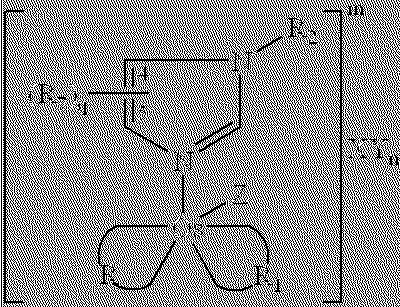Patents
Literature
96results about How to "Eliminating, or" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
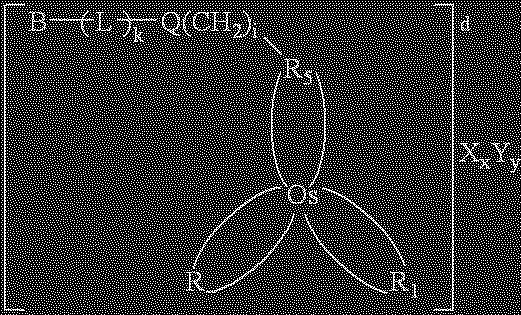
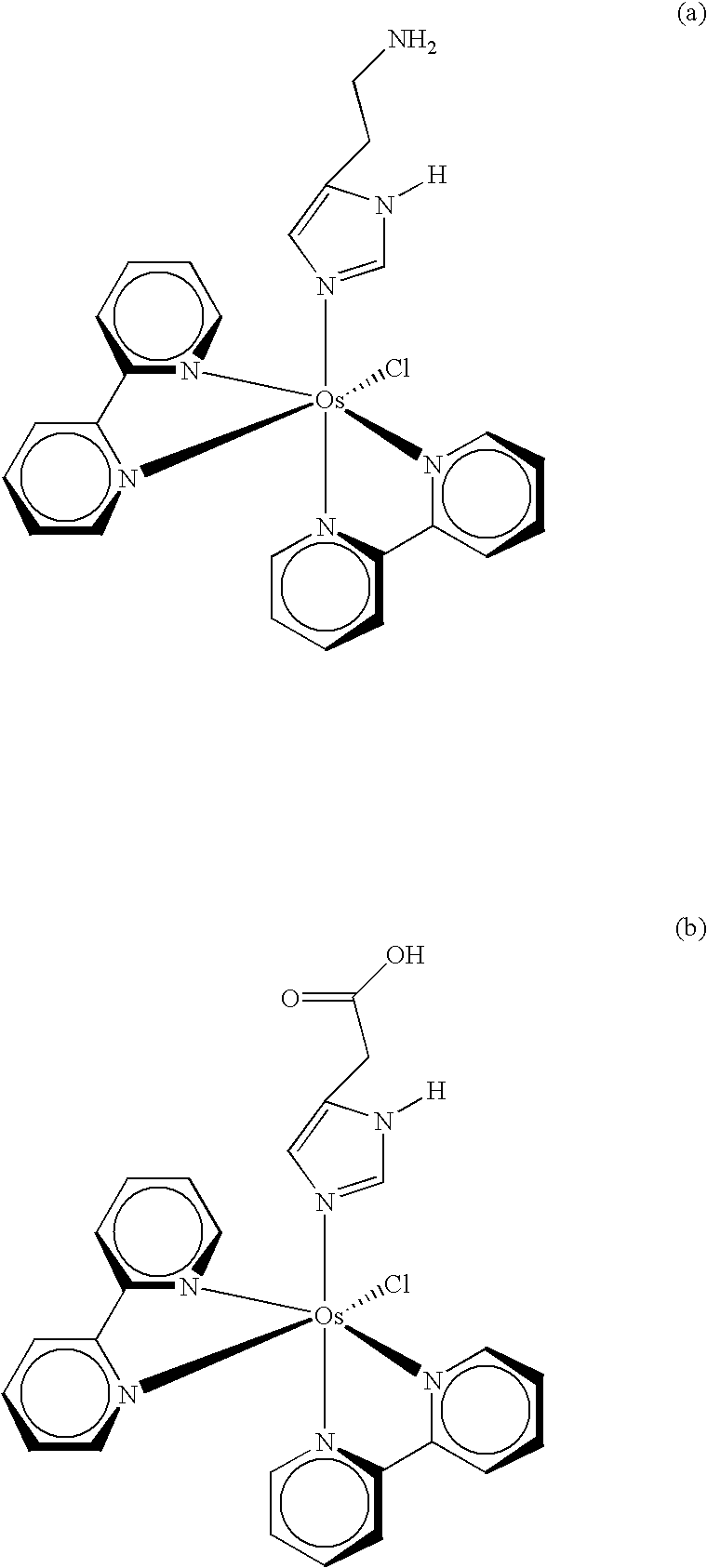
Redox reversible bipyridyl-osmium complex conjugates
InactiveUS7045310B2High measurement accuracyImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRedoxElectrochemistry
Novel bipyridyl-osmium complex conjugates and their use in electrochemical assays are described. The redox reversible-osmium complexes can be prepared to exhibit unique reversible redox potentials and can thus be used in combination with other electroactive redox reversible species having redox potentials differing by at least 50 millivolts in electrochemical assays designed for use of multiple electroactive species in the same cell and in the same sample without interference between the two or more redox coupled conjugate systems.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
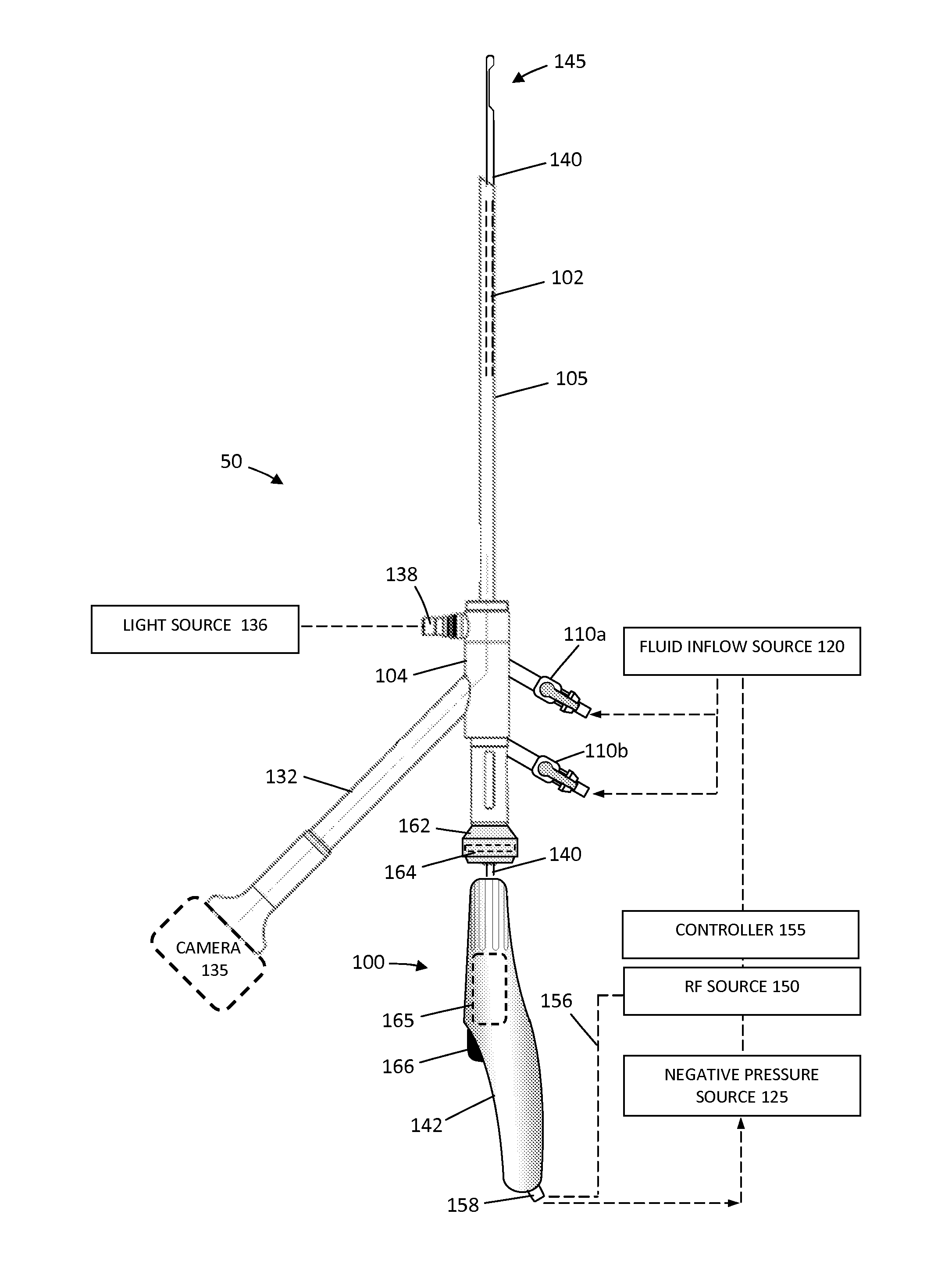
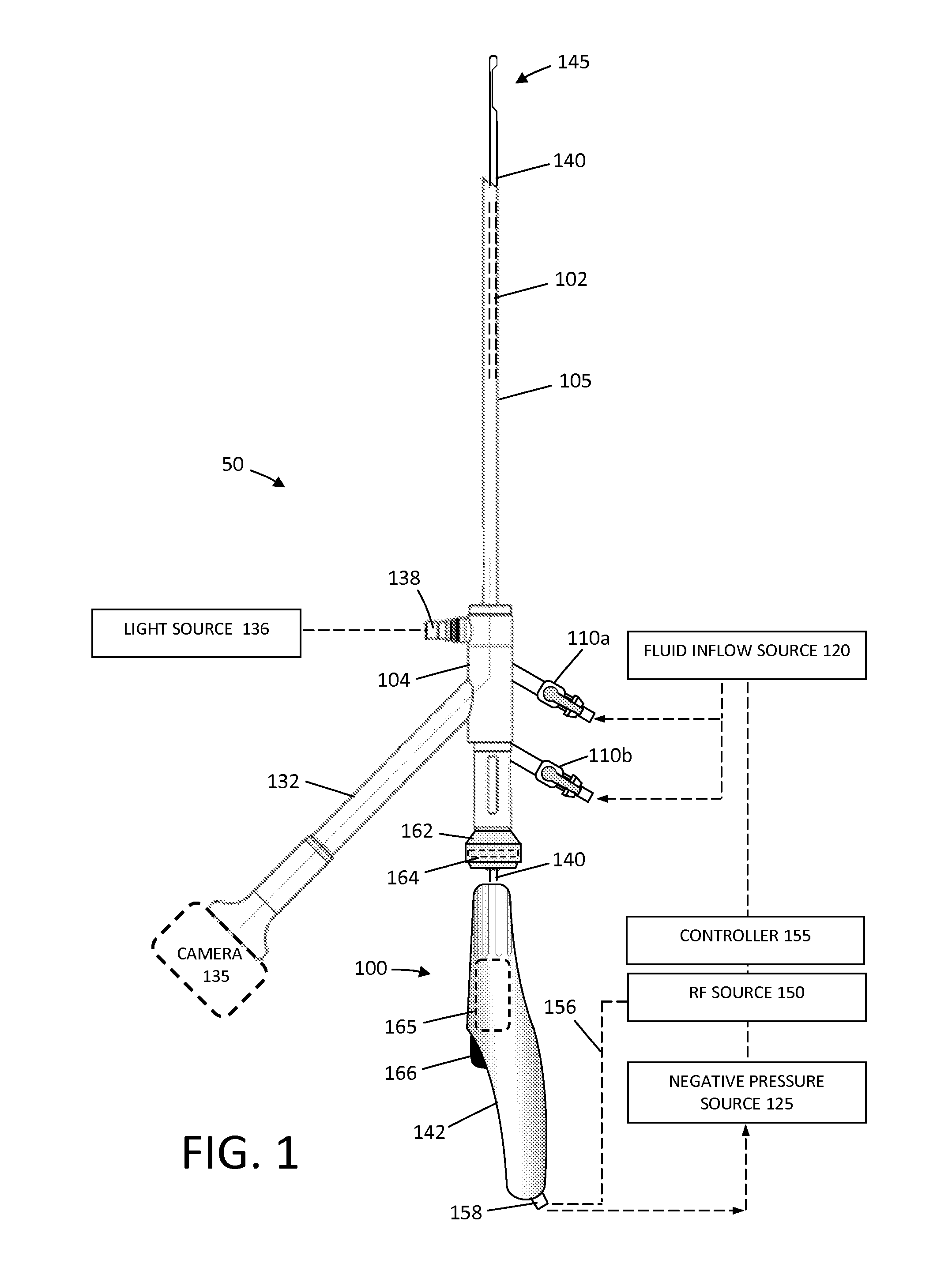
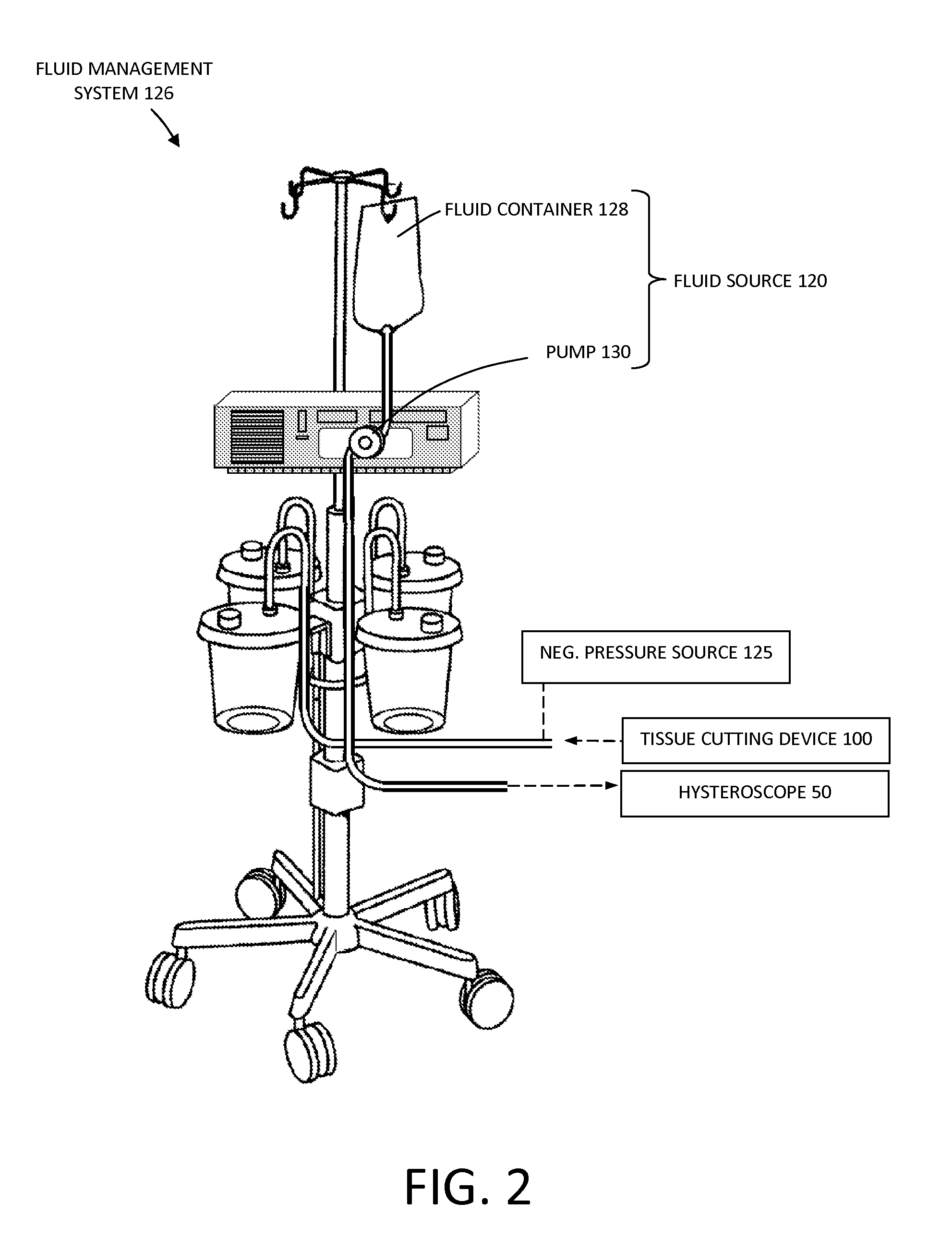
Tissue cutting systems and methods
ActiveUS20130172870A1Avoid the needEliminating orEndoscopesSurgical instruments for heatingRadio frequency energySurgery
A probe for resecting and coagulating tissue comprises an outer sleeve having a tissue cutting window and an inner sleeve having a tissue cutting distal end. And RF cutting region is formed at the distal end of the inner member and an RF coagulation region is formed on an exterior surface of the inner member immediately proximal to the cutting surface. A single power supply providing a single RF energy mode can be connected to both RF applicator regions to simultaneously cut and coagulate tissue.
Owner:MINERVA SURGICAL
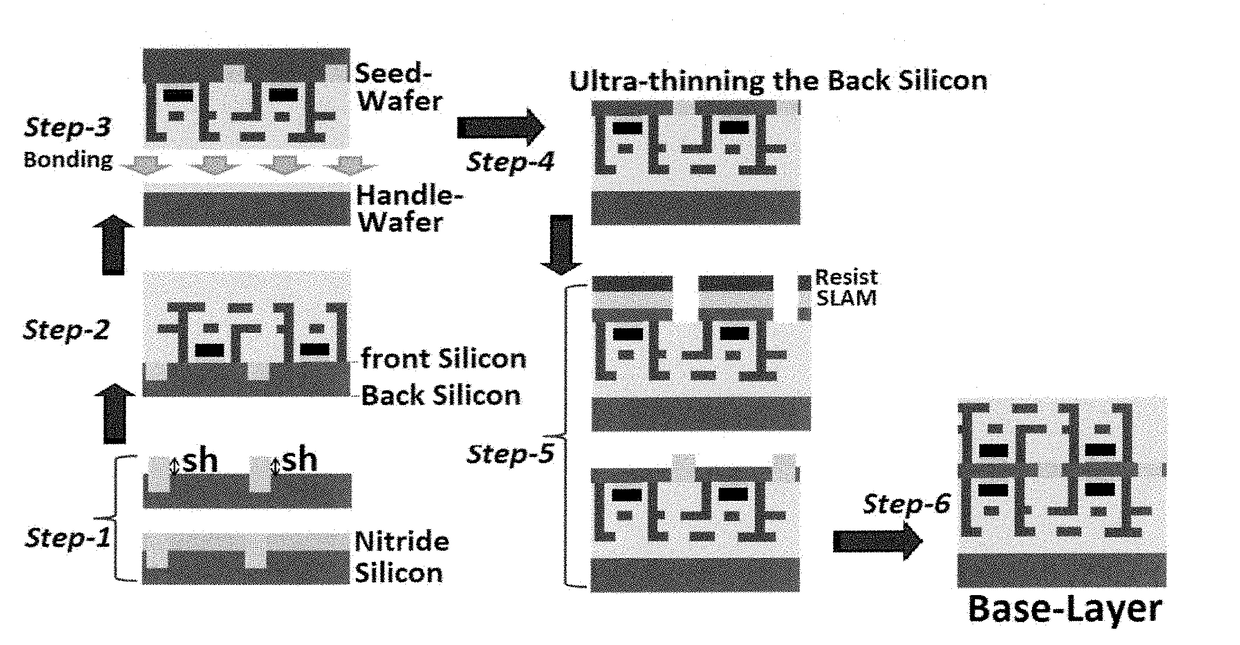
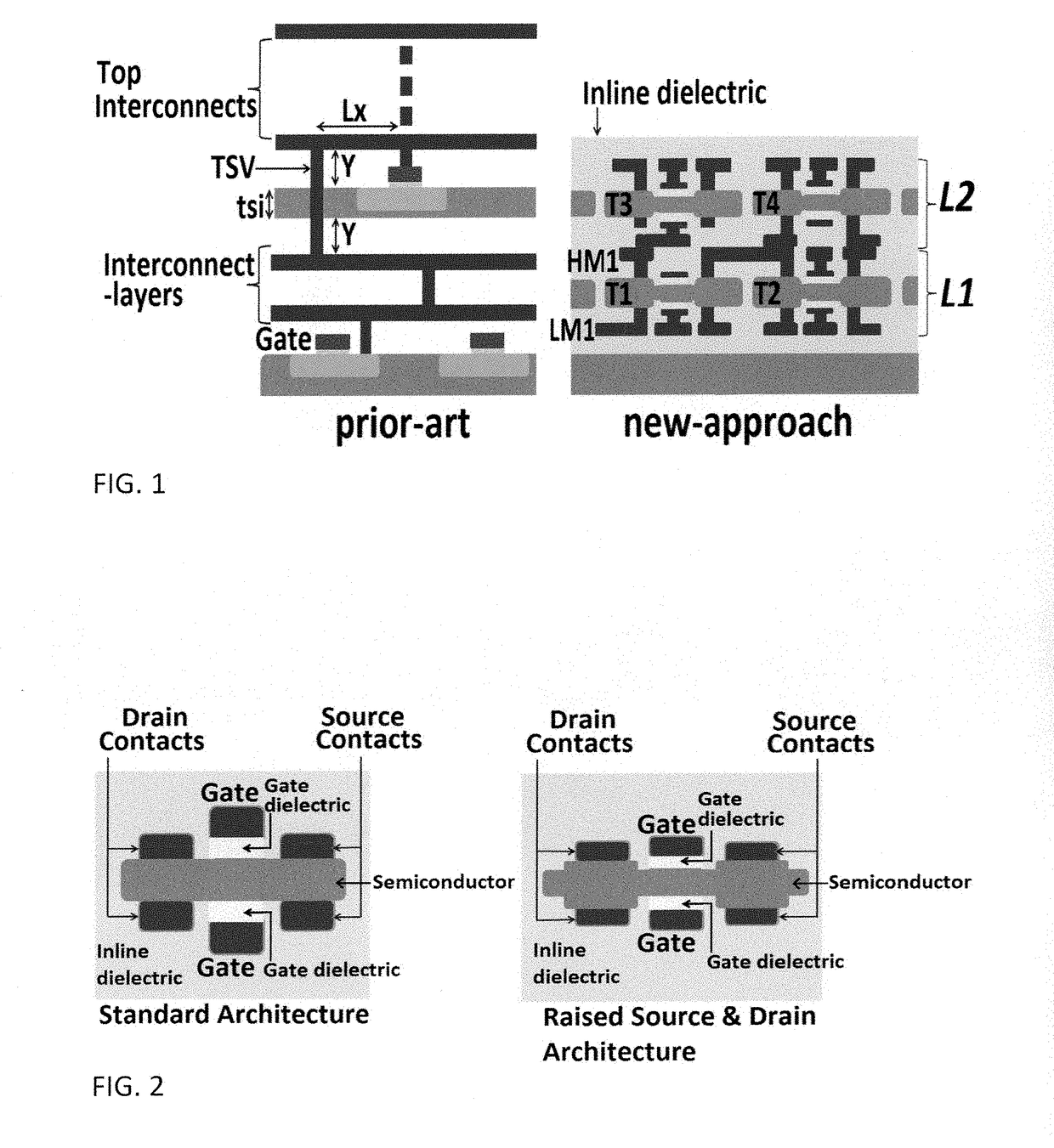
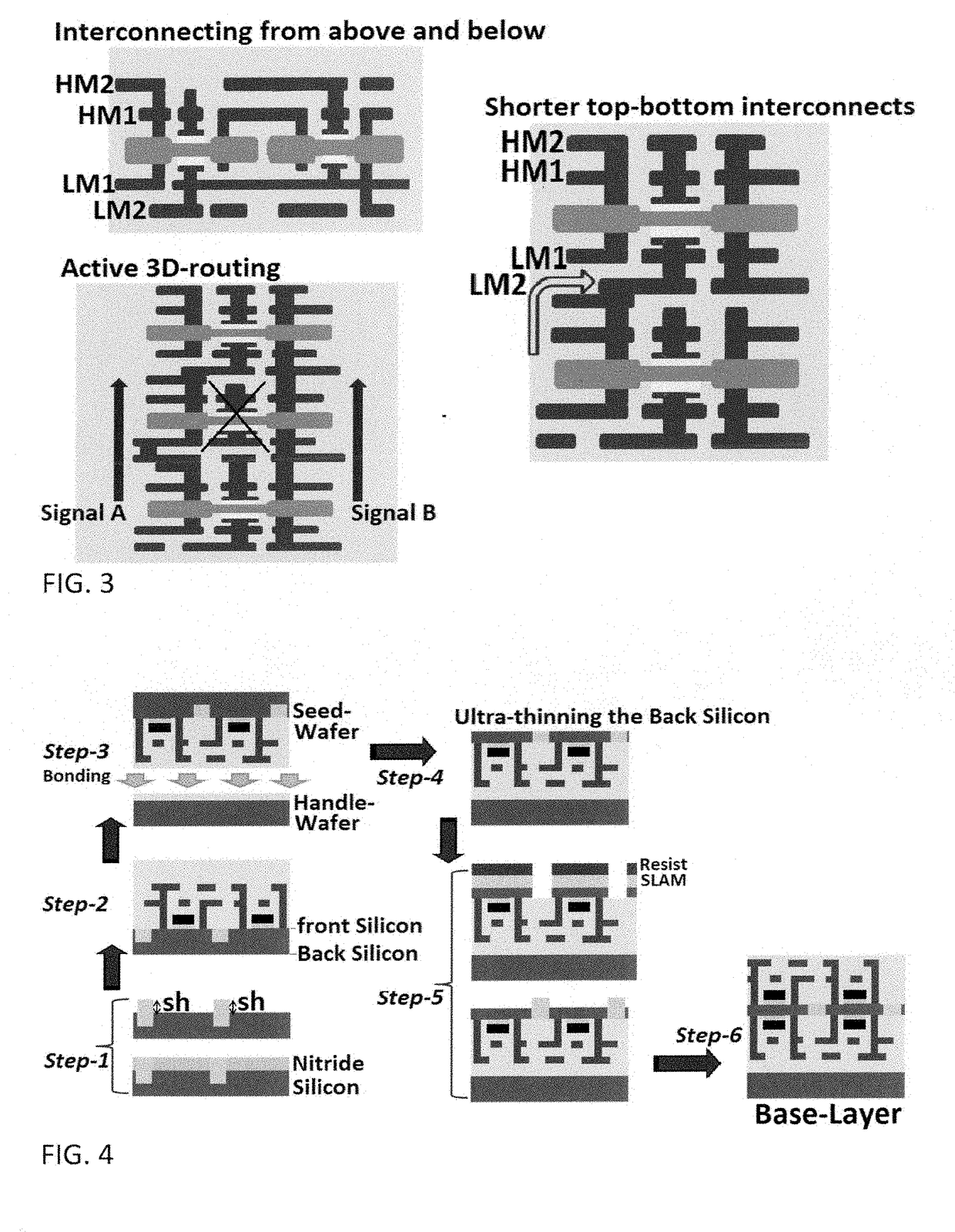
Approach to the manufacturing of monolithic 3-dimensional high-rise integrated-circuits with vertically-stacked double-sided fully-depleted silicon-on-insulator transistors
ActiveUS20180294284A1Increase its VTLow powerTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHigh rise
Method to fabricate high-rise three-dimensional Integrated-Circuits (3D-ICs) is described. It has the major advantage over all the other known methods and prior arts to fabricate or manufacture 3D-ICs in that it substantially reduces RC-delays and fully eliminates or very substantially reduces the large and bulky electrically conductive Through-Silicon-VIAs in monolithic 3D integration. This enables the 3D-ICs to have faster operational speed with denser device integration.
Owner:TARAKJI AHMAD +1
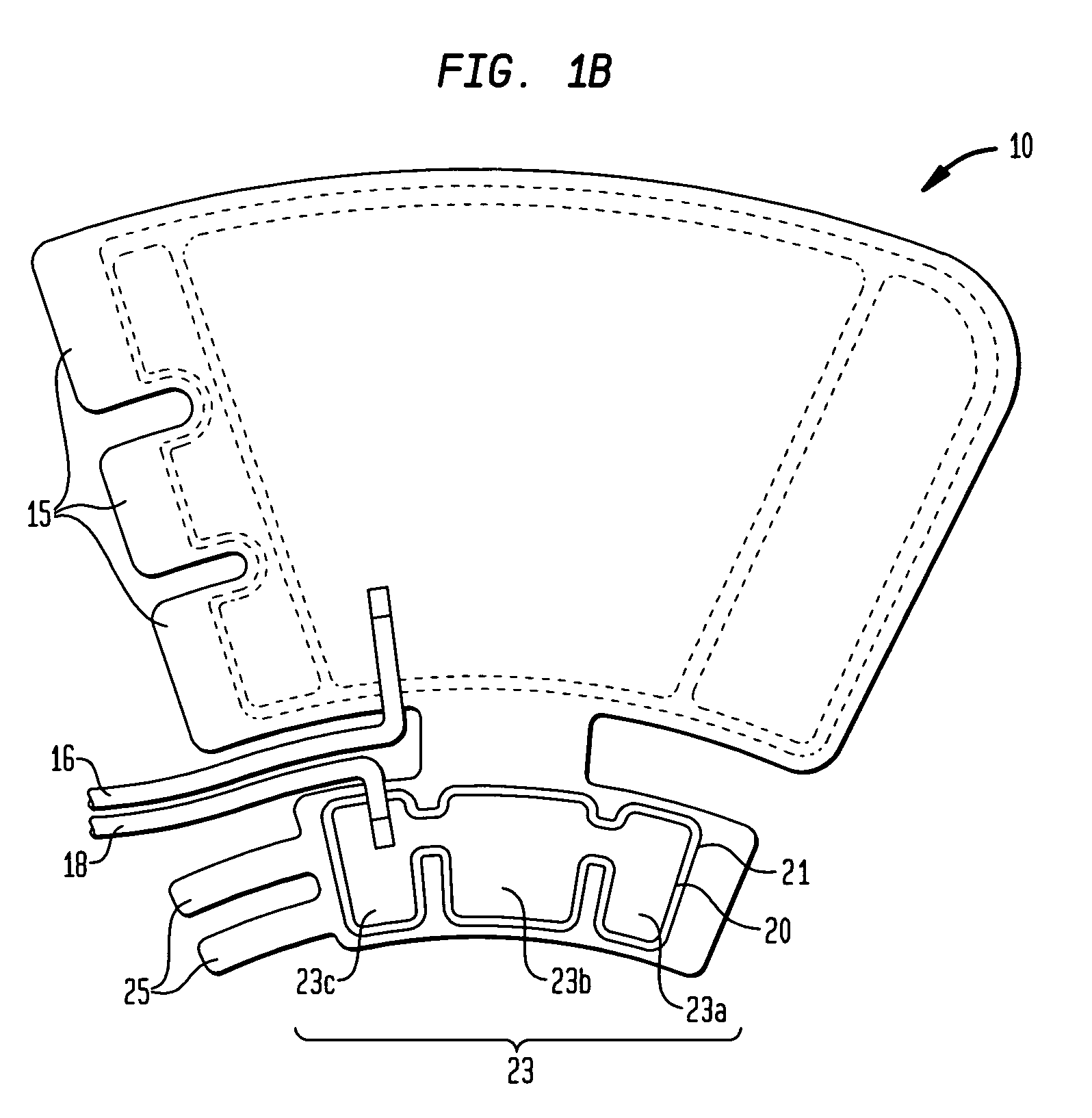
Bioresorbable Spinal Implant and Related Methods
A prosthesis for the replacement of an intervertebral disc of the spine comprises a block of an elastomeric material, which is held under compression by an encapsulating textile fabric. A preferred version of the invention has flanges that are continuations of the encapsulating fabric forming an interdigitation, with the continuation of the upper fabric passing through a hole in the lower fabric and being attached to the lower vertebral body and the continuation of the lower fabric crossing to its fixation site on the upper vertebral body. Optionally, the flanges are resorbable, over time leaving only the implant core and encapsulation fabric in the intervertebral space.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Benzoimidazole compounds
Benzoimidazole compounds, compositions, and methods of using them in leukocyte recruitment inhibition, in modulating H4 receptor, and in treating conditions such as inflammation, H4 receptor-mediated conditions, and related conditions.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Compression garment with heel elevation
InactiveUS20070161933A1Reducing and mitigating pressureEliminating orOperating chairsOperating tablesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationHeel strike
A garment that includes at least one inflatable chamber for applying compression to a limb for assisting venous return, and an elevation member to elevate the limb. The elevation member may comprise an inflatable chamber, and the garment may be configured for compressive therapy of the leg while elevating the heel, eliminating or otherwise reducing or mitigating pressure on an individual's heel while the leg is in an extended position and undergoing compressive therapy.
Owner:SUN SCI
Satellite refuelling system and method
ActiveUS8074935B2Eliminating orReduce riskAircraft componentsCosmonautic ground equipmentsRobotic armActuator
The present invention provides a method, system and apparatus for robotic refueling of satellites. The system may include a dedicated refueling satellite launched directly from either earth, or alternatively it could be launched from another larger mother spacecraft or space station in which the refueling satellite is ferried into space in the case of the larger space craft or it may be stored on the space station until needed from which it can be launched. The system includes a robotic arm, suitable tools which can be affixed to the end effector of the robotic arm required for accessing, opening and closing the fuel fill valve on the satellite being serviced, storage and retrieval stations on a tool caddy on which the tools and various fuel fill valve caps are stored. The system is under teleoperation by a remotely located operator, for example located on earth, in the mother station or in the space station. Cameras are included focussed on the robotic arm and end effector and images are transmitted to the operator to allow the operator to direct and control the refueling procedure. The system may also be configured to be operated autonomously under computer control.
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
Flow regulation vent
ActiveUS8439035B2Decreasing gas flow areaReduce gas flow rateOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksAirflowHinge angle
A flow regulation vent includes a fixed portion adapted to engage a gas supply conduit and a spring force biased movable portion connected by a hinge to the fixed portion and flowingly connected to the pressurized gas supply. The fixed portion includes a gas flow orifice. The movable portion is pivotally movable between 1) a relaxed position, whereby at a specified minimum operating pressure, the movable portion is pivoted by the spring force away from the fixed portion to a position to establish a first gas washout flow area between the movable portion and the gas flow orifice; and 2) a fully pressurized position, whereby at a specified maximum operating pressure, the pressurized gas offsets the spring force to pivot the movable portion to a position adjacent the fixed portion to establish a minimum gas washout flow area between the movable portion and the gas flow orifice.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Satellite refuelling system and method
ActiveUS20080237400A1Prevent be damageEliminating orAircraft componentsCosmonautic ground equipmentsSatelliteSpacecraft
The present invention provides a method, system and apparatus for robotic refueling of satellites. The system may include a dedicated refueling satellite launched directly from either earth, or alternatively it could be launched from another larger mother spacecraft or space station in which the refueling satellite is ferried into space in the case of the larger space craft or it may be stored on the space station until needed from which it can be launched. The system includes a robotic arm, suitable tools which can be affixed to the end effector of the robotic arm required for accessing, opening and closing the fuel fill valve on the satellite being serviced, storage and retrieval stations on a tool caddy on which the tools and various fuel fill valve caps are stored. The system is under teleoperation by a remotely located operator, for example located on earth, in the mother station or in the space station. Cameras are included focussed on the robotic arm and end effector and images are transmitted to the operator to allow the operator to direct and control the refueling procedure. The system may also be configured to be operated autonomously under computer control.
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
Satellite refuelling system and method
ActiveUS20120112009A1Eliminating orReduce riskCosmonautic ground equipmentsCosmonautic partsRobotic armActuator
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
Telephone-linked commodity-billing method
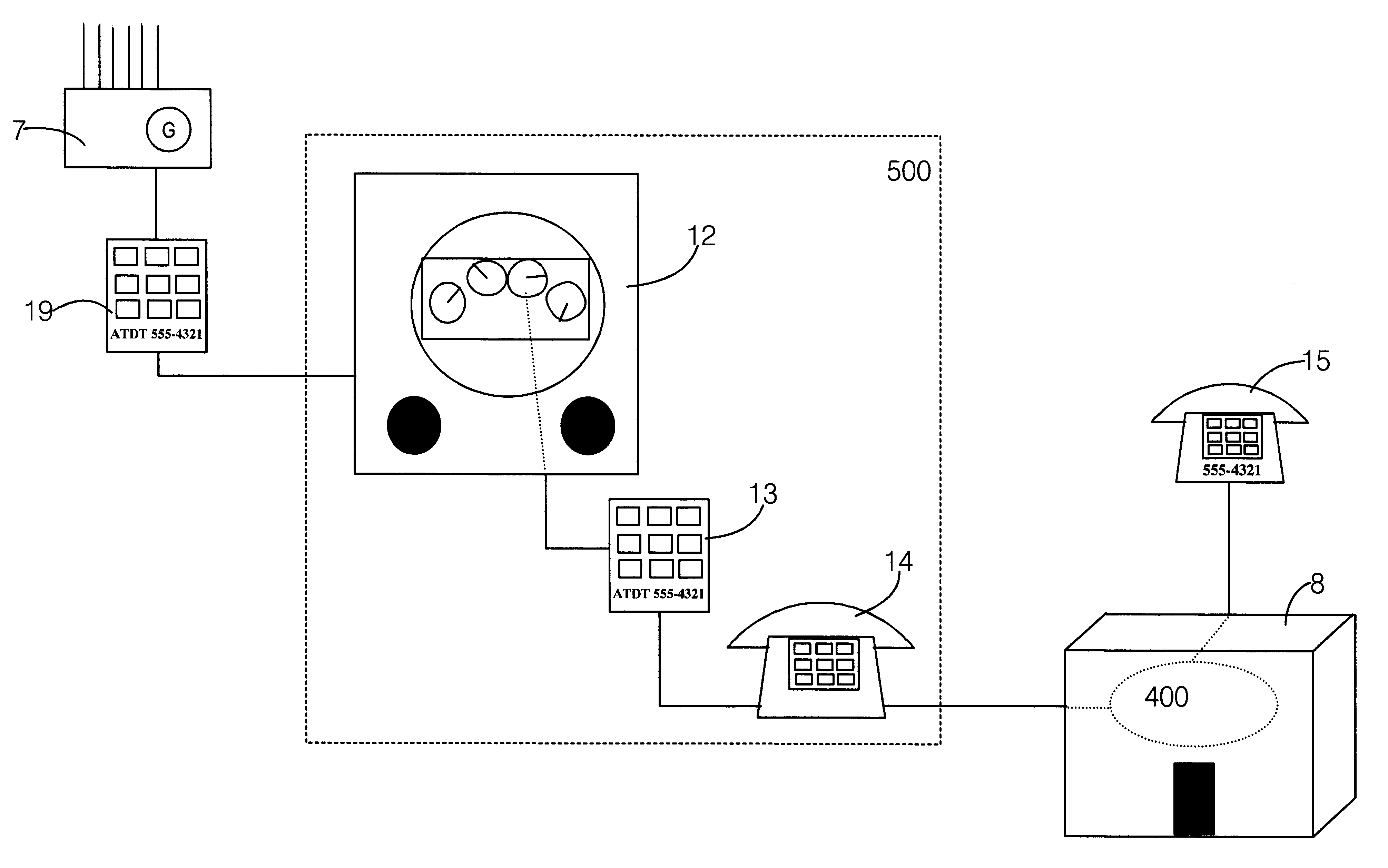
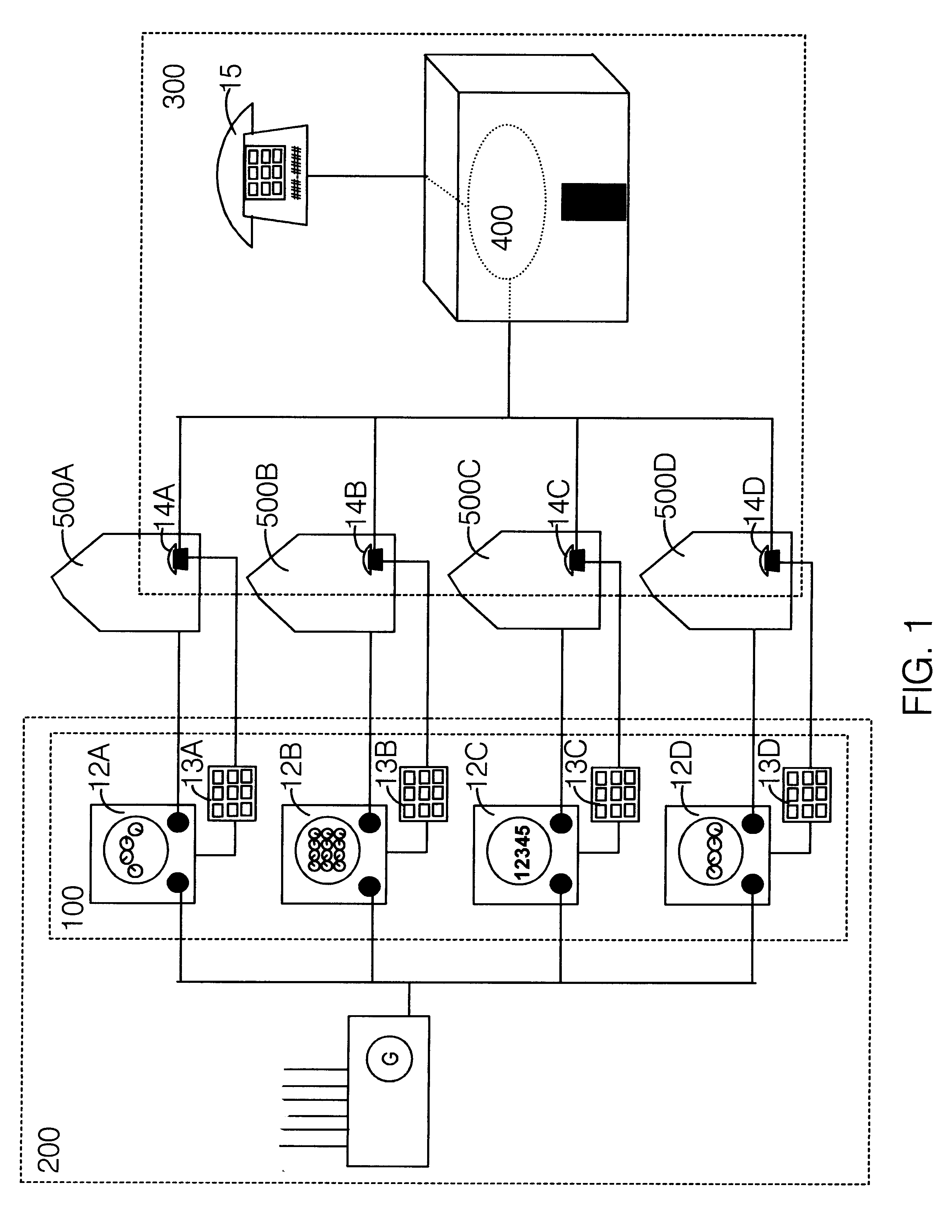
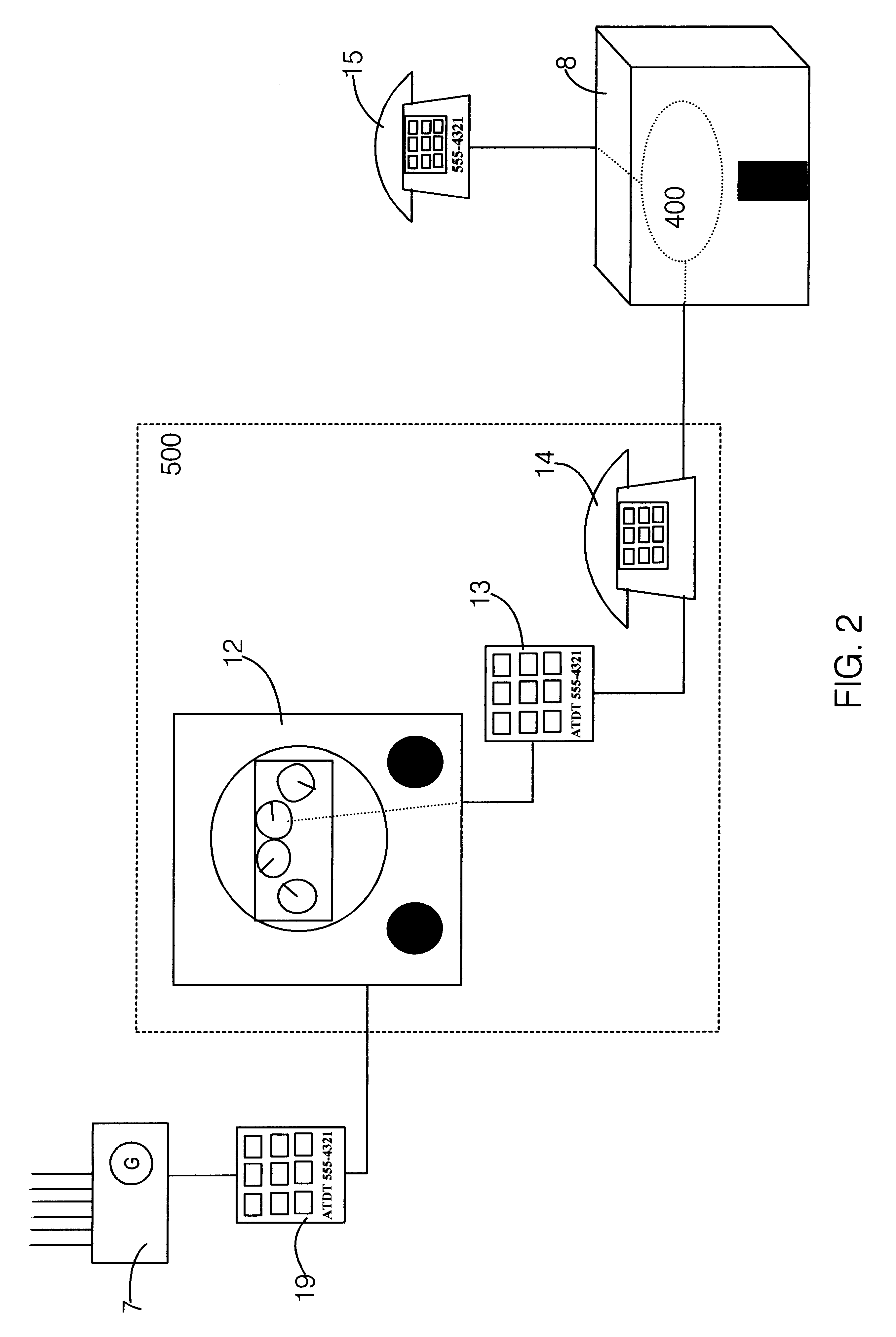
InactiveUS6240167B1Reduce eliminateEliminating orTelephonic communicationPayment architectureLine itemElectric power
A method for billing consumers of on-demand commodities consumed at a site remote from the site at which they are produced. It is modeled after certain contemporary telephone-company billing practices, though it is not limited to use with telephone companies. In one embodiment the method uses a telephone service provider to bill and collect for monies owed to the producer of the commodity for the amount of the full commodity units consumed during a billing period. In a simple embodiment of the method, commodity-consumption information is sent to the billing service by an automatically reading meter located at the point where the commodity is delivered for consumption. In particular, this commodity meter-such as an electric power meter-is designed to generate a discrete signal each time that a predetermined commodity-billing-unit has been consumed. Further in this particular embodiment, a coupling device for coupling the meter to the telephone line of the consumer is designed to receive this discrete signal and, each time that it does, to call a predetermined telephone number. The coupling device then disconnects the telephone connection immediately upon receiving verification of a telephone connection, without the transfer of any data. In that manner, the billing facility at the telephone is able to record that the particular customer identified by the number from which the call came had consumed one more billing-cost-unit of the commodity. This information is then utilized by the accounting computer at the telephone company to generate a line item or a billing section on the next telephone bill sent to that particular customer, a line item or a billing section corresponding to the cost of the commodity in question consumed by that customer during the billing period.
Owner:MICHAELS RAYMOND JOSEPH
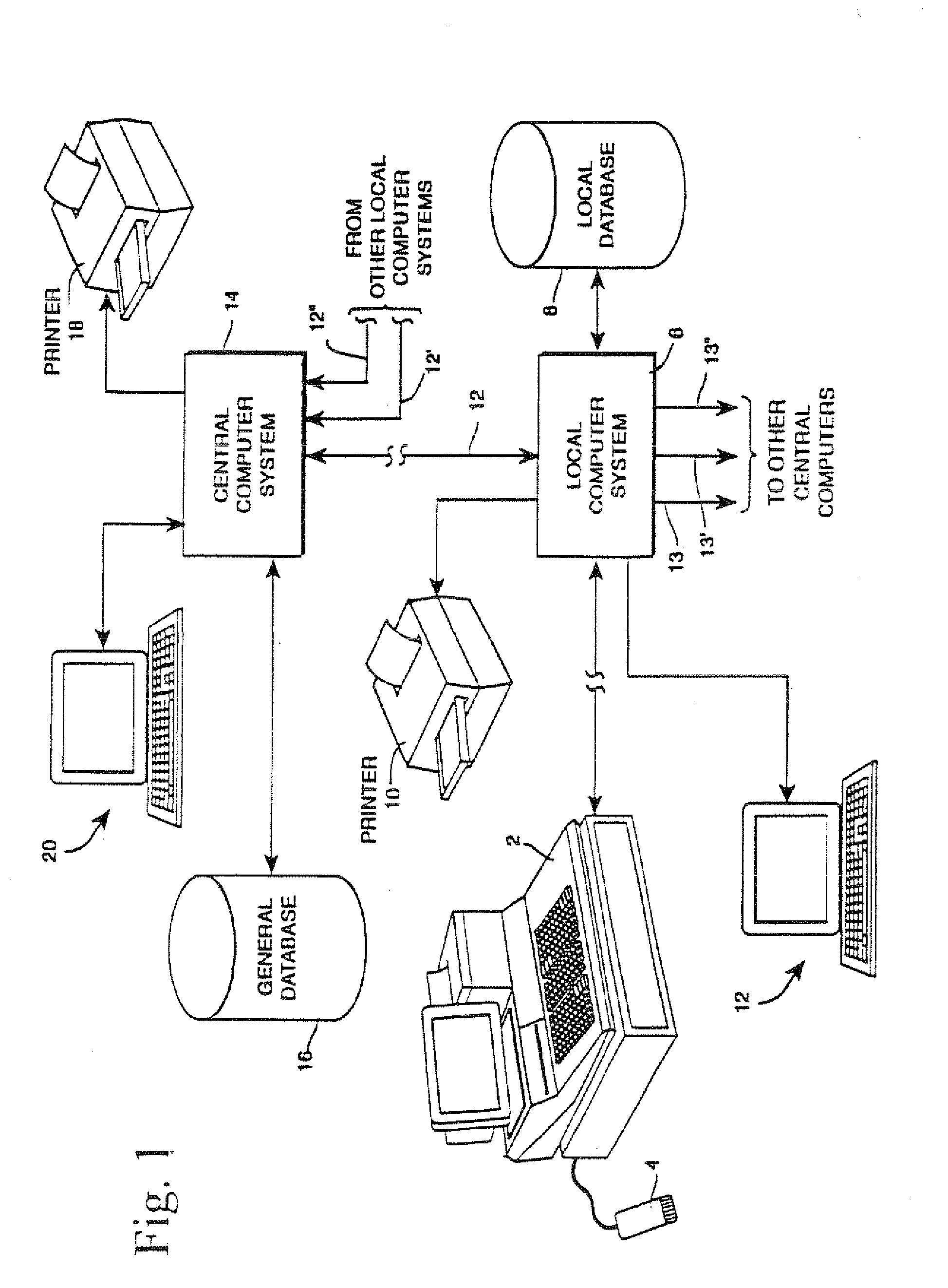
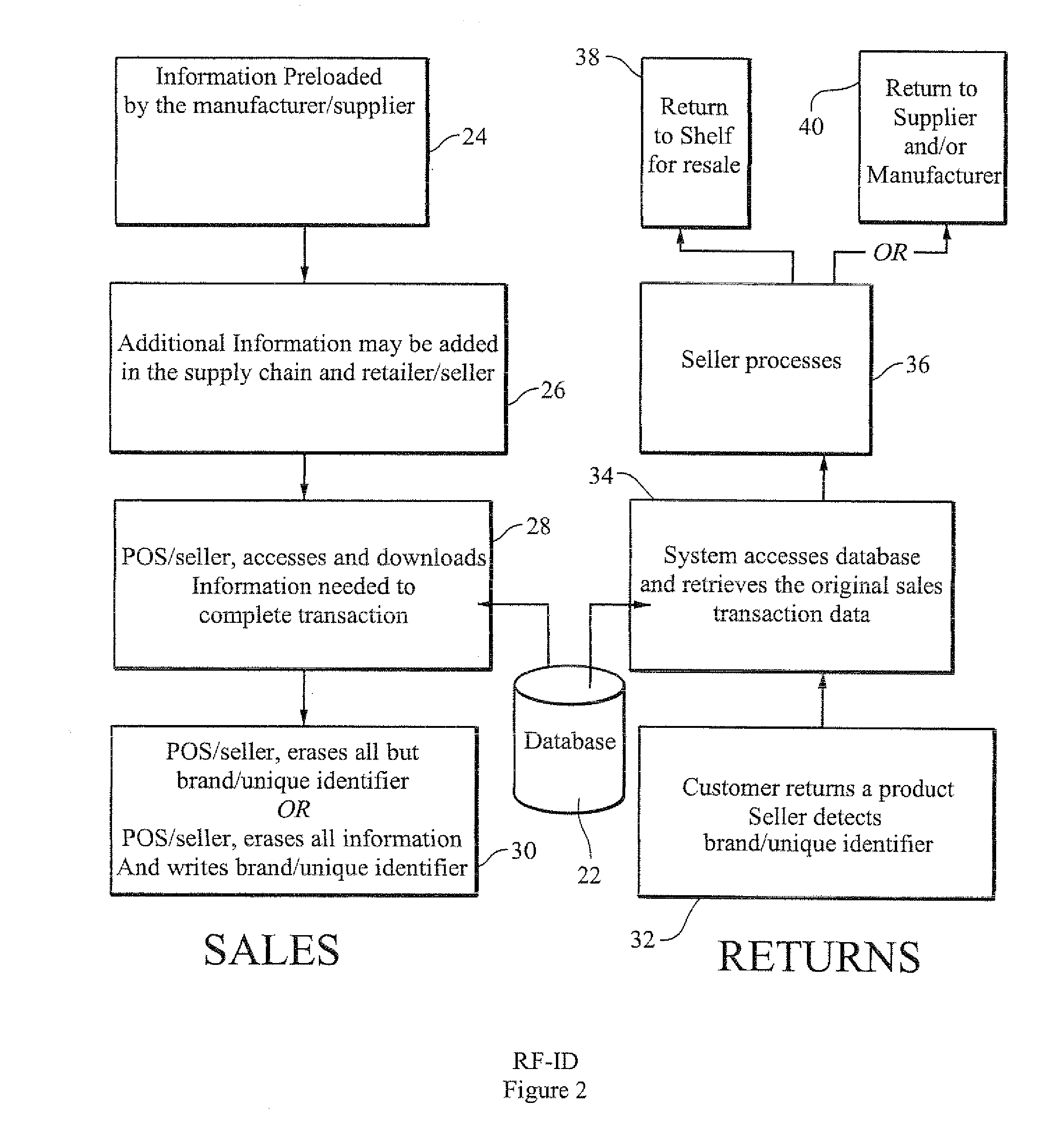
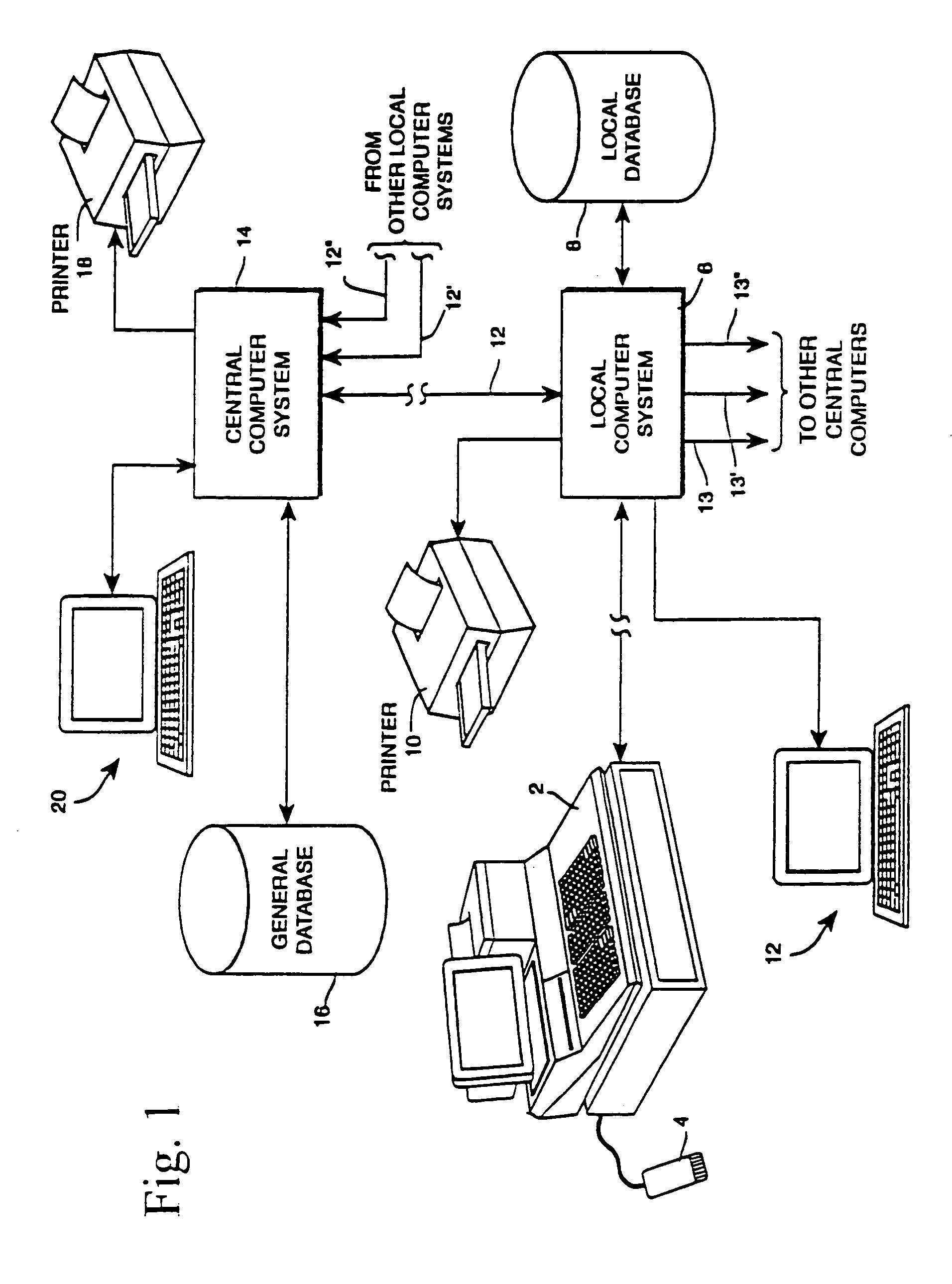
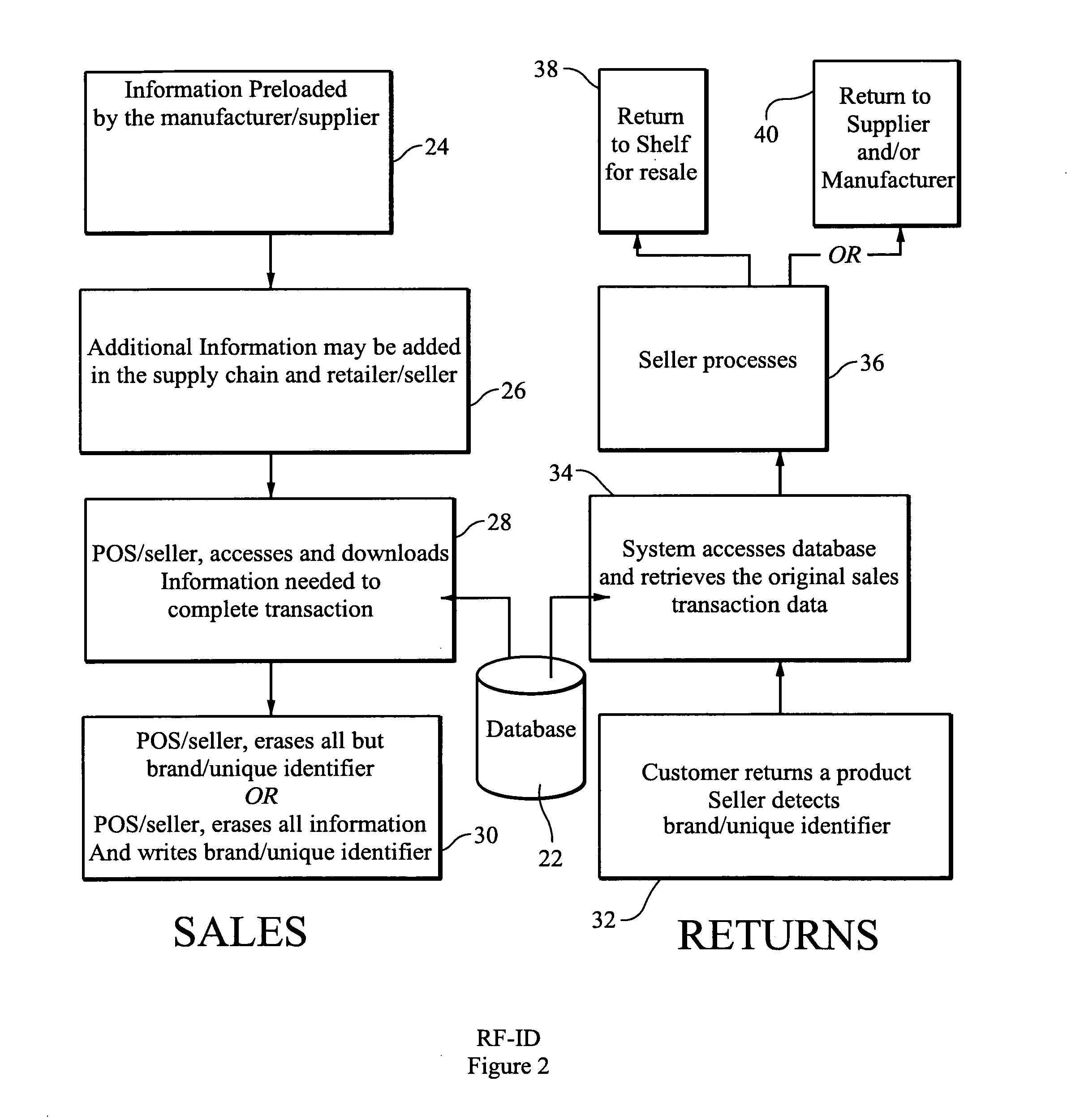
Rf-id product tracking system with privacy enhancement
ActiveUS20110029397A1Easy to useEliminating, orLogisticsPoint-of-sale network systemsIdentification deviceSecurity question
Owner:E2INTERACTIVE INC D B A E2INTERACTIVE
Compression garment with heel elevation
InactiveUS7967766B2Eliminating orReducing and mitigating pressureOperating chairsOperating tablesVeinPhysical therapy
A garment that includes at least one inflatable chamber for applying compression to a limb for assisting venous return, and an elevation member to elevate the limb. The elevation member may comprise an inflatable chamber, and the garment may be configured for compressive therapy of the leg while elevating the heel, eliminating or otherwise reducing or mitigating pressure on an individual's heel while the leg is in an extended position and undergoing compressive therapy.
Owner:SUN SCI
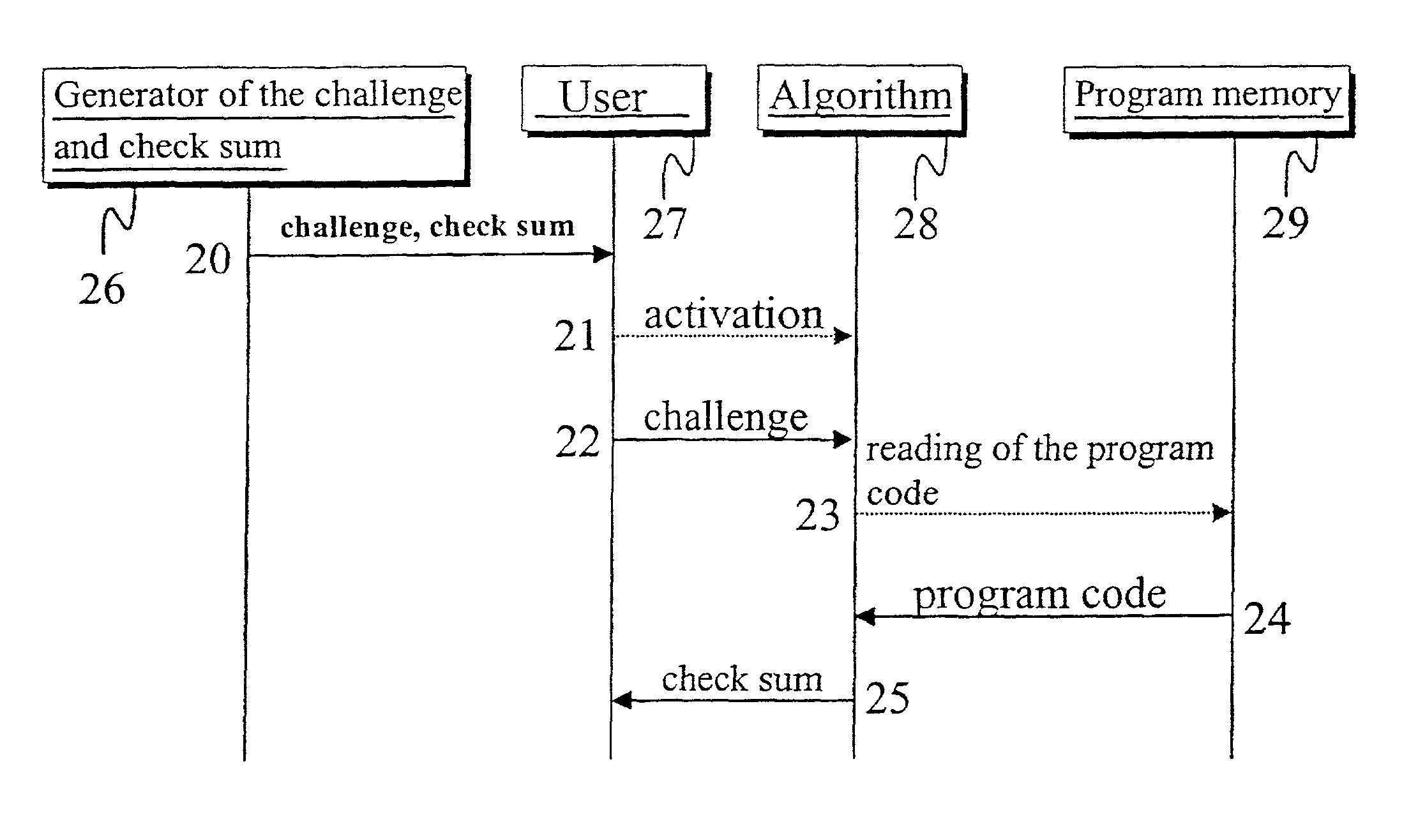
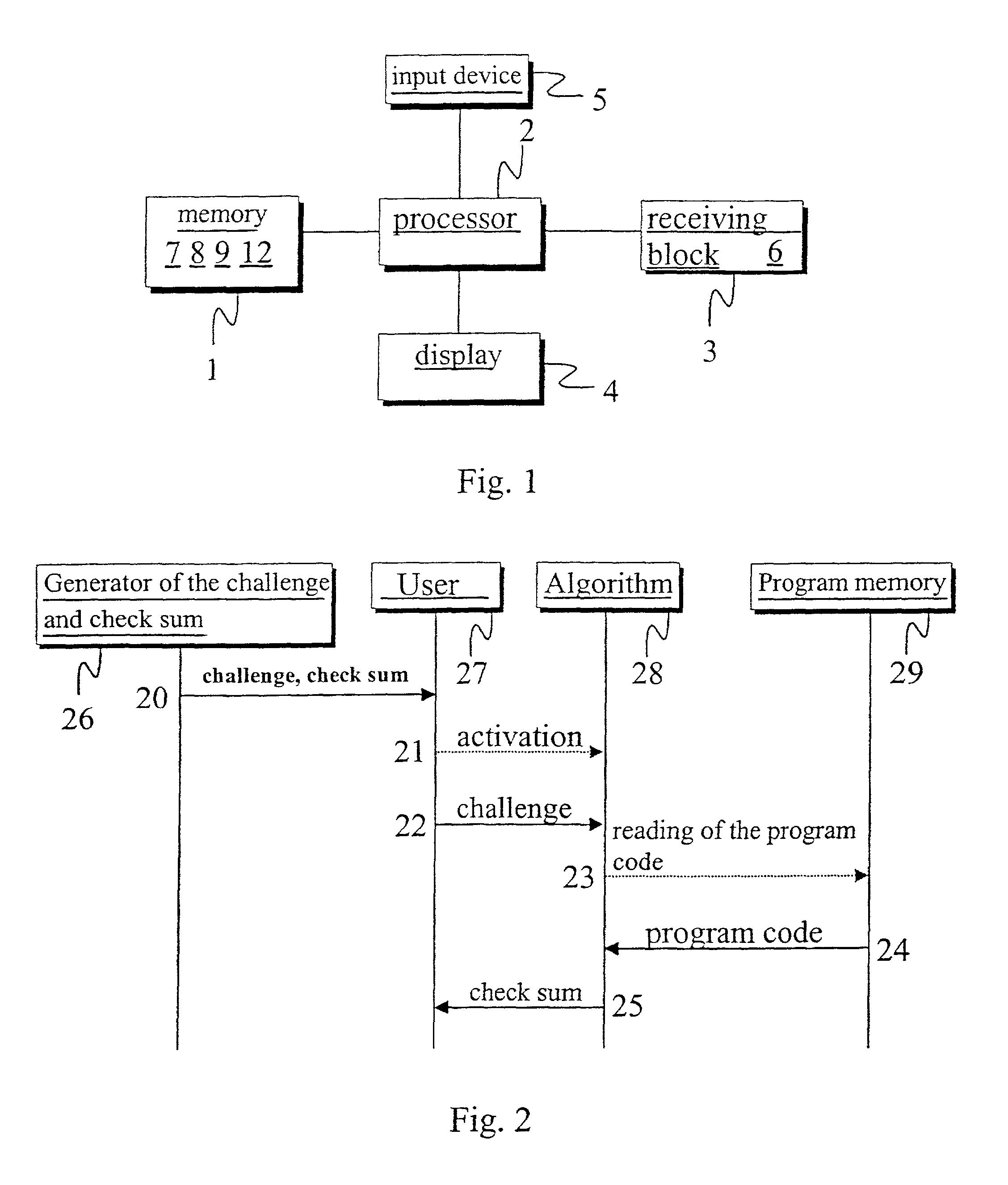
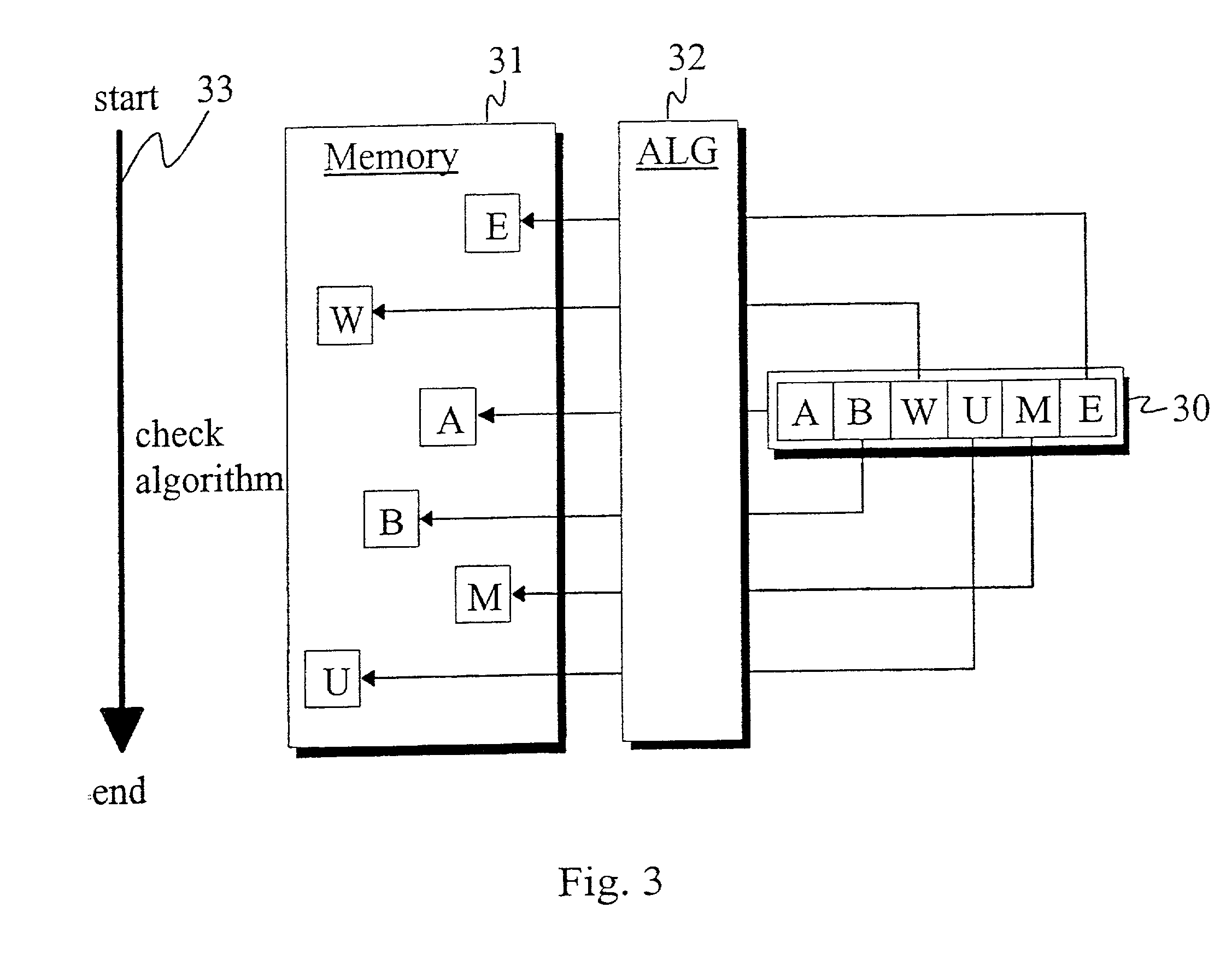
Method and device for authenticating locally-stored program code
ActiveUS20020091938A1Eliminating, orReducing, the drawbacks and deficienciesDigital data processing detailsHardware monitoringDisplay deviceChecksum
In a method and system for authenticating locally-stored program code, a first checksum is computed using the locally-stored program code, the computed checksum is compared with a second checksum known to be valid and, if the two checksums are determined to match, the locally-stored program code is deemed valid and authentic. For increased certification reliability and dependability, before computation of the first checksum a predetermined challenge is added to the stored program code, so that the first checksum is computed from the combination of the stored program code and the challenge. This enhancement enables secure use of stored program code in applications that demand high security. Users of such software may therefore rely on the authenticity of the data processed by the software and of the data and results reported on the display of a mobile phone or keyboard throughout the entire process or transaction.
Owner:GIESECKE & DEVRIENT MOBILE SECURITY GMBH
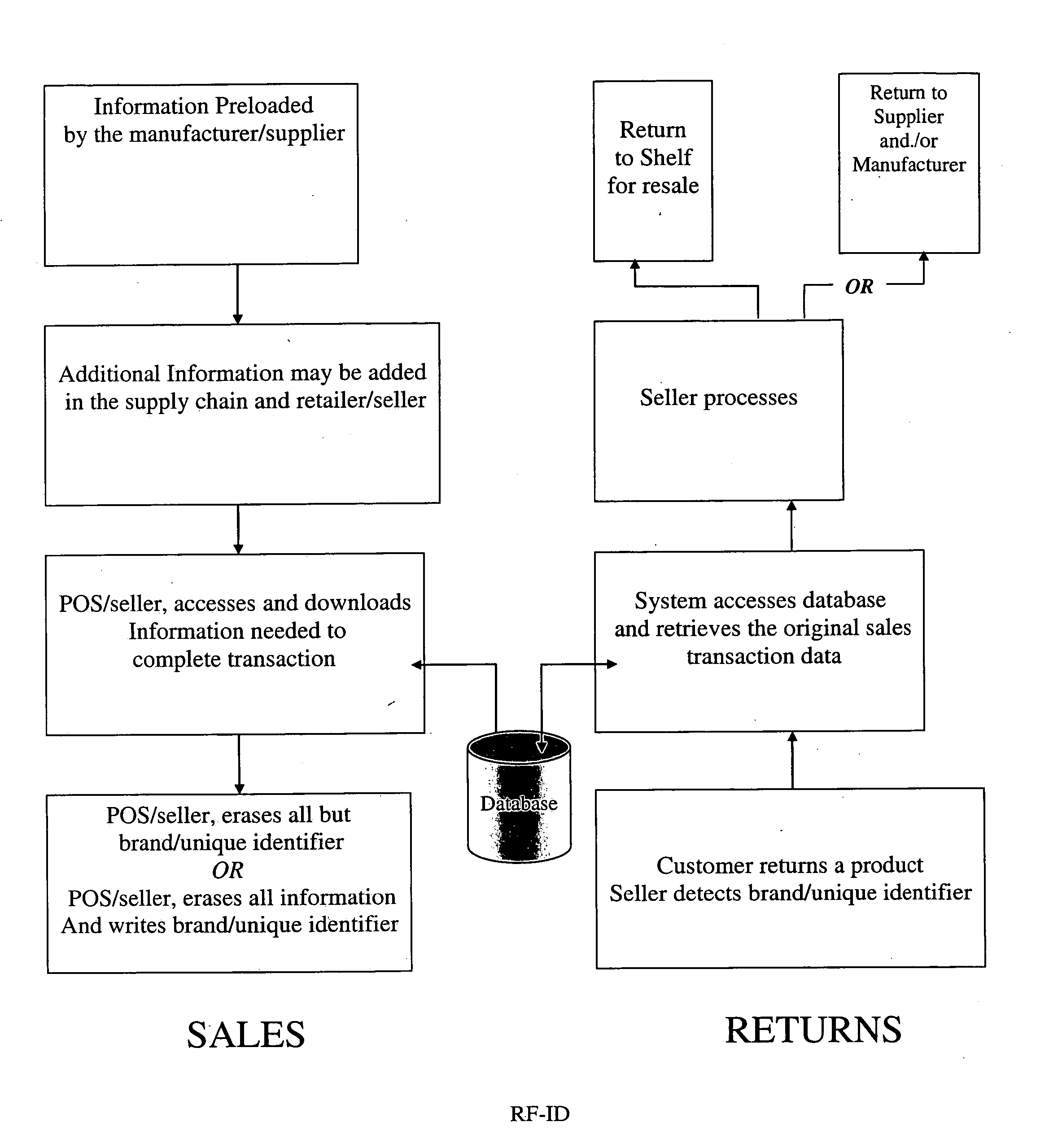
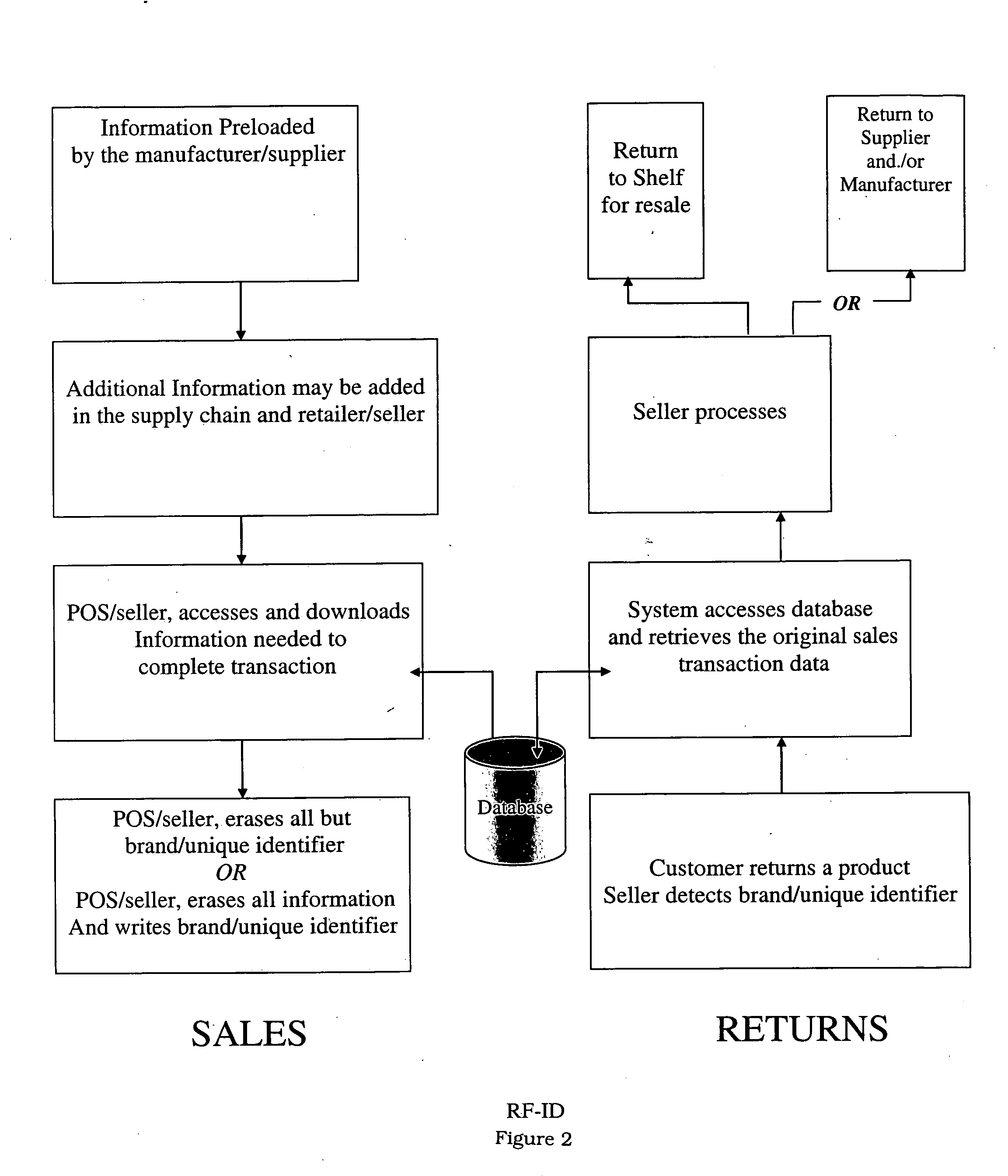
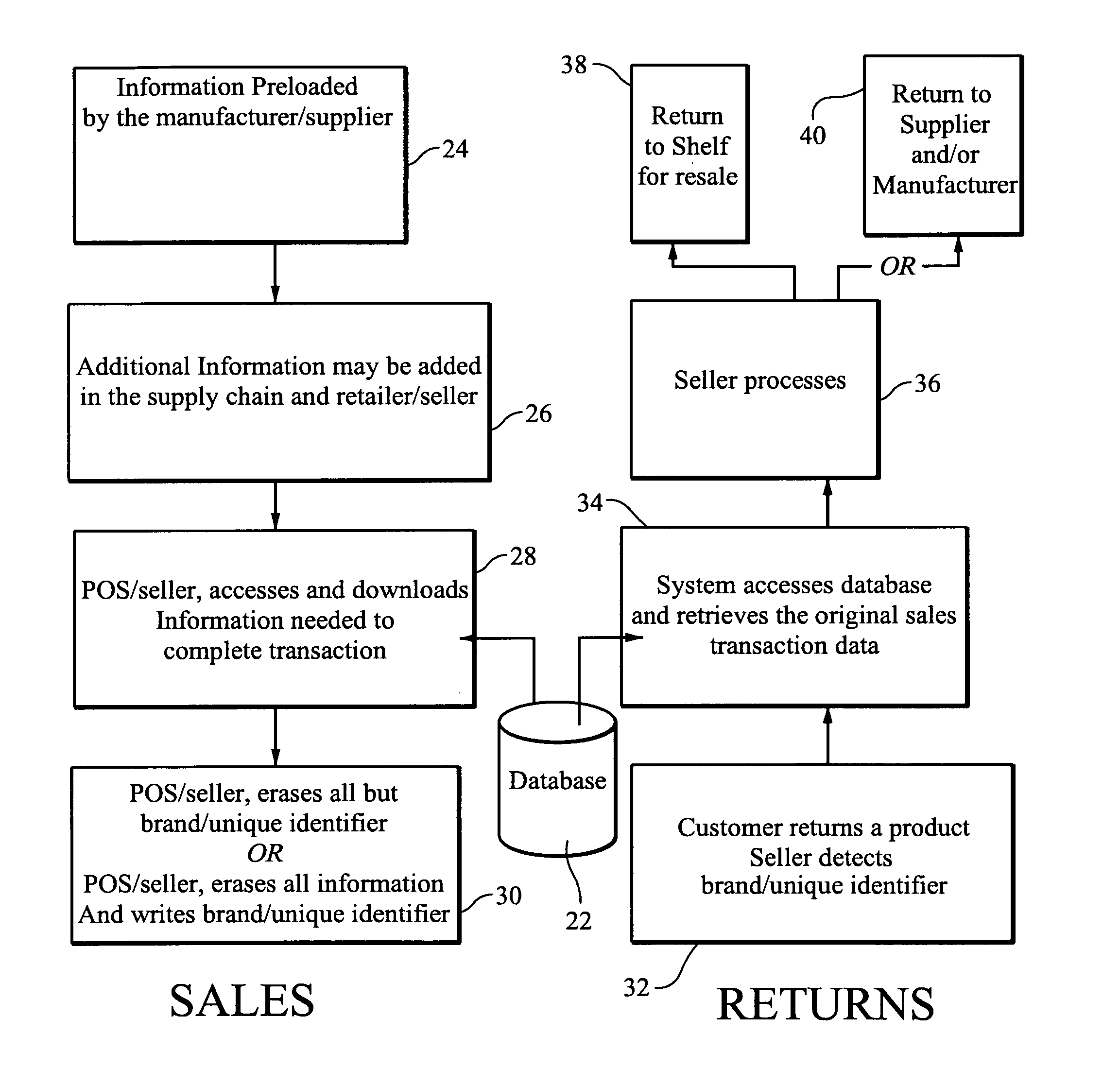
RF-ID product tracking system with privacy enhancement
ActiveUS20050131763A1Reduces privacy concernEasy to useElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing details
A method for using electronic product identification devices to track product sales and enable sales transactions to be registered in an electronic registration (ER) system without causing privacy or security concerns for the purchasers. RF-ID devices are placed on products being sold and include detailed information about the products. When the products are purchased, the detailed information is loaded into an ER database and all but a limited amount of information is removed from the RF-ID device. The limited information is sufficient to enable the detailed information to be located in the ER database by authorized individuals in connection with a return transaction or the like.
Owner:E2INTERACTIVE INC D B A E2INTERACTIVE
RF-ID product tracking system with privacy enhancement
ActiveUS7840439B2Easy to useEliminating, orElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsIdentification deviceSecurity question
A method for using electronic product identification devices to track product sales and enable sales transactions to be registered in an electronic registration (ER) system without causing privacy or security concerns for the purchasers. RF-ID devices are placed on products being sold and include detailed information about the products. When the products are purchased, the detailed information is loaded into an ER database and all but a limited amount of information is removed from the RF-ID device. The limited information is sufficient to enable the detailed information to be located in the ER database by authorized individuals in connection with a return transaction or the like.
Owner:E2INTERACTIVE INC D B A E2INTERACTIVE
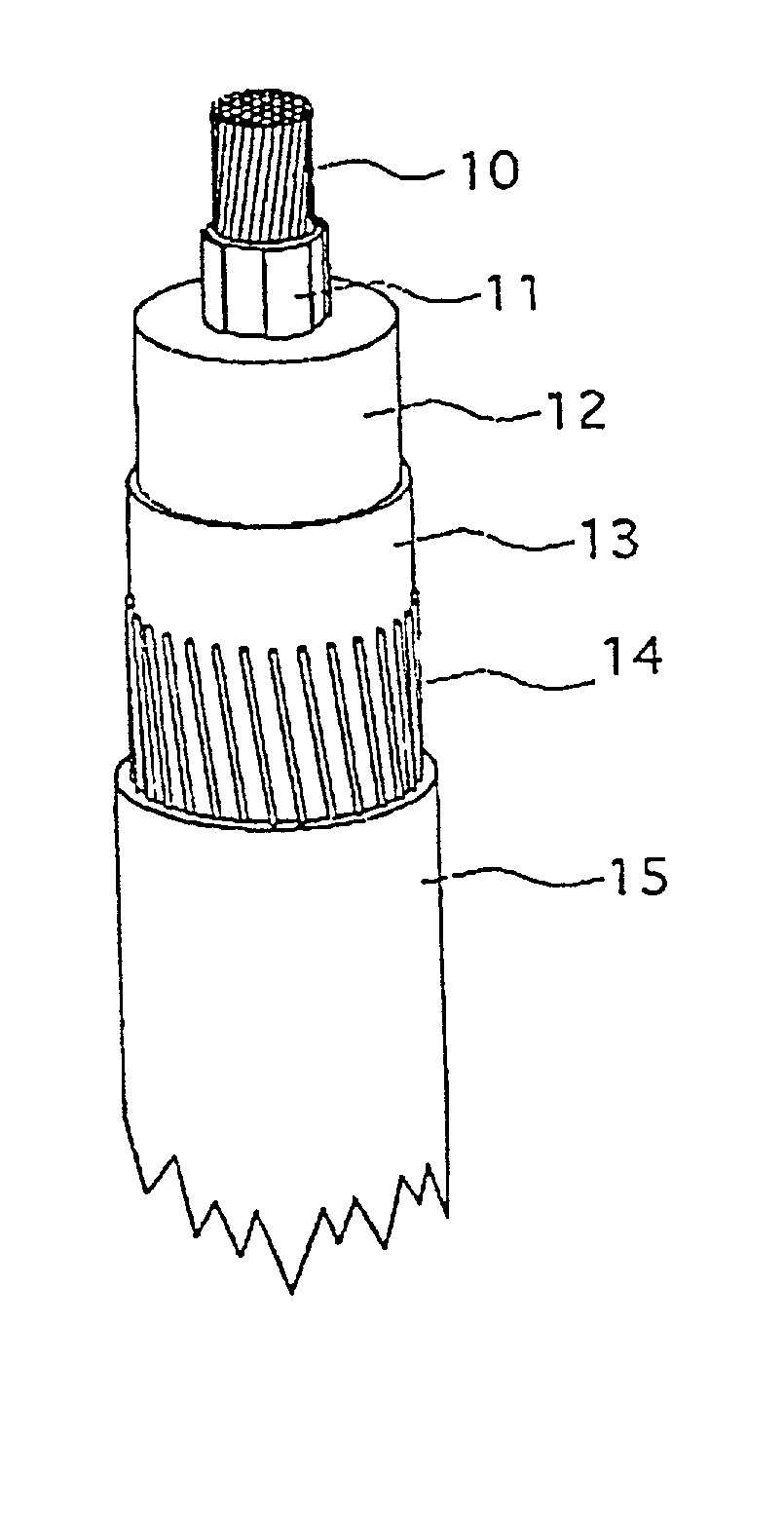
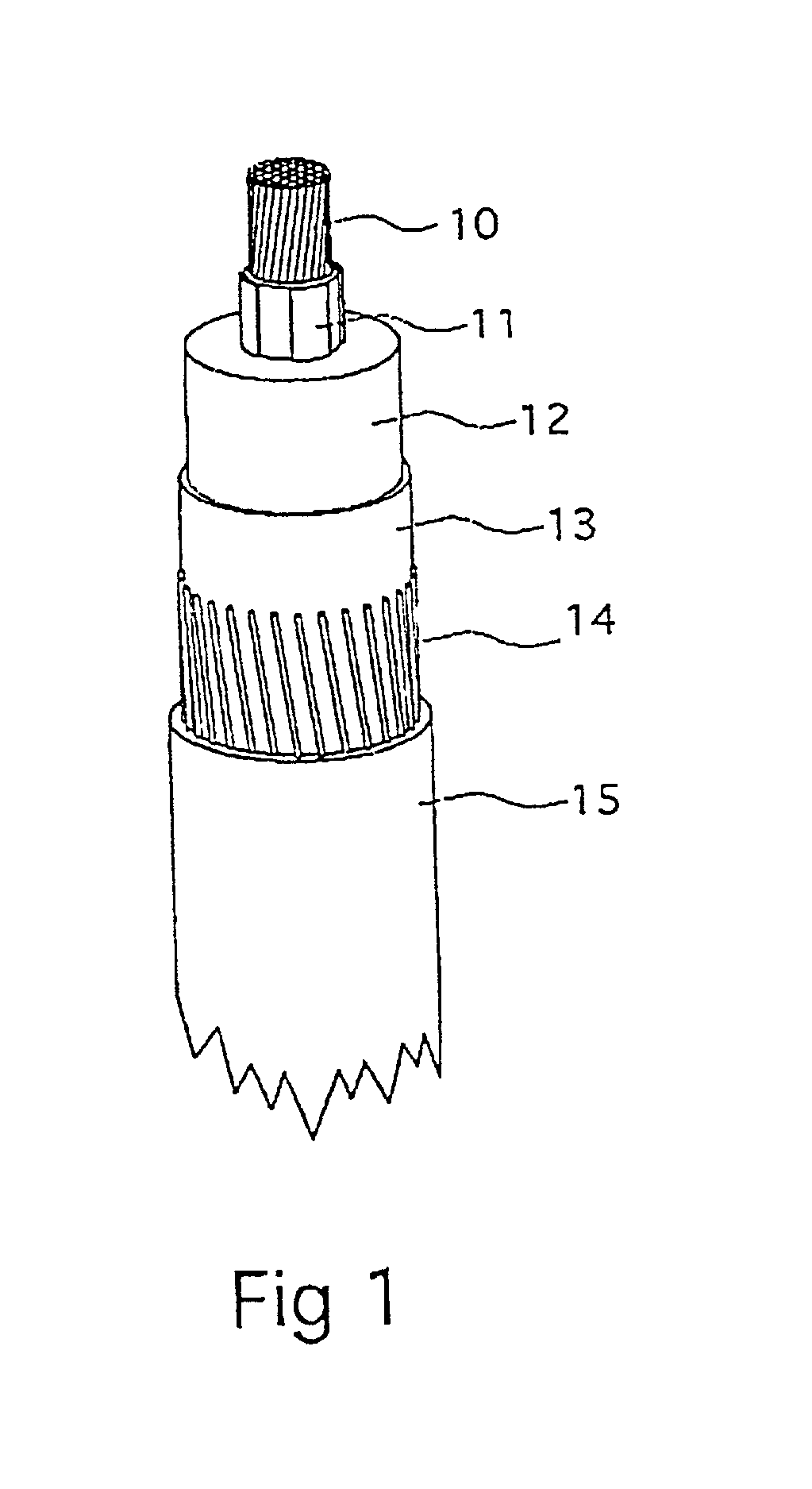
Electric DC-cable with an insulation system
InactiveUS20020039654A1Shorten production timeLow production costPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsYarnCross-linkElectrical conductor
An insulated DC-cable and method for production of an insulated DC-cable with an insulating system comprising an extruded cross-linked polyethylene based insulation disposed around the conductor. The extruded polyethylene based compound comprises additives such as cross-linking agent, scorch retarding agent and antioxidant. The scorch retarding agent comprises a compound (D), 2,4-diphenyl-4-methyl-pentene-1 and the antioxidant comprises a compound (C), a diester of 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionicacid and thiodiglycol. The compounded polyethylene based resin composition is extruded and cross-linked at a temperature and for a period of time sufficient enough to cross link the insulation. The temperature and the period of time upon extrusion and cross-linking are limited so as to substantially suppress or essentially avoid undesired polar by-products being formed in the cross-linked composition.
Owner:GUSTAFSSON BILL +7
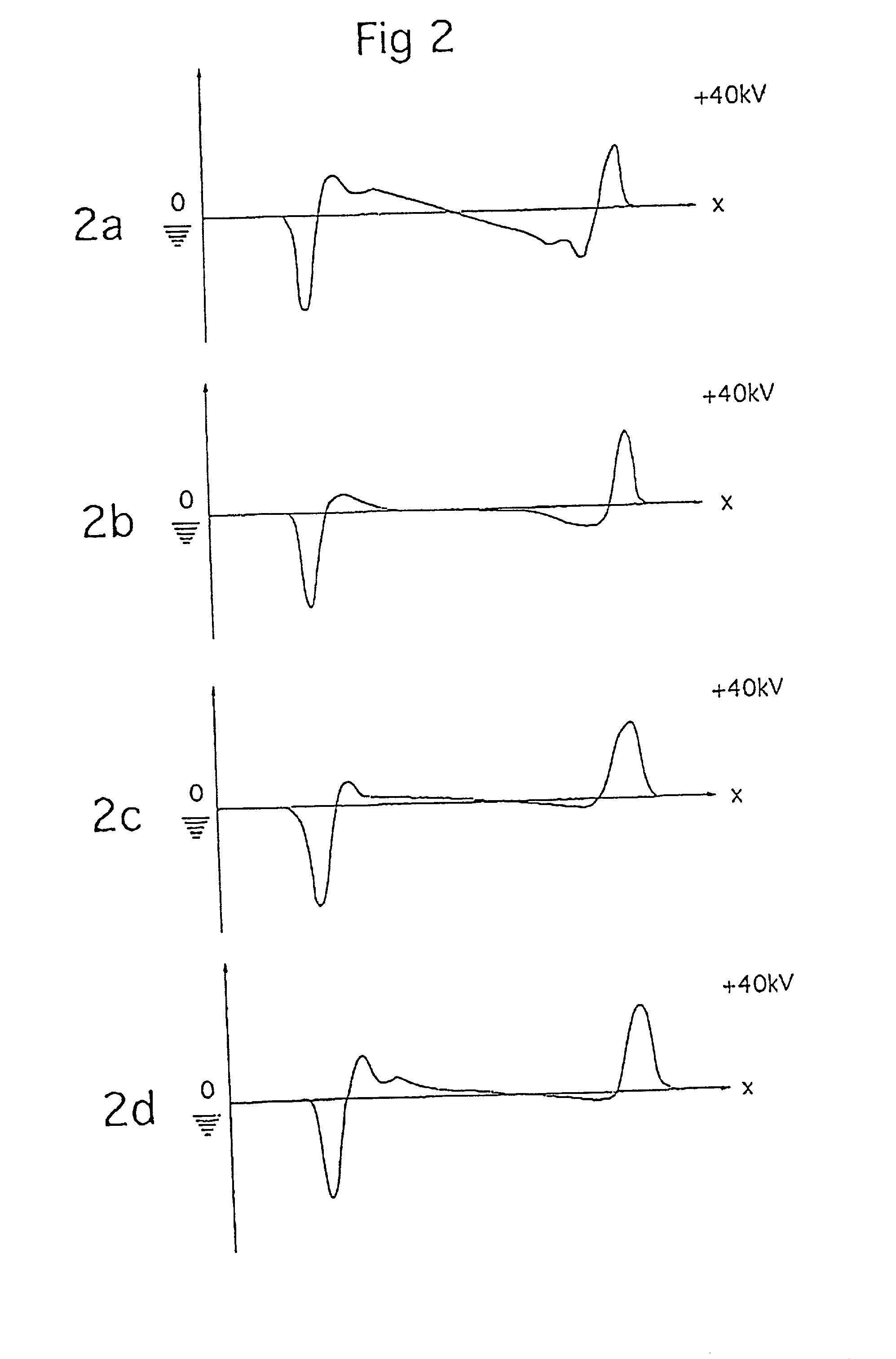
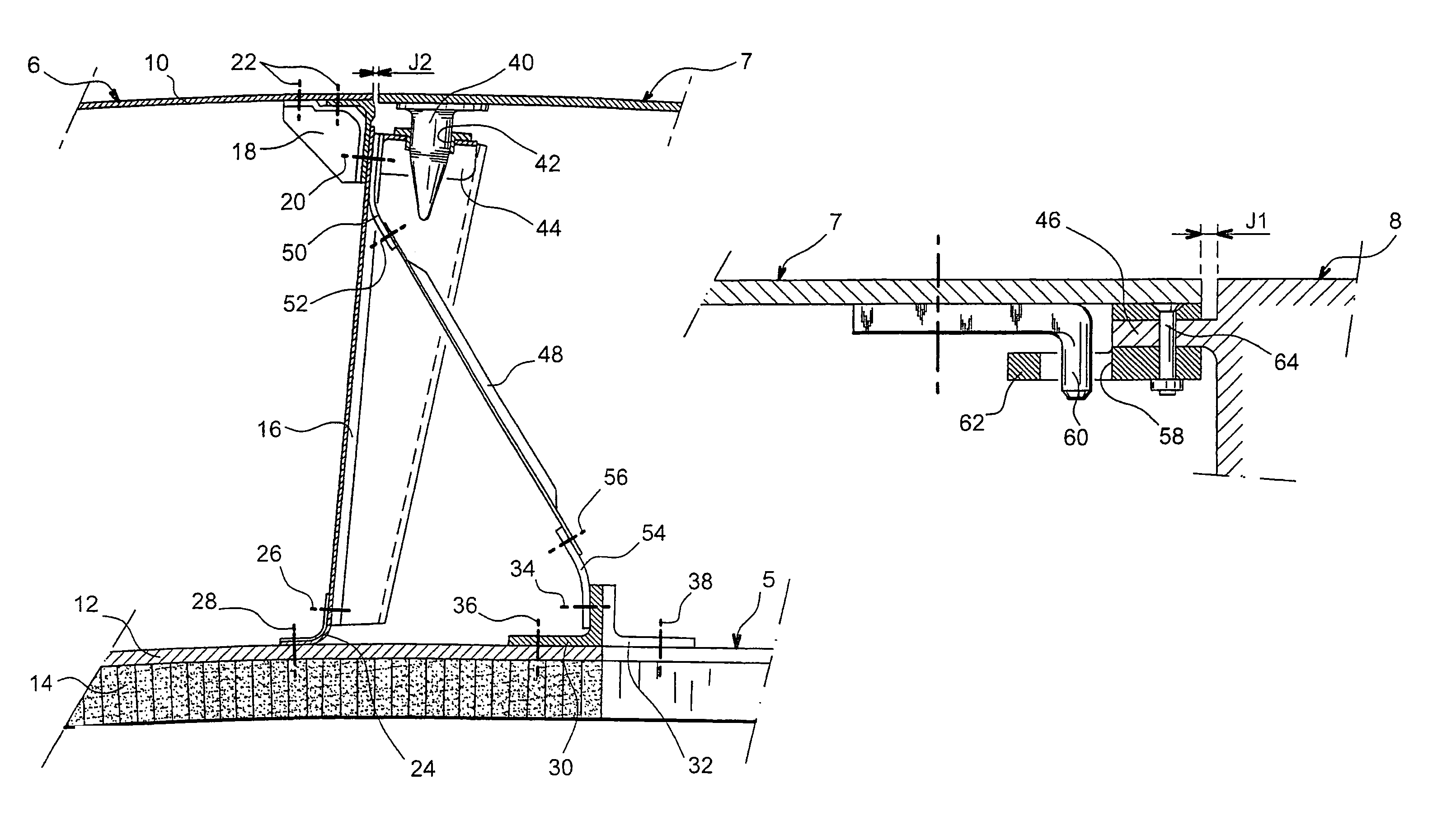
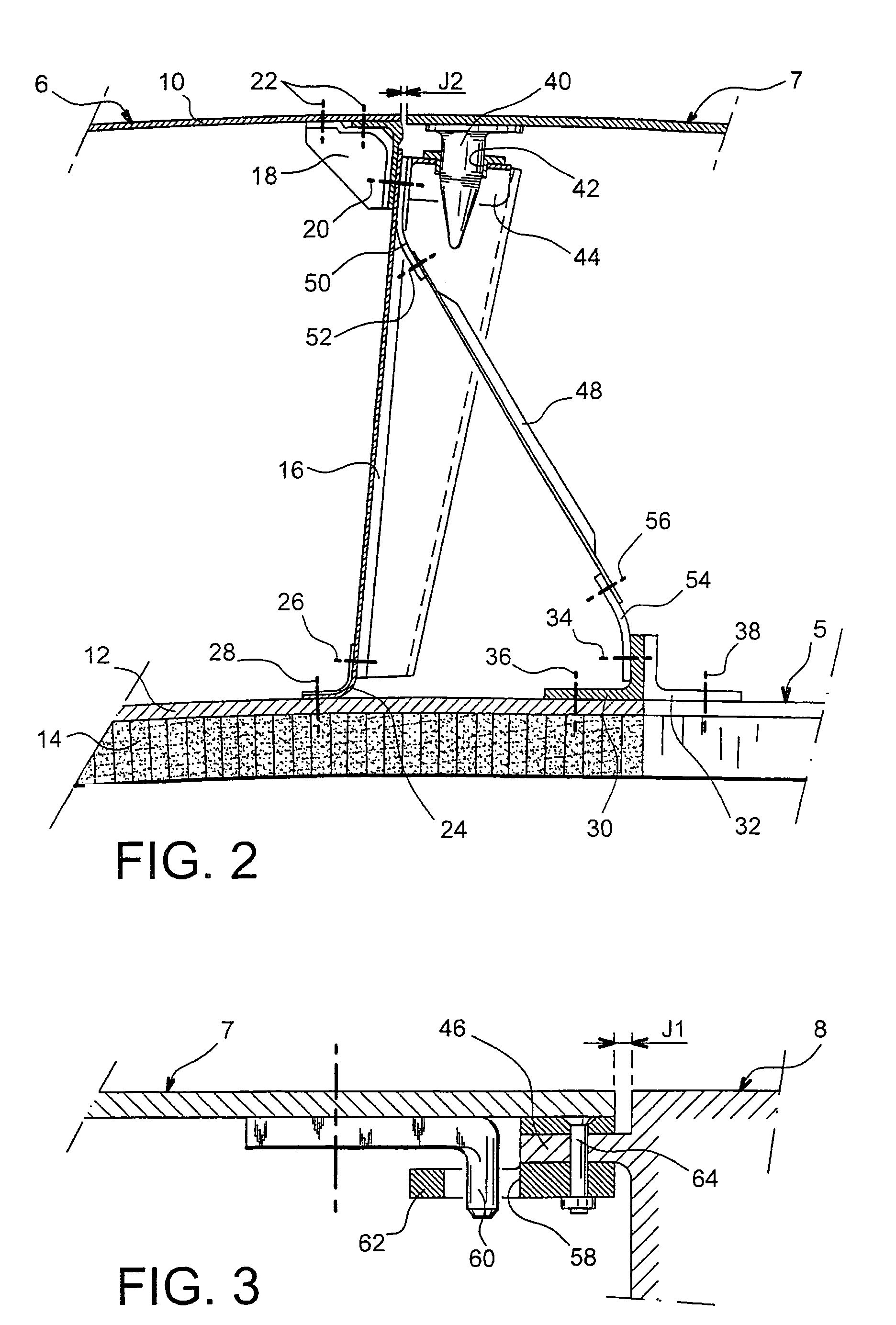
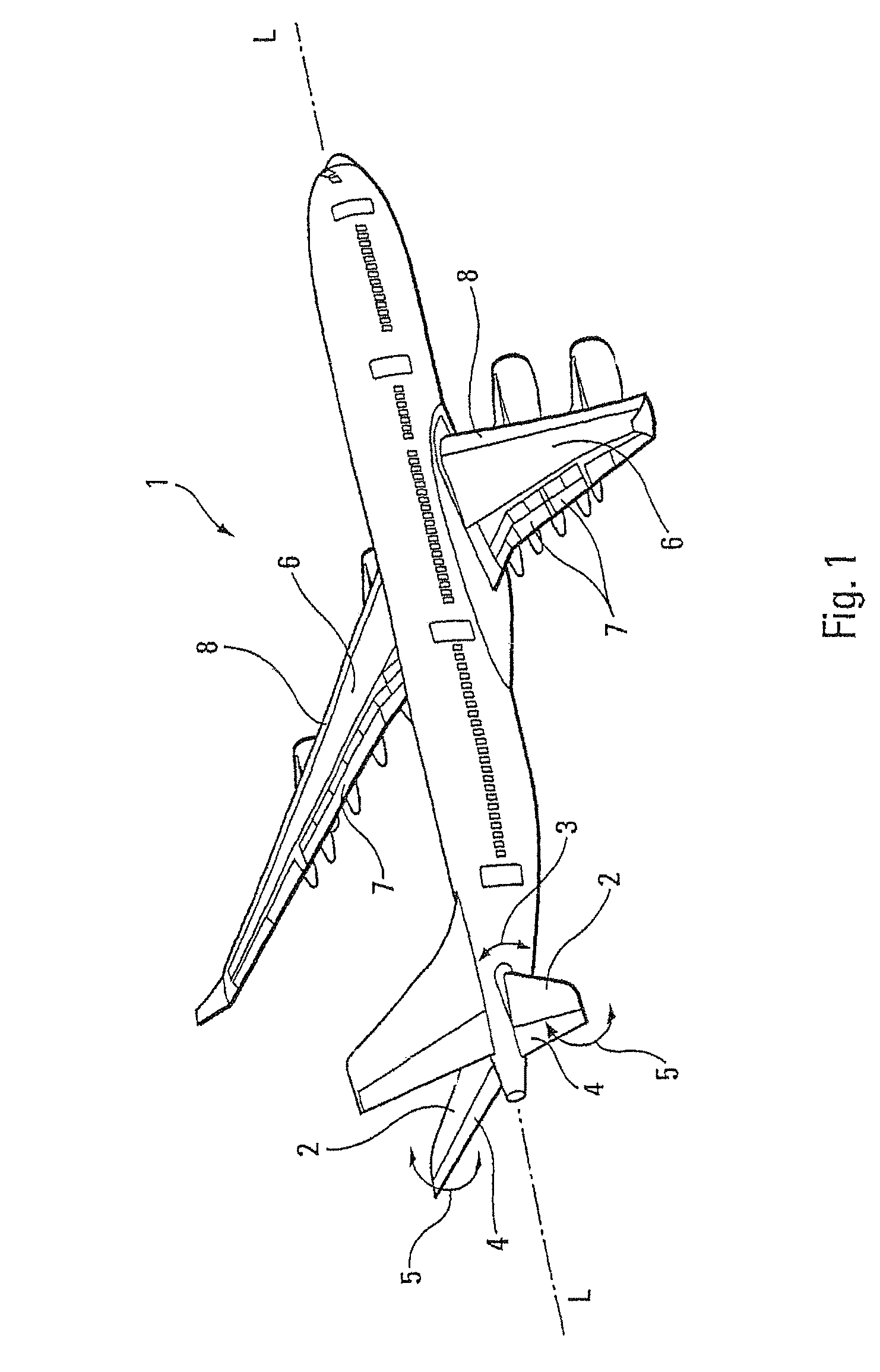
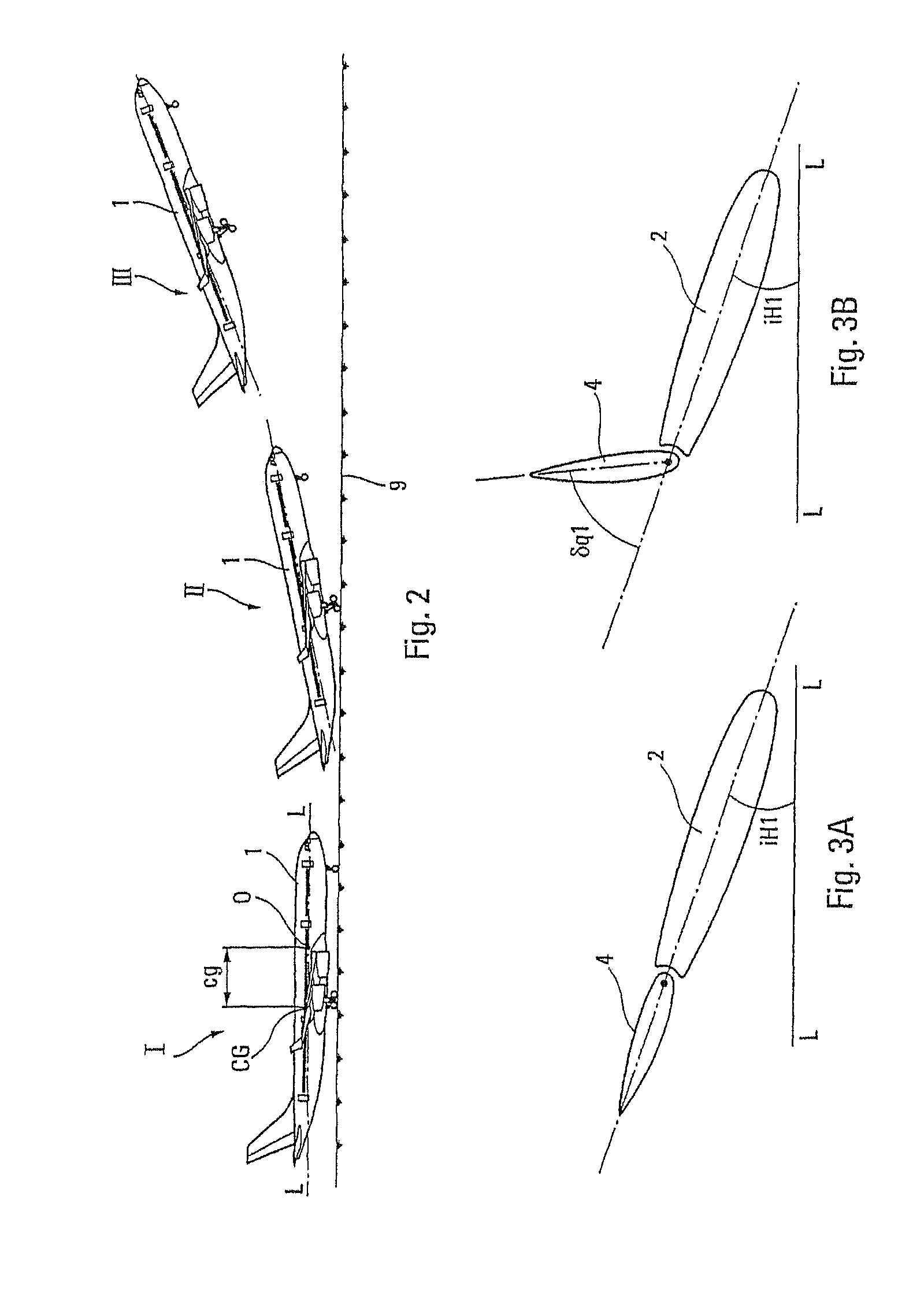
Aircraft engine in which there is a small clearance separating the fan cowls and the thrust inverter cowls
ActiveUS7334393B2Reduce fuel consumptionLimit parasite dragPower plant inspection panelsEfficient propulsion technologiesPressure differenceAirplane
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Bioresorbable spinal implant and related methods
A prosthesis for the replacement of an intervertebral disc of the spine comprises a block of an elastomeric material, which is held under compression by an encapsulating textile fabric. A preferred version of the invention has flanges that are continuations of the encapsulating fabric forming an interdigitation, with the continuation of the upper fabric passing through a hole in the lower fabric and being attached to the lower vertebral body and the continuation of the lower fabric crossing to its fixation site on the upper vertebral body. Optionally, the flanges are resorbable, over time leaving only the implant core and encapsulation fabric in the intervertebral space.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Locking/release device
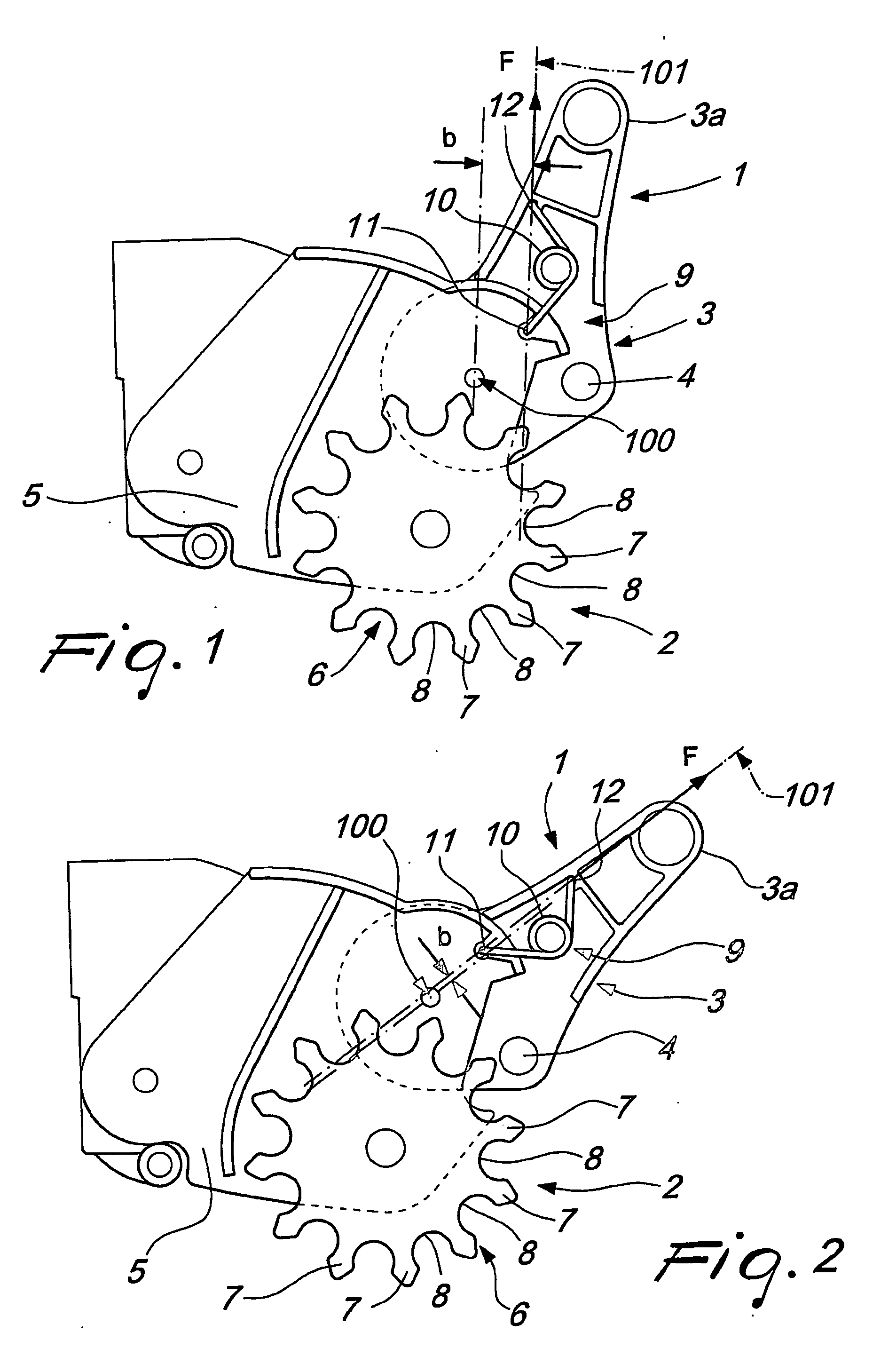
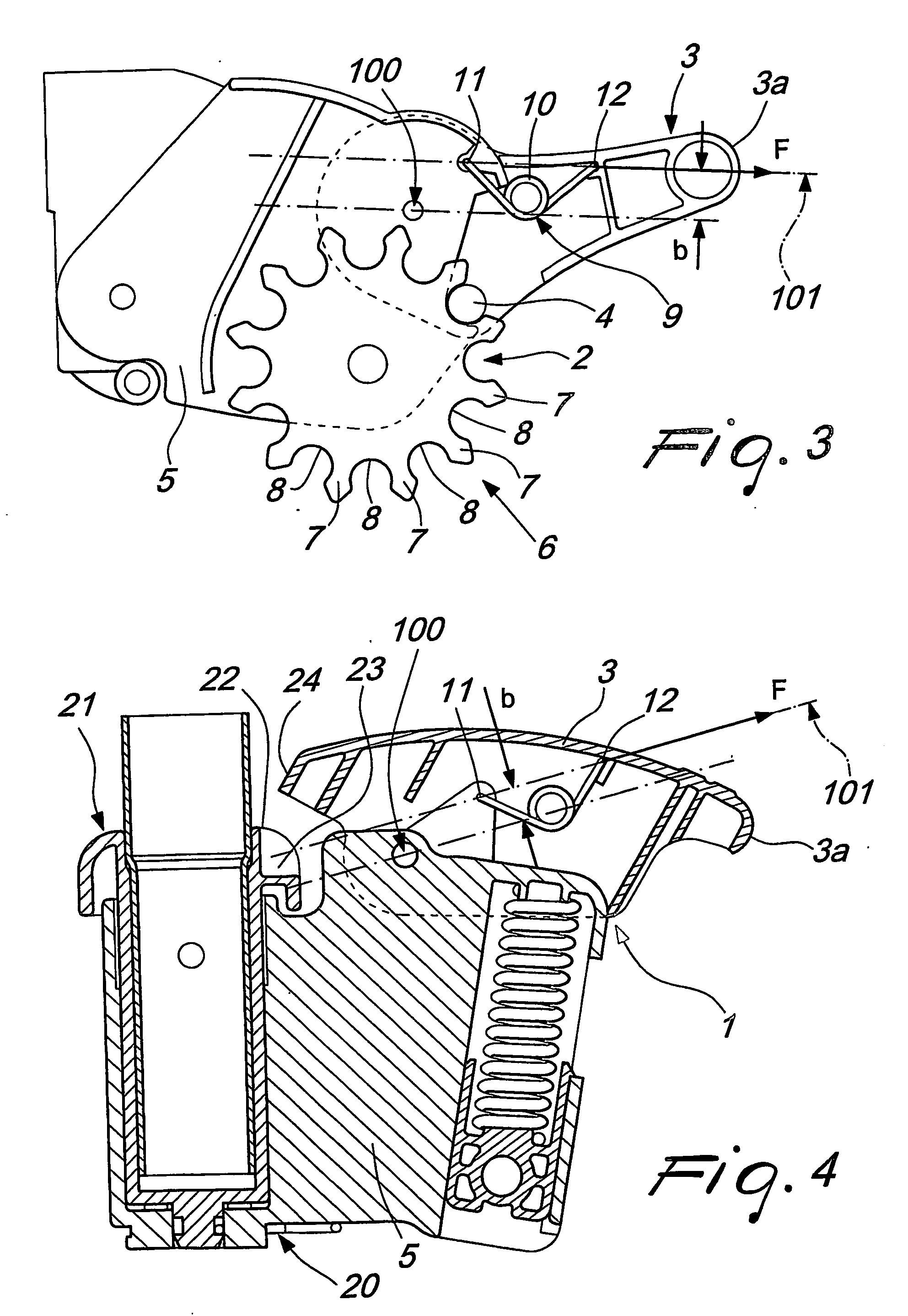
InactiveUS20060151259A1Eliminating orReducing significantly the drawback suffered by known devicesCarriage/perambulator accessoriesBraking element arrangementsCouplingEngineering
A locking / release device particularly for pushchairs, prams or the like, comprising an actuation lever system supporting an engagement device and articulated to a supporting structure movable with respect to a locking element, having one abutment region and at least one engagement seat; the actuation lever system is mounted rotatable about a pivoting axis to pass from a release position, to a locking position of the locking element; in an abutment position, the engagement device abuts against at least one portion of the abutment region. An elastic loading element of the device acts between a first coupling portion of the supporting structure and the actuation lever system.
Owner:LINGLESINA BABY
Tag assembly
ActiveUS20140319225A1Improve distributionEasy to storeStampsRecord carriers used with machinesBiomedical engineeringEngineering
A tag assembly is described wherein the tag assembly is affixable to clothing and / or a body and wherein the assembly includes a support sheet; a tag disposed on the support sheet, the tag being configured to transmit a signal to a receiver; and, an expandable spacer structure disposed the support sheet, the expandable spacer structure providing a predetermined spacing between the tag and the body, the expandable spacer being configured to expand from a thin non-expanded state to a expanded state of a predetermined spacer thickness.
Owner:MYLAPS BV
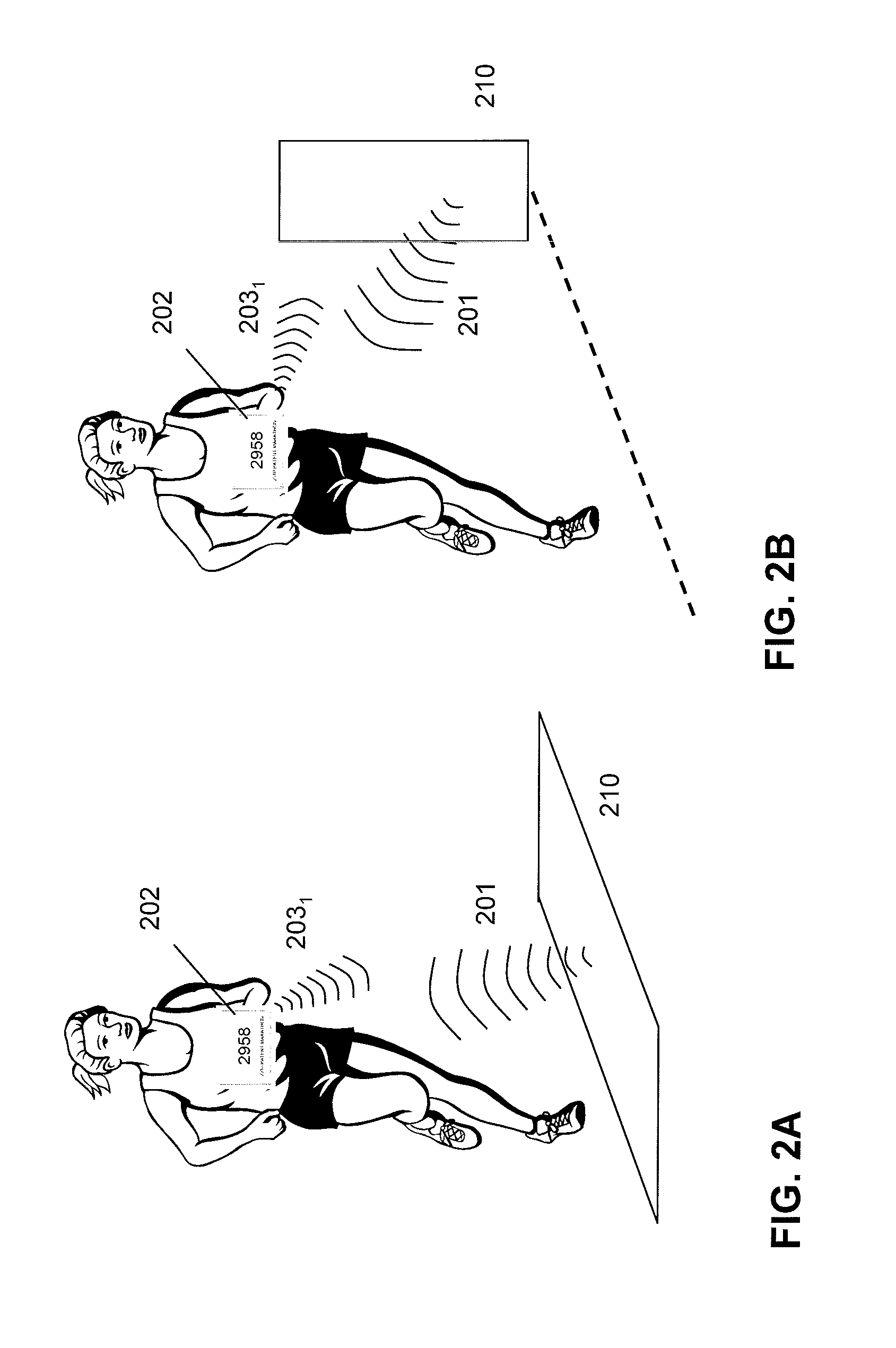
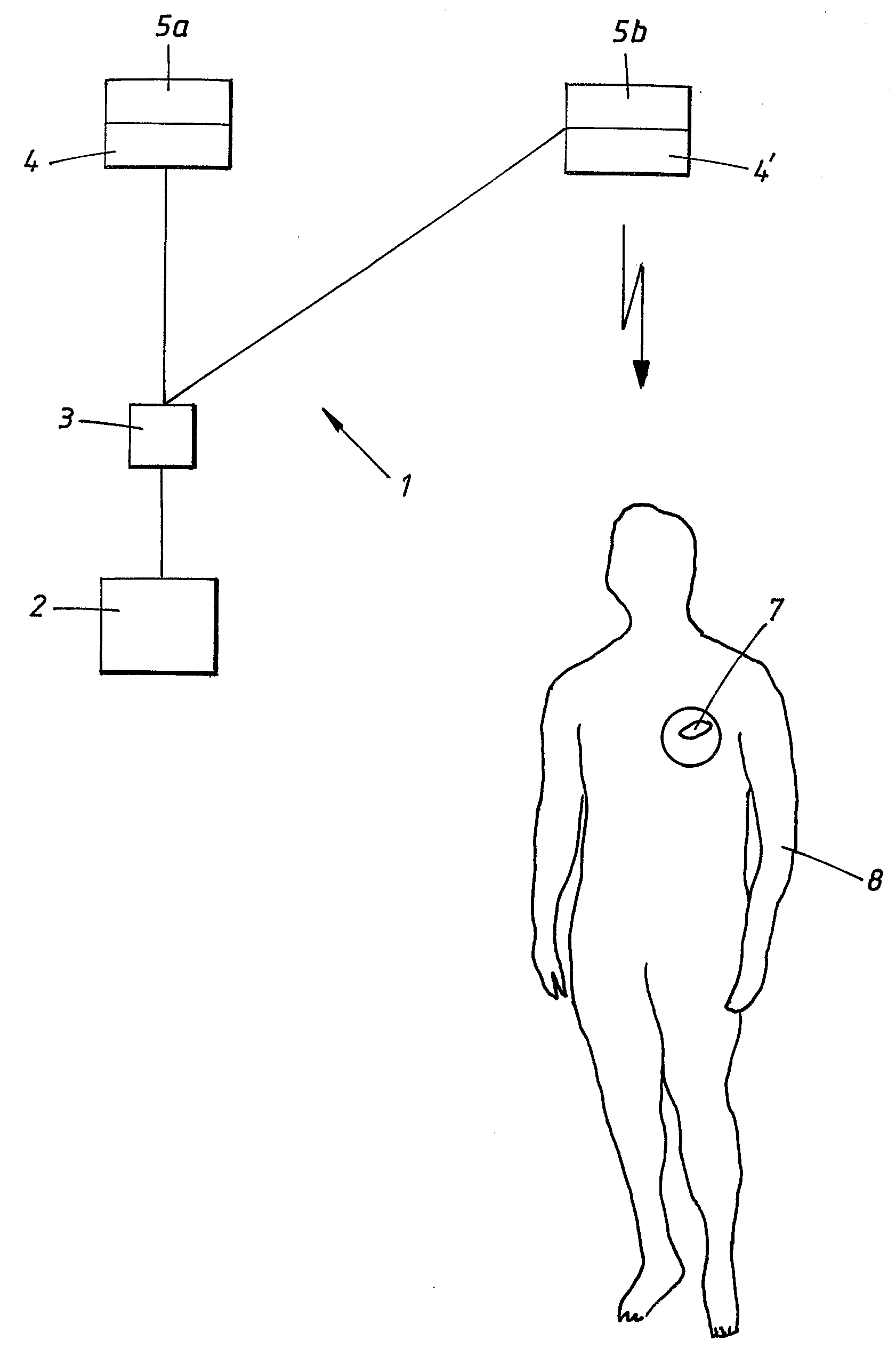
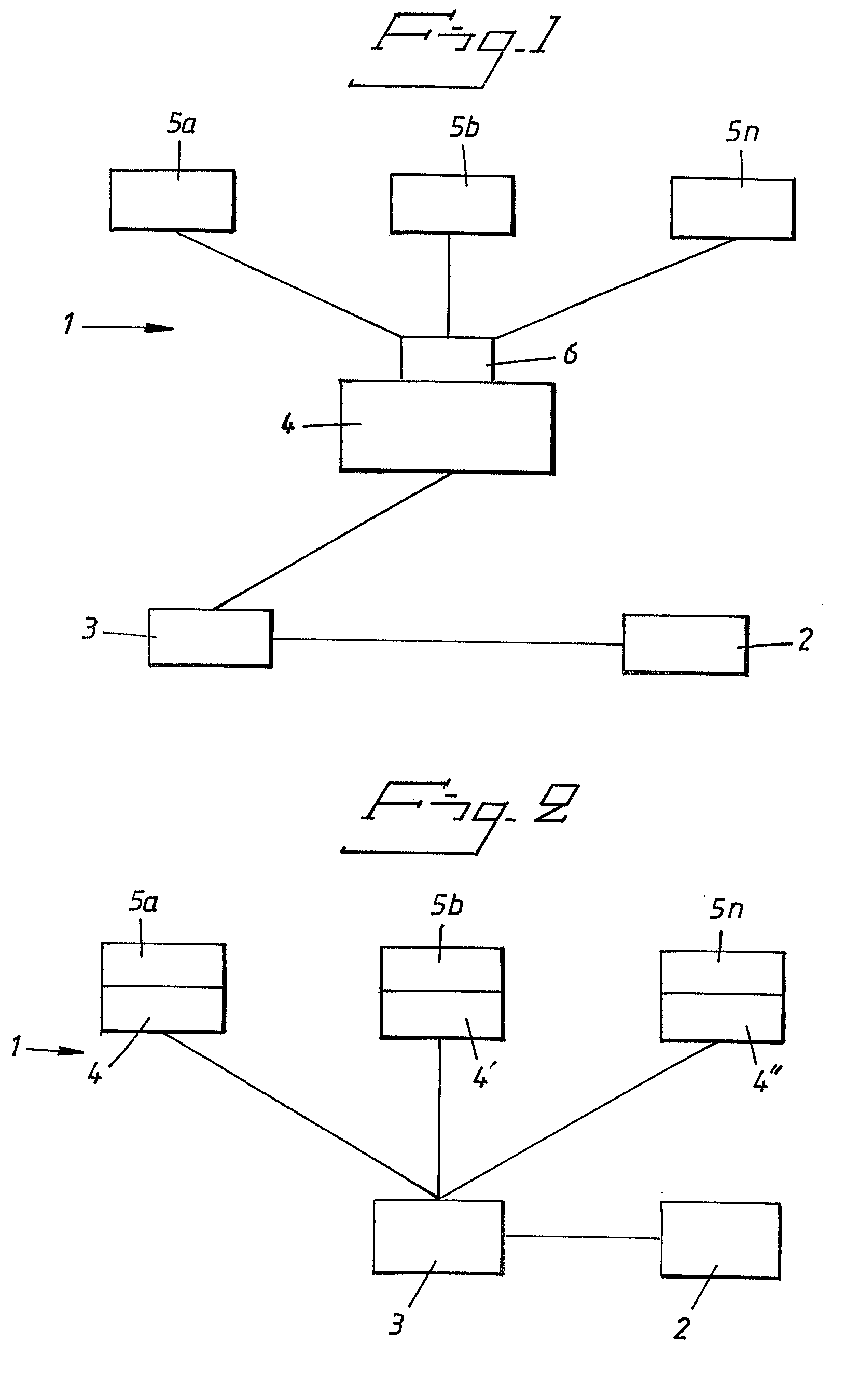
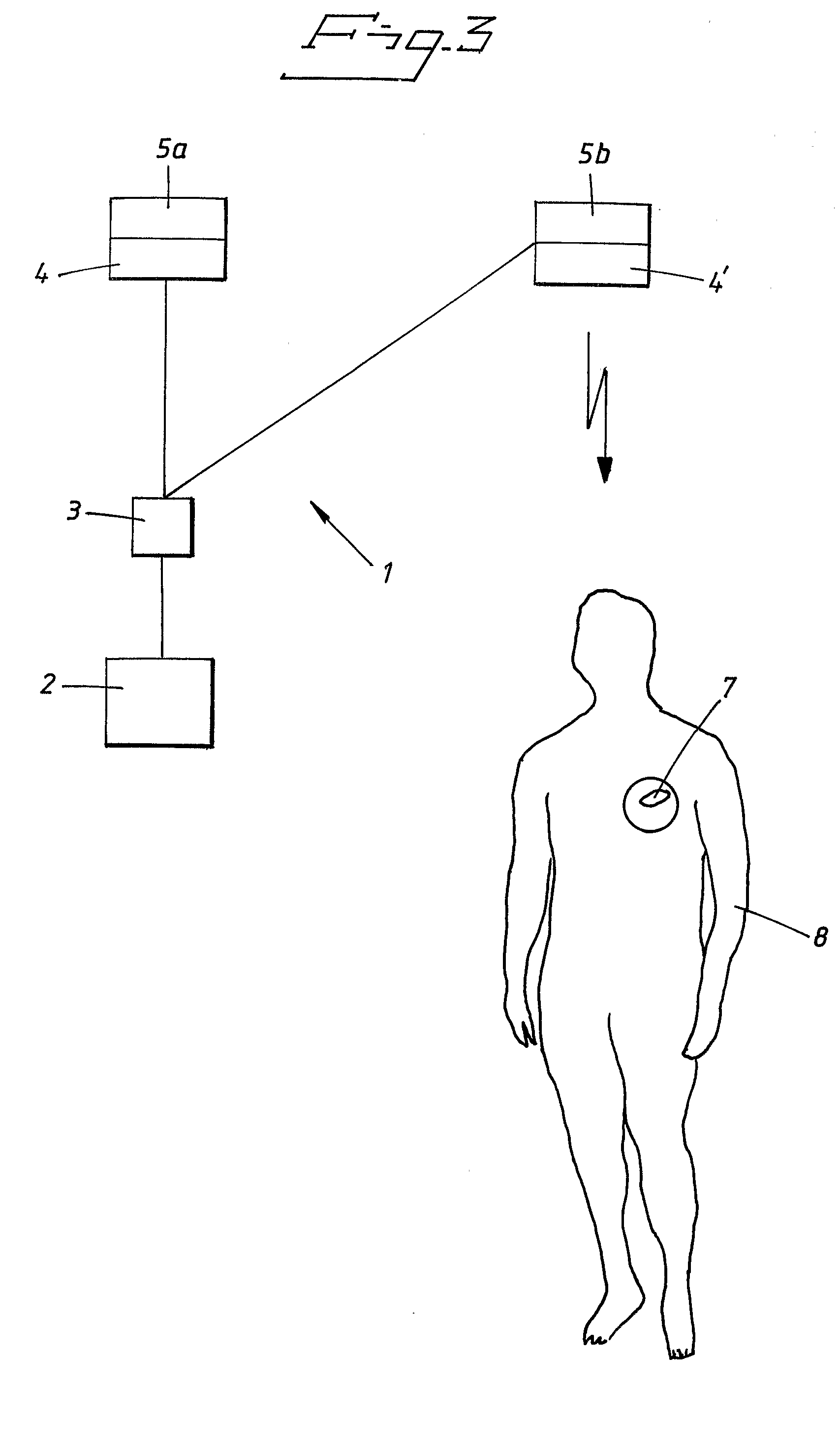
Medical apparatus and system
InactiveUS20090132008A1Reliable and reliableEasily and conveniently optimizedElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringWired communicationTelecommunications link
A medical system includes an implantable medical device configured for implantation in a living subject to interact with the subject, an extracorporeal device having a processor that processes information such as programming instructions for the implantable medical device or monitoring data received from the implantable medical device, and at least two antenna devices located at respectively different locations. The implantable medical device communicates with at least one of the two antenna devices, and the extracorporeal device also communicates with the at least two antenna devices to exchange the aforementioned information with the implantable medical device via at least one of the two antenna devices. The at least two antenna devices are physically separated from the extracorporeal device and the extracorporeal device communicates with each of the at least two antenna devices via a communication link that allows the extracorporeal device to be freely moved relative to the at least two antenna devices. The communication link can be a hard-wired communication link or a wireless communication link.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for positioning reinforcing members within hardened material structures
InactiveUS20090120030A1Accurate and efficient positioningMaterial minimizationPaving reinforcementsBuilding reinforcementsPlastic materialsEngineering
Owner:EDELL SHAPIRO & FINNAN
Reconfigurable heel elevator
ActiveUS20070095353A1Reducing and mitigating pressureEliminating orOperating chairsOperating tablesEngineeringHeel region
A method and apparatus for eliminating or otherwise reducing or mitigating pressure on an individual's heel while the leg is in an extended position, while allowing for ambulation without completely removing the device. An apparatus comprises a support member configured to be attached to a lower leg portion of an individual between the calf and heel region, the support member having an inner surface portion to be disposed facing the leg when attached thereto, and having an opposite outer surface; and a reconfigurable elevation member configured (i) to be disposed at the outer surface of the support member such that when the support member is attached to the lower leg portion of the individual the elevation member is selectively capable of providing elevation of the heel from an underlying surface in the event that the lower leg portion is extended above the underlying surface, and (ii) to be reconfigured for ambulation without removing said support member from the lower leg. In some implementations, the reconfigurable elevation member is integral with the support member and is inflatable and deflatable. In other implementations, the reconfigurable elevation member is removably attachable to the support member, and may be removed for ambulation while the support member remains securely in place such that the elevation member may be reattached thereto.
Owner:SUN SCI
Wafer boat for reducing wafer warpage
InactiveUS20060027171A1Minimize contact surfaceReduce Particle GenerationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingAcute angleMechanical engineering
A wafer boat which is suitable for supporting wafers in a process furnace is disclosed. The wafer boat includes a base plate, multiple support rods carried by the base plate and multiple wafer support pins carried by each of the support rods. Each of the wafer support pins has an upper surface disposed at an acute angle with respect to a longitudinal axis of each of the support rods. This causes contact of the wafer support pins with the wafer at the wafer's center of gravity and minimizes the contact surface area between the wafer support pins and each wafer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Microscope System and Method
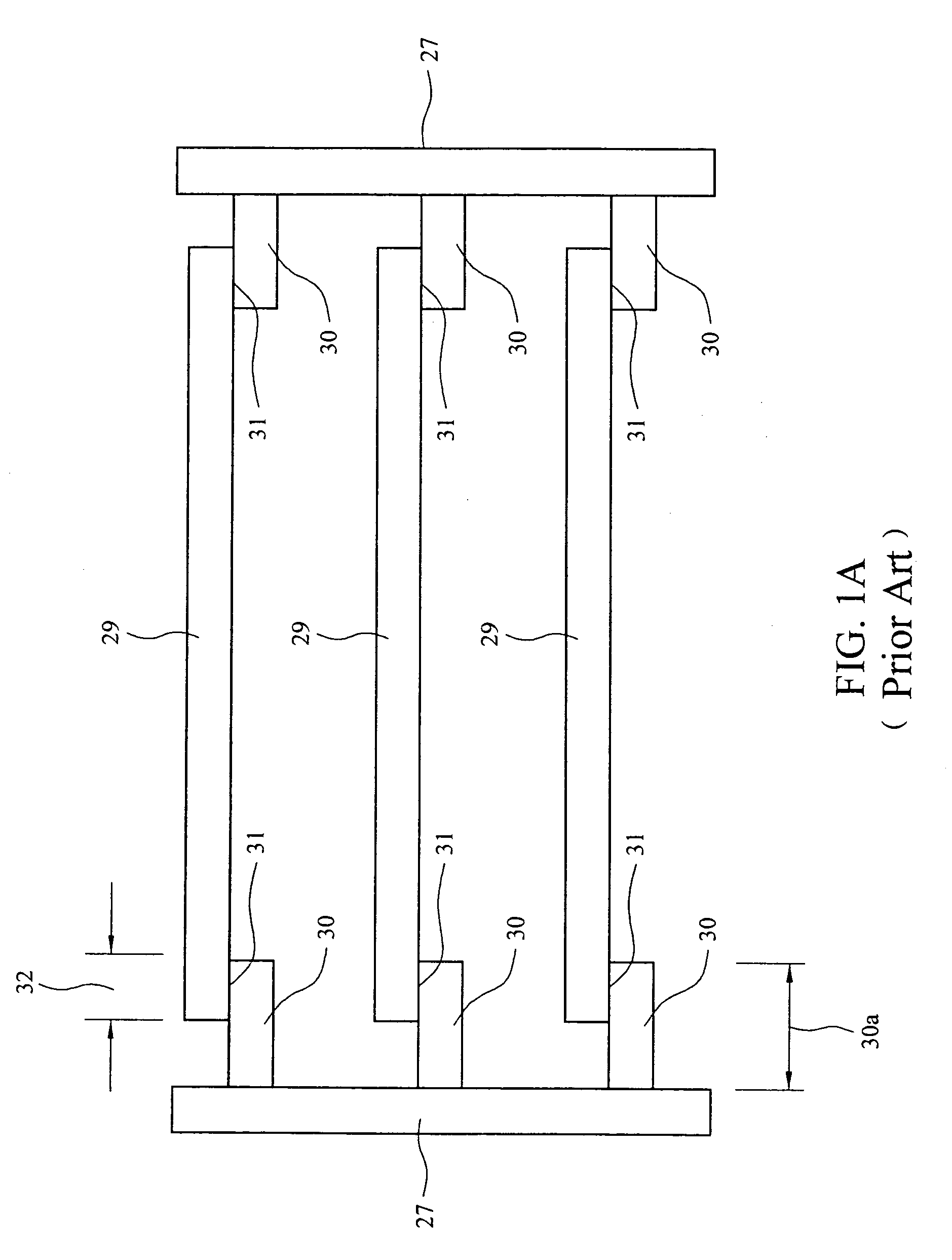
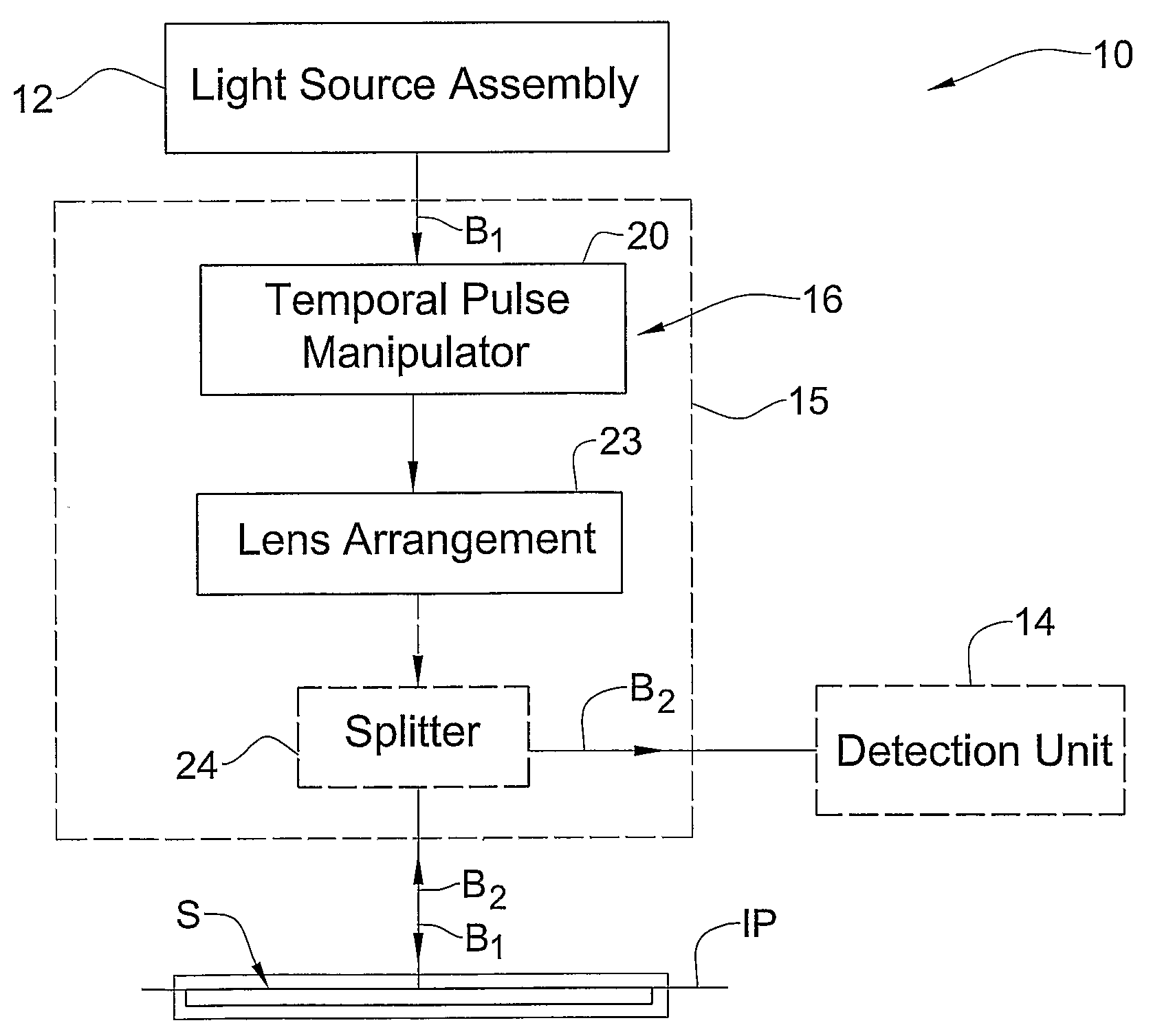
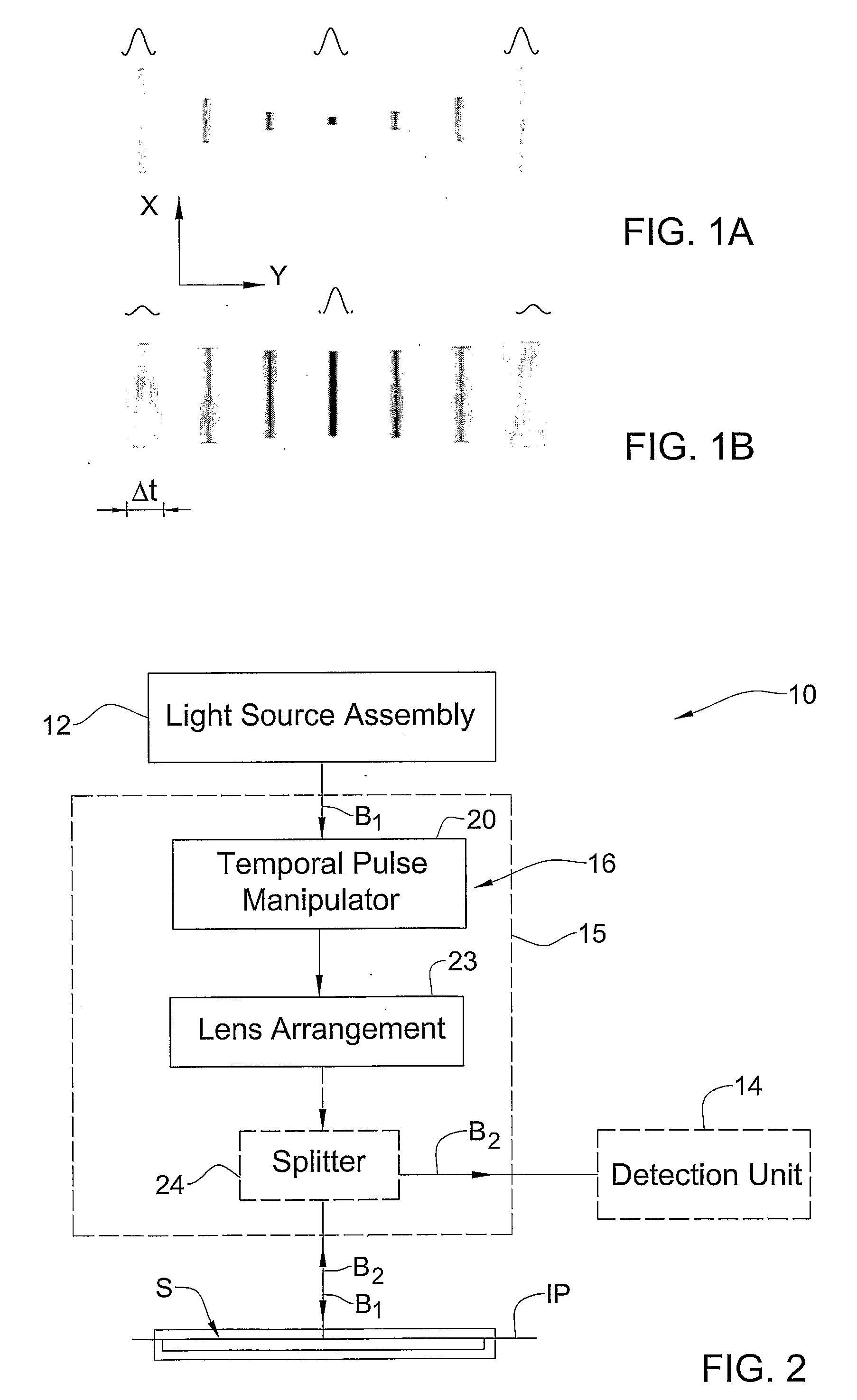
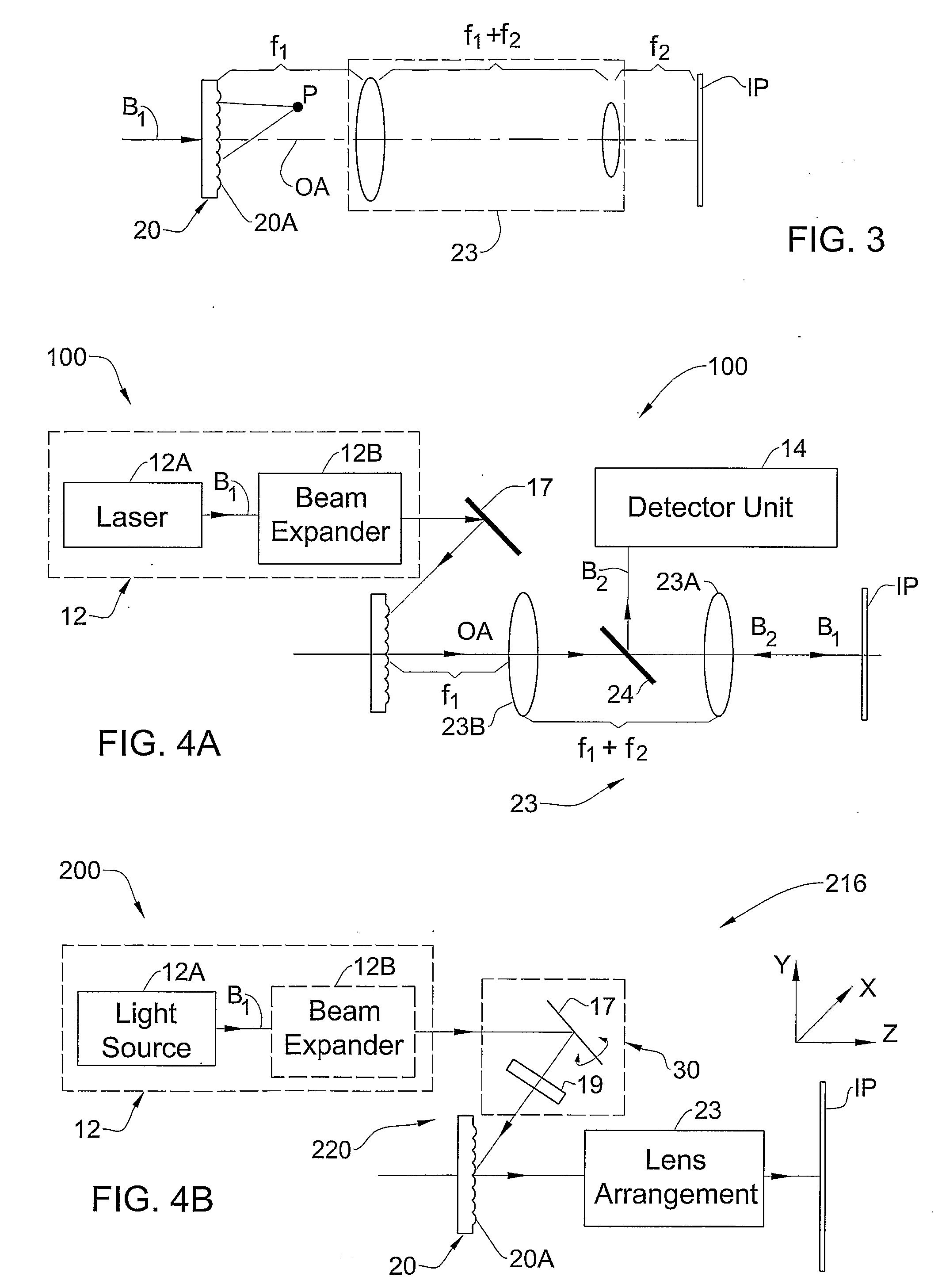
ActiveUS20080130093A1Enhance the imageEliminating orComputer controlMaterial analysis by optical meansSystem configurationMicroscope
The microscope (10) includes such main constructional parts as a light source assembly (12); and an optical system (16) configured according to the invention, and in the present example of microscope (generally imaging) system configuration includes also a detection unit (14) (shown in the figure in 5 dashed lines). The detection unit (14) may be configured to define an array of image pixels (e.g. CCD), may be configured for intensified or not intensified light detection, as well as for gated or not-gated light detection. It should be understood that the light source, as well as the detector, may or may not be accommodated in the same housing (15) enclosing the optical path of an input pulse of an initial profile, and system (16). For example, the light source and / or detector may be accommodated outside the housing (15) and light may be guided towards and / or away from a sample S via light guiding means (either in free space or in optical fibers).
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
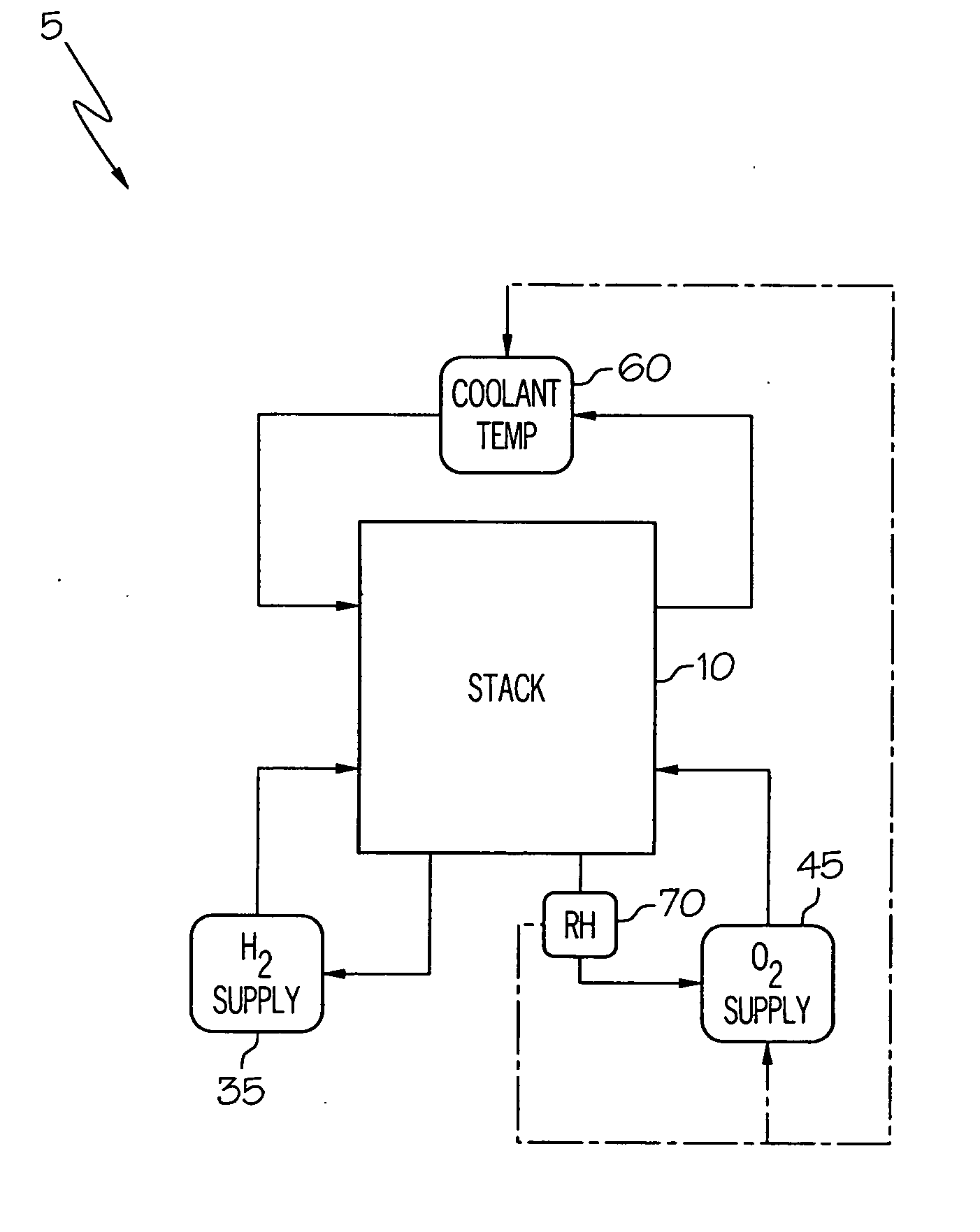
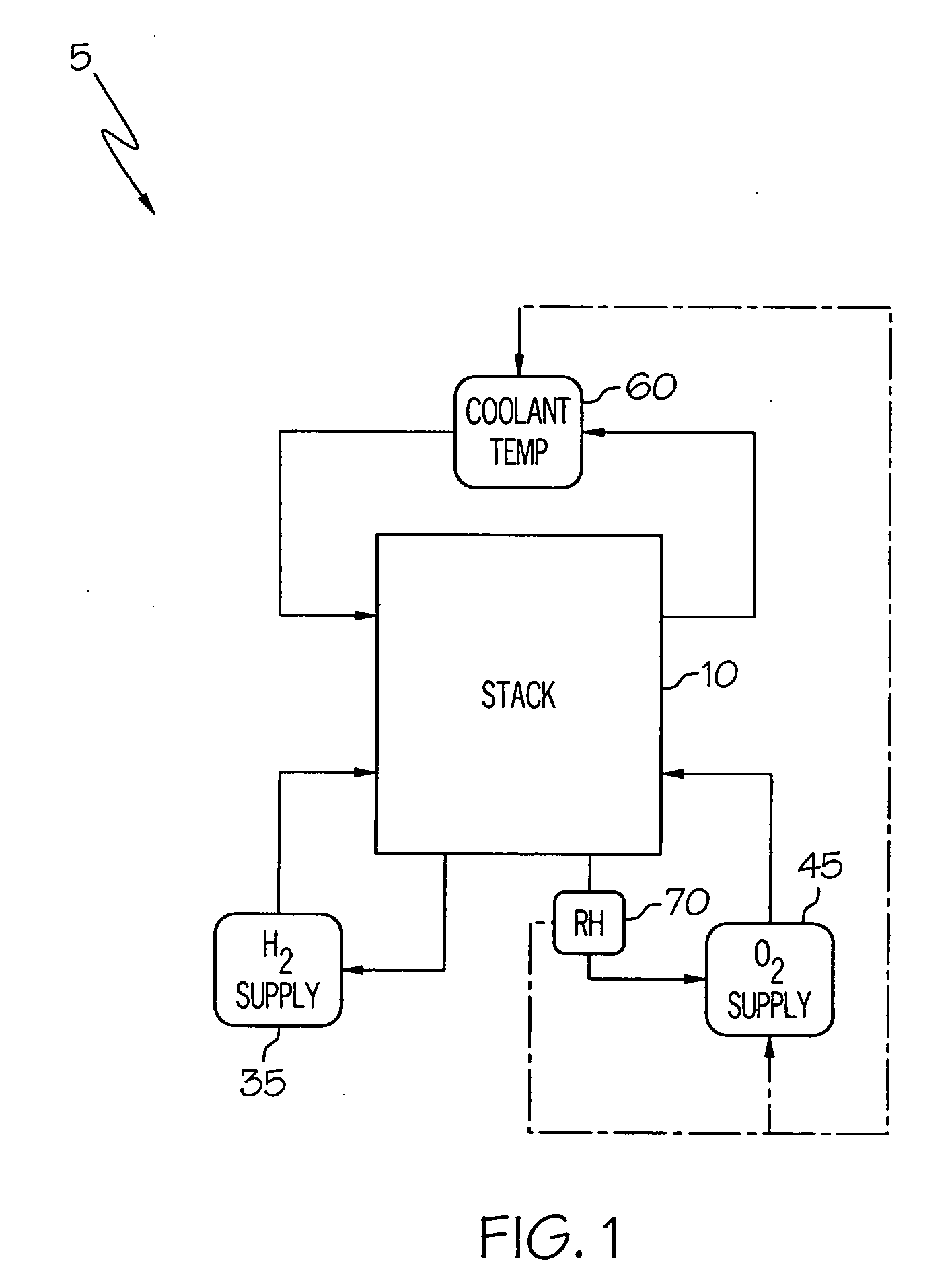
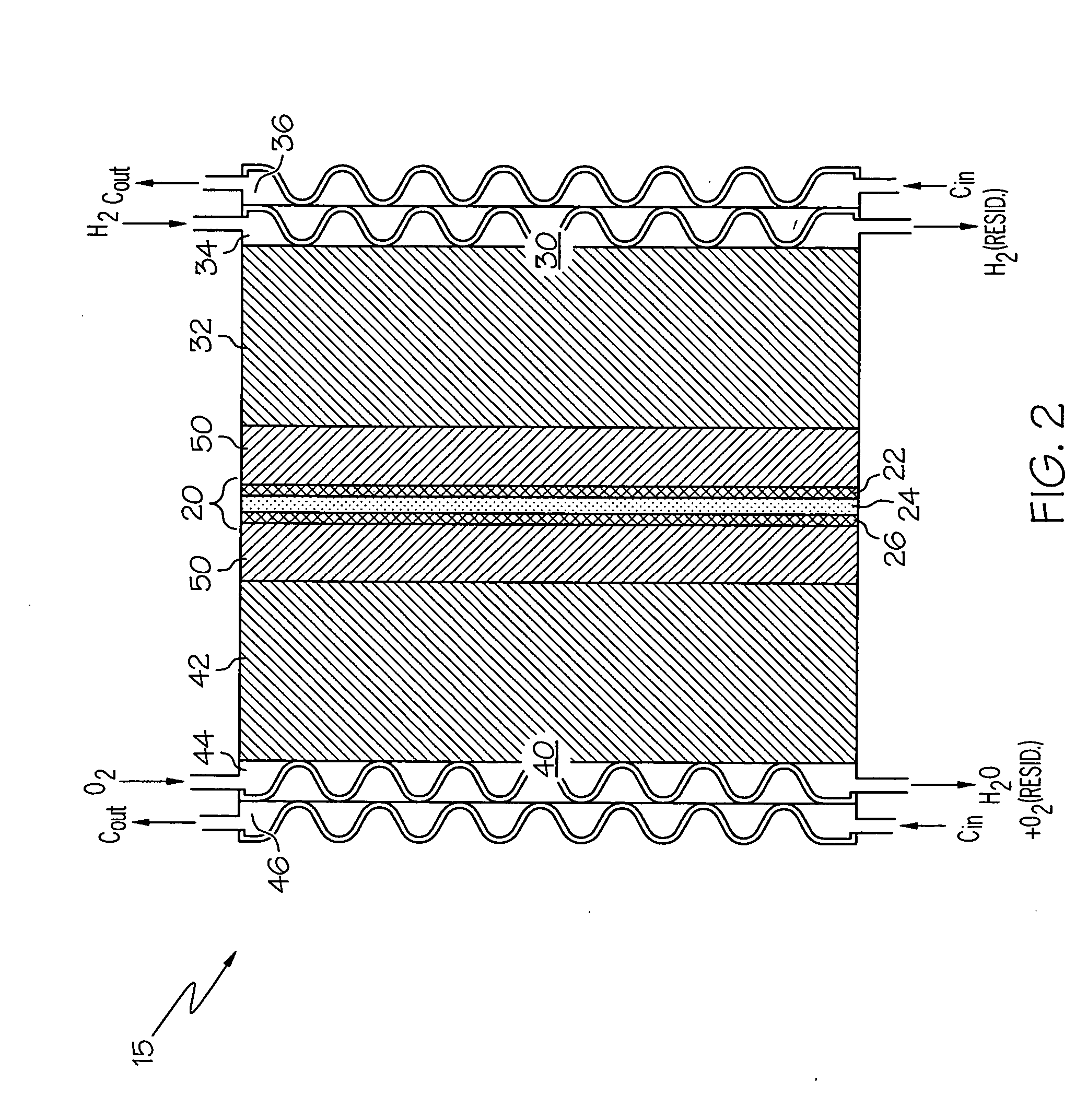
Control of RH conditions in electrochemical conversion assembly
InactiveUS20060154124A1Increase humidityReducing and excessive humidityFuel cell heat exchangeCell component detailsVapor barrierTemperature control
A system and method for controlling an electrochemical conversion assembly are provided. The system is configured such that operation of one or both of the second reactant supply and the temperature controller responds to the cathode-side RH signal to a degree sufficient to maintain relative humidity within the second flowfield portion within a suitable humidification range. The suitable humidification range is a function of the degree to which the vapor barrier layers inhibit the migration of water molecules from the membrane electrode assembly.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
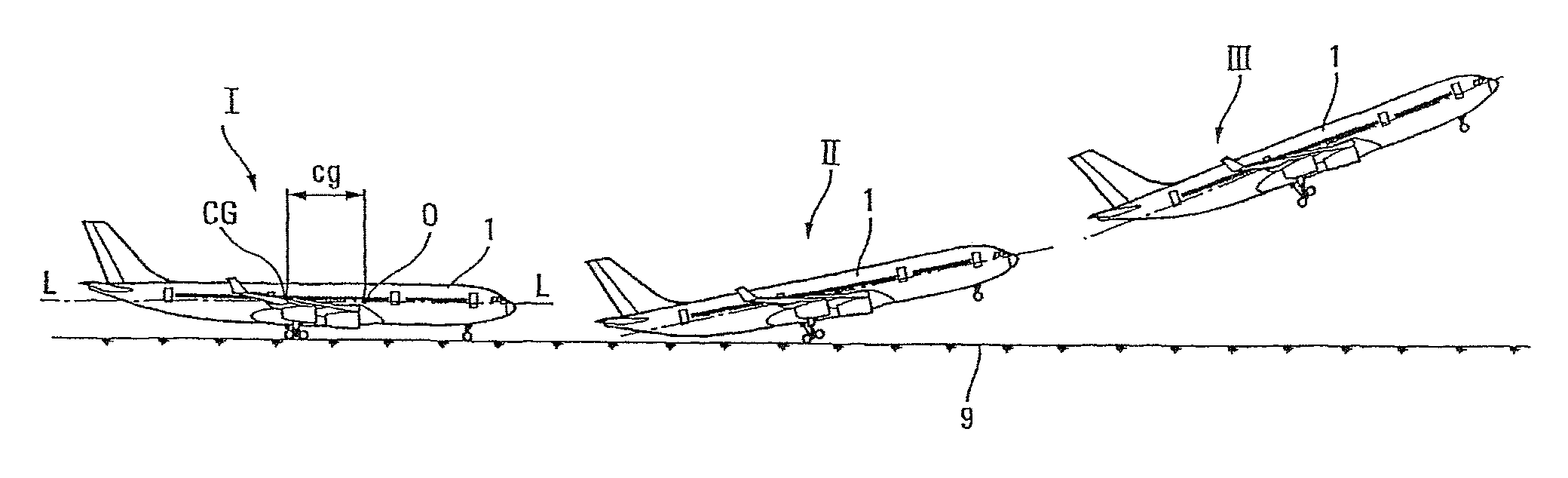
Assisted take-off method for aircraft
ActiveUS8014910B2Reducing effect of variationCompromise valuePropellersAnalogue computers for trafficControl theoryAirplane
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
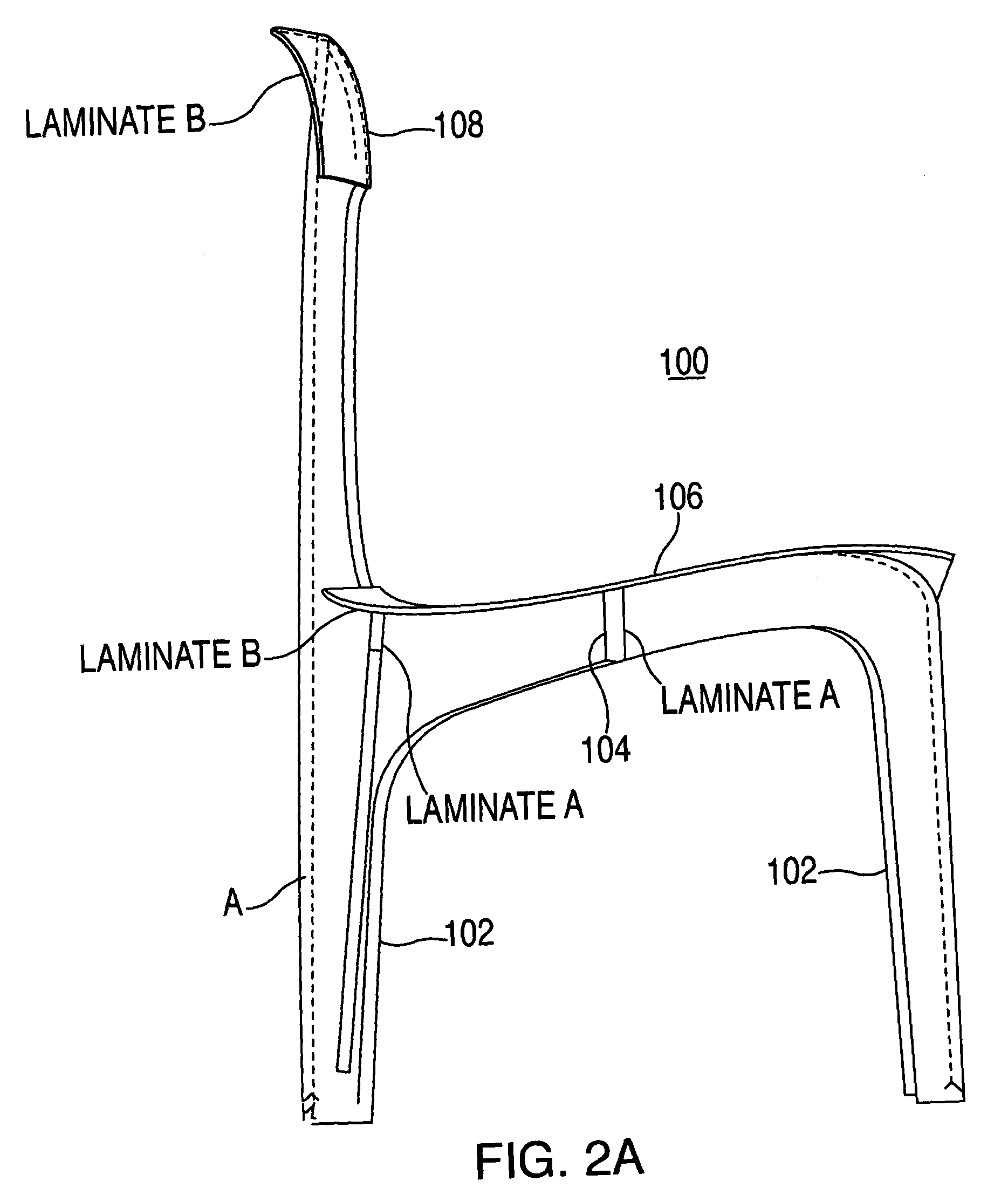
Laminate materials for furniture and furniture pieces incorporating the same
ActiveUS20050069690A1Good dimensional stabilityResists warpingFibreboardSynthetic resin layered productsWood veneerComposite material
Several laminate materials are provided that are particularly useful for making furniture pieces. The laminate materials may include several interleaved wood veneer and carbon fiber layers. The thickness and characteristics of these layers are chosen so that the resultant material can be used either as a support member, such as a leg, that must withstand large tensile and / or compressive forces, or is thin and flexible, for example for making chair seats or backrest. Another laminate material includes a thick stiff core. This laminate material is used for furniture members that must resist warping, such as table tops.
Owner:WALZ KEVIN RANDALL
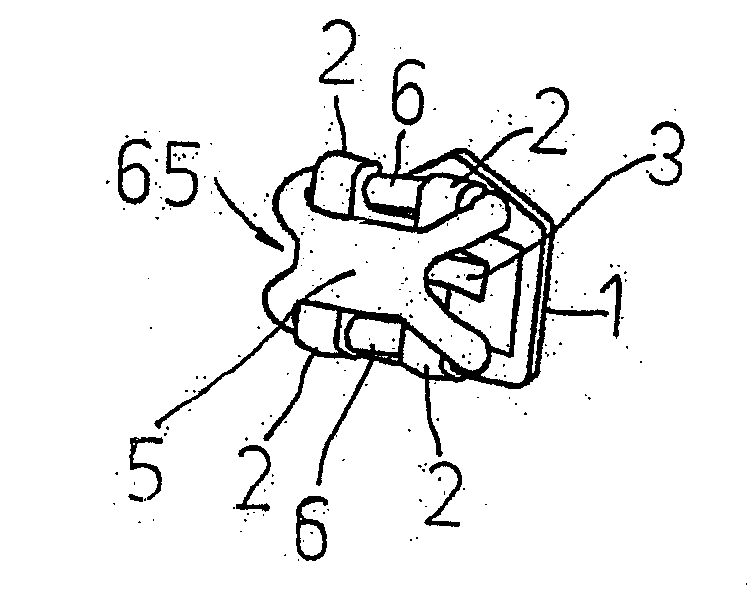
Ligature device
InactiveUS20080032249A1Reduce inconvenienceEliminating orArch wiresBracketsEngineeringOrthodontic ligature
Ligature device for orthodontic brackets, consisting of an elastic body with a central portion (5) and two lateral rings (6) positioned on two mesodistal sides of the central portion (5), on opposite sides with respect to the latter, the rings being intended to be stretched to be coupled with the wings (2) of an orthodontic bracket so that the central portion (5) results above the same bracket wings (2), characterized in that the lateral rings (6) form at least a curve (65) corresponding to a mesodistal side of the orthodontic bracket at the height of the wings (2), the vertex of the at least one curve (65) being turned toward the orthodontic bracket, that is to say toward the central portion (5) of the ligature device, the length (a) of each of the rings (6) exceeding the length (c) of the central portion (5) both when the rings (6) are stretched and un-stretched, so that the value of the ratio (a) / (c) is less than one in both the stretched and un-stretched configurations.
Owner:LEONE SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com