Patents
Literature
440 results about "Fuze" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
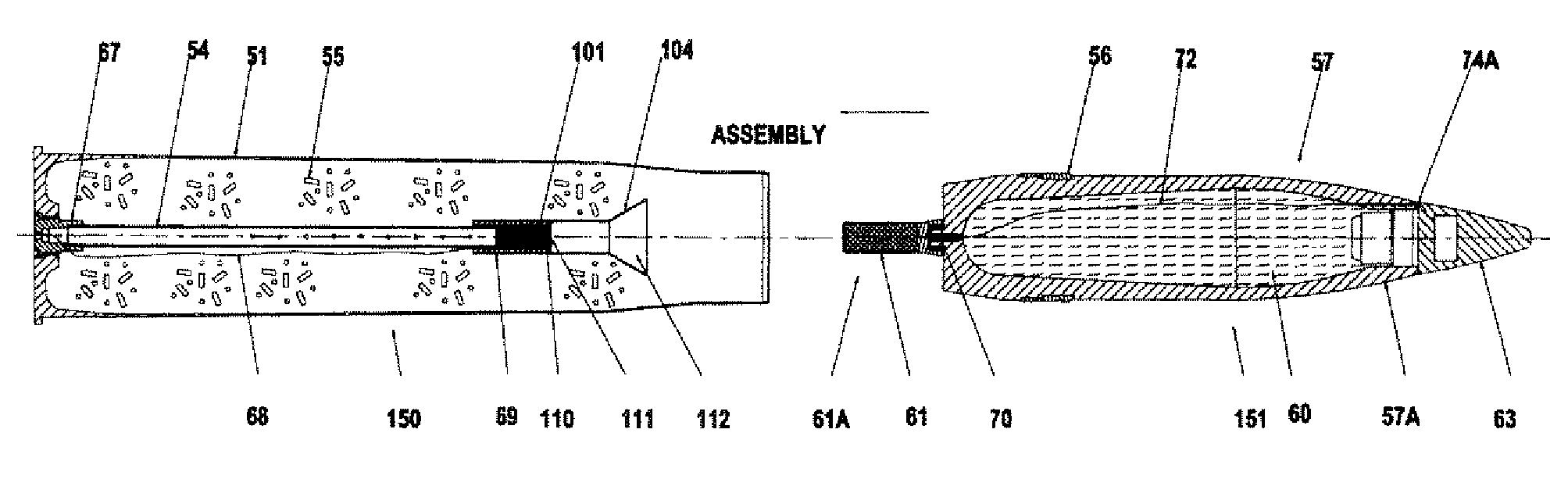
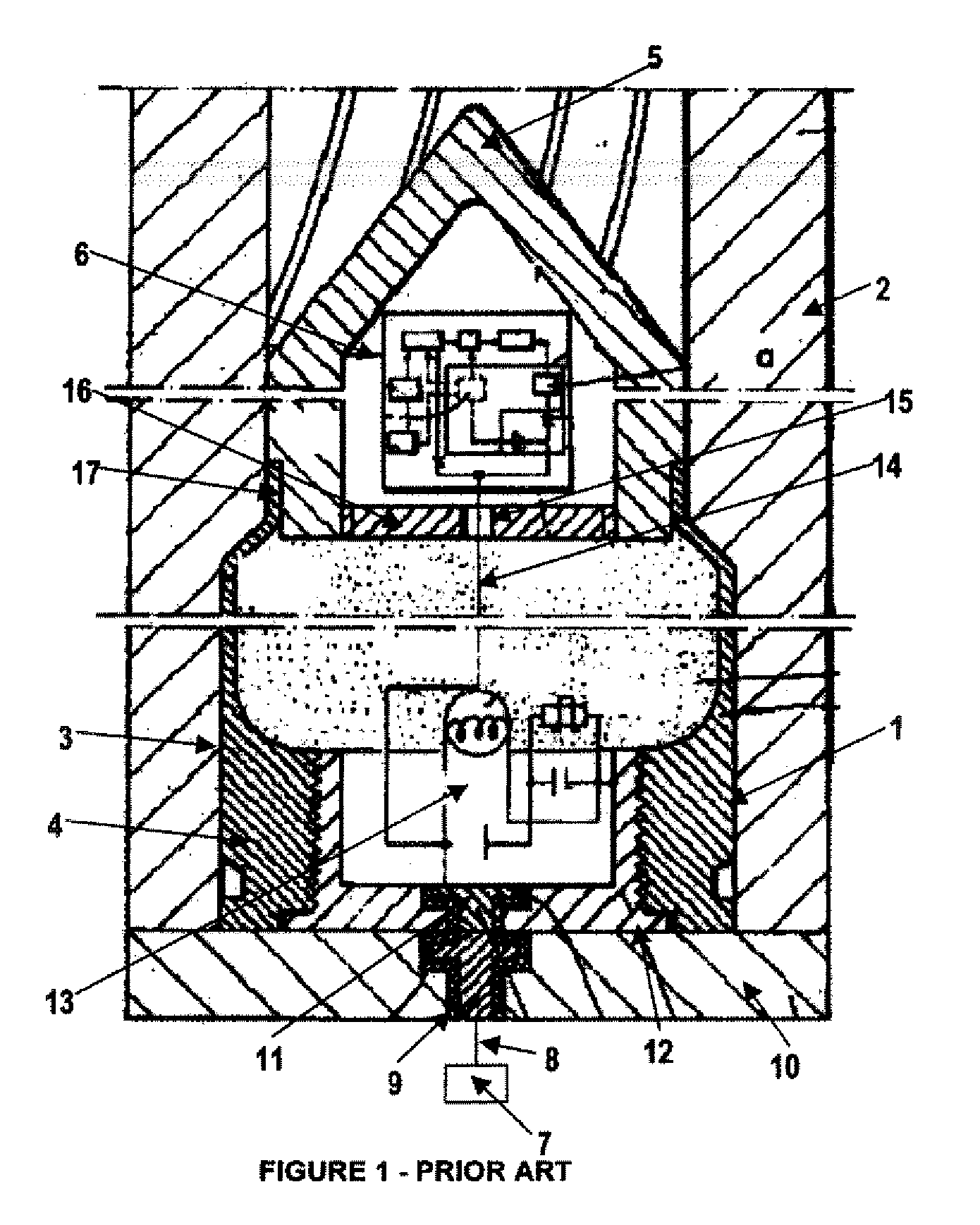
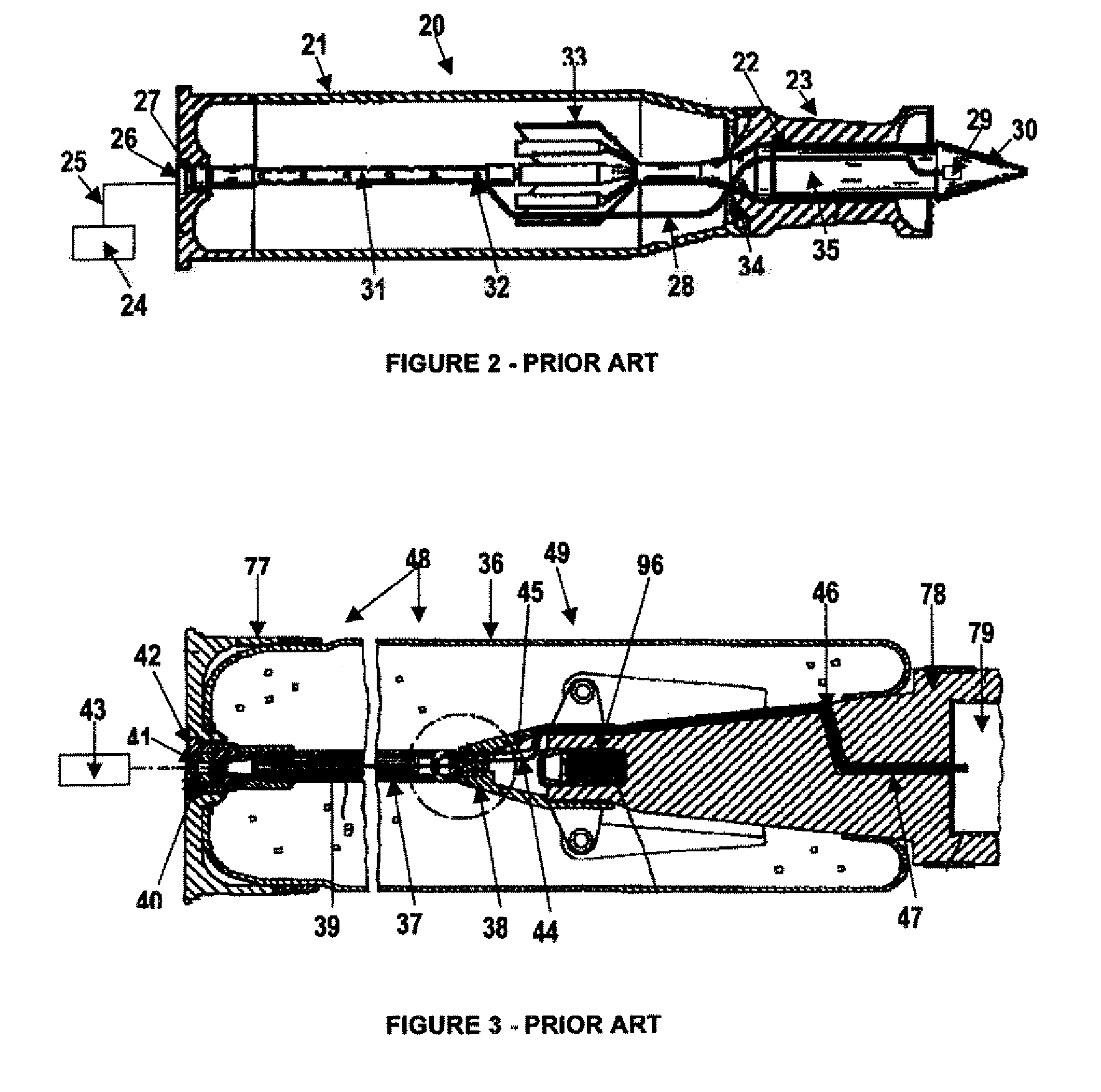
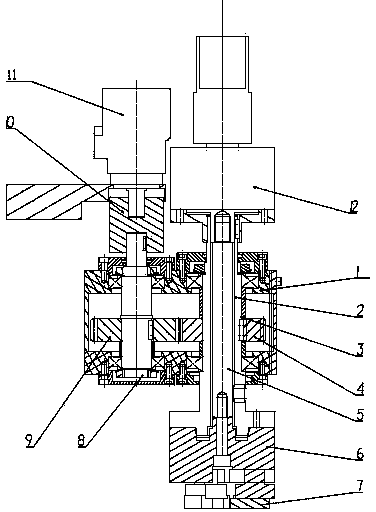
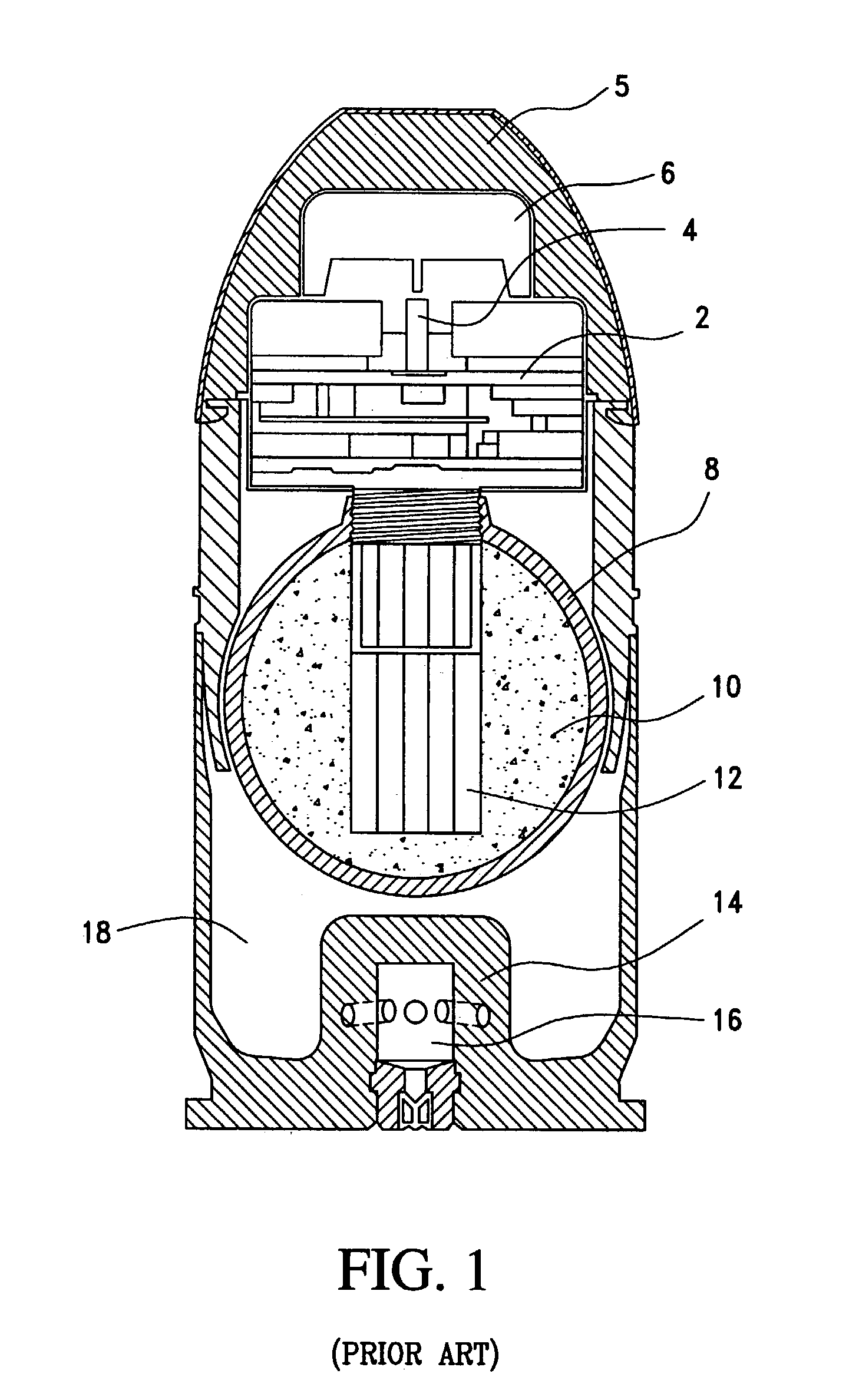
In military munitions, a fuze (sometimes fuse) is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams.
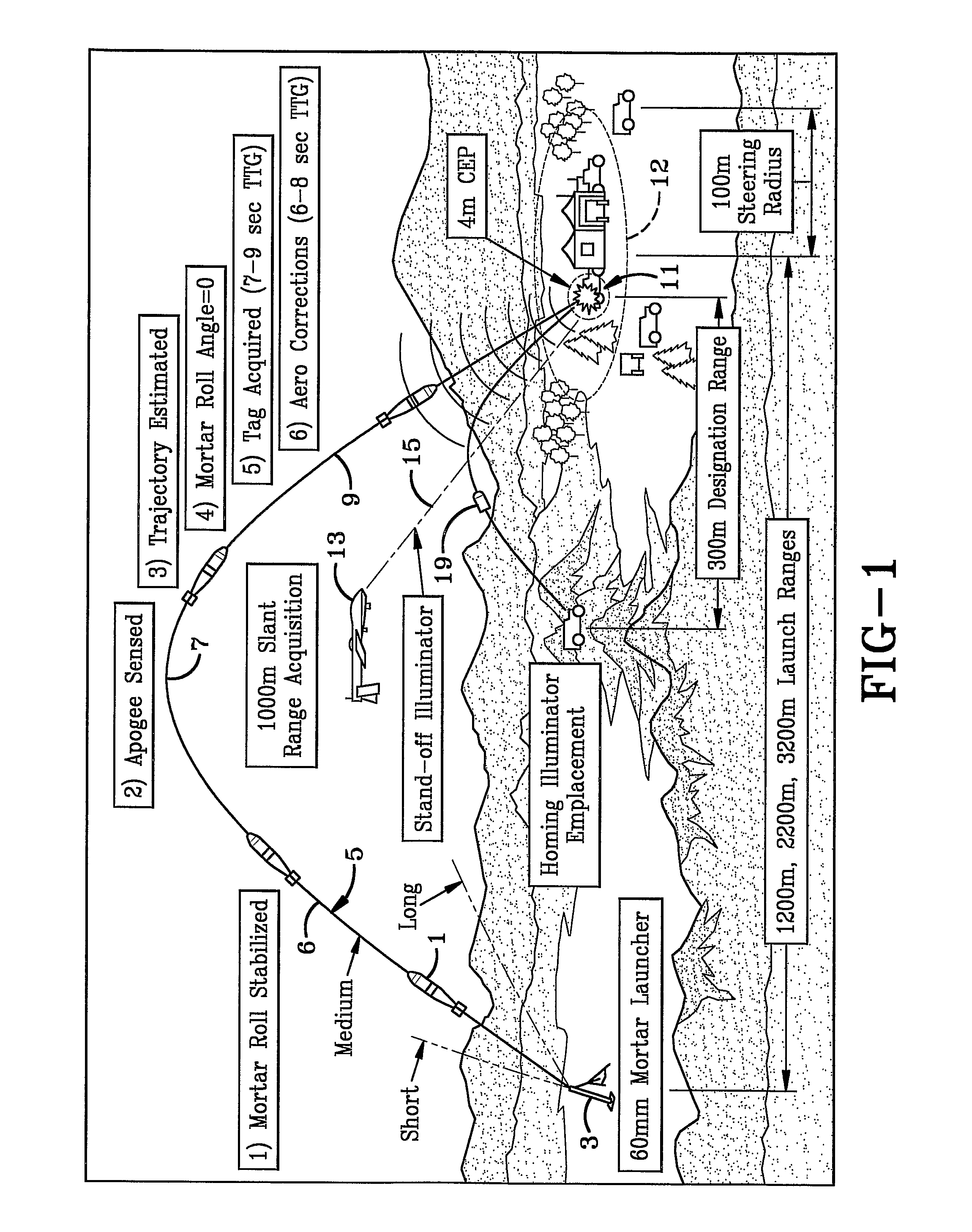
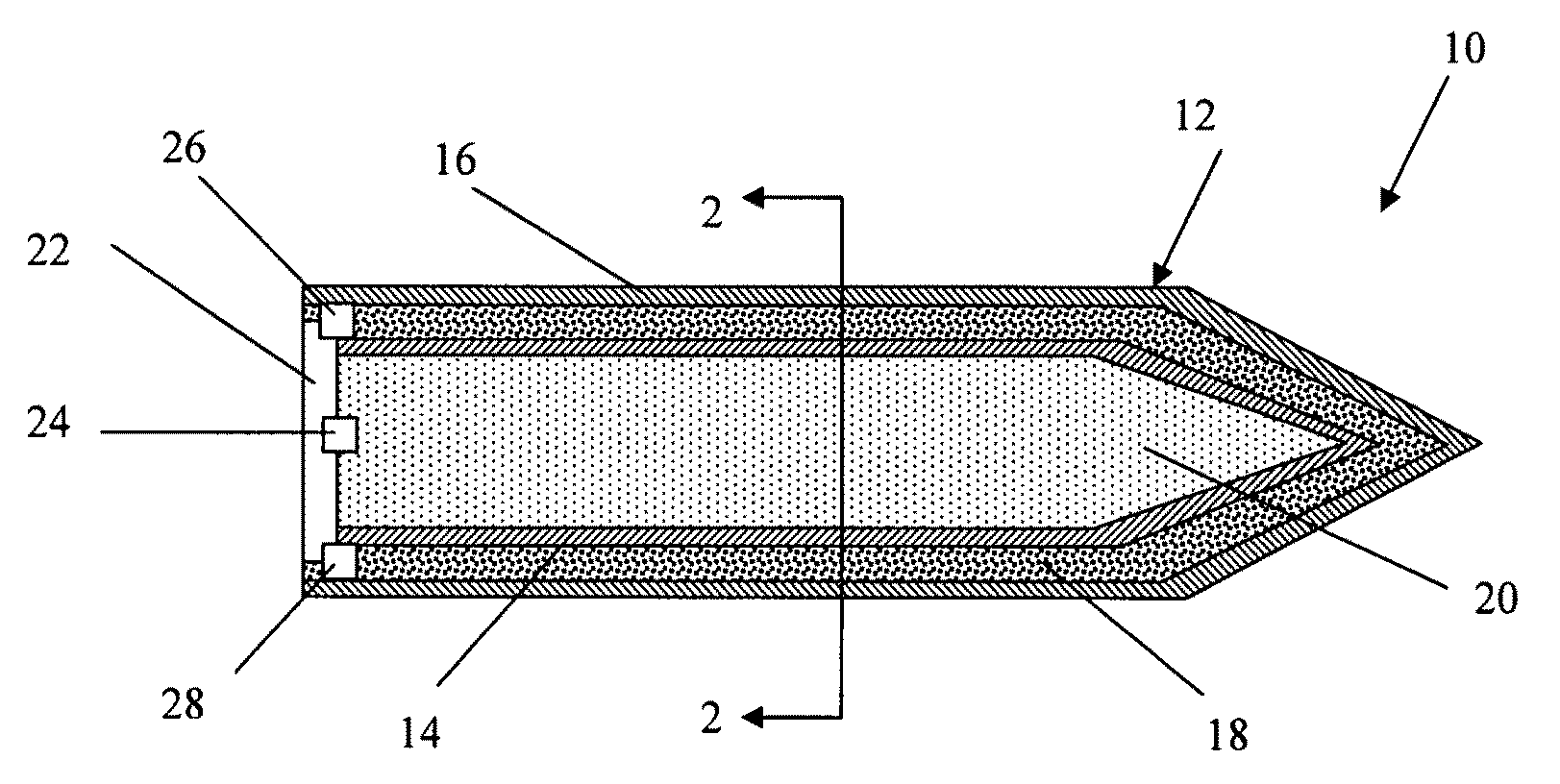
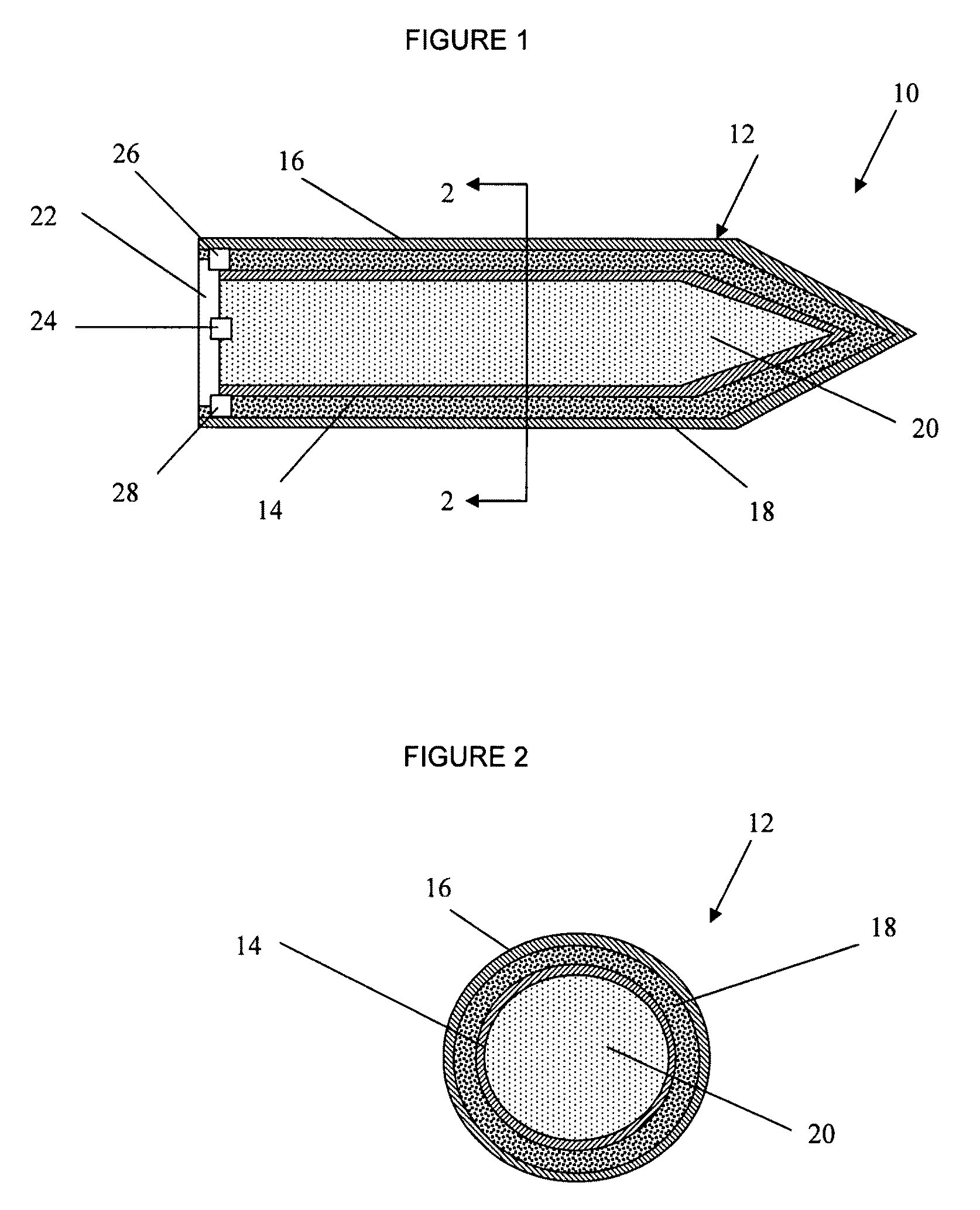
Imaging-infrared skewed-cone fuze
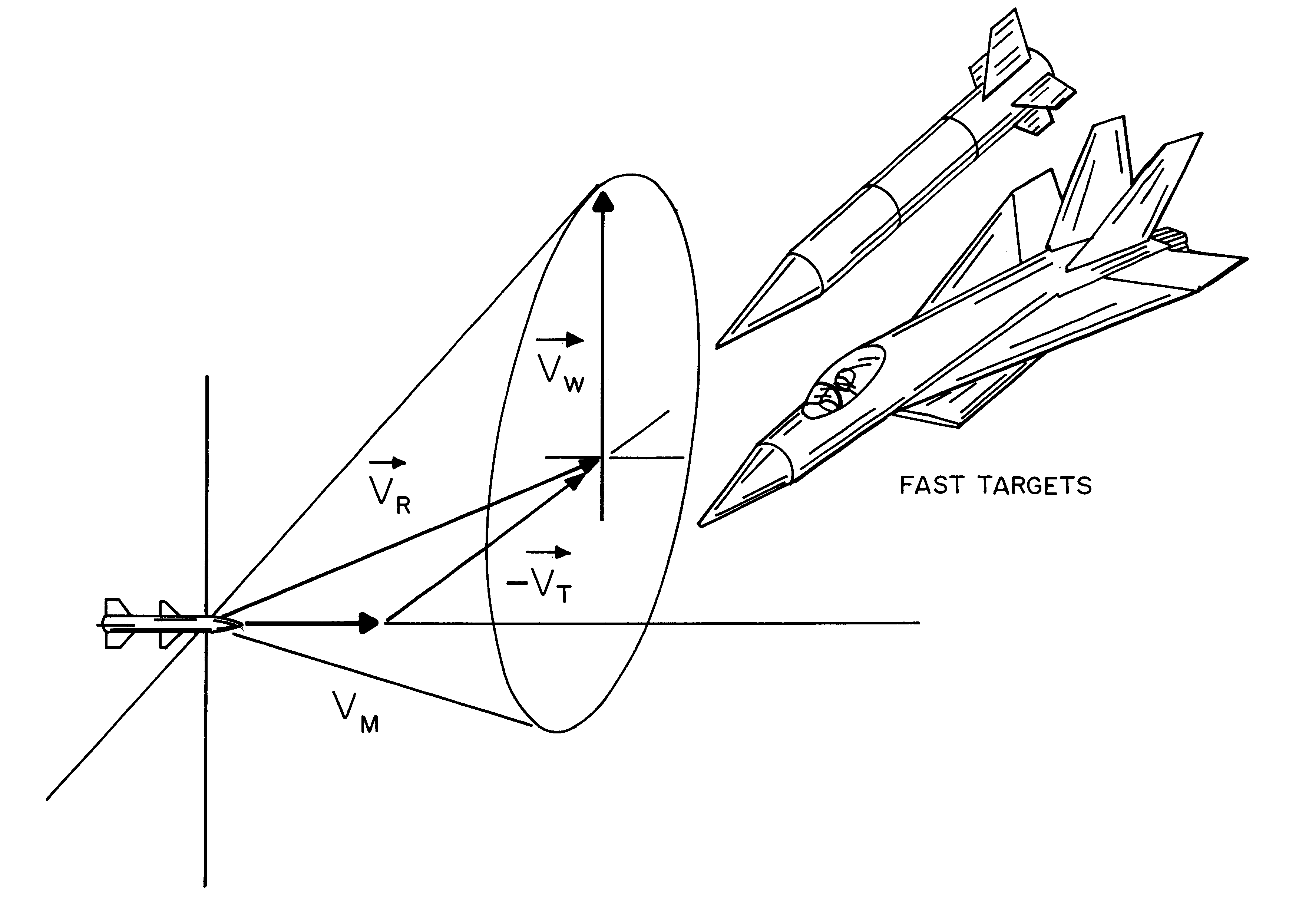
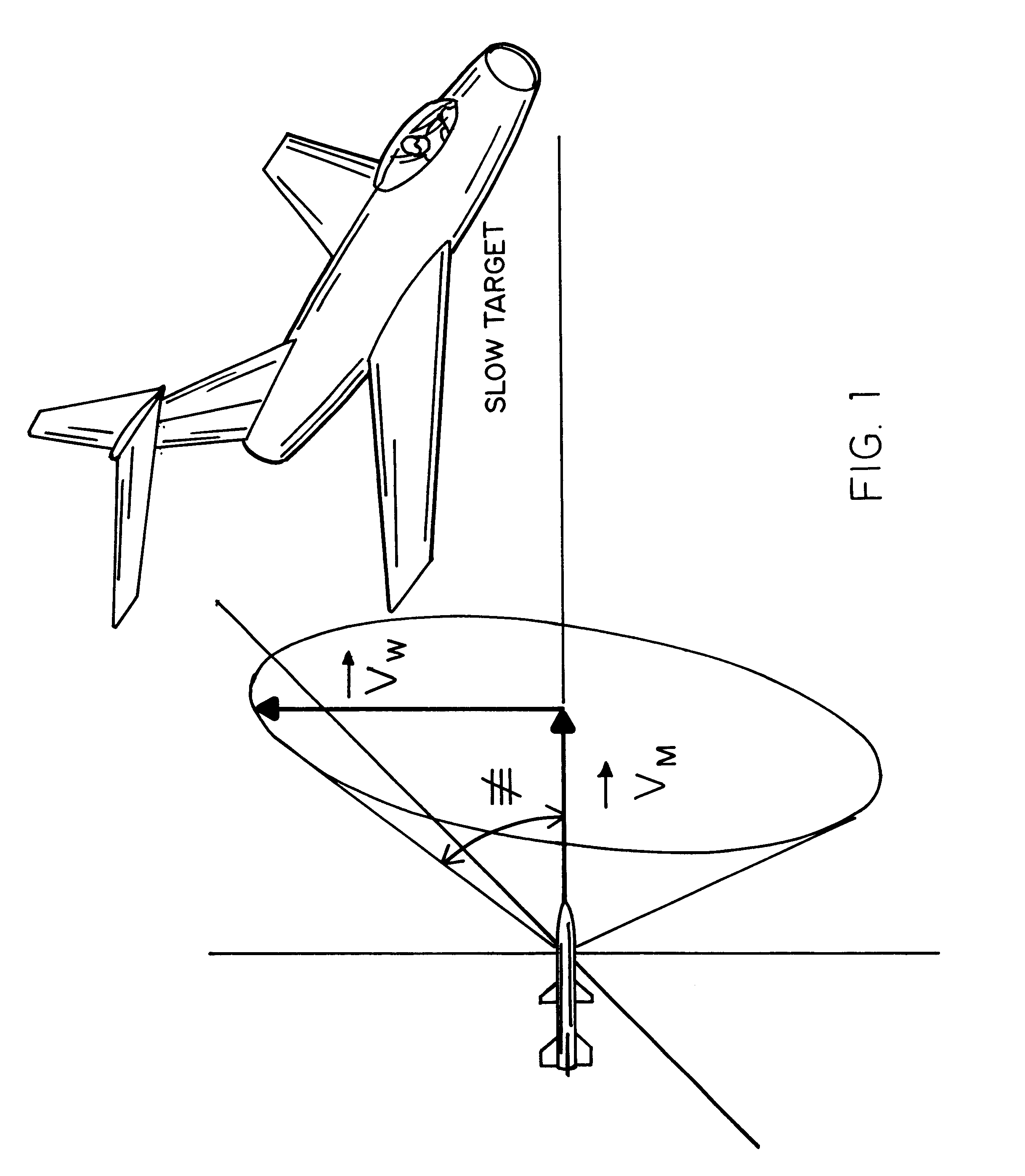
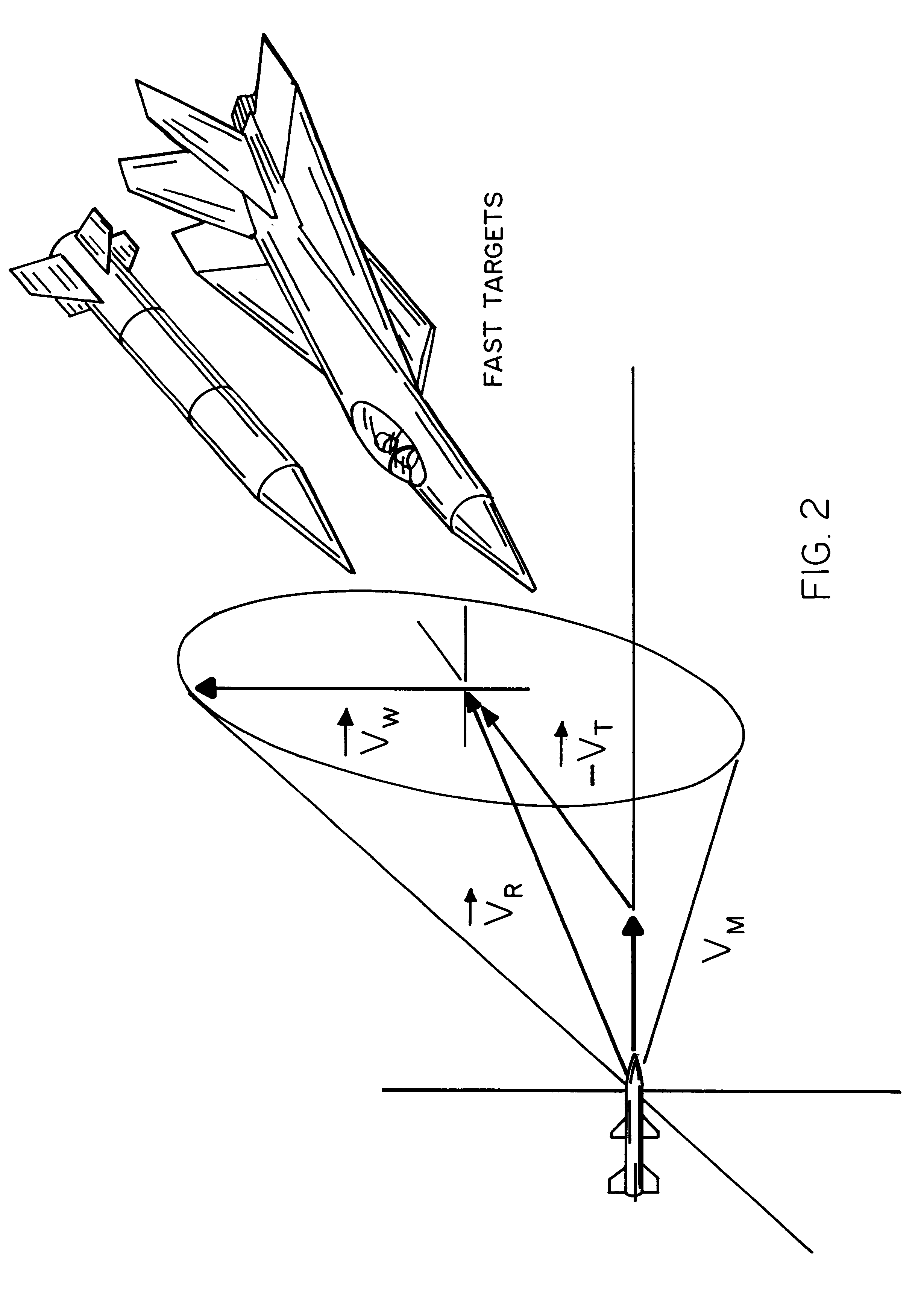
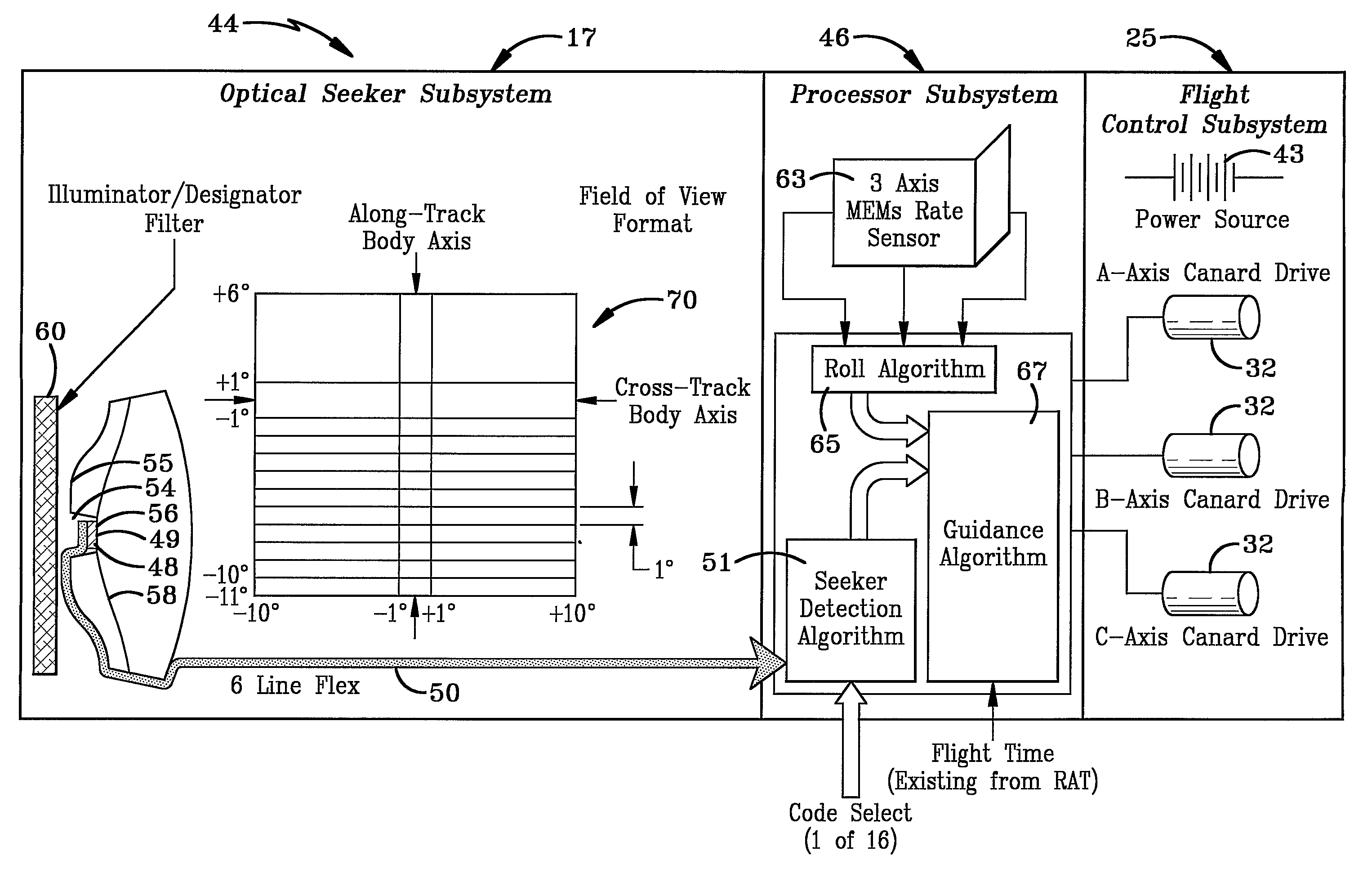
A fuzing system for non-spinning or substantially non-spinning weapons is implemented by means of wide angle optics providing at least forward-hemisphere coverage, an array of infrared detectors and a microprocessor for image and data processing, aim-point selection, directional-warhead aiming and skewed-cone fuzing. The skewed-cone fuzing has a generatrix which is the vector sum of missile velocity, warhead velocity and the negative of target velocity.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for autonomous detonation delay in munitions
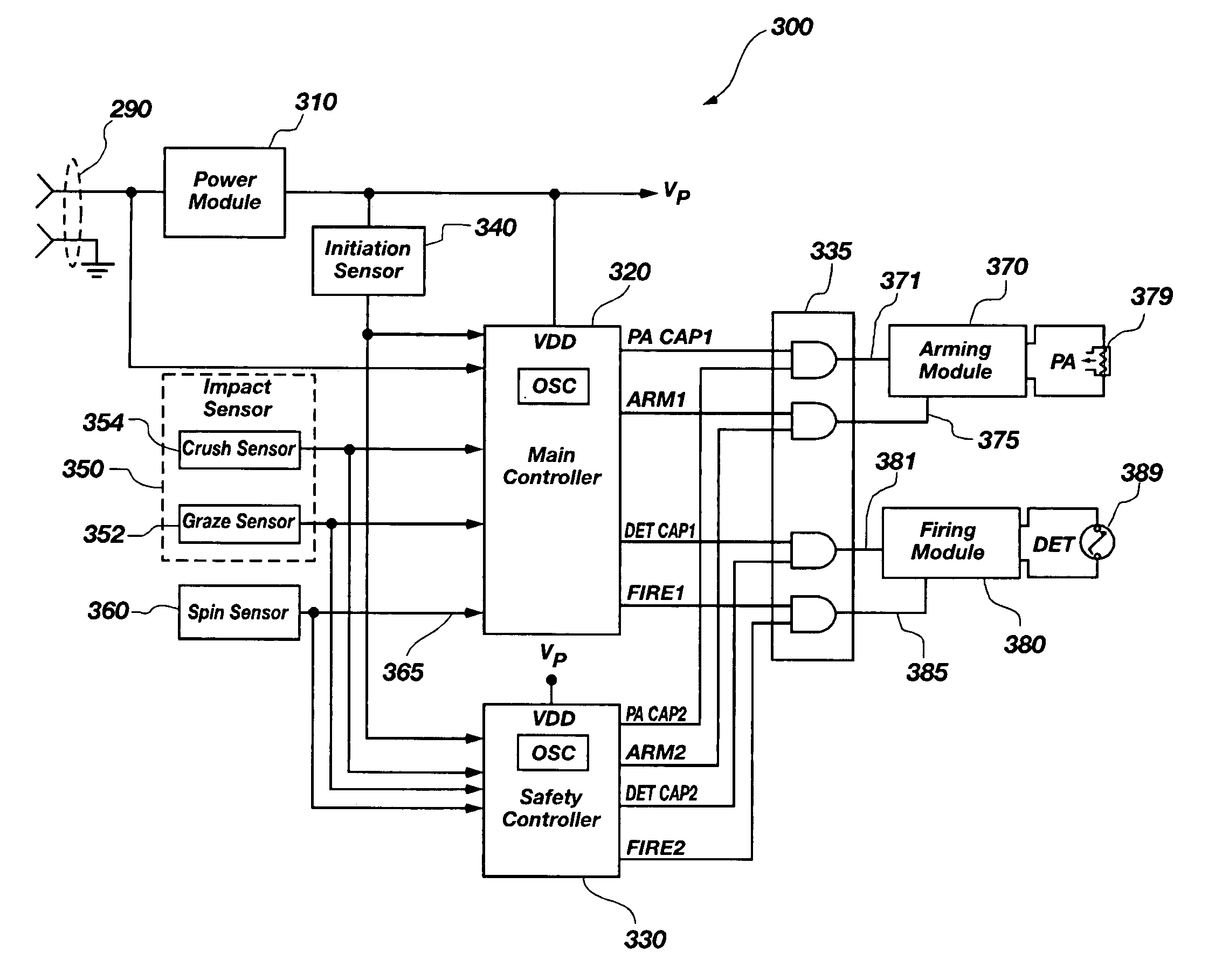
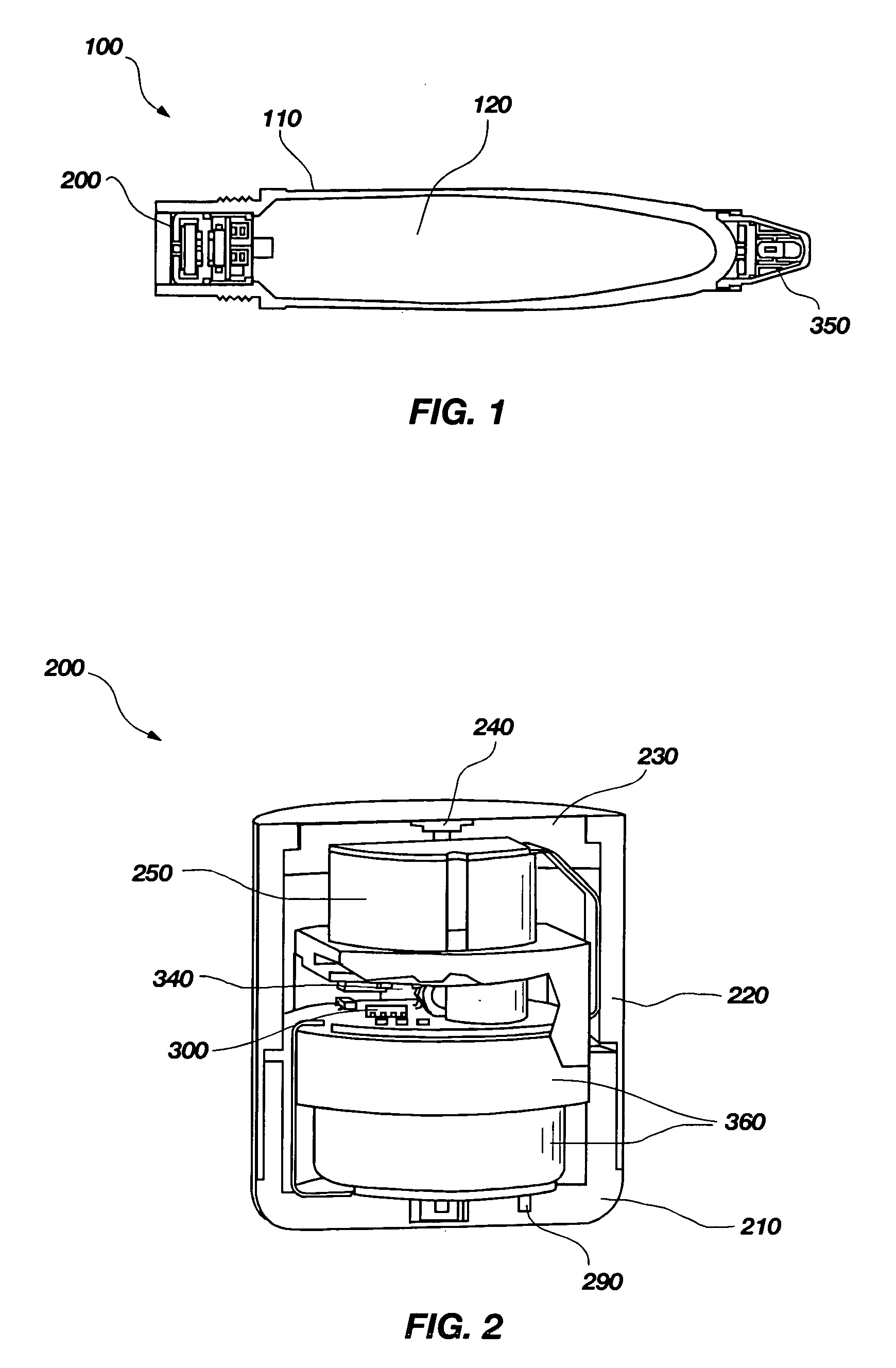
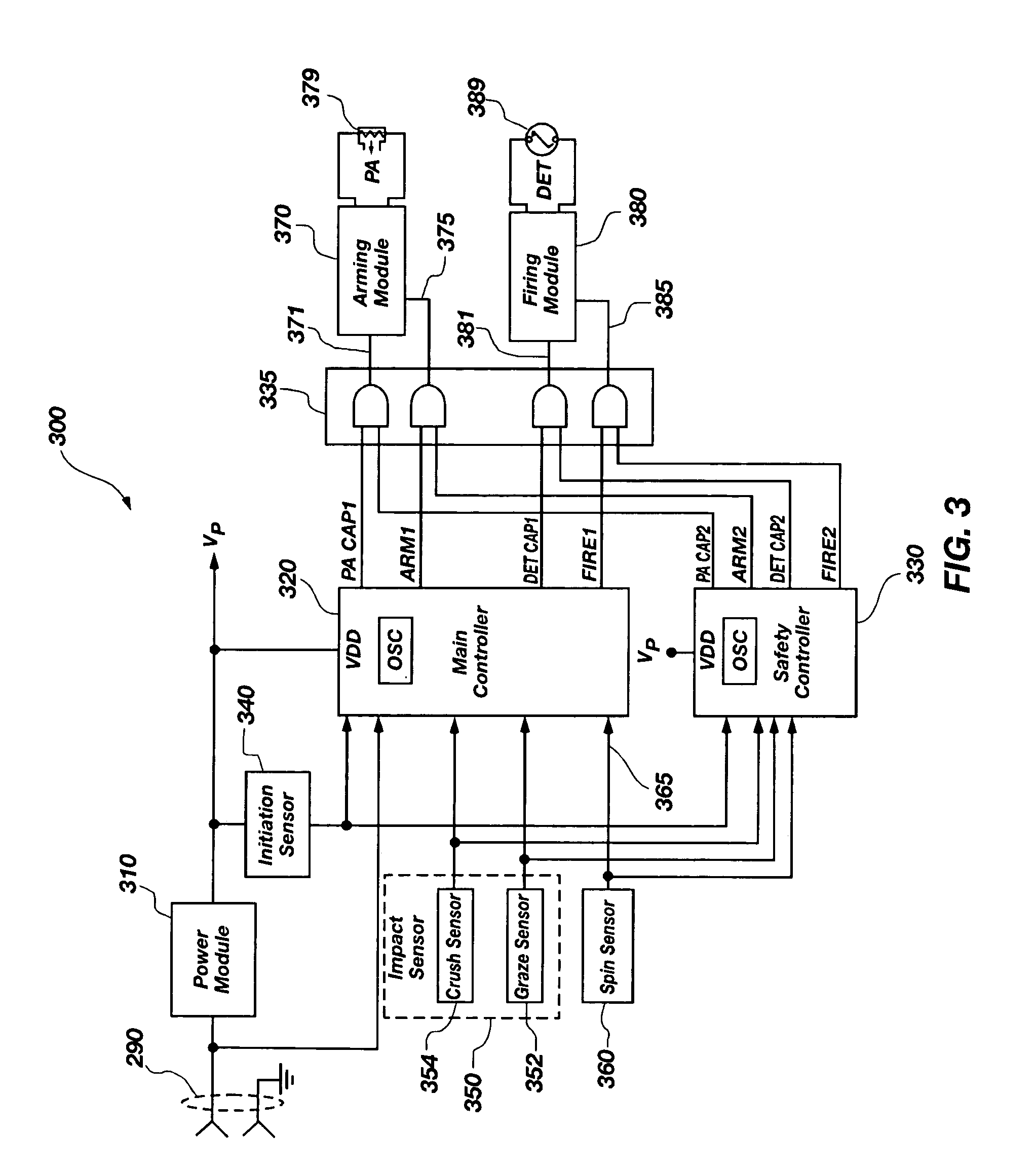
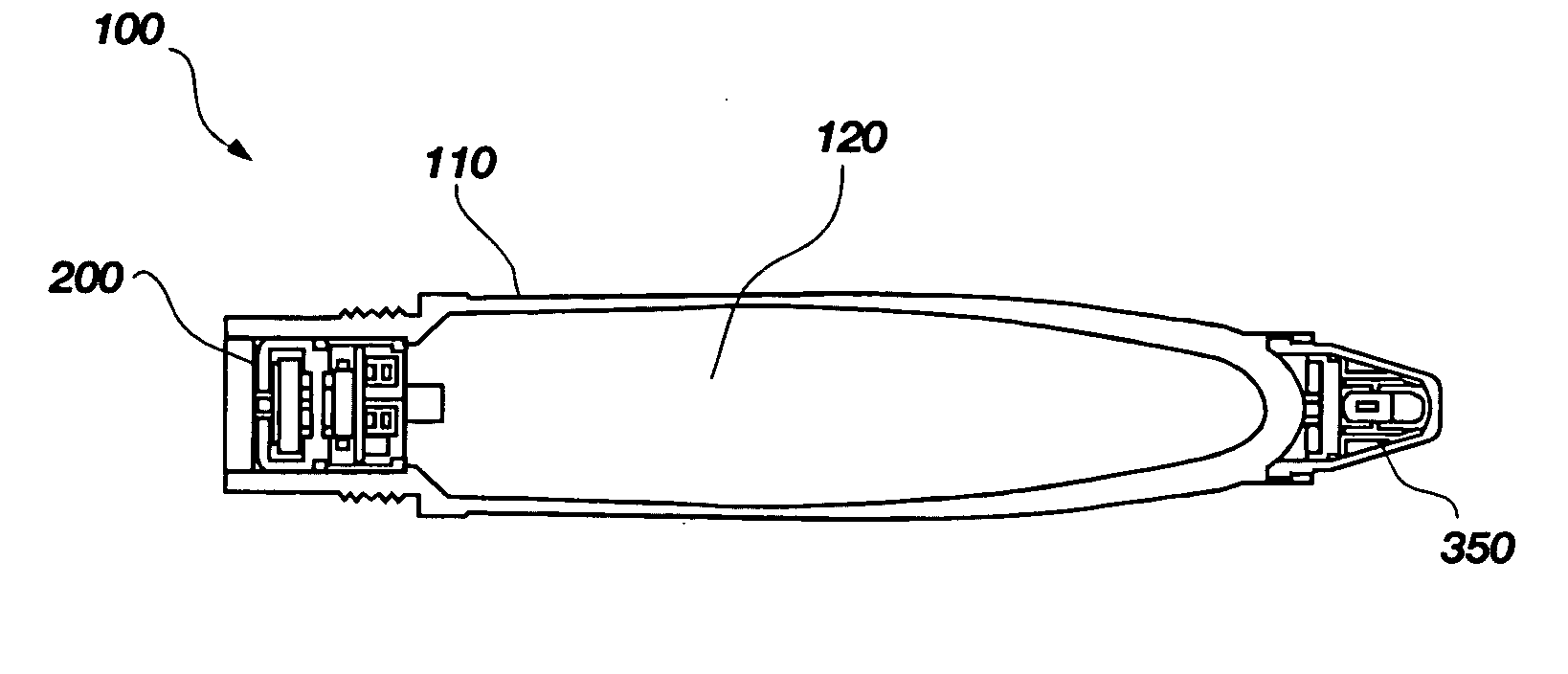
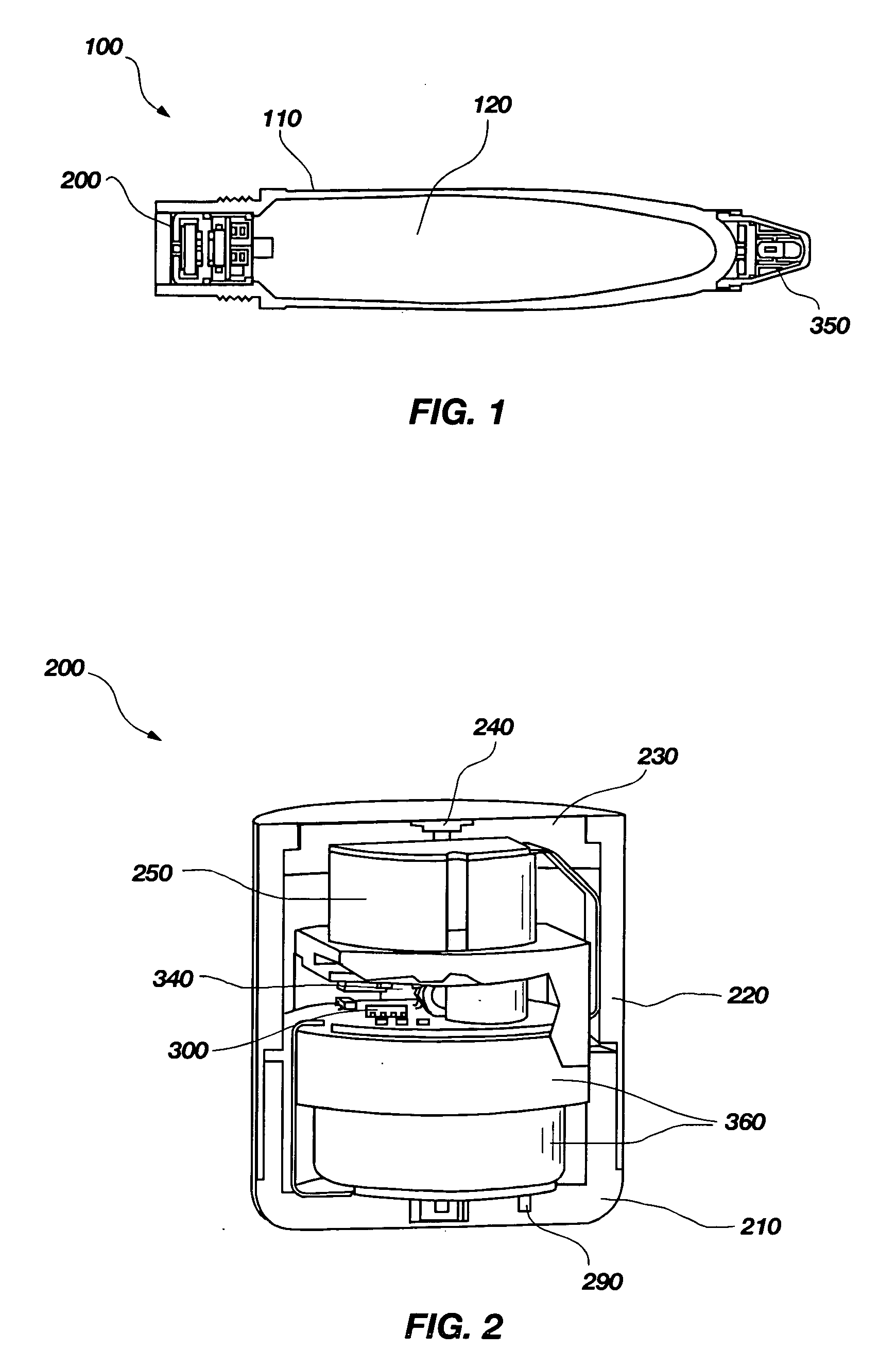
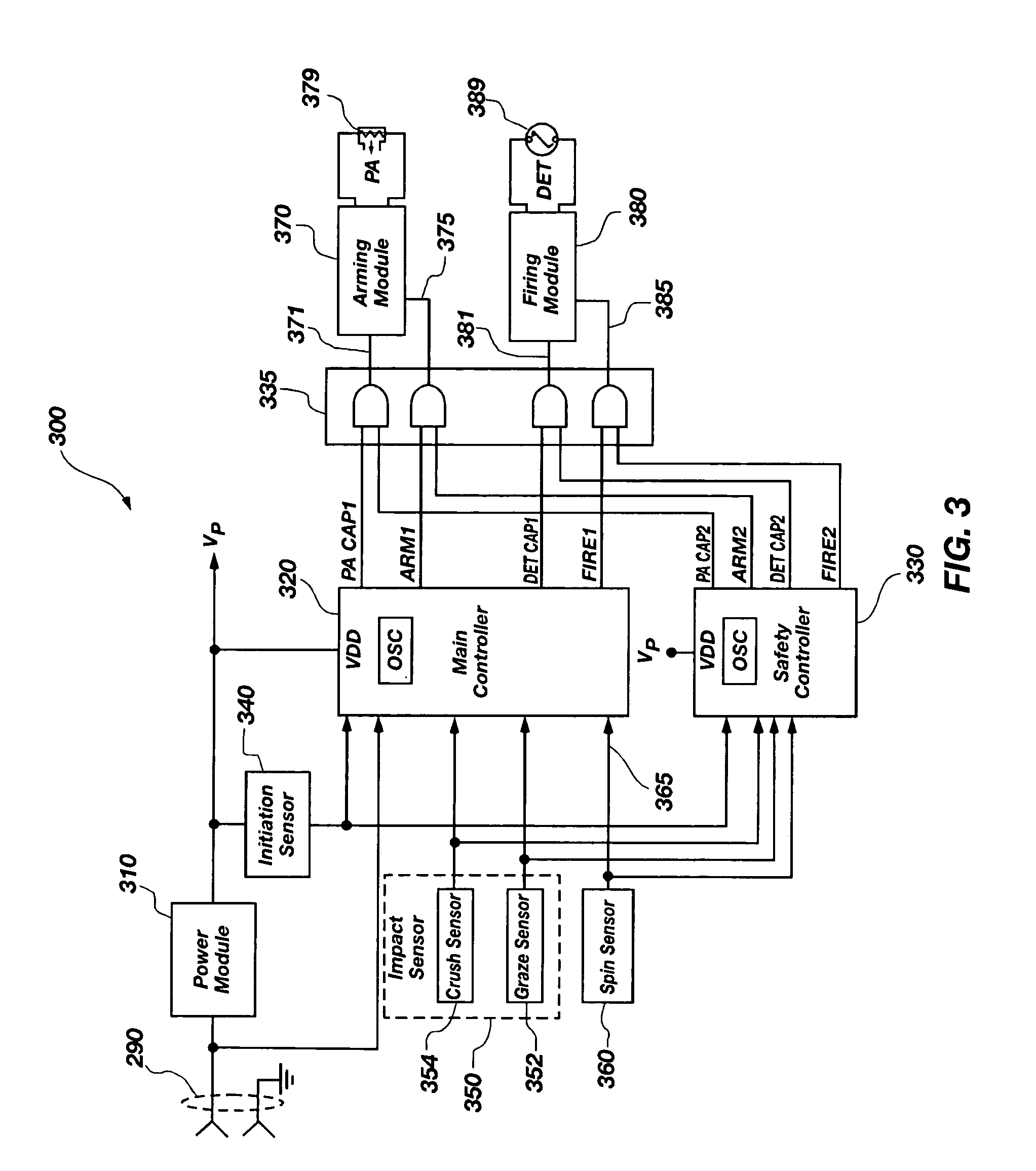
A detonation timing apparatus and method of determining a detonation time is disclosed. The detonation timing apparatus comprises an initiation sensor, at least one impact sensor, and at least one controller. The at least one controller may be configured for sensing an initiation event associated with the initiation sensor and sensing an impact event associated with the at least one impact sensor. The at least one controller is further configured for determining an impact velocity estimate proportional to a temporal difference between the initiation event and the impact event, using the impact velocity estimate to determine the detonation delay, and generating the detonation event at the detonation delay after the impact event. The timing apparatus and method of determining a detonation time may be incorporated in a fuze, which may be incorporated in an explosive projectile.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Medium caliber high explosive dual-purpose projectile with dual function fuze
InactiveUS20030140811A1More reliableLess expensiveAmmunition projectilesBlasting cartridgesElectricityDetonation
A multi-mode fuze for a munition has at least one sensor that generates an electrical output dependent on a rate of deceleration when the munition impacts a target, a logic circuit electrically coupled to the at least one sensor effective to discriminate between a soft target and a hard target dependent on the electrical output and a fuze that transmits a detonation signal to an initiating explosive to thereby detonate the munition. The detonation signal is transmitted at a time dependent on target discrimination. The multi-mode fuze of the invention may be incorporated into an explosive projectile that includes an aerodynamically shaped metallic casing, an explosive contained within the metallic casing and an initiating explosive contacting the explosive. The multi-mode fuze communicates with the initiating explosive to trigger detonation of the explosive either on impact with a hard target or following a delay on impact with a soft target.
Owner:GEN DYNAMICS ORDNANCE & TACTICAL SYST
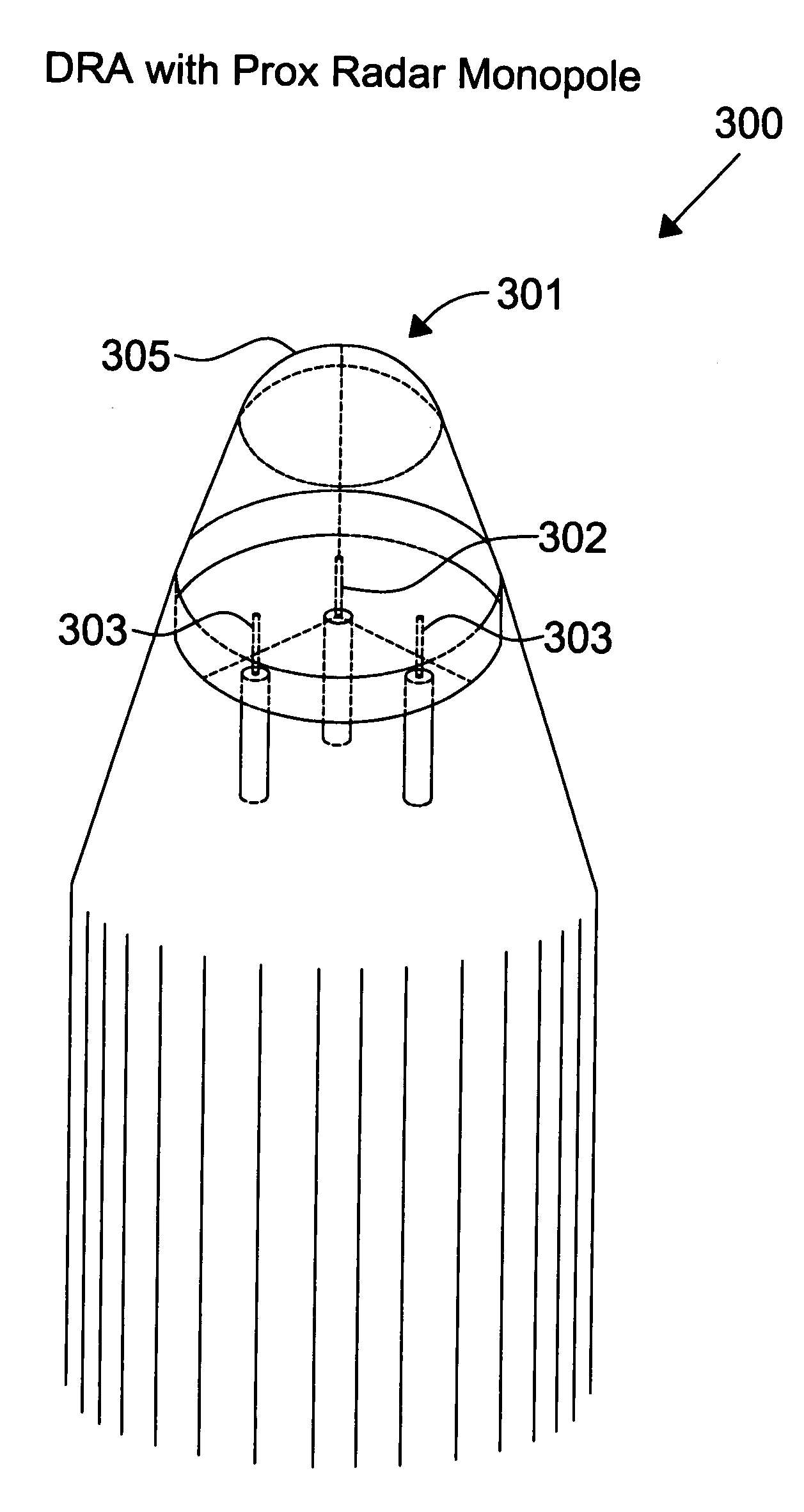
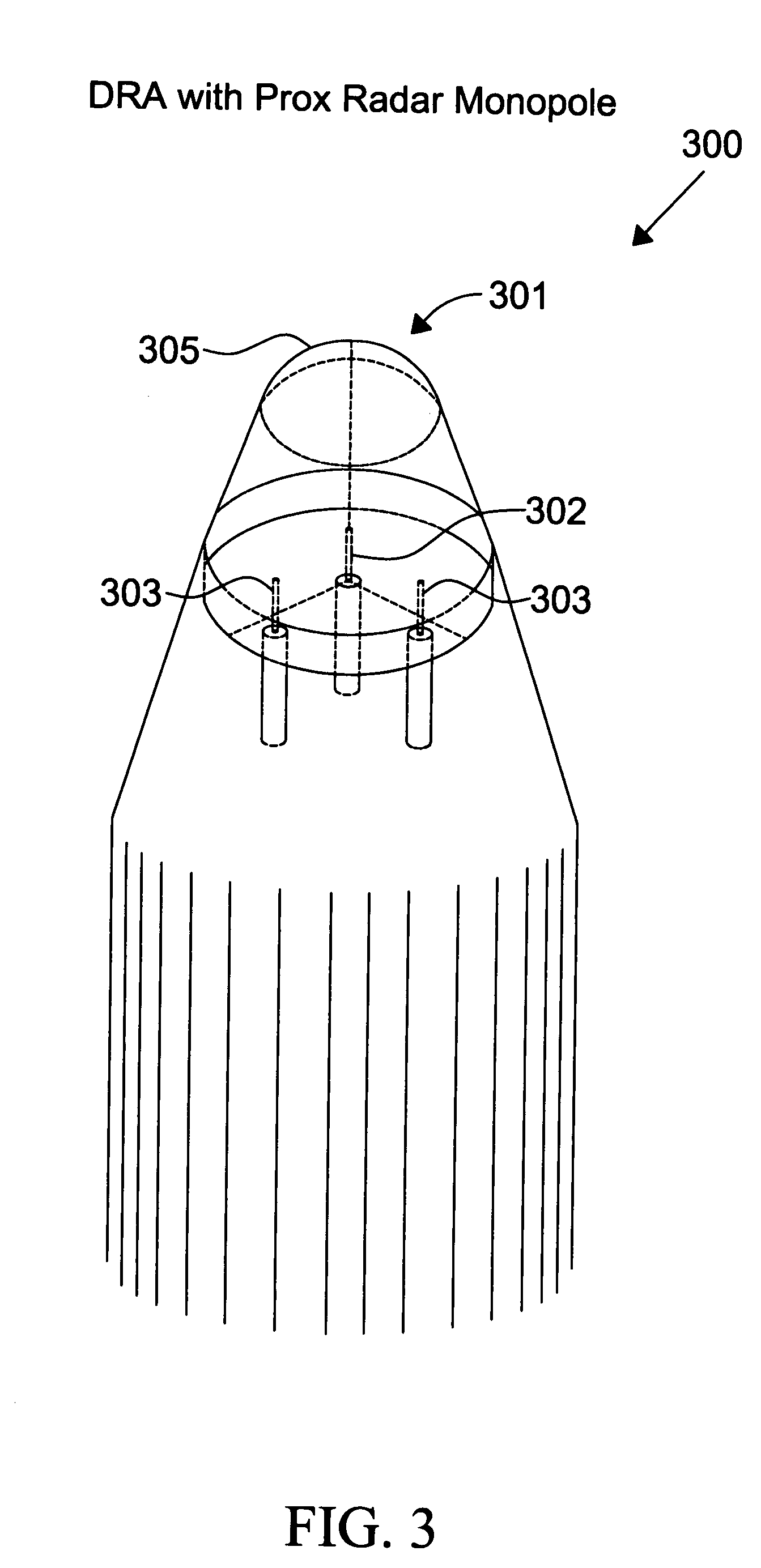
Proximity radar antenna co-located with GPS DRA fuze
ActiveUS7498969B1Improve approachReduce the amount requiredDirection controllersAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadar antennasDielectric resonator antenna
The present invention is directed to a fuze application capable of GPS (Global Positioning System) and proximity radar functionality by co-locating a proximity radar antenna with a GPS DRA (Dielectric Resonator Antenna) fuze. The GPS DRA fuze has a HE11δ mode structure resulting in an E-field null at the center. The monopole proximity radar antenna is mounted in the E-field null center and is thus electrically isolated from the GPS DRA fuze. The high dielectric constant permits the GPS DRA fuze to operate in the L1 frequency and the electrically shortened proximity radar antenna to resonate in the C-Band within a small form factor. The GPS DRA fuze maintains a forward-looking CP (circular polarization) pattern while proximity antenna maintains a desirable monopole pattern. Nesting allows mounting of both GPS and proximity radar antennas on the fuze nose while reducing the total space occupied.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
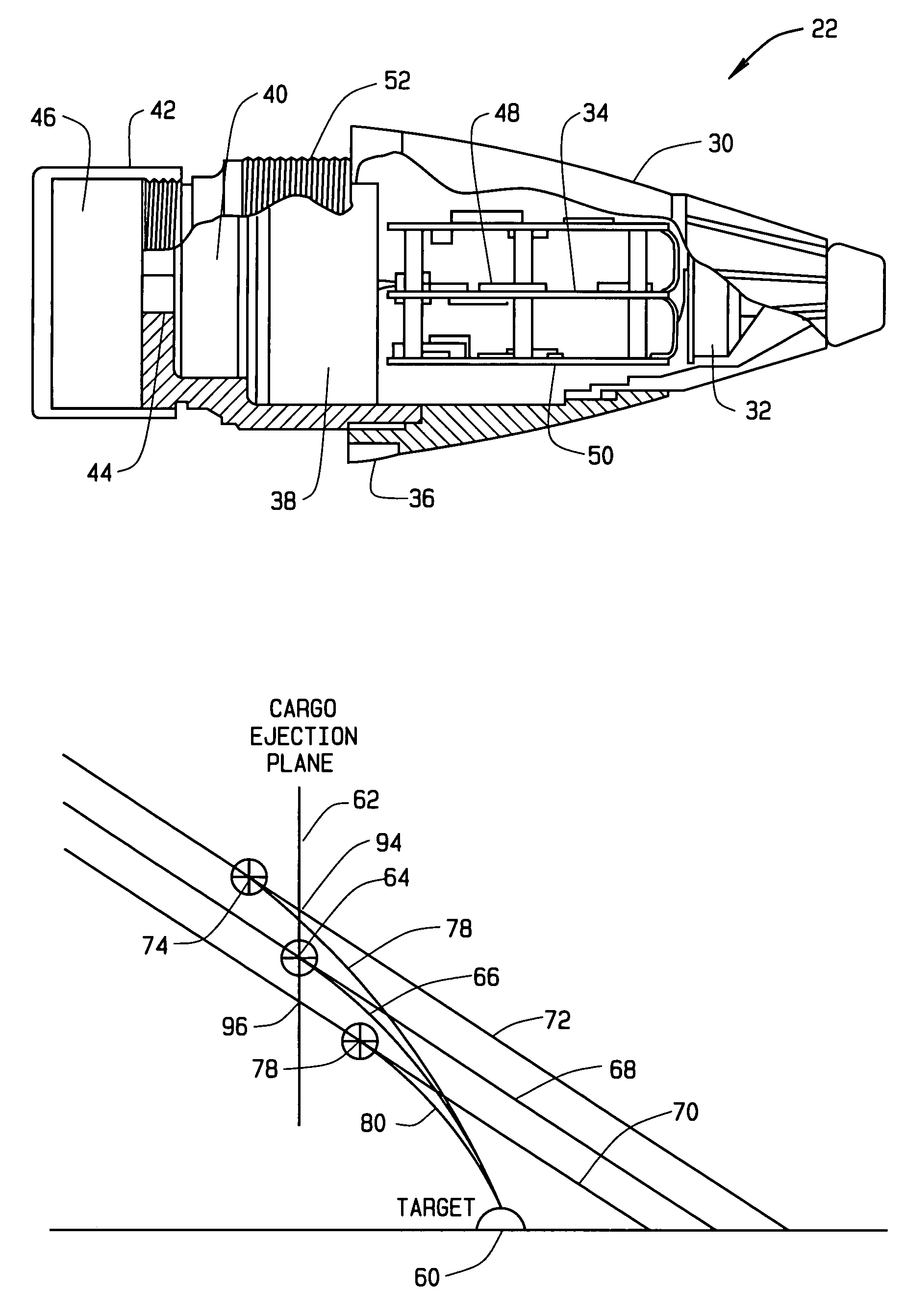
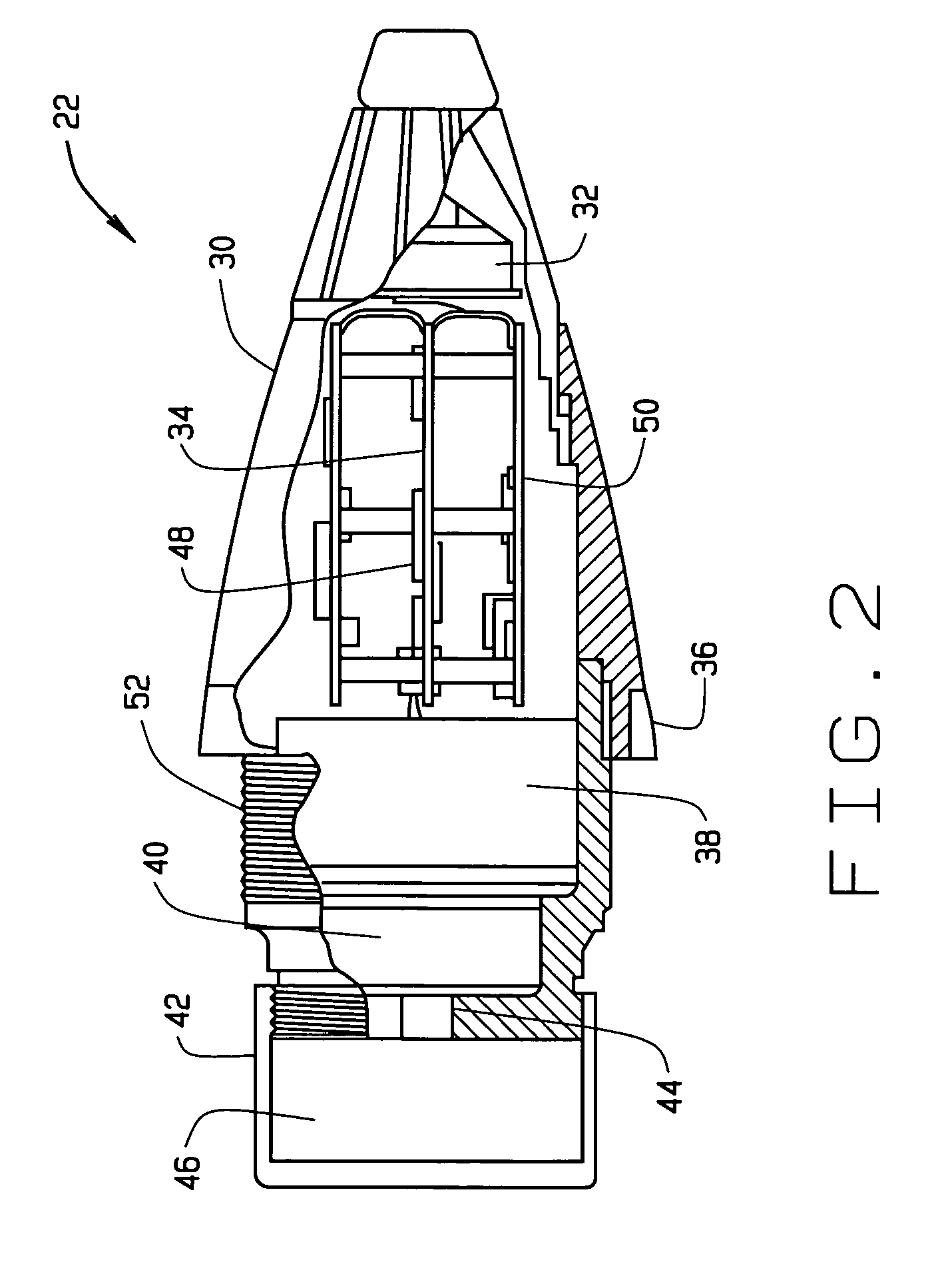
Accuracy fuze for airburst cargo delivery projectiles
InactiveUS7121210B2Low costReduce in quantityAmmunition projectilesProximity fuzesRadio navigationFuze
In one aspect, an artillery projectile apparatus is provided that includes a carrier projectile containing a payload, and a fuze disposed at an ogive of the projectile and which is configured to eject the payload when the fuze is detonated. The fuze includes a receiver configured to receive location information from a radionavigation source and a processor configured to acquire position data from the receiver. The processor is also configured to estimate a projectile flight path using the position data, to determine intercept parameters of the artillery projectile relative to an ejection plane of its payload cargo, and to adjust an ejection event initiation command time of the payload in accordance with the determined intercept parameters. In some configurations, the present invention dramatically decreases range errors typically associated with delivering artillery payloads to specific targets.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
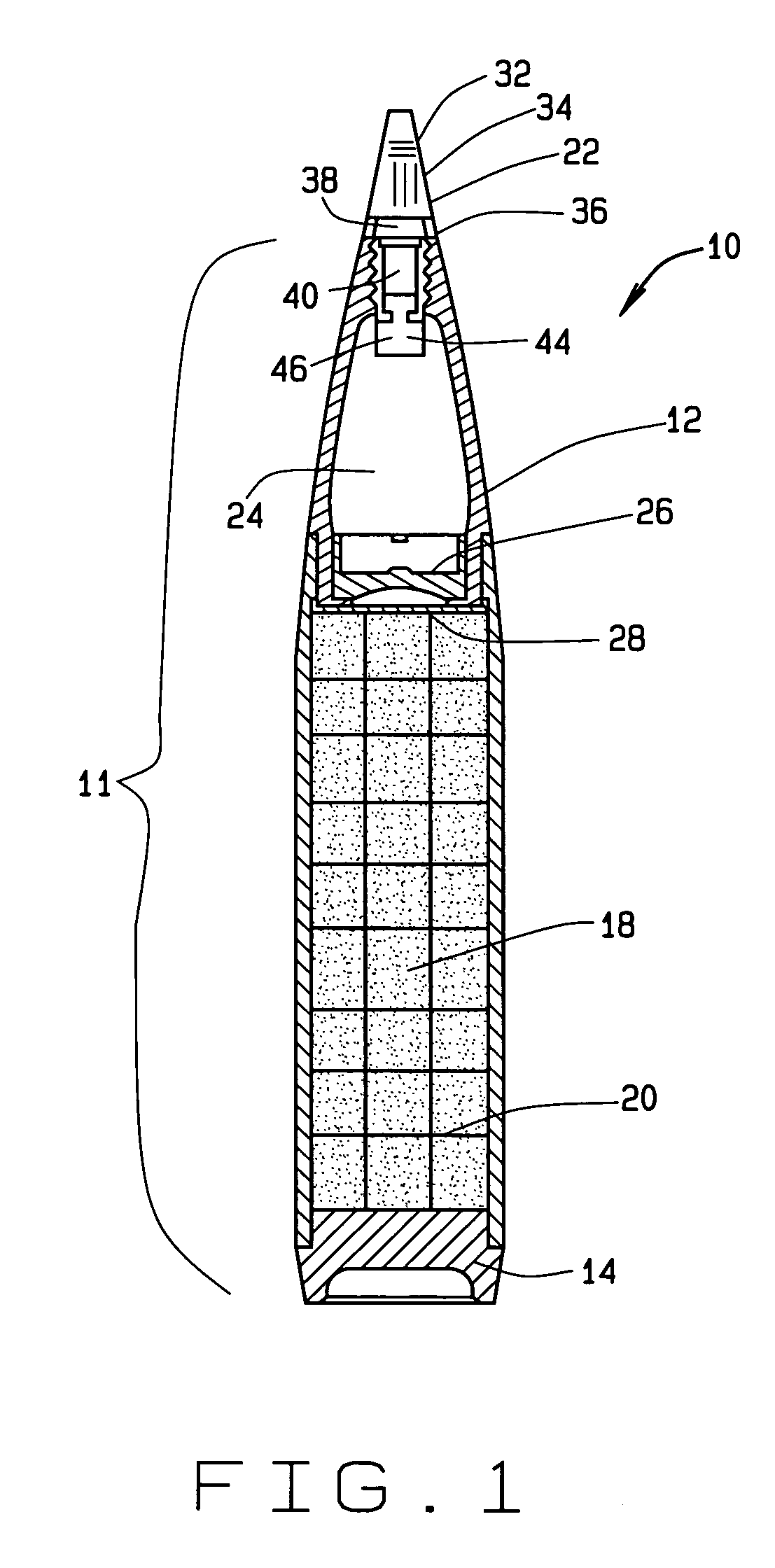
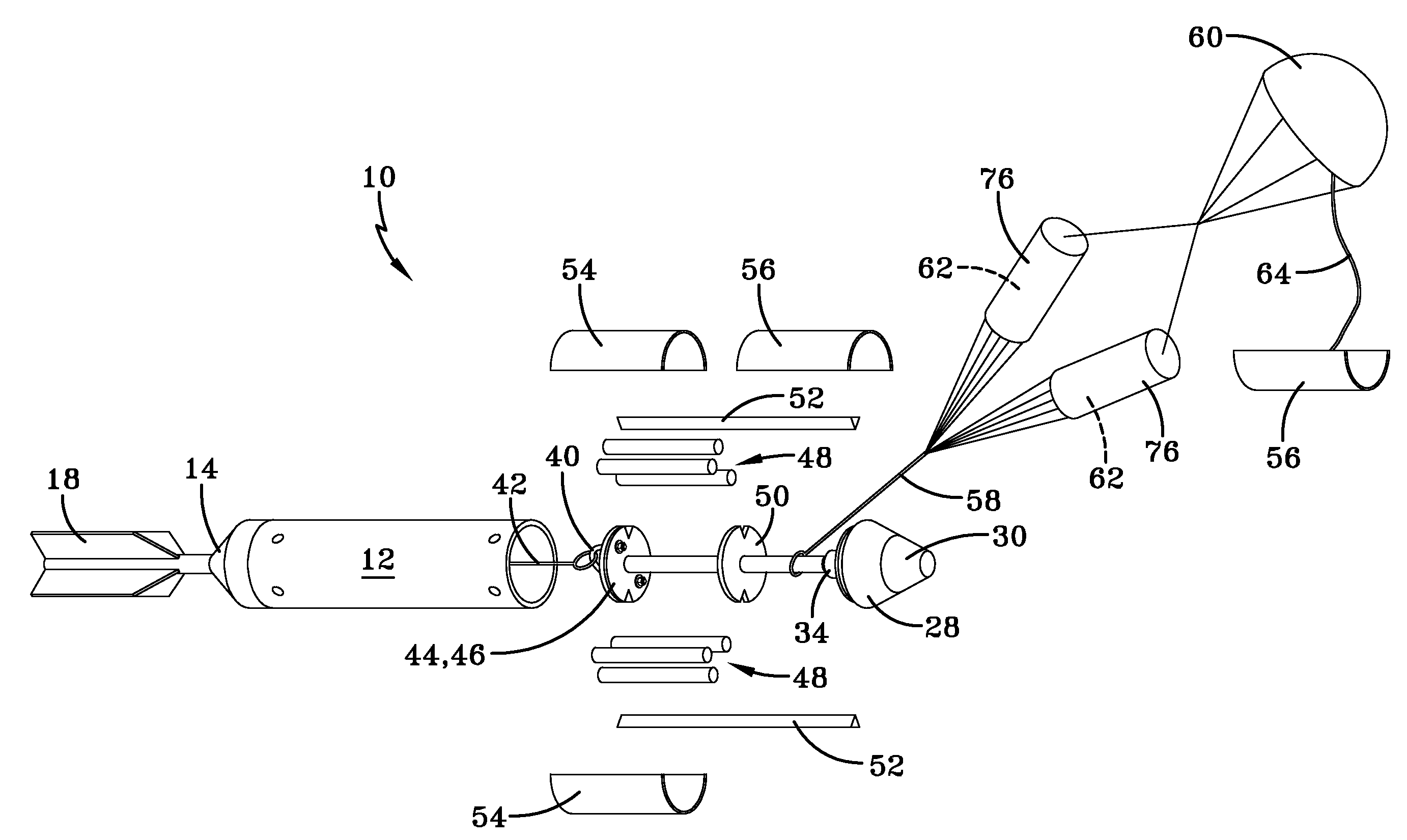
Non-lethal cargo projectile
InactiveUS7360489B1Minimizes ejection forceAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionEngineeringStern
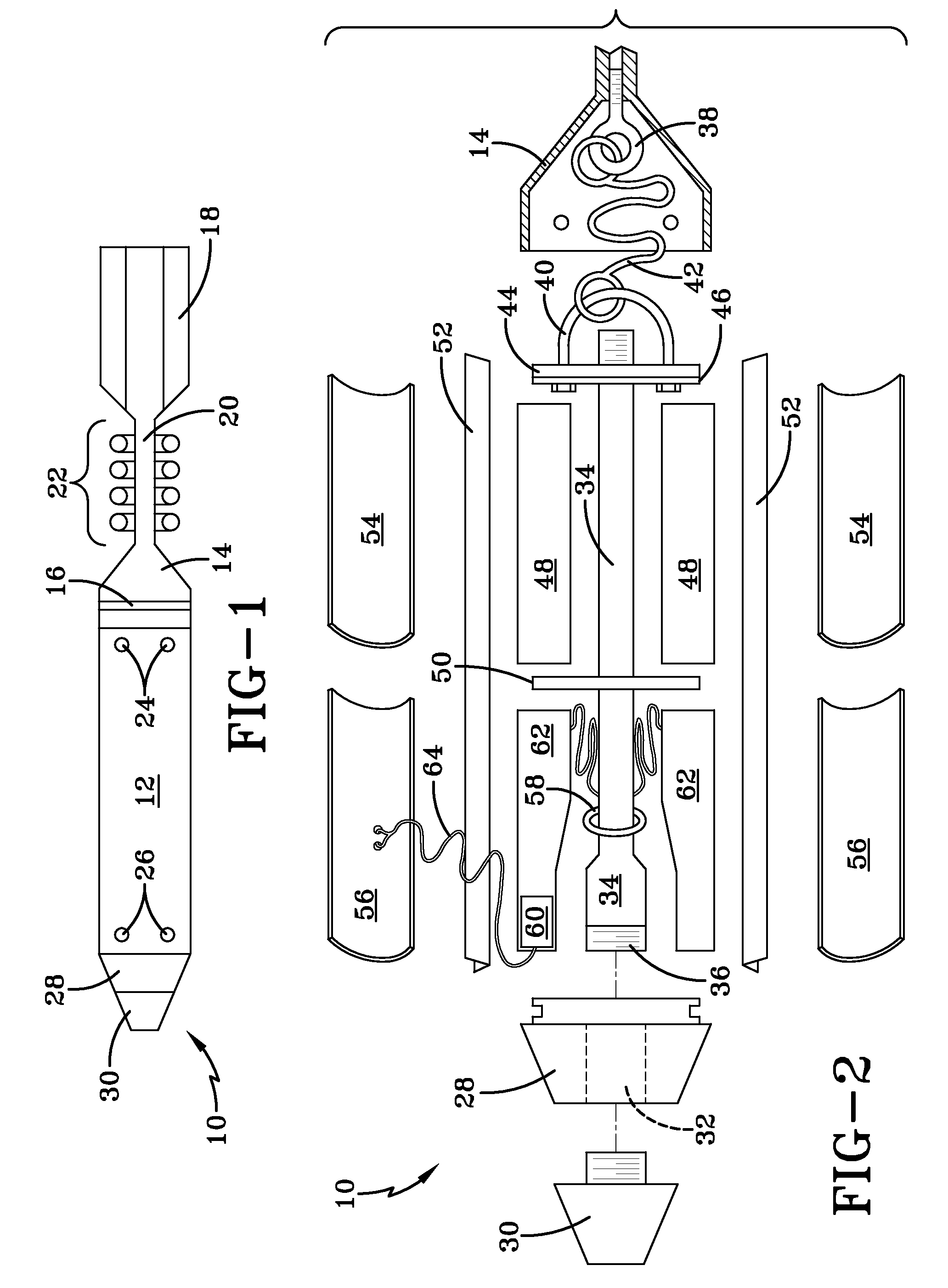
A non-lethal cargo projectile comprises a projectile body; a fuze adapter attached to a front of the projectile body; a fuze attached to the fuze adapter; a boattail attached to a rear of the projectile body; a pressure tube extending from the fuze adapter to the boattail; a decelerator and drogue chute disposed aft of the fuze adapter; a flexible line that connects the pressure tube to the decelerator; a center disc disposed aft of the decelerator and drogue chute; a rear disc disposed aft of the center disc, the center disc and the rear disc defining a payload volume therebetween; a second flexible line that connects the rear disc to the boattail; at least one shearable fastener that fastens the projectile body to the fuze adapter; and at least one vent extending from the boattail to the fuze adapter.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Airborne vehicle for firefighting
InactiveUS7121353B2Good effectImprove efficiencyAmmunition projectilesDirection controllersDetonatorFlight vehicle
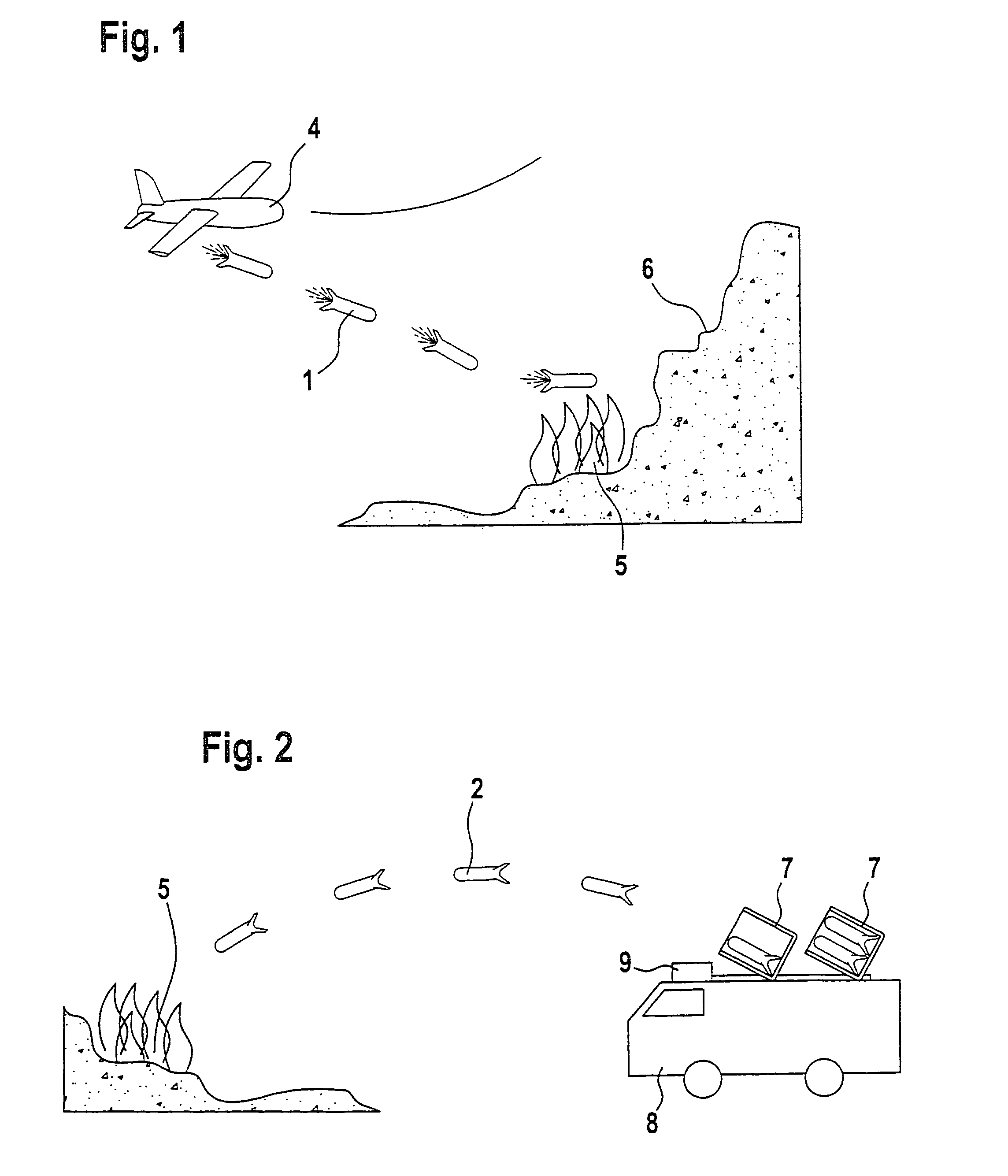
An airborne vehicle (1, 2, 10) which is equipped with an extinguishant container (12) for mist extinguishing is specified for efficient firefighting. A detonator (18) which is located on the extinguishant container (12) can be detonated via a fuze (19). The detonator (18) is attached to the airborne vehicle (1, 2, 10) such that, on firing the extinguishant which is contained in the extinguishant container (12) produces an extinguishant mist.
Owner:BODENSEEWERK GERATETECHNIK GMBH
Mechanism for reducing the vulnerability of high explosive loaded munitions to unplanned thermal stimuli
InactiveUS7025000B1Reduce vulnerabilityImprove personnel safetyAmmunition storageAmmunition loadingPersonnel safetyFuze
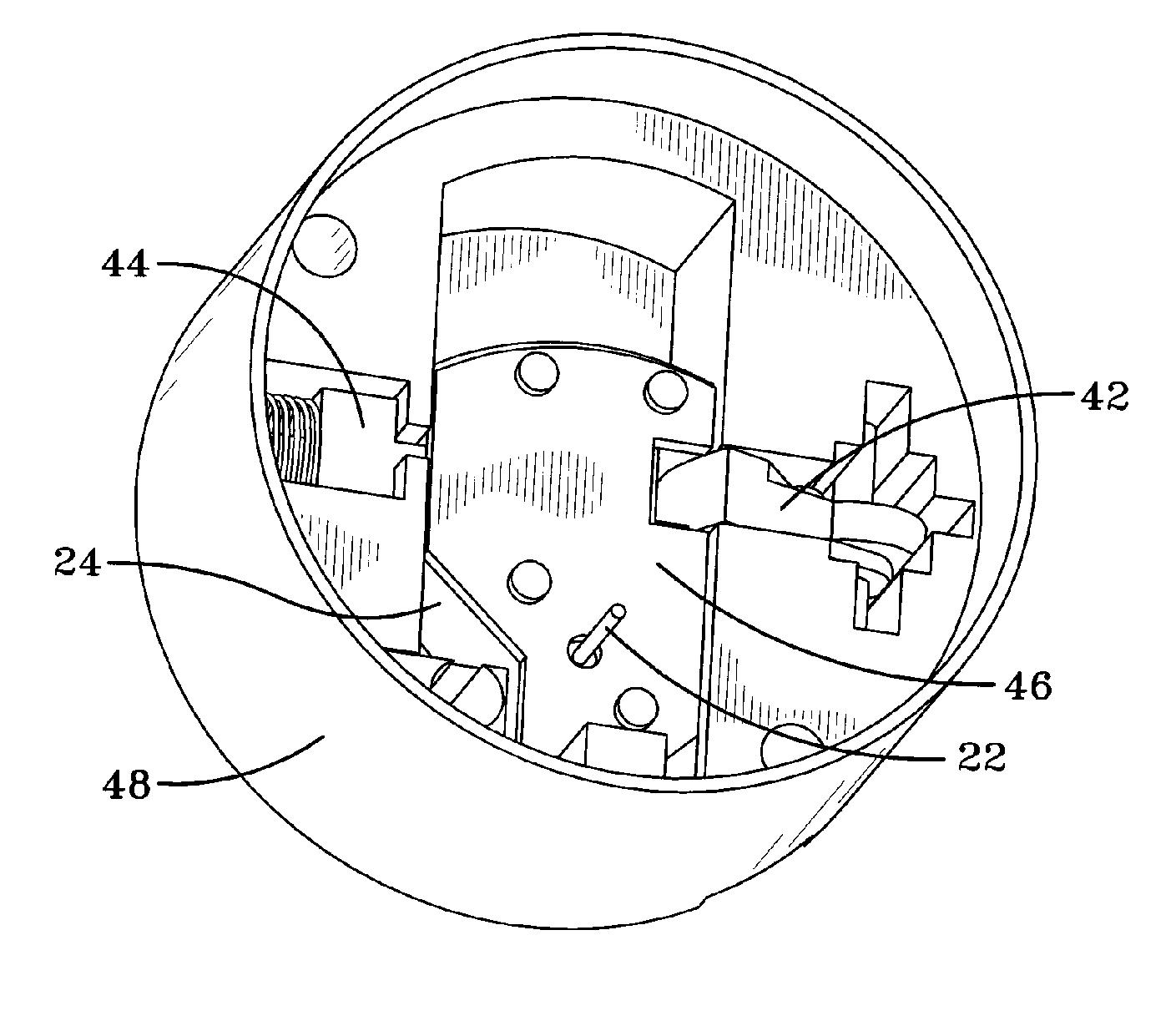
A new mechanism substantially reduces the vulnerability of explosive load munitions to thermal stimuli, such as fire or heat during transport and storage, thus enhancing personnel safety and the survivability of adjacent munitions. The mechanism includes a threaded fuze adapter made of plastic and having a melting temperature that is lower than the auto-ignition temperature of the explosive. The adapter secures a fuze or metal closing plug to an explosive loaded projectile and is designed to permit venting of combustion gases through the nose of the projectile upon auto-ignition of the explosive, thereby preventing detonation of the explosive and fragmentation of the projectile body. A plastic or metal ring is utilized to support the body of an explosive loaded projectile within a fiberboard packing tube, thus allowing the fuze to readily separate from the projectile body upon the melting of the plastic threaded fuze adapter and subsequent combustion of the explosive during an unplanned thermal stimulus event. An intumescent coating is deposited on the metal ammunition container that is used to package explosive loaded cartridges, to reduce the rate of thermal stimuli to the munitions, thereby ensuring that the plastic fuze adapter of the present invention reaches its melting temperature prior to the explosive attaining its auto-ignition temperature.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
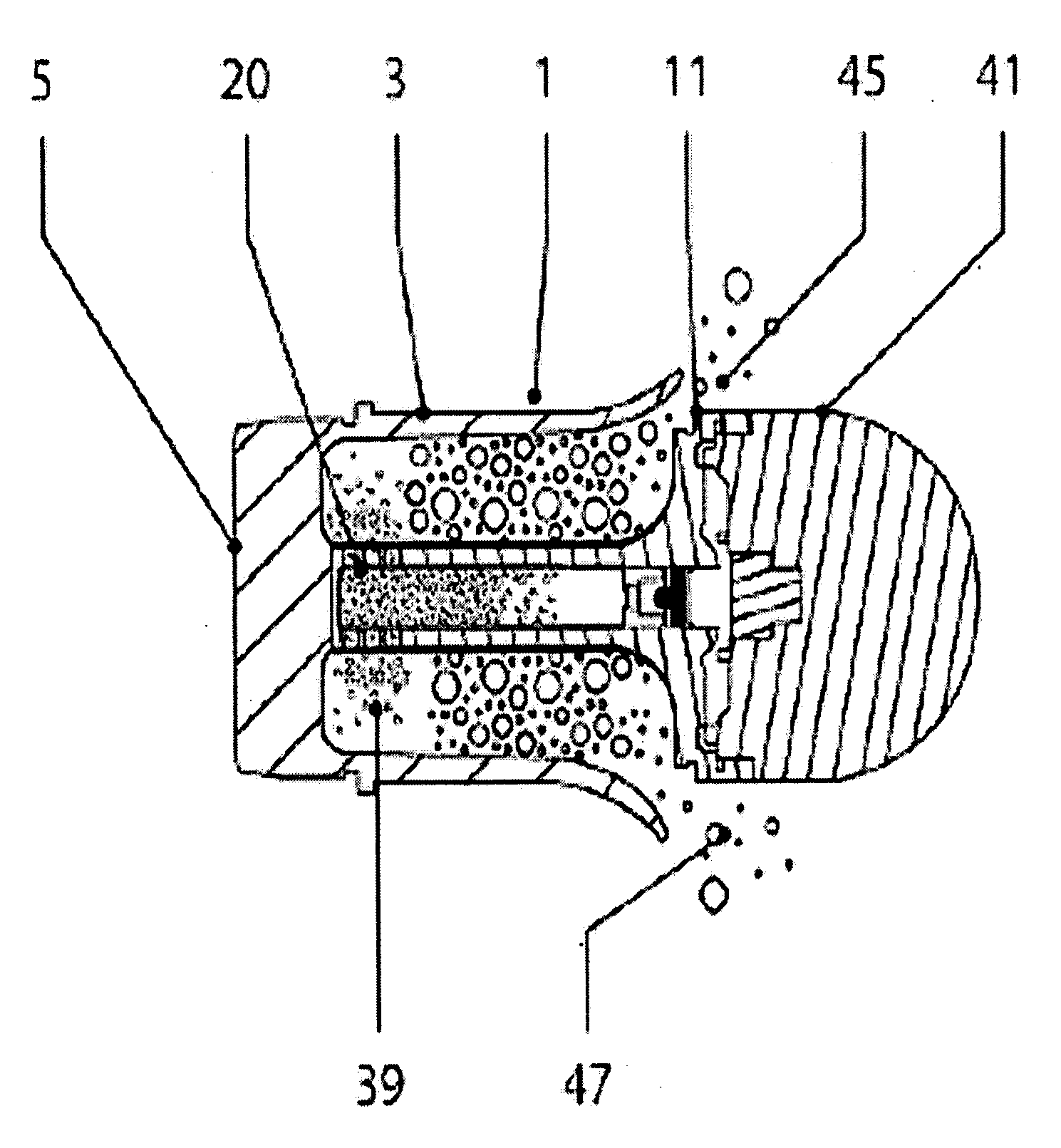
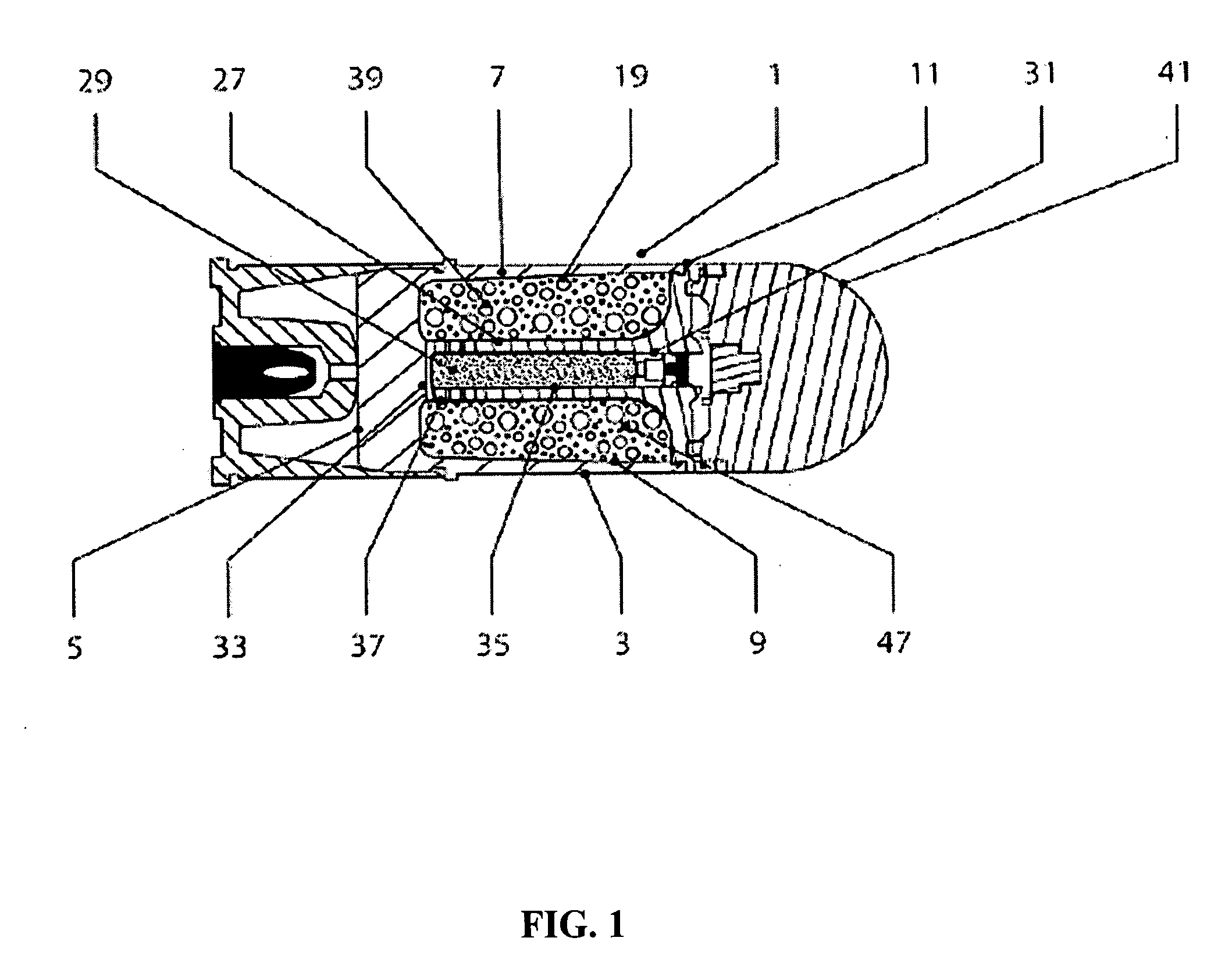
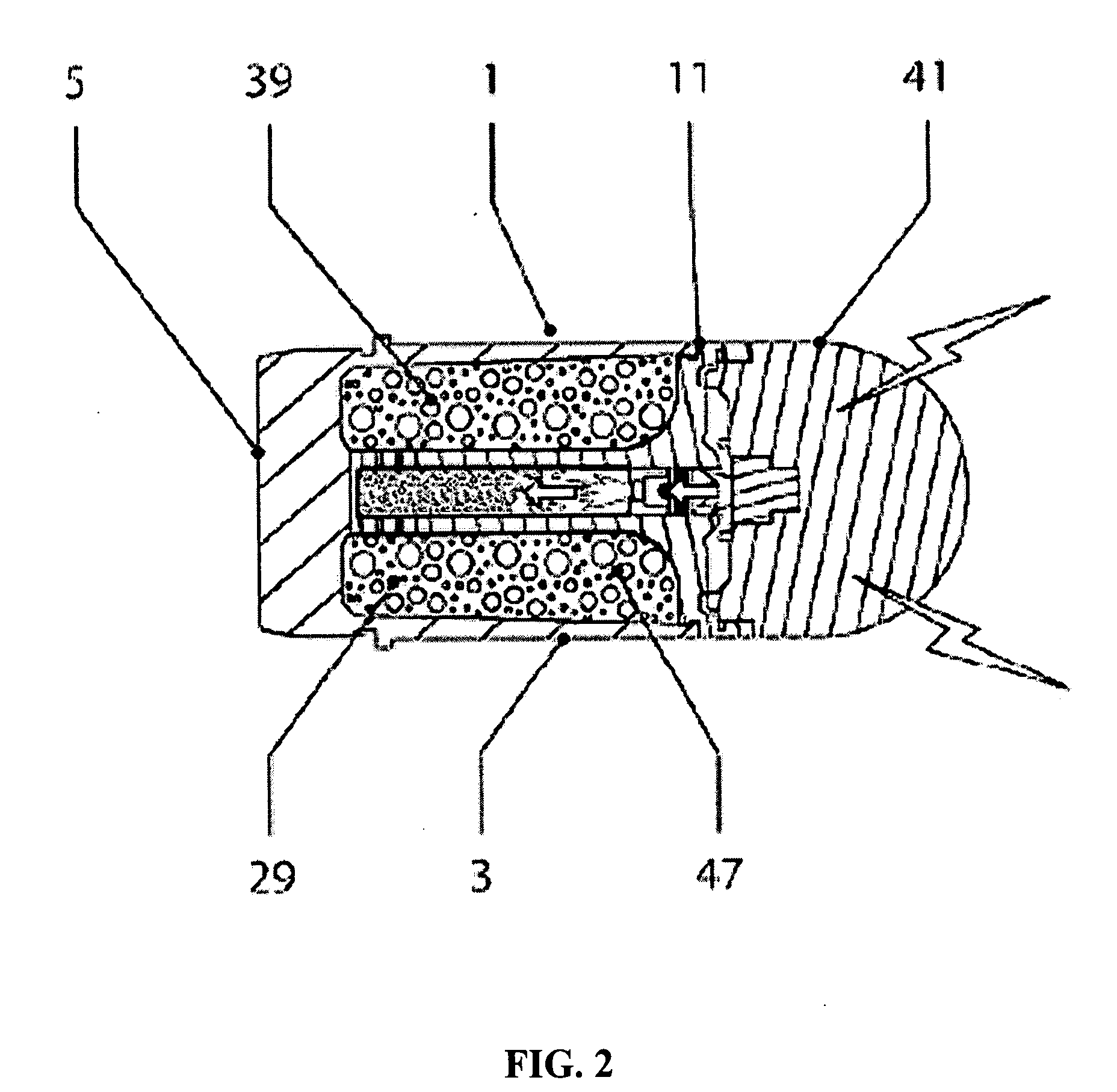
Time detonating fuse of antiaircraft gun hail-suppression precipitation increasing bomb
ActiveCN106338224AImprove reliabilityLarge chargeWeather influencing devicesAmmunition fuzesSilver iodideTime delays
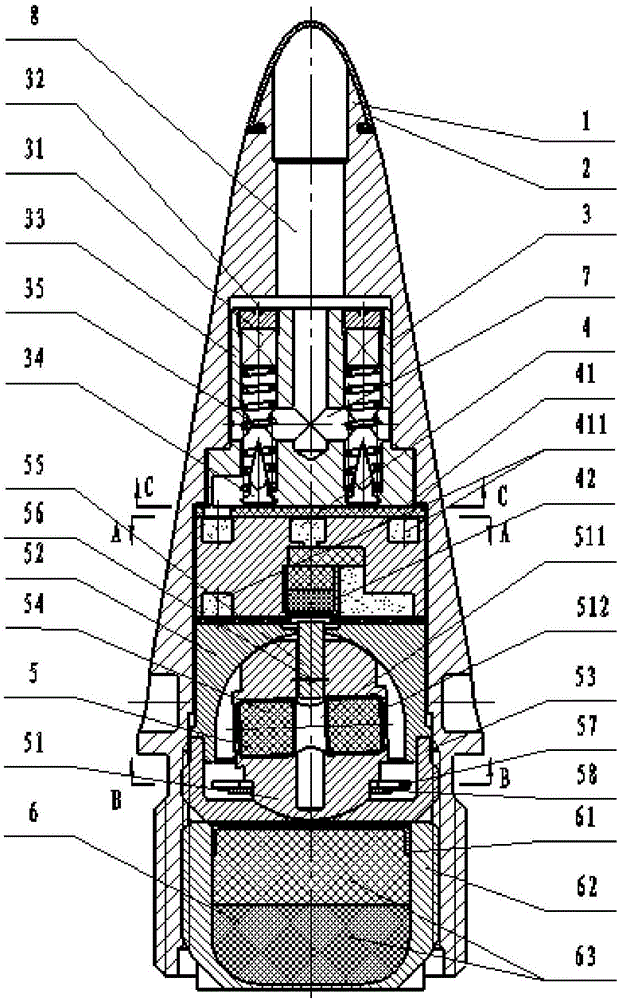
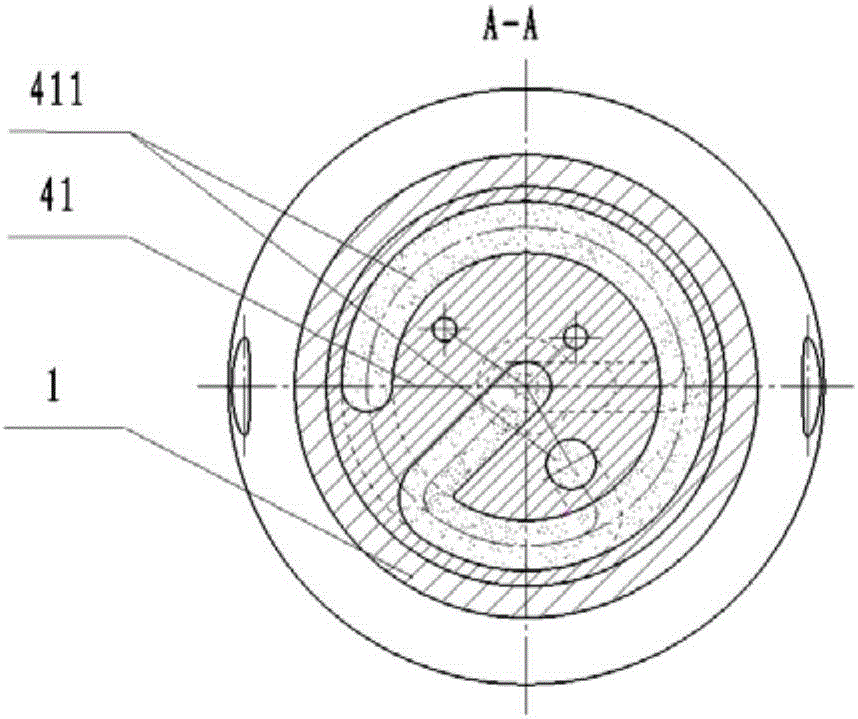
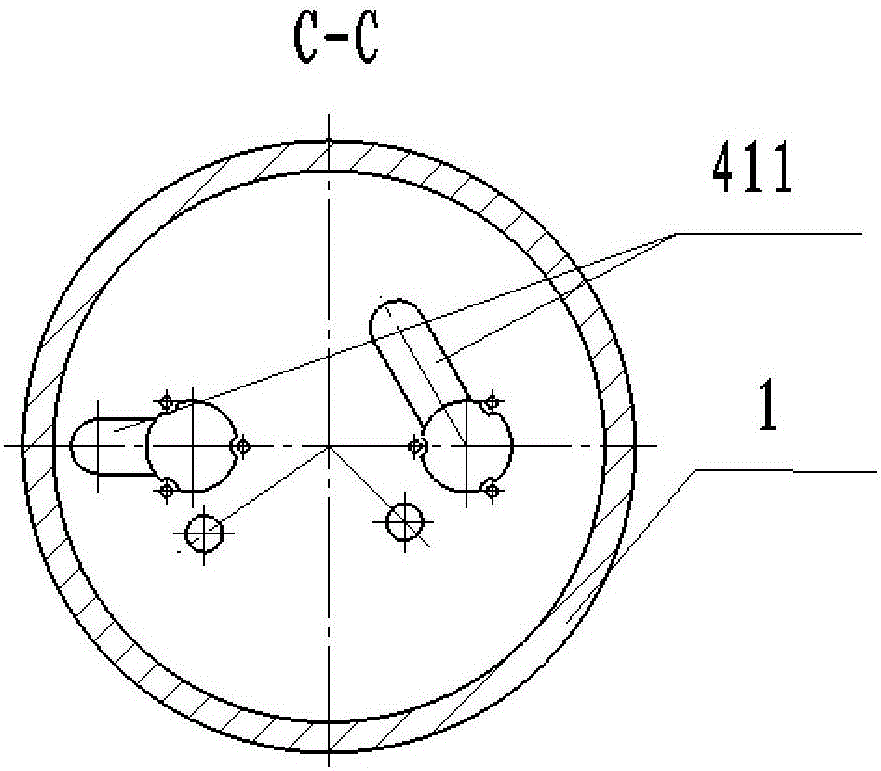
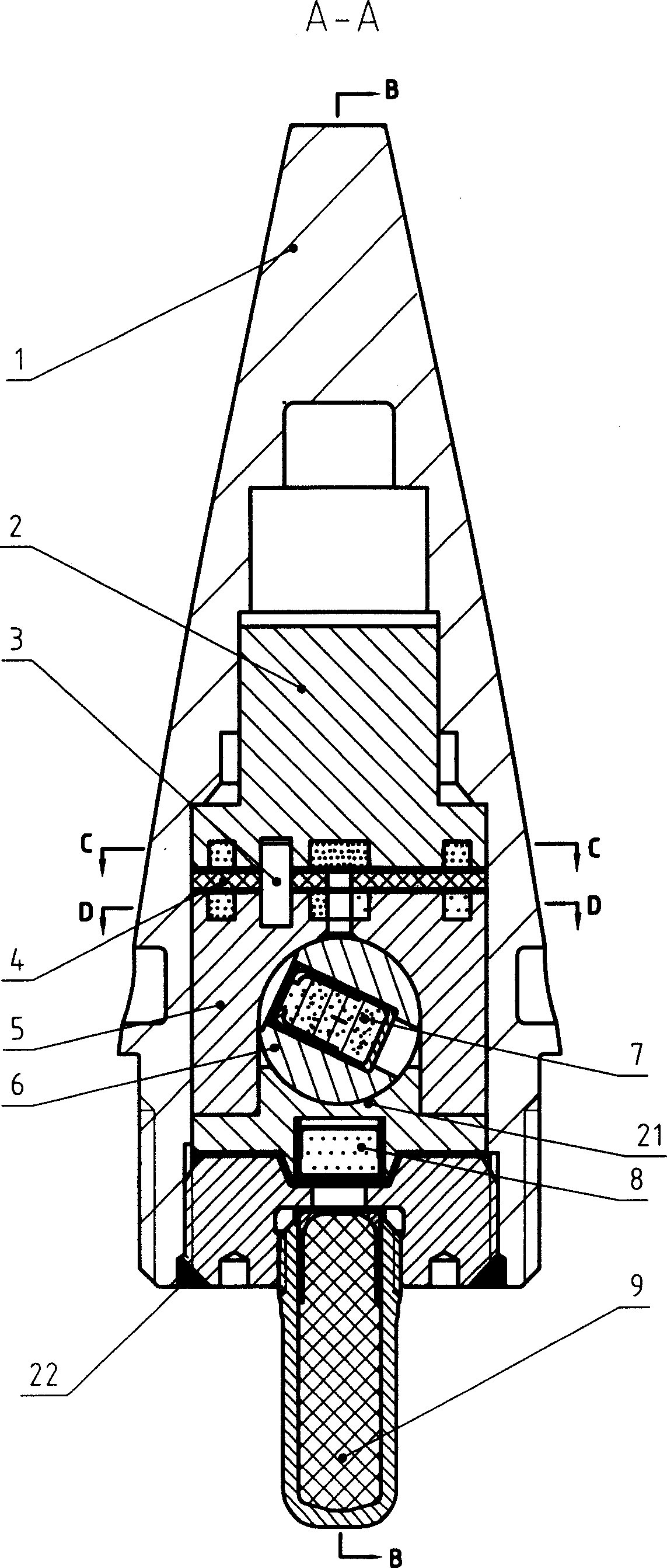
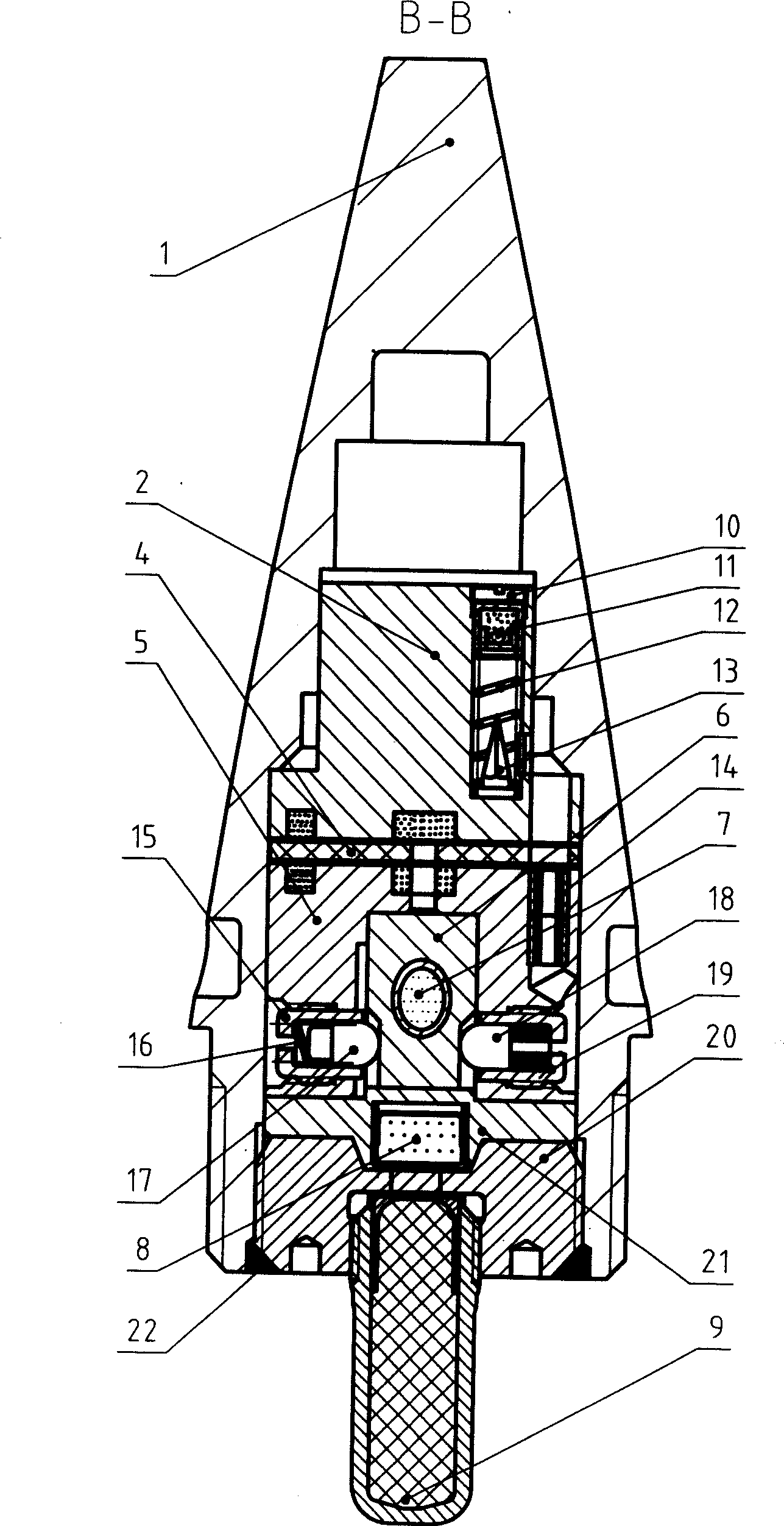
The invention discloses a time detonating fuse of an antiaircraft gun hail-suppression precipitation increasing bomb. The time detonating fuse comprises a fuse body (1), a hood (2), a firing mechanism (3), a medicament tray time-delay mechanism (4), a ball rotor safe and arming mechanism (5) and a detonating primer (6), wherein the hood (2) covers the front end of the fuse body (1), the firing mechanism (3), the medicament tray time-delay mechanism (4), the ball rotor safe and arming mechanism (5) and the detonating primer (6) are arranged in the cavity of the fuse body (1), the firing mechanism (3) is located on the front part of the fuse body (1), the medicament tray time-delay mechanism (4) which has a time-delay function is located between the firing mechanism (3) and the ball rotor safe and arming mechanism (5), the front end of the detonating primer (6) is connected with the ball rotor safe and arming mechanism (5), and the back end of the detonating primer (6) is used as the output end of the fuse and is used for detonating a charged projectile containing the silver iodide grain. The time detonating fuse of the antiaircraft gun hail-suppression precipitation increasing bomb has the advantages of high reliability and good safety.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optically guided munition
ActiveUS7533849B2Low costAvoid explosionAmmunition projectilesDirection controllersSurvivabilityDrive motor
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
Air-powered electro-mechanical fuze for submunition grenades
InactiveUS7316186B1Improves fuze safetyImprove reliabilityAmmunition fuzesElectricityElectric generator
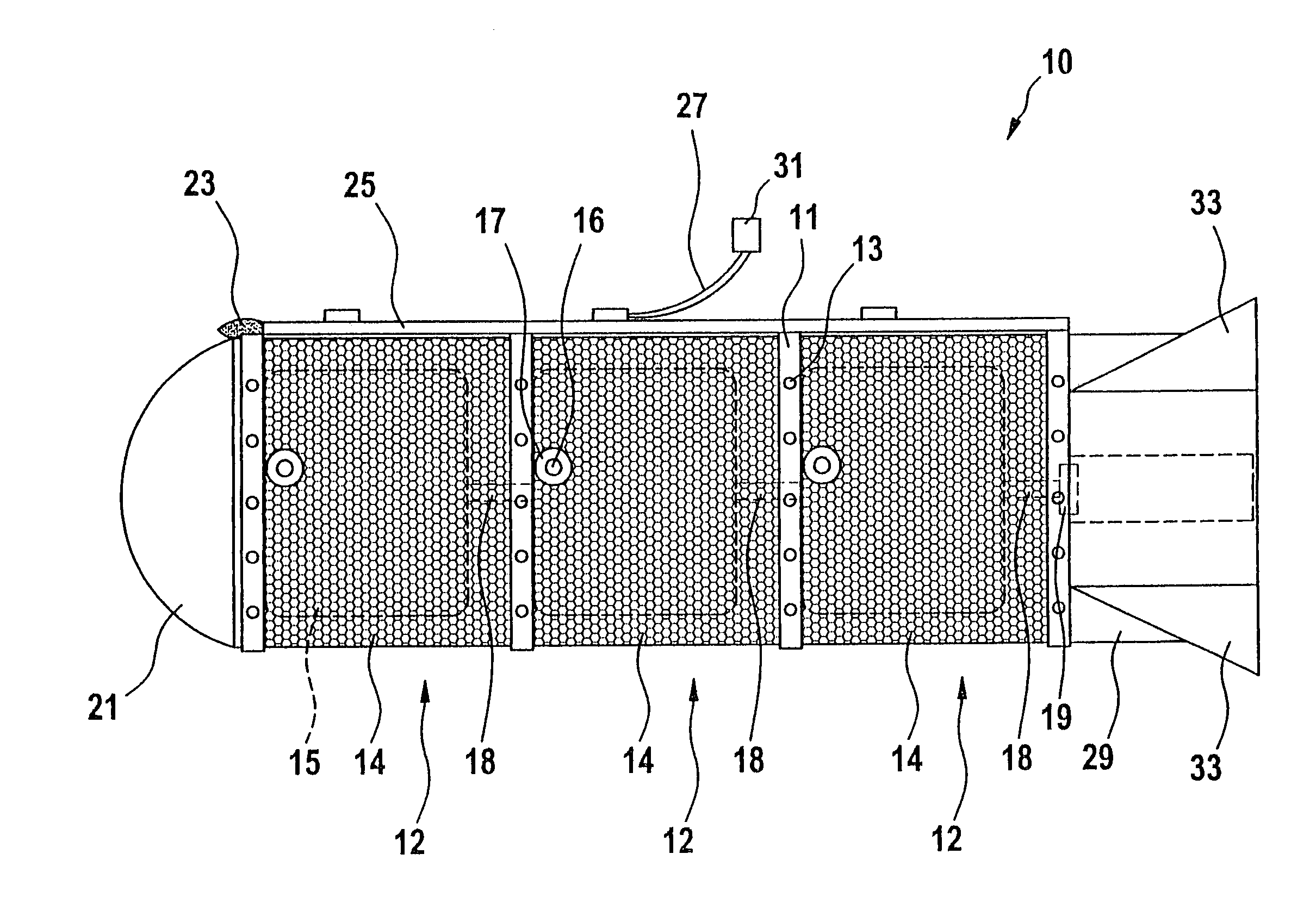
A fuze for a submunition comprises a fuze housing with a stabilizer ribbon for aerodynamic orientation, a fuze slider released by tension on the stabilizer ribbon, an air-powered electric generator extended into the airstream by the fuze slider and powered in flight by high-speed airflow, a MEMS safety and arming device, a fuze circuit board including an explosive fireset, and an electrically initiated firetrain. The fuze is fixed to and communicates explosively with the end of a grenade warhead.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Full insurance type artificial rain bullet detonator
A full-insurance rain bomb fuze relates to an artificial hail-suppressing rain bomb fuze for antiaircraft guns. The present invention mainly includes a fuze body, an upper drug tray, a lower drug tray, a rotary body, a bracket, a pressure screw, and a detonator tube. There is a 134-136° circular groove on the bottom surface of the medicine tray and the top surface of the medicine tray respectively. The gunpowder column is installed on the side, and the gyratory body is installed in the medicine feeding tray. The left and right sides of the medicine feeding tray and the gyratory body are respectively equipped with centrifugal safety screw plugs, centrifugal springs, centrifugal pins and safety pins, and gunpowder safety screw plugs. The dimensions of the booster tube have also been improved. The invention has the advantages of small fragments, sufficient explosion, safe use, good delay reliability and more complete detonation.
Owner:CHANGAN AUTOMOBILE (GRP) CO LTD
Remote Setting for Electronic Systems in a Projectile for Chambered Ammunition
ActiveUS20090217836A1Installation economyEasy to installAmmunition projectilesIncandescent ignitionElectronic systemsMechanical engineering
A fuze setting circuit in an artillery or tank shell having a case with a press-fitted head assembly is provided with an electromechanical fuze-wiring link that is completed electrically by mechanical assembly of a tracer-carrying projectile on the shell casing, and by the rotational attachment of a programmable fuze onto the projectile.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS ORDNANCE & TACTICAL SYST CANADA VALLEYFIELD INC
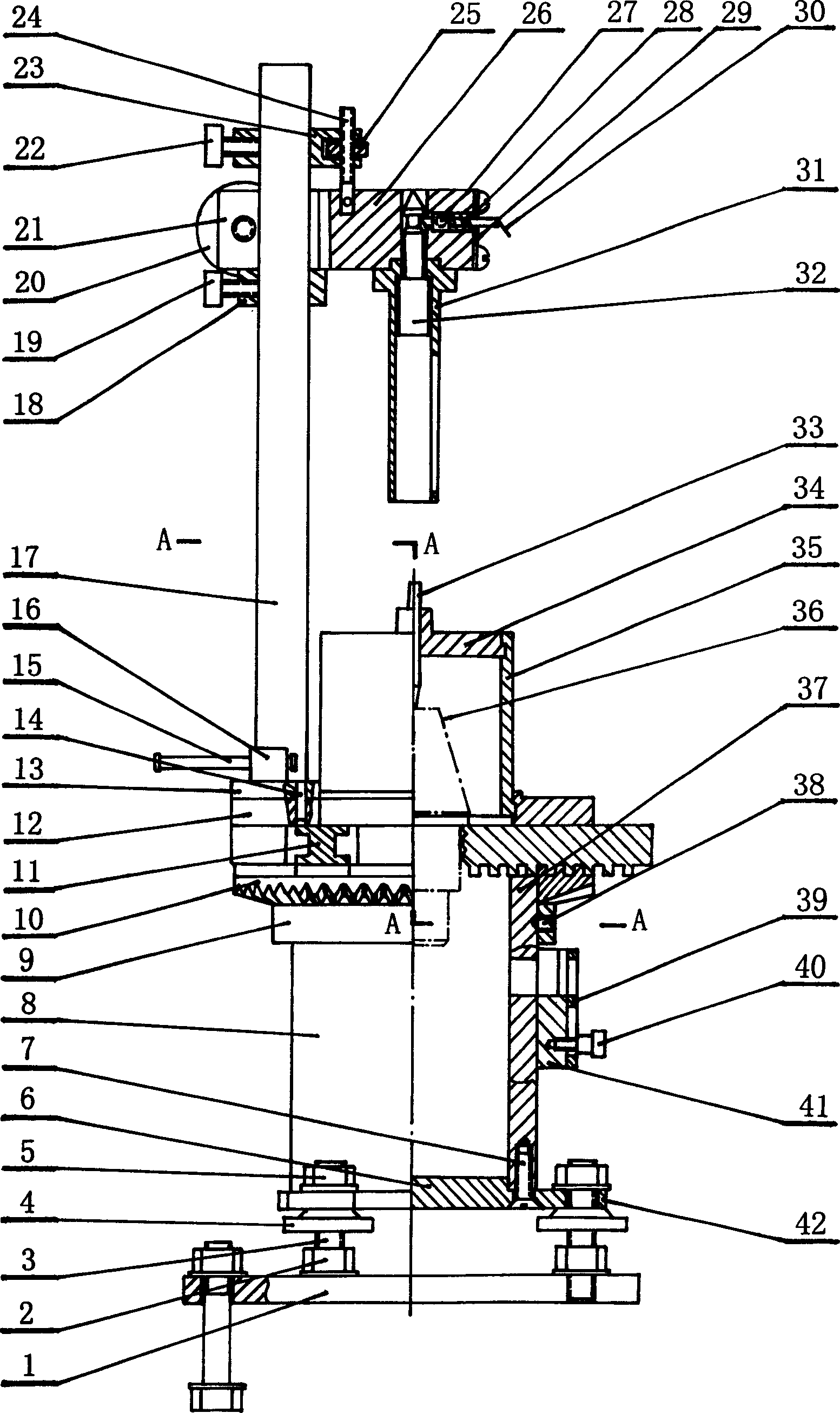
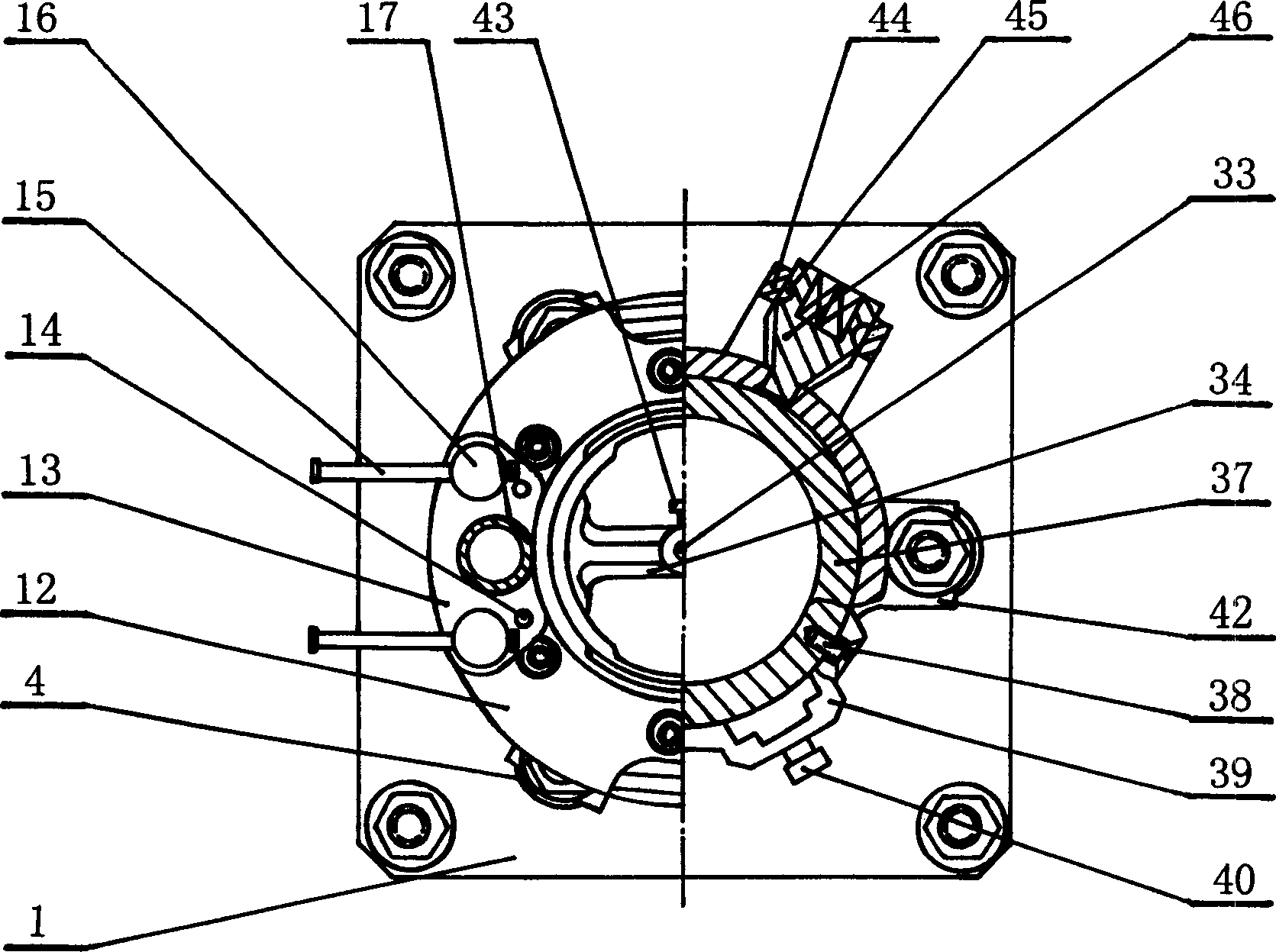
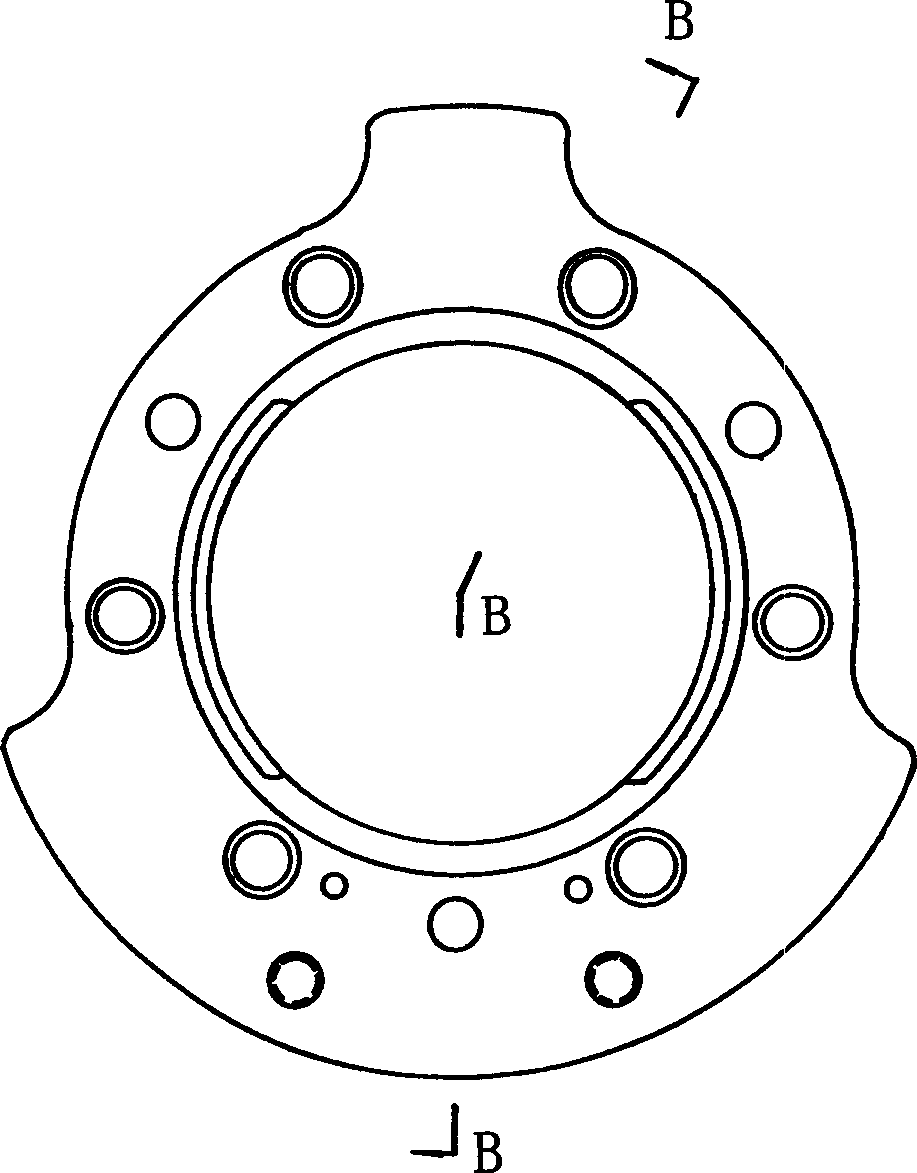
Fuze rotary demounting device for small-caliber aircraft projectiles
The invention relates to a fuze rotary demounting device for small-caliber aircraft projectiles and belongs to an automatic demounting line for the small-caliber aircraft projectiles. The fuze rotary demounting device comprises a rotary demounting power head, a projectile positioning clamping mechanism, a positioning lifting slide table, a fuze-moving-out mechanical arm, a counter weight mechanism and a rack. A hydraulic floating jaw and a spring seat are used for solve the key technical problem of fuze streamline conical surface clamping, reliable projectile positioning is guaranteed by the shape-following design of the cartridge jaw, and safe and reliable operation of the device is guaranteed by the clamping force for hydraulic clamping a fuze and a battle part. A rotary demounting separating end falls by the aid of the axial force and self weight, rotary demounting is performed according to screw pitch, and disordered fastening is avoided. By the fuze rotary demounting device, safe, fast and automatic fuze rotary demounting is achieved through electric, gas and liquid linkage control, automatic demounting of the small-caliber aircraft projectiles is achieved, and good technical support is provided for retired ammunition demounting.
Owner:CHANGCHUN EQUIP TECH RES INST
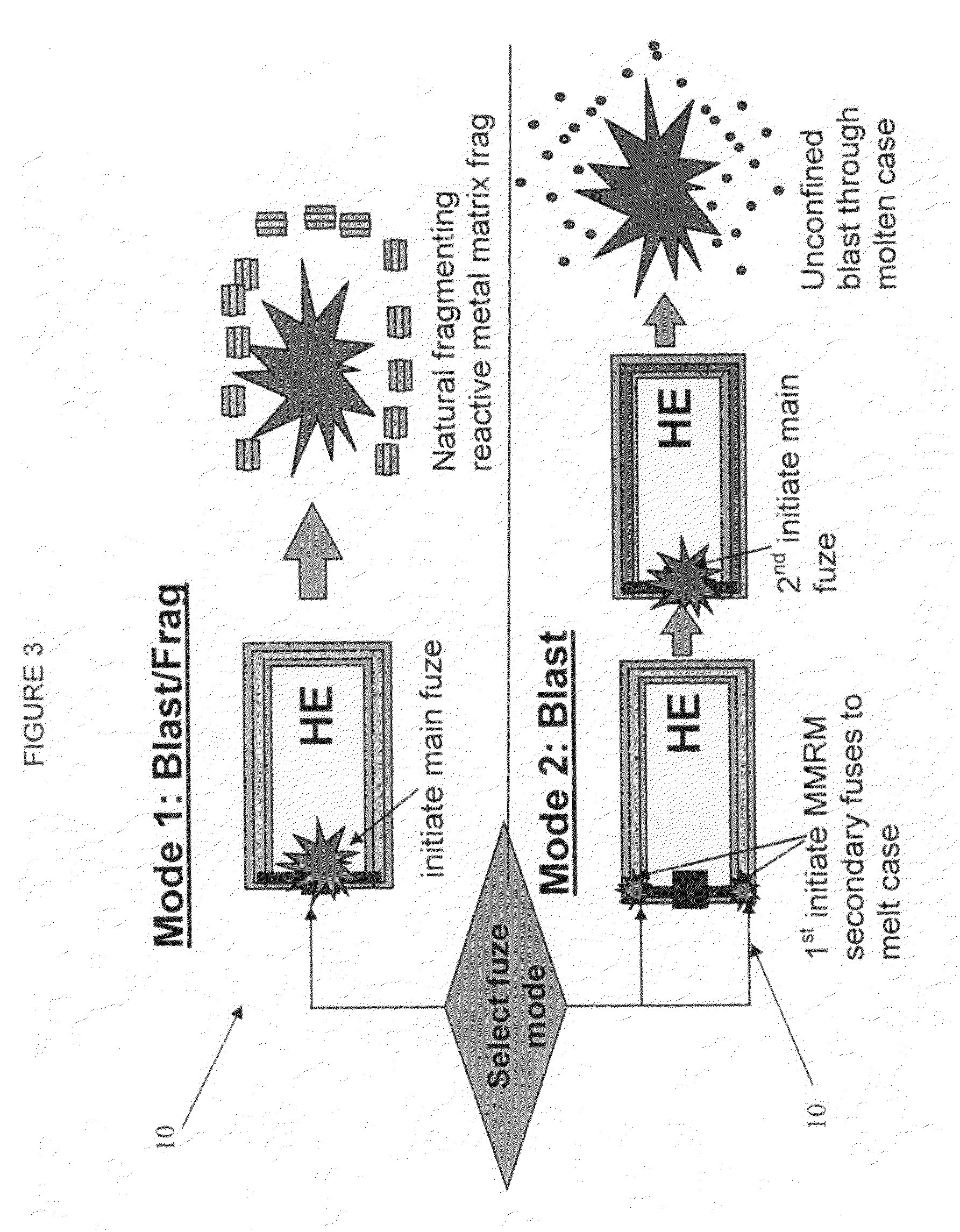
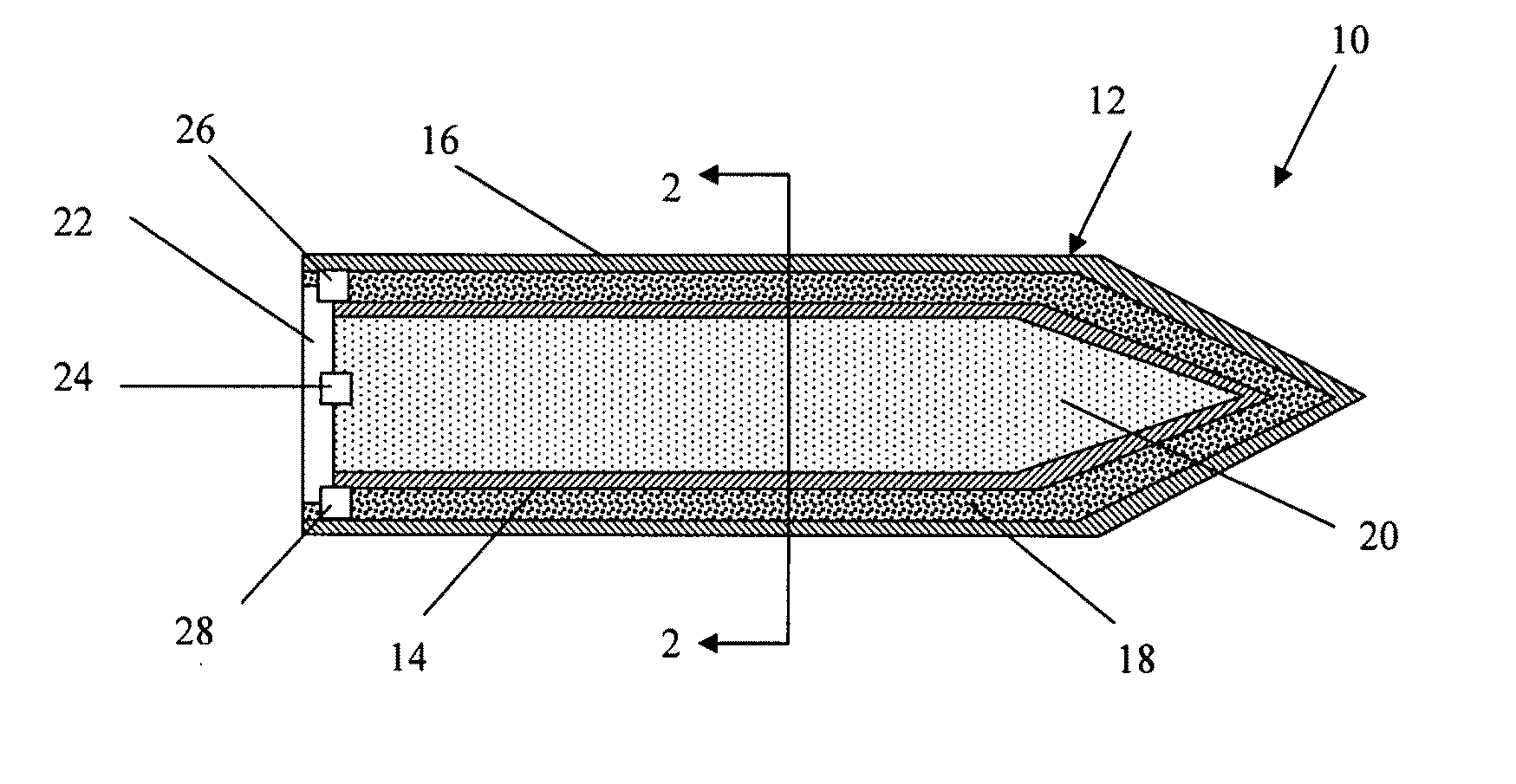
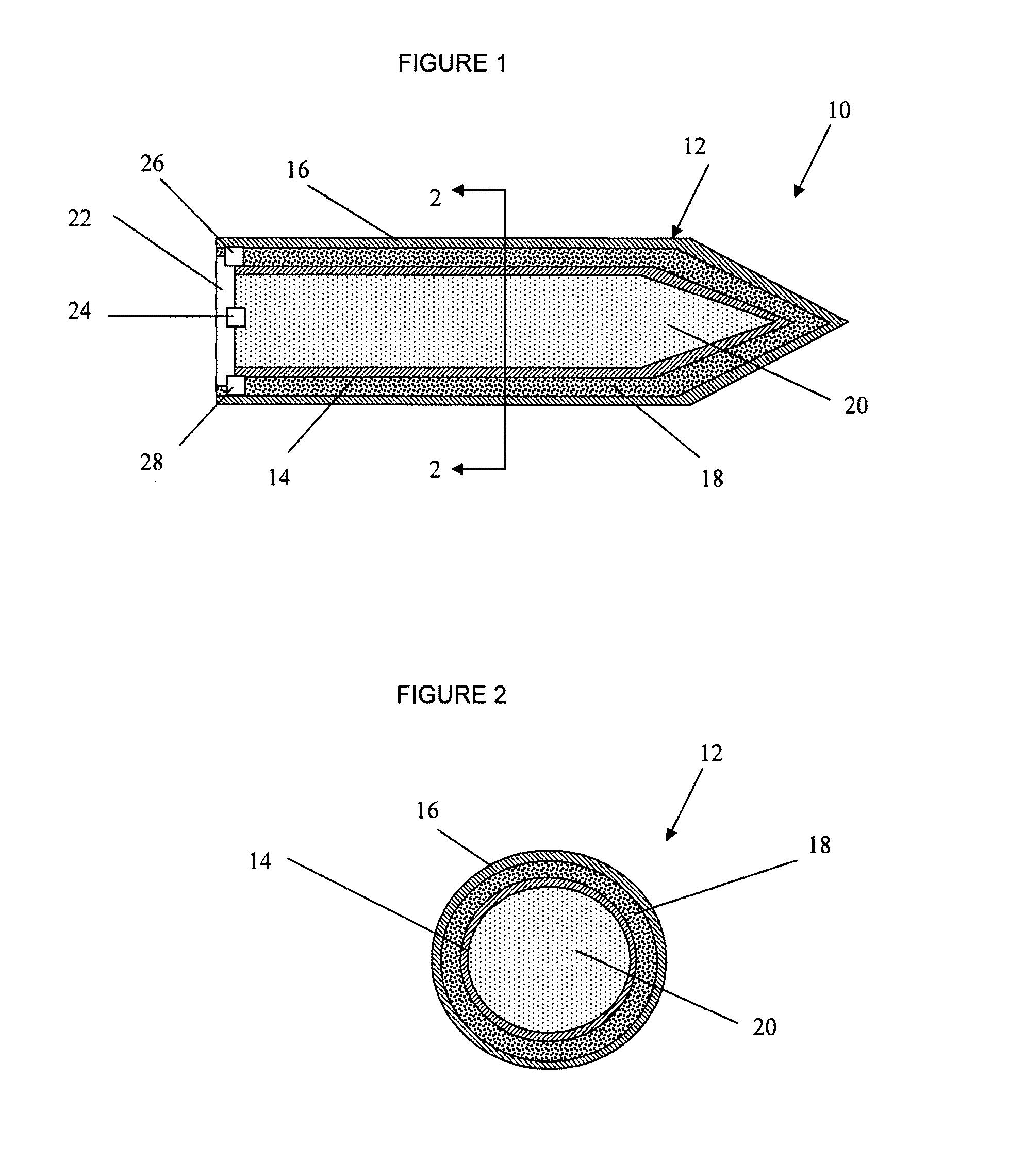
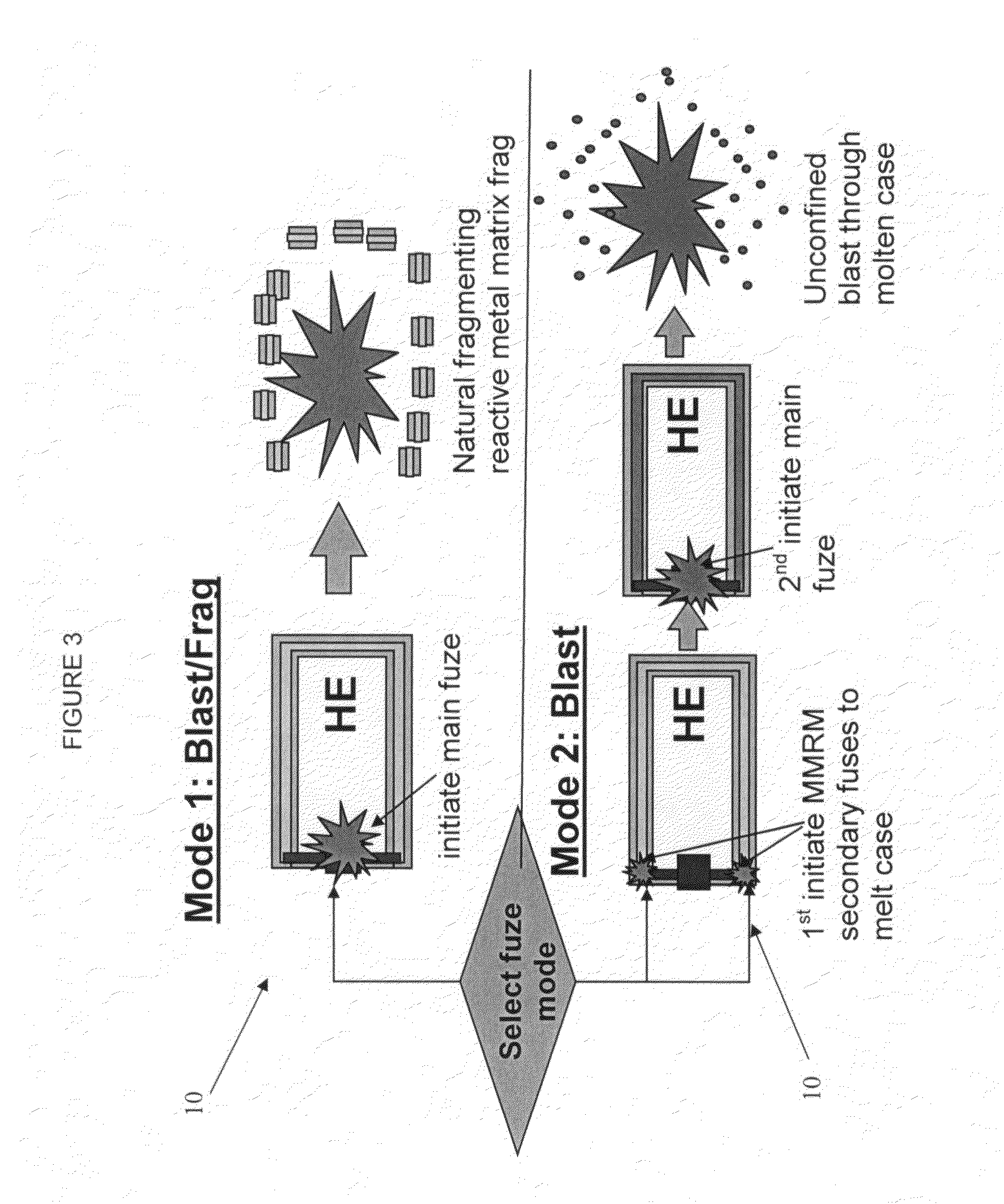
Selectable effect warhead
ActiveUS7845282B2Reduce impactSelectively eliminatedAmmunition projectilesProjectilesBlast effectsOperation mode
A munition includes a casing, the casing formed at least in part from a material comprising (i) a meltable or phase-changing material, and (ii) an energetic material; an explosive payload contained within the casing; and a fuze arrangement, the fuze arrangement comprising a main fuze configured and arranged to ignite the high explosive, and at least one secondary fuze configured and arranged to cause the casing material to melt or undergo a phase change. A method of selectively altering the mode of operation of a munition includes: forming a casing, the casing comprising a material comprising (i) a meltable or phase-changing material, and (ii) an energetic material; introducing an explosive payload into the casing; providing a fuze arrangement comprising a main fuse and at least one secondary fuze configured and arranged to cause the casing material to melt or undergo a phase change; and selectively activating the main fuze and the at least one secondary fuze in a manner that provided at least a first and a second mode of operation, the first mode of operation comprising blast coupled with fragmentation effects, and the second mode of operation comprising mainly blast effects.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Selectable effect warhead
ActiveUS20100282115A1Reduce impactSelectively eliminatedAmmunition projectilesProjectilesExplosive AgentsBlast effects
A munition includes a casing, the casing formed at least in part from a material comprising (i) a meltable or phase-changing material, and (ii) an energetic material; an explosive payload contained within the casing; and a fuze arrangement, the fuze arrangement comprising a main fuze configured and arranged to ignite the high explosive, and at least one secondary fuze configured and arranged to cause the casing material to melt or undergo a phase change. A method of selectively altering the mode of operation of a munition includes: forming a casing, the casing comprising a material comprising (i) a meltable or phase-changing material, and (ii) an energetic material; introducing an explosive payload into the casing; providing a fuze arrangement comprising a main fuse and at least one secondary fuze configured and arranged to cause the casing material to melt or undergo a phase change; and selectively activating the main fuze and the at least one secondary fuze in a manner that provided at least a first and a second mode of operation, the first mode of operation comprising blast coupled with fragmentation effects, and the second mode of operation comprising mainly blast effects.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method and apparatus for autonomous detonation delay in munitions
A detonation timing apparatus and method of determining a detonation time is disclosed. The detonation timing apparatus comprises an initiation sensor, at least one impact sensor, and at least one controller. The at least one controller may be configured for sensing an initiation event associated with the initiation sensor and sensing an impact event associated with the at least one impact sensor. The at least one controller is further configured for determining an impact velocity estimate proportional to a temporal difference between the initiation event and the impact event, using the impact velocity estimate to determine the detonation delay, and generating the detonation event at the detonation delay after the impact event. The timing apparatus and method of determining a detonation time may be incorporated in a fuze, which may be incorporated in an explosive projectile.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Base mounted airburst fuze for projectile
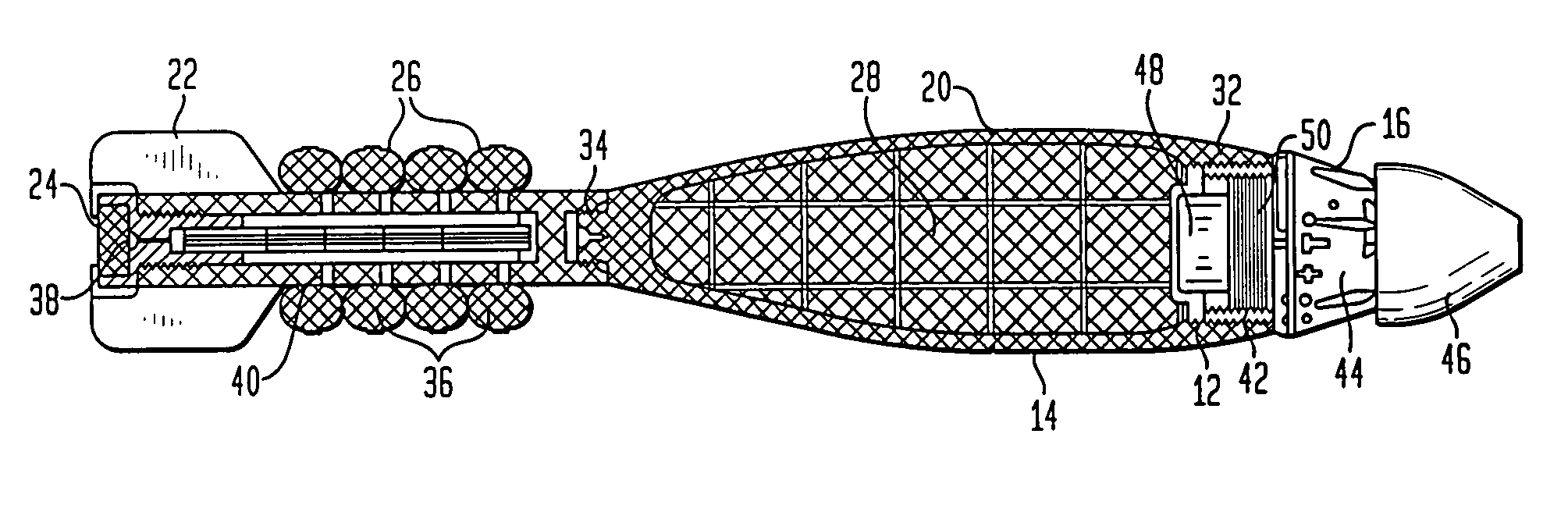
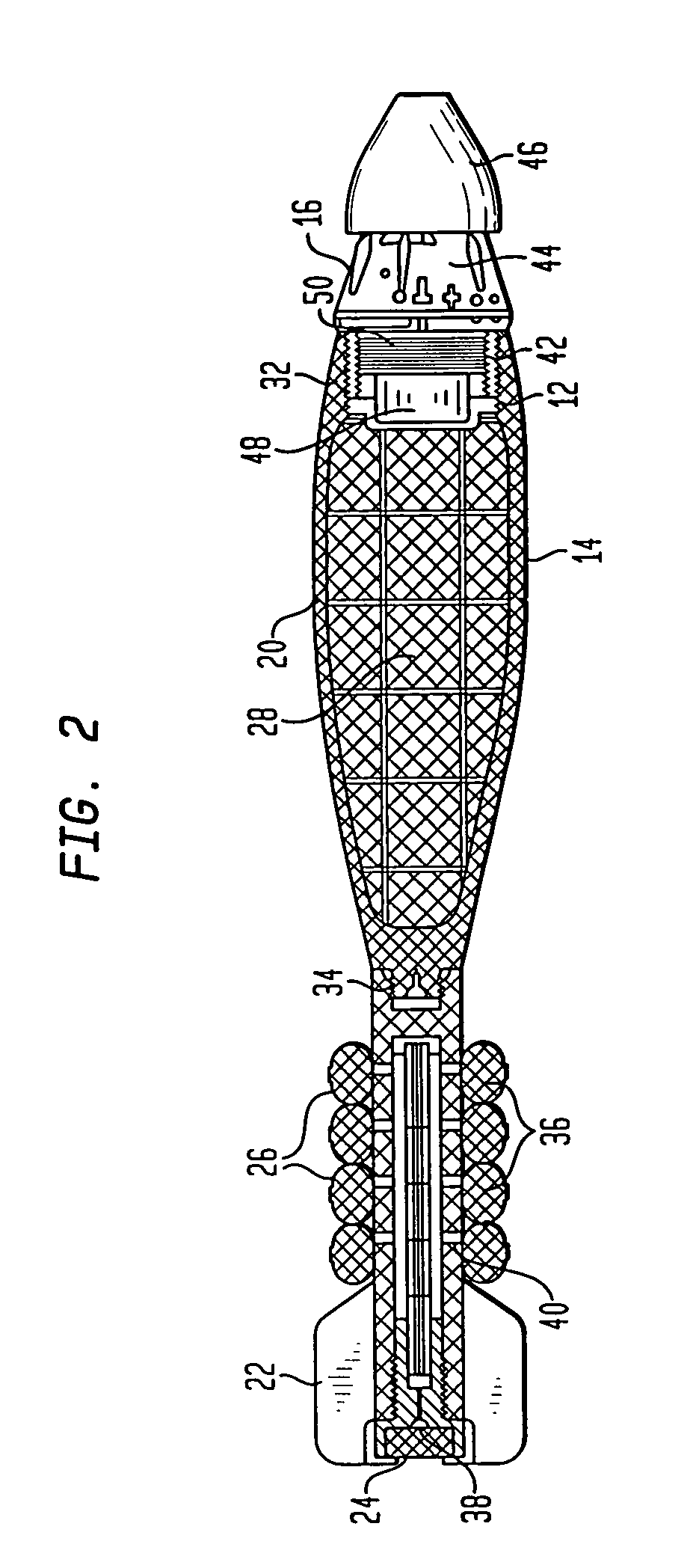
A projectile comprises a payload portion and an airburst fuze mounted on a rear of the projectile and explosively connected to the payload portion. The airburst fuze comprises an arming and firing electrical circuit including a setback generator; a slider that is movable from a safe position to an armed position, the slider including a detonator attached thereto; a setback lock and a spin lock that lock the slider in the safe position and, in response to a setback acceleration and a spin rate, respectively, unlock the slider; and an actuator that moves the slider to the armed position in response to a first input from the arming and firing electrical circuit; wherein a second input from the arming and firing circuit activates the detonator when the slider is in the armed position.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Method for detecting Japan abandoned chemical weapons in water areas
InactiveCN103645515ASolve the detection problemHigh sensitivityWater resource assessmentSatellite radio beaconingGas cylinderChemical weapon
The invention pertains to the technical field of underwater exploration, and specifically relates to a method for detecting Japan abandoned chemical weapons in water areas, wherein the method is suitable for detecting Japan abandoned chemical weapons, such as single or multiple chemical bombs, poison gas cylinders, chemical aerial bombs, bulk toxic agent barrels, etc., in various water area environments. The method of the invention is completed through six steps, the advantage of high magnetic method detection sensitivity can be realized, and the method plays an irreplaceable role in the detection of deeply-buried ammunition. In terms of technology safety, the magnetic method detection is use to passively measure the magnetic field strength generated by a target body, pulse currents and electromagnetic waves do not need to be transmitted to the underground, and no risk factor exists even for Japan abandoned chemical bombs and aerial bombs provided with fuzes. In terms of detection operation efficiency, a magnetometer has advantages over other instruments. The Japan abandoned chemical weapons comprise chemical bombs, poison gas cylinders, chemical aerial bombs and barreled toxic agent, the common characteristic of the chemical weapons is that all of the chemical weapons is provided with a ferromagnetism metal housing, so typical conditions of the magnetic method detection can be satisfied.
Owner:中国人民解放军防化学院
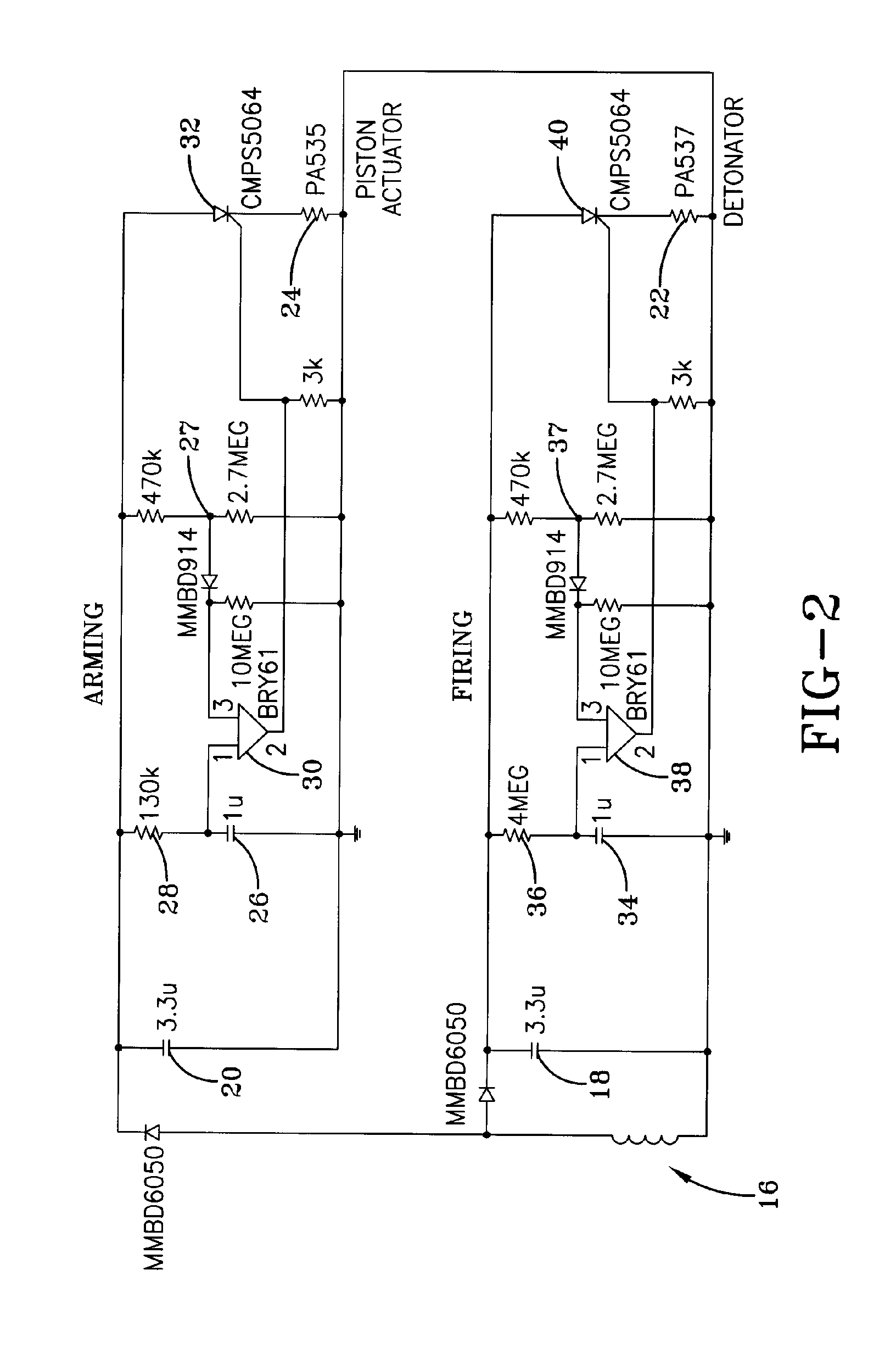
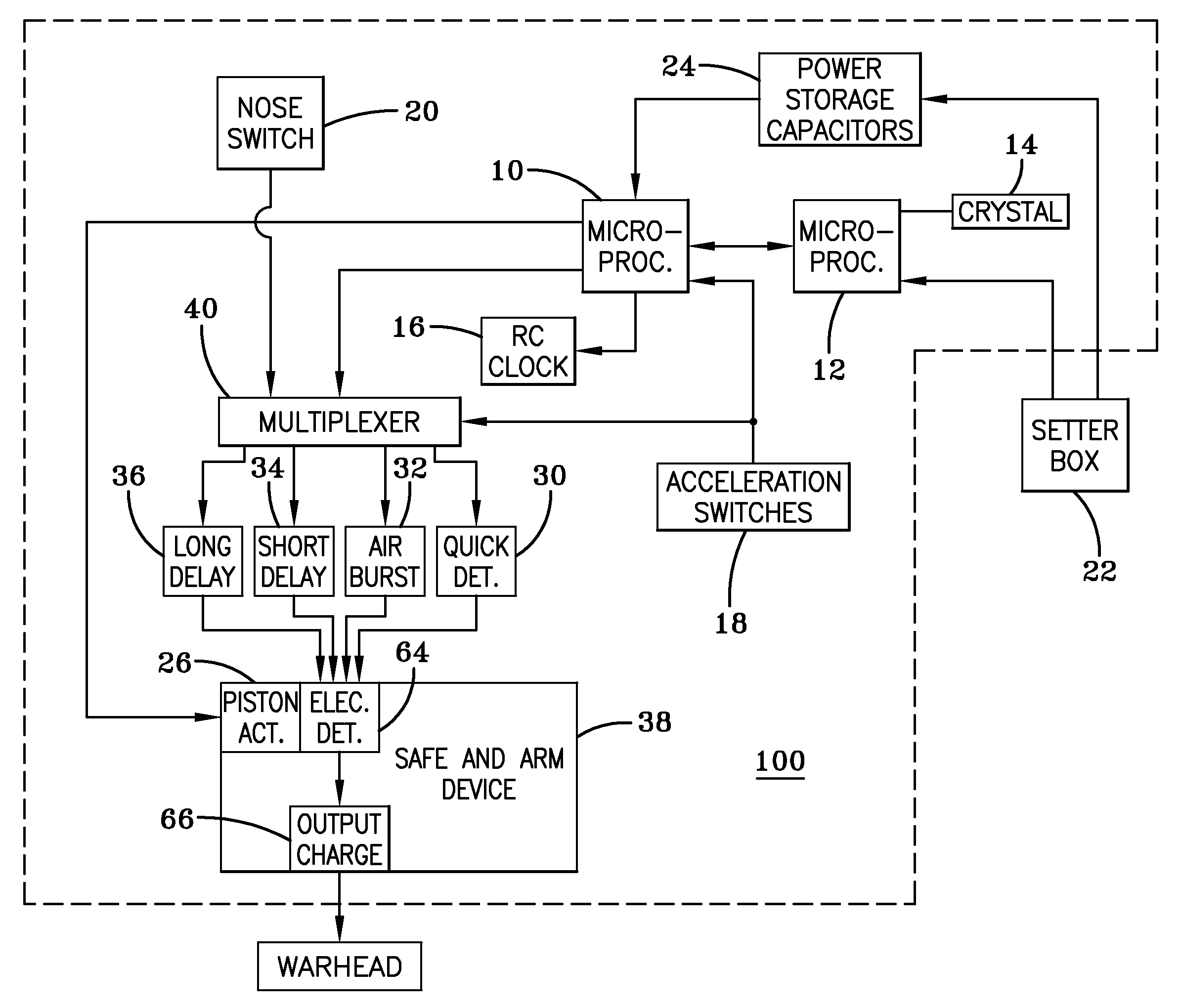
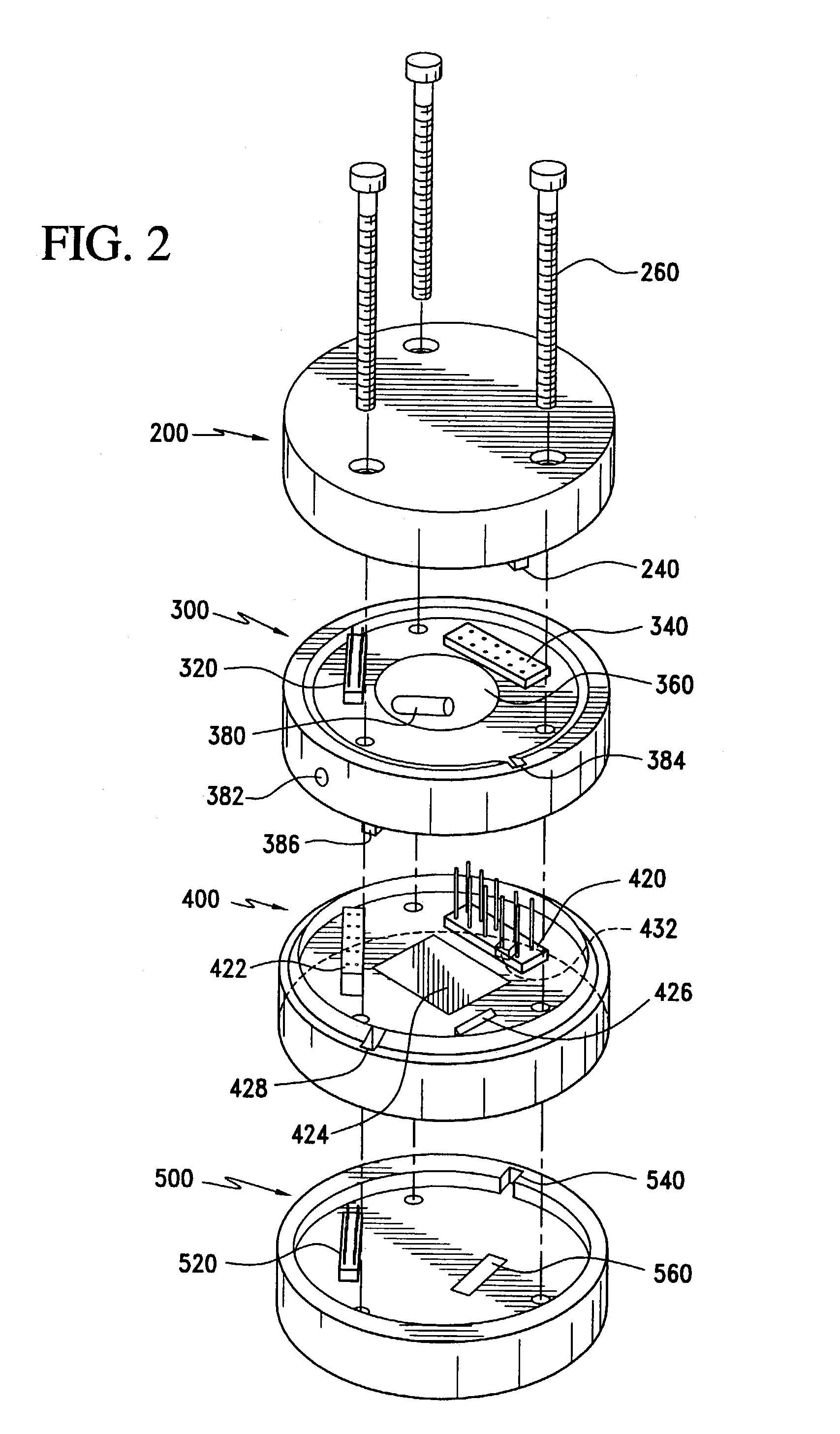
Multi-mode fuze
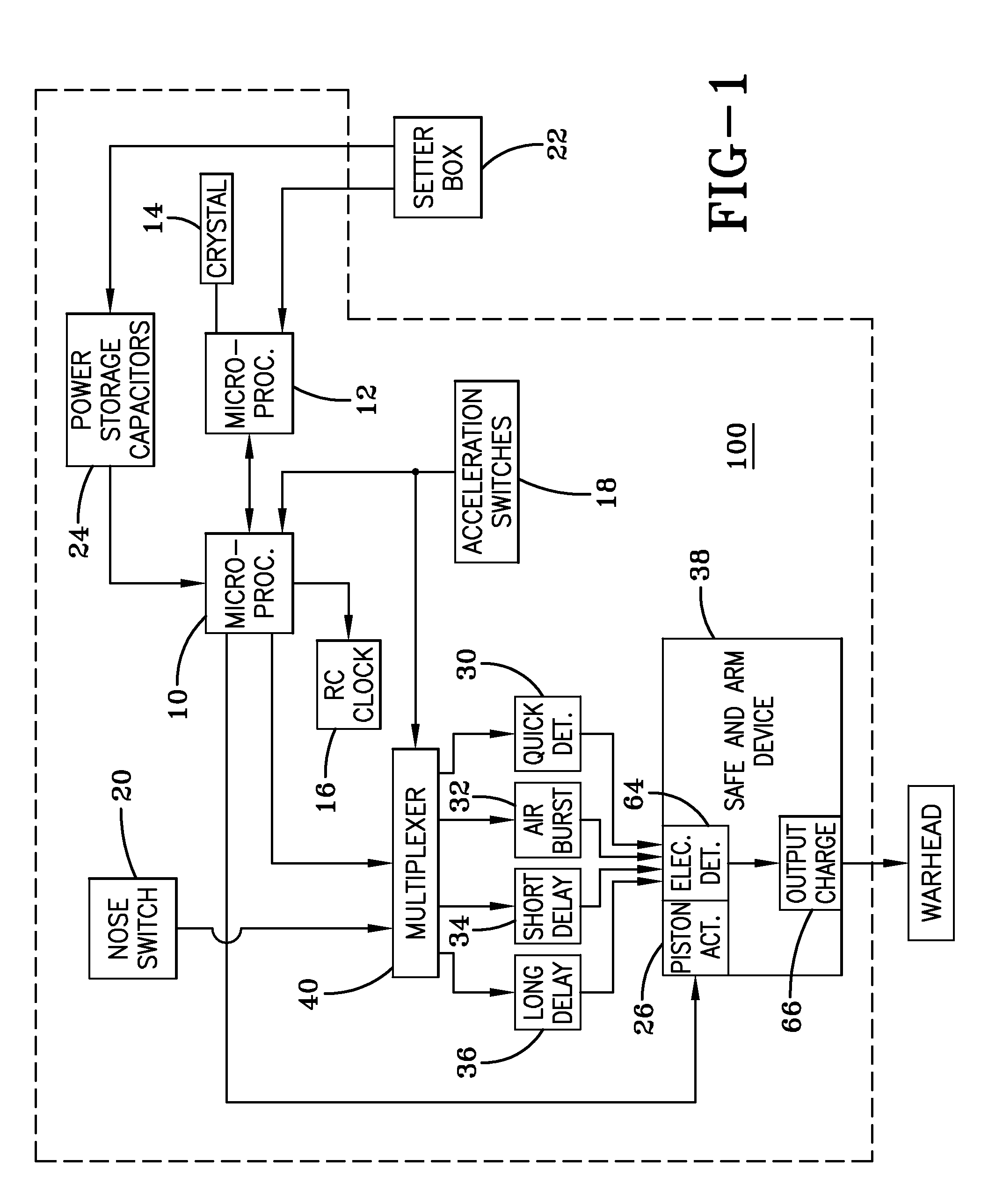
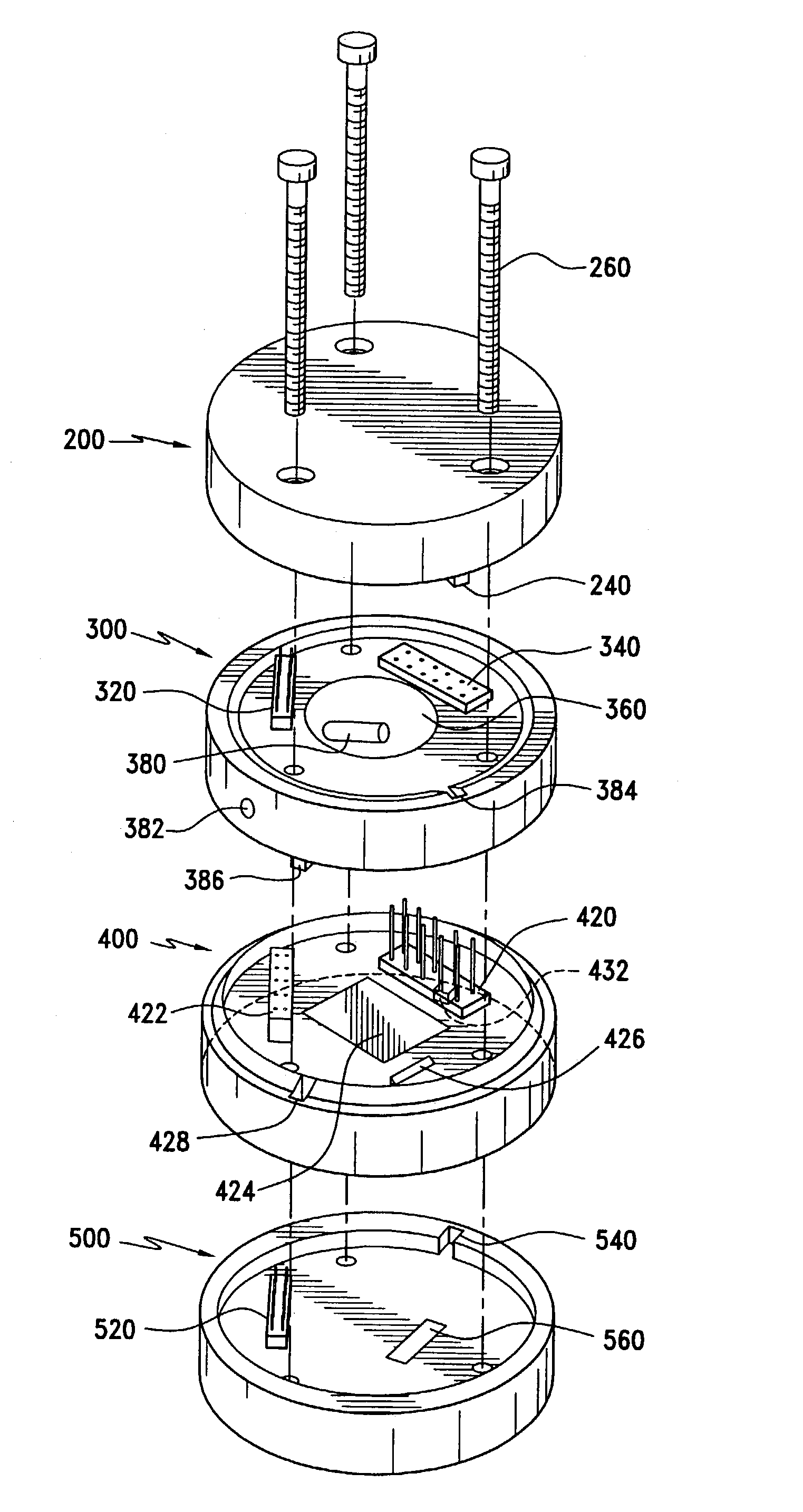
A multi-mode fuze includes first and second microprocessors, the first microprocessor being connected to a resistor / capacitor oscillator and the second microprocessor being connected to a quartz crystal oscillator, the first and second microprocessors being connected to each other, the second microprocessor being operable to time calibrate the first microprocessor; a safe and arm device connected to the first microprocessor; power storage capacitors connected to the first microprocessor; a nose mounted impact switch connected to the first microprocessor; at least one impact delay circuit connected to the first microprocessor; and at least one acceleration switch connected to the first microprocessor.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Modular electronic fuze
InactiveUS7213518B2Readily assembled into military ordnanceReadily signaling deviceIncandescent ignitionTime fuzesModularityEngineering
A modular fuze assembly is provided for use in multiple types of military ordnance. The fuze comprises a base unit having an initiator for arming the fuze; a timer assembly that includes a programmable clock package; a trigger assembly comprising a line monitoring circuit and a photo-capacitor; and a top cover unit. Each of the individual components are interconnected together to form a single, unitized system. Multiple initiation stages are provided to ensure payload activation.
Owner:ENGEL BALLISTIC RES
Burping projectile
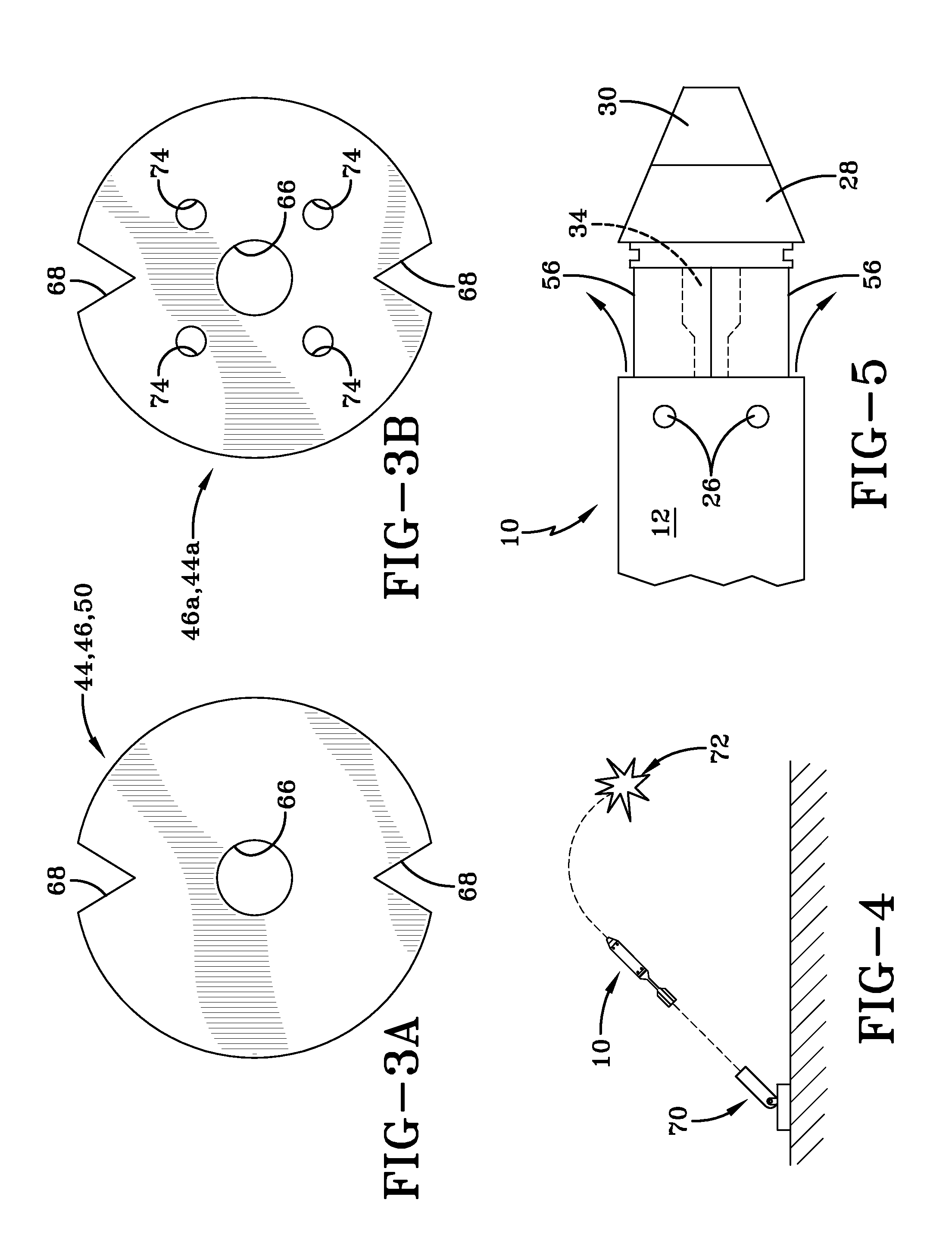
The present invention provides a burping projectile and, particularly, a non-lethal projectile having a nose-mounted fuze thereon, which initiates an expulsion charge via an ignition shaft in the payload cup of the projectile body at a preset distance from target impact, resulting in sufficient expansion of the projectile body via the forces of propellant gases to create an annular opening between the projectile body side wall and projectile body forward end. The payload is then ejected from this annular opening, the resulting forward velocity of the escaping payload producing a rearward thrust on the projectile, and a concomitant deceleration thereof to a non-lethal forward velocity or a total reverse in direction of travel.
Owner:DINDL FRANK J +1
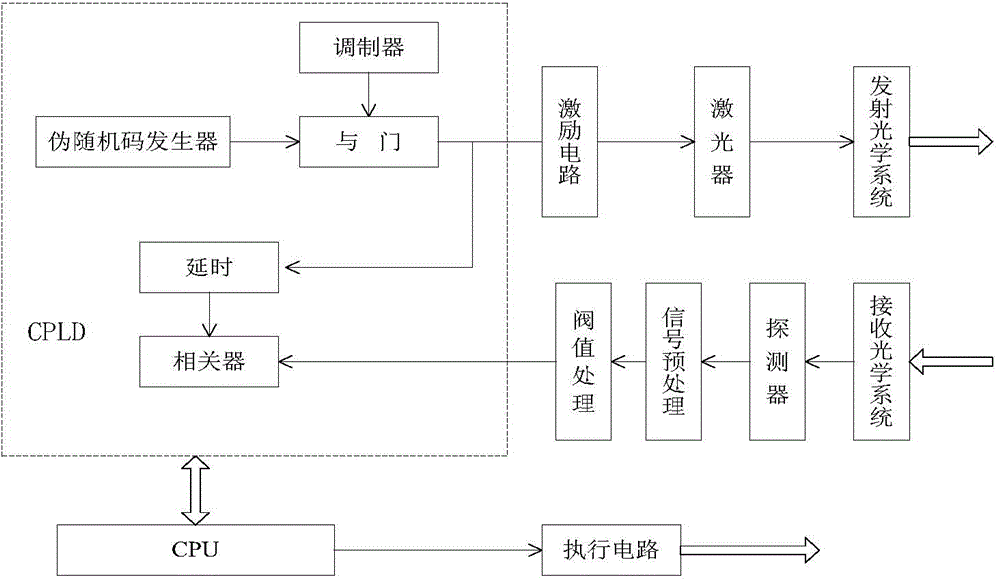
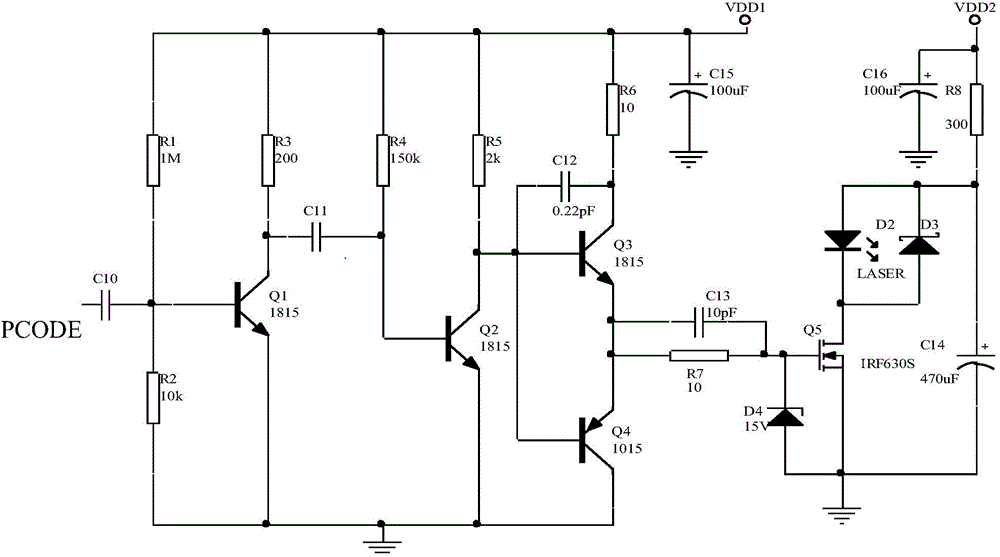
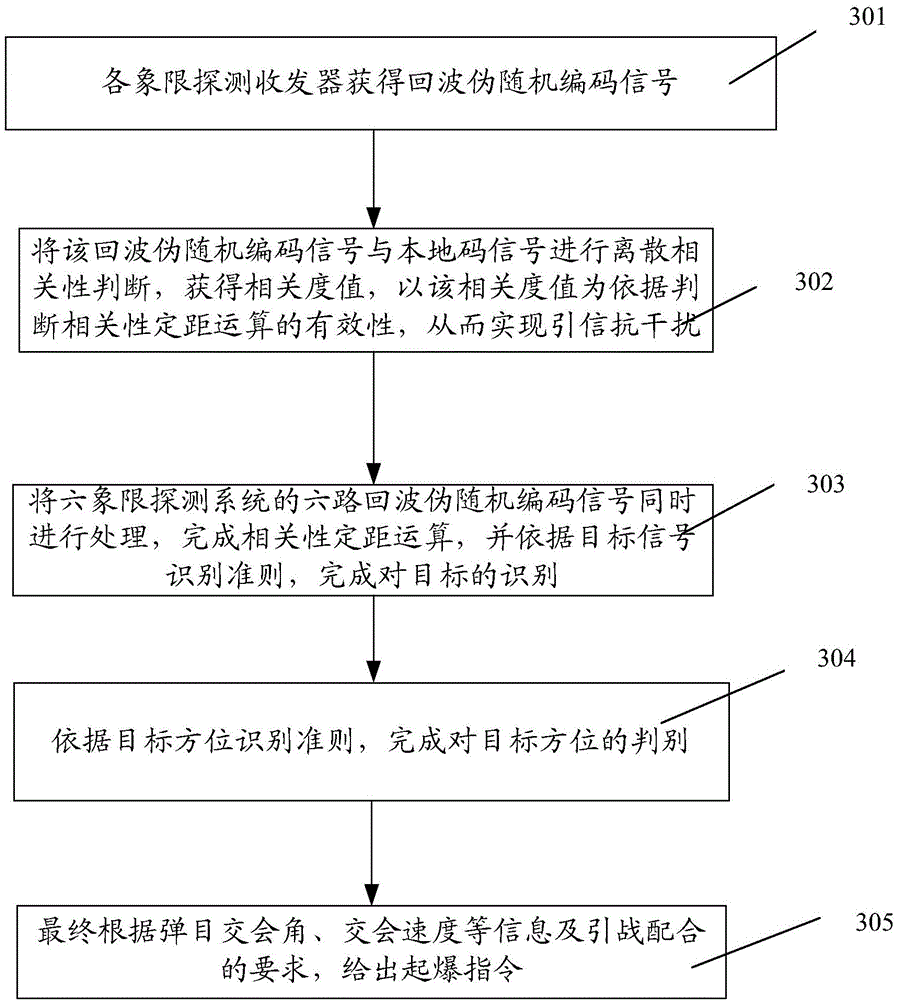
Pseudo-random code system-based laser fuze system and target identification method thereof
InactiveCN104457452AImprove recognition accuracyImprove coordination efficiencyProximity fuzesTransceiverSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses a pseudo-random code system-based laser fuze system and a target identification method thereof. The laser fuze system adopts a six-quadrant detection scheme, and each pair of detection transceiver systems comprises a pseudo-random code generator, an excitation circuit, a laser, a detector, a signal processing circuit, and transmitting and receiving optical systems; the pseudo-random code generator is used for generating a pseudo-code signal with certain code element width and frequency, the pseudo-code signal is modulated to obtain a pseudo-code pulse signal meeting the requirement of pulse width of the laser, and the pseudo-code pulse signal is excited by the excitation circuit to drive the laser to transmit encoded laser pulse; finally, a laser beam irradiates to a target after being collimated or extended by a transmitting optical system, and the optical energy reflected from the target is received by the receiving optical system; meanwhile, the filtering of a filter and the focusing of the light beam are completed, and after the detector completes the photoelectric conversion and the signal preprocessing of the signal processing circuit, an echo pseudo-random coded signal is obtained after threshold comparison.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
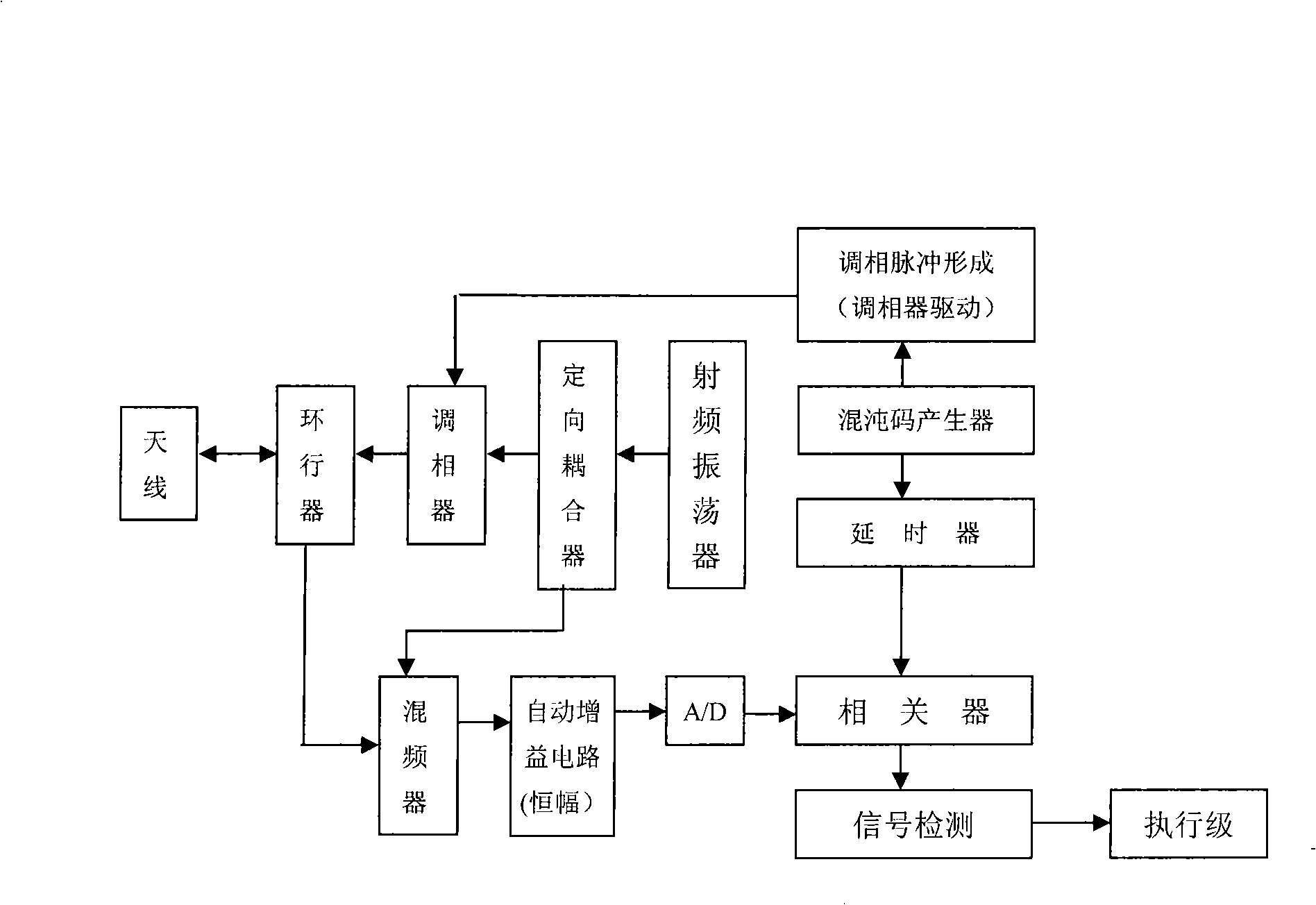
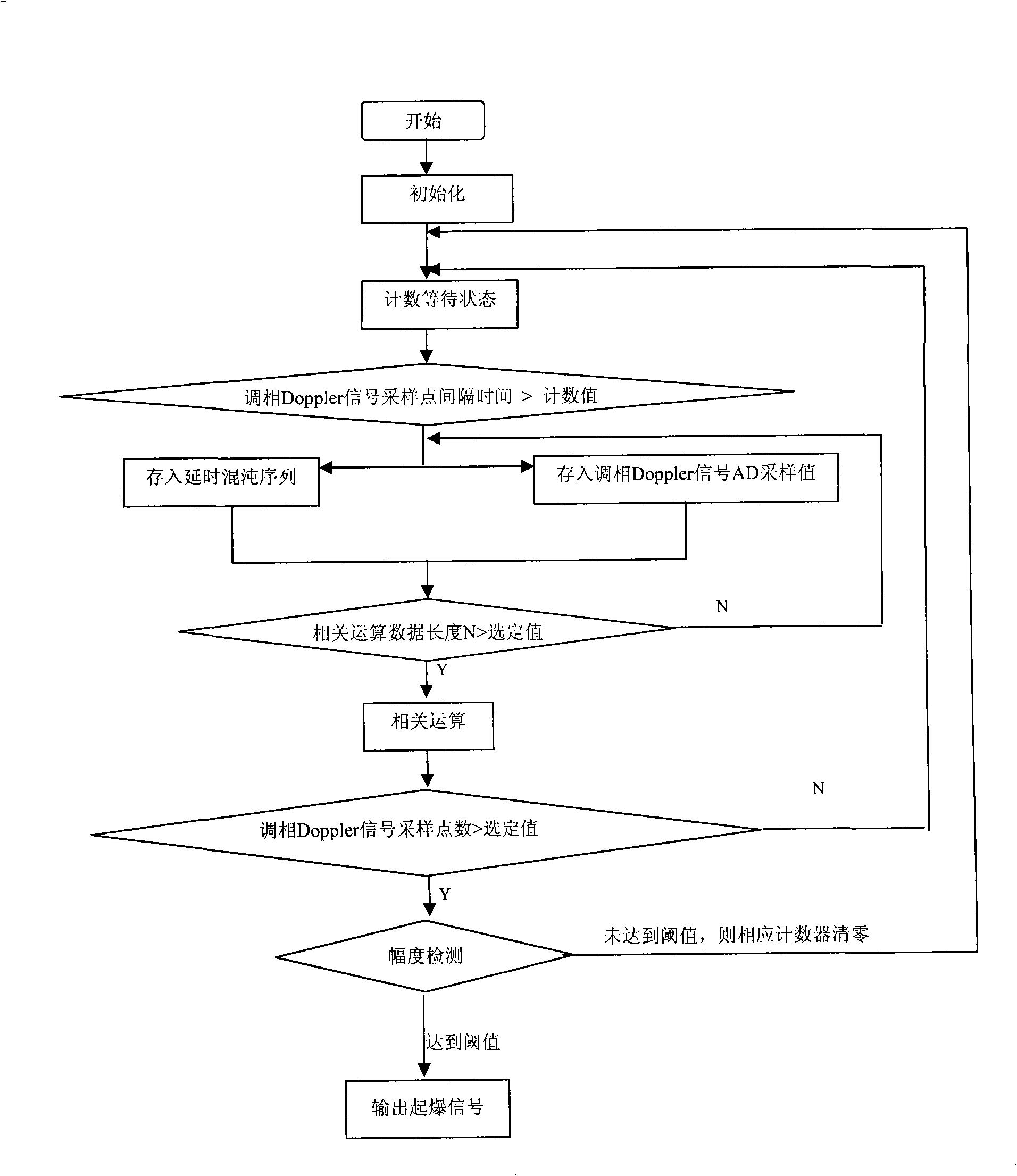
Continuous wave chaos phase-modulation radio fuse detection system and demodulation method
InactiveCN101256230AEasy to adjustControl real-timeWave based measurement systemsModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention provides a continuous wave chaos phase modulation firebird detecting system, especially a continuous wave chaos phase modulation firebird detecting system implemented based on the generation of modulation signal of FPGA and the quick digital correlative demodulation arithmetic of signal after modulating. The system comprises chaos code generator, retarder, radio frequency oscillator, directional coupler, phase modulator, circulator, aerial, mixer, automatic gain control amplifier, correlator and signal detecting part. The invention has important application value in aspect of realizing fuze anti-interference. The system not only can make the fuze with very perfect distance, speed resolution and distance measurement, distance measurement accuracy, but also with better anti-capturing performance due to diversity and initial value sensitivity of generating method of chaos signal.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Detector for light fuse sensitivity and igniting property
The detector for the sensitivity and igniting property of light fuse consists of fuse holder and its seat board and levelness regulator, locating sleeve to avoid explosion gas diffusion, striker and its centralizer, and drop hammer and its fall height determiner. It is used in the detecting the sensitivity and igniting property of different kinds of mechanical fuse, mechanical timing fuse and powder disc timing fuse with the first stage of igniting element being needle percussion cap or needle detonator. It is portable and may be used in field.
Owner:ORDNANCE TECH RES INST OF THE GENERAL ARMAMENT DEPT PLA
Universal smart fuze for unmanned aerial vehicle or other remote armament systems
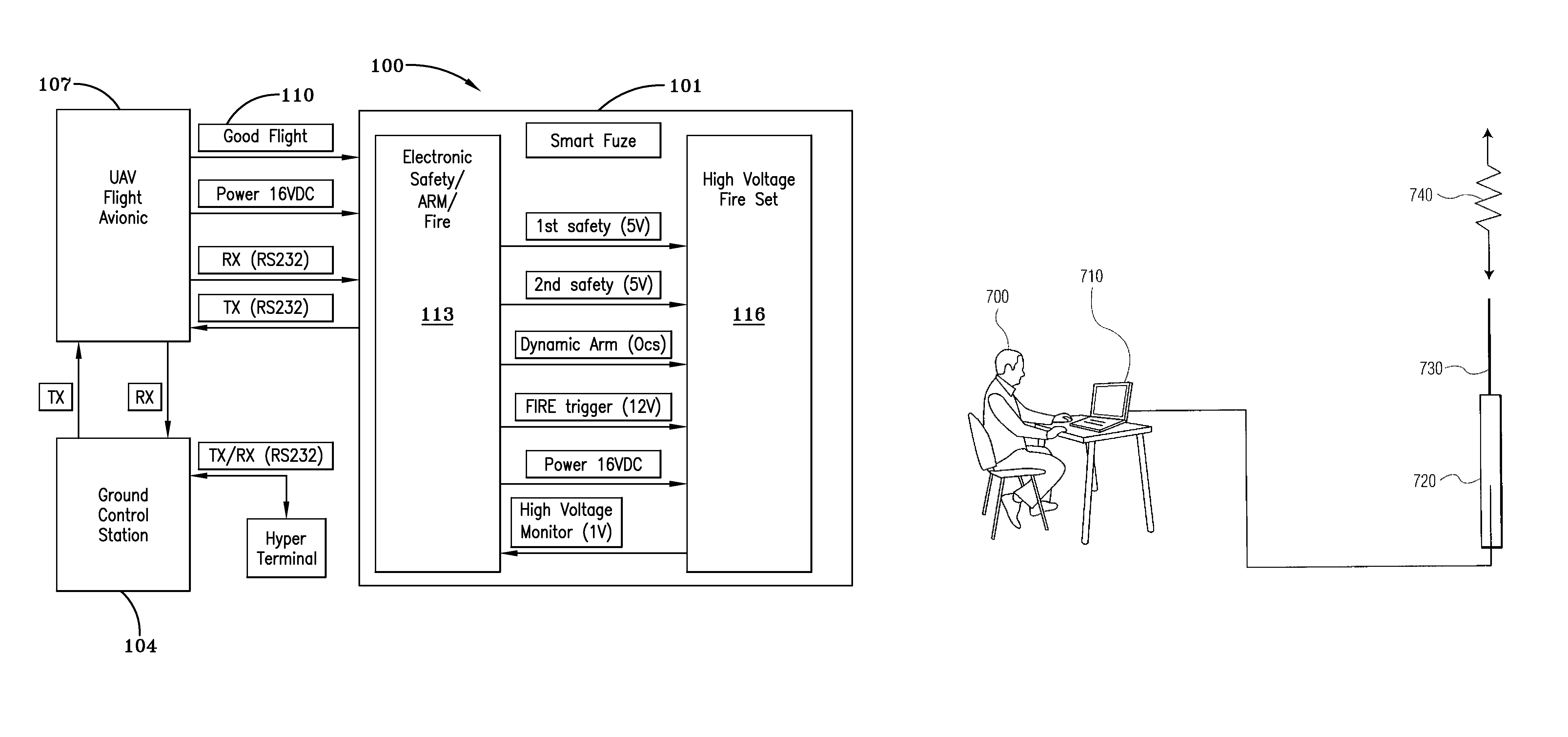
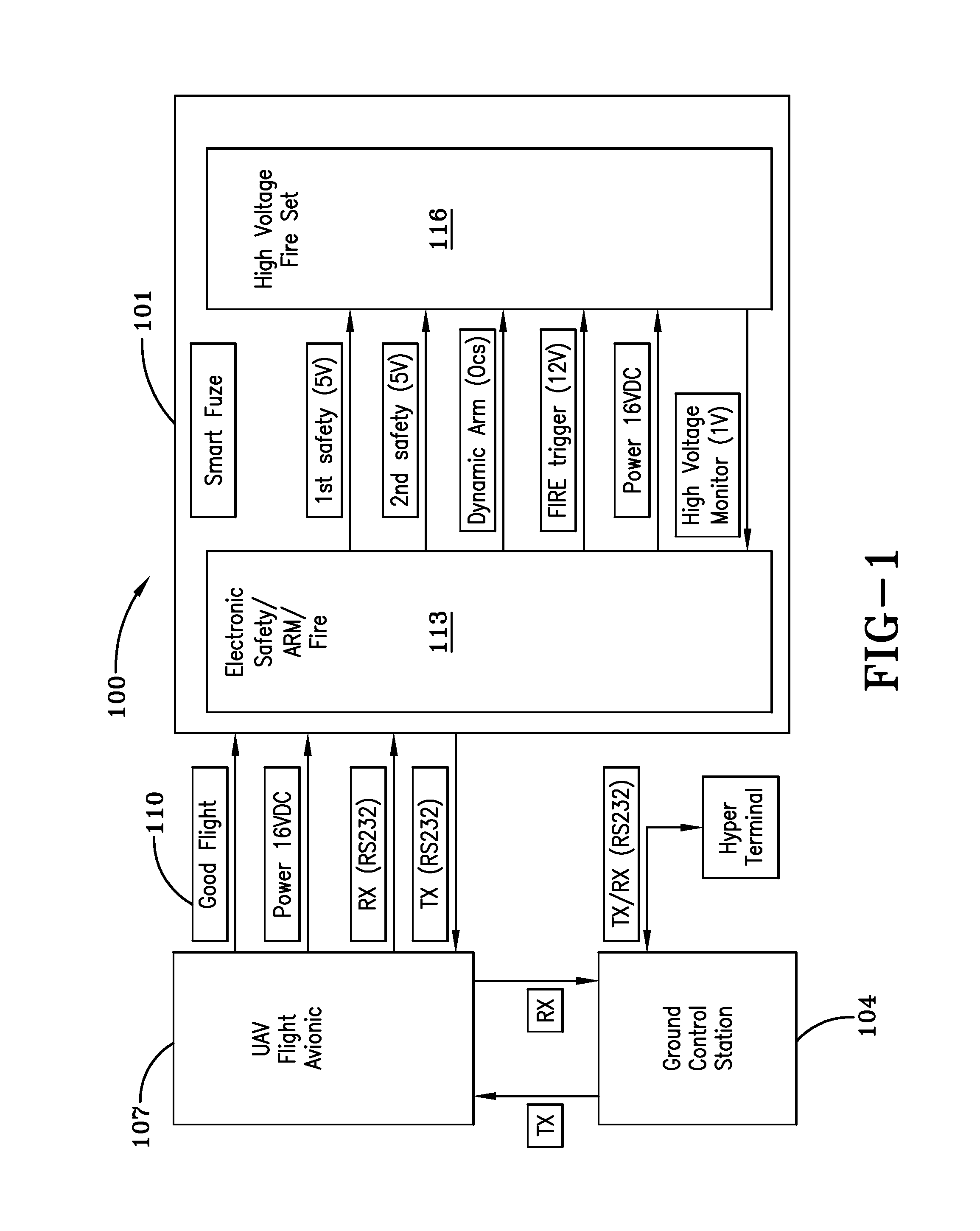
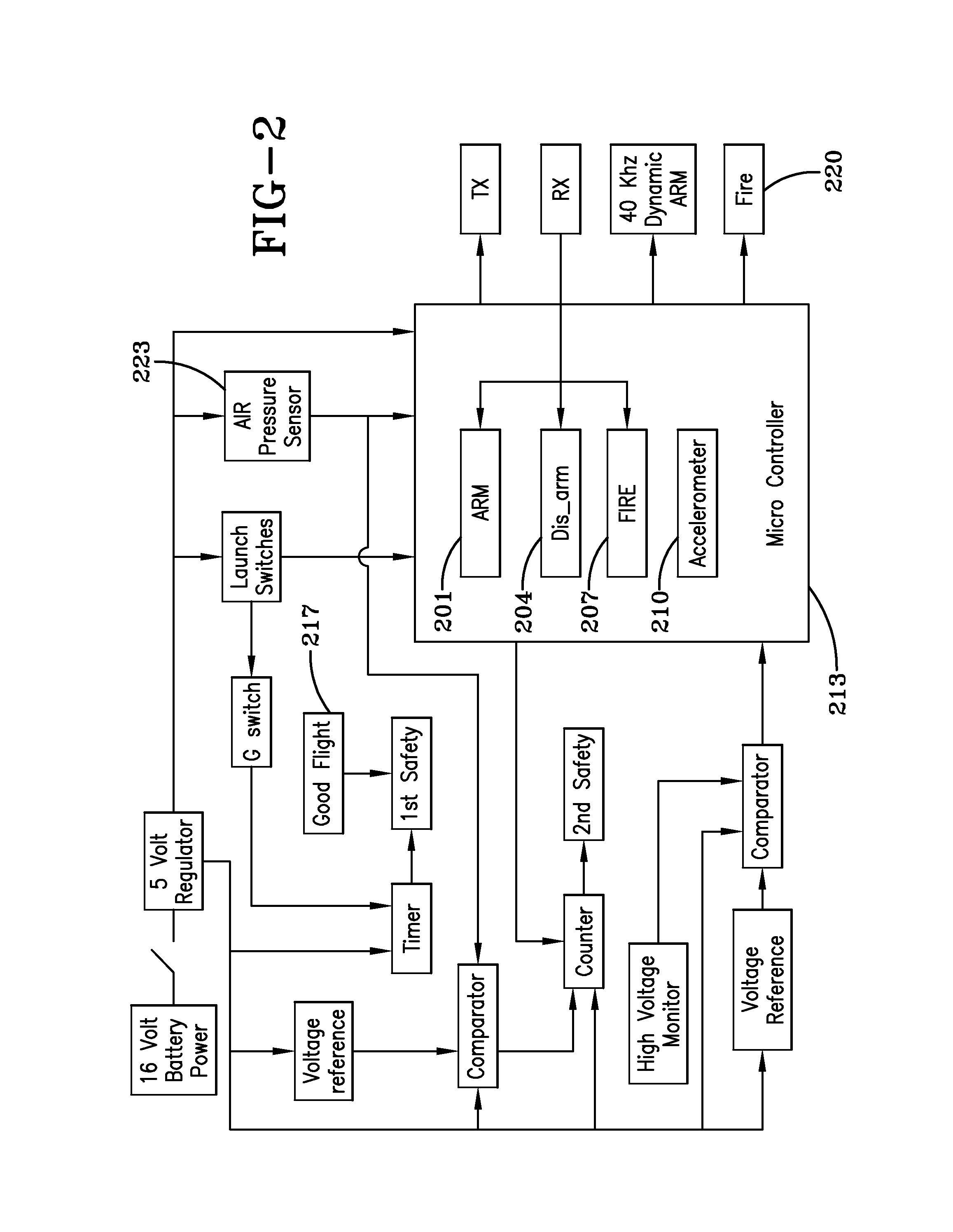
An unmanned aerial vehicle is equipped to carry a payload of explosives for remote delivery upon a target. The vehicle includes a small TV camera, global positioning system, and auto pilot homing target software. The modified vehicle is capable of being detonated upon an impact or selectively while still in flight. Vehicle flight is monitored by an operation person at a ground control station. The vehicle includes universal smart fuze circuitry for enabling the multiple functions for the vehicle and for enabling communications / commands from the operator at the ground control station. The fuze continuously communicates aspects of fuze status back to the ground control station; measures flight velocity by sensing air speed of the UAV; arms / disarms an explosives warhead package in the vehicle; in flight fires the explosives or else detonates the explosives warhead package upon impact with a select target. The camera images are communicated back to the operator who can make a decision on completing / aborting a mission. The wind speed indications, also fed back to the operator, can further aid in verifying a successful launch / good flight for decision of completing / aborting a mission.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Process for removing the fuze from explosive projectiles using fluid jet technology
A process for defuzing explosive projectiles using fluid jet technology. It is preferred that two or more projectiles be defuzed simultaneously in the same defuzing apparatus. The explosive material can also be removed from the casing by fluid jet technology, after the projectile has been defuzed.
Owner:BREMER BANK NAT ASSOC
Course self-correcting projectile
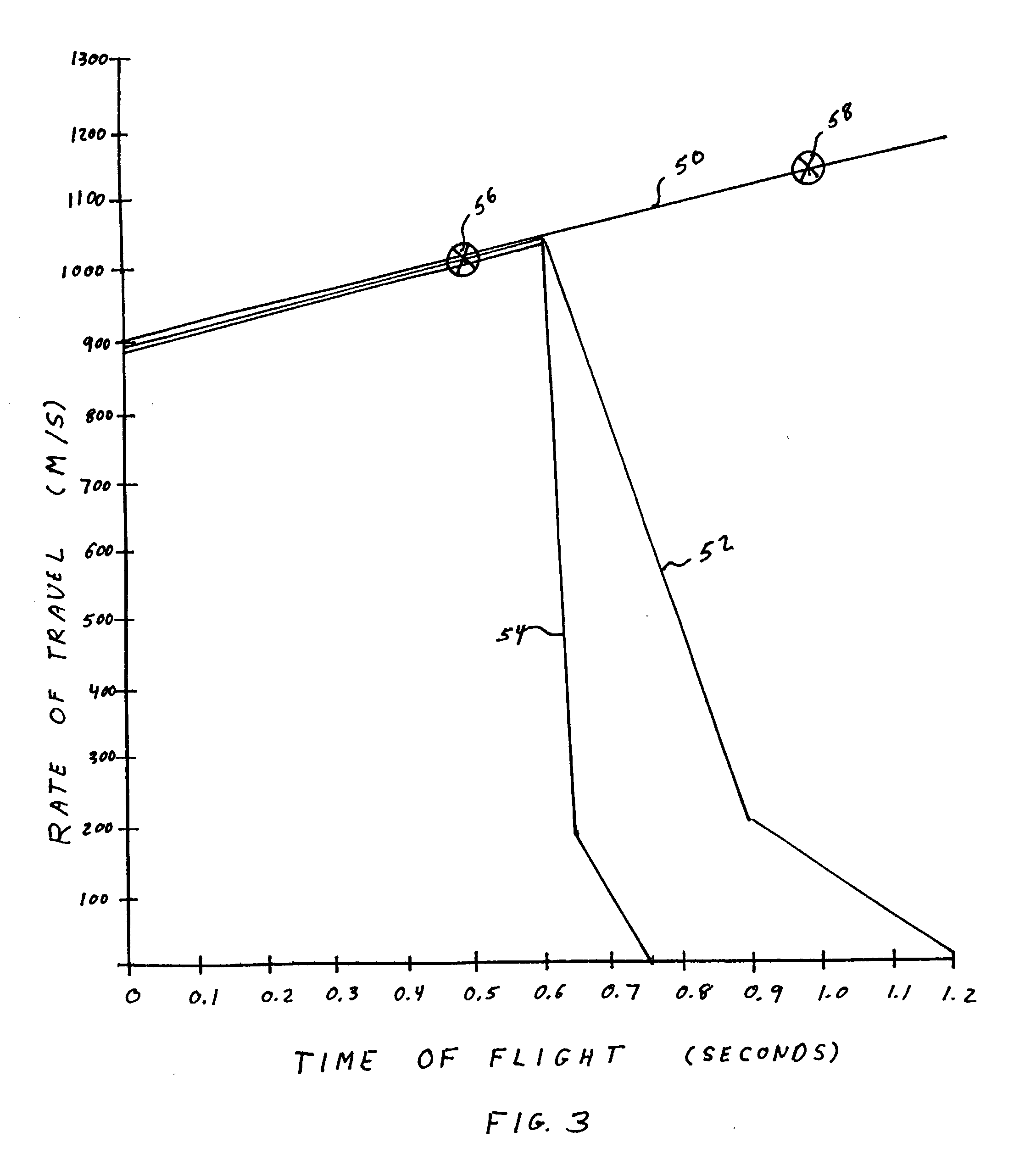
ActiveUS9115968B1Improve accuracyReduces projectile miss-distanceAmmunition projectilesDirection controllersEngineeringTime of flight
A new fuze that reduces projectile miss-distance to a target, by correcting for discrepancies in anticipated round velocities through its flight. As a result, the fuze-equipped projectile is nominally aimed at a target and maintains improved accuracy relative to a conventional round. The fuze adjusts for the discrepancies in velocity by using an internal electric motor to mechanically actuate a drag-altering surface on the fuze body. In order to adjust for errors in the anticipated velocity, the fuze compares its preprogrammed velocity to its actual velocity at a given point in time during flight. An anticipated velocity table versus time in flight is constantly referenced so that appropriate adjustments in velocity can be made.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
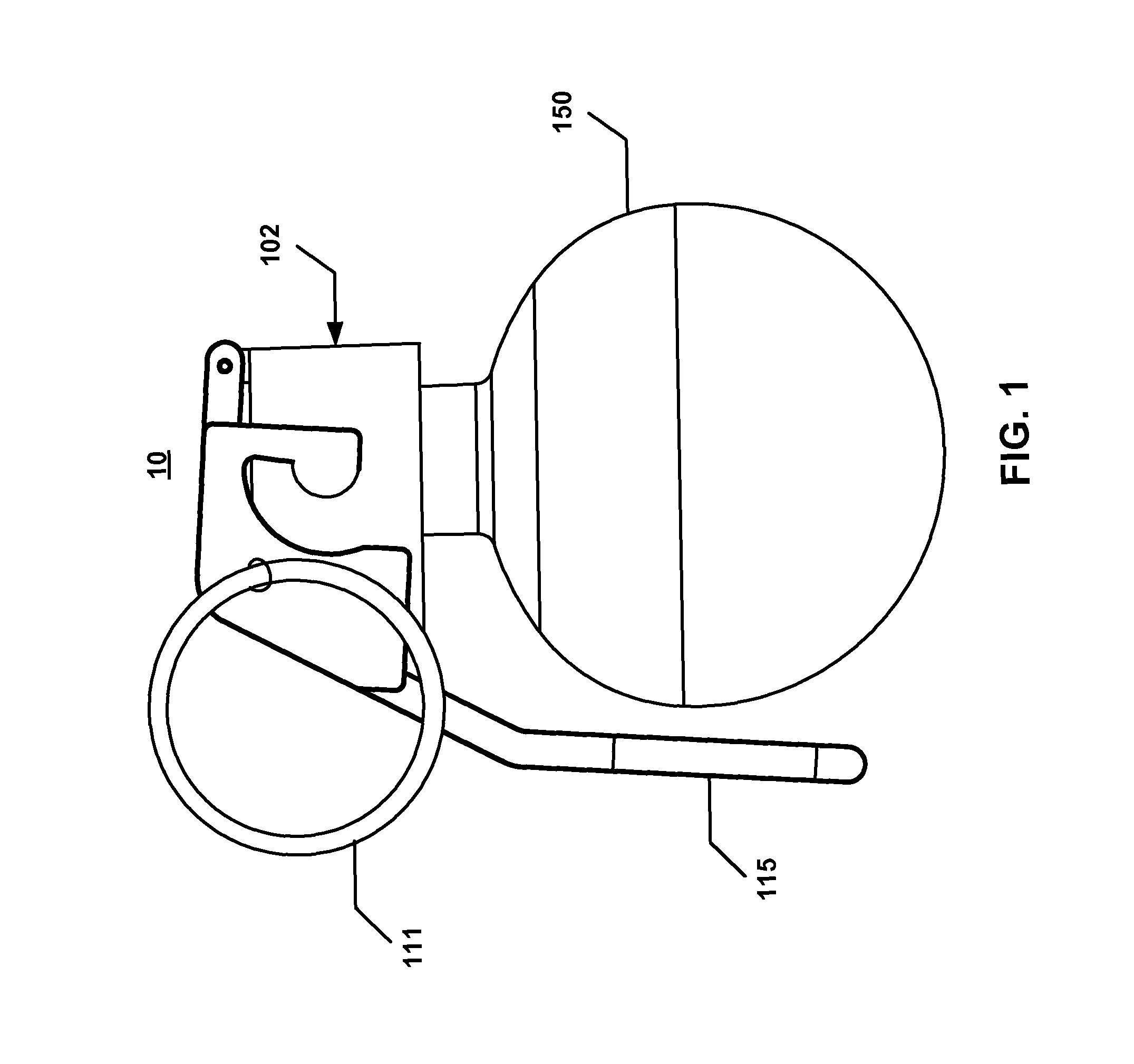
Hand grenade fuze
InactiveUS7712419B1Improved IM performanceHand grenadesMechanical fuzesDetonatorReciprocating motion
A detonator for a hand grenade fuze comprises a detonator case; a slider that is transversely reciprocable in the detonator case from an unarmed position to an armed position, the slider including a longitudinal through-hole filled with a primary explosive; a spring that biases the slider to the unarmed position; an arming mechanism attached to the slider, the arming mechanism comprising a shape memory alloy; an explosive lead disposed below the slider; and a booster charge disposed below the explosive lead.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
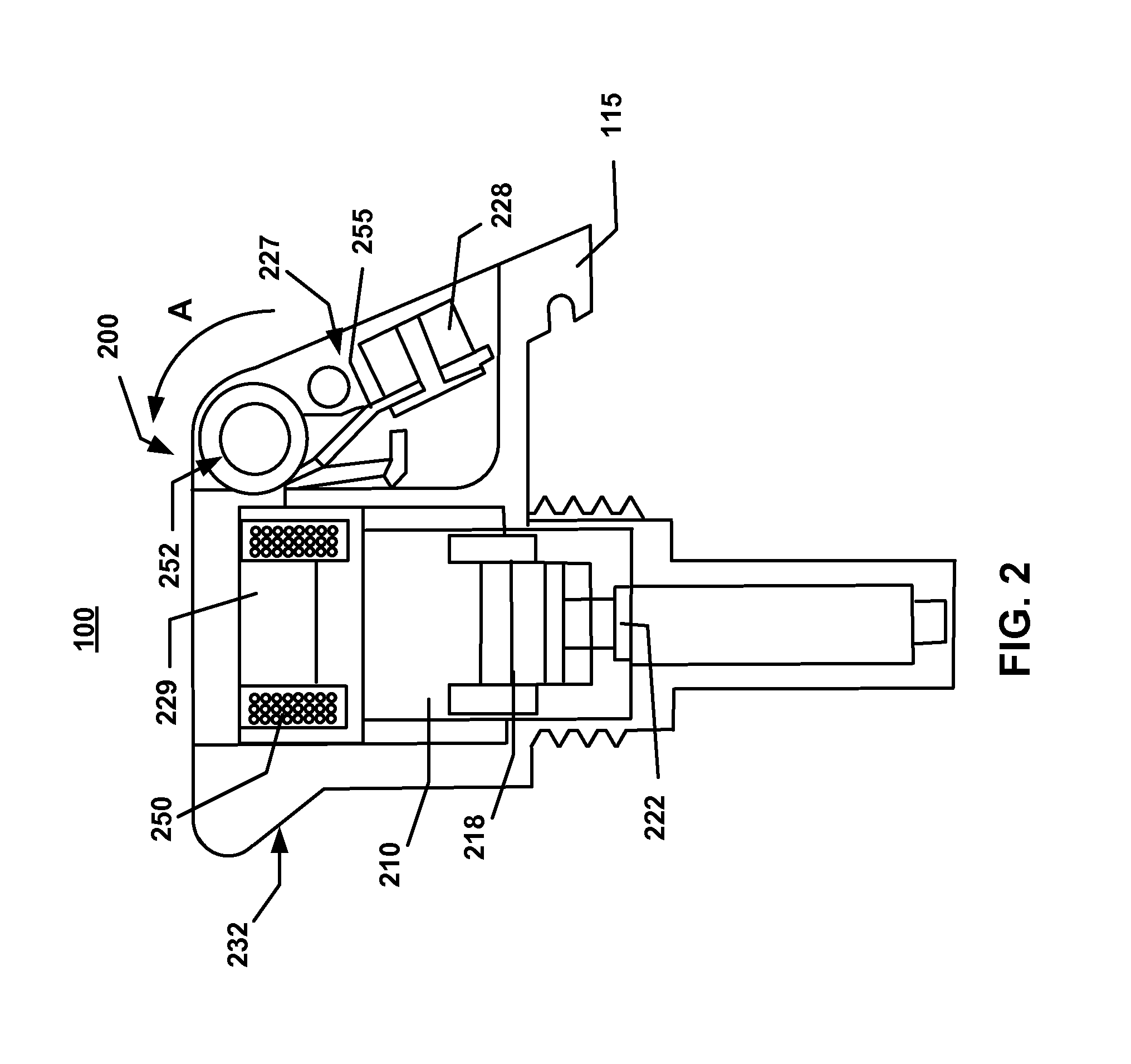
Electro-mechanical fuze for hand grenades
InactiveUS8887640B1Improve reliabilityImprove securityHand grenadesDomestic stoves or rangesBobbinPower flow
A safety fuze includes a magneto striker generator (MSG) as its a power generation source. The MSG provides energy to energize an electronic unit and a safety and arming device. The safety fuze allows safety and arming of military hand grenades, with a fully out-of-line explosive initiator and an integrated power generation means, for improving safety and performance. The MSG includes a striker and a receiving bobbin that houses a conductive coil. The striker comprises a permanent magnet that is mounted on a pivot mechanism for allowing a rotational displacement of the permanent magnet, into the bobbin, in order to generate an electrical current. As the permanent magnet is being inserted inside the bobbin, the magnetic flux change induces an electric current in the coil, creating the necessary energy for the fuze operation.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com