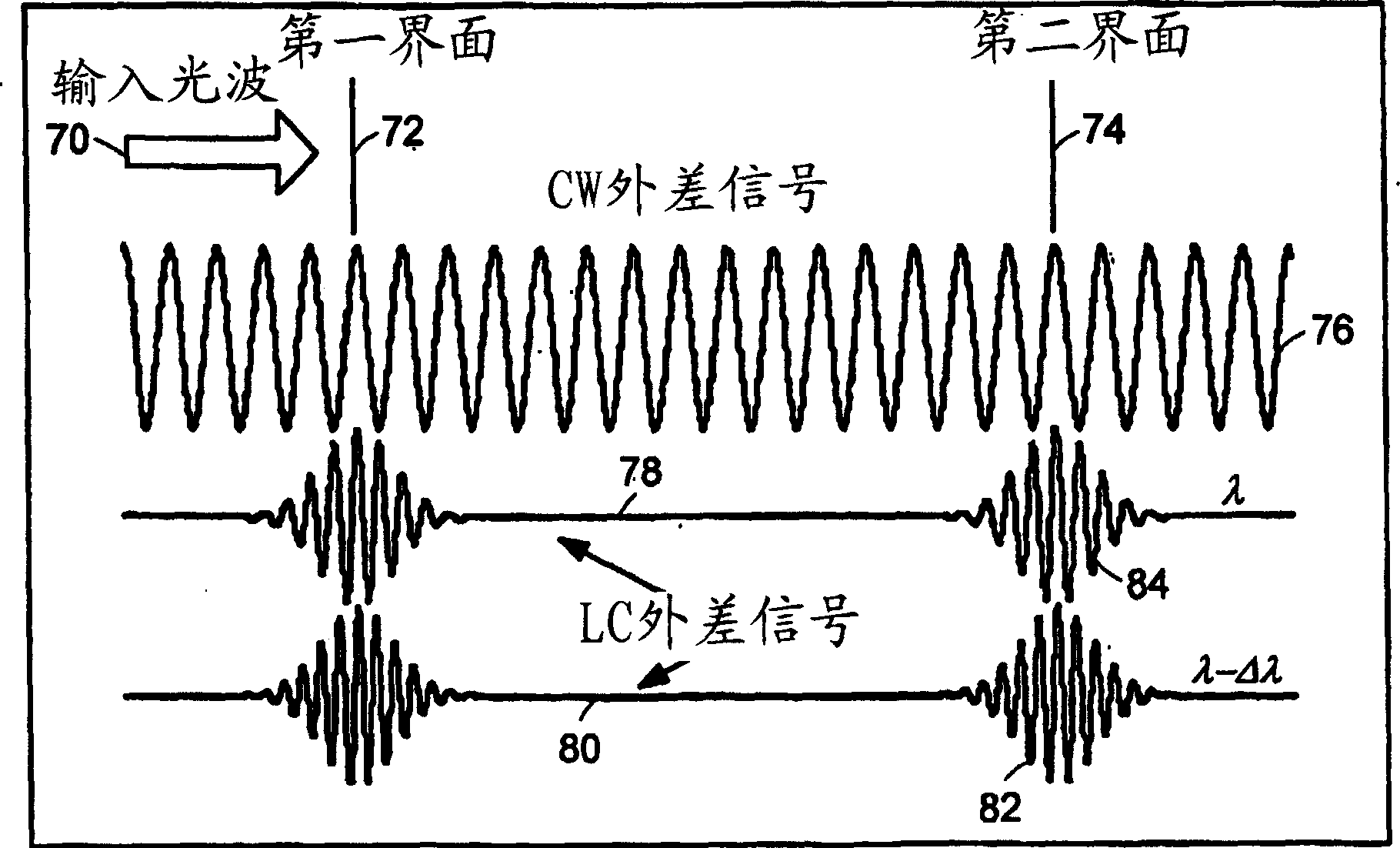
Systems and methods for phase measurements
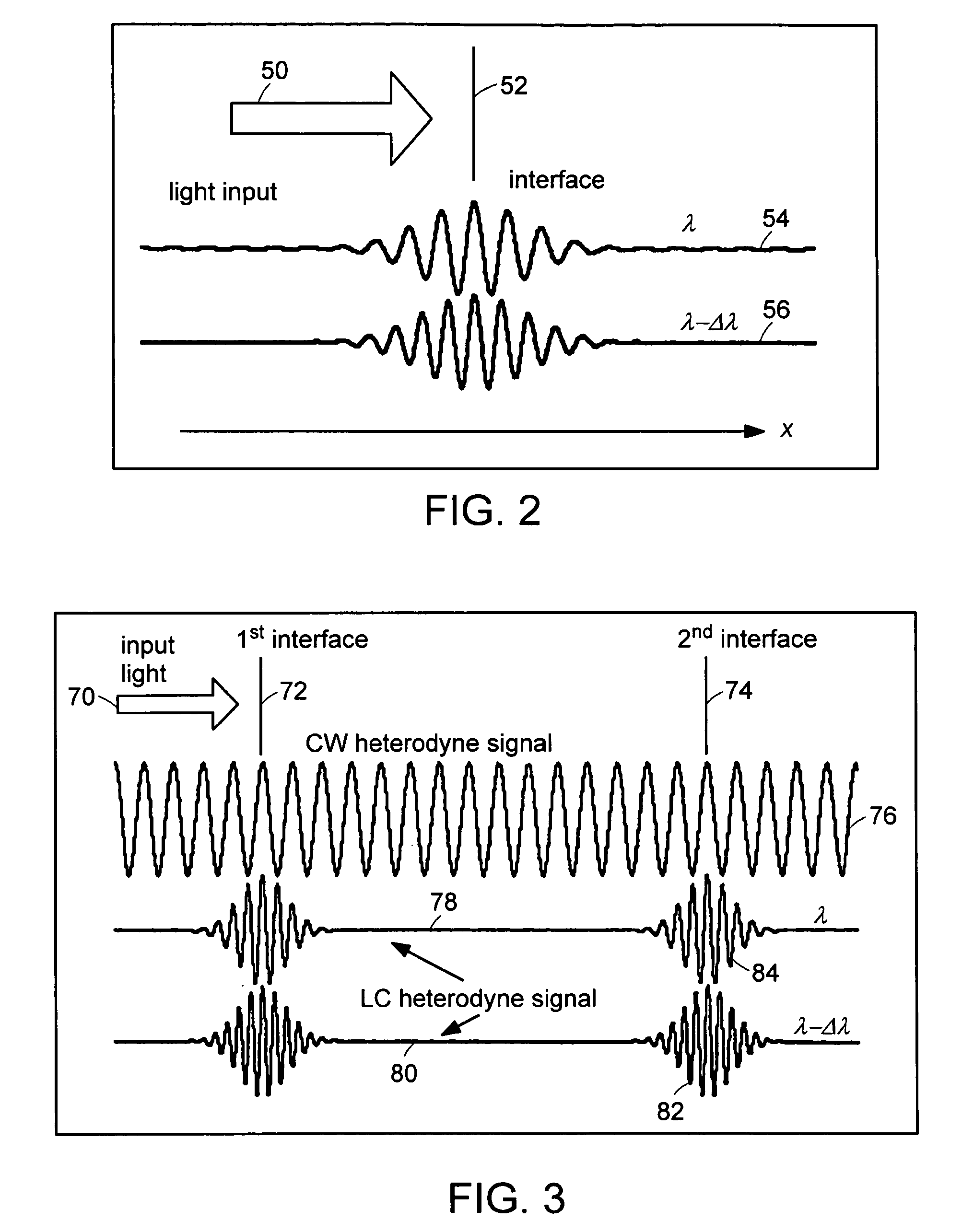
InactiveUS20050057756A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsCellular componentPhase noise
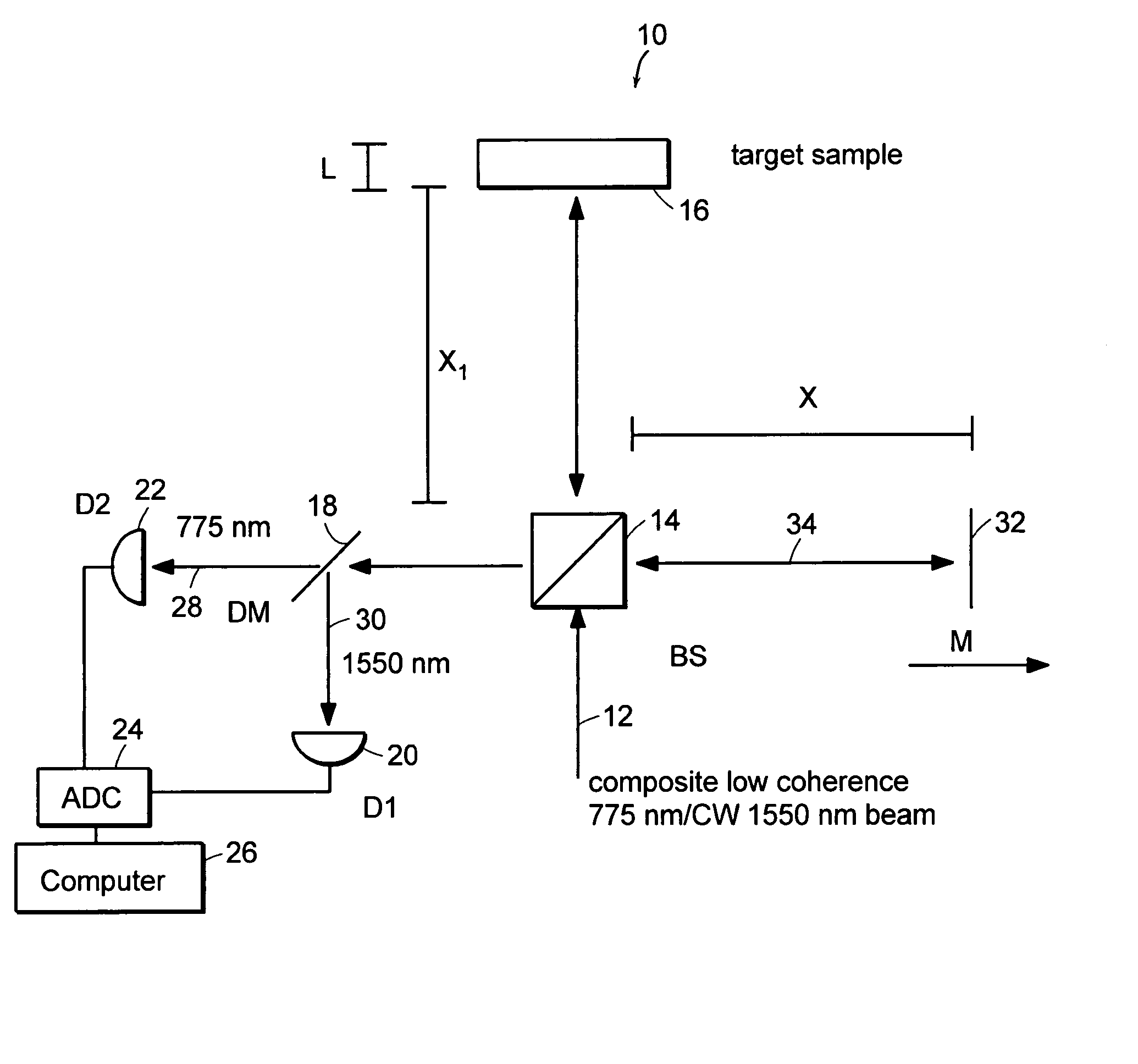
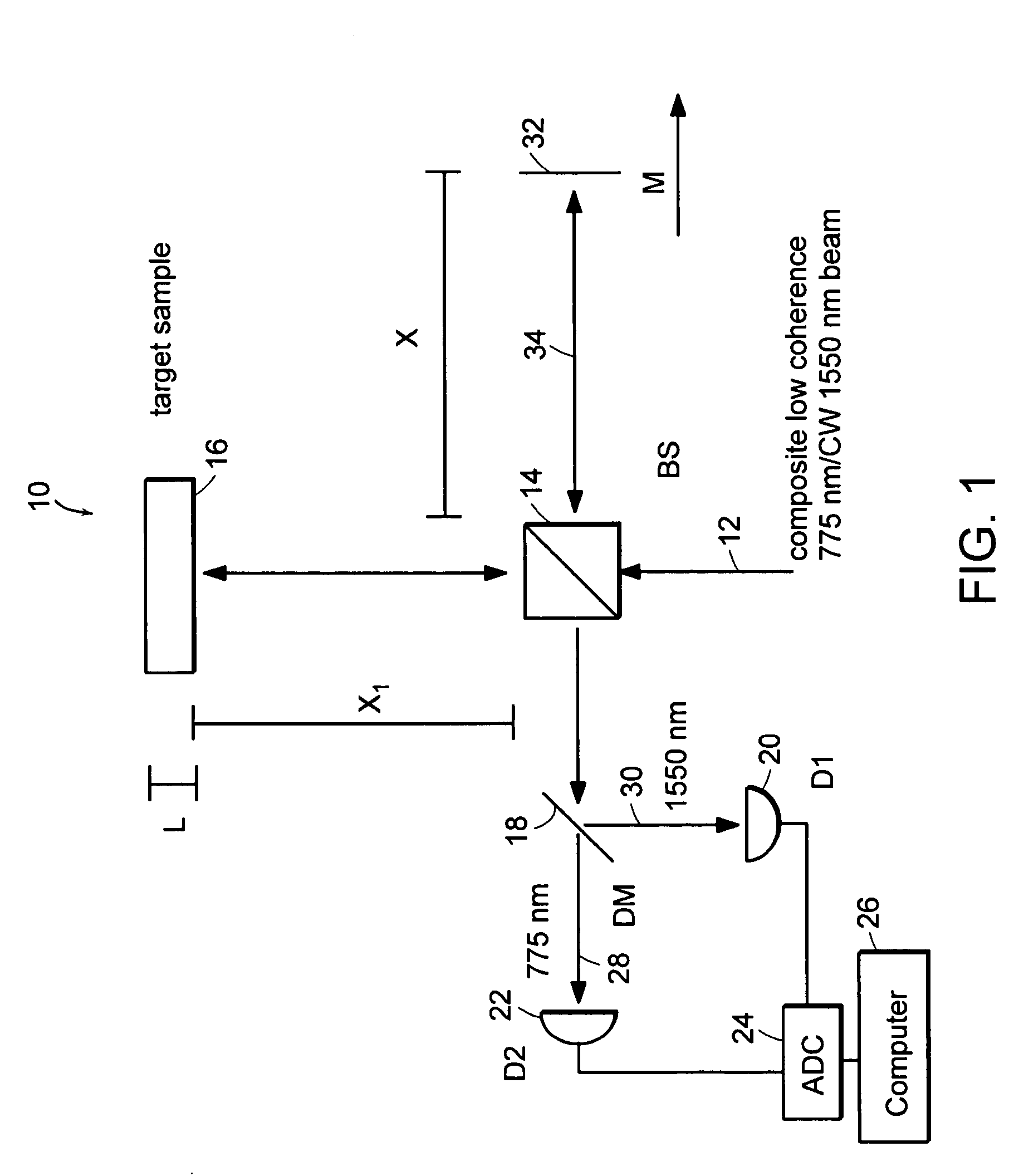
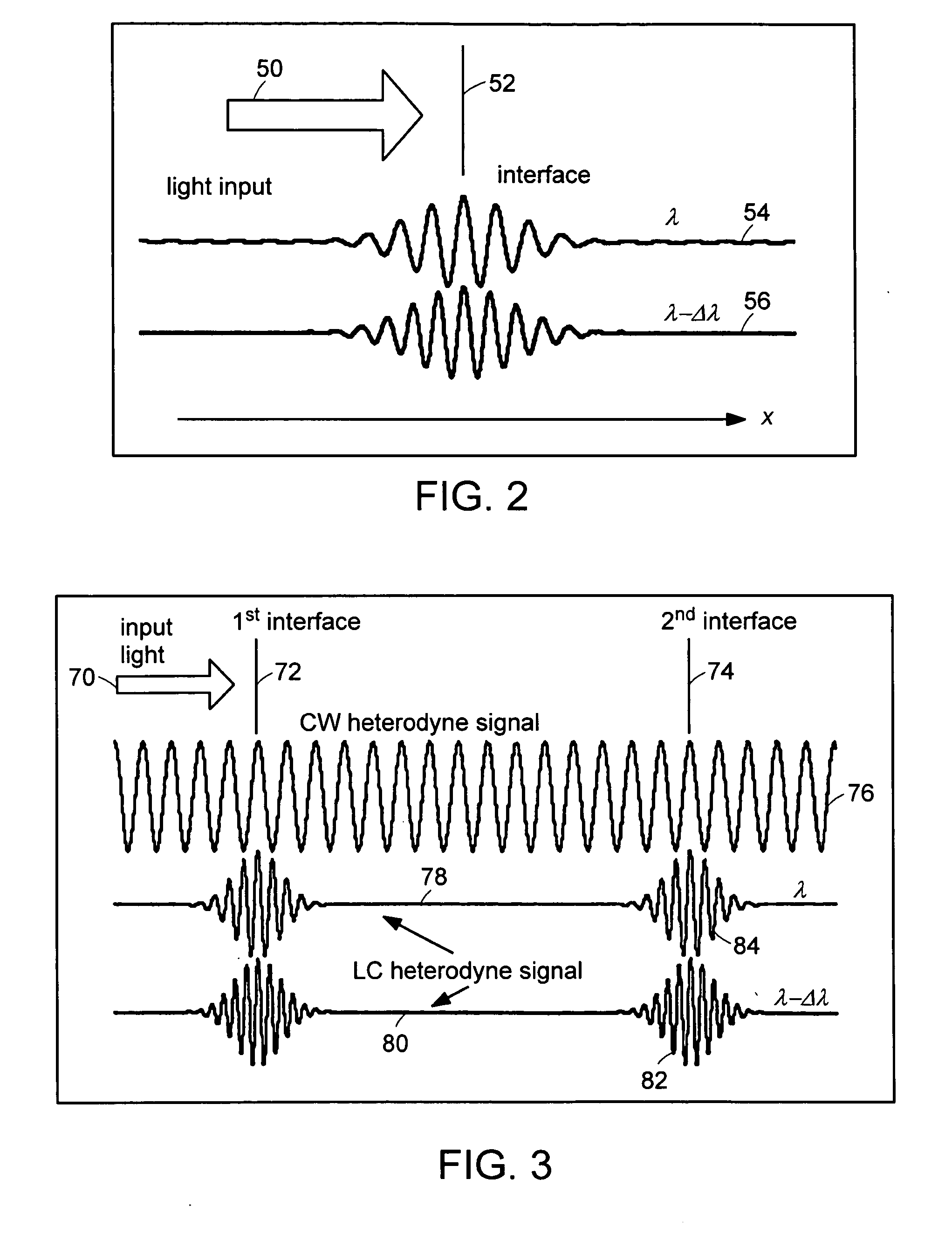
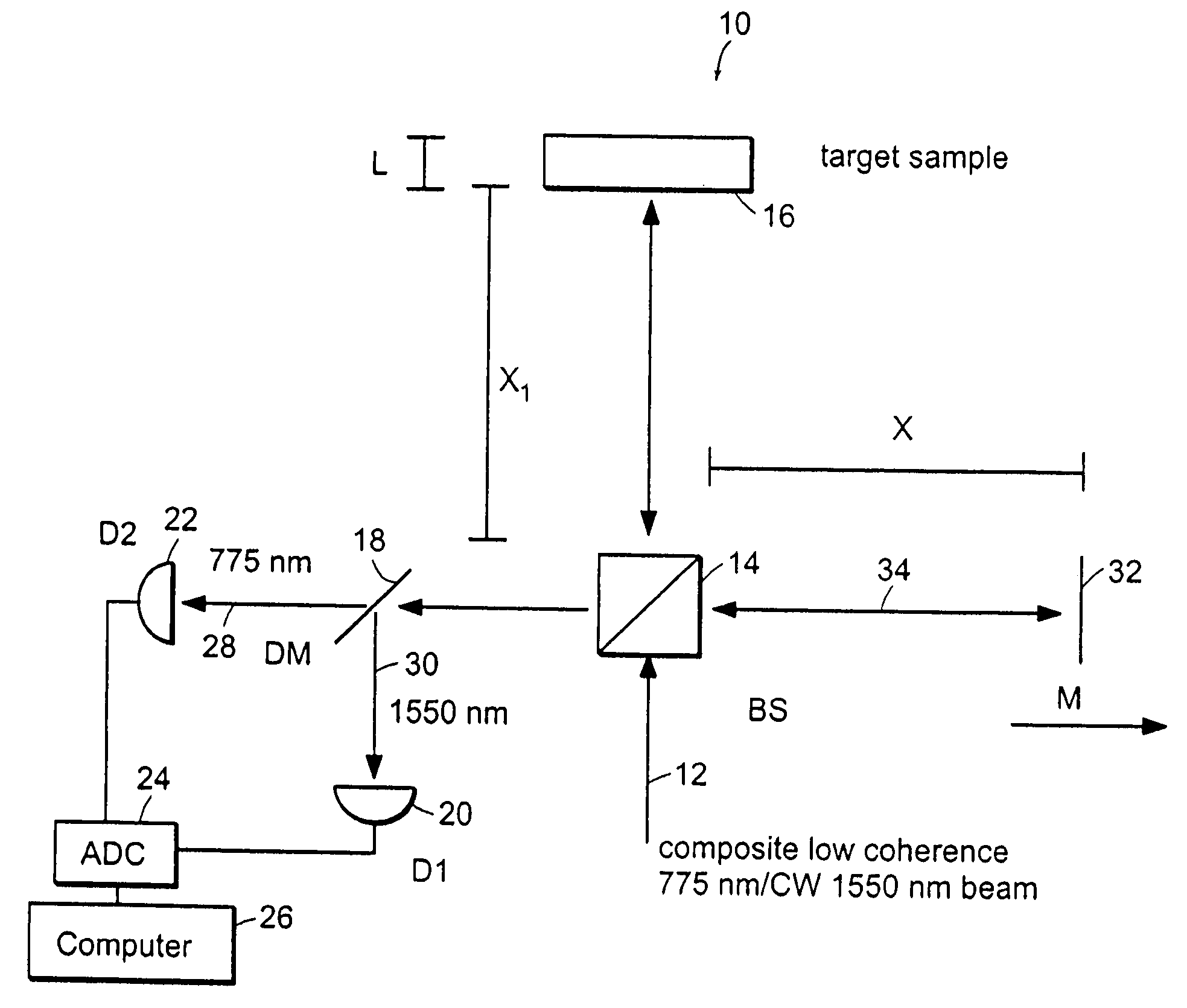
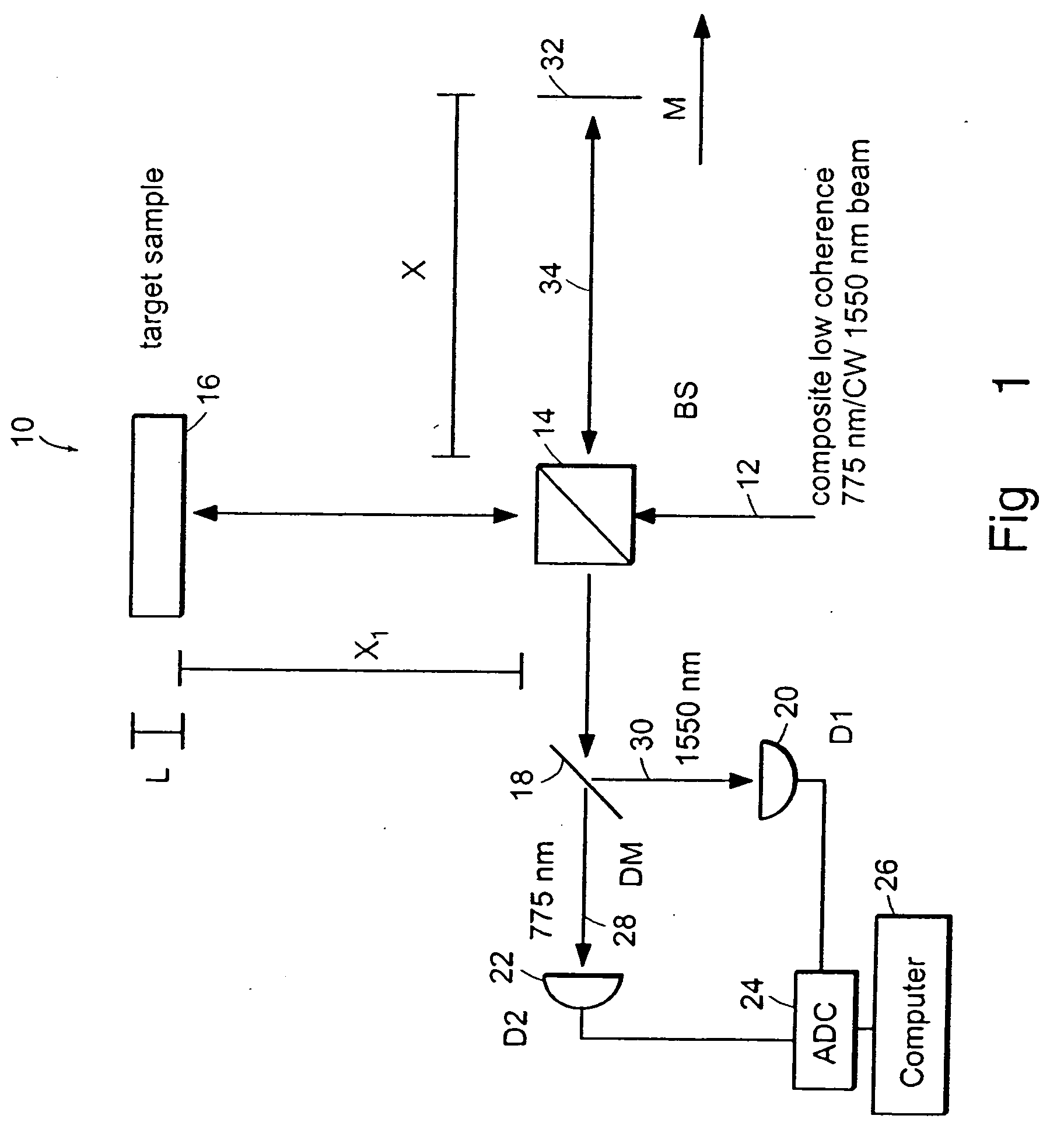
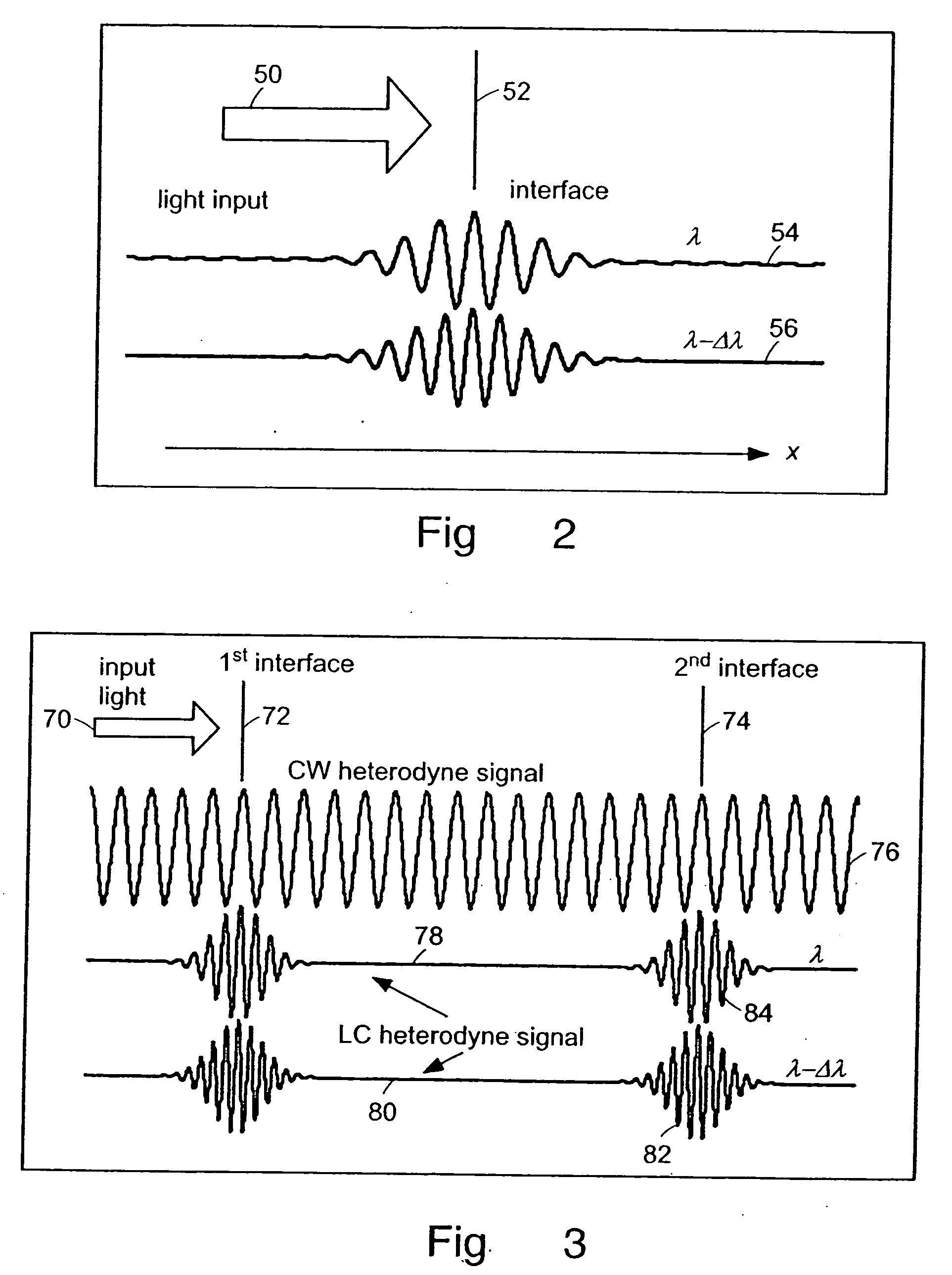
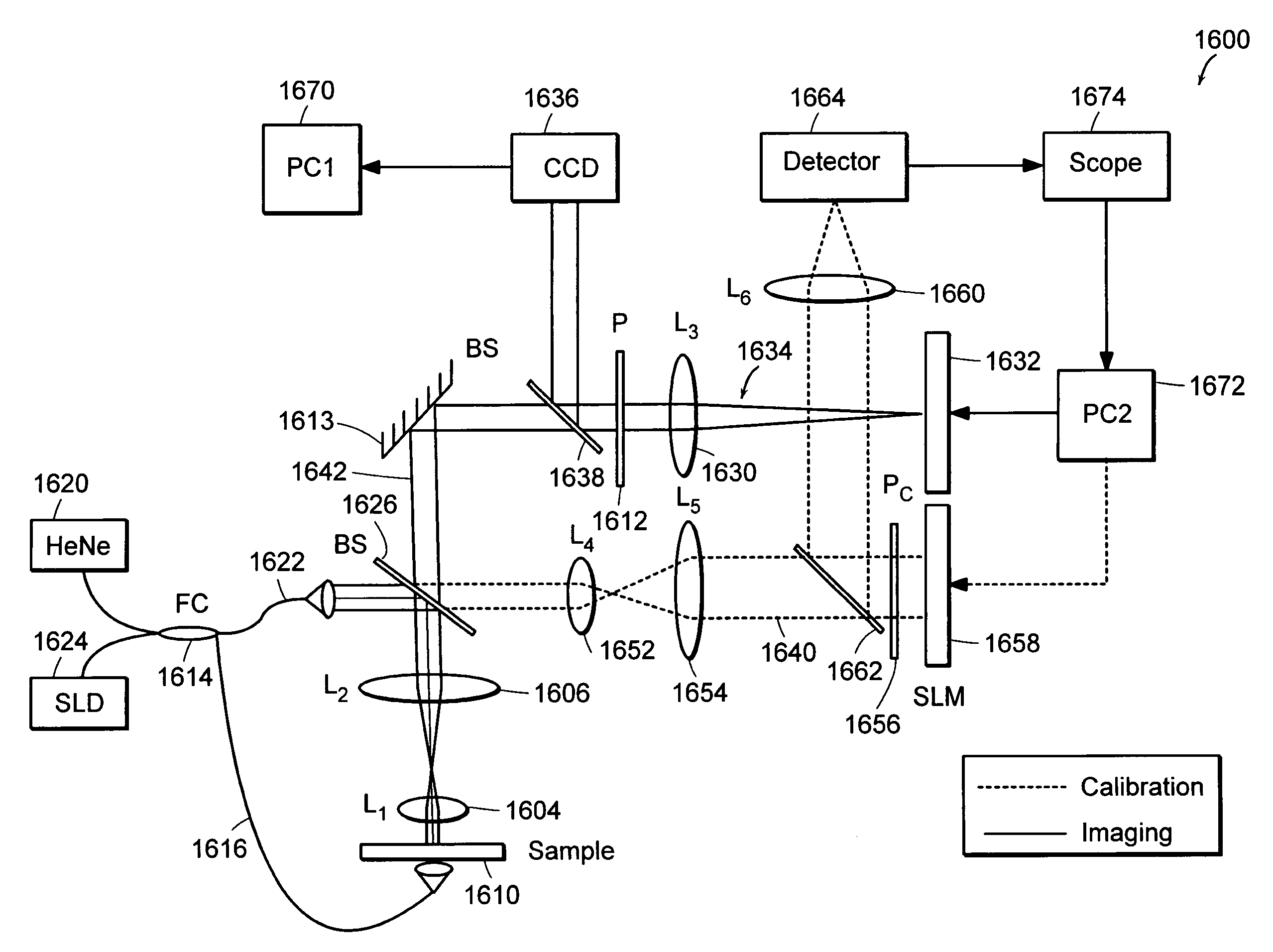
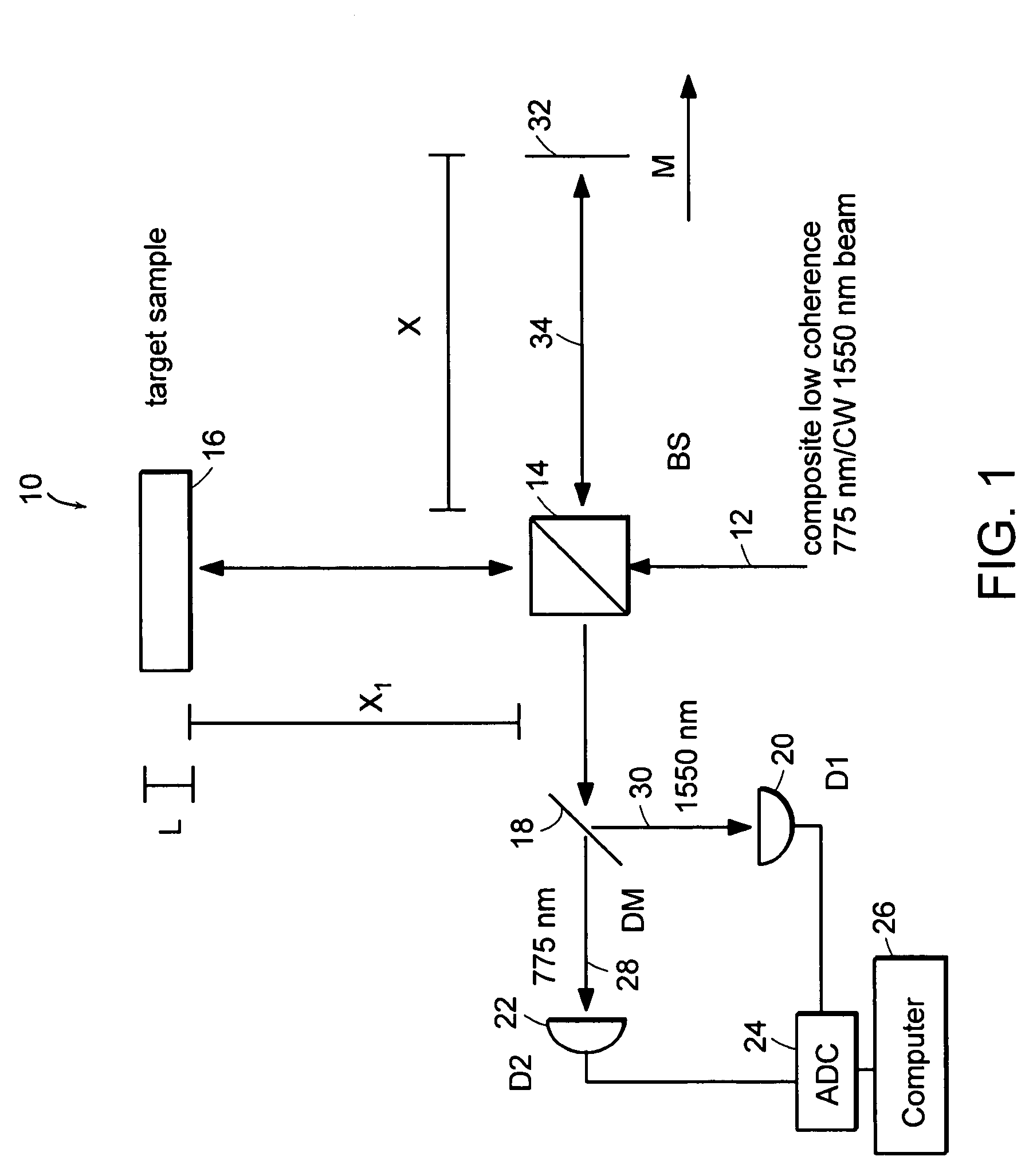
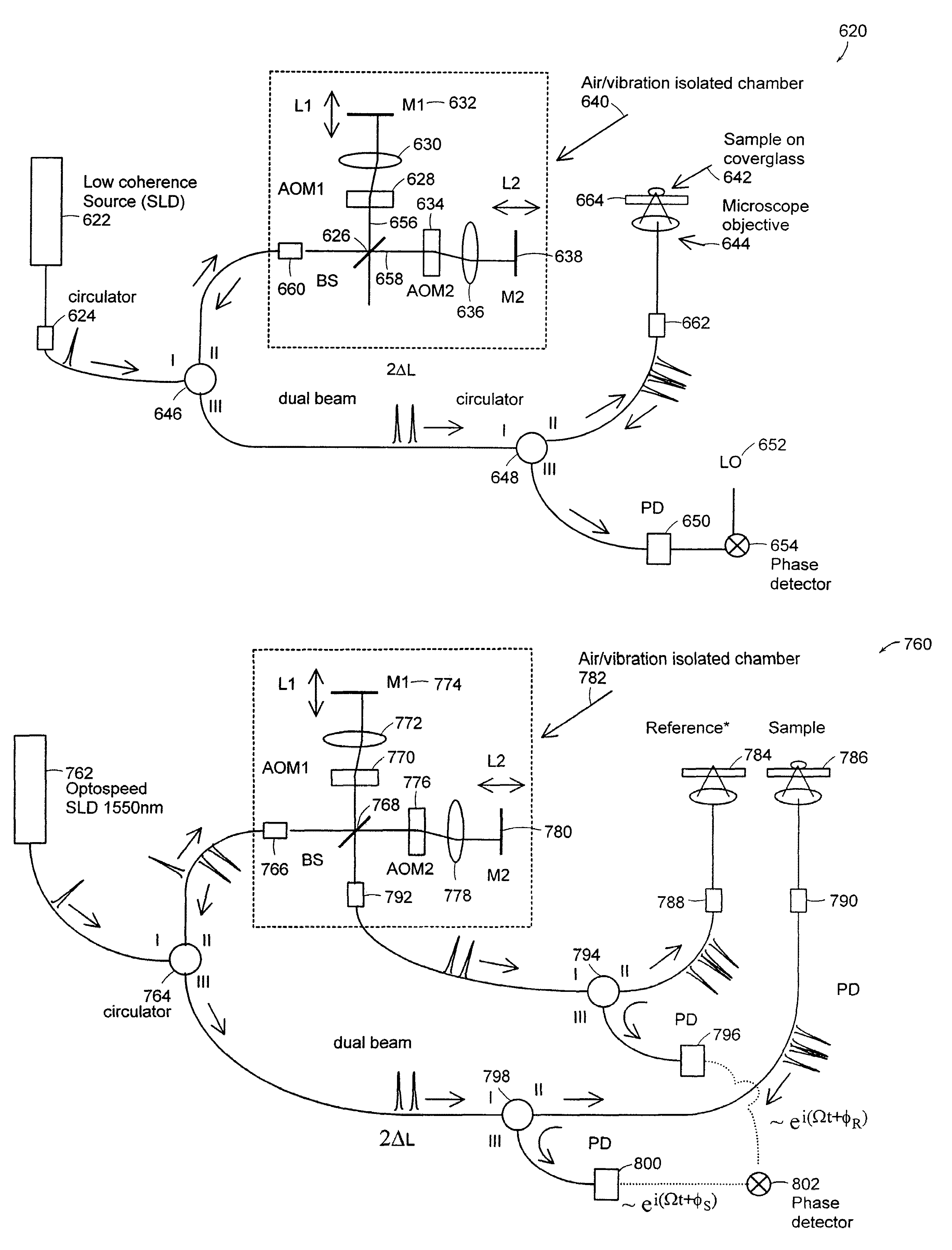
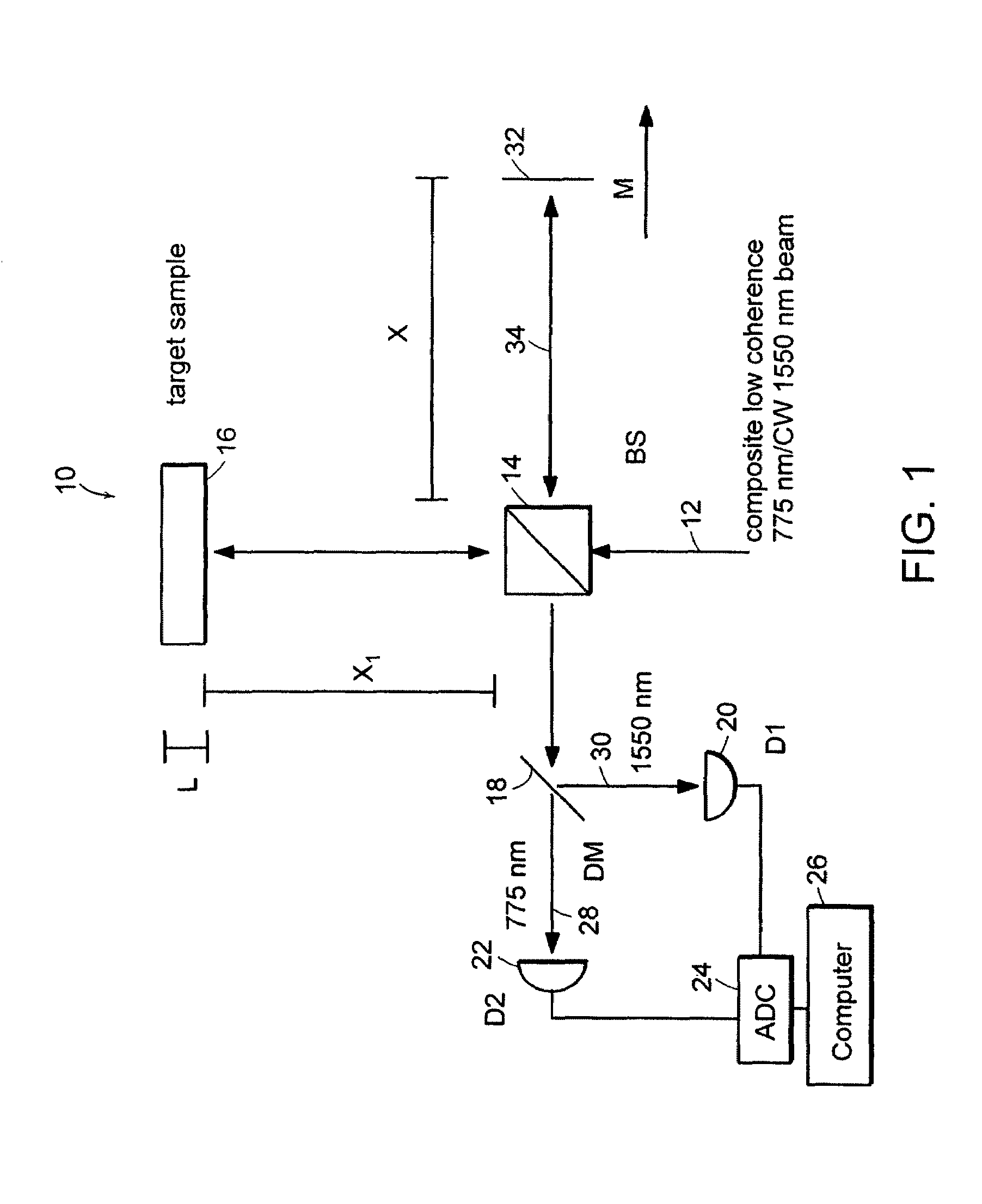
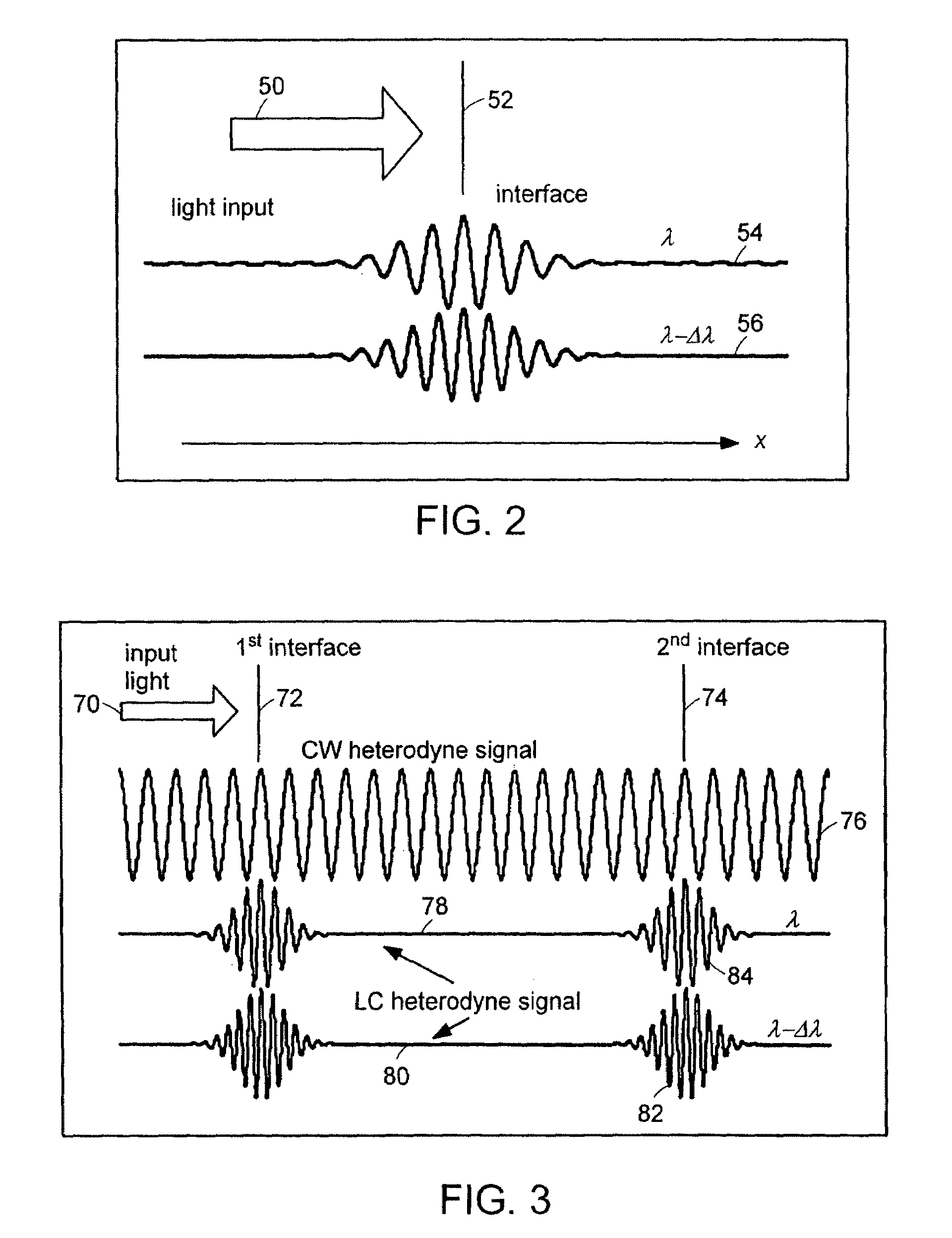
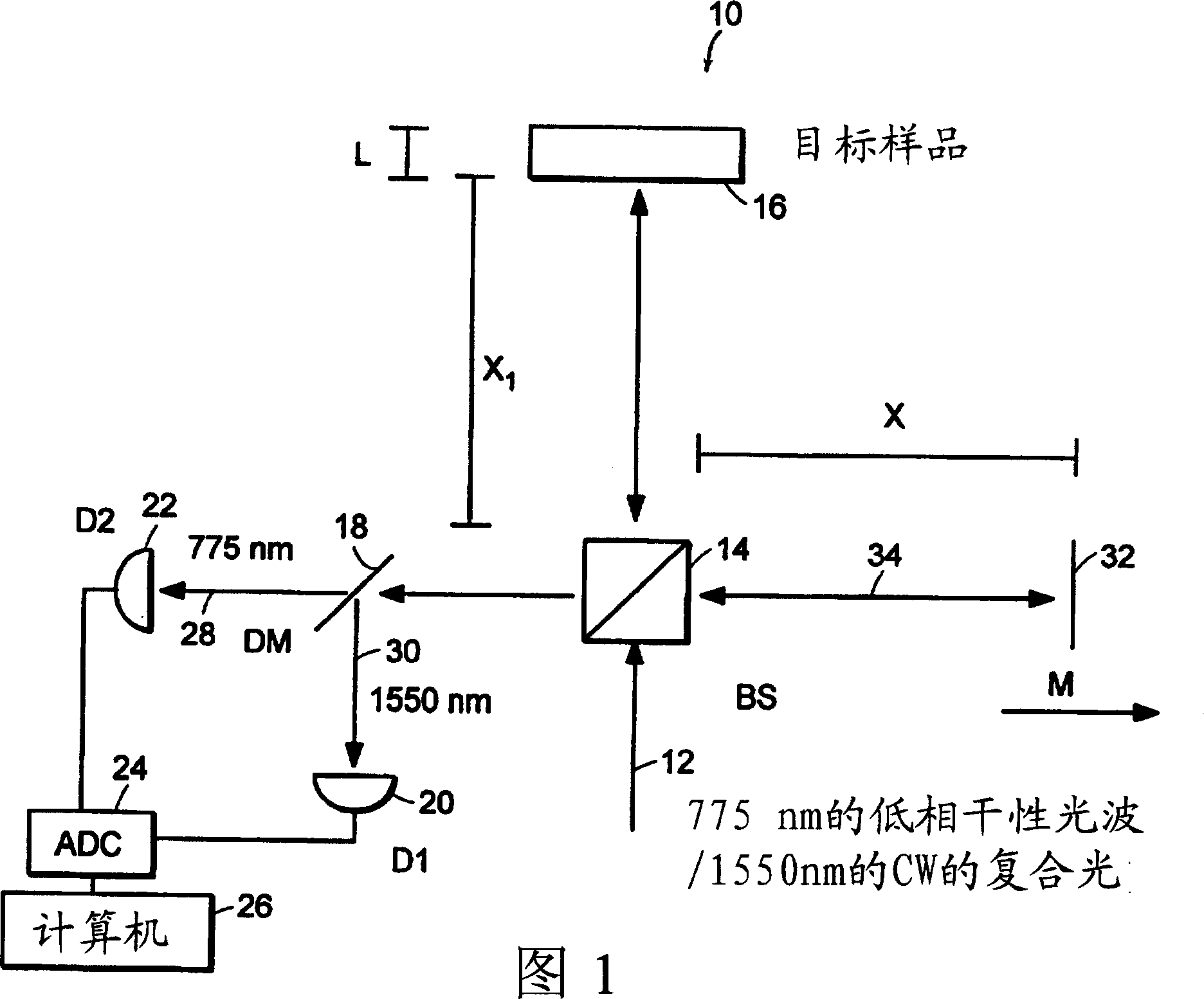
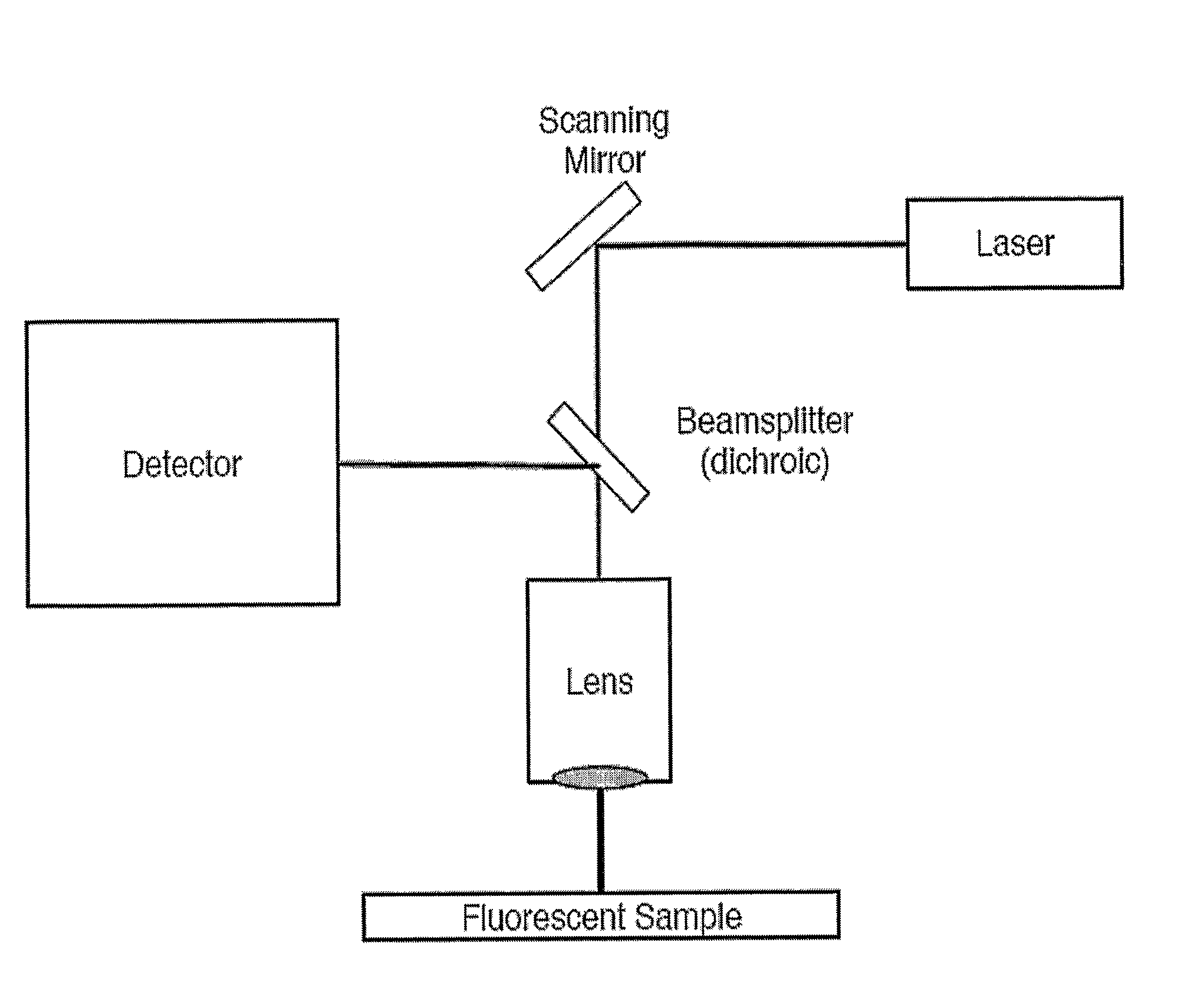
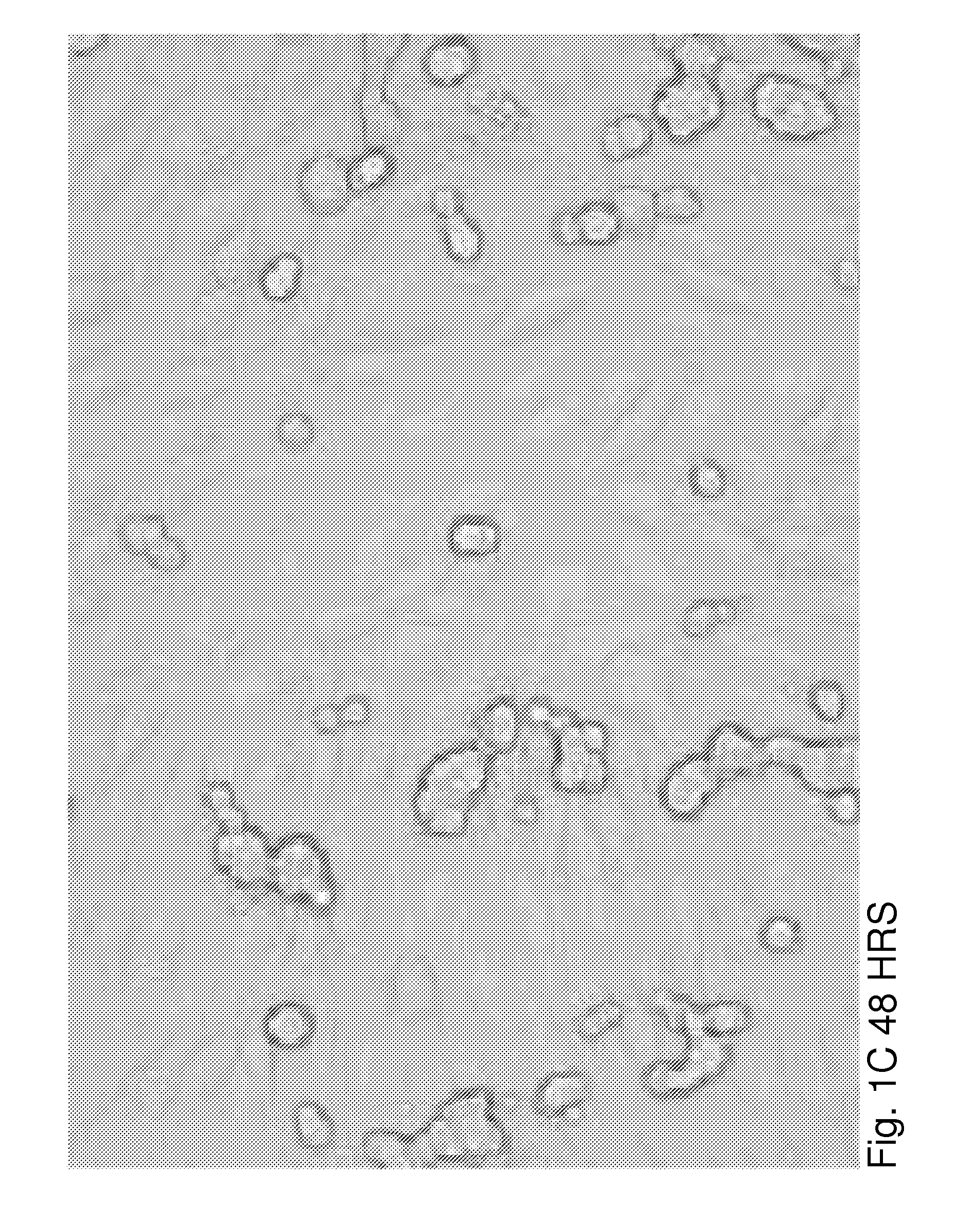
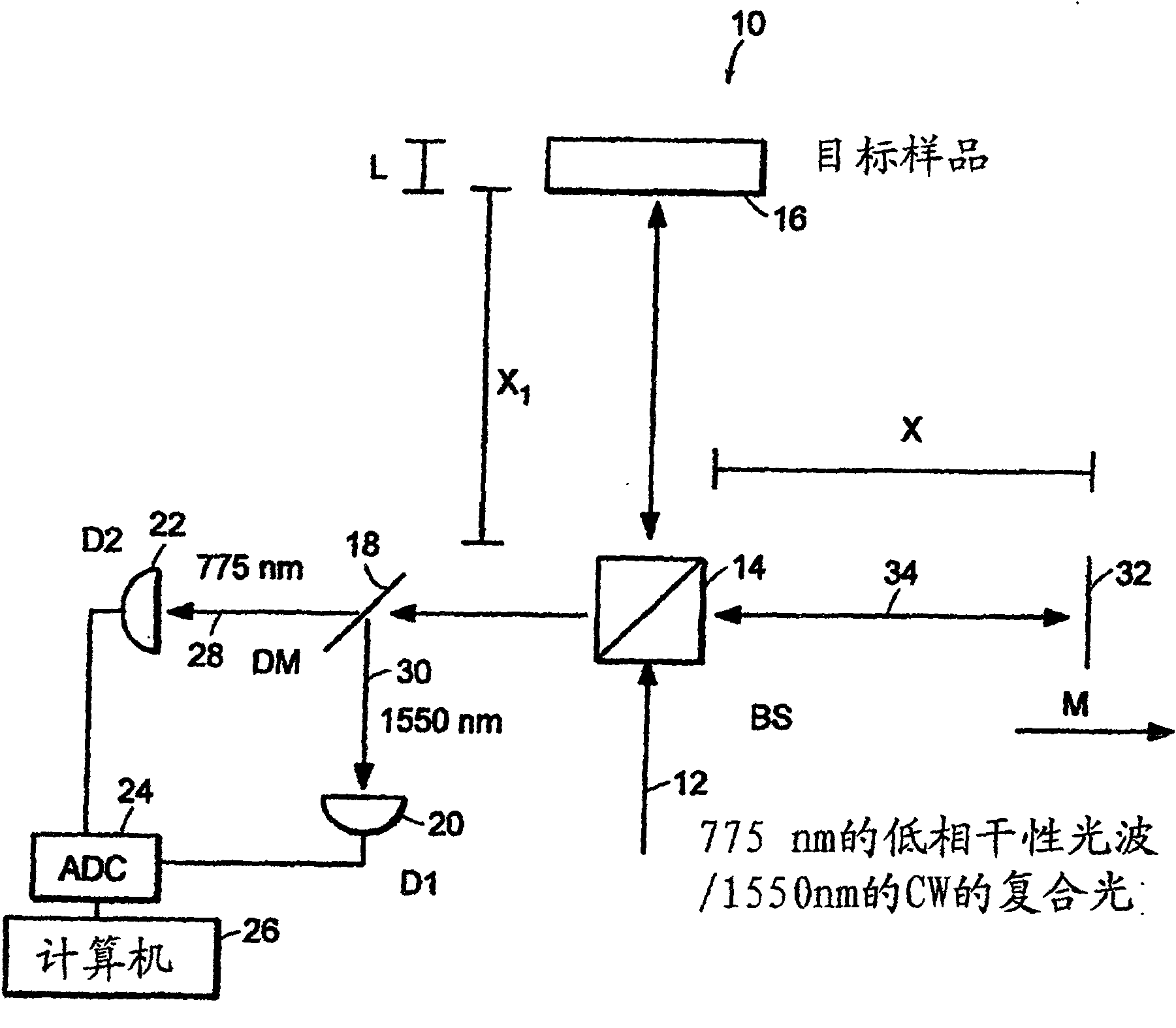
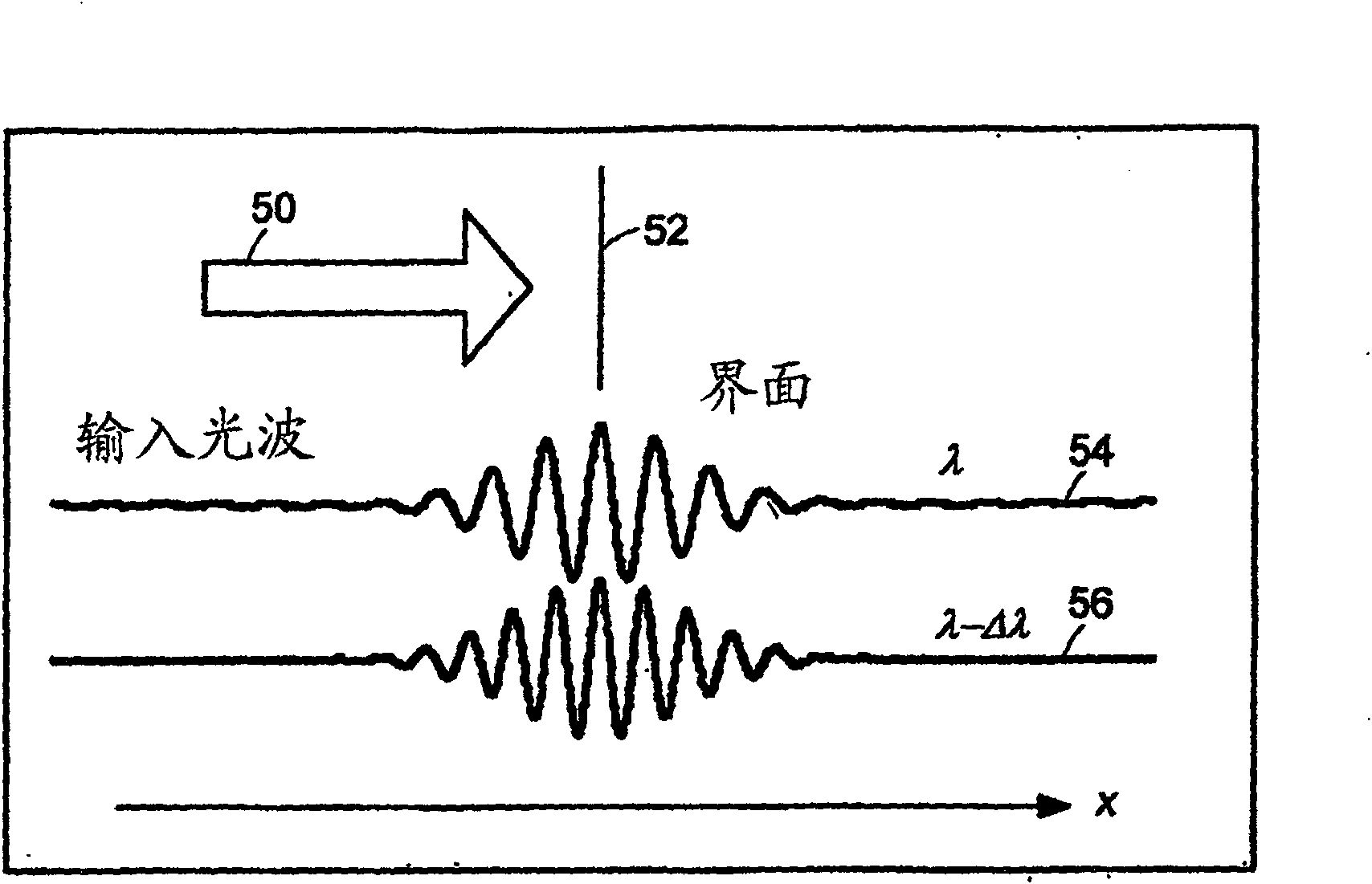
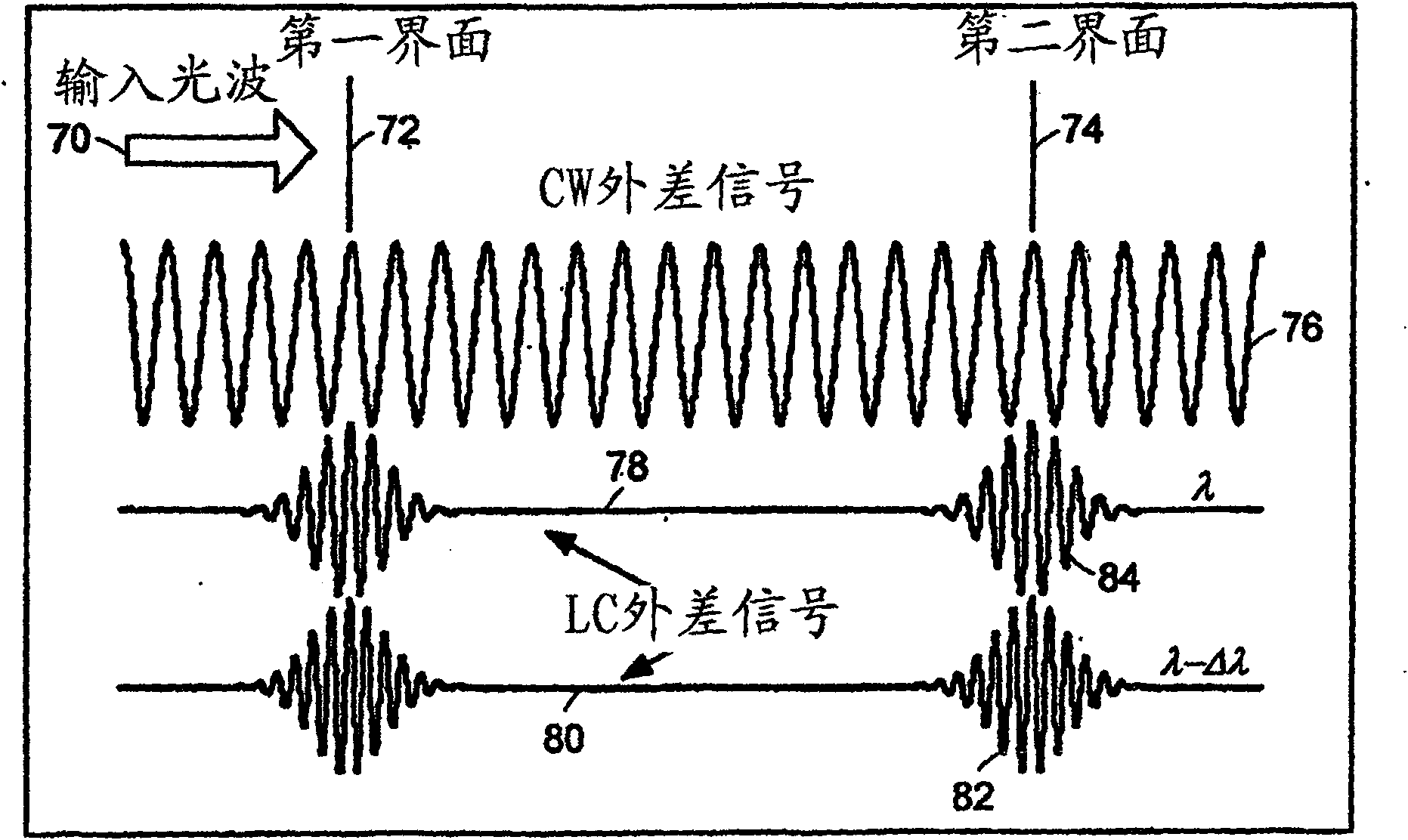
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7365858B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
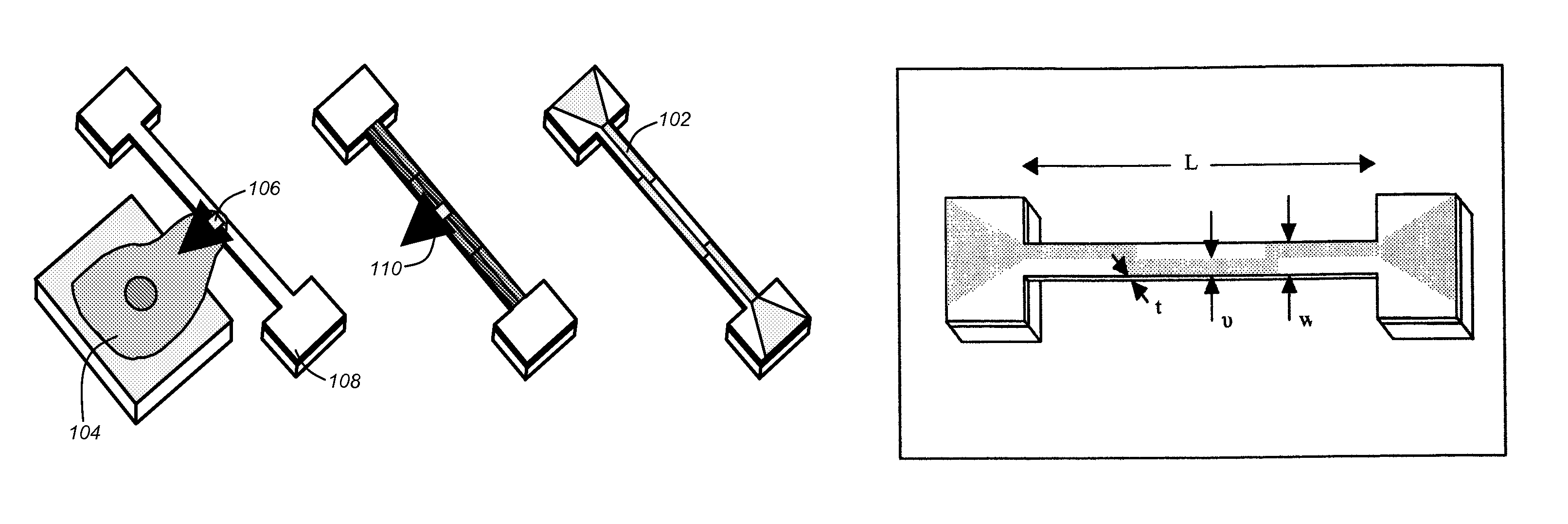
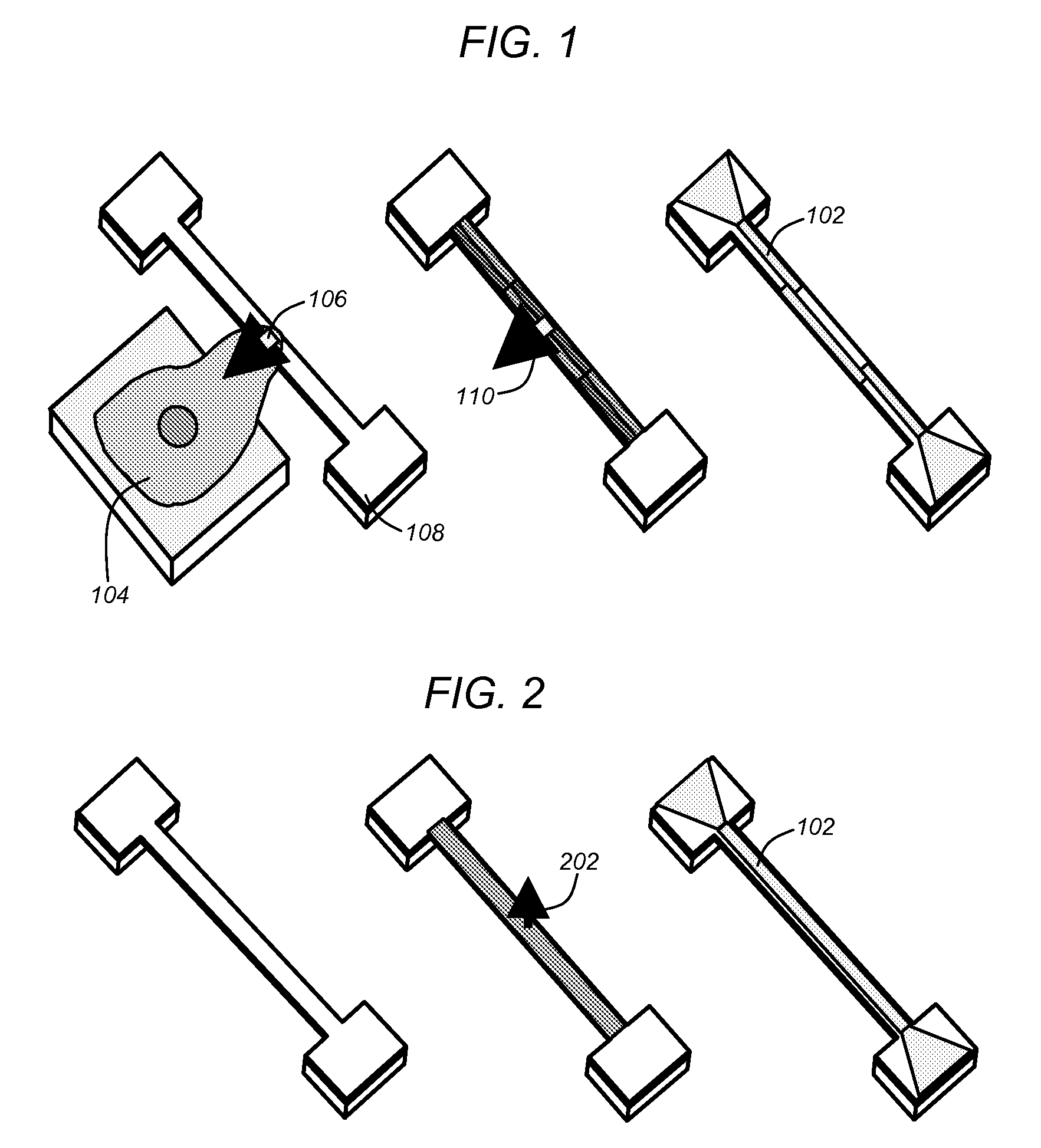
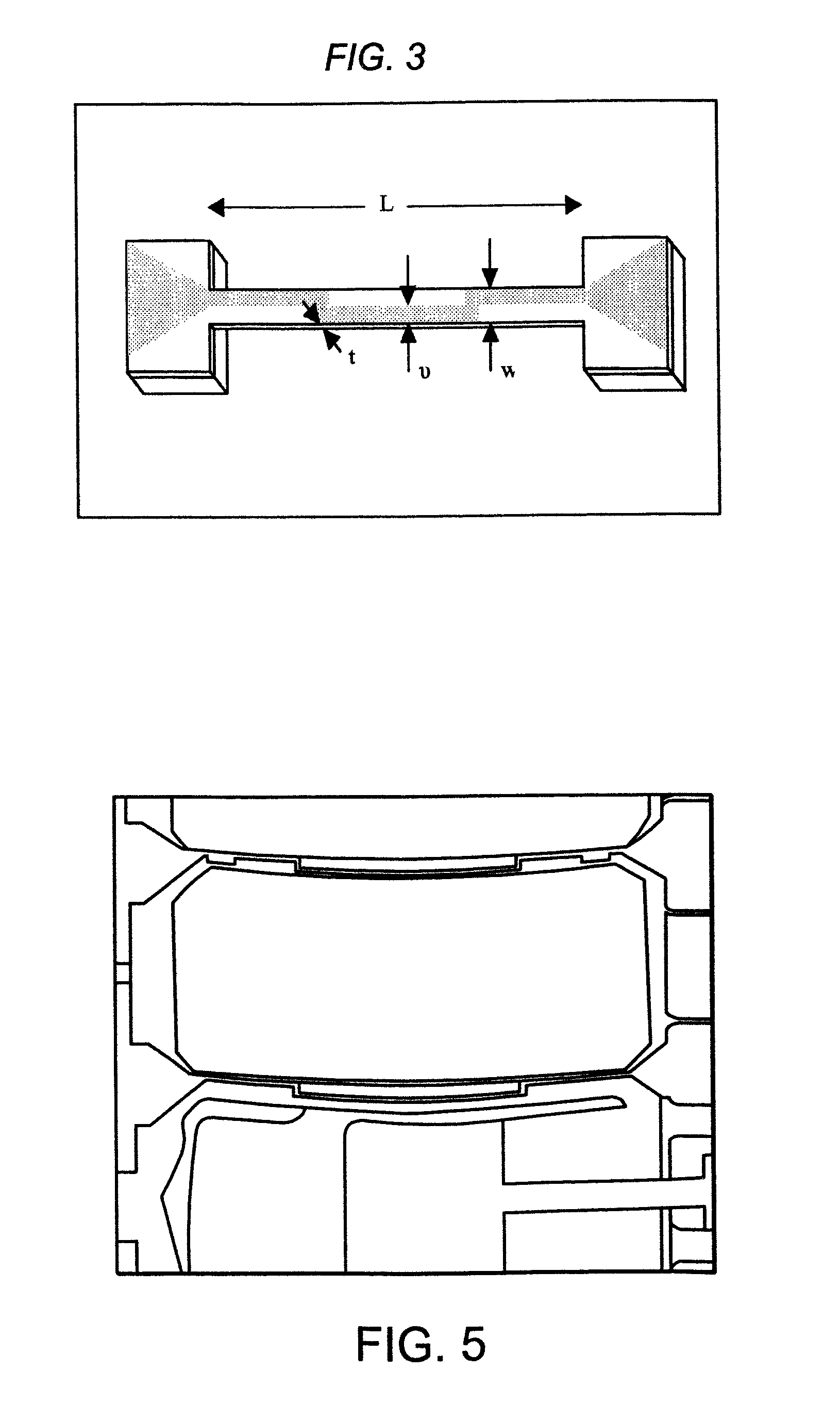
Polymer nems for cell physiology and microfabricated cell positioning system for micro-biocalorimeter
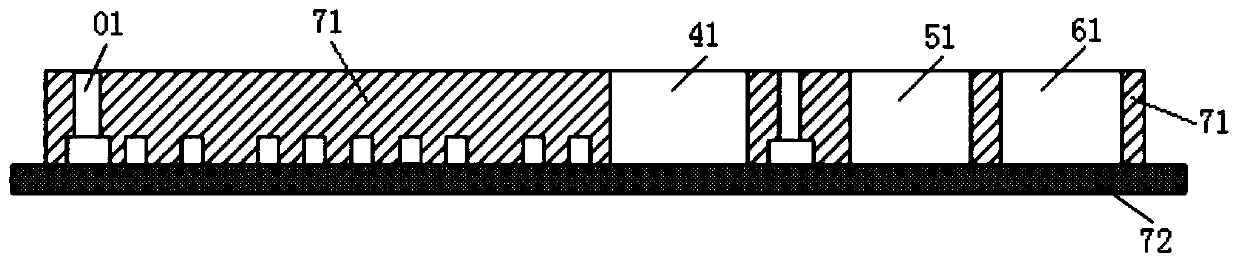
ActiveUS20100024572A1Rapid and parallel implementationShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsForce measurement by measuring frquency variationsParyleneThermopile
A microfluidic embedded nanoelectromechanical system (NEMs) force sensor provides an electrical readout. The force sensor contains a deformable member that is integrated with a strain sensor. The strain sensor converts a deformation of the deformable member into an electrical signal. A microfluidic channel encapsulates the force sensor, controls a fluidic environment around the force sensor, and improves the read out. In addition, a microfluidic embedded vacuum insulated biocalorimeter is provided. A calorimeter chamber contains a parylene membrane. Both sides of the chamber are under vacuum during measurement of a sample. A microfluidic cannel (built from parylene) is used to deliver a sample to the chamber. A thermopile, used as a thermometer is located between two layers of parylene.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7557929B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for measuring phase
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods for the treatment of HIV-1 related fat maldistribution, fasting hyperlipidemia and modification of adipocyte physiology
InactiveUS20080114065A1Treating and preventing and normalizing lipoatrophyIncreased serum lipidsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsThiolSecondary hyperlipidemia
Methods for treating or preventing metabolic dysregulation of adipocytes resulting from HIV-1 infection or chronic inflammation are disclosed. The compositions contain a conjugated fatty acid, a thiol-containing compound and a bioavailable form of trivalent chromium.
Owner:POPULATION RES
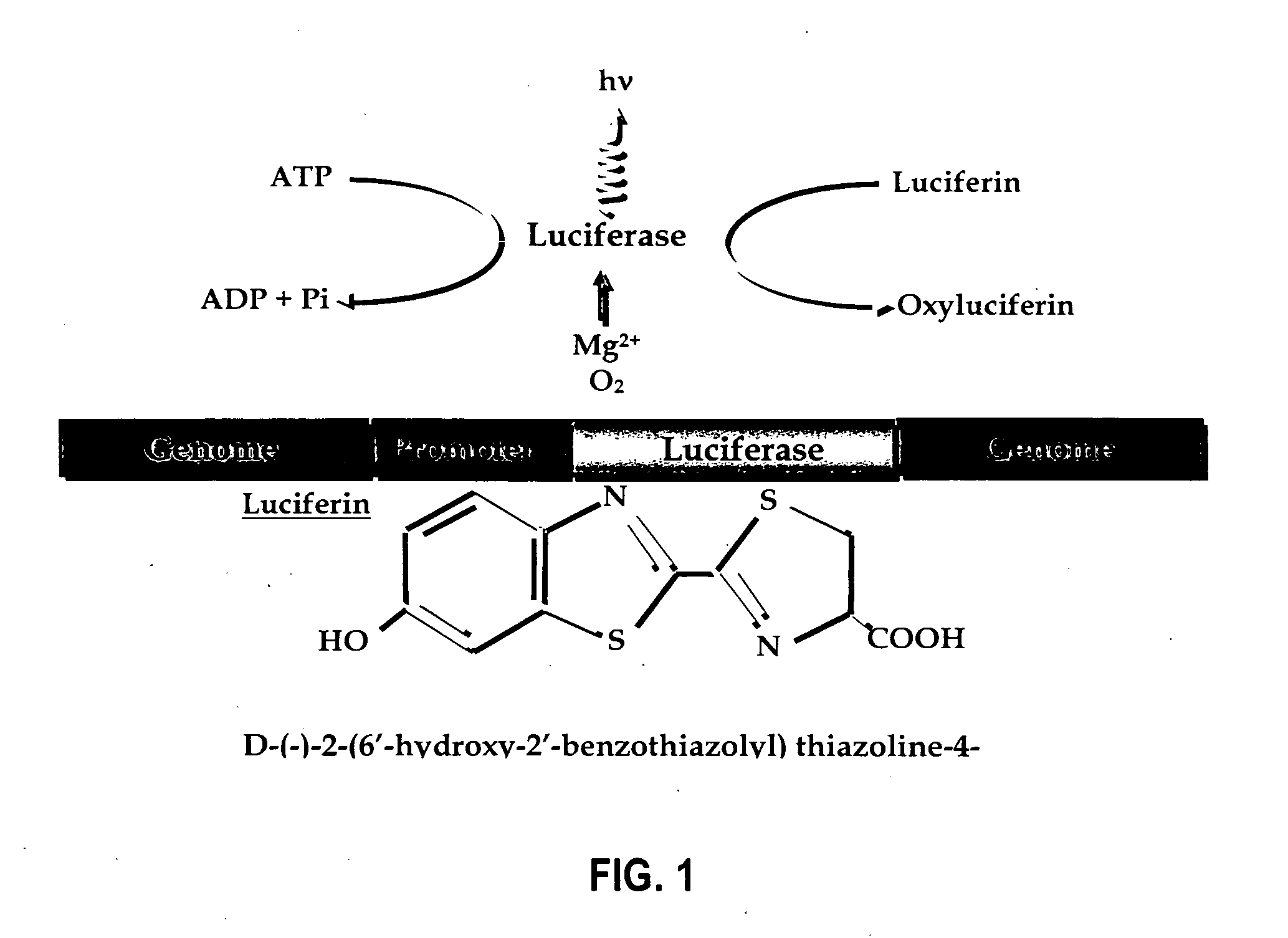
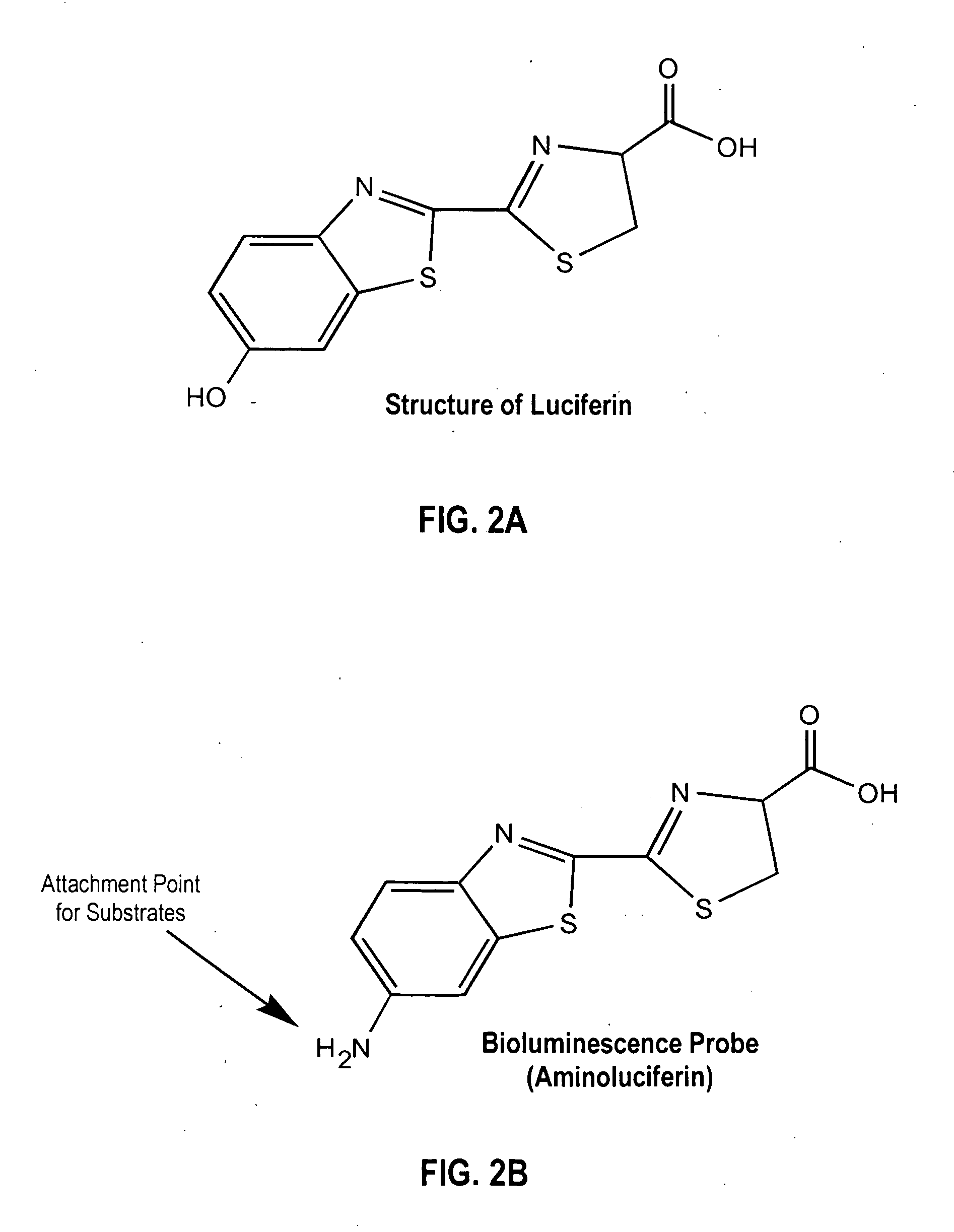
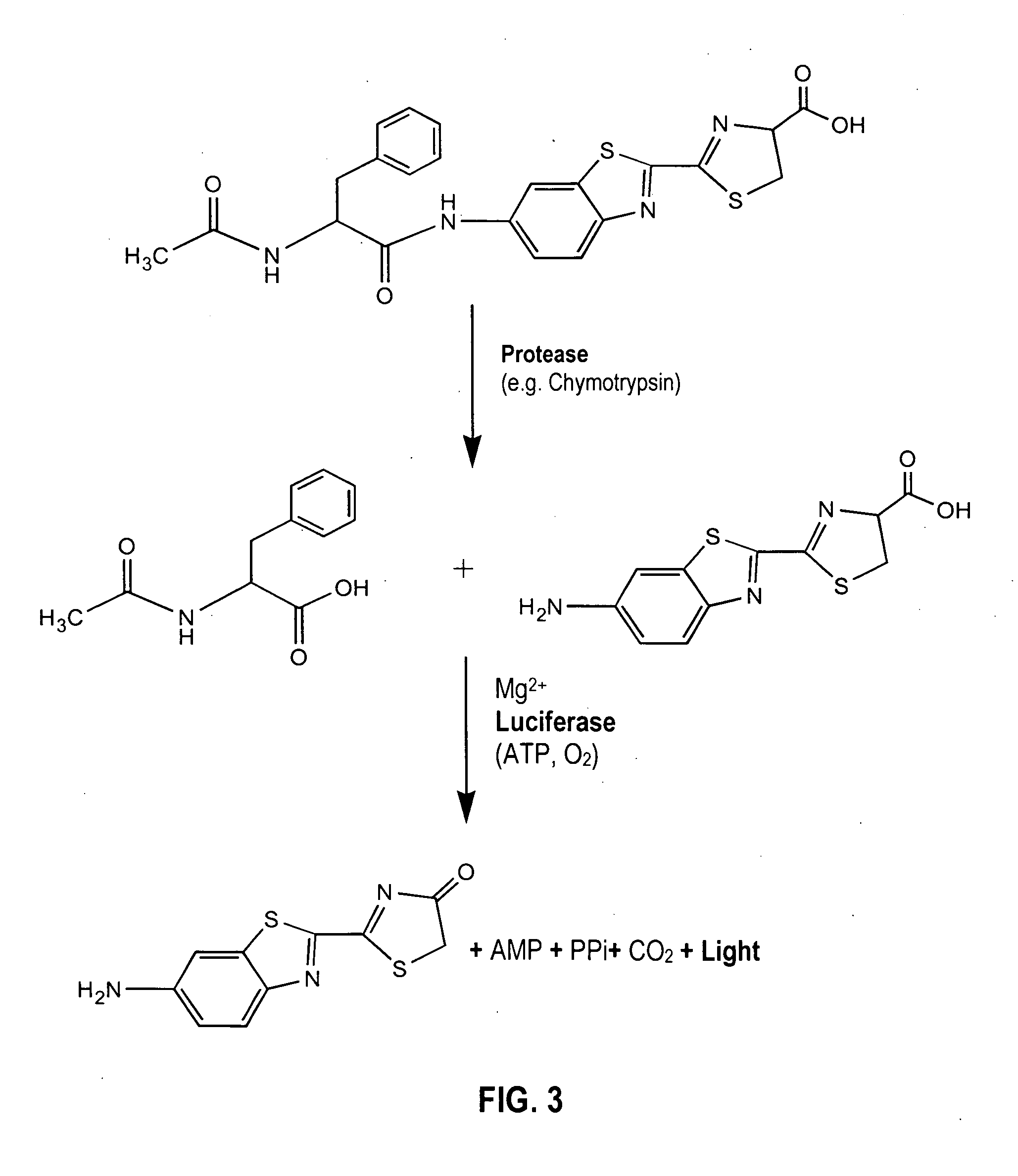
Luciferyl peptide substrate
InactiveUS20060073529A1Promote localizationPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementLuciferase GeneCell membrane
Provided are luciferyl peptide substrates that are produced by attaching specifically prepared peptide conjugates to luciferin, and / or its analogs and derivatives. The luciferyl peptide substrates are incapable of penetrating cell membranes and tissue barriers. Cleavage of the peptide conjugates from the luciferyl peptide substrates releases the luciferin, which upon contact with luciferase emits photons for easy detection. The luciferyl peptide substrates may be used in assays to detect pathogens, test protease inhibitors, probe cell physiology, assess protease activity in oncogenesis, and improve specific and regulated drug delivery.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Cancer individuation intervention strategy selection method based on molecular physiome
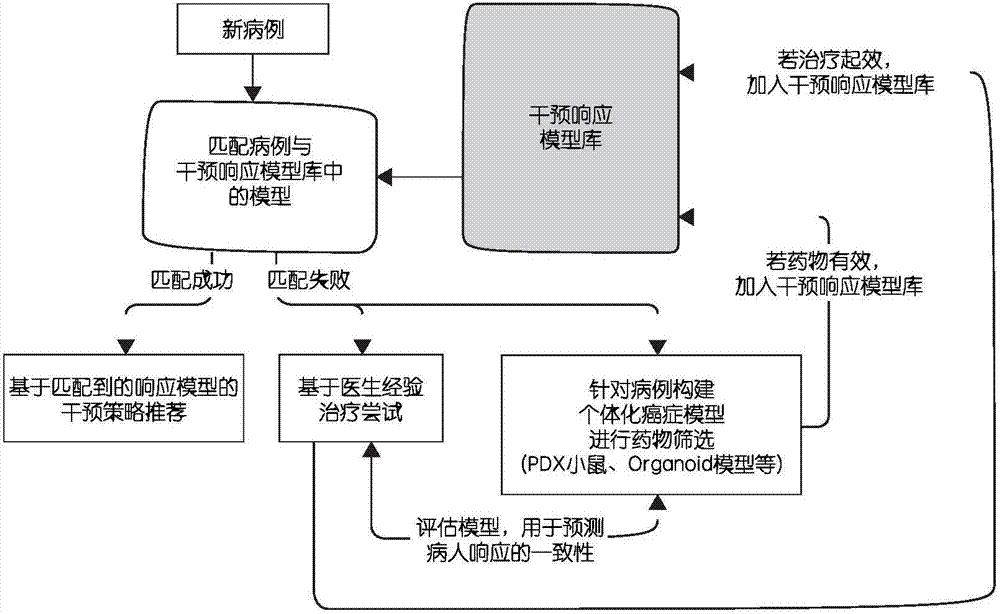
InactiveCN106897549ASimplify the diagnostic cycleImprove follow-up intervention responseMedical data miningMedical automated diagnosisResponse effectMolecular level
The invention discloses a cancer individuation intervention strategy selection method based on molecular physiome. The method comprises the following steps that: establishing an intervention response model library; when a new case appears, comparing the new case with the pre-administration proteomics difference of a model; and analyzing biological approaches / physiological function differences and the like which may be caused by the difference. A sample data type on which the method depends has high dependency with a physiological level phenotype. Proteomics data related to cell physiology and functions including protein and the like can be transcribed and subjected to epigenetic inheritance. The method is more sensitive to the intervention response effect of diseases, can provide rich indexes to observe molecular level physiological changes caused by diseases, and is suitable for clinic transformation and practical popularization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Polymer NEMS for cell physiology and microfabricated cell positioning system for micro-biocalorimeter
ActiveUS7966898B2Fast implementationReduce problem sizeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsForce measurement by measuring frquency variationsParyleneThermopile
A microfluidic embedded nanoelectromechanical system (NEMs) force sensor provides an electrical readout. The force sensor contains a deformable member that is integrated with a strain sensor. The strain sensor converts a deformation of the deformable member into an electrical signal. A microfluidic channel encapsulates the force sensor, controls a fluidic environment around the force sensor, and improves the read out. In addition, a microfluidic embedded vacuum insulated biocalorimeter is provided. A calorimeter chamber contains a parylene membrane. Both sides of the chamber are under vacuum during measurement of a sample. A microfluidic cannel (built from parylene) is used to deliver a sample to the chamber. A thermopile, used as a thermometer is located between two layers of parylene.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Cell impedance sensor based on DFP-ITO electrode and application of cell impedance sensor
InactiveCN104820004AGood light transmissionReduce processing difficultyMaterial analysis by optical meansMaterial electrochemical variablesCuvetteLight sensing
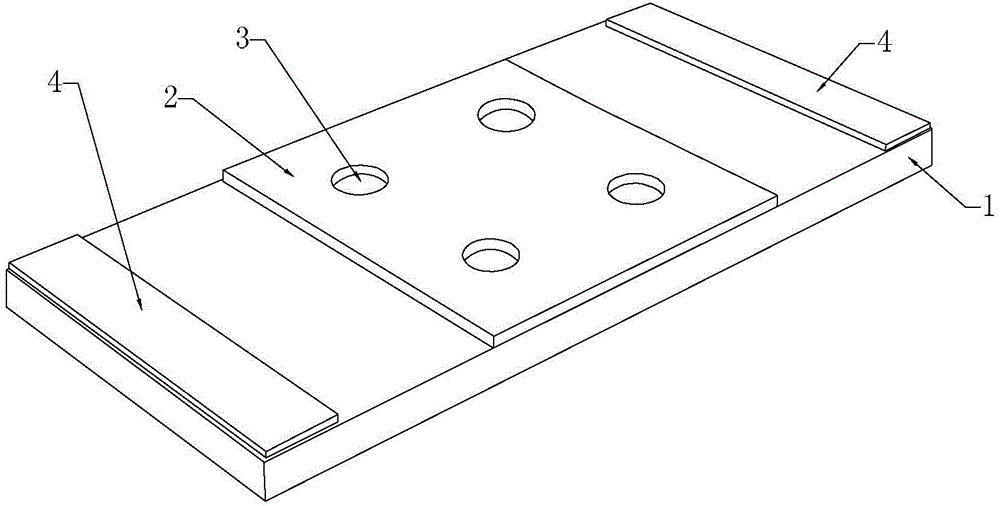
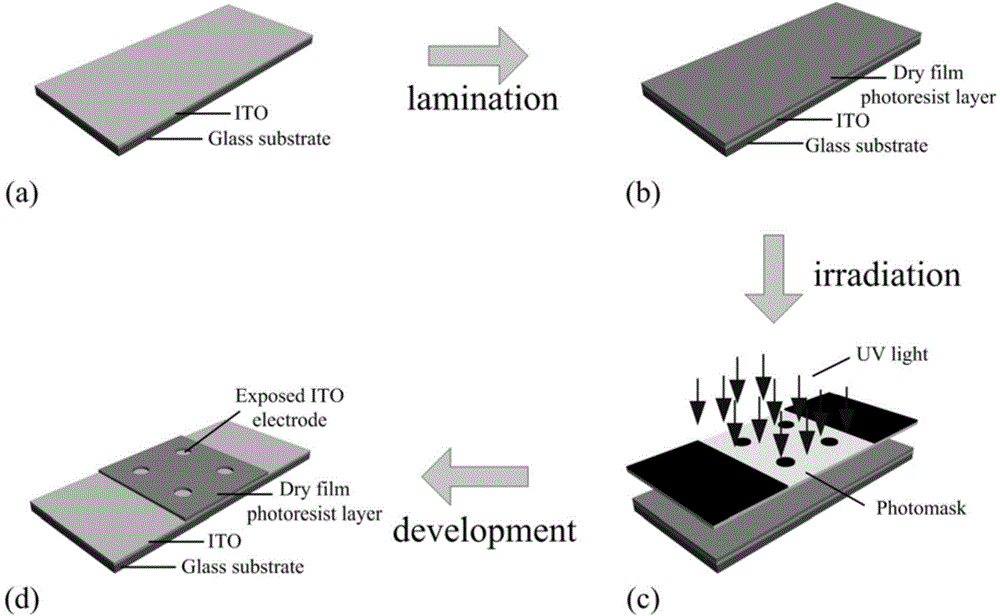
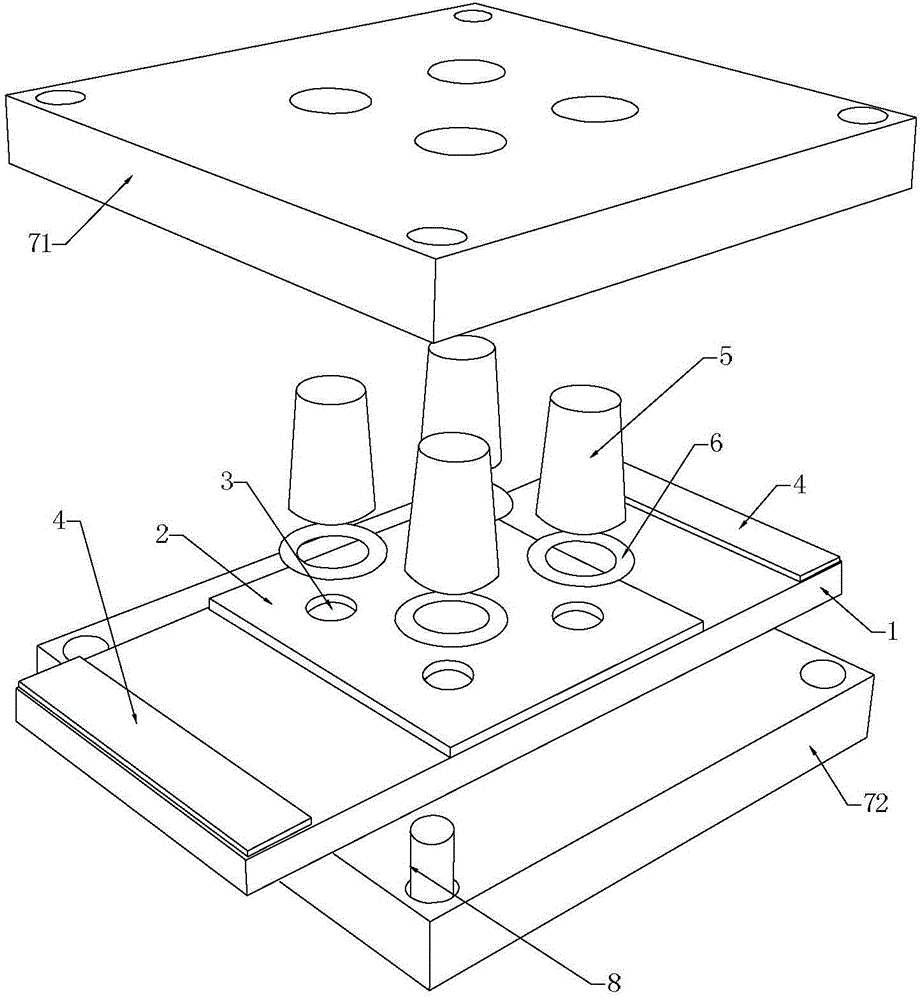
The invention belongs to the technical field of cell impedance sensors and particularly relates to a cell impedance sensor based on a DFP-ITO electrode and application of the cell impedance sensor. The DFP-ITO electrode comprises a conductive substrate layer and an insulating layer located on the conductive substrate layer, wherein the insulating layer is provided with electrode holes, the conductive substrate layer is further provided with lead ports, the conductive substrate layer is indium tin oxide conductive glass, and the insulating layer is a light-sensing dry film. The cell impedance sensor comprises the DFP-ITO electron and a measuring cuvette. The cell impedance sensor is simple in structure, easy to machine, capable of acquiring the morphology and impedance feature values of cells on the DFP-ITO electrode at the same time, capable of being popularized in common labs, and applicable to research fields such as cell physiology and pathology behaviors and drug screening.
Owner:AFFILIATED YONGCHUAN HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
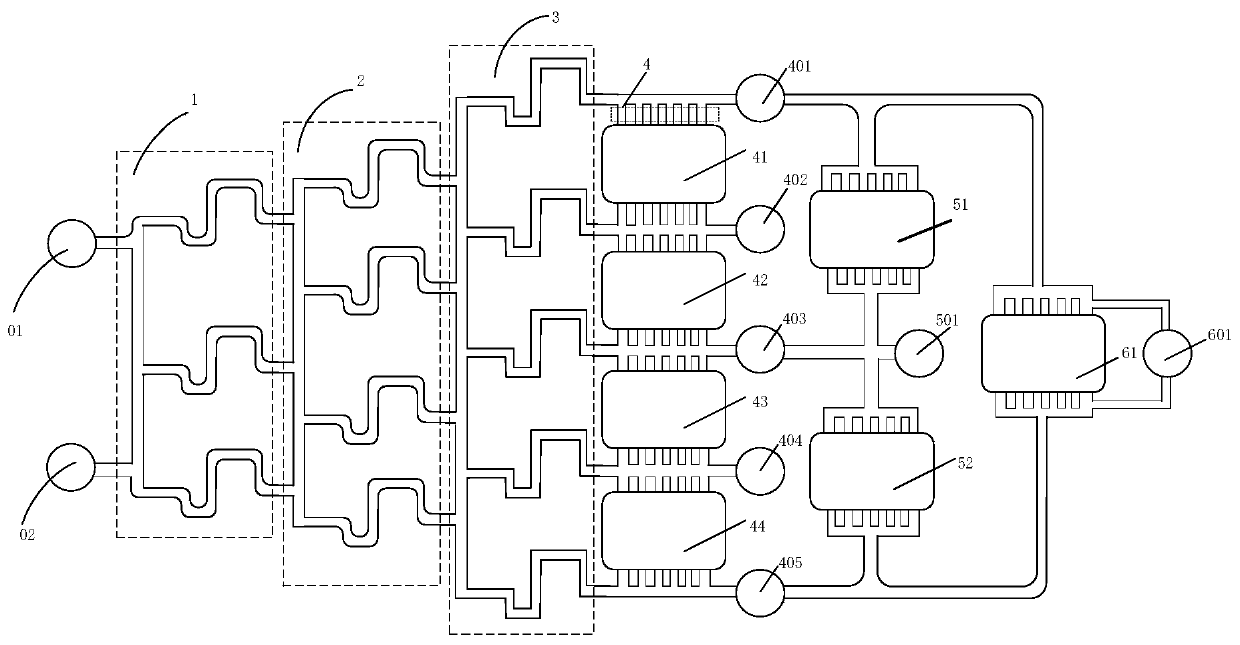
Concentration gradient generation device for gel 3D cell culture and preparation and application method
ActiveCN110586210AReduce volumeLow costMaterial analysis by optical meansLaboratory glasswaresCell behaviour3D cell culture
The invention discloses a concentration gradient generation device for gel 3D cell culture. The device comprises multi-stage mixing and concentration gradient generation modules and gel chambers of multi-stage concentration gradient ranges, wherein a plurality of gel samples can be carried simultaneously; through application of sectional concentration gradients, detection and evaluation on cell behaviors in gel within different concentration gradient ranges can be performed simultaneously; and through setup of the multi-stage concentration gradient ranges, samples of different concentration spans can be simultaneously detected on a same fluid chip. The fluid chip provided by the invention has the advantages of being small in volume, low in cost, good in integration with a trace amount of gel, and the like, and has wide application prospects in aspects such as cell physiology, pathology, drug screening, biomedicines and environmental monitoring. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses a preparation method and an application method of the concentration gradient generation device.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
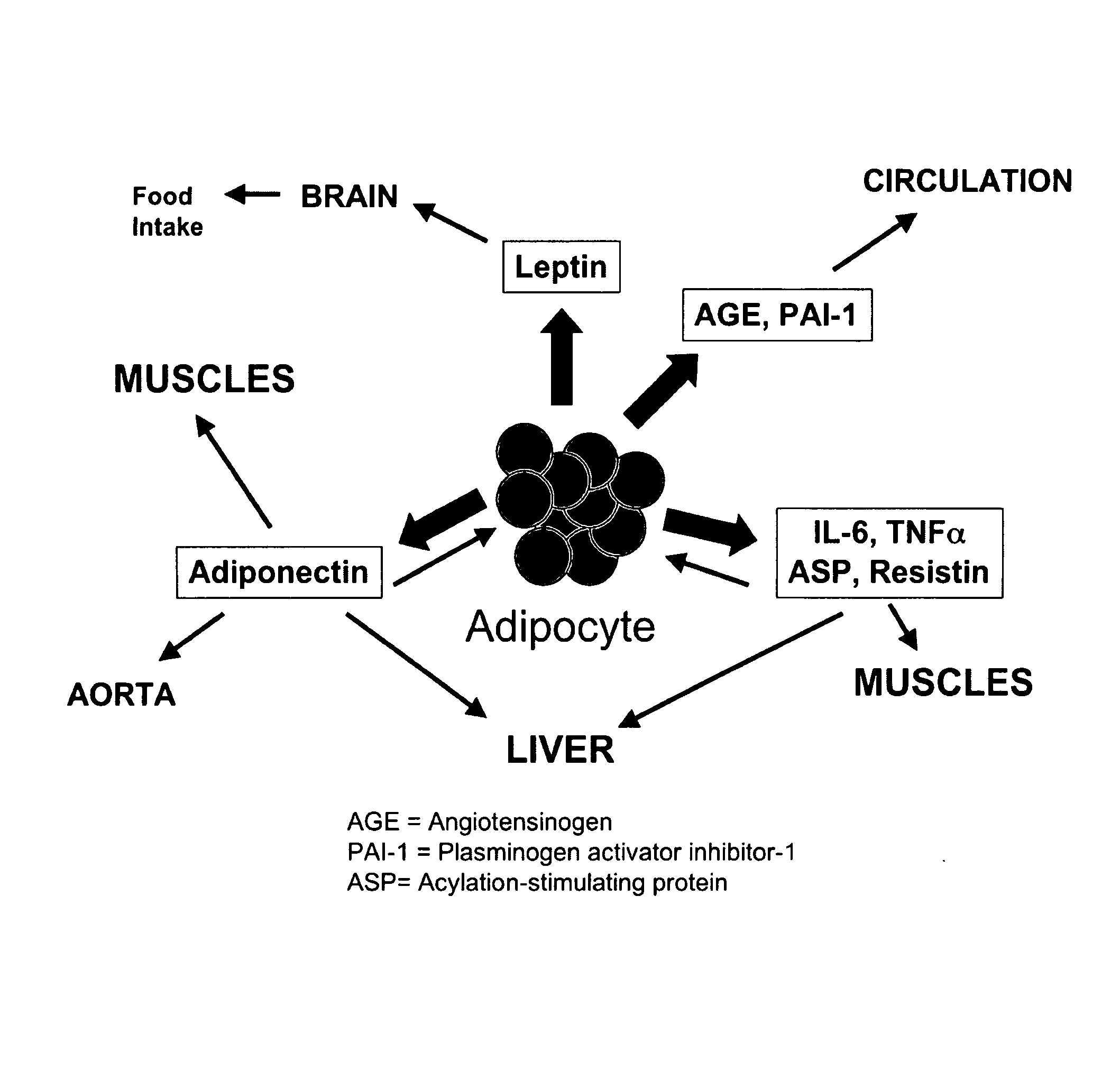
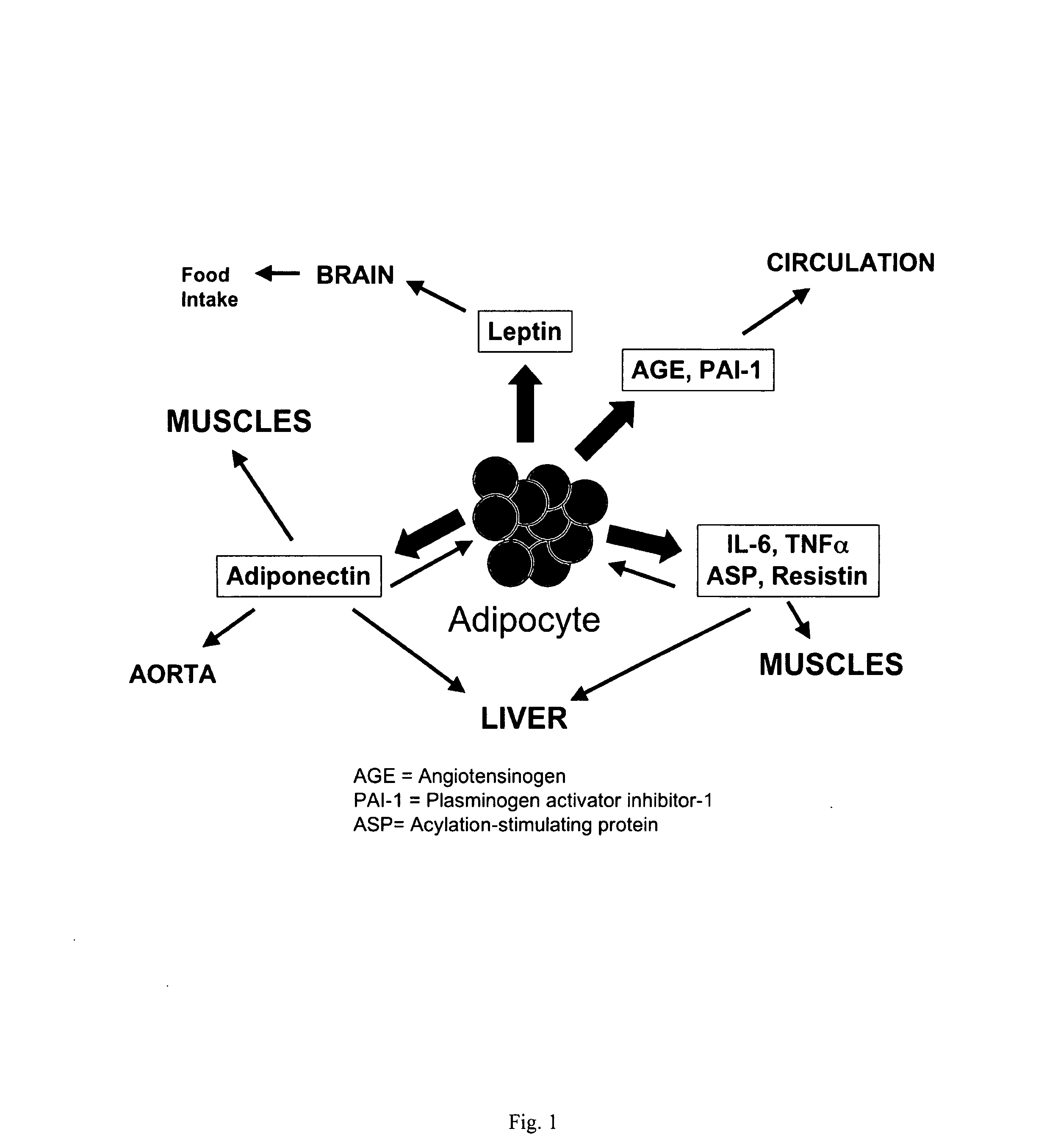
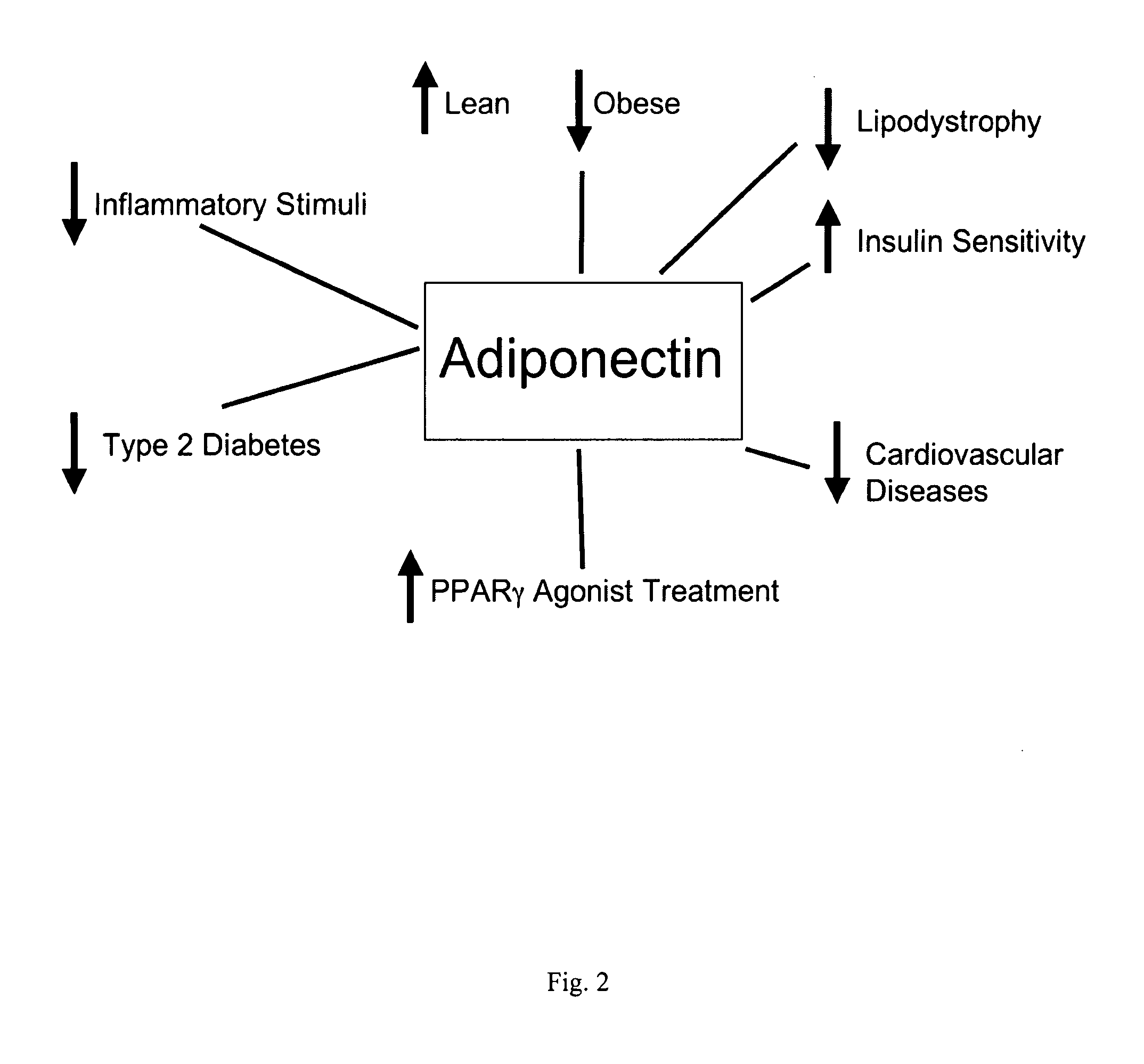
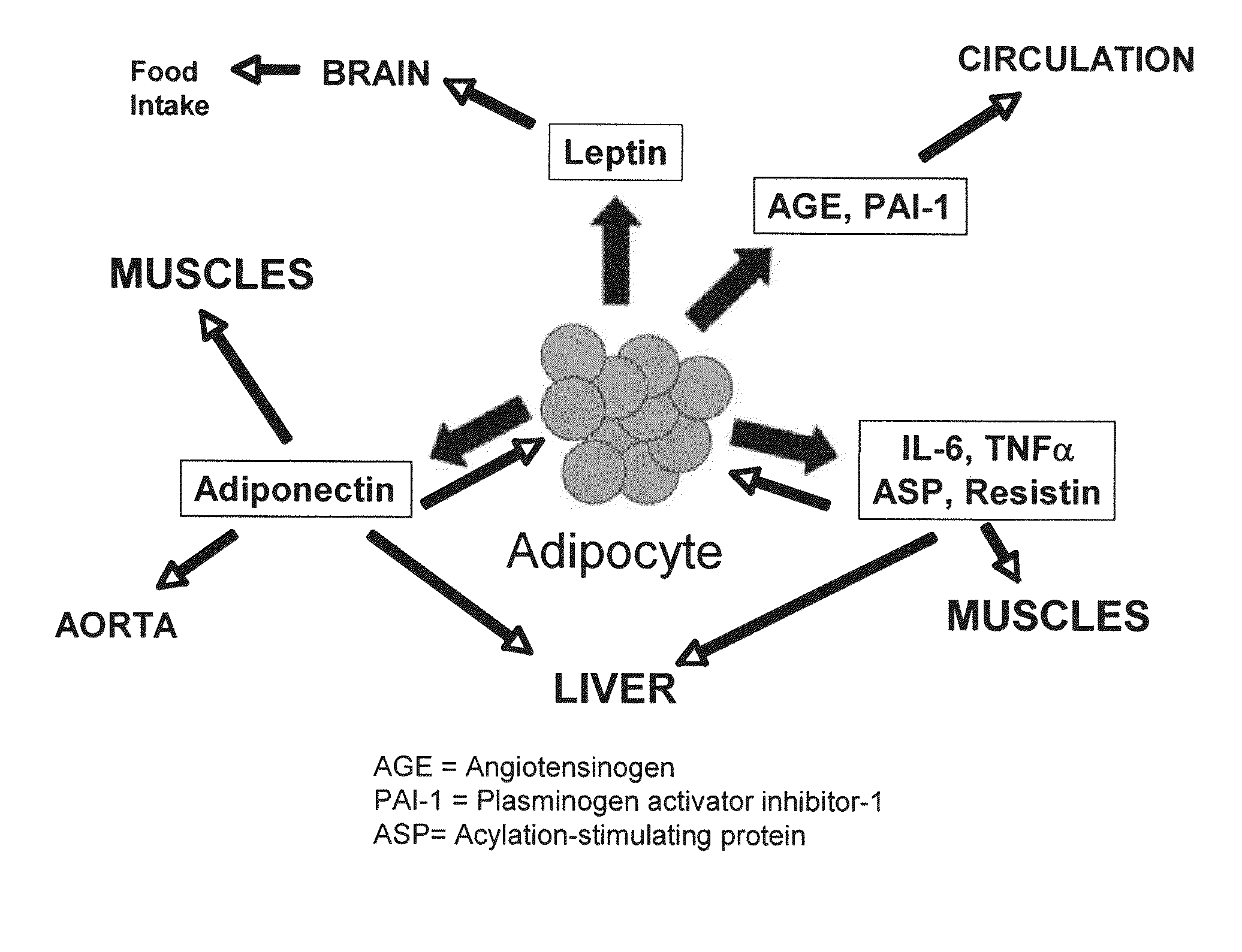
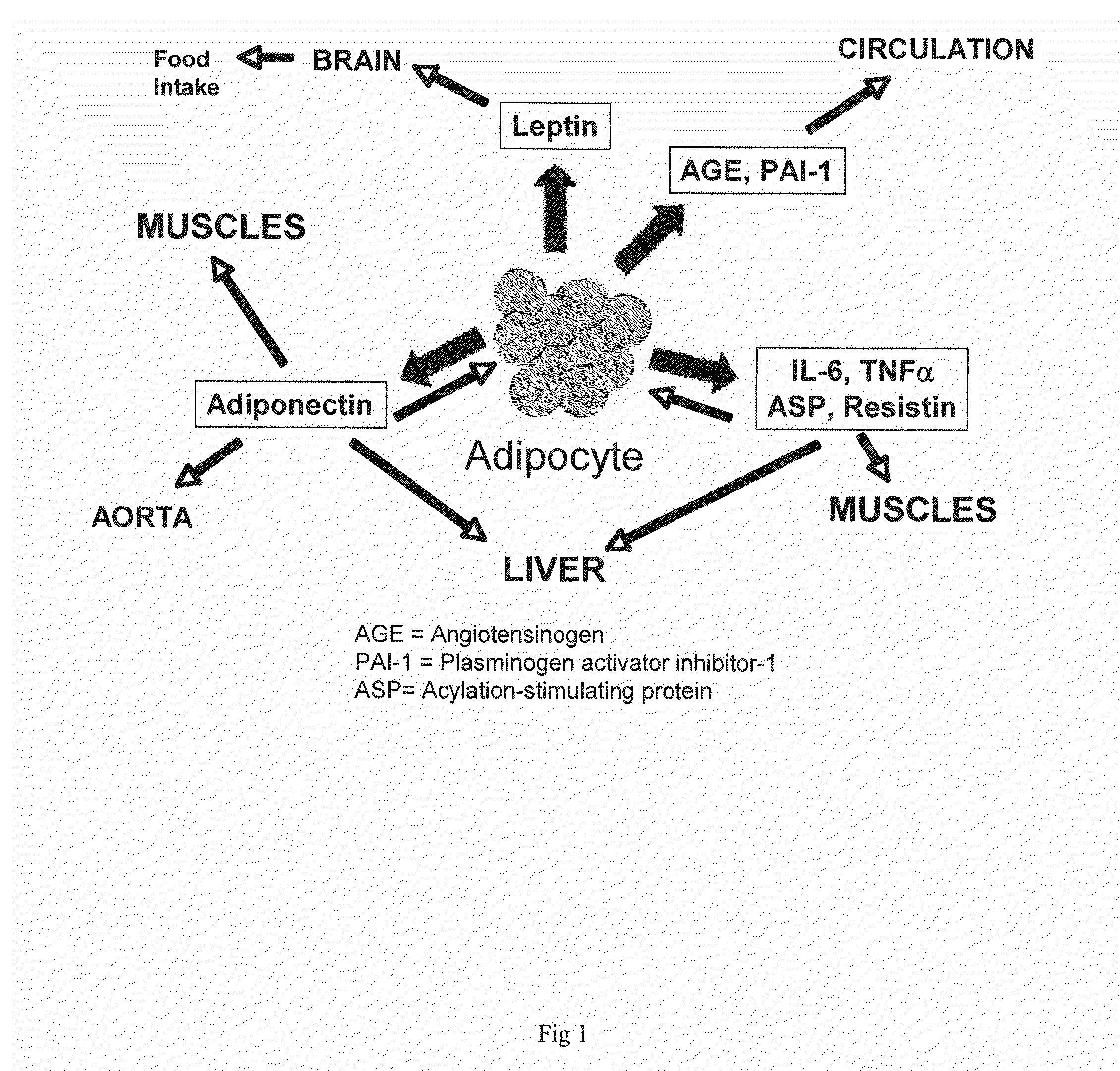
Novel mitochondrial uncoupling methods and compositions for enhancing adipocyte thermogenesis
InactiveUS20100215782A1Assist in weight lossQuality improvementBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsWeight gainingPhytochemical
Disclosed are methods, compounds, and compositions comprising botanically based drugs, medical foods, and dietary supplements for the prevention and treatment of metabolic disorders, in particular obesity, weight gain, insulin resistance syndromes, diabetes, fasting hyperlipidemia and osteoarthritis. More specifically, the invention relates to pharmaceutical therapeutic methods and compositions utilizing phytochemicals, natural plant extracts and combinations to modify adipocyte physiology to enhance thermogenesis and modify cytokine secretion.
Owner:METAPROTEOMICS
Image metrics in the statistical analysis of DNA microarray data
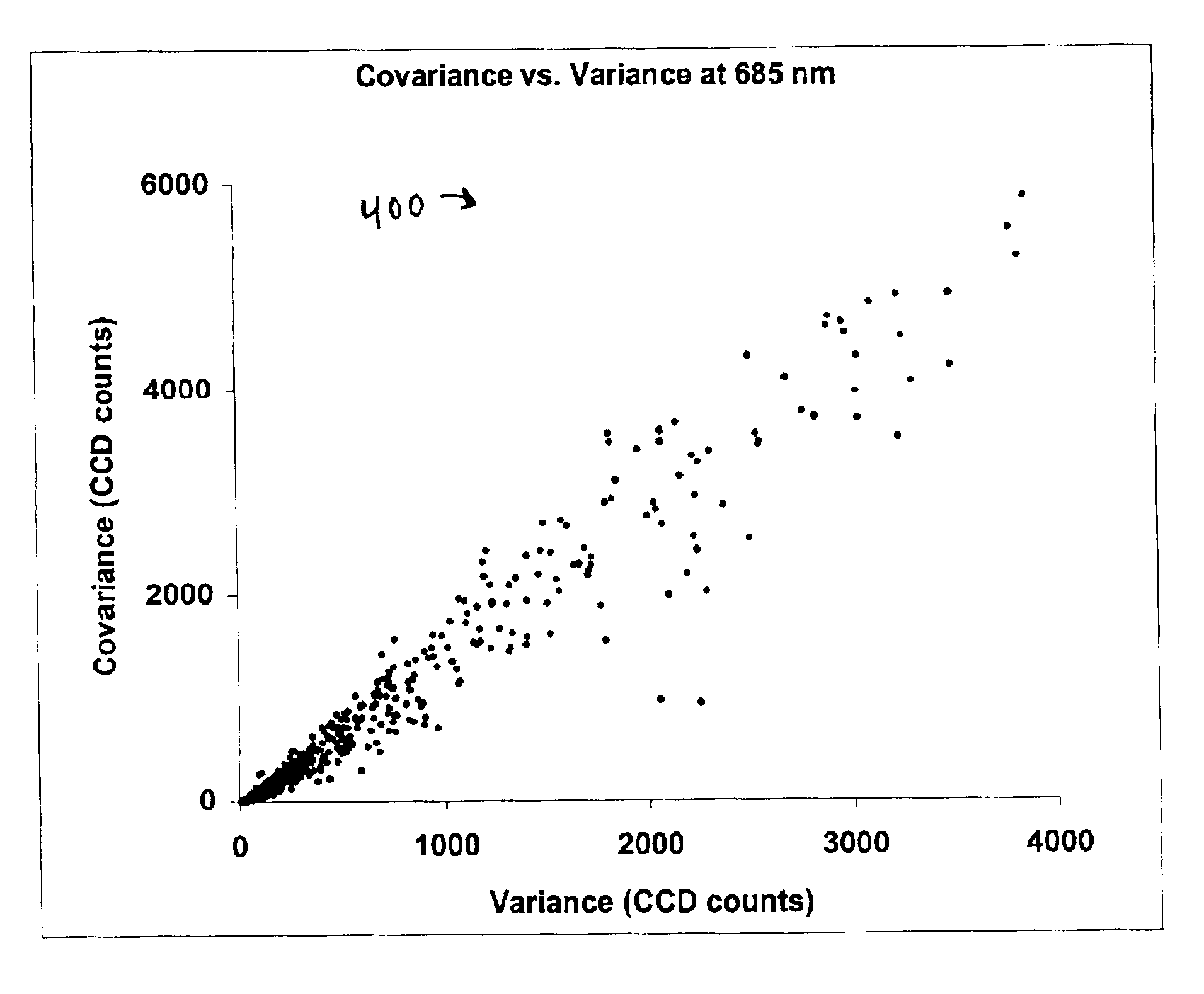
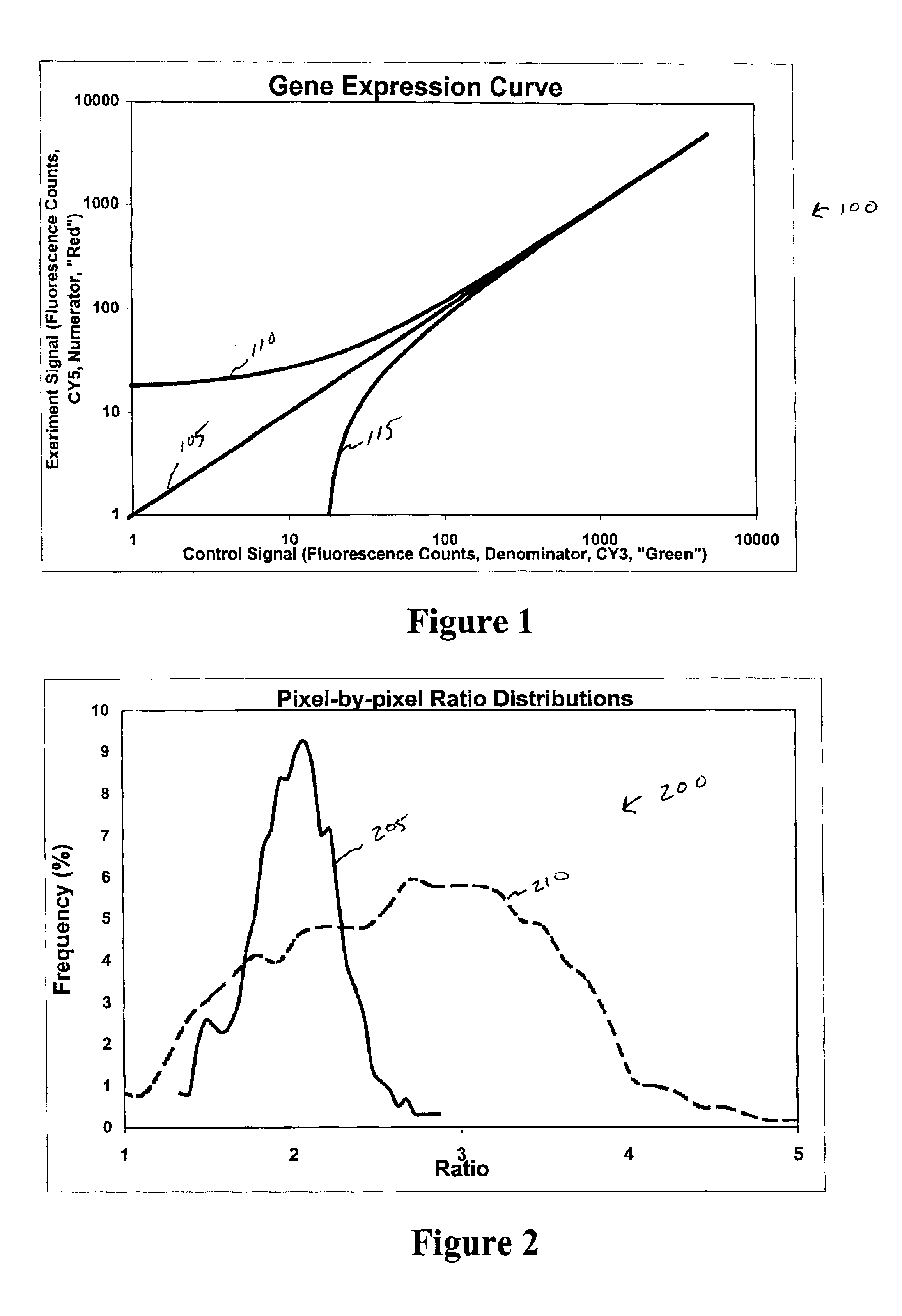
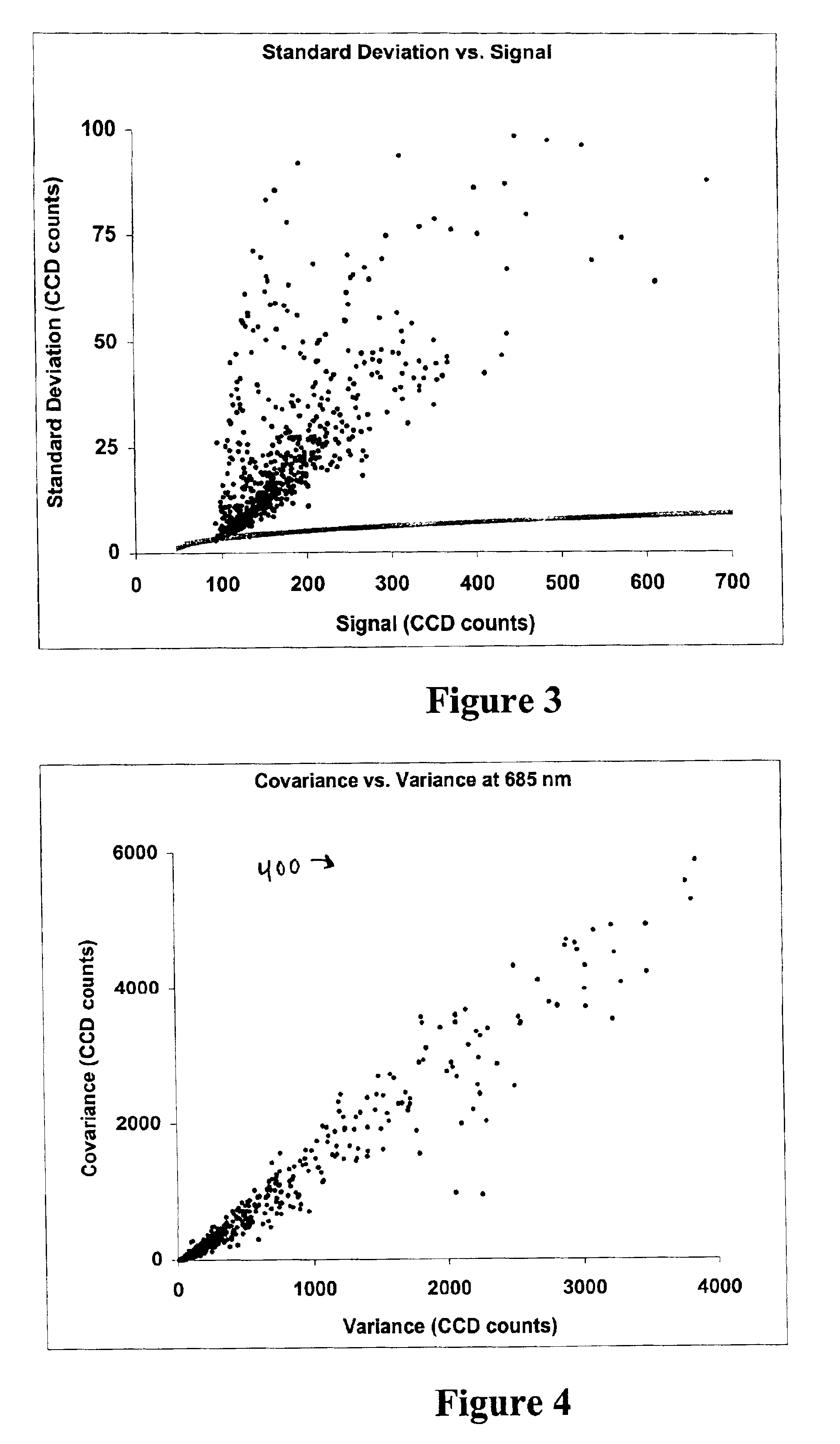
Expression profiling using DNA microarrays is an important new method for analyzing cellular physiology. In “spotted” microarrays, fluorescently labeled cDNA from experimental and control cells is hybridized to arrayed target DNA and the arrays imaged at two or more wavelengths. Statistical analysis is performed on microarray images and show that non-additive background, high intensity fluctuations across spots, and fabrication artifacts interfere with the accurate determination of intensity information. The probability density distributions generated by pixel-by-pixel analysis of images can be used to measure the precision with which spot intensities are determined. Simple weighting schemes based on these probability distributions are effective in improving significantly the quality of microarray data as it accumulates in a multi-experiment database. Error estimates from image-based metrics should be one component in an explicitly probabilistic scheme for the analysis of DNA microarray data.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Method for Drug Screening and Characterization by Calcium Flux
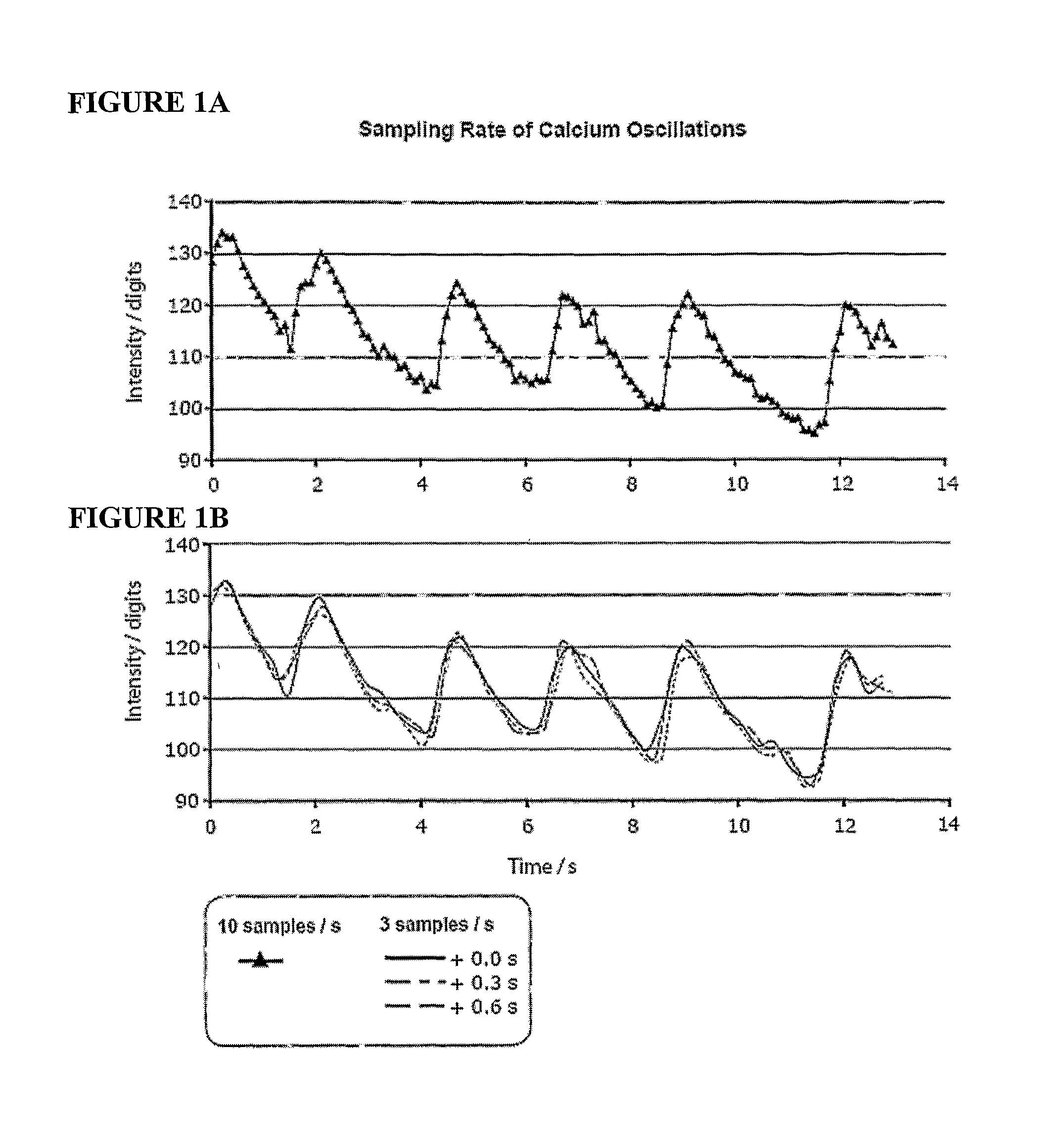
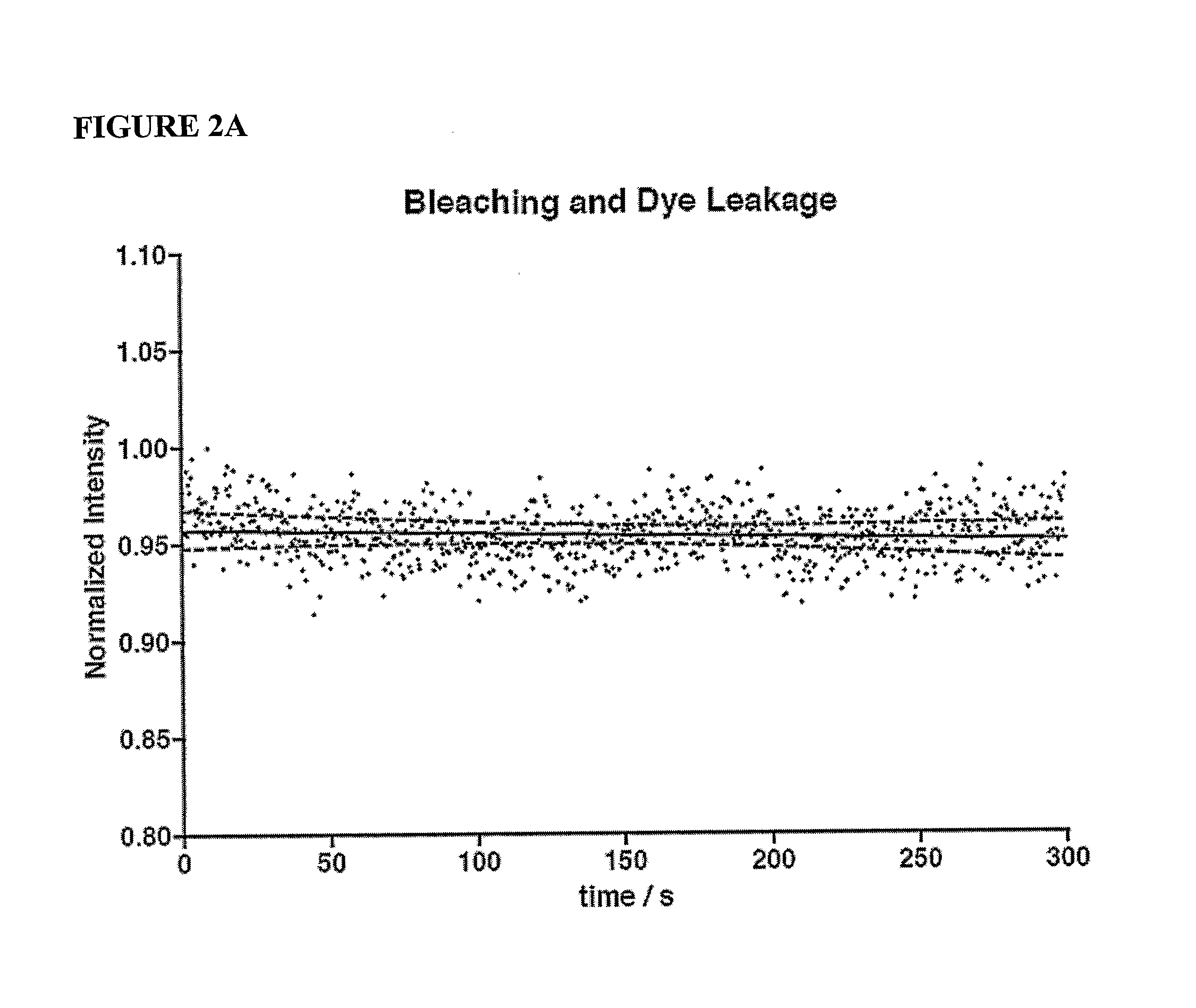
The instrumentation and methods described herein are based on imaging and measuring single cell dose response by fluorescent ion imaging that records live cell responses to drug doses with no apparent damage to the cells or toxic side effects. Dose response curves and other pharmacological parameters can be computed by imaging and measuring oscillation changes for each dose and each cell. Large variability of cellular responses under the same experimental conditions indicates that pharmacological benchmarks are determined by statistical distribution of cells and cellular physiology. The instrumentation and methods described herein provide a means of measuring statistical variability of cell populations for improved screening and development methods for drugs.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
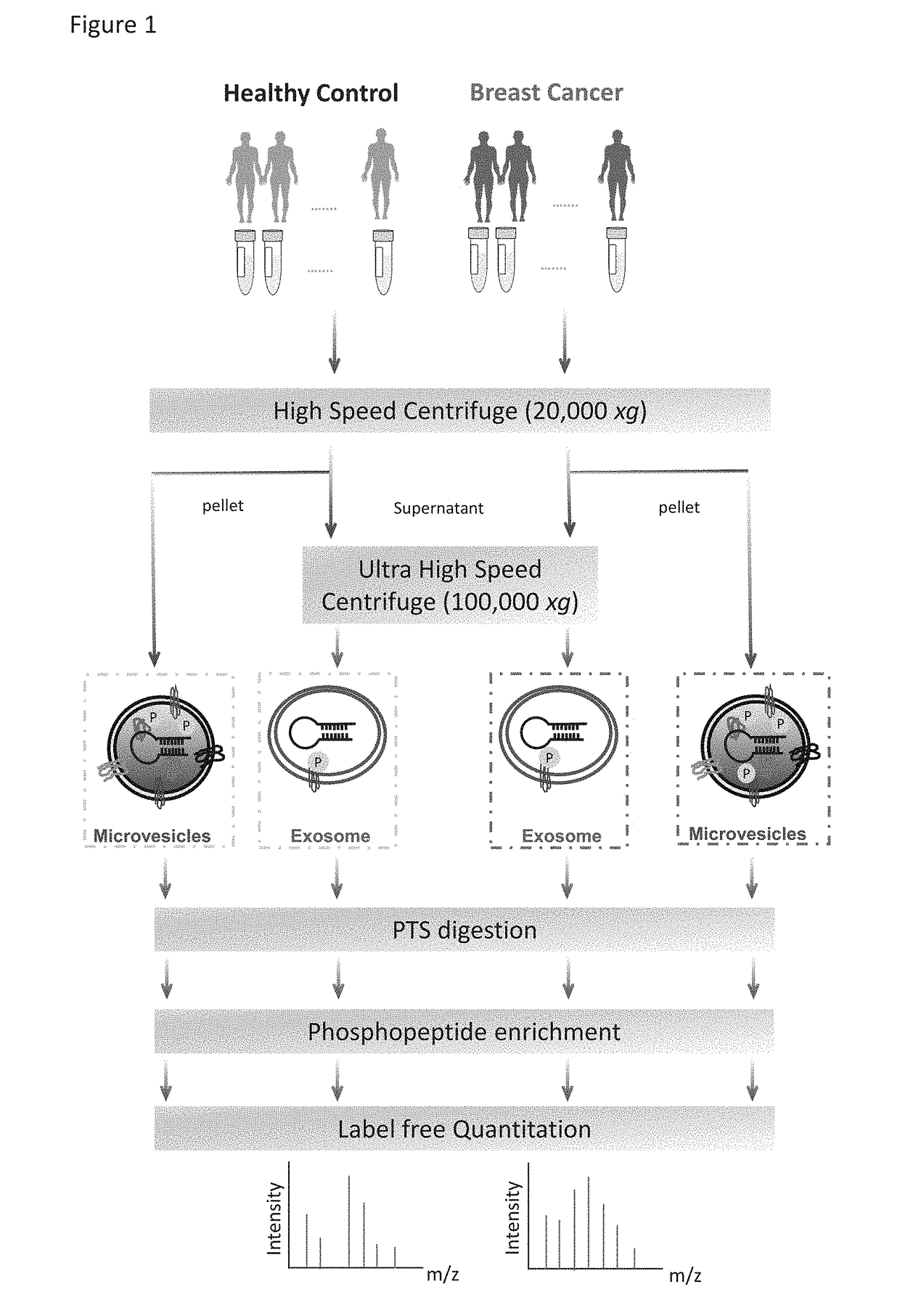
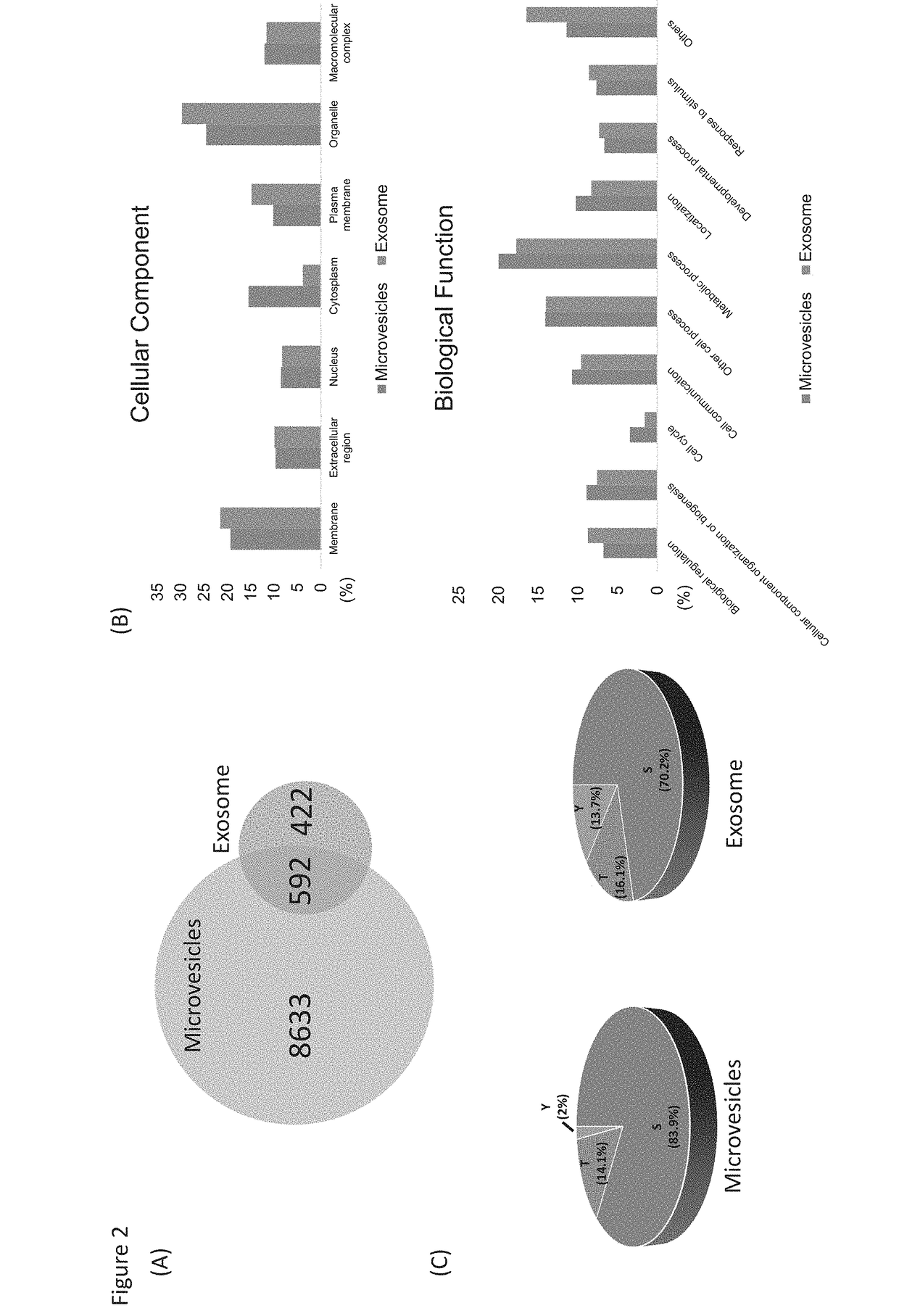
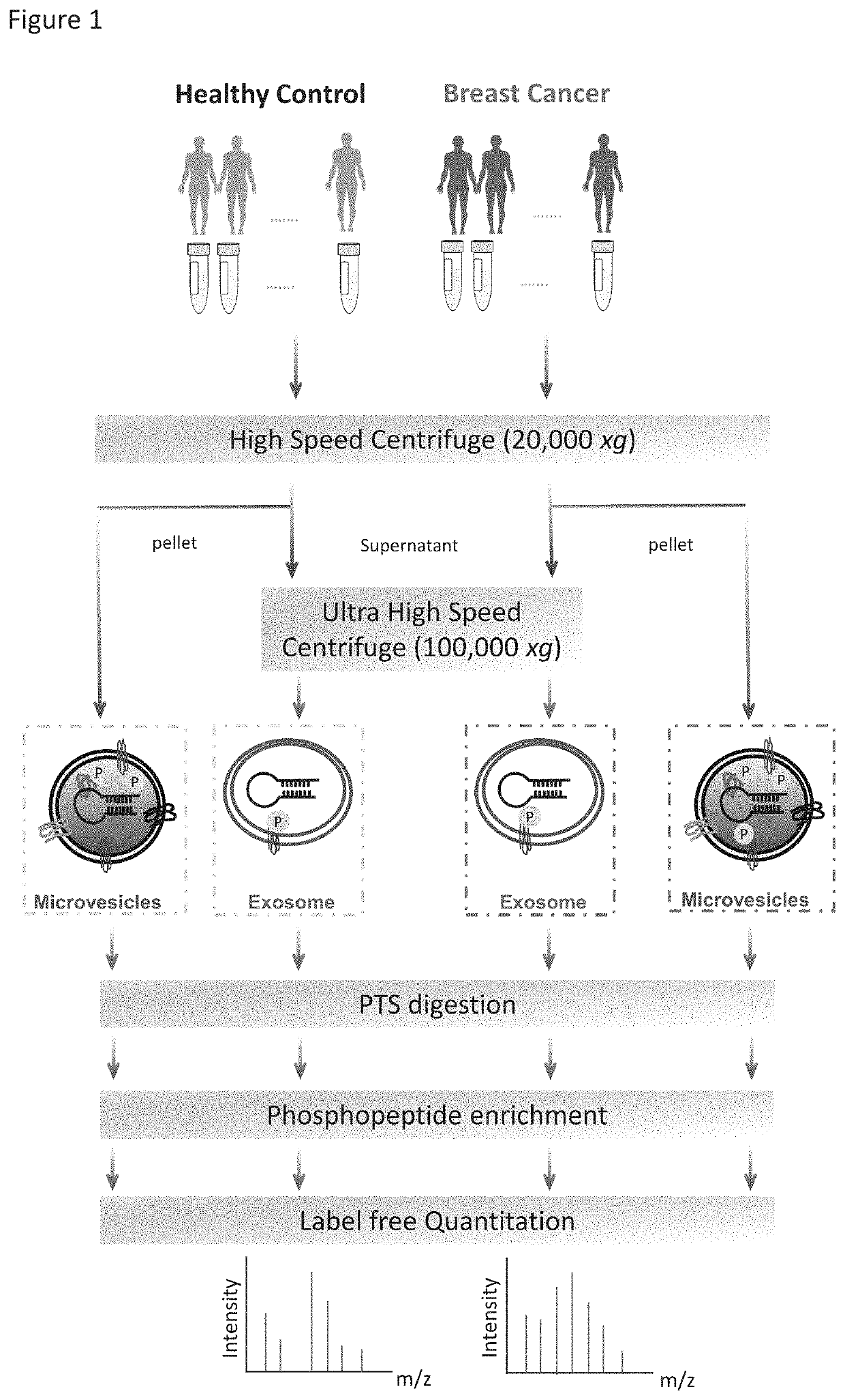
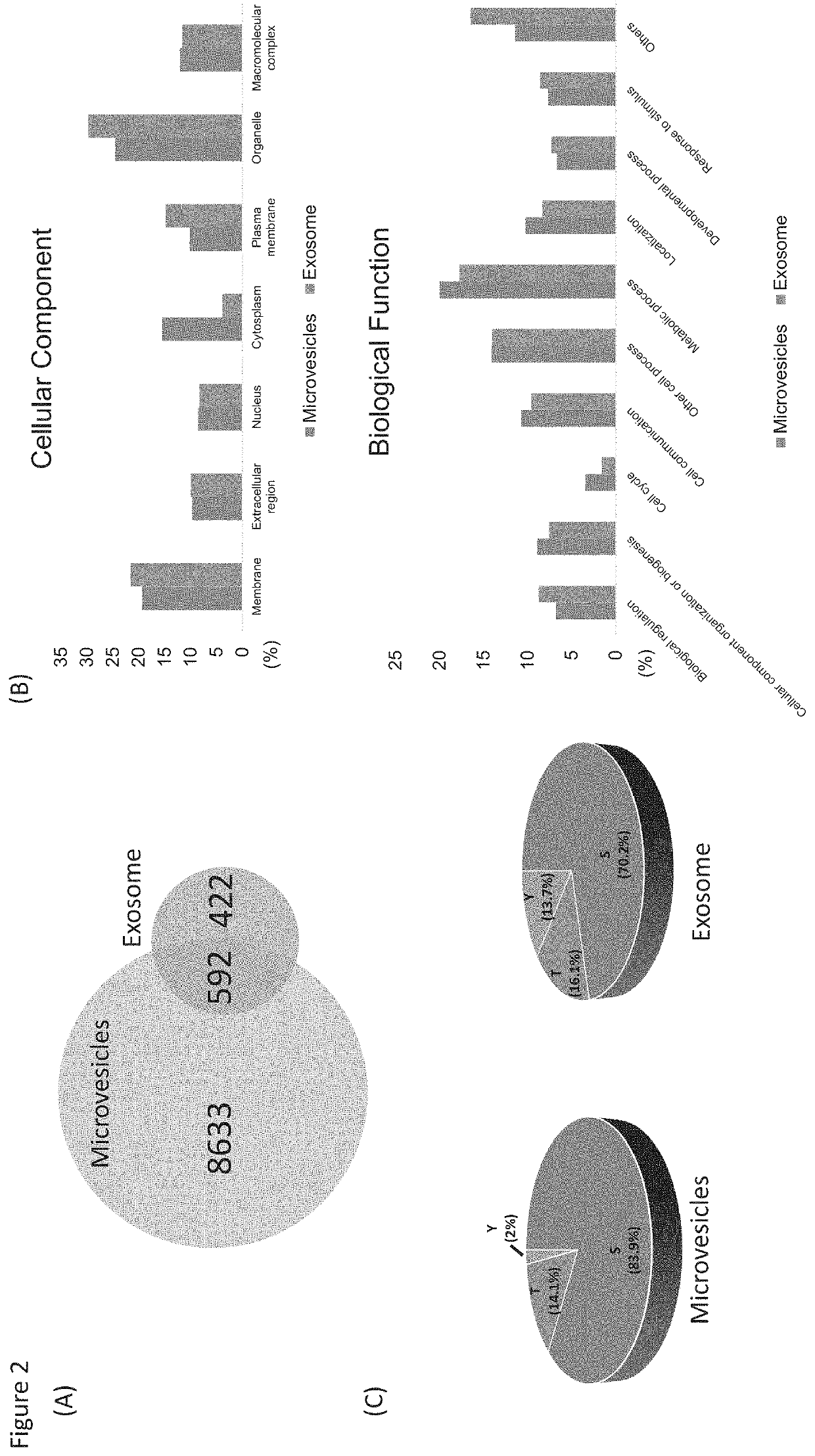
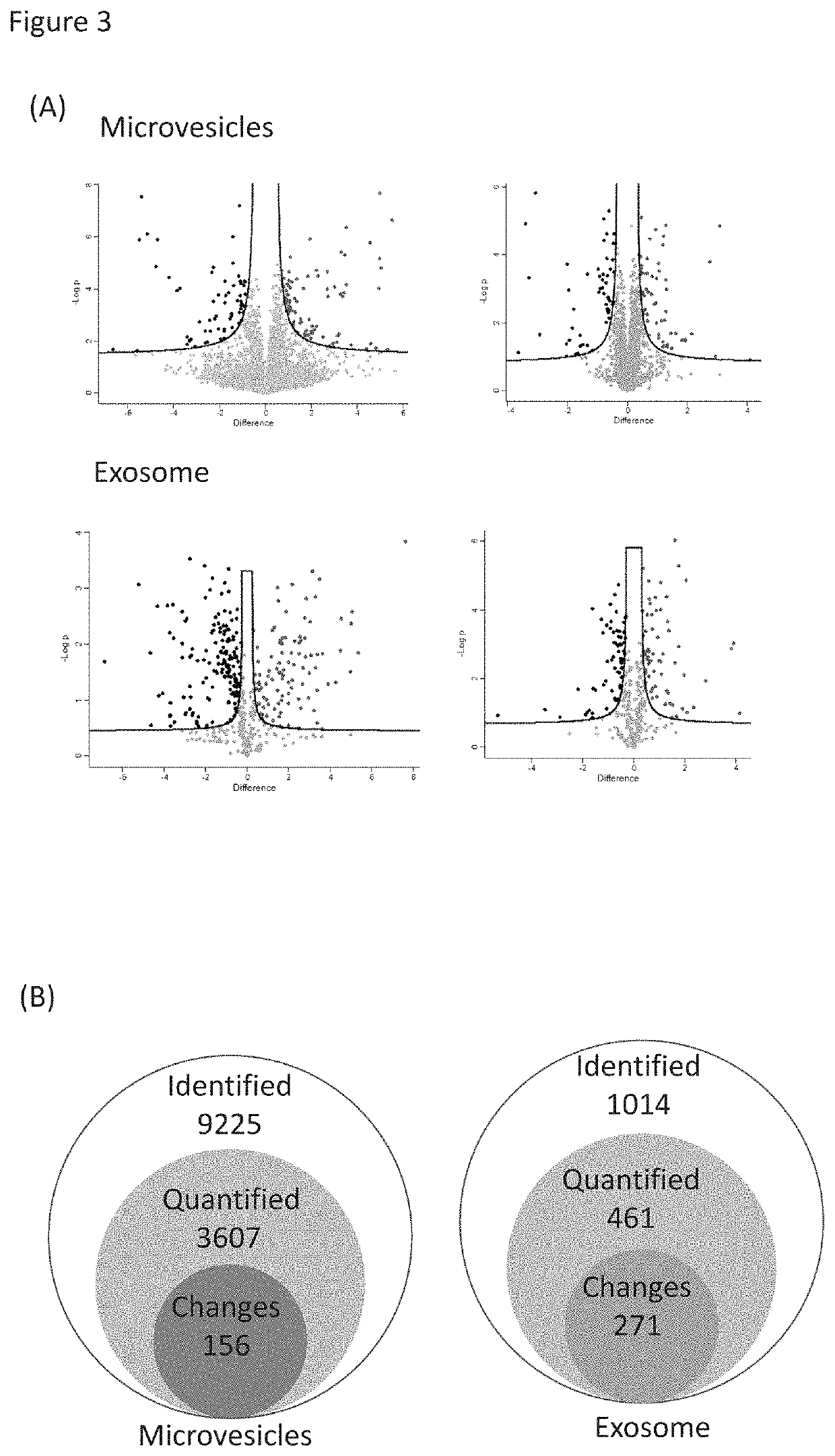
Phosphoproteins in Extracellular Vehicles as Candidate Markers for Breast Cancer
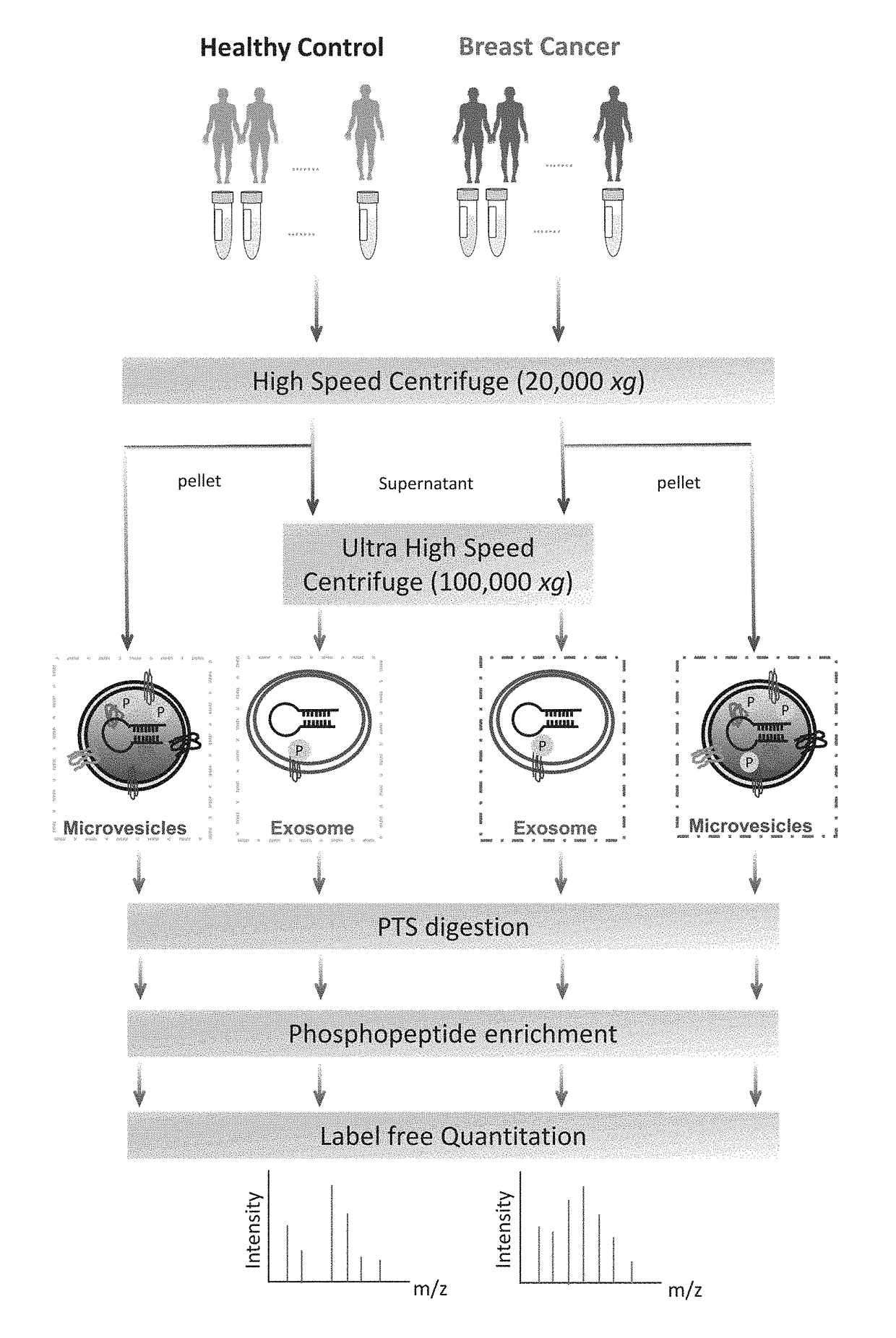
The state of protein phosphorylation and glycosylation can be key determinants of cellular physiology such as early stage cancer, but the development of phosphoproteins and / or glycoproteins in biofluids for disease diagnosis remains elusive. Here we demonstrate, for the first time, a strategy to isolate and identify phosphoproteins / glycoproteins in extracellular vehicles (EVs) from human plasma as potential markers to differentiate disease from healthy states. We identified close to 10,000 unique phosphopeptides in EVs by isolating from small volume of plasma samples. Using label-free quantitative phosphoproteomics, we identified 144 phosphoproteins in plasma EVs that are significantly higher in patients diagnosed with breast cancer than in healthy controls. Several novel biomarkers were validated in individual patients using Paralleled Reaction Monitoring for targeted quantitation. Similarly a group of glycoproteins in plasma EVs are identified. The study demonstrated that the development of phosphoproteins and / or glycoproteins in plasma EV as disease biomarkers is highly feasible and may transform cancer screening and monitoring.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for inducing the formation of islet structures and improving beta cell function
InactiveUS20160017288A1Avoid the needStraightforward and rapid methodPancreatic cellsArtificial cell constructsECM ProteinΒ cell function
Insulin producing β cells are found in three dimensional (3D) structures, the Islet of Langerhans. The 3D structure is required for normal β cell function and survival. β cell pseudoislets (PIs) are useful for study of β cell physiology. Co-culturing of primary human islets and β cell lines together with islet-derived epithelial cells can improve β cell function and survival and maintain the cells' 3D structure, resulting a rapid and spontaneous formation of free-floating PIs. β cells in PIs were similar in size to native islets and showed increased percentage of pro-insulin-positive cells, increased insulin gene expression in response to glucose stimulation, improved glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, and reduced β cell death. Key ECM proteins, absent in monolayer β cells, are deposited by iECs in and round the PIs. iEC induced PIs are a useful tool for examining β-cell / iEC interactions and studying β-cell function in a native 3D configuration.
Owner:AKIRAV EITAN MOSHE
System and method for measuring phase
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light.These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imagingorigins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in theirnative state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference withinthe cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Bio-optical composite material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110200994AFunction increaseImprove eyesightHeavy metal active ingredientsInorganic boron active ingredientsCinnabarMirabilite
The invention belongs to the technical field of composite materials, and particularly discloses a bio-optical composite material, a preparation method and an application thereof. The bio-optical composite material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 0.5-3 parts of mica, 0.5-2 parts of mirabilite, 0.5-3 parts of haematite, 0.5-1 part of gypsum, 0.5-1 part of magnetite, 0.5-3 parts of cinnabar, 0.5-2 parts of tourmaline, 0.5-3 parts of alum and 0.5-2 parts of medical stone. The raw material fine powder of the bio-optical composite material is evenly mixed in a high-speed mixer, and is irradiated for 12-24 hours by a laser with 457-600nm frequency band and a continuous output power of 400mW. The composite material can convert infrared waves emitted by human bodies to generate short-wave biological waves, can promote cell metabolism, improve cell pathology and improve cell physiology, has the functions of quickly relieving pain, repairing cell damage, dispelling glandhyperplasia, improving cell hypoxia, enhancing muscle fiber strength, strengthening physiological state of human organs and the like, can be used for medical treatment and human body rehabilitation health care, such as preparing multiple medical patches, eyeglass frames and other human body contact articles for daily use.
Owner:上海华芝隆科技有限公司
Fluorescence tracking method for transportation direction and route of assimilate of in-vitro lily plant
InactiveCN109520978AHigh quantum yieldMicroautoradiography SafetyFluorescence/phosphorescenceDevelopmental stageQuantum yield
The invention relates to the research technique of plant stoichiology and aims at providing a fluorescence tracking method for the transportation direction and route of assimilate of an in-vitro lilyplant. The fluorescence tracking method comprises the following steps: applying medical absorbent cotton wetted by a CFDA solution to outer-layer scale notches of bulbs or cross sections of vascular bundles of leaves of an in-vitro lily, carrying out packaging by virtue of a paraffin sealing film, and covering by virtue of tin foil paper; continuing to carry out culturing for 72 hours under the original culture condition; carrying out freehand section sampling at an observed part, observing distribution images of CF in the notches by virtue of a fluorescence microscope, and taking a picture. Afluorescent dye CFDA adopted in the invention has no toxin or chemical inertness to cells, the quantum yield is relatively high, the transportation direction and route of the assimilate in the lily bulbs in different developmental stages can be properly tracked in a cell level, and compared with a traditional microradioactive autographing technique, the method is relatively safe and simple. The special sample treatment is omitted, the cost is low, and an ideal marking result can be rapidly and effectively achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
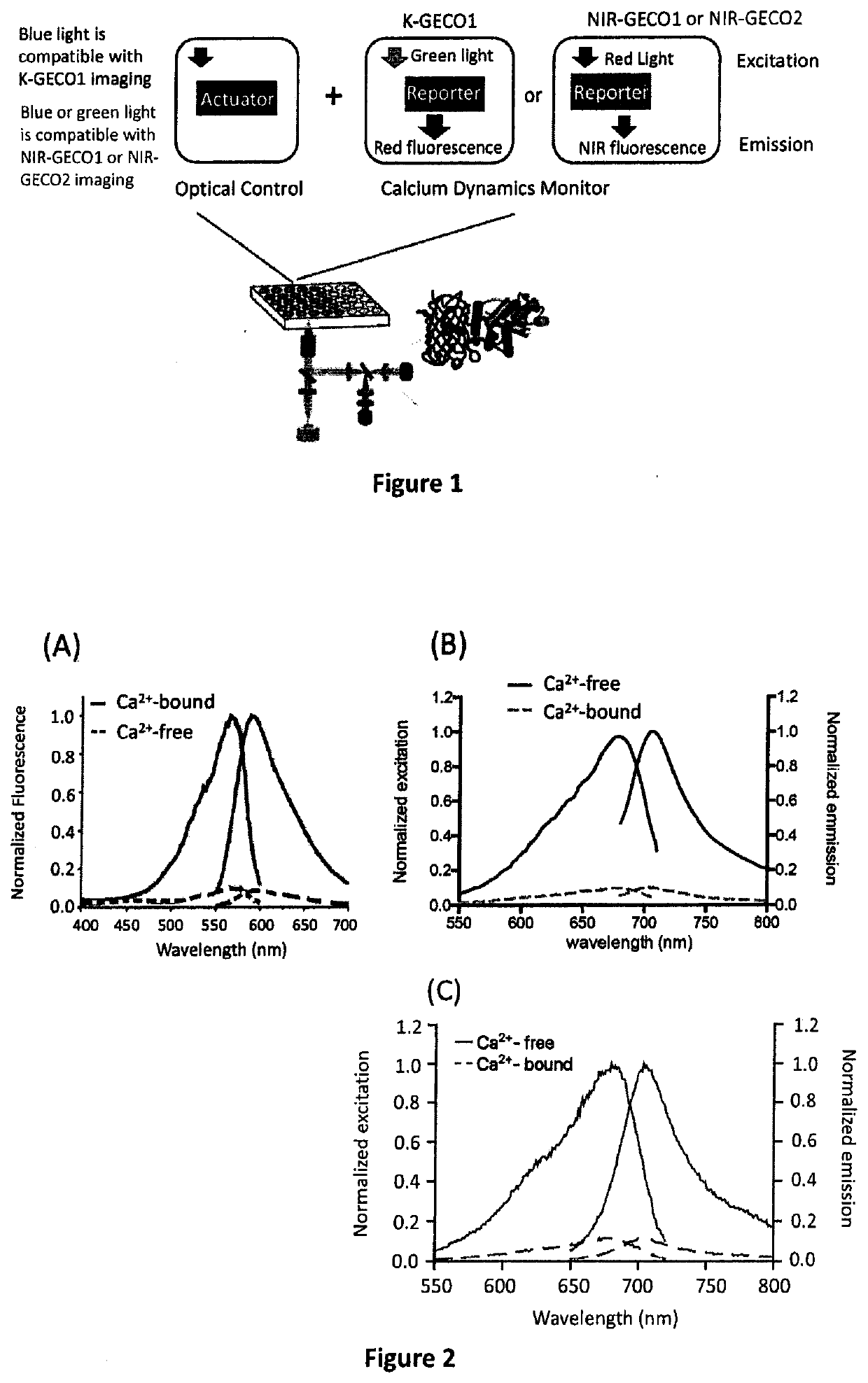
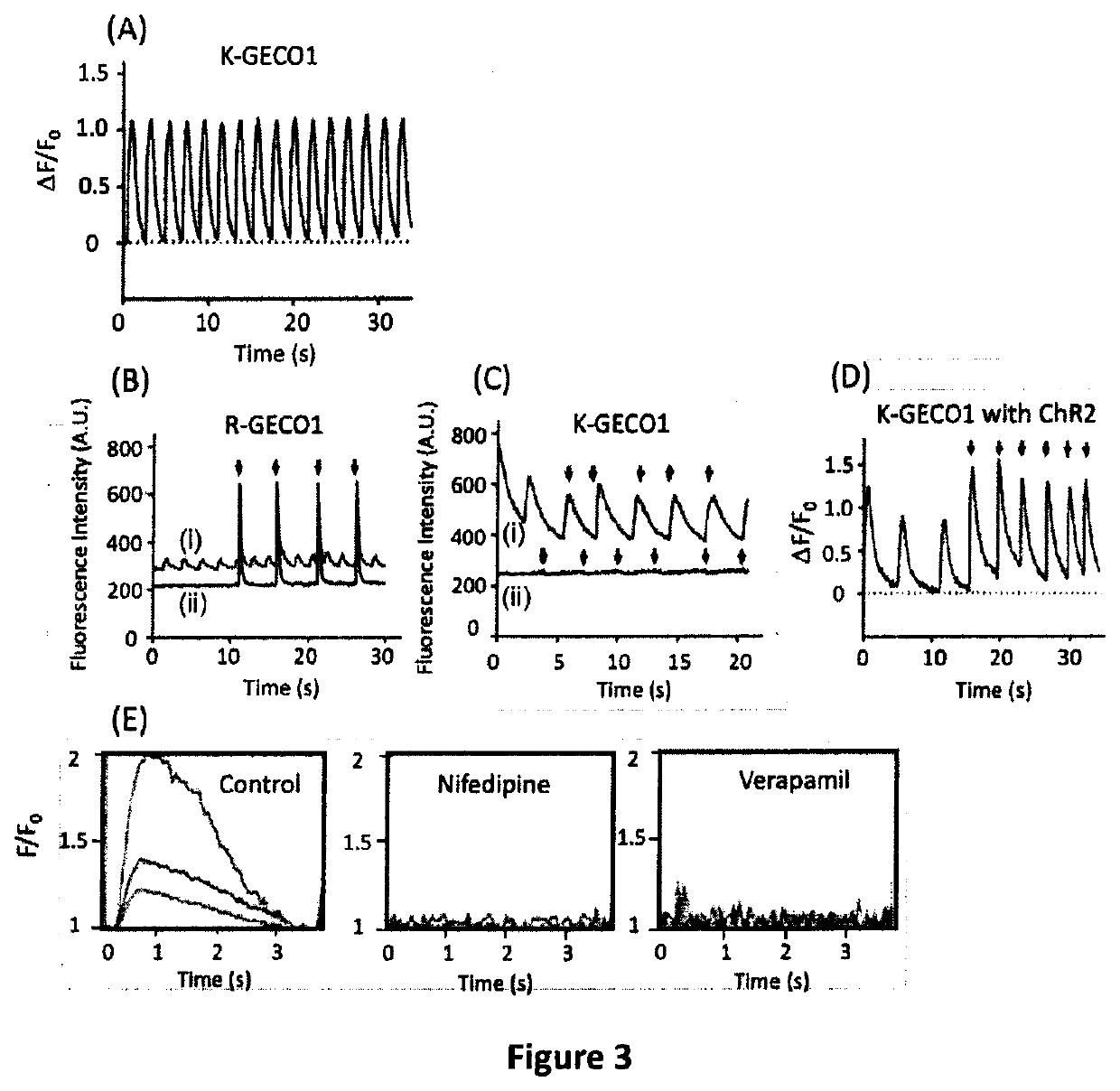
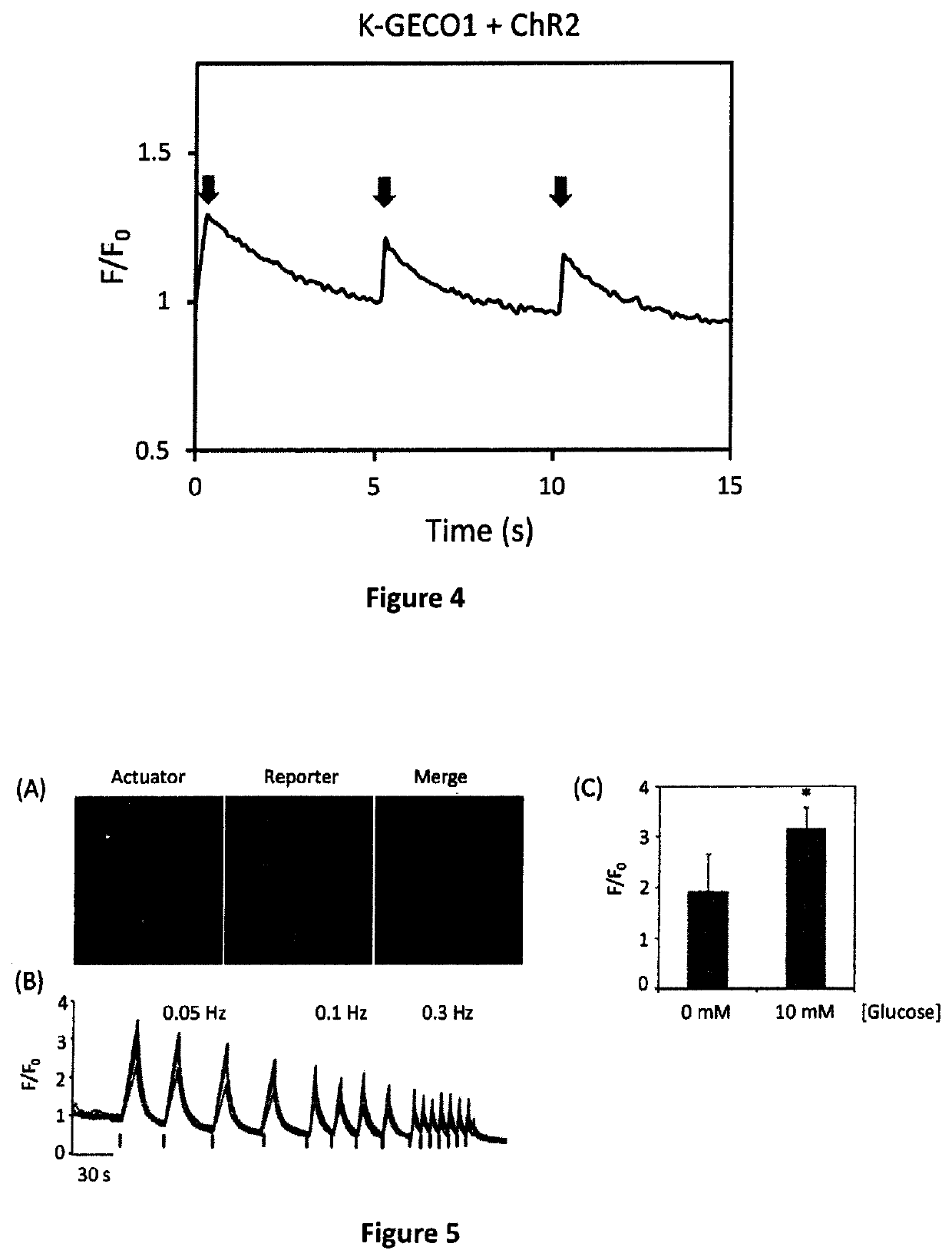
Genetically encoded fluorescent indicators under optogenetic control and uses thereof
PendingUS20220017976A1Microbiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesOptogeneticsFunctional imaging
Disclosed are methods and compositions for real-time monitoring cellular calcium ion dynamics by red-shifted genetically encoded indicators under optogenetic control, in which millisecond-timescale of temporal control of optical activation or inactivation and signal recording can be achieved. The methods include artifact-free functional imaging in conjunction with optogenetic tools for studying cellular physiology, signal transduction and neuronal activity. Thus, all-optical and non-invasive approaches for drug screening, toxicity testing and assessment of cell functions may be provided.
Owner:LUMISTAR BIOTECHNOLOGY INC +1
Phosphoproteins in extracellular vesicles as candidate markers for breast cancer
The state of protein phosphorylation and glycosylation can be key determinants of cellular physiology such as early stage cancer, but the development of phosphoproteins and / or glycoproteins in biofluids for disease diagnosis remains elusive. Here we demonstrate, for the first time, a strategy to isolate and identify phosphoproteins / glycoproteins in extracellular vesicles (EVs) from human plasma as potential markers to differentiate disease from healthy states. We identified close to 10,000 unique phosphopeptides in EVs by isolating from small volume of plasma samples. Using label-free quantitative phosphoproteomics, we identified 144 phosphoproteins in plasma EVs that are significantly higher in patients diagnosed with breast cancer than in healthy controls. Several novel biomarkers were validated in individual patients using Paralleled Reaction Monitoring for targeted quantitation. Similarly a group of glycoproteins in plasma EVs are identified. The study demonstrated that the development of phosphoproteins and / or glycoproteins in plasma EV as disease biomarkers is highly feasible and may transform cancer screening and monitoring.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
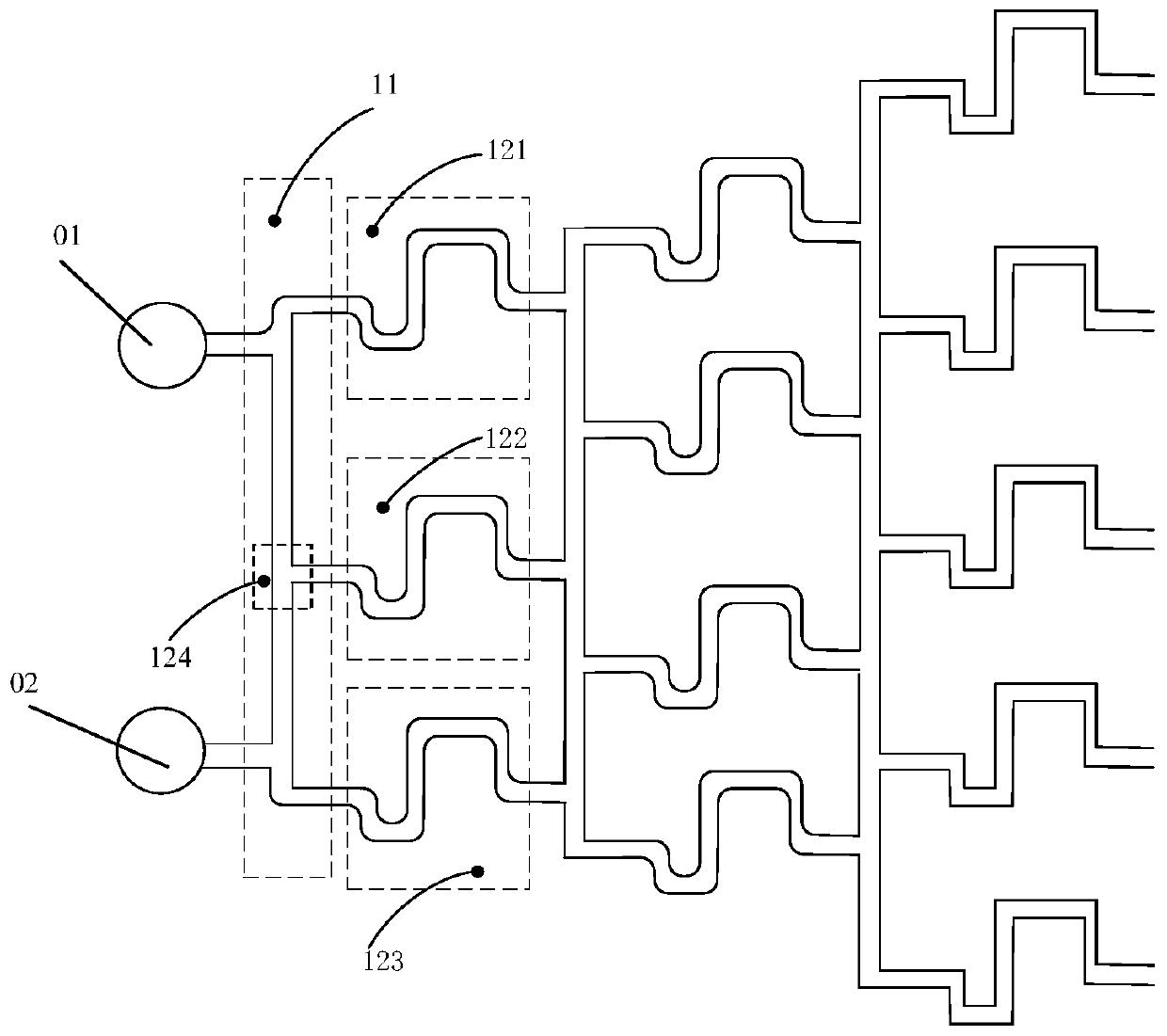
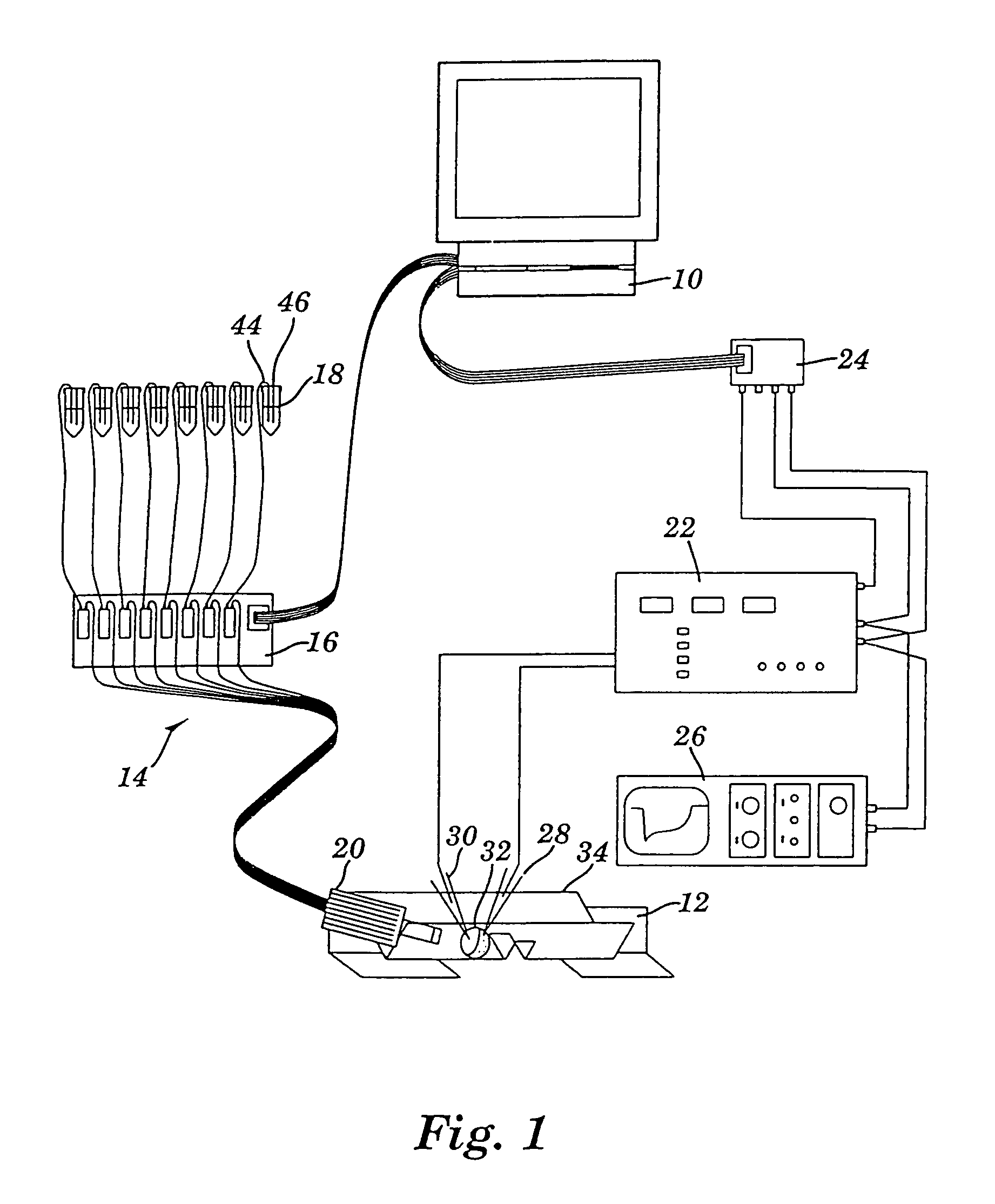
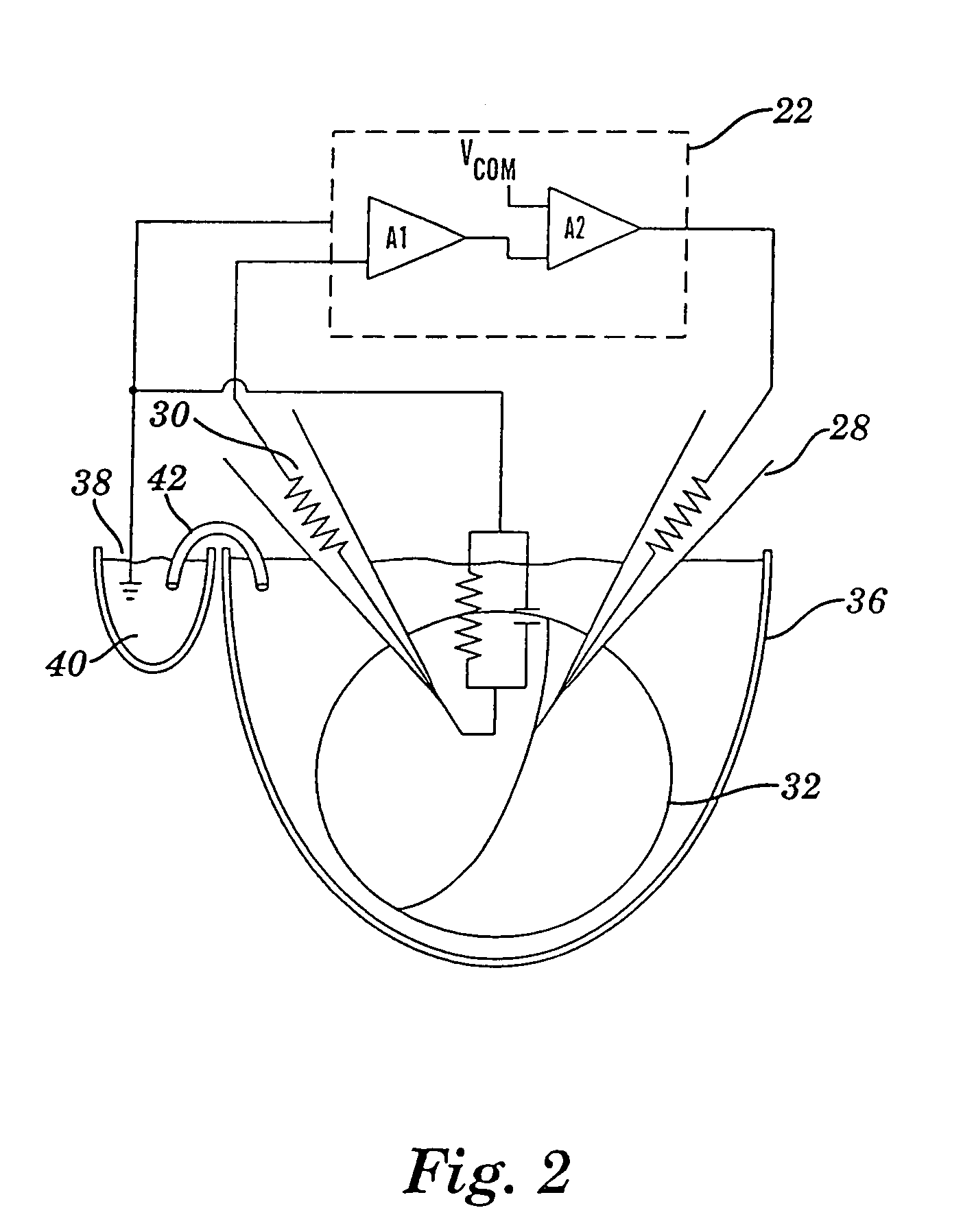
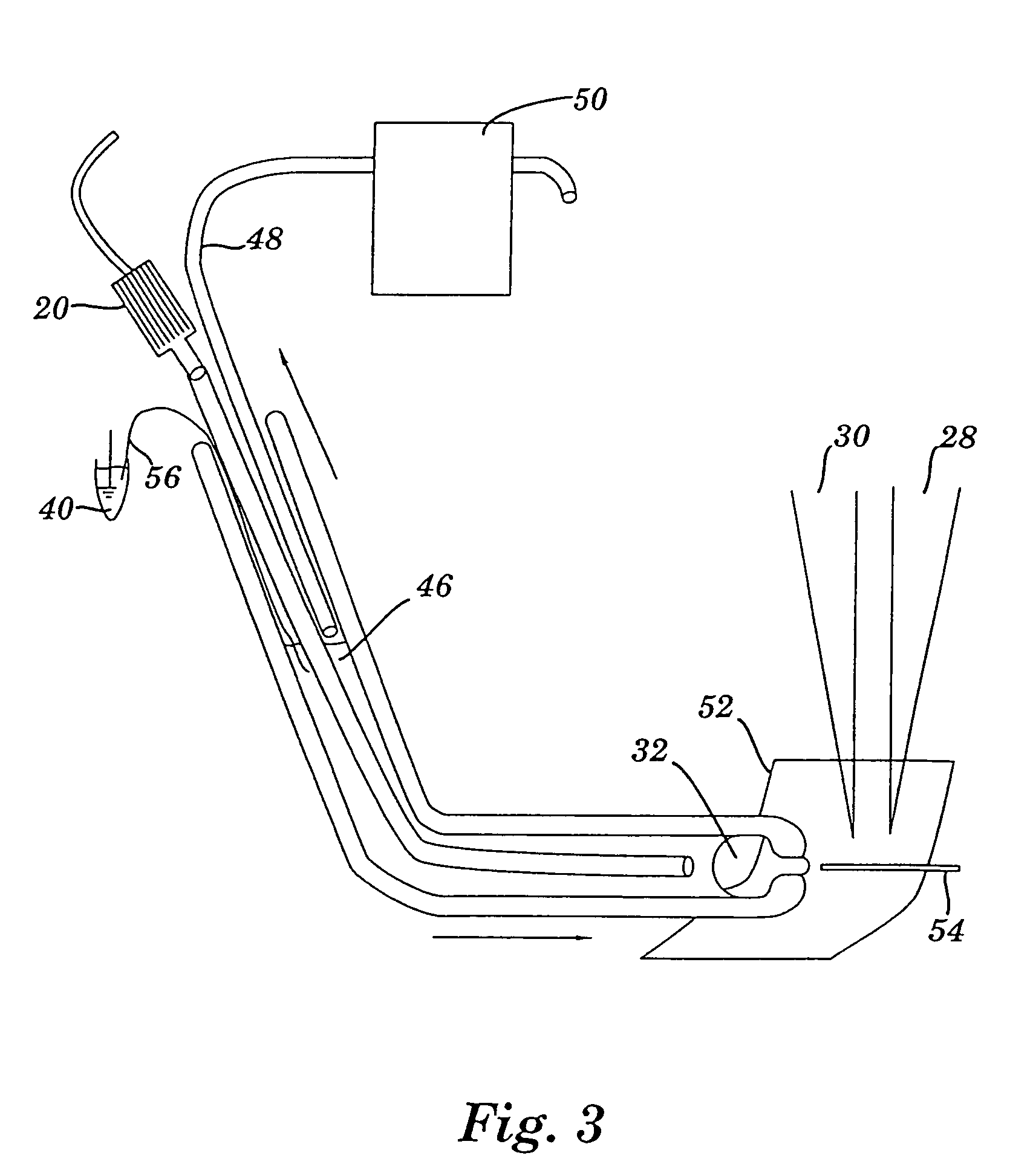
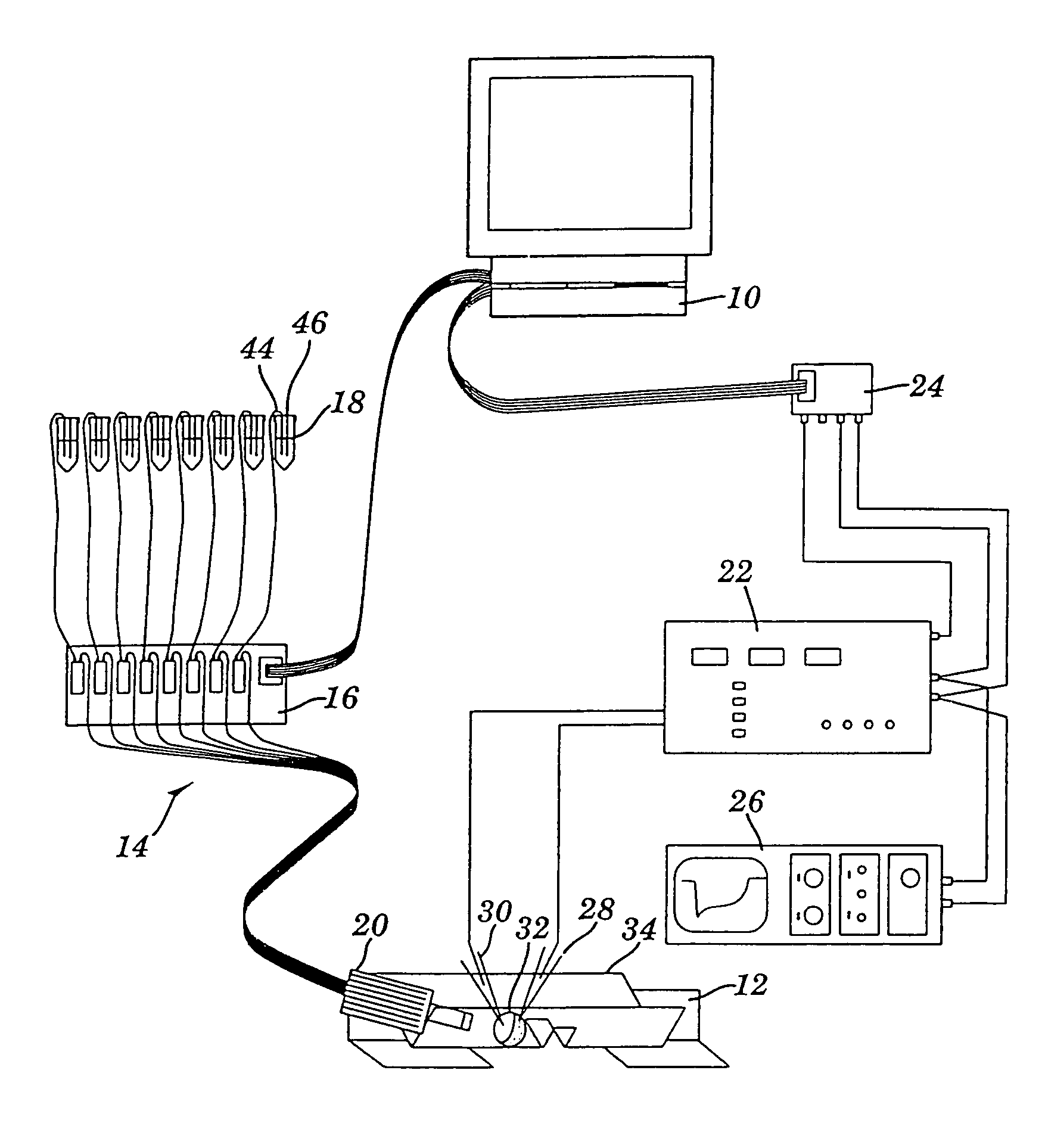
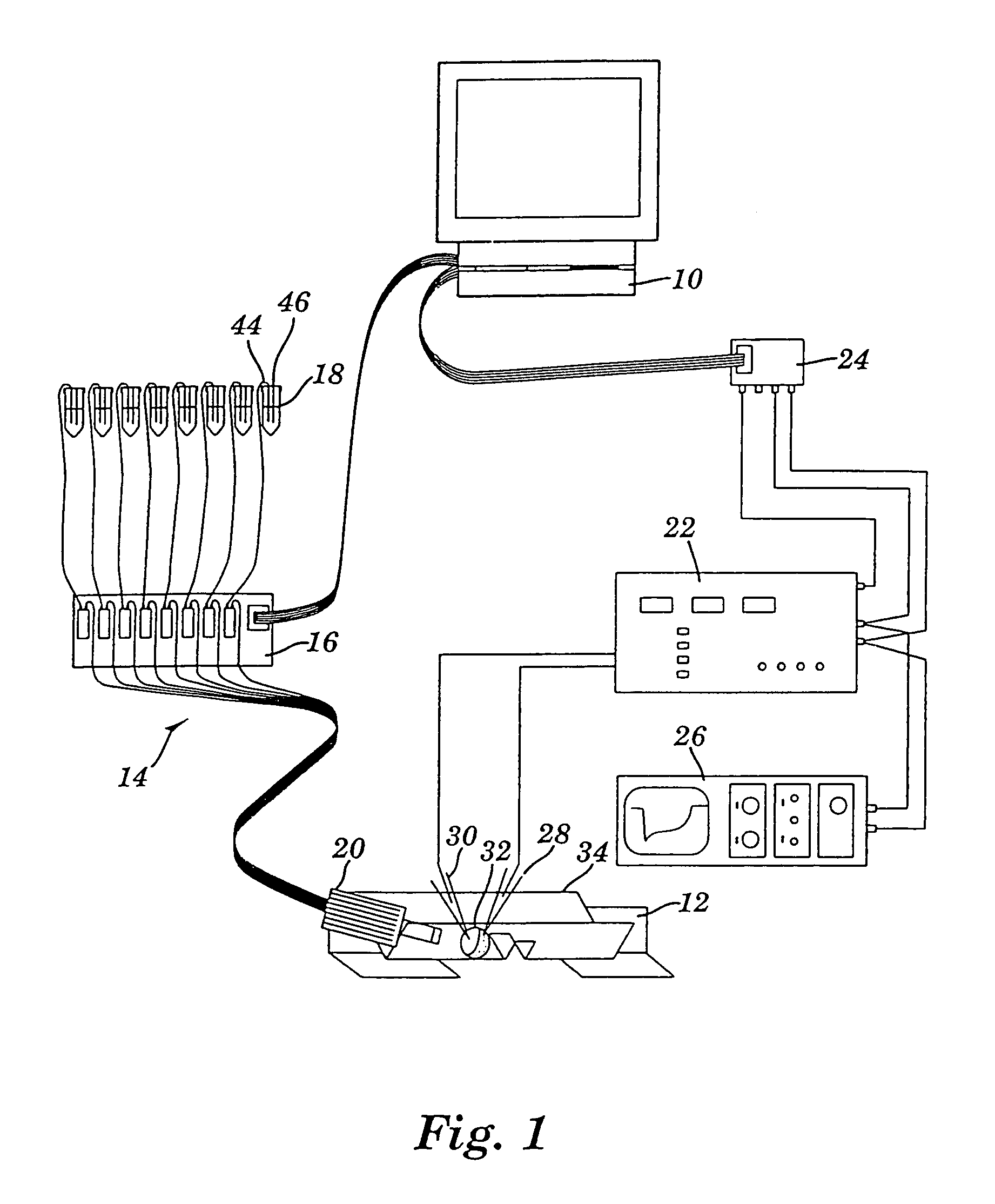
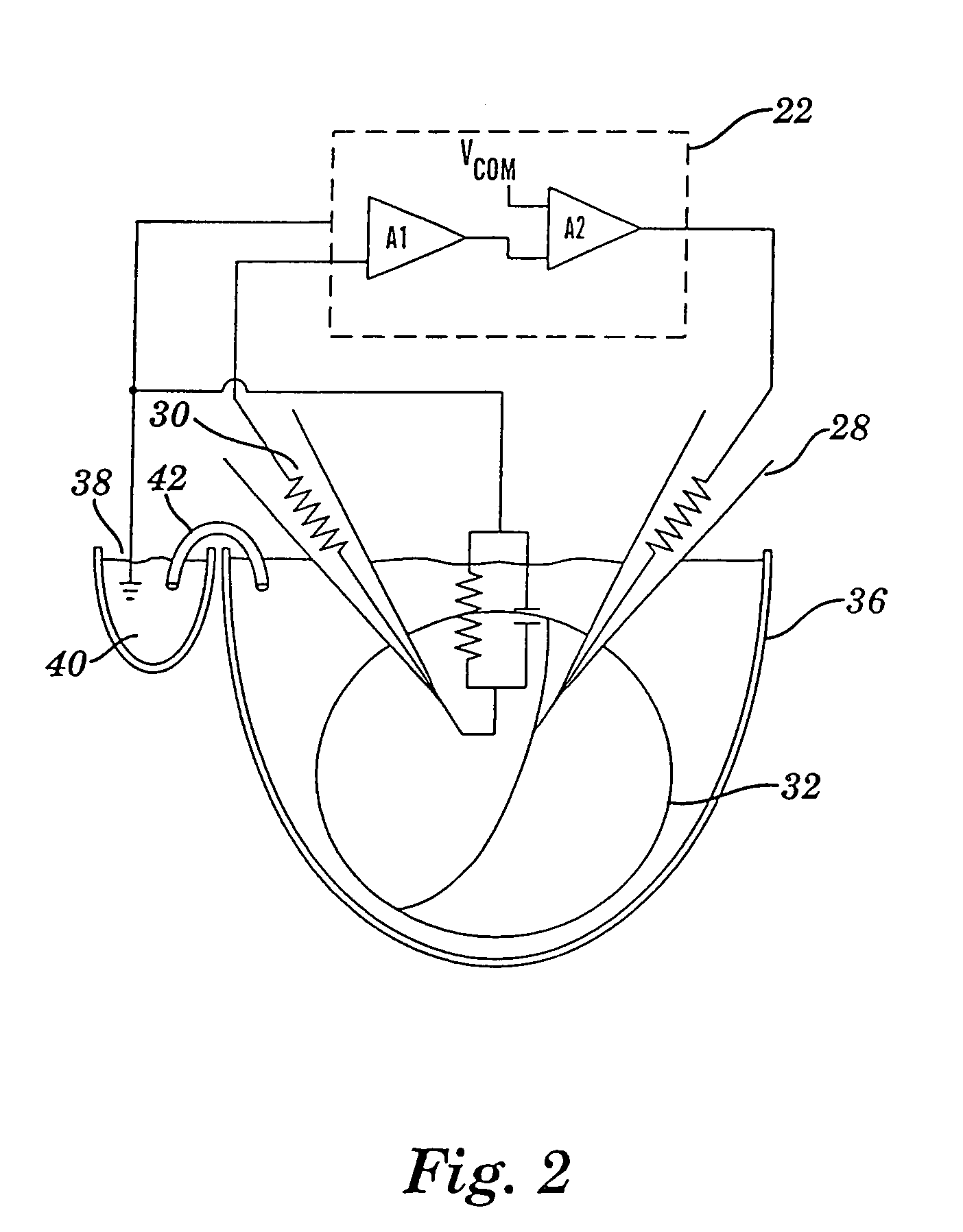
Apparatus for detecting and recording cellular responses
InactiveUS7799539B2Easy to adaptBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsData acquisitionWorkstation
Cellular physiology workstations for automated data acquisition and perfusion control are described. The cellular physiology workstation may be used for physiological and electrophysiological experiments. Methods for employing such cellular physiology workstations in physiological and electrophysiological experiments are also disclosed. The cellular physiology workstations comprise one or more recording chambers each for holding one or more cells to be measured. One or more cells are place in each recording chamber. Perfusions means, such as an automatic perfusion system is connected to the recording chamber to perfuse the cells with a plurality of solutions containing different concentration of one or more agents to be tested. Biosensors, such as patch clamps, electrodes, or microscopes are positioned to detect a response from the cell. The cellular physiology workstation may optionally comprise injecting means for introducing an injection solution into the cell before and during analysis.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
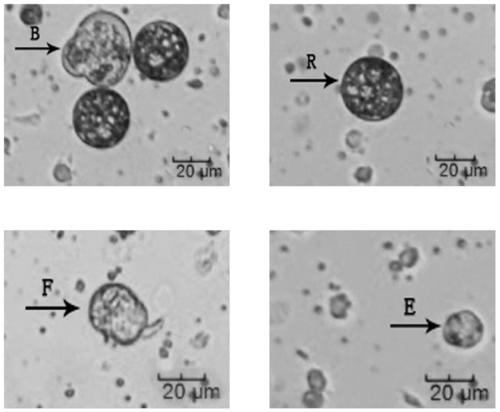
A method for the isolation and primary culture of Chinese mitten crab hepatopancreatic cells
ActiveCN106635956BCultivate stableCell dissociation methodsPancreatic cellsPenicillinPancreatic A Cells
The invention relates to an Eriocheir hepatopancreas cell separation and primary culture method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) cleaning Eriocheir pancreatic tissues with cell separation liquid, cutting the cleaned Eriocheir pancreatic tissues to tissue blocks of 1mm<2> with a shear, adding a proper quantity of tissue blocks into the separation liquid, blowing and filtering with a suction tube, and centrifuging the filtrate to obtain yellow precipitate; (2) adding the yellow precipitate into a culture medium containing 100UI / ml penicillin and 100mug / ml streptomycin, blowing uniformly, inoculating into a culture plate, and culturing in a CO2 cell incubator. By adopting the method, Eriocheir hepatopancreas cells can be stably cultured till the survival rate with 72 hours is higher than 50 percent, a theoretical basis is laid for building of a subsequent cell line, and a cell tool is provided for researches in relevant fields of cell physiology, gene engineering and the like.
Owner:XICHANG COLLEGE
Preparation having functions of tinnitus treatment and ear health care as well as preparation method thereof
PendingCN108939078AReduce doseToxic and side effectsSenses disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntioxidantNose
The invention belongs to the technical field of treatment of ear diseases in ear, nose and throat departments and ear health care, and particularly relates to a preparation having functions of tinnitus treatment and ear health care as well as a preparation method thereof. The preparation having the functions of tinnitus treatment and ear health care is prepared by refining a biological tinnitus relief agent, a cell physiology function regulator, a cell protecting agent, a cell agonist, a blood activation and channel dredging agent, an intelligence strengthening agent, an antioxidant, a cell normal growth metabolism required agent and an auxiliary through a mild environmental-protection process. The preparation has the functions and effects of activating blood and dredging channels, dispelling the wind and inducing resuscitation, removing necrosis and promoting granulation, resisting inflammation and aging, inhibiting bacteria and relieving itching, nourishing neurovascular of ears andbrain and muscles and improving auditory nerve conduction capabilities. Compared with a conventional tinnitus treatment agent, the preparation disclosed by the invention has the advantages that tinnitus can be treated, and the preparation also can be used as an ear health-care product of ordinary people, and can be used for conditioning or recovering the neurovascular of ears and brain and musclecells; the preparation has the function of drugs and also has the security of health-care food and cosmetics. The preparation is convenient to use and has a good effect.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU LANCI BIOENG CO LTD
Cellular physiology workstations for automated data acquisition and perfusion control
InactiveUS20080227187A1Desirable effectEasy to adaptBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsData acquisitionWorkstation
Cellular physiology workstations for automated data acquisition and perfusion control are described. The cellular physiology workstation may be used for physiological and electrophysiological experiments. Methods for employing such cellular physiology workstations in physiological and electrophysiological experiments are also disclosed. The cellular physiology workstations comprise one or more recording chambers each for holding one or more cells to be measured. One or more cells are place in each recording chamber. Perfusions means, such as an automatic perfusion system is connected to the recording chamber to perfuse the cells with a plurality of solutions containing different concentration of one or more agents to be tested. Biosensors, such as patch clamps, electrodes, or microscopes are positioned to detect a response from the cell. The cellular physiology workstation may optionally comprise injecting means for introducing an injection solution into the cell before and during analysis.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Biochloride Generation and Methods
InactiveUS20190381094A1Enhance zeta potentialMaintain efficiencyChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentMetaboliteReprogramming
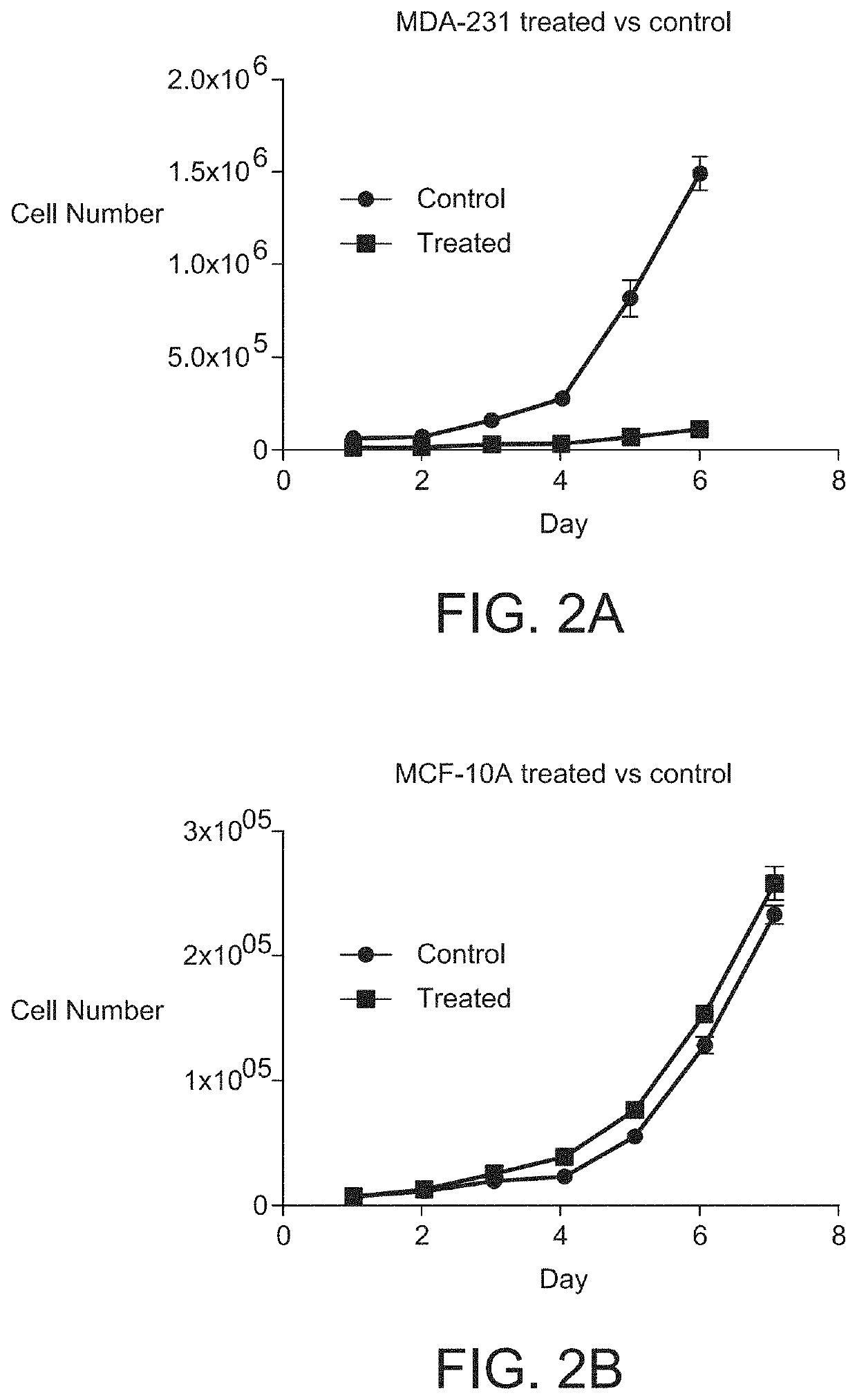
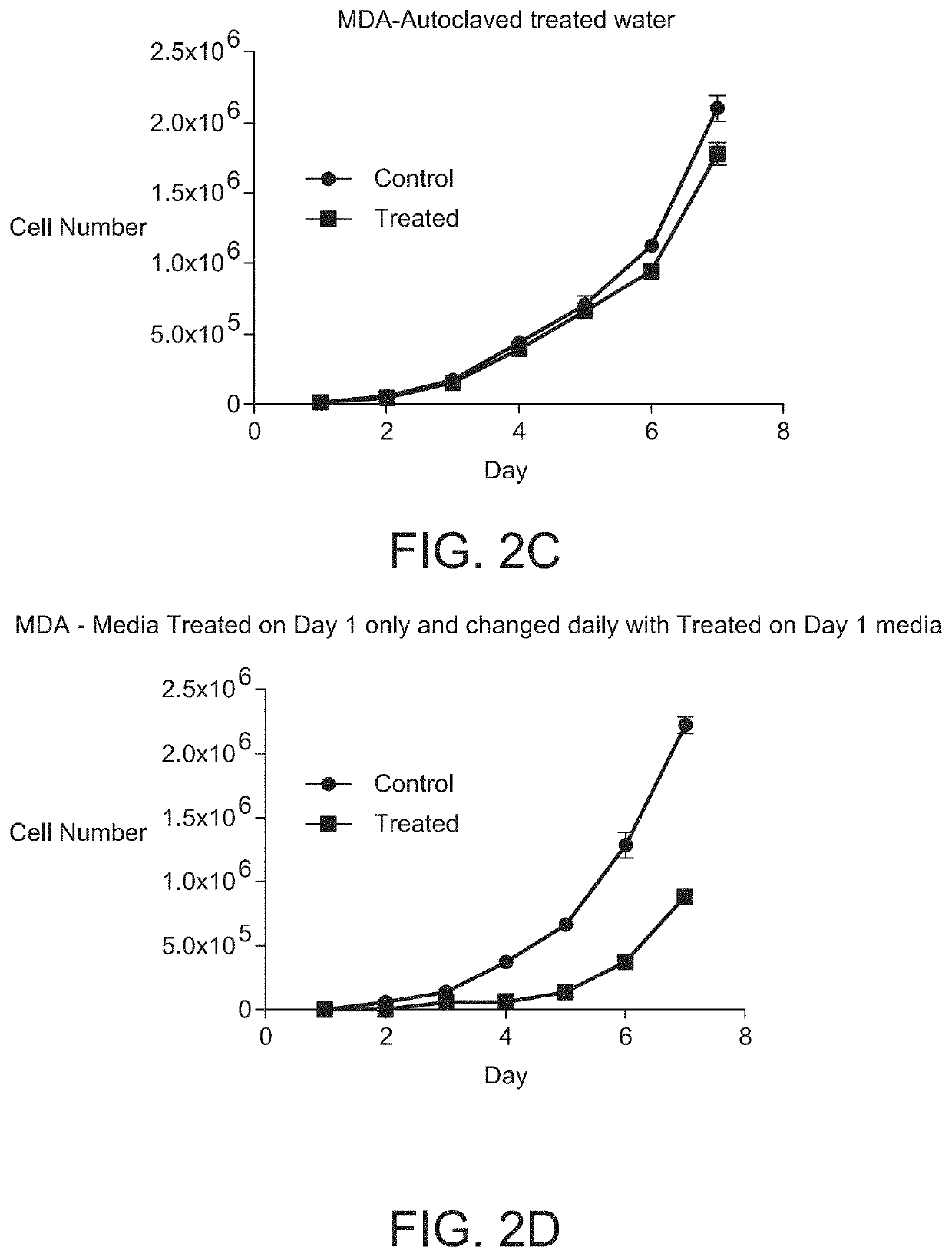
The method of enhancing diamagnetic anisotropy in cell membranes that occur under the influence of disassociated polymorphic bCl− comprising changes in chloride ion channel expression and cell physiology. Direct current from a device generates an electromagnetic field in a 3 hypotonic saline solution leading to a dielectrophoretic disassociation of the chloride ion from its chloro-metabolites transforming it into a polymorphic diamagnetically disassociated bio-chloride (bCl−). This field treated aqueous solution induces a magnetic moment change in solution for some hours when no longer under the influence of the direct current; for when this field influenced solution is used to reconstitute growth media of human breast carcinoma (MDA-MB-231) and human breast epithelial (MCF-10A) cells in vitro, significant changes in chloride ion channel expression, membrane potential, cell volume, and a massive transcriptional reprogramming of 2,468 genes expressions by Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Gene Chip Array (Affymetrix) analyses occur.
Owner:MCP IP
The beauveria bassiana analogue is applied as micromolecular agonist of APC/C
ActiveCN112569341AWide variety of sourcesEasy to expand and cultureCyclic peptide ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseAgonist
The invention discloses an application of a beauveria bassiana analogue as a small molecular agonist of APC / C. The invention discloses the function of activating APC / C of the beauveria bassiana analogue with the natural source as shown in the formula I for the first time, and the beauveria bassiana analogue is a powerful agonist of a late-stage promoter compound (APC / C-Cdh1) or a late-stage promoter compound (APC / C-Cdc20). As a small molecular agonist of APC / C, the compound has important application value in the research fields of cell physiology change caused by APC / C protein activity disorder, targeted activation of APC / C to control cell proliferation disorder diseases and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Application of Beauveriacin Analogs as Small Molecule Agonists of APC/C
ActiveCN112569341BWide variety of sourcesEasy to expand and cultureCyclic peptide ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAgonistProteinoid
The invention discloses the application of a beauverian analogue as a small molecule agonist of APC / C. The present invention discloses for the first time that the natural source beauvericin analog shown in formula I activates the function of APC / C, which is a powerful anaphase-promoting factor complex (APC / C-Cdh1) or anaphase-promoting factor complex (APC / C‑Cdc20). As a small molecule agonist of APC / C, this kind of compound has important application value in the research fields of cell physiological changes caused by APC / C protein activity disorder, targeted activation of APC / C to control cell proliferation disorders and other diseases.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
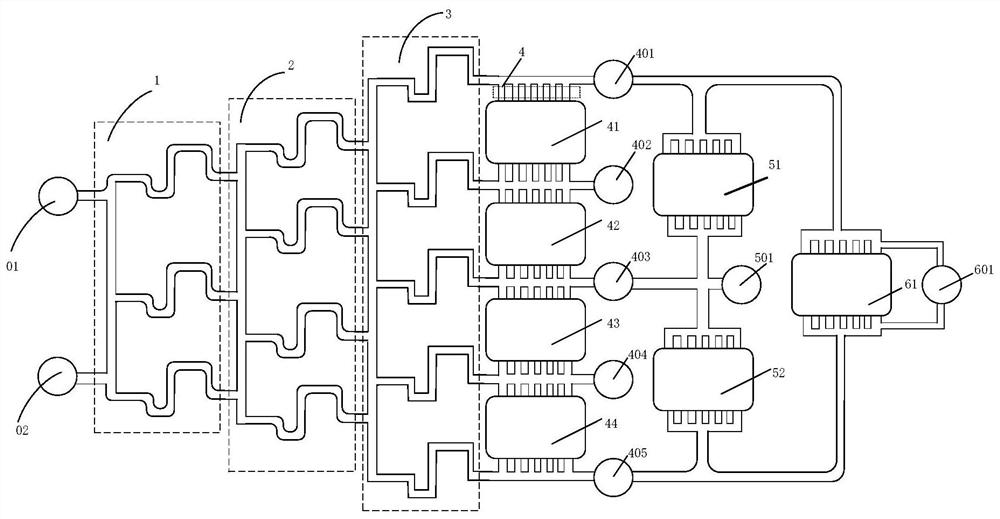
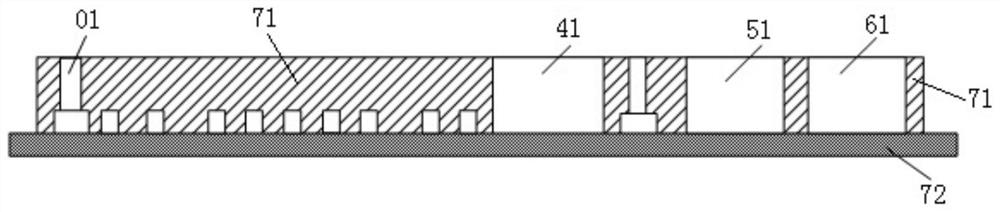
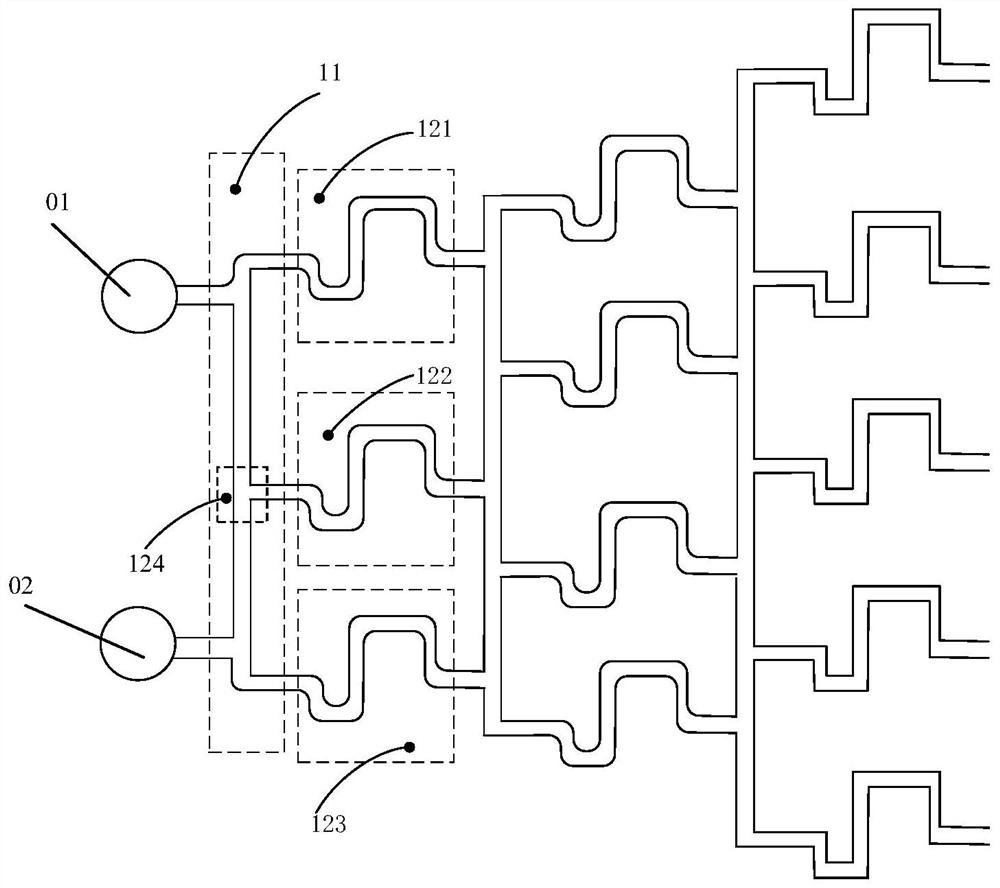
A concentration gradient generating device, preparation and application method for gel 3D cell culture
ActiveCN110586210BReduce volumeLow costMaterial analysis by optical meansLaboratory glasswaresCell behaviour3D cell culture
The invention discloses a concentration gradient generation device for gel 3D cell culture, which includes a multi-stage mixing and concentration gradient generation module, and a gel chamber with a multi-stage concentration gradient range, which can simultaneously load multiple gel samples , and through the application of segmental concentration gradients, the detection and evaluation of cell behavior in gels in different concentration gradient ranges is carried out at the same time; the establishment of multi-level concentration gradient ranges can simultaneously detect cells in different concentrations on the same fluid chip. span samples; the fluid chip provided by the present invention has the advantages of small size, low cost, and good integration performance with microgels, and has broad applications in in vitro tissue reconstruction, cell physiology, pathology, and drug screening, biomedicine, and environmental monitoring. Application prospect; at the same time, the invention also discloses its preparation method and application method.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com