Method for separating exosome from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell source and application thereof
A technology of stem cells and exosomes, which is applied in the field of obtaining membrane vesicles involved in cell biological activities, can solve the problems of inability to guarantee the amount of exosomes obtained, uneven quality of exosomes, and lengthy step-by-step centrifugation time. The effect of improved damage repair, shortened preparation time, and simplified operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
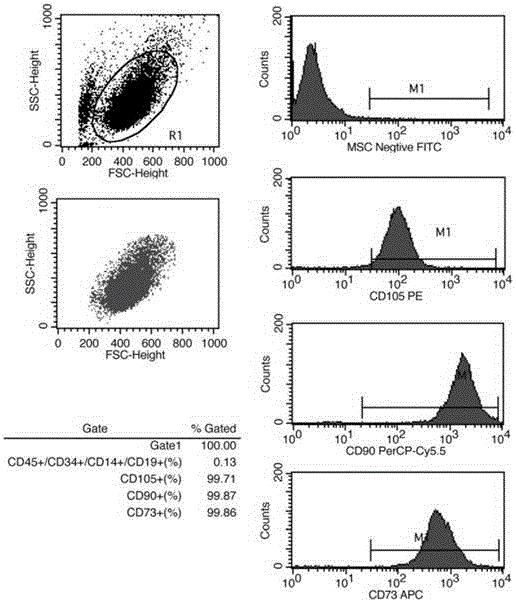
[0043] Example 1 Isolation, preparation and identification of placental mesenchymal stem cells
[0044] Neonatal placenta authorized with maternal consent was used as a source of mesenchymal stem cells.
[0045] The postpartum fresh placenta was taken under aseptic conditions, and the placenta was preserved and transported using placenta preservation solution (see Chinese invention patent No. ZL201410028687.X) and placenta collection and storage device (see Chinese utility model patent No. ZL2014203904164). Under aseptic conditions within 48 hours, the amniotic membrane was mechanically peeled off from the placenta tissue, and then the placental chorion was carefully cut to remove as much connective tissue as possible on the chorion. Soak and rinse 3 to 5 times, and cut the rinsed chorion into about 1mm with ophthalmic scissors 3 Fragments were digested by adding type II collagenase (0.1% final enzyme digestion concentration) at 37° C. for 90 min, and shaken at 200 rpm. Add ...
Embodiment 2
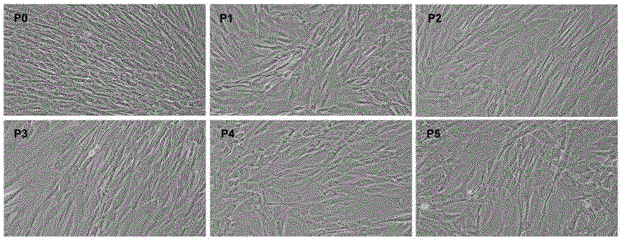
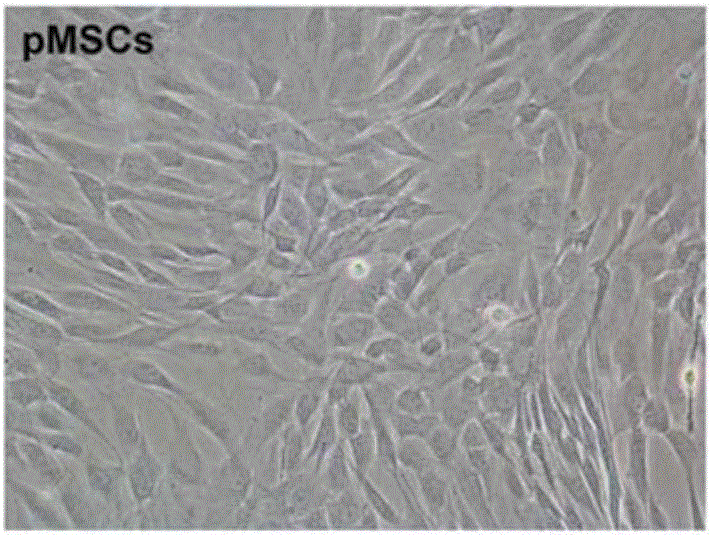
[0047] Example 2 Subculture of placental mesenchymal stem cells, morphological observation and culture medium collection
[0048] Take P0~P5 cultured cells, 5×10 4 Inoculated on 10×10 cell culture dishes, 37°C, 5% CO 2 , static culture in saturated humidity, using the serum-free medium for placental mesenchymal stem cells described in CN103805562B for culture, changing the medium every 3 days, and collecting the supernatant of the medium when the hPMSCs cell confluence reaches 85% to 90%. When the confluence of P0-P5 generation cells reached 85%-90%, the phase-contrast microscope morphology was observed and photographed (see image 3 ). Such as image 3 As shown, observed under an inverted phase-contrast microscope, 48 hours after inoculation of the primary cultured PMSCs, most of the cells adhered to the wall, and the morphology was typical fibroblast-like. Scattered some translucent round miscellaneous cells. The P0, P1, P2, and P3 generations were all long-spindle-shap...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3 Acquisition of exosome
[0050] Extract 10ml-20ml of cell culture supernatant, filter it with a 0.22μm filter membrane at 4°C; then centrifuge at 10,000×g for 30min, discard the precipitate (remove subcellular components); collect the centrifuged supernatant by volume 1:1 Proportionally add 0w / v%, 9w / v%, 10w / v%, 11w / v%, 12w / v% and 13w / v% polyethylene glycol culture supernatant solution, 120,000×g for the second time After centrifugation for 75 minutes, the resulting precipitate is the exosome.
[0051] Re-suspend the precipitate with 30ml of PBS solution, mix well and then centrifuge at 120,000×g for 75min, suspend the purified exosome solution with 1ml of PBS solution, put them into eppendorf tubes, store them in a -80°C refrigerator for later use, and carry out the yield analysis. Analysis see Figure 5 , in which the 12% PEG group had the highest yield of exosome.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com