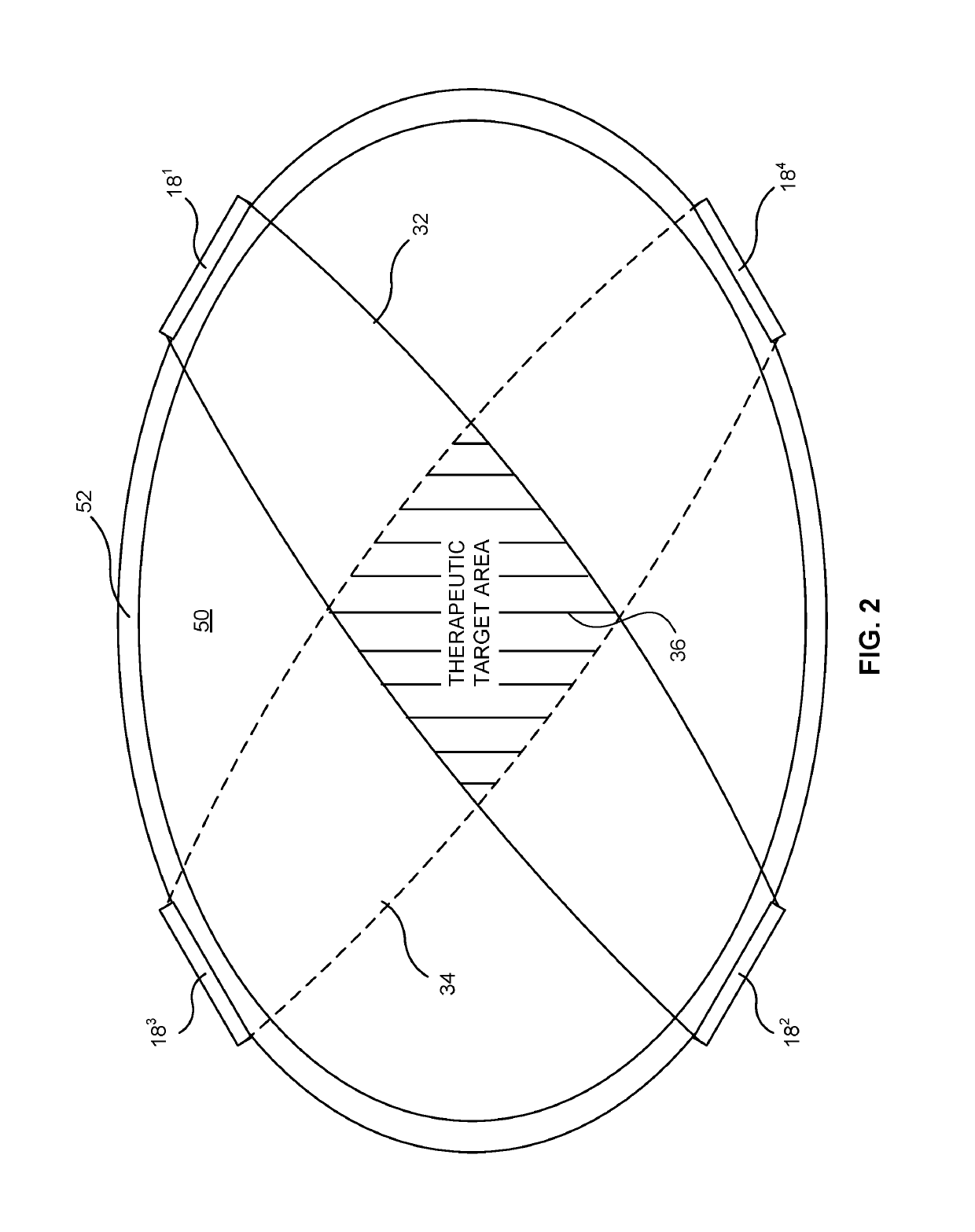
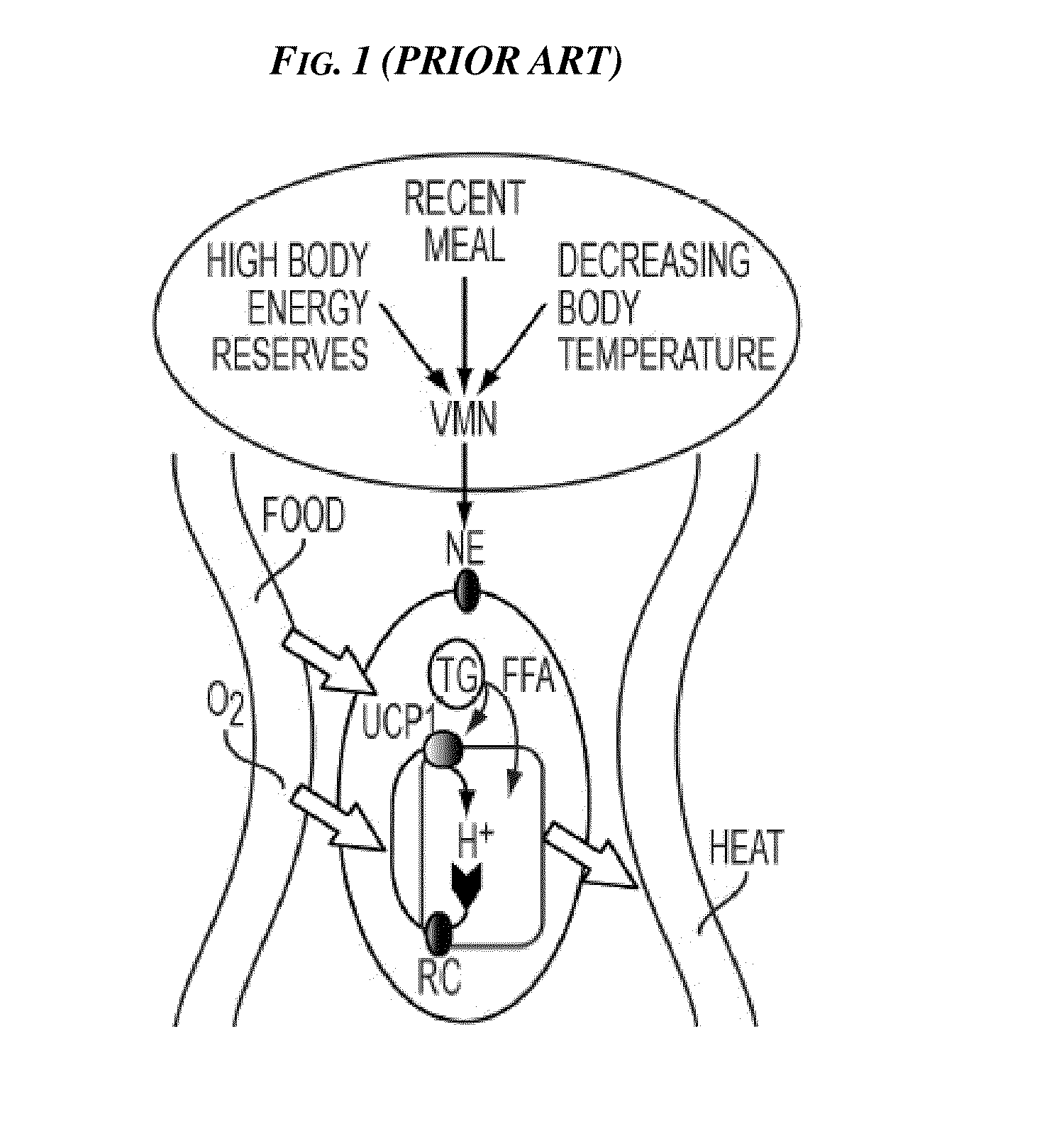
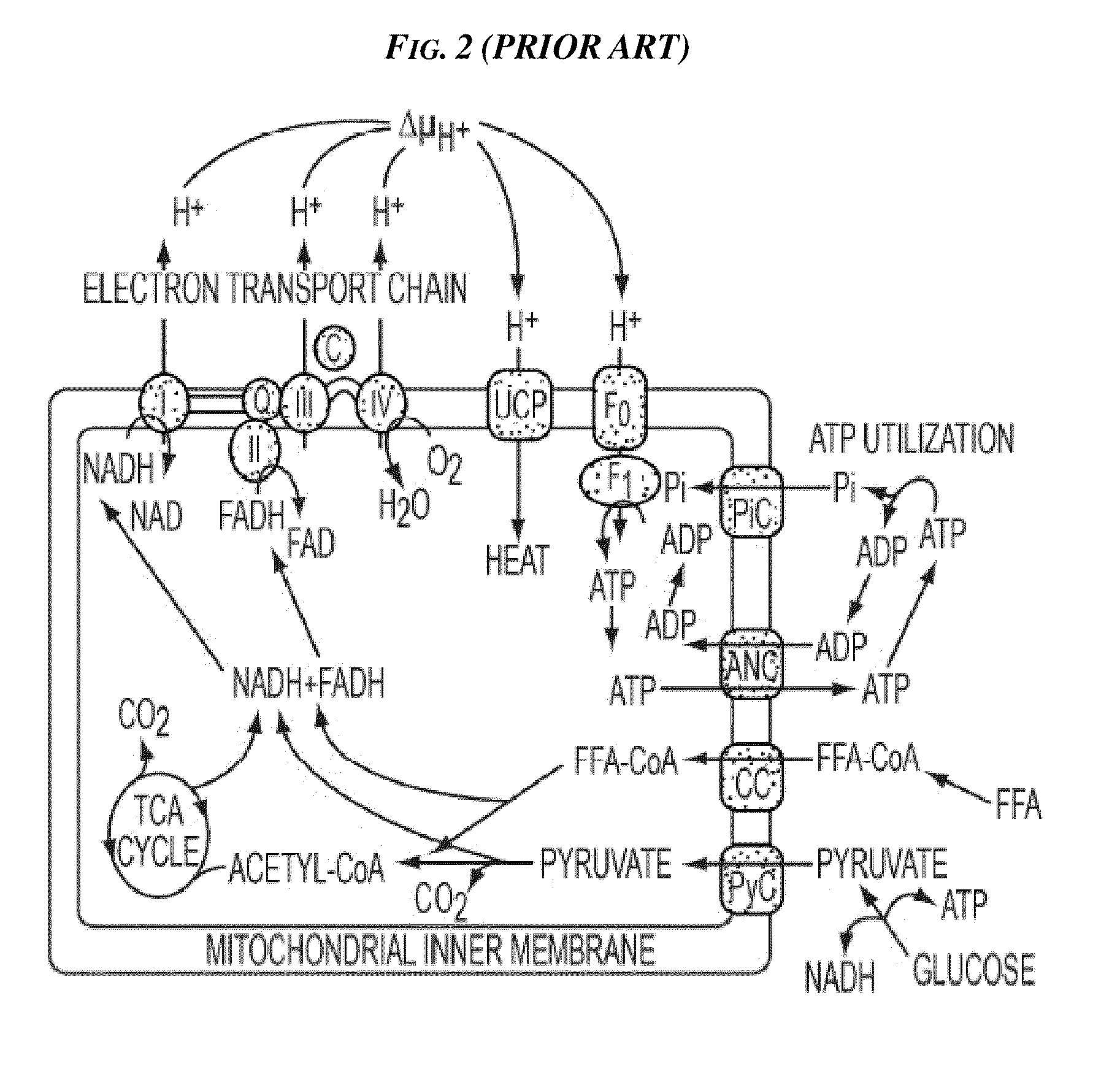
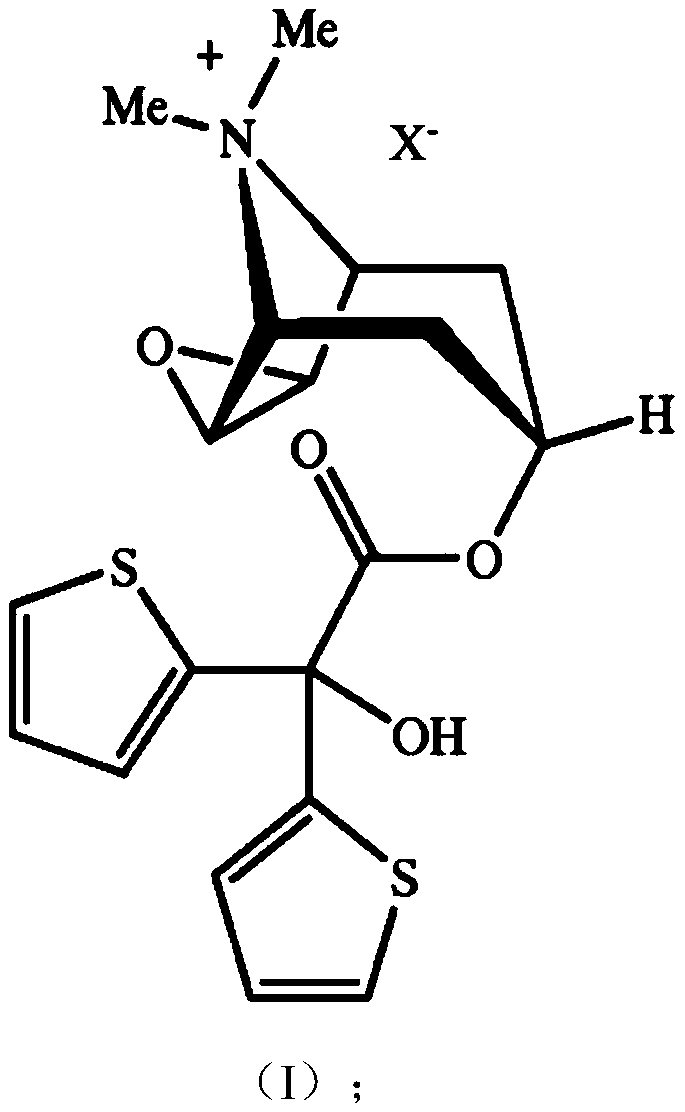
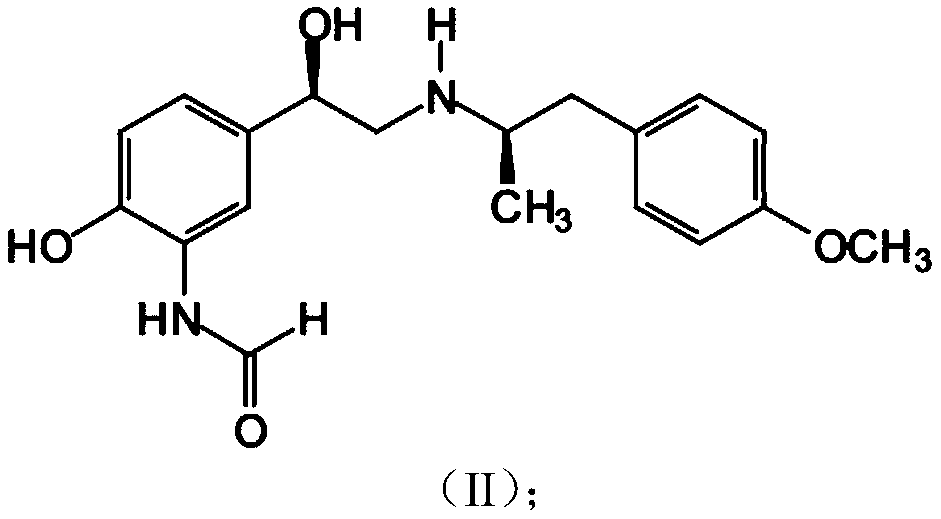
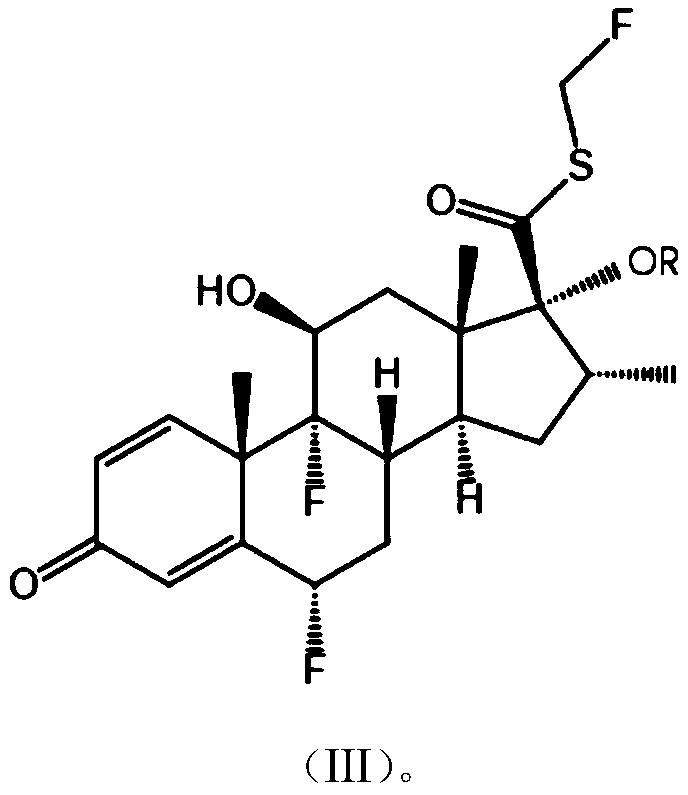
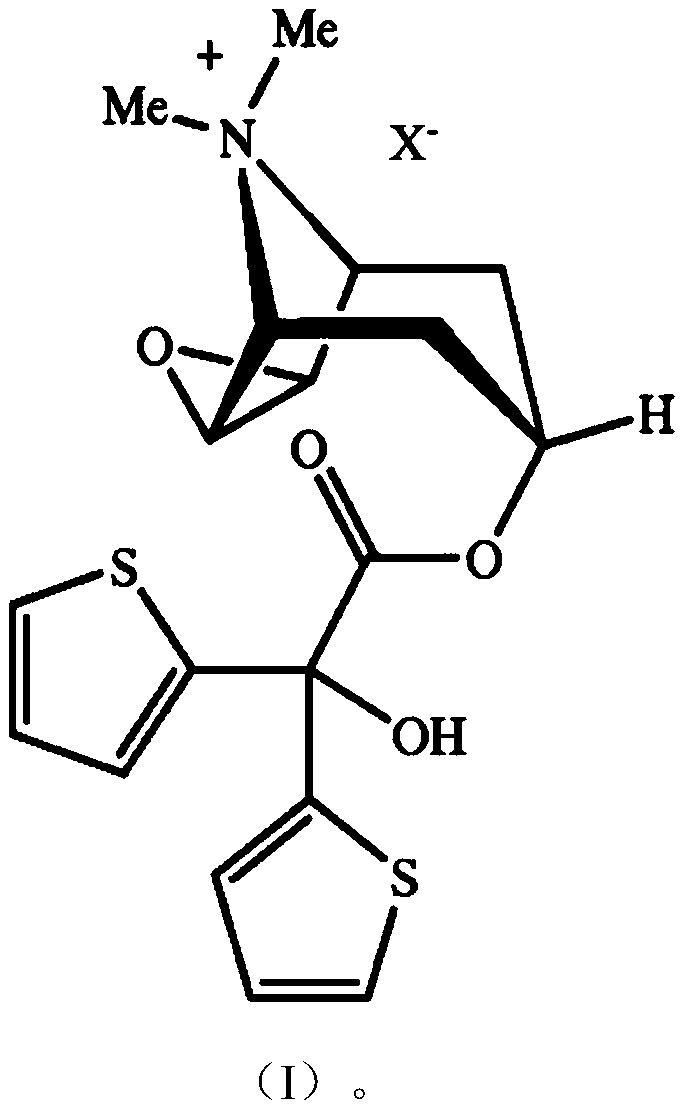
Patents
Literature
52 results about "Parasympathetic nerve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the brain, the parasympathetic system arises from the oculomotor nerve, the facial nerve, the glossopharyngeal nerve, and the vagus nerve. Near the tailbone, the PNS originates from the second, third, and fourth sacral nerves.
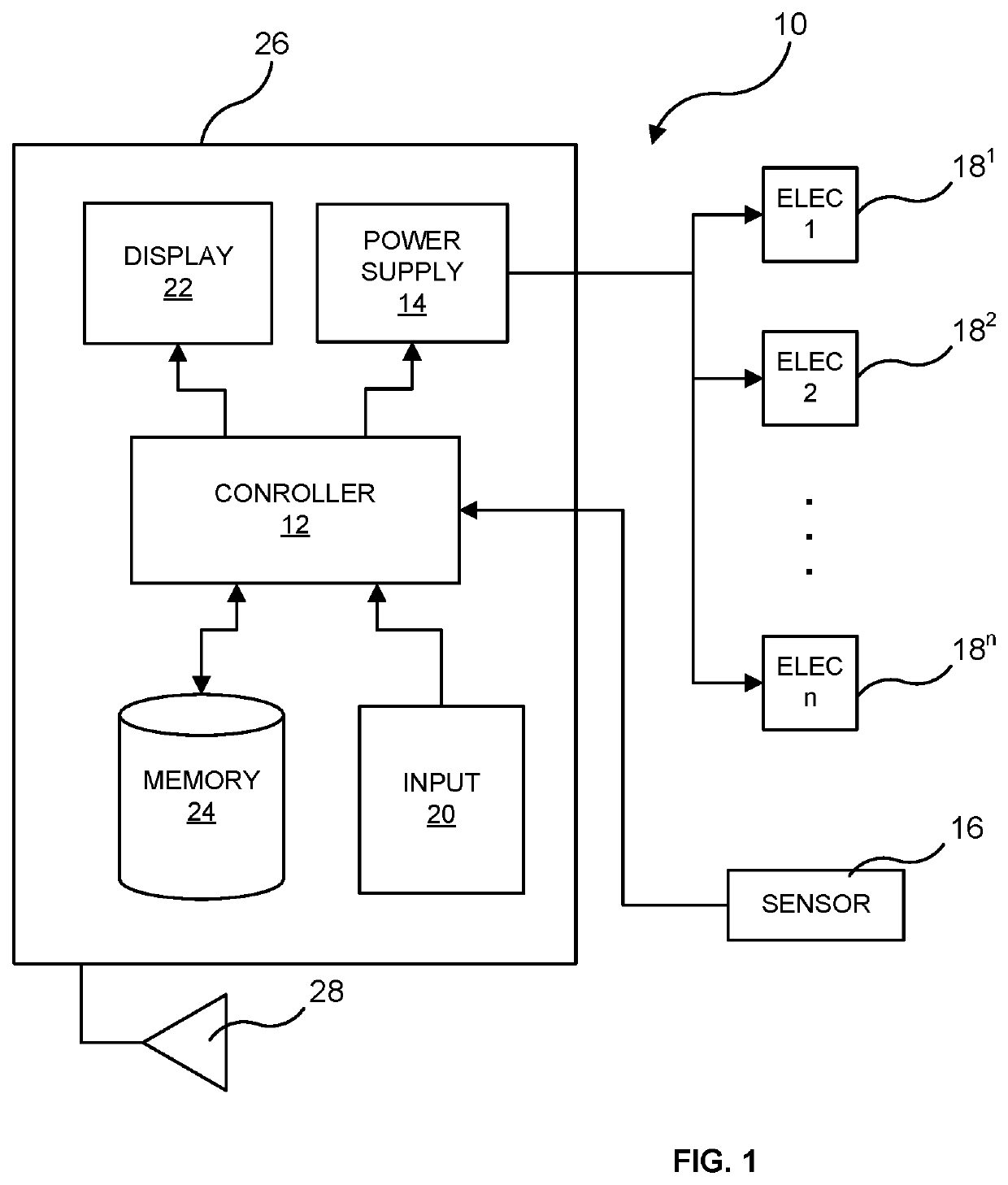
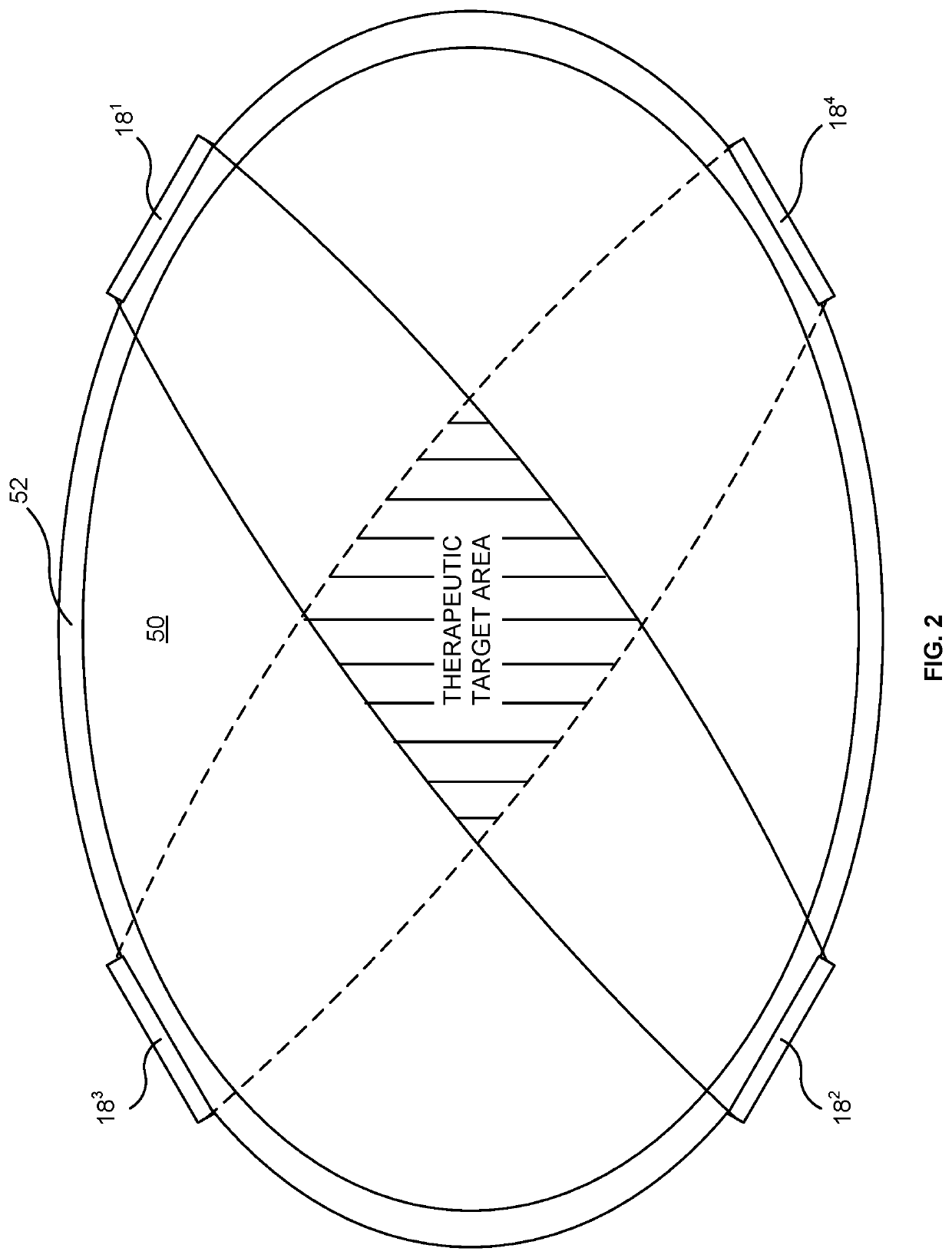
Parasympathetic nerve stimulation
InactiveUS20120303080A1Optimal ventricular rateSlow heart rateSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsPower flowMedicine
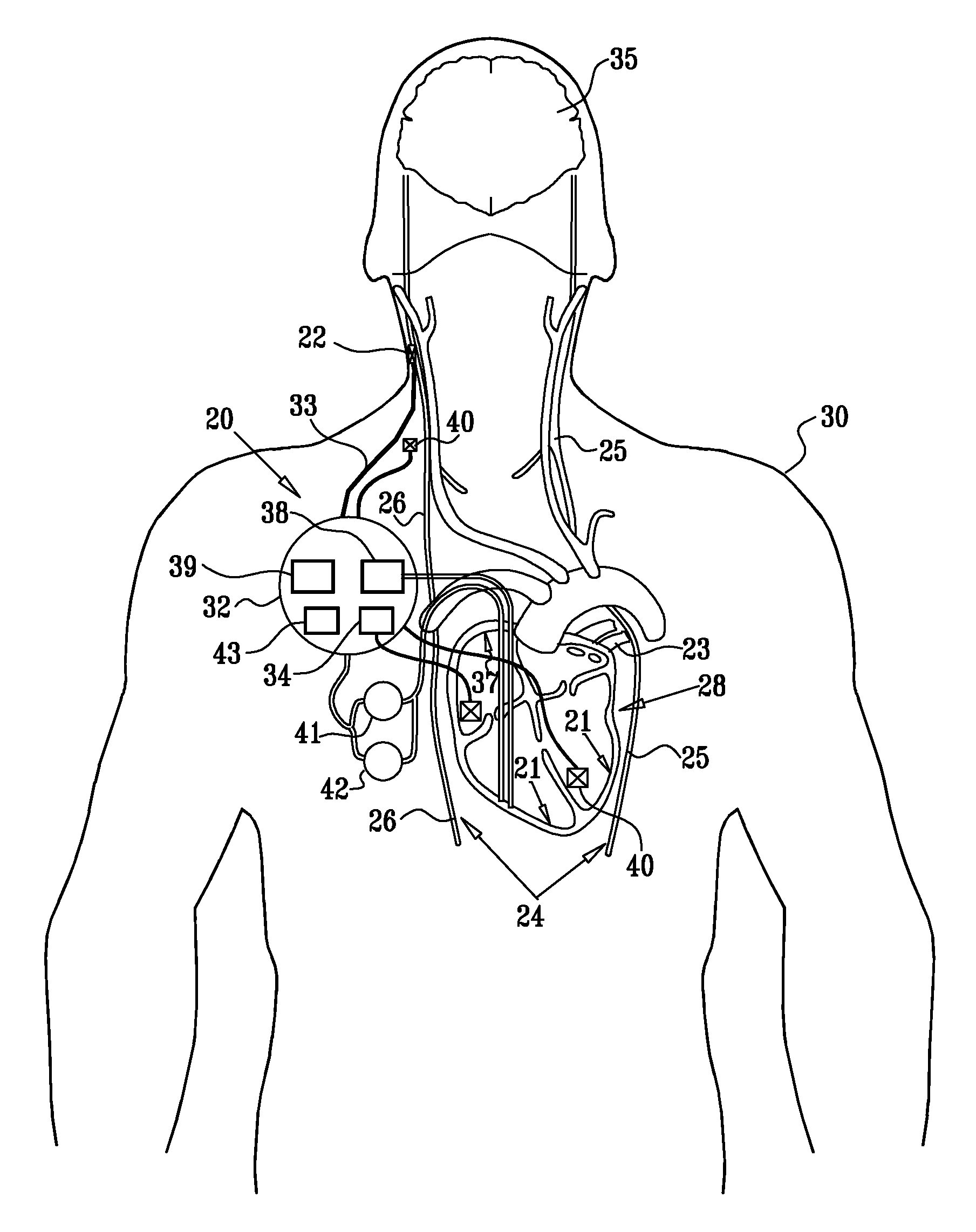
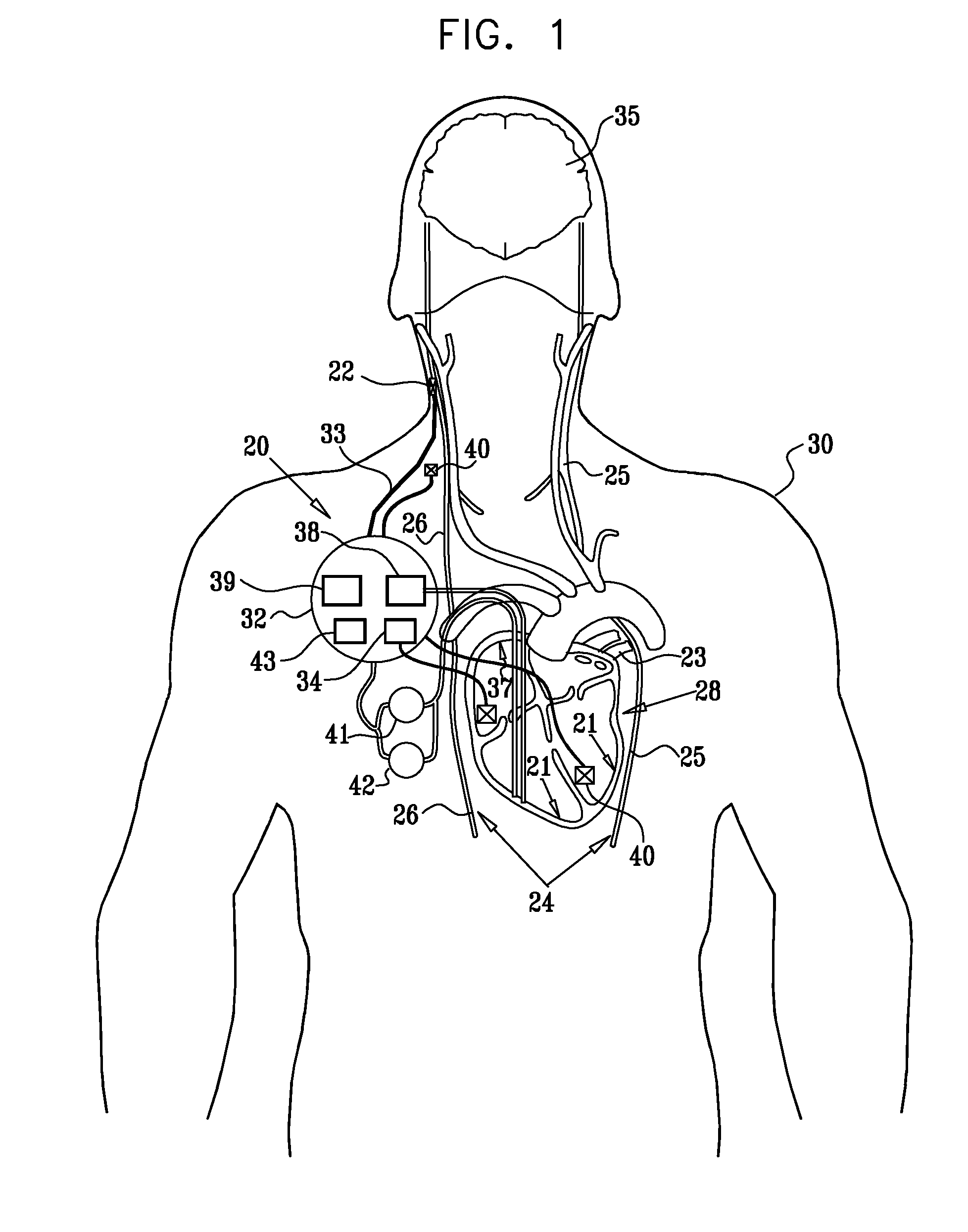
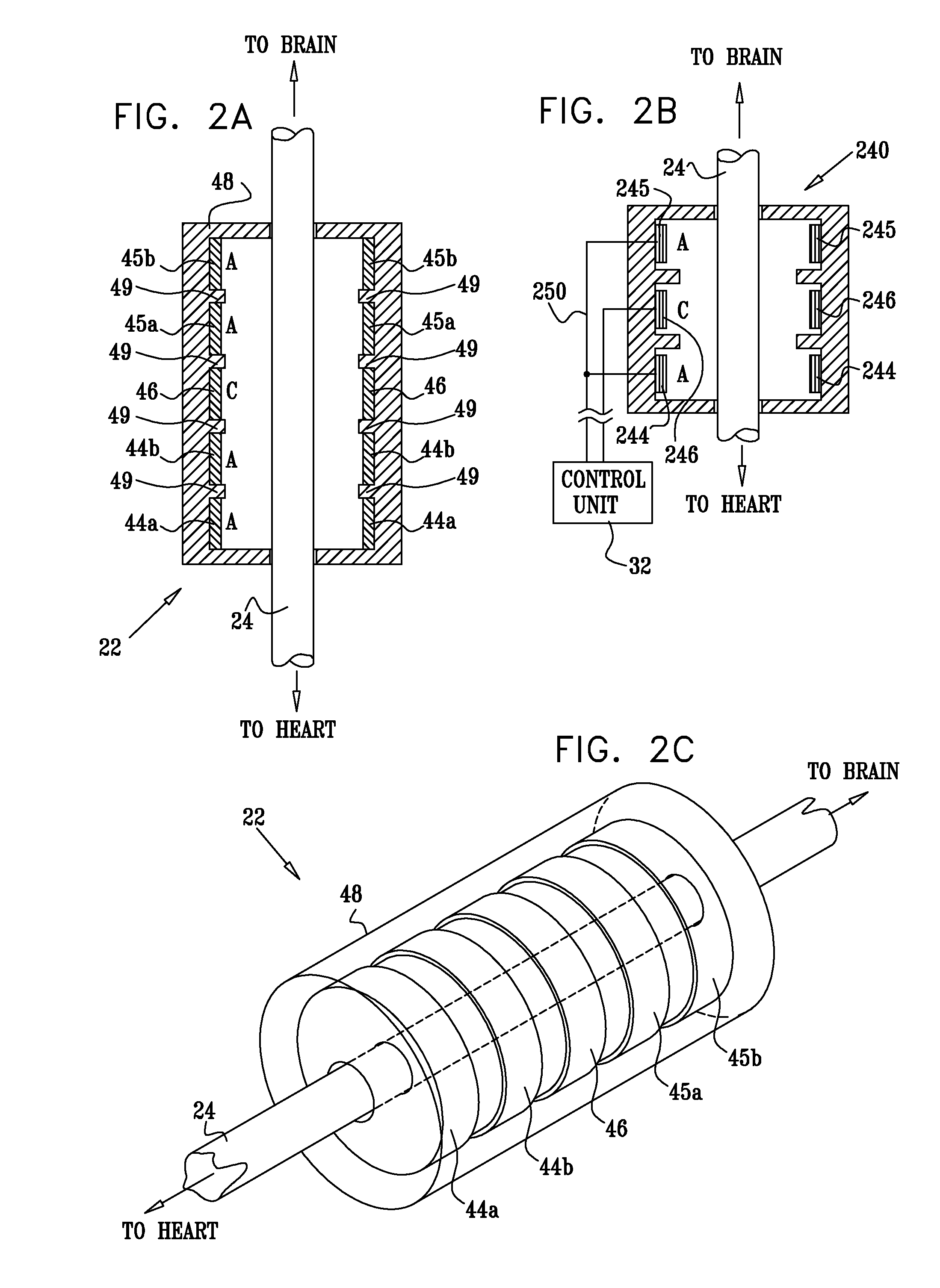
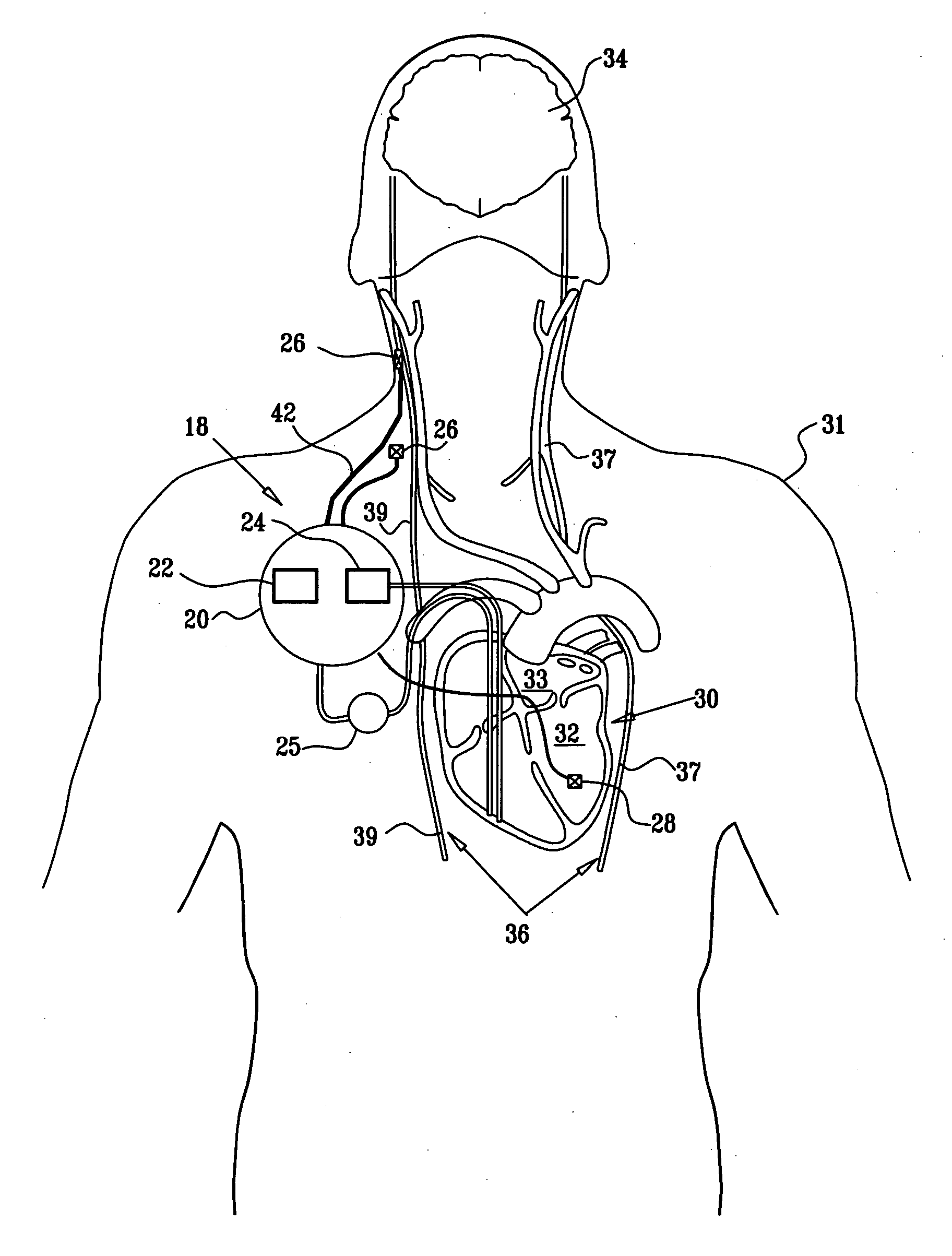
A method is provided, including identifying that a subject is at risk of suffering from atrial fibrillation (AF). Responsively to the identifying, a risk of an occurrence of an episode of the AF is reduced by coupling an electrode device to a site of a subject containing parasympathetic nervous tissue; driving, by a control unit, the electrode device to apply an electrical current to the site not responsively to any physiological parameters sensed by any device directly or indirectly coupled to the control unit; and configuring the current to stimulate autonomic nervous tissue in the site. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Parasympathetic pacing therapy during and following a medical procedure, clinical trauma or pathology
ActiveUS20060206155A1Increase parasympathetic toneReduced responseSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsParasympathetic ganglionPathology diagnosis
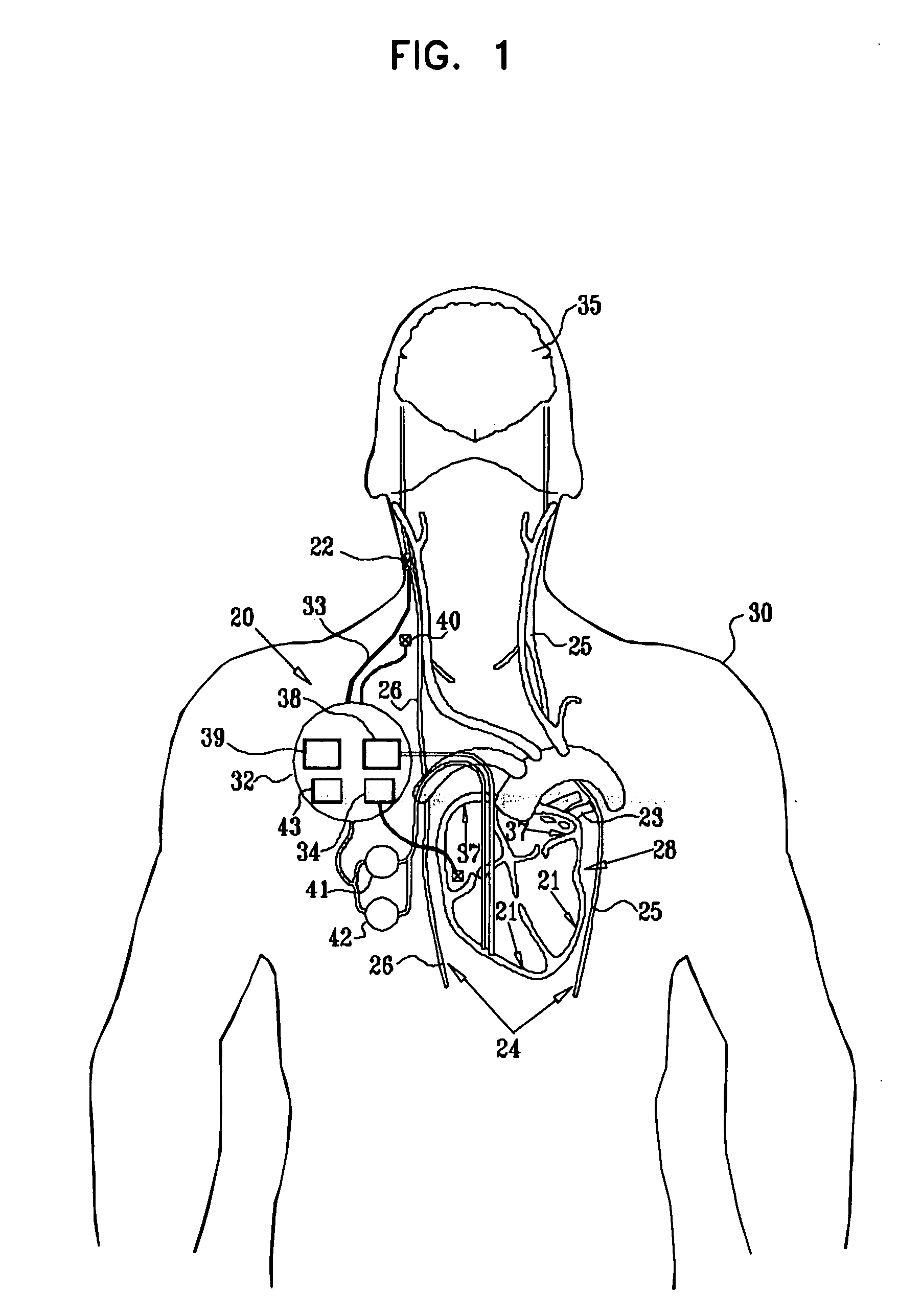
A treatment method is provided, including identifying a subject as one who is selected to undergo an interventional medical procedure, and, in response to the identifying, reducing a likelihood of a potential adverse effect of the procedure by applying an electrical current to a parasympathetic site of the subject selected from the group consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a jugular vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, a parasympathetic ganglion of the subject, and a parasympathetic nerve of the subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
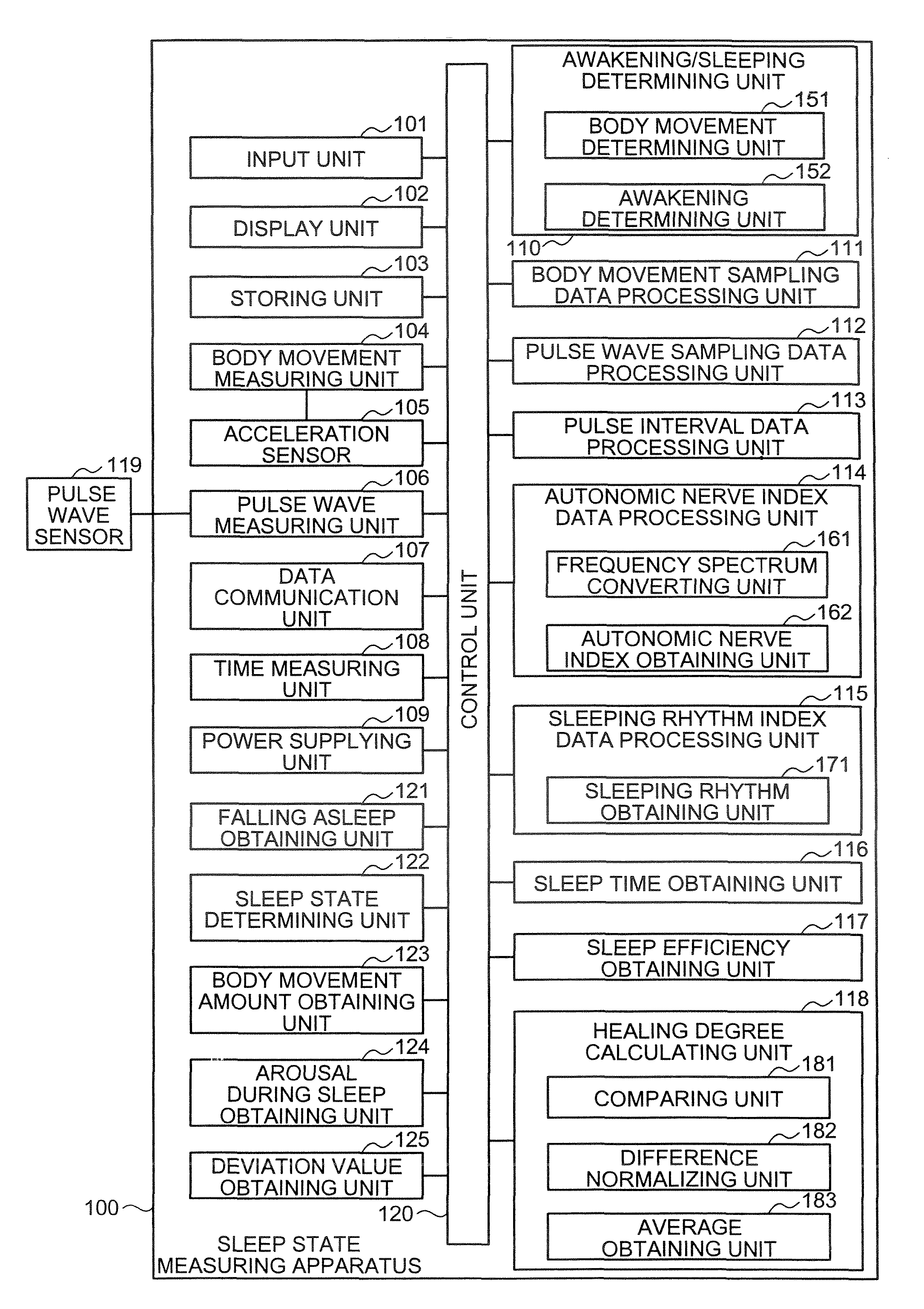
Apparatus, method and system of measuring sleep state
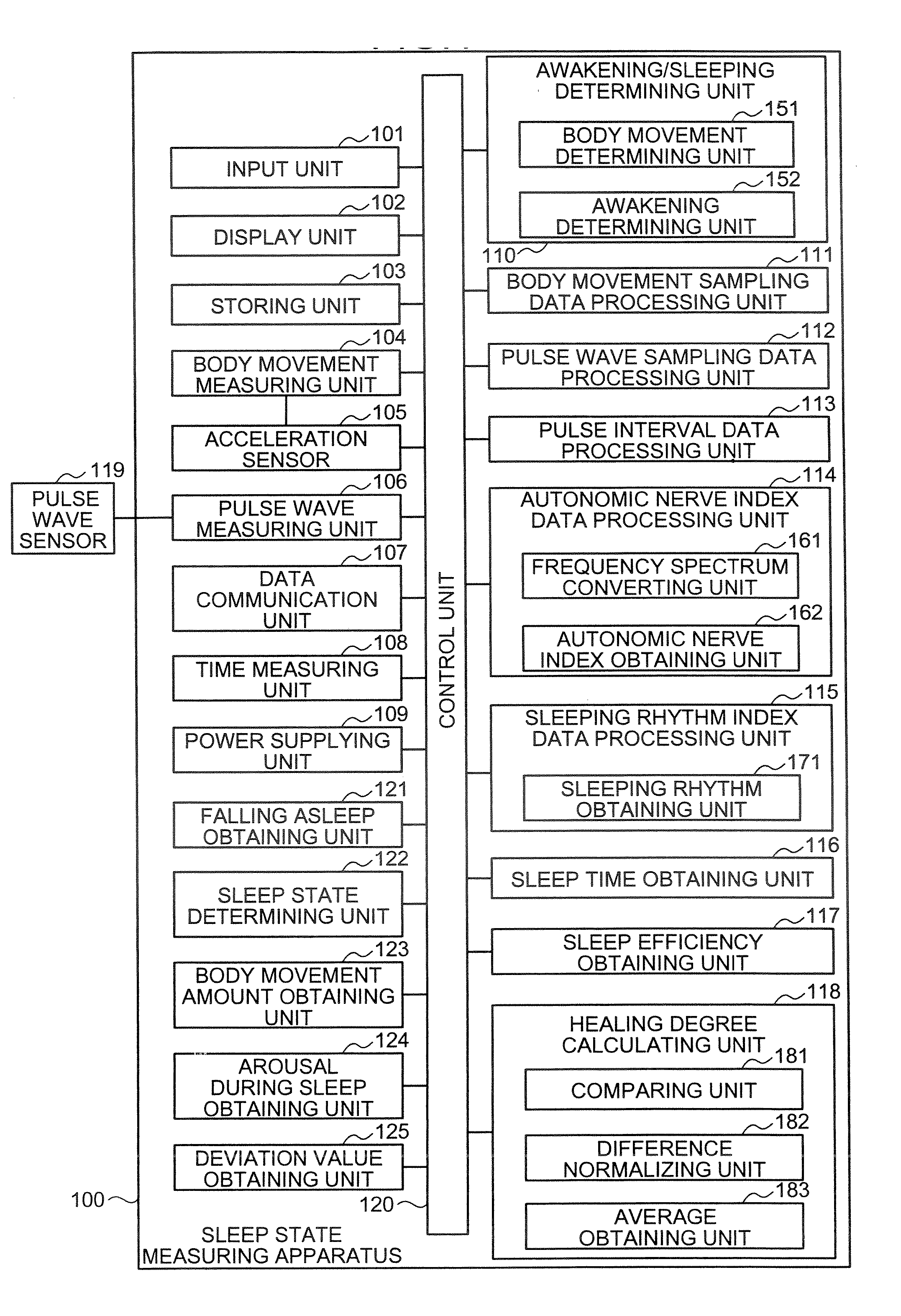
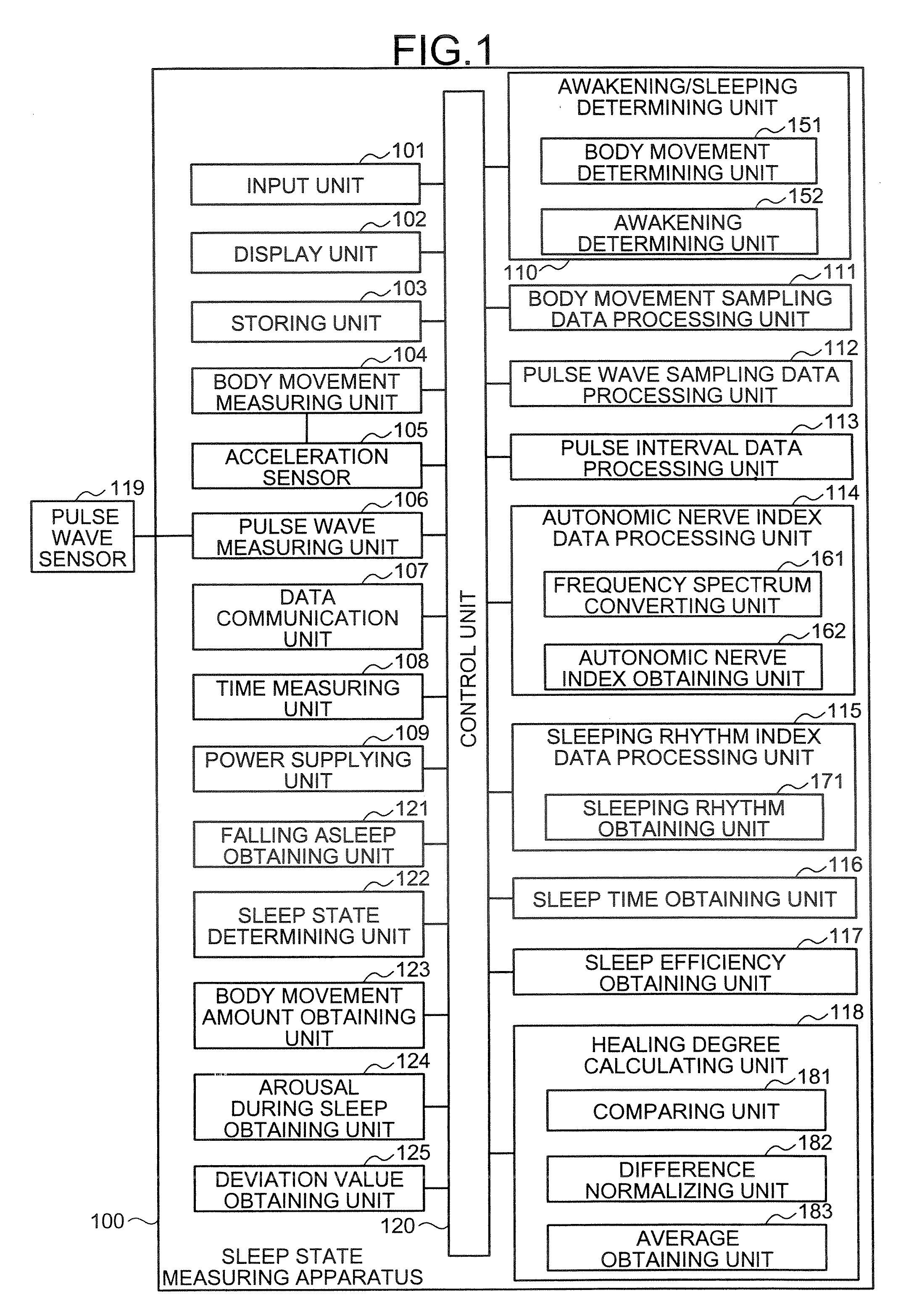
A sleep state measuring apparatus includes an autonomic nerve index obtaining unit that obtains a user's autonomic nerve index; and a sleep periodicity index calculating unit that calculates a sleep periodicity index based on a temporal change of the autonomic nerve index and a change in a user's sleeping cycle, wherein the sleep periodicity index indicates whether the user is sleeping or not according to a user's ideal sleeping cycle as an index, or a dominance index calculating unit that calculates a parasympathetic nerve dominance index which shows dominance of a parasympathetic nerve index included in the autonomic nerve index with respect to a sympathetic nerve index included in the autonomic nerve index for a user during sleep.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Treatment for disorders by parasympathetic stimulation
InactiveUS20080086182A1Increase parasympathetic toneReduced responseSpinal electrodesHeart defibrillatorsDiseaseParasympathetic ganglion
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus, method and system of measuring sleep state
A sleep state measuring apparatus includes an autonomic nerve index obtaining unit that obtains a user's autonomic nerve index; and a sleep periodicity index calculating unit that calculates a sleep periodicity index based on a temporal change of the autonomic nerve index and a change in a user's sleeping cycle, wherein the sleep periodicity index indicates whether the user is sleeping or not according to a user's ideal sleeping cycle as an index, or a dominance index calculating unit that calculates a parasympathetic nerve dominance index which shows dominance of a parasympathetic nerve index included in the autonomic nerve index with respect to a sympathetic nerve index included in the autonomic nerve index for a user during sleep.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Combined parasympathetic stimulation and cardiac pacing
InactiveUS20080091245A1Reduce frequencyIncreased riskHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsThrombusControl cell
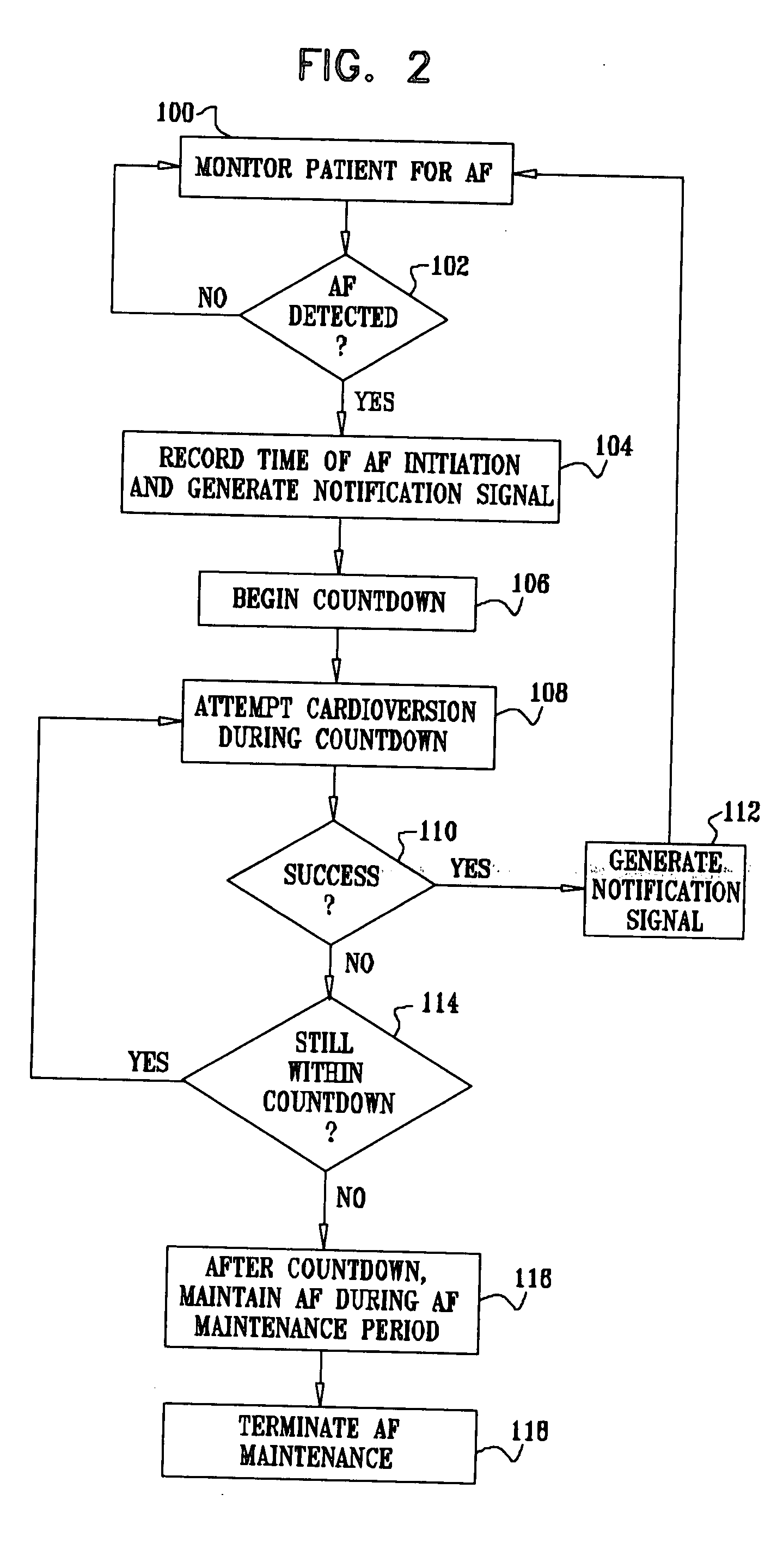
Apparatus for treating a subject suffering from spontaneous atrial fibrillation includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a vagus nerve of the subject, and a control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply an electrical current to the vagus nerve, and to configure the current to maintain the spontaneous AF for at least about 24 hours, so as to modify blood flow within the atria and reduce risk of thromboembolic events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Sleep condition measuring apparatus and method
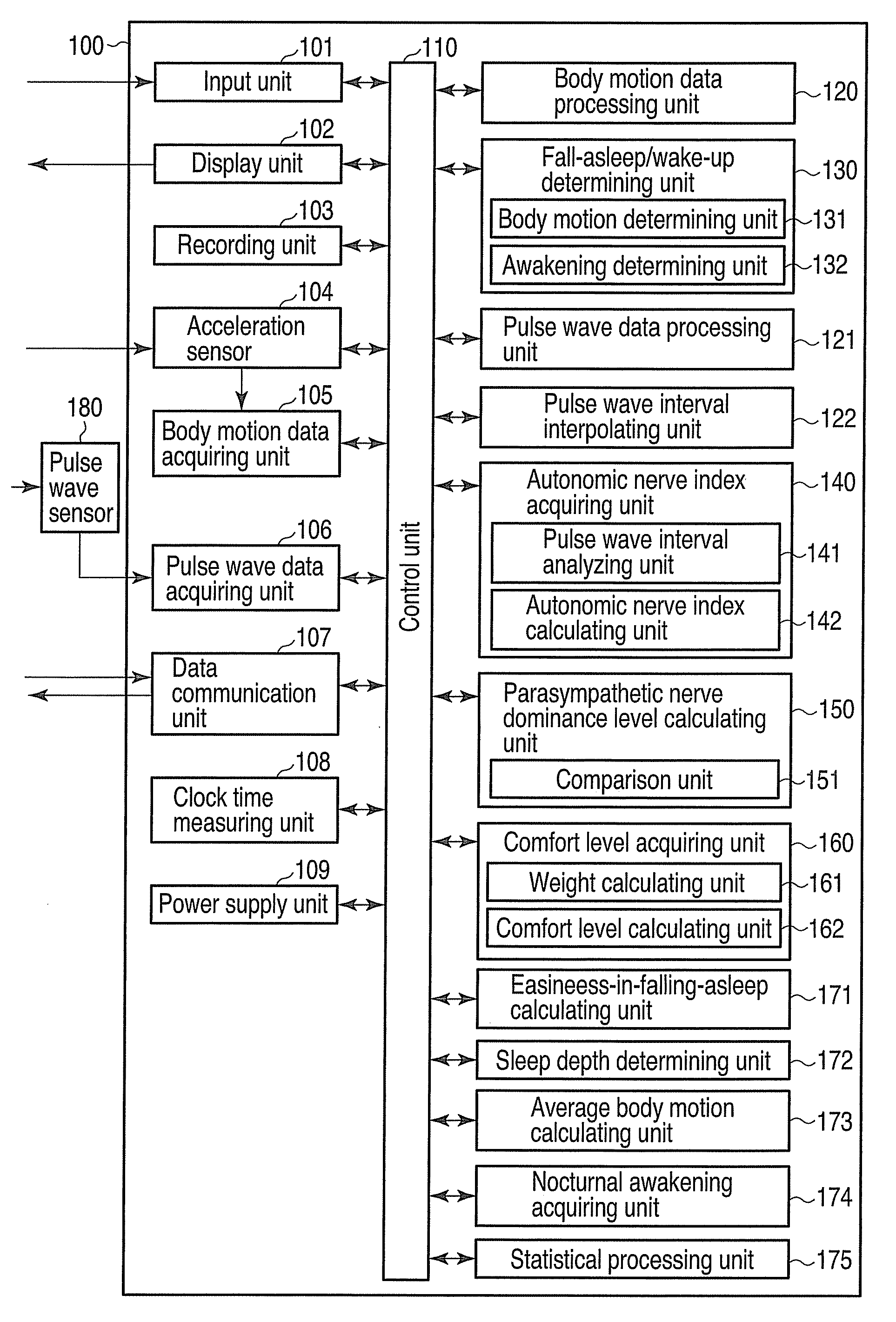
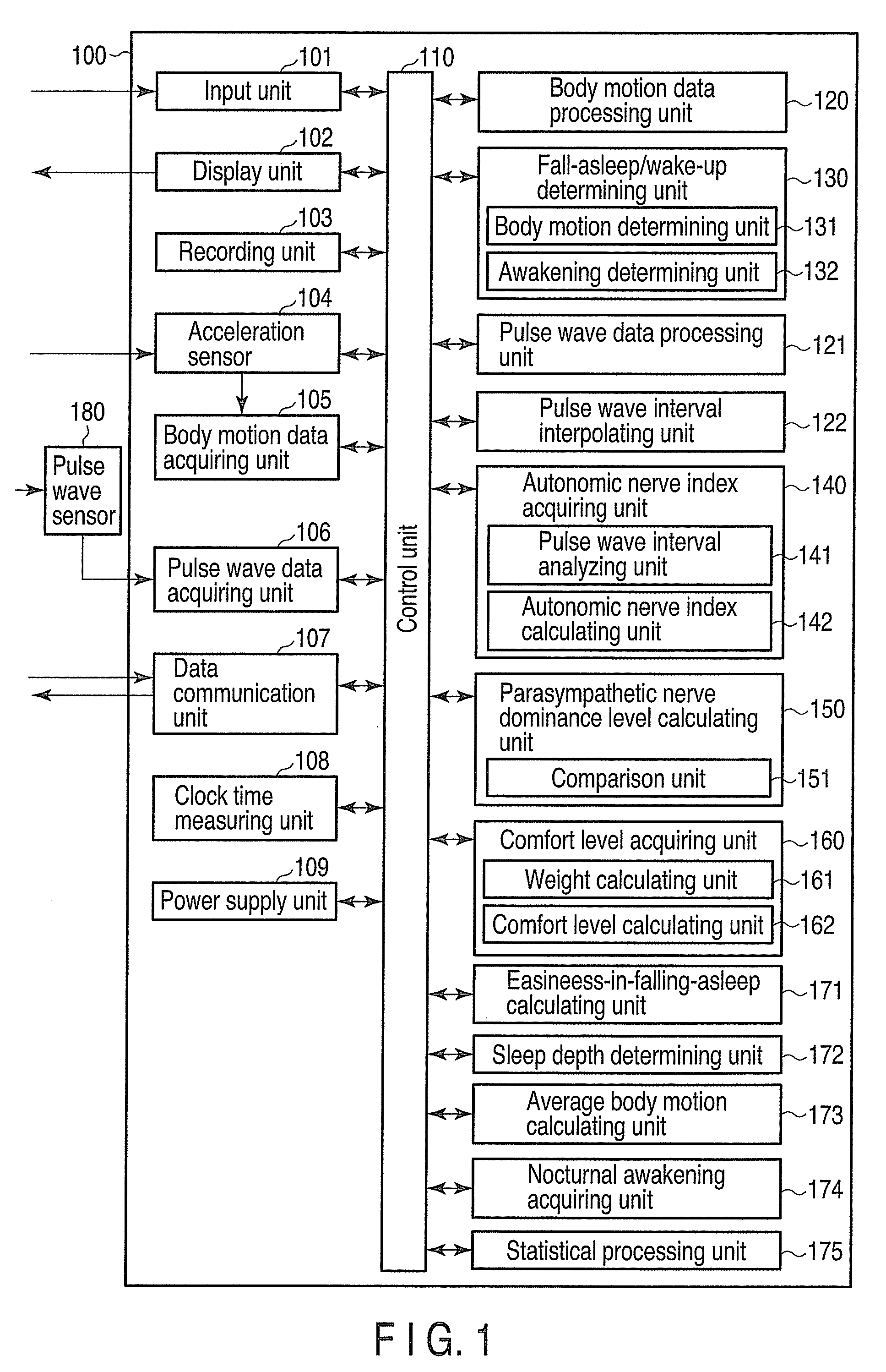
A sleep condition measuring apparatus includes a determination unit configured to determine a first timing indicating that the user has fallen asleep and a second timing indicating that the user has waken up, based on body motion of a user, an acquisition unit configured to acquire a first index indicating activity of a sympathetic nerve of the user and a second index indicating activity of a parasympathetic nerve of the user, based on a pulse wave interval of the user, a calculation unit configured to calculate a dominance level of the second index over the first index every predetermined time, and a calculation unit configured to calculate a third index indicating quality of sleep of the user from the first timing until the second timing, using the dominance level and a weight decreasing as time elapses from the first timing.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
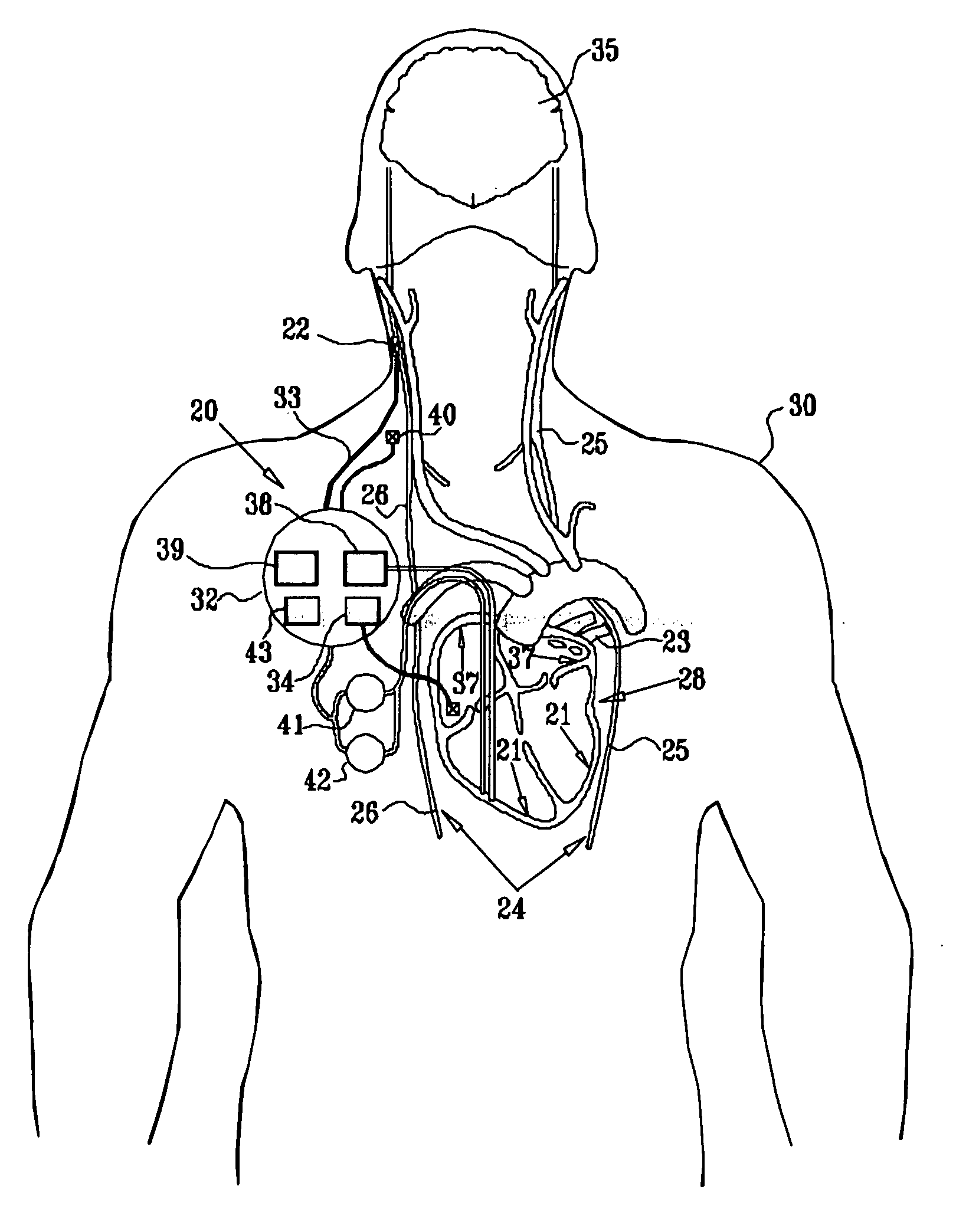
Wholly implantable non-natural heart for humans
InactiveUS20090287305A1Efficient solutionSuitable for miniaturizationControl devicesBlood pumpsHigh energyBreast bone
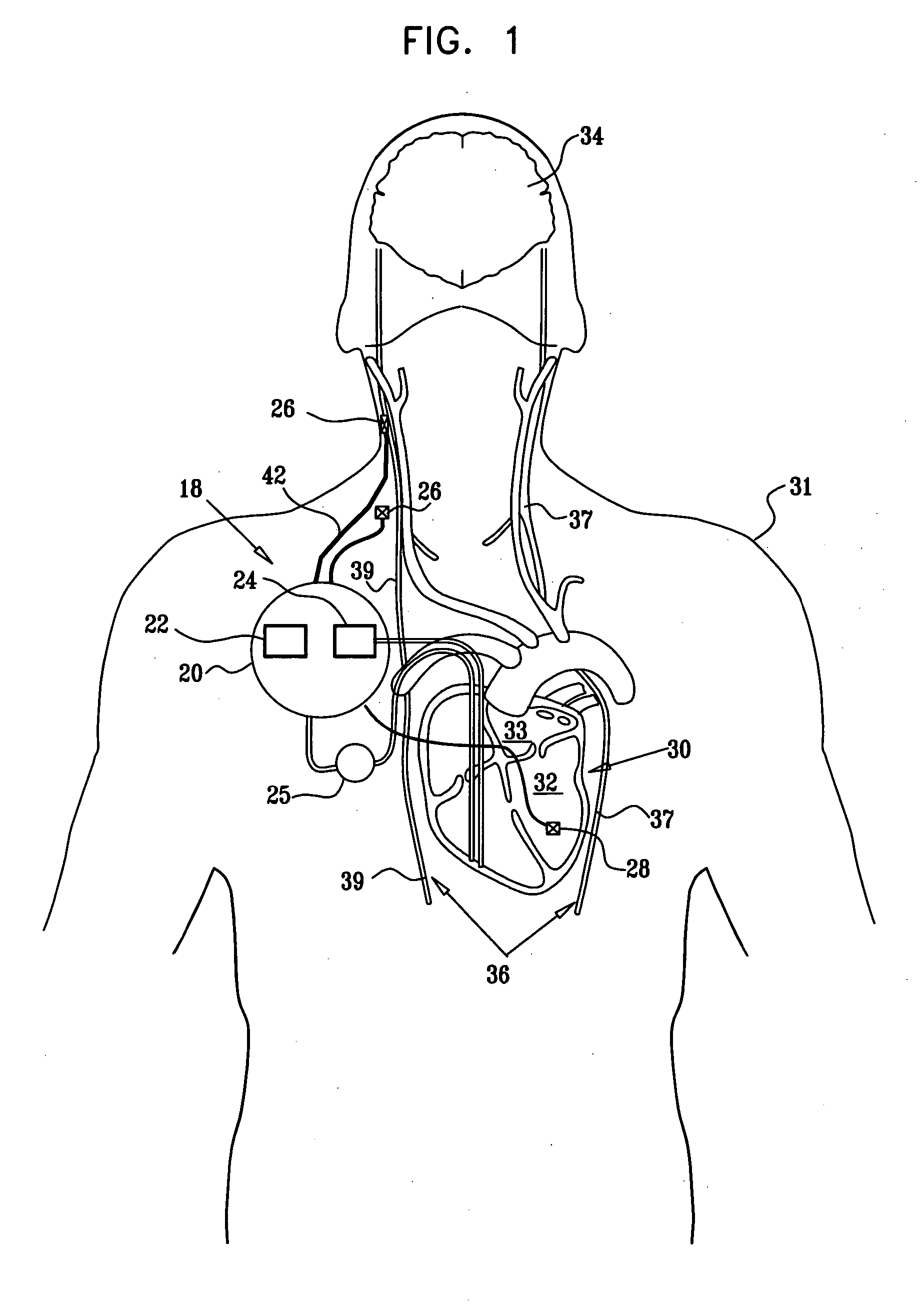
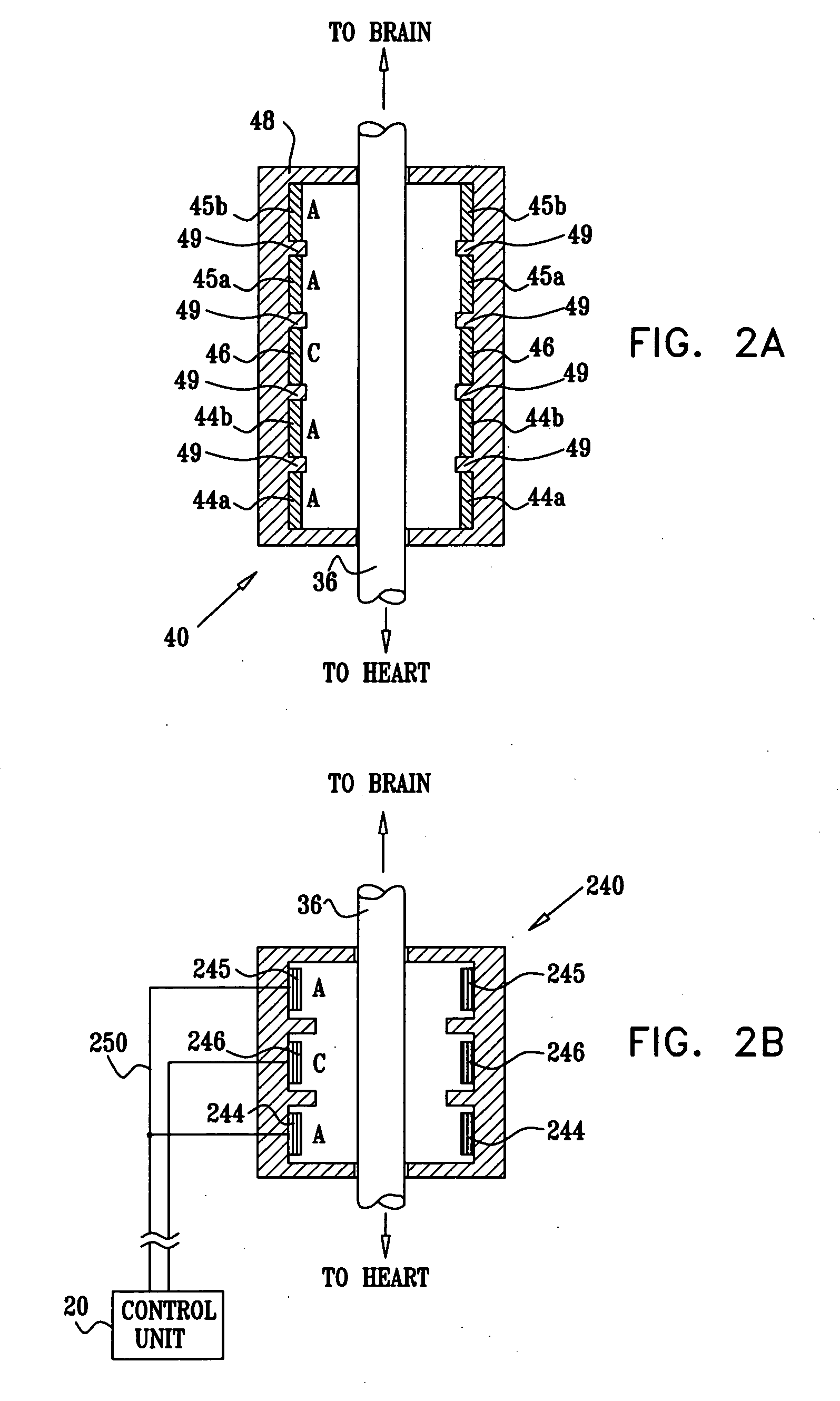
A wholly implantable non-natural heart for humans is a double pump configuration provided with two auricles and two ventricles. Both the said auricles and ventricles are driven by solenoid actuators interacting with high energy magnets; the auricles and ventricles which are hollow chambers are provided with one-way valves in the usual manner, for the purpose of effectively and rhythmically moving blood to and from the said chambers; power generation for driving said solenoid actuators, as well as an electronic control unit is accomplished by a power generating module which could be a simple battery, a miniature spring-driven generator, a mems generator or a redundant self-sustaining generator or a combination of all of the above; the self-sustaining generator has been proposed and designed to power this present artificial heart and will be presented in a separate patent application in the near future as a follow up to this present one; the aforementioned electronic control unit is preferably configured to amplify the signals from the power generating unit as well as utilizing input / output signals from temperature and pressure sensors embedded in the heart to vary contractile force and frequency of beats, based on bodily requirements, thereby mimicking some functions of the natural heart; the electronic unit is also preferably provided with a translator chip that converts signals from the cardiac / vargus trunks (sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves) via electrodes into clear electric currents for varying actuator outputs; the heart would be implanted in the normal position in the chest, atop the diaphragm, while the electronic control unit and the power generation module would preferably be implanted behind the breastbone and lower abdomen respectively; all components of the present invention are amenable to current mass production techniques and miniaturization for the purpose of fitting into individuals of various sizes; as is clearly shown in FIG. 1, this present invention is an integral three-tiered configuration constituted of pumping unit I, the power generating unit II and the controller III. Also, as aforementioned, additional signals from the embedded temperature and pressure sensors, as well as nerve connecting electrodes are used to manipulate instantaneous outputs. The said electrodes are in the form of cuffs and are to be implanted on the vargus nerves (sympathetic and parasympathetic); Texas Instruments (TI) manufactures reliable operational and instrumentation amplifiers which can detect condition, and amplify nerve signals. The VCO in the controller uses the signals to manipulate instantaneous outputs of the actuating solenoids.
Owner:AMALAHA LEONARD D
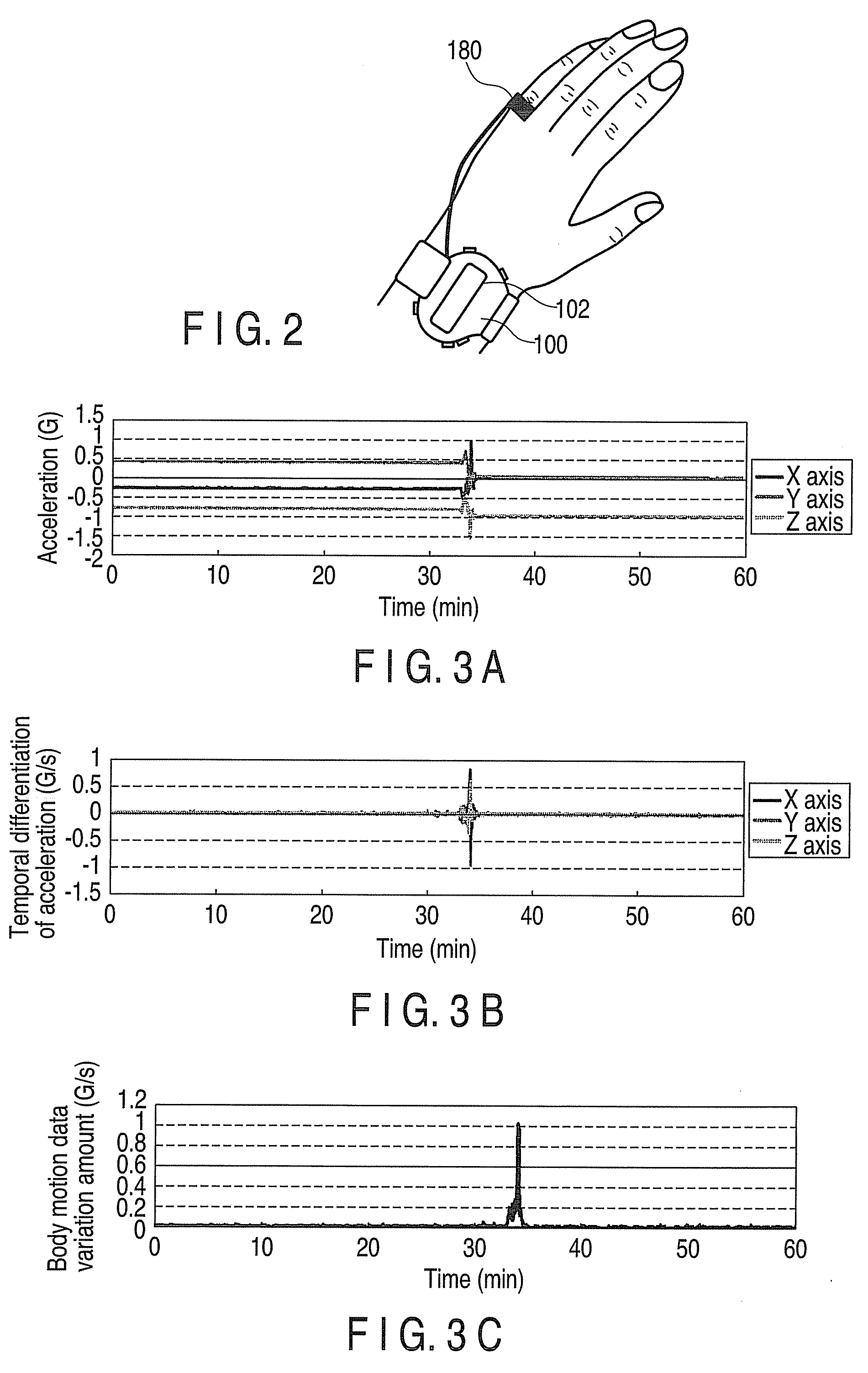
Method and device for measuring autonomic nerve heart regulation and control function
ActiveCN105455797AReduce the influence of other factorsIdeal control function measurement environmentEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsControl disordersHeart regulation
The invention relates to a method and device for measuring the autonomic nerve heart regulation and control function. The wearable device, an autonomic nerve heart regulation and control function mathematical model and an autonomic nerve heart regulation and control system parameter calculation method are involved in the method. The wearable device is used for measuring motion data, continuous blood pressure and a heart rate value sequence in a human body standing-up or inclining test. The autonomic nerve heart regulation and control function mathematical model is used for quantitatively describing the blood pressure and heart rate regulation and control process in the standing-up process. According to the autonomic nerve heart regulation and control system parameter calculation method, a series of autonomic nerve heart regulation and control system parameters such as pressure sensor sensitivity and sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic nerve activity are solved based on the autonomic nerve heart regulation and control function mathematical model and the continuous blood pressure and the heart rate value sequence measured in the standing-up or inclining test through the wearable device. Autonomic nerve regulation and control disorders are represented by reduction of the pressure sensor sensitivity and reduction of the sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic nerve activity, which are the occurrence origins and independent indexes of many lethal cardiovascular diseases. Quantitative measurement of the pressure sensor sensitivity and the sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic nerve activity is of great significance on effective diagnosis and prevention of cardiovascular diseases, evaluation of treatment effects and recovery of patients.
Owner:南京茂森电子技术有限公司
Biological feedback control method and system based on HRV heart rate variability training
PendingCN107411726AImprove mental conditionPromote breathingInput/output for user-computer interactionGymnastic exercisingDiseaseBiological feedback
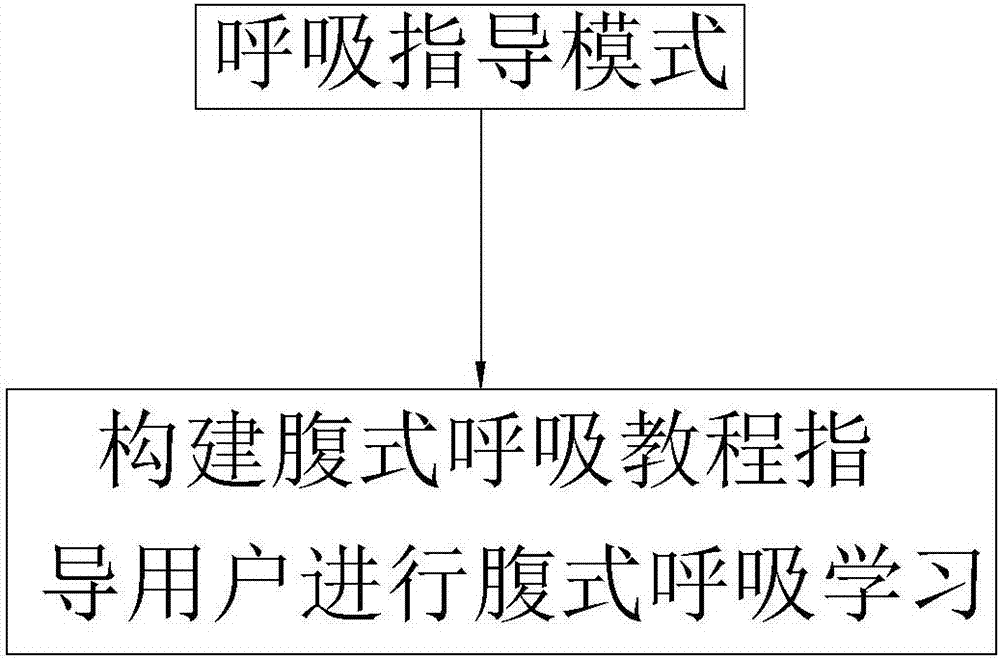
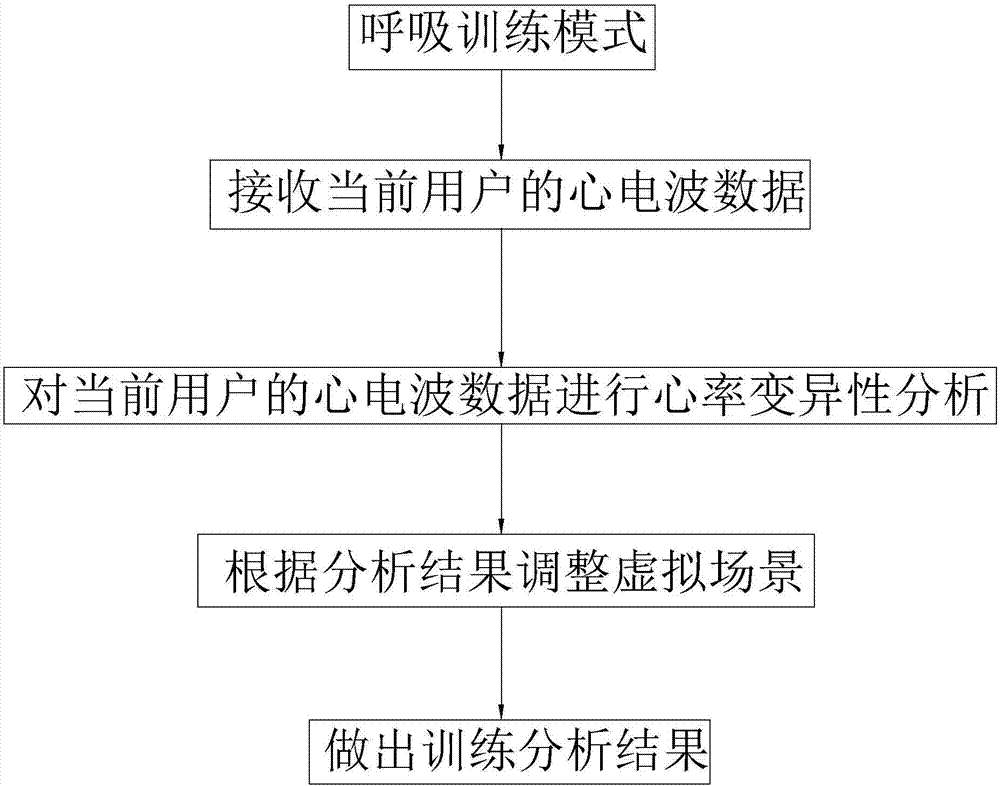
The invention provides a biological feedback control method and system based on HRV heart rate variability training. The biological feedback control method comprises the steps that S1, mode options of any one or more combinations including a breathing guiding mode, a breathing training mode and a state evaluating mode are provided for a user to select; and S2, a corresponding mode interface is entered according to the selecting operation of the user, and heart rate variability analyzing is conducted on the current user when the user selects the breathing training mode or the state evaluating mode. The biological feedback control method has the advantages that the biological feedback control method is not limited to simple evaluation any longer, by conducting pointed breathing trainings with different rhythms on the user, impaired parasympathetic nerves (or sympathetic nerves) can recover to be balanced, and the purpose of effective preventing or relieving some diseases is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FANJU SCI & TECH
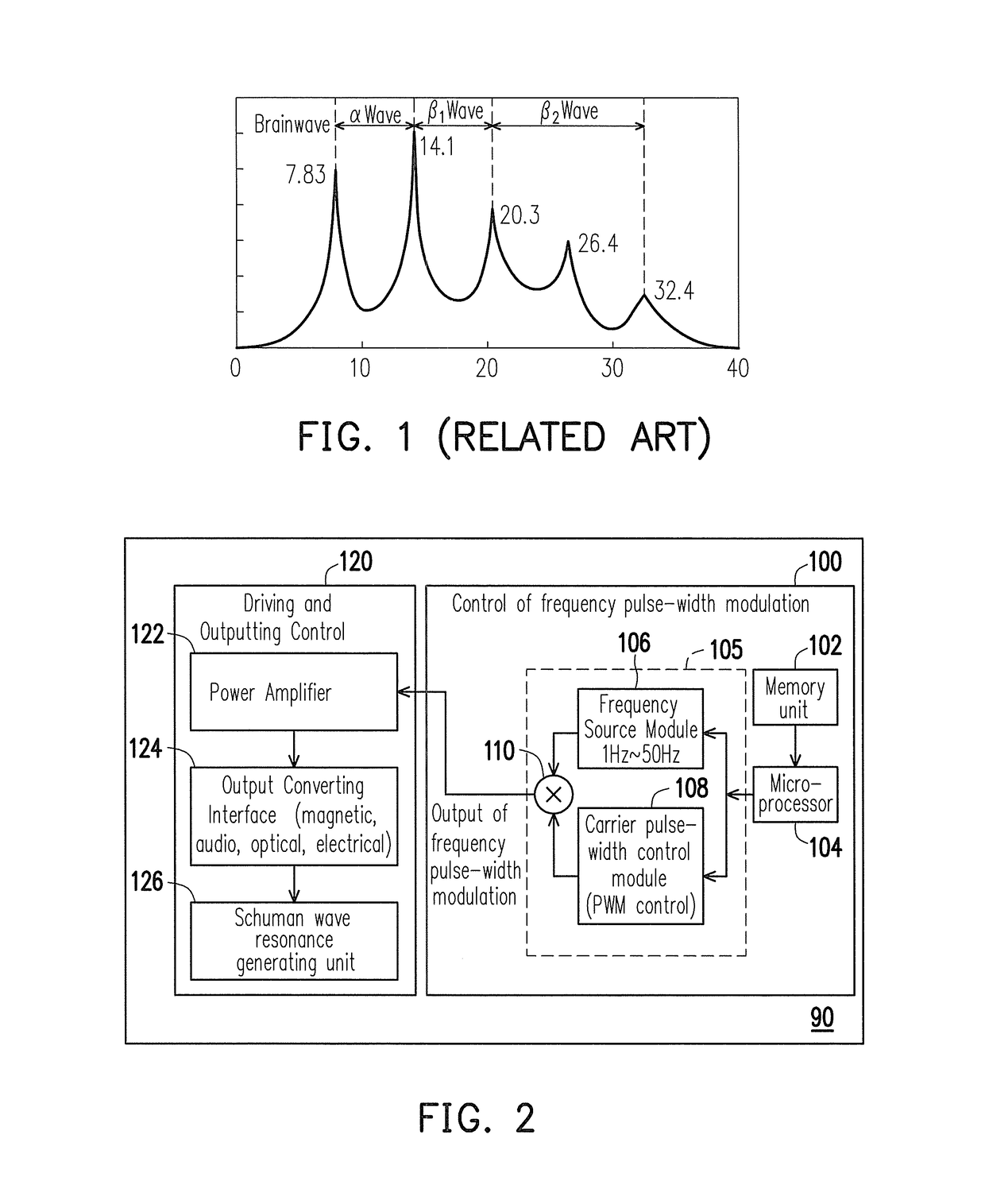
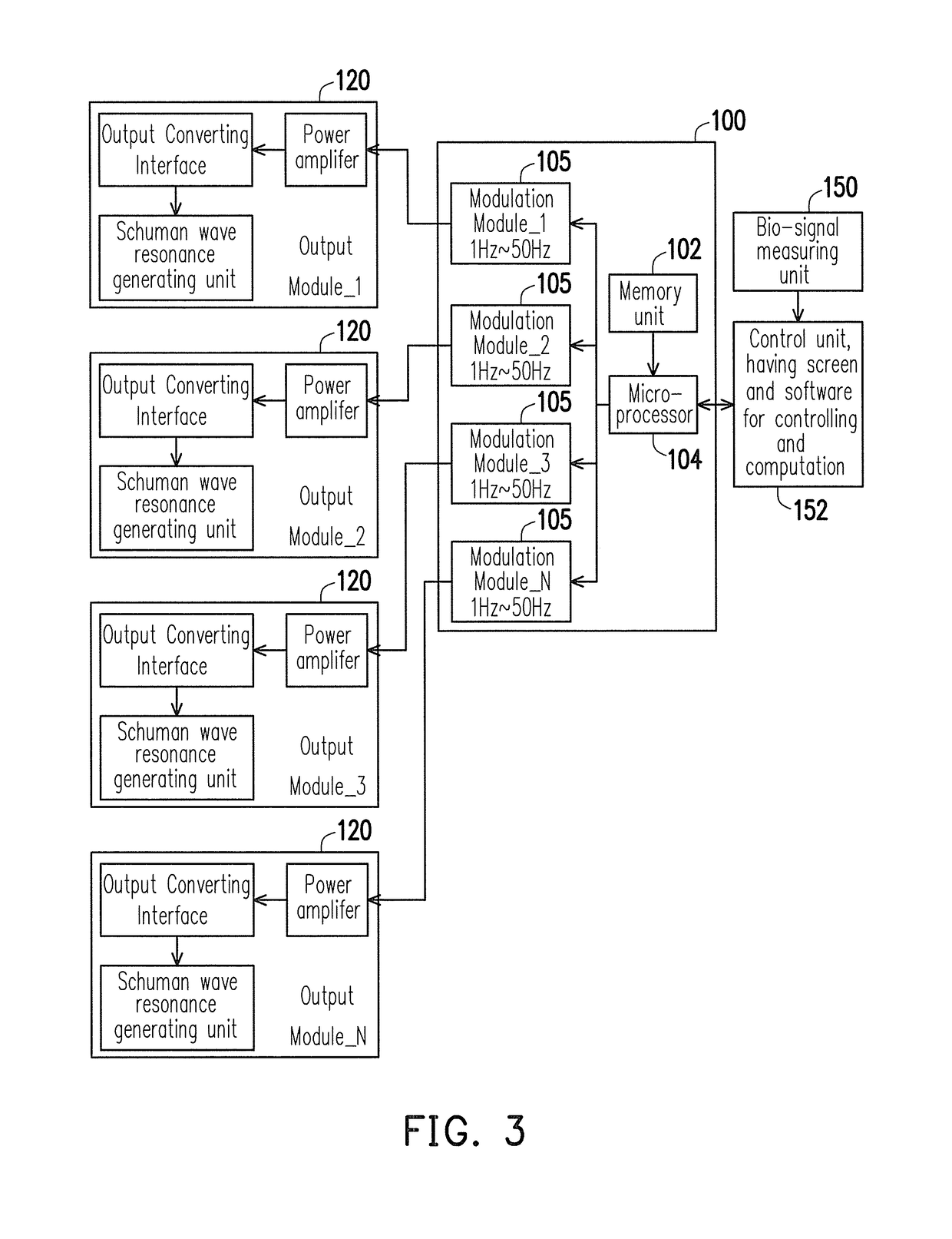
Pressure relief apparatus with brain entrainment
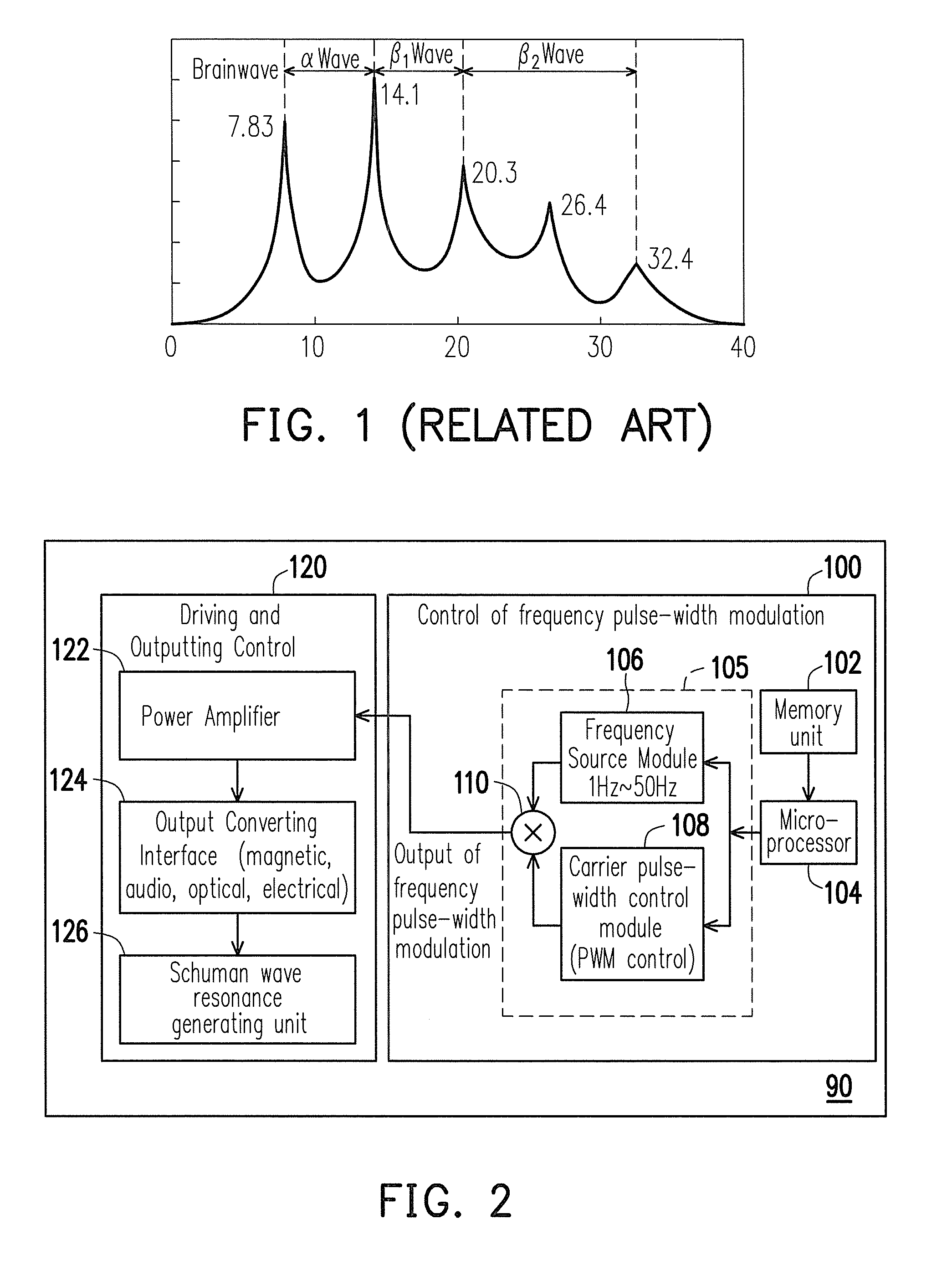
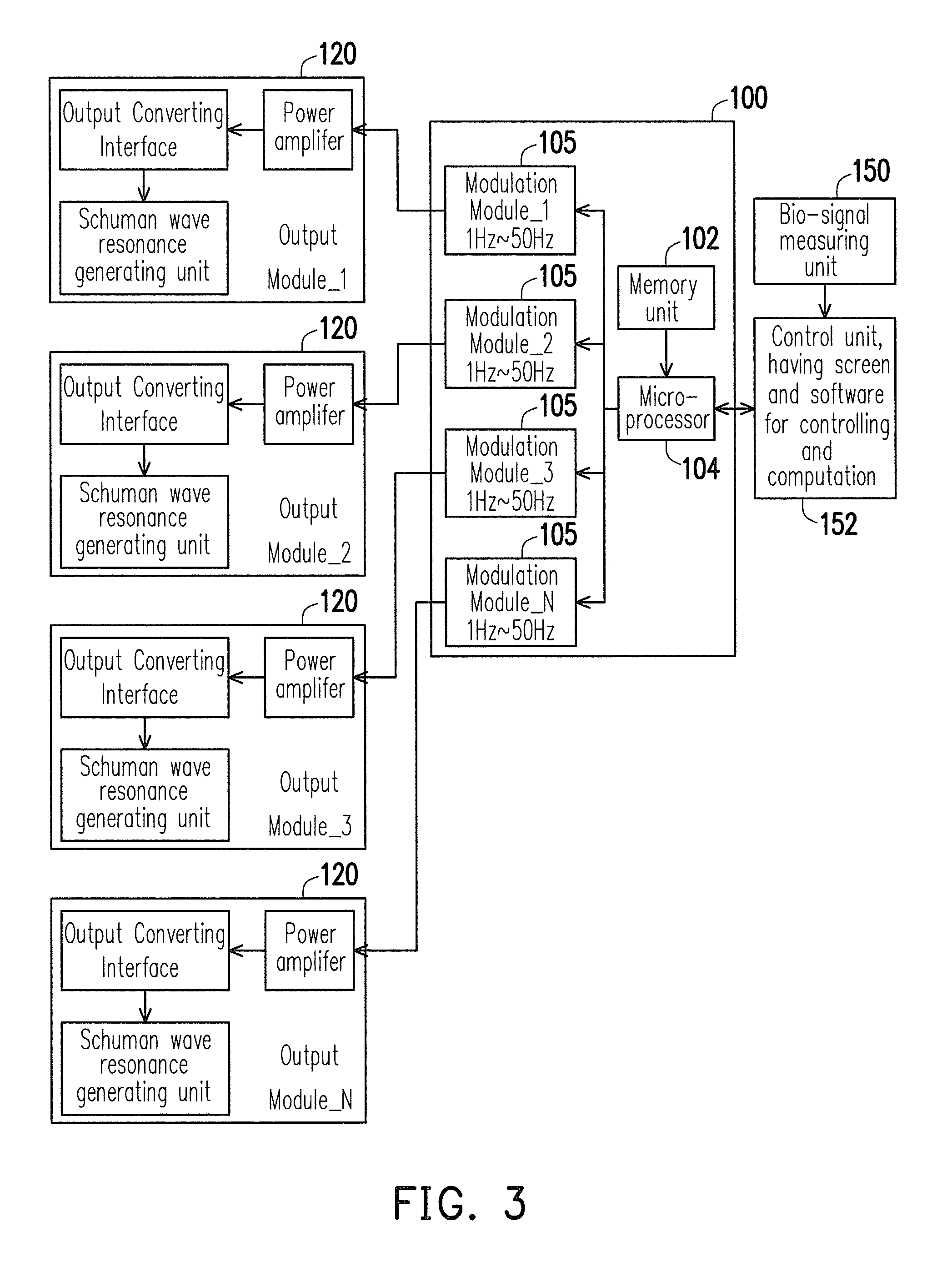
A pressure relief apparatus with brain entrainment includes a resonant wave generating module and a bio-signal measuring unit. The resonant wave generating module includes multiple resonant devices, divided into multiple regions. Each of the resonant regions can respectively generate a resonant wave being changeable or turned off. The bio-signal measuring unit at least measures an energy of autonomic sympathetic nerve system LH and an energy of autonomic parasympathetic nerve system HF. According to a current one of a set of present conditions, a set of feedback control signals is output to the resonant wave generating module to modulate the resonant devices.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
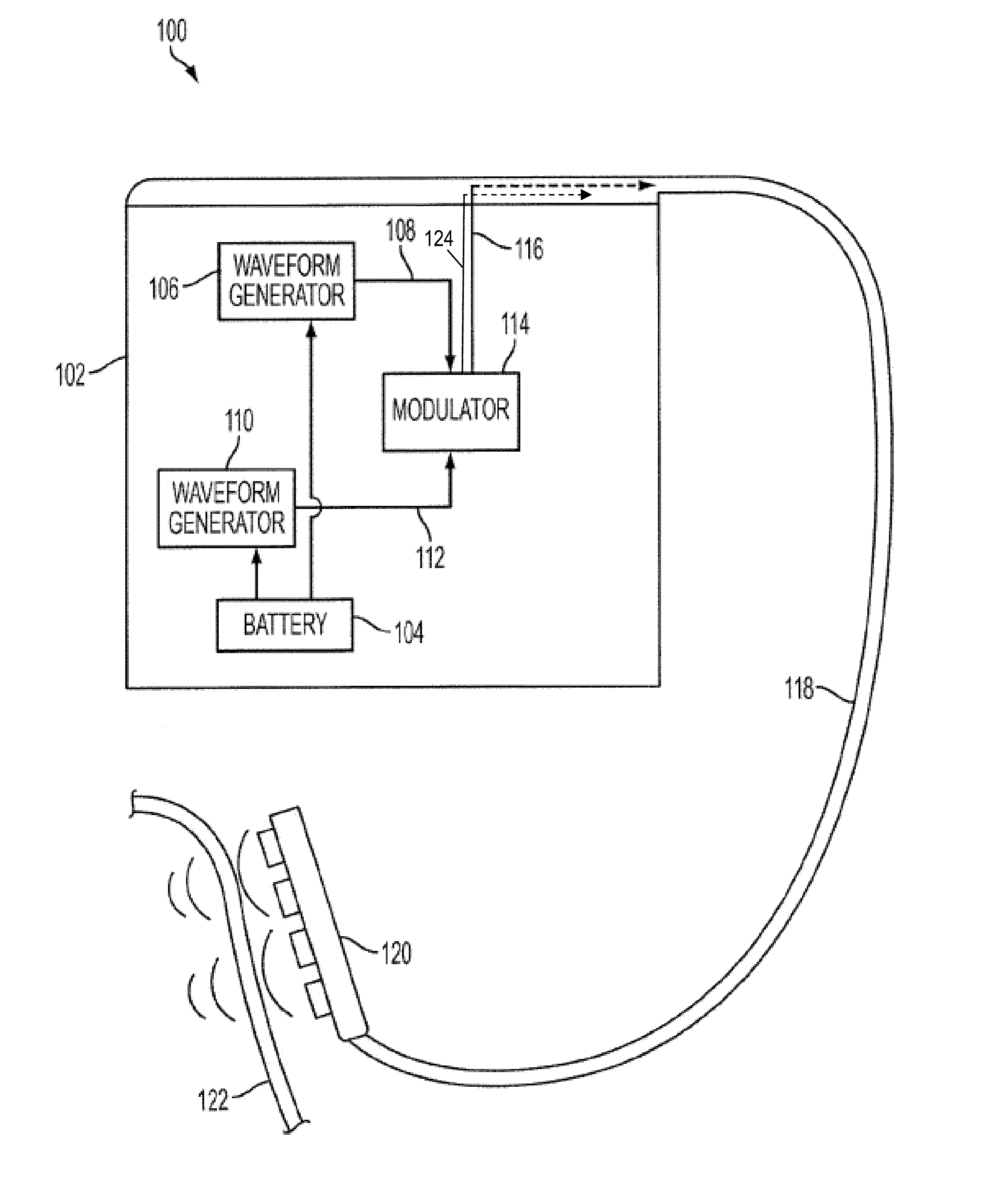
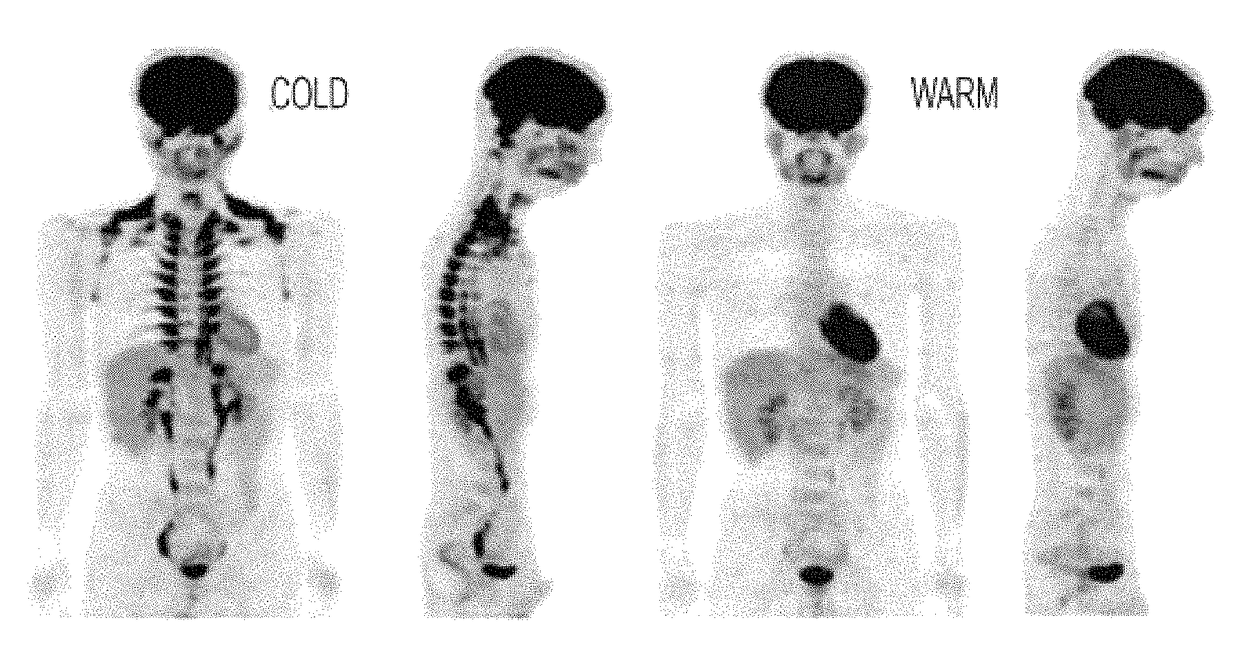
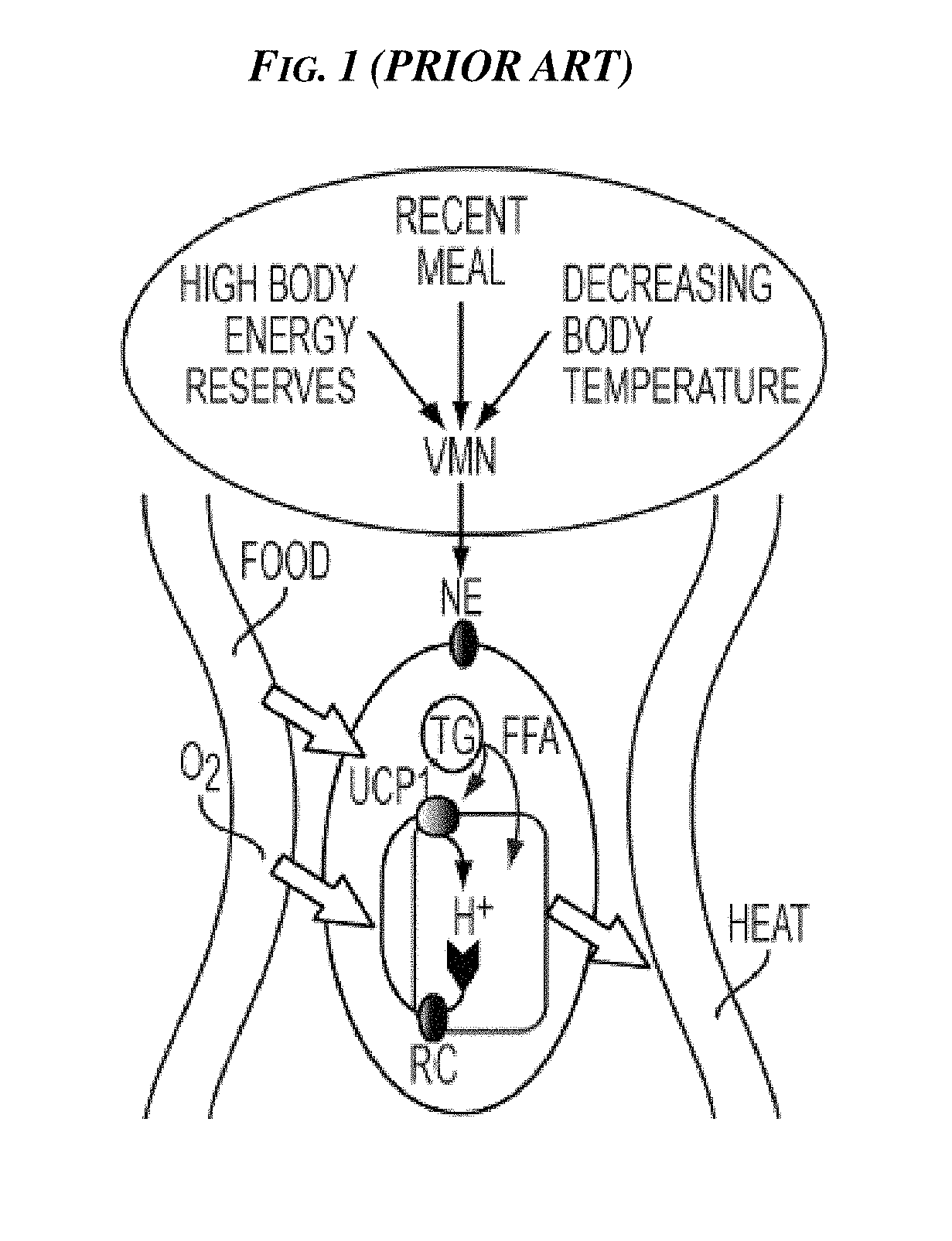
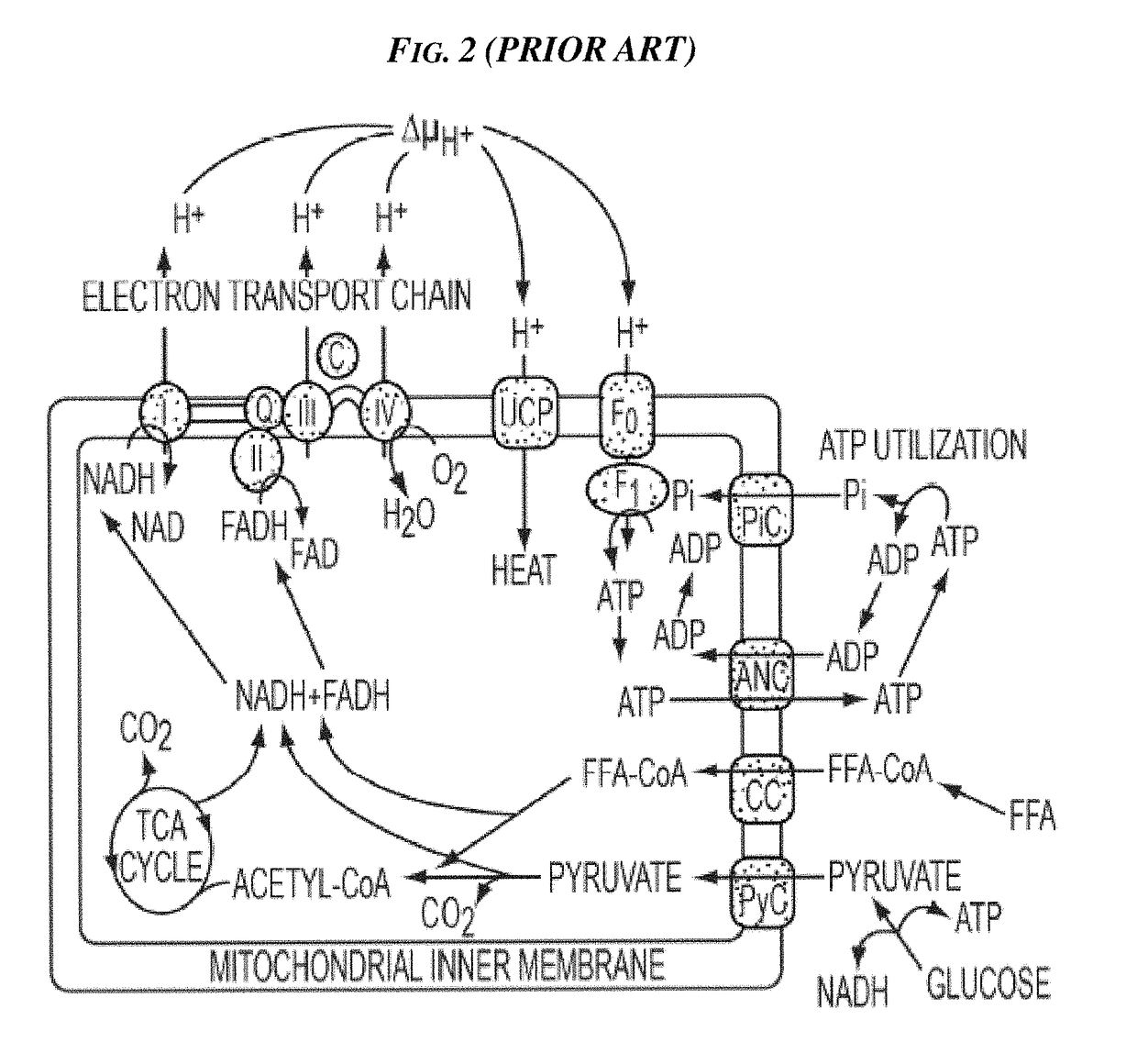
Methods and Devices for Inhibiting Nerves When Activating Brown Adipose Tissue
ActiveUS20160184568A1Increased energy expenditureMedical devicesMedical applicatorsMicrochiropteraBrown adipose tissue
Methods and devices are provided for inhibiting nerves when activating brown adipose tissue (BAT). In general, a first nerve type (e.g., sympathetic nerves) innervating BAT can be activated while at least one other nerve type (e.g., parasympathetic nerves and / or sensory nerves) innervating BAT is being suppressed. A first neuromodulator (e.g., an electrical signal, a chemical, a light, cooling, etc.) can be applied to activate the first nerve type, and a second neuromodulator can be applied to inhibit the at least one other nerve type. In this way, parasympathetic nerves and / or sensory nerves innervating BAT can be inhibited when activating sympathetic nerves innervating BAT.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
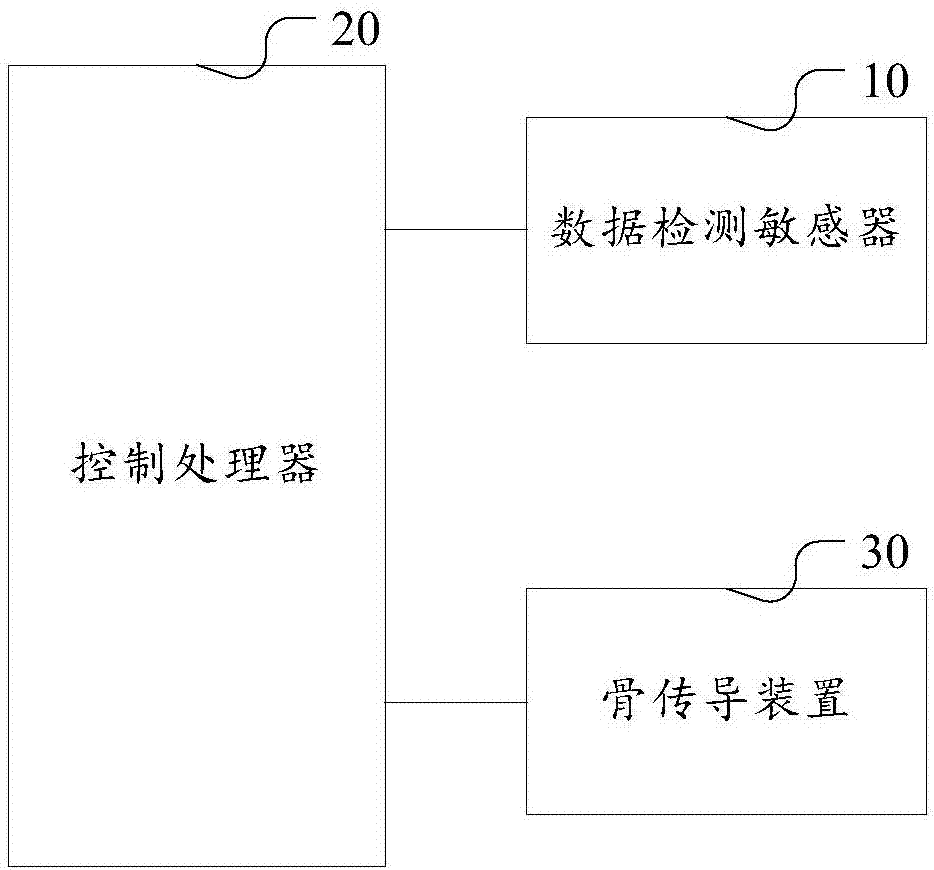
Sleep detecting and analyzing closed-loop system and device and intelligent pillow
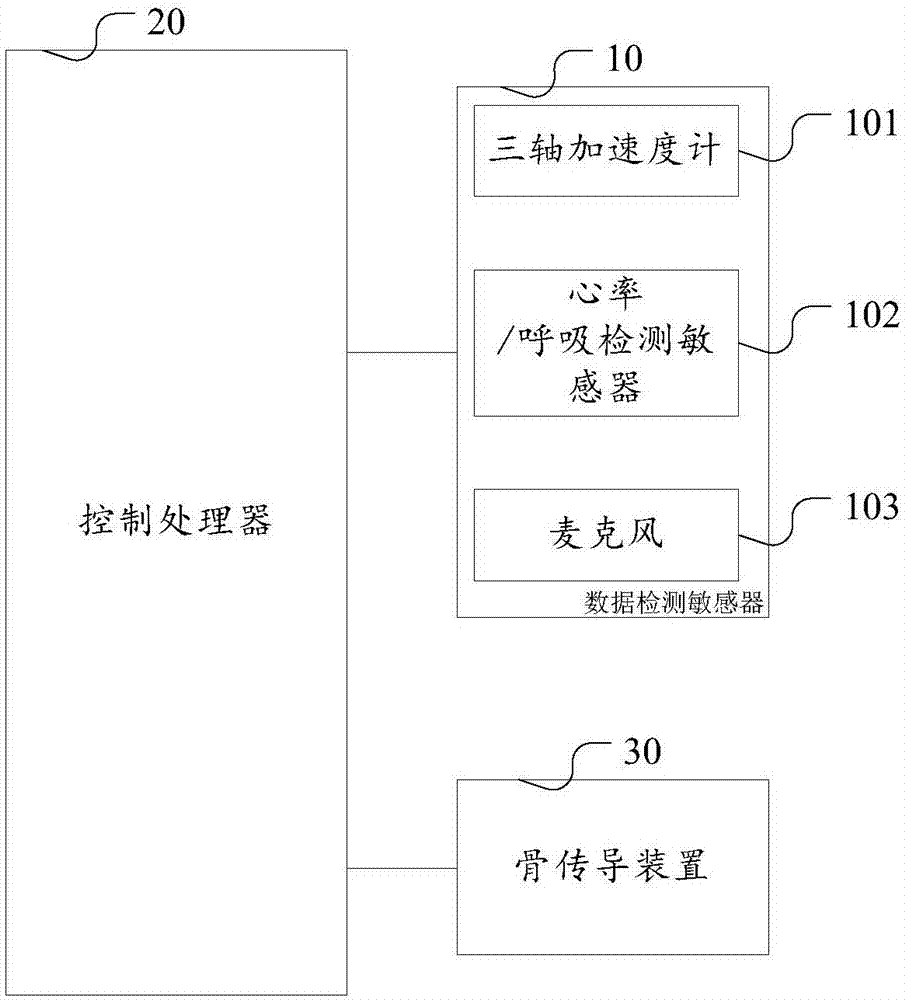
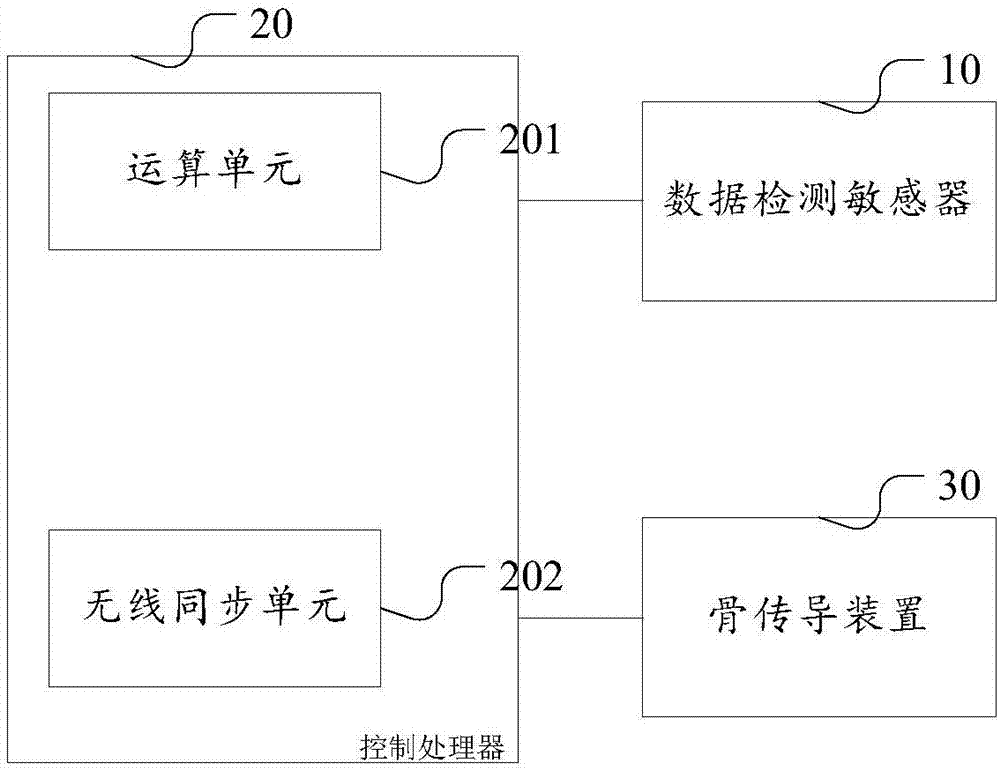
InactiveCN107374223AAdequate basis for diagnosis and treatmentCalm body and mindPillowsDiagnostic signal processingClosed loopBone conduction hearing
The invention discloses a sleep detecting and analyzing closed-loop system and device and an intelligent pillow. The device comprises a data detection sensor, a control processor and a bone conduction device. Data acquired through detection with the data detection sensor are comprehensive and capable of reflecting sound signals in sleeping; a music low-frequency portion is highlighted through the bone conduction device to stimulate the parasympathetic nerve of a user so as to further improve sleep quality. The system comprises the closed-loop device and an intelligent terminal / server and further realizes that complete statistical data are obtained by statistics and analysis of the signals through cooperation of a control processor and the intelligent terminal, and people can know whether sleep quantitative indexes tend to be healthy or not after music listening according to the statistical data and know which kind of music is more helpful to sleep. The pillow comprises first, second and third fill bags through which head, cervical vertebra and shoulder curves of the pillow are designed to improve shoulder and cervical vertebra comfort of people.
Owner:赛博龙科技(北京)有限公司
System and method for mapping the functional nerves innervating the wall of arteries, 3-d mapping and catheters for same
InactiveUS20210145342A1Accurate and precise locationAccurate locationUltrasound therapyEvaluation of blood vesselsKidney arteriesRadial nerve branch
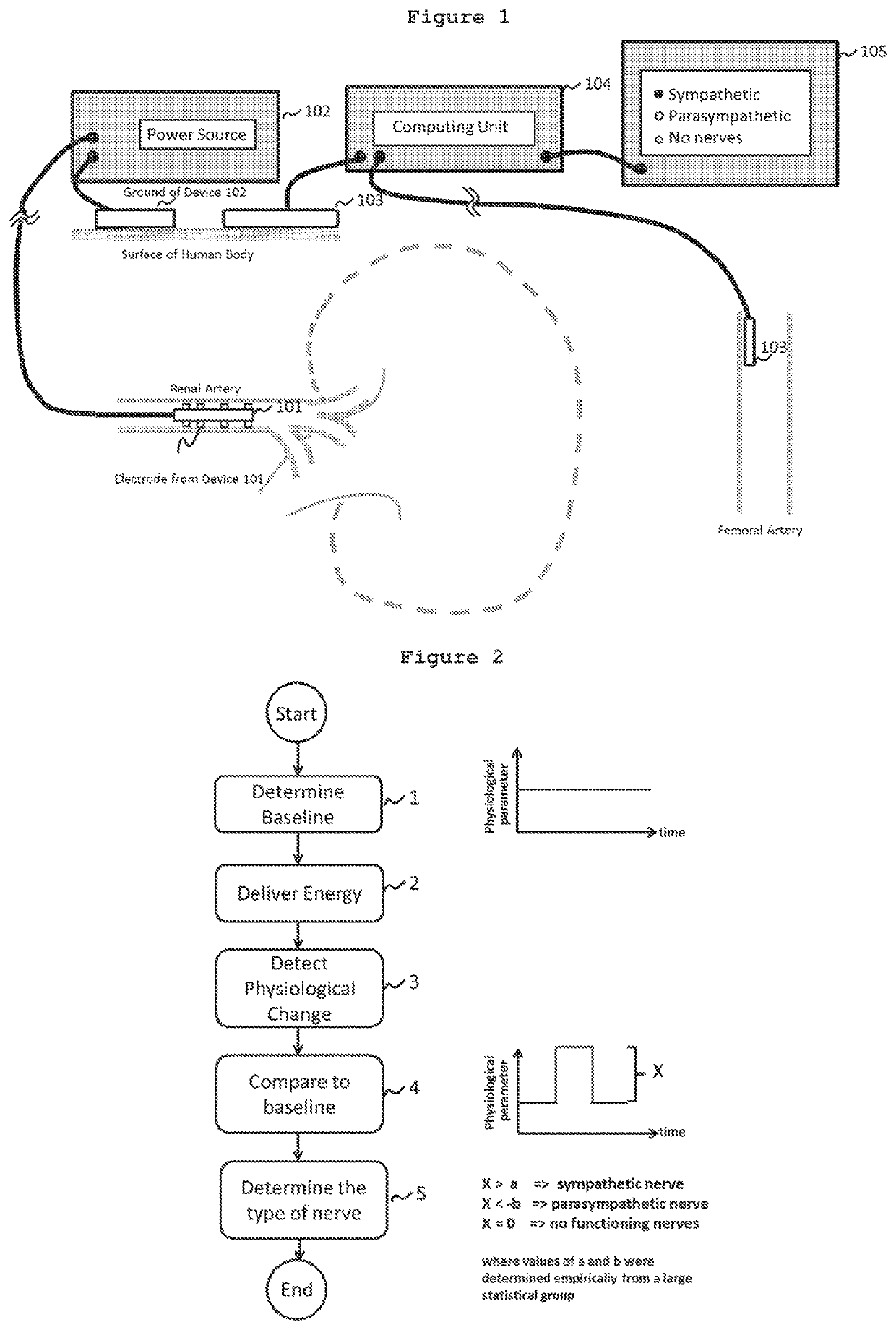
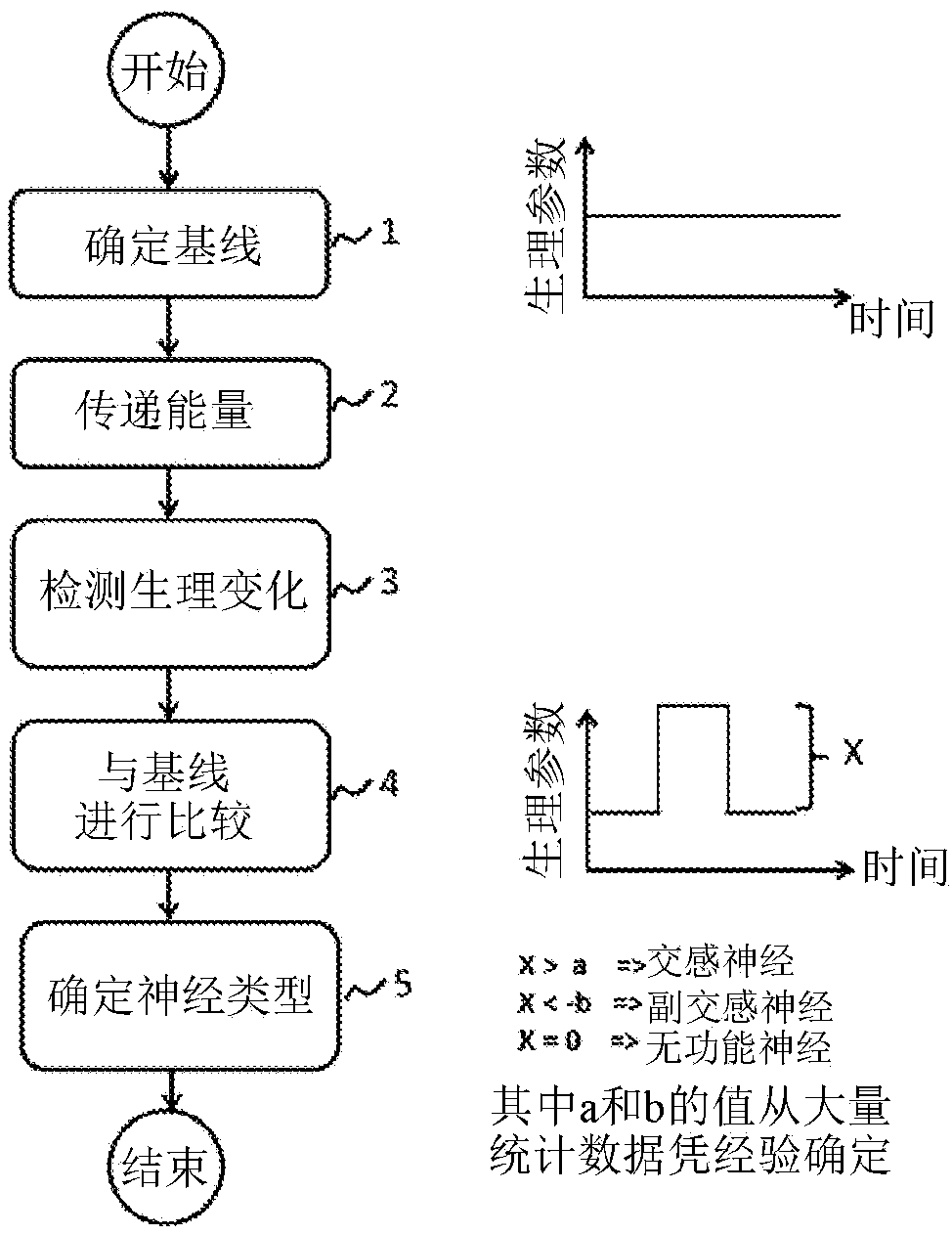
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for locating and identifying nerves innervating the wall of arteries such as the renal artery. The present invention identifies areas on vessel walls that are innervated with nerves; provides indication on whether energy is delivered accurately to a targeted nerve; and provides immediate post-procedural assessment of the effect of energy delivered to the nerve. The methods include evaluating a change in physiological parameters after energy is delivered to an arterial wall; and determining the type of nerve that the energy was directed to (sympathetic or parasympathetic or none) based on the evaluated results. The system includes at least a device for delivering energy to the wall of blood vessel; sensors for detecting physiological signals from a subject; and indicators to display results obtained using said method. Also provided are catheters for performing the mapping and ablating functions.
Owner:SYMAP MEDICAL (SUZHOU) LIMITED
Methods and devices for inhibiting nerves when activating brown adipose tissue
ActiveUS10092738B2Increased energy expenditureMedical devicesMedical applicatorsMicrochiropteraBrown adipose tissue
Methods and devices are provided for inhibiting nerves when activating brown adipose tissue (BAT). In general, a first nerve type (e.g., sympathetic nerves) innervating BAT can be activated while at least one other nerve type (e.g., parasympathetic nerves and / or sensory nerves) innervating BAT is being suppressed. A first neuromodulator (e.g., an electrical signal, a chemical, a light, cooling, etc.) can be applied to activate the first nerve type, and a second neuromodulator can be applied to inhibit the at least one other nerve type. In this way, parasympathetic nerves and / or sensory nerves innervating BAT can be inhibited when activating sympathetic nerves innervating BAT.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Sleepiness judging device
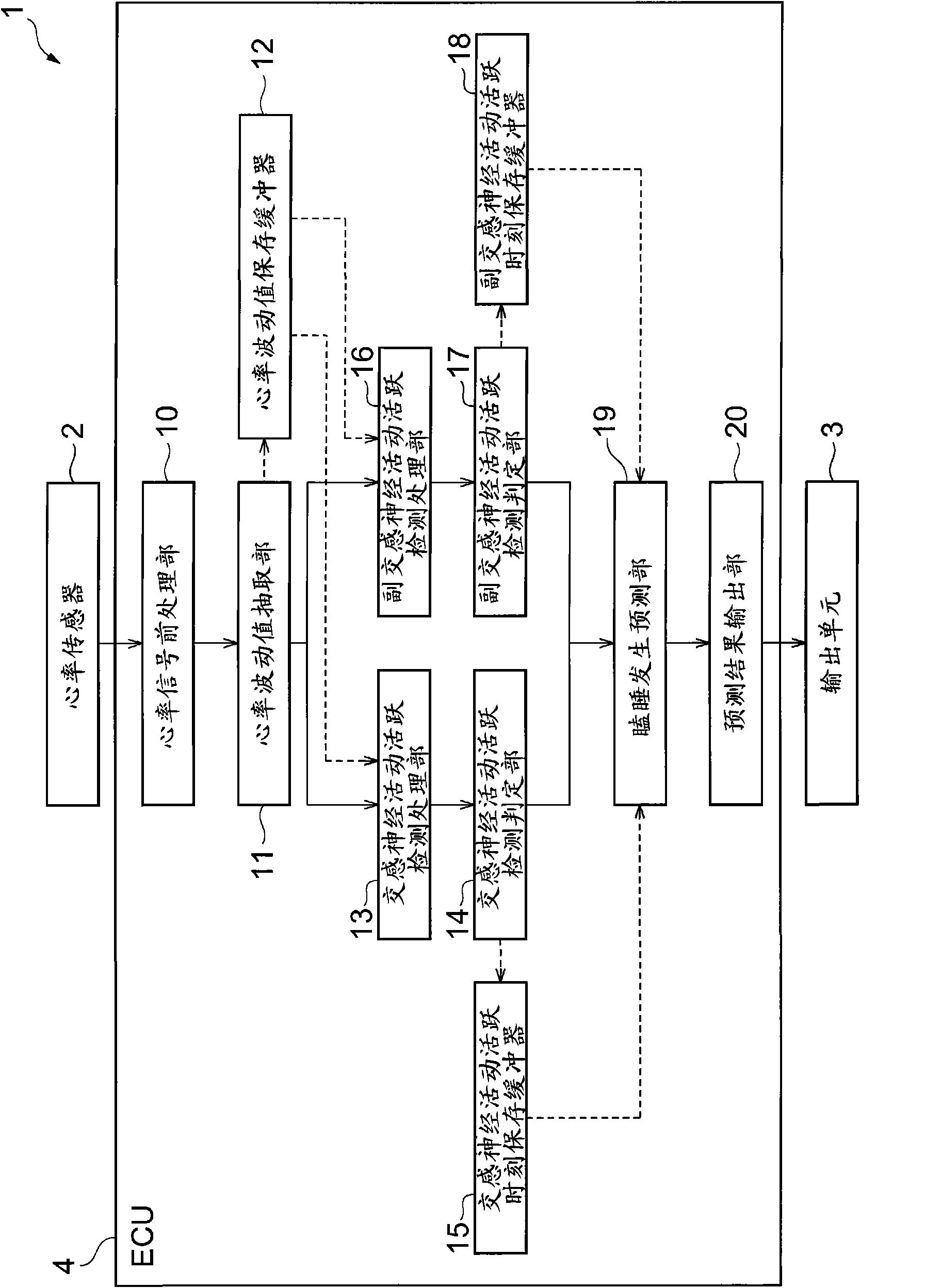
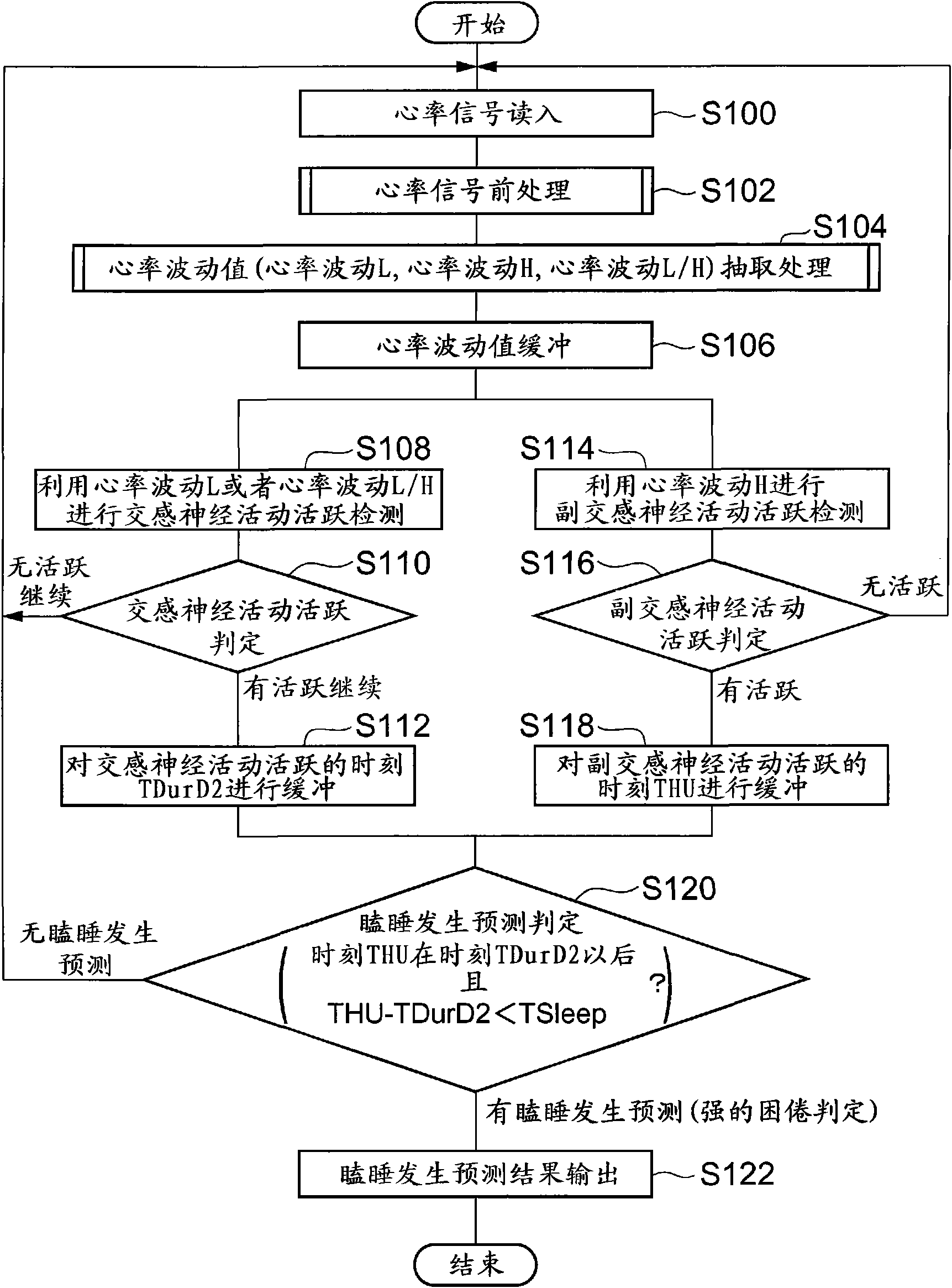
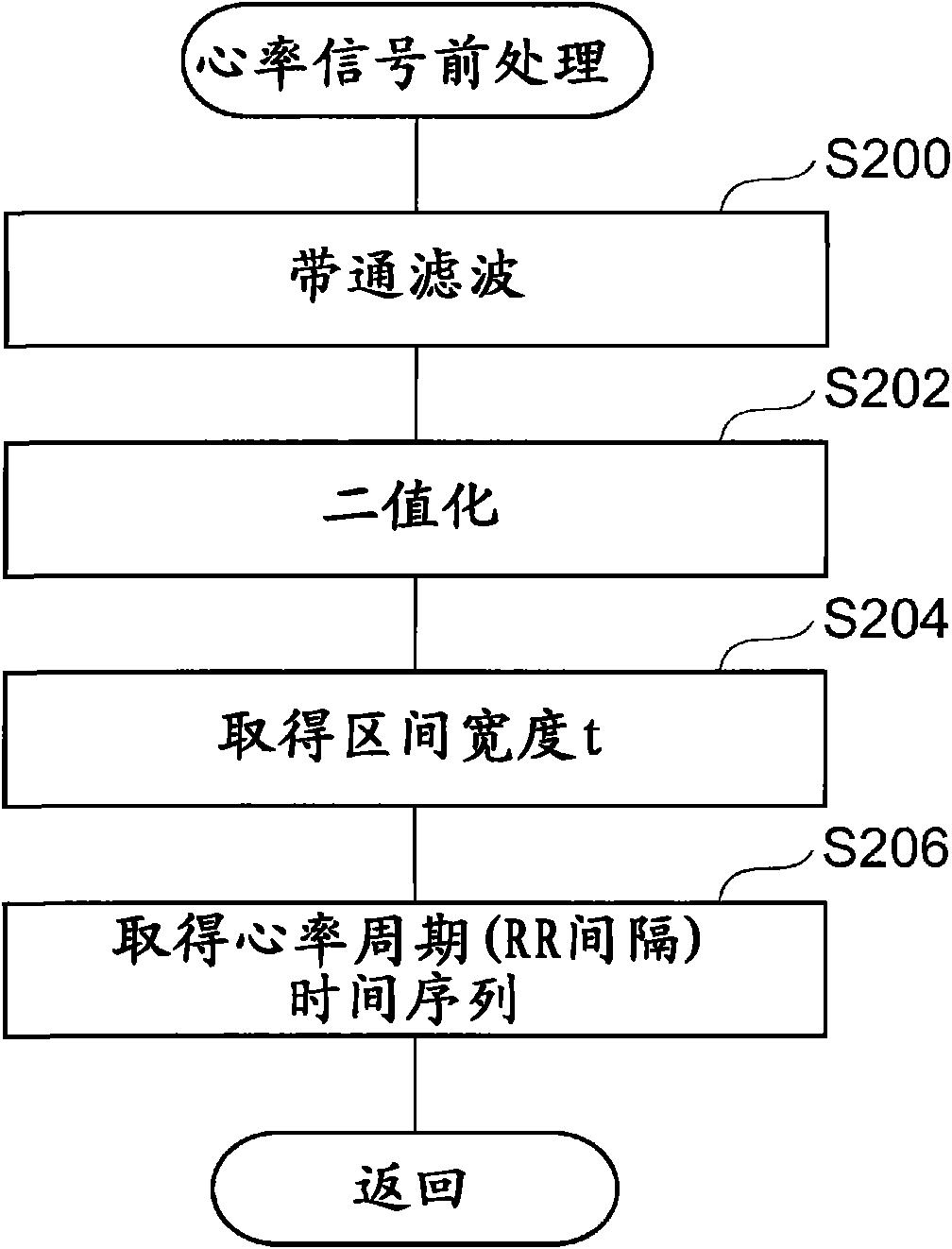
InactiveCN101686816AJudging sleepinessAnti-collision systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringParasympathetic nerveMedicine
A sleepiness judging device for judging a strong sleepiness before a subject comes to doze. Sleepiness judging device (1) is characterized by comprising a sympathetic parameter acquiring unit (2,11) for acquiring a parameter concerning the sympathetic nerve of a subject, a parasympathetic parameter acquiring unit (2, 11, 16) for acquiring a parameter concerning the parasympathetic nerve of the subject, a sympathetic increase judging unit (13, 14) for judging whether or not the magnitude of the sympathetic parameter is larger than a sympathetic threshold, and a sleepiness judging unit (19) forjudging the sleepiness of the subject from the increase / decrease relation between the sympathetic parameter and the parasympathetic parameter if the magnitude of the sympathetic parameter is judged tobe larger than the sympathetic threshold.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Medical cuff employing electrical stimulation to control blood flow
ActiveUS10456573B1Eliminating (or at least mitigating) needEliminating (orBlood flow measurement devicesTourniquetsArteriolar VasoconstrictionBlood flow
A device covering for controlling blood flow includes a cuff configured to be mounted to an extremity of a patient. The cuff includes a plurality of electrodes electrically connectible to a stimulation power supply. Upon receipt of power from the stimulation power supply, the electrodes supply electrical impulses to the anatomical site in order to stem or stop blood flow. In some cases, the stimulation power supply is an interferential therapy power supply, and a pair of electrodes supplies electrical impulses at two different frequencies, the electrical impulses provided at two different frequencies giving rise to at least one beat impulse having an interference frequency. The beat impulse activates the sympathetic nerves to induce vasoconstriction in the local blood vessels. Alternatively, the beat impulse can be programmed to target the parasympathetic nerves if vasodilatation is desired.
Owner:FEINSTEIN PATENTS
Methods and Devices for Activating Brown Adipose Tissue Using Electrical Energy
ActiveUS20160184574A1Small diameterSpinal electrodesSubcutaneous electrodesElectricityNerve fiber bundle
Methods and devices are provided for activating brown adipose tissue (BAT) using electrical energy. In general, the methods and devices can facilitate activation of BAT to increase thermogenesis. The BAT can be activated by applying an electrical signal thereto that can be configured to target sympathetic nerves that can directly innervate the BAT. The electrical signal can be configured to target the sympathetic nerves using fiber diameter selectivity. In other words, the electrical signal can be configured to activate nerve fibers having a first diameter without activating nerve fibers having diameters different than the first diameter. Sympathetic nerves include postganglionic unmyelinated, small diameter fibers, while parasympathetic nerves that can directly innervate BAT include preganglionic myelinated, larger diameter fibers. The electrical signal can be configured to target and activate the postganglionic unmyelinated, small diameter fibers without activating the preganglionic myelinated, larger diameter fibers.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Pharmaceutical composition preparation
InactiveCN111467498AReduce exacerbationsImprove lung functionRespiratory disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsAnticholinergic DrugsGlucocorticoid
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition preparation. The pharmaceutical composition preparation comprises an anticholinergic drug tiotropium or a hydrate thereof, a beta 2-receptor agonistarformoterol or a salt thereof, and an inhaled glucocorticoid fluticasone or an ester derivative thereof; tiotropium bromide acts on a muscarinic receptor on bronchial smooth muscles, the cholinergiceffect of acetylcholine released by the tail ends of parasympathetic nerves can be inhibited, and muscular tension is blocked; the arformoterol acts on a beta 2-receptor on an airway smooth muscle cell membrane, so that the release of degranulation and media of mast cells and basophils is reduced, the permeability of capillaries is reduced, and swinging of airway epithelial cilia is increased; the fluticasone is an effective anti-inflammatory drug, and when the three drugs are combined for use, the three mechanisms jointly exert the bronchus relaxing effect and the anti-inflammatory effect; the application range of the triple therapy is wider on the important clinical indexes of reducing acute exacerbation of patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, reducing total-cause mortality rate, improving the lung function of the patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, improving the living quality and the like.
Owner:王兆霖
Device and method for measuring autonomic nervous cardiovascular system using stand-up experiment
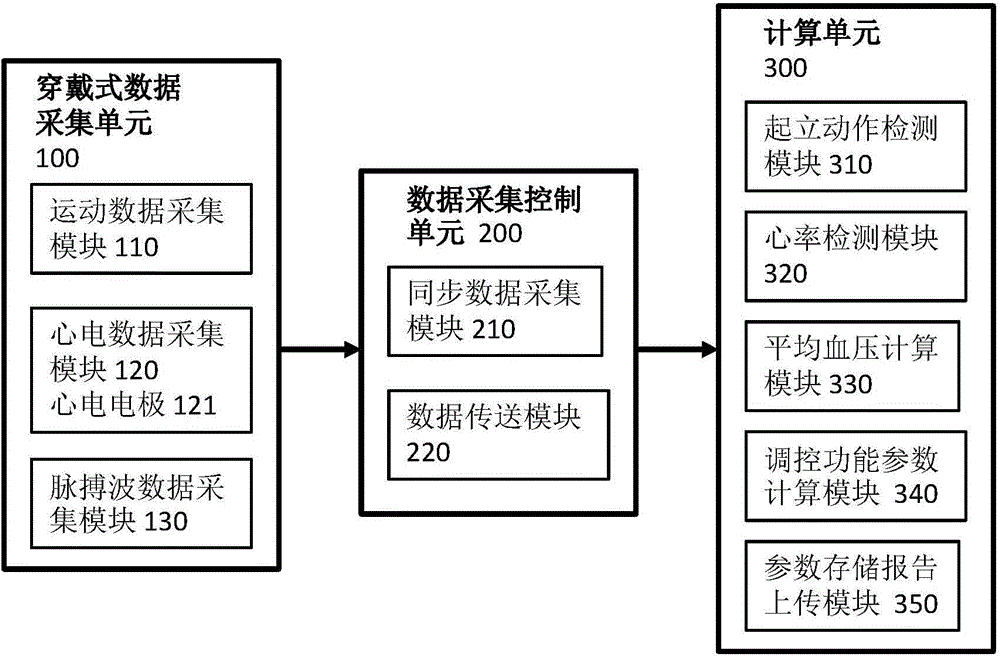
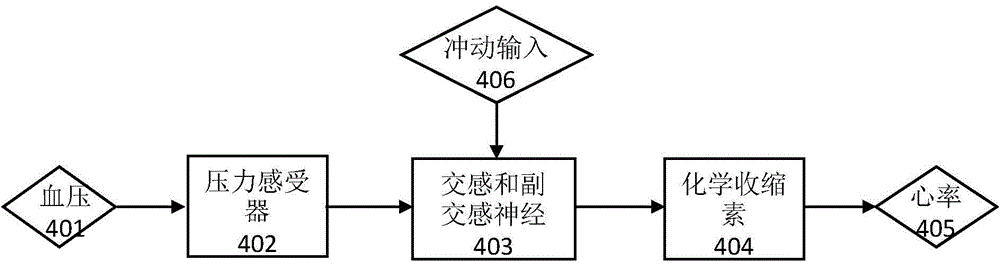
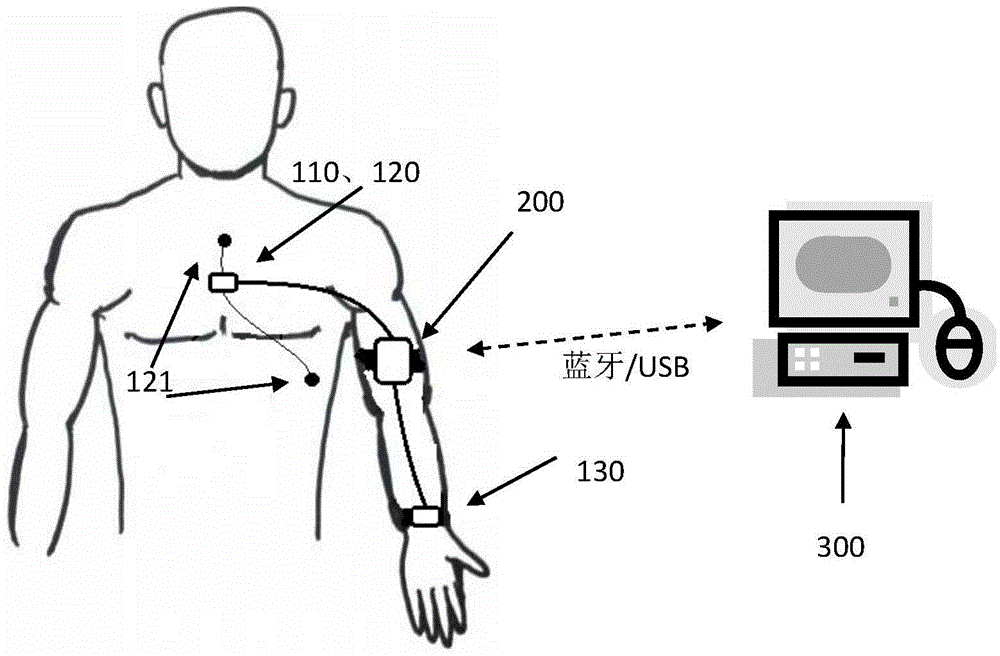
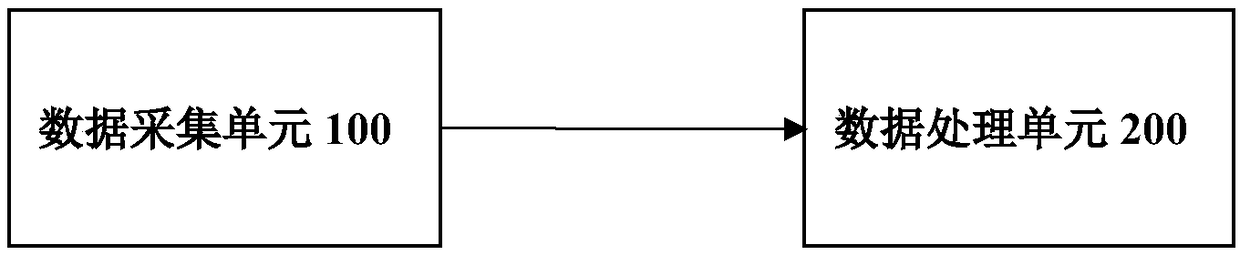
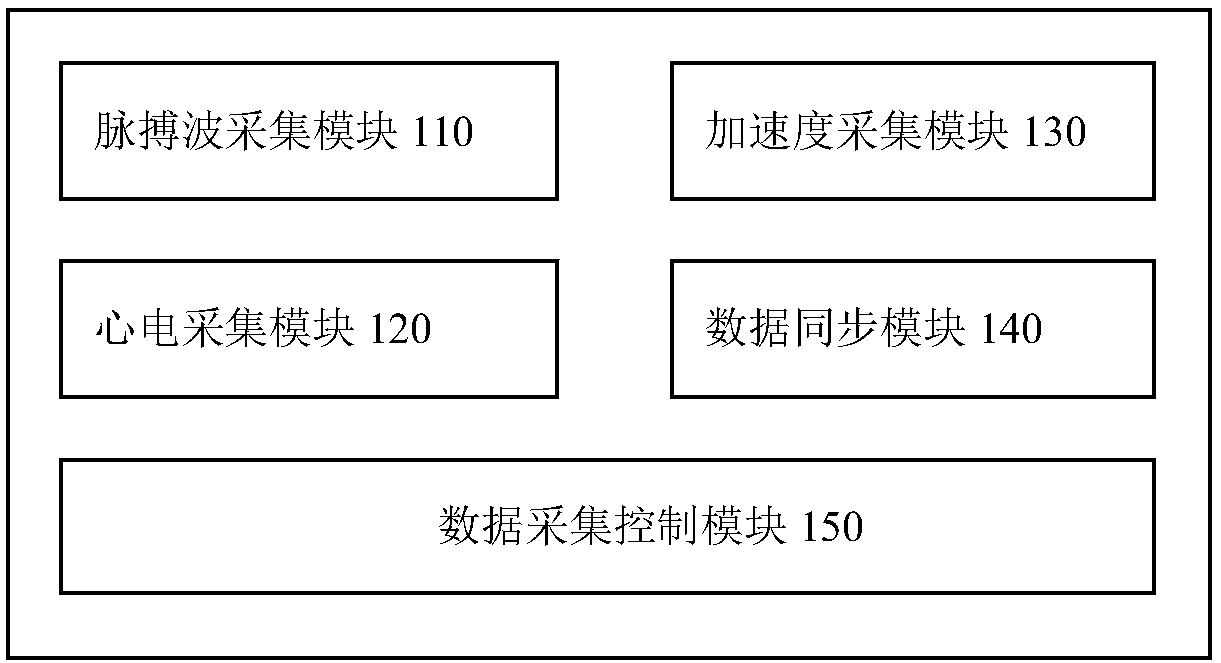
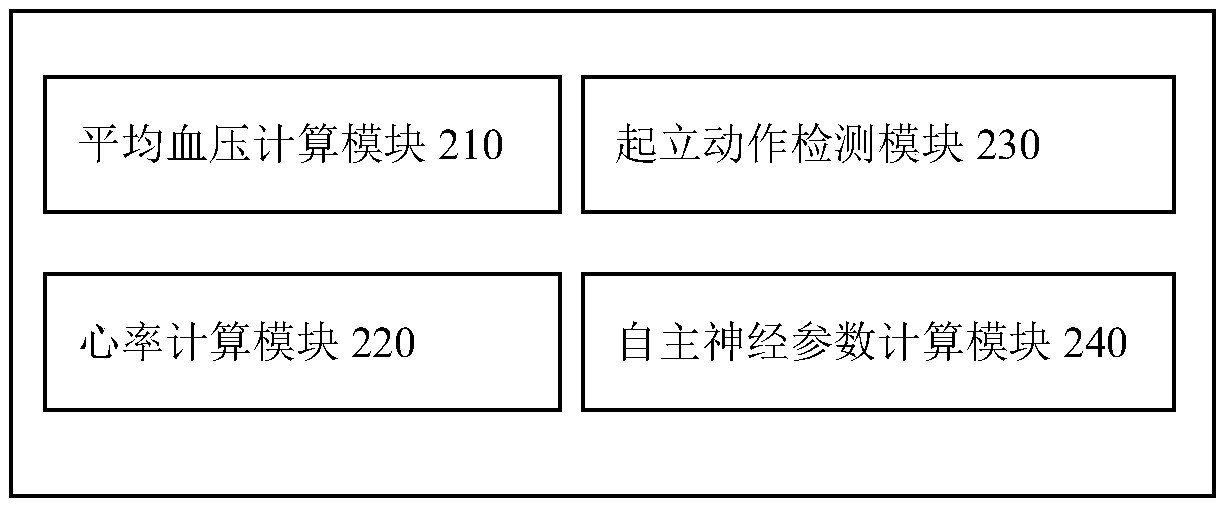
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring an autonomic nervous cardiovascular system using a stand-up experiment. The device comprises a data acquisition unit (100) and a data processing unit (200). The data acquisition unit (100) is used for synchronously acquiring acceleration signals, electrocardiogram signals and pulse wave signals of a subject in a standing experiment and sending them to the data processing unit (200). The data processing unit (200) is configured to calculate the heart rate and the average blood pressure of the measured person, and calculate the personalized parameters of the autonomic nerve cardiac regulation model, and finally calculate the sensitivity of the baroreceptor and the activity of the sympathetic parasympathetic nerve. As that baroreceptor sensitivity and the sympathetic parasympathetic activity are use as the indexes for measure the cardiac regulation state of the autonomic nerve for real-time display, the purpose of clinically evaluating the dynamic function of the cardiovascular system is achieved.
Owner:中科数字健康科学研究院(南京)有限公司
System and method for mapping functional nerves innervating wall of arteries, 3-d mapping and catheters for same
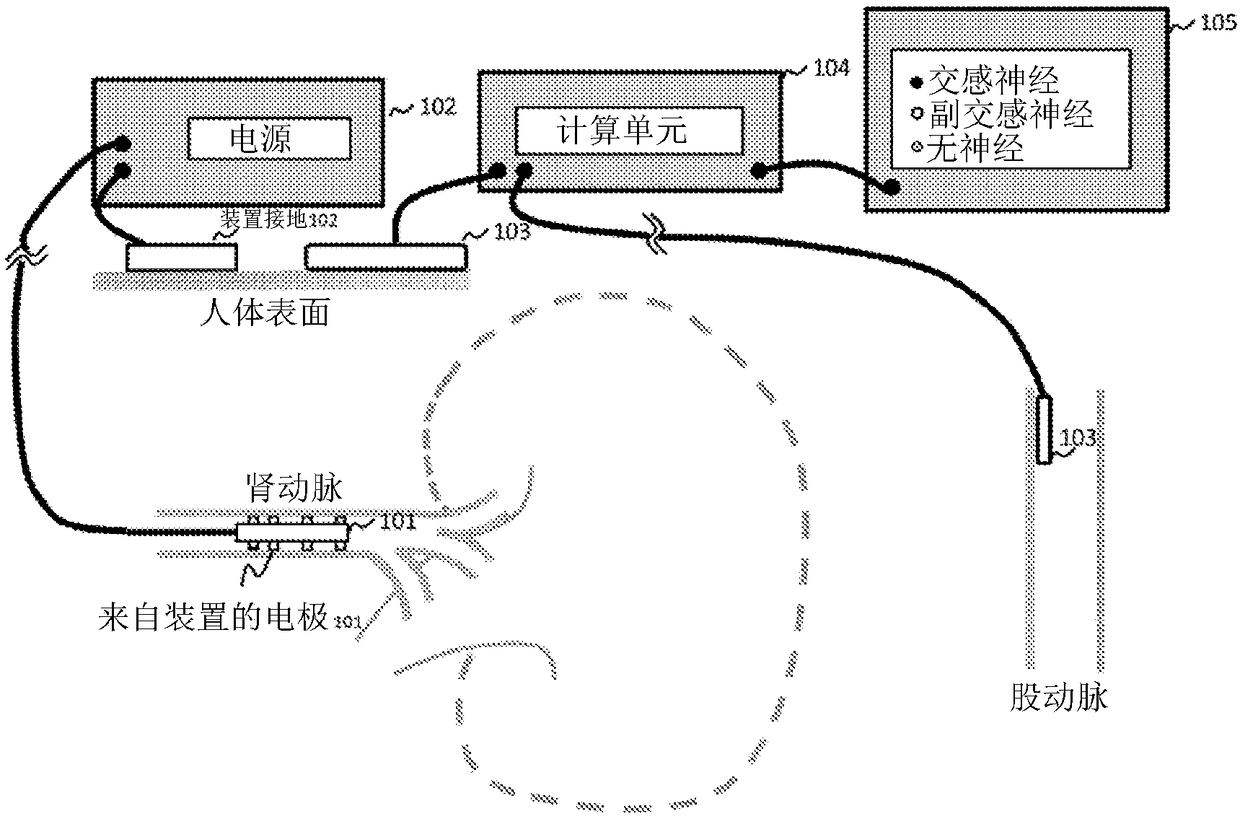
Disclosed herein are a system and method for locating and identifying nerves innervating the wall of arteries such as the renal artery. The system identifies an area on a vessel wall innervated with nerves; provides indication on whether energy is delivered accurately to a targeted nerve; and provides immediate post-procedural assessment of the effect of energy delivered to the nerve. The method includes evaluating a change in physiological parameters after energy is delivered to arterial wall; and determining the type of nerve that the energy was directed to (sympathetic or parasympathetic ornone) based on the evaluated results. The system includes at least a device (101) for delivering energy to the wall of a blood vessel; a sensor (103) for detecting physiological signals from a subject; and an indicator (105) to display results obtained using said method. Also provided are catheters (2510, 2520) for performing the mapping and ablating functions.
Owner:SYMAP MEDICAL (SUZHOU) LIMITED
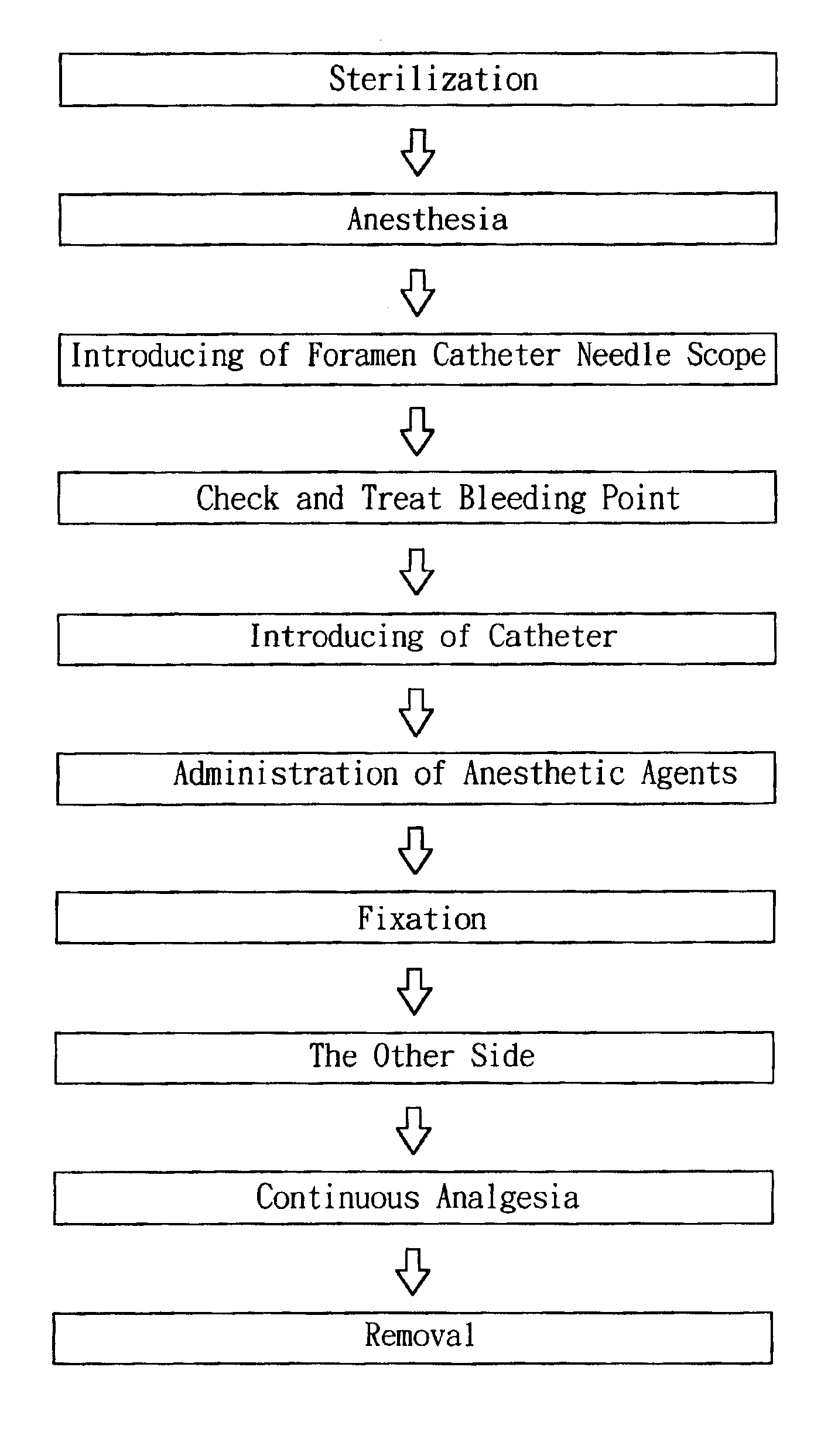
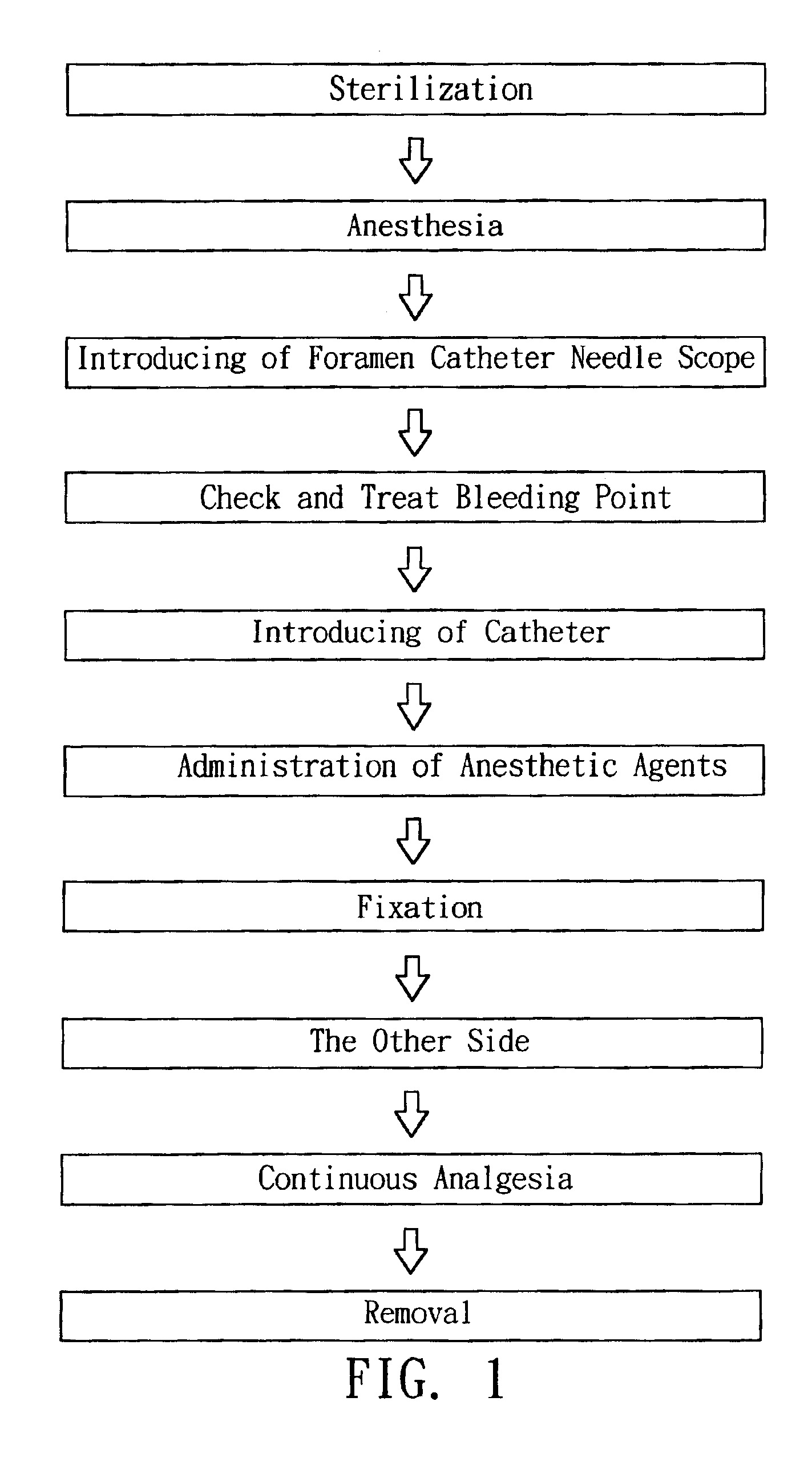
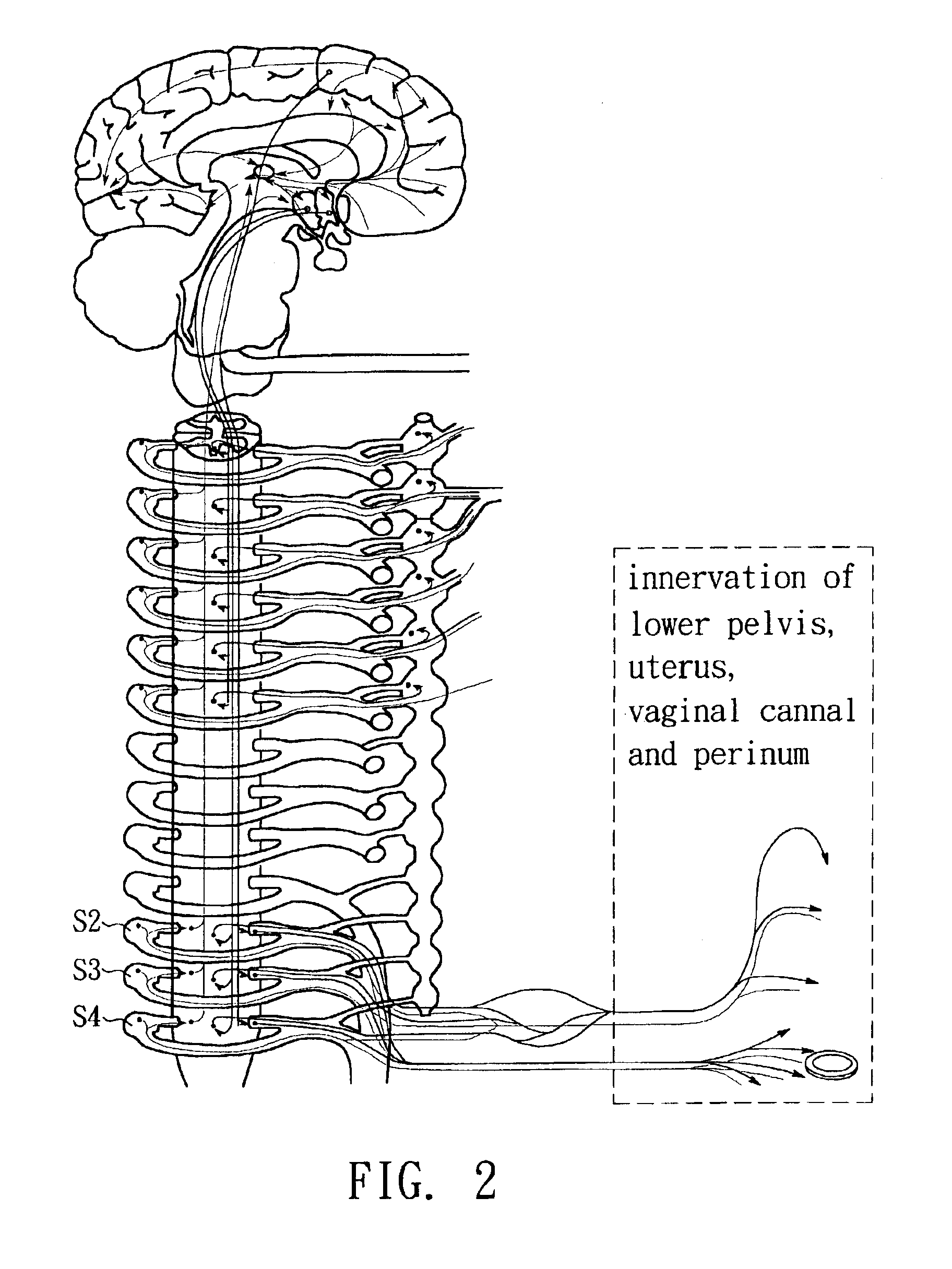
Method and apparatuses of using foramen catheter needle scope to induce temporary blockade of sacral nerves
A using method and apparatuses of foramen catheter needle scope of the present invention uses a new approach, new sites and set of apparatuses to block sacral nerves or nerve plexus to reduce pain during operating. The present invention uses an endoscopic video system with foramen catheter needle scope to introduce anesthetic agents via catheter through foramen of sacral bone to block the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve fibers of lower pelvis, which includes the innervation of uterus, vaginal canal and perineum.
Owner:HO ESTHER SHIH CHU +4
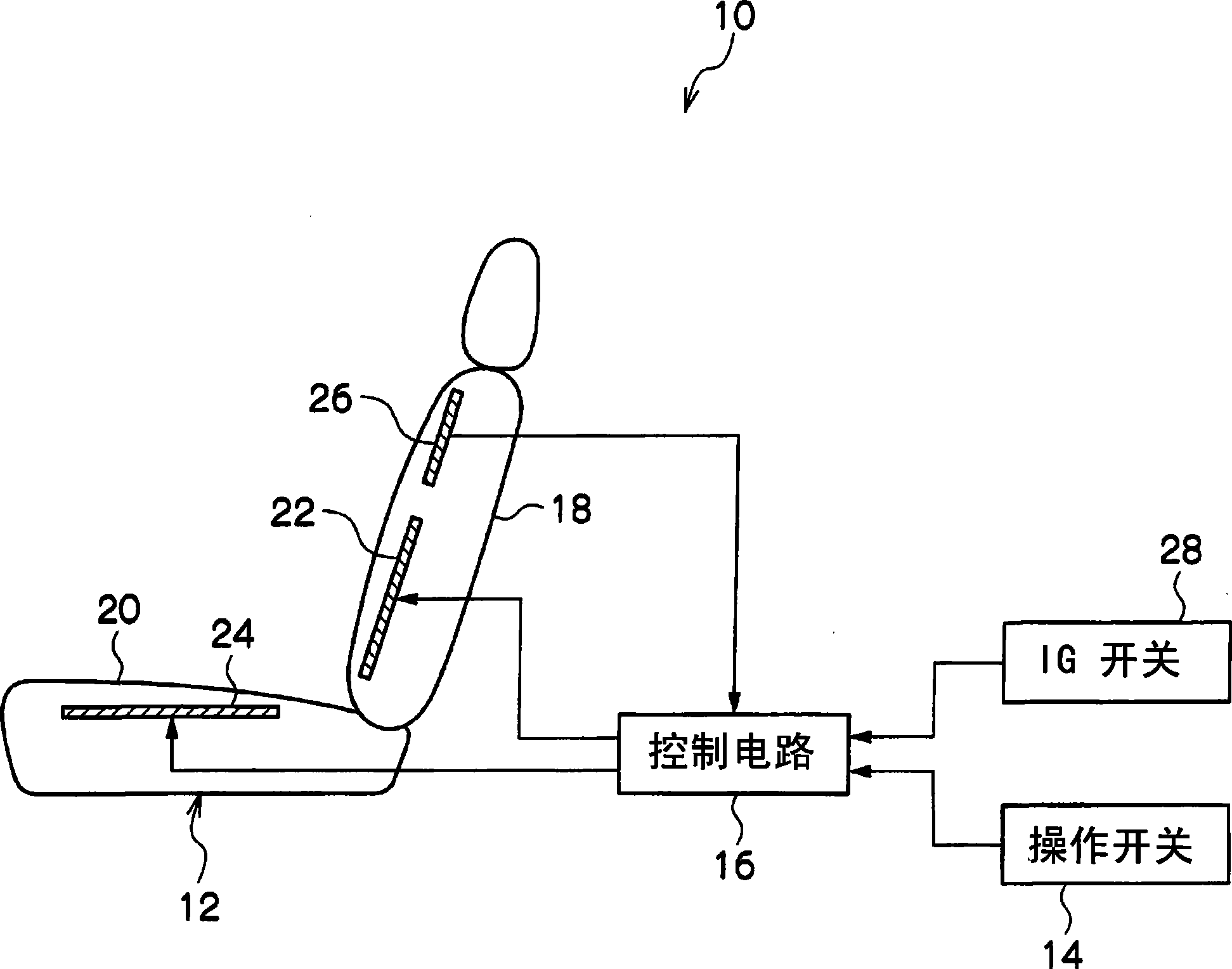
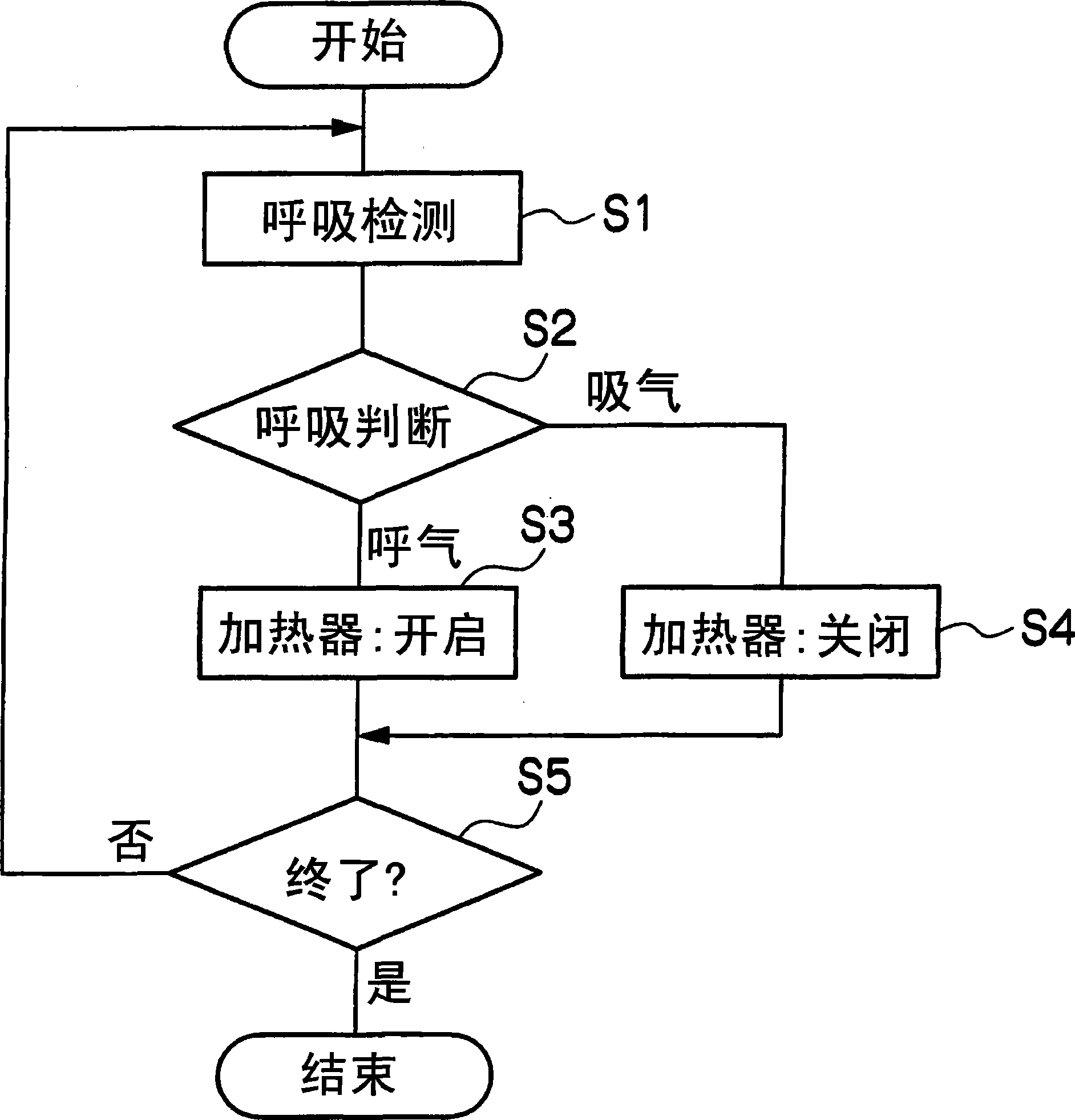
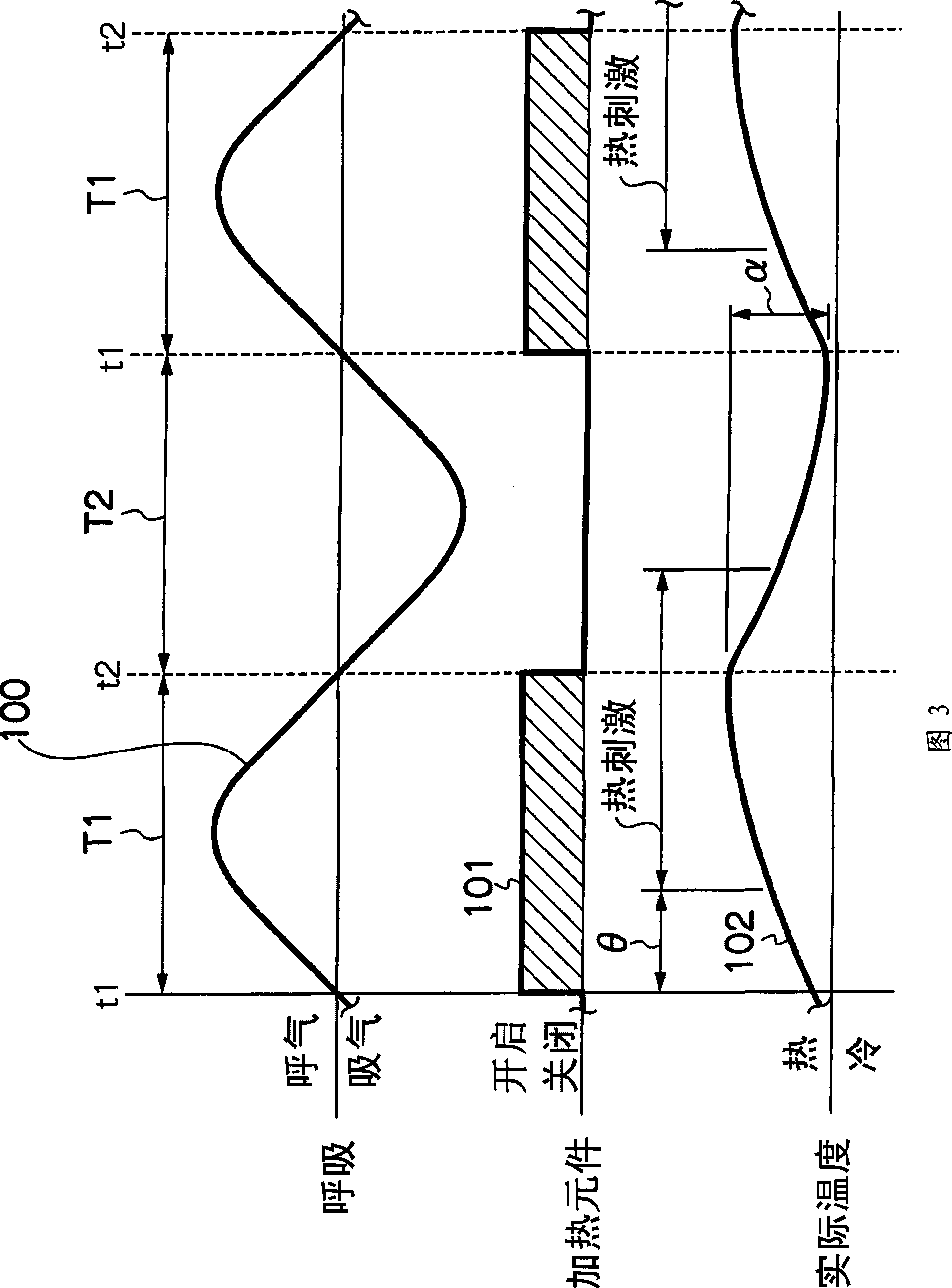
Thermal stimulation apparatus for vehicles
InactiveCN101378802AReduce fatigueEnhance physical fitnessVehicle seatsMedical devicesThermal stimulationEngineering
It is intended to provide a thermal stimulation apparatus for vehicles which can exert effects of, for example, reducing fatigue and improving physical conditions on a crew member in a vehicle. In a thermal stimulation apparatus for vehicles (10), when the biorhythm (for example, respiration rhythm) with periodical changes of a crewmember is detected by a piezoelectric sensor (26), heater elements (22, 24) are switched on by a control circuit (16) based on the detection data and thus thermal stimuli synchronizing the respiration rhythm of the crew member are provided to the crew member by switching on / off the heater element (22, 24). As a result, the autonomic nerve (parasympathetic nerve) activity of the crew member can be enhanced. Therefore, it becomes possible to exert effects of, for example, reducing fatigue and improving physical conditions on a crew member in a vehicle.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Methods and devices for activating brown adipose tissue using electrical energy
Methods and devices are provided for activating brown adipose tissue (BAT) using electrical energy. In general, the methods and devices can facilitate activation of BAT to increase thermogenesis. The BAT can be activated by applying an electrical signal thereto that can be configured to target sympathetic nerves that can directly innervate the BAT. The electrical signal can be configured to target the sympathetic nerves using fiber diameter selectivity. In other words, the electrical signal can be configured to activate nerve fibers having a first diameter without activating nerve fibers having diameters different than the first diameter. Sympathetic nerves include postganglionic unmyelinated, small diameter fibers, while parasympathetic nerves that can directly innervate BAT include preganglionic myelinated, larger diameter fibers. The electrical signal can be configured to target and activate the postganglionic unmyelinated, small diameter fibers without activating the preganglionic myelinated, larger diameter fibers.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Pressure relief apparatus with brain entrainment
A pressure relief apparatus with brain entrainment includes a resonant wave generating module and a bio-signal measuring unit. The resonant wave generating module includes multiple resonant devices, divided into multiple regions. Each of the resonant regions can respectively generate a resonant wave being changeable or turned off. The bio-signal measuring unit at least measures an energy of autonomic sympathetic nerve system LH and an energy of autonomic parasympathetic nerve system HF. According to a current one of a set of present conditions, a set of feedback control signals is output to the resonant wave generating module to modulate the resonant devices.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Pharmaceutical preparation containing tiotropium bromide and arformoterol
InactiveCN111481550AReduce exacerbationsImprove lung functionRespiratory disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsCell membraneBronchial epithelium
Owner:王兆霖
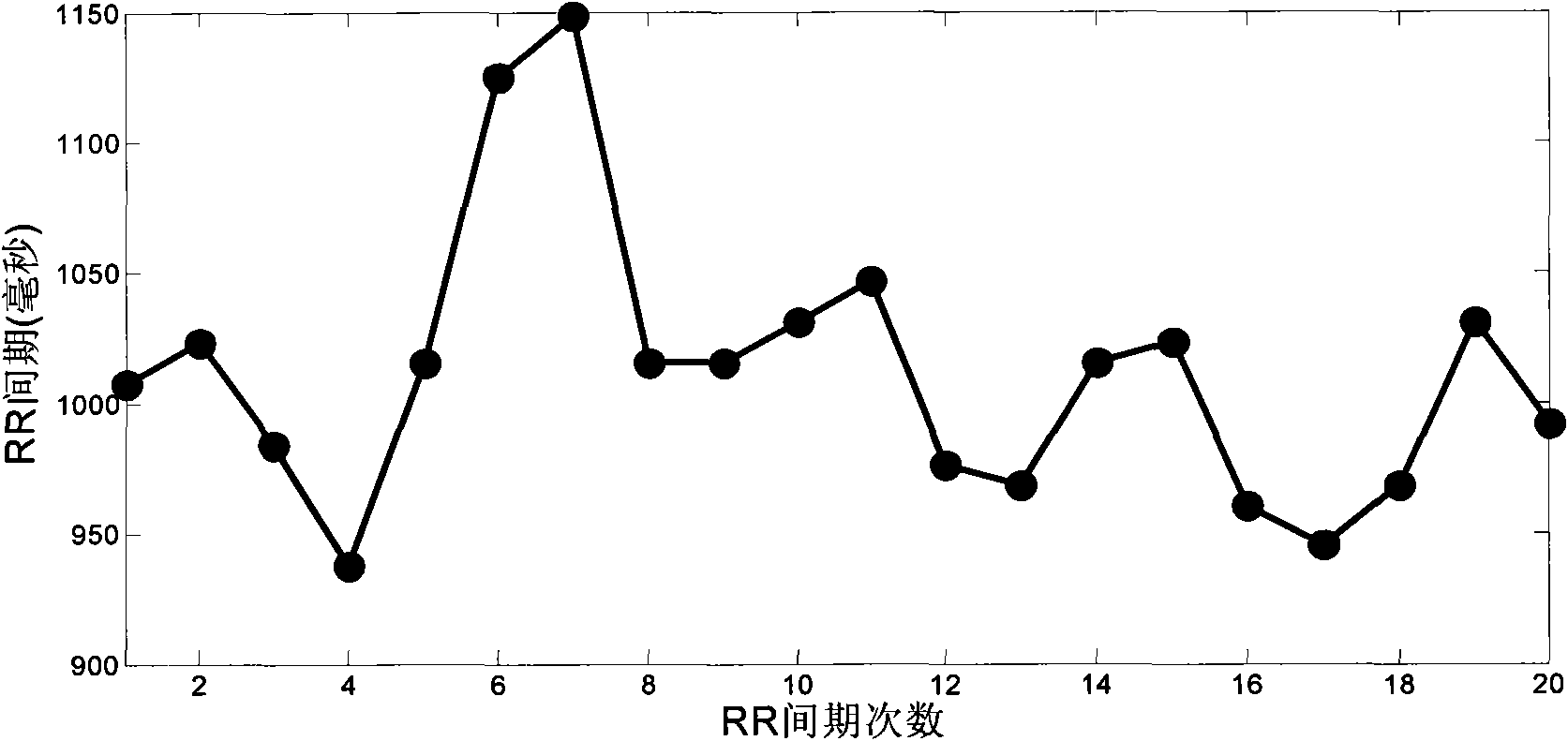
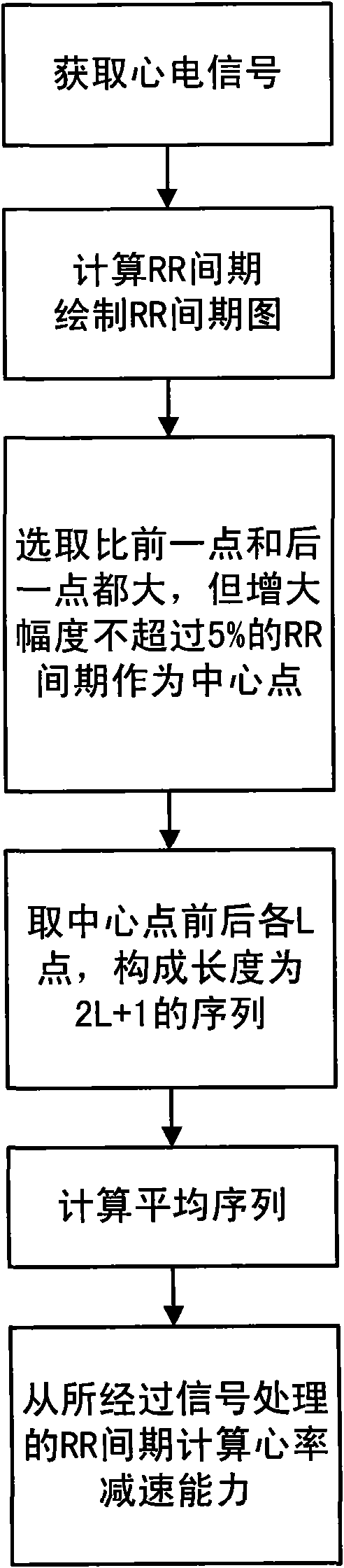
Method and device for testing heart rate deceleration capacity
InactiveCN101558994AEffective assessmentDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRR intervalNervous system
The invention discloses a method and a device for testing heart rate deceleration capacity. The method and the device calculate RR interval from a recorded electrokardiagram, and draws an RR interval graph taking the frequency of the RR interval as a horizontal coordinate and the RR interval as a vertical coordinate; a central point is selected from the RR interval graph, L points are taken from the front of the central point and the back of the central point respectively to form RR interval sequence with the length of 2L+1; points with the same subscript in all sequences are calculated to obtain an average value, and the average value is taken as a value of a point corresponding to the subscript in average sequence; and the heart rate deceleration capacity is calculated from the obtained average sequence. The method and the device can be used for testing the activity evaluating index of parasympathetic nerve of the heart rate deceleration capacity, and provide a reliable tool for clinically researching an autonomic nervous system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Medical wound covering employing electrical stimulation to control blood flow
ActiveUS10646710B2Eliminating (orNeed for manyElectrotherapySurgical drapesElectrical stimulationsBlood vessel
Owner:FEINSTEIN PATENTS
Building animal model of asthenopia based on tupaia belangeri as experiment animal
Forcing eyes of tupaia belangeri to be adjusted overly (positive adjustment) makes parasympathetic nerves, which controls eye adjustment, erethism. Thus, excitability of sympathetic nerve is changed correspondingly; ciliary muscle and sphincter pupillae are durative shrinked so as to cause dynamic dysequilibrium between sympathetic nerve and parasympathetic nerves for adjusting eyes. Asthenopia model of tupaia belangeri is built thorugh experimental media. The model can be utilized to study pathogenesis, prevent and treat asthenopia, filtrate out new drug and evaluate method for treating asthenopia.
Owner:张堰黎
Biological negative electricity insomnia recovery therapeutic apparatus equipment system
InactiveCN102100940ASuitable for long-term useAvoid electromagnetic radiation, interfere with bioelectricity, and have disadvantages of side effectsElectrotherapyPhysical therapy involving specific reflex pointsMedical equipmentEndocrine functions
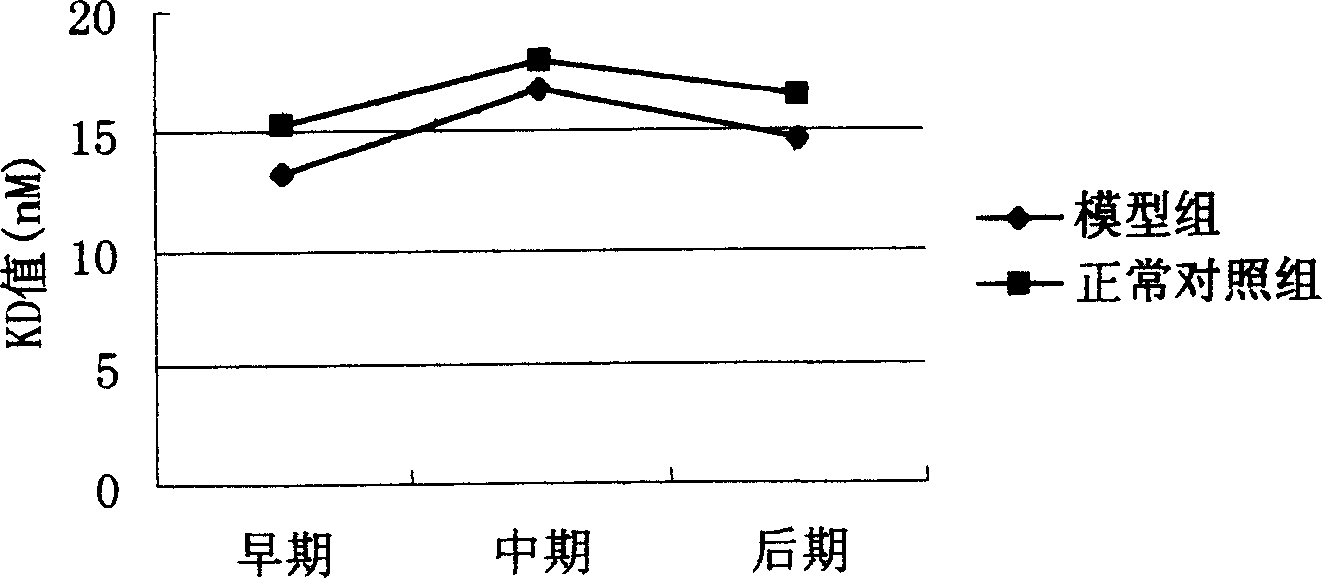
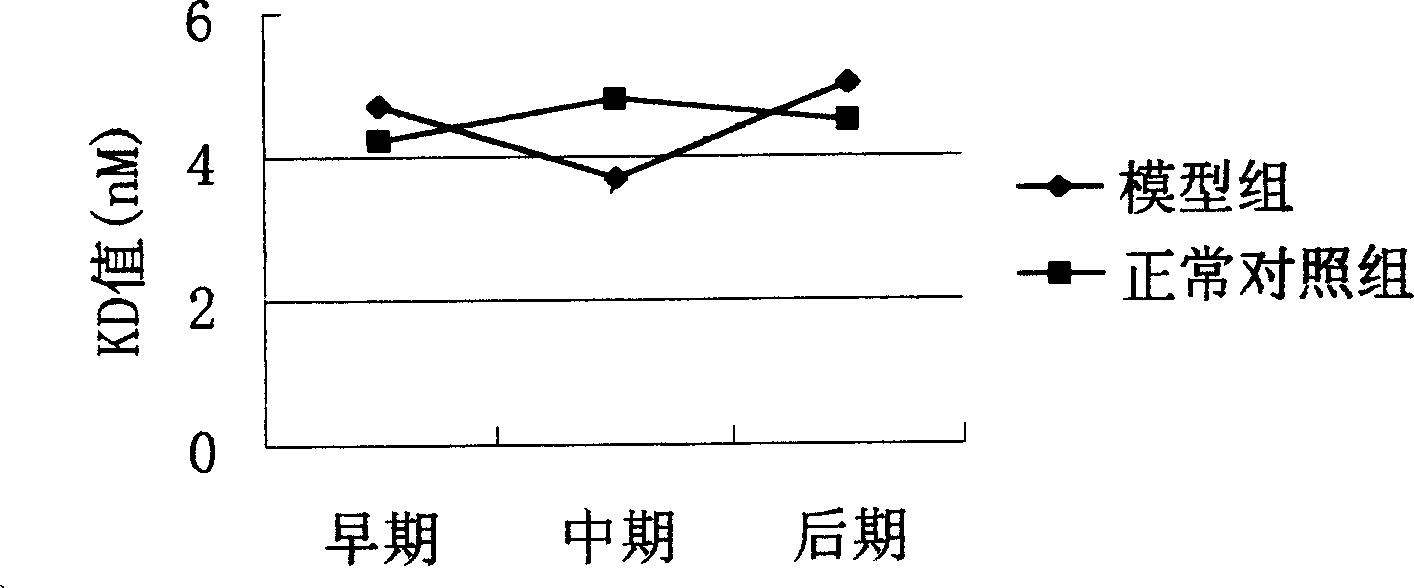
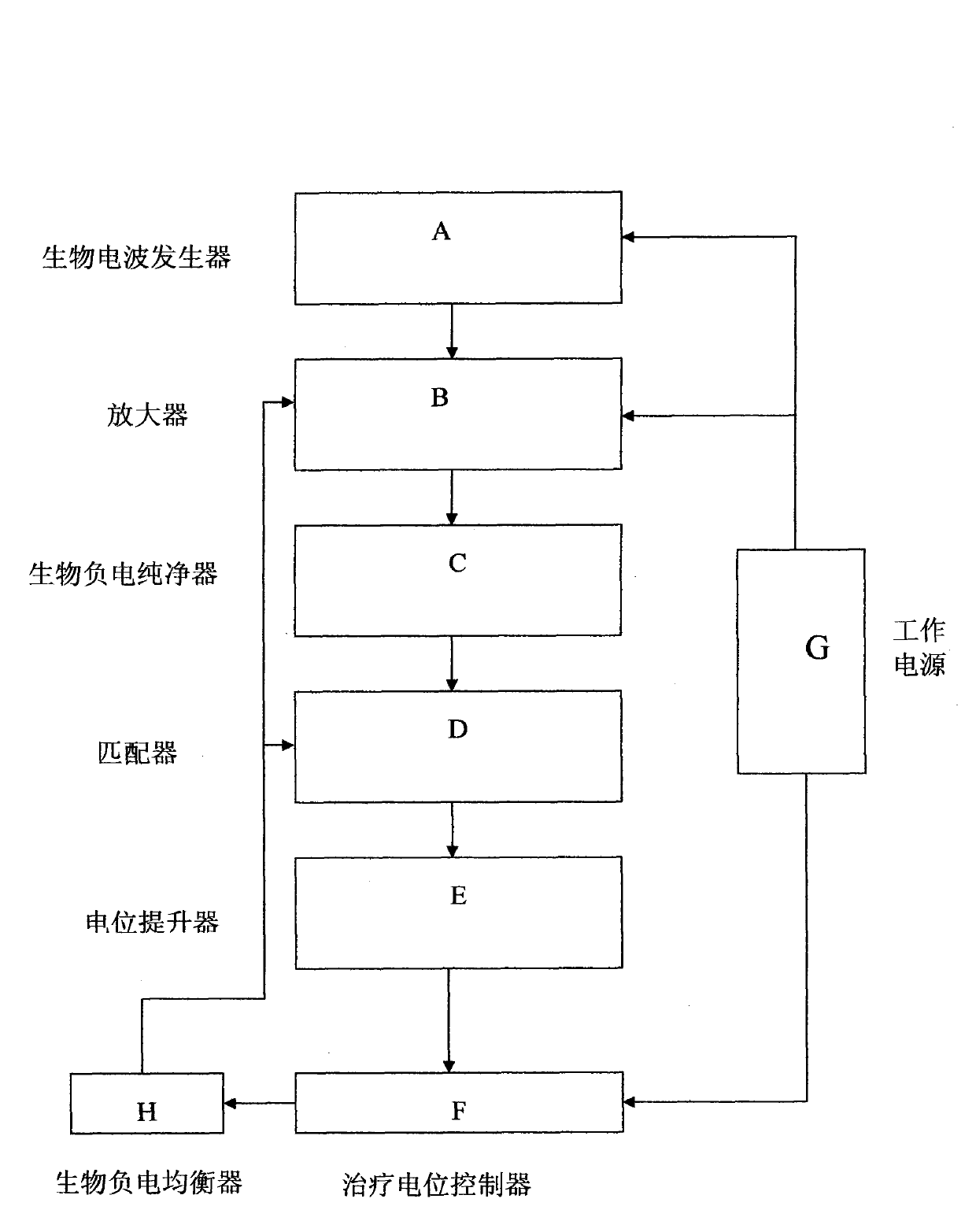
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering-electronic medical equipment, in particular relates to a biological negative electricity insomnia recovery therapeutic apparatus equipment system which comprises a host computer, a biological negative electricity conveyer and a biological negative electricity stimulator. A recovery therapeutic method of the biological negative electricity insomnia recovery therapeutic apparatus equipment system comprises the steps of: generating a direct current negative potential same with a potential of a cell membrane of the human body by using the system, placing an insomniac in a biological negative electric field, enabling the in vivo tissue to generate a physical effect through the action of the negative electric field to the insomniac, regulating the cerebral cortex, the autonomic nervous system and the incretion function; and stimulating meridian points related to the autonomic nervous system by using a biological negative electricity stimulator according to the principle of meridian science and science of acupuncture and moxibustion in traditional Chinese medicine to activate weak parasympathetic nerve, restore the function of inhibiting the excitation, improve the sleep and cure the insomnia.
Owner:重庆新大地电子有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com