Patents
Literature
197 results about "Vena cava" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
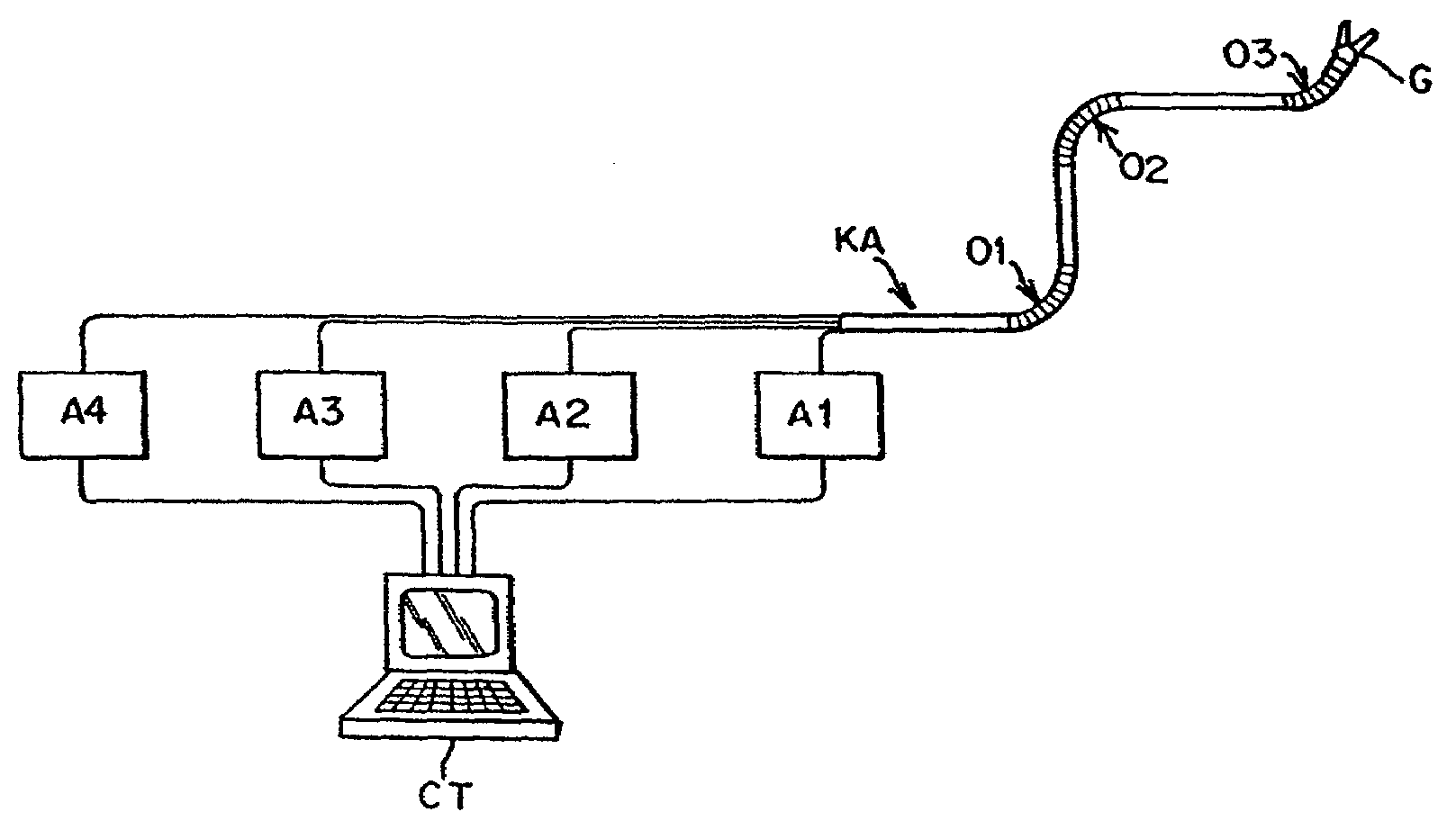
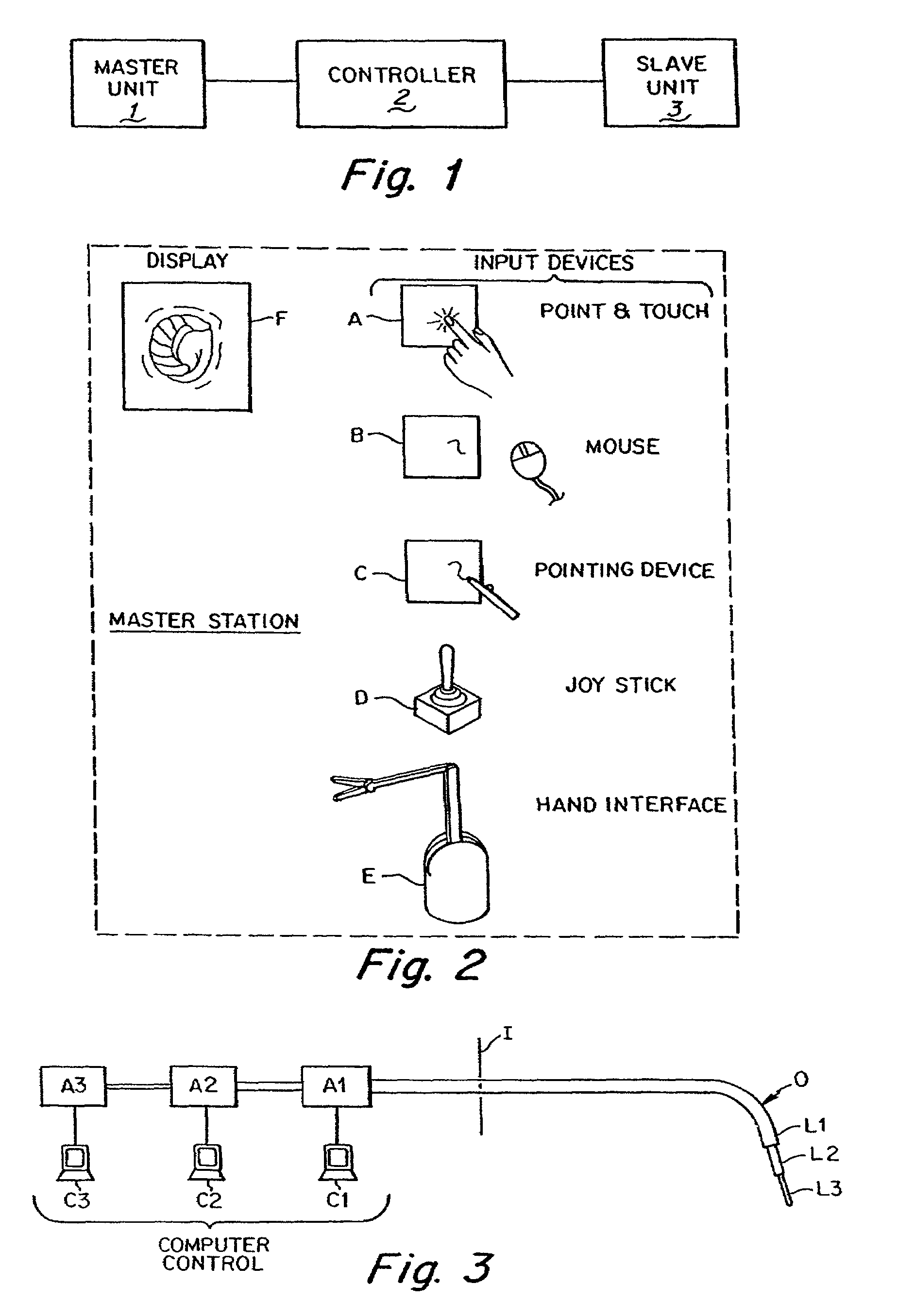
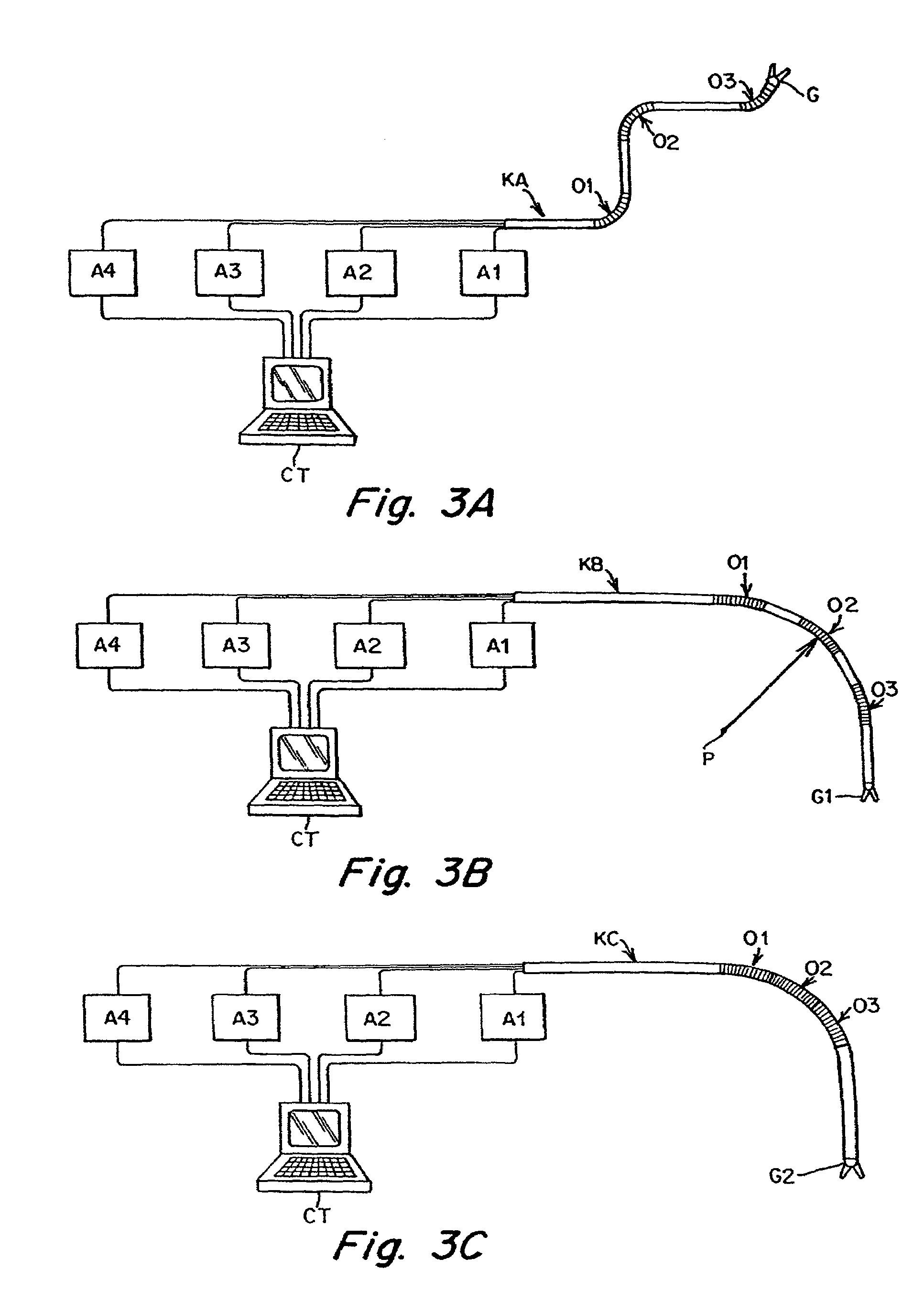
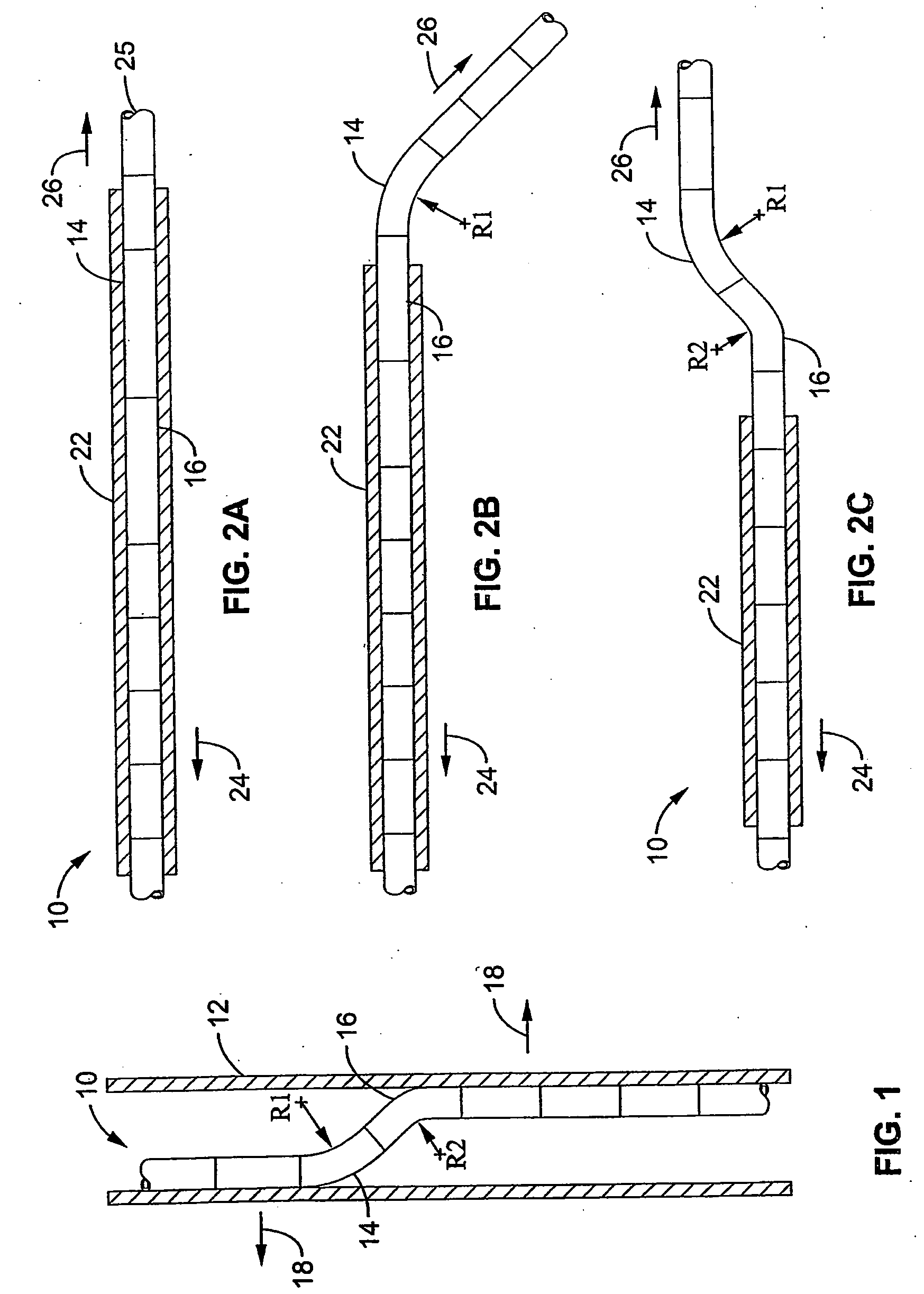
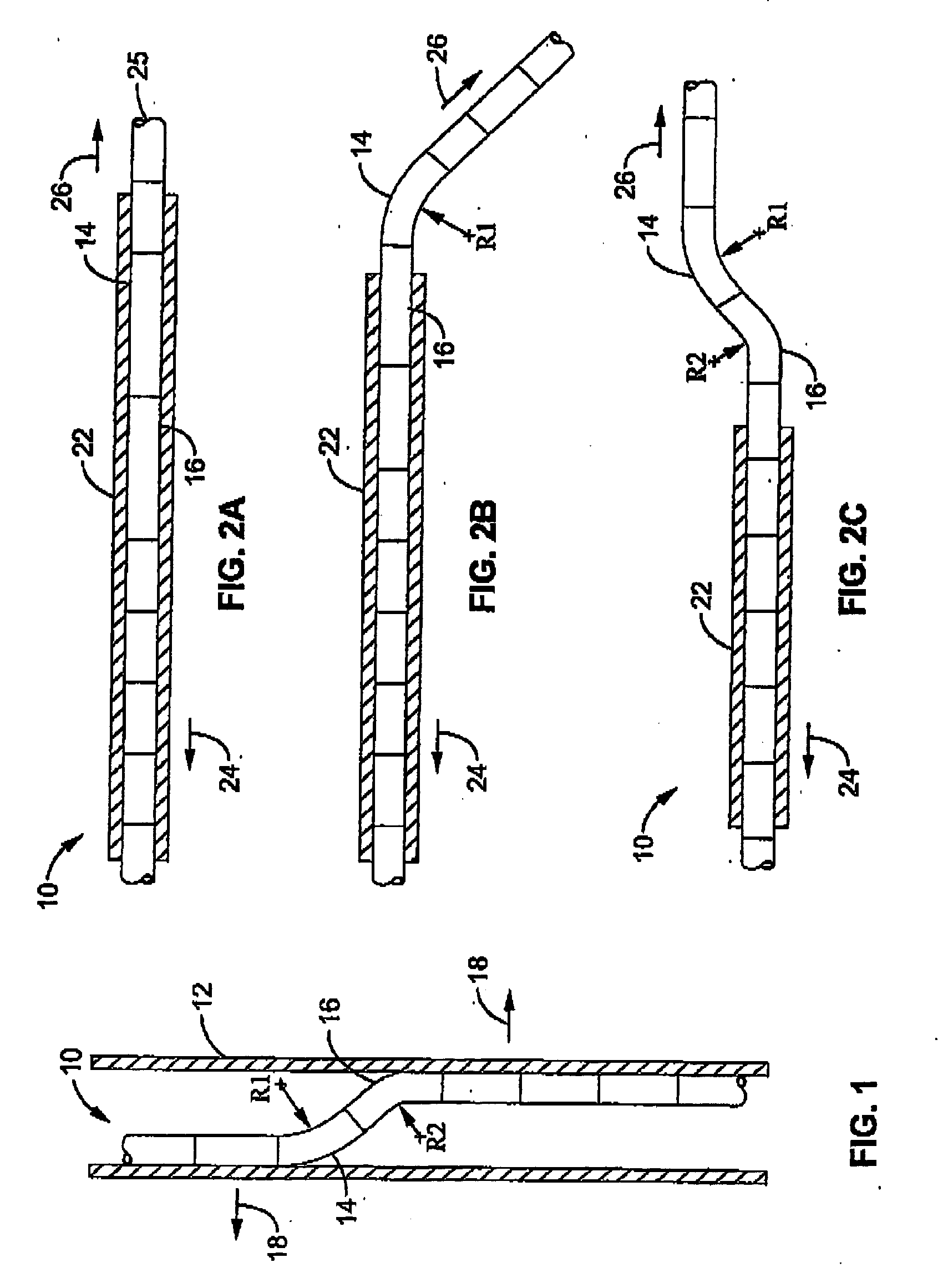
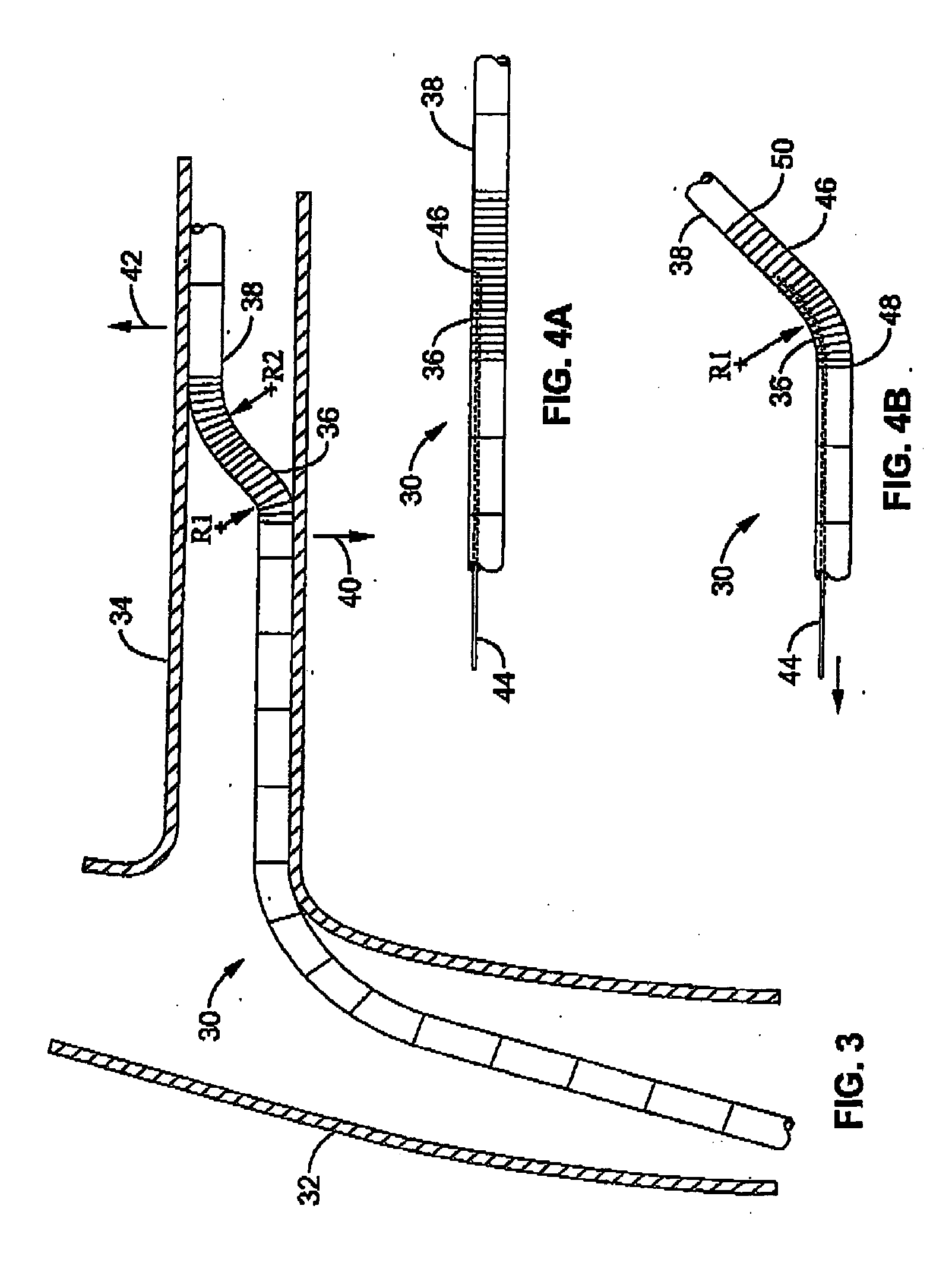
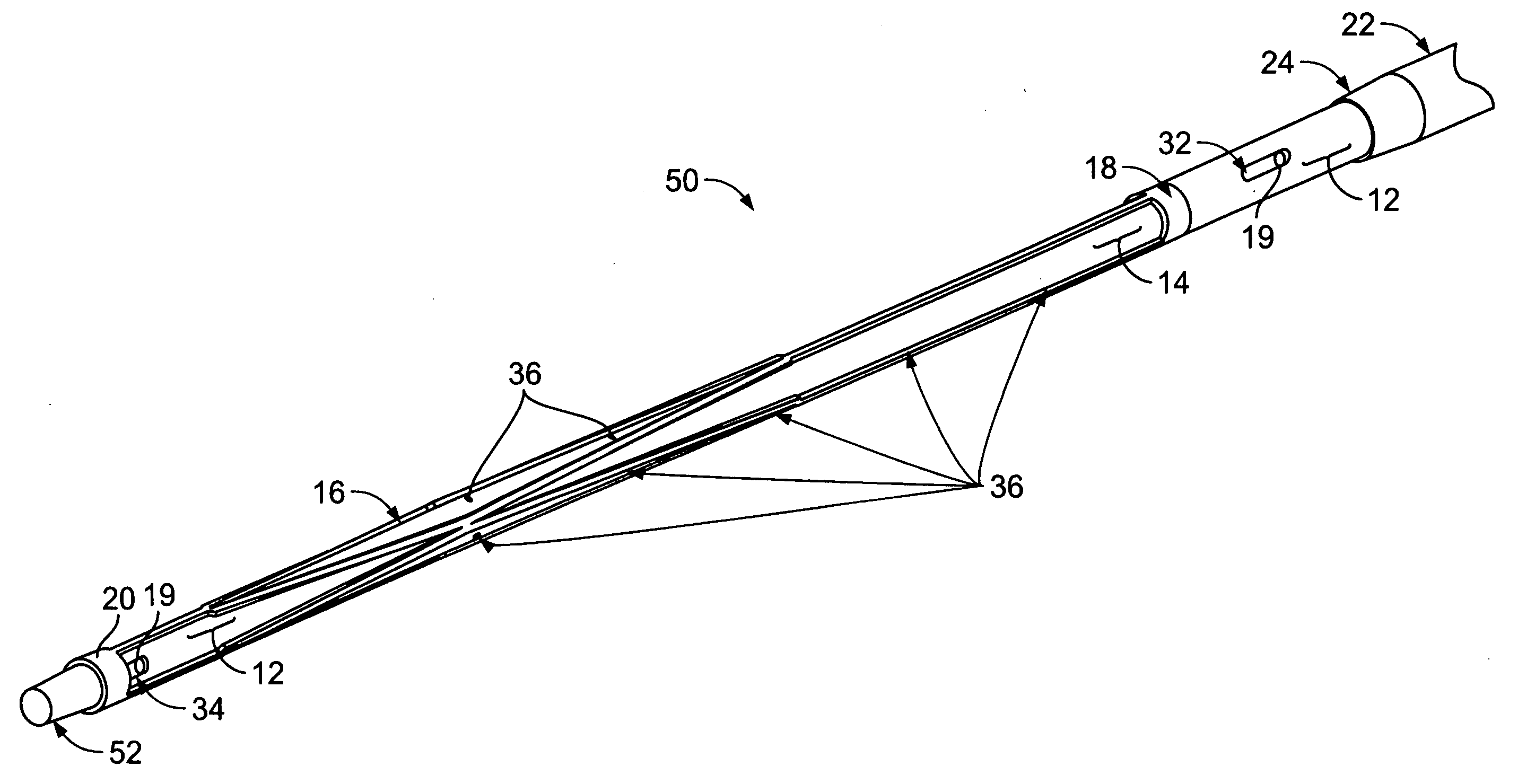
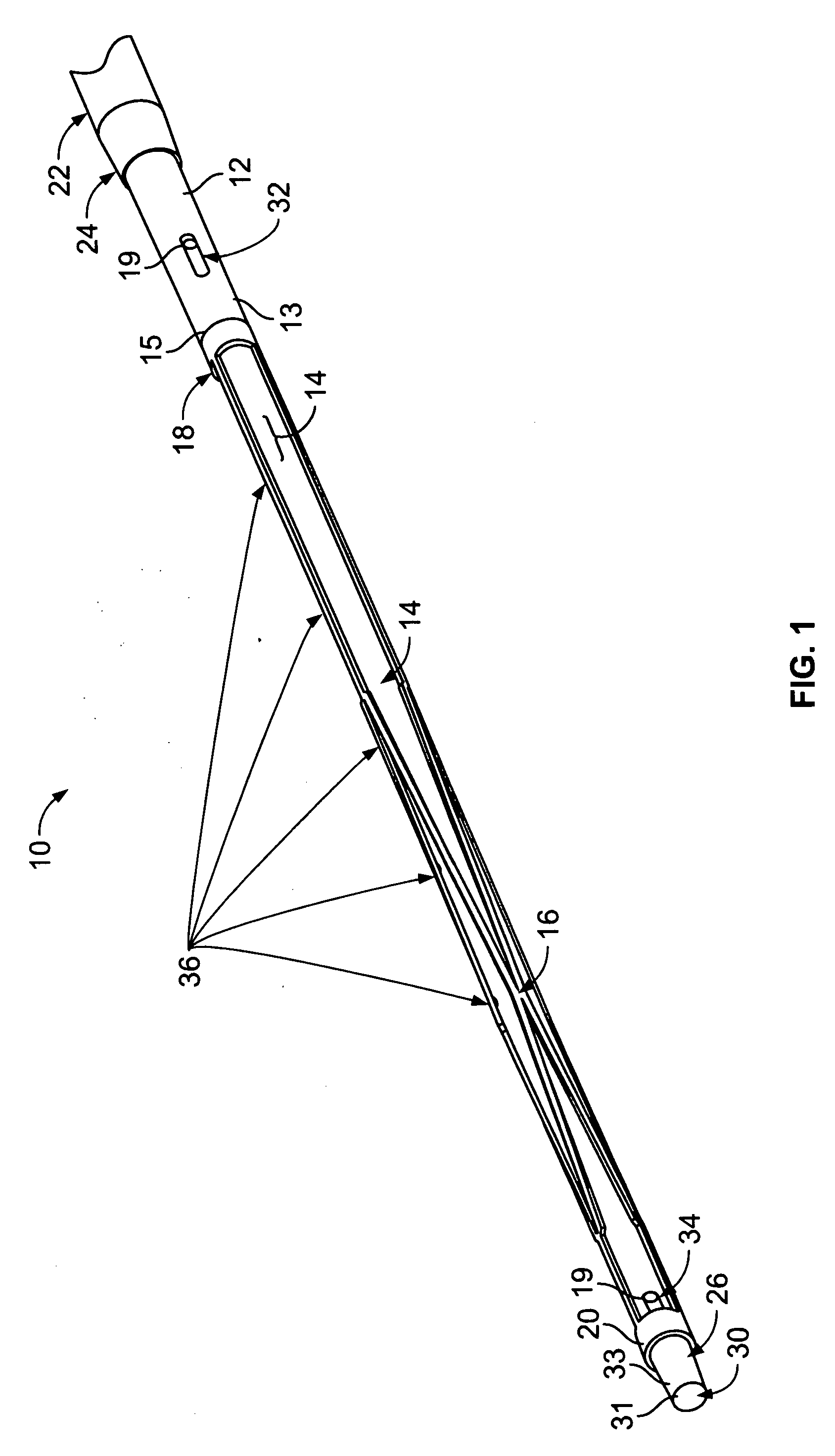
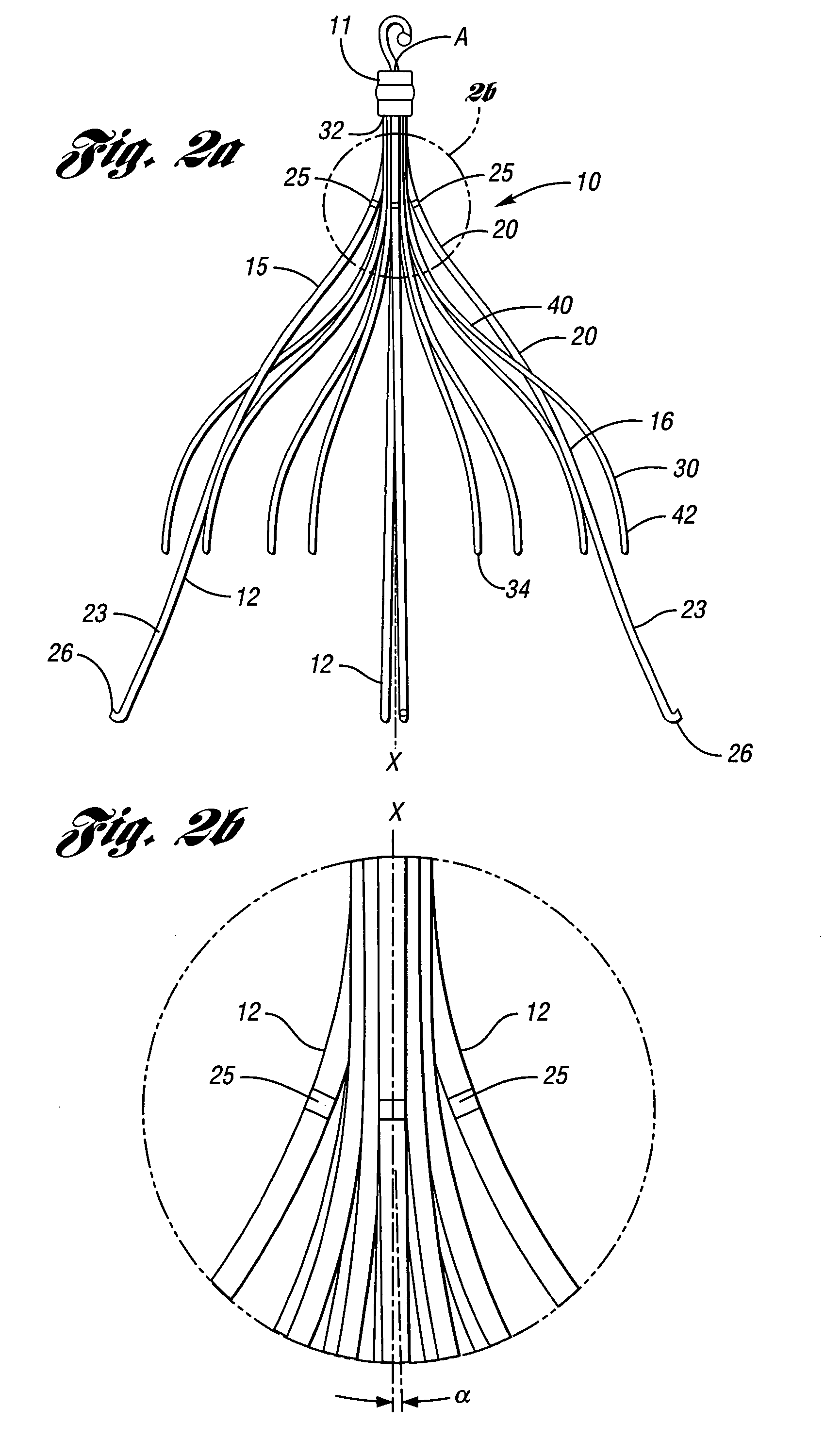
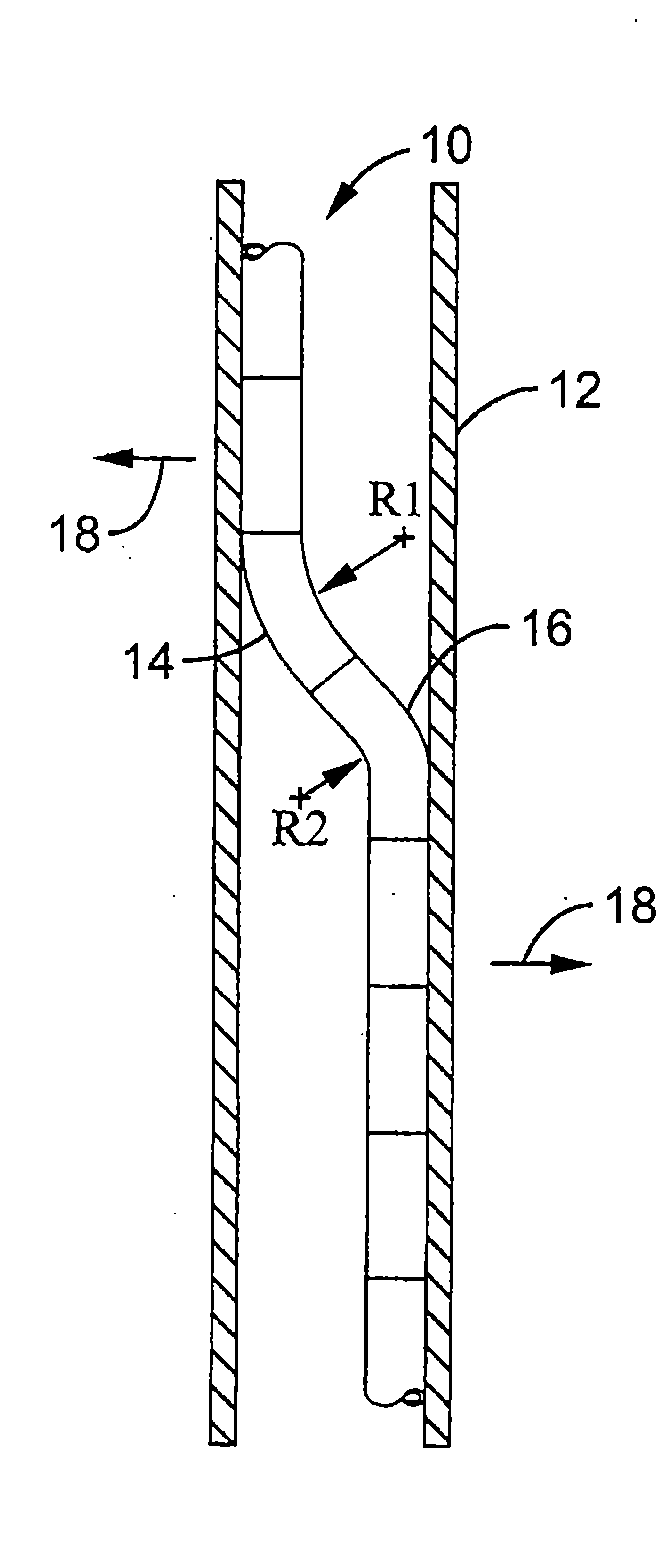
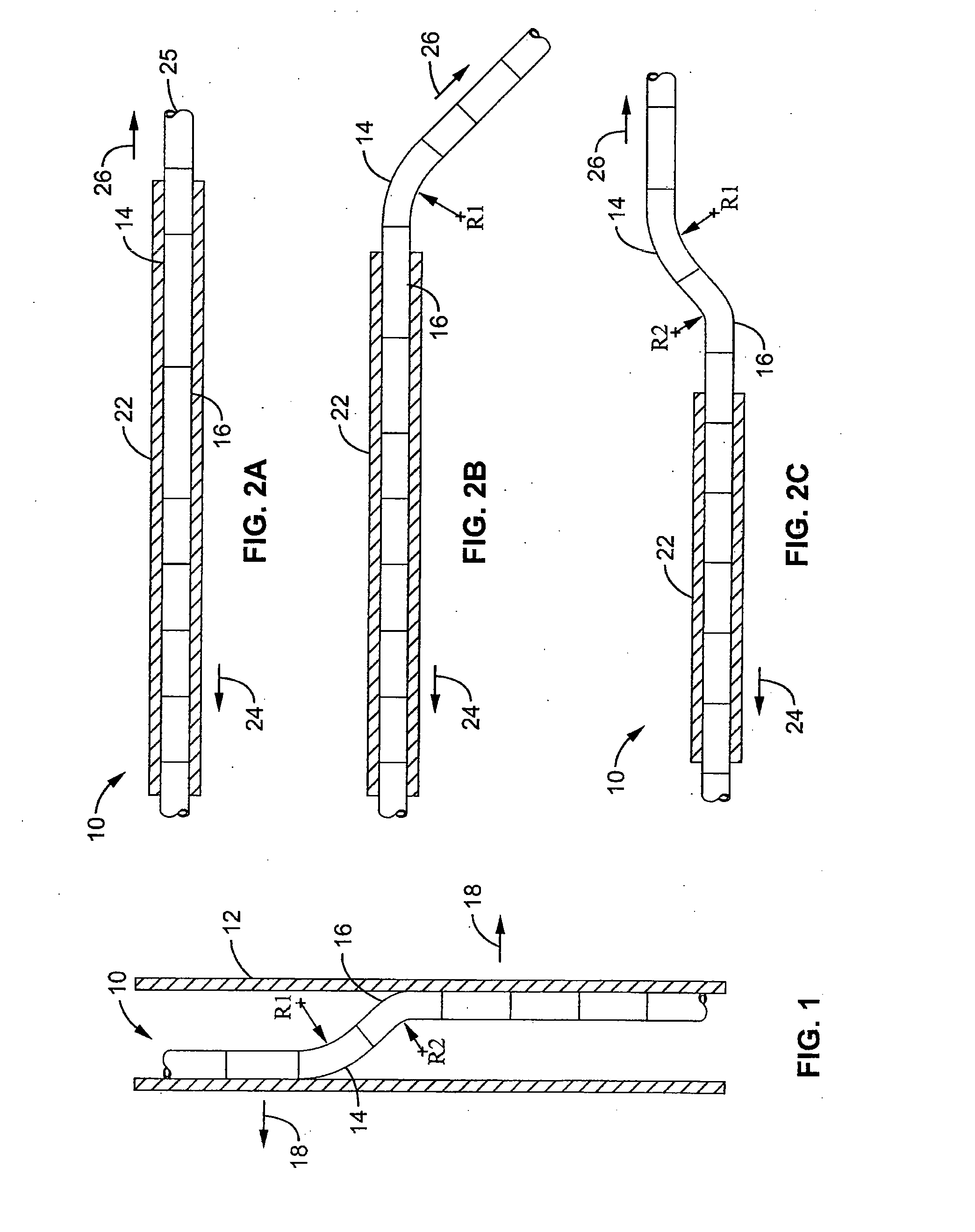
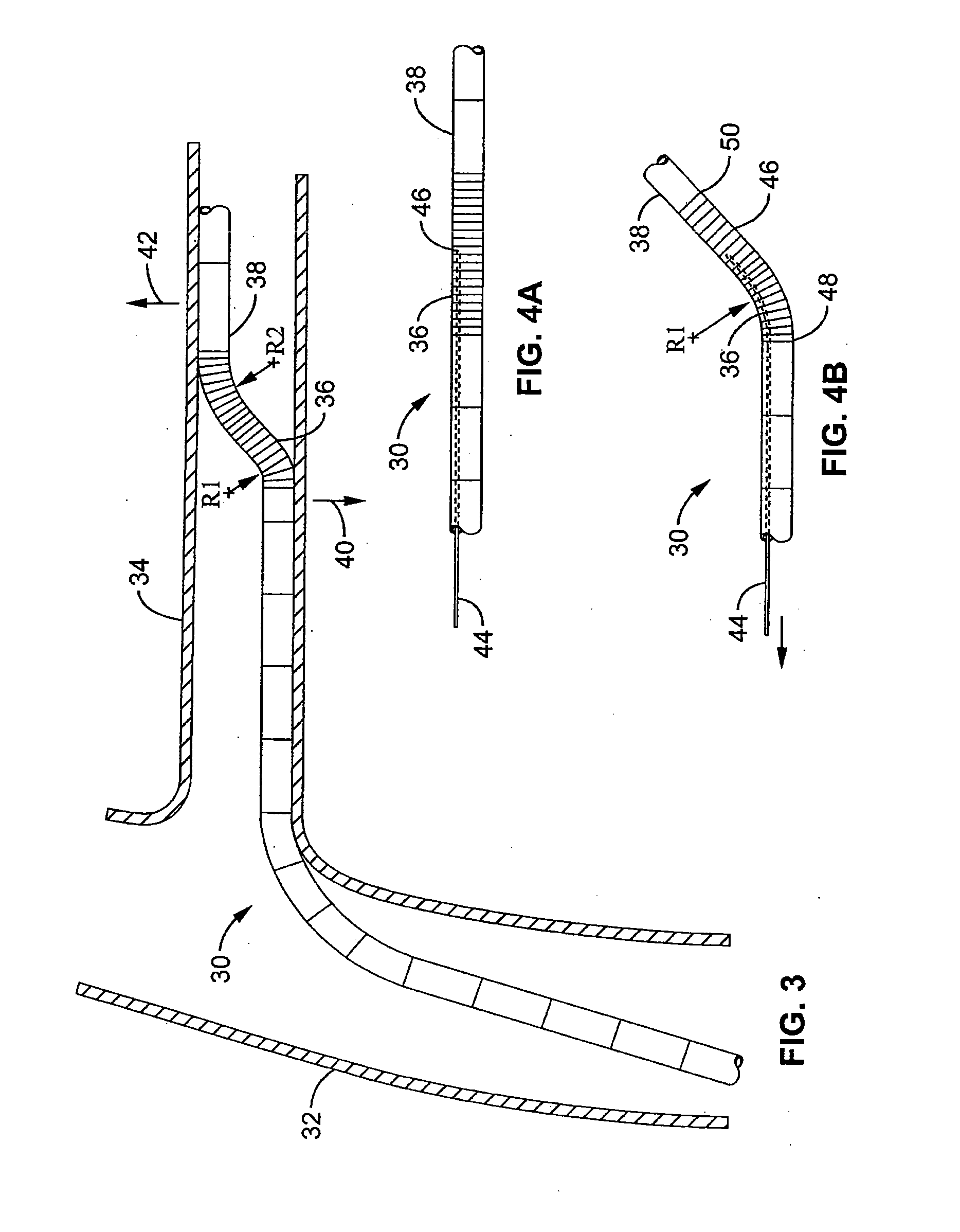
Flexible instrument
A method of performing a medical procedure on a patient comprises conveying control signals from a remote controller to a drive unit, intravenously introducing the catheter into a heart of the patient (e.g., via the vena cava into the right atrium), and creating a puncture within a wall between two chambers (e.g., the left and right atria) of the heart. The method further comprises creating a puncture within a wall between two chambers of the heart, and operating the drive unit in accordance with the control signals to advance a working catheter within the guide catheter through the puncture.
Owner:HANSEN MEDICAL INC
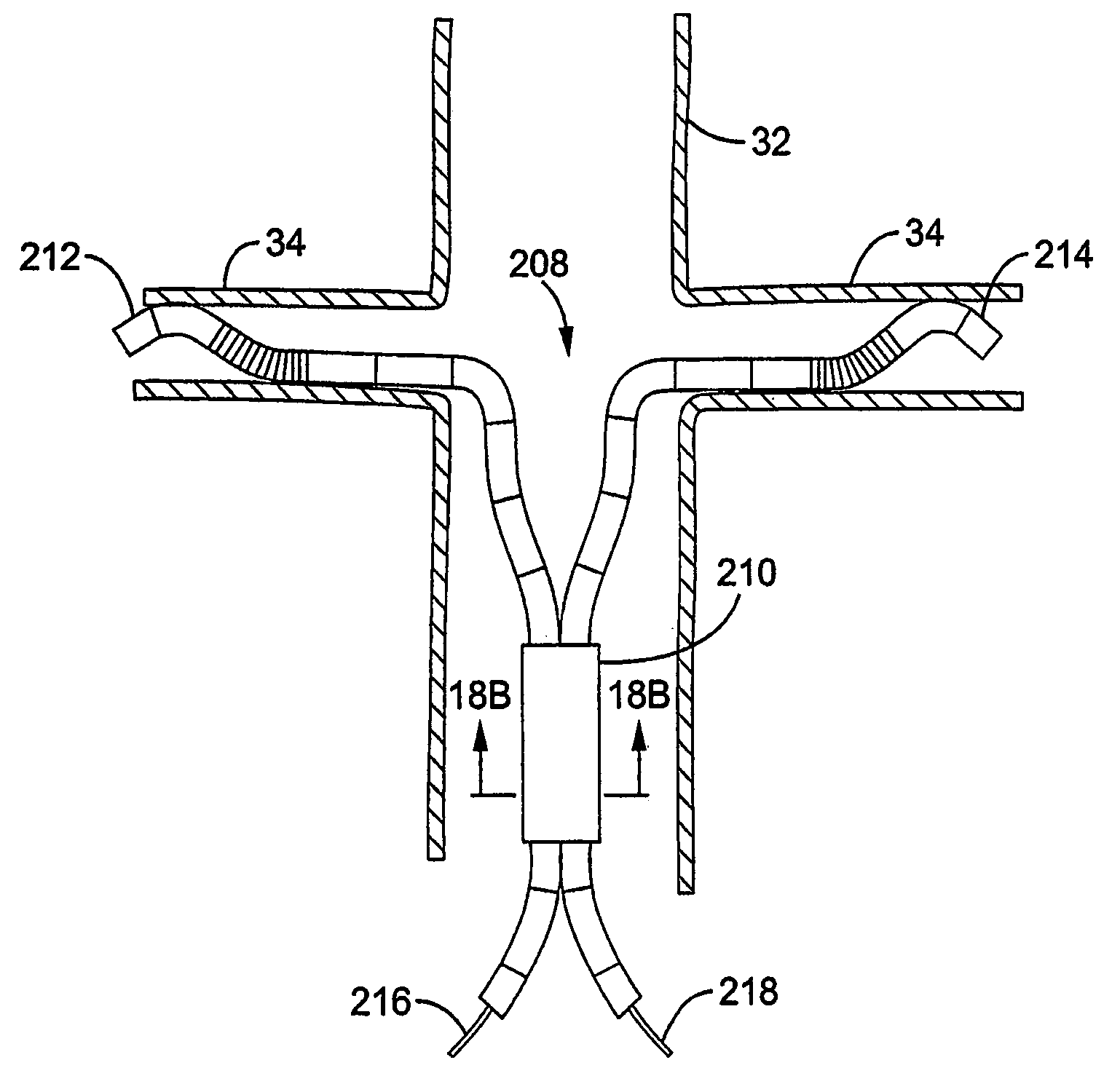
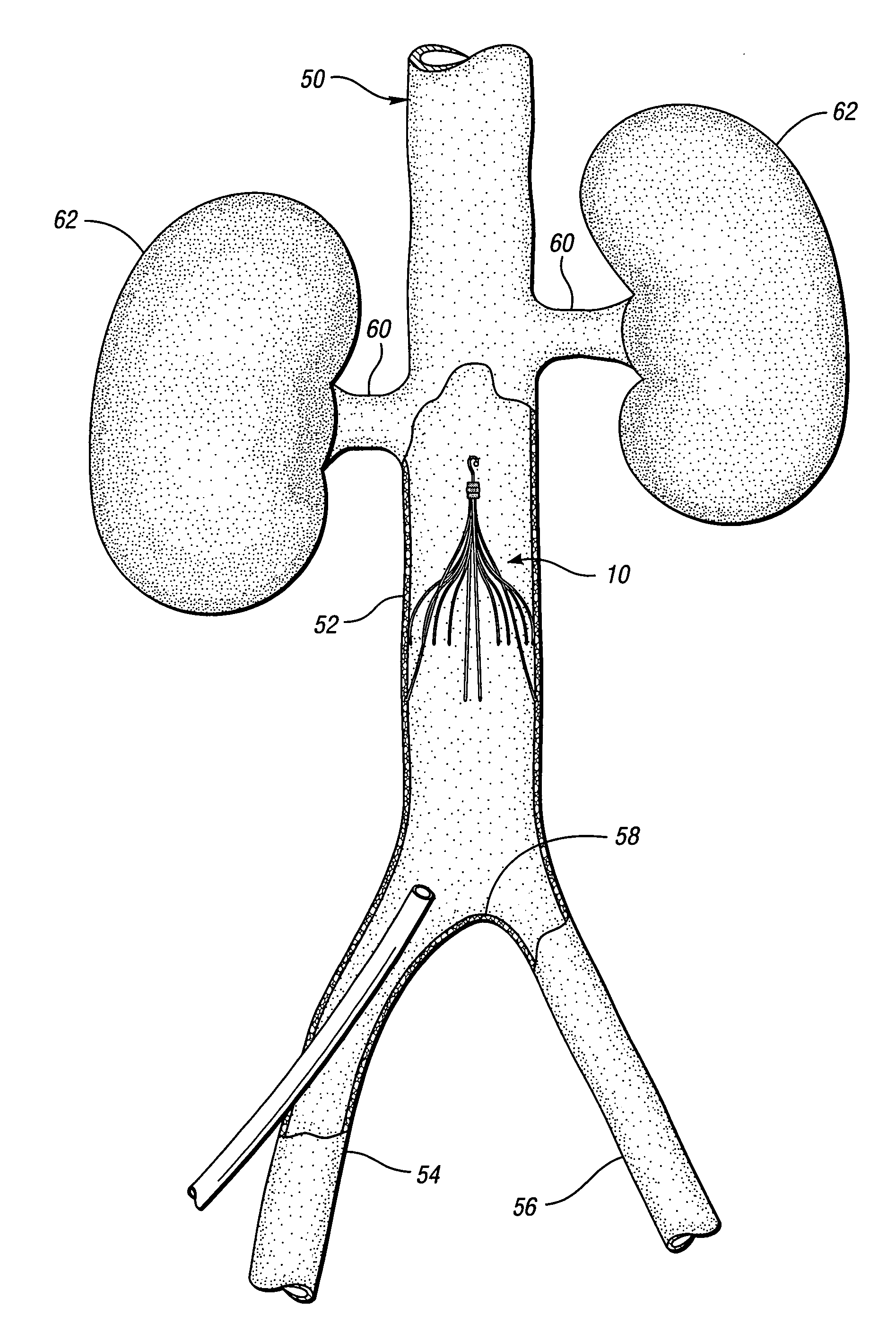
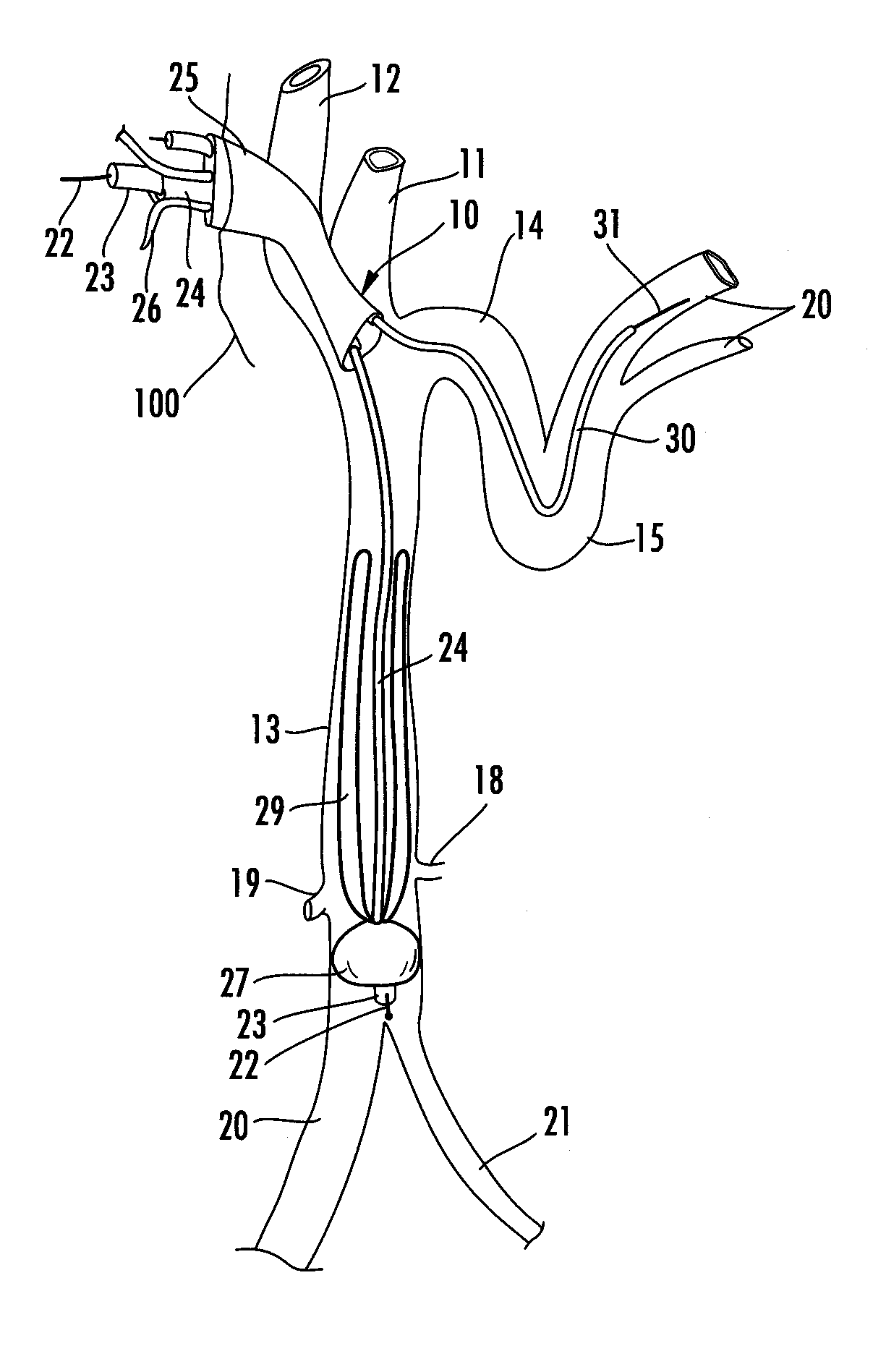
Systems and methods for performing bi-lateral interventions or diagnosis in branched body lumens
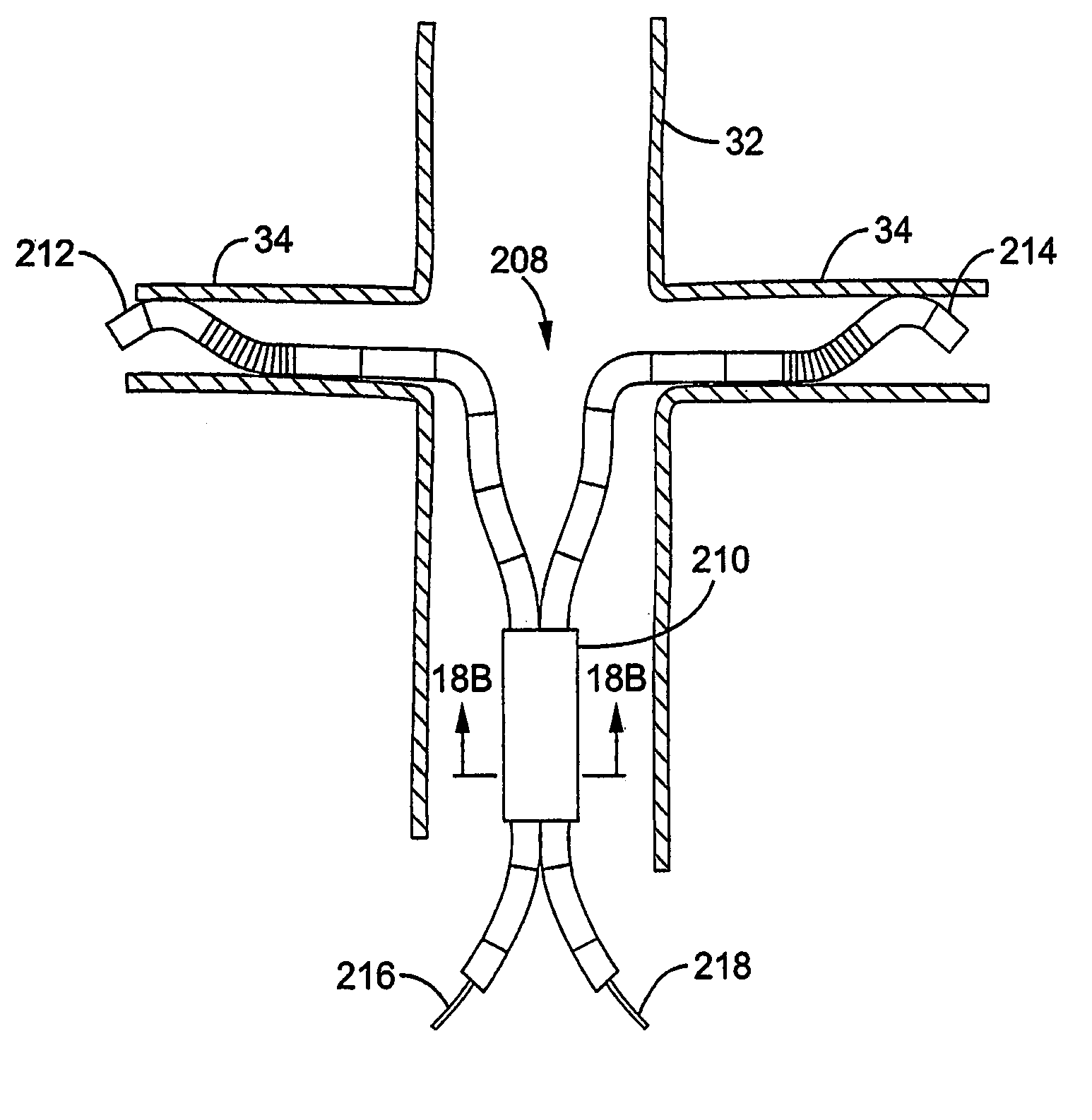
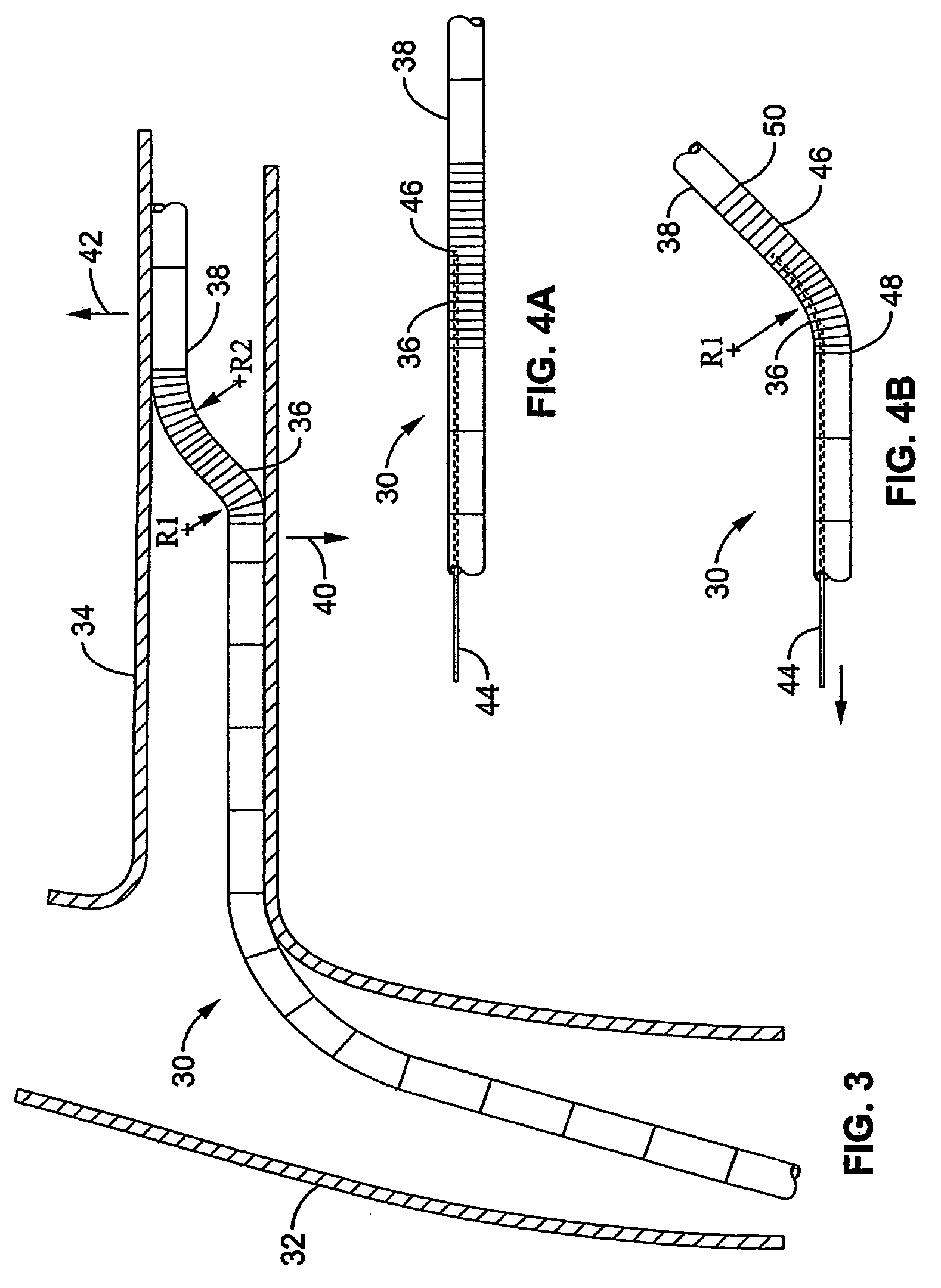
Bifurcated delivery assemblies provide bilateral access to first and second branch lumens extending from a main body space or lumen in a patient. One or more interventional devices are combined with the delivery assemblies for delivery s into one or both of the branch lumens. Bilateral renal stenting or embolic protection procedures are performed using the combination delivery / interventional device assemblies. Fluids may also be injected or aspirated from the assemblies. A bifurcated catheter has a first fluid port located on one bifurcation branch, a second fluid port located on a second branch of the bifurcation, and a third fluid port positioned so as to be located within a vena cava when the first and second ports are positioned bilaterally within first and second renal veins.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
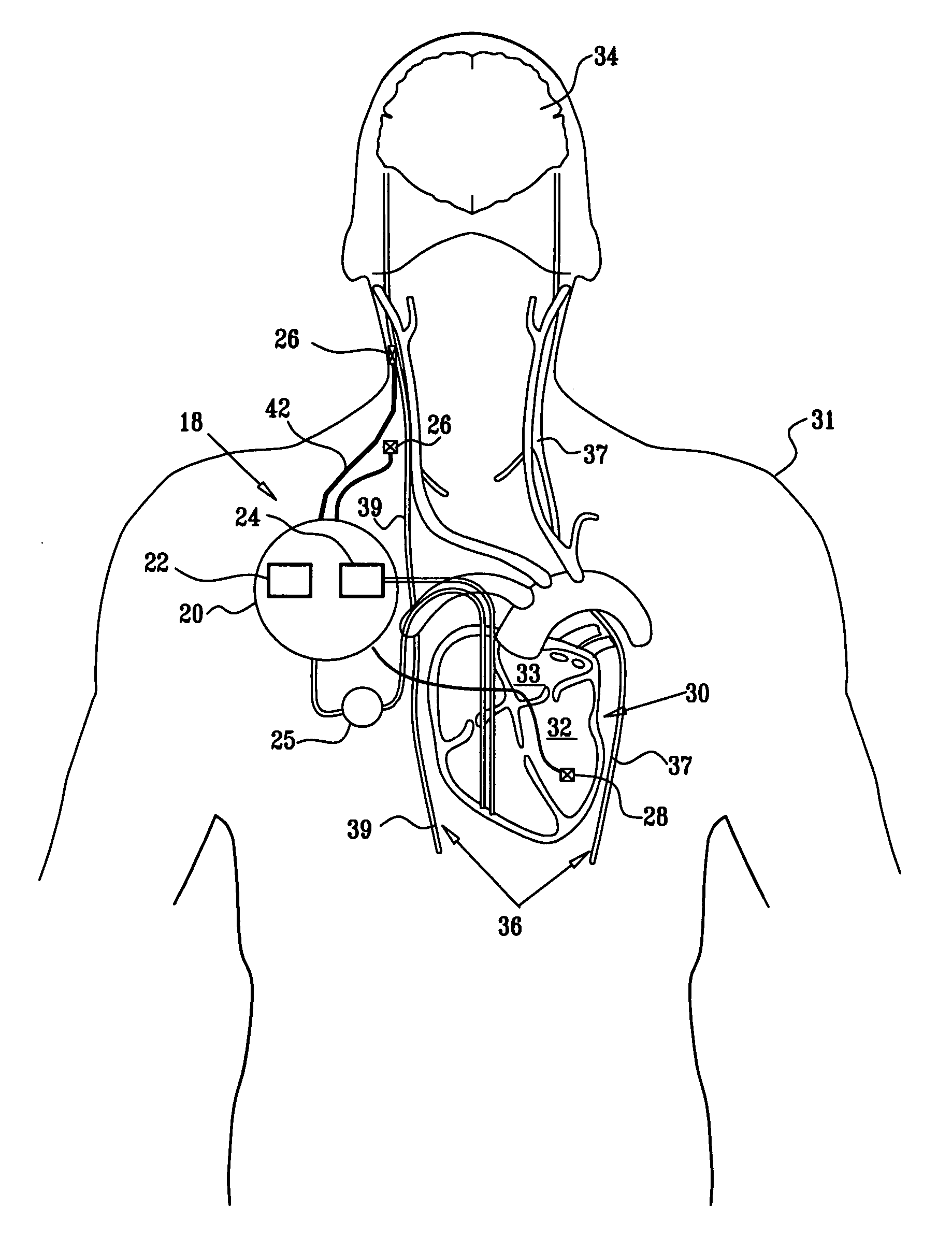
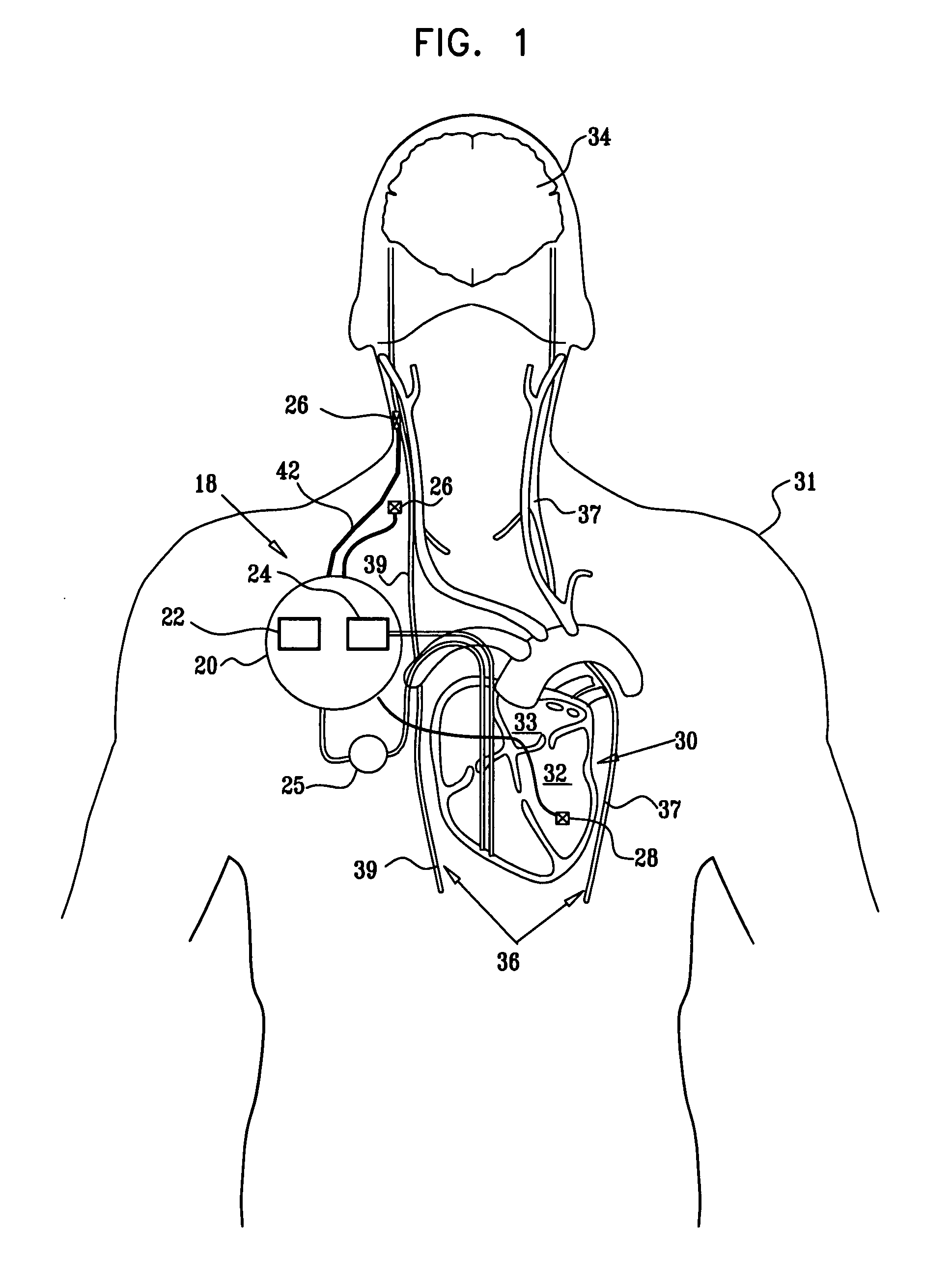
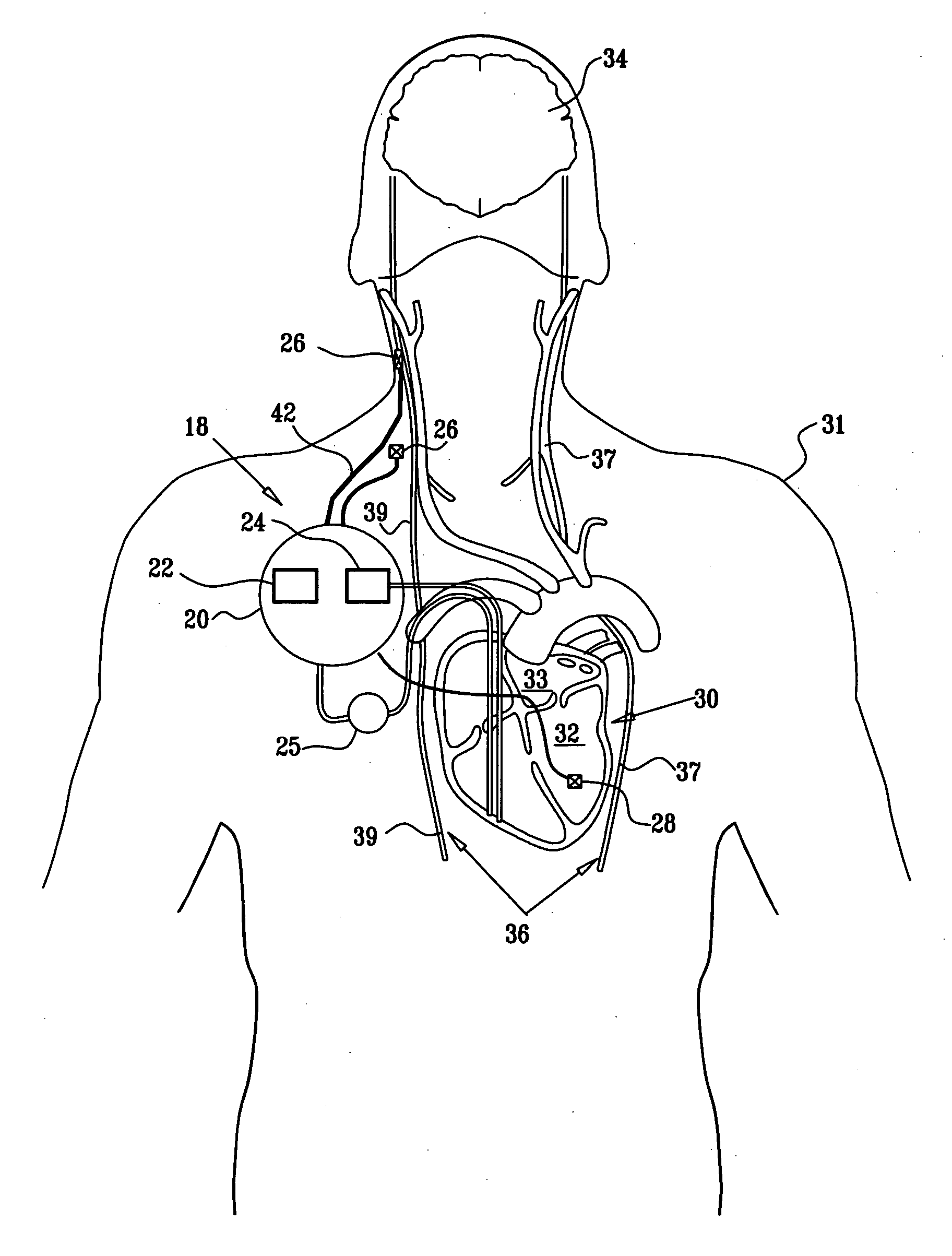
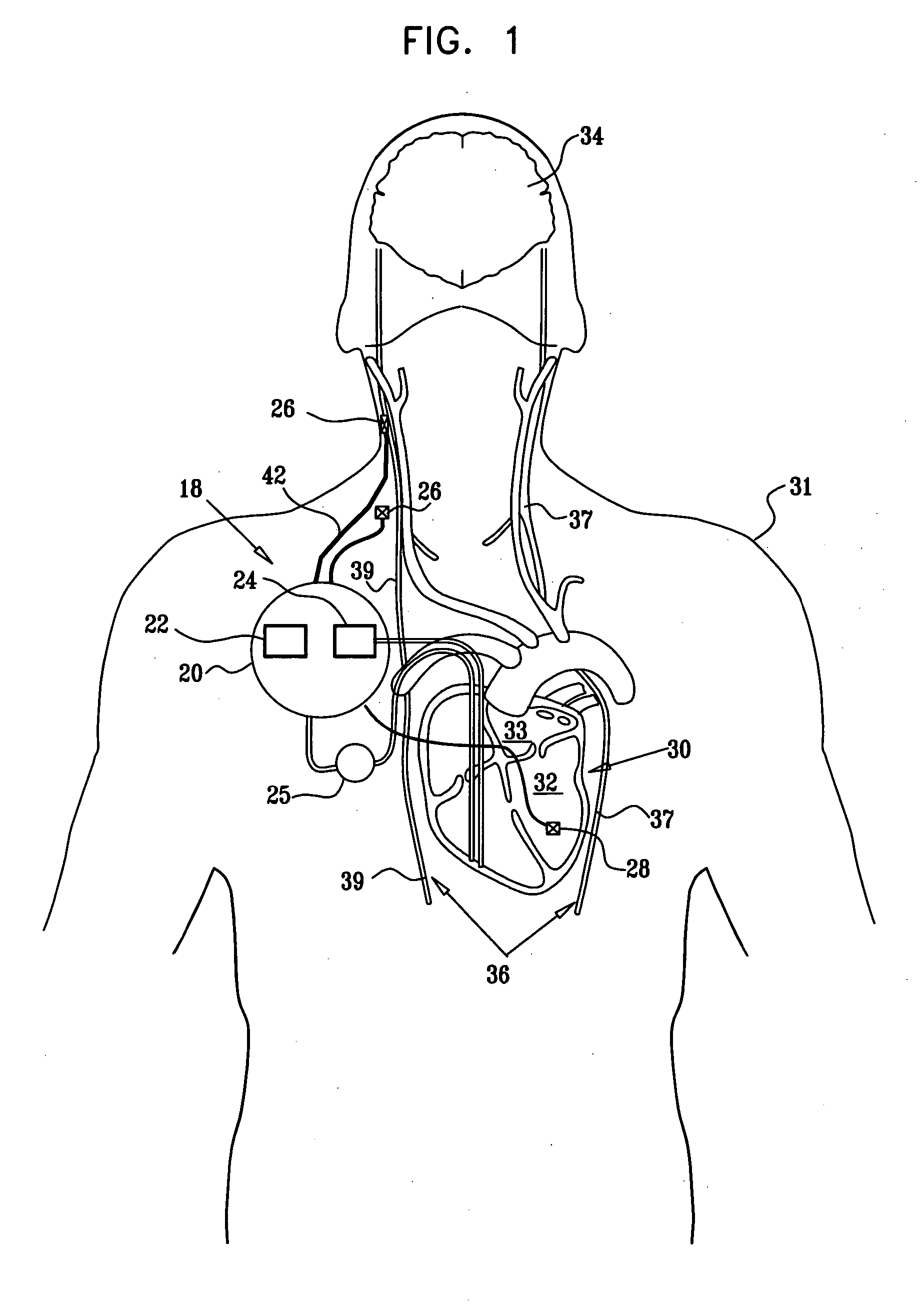
Techniques for applying, configuring, and coordinating nerve fiber stimulation
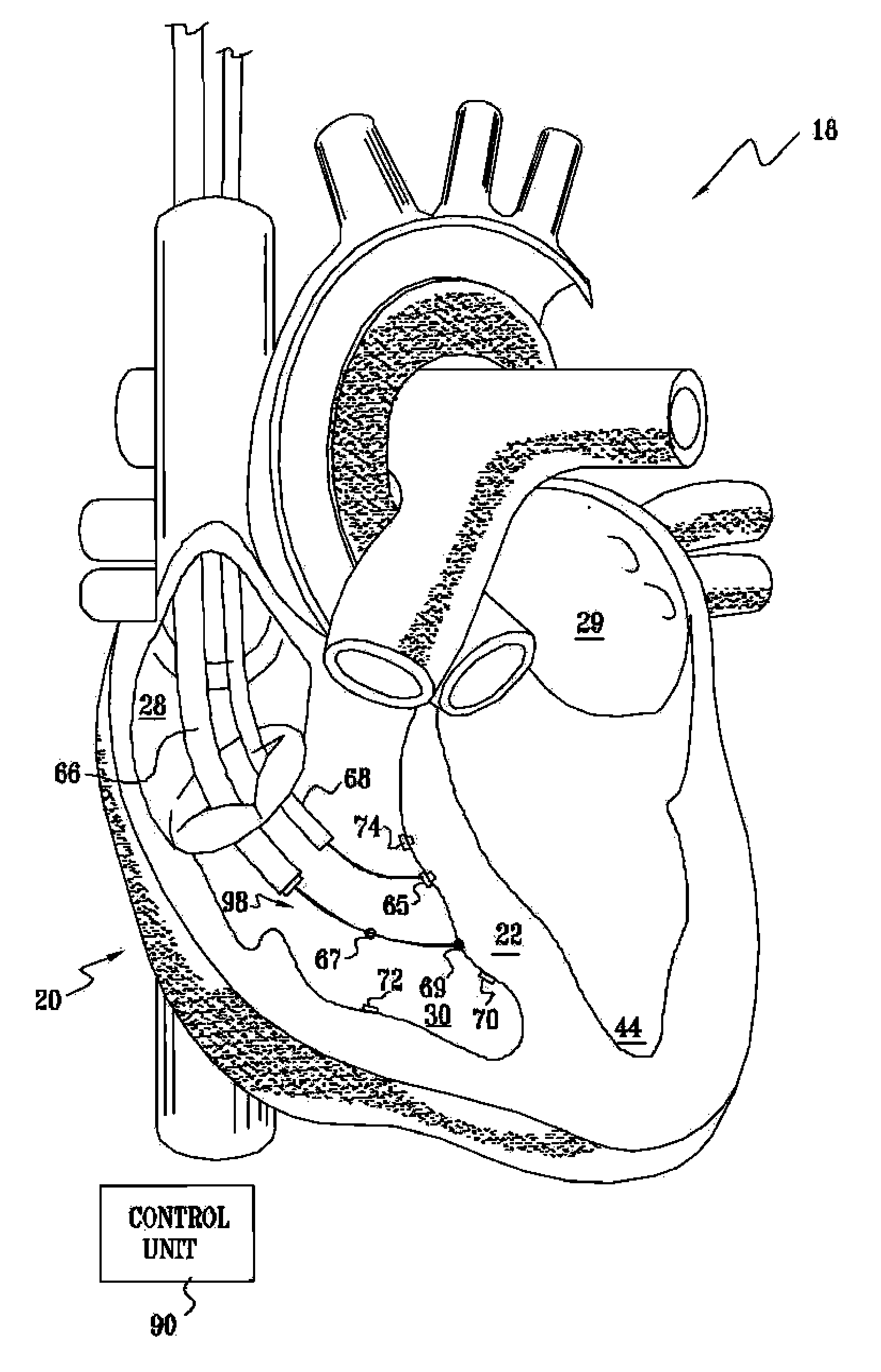
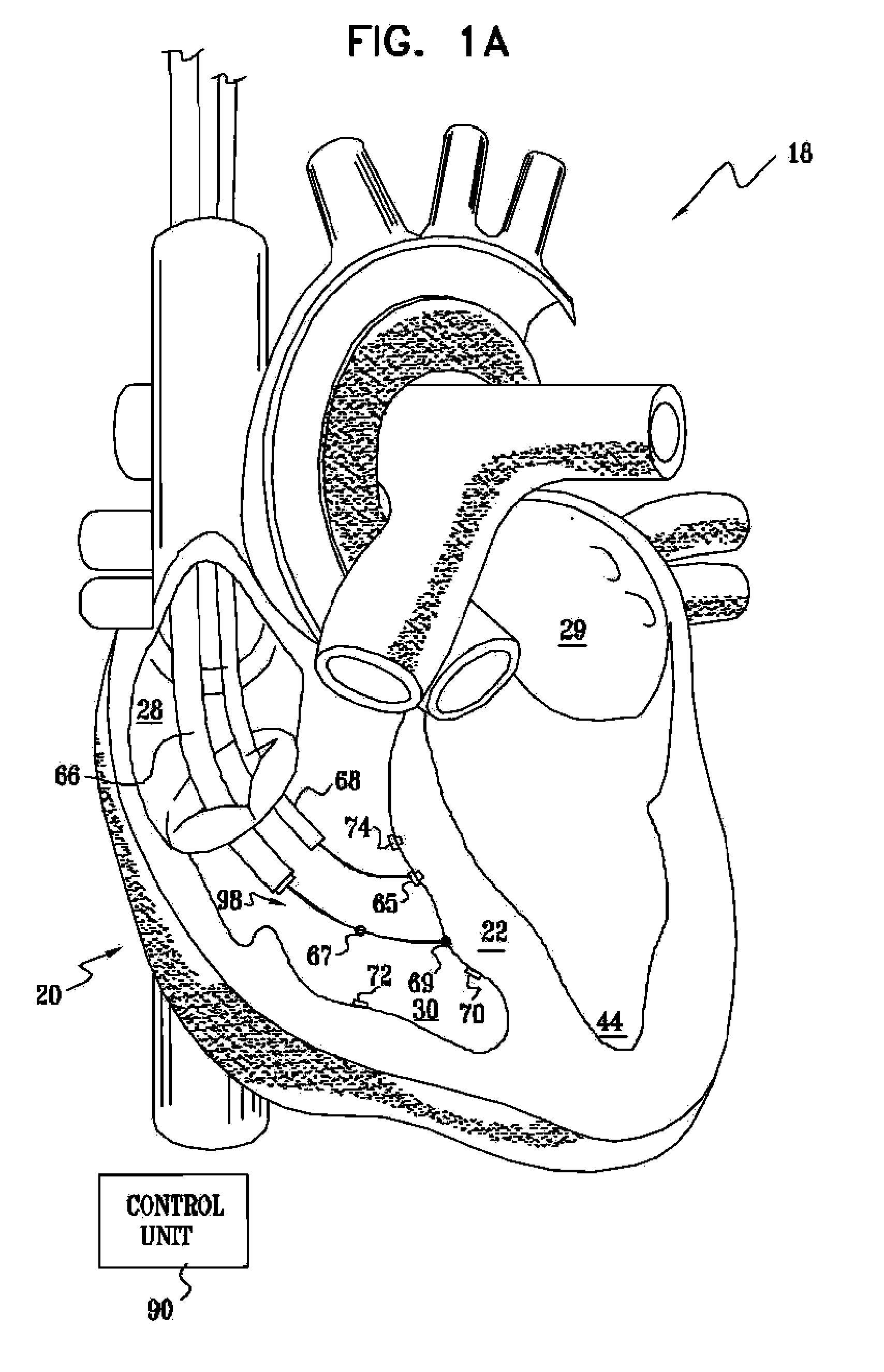
ActiveUS20050267542A1Decreased heart rateEliminate side effectsSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsCardiac arrhythmiaCarotid sinus
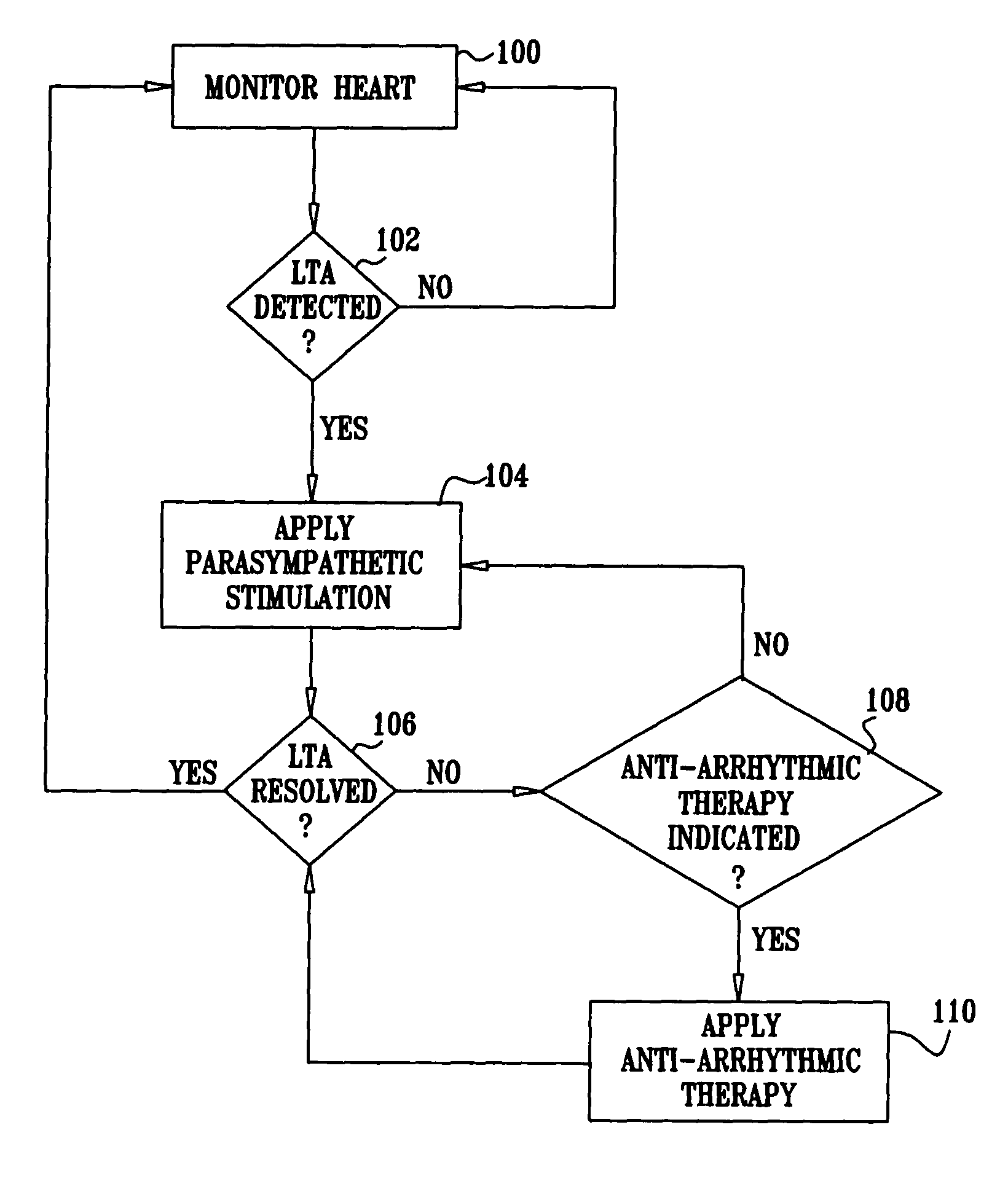
Apparatus is provided including an implantable sensor, adapted to sense an electrical parameter of a heart of a subject, and a first control unit, adapted to apply pulses to the heart responsively to the sensed parameter, the pulses selected from the list consisting of: pacing pulses and anti-arrhythmic energy. The apparatus further includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, and a jugular vein of the subject; and a second control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the site a current that increases parasympathetic tone of the subject and affects a heart rate of the subject. The first and second control units are not under common control. At least one of the control units is adapted to coordinate an aspect of its operation with an aspect of operation of the other control unit. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
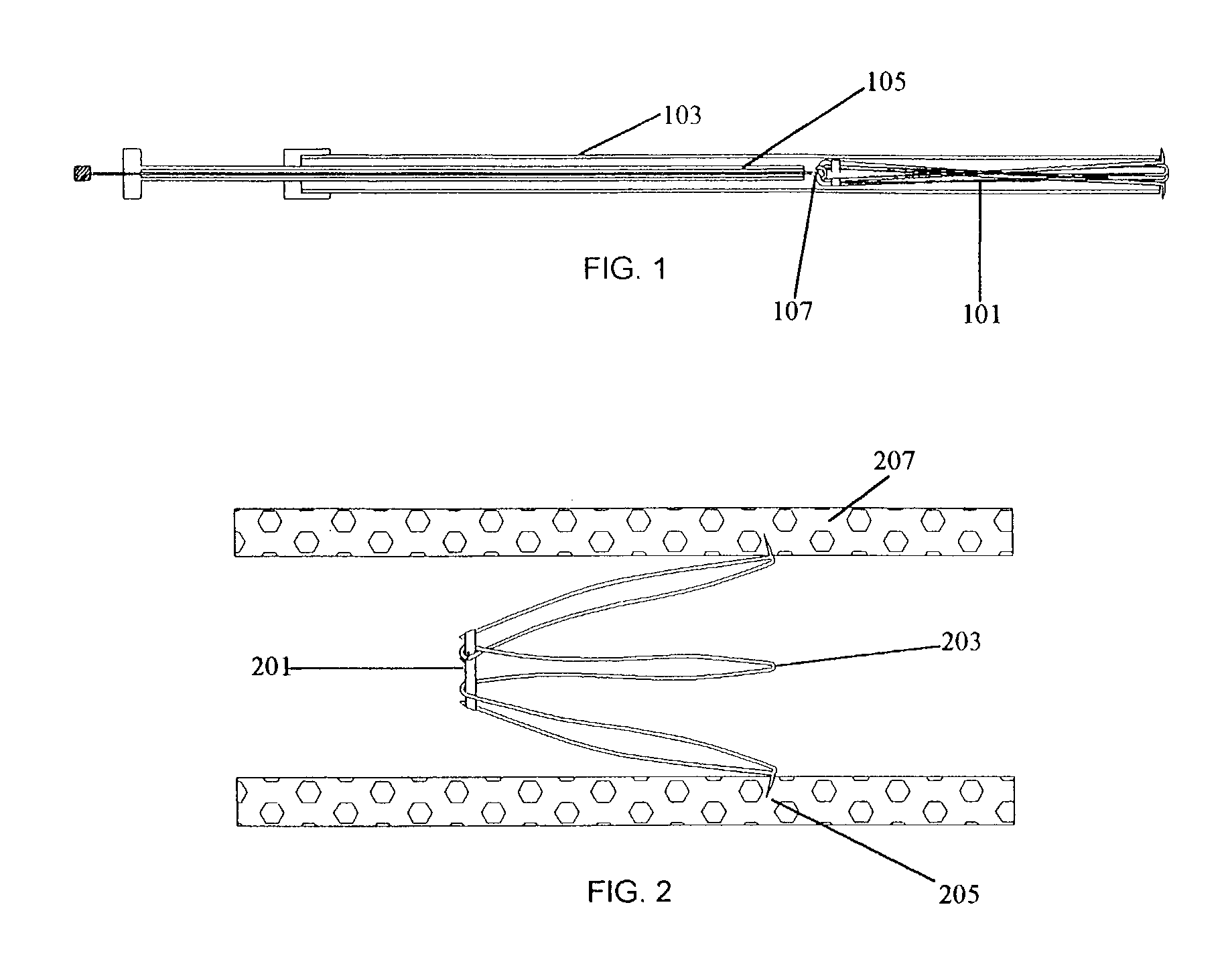
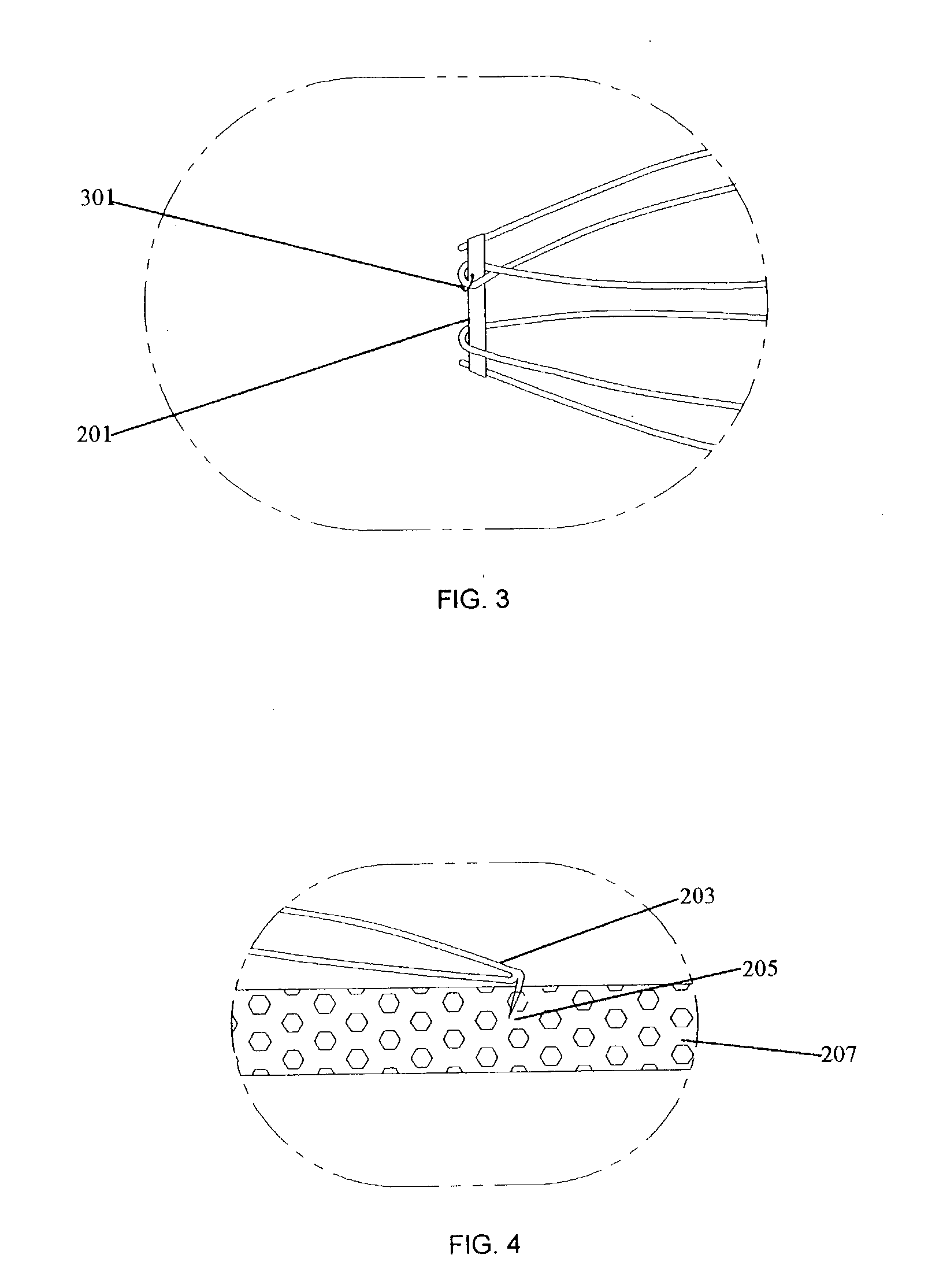
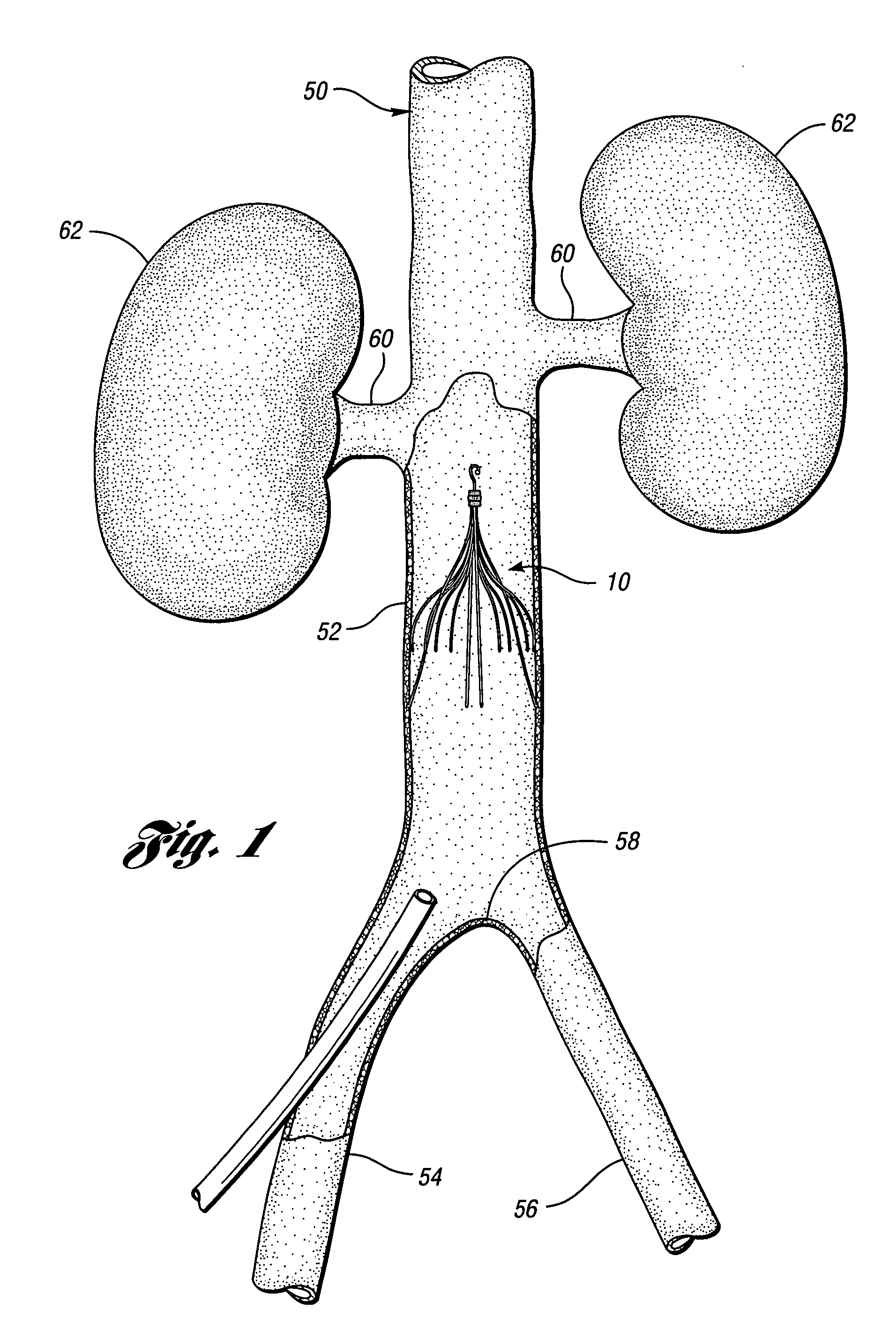
Convertible blood clot filter
A vena cava blood clot filter is described that is attached to the walls of the vena cava by barbed anchors. In its filtering state, the filter is cone shaped which causes the blood to be filtered. The cone shape is formed by an appropriate restraining mechanism. When it is desired to stop filtering, the restraining mechanism is released and the filter takes a cylindrical shape. The cylindrical shaped filter will then line the vena cava wall and cease filtration of the blood.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Systems and methods for performing bi-lateral interventions or diagnosis in branched body lumens
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Method and apparatus for selective material delivery via an intra-renal catheter
Two renal delivery members have two distal ports that are adapted to be positioned within two renal arteries via their corresponding renal ostia at unique locations along an abdominal aortic wall. A proximal coupler assembly is outside the body and is coupled to deliver material to the two distal ports for bi-lateral renal therapy. One or both of the delivery members may be self-cannulating into the corresponding renal ostium, or may be controllably steered into the respective ostium. Non-occlusive anchors may be coupled with one or both of the delivery members at anchoring positions in the renal artery or abdominal aorta to secure the renal delivery member within the renal artery. Renal-active fluid agents are coupled to the bi-lateral delivery system. Another renal therapy system cannulates a renal vein from the vena cava and controls a retrograde delivery of agents to the respective kidney.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Parasympathetic pacing therapy during and following a medical procedure, clinical trauma or pathology
ActiveUS20060206155A1Increase parasympathetic toneReduced responseSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsParasympathetic ganglionPathology diagnosis
A treatment method is provided, including identifying a subject as one who is selected to undergo an interventional medical procedure, and, in response to the identifying, reducing a likelihood of a potential adverse effect of the procedure by applying an electrical current to a parasympathetic site of the subject selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a jugular vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, a parasympathetic ganglion of the subject, and a parasympathetic nerve of the subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
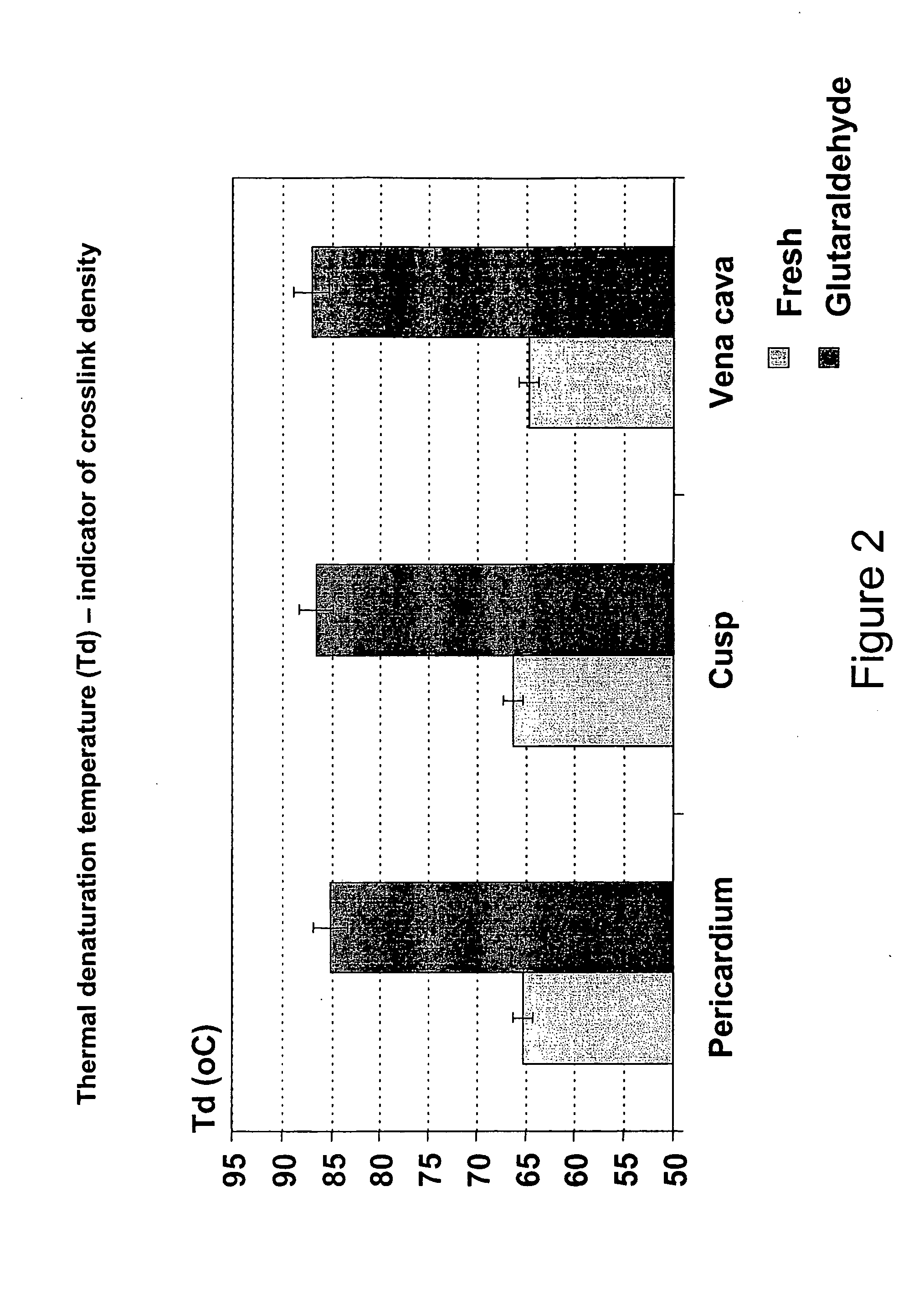
Tissue material and process for bioprosthesis
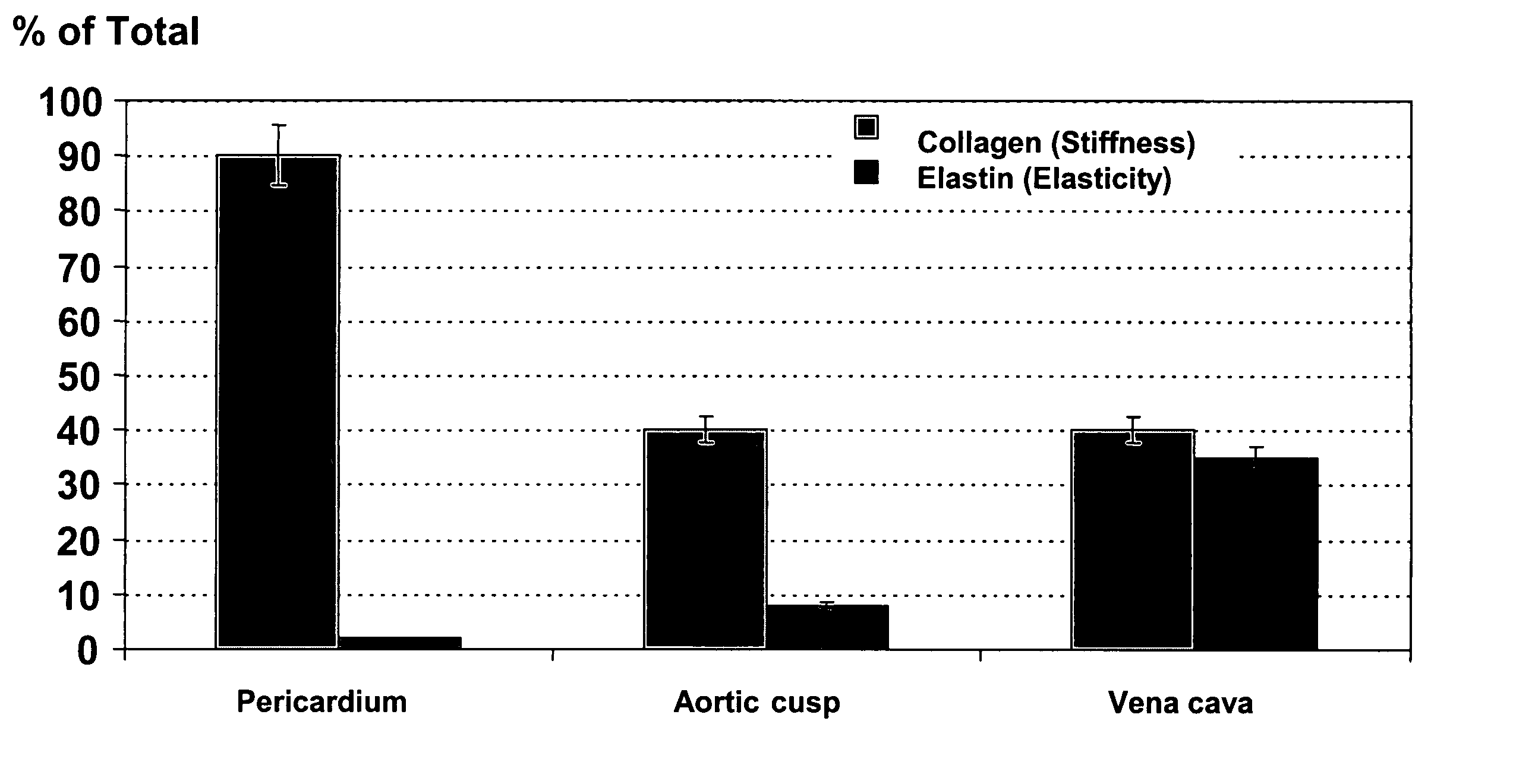
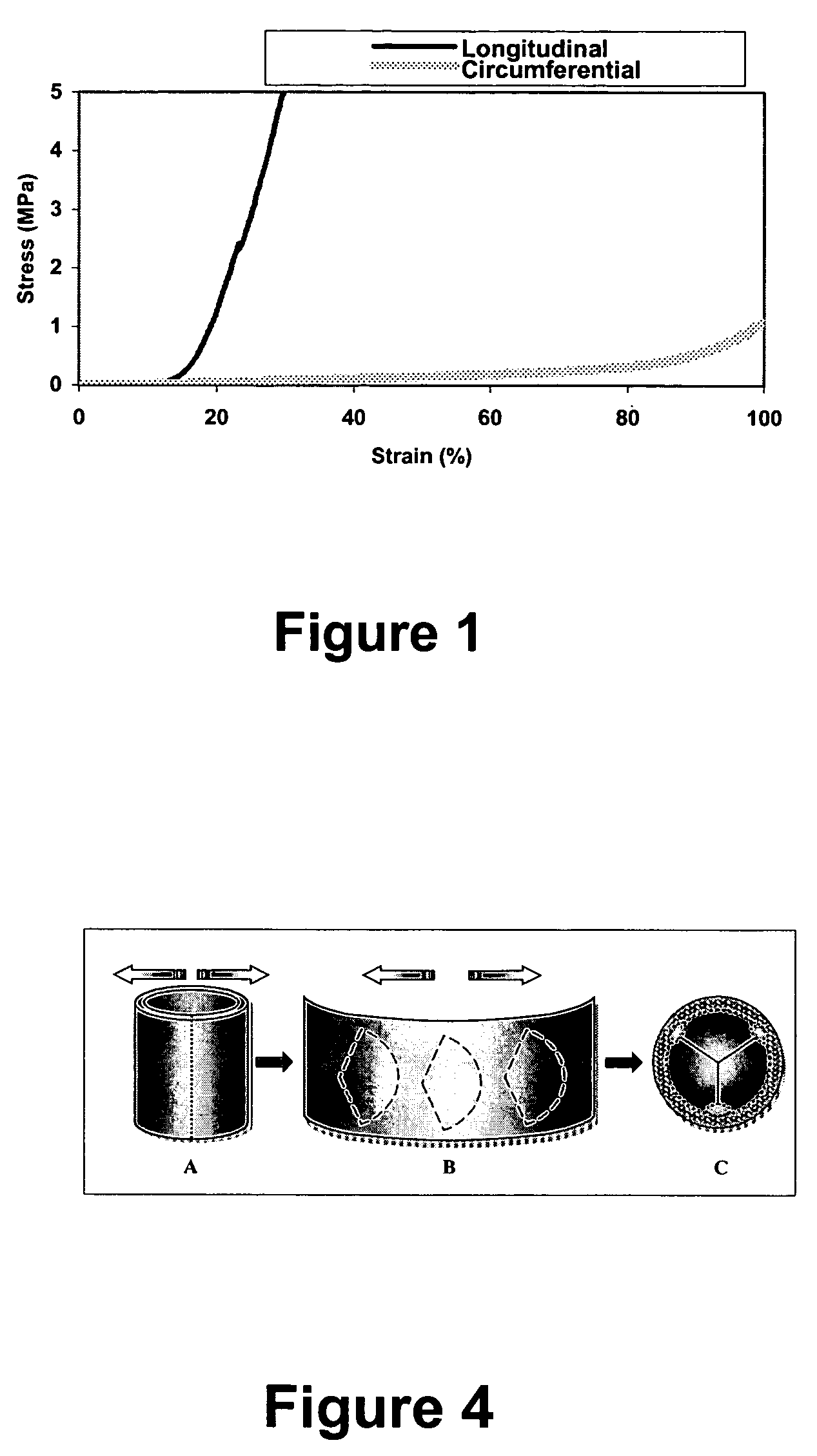
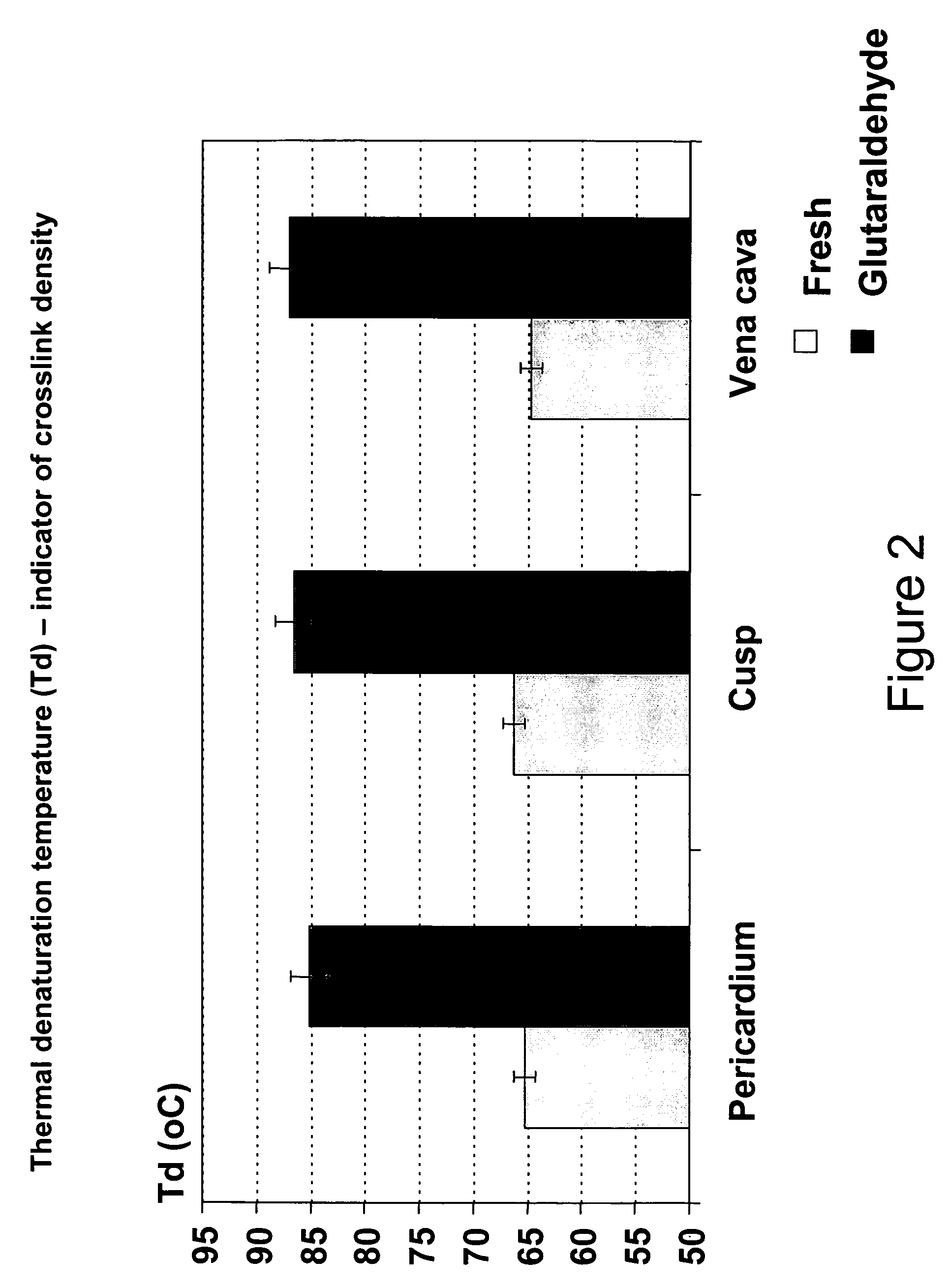
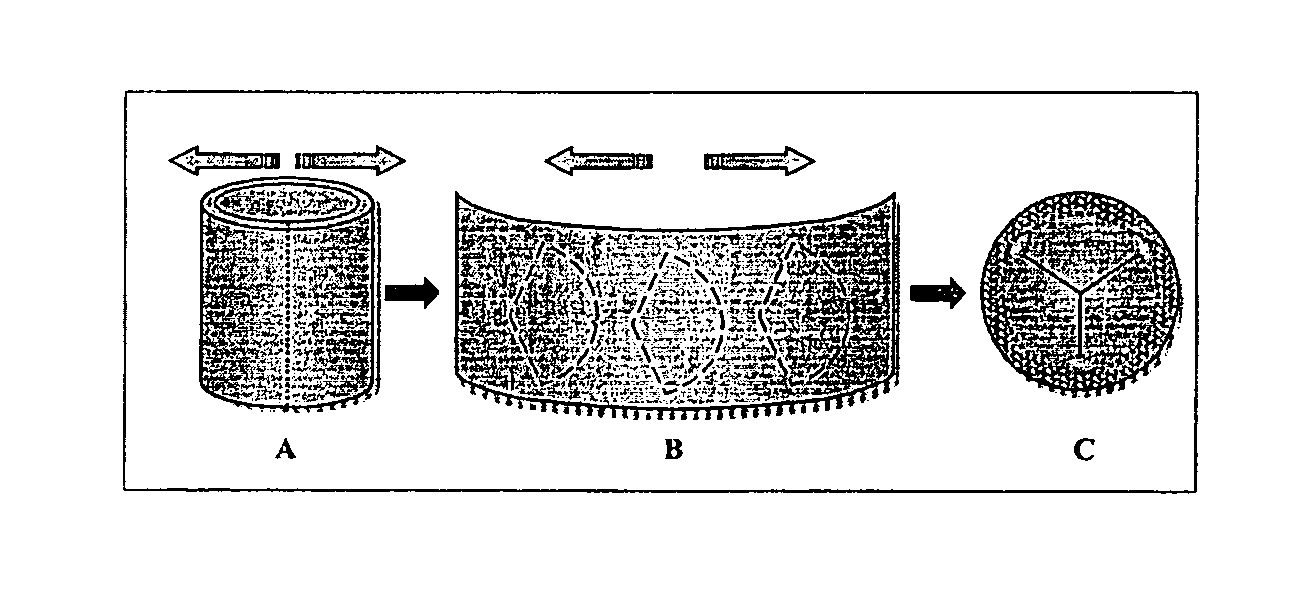
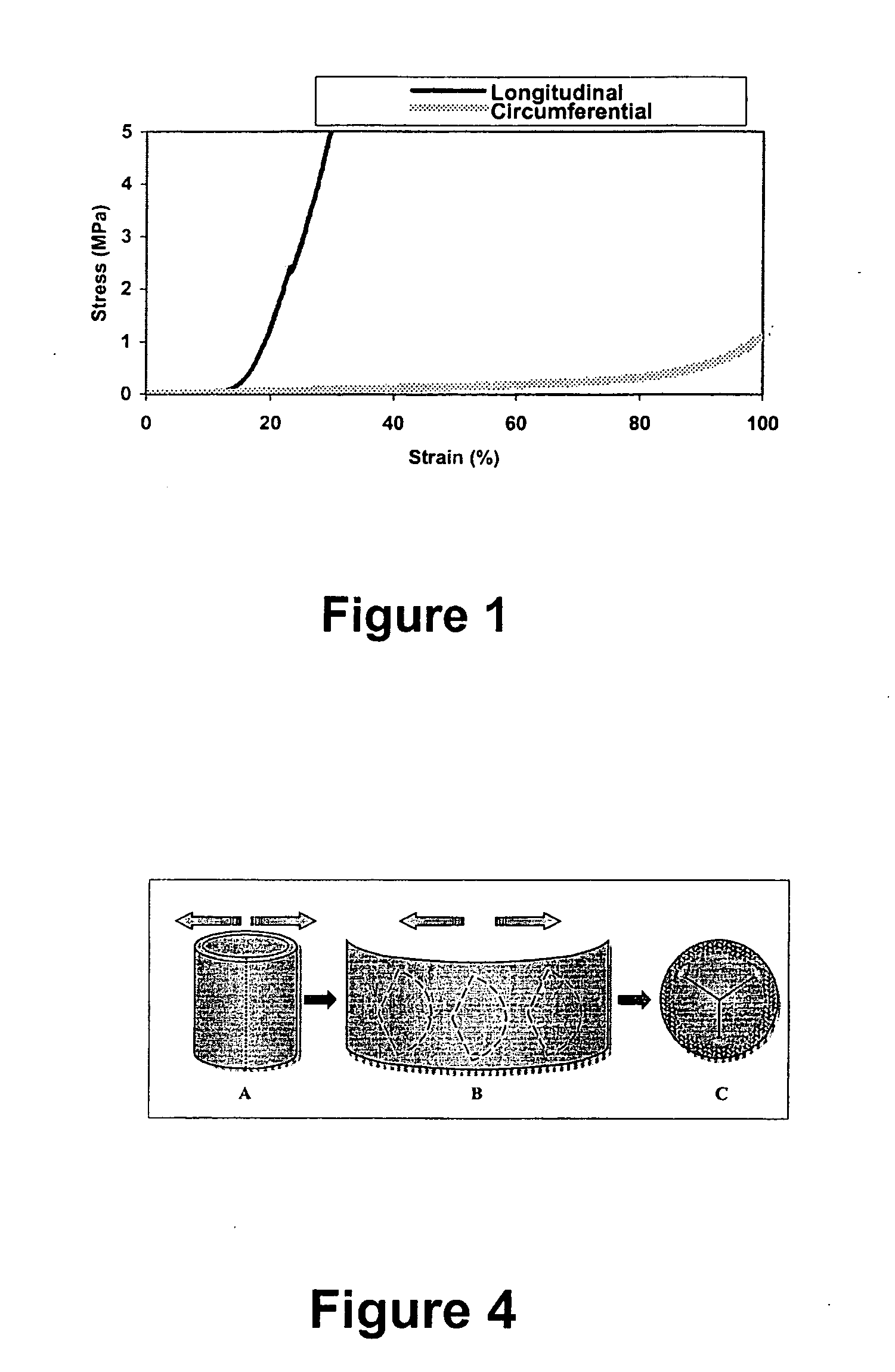
A biomaterial useful for bioprostheses such as bioprosthetic heart valves is provided in which the fixed tissue has improved elastic properties. The high elastin-containing biomaterial is further characterized by having anisotropic properties wherein the biological material has a greater stiffness in one direction and a greater elasticity in a cross direction. For instance, the biological material has an elastin content of about 30% by weight. In one embodiment, the biological material is vena cava tissue.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
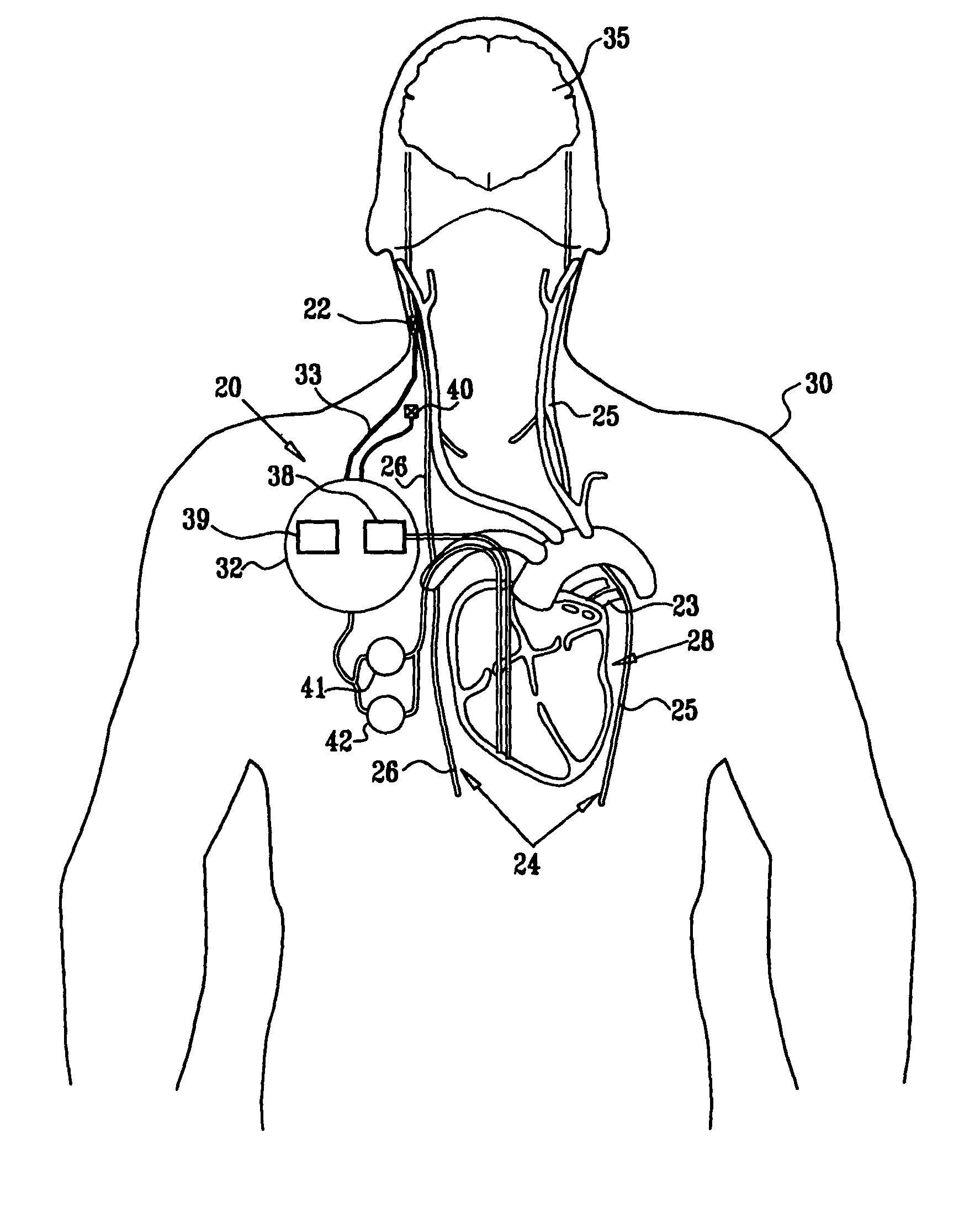
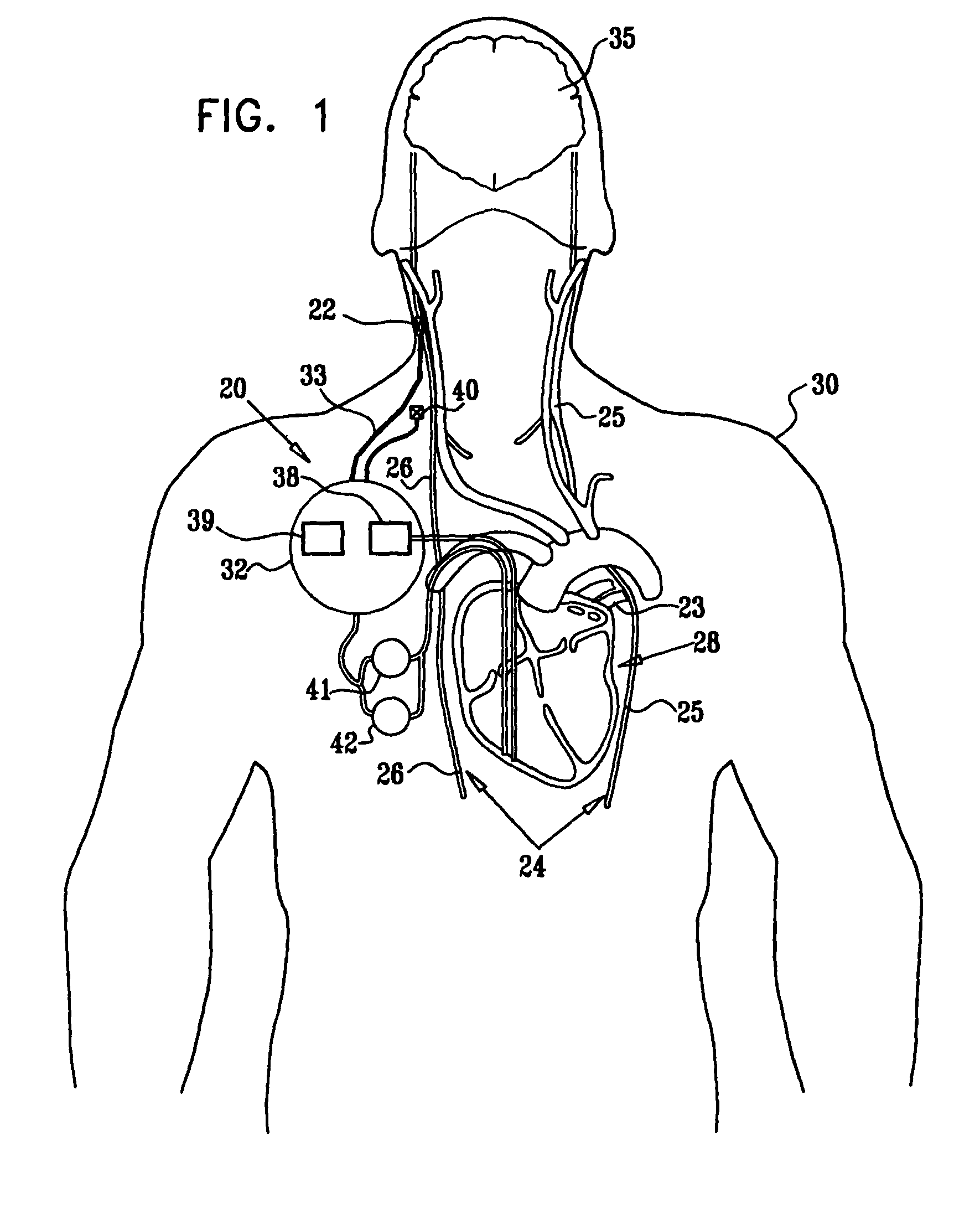
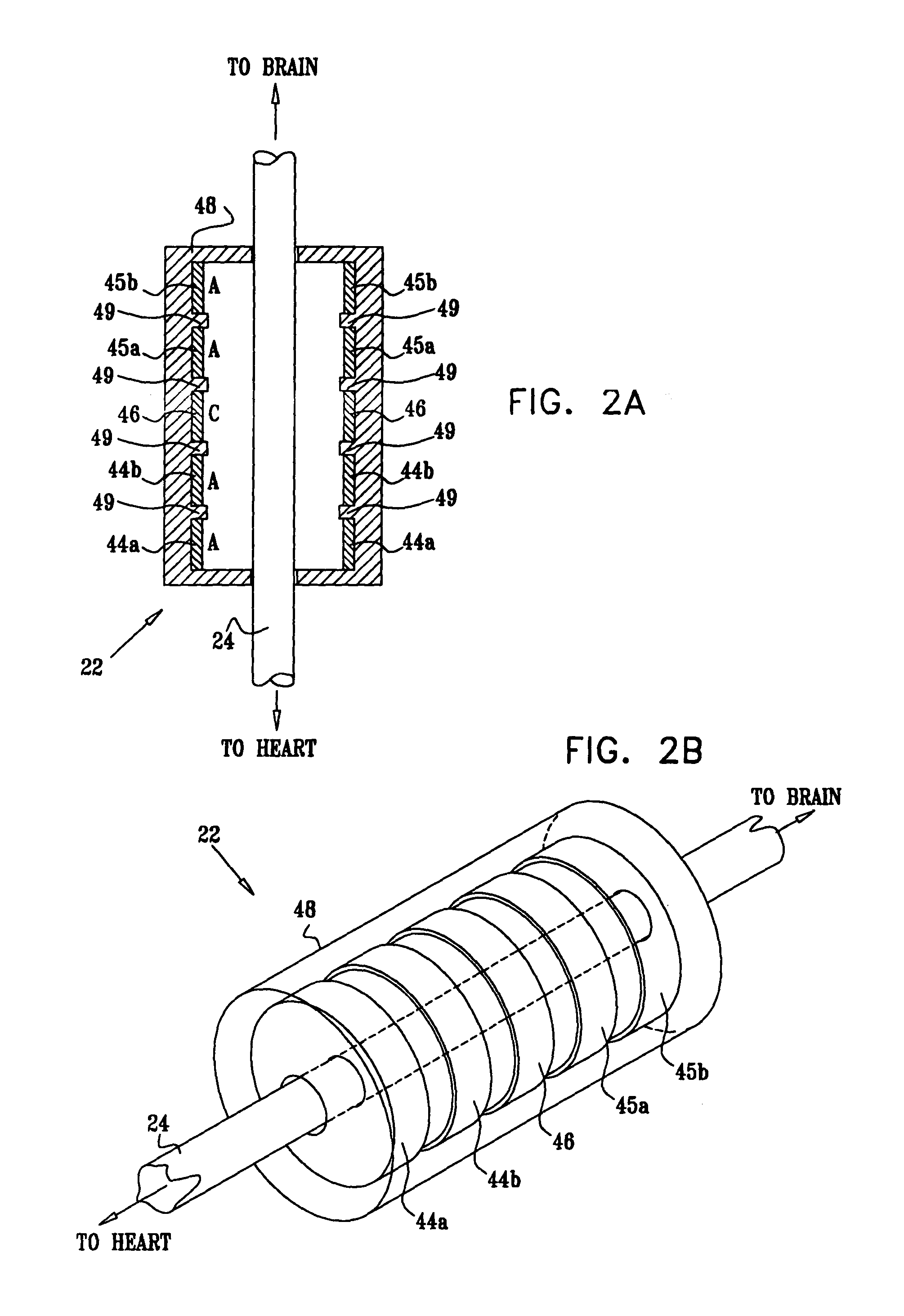
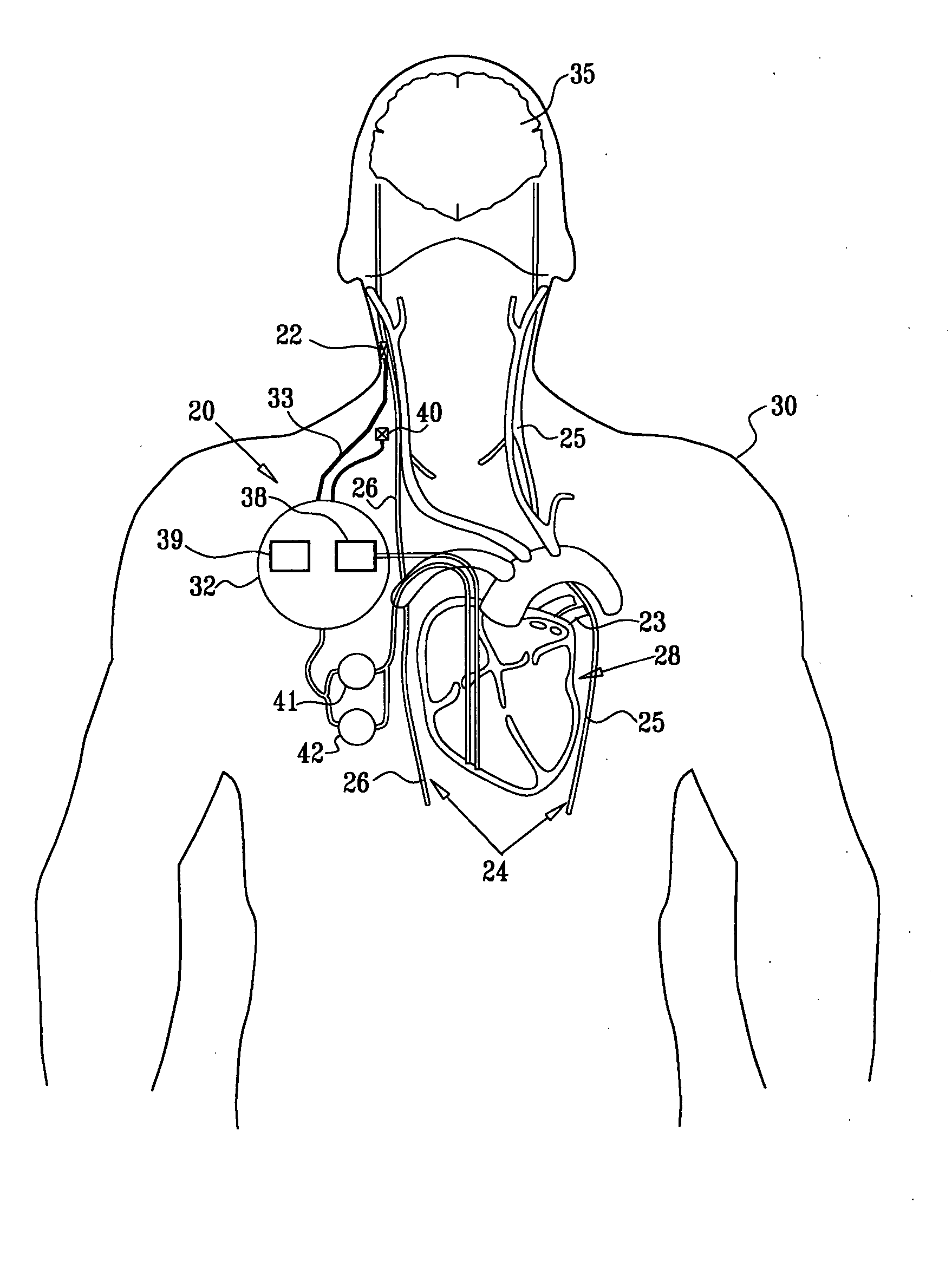
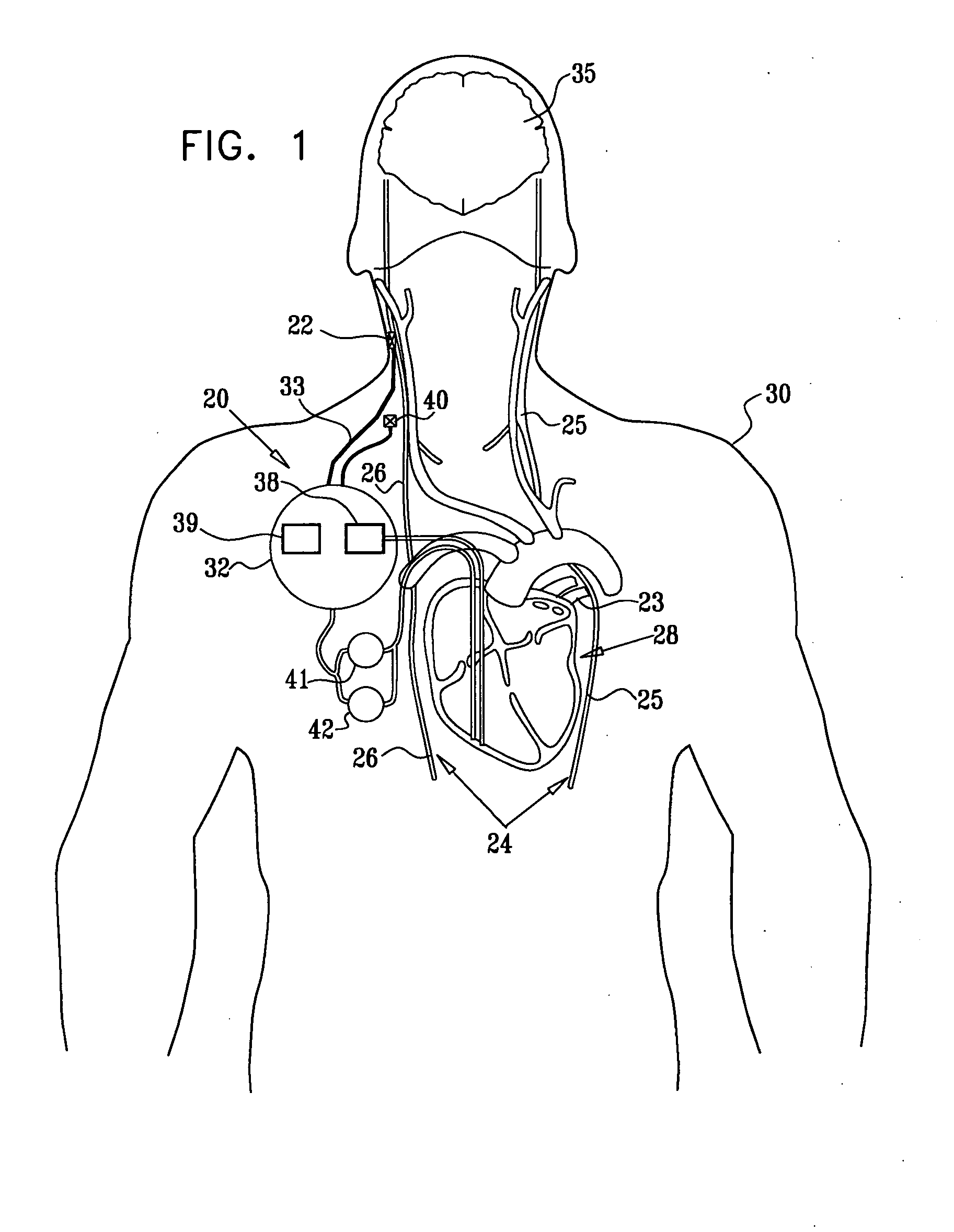
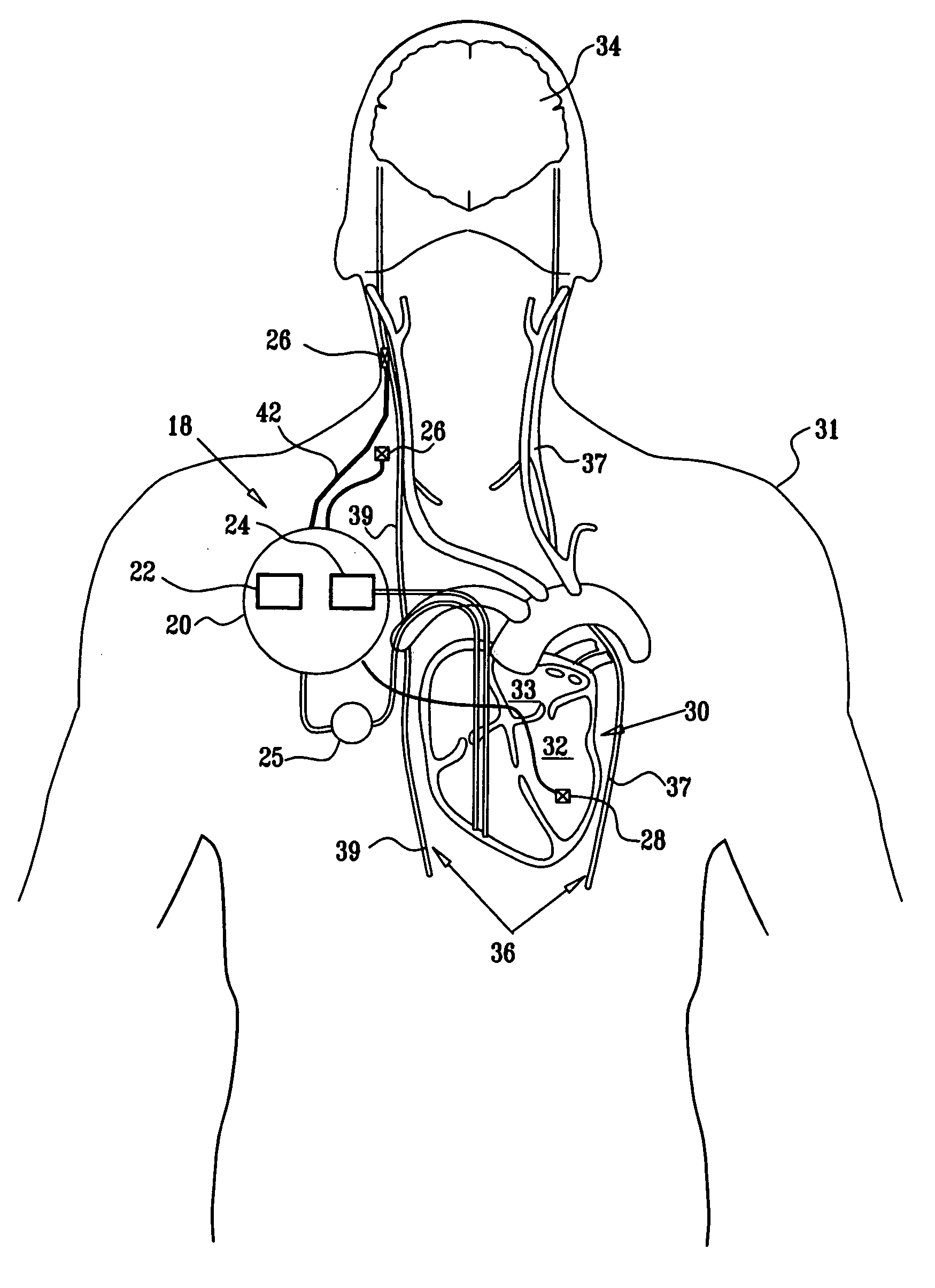
Endovascular lead for chronic nerve stimulation
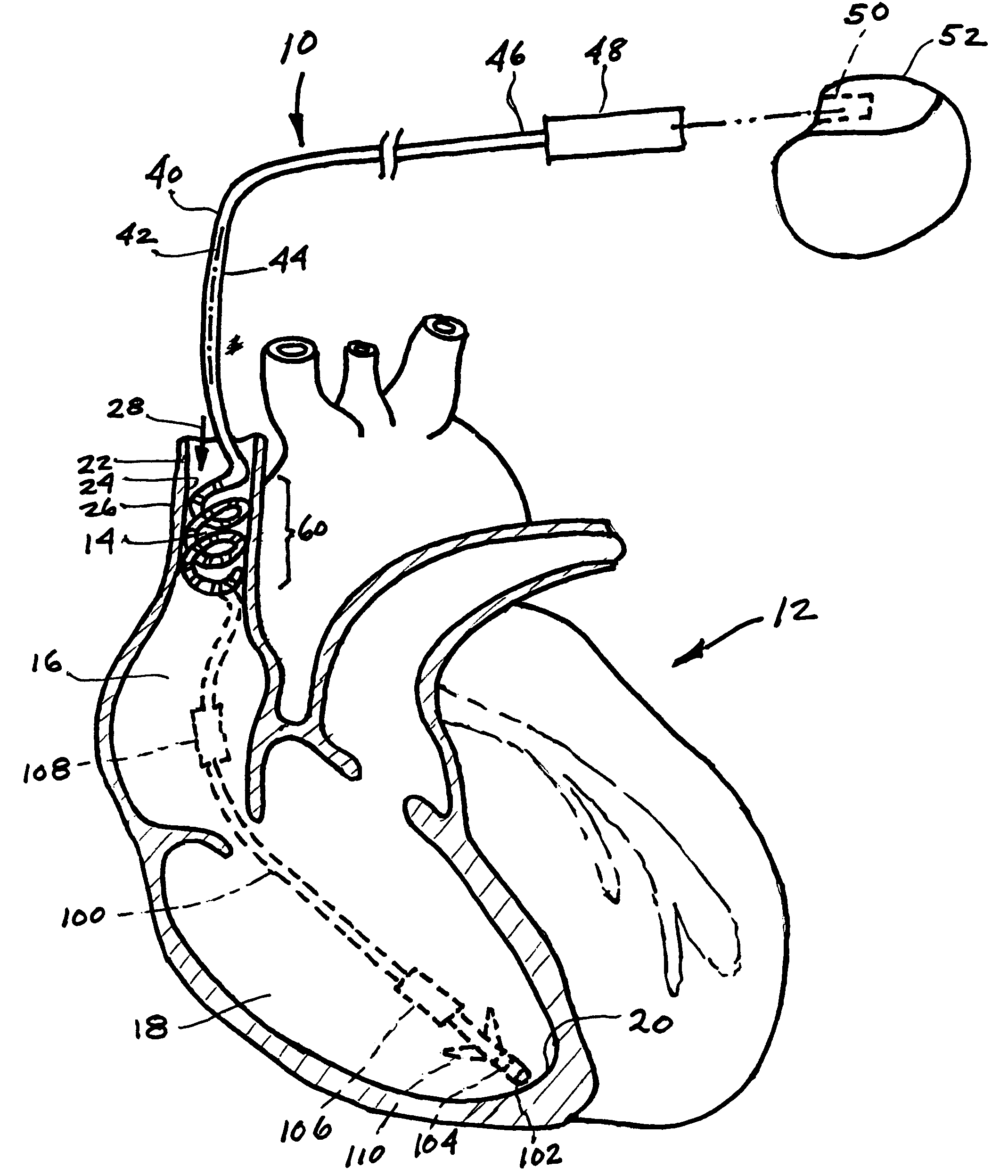
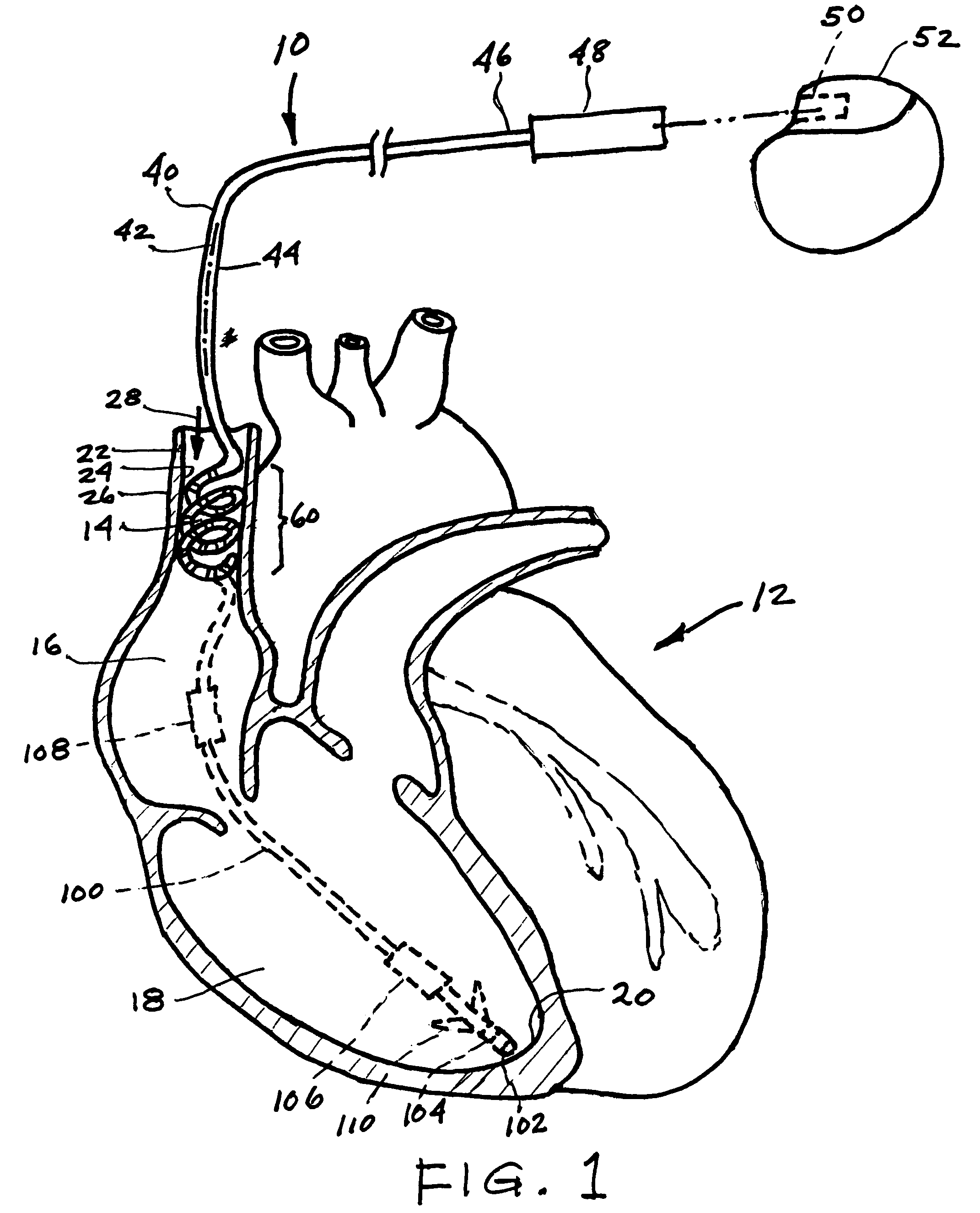
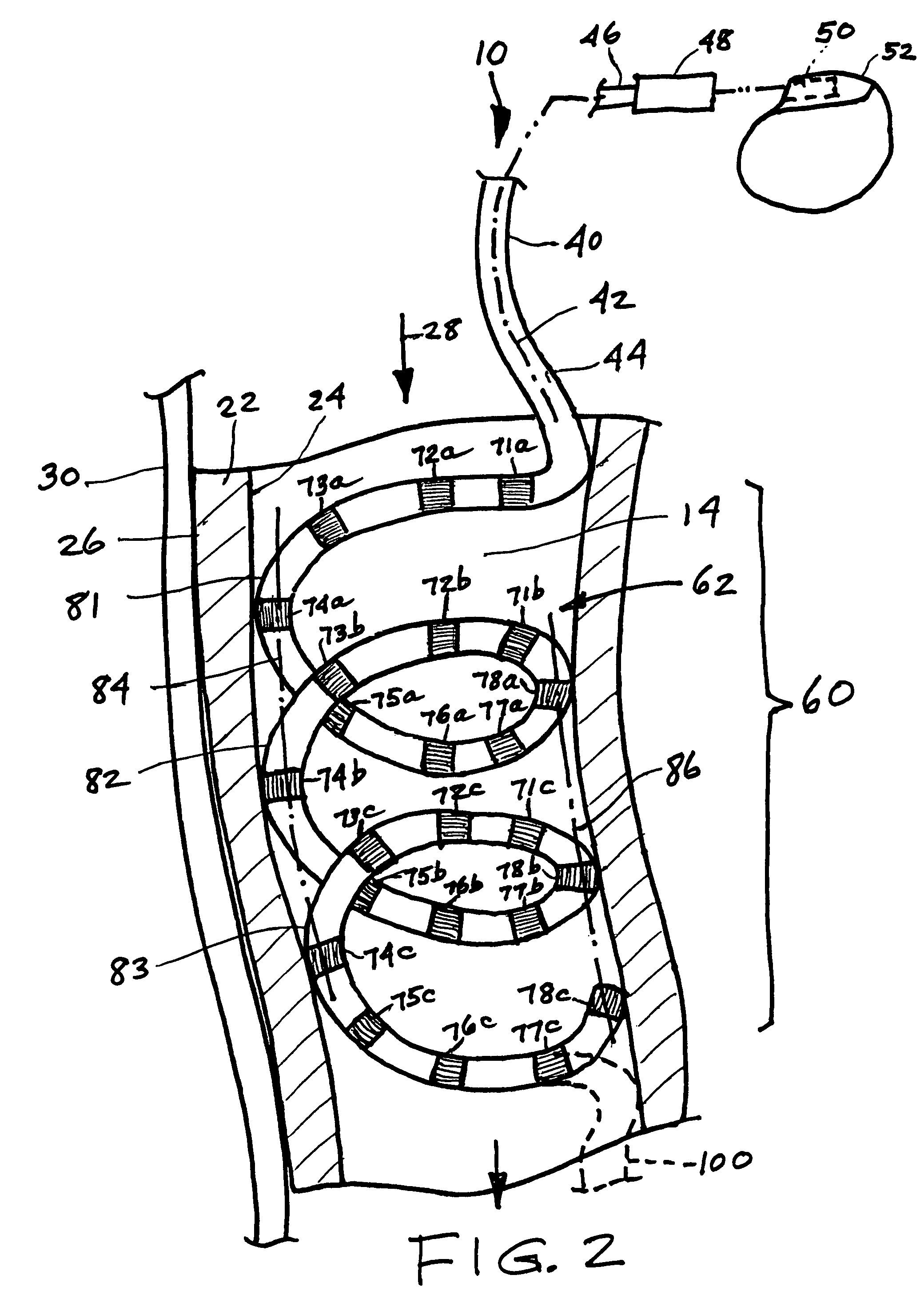
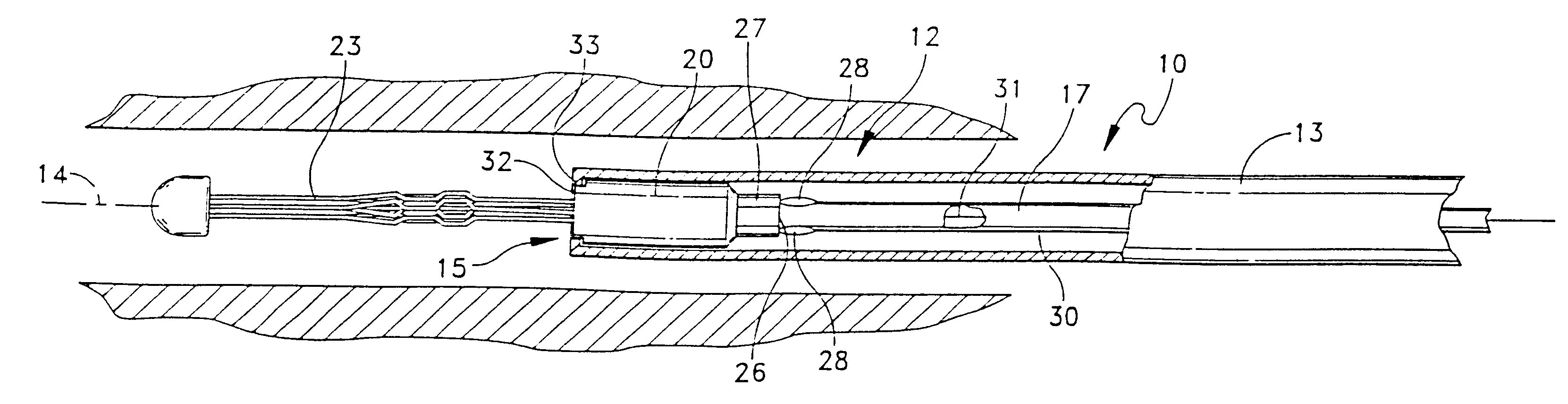
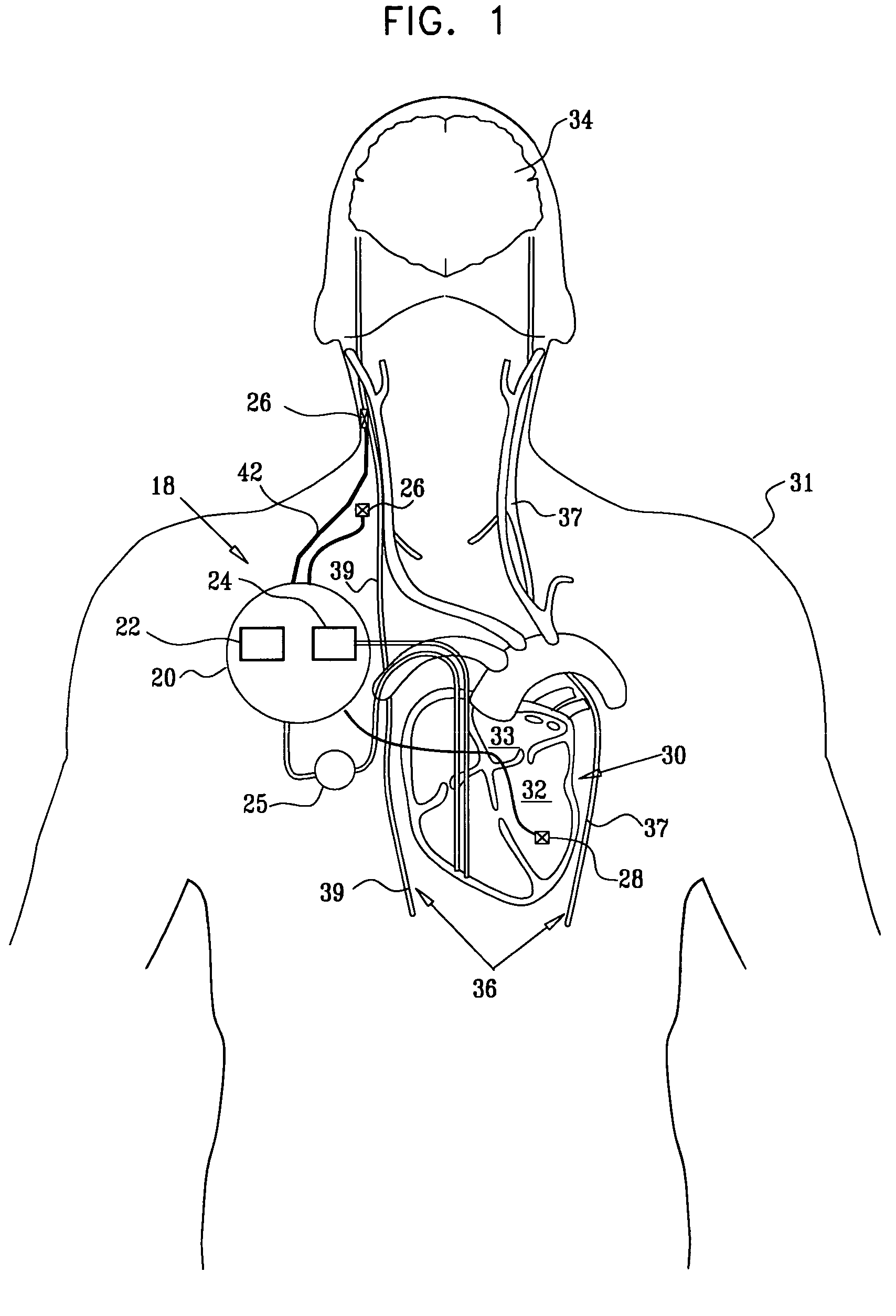
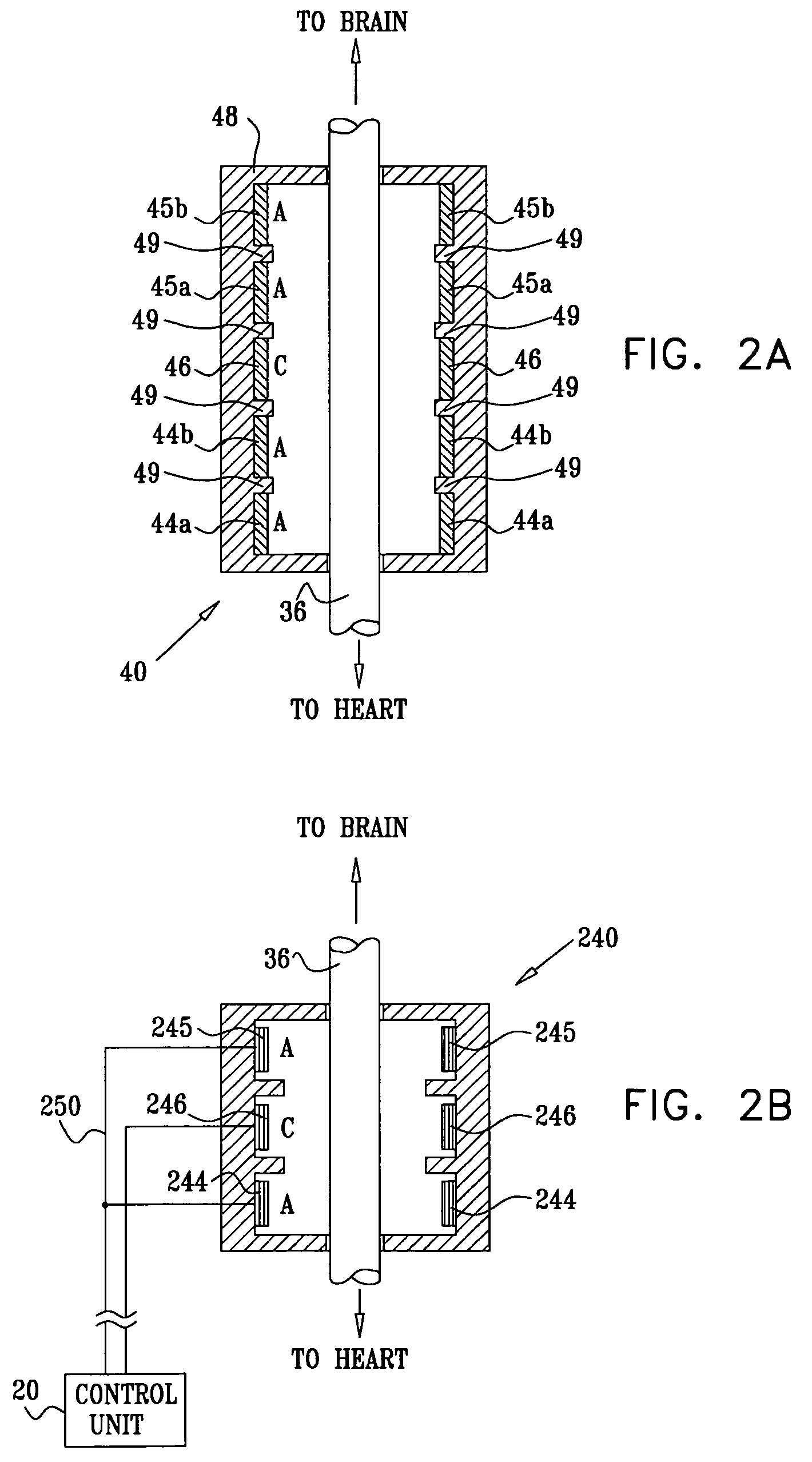
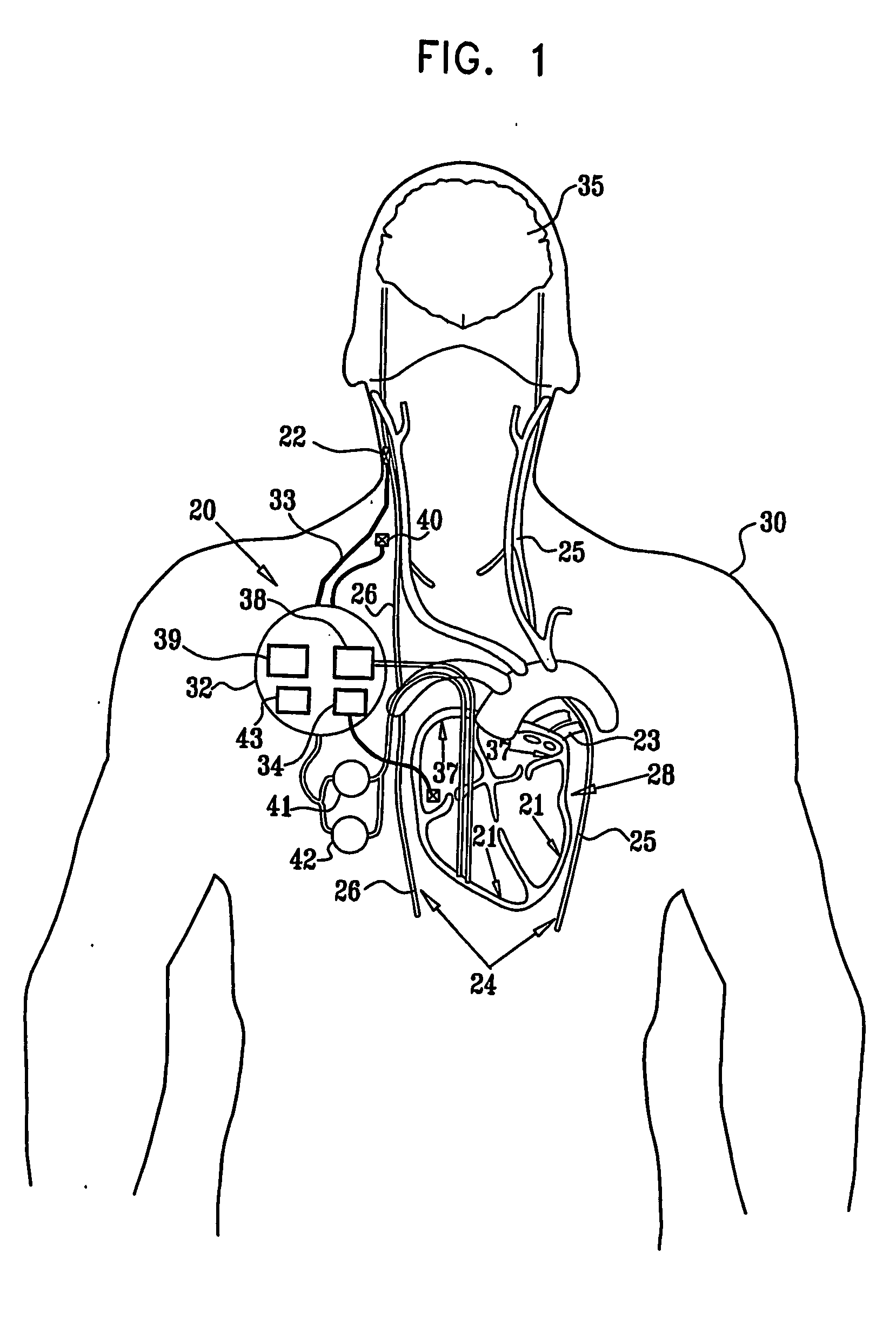
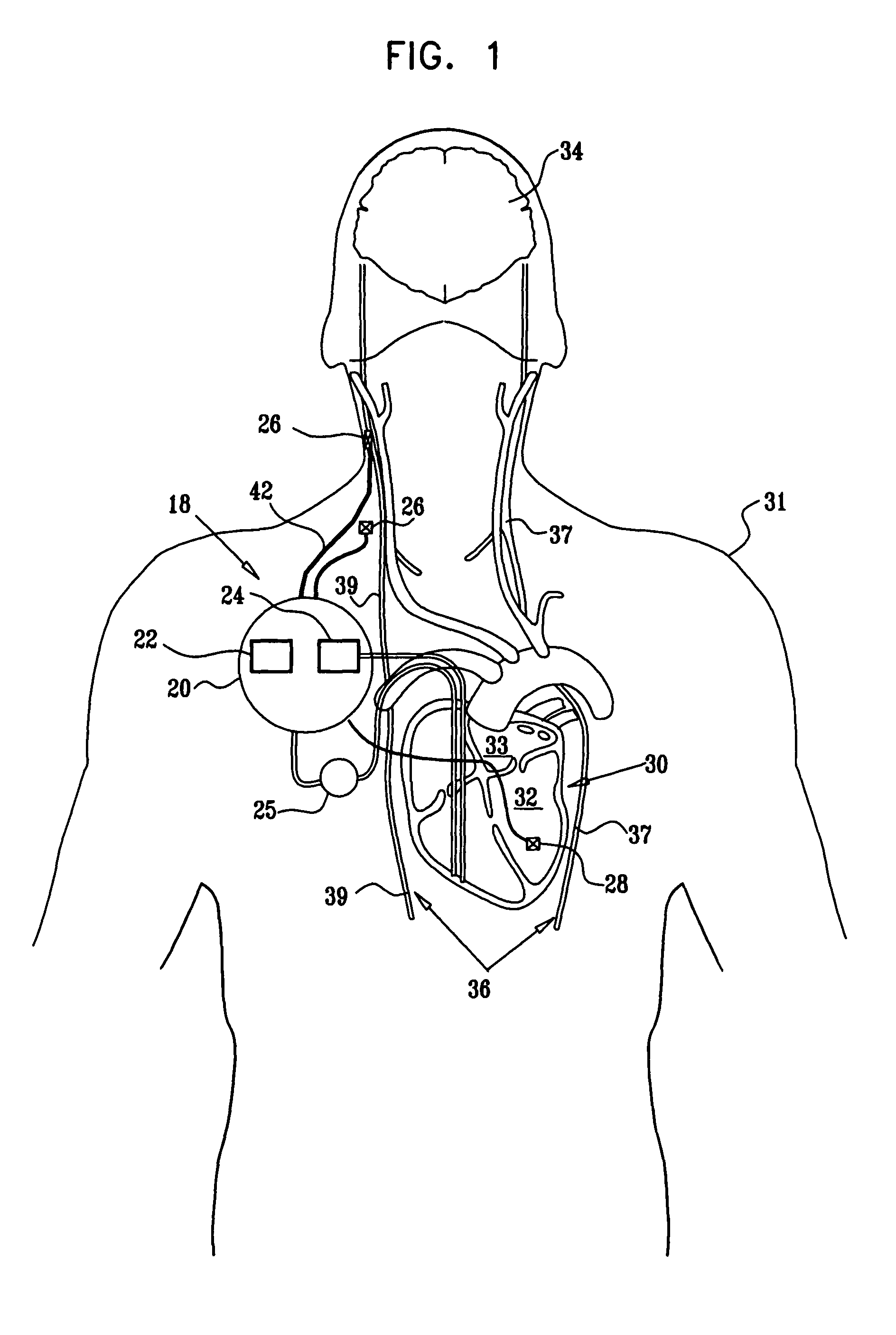
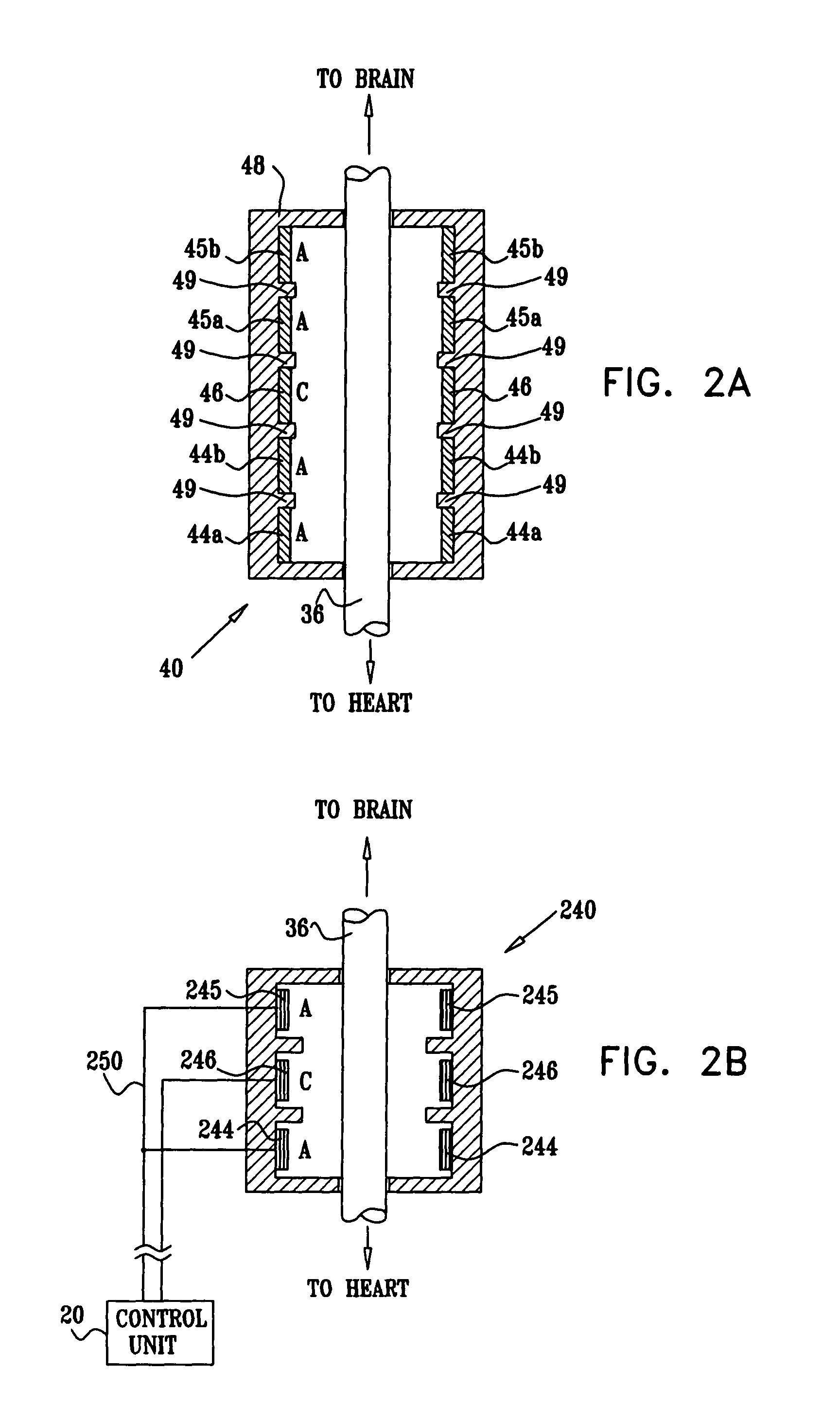
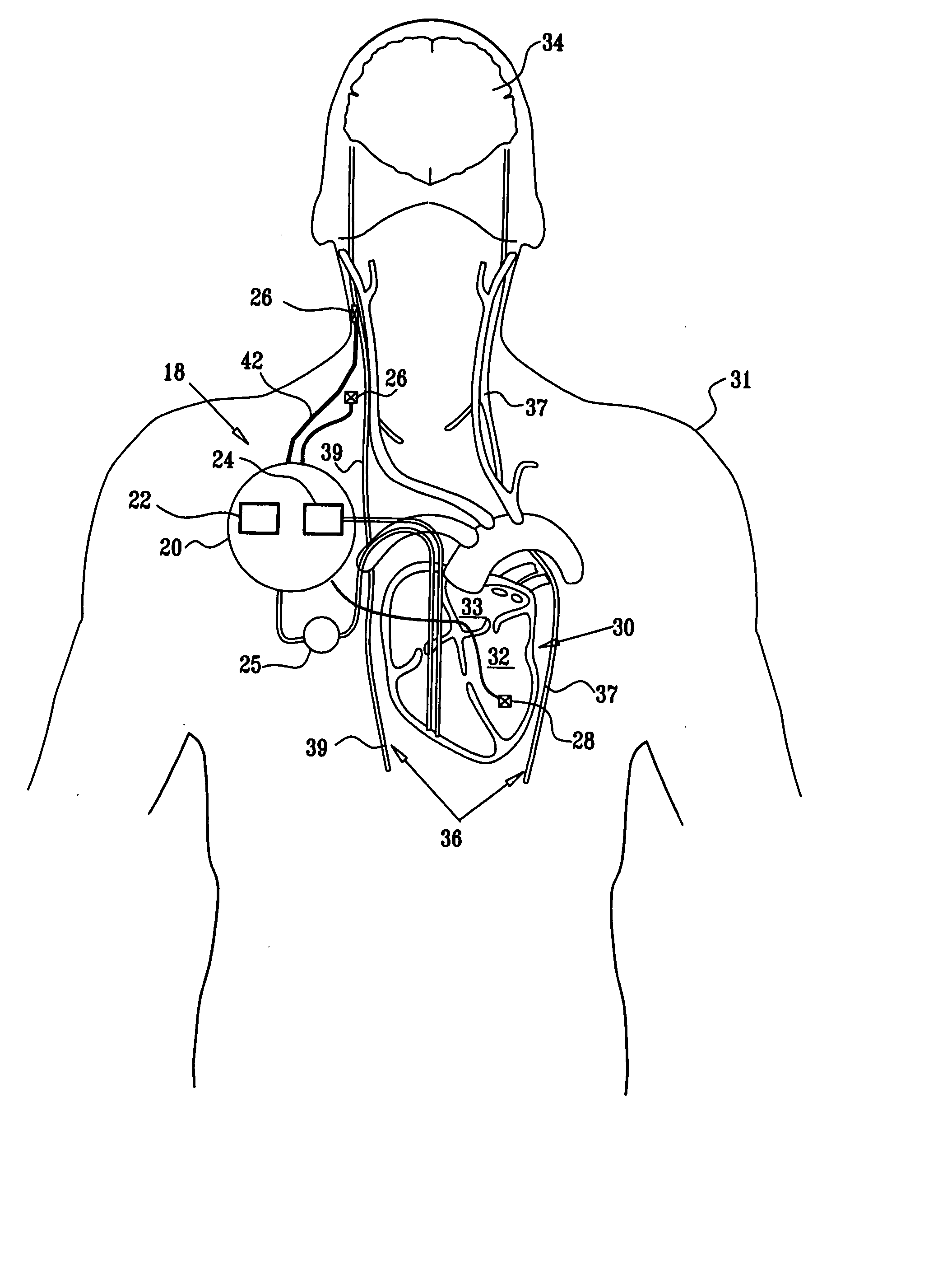
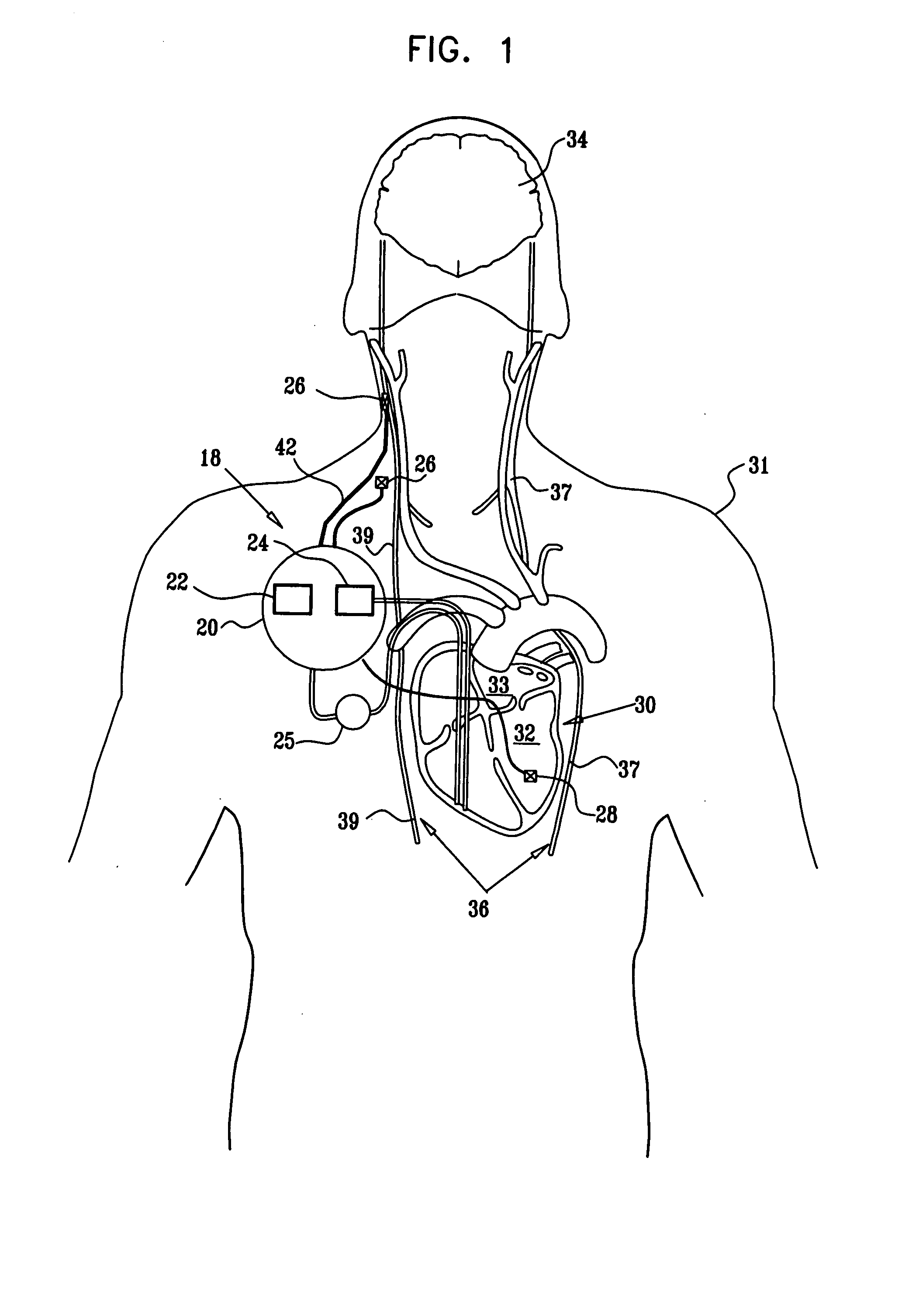
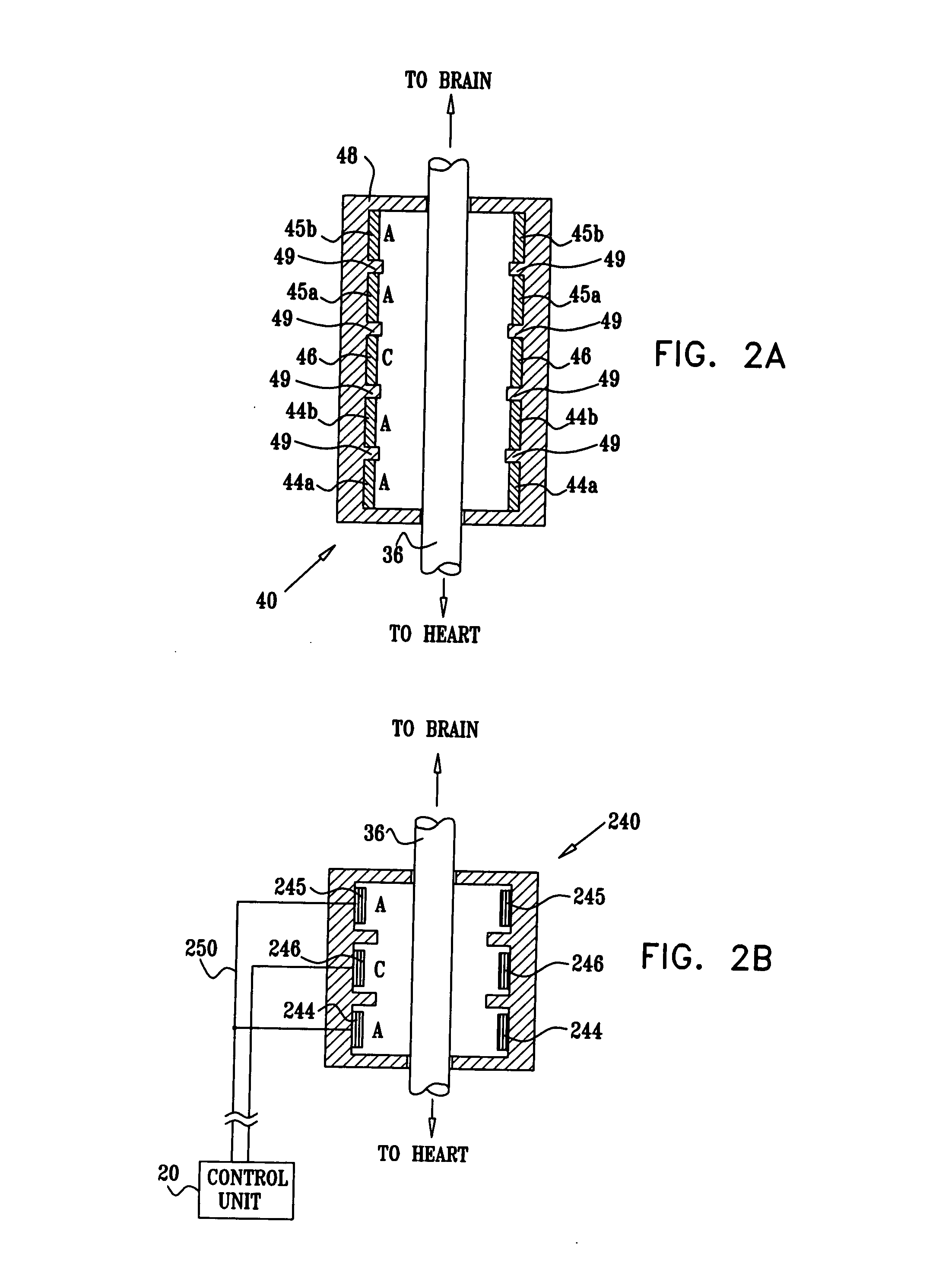
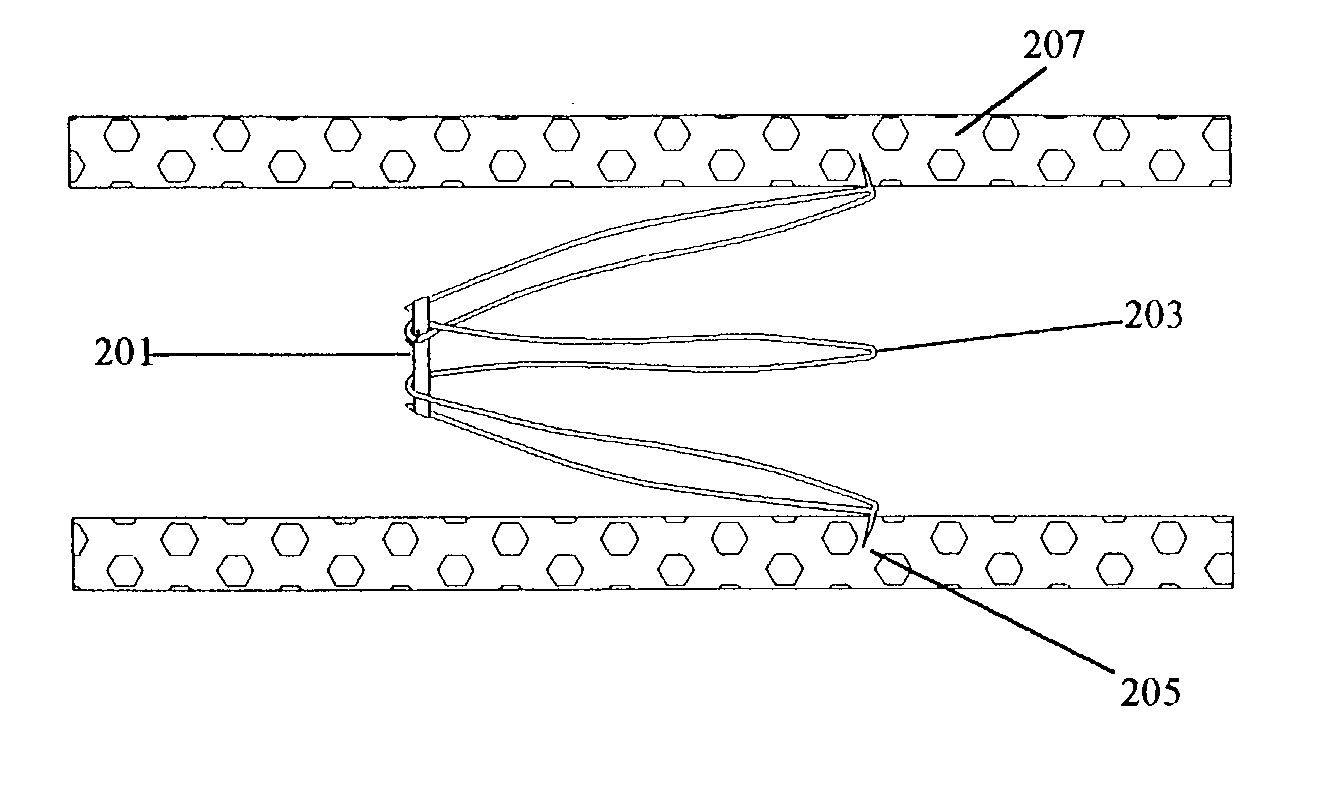
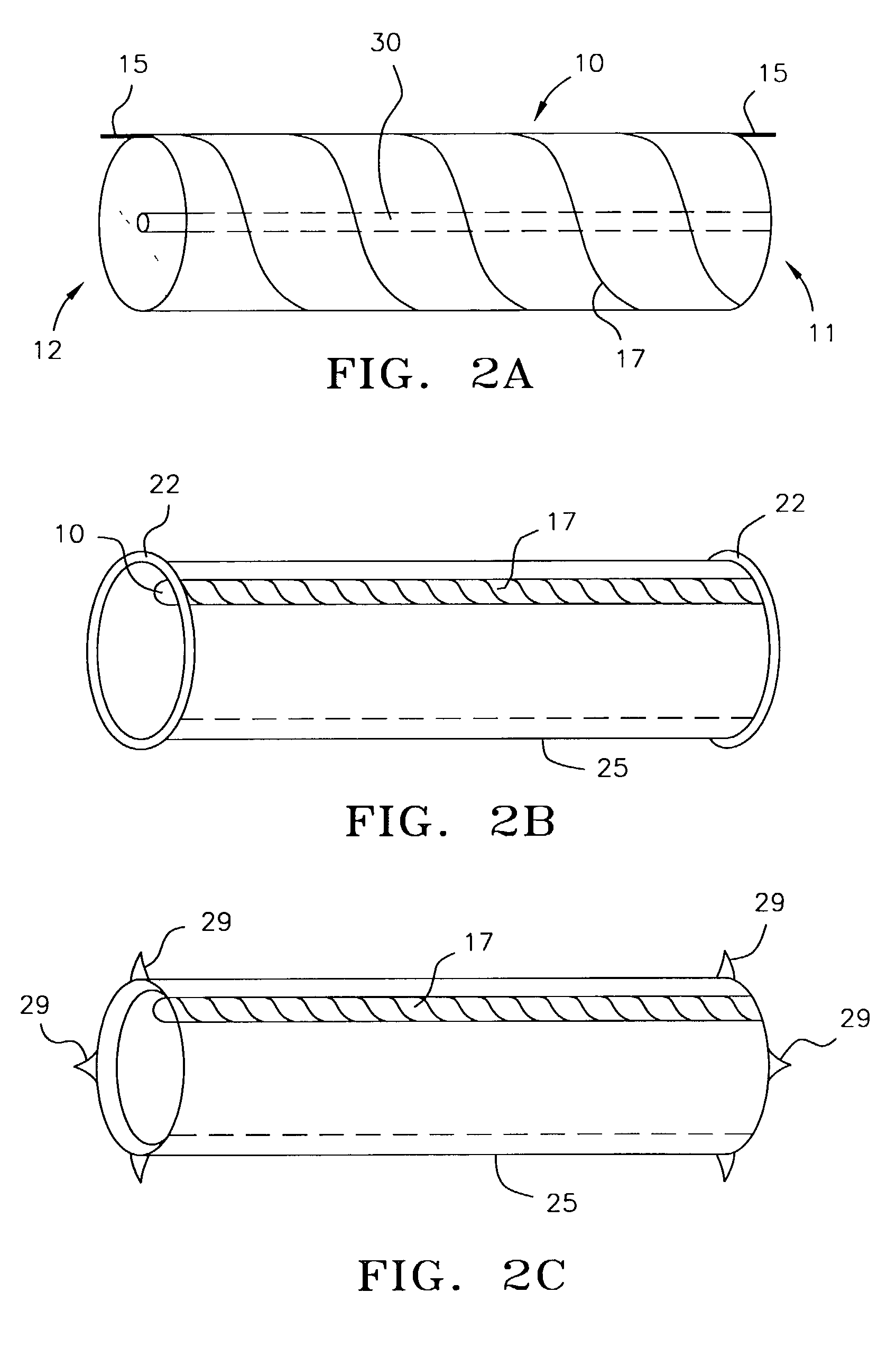
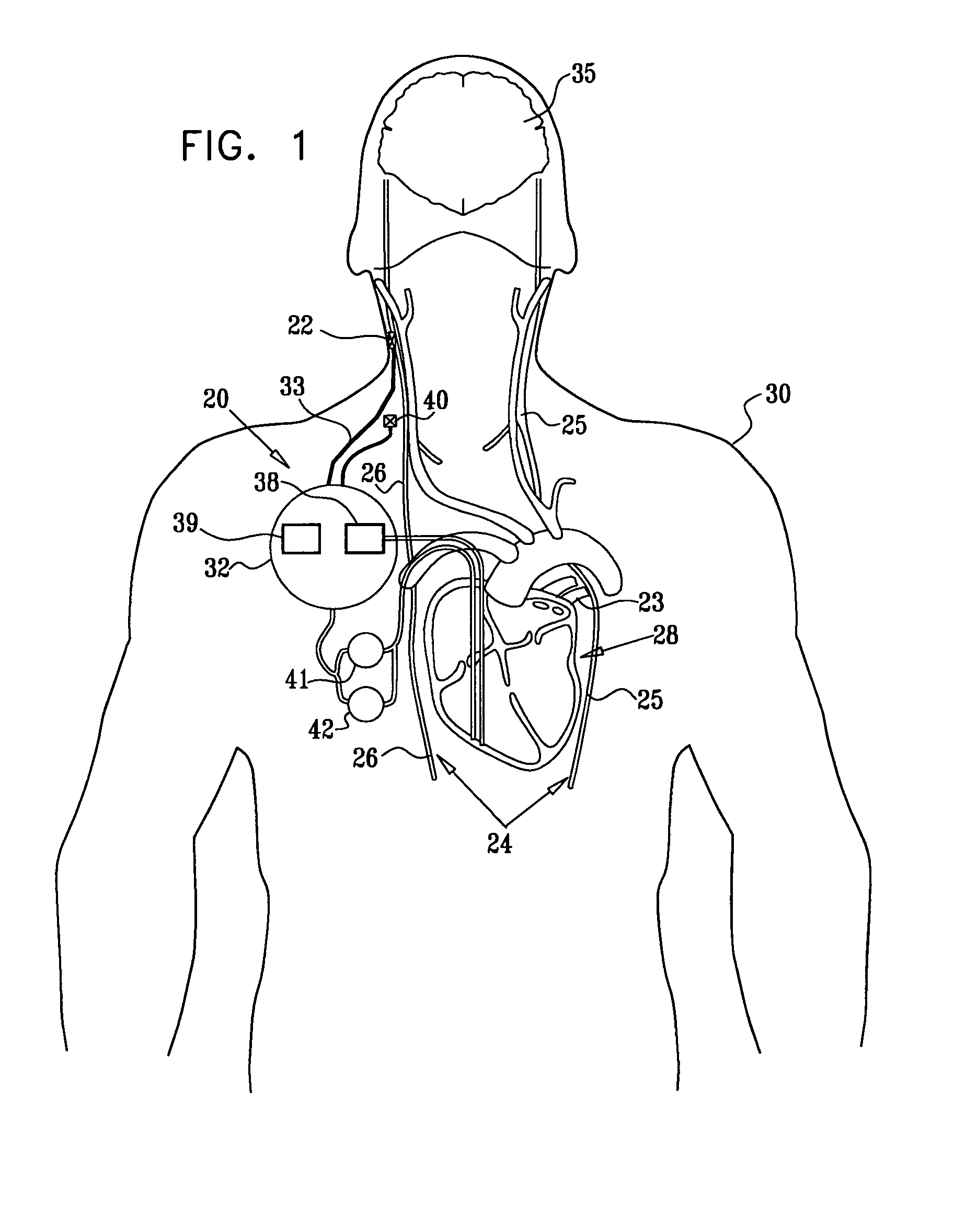
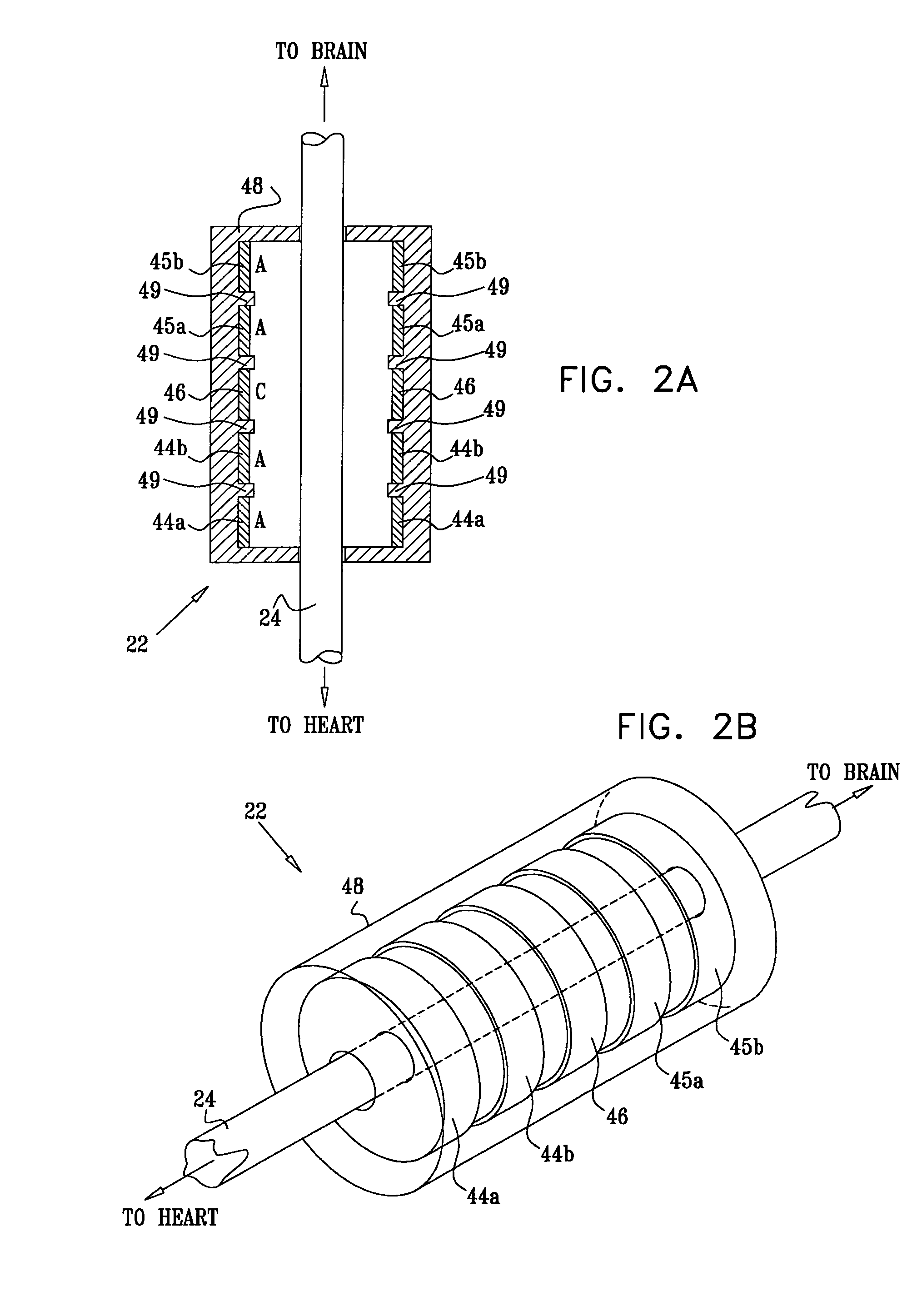
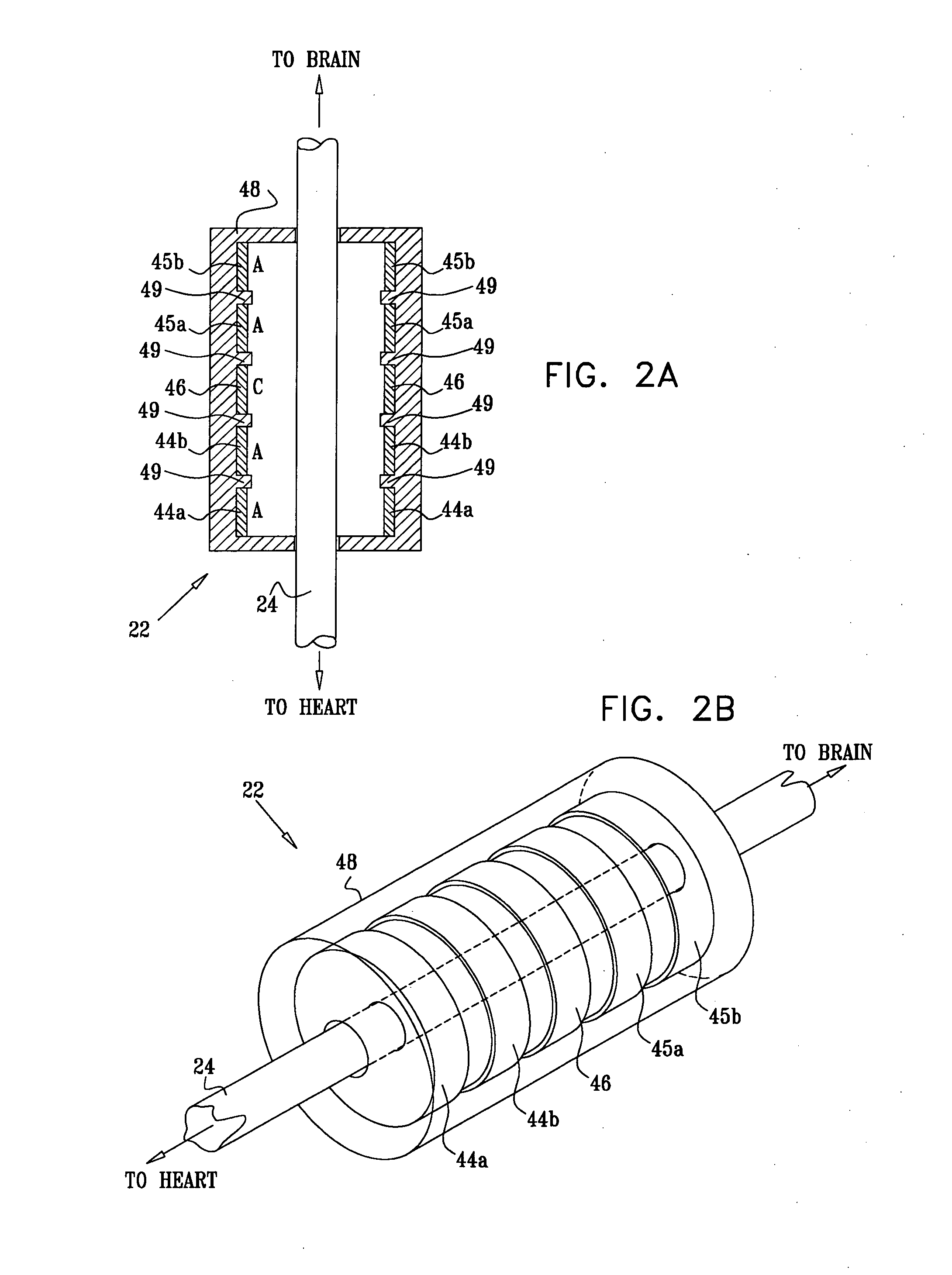
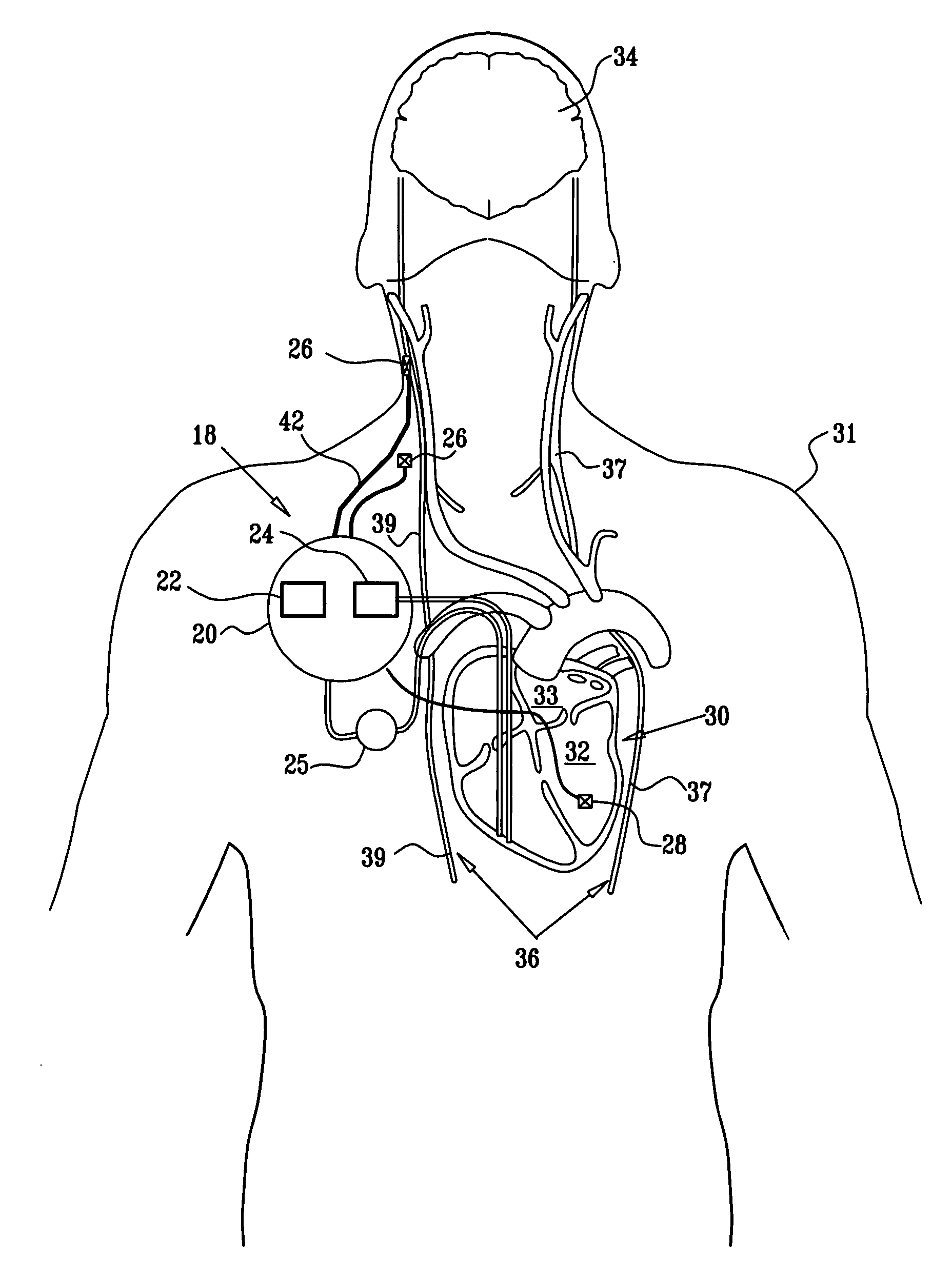
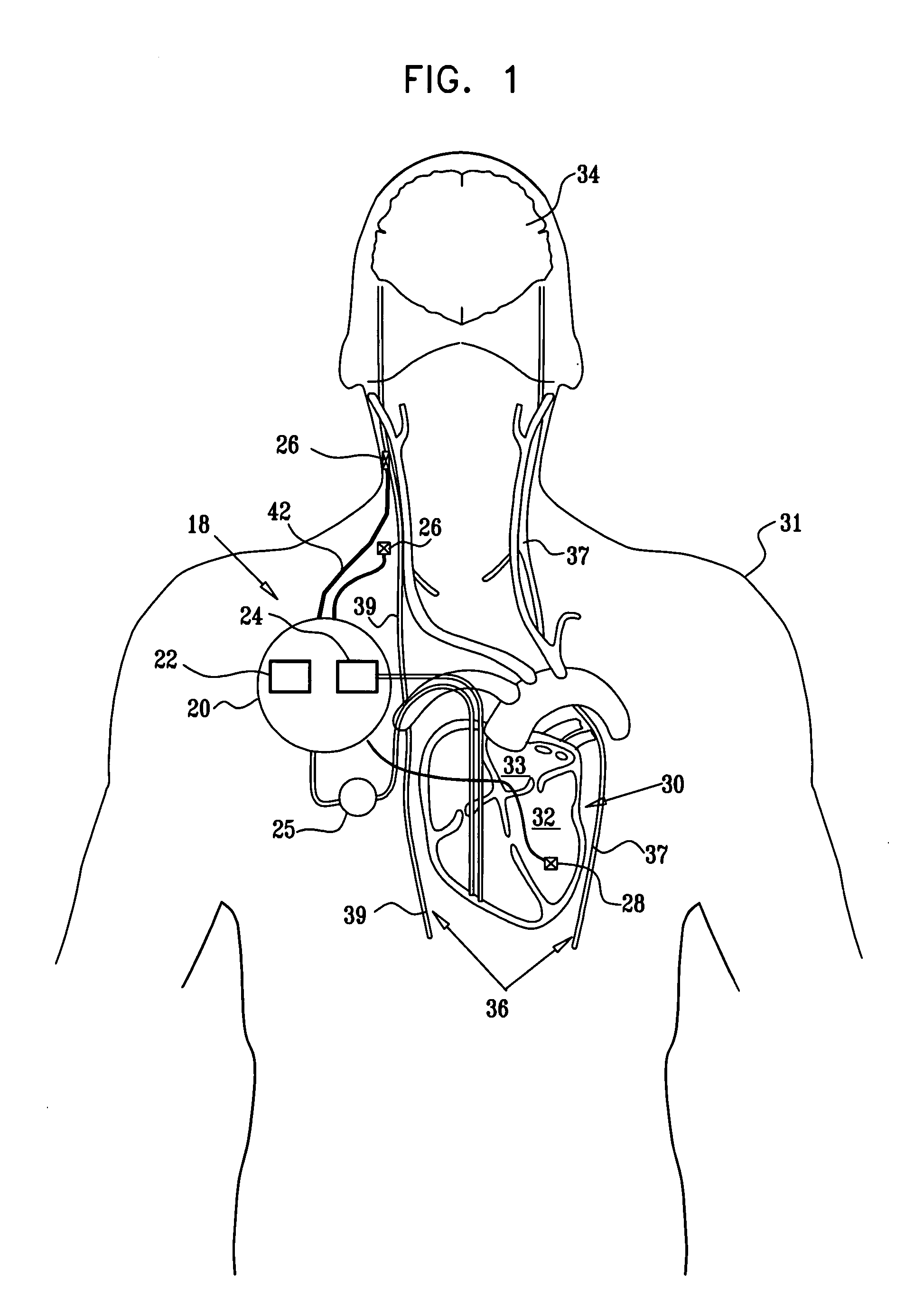
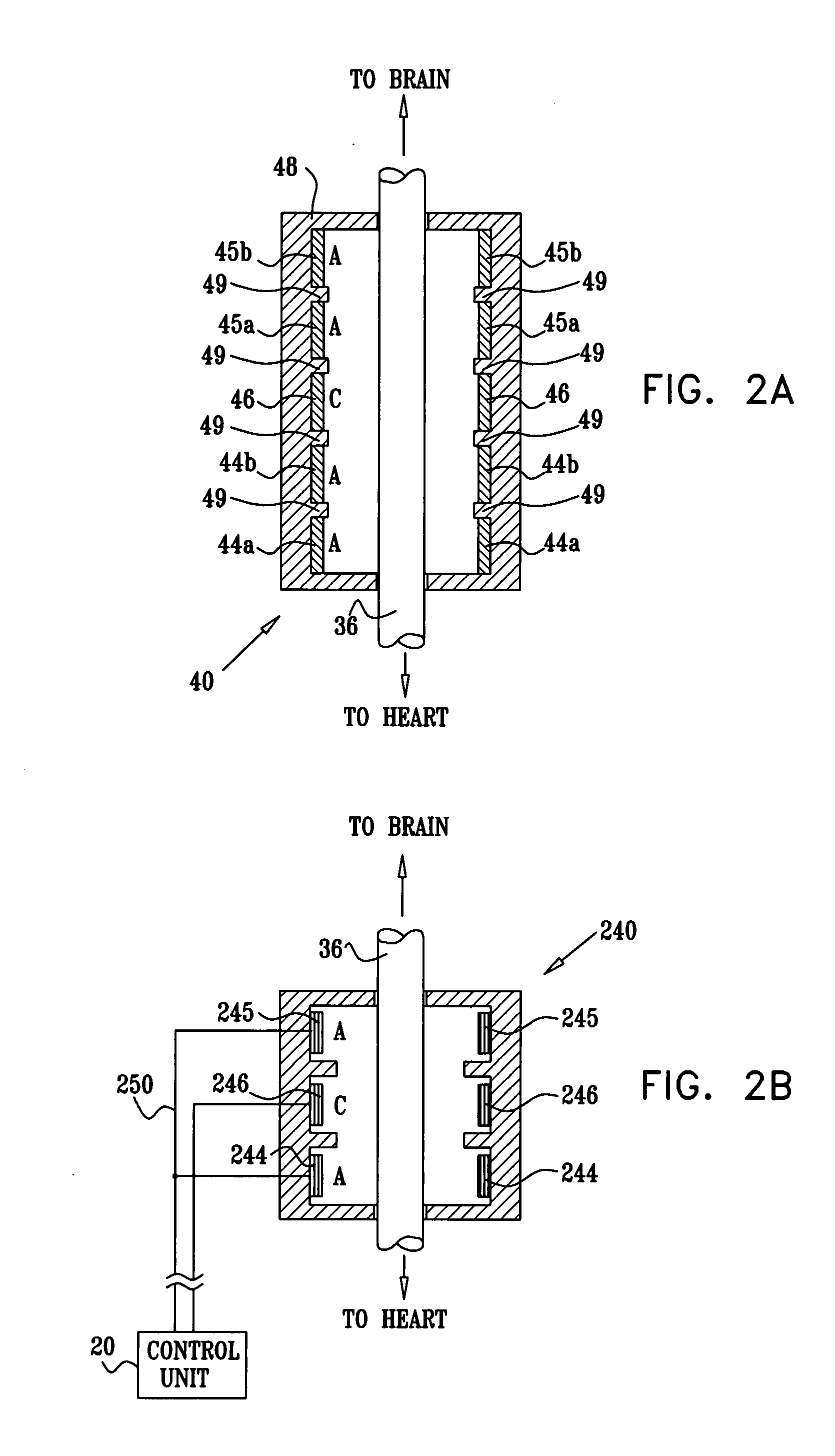
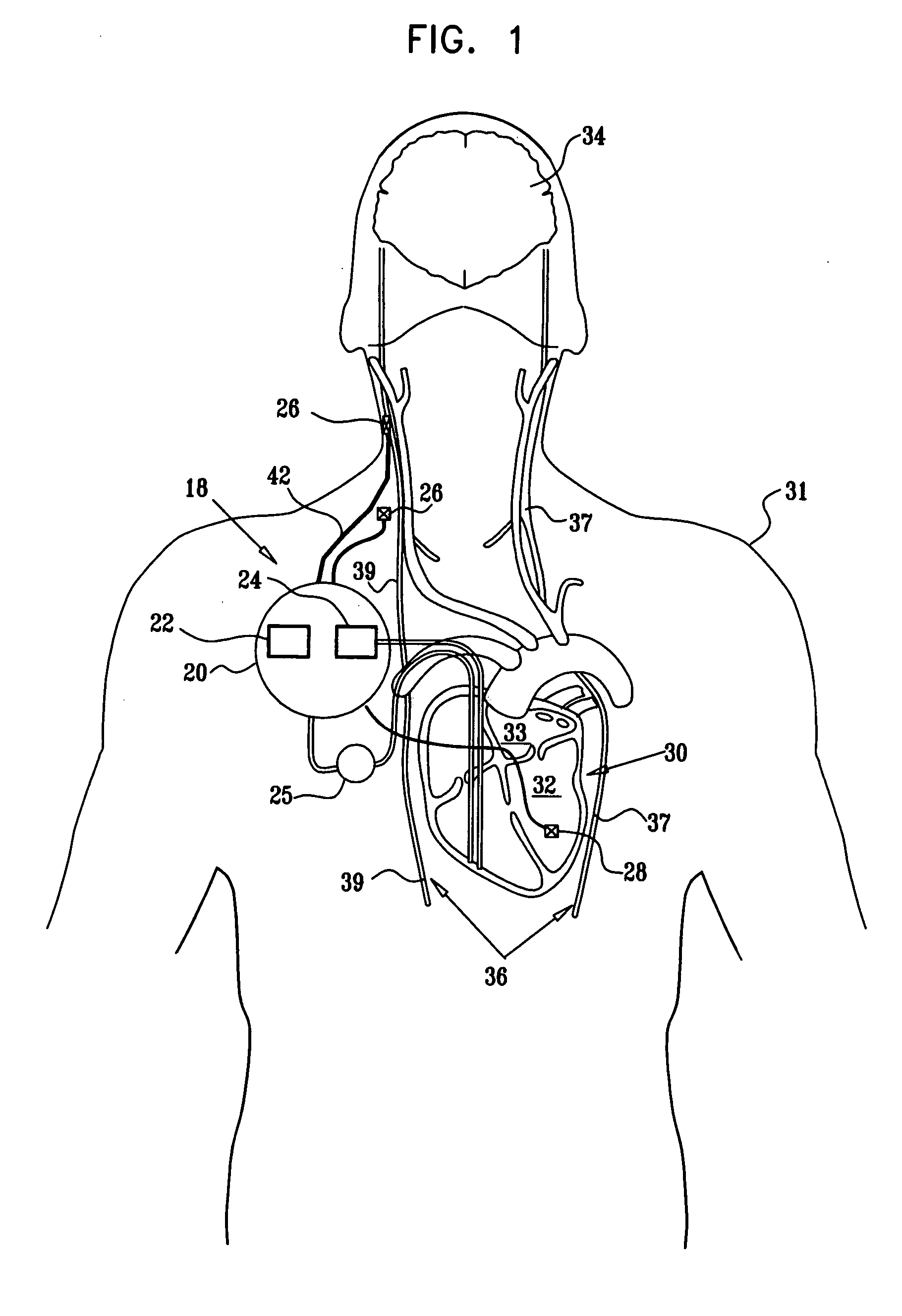
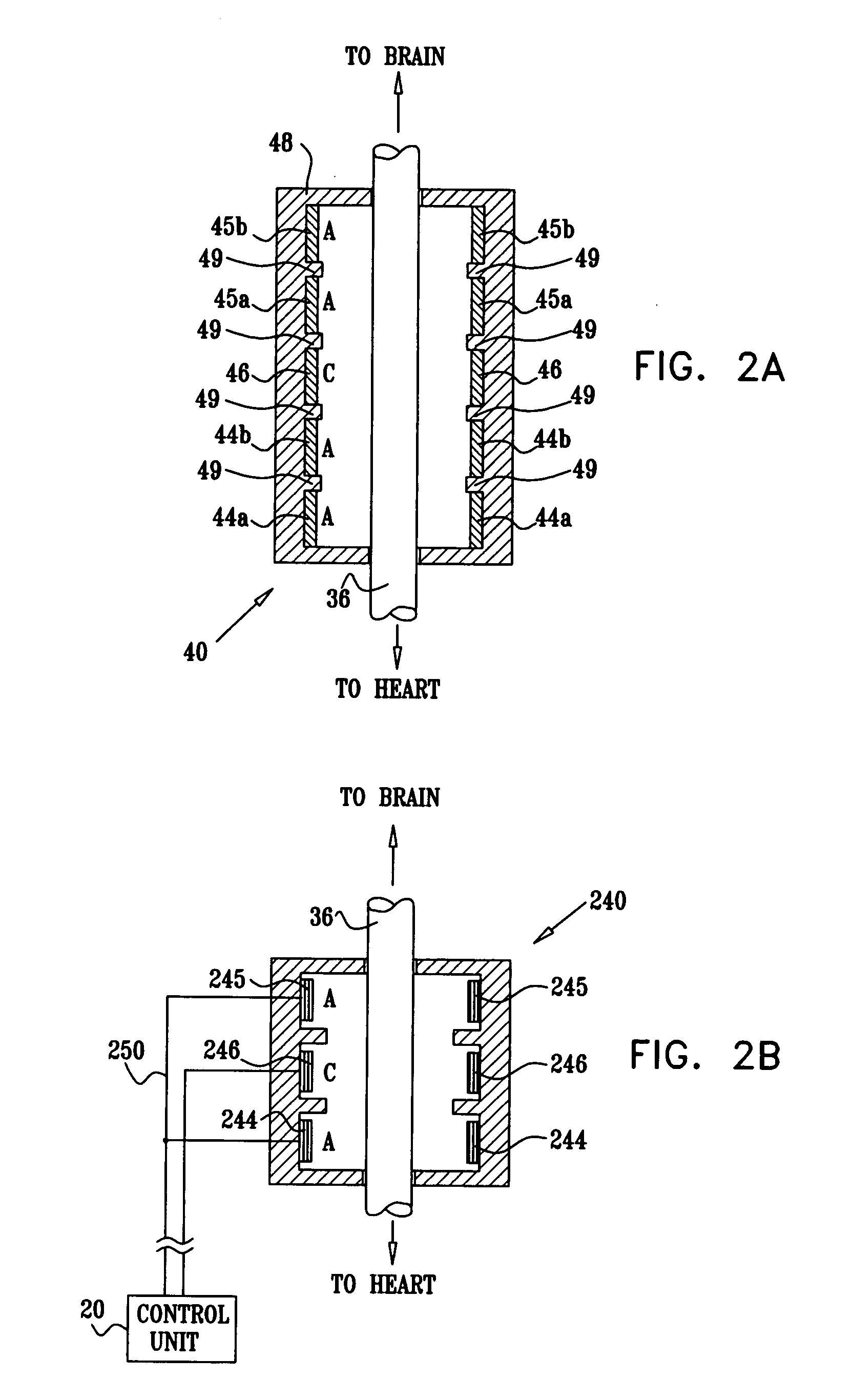
A lead of the present invention comprises an electrode array adapted to be stably anchored at a selected location within the vena cava of a human patient. The electrode array may take various shapes, including helical, annular and linear. The electrode array is connectable to an electrical stimulation means such as an implantable pulse or signal generator. Electrical stimulation applied to a selected region of the vena cava and across the wall of the vein, that is, transvascularly, to the vagus nerve or branches thereof, depolarizes the nerve to thereby effect control of the heart rate.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
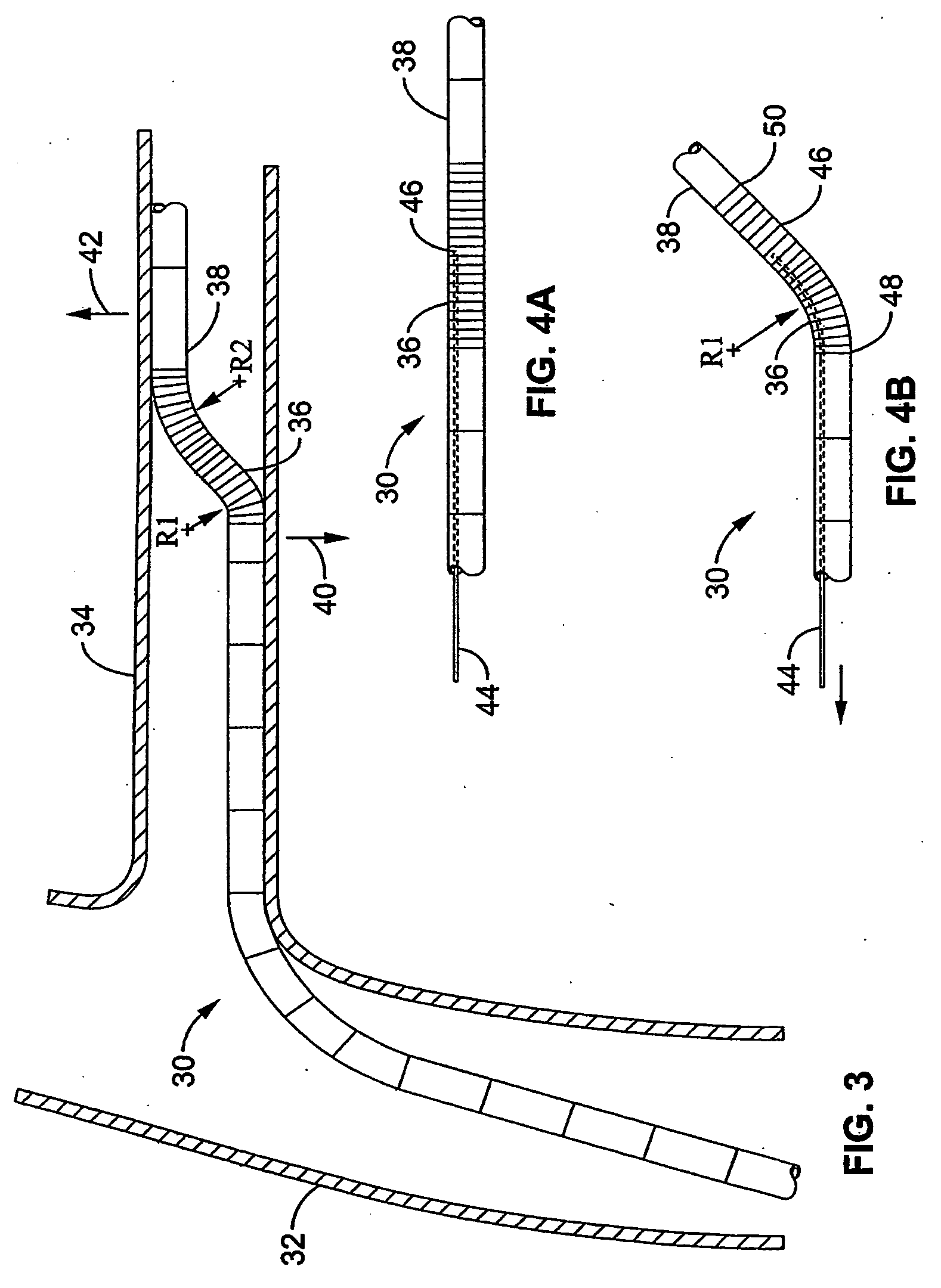
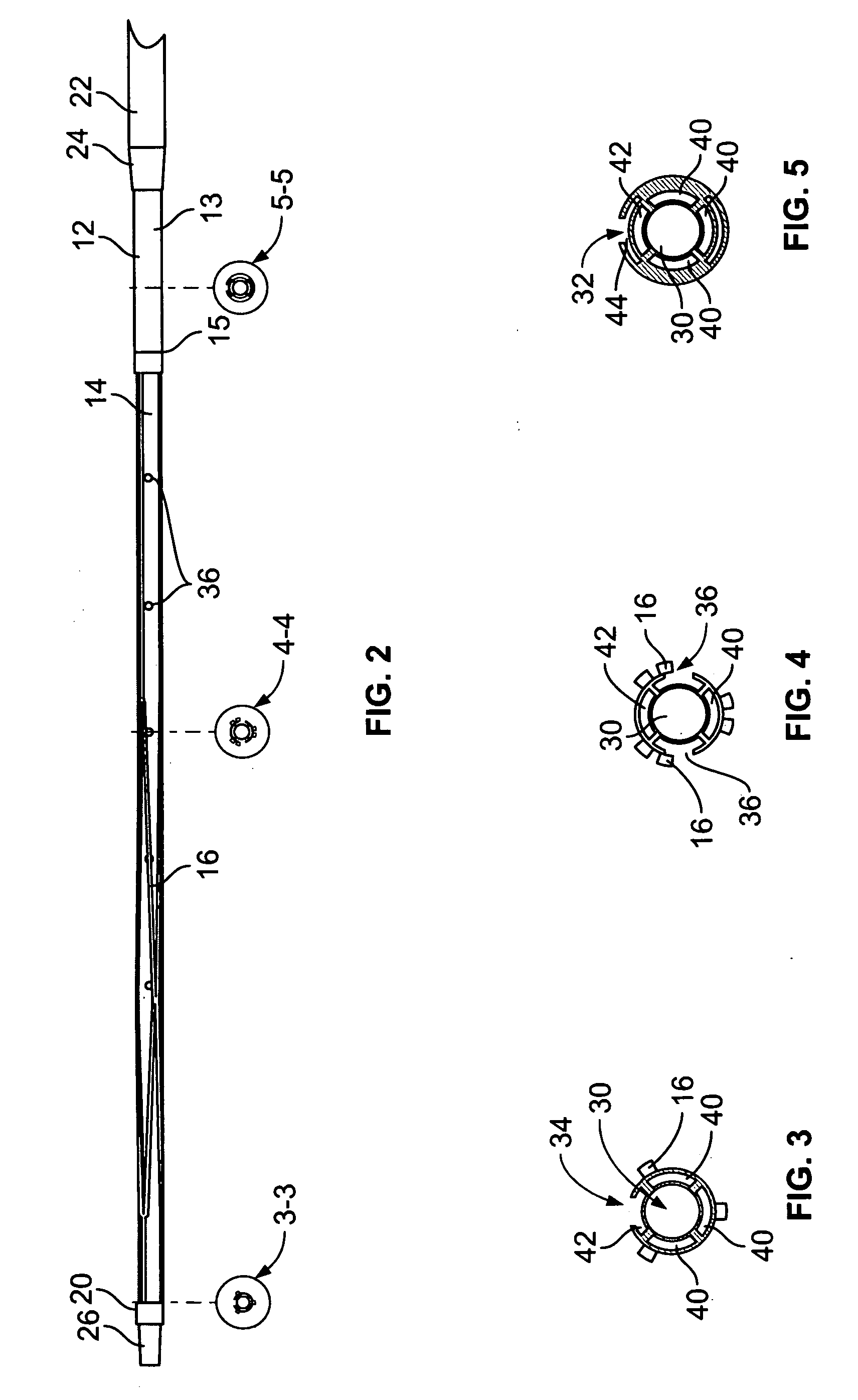
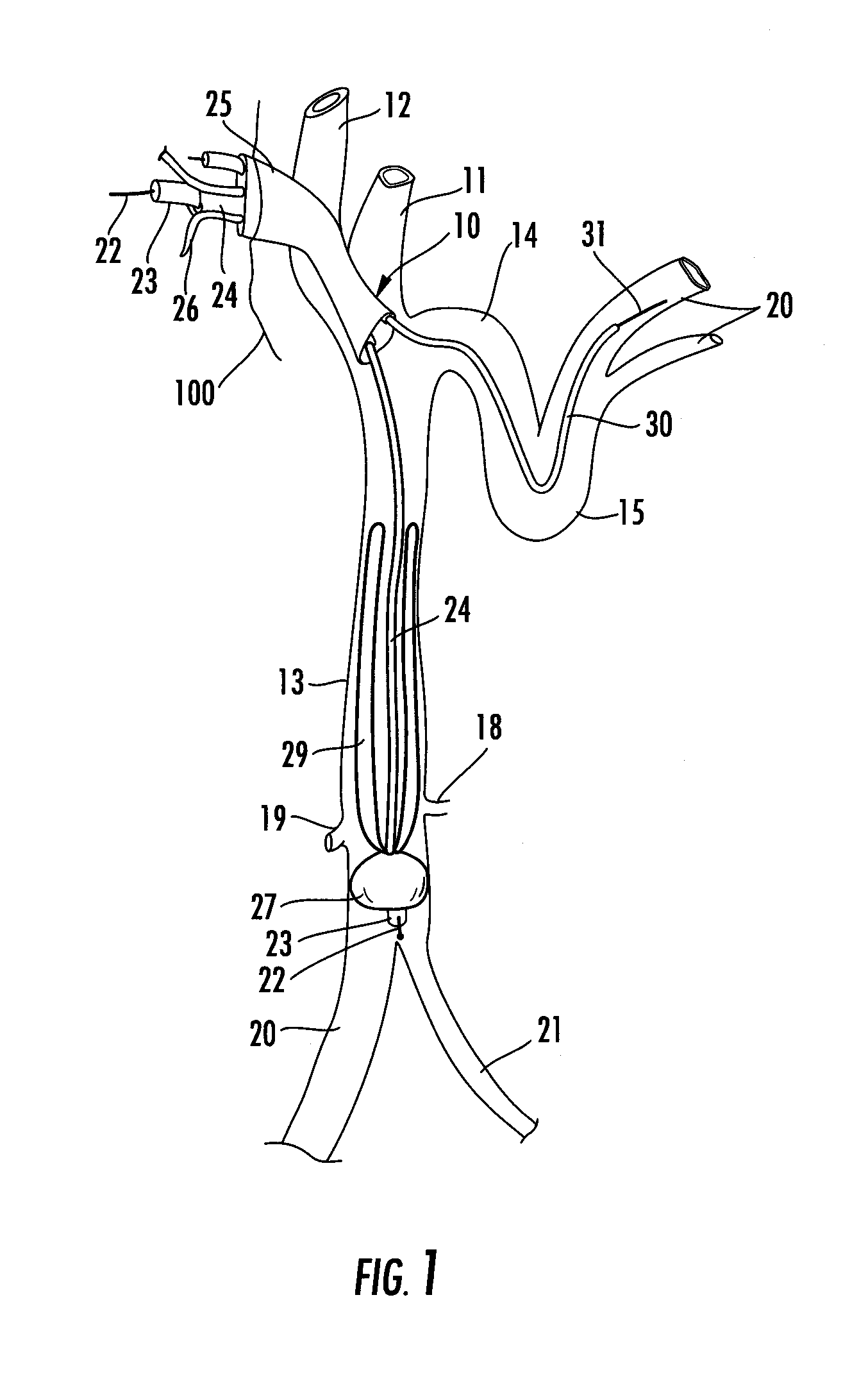
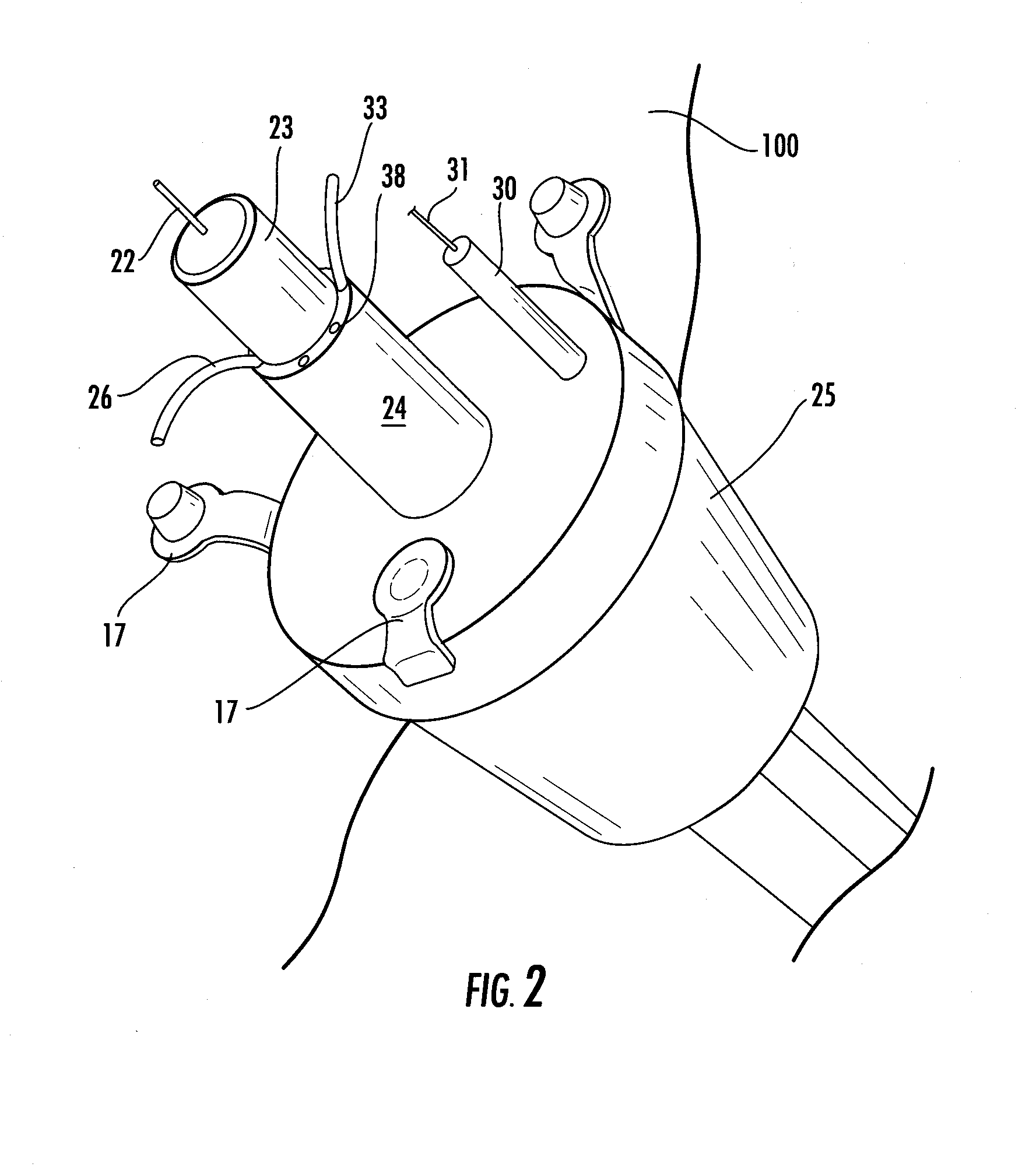
Vena cava delivery system
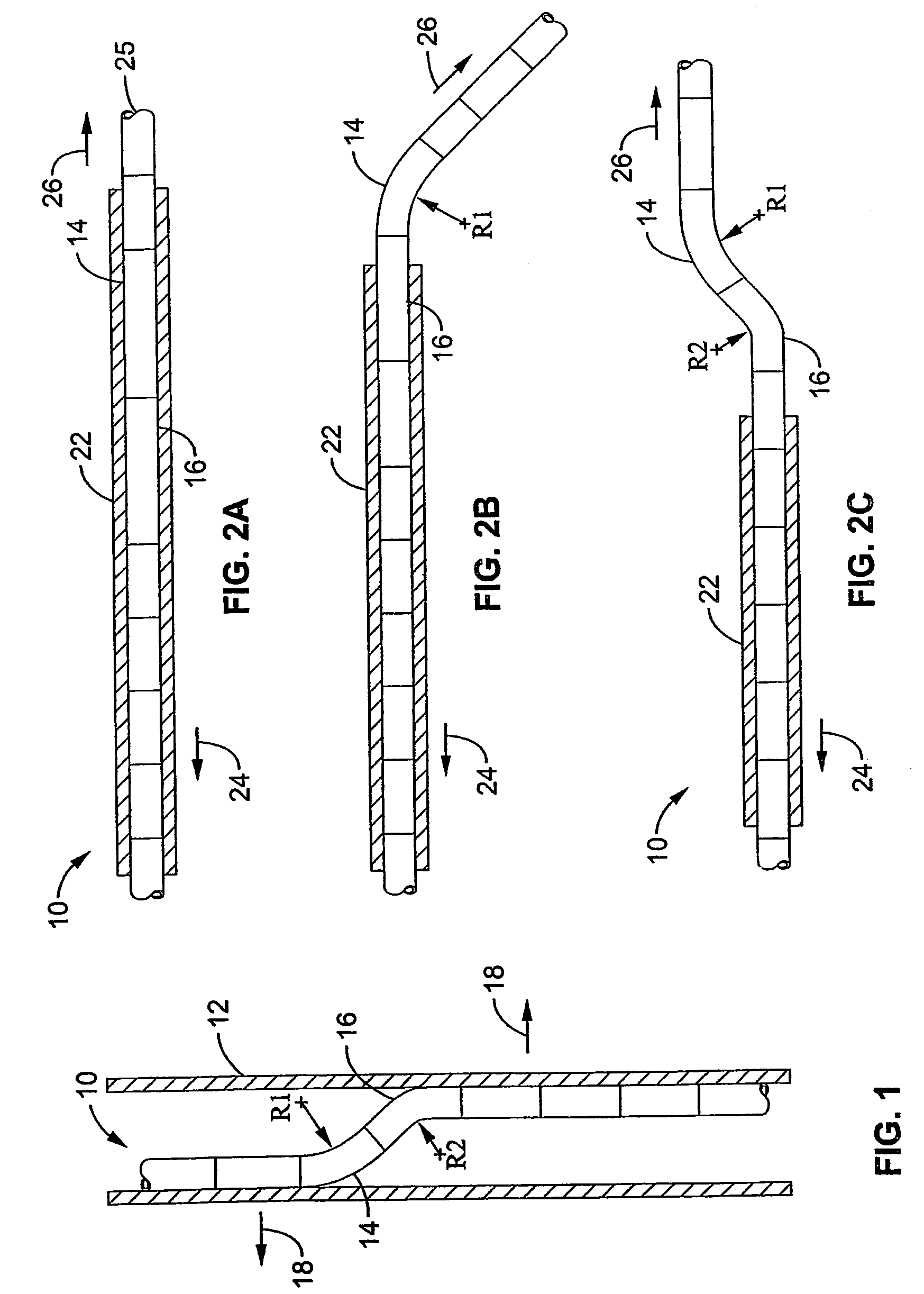
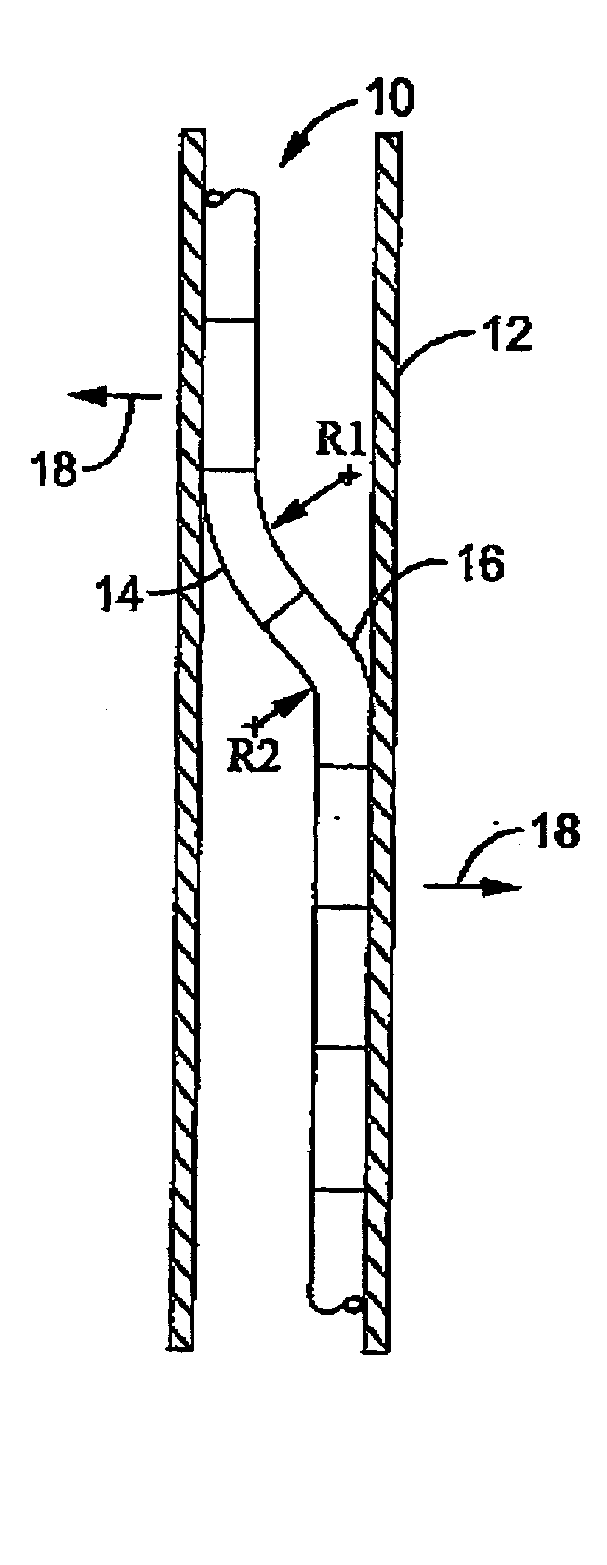
A delivery system for delivery and deployment of devices having abrading portions within a patient's lumen. A lumen in a flexible catheter that extends proximally from a distal end of the catheter receives the device in a compact form. At least one impervious segment positioned in the lumen overlies the abrading portions of the device to shield and buffer the surface of the lumen from the abrading portions. The segment is of a relatively short length so that the catheter remains relatively flexible therealong to enable relative ease in the transit of the catheter through the patient's lumen to a delivery site. Additional segments may be disposed in the catheter distally of the segment or the segment may move with the device to the distal end to buffer the walls of the catheter during the deployment of the device. Additional segments mate with the segment so that engaged ones of the segments are relatively radial deflectable.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
Treatment of infarct expansion by partially occluding vena cava
InactiveUS20060064059A1Reduces severity and complicationReduce expansionBalloon catheterSurgeryVeinVenous blood flow
A method and apparatus for prevention and reduction of myocardial infarct size and / or expansion and heart remodeling by partial, controllable and reversible obstruction of the venous blood flow to the heart. As a result, the ventricular wall stress and dilation are reduced. Blood flow is maintained at a safe level for the duration of treatment. The apparatus consists of a catheter with an occlusion balloon and a control and monitoring system.
Owner:GELFAND MARK +1
Techniques for reducing pain associated with nerve stimulation
Apparatus is provided including an electrode device and a control unit. The electrode device is configured to be coupled to a site of a subject selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve, an epicardial fat pad, a pulmonary vein, a carotid artery, a carotid sinus, a coronary sinus, a vena cava vein, a right ventricle, a right atrium, and a jugular vein. The control unit is configured to drive the electrode device to apply to the site a current in at least first and second bursts, the first burst including a plurality of pulses, and the second burst including at least one pulse, and set (a) a pulse repetition interval (PRI) of the first burst to be on average at least 20 ms, (b) an interburst interval between initiation of the first burst and initiation of the second burst to be less than 10 seconds, (c) an interburst gap between a conclusion of the first burst and the initiation of the second burst to have a duration greater than the average PRI, and (d) a burst duration of the first burst to be less than a percentage of the interburst interval between, the percentage being less than 67%. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
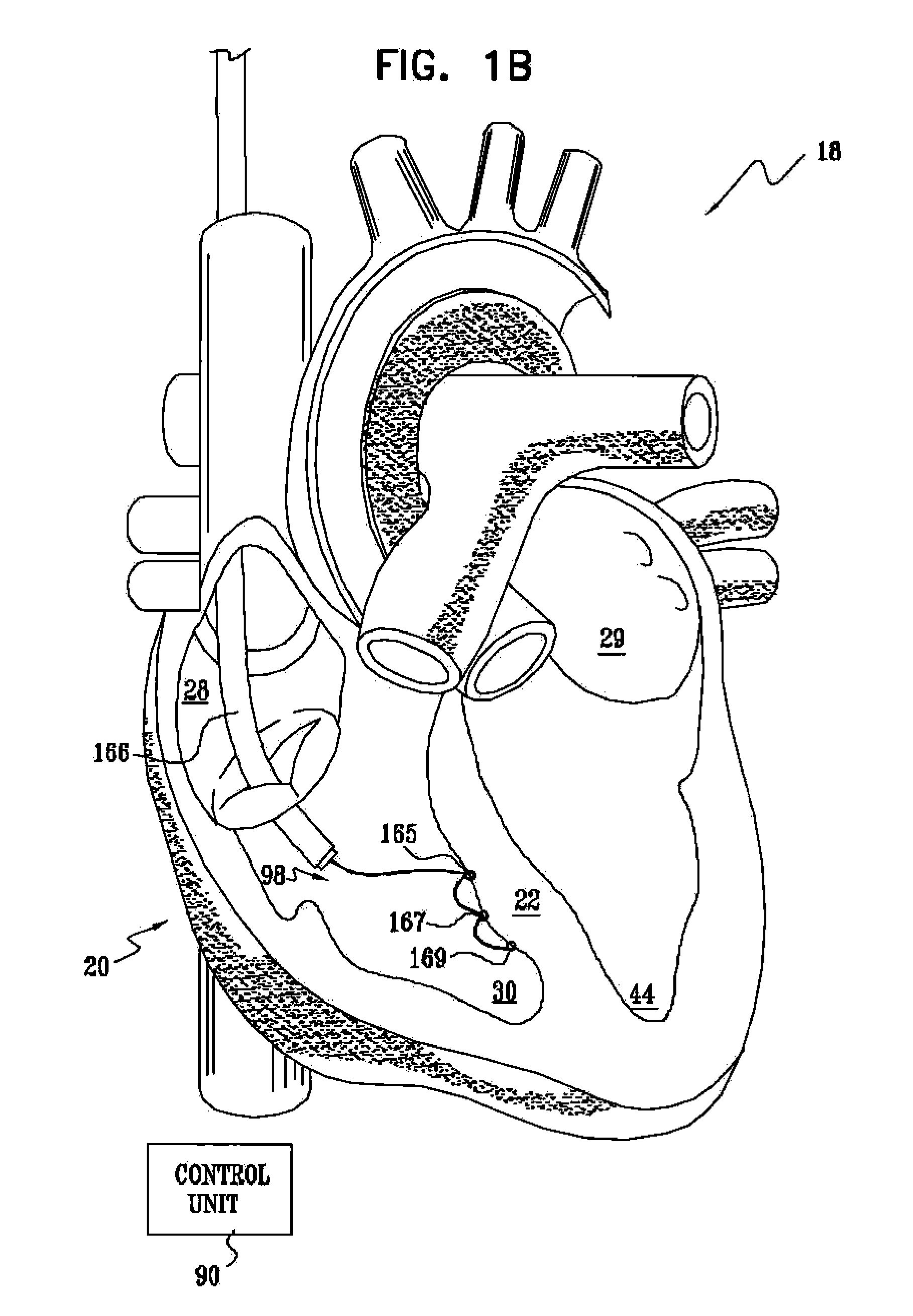
Vagal stimulation for anti-embolic therapy
InactiveUS20060271115A1Increase volumeIncrease stimulationSpinal electrodesHeart defibrillatorsEmbolization TherapyBlood flow
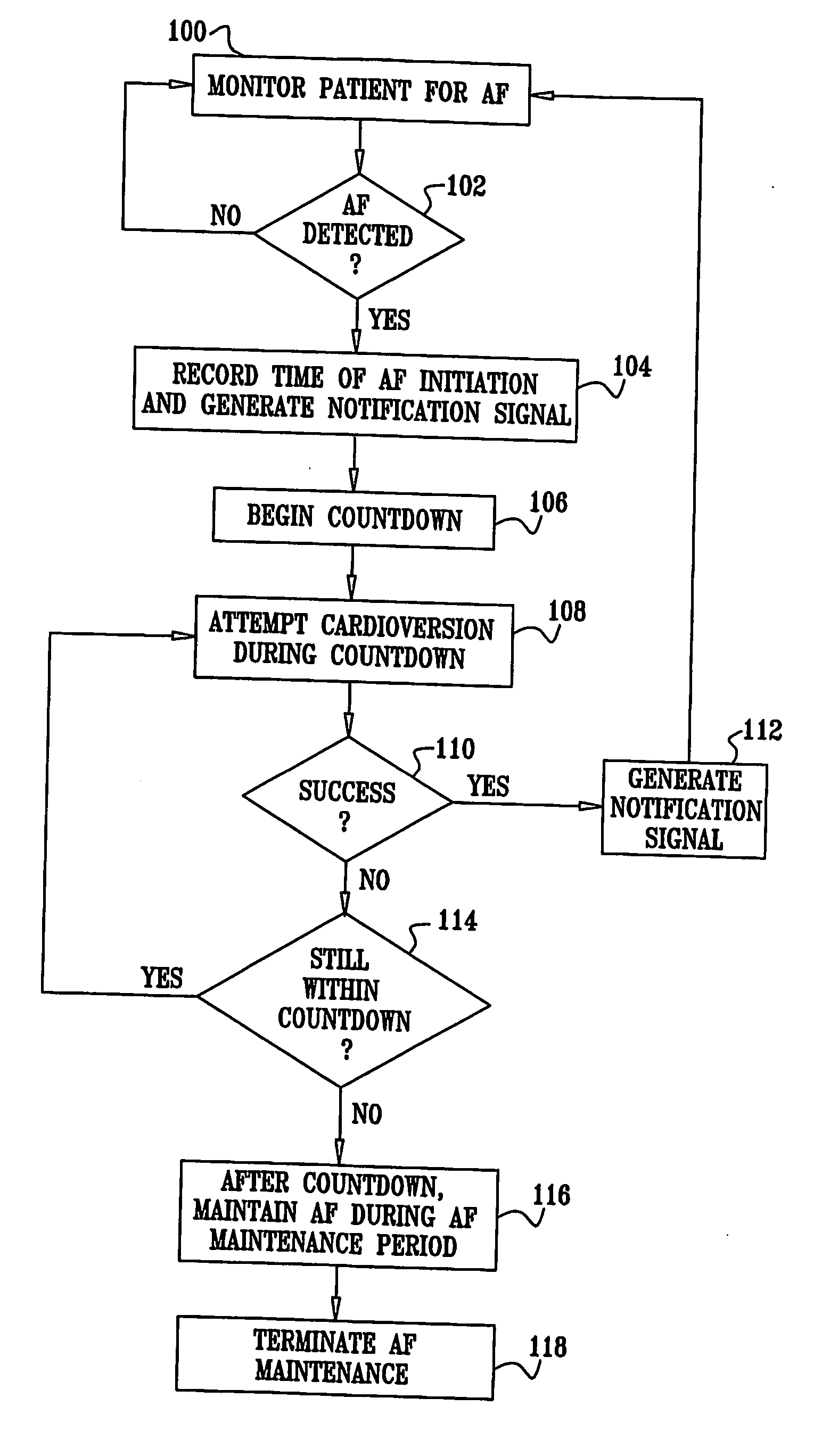
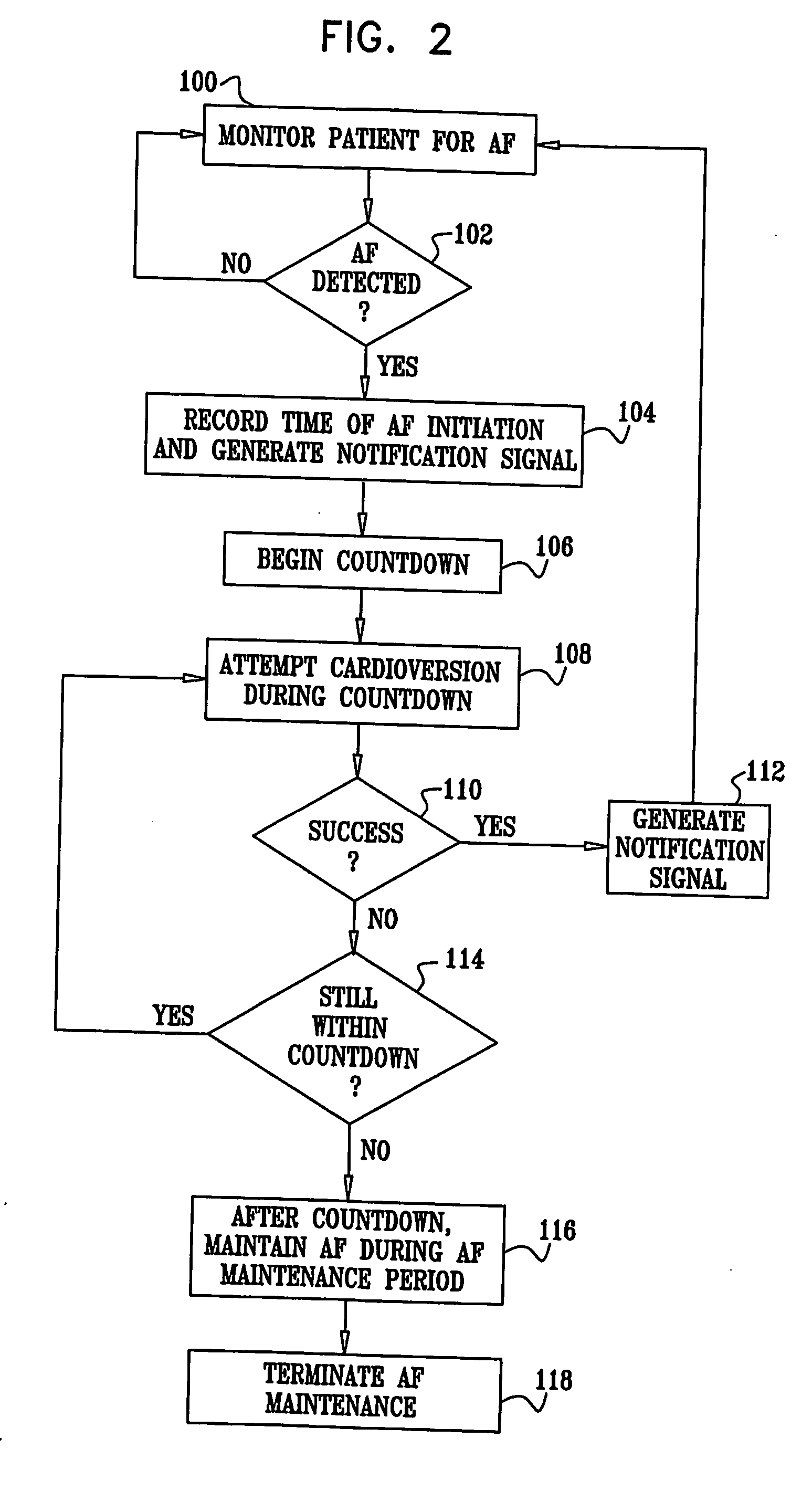
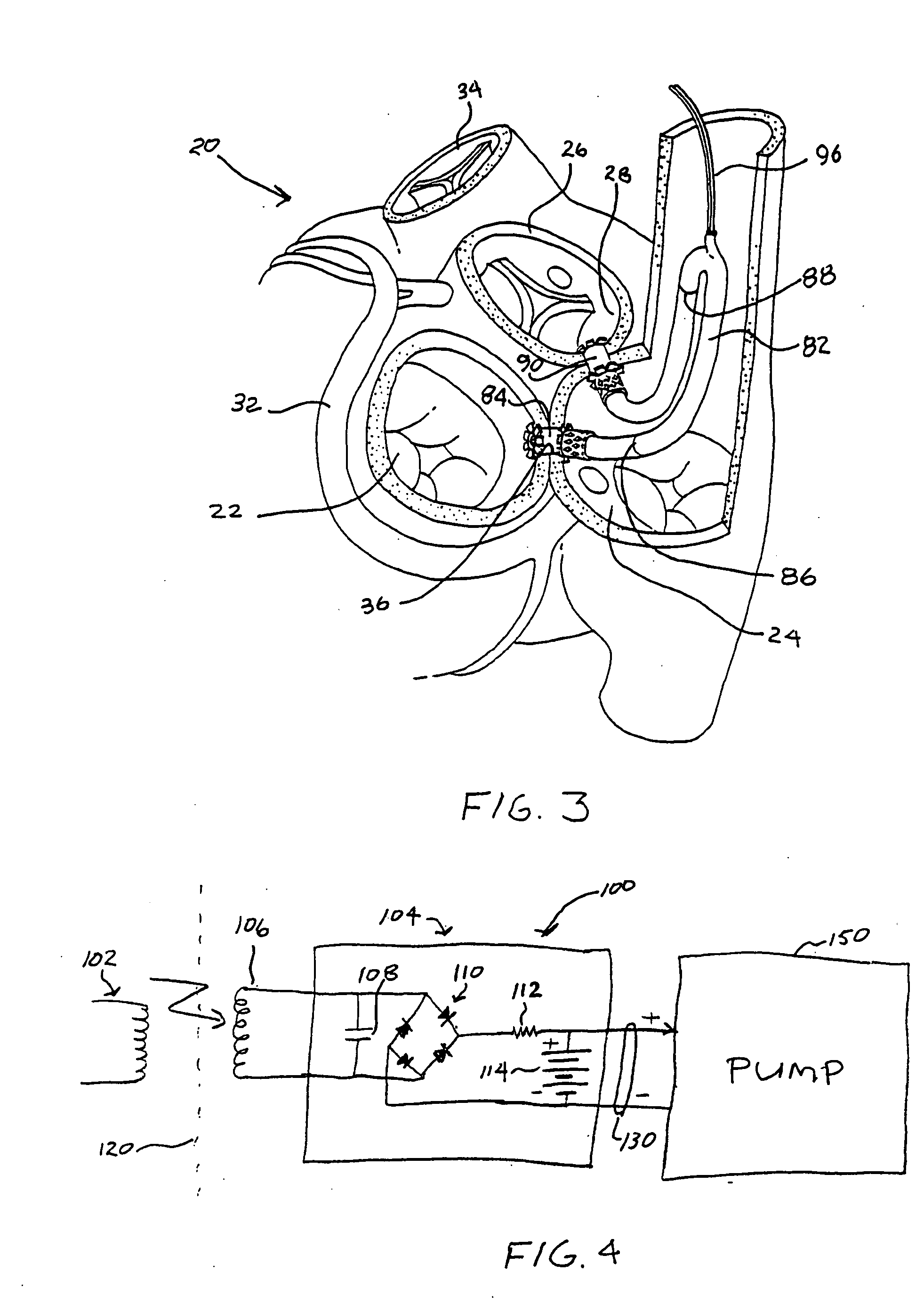
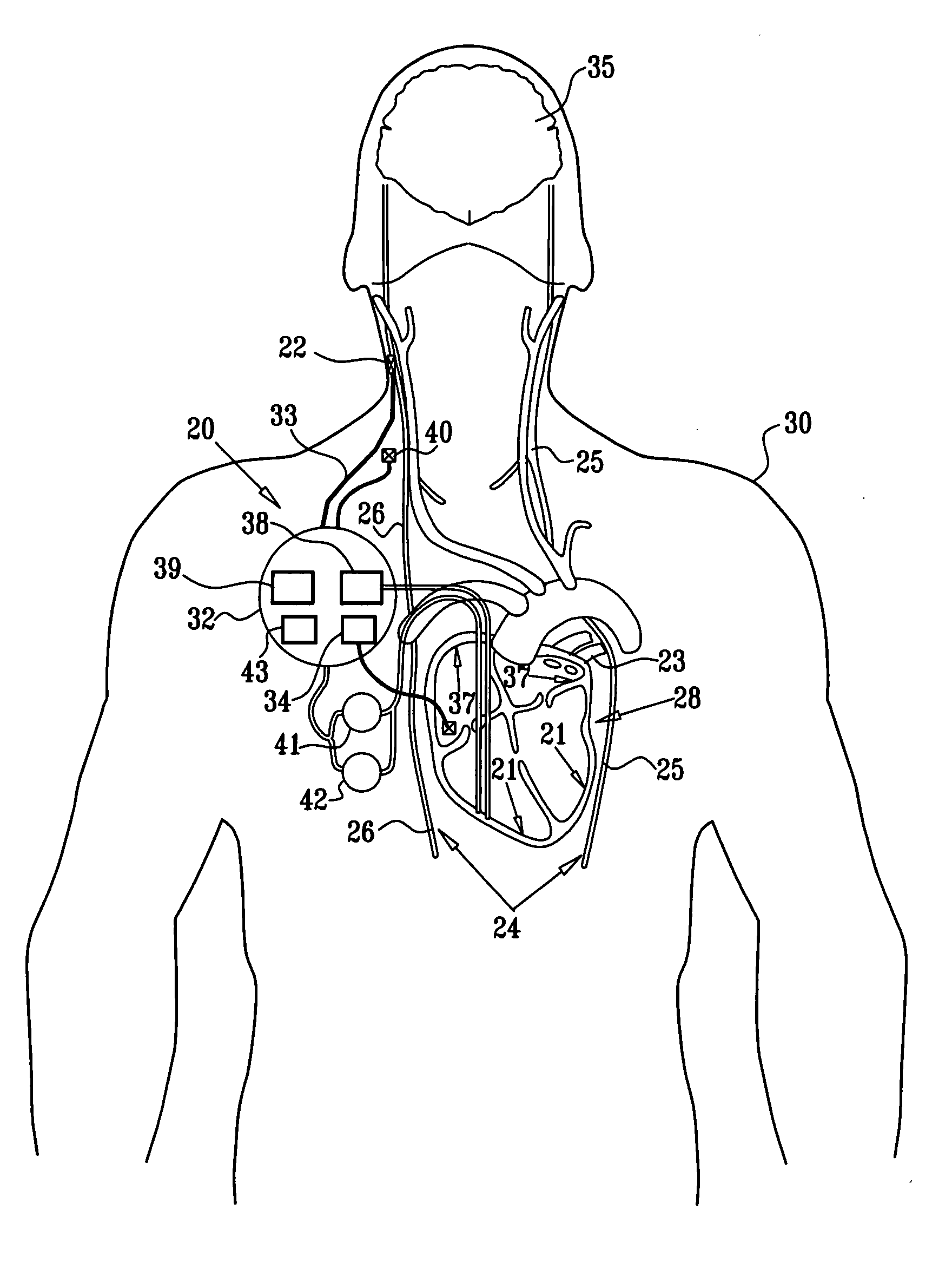
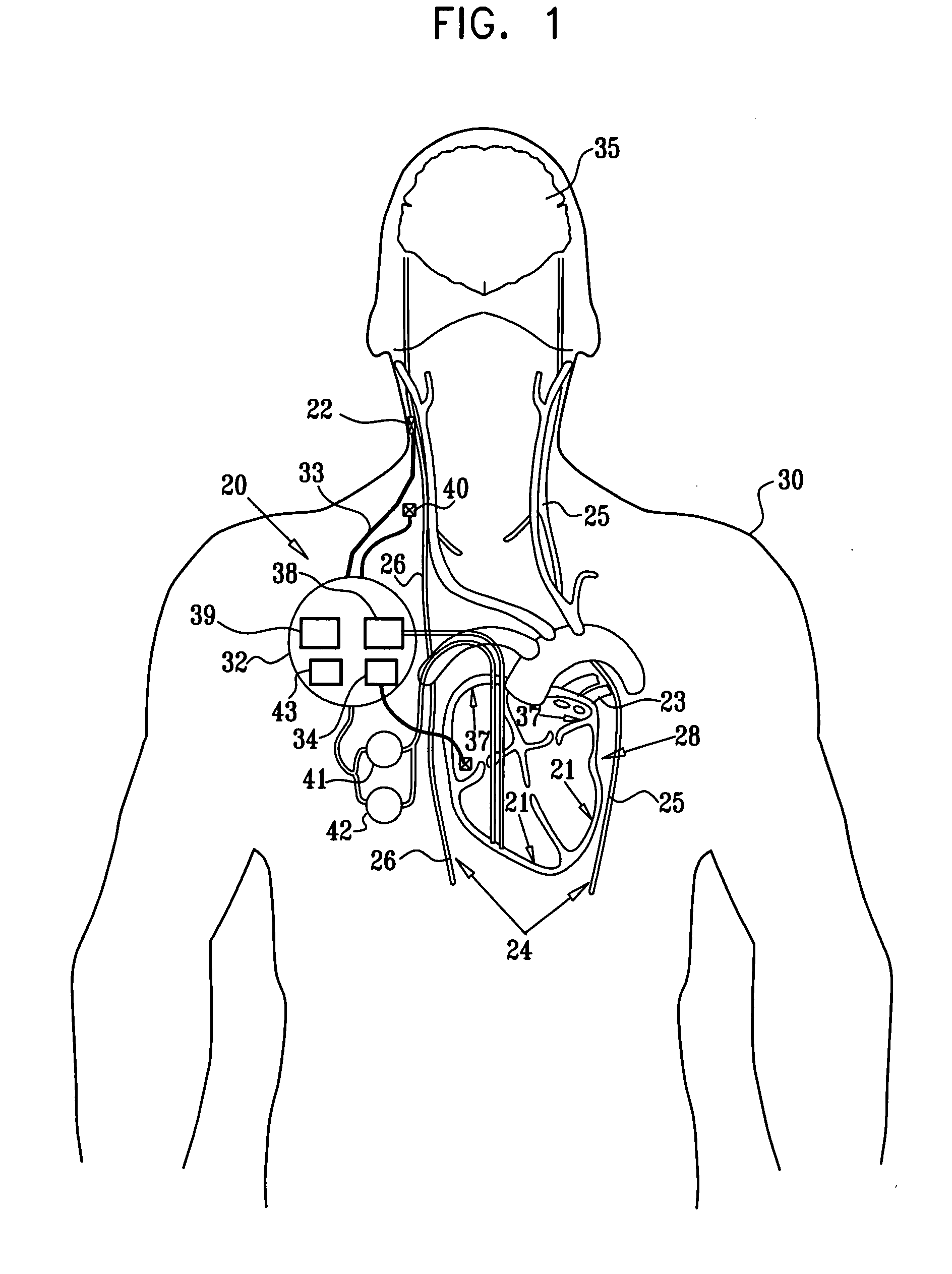
Apparatus (20) for treating a subject (30) suffering from spontaneous atrial fibrillation includes an electrode device (22), adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject (30) selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve (24) of the subject (30), an epicardial fat pad of the subject (30), a pulmonary vein of the subject (30), a carotid artery of the subject (30), a carotid sinus of the subject (30), a vena cava vein of the subject (30), and an internal jugular vein of the subject (30), and a control unit (32), adapted to drive the electrode device (22) to apply an electrical current to the site, and to configure the current to maintain the spontaneous AF for at least about 24 hours, so as to modify blood flow within the atria and reduce risk of thromboembolic events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Parasympathetic stimulation for treating ventricular arrhythmia
InactiveUS7904151B2Reduce riskFew potential side effectHeart defibrillatorsCardiac arrhythmiaCarotid sinus
Apparatus is provided including an implantable sensor, adapted to sense an electrical parameter of a heart of a subject, and a first control unit, adapted to apply pulses to the heart responsively to the sensed parameter, the pulses selected from the list consisting of: pacing pulses and anti-arrhythmic energy. The apparatus further includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, and a jugular vein of the subject; and a second control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the site a current that increases parasympathetic tone of the subject and affects a heart rate of the subject. The first and second control units are not under common control. At least one of the control units is adapted to coordinate an aspect of its operation with an aspect of operation of the other control unit. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Tissue material and process for bioprosthesis
ActiveUS20070005132A1Increase stiffnessIncrease elasticityHeart valvesTubular organ implantsTissue materialProsthesis
A biomaterial useful for bioprostheses such as bioprosthetic heart valves is provided in which the fixed tissue has improved elastic properties. The high elastin-containing biomaterial is further characterized by having anisotropic properties wherein the biological material has a greater stiffness in one direction and a greater elasticity in a cross direction. For instance, the biological material has an elastin content of about 30% by weight. In one embodiment, the biological material is vena cava tissue.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
Parasympathetic stimulation for prevention and treatment of atrial fibrillation
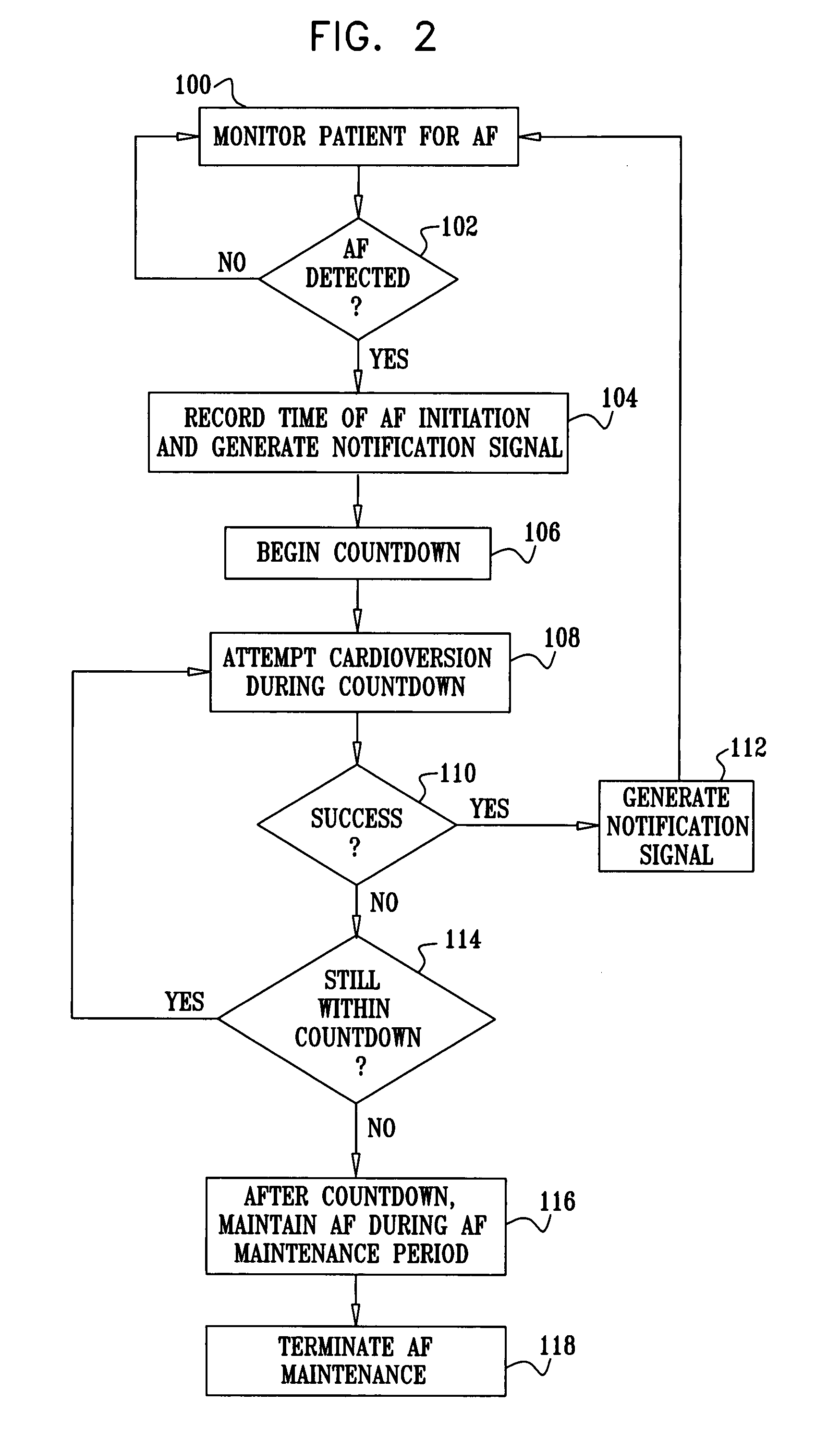
A method is provided, including identifying that a subject is at risk of suffering from atrial fibrillation (AF). Responsively to the identifying, a risk of an occurrence of an episode of the AF is reduced by applying an electrical current to a site of the subject selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve, a sinoatrial (SA) node fat pad, a pulmonary vein, a carotid artery, a carotid sinus, a coronary sinus, a vena cava vein, a jugular vein, an azygos vein, an innominate vein, and a subclavian vein, and configuring the current to stimulate autonomic nervous tissue in the site. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Parasympathetic stimulation for treating ventricular arrhythmia
InactiveUS20080091240A1Decreased heart rateEliminate side effectsHeart stimulatorsCardiac arrhythmiaCarotid sinus
Apparatus is provided including an implantable sensor, adapted to sense an electrical parameter of a heart of a subject, and a first control unit, adapted to apply pulses to the heart responsively to the sensed parameter, the pulses selected from the list consisting of: pacing pulses and anti-arrhythmic energy. The apparatus further includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, and a jugular vein of the subject; and a second control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the site a current that increases parasympathetic tone of the subject and affects a heart rate of the subject. The first and second control units are not under common control. At least one of the control units is adapted to coordinate an aspect of its operation with an aspect of operation of the other control unit. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Convertible blood clot filter
A vena cava blood clot filter is described that is attached to the walls of the vena cava by barbed anchors. In its filtering state, the filter is cone shaped which causes the blood to be filtered. The cone shape is formed by an appropriate restraining mechanism. When it is desired to stop filtering, the restraining mechanism is released and the filter takes a cylindrical shape. The cylindrical shaped filter will then line the vena cava wall and cease filtration of the blood.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
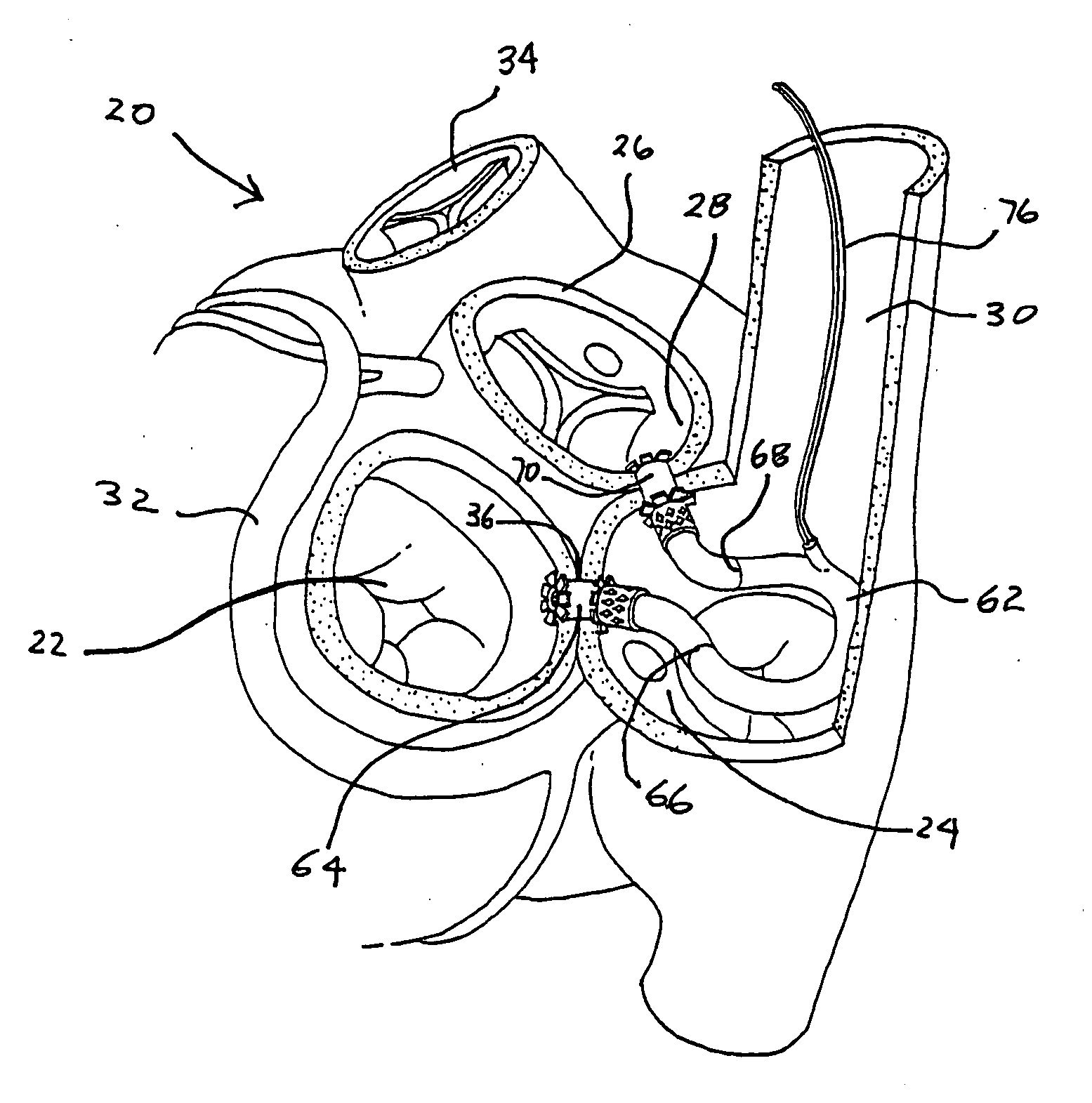
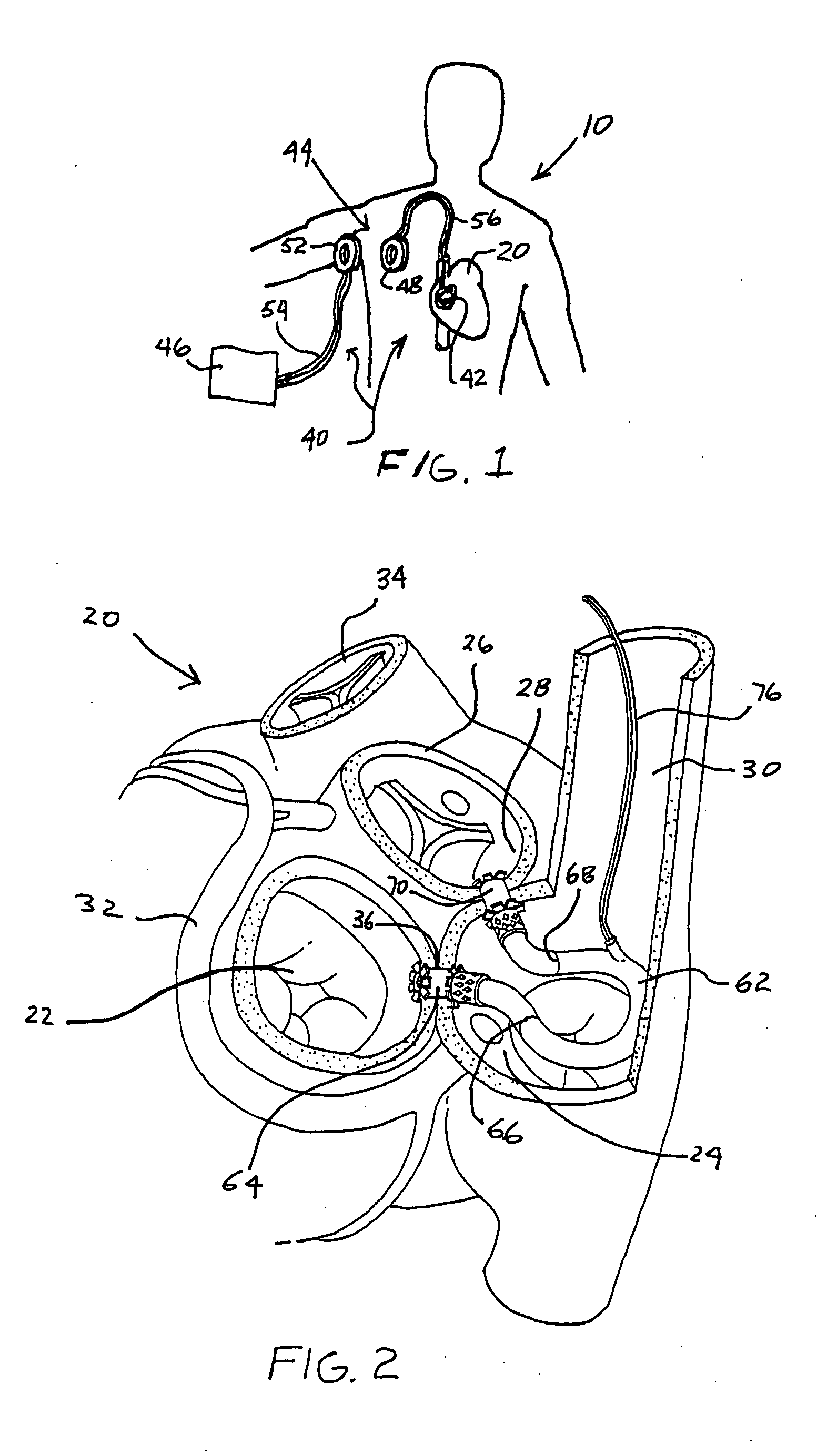
Endoscopic arterial pumps for treatment of cardiac insufficiency and venous pumps for right-sided cardiac support
Methods for using blood pumps to treat heart failure are disclosed. The pump is mounted on an interior of a stent, and the stent is releasably mounted on a distal end of a catheter. The distal end of the catheter is inserted into a peripheral artery and advanced to position at a region of interest within the descending aorta, the ascending aorta, or the left ventricle. The stent and the pump are released from the catheter, and the pump is activated to increase blood flow downstream of the pump. The pump can also be positioned in the vena cava or used to treat right-sided heart failure following the insertion of an LVAD, or to improve venous return in patients with varicose veins. Non-stent pumps are described for insertion between the pulmonary vein and aorta, and between the vena cava and pulmonary artery designed for use during cardiac surgery.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE R +2
Techniques for prevention of atrial fibrillation
A method is provided, including identifying that a subject is at risk of suffering from atrial fibrillation (AF). Responsively to the identifying, a risk of an occurrence of an episode of the AF is reduced by applying an electrical current to a site of the subject selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve, a sinoatrial (SA) node fat pad, a pulmonary vein, a carotid artery, a carotid sinus, a coronary sinus, a vena cava vein, a jugular vein, an azygos vein, an innominate vein, and a subclavian vein, and configuring the current to stimulate autonomic nervous tissue in the site. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Multi-lumen central access vena cava filter apparatus and method of using same
ActiveUS20100217304A1Rate be on riseEasy to disassembleMulti-lumen catheterSurgeryVena cava filtersVein
A combined multi-lumen central access catheter and an embolic filter including ports proximal and distal the filter for fluid infusion and / or pressure sensing and infusion ports in the catheter to permit infusion of bioactive agents, flushing agents and / or contrast agents. The embolic filter may be removably coupled to the multi-lumen catheter for temporary placement and retrieval under recommended indications.
Owner:BIO2MEDICAL
Removable vena cava filter comprising struts having axial bends
ActiveUS20060069406A1Simple deliveryMinimizes entanglementSurgeryDilatorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A removable vena cava filter configured for simplified delivery to and retrieval from the vena cava of a patient is disclosed. The filter includes struts configured to be arranged in consistent orientation together between expanded (opened) and collapsed (closed) configurations, thereby minimizing entanglement of the struts. Each of the struts has a circumferential bend relative to the longitudinal axis of the filter. The circumferential bends allow for consistent orientation of the struts when moved between the expanded and collapsed configurations and when placed in the closed configuration of the filter.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Techniques for prevention of atrial fibrillation
ActiveUS20070179543A1Prevent electrical remodelingReduce riskSpinal electrodesHeart defibrillatorsInnominate veinBiology
A method is provided, including identifying that a subject is at risk of suffering from atrial fibrillation (AF). Responsively to the identifying, a risk of an occurrence of an episode of the AF is reduced by applying an electrical current to a site of the subject selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve, a sinoatrial (SA) node fat pad, a pulmonary vein, a carotid artery, a carotid sinus, a coronary sinus, a vena cava vein, a jugular vein, an azygos vein, an innominate vein, and a subclavian vein, and configuring the current to stimulate autonomic nervous tissue in the site. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method for surgically implanting an electrode device
InactiveUS20080161894A1Reduce riskFew potential side effectSpinal electrodesSurgeryCarotid sinusRight ventricles
Apparatus is provided including an implantable sensor, adapted to sense an electrical parameter of a heart of a subject, and a first control unit, adapted to apply pulses to the heart responsively to the sensed parameter, the pulses selected from the list consisting of: pacing pulses and anti-arrhythmic energy. The apparatus further includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, and a jugular vein of the subject; and a second control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the site a current that increases parasympathetic tone of the subject and affects a heart rate of the subject. The first and second control units are not under common control. At least one of the control units is adapted to coordinate an aspect of its operation with an aspect of operation of the other control unit. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for selective material delivery via an intra-renal catheter
Two renal delivery members have two distal ports that are adapted to be positioned within two renal arteries via their corresponding renal ostia at unique locations along an abdominal aortic wall. A proximal coupler assembly is outside the body and is coupled to deliver material to the two distal ports for bi-lateral renal therapy. One or both of the delivery members may be self-cannulating into the corresponding renal ostium, or may be controllably steered into the respective ostium. Non-occlusive anchors may be coupled with one or both of the delivery members at anchoring positions in the renal artery or abdominal aorta to secure the renal delivery member within the renal artery. Renal-active fluid agents are coupled to the bi-lateral delivery system. Another renal therapy system cannulates a renal vein from the vena cava and controls a retrograde delivery of agents to the respective kidney.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Treatment for disorders by parasympathetic stimulation
InactiveUS20080086182A1Increase parasympathetic toneReduced responseSpinal electrodesHeart defibrillatorsDiseaseParasympathetic ganglion
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Left ventricular function assist system and method
InactiveUS20050187425A1Assist left ventricular functionBlood pumpsMedical devicesVeinLeft ventricular size
A pump assists left ventricular function of a heart. The pump is configured for implant in the body and has an input connectable to the left atrium and an output connectable to the aorta for pumping blood from the left atrium to the aorta. A power source for powering operation of the pump is connectable to the pump. The pump may be configured for implant within the heart, such as, for example, in the atrium, the super vena cava, or partly within each of the right atrium and the superior vena cava.
Owner:SCOUT MEDICAL TECH
Vagal stimulation for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS20080091241A1Reduce frequencyIncreased riskSpinal electrodesHeart defibrillatorsBlood flowThrombus
Apparatus (20) for treating a subject (30) suffering from spontaneous atrial fibrillation includes an electrode device (22), adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject (30) selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve (24) of the subject (30), an epicardial fat pad of the subject (30), a pulmonary vein of the subject (30), a carotid artery of the subject (30), a carotid sinus of the subject (30), a vena cava vein of the subject (30), and an internal jugular vein of the subject (30), and a control unit (32), adapted to drive the electrode device (22) to apply an electrical current to the site, and to configure the current to maintain the spontaneous AF for at least about 24 hours, so as to modify blood flow within the atria and reduce risk of thromboembolic events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Signal Delivery Through The Right Ventricular Septum
InactiveUS20070162079A1Improve heart functionReduced contractilityHeart stimulatorsVeinLeft ventricle wall
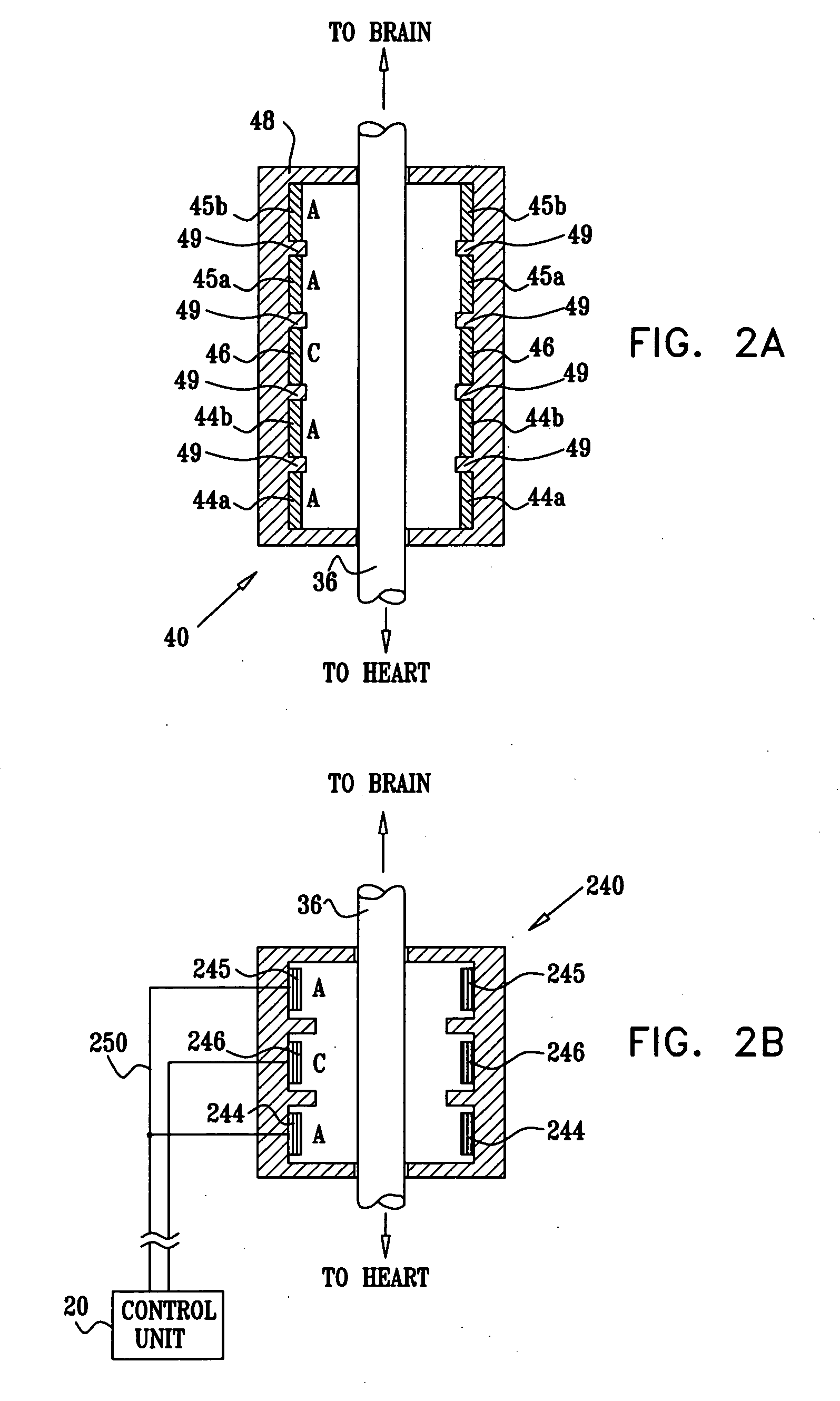
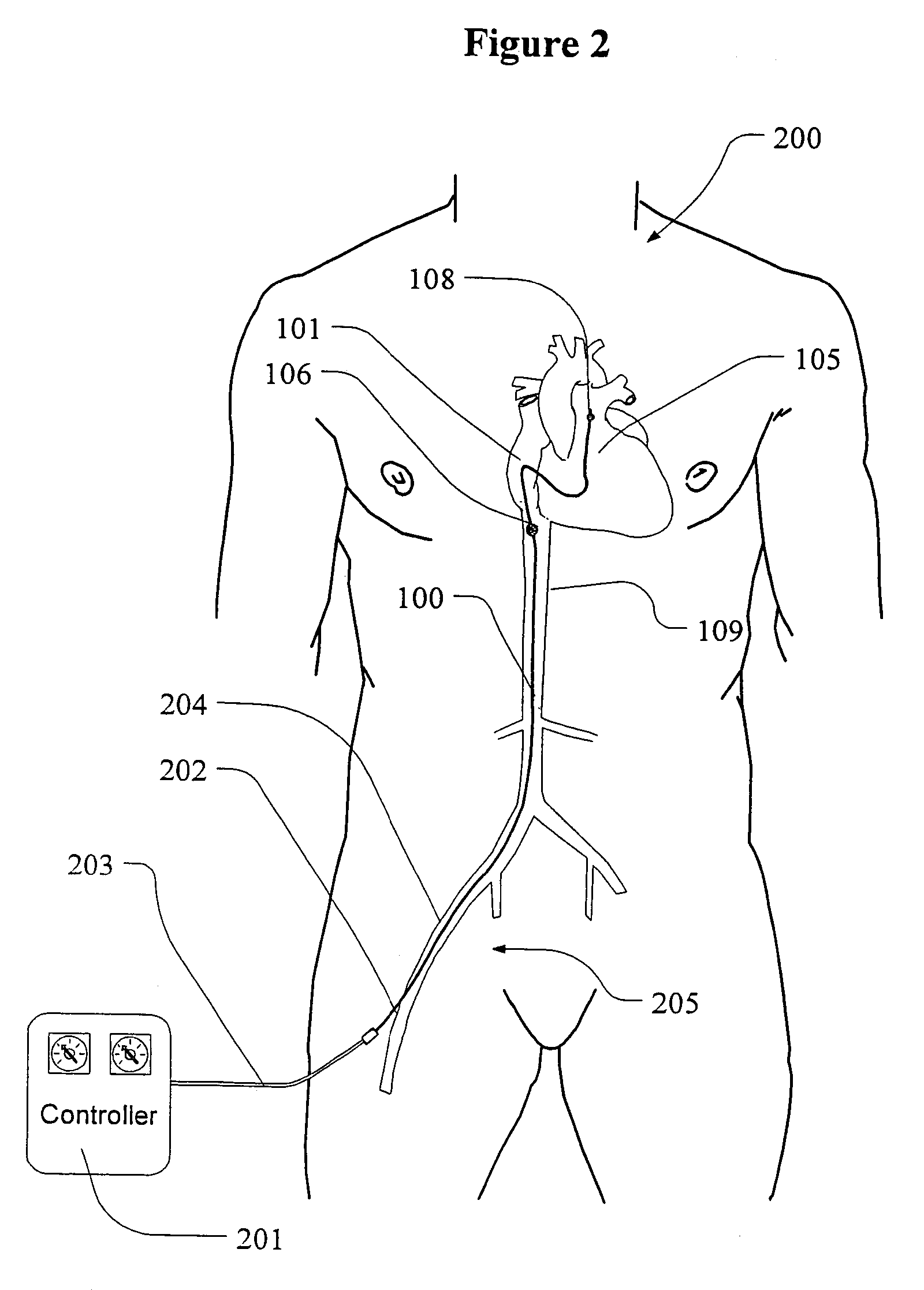
A method is provided for use with a human subject. The method includes accessing a cardiac site via a vena cava of the subject, and alleviating heart failure of the subject by applying to the cardiac site, during a refractory period of the site, a refractory-period signal that affects the left ventricle of the subject's heart. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:IMPULSE DYNAMICS NV
Catheter for treatment of severe pulmonary emboli
A catheter system for treating pulmonary emboli has an multi-channel access port for establishing and maintaining communication with the vascular system and provide guidance for endovascular catheterization. One catheter may traverse the port and extend through the heart to the pulmonary arteries to inject lysing agents, contrast media, medicaments and to remove blood clots. Another catheter may traverse the port and extend through the vena cava to other parts of the venous tree to supply the same agents and to remove blood clots there. A third catheter may telescope over the treatment catheter through the vena cava and occlude the affected vein. Gas pervious tubules on the third catheter provide oxygen enrichment of the venous blood.
Owner:LARY RES & DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com