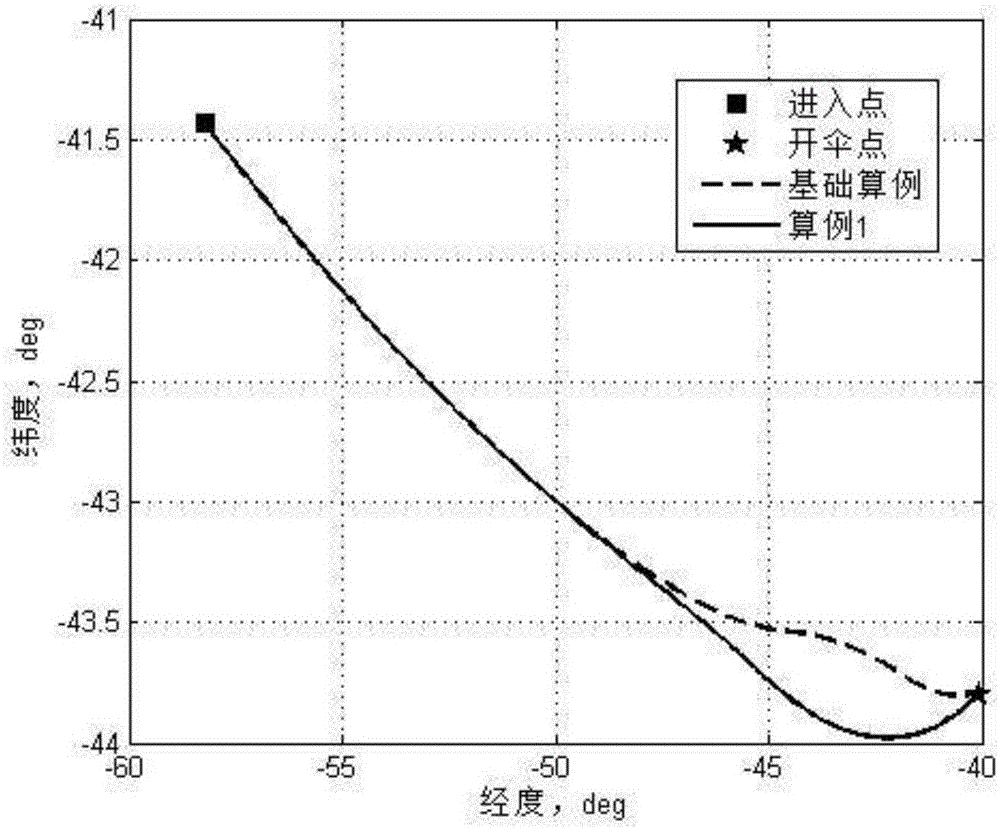
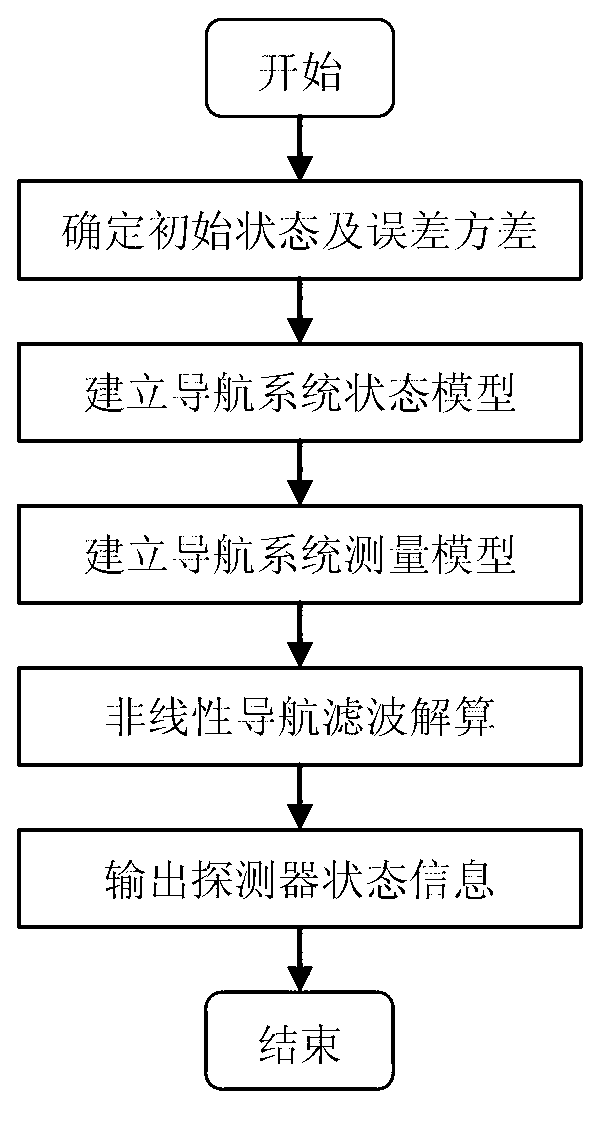
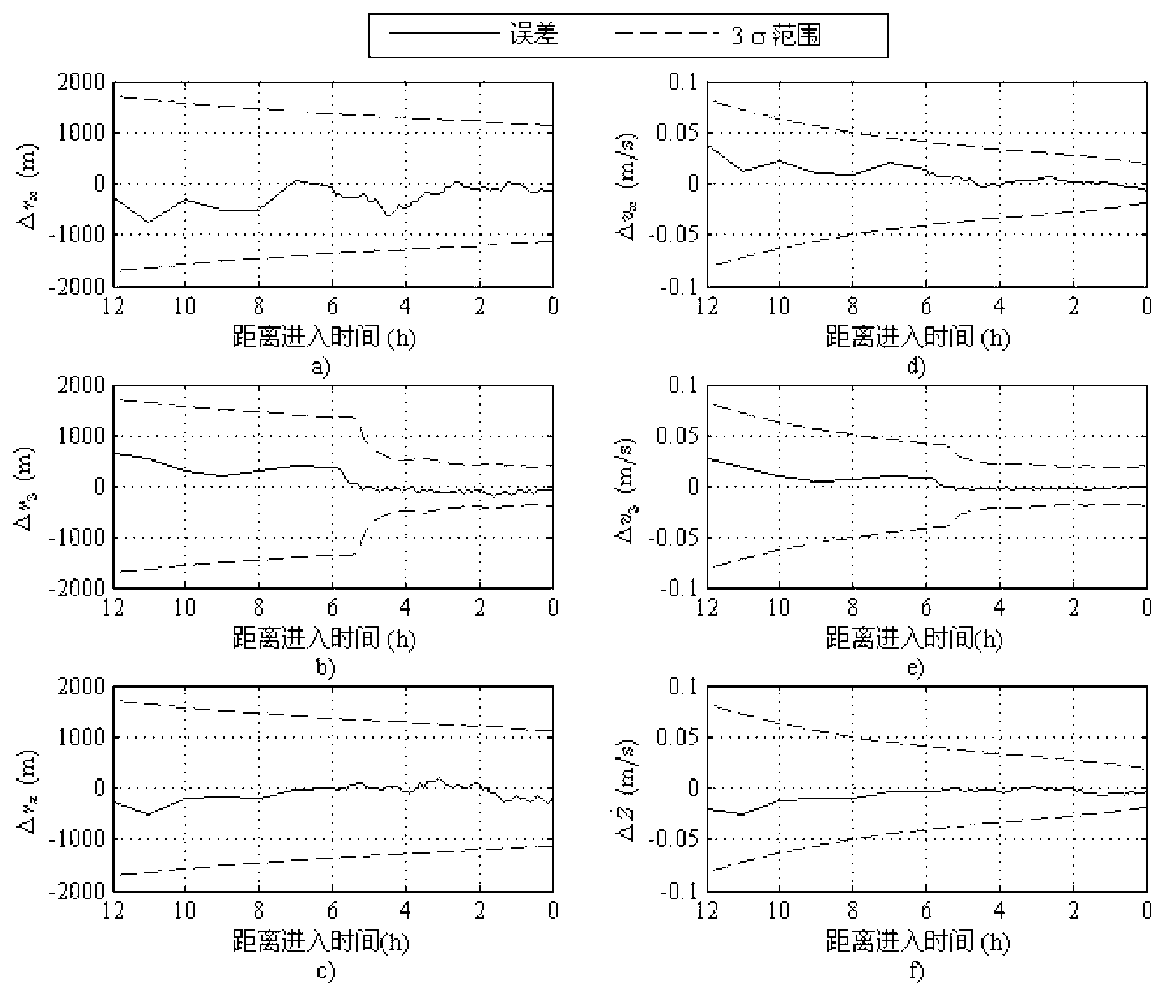
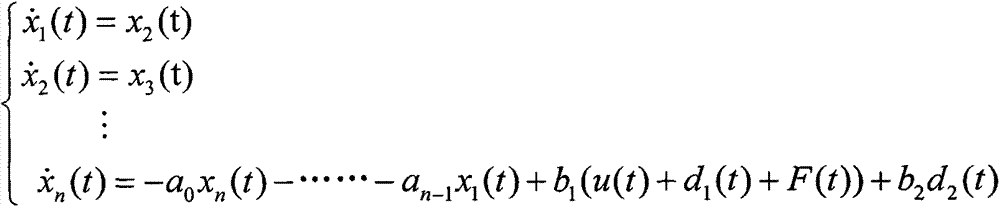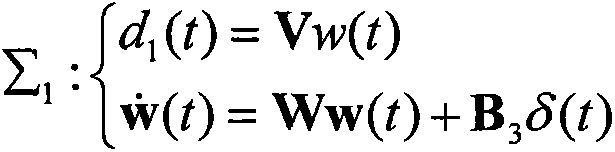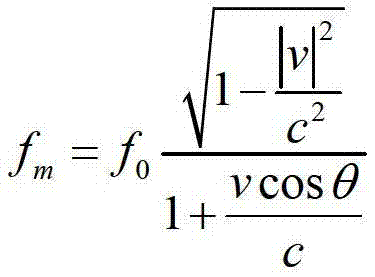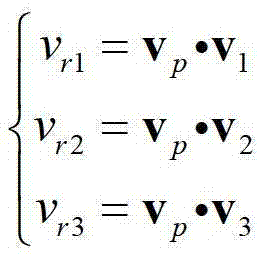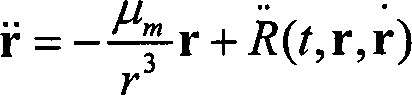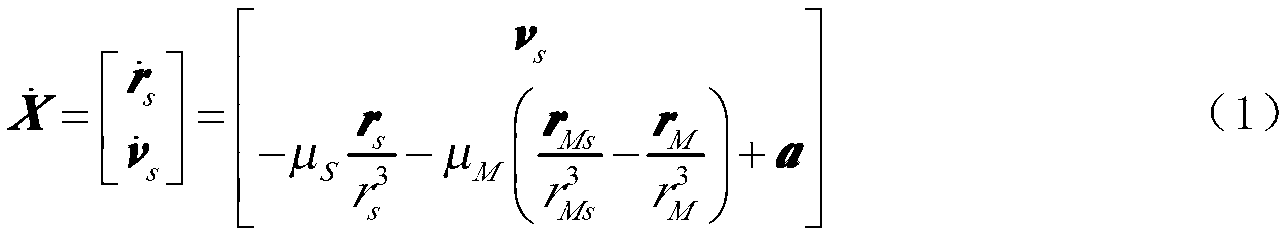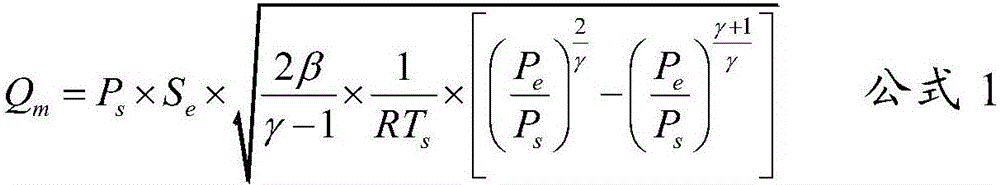Patents
Literature
584 results about "Deep space exploration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Deep space exploration (or deep-space exploration) is the branch of astronomy, astronautics and space technology that is involved with exploring the distant regions of outer space. However, there is little consensus on the meaning of "distant" regions. In some contexts, it is used to refer to interstellar space. The International Telecommunication Union defines "deep space" to start at a distance of 2 million km from the Earth's surface. NASA's Deep Space Network has variously used criteria of 16,000 to 32,000 km from Earth. Physical exploration of space is conducted both by human spaceflights (deep-space astronautics) and by robotic spacecraft.
Sliding-mode control method with anti-interference fault-tolerance performance
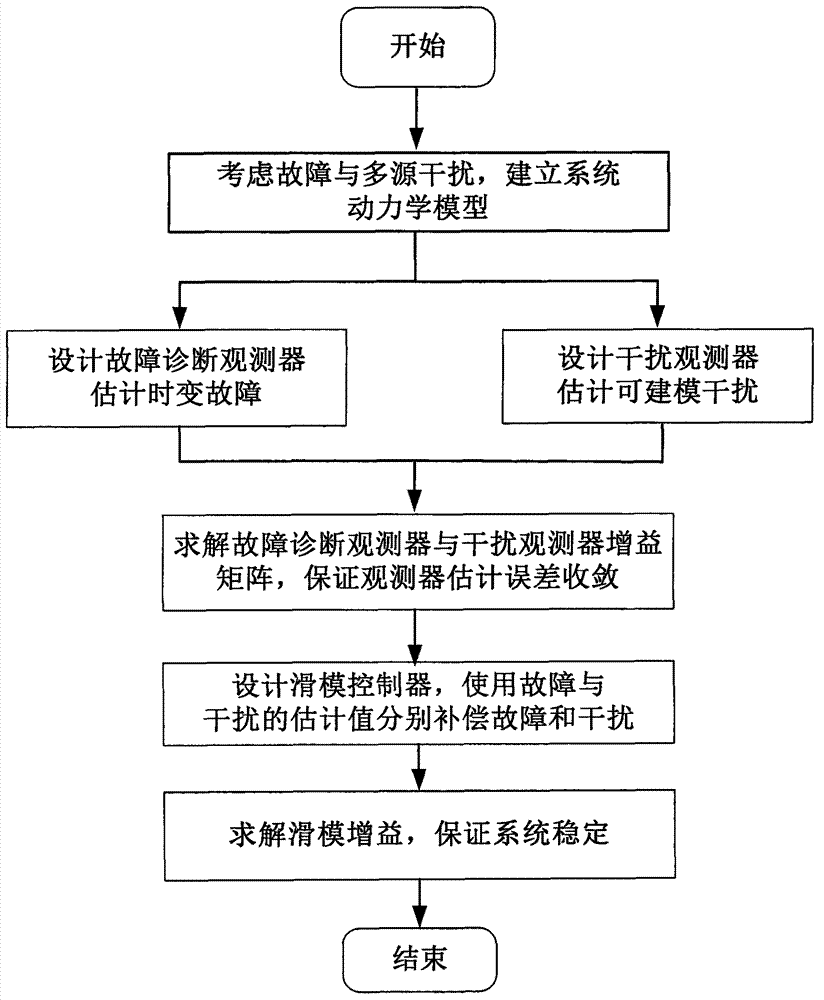
Provided is a sliding-mode control method with anti-interference fault-tolerance performance. A sliding-mode controller with anti-interference fault-tolerance performance is designed and is specific to a system containing faults and interferences. Firstly, faults and multi-source interferences in the system are considered, so that a dynamical model of the system is established. Secondly, a fault diagnosis observer and a disturbance observer are designed to estimate the faults and interferences capable of being modeled. Thirdly, the gain matrix of the disturbance observer and the fault diagnosis observer is solved. Then, the sliding-mode controller is designed to offset faults and interferences respectively by using the estimated value of faults and interferences. Finally, stability of the controller is analyzed and the sliding-mode yield value is determined on the premise that the system input is saturated. According to the sliding-mode control method with anti-interference fault-tolerance performance, the anti-interference and fault-tolerance performance of the system are guaranteed, the buffeting of the sliding-mode control is improved, and the sliding-mode control method can be applied to the attitude control system of the fields of aviation, aerospace and deep space exploration.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
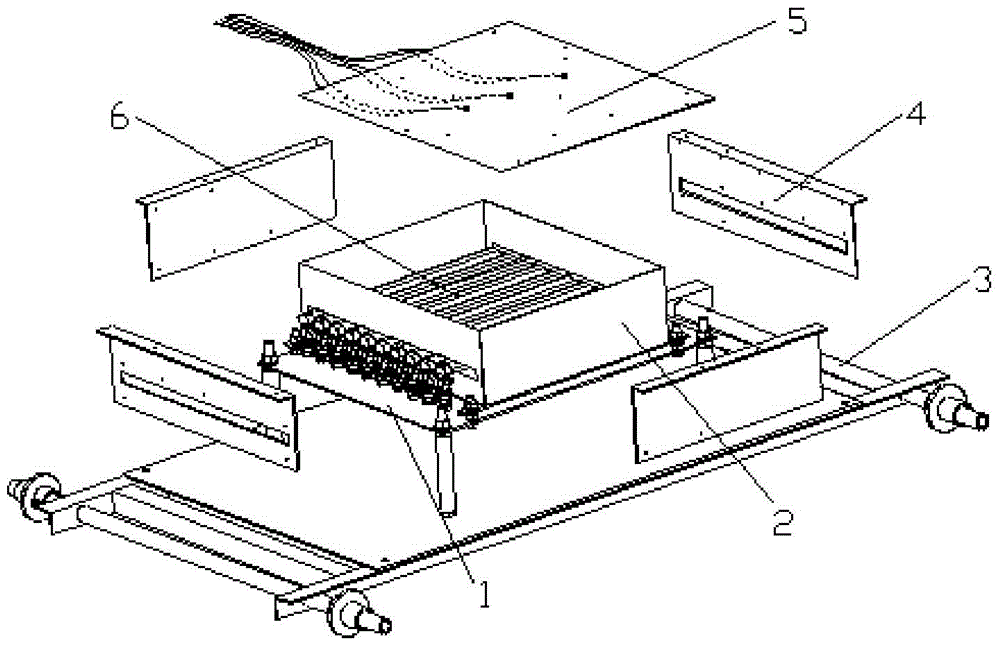
High heat flow simulator for spacecraft vacuum heat tests
InactiveCN103600851ASolve high temperatureSolve the technical difficulties of high heat flow simulationCosmonautic condition simulationsAircraft components testingHeat fluxInfrared lamp
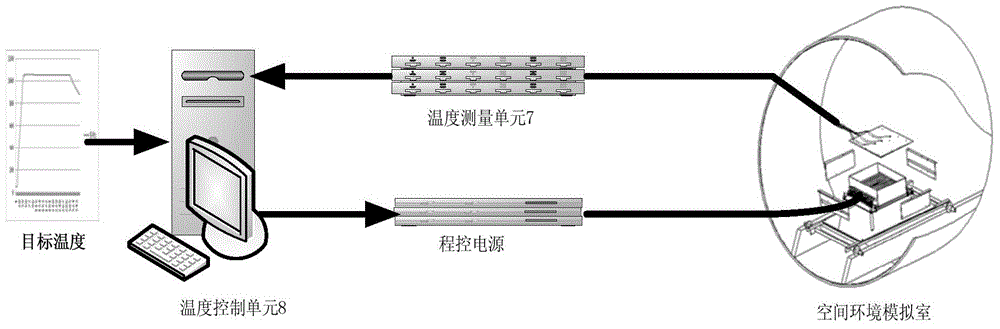
The invention discloses a high-temperature high heat flow simulator for spacecraft vacuum heat tests in a space environment simulating chamber. The simulator mainly comprises infrared light arrays, a high-temperature insulation component unit, moving units, a temperature measuring unit and a temperature controlling unit. A plurality of infrared lights in the infrared light arrays are provided with reflective screens, the infrared lights are arrayed and combined to form the infrared light arrays according to requirements of heat flux density and uniformity, baffles surround the periphery of the infrared light arrays, high-temperature multi-layer insulation components are mounted among the infrared lights, a mounting baseplate and the baffles, and a high temperature region is limited in region formed through specimen irradiated face and the infrared light array high-temperature insulation components. According to the high-temperature high heat flow simulator, by means of unique design of the infrared light arrays and the high-temperature insulation components, technical difficulties of high-temperature high heat flow simulation when vacuum heat tests are performed on a spacecraft are solved, high-temperature high heat flow space environment can be simulated when vacuum heat tests are performed on spacecrafts in series of deep space exploration and space shuttles, and the spacecrafts can be tested.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
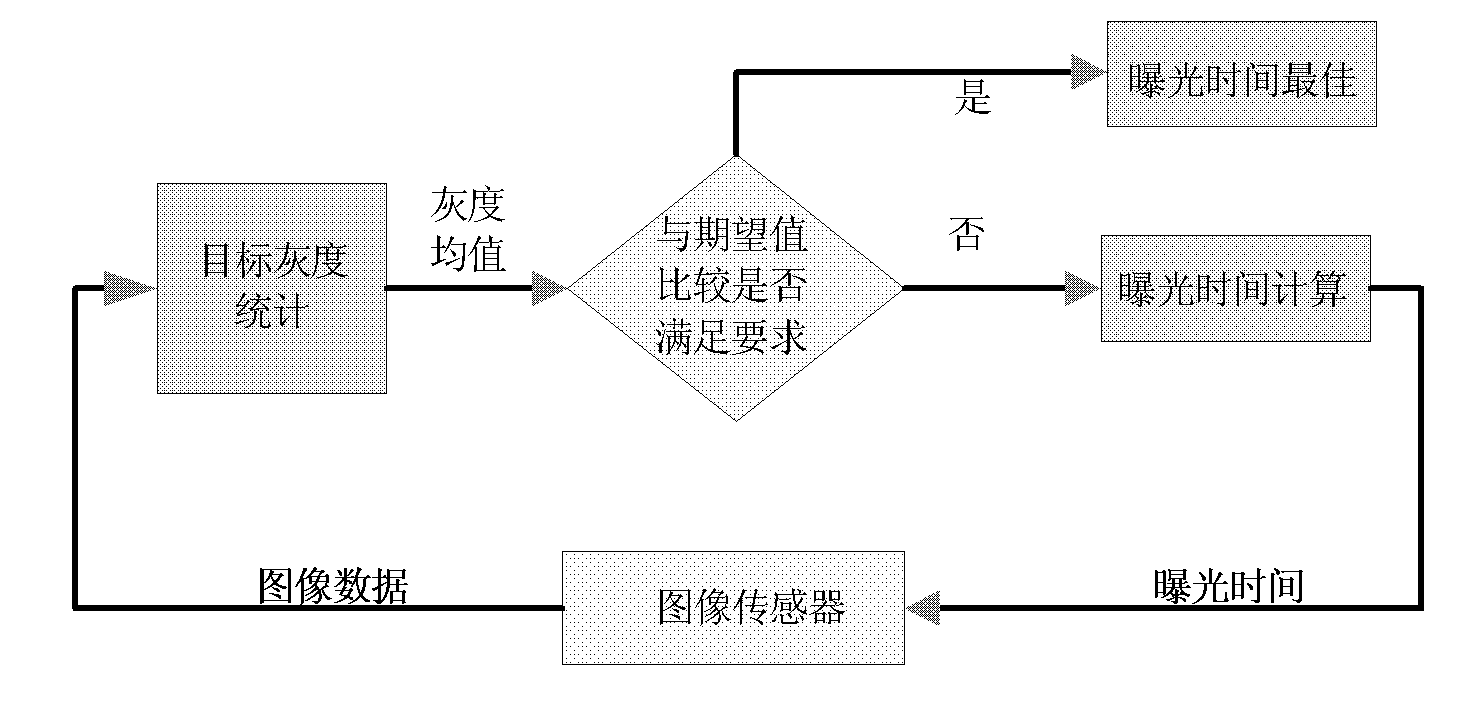
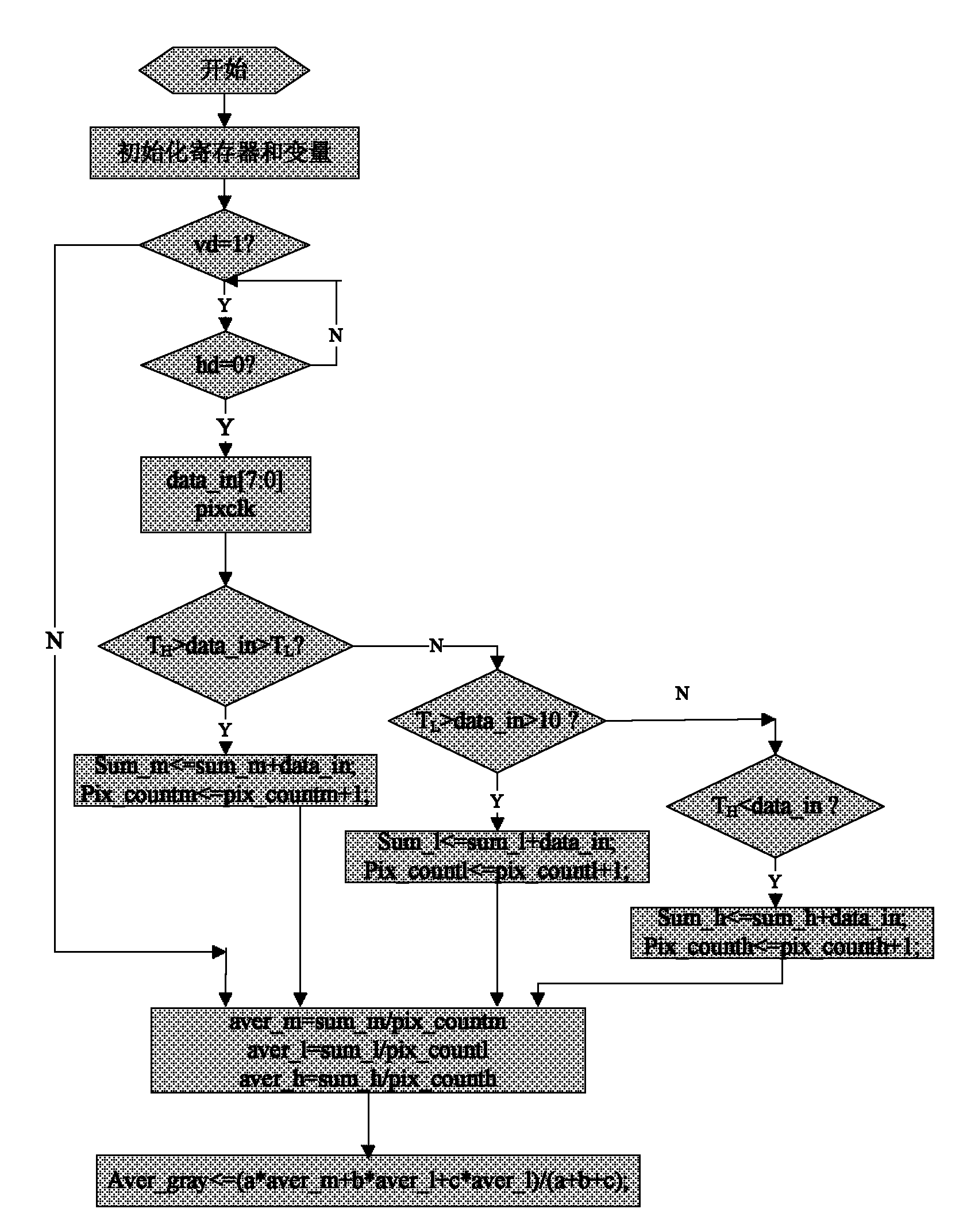
Automatic exposure method based on analogous column diagram
InactiveCN101783888AInfluence IgnoreIncrease exposureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl mannerStatistical analysis
The invention provides an automatic exposure method based on an analogous column diagram, which has favourable exposure effect on various situations, such as dark background light target, target size uncertainty and the like in deep space exploration. An automatic exposure control system is a closed loop control system and mainly comprises three modules: target gray level statistics, comparative judgment with expected values and exposure time calculation; data statistics analysis is carried out by gray scale region division, gray scale value weighting average calculation and the like so as to determine exposure required by shooting. Because of having low requirement on hardware, the invention can be suitable for different hardware platforms by slightly modifying, and can balance calculation speed, logic resource use, system time sequence requirement and the like according to the practical situation so as to choose different control modes.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
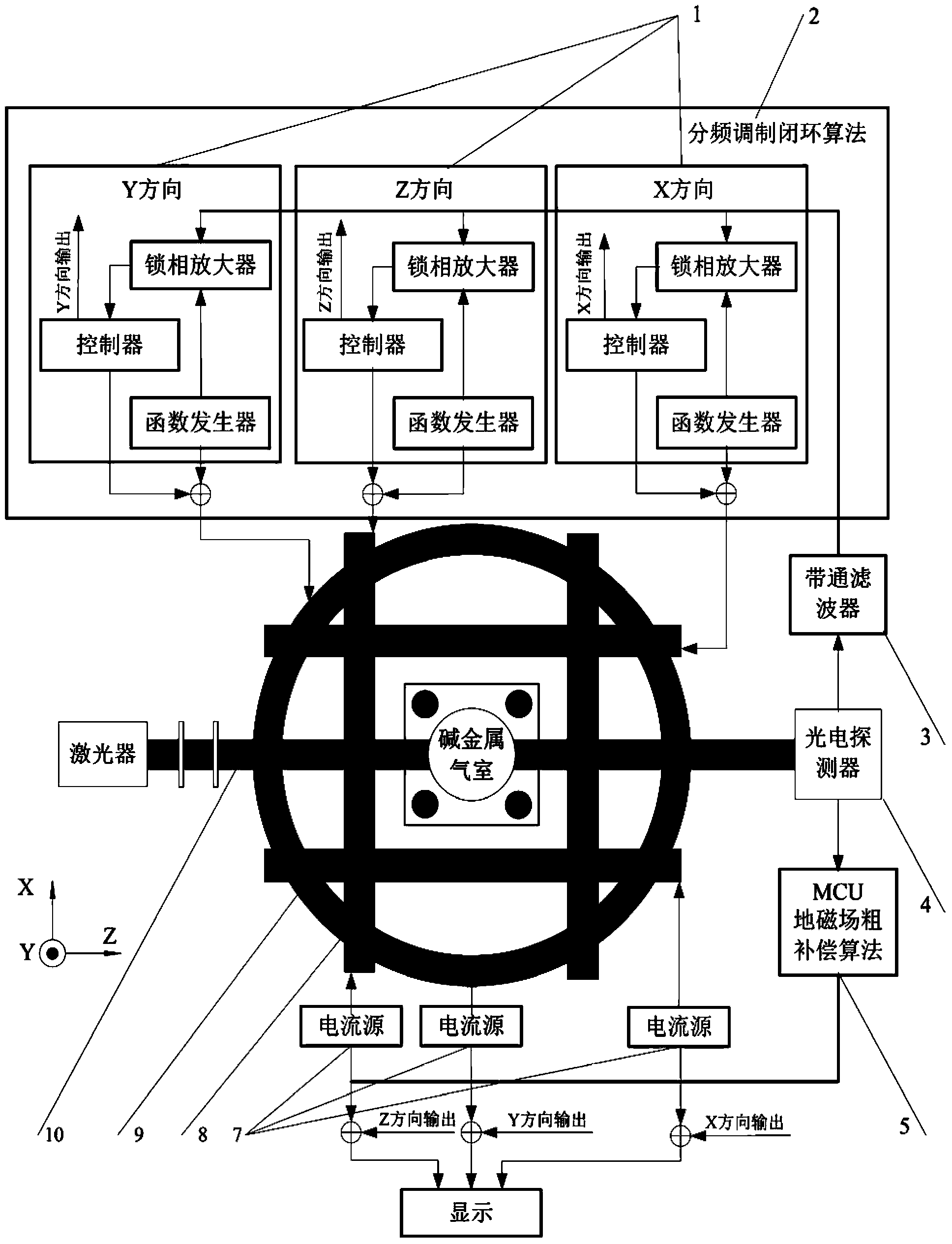
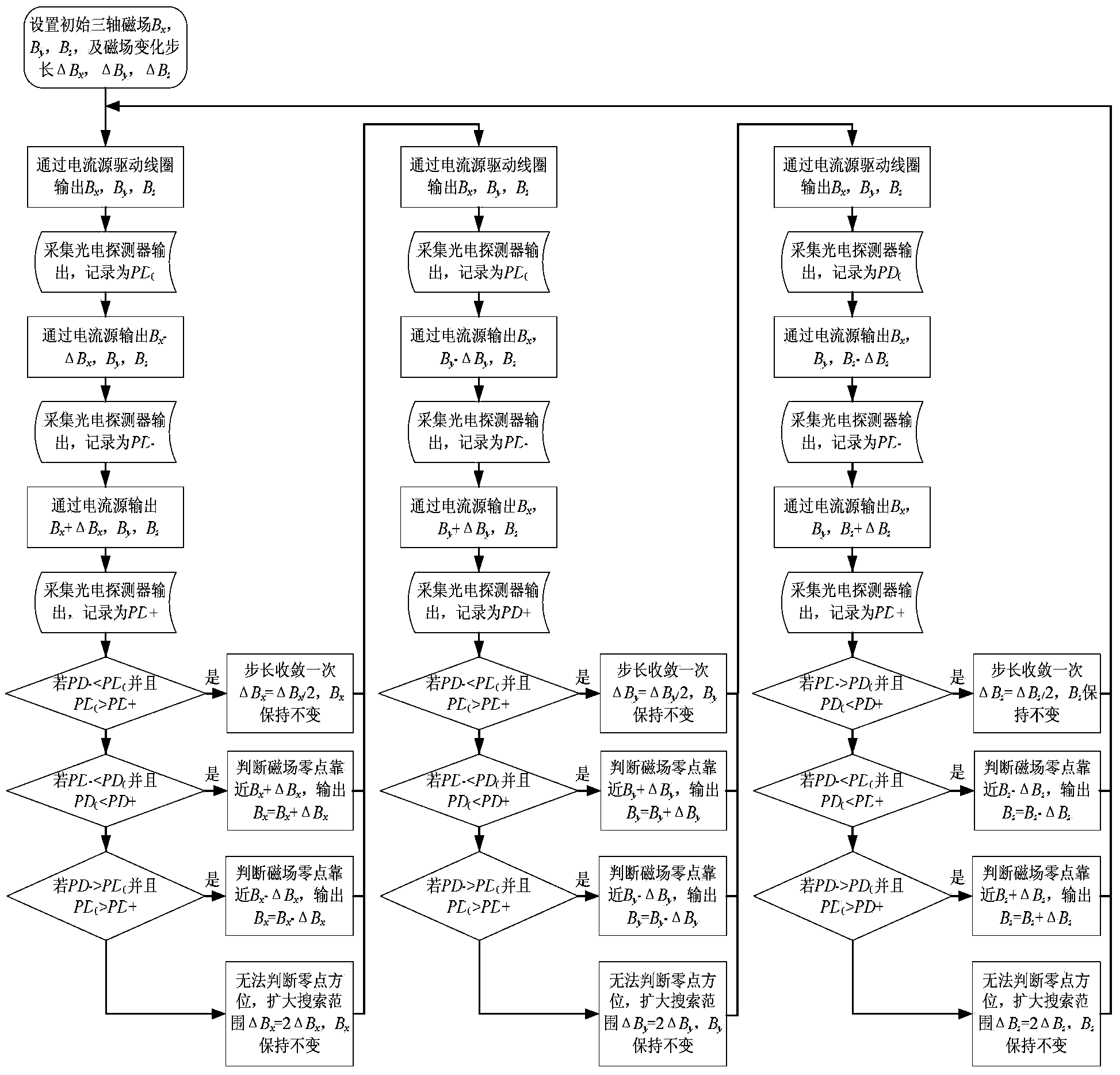
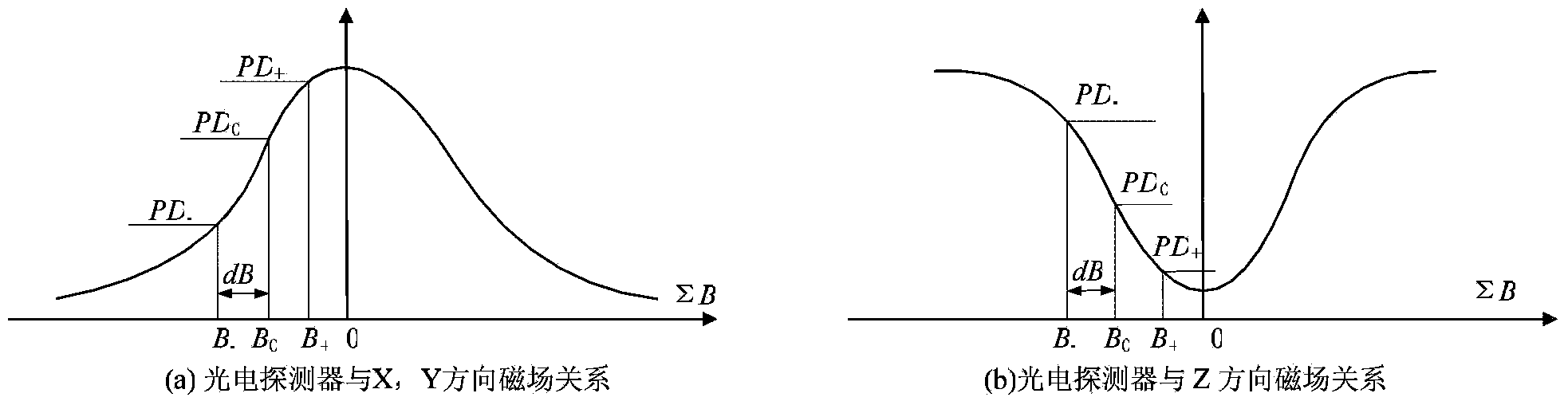
Single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer and detection method thereof
InactiveCN103412268AHigh sensitivitySimple structureMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesClosed loopAlkali metal
The invention discloses a single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer and a detection method of the single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer. The single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer comprises two sets of triaxial orthogonal coils, wherein one set of triaxial orthogonal coils are used for geomagnetic field coarse compensation and the other set of triaxial orthogonal coils are used for closed loop frequency-division modulation. A single beam of pumped laser passes through a heated alkali metal gas chamber and then is received by a photoelectric detector. The detection method of the single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer comprises the following steps that firstly, a geomagnetic field is counteracted by the triaxial orthogonal coils which are controlled in a feedback mode according to a geomagnetic field coarse compensation algorithm of a micro control unit (MCU), and a weak magnetic field environment is created in the gas chamber; secondly, fine compensation for a residual field is completed according to a closed loop frequency-division modulation algorithm; finally, the feedback amount of geomagnetic field coarse compensation and the feedback amount of closed loop frequency-division modulation are added together, so that the size of an external magnetic field is obtained. The single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer and the detection method of the single-beam unshielded atom magnetometer are high in integration level and sensitivity, and capable of obtaining triaxial magnetic field vector information simultaneously, and having wide application prospects in the fields such as deep space exploration and mineral resource exploration.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for manufacturing antenna reflecting surface with aluminum skin honeycomb sandwich structure
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing an antenna reflecting surface with an aluminum skin honeycomb sandwich structure, which relates to a technology for manufacturing the antenna reflecting surface in the fields of satellite communication, radio measurement and control, deep space exploration, large radio telescopes and the like. The method adopts a high-precision enveloping mold forrealizing the stretch forming of an inner skin and an outer skin, imposes the negative pressure through sealing and a vacuum device, presses and attaches the two layers of the skins, a honeycomb andother separating components on the mold, carries out adhesive curing and molding to form a whole by a bonding agent, and forms a high-precision aluminum skin honeycomb sandwich antenna reflecting surface unit after releasing vacuum negative pressure. The method has the advantages of high precision, light weight, great rigidness, great strength, simple processing technology, stable and reliable performances, low manufacturing cost, easy realization of production environment, mass production and the like, thereby being particular applicable to manufacturing the high-precision antenna reflectingsurfaces above ka frequency band and Q frequency band.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
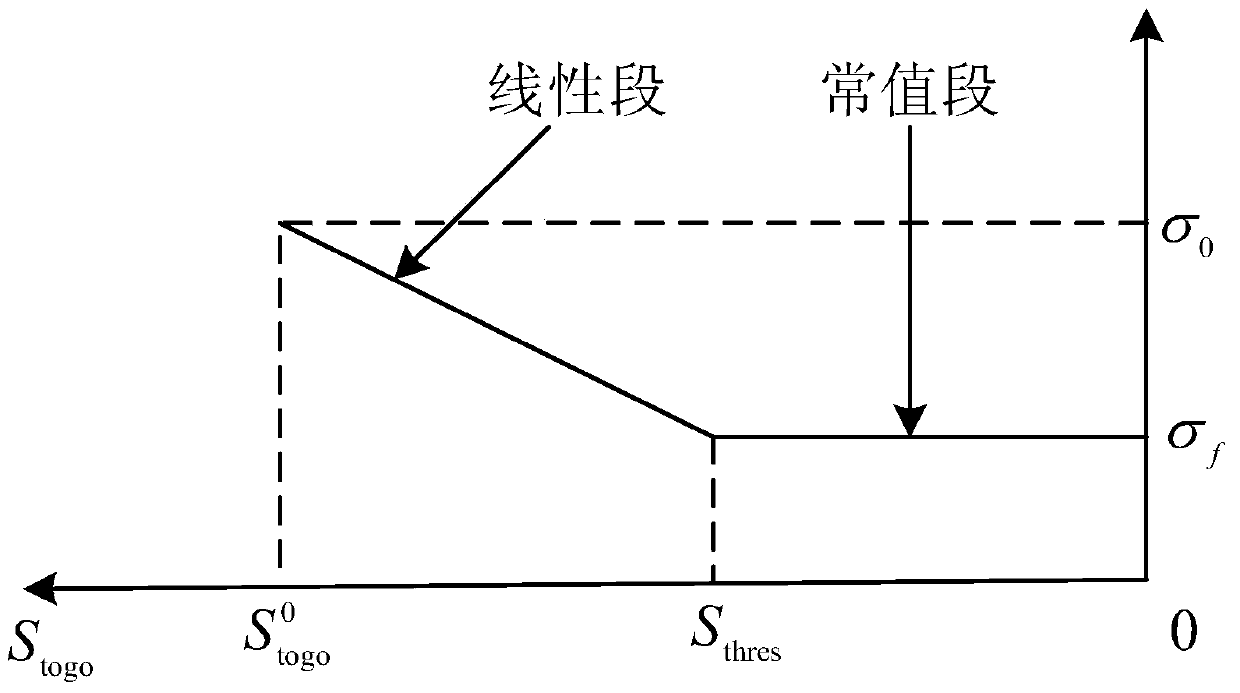
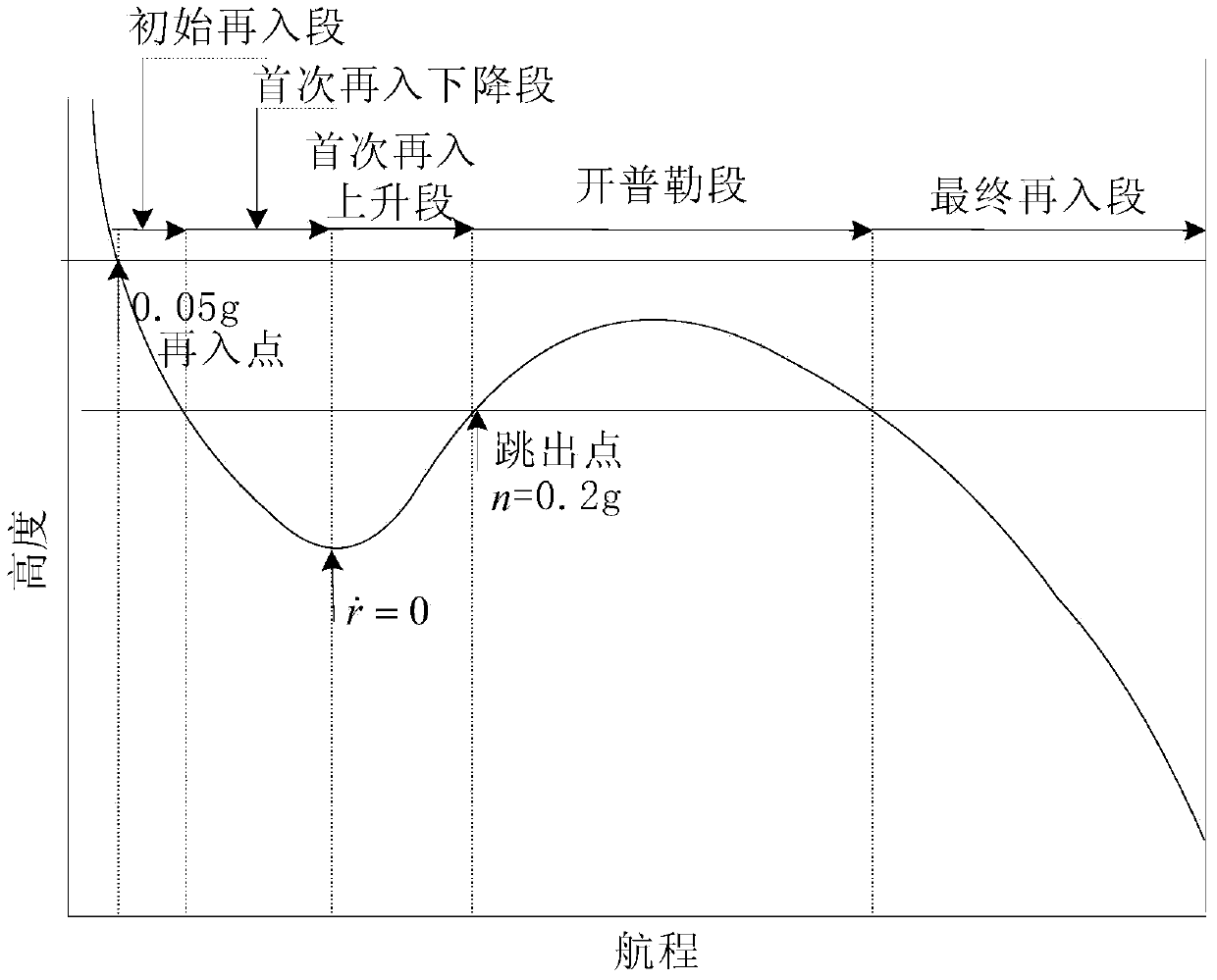
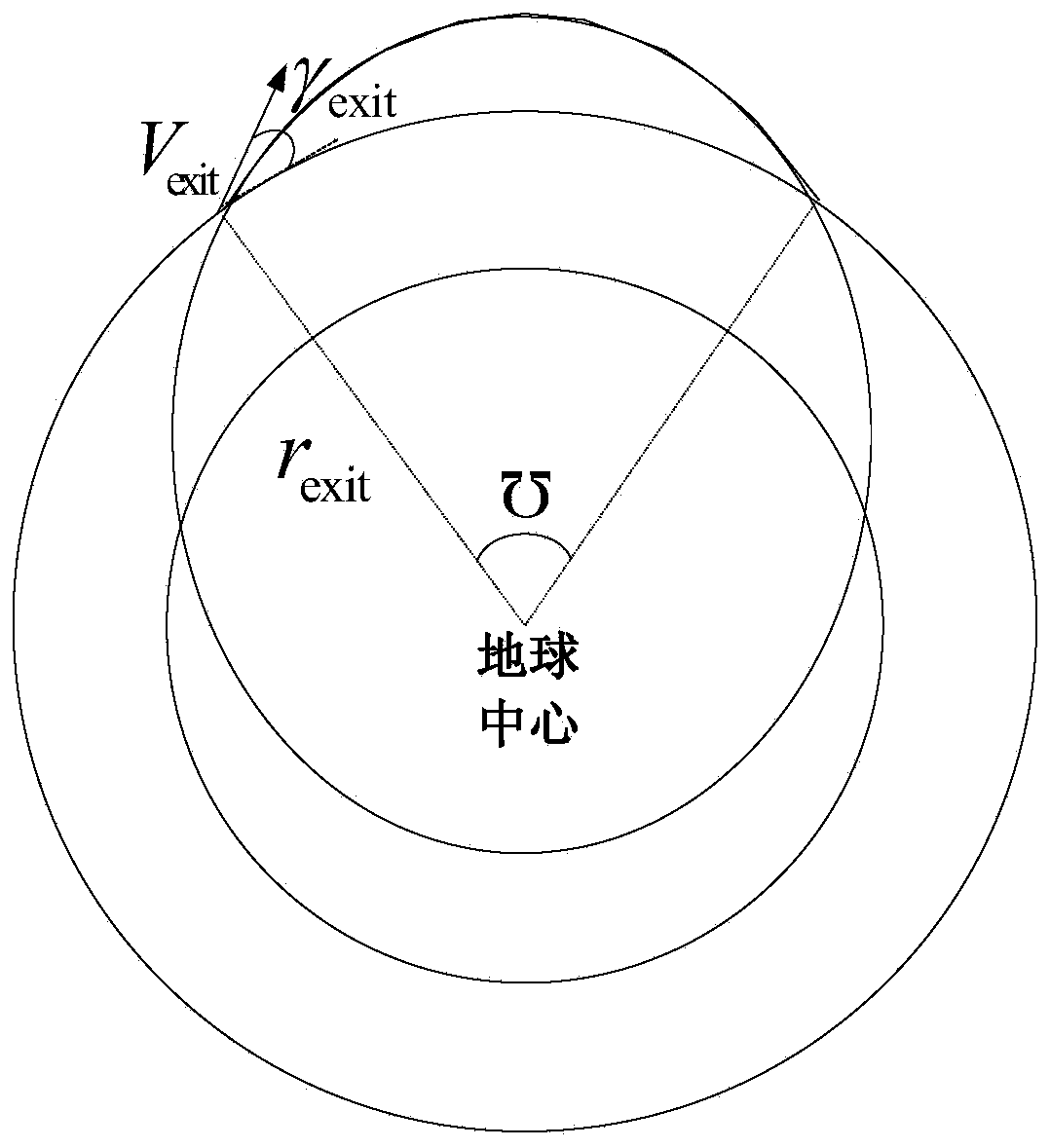
Prediction correcting guidance method of deep space exploration returning process
ActiveCN103863579ANo added complexityIncrease flight rangeSystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesCurrent pointDeep space exploration
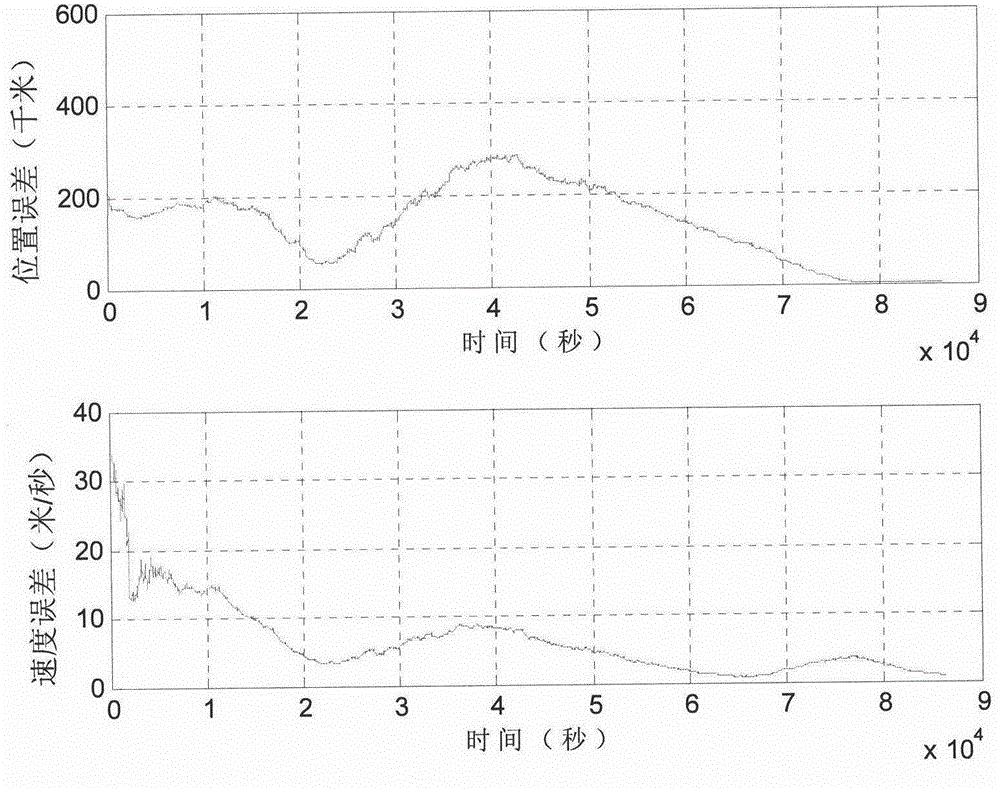
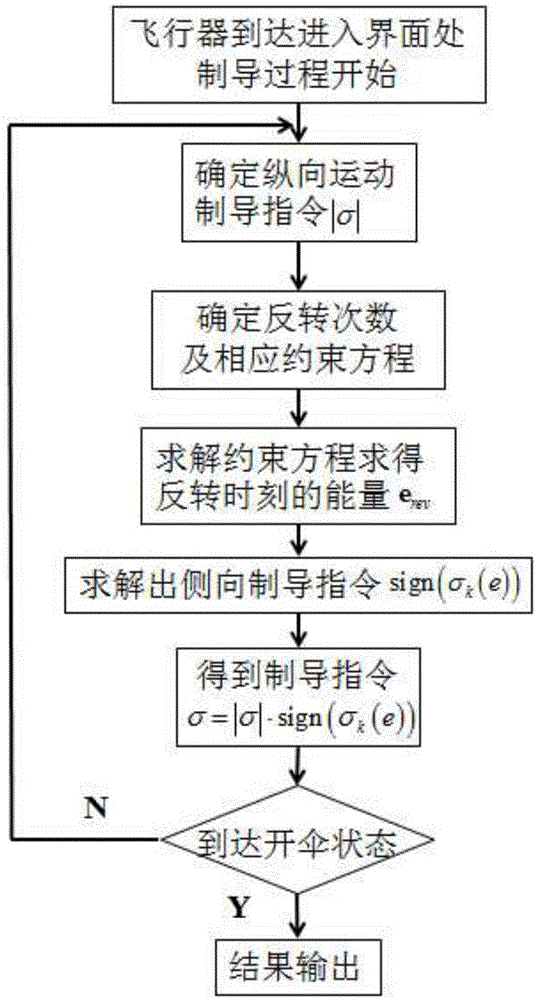
A prediction correcting guidance method of a deep space exploration returning process comprises the steps that (1) a heeling angle section used for deep space exploration returning process track prediction is determined; (2) the amplitude value | sigma 0 | of the heeling angle of a current point is computed in an iterative mode; (3) a salutatory reentry flight track of a returning device is divided into an initial reentry stage, a primary reentry descending stage, a primary reentry ascending stage, a Kepler stage and a final reentry stage, a final guidance rule of the returning device is determined, and the final guidance rule is that when the returning device is in the initial reentry stage or the primary reentry descending stage or the primary reentry ascending stage or the final reentry stage, the amplitude value | sigma 0 | determined in the step (2) of the heeling angle sigma 0 of the current point is used for guidance; and when the returning device is in the Kepler stage, | sigma 0 | = 180 degrees is used for guidance, and accordingly prediction correcting guidance of the deep space exploration returning process is completed. The guidance rule is designed at the Kepler stage of the track for achieving overload restrain on the deep space exploration returning process, and safe and accurate landing of the returning device is guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
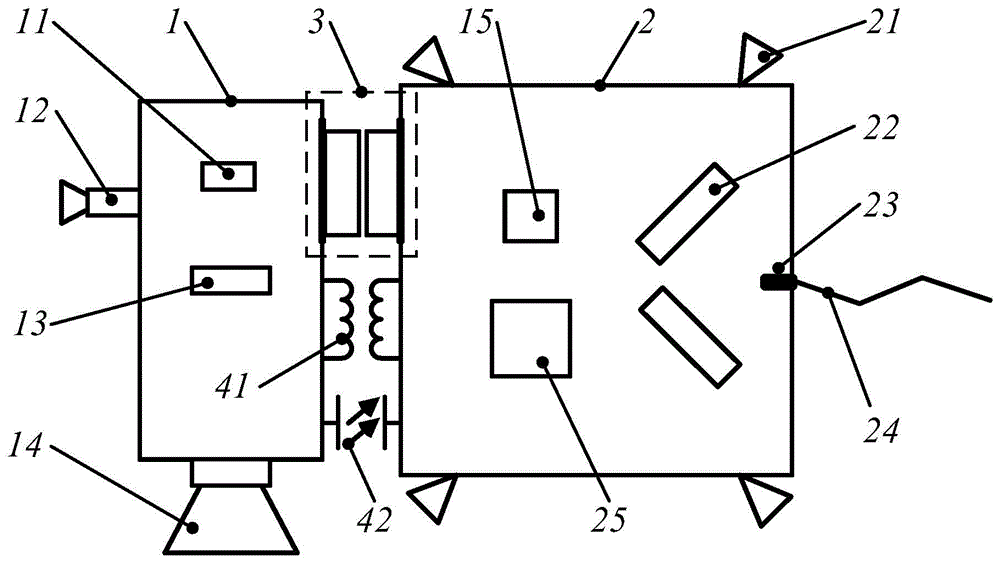
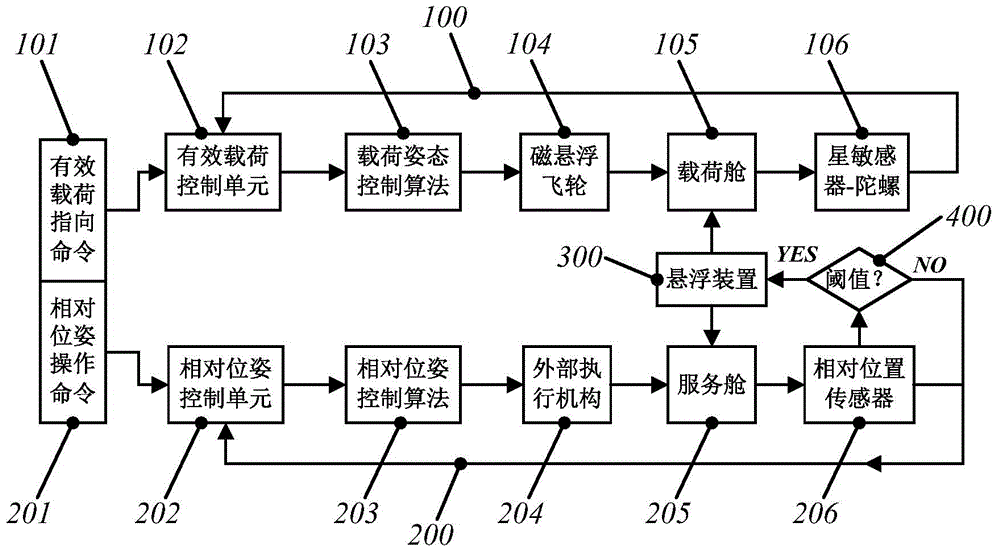
Follow-up tracking dynamic and static isolation type dual-super satellite platform and working mode implementation method thereof
ActiveCN104129509ASolve the problem of super precision and super stabilityTo achieve the purpose of keeping quiet while movingCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsDeep space explorationAstronomical telescopes
The invention discloses a follow-up tracking dynamic and static isolation type dual-super satellite platform and a working mode implementation method thereof. The follow-up tracking dynamic and static isolation type dual-super satellite platform is suitable for sensitive load spacecrafts with the ultra-precision and ultra-stability requirement. Dynamic and static isolation is used as the means, a satellite is divided into a load cabin and a service cabin, the load cabin can ensure that the effective load meets the expected ultra-precision and ultra-stability control requirement through a high-performance magnetic levitation flywheel arranged on the load cabin, the service cabin can resist environmental disturbance and track the load cabin in a follow-up mode through an external actuator mounted on the service cabin, and accordingly the two cabins can meet the expected relative pose requirement. The load cabin is connected with the service cabin through a suspension device in a non-contact mode, vibration disturbance of the service cabin can be effectively isolated, and the vibration isolation effect cannot be affected by the sensor performance. The satellite based on the dual-super satellite platform at least has the launching, ultra-precision and ultra-stability, anti-collision or mobility working mode. The dual-super satellite platform can be applied to high resolution sensitivity effective load spacecrafts such as a high resolution remote sensing satellite and a deep space exploration astronomical telescope.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
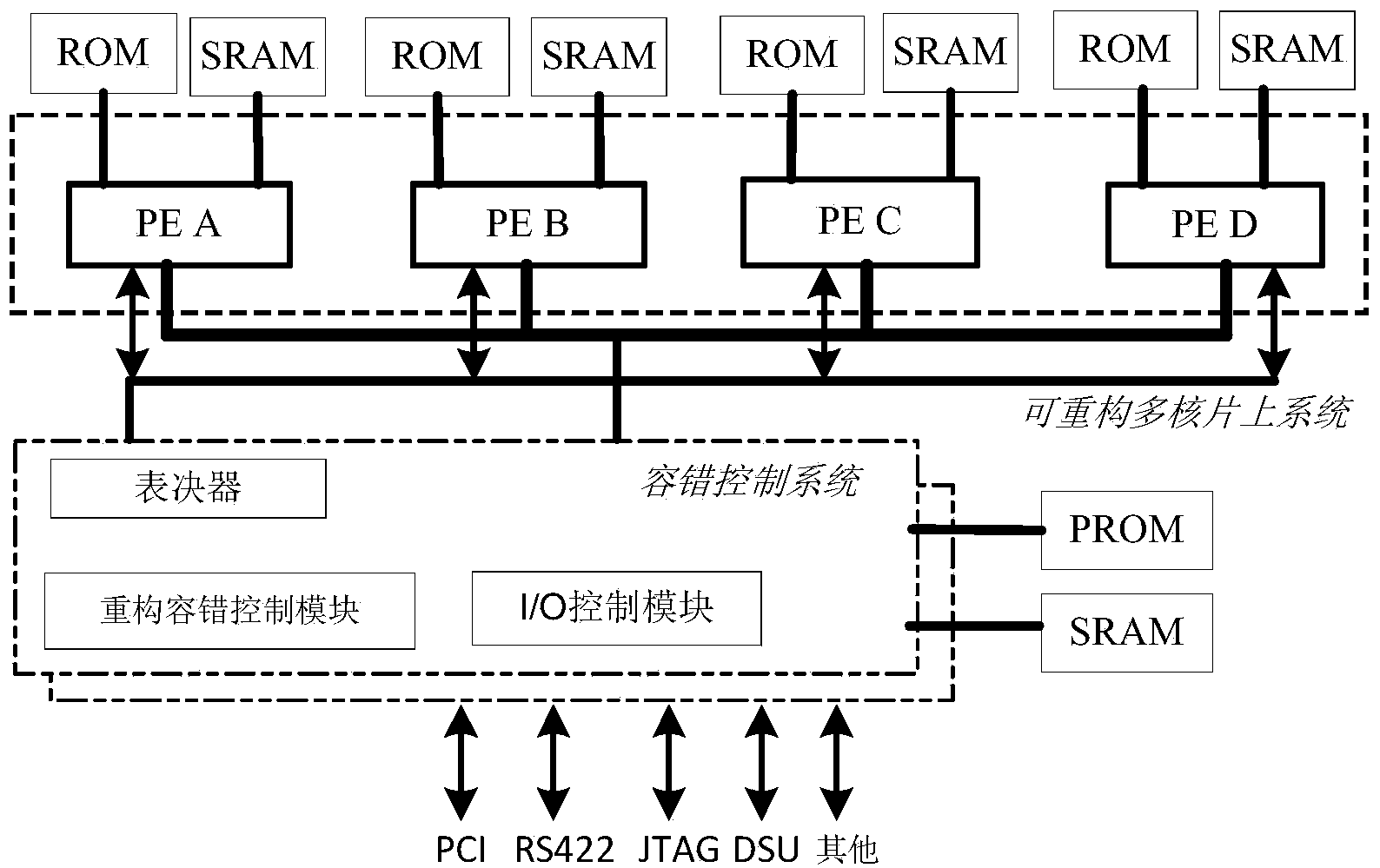
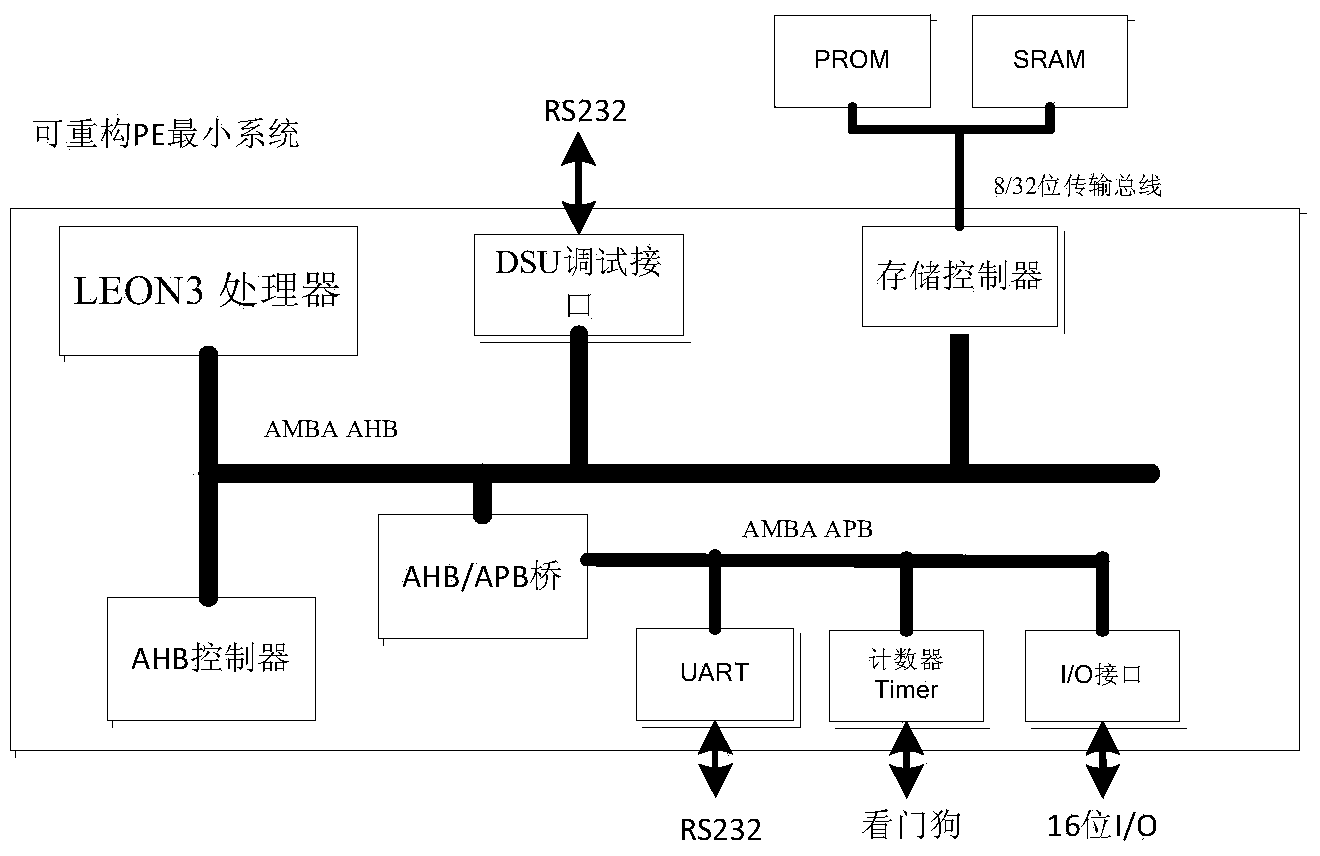
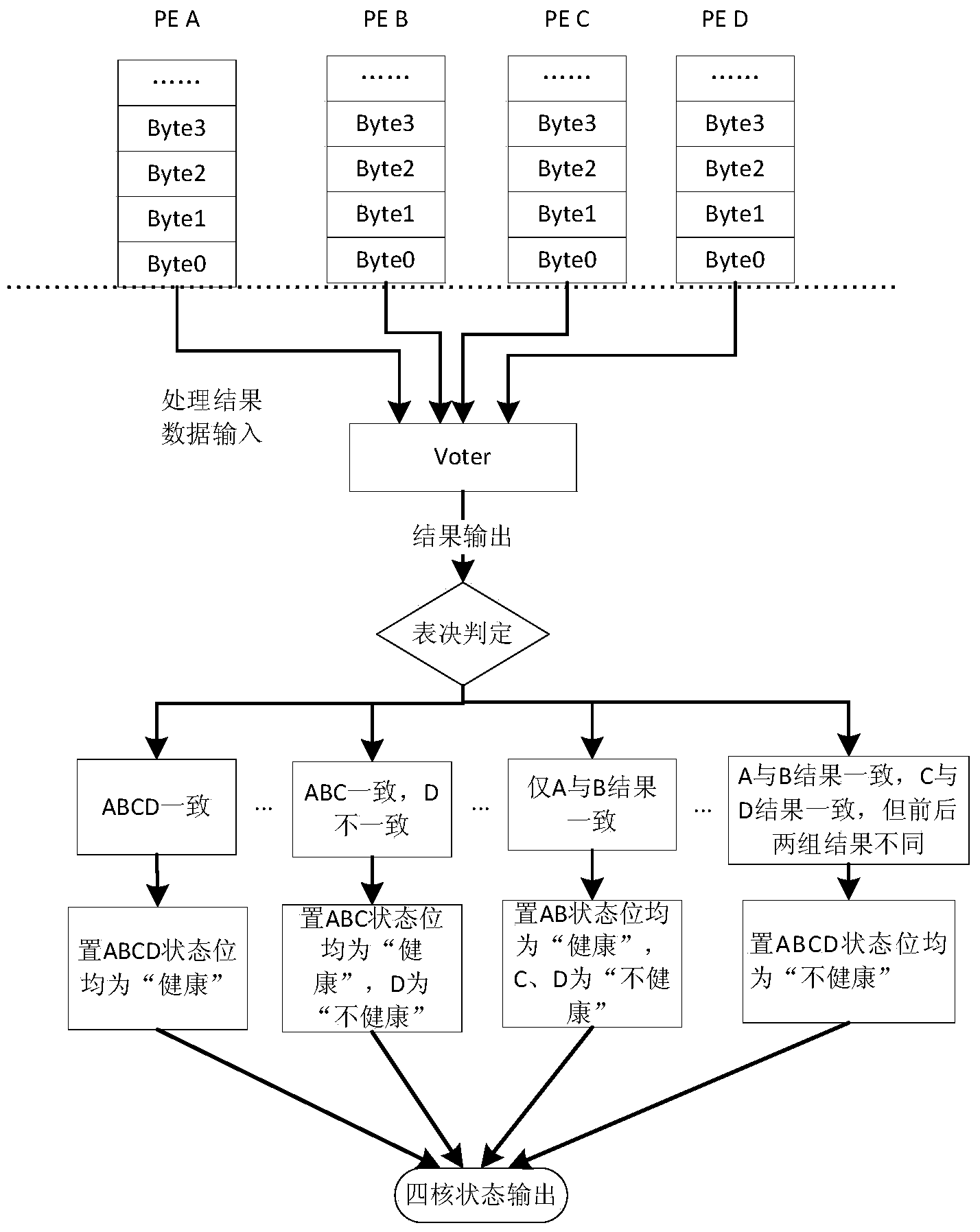
Multicore-oriented reconfigurable fault tolerance system and multicore-oriented reconfigurable fault tolerance method
InactiveCN103870353ALow coupling designReduce the risk of fault propagationFault responseFault toleranceDeep space exploration
The invention provides a multicore-oriented reconfigurable fault tolerance system and a multicore-oriented reconfigurable fault tolerance method. A multi-core processor reconfiguration strategy based on an SOC (System On chip) is adopted for design, a multicore fault tolerance mechanism based on system degradation is provided; by virtue of reconfiguration of working modes of a multi-core processor, the reliability and fault tolerance capability of the system are improved, so that the multicore-oriented reconfigurable fault tolerance system is applicable to complex and severe-environment engineering application such as deep-space exploration.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
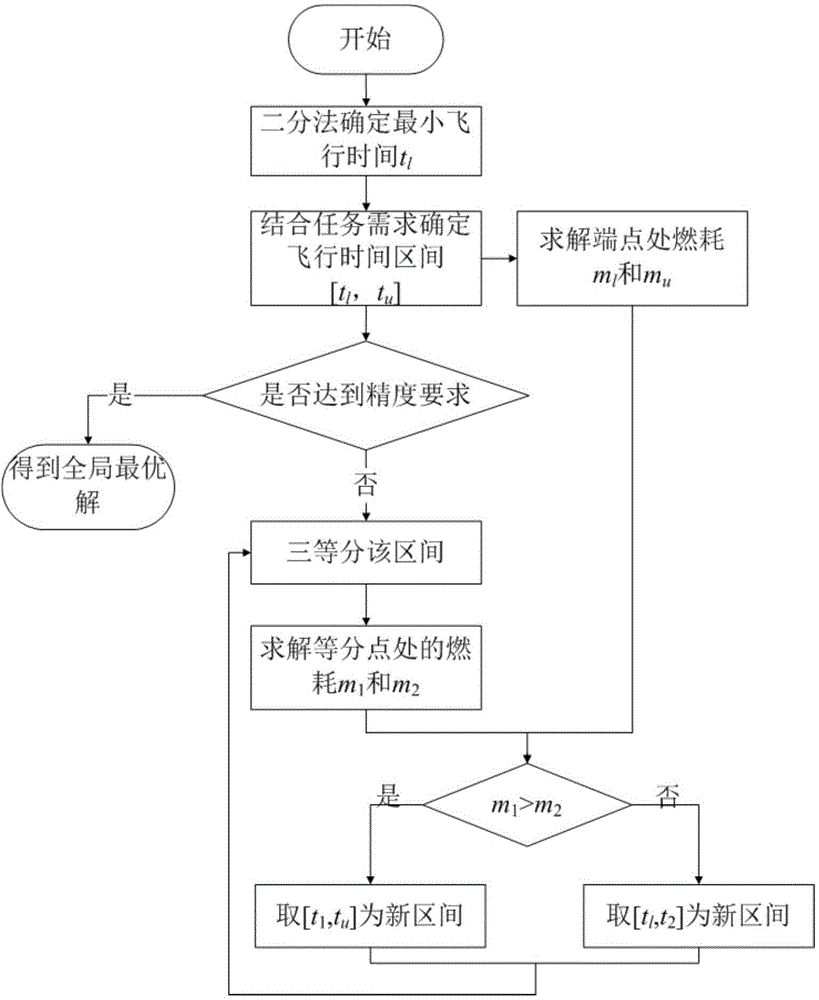
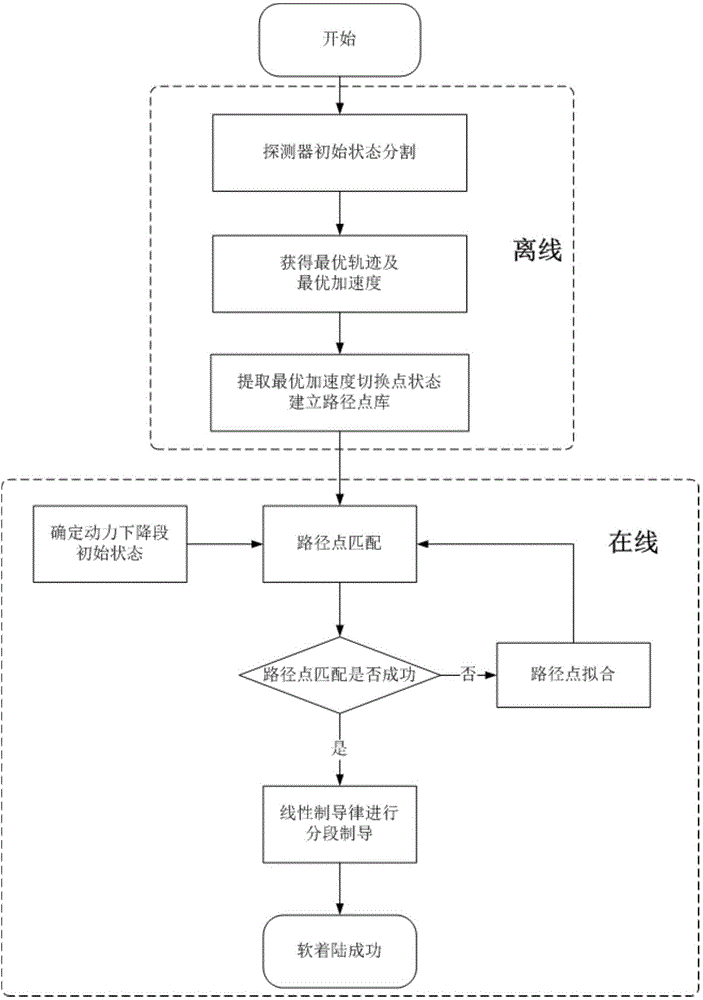
Mars probe landing guidance method based on fuel minimization
ActiveCN104590589AReduce the amount of online calculationsAchieve a soft landingSpacecraft guiding apparatusDeep space explorationEngineering
The invention relates to a mars soft landing guidance method, in particular to a mars probe landing guidance method based on fuel minimization, and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. The mars probe landing guidance method based on fuel minimization solves the problems that fuel minimization guidance can not be achieved through an existing explicit guidance law, and the optimal guidance law must store an entire track, so that a large storage space is occupied. The technical scheme includes the steps that a fuel optimal solution of a probe is acquired; path points are set and a path point library is established; a linear feedback guidance law is designed, if initial state information of the probe is matched with path point information of the path point library, landing is executed, and otherwise, landing is executed after the path points are fitted. Through the guidance strategy of the path points and the linear guidance law, the method can achieve the fuel optimal guidance of a power descent section of the mars probe based on a small storage space. The mars probe landing guidance method based on fuel minimization is suitable for the guidance law of the power descent section of the mars probe.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Lunar-environment-simulated cutting test device
ActiveCN102798577ARealize visualizationExtended testInvestigating machinabilityDeep space explorationEngineering
The invention discloses a lunar-environment-simulated cutting test device. According to the lunar-environment-simulated cutting test device, a vacuum environment existing during lunar surface drilling is simulated by adopting a vacuum tank, the structure of a lunar surface is simulated by adopting a drilling load, and a heat-insulating drilling load in a lunar vacuum environment is simulated more really by using a heat insulation technology; the control on drilling parameters and procedures is carried out on drilling sampling during the process of cutting, the drilling parameters and drilling temperature can be monitored, acquired and analyzed, the temperature distribution and the highest temperature limit of a drilling tool are determined, and the vacuum seal for a drilling sampling device during the process of drilling is realized through a magnetofluid sealing device; and the visualization of a vacuum device is realized by adopting an observation window. The lunar-environment-simulated cutting test device also can be applied to the test and development of other drilling unmanned autonomous samplers for deep space exploration in an expanding manner; and in addition, the lunar-environment-simulated cutting test device also has a wide application prospect in the field of vacuum sealing and precise measurement.
Owner:BEIJING SATELLITE MFG FACTORY
Method for designing Mars entry phase autonomous navigation scheme based on observability degree analysis
InactiveCN103076017AImprove ObservabilitySpeed upInstruments for comonautical navigationControl engineeringDeep space exploration
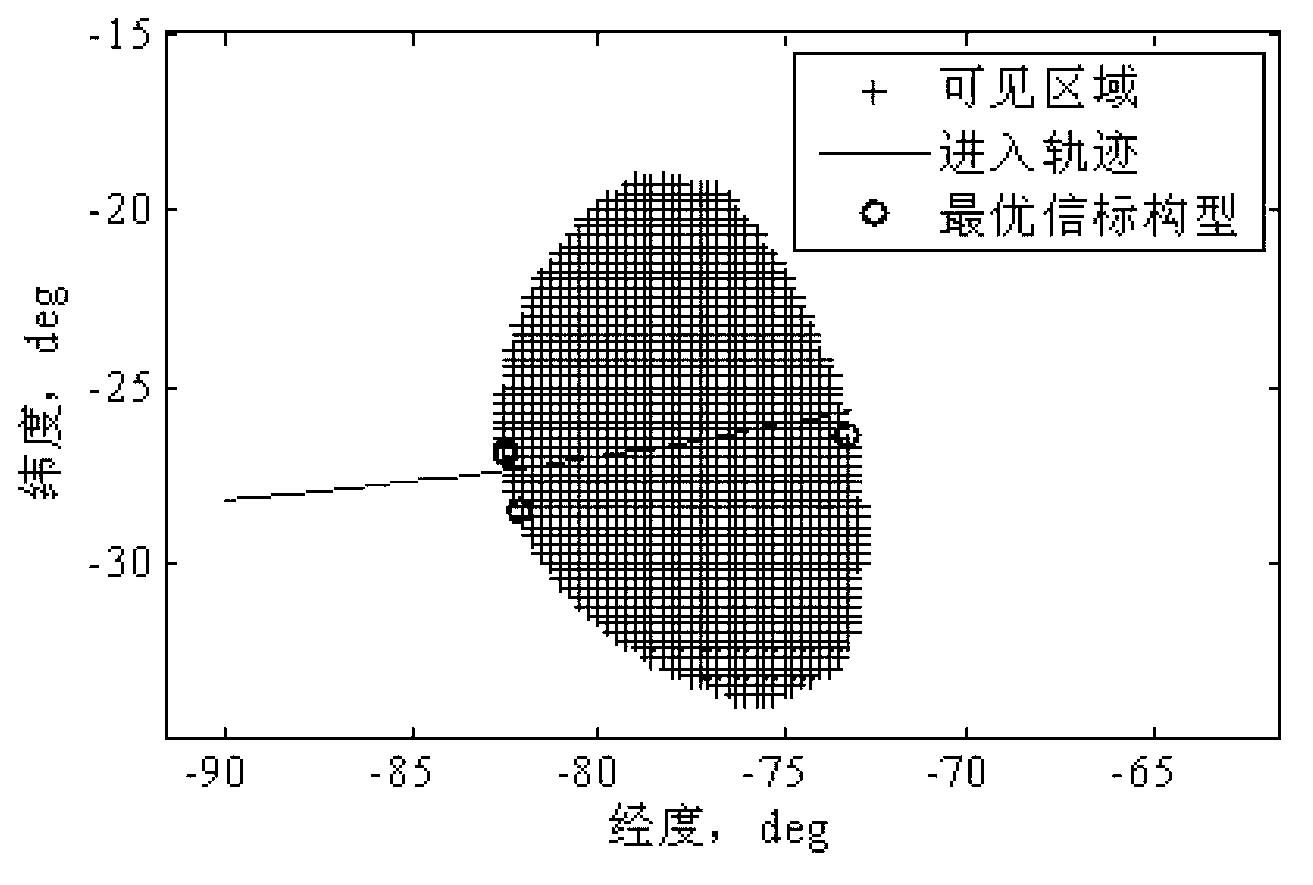
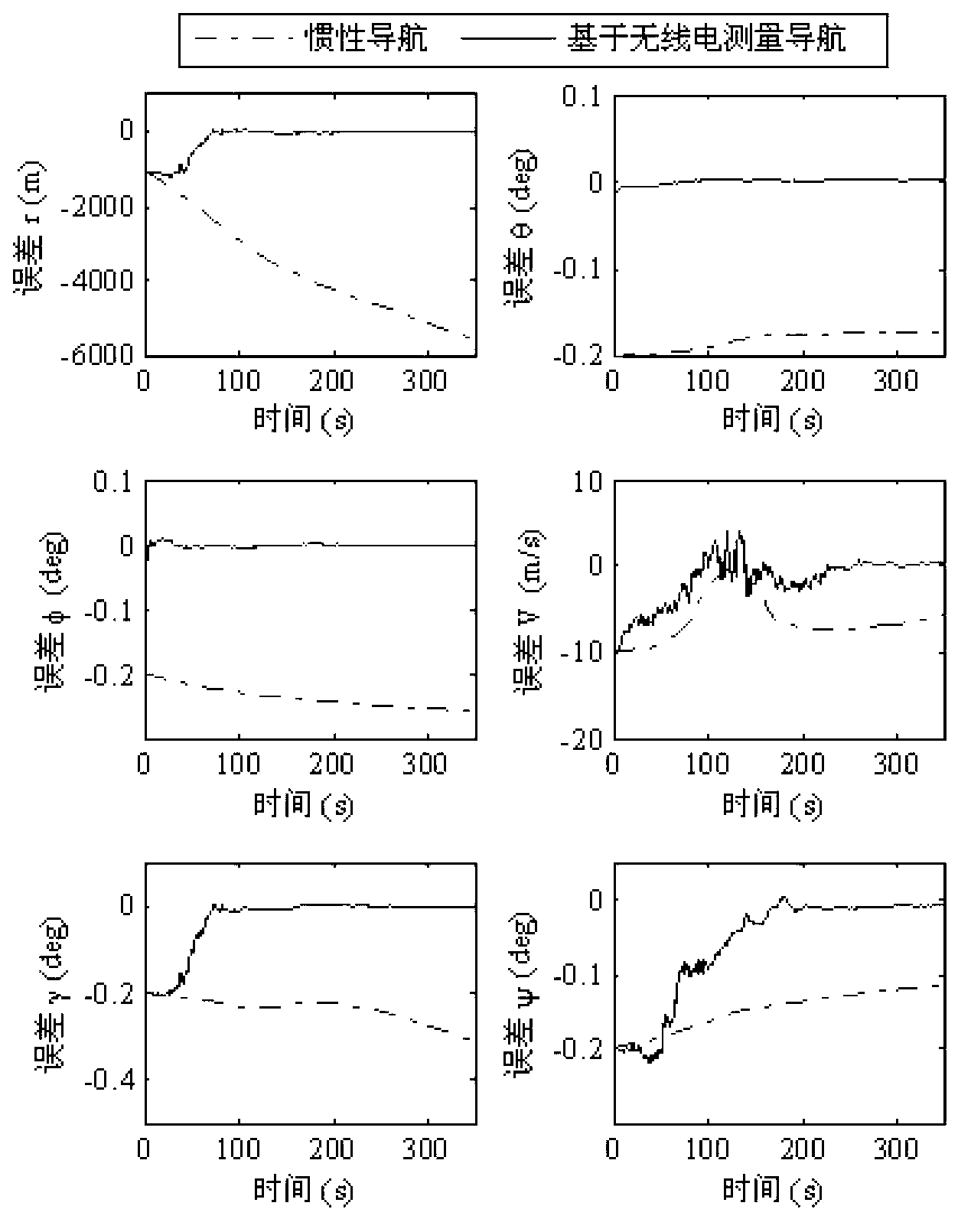
The invention relates to a method for designing a Mars entry phase autonomous navigation scheme based on observability degree analysis, belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration, and particularly aims to optimize the geometric configuration of a navigation beacon so as to realize the design of the Mars entry phase autonomous navigation scheme and ensure the optimal navigation property by utilizing observability degree of a navigation system to represent the property of the navigation system and by combining the Mars entry phase autonomous navigation scheme based on radio measurement. According to the method provided by the invention, the observability matrix is calculated through a linearization method, the calculation amount is small, and the calculation speed is high; the observability degree of the navigation system is defined by inverse of the condition number of the observability matrix, and a quantitative gauge is provided for observability of the navigation system; and the observability degree of the navigation system can be maximized, so that the property of the navigation system can be further improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Gravity-gradient-invariant-based method for estimating orbit element
ActiveCN107065025AStrong autonomyImprove anti-interference abilityGravitational wave measurementState parameterDecomposition
The invention provides a gravity-gradient-invariant-based method for estimating an orbit element. The method comprises: step one, carrying out preparation work; step two, carrying out decomposition of an ideal gravity gradient tensor under an east-noth-up (ENU) coordinate system and obtaining feature values; step three, solving decomposition of a measuring epoch J2 model gravity field tensor under the ENU coordinate system and obtaining feature values; step four, solving all measuring epochs r and phi by using feature values of a J2 gravity gradient matrix; step five, calculating an initial orbit element by using the r and phi; and step six, carrying out orbit element smoothing. Therefore, with utilization of the gravity gradient matrix invariant information measured during the satellite operating process, a geometrical distance between the satellite and the earth's core and the latitude of the earth's core are obtained by iterative solution; a measurement equation that uses a semi-major axis, an eccentricity ratio, an orbit inclination angle, a perigee depression angle, and a true anomaly in an orbital element as state parameters is provided by using an obtained data as an observed quantity; and a perturbation kinetic equation of the orbital element is introduced innovatively and five orbital elements are estimated by using a batching least square method. The gravity-gradient-invariant-based method has advantages of high autonomous degree, high anti-interference capability, and low building cost and the like and has advantages that the traditional method does not have in the deep space exploration field.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
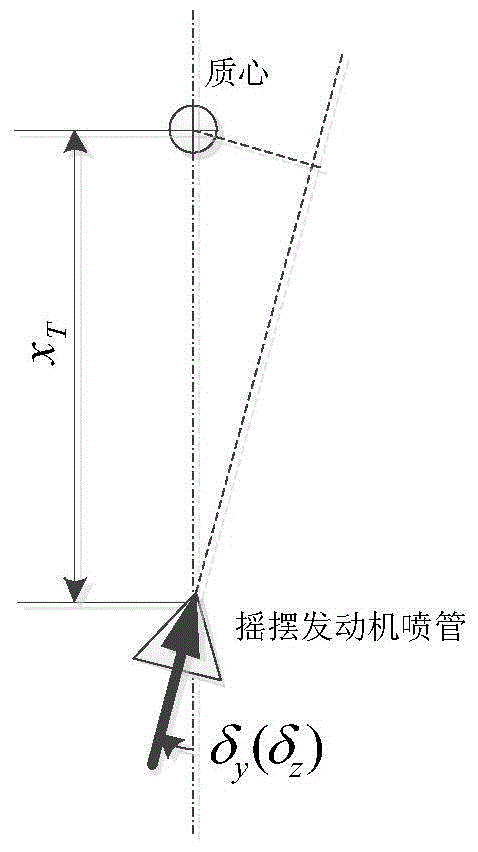
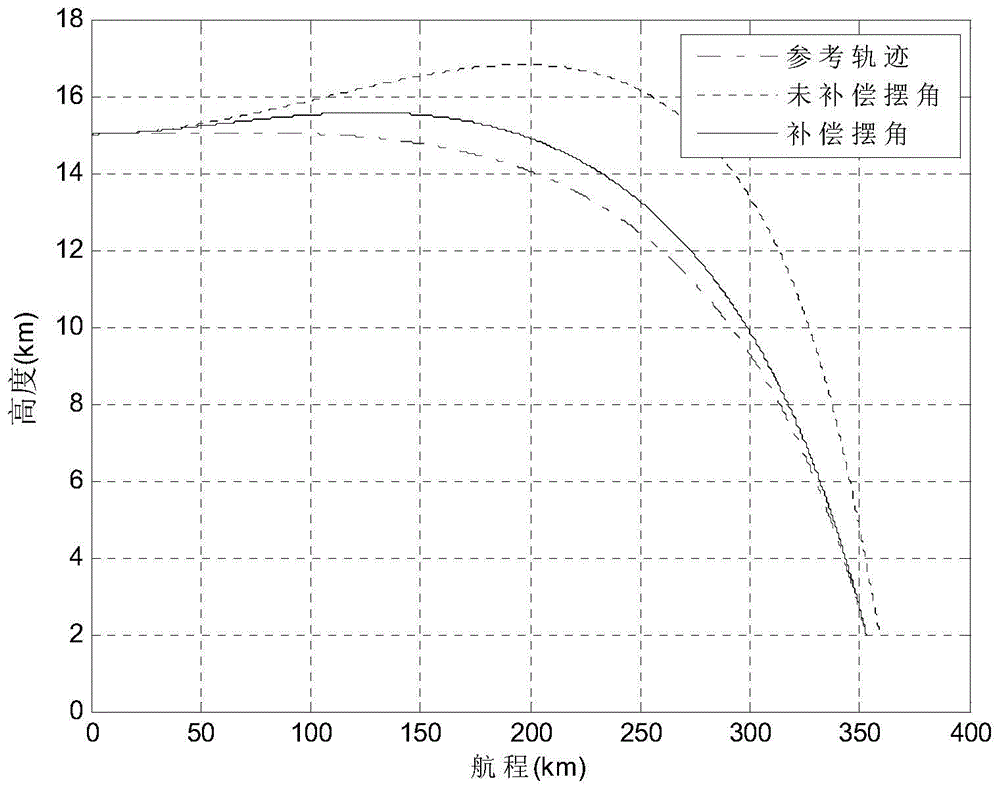
Posture and path coupling control method for deep space exploration soft landing process
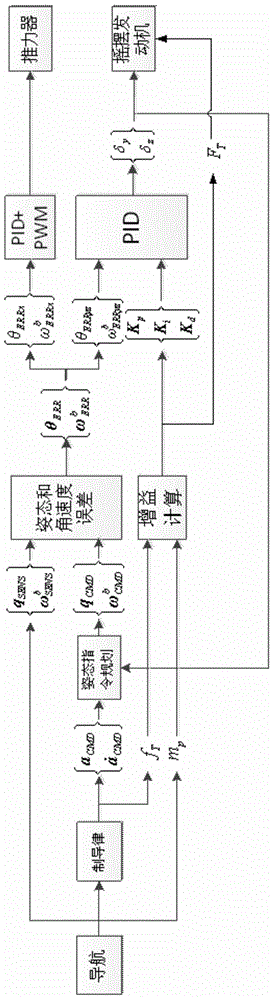
ActiveCN103955223AImprove consistencyReduce the impactAttitude controlAttitude controlCelestial body
The invention relates to a posture and path coupling control method for the deep space exploration soft landing process. In the deep space celestial body soft landing process, a thrust-variable swing engine is used for conducting posture control, and therefore a landing path is disturbed. Important measures for reducing posture control and path control coupling of the thrust-variable swing engine includes that a part, used for eliminating centroid skewing, in a swing angle of the thrust-variable swing engine is estimated on line, and flight postures are amended. According to the posture and path coupling control method, the swing angle of the thrust-variable swing engine is required to be estimated on line firstly, and stable components of the swing angle are extracted; then the target flight postures are amended through the stable components of the swing angle, the amended thrust direction is coincident with the thrust direction expected in a guidance law, and influences of posture control swing of the thrust-variable swing engine on guidance are initiatively eliminated. By means of the posture and path coupling control method, disturbance to the guidance is reduced to the maximum degree while the posture control is carried out, and even though the guidance has no three-direction position control capacity, it can be guaranteed that the flight path is coincident with an ideal path as far as possible.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
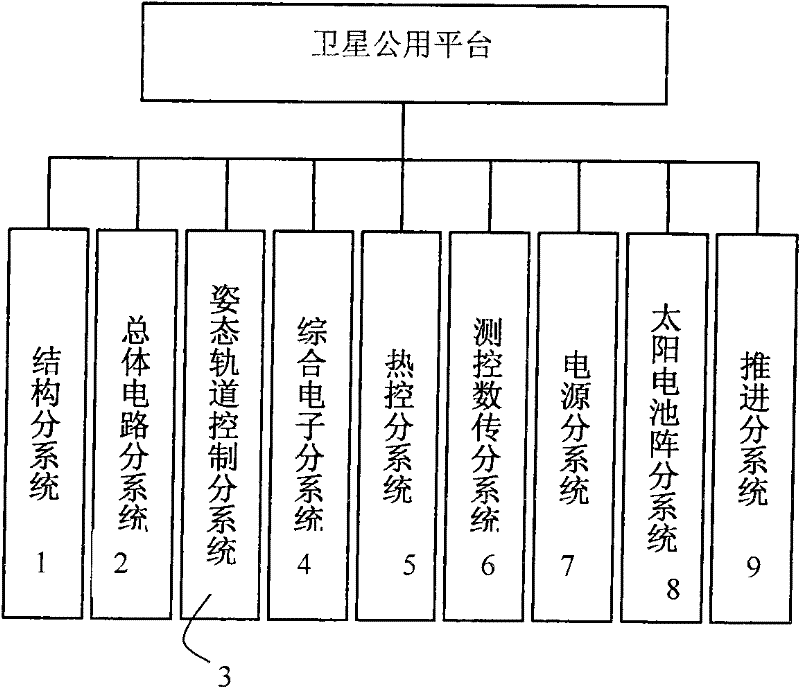
Common platform for satellite
ActiveCN102530267ASolve the real problemMeet electricity demandCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsAttitude controlDeep space exploration
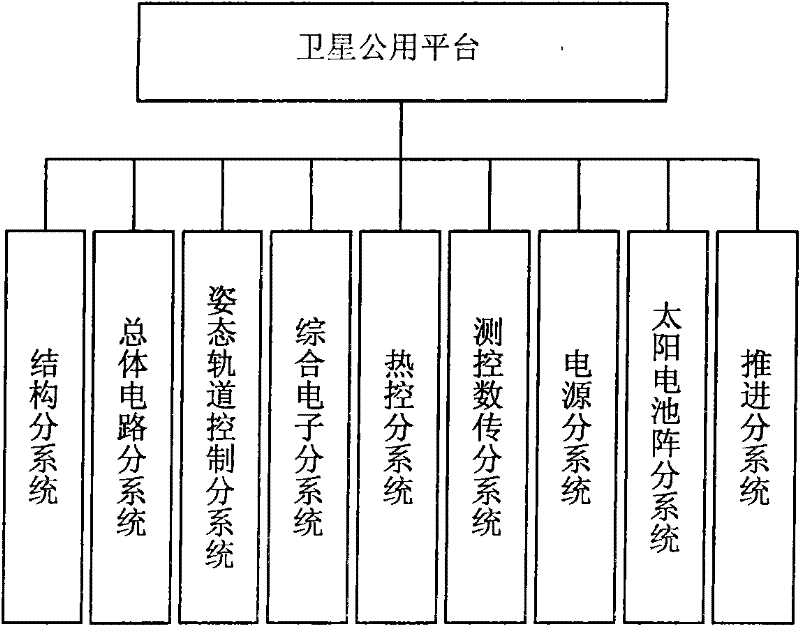
The invention relates to a common platform with the deep space exploration capability for a satellite. The common platform comprises systems such as a structure, a thermal control, a solar cell array, an attitude control, propulsion, a power supply, integrated electronics, measurement and control digital transmission, a total circuit and the like. According to the common platform disclosed by the invention, the problem of the common platform for the satellites in the filed of deep space exploration is solved; and the common platform has the characteristics of small size, light weight, low research cost, short period, low risk, capability of meeting the carrying requirement and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Mars ultimate approach segment autonomous navigation method based on multi-source information fusion
InactiveCN104567880AGood autonomyHigh implementabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationFault toleranceFilter algorithm
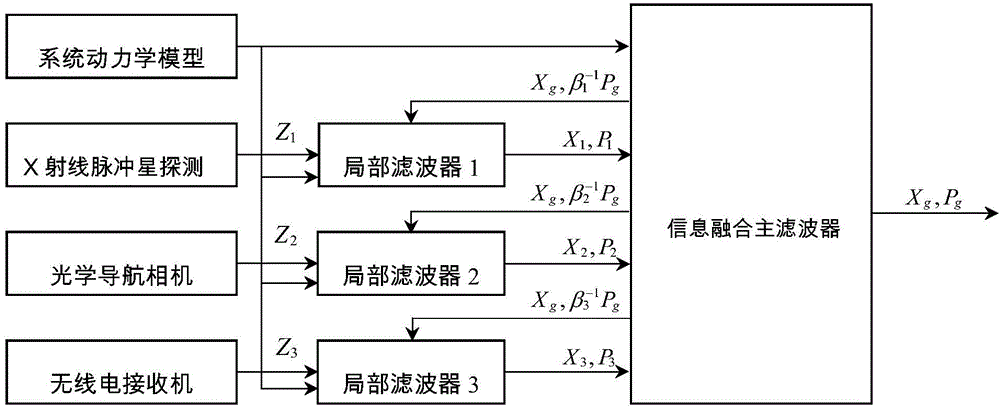
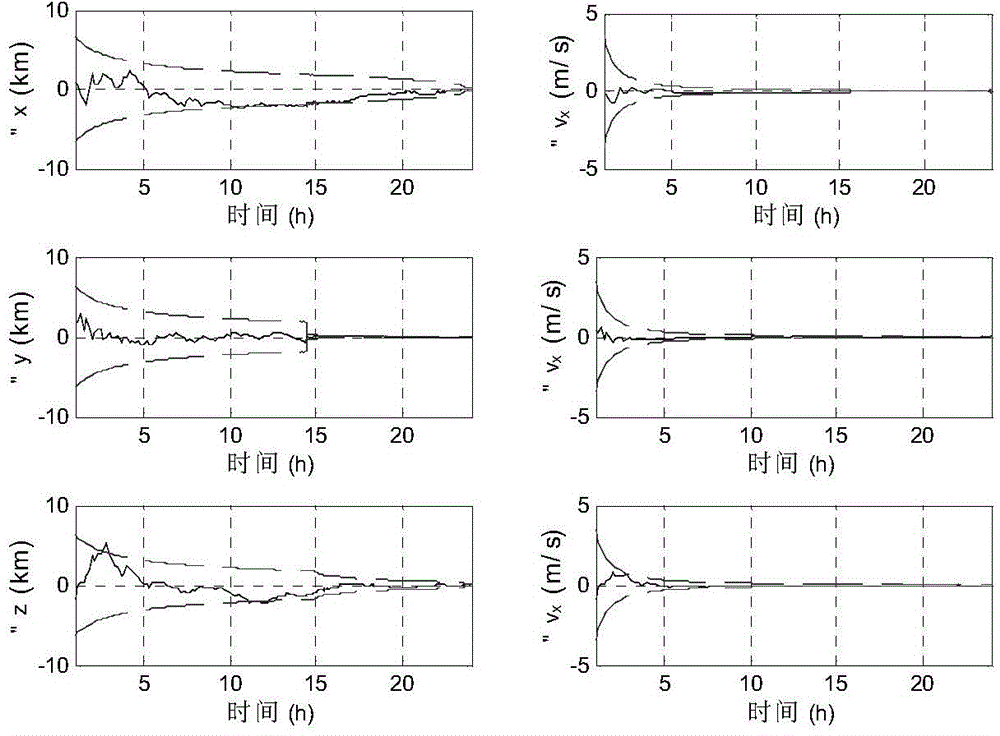
The invention discloses a mars ultimate approach segment autonomous navigation method based on multi-source information fusion, relates to a mars ultimate approach segment autonomous navigation method and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. The method is characterized in that optical measurement, radio measurement based on a mars orbiter and X-ray pulsar measurement information are combined based on a mars ultimate approach segment dynamical model, are effectively fused in the application range based on a federated filtering structure and are standby for one another, and the advantages of various navigation systems are fully exerted; on the basis of establishing a mars ultimate approach segment state model and a mars ultimate approach segment autonomous navigation model, detector real-time navigation status information is resolved by the utilization of an integrated navigation filtering algorithm of a federation structure to realize the mars ultimate approach segment autonomous navigation. According to the mars ultimate approach segment autonomous navigation method, the precision and the real time of the mars ultimate approach segment autonomous navigation can be improved, and the reliability and the fault tolerance of a navigation system can be improved. The method can provide a technical support for the design of a future mars exploration task autonomous navigation solution.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
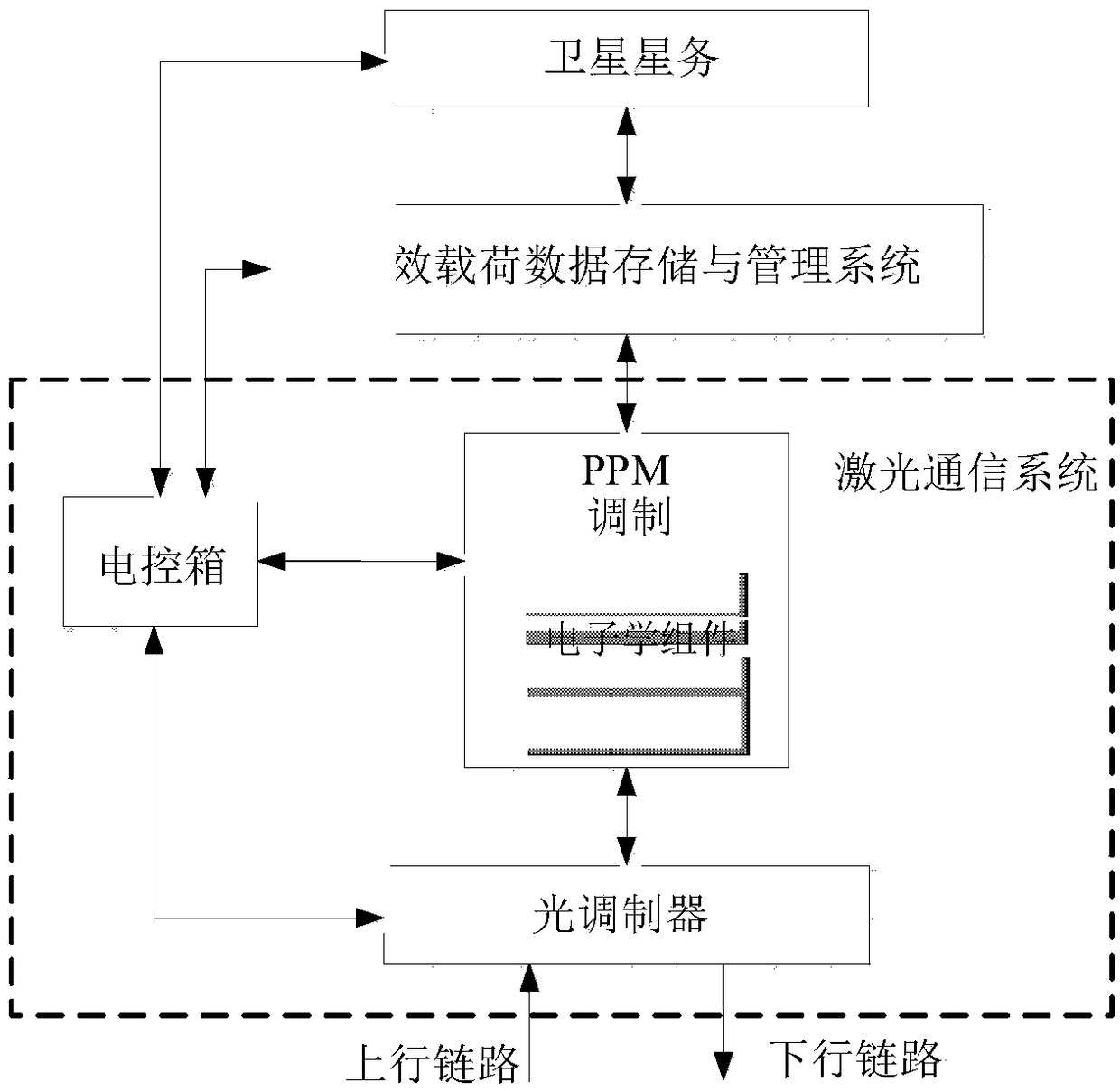
Ultra-long distance optical communication system and ultra-long distance optical communication method based on single-photon detection
The invention discloses an ultra-long distance optical communication system and an ultra-long distance optical communication method based on single-photon detection, which is particularly applicable to the occasions with ultra-long distance communication. In the invention, aiming at the contradictions between the international requirements on deep-space exploration and deep-space communication and the limits of traditional microwave communication system on power consumption, bandwidth and the like, the spatial optical communication mode with the following advantages is adopted: large channel capacity, low power consumption, small volume, light weight, high confidentiality, strong anti-interference and the like; based on the rising single-photon detection technology, the invention provides the ultra-long distance optical communication system and the ultra-long distance optical communication method based on single-photon detection; the coding modulation mode in which the differential pulse position modulation and the polarization modulation are combined with each other is adopted; furthermore, the spatial high-precision tracking, capturing and aiming technology is adopted; by the optical machine structure with reasonable design and the communication method of the system, the chain and system consumption of the spatial optical communication can be reduced; the communication bandwidth can be improved; and the power consumption of communication system can be greatly reduced, thus meeting the requirement on the ultra-long distance optical communication, therefore, the system and the method are especially applicable to the occasions with ultra-long distance optical communication.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
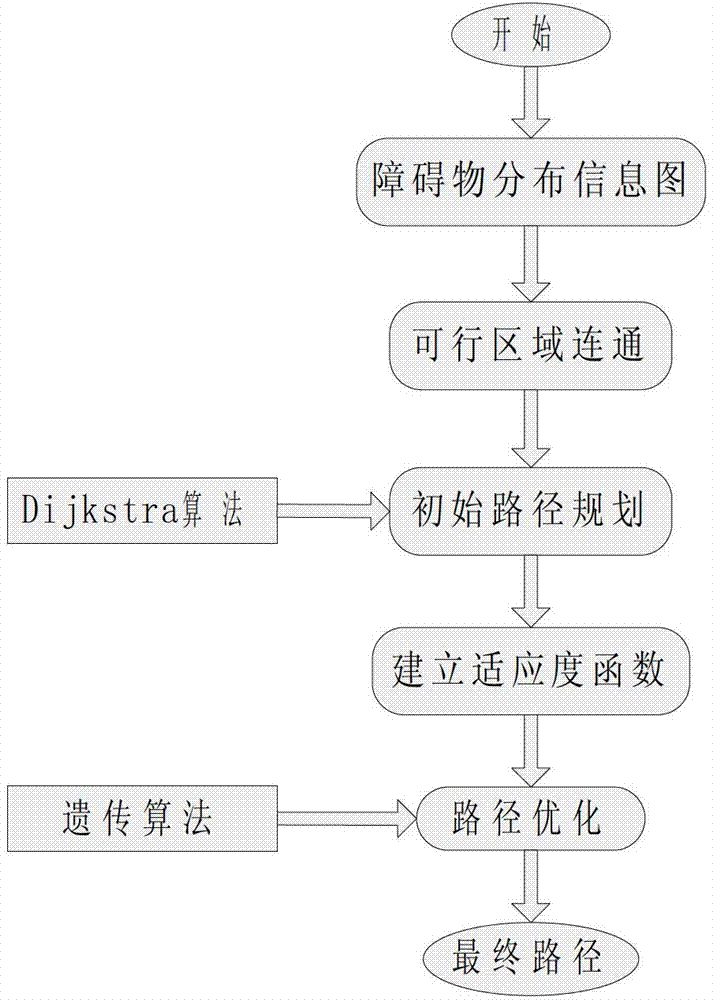
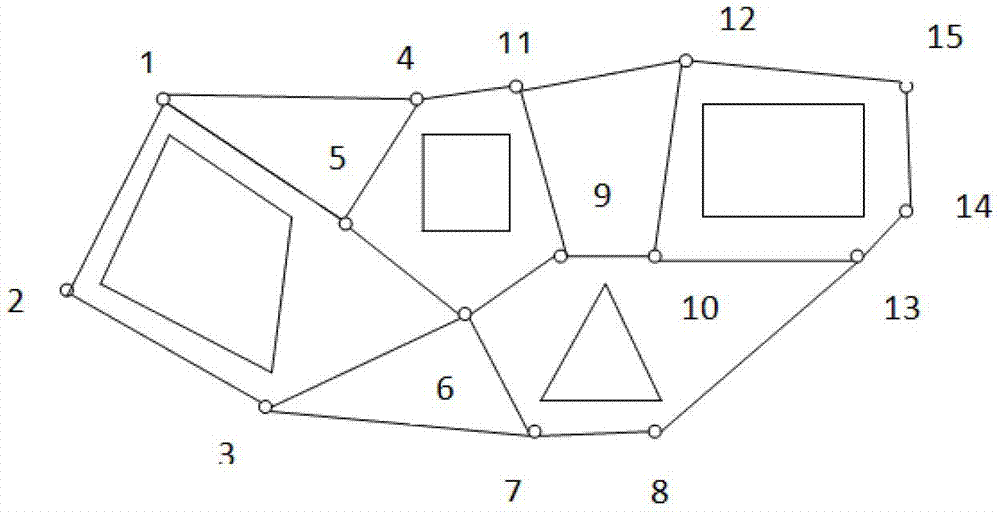
Rapid planning method for surface global path of planet
InactiveCN102929286AImprove versatilityEasy to mixPosition/course control in three dimensionsPath lengthAlgorithm
The invention relates to a rapid planning method for a surface global path of a planet, and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly obtaining an obstacle distribution information graph in a region to be subjected to path planning, carrying out analysis process on the graph, selecting a plurality of feasible nodes in the feasible region capable of avoiding obstacles and carrying out path connection in the feasible region according to the selected nodes; obtaining the coordinate information of the nodes, creating a network topology which the path planning needs by adopting a Dijkstra algorithm and planning an initial optimal path through taking the length of the path as the constraint condition; and taking the path length function as a fitness function, taking the mathematical function relationship followed in the process of selecting the nodes and the constraint range of the coordinates as a to-be-optimized object and the constraint condition of a genetic algorithm, optimizing the initial optimal path by adopting the genetic algorithm and outputting the optimization result used as the final planning path. The method has the advantages of simplicity in algorithm, high efficiency, good generality and strong expandability.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Parameterization simulation method of lunar probe soft landing dynamics
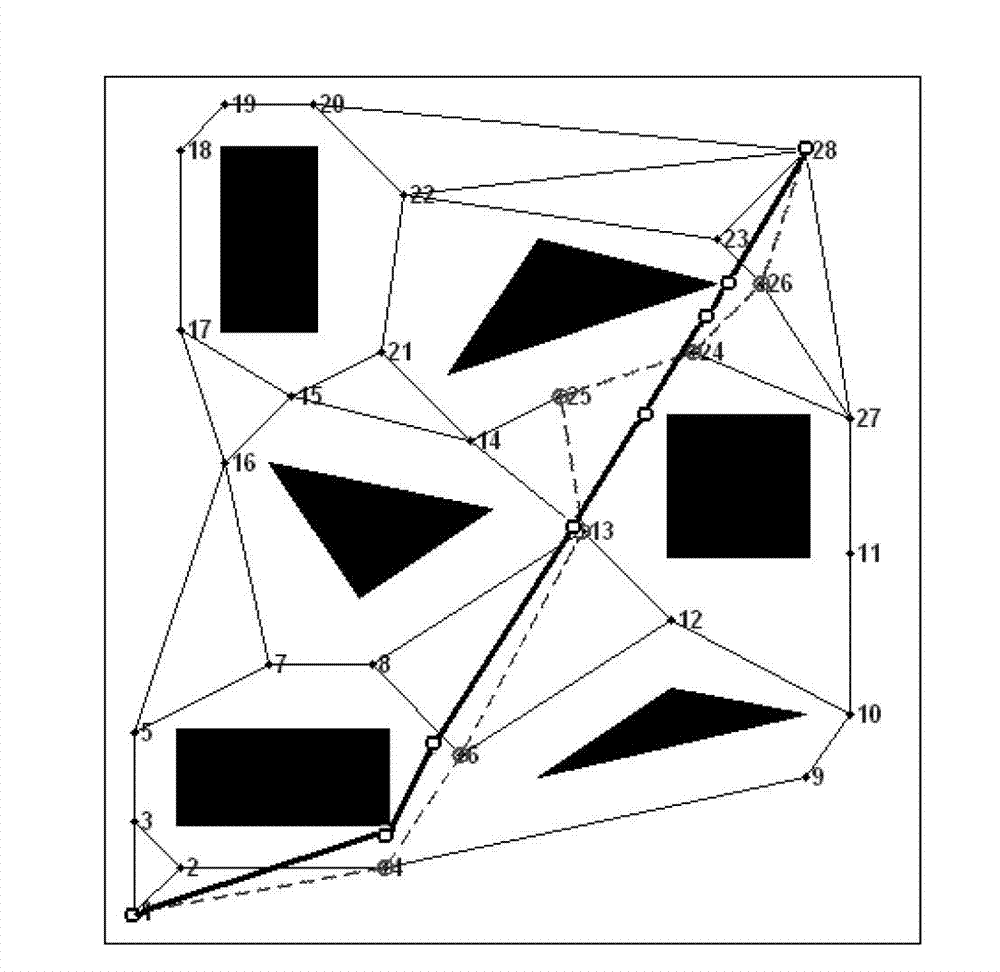
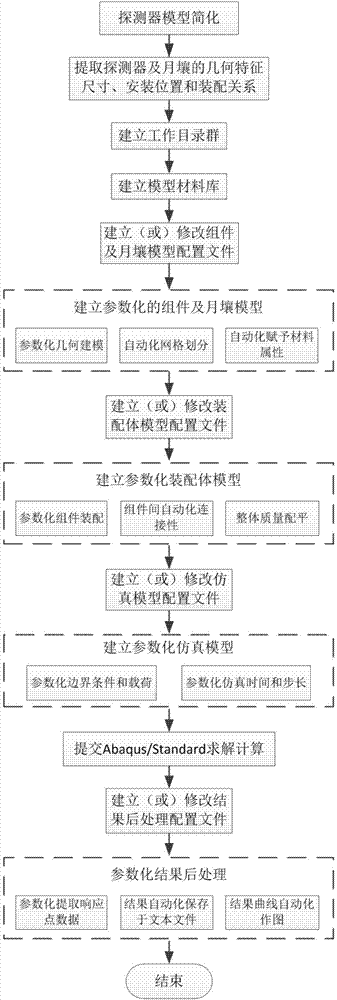
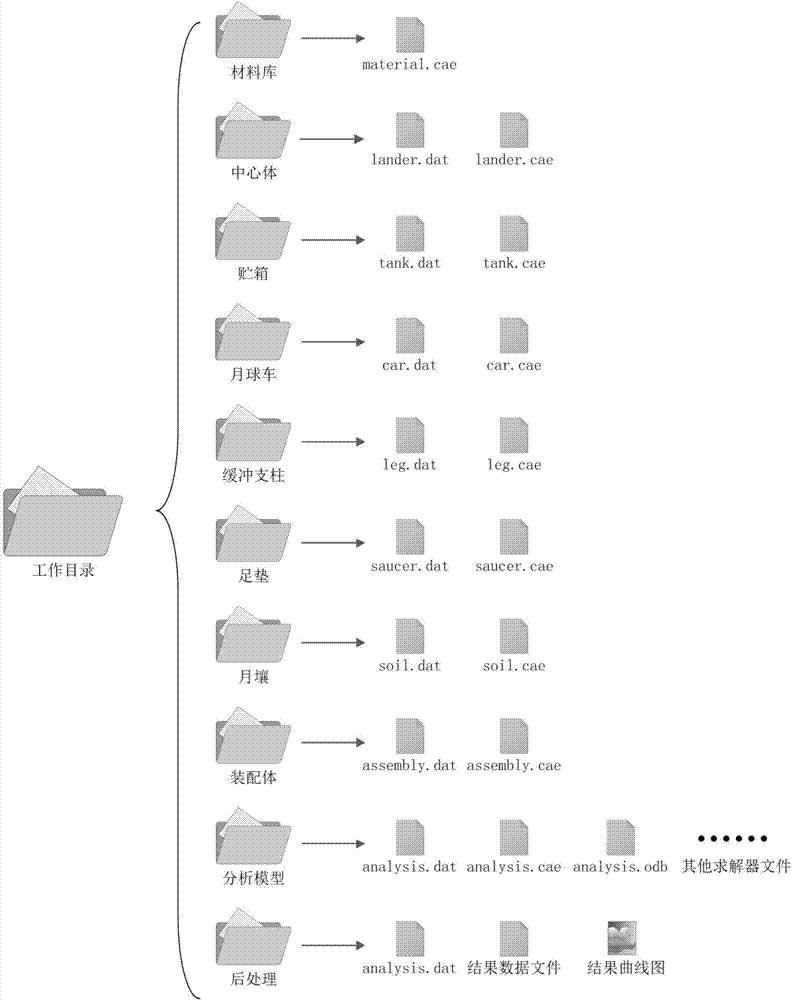
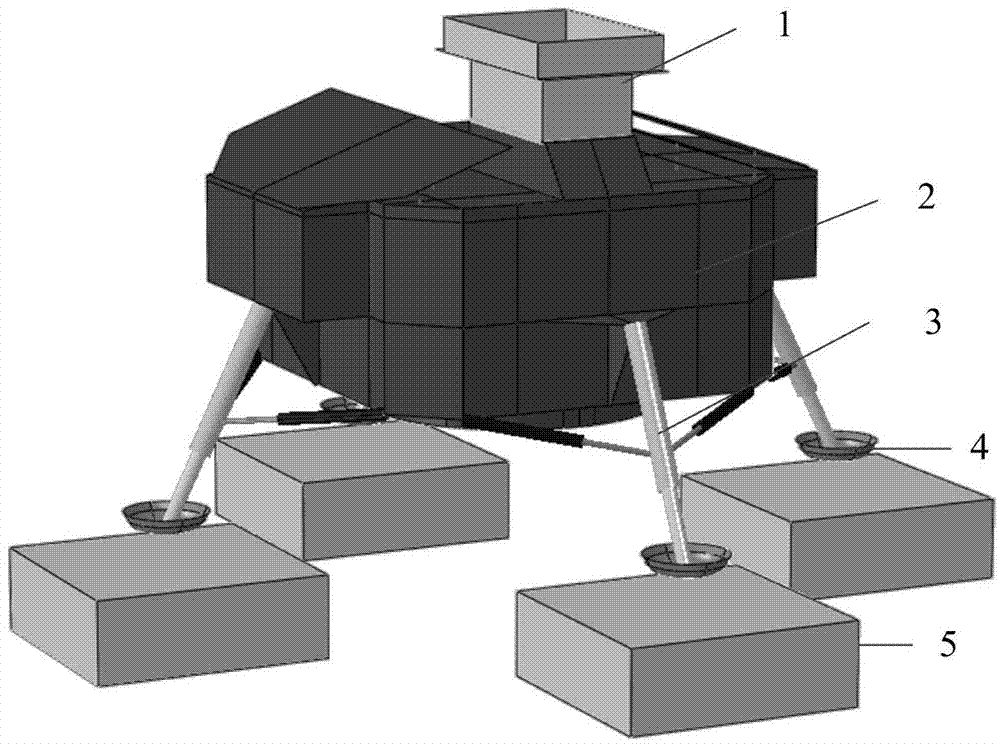
InactiveCN103678824AAutomate the creationSimple designSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelDeep space exploration
The invention relates to a parameterization simulation method of lunar probe soft landing dynamics, and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. The method integrates finite element modeling, solving calculating and result post-processing, finite element models of all components (including a center body, a fuel storage box, a lunar rover, buffering pillars and a foot pad) of a probe can be generated, and assembly, working condition setting, solving calculating and result extracting can be finished automatically. By means of the method, automatic establishing of a parameterization model of the lunar probe soft landing dynamics is realized, re-handling brought to designing personnel by re-meshing and component connection relationship re-setting which are caused by the fact that a certain characteristic is changed in the finite element modeling process of the lunar probe is avoided, and the problem of designing efficiency in the dynamics analysis of the lunar probe soft landing process in the prior art is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
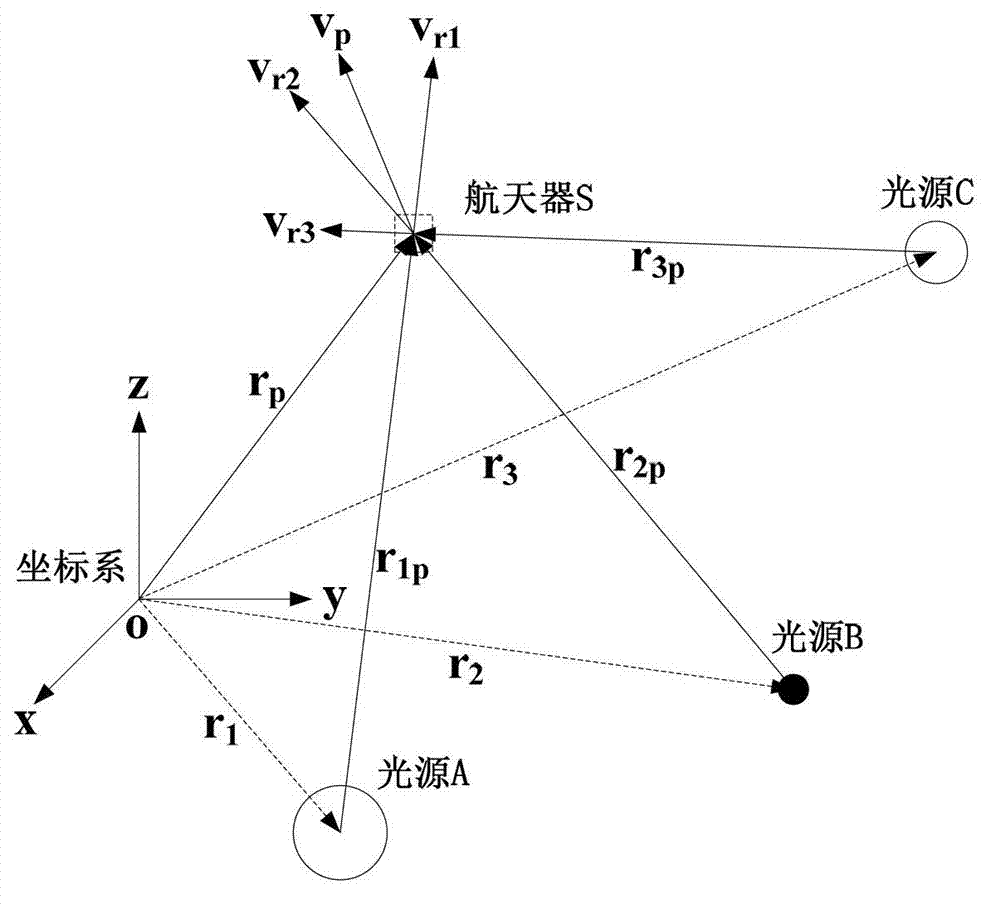
Spectrum red shift antimonous navigation method for spacecraft
ActiveCN103206955ARealize autonomous navigationNo delayInstruments for comonautical navigationCelestial bodyDeep space exploration
The invention provides a spectrum red shift antimonous navigation method for spacecraft. The method includes: directly using solar celestial bodies as light emitters in the solar system; allowing a spacecraft to receive spectral information by spacecraft-carrying spectrum red shift measurement sensors; acquiring speed parameter of the spacecraft according to spectrum red shift measured parameters and spacecraft attitude information measured by spacecraft starlight sensors; and acquiring location parameters of the spacecraft by integration. The principle of the method is simple, the method is novel and is new breakthrough in spacecraft autonomous navigation methods, the means of spacecraft navigation is expanded, navigation capacity is increased, and true autonomous spacecraft navigation is realized. The method is directly applicable to autonomous navigation tasks for deep space exploration in China, has promising application prospect in the field of deep space exploration, and provides references for antimonous navigation in near-earth spacecraft.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
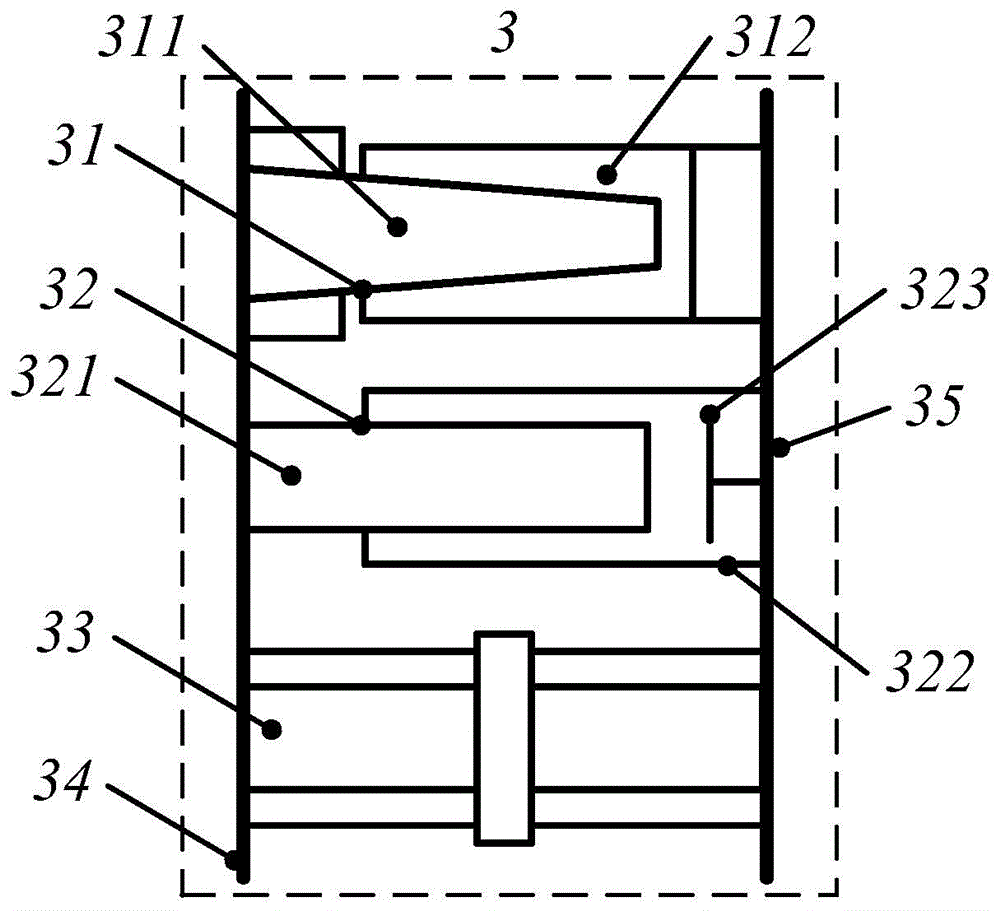
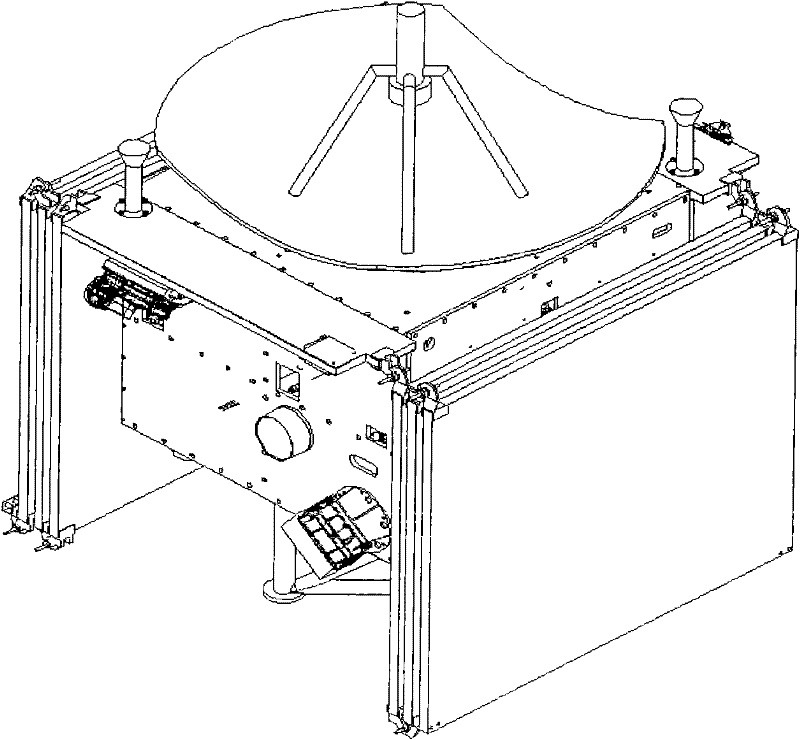
Eight-rod-connecting type non-contact satellite platform configuration and assembling method
ActiveCN104058102AFocus on ultra-precise and ultra-stable tasksFine-grained controlCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesDeep space explorationAstronomical telescopes
The invention provides an eight-rod-connecting type non-contact satellite platform configuration and an assembling method. The eight-rod-connecting type non-contact satellite platform configuration comprises an upper connecting plate, a lower connecting plate, four same vertical mounting force actuators and four same horizontal mounting force actuators; both the vertical mounting force actuators and the horizontal mounting force actuators are connected between the upper connecting plate and the lower connecting plate and are arranged in a circumference manner; the vertical mounting force actuators and the horizontal mounting force actuators are arranged along the same circumference in a staggered and orthorhombic manner; the vertical mounting force actuators are vertical to the horizontal mounting force actuators. The eight-rod-connecting type non-contact satellite platform configuration implements complete isolation of an effective load on platform vibration and interference response, can be applied to spacecrafts with high-resolution sensitive effective load, such as a very-high accuracy remote sensing satellite, a deep space exploration astronomical telescope and the like, and can greatly improve exploration performance of spacecrafts.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Space-based deep space relay communication satellite networking system
ActiveCN108494472AAvoid too small a problemReduce manufacturing costRadio transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersData accessGround station
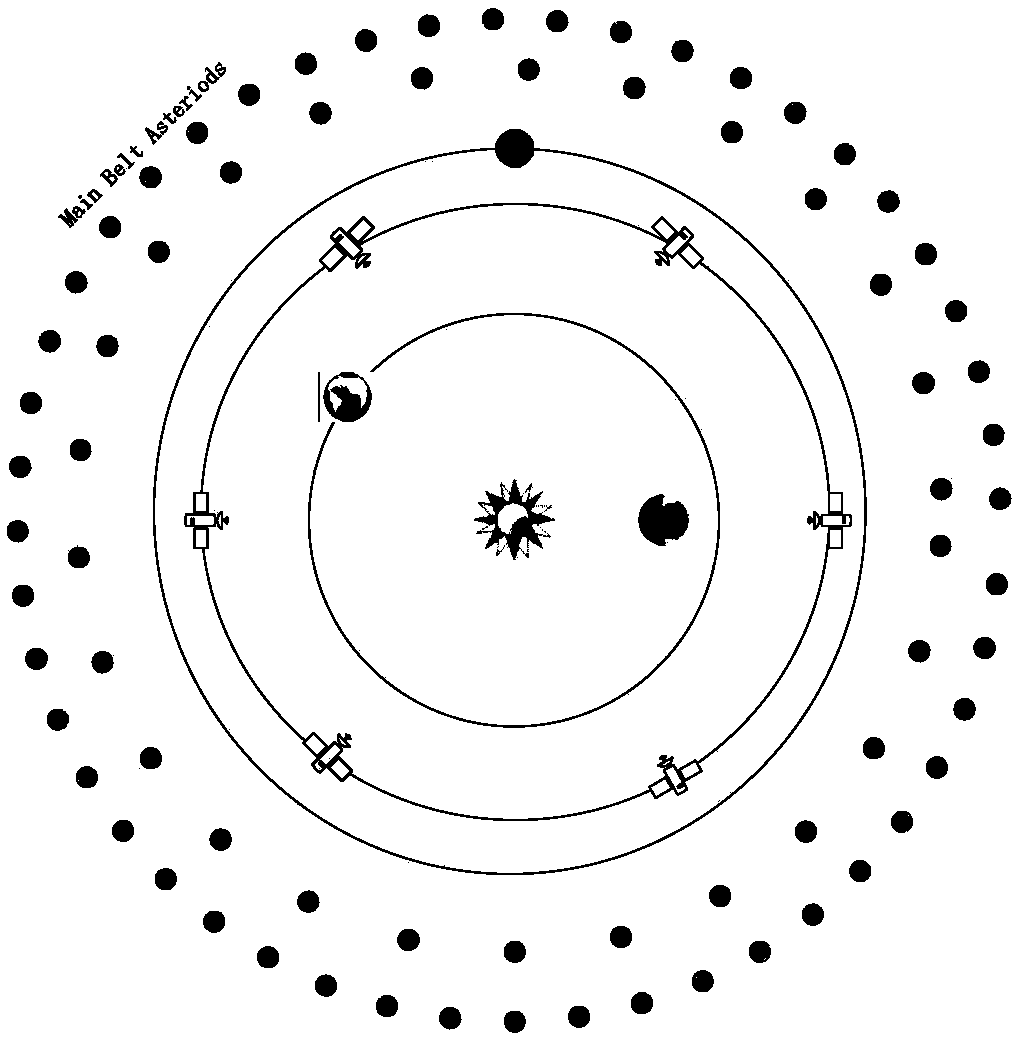
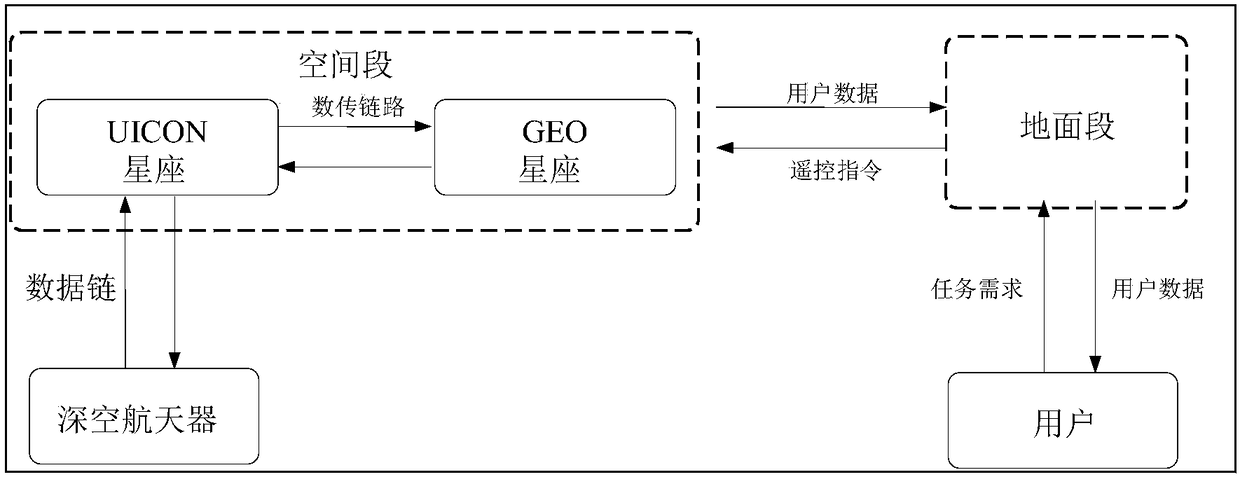
The invention discloses a space-based deep space relay communication satellite networking system. The system comprises a spacecraft and a ground station, wherein the spacecraft comprises a UNICON heliocentric constellation and a geosynchronous orbit constellation; the heliocentric constellation comprises six UNICON communication satellites which are arranged on a heliocentric orbit through constellation layout, and the geosynchronous orbit constellation comprises three GEO satellites which are located on a geosynchronous orbit; a user deep space detector transmits data to the UNICON heliocentric constellation and then sends the data to the ground station through the geosynchronous orbit constellation; two laser communication telescopes are arranged at the top of each UNICON communication satellite, each laser communication telescope can rotate by 180 degrees along the longitudinal axis, so that 360-degree scanning is realized, and laser communication can be carried out between every two communication satellites. The satellite system can provide high-speed uplink and downlink data access services for deep space exploration tasks of different data rates and different orbits.
Owner:北京中科深链空间科技有限公司
Spacecraft resource constraint processing method based on time topological sorting
InactiveCN104573856AEfficient use ofImprove computing efficiencyResource allocationForecastingTopological sortingResource constraints
The invention relates to a spacecraft resource constraint processing method based on time topological sorting and belongs to the technical field of autonomous control on spacecraft. The method comprises steps as follows: firstly, performing topological sorting on actions in planning results according to execution time of the actions; then layering the actions in a resource constraint network according to changes of resource numbers by the actions, and processing each resource mutation to improve the resource number computing efficiency. The method is particularly applicable to resource management in autonomous planning of spacecraft tasks in deep-space exploration. According to the method, the resource constraint network is adopted to describe resource information in planning, the changes of the resource numbers when a spacecraft executes the actions along with time are acquired through analysis of changes of apexes and edges in the network, advantages of an augmenting path method and a pre-flow push method for the maximum flow problem are combined, topological sorting is performed on resource mutations according to execution time, and the resource number computing process is optimized; resource constraint in the planning results can be effectively processed, and the computing efficiency is significantly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
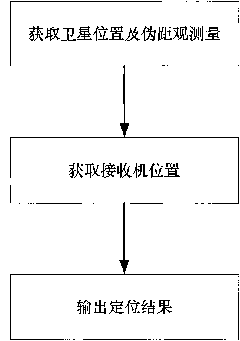
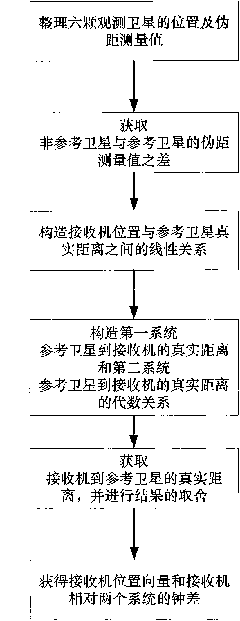
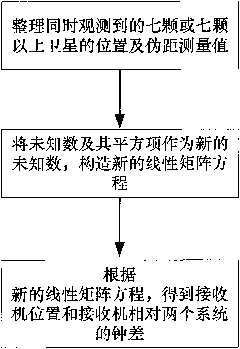
Method for positioning dual-system combined satellite navigation receiver
InactiveCN101799552APositioning results are reliableGuaranteed reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingDeep space explorationSystem combination
The invention discloses a method for positioning a dual-system combined satellite navigation receiver, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, acquiring positions of satellites and the pseudo-range observed quantity; secondly, according to different conditions for observing the satellites, adopting different steps to finish the positioning of the receiver so as to acquire the position of the receiver; and finally, outputting positioning results The method has two solutions according to the number of visible satellites: firstly, under the condition that two satellite systems have three visible satellites respectively, the position of the receiver can be acquired finally by using an algebraic processing method of a unary quadratic equation; and secondly, under the condition that the two satellite systems has seven or more visible satellites respectively, an observation equation set is converted into a linear equation set by using the redundancy of observation information, and a least square method is finally used to perform processing directly. The method needs no initial estimated value of a navigation position and also needs no iterated operation processing to ensure that the receiver can obtain a reliable positioning result during a deep space exploration and in other special environments.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
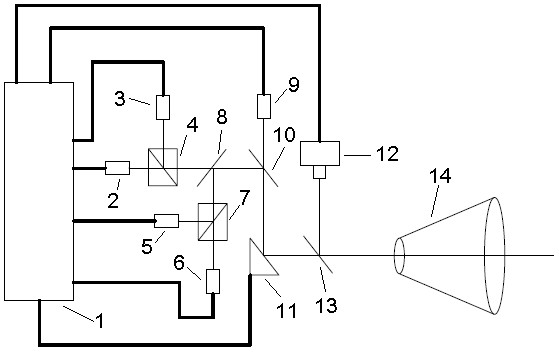
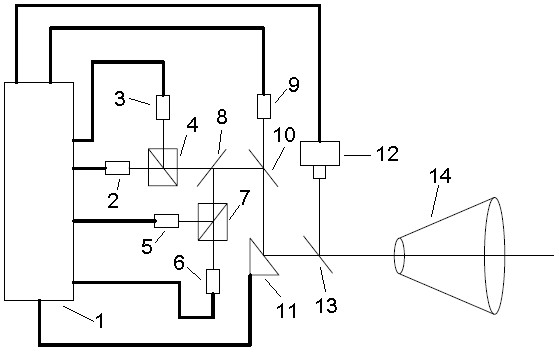
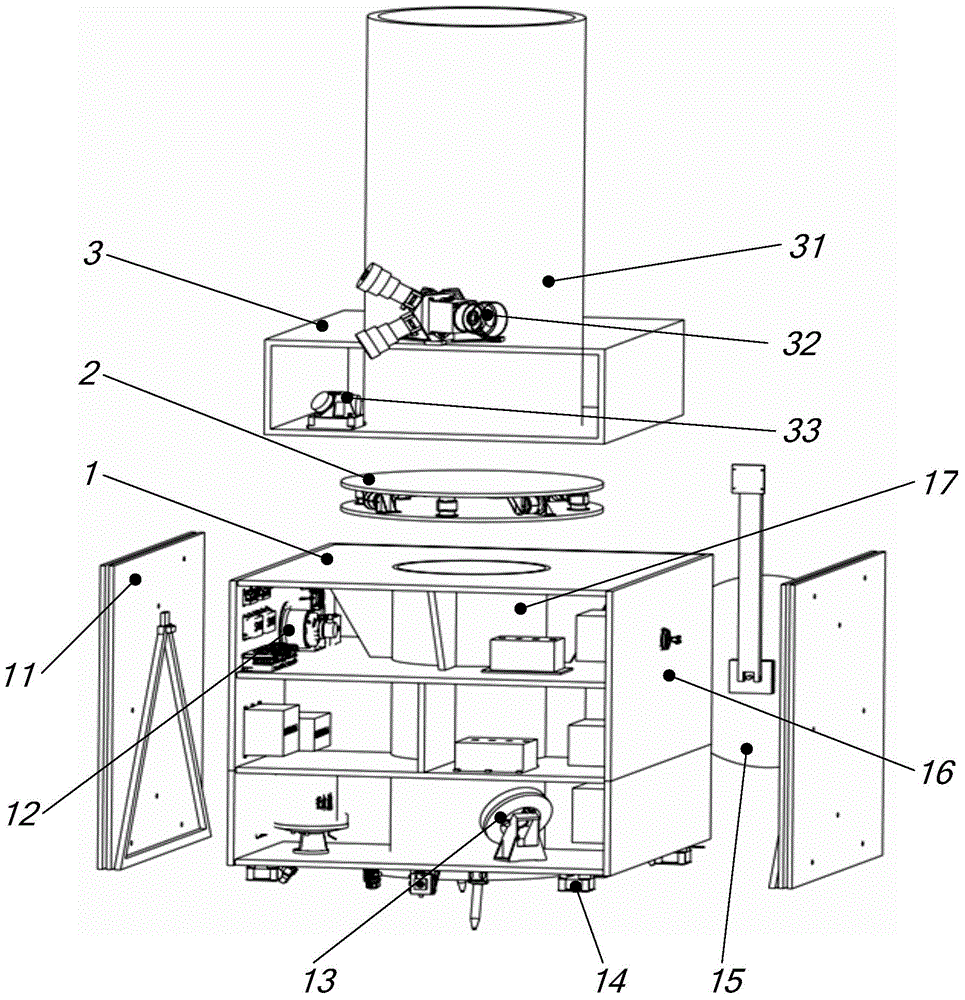
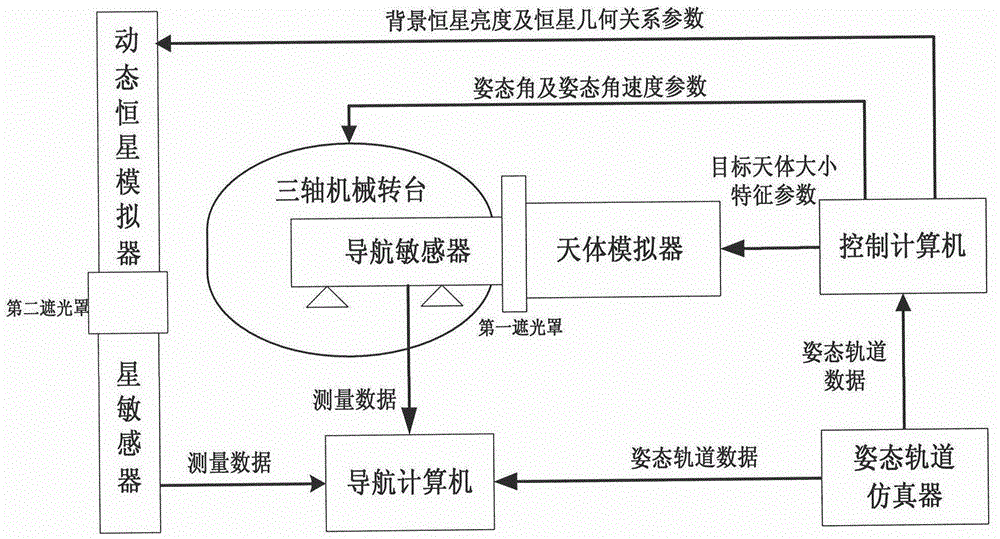
Optical imaging autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation testing system for deep space exploration proximity process
An optical imaging autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation testing system for a deep space exploration proximity process is characterized in that a navigation sensor is mounted on a rotary table to be docked with a celestial simulator, a star sensor is docked with a dynamic fixed star simulator, an attitude and orbit simulator generates deep space probe reference attitude and orbit data and transmits the data to a control computer and a navigation computer, the control computer drives the celestial simulator, the dynamic fixed star simulator and the rotary table to move, the celestial simulator simulates position changes of a deep space probe and a target celestial body, the dynamic fixed star simulator simulates inertial attitude changes of the deep space probe, the rotary table simulates attitude disturbance of the deep space probe, and the navigation computer acquires measurement data of the navigation sensor and the star sensor, performs navigation filtering computation and compares a computed result with the reference data so that autonomous navigation precision is obtained. The optical imaging autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation testing system for the deep space exploration proximity process achieves hardware-in-the-loop semi-physical simulation testing on the basis of real measurement data of the sensors and can effectively test and verify the performances of an optical imaging autonomous navigation system for the deep space exploration proximity process on the ground.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Method for lateral prediction correction guidance in stage of entering mars atmosphere
InactiveCN105115512AGuaranteed accuracyFlexible planningInstruments for comonautical navigationDeep space explorationOrbit
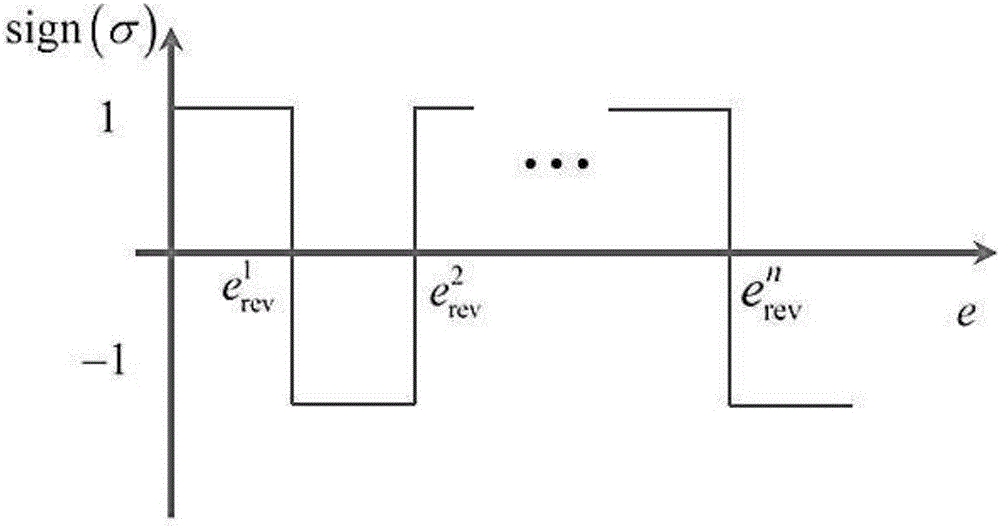
The invention discloses a method for lateral prediction correction guidance in the stage of entering mars atmosphere, relates to a lateral prediction correction guidance method and belongs to the technical field of deep-space exploration. On the basis of a conventional longitudinal prediction correction guidance method, the prediction correction method is introduced into design of a detector lateral motion guidance law. Firstly, lateral motion constraint conditions required by a landing detection task are determined, so as to determine heeling angle inversion frequency required by a detector at the entering stage; then, lateral motion constraint conditions are solved to determine energy of the detector at the heeling angle inversion moment, and when the energy of the detector exceeds energy at the heeling angle inversion moment, heeling angle inversion is carried out. After the constraint conditions are met, next heeling angle inversion energy is determined; finally, a current guidance cycle is determined by combing energy at the heeling angle inversion moment and the longitudinal guidance law and output is guided finally. By adopting the method provided by the invention, while parachute-opening point position accuracy is ensured, lateral motion of the detector entering an orbit can be flexibly planned according to task needs and fuel is saved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Autonomous navigation method for planet in final approaching section
InactiveCN103234538AHigh implementabilityHigh measurement accuracyNavigation instrumentsPulsarState model
The invention relates to an autonomous navigation method for a planet in a final approaching section, which belongs to the field of deep space exploration. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a state model of the planet in the final approaching section; carrying out radio measurement and communication through a detector and planetary orbiters determined by n positions, observing m pulsars and establishing an autonomous navigation measurement model of the planet in the final approaching section; and calculating the state of the detector through navigation filtering based on the two models. According to the invention, measurement characteristics of pulsar navigation and radio navigation are combined in the autonomous navigation method, a non-linear filtering method is employed, so autonomous navigation of the planet in the final approaching section is realized, precision and instantaneity of autonomous navigation of the planet in the final approaching section are improved, and the autonomous navigation method has good exploitativeness and high measurement precision and can satisfy the requirement for instantaneity of autonomous navigation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Planet landing motion simulation system and method based on air-floating platform
The invention discloses a planet landing motion simulation system and method based on an air-floating platform, wherein the system comprises of a three degree-of-freedom air flotation supporting subsystem, a single degree-of-freedom air flotation supporting subsystem, a motion assisting subsystem, an air flotation system main platform, a thrust executing subsystem, a pose measurement subsystem and a controller. According to the invention, the three degree-of-freedom air flotation supporting subsystem, the single degree-of-freedom air flotation supporting subsystem, the air flotation system main platform and the thrust executing subsystem are used for simulating the motion of a spacecraft in space, a force applying device with a given original state is used for driving the spacecraft to reach an original operation state, a gravitation simulating applied force device is used for simulating gravitation between the spacecraft and a planet. By using the planet landing motion simulation system and method, a complex deep-space environment can be simulated, full physical simulation of the planet landing motion is realized, the cost-effectiveness of an aircraft is improved, the risk is reduced, the development cycle is shortened, and the planet landing motion simulation system and method have significant meanings on deep space exploration, planet landing research and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
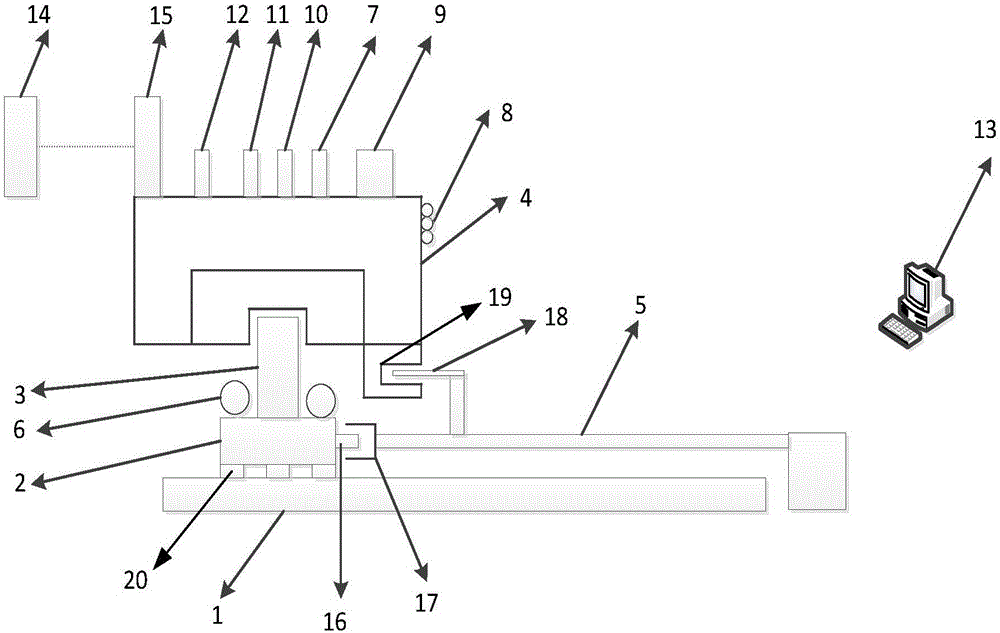
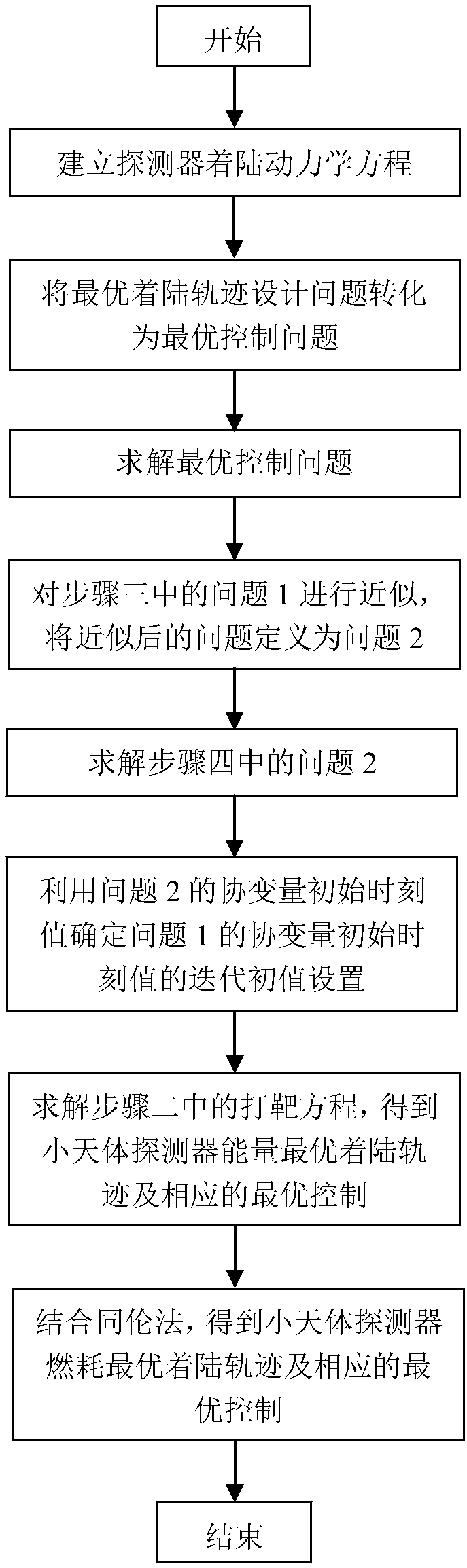
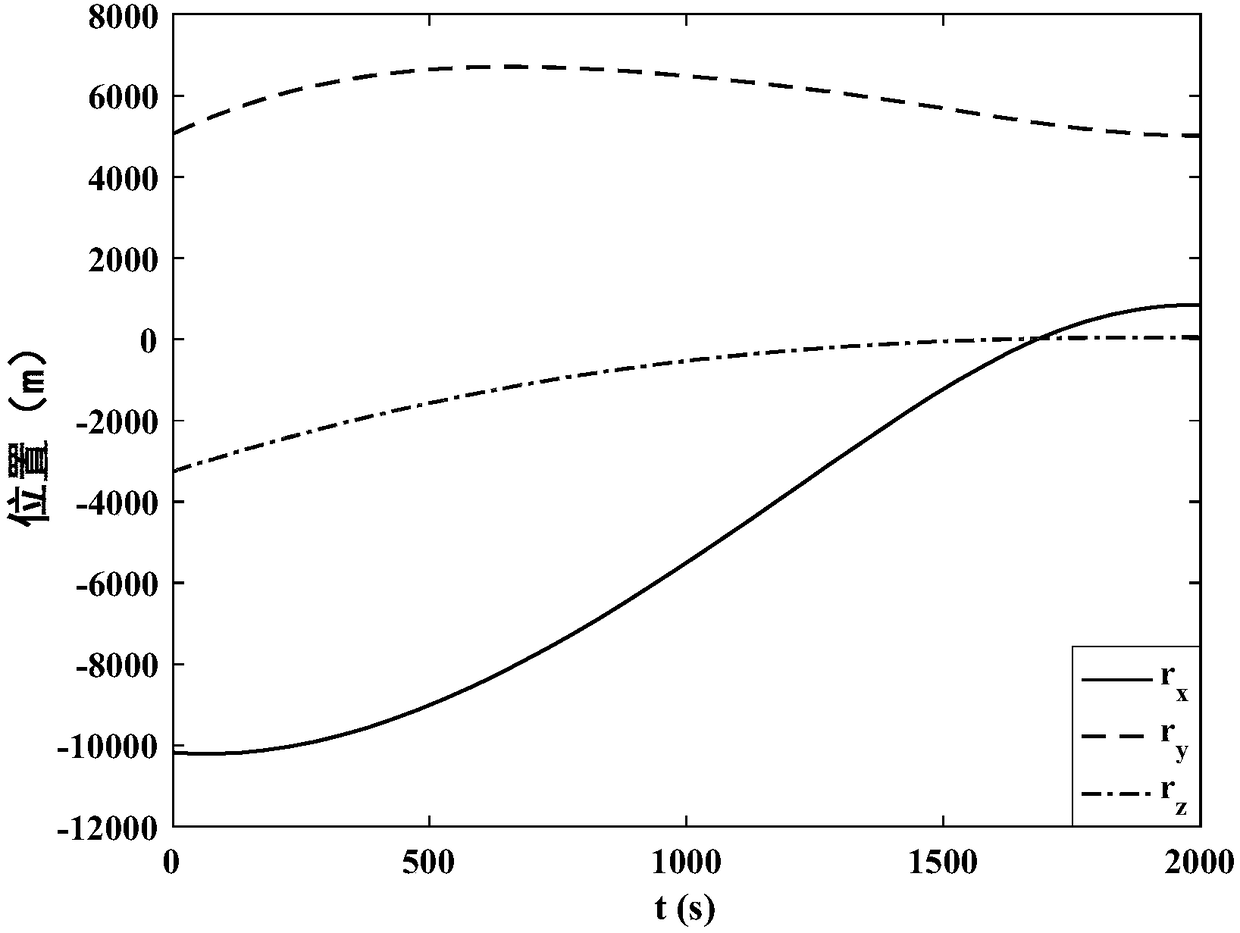
Covariant initial value determination method for optimal landing track design
ActiveCN108196449ASolve the defects that are not easy to solveSmall amount of calculationAdaptive controlDeep space explorationOptimal control
The invention discloses a covariant initial value determination method for the optimal landing track design and belongs to the field of deep space exploration. The covariant initial value determination method includes building a small body fixing coordinate system and corresponding detector landing kinetic equations; converting the optimal design problem of the small body landing track into the optimal control problem and the corresponding two-point boundary value problem, and defining the problems as the problem 1; approximating the problem 1, and defining the approximated problem 1 as the problem 2; solving the covariant initial values lambda<r2(t0)> and lambda<v2(t0)> of the problem 2, setting the the covariant initial values lambda<r2(t0)> and lambda<v2(t0)> of the problem 2 as iterative initial values of the covariant initial values lambda<r1(t0)> and lambda<v1(t0)> of the problem 1, determining the iterative initial value of the covariant initial value lambda<m1(t0)> of the problem 1 according to the setting of the iterative initial values, namely lambda<r2(t0)> and lambda<v2(t0)>, of the covariant initial values lambda<r1(t0)> and lambda<v1(t0)> of the problem 1, thereby achieving the iterative initial value setting of the covariant initial values for the optima landing track design. The defect that it is difficult to solve the two-point boundary value problem due to improper initial value setting can be avoided by application of the method.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
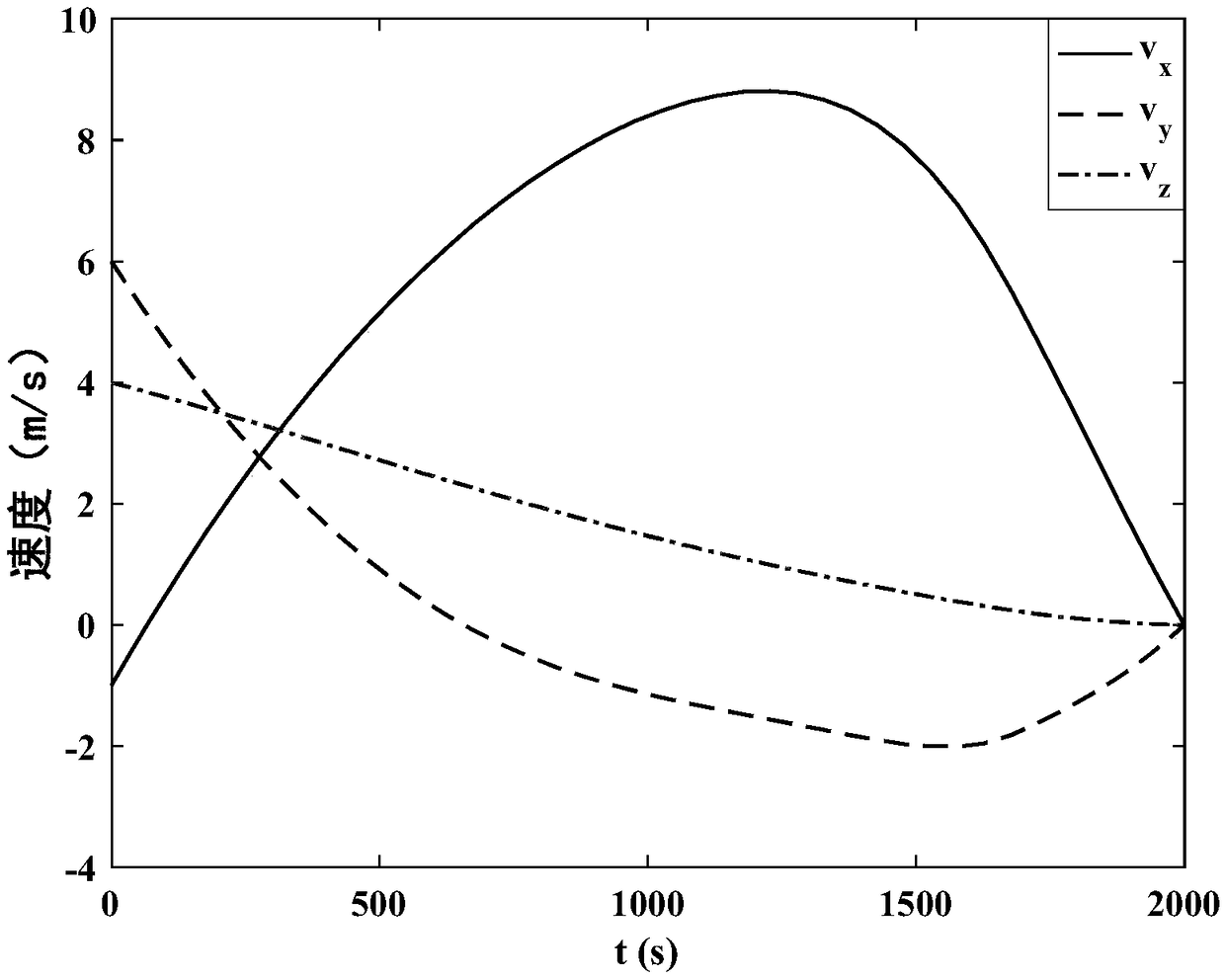
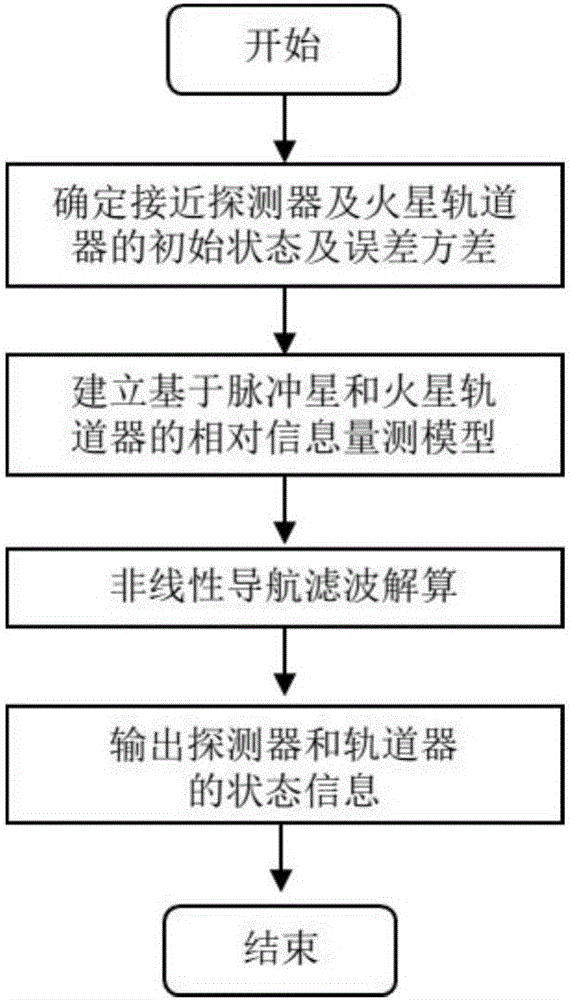
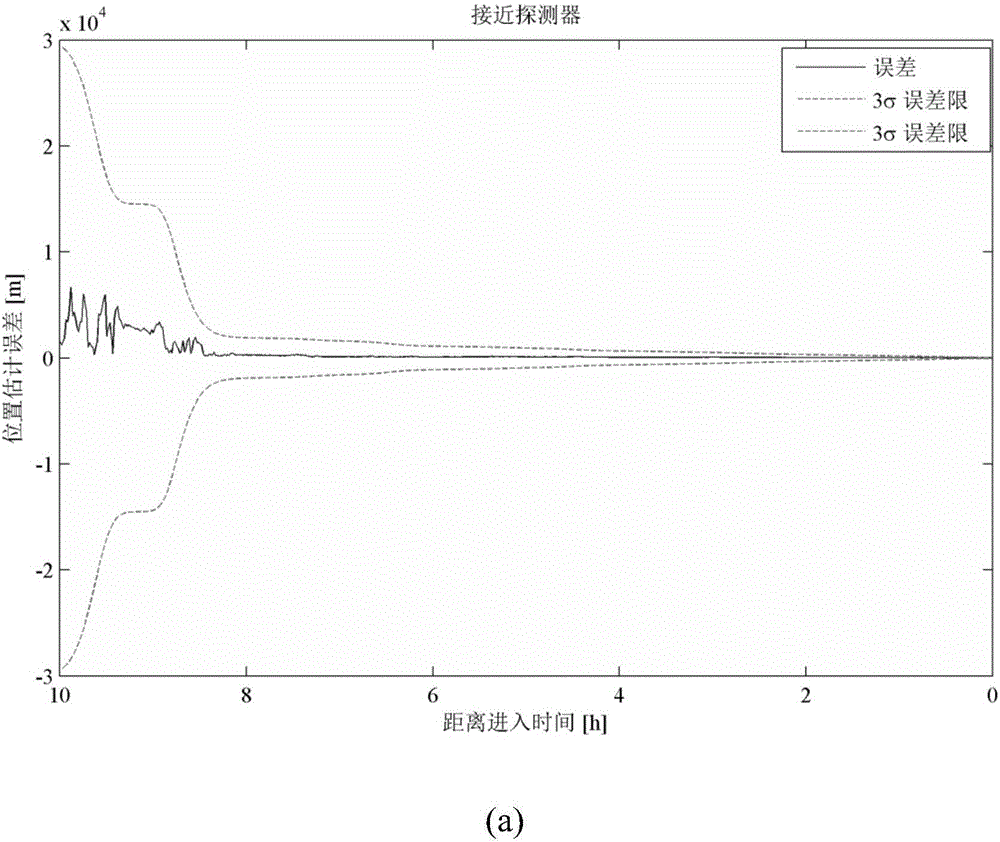
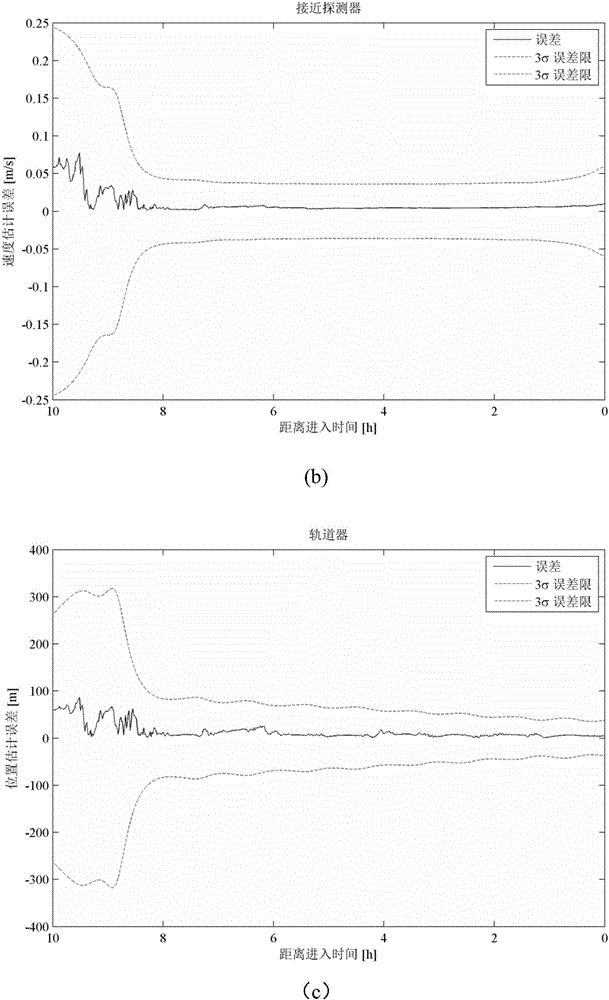
Mars final approaching section autonomous navigation method based on relative measurement information
ActiveCN106679675AHigh precisionFast convergenceInstruments for comonautical navigationNonlinear filterEntry point
The invention discloses a Mars final approaching section autonomous navigation method based on relative measurement information, and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. For achieving Mars final approaching section autonomous navigation, a final approaching and surrounding dynamic model is established. According to differential information of X-ray pulsar arrival time and Doppler velocity measurement information of a Mars orbiter, based on nonlinear filtering algorithm, the states of an approaching detector and the Mars orbiter undergo joint estimation, absolute navigation is achieved through utilization of two kinds of relative measurement information including the differential information of X-ray pulsar arrival time and the Doppler velocity measurement information of the Mars orbiter, and the accuracy of Mars final approaching section autonomous navigation and the accuracy of entry point state estimation are improved. The method has the following advantages: introduction of a planet ephemeris error is avoided, the adverse effect on navigation performance due to nondeterminacy of pulsar parameters is limited, the problem of state divergence resulting from long observation time of pulsars is overcome, the navigation performance of two detectors is improved at the same time, and the navigation filter accuracy and the convergence speed are increased.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Planet landing obstacle avoidance control method based on collision probability
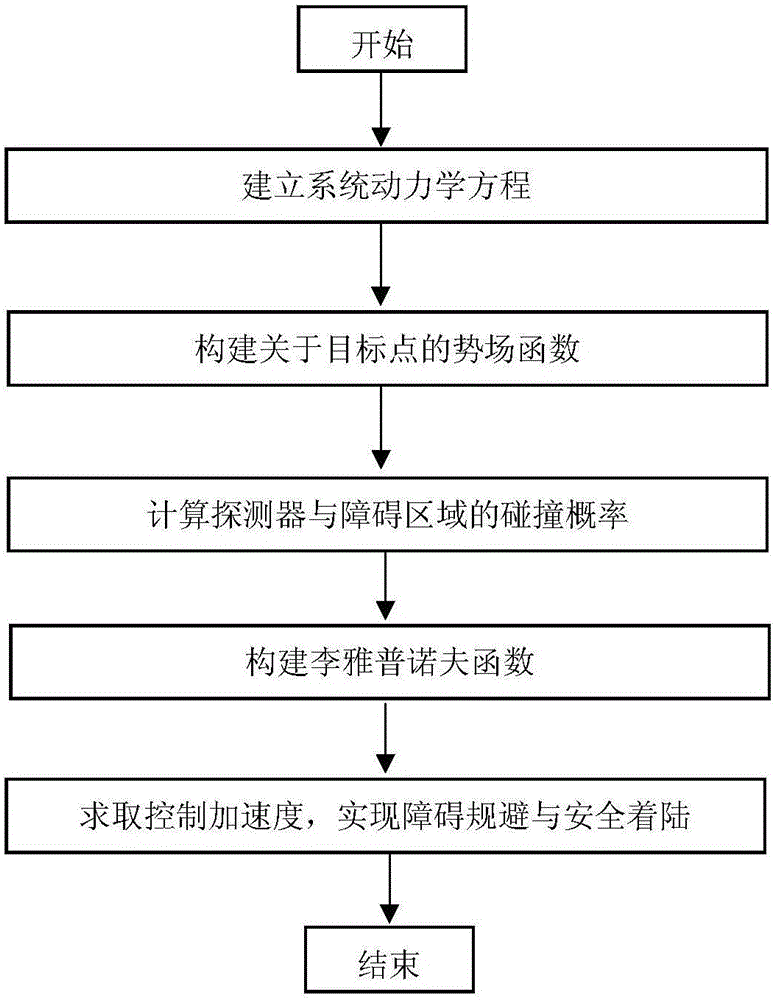
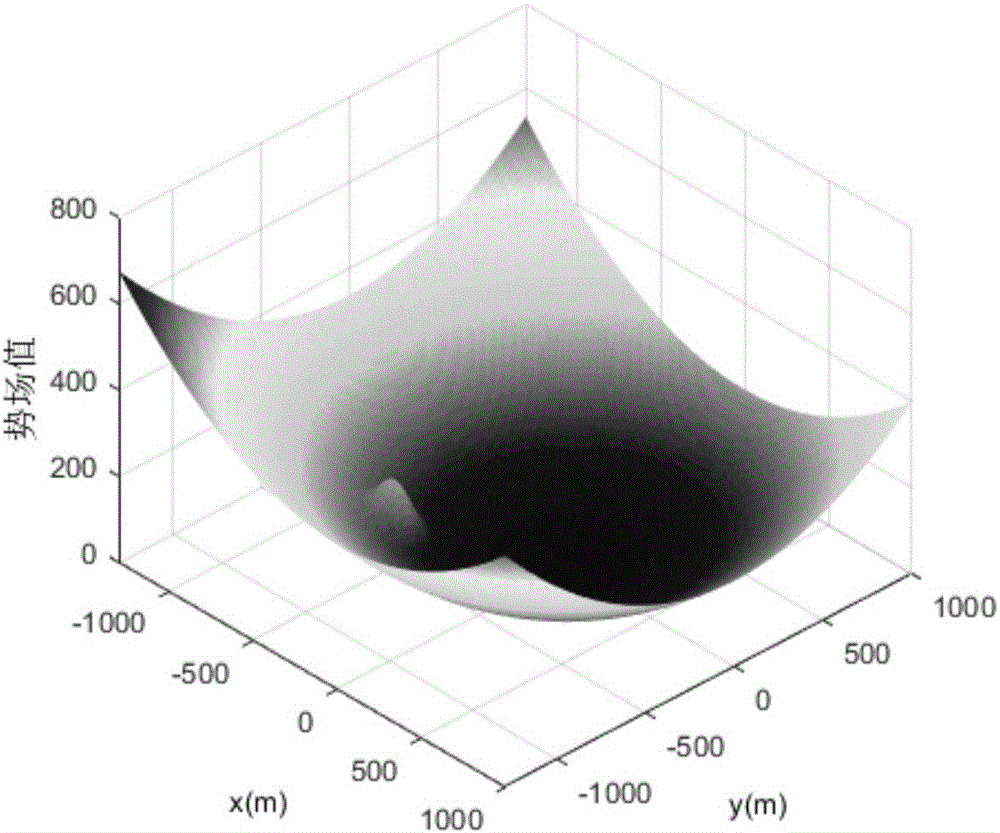
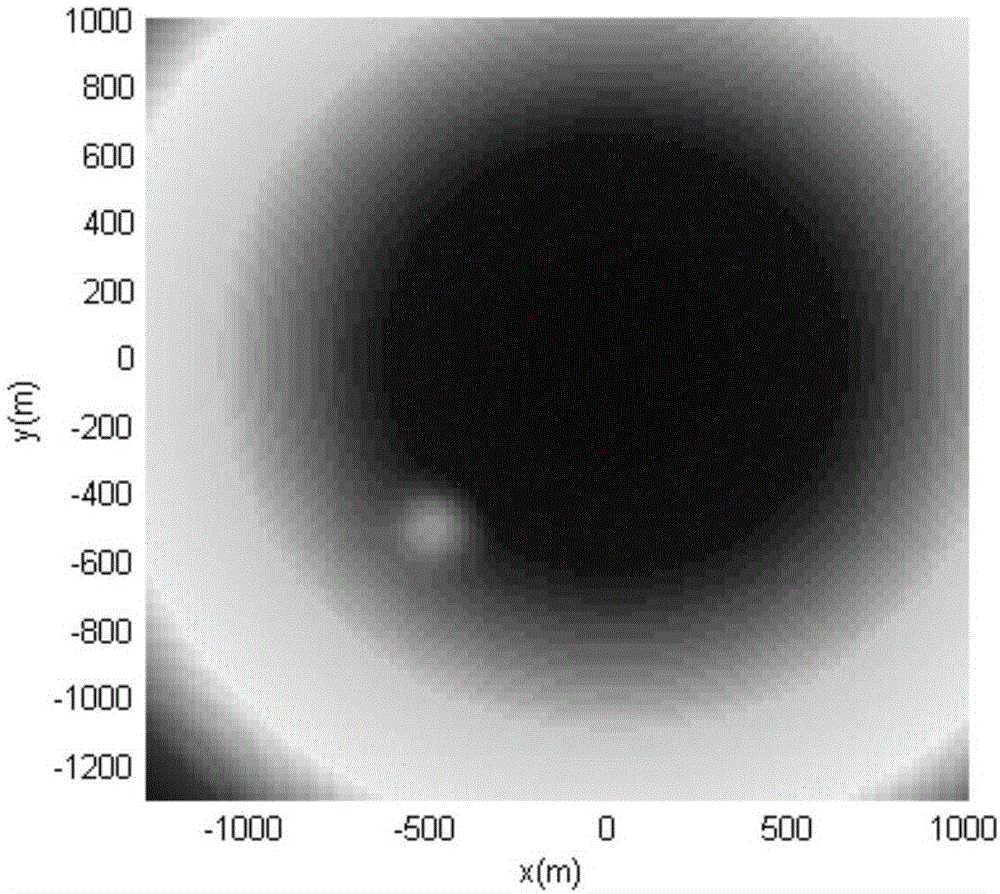
ActiveCN106249756AEvasion is effectiveRealize autonomous safe and precise landingPosition/course control in three dimensionsLyapunov stabilityDeep space exploration
The invention discloses a planet landing obstacle avoidance control method based on a collision probability, which relates to a planet landing obstacle avoidance control method and belongs to the field of deep space exploration. The realization method comprises steps: a system dynamics equation is built; a potential function about a target point in a Lyapunov function is built, a detector is ensured to approach the target landing point, and the target landing speed is also met; a covariance matrix for the detector position is introduced, and the collision probability between the detector and each obstacle area is calculated; based on the collision probability, the Lyapunov function is built, a Lyapunov stability principle is used for acquiring a control acceleration, the acquired acceleration is used for controlling the detector landing trajectory. Influences on the detector obstacle avoidance control by multiple perturbations on the surface of the planet and an uncertain environment can be reduced, complicated obstacles on the surface of the planet can be effectively avoided, and autonomous, safe and accurate landing is realized. The method of the invention also has the advantages of good robustness and high real-time performance.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com