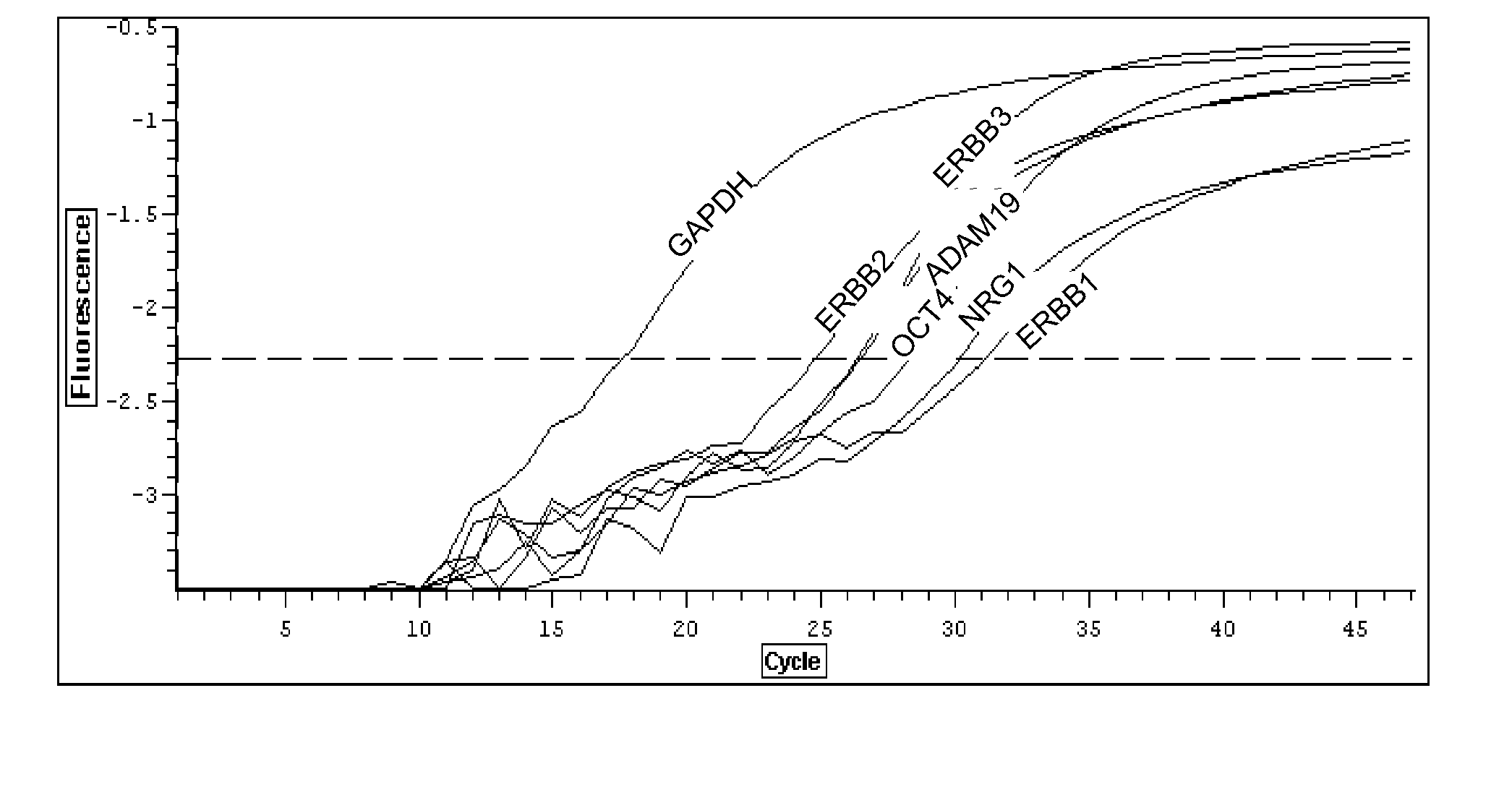
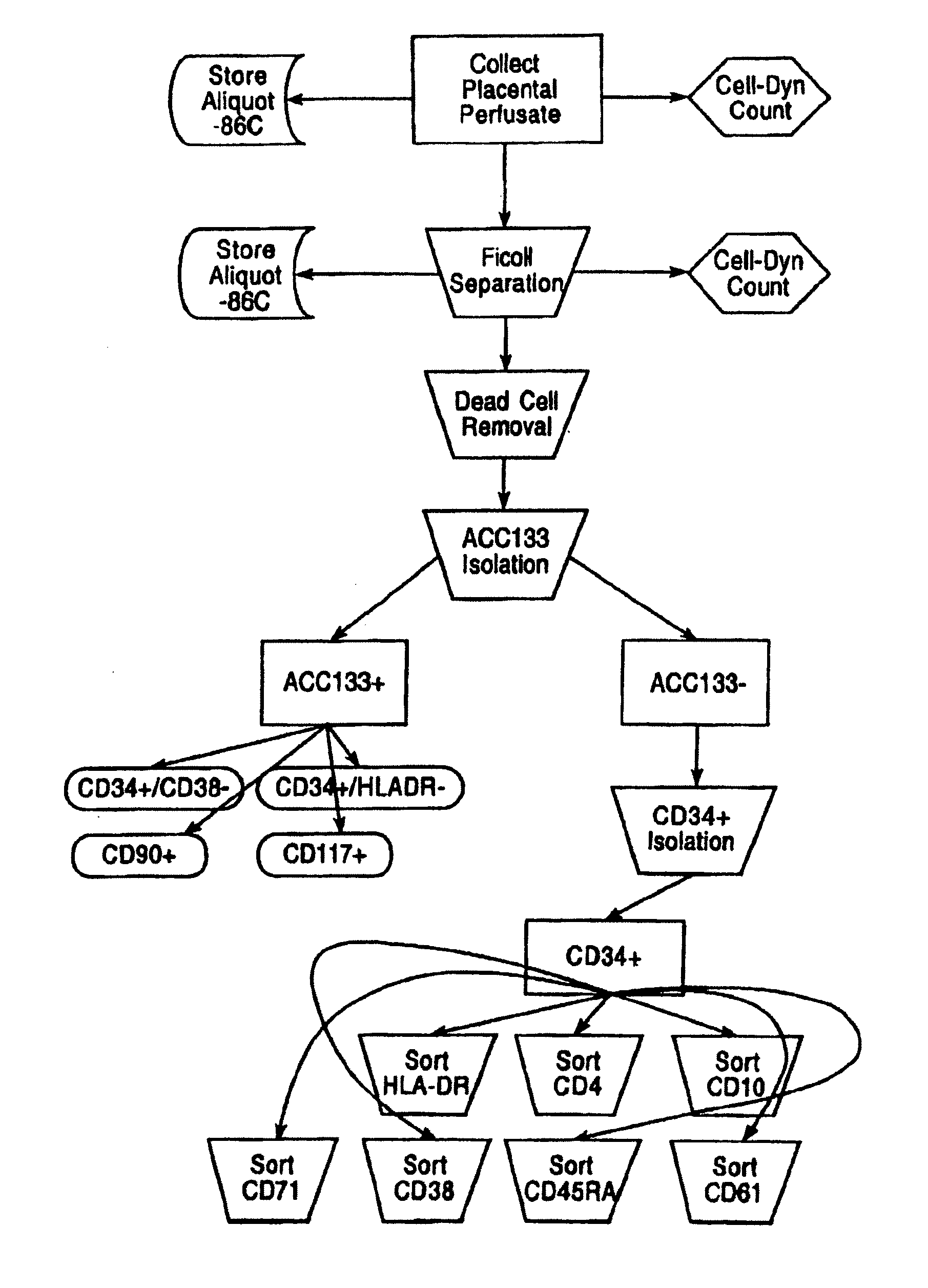
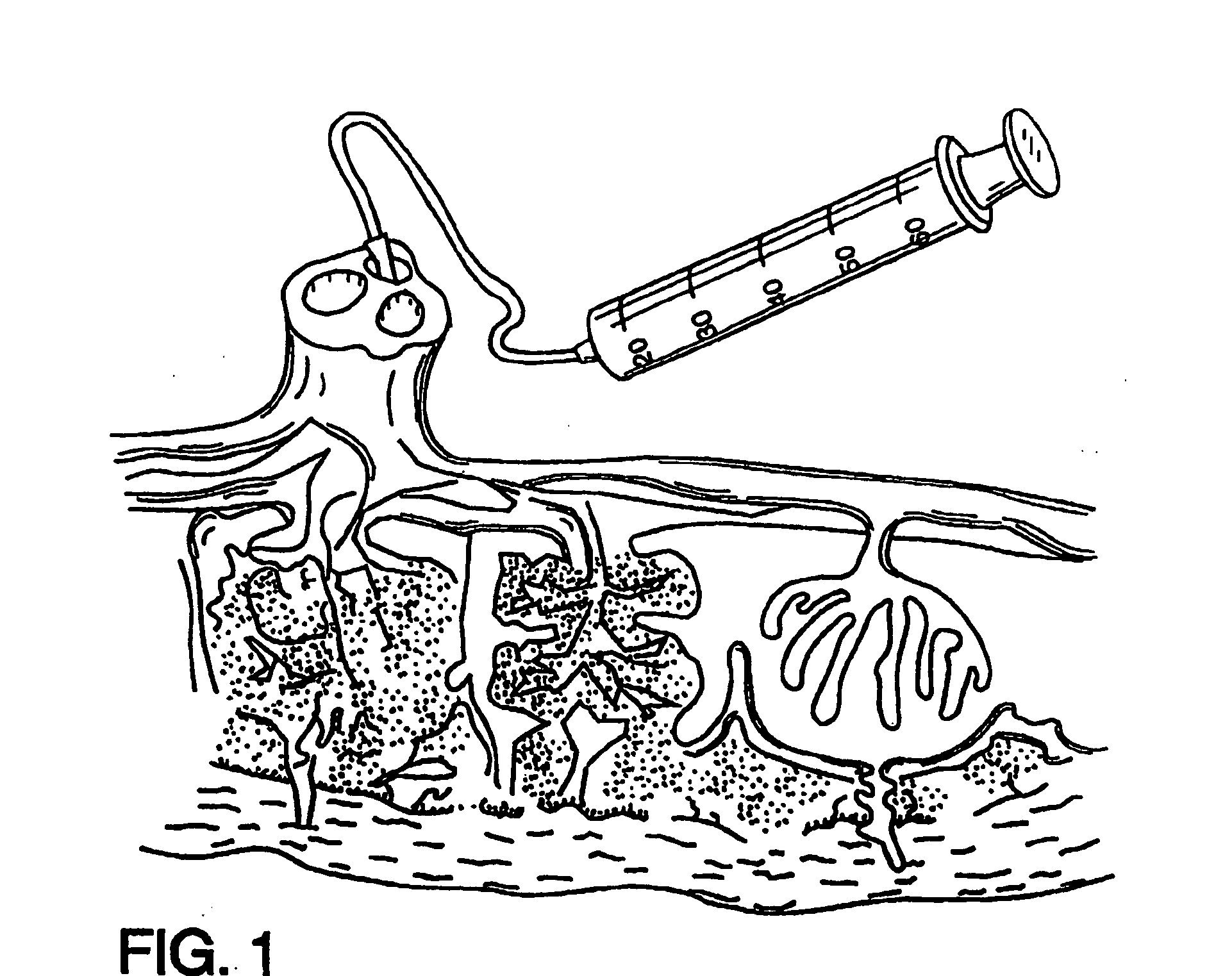Patents
Literature
3770results about "Cell dissociation methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
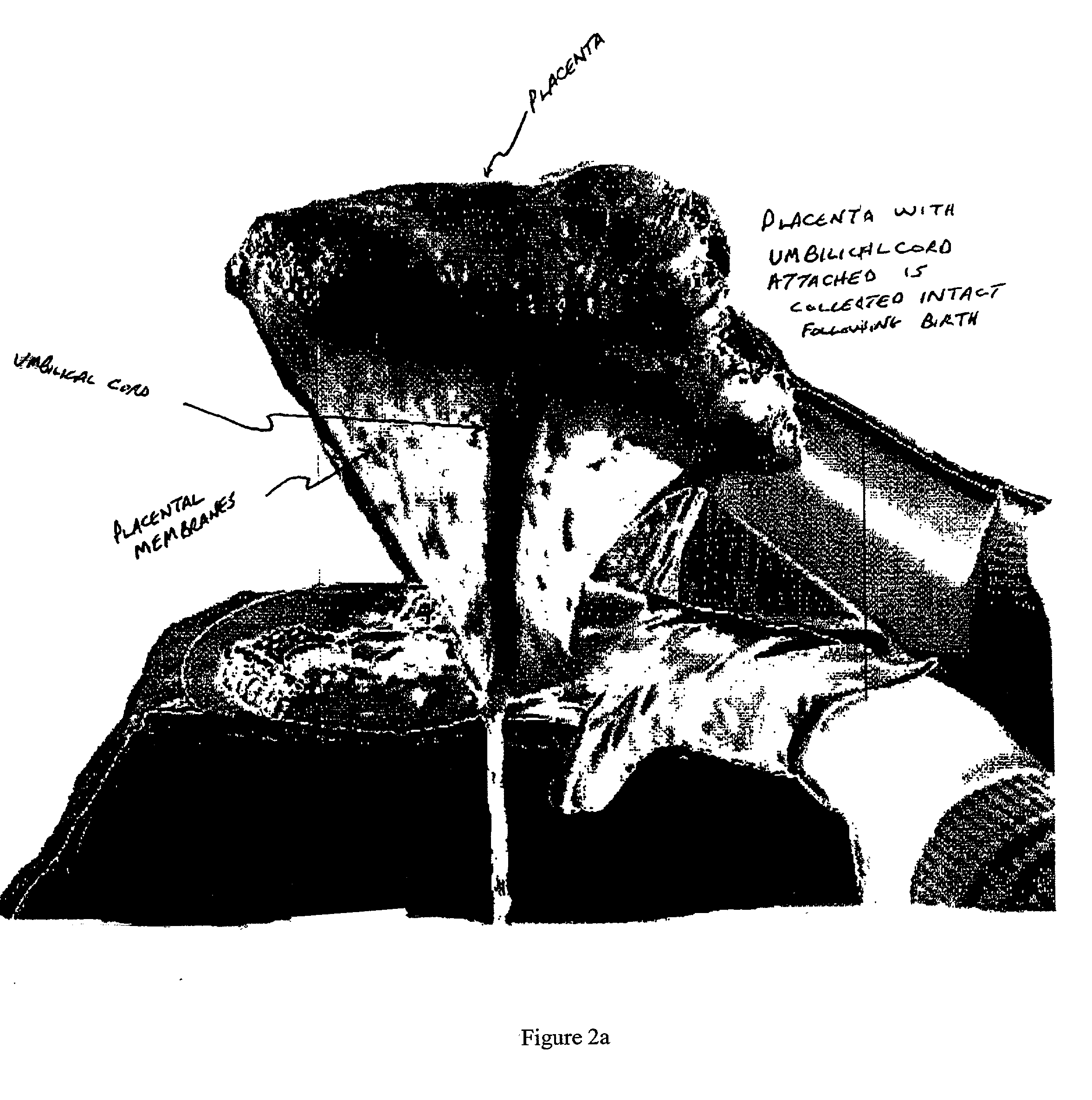
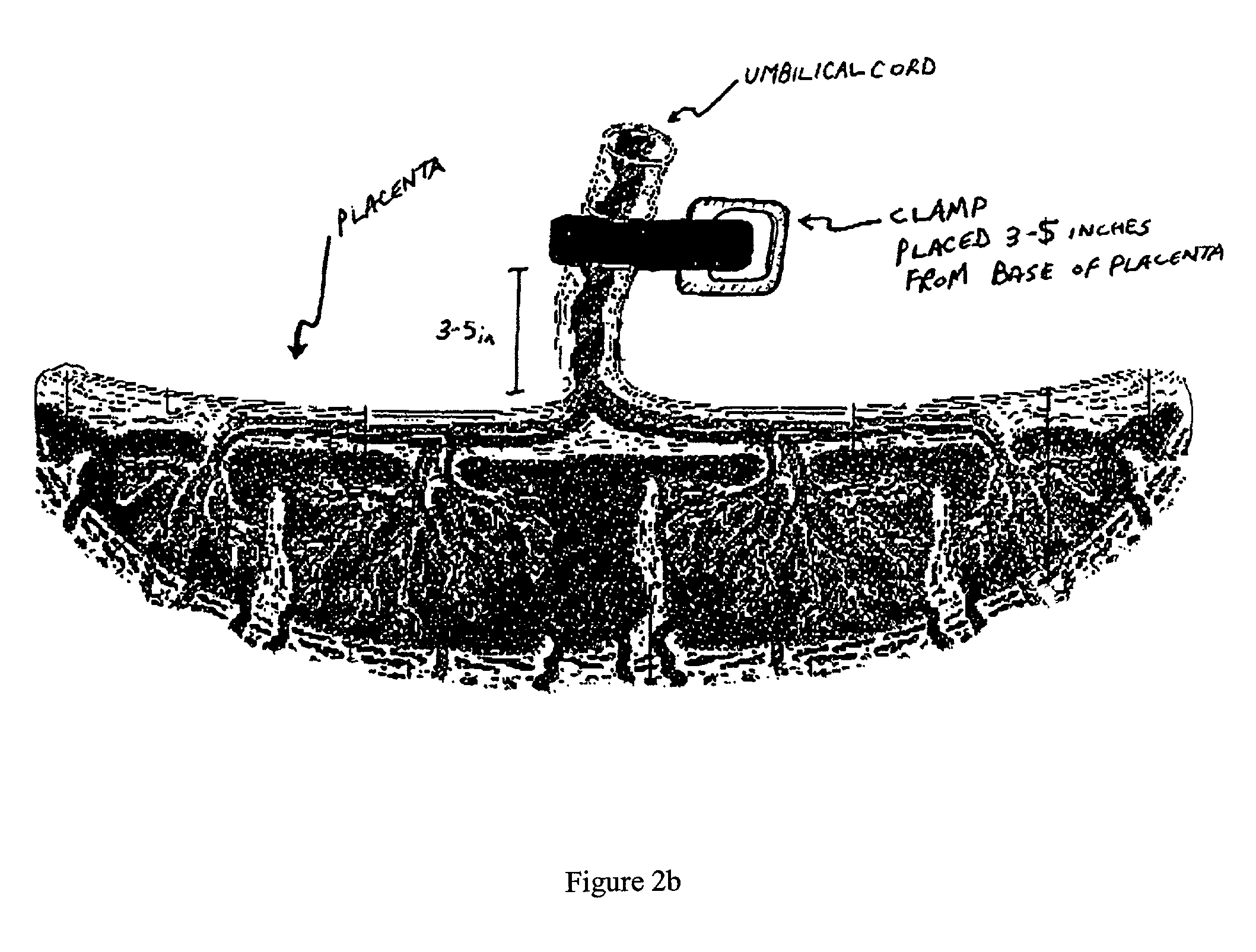
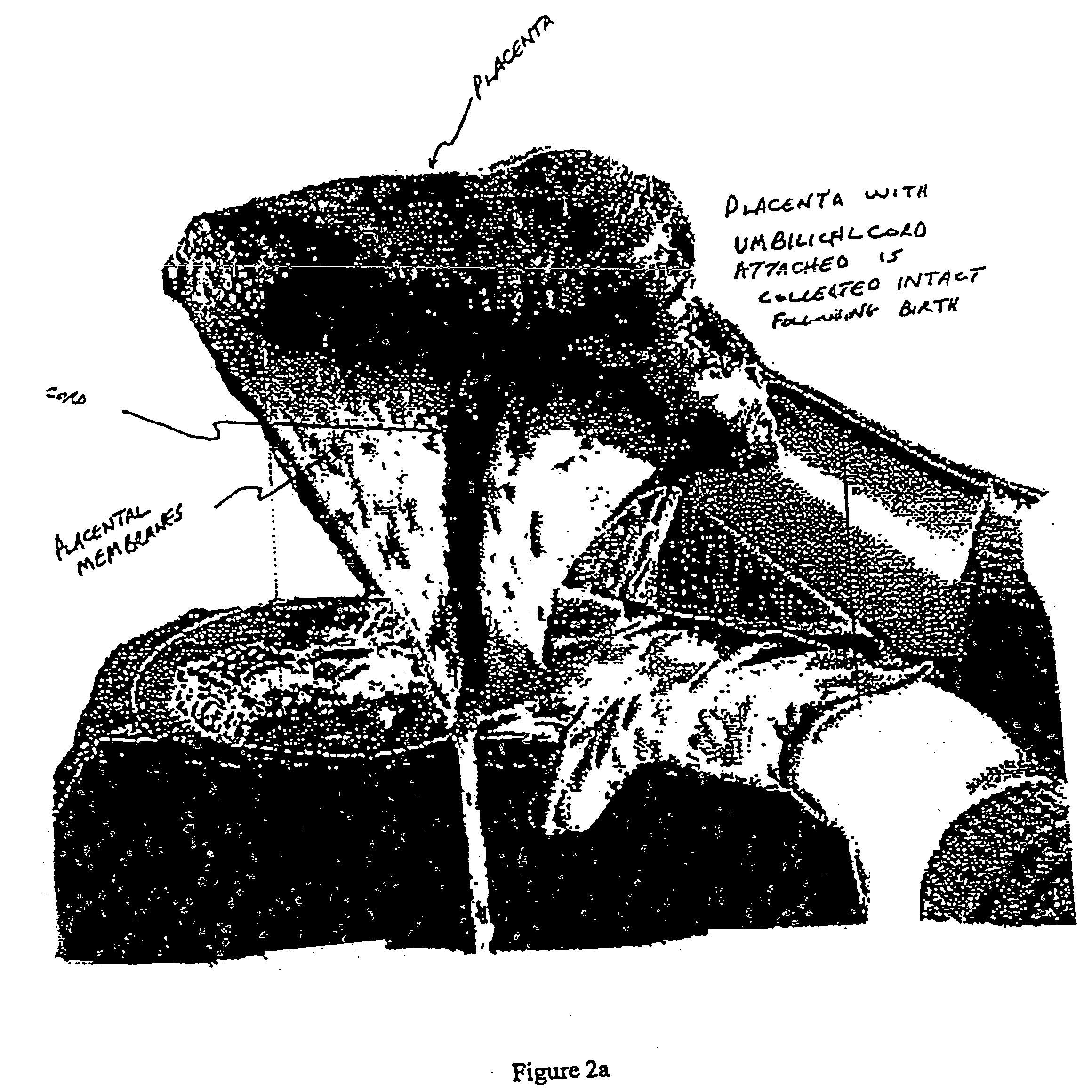
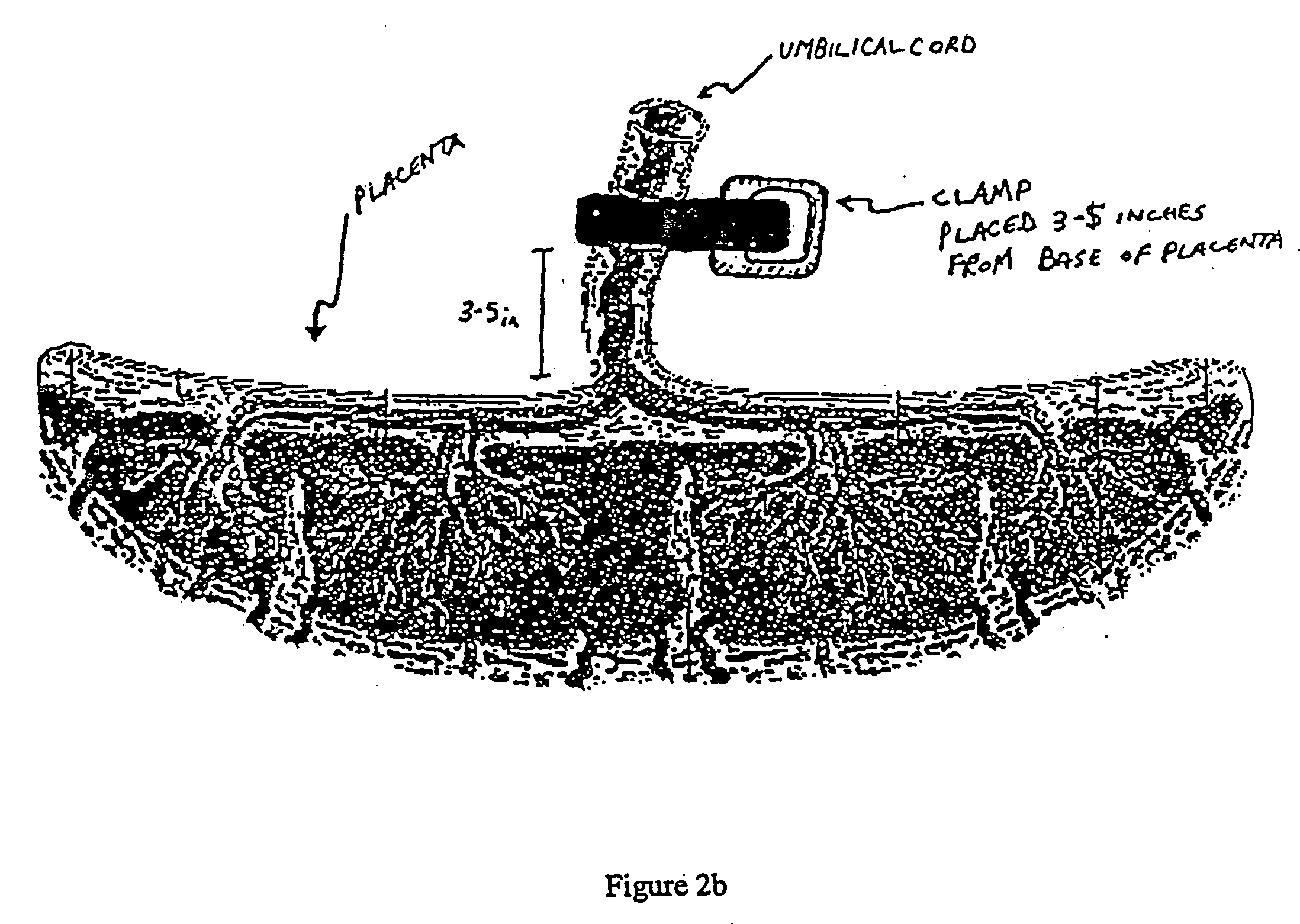
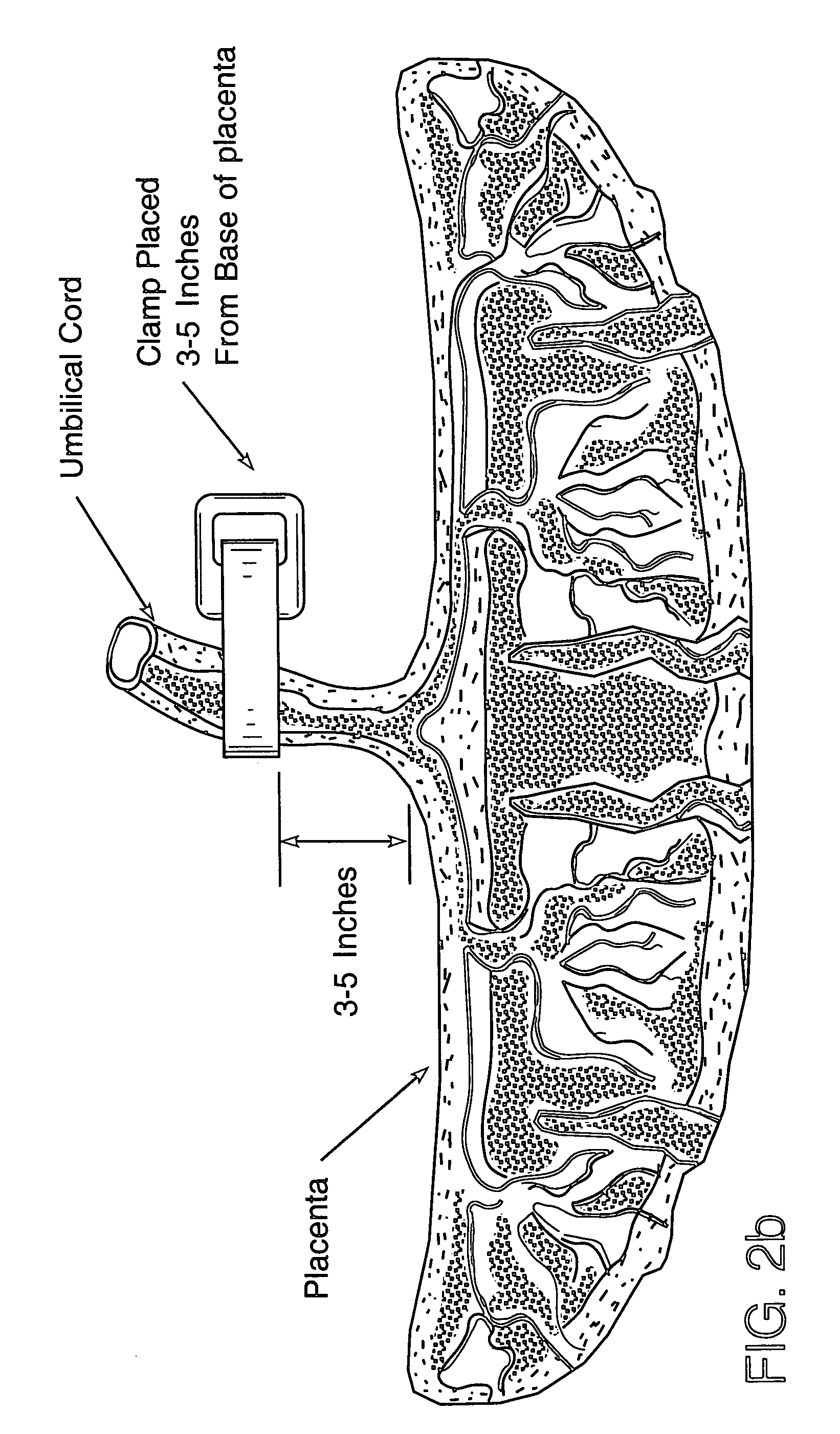
Post-partum mammalian placenta, its use and placental stem cells therefrom
InactiveUS20030032179A1Enhance exsanguinationEnhance sterile conditionSenses disorderAntipyreticAnticoagulant AgentEmbryo
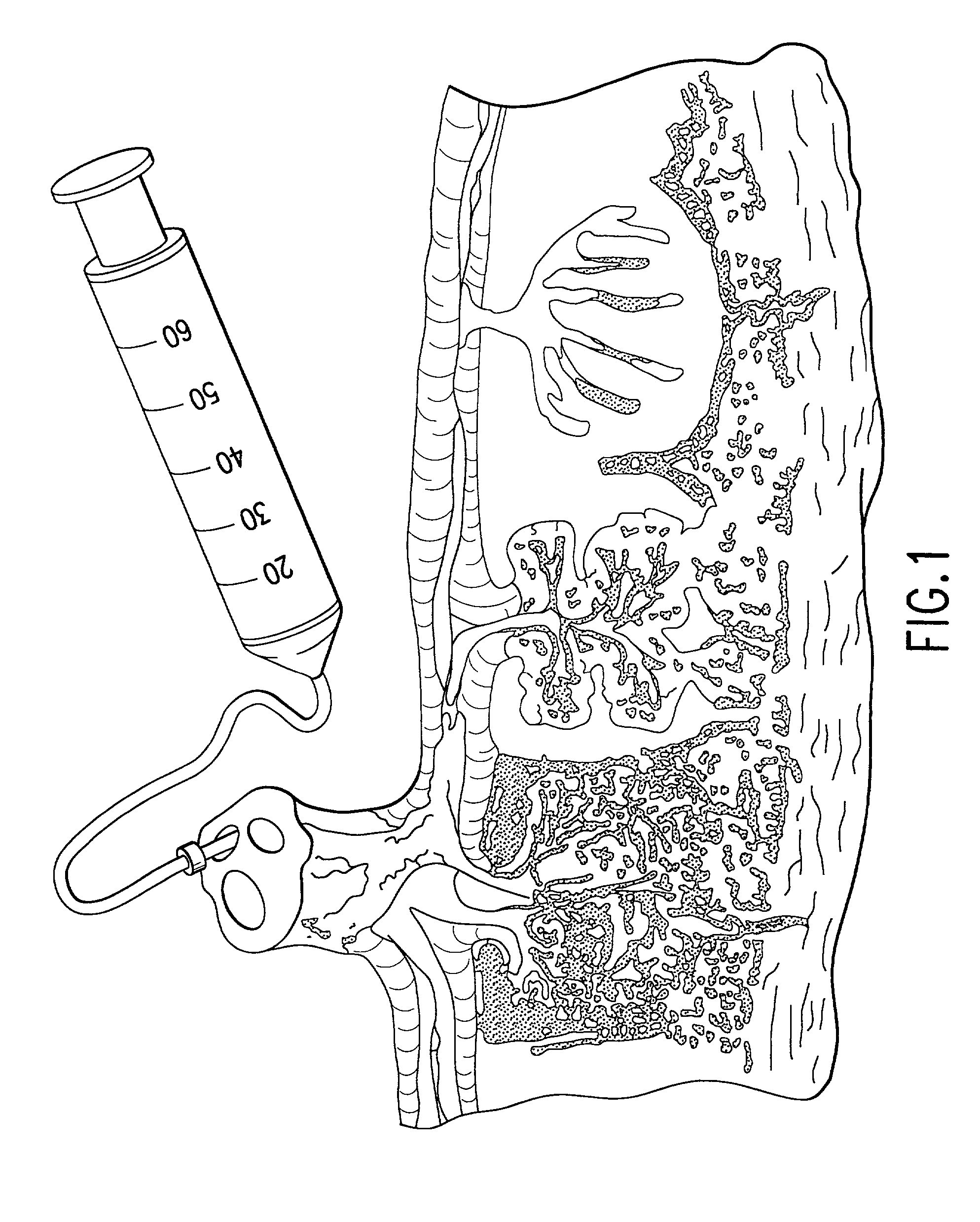
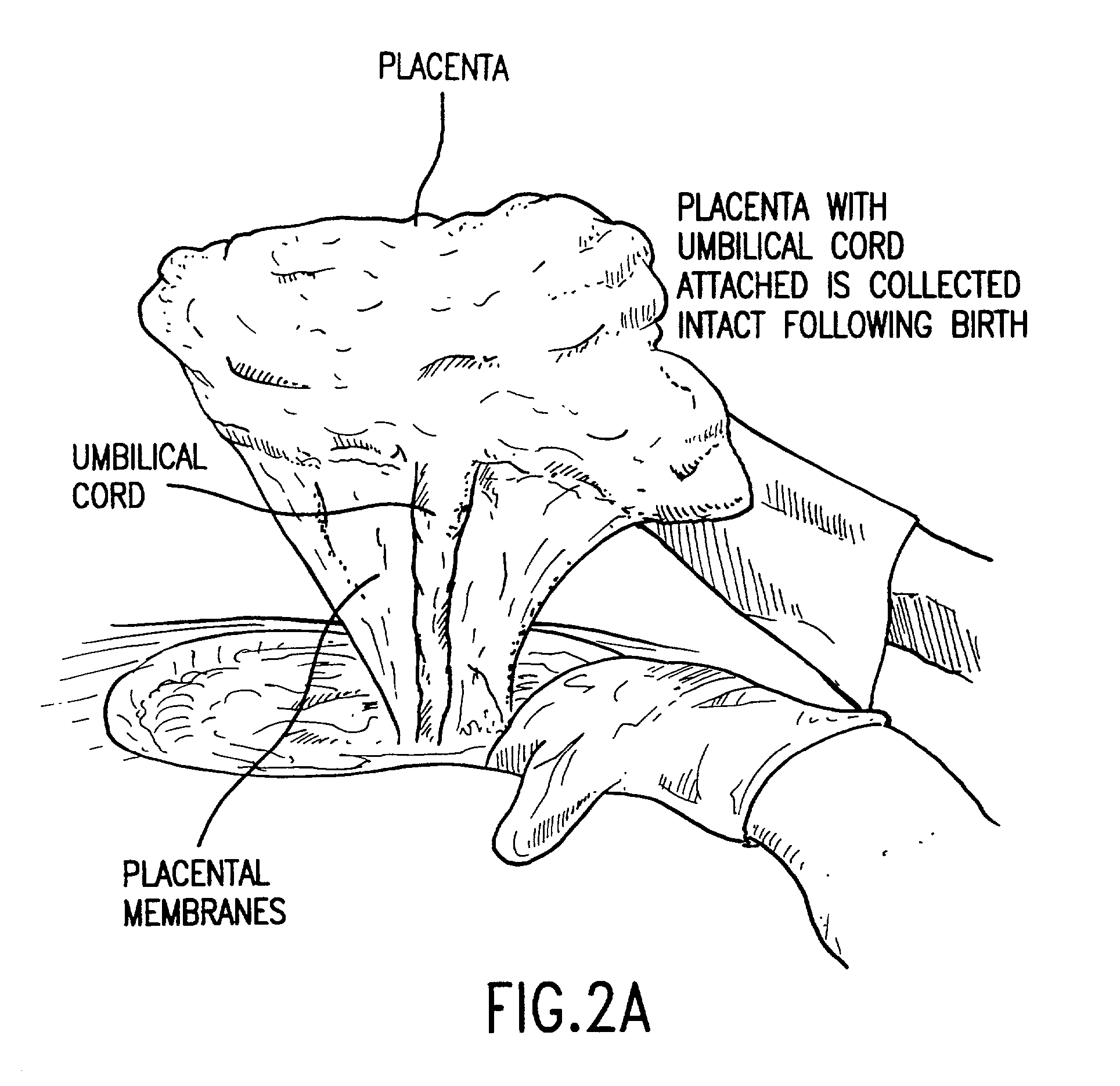
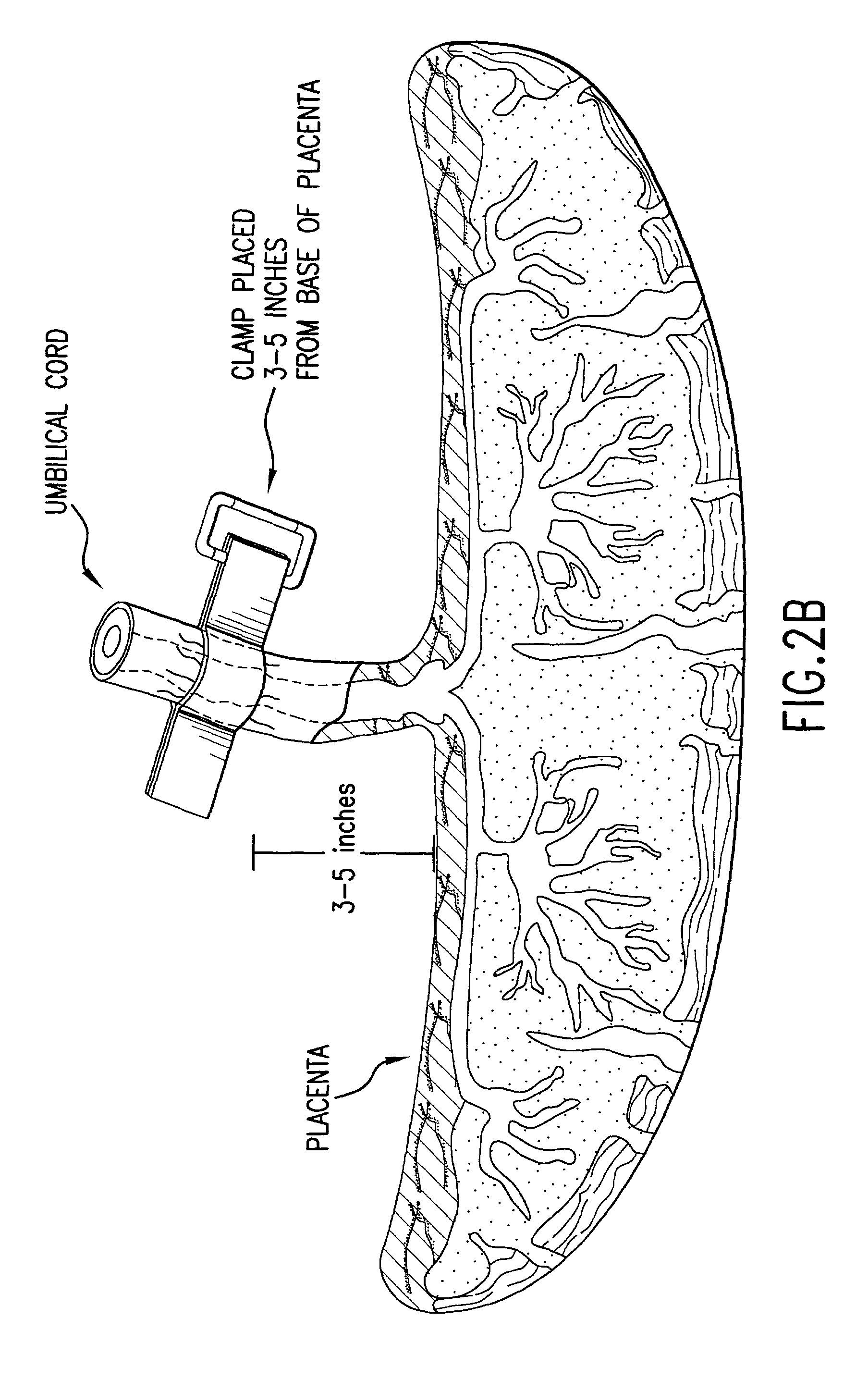
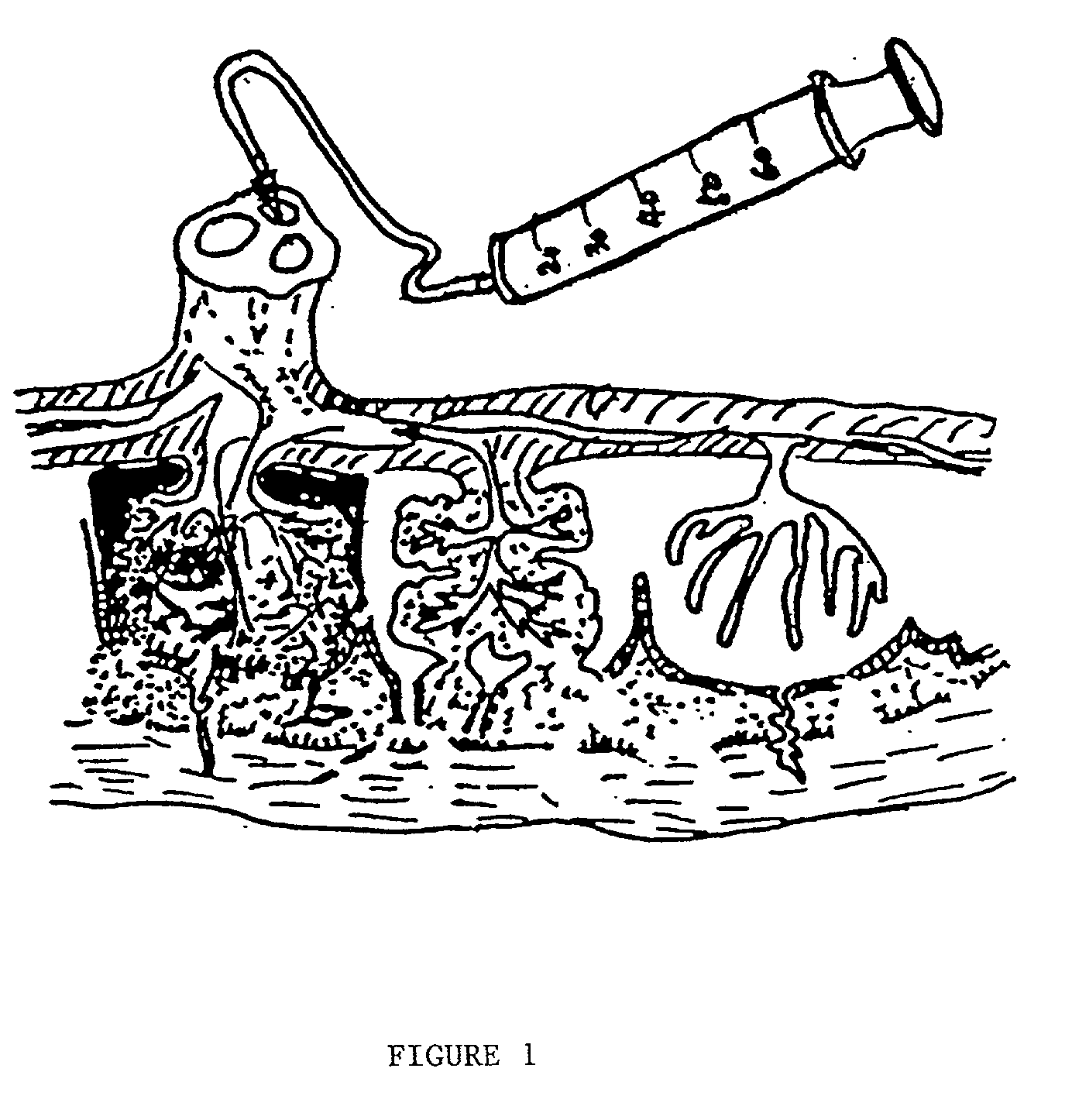
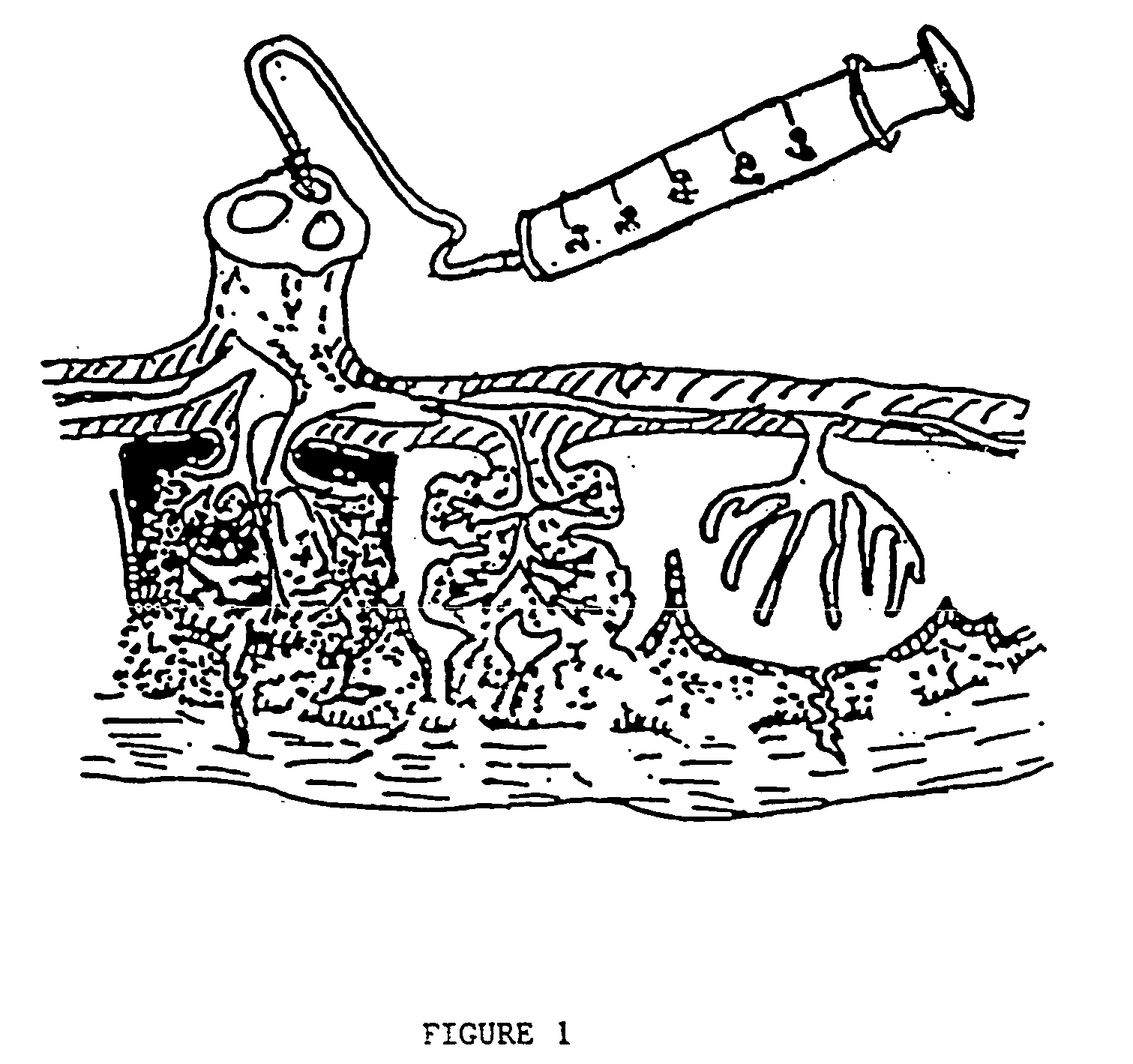
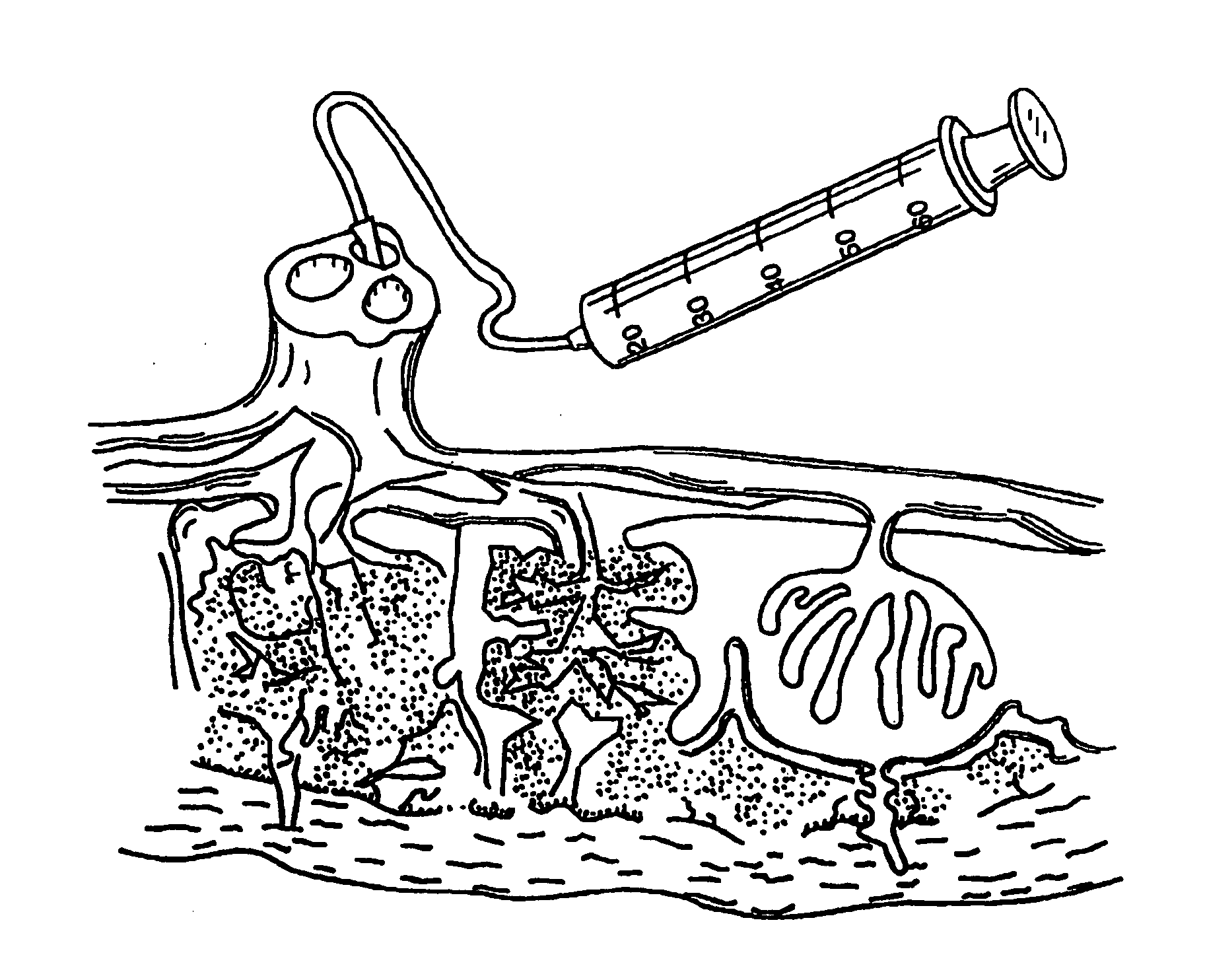
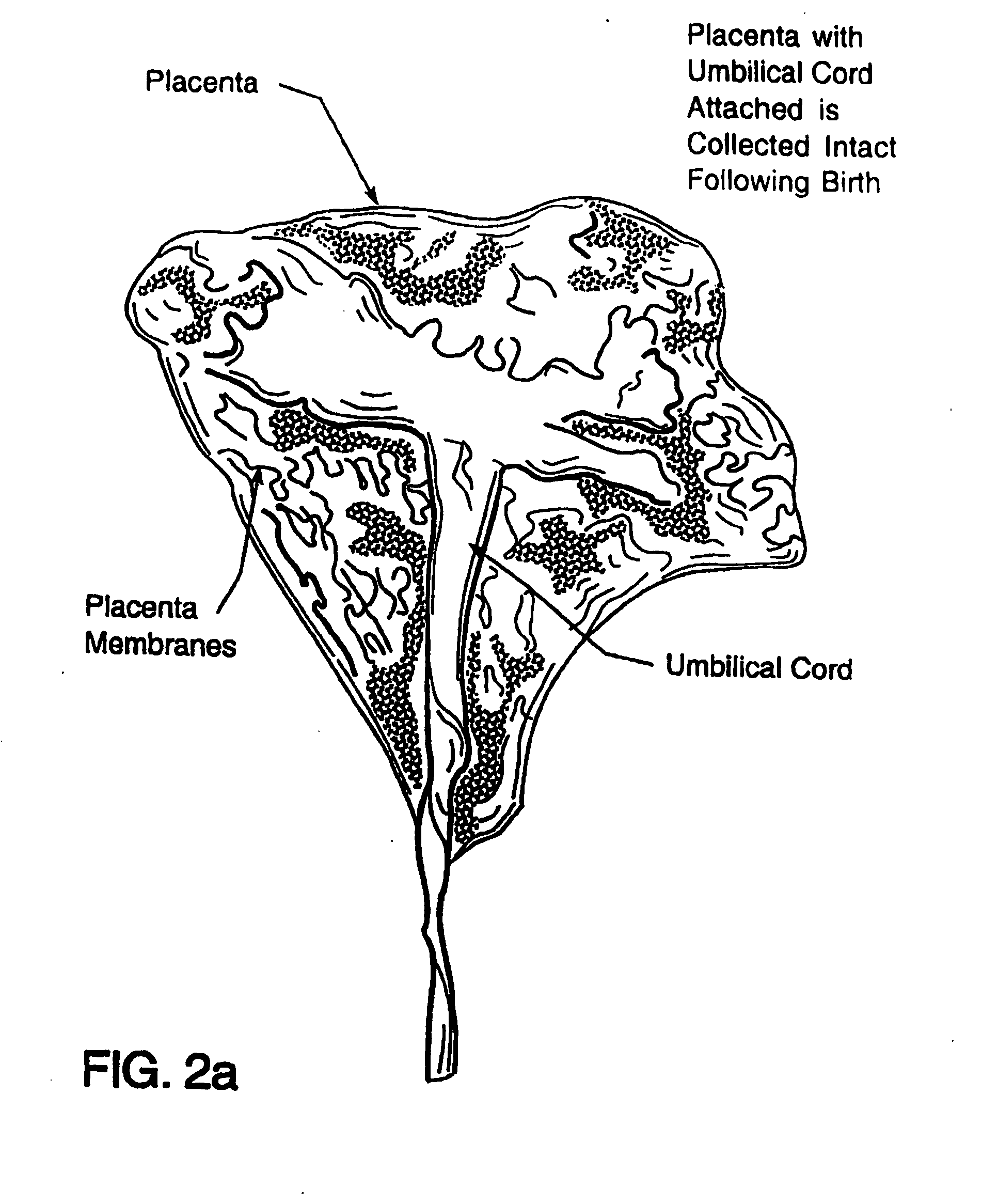
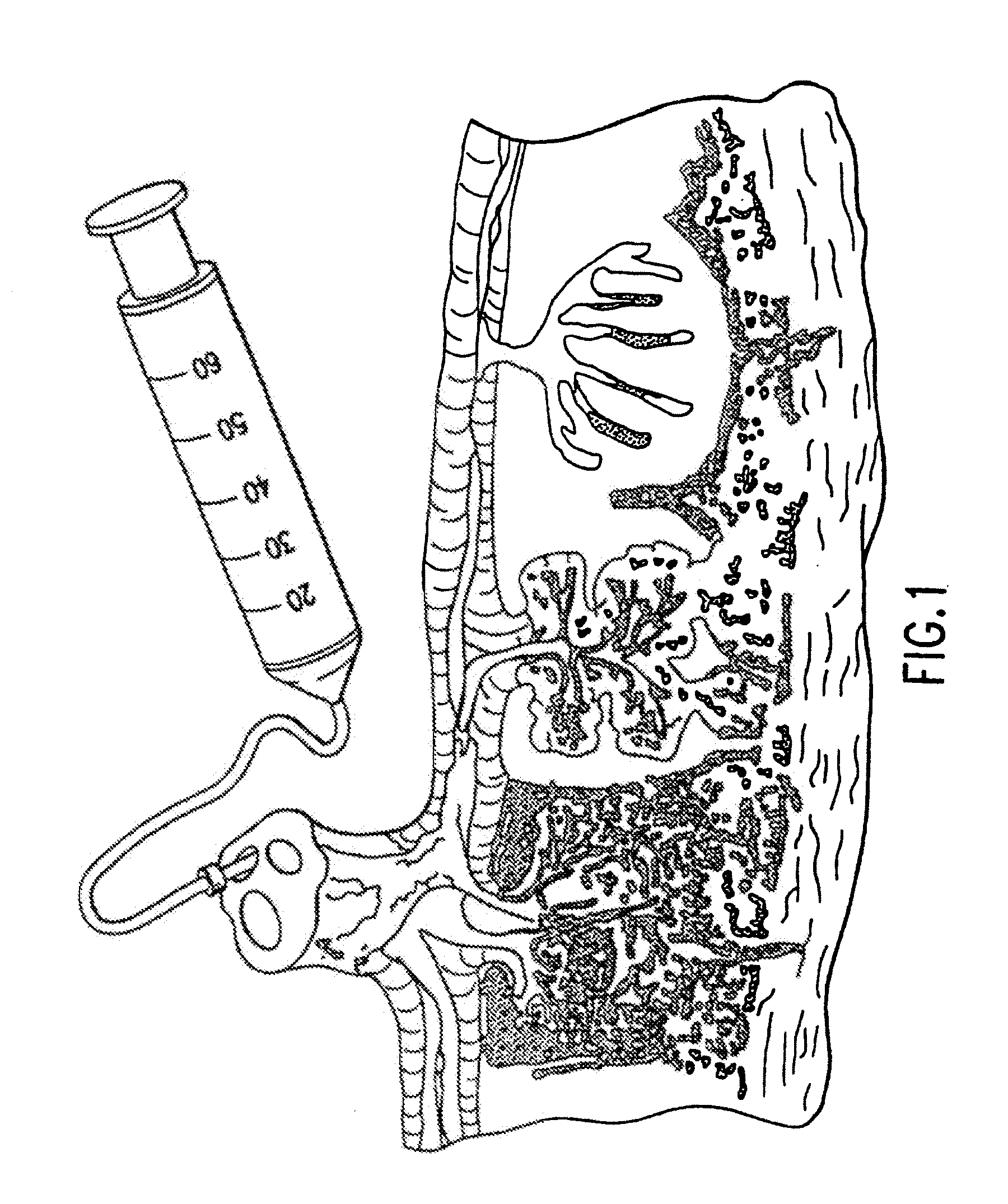
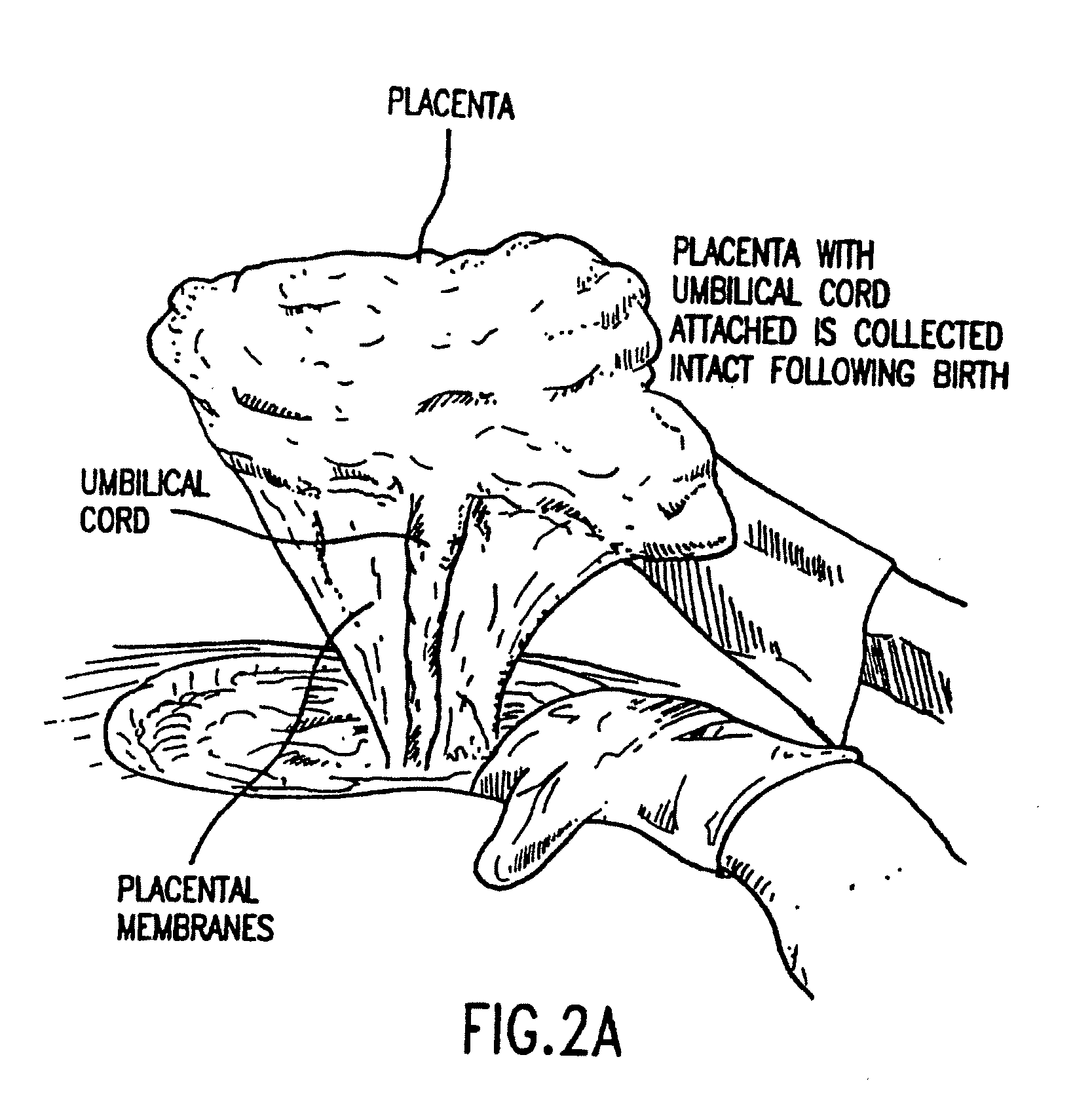
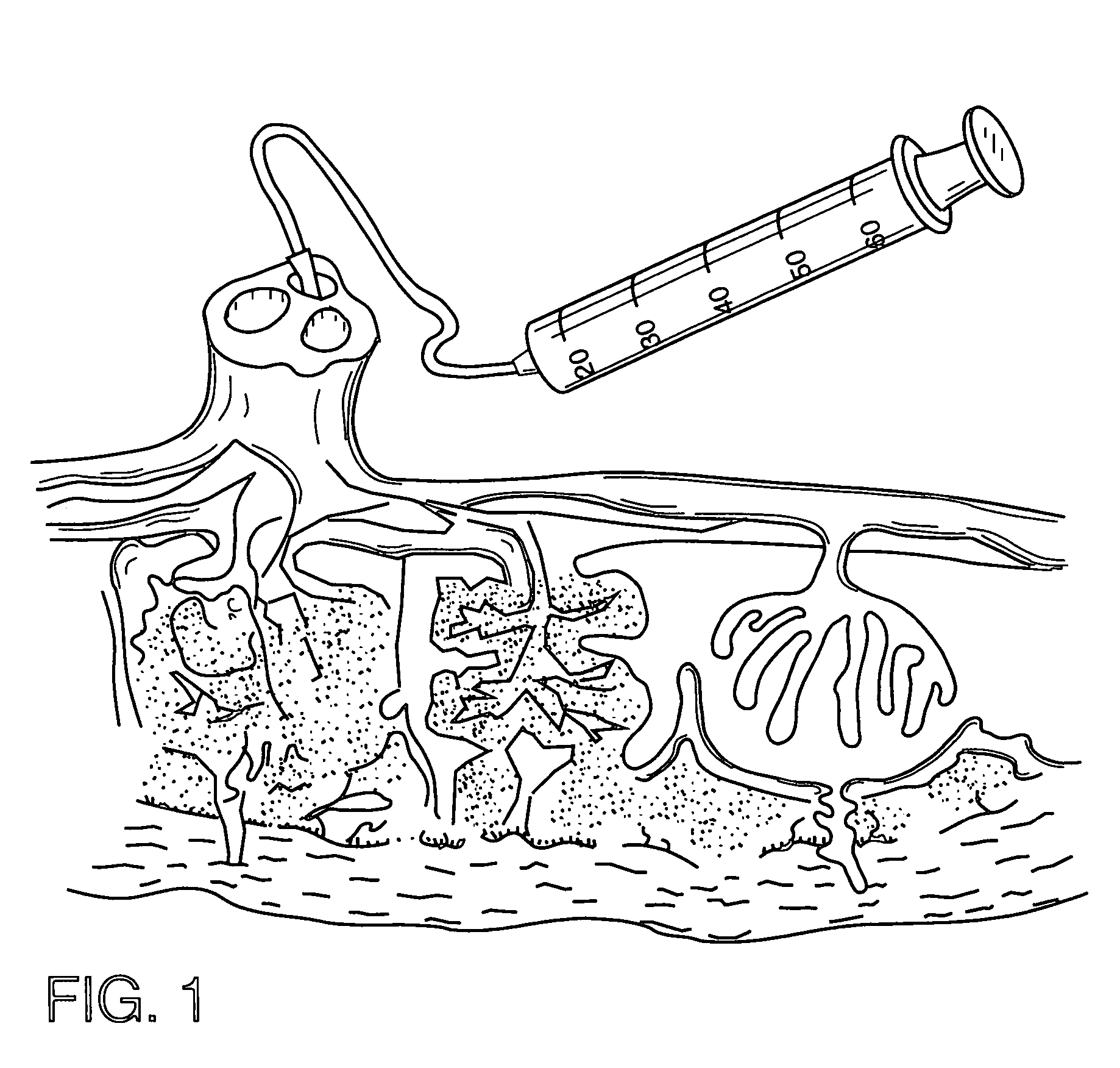
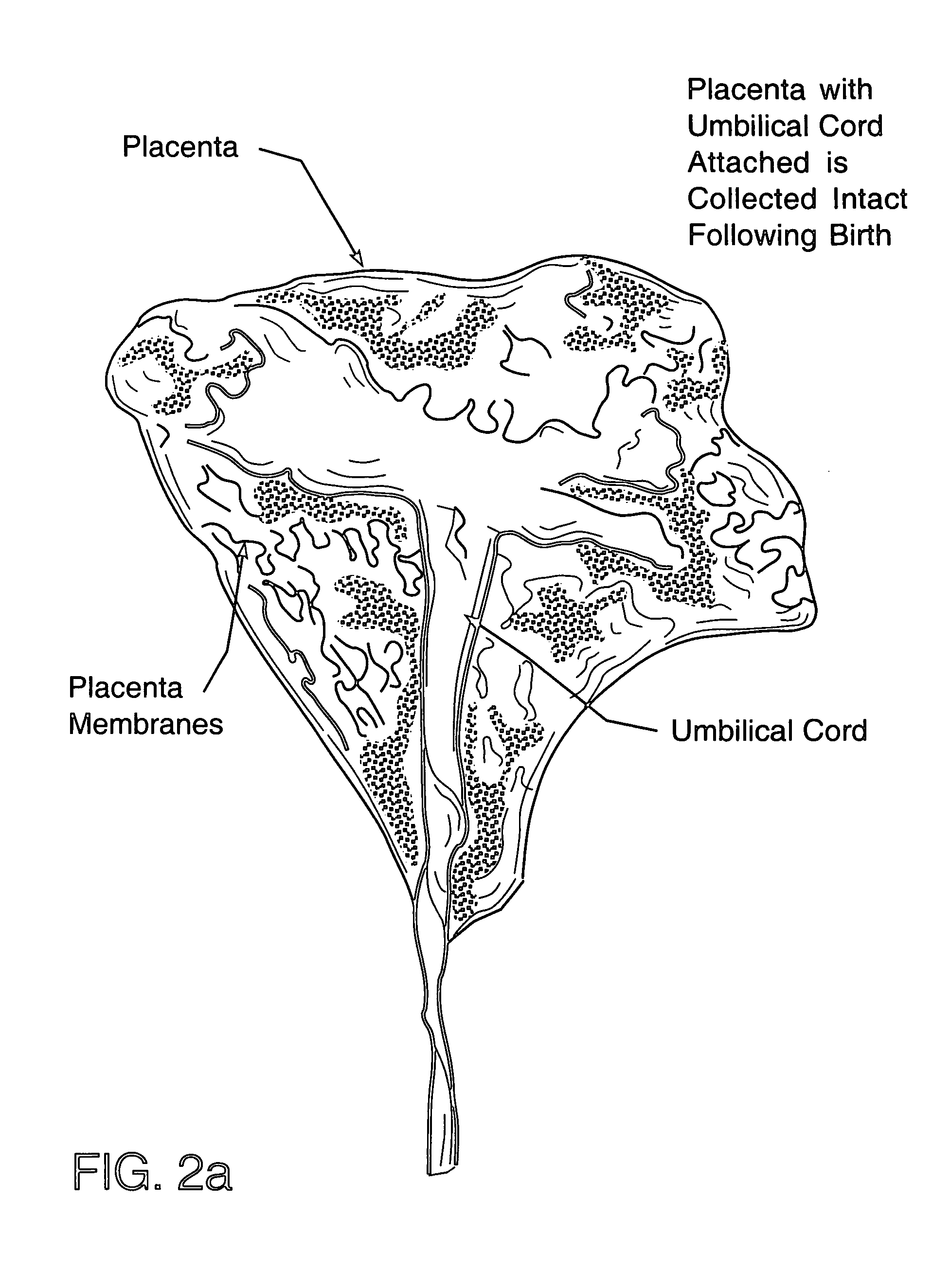
The present invention provides a method of extracting and recovering embryonic-like stem cells, including, but not limited to pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, from an exsanguinated human placenta. A placenta is treated to remove residual umbilical cord blood by perfusing an exsanguinated placenta, preferably with an anticoagulant solution, to flush out residual cells. The residual cells and perfusion liquid from the exsanguinated placenta are collected, and the embryonic-like stem cells are separated from the residual cells and perfusion liquid. The invention also provides a method of utilizing the isolated and perfused placenta as a bioreactor in which to propagate endogenous cells, including, but not limited to, embryonic-like stem cells. The invention also provides methods for propagation of exogenous cells in a placental bioreactor and collecting the propagated exogenous cells and bioactive molecules therefrom.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Cartilage and bone repair and regeneration using postpartum-derived cells
Cells derived from postpartum tissue and methods for their isolation and induction to differentiate to cells of a chondrogenic or osteogenic phenotype are provided by the invention. The invention further provides cultures and compositions of the postpartum-derived cells and products related thereto. The postpartum-derived cells of the invention and products related thereto have a plethora of uses, including but not limited to research, diagnostic, and therapeutic applications, for example, in the treatment of bone and cartilage conditions.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Method of collecting placental stem cells
InactiveUS20020123141A1Increase concentrationImprove the environmentSenses disorderAntipyreticCord blood stem cellEmbryo
A method of collecting embryonic-like stem cells from a placenta which has been treated to remove residual cord blood by perfusing the drained placenta with an anticoagulant solution to flush out residual cells, collecting the residual cells and perfusion liquid from the drained placenta, and separating the embryonic-like cells from the residual cells and perfusion liquid. Exogenous cells can be propagated in the placental bioreactor and bioactive molecules collected therefrom.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Embryonic-like stem cells derived from post-partum mammalian placenta, and uses and methods of treatment using said cells
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Post-partum mammalian placenta, its use and placental stem cells therefrom
The present invention provides a method of extracting and recovering embryonic-like stem cells, including, but not limited to pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, from an exsanguinated human placenta. A placenta is treated to remove residual umbilical cord blood by perfusing an exsanguinated placenta, preferably with an anticoagulant solution, to flush out residual cells. The residual cells and perfusion liquid from the exsanguinated placenta are collected, and the embryonic-like stem cells are separated from the residual cells and perfusion liquid. The invention also provides a method of utilizing the isolated and perfused placenta as a bioreactor in which to propagate endogenous cells, including, but not limited to, embryonic-like stem cells. The invention also provides methods for propagation of exogenous cells in a placental bioreactor and collecting the propagated exogenous cells and bioactive molecules therefrom.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Soft tissue repair and regeneration using postpartum-derived cells
ActiveUS20050058629A1Reduce productionReduce risk of rejectionSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSoft tissue repairSupporting cell
Cells derived from postpartum tissue having the potential to support cells of and / or differentiate to cells of a soft tissue lineage, and methods of preparation and use of those postpartum tissue-derived cells, are provided by the invention. The invention also provides methods for the use of such postpartum-derived cells and products related thereto in therapies for conditions of soft tissue.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Postpartum-derived cells for use in treatment of disease of the heart and circulatory system
Cells derived from postpartum tissue are disclosed along with methods for their therapeutic use in diseases of the heart or circulatory system are disclosed. Cells may be used therapeuticall in either differentiated or undifferentiated forms, in homogenous cultures, or as populations with other cells, and in conjunction with other bioactive factors.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Cartilage and bone repair and regeneration using postpartum-derived cells
Cells derived from postpartum tissue and methods for their isolation and induction to differentiate to cells of a chondrogenic or osteogenic phenotype are provided by the invention. The invention further provides cultures and compositions of the postpartum-derived cells and products related thereto. The postpartum-derived cells of the invention and products related thereto have a plethora of uses, including but not limited to research, diagnostic, and therapeutic applications, for example, in the treatment of bone and cartilage conditions.
Owner:ETHICON INC
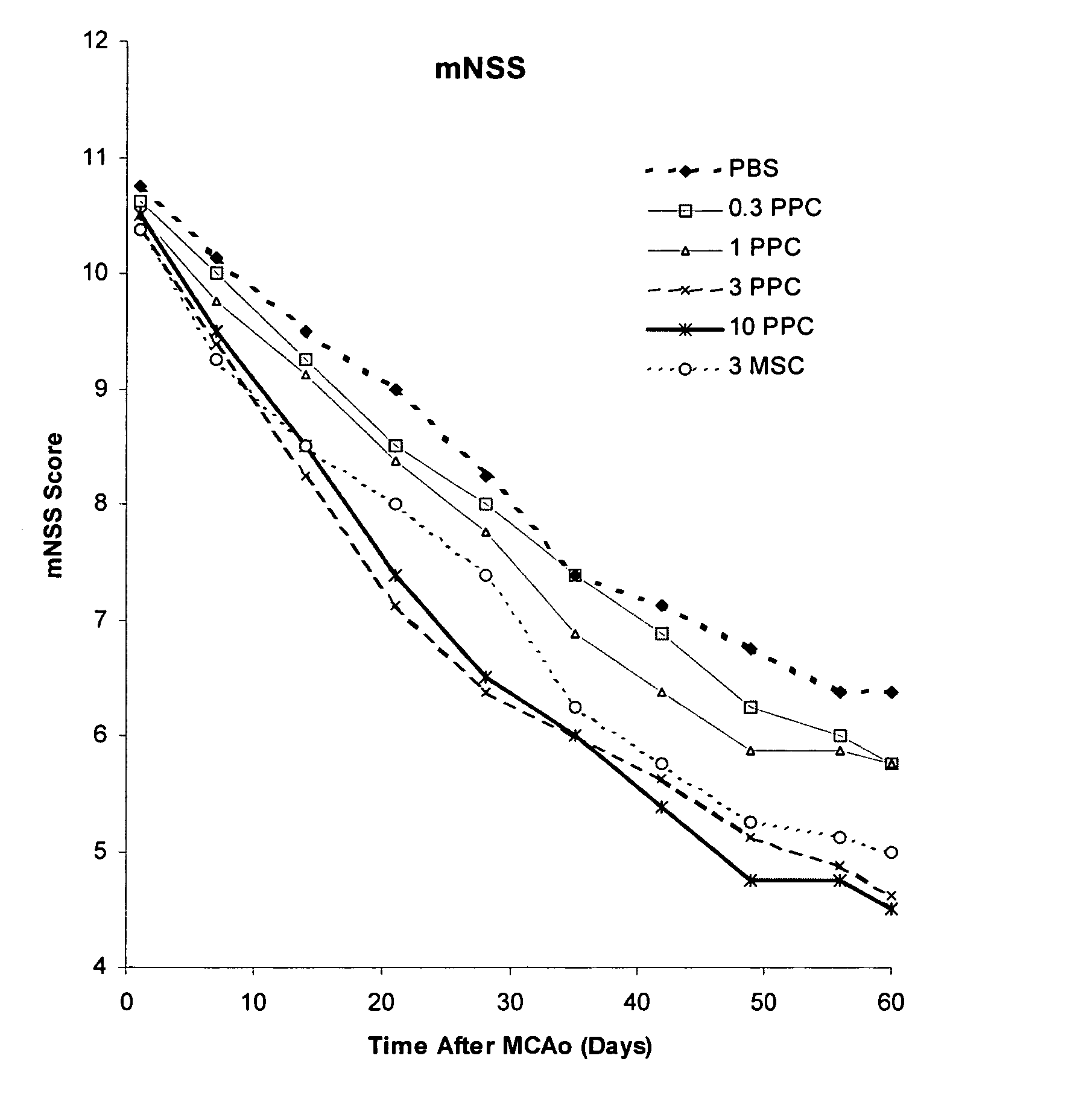
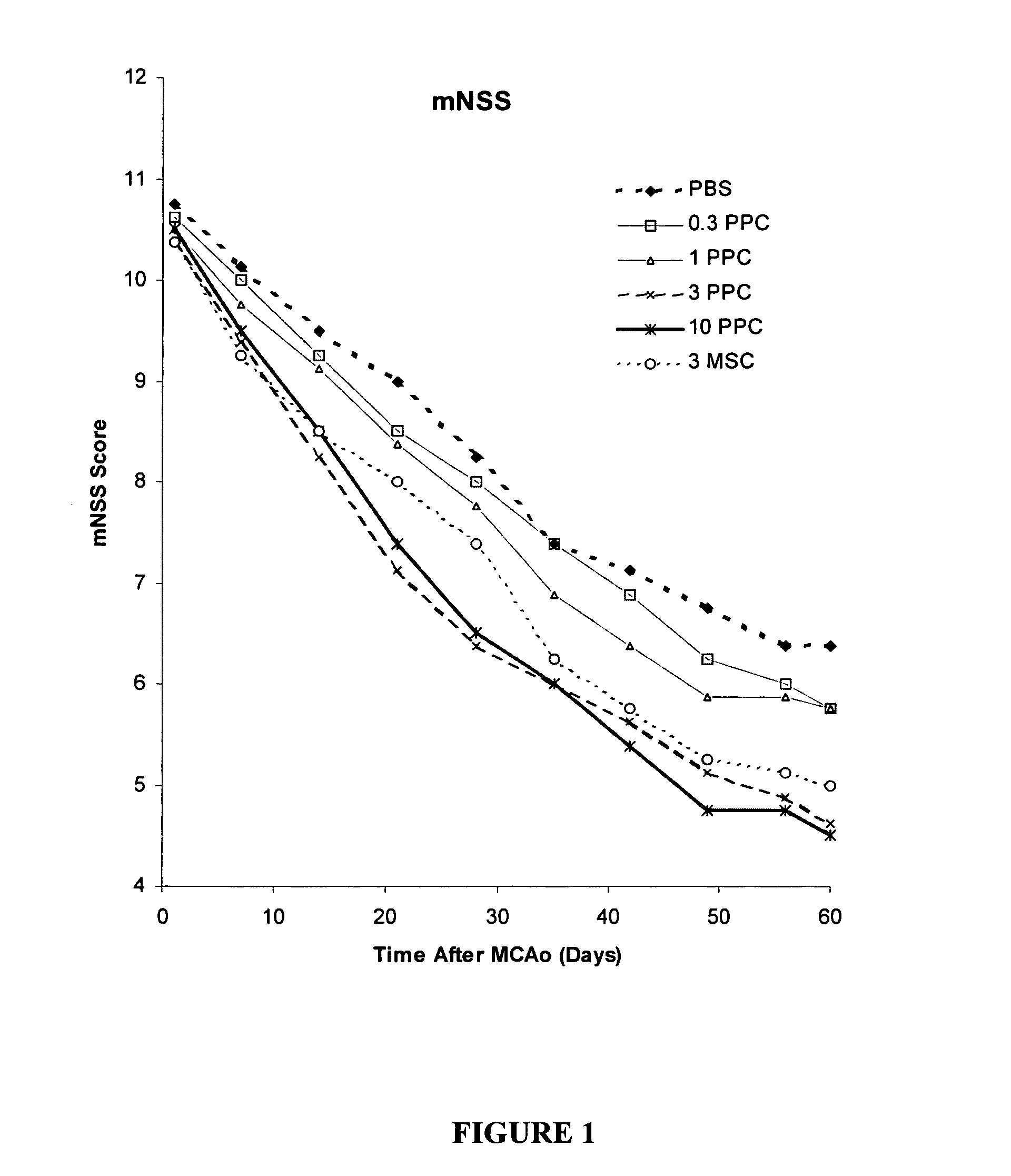
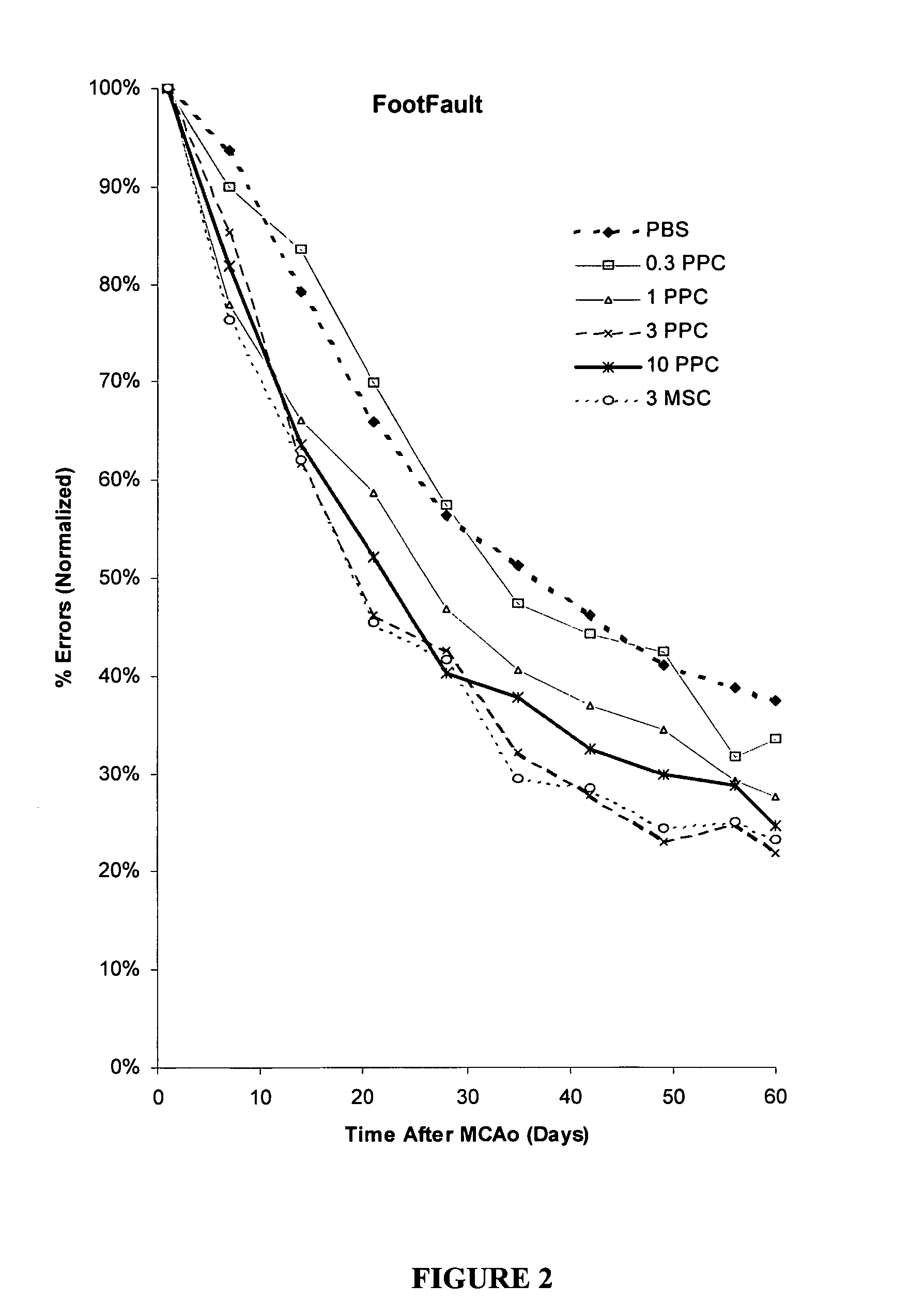
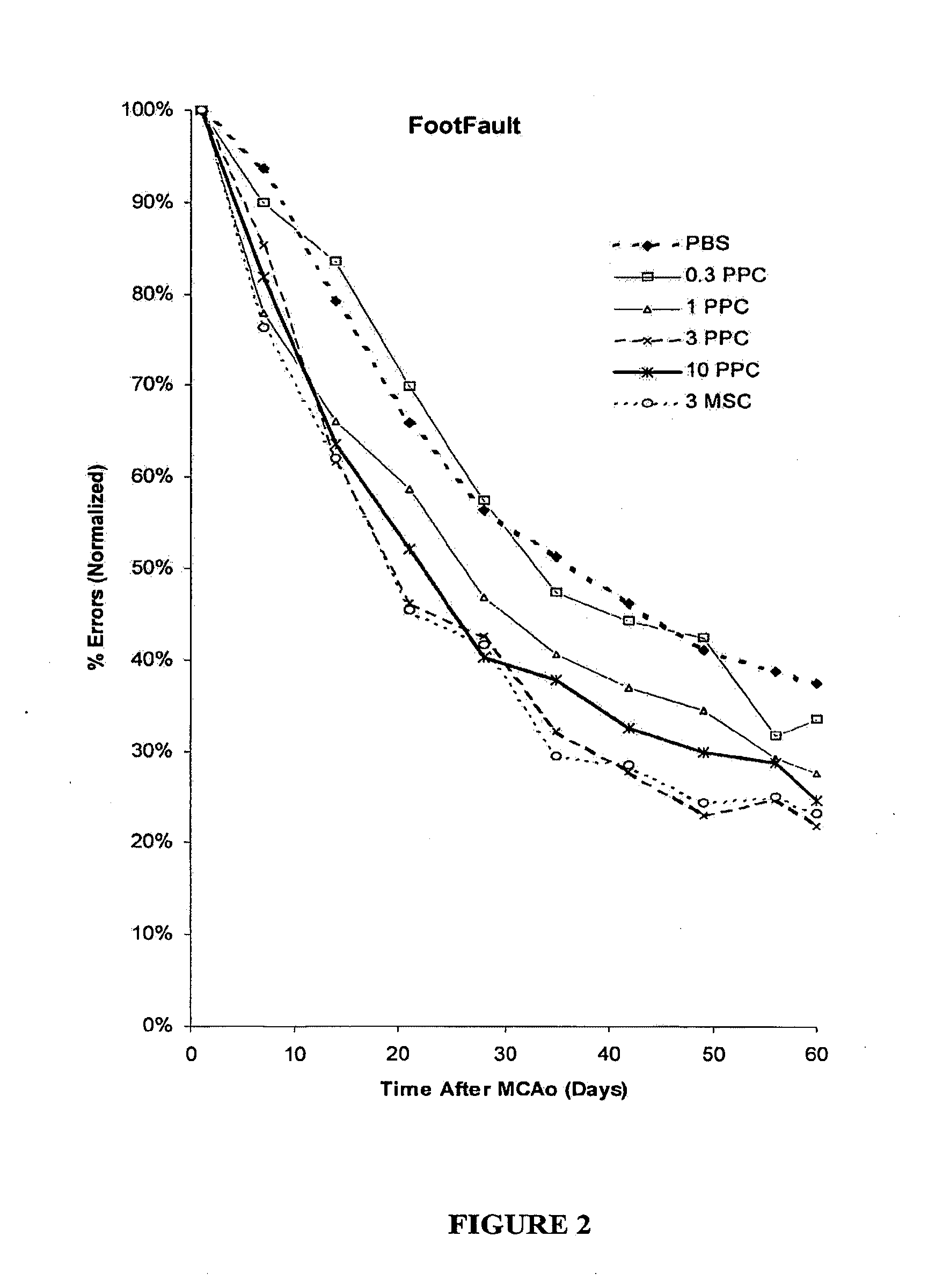
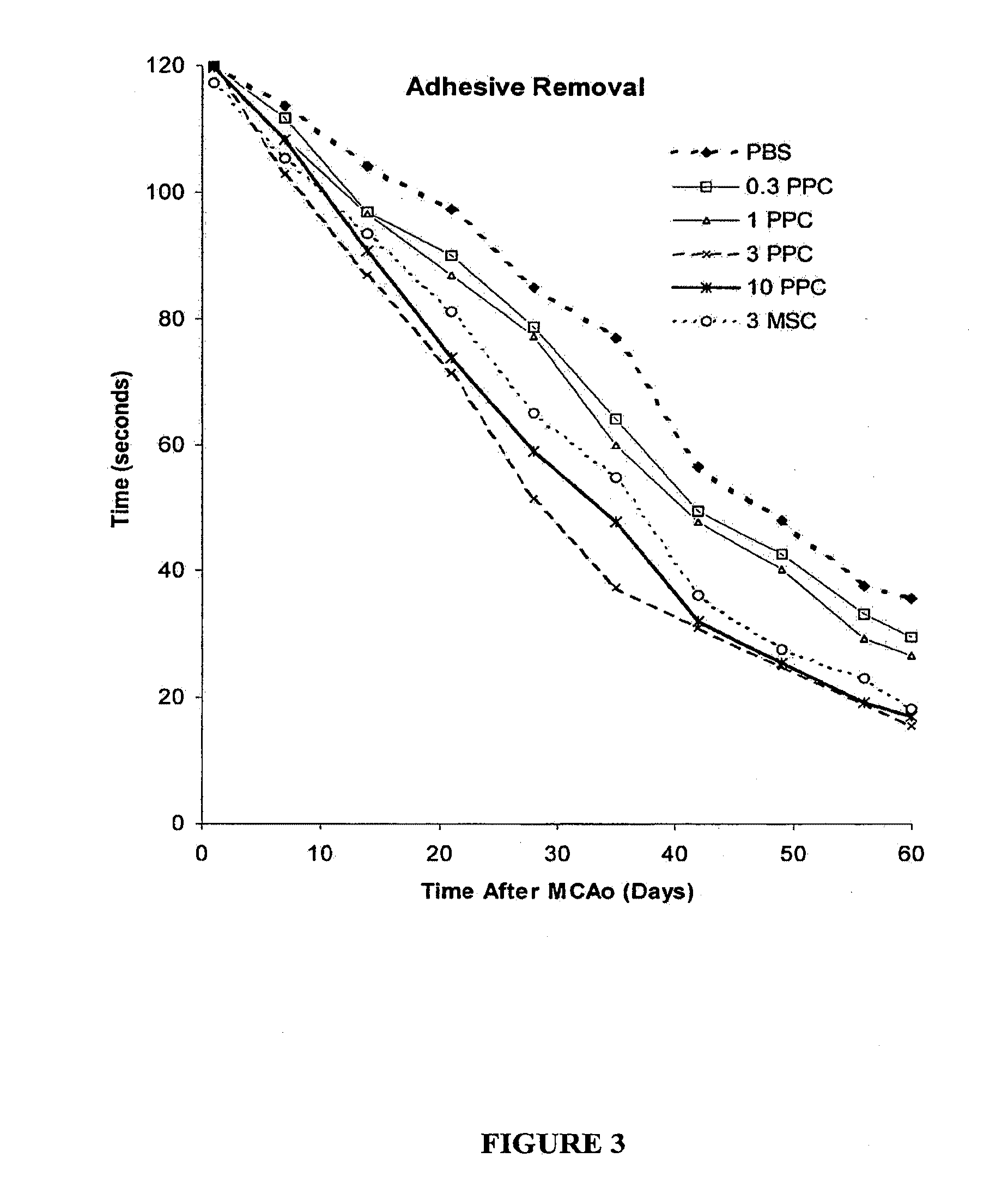
Treatment of stroke and other acute neuraldegenerative disorders using postpartum derived cells
InactiveUS20060233765A1BiocideMammal material medical ingredientsPhysiologyNeuro-degenerative disease
Cells derived from postpartum tissue such as the umbilical cord and placenta, and methods for their use to regenerate, repair, and improve neural tissue, and to improve behavior and neurological function in stroke patients are disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Soft tissue repair and regeneration using stem cell products
Stem cells products having the potential to support cells of a soft tissue lineage, and methods of preparation and use of those stem cell products are disclosed. The invention also relates to methods for the use of such stem cells products in the regeneration and repair of soft tissue, and in cell-based therapies for of soft tissue conditions.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Renovation and repopulation of decellularized tissues and cadaveric organs by stem cells
A method of manufacturing a tissue matrix for implantation into a patient is disclosed. The method sets forth collecting embryonic stem cells from a placenta which has been treated to remove residual cord blood and seeding the collected stem cells onto or into a tissue matrix. The seeded tissue matrix is then implanted on or into a patient. The seeded tissue matrix made by the method of the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Use of adipose tissue-derived stromal stem cells in treating fistula
Provided herein are novel methods and compositions utilizing adipose tissue-derived stromal stem cells for treating fistulae.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS UNIVERSITY OF MADRID +1
Automated method and apparatus for embryonic stem cell culture
ActiveUS20090029462A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyCell cluster
The invention concerns methods for automated culture of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) such as human ESCs. In some aspects, methods of the invention employ optimized culture media and limited proteolytic treatment of cells to separate cell clusters for expansion. Automated systems for passage and expansion of ESCs are also provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Methods of Preparing and Using Novel Stem Cell Compositions and Kits Comprising the Same
The present invention provides novel stem cell compositions having significant therapeutic and practical advantages, as well as methods of preparing and using such compositions for the treatment and prevention of injury and disease in patients. The invention may be applied to stem cell populations isolated from a wide variety of animals, including humans, and tissues. In particular applications, the invention is used to prepare a stem cell composition from a collagen-based tissue, such as adipose tissue, isolated from a patient, and the stem cell composition is subsequently provided to a site of actual or potential injury in the patient. The invention further includes related kits comprising the stem cell compositions, which are remarkably stable and retain viability and efficacy during storage and shipment.
Owner:VETSTEM INC
Tissue matrices comprising placental stem cells
A method of manufacturing a tissue matrix for implantation into a patient is disclosed. The method sets forth collecting embryonic stem cells from a placenta which has been treated to remove residual cord blood and seeding the collected stem cells onto or into a tissue matrix. The seeded tissue matrix is then implanted on or into a patient. The seeded tissue matrix made by the method of the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Method of collecting placental stem cells
A method of collecting embryonic-like stem cells from a placenta which has been treated to remove residual cord blood by perfusing the drained placenta with an anticoagulant solution to flush out residual cells, collecting the residual cells and perfusion liquid from the drained placenta, and separating the embryonic-like cells from the residual cells and perfusion liquid. Exogenous cells can be propagated in the placental bioreactor and bioactive molecules collected therefrom.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
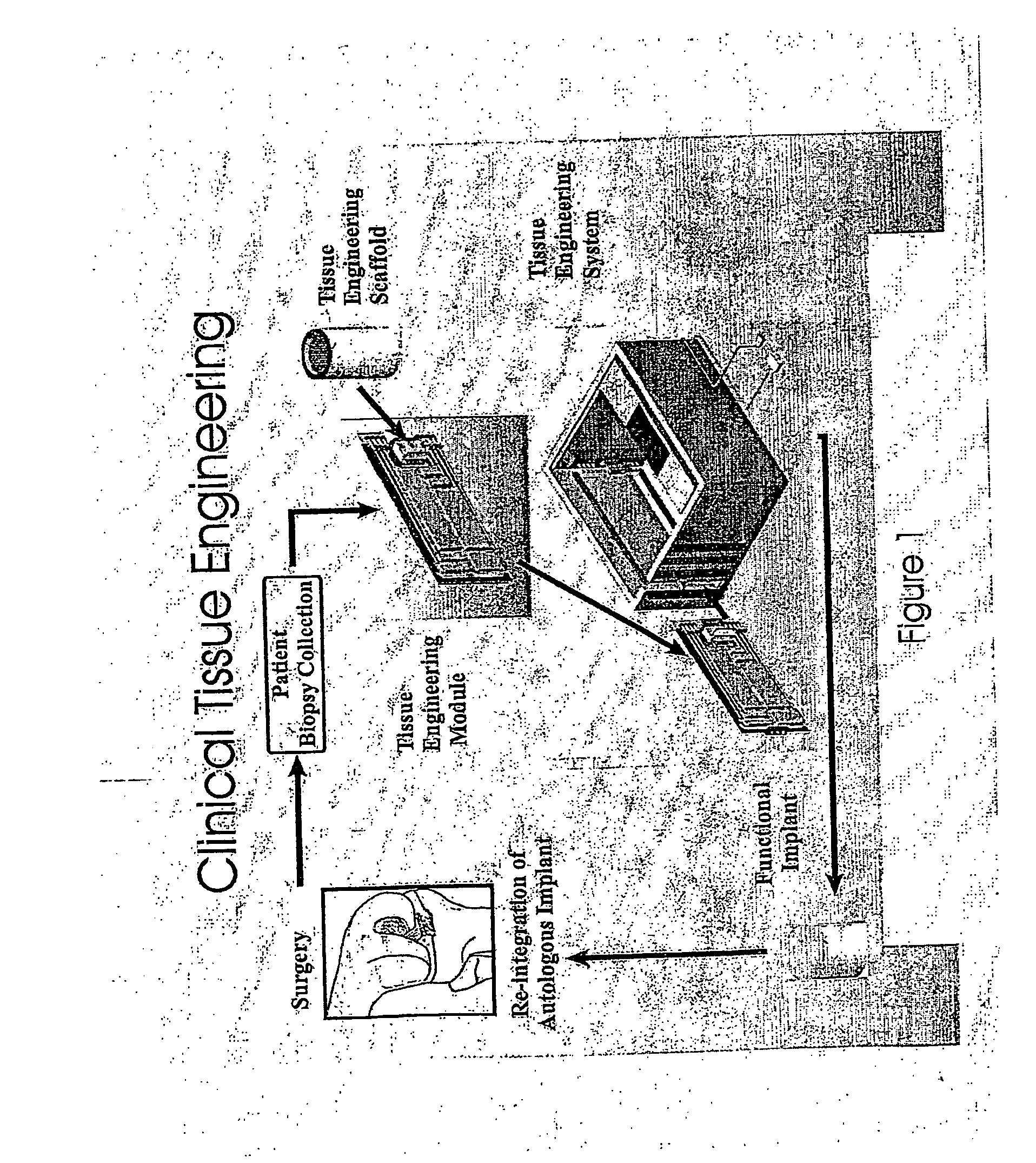
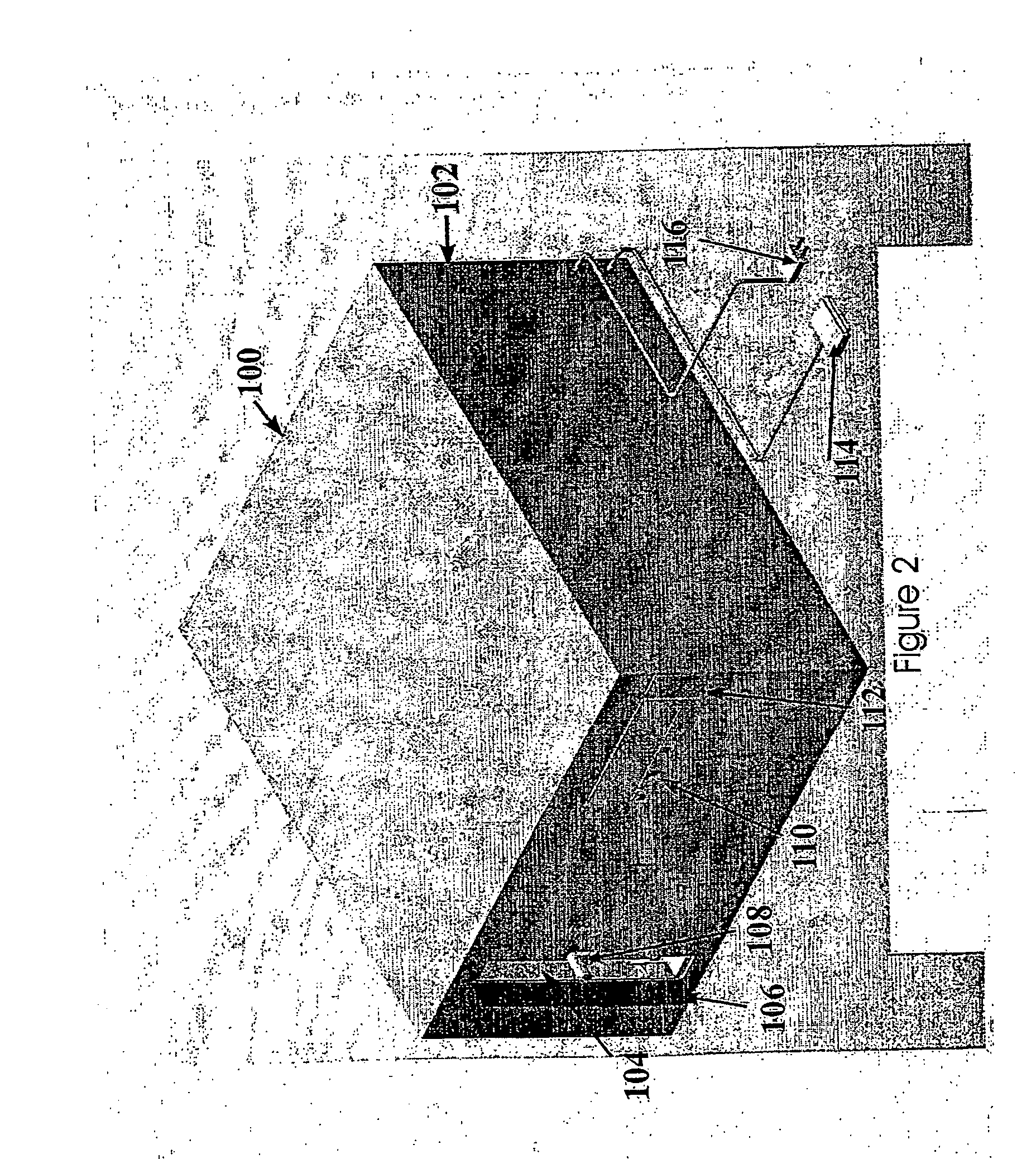
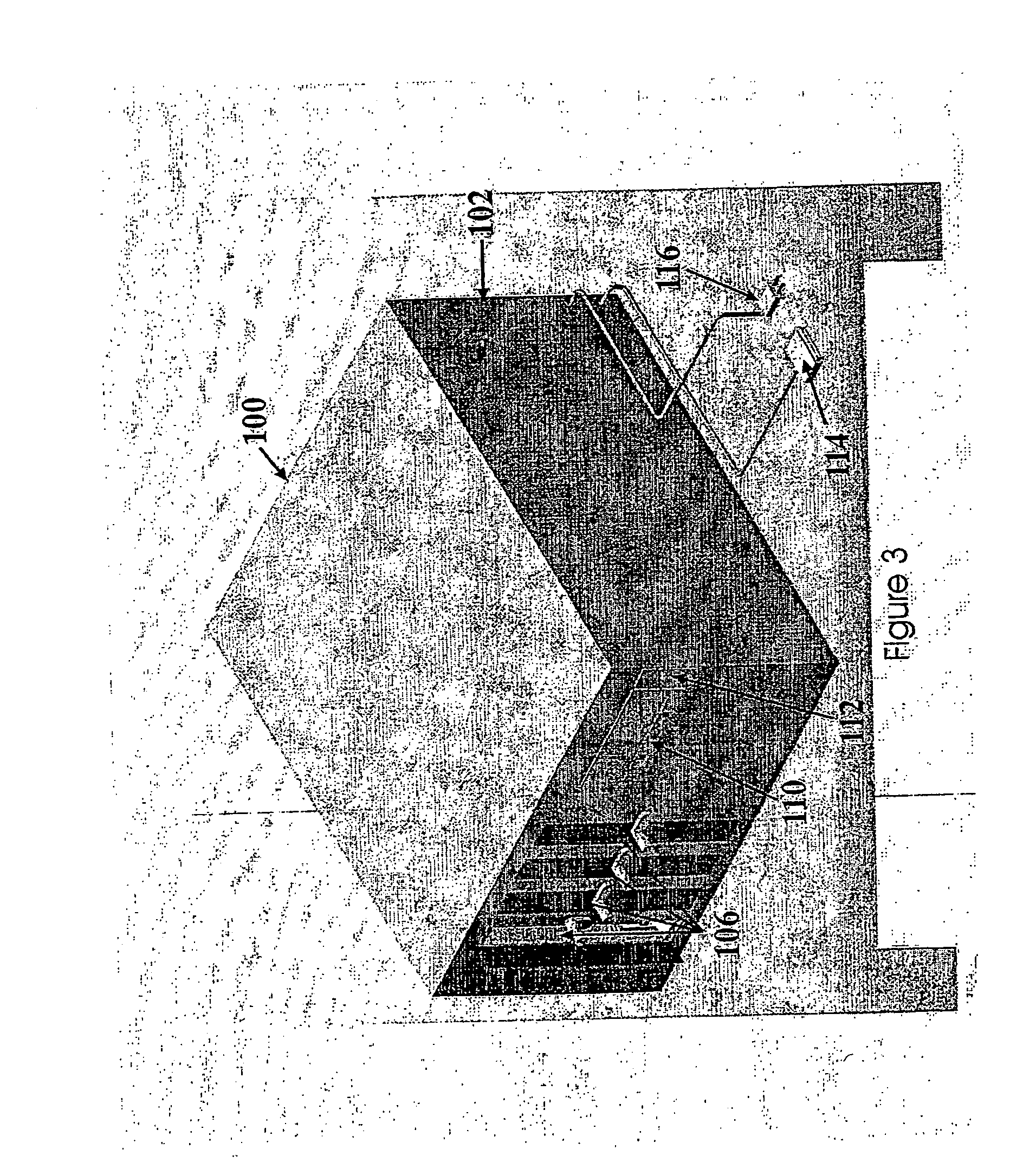
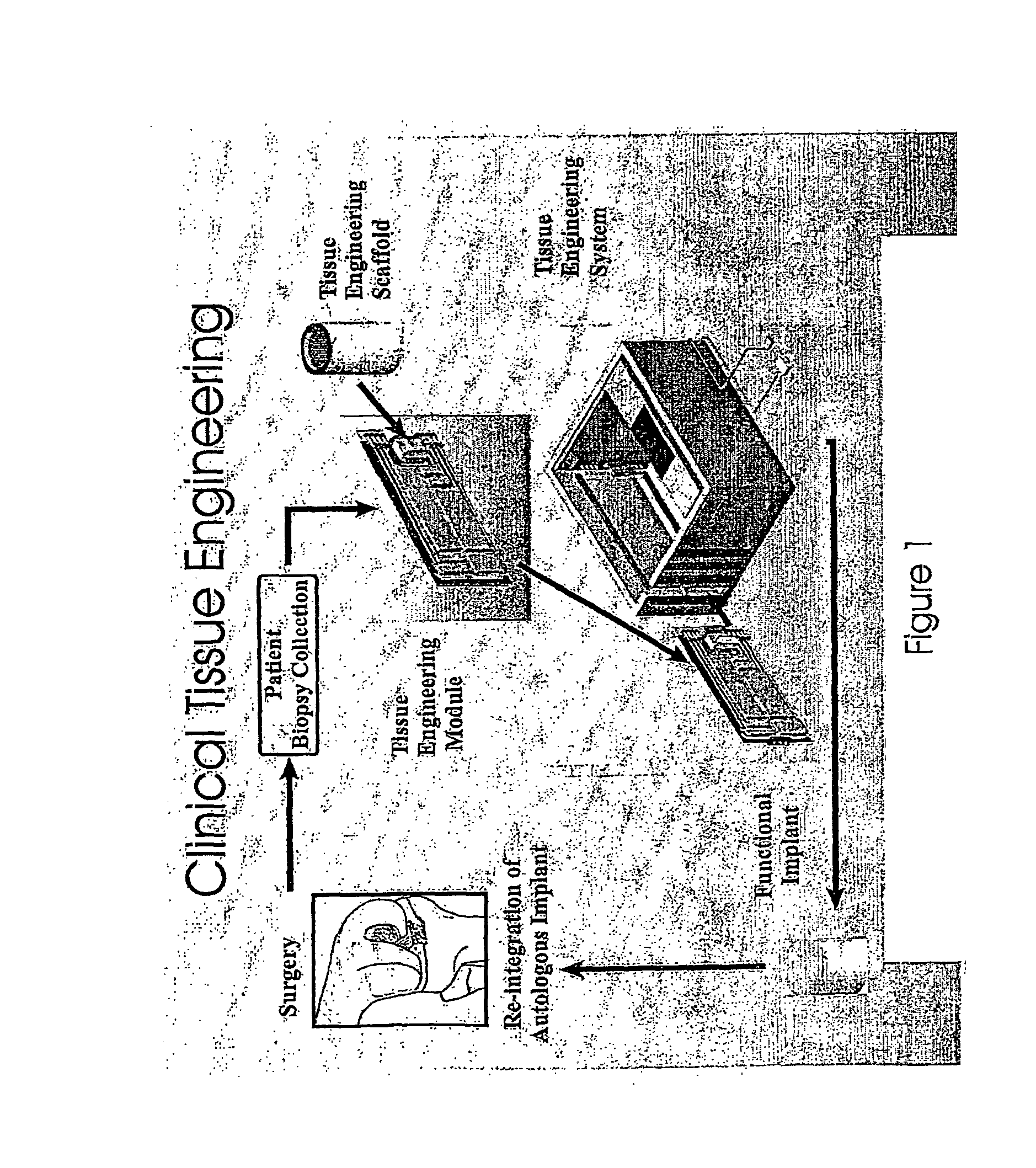
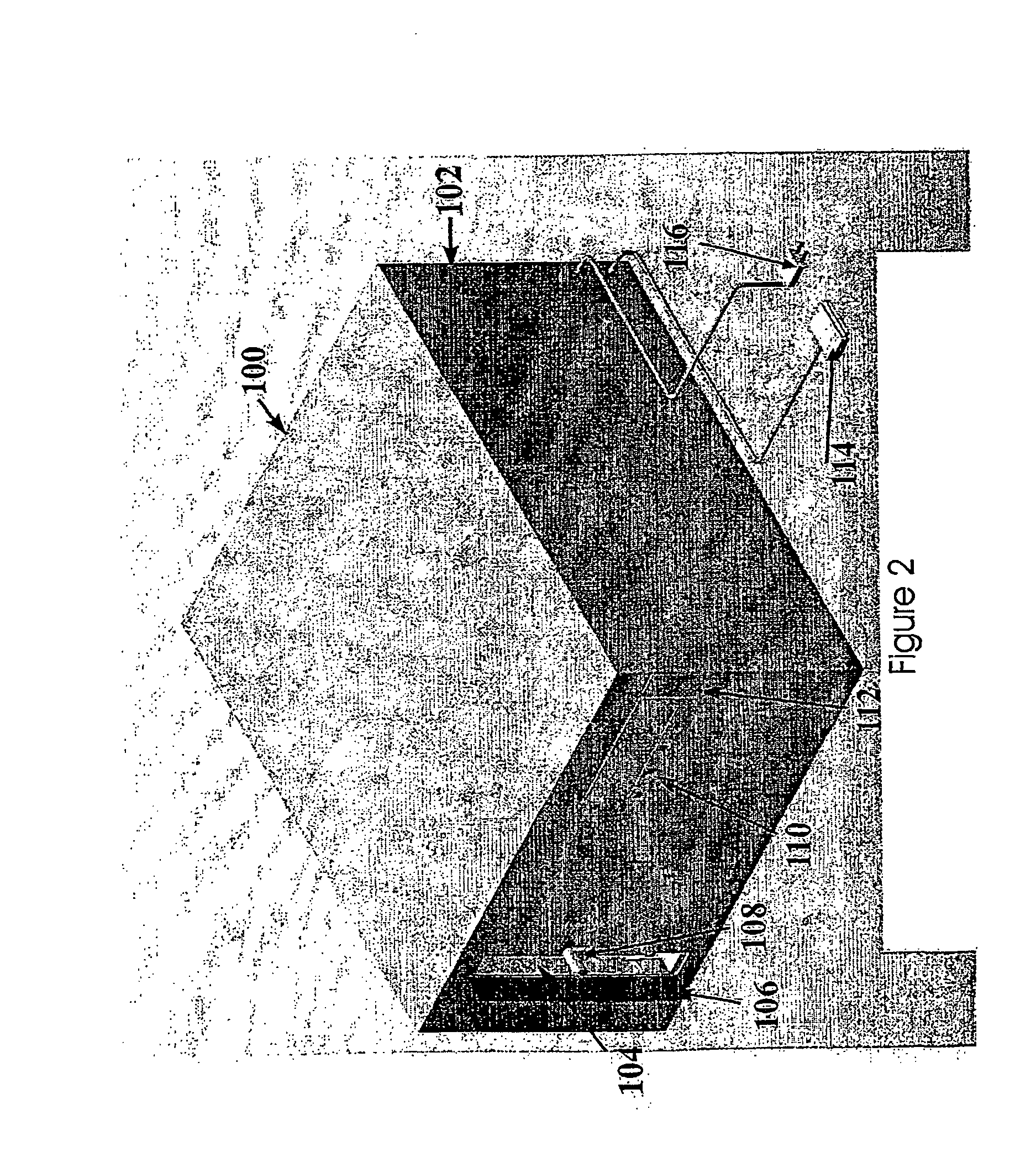
Automated tissue engineering system
ActiveUS20060141623A1Safe preparationImproving patient recoveryBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsComputer moduleCellular functions
The invention provides systems, modules, bioreactor and methods for the automated culture, proliferation, differentiation, production and maintenance of tissue engineered products. In one aspect is an automated tissue engineering system comprising a housing, at least one bioreactor supported by the housing, the bioreactor facilitating physiological cellular functions and / or the generation of one or more tissue constructs from cell and / or tissue sources. A fluid containment system is supported by the housing and is in fluid communication with the bioreactor. One or more sensors are associated with one or more of the housing, bioreactor or fluid containment system for monitoring parameters related to the physiological cellular functions and / or generation of tissue constructs; and a microprocessor linked to one or more of the sensors. The systems, methods and products of the invention find use in various clinical and laboratory settings.
Owner:OCTANE BIOTECH +1
Method of isolating epithelial cells, method of preconditioning cells, and methods of preparing bioartificial skin and dermis with the epithelial cells or the preconditioned cells
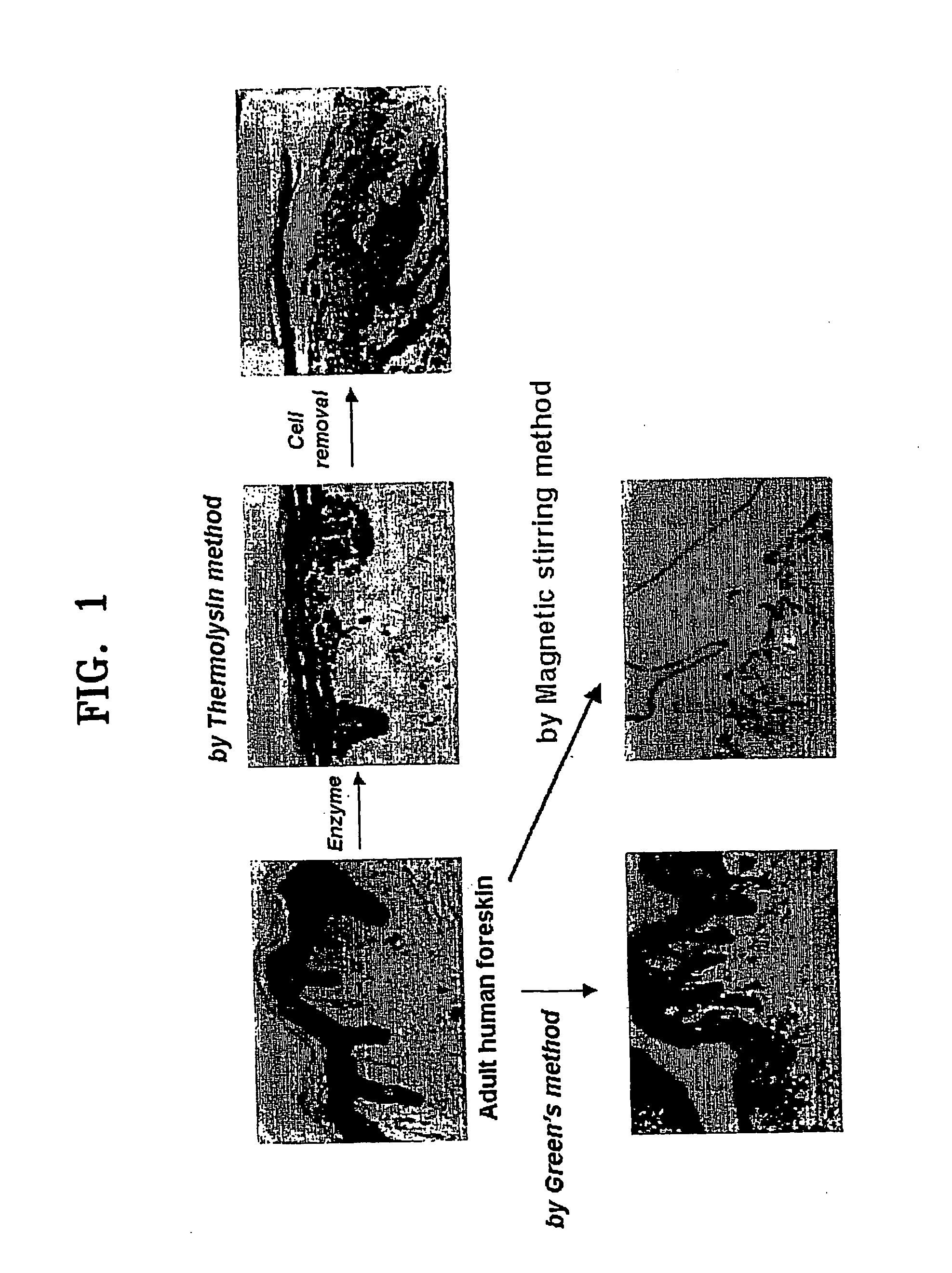
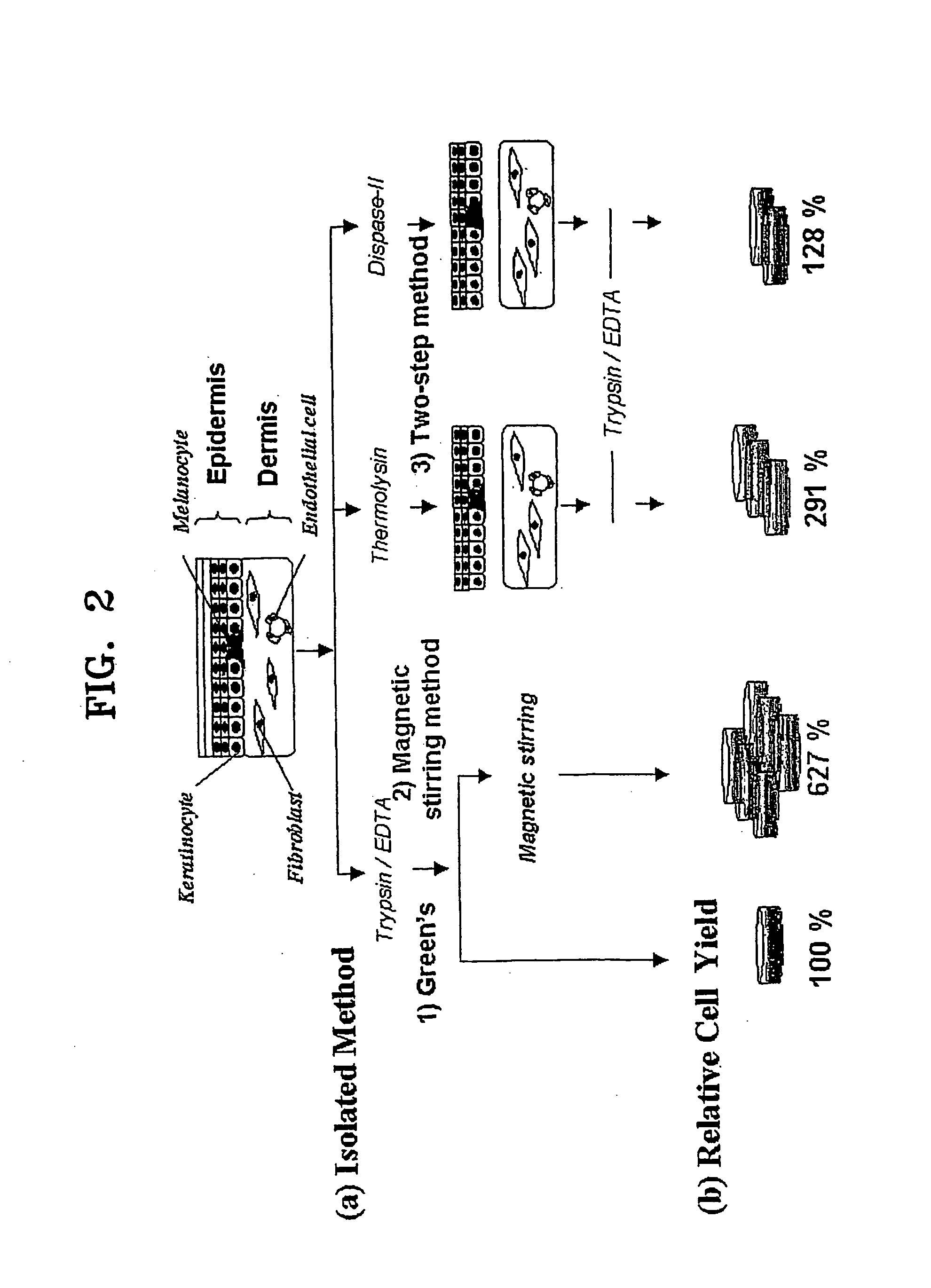
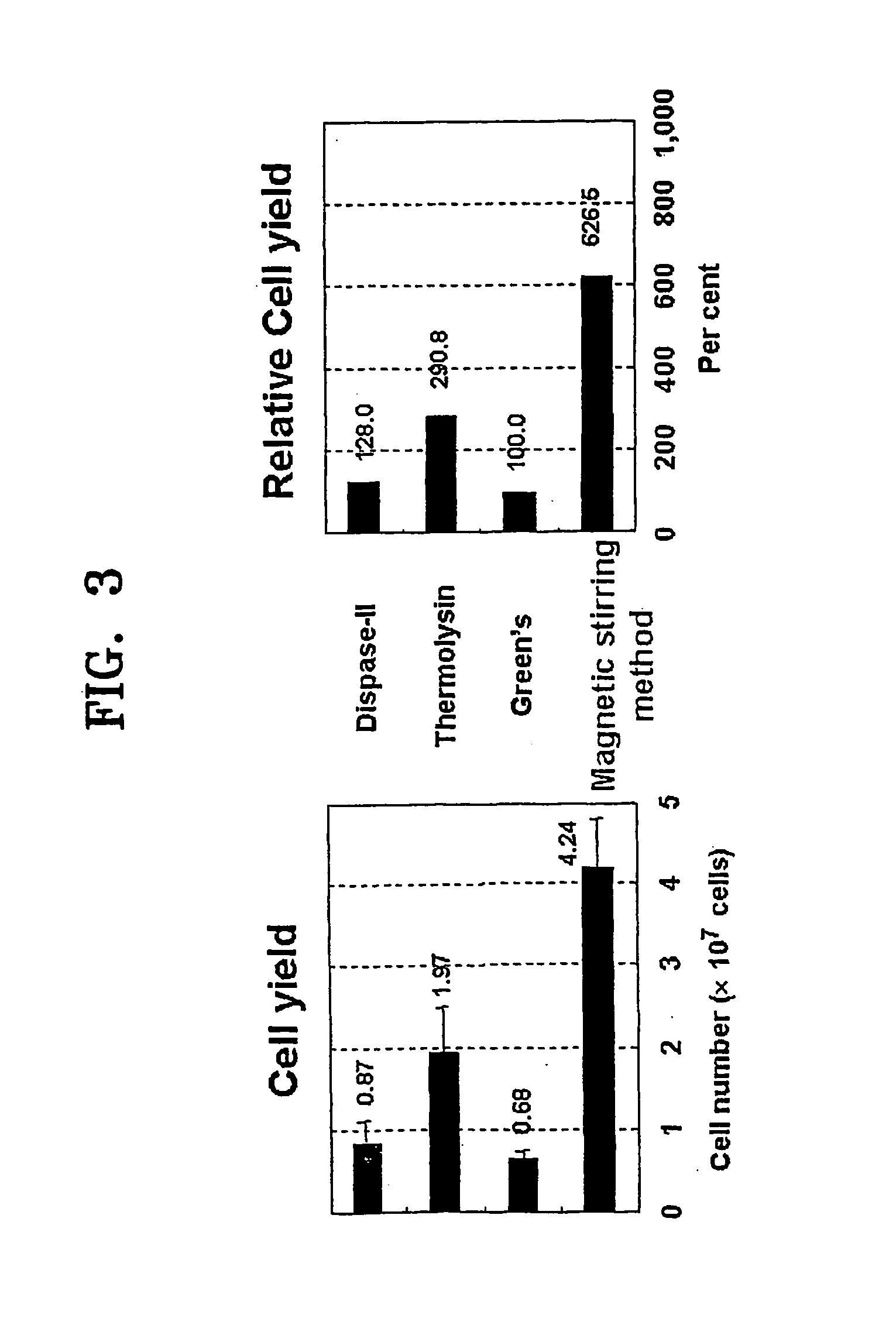
InactiveUS20060105454A1Increased cell yieldEasy to implantCell dissociation methodsEpidermal cells/skin cellsDamages tissueTrypsin
A method of isolating epithelial cells from a human skin tissue or internal organ tissue using trypsin and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) simultaneously with the application of magnetic stirring, a method of preconditioning isolated biological cells by the application of physical stimulus, i.e., strain, are provided. Epithelial cells can be isolated by the method with increased yield, colony forming efficiency (CFE), and colony size. Also, the increased percentage of stem cells in isolated cells is advantageous in therapeutic tissue implantation by autologous or allogeneic transplantation. In skin cells preconditioned by the application of strain, cell division is facilitated, and the secretion of extracellular matrix components and growth factors and the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are improved. When preconditioned cells are implanted by autologous or allogeneic transplantation to heal a damaged tissue, the improved cell adhesion, mobility, and viability provides a biological adjustment effect against a variety of stresses or physical stimuli which the cells would undergo after implantation, with improved capability of integration into host tissue, thereby markedly improving the probability of success in skin grafting.
Owner:KOREA INST OF RADIOLOGICAL & MEDICAL SCI
Pluripotent stem cell that can be isolated from body tissue
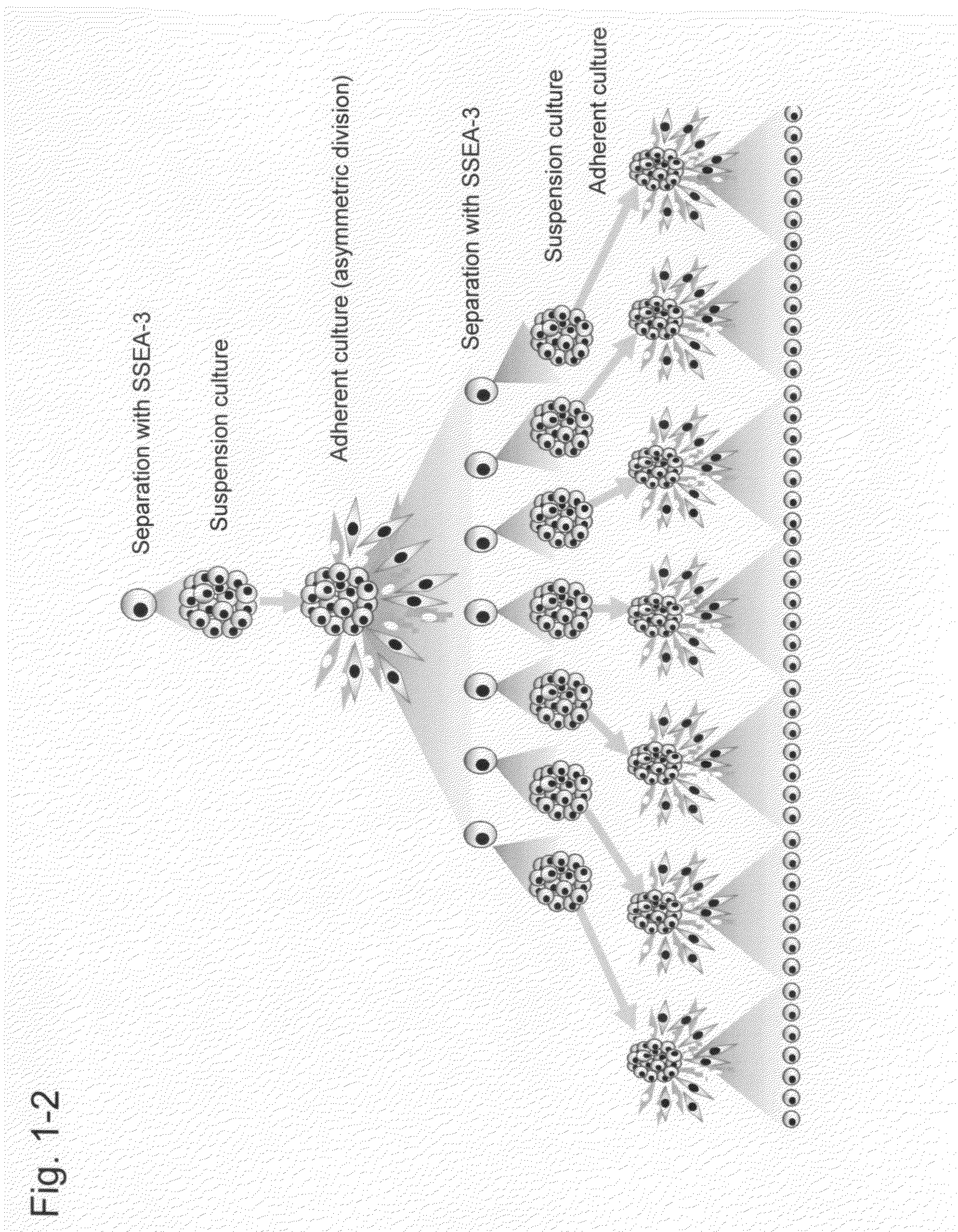
Objects of the present invention are to provide a method for directly obtaining pluripotent stem cells from body tissue and the thus obtained pluripotent stem cells. The present invention relates to SSEA-3 (+) pluripotent stem cells that can be isolated from body tissue.
Owner:DEZAWA MARI +3
Lung and lung cancer tissue culture method and method using lung and lung cancer tissue culture method to build lung cancer mouse animal model
ActiveCN106967672AGenetic stabilityGenetic uniformityCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsImmunofluorescent stainLung tissue
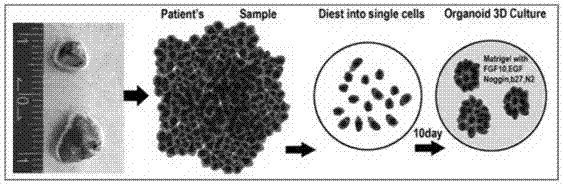
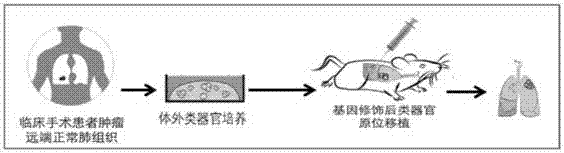
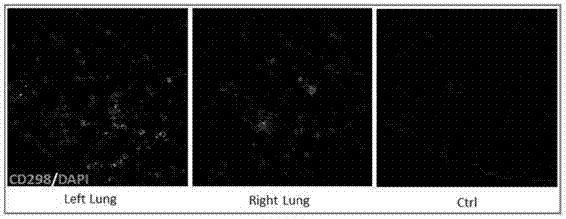
The invention discloses a method for culturing normal human lung tissue and a lung cancer tissue organoid in an in-vitro manner. The method includes: acquiring fresh human-derived lung tissue cells, and performing collagen digestion on the fresh human-derived lung tissue cells to obtain single cells; culturing human lung tissue and the lung cancer tissue organoid under in-vitro 3D culture conditions; performing H&E staining to determining the structure and form, and using q-PCR to detect related gene expression; using immunofluorescent staining to authenticate cell sources and detect related protein expression. The invention further discloses a method for building a mouse animal model based on the organoid. The method for culturing the normal human lung tissue and the lung cancer tissue organoid and the method for building the mouse animal model have the advantages that the methods are significant to the building of large-scale and good-consistency human-derived in-situ lung cancer animal models, and a good basis and related application prospect are provided for the fundamental researches of lung cancer.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Treatment of stroke and other acute neural degenerative disorders using postpartum-derived cells
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Microfluidic chip and cell screening method for screening specific cells
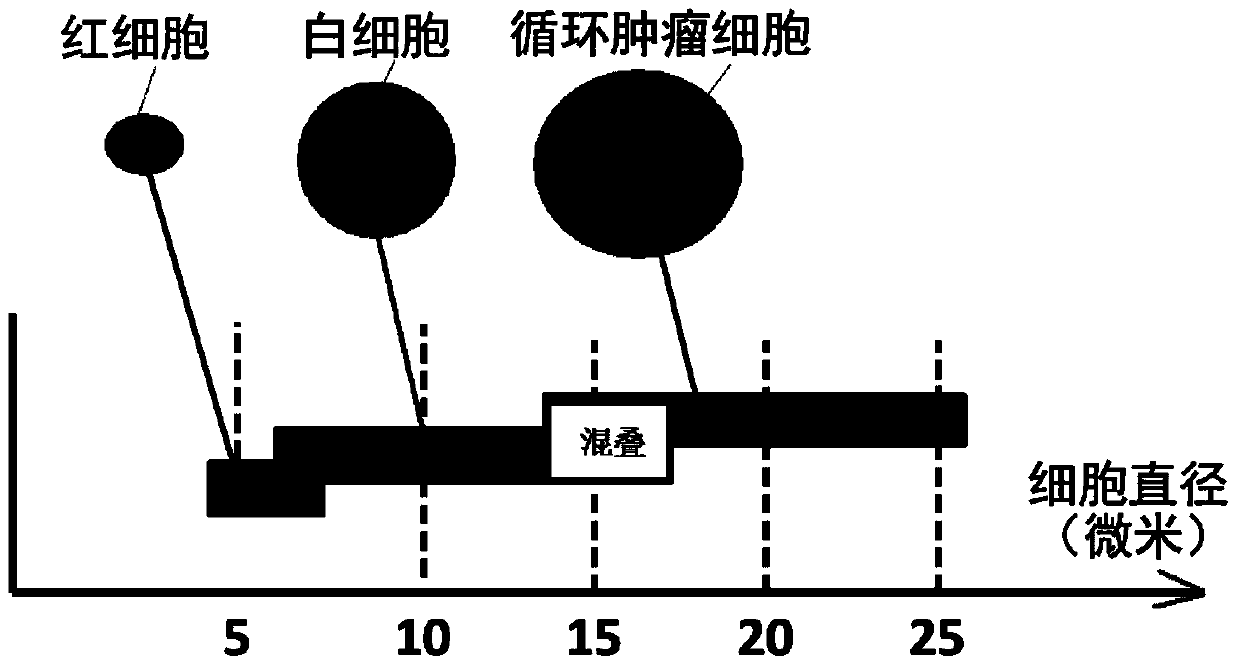
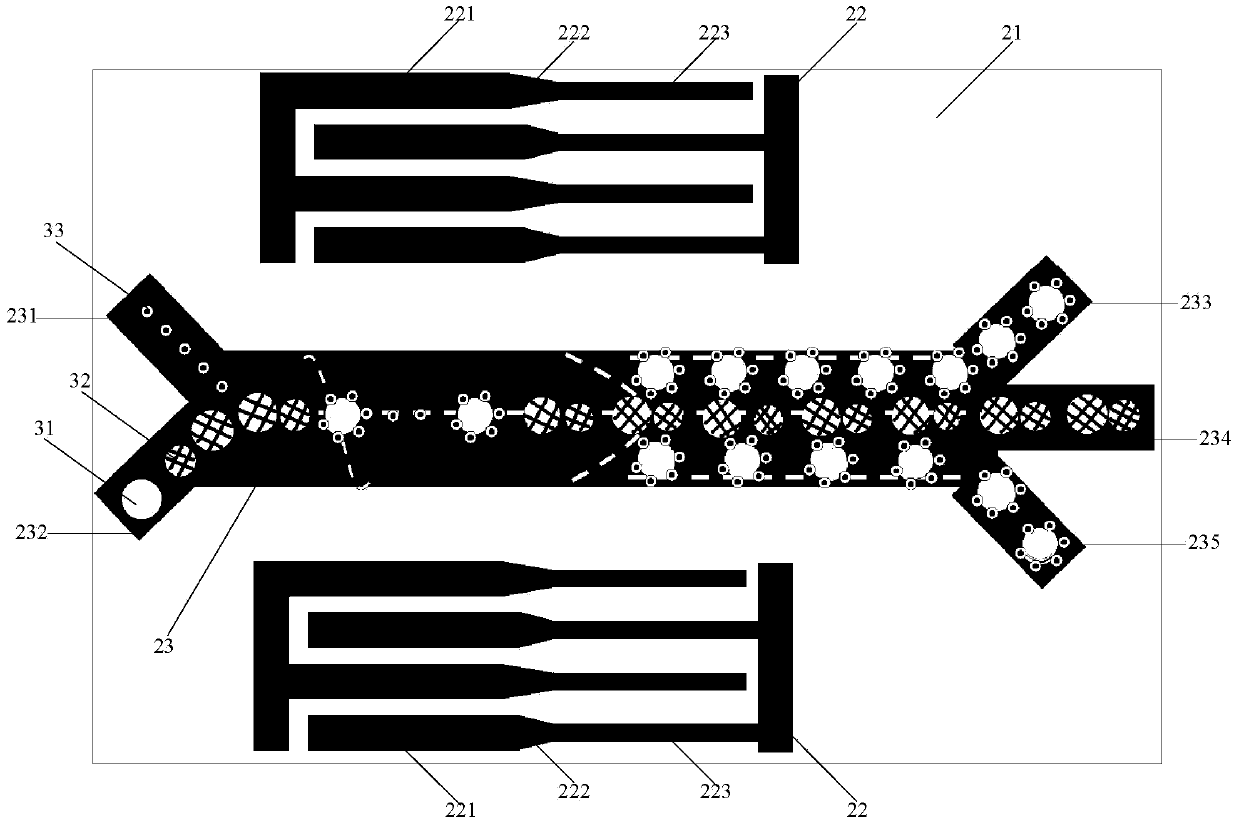
ActiveCN104195028ATo achieve the purpose of screening specificityCell dissociation methodsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsScreening methodAcoustic wave
The invention discloses a microfluidic chip and a cell screening method for screening specific cells. The chip comprises a substrate, a cavity and an acoustic excitation source, wherein the cavity comprises a middle channel, an inlet and an outlet; the acoustic excitation source is positioned on the substrate and at two sides of the middle channel and comprises two parts which extend to a direction of the outlet along the middle channel, wherein the corresponding acoustic resonance frequency of the second part close to the outlet is integer multiples of the corresponding acoustic resonance frequency of the first part far away from the outlet. Based on an acoustic streaming effect formed by targeted microbubbles and asymmetric sound fields, the microbubbles are adhered to the surfaces of the specific cells, so that the enriched cells which flow past the first part can still move in a straight line and cannot diffuse due to a laminar flow characteristic of microfluidics, and the specific cells bonded with the targeted microbubbles can shift because the acoustic resonance frequency of the second part is different from that of the first part. Thus, the screening of the specificity of the specific cells in blood is realized.
Owner:广州康臣药业有限公司
Automated tissue engineering system
ActiveUS8492140B2Minimize risk of contaminationImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue constructCellular functions
The invention provides systems, modules, bioreactor and methods for the automated culture, proliferation, differentiation, production and maintenance of tissue engineered products. In one aspect is an automated tissue engineering system comprising a housing, at least one bioreactor supported by the housing, the bioreactor facilitating physiological cellular functions and / or the generation of one or more tissue constructs from cell and / or tissue sources. A fluid containment system is supported by the housing and is in fluid communication with the bioreactor. One or more sensors are associated with one or more of the housing, bioreactor or fluid containment system for monitoring parameters related to the physiological cellular functions and / or generation of tissue constructs; and a microprocessor linked to one or more of the sensors. The systems, methods and products of the invention find use in various clinical and laboratory settings.
Owner:OCTANE BIOTECH +1
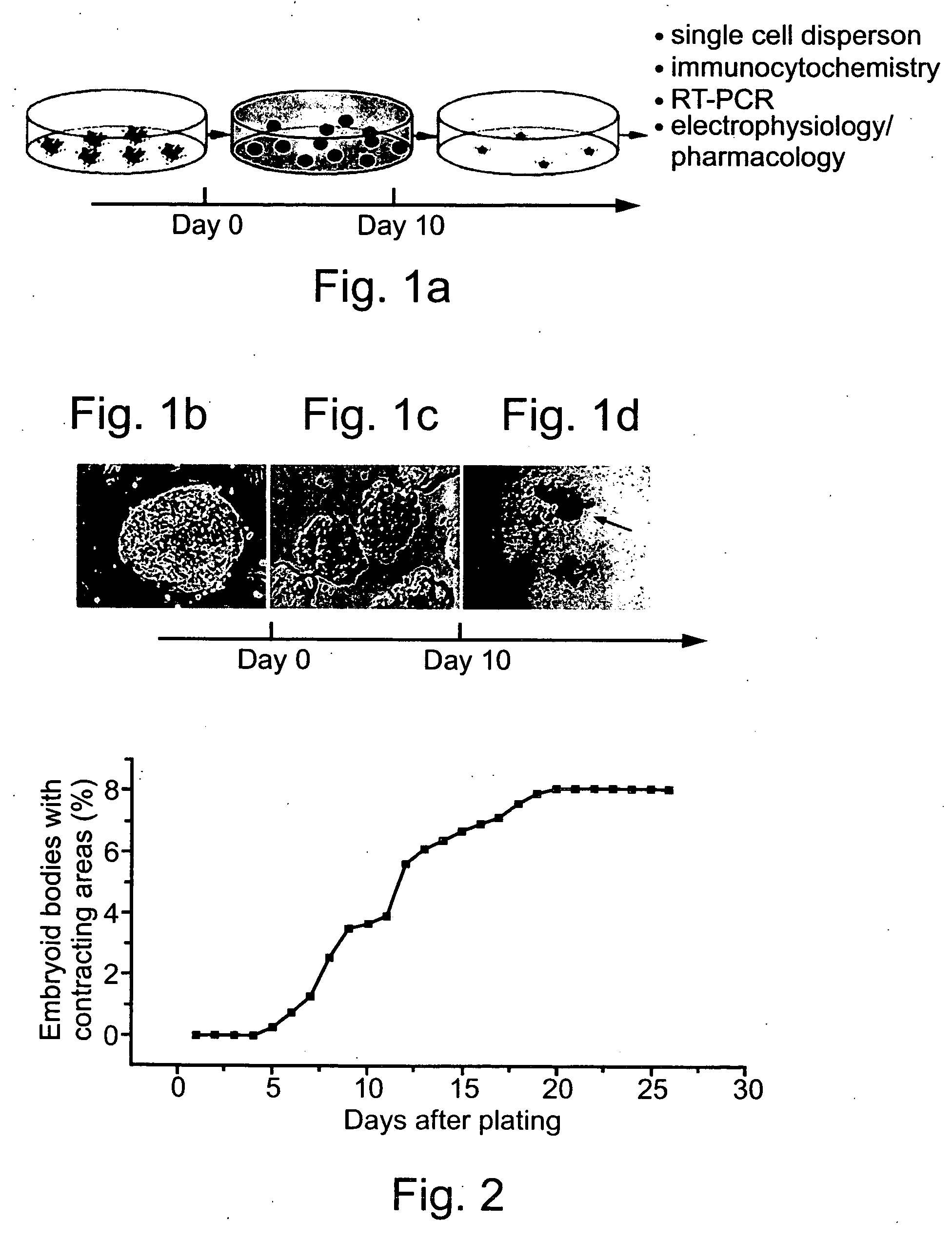
Methods of generating human cardiac cells and tissues and uses thereof
A method of generating cells predominantly displaying at least one characteristic associated with a cardiac phenotype is disclosed. The method comprises (a) partially dispersing a confluent cultured population of human stem cells, thereby generating a cell population including cell aggregates; (b) subjecting said cell aggregates to culturing conditions suitable for generating embryoid bodies; (c) subjecting said embryoid bodies to culturing conditions suitable for inducing cardiac lineage differentiation in at least a portion of the cells of said embryoid bodies, said culturing conditions suitable for inducing cardiac lineage differentiation including adherence of said embryoid bodies to a surface, and culture, medium supplemented with serum, thereby generating cells predominantly displaying at least one characteristic associated with a cardiac phenotype.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Tissue transplantation compositions and methods
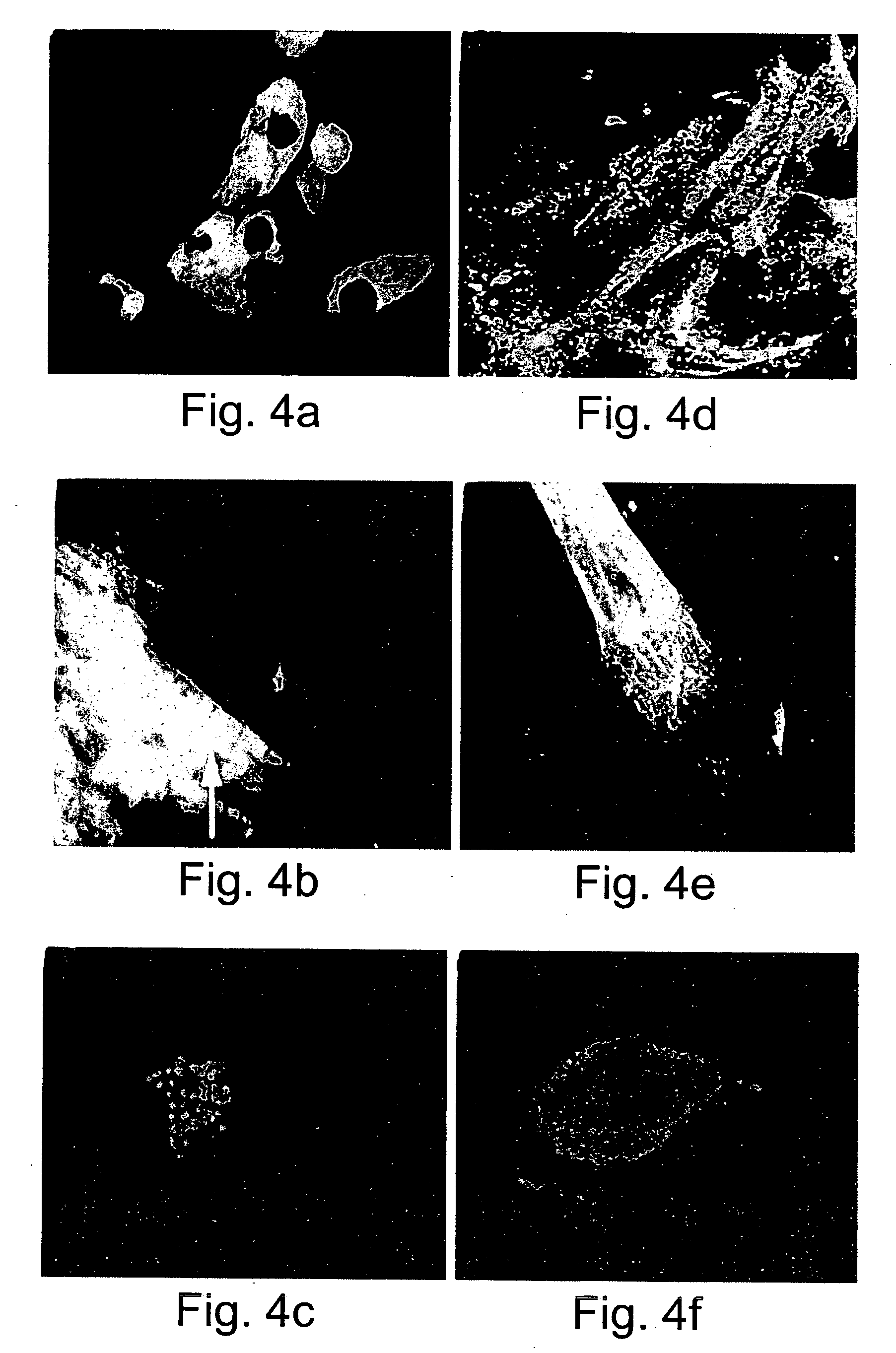
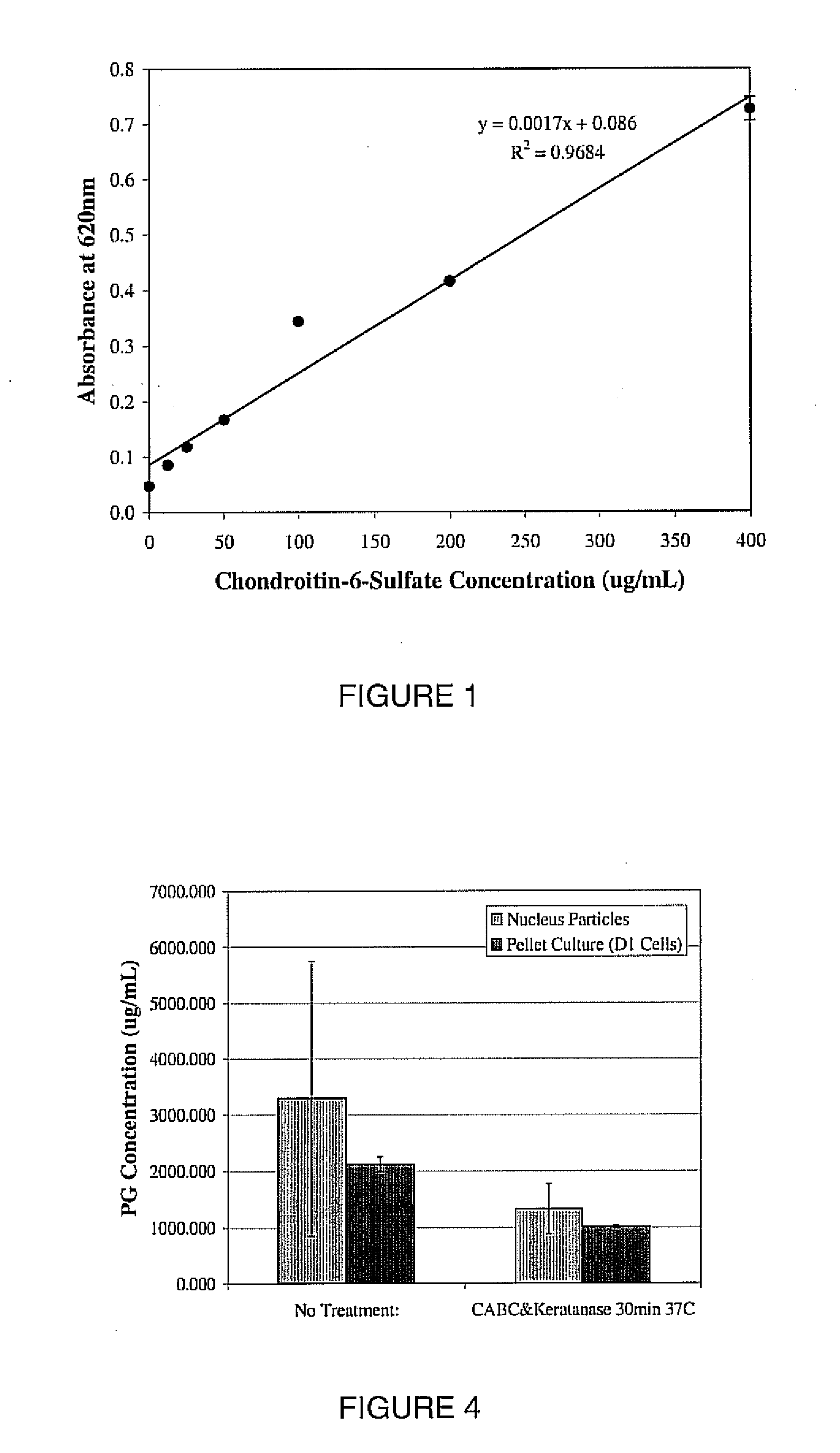
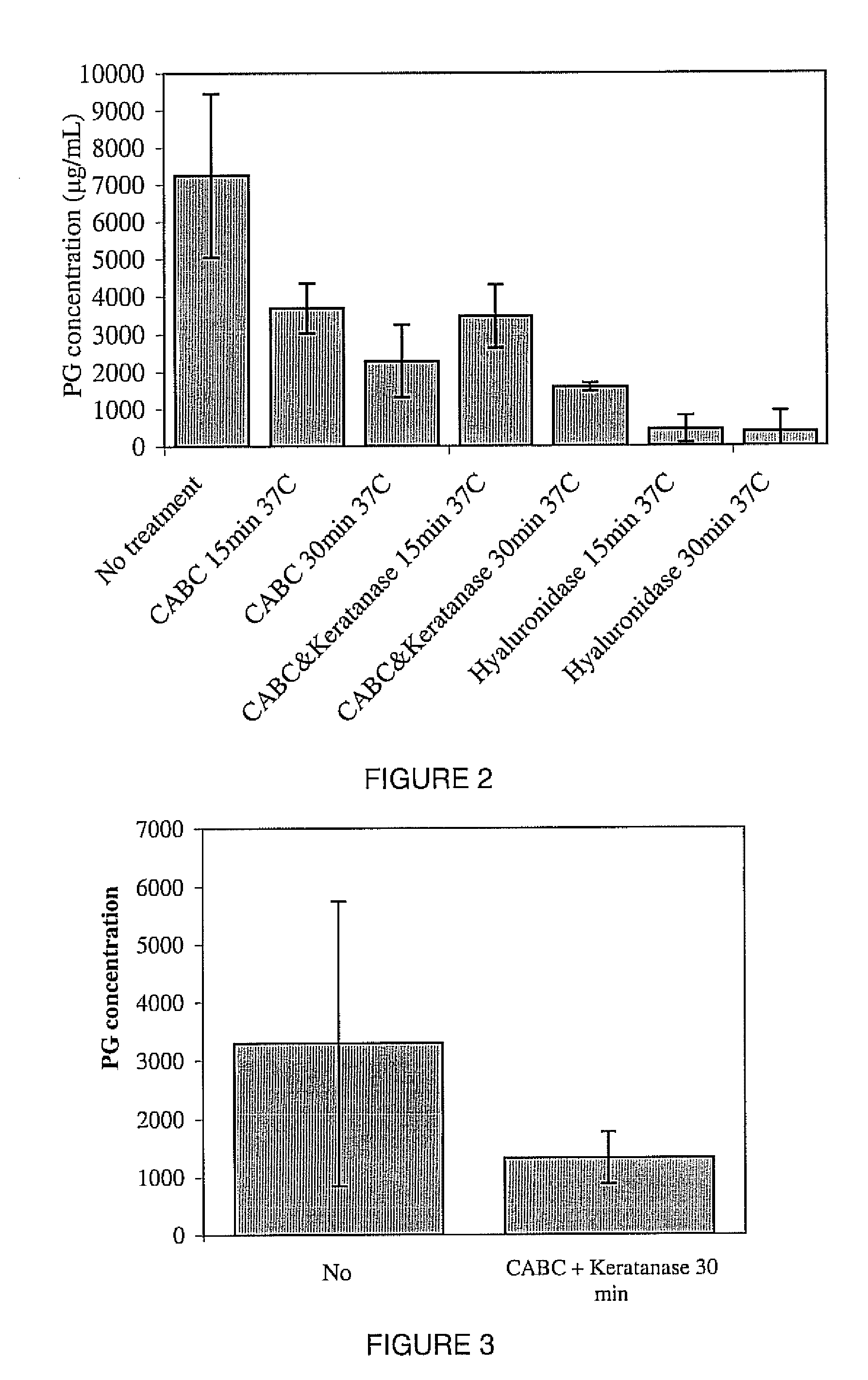
A biomedical material for transplant to a subject is provided according to embodiments of the present invention which includes an isolated donor tissue enzyme-treated to reduce the amount of proteoglycans in the donor tissue compared to untreated tissue. Isolated cells are optionally added to the enzyme-treated donor tissue, including leukocytes, particularly monocytes; macrophages; platelets; cells derived from an intervertebral disc such as chondrocyte-like nucleus pulposus cells; fibrocytes; fibroblasts; mesenchymal stem cells; mesenchymal precursor cells; chondrocytes; or a combination of any of these. The isolated donor tissue is articular cartilage or an intervertebral disc tissue such as nucleus pulposus tissue and / or annulus fibrosis tissue enzyme-treated to remove proteoglycans normally present in these tissues. A biomedical material of the present invention is administered to a subject to treat a disorder or injury, such as a disorder or injury to connective tissue.
Owner:FERREE BRET
Allografts combined with tissue derived stem cells for bone healing
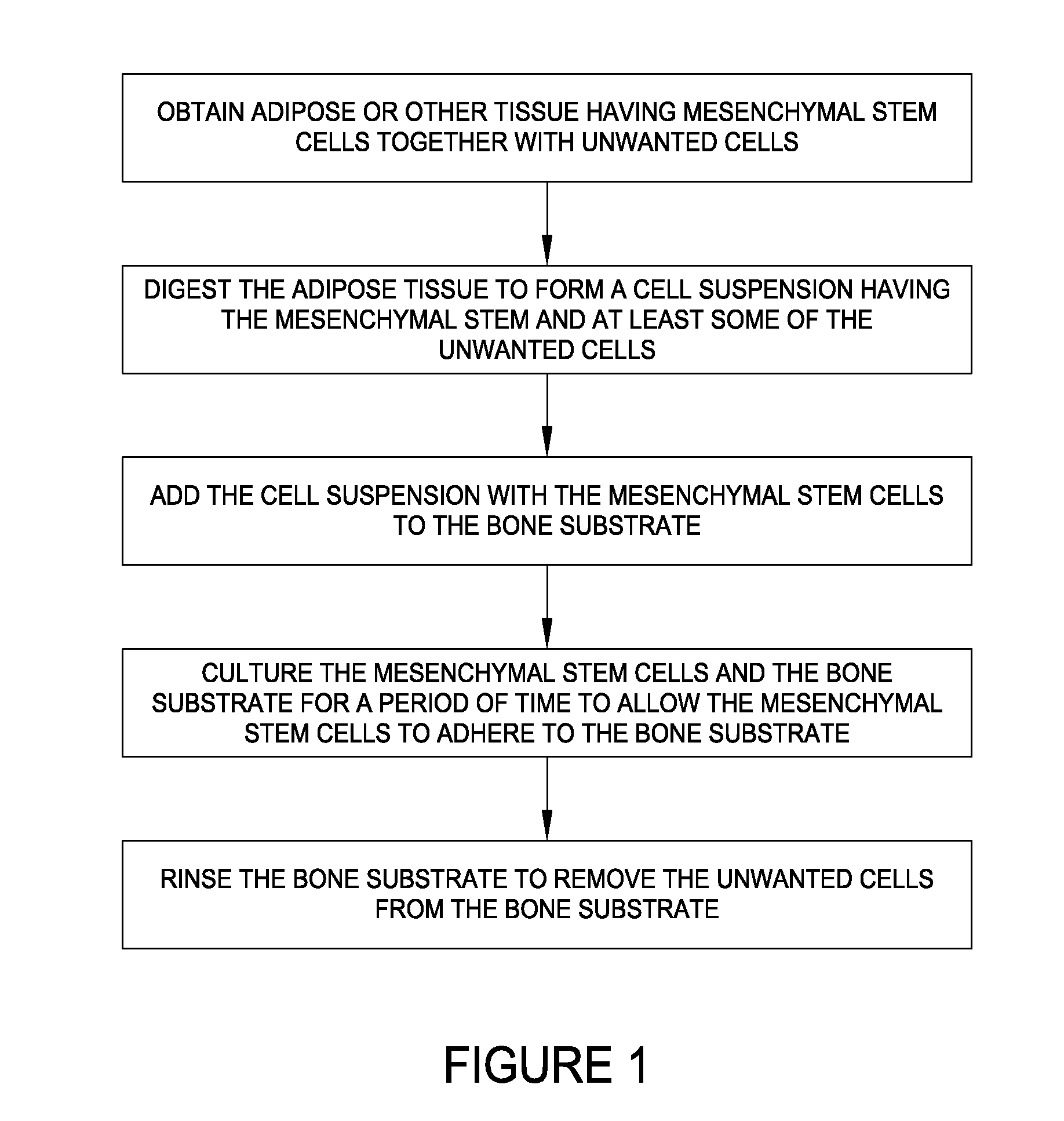
ActiveUS20100124776A1Smooth appearanceCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsWound healingMuscle tissue
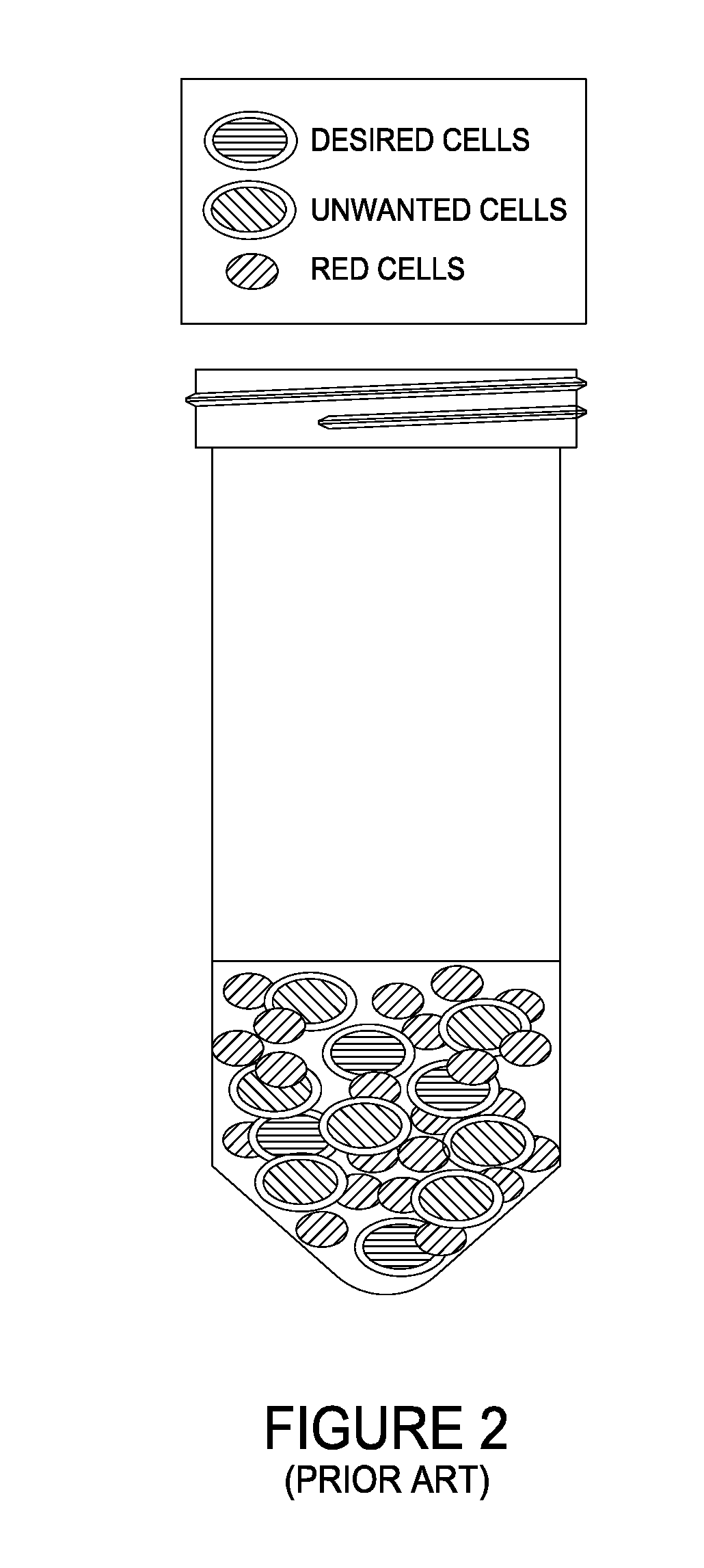
There is disclosed a method of combining mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) with a bone substrate. In an embodiment, the method includes obtaining tissue having MSCs together with unwanted cells. The tissue is digested to form a cell suspension having MSCs and unwanted cells. The cell suspension is added to the substrate. The substrate is cultured to allow the MSCs to adhere. The substrate is rinsed to remove unwanted cells. In various embodiments, the tissue is adipose issue, muscle tissue, or bone marrow tissue. In an embodiment, there is disclosed an allograft product including a combination of MSCs with a bone substrate in which the combination is manufactured by culturing MSCs disposed on the substrate for a period of time to allow the MSCs to adhere to the substrate, and then rinsing the substrate to remove unwanted cells from the substrate. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:ALLOSOURCE
Method for separating exosome from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell source and application thereof
PendingCN106282107AImprove acquisitionEasy to operateCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsFiltrationCentrifugation
The invention relates to a method for separating exosome from a human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell source. The method comprises the following steps: when the P2-P3 placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell convergence rate reaches 85-90%, obtaining a cell culture supernate, carrying out membrane filtration, and collecting the filtrate; centrifugating the filtrate, collecting the centrifugal supernate, adding a 10w / v%-12w / v% polyethyleneglycol culture medium supernate solution into the centrifugal supernate according to the volume ratio of 1:1, sufficiently and uniformly mixing, and carrying out secondary centrifugation, wherein the finally obtained precipitate is the exosome. The method is convenient for taking materials, is easy for enrichment amplification culture, reutilizes the P2-P3 placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell culture medium supernatant to obtain the exosome, and does not refer to the problem of medical ethics. In the exosome separation process, membrane filtration, centrifugation, polyethyleneglycol solution addition and other means are adopted to effectively increase the exosome enrichment, so the method has the advantages of short time consumption and low cost.
Owner:章毅 +7
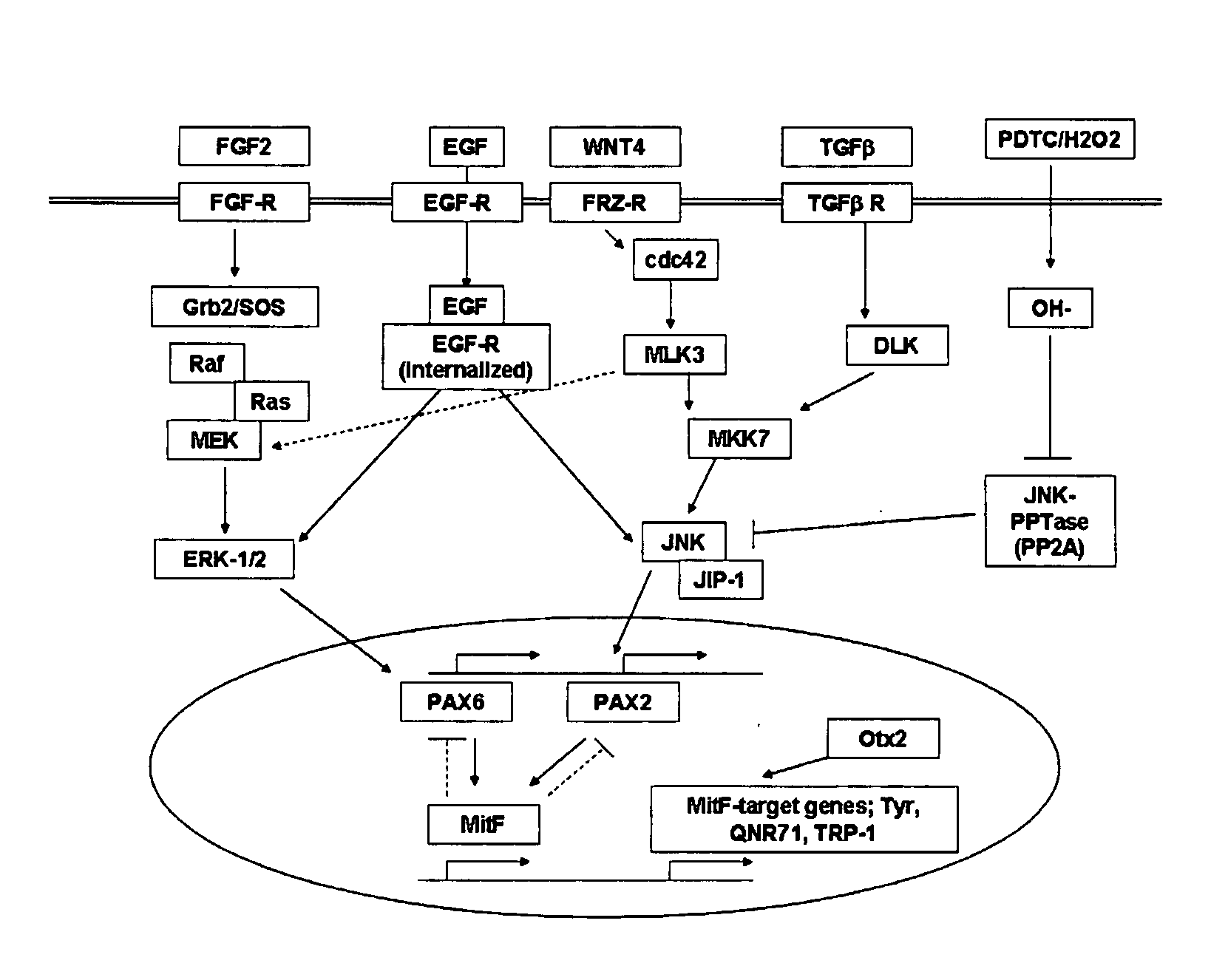
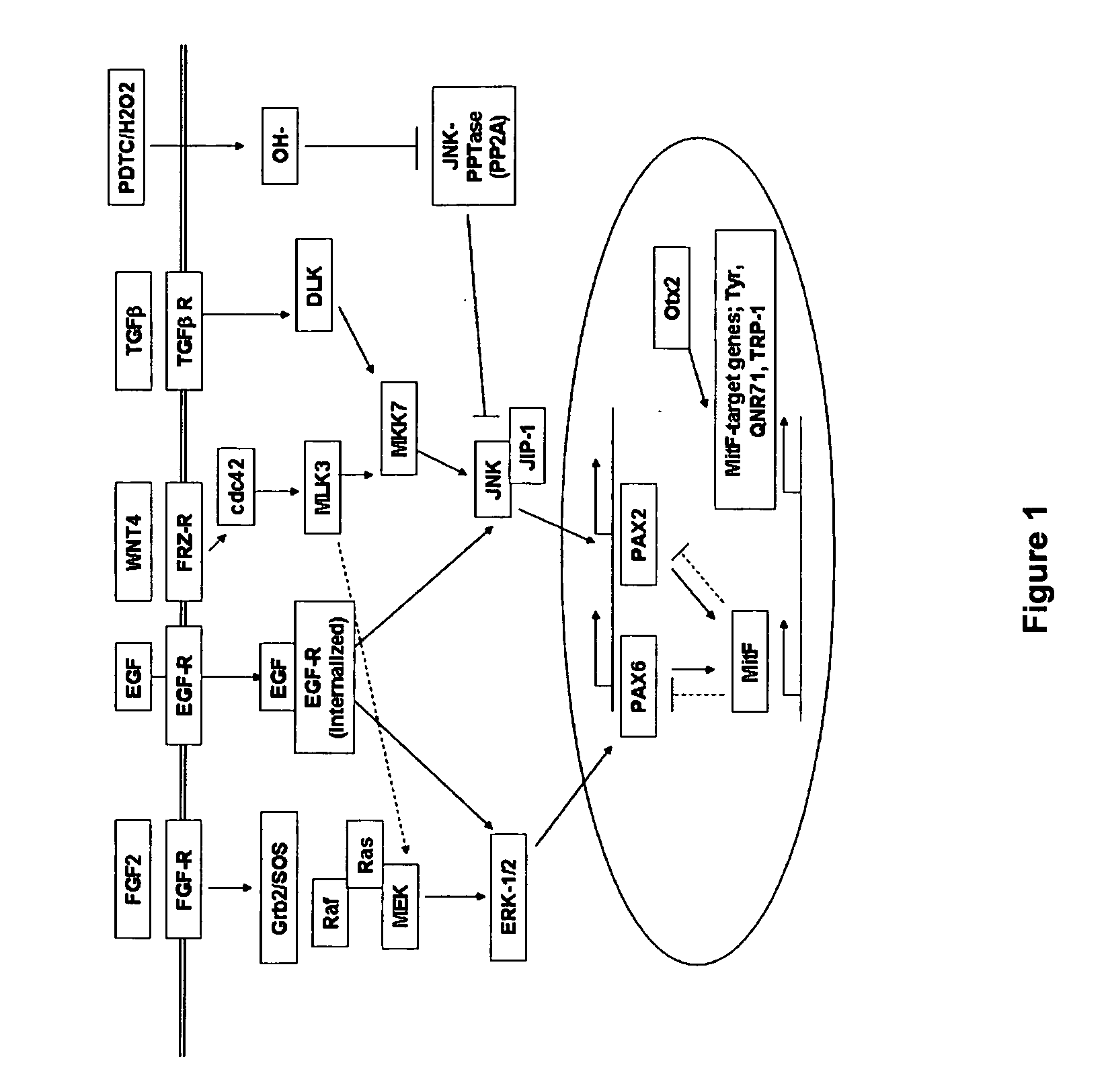
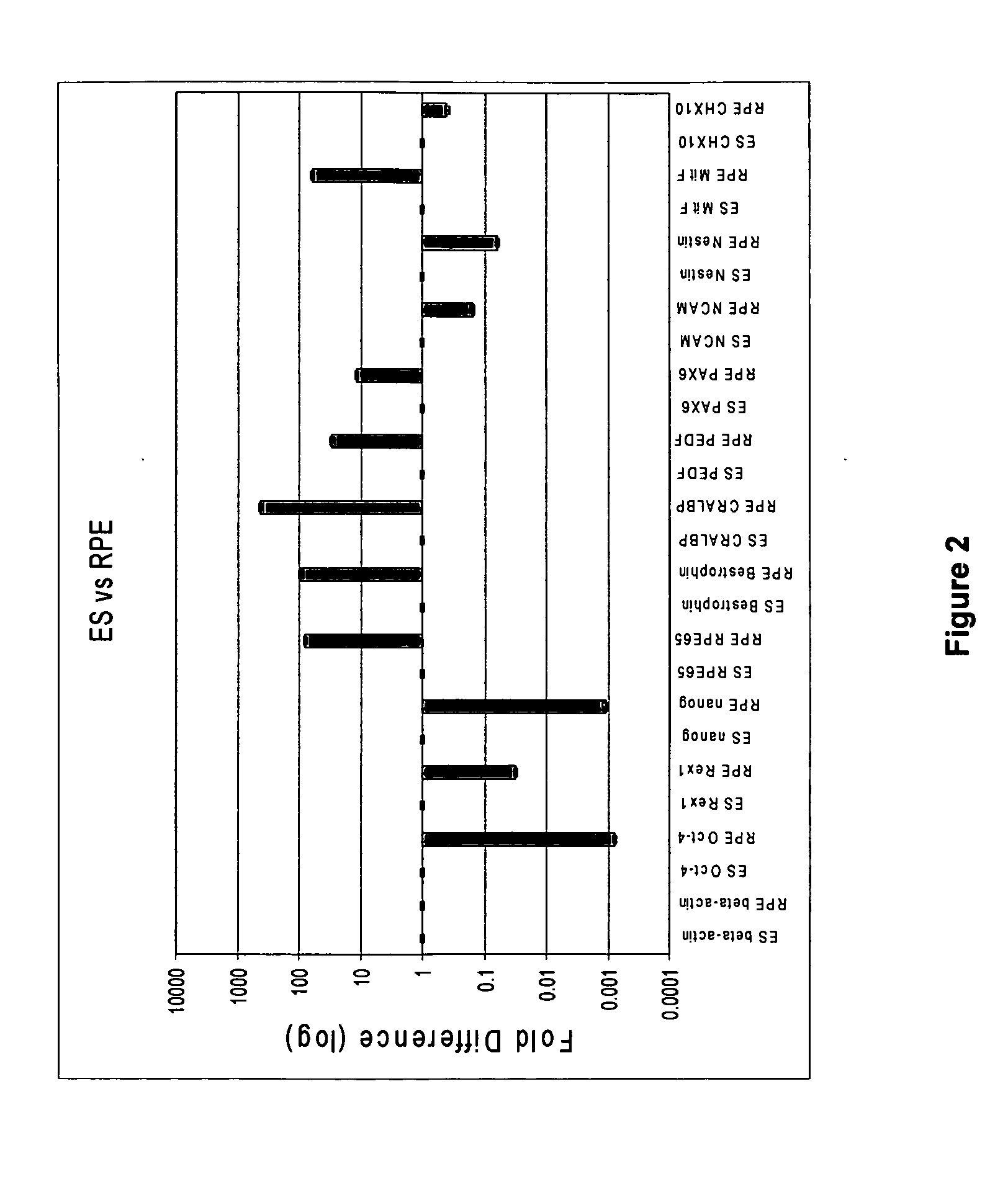
Methods of Producing RPE Cells and Compositions of RPE Cells
InactiveUS20110274662A1Reduce riskMaximize likelihoodBiocideSenses disorderInduced pluripotent stem cellRetinal pigment epithelial cell
The present invention provides improved methods for producing RPE cells from human embryonic stem cells or from other human pluripotent stem cells. The invention also relates to human retinal pigmented epithelial cells derived from human embryonic stem cells or other human multipotent or pluripotent stem cells. hRPE cells derived from embryonic stem cells are molecularly distinct from adult and fetal-derived RPE cells, and are also distinct from embryonic stem cells. The hRPE cells described herein are useful for treating retinal degenerative diseases.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com