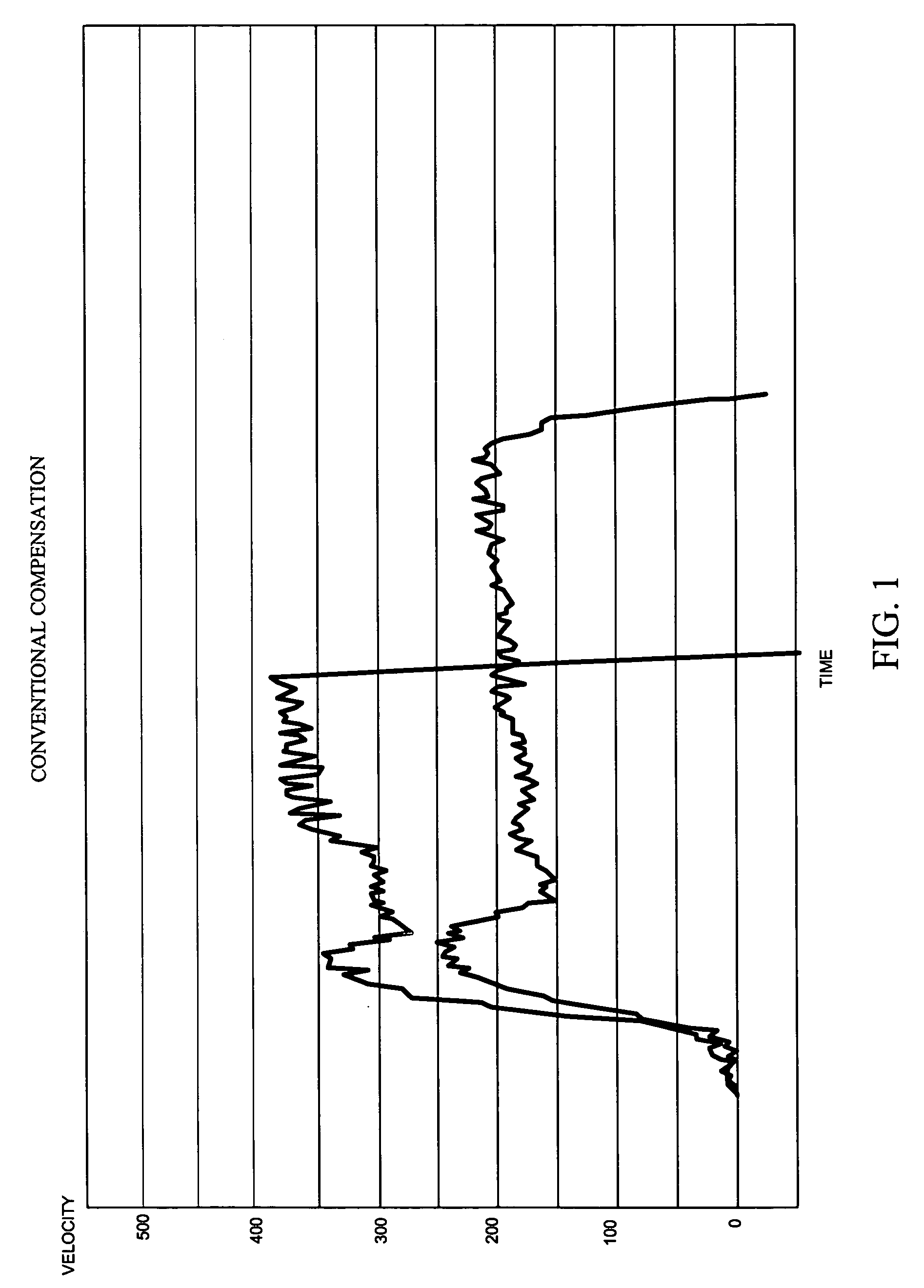
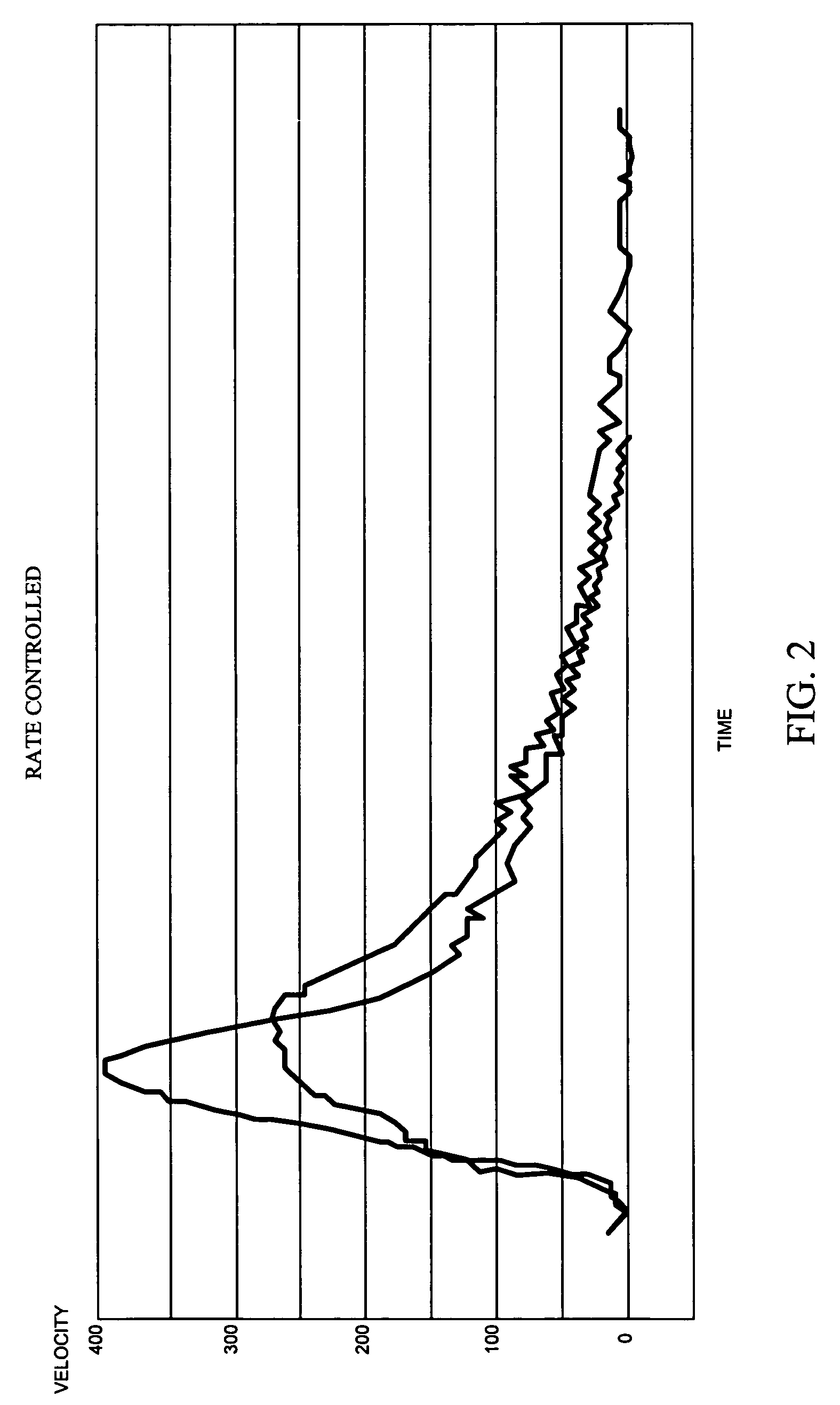
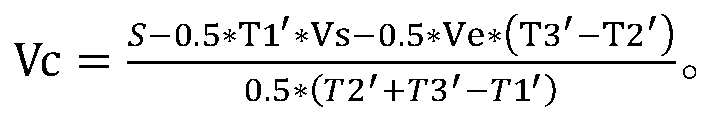Patents
Literature
72 results about "Terminal velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Terminal velocity is the maximum velocity attainable by an object as it falls through a fluid (air is the most common example). It occurs when the sum of the drag force (Fd) and the buoyancy is equal to the downward force of gravity (FG) acting on the object. Since the net force on the object is zero, the object has zero acceleration.
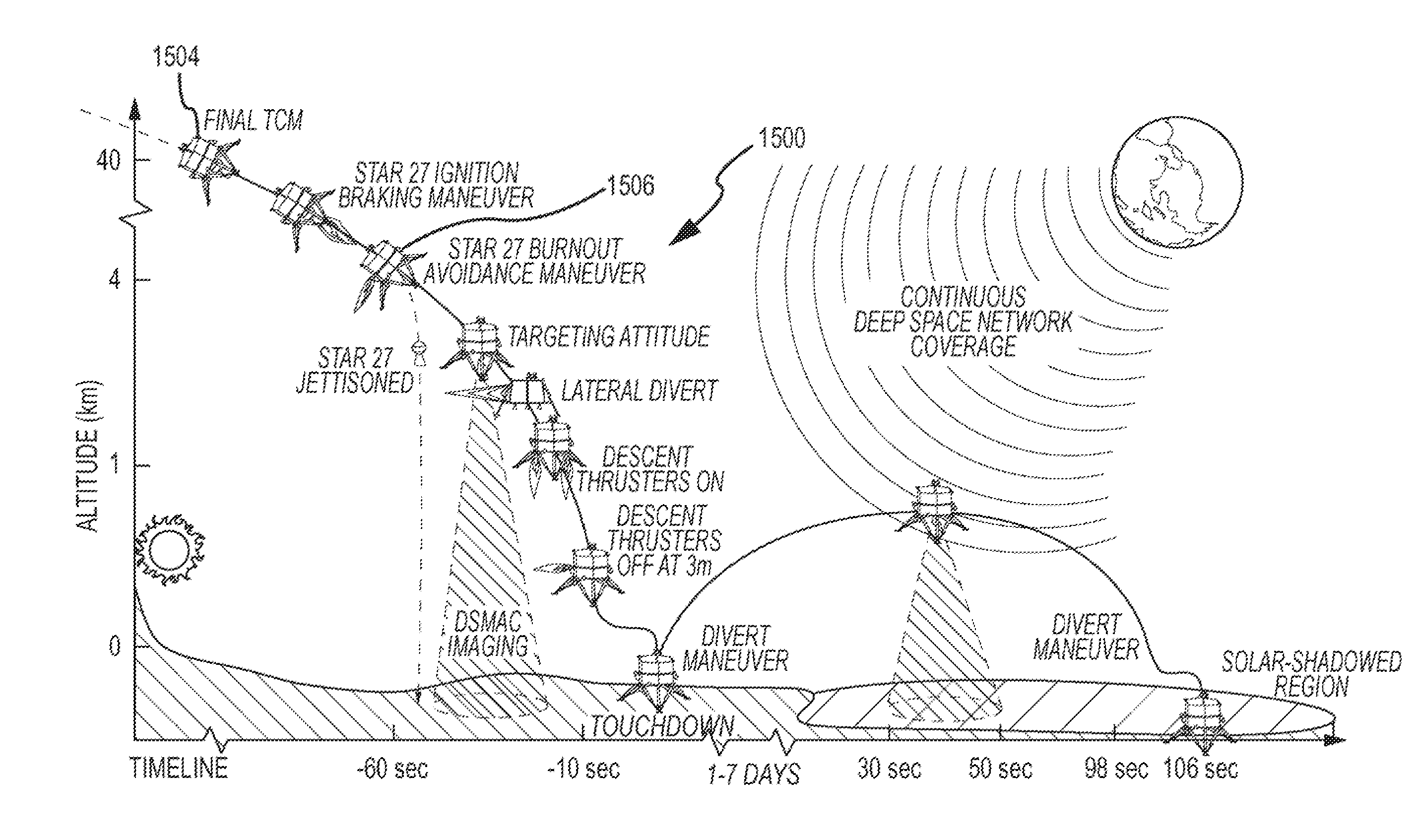
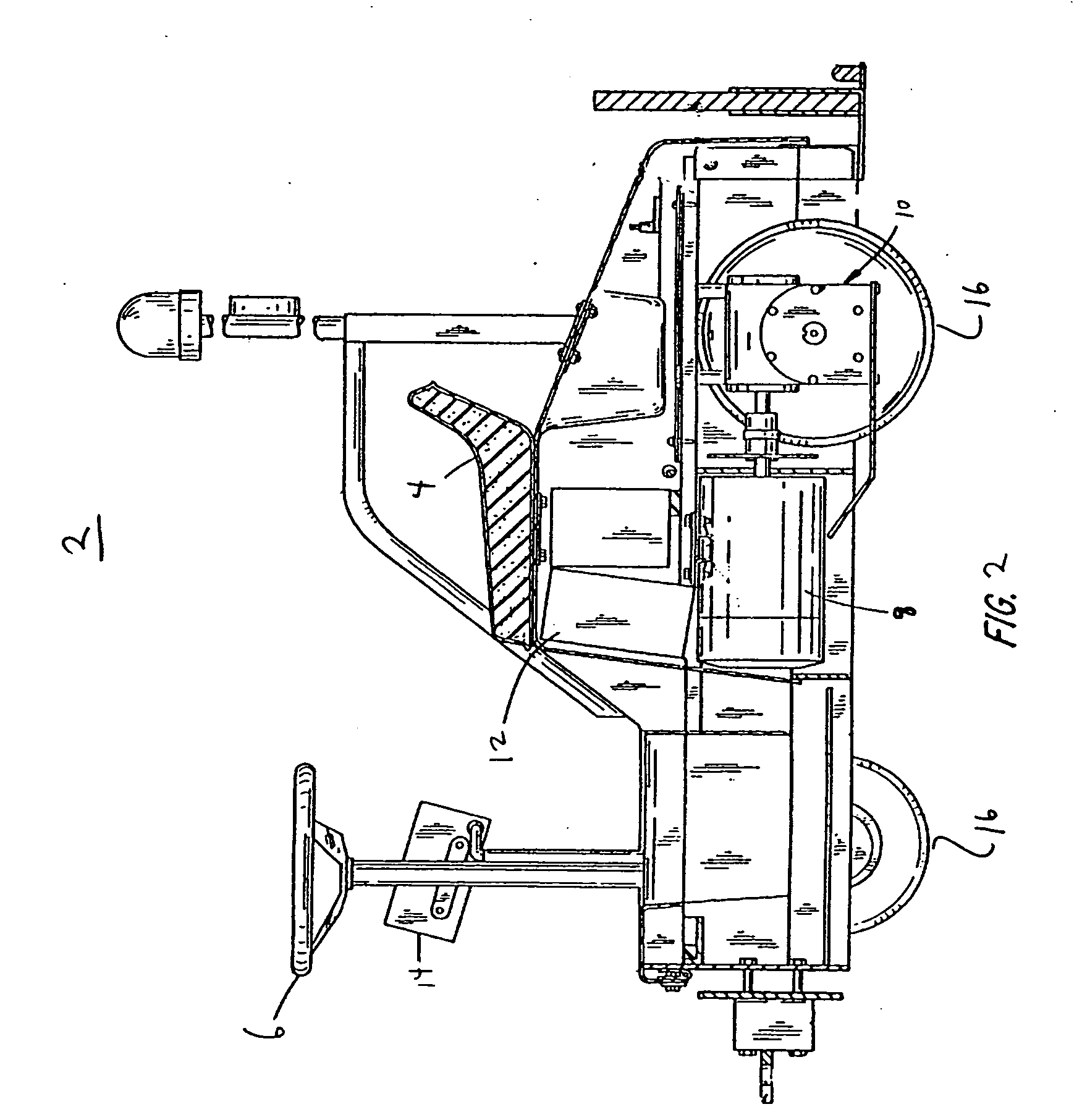
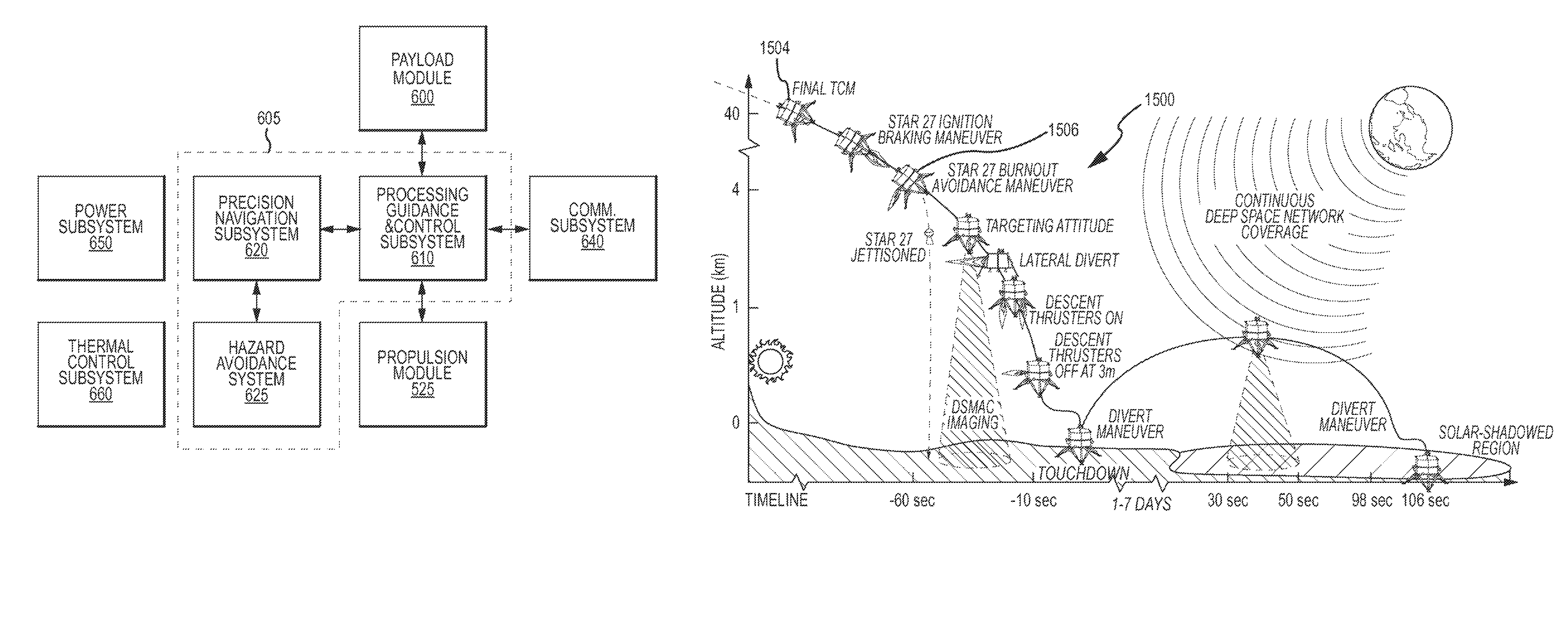
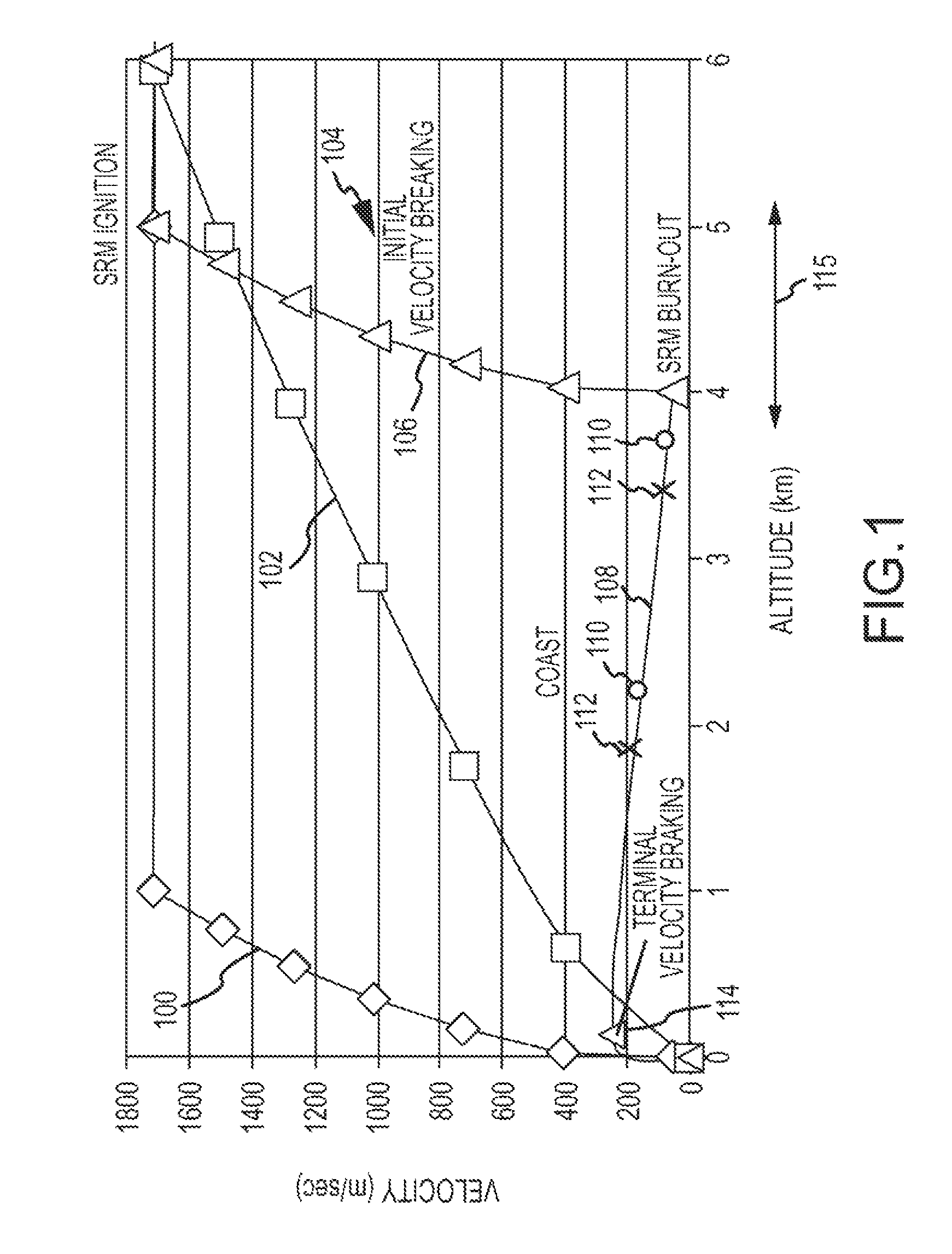
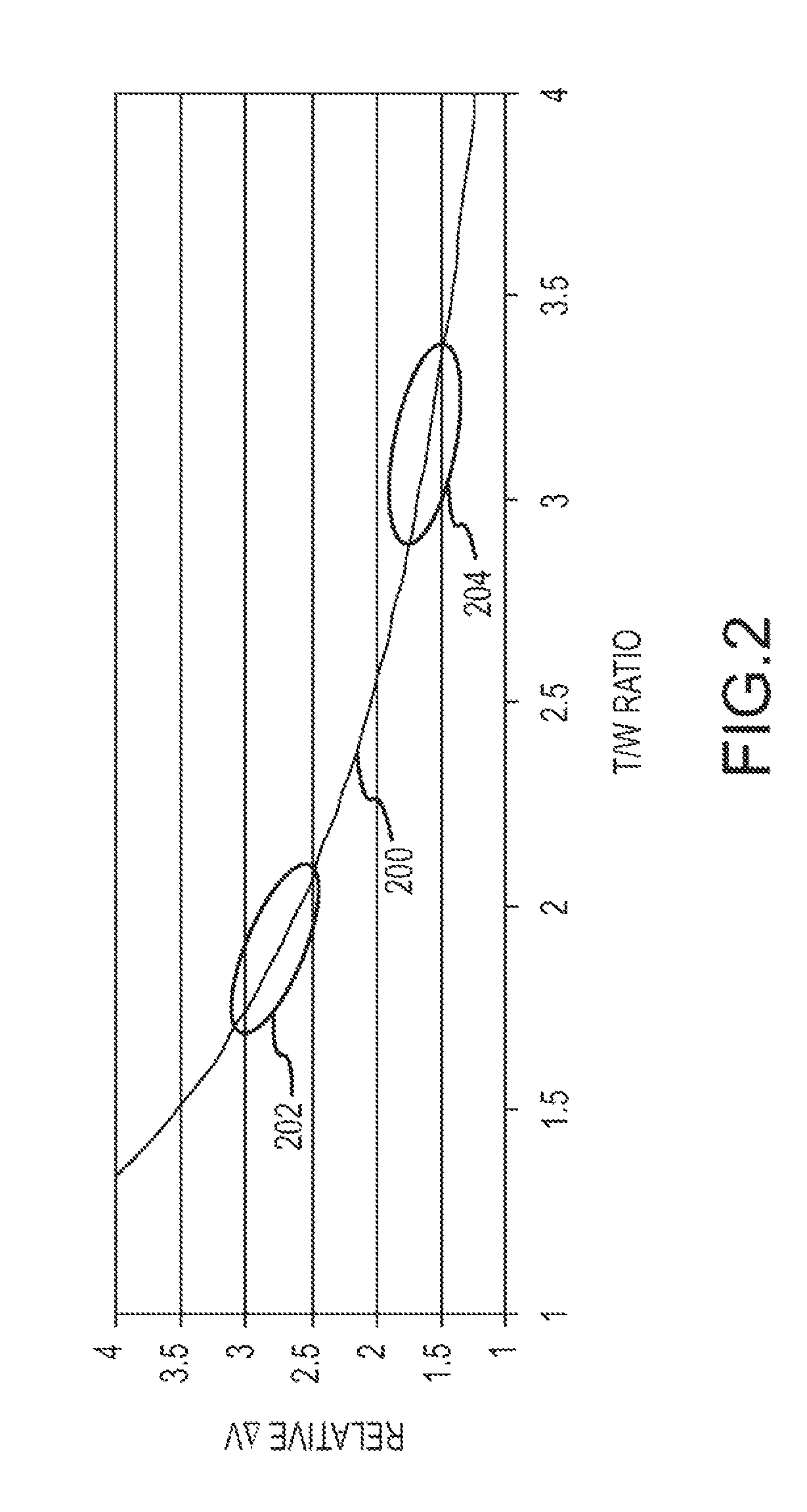
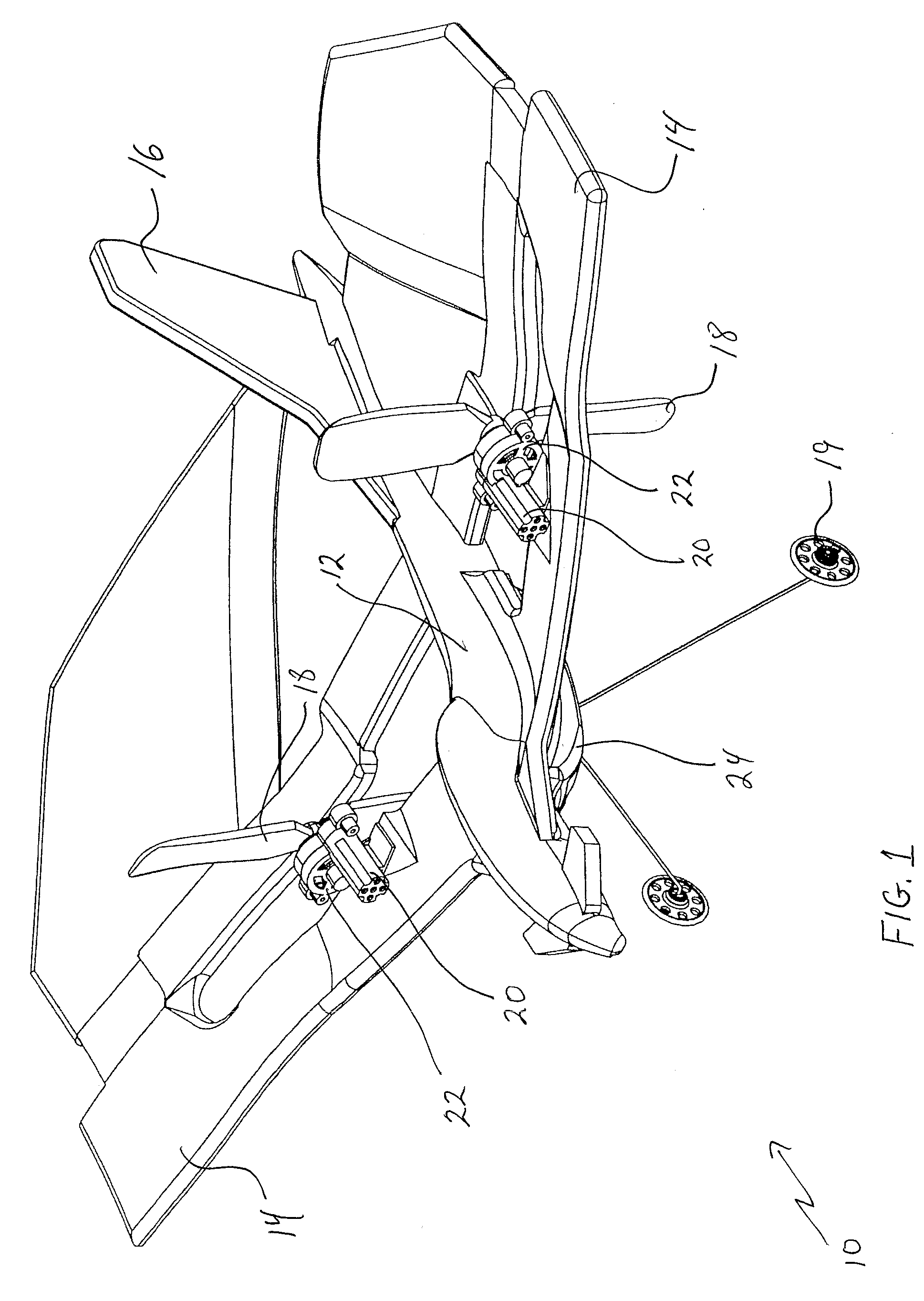
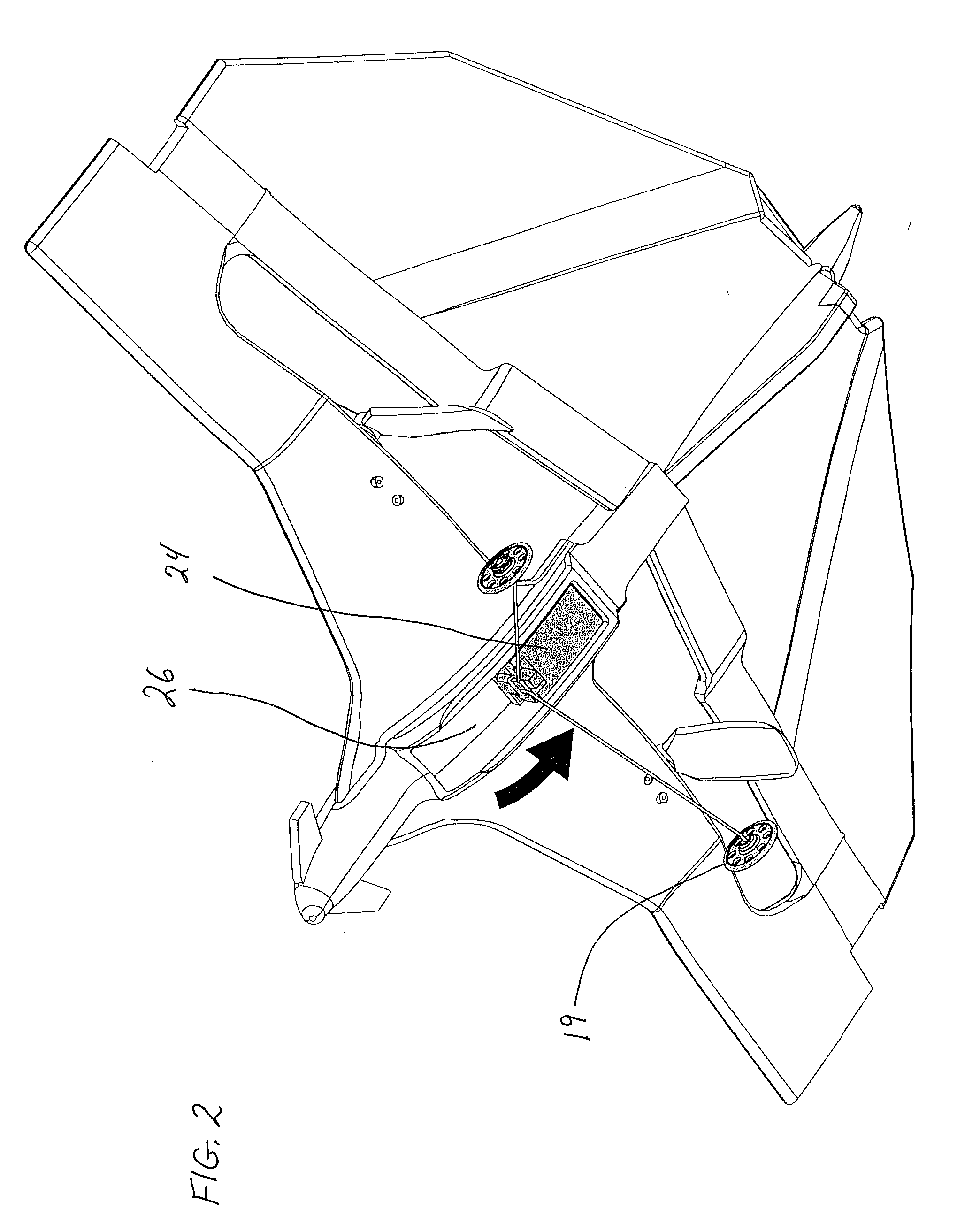
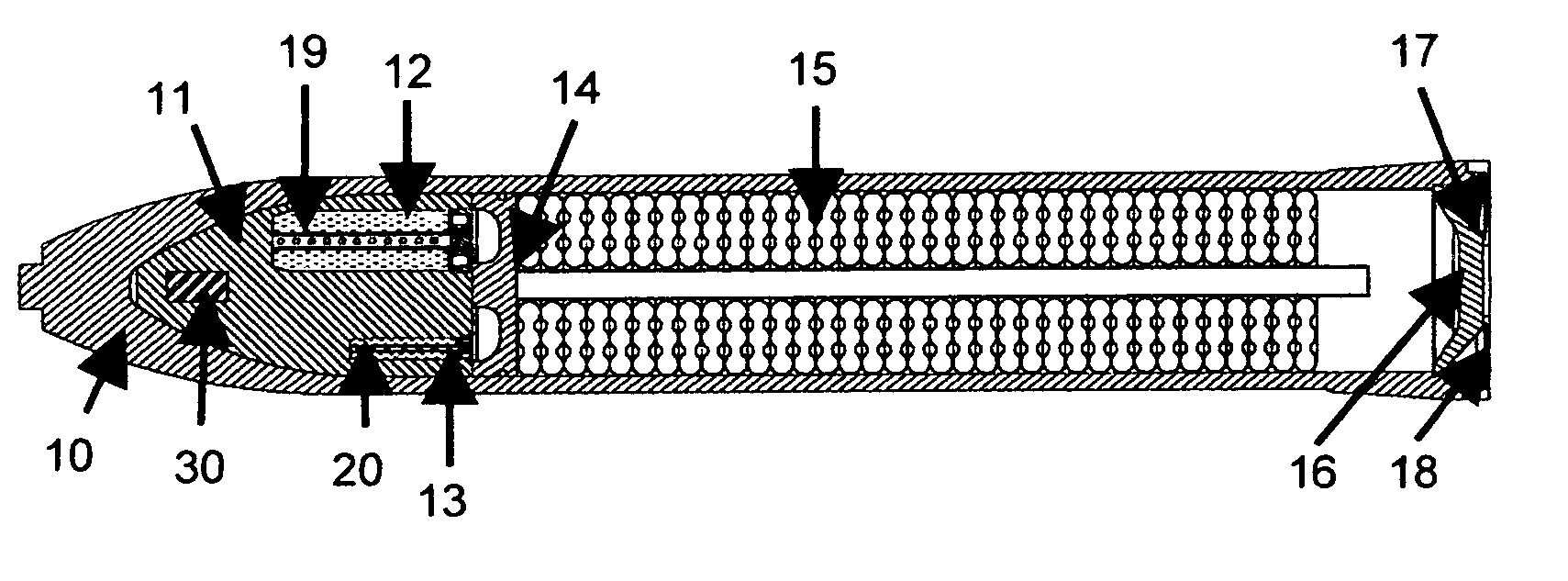
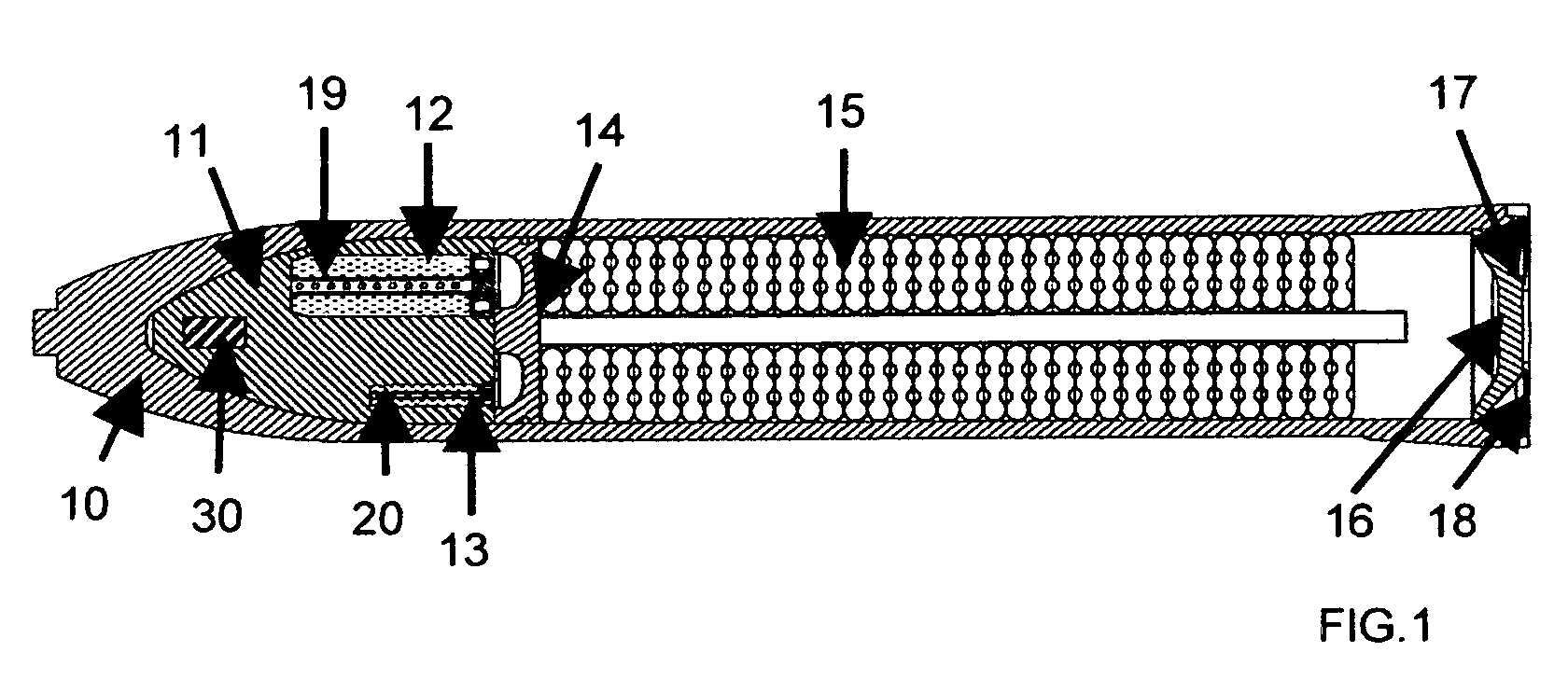
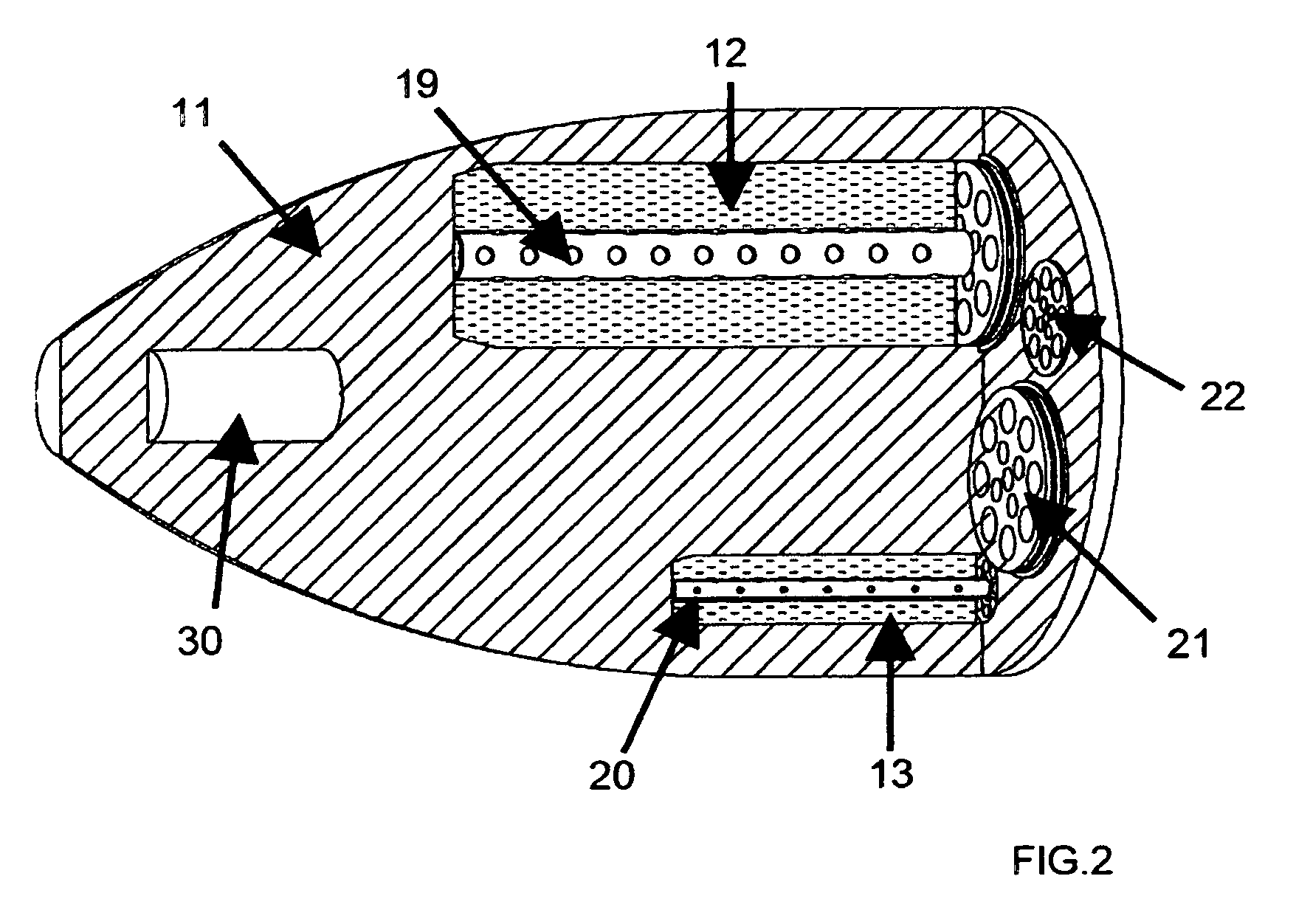
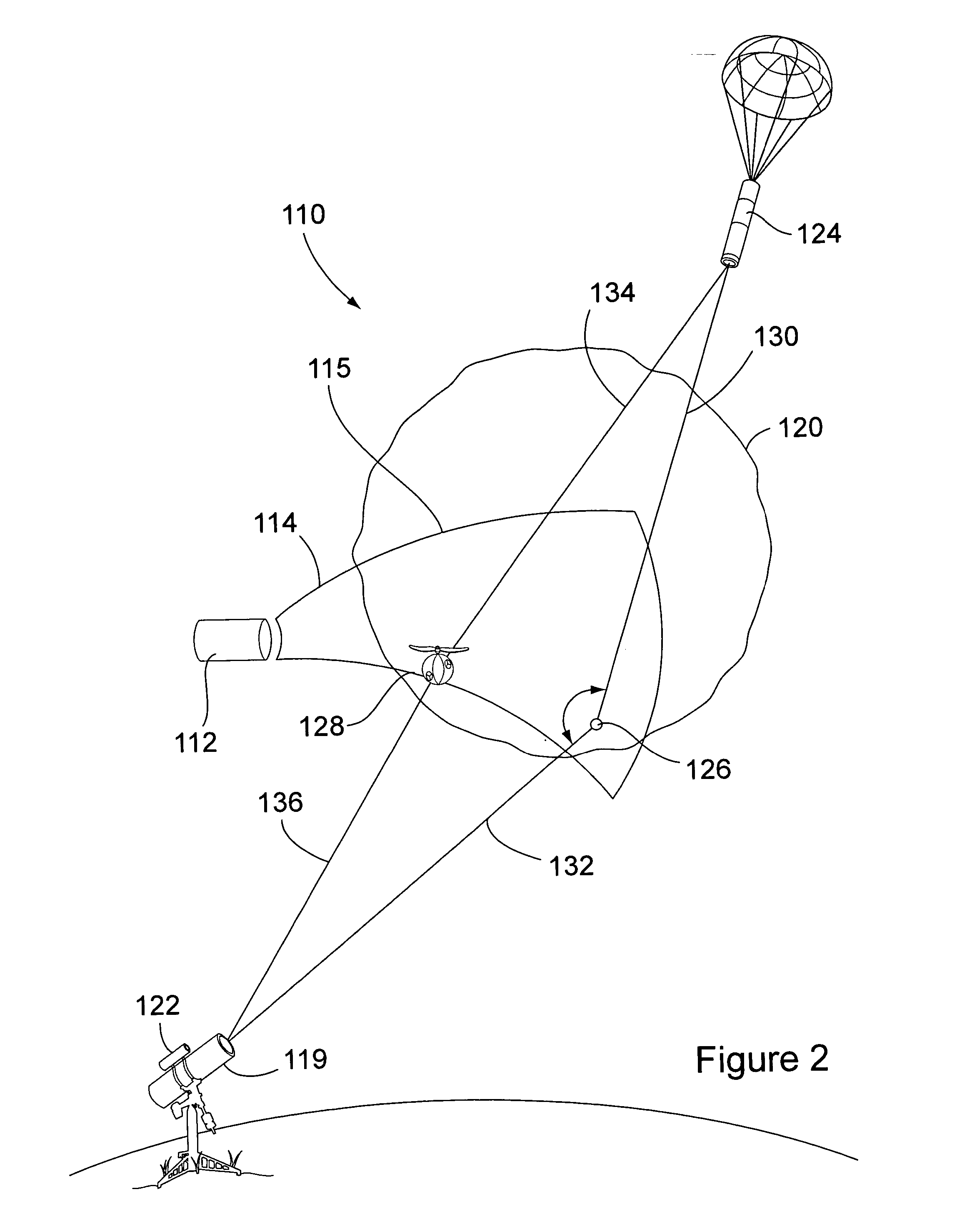
Autonomous Space Flight System and Planetary Lander for Executing a Discrete Landing Sequence to Remove Unknown Navigation Error, Perform Hazard Avoidance and Relocate the Lander and Method
ActiveUS20080023587A1Detect and avoid hazardIncreased payload capacityCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusInstruments for comonautical navigationReference mapImage resolution
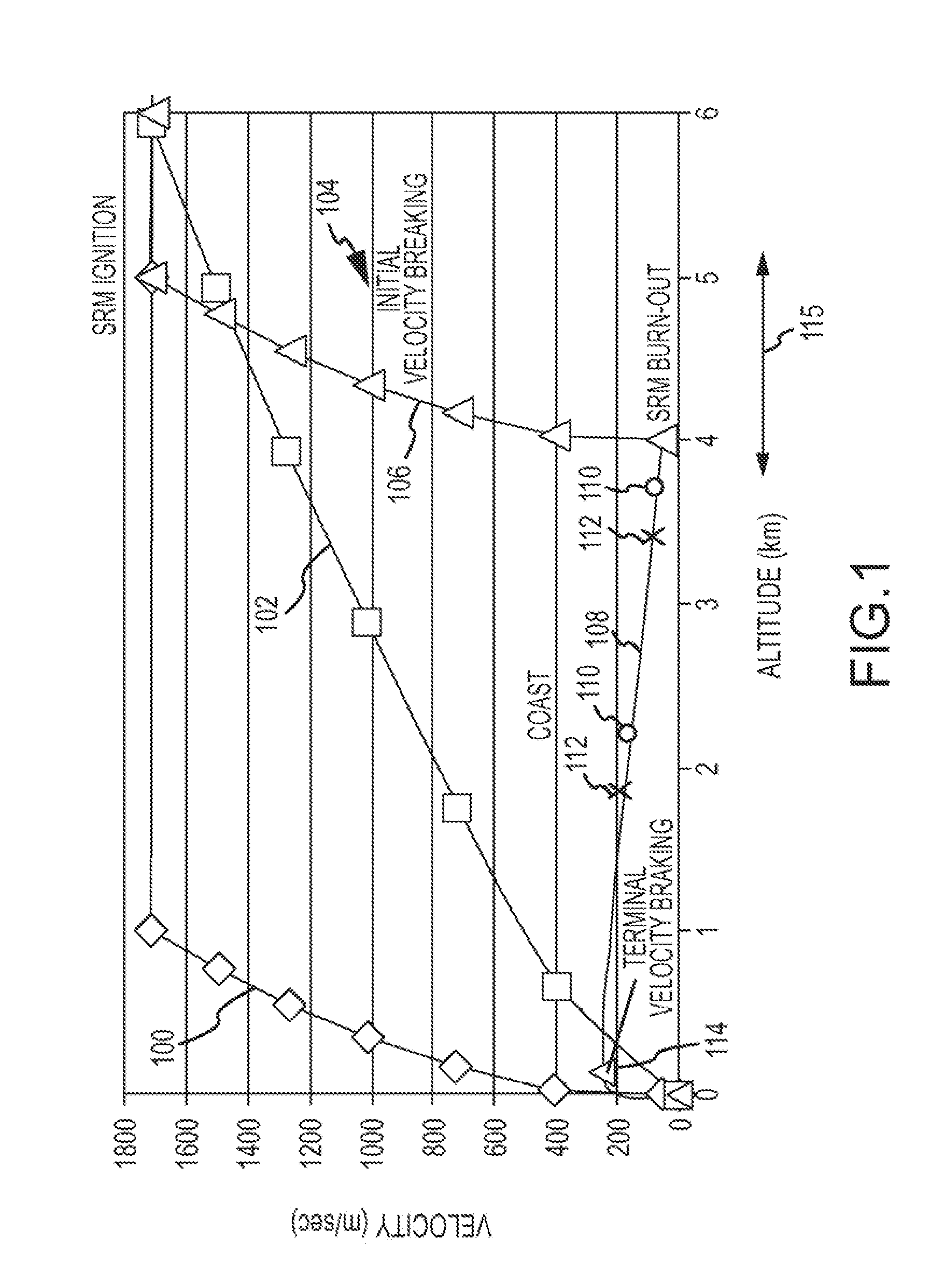
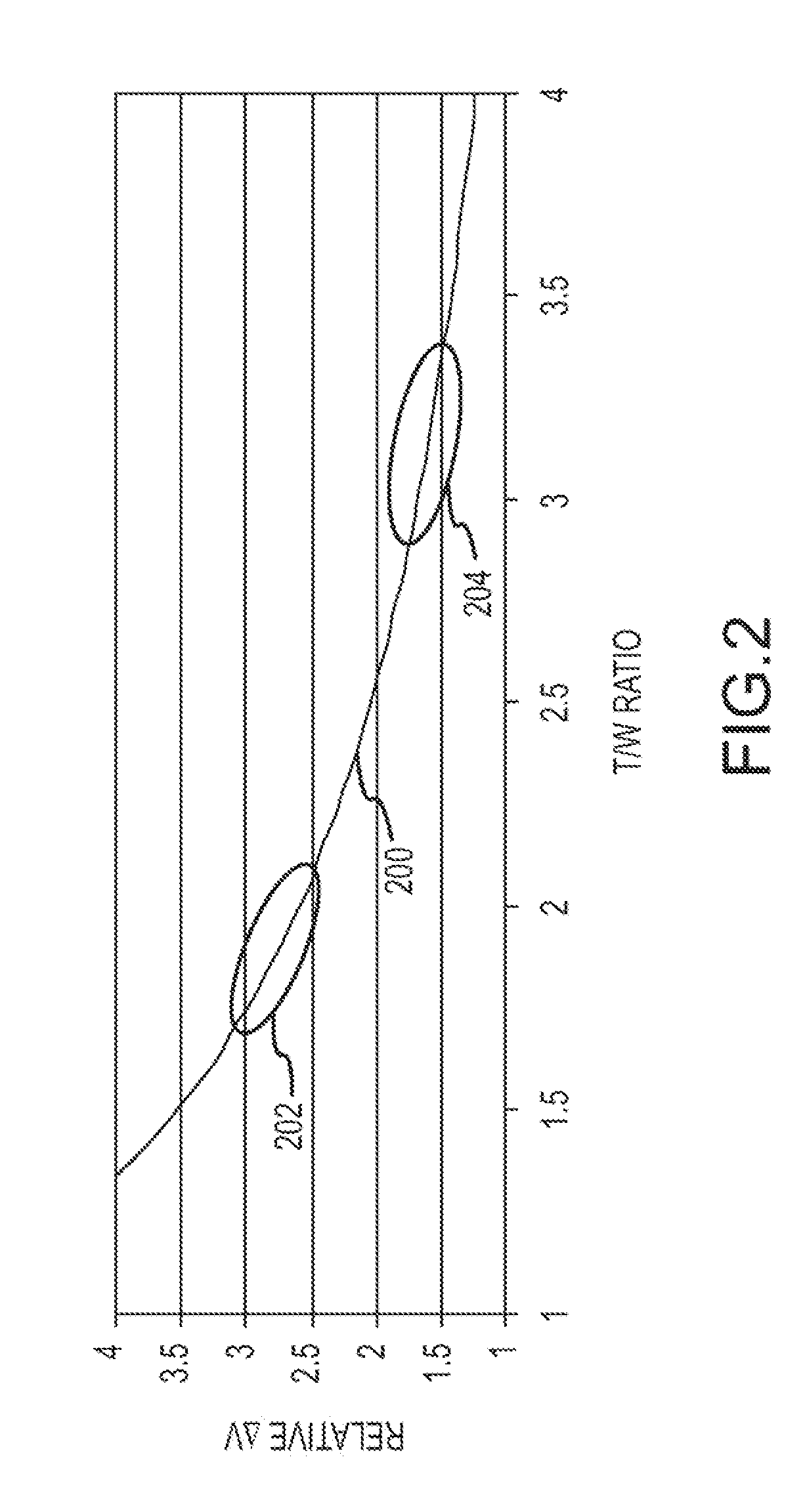
An autonomous unmanned space flight system and planetary lander executes a discrete landing sequence including performing an initial velocity braking maneuver to remove velocity at altitude, coasting during which the planet surface is imaged and correlated to reference maps to estimate cross-track and along-track navigation errors and one or more lateral braking maneuvers are performed to reduce cross-track navigation error, and performing a terminal velocity braking maneuver(s) to reduce the along-track braking maneuver and remove the remainder of the velocity just prior to landing. A bi-propellant propulsion system provides a very high T / M ratio, at least 15:1 per nozzle. Short, high T / M divert maneuvers provide the capability to remove cross-track navigation error efficiently up to the maximum resolution of the reference maps. Short, high T / M terminal velocity braking maneuver(s) provide the capability to remove along-track navigation error to a similar resolution and remove the remaining velocity in a very short time window, approximately 3-15 seconds prior to touchdown. The propulsive efficiency frees up mass which can be allocated to a fuel to remove the unknown navigation errors, perform hazard avoidance and / or relocate the lander by flying it to another site or be allocated to additional payload.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
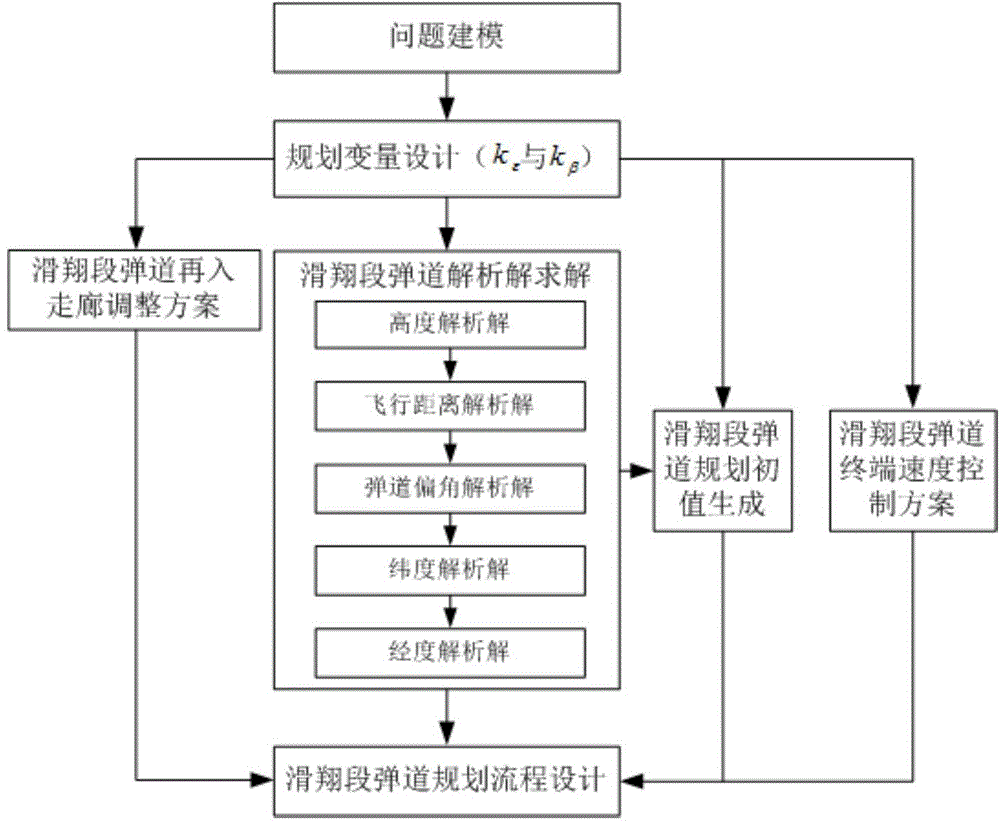
Quick trajectory programming method based on smooth glide trajectory analytic solution
The invention discloses a quick trajectory programming method based on a smooth glide trajectory analytic solution. The quick trajectory programming method based on the smooth glide trajectory analytic solution includes that step 1, modeling glide trajectory programming problems; step 2, designing glide trajectory programming variables; step 3, calculating a glide trajectory analytic solution; step 4, designing a glide trajectory terminal speed control scheme; step 5, designing a glide trajectory re-entry corridor regulating proposal; step 6, generating initial values of glide trajectory programming; step 7, designing a glide trajectory programming flow. The quick trajectory programming method based on the smooth glide trajectory analytic solution uses longitudinal maneuvering acceleration proportion coefficients and transverse maneuvering acceleration proportion coefficients as the glide trajectory programming variables so that differential equations of the trajectory inclination angle, trajectory deflection angle, height, longitude and latitude in motion equations do not comprise a speed item. The quick trajectory programming method based on the smooth glide trajectory analytic solution obtains the glide trajectory analytic solution corresponding to a fixed longitudinal maneuvering acceleration proportion coefficient and a fixed transverse maneuvering acceleration proportion coefficient.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
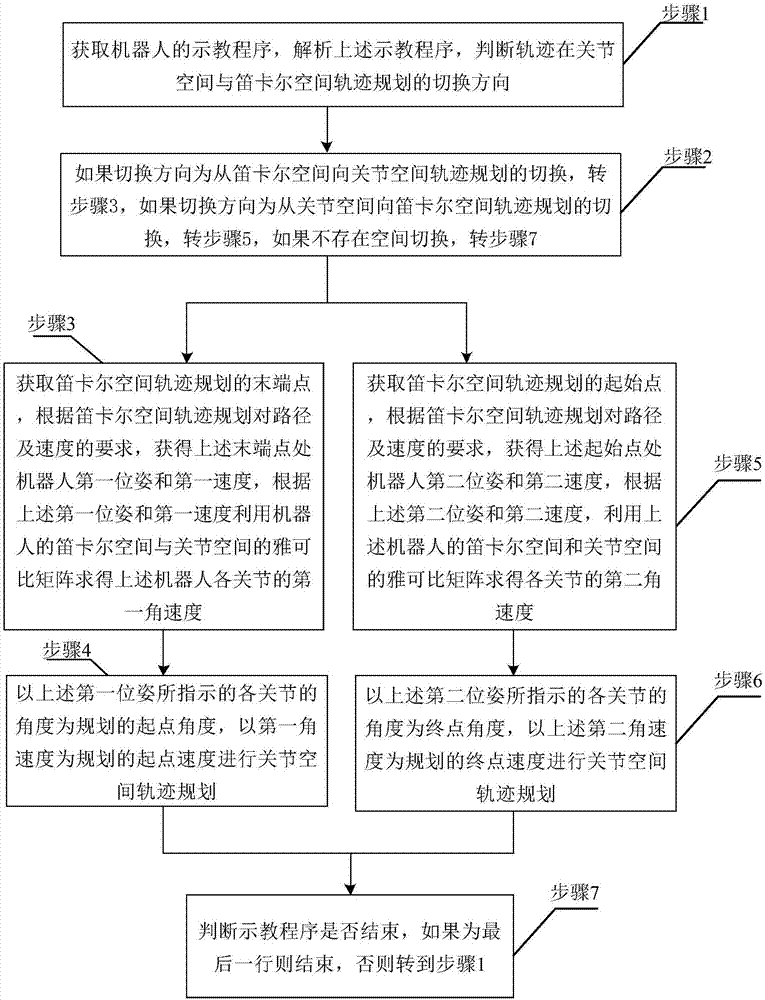
Smooth transition method of multi-space trajectory planning of teaching robot, and devices
ActiveCN107571261ASolve the stall problemImprove work efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorTeaching programAngular velocity
The invention relates to the field of robot trajectory planning, and provides a smooth transition method of multi-space trajectory planning of a teaching robot, aiming at solving the unsmooth problemin the trajectory switching process. The smooth transition method comprises the steps that a teaching program of the teaching robot is analyzed, the switching direction of the trajectory planning is judged, if the trajectory planning is that the switching direction is from cartesian space to joint space, a tail end of cartesian space trajectory planning is acquired, according to the requirements on a path and a velocity, a first posture and a first velocity at the tail end are acquired, first angular velocities of various joints are obtained by employing a jacobi matrix, and by taking an angleindicated by the first posture as a starting angle and the first angular velocities as starting velocities, joint space trajectory planning is carried out; or else, a starting point of the cartesianspace trajectory planning is acquired, a second posture at the starting point and second angular velocities of the various joints are obtained, and by taking an angle indicated by the second posture as a terminal angle and the second angular velocities as terminal velocities, the joint space trajectory planning is carried out. Smooth transition of the trajectory planning in space switching is realized.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Power-assisted cart retriever with attenuated power output
ActiveUS7389836B2Avoid damageExtended service lifeDigital data processing detailsElectric propulsion mountingBrief periodsHeavy load
The present invention is a motorized shopping cart retriever that includes a controller that attenuates the power provided to the drive system of the retriever to prevent the retriever from being utilized to move an excessively heavy load of shopping carts. By preventing the retriever and carts from being subjected to overloaded conditions, the operational lives of the retriever and carts are maximized. The retriever is also provided with a burst mode that allows the power provided to the drive system to rapidly increase past the normal attenuated level for a brief period of time in order to reduce the time required to accelerate a retriever loaded with carts to a terminal velocity.
Owner:DANE TECH
System for debris elimination and item separation and method of use thereof
InactiveUS6293407B1Reduce labor costsReduce water consumptionGas current separationFlotationHigh densityMedium density
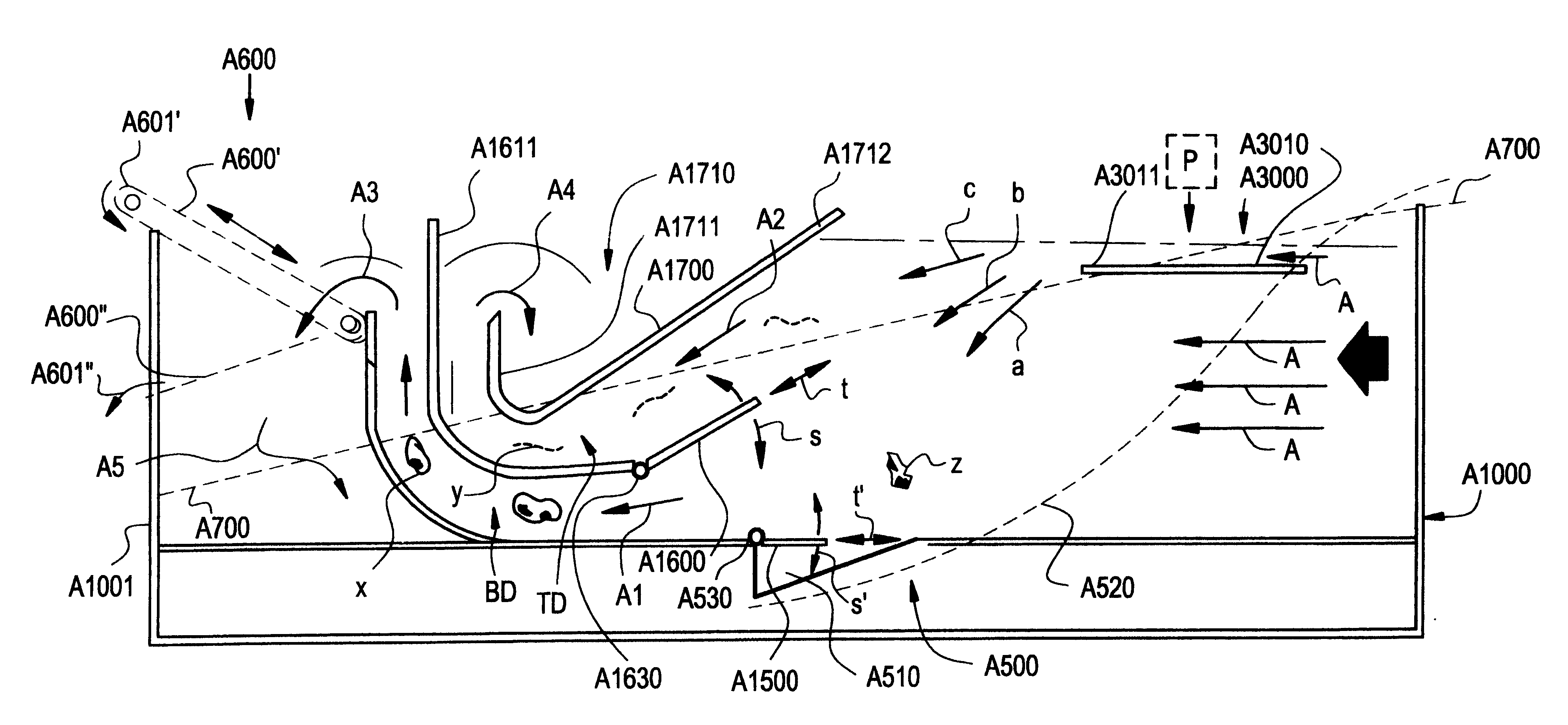
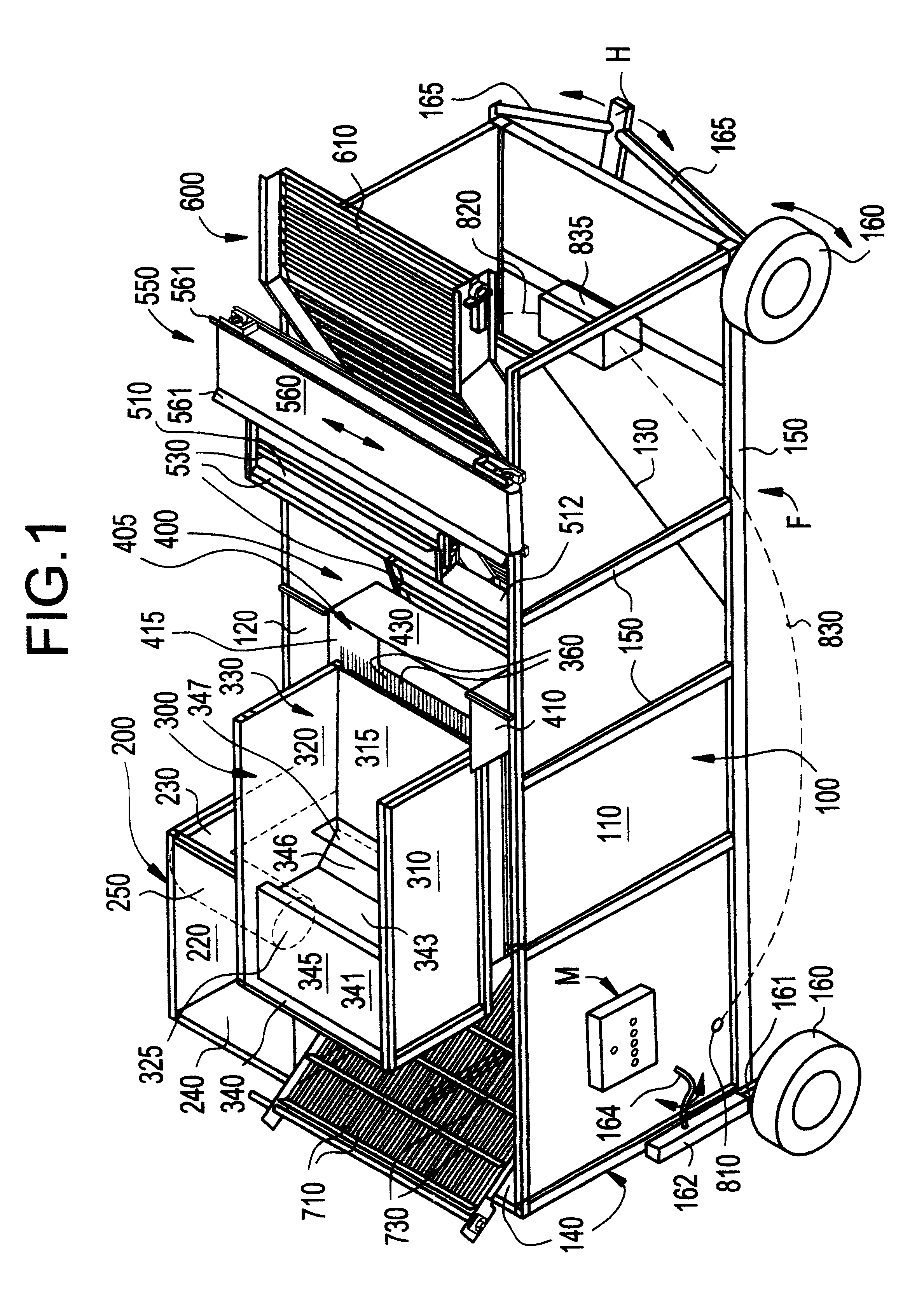
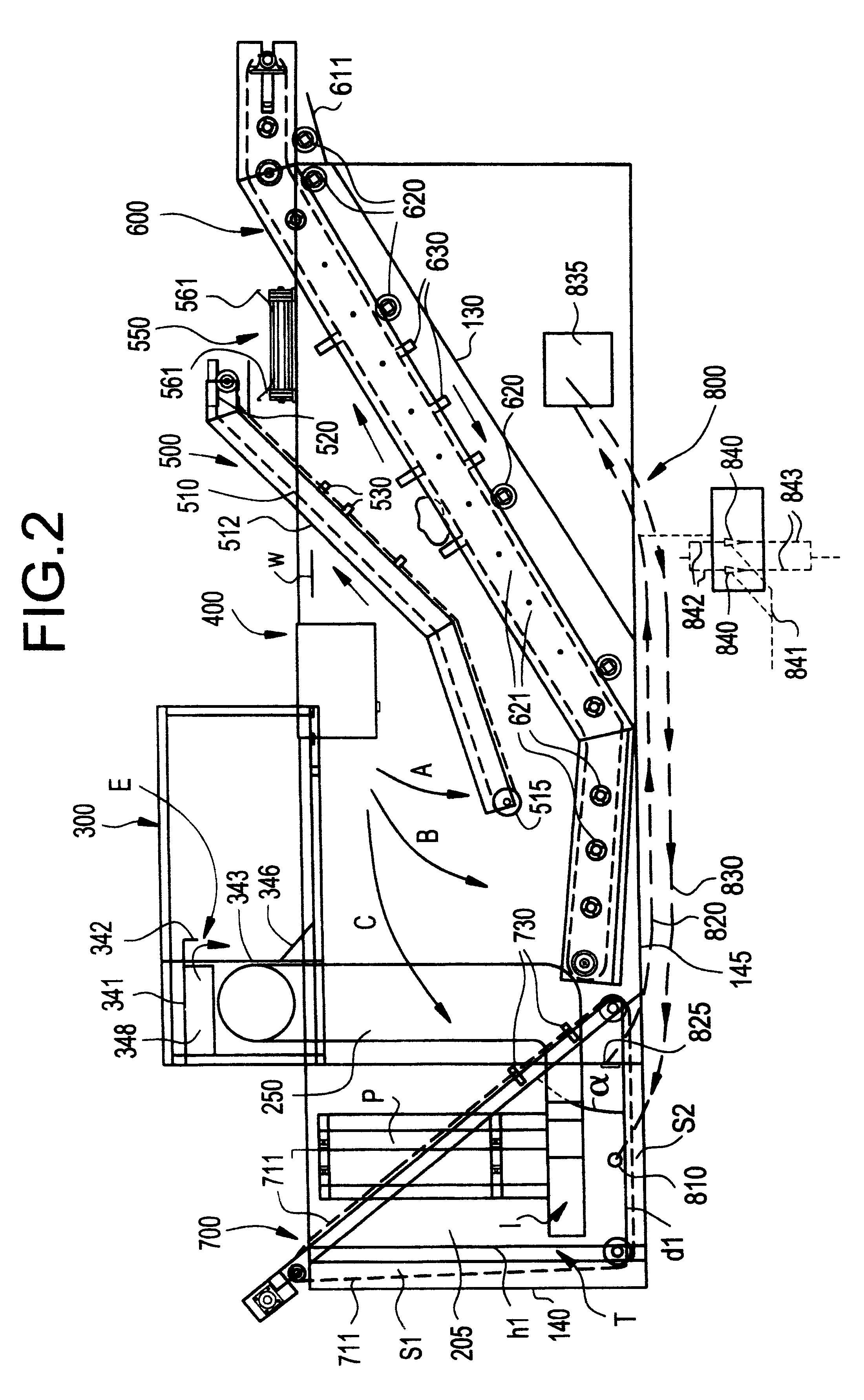
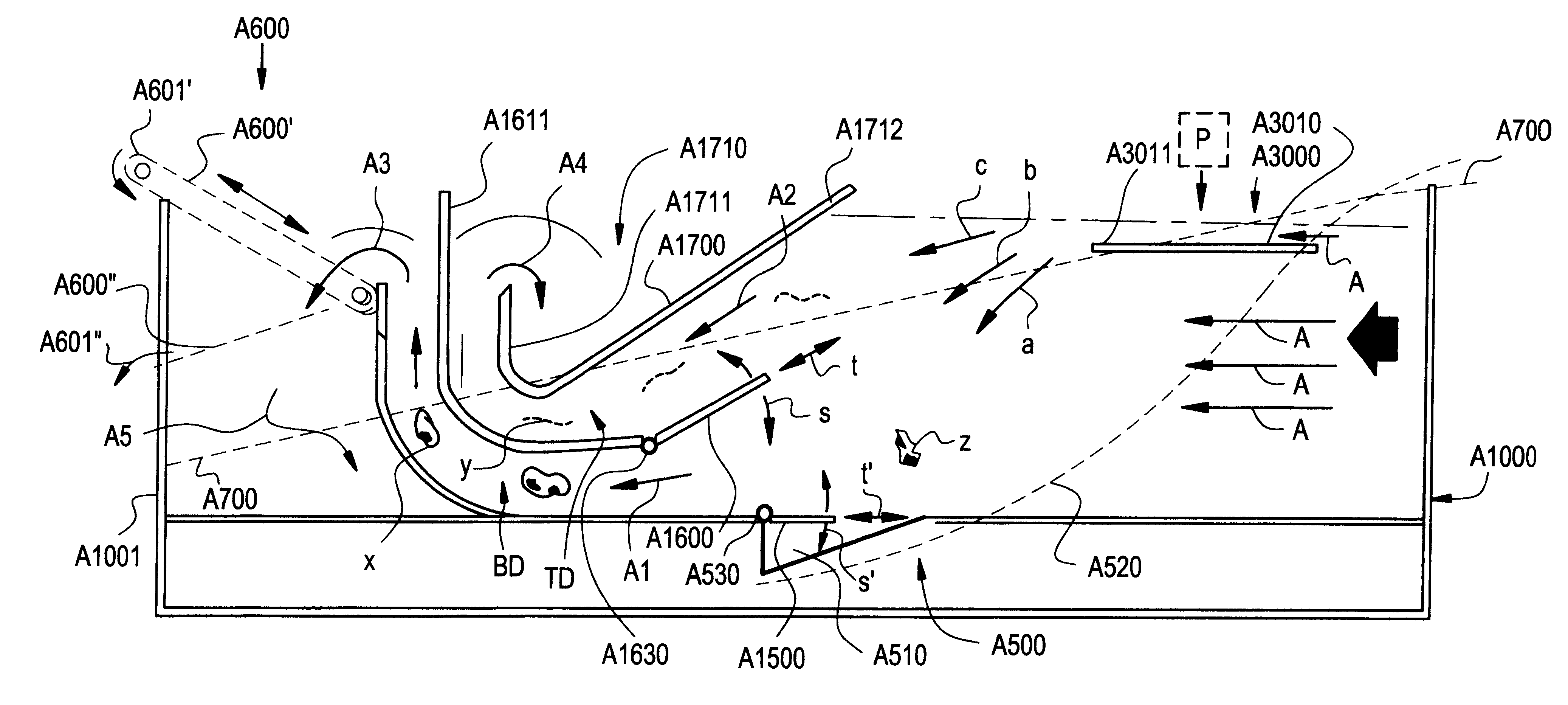
A item separating or debris eliminating system includes a tank and a pump for circulating water from one end of the tank around through a duct and back into the opposite end of the tank. A medium density object collector is located within the tank, and a light debris collector is located within the tank. A conveyor filter is included through which substantially all of the water in the tank is circulated. The debris eliminating system preferably also includes a high density object collector within the tank. The system can be used to separate a variety of objects having different densities and terminal velocities in a fluid. Most preferably, the system is utilized for separating debris from potatoes and the like produce.
Owner:FRITO LAY NORTH AMERICA INC
System for debris elimination and item separation and method of use thereof
InactiveUS6213308B1Reduce labor costsReduce water consumptionSievingScreeningHigh densityMedium density
A item separating or debris eliminating system includes a tank and a pump for circulating water from one end of the tank around through a duct and back into the opposite end of the tank. A medium density object collector is located within the tank, and a light debris collector is located within the tank. A conveyor filter is included through which substantially all of the water in the tank is circulated. The debris eliminating system preferably also includes a high density object collector within the tank. The system can be used to separate a variety of objects having different densities and terminal velocities in a fluid. Most preferably, the system is utilized for separating debris from potatoes and the like produce.
Owner:FRITO LAY NORTH AMERICA INC
Power-assisted cart retriever with attenuated power output
ActiveUS20050098364A1Avoid damageExtended service lifeDigital data processing detailsElectric propulsion mountingBrief periodsControl theory
The present invention is a motorized shopping cart retriever that includes a controller that attenuates the power provided to the drive system of the retriever to prevent the retriever from being utilized to move an excessively heavy load of shopping carts. By preventing the retriever and carts from being subjected to overloaded conditions, the operational lives of the retriever and carts are maximized. The retriever is also provided with a burst mode that allows the power provided to the drive system to rapidly increase past the normal attenuated level for a brief period of time in order to reduce the time required to accelerate a retriever loaded with carts to a terminal velocity.
Owner:DANE TECH
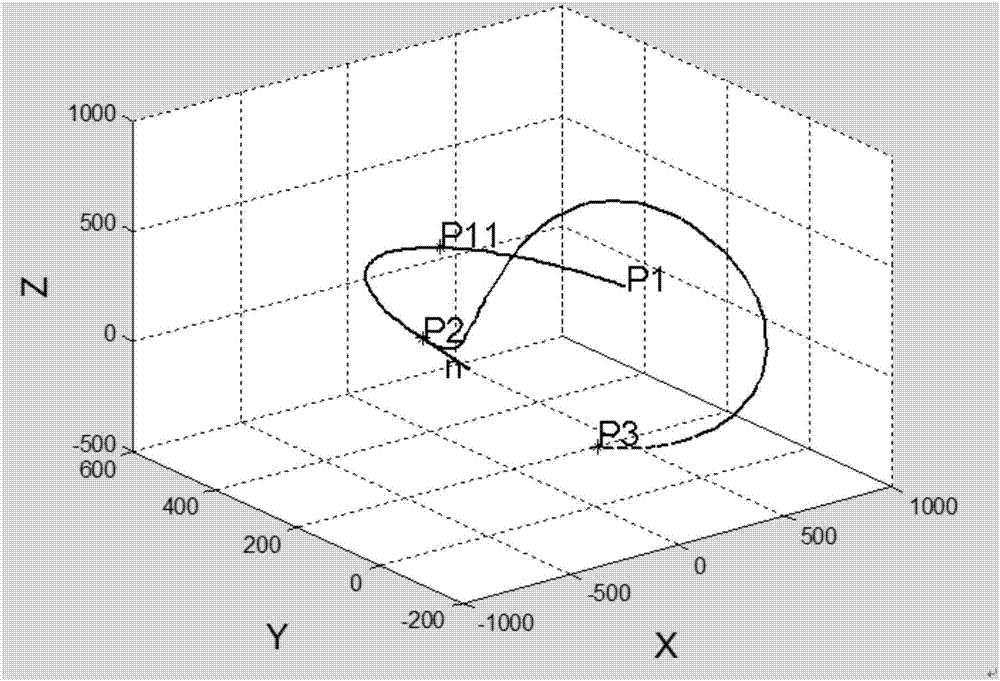
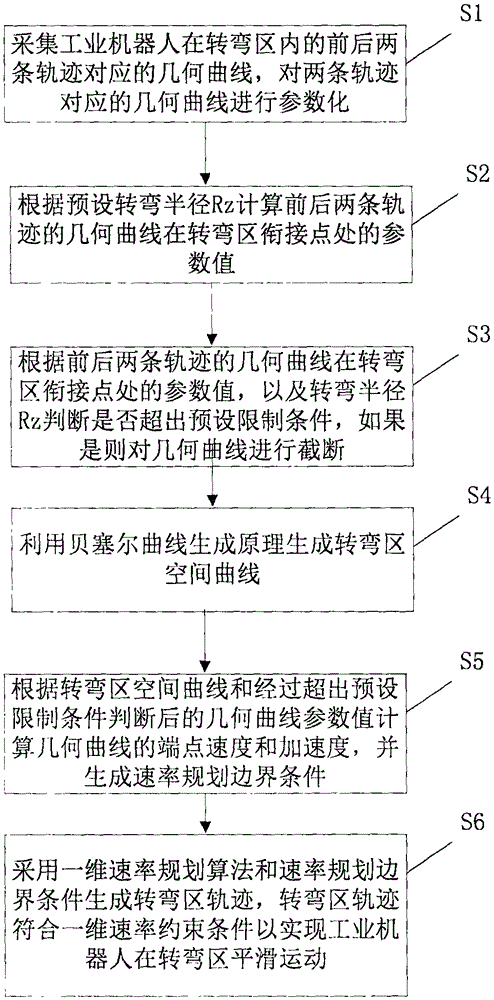
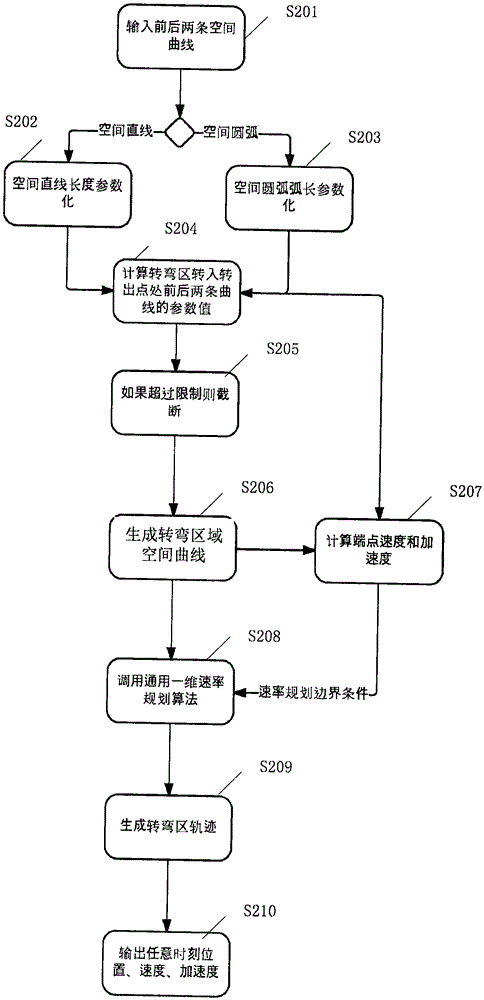
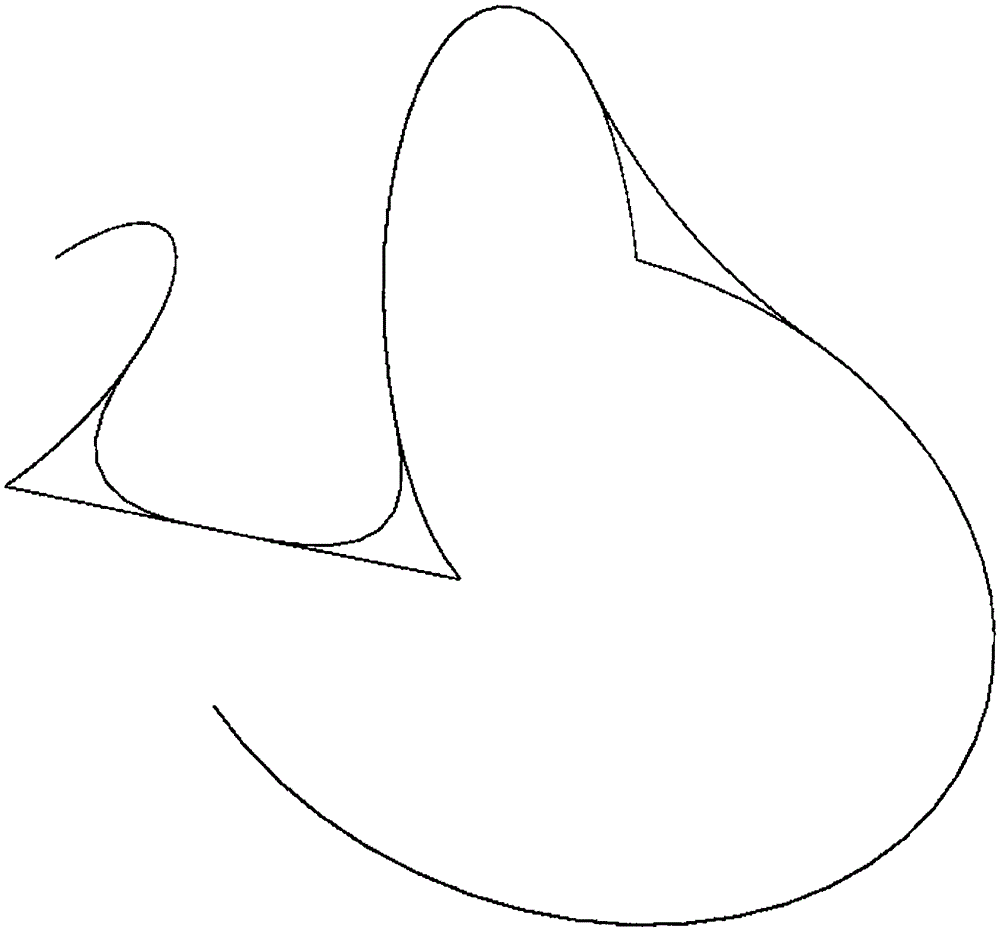
Industrial robot Cartesian space trajectory geometric smoothing method
ActiveCN105573315AGuaranteed continuous curvatureGuaranteed accuracyPosition/course control in two dimensionsThermal velocityComputer science
The invention provides an industrial robot Cartesian space trajectory geometric smoothing method. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out parameterization on geometrical curves corresponding to front and back two trajectories in a turning area; calculating parameter values of the geometrical curves of the front and back two trajectories in a turning area connecting point; judging whether the geometrical curves surpass preset limit conditions according to the parameter values of the geometrical curves of the front and back two trajectories in the turning area connecting point and turning radius, and if so, cutting off the geometrical curves; generating a turning area space curve by utilizing the Bezier curve generation principle; calculating terminal velocity and acceleration velocity of the geometrical curves; and generating a turning area trajectory by utilizing a one-dimensional velocity planning algorithm and velocity planning boundary conditions. The method enables the front and back two trajectories of an industrial robot in the turning area to realize geometric superposition smoothing to ensure curvature continuity of the geometrical curves corresponding to the trajectories; and velocity planning is carried out on the smoothed geometrical curves to achieve the purpose of speed control of the turning area.
Owner:苏州科诺机器人有限责任公司
Autonomous space flight system and planetary lander for executing a discrete landing sequence to remove unknown navigation error, perform hazard avoidance and relocate the lander and method
ActiveUS7967255B2Increased payload capacityReduce errorsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusInstruments for comonautical navigationReference mapImage resolution
An autonomous unmanned space flight system and planetary lander executes a discrete landing sequence including performing an initial velocity braking maneuver to remove velocity at altitude, coasting during which the planet surface is imaged and correlated to reference maps to estimate cross-track and along-track navigation errors and one or more lateral braking maneuvers are performed to reduce cross-track navigation error, and performing a terminal velocity braking maneuver(s) to reduce the along-track braking maneuver and remove the remainder of the velocity just prior to landing. A bi-propellant propulsion system provides a very high T / M ratio, at least 15:1 per nozzle. Short, high T / M divert maneuvers provide the capability to remove cross-track navigation error efficiently up to the maximum resolution of the reference maps. Short, high T / M terminal velocity braking maneuver(s) provide the capability to remove along-track navigation error to a similar resolution and remove the remaining velocity in a very short time window, approximately 3-15 seconds prior to touchdown. The propulsive efficiency frees up mass which can be allocated to a fuel to remove the unknown navigation errors, perform hazard avoidance and / or relocate the lander by flying it to another site or be allocated to additional payload.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
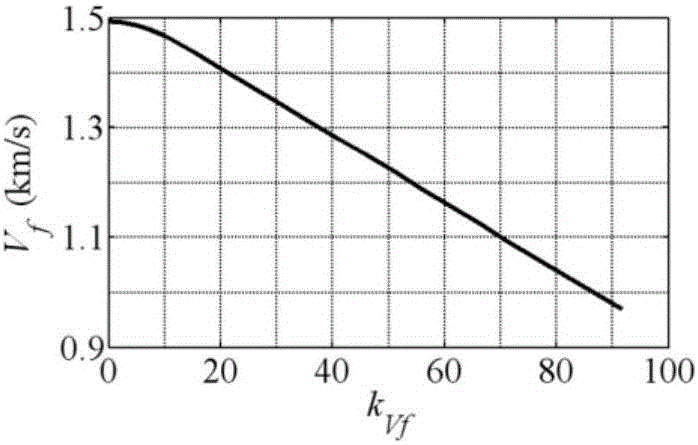
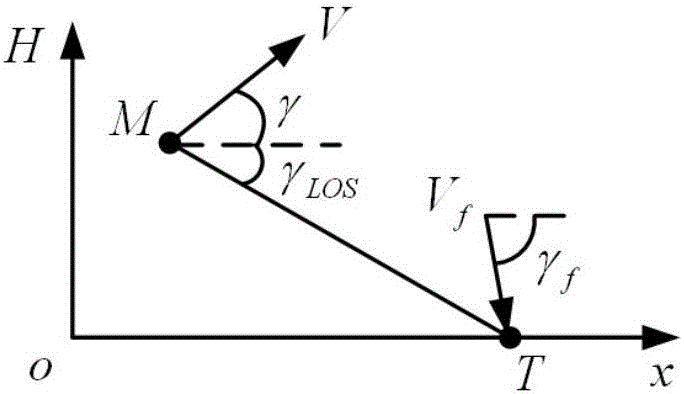
Explicit guidance law for rocket with terminal speed, trajectory inclination angle and overload constraint
InactiveCN106843272AManeuvering Acceleration DecayPosition/course control in three dimensionsGuidance systemCorrection algorithm
The present invention provides an explicit guidance law for a rocket with a terminal speed, a trajectory inclination angle and overload constraint. The explicit guidance law for a rocket is formed by integration of an optimal trajectory-shaping guidance law and a terminal speed control scheme. The optimal trajectory-shaping guidance law can control an aircraft to hit a target from a predetermined direction, the terminal speed control scheme controls the transverse maneuverable accelerated speed of the aircraft bending so as to control the prolonging of flight distance to regulate the size of the terminal speed, and the size of the transverse maneuverable accelerated speed is determined through an iteration correction algorithm. The analysis guidance law can satisfy the terminal trajectory inclination angle and the terminal speed constraint, and allow an aircraft to approach to the maneuverable accelerated speed of the target to gradually decrease to 0; further, the present invention provides a method for determination of coefficients of guidance law for a rocket, namely the coefficients of guidance law for a rocket are determined through proper selection of features of a linear approximation system; and moreover, a coefficient stability domain of the guidance law for the rocket is obtained so as to strictly prove that only if the coefficients of guidance law for a rocket are in the stability domain the guiding system is stable and the aircraft hits a target at a small angle of attack.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
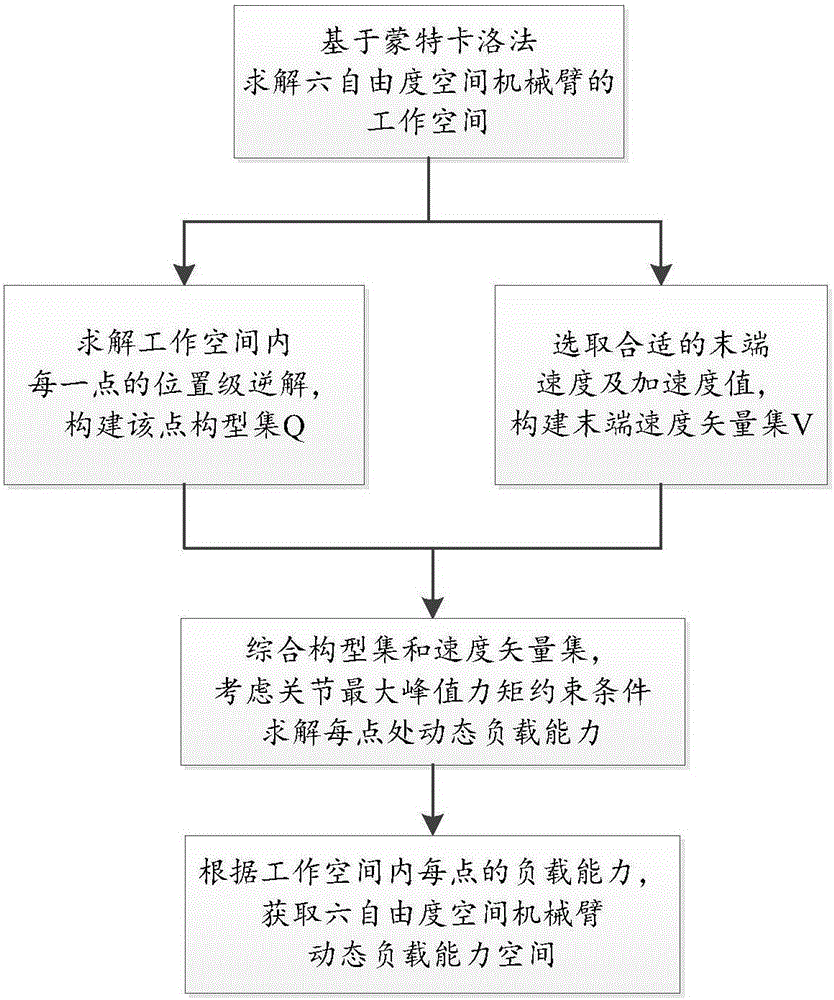
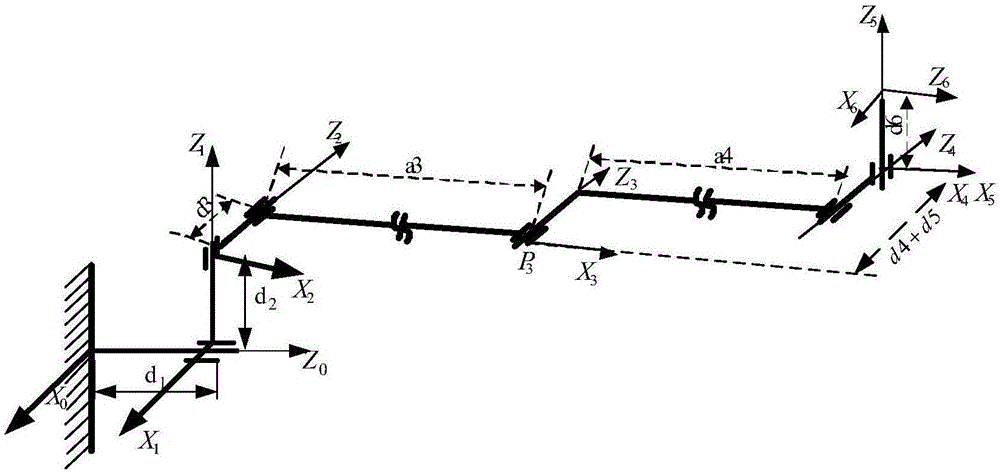
Method for analyzing dynamic load capacity work space of six-degree of freedom space manipulator
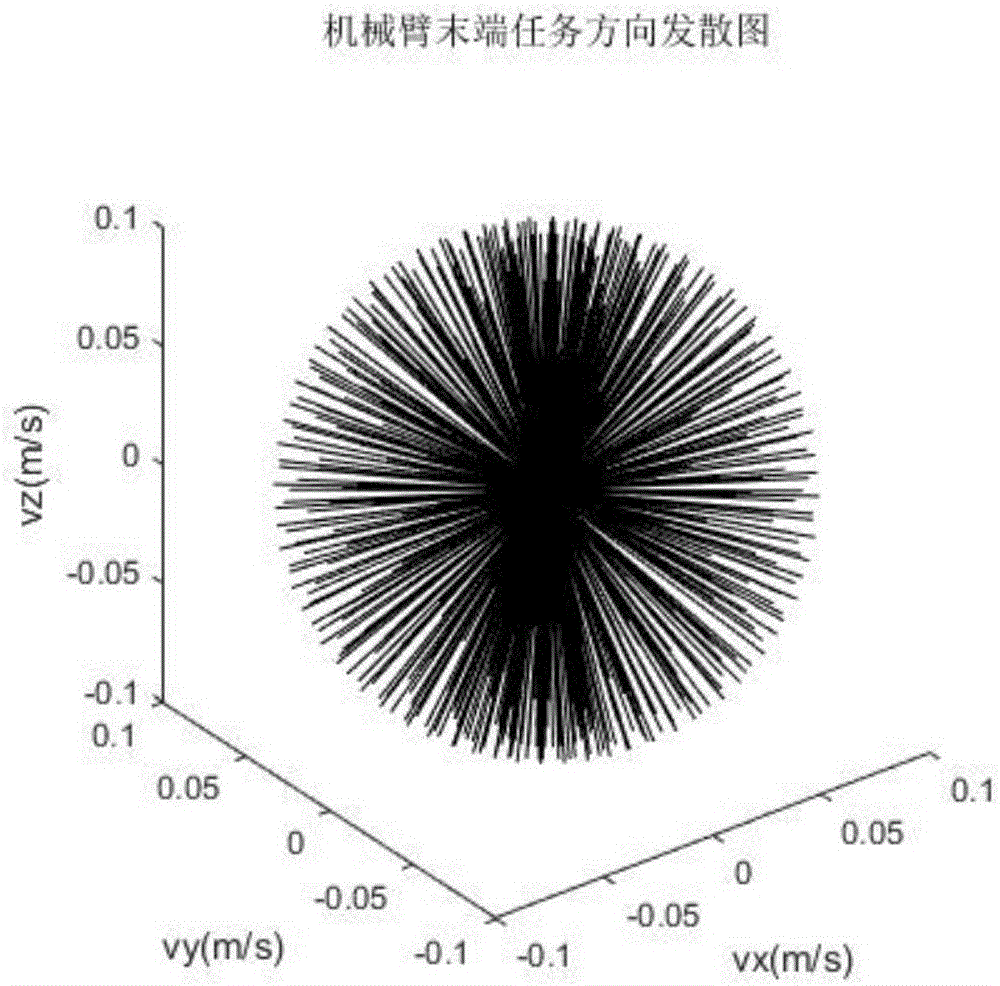
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for analyzing a dynamic load capacity work space of a six-degree of freedom space manipulator. The method is used for realizing the analysis and evaluation for the dynamic load capacity of the work space of the six-degree of freedom space manipulator. The method comprises the following steps of: solving the work space of the six-degree of freedom space manipulator on the basis of Monte Carlo method; constructing a configuration set and a terminal velocity vector set of each point in the work space; compounding the configuration set with the terminal velocity vector set; and considering the maximum peak torque of the joint and solving the dynamic load capacity of each point, thereby acquiring the dynamic load capacity work space of the six-degree of freedom space manipulator. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the analysis and evaluation for the dynamic load capacity of the work space of the six-degree of freedom space manipulator can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
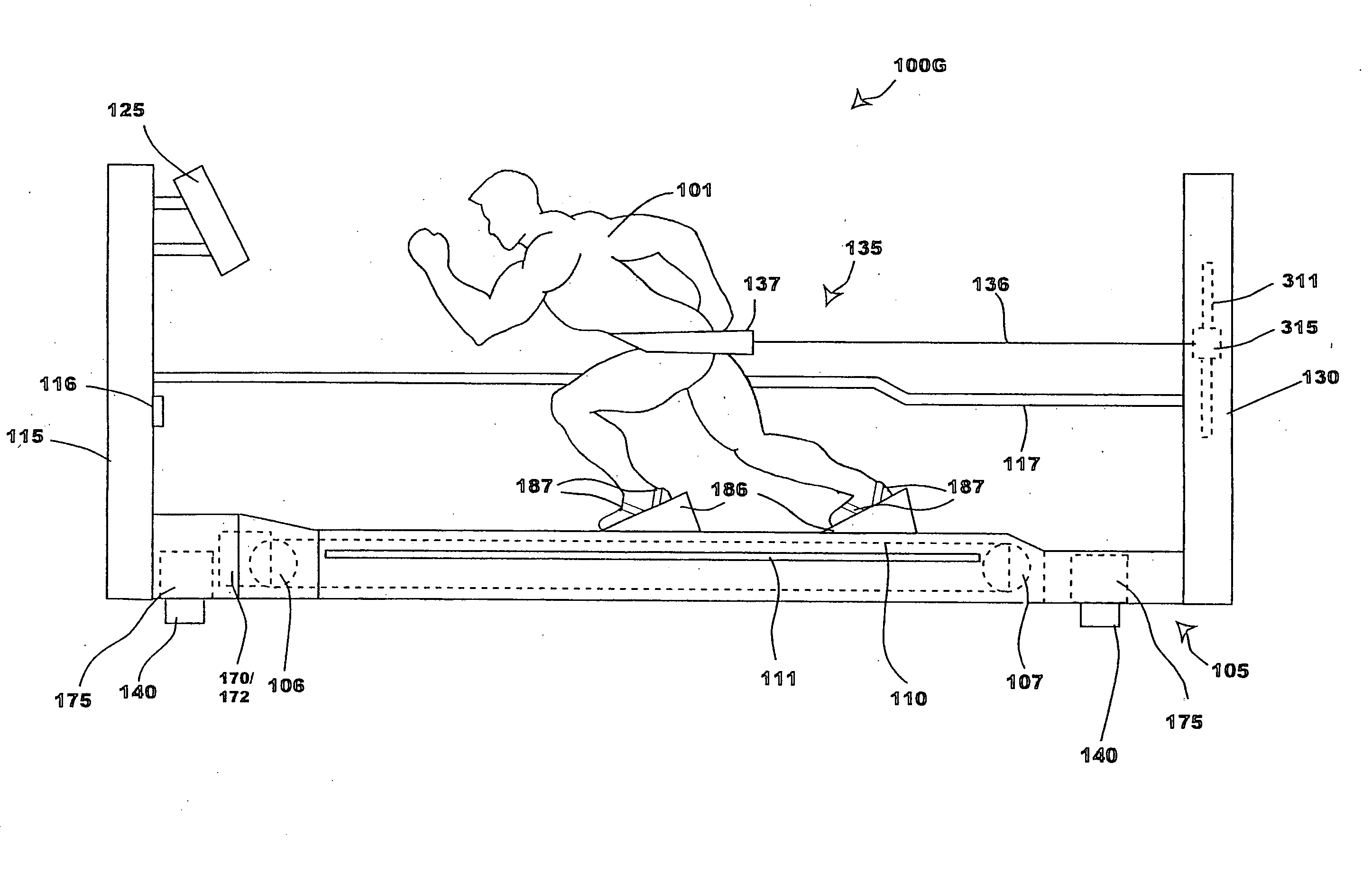
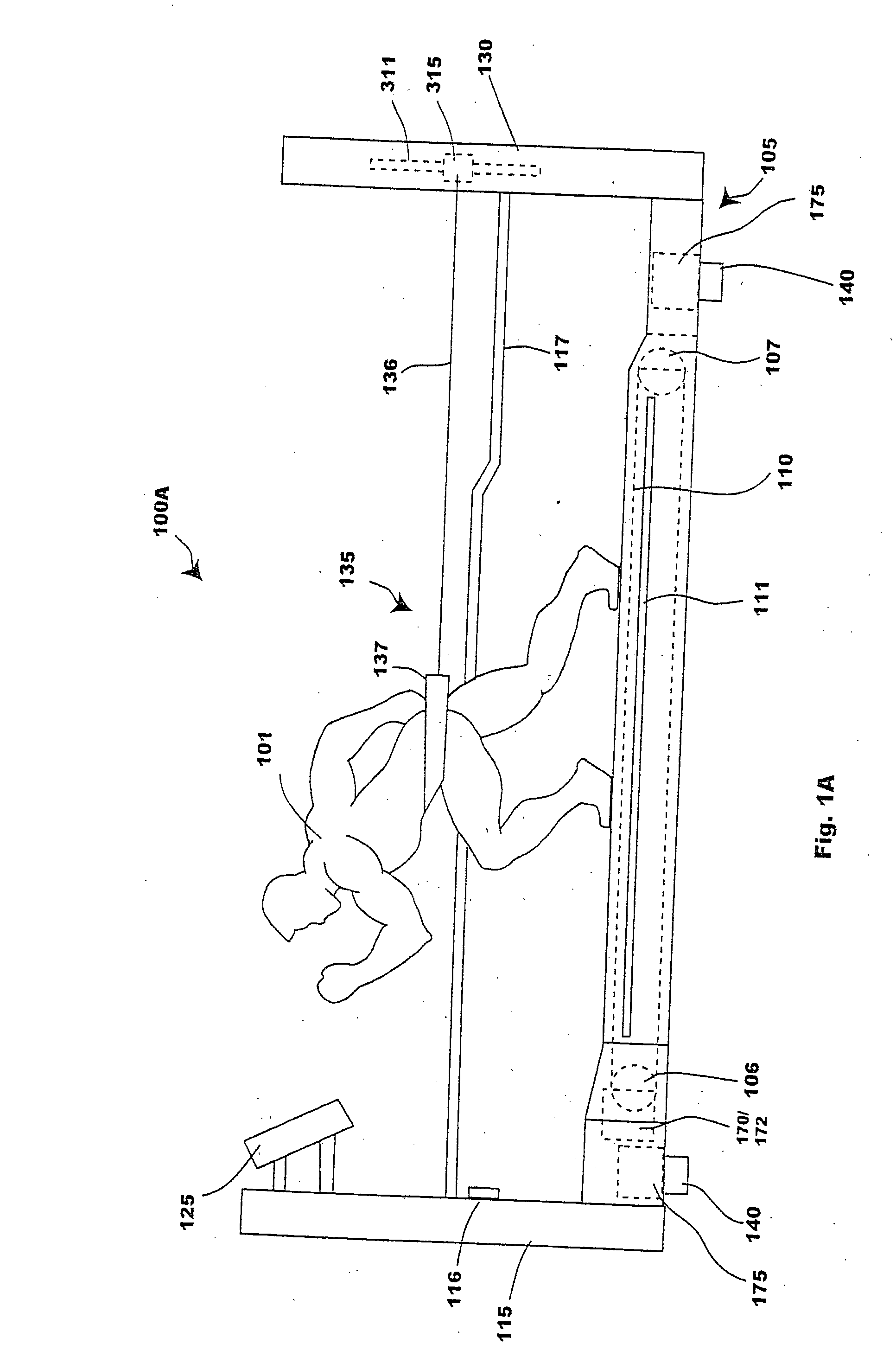
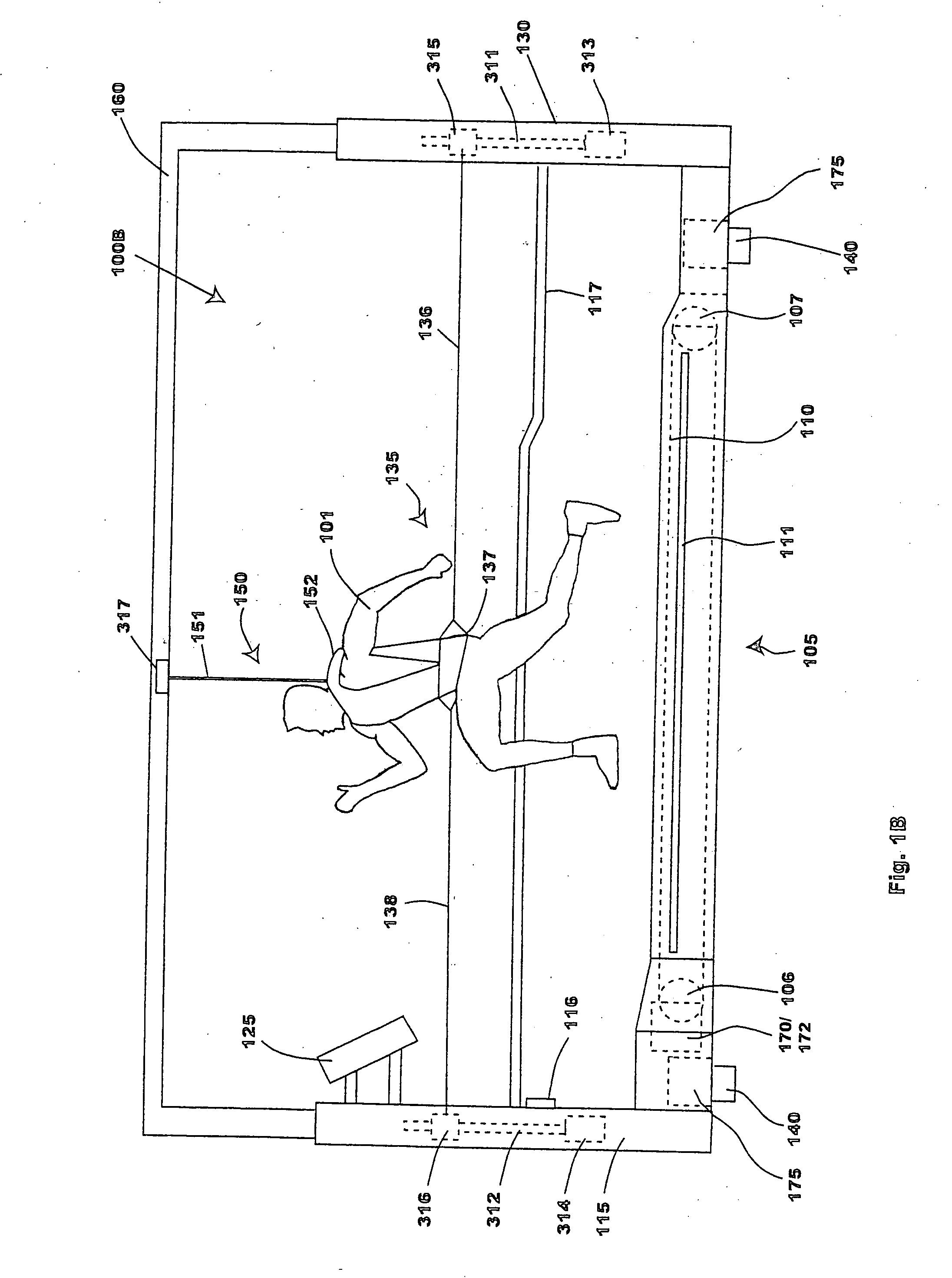
Bipedal locomotion training and performance evaluation device and method
An exercise and performance evaluation apparatus includes a revolving belt on which a subject can perform bipedal locomotion, a harness for securing the subject at a fixed position relative to the apparatus, a means for measuring the force applied by the subject to the belt, and a means for monitoring and controlling the velocity of the belt. The harnessing of the subject allows monitoring of the velocity as a function of time. An overhead harness may be used to alter the effective mass of the subject. The velocity of the belt may be controlled by a motor and brake system, where the motor may be uni-directional or bi-directional. A digital processor may be used to control the motor and / or brake as a function of the applied forces to simulate real-world or virtual world environments, allowing the operation of the device in modes such as constant-force modes, constant-load modes, constant velocity modes, sprint simulation mode, bob sled simulation mode, terminal velocity determination mode, isokinetic overspeed mode, and isotonic overspeed mode. Processing of the velocity and force as a function of time allows for the recording and analysis of data such as the maximal exertion force-velocity curve, left leg / right leg performance, force as a function of stride, etc.
Owner:RADOW SCOTT B
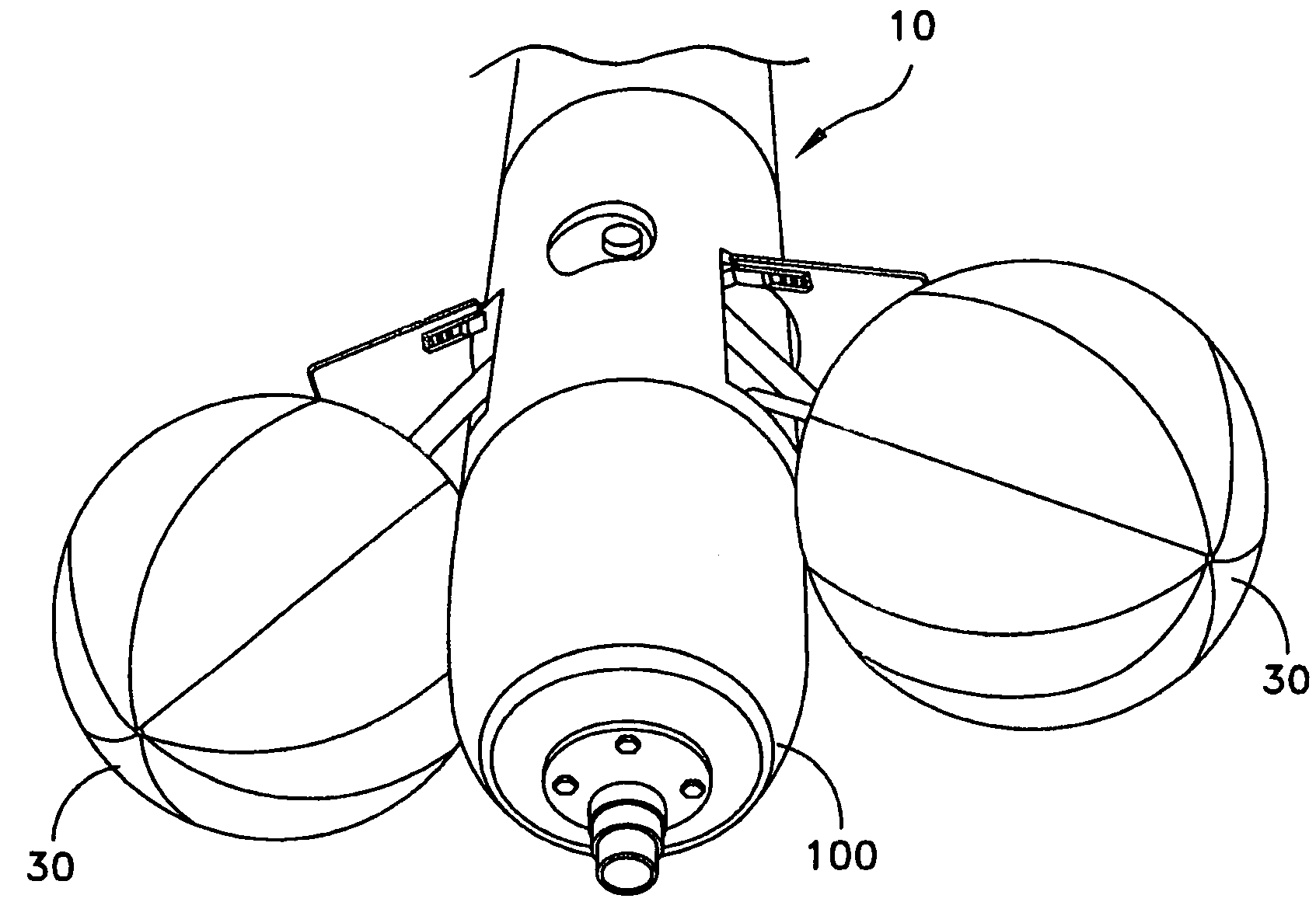
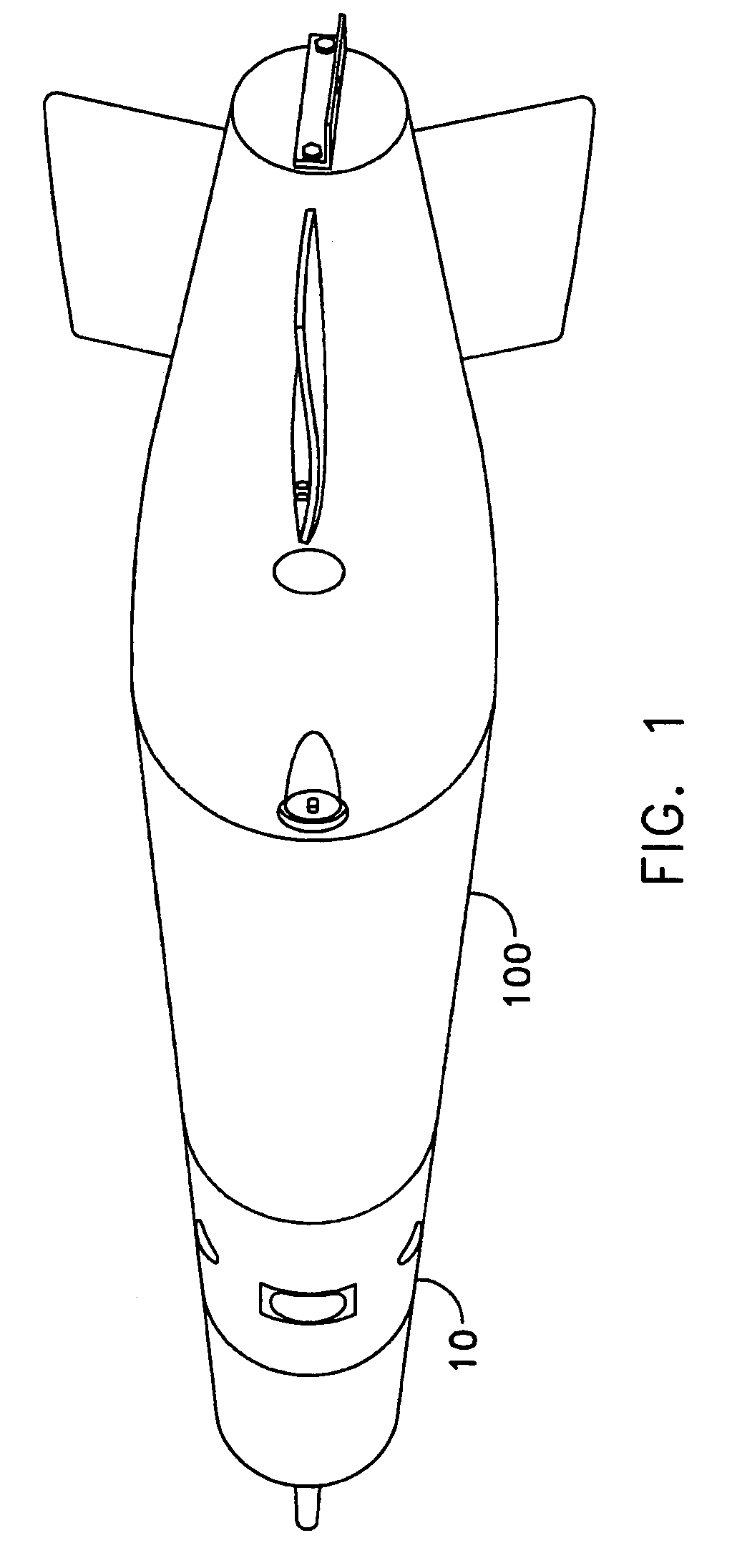
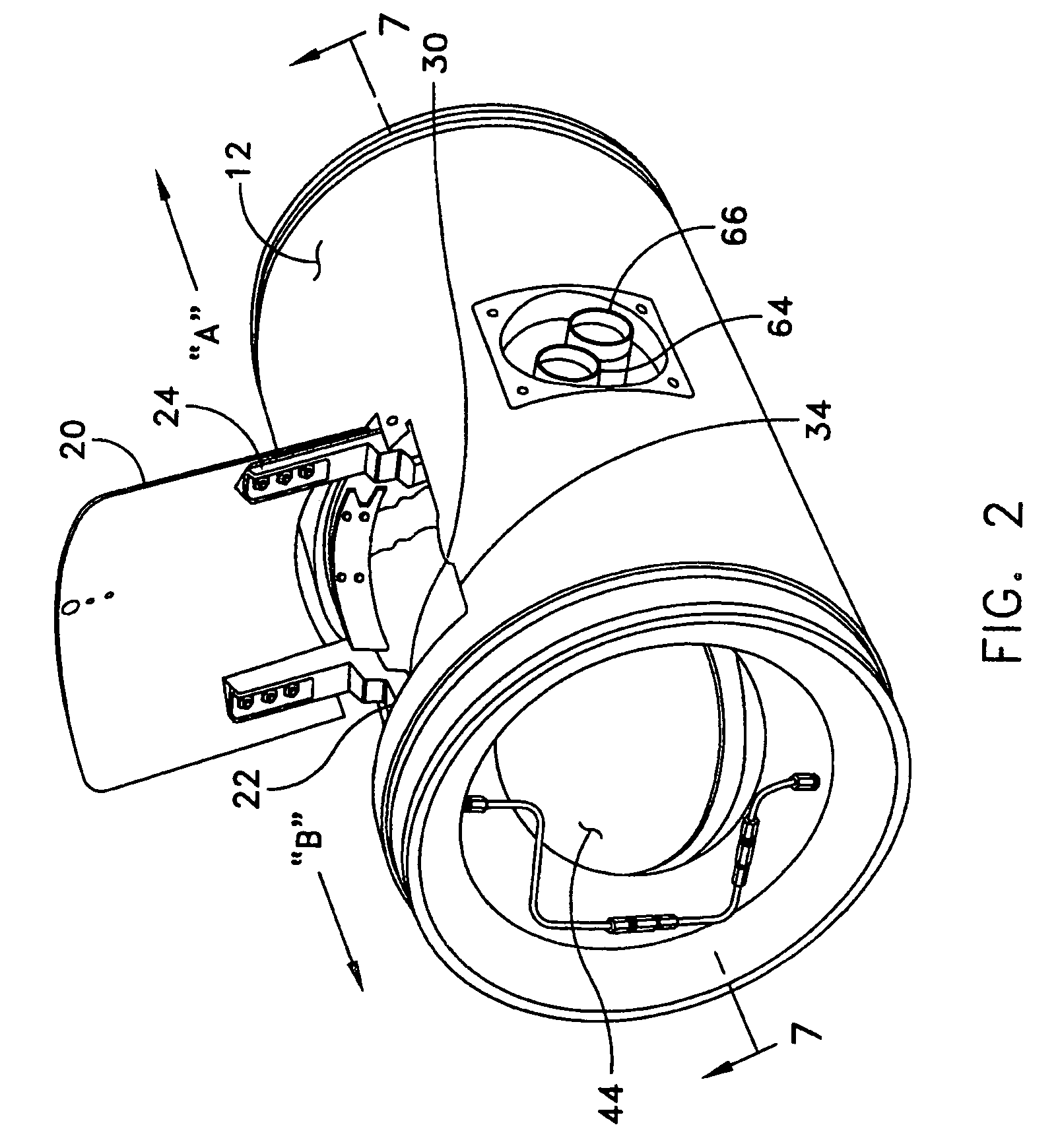
Underwater vehicle deceleration and positive buoyancy assembly
InactiveUS7250568B1Reduce depthShorten the timeMarine torpedoesSelf-propelled projectilesTerminal velocityHydrodynamic forces
An assembly for vehicle deceleration and buoyancy comprises a pair of doors enclosing flotation bags inflatable for buoyant recovery of the torpedo. In operation, the doors are controllably forced open to an initial angle off a longitudinal axis of the assembly to a fully-deployed position by hydrodynamic forces of the movement of the vehicle. From the doors blocking the hydrodynamic forces, the vehicle decelerates. The hydrodynamic braking action of the doors reduces the time required to reach terminal velocity, thus reducing the depth the vehicle sinks and enabling recovery with less gas required for inflation.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Air shifter toy model
InactiveUS20100330866A1Avoid difficult choicesToy aircraftsRemote-control toysJet aeroplaneOutdoor area
The present invention provides an unconventional and proprietary radio control (RC) or infrared remote control (IR) toy model / airplane which can intentionally shift or change its center of gravity (COG) to different positions along the longitudinal centerline of the aircraft or fuselage. The incremental shifting or moving of the COG from front to rear or vice versa incrementally changes the “angle of attack” of the wing, thereby producing a variable range of viable flight attitudes and resultant terminal velocities (top speeds). Therefore, users can easily select an appropriate speed for the airplane to fly in limited indoor spaces or in larger outdoor areas. Additionally, the COG shifting of the present invention can be applied not only to RC and IR controlled toy models / aircrafts but may also be implemented into real aircrafts including manned and unmanned aircraft for civilian and / or military applications.
Owner:TOP NOTCH TOYS
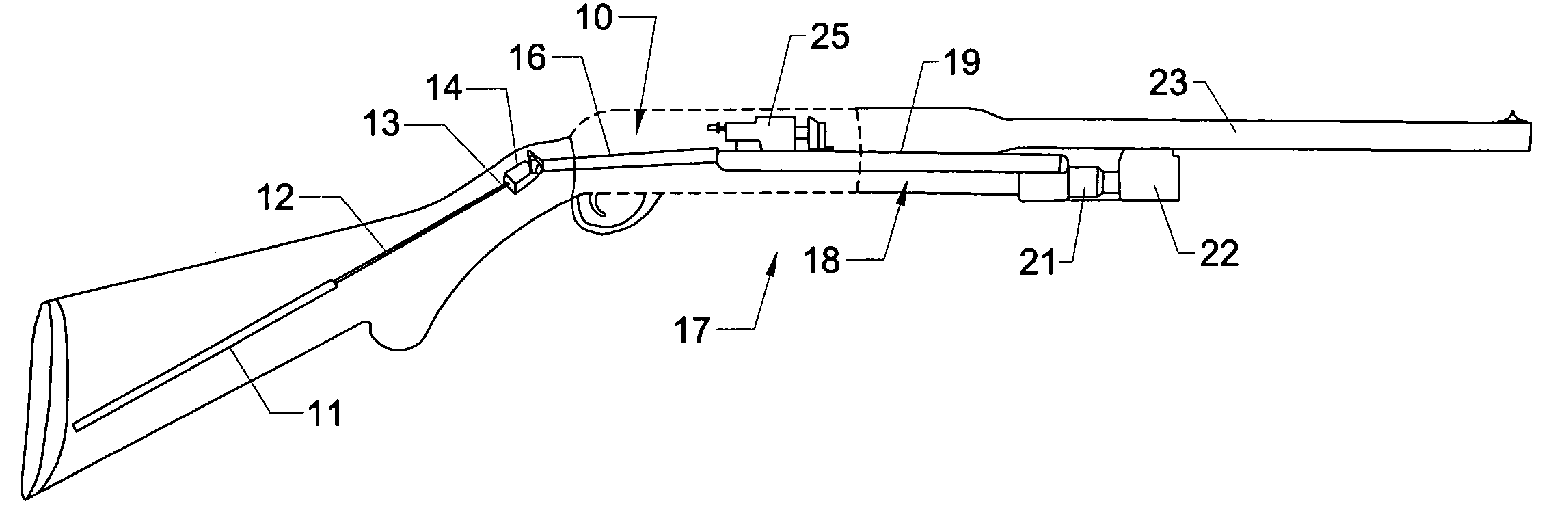
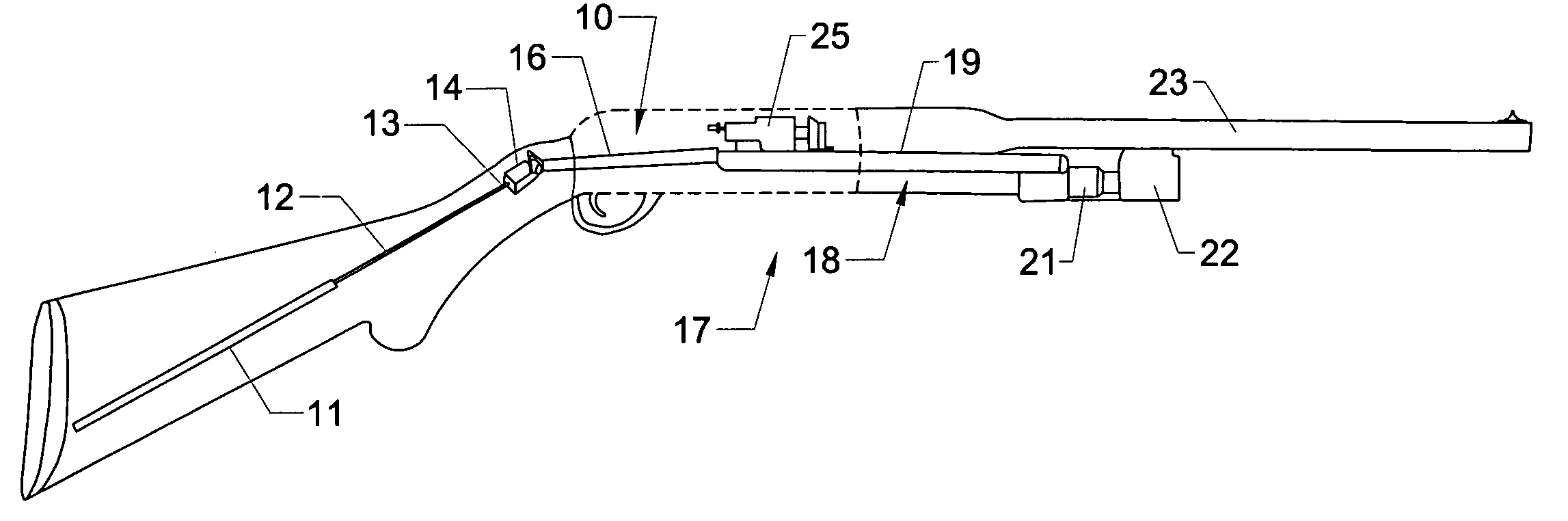
Action rate control system
An action rate control system for a gas operated firearm that includes an action sleeve and an action rate control cylinder. The action sleeve moves in a rearward direction in response to a volume of combustion gases that are generated during firing of the firearm and diverted from the barrel of the firearm through gas ports. The action rate control cylinder is connected to the action sleeve by a linkage that controls movement and slowing of the action sleeve as it approaches a rear limit for its movement. The resistance force generated by the rate control cylinder is a function of the velocity of the action sleeve during its movement. In another aspect, a gas operated firearm includes a barrel, a bolt assembly, an action system coupled to the bolt assembly, and a rate control cylinder coupled to the action system. The action system includes a sleeve assembly that is driven by a volume of combustion gases that are diverted from the barrel when a round of ammunition is fired. The rate control cylinder controls a terminal velocity of the sleeve assembly being driven by the volume of combustion gases. A resistance force generated by the rate control cylinder is a function of the velocity of the bolt assembly during the bolt assembly's rearward movement. The velocity of the bolt assembly follows a controlled and gradual reduction as the energy load associated with the firing is absorbed by the rate control cylinder.
Owner:REM TML HLDG LLC
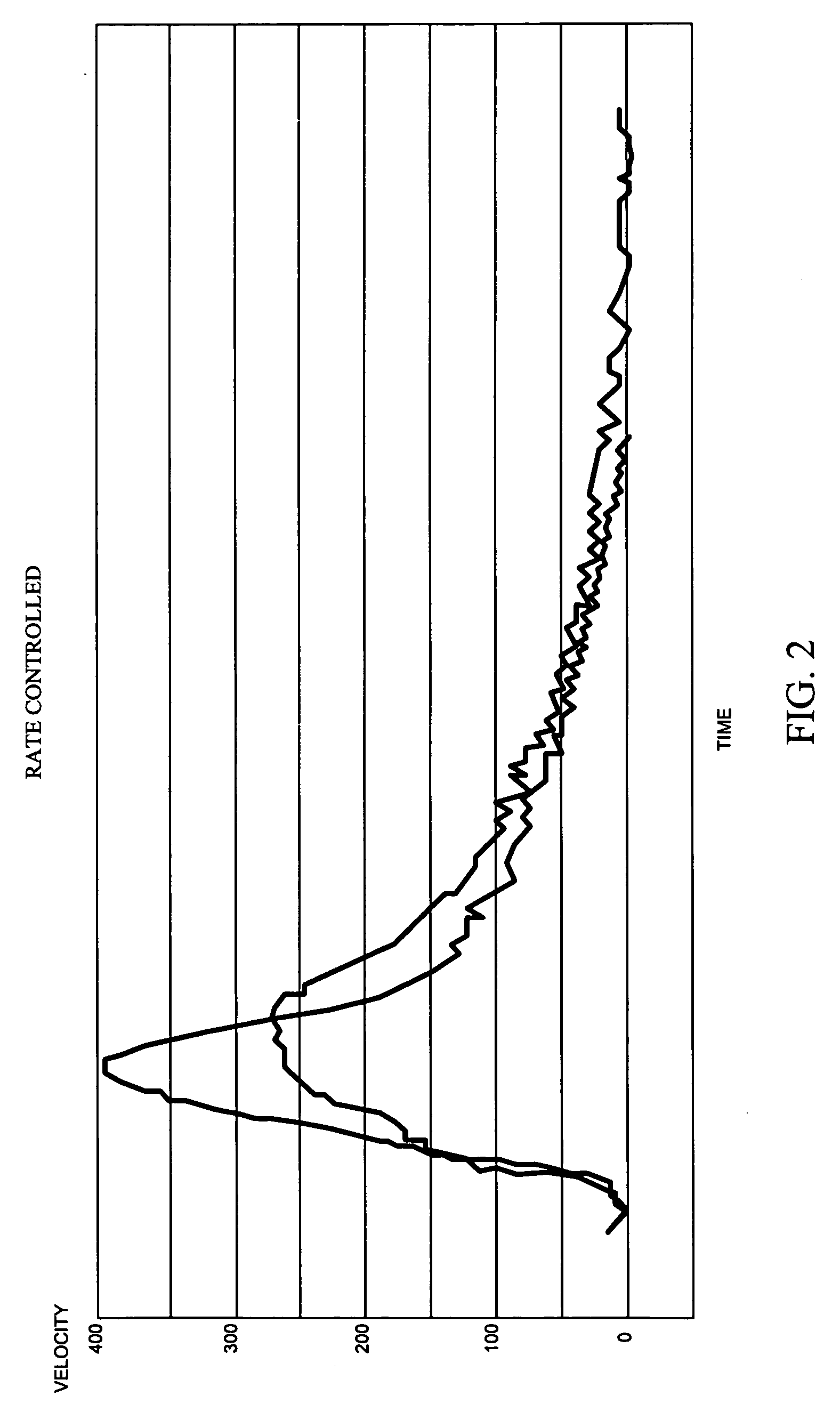
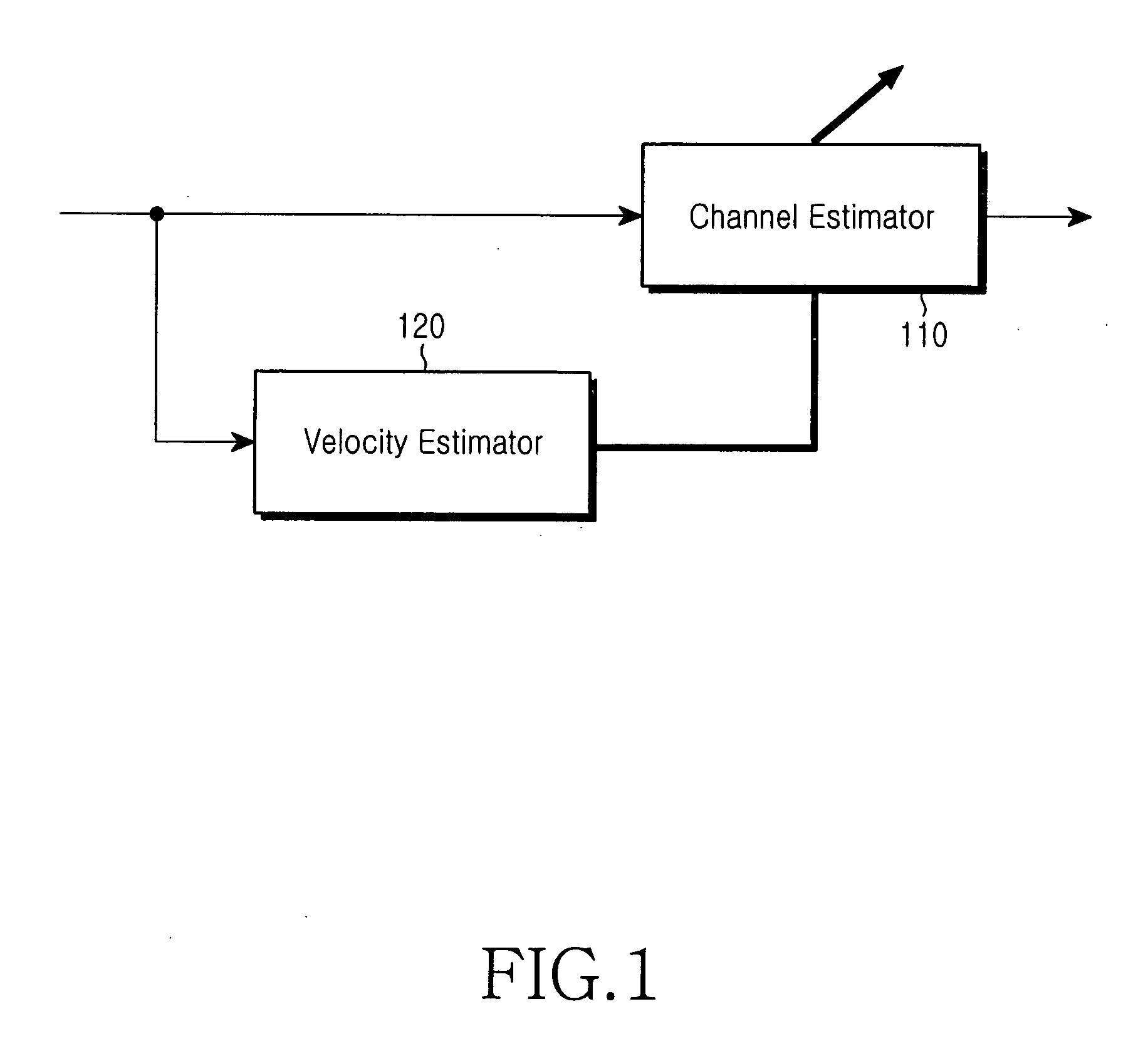
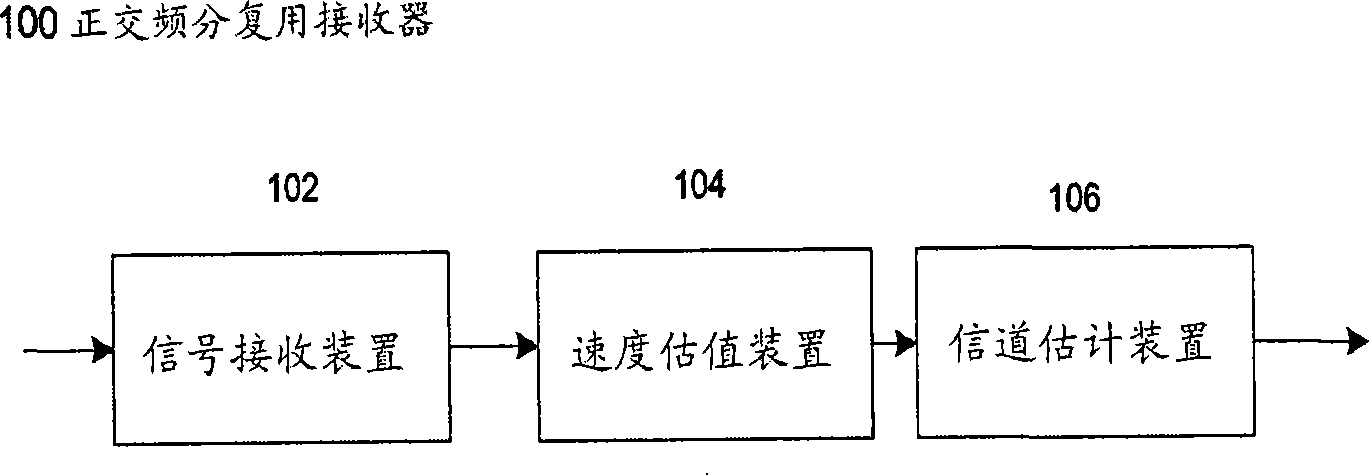
Apparatus and method for estimating a velocity of a mobile terminal in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050060094A1Improve reception performanceRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsRoad vehicles traffic controlControl signalBoundary values
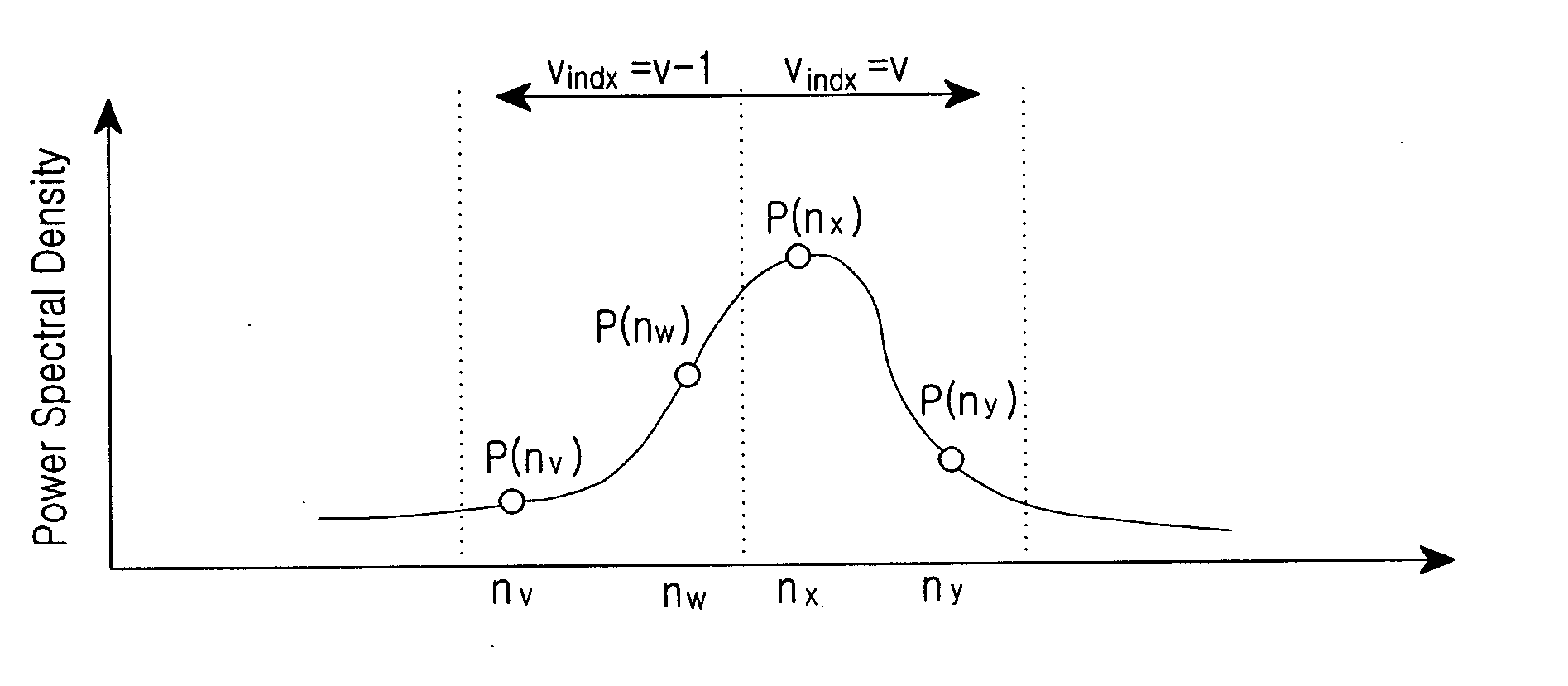
Apparatus and method are provided in a BS (Base Station) apparatus of a mobile communication system including a velocity estimator for estimating a velocity of a mobile station (MS) and a channel estimator for performing channel estimation using a plurality of channel estimation coefficients according to a control signal of the velocity estimator. The apparatus and method comprise estimating reception performance of individual channel estimation coefficients of the channel estimator, and selecting boundary frequencies of a plurality of Doppler frequency bands corresponding to a channel estimation coefficient having the best reception performance; measuring a power spectrum associated with a minimum number of frequency indexes capable of classifying the plurality of Doppler frequency bands; and controlling a detection position such that a Doppler frequency boundary value measured when a weight value is applied to the measured power spectrum approximates a desired Doppler frequency boundary value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
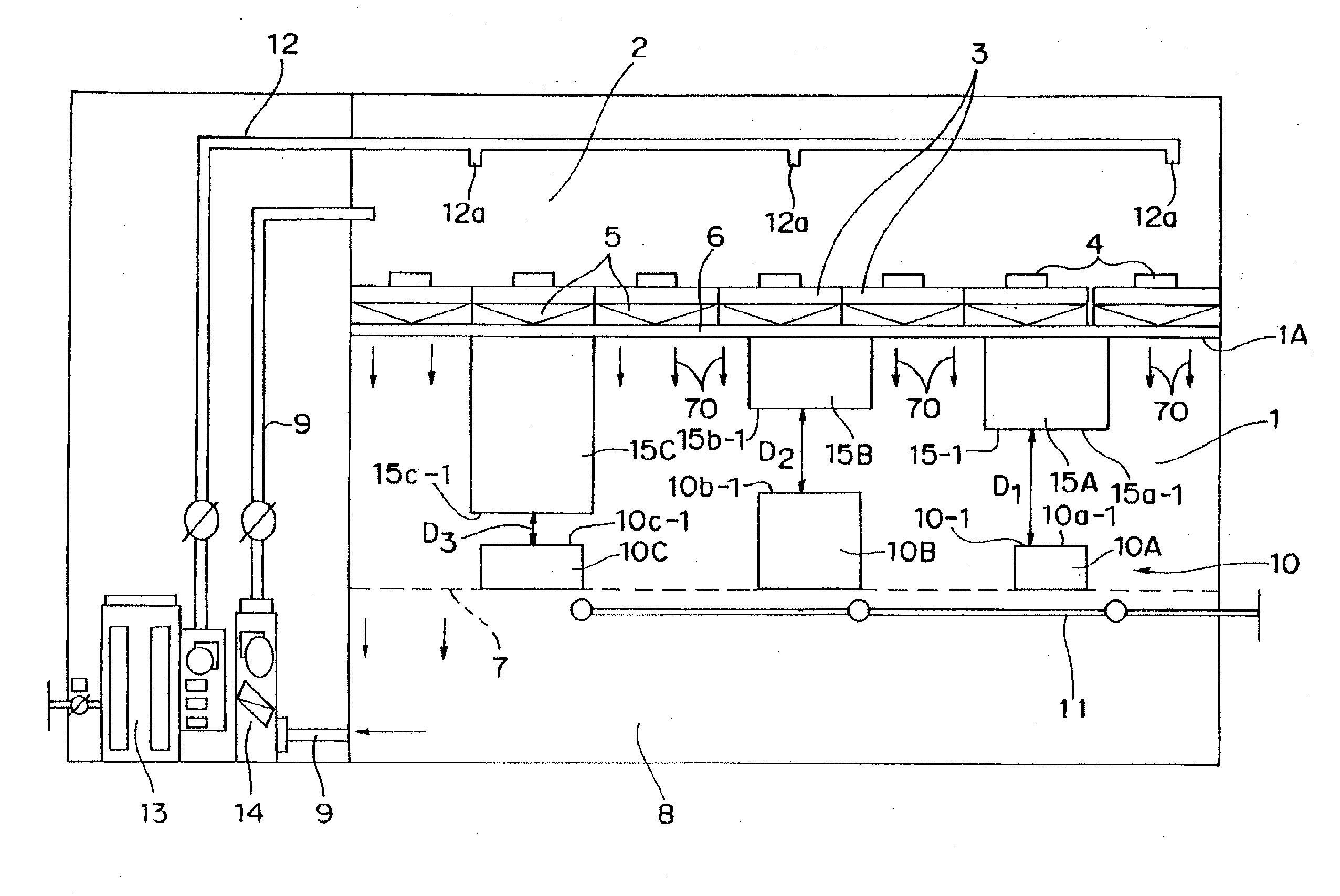
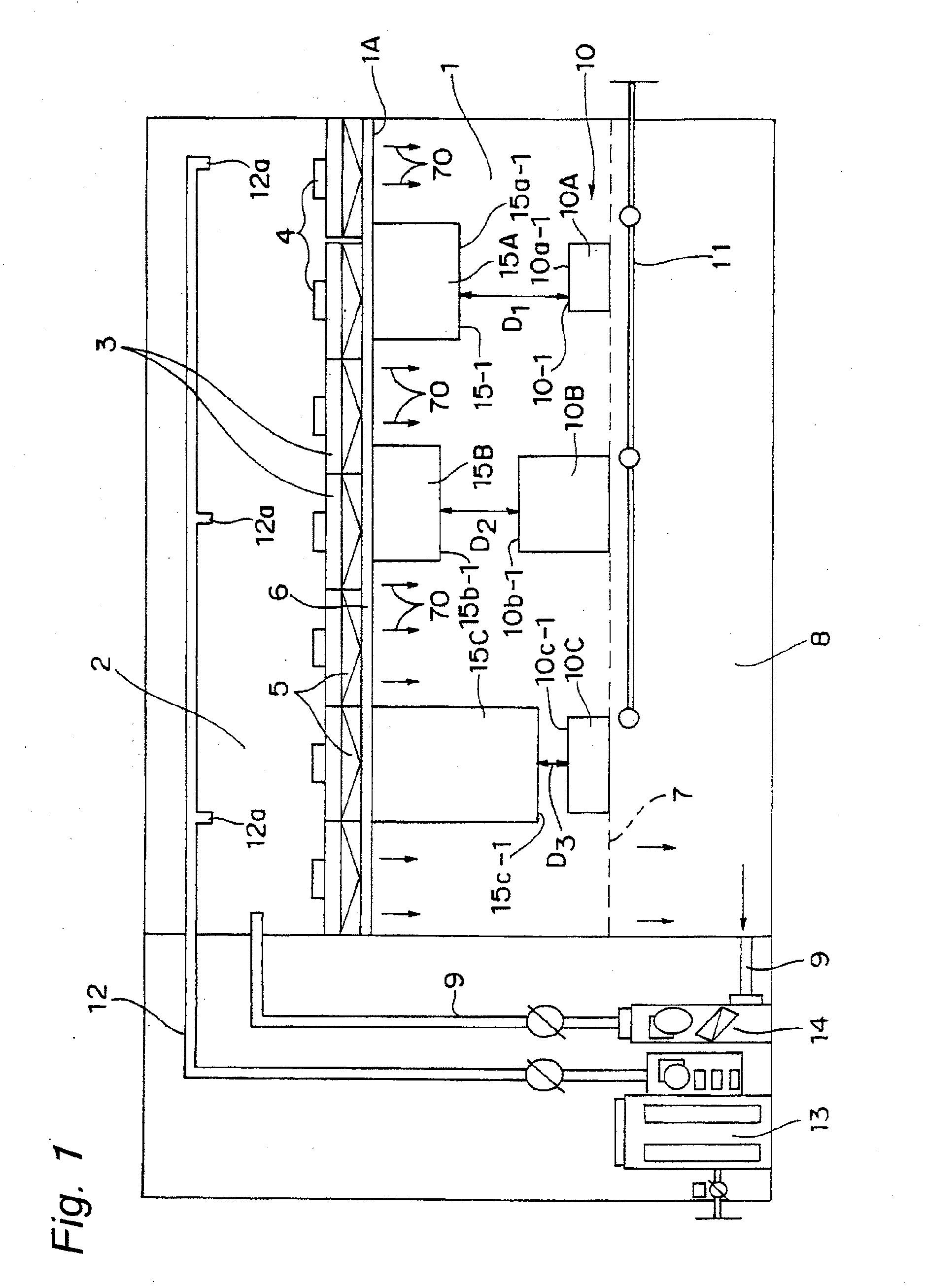
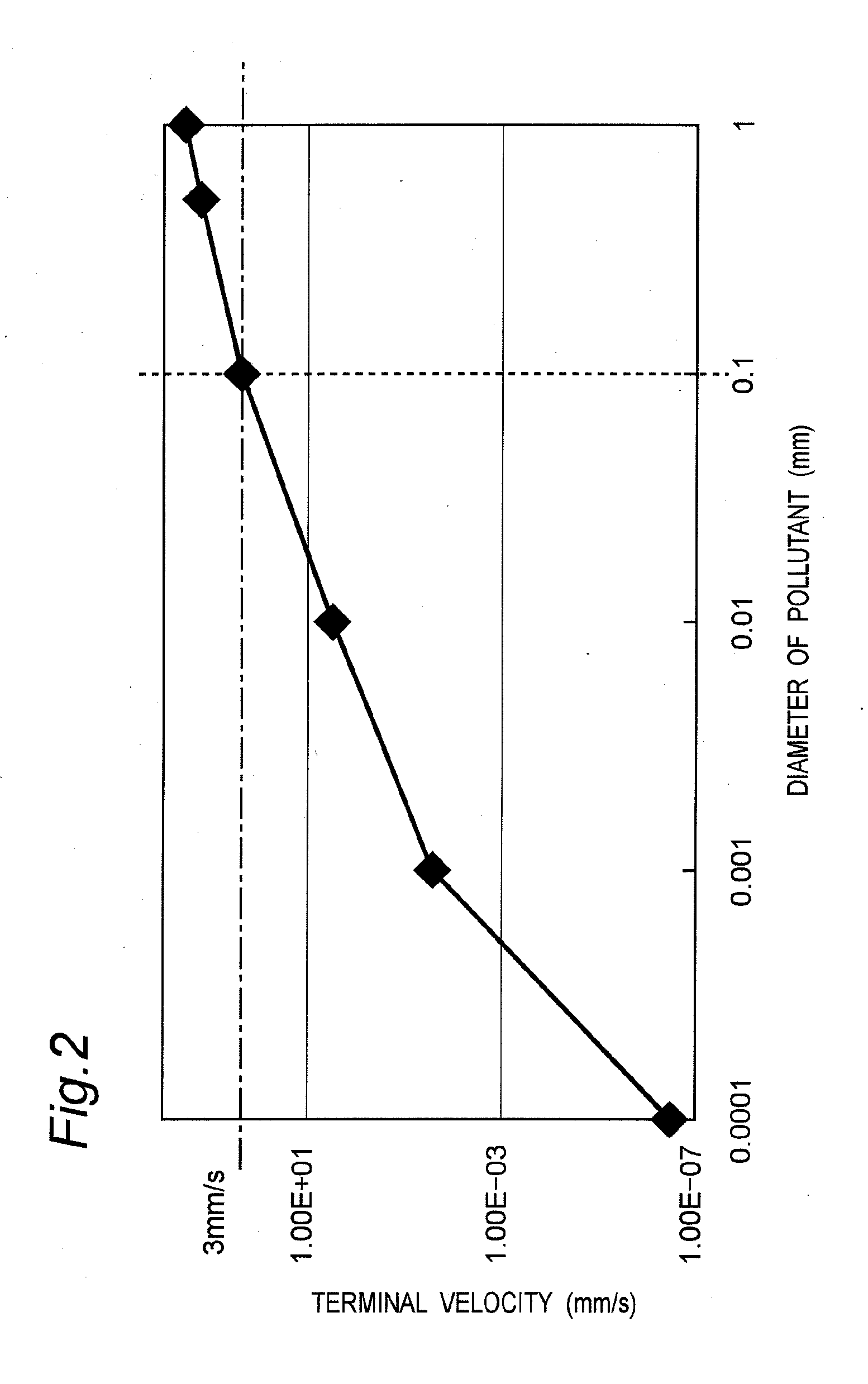
Clean room
InactiveUS20100022179A1Increase airflowPrevent fallingMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusParticulatesAerodynamic drag
A dust-exhaust acceleration face of a dust-exhaust assistant member is disposed so as to face a top face of a heat radiating member of a production facility or the like so that a gap between the top face of the heat radiating member and the dust-exhaust acceleration face of the dust-exhaust assistant member is occupied by ascending air flows, each having a falling velocity (terminal velocity) that is not accelerated beyond a fixed velocity, to form a balanced state between the size of an object, such as a dust particulate or a chemical substance particulate, and air resistance when the object is freely falling in the air; thus, the object, such as a dust particulate and a chemical substance particulate, is prevented from falling onto the heat radiating member.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
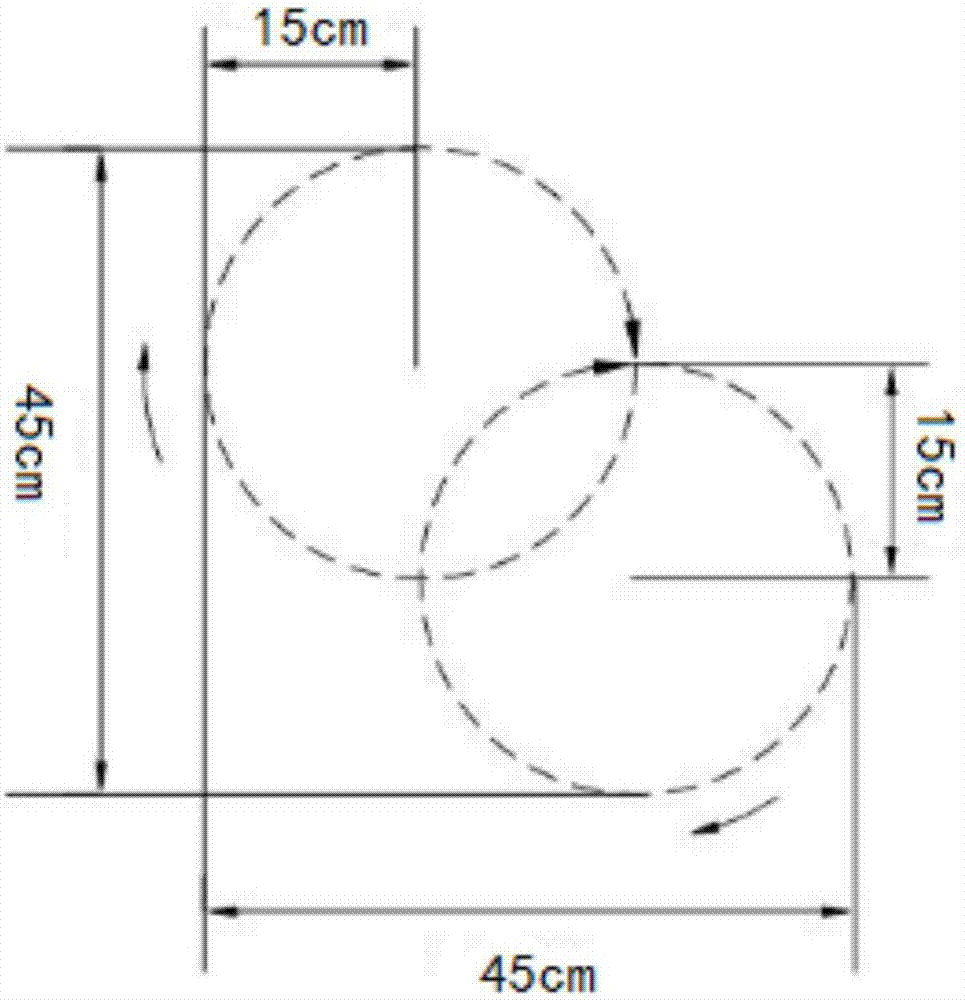
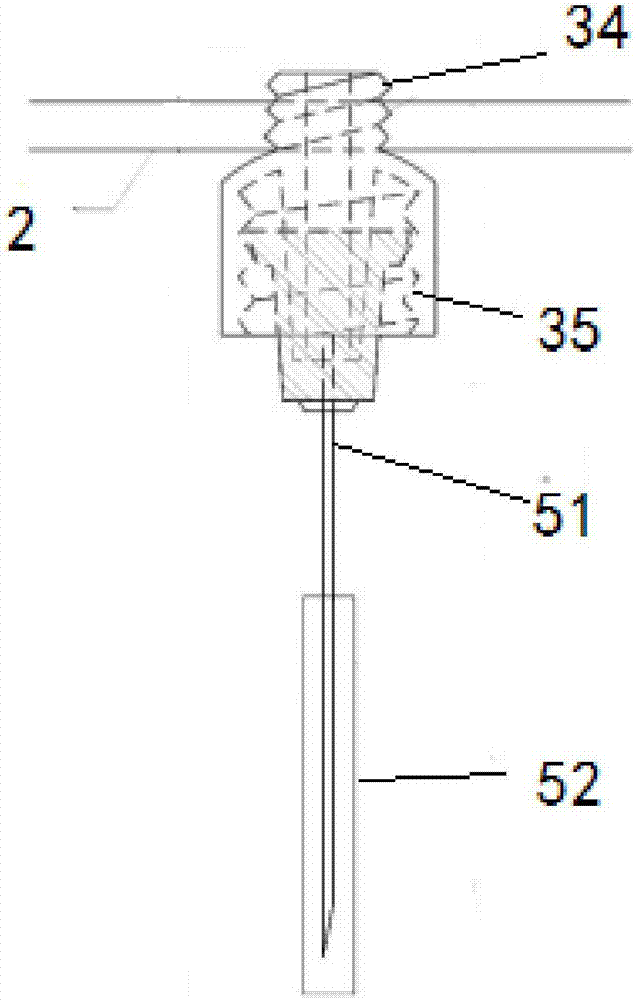
Needle type rainfall simulation device and method
InactiveCN107544593AEfficiently reproduce the distributionHighly consistent and evenly distributedEducational modelsSimultaneous control of multiple variablesRainfall simulationPeristaltic pump
The invention relates to a needle-type simulated rain device and a method for simulating rainfall thereof. The simulated rain device includes a rain device and a water supply device, wherein the rain device includes a frame, a transmission device and a rain collection box; the frame has two vertically connected frames; the transmission The device includes two identical sub-transmission systems fixed on the two frames; the rain collection box is a sealed cuboid, and two adjacent sides are connected to the two sub-transmission devices. The upper end of the rain collection box is equipped with a reactor, and the lower The end face is connected with a plurality of raindrop generators. The water supply unit includes a peristaltic pump. The present invention can fine-tune the size of raindrops, conveniently control the range of rain intensity and rainfall height, and is convenient to install and adjust the needle-type rainfall device indoors and outdoors, and is used for studying rainfall characteristic parameters such as raindrop diameter, rain intensity, raindrop terminal velocity, and raindrop kinetic energy.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
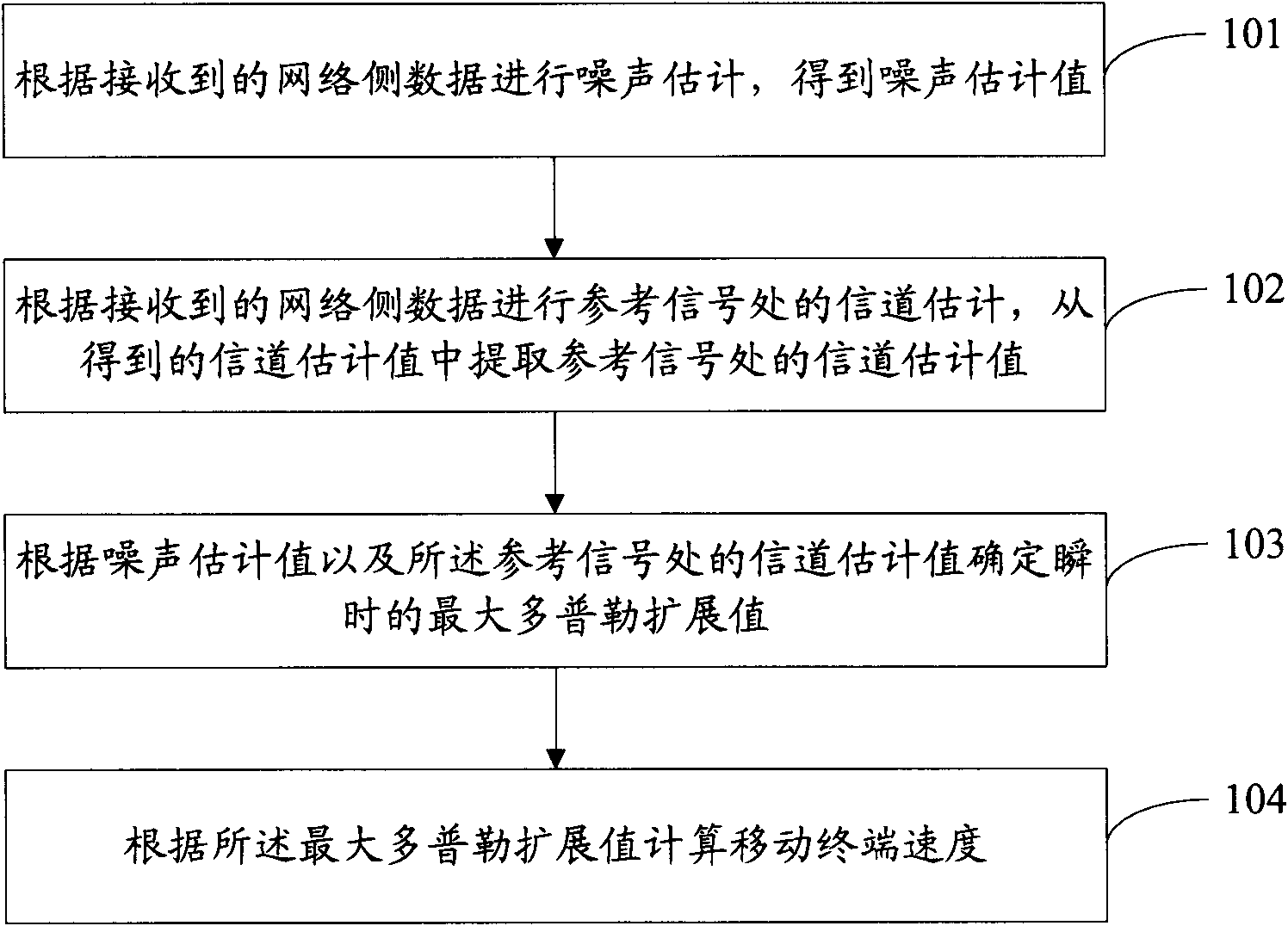
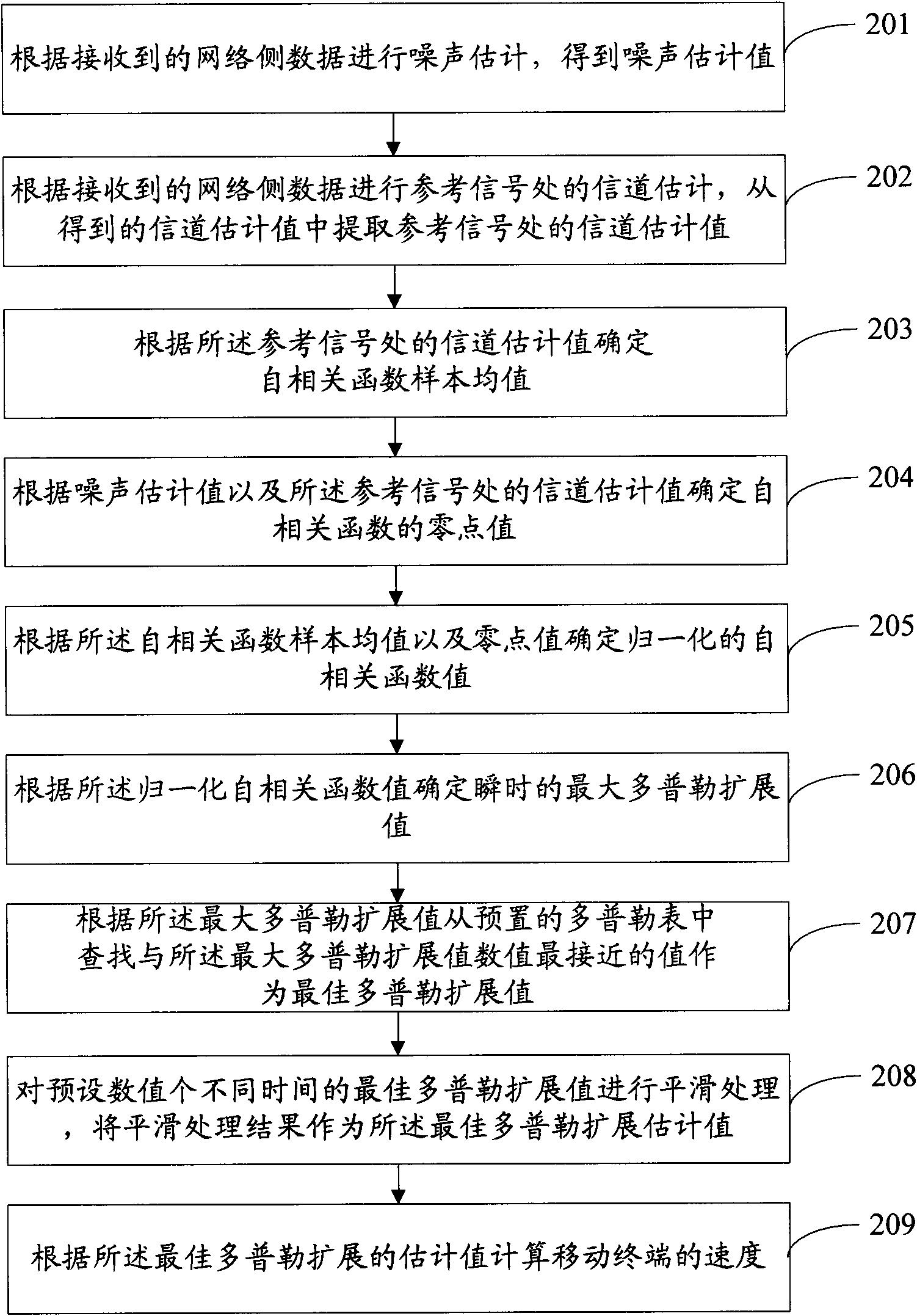
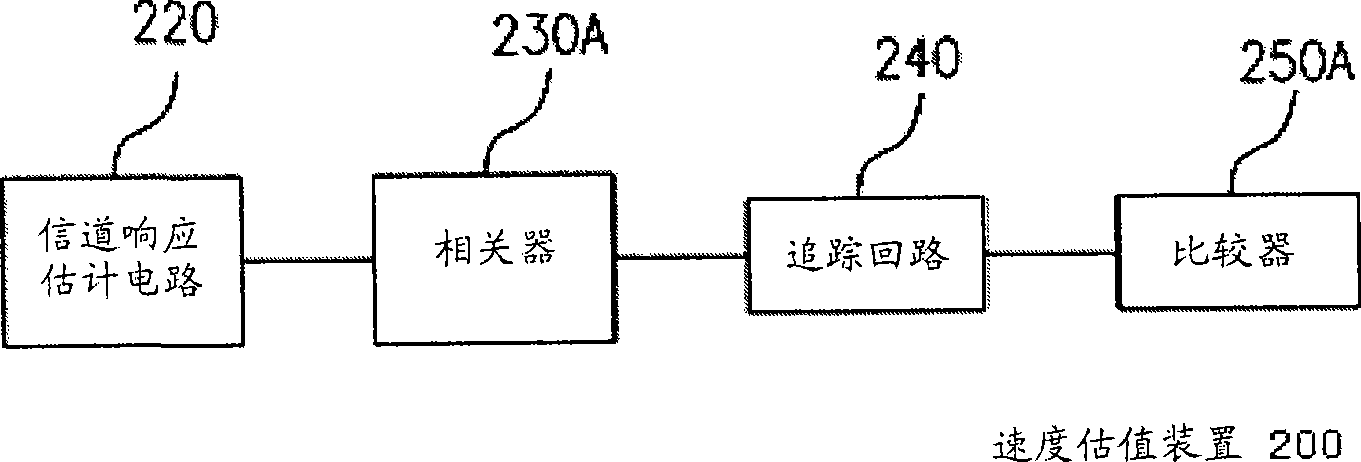
Method and device for detecting speed of mobile terminal
ActiveCN101965047AAccurate detectionMulti-frequency code systemsUsing reradiationDoppler spreadComputer terminal
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting the speed of a mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps of: performing noise estimation according to received network side data to obtain noise estimation values; performing channel estimation according to the received network side data and extracting a channel estimation value at a reference signal from obtained channelestimation values; determining an instantaneous maximum Doppler spread value according to the noise estimation values and the channel estimation value at the reference signal; and computing the speedof the mobile terminal according to the maximum Doppler spread value. In the method and the device, the more accurate speed of the mobile terminal can be detected in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Payload expulsion system for deep-target penetrators
Improved deep target penetrating munitions are disclosed which bring about controlled ejection of the payload following the penetration by the munition of the ceiling of a hardened facility. The ejection results from a plurality of selected propelling charges, which are activated following a signal from a fuze by a shock-hardened electronic trigger system. The shock-hardened electronic trigger system is programmed to automatically select the appropriate charges to match and cancel out the instantaneous terminal velocity of the munitions following the penetration of the ceiling of a hardened target facility. In this manner, the payload is deployed within the target facility for maximum effect and minimum collateral damage.
Owner:SALIZZONI RANDY M +2
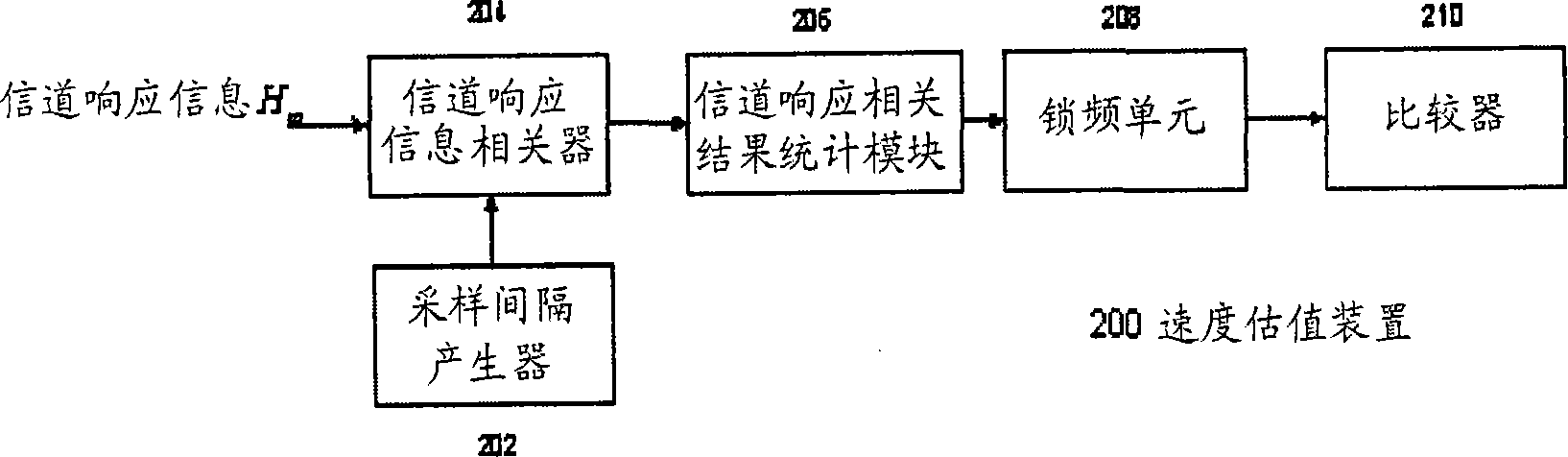
Apparatus and method for estimating wireless terminal velocity
ActiveCN101252764ASmall space requirementAvoid defectsPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime domainCarrier signal
The invention provides a method and a device for estimating the velocity of a wireless terminal. The velocity estimating device used in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system is used for receiving a plurality of pieces of channel responding information of the orthogonal frequency division multiplexing element, and the velocity estimating result is obtained according to the sampling interval. The device comprises a correlation device used for relevant operation of a plurality of pieces of channel responding information corresponding to the sub-carrier wave with the time field interval being the sampling interval, to obtain a plurality of pieces of relevant result information; a statistical module connected with the correlation device and used for statistical operation of a plurality of pieces of relevant result information, to obtain the relevant result statistical information; a comparator which is connected with the statistical module, compares the relevant result statistical information with the threshold value according to a first threshold value of the comparator, to obtain the velocity estimating result. The velocity estimating device and method applied in the invention can greatly reduce the space demand on the storing device in the estimating value process and greatly enhance the operating speed.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
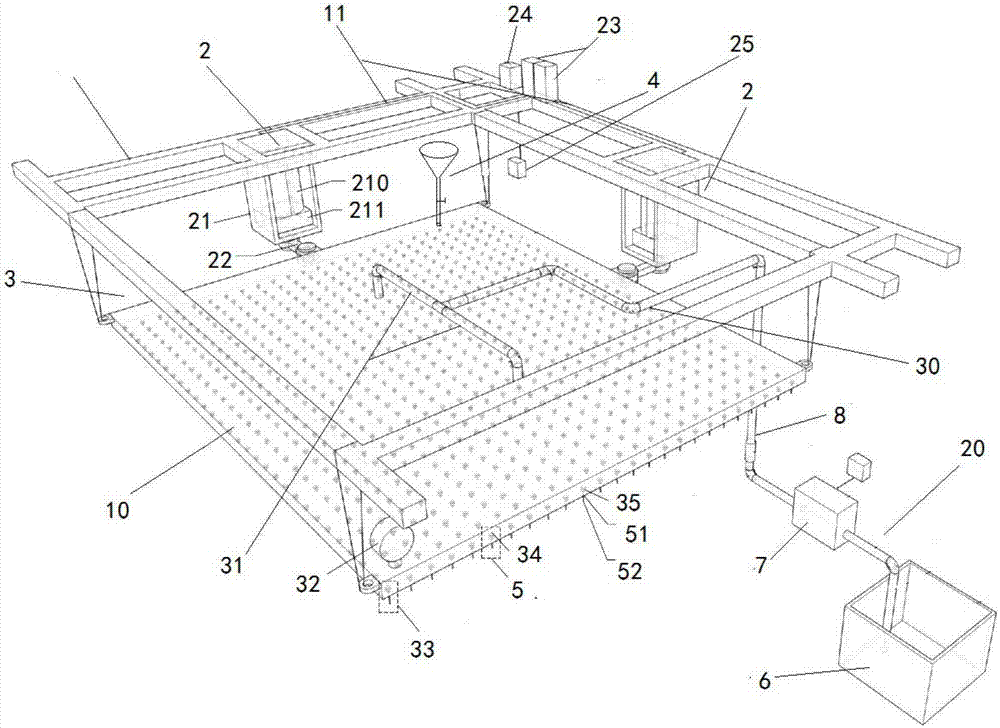
Indoor simulation system applied to pollutant migration process researches under artificial rainfall
InactiveCN103969419AHigh rainfall stabilityHigh similarityEarth material testingCollection systemControl system
The invention provides an indoor simulation system applied to pollutant migration process researches under artificial rainfall. The indoor simulation system can satisfy similarity conditions of the rainfall uniformity, the median raindrop diameter, the terminal velocity and the raindrop spectrum, can be directly used in the researches and stimulation of the migration process of soil (deposit)-water interface pollutants under the artificial rainfall conditions, and mainly includes a rainfall control system, a pollutant vertical transport simulation system and a sample collection system; and the above simulation device can be used as an experimental device for carrying out migration conversion and repair mechanism researches of pollutants in soil / sediment. The simulation device has the characteristics of strong practicability, high reliability, low cost, compact structure, convenient installation, demounting and replacement of parts, suitable simulation conditions, maneuverability and good application popularization value.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
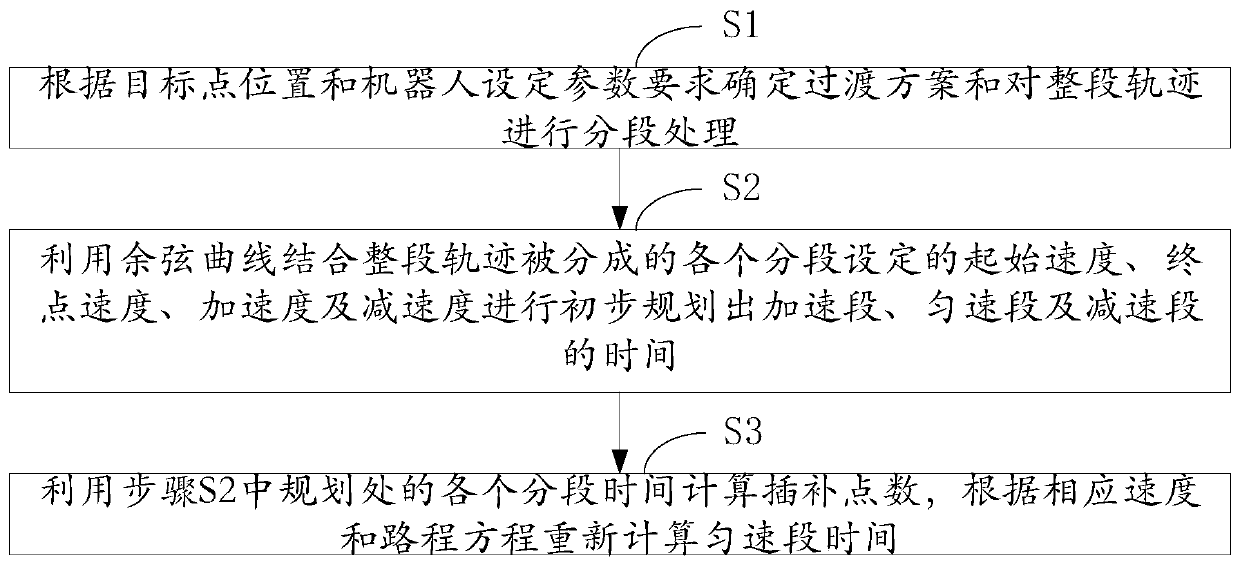
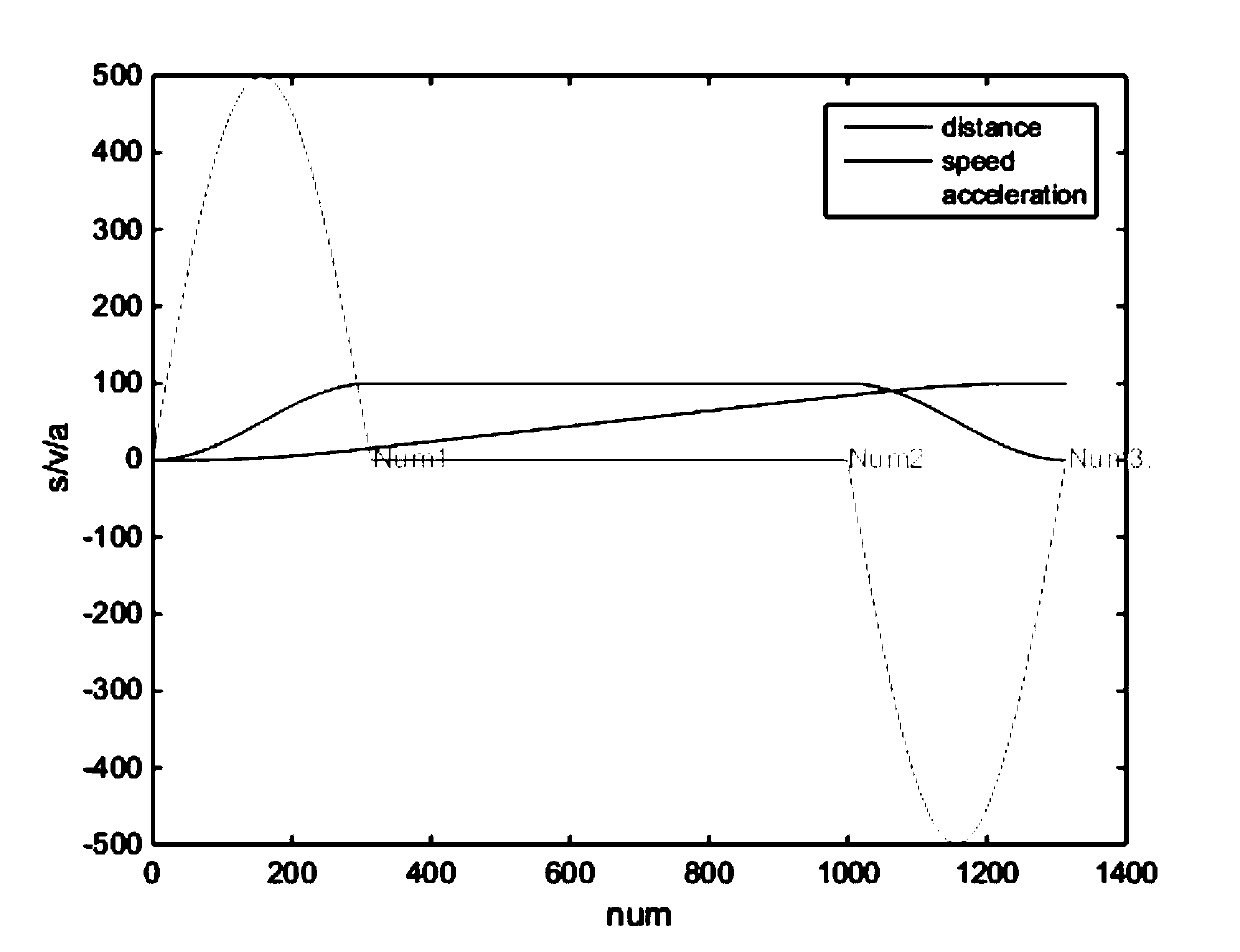
Cosine interpolation method of industrial robot under spatial linear movement
ActiveCN110147077APrevent high driving torqueTo prevent the phenomenon that the imputation cannot be completedProgramme controlComputer controlEquation of the centerThermal velocity
The invention is applied to the field of movement trajectory technology improvement, and provides a cosine interpolation method of an industrial robot under spatial linear movement. The method comprises the steps: 1, a transition scheme is determined according to the target point position and the robot setting parameter requirements, and segmentation processing is conducted on an overall trajectory; 2, times of an accelerating segment, a uniform velocity segment and a decelerating segment are preliminarily planned by combining a cosine curve with starting velocities, terminal velocities, accelerating velocities and decelerating velocities which are set for various segments obtained by segmenting the overall trajectory; and 3, the interpolation point number is calculated by means of the various segment times planned in the step 2, and the time of the uniform velocity segment is recalculated according to a corresponding velocity and journey equation. The various trajectory segments are interpolated by adopting the cosine curve interpolation method, not only does the accelerating velocities distributed in various intervals become smooth, but also the accelerating velocities become smooth.
Owner:SHENZHEN COLIBRI TECH
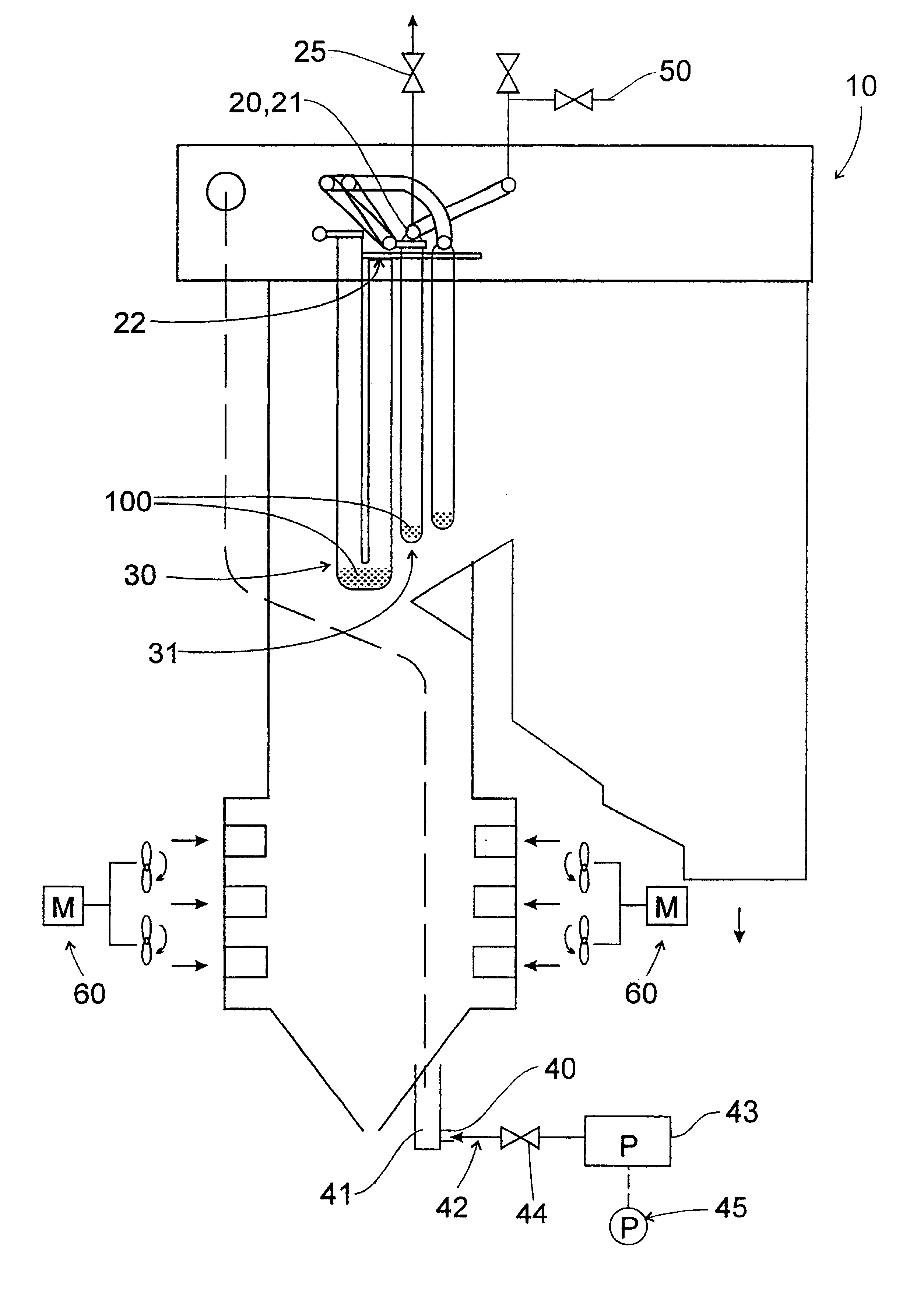
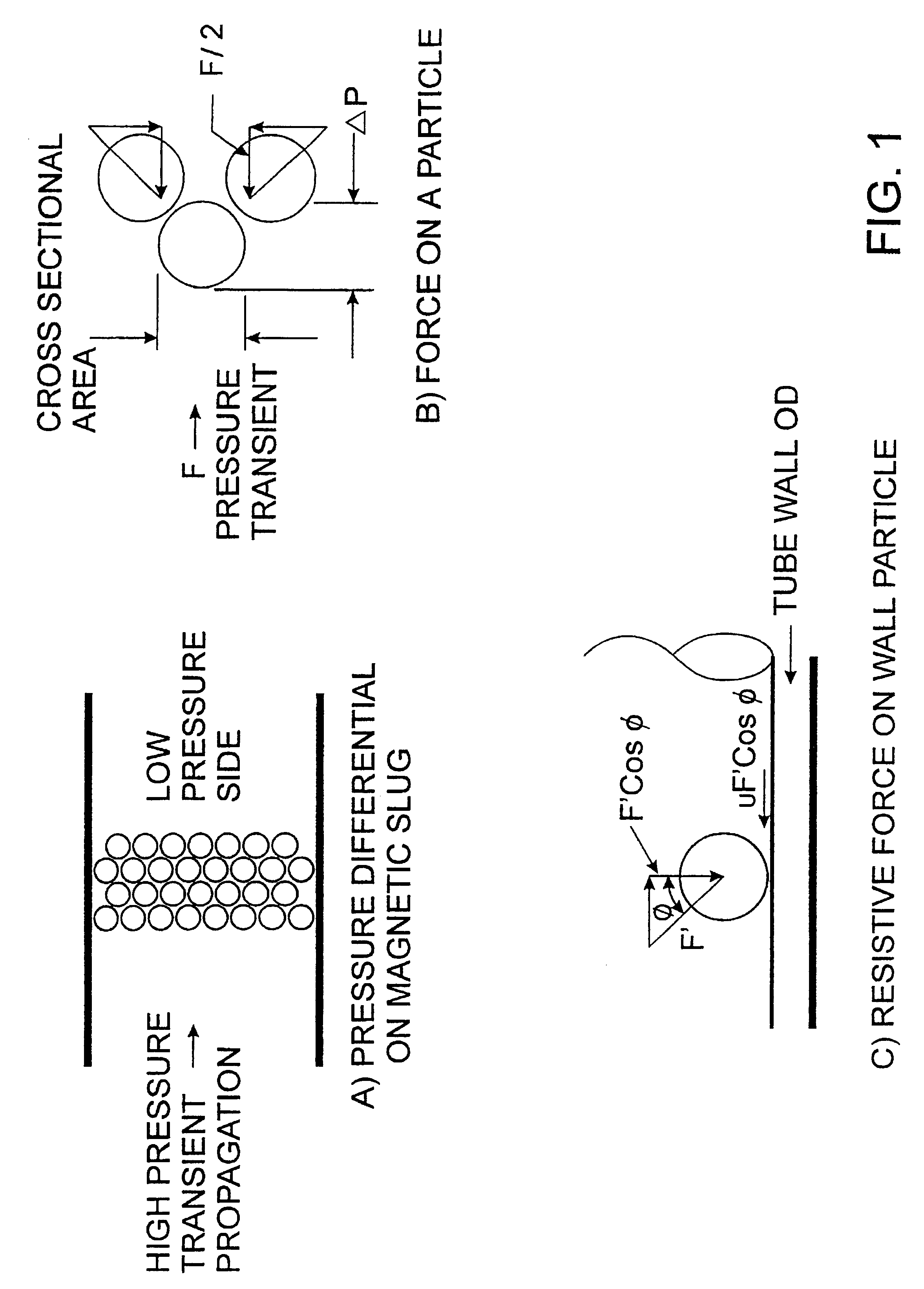
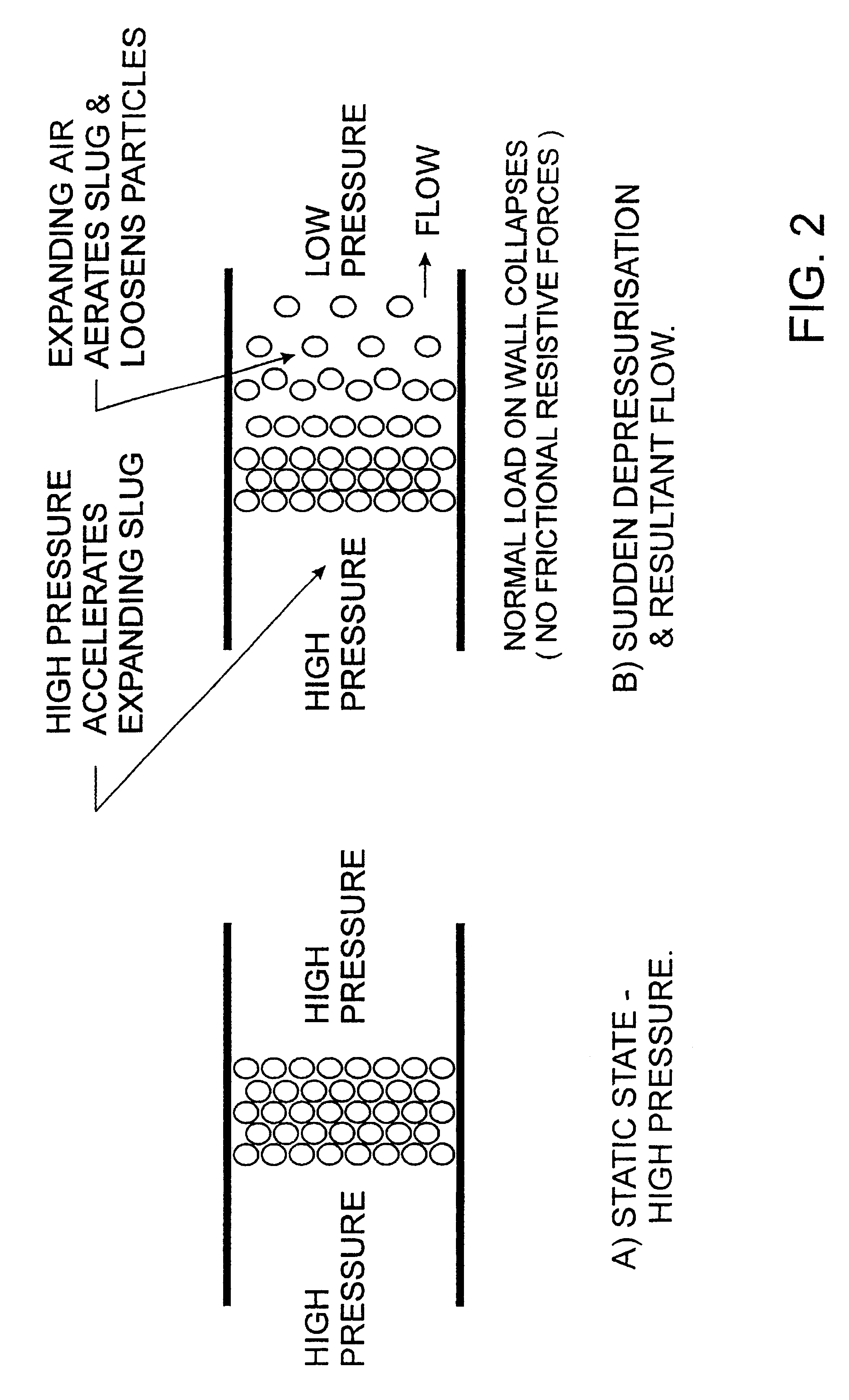
Exfoliated magnetite removal system and controllable force cooling for boilers
InactiveUS6523502B1Rapidly and controllably coolMinimal capital costBoiler cleaning apparatusMachines/enginesMagnetiteProduct gas
A method of controllable cooling of a boiler (10) and removing exfoliated magnetite from the boiler tubes (30, 31) employs flowing dry gas through the boiler tubes (30, 31) at a flow velocity above the terminal velocity of the magnetite flakes as the boiler (10) is cooled from a temperature above the temperature at which exfoliation occurs. A method of removing magnetite blockages (100) from boiler tubes (30, 31) is also disclosed.
Owner:CS ENERGY
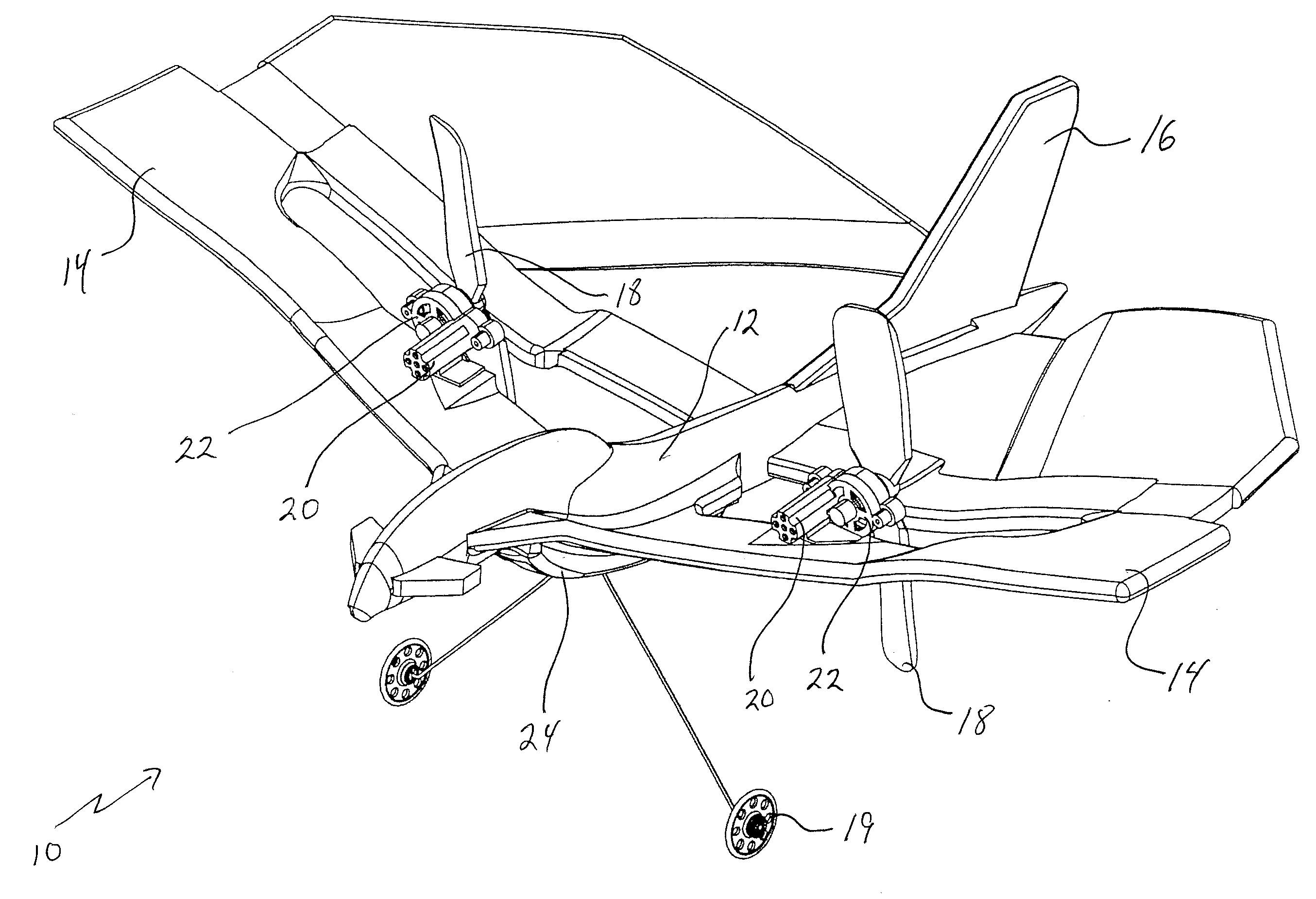
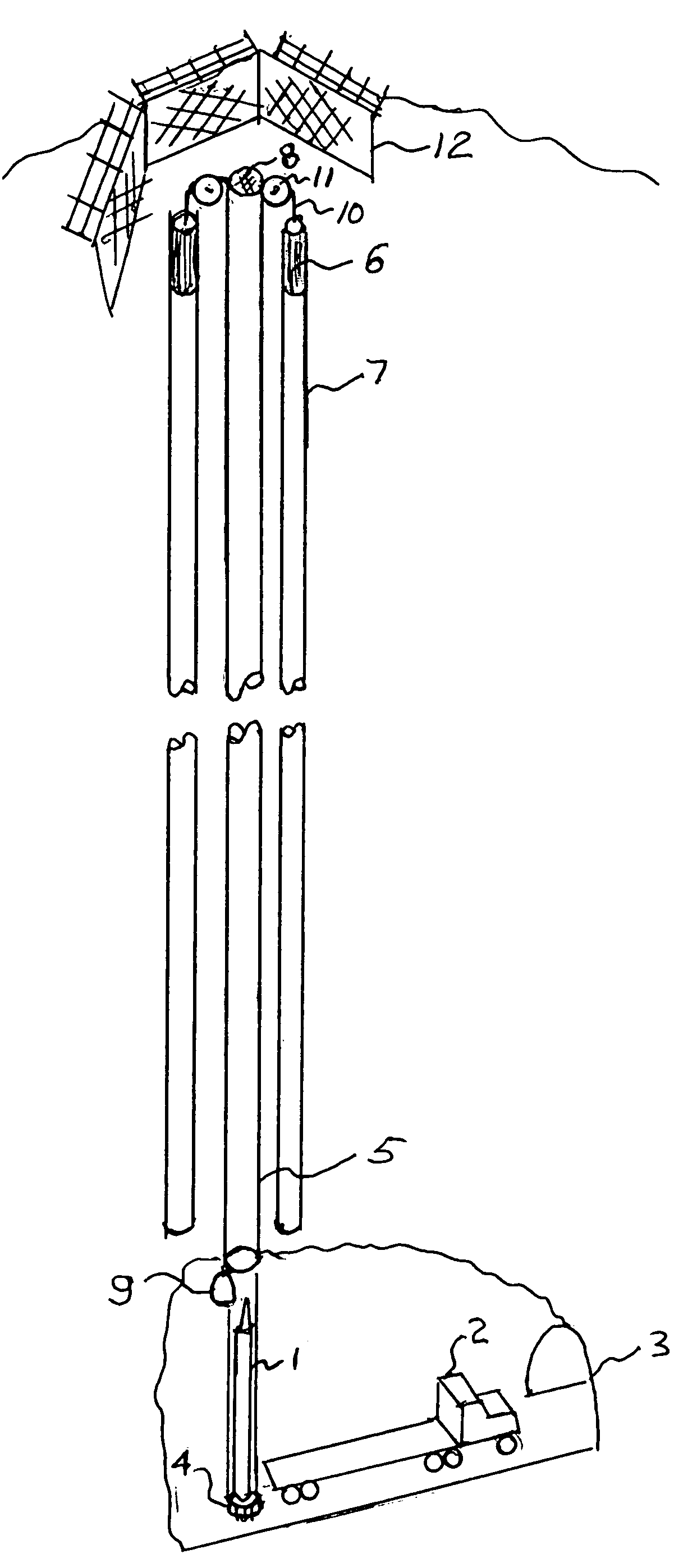
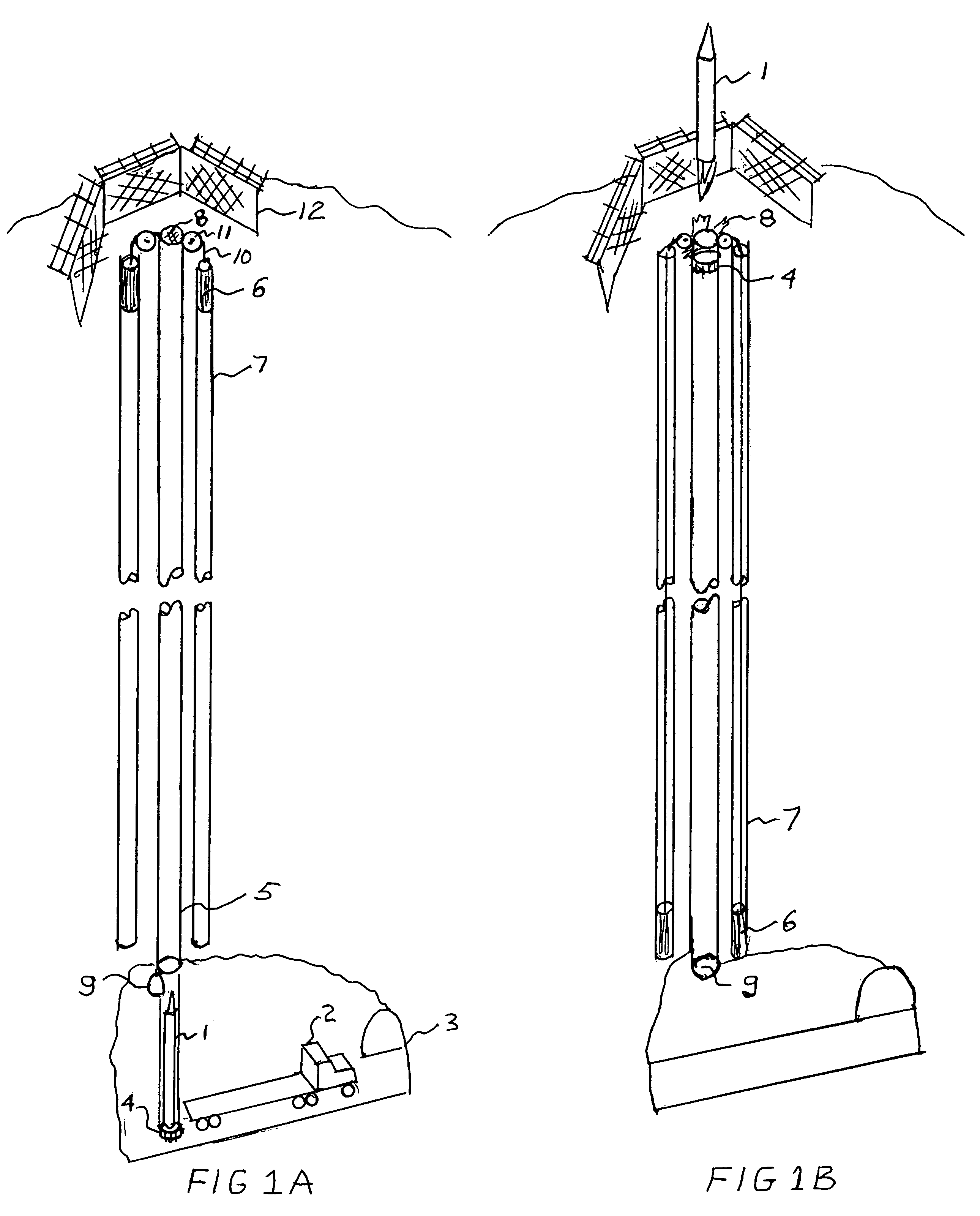
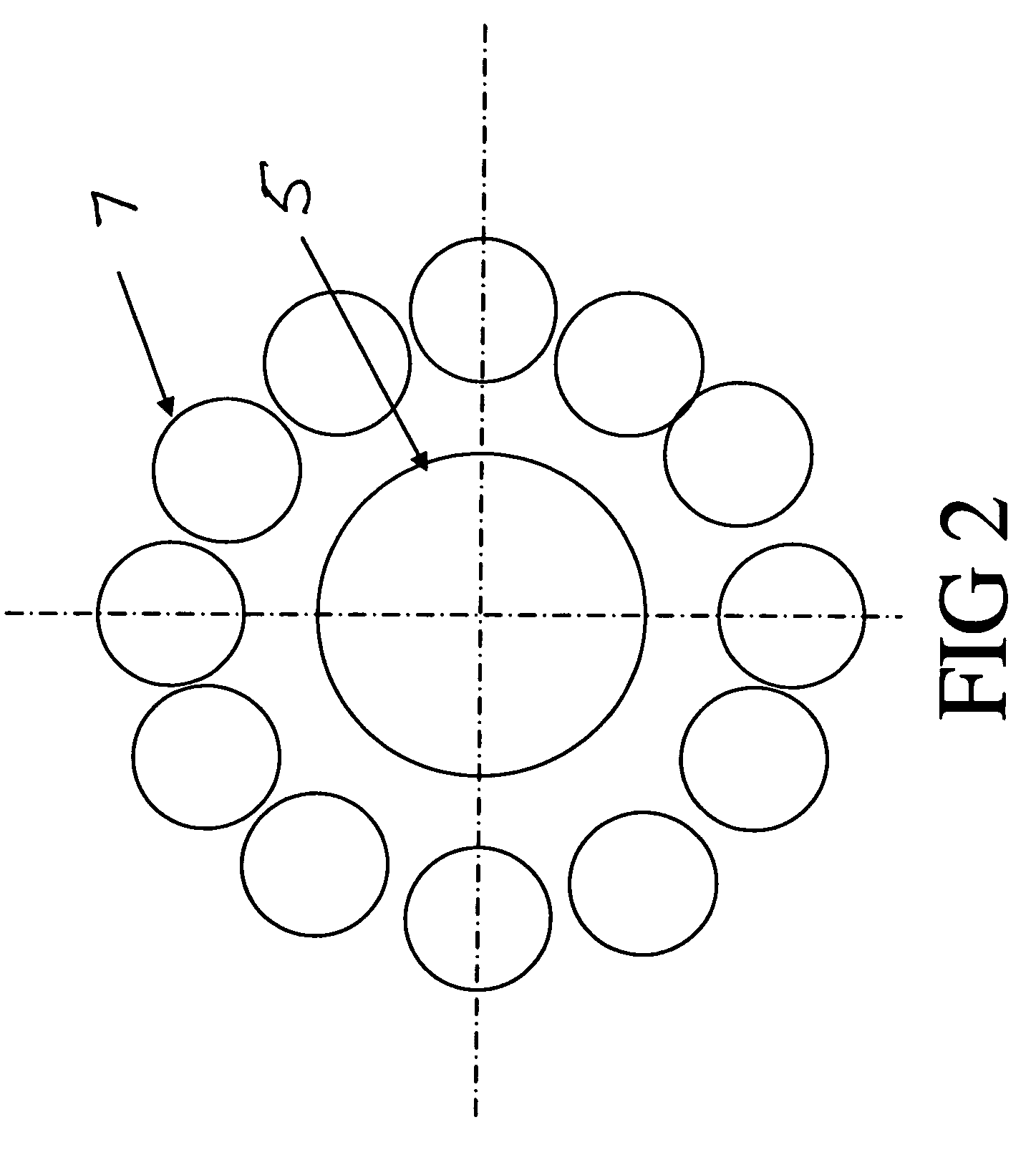
Counterweight based rocket launch platform
A counterweight based rocket launch platform system and method uses gravity acting upon a counterweight to provide the initial assent for a rocket. This counterweight system is preferably built inside of a mountain so as to use the mountain as the supporting structure. By covering the exit opening with a thin membrane and closing the bottom, the system can have the air evacuated providing a free ascent without a terminal velocity. During the final moments of the ascent or after the rocket leaves the tube, the rocket will ignite carrying the payload into space. The velocity imparted to the rocket from the gravity assist in combination with bypassing the thickest part of the atmosphere will lower the amount of fuel required to lift payloads into space. This will result in increased payloads of existing rockets or the use of smaller and less expensive rockets.
Owner:WATTS KEITH PETER
Action rate control system
An action rate control system for a gas operated firearm that includes an action sleeve and an action rate control cylinder. The action sleeve moves in a rearward direction in response to a volume of combustion gases that are generated during firing of the firearm and diverted from the barrel of the firearm through gas ports. The action rate control cylinder is connected to the action sleeve by a linkage that controls movement and slowing of the action sleeve as it approaches a rear limit for its movement. The resistance force generated by the rate control cylinder is a function of the velocity of the action sleeve during its movement. In another aspect, a gas operated firearm includes a barrel, a bolt assembly, an action system coupled to the bolt assembly, and a rate control cylinder coupled to the action system. The action system includes a sleeve assembly that is driven by a volume of combustion gases that are diverted from the barrel when a round of ammunition is fired. The rate control cylinder controls a terminal velocity of the sleeve assembly being driven by the volume of combustion gases. A resistance force generated by the rate control cylinder is a function of the velocity of the bolt assembly during the bolt assembly's rearward movement. The velocity of the bolt assembly follows a controlled and gradual reduction as the energy load associated with the firing is absorbed by the rate control cylinder.
Owner:REM TML HLDG LLC
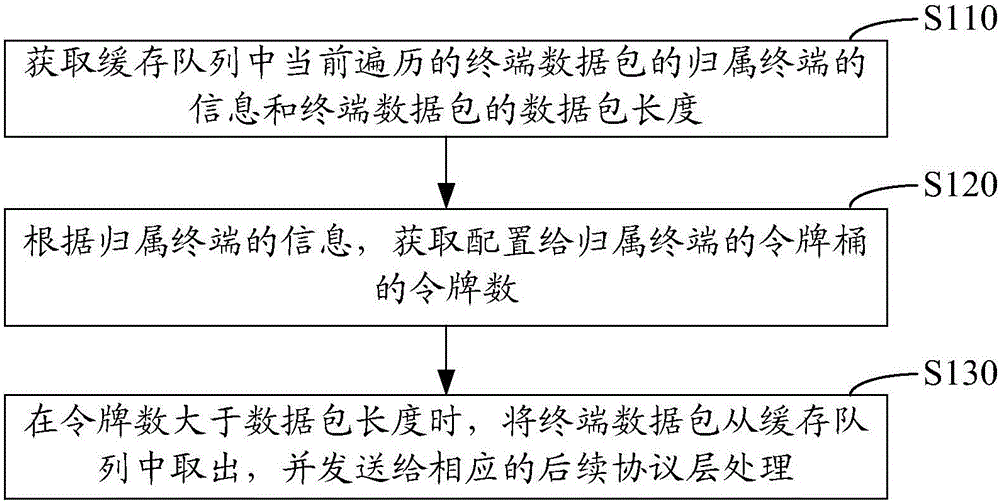
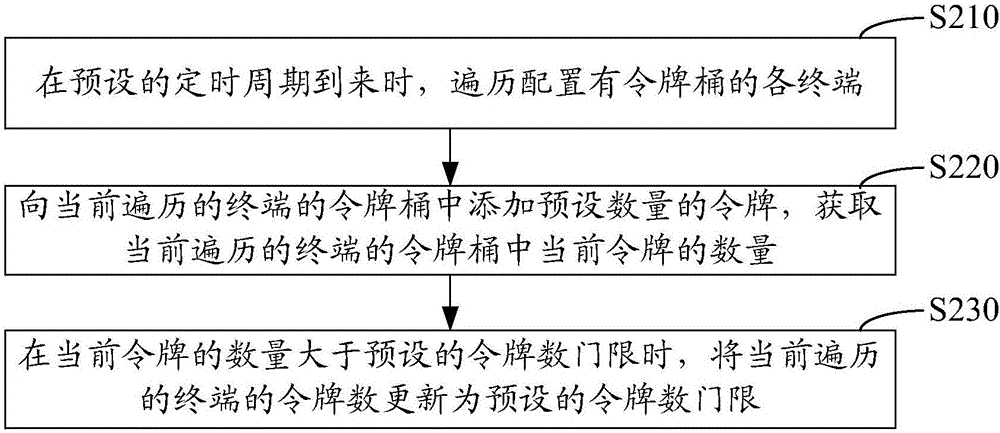
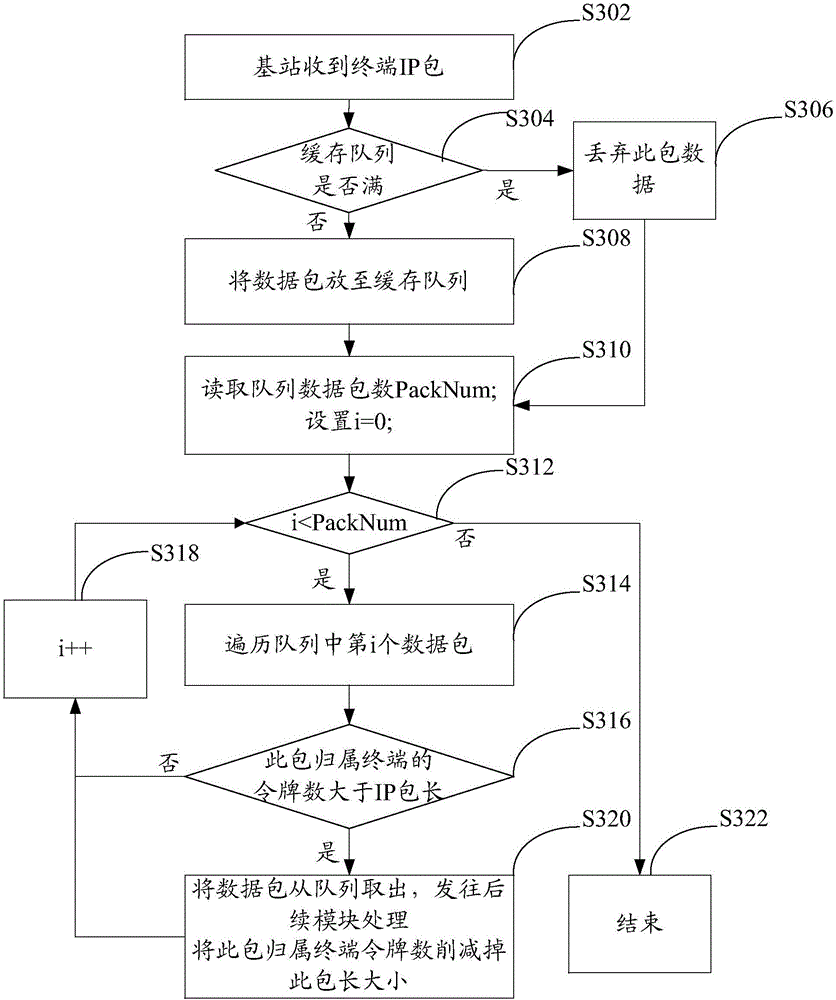
Terminal velocity control method, terminal velocity control device and terminal velocity control base station
ActiveCN106413002AEasy to useSave transmission bandwidthNetwork traffic/resource managementComputer terminalProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
The invention relates to a terminal velocity control method, a terminal velocity control device and a terminal velocity control base station. The terminal velocity control method comprises the following steps: getting the information of a home terminal of a currently traversed terminal data packet in a cache queue and the data packet length of the terminal data packet; getting the token number of a token bucket configured to the home terminal according to the information of the home terminal, wherein the token number is configuration data obtained by updating the number of tokens in the token bucket on the arrival of a preset timing cycle; and when the token number is greater than the data packet length, taking the terminal data packet out from the cache queue, and sending the terminal data packet to a corresponding follow-up protocol layer for processing. The method is based on re-optimization of a token-controlled base station internal protocol (GTP). The sending of data of a user of which the transmission rate overruns and the number of tokens is insufficient is postponed until the number of tokens is enough, and the overrun rate peak of the terminal is limited.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
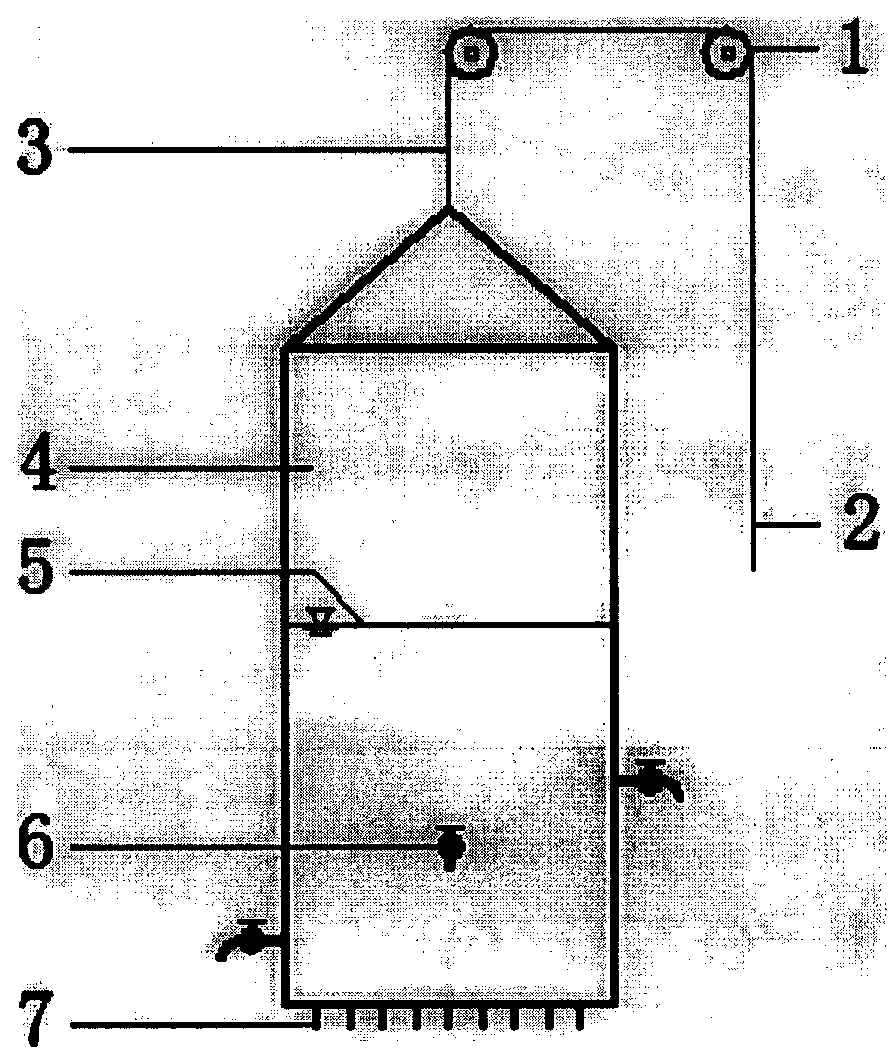
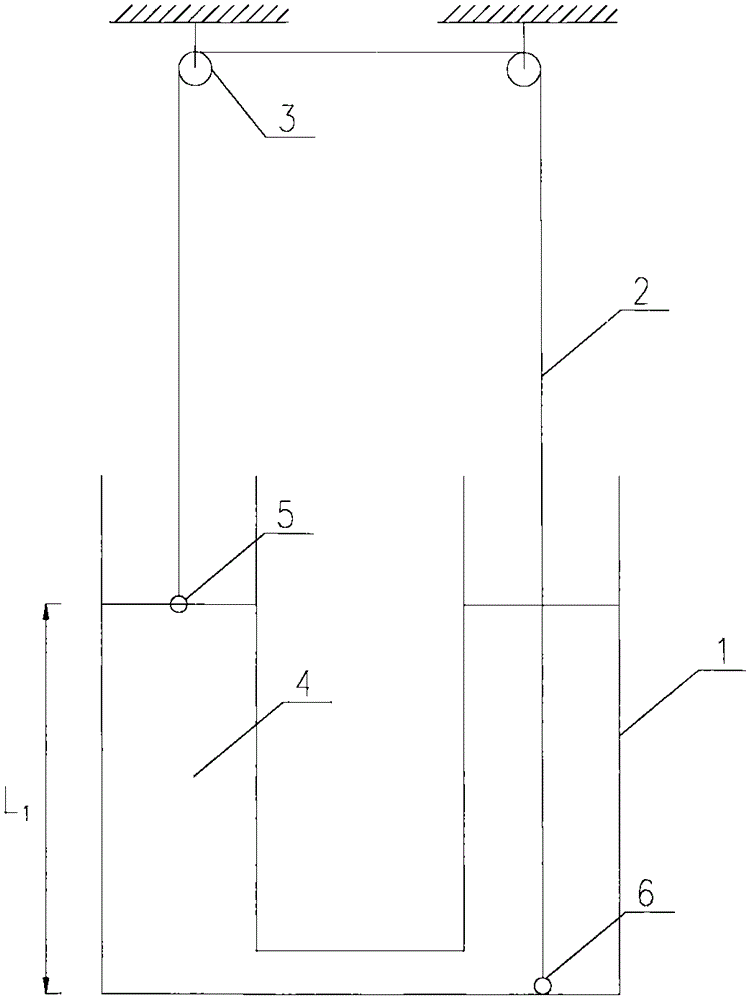
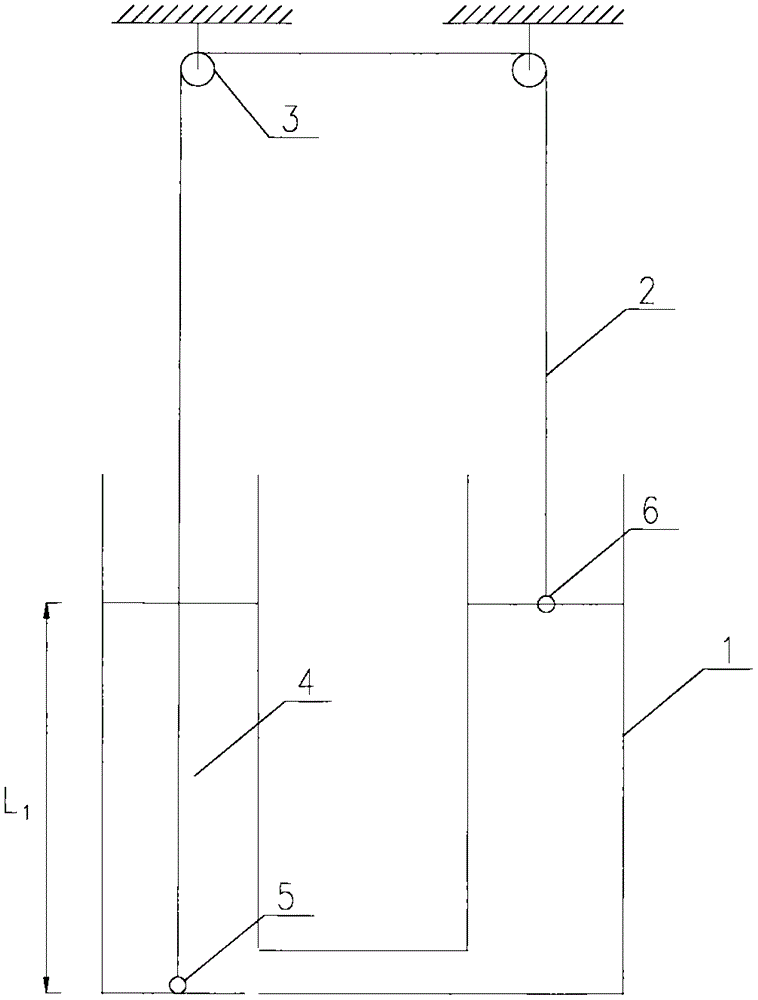
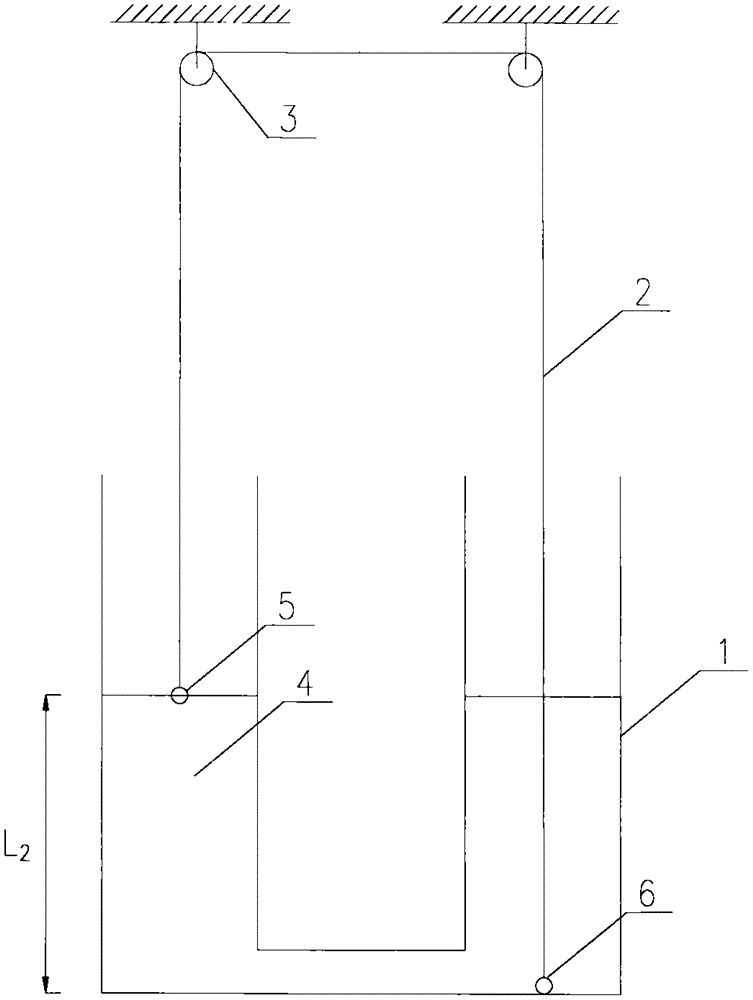
Experimental device and method for measuring liquid viscosity coefficient through U-shaped tube
InactiveCN105606491AControl the falling speedAccurate measurement of viscosity coefficientFlow propertiesLiquid densityExperimental methods
The invention discloses an experimental device and method for measuring a liquid viscosity coefficient through a U-shaped tube. The experimental device is composed of the U-shaped tube, a thin filament, a pulley block, a driving small ball, a driven small ball and experimental liquid. By analyzing the linkage movement of the two small balls connected to the two ends of the thin filament on the two sides of the U-shaped tube, and the liquid viscosity coefficient is obtained under the condition that the liquid density is not precisely measured and buoyancy is not calculated. According to the experimental method, by means of the stress of the small balls in the balanced state and the Stokes formula, the relation between the liquid viscosity coefficient and the terminal velocity of the small balls is acquired. The experimental method further includes the step that by changing the liquid level height, measuring the terminal velocity of the small balls and changing the average density of the driven small ball, the Reynolds number of the viscosity coefficient is corrected. The experimental device and method are clear in principle, equipment is simple, operation is fast, the falling speed of the driving small ball is effectively controlled by arranging the driven small ball, and the experimental device and method are suitable for measuring the liquid viscosity coefficient of small-viscosity liquid and are also suitable for physical experiment teaching.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Co-deployed optical referencing for responsive dust-based sensing system
ActiveUS20060262299A1High light reflectivityPromote absorptionPhotometry using reference valueWave based measurement systemsEngineeringRetroreflector
Apparatus and methods for calibrating an optical detector. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention provides a reference that includes a body and a surface of the body. At least a portion of the surface has a reflectance that can vary. The reference is adapted to be deployed with a cloud of optical sensors and has a terminal velocity that is about the same as the terminal velocity of the sensors. Further, the variation of the reflectance can be caused by a rotation of the reference (caused by an aerodynamic member) or by a controller that controls an electo optic material of the surface. In a preferred embodiment, the sensors are porous silicon optical sensors and the reference includes a retroreflector. The invention also provides a method of referencing an optical signal. The method includes deploying a reference with a cloud of sensors and detecting a variation in its reflectance.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
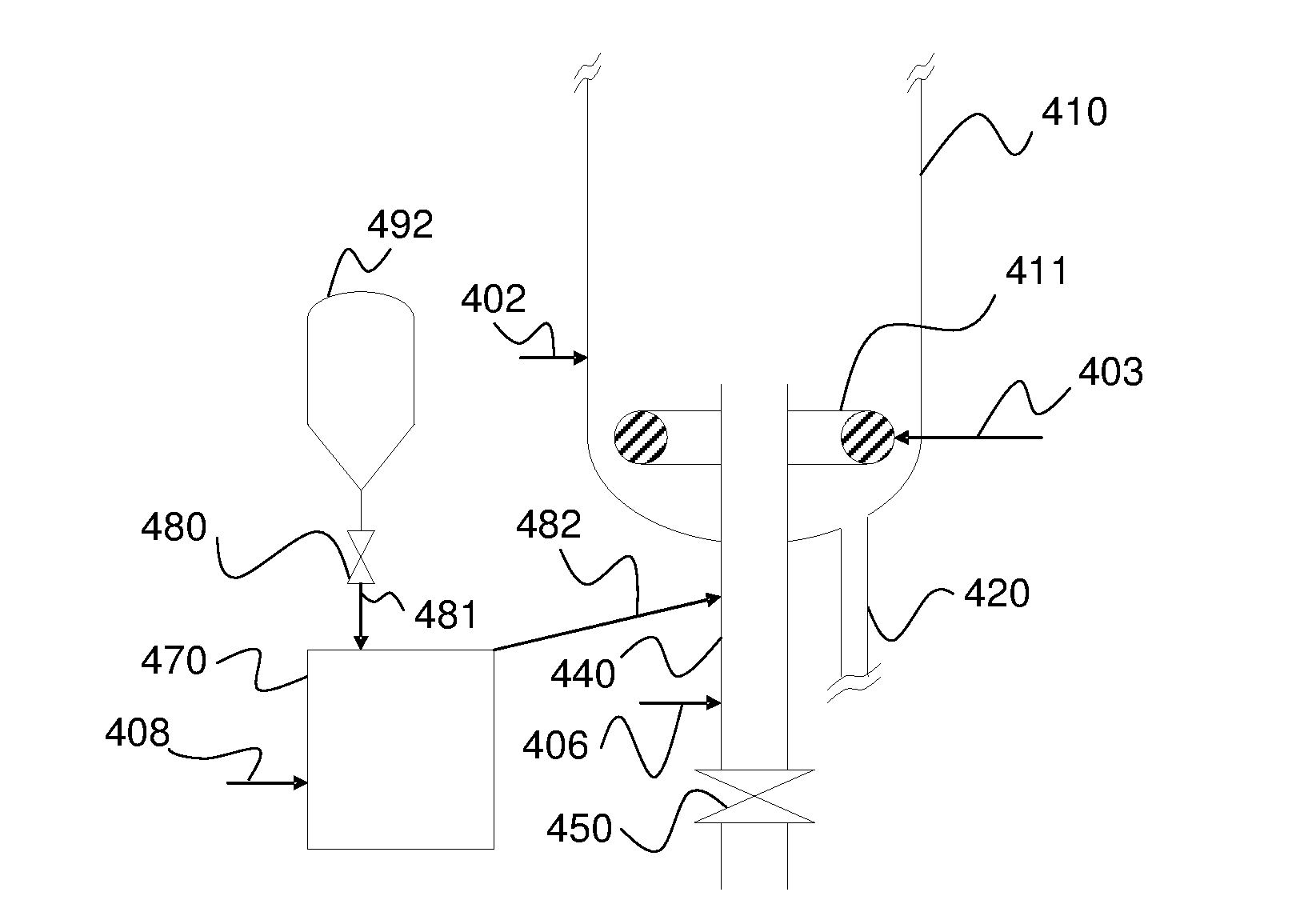
Method and plant for redox chemical looping combustion of a solid hydrocarbon feedstock
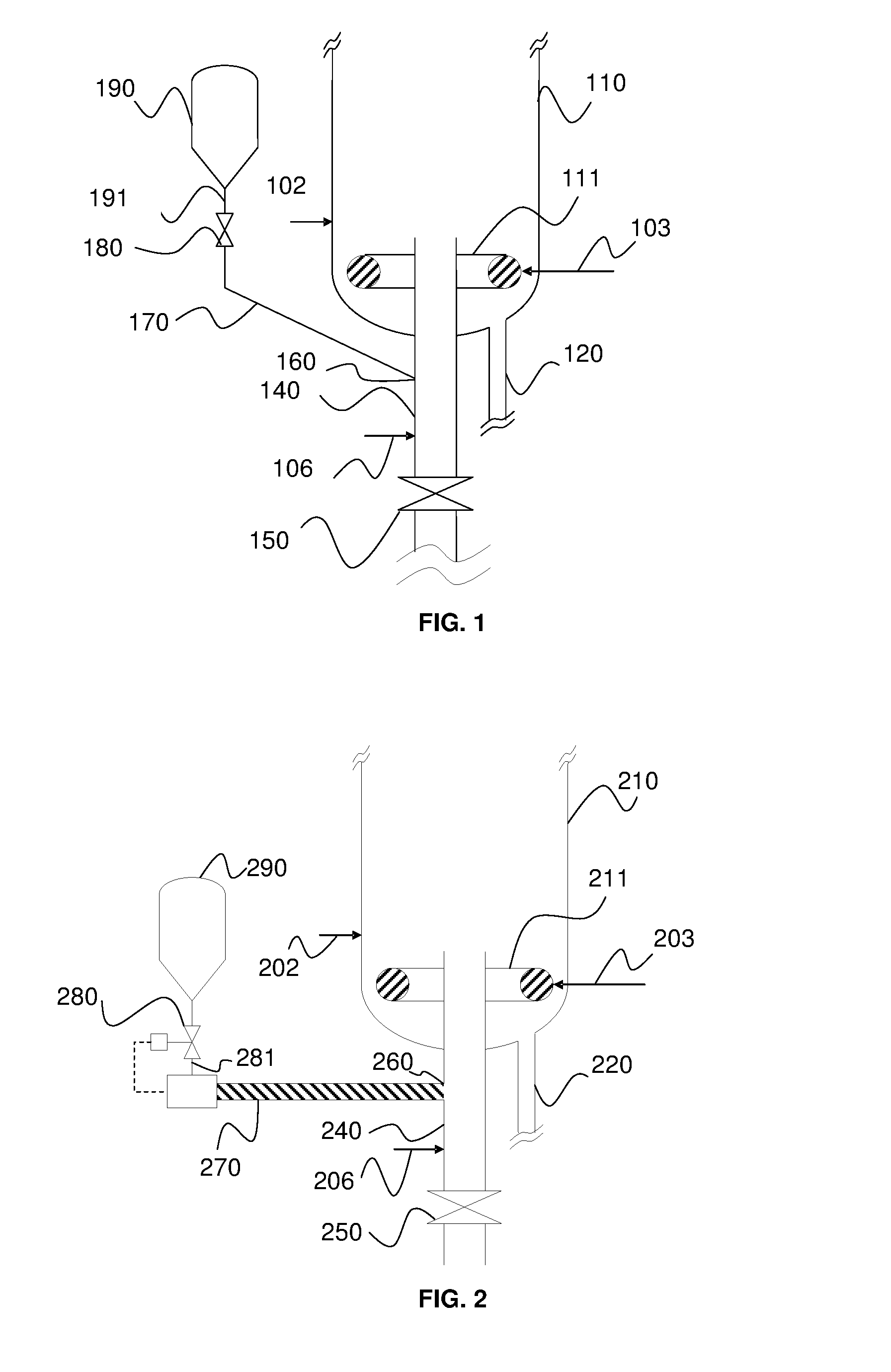
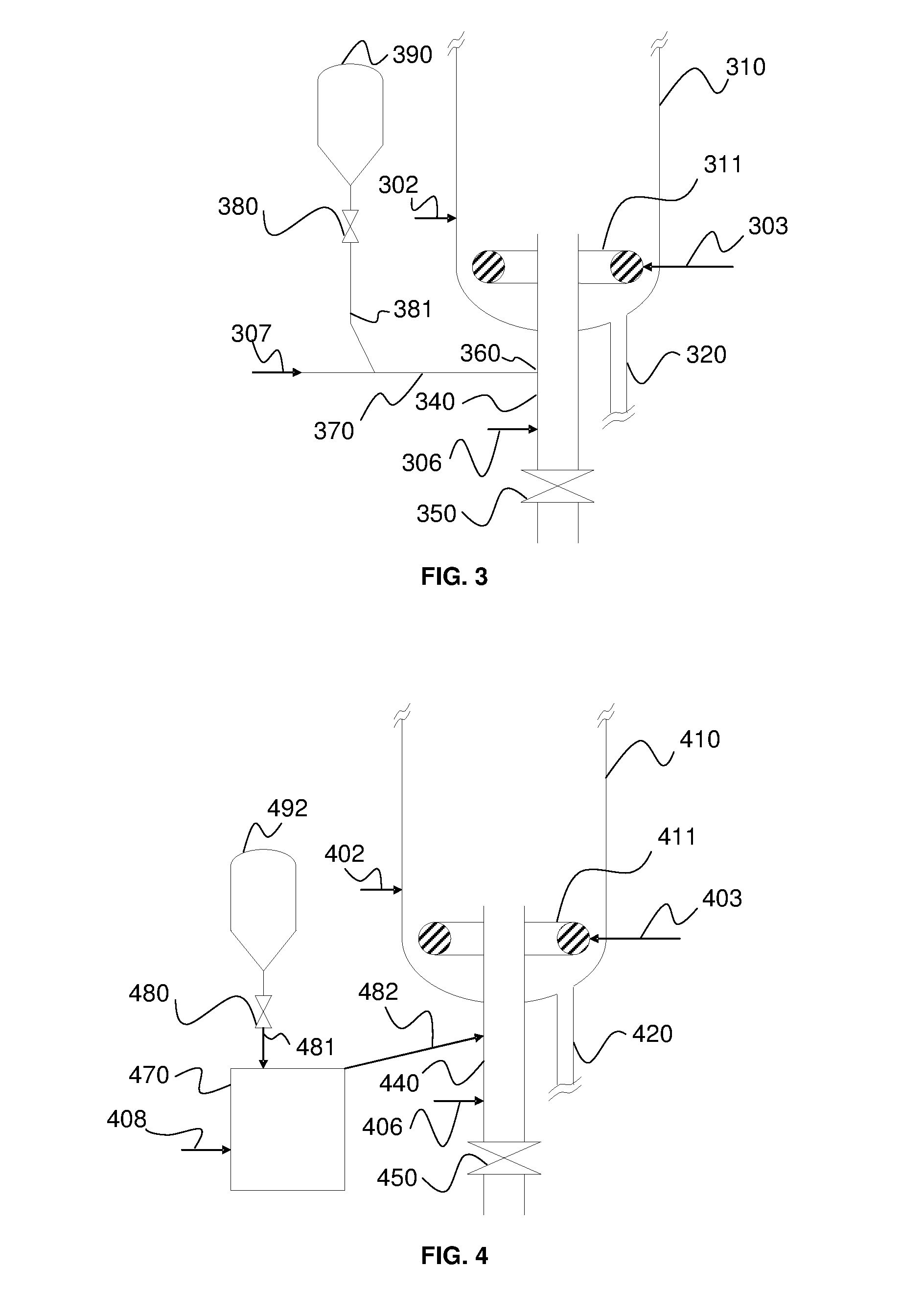
ActiveUS20160146456A1Good dispersionReduce stepsFluidized bed combustionFurnace componentsOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
The invention relates to a method and to a device for chemical looping combustion CLC of a solid hydrocarbon feed wherein it is proposed to inject the solid hydrocarbon feed so as to limit any occurrence of sticking of the feed to the walls of the injection device. The solid feed is fed into a conveying zone operating under fluidized bed conditions and opening into a combustion reactor. A fluidization gas is injected into this conveying zone while controlling the flow of gas in such a way that the superficial velocity of the gas in the conveying zone is higher than the terminal velocity of the solid hydrocarbon feed particles and the terminal velocity of solid particles present in the combustion reactor, and while controlling the fluidization gas temperature in such a way that the temperature in the conveying zone is less than or equal to 500° C.
Owner:TOTALENERGIES ONETECH +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com