Patents
Literature
246 results about "Perfusion fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
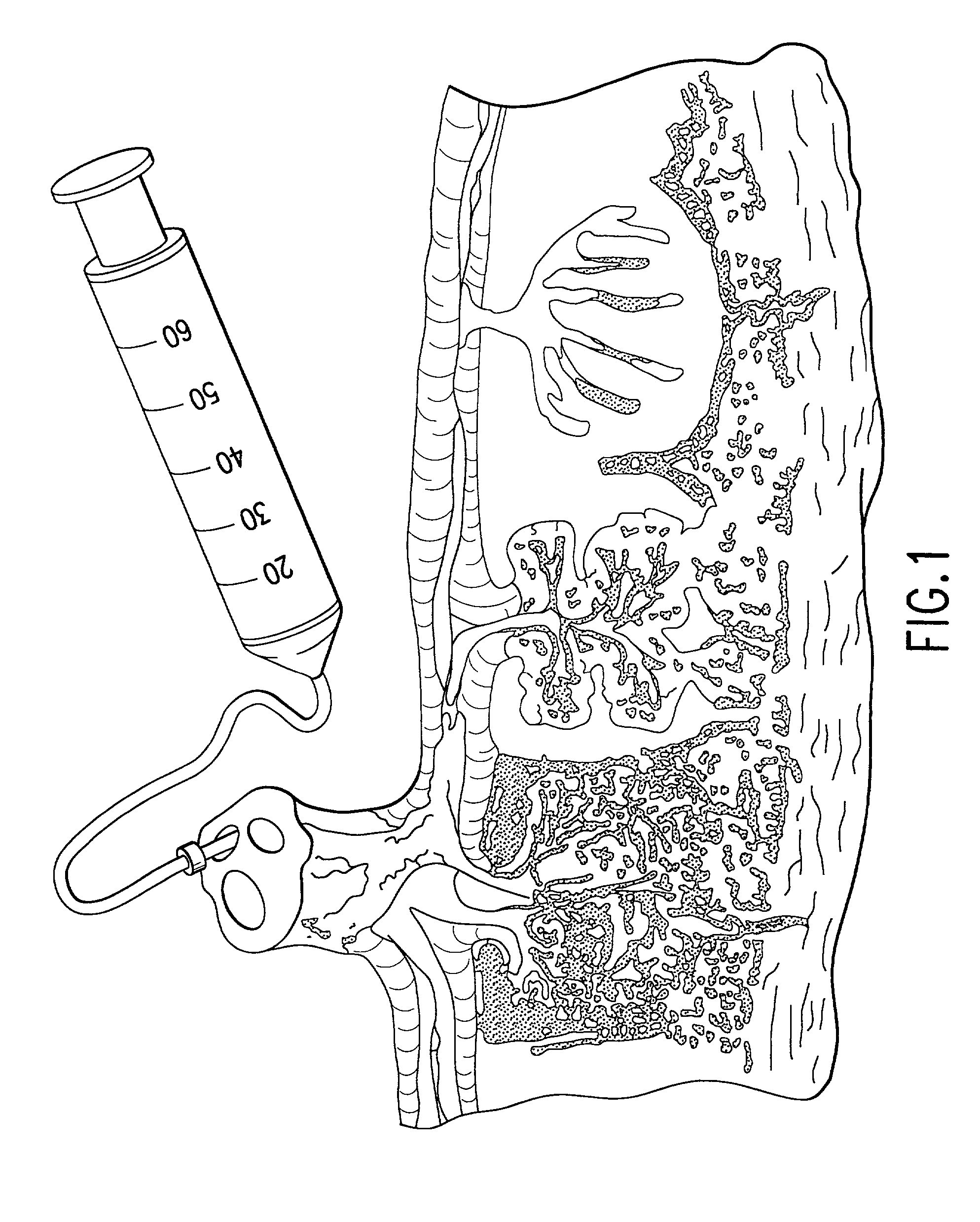
Perfusion fluids play a vital role in this matter. The perfusion fluid is used to perfuse and preserve the kidney prior to transplantation and acts as a medium in which organisms can grow.
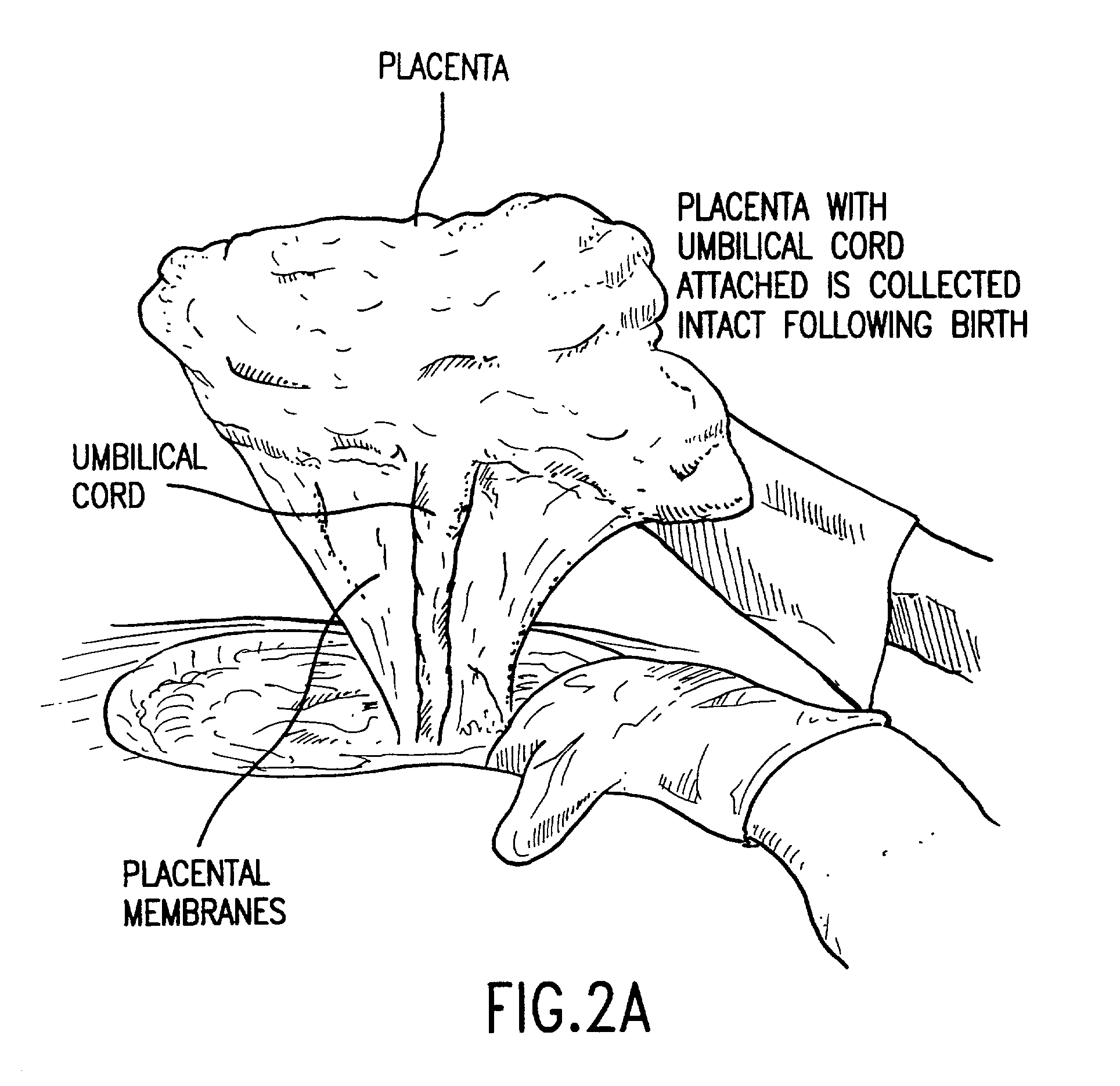
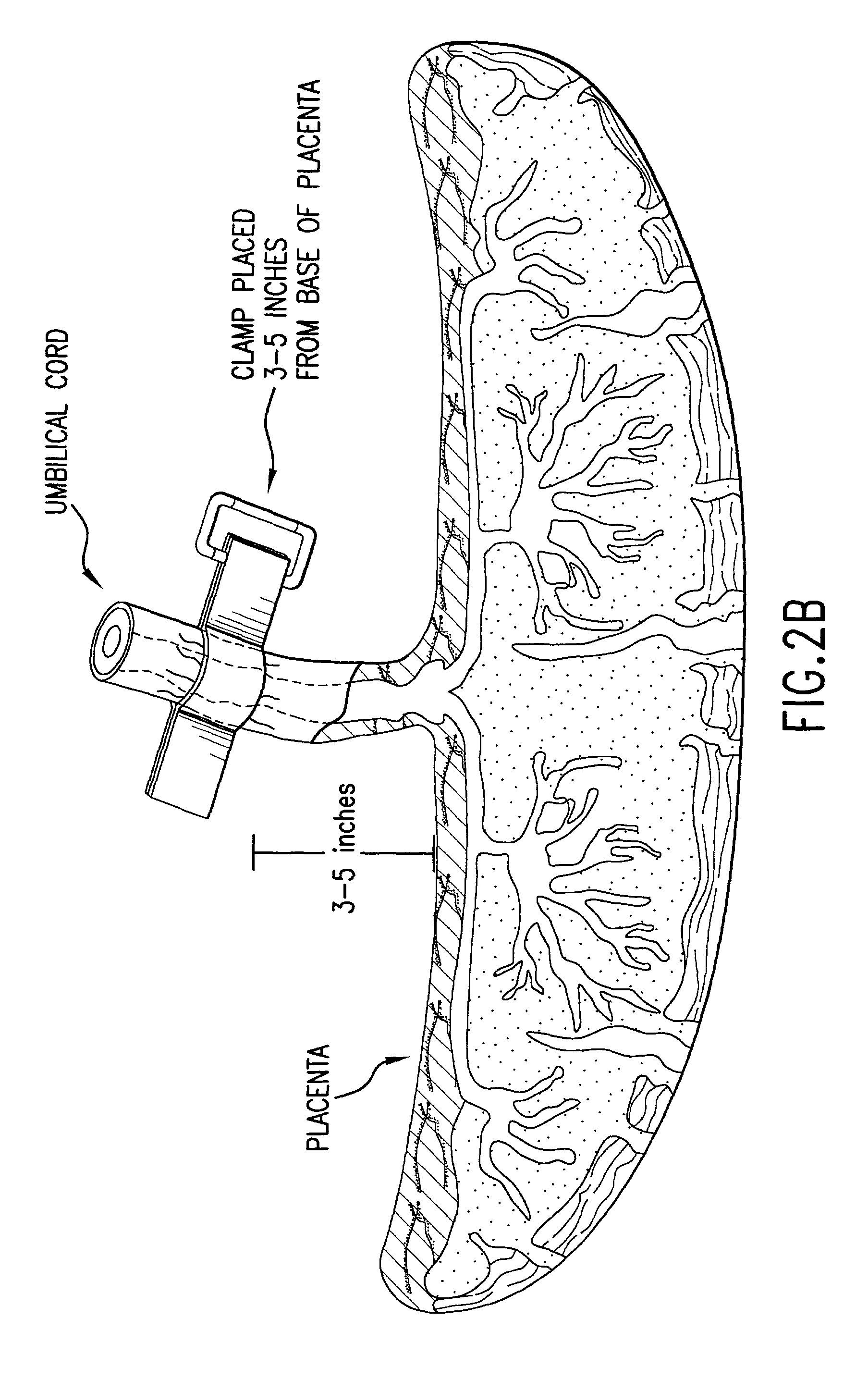
Post-partum mammalian placenta, its use and placental stem cells therefrom
InactiveUS20030032179A1Enhance exsanguinationEnhance sterile conditionSenses disorderAntipyreticAnticoagulant AgentEmbryo
The present invention provides a method of extracting and recovering embryonic-like stem cells, including, but not limited to pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, from an exsanguinated human placenta. A placenta is treated to remove residual umbilical cord blood by perfusing an exsanguinated placenta, preferably with an anticoagulant solution, to flush out residual cells. The residual cells and perfusion liquid from the exsanguinated placenta are collected, and the embryonic-like stem cells are separated from the residual cells and perfusion liquid. The invention also provides a method of utilizing the isolated and perfused placenta as a bioreactor in which to propagate endogenous cells, including, but not limited to, embryonic-like stem cells. The invention also provides methods for propagation of exogenous cells in a placental bioreactor and collecting the propagated exogenous cells and bioactive molecules therefrom.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
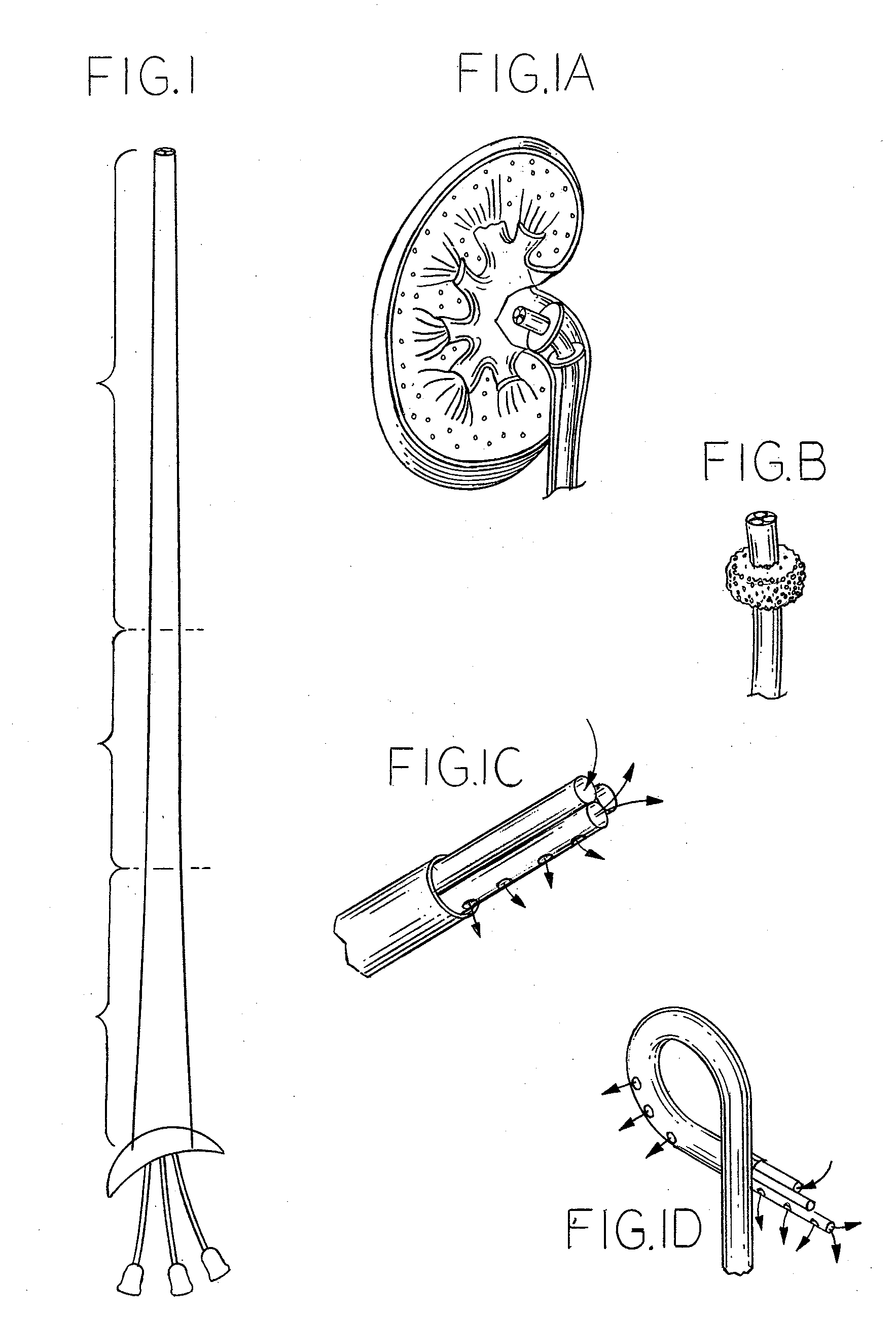
Process and System For Systematic Oxygenation and Renal Preservation During Retrograde Perfusion of the Ischemic Kidney
A delivery system to provide end organ oxygenation and even systematic oxygenation in the face of ischemic result. The deliver system including a retrograde oxygenation and perfusion stent. The stent employing at least two and possibly more channels to allow flow of the perfusate from the device to the renal pelvis then to a back out to a collection apparatus. The stent may include various vital sign monitors, such as a renal pressure monitor, temperature monitor, and even an oxygenation monitor. The stent may include an anchoring device to allow the stent to be anchored into the renal pelvis in a temporary way during the retrograde oxygenation process.
Owner:HUMPHREYS MITCHELL R
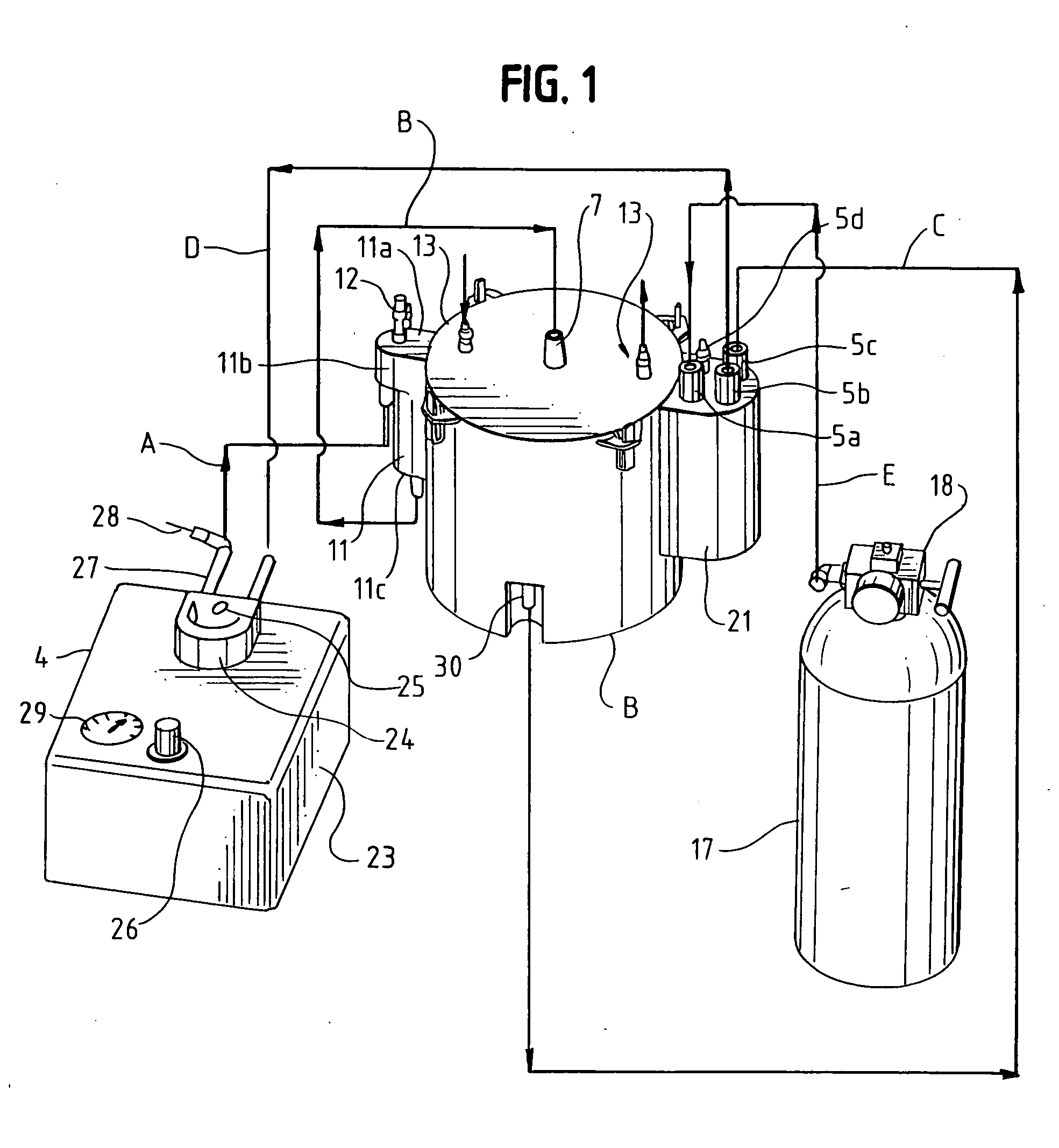
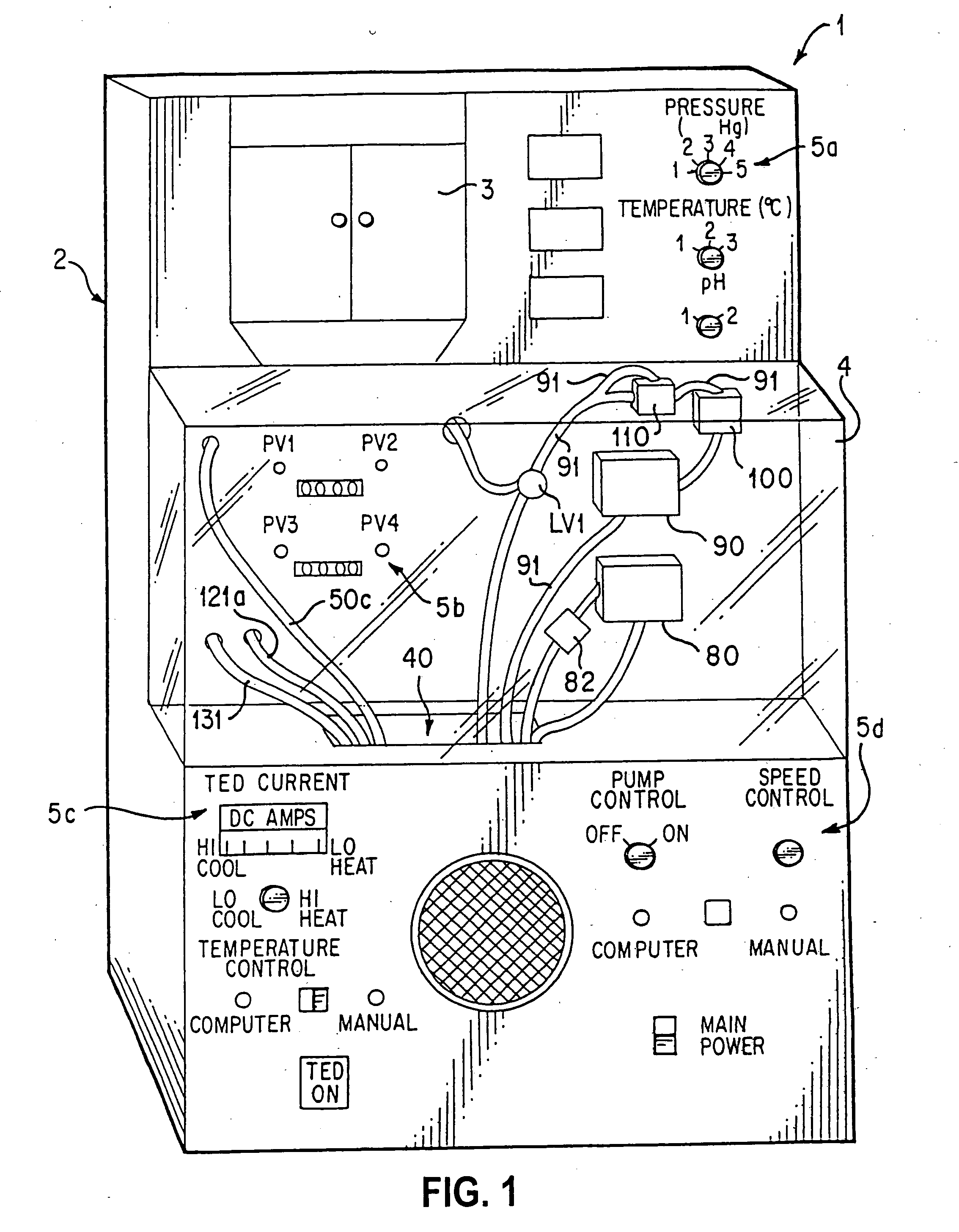
Organ preservation apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20050153271A1Increase the lengthReduce decreaseDead animal preservationMachines using electric/magnetic effectsNutrient solutionOxygen
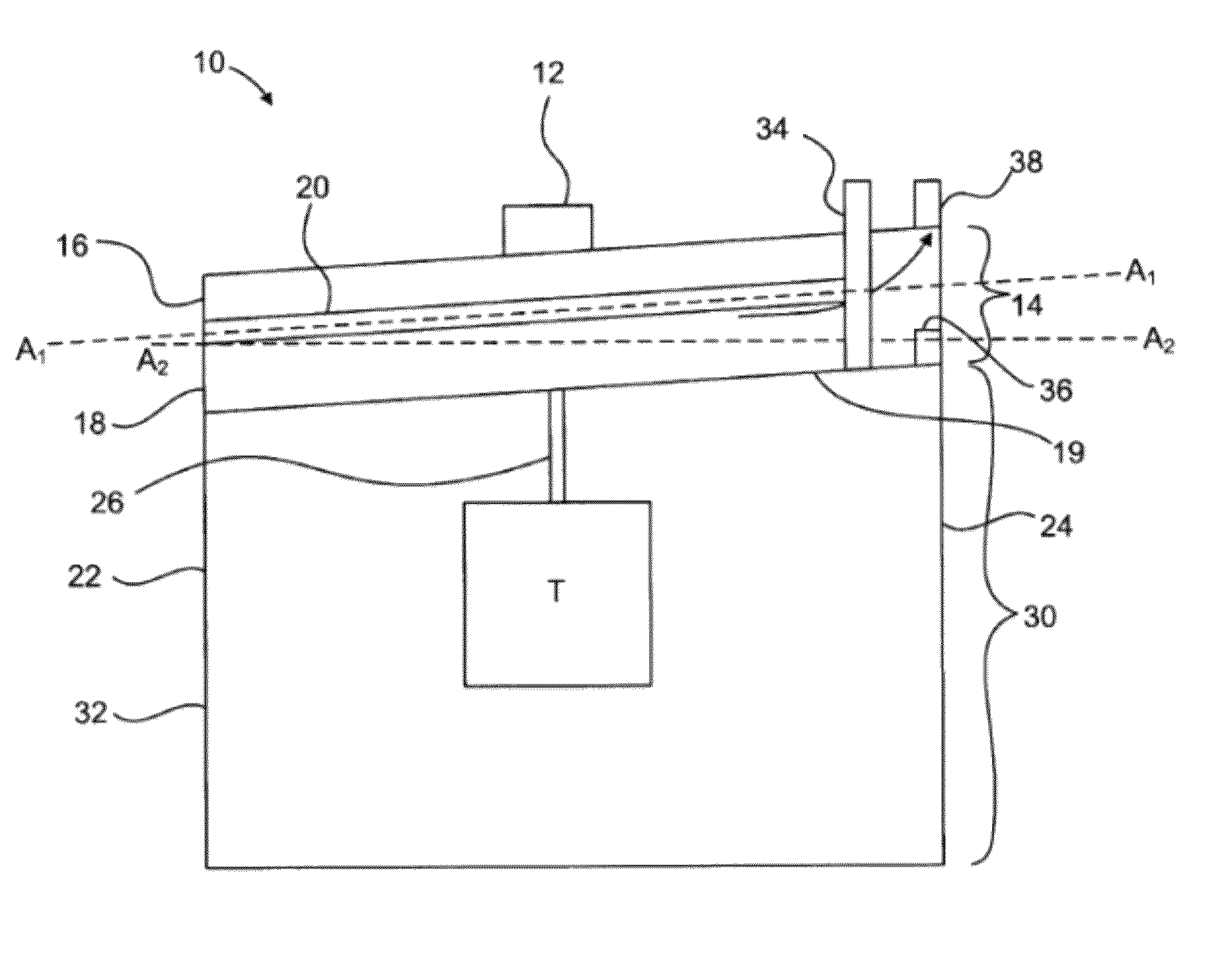
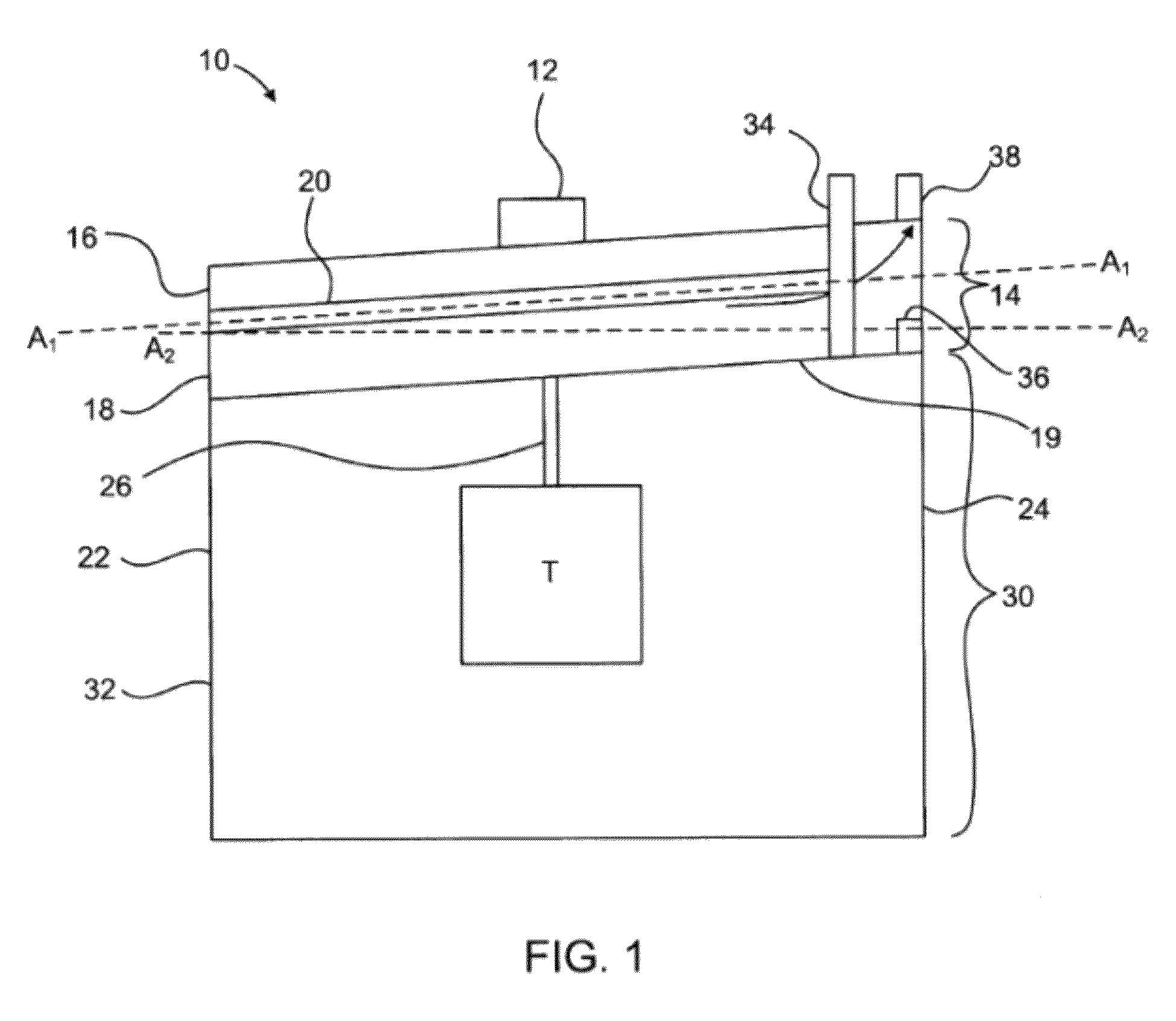
This invention is a transportable organ preservation system that substantially increases the time during which the organ can be maintained viable for successful implantation into a recipient. A chilled oxygenated nutrient solution can be pumped through the vascular bed of the organ after excision of the organ from the donor and during transport. The device of the present invention uses flexible permeable tubing to oxygenate the perfusion fluid while the CO2 produced by the organ diffuses out of the perfusion fluid. One pressurized two-liter “C” cylinder can supply oxygen for up to 34 hours of perfusion time. The device can use a simple electric pump driven by a storage battery to circulate the perfusion fluid through the organ being transported. The vessel containing the organ to be transported can be held at a suitable temperature by a chiller.
Owner:ORGAN TRANSPORT SYST
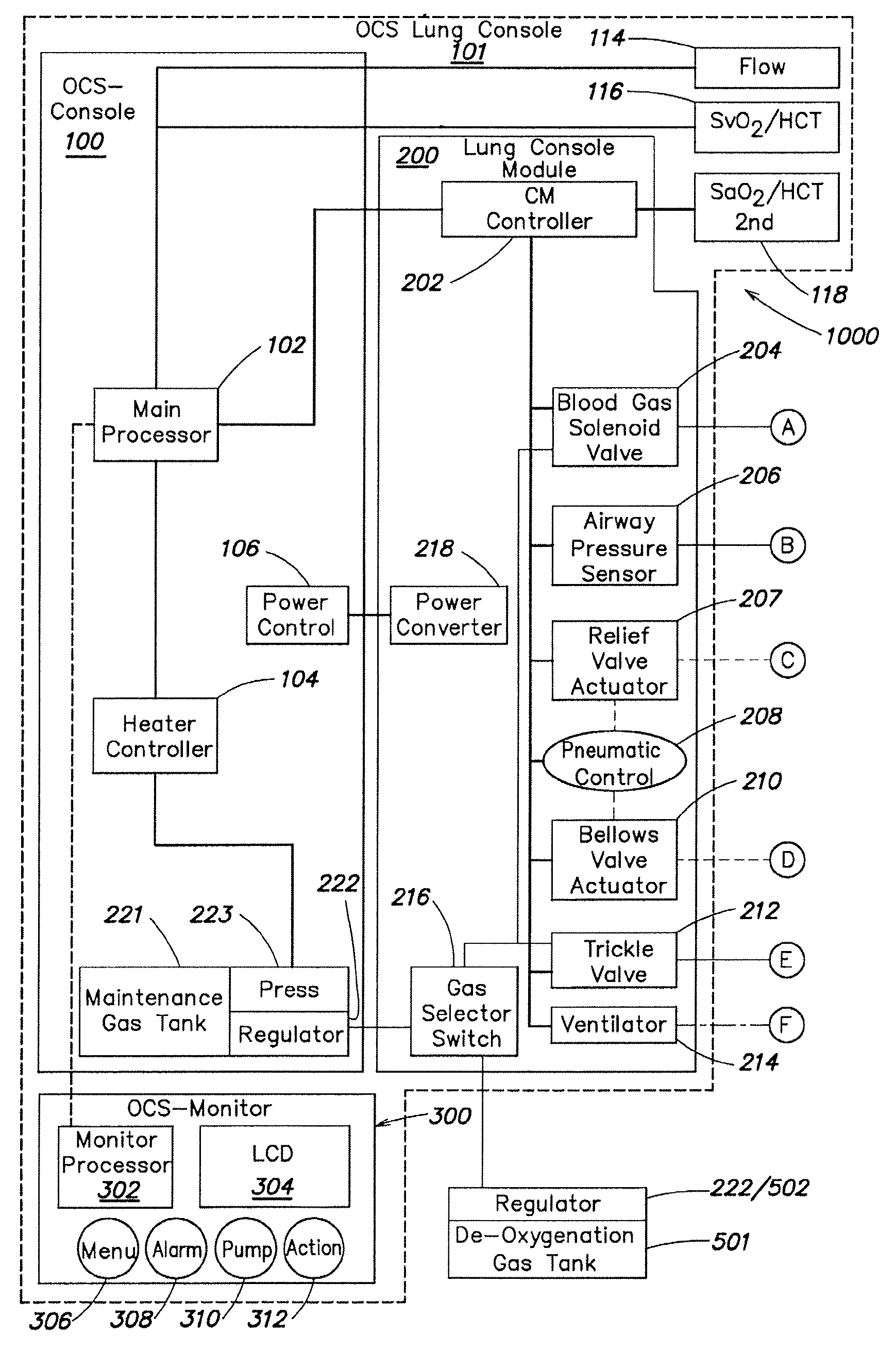
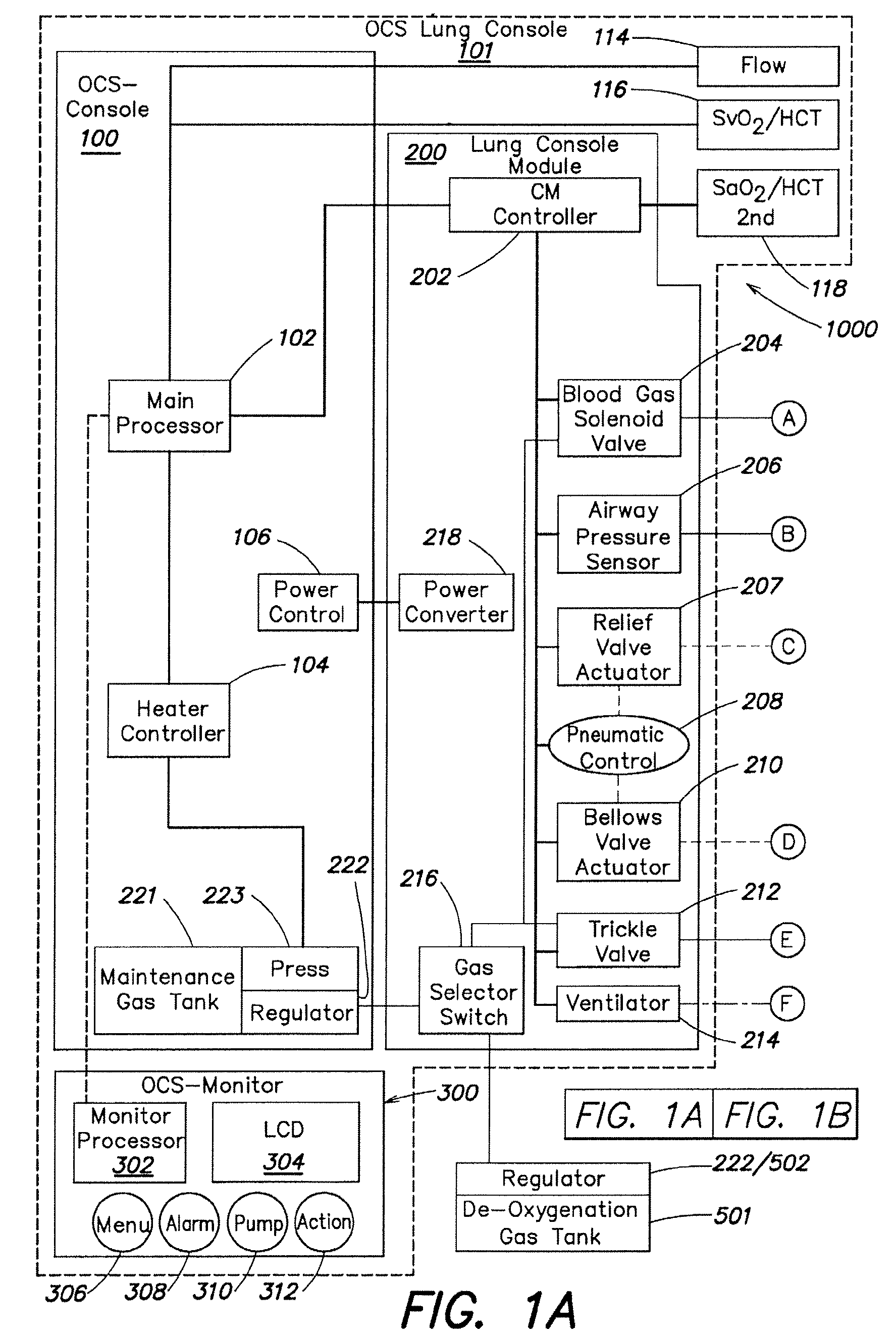
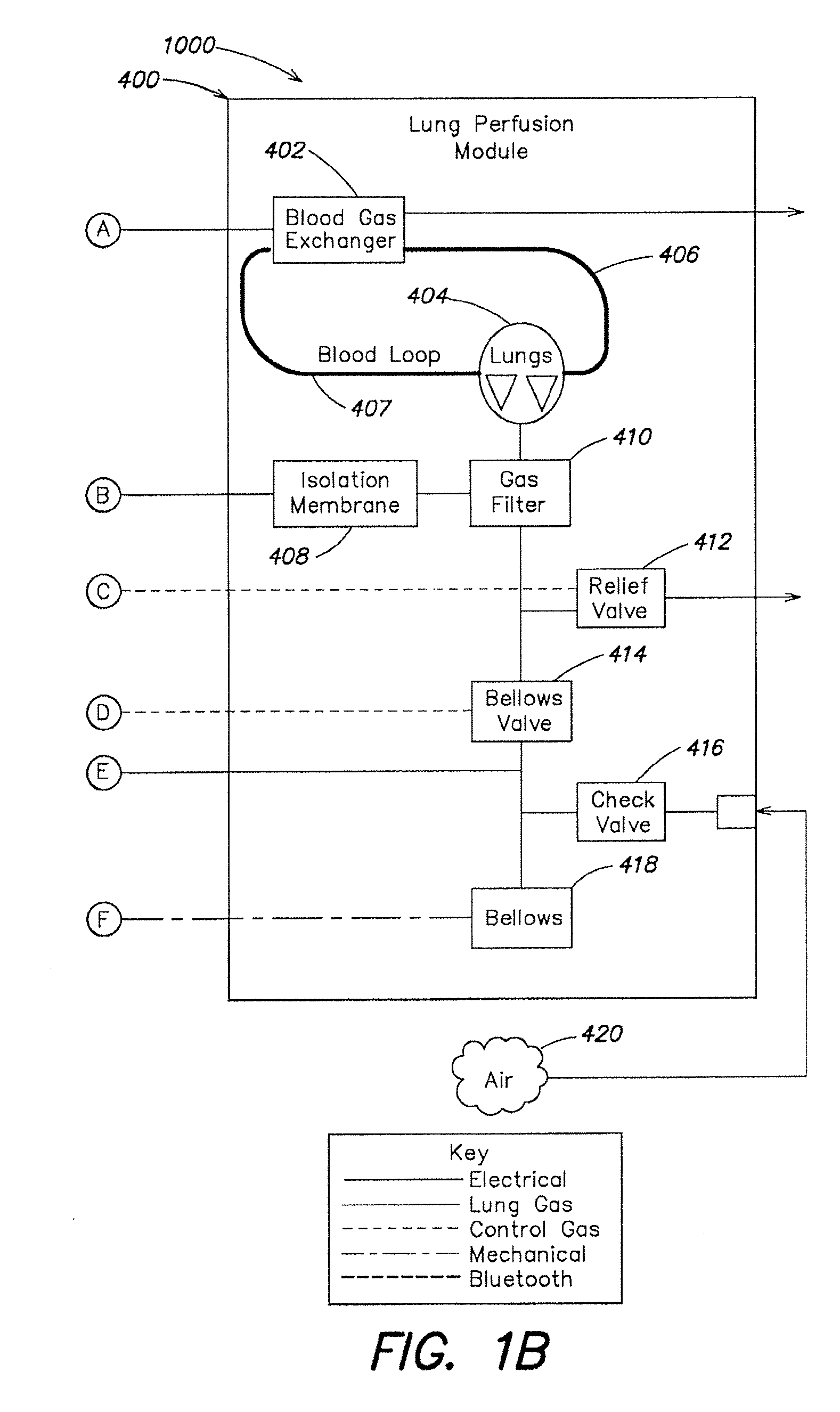
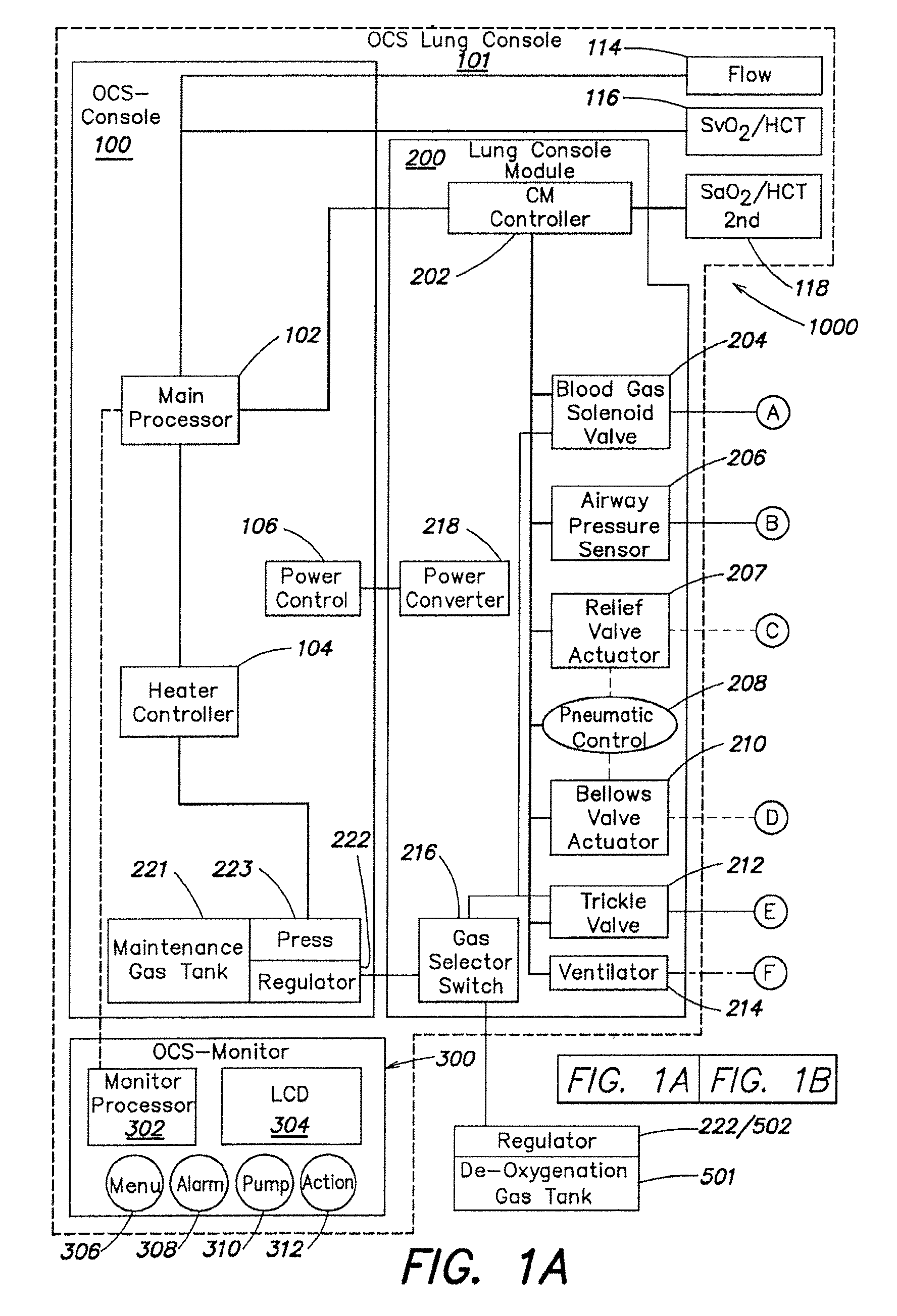
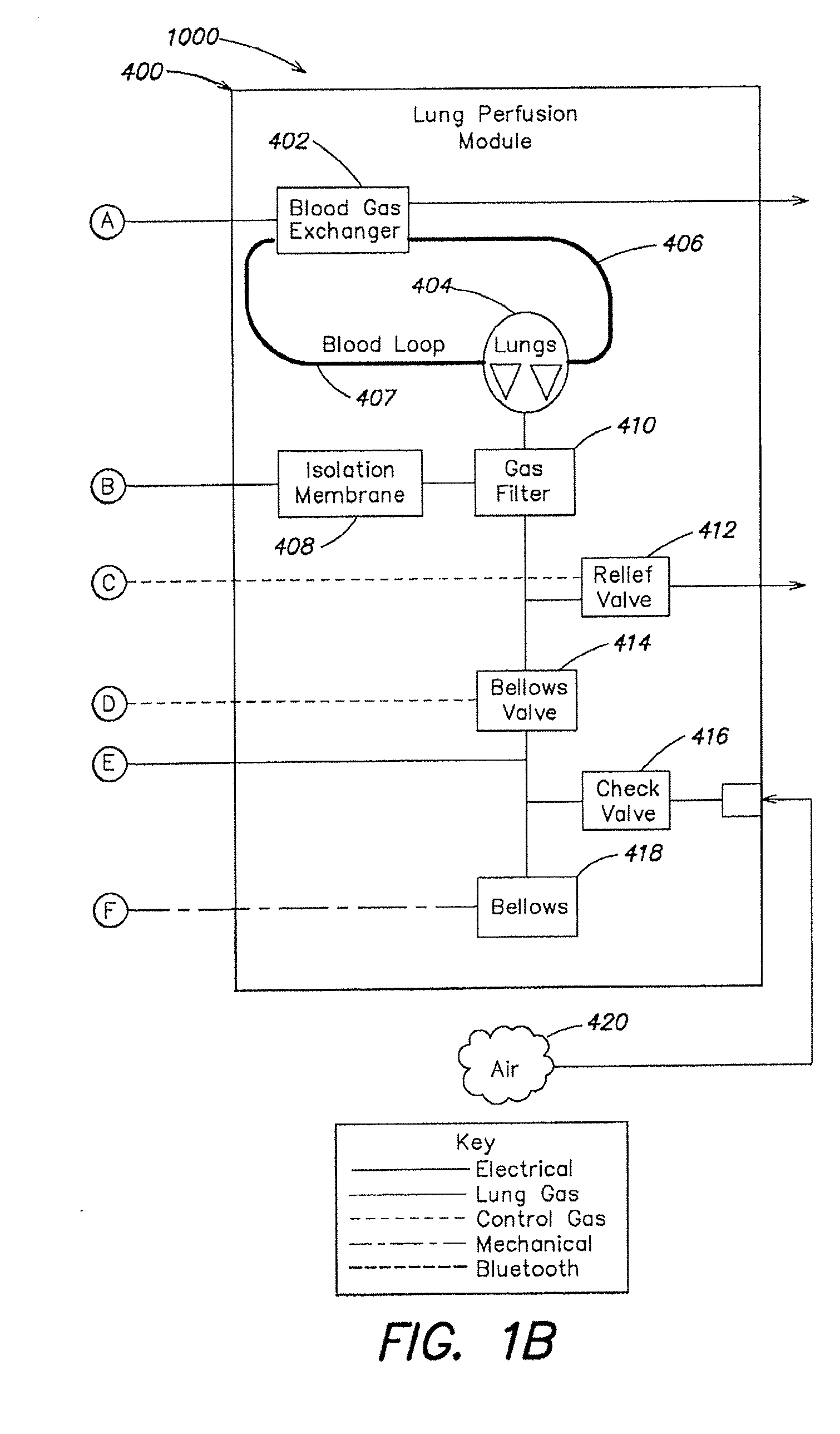
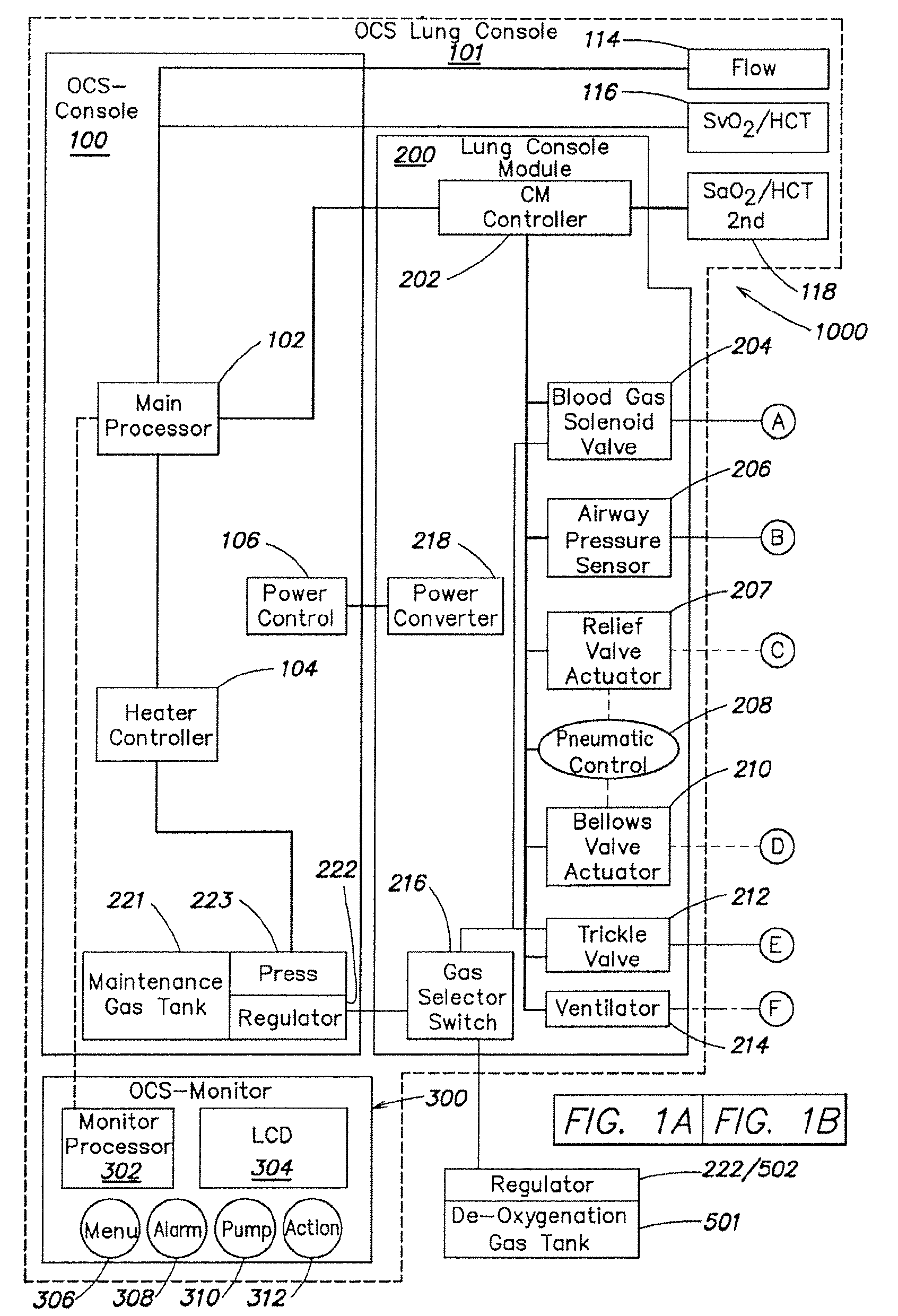
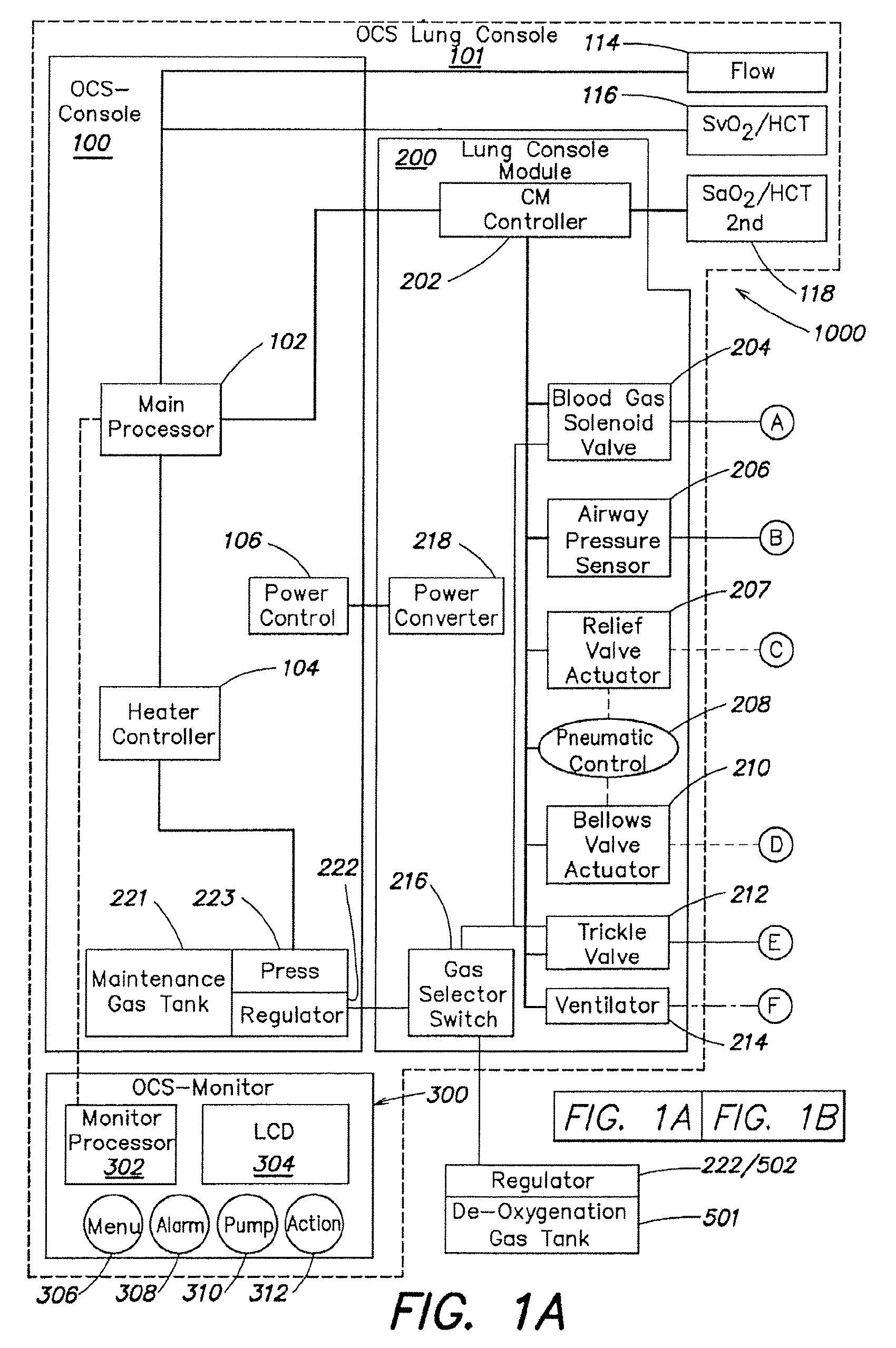
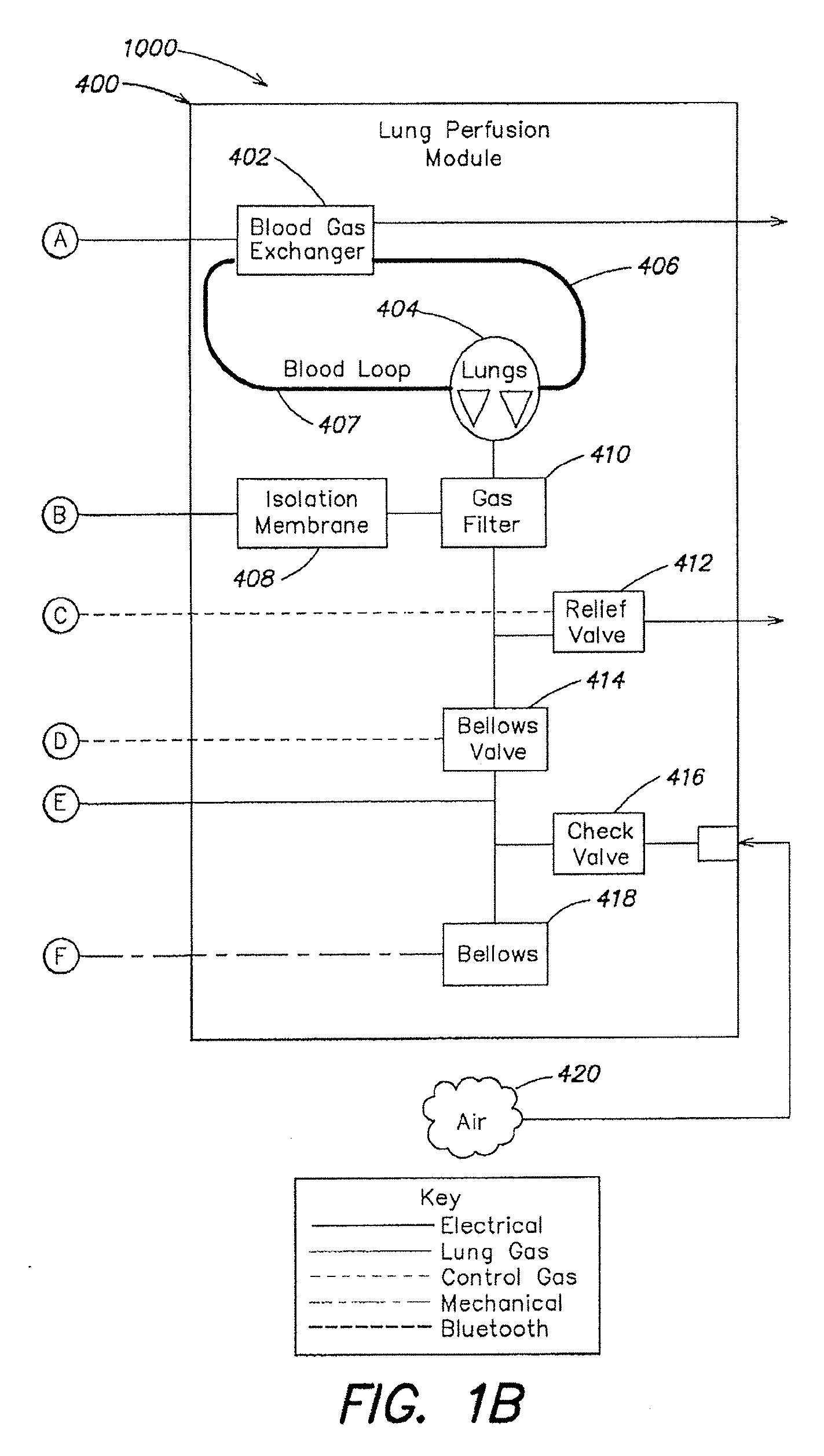
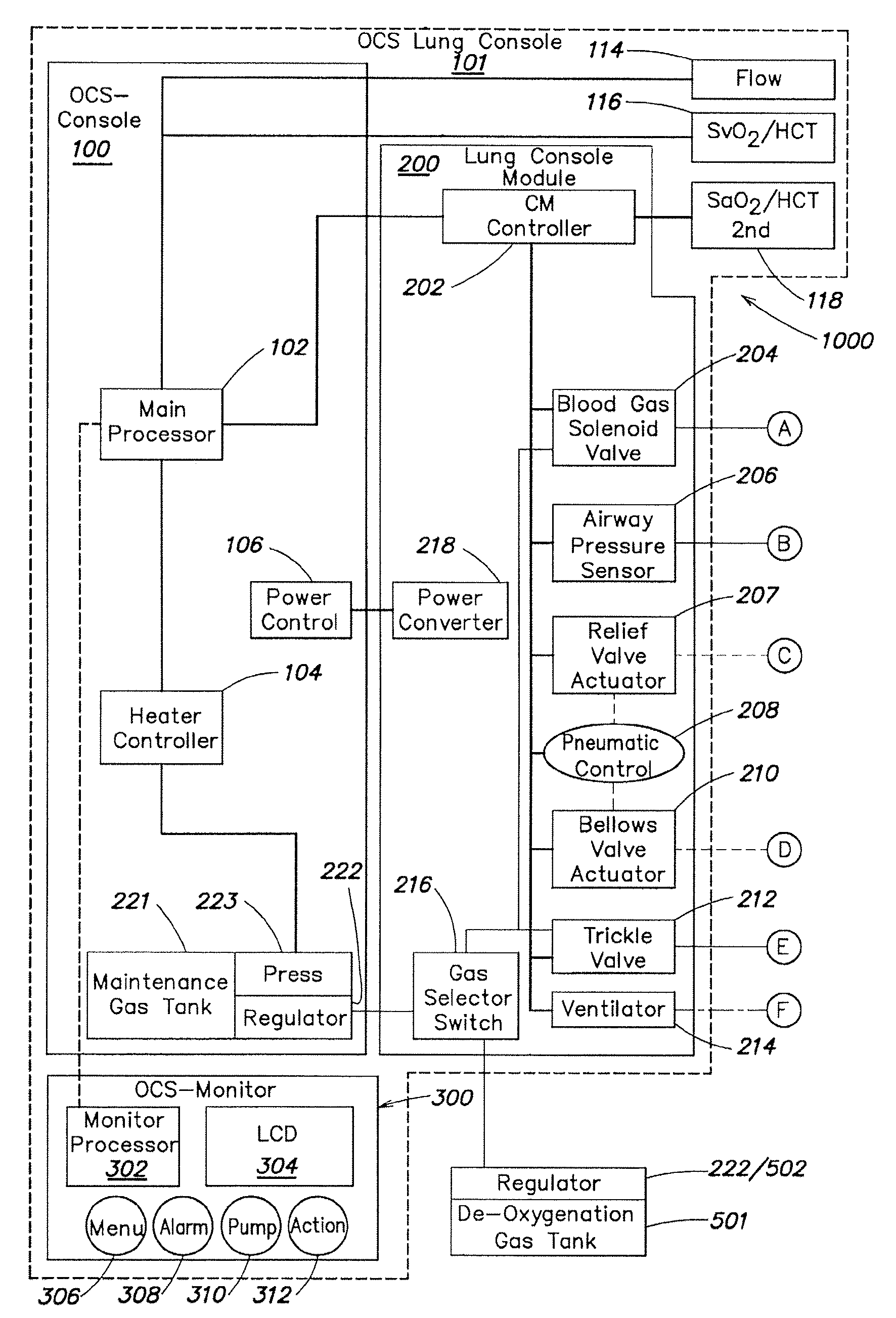
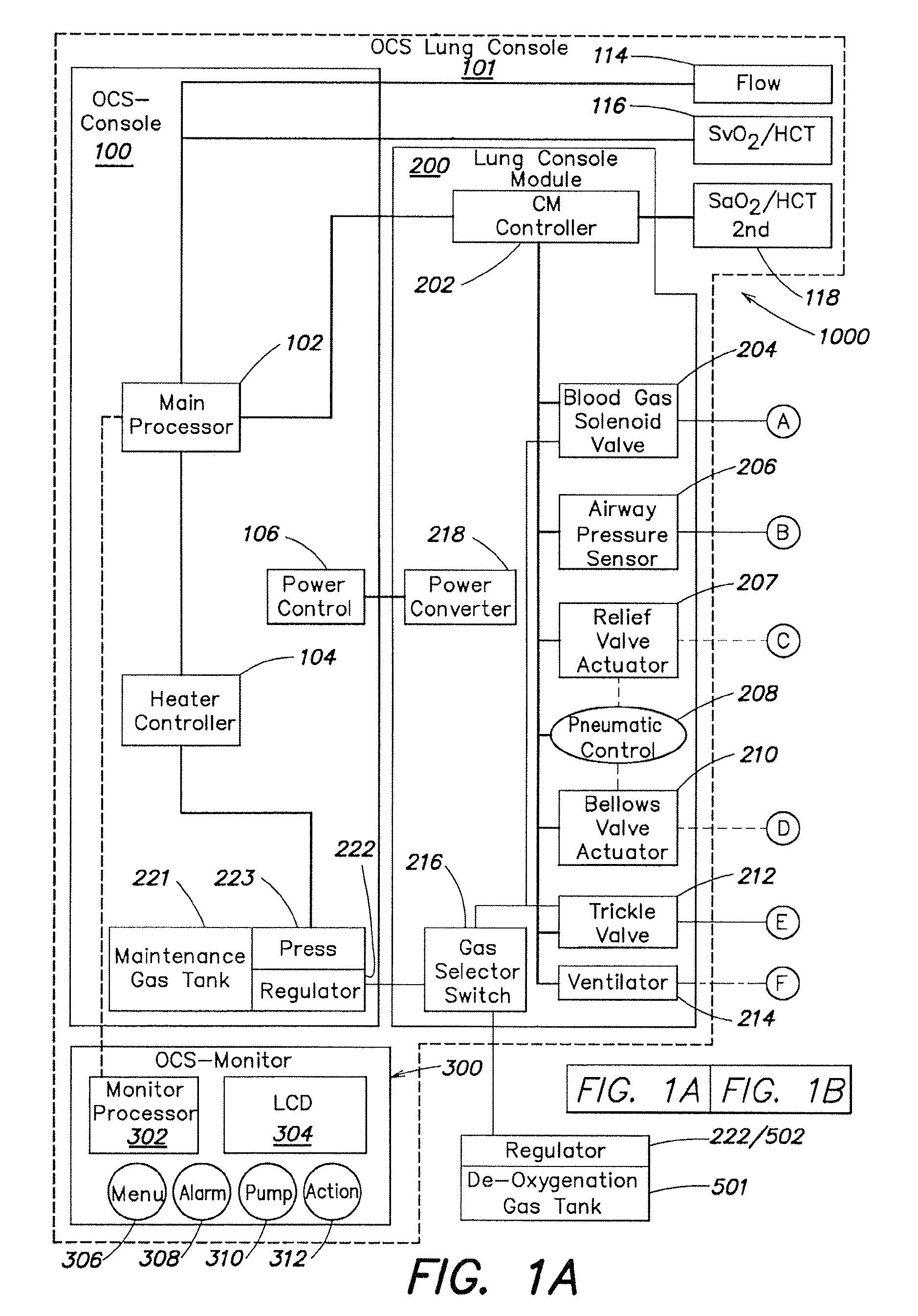
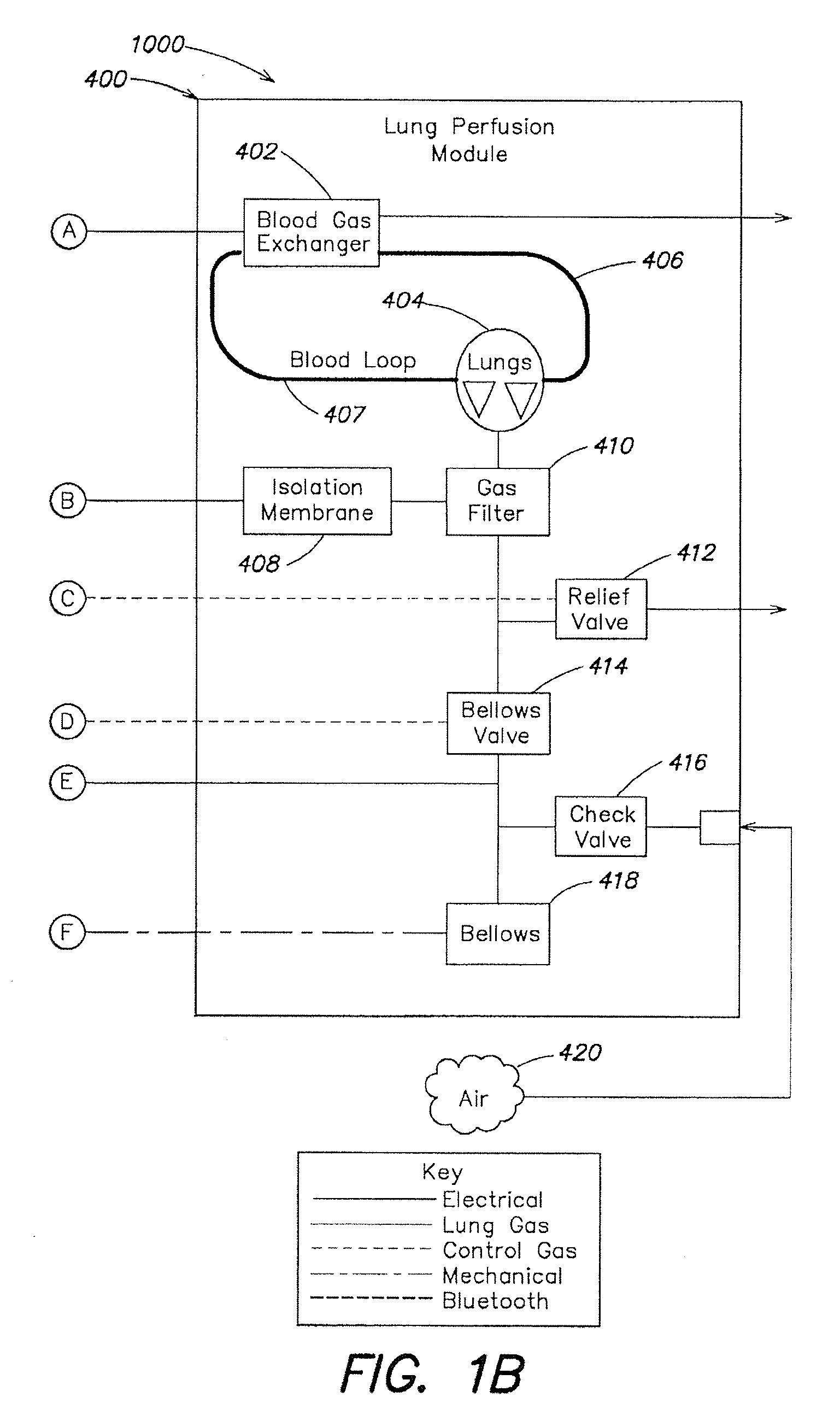
Systems and methods for ex vivo lung care
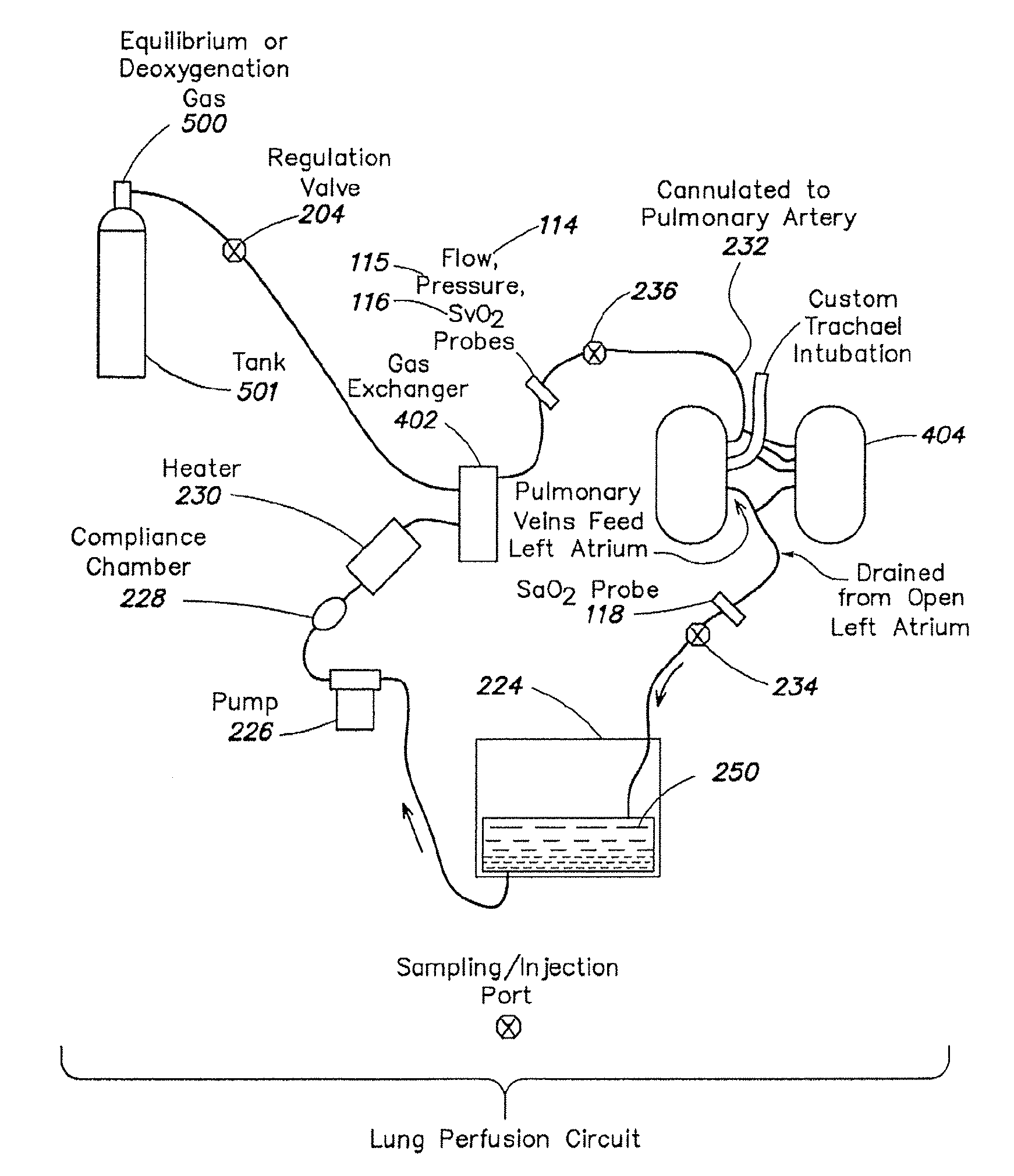
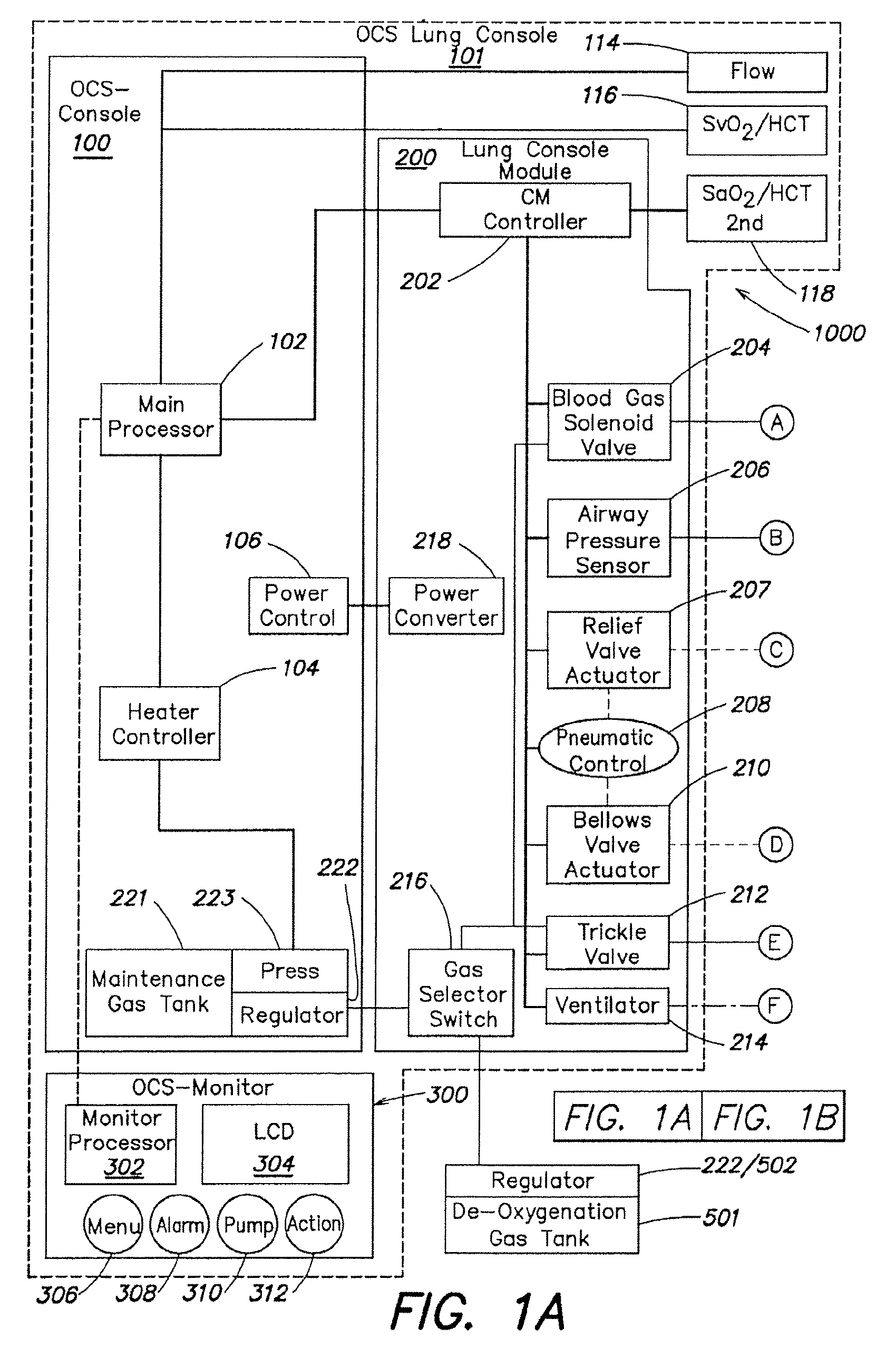
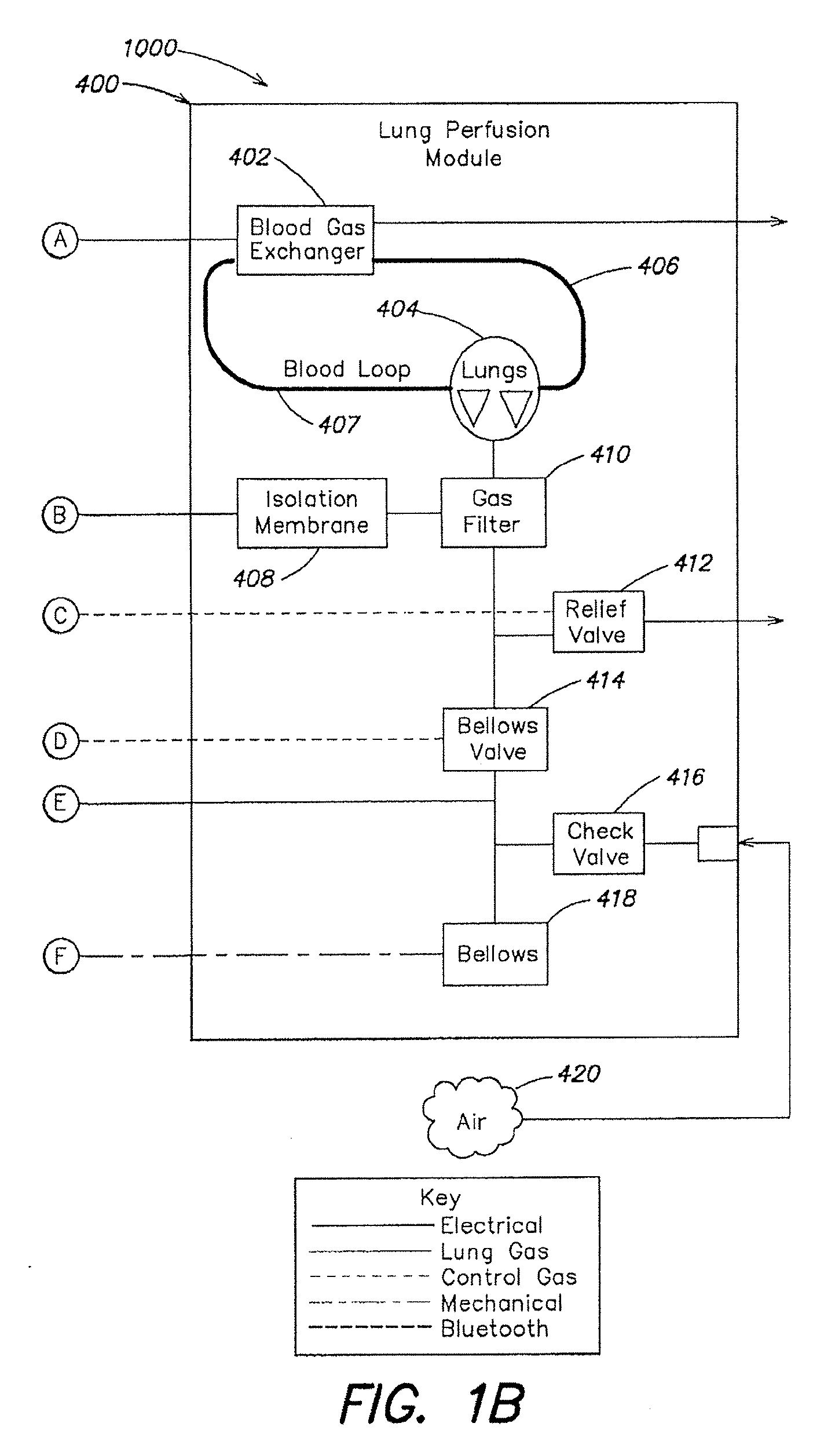
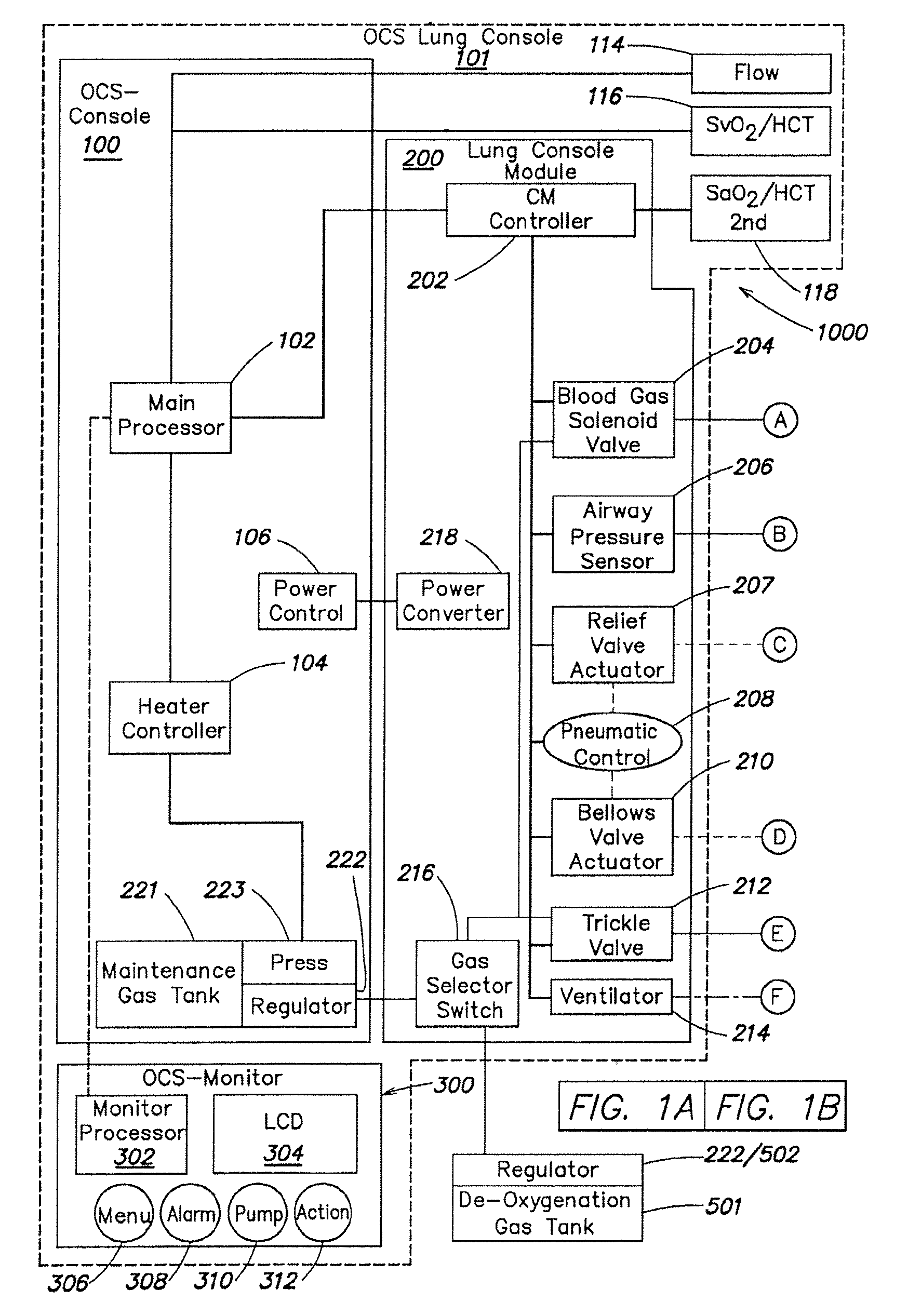
Methods and systems of maintaining, evaluating, and providing therapy to a lung ex vivo. The methods and systems involve positioning the lung in an ex vivo perfusion circuit; circulating a perfusion fluid through the lung, the fluid entering the lung through a pulmonary artery interface and leaving the lung through a left atrial interface; and ventilating the lung by flowing a ventilation gas through a tracheal interface. Maintaining the lung for extended periods involves causing the lung to rebreath a captive volume of air, and reaching an equilibrium state between the perfusion fluid and the ventilation gas. Evaluating the gas exchange capability of the lung involves deoxygenating the perfusion fluid and measuring a time taken to reoxygenate the perfusion fluid by ventilating the lung with an oxygenation gas.
Owner:TRANSMEDICS
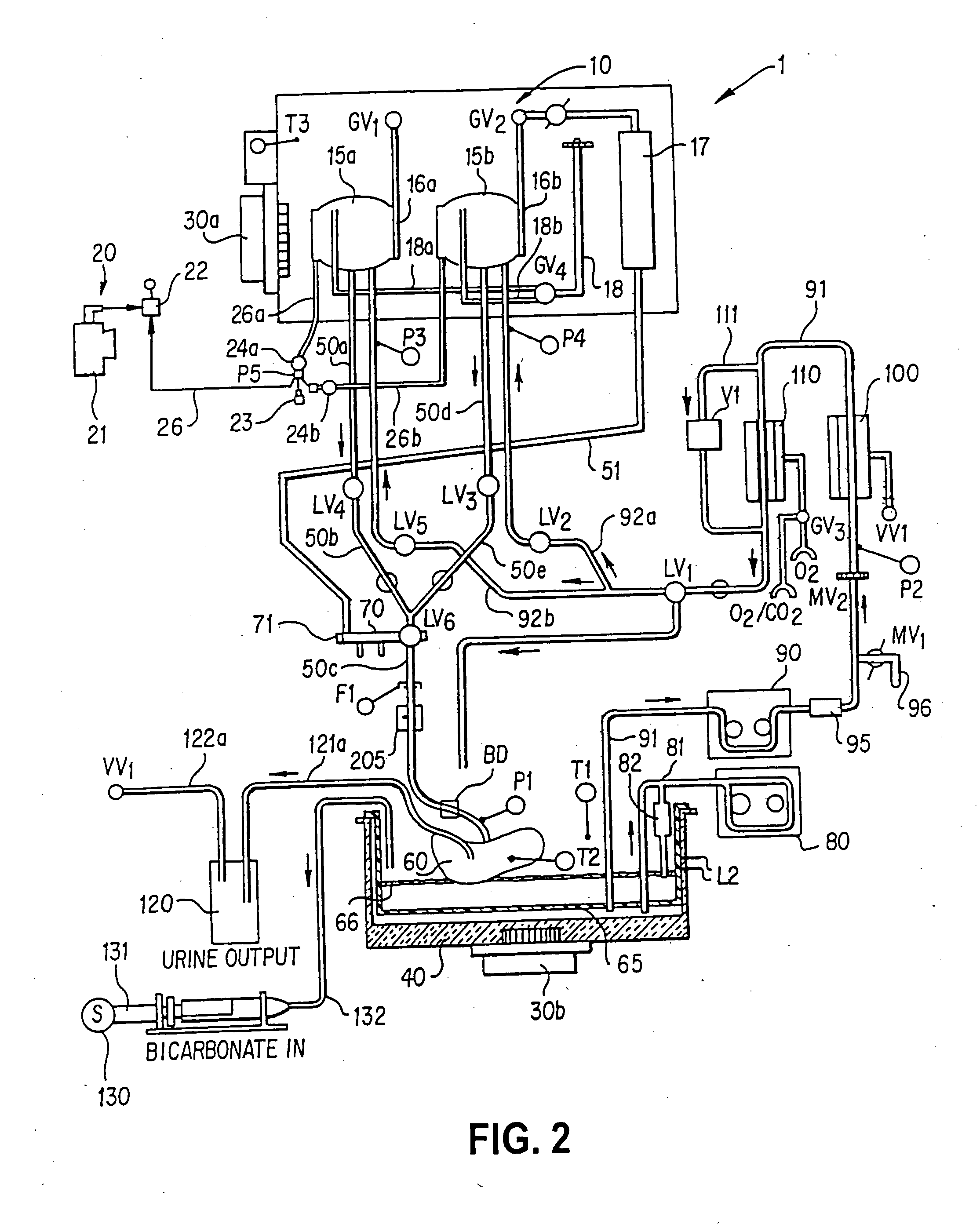
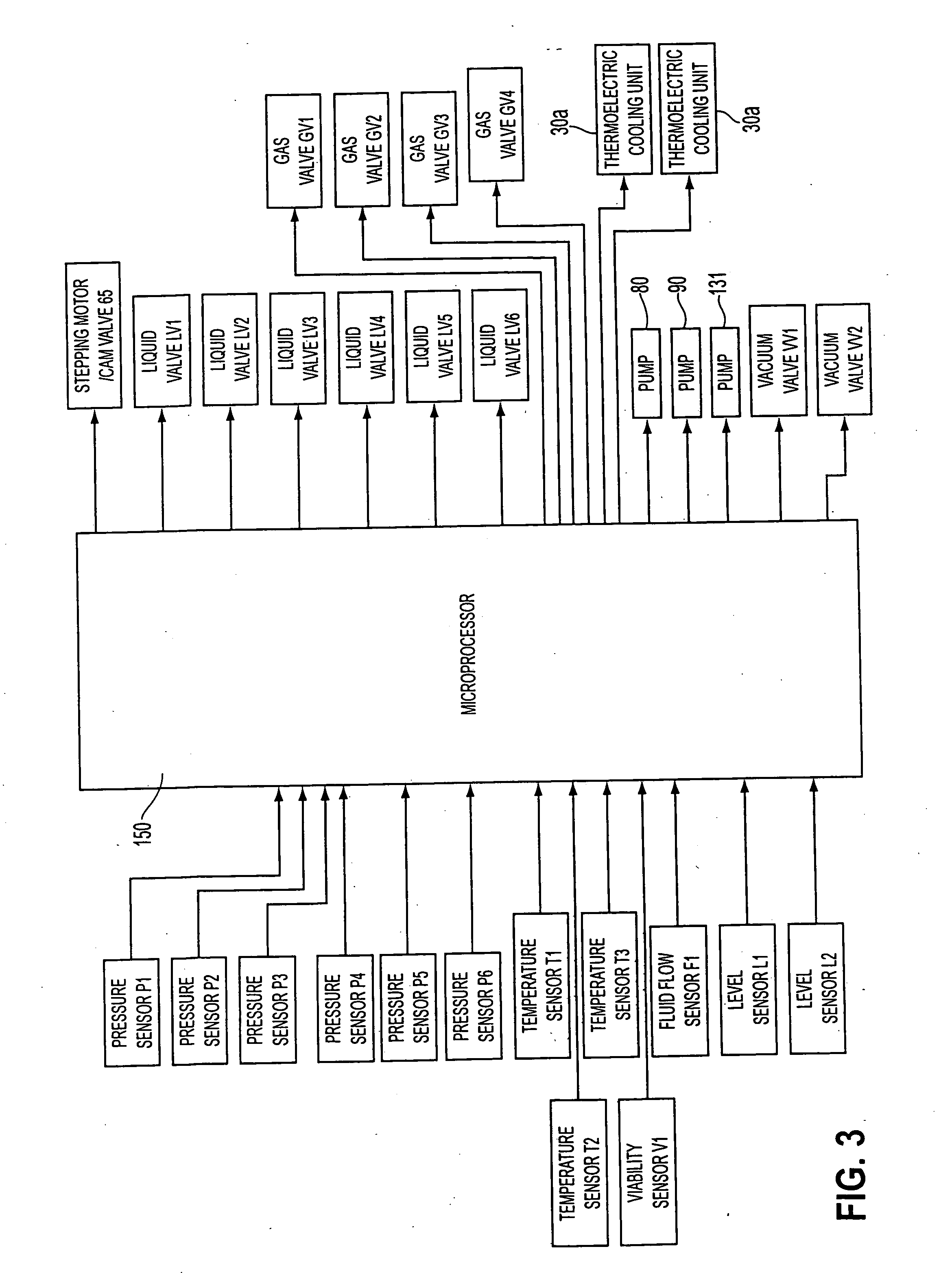
Apparatus and method for perfusing an organ or tissue for isolating cells from the organ or tissue
ActiveUS20050221269A1Avoid damageMonitor and sustain and restore viabilitySurgeryDead animal preservationBiomedical engineeringOrgan of Corti
An organ perfusion apparatus and method monitor, sustain and / or restore viability of organs and preserve organs for storage and / or transport. Other apparatus include an organ transporter, an organ cassette and an organ diagnostic device. The method includes perfusing the organ at hypothermic and / or normothermic temperatures. The methods further include perfusing the organ at hypothermic and / or normothermic temperatures with a second perfusate containing a substance for reacting with the organ. Condition of the organ may be automatically monitored, and the perfusion process can be automatically controlled using a control program.
Owner:ORGAN RECOVERY SYST
Compositions and methods for treating diseases
This invention relates to compositions and methods for treatment of vascular conditions. The invention provides arginine polymers and arginine homopolymers for the treatment and / or prevention of glaucoma, pulmonary hypertension, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, erectile dysfunction, Raynaud's syndrome, heparin overdose, vulvodynia, and wound healing. The invention also provides arginine polymers and arginine homopolymers for use in organ perfusate and preservation solutions.
Owner:LUMEN THERAPEUTICS
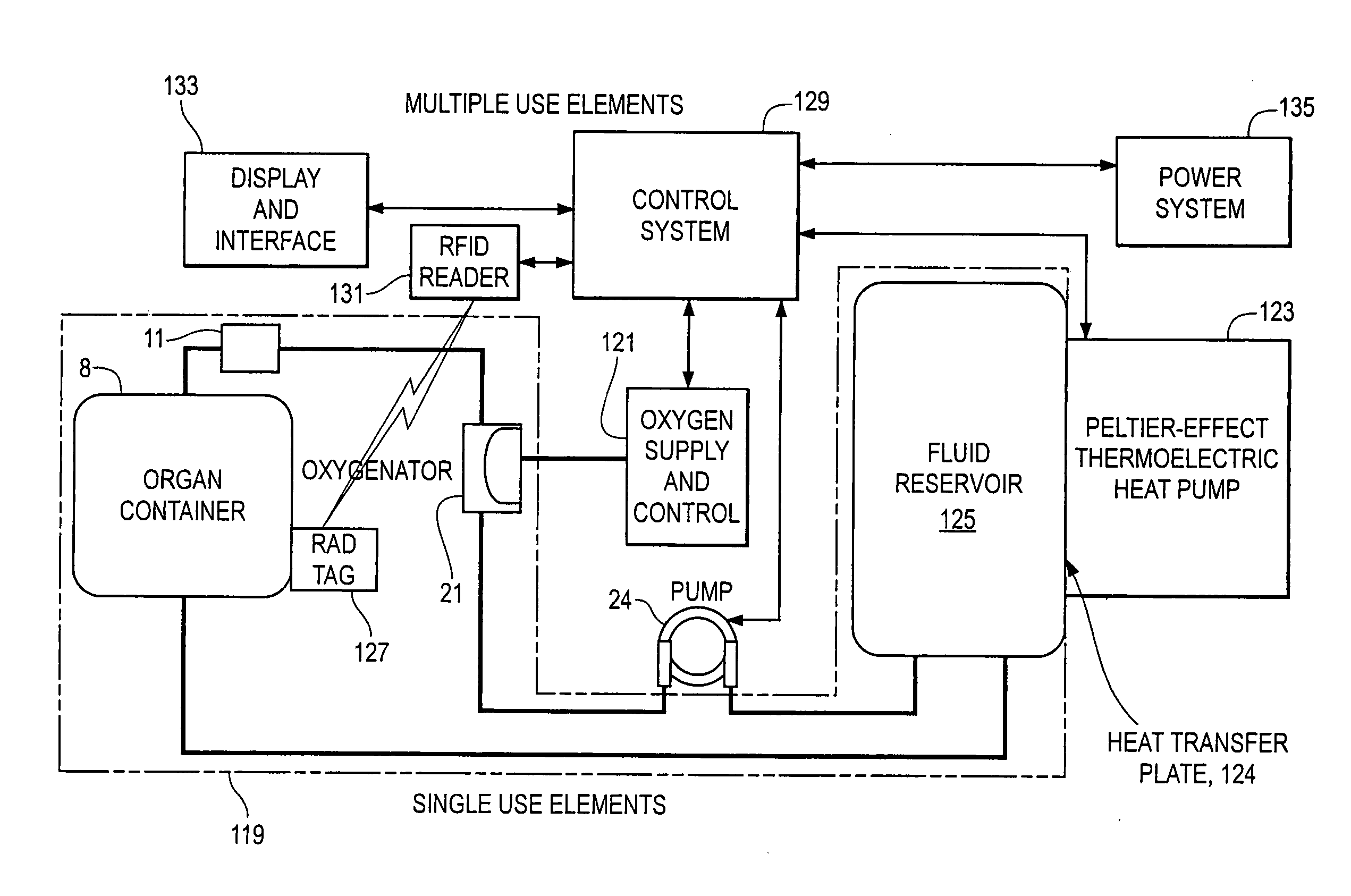
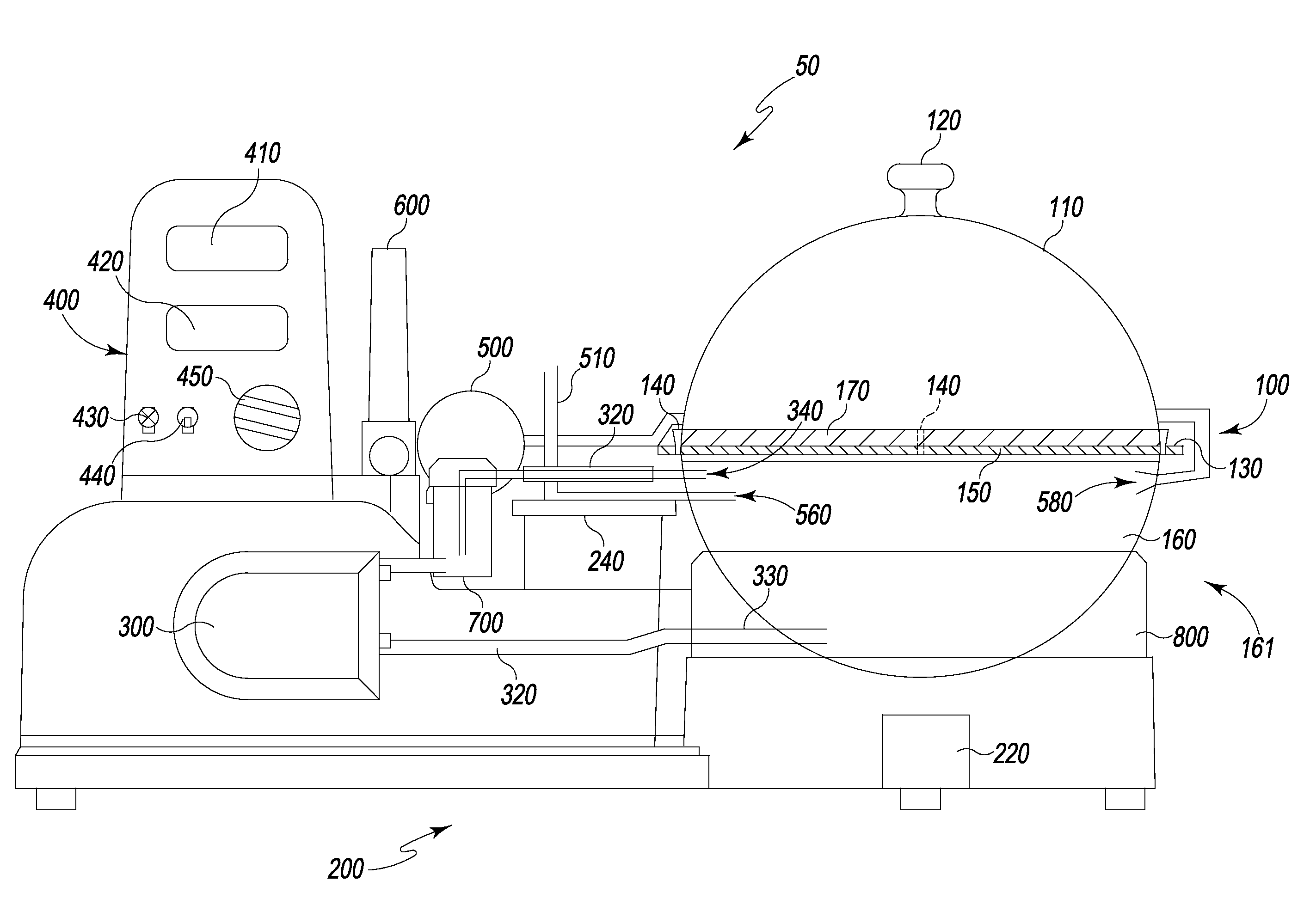
Organ Preservation System
An organ preservation system having an organ chamber with a perfusate reservoir surrounded by a heat exchanger. The system has a pump for circulating perfusate, which draws perfusate from the reservoir and passes the perfusate through a bubble trap, and temperature and pressure sensors prior to entering the chamber where the organ is perfused. An oxygenator with a platform and a filter is situated within the perfusate reservoir such that perfusate leaving the organ which rests on the platform passes through the filter before dripping into the perfusate reservoir below. The pump re-circulates perfusate from the perfusate reservoir. The oxygenator has gas permeable tubes wound around support legs of the oxygenator. Circulation of oxygen through the tubes allows for gas exchange by diffusion across the membrane to oxygenate perfusate flowing around the tubes.
Owner:BRASSIL JOHN
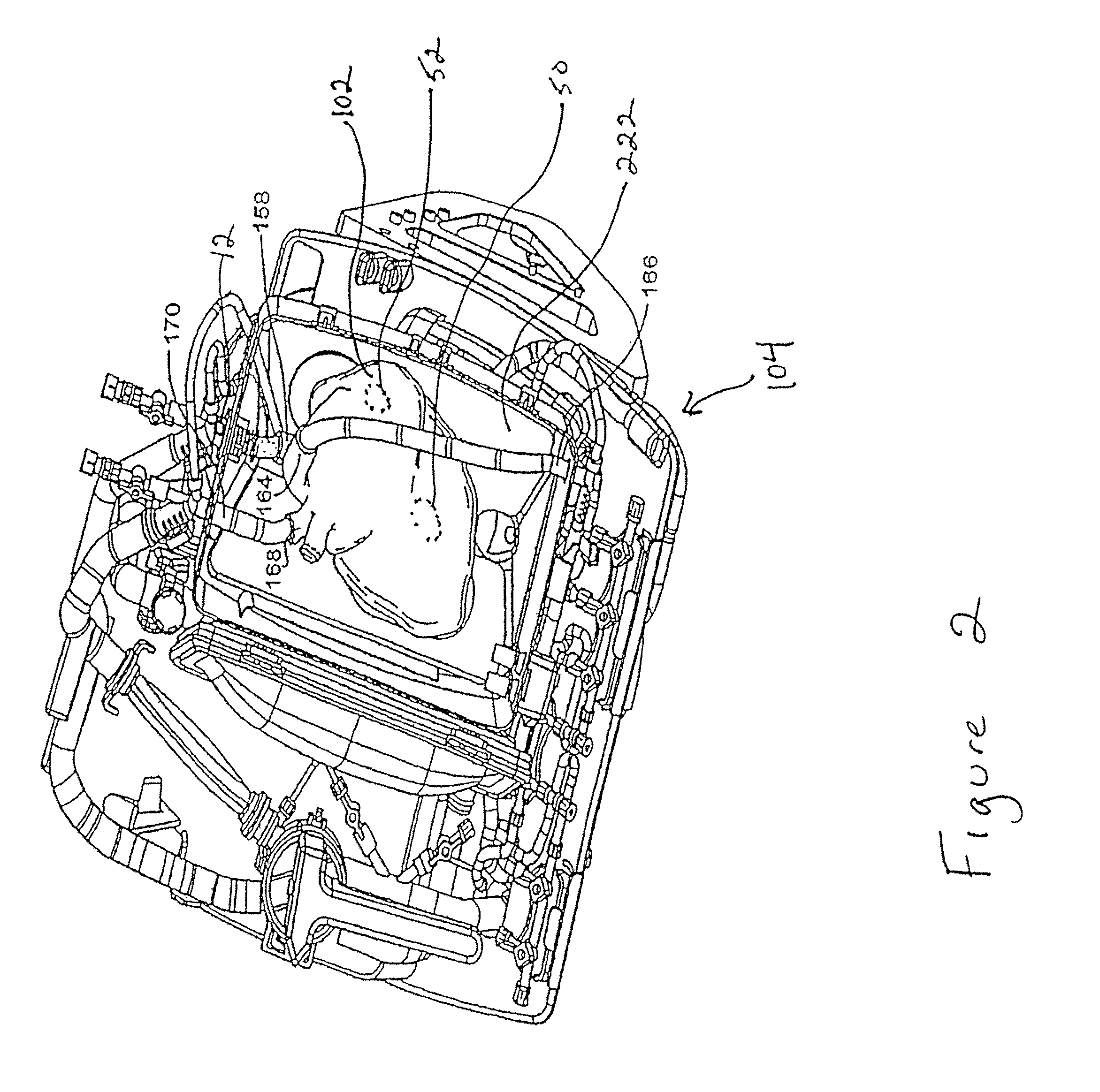
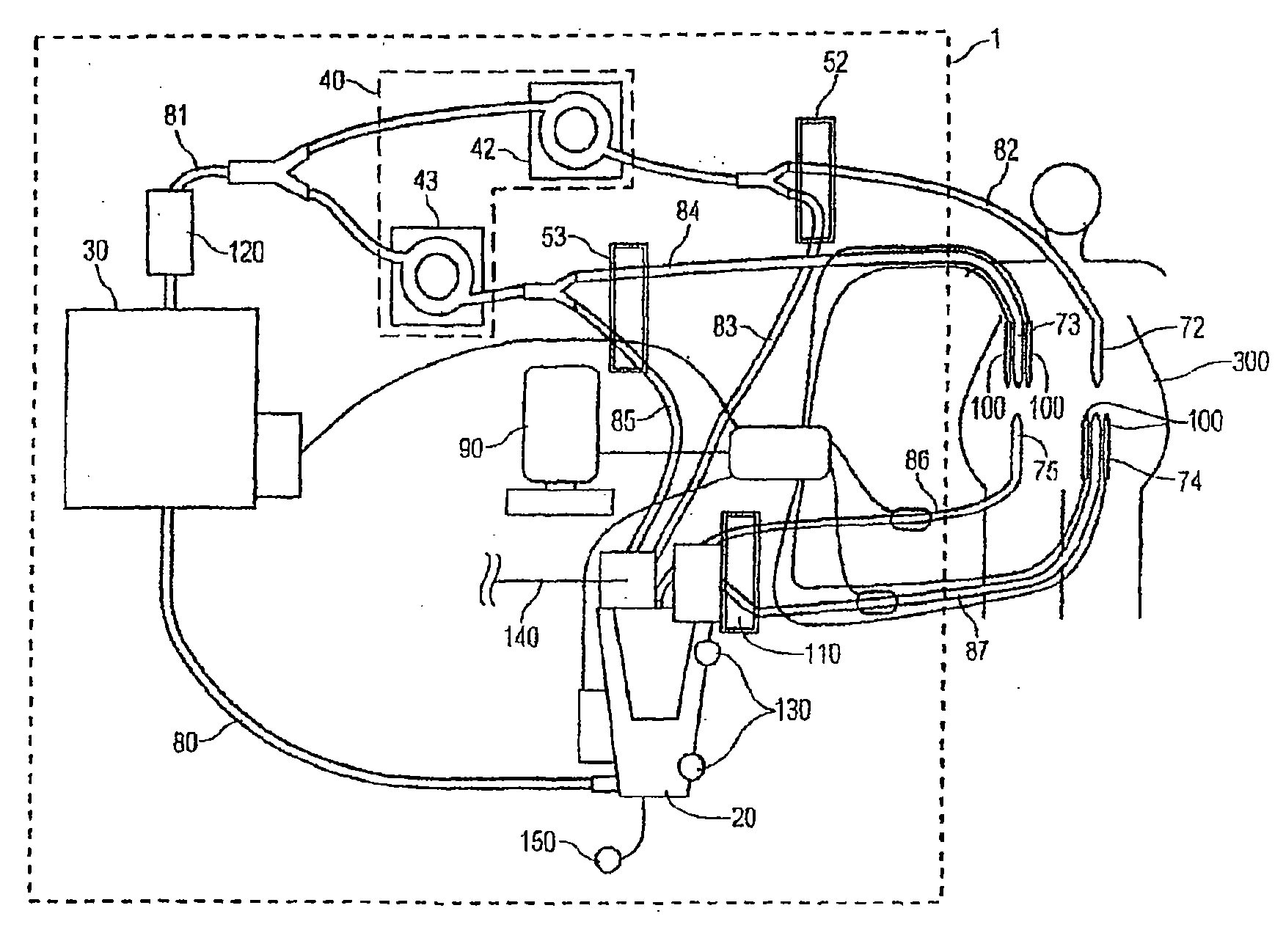
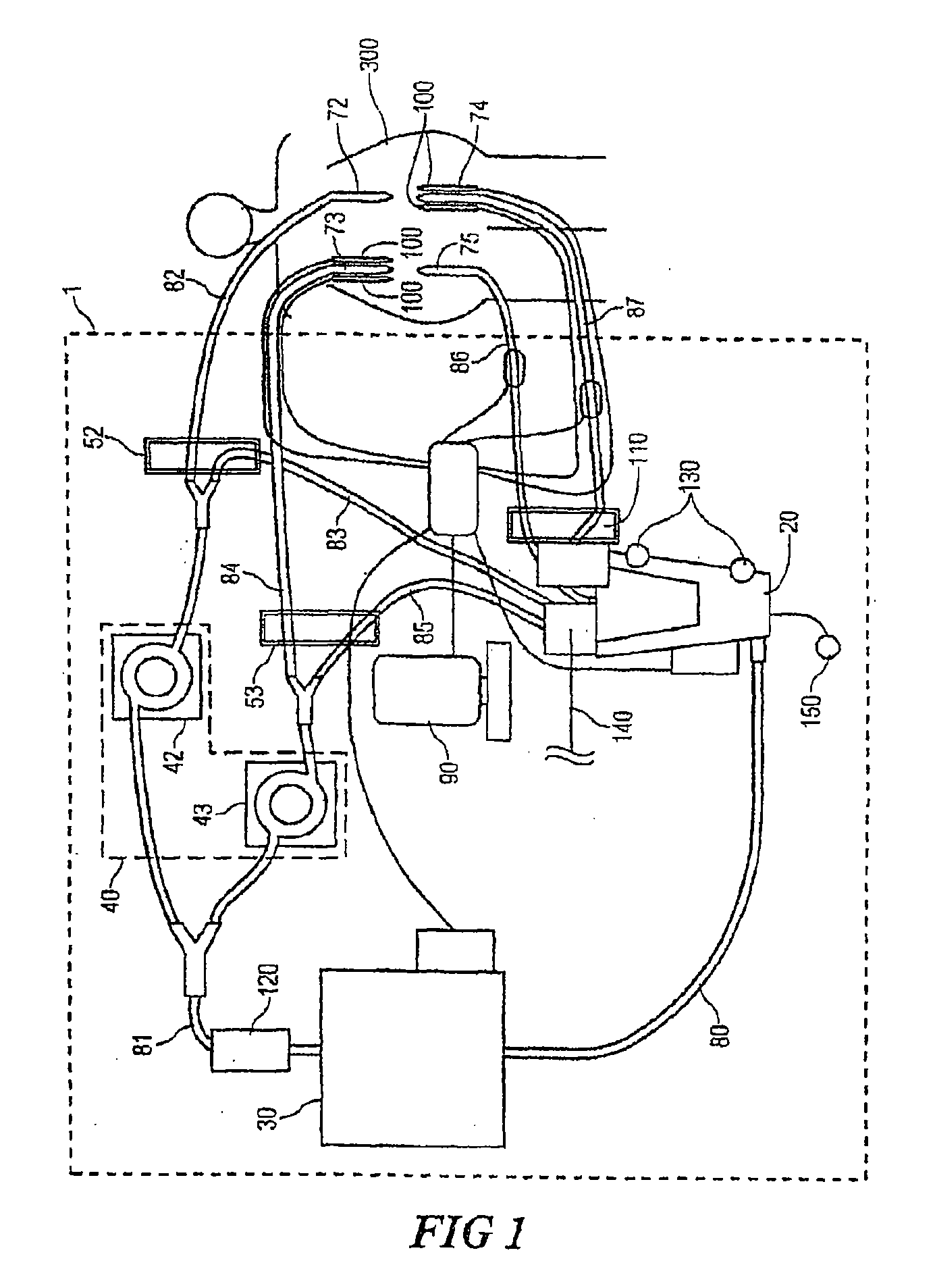
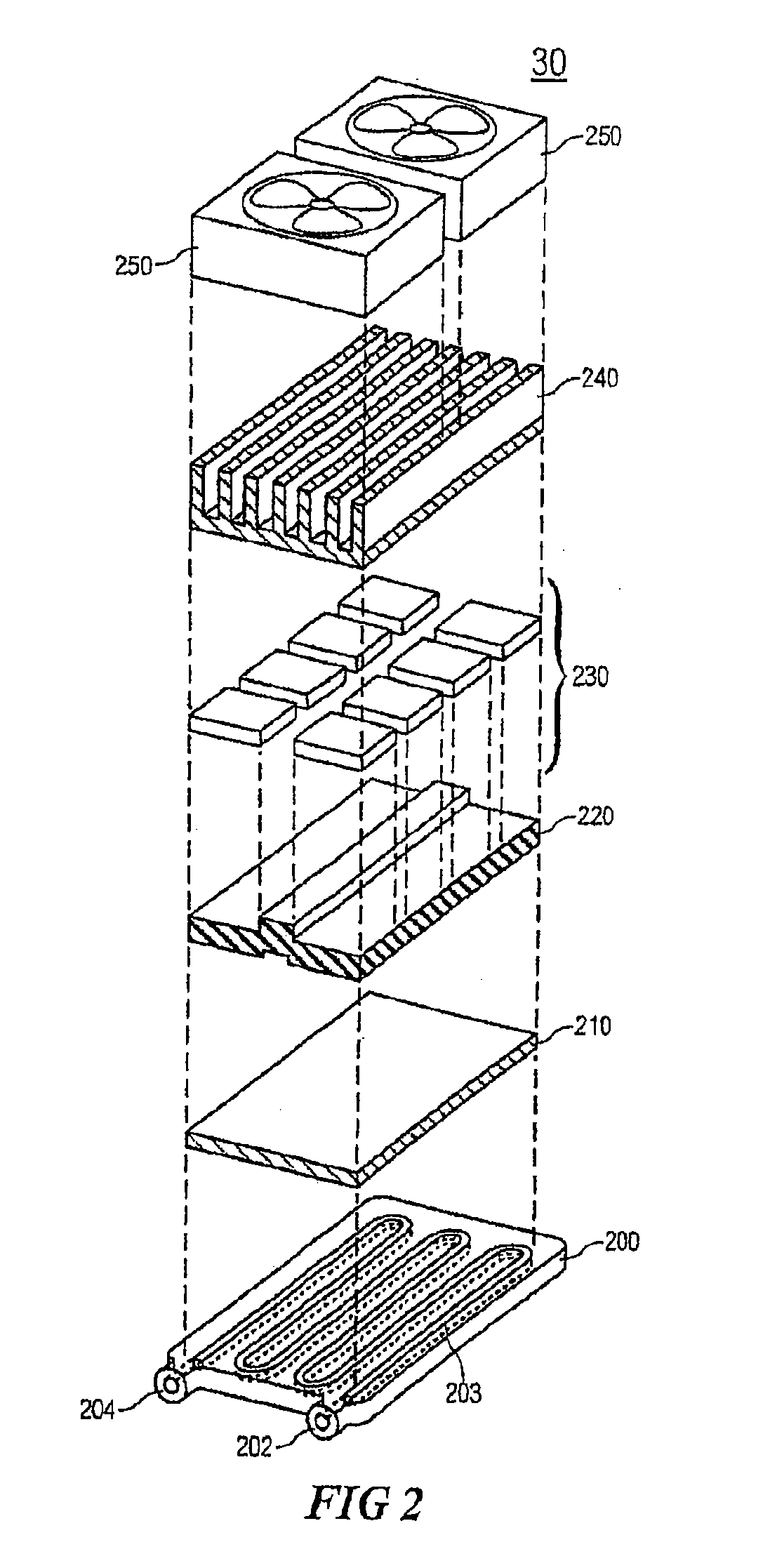
Systems for monitoring and applying electrical currents in an organ perfusion system
ActiveUS20080234768A1Reliable electrical connectionDifferent shapesDead animal preservationExternal electrodesOxygenRight atrium
Electrode systems have been developed for use in perfusion systems to measure the electrical activity of an explanted heart and to provide defibrillation energy as necessary. The perfusion systems maintain the heart in a beating state at, or near, normal physiological conditions; circulating oxygenated, nutrient enriched perfusion fluid to the heart at or near physiological temperature, pressure and flow rate. These systems include a pair of electrodes that are placed epicardially on the right atrium and left ventricle of the explanted heart, as well as an electrode placed in the aortic blood path.
Owner:TRANSMEDICS
System and method for microfluidic cell culture
ActiveUS20120009671A1Shorten speedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGravitational forceEngineering
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Systems and methods for ex vivo lung care
Methods and systems of maintaining, evaluating, and providing therapy to a lung ex vivo. The methods and systems involve positioning the lung in an ex vivo perfusion circuit; circulating a perfusion fluid through the lung, the fluid entering the lung through a pulmonary artery interface and leaving the lung through a left atrial interface; and ventilating the lung by flowing a ventilation gas through a tracheal interface. Maintaining the lung for extended periods involves causing the lung to rebreath a captive volume of air, and reaching an equilibrium state between the perfusion fluid and the ventilation gas. Evaluating the gas exchange capability of the lung involves deoxygenating the perfusion fluid and measuring a time taken to reoxygenate the perfusion fluid by ventilating the lung with an oxygenation gas.
Owner:TRANSMEDICS
SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR Ex vivo LUNG CARE
Methods and systems of maintaining, evaluating, and providing therapy to a lung ex vivo. The methods and systems involve positioning the lung in an ex vivo perfusion circuit; circulating a perfusion fluid through the lung, the fluid entering the lung through a pulmonary artery interface and leaving the lung through a left atrial interface; and ventilating the lung by flowing a ventilation gas through a tracheal interface. Maintaining the lung for extended periods involves causing the lung to rebreath a captive volume of air, and reaching an equilibrium state between the perfusion fluid and the ventilation gas. Evaluating the gas exchange capability of the lung involves deoxygenating the perfusion fluid and measuring a time taken to reoxygenate the perfusion fluid by ventilating the lung with an oxygenation gas.
Owner:TRANSMEDICS
Systems and methods for ex vivo lung care
Methods and systems of maintaining, evaluating, and providing therapy to a lung ex vivo. The methods and systems involve positioning the lung in an ex vivo perfusion circuit; circulating a perfusion fluid through the lung, the fluid entering the lung through a pulmonary artery interface and leaving the lung through a left atrial interface; and ventilating the lung by flowing a ventilation gas through a tracheal interface. Maintaining the lung for extended periods involves causing the lung to rebreath a captive volume of air, and reaching an equilibrium state between the perfusion fluid and the ventilation gas. Evaluating the gas exchange capability of the lung involves deoxygenating the perfusion fluid and measuring a time taken to reoxygenate the perfusion fluid by ventilating the lung with an oxygenation gas.
Owner:TRANSMEDICS
System and method for microfluidic cell culture
InactiveUS20130115606A1Avoid the needHigh densityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGravitational forceEngineering
Microfluidic devices and methods for perfusing a cell with perfusion fluid are provided herein, wherein the gravitational forces acting on the cell to keep the cell at or near a retainer or a retaining position exceed the hydrodynamic forces acting on the cell to move it toward an outlet. Also provided, are methods for assaying cell products within the microfluidic device.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Systems and methods for ex vivo lung care
Methods and systems of maintaining, evaluating, and providing therapy to a lung ex vivo. The methods and systems involve positioning the lung in an ex vivo perfusion circuit; circulating a perfusion fluid through the lung, the fluid entering the lung through a pulmonary artery interface and leaving the lung through a left atrial interface; and ventilating the lung by flowing a ventilation gas through a tracheal interface. Maintaining the lung for extended periods involves causing the lung to rebreath a captive volume of air, and reaching an equilibrium state between the perfusion fluid and the ventilation gas. Evaluating the gas exchange capability of the lung involves deoxygenating the perfusion fluid and measuring a time taken to reoxygenate the perfusion fluid by ventilating the lung with an oxygenation gas.
Owner:TRANSMEDICS
Method for perfusing an organ and for isolating cells from the organ
ActiveUS7504201B2Avoid damageMonitor and sustain and restore viabilitySurgeryDead animal preservationBiomedical engineeringOrgan of Corti
An organ perfusion apparatus and method monitor, sustain and / or restore viability of organs and preserve organs for storage and / or transport. Other apparatus include an organ transporter, an organ cassette and an organ diagnostic device. The method includes perfusing the organ at hypothermic and / or normothermic temperatures. The methods further include perfusing the organ at hypothermic and / or normothermic temperatures with a second perfusate containing a substance for reacting with the organ. Condition of the organ may be automatically monitored, and the perfusion process can be automatically controlled using a control program.
Owner:ORGAN RECOVERY SYST
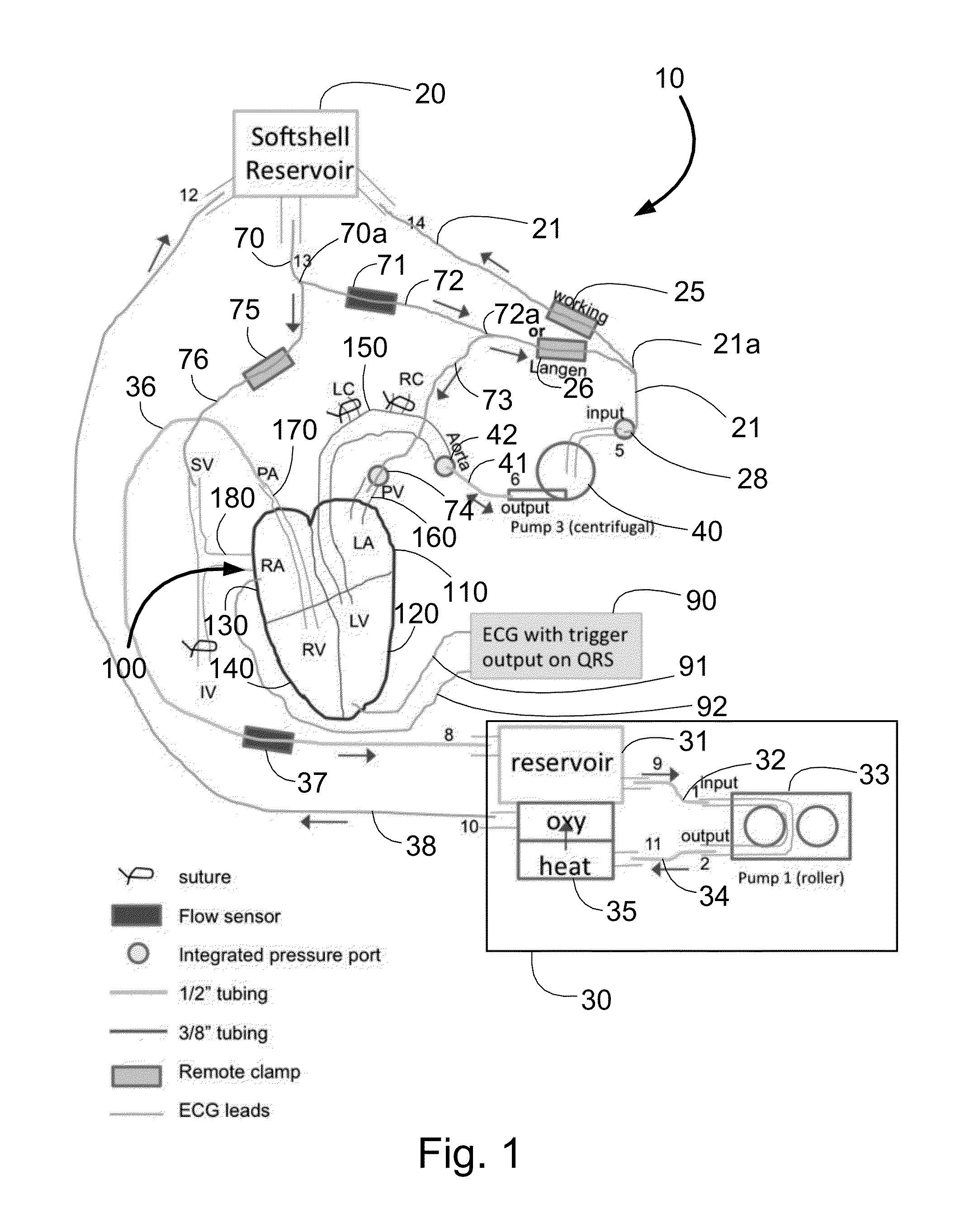
Heart-lung preparation and method of use
InactiveUS20140370490A1Easy to produceMaintain activityDead animal preservationEducational modelsPulmonary vasculatureLung structure
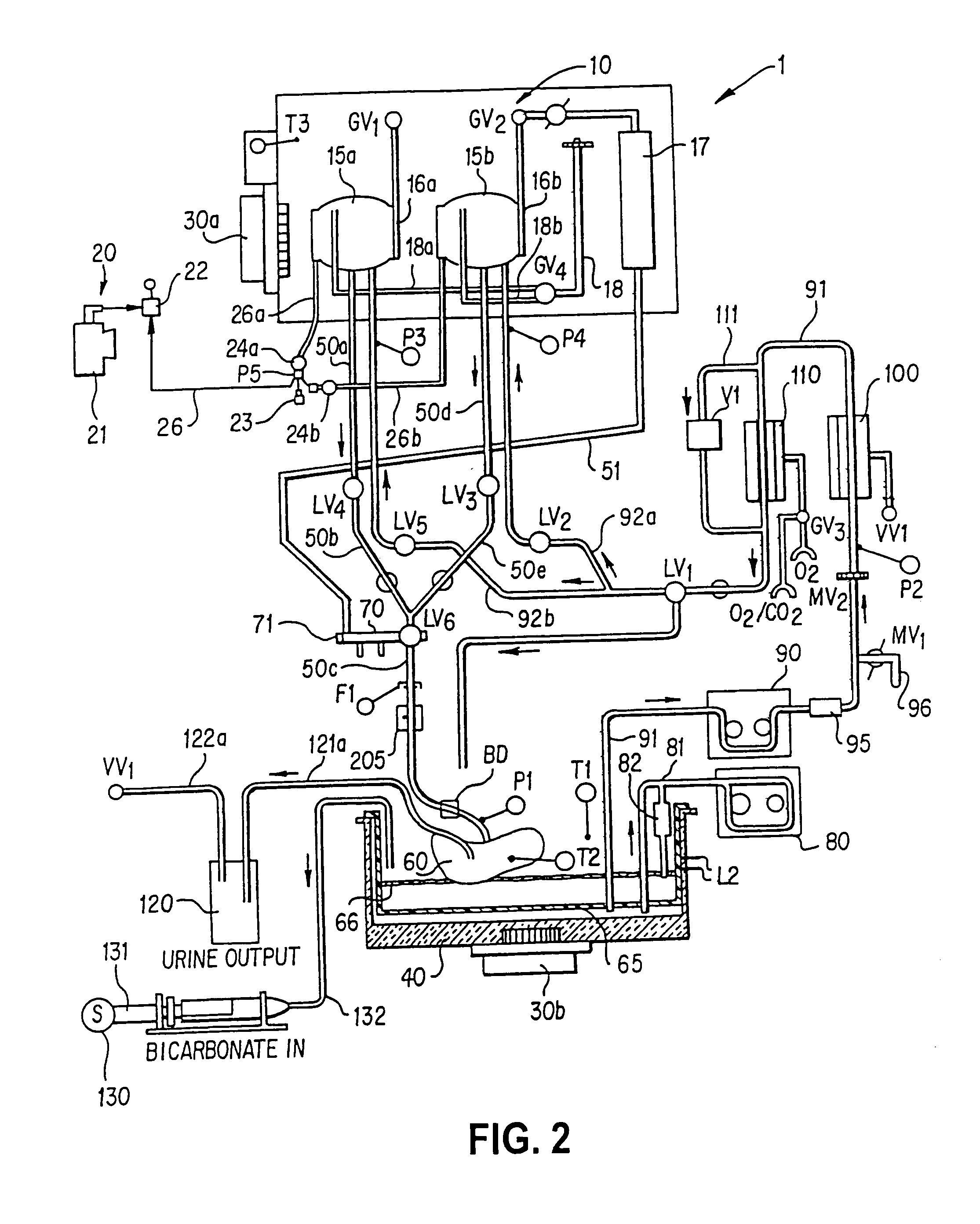
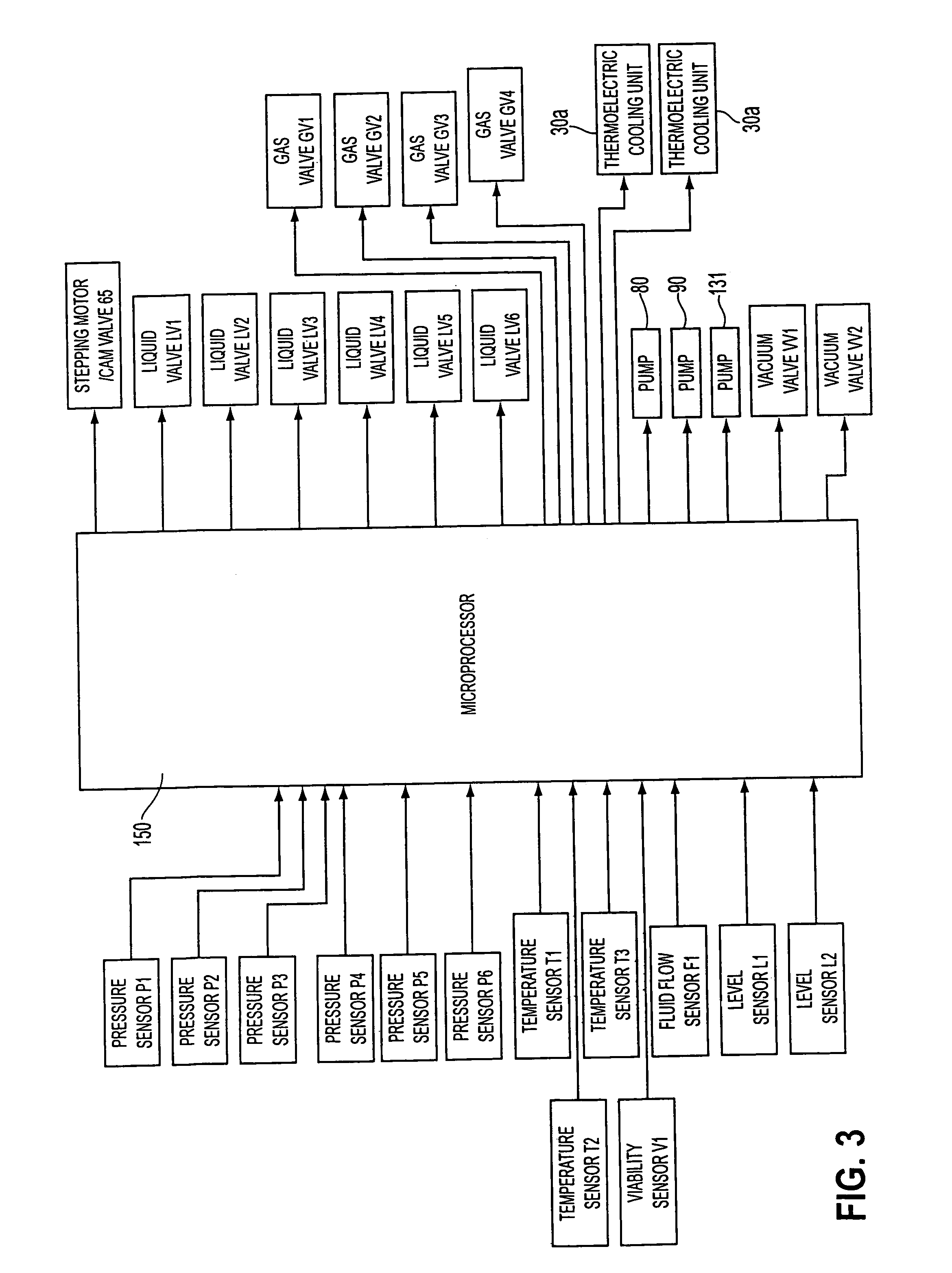
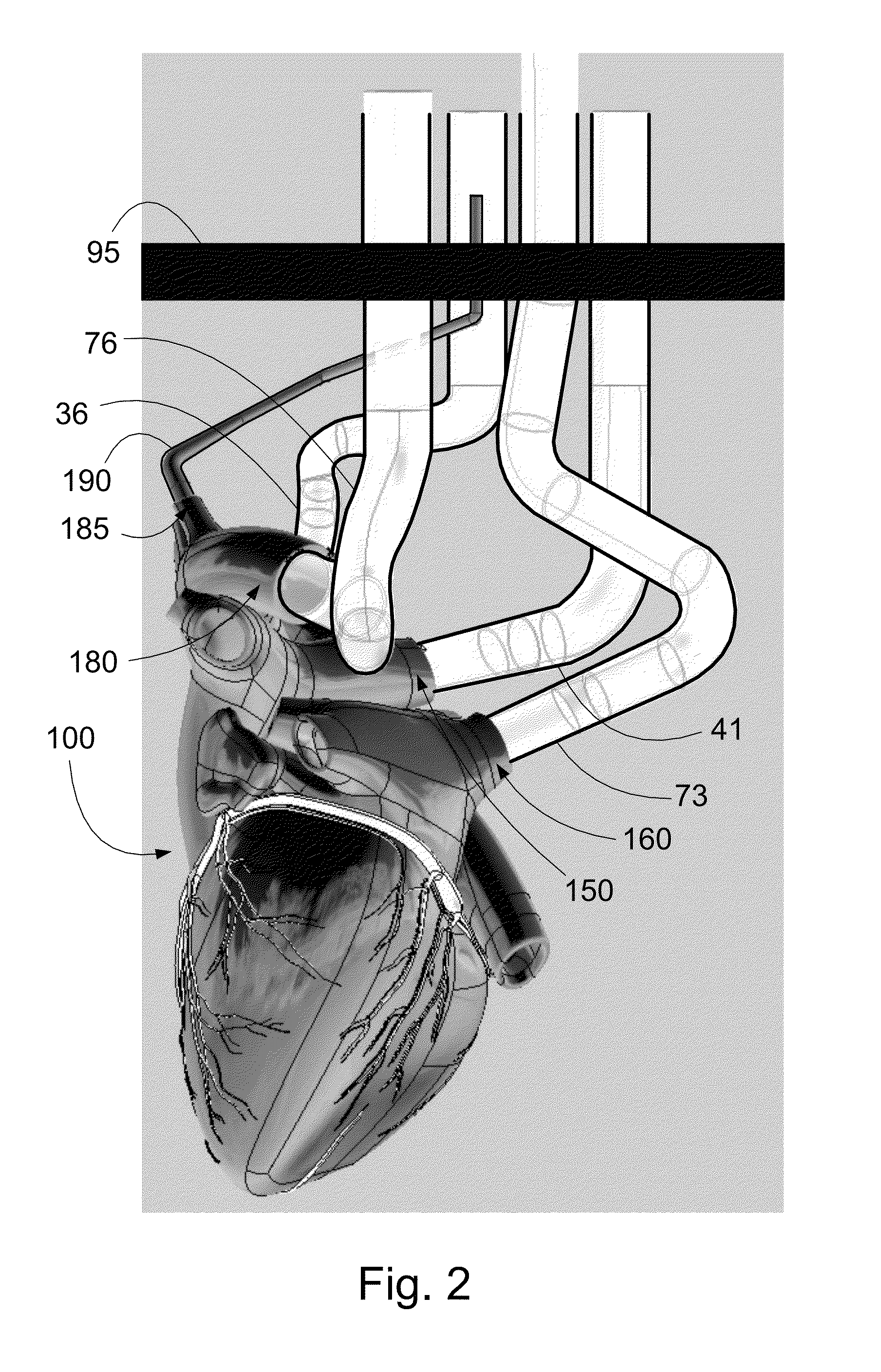
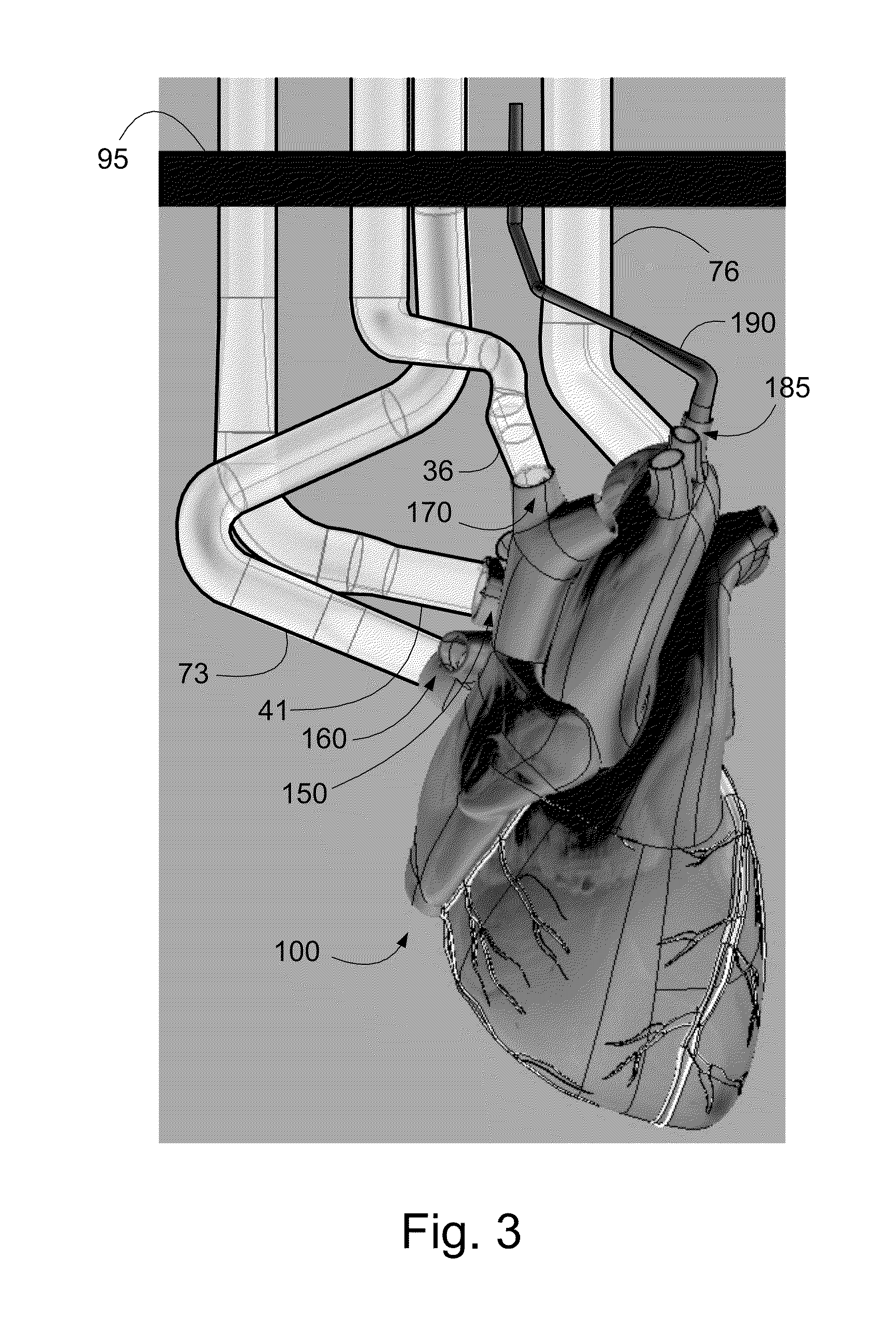
An isolated heart or heart-lung preparation in which essentially normal pumping activity of all four chambers of the heart is preserved, allowing for the use of the preparation in conjunction with investigations of electrode leads, catheters, ablation methods, cardiac implants and other medical devices intended to be used in or on a beating heart. The system can be designed to be used within a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) unit or a X-ray computed tomography (CT) scanner. The preparation may also be employed to investigate heart and lung functions, in the presence or absence of such medical devices. In order to allow comparative imaging visualizations of either or simultaneously the heart and / or lung structures and devices located within the chambers of the heart or vessels or bronchi within the lungs, a clear perfusate such as a modified Krebs buffer solution with oxygenation is circulated through all four chambers of the heart and thus the coronary and / or pulmonary vasculatures. A ventilator with intubation tube can be used to inflate / deflate the lungs and / or provide oxygen to the isolated organs. The preparation and recordings of the preparation may be used in conjunction with the design, development and evaluation of devices for use in or on the heart and / or lungs, as well as for use as an investigational and teaching aid to assist physicians and students in understanding the operation of the cardiopulmonary system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Organ preservation apparatus and methods
InactiveUS7176015B2Maintain qualityMaintaining viabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNutrient solutionOxygen
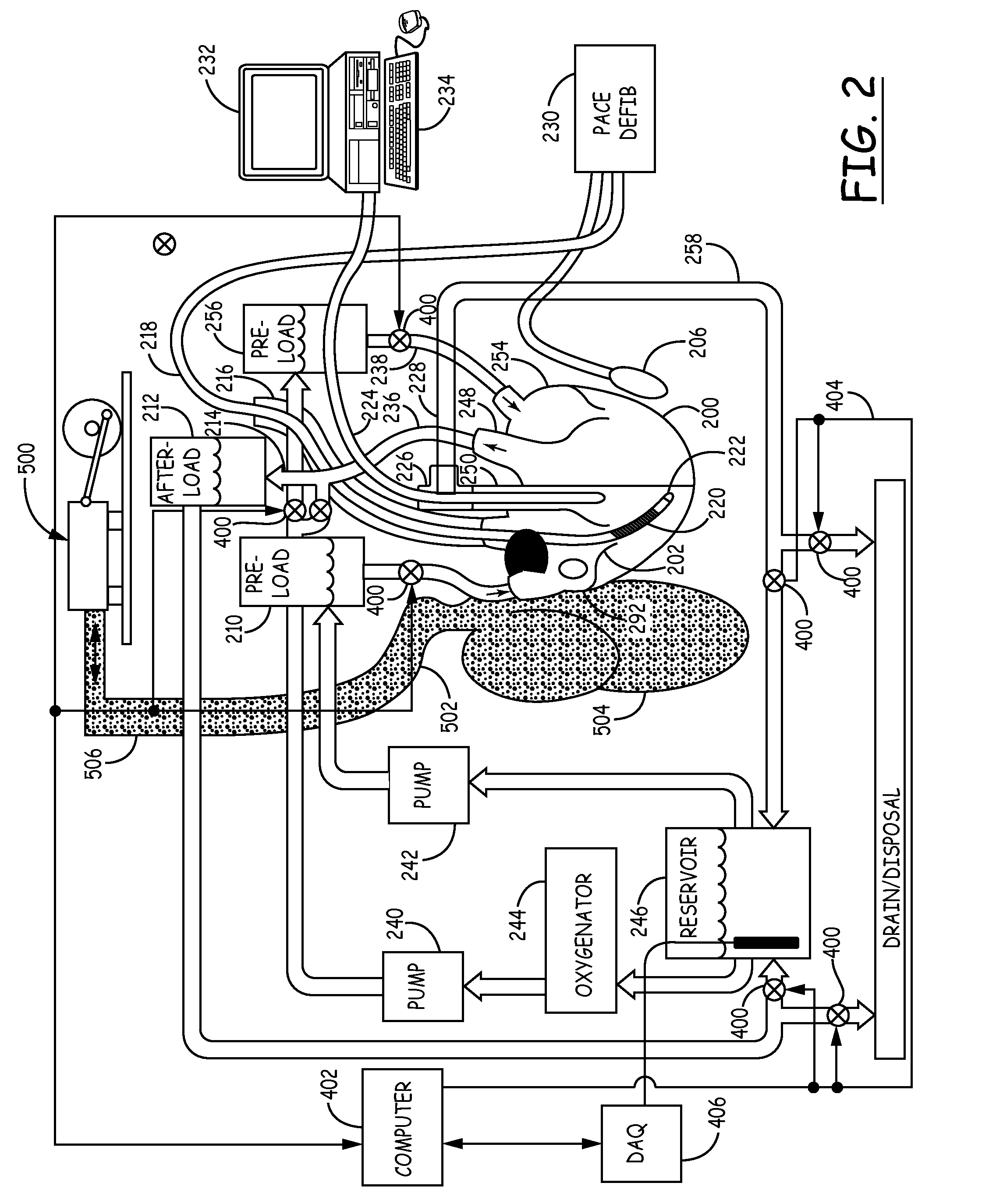
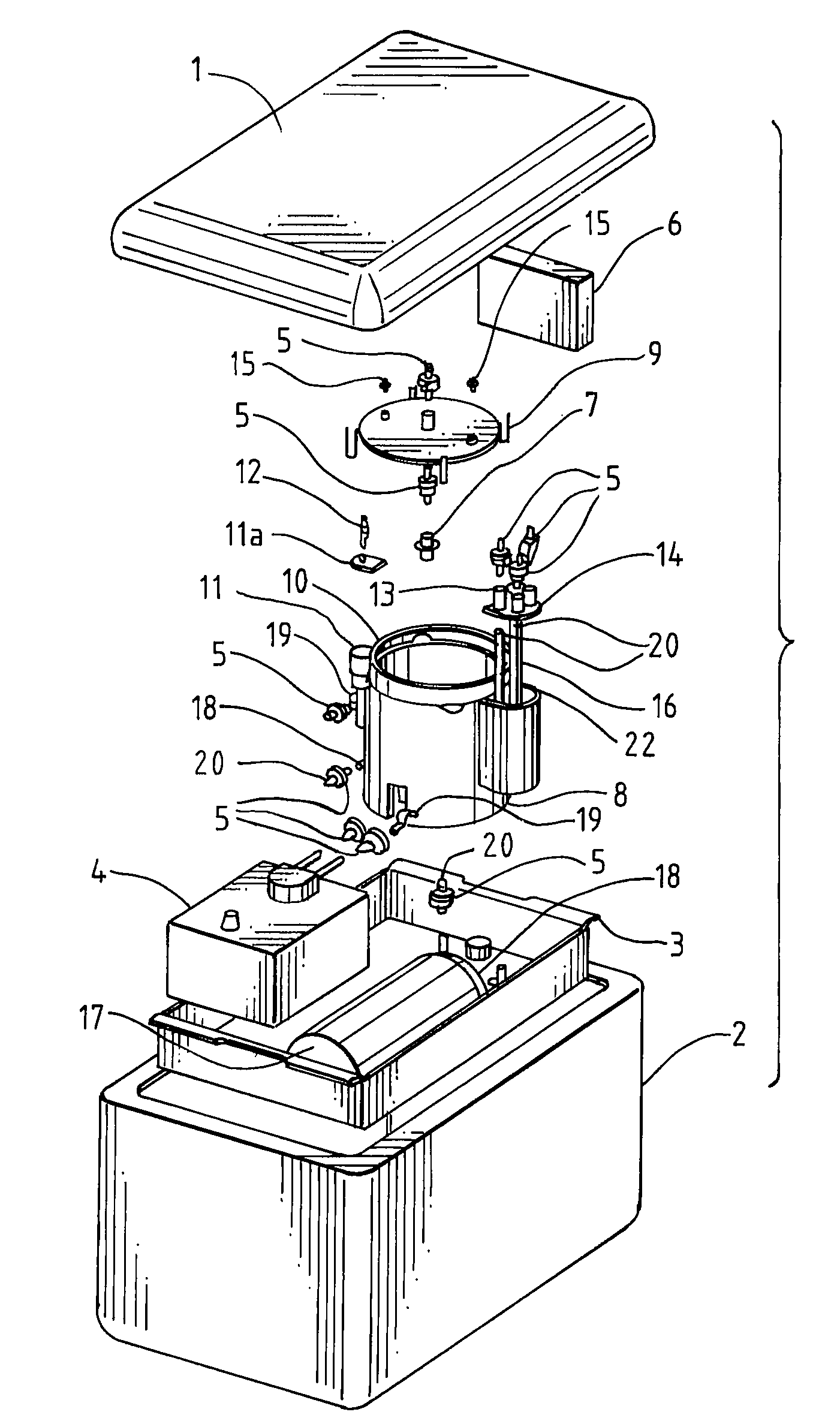
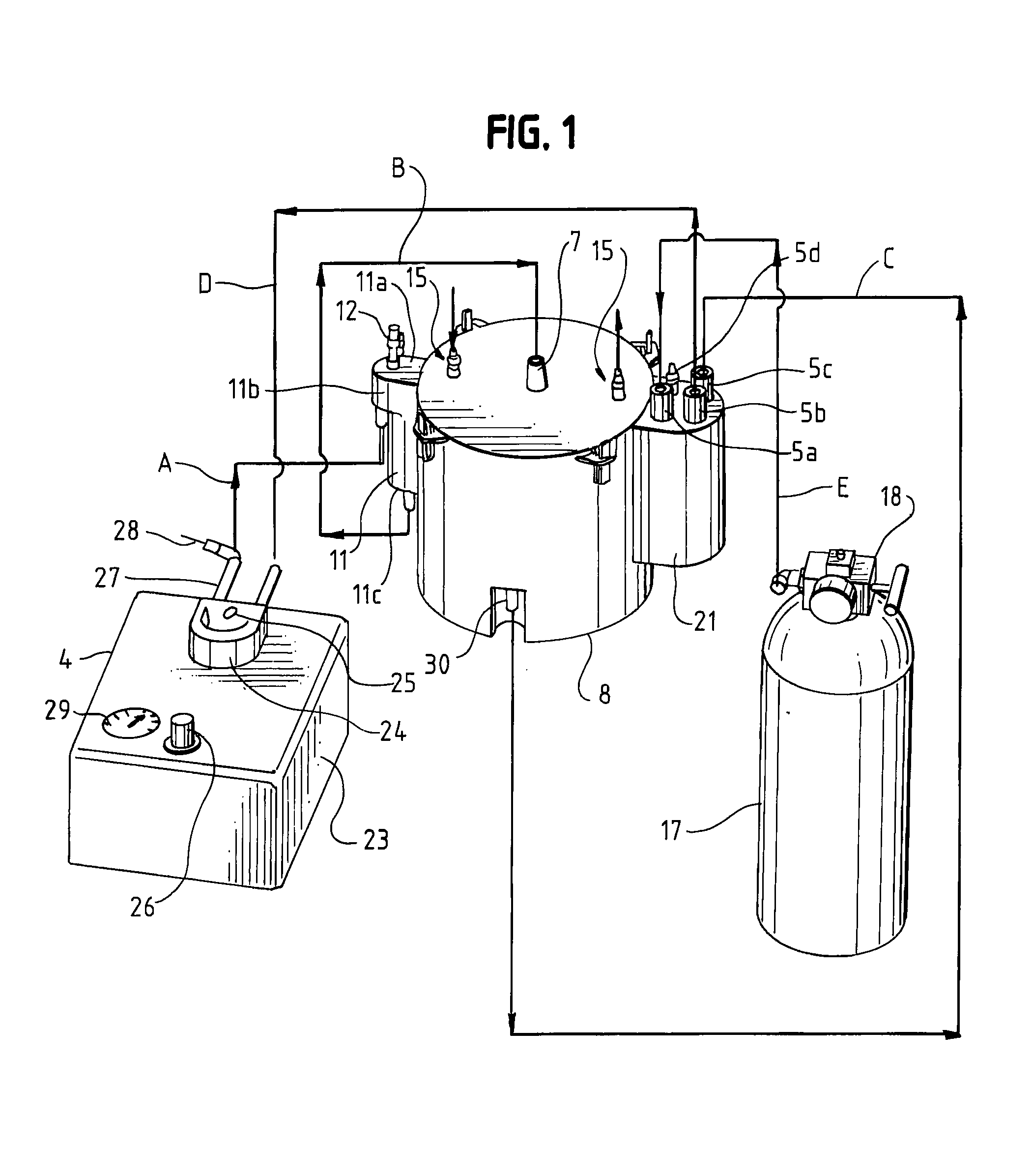
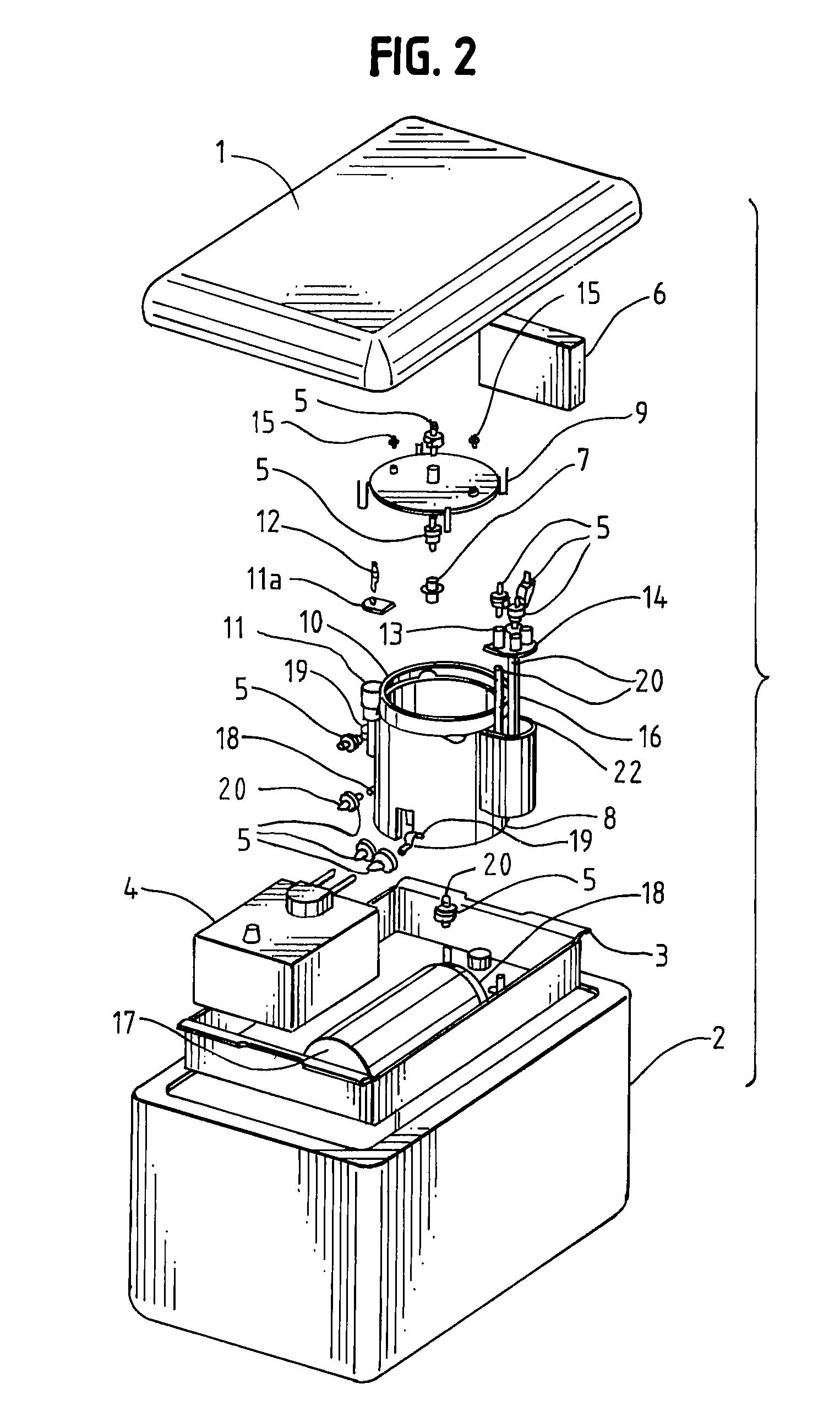
This invention is a transportable organ preservation system that substantially increases the time during which the organ can be maintained viable for successful implantation into a human recipient. A chilled oxygenated nutrient solution is pumped through the vascular bed of the organ after excision of the organ from the donor and during transport. The device of the present invention uses flexible permeable tubing to oxygenate the perfusion fluid while the CO2 produced by the organ diffuses out of the perfusion fluid. One pressurized two liter “C” cylinder that contains 255 liters of oxygen at standard temperature and pressure can supply oxygen for up to 34 hours of perfusion time. The device uses a simple electric pump driven by a storage battery to circulate the perfusion fluid through the organ being transported. The vessel containing the organ to be transported is held at 4° C. by coolant blocks.
Owner:BRIDGE TO LIFE LTD
Organ preservation apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20090291486A1Increase the lengthReduce decreaseDead animal preservationMachines using electric/magnetic effectsNutrient solutionOxygen
A transportable organ preservation system that substantially increases the time during which the organ can be maintained viable for successful implantation into a recipient is disclosed. A chilled oxygenated nutrient solution can be pumped through the vascular bed of the organ after excision of the organ from the donor and during transport. The device of the present invention uses flexible permeable tubing to oxygenate the perfusion fluid while the CO2 produced by the organ diffuses out of the perfusion fluid. One pressurized two-liter “C” cylinder can supply oxygen for up to 34 hours of perfusion time. The device can use a simple electric pump driven by a storage battery to circulate the perfusion fluid through the organ being transported. The vessel containing the organ to be transported can be held at a suitable temperature by a chiller.
Owner:ORGAN TRANSPORT SYST
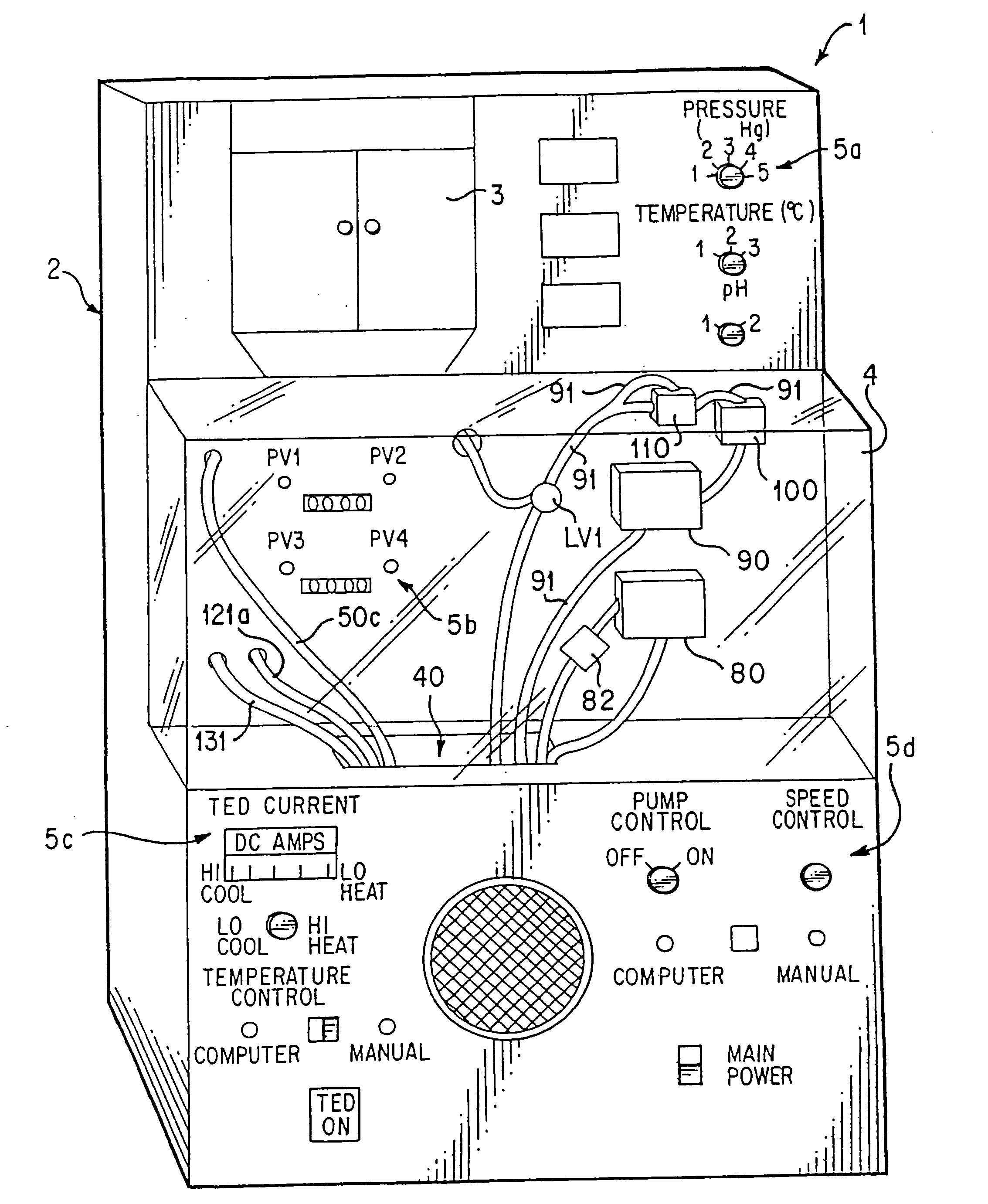
System For Chemohyperthermia Treatment
InactiveUS20080097562A1Easy to controlSmall weightCatheterIntravenous devicesGuide tubeHeating system
The present invention provides a system for chemohyperthermia treatment. The chemohyperthermia treatment system comprises a reservoir for storing fluid; a heating / cooling system coupled to the reservoir so that the fluid can be transferred from the reservoir to the heating system, wherein the heating / cooling system comprises a heating / cooling exchange module having a channel within which the fluid can flow; and a plurality of peltier modules coupled to the heating / cooling module, wherein the plurality of peltier modules heat up the fluid flowing through the channel, and wherein in the cooling mode, the plurality of peltier modules cool the fluid flowing through the channel; a pumping means coupled to the heating / cooling system, wherein the pumping means pump the perfusion fluid from the reservoir to the heating / cooling system, thereby allowing the heating / cooling system to change the temperature of the fluid; at least one inflow catheter coupled to the pumping means, wherein the at least one inflow catheter delivers the heated / cooled fluid to an object; and at least one outflow catheter coupled to the reservoir, wherein the at least one outflow catheter drains the fluid from the object to the reservoir.
Owner:DYAMED BIOTECH PTE
Multifunctional perfusion and suction platform and using method
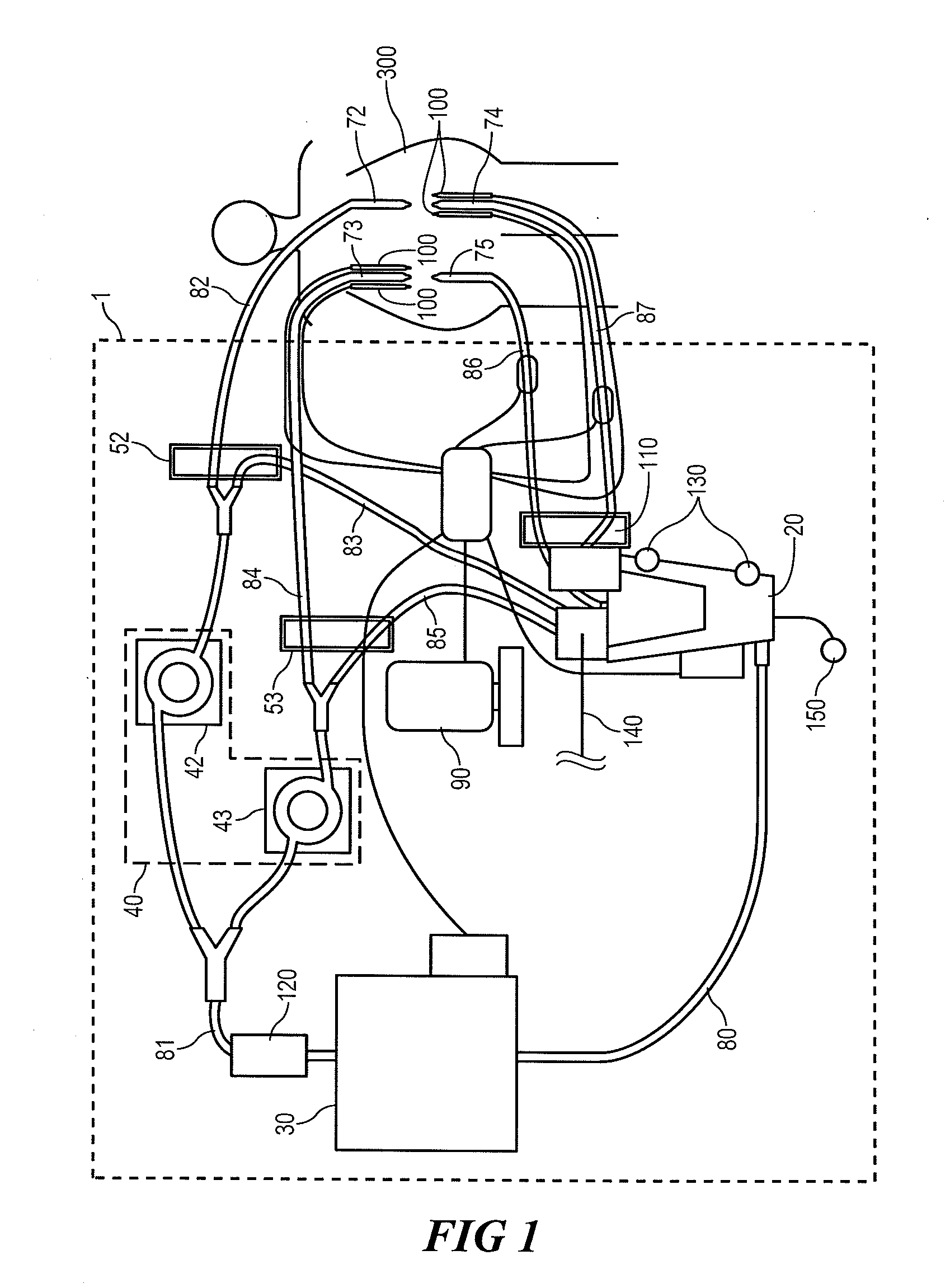
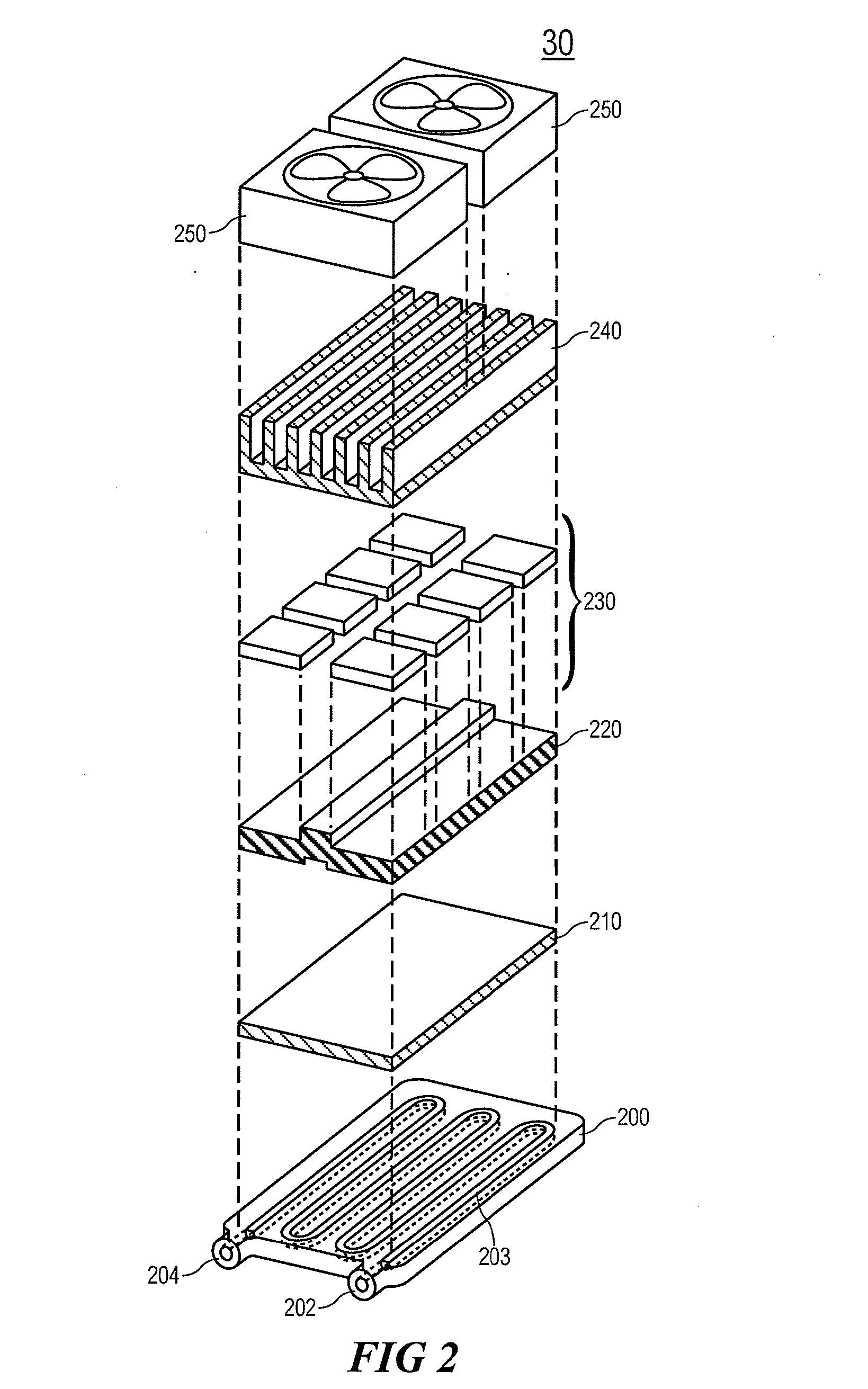
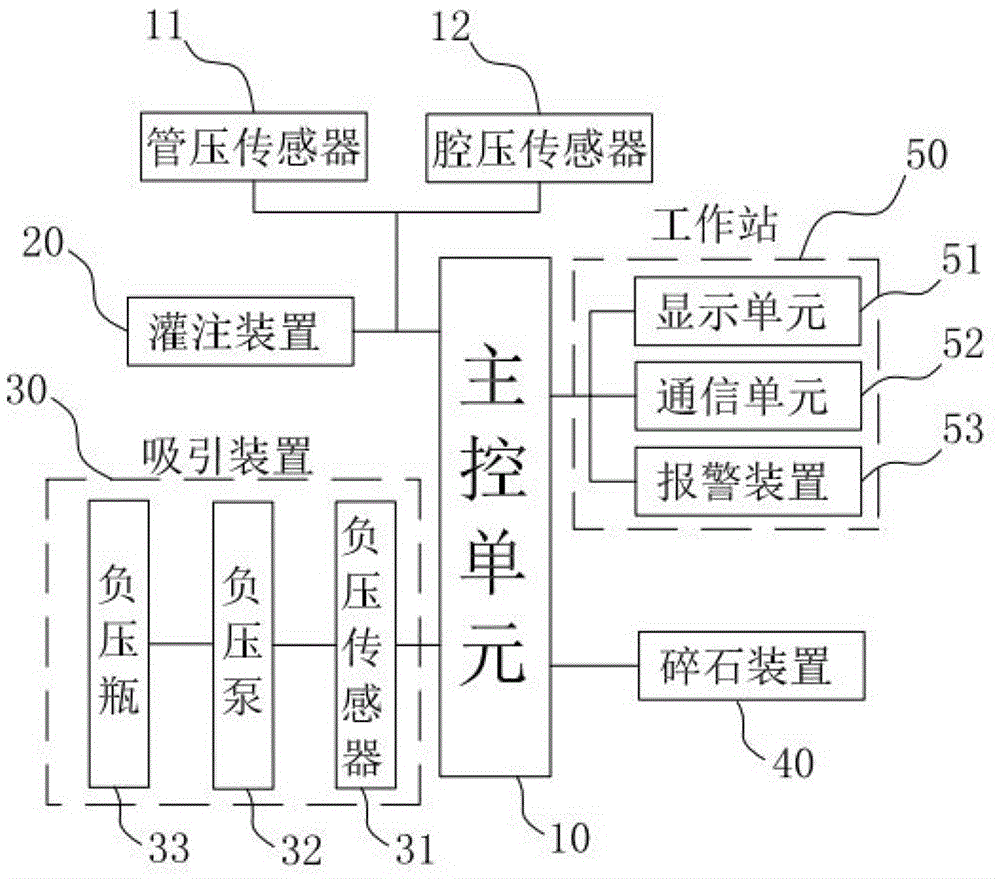
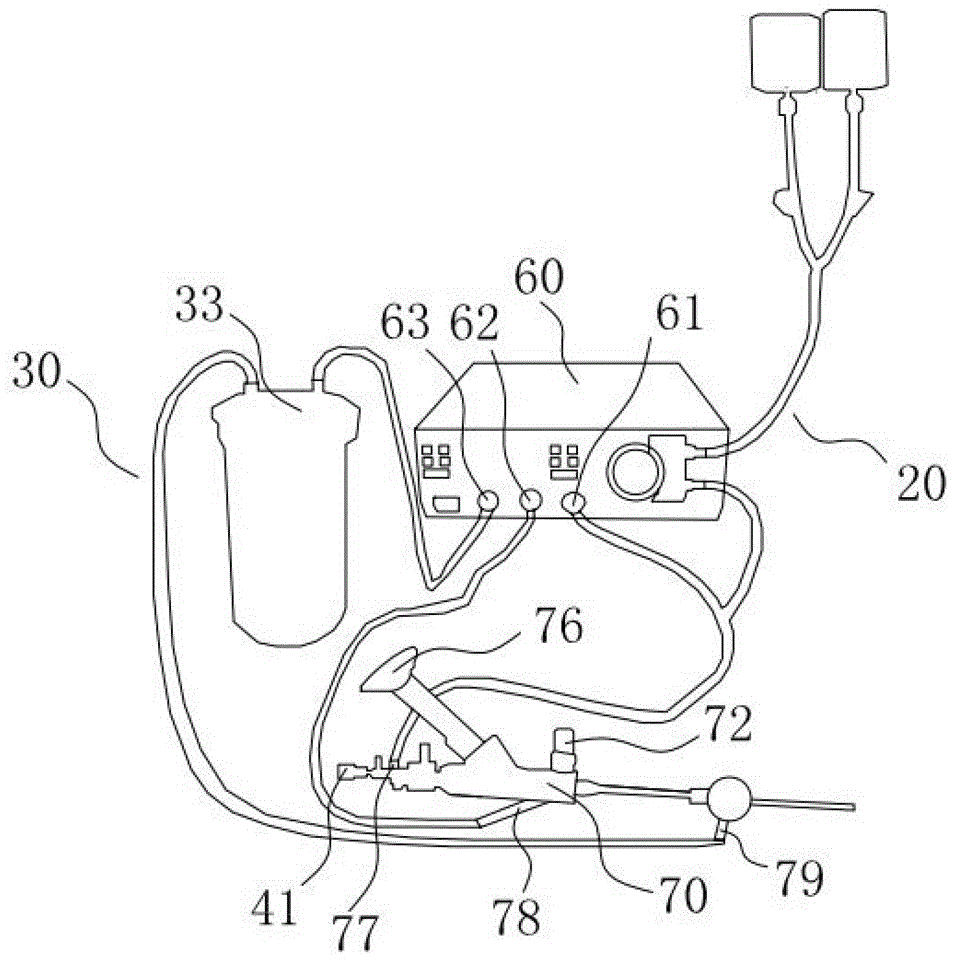
InactiveCN106237417AEasy to operateImprove surgical safetyEnemata/irrigatorsSurgeryMedicineEngineering
The invention relates to a multifunctional perfusion and suction platform and a using method. The perfusion and suction platform at least comprises a perfusion device and a main control unit and further comprises a pipe pressure sensor for measuring pressure in a perfusion fluid channel of the perfusion device, a cavity pressure sensor for measuring pressure of an inner cavity and an alarming device; the pipe pressure sensor, the cavity pressure sensor and the alarming device are all connected with the main control unit, limit reference values of the pipe pressure sensor and the cavity pressure sensor are preset in the main control unit, and on the condition that the pressure measured by the pipe pressure sensor or the pressure measured by the cavity pressure sensor exceeds the corresponding limit reference value, the alarming device is started. The structure has the advantages that the pipe pressure and the cavity pressure are monitored simultaneously, double insurance is formed, a doctor can know a failure through the alarming device and make a right judgment at first time according to the pressure measured by the other sensor even if one of the sensors fails, and therefore the operation safety is greatly improved.
Owner:黄健
Nasal irrigation systems
InactiveUS20130012869A1Facilitate mixing and removalIncrease contactCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsNasal cavityIntensive care medicine
Nasal irrigation systems for irrigating and / or rinsing a subject's nasal cavity are disclosed herein. Irrigation fluid may be drawn through the nasal cavity while utilizing a staged treatment procedure which allows for an initial infusion or flushing of irrigation fluid, circulation of the fluid, and subsequent flushing of the effluent from the nasal cavity. The system allows for reversible flow of the fluid during irrigation as well as use of vibration to disrupt debris within the nasal cavity to facilitate the mixing and removal of the debris. Additionally, peristaltic flow of the irrigation fluid may be used to facilitate contact between the fluid and debris during fluid circulation. Moreover, the irrigation fluid may also incorporate air or a gas into the fluid flow to create discrete volumes or boluses of pressured fluid to further facilitate thorough irrigation of the nasal cavity.
Owner:CHA ALBERT +2
Isolated organ preserving device and preserving method thereof
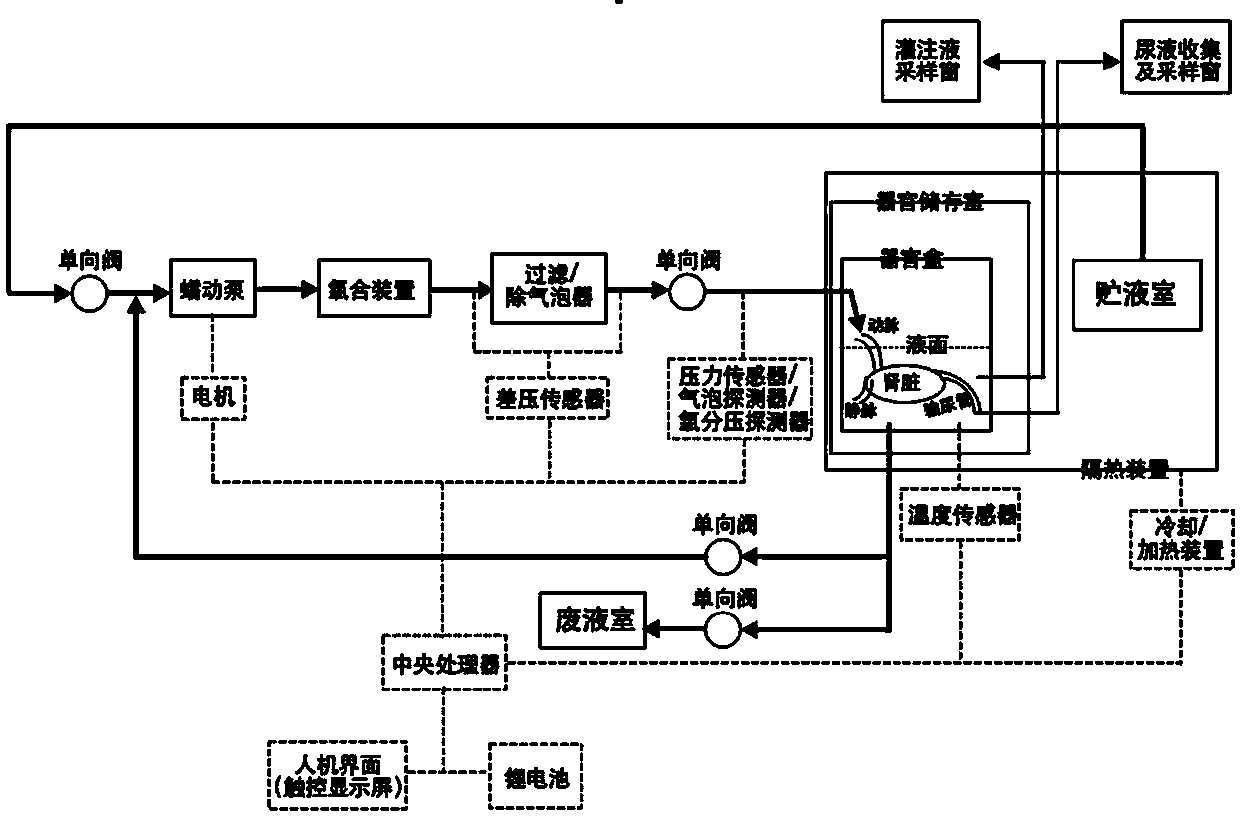
ActiveCN103719075AGuaranteed sterility requirementsGuaranteed partial pressure of oxygenDead animal preservationEthylene Oxide SterilizationCell metabolite
The invention relates to an isolated organ preserving device and a preserving method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medical equipment. The isolated organ preserving device is structurally characterized in that continuous mechanical irrigation and membrane oxygenation are adopted, an isolated organ continuously obtains nutrients and the oxygen supply, a cell metabolite is removed in time, and a cell microenvironment is better maintained, so that the function normality is ensured. The isolated organ preserving device disclosed by the invention can be used for directly contacting the organ perfusate and the organ perfusion instrument by adopting a disposable consumable material sterilized through epoxyethane, thereby meeting the requirement for sterility of a system. Besides, the isolated organ preserving device disclosed by the invention can be used for judging the consumption of the nutrients contained in the organ perfusate and the gathering degree of metabolic wastes by monitoring the pH value of the organ perfusate in real time and can be used for abandoning the organ perfusate after a certain standard is achieved and replacing the fresh organ perfusate, thereby further ensuring the possibility of long-time preservation; the isolated organ preserving device can be used for evaluating the damage condition of the isolated organ by monitoring the front and back perfusion pressure of the isolated organ in real time and converting the perfusion resistance by combining a flow number.
Owner:江苏赛谷细胞工程研究院有限公司
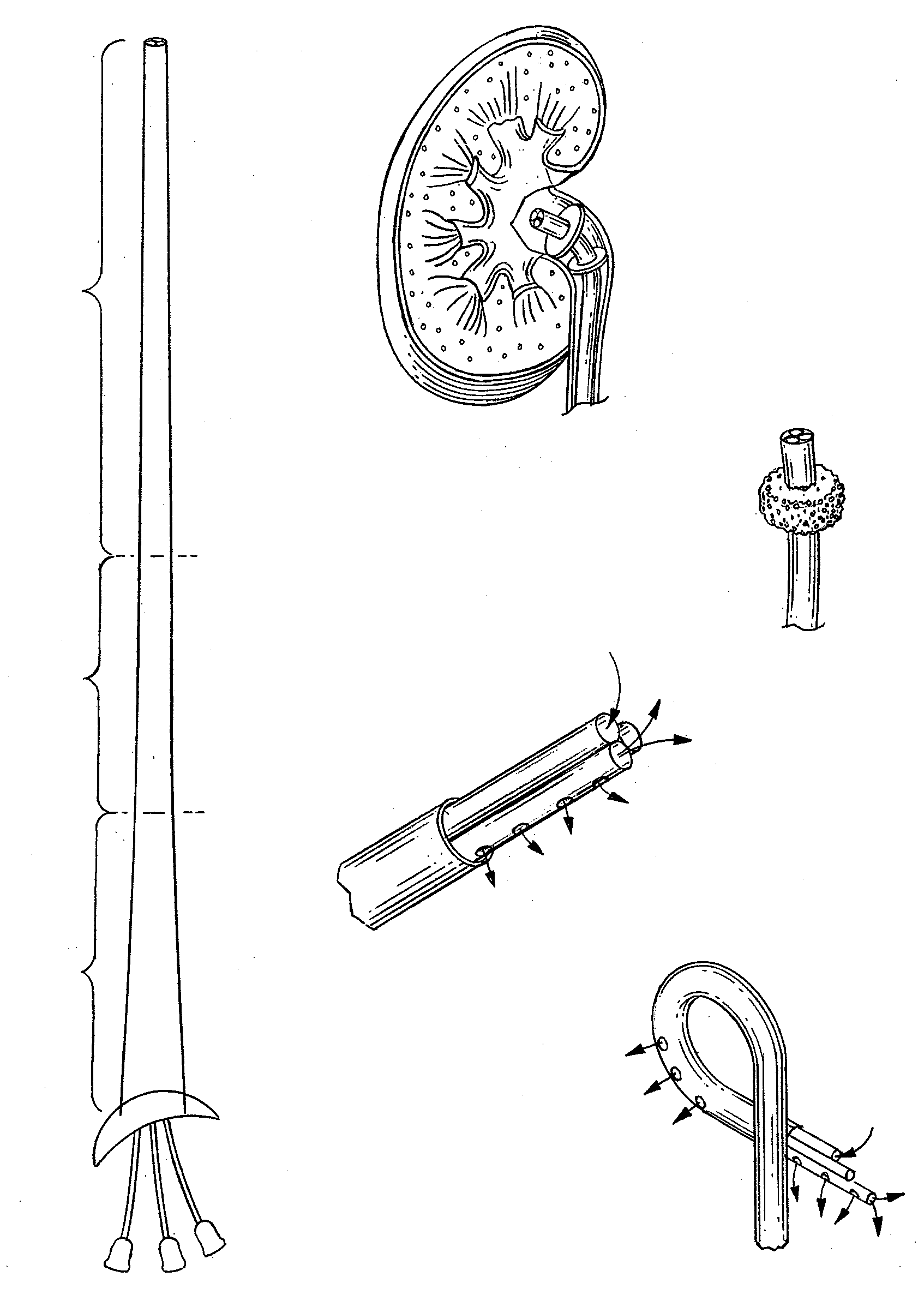
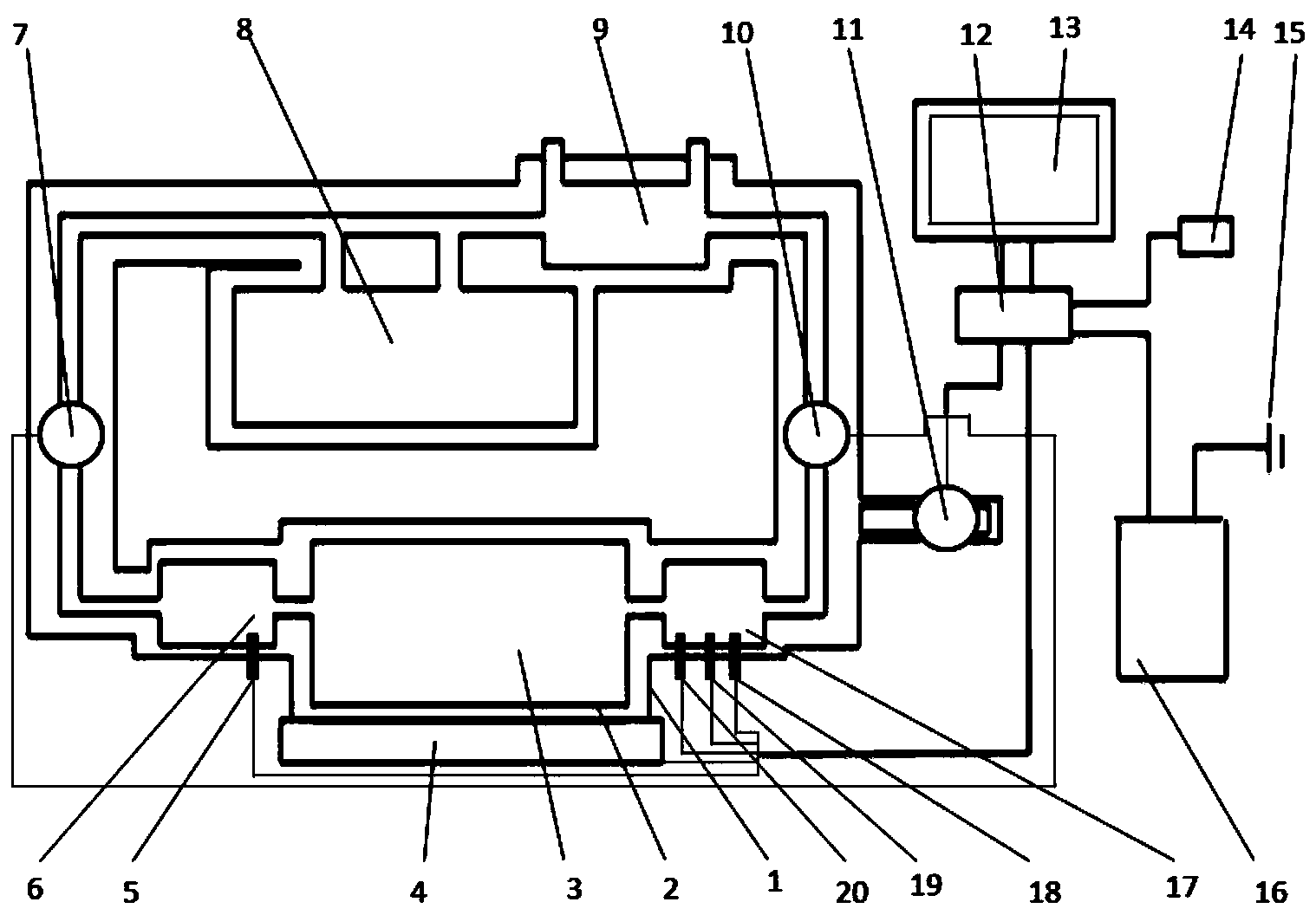
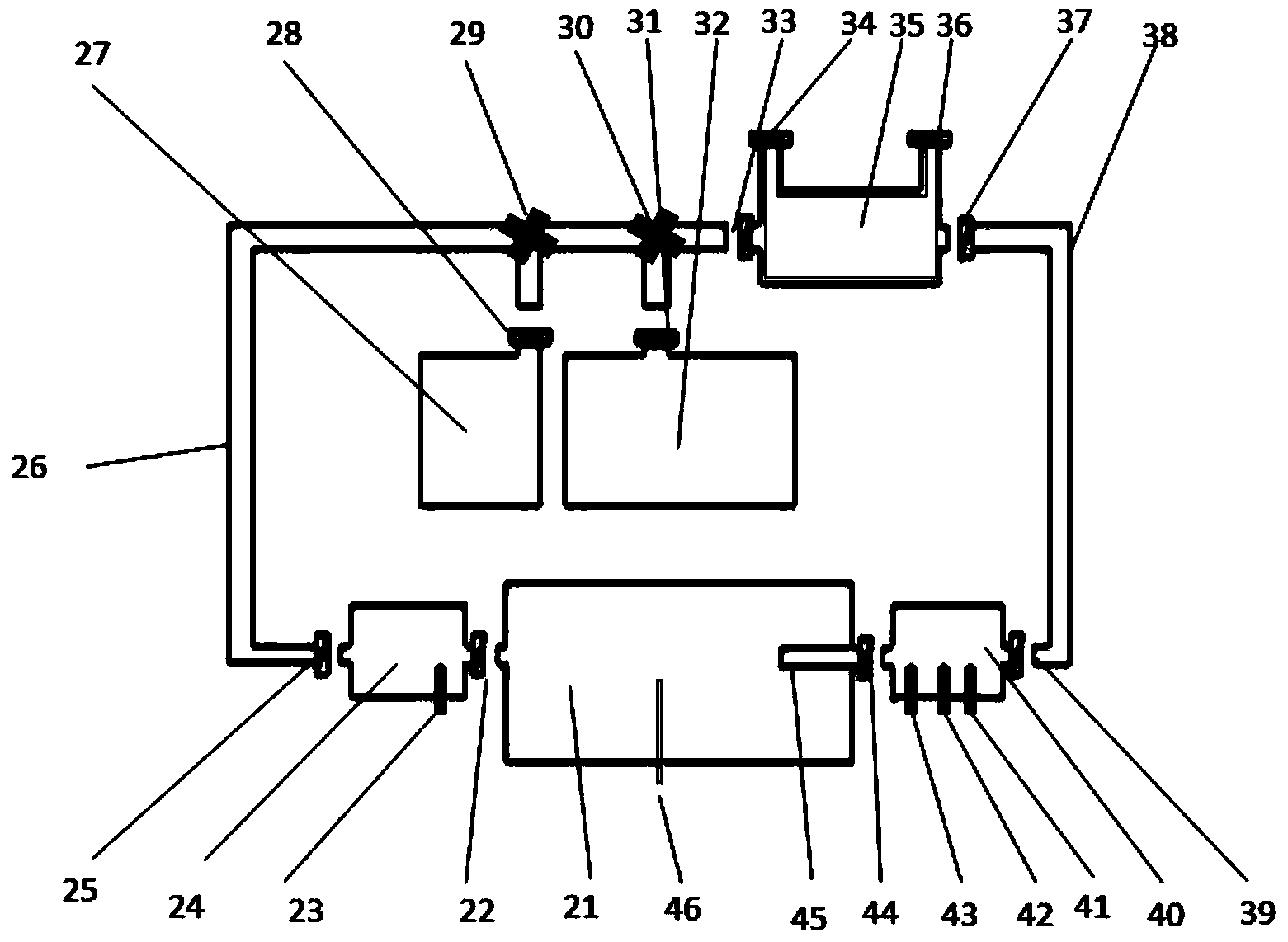
Sub-normal-temperature or low-temperature isolated kidney storage device
The invention relates to a kidney storage device and provides a sub-normal-temperature or low-temperature isolated kidney storage device comprising an organ storage box, a liquid storage chamber, a perfusing pipeline and a controller, wherein the liquid storage chamber is connected with an input opening of the perfusing pipeline through a one-way valve; an output opening of the perfusing pipeline is connected with the organ storage box through a one-way valve; the organ storage box is connected with the input opening of the perfusing pipeline through a one-way valve; the organ storage box is also connected with a urine and perfusate collecting and sampling window; a detecting device connected with the controller is arranged between the perfusing pipeline and the organ storage box; and the organ storage box is provided with a temperature control device. The sub-normal-temperature or low-temperature isolated kidney storage device is used for storing kidneys.
Owner:THE 309TH HOSPITAL OF CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Apparatus and method for perfusing an organ or tissue for isolating cells from the organ or tissue
ActiveUS20090226878A1Avoid damageMonitor and sustain and restore viabilitySurgeryDead animal preservationBiomedical engineeringOrgan of Corti
An organ perfusion apparatus and method monitor, sustain and / or restore viability of organs and preserve organs for storage and / or transport. Other apparatus include an organ transporter, an organ cassette and an organ diagnostic device. The method includes perfusing the organ at hypothermic and / or normothermic temperatures. The methods further include perfusing the organ at hypothermic and / or normothermic temperatures with a second perfusate containing a substance for reacting with the organ. Condition of the organ may be automatically monitored, and the perfusion process can be automatically controlled using a control program.
Owner:ORGAN RECOVERY SYST
Systems for monitoring and applying electrical currents in an organ perfusion system
ActiveUS9457179B2Reliable electrical connectionReduce the possibilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRight atriumLeft ventricle wall
Electrode systems have been developed for use in perfusion systems to measure the electrical activity of an explanted heart and to provide defibrillation energy as necessary. The perfusion systems maintain the heart in a beating state at, or near, normal physiological conditions; circulating oxygenated, nutrient enriched perfusion fluid to the heart at or near physiological temperature, pressure and flow rate. These systems include a pair of electrodes that are placed epicardially on the right atrium and left ventricle of the explanted heart, as well as an electrode placed in the aortic blood path.
Owner:TRANSMEDICS
System for chemohyperthermia treatment
InactiveUS20100298771A1Risk minimizationReduce flow rateCatheterIntravenous devicesHeating systemTreatment system
A chemohyperthermia treatment system includes a reservoir for storing fluid, a heating / cooling system coupled to the reservoir so that the fluid can be transferred from the reservoir to the heating system, wherein the heating / cooling system comprises a heating / cooling exchange module having a channel within which the fluid can flow, and a plurality of peltier modules / heating strips coupled to the heating / cooling module, wherein the plurality of peltier modules / heating strips heat up the fluid flowing through the channel, and wherein in the cooling mode, the plurality of peltier modules cool the fluid flowing through the channel. A pumping means is coupled to the heating / cooling system, wherein the pumping means pump the perfusion fluid from the reservoir to the heating / cooling system, thereby allowing the heating / cooling system to change the temperature of the fluid. A least one inflow catheter is coupled to the pumping means, wherein the at least one inflow catheter delivers the heated / cooled fluid to an object. At least one outflow catheter coupled to the reservoir, wherein the at least one outflow catheter drains the fluid from the object to the reservoir.
Owner:DYAMED BIOTECH PTE
Mesoscale bioreactor platform for perfusion
InactiveUS20110104730A1Risk minimizationEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPerfusionEngineering
Disclosed is a mesoscale bioreactor platform including two or more liquid reservoirs in fluid communication with a culture chamber which chamber is in fluid communication with an exit. The platform allows the chamber to be perfused with a flow of liquid from one or more of the liquid reservoirs. The integrated reservoirs for liquids remove the need for external supplies of liquid to the culture chamber during cell culture experiments requiring perfusion of liquids. Moreover, with two or more reservoir it is possible to supply the culture chamber with different types of liquids.
Owner:SMART BIOSYST
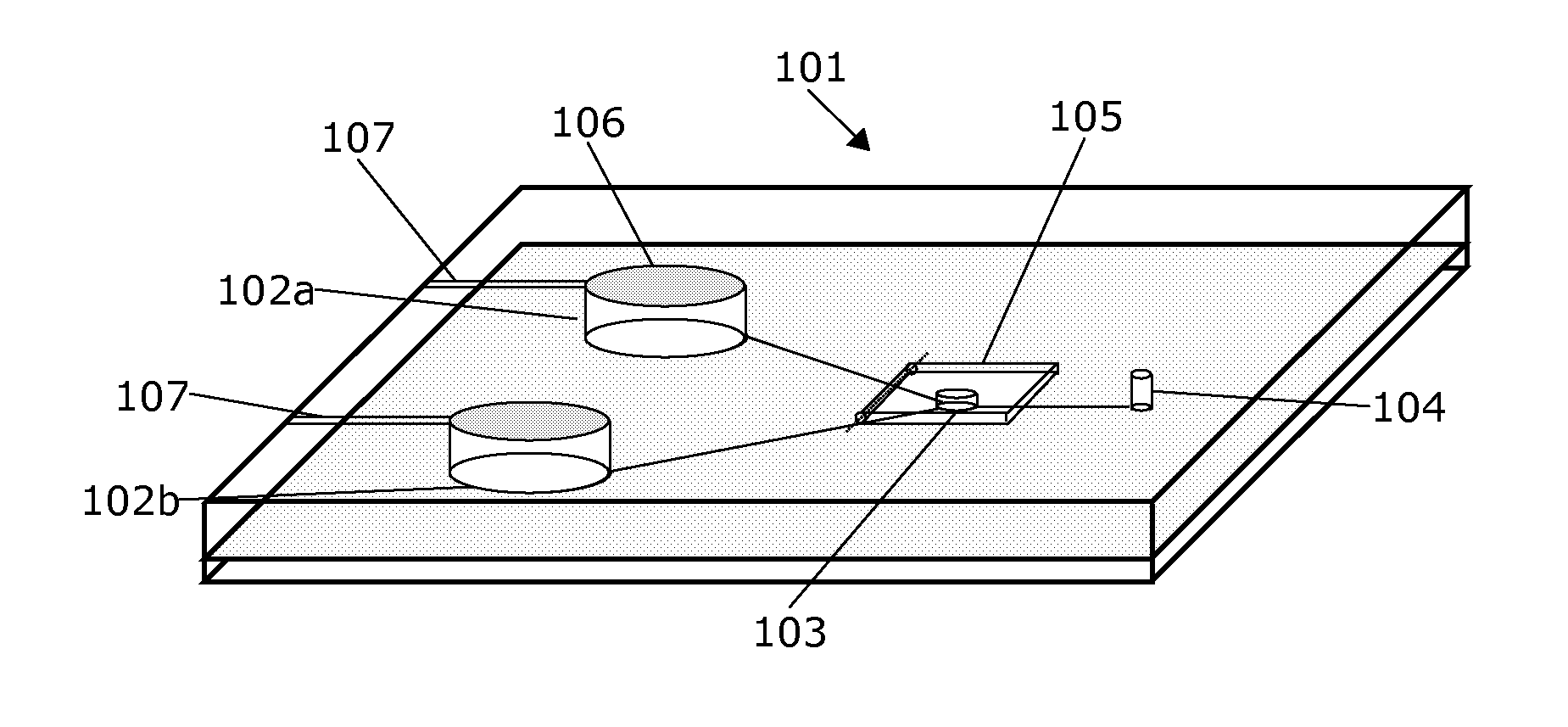
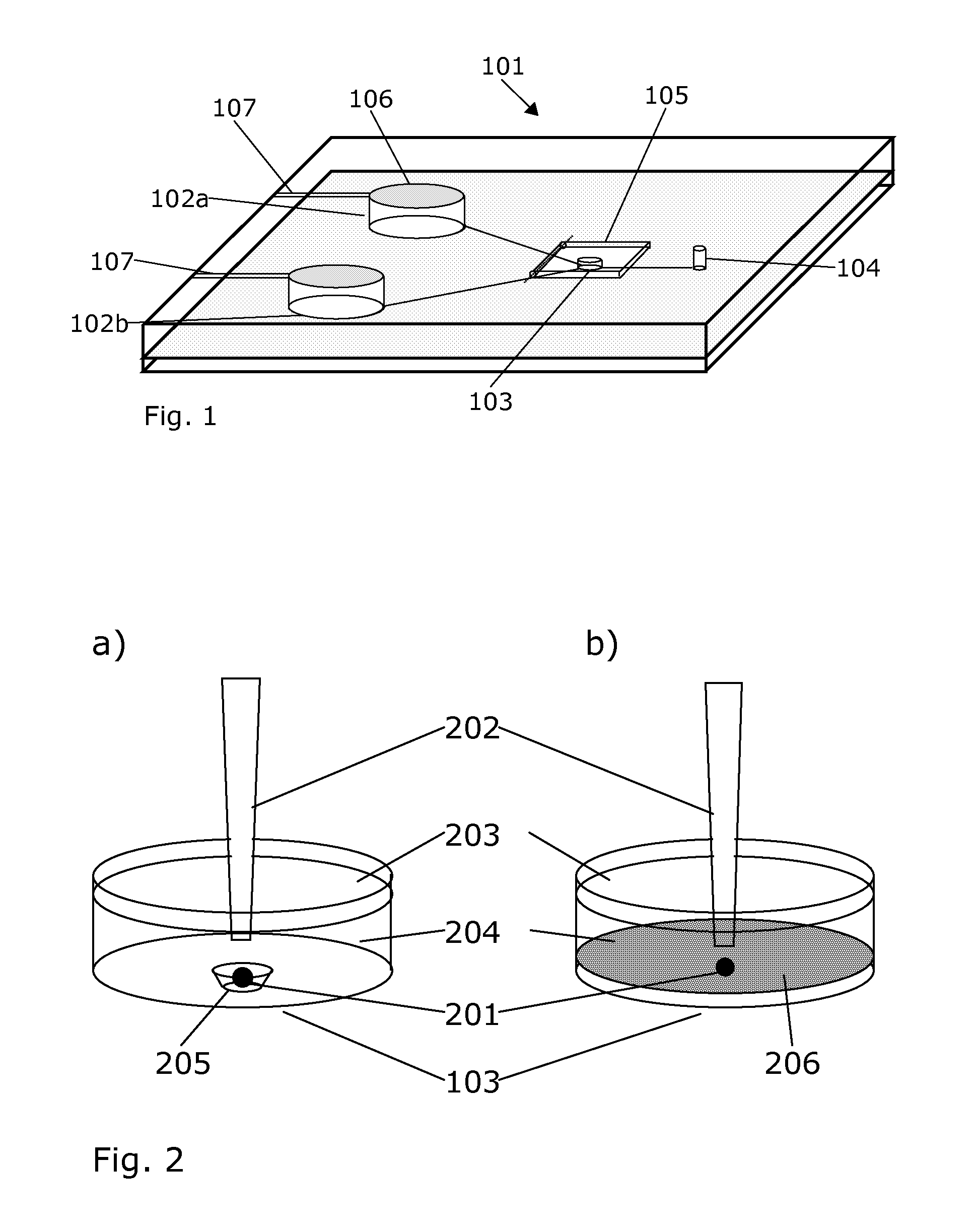
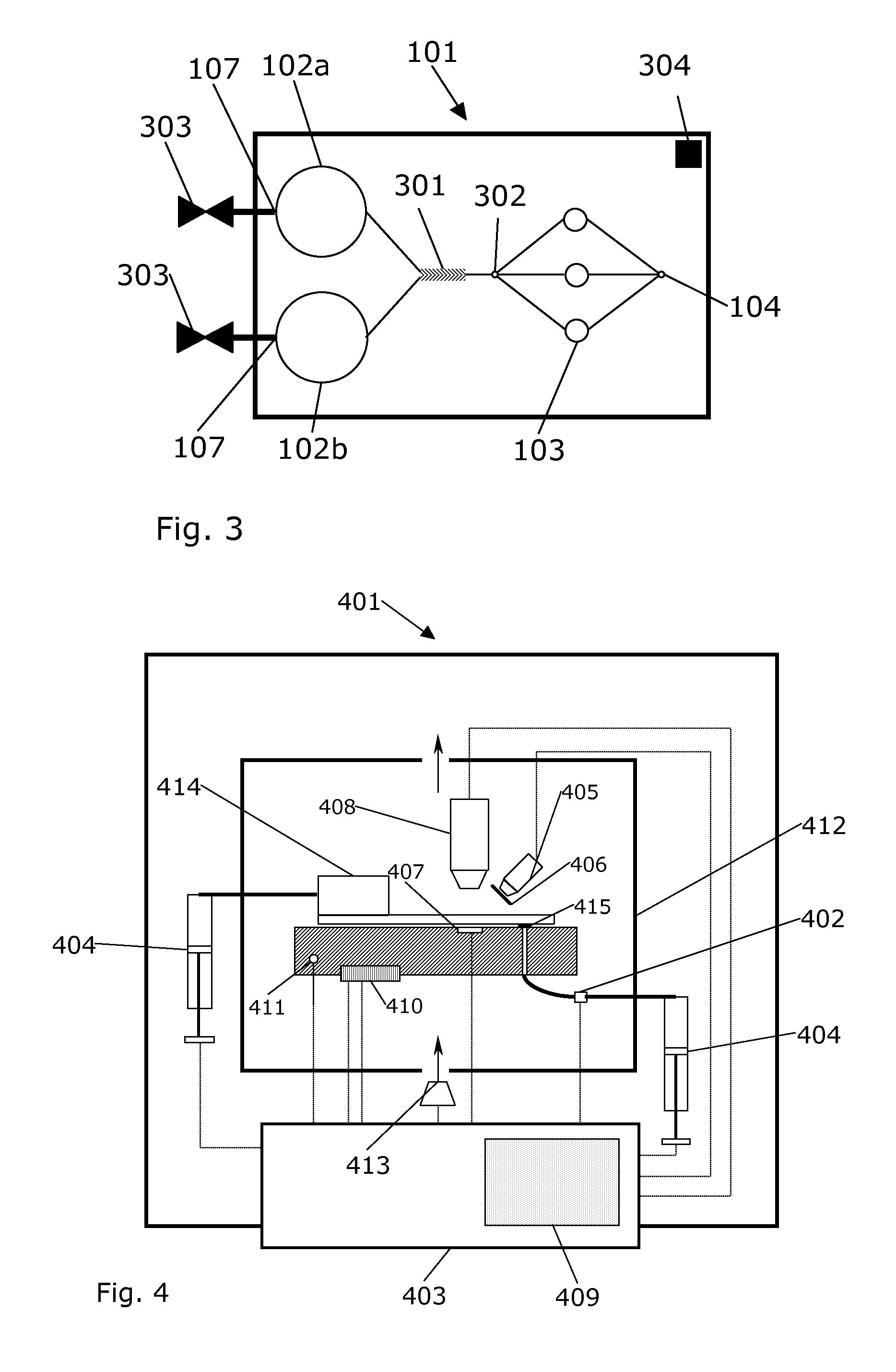
Apparatus for testing, assessment, and maintenance of harvested hearts for transplanting
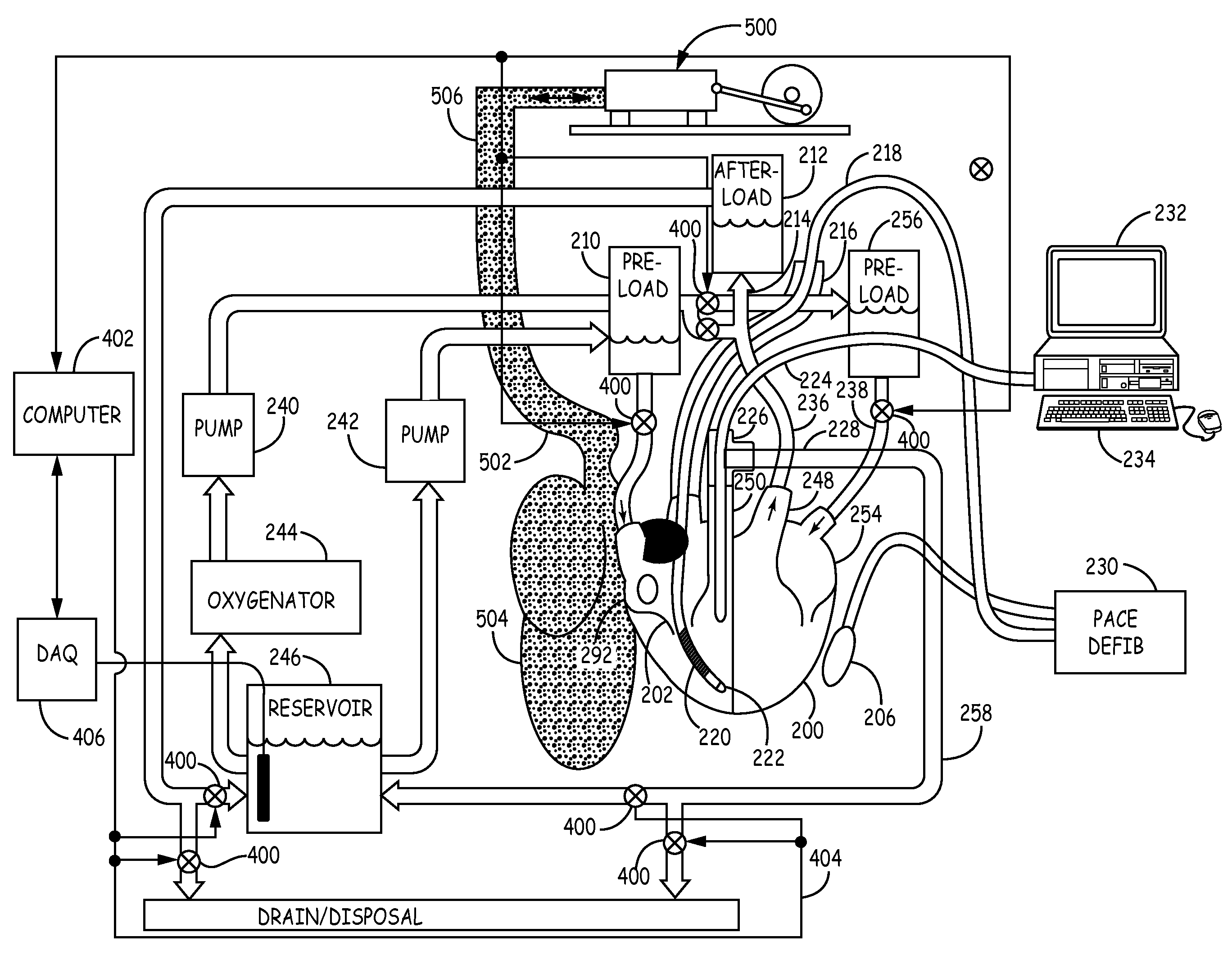
An apparatus, a system, and methods for receiving, perfusing and maintaining and assessing excised donor heart physiological functionality, The system generally comprises an apparatus for receiving and holding an excised heart that is interconnected with: (i) a perfusate-processing system, (ii) a bidirectional perfusate pumping system, (in) flow sensors for monitoring the flow of perfusate to and from an installed heart's aorta, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, and vena cava, (iv) an ECG apparatus interconnectable with the installed heart, and (v) probes interconnecting the installed heart with instruments for monitoring the heart's physiogical functionality using load independent indices and load dependent indices.
Owner:TEVOSOL INC
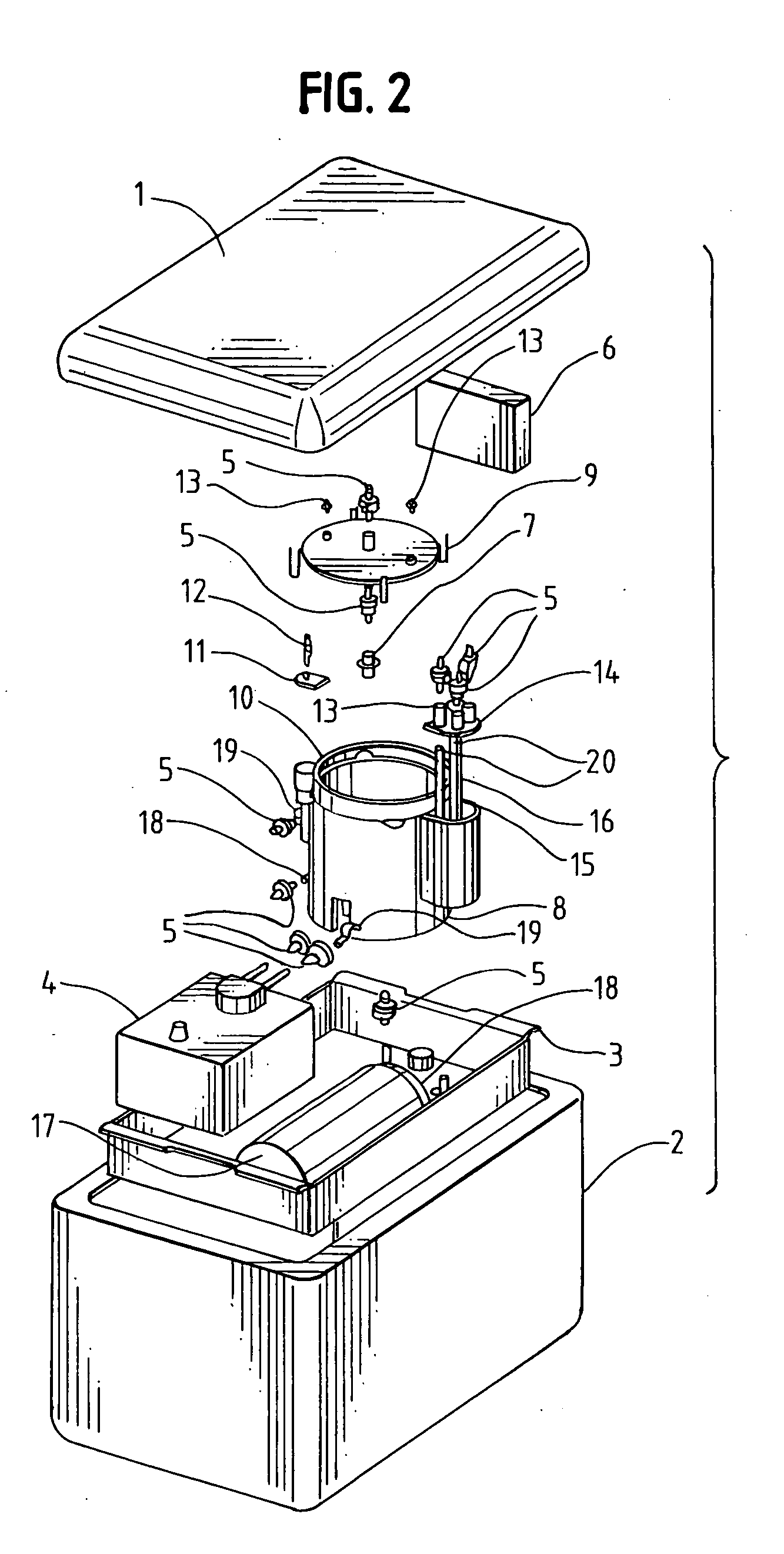
Apparatus for oxygenation and perfusion of tissue for organ preservation
Owner:PARAGONIX TECH
Vascular tissue engineering reactor having vas stretch and pulsating flow pouring functions
ActiveCN101372663AWith rotation functionEnhanced mass transferBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVascular tissueBlood Vessel Tissue
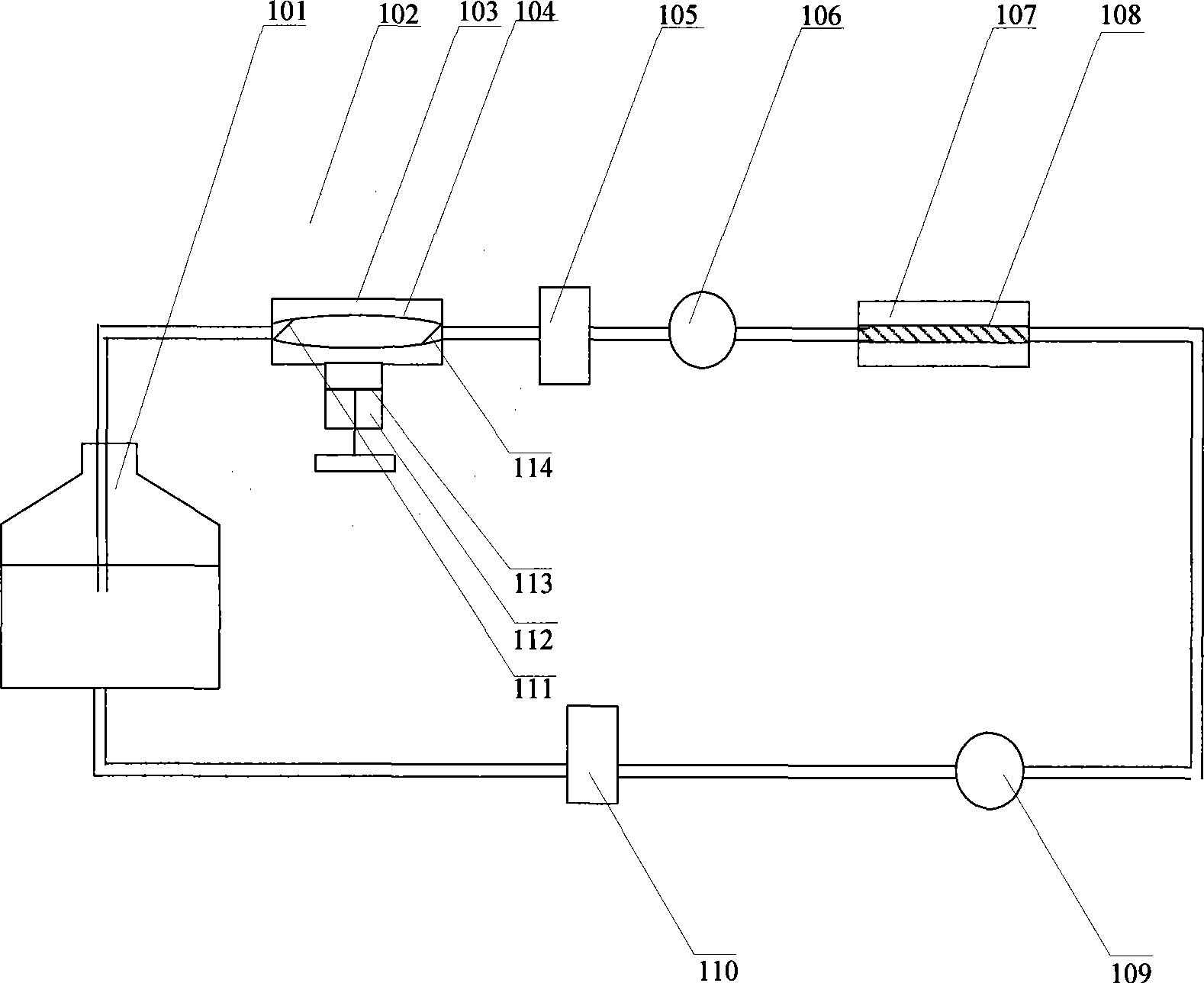
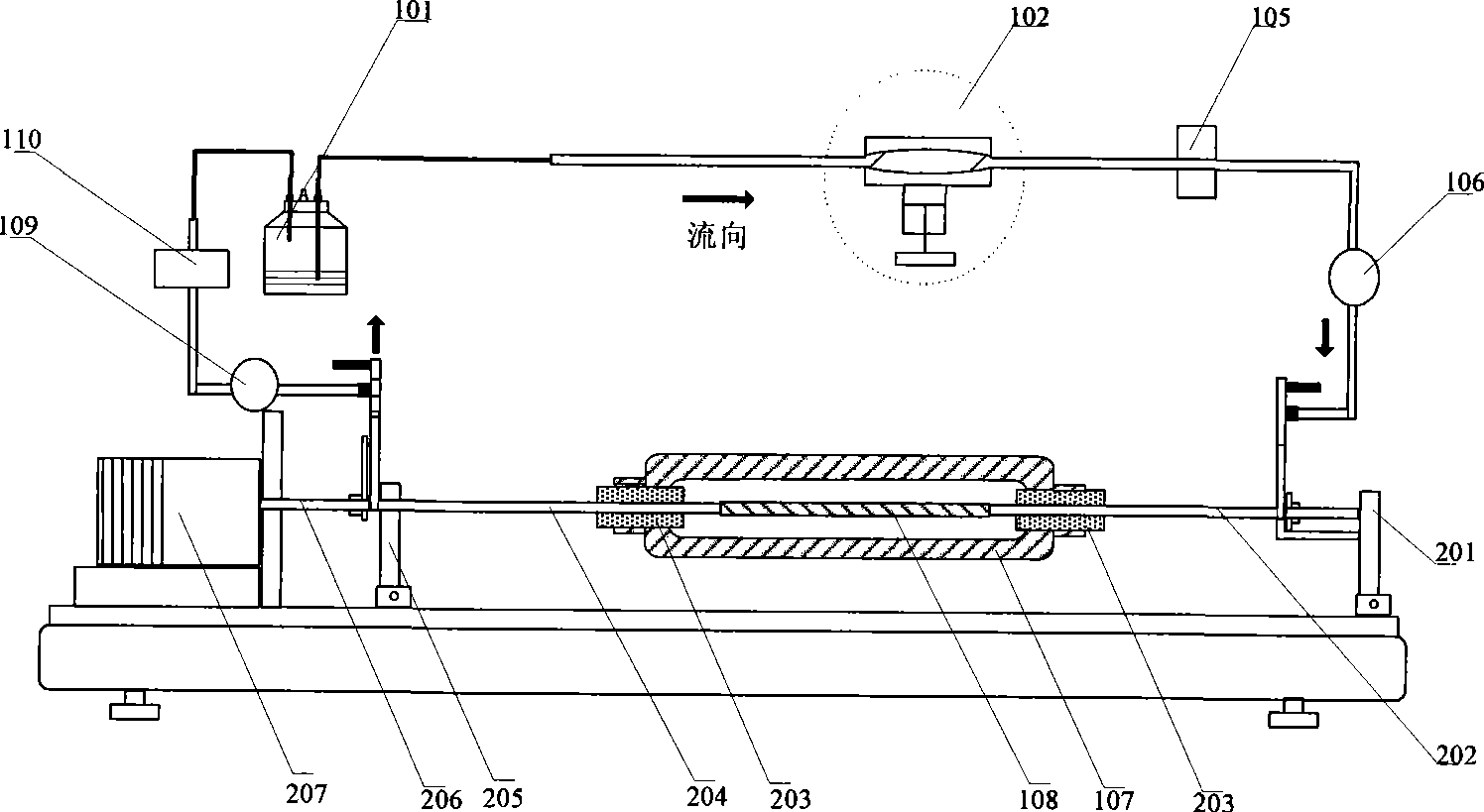
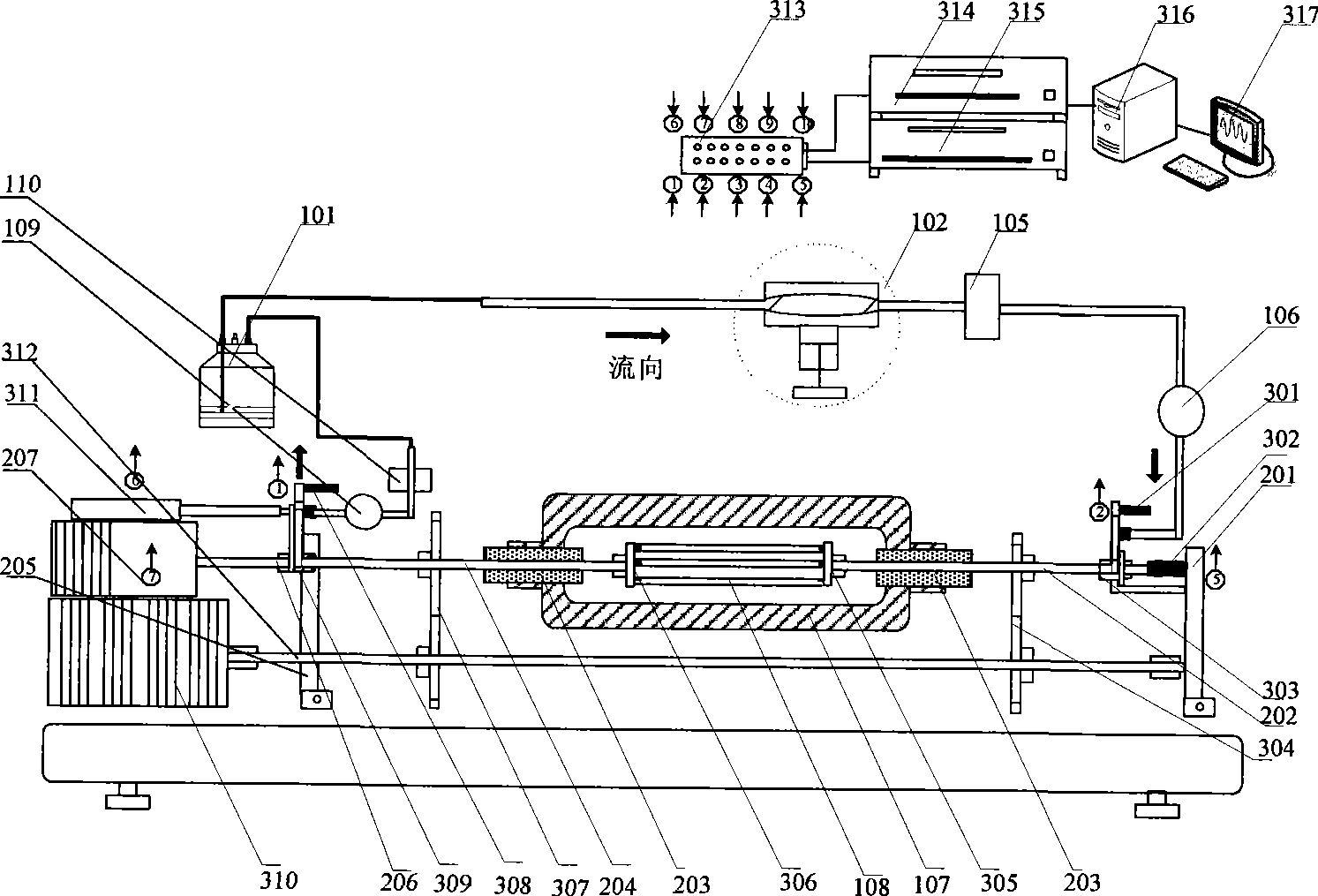
The invention relates to a vascular tissue engineering reactor which is characterized by comprising intravascular perfusion liquid storage bottles (101) which are connected with each other in sequence by pipelines, a pulsation source (102) which is taken as an intravascular perfusion liquid driving device, a culture cavity inlet pipeline (202) of an intravascular perfusion circuit, and a vascular tissue culture cavity (107), wherein, one end of an inlet pipeline (104) of the culture cavity enters the vascular tissue culture cavity (107), and is connected with one end of a vascular tissue (108) to be cultured so as to cause the culture solution from the perfusion liquid storage bottle (101) to flow into the vascular tissue (108). The reactor further comprises a culture cavity outlet pipeline (204) of the intravascular perfusion circuit, one end of the culture cavity outlet pipeline (204) enters the vascular tissue culture cavity (107), and is connected with the other end of the vascular tissue (108) to be cultured so as to export the culture solution from the inner part of the vascular tissue (108).
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com