Patents
Literature
634results about "Systems for re-entry to earth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
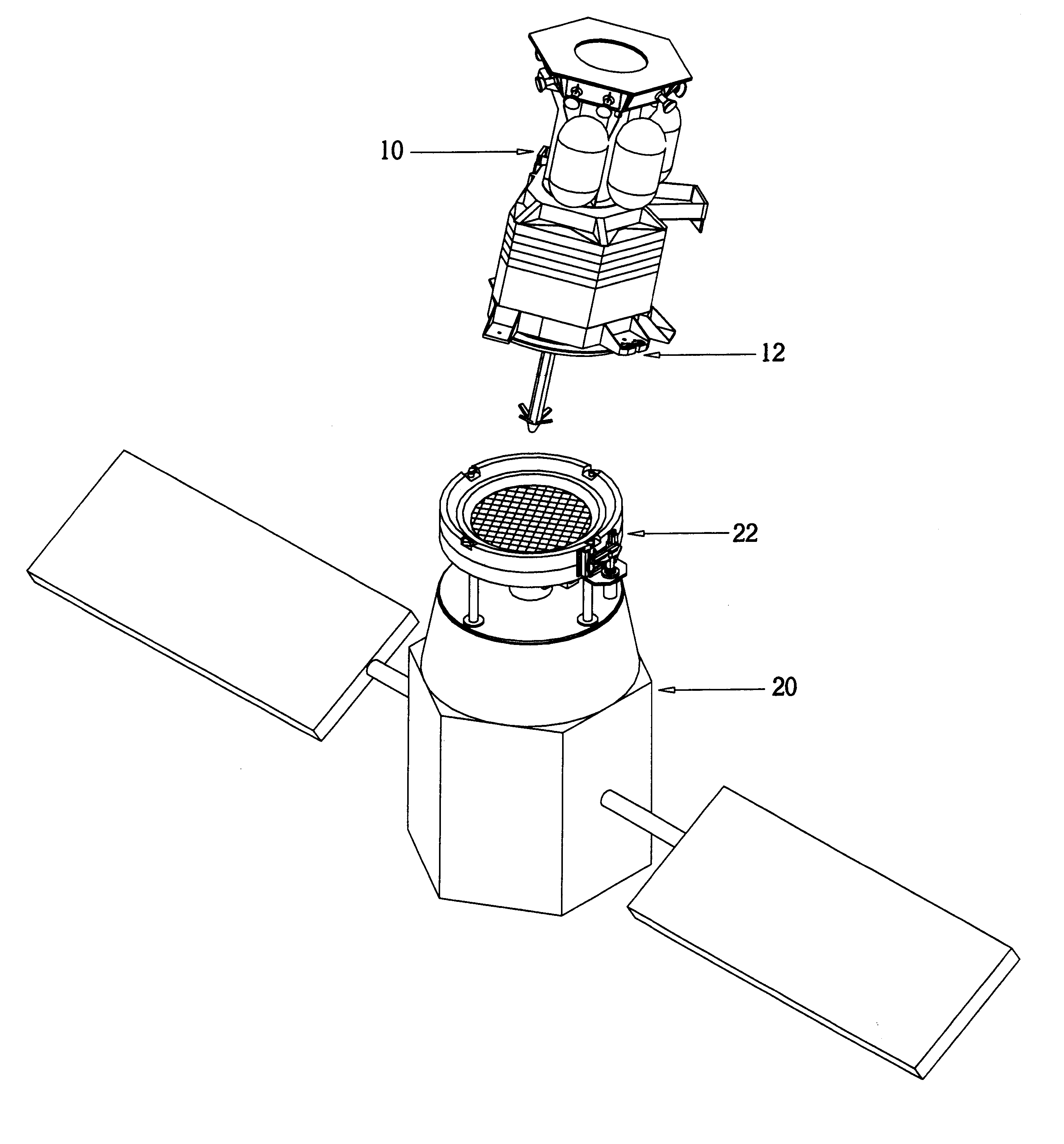
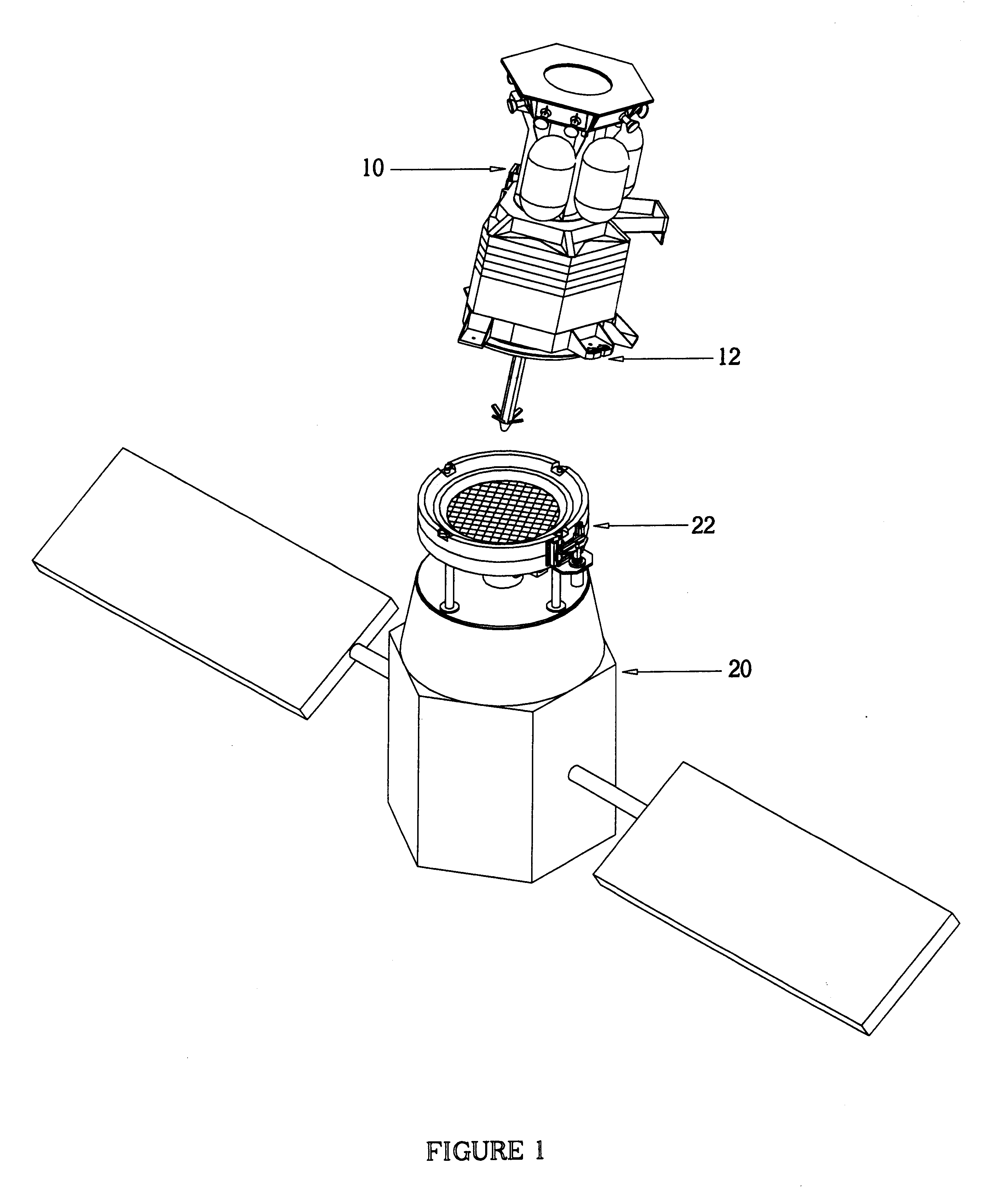
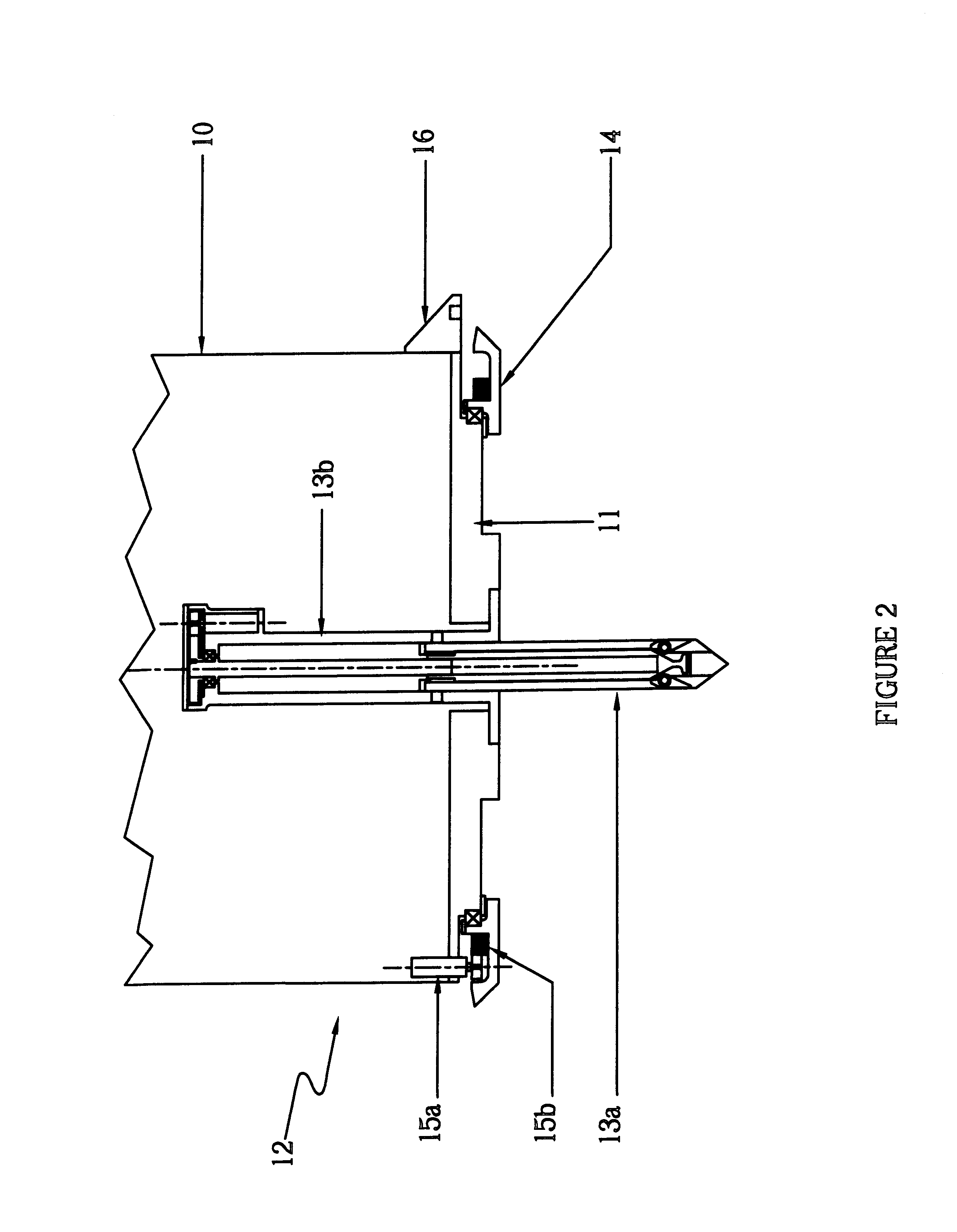
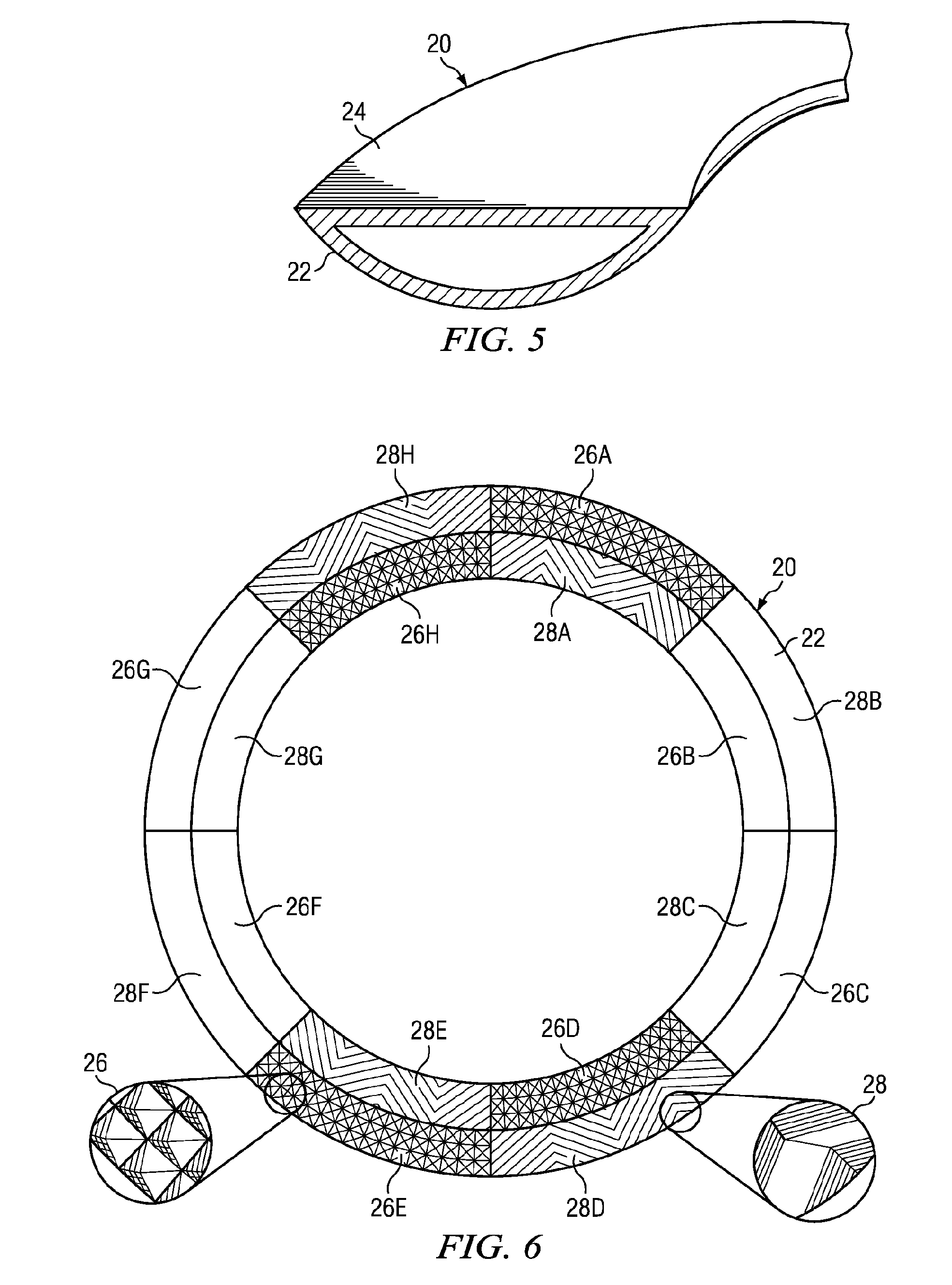
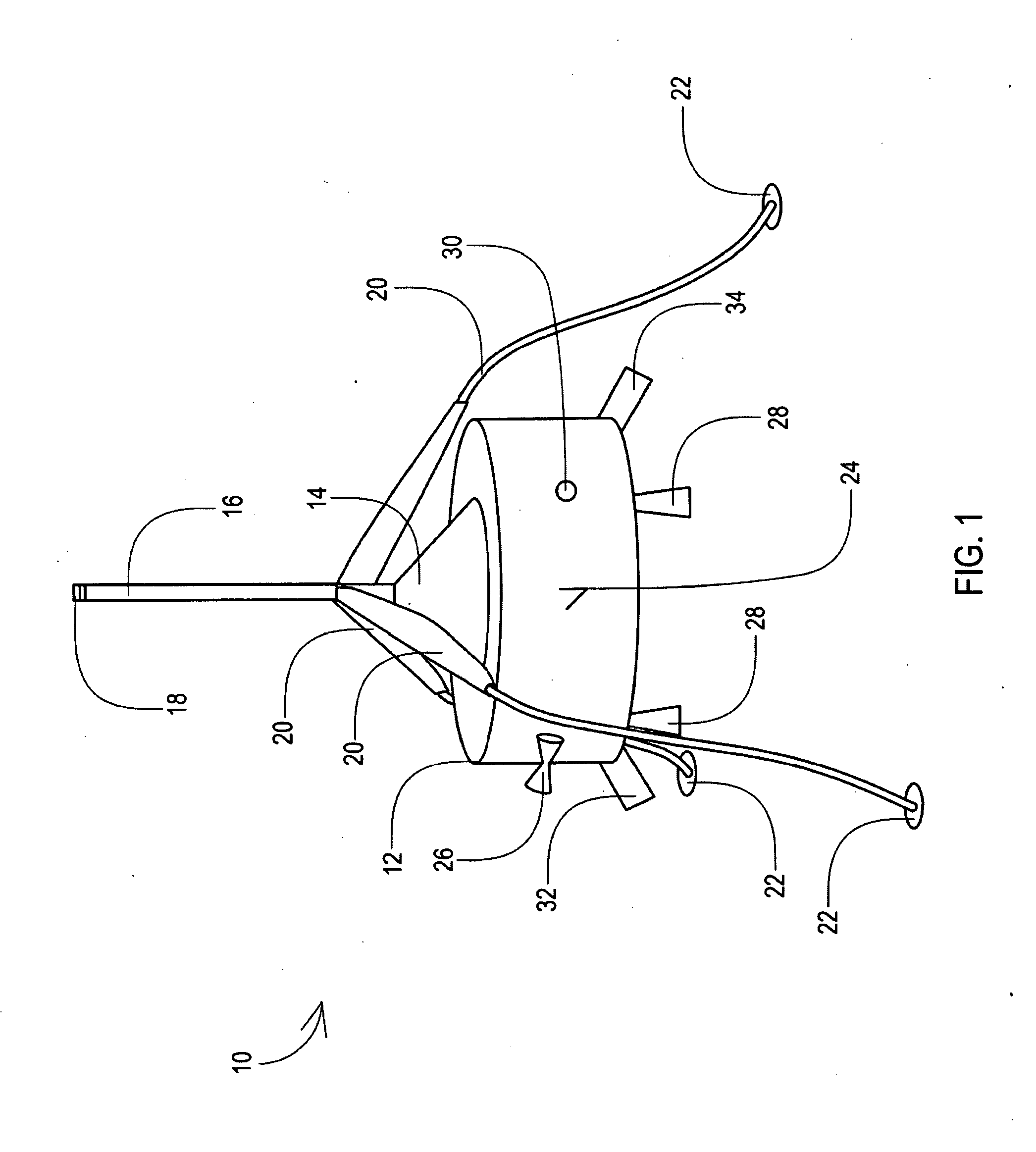
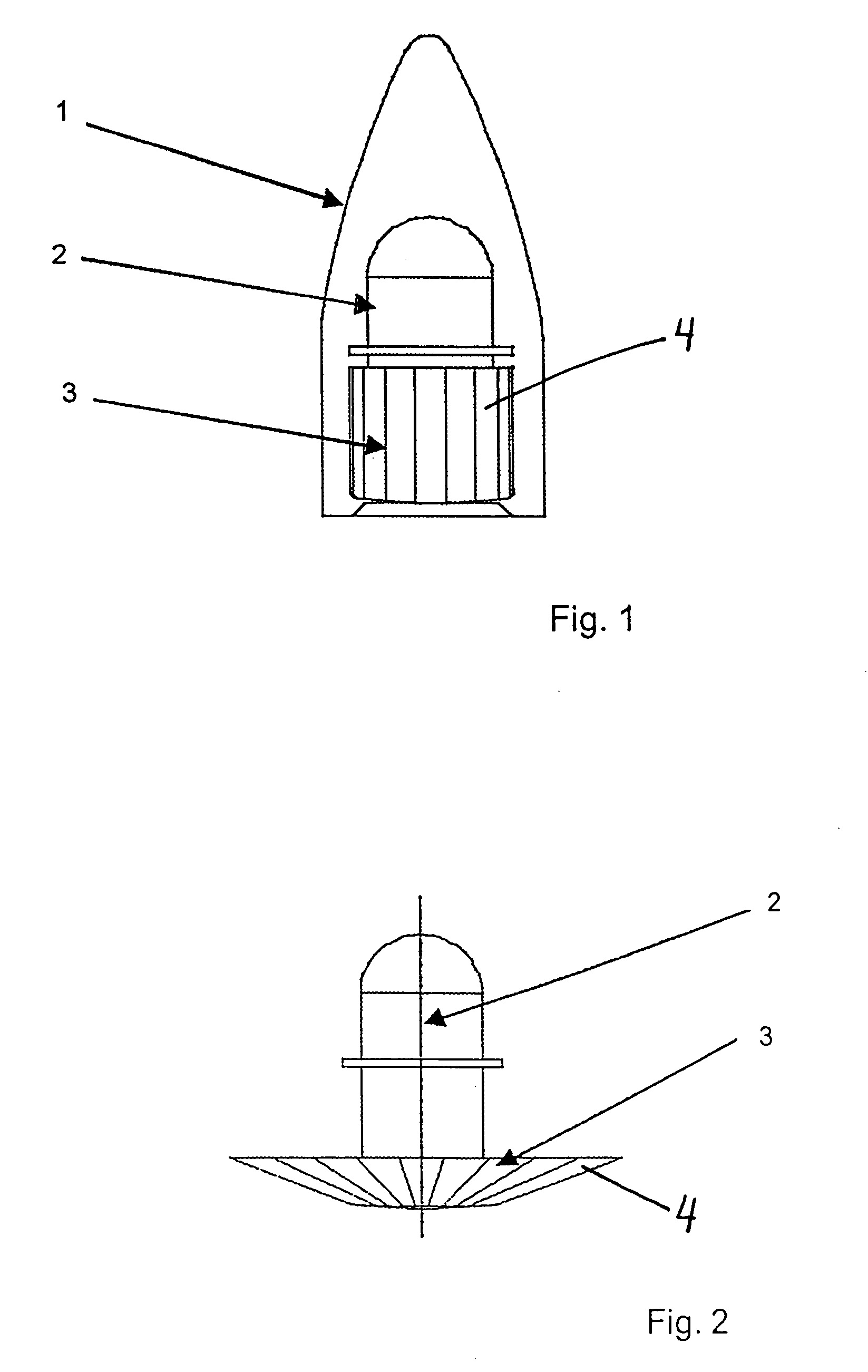
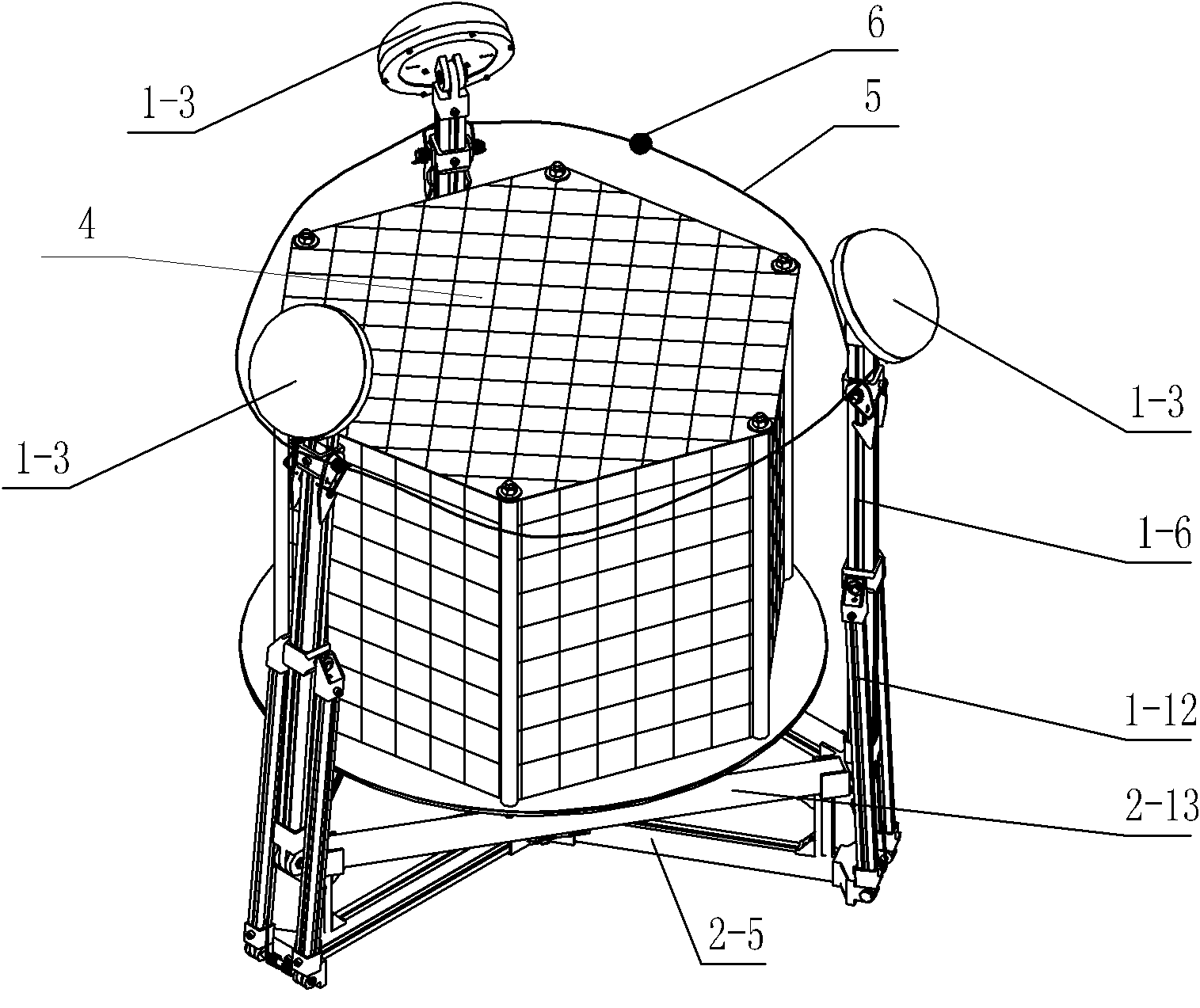
Spacecraft capture and docking system
InactiveUS6299107B1Robust, fail-safe and reliableReduces risk of collision and damageCosmonautic vehiclesSystems for re-entry to earthRotary stageUnderwater vehicle
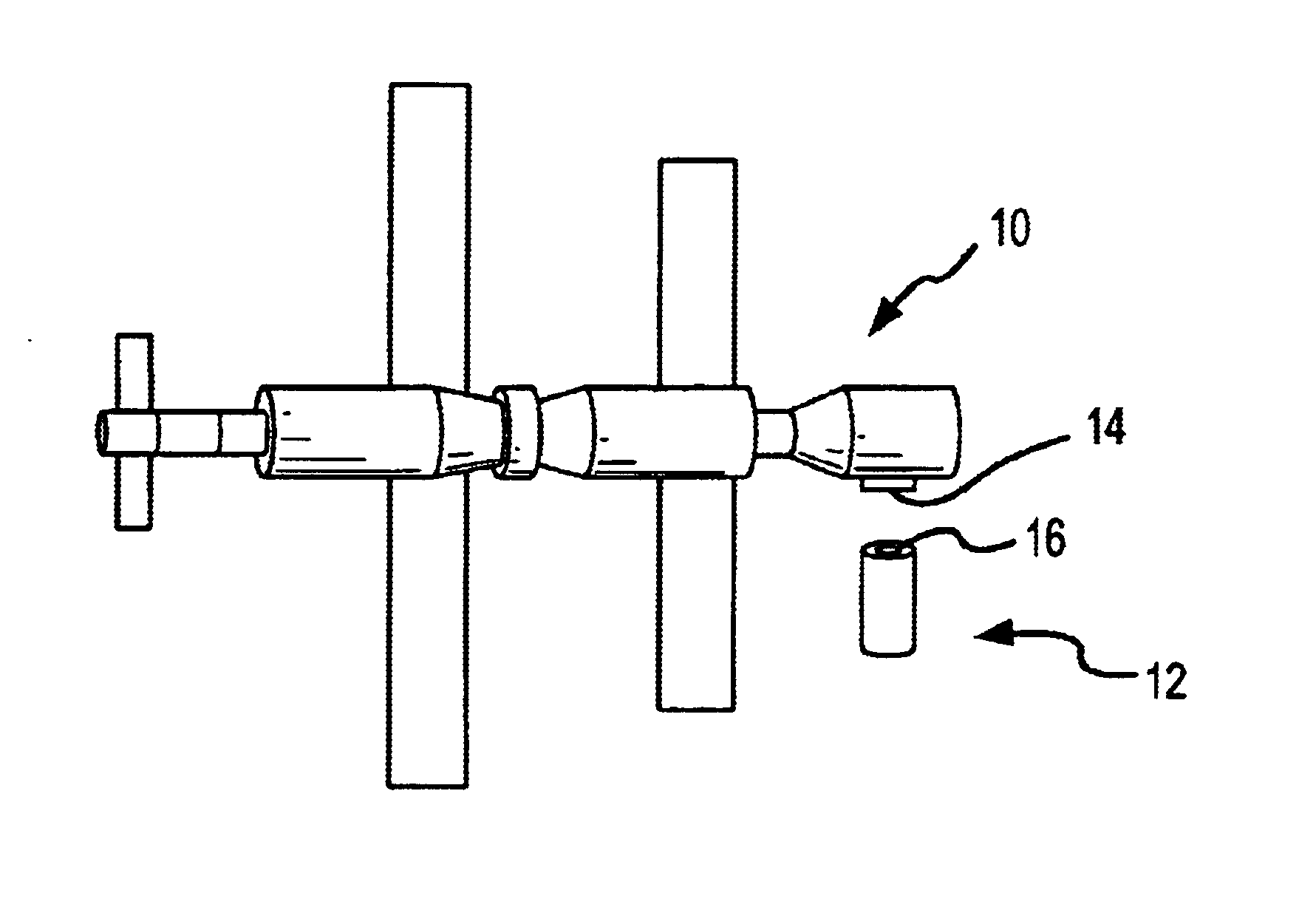
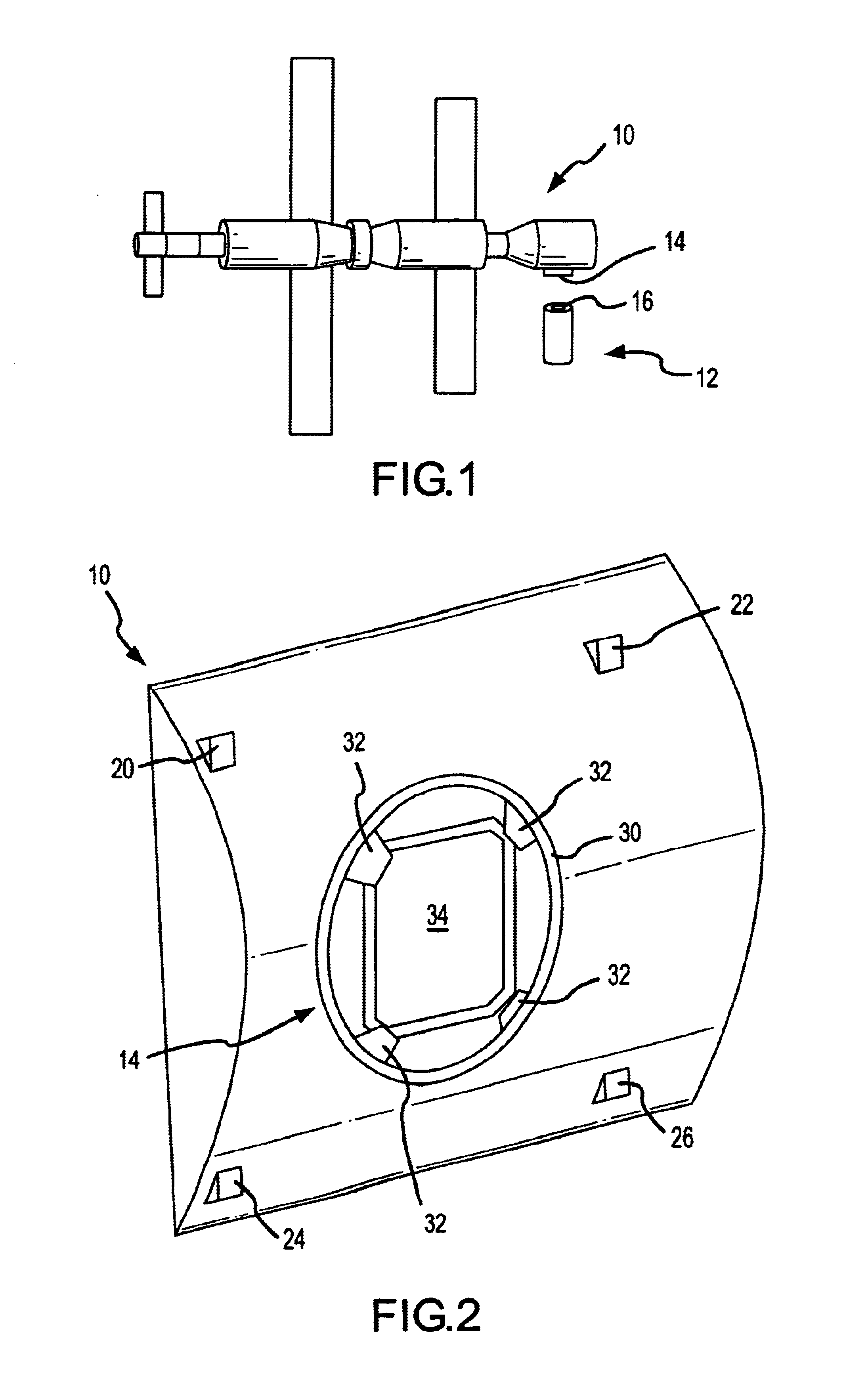
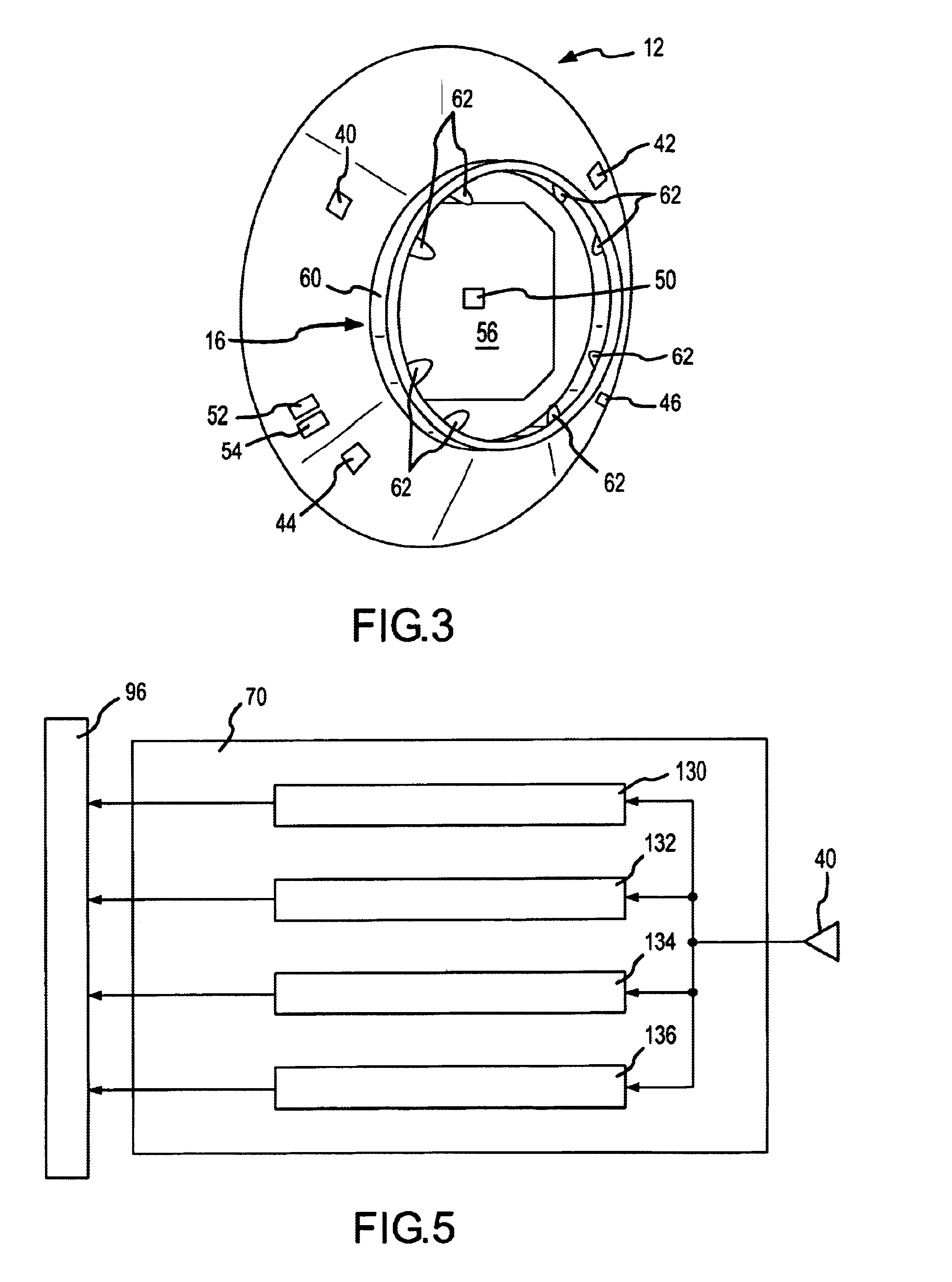
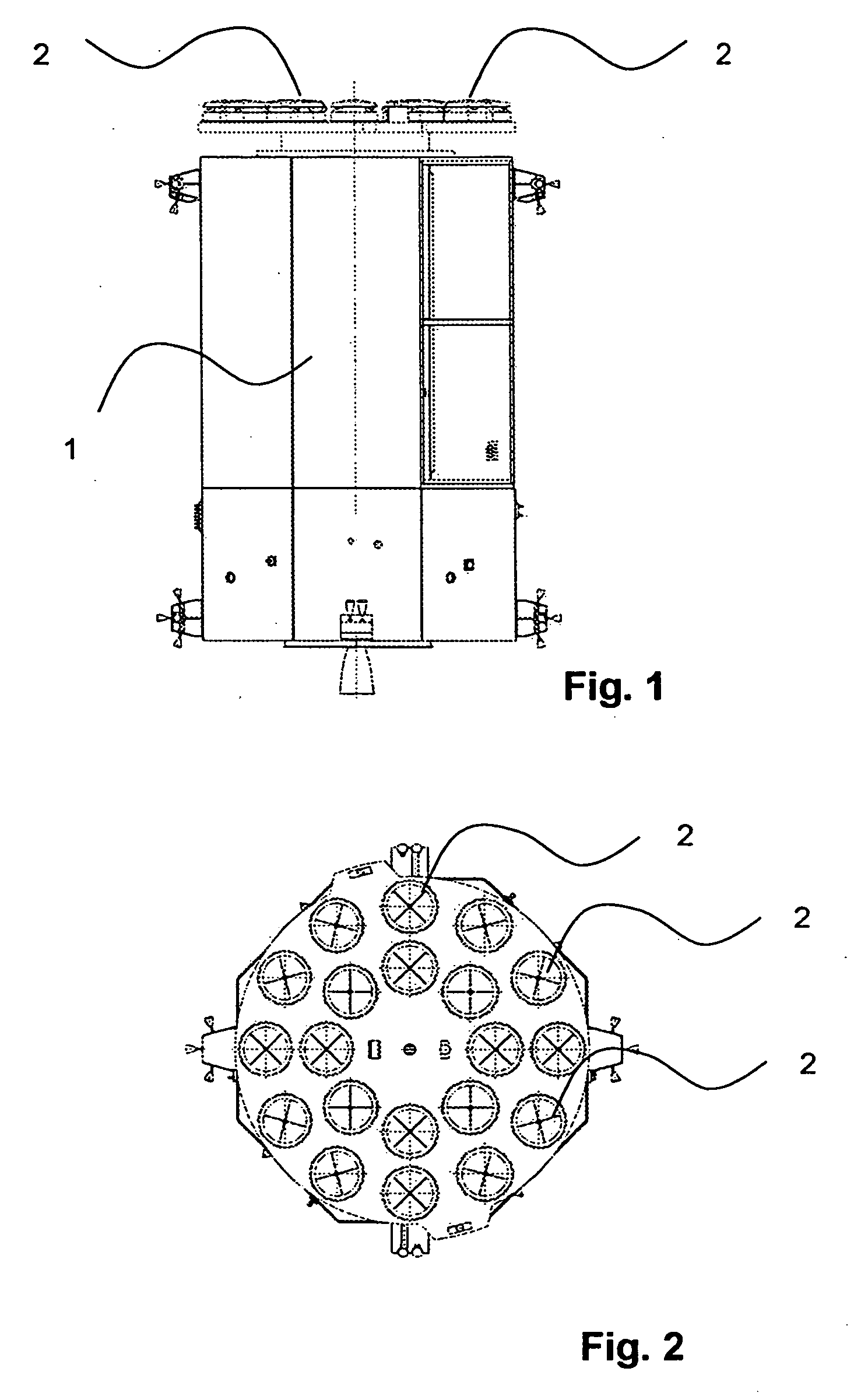
A system for capturing and docking an active craft to a passive craft has a first docking assembly on the active craft with a first contact member and a spike projecting outwardly, a second docking assembly on the passive craft having a second contact member and a flexible net deployed over a target area with an open mesh for capturing the end of the spike of the active craft, and a motorized net drive for reeling in the net and active craft to mate with the passive craft's docking assembly. The spike has extendable tabs to allow it to become engaged with the net. The net's center is coupled to a net spool for reeling in. An alignment funnel has inclined walls to guide the net and captured spike towards the net spool. The passive craft's docking assembly includes circumferentially spaced preload wedges which are driven to lock the wedges against the contact member of the active craft. The active craft's docking assembly includes a rotary table and drive for rotating it to a predetermined angular alignment position, and mating connectors are then engaged with each other. The system may be used for docking spacecraft in zero or low-gravity environments, as well as for docking underwater vehicles, docking of ancillary craft to a mother craft in subsonic flight, in-flight refueling systems, etc.
Owner:HONEYBEE ROBOTICS
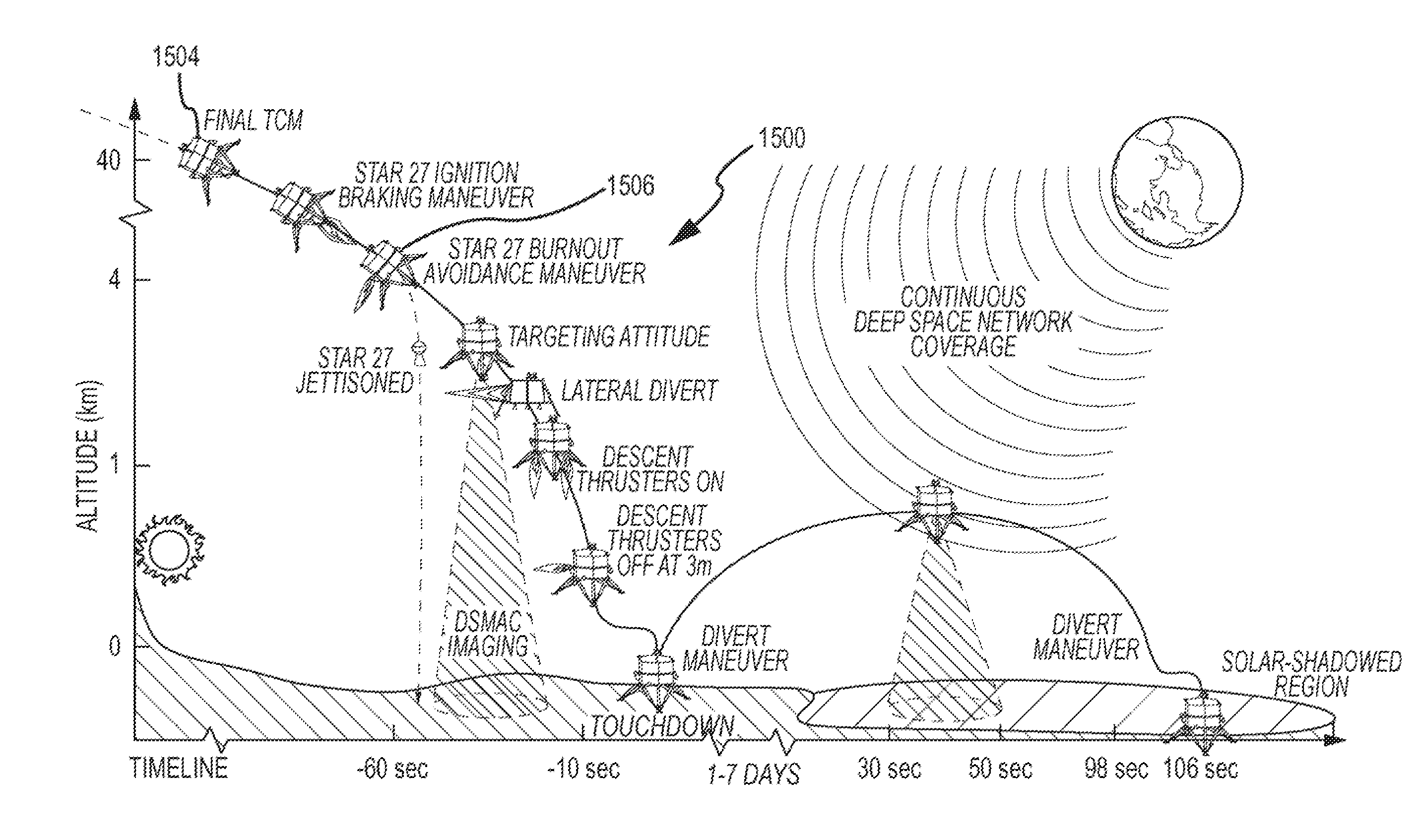
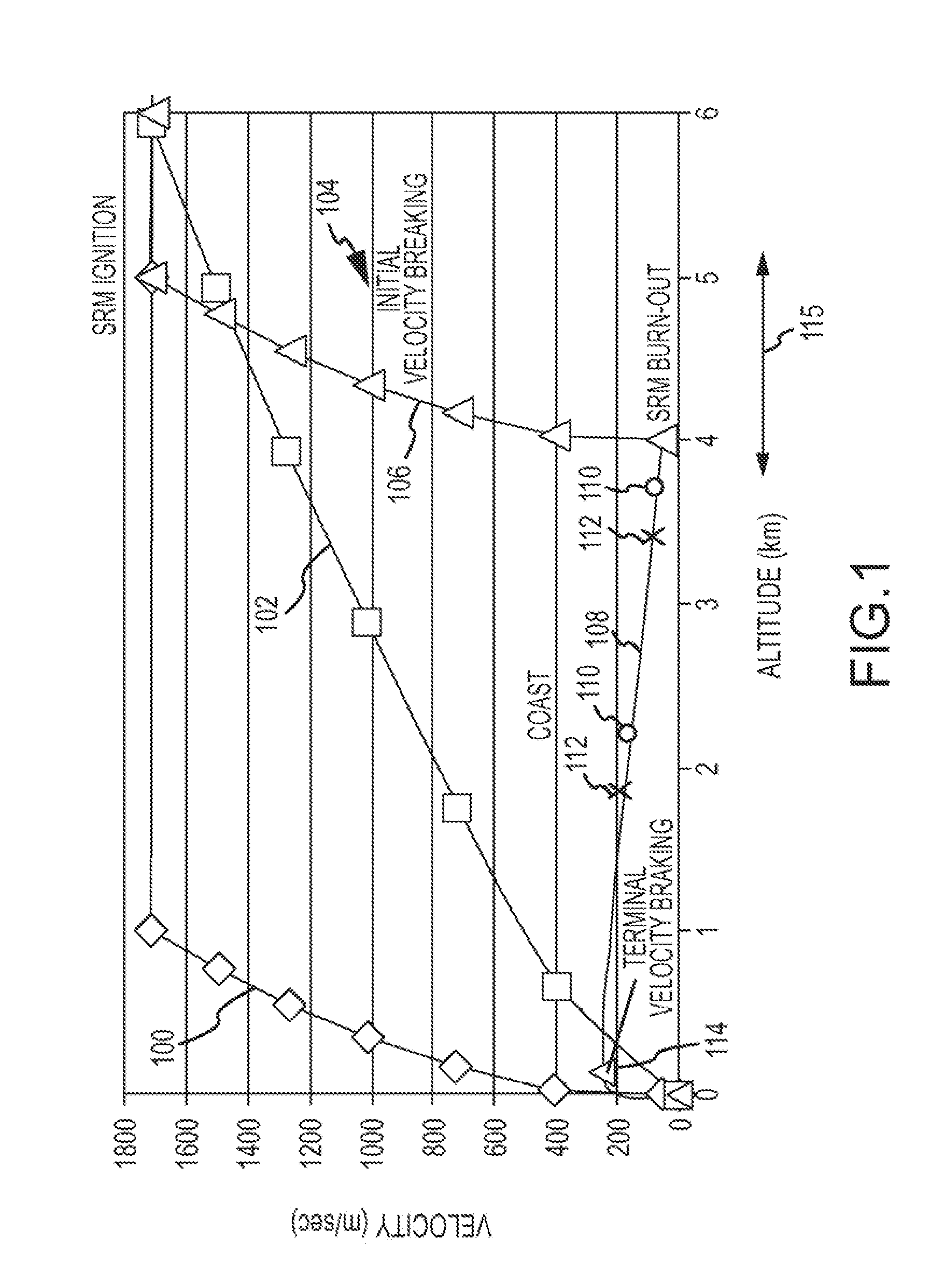
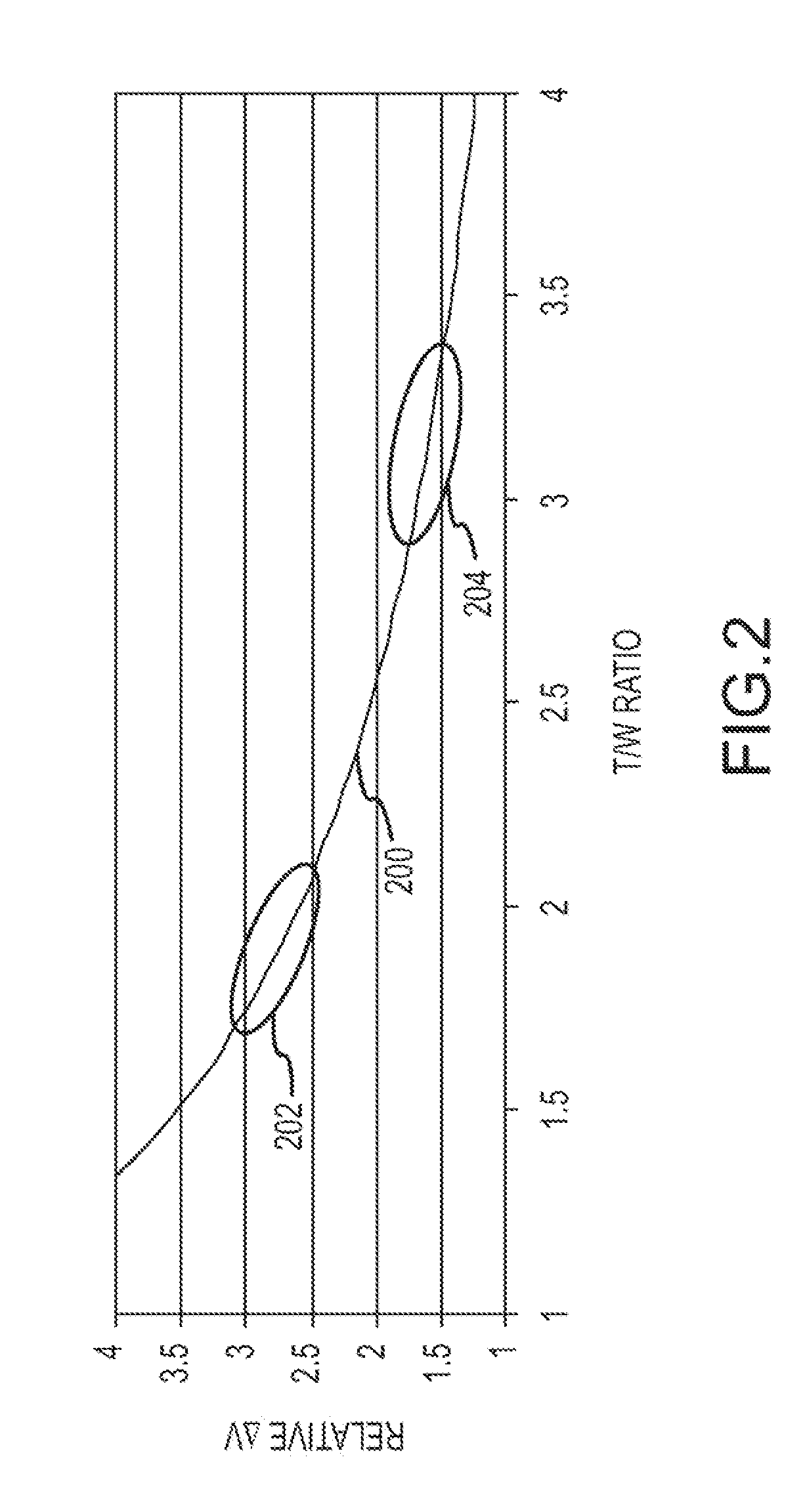
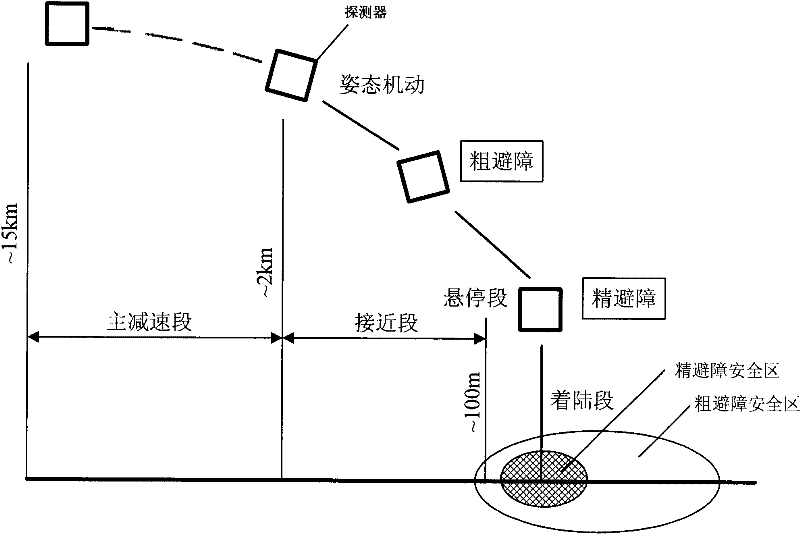
Autonomous Space Flight System and Planetary Lander for Executing a Discrete Landing Sequence to Remove Unknown Navigation Error, Perform Hazard Avoidance and Relocate the Lander and Method
ActiveUS20080023587A1Detect and avoid hazardIncreased payload capacityCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusInstruments for comonautical navigationReference mapImage resolution
An autonomous unmanned space flight system and planetary lander executes a discrete landing sequence including performing an initial velocity braking maneuver to remove velocity at altitude, coasting during which the planet surface is imaged and correlated to reference maps to estimate cross-track and along-track navigation errors and one or more lateral braking maneuvers are performed to reduce cross-track navigation error, and performing a terminal velocity braking maneuver(s) to reduce the along-track braking maneuver and remove the remainder of the velocity just prior to landing. A bi-propellant propulsion system provides a very high T / M ratio, at least 15:1 per nozzle. Short, high T / M divert maneuvers provide the capability to remove cross-track navigation error efficiently up to the maximum resolution of the reference maps. Short, high T / M terminal velocity braking maneuver(s) provide the capability to remove along-track navigation error to a similar resolution and remove the remaining velocity in a very short time window, approximately 3-15 seconds prior to touchdown. The propulsive efficiency frees up mass which can be allocated to a fuel to remove the unknown navigation errors, perform hazard avoidance and / or relocate the lander by flying it to another site or be allocated to additional payload.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Balloon device for lowering space object orbits
InactiveUS6830222B1Reduce spacingIncreasing atmospheric drag on the envelopeLaunch systemsAir braking surfacesControl systemSpace object
An apparatus for lowering an orbit of a space object includes an envelope, an inflation system for inflating the envelope, an inflation control system for controlling the inflation system, and attachment hardware for connecting the apparatus and the space object. Inflating the envelope increases an effective drag area of the envelope for increasing atmospheric drag on the envelope.
Owner:GLOBAL AEROSPACE
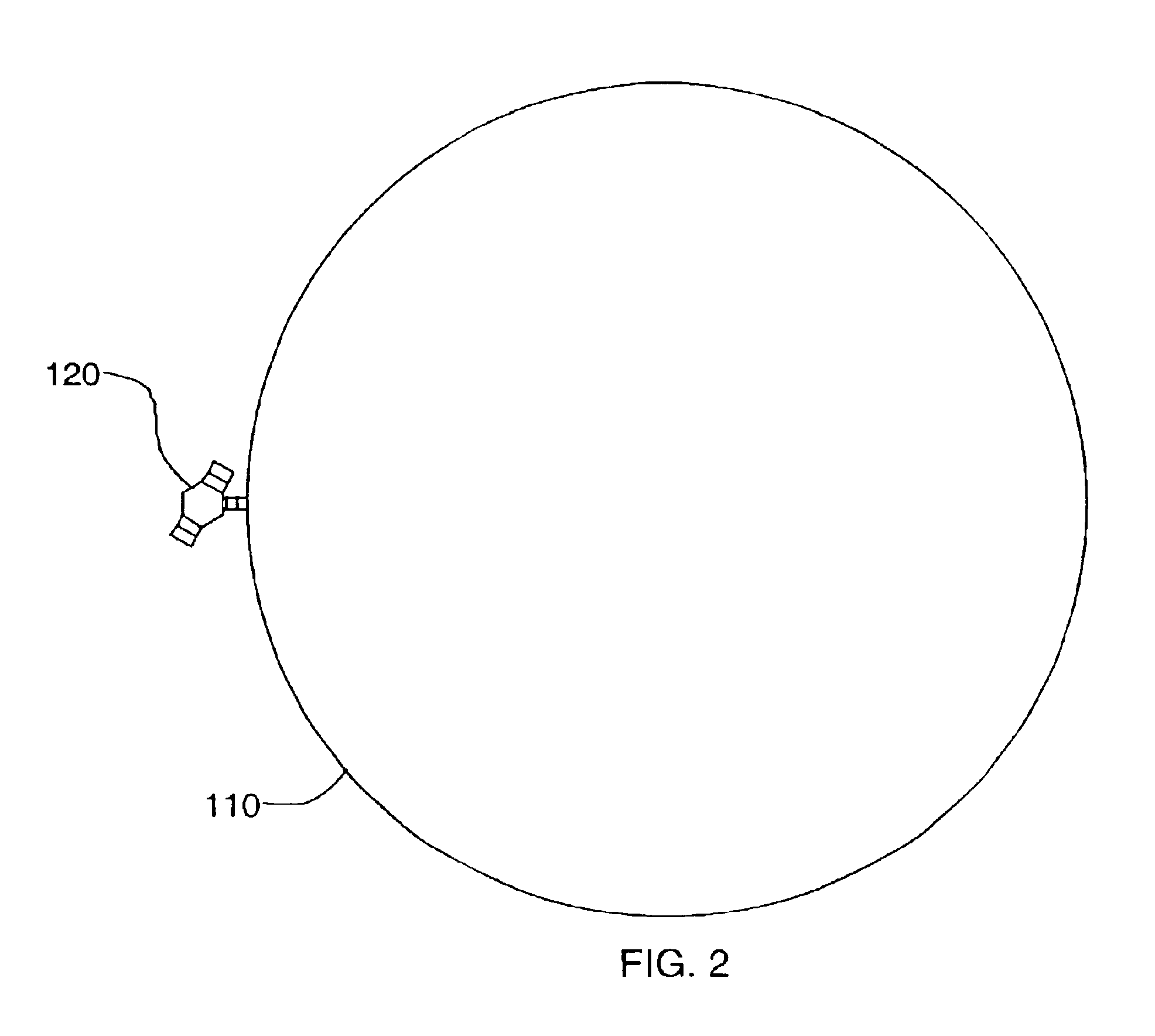
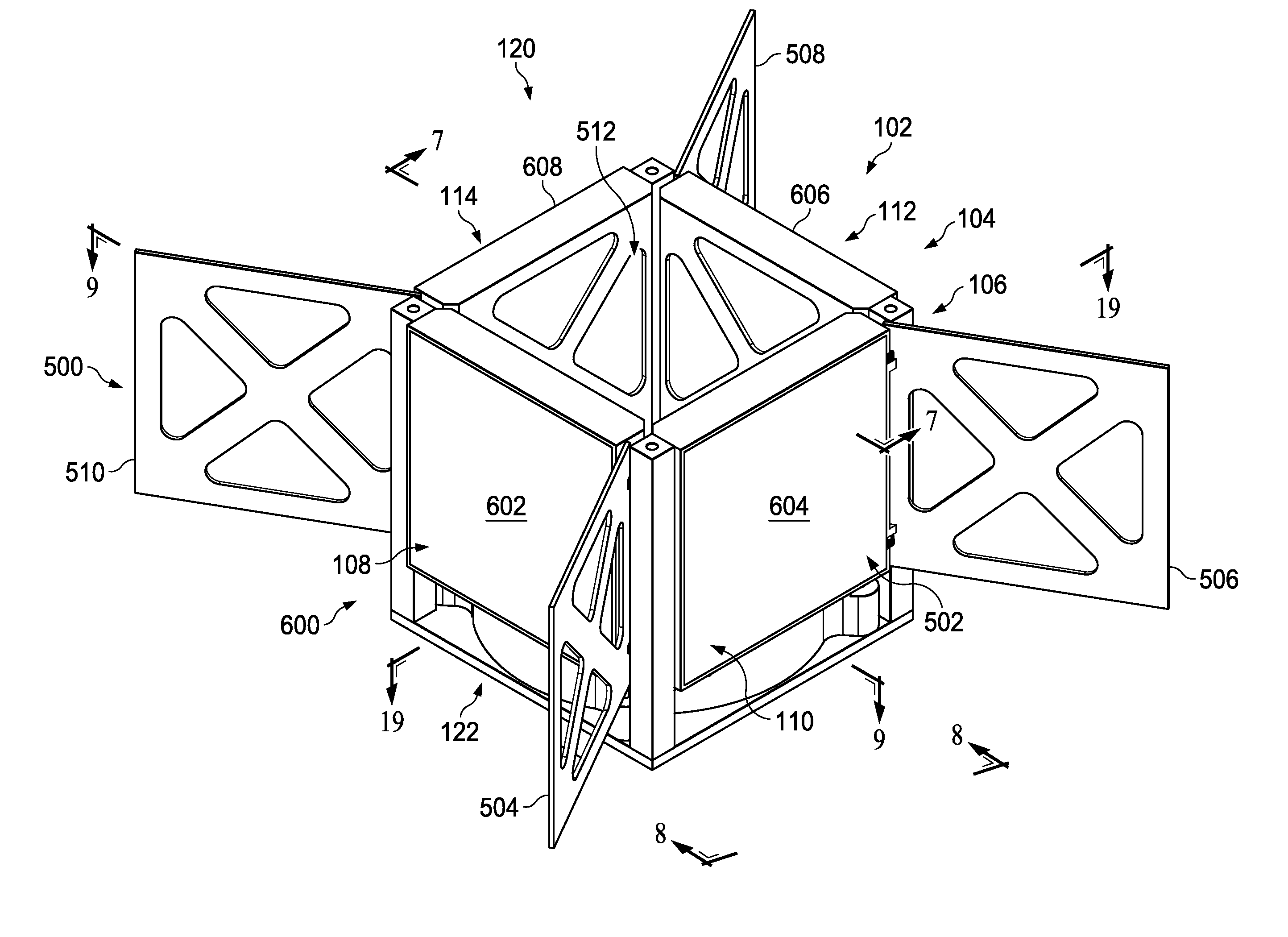
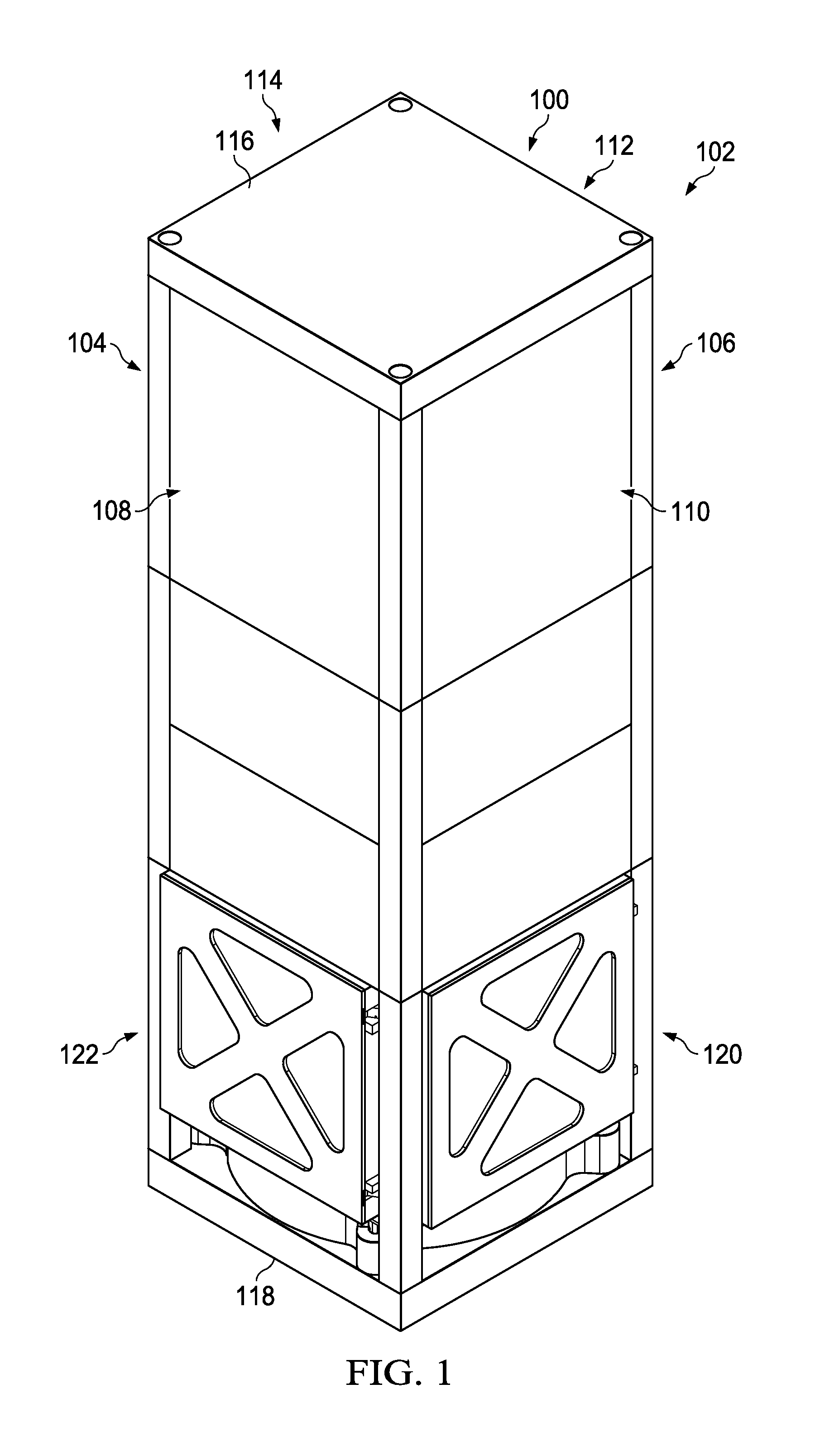
Component Deployment System
A method and apparatus for deploying a group of panels. An apparatus comprises a group of panels in a folded configuration against a side of a spacecraft, a group of flexible members connected to the group of panels, and an interface system associated with the group of panels and the group of flexible members. The interface system is configured to move the group of panels from the folded configuration to a deployed configuration when the group of flexible members is extended from the spacecraft.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Automated docking of space vehicles
InactiveUS6866232B1Facilitate automated dockingImprove securityCosmonautic vehiclesSystems for re-entry to earthEngineeringAngular orientation
An automated docking system for space vehicles that includes a plurality of antennas on each of a target vehicle and a chase vehicle. A pseudo random code is transmitted via one of the antennas located on one of the vehicles and received by one of the antennas located on the other vehicle. The pseudo random code is then sent back to the original vehicle via transmissions from the plurality of antennas on the second vehicle and received by the plurality of antennas on the original vehicle. The distance from each of the antennas on the other vehicle to each of the antennas on the originating vehicle can be measured in this fashion. The antennas on each of the vehicles are located in a spaced-apart arrangement so that the angular orientation or attitude of each of the vehicles to each other can also be determined. A plurality of video cameras is provided on the exterior of one of the vehicles and video information from these cameras is transmitted to the other vehicle for display to operators in that vehicle. Commands between the vehicles can also be communicated.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
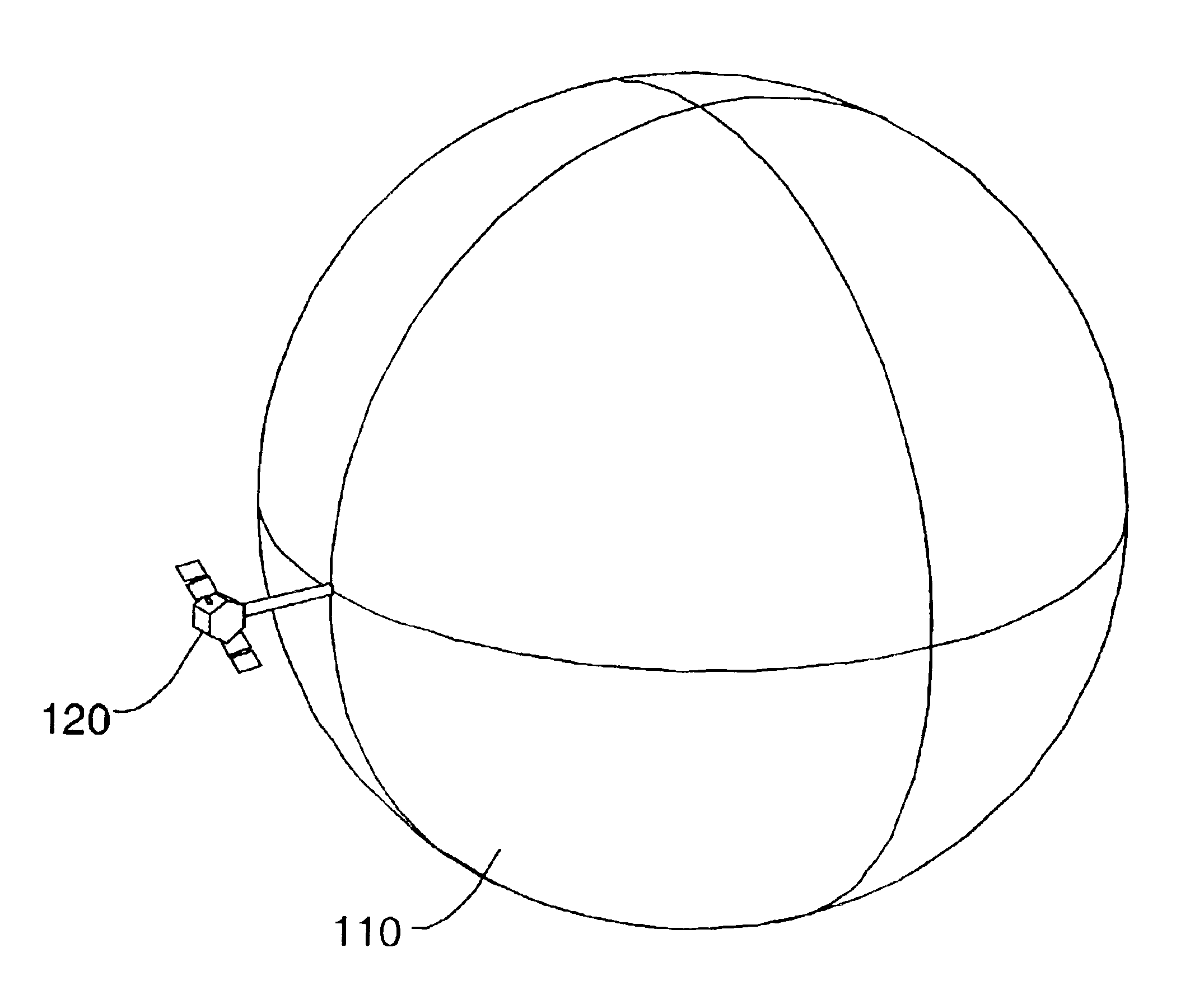
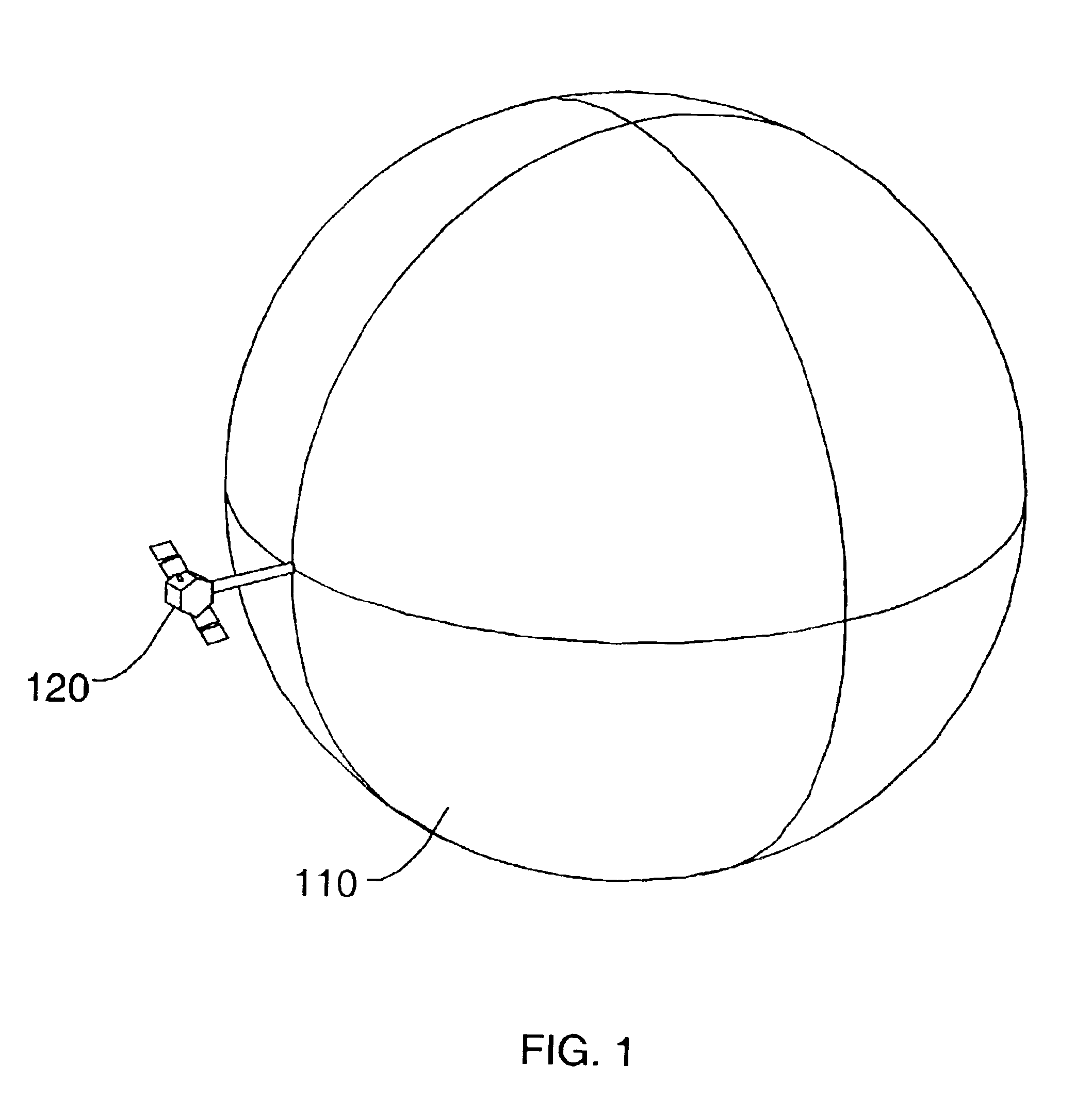
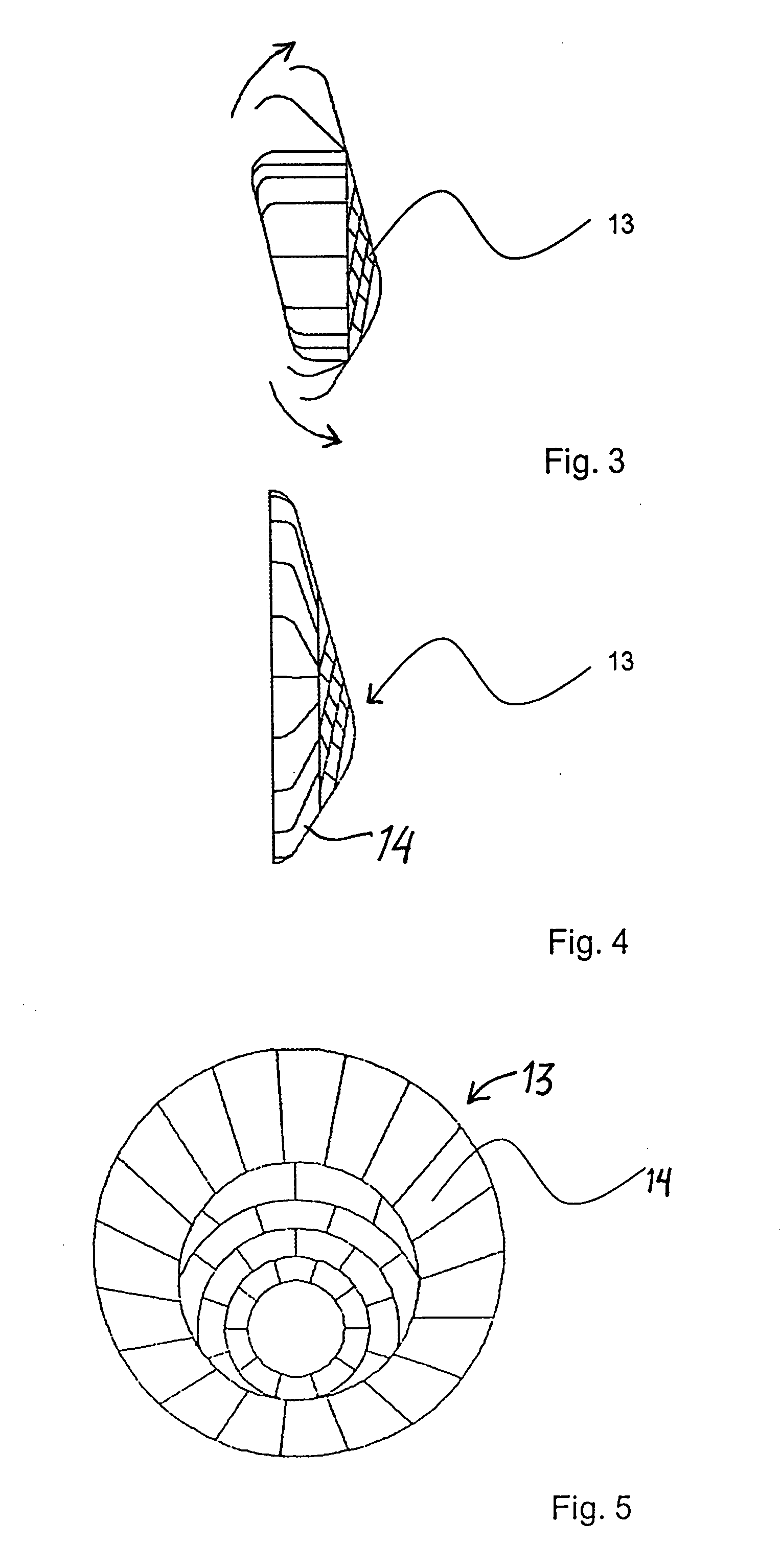
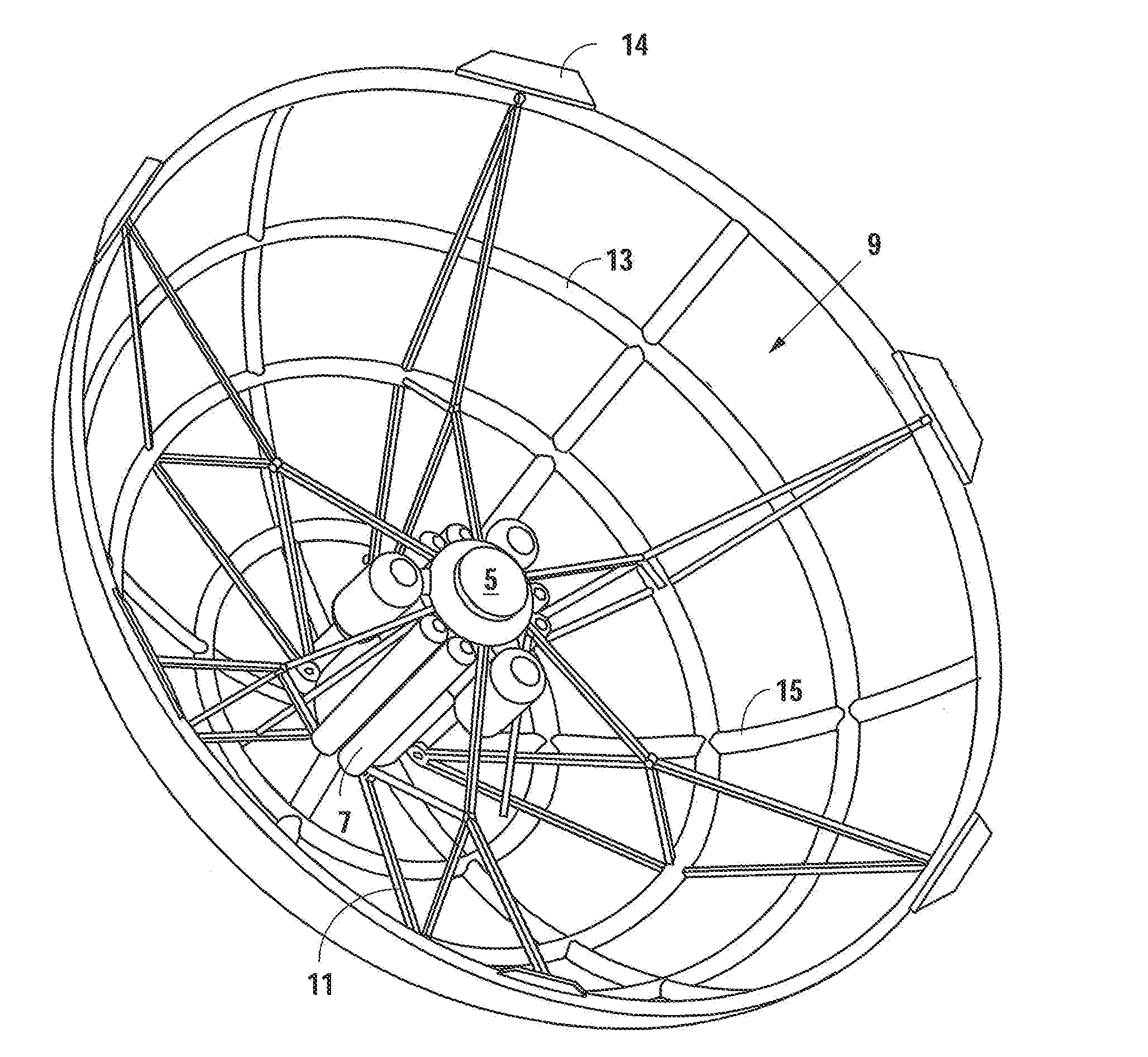
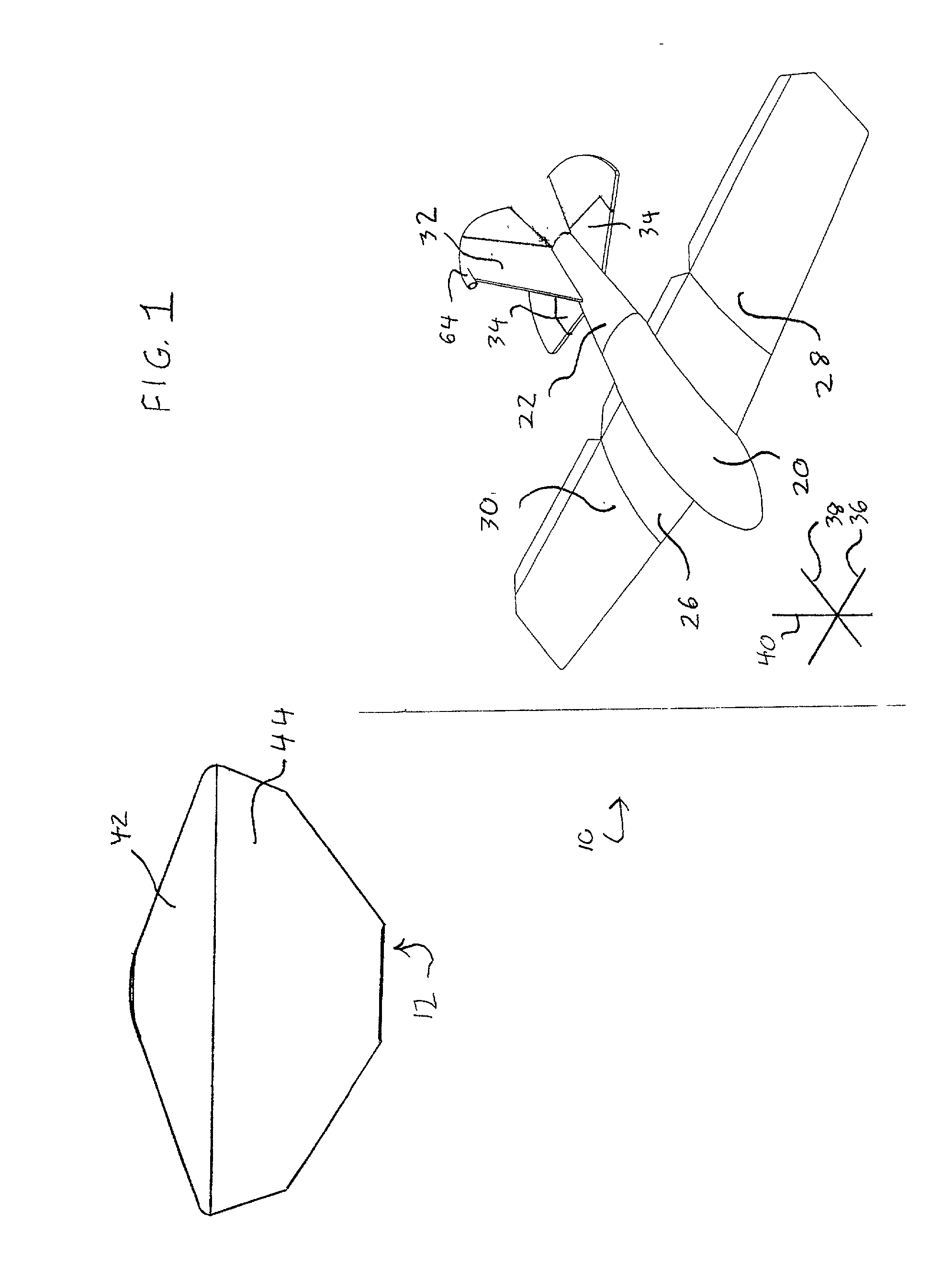
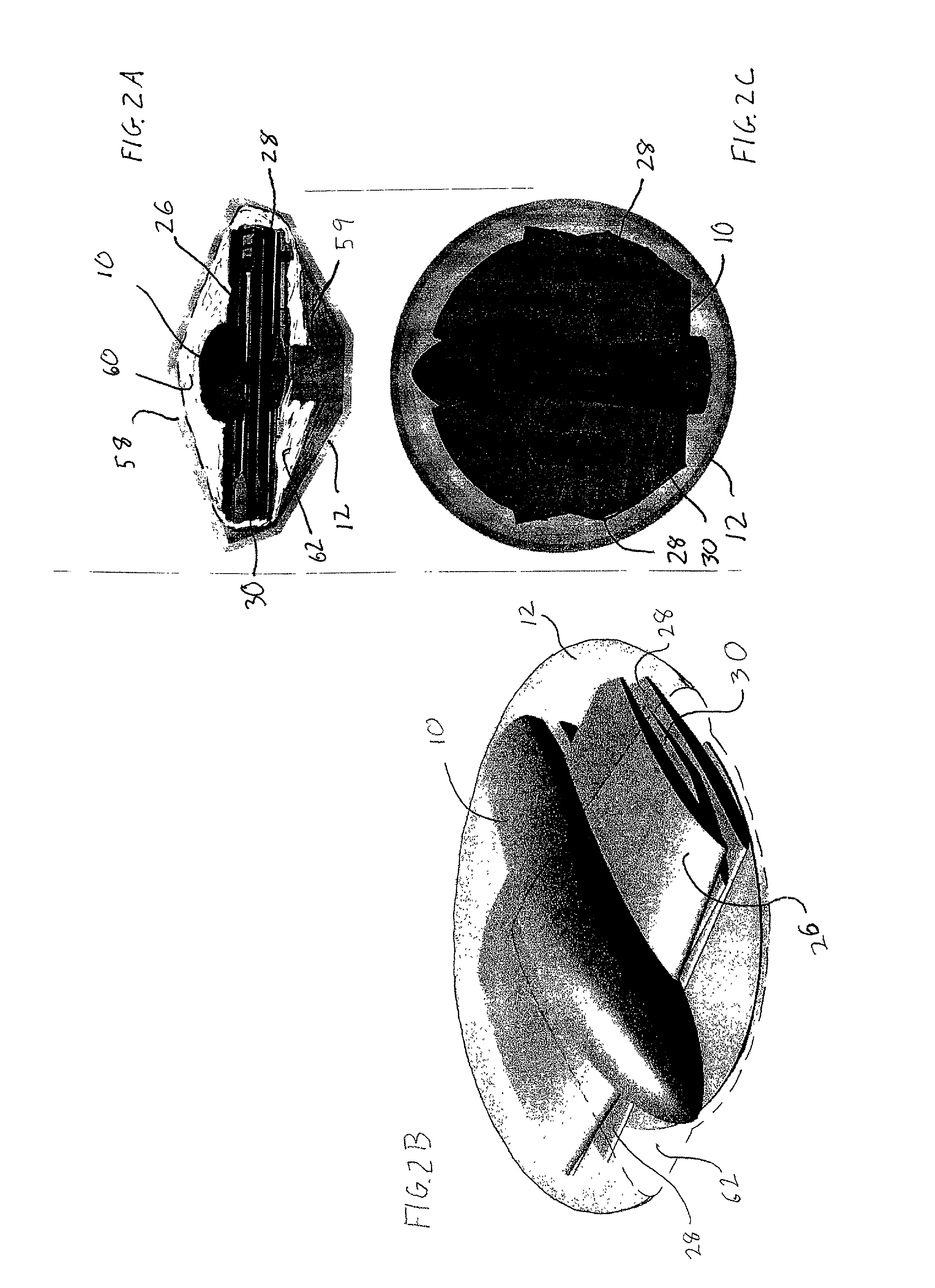
System for capturing and recovering free-flying objects in space
ActiveUS20050103939A1Safe spacing distanceArtificial satellitesSystems for re-entry to earthAcute angleEngineering
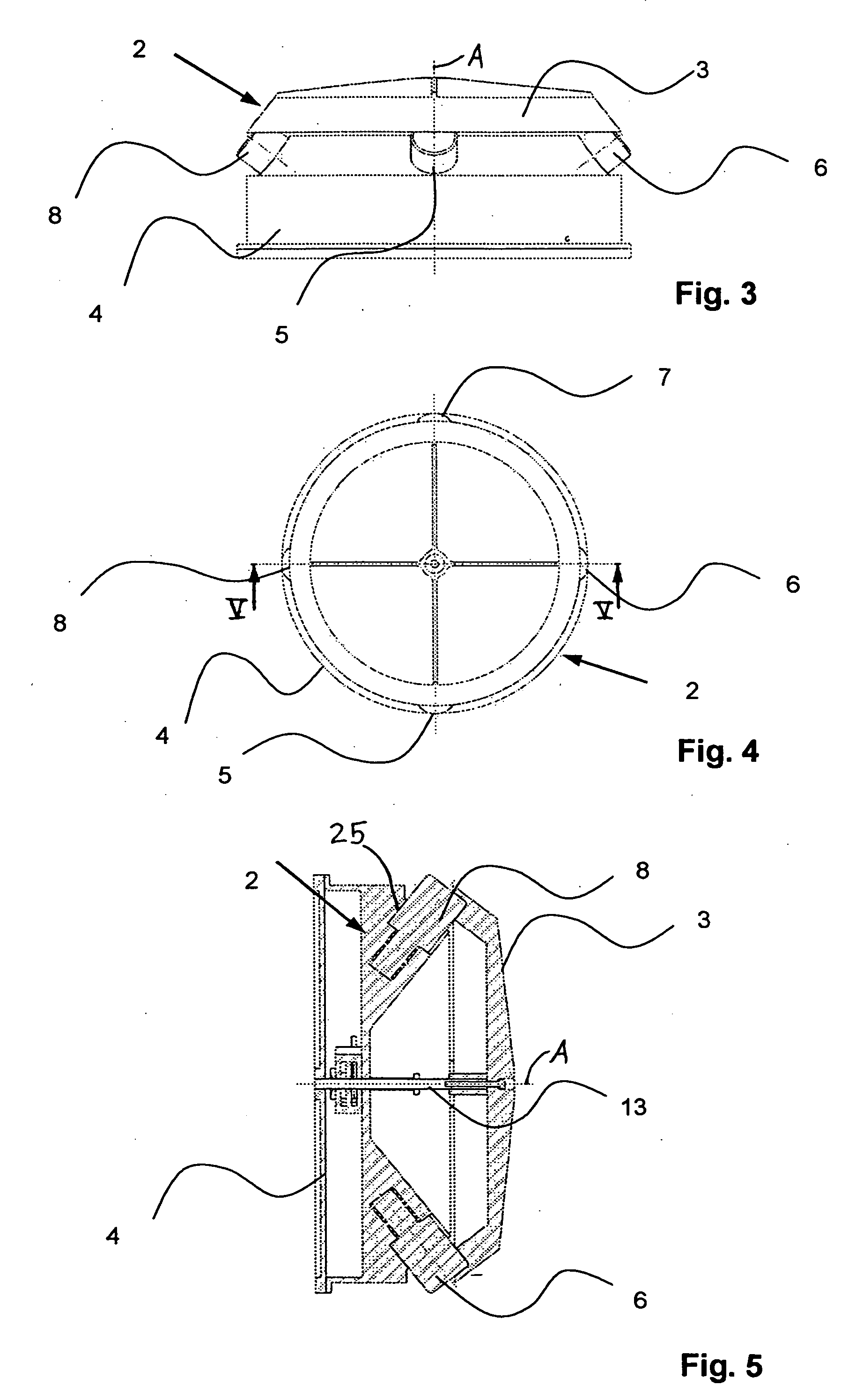
Capture devices are mounted on a space platform such as a spacecraft or utility satellite. Each capture device includes a folded capture net stored in a housing, guide weights connected to the net and received in spring-loaded ejection tubes oriented at an acute angle relative to the axis of the housing around the perimeter thereof, and a spring-loaded releasable cover that is connected to the net, covers the net in the housing, and holds the weights in the ejection tubes. When the cover is released, it is spring-ejected from the housing while pulling out and unfolding the net, and the weights are spring-ejected out of the ejection tubes while spreading out the net. After the net wraps around a free-flying target object in space, net closure mechanisms reel-in a net pursing line to close the net, which is connected to the space platform by a tether line on a winch.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
Variable surface landing platform (varslap)
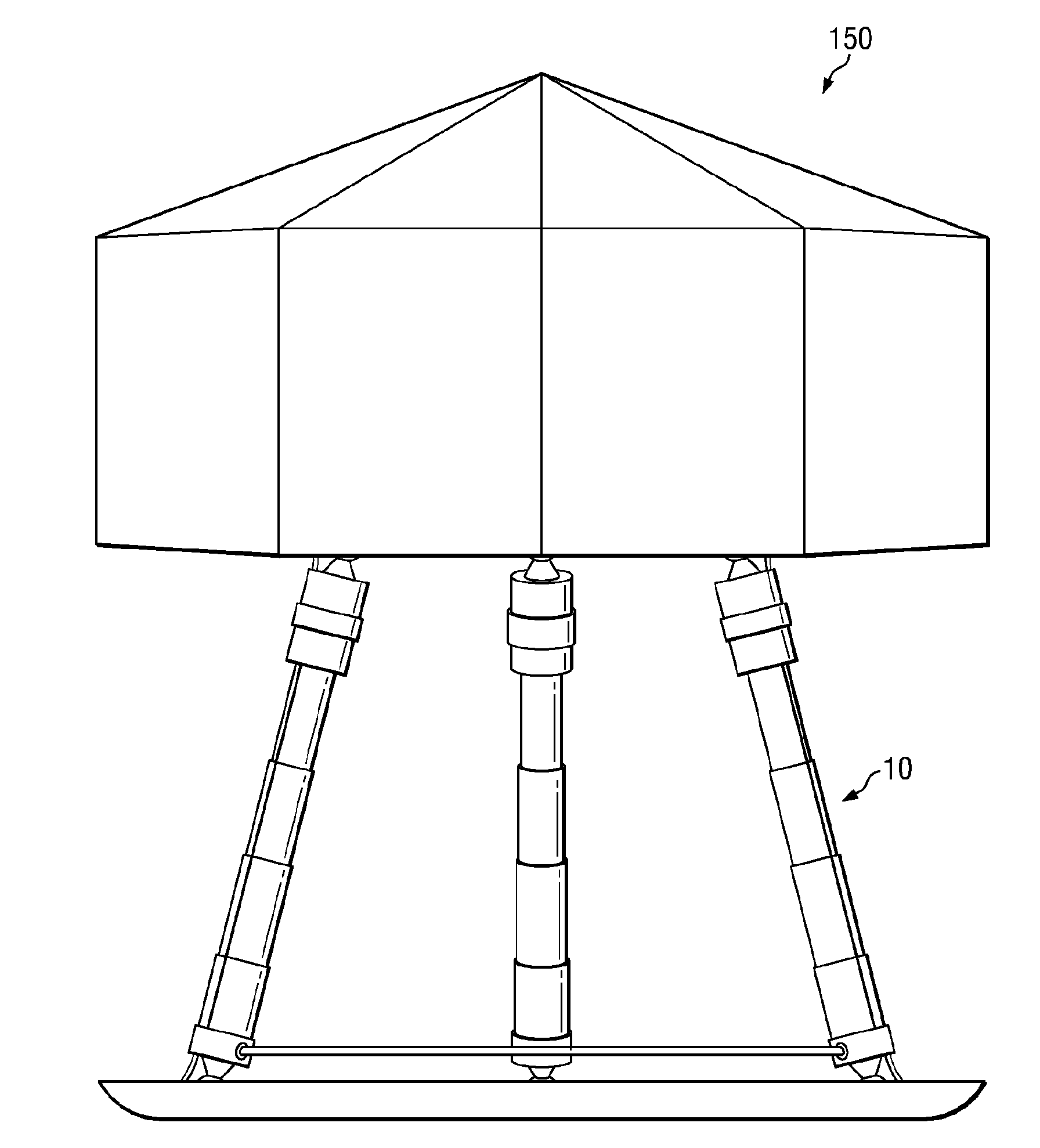
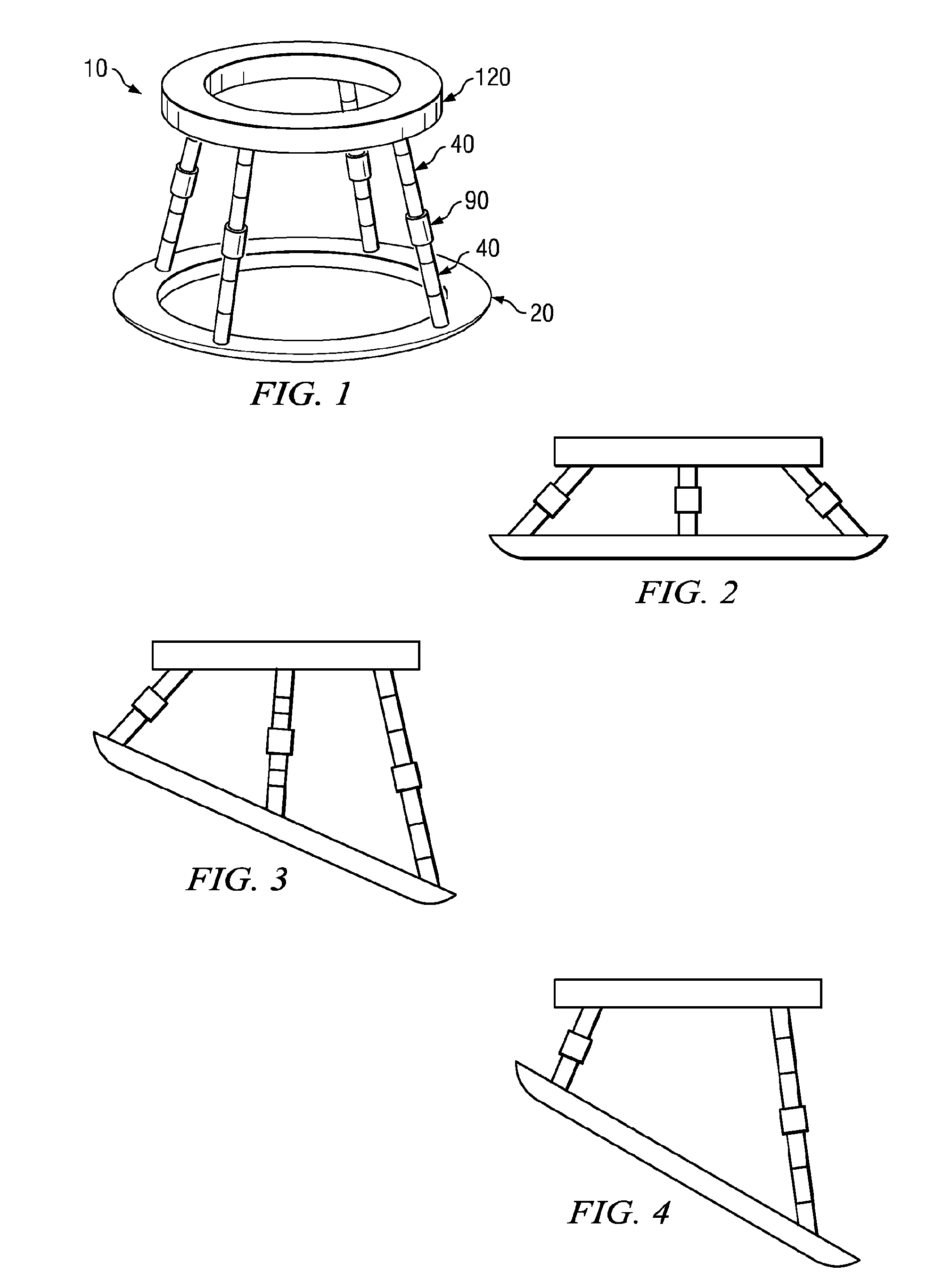
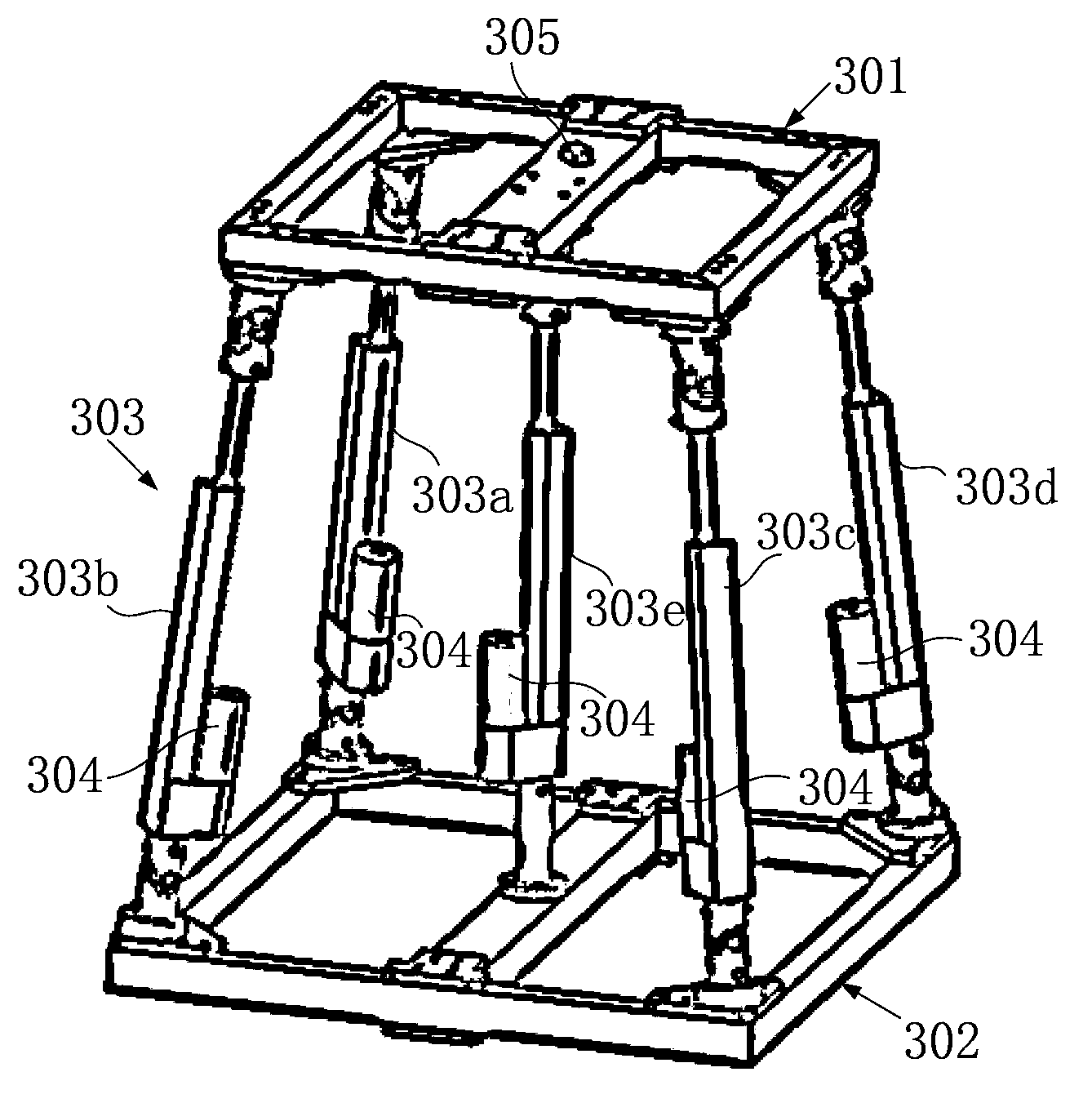
In one embodiment, a variable surface landing platform (VARSLAP) includes a base for contacting a landing surface; at least 3 adjustable struts interconnected with the base, wherein each strut is bisected by a strut actuator-housing, and wherein the at least 3 adjustable struts are interconnected to a main body aerospace craft (MAC); a sensor array on the base; and an attitude determination and control system (ADCS).
Owner:CARREKER RAYMOND GEORGE
Spin-stabilized lander
InactiveUS20090206204A1Low costAdditive manufacturing apparatusCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusNatural satelliteCelestial body
The invention provides a novel, low-cost, spin-stabilized lander architecture capable (with appropriate system scaling tailored to the attributes of the target) of performing a soft-landing on a solar-system body such as Earth's Moon, Mars, Venus, the moons of Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, selected near-Earth and main-belt asteroids, comets and Kuiper belt objects and even large human-made objects, and also moving about on the surface of the target solar-system body after the initial landing in movement akin to hopping.
Owner:ECLIPTIC ENTERPRISES CORP
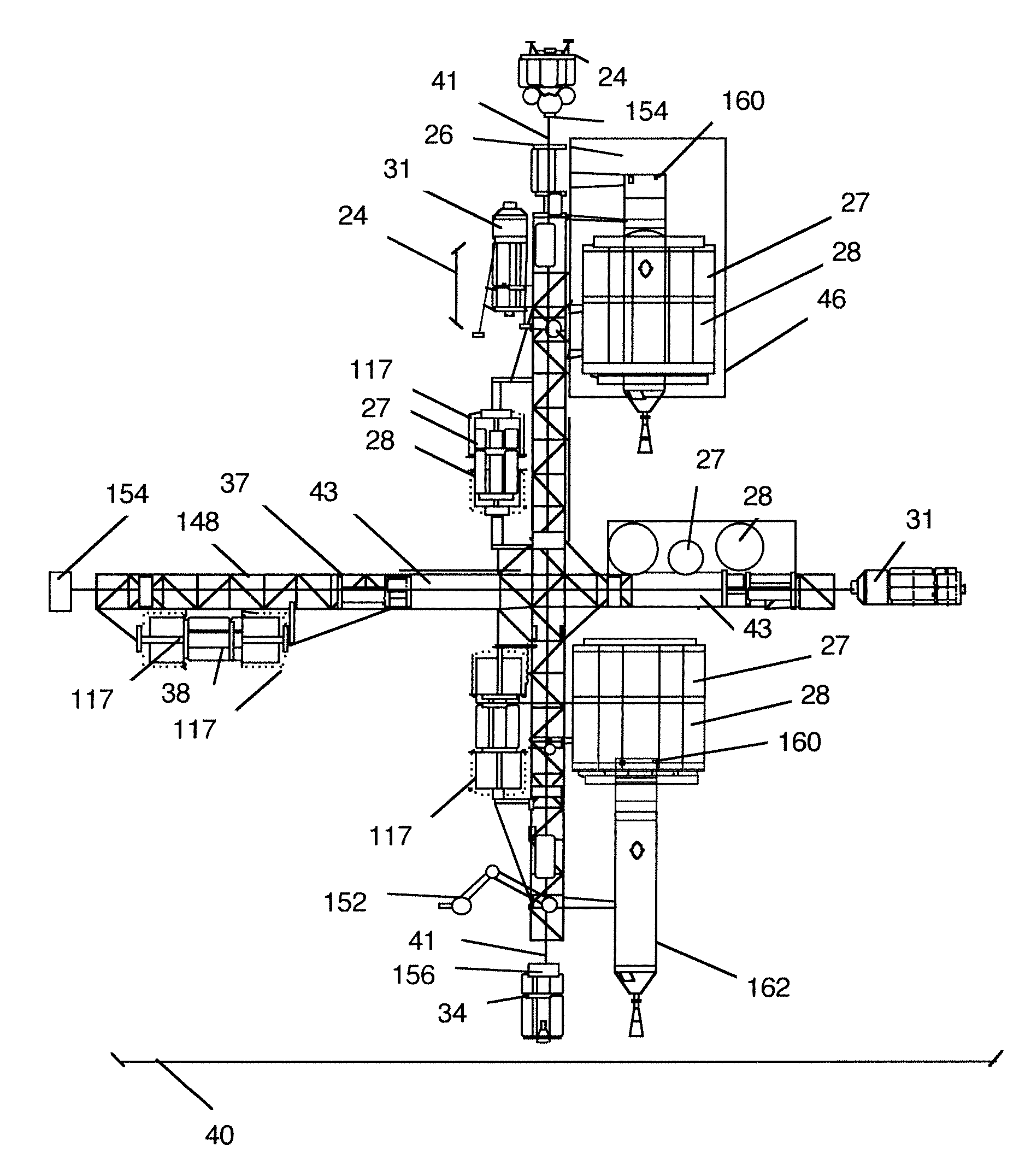
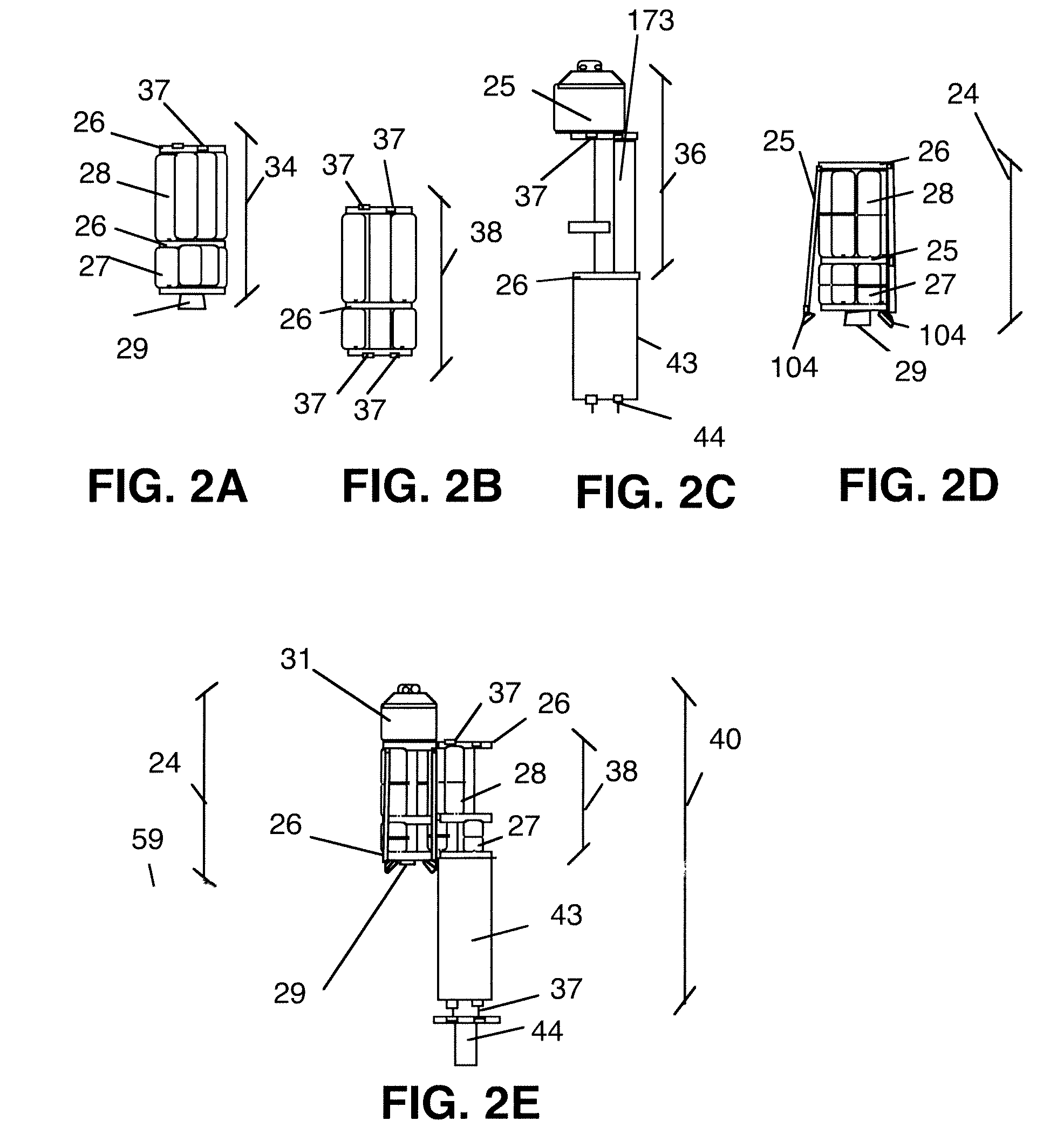
Anchor positioning system for detecting planetoid lander
InactiveCN101786504ALower launch costsRisk of drifting away eliminatedCosmonautic vehiclesSystems for re-entry to earthCelestial bodyEngineering
The invention relates to an anchor positioning system for detecting a lander, in particular to the anchor positioning system for detecting a planetoid lander. The anchor positioning system solves the following problems of a telescopic sleeve connecting and positioning system: an anchor bill is inclined when in incidence and transverse impact load is acted on the lander, so as to damage instruments at the inner part of the lander; a moving part of a telescopic sleeve is changed in quality during the incidence, so as to cause difficulty in estimating initial emission energy. An advancing mechanism is fixedly arranged on the side face of a cable box body, a winding mechanism is fixedly arranged on a rear end cover of the cable box body, a locking and unlocking mechanism is fixedly arranged on a right shell body of the winding mechanism, a connecting rope is stored in the cable box body, one end of the connecting rope is fixed on an anchor rod pin, and the other end of the connecting ropeis fixedly connected with a winding reel. A winding motor and an unlocking motor are connected with a pin socket by a lead wire. The anchor positioning system can also be used not only for detecting the lander of a small celestial body with weak surface gravitation such as the comet and the like, but also for automatic operation of a robot in dangerous environments.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
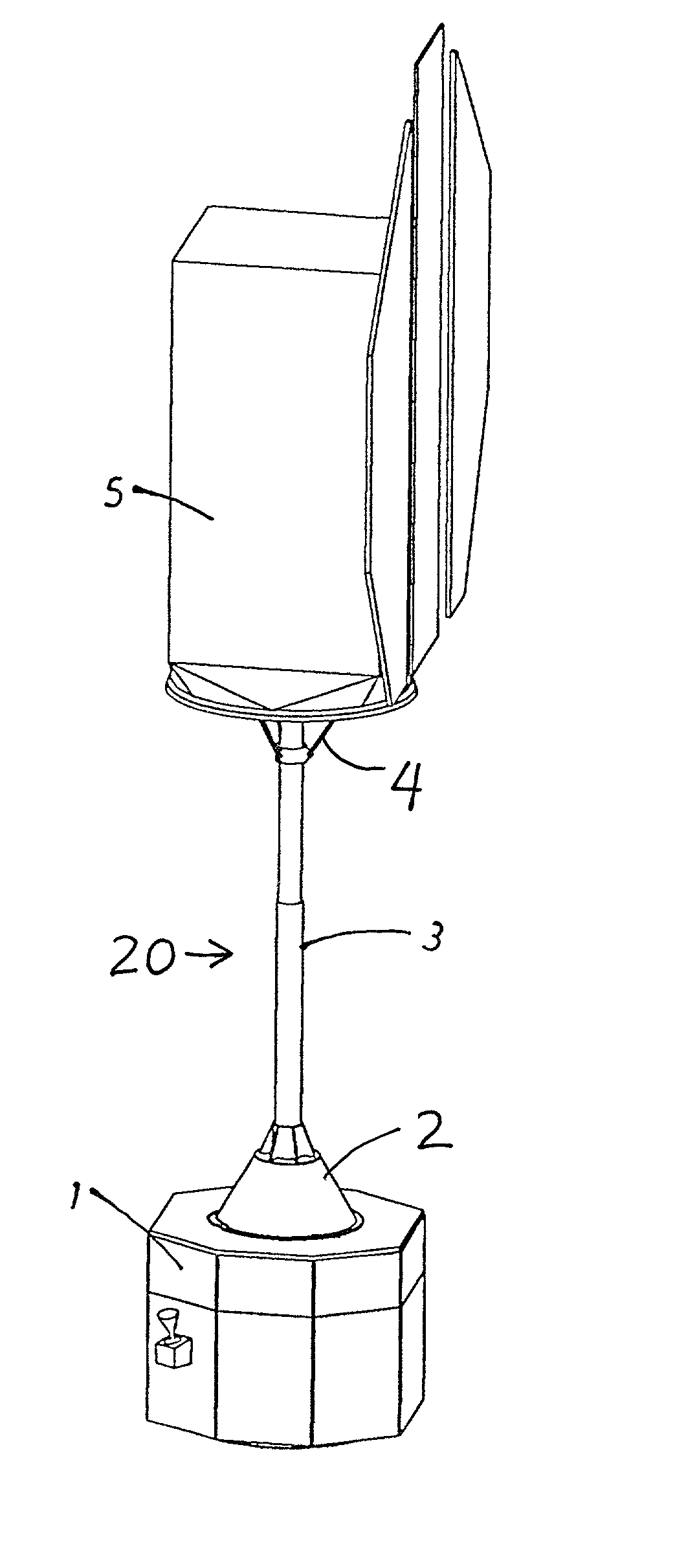
Deployable heat shield and deceleration structure for spacecraft
InactiveUS20080078884A1Reliable functionInexpensive mannerCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic thermal protectionFiberFlight direction
An apparatus for heat shielding and deceleration of a spacecraft comprises an unfoldable shield of individual panels made of a high temperature resistant fiber reinforced ceramic and pivotally mounted on the outer structure of the spacecraft. An unfolding ring slides axially along the body of the spacecraft. The panels are pivotally connected to the unfolding ring by compression struts acting as toggle levers. Tension springs pull the unfolding ring axially along the spacecraft body to toggle out the compression struts so as to outwardly pivotally deploy the panels. The unfoldable shield can be arranged on the forward end or the rear end of the spacecraft relative to its flight direction upon entry into the atmosphere.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
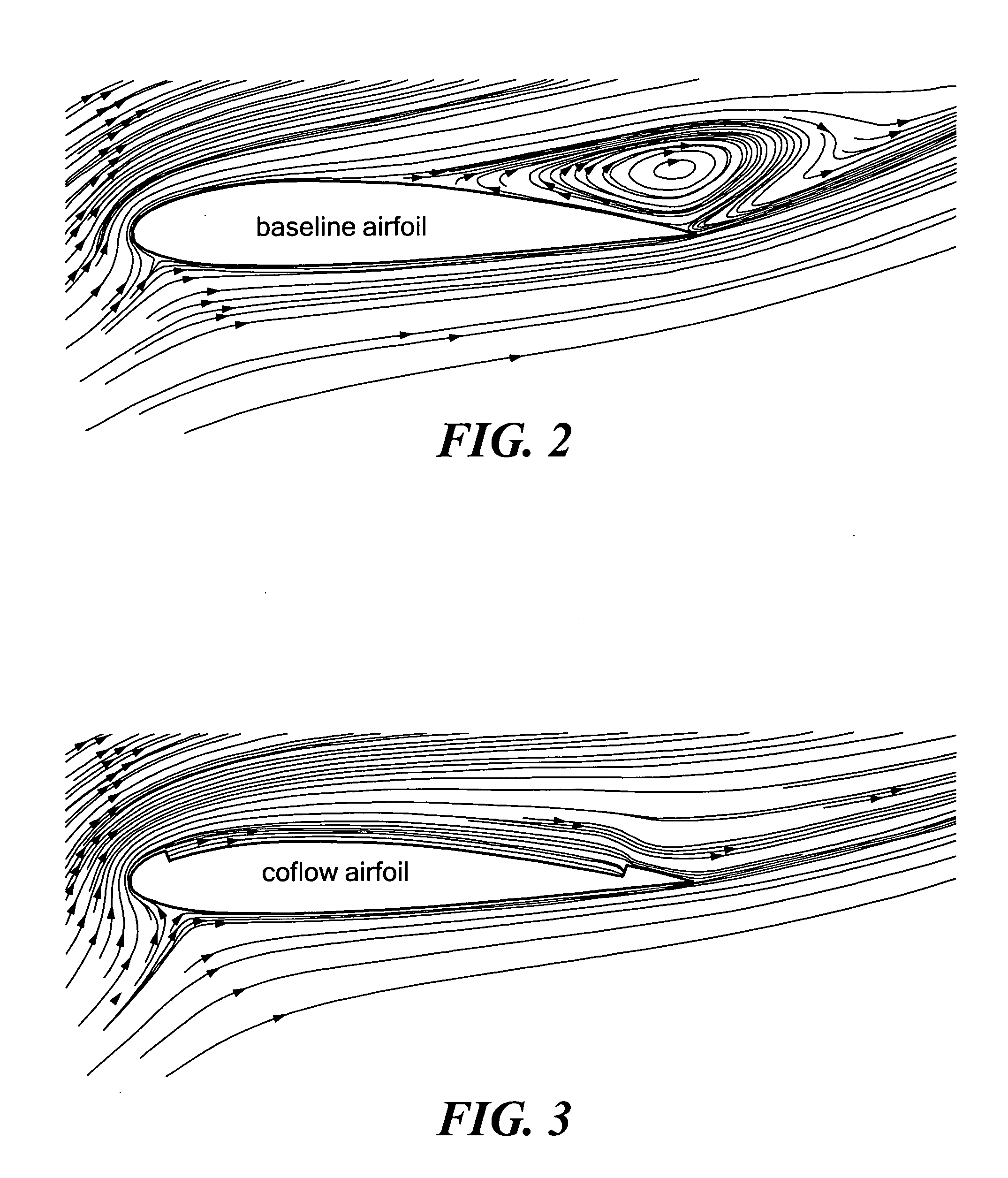
Emissionless silent and ultra-efficient airplane using cfj airfoil
InactiveUS20090065631A1Reduce energy consumptionEasy to operateAircraft navigation controlBoundary layer controlsJet enginePropeller
The present invention provides an aircraft having one or more fixed wings in a flying wing configuration, where the aircraft further includes a high performance co-flow jet (CFJ) circulating about at least a portion of an aircraft surface to produce both lift and thrust rather than a conventional propulsion system (i.e., a propeller or jet engine).
Owner:MIAMI UNIVERISTY OF
Propellant depot in space
InactiveUS7559508B1Improve efficiencyLow costLaunch systemsCosmonautic power supply systemsPropellant depotMature technology
A space transportation propellant depot has multiple locations, sources and capabilities. Maximizing known mature technologies coupled with realistic industrial techniques results in the incremental development of a propellant source on the moon. Propellant depots are economically driven locations with defined services, sources of propellant and innovation in the pursuit of transportation related commerce as mankind explores for resources beyond Earth.
Owner:TAYLOR THOMAS C +2
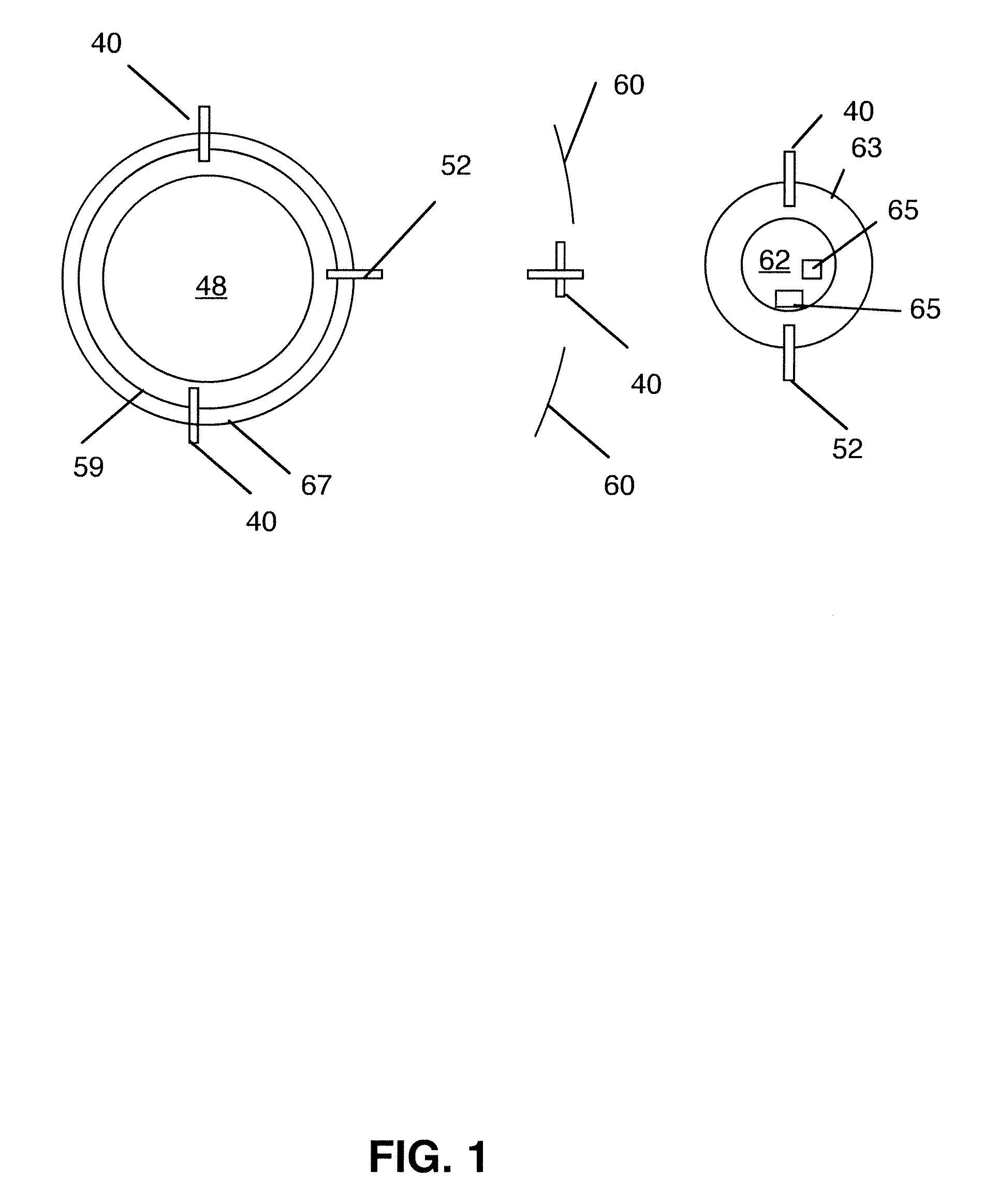
Attached mechanism of small star lander
InactiveCN102167166AOvercoming the defect of easy drifting awayGuaranteed to workSystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesMassive gravityElectricity
The invention discloses an attached mechanism of a small star lander, which relates to the attached mechanism of a lander, and aims to solve the problems that the lander safely lands on the surface of a small star and the land is easy to float away due to the small gravitation of the surface of the small star. One or two anchor positioning systems are arranged on the star-shaped bracket rod pieces of a triangular space truss type bracket; a universal joint mechanism is arranged on a landing mechanism; an executive tail end of the universal joint mechanism is connected with the buffer rod of ahydraulic buffer of a buffer mechanism; the sliding barrel of the buffer mechanism is inserted into an apparatus platform; the anchor positioning system is electrically connected with the pin socket of an electrical interface through a motor control wire; the signal detecting sleeve of the boosting mechanism of the anchor positioning system is electrically connected with the pin socket of the electrical interface by a feedback signal wire; the pin socket of the electrical interface is electrically connected with an electrical system and a control system by the plug wires of signal wires; and the motors of the motor driving mechanism of the universal joint mechanism and corresponding sensors are electrically connected with the electrical system and the control system by the plug wires of the signal wires. The attached mechanism of the small star lander is applied to lander detecting activities.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
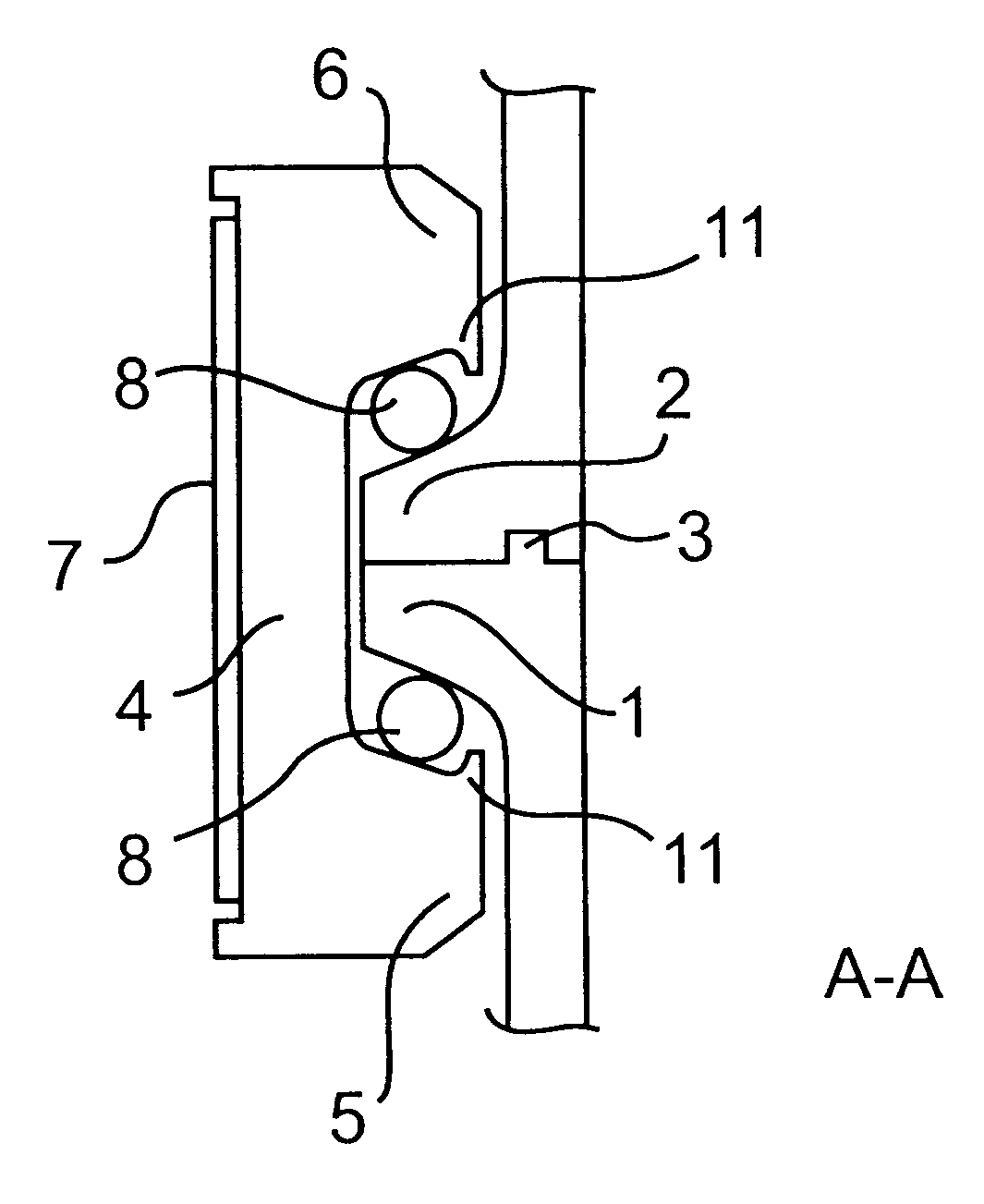
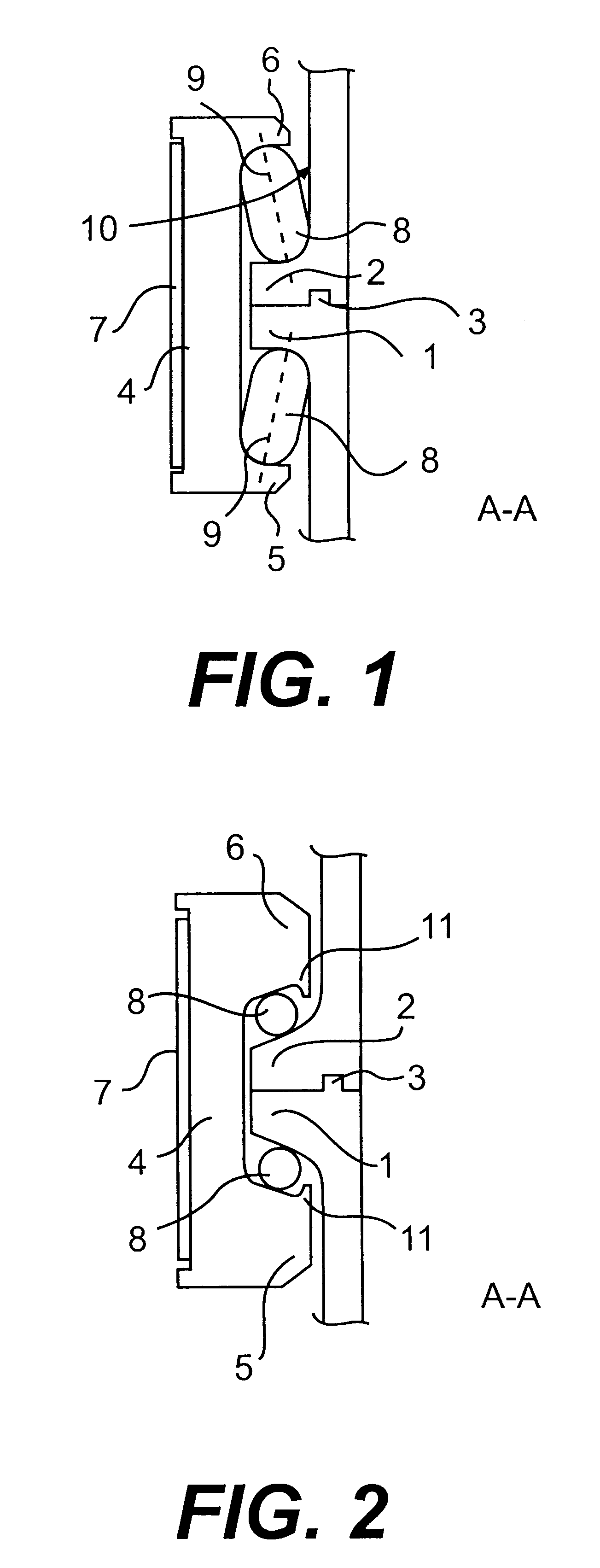
Joint for space vehicle
A joint in a space vehicle to hold together a first part of the vehicle and a second part of the vehicle that can be separated from the first part, in which the joint includes a first flange member (1) attached to the first part of the vehicle and a second flange member (2) attached to the second part of the vehicle. A number of clamps (4) equipped with two clamping lips (5, 6) are distributed around the perimeter of the flange members (1, 2) that transfer radial force from a tensioning means (7), arranged around the clamps (4), to both of the flange members (1, 2) in order to press these together, whereby rolling members (8) are arranged between at least one of the clamping lips (5, 6) of the respective clamps (4) and the adjacent first (1) or second (2) flange member.
Owner:SAAB ERICSON SPACE
Attitude-adjustable moon soft lander
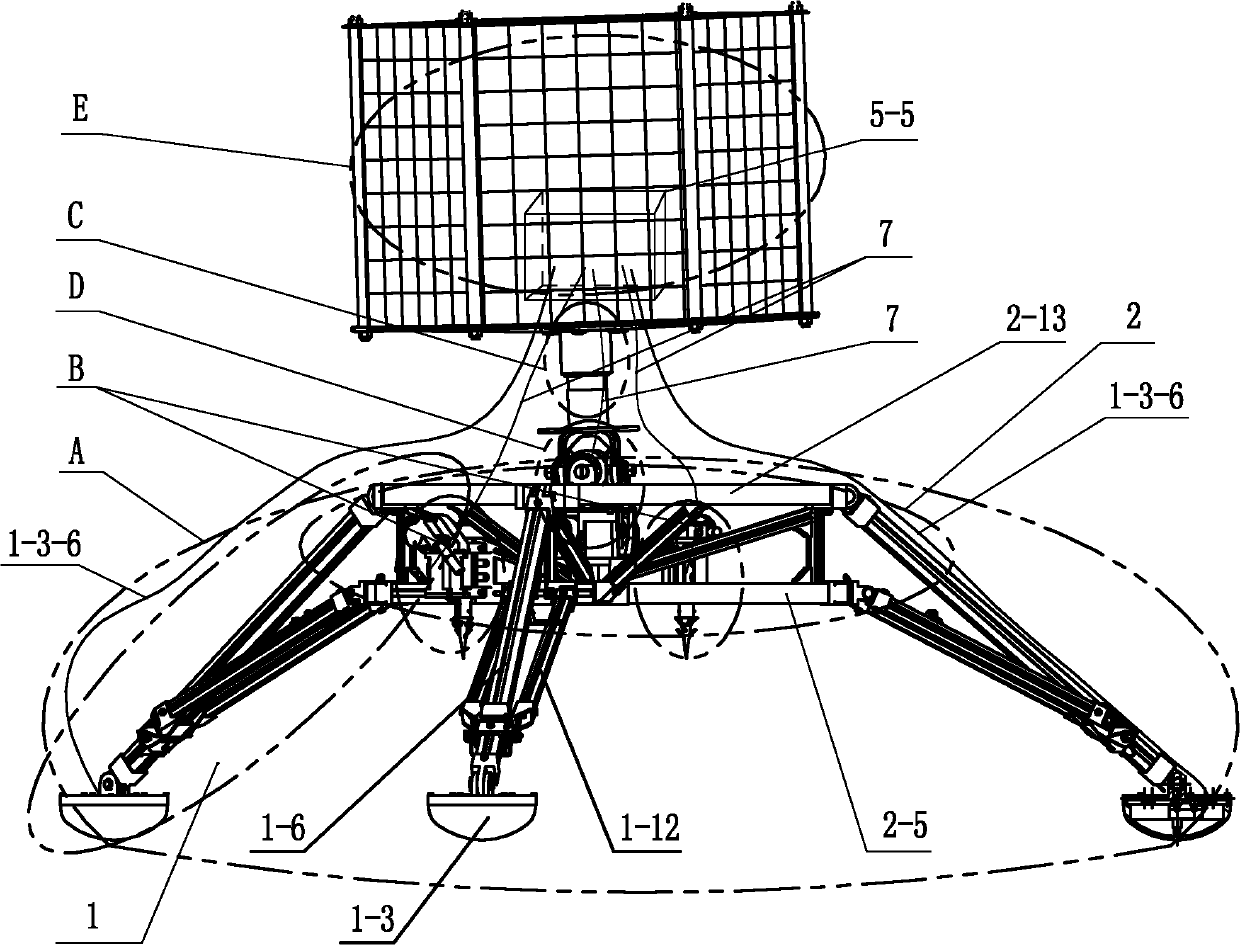
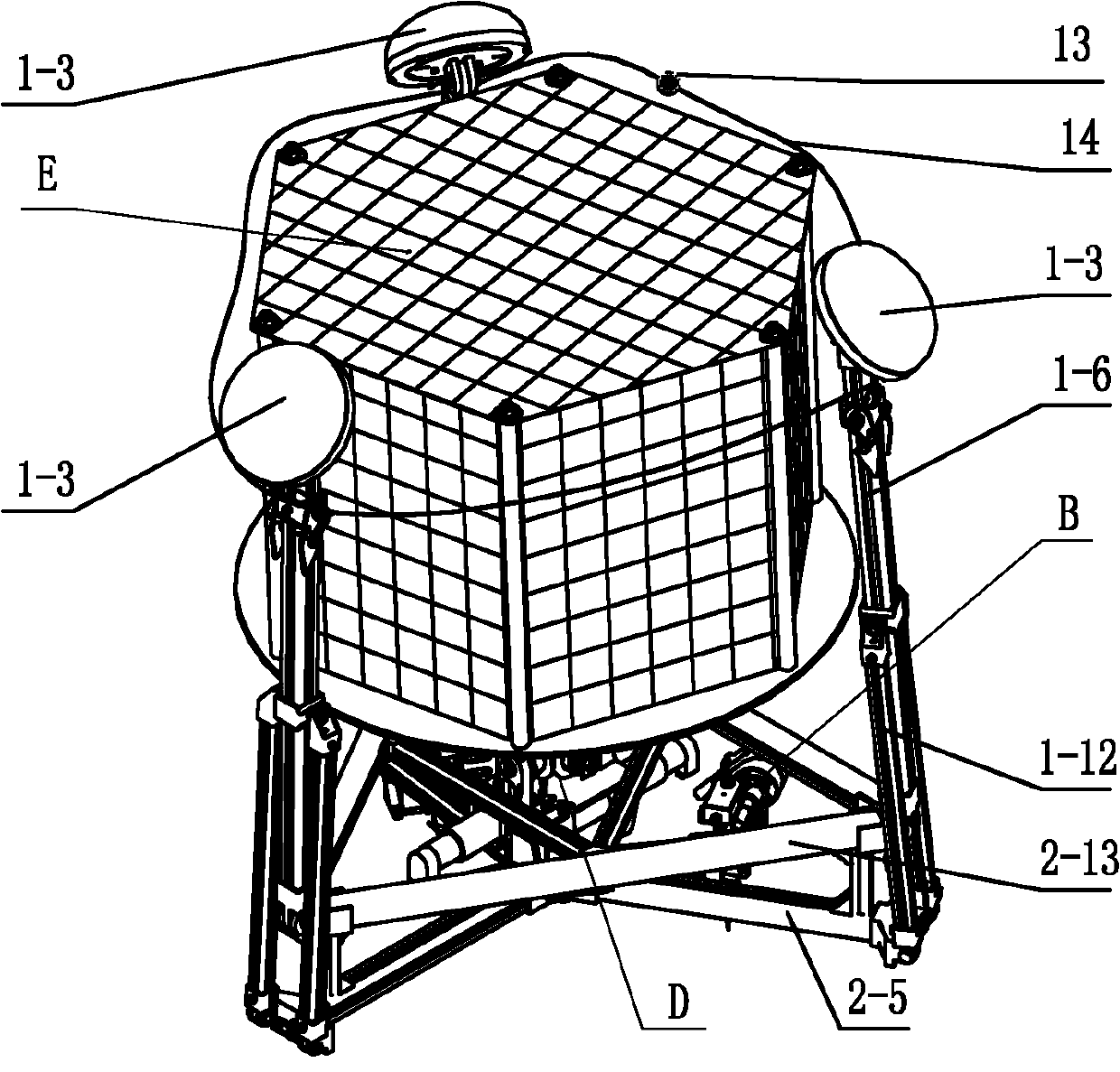
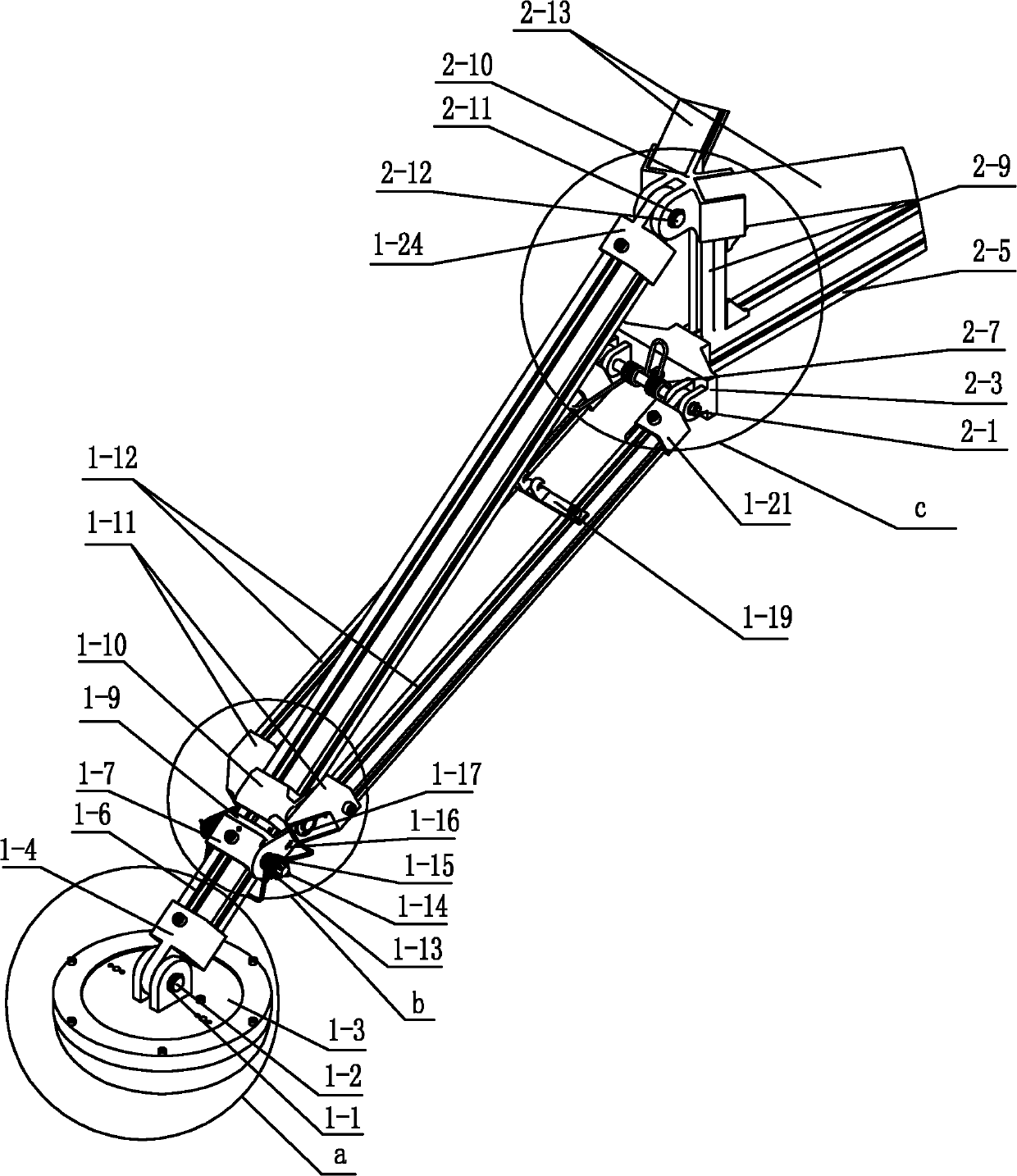
ActiveCN103350758AMeet the working conditions of the payloadMeet working conditionsSystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesEngineeringDegrees of freedom
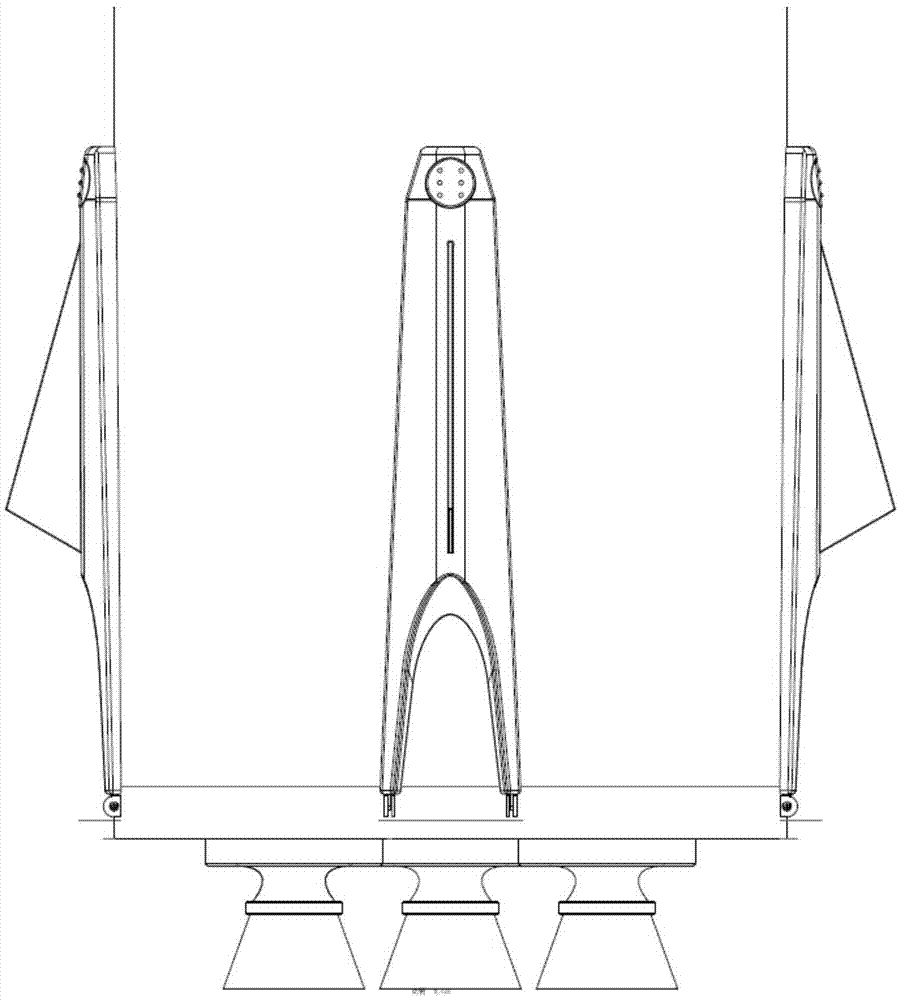
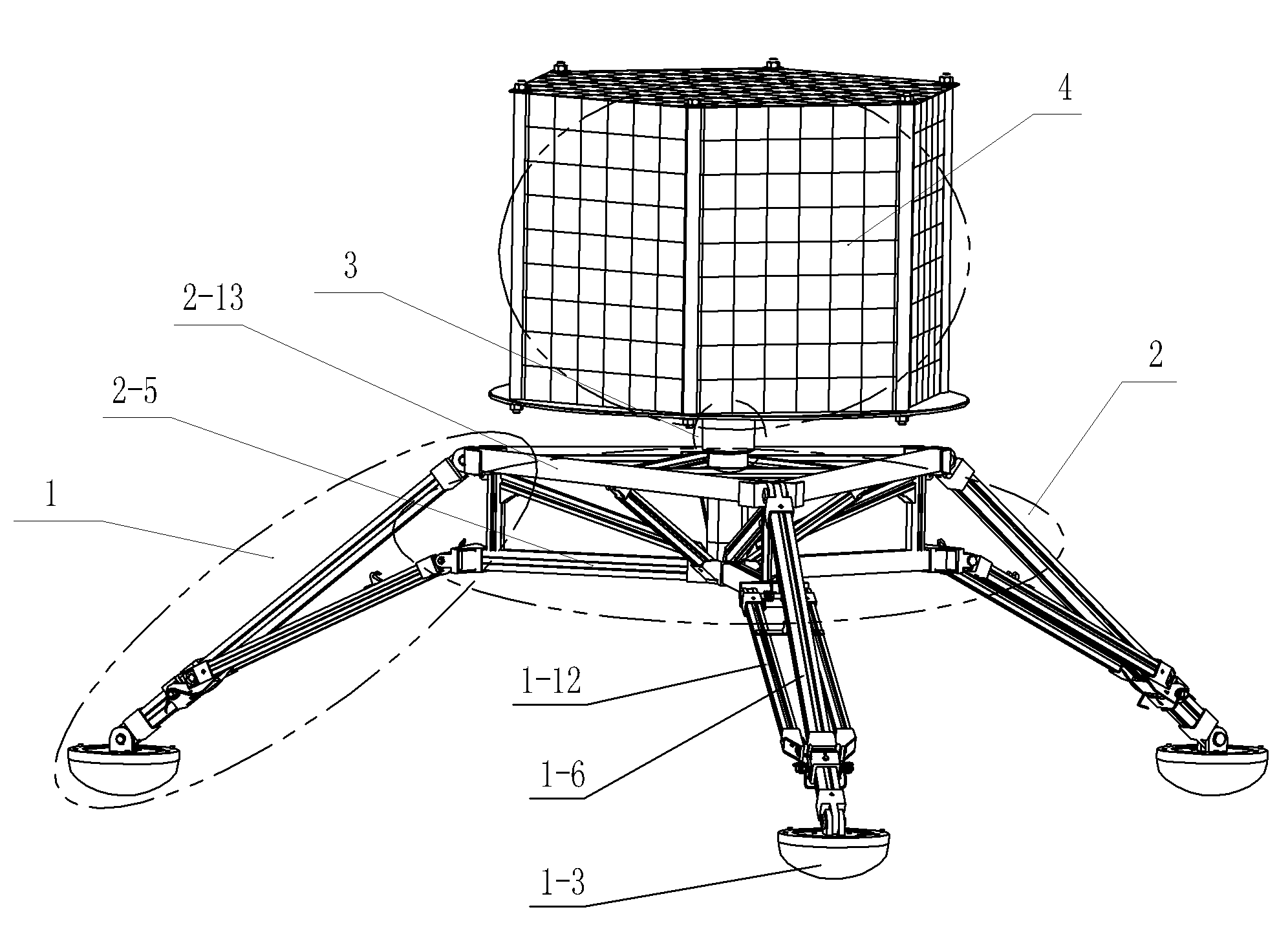
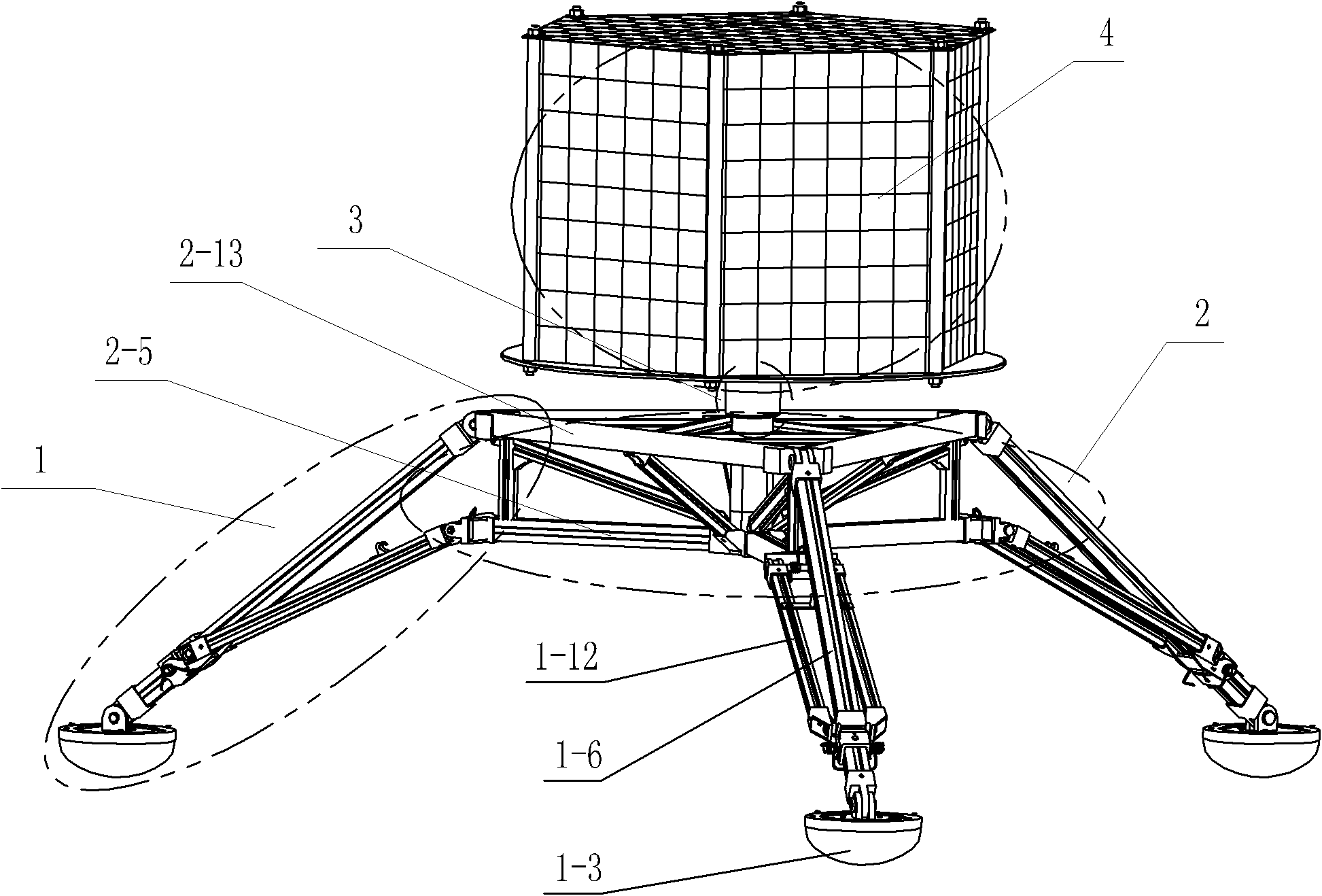
The invention discloses an attitude-adjustable moon soft lander which comprises a lander body and buffering leg components, wherein the buffering leg components are uniformly mounted on the circumferential side wall of the lander body and can realize stable landing. An attitude-adjustable effective load carrying platform is mounted inside the lander body and adopts a four-degree-of-freedom parallel connection platform which comprises an upper platform, a lower platform and five electric push rods connected with the upper platform and the lower platform, wherein displacement sensors which are used for acquiring a distance between the electric push rods and the upper and lower platforms in real time are mounted at body ends of the five electric push rods; a double-shaft tilt angle sensor used for acquiring attitude information of the upper platform is mounted on the upper platform; and the five electric push rods are controlled to realize attitude adjustment of the moon soft lander. Solar panels used for charging the soft lander are mounted on the side walls of the soft lander body through torsional springs, and the torsional springs and electromagnets mounted on the side walls of the soft lander body are used for unfolding and folding the solar panels. The attitude-adjustable moon soft lander has the benefits as follows: soft landing can be stably realized, and the attitude can be adjusted.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Prediction correcting guidance method of deep space exploration returning process
ActiveCN103863579ANo added complexityIncrease flight rangeSystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesCurrent pointDeep space exploration
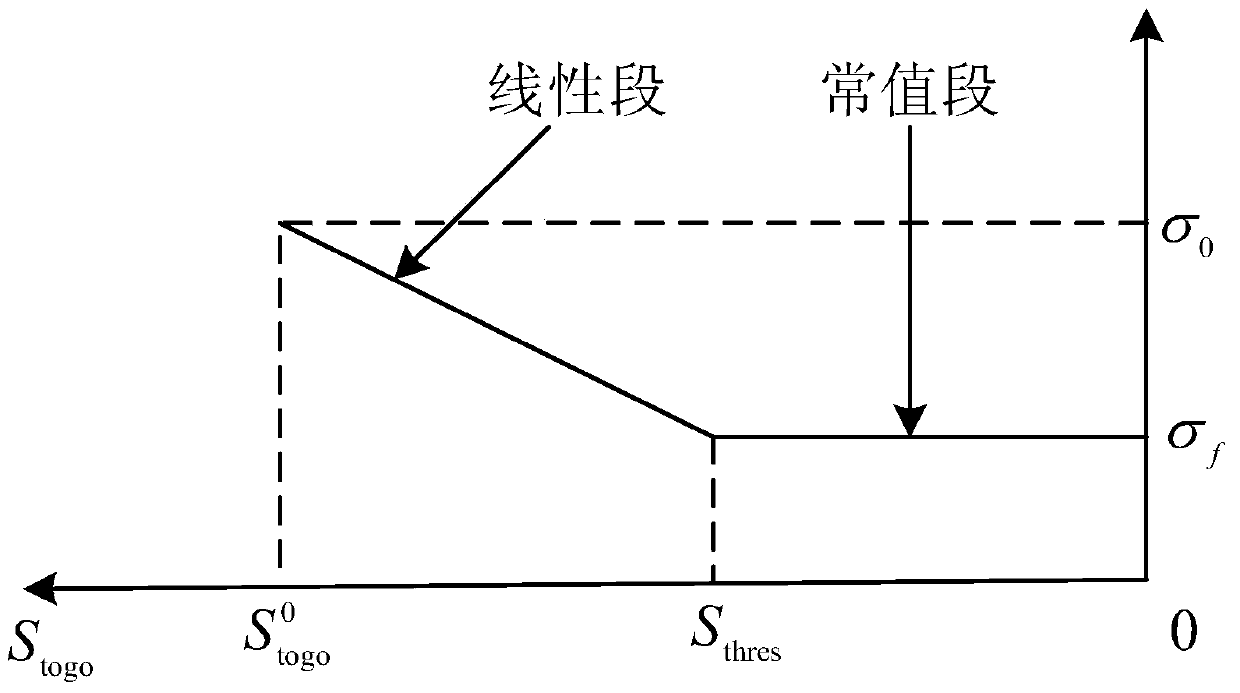
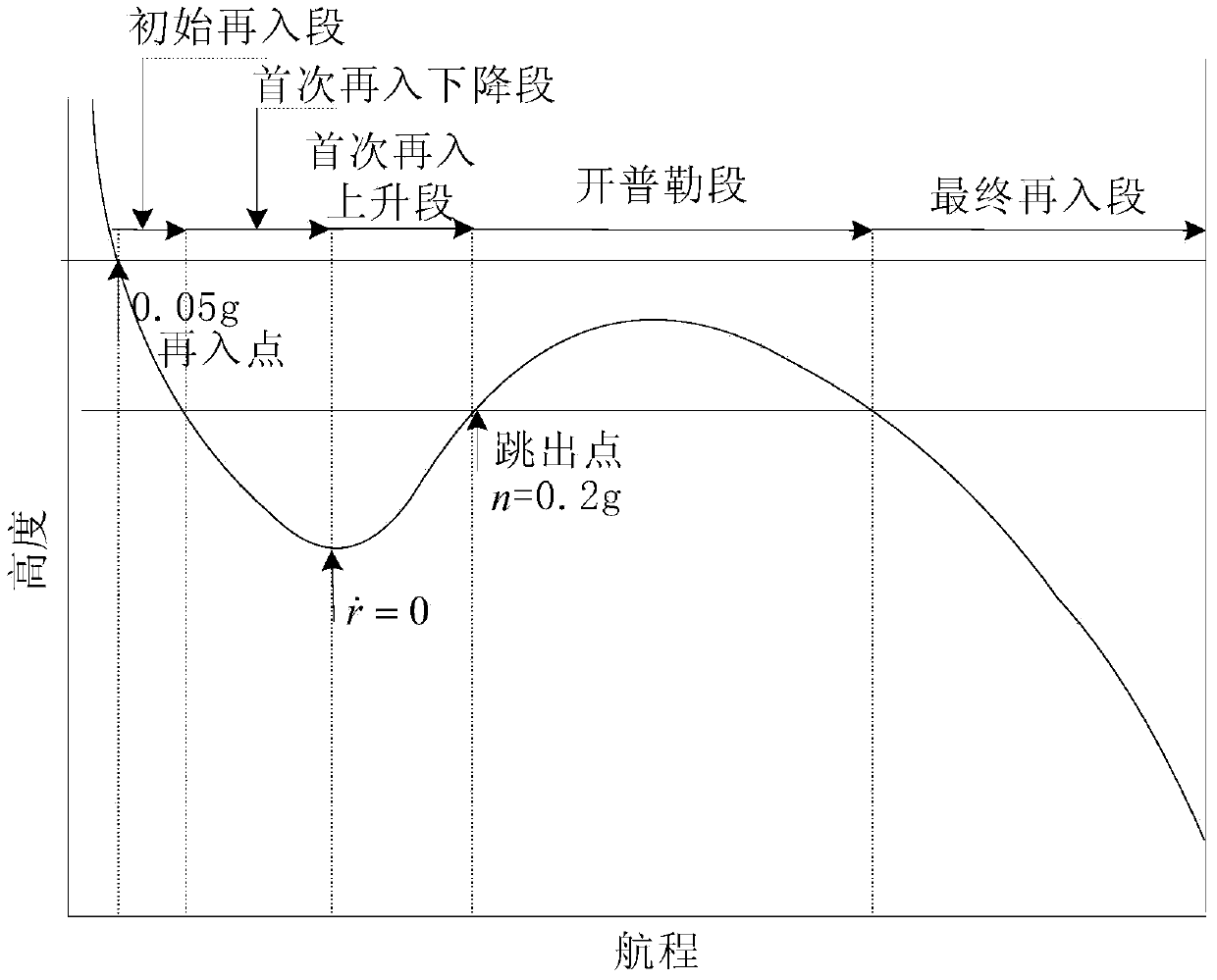
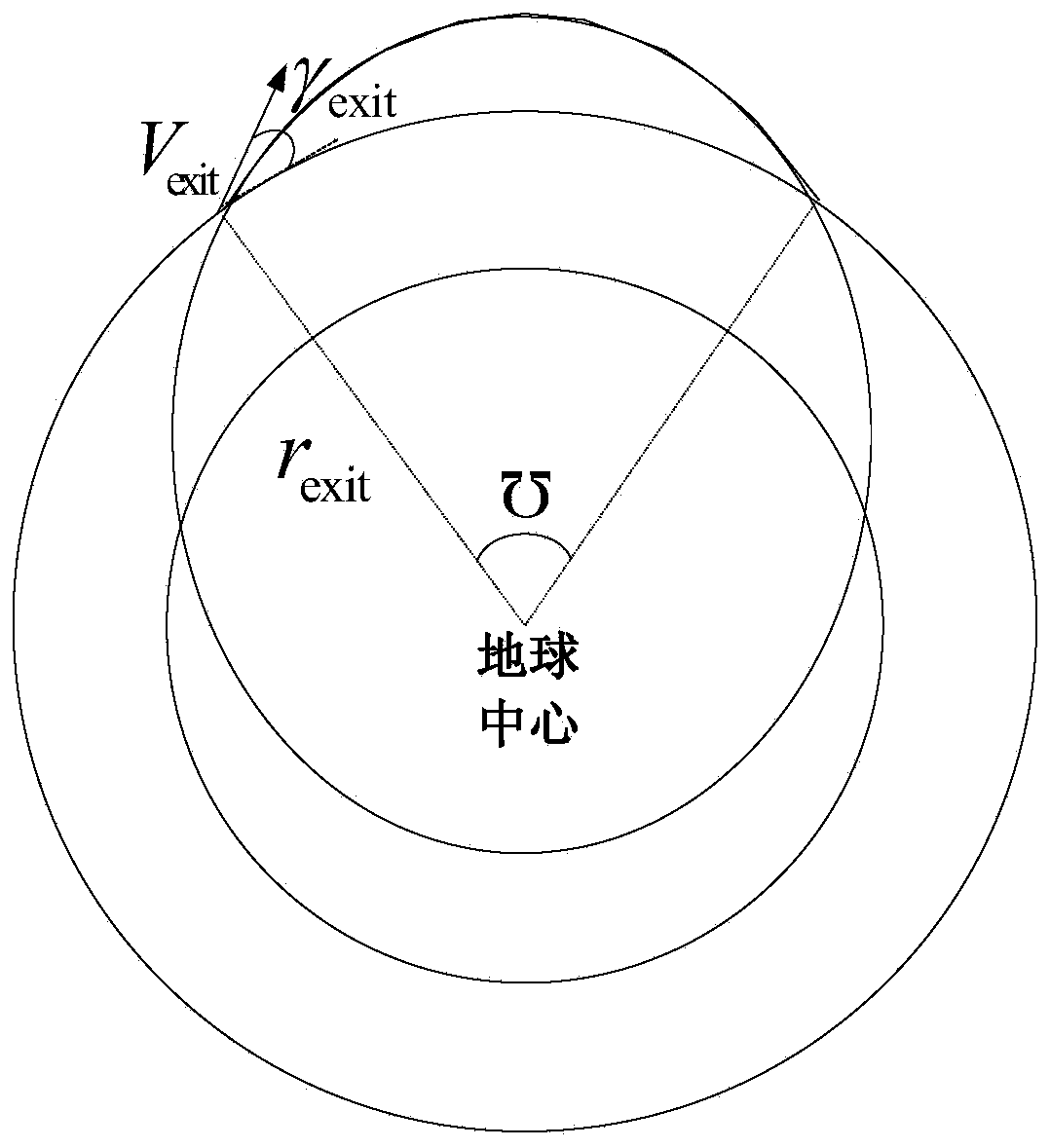
A prediction correcting guidance method of a deep space exploration returning process comprises the steps that (1) a heeling angle section used for deep space exploration returning process track prediction is determined; (2) the amplitude value | sigma 0 | of the heeling angle of a current point is computed in an iterative mode; (3) a salutatory reentry flight track of a returning device is divided into an initial reentry stage, a primary reentry descending stage, a primary reentry ascending stage, a Kepler stage and a final reentry stage, a final guidance rule of the returning device is determined, and the final guidance rule is that when the returning device is in the initial reentry stage or the primary reentry descending stage or the primary reentry ascending stage or the final reentry stage, the amplitude value | sigma 0 | determined in the step (2) of the heeling angle sigma 0 of the current point is used for guidance; and when the returning device is in the Kepler stage, | sigma 0 | = 180 degrees is used for guidance, and accordingly prediction correcting guidance of the deep space exploration returning process is completed. The guidance rule is designed at the Kepler stage of the track for achieving overload restrain on the deep space exploration returning process, and safe and accurate landing of the returning device is guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
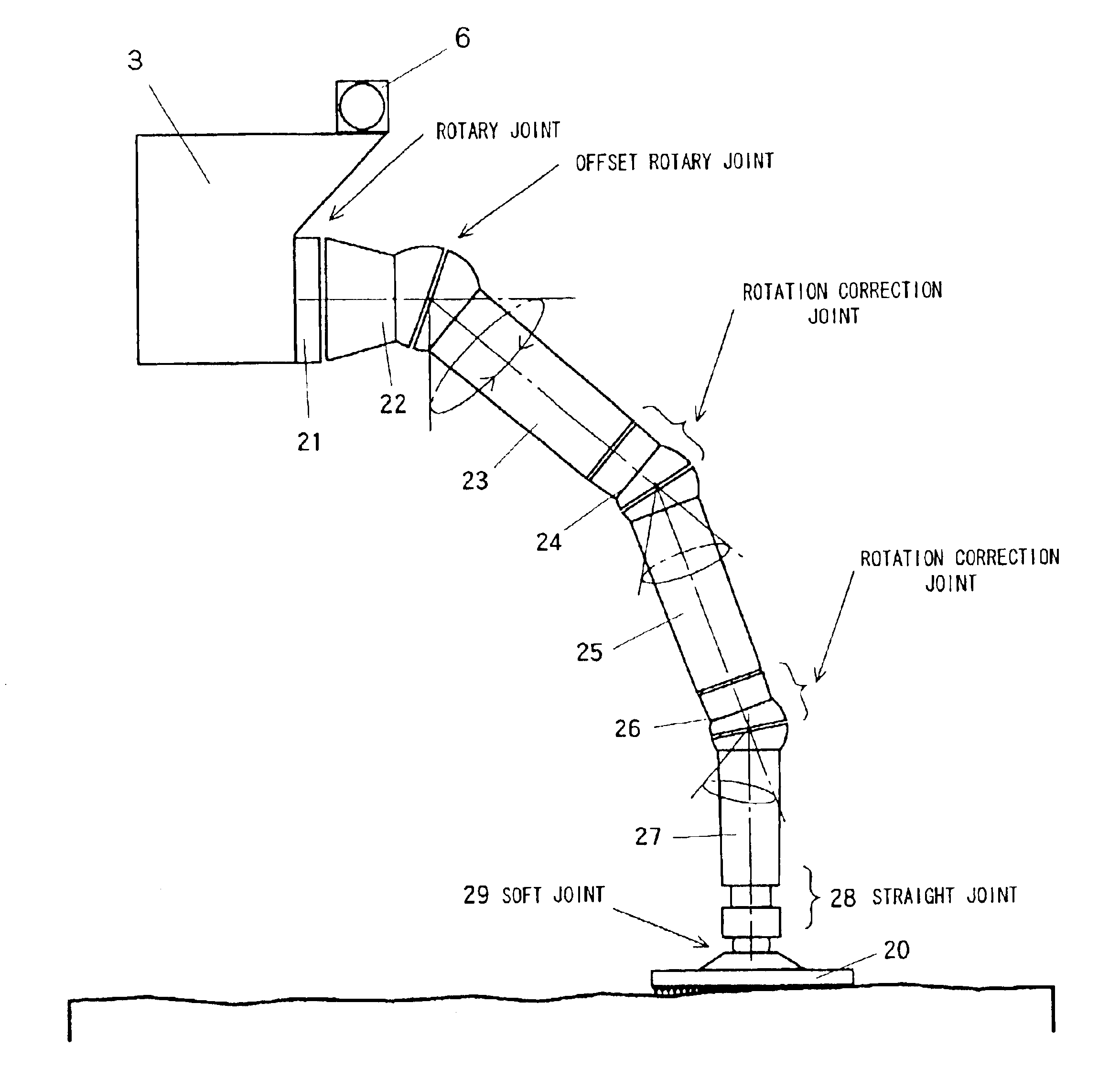
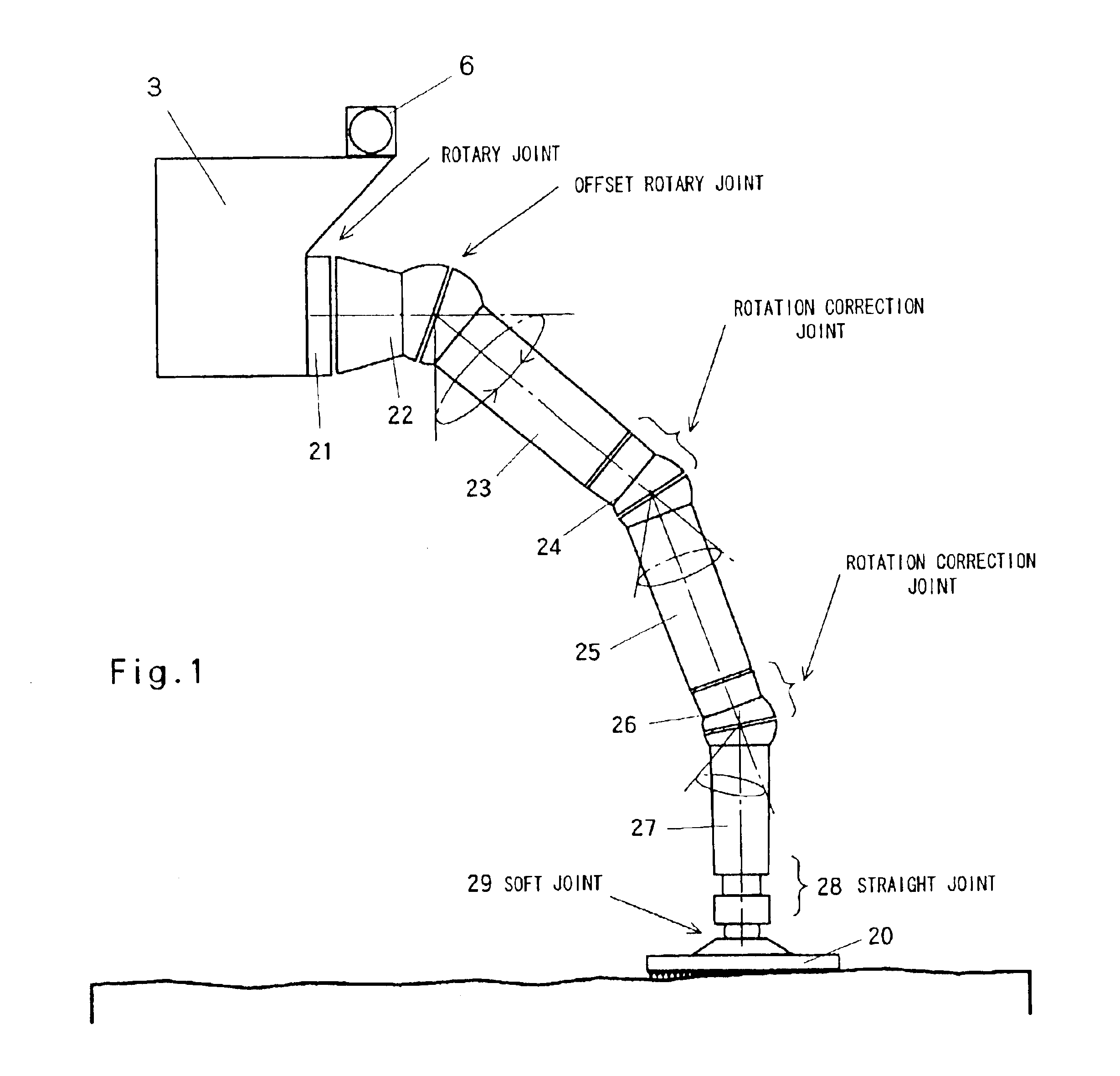
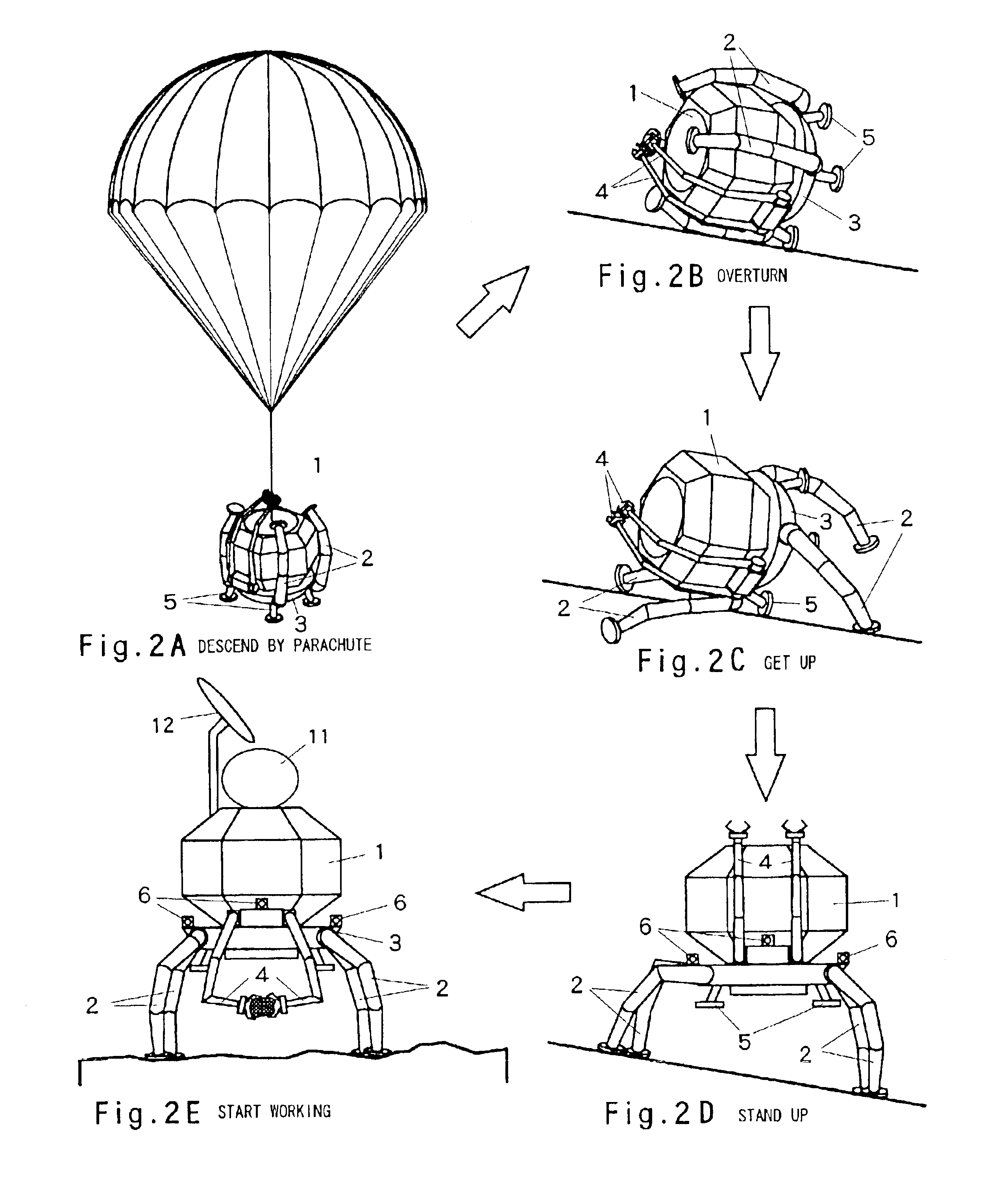
Robot having offset rotary joints
InactiveUS6922610B2Take-off and landing on uneven ground is facilitatedAvoid shockProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsHand partsSimulation
A robot is obtained having various functions that are demanded for planetary landing vehicles, extreme operations robots or the like, in particular to provide a leg structure for a robot that is capable of getting up itself when overturned, facilitating take-off and landing on uneven ground, and that has a walking function and that has a hand function capable of three-dimensional operation. A robot comprises a main robot body and at least three legs mounted on this main body for enabling three-dimensional movement of the main robot body such as a self-erecting action or walking action; each leg is constituted by a multi-joint arm having a plurality of said offset rotary joints linked together and has a ground-engaging member mounted at the leading end of the arm, so that each leg is capable of independently controlled three-dimensional movement and drive.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
External electric folding landing mechanism
ActiveCN105438502ADoes not affect layoutIncrease buffer strokeSystems for re-entry to earthLiquid based dampersRocketVertical take off and landing
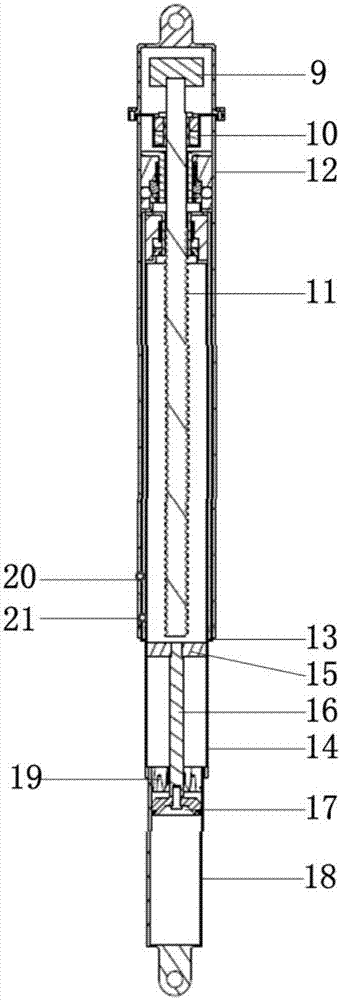
The invention provides an external electric folding soft landing mechanism. The external electric folding soft landing mechanism comprises at least three groups of the same supporting mechanisms arranged on a vehicle body, each of the supporting mechanism groups comprises a damping post and a landing leg, wherein the damping post comprises an electric transmission mechanism and a hydraulic damping device; the electric transmission mechanism comprises a motor, a bearing, a lead screw and a plurality of stage transmission sleeves which are sequentially nested; the hydraulic damping device comprises a spiral fastening device, a piston rod, a piston head, a buffer outer cylinder and a sealing device. The landing mechanism disclosed by the invention is suitable for repeated use in perpendicular ascending and descending, and is stuck to the outer surface of the vehicle under a folding state, so that the aerodynamic influence on the vehicle is reduced, and the folding rigidity is good; when the landing mechanism disclosed by the invention is under an unfolding state, the supporting area is large, and the bearing capacity is strong; the landing mechanism disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of light in weight, simple in preparation technology, smooth in buffering process, free from rebounding during processes, and high in buffering efficiency, and can be repeatedly utilized; a protrusion structure of a mechanism casing can also achieve the effect that a rocket empennage is aerodynamically stabilized.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
Folding lightweight landing mechanism
InactiveCN102092484ASimple configurationSimple designSystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesInstrumentationAsteroid
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
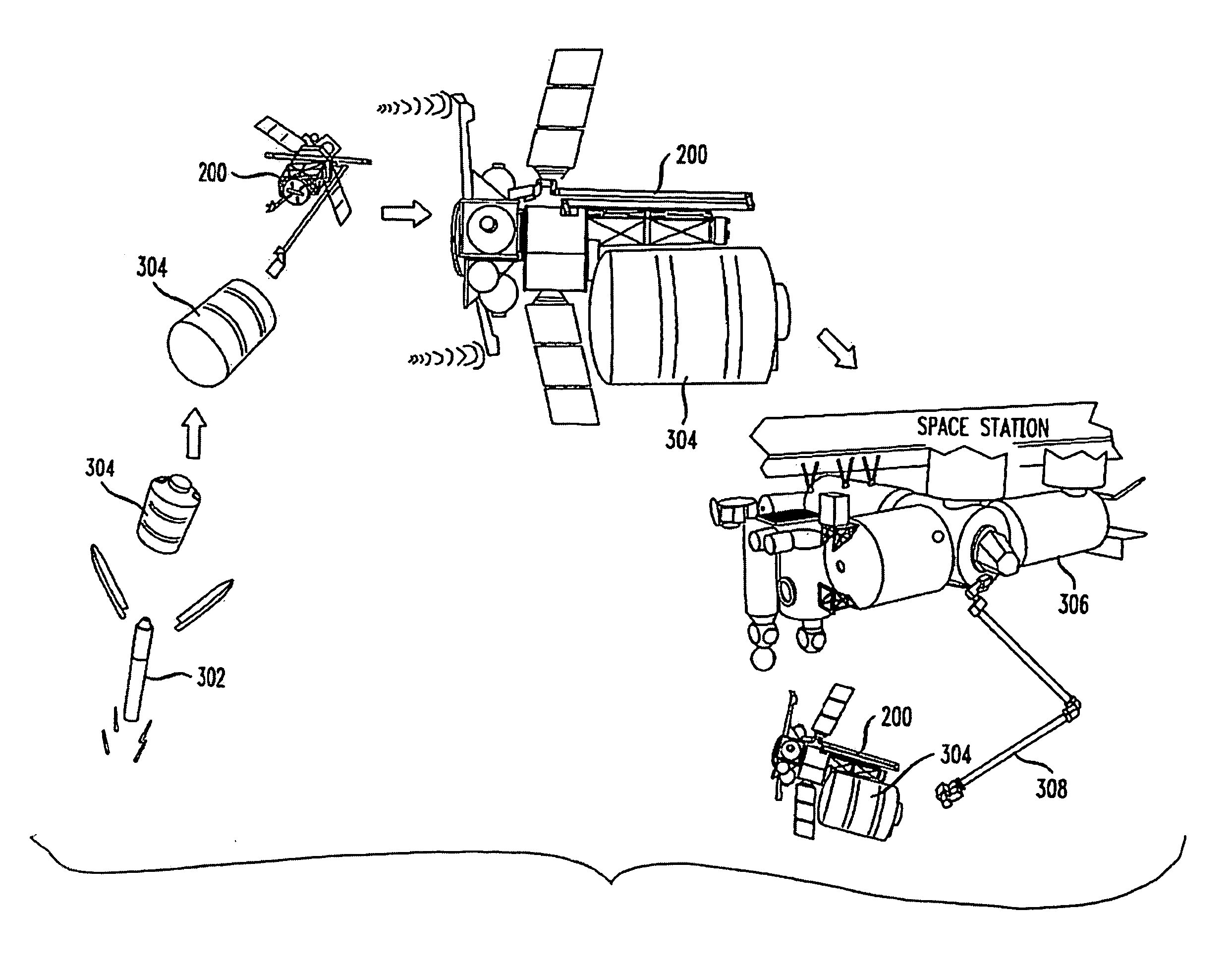
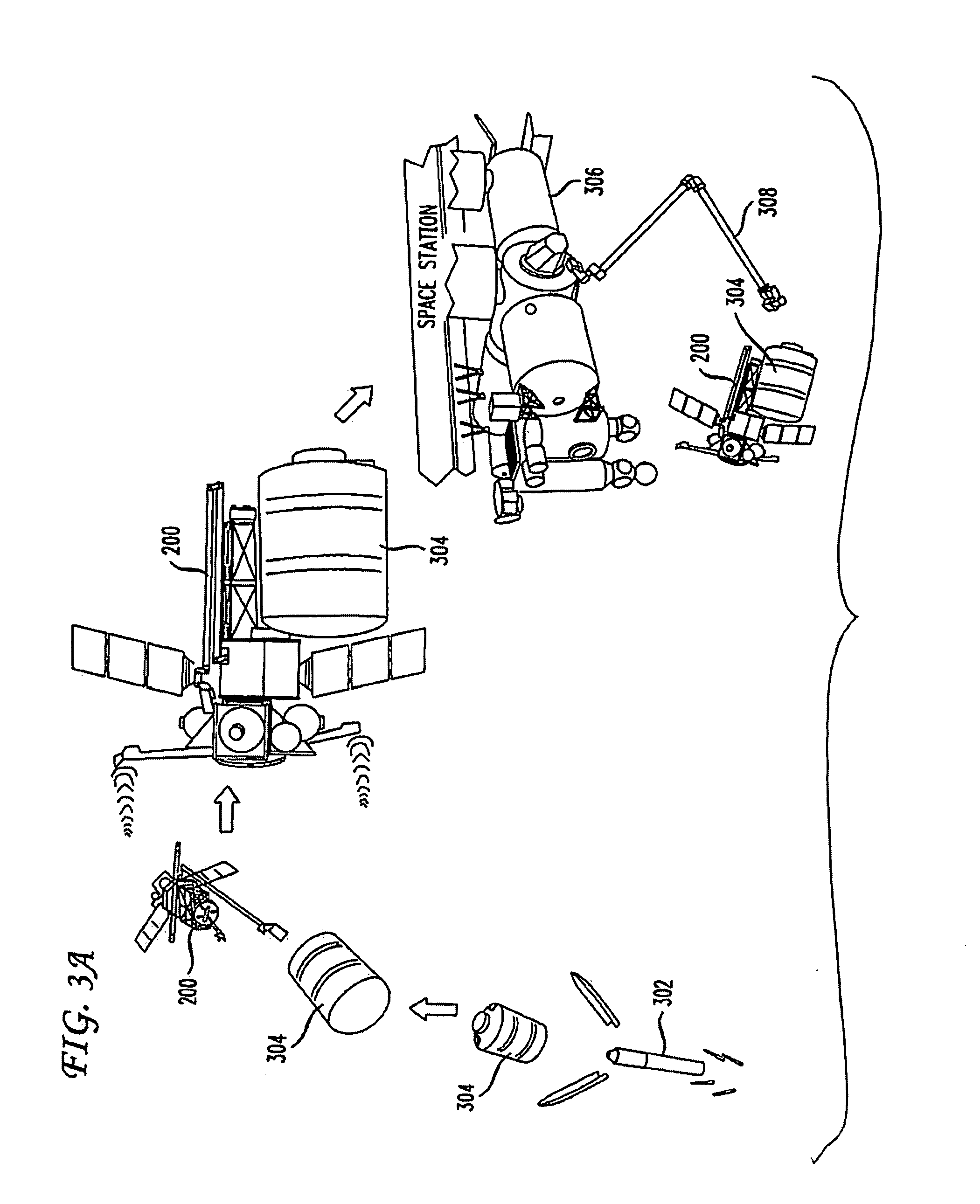
System and method for transferring cargo containers in space
InactiveUS20100038491A1Safe returnLaunch systemsSystems for re-entry to earthCouplingInternational Space Station
Disclosed is a Host Transfer Vehicle methods and computer-readable medium for enabling the capture and berthing of passive cargo containers in space with an orbiting system, such as the International Space Station. A method embodiment positions a Host Transfer Vehicle (HTV) in proximity to an orbiting system, captures a passive cargo container launched from a ground by a grappling arm of the HTV, couples the passive cargo container to the HTV to form an HTV / cargo container stack, propels the HTV / cargo container stack within proximity of an orbiting system, and through the use of a grappling arm of the orbiting system berths the HTV / cargo container stack via a coupling structure on the cargo container to the orbiting system. The cargo container can then receive cargo from the orbiting system and either return to the ground or the cargo container can be burned up in the atmosphere.
Owner:NASA
System for Emergency Crew Return and Down-Mass from Orbit
ActiveUS20160264266A1High level of operation safetyEconomy of scaleCosmonautic thermal protectionArtificial satellites3d shapesHuman use
A system for emergency crew return and down-mass orbit comprising a stowable, self-contained, deployable maneuvering reentry vehicle for automated, on-demand reentry to ground for cargo of 1-10 kilograms or up to single or multiple human use for evacuation of orbital facilities. The system includes a deployable “aeroshell” that is contiguous (a single geometric object—surface or hollow shape—that can morph in 3D shape), modular (a collection of modular components externally acting as a contiguous shape, but morphed in 3D via actuators contained in each modular member to create a general asymmetric geometry), or discontiguous (a collection of independently controlled surfaces or bodies that morph to form desirable asymmetric drag configurations). The system contains traditional spacecraft guidance, navigation and control, propulsion, and attitude control elements, in addition to communications, power, and actuator energetics systems for controlling the vehicle aeroshell shape during reentry, thus, minimizing the landing footprint of the vehicle.
Owner:STONE WILLIAM C
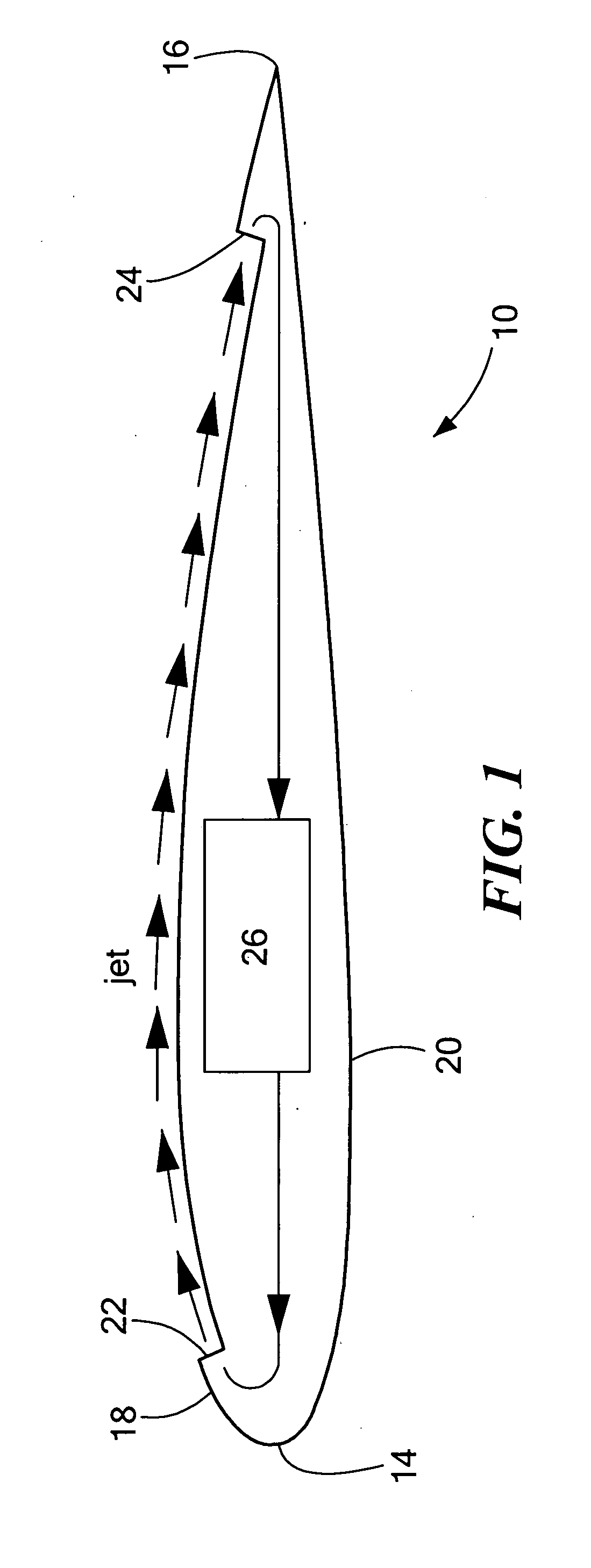
Shock wave modification method and system
InactiveUS20050061908A1Reduce pressureHigh speed of soundFluid dynamicsSystems for re-entry to earthElectric dischargeEngineering
A shock wave in a gas is modified by emitting energy to form an extended path in the gas; heating gas along the path to form a volume of heated gas expanding outwardly from the path; and directing a path. The volume of heated gas passes through the shock wave and modifies the shock wave. This eliminates or reduces a pressure difference between gas on opposite sides of the shock wave. Electromagnetic, microwaves and / or electric discharge can be used to heat the gas along the path. This application has uses in reducing the drag on a body passing through the gas, noise reduction, controlling amount of gas into a propulsion system, and steering a body through the gas. An apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:KREMEYER KEVIN
Airship shaped space craft
InactiveUS6471159B1Launch safetyReduce the average velocitySpace shuttlesSystems for re-entry to earthReverse orderJet engine
The present airship-shaped space craft has a middle fuselage extending in a fore-and-aft direction, and a pair of two outer fuselages extending in the fore-and-aft direction located symmetrically on both sides of the middle fuselage. In the above fuselages, gas of a specific gravity of which is smaller than that of air is filled, and the middle fuselage is connected with the outer fuselages by a horizontal wing. The horizontal wing is provided with propelling devices supported in a gimbal fashion for generating thrust in any optional direction, jet engines with backwards directed nozzles to be controlled within a range from a slantwise upward direction to a slantwise downward direction, and rocket engines with ejection nozzles to be controlled in right-and-left and up-and-down directions. During ascent of the space craft, at first the propelling devices, then the jet engines and at last the rocket engines are actuated so as to make the space craft reach and fly along a satellite orbit. Upon return of the space craft, the rocket engines, the jet engines and the propelling devices are actuated in reverse order, and aerodynamic heating at reentry into the atmospheric space can be reduced by making the space craft descend slowly. Also, control of the flight in the atmospheric space becomes easy, so that the space craft can safely and easily land on a predetermined narrow area of the ground.
Owner:BUNDO MUTSURO
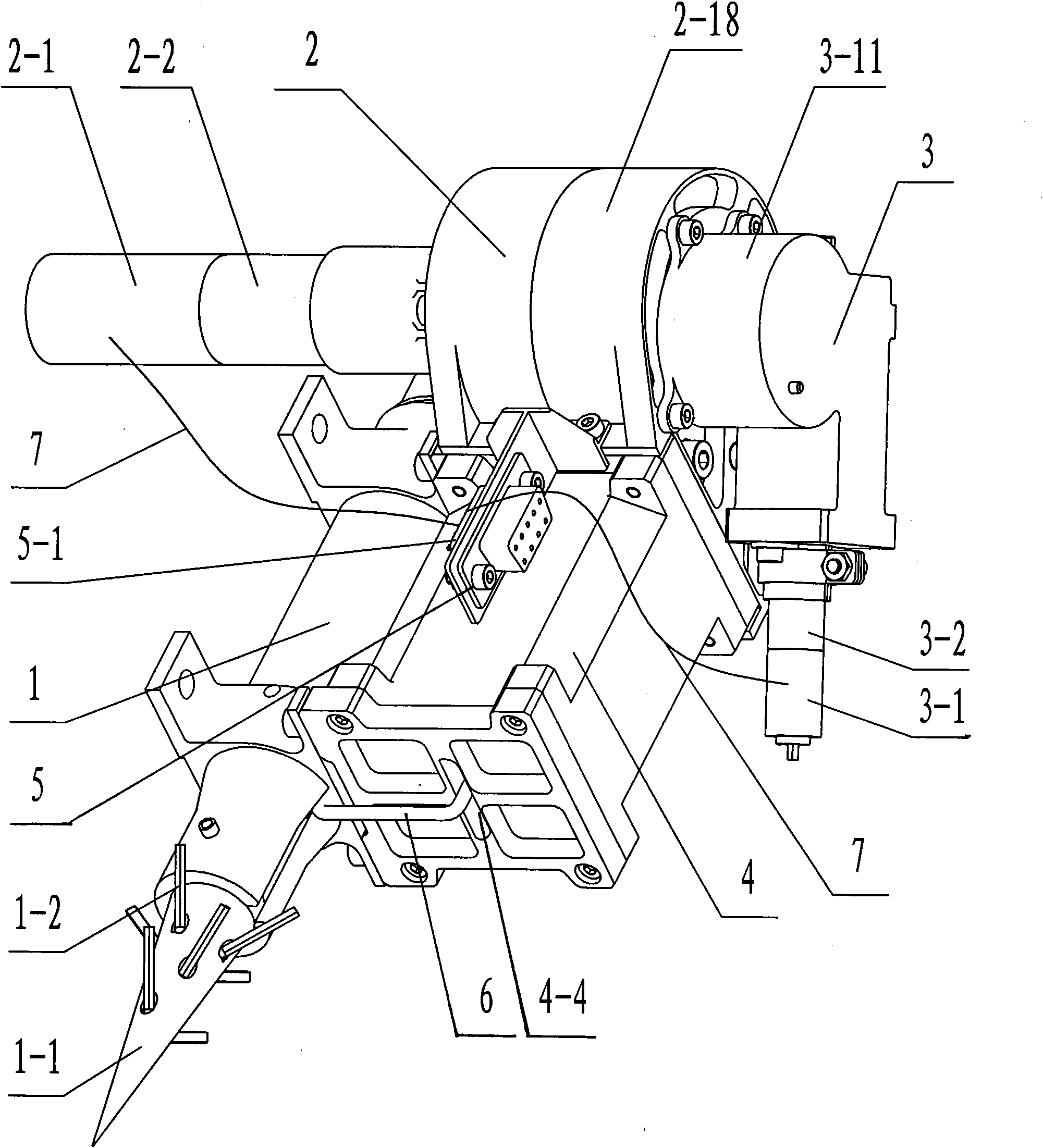
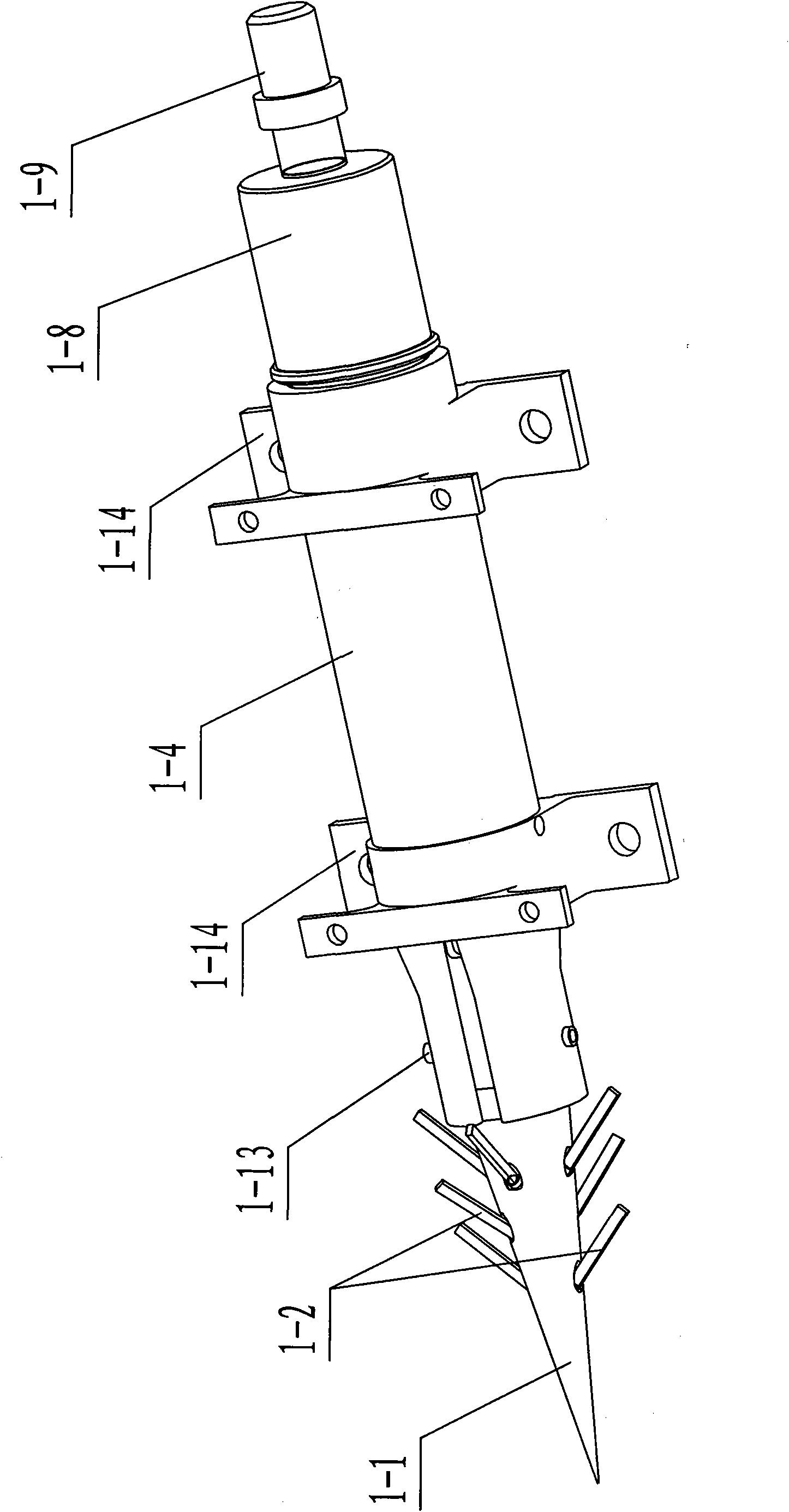
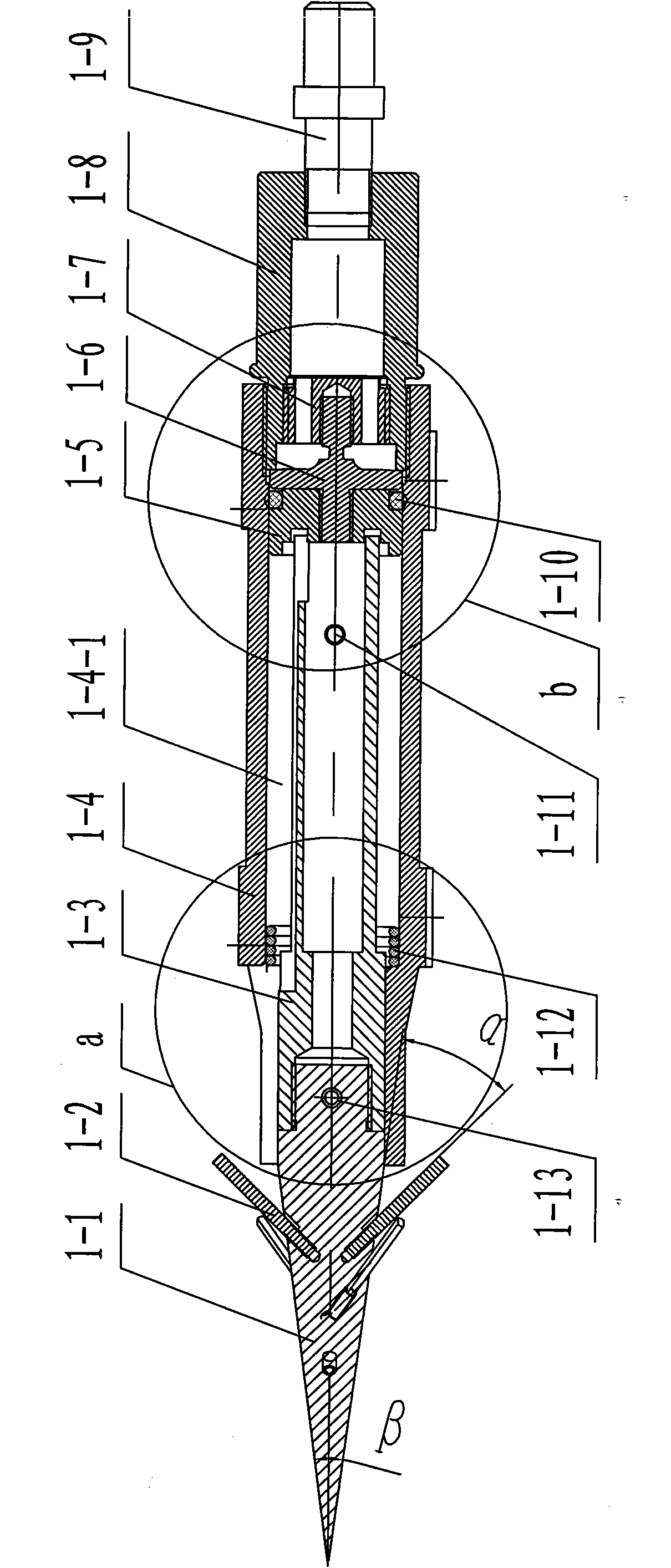
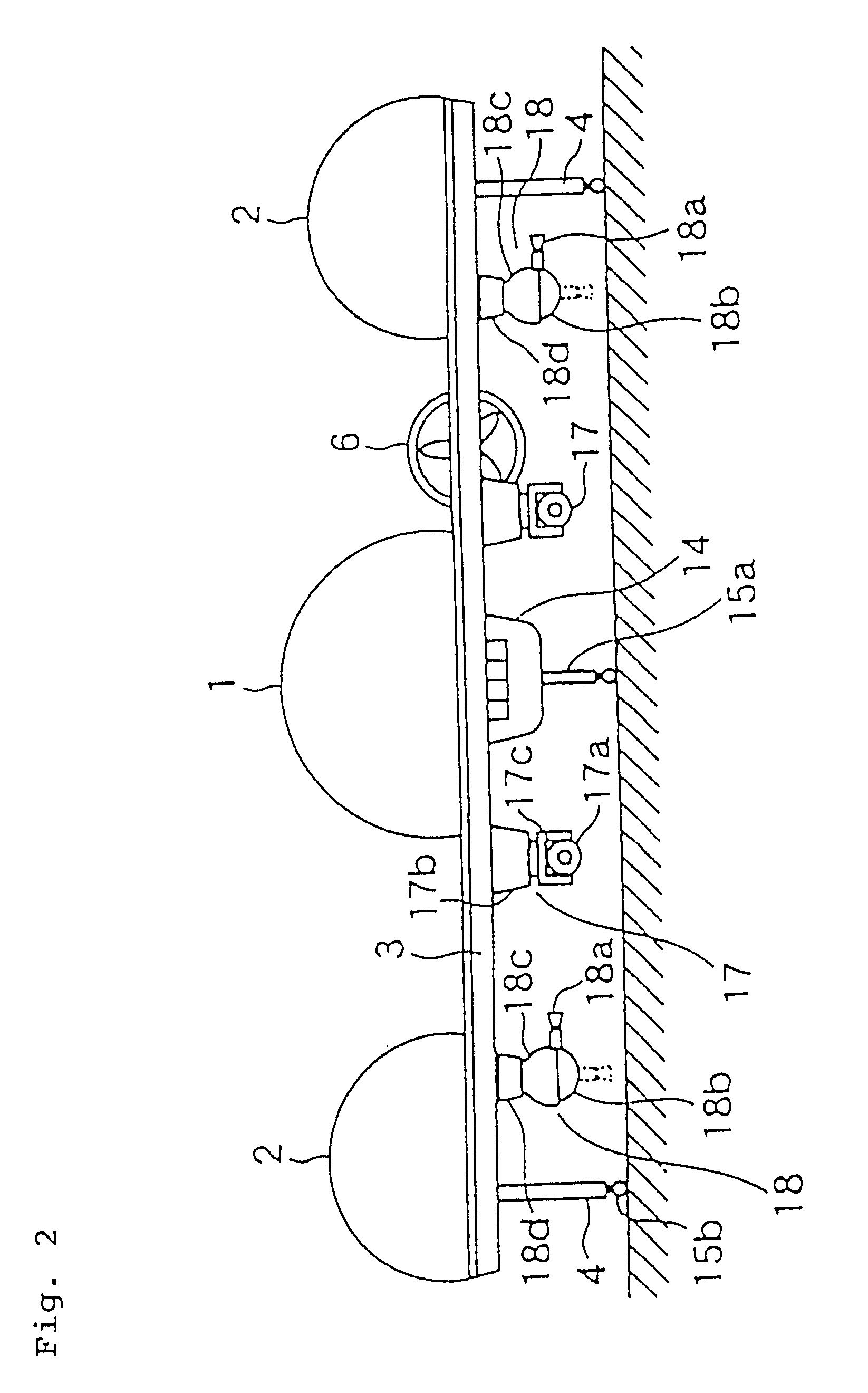
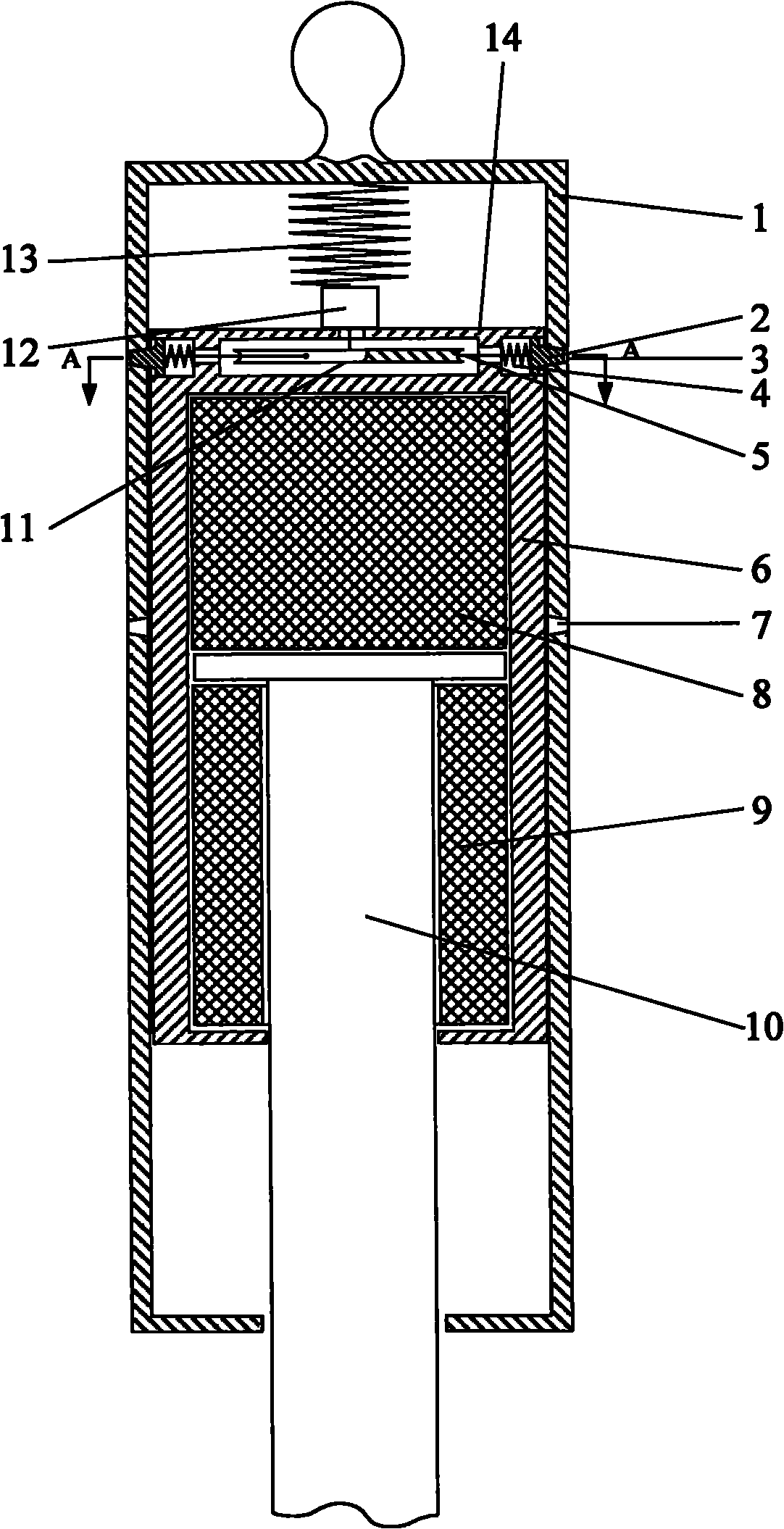
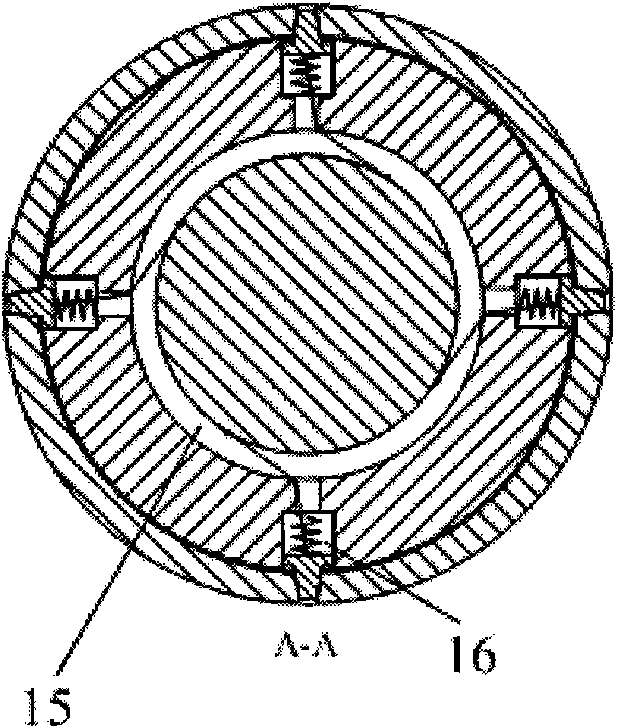
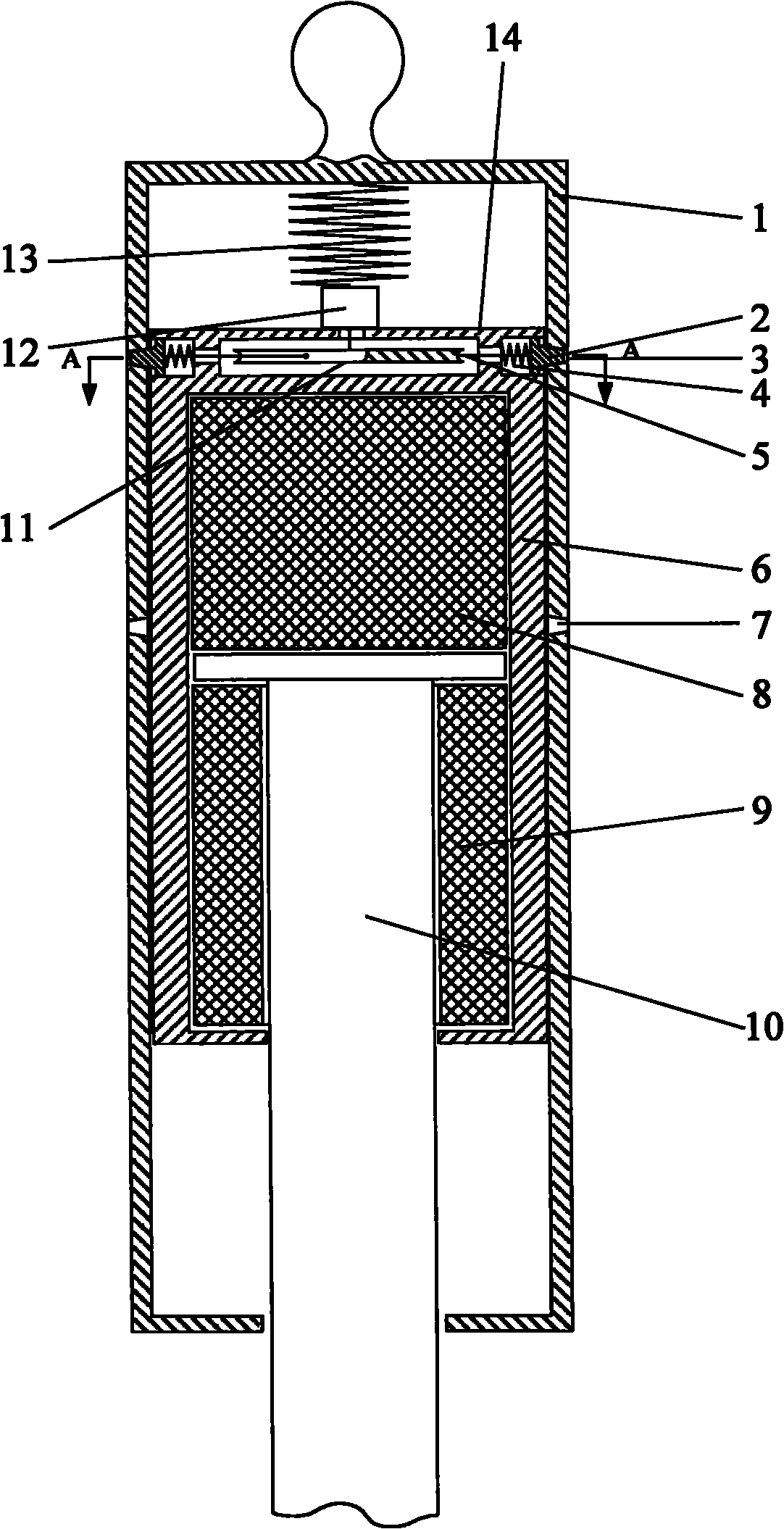
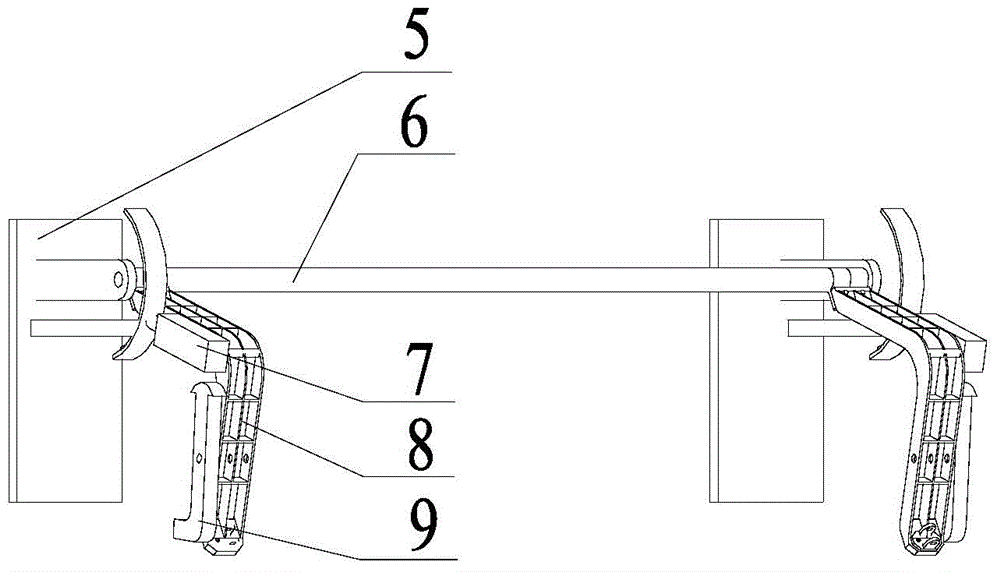
Landing leg pressing, unfolding and locking device of lander
InactiveCN101780841ALow movement friction resistanceImprove structural rigiditySystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesLeg pressLocking mechanism
The invention relates to a landing leg pressing, unfolding and locking device of a lander, which belongs to the landing leg unfolding and locking mechanism. The device comprises an outer support cylinder (1) and an inner support cylinder (6); the top part of the inner support cylinder (6) is provided with a top inner cylinder cover (14), a mounting chamber is formed between the top part of the inner support cylinder (6) and the top inner cylinder cover (14); a stepper motor (12) is arranged above the top inner cylinder cover (14) and is connected with the top part of the outer support cylinder (1) through an axial spring (13); a turntable (11) is arranged on a motor shaft and is connected with a bolt (2) through a radial spring (4) which penetrates through a locking spring chamber (16); and the outer support cylinder (1) is also provided with an upper locking hole (3) which is matched with the bolt (2) and is used for locking the inner support cylinder before the landing leg is unfolded and a lower locking hole (7) which is matched with the bolt (2) and is used for locking the inner support cylinder after the landing leg is unfolded. The invention has the advantages of simple mechanism and high reliability.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
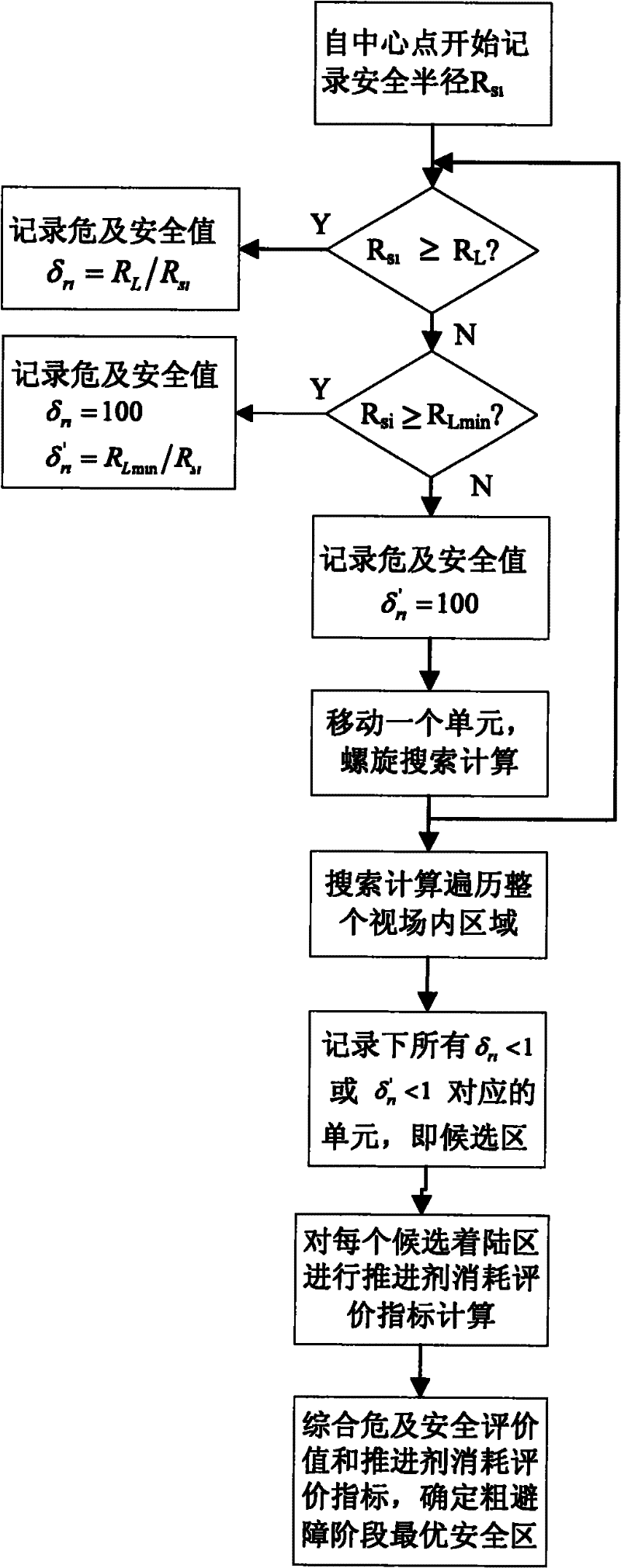
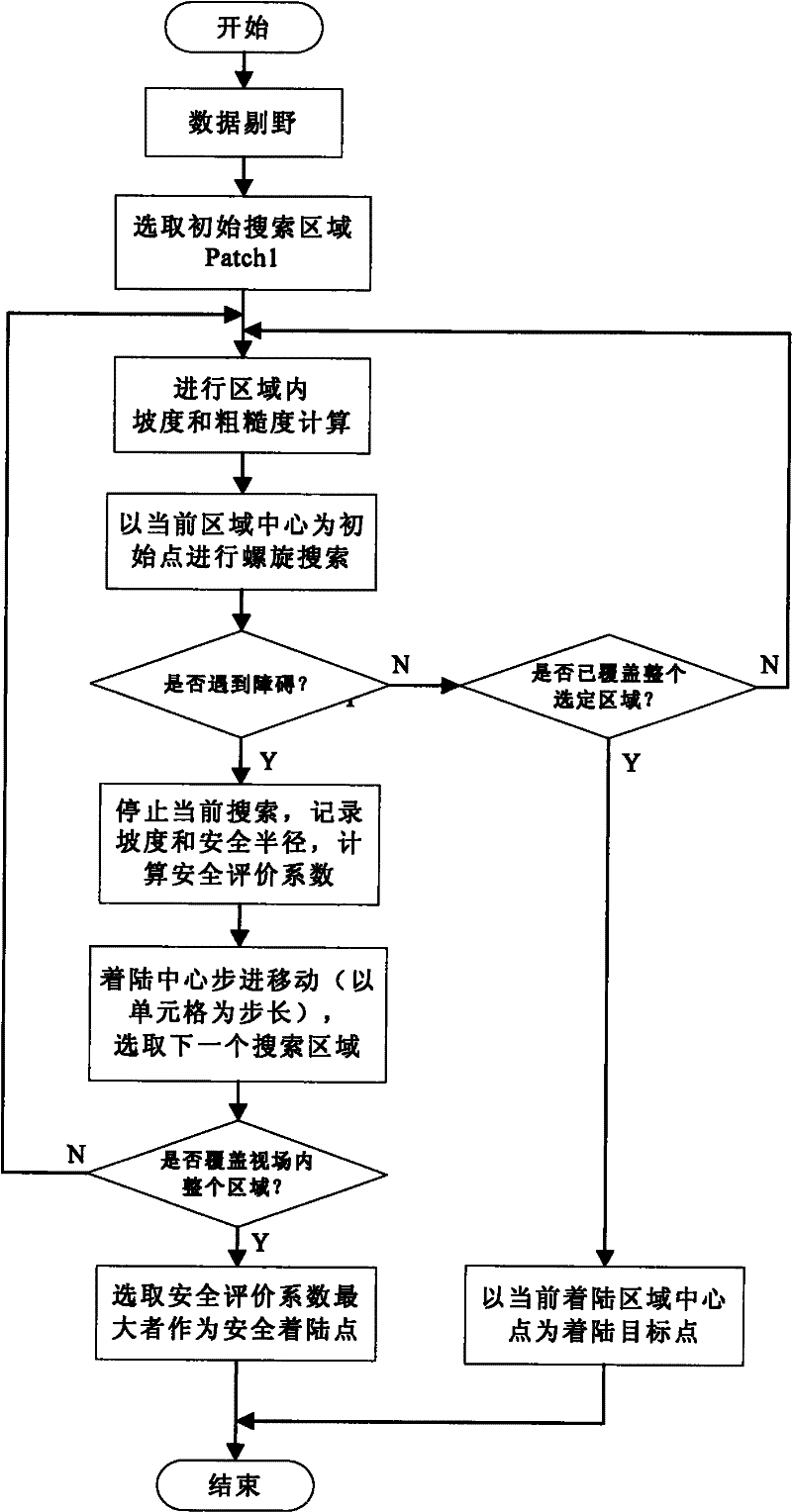
Soft landing relay obstacle avoiding method
ActiveCN102173313AGood autonomyImprove reliabilitySystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesTerrainCelestial body
The invention discloses a soft landing relay obstacle avoiding method which is used for completing soft landing of a celestial body through two matched stages, namely a rough obstacle avoiding stage and a fine obstacle avoiding stage, wherein in the rough obstacle avoiding stage, a visible-light camera is used for carrying out rough detection on a larger range and larger obstacles to remove largeobstacles which directly threaten landing safety; and then the surface of the celestial body is subjected to accurate three-dimensional obstacle detection by utilizing laser scanning in a safe area selected in the rough obstacle avoiding stage so as to obtain and remove obstacles with smaller dimensions and ensure landing safety to the maximum extent. The soft landing relay obstacle avoiding method disclosed by the invention has good autonomy and high reliability, can be used for soft landing detection of the celestial body with more complicated terrain, and is especially applicable to soft landing of deep-space unmanned celestial bodies in a longer distance; the soft landing relay obstacle avoiding method greatly improves the obstacle avoiding capacity and lengthens the obstacle avoidingdistance, and improves the landing safety; and the soft landing relay obstacle avoiding method reduces the technical index requirement on sensors, reduces the difficulty in research of visible-light / laser imaging sensors, and is beneficial to engineering application.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
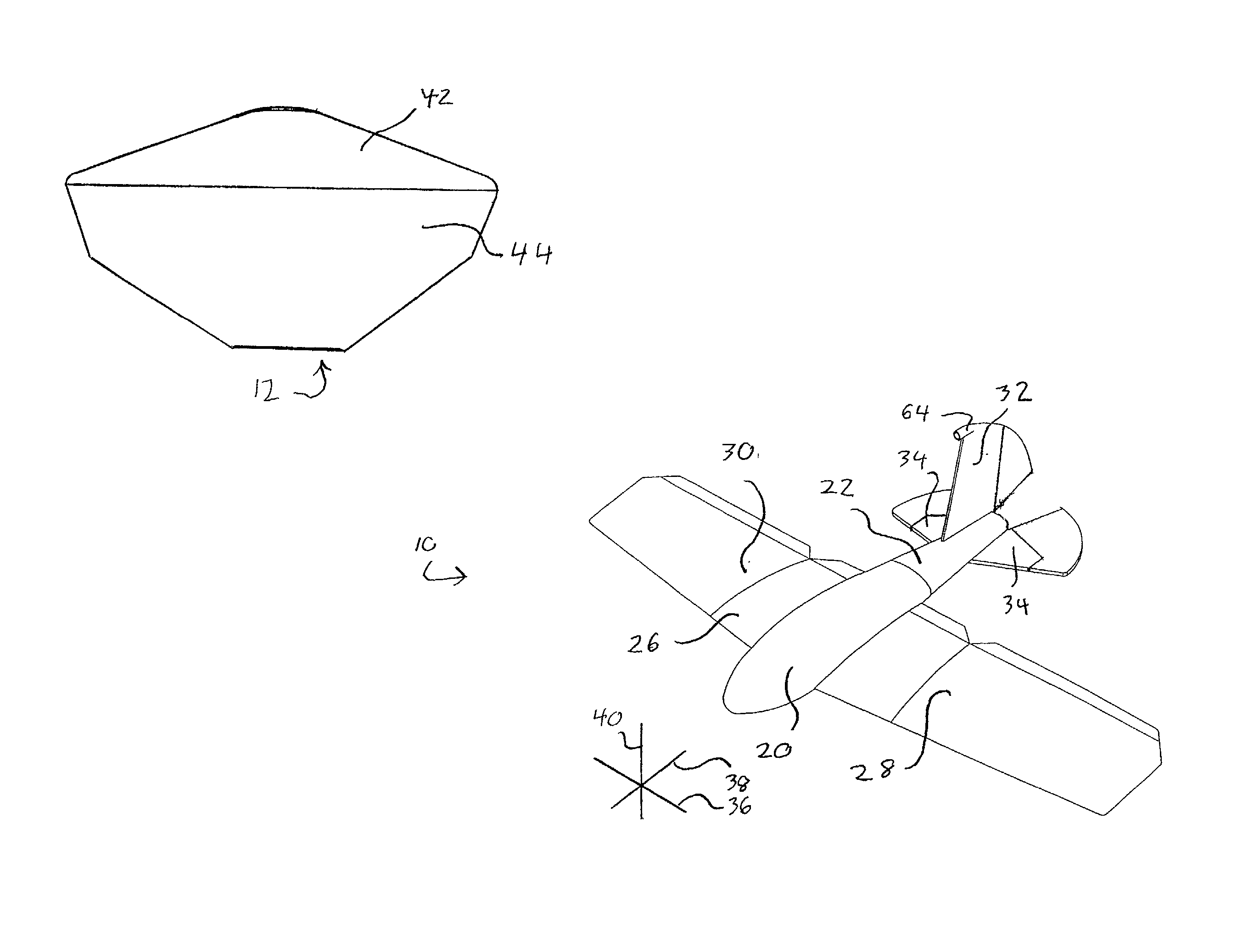
Payload delivery system
InactiveUS20020066825A1Effective placementShorten the lengthUnmanned aerial vehiclesArtificial satellitesFree fallingMission Command
Disclosed is a spacecraft carrying a number of pods, each containing an aircraft that has been folded to fit in the pod. Each aircraft has a vertical stabilizer and outboard wing-portions that fold around fore-and-aft axes. Each aircraft also has a fuselage that folds around a lateral axis. The spacecraft releases one or more of the pods into an atmosphere. Each of the pods is configured with an ablative heat shield and parachutes to protect its aircraft when the pod descends through the atmosphere. The pod releases its aircraft at a desired altitude or location, and the aircraft unfolds while free-falling. The aircraft then acquires and follows a flight path, and activates scientific experiments and instruments that it carries. The aircraft relays results and readings from the experiments and instruments to the spacecraft, which in turn relays the results and readings to a mission command center.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
Shock wave modification method and system
InactiveUS7063288B1Reduce pressureHigh speed of soundSystems for re-entry to earthFire rescueShock waveModified method
A system for modifying a shock wave formed in a fluid by a body to modify effects of the shock wave on an object released from the body including heating fluid along a path to form a volume of heated fluid expanding outwardly from the path, the path extending from the body and through the shock wave, releasing the object from the body, and timing a release of the object relative to the heating of the fluid along the path to modify certain effects of the shock wave on the object.
Owner:KREMEYER KEVIN
Multipurpose modular spacecraft
InactiveUS7219859B2Artificial satellitesSystems for re-entry to earthModularityElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:SPACEHAB
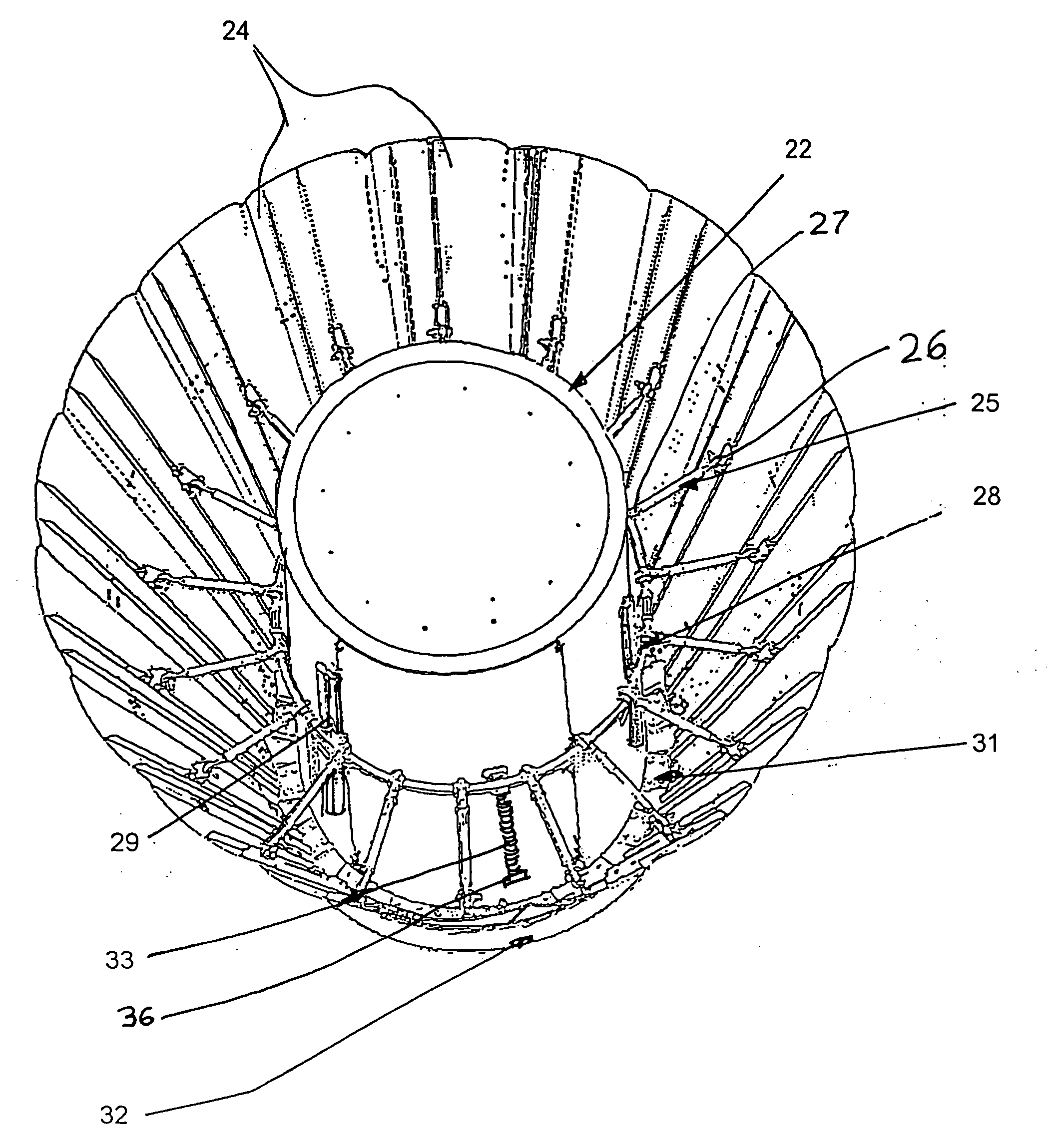
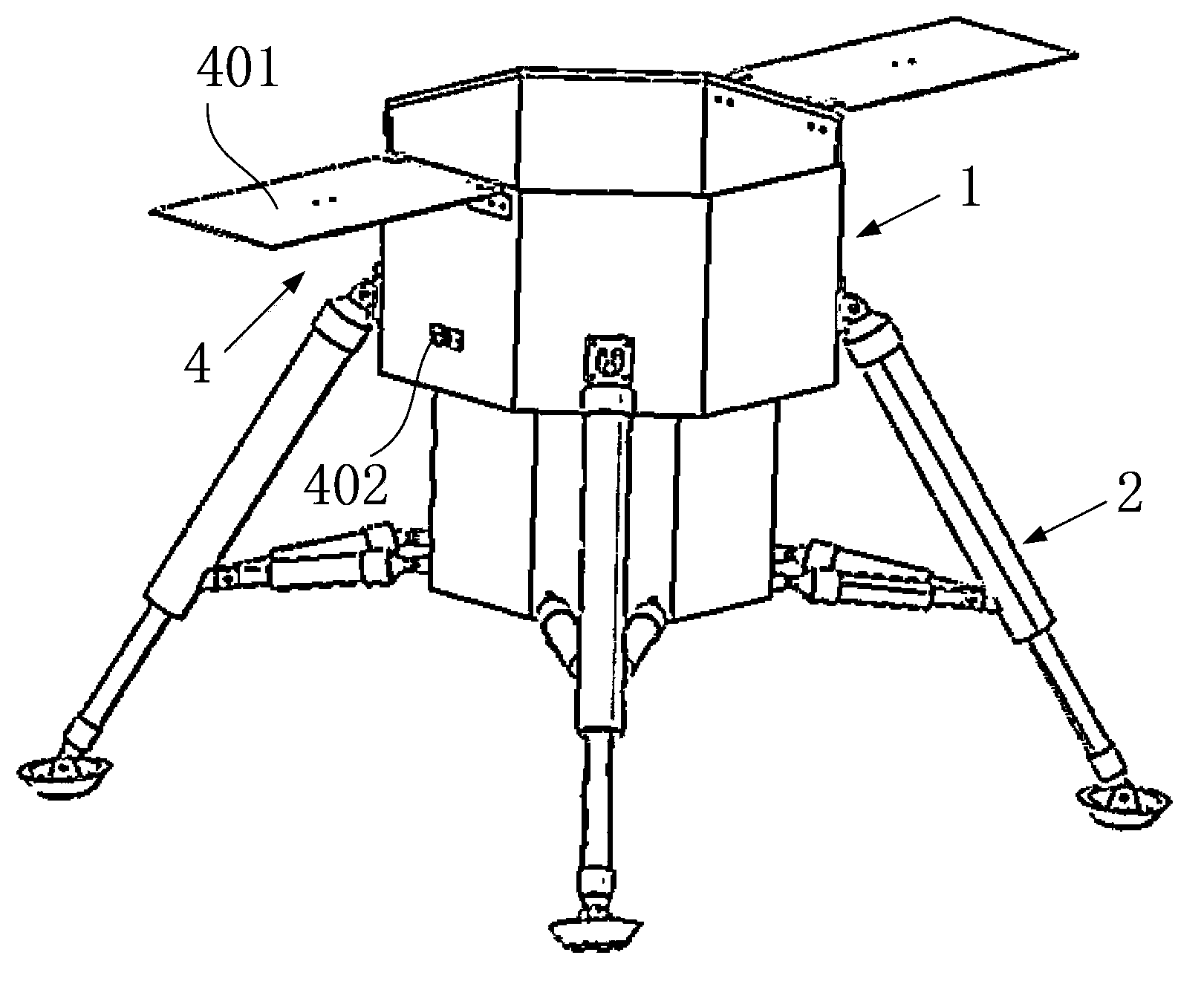
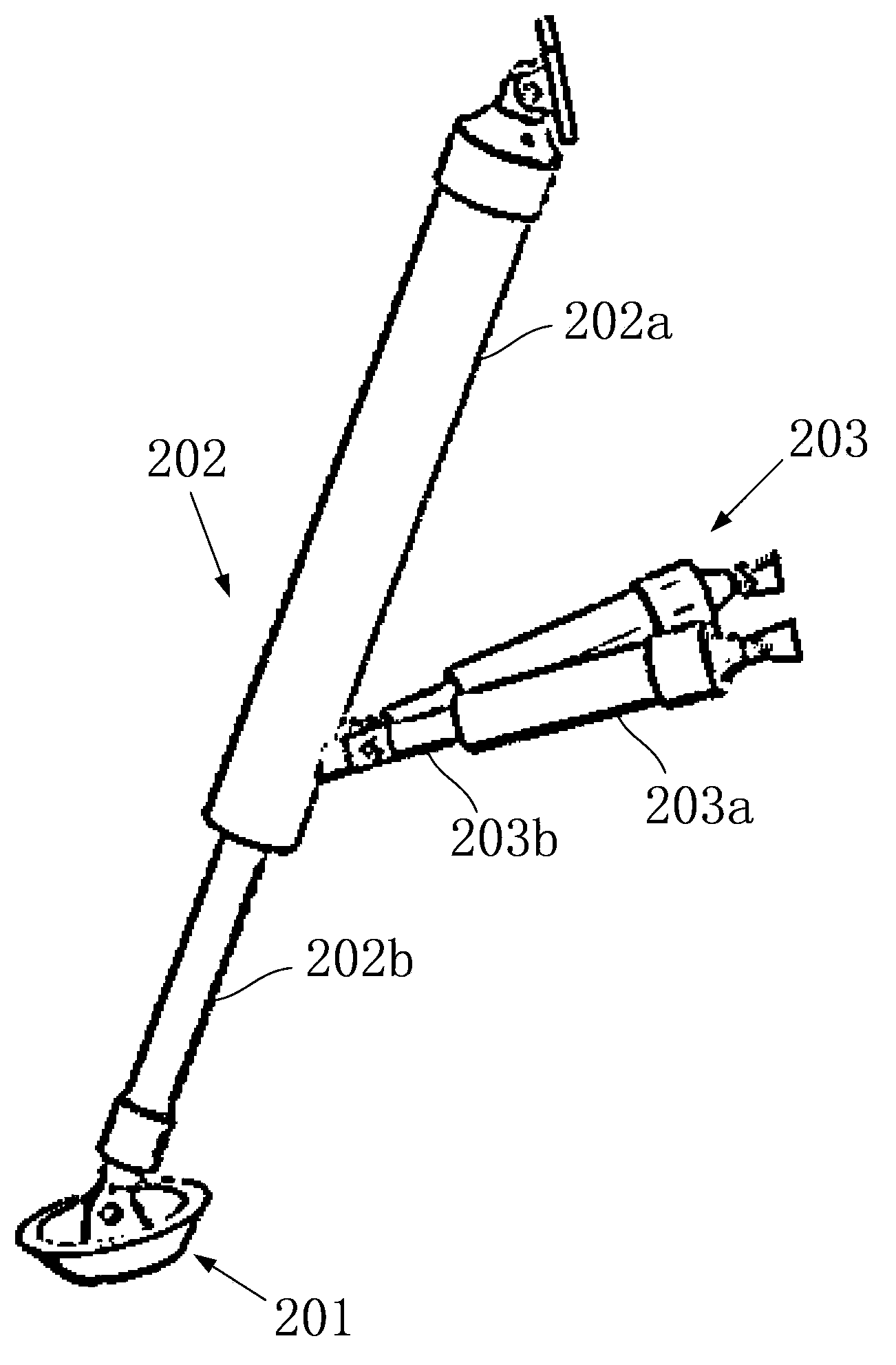
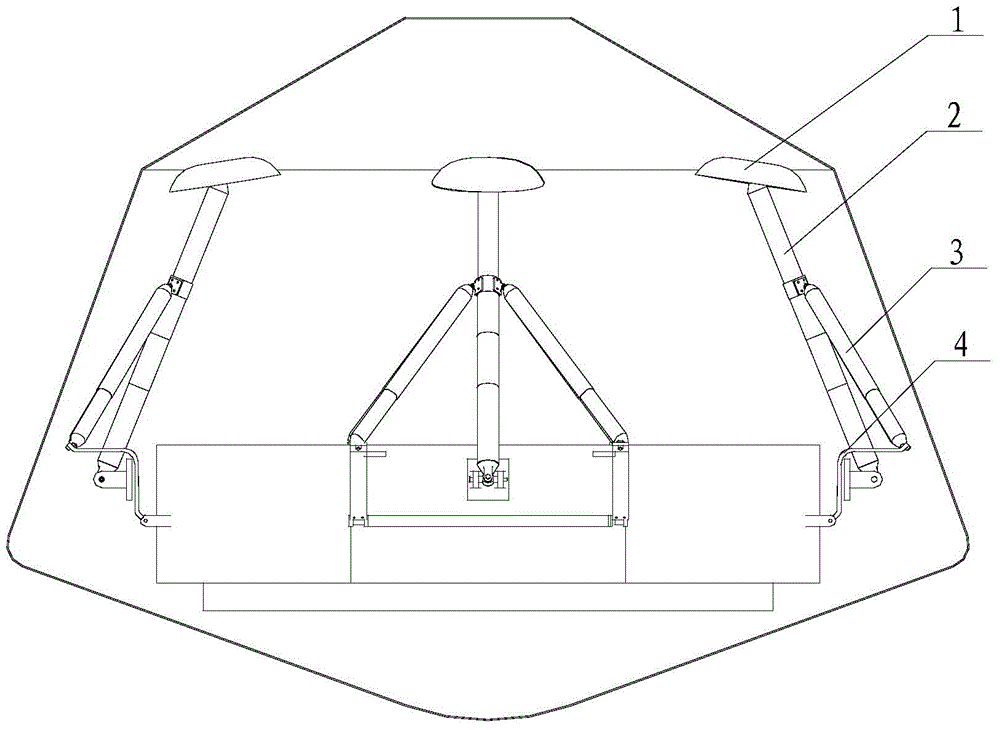
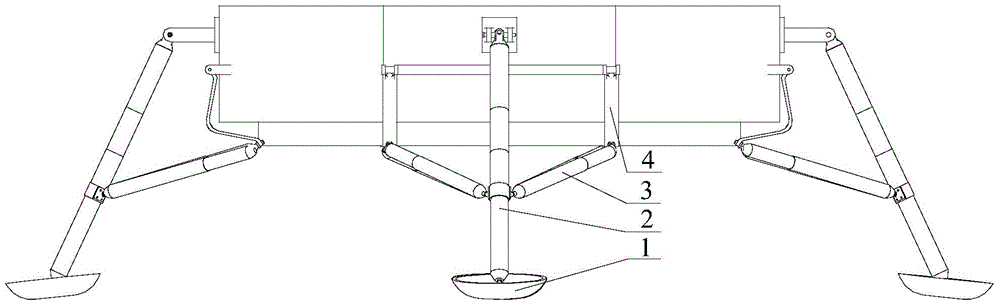
Mars exploration landing buffer device
ActiveCN104627390AIncrease spanImprove motion stabilitySystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesLocking mechanismUniversal joint
A Mars exploration landing buffer device comprises three or four sets of landing legs symmetrically distributed on the periphery of a Mars exploration lander body mechanism. Each set of landing legs is composed of a foot pad (1), a main leg (2), an auxiliary leg (3) and an unfolding locking mechanism (4), wherein the foot pad (1), the main leg (2), the auxiliary leg (3) and the unfolding locking mechanism (4) of the same set of landing legs are connected with one another through universal joints or rotating shafts, and the main leg (2), the auxiliary leg (3), the unfolding locking mechanism (4) of each set of landing legs and the lander body mechanism form a four-bar mechanism so that the landing buffer device can be overturned outwards up and down. The upturning folding structure enables the mass center of the lander to move forwards, the movement stability of the lander in an entering stage is improved, in addition, energy is absorbed through own movement deformation of buffer cellular structures in the main legs (2) and the auxiliary legs (3), soft landing of the lander is achieved, and the device can be applied to design of soft landing buffer mechanisms for landing detection on a planet or a satellite with atmosphere.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Arrangement for recovering spacecraft
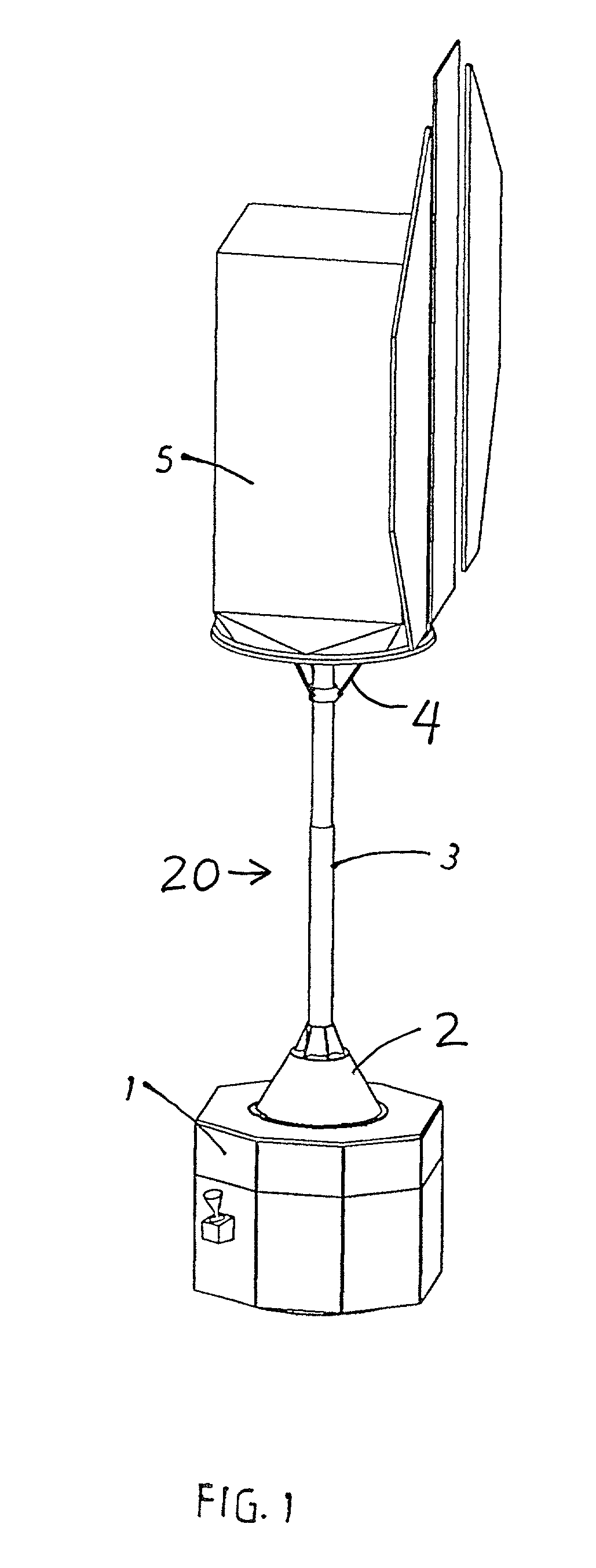
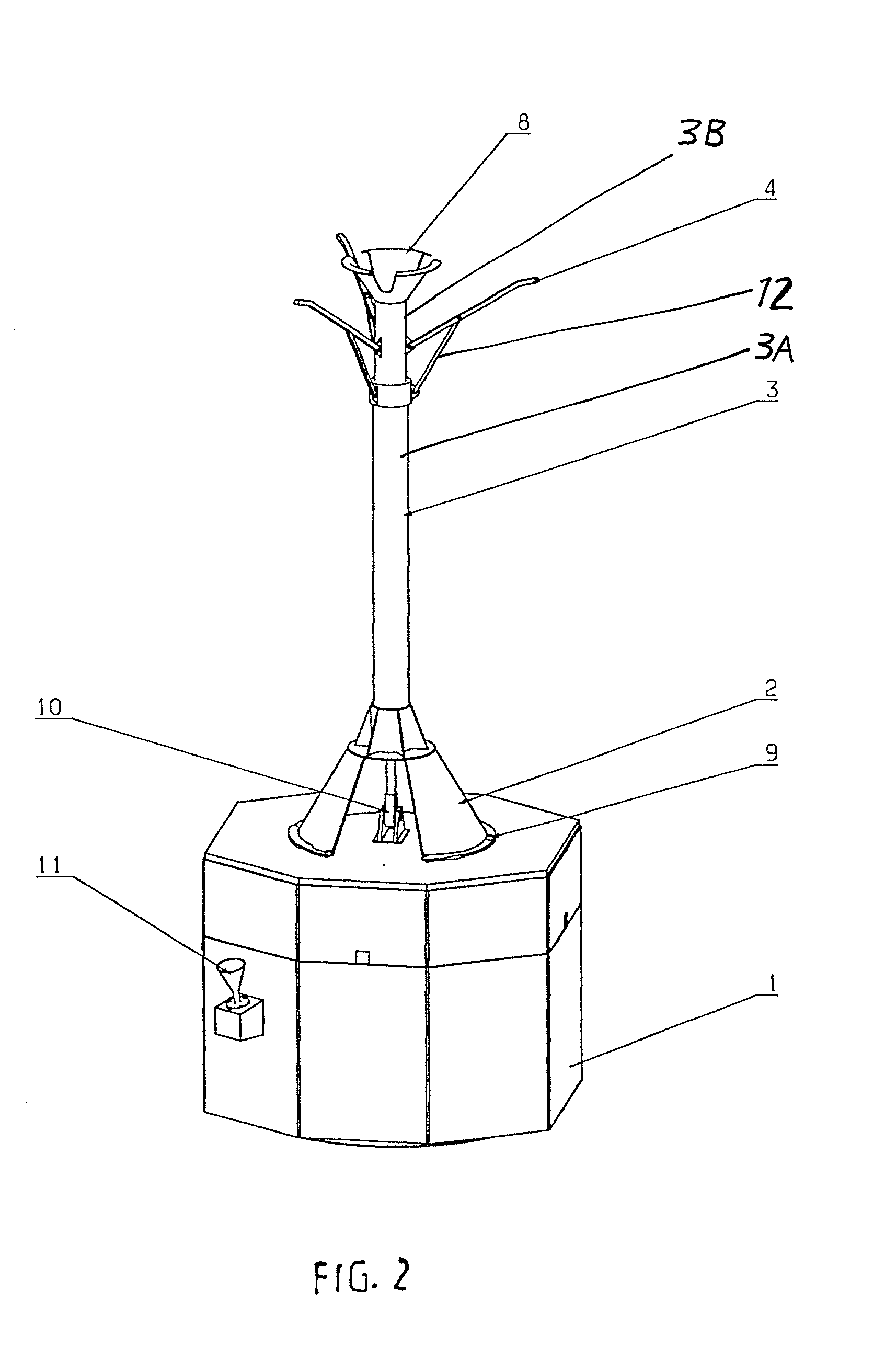
InactiveUS20020063188A1Easy to implementMechanically simpleArtificial satellitesSystems for re-entry to earthFlight vehicleCoupling
A recovery craft with a coupling arrangement captures, engages, and transports a defective or expended non-maneuverable spacecraft. The coupling arrangement includes a coupling mast (e.g. a telescoping pipe), a releasable rigid mount that secures one end of the coupling mast to the recovery craft, and spreader arms that are radially spreadable from the other end of the coupling mast. The spreader arms are initially radially inwardly retracted, and are inserted into an interface ring of the spacecraft. Then the spreader arms are radially outwardly extended to engage behind a protruding rim of the interface ring. A spring braces against the spacecraft. Next, the rigid mount is released and the coupling mast remains connected to the recovery craft only by a tension-transmitting cable. Thrusters of the recovery craft are activated to tow the spacecraft to a new target position, orbit, or trajectory.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com