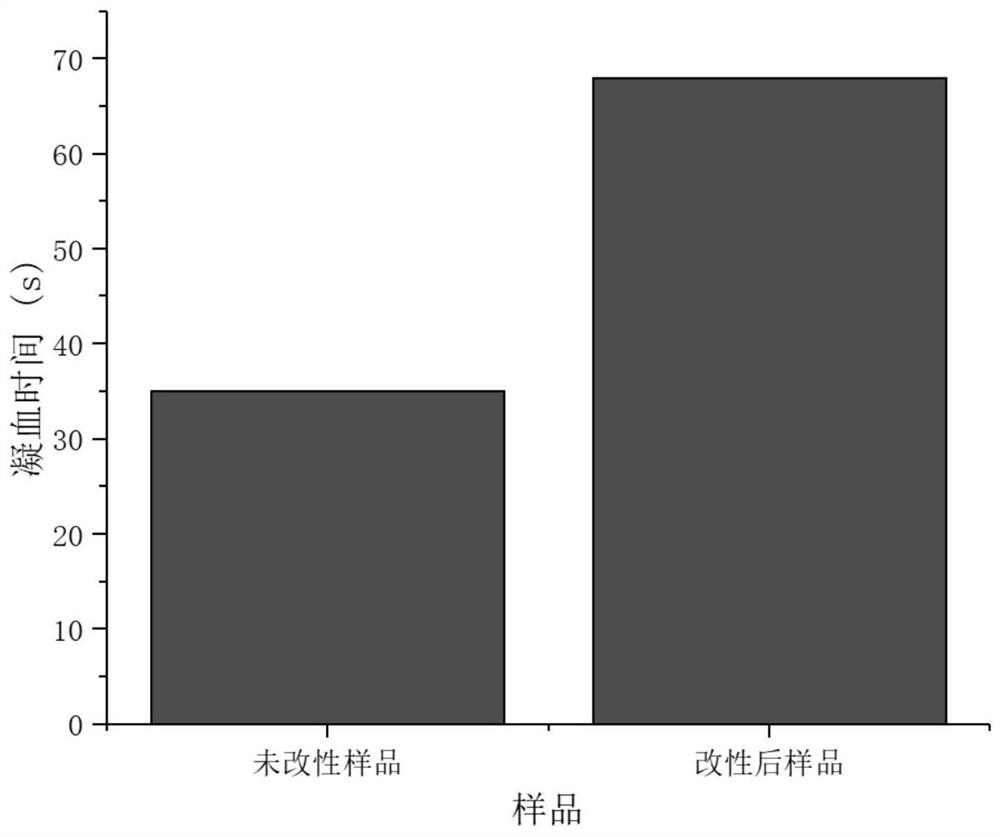
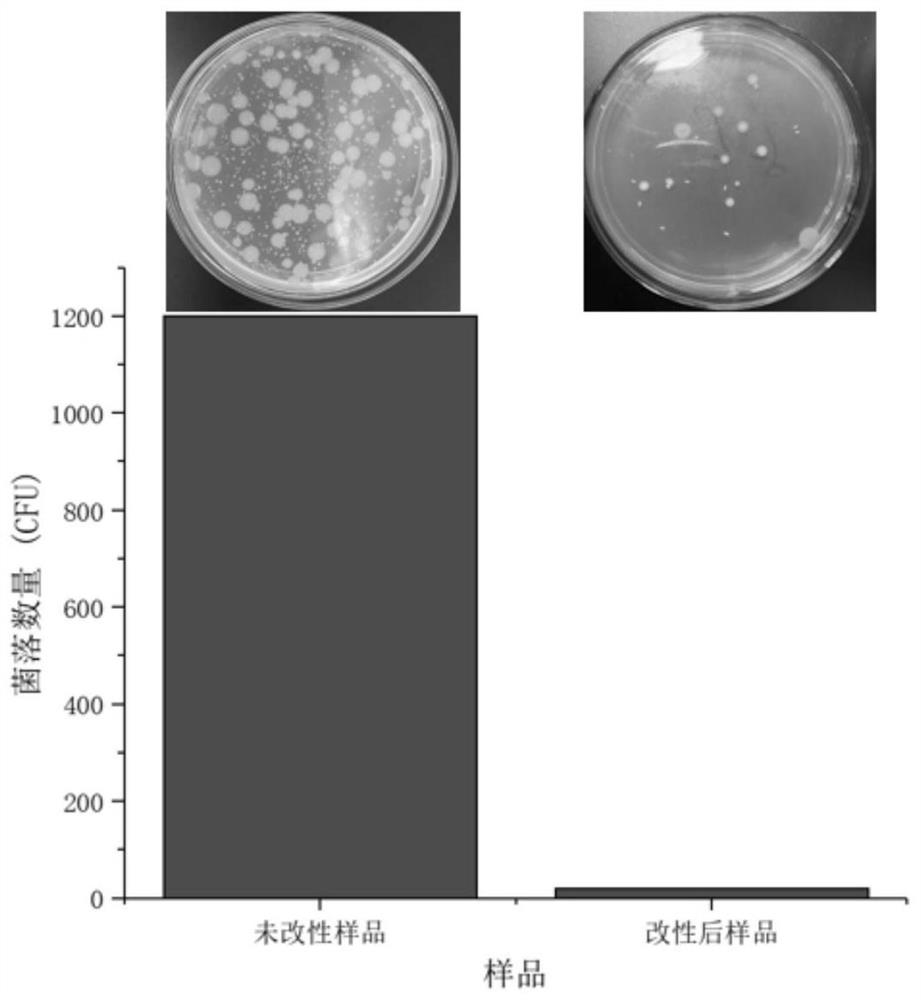
Patents
Literature
98 results about "Anticoagulant Agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A substance that is used to prevent and treat blood clots in blood vessels and the heart.
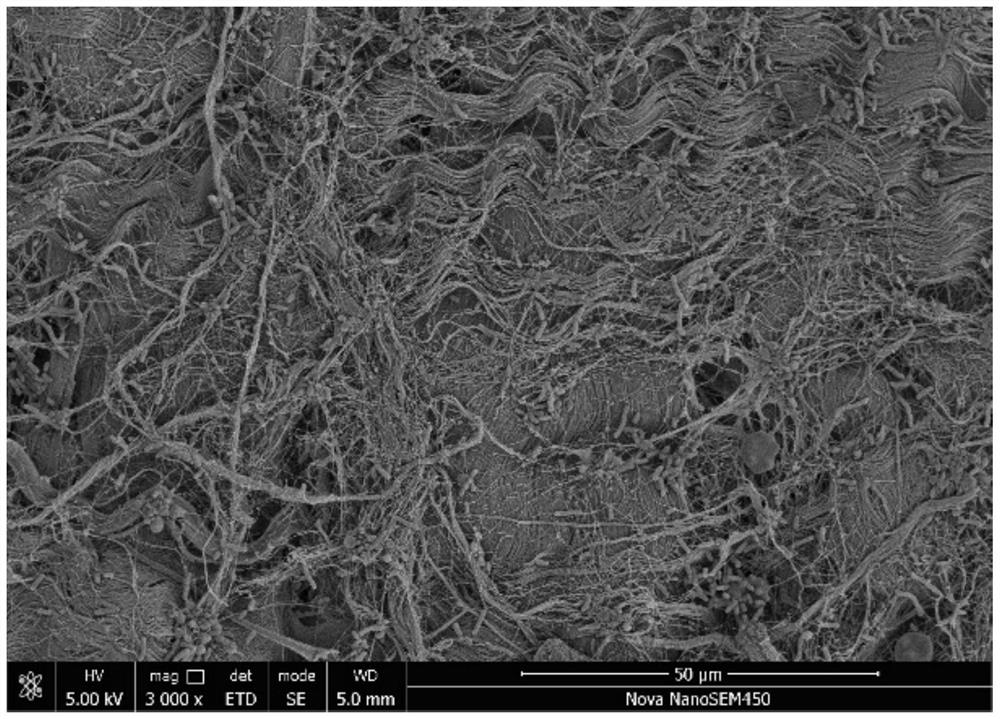
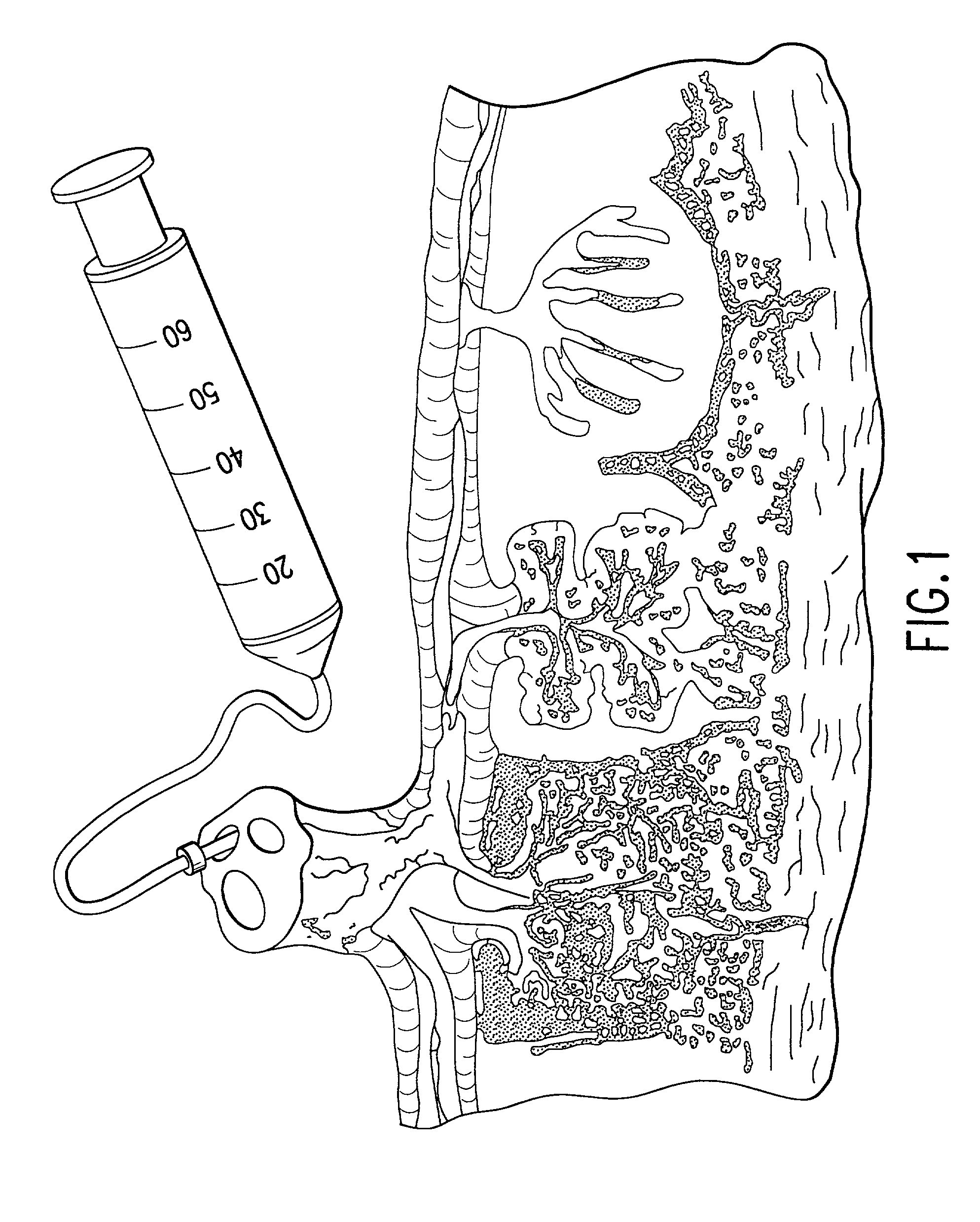
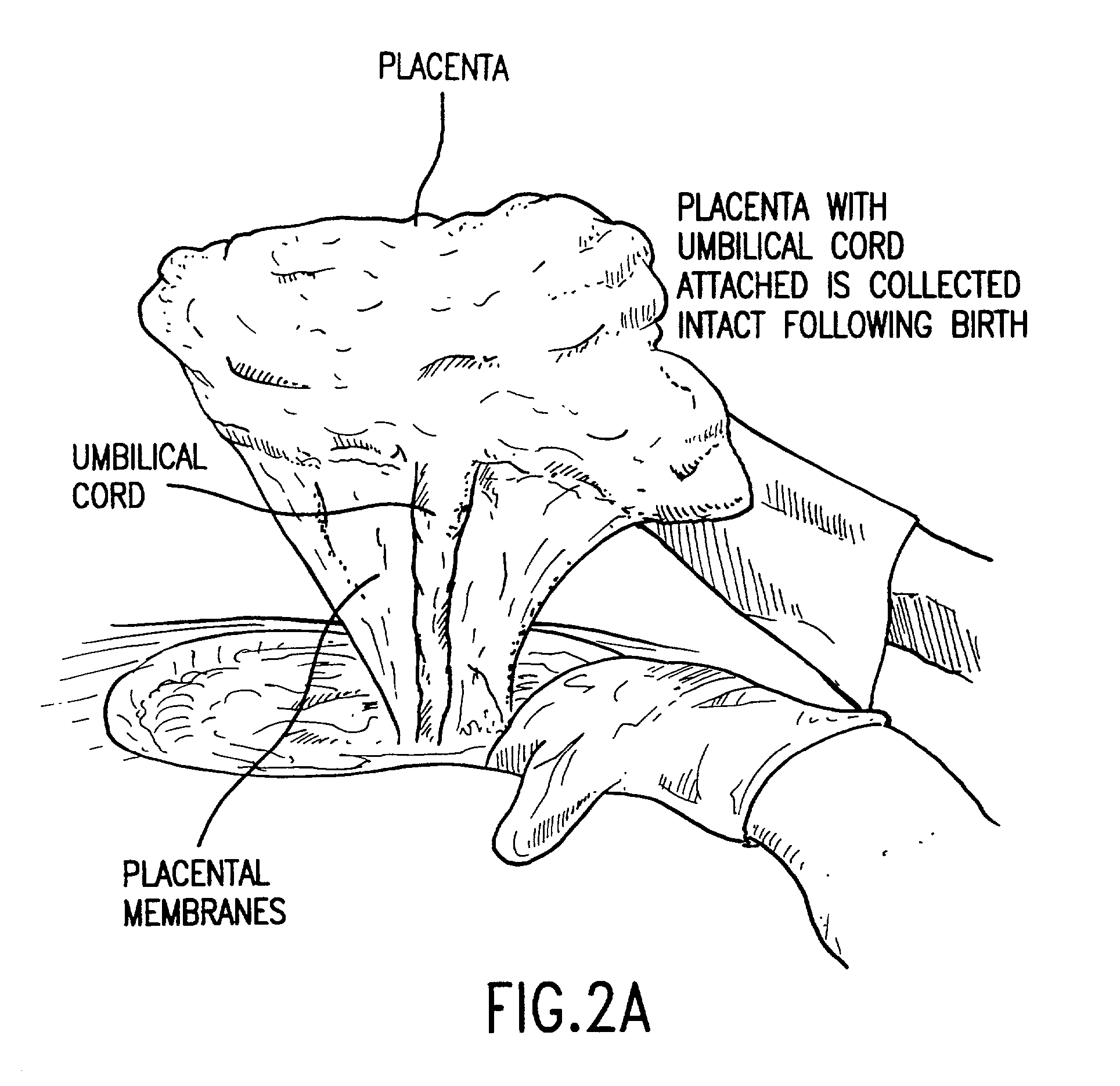
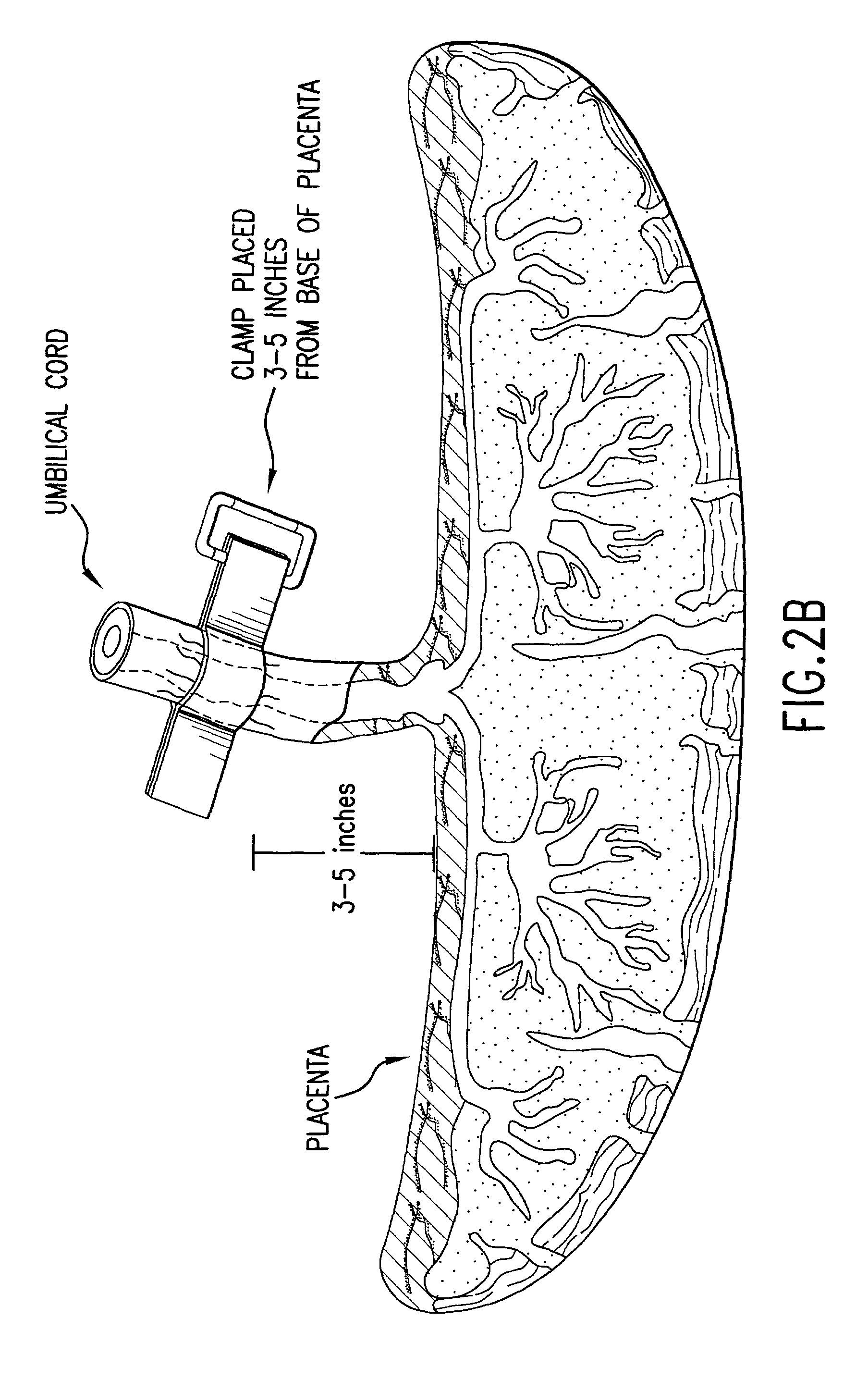
Post-partum mammalian placenta, its use and placental stem cells therefrom
InactiveUS20030032179A1Enhance exsanguinationEnhance sterile conditionSenses disorderAntipyreticAnticoagulant AgentEmbryo
The present invention provides a method of extracting and recovering embryonic-like stem cells, including, but not limited to pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, from an exsanguinated human placenta. A placenta is treated to remove residual umbilical cord blood by perfusing an exsanguinated placenta, preferably with an anticoagulant solution, to flush out residual cells. The residual cells and perfusion liquid from the exsanguinated placenta are collected, and the embryonic-like stem cells are separated from the residual cells and perfusion liquid. The invention also provides a method of utilizing the isolated and perfused placenta as a bioreactor in which to propagate endogenous cells, including, but not limited to, embryonic-like stem cells. The invention also provides methods for propagation of exogenous cells in a placental bioreactor and collecting the propagated exogenous cells and bioactive molecules therefrom.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Methods of treatment of patients at increased risk of development of ischemic events and compounds hereof
InactiveUS20130040898A1Impair thrombus formationIncreased riskElcosanoid active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsBeta blockerPlatelet inhibitors
The present invention relates to compounds for treatment that protects the endothelium, prevents pathologic thrombus formation in the microcirculation and preserves platelet number and function and thus may be related to treatment or prevention of ischemic events in patients with cardiovascular disease. The present invention is particularly useful for patients having or being at increased risk of development of an ischemic event such as an acute myocardial infarction and / or no-reflow phenomena and / or ischemia-reperfusion injury by administration of agent(s) modulating and / or preserving endothelial integrity. The compounds may be administered in combination with standard treatment of acute cardiovascular ischemic events such as Platelet inhibitors such as aspirin (ASA), Thienopyridins, GPIIb / IIIa inhibitors), Parenteral anticoagulants such as unfractioned heparin (UFH), bivalirudin, enoxaparin, and fondaparinux, Verapamil, Adenosine, Sodium nitroprusside, Nitroglycerin, Epinephrine, Beta-blockers and surgical methods such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), PCI with thrombus aspiration, PCI with stents.
Owner:THROMBOLOGIC
Anti-Thrombotic Agents
InactiveUS20080219998A1Improve efficacyImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesAntithrombotic AgentAnticoagulant Agent
The present invention embodies: methods; compounds, their pharmaceutically acceptable analogs, isomer, salts, hydrates, solvates and prodrug derivatives, and pharmaceutically acceptable compositions thereof that have particular biological properties; devices; diagnostic and other assays; and the uses of such methods, compounds, devices and assays. Common throughout these embodiments is specific selective reduction of intravascular thromboplastin antecedent activity, which results in a safe antithrombotic effect. A particularly prominent application or the invention relates to diagnosis and treatment of patients which have, or are at risk of, developing thrombosis, thrombotic injury, or vaso-occlusive diseases, such as myocardial infarction, stroke, restenosis after angioplasty, thrombotic diseases, etc. Another particularly prominent feature of the present invention is its high level of hemostatic safety at optimal efficacy. Also, the present invention is compatible for use in combination with other traditional therapeutic agent such as another antithrombotic, antiplatelet, thrombolytic, or anticoagulant agents.
Owner:GRUBER ANDRAS
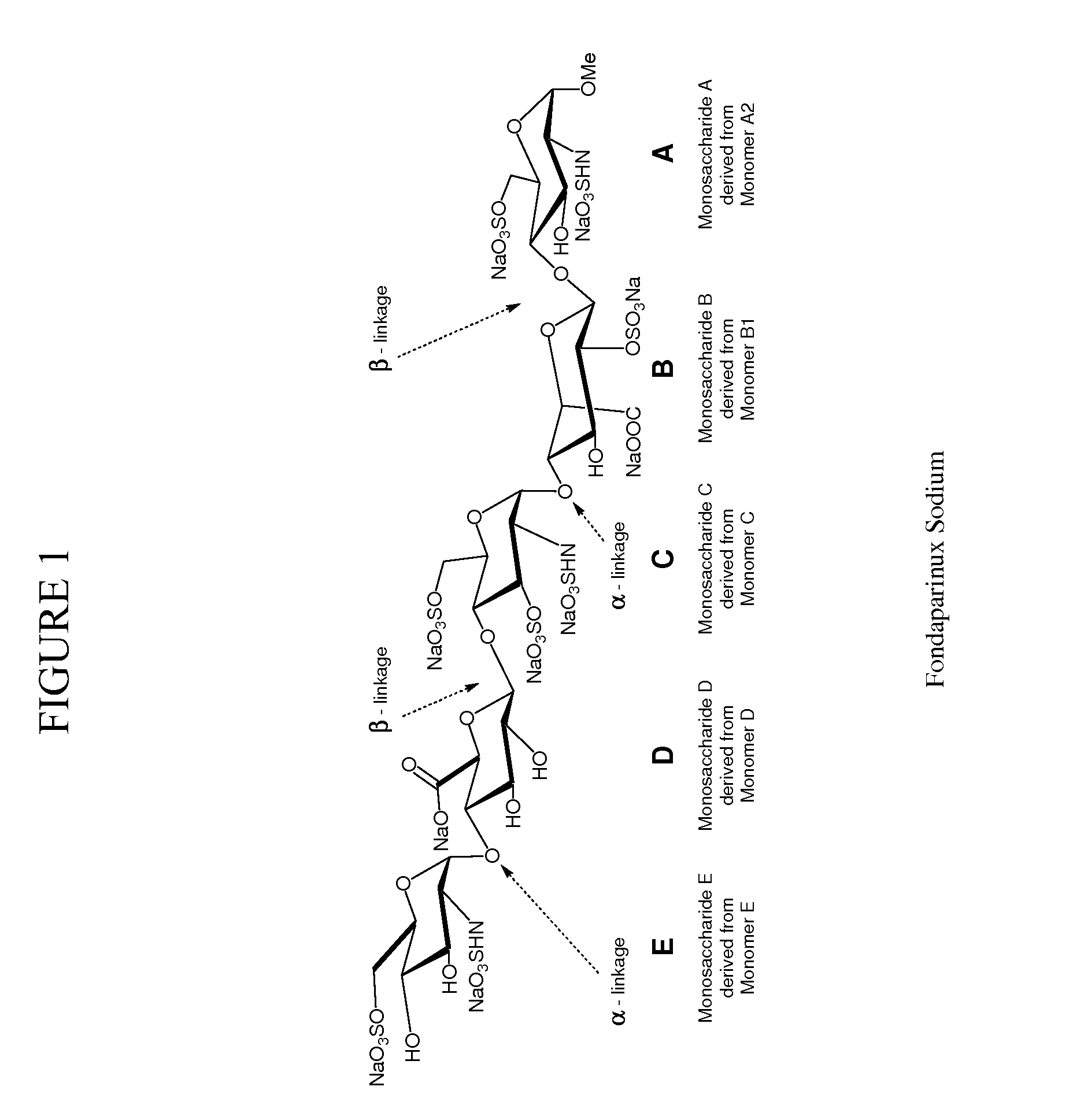
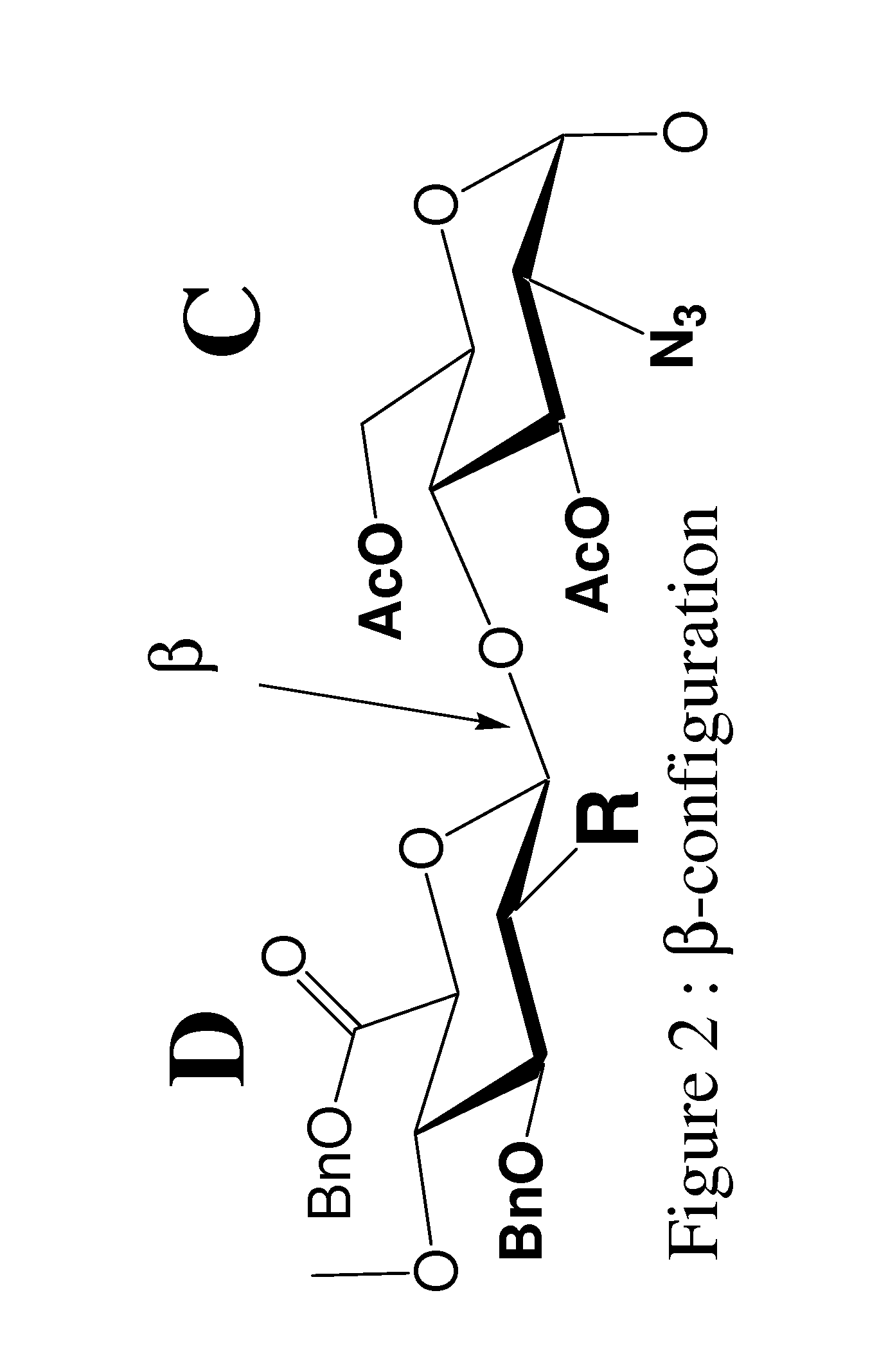
Process for preparing Fondaparinux sodium and intermediates useful in the synthesis thereof
ActiveUS8288515B2Highly efficient glycosylation reactionGood yieldEsterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsAnticoagulant AgentCombinatorial chemistry
Processes for the synthesis of the Factor Xa anticoagulent Fondaparinux, and related compounds are described. Also described are protected pentasaccharide intermediates as well as efficient and scalable processes for the industrial scale production of Fondaparinux sodium by conversion of the protected pentasaccharide intermediates via a sequence of deprotection and sulfonation reactions.
Owner:RELIABLE BIOPHARM LLC
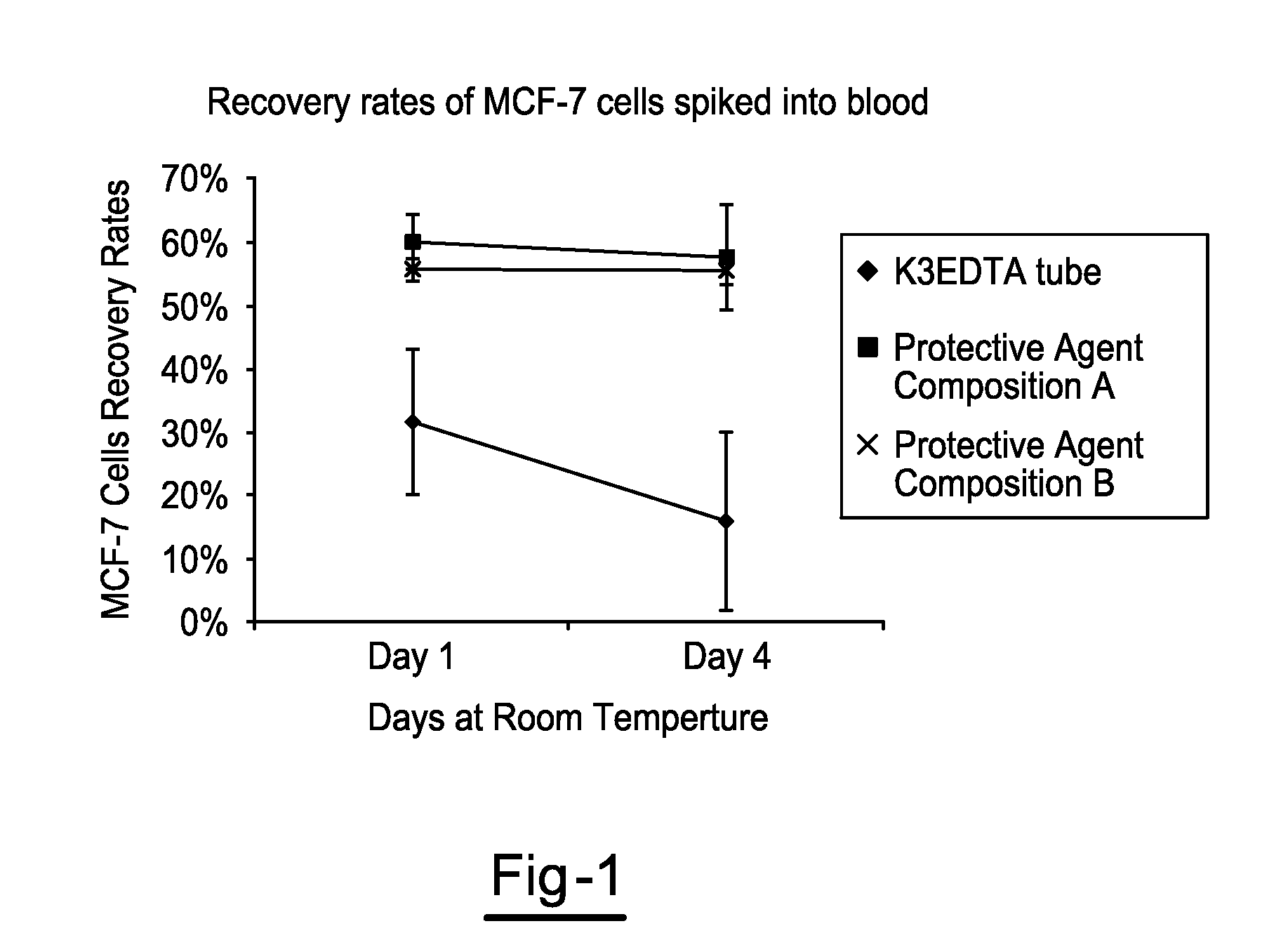
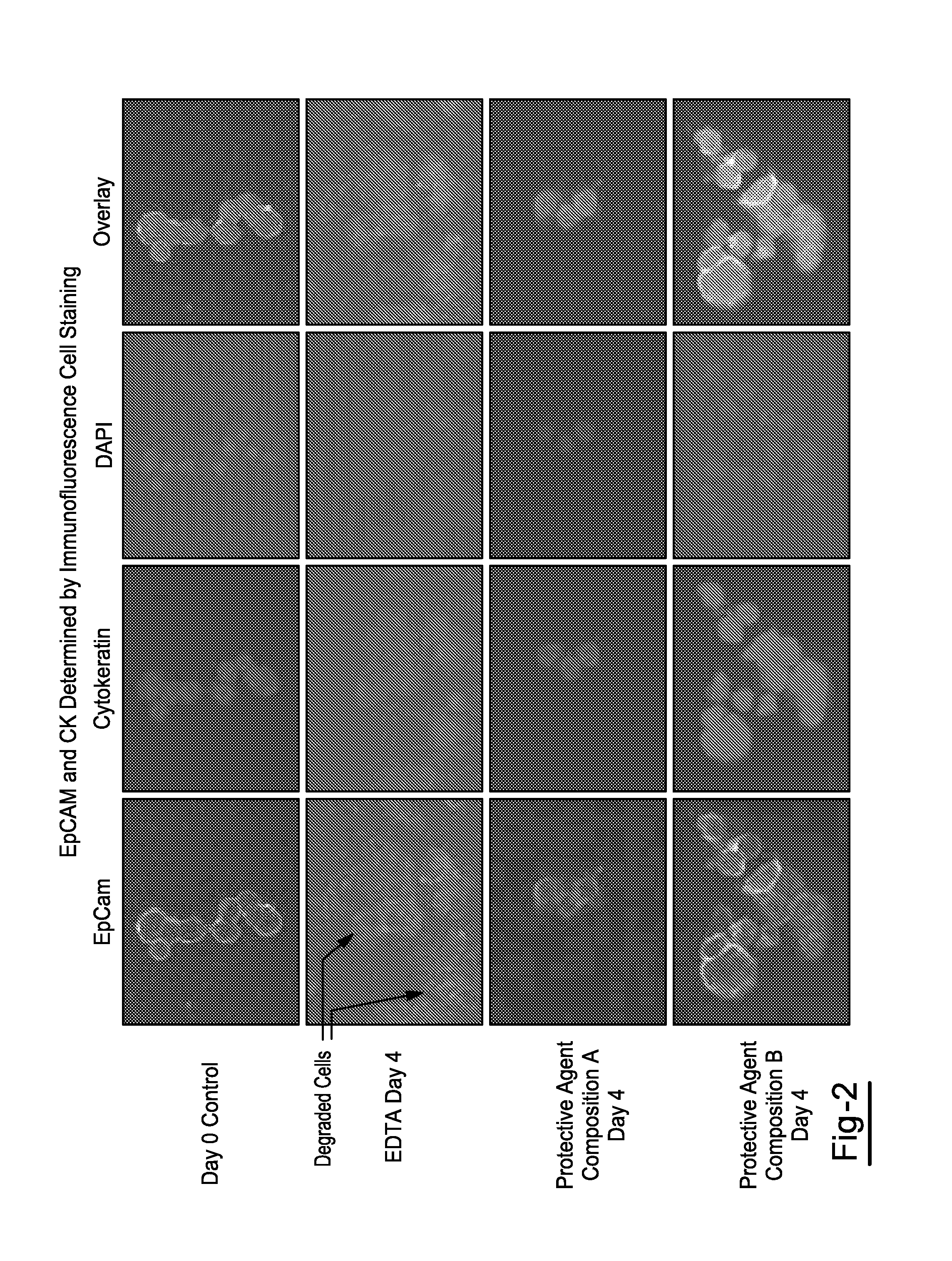
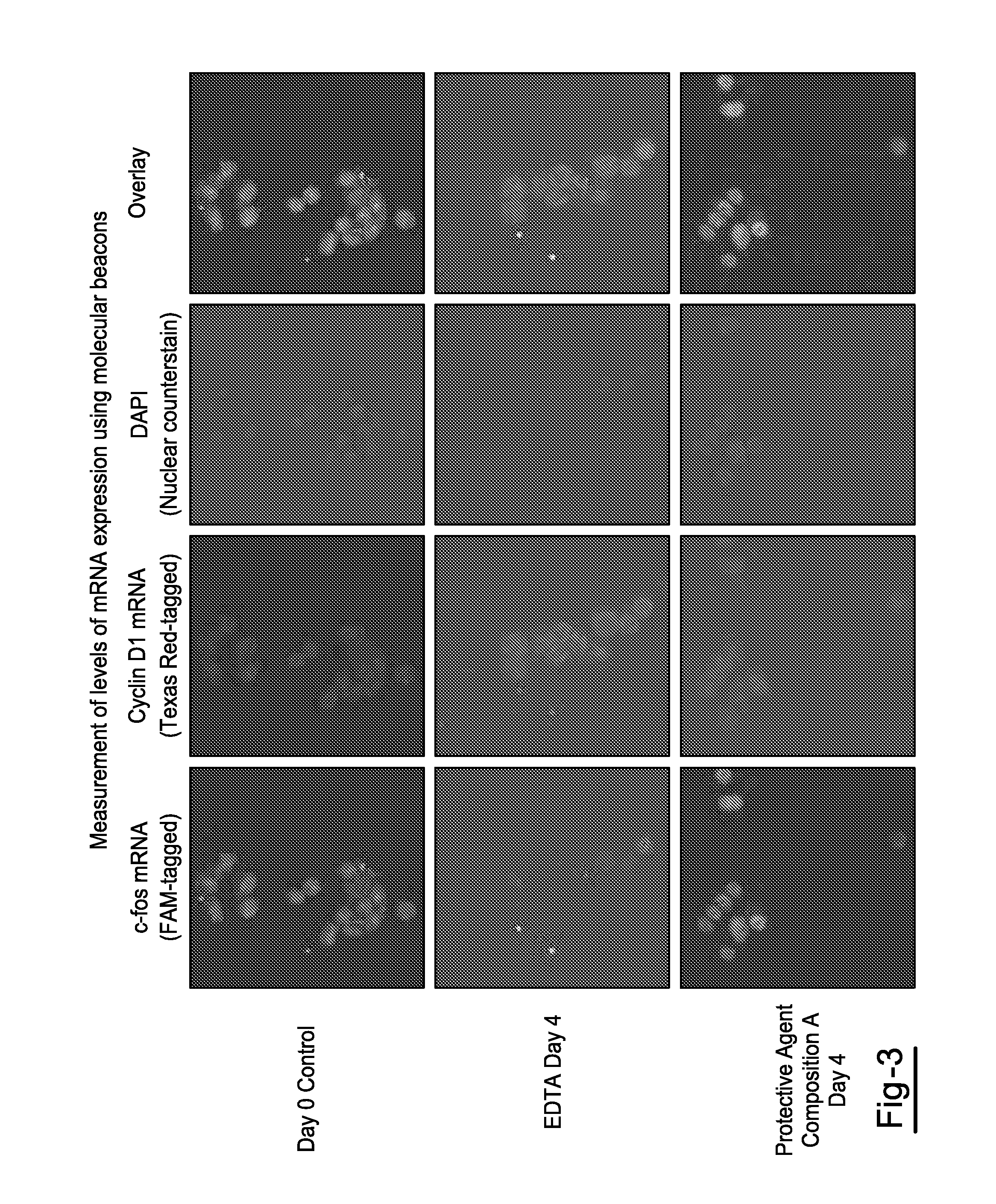
Compositions and Methods for Stabilizing Circulating Tumor Cells
ActiveUS20160174544A1Improves downstream clinical analysisReduced activityDead animal preservationTissue culturePreservativeSubject matter
Compositions and Methods for Stabilizing Circulating Tumor Cells Methods and compositions for stabilizing a biological sample for analysis, comprising the steps of obtaining in a sample collection device a biological sample from a subject, especially blood, the biological sample including at least one circulating tumor cell from the subject. The methods may include a step of contacting the biological sample with a protective agent composition that includes a preservative agent, an optional anticoagulant, and a quenching agent to form a mixture that includes the protective agent composition and the sample.
Owner:STRECK LLC
Cell preservation solution and application thereof
PendingCN107410287AEasily brokenAvoid destructionDead animal preservationTreatment effectAnticoagulant
The invention provides a cell preservation solution and application thereof. The cell preservation solution is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 60 to 1000 parts of pH buffer, 10 to 150 parts of osmotic pressure maintenance agent, 4 to 55 parts of anticoagulant, 1 to 30 parts of mucolytic agent, 800 to 5000 parts of fixing agent, 1 to 150 parts of component A, 10 to 30 parts of component B and 10000 to 20000 parts of water, wherein the component A is prepared from sodium azide and lauryl sodium sulfate according to a weight ratio of (1 to 10) to (2 to 110); the component B is carbon disulfide. The cell preservation solution of the invention has a better impurity treatment effect, and reduces the interference factors in cell samples; at the same time, target cells therein can retain the characteristics of structural morphology for a long time, thereby facilitating the medical detection and analysis of the target cells, and the cost is low.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HONGQI OPTICAL INSTR TECH
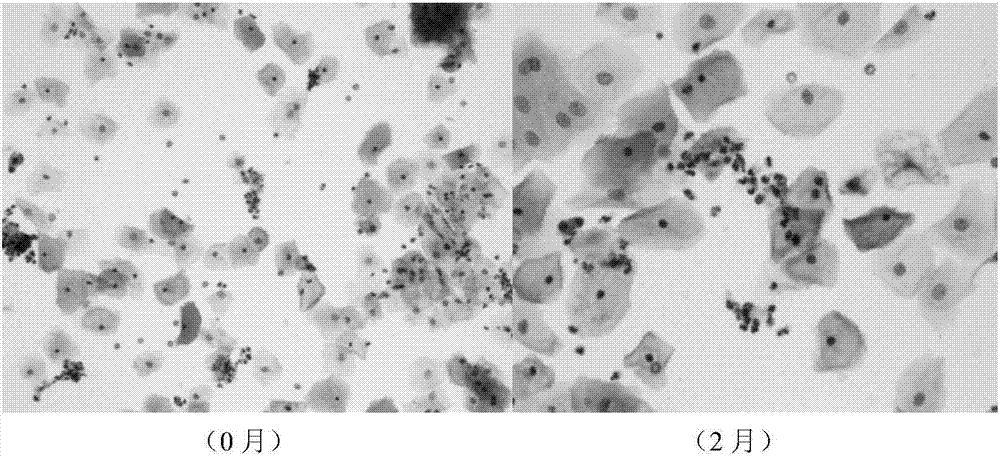
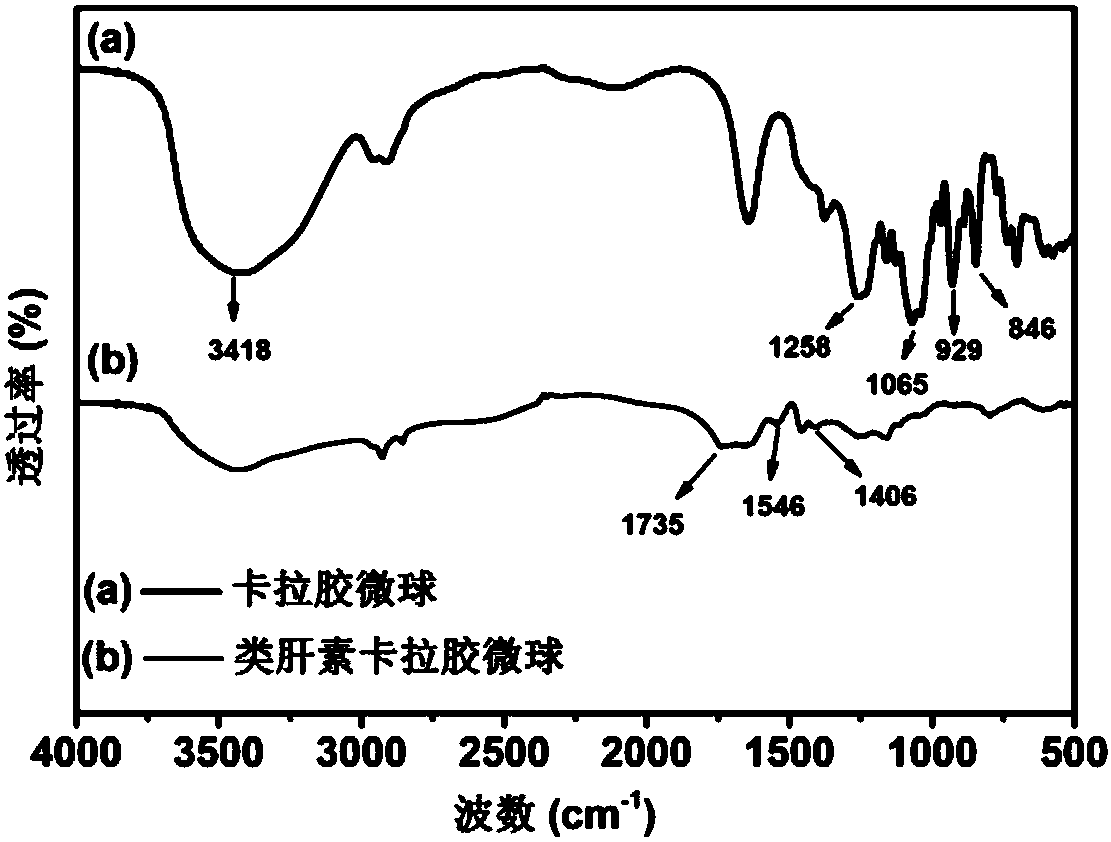
Carrageenan-based self-anticoagulant heparitin microsphere, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108530670AGood biocompatibilityLow cytotoxicityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesCarrageenanDouble network
The invention discloses a carrageenan-based self-anticoagulant heparitin microsphere, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The carrageenan-based self-anticoagulant heparitin microsphere comprises a carrageenan microsphere of a network structure and a polyacrylic acid crosslinked network constructed by a crosslinking agent and interspersed with a carrageenan microsphere network.The microsphere is low in cytotoxicity and high in biocompatibility and anticoagulant property and has a structure and functional group similar to anticoagulant heparitin. The interspersed carrageenan network and polyacrylate crosslinked network form double networks and the double networks are restricted by each other, so that the mechanical strength of the microsphere is strengthened, the swelling rate is limited, breakage of the microsphere in a using process can be effectively avoided, the dimensional stability of the microsphere can be maintained in use and the microsphere is a novel adsorption material with application prospect for a hemoditoxifier.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Heparin compound, and its preparing method and use
InactiveCN1580080AImprove efficacyDoes not affect testingOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderSolubilityZinc hydroxide
The invention refers to a heparin compound and its preparation method and application. The heparin compound is a heparin zinc-potassium double salt demonstrated by the formula of R(ZnOH)aKb. The R represents the heparin radical and a is between 3 and 5, b between 1 and 3. The heparin compound can be made through the following preparation method: dissolve the sodium heparin into the water and contact with the cinnamene cation exchange resin to get the heparin solution; add an amount of zinc hydroxide and potassium hydroxide to the heparin solution, whisk and dry it and get the mentioned solid heparin compound. The heparin compound can be used as the anticoagulant agent as well as the main material of the anti thrombus medicine. The heparin zinc-potassium as the anticoagulant agent meets not only the requirements of not affecting the components' balance and stability of the blood samples to be tested but also the requirement of the solubility in the blood. When it is chosen as the main resource of the anti thrombus medicine, the heparin zinc-potassium releases slowly, has long effect of medicine and no toxicity and is good for the zinc-adding of the human body.
Owner:汕头市金丰医疗器械科技有限公司
Blood virus RAN protective agent and blood sampling tube
ActiveCN109679946AAvoid degradationAvoid pollutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSodium thiocyanatePollution
The invention provides a blood virus RAN protective agent and a blood sampling tube. The blood virus RAN protective agent is prepared by dissolving the following components in DEPC (diethyl pyrocarbonate) solution 100-500mg / ml glycine, 1-5mg / ml aprotinin, 1-5mg / ml wortmannin, 10-40mg / ml glutathione, 100-500mg / ml sodium thiocyanate, 1-3mg / ml anticoagulant and 5-20mg / ml membrane protective agent. The blood virus RAN protective agent provided by the invention is capable of supplying long-term protection to virus RNA in blood under room temperature, preventing degradation and pollution of virus RNA and effectively guaranteeing accuracy and validity of blood sample.
Owner:NINGBO AJCORE BIOSCIENCES INC
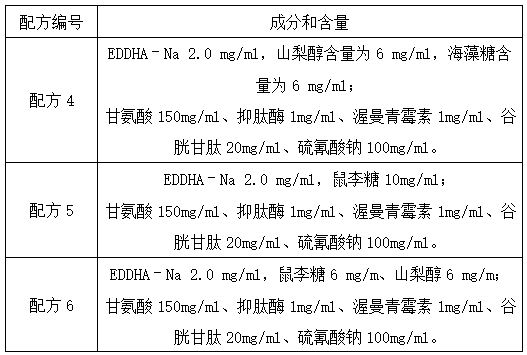
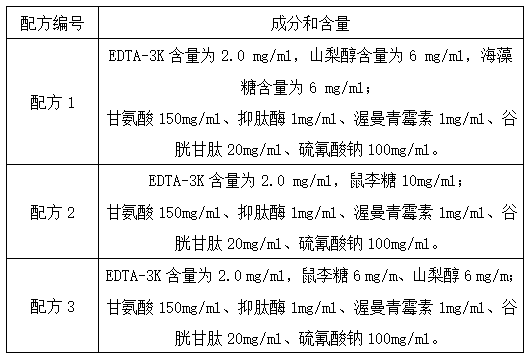
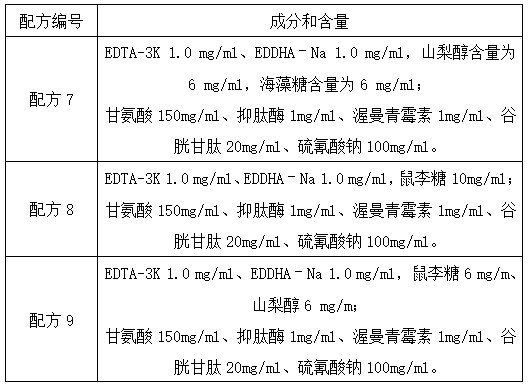
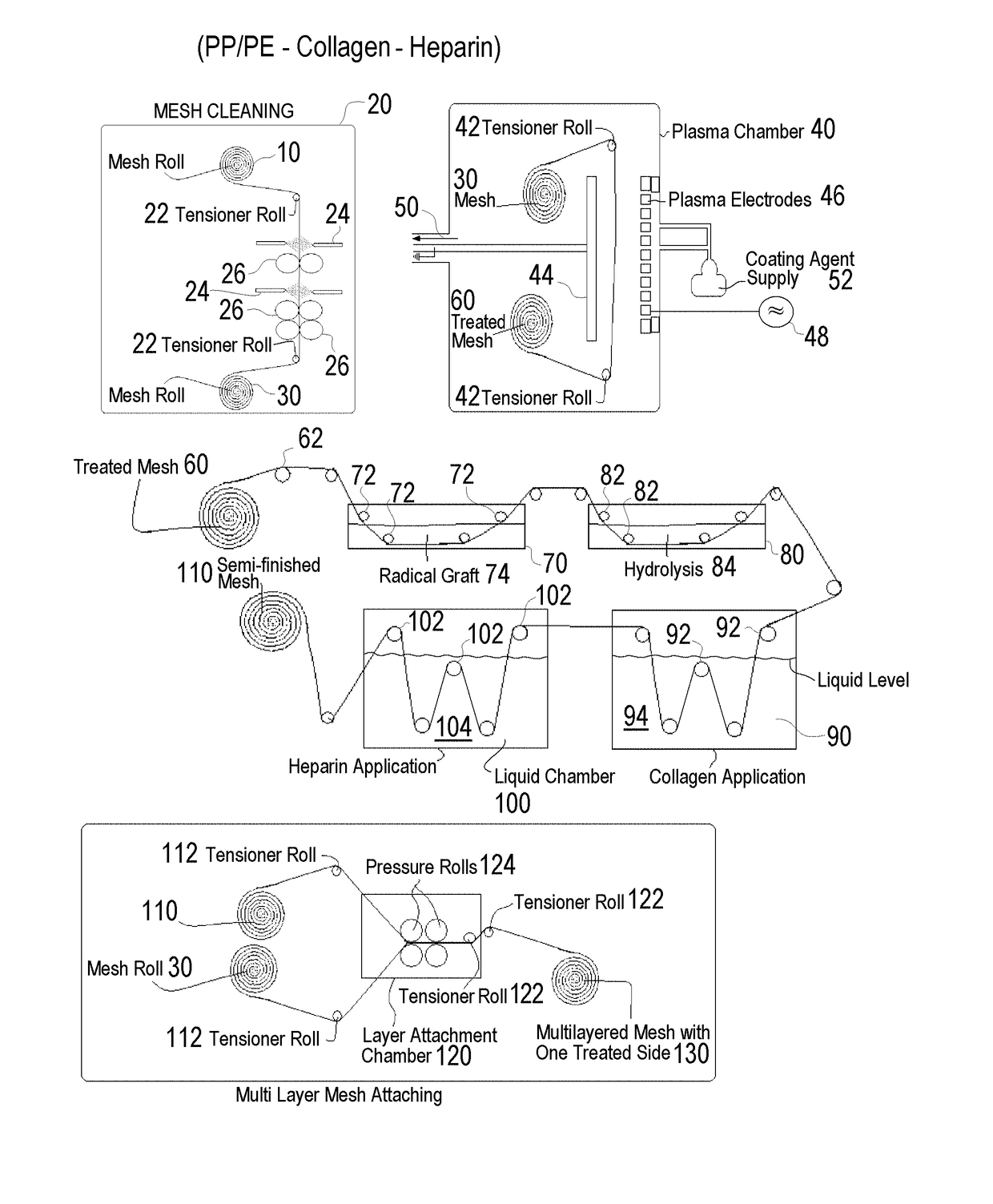
Methods of surface treating tubular medical products
A method of treating a tubular medical device with a biomolecule comprises the steps of: a) providing a polyolefin tubular substrate forming a tubular medical device; b) cleaning the tubular polyolefin substrate; c) exposing the tubular polyolefin substrate to a reactive gas containing at least one of acrylic acid and siloxane and to plasma energy to yield a plasma-deposited coating on at least one surface of the tubular polyolefin substrate; and d) attaching a biomolecule to the polyolefin substrate following formation of the plasma-deposited coating on at least one surface of the tubular polyolefin substrate, and wherein the biomolecule is at least one of an antibacterial agent, antimicrobial agent, anticoagulant, heparin, antithrombotic agent, platelet agent, anti-inflammatory, enzyme, catalyst, hormone, growth factor, drug, vitamin, antibody, antigen, protein, nucleic acid, dye, a DNA segment, an RNA segment, protein, and peptide.
Owner:ENSION
Activated blood coagulation factor x (FXA) inhibitor
InactiveUS20110275666A1Effective treatmentReduce riskBiocideOrganic chemistryAnticoagulant AgentCvd risk
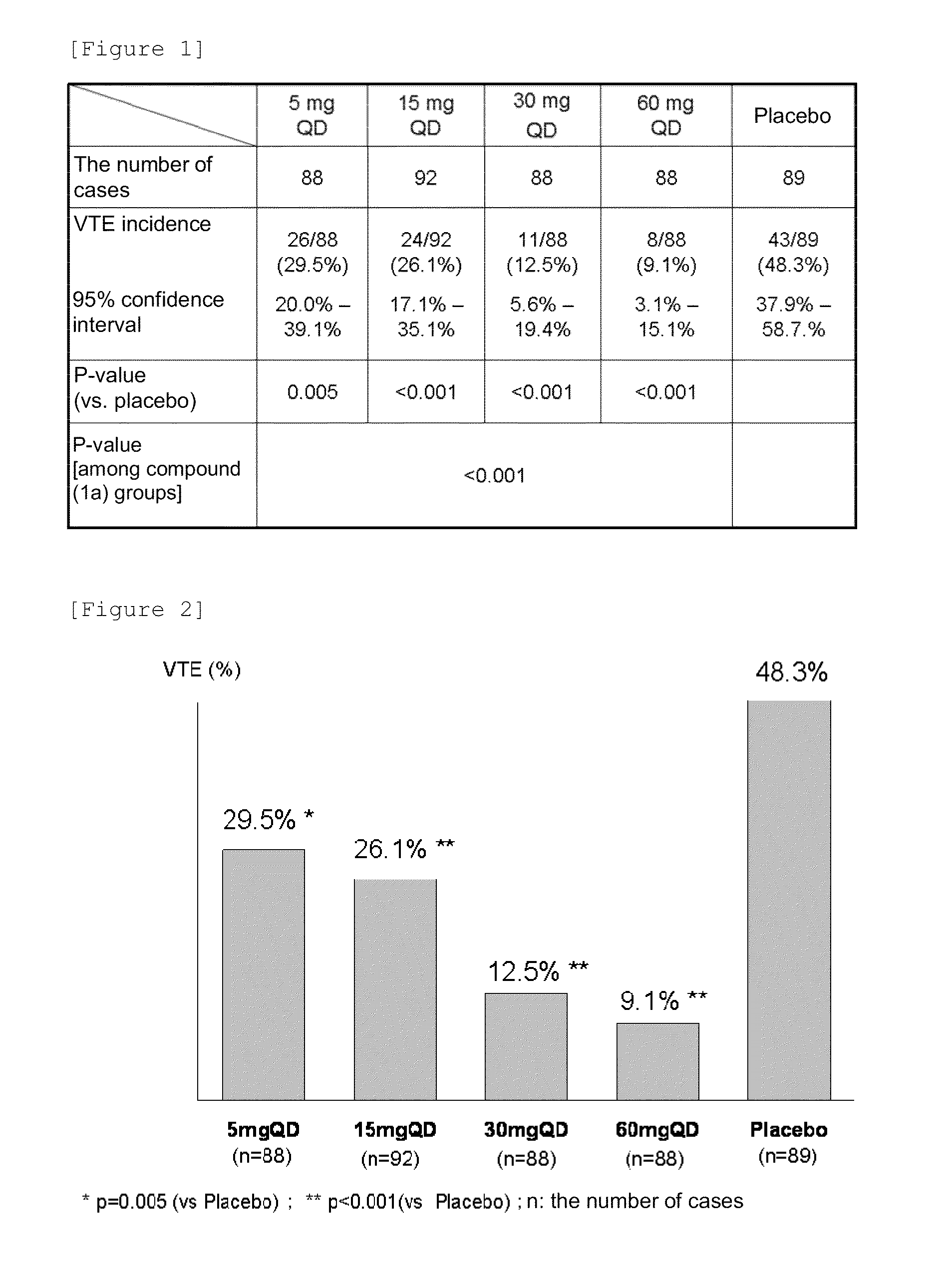
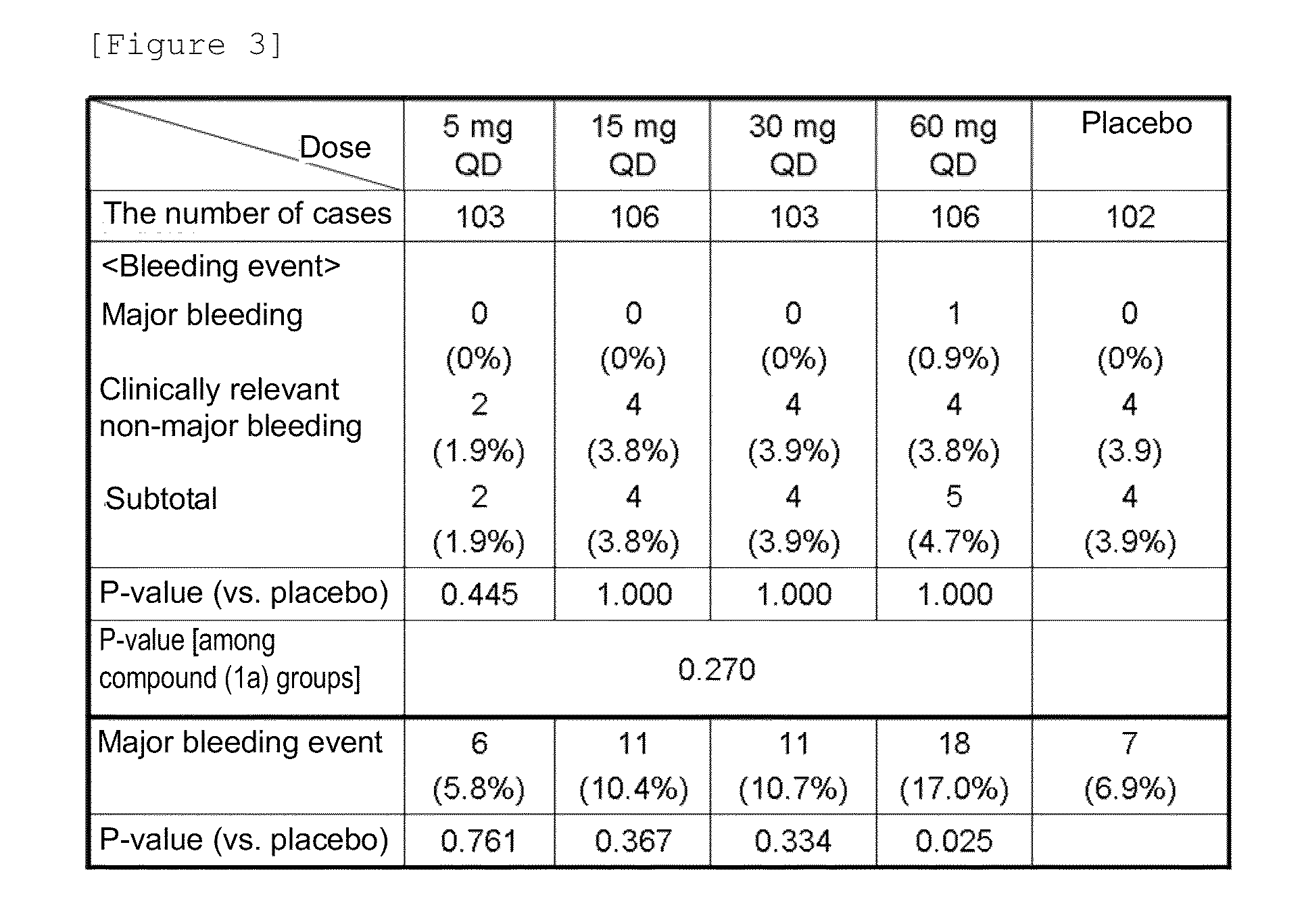
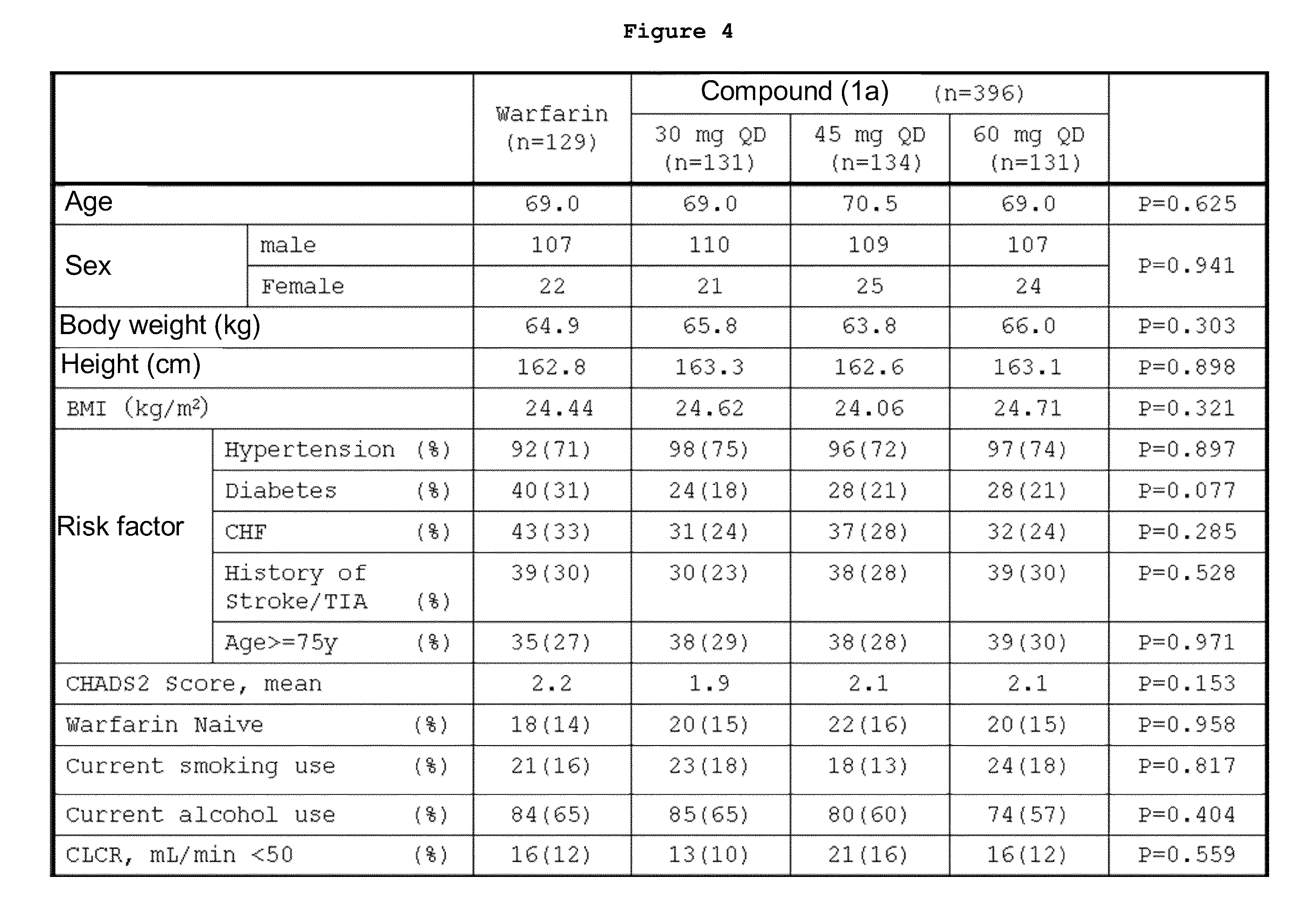
An object of the present invention is to provide an activated blood coagulation factor X (FXa) inhibitor that reduces the risk of bleeding caused by the treatment of thromboembolism. The present invention provides an oral anticoagulant agent comprising a compound represented by the following formula (1):or a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof, or a hydrate thereof, as an active ingredient, wherein (A) a factor involved in the risk of bleeding caused by the anticoagulant agent is selected as a dose determinant; (B) a reference value of the dose determinant is set; (C) the dose determinant of a patient in need of administration is measured; and (D) the dose of the anticoagulant agent is selected with the reference value as an index.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Blood anticoagulant
InactiveCN104072600ABlood hemolysisThe original aggregation phenomenon is solvedDead animal preservationAnimals/human peptidesHemolysisAnticoagulant Agent
The invention discloses a blood anticoagulant which consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2.5-3 parts of sodium citrate, 0.3-0.4 part of citric acid, 2.2-2.6 parts of glucose, 0.2-0.25 part of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 1-1.5 parts of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt and 100 parts of water, wherein the raw materials are sequentially added into 100 parts of water, dissolved and uniformly stirred at normal temperature, and 14ml of the blood anticoagulant is dissolved in 100ml of pig blood. The anticoagulation effect of the blood anticoagulant disclosed by the invention is not less than 3 days, and then the phenomenon of blood hemolysis is solved. By adopting the blood anticoagulant, the fibrinogen aggregation phenomenon of the blood is solved.
Owner:桐城市雨润生物科技有限公司
Manufacturing method of coaxial electrostatic spinning magnetic anastomosed artificial blood vessel
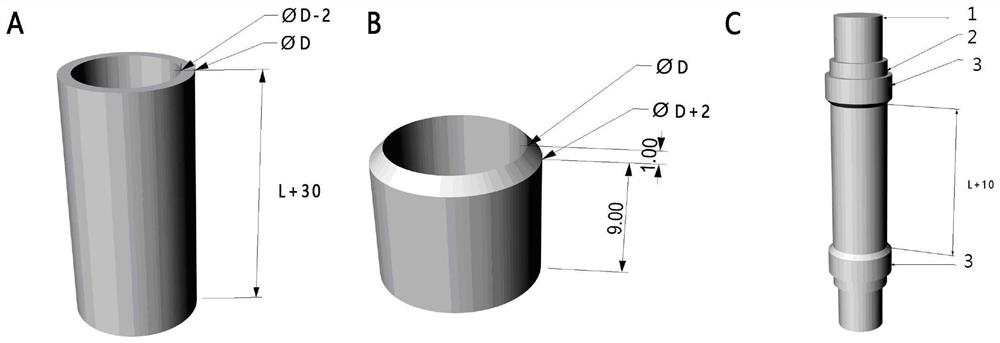
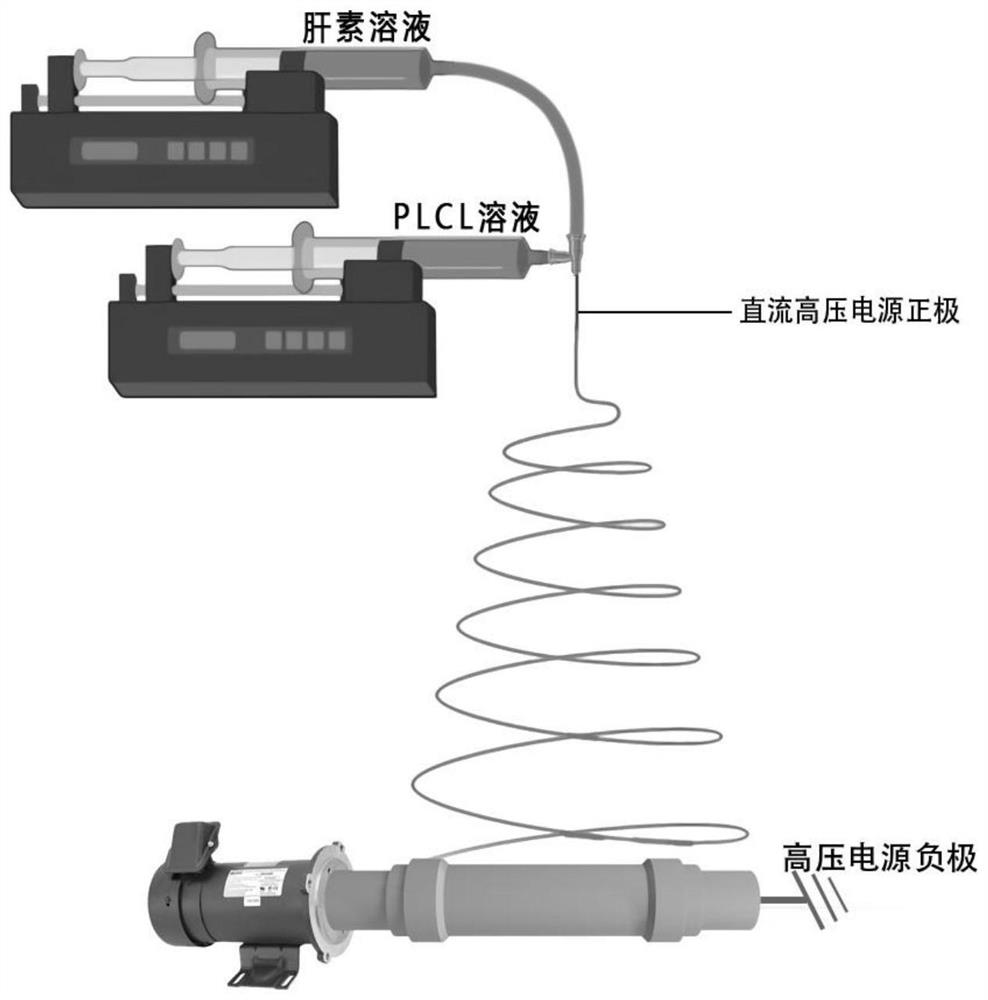
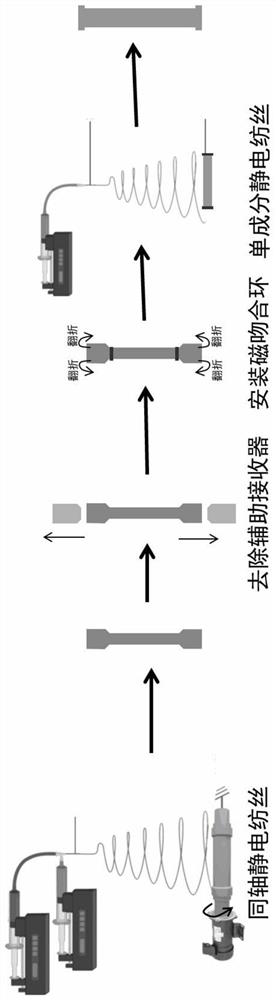
PendingCN111603267AGood microscopic appearanceImprove mechanical propertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatusFilament/thread formingAnticoagulant AgentPoly dl lactide
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of a coaxial electrostatic spinning magnetic anastomosed artificial blood vessel. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a coaxial electrostatic spinning solution; and preparing two solutions: namely a heparin sodium solution and a poly L-lactide-caprolactone solution, wherein the heparin sodium solution is a core layer solution for coaxial electrostatic spinning, and the PLCL solution is a shell layer solution for coaxial electrostatic spinning; 2) carrying out 3D printing of an electrostatic spinning receiver: 2.1) carrying outCT angiography examination on a patient before an operation; 2.2) measuring the blood vessel length L and the blood vessel diameter D, which need to be replaced; 2.3) drawing a 3D model of an electrostatic spinning receiver by using SolidWorks software; and 2.4) manufacturing an electrostatic spinning receiver by using a 3D printer; and 3) manufacturing a coaxial electrostatic spinning magnetic anastomosed artificial blood vessel. The prepared magnetic anastomosed artificial blood vessel has a good microstructure, hydrophilicity and stable heparin slow release performance, and the blood compatibility, mechanical properties and animal in-vivo implantation experiments show that the magnetic anastomosed artificial blood vessel has the advantages that the anastomosis process is convenient andrapid, an anastomosed stoma is not narrow, and anticoagulant application is avoided.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL COLLEGE OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
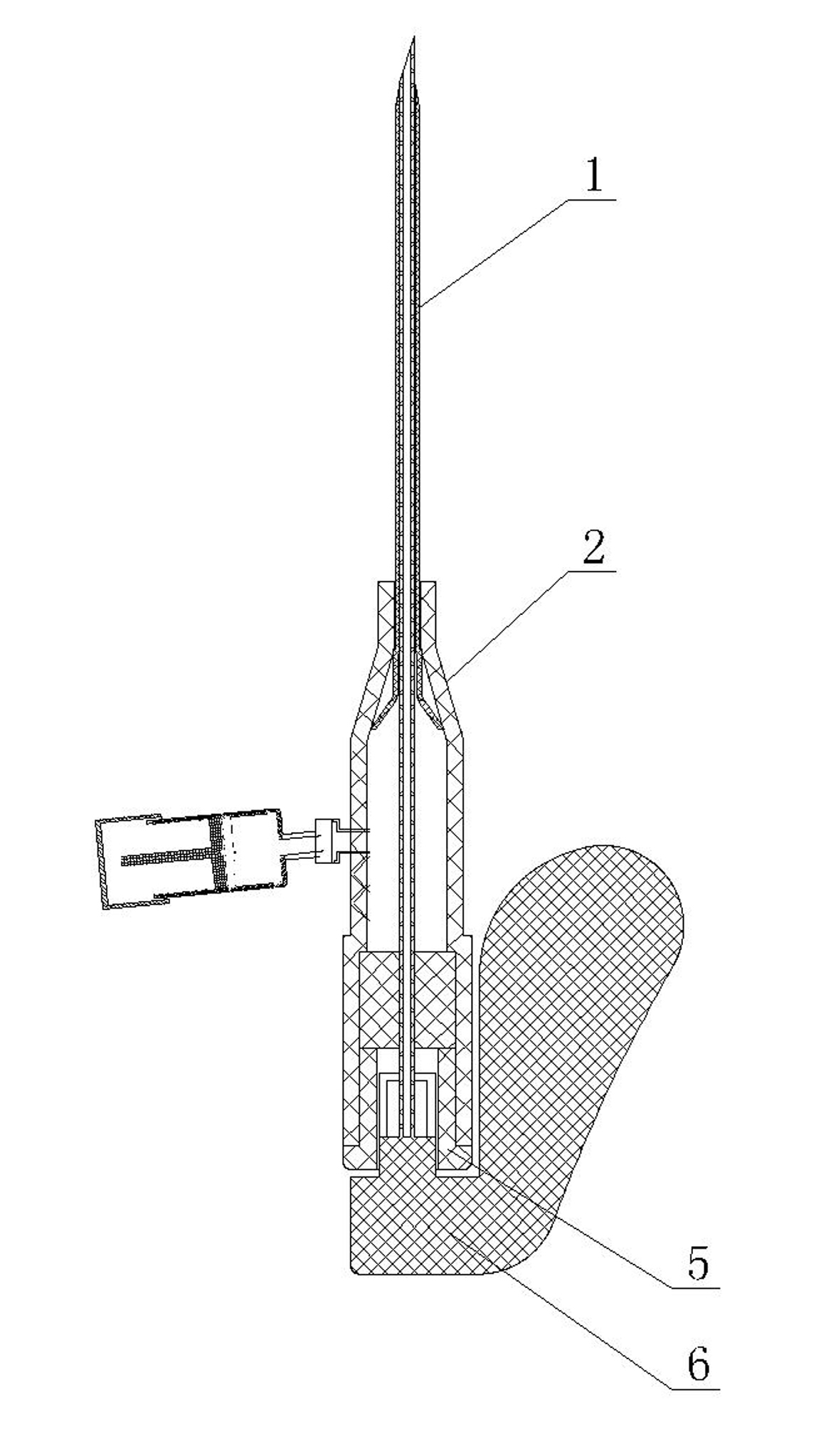
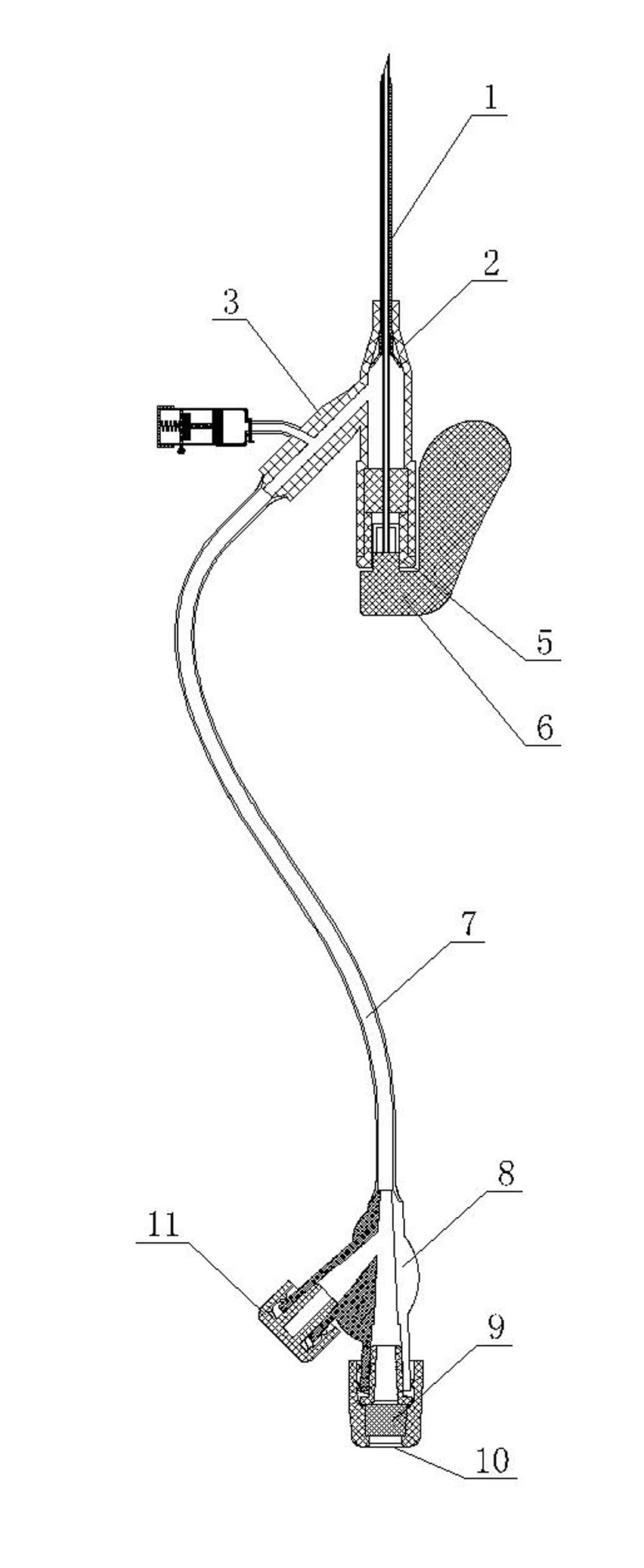
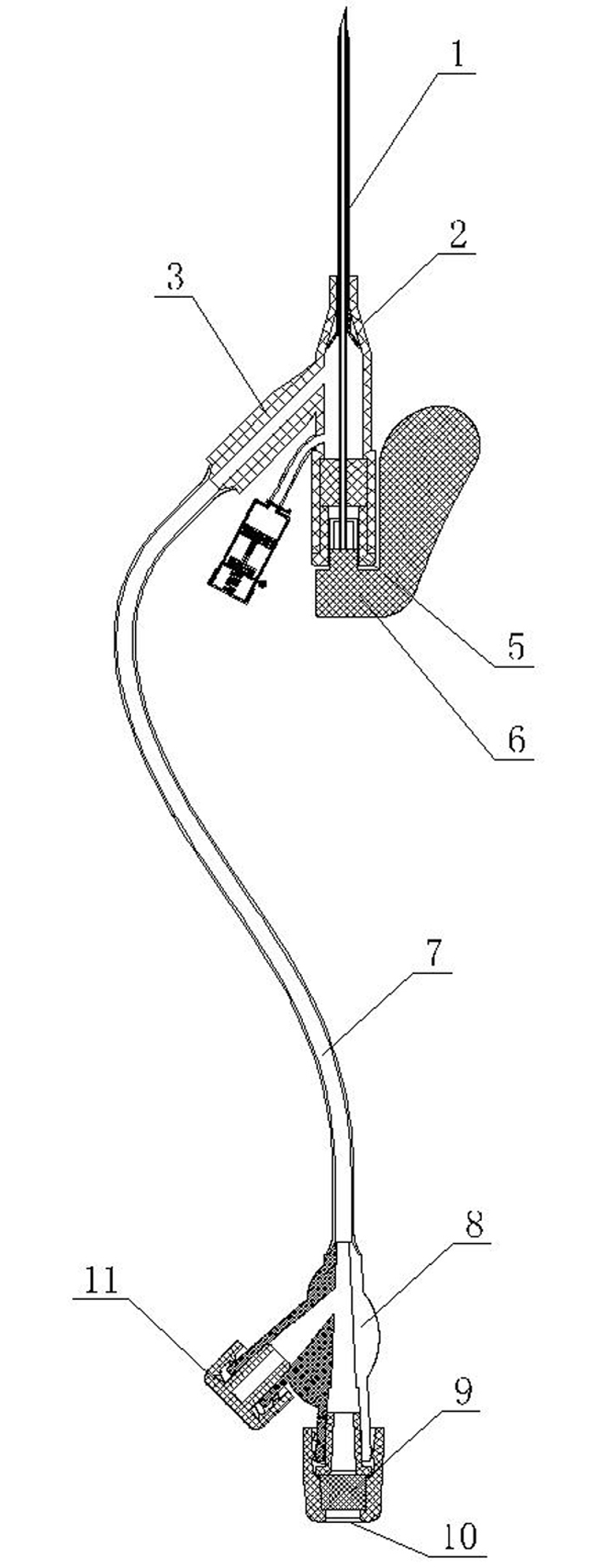
Vein remaining needle
InactiveCN102038986AGuaranteed smoothBlood clots will not occurInfusion needlesVeinAnticoagulant Agent
The invention relates to a vein remaining needle which mainly comprises a remaining rubber tube, a puncture needle guide disc, a sealing tube plug and a puncture needle, wherein the vein remaining needle is provided with at least one hirudin injection device capable of preventing blood from forming thrombi in the vein remaining needle; the liquid injection outlet at the bottom of the hirudin injection device can be selectively communicated with the inner cavity of the vein remaining needle; and the inner cavity of the hirudin injection device is filled with a hirudin biological anticoagulant, and the top is provided with a driving device capable of driving the hirudin biological anticoagulant in the inner cavity to be injected into the inner cavity of the vein remaining needle. Because the vein remaining needle adopts the hirudin as an anticoagulant and fully utilizes the super strong and super long anticoagulation properties of the hirudin biological anticoagulant, the vein remaining needle fully guarantees that the blood flowing back into the vein remaining needle because of a negative pressure can not generate thrombi, thereby ensuring the smoothness of each channel of the vein remaining needle, avoiding the adverse impact resulted from puncturing again and utilizing heparin sodium which should be used immediately after being prepared, and effectively reducing the pain of patients and the labor strength of medical personnel. Besides, the invention has the advantages of easy manufacturing process and simple implementation, and is beneficial to popularization.
Owner:柯丽红
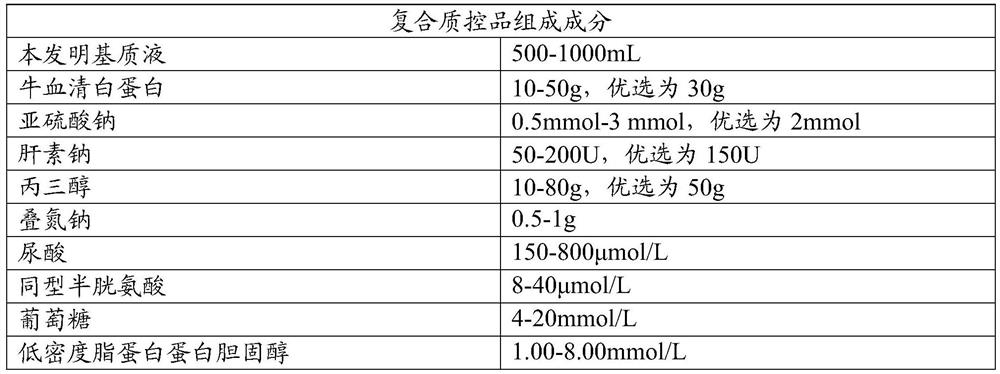
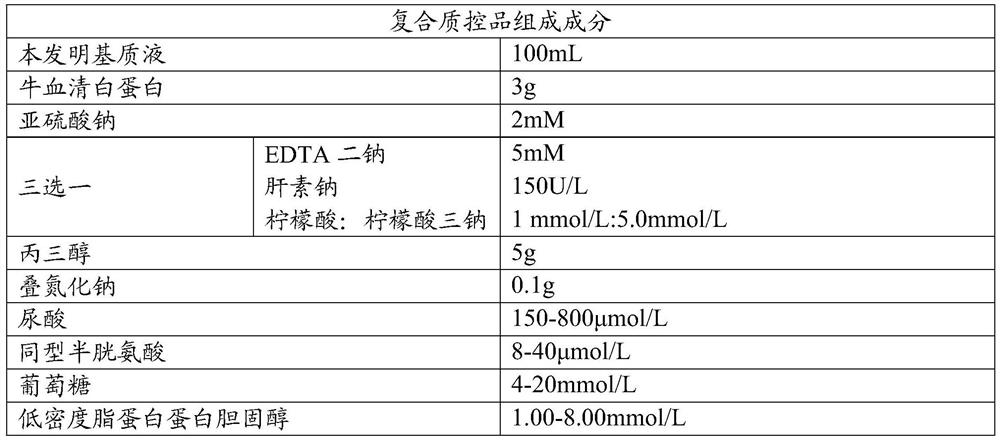
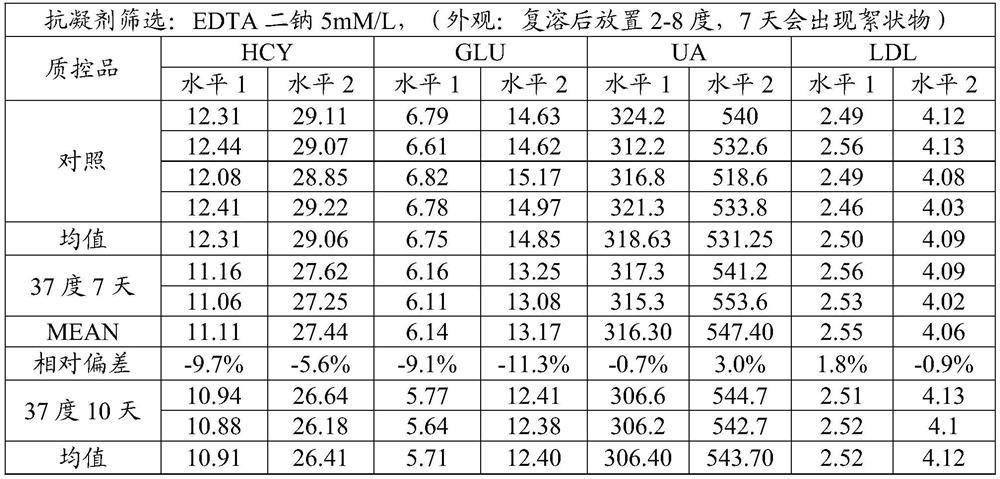
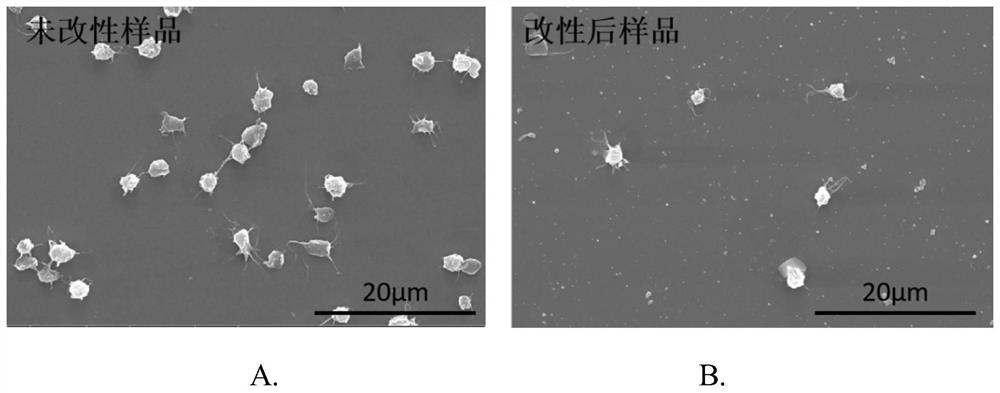
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular and diabetes related four-high index composite quality control product and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112180095APromote formationEnsure consistencyDisease diagnosisBiological testingAnticoagulant AgentA lipoprotein
The invention relates to the technical field of medical diagnosis, and discloses a cardiovascular and cerebrovascular and diabetes related four-high index composite quality control product and a preparation method thereof. The composite quality control product comprises a matrix liquid, a reducing agent, bovine serum albumin, an anticoagulant, polyol, uric acid, homocysteine, glucose, low-densitylipoprotein cholesterol and a preservative. The composite quality control product which can be used for testing four cardiovascular and cerebrovascular and diabetic indexes of Glu, Hcy, UA and LDL-C at the same time can be prepared at a time, healthy human plasma is selected as a matrix liquid raw material, the components are basically consistent with those of serum after treatment, and the matrixeffect is reduced to the maximum extent; meanwhile, by matching with other components, the prepared four-high quality control product has good uniformity and stability, stable performance, long preservation time and simplicity and convenience in use, meanwhile, the accuracy of quality control during joint inspection is greatly improved, and a more accurate basis is provided for clinical diagnosisof cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and diabetes related diseases.
Owner:SINOCARE
Valve material with synergistic anticoagulation and anti-calcification functions and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111658824ALong-term anti-corruptionExtended service lifePharmaceutical containersPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAnticoagulant AgentVenous valve
The invention provides a valve material with synergistic anticoagulation and anti-calcification functions and a preparation method of the valve material. The preparation method comprises the followingsteps: carrying out glutaraldehyde crosslinking treatment on an animal-derived biological valve material; immersing the treated valve material in confining liquid containing an amino compound to perform treatment for 0.5-6 h, and then confining aldehyde groups remaining after glutaraldehyde crosslinking; then putting the valve material into a reaction solution containing an anticoagulant and a cross-linking agent, and carrying out cross-linking treatment for 6-24 hours at 4-37 DEG C; and finally, cleaning the valve material to obtain the valve material, and storing the valve material in a glutaraldehyde or isopropanol / glycerol mixed solvent. The method can effectively solve the problems of easy calcification and thrombus formation caused by aldehyde group residue in the valve material prepared by an existing method, and the valve material prepared by the method disclosed by the invention can be used as a valve material required by aortic valve, pulmonary valve, venous valve, mitral valve and tricuspid valve replacement.
Owner:JILIN VENUS HAOYUE MEDICAL LTD
Anticoagulant and metal-organic framework compound dual-modified in-vitro blood circulation pipeline coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN113082301AReduce the risk of bacterial infectionAvoid inactivationPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingHemodialysisAnticoagulant Agent
The invention discloses an anticoagulant and metal-organic framework compound dual-modified in-vitro blood circulation pipeline coating and a preparation method thereof. The anticoagulant of the coating is selected from heparin, hirudin, citric acid or argatroban, and the metal-organic framework compound in the coating is MOF-Ag or MOF-Cu; the coating is obtained by fixing the metal-organic framework compound on the inner wall of an in-vitro blood circulation pipeline through dopamine and then fixing the anticoagulant on a dopamine layer with the metal-organic framework compound in a chemical grafting mode. The coating is high in stability, can improve blood compatibility and has excellent anticoagulation and antibacterial effects; and the in-vitro blood circulation pipeline with the coating can be applied to conventional hemodialysis, blood adsorption and continuous blood purification treatment.
Owner:重庆天外天生物技术有限公司
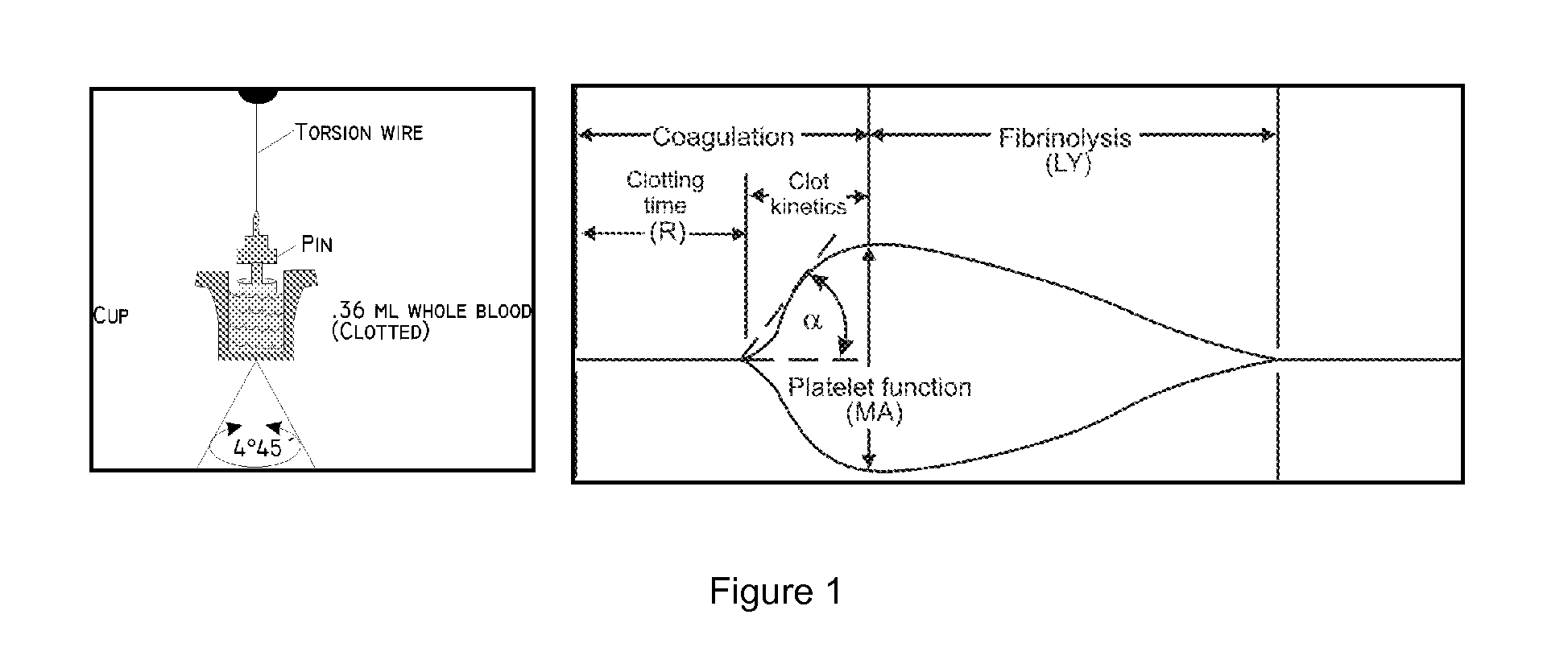
Methods and devices for detection of anticoagulants in plasma and whole blood
PendingCN111094990AUnderstanding PathophysiologyPeptide/protein ingredientsLaboratory glasswaresAnticoagulant AgentAnti coagulation
Methods and devices for evaluating coagulation are described, including methods and devices for detecting an anticoagulant agent or a coagulation abnormality. In various embodiments, the methods and devices of the invention measure the coagulation of a sample in response to a gradient of one or more coagulation factors. These responses can be evaluated to accurately profile the coagulation impairments of the sample, including the presence of anticoagulant medication. In various embodiments, the invention provides the point-of-care or bedside testing with a convenient, microfluidic device thatcan be used by the minimally trained personnel.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
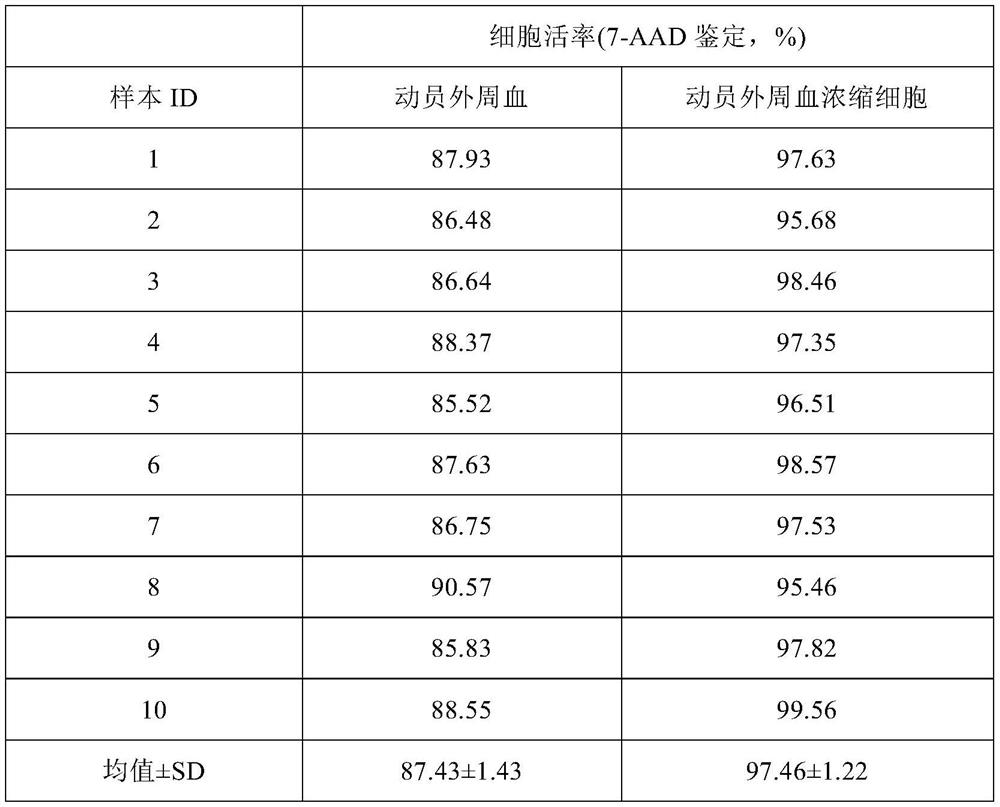
Peripheral blood mobilization concentrated cell therapeutic agent for treating premature ovarian failure
PendingCN114196619AQuality improvementReal-time processingCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsAnticoagulant AgentThrombus
The invention relates to a peripheral blood mobilizing concentrated cell therapeutic agent for treating premature ovarian failure. The method for preparing peripheral blood, such as mobilized peripheral blood concentrated cells, comprises the following steps: providing peripheral blood, such as mobilized peripheral blood concentrated cells, of a biological sample, and placing the peripheral blood in a sterile bag containing an anticoagulant for later use; a protective cap on an input tube of the automatic cell separation system is taken down, an injector is connected to a Luer locking connector of the input tube and passes through a thrombus filter at a slow and stable speed, an anticoagulant biological sample is transferred into a disposable sterile separation cup, and the mixed sample is shaken along a horizontal shaft; the automatic cell separation system is a closed PXP separation system and consists of four parts, namely a disposable sterile separation cup, a control module, a separation base and a software processing system, and putting the disposable separation cup into a control module, and centrifuging in a programmable centrifugal machine to obtain mobilized peripheral blood concentrated cells. The method disclosed by the invention has excellent effects as described in the specification.
Owner:深圳博雅感知医疗科技有限公司
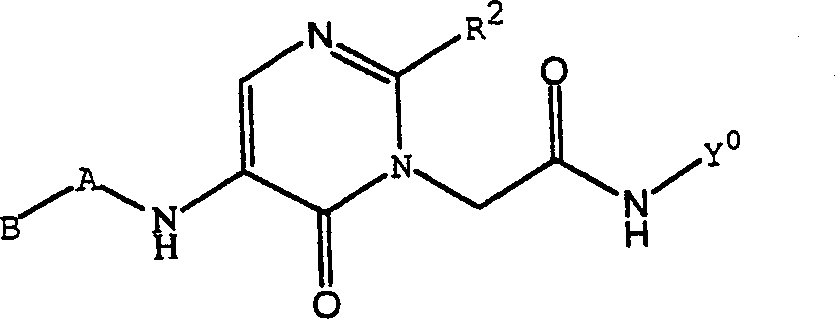
Substituted polycyclic aryl and heteroaryl pyrymidinones useful as anticoagulants agents
The invention relates to substituted polycyclic aryl and heteroaryl pyrimidinone compounds useful as inhibitors of serine proteases of the coagulation cascade and compounds, compositions and methods for anticoagulant therapy for the treatment and prevention of a variety of thrombotic conditions including coronary artery and cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:PHARMACIA CORP
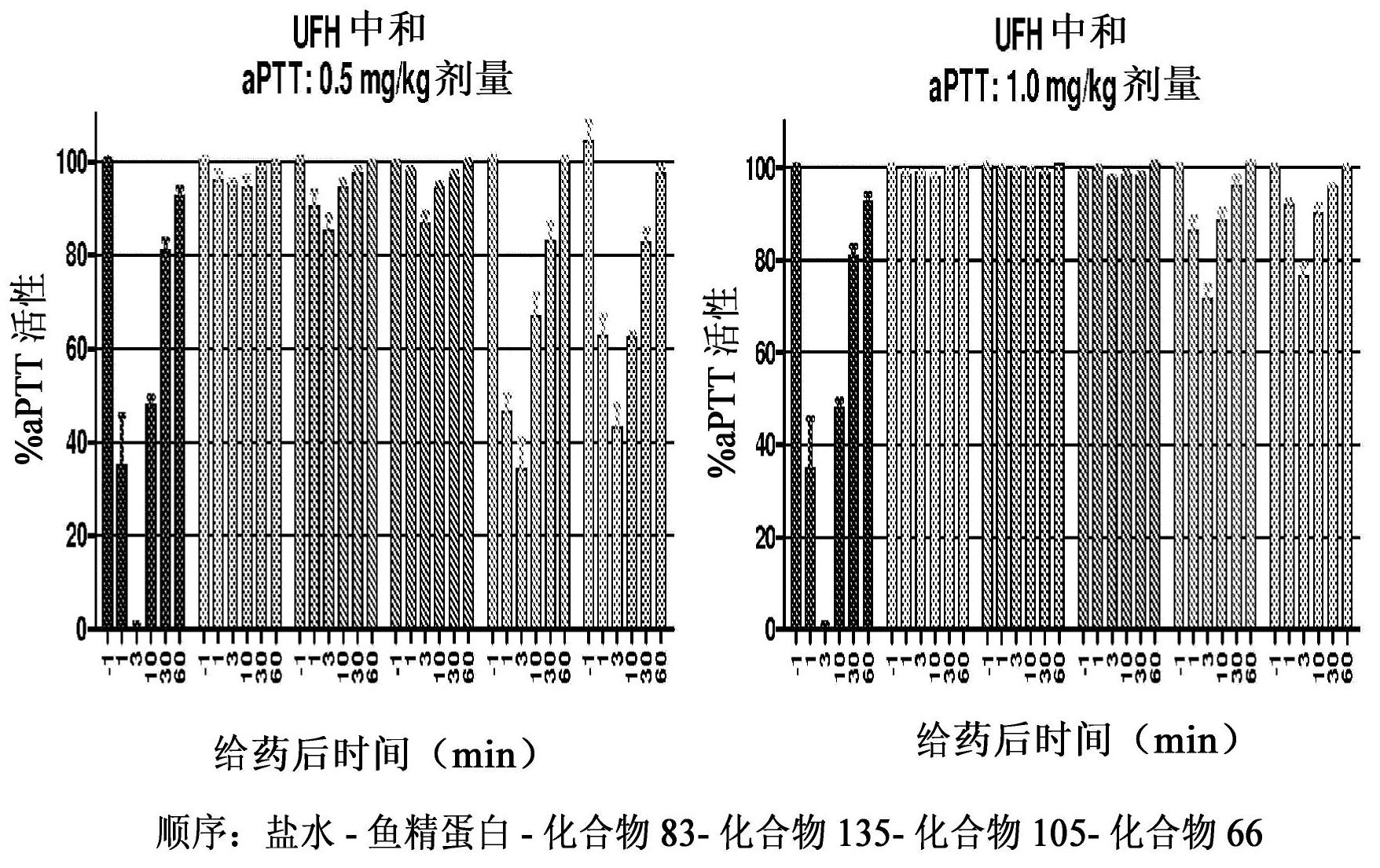
Anti-heparin compounds
The present invention provides compounds and methods for antagonizing the anticoagulant effect of an anticoagulant agent that is selected from UFH, LMWH, and a heparin / LMWH derivative in a patient comprising administering to the patient a compound of the invention or a salt thereof, or a composition comprising the same.
Owner:CELLCEUTIX CORP
Freeze-dried platelet derivative compositions for treating anticoagulant-induced coagulopathy
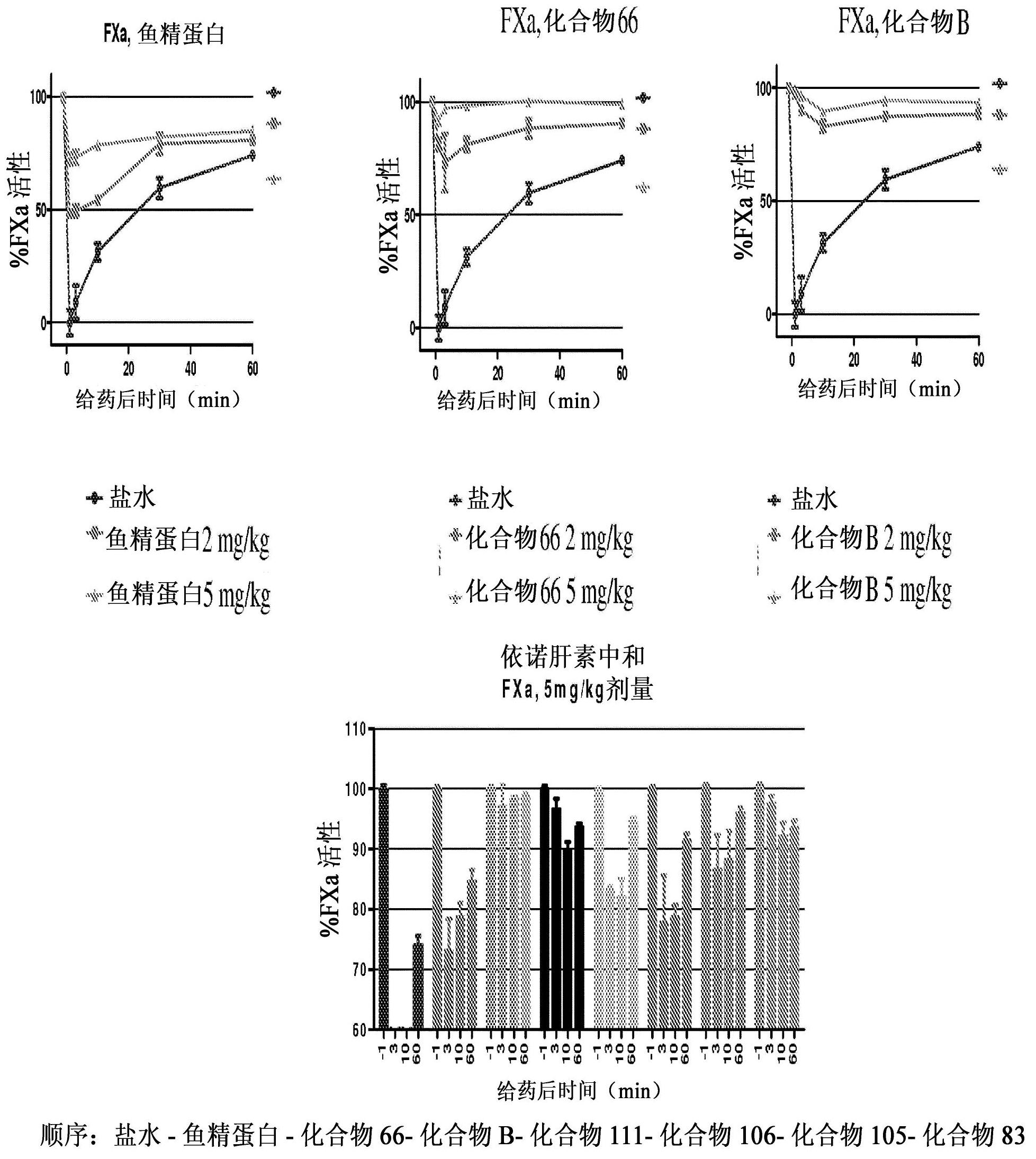
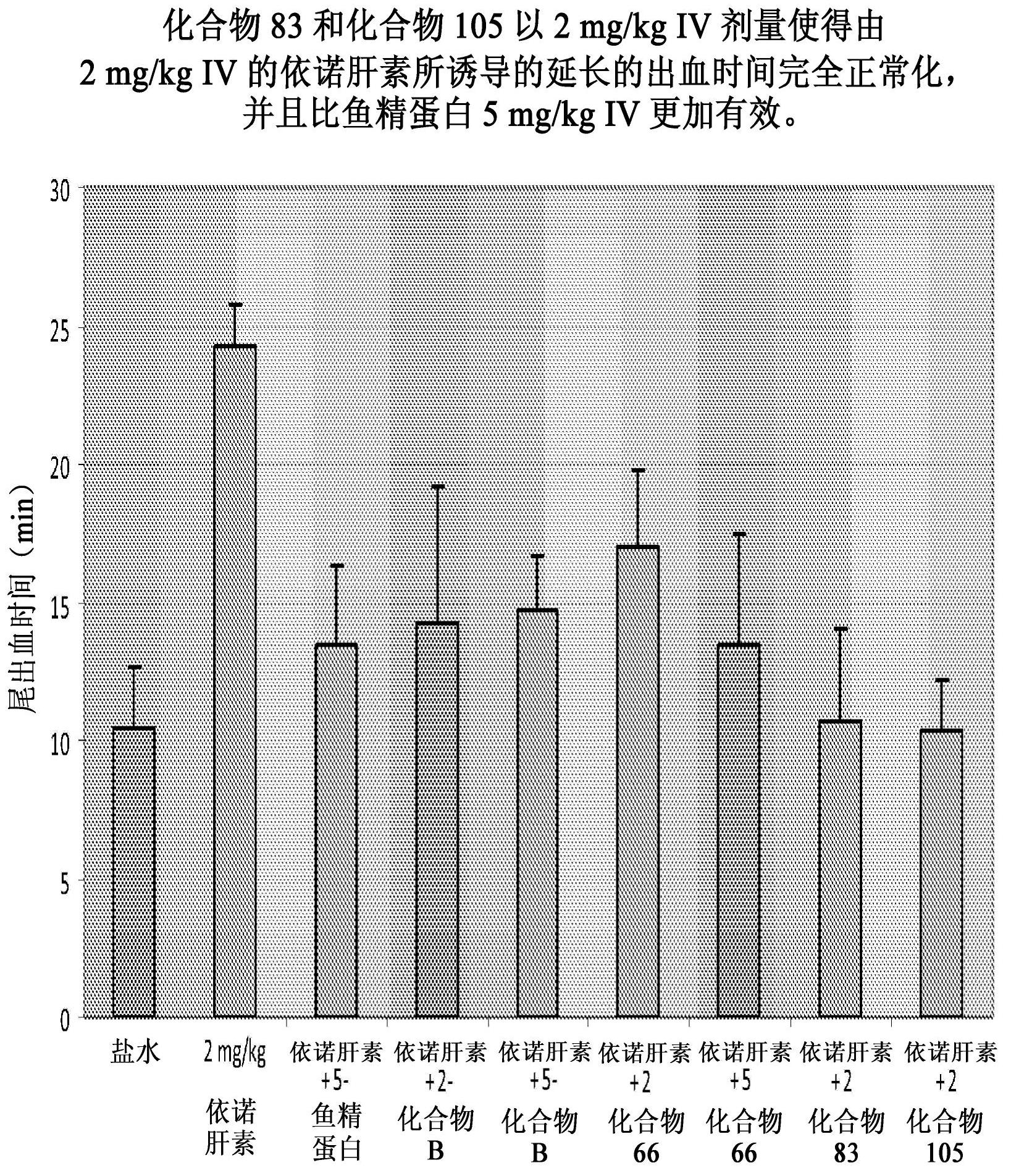
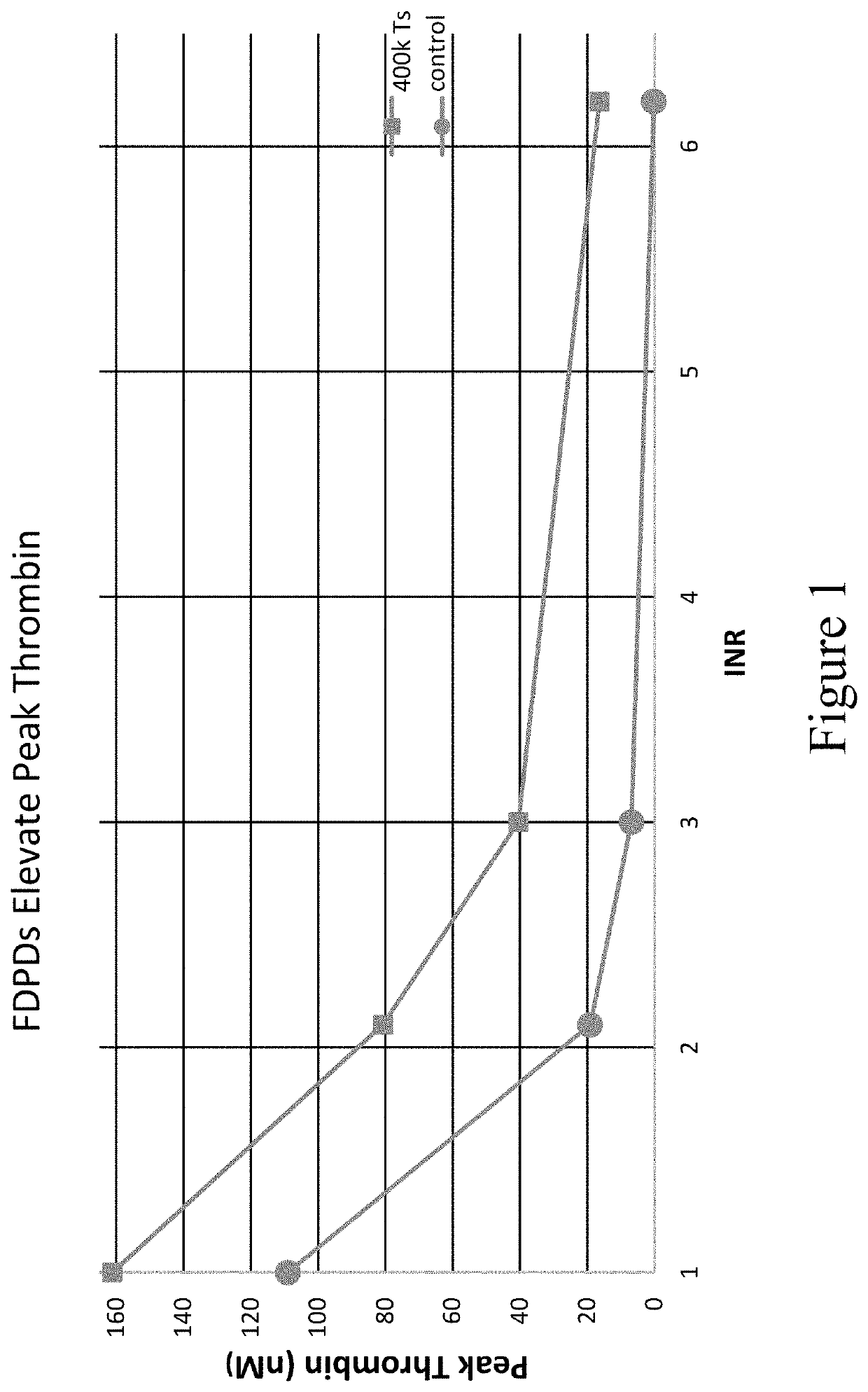
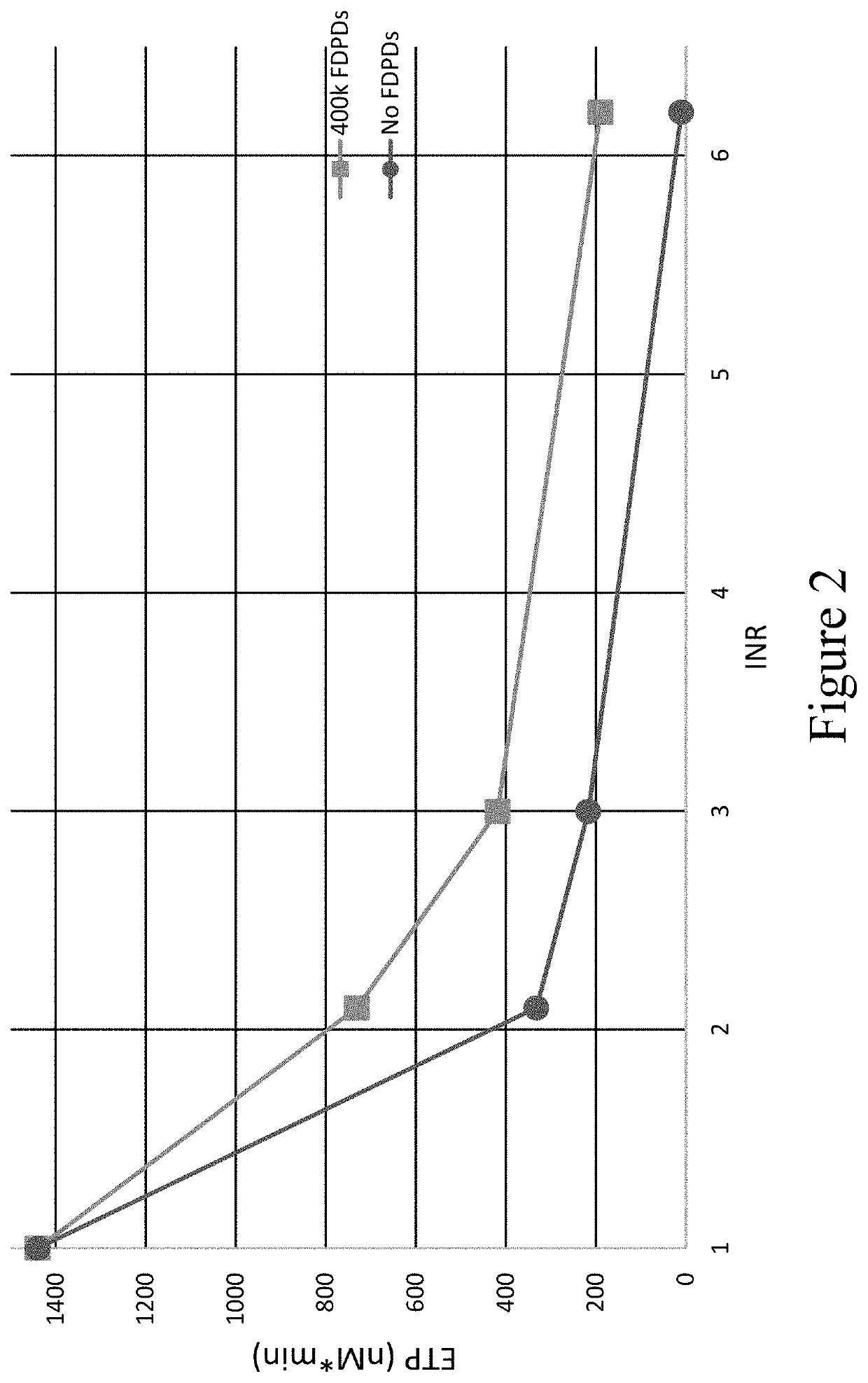
PendingUS20220279777A1Restore hemostasisIncreased bleeding potential of a subjectPeptide/protein ingredientsCulture processAnticoagulant AgentPlatelet
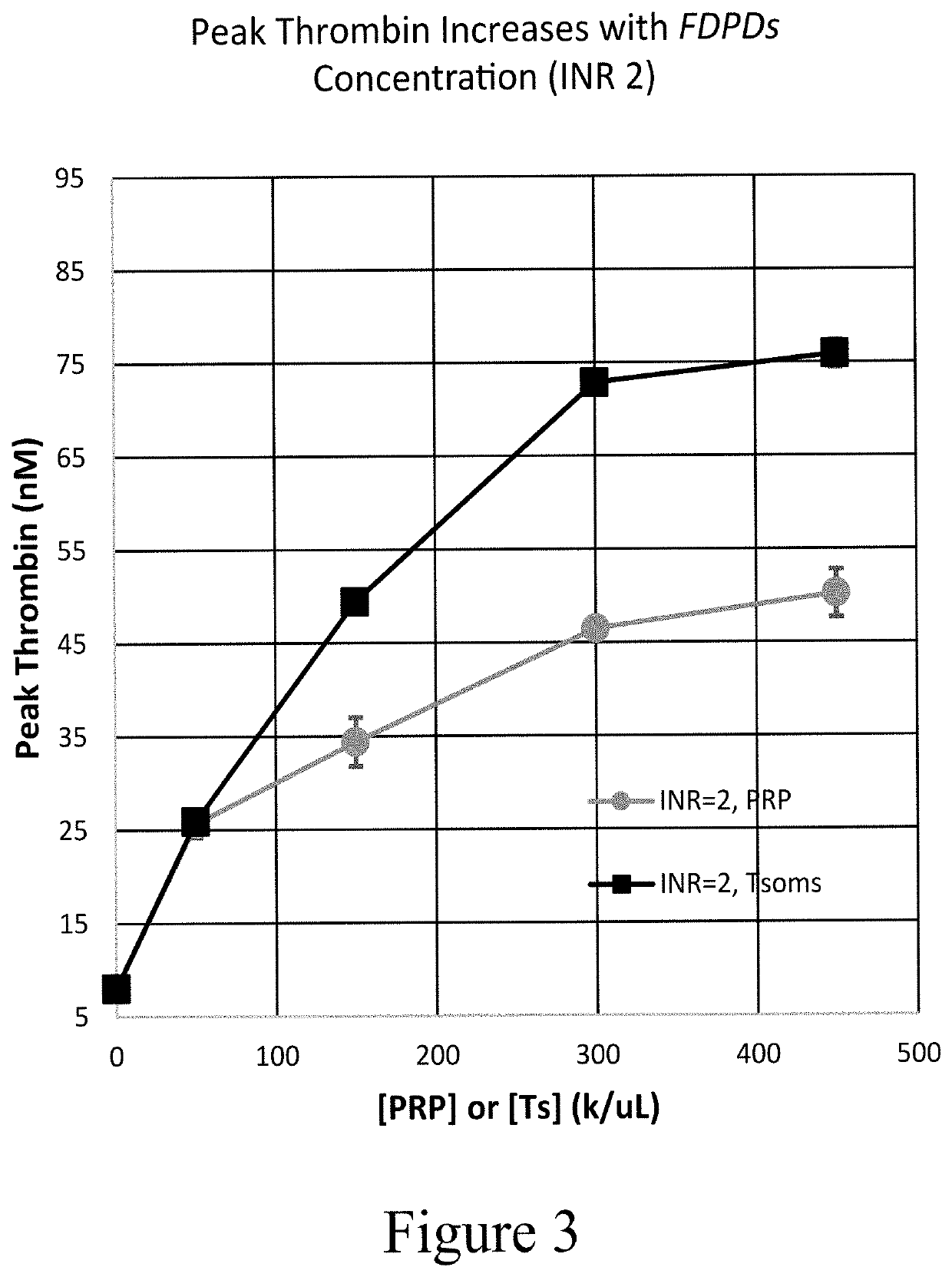
Provided herein are methods and compositions for treating a coagulopathy in a subject. Such methods can include administering to the subject in need thereof, for example because they have been administered an anticoagulant agent, an effective amount of a composition including platelets, or in illustrative embodiments platelet derivatives, and in further illustrative embodiments freeze-dried platelet derivatives (FDPDs). Various properties of exemplary embodiments of such methods and platelet derivatives used therein, as well as numerous additional aspects and embodiments are provided herein.
Owner:CELLPHIRE INC
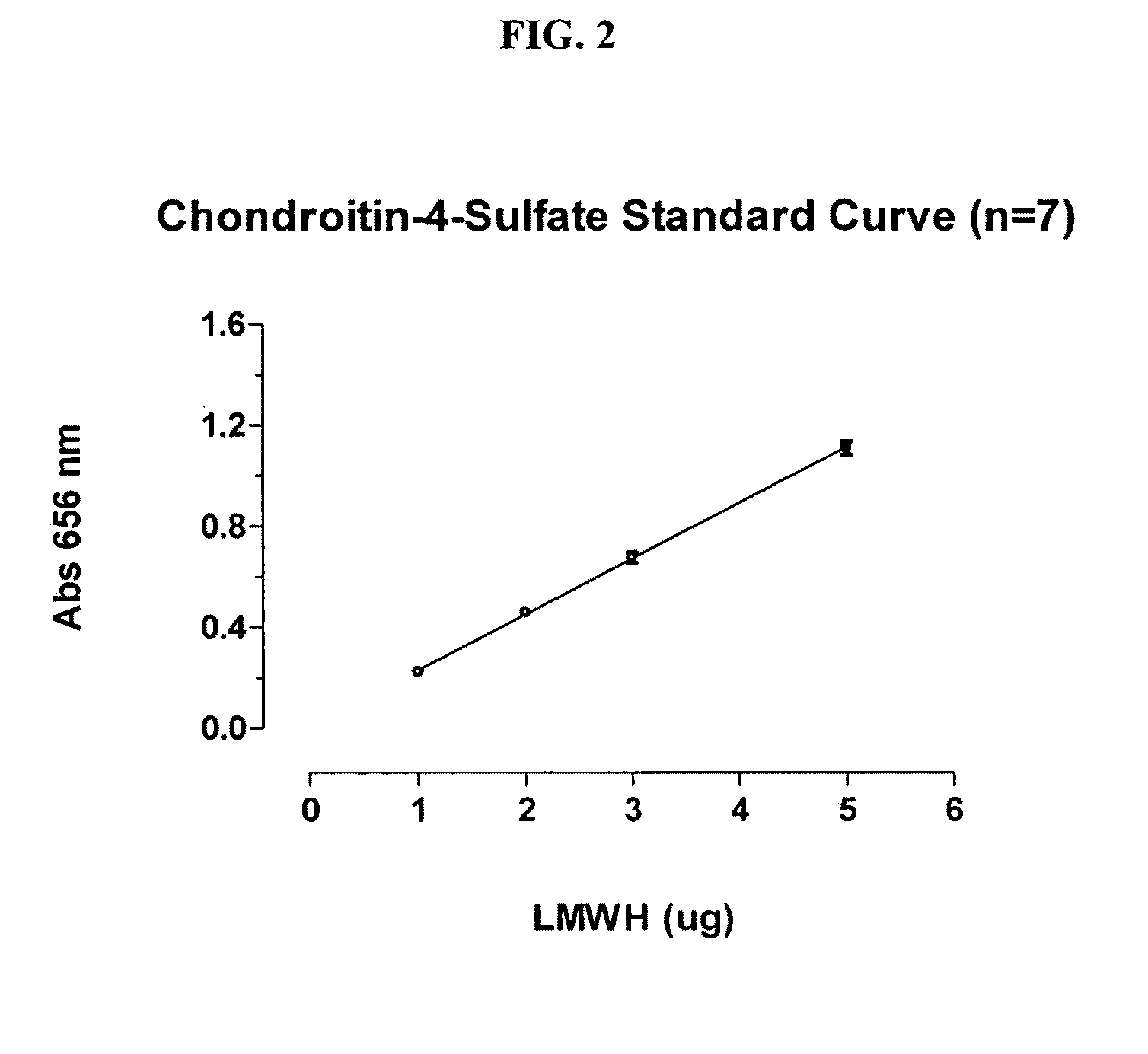
Method for measuring the concentration of a glycosaminoglycan anticoagulant
ActiveUS20090042303A1Performed easily and quicklyImprove throughputSamplingElectrostatic cleaningAnticoagulantGlycosaminoglycan
The invention provides an accurate, economical, automatable, high throughput method for the determination of the concentration of glycosaminoglycan anticoagulants, including low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) anticoagulants, in aqueous solutions. A method for cleaning a unit of manufacturing equipment used in the preparation of a LMWH to obtain an acceptable residual concentration of LMWH is further provided.
Owner:ACTIVE BIOMATERIALS
A kind of cell preservation solution and its application in flow cytometry sample preservation
ActiveCN106386785BFor long-term storageDetect stable and correctPreparing sample for investigationDead animal preservationAnticoagulant AgentPolyethylene glycol
The invention provides the application of a cell preservation liquid in flow cytometry detection. During detection, the typing of leukemia and lymphoma is completed. The cell preservation liquid comprises Na2HPO4, KH2PO4, NaCl, KCl, polyethylene glycol, chromium chloride and any optionally selected anticoagulant. In addition, the invention also discloses a method for preparing the cell preservation liquid and a method for preserving a flow-type cell sample. The cell preservation liquid can be used for the long-time and stable preservation of clinical cell samples. Especially for flow-type cell samples, the long-term and stable preservation effect is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BOZHEN BIOTECH CO LTD
Cell preserving fluid for in-vitro analysis and detection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113966737AReduce autolytic spoilageImprove integrityDead animal preservationAnticoagulant AgentIn vitro analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of biological preserving fluid, in particular to cell preserving fluid for in-vitro analysis and detection and a preparation method thereof. The cell preserving fluid is prepared from the following components in a concentration range: 60 to 75 v / v percent of a cell fixing agent, 0.6 to 0.9 g / 100 mL of an osmotic pressure regulator, 0.2 to 0.5 g / 100 mL of an anticoagulant, 0.3 to 0.6 g / 100 mL of chitosan quaternary ammonium salt and 0.05 to 0.2 g / 100 mL of trehalose; and the solvent is ultra-pure water, and the pH value is 7.0-7.6. A small amount of trehalose and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt are combined, so that the protective effect can be effectively enhanced, autolysis decay of cells is effectively reduced, and the integrity of cell preservation is improved. When the cell preserving fluid is prepared, ultra-pure water is used for dissolving components except the cell curing agent, the dissolving effect of the components can be effectively improved, the uniform and stable cell preserving fluid is obtained, and batch production of the cell preserving fluid is facilitated.
Owner:深圳市华晨阳科技有限公司
Cell therapeutic agent for treating premature ovarian failure by using umbilical cord blood concentrated cells
PendingCN114177203ASatisfied with the effectCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsAnticoagulant AgentThrombus
The invention relates to a cell therapeutic agent for treating premature ovarian failure by using umbilical cord blood concentrated cells. On one hand, the method for preparing the umbilical cord blood concentrated cell preparation comprises the following steps: providing a biological sample umbilical cord blood, and putting the biological sample umbilical cord blood into a sterile bag containing an anticoagulant for later use; a protective cap on an input tube of the automatic cell separation system is taken down, an injector is connected to a Luer locking connector of the input tube and passes through a thrombus filter at a slow and stable speed, an anticoagulant biological sample is transferred into a disposable sterile separation cup, and the mixed sample is shaken along a horizontal shaft; and putting the disposable separation cup into a control module, and centrifuging in a programmable centrifugal machine to obtain the umbilical cord blood concentrated cell preparation. The invention also relates to the umbilical cord blood concentrated cell preparation prepared by the method, and application of the umbilical cord blood concentrated cell preparation in preparation of a cell therapeutic agent for treating premature ovarian failure. The cell preparation disclosed by the invention shows an excellent effect.
Owner:BOYALIFE
Methods using four-layer filter for PCR sample preparation
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a device, method and kit for detecting any genetic material containing moieties. The present invention enables identification of known or unknown virions or bacteria contained in a fluid therein, such as virions in a blood sample. It also provides for an amenable and highly automatable device for massed screenings and the discovery of sequence variants of known virions, previously undetected virions, and other genetic material containing moieties. In one aspect, the present invention provides a method for storage and analysis of a nucleic acid containing moiety in a biological sample, the method comprising providing a device comprising a plurality of layers, wherein the plurality of layers comprises a collection layer comprising a neutral porous matrix and a dry anticoagulant or liquefying agent, a filter layer comprising a dry solid medium comprising a solid matrix having a particle size limit that precludes eukaryotic cells, but not prokaryotic cells or virions, a separator layer, and an isolation layer comprising a dry solid medium comprising a neutral solid matrix having sorbed thereto a composition comprising a detergent; applying a biological sample to the collection layer; filtering remaining components of the biological sample through the collection layer to the filter layer; filtering remaining components of the biological sample through the filter layer to the separator layer; filtering remaining components of the biological sample through the separator layer to the isolation layer; retaining nucleic acid components in the isolation layer while removing a plurality of non-nucleic acid components; drying the isolation layer; providing at least one primer; and analyzing the nucleic acid components using PCR techniques, wherein at least two PCR primers are used.
Owner:WHATMAN PLC
Method for treating warm-blooded vertebrates with a salt of a halide-free glucosamine base and a therapeutic drug
InactiveUS20070248677A1Inhibition formationGood release effectPowder deliveryBiocideAntiparkinsoniansAnti-coagulants
A method of treating a warm-blood vertebrate. The verebrate may be a human being or a lower animal. The treatment method involves administering to the vertebrate in need of such treatment a pharmaceutically effective amount of a salt of a halide-free glucosamine base and a therapeutic drug containing at least one acid functionality, e.g., a carbonyl moiety, a carboxyl moiety, a sulfoxide moiety, etc. Preferably, the salt is stabilized by coating it with at least one pharmaceutically acceptable polymer comprising a water-soluble, water-immiscible and / or water-swellable homopolymer and / or copolymer. Suitable polymers include carboxypolymethylene homopolymers and copolymers; polyethylene glycol homopolymers and copolymers, povidone homopolymers and copolymers; polyacrylic acid homopolymers and copolymers; polyacrylamide homopolymers and copolymers; polysaccharides; and mixtures of two or more of the foregoing polymers. The resultant coated halide-free glucosamine-therapeutic drug salt composition will be stable upon exposure to ambient temperature and / or the atmosphere. Suitable therapeutic drugs containing at least one acid functionality may be found in one or more of the following classes of therapeutic drugs. α- and β-Adrenergic Agonists; Narcotic and Non-Narcotic Analgesics; Anorexics; Antiallergics; Antianginals; Antiarrhythmics; Antiasthmatics; Antibiotics; Anti-coagulants; Anticonvulsants; Antidepressants; Antidiabetics; Antihistaminics; Anti-hypertensives; Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatories; Antimigraines; Antineoplastics; Antiparkinsonians; Antipsychotics; Antipyretics; Antispasmodics; Antithrombotics; Anti-ulceratives; Anxiolytics; Decongestants; Diuretics; Hepatoprotectants; Sedatives; and Vasodilators.
Owner:GLUCONOVA
Materials and Methods for Control of Insect Pests Using Entomopathogenic Fungi
PendingUS20200390106A1Preventing and reducing and eliminating infection and spreadReduce nuisanceBiocideClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyAnticoagulant Agent
The subject invention relates to the production and use of entomopathogenic fungi for the control of arthropod pests. Specifically, the subject invention provides methods for producing Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana, as well as methods of their use, as biopesticidal compositions. Compositions are also provided for controlling arthropod pests, comprising one or more entomopathogenic fungi, a chitinase inducer, diatomaceous earth, and an anticoagulant.
Owner:LOCUS SOLUTIONS IPCO LLC
High-temperature-resistant precipitation antagonist for hydraulic oil
ActiveCN113698975ANon-flammableNot volatileChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsAdditivesAnticoagulant AgentCresol
The invention relates to the technical field of hydraulic oil, in particular to a high-temperature-resistant precipitation antagonist for hydraulic oil. The precipitation antagonist is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 70 to 80 percent of base oil, 2 to 6 percent of 6-butylated hydroxytoluene, 2 to 5 percent of zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate, 2 to 10 percent of anticoagulant, 1 to 3 percent of dispersing agent, 1 to 3 percent of accelerant, 1 to 3 percent of PH regulator, 2 to 5 percent of stabilizer, 3 to 8 percent of water retention agent, 2 to 5 percent of defoaming agent and 1 to 2 percent of clarifying agent. The main shaft drives the pushing mechanism to rotate, so that the roller rolls along the disc, and the roller is in intermittent rolling fit with the curved surface block. When the rollers roll along the curved surface blocks, the rollers roll to drive the limiting rods to move downwards, and the limiting rods push the walking plates to slide downwards along the sliding grooves; and meanwhile, the walking plate extrudes the shaking spring, and the walking plate is pushed to slide upwards under the elastic action of the shaking spring; the operations are repeated so as to make the walking plate to shake vertically, so that the intermediate product C is filtered and purified, and the precipitate antagonist is prepared.
Owner:山东恒利导热油工程技术研究所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com