Patents
Literature
206results about "Proximity fuzes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
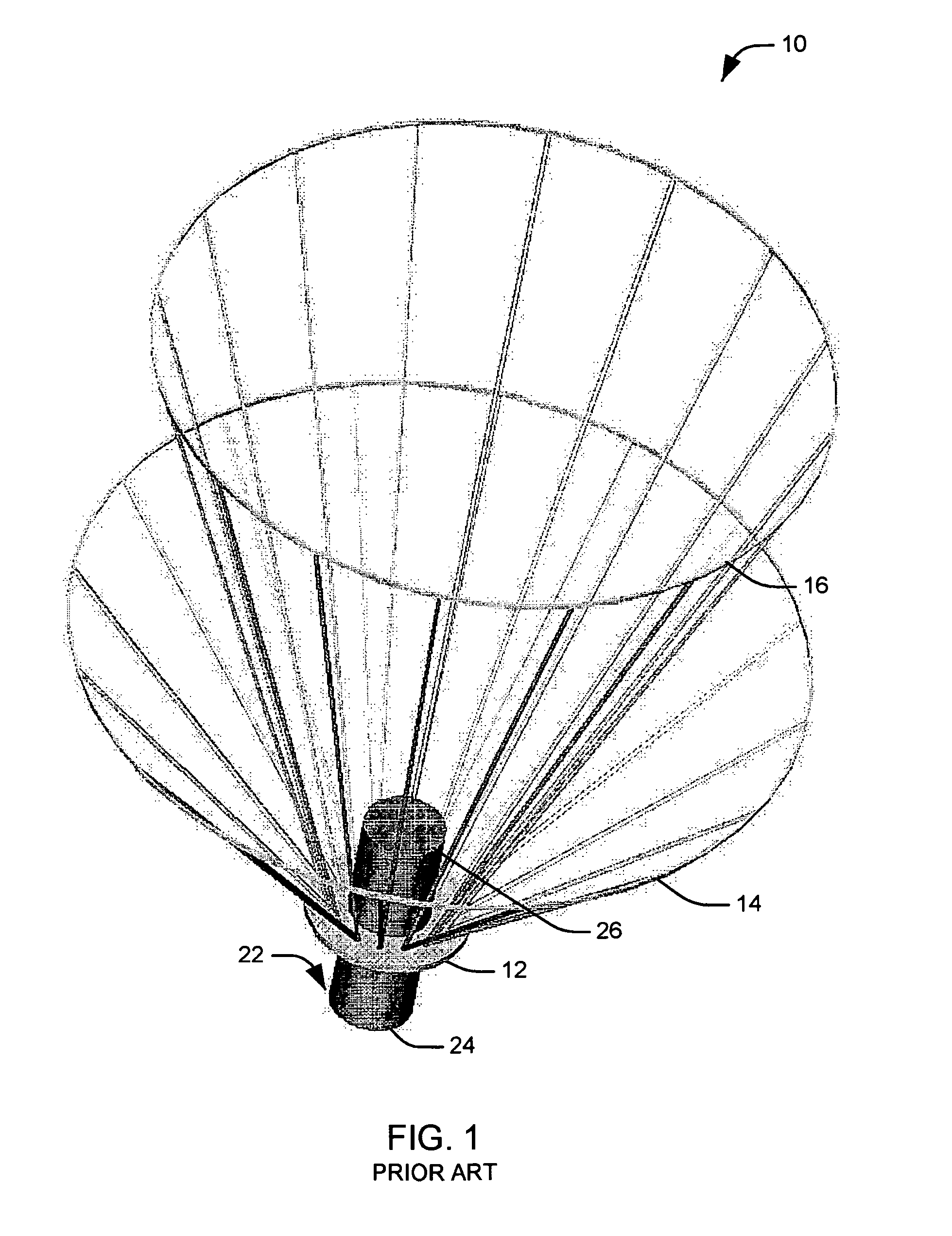
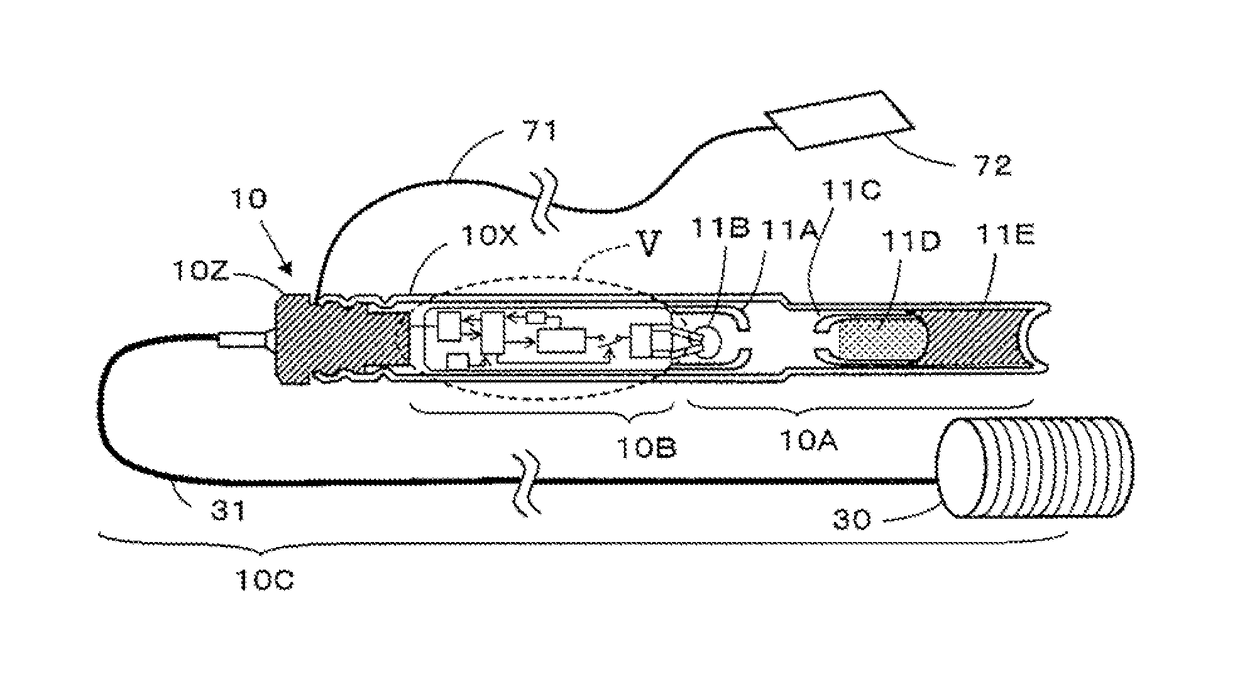
Wireless detonator assemblies, corresponding blasting apparatuses, and methods of blasting
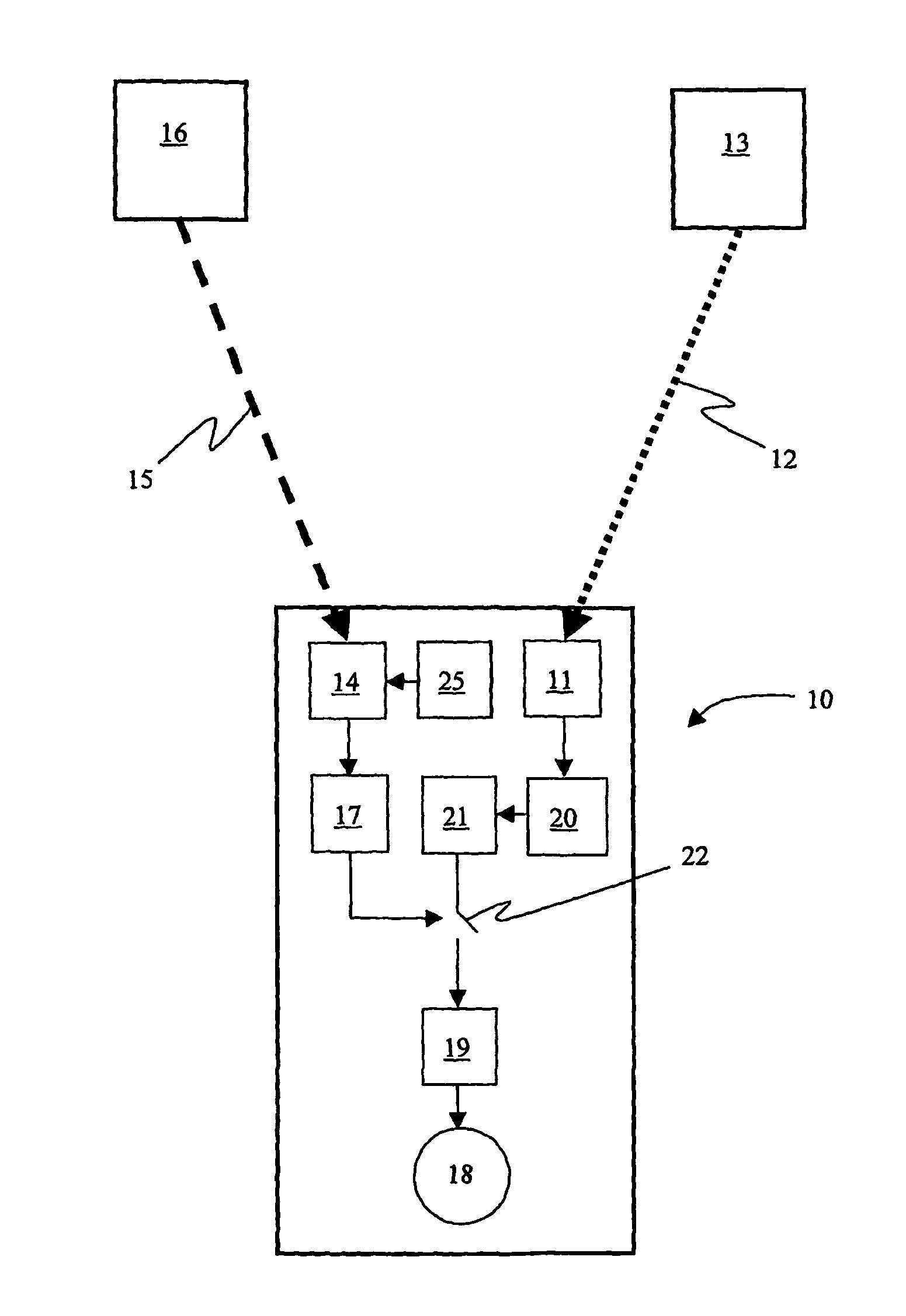
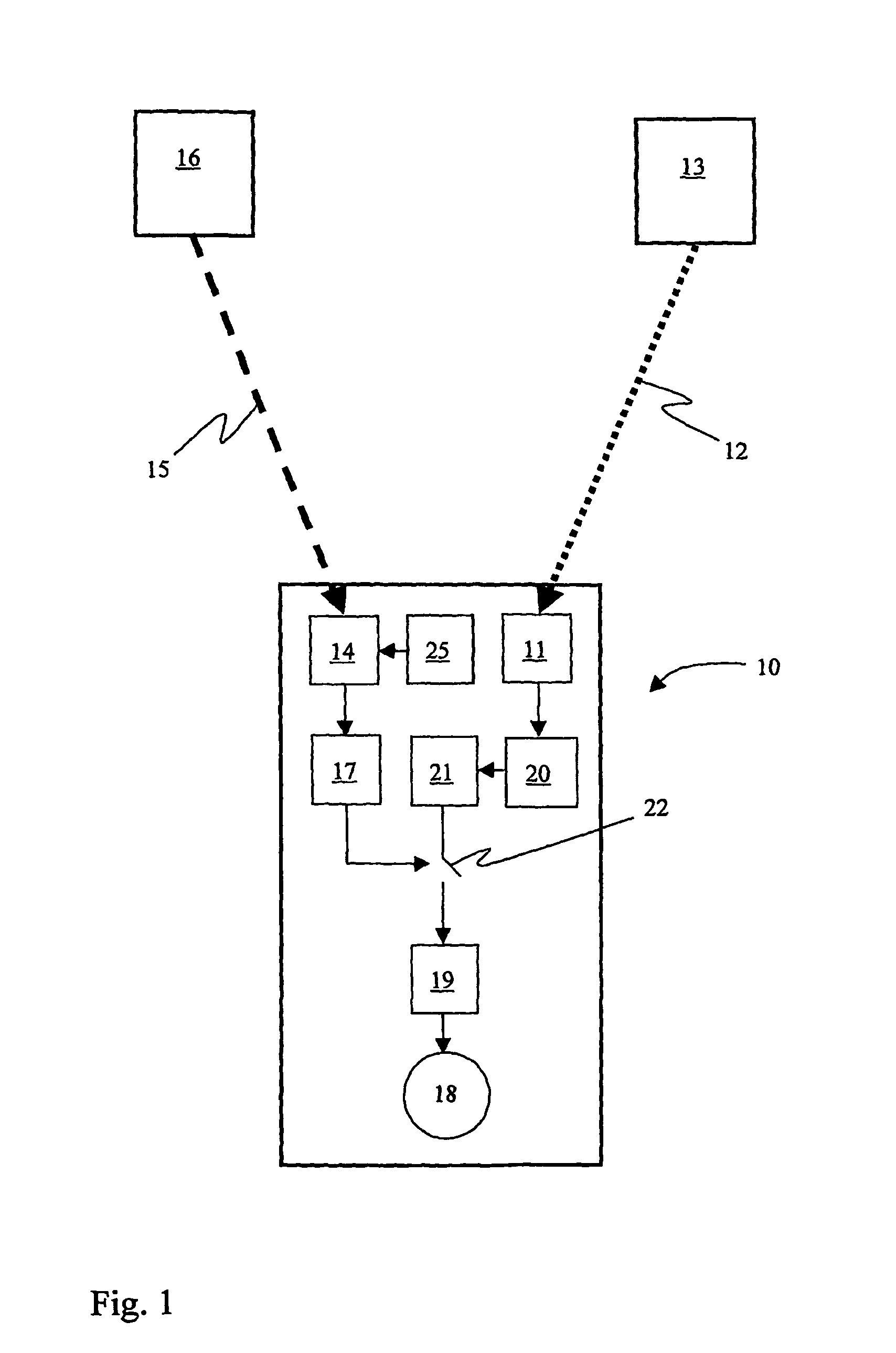
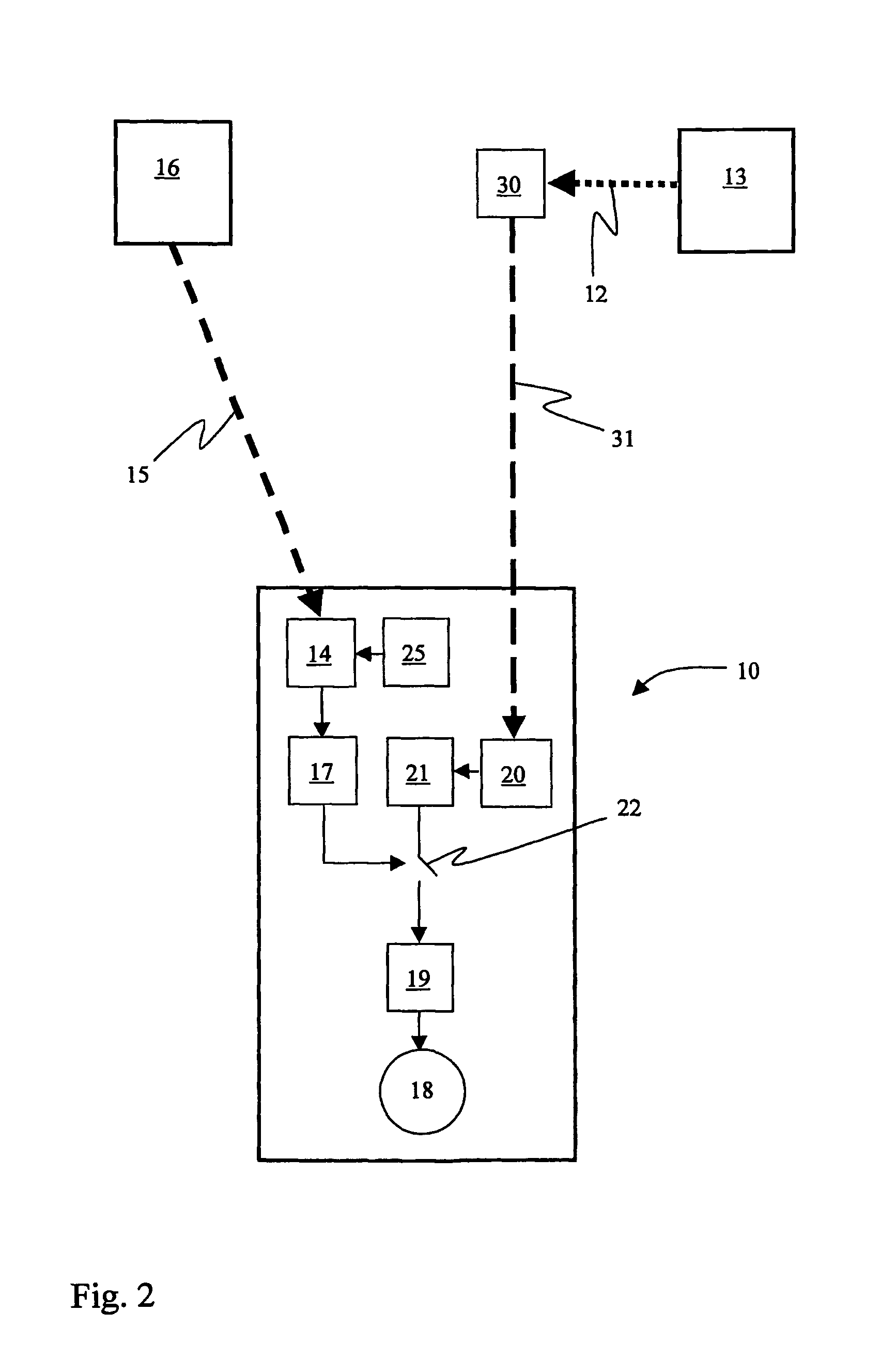
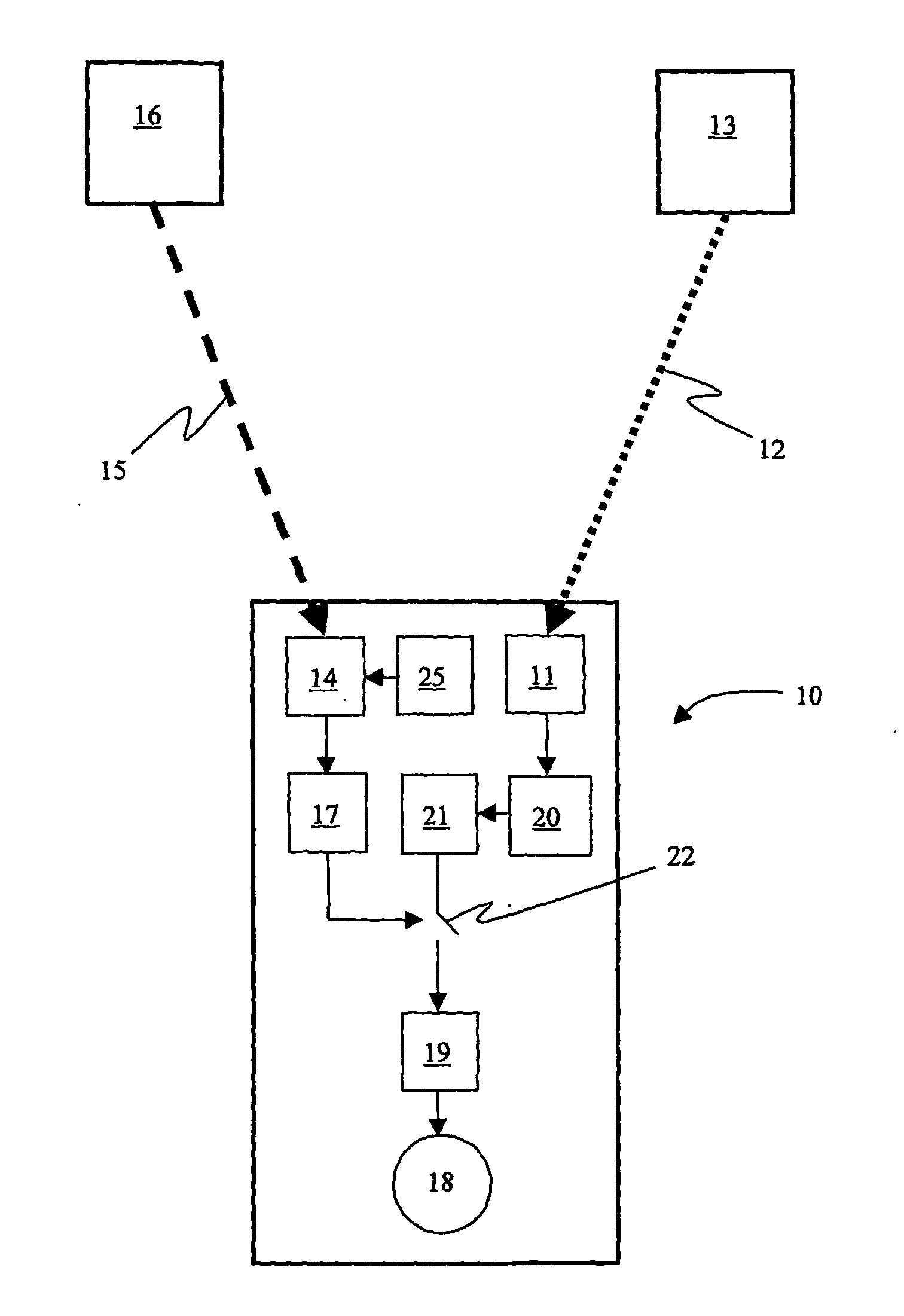
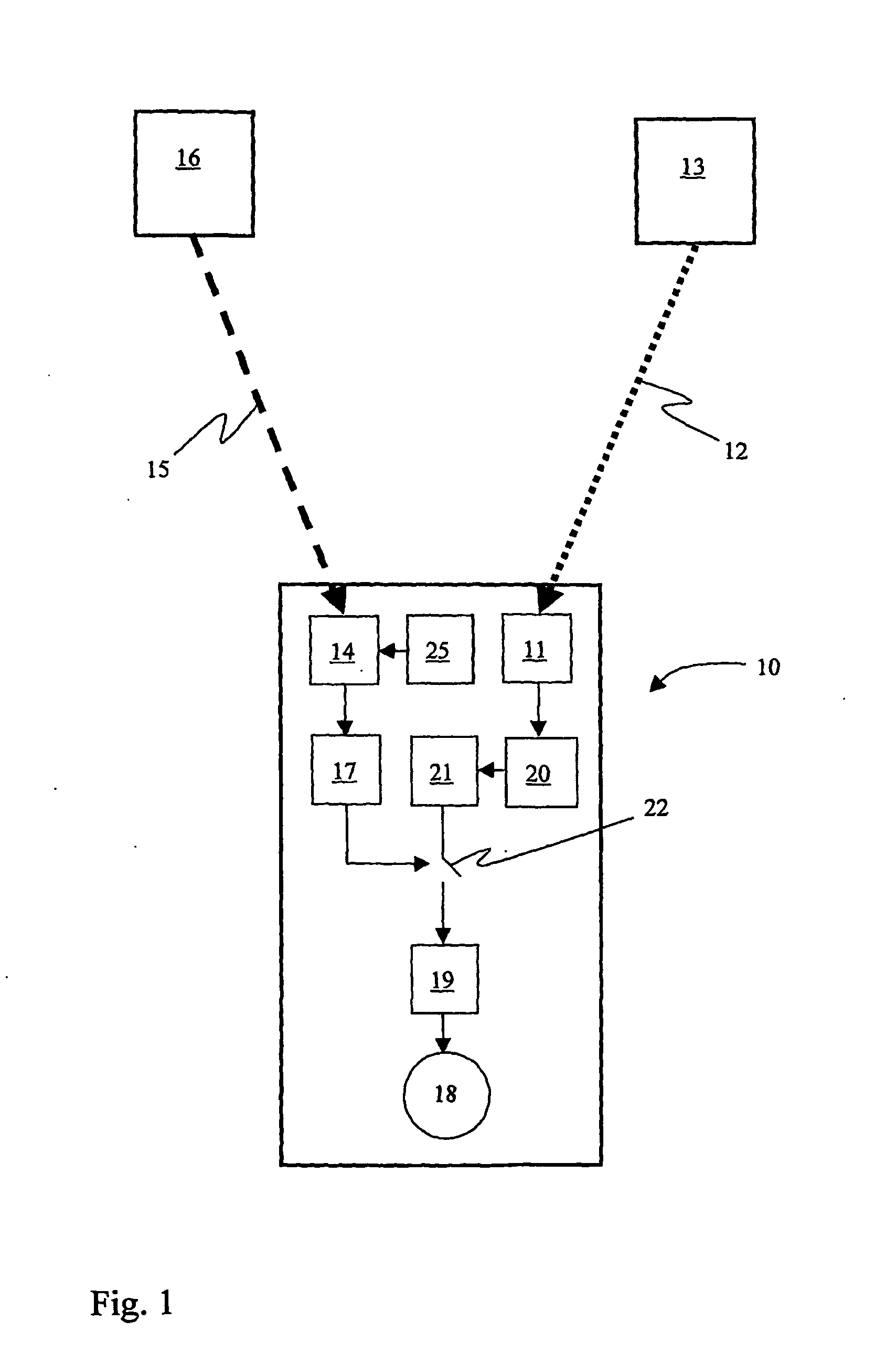
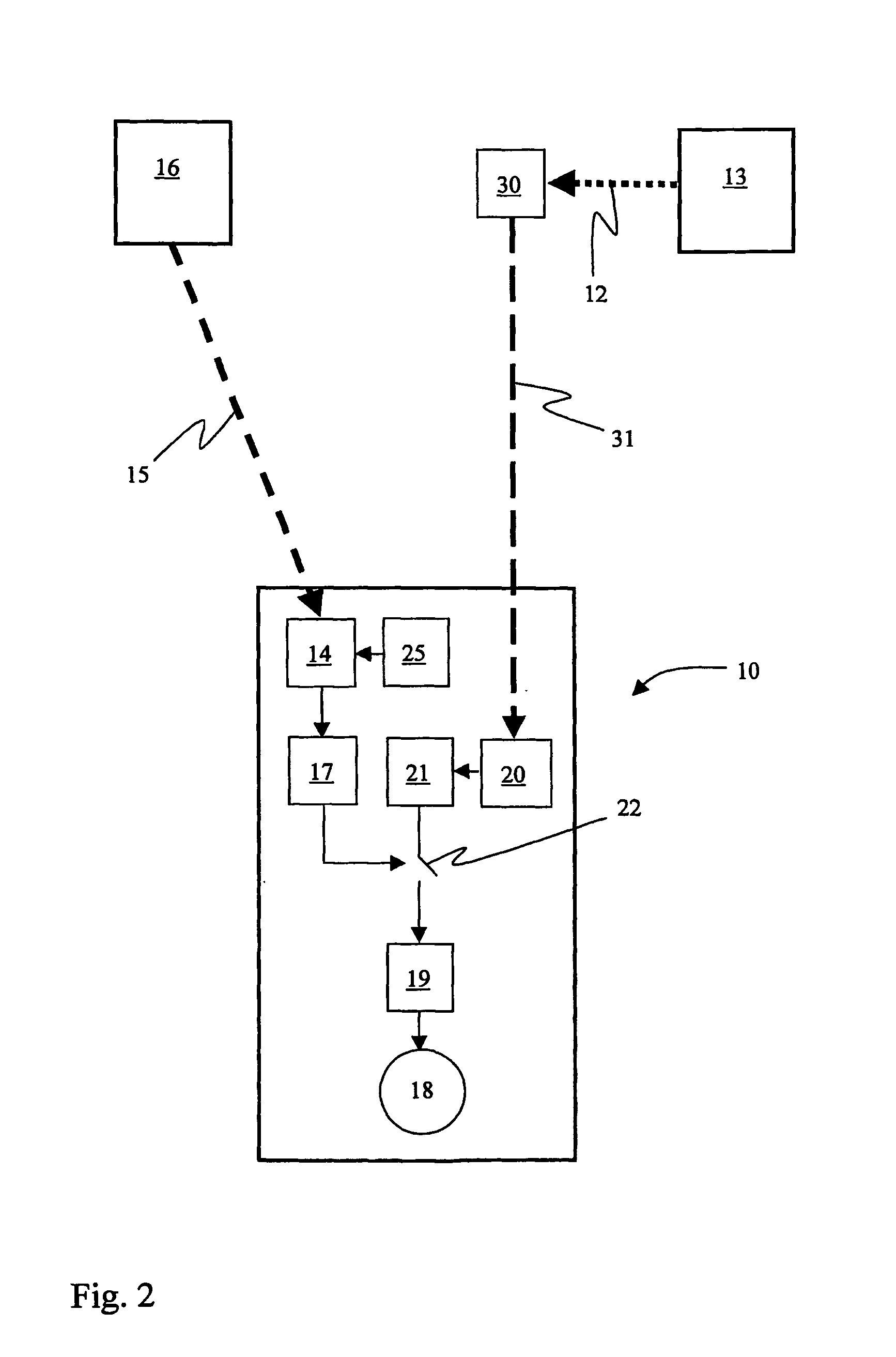
A wireless or partially wireless detonator assembly (10) and corresponding blasting apparatus, that may be “powered Up” by a remote source of power (13) that is entirely distinct from the energy used for general command signal communications (16). In one embodiment, the detonator assembly (10) may include an active power source (25) with sufficient power for communications, but insufficient power to cause intentional or inadvertent actuation of the detonator (10).
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
Imaging-infrared skewed-cone fuze
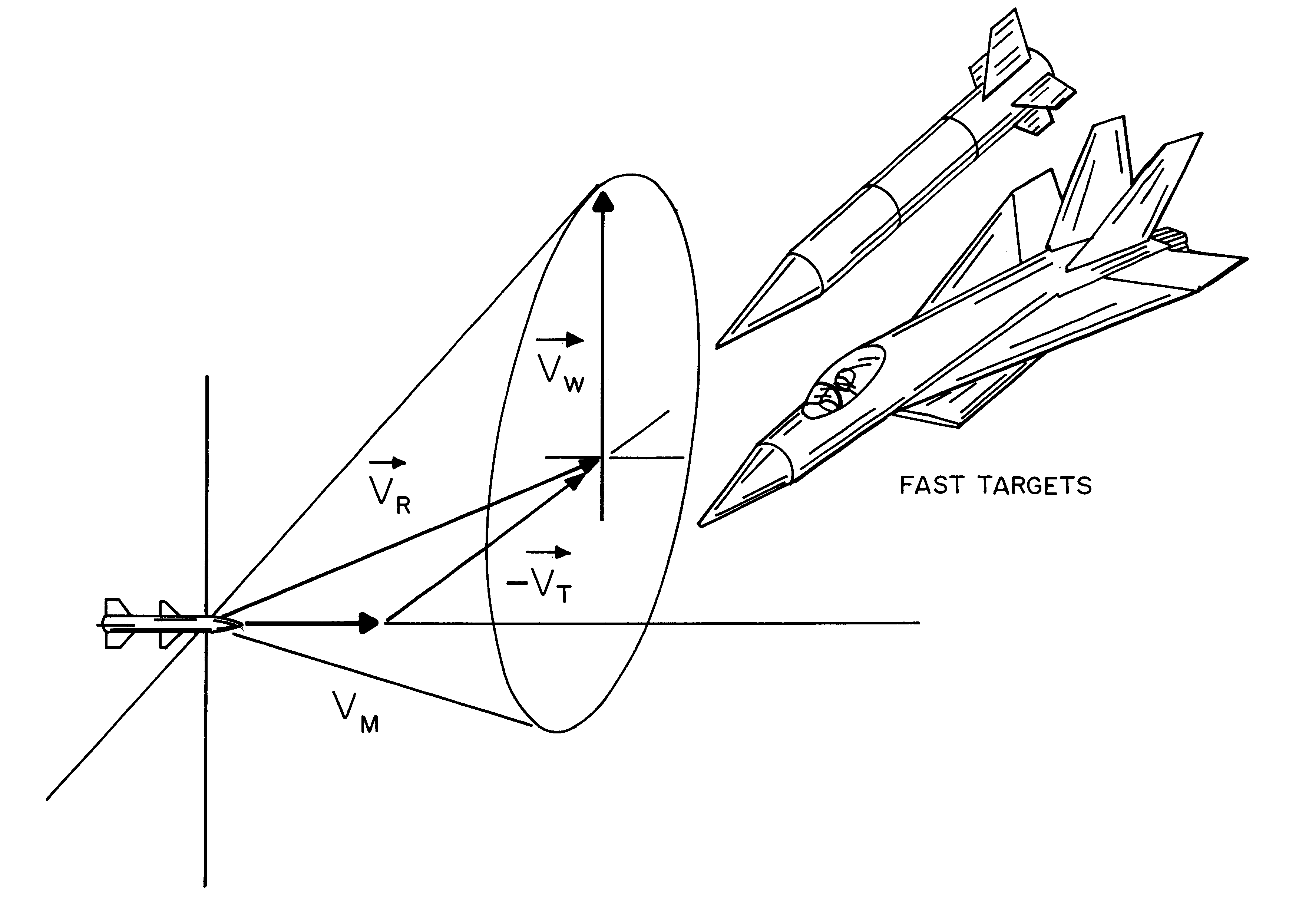
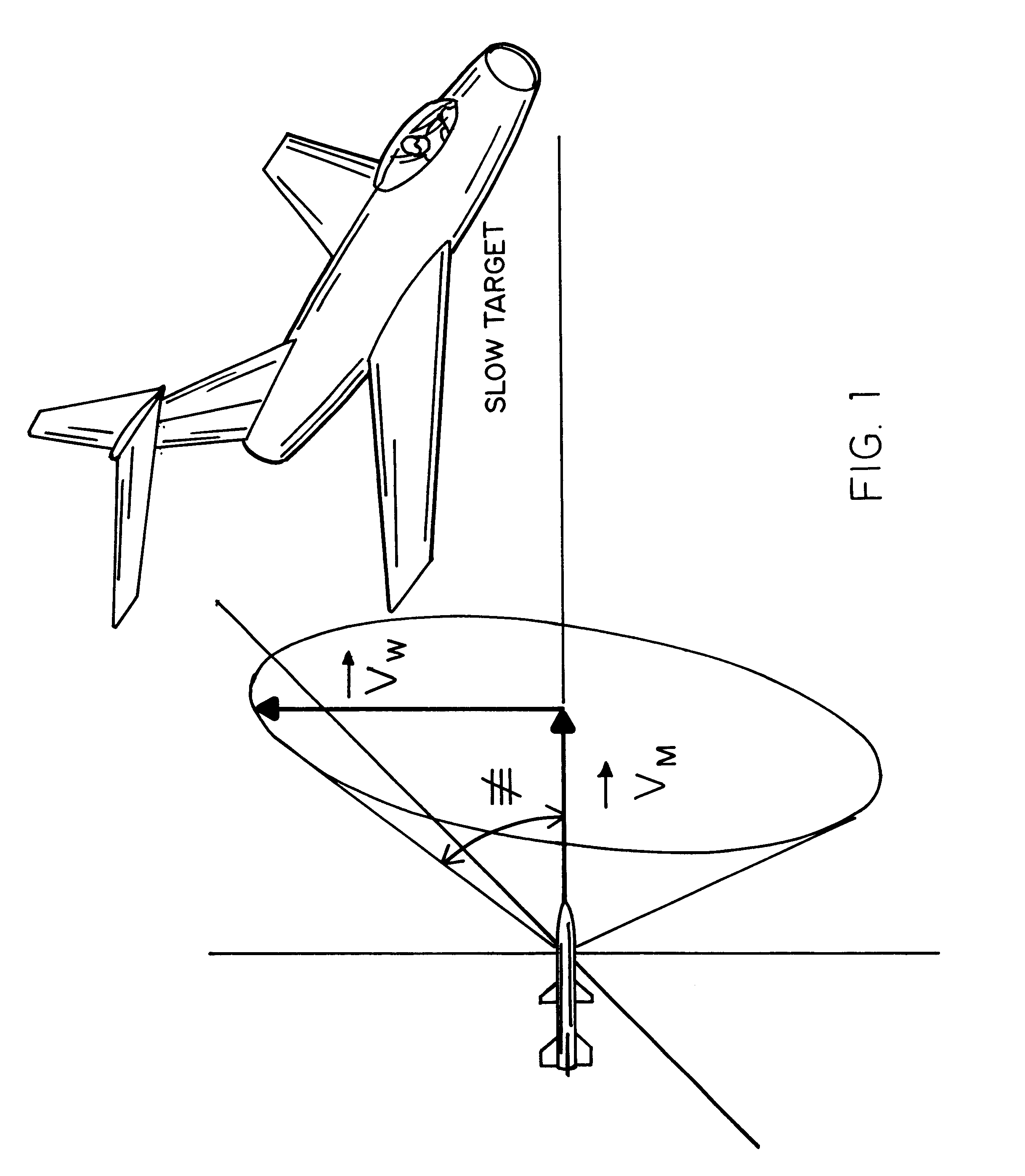
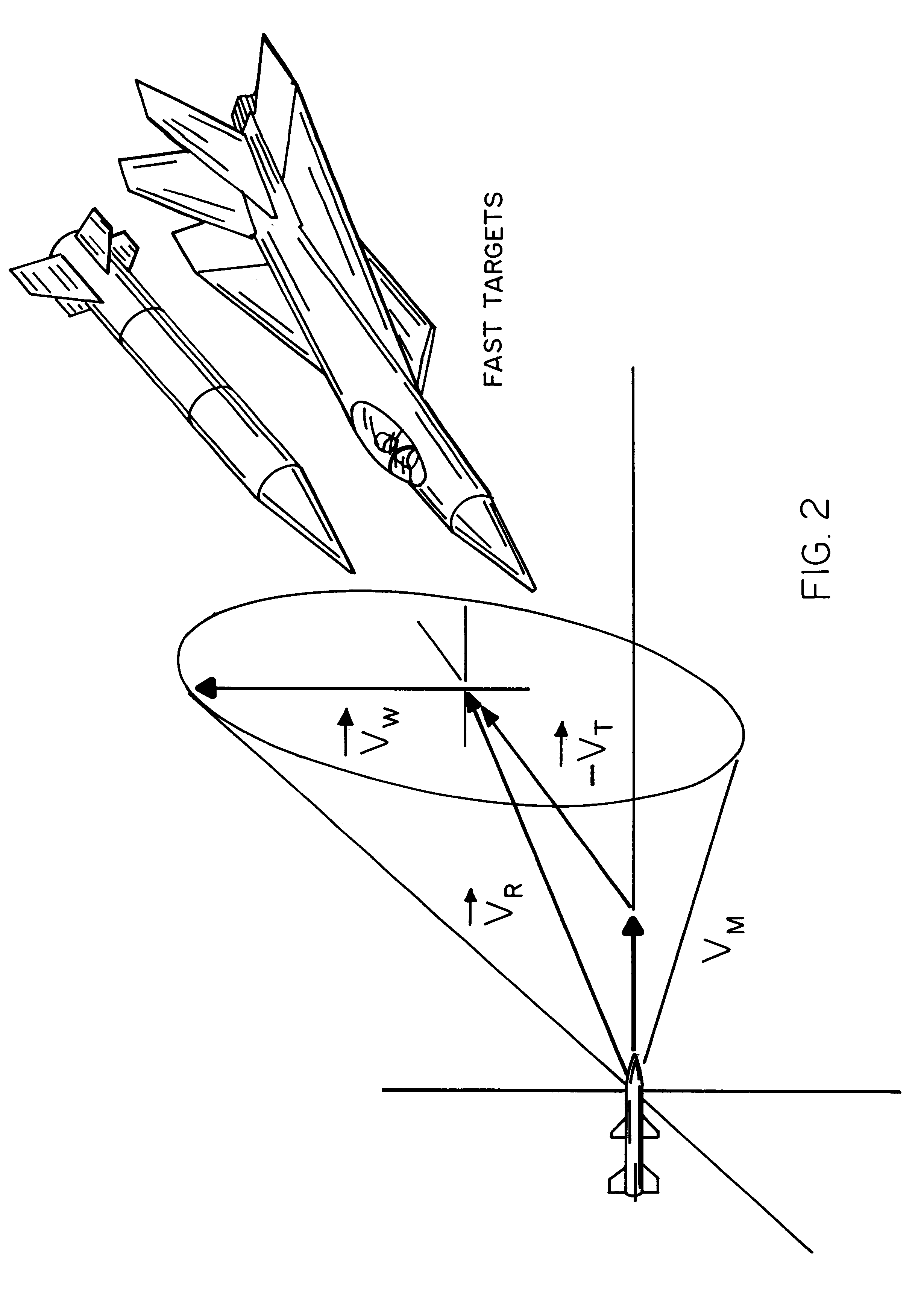
A fuzing system for non-spinning or substantially non-spinning weapons is implemented by means of wide angle optics providing at least forward-hemisphere coverage, an array of infrared detectors and a microprocessor for image and data processing, aim-point selection, directional-warhead aiming and skewed-cone fuzing. The skewed-cone fuzing has a generatrix which is the vector sum of missile velocity, warhead velocity and the negative of target velocity.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Vehicle-borne system and method for countering an incoming threat
InactiveUS6920827B2Effective destructionEffectively destroying and altering flight pathAmmunition projectilesProximity fuzesEngineeringProtection system
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
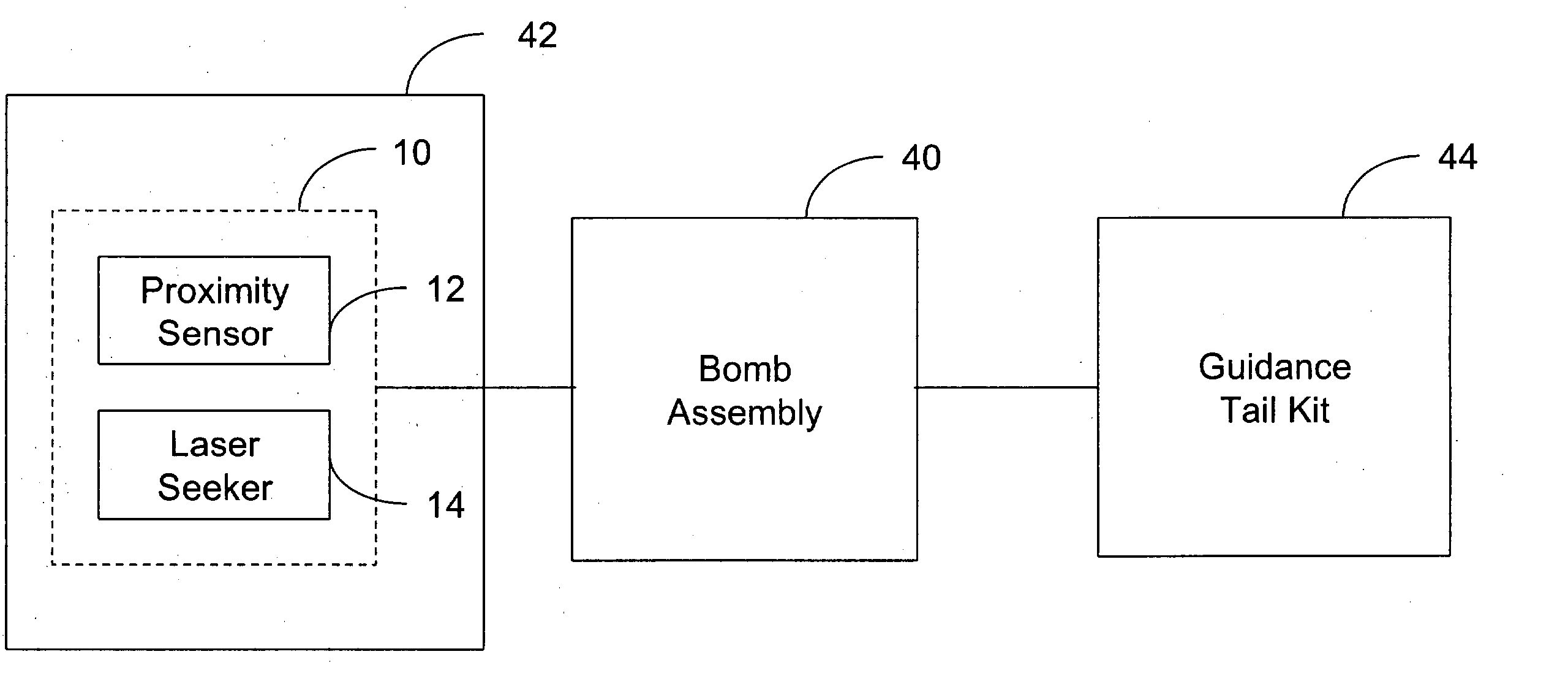
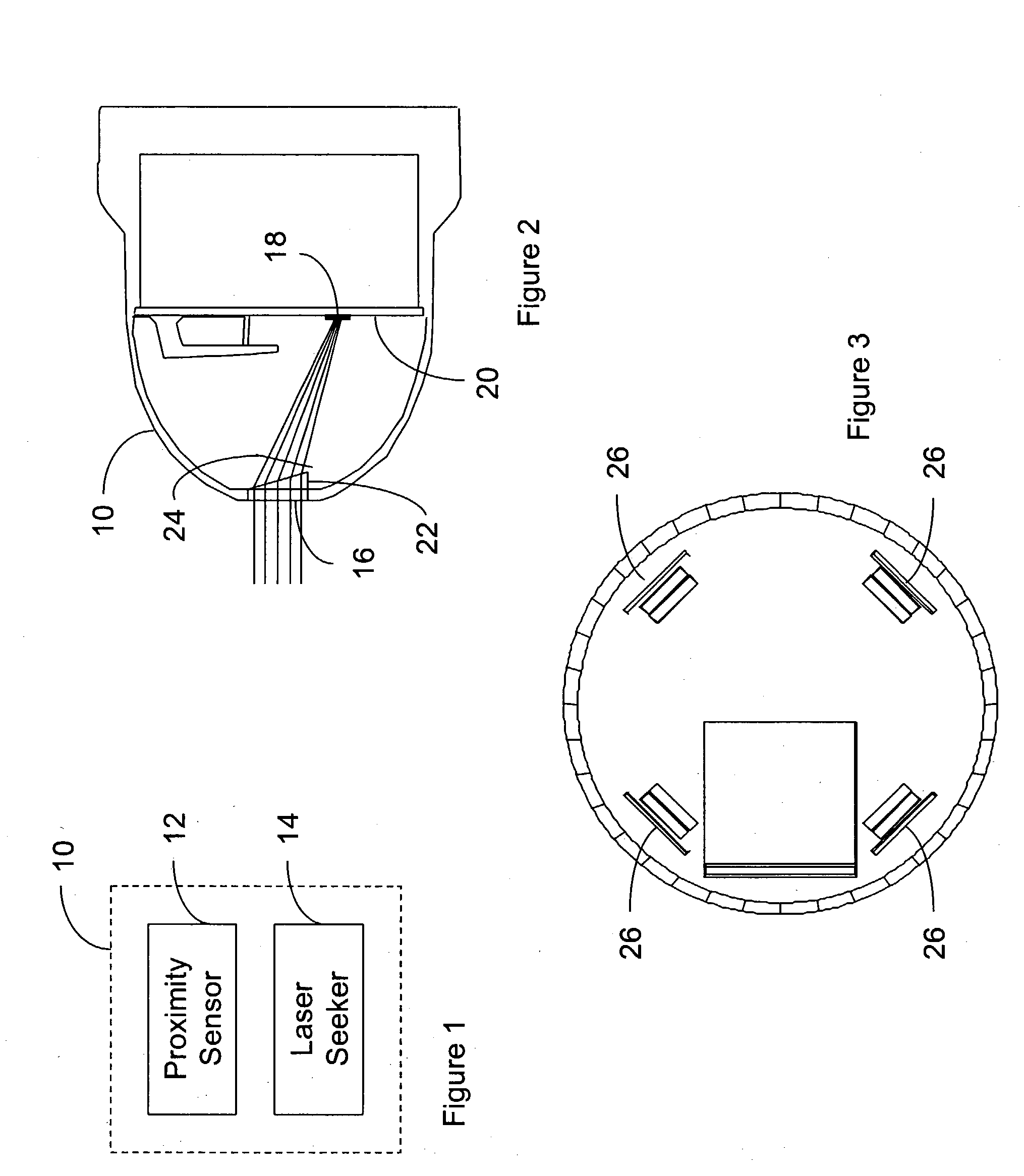
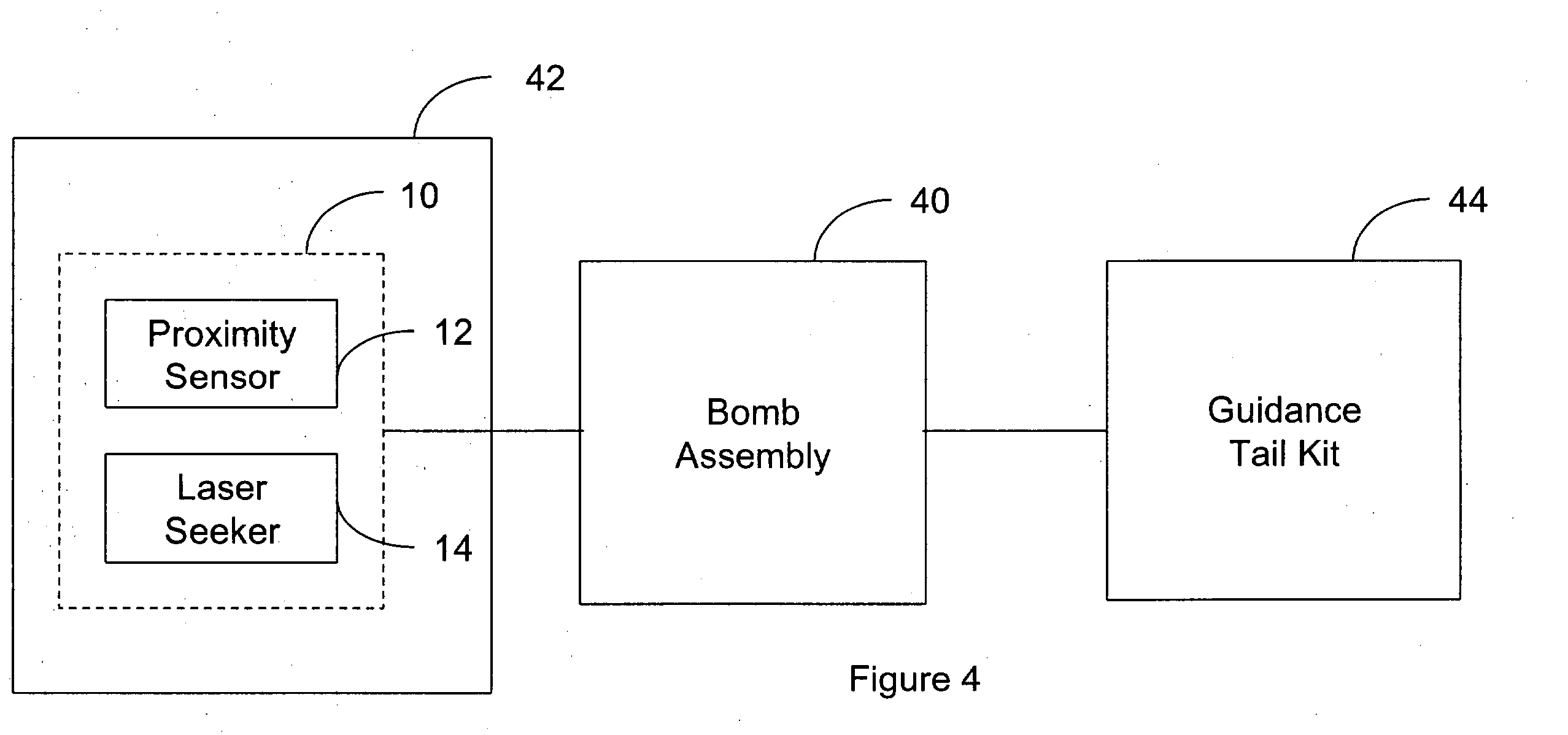
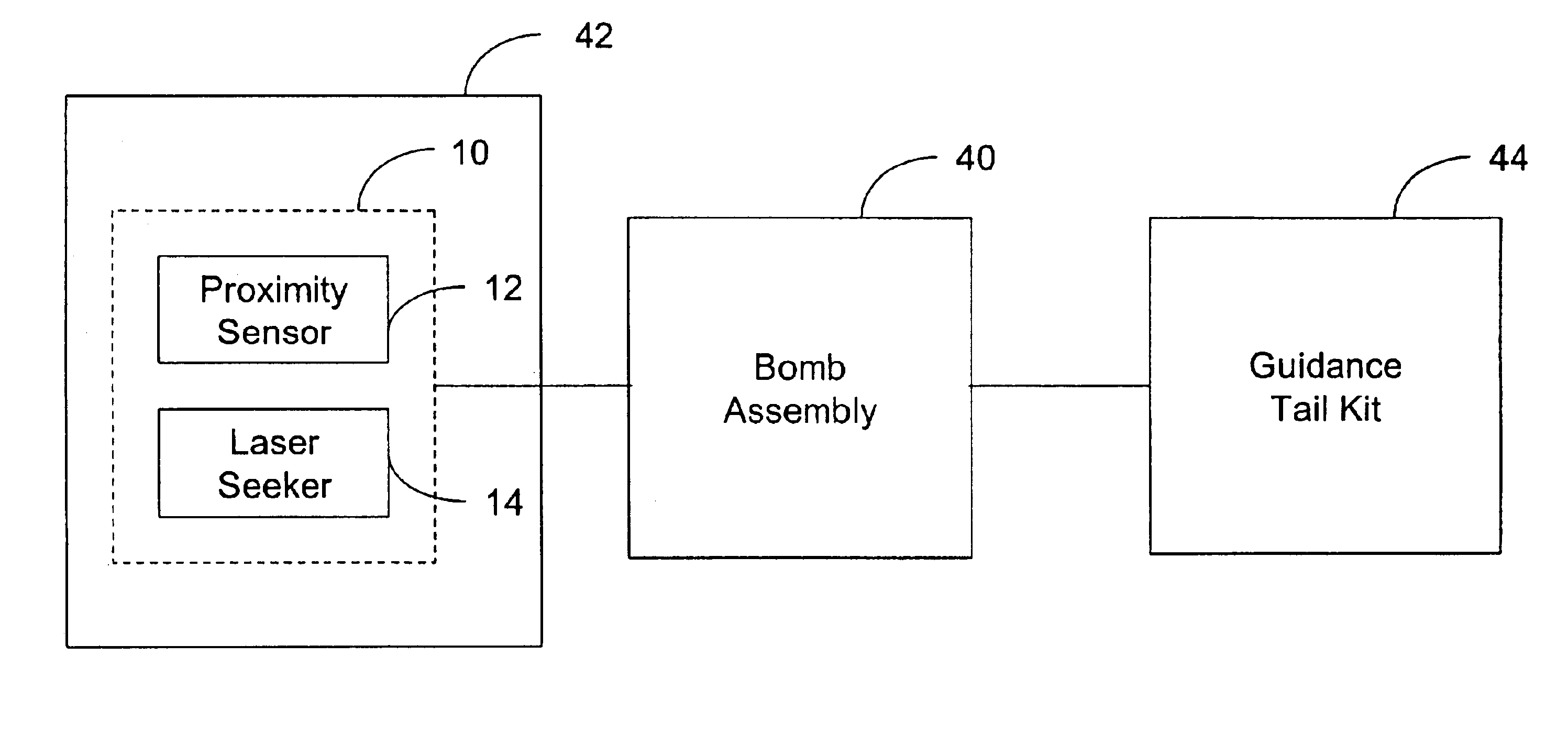
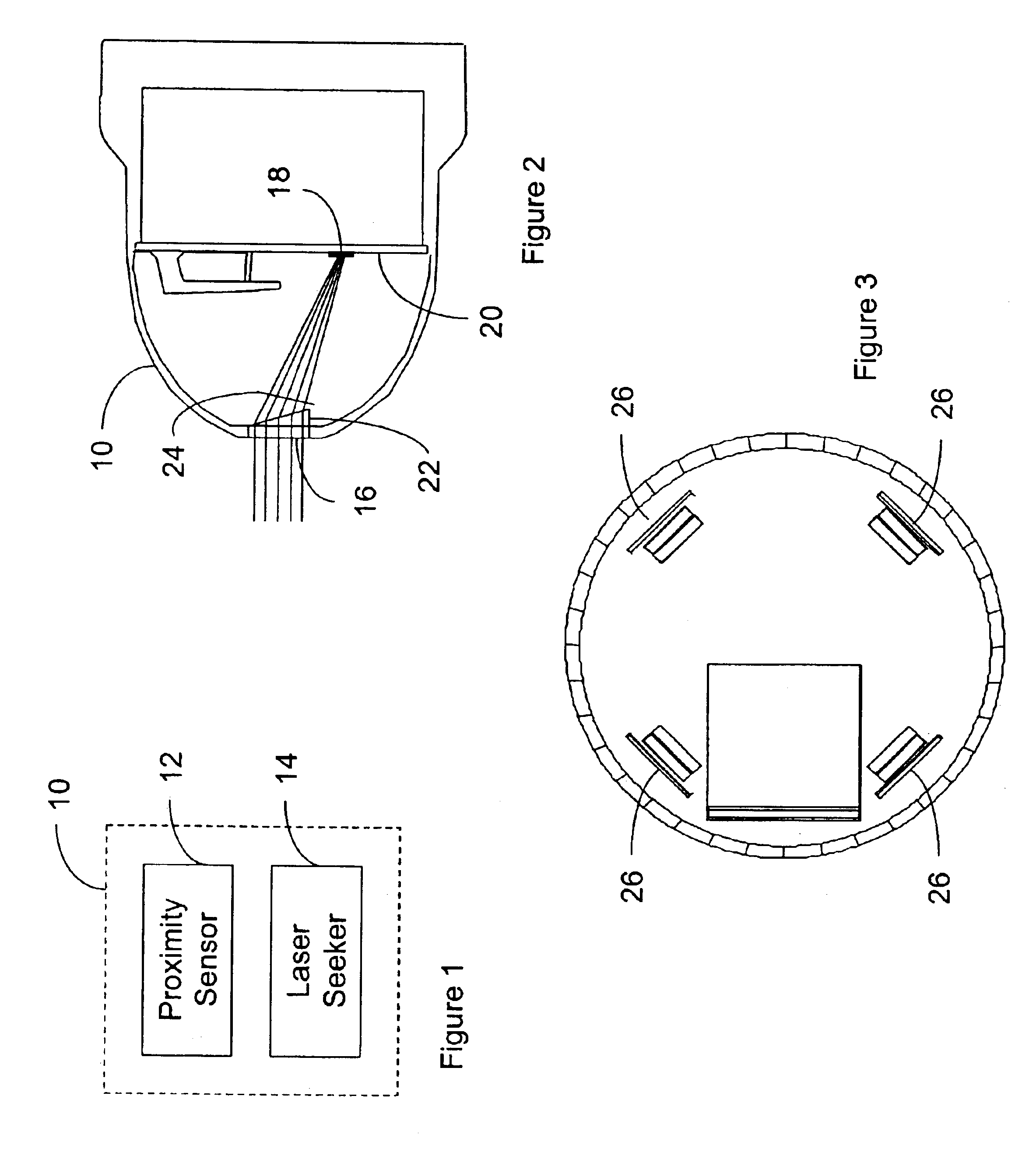
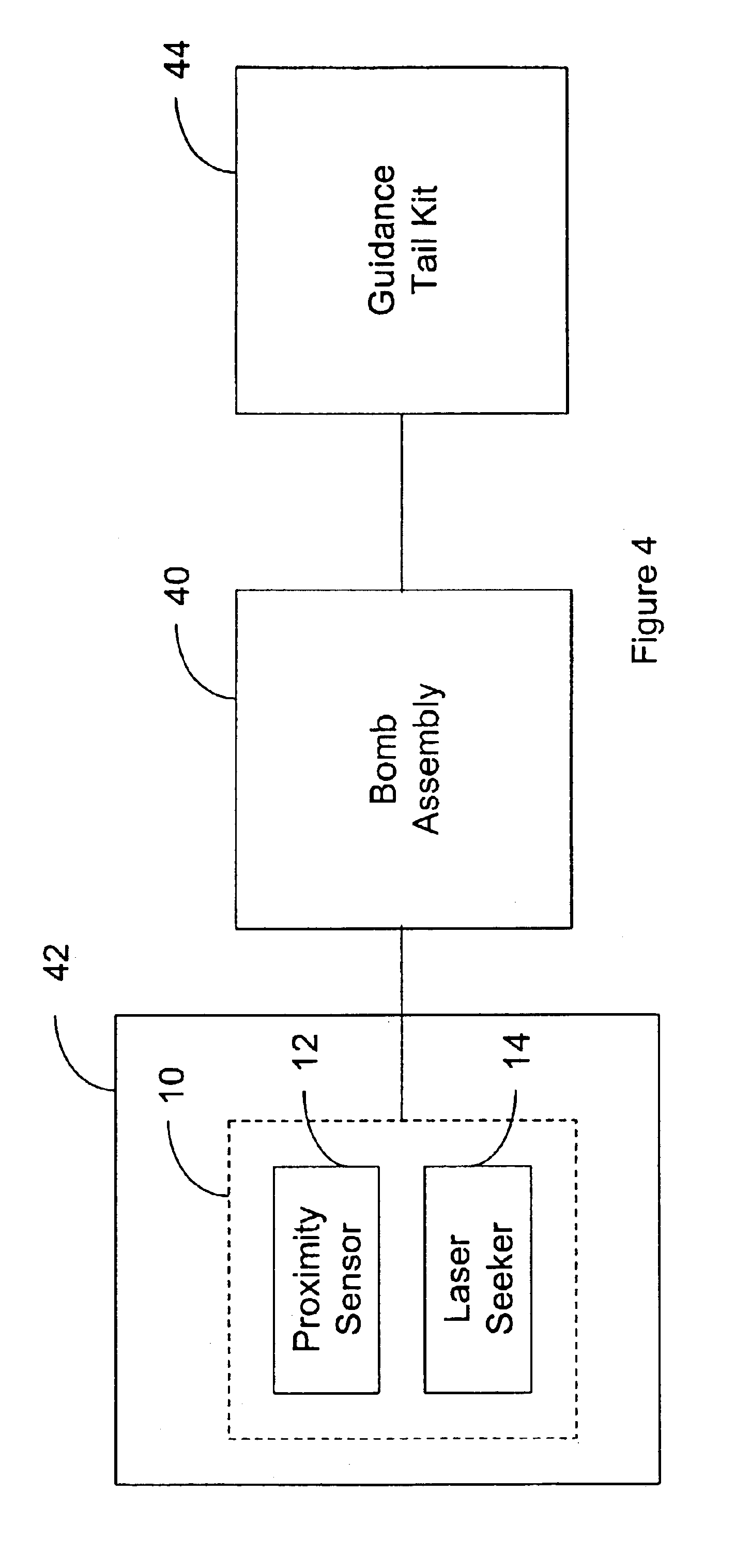
Integration of a semi-active laser seeker into the dsu-33 proximity sensor
InactiveUS20050030219A1High proximityAmmunition projectilesDirection controllersElevation angleSemi active
A proximity sensor for use with a guidance system of a smart bomb including a ranging radar proximity sensor configured for mounting on a smart bomb and a radome connected to the ranging radar proximity sensor. A laser radiation sensor system is attached to the proximity sensor, which is configured and arranged to detect laser radiation reflected from a target which passes through the radome and output the azimuth and elevation angles to the target to the guidance system.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
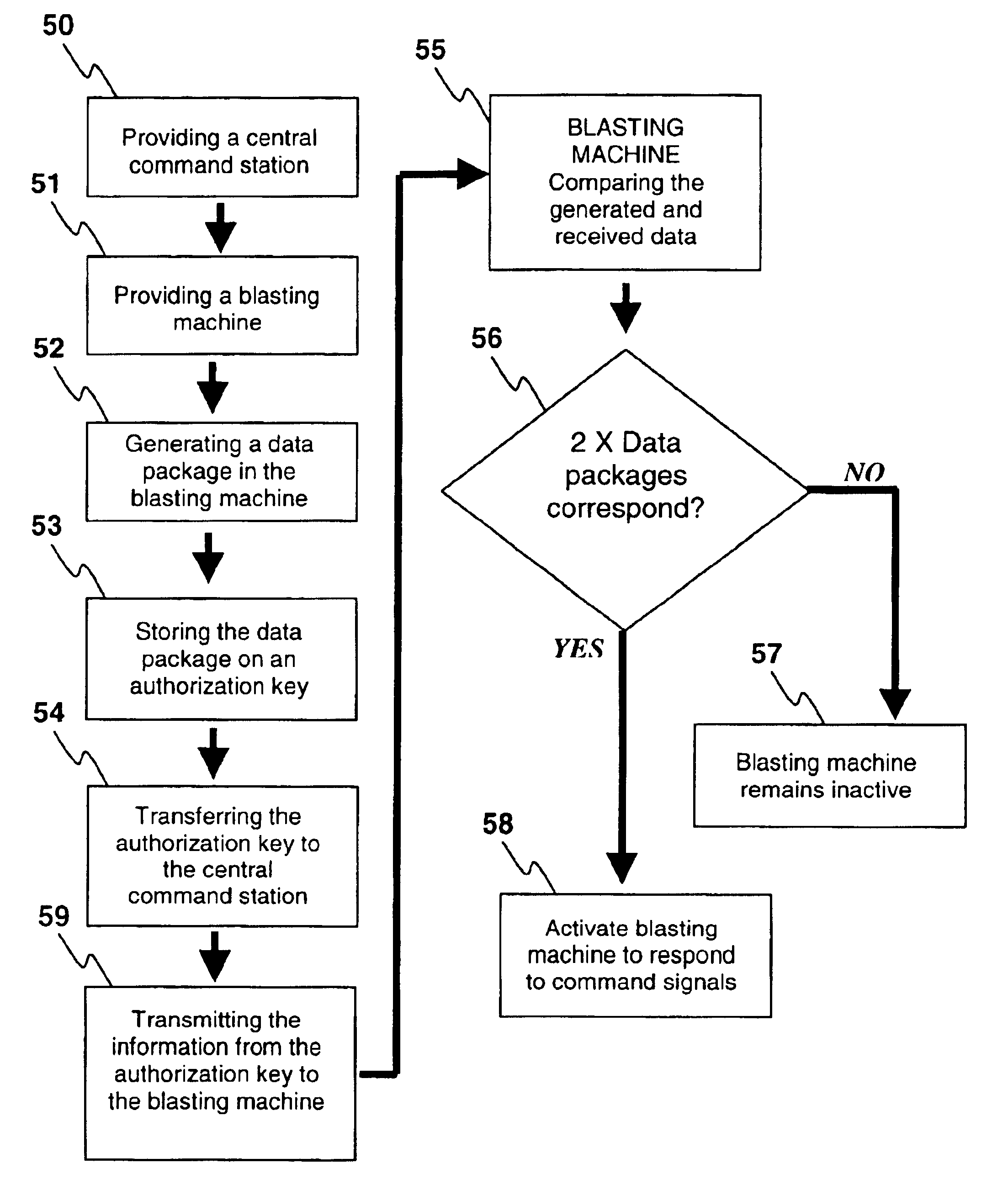
Access control for electronic blasting machines
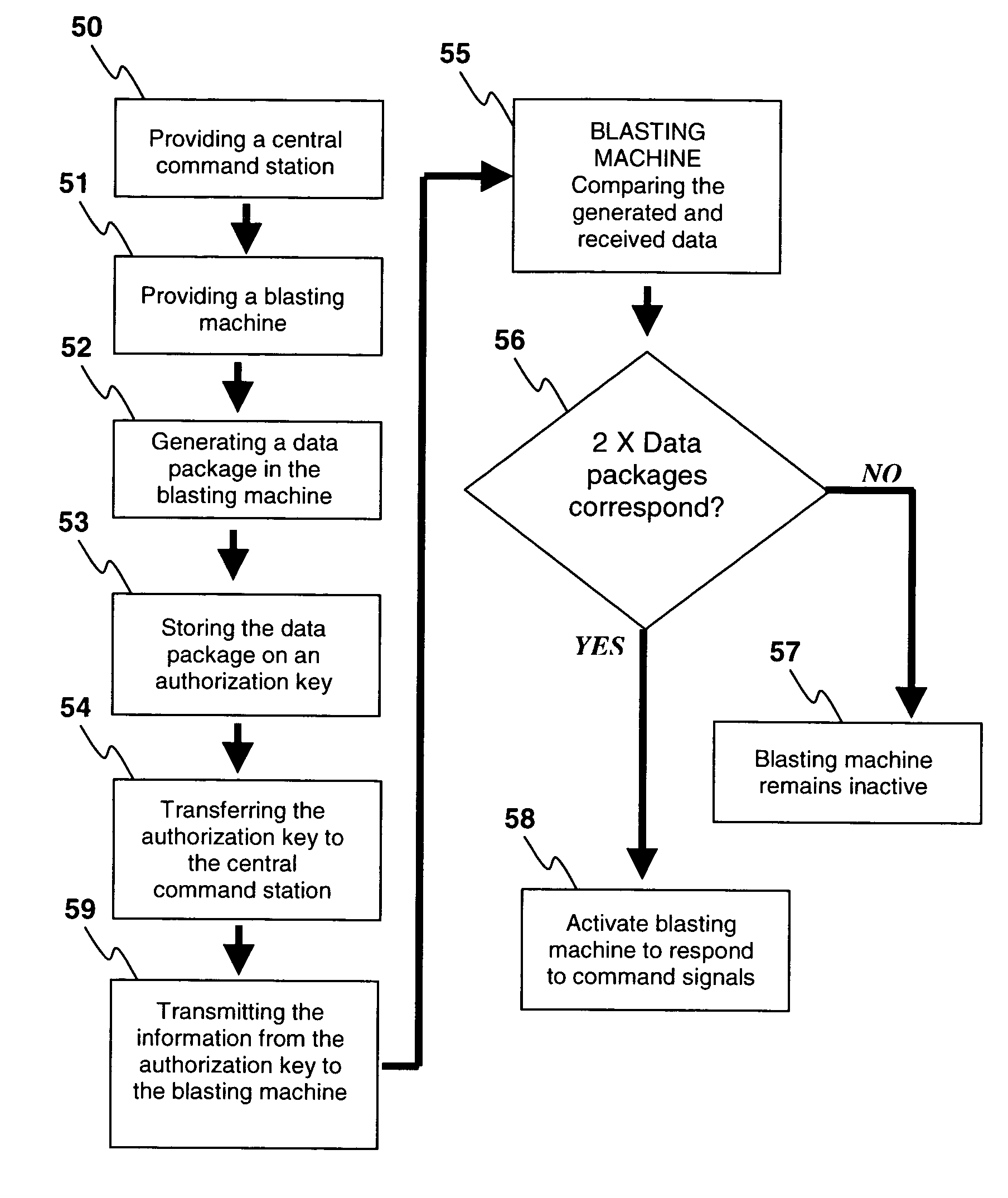
Blasting apparatuses and methods control actuation of a plurality of detonators, and involve the use of one or more authorization keys each associated with a blasting machine. The authorization key(s) are transferable from the blasting machine(s) to a central command station, each authorization key storing a data package comprising a randomly generated access code generated by its corresponding blasting machine. Transfer of the one or more authorization keys to a central command station allows the data packages (and associated randomly generated access codes) to be transmitted by the central command station for receipt by the blasting machine(s).
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
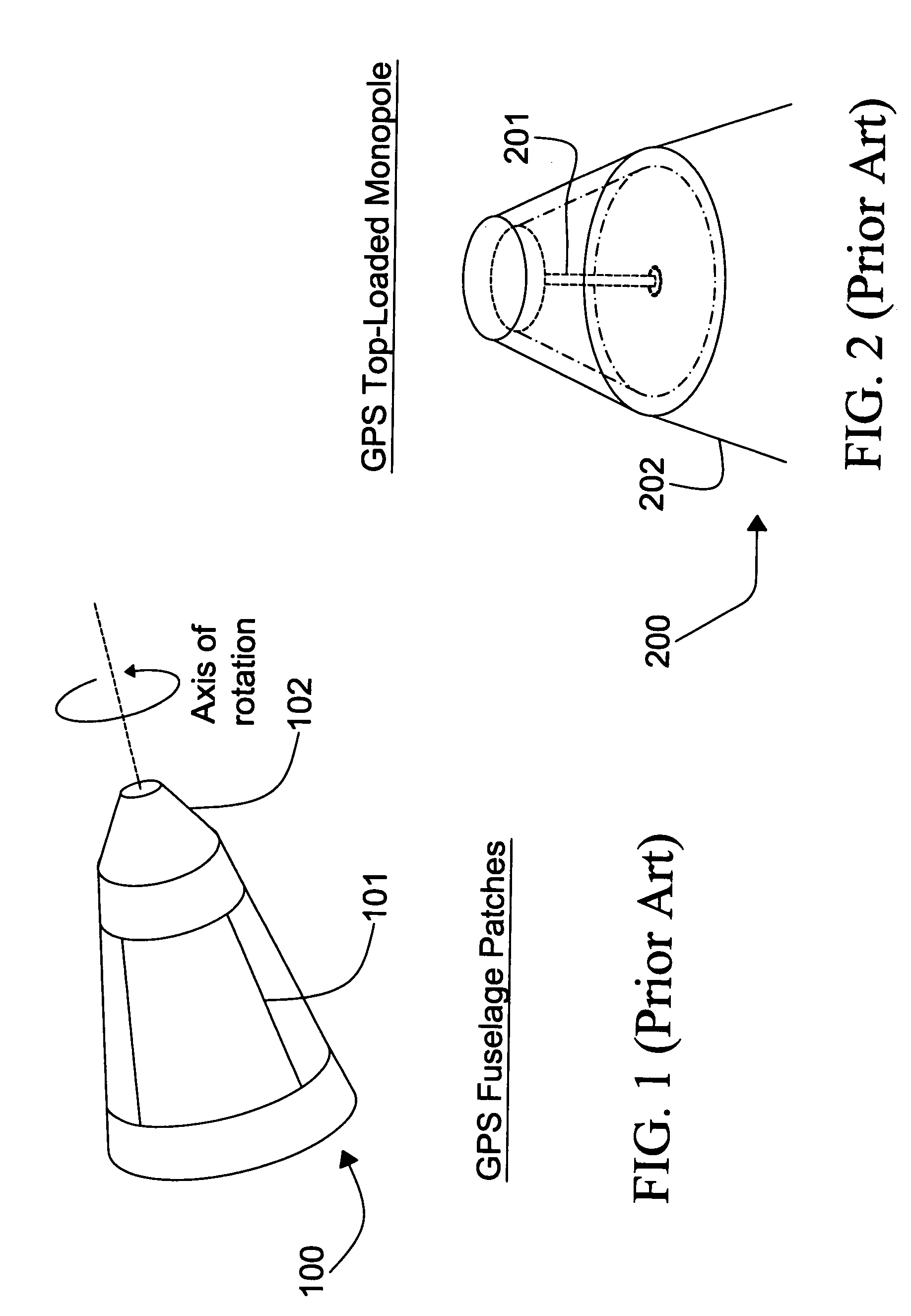
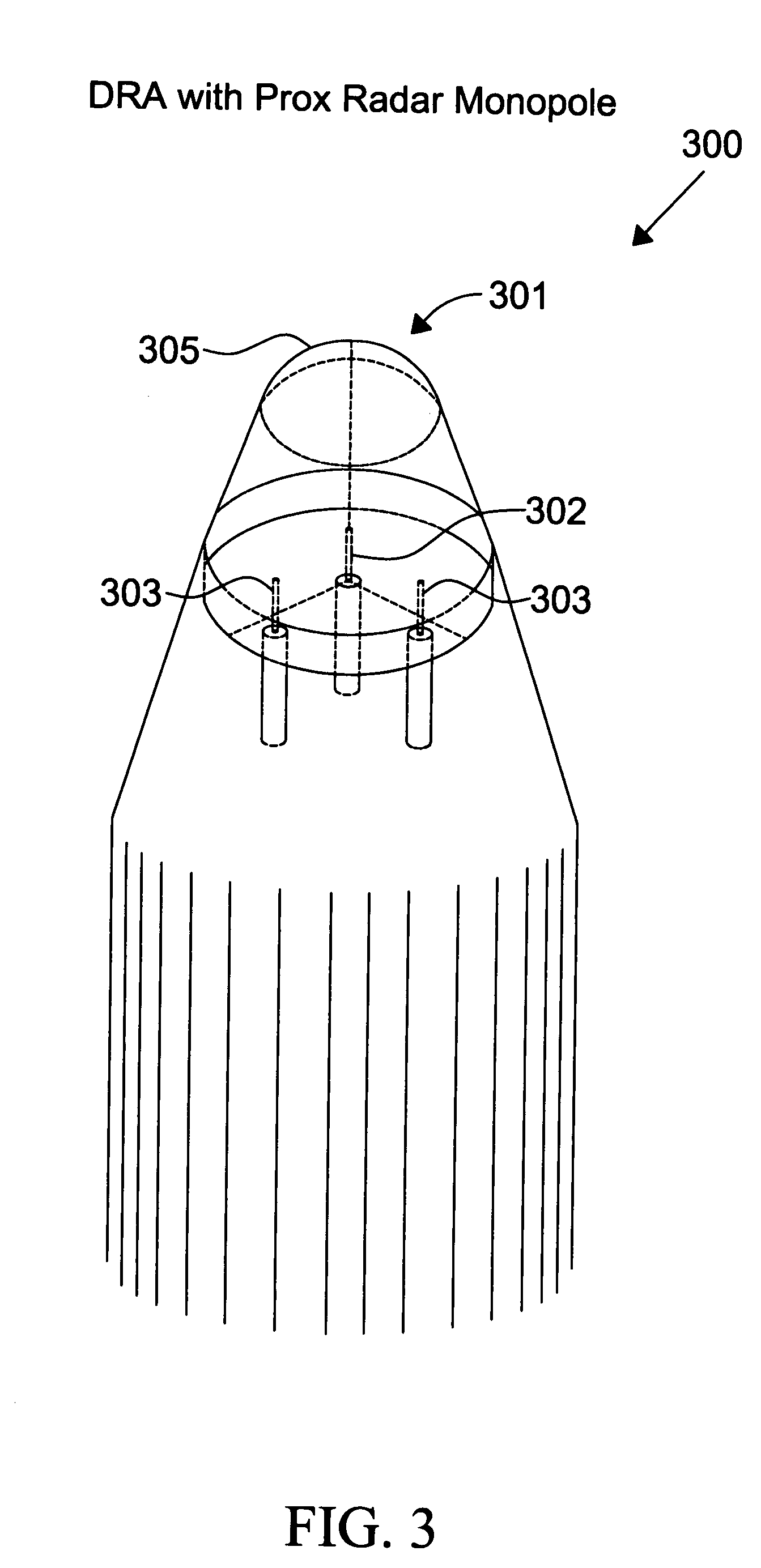
Proximity radar antenna co-located with GPS DRA fuze
ActiveUS7498969B1Improve approachReduce the amount requiredDirection controllersAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadar antennasDielectric resonator antenna
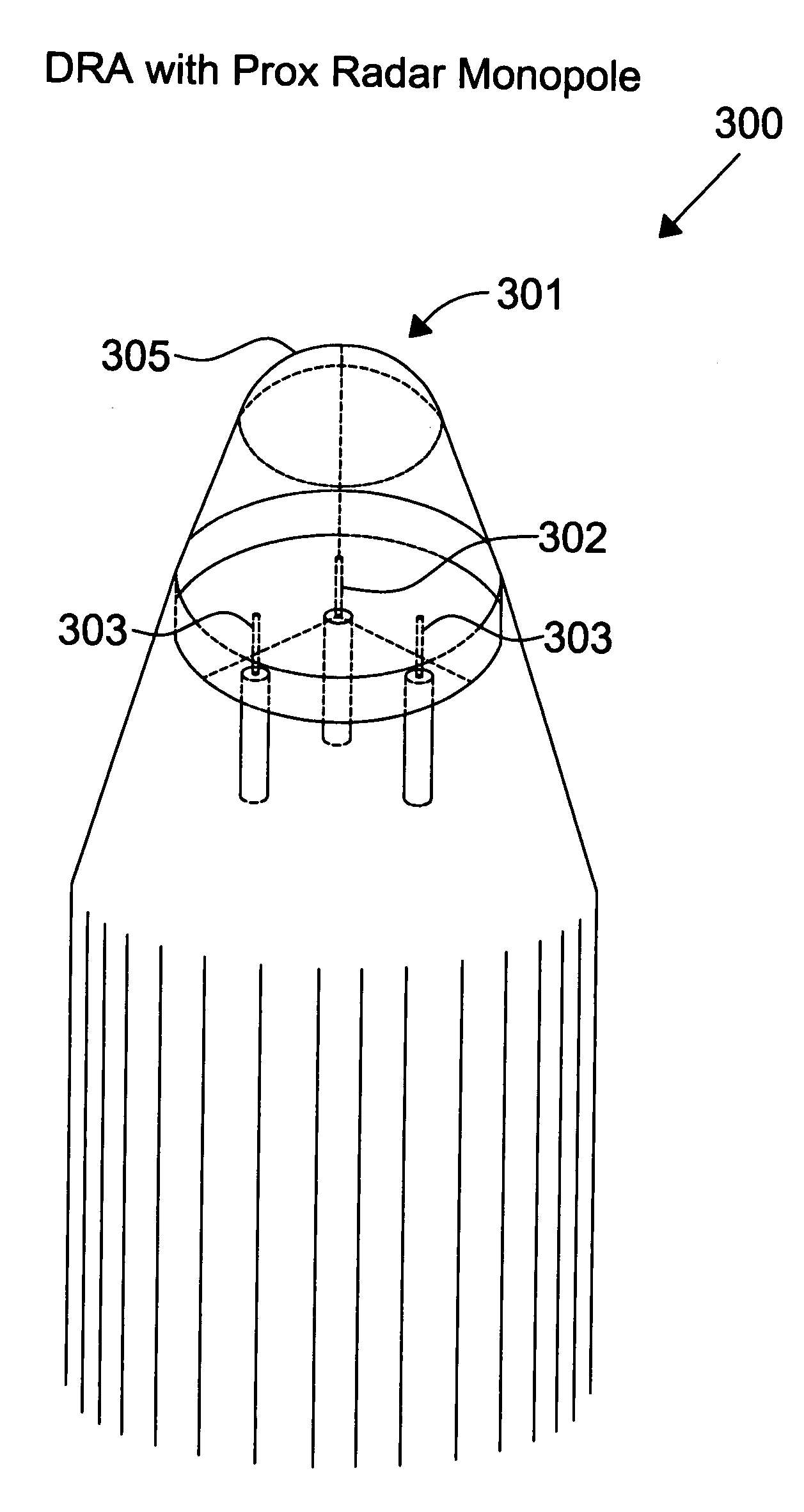
The present invention is directed to a fuze application capable of GPS (Global Positioning System) and proximity radar functionality by co-locating a proximity radar antenna with a GPS DRA (Dielectric Resonator Antenna) fuze. The GPS DRA fuze has a HE11δ mode structure resulting in an E-field null at the center. The monopole proximity radar antenna is mounted in the E-field null center and is thus electrically isolated from the GPS DRA fuze. The high dielectric constant permits the GPS DRA fuze to operate in the L1 frequency and the electrically shortened proximity radar antenna to resonate in the C-Band within a small form factor. The GPS DRA fuze maintains a forward-looking CP (circular polarization) pattern while proximity antenna maintains a desirable monopole pattern. Nesting allows mounting of both GPS and proximity radar antennas on the fuze nose while reducing the total space occupied.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
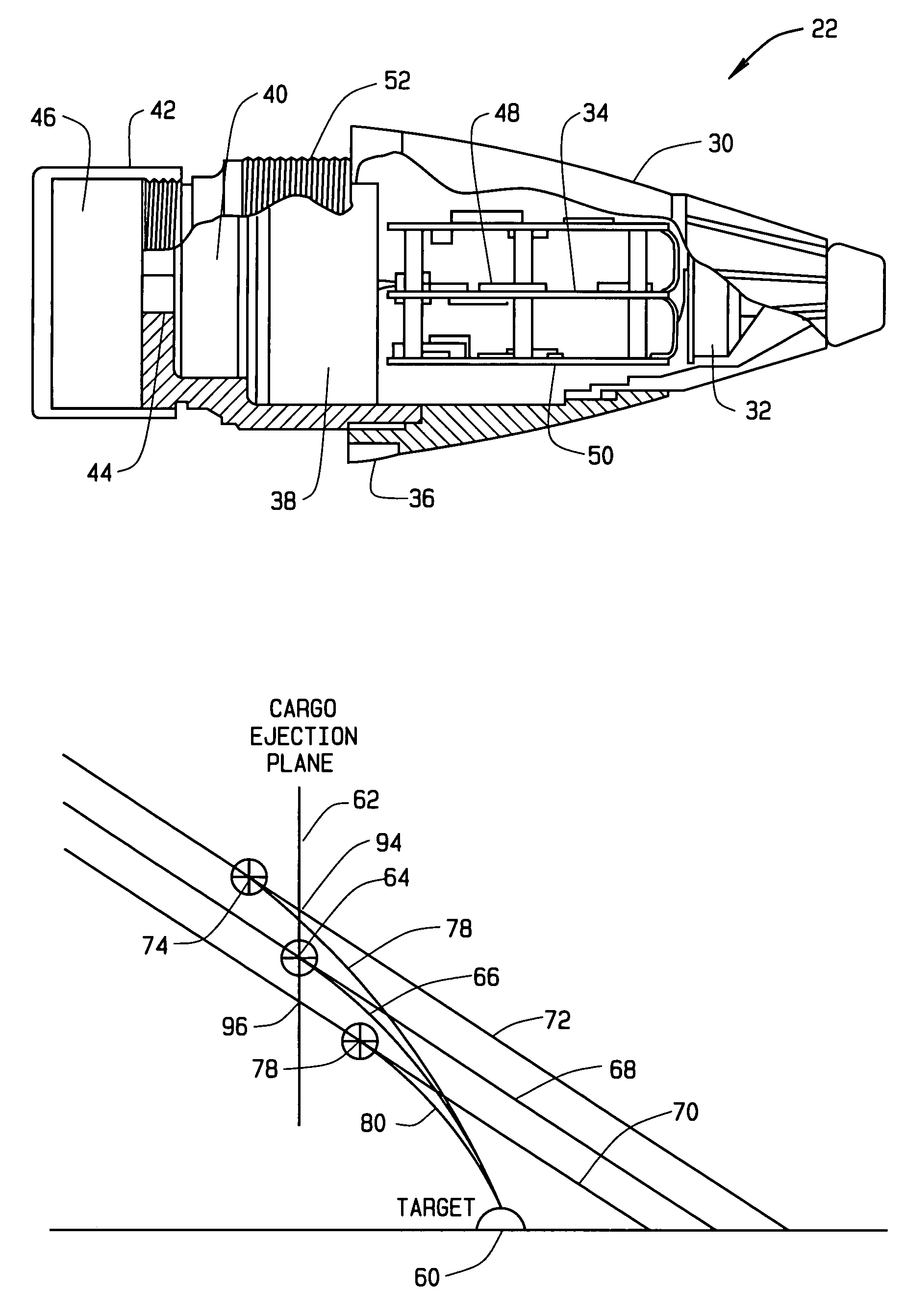
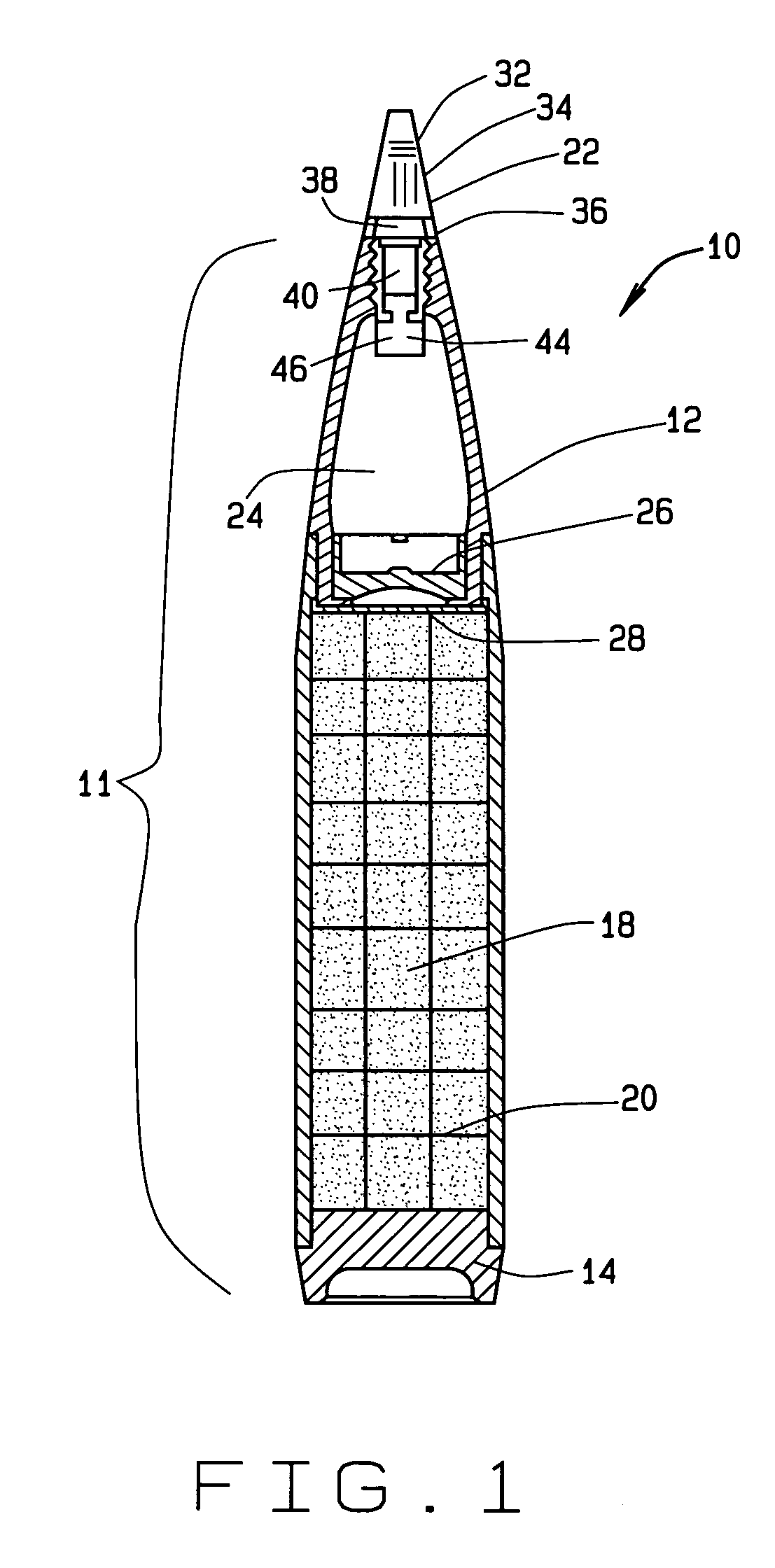
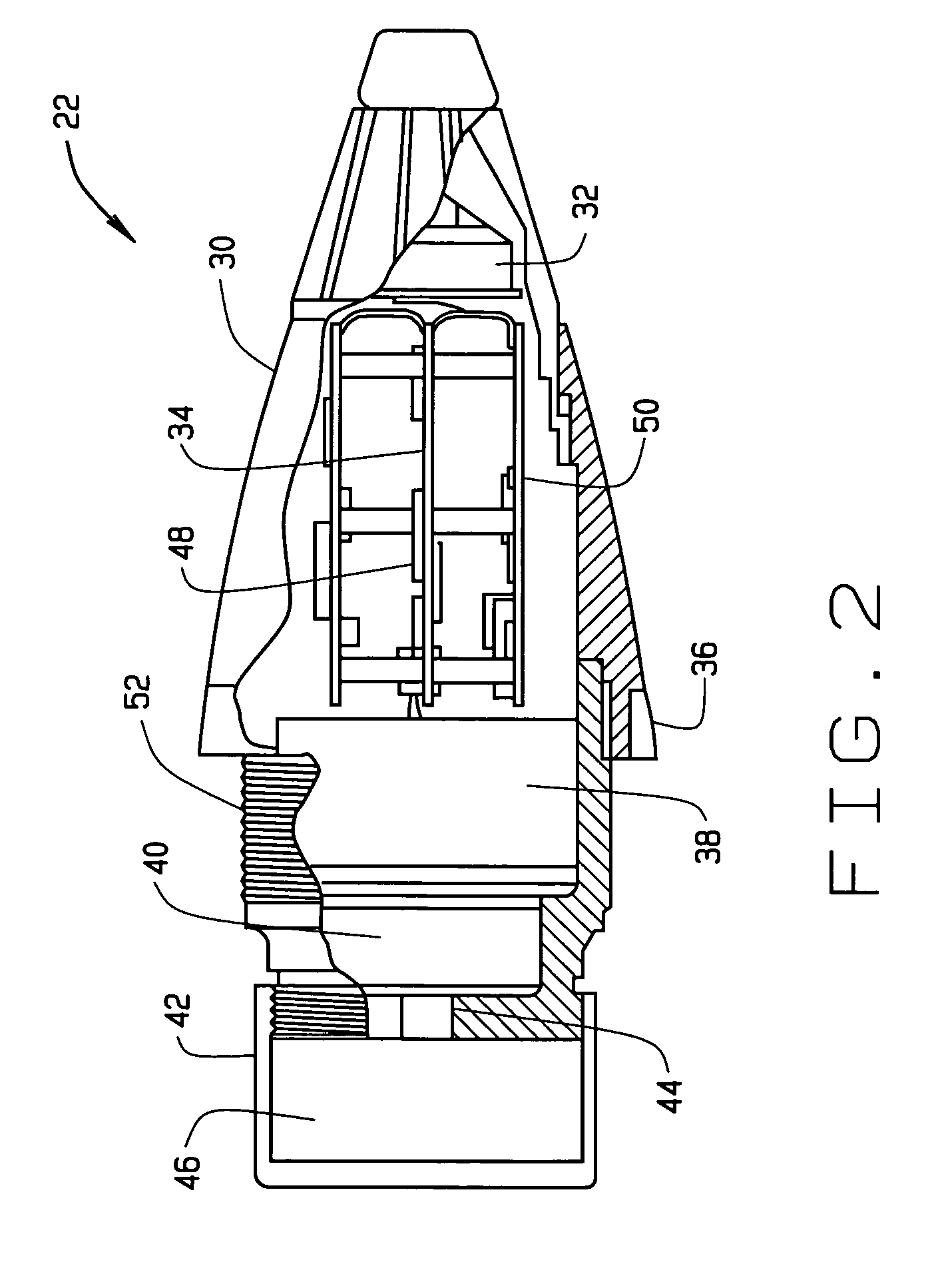
Accuracy fuze for airburst cargo delivery projectiles
InactiveUS7121210B2Low costReduce in quantityAmmunition projectilesProximity fuzesRadio navigationFuze
In one aspect, an artillery projectile apparatus is provided that includes a carrier projectile containing a payload, and a fuze disposed at an ogive of the projectile and which is configured to eject the payload when the fuze is detonated. The fuze includes a receiver configured to receive location information from a radionavigation source and a processor configured to acquire position data from the receiver. The processor is also configured to estimate a projectile flight path using the position data, to determine intercept parameters of the artillery projectile relative to an ejection plane of its payload cargo, and to adjust an ejection event initiation command time of the payload in accordance with the determined intercept parameters. In some configurations, the present invention dramatically decreases range errors typically associated with delivering artillery payloads to specific targets.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Game set including projectiles with internal distance measuring means
InactiveUS20060267286A1Accurately determineLevel accuracyIndoor gamesBall sportsExact locationEngineering
The present invention is a game set for use in an object throwing game in which projectiles are rolled, tossed or otherwise moved towards a target object. Each projectile includes a distance measuring means disposed within the projectile that can send and receive signals from a control device. The distance measuring system including the measuring means and the control devices allow for an individual or individuals playing the game to measure in a highly accurate manner the positioning of the projectiles with regard to the target object and with regard to one another in order to determine the exact locations of the projectiles, and which projectile or projectiles are positioned closer to the target object than the remaining projectiles. All information regarding the distance between the projectiles and the target object can be received and displayed on the control device for easy administration of the game.
Owner:HICKEY IP
Wireless Detonator Assemblies, Corresponding Blasting Apparatuses, and Methods of Blasting
A wireless or partially wireless detonator assembly (10) and corresponding blasting apparatus, that may be “powered Up” by a remote source of power (13) that is entirely distinct from the energy used for general command signal communications (16). In one embodiment, the detonator assembly (10) may include an active power source (25) with sufficient power for communications, but insufficient power to cause intentional or inadvertent actuation of the detonator (10).
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
Sensor system with modular optical transceivers
An optical sensor system and method includes a plurality of optical transceiver modules arranged across the surface of the optical sensor in a predetermined pattern. A given optical transceiver module includes an optical transmitter that produces at least one light beam and an optical receiver that detects reflected light from the at least one light beam. The optical transceiver module further includes housing for housing the optical transmitter and the optical receiver.
Owner:LITTON SYST INC
Access control for electronic blasting machines
InactiveUS6851369B2Improve securityIncandescent ignitionBlasting cartridgesDetonatorComputer hardware
Blasting apparatuses and methods control actuation of a plurality of detonators, and involve the use of one or more authorization keys each associated with a blasting machine. The authorization key(s) are transferable from the blasting machine(s) to a central command station, each authorization key storing a data package comprising a randomly generated access code generated by its corresponding blasting machine. Transfer of the one or more authorization keys to a central command station allows the data packages (and associated randomly generated access codes) to be transmitted by the central command station for receipt by the blasting machine(s).
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
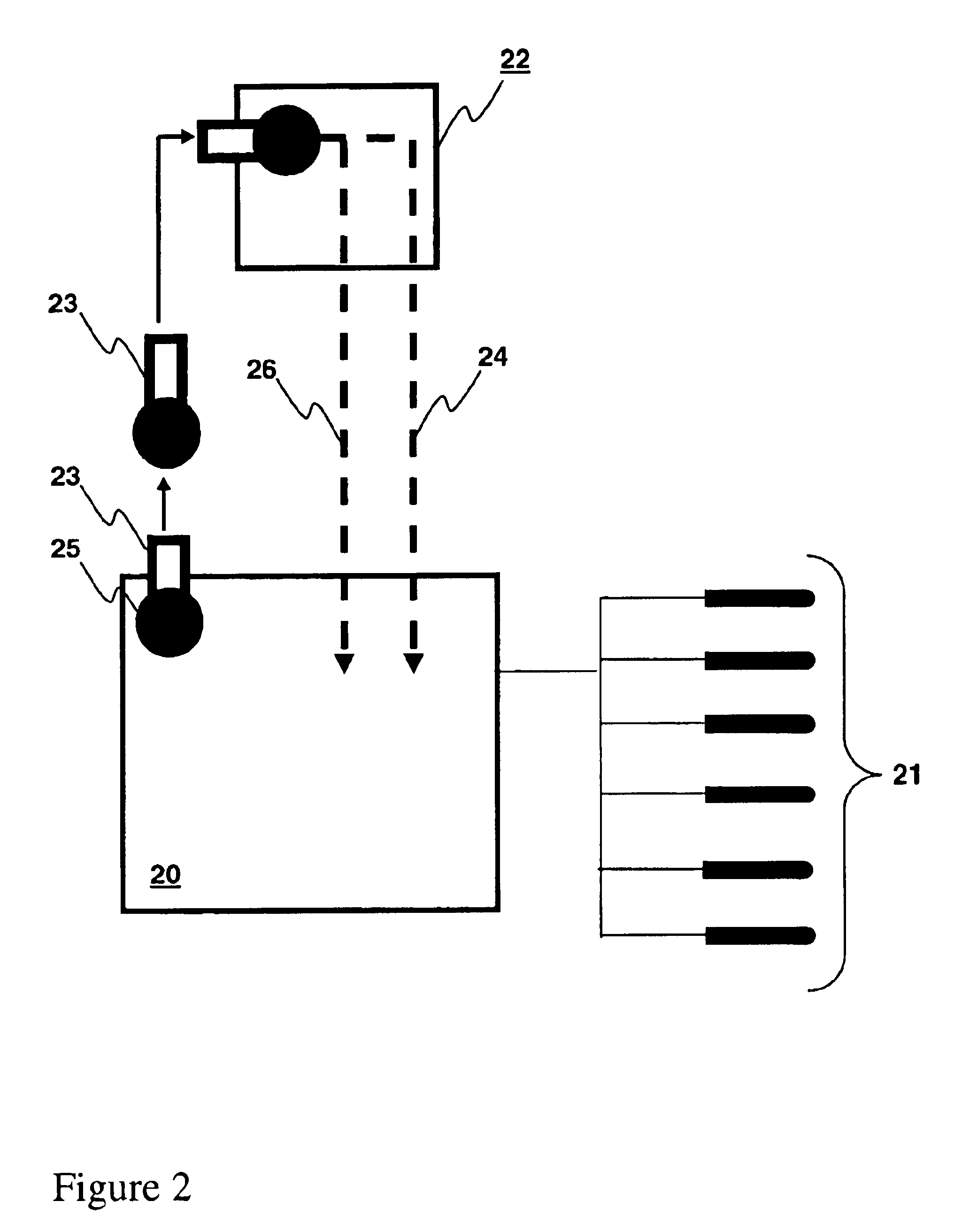
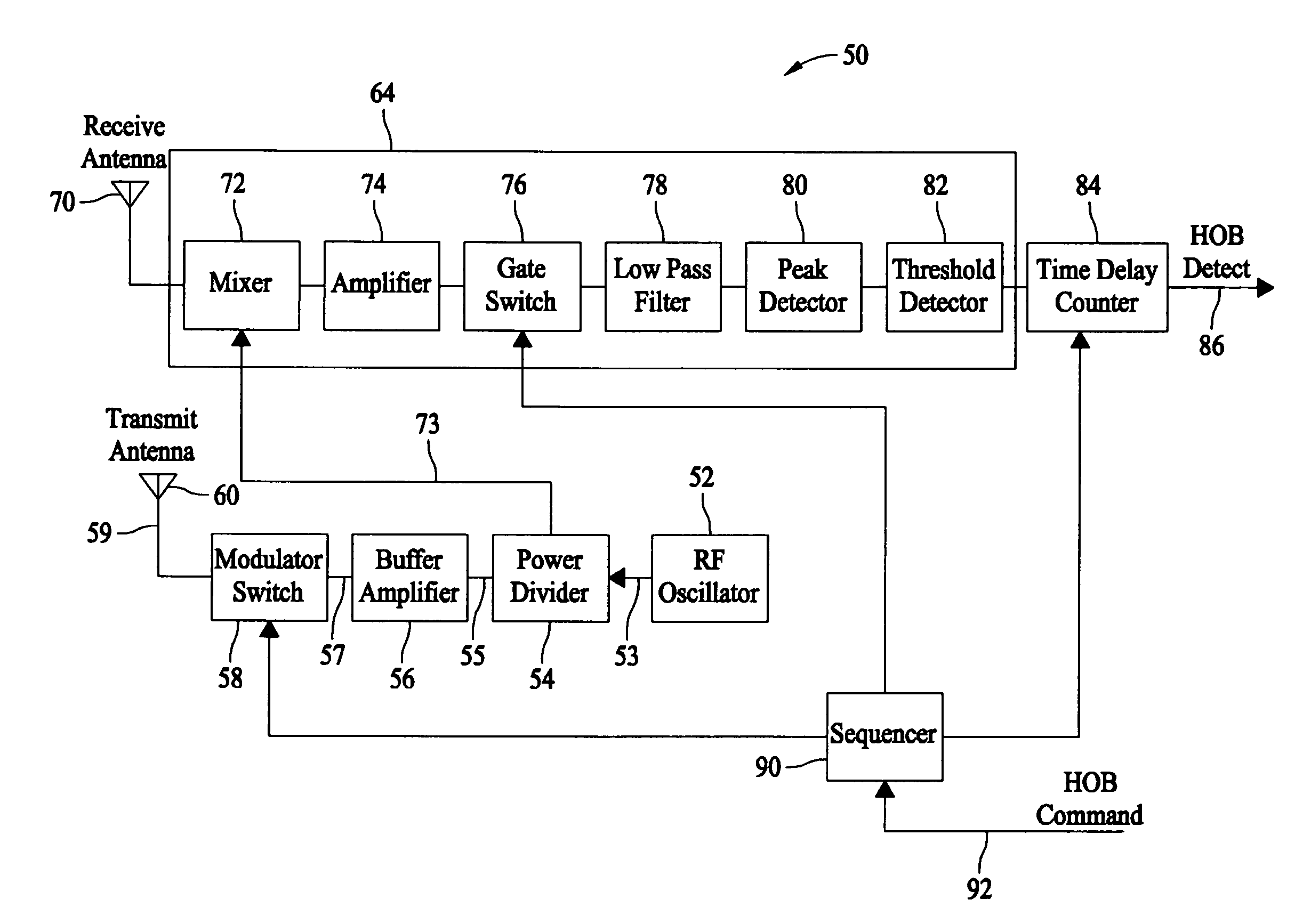
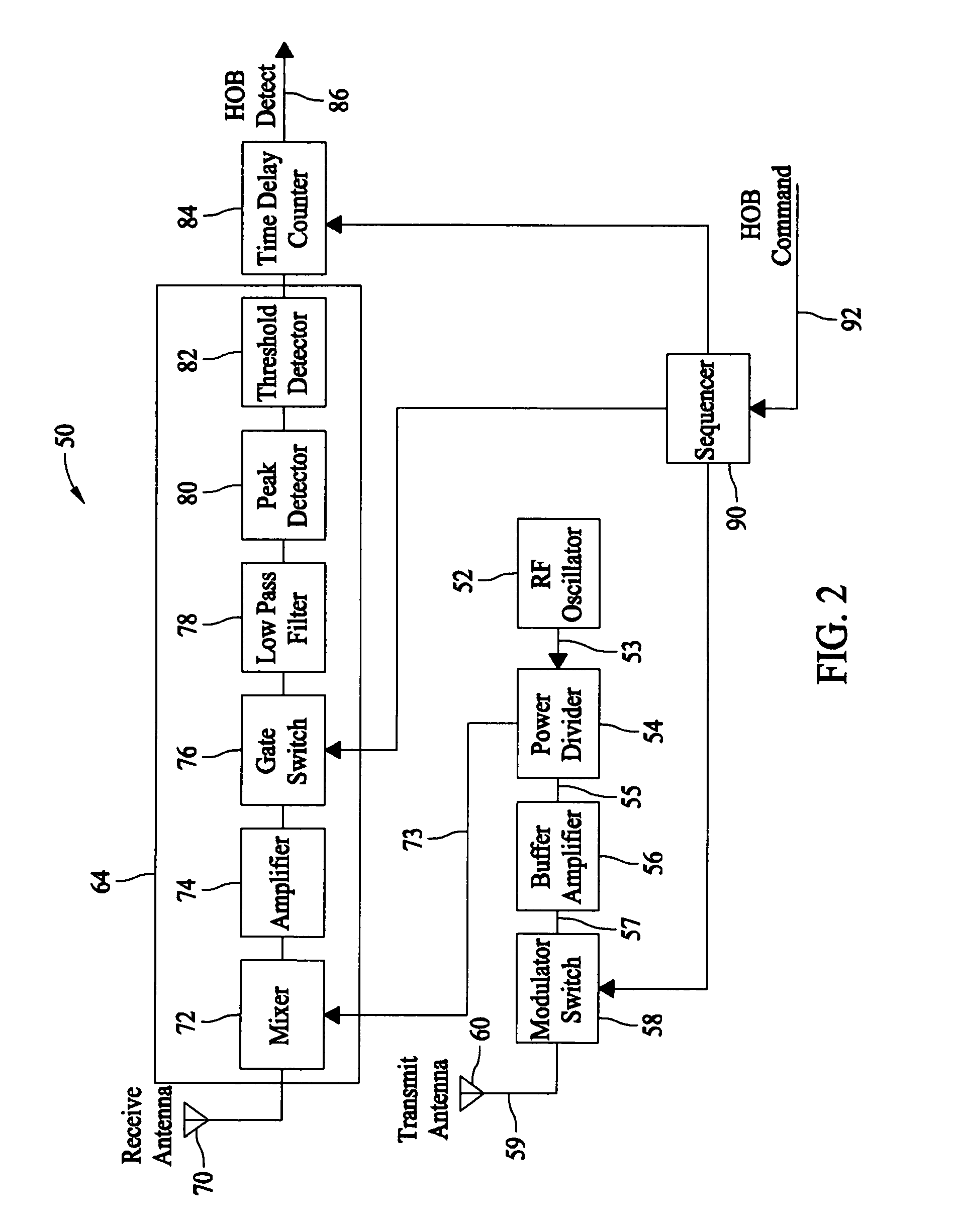
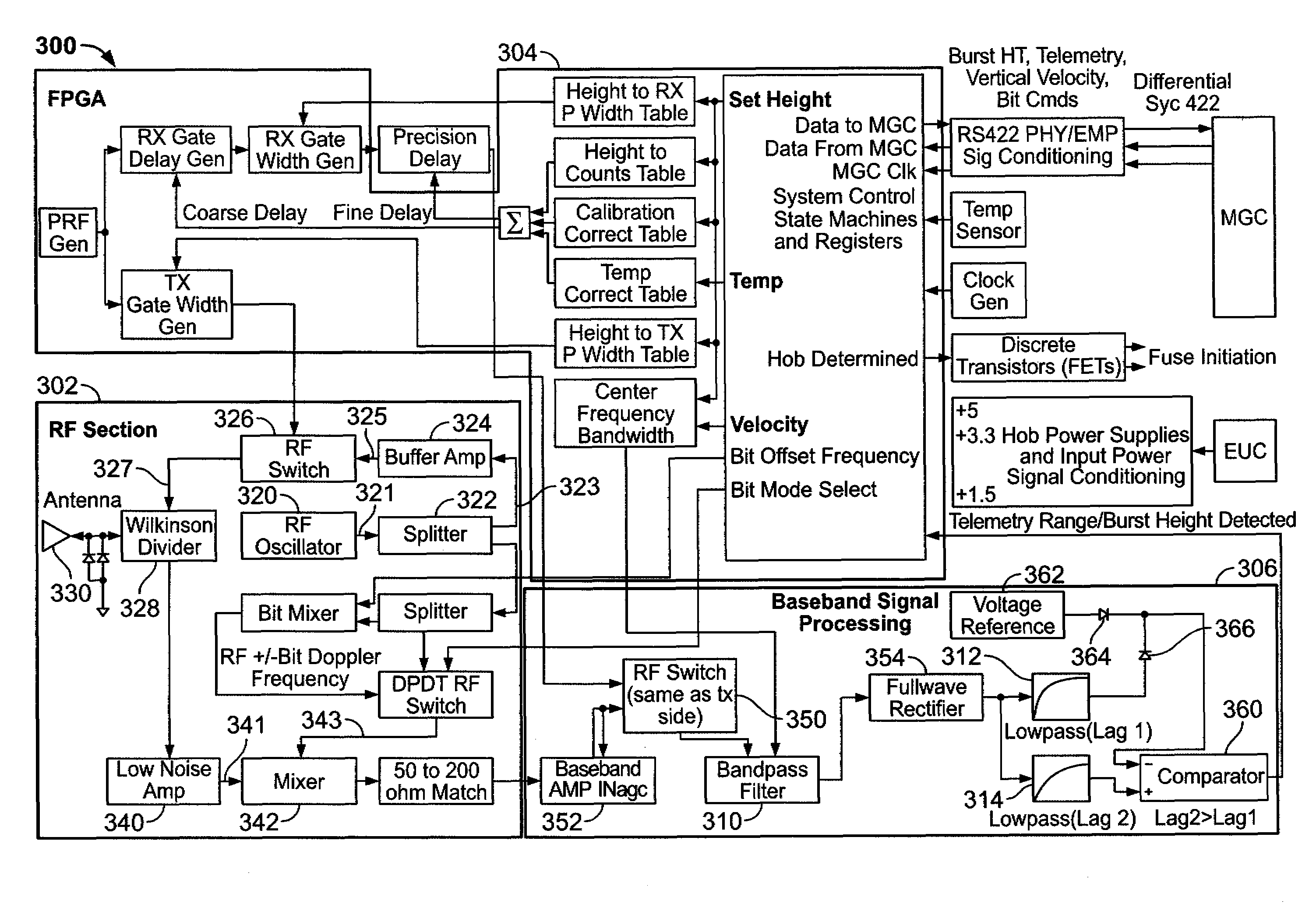
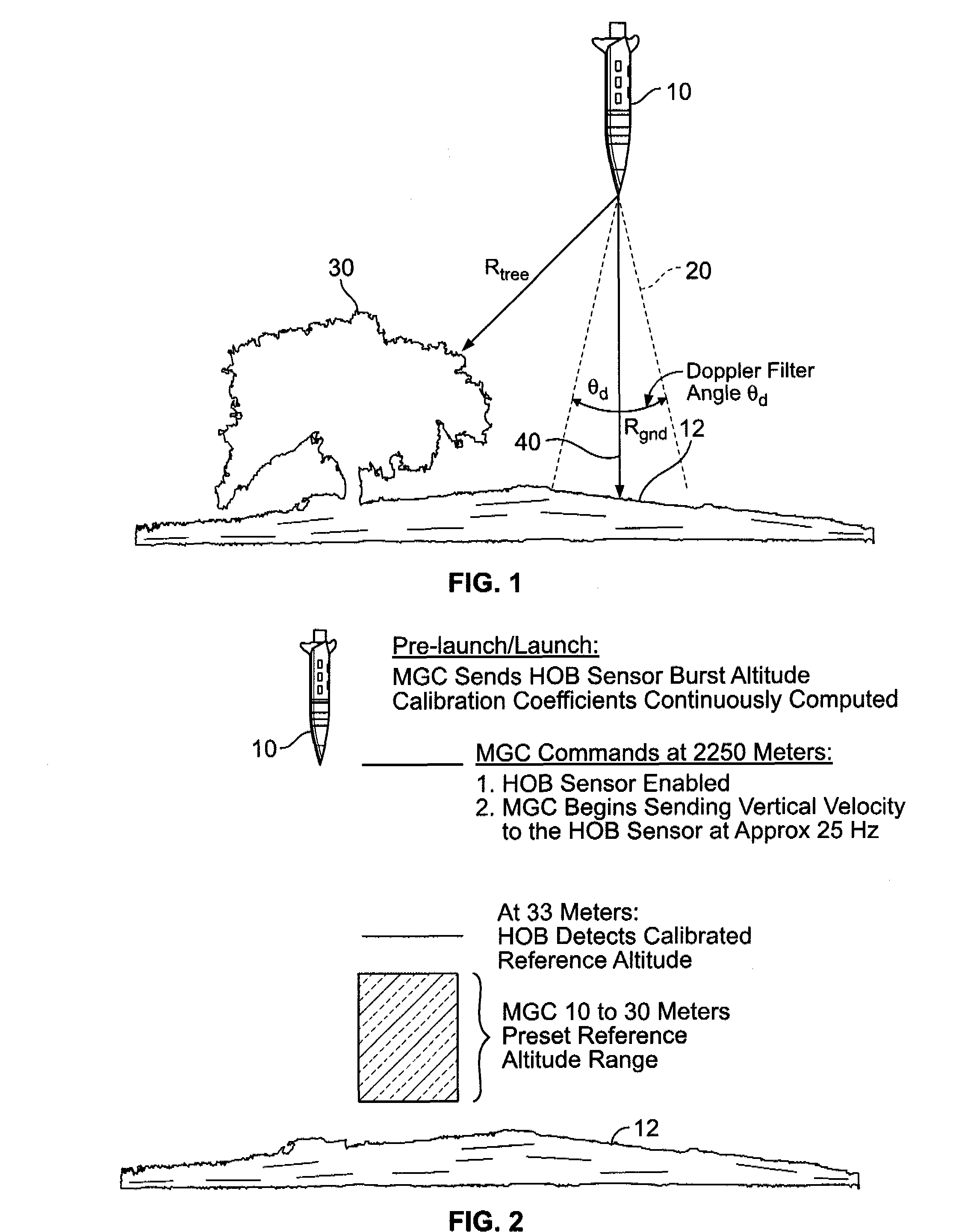
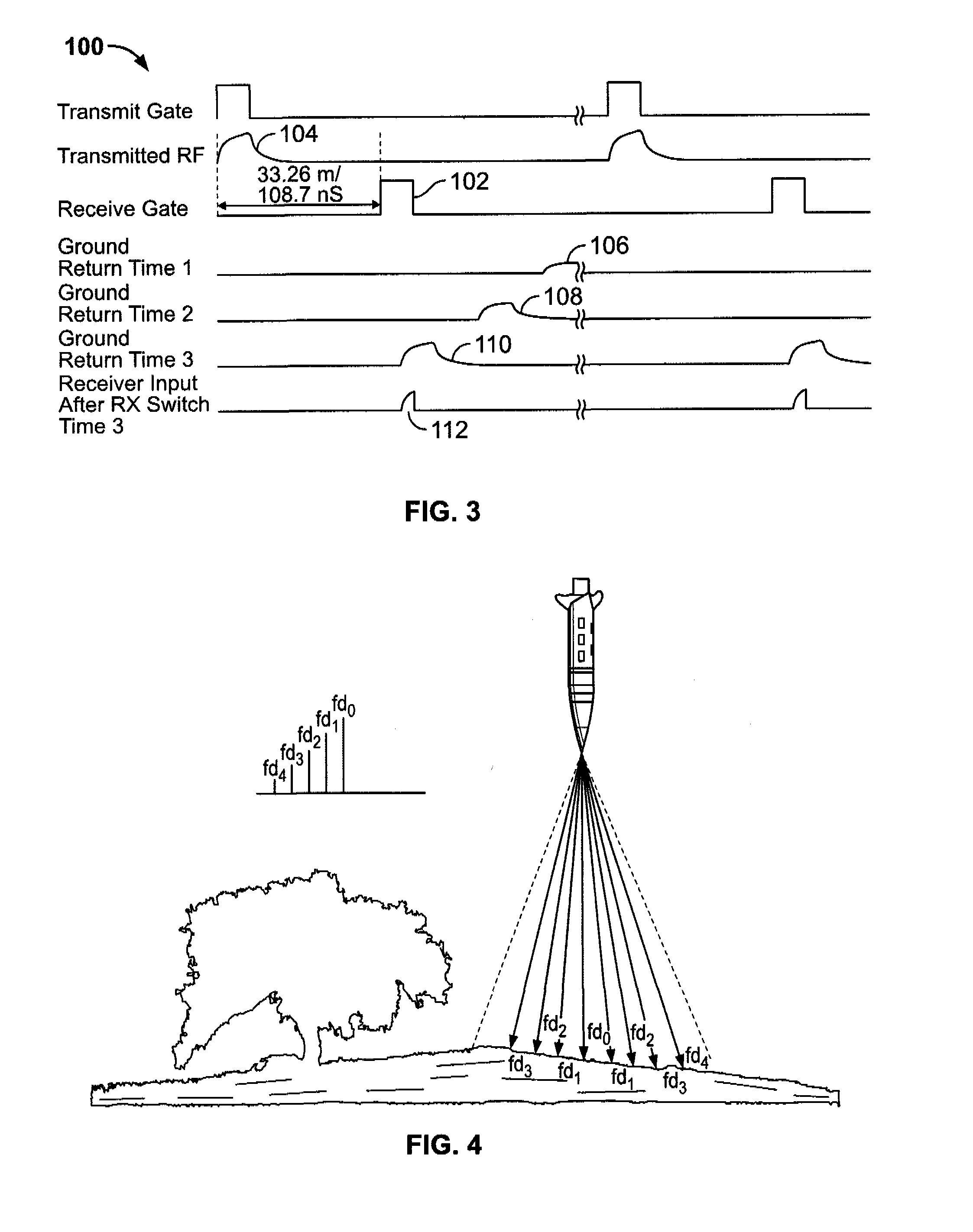
Methods and systems for controlling a height of munition detonation
A unit is described that is configured to control detonation of a munition such that the munition is detonated at a desired altitude. The unit includes a radar transmitter, a radar receiver that includes a radar range gate, and a sequencer. The sequencer is configured to receive a detonation altitude and set the range gate based on the received detonation altitude. The unit is also configured to output a detonation signal when radar return pulses received by the receiver aligned with gate delay pulses from the range gate.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
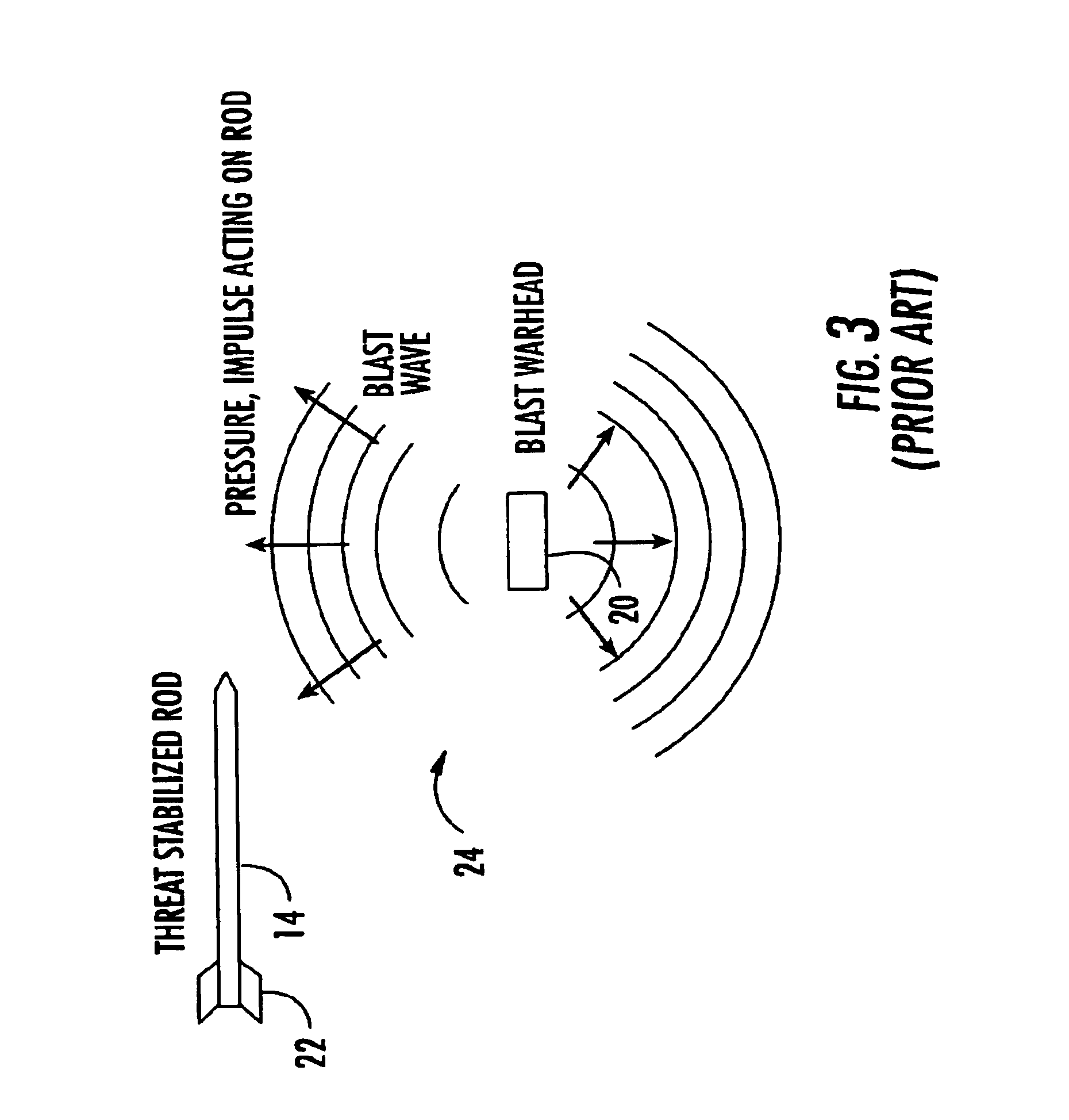
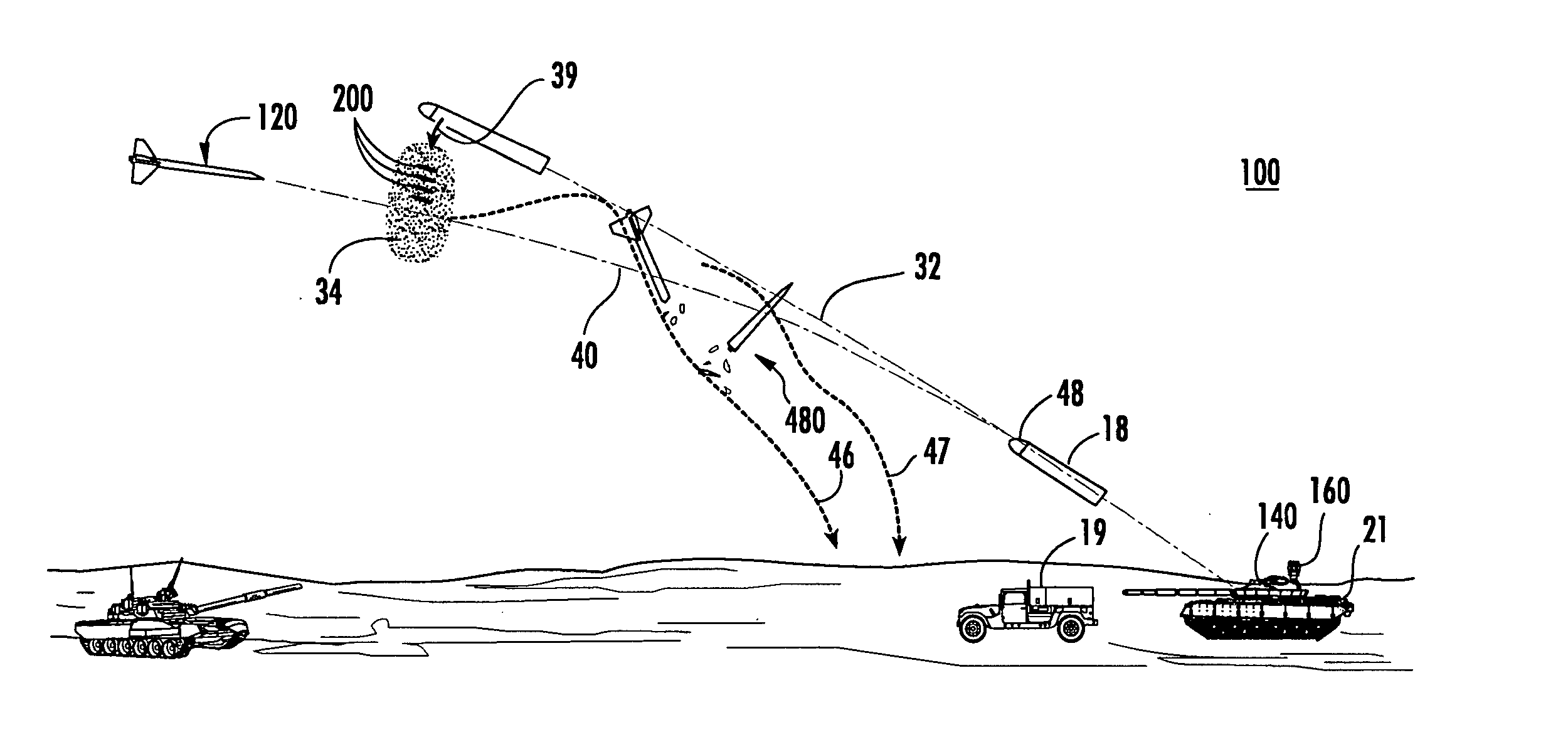
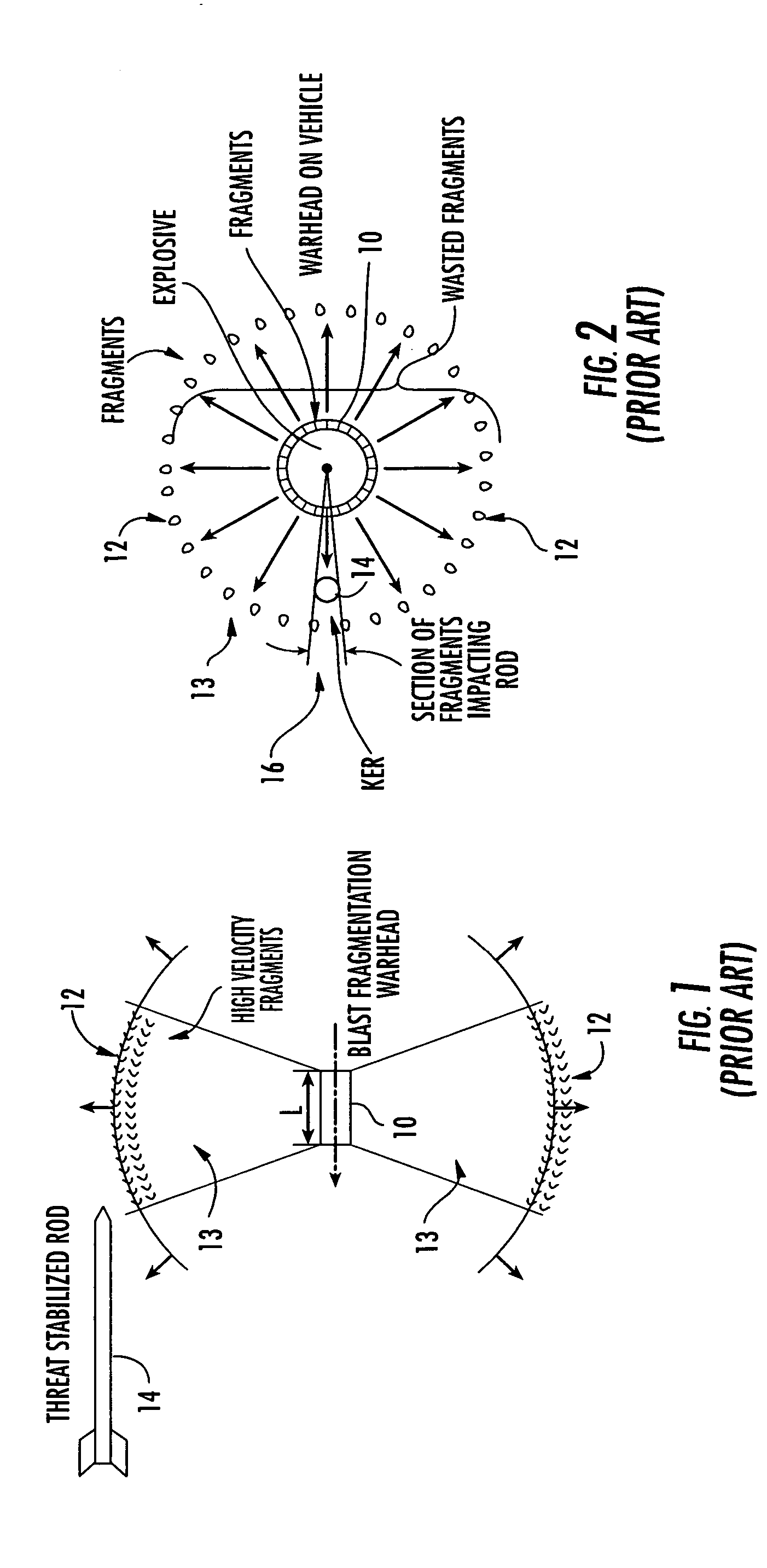
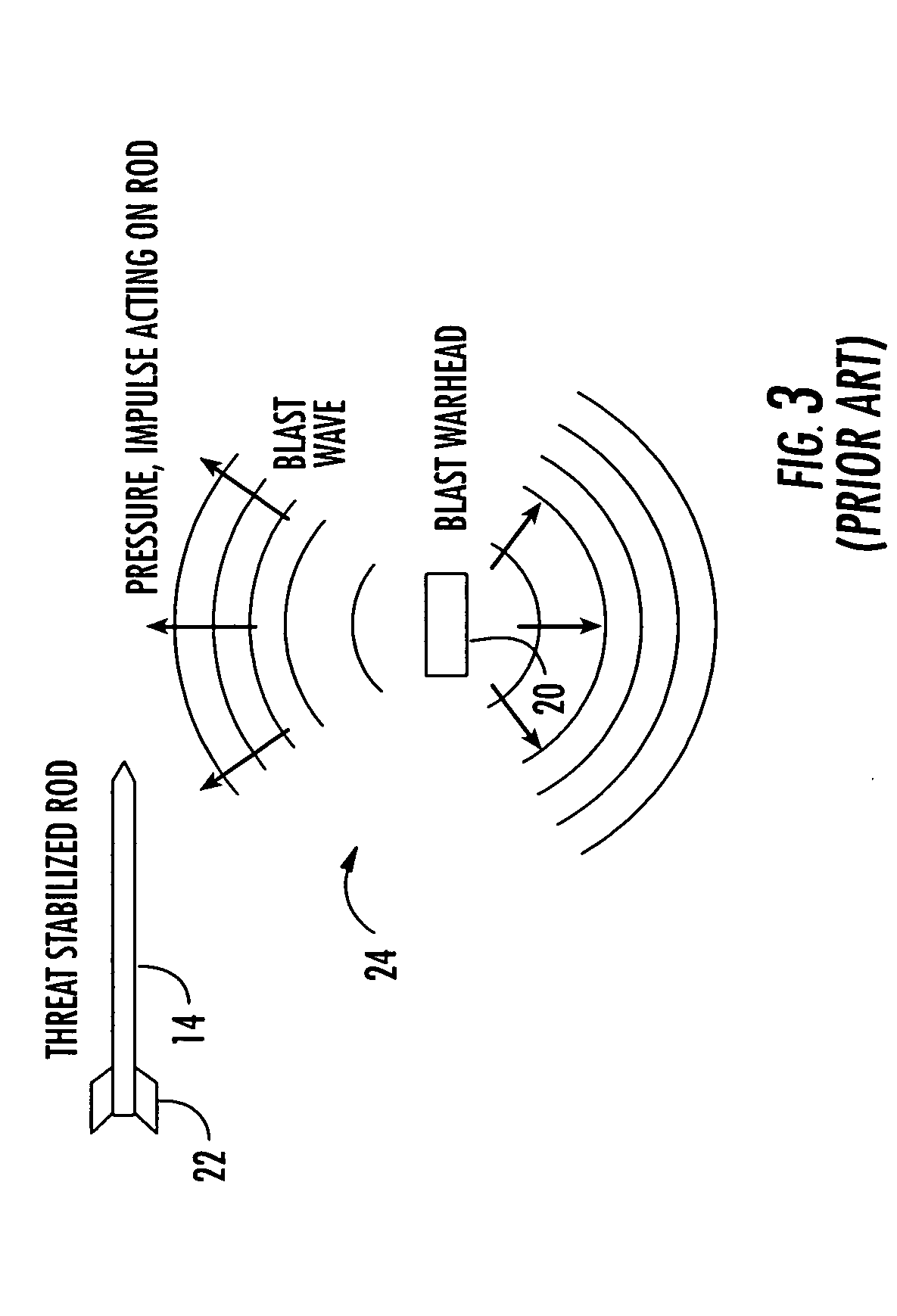
Vehicle-borne system and method for countering an incoming threat
ActiveUS20050115450A1Effectively breakEffectively fracturesAmmunition projectilesProximity fuzesEngineeringProtection system
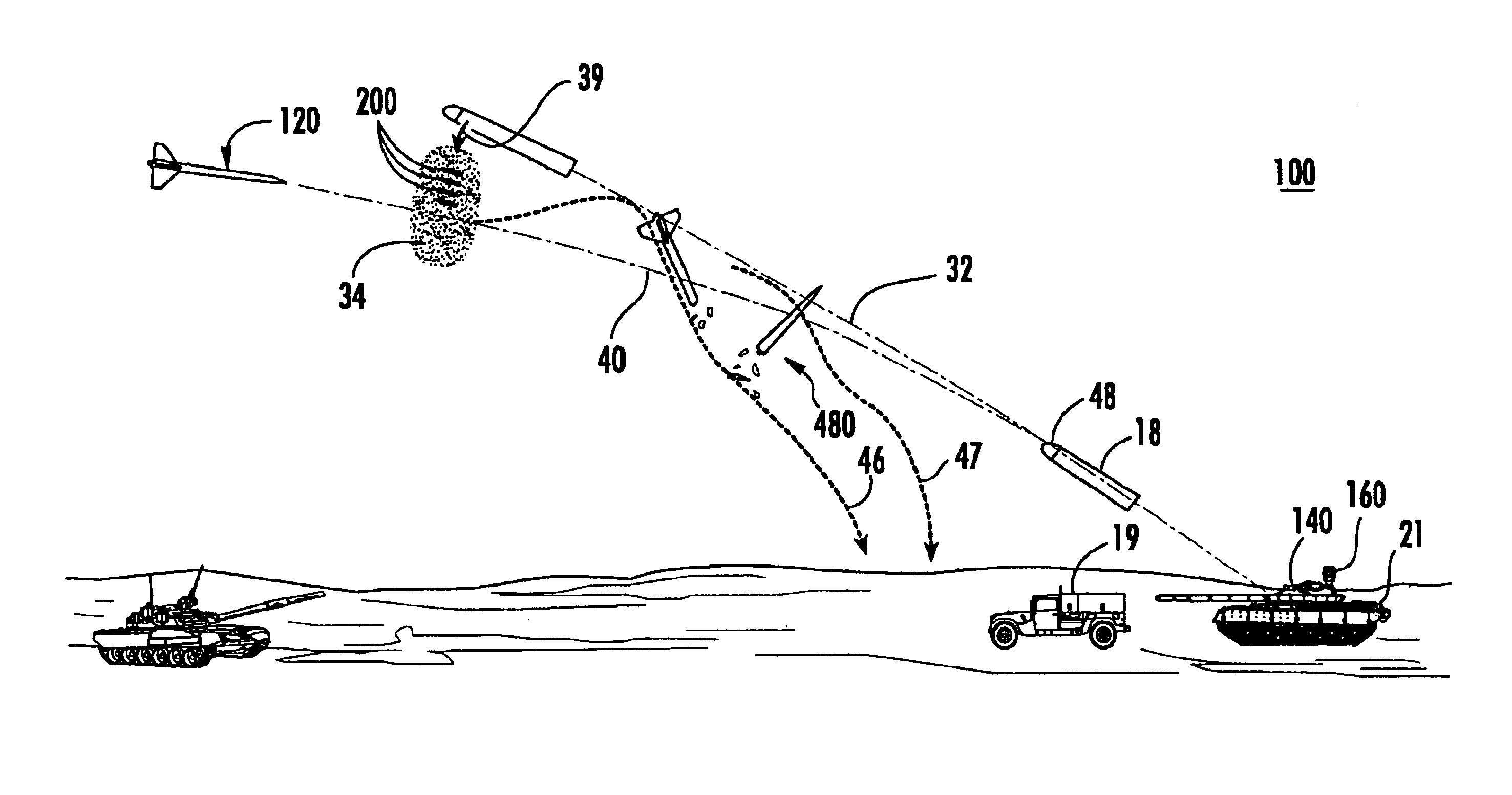
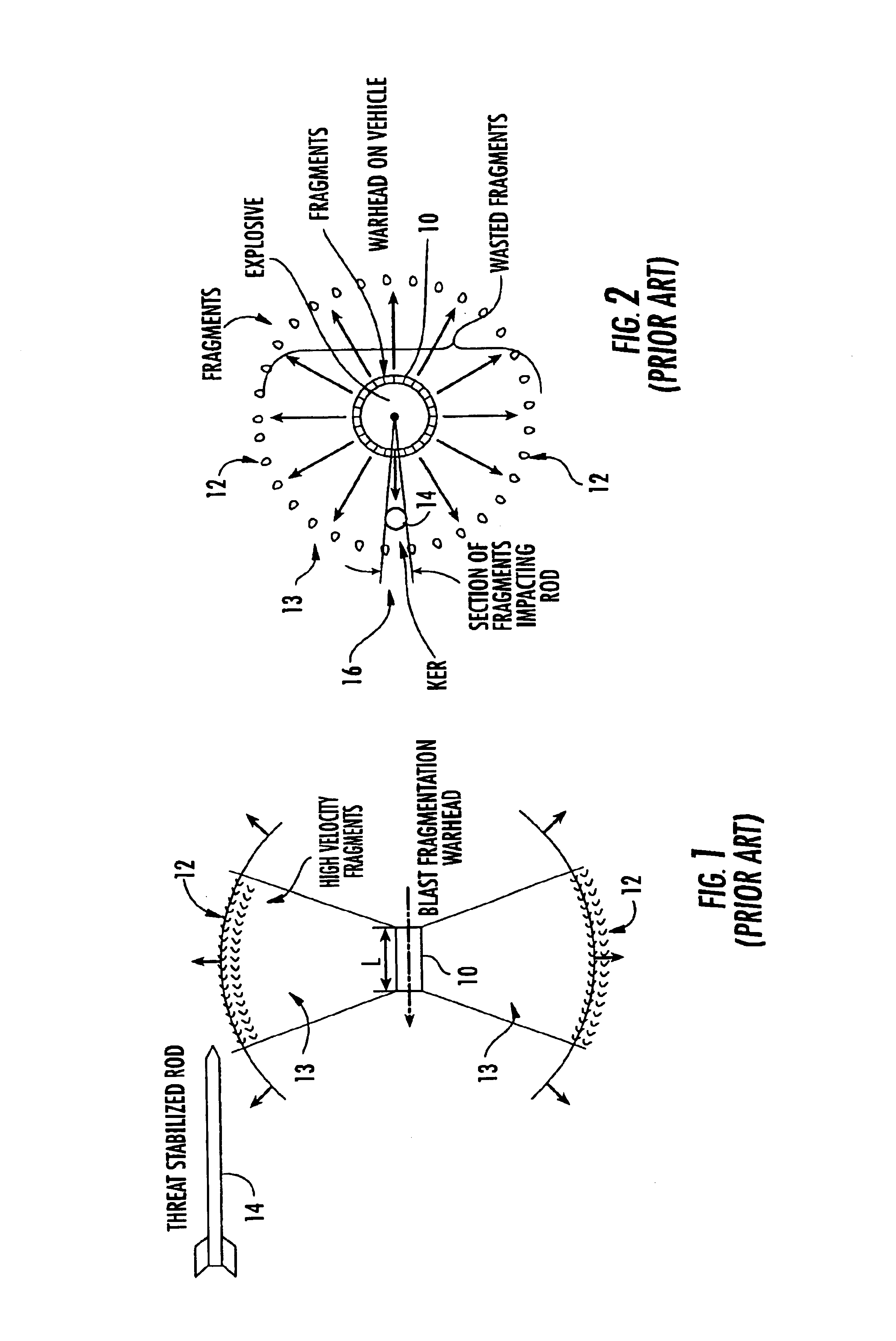
A vehicle-borne system for countering an incoming threat, the system including a sensing device configured to sense an incoming threat, and an active protection system including a maneuverable interceptor incorporating a plurality of kinetic energy rods and an aimable explosive charge configured to deploy the kinetic energy rods in a predetermined direction; the active protection system further including a detection subsystem configured to maneuver the interceptor to intercept the incoming threat, the detection subsystem further configured to determine if the interceptor will miss the threat, and then initiate the explosive charge to aim the kinetic energy rods into a disbursed cloud in the trajectory path of the incoming threat and between the incoming threat and the vehicle.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Wireless detonation system, wireless detonation method, and detonator and explosive unit used in same
ActiveUS9709373B2Reduce the overall diameterReduce the amount requiredBlastingProximity fuzesDetonatorDetonation
Owner:NOF CORP
Composites for antennas and other applications
Composite material, devices incorporating the composite material and methods of forming the composite material are provided. The composite material includes interstitial material that has at least one of a select relative permittivity property value and a select relative permeability property value. The composite material further includes inclusion material within the interstitial material. The inclusion material has at least one of a select relative permeability property value and a select relative permittivity property value. The select relative permeability and permittivity property values of the interstitial and the inclusion materials are selected so that the effective intrinsic impedance of the interstitial and the inclusion material match the intrinsic impedance of air. Devices made from the composite include metamaterial and / or metamaterial-inspired (e.g. near-field LC-type parasitic) substrates and / or lenses, front-end protection, stealth absorbers, filters and mixers. Beyond the intrinsic, applications include miniature antenna and antenna arrays, directed energy weapons, EMI filters, RF and optical circuit components, among others.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Blasting system and method
The invention provides a blasting system which includes a plurality of electronic detonators which are configured in a blast array which has at least one row and a plurality of detonators in the row, each detonator including a memory in which is stored at least a respective identity code which is dependent, at least, on the row on which the detonator is, and on the detonator's position in the row, a harness which interconnects the detonators, and at least one control unit, connected to the harness, which generates a signal to fire the detonators.
Owner:DETNET SOUTH AFRICA (PTY) LTD
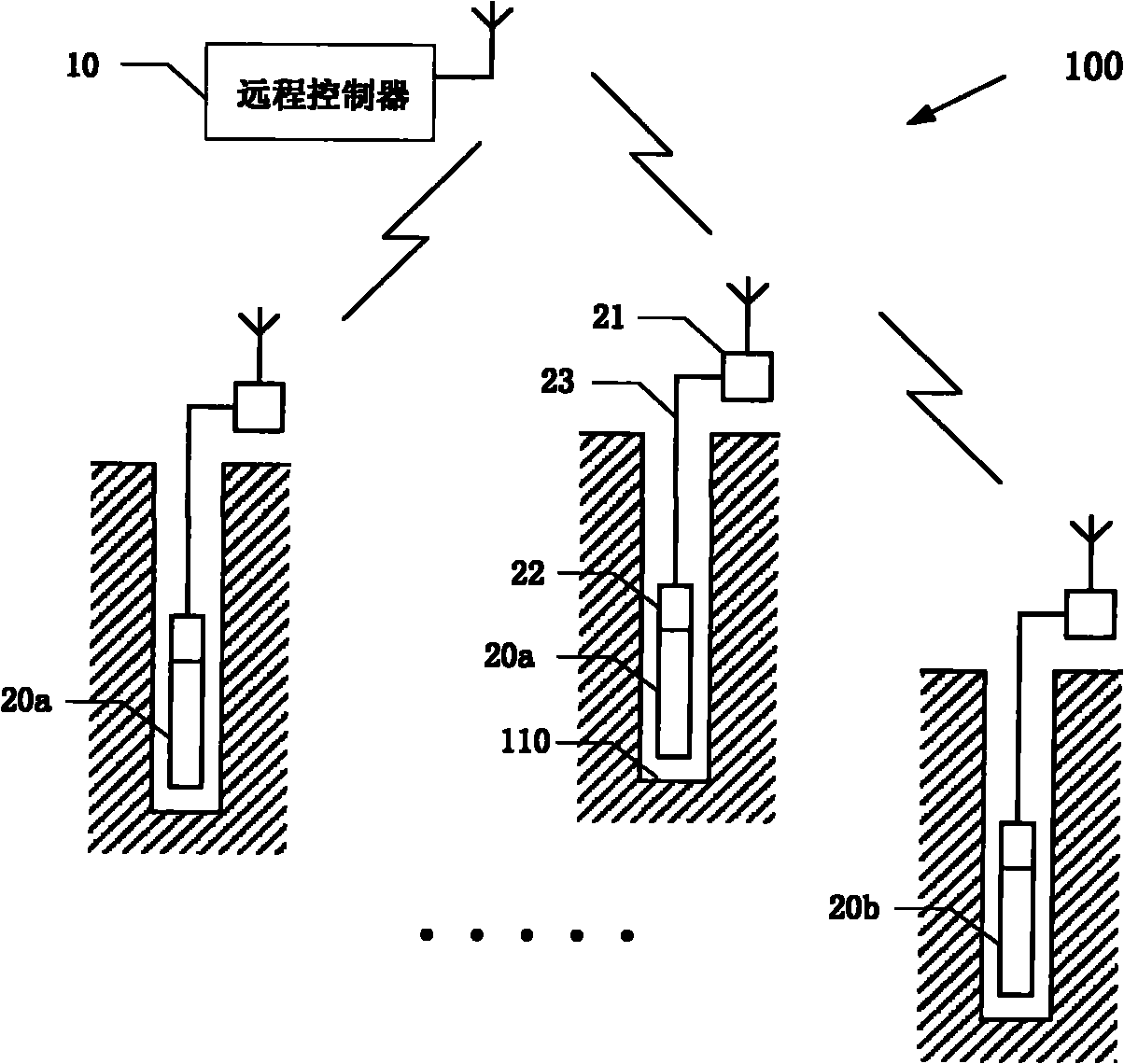
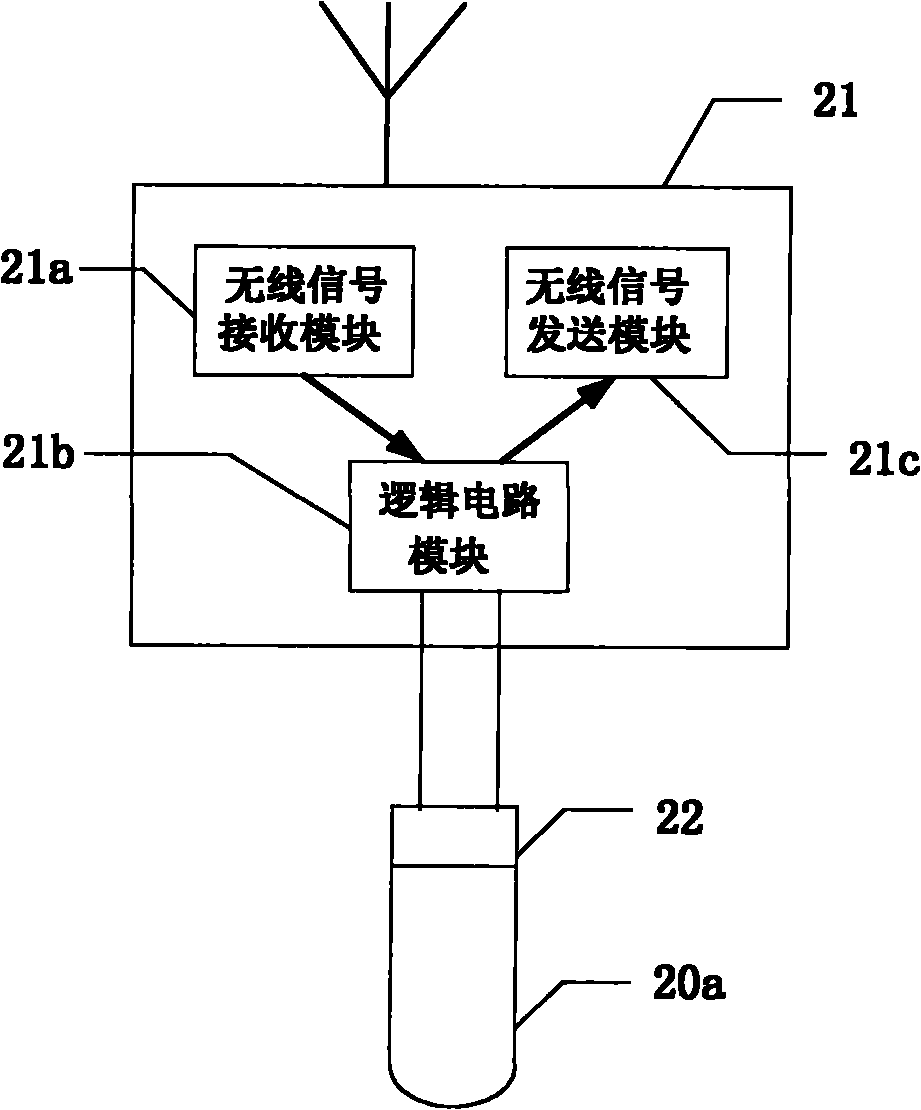
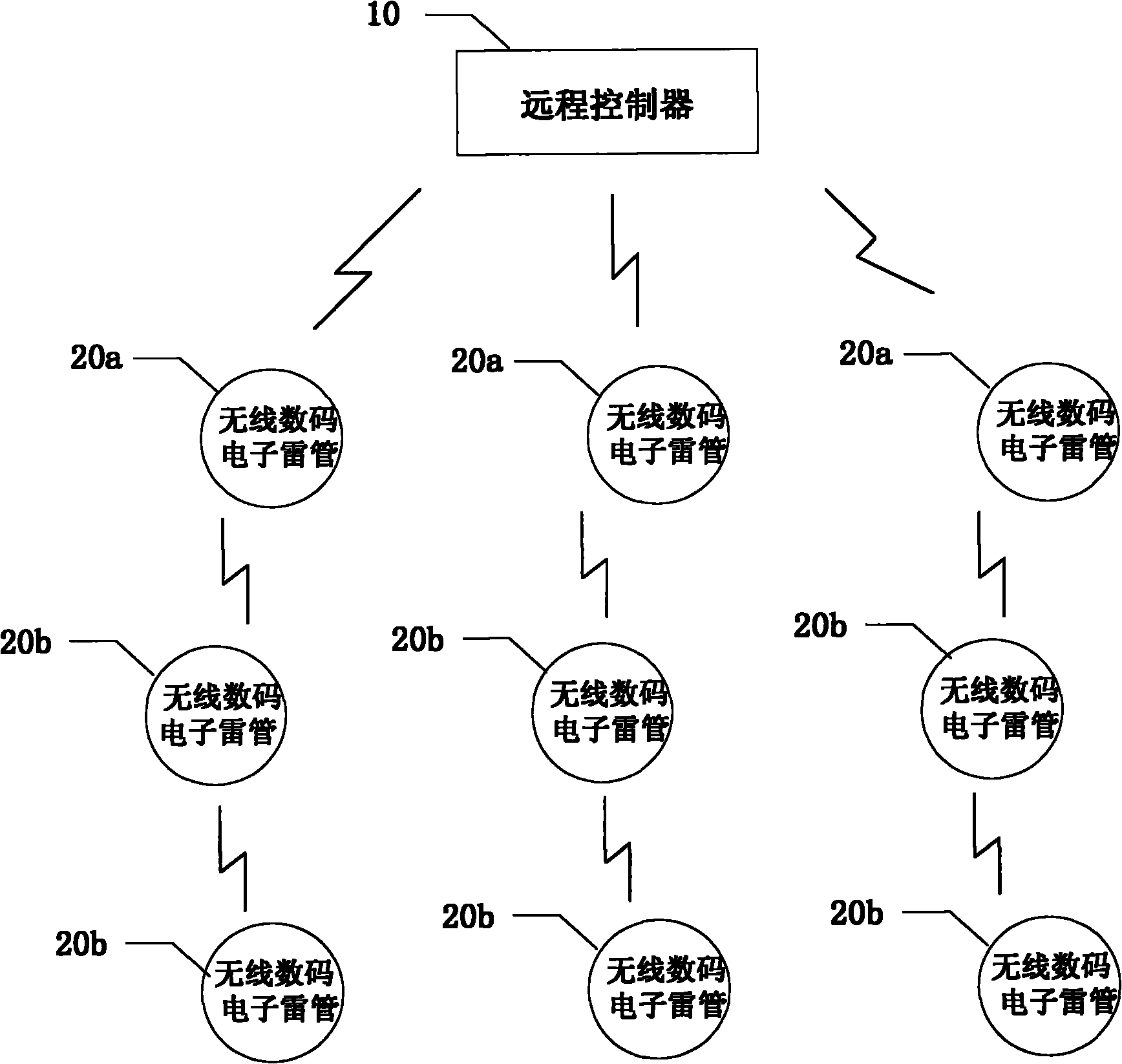
Wireless blasting system and communication method thereof
The invention discloses a blasting system, which comprises a remote controller and at least two wireless digital electronic detonators. The remote controller and the wireless digital electronic detonators are directly or indirectly communicated through a wireless signal, and the wireless digital electronic detonators comprise a wireless signal transceiver which is used for receiving instruction information sent by the remote controller, and the instruction information comprise detonating information; and the wireless digital electronic detonators work and detonate through work voltage and firing voltage according to the received detonating information. The invention also provides a communication method of the blasting system. According to the invention, the security and the reliability ofthe blasting system in the blasting work can be improved, an organized wireless digital electronic detonator network benefits the successful transmission of the wireless signal, the possibility of misoperations is reduced, a programmer and an exploder in the work process can be recycled, and the work trash after the blasting can be reduced at the same time to benefit the environment protection.
Owner:RONGGUI SICHUANG BEIJING TECH
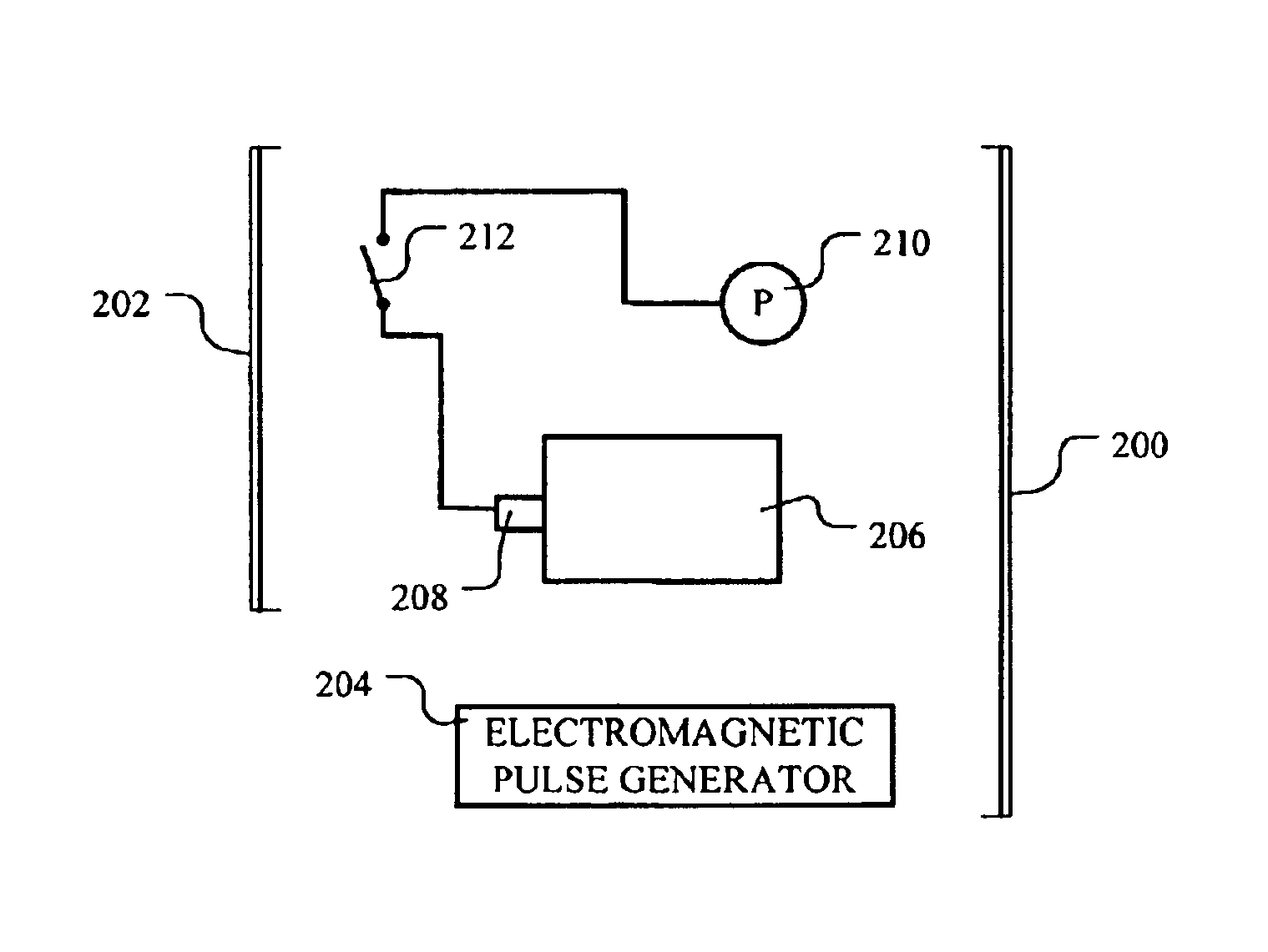
Electromagnetic pulse transmitting system and method
A plasma antenna generator includes an ionizable material, an explosive charge capable of projecting the ionizable material upon detonation, and a detonator coupled with the explosive charge. An electromagnetic pulse transmitting system includes an electromagnetic pulse generator and a plasma antenna generator capable of reradiating an electromagnetic pulse emitted from the electromagnetic pulse generator. A method includes providing an explosive device comprising an ionizable material, detonating the explosive device to propel the ionizable material, and ionizing the ionizable material to form at least one plasma trail. A sensing system includes an electromagnetic pulse generator, a plasma antenna generator capable of reradiating an electromagnetic pulse emitted from the electromagnetic pulse generator, and a sensing system capable of receiving and analyzing at least a portion of the electromagnetic pulse after being reflected from an interface.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Passive doppler fuze
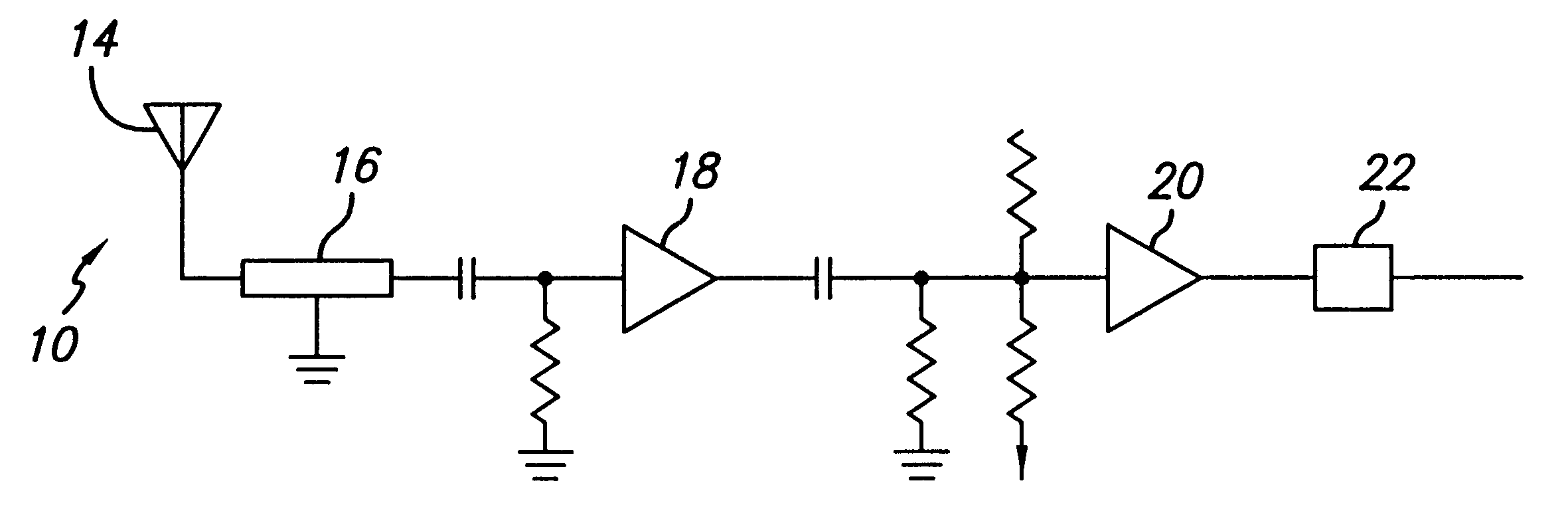
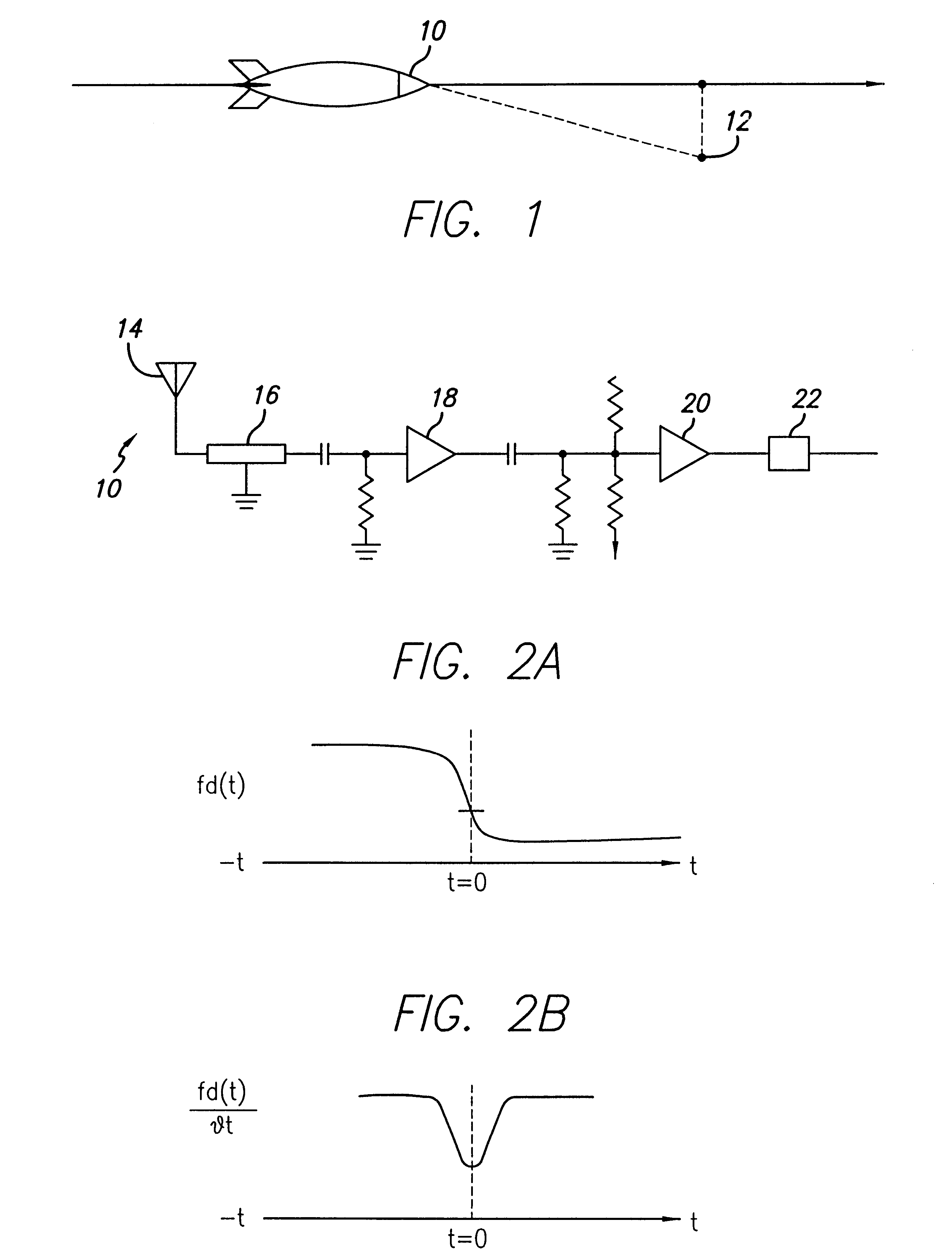
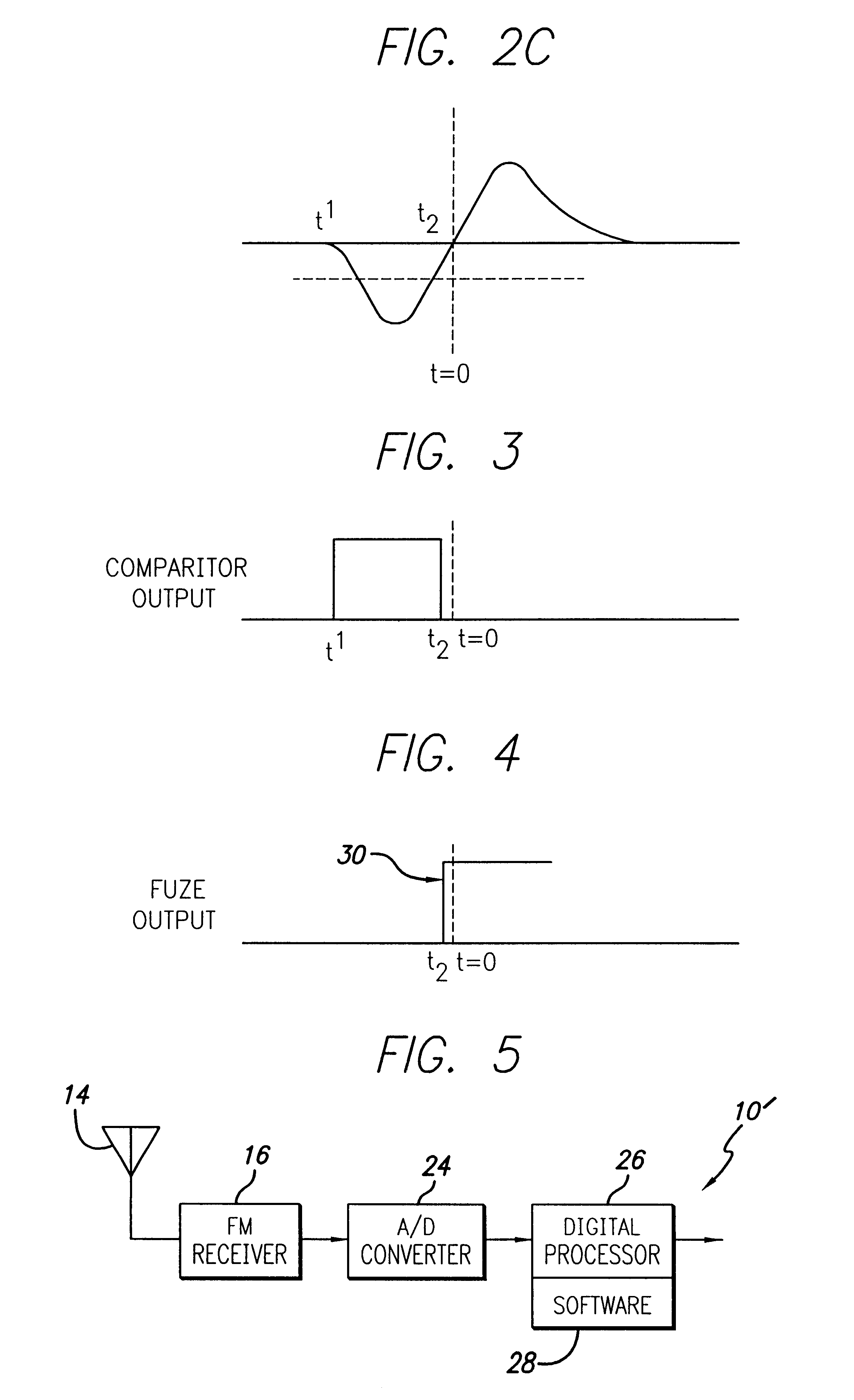
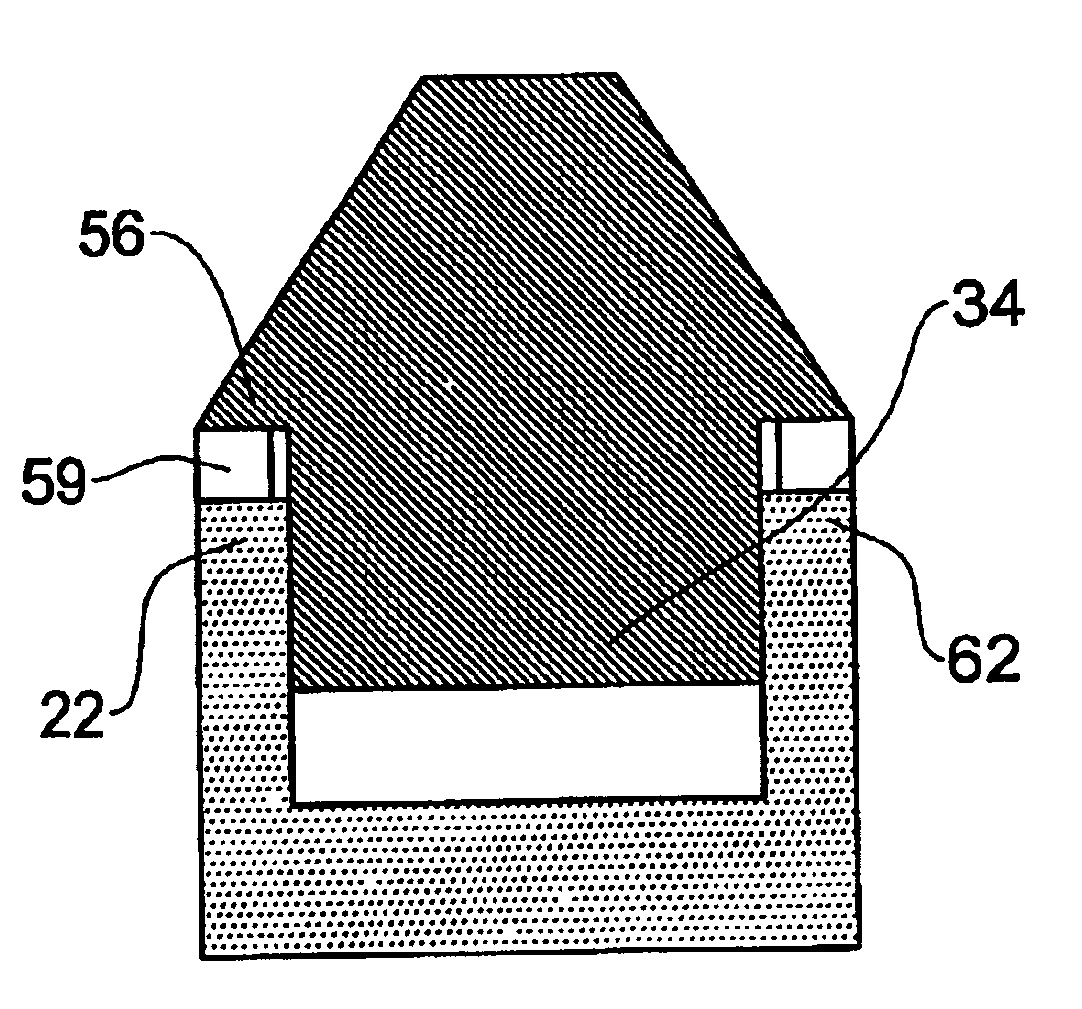
A passive proximity fuze. The inventive fuze (10) is adapted to be mounted on a munition (11) and includes a receiver (16) adapted to lock on to a signal transmitted by a target transmitter (12). The receiver (16) detects a Doppler shift in the signal as the munition approaches the target. When a closest point of approach is reached the Doppler shift changes from increasing to decreasing. The inventive fuze (10) includes a mechanism for detecting this change in the Doppler shift and provides a detonation signal in response thereto. In the illustrative embodiment, the receiver (16) is an FM receiver. The mechanism for detecting a change in the Doppler shift may be implemented with discrete analog circuitry or digital circuitry. In an illustrative analog implementation, first and second resistive / capacitive networks (R1C1 and R2C2) are employed to compute a second derivative of the Doppler shift signal output by the receiver (16). This signal is then amplified and thresholded to provide the output detonation signal. In an illustrative digital implementation, the output of the receiver (16) is converted to digital and processed by a digital signal processor (26). The DSP 26 computes the second derivative of the Doppler shift signal output by the receiver (16) in response to a stored program for computing same. The output of the DSP is the detonation signal. Hence, detonation is achieved at the closest point of approach of the munition (11) to the target (12) with an inexpensive passive solution (10).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Integration of a semi-active laser seeker into the DSU-33 proximity sensor
A proximity sensor for use with a guidance system of a smart bomb including a ranging radar proximity sensor configured for mounting on a smart bomb and a radome connected to the ranging radar proximity sensor. A laser radiation sensor system is attached to the proximity sensor, which is configured and arranged to detect laser radiation reflected from a target which passes through the radome and output the azimuth and elevation angles to the target to the guidance system.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Imaging device and method
Owner:GEO T VISION
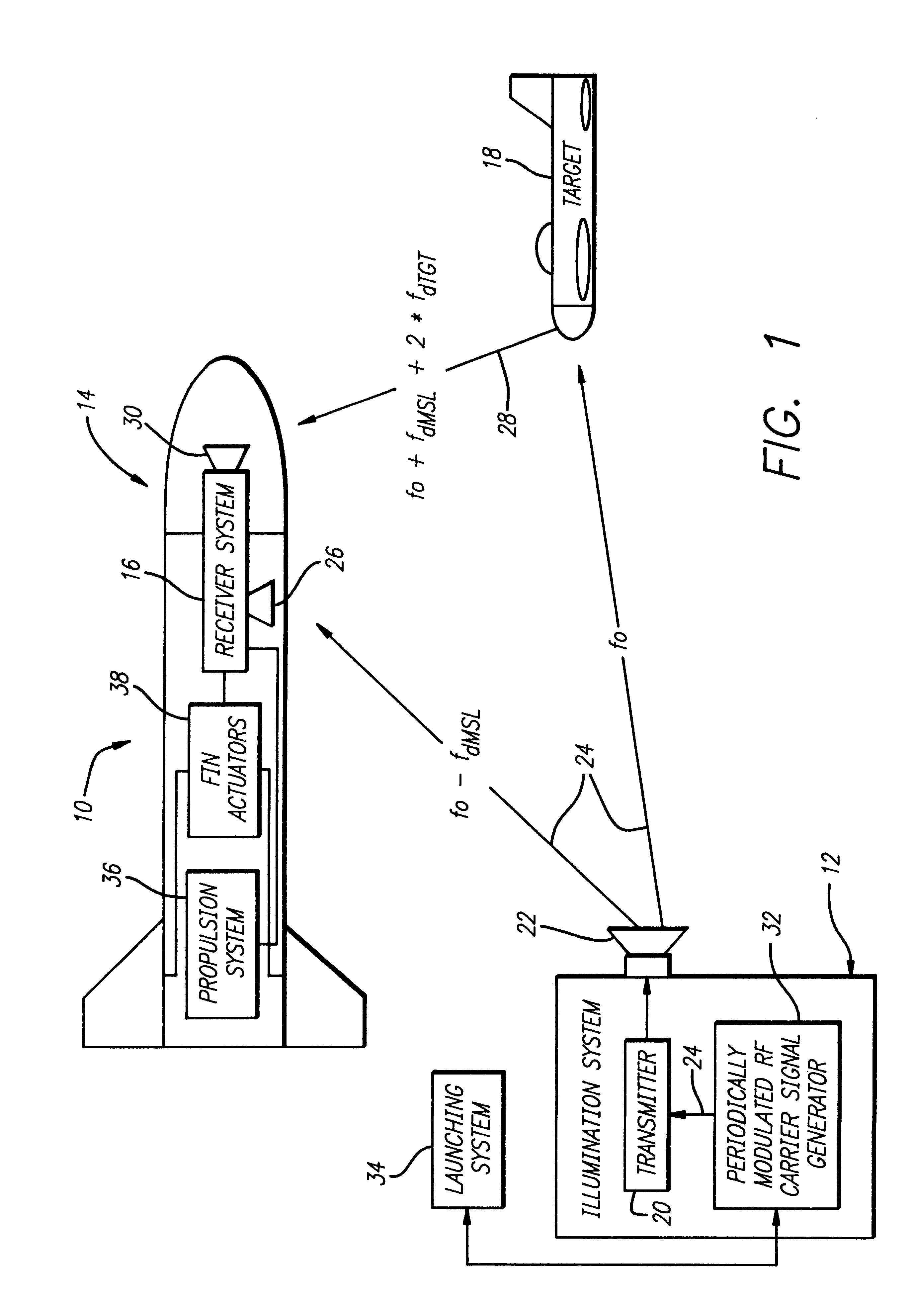
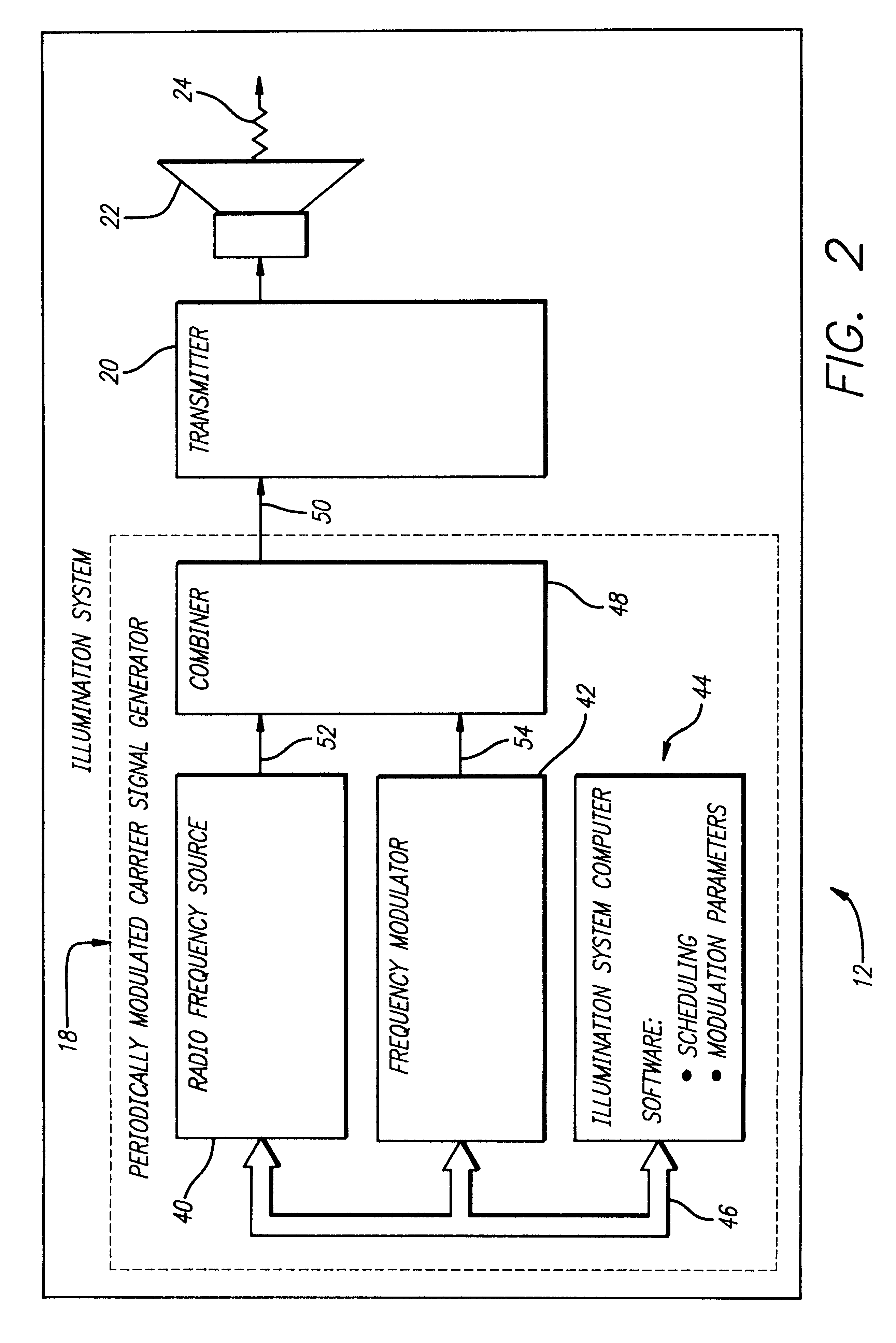
System and method for obtaining precise missile range information for semiactive missile systems
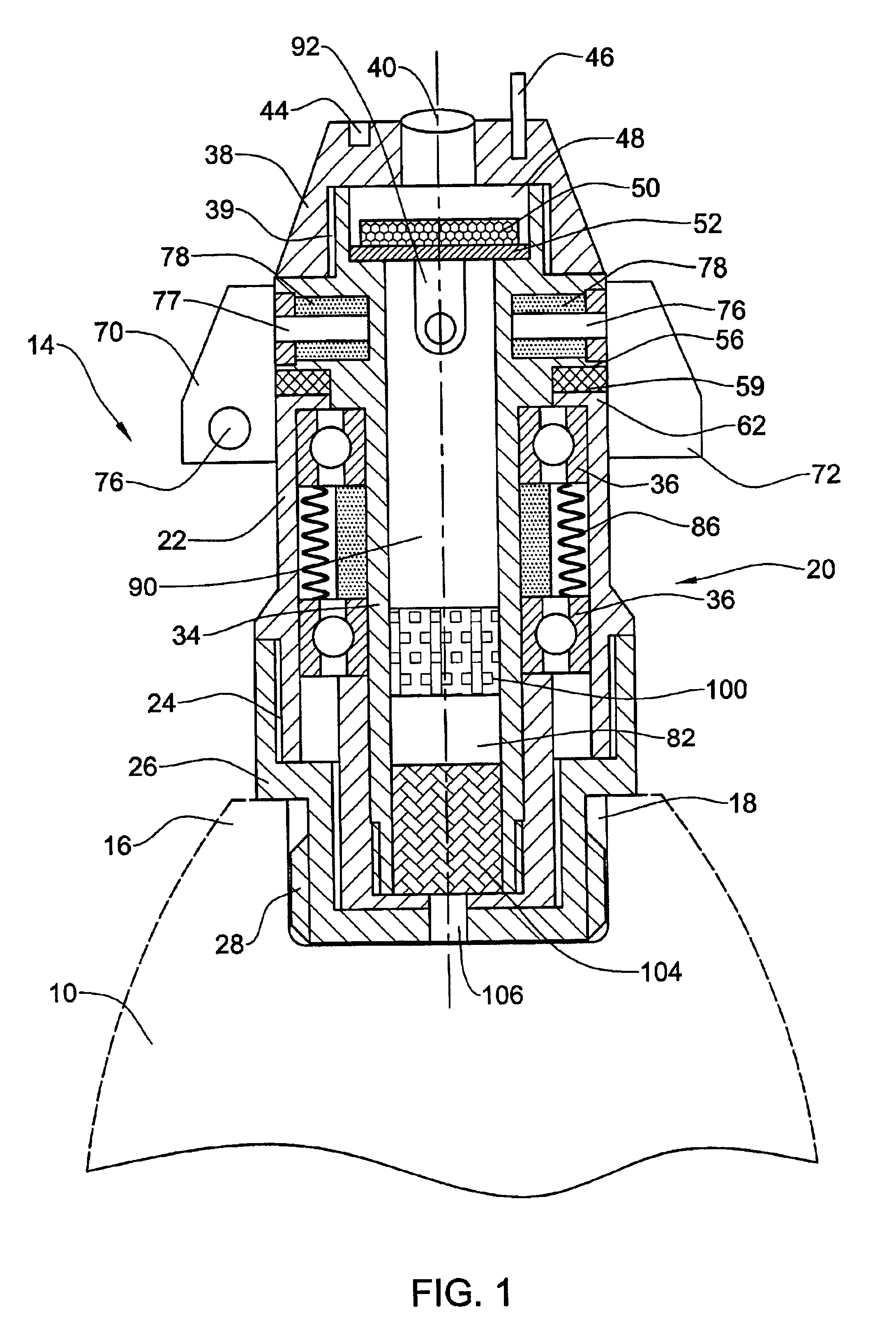
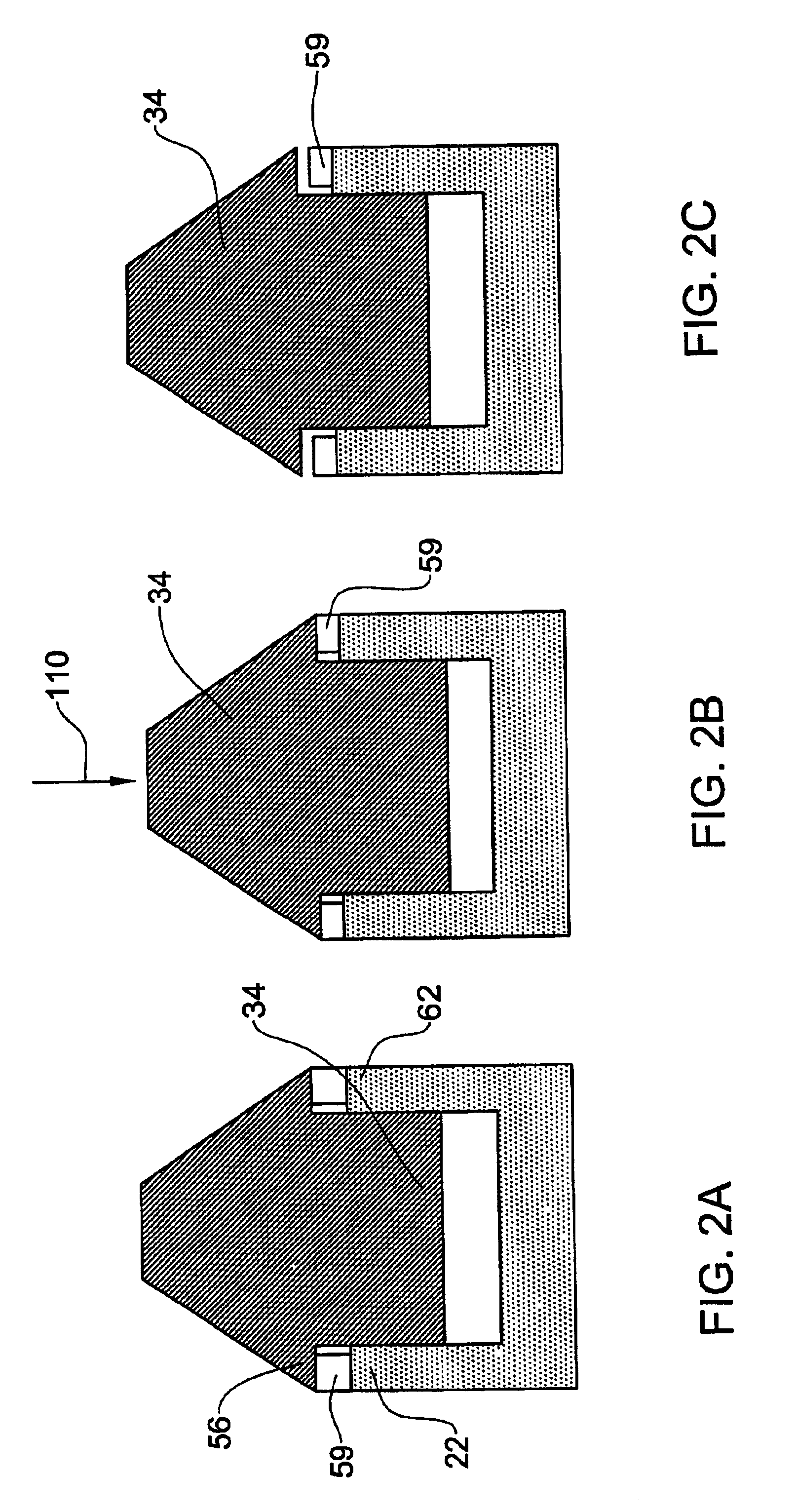
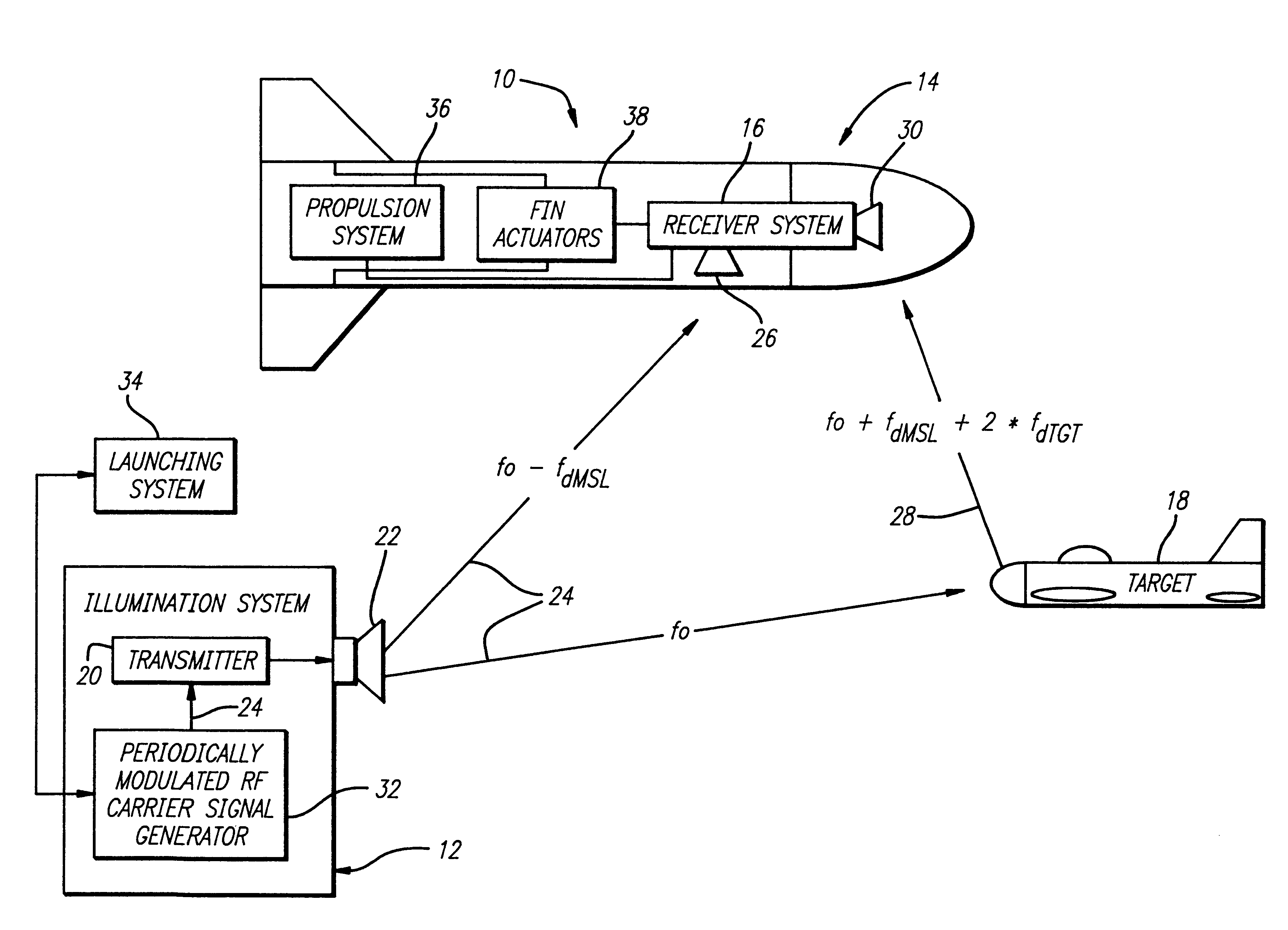
A system (10) for determining the range between a missile (14) and a target (18) adapted for use with a semi-active missile system. The system (10) includes a first circuit (12) for generating a periodic signal (24) that is periodically frequency modulated. A second circuit (16) determines a closing rate at which the missile 14 is approaching the target 18 via the periodic signal 24. A third circuit (16) determines a value containing information corresponding to the range and the closing rate via the periodic signal. A fourth circuit (16) determines the range from the closing rate and the value. In a specific embodiment, the first circuit (12) includes an illumination system (12). The illumination system (12) includes a periodically modulated carrier signal generator (32) that generates the periodic signal (24). The periodically modulated carrier signal generator (32) includes a frequency source, a frequency modulator, and an illumination system computer. The illumination system computer runs software for adjusting the modulation parameters of the frequency modulator. The second, third and fourth circuits (16) are included in a receiver system (16) onboard the missile (14). The receiver system (16) includes a front receiver located near the front of the missile and a rear receiver located near the rear of the missile (14). A receiver system computer runs software that implements the fourth circuit (16). The receiver system (16) includes a local oscillator for providing a reference frequency for the receiver system. The local oscillator derives the reference frequency from the periodic signal provided by the first circuit. In illustrative embodiment, the fourth circuit (16) runs computer software that subtracts the closing rate from the combination of closing rate and range and provides the range in response thereto.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
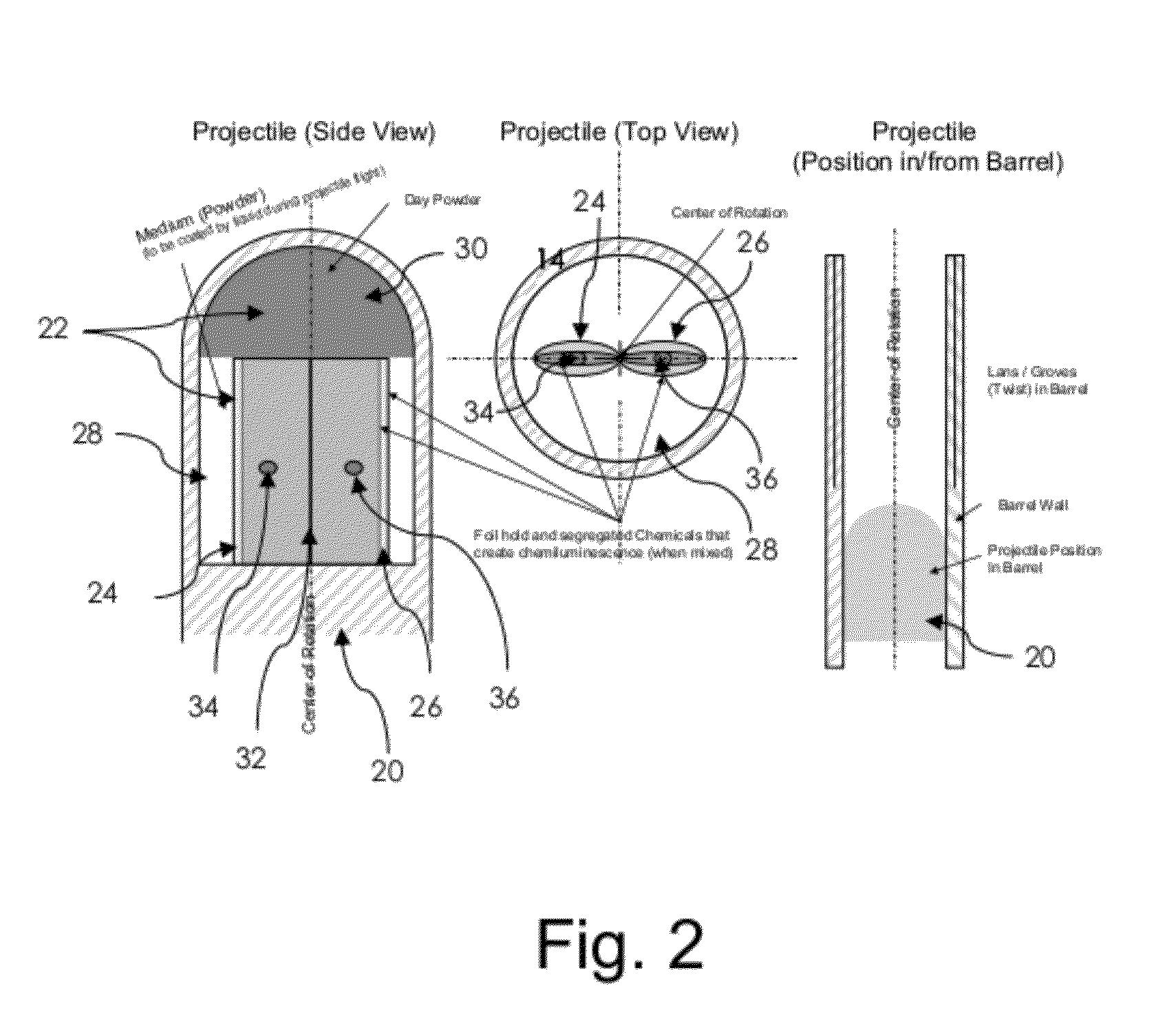
Impact locating day and night marker for a projectile
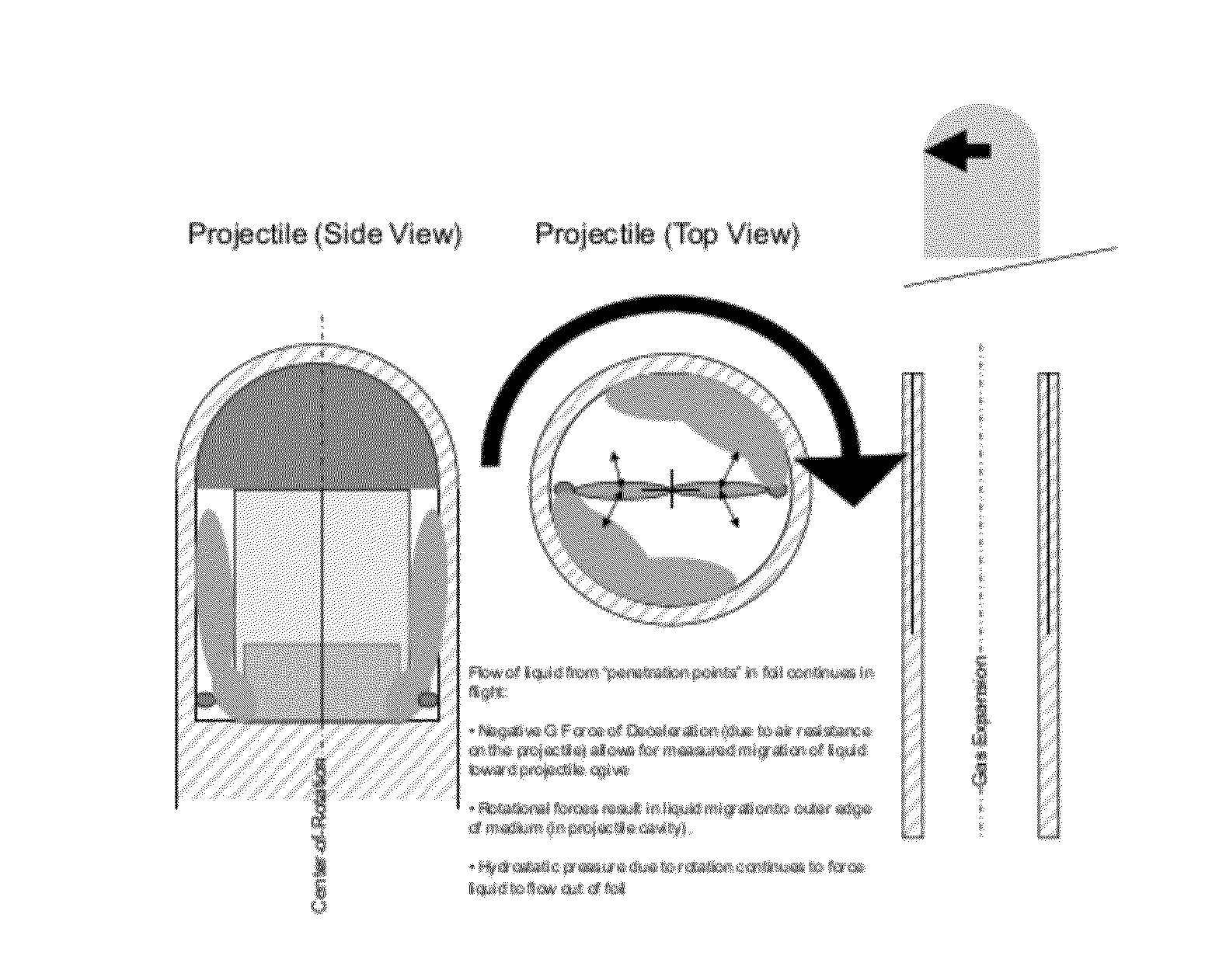
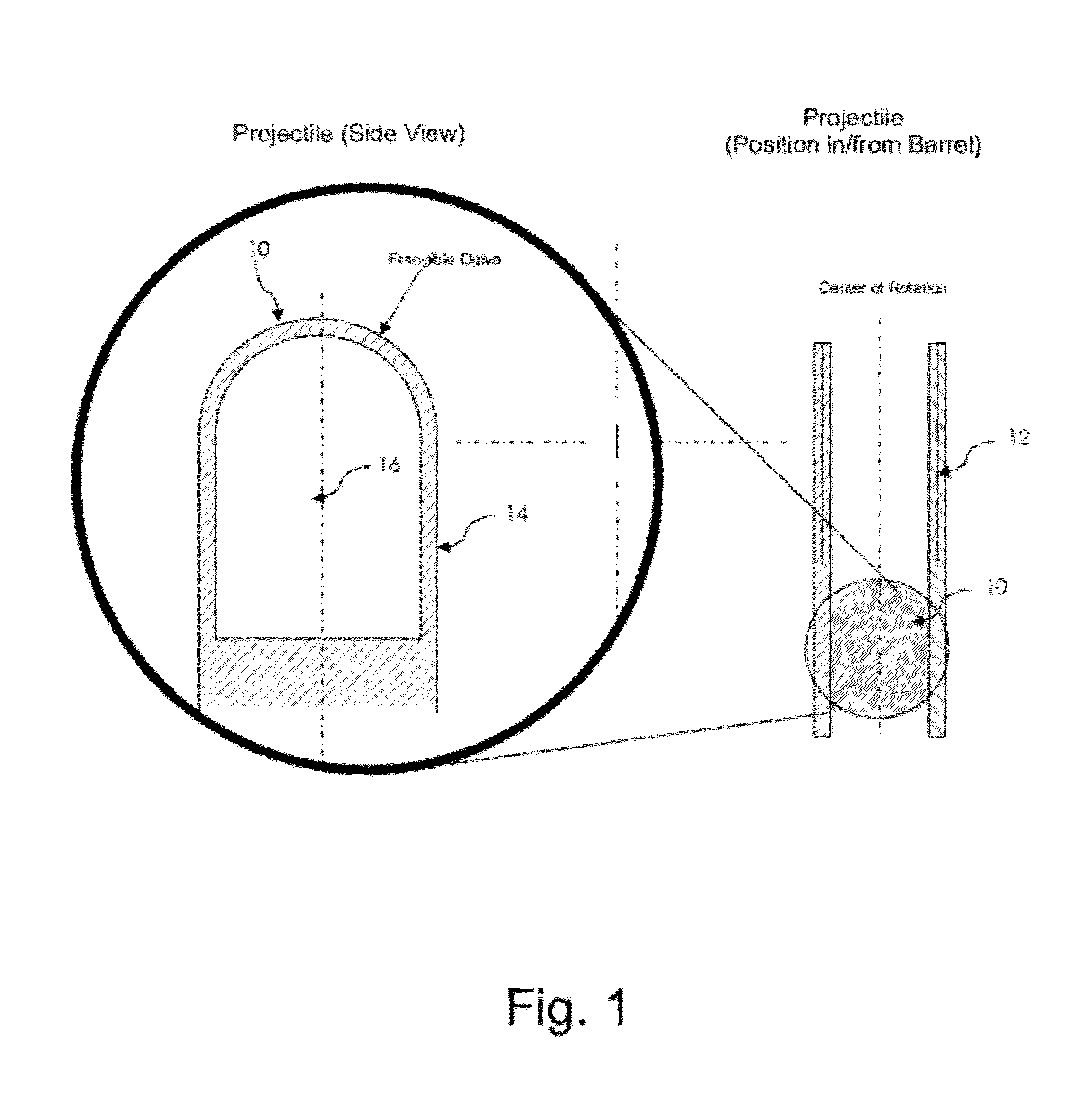
A marking projectile comprises separate compartments that break during launch due to rotation of the projectile as it leaves the barrel of a weapon. Metal pellets contained within the compartments are pressed outward and pierce the compartment walls. This allows for mixing of chemical materials contained within the compartments, so that the materials substantially react by the time the projectile strikes a target. The chemical materials may be a pair of chemi-luminescent components, or components that create heat for thermal marking.
Owner:RHEINMETALL WAFFE MUNITION GMBH
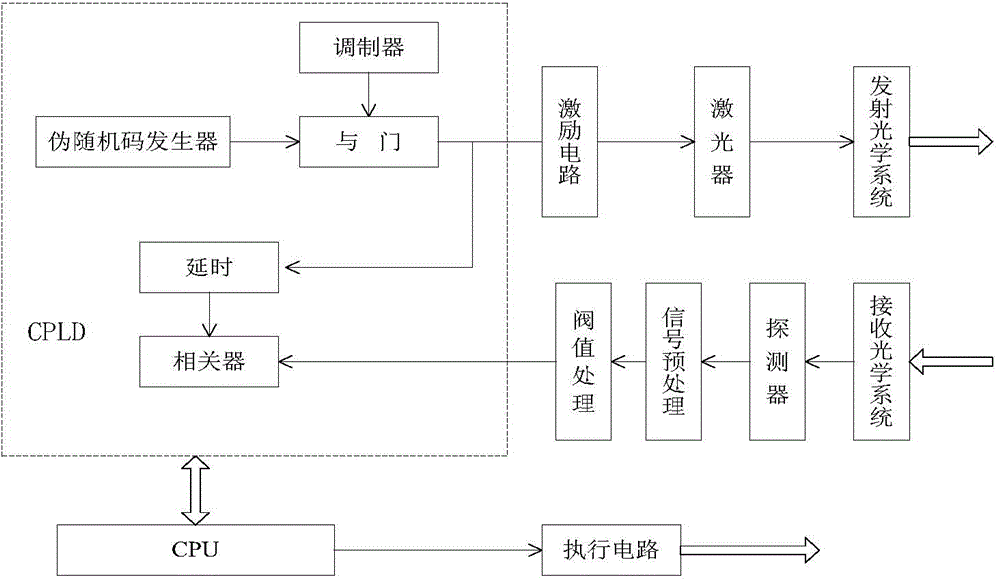
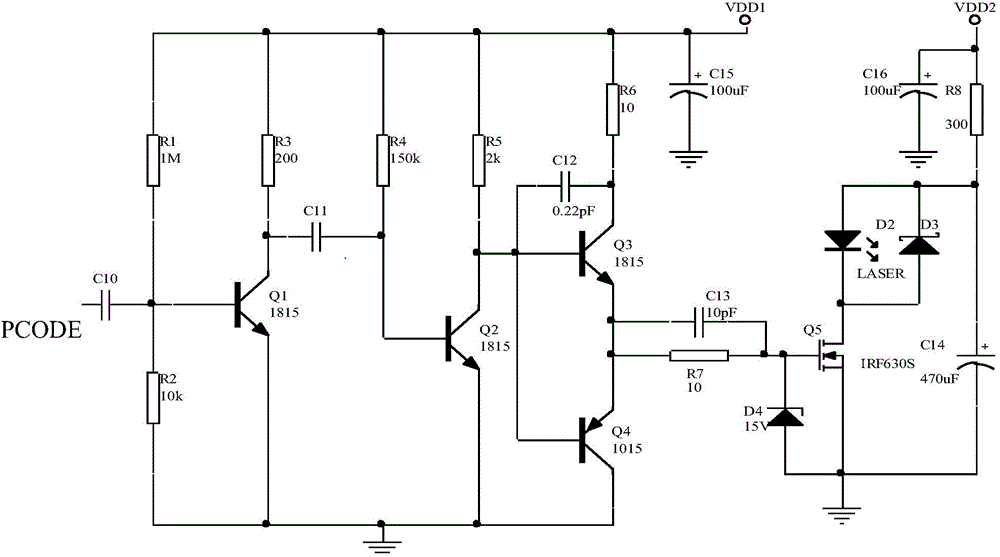
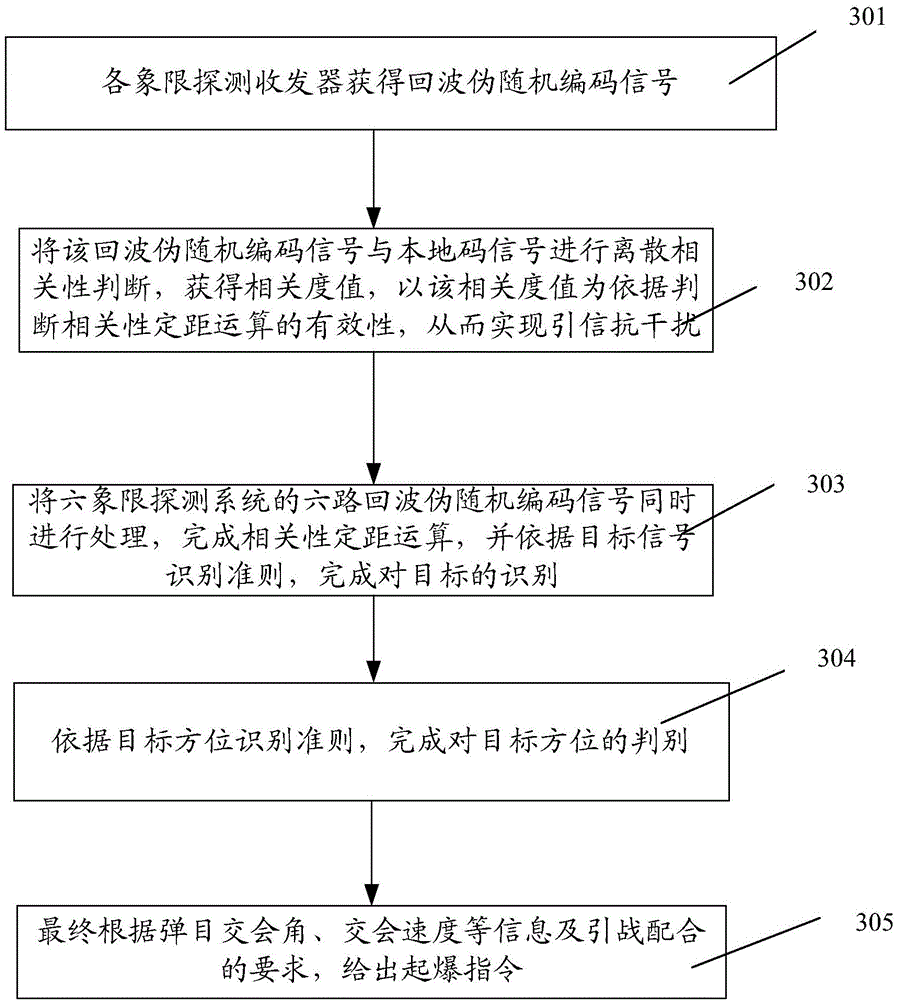
Pseudo-random code system-based laser fuze system and target identification method thereof
InactiveCN104457452AImprove recognition accuracyImprove coordination efficiencyProximity fuzesTransceiverSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses a pseudo-random code system-based laser fuze system and a target identification method thereof. The laser fuze system adopts a six-quadrant detection scheme, and each pair of detection transceiver systems comprises a pseudo-random code generator, an excitation circuit, a laser, a detector, a signal processing circuit, and transmitting and receiving optical systems; the pseudo-random code generator is used for generating a pseudo-code signal with certain code element width and frequency, the pseudo-code signal is modulated to obtain a pseudo-code pulse signal meeting the requirement of pulse width of the laser, and the pseudo-code pulse signal is excited by the excitation circuit to drive the laser to transmit encoded laser pulse; finally, a laser beam irradiates to a target after being collimated or extended by a transmitting optical system, and the optical energy reflected from the target is received by the receiving optical system; meanwhile, the filtering of a filter and the focusing of the light beam are completed, and after the detector completes the photoelectric conversion and the signal preprocessing of the signal processing circuit, an echo pseudo-random coded signal is obtained after threshold comparison.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
Detonator system and method in connection with the same
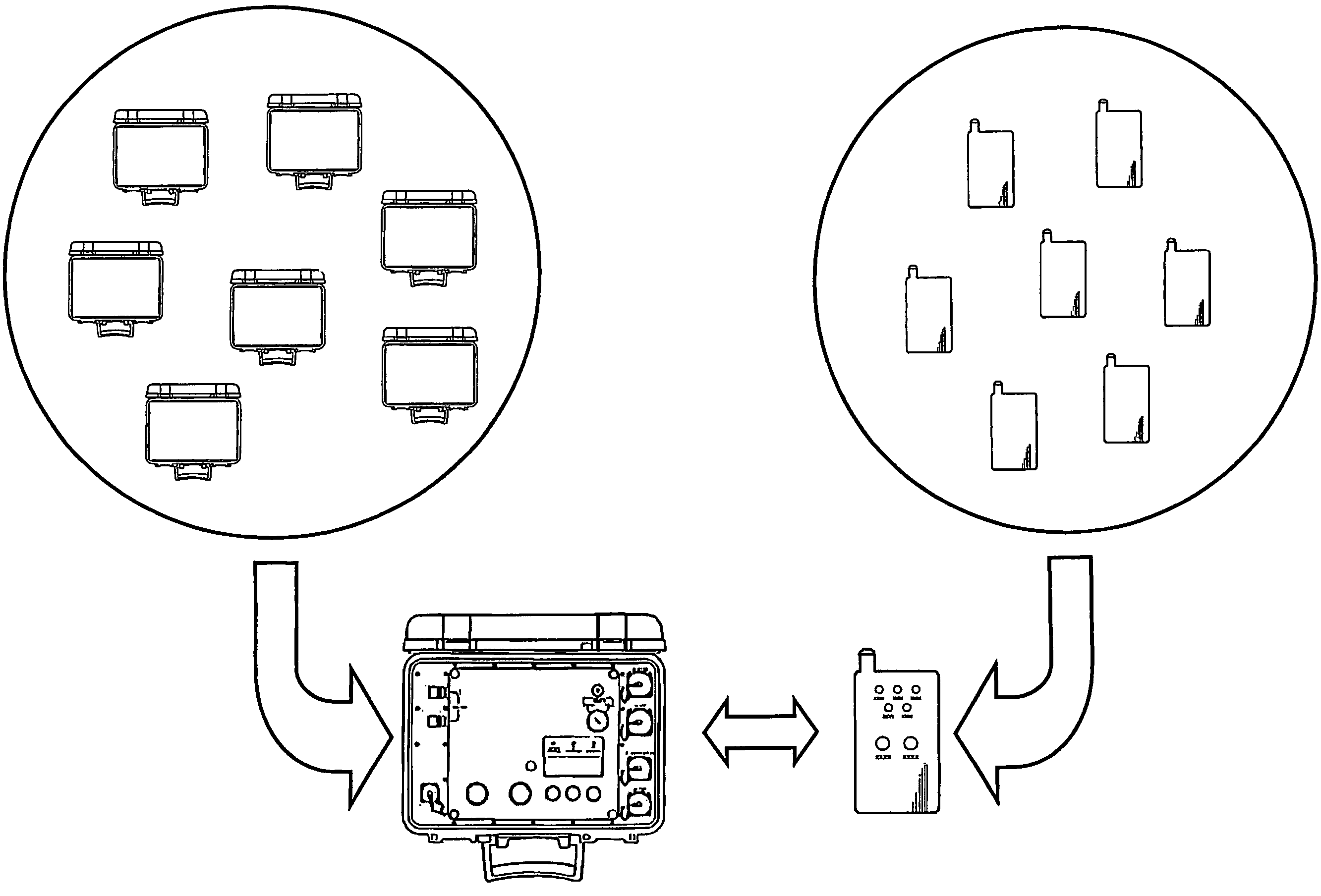
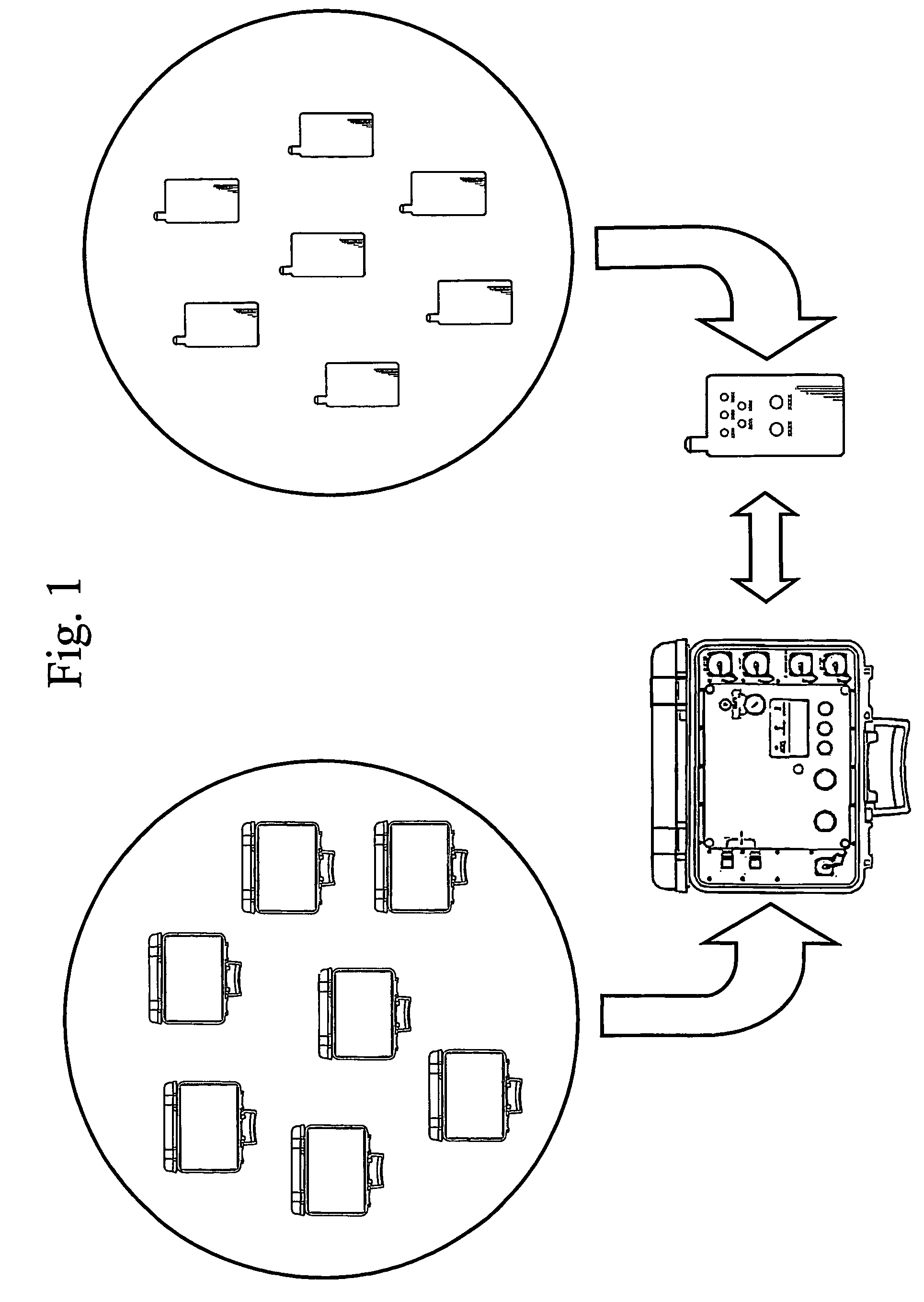
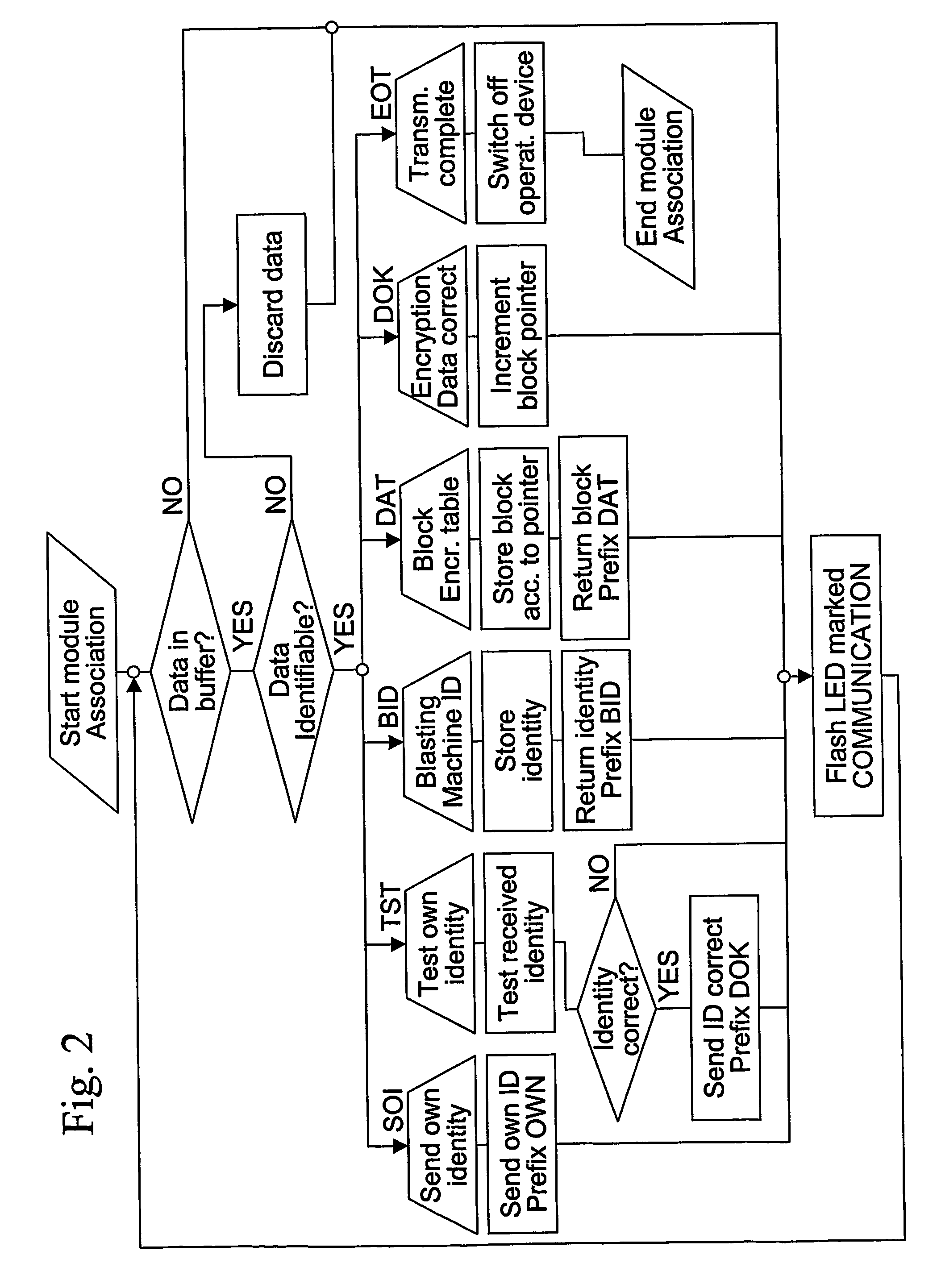
A method for wirelessly transmitting data to a control unit, such as a blasting machine, selected from a plurality of control units from an operating device selected from a plurality of operating devices, and a system intended for the method. The control unit is connected to a plurality of detonators, which are controlled by the control unit via an electrical wire or a fuse. The operating device is associated with the appropriate control unit in a step in which address data and / or encryption data is exchanged between the units. Only one operating device can be associated with a pre-determined control unit at any given moment. The data transmitted in accordance with the method preferably comprises at least a fire command, which instructs the control unit to fire the detonators.
Owner:DETNET SOUTH AFRICA (PTY) LTD
Remotely controlled ignition system for pyrotechnics
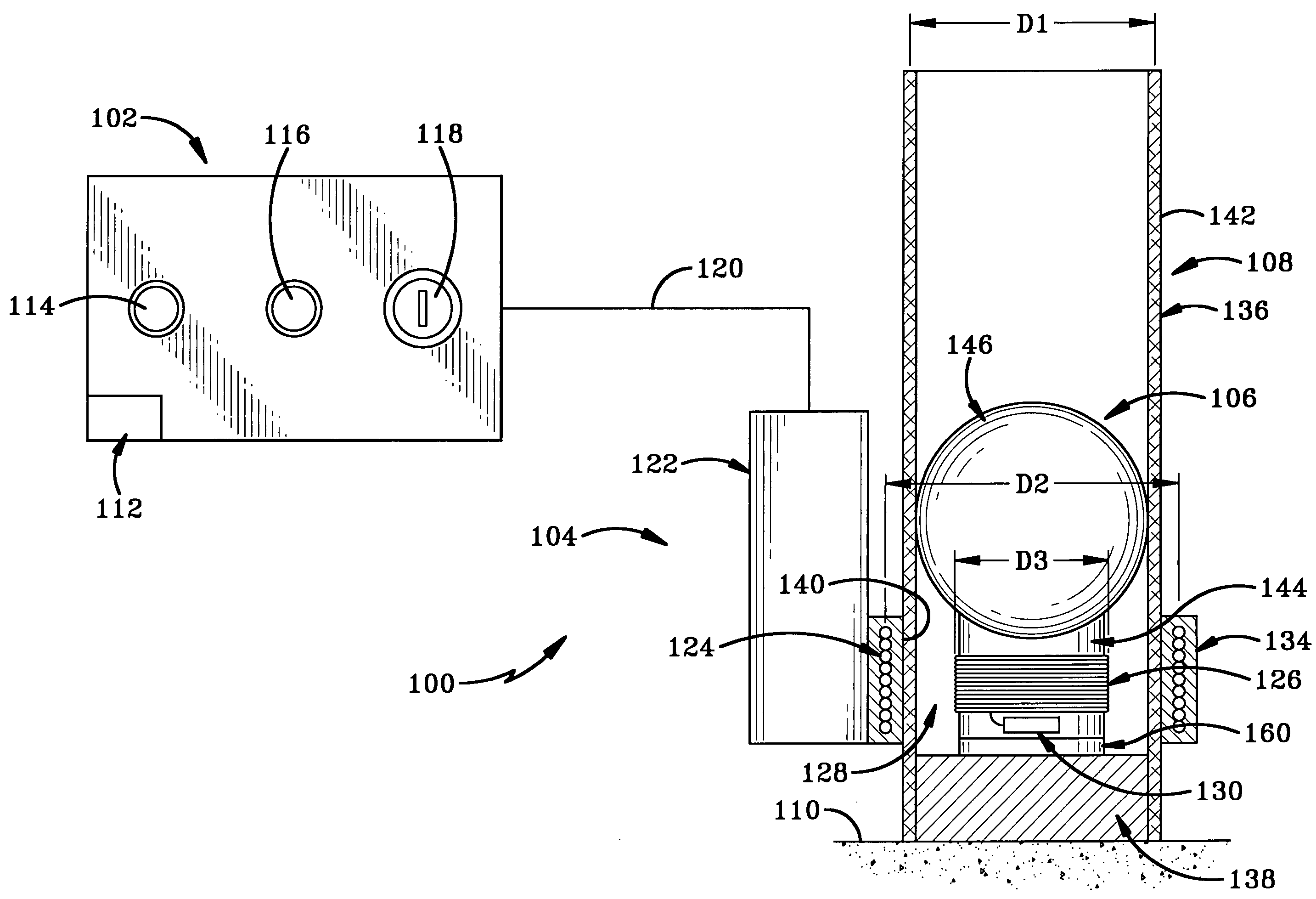
A remote pyrotechnic ignition system includes a power supply for producing an electrical current in a transmitting induction coil to induce an electrical current in a receiving induction coil for igniting a pyrotechnic device. Thus, a wireless ignition communication section allows pyrotechnic mortars to be reused and substantially reduces set-up time by eliminating the wiring of fireworks normally required for a pyrotechnic production. Optionally, a capacitor is charged by the power source via a charging circuit and discharged via a firing circuit to produce the electric current in the transmitting coil in a pulse. The capacitor provides a two-stage firing safety feature. An electronic control device such as a circuit board may be mounted on the pyrotechnic device for controlling ignition of the pyrotechnic device and is especially useful in controlling ignition sequencing and overall ignition timing of a lift charge and burst charge of the pyrotechnic device.
Owner:DEYE JAMES G
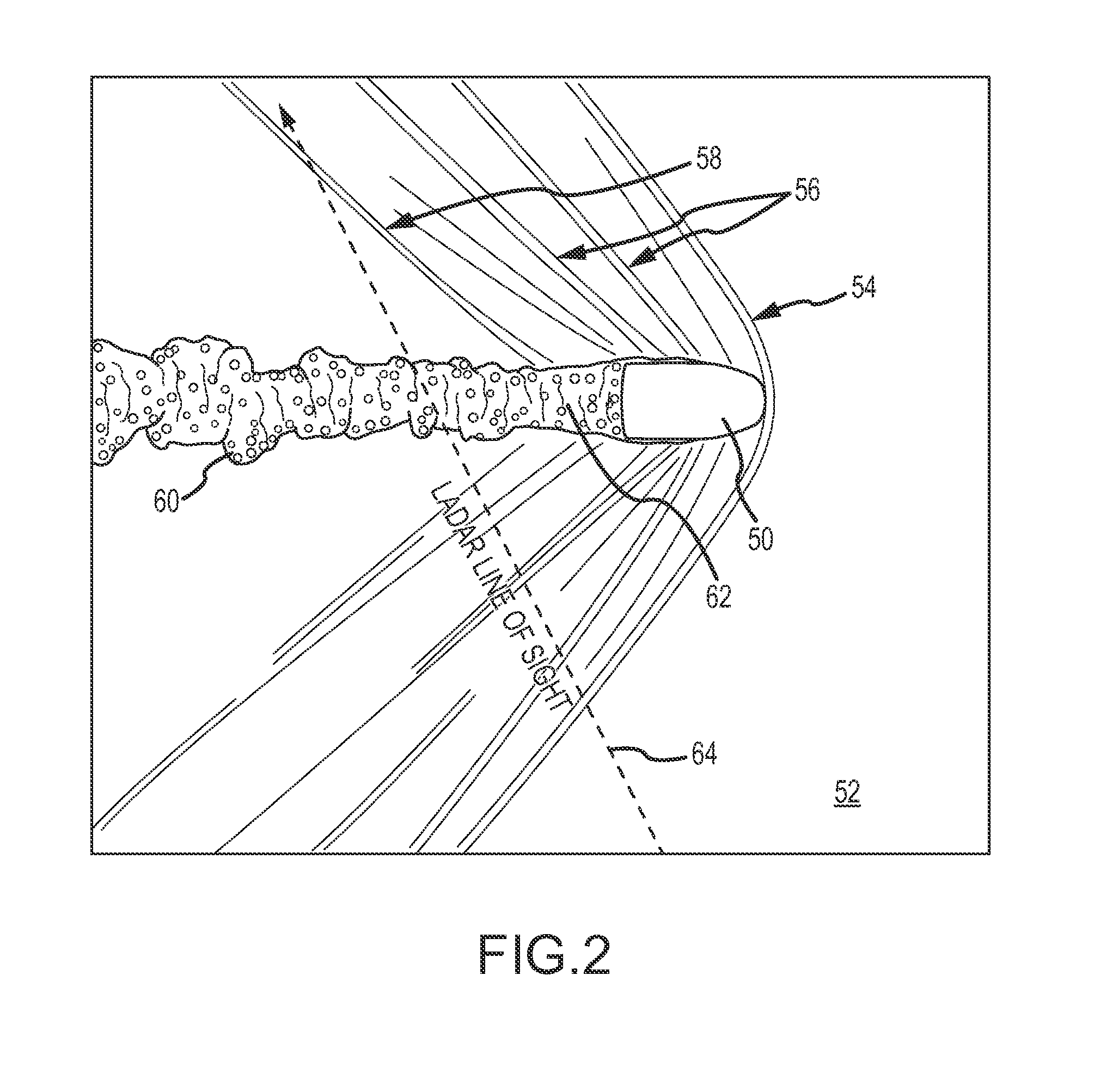
Ladar backtracking of wake turbulence trailing an airborne target for point-of-origin estimation and target classification
A weapon-locating ladar system estimates a backward trajectory of an airborne target by using flow field measurements to follow the wake turbulence trailing the airborne target from a position at which the target is detected backwards until the wake is no longer observable. The system may use the backward trajectory to estimate the point-of-origin of the target. The system may also use the flow field measurements along the backward trajectory to classify the target. Target classification may be used to refine the point-of-origin estimate, to influence counter-fire or to adapt the flow field measurements.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Projectile having a casing and/or interior acting as a communication bus between electronic components
InactiveUS6892644B2Overcome disadvantagesStar/tree networksProximity fuzesElectronic componentProjectile
A projectile including: at least two electronic or electrical components; and a casing, the casing having at least a portion thereof acting as a communication bus for connecting the at least two electronic / electrical components. The projectile casing can further have a window for inputting a signal or charging an internal power storage device.
Owner:OMNITEK PARTNERS LLC
Methods and systems providing an adaptive threshold for a beam sharpened pulse radar
InactiveUS20070273572A1Fast rise timeProximity fuzesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSelf adaptiveAcoustics
A radar sensor is described that includes a radar transmitter, a radar receiver configured to receive reflected returns of signals output by the radar transmitter, and a signal processing unit configured to process signals received by the radar receiver. The signal processing unit includes a comparator, a first filter comprising an output coupled to a reference input of the comparator, and a second filter comprising an output coupled to a signal input of the comparator. The first and second filters are configured to receive a common input related to the reflected returns. The first filter is configured to have a time constant such that a rise time of the first filter output is faster than a rise time of the second filter output.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Munition article with antenna for satellite navigation
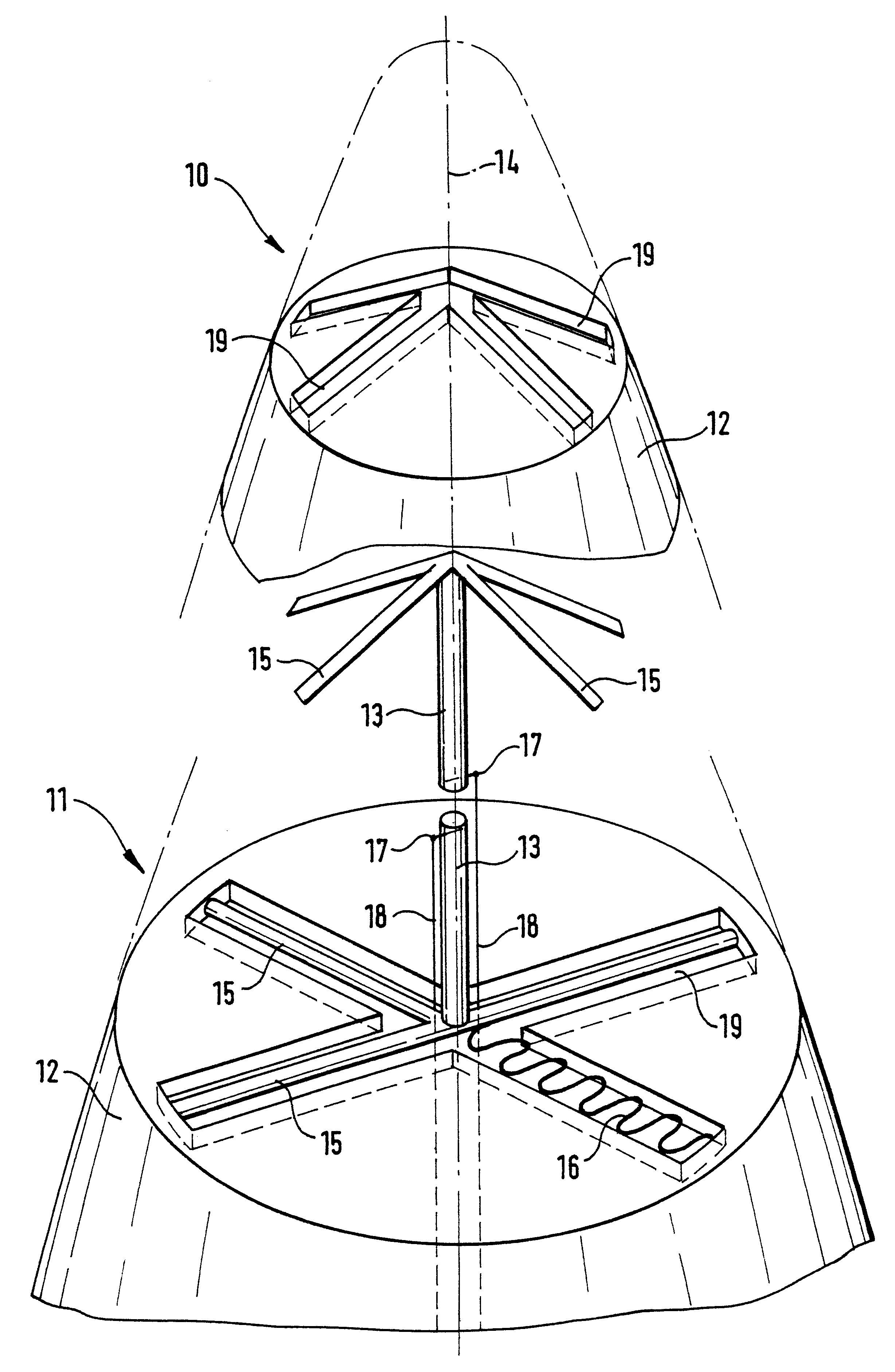
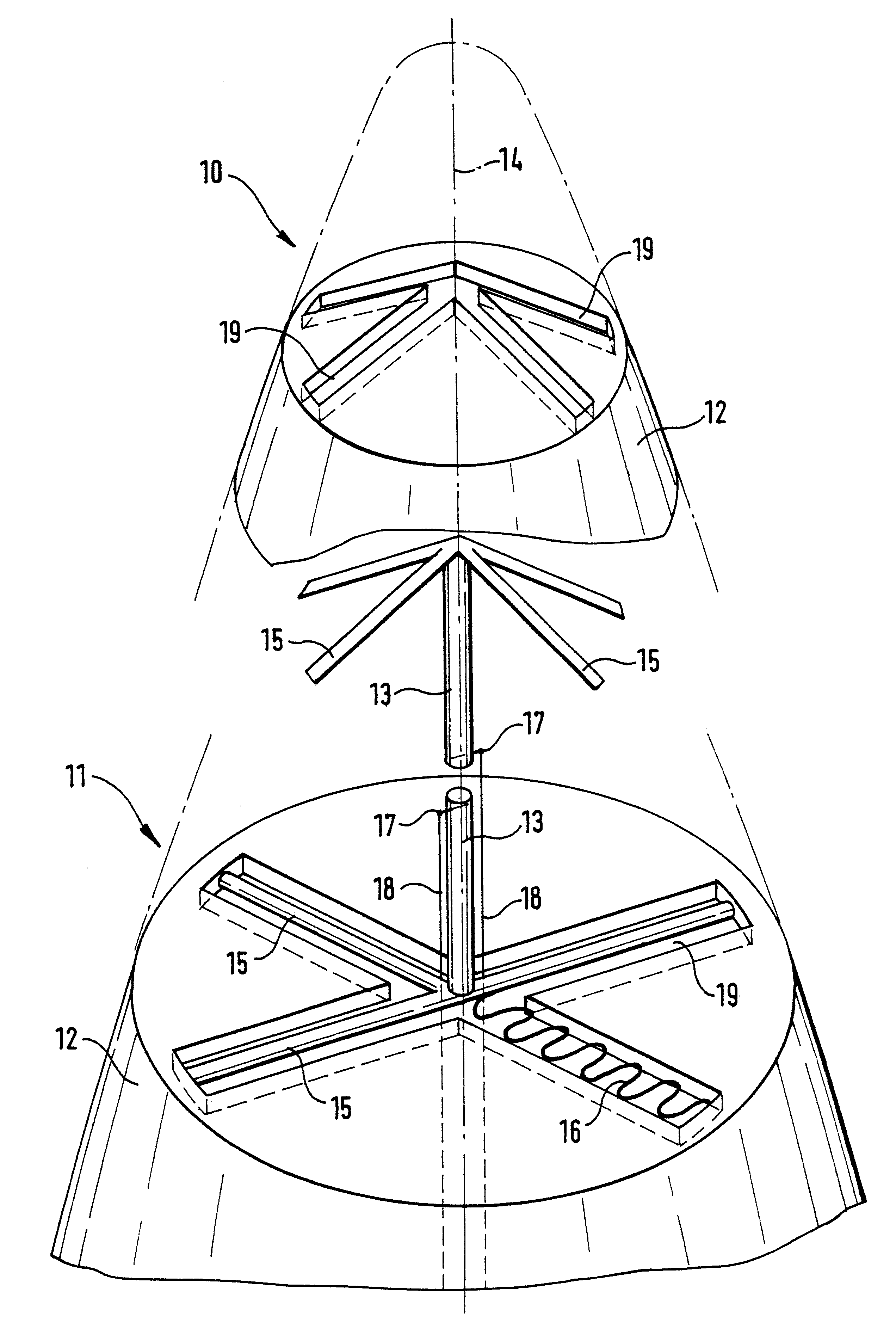
A munition article is to be provided with an antenna which, by virtue of a characteristic which is uniform all around, permits interference-free reception of items of satellite navigation information, even if in the manner of an artillery projectile it is fired with spin along an elongate ballistic trajectory, so that a tail antenna with a spherical characteristic does not allow the expectation of good reception factors in relation to navigation satellites which are as high as possible above the horizon. Therefore the tip (10) of the fuse tip (11) of the projectile is equipped with a dipole satellite antenna which faces in the direction of flight. Connected to the dipole (13) which is arranged concentrically with respect to the longitudinal axis (14) of the projectile are symmetrically disposed conductor portions (15) which rest with a close fit in recesses (19) in the ballistic cap (12).
Owner:DIEHL BGT DEFENCE GMBH & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com