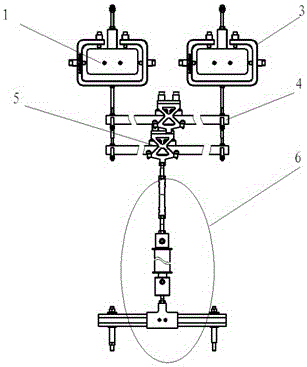
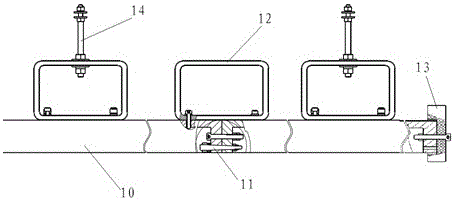
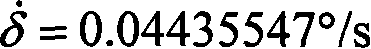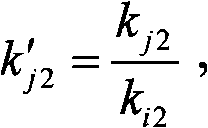Patents
Literature
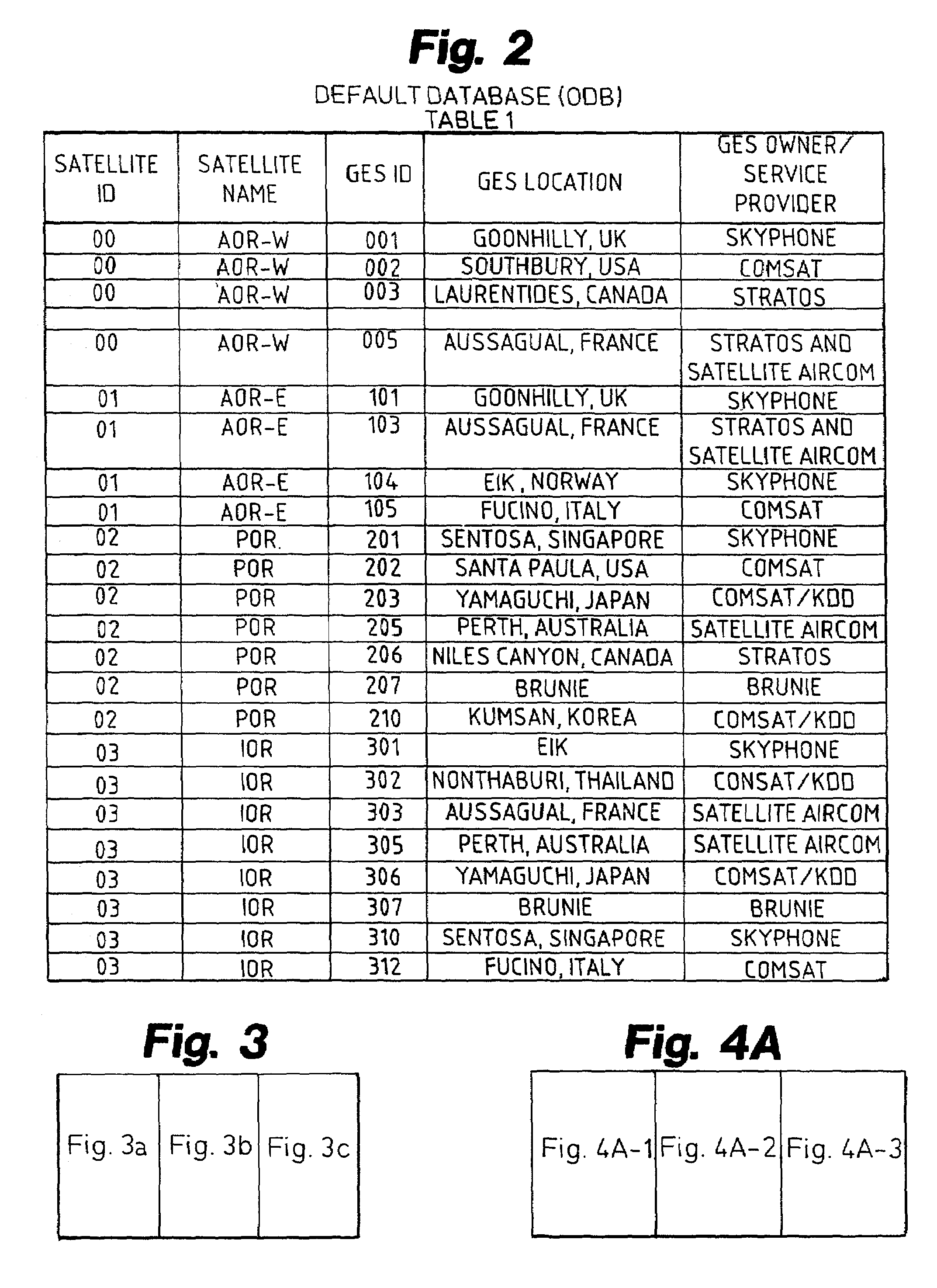
79 results about "Space craft" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Satellite refuelling system and method
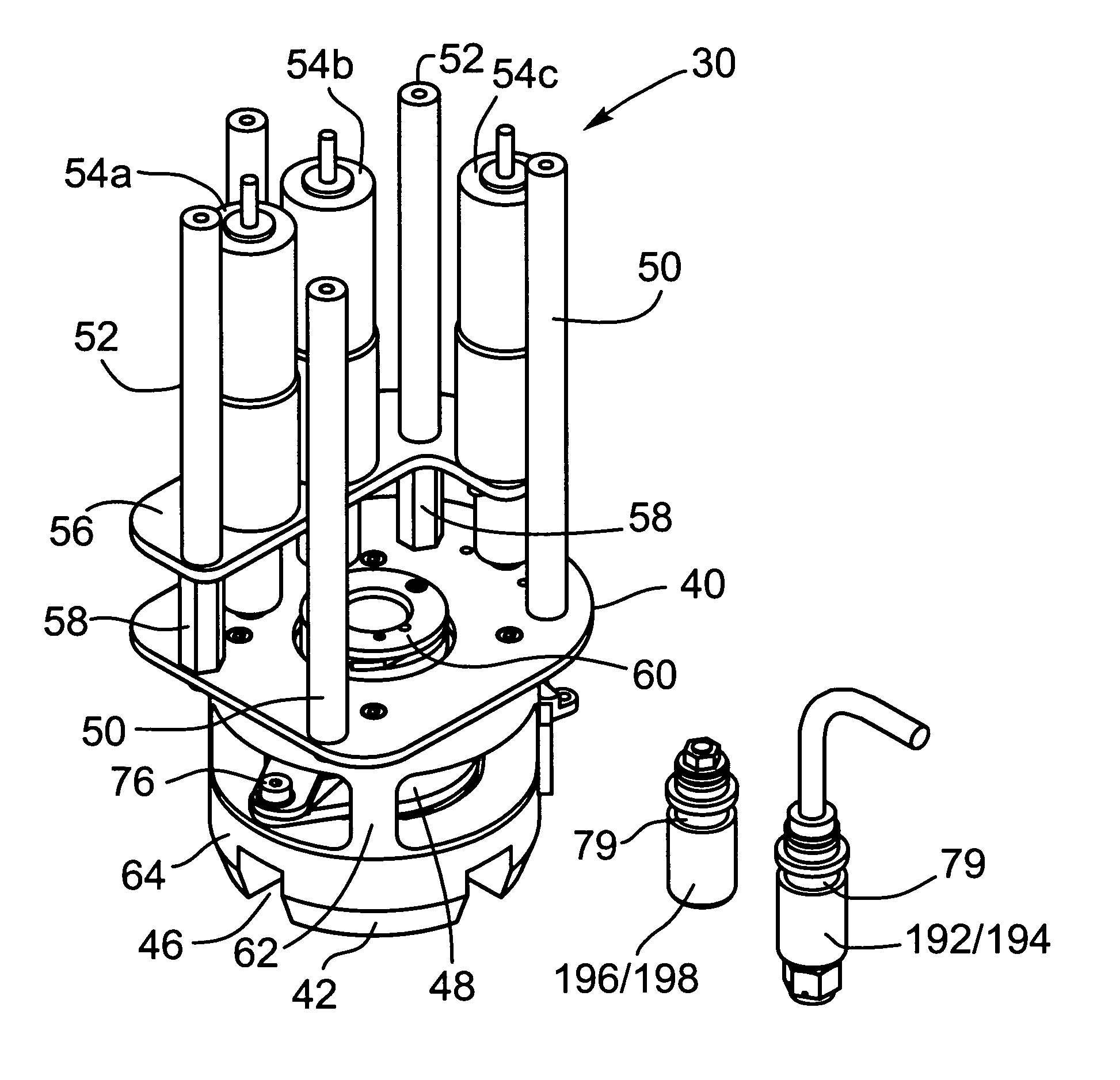
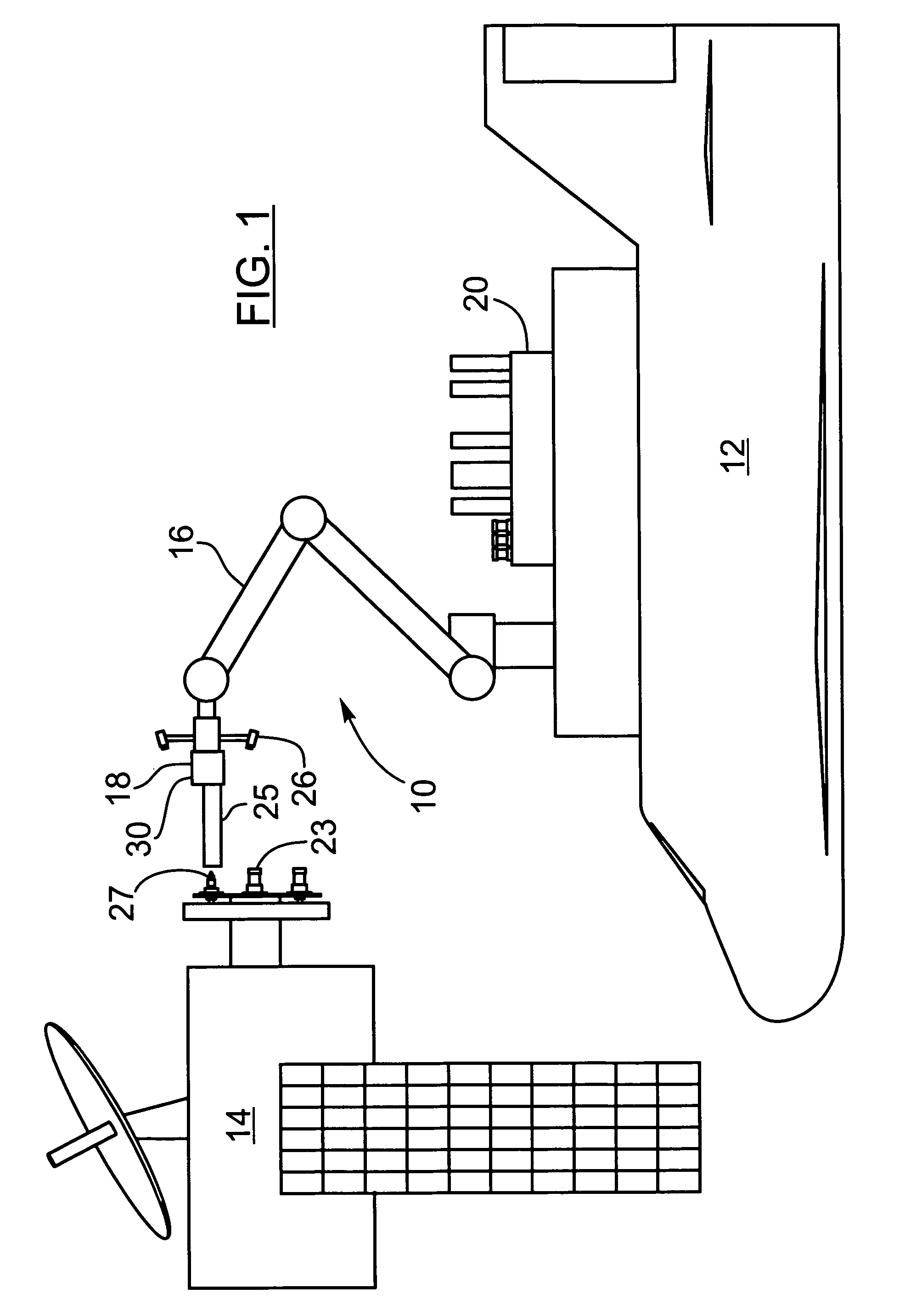
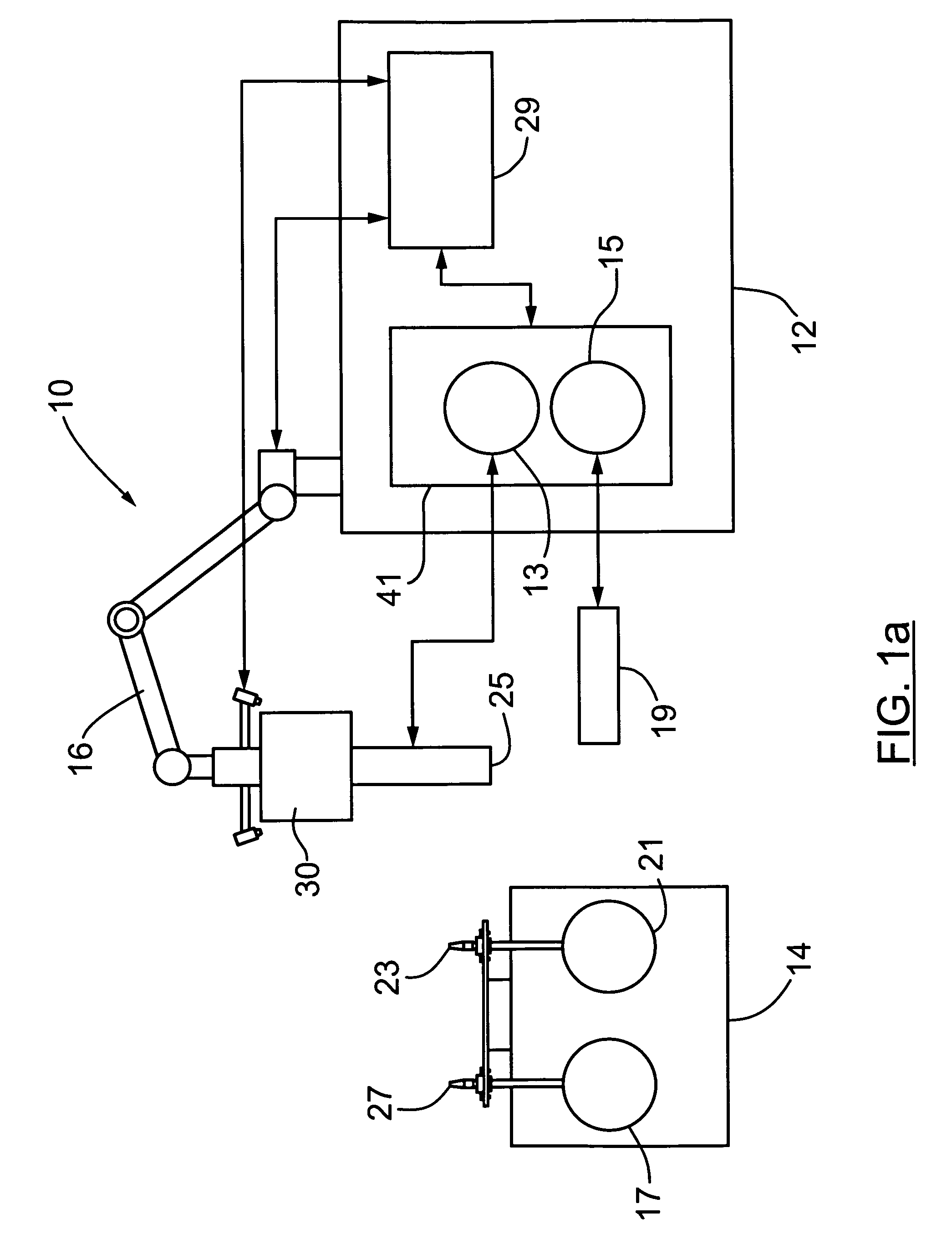
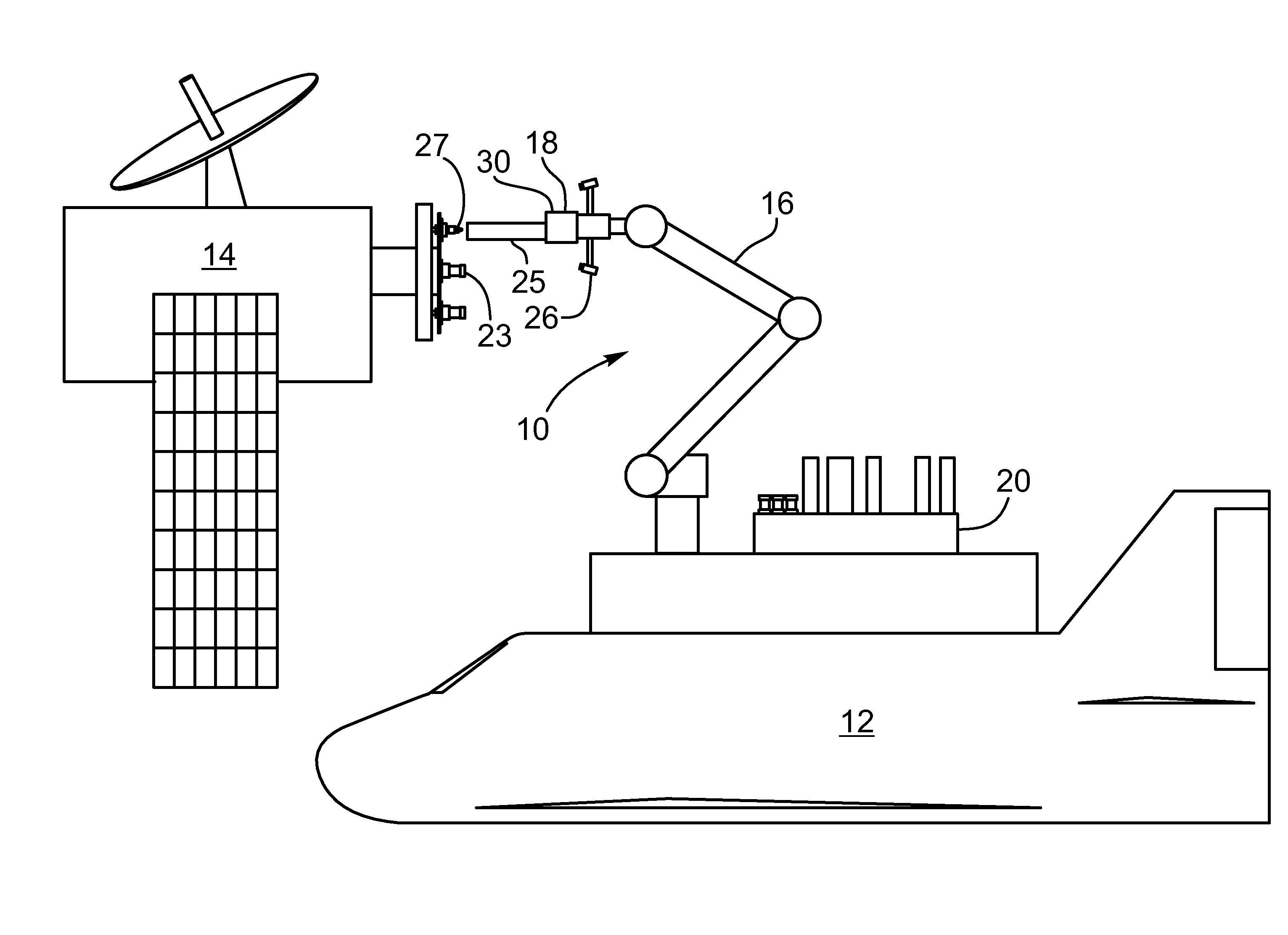
ActiveUS8074935B2Eliminating orReduce riskAircraft componentsCosmonautic ground equipmentsRobotic armActuator
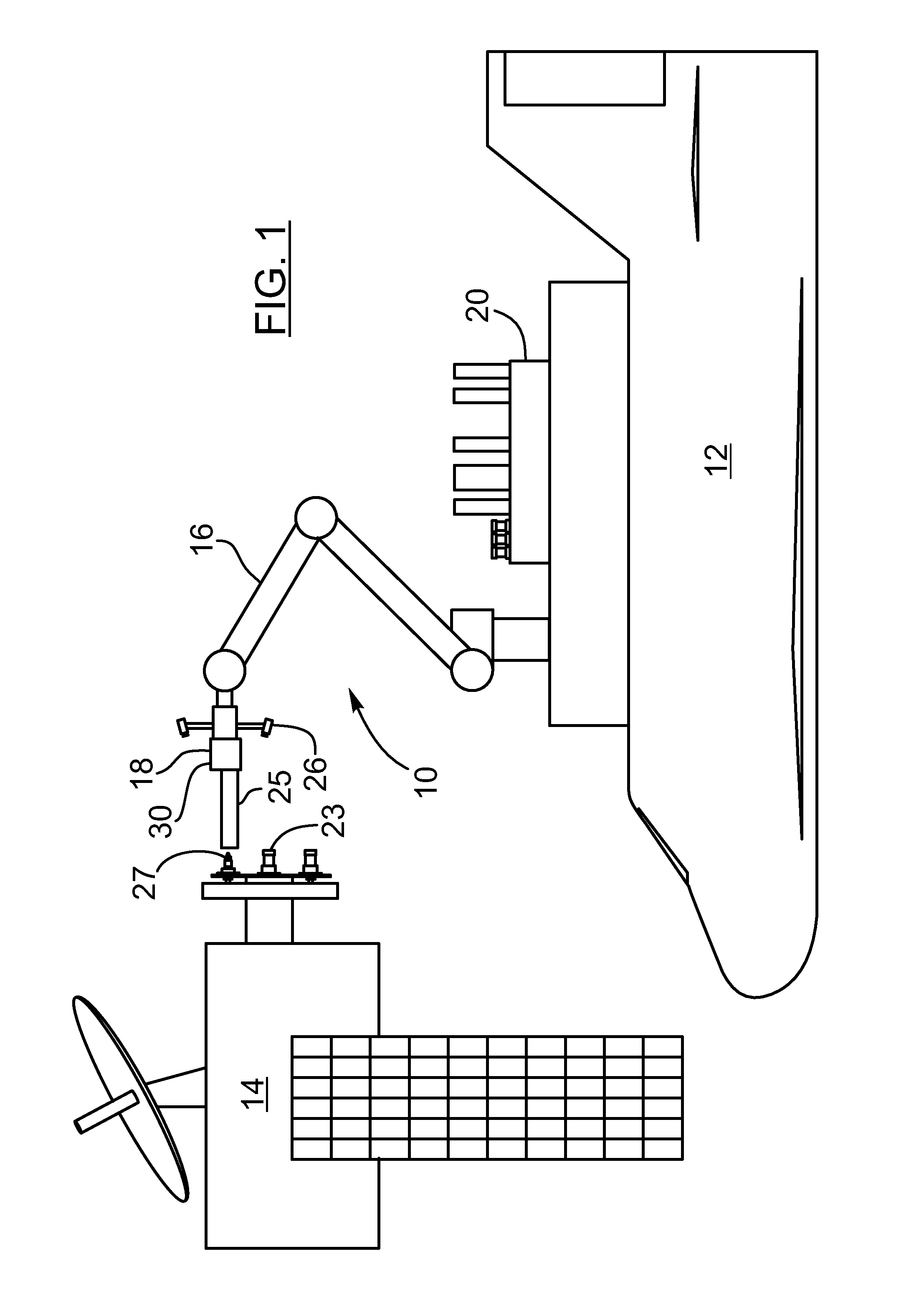
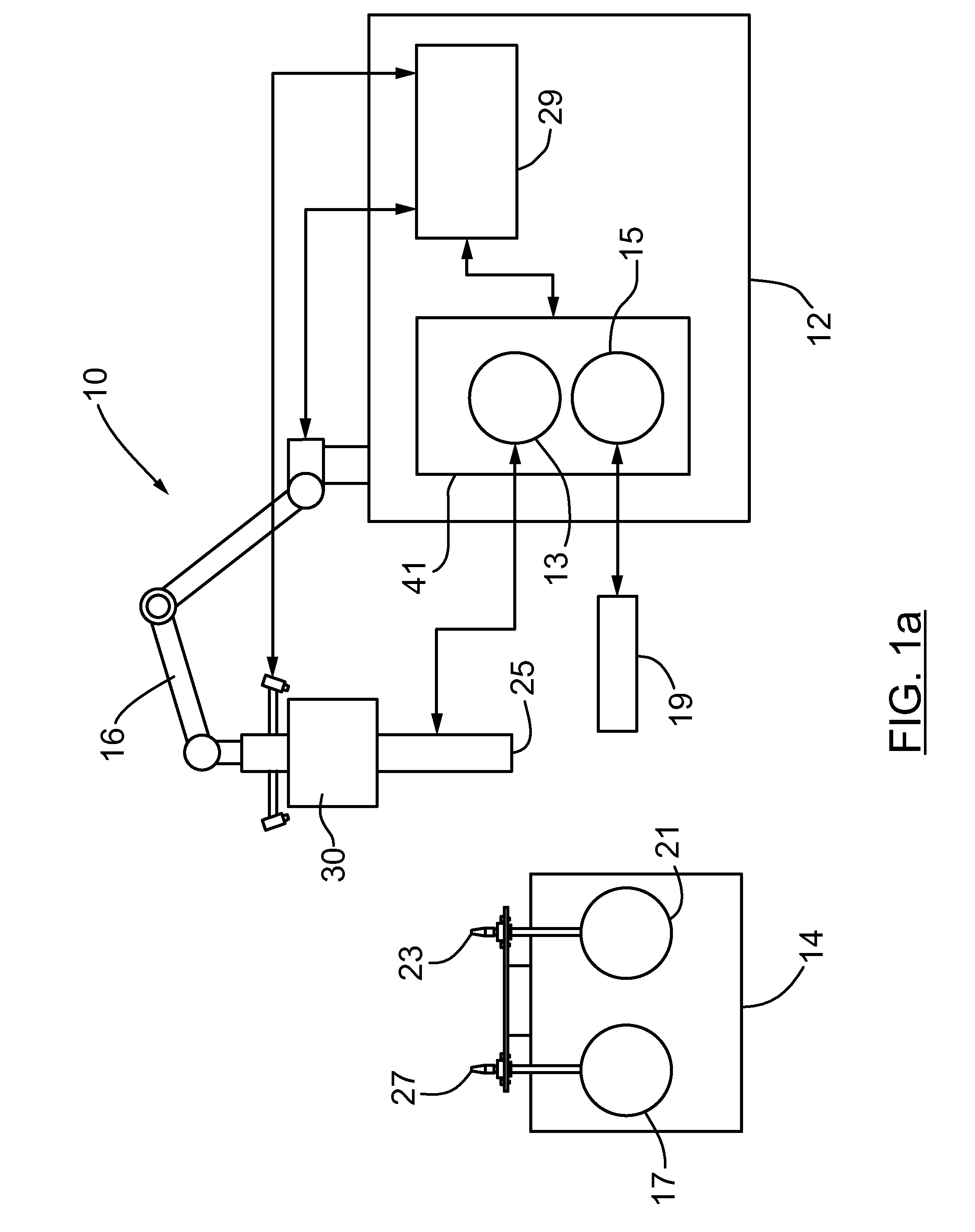
The present invention provides a method, system and apparatus for robotic refueling of satellites. The system may include a dedicated refueling satellite launched directly from either earth, or alternatively it could be launched from another larger mother spacecraft or space station in which the refueling satellite is ferried into space in the case of the larger space craft or it may be stored on the space station until needed from which it can be launched. The system includes a robotic arm, suitable tools which can be affixed to the end effector of the robotic arm required for accessing, opening and closing the fuel fill valve on the satellite being serviced, storage and retrieval stations on a tool caddy on which the tools and various fuel fill valve caps are stored. The system is under teleoperation by a remotely located operator, for example located on earth, in the mother station or in the space station. Cameras are included focussed on the robotic arm and end effector and images are transmitted to the operator to allow the operator to direct and control the refueling procedure. The system may also be configured to be operated autonomously under computer control.
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
Satellite refuelling system and method
ActiveUS20120112009A1Eliminating orReduce riskCosmonautic ground equipmentsCosmonautic partsRobotic armActuator
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
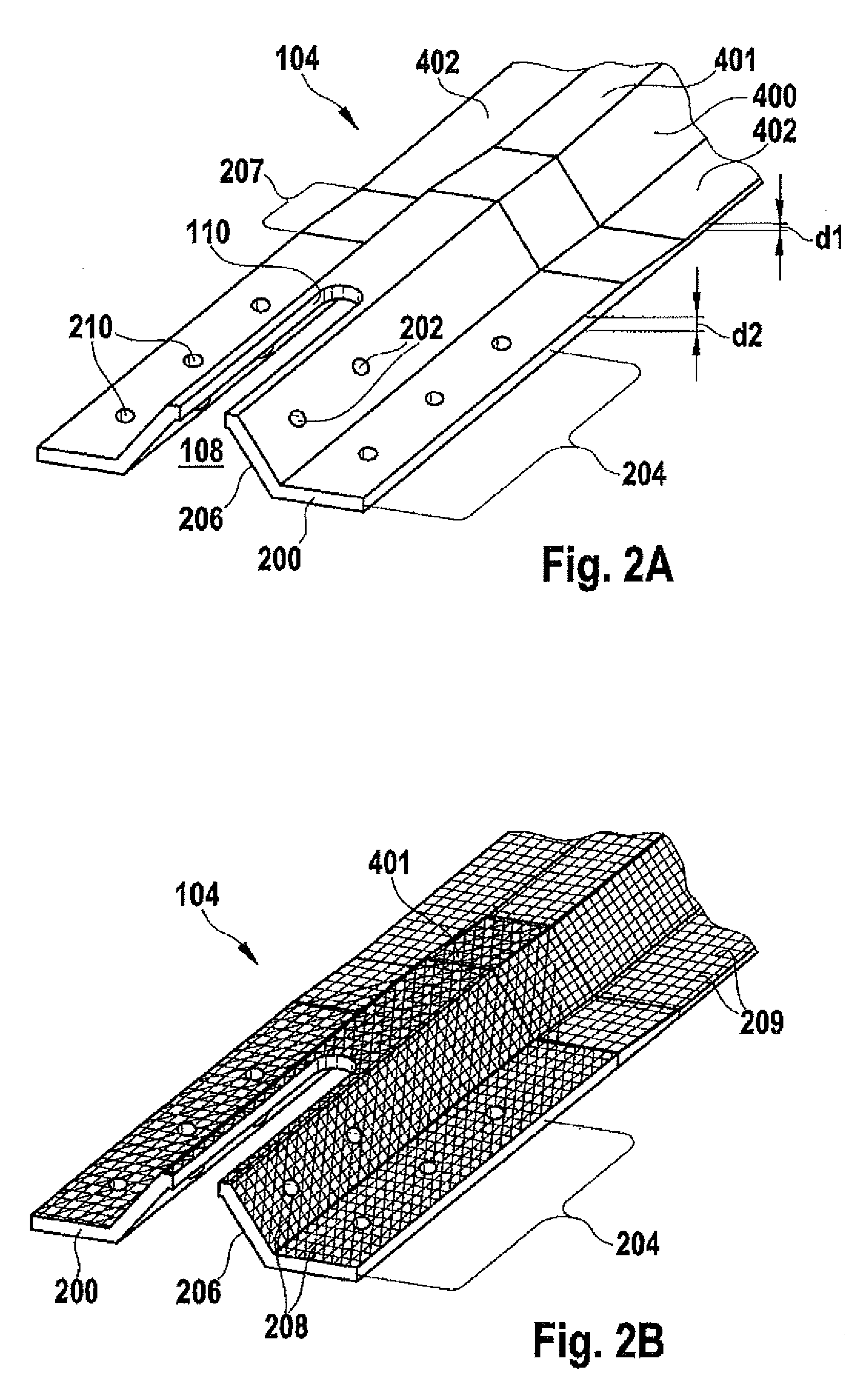
Method for Coupling Stiffening Profile Elements and Structural Component
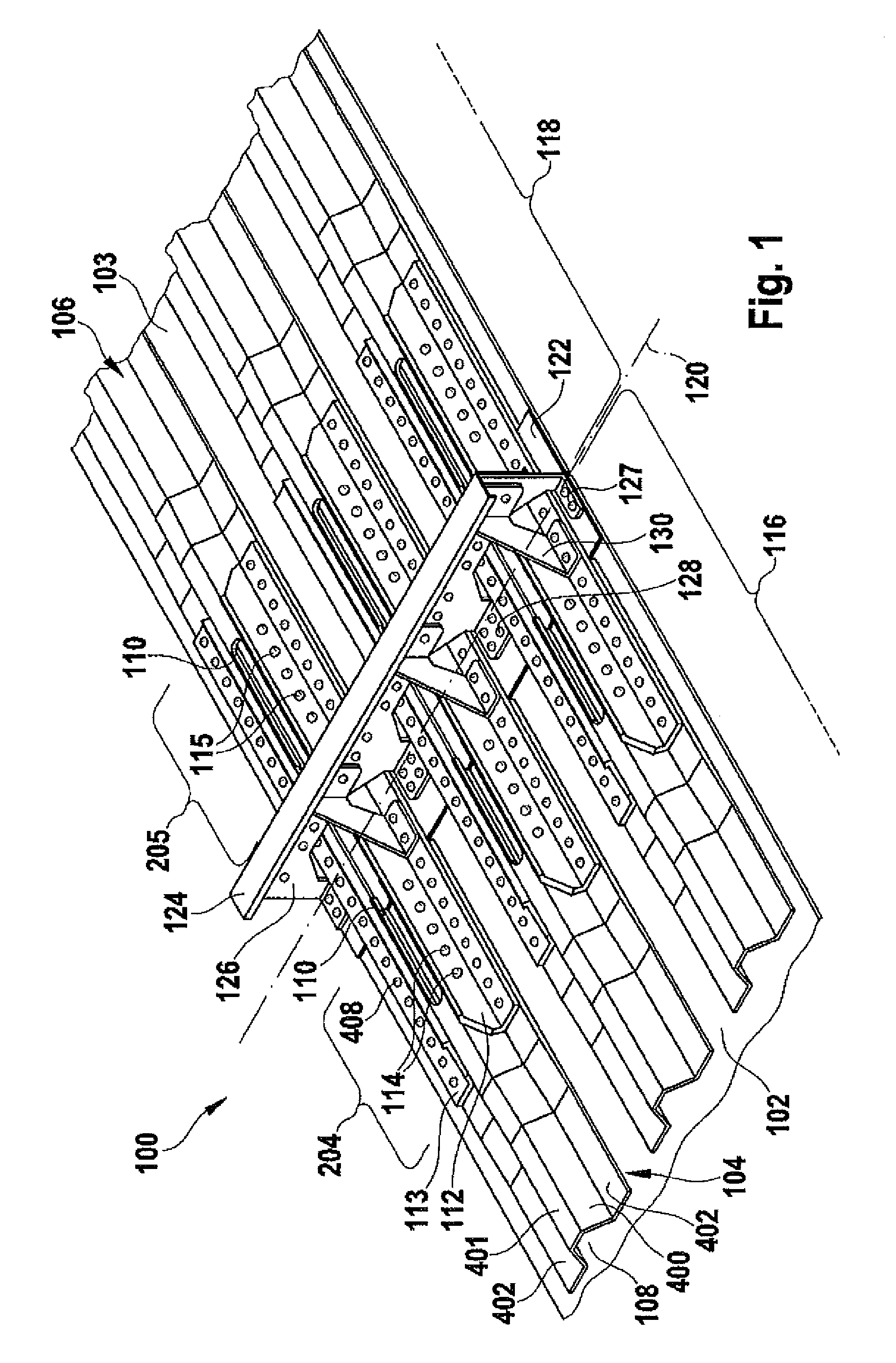
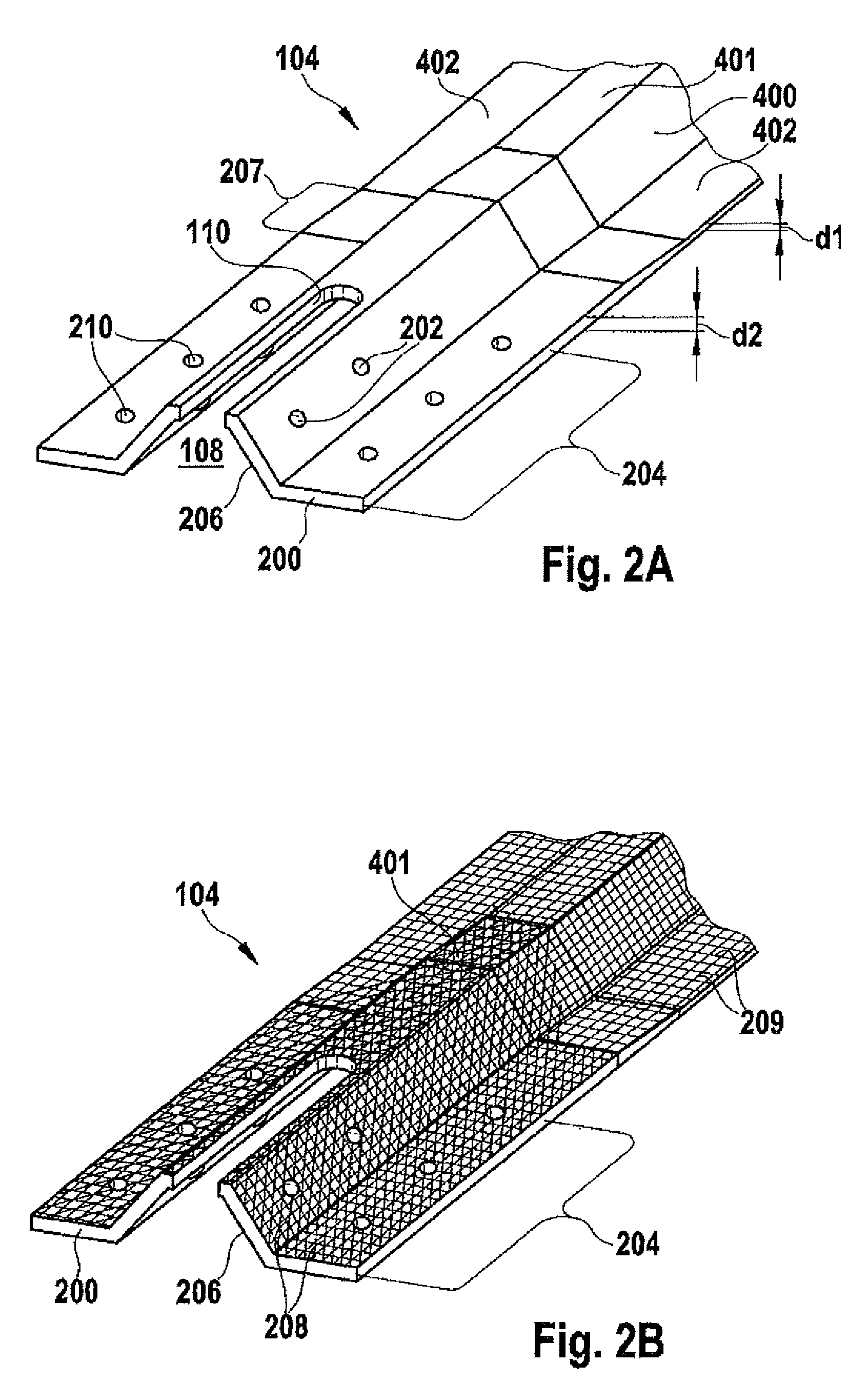
ActiveUS20100272954A1Reliable quality controlEnhanced couplingLayered productsEfficient propulsion technologiesCouplingEngineering
This invention provides a coupling method for coupling a first and a second stiffening profile element for an outer skin of an aircraft or space craft. In a first step the stiffening profile elements are arranged on the outer skin in such a manner that the stiffening profile elements oppose each other with their respective front sides and enclose within themselves a cavity. Furthermore, a fixing hole is formed through a wall of at least one of the stiffening profile elements in the cavity inside a coupling zone of the stiffening profile element. An access opening is formed through the wall in the cavity along the coupling zone. A coupling strap, which couples the stiffening profile elements together, is fastened to the coupling zone by means of a fastening element guided through the fixing hole.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
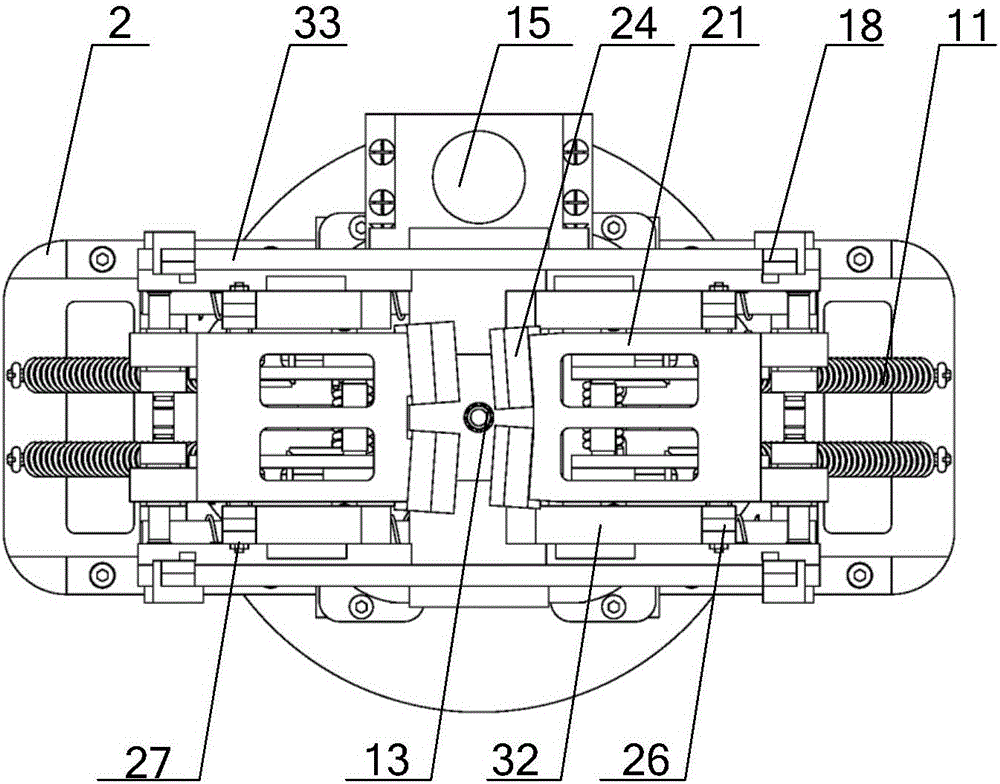
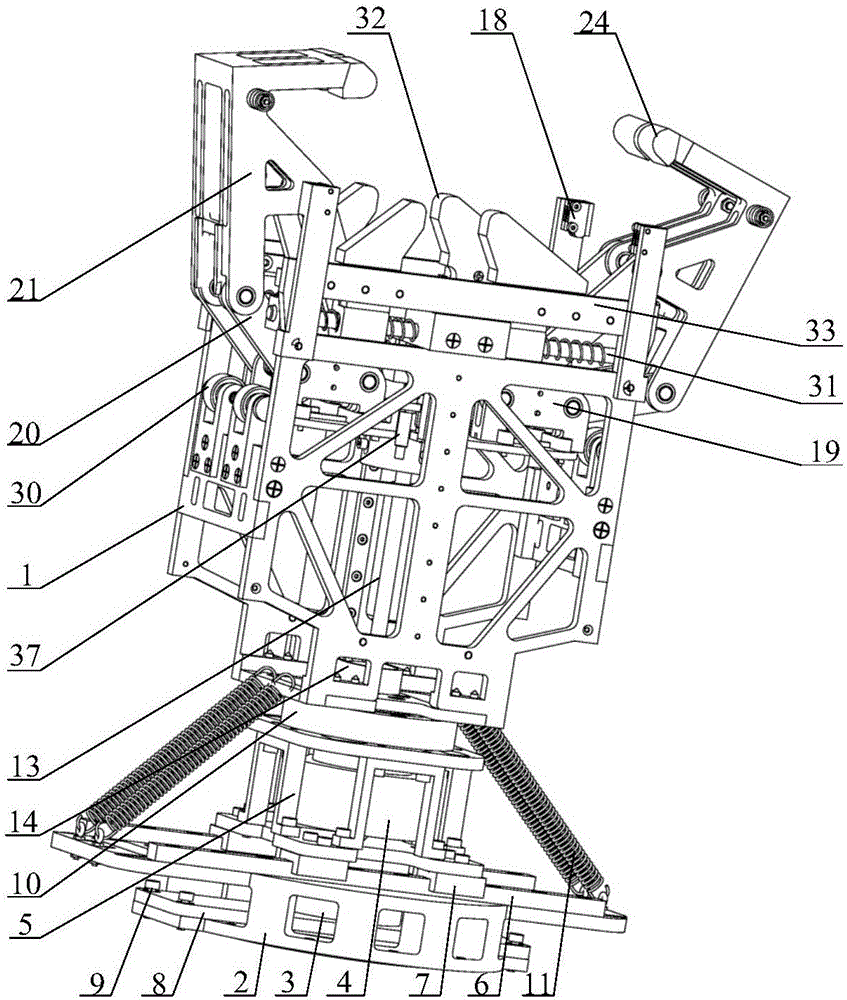
Non-cooperative target satellite acquisition device and acquisition method
The invention discloses a non-cooperative target satellite acquisition device and an acquisition method, and belongs to the technical field of aerospace. The non-cooperative target satellite acquisition device includes an outer shell, two four-link capturing pawl mechanisms, four horizontal locking mechanisms, a screw rod and a controller; the two four-link capturing pawl mechanisms are arranged in the outer shell face to face, and the lower parts thereof are fixedly connected with an installing bottom plate; the lower end of the screw rod crosses through the installing bottom plate, and the lower end thereof is connected with a driving mechanism; four horizontal locking mechanisms are respectively located at outside of the two four-link capturing pawl mechanisms, and every two horizontal locking mechanisms are installed on the upper part of the outer shell; both sides of the upper part of the four-link capturing pawl mechanisms are respectively equipped with pressure lever mechanisms; when the four-link capturing pawl mechanisms are descended, the pressure lever mechanisms compress the horizontal locking mechanism to horizontally glide towards inside; the top part of the outer shell is equipped with a photoelectric sensor, and the photoelectric sensor and the driving mechanism are electrically connected with the controller. The non-cooperative target satellite acquisition device is widely applied to the acquisition of various space crafts, and the non-cooperative target satellite acquisition device is wide in application range, big in tolerance, quick in response speed, high in reliability, and others.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
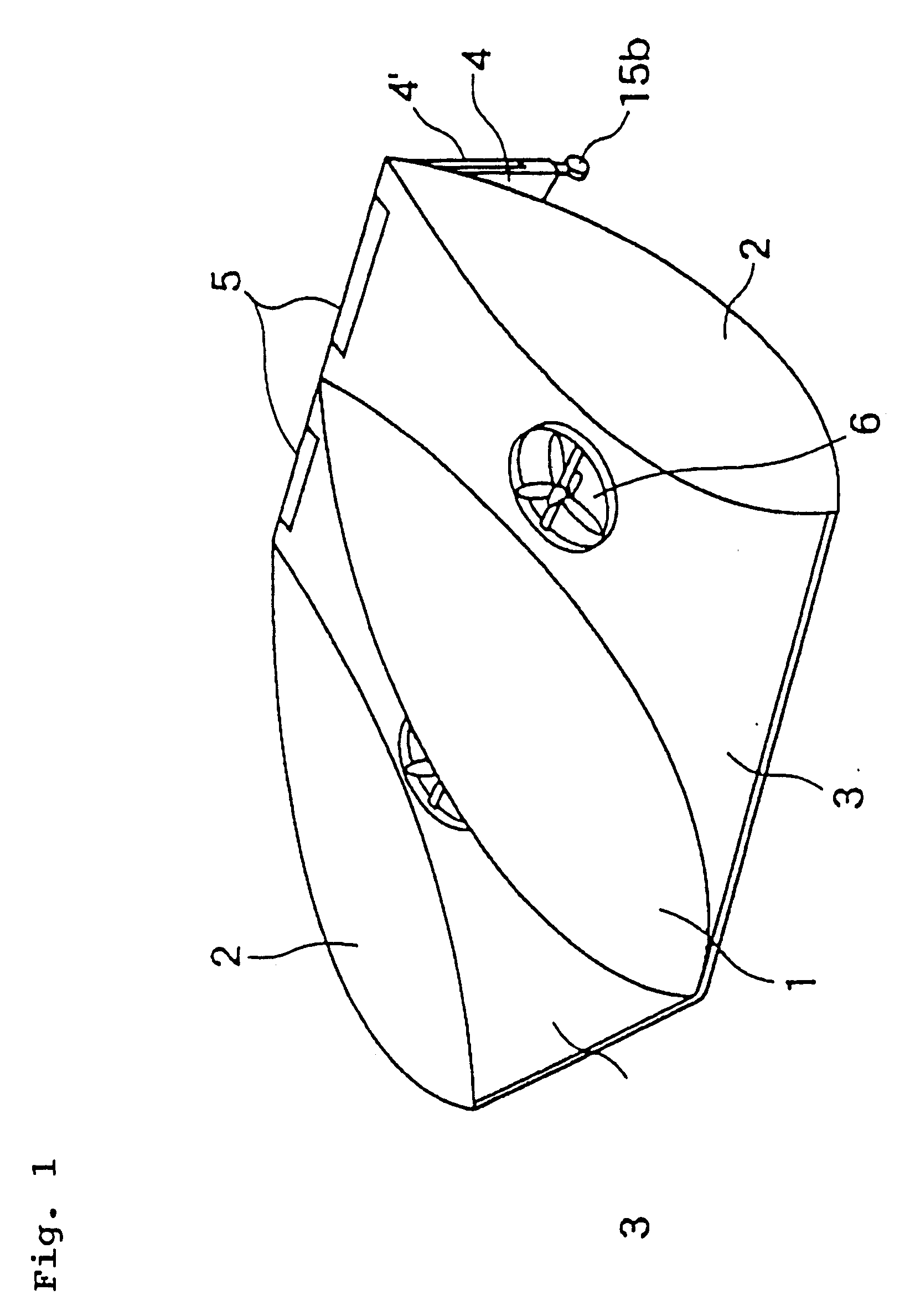
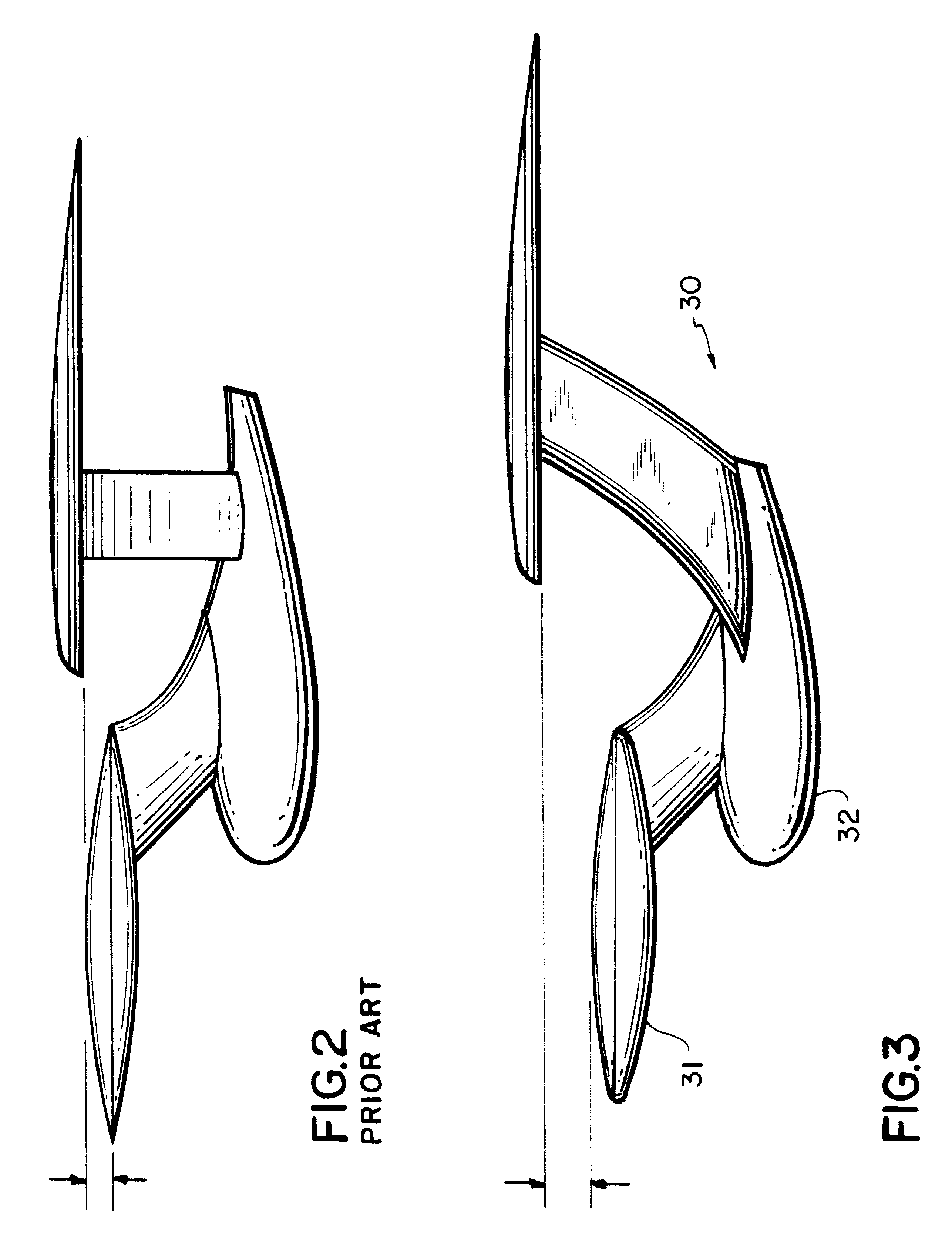
Airship shaped space craft
InactiveUS6471159B1Launch safetyReduce the average velocitySpace shuttlesSystems for re-entry to earthReverse orderJet engine
The present airship-shaped space craft has a middle fuselage extending in a fore-and-aft direction, and a pair of two outer fuselages extending in the fore-and-aft direction located symmetrically on both sides of the middle fuselage. In the above fuselages, gas of a specific gravity of which is smaller than that of air is filled, and the middle fuselage is connected with the outer fuselages by a horizontal wing. The horizontal wing is provided with propelling devices supported in a gimbal fashion for generating thrust in any optional direction, jet engines with backwards directed nozzles to be controlled within a range from a slantwise upward direction to a slantwise downward direction, and rocket engines with ejection nozzles to be controlled in right-and-left and up-and-down directions. During ascent of the space craft, at first the propelling devices, then the jet engines and at last the rocket engines are actuated so as to make the space craft reach and fly along a satellite orbit. Upon return of the space craft, the rocket engines, the jet engines and the propelling devices are actuated in reverse order, and aerodynamic heating at reentry into the atmospheric space can be reduced by making the space craft descend slowly. Also, control of the flight in the atmospheric space becomes easy, so that the space craft can safely and easily land on a predetermined narrow area of the ground.
Owner:BUNDO MUTSURO
Device for supporting systems
ActiveUS20080296443A1Cost efficientLow production costCandle holdersLighting support devicesSupporting systemEngineering
The present invention relates to a device for supporting systems, for example an electric cable or a fluid-carrying pipe, on a structure of an aircraft or space craft, and to an aircraft or space craft with such a device. The device has a basic bracket arrangement which can be fastened to at least one predetermined fastening section of the structure, and also has at least one system bracket for supporting the systems. The at least one system bracket can be fastened to the basic bracket arrangement locationally variable with respect to the fastening section. The advantage of the invention consists in the fact that a route of a system can be flexibly varied even during the equipment assembly, i.e. the structure is no longer modifiable or is only modifiable at considerable expense.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
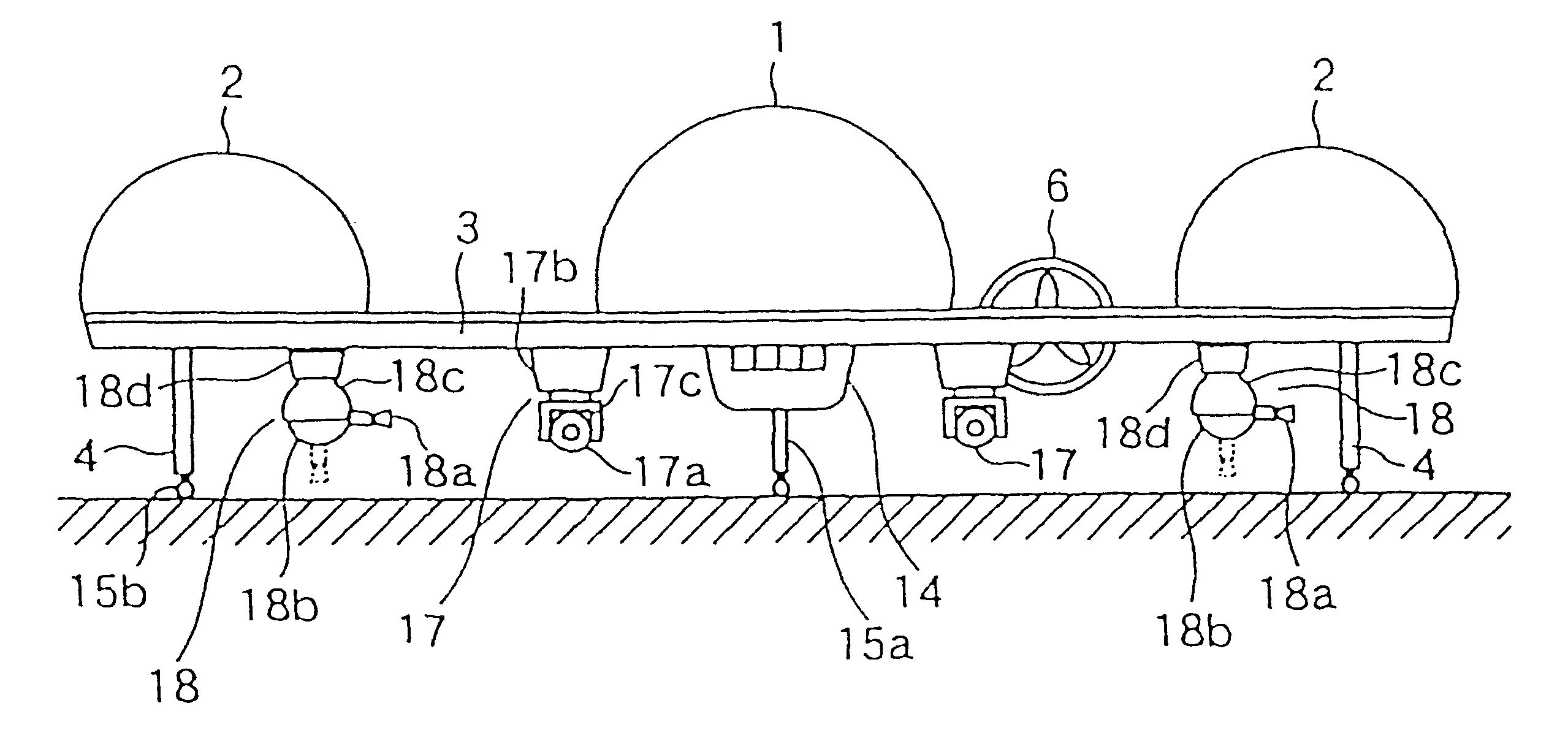
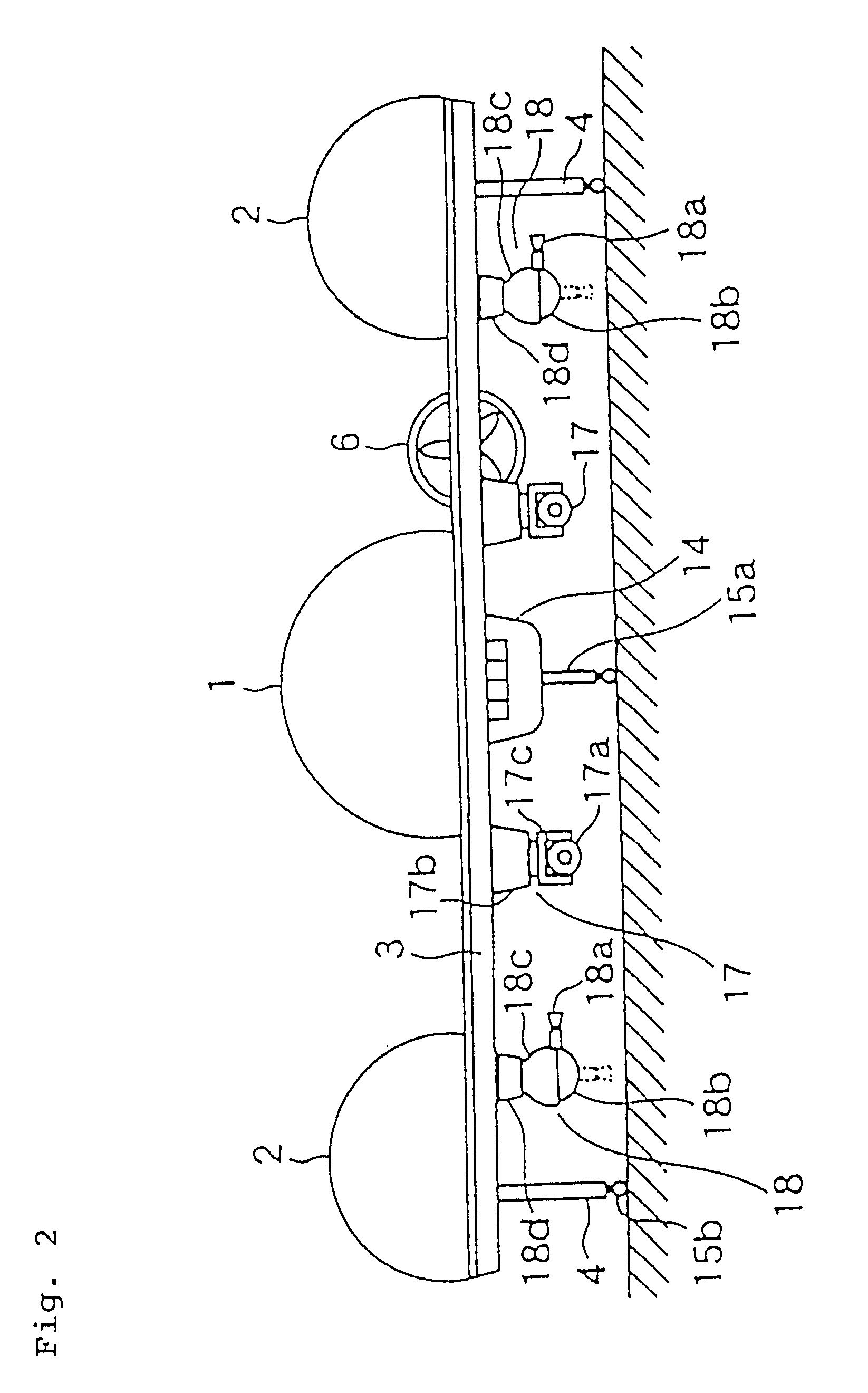
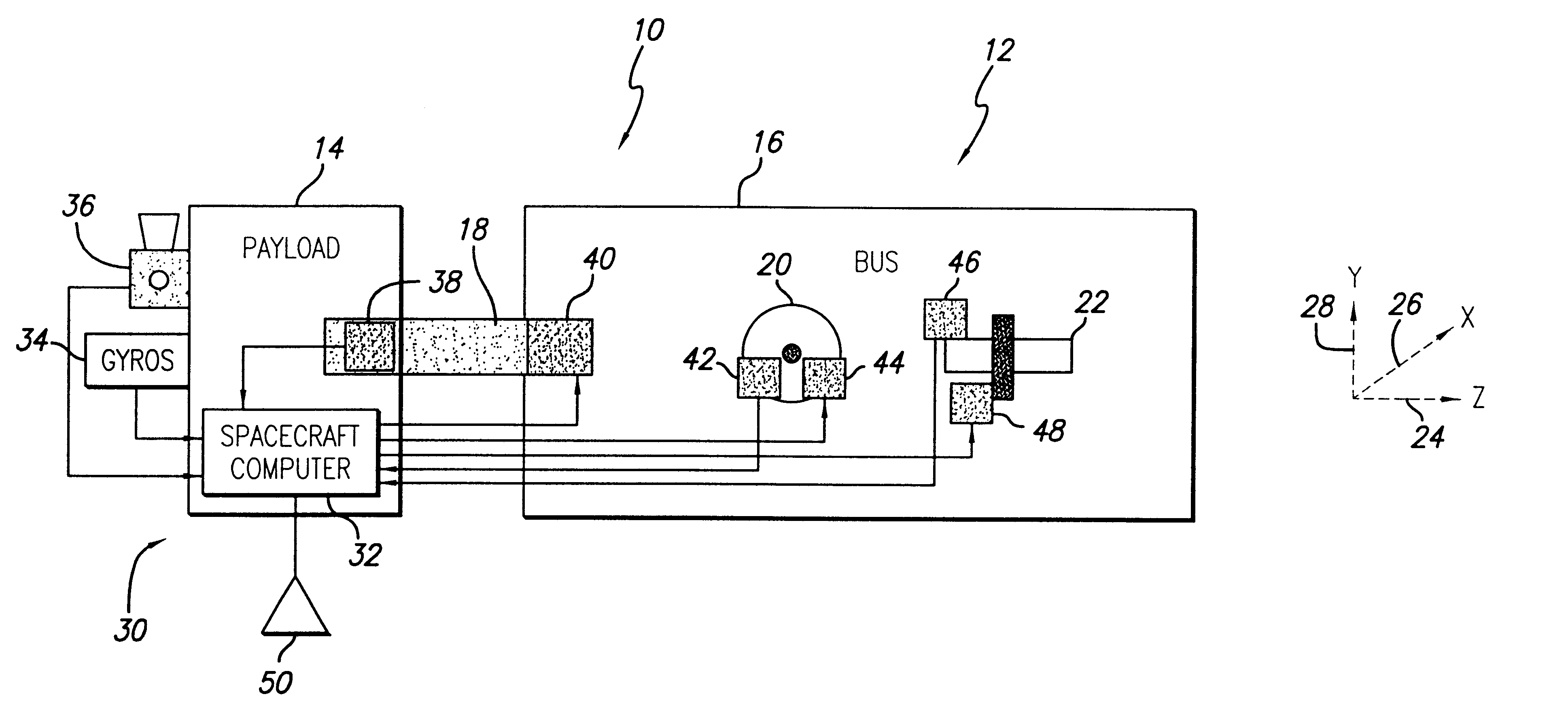
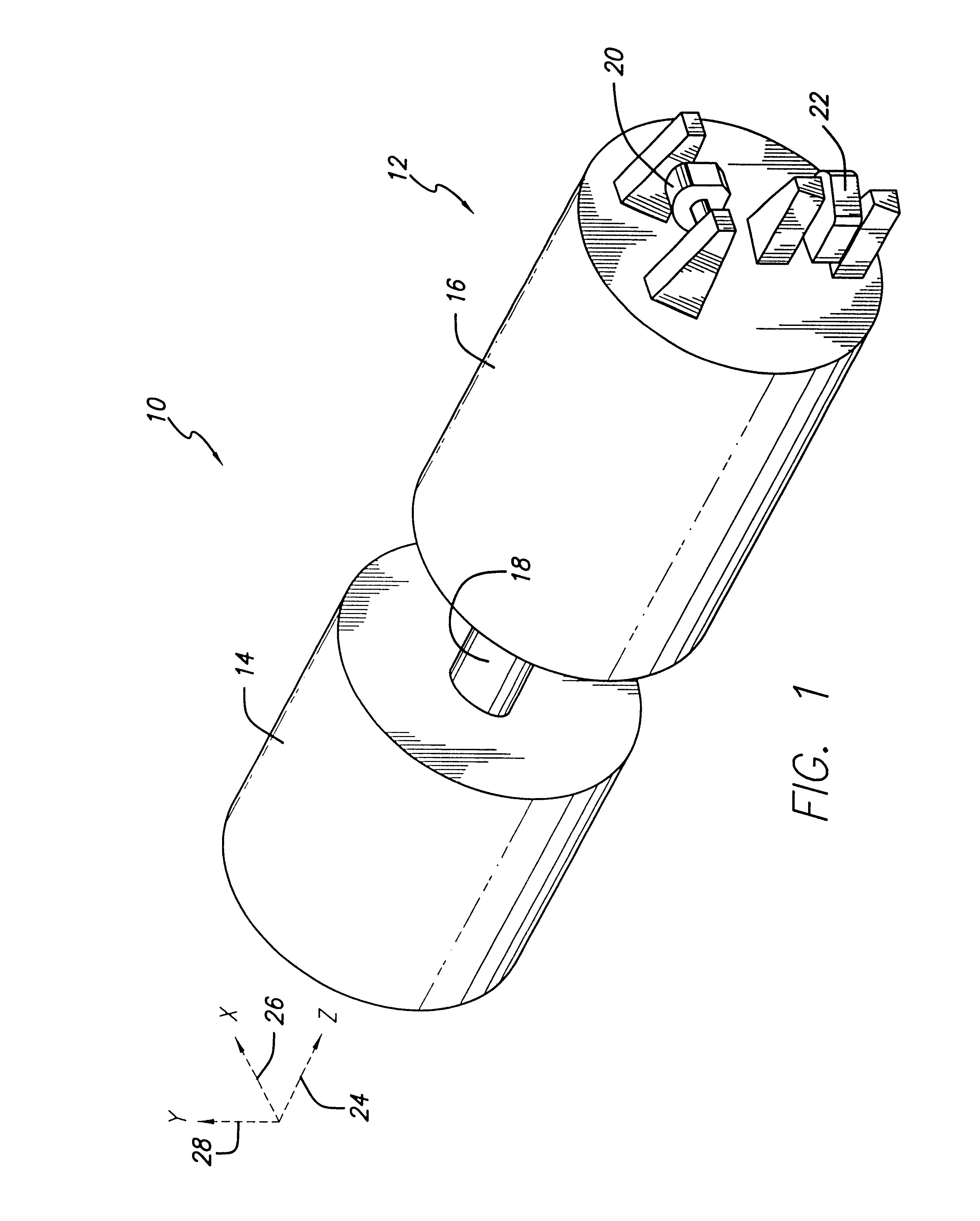
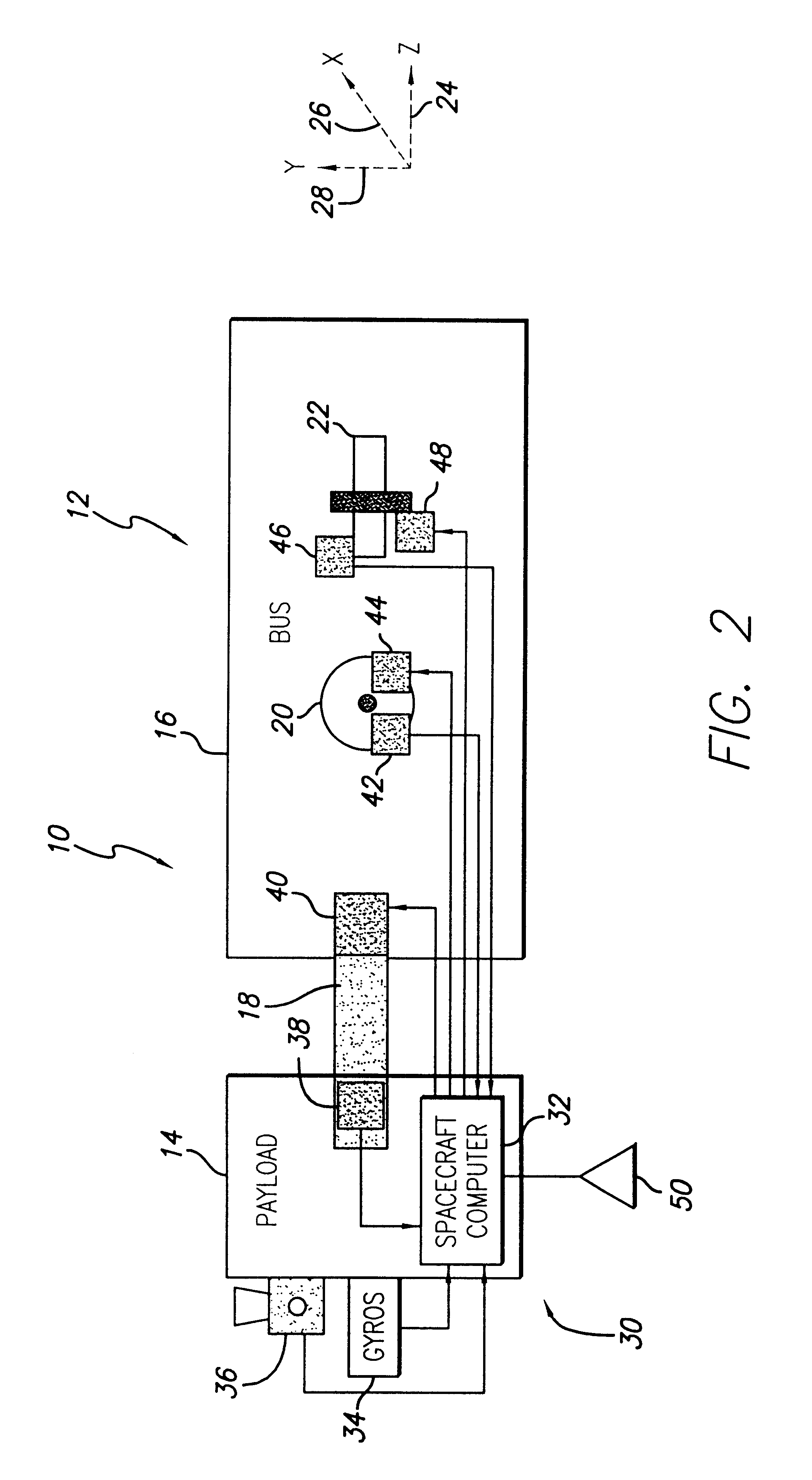
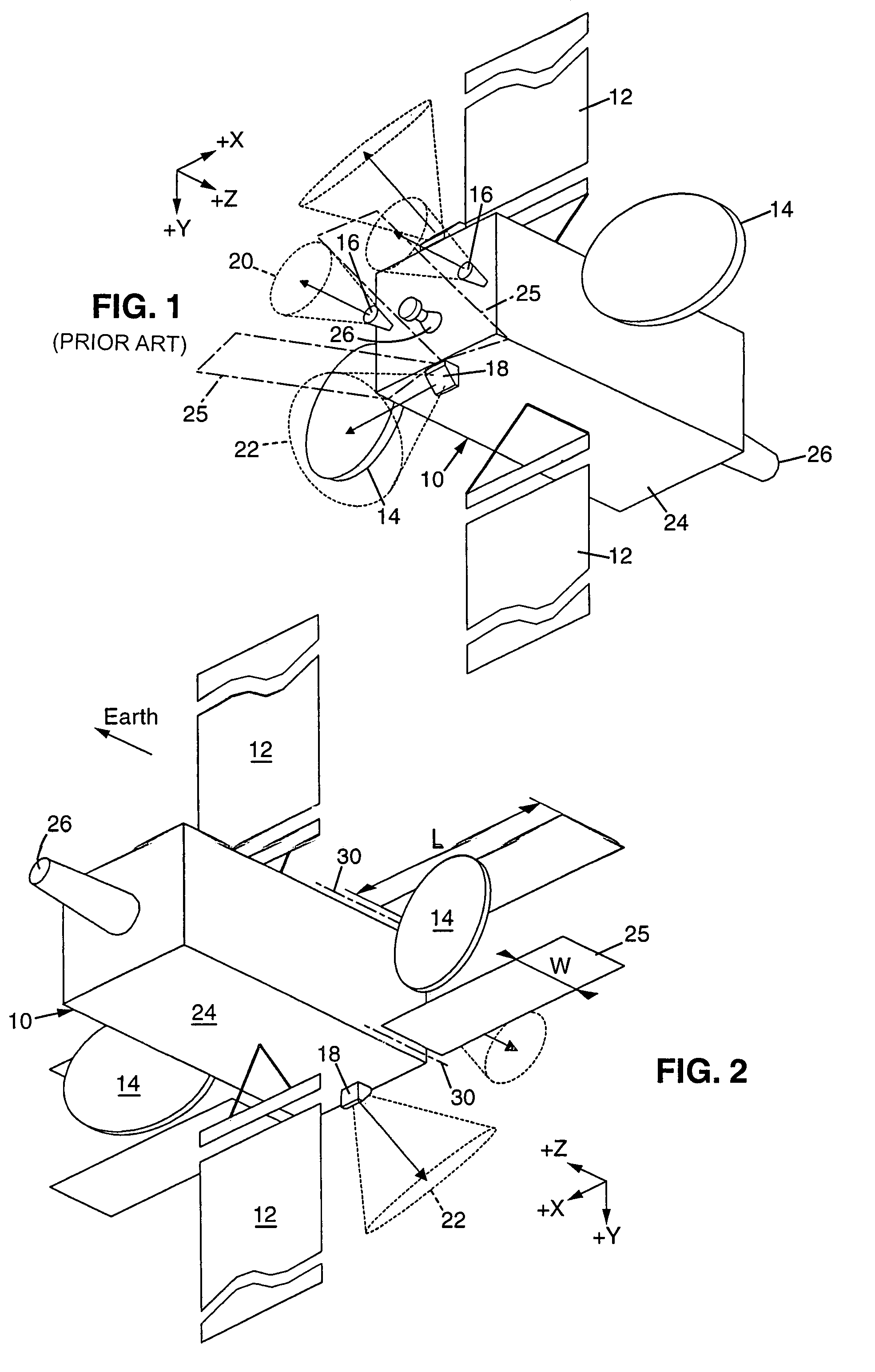
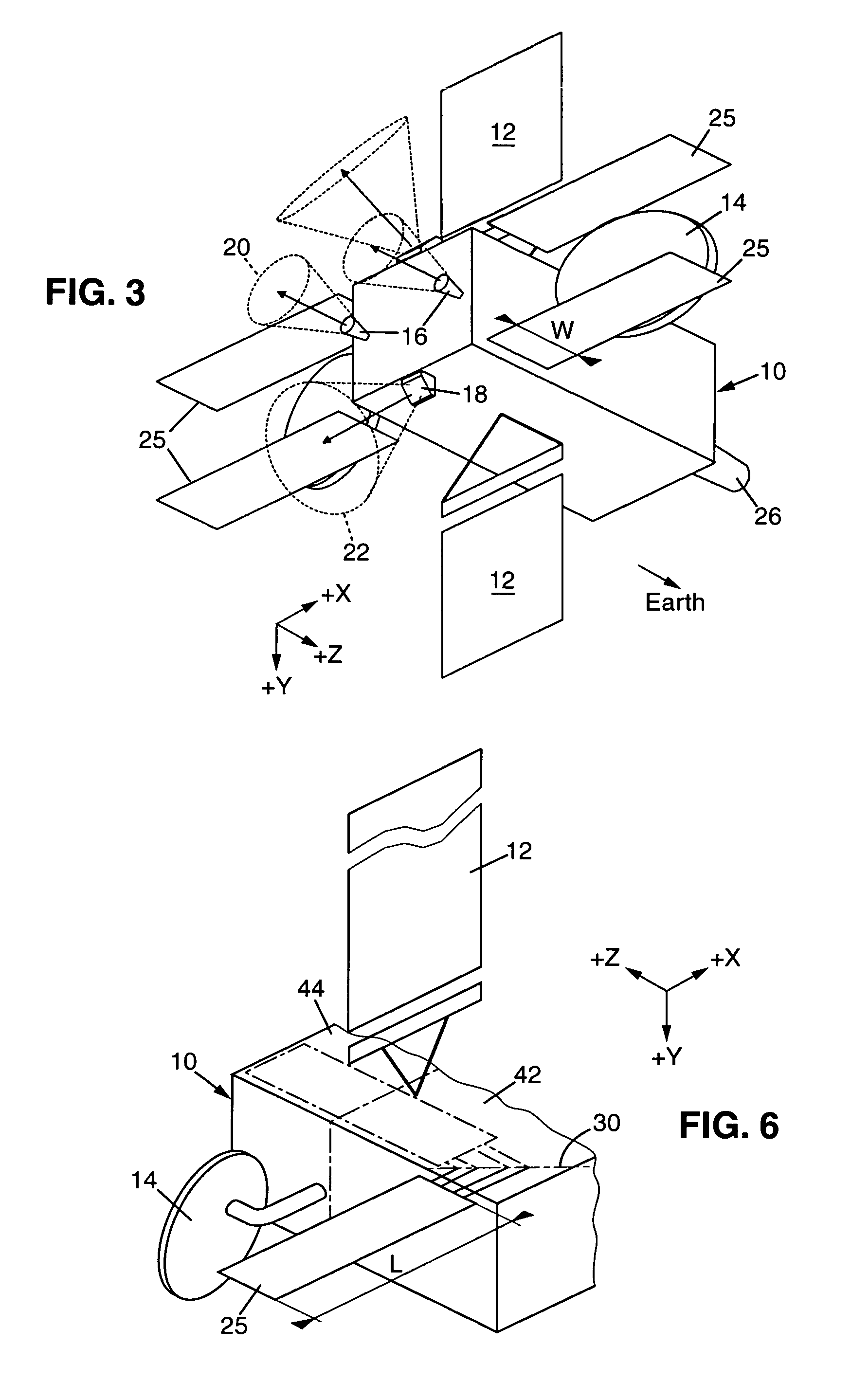
System and method for controlling the attitude of a space craft
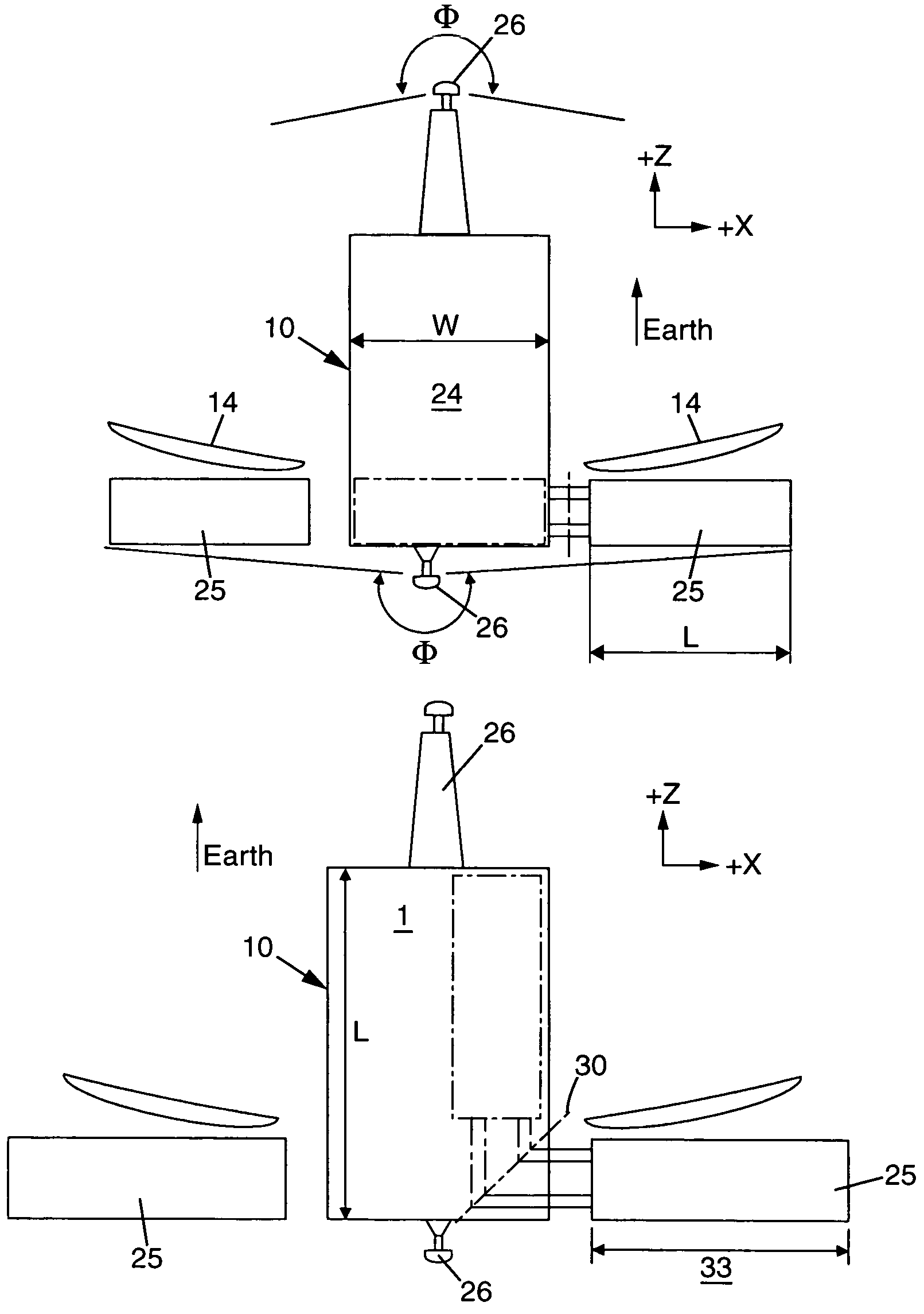
A system (30) for adjusting the orientation of a spacecraft adapted for use with a satellite (10). The system (30) includes a first control circuit (32, 38, 40) for canceling any momentum of the spacecraft via a counter-rotating spacecraft bus (16, 18). A second controller (32, 42, 44, 46, 48) orients the spacecraft via the application of internal spacecraft forces. In a specific embodiment, the spacecraft bus (16, 18) serves a dual use as storage section and includes a mass (16) having a moment of inertia on the same order as the moment of inertia of the satellite (10). The satellite (10) includes a bus section (16) and a payload section (14). The mass (16) includes the bus section (16). The first control circuit (32, 38, 40) runs software to selectively spin the mass (16) to cancel the momentum of the satellite (10). The software computes an actuator control signal, via a computer (32), that drives a first actuator (38) that spins the mass (16). The first control circuit (32, 38, 40) further includes a circuit for determining the inertial angular rate of the satellite (10) that includes a gyroscope sensor package (34) in communication with the computer (32). The gyroscope sensor package (34) provides a rate signal to the computer (32) that is representative of the momentum of the satellite (10). The computer (32) runs software for generating the actuator control signal in response to the receipt of the rate signal from the gyroscope sensor package (34). The second controller (32, 42, 44, 46, 48) includes a first reaction wheel (20) having an axis of rotation (26) approximately perpendicular to an axis of rotation (28) of a second reaction wheel (22). The first and second reaction wheels (20, 22) are rigidly mounted to the spacecraft bus (18, 16) and are free to spin about their respective axis. The first and second reaction wheels (20, 22) are selectively spun via first and second actuators (44, 48), respectively, in response to the receipt of first and second steering control signals, respectively.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Telescope sparse array not requiring the use of laser interferometry
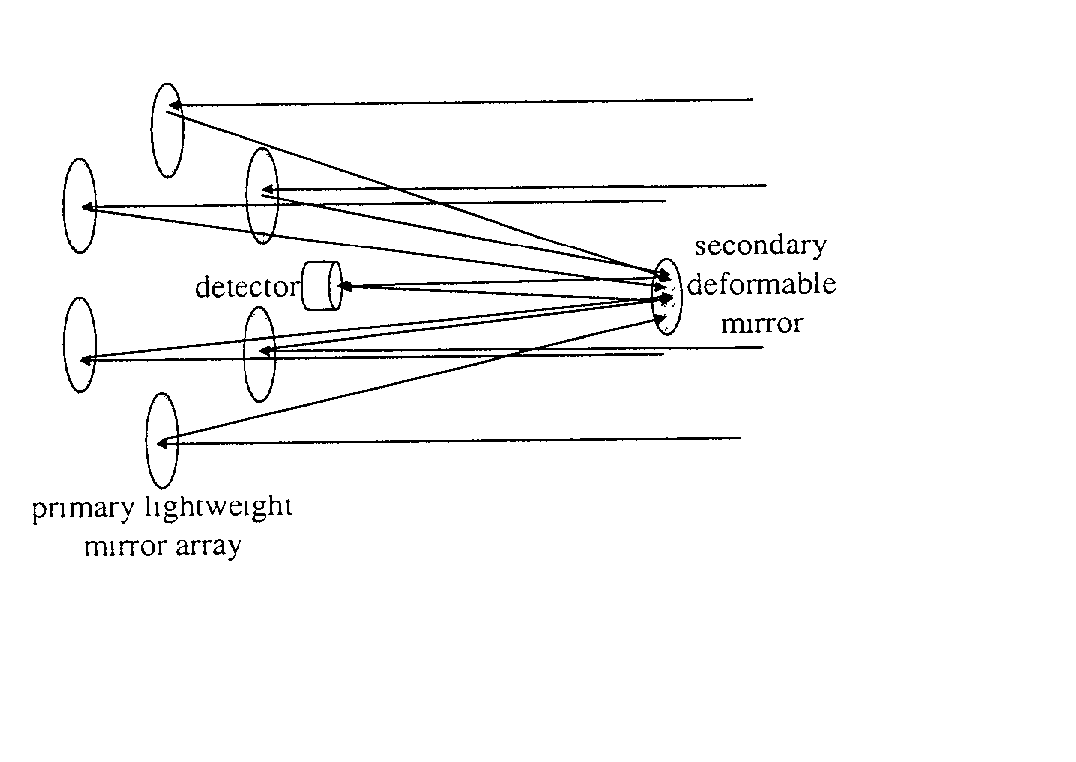
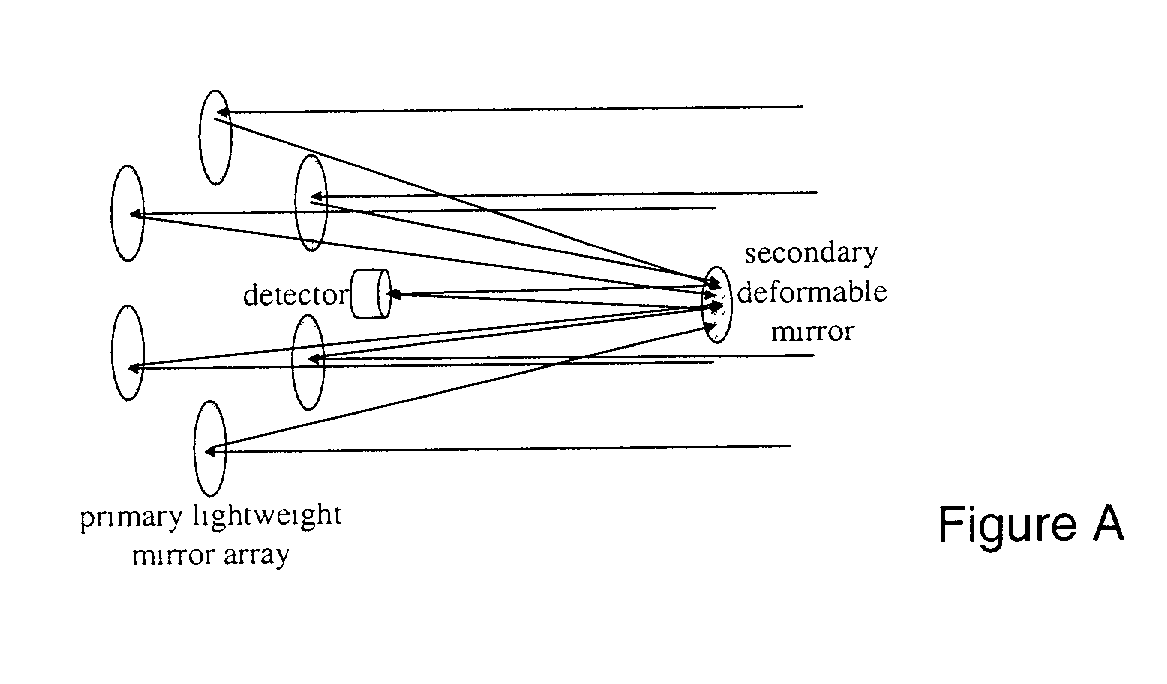
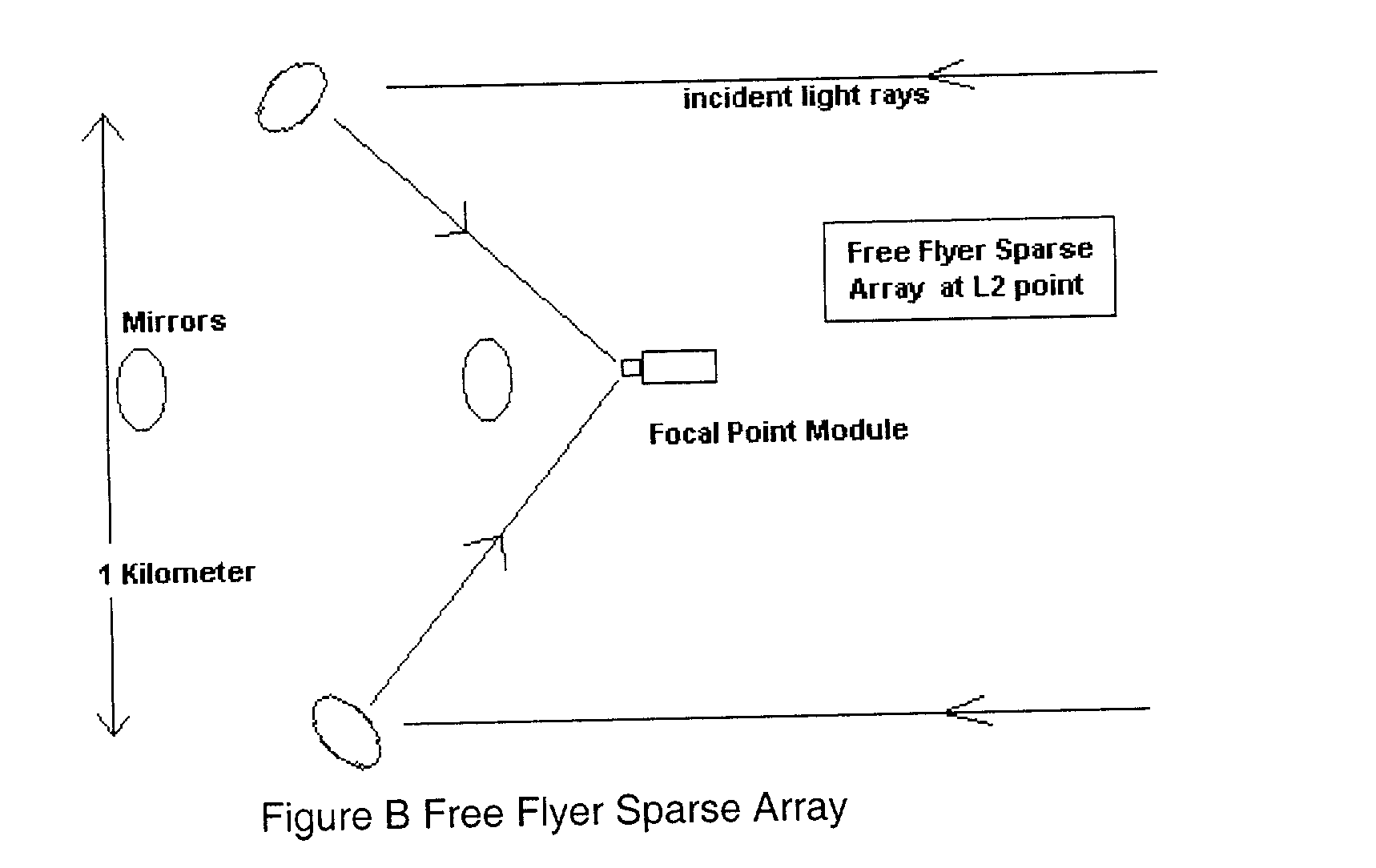
InactiveUS20030227696A1Rapid Strehle ratio maximizationHigh resolutionMirrorsTelescopesLight beamClassical mechanics
Recent schemes have been accepted by NASA in its TPF program for simple sparse arrays. But these methods require a great deal of interferometric control of tip tilt and other motion. But with this invention we just need (actuated) flats on a parabola with a central focal point module. The mirrors will be on the order of a kilometer distant from that module so that tip tilt can be sensed (and then controled) by sensors on the module that also detect beam pointing. The actual (high SNR) star the planet is orbiting can be used for rapid Strehle ratio maximization so that NO laser interferometry is needed at all. Fine mirror control can be done by variable reflectivity of the backside of the mirrors. The mirrors can be placed at L2 so that their orbits are all the same. A lot of this multi space craft control has already been accomplished with the ESA "Cluster".
Owner:MAKER DAVID JOEL
Integrated shock absorbing vibrating isolation device for stellite
InactiveCN1911734ASo as not to damageLower launch costsCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsStellite alloyIsolating mechanisms
Owner:郑钢铁 +3
Rod pin type blind alignment space butt joint mechanism
InactiveCN106428647ASpace Rescue FavorableAxialCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic component separationButt jointCircular cone
The invention provides a rod pin type blind alignment space butt joint mechanism. An outer truncated cone and an inner truncated cone are installed on two space crafts respectively, one end of a lead screw pushing rod is an outer thread and penetrates through a central hole of a flange to be in threaded connection with a straight thread sleeve, and a boss of the side wall of the lead screw pushing rod is matched with an axial groove formed in the inner wall of the central hole of the flange. The other end of the lead screw pushing rod is a conical face. A radial through hole is formed in the conical face of the outer truncated cone, and a pin is installed in a through hole through a compression spring. The inner wall of the inner truncated cone is provided with an annular groove in the axial direction, the flange is fixed to the bottom face of the outer truncated cone, and the straight thread sleeve pushes the lead screw pushing rod to perform axial motion on the outer truncated cone and pushes the pin to get over the spring and extend out of the outer conical face of the outer truncated cone to be in clearance fit with the annular groove during rotation. The rod pin type blind alignment space butt joint mechanism can perform bidirectional initiative butt joint, is high in butt joint reliability and butt joint speed and can work repeatedly.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Orbit changing method for reducing space craft gravity loss
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Low-damping suspension hanging type deployment test device
InactiveCN106218926AShorten the development cycleSmooth motionCosmonautic condition simulationsStructural/machines measurementDistribution systemWeightlessness
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
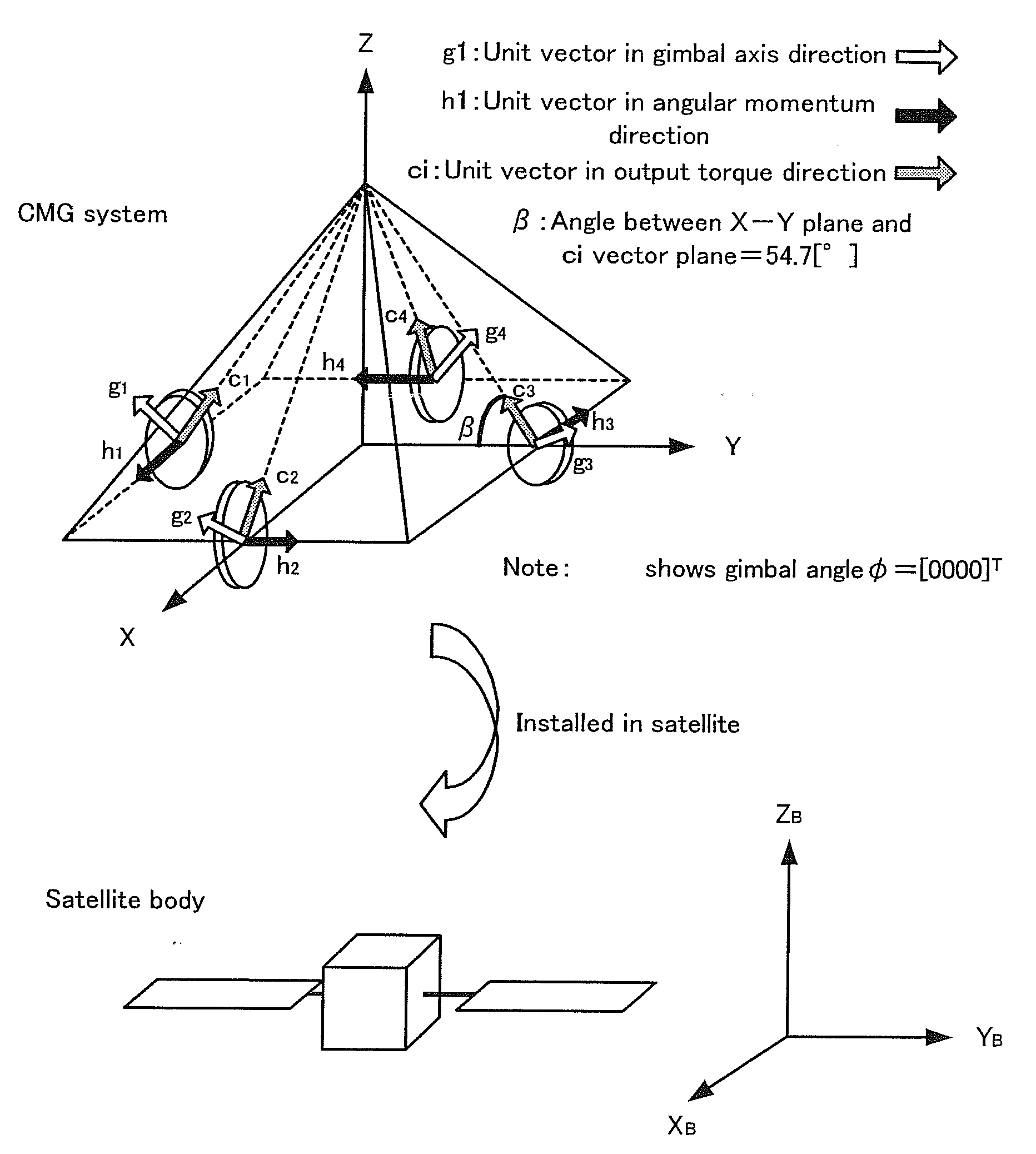
Attitude Change Control Method, Attitude Change Control System, Attitude Change Control Program and Program Recording Medium
InactiveUS20090039202A1Raise the ratioEfficiently outputting such torqueCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsControl systemAngular velocity
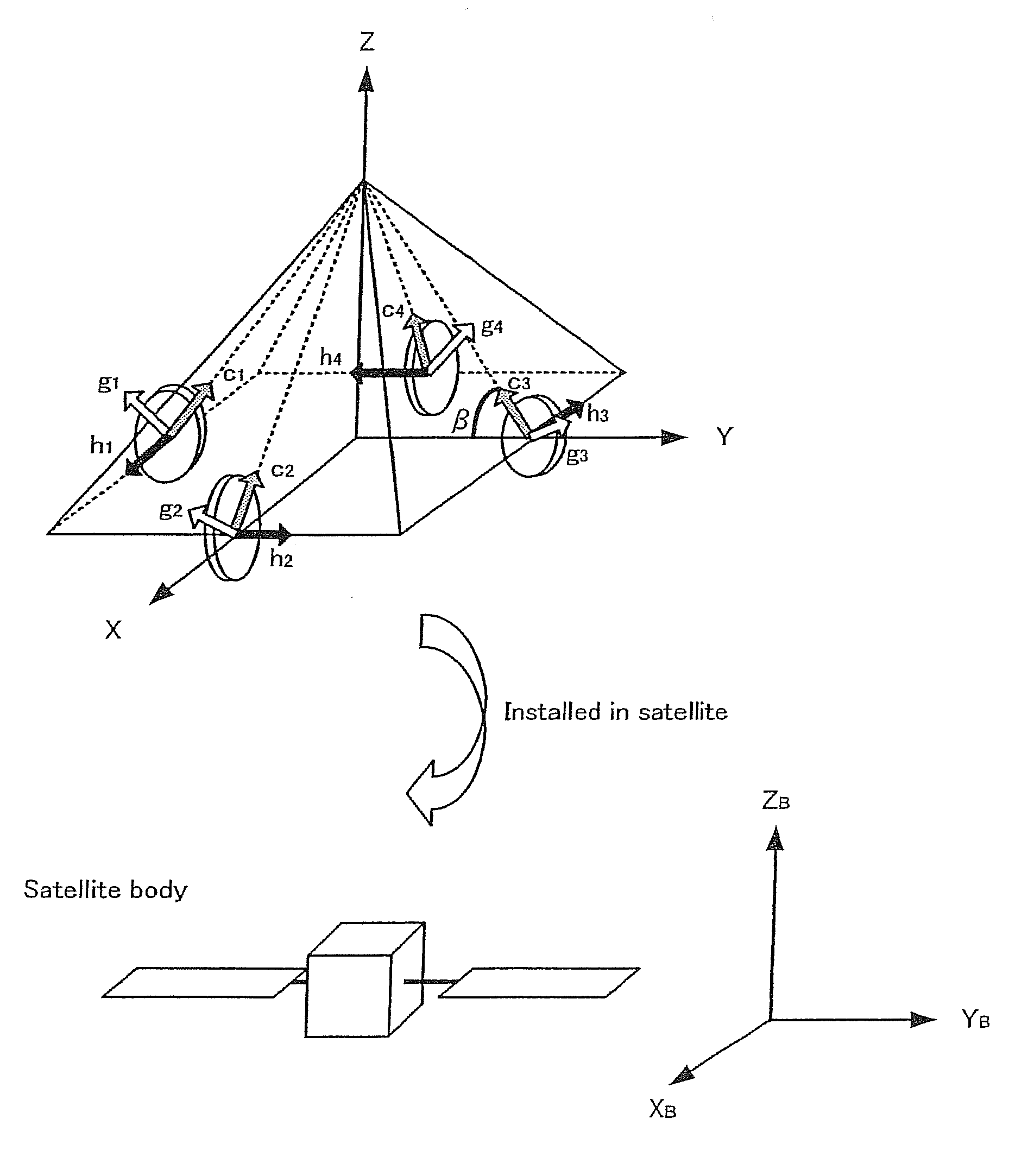
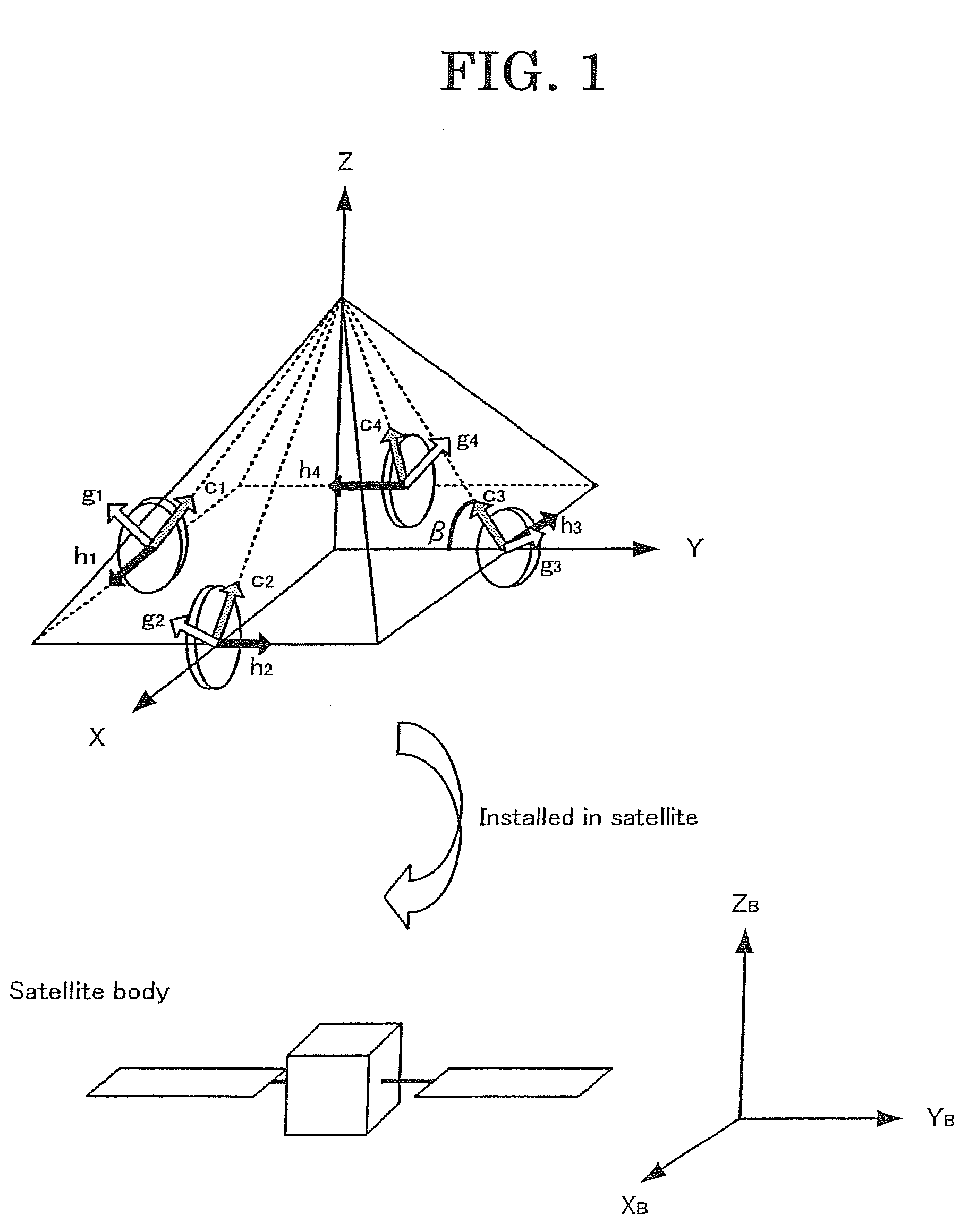
Disclosed is an attitude change control system that is designed to efficiently output a torque for attitude change of a space craft using CMGs and realizes a real time CMG driving rule. A CMG gimbal steering law 15 generates target profiles for setting angle and angular velocity for each gimbal by applying an anisotropic weighted gradient method based upon the necessary torque calculated by a feed back controller 13 and a feed forward controller 14 from the angle and angular velocity in the target direction from the attitude navigator 12 and the current angle and angular velocity of the space craft estimated by the attitude estimator 11 as well as the current condition of each gimbal from the CMG 40, thereby controlling the CMG 40 for changing the attitude of the space craft dynamics 50 to the target direction.
Owner:NEC TOSHIBA SPACE SYST
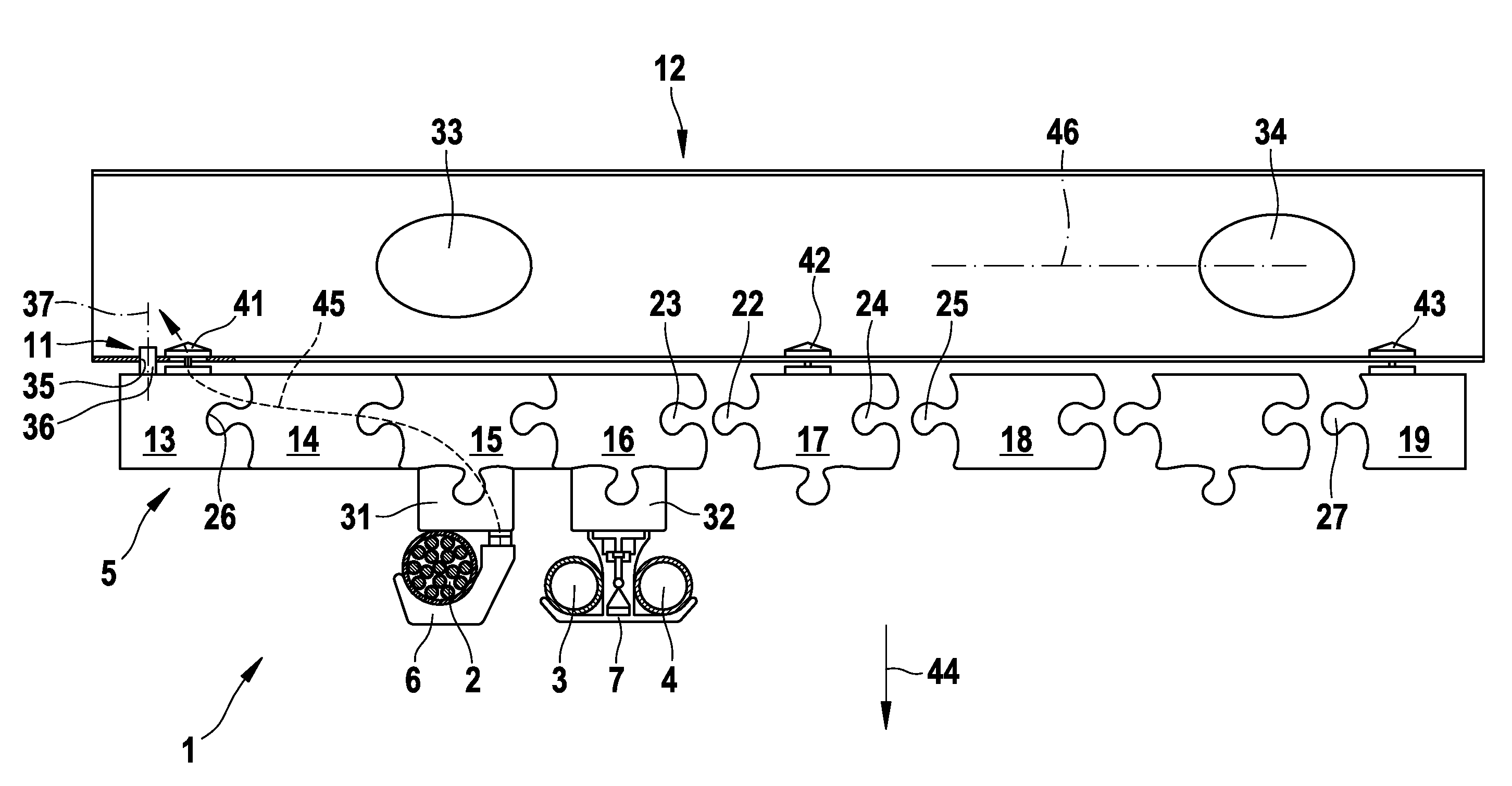
Space micro generation module integrating light, temperature difference and thermal ion electric conversion into one body
InactiveCN1716749AEasy to manufactureProduction is feasiblePV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationMicro cellEngineering
The present invention provides one micro space generation module with photoelectric converter, thermoelectric converter and plasma-to-electricity converter integrated together, and the module has deposited photoelectronic film and hot ion emitting film, semiconductor photoelectronic element and other micro cell module units. The micro space generation module can realize excellent stepped energy utilization and may be used in various fields, especially as the high efficiency and long life cell for micro space craft and other effective load after being provided with isotope fuel. It may be used in desert and other places with rich solar energy, and may be miniaturized for use in micro electromechanical system.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Model space craft glider
InactiveUS6435932B1Promote effective stabilityIncreasing side profile areaToy aircraftsFlight vehicleFuselage
A model space vehicle having a fixed circular wing, streamlined fuselage, fins with booms attached thereto all efficiently configured to result in an article possessing suitable aerodynamic properties to enable it to glide smoothly through the air for a substantial period of time and substantial distance relative to its size and weight.
Owner:LYNN ANTHONY
Attitude and orbit control method based on fore and after arrangement of engine
ActiveCN101758933AHas a positionCapable of attitude controlSpecial data processing applicationsSpacecraft guiding apparatusAttitude controlOrbit
The invention provides an attitude and orbit control method based on fore and after arrangement of an engine. In the method, the front end and the rear end of a spacecraft are respectively provided with a translation engine; starting-up of the engines is combined to control the position and attitude of the spacecraft at the transverse moving direction, pitching direction and yawing direction of the spacecraft respectively. According to the barycentre position of the spacecraft, startup factor ki1 of positions of the front and rear engines is calculated by the translating control force according to a principle that magnitudes and directions of thrust generated by the front and rear engines at the same direction of the spacecraft are the same as the requirement of control force, and the magnitudes of torques generated by the front engine and the rear engine are the same; startup factor ki2 of attitudes of the front engine and the rear engine is calculated by the attitude control torque requirement according to the principle that the magnitudes and directions of torques generated by the front and rear engines at opposite directions of the space craft are the same as the control torque requirement, and the magnitudes of the thrust generated by the front and rear engines at the opposite directions are the same; and finally, the total startup factor ki equaling to ki1 plus ki2 of the translation engines are calculated, and the engine is started to complete attitude and orbit control after normalization processing.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Process and device for coating silver on molybdenum foil used for solar cell paddle of aerospace aircraft
InactiveCN101393947AElectric discharge tubesFinal product manufactureSolar cellBiological activation
The invention relates to a silver electroplating technology for molybdenum foils used for panel substrate interconnecting flakes of solar cells of a space craft. The technology comprises the steps of molybdenum foils buffing and degreasing treatment, acid cleaning activation treatment, silver metal plasma injection, high temperature annealing treatment, silver leaching treatment, silver electroplating, EDS testing on the constituents of an electroplated layer, shape and morphology SEM observation, passivation for the electroplated molybdenum foils, and testing on the conductibility and the weldability of the electroplated molybdenum foils. The vacuum metal plasma injection technology provided by the invention comprises the following steps: injecting metallic elements as per certain energy and dosage into the molybdenum foil interconnecting flake material processed by buffing, degreasing treatment and acid cleaning activation treatment; carrying out silver leaching treatment after vacuum high temperature annealing; and carrying out non-cyanide silver electroplating so as to achieve a silver plating layer on the molybdenum foils, which is characterized by seamlessness, fine and round crystal grains and dense structure. The passivation treatment for the electroplated molybdenum foils gives the silver plating layer the ability to prevent the silver plating layer from being corroded by sulfide. Meanwhile, the conductibility and the weldability of electroplated aluminum foils are greatly improved without being affected by the passivation treatment.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Spacecraft with extensible radiators
InactiveUS7036772B2View field is obstructedAvoid viewingCosmonautic environmental control arrangementCosmonautic vehiclesOmnidirectional antennaEngineering
The invention concerns a space craft, such as a telecommunication geostationary satellite, comprising a body, at least one main telecommunication antenna having a specific orientation relative to the body, at least a omnidirectional antenna having a field of view opposite to that of the main antennae and at least a radiator extensible by tilting about an axis linked to the craft body between a stowing position wherein it is pressed against the body and an extended position. The axis is positioned substantially in the plane of one surface of the body parallel to the orientation of the omnidirectional antenna and to the surfaces or the surface bearing the main antenna. The radiator tilts at an angle close to 180° from a position wherein it is pressed against one surface bearing a solar panel to a position wherein it extends substantially in the plane of the surface which bears it when it is stowed.
Owner:EADS ASTRIUM SAS
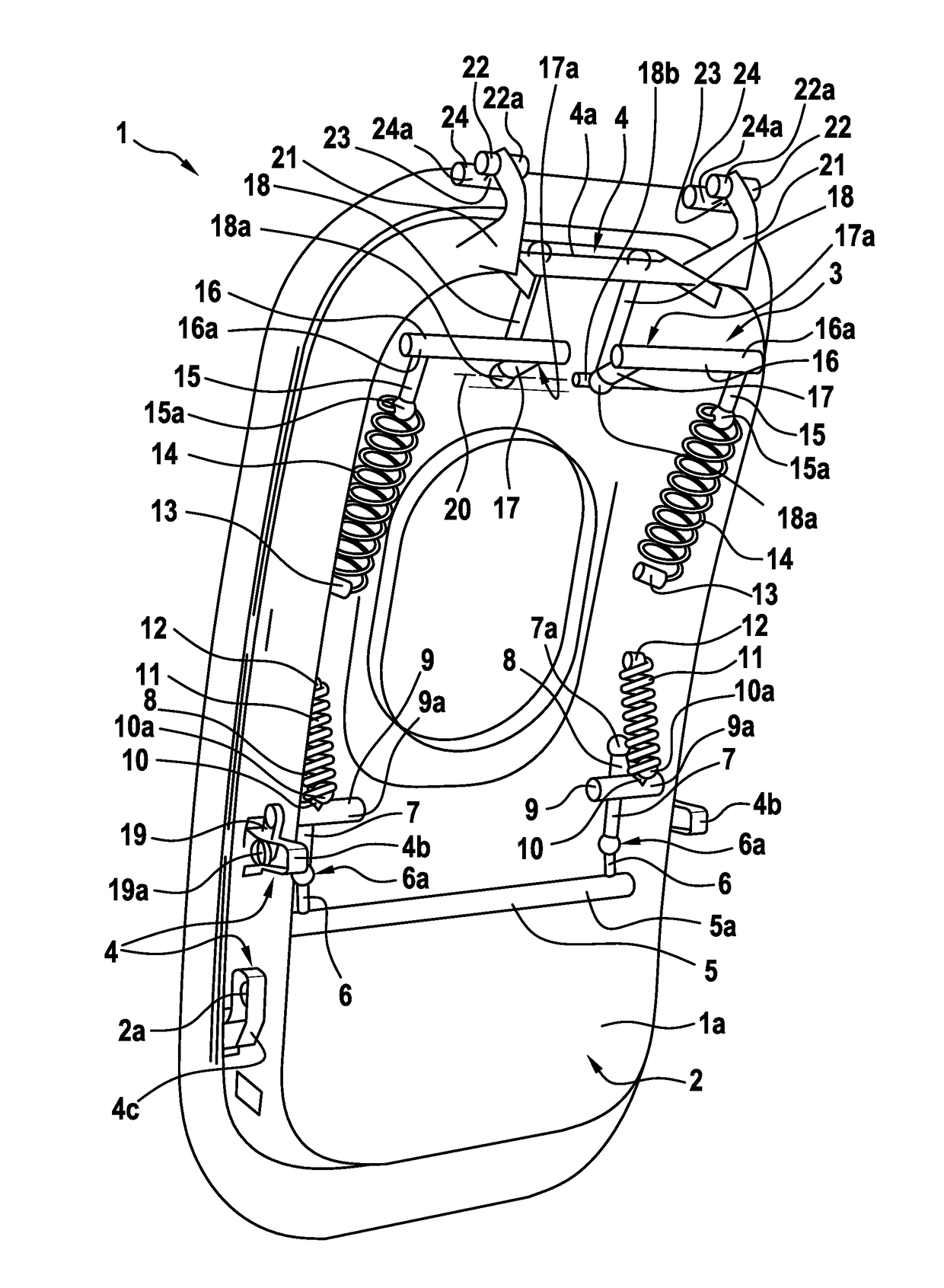
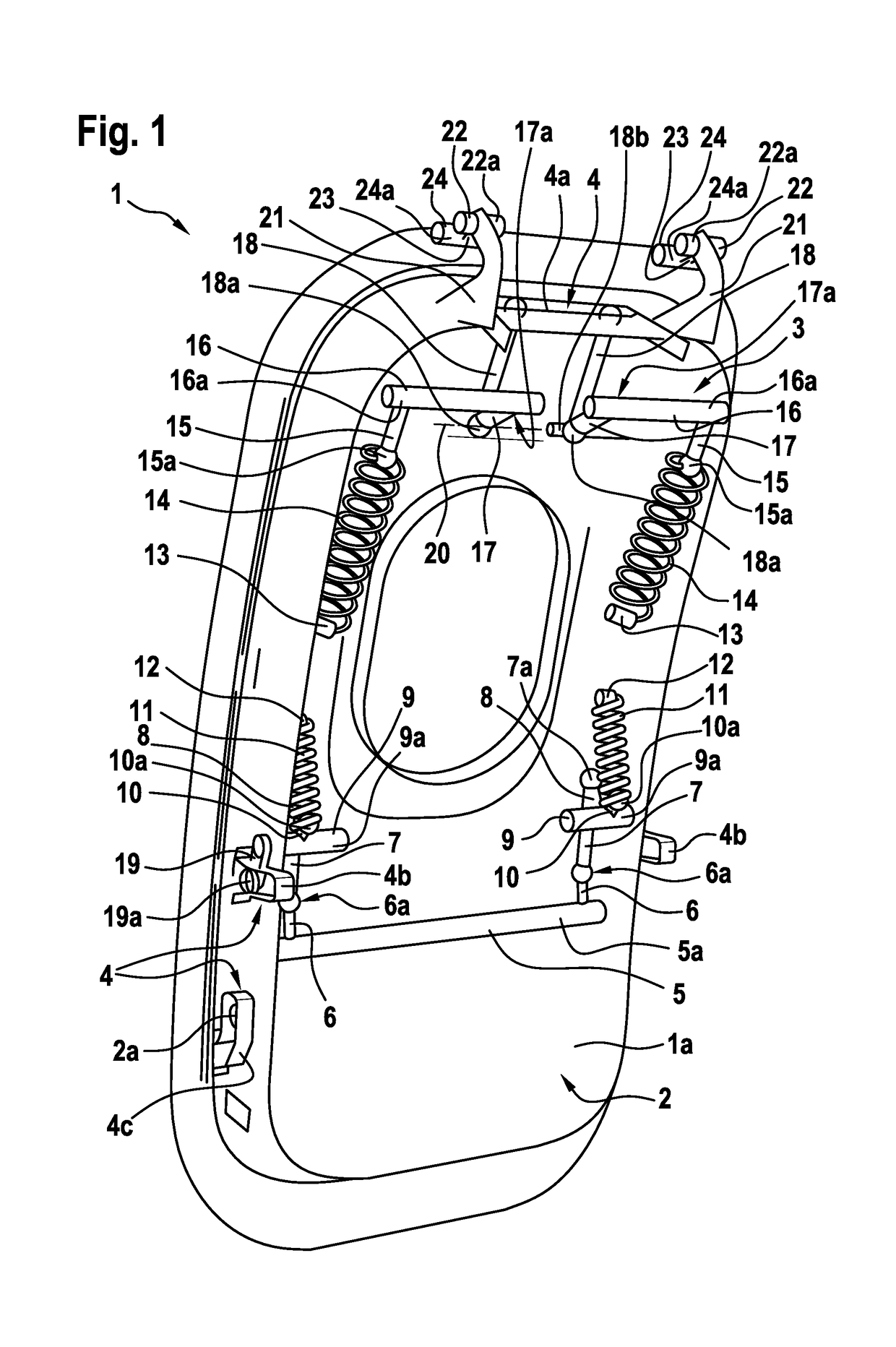
Actuatable emergency exit door and an aircraft or space craft with a pressurized cabin having such an actuatable emergency exit door
ActiveUS20180134366A1Low costReduce weightCosmonautic crew accomodationsAircraft doorsEmergency exitEngineering
An actuatable emergency exit door with a door actuating device that comprises at least two connection rods that are pivotally mountable to an associated structural frame that is adapted for accommodating the actuatable emergency exit door in closed state, the at least two connection rods being provided for enabling an opening movement of the actuatable emergency exit door with respect to the associated structural frame during opening, wherein at least one door-mounted goose neck-shaped structure is mountable to the associated structural frame for enabling an initial translational opening movement and subsequently a swiveling opening movement of the actuatable emergency exit door with respect to the associated structural frame during opening. The invention is further related to an aircraft or space craft with a pressurized cabin having such an actuatable emergency exit door.
Owner:AIRBUS HELICOPTERS DEUT GMBH
Heat storing and electricity generating device for wireless transmission of energy by laser
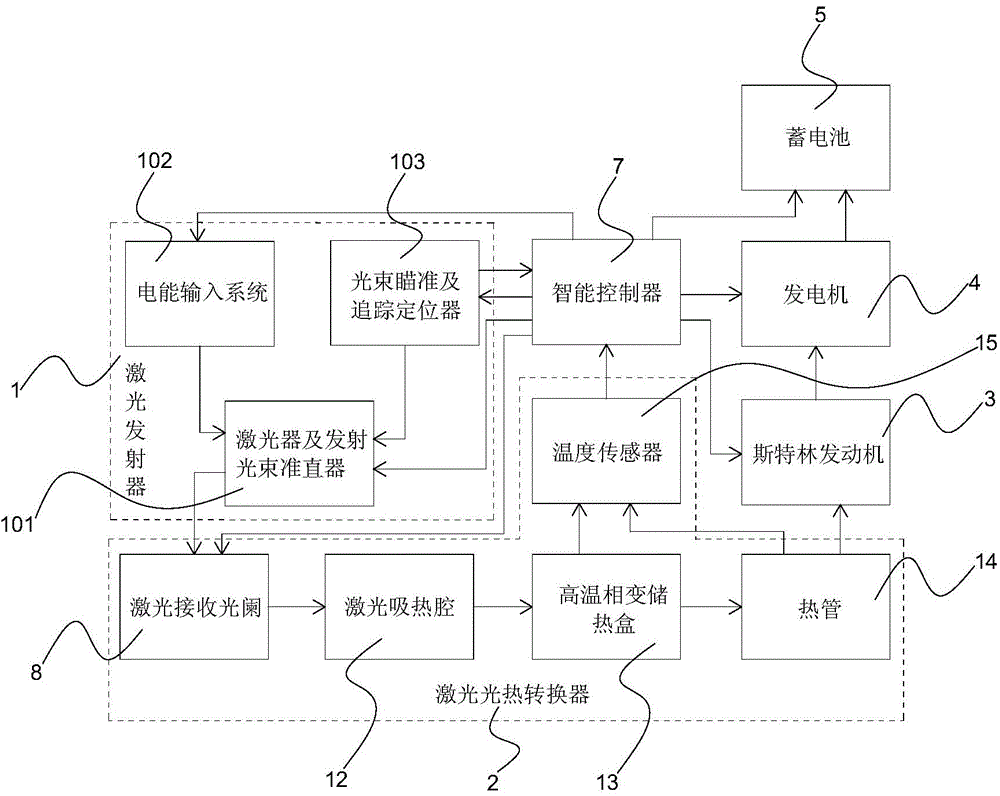
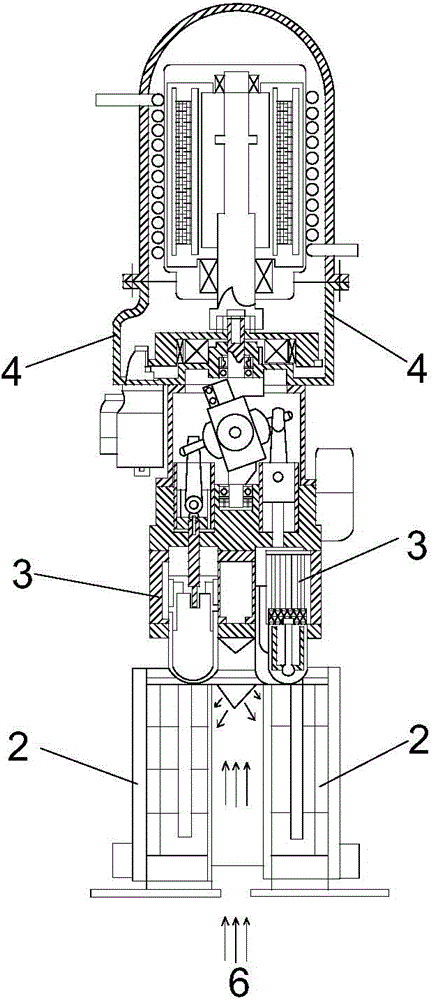
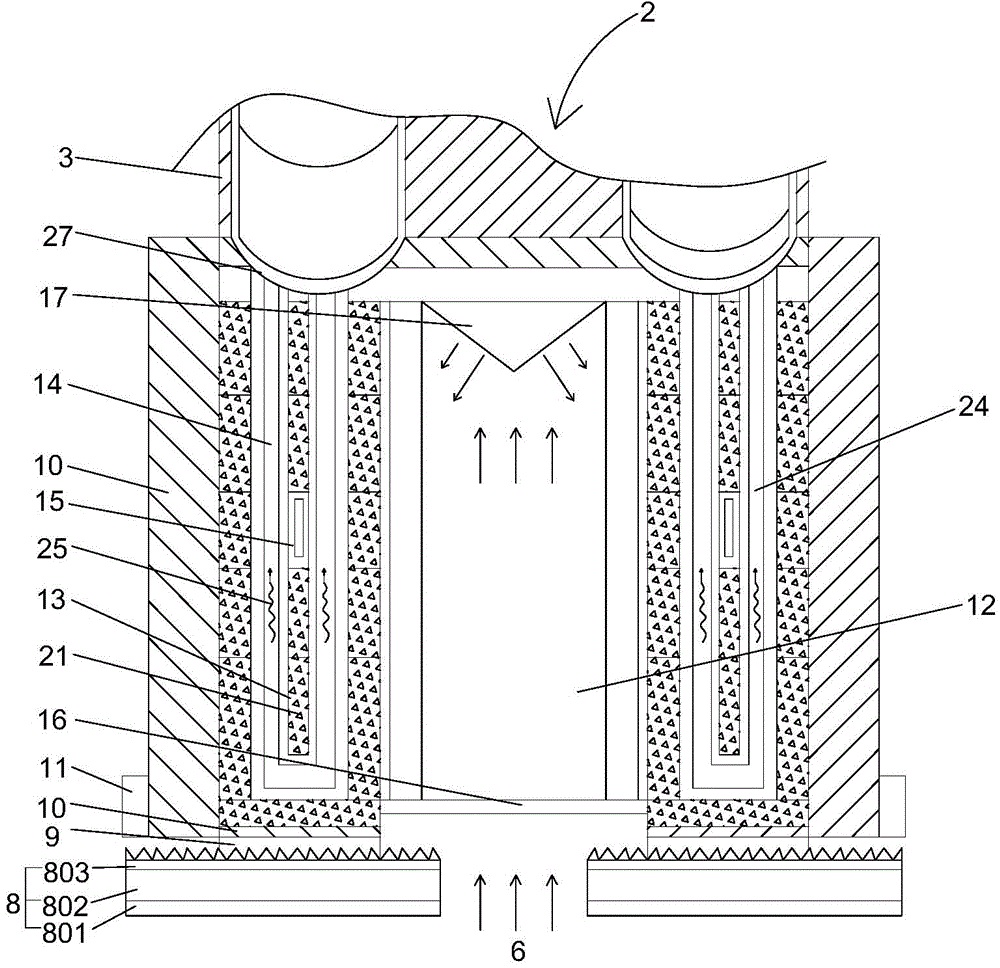
InactiveCN104696173AIncrease energy densityFast convergenceElectromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsLaser transmitterElectric power system
The invention relates to a heat storing and electricity generating device for wireless transmission of energy by a laser. The heat storing and electricity generating device comprises a laser transmitter, laser photo-thermal converters, Stirling engines, electricity generators, an accumulator and an intelligent controller, wherein each laser photo-thermal converter comprises laser receiving diaphragms, a laser heat absorbing cavity, high-temperature phase change heat storing boxes, heat pipes and temperature sensors; a laser beam generated by the laser transmitter penetrates through the laser receiving diaphragms to enter the laser heat absorbing cavity, and heat is transferred to the high-temperature phase change heat storing boxes by the laser heat absorbing cavity; the heat pipe is connected with the hot ends of the Stirling engines, and the Stirling engines are connected with the electricity generators. The heat storing and electricity generating device disclosed by the invention can be used for a space solar power station and an electrical power system for transmitting energy to the ground in a wireless manner, the heat storing and electricity generating device can be applied to wireless transmission of air-to-ground, air-to-air and ground energy, wireless energy transmission between satellites, wireless energy transmission between space crafts, space shuttles and airships and wireless energy transmission between unmanned aircrafts, unmanned vehicles, unmanned ships and warships and robots.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Attitude change control method, attitude change control system, attitude change control program and program recording medium
ActiveUS20080203230A1Efficient outputCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsControl systemAngular velocity
Disclosed is an attitude change control system that is designed to efficiently output a torque for attitude change of a space craft using CMGs and realizes a real time CMG driving rule. A CMG gimbal steering law 15 generates target profiles for setting angle and angular velocity for each gimbal by applying an anisotropic weighted gradient method based upon the necessary torque calculated by a feed back controller 13 and a feed forward controller 14 from the angle and angular velocity in the target direction from the attitude navigator 12 and the current angle and angular velocity of the space craft estimated by the attitude estimator 11 as well as the current condition of each gimbal from the CMG 40, thereby controlling the CMG 40 for changing the attitude of the space craft dynamics 50 to the target direction.
Owner:NEC CORP
Fan, airfoil and vehicle propulsion systems
InactiveUS20100150714A1Preferred liftPreferred thrustCircumferential flow pumpsPump componentsAviationJet aeroplane
Vehicle propulsion systems and methods of propulsion are disclosed, as well as embodiments of fans and airfoils, technology that in some applications of the invention can provide both lift and thrust, and propulsion via cross flow fan, manifold and a plurality of airfoils. In some embodiments the invention is directed to the production of lift and thrust, and propulsion generally, based from air produced by a cross flow fan in accordance with the invention disclosed herein. In still further embodiments, lift and thrust may yet be generated from air produced from the cross flow fan even when unpowered, such as in a loss of power or in a stall condition. Applications of the invention apply broadly to propulsion systems, generally; however, some preferred embodiments have particular application for vehicles characterized or used in application such as traditional private and commercial aircraft, ground effects vehicles, military applications, amphibious applications, aerospace, aeronautical, and non-traditional vehicles such as experimental air planes, space craft, hover craft, and the like. The invention in some embodiments comprises technologies addressing preferred air flow, lift, and thrust and the reduction of drag and circulation losses. The invention may be further applicable for incorporation in aircraft and other vehicles wherein the ability to maximize initial vertical lift and takeoff is important, such as in instant take-off and landing, as well as the abilities to hover, to control the flight and landing of aircraft, and control in power-loss scenarios, addressing the prevention of stalls and allowing for controlled descents under continued propulsion. In some embodiments, the invention is further applicable for aircraft, shuttles and other vehicles as a ram jet engine system as a further alternative propulsion technology, having no requirement for forward movement for propulsion upon take-off.
Owner:KOLACNY GORDON S +1
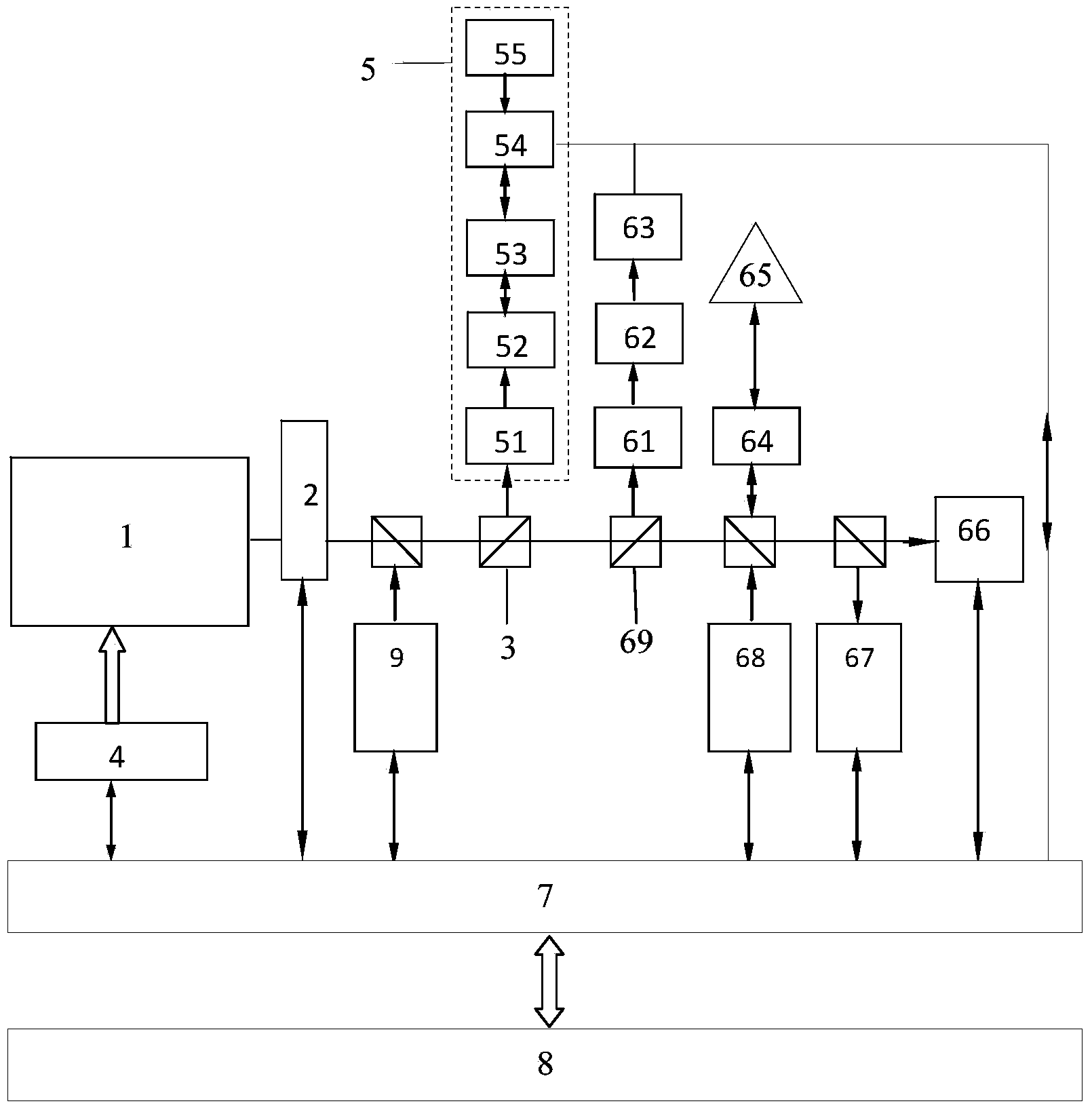
System for direct communications with a space craft
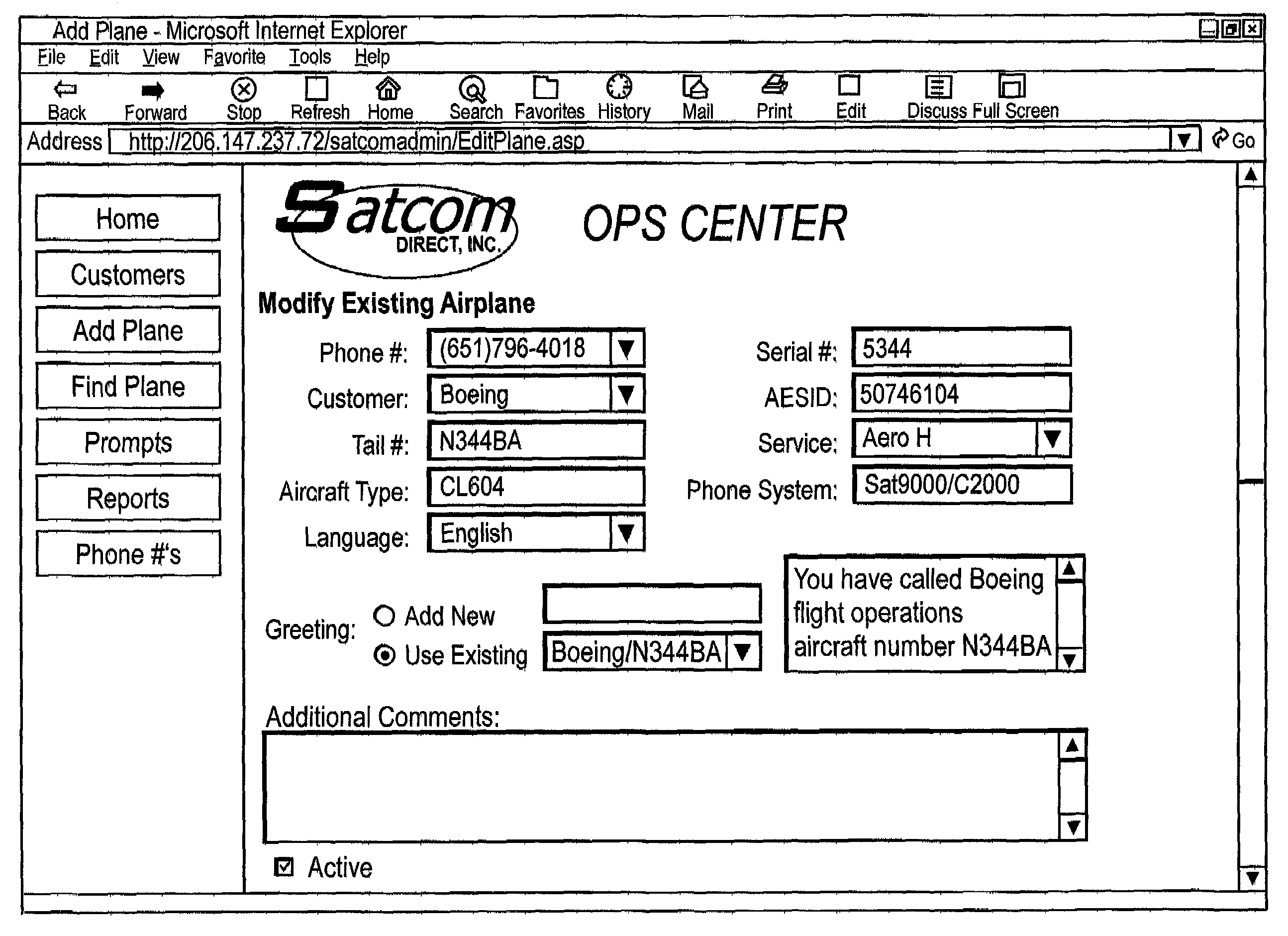
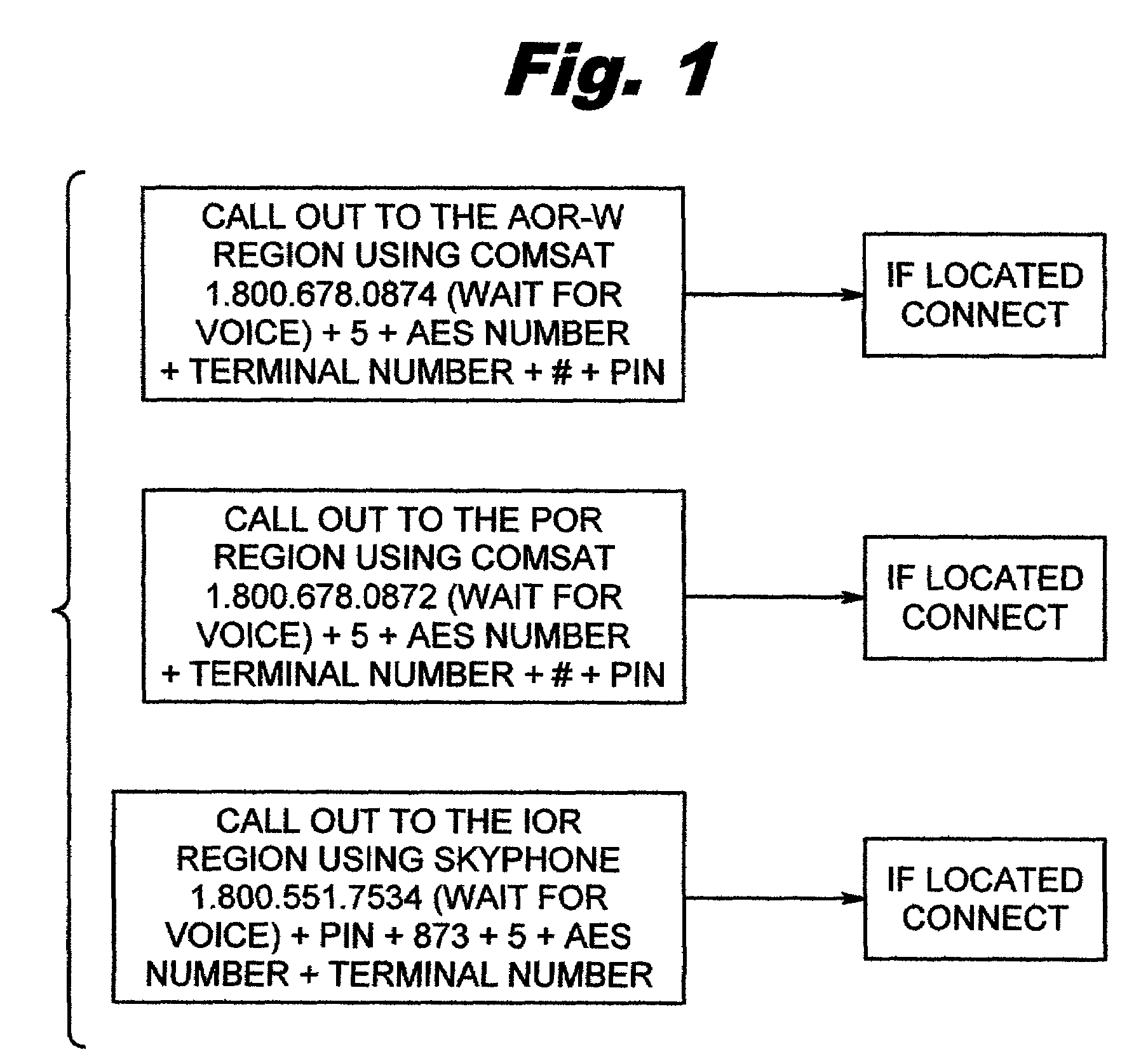
InactiveUS6970704B2Efficient and reliable communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionCommunications systemDirect communication
An automated communication system for communicatively connecting a caller with a communications device to an space craft. The system includes a port for accepting a call and a call management program that uses a spacecraft identifier to automatically effect the communication to the space craft via a ground earth station and a satellite. The satellite retransmits the communication to a dedicated spacecraft receiver in the space craft. The system provides Internet-based call monitoring and billing capabilities. The system reduces cost and overall connection time by using the Internet to verify the spacecraft's flying status through the ground station databases before initiating a call.
Owner:SATCOM DIRECT
Space micro generation module integrating light, temperature difference and thermal ion electric conversion into one body
InactiveCN100593281CRealize cascade utilizationImprove efficiencyPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationMicro cellEngineering
The present invention provides one micro space generation module with photoelectric converter, thermoelectric converter and plasma-to-electricity converter integrated together, and the module has deposited photoelectronic film and hot ion emitting film, semiconductor photoelectronic element and other micro cell module units. The micro space generation module can realize excellent stepped energy utilization and may be used in various fields, especially as the high efficiency and long life cell for micro space craft and other effective load after being provided with isotope fuel. It may be usedin desert and other places with rich solar energy, and may be miniaturized for use in micro electromechanical system.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fan, airfoil and vehicle propulsion systems
InactiveUS8157520B2Preferred liftPreferred thrustCircumferential flow pumpsPump componentsAviationJet engine
Vehicle propulsion systems and methods of propulsion are disclosed, as well as embodiments of fans and airfoils, technology that in some applications of the invention can provide both lift and thrust, and propulsion via cross flow fan, manifold and a plurality of airfoils. In some embodiments the invention is directed to the production of lift and thrust, and propulsion generally, based from air produced by a cross flow fan in accordance with the invention disclosed herein. In still further embodiments, lift and thrust may yet be generated from air produced from the cross flow fan even when unpowered, such as in a loss of power or in a stall condition. Applications of the invention apply broadly to propulsion systems, generally; however, some preferred embodiments have particular application for vehicles characterized or used in application such as traditional private and commercial aircraft, ground effects vehicles, military applications, amphibious applications, aerospace, aeronautical, and non-traditional vehicles such as experimental air planes, space craft, hover craft, and the like. The invention in some embodiments comprises technologies addressing preferred air flow, lift, and thrust and the reduction of drag and circulation losses. The invention may be further applicable for incorporation in aircraft and other vehicles wherein the ability to maximize initial vertical lift and takeoff is important, such as in instant take-off and landing, as well as the abilities to hover, to control the flight and landing of aircraft, and control in power-loss scenarios, addressing the prevention of stalls and allowing for controlled descents under continued propulsion. In some embodiments, the invention is further applicable for aircraft, shuttles and other vehicles as a ram jet engine system as a further alternative propulsion technology, having no requirement for forward movement for propulsion upon take-off.
Owner:KOLACNY GORDON S +1
Method for coupling stiffening profile elements and structural component
ActiveUS8715808B2Reliable quality controlEnhanced couplingFuselage framesCellulosic plastic layered productsCouplingEngineering
This invention provides a coupling method for coupling a first and a second stiffening profile element for an outer skin of an aircraft or space craft. In a first step the stiffening profile elements are arranged on the outer skin in such a manner that the stiffening profile elements oppose each other with their respective front sides and enclose within themselves a cavity. Furthermore, a fixing hole is formed through a wall of at least one of the stiffening profile elements in the cavity inside a coupling zone of the stiffening profile element. An access opening is formed through the wall in the cavity along the coupling zone. A coupling strap, which couples the stiffening profile elements together, is fastened to the coupling zone by means of a fastening element guided through the fixing hole.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
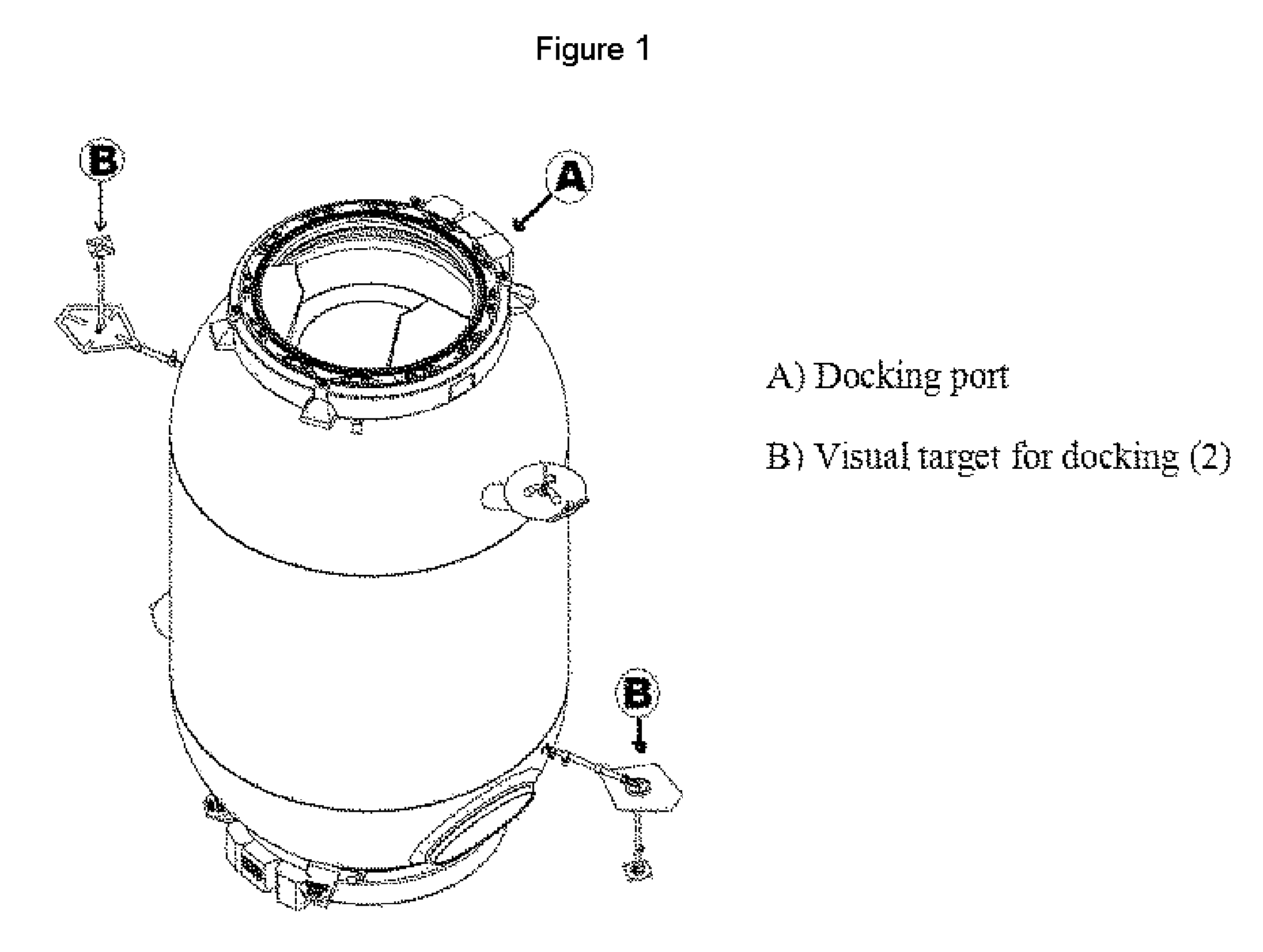
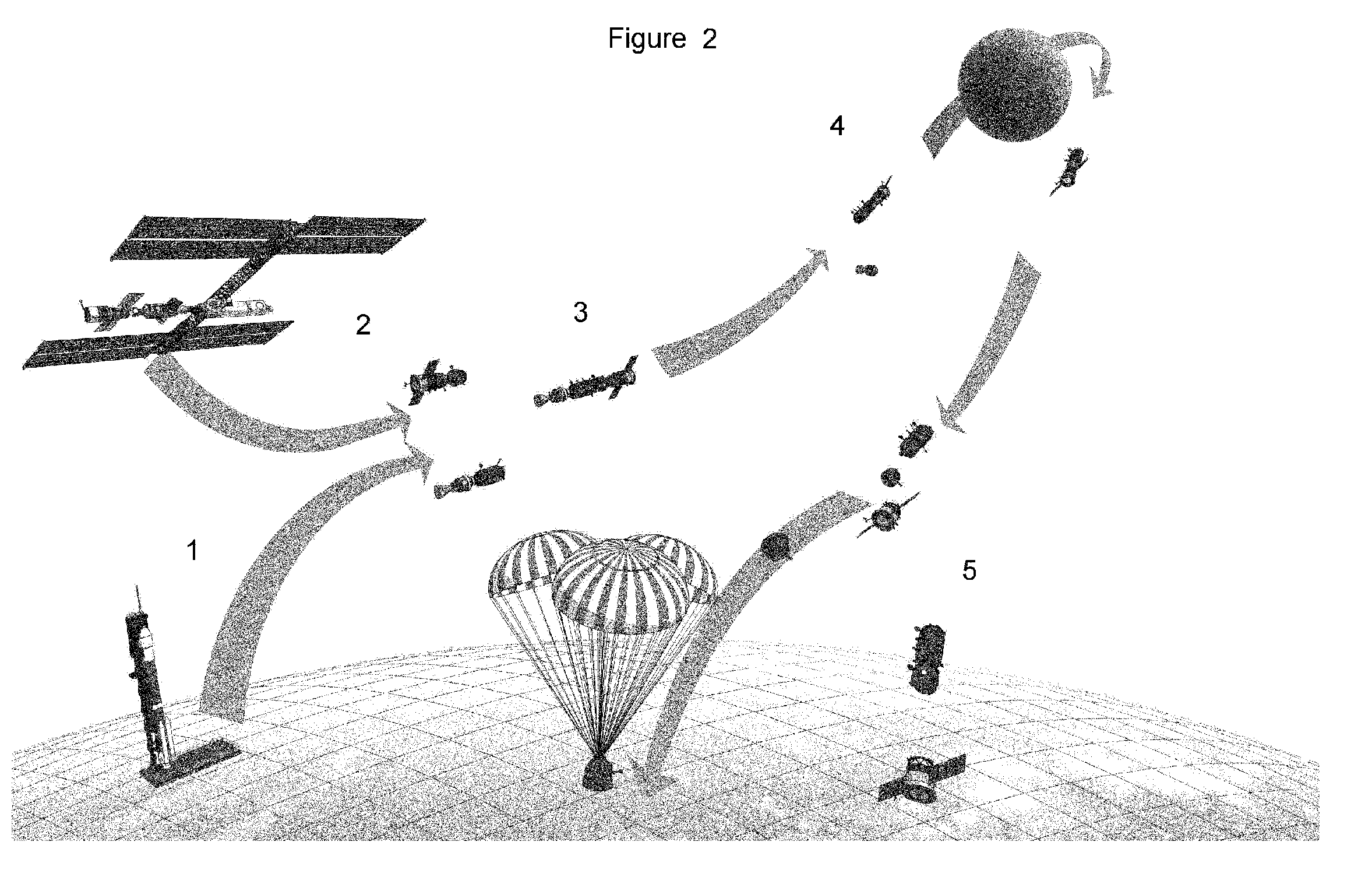
Method and apparatus for utilizing a lifeboat for a space station in earth orbit to serve as a lunar spacecraft
InactiveUS7392964B1Low costVast supplyLaunch systemsCosmonautic thermal protectionFlight vehicleEngineering
Methods and an apparatus for a lifeboat of a space station in orbit to be docked with and used in combination with a separately launched logistics module having an upper stage propulsion capability as a space craft for human pilots and passengers to be flown to orbits and trajectories in deep space beyond low Earth orbit including the Moon, at the lowest practical cost.
Owner:ANDERMAN DAVID
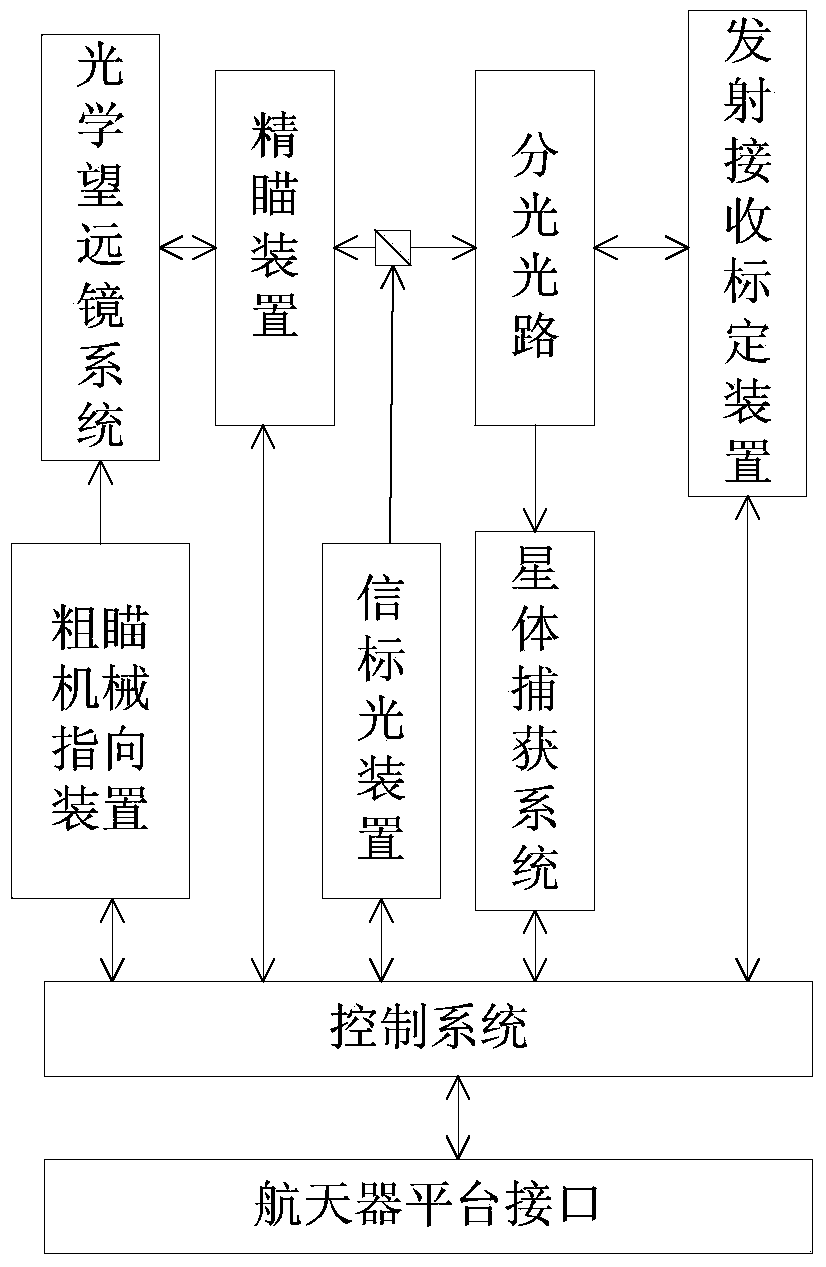
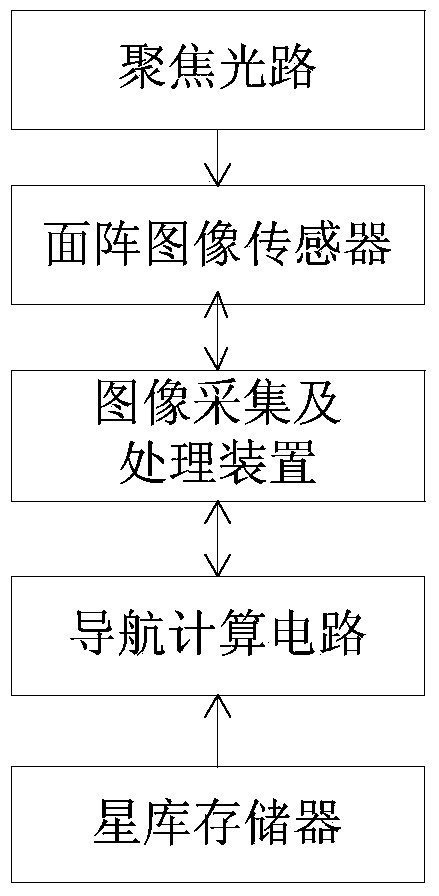
Autonomous navigation system and autonomous navigation method thereof based on laser space communication transceiver
InactiveCN104296754AReduce volumeReduce weightInstruments for comonautical navigationNatural satelliteFixed stars
The invention discloses an autonomous navigation system and an autonomous navigation method thereof based on a laser space communication transceiver. Based on the traditional laser space communication transceiver, a star capturing system is added, so that fixed stars and planets or satellites thereof can be recognized and the azimuth information can be obtained; by calculating the included angle among the fixed stars-space crafts-planets (or planets thereof), the position information of the space crafts can be obtained finally so as to achieve the navigation process. The laser space communication transceiver can obtain the navigation information without a set of additional autonomous navigation device, so that the relevant research, development, launch and running expense is saved, and the volume, weight and power consumption of the effective load of the aircrafts are reduced; the integral performance of the autonomous navigation system is improved; approximate real-time flight track correction is provided for deep space exploration according to the navigation result, so that not only can the signal round-trip delay between satellites and the ground be eliminated, but also ground data processing can be omitted.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
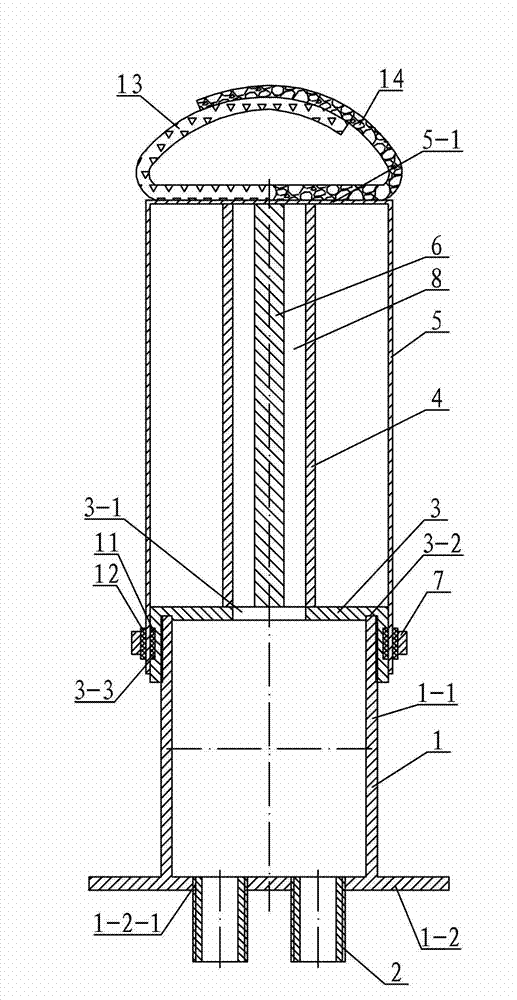
Rapidly-inflatable-deployment thin-film support tube for space craft
ActiveCN102887234ARealize large-scaleStable and firmCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsDeployment timeEngineering
The invention discloses a rapidly-inflatable-deployment thin-film support tube for a space craft, and relates to an inflatable-deployment thin-film support tube for a space craft, for solving the problems of high self-weight, limit on the length after deployment, and long deployment time of the present inflatable-deployment thin-film support tube for a space craft due to a mechanical deployment structure. According to the invention, an upper end cover is arranged at the upper end of a barrel body and in threaded connection with the barrel body; an airflow guide tube is vertically arranged at the centre of the upper end surface of the upper end cover; the inner cavity of the airflow guide tube is connected with an air vent; one end of a folding thin-film tube is sleeved on the upper end cover; one end of the folding thin-film tube is fastened with the upper end cover via a hoop, and the other end of the folding thin-film tube is a closed-type top; a direction indicator is vertically arranged on the inner wall of the closed-type top; the section shape of the direction indicator is fitted with the section shape of the inner cavity of a direction indicator guide tube; at least three connection tubes are arranged on the outer end surface of a flange; and each lower thread hole is in threaded connection with one connection tube. The rapidly-inflatable-deployment thin-film support tube disclosed by the invention is used for supporting various micro cameras and various magnetometers on satellite detectors and lunar detectors.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Device for supporting systems
ActiveUS8534624B2Cost efficientLow production costCandle holdersLighting support devicesSupporting systemFlight vehicle
The present invention relates to a device for supporting systems, for example an electric cable or a fluid-carrying pipe, on a structure of an aircraft or space craft, and to an aircraft or space craft with such a device. The device has a basic bracket arrangement which can be fastened to at least one predetermined fastening section of the structure, and also has at least one system bracket for supporting the systems. The at least one system bracket can be fastened to the basic bracket arrangement locationally variable with respect to the fastening section. The advantage of the invention consists in the fact that a route of a system can be flexibly varied even during the equipment assembly, i.e. the structure is no longer modifiable or is only modifiable at considerable expense.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com