Pseudo-random code system-based laser fuze system and target identification method thereof
A pseudo-random code and laser fuze technology, which is applied in the field of laser fuze, can solve the problems of early missile bombing, loss of combat opportunities, blind fire, etc., and achieve the effect of accurate target recognition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0047] The embodiments of the present invention will be described below through specific examples and in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, and those skilled in the art can easily understand other advantages and effects of the present invention from the contents disclosed in this specification. The present invention can also be implemented or applied through other different specific examples, and various details in this specification can also be modified and changed based on different viewpoints and applications without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
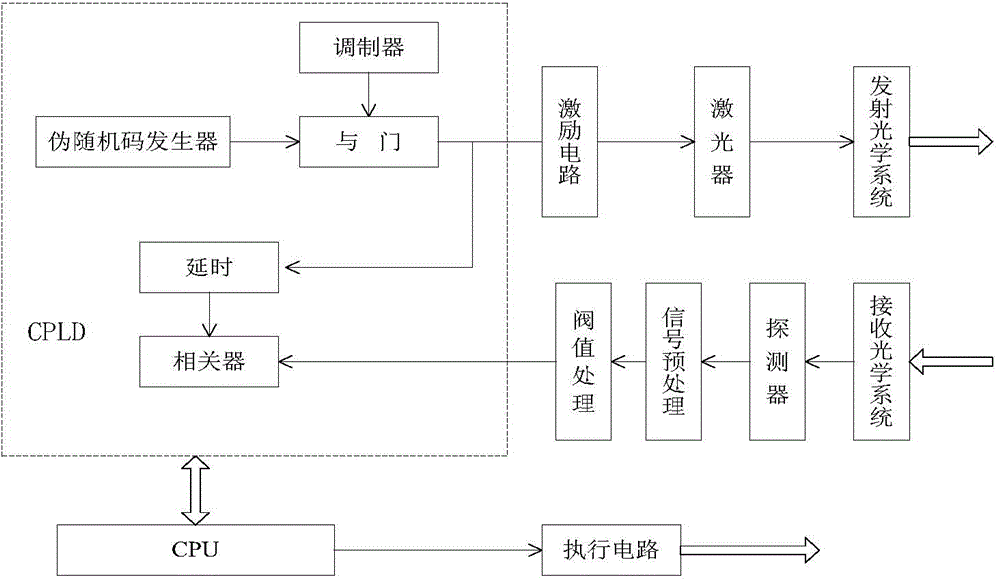
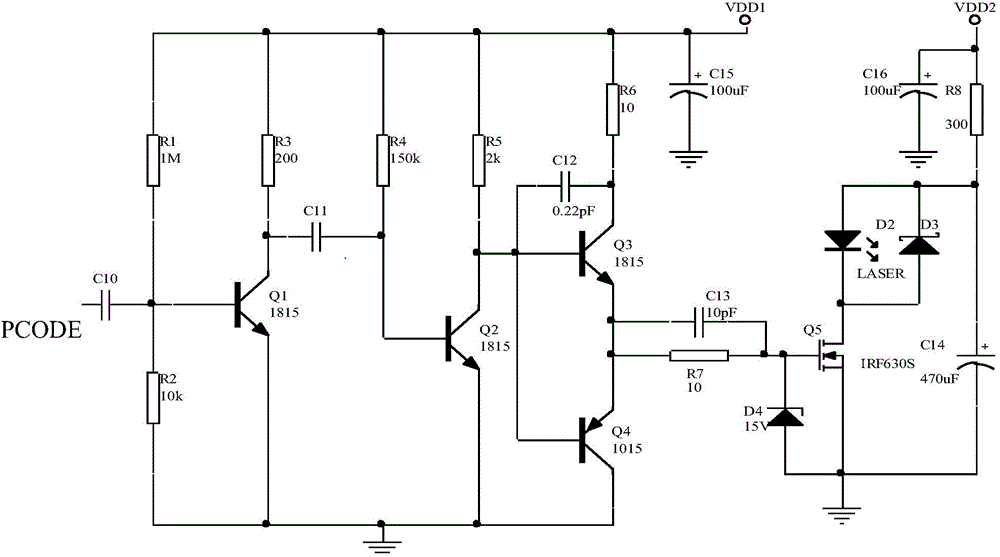
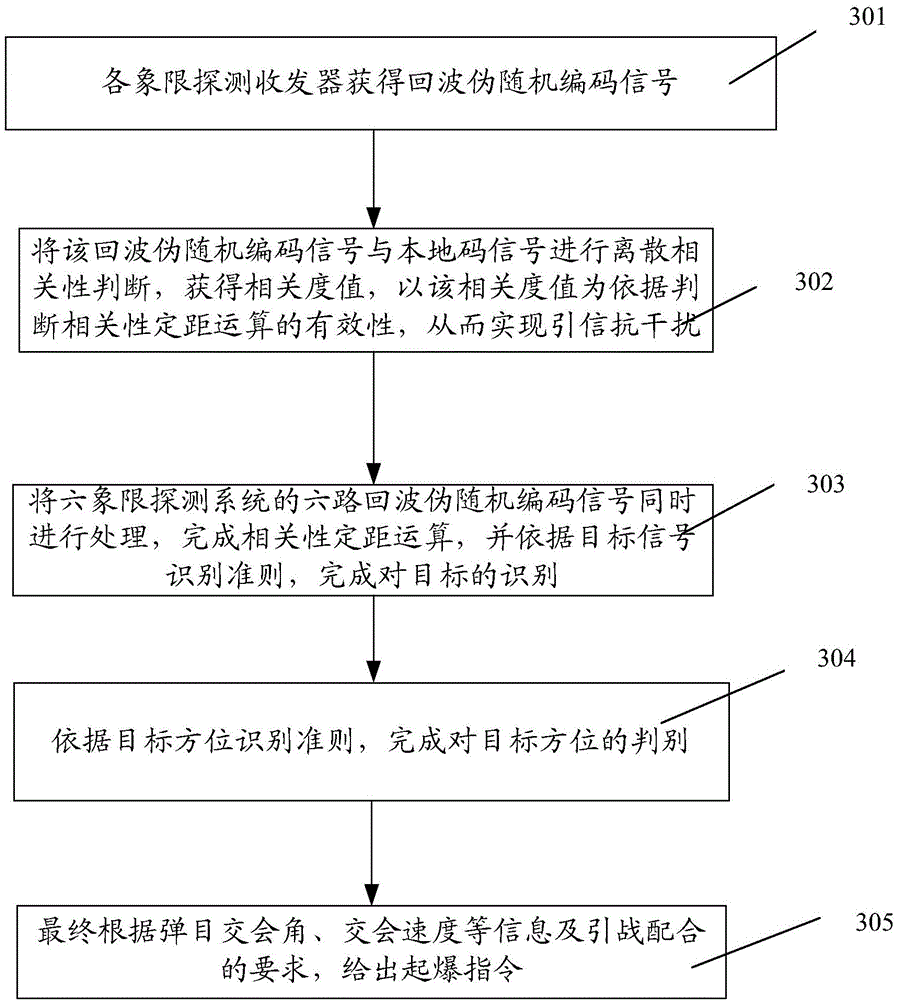
[0048] figure 1It is a system block diagram of a pseudo-random code system laser fuze system of the present invention. The present invention adopts a six-quadrant detection scheme. Six pairs of detection transceiver systems are evenly arranged along the circumferential direction of the projectile equatorial plane, with a difference of 60° from each other. Processing circuitry, transmit and receive ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com