Patents
Literature
1135results about "Seismic energy generation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
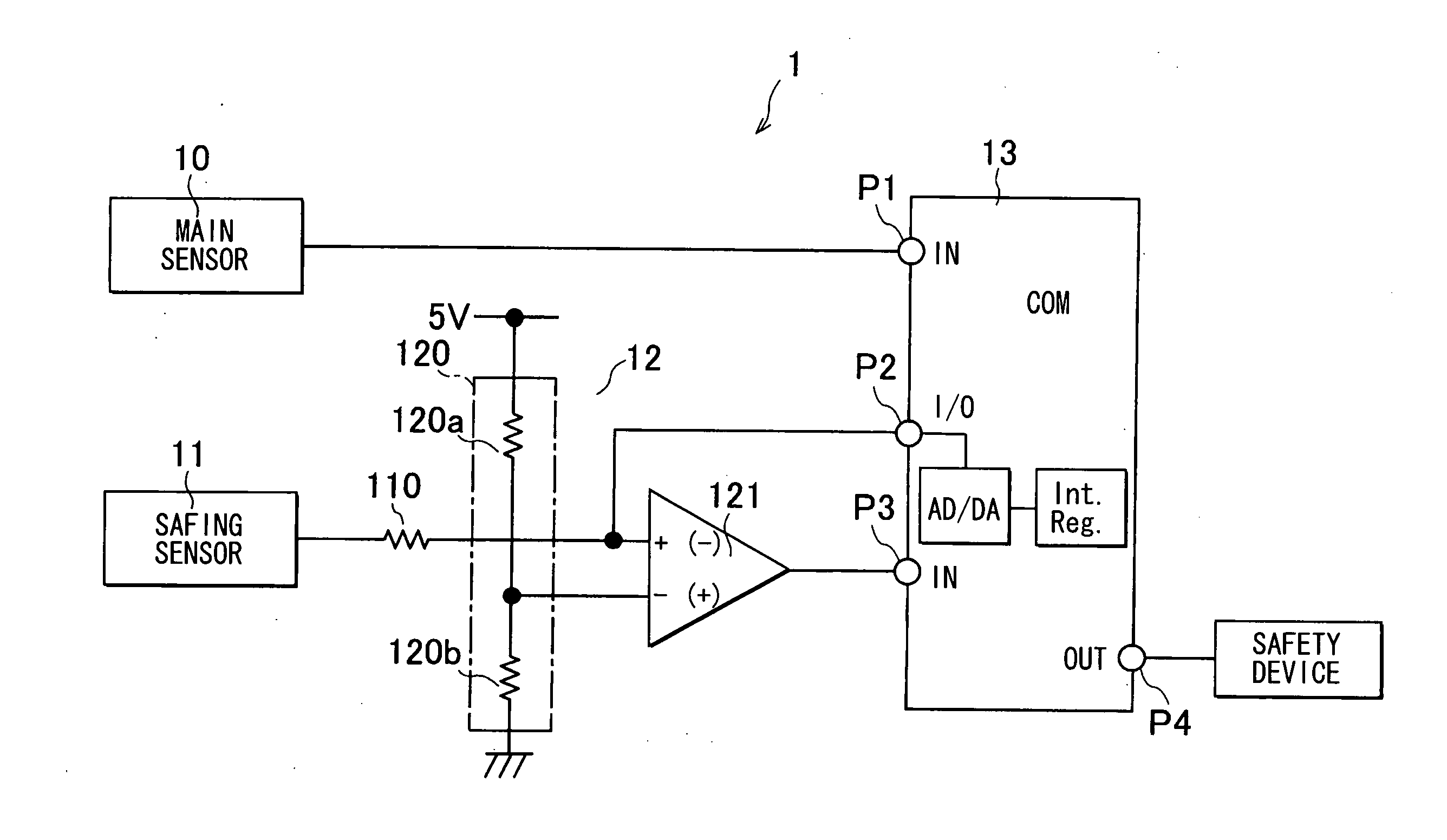
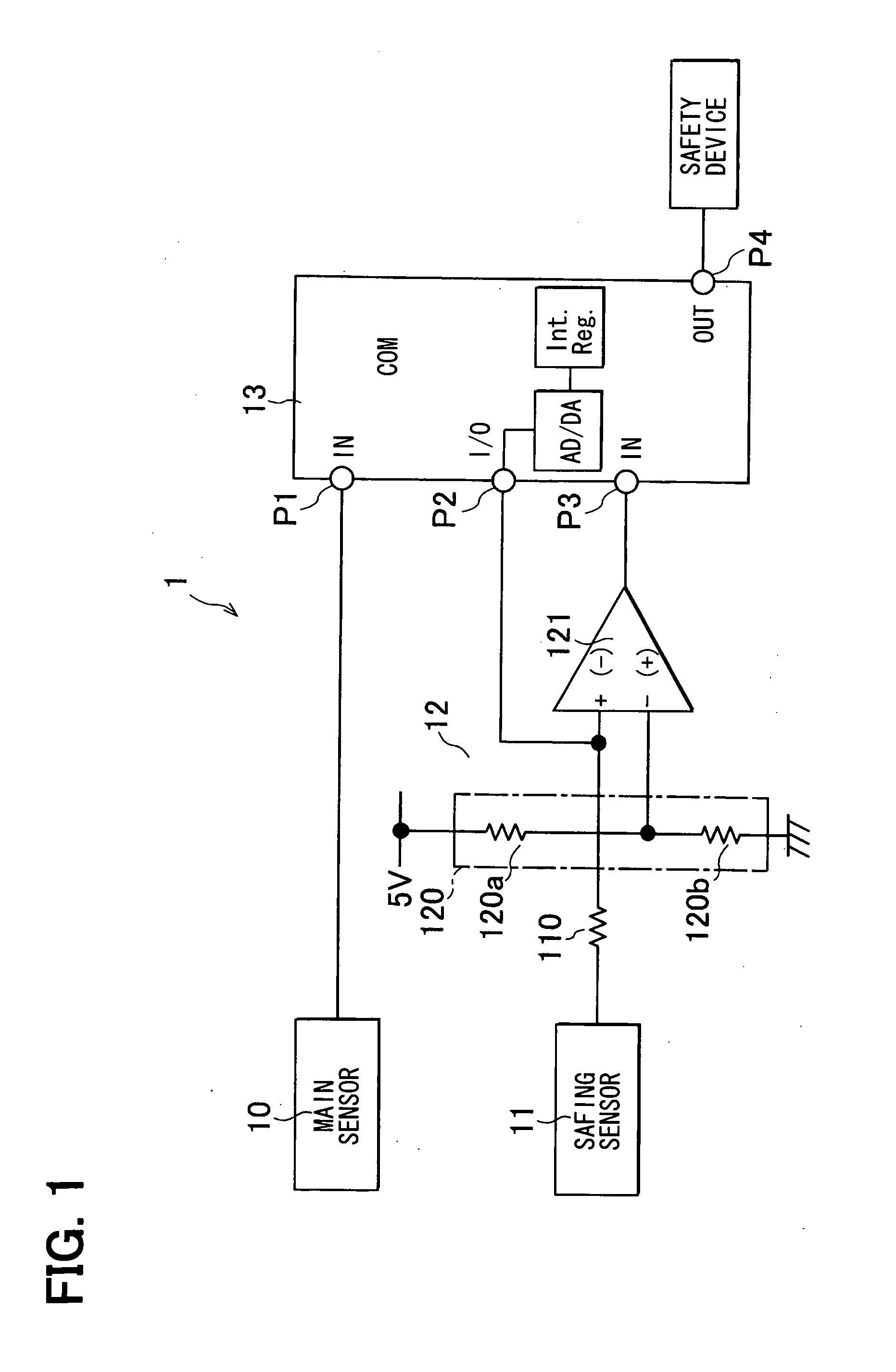
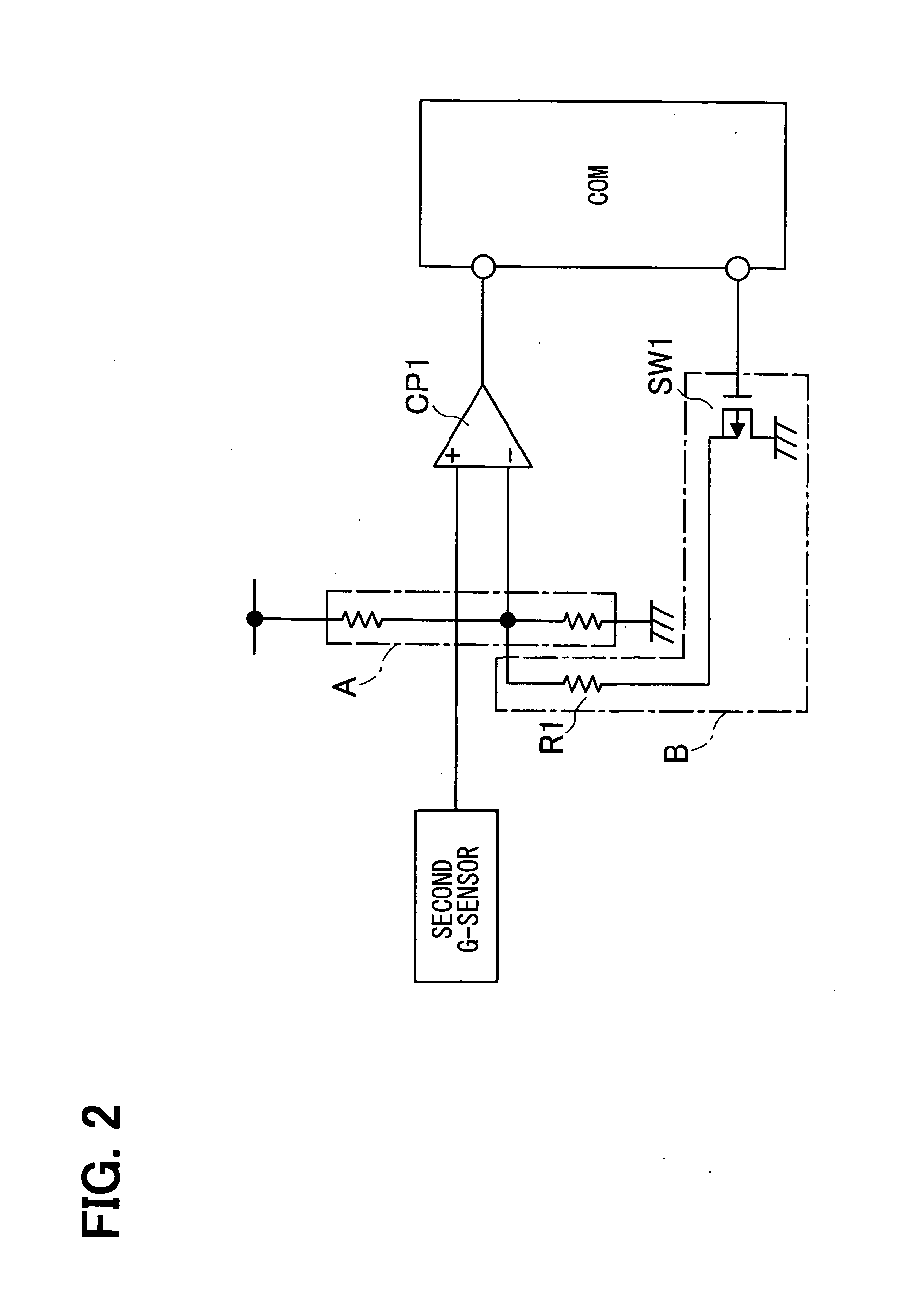
Electronic safing system
InactiveUS20100121521A1Improve reliabilityLow costVehicle testingIncandescent ignitionMicrocomputerProcessor register
The electronic safing system is provided with a safing sensor, a comparator, and a microcomputer. The microcomputer has a programmable analog I / O port which is connected to a built-in AD-DA converter. The programmable analog I / O port can be switched to an analog input port and an analog output port according to an internal register. The programmable analog I / O port is connected to an input terminal of the comparator. When diagnosing the comparing circuit, the microcomputer switches the programmable analog I / O port to the analog output port and outputs a predetermined voltage for diagnosis. Then, the microcomputer diagnoses the comparing circuit by monitoring the output of the comparing circuit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
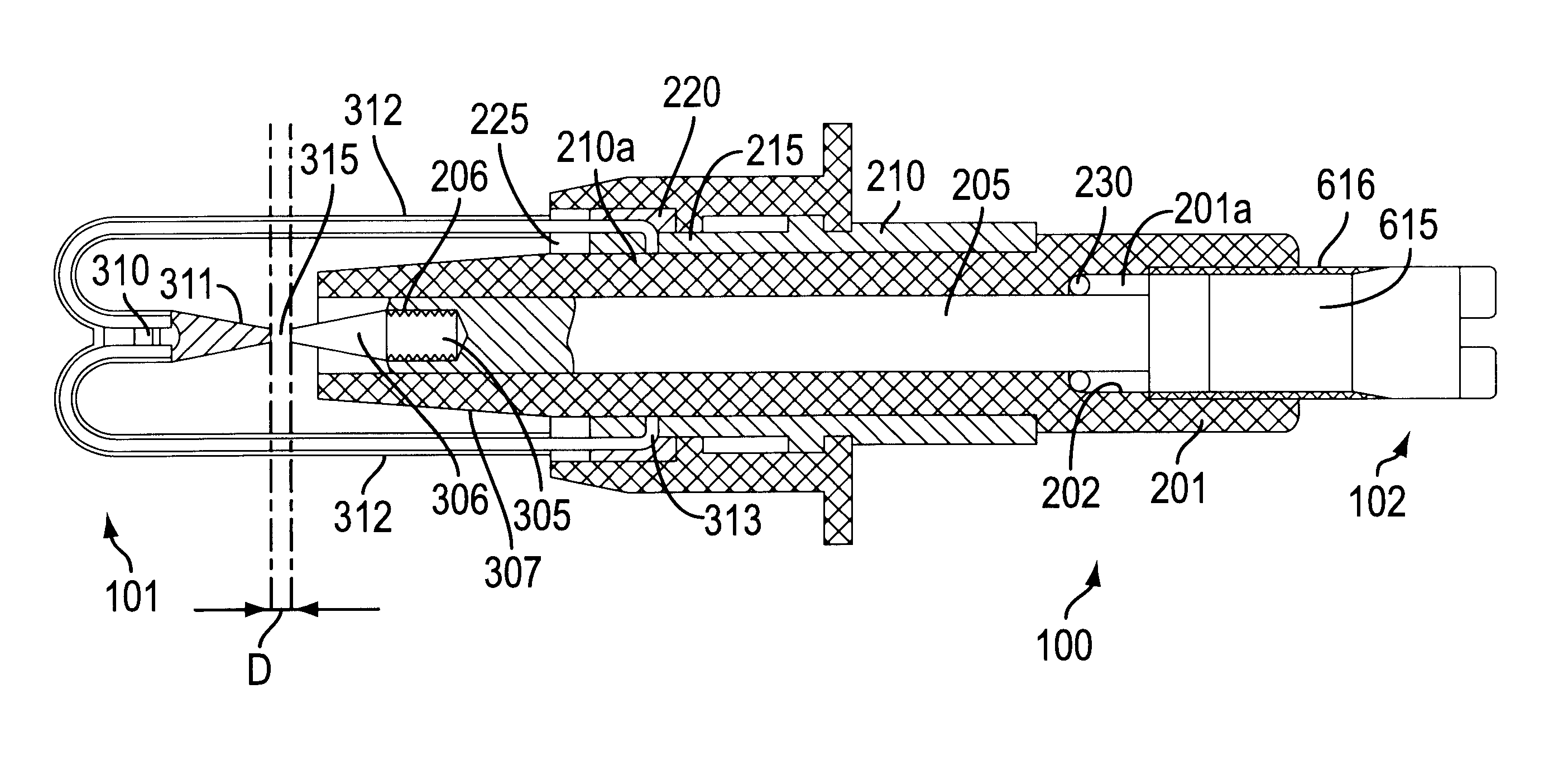
Adjustable electrode and related method
InactiveUS6217531B1Broad spectrumEasy to replaceChiropractic devicesEye exercisersElectricityElectrical conductor
The present invention relates to a electrode assembly and related method that includes a insulator assembly, an electrode assembly, a charging system, a mechanism for measuring electrical voltages, a mechanism for adjusting the distance between inner and outer electrode tips, and a controller. The insulator assembly includes an insulator body having a hollow central portion with a threaded inner wall. The insulator assembly includes inner and outer conductors that are electrically connected to the charging system and are physically connected to inner and outer electrodes, respectively. The electrodes are positioned such that their longitudinal axes are aligned and the tips of the electrodes are in relatively close physical proximity. The distance between the tips is defined as the spark gap. The charging system charges a capacitor that discharges and forms a spark across the spark gap. The electrical measuring mechanism measures the discharge voltage of the capacitor and the controller compares it to a reference voltage, issuing a correction signal to the adjusting mechanism that repositions the electrodes, thus optimizing the spark gap. An alternate embodiment analyzes the charge and discharge characteristics of an electrode assembly that utilizes a second capacitor and an inductor to adjust the spark gap.
Owner:MTS MEDICAL TECH & SERVICES
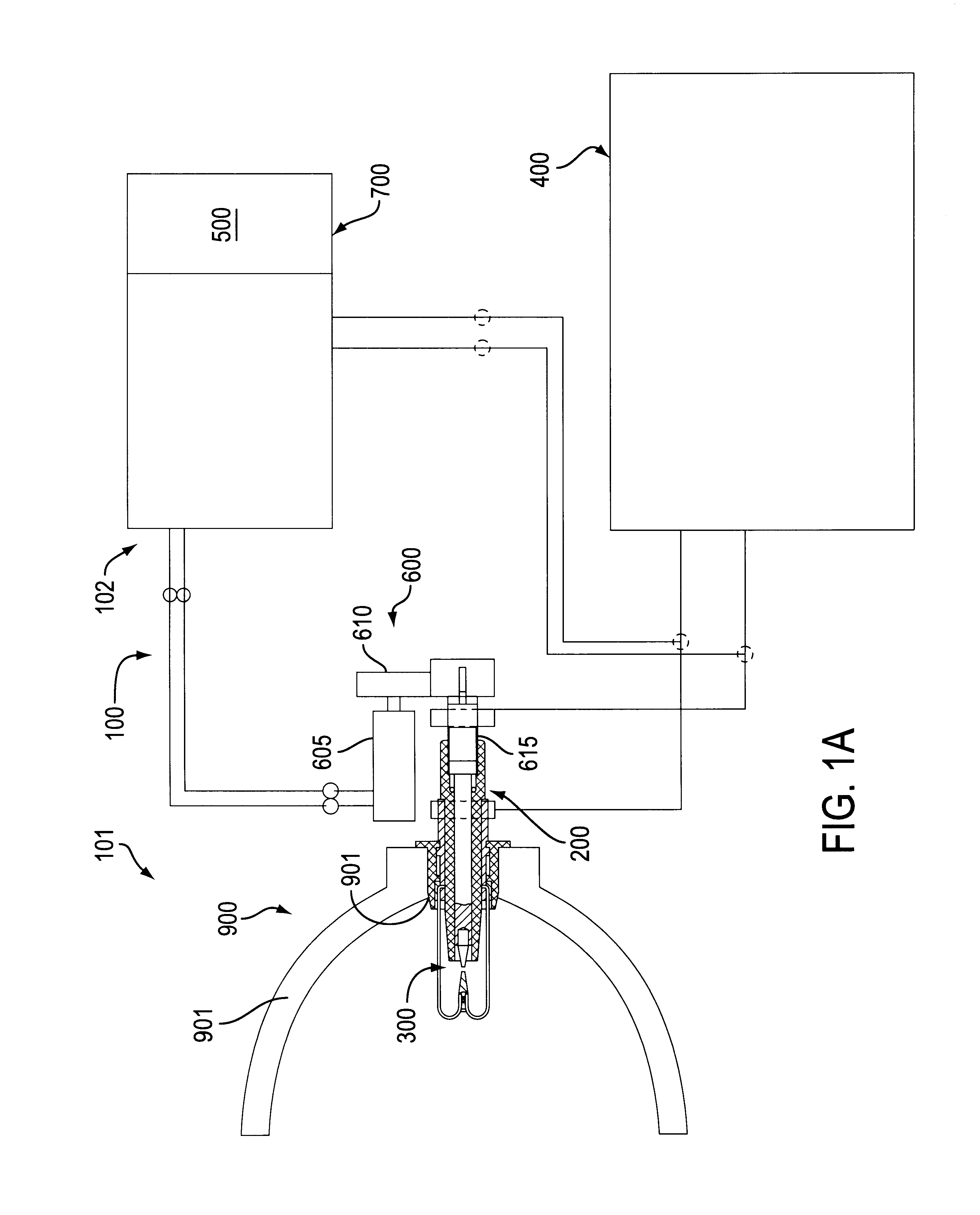
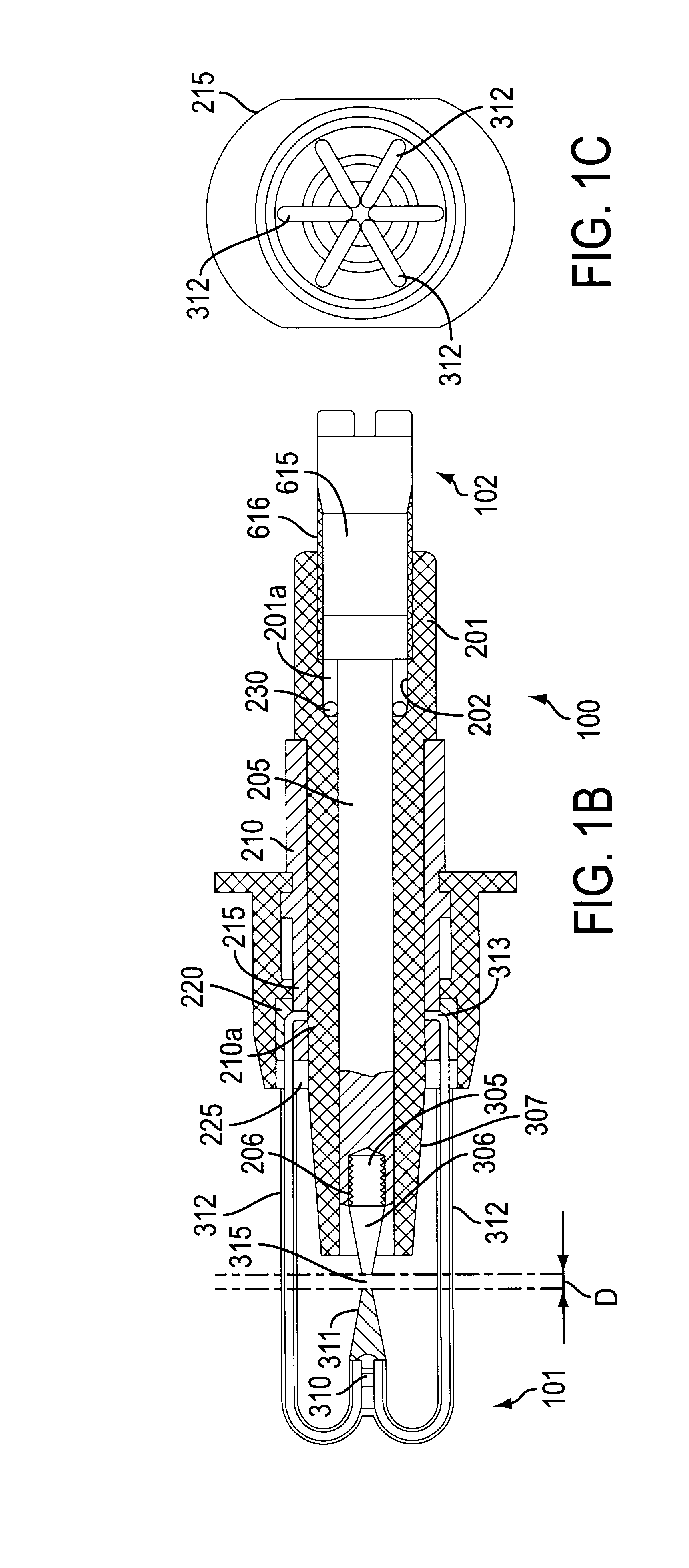
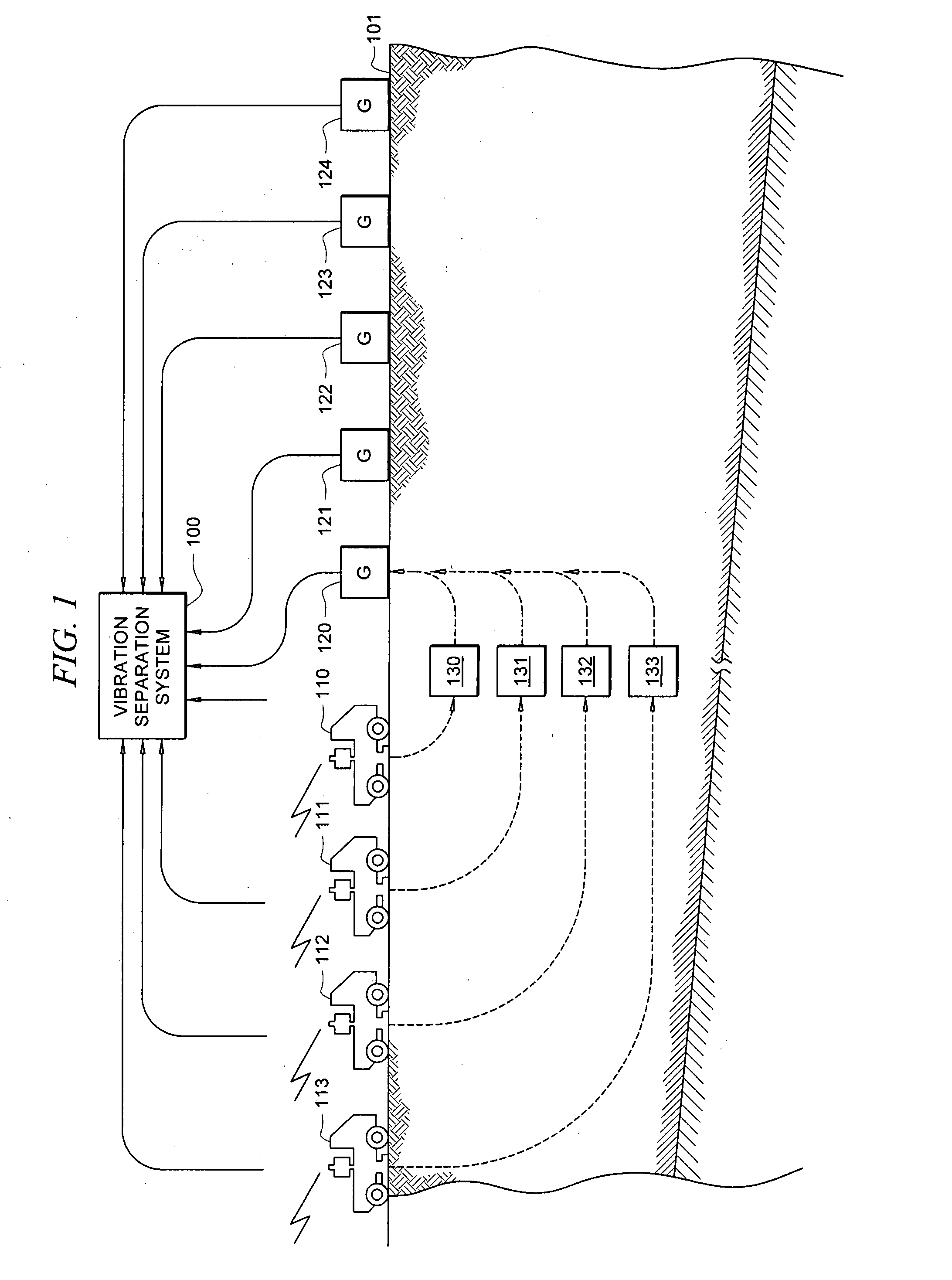
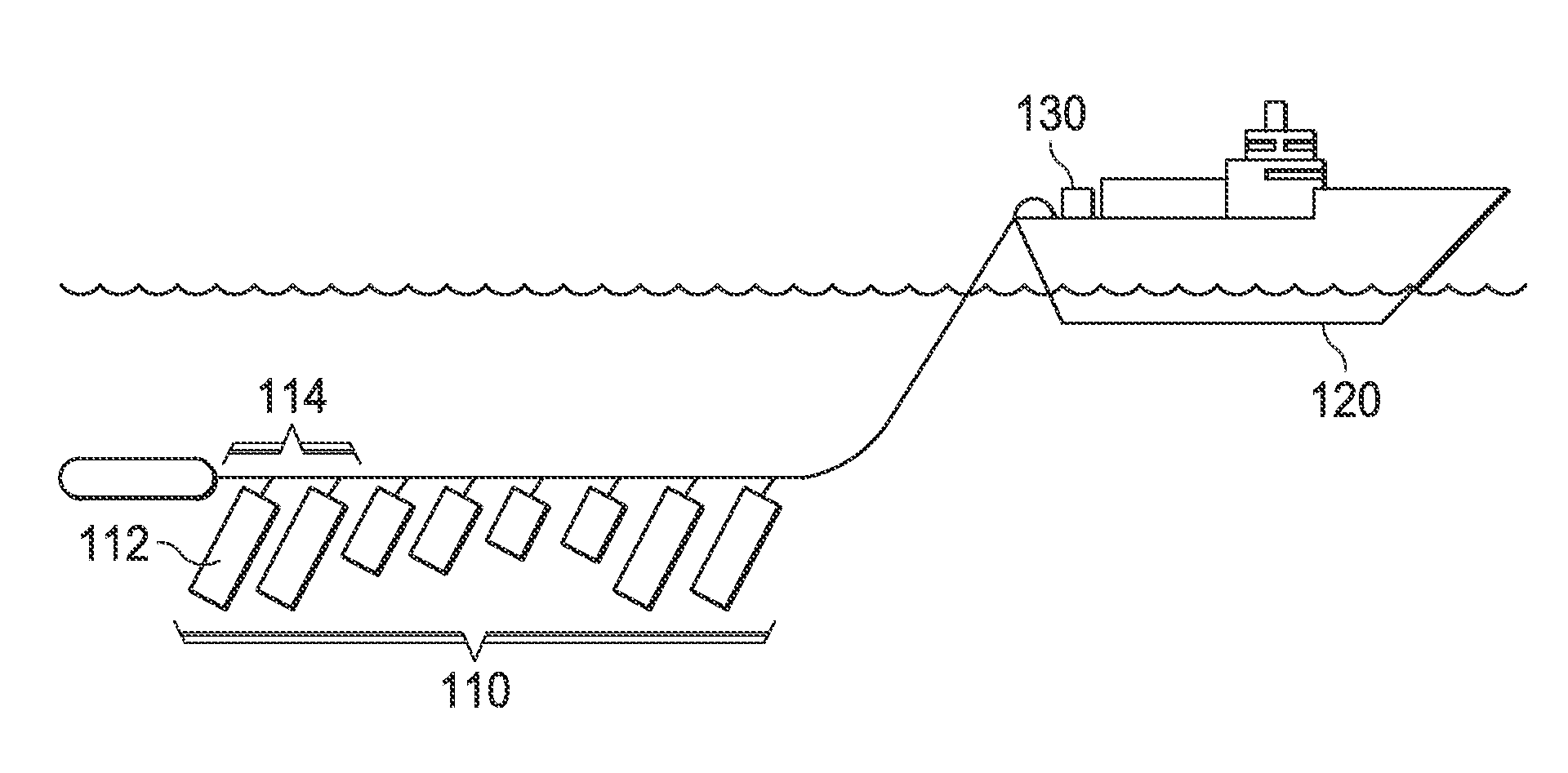
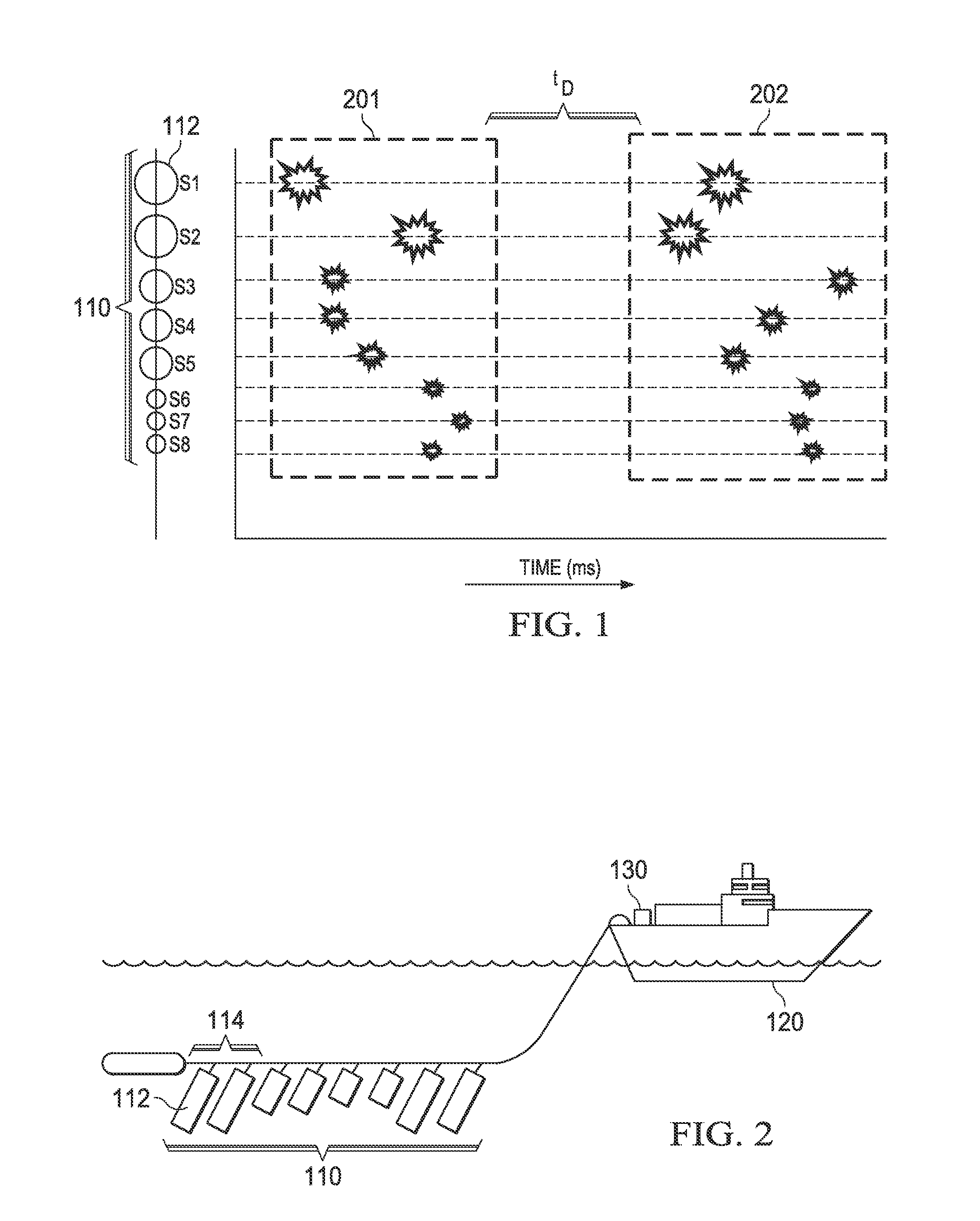
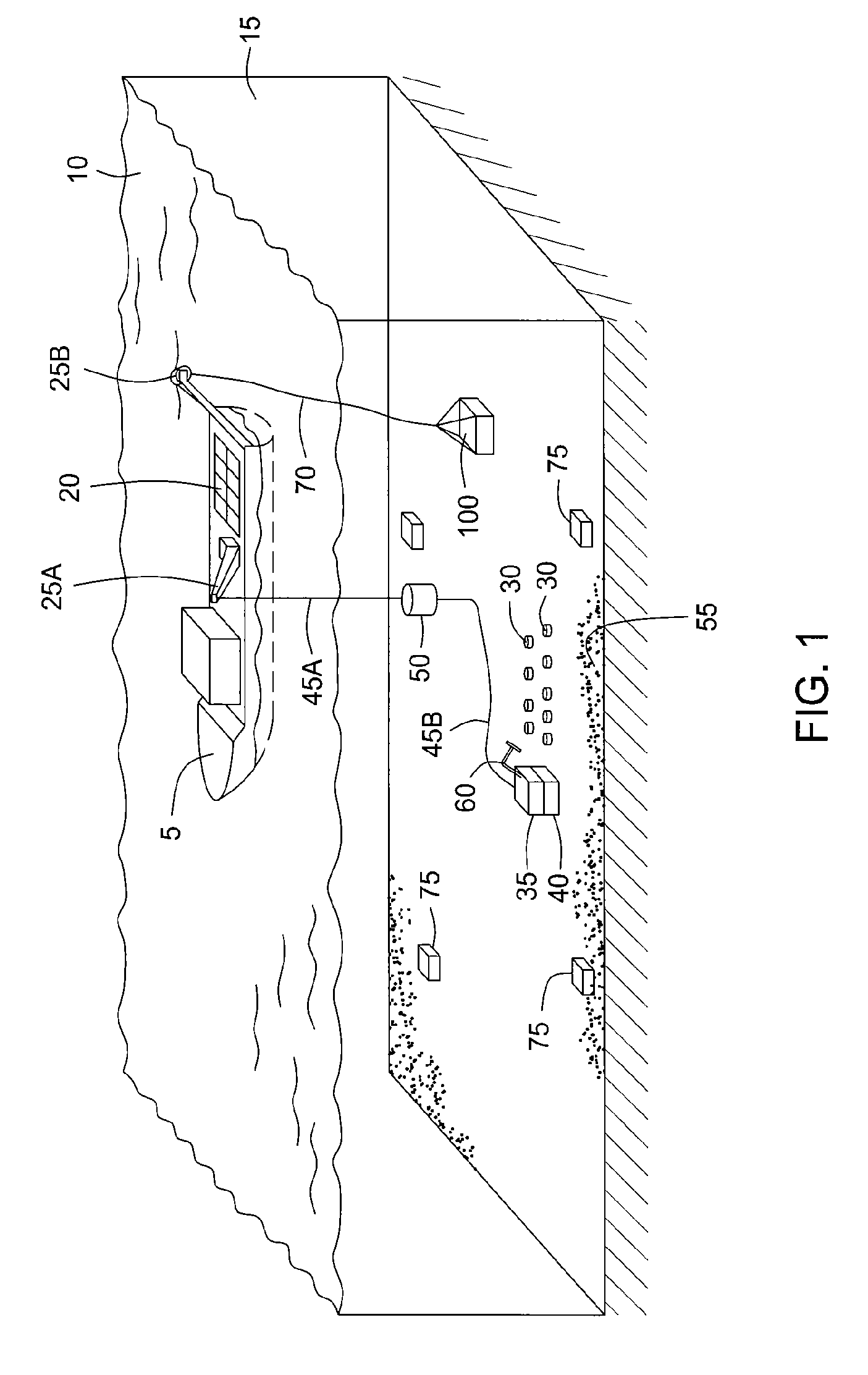
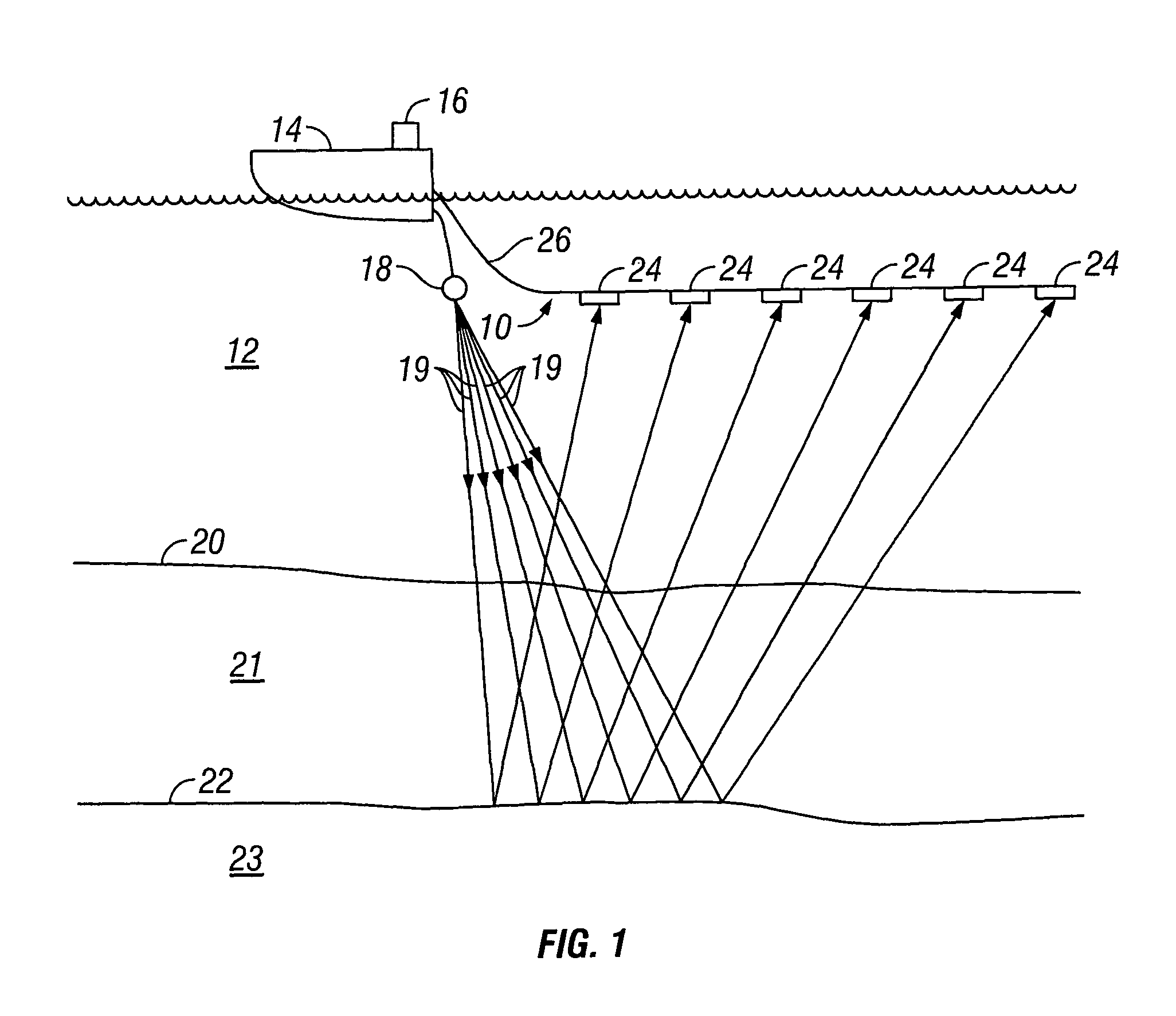
Method and system for acquiring marine seismic data using multiple seismic sources
InactiveUS6906981B2Easy to foldIncrease the lengthSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationSeismic surveySurveyor
A method for seismic surveying is disclosed which includes towing a first seismic energy source and at least one seismic sensor system. A second seismic energy source is towed at a selected distance from the first source. The first seismic energy source and the second seismic energy source are actuated in a plurality of firing sequences. Each of the firing sequences includes firing of the first source, waiting a selected time firing the second source and recording signals generated by the seismic sensor system. The selected time between firing the first source and the second source is varied between successive ones of the firing sequences. The firing times of the first and second source are indexed so as to enable separate identification of seismic events originating from the first source and seismic events originating from the second source in detected seismic signals.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Integrated detonators for use with explosive devices
A detonator assembly is provided for use in oilfield operations to detonate an explosive downhole including a capacitor discharge unit and initiator electrically connected together to form a single unit. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
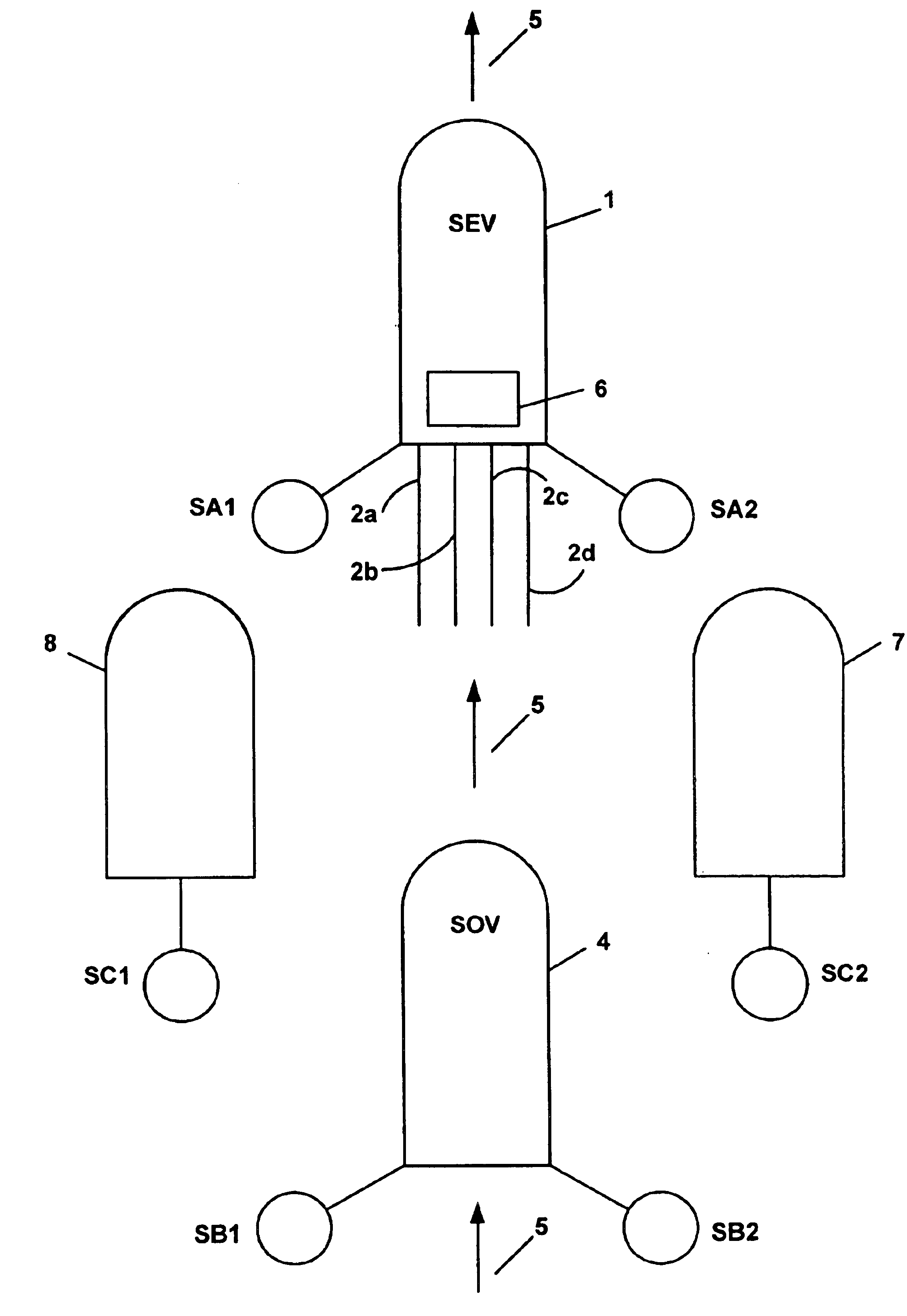
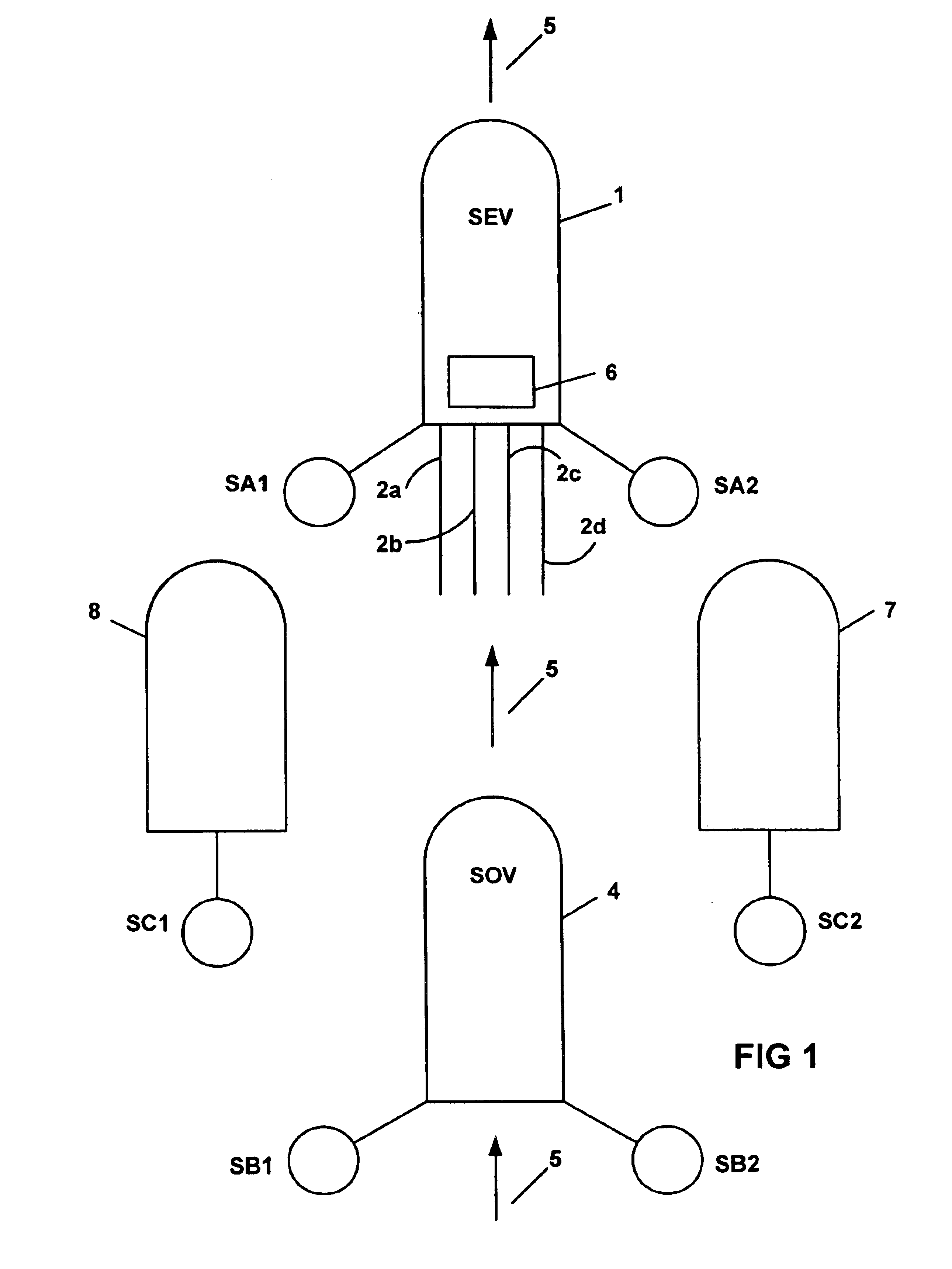
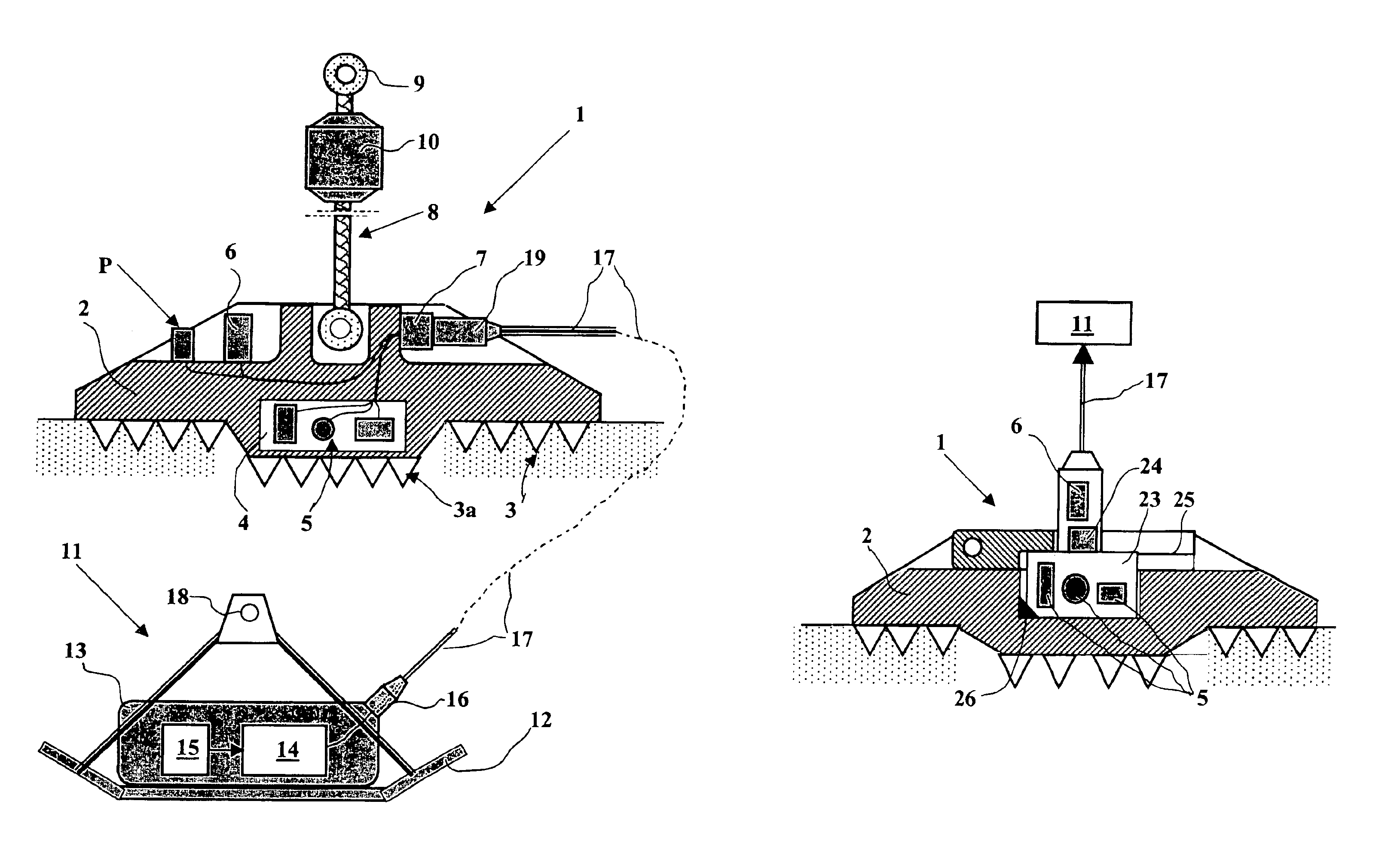
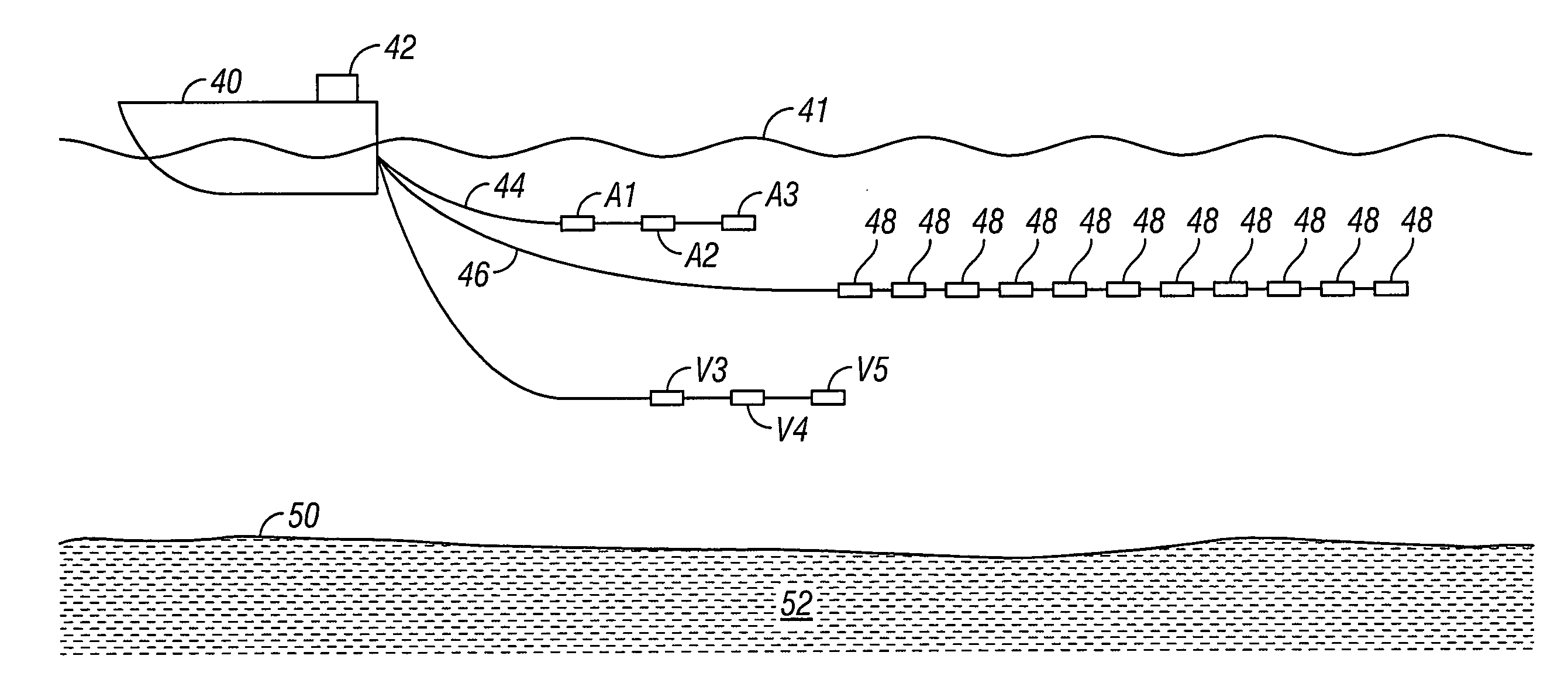
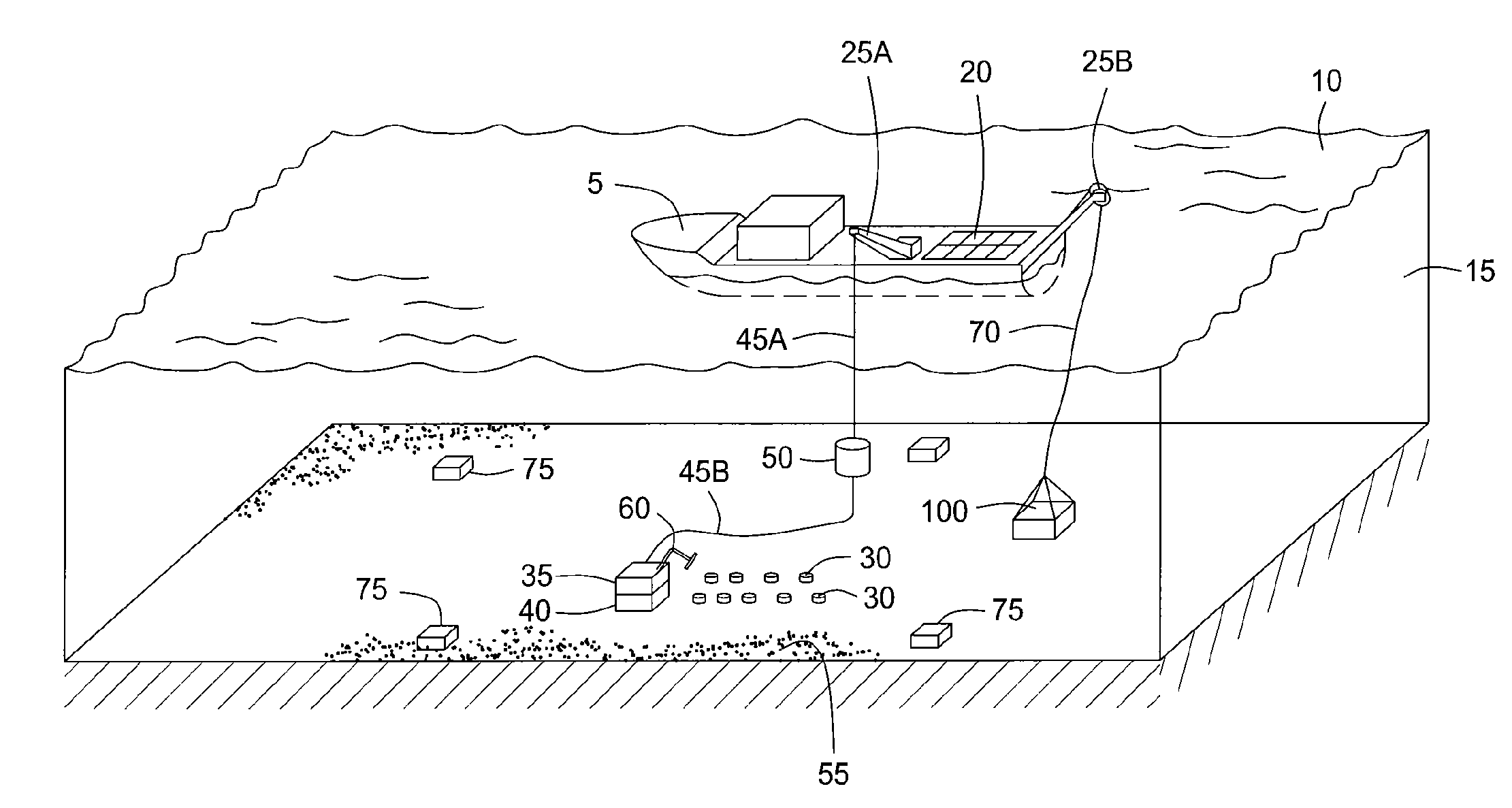
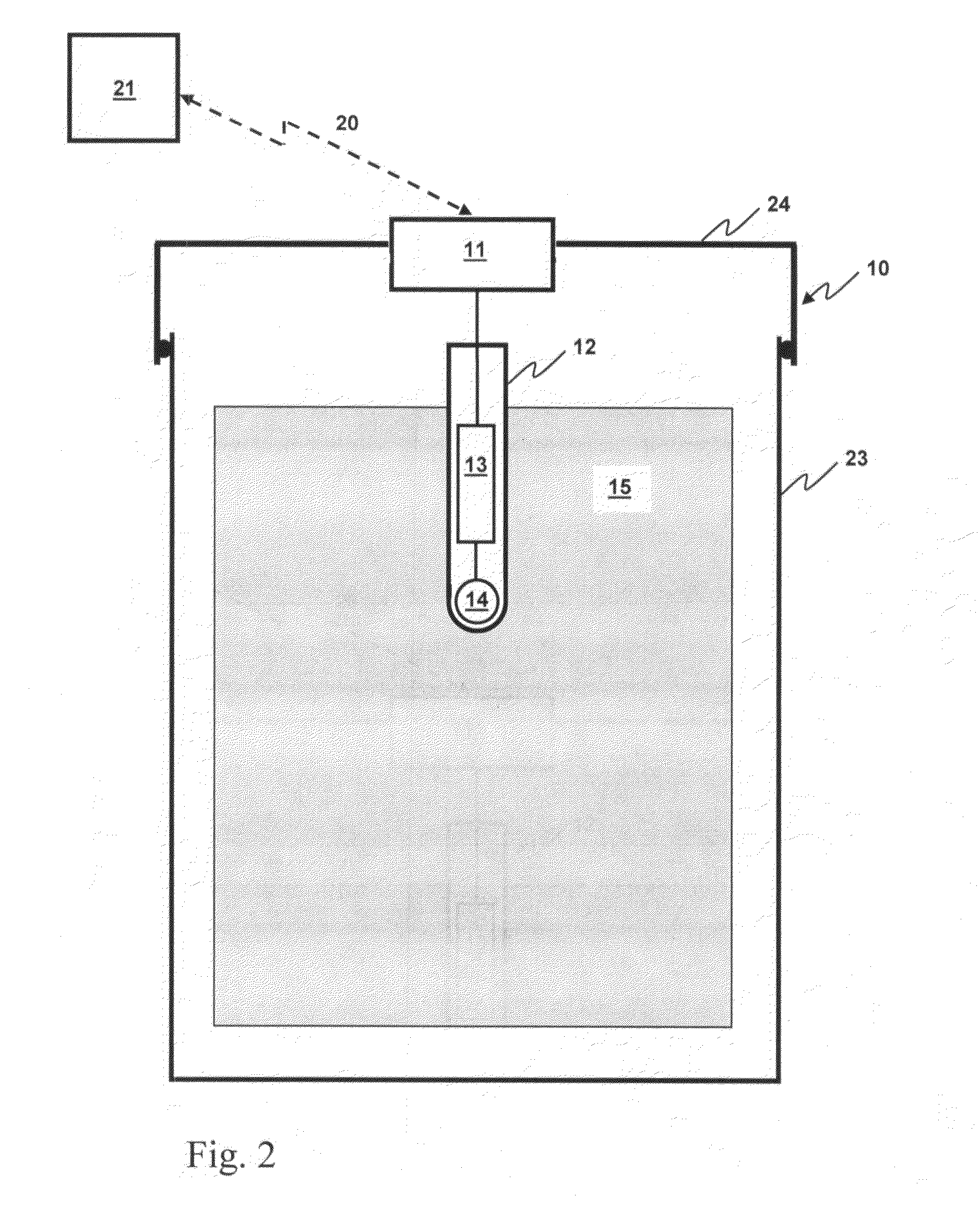
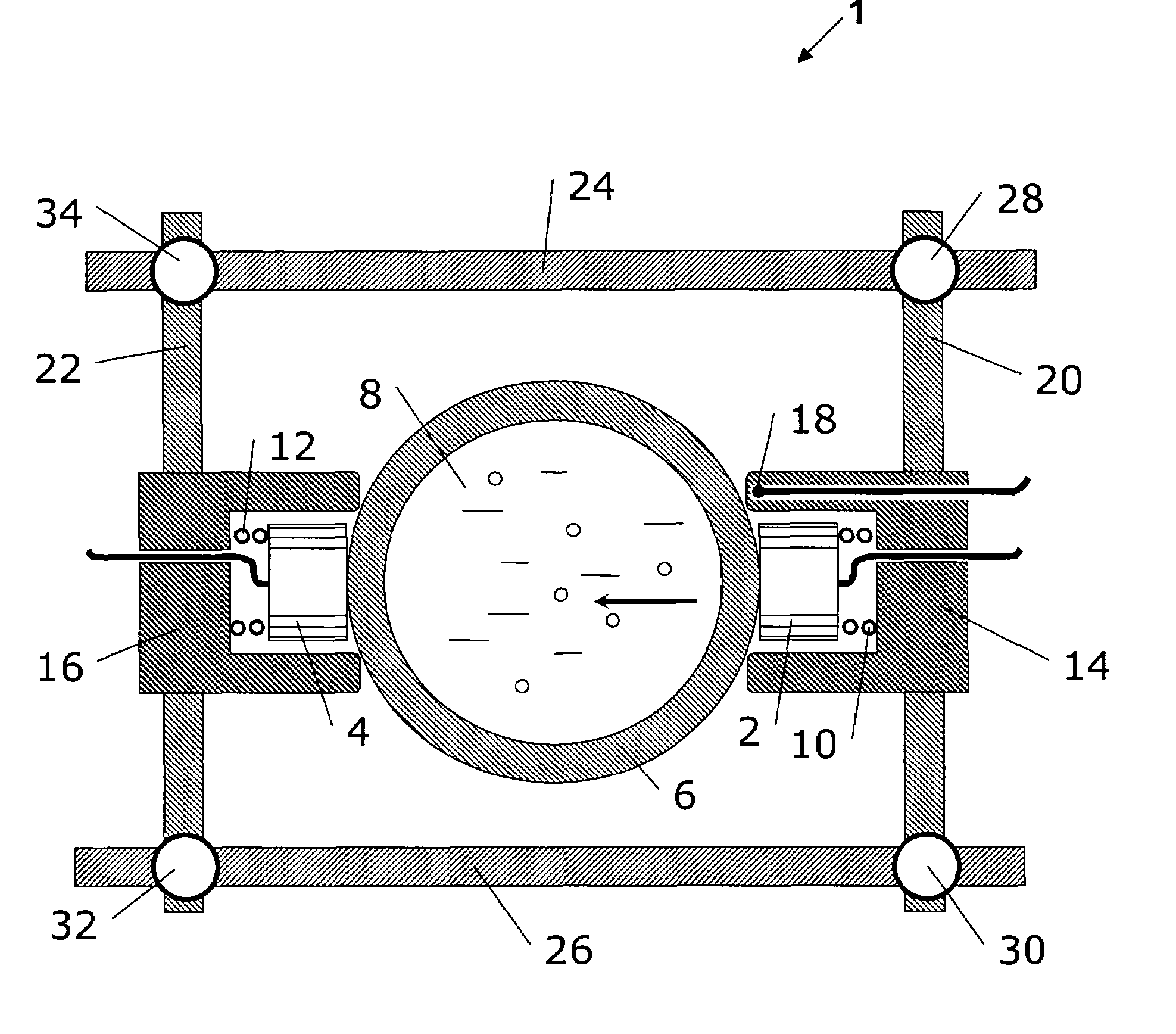
Acquisition method and device for seismic exploration of a geologic formation by permanent receivers set on the sea bottom
InactiveUS6932185B2Good flexibilityFine divisionSeismic energy generationSeismic signal receiversGeophoneHydrophone
A method and device for seismic exploration of a subsea geologic formation by pickups set on the sea bottom and intermittently connectable to active data acquisition stations (11) brought nearby. Permanent passive reception stations (1) comprising a heavy pedestal provided with housings for seismic pickups (geophones (6), hydrophone (7) which receive acoustic or seismic signals from the underlying formation are arranged at the bottom of the water body. When collection sessions for the signals received by the pickups are scheduled, mobile active acquisition stations (11) connected to permanent passive reception stations (1) are positioned at the bottom of the water body. The signals picked up are then recorded, for the time required to carry out at least one session of acquisition and recording of the acoustic or seismic signals received by the passive stations in response to the emission of seismic waves by one or more seismic sources. The mobile active acquisition stations (11) are thereafter recovered at the surface and the records acquired by each one are transferred to a central collection laboratory.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
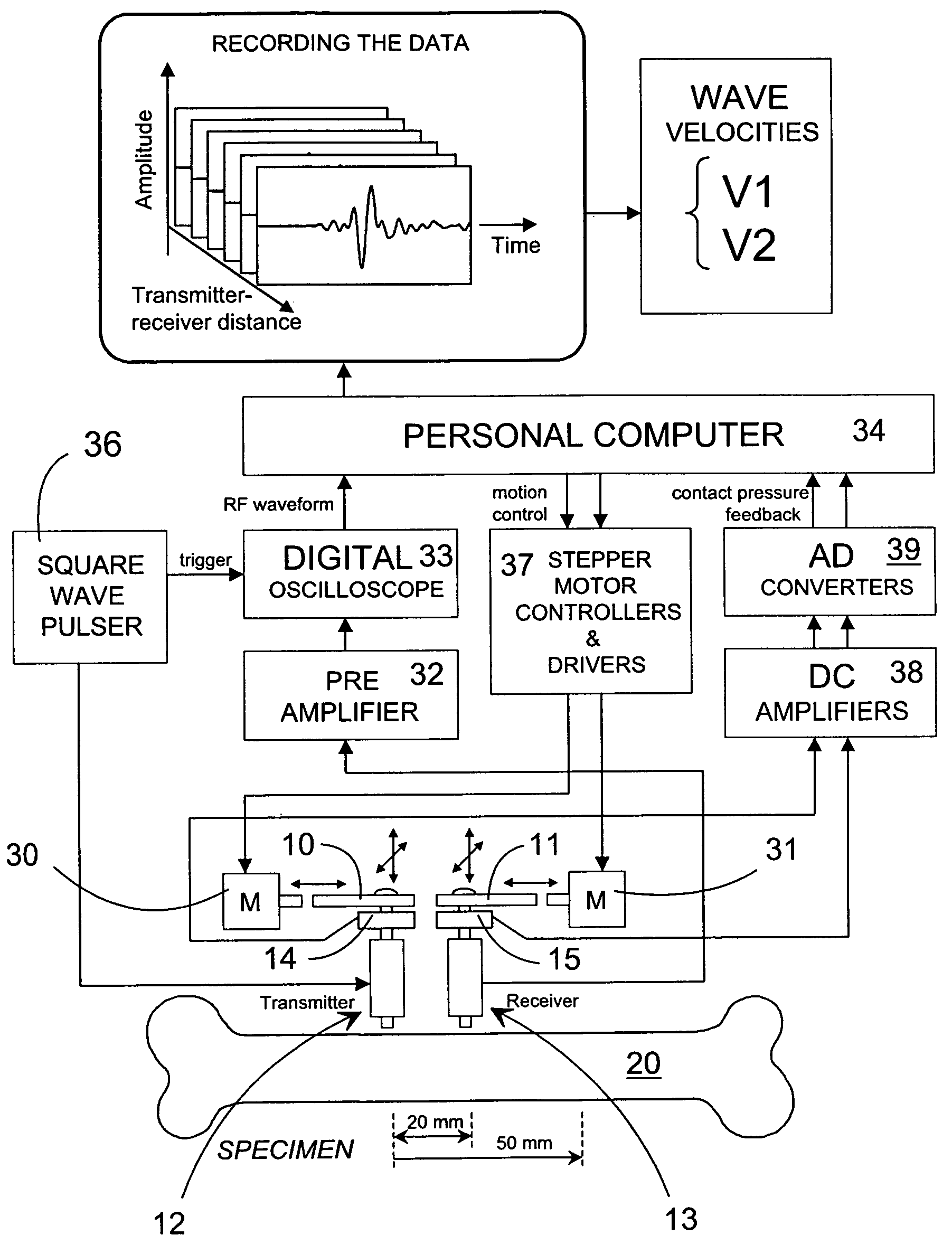
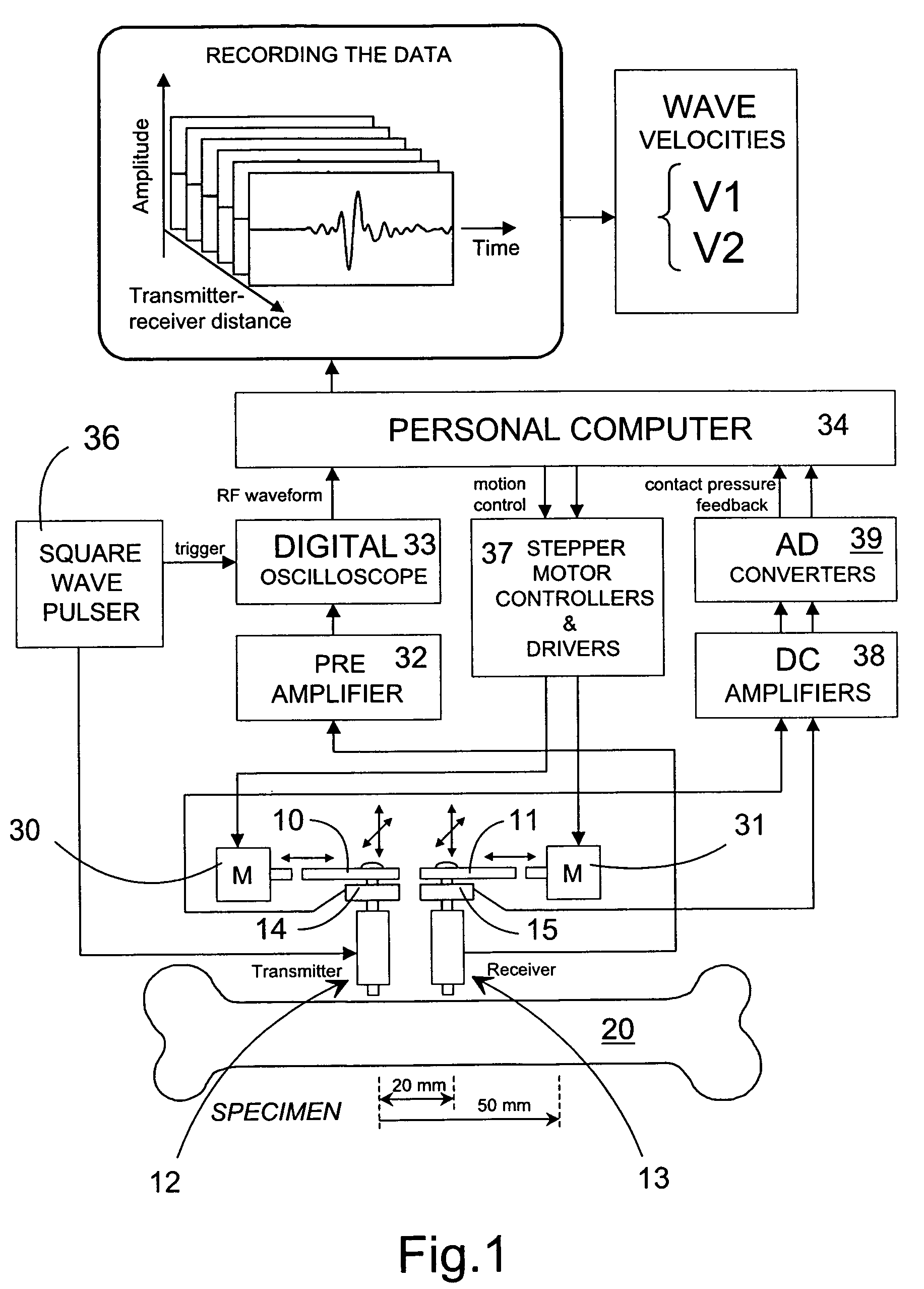
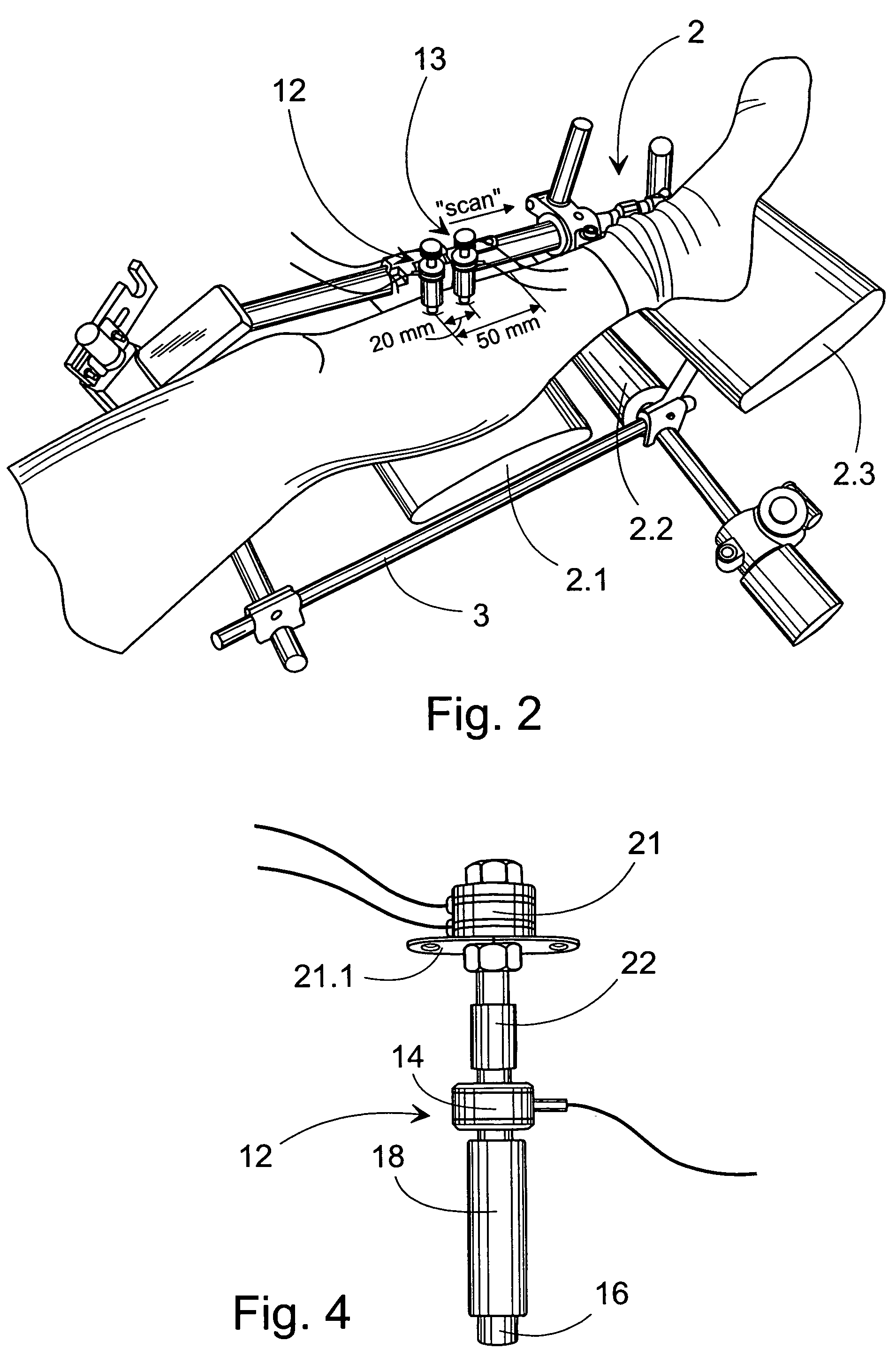
Method and device for the non-invasive assessment of bones
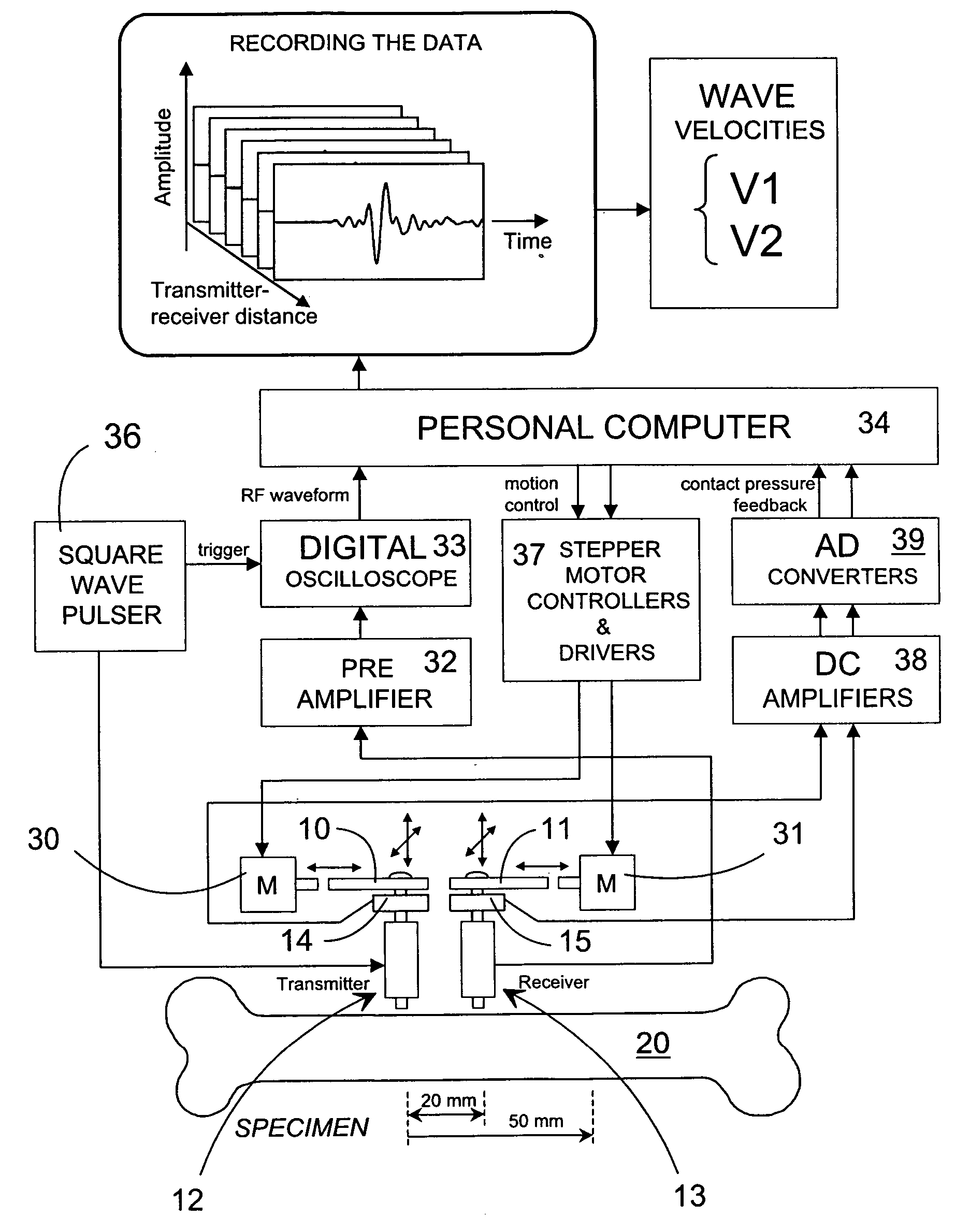
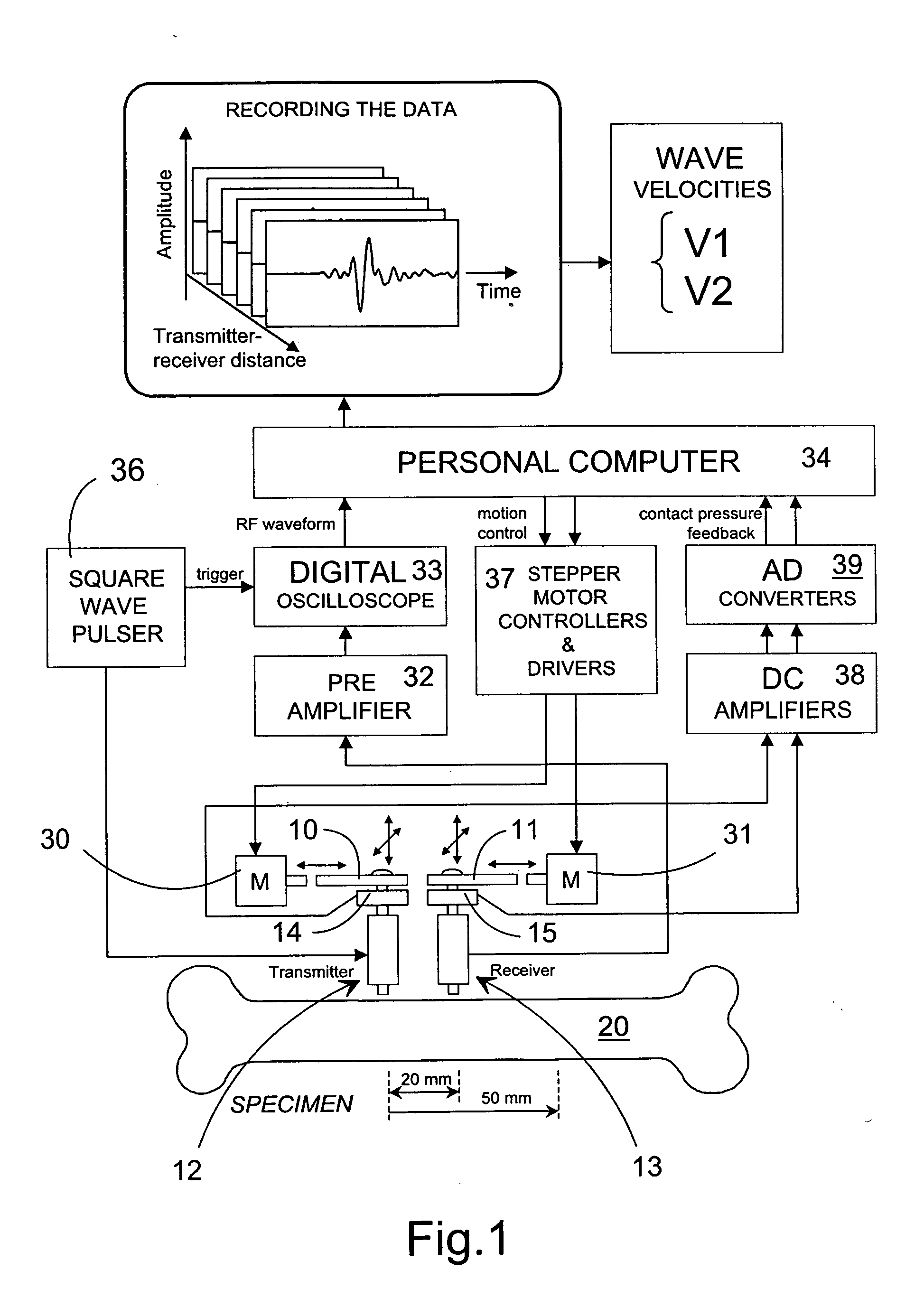
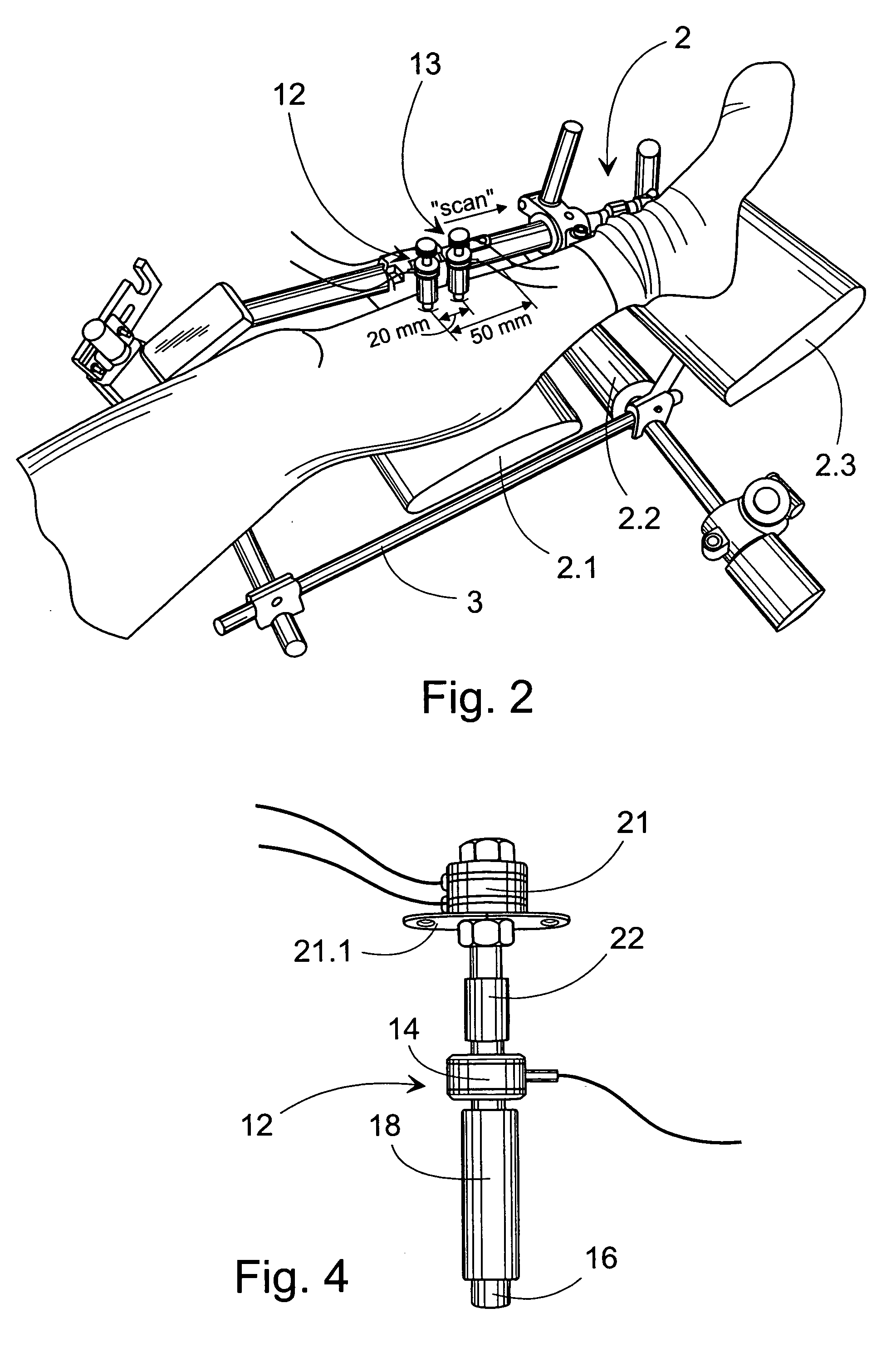
ActiveUS7601120B2Enhanced thickness-dependenceMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidBone densityTransducer
A method for the in vivo non-invasive characterization of the material and architectural properties of a bone in which an ultrasonic wave is introduced into a bone in such way as to produce one or more guided wave modes within the bone, and the signals emerging from the bone are stored and analyzed to determine the propagation characteristics of the guided wave / s. These measured guided wave propagation characteristics are then processed to obtain estimates of desired bone properties such as cortical thickness, bone density and bone elastic constants. The invention also includes an unltrasound arrangement with movable transducers.
Owner:OSCARE MEDICAL
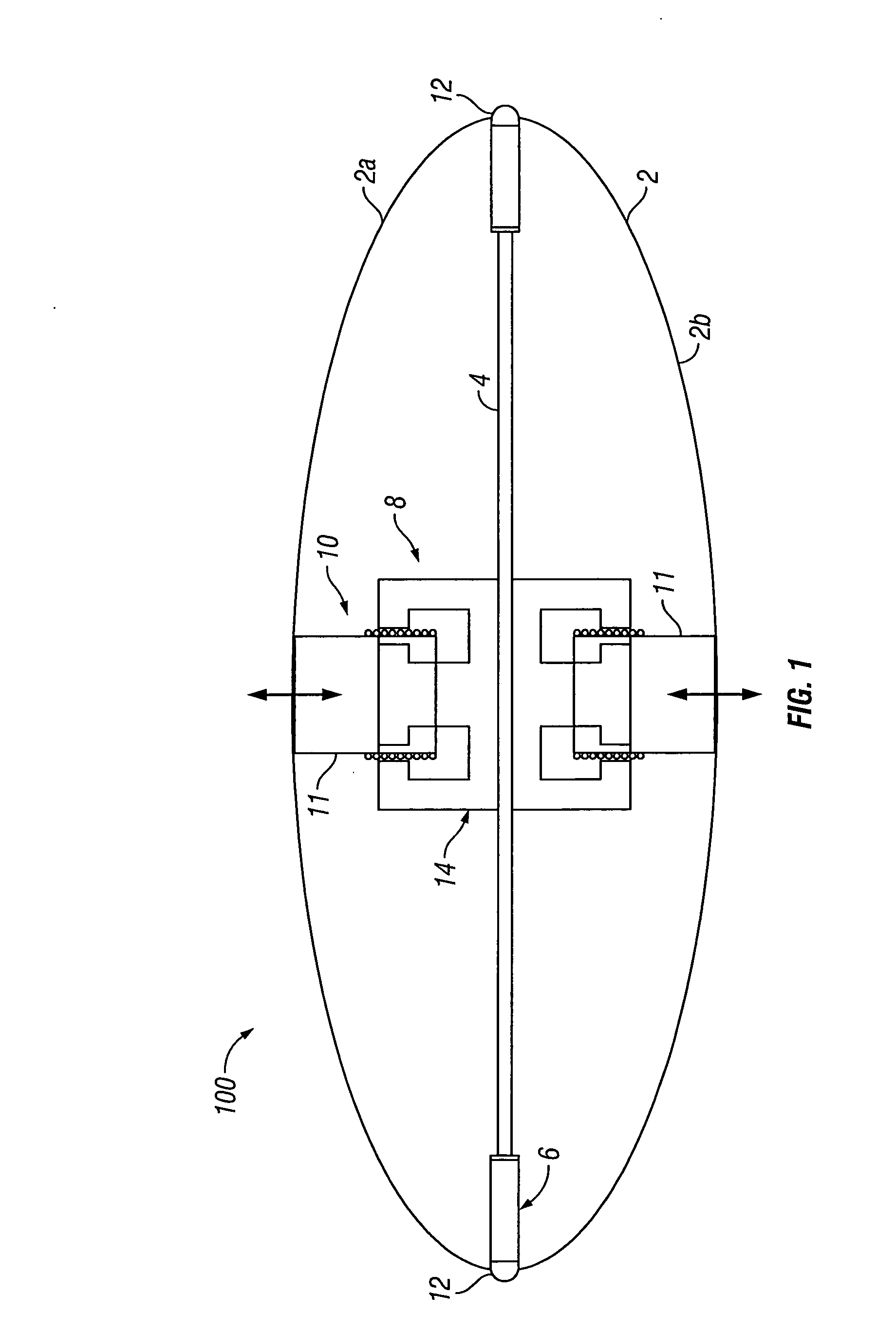
Electrohydraulic pressure wave projectors
A projector (10) for creating electrohydraulic acoustic and pressure waves comprising an energy source (21) (such as a capacitor) within approximately one meter of an electrode array (23). Larger projectors may be formed by arraying the projectors, and still larger projectors by arraying them.
Owner:SDG LLC
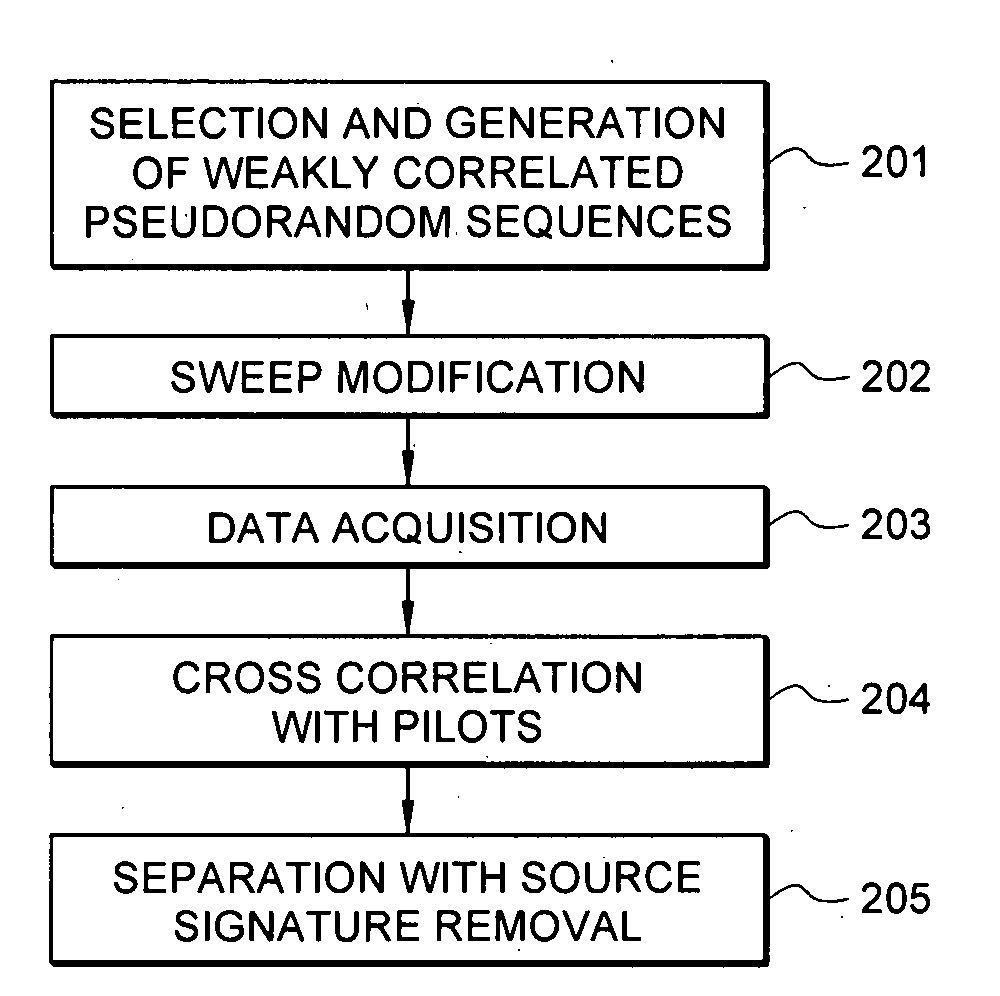
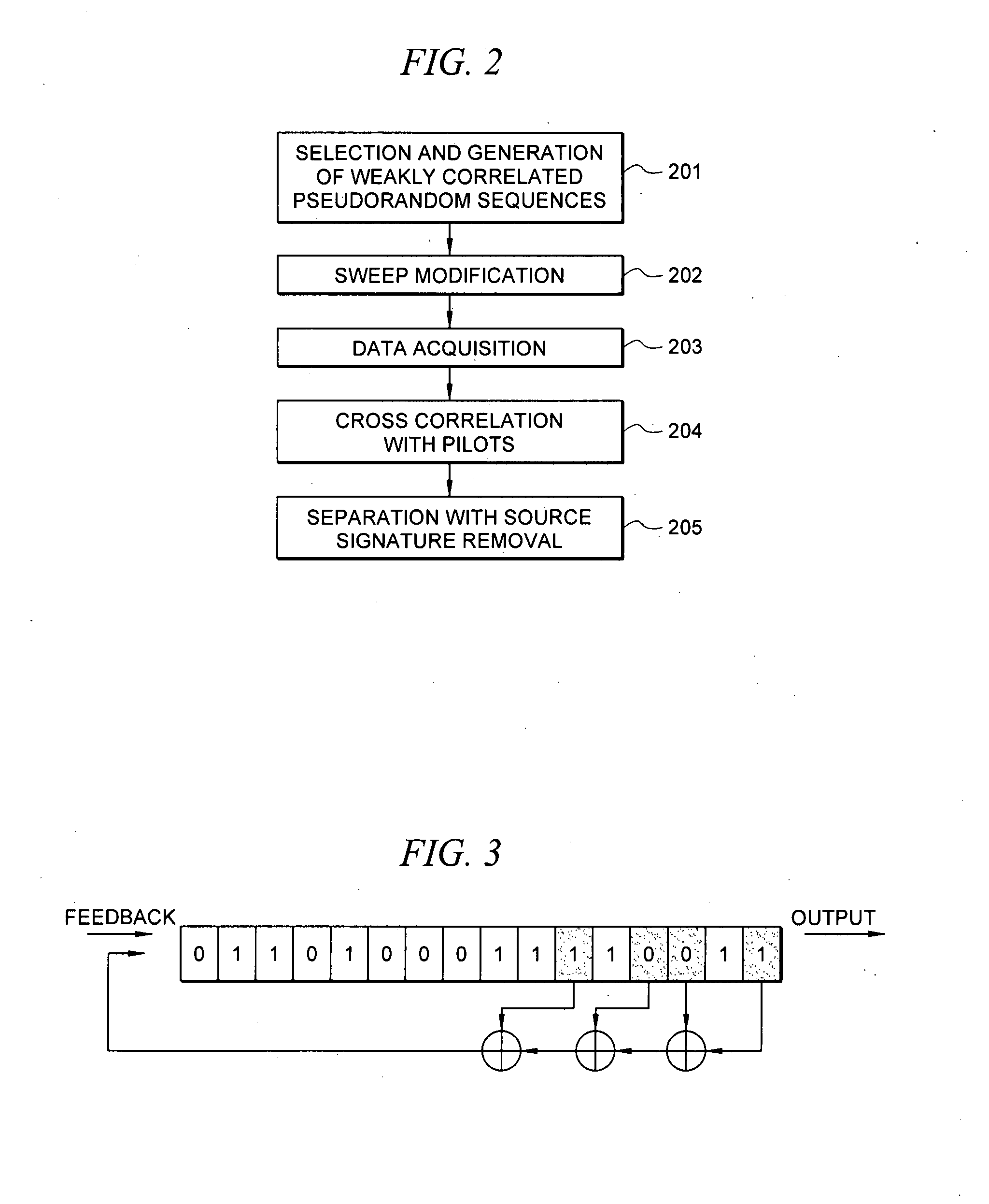
Efficient seismic data acquisition with source separation
ActiveUS20090010103A1Minimize crosstalkSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationTime domainFrequency spectrum
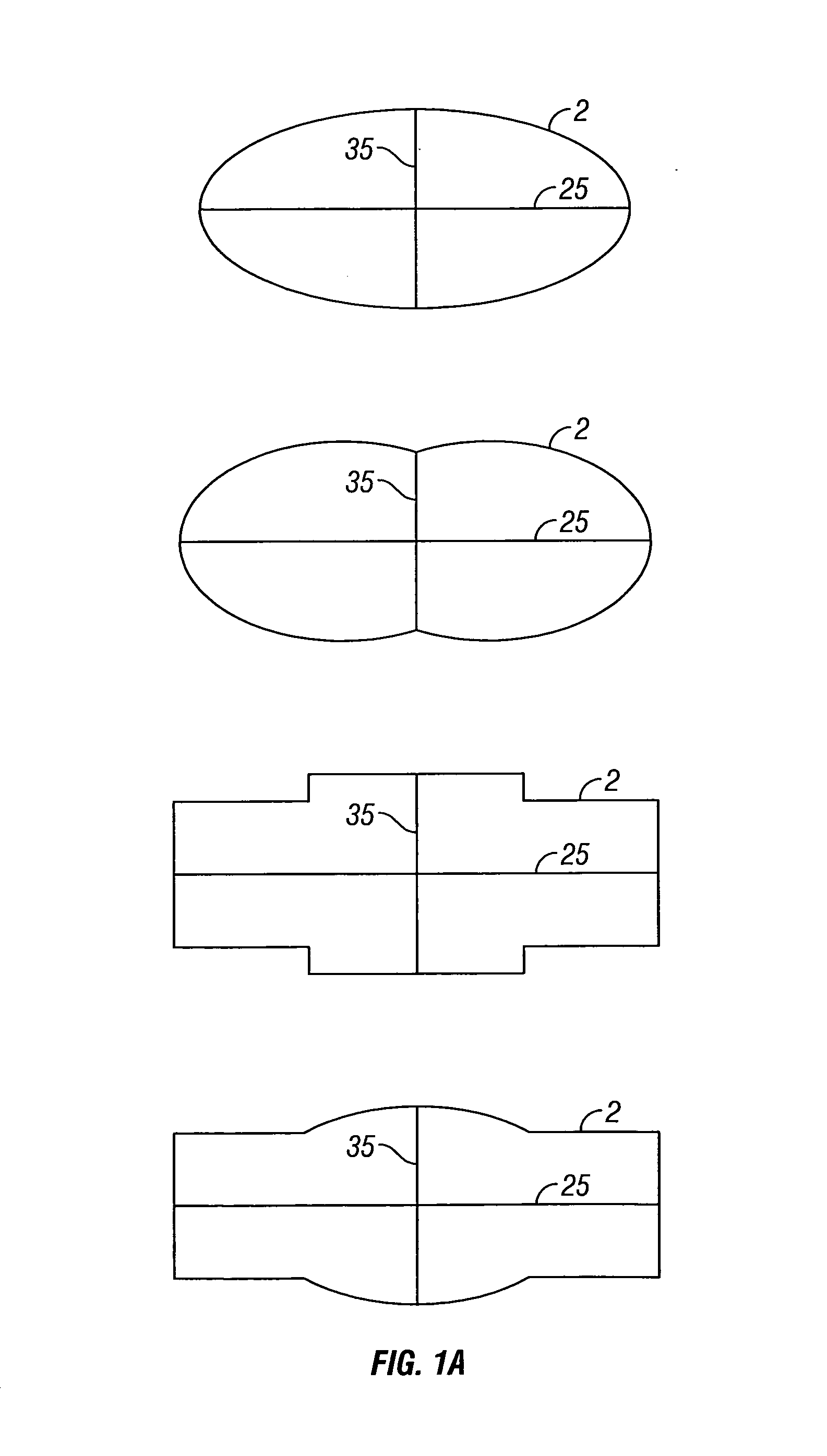
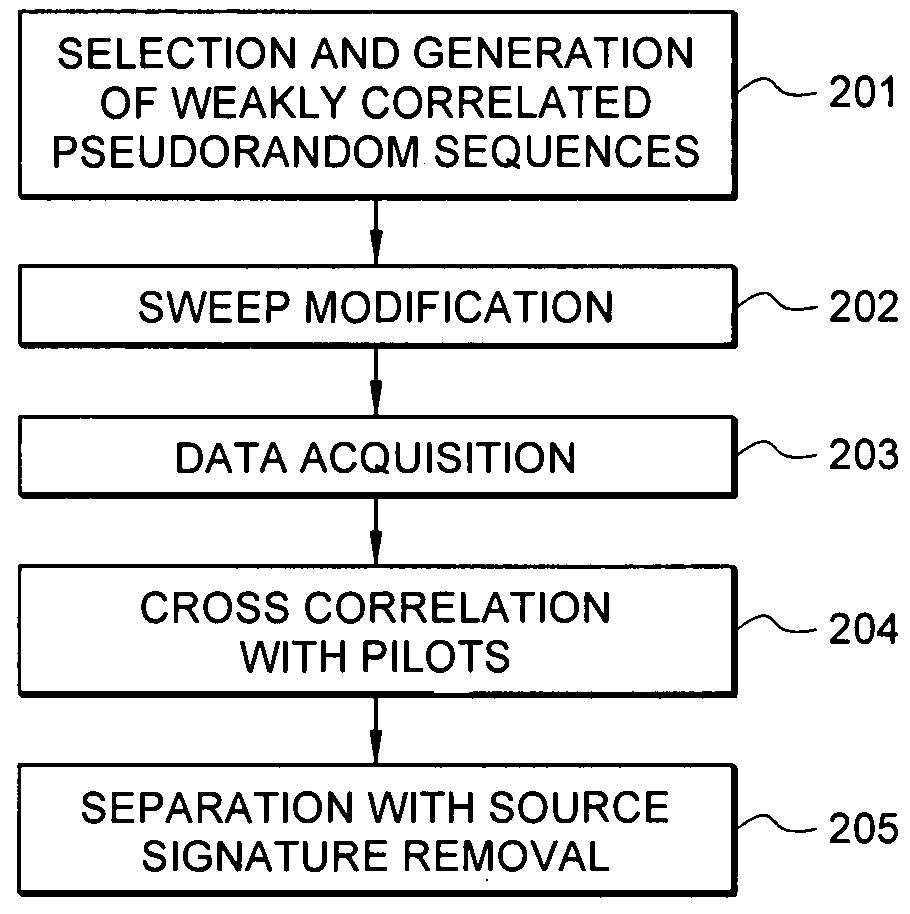
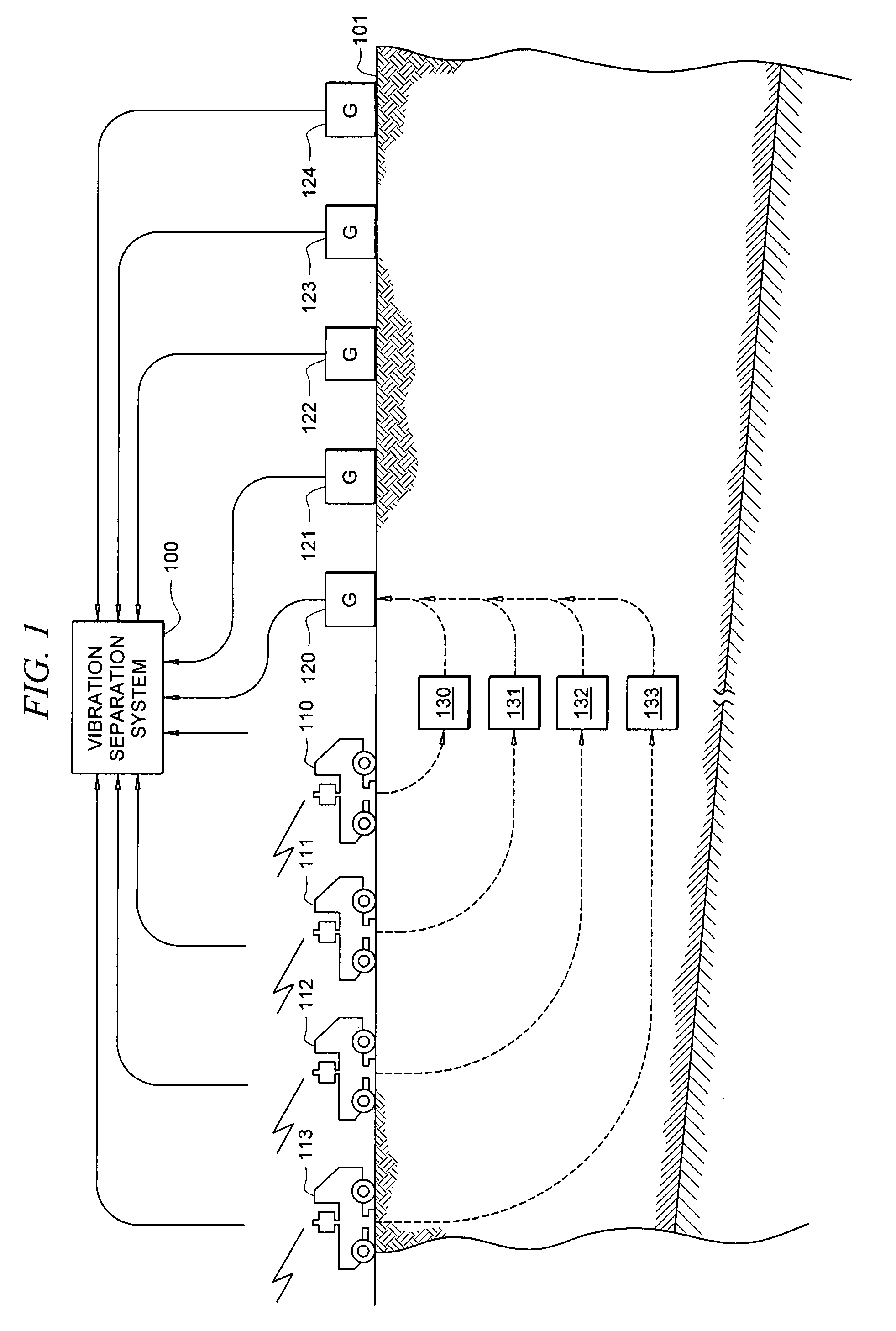
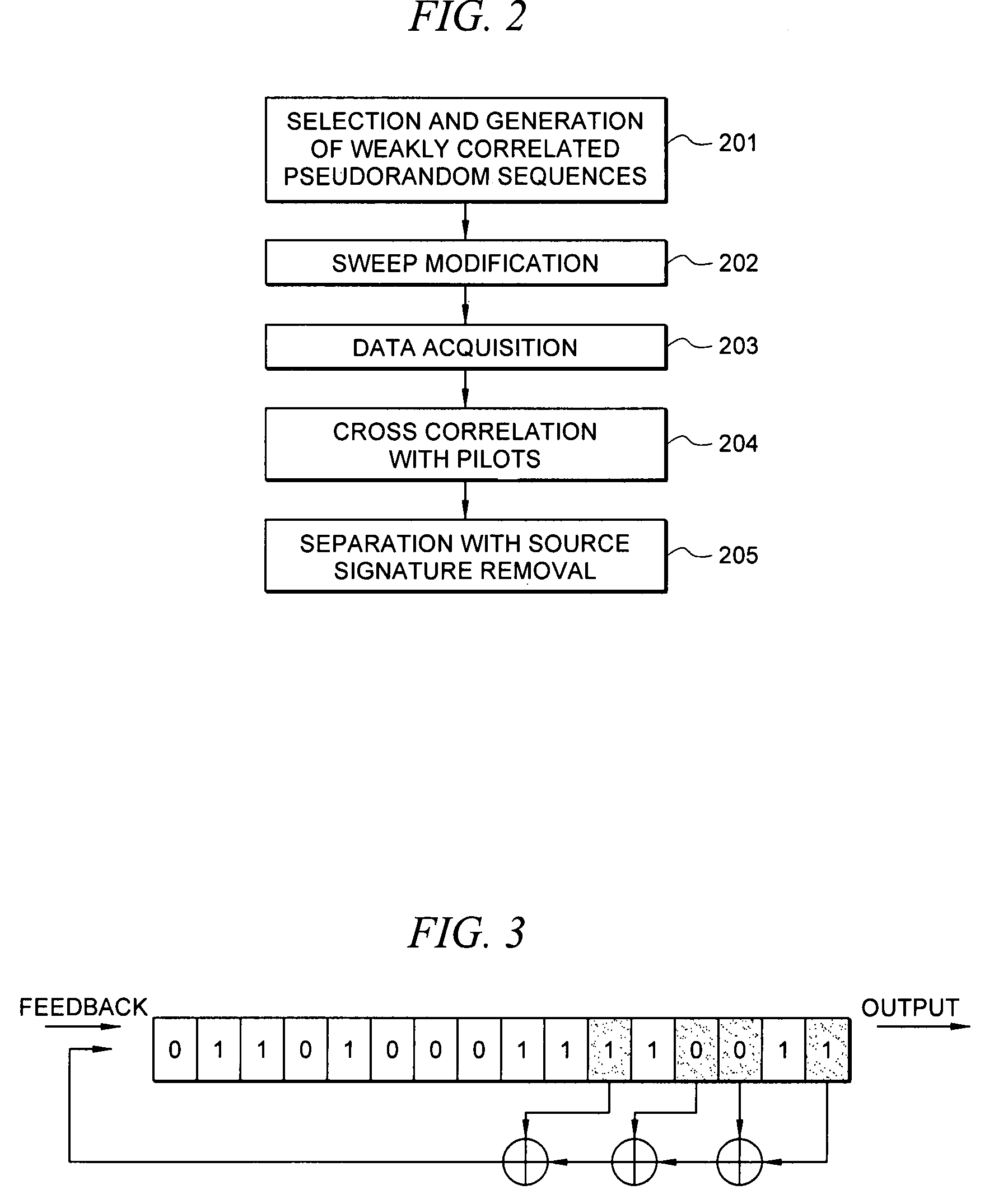
A method for the simultaneous operation of multiple seismic vibrators using unique modified pseudorandom sweeps and recovery of the transmission path response from each vibrator is disclosed. The vibrator sweeps are derived from pseudorandom binary sequences modified to be weakly correlated over a time window of interest, spectrally shaped and amplitude level compressed. Cross-correlation with each pilot signal is used to perform an initial separation of the composite received signal data set. Recordings of the motion of each vibrator are also cross-correlated with each pilot, windowed, and transformed to form a source cross-spectral density matrix in the frequency domain useful for source signature removal and for additional crosstalk-suppression between the separated records. After source signature removal in the frequency domain an inverse transform is applied to produce an estimate of each source-to-receiver earth response in the time domain. The method has application to both land and marine geophysical exploration.
Owner:SERCEL INC
Seismic acquisition method and system
ActiveUS20120147701A1Reduce impactReduce outputSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationImaging qualityBiological activation
The maximum output of a seismic source array may be reduced by activating the individual seismic sources within these seismic source array in a pattern that is extended in time rather than by the presently employed conventional simultaneous activation of a large number of individual seismic sources. Methods are disclosed which take data shot with patterned sources and may use a sparse inversion method to create data with the about same image quality as that of conventional sources. In this manner the output of the maximum impulse of a seismic source array may be reduced by an amplitude factor of about 10 in the examples shown here, corresponding to a reduction of about 20 dB while maintaining virtually the same seismic image quality. The disclosed methods may be used in combination with any simultaneous sourcing technique. In addition, the disclosed methods may be used with a plurality of source arrays.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Marine acoustic vibrator having enhanced low-frequency amplitude
InactiveUS20110317515A1Seismic energy generationSound producing devicesVibration amplitudeSeismic survey
A seismic source includes a flextensional shell defining a longer axis and a shorter axis and at least one driver coupled to the flextensional shell proximate an end of the shorter axis. The seismic source may be a component of a marine seismic survey system. The marine seismic survey system may be utilized in a method of marine seismic surveying.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Efficient seismic data acquisition with source separation
A method for the simultaneous operation of multiple seismic vibrators using unique modified pseudorandom sweeps and recovery of the transmission path response from each vibrator is disclosed. The vibrator sweeps are derived from pseudorandom binary sequences modified to be weakly correlated over a time window of interest, spectrally shaped and amplitude level compressed. Cross-correlation with each pilot signal is used to perform an initial separation of the composite received signal data set. Recordings of the motion of each vibrator are also cross-correlated with each pilot, windowed, and transformed to form a source cross-spectral density matrix in the frequency domain useful for source signature removal and for additional crosstalk-suppression between the separated records. After source signature removal in the frequency domain an inverse transform is applied to produce an estimate of each source-to-receiver earth response in the time domain. The method has application to both land and marine geophysical exploration.
Owner:SERCEL INC
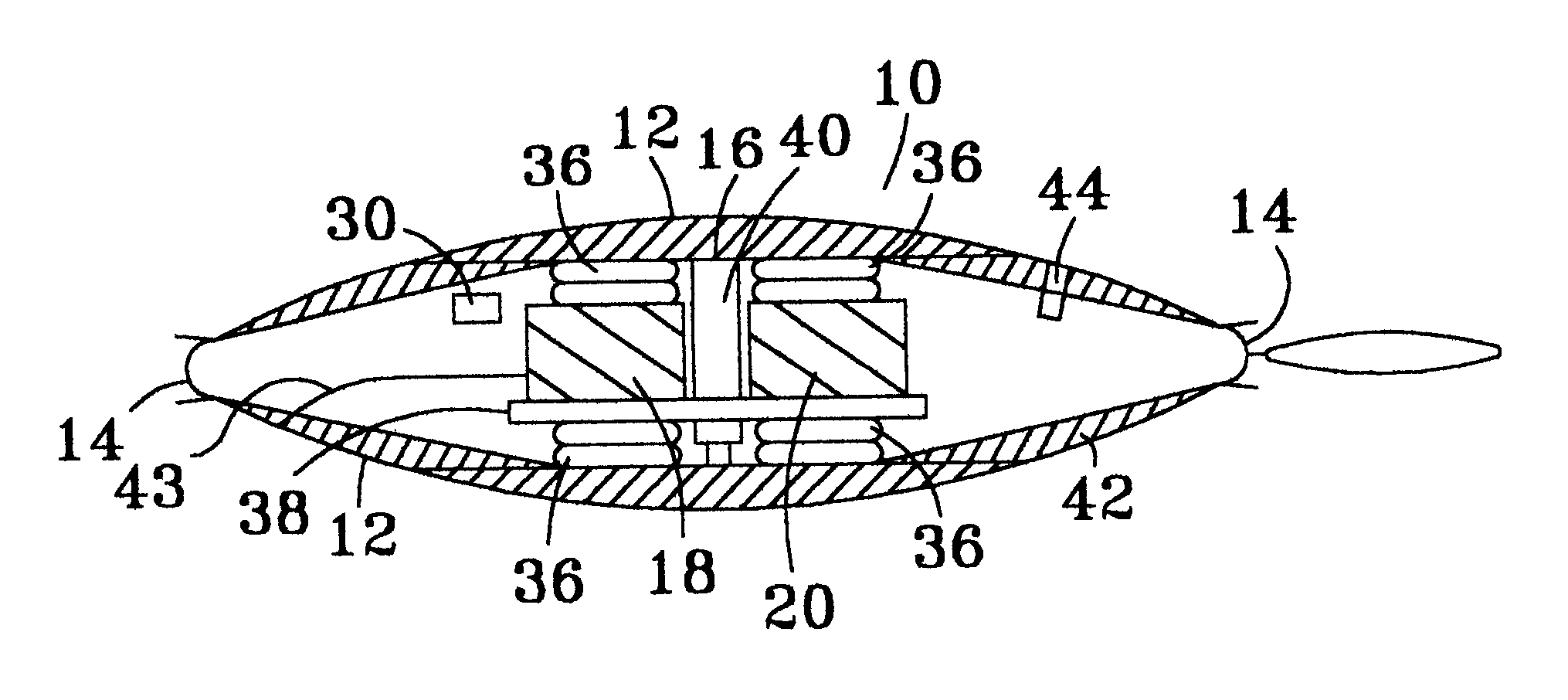
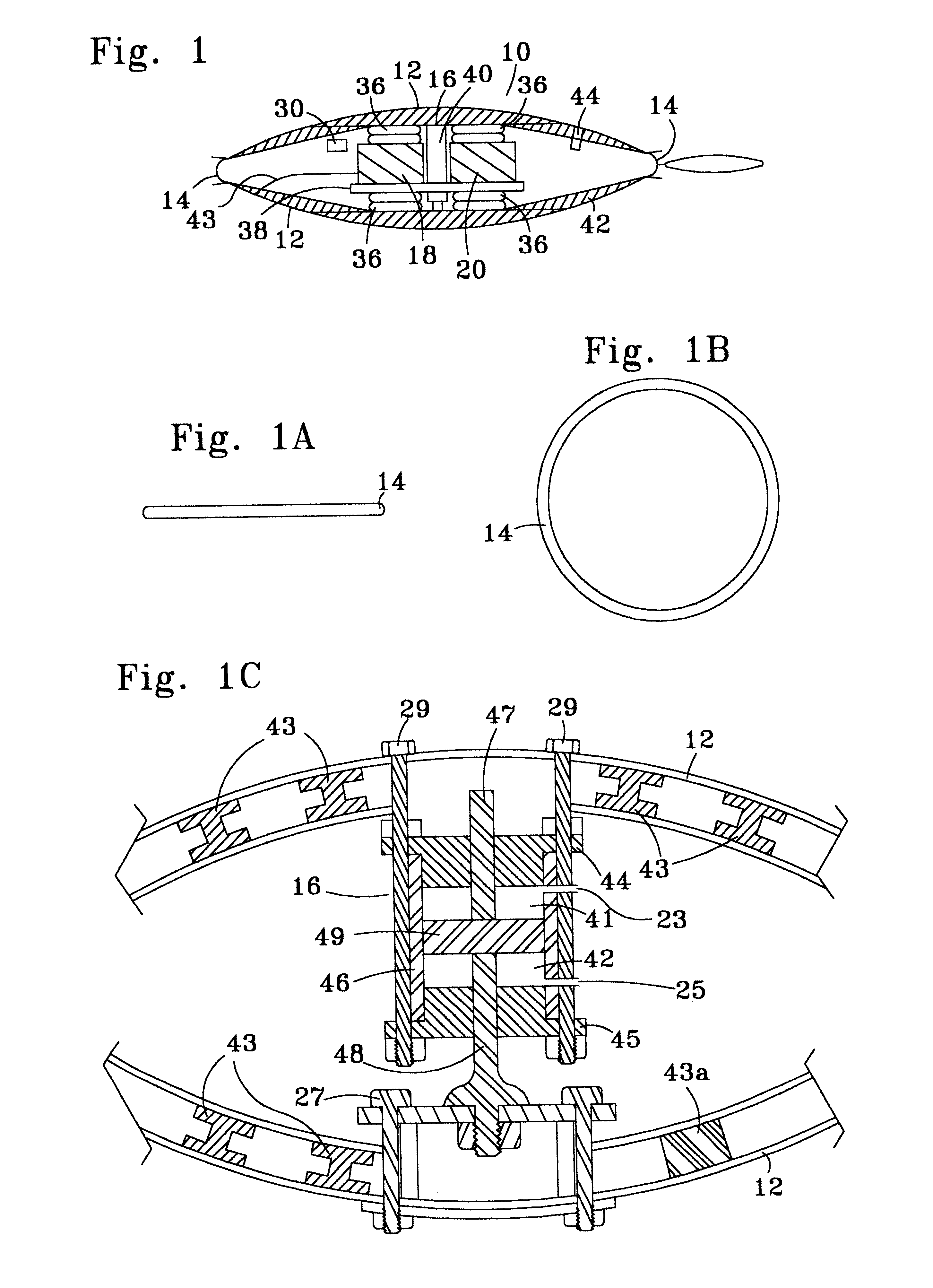
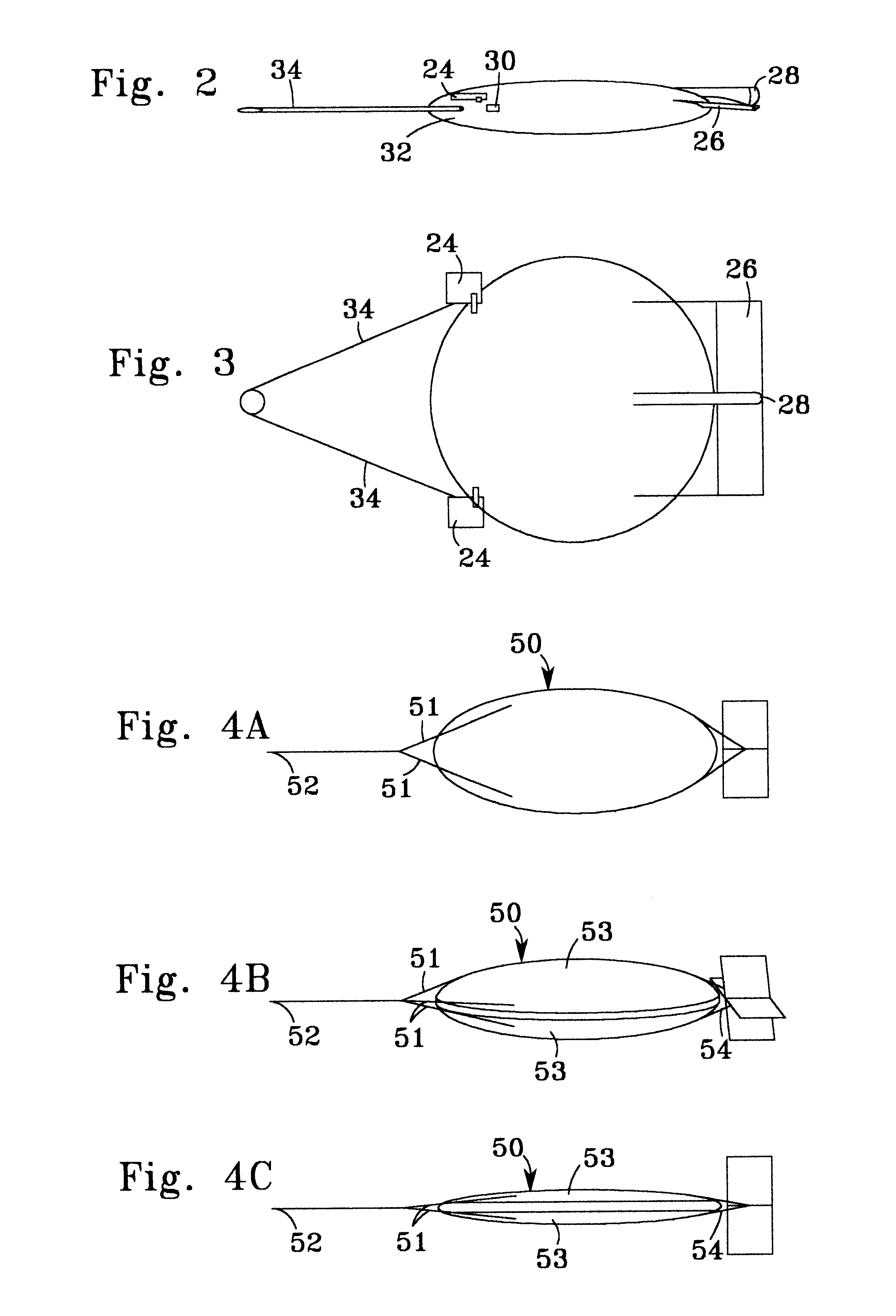
Marine vibrator
InactiveUS6230840B1Reduce hydrodynamic dragReducing hydrodynamic dragSeismic energy generationSound producing devicesCurve shapeEngineering
A marine vibrator has a hollow body formed of one shell or of two opposed shells defining an inner space therein with vibrator apparatus within the hollow body. At least one shell has a curved shape, and the shell can have a streamlined shape with relatively low hydrodynamic drag. Certain embodiments include one or more exterior control members to facilitate positioning of the vibrator in water. Other than their mating ends, when two shells are used the two shells may be different in shape and volume or they may be identical. In preferred two-shell embodiments, there is a flexible seal between and connecting the two opposed shells. In certain aspects the inner space is filled with gas. A vibrator apparatus in one aspect applies equal and opposite forces to the shells of a two-shell vibrator or to opposed sides of a single shell vibrator.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
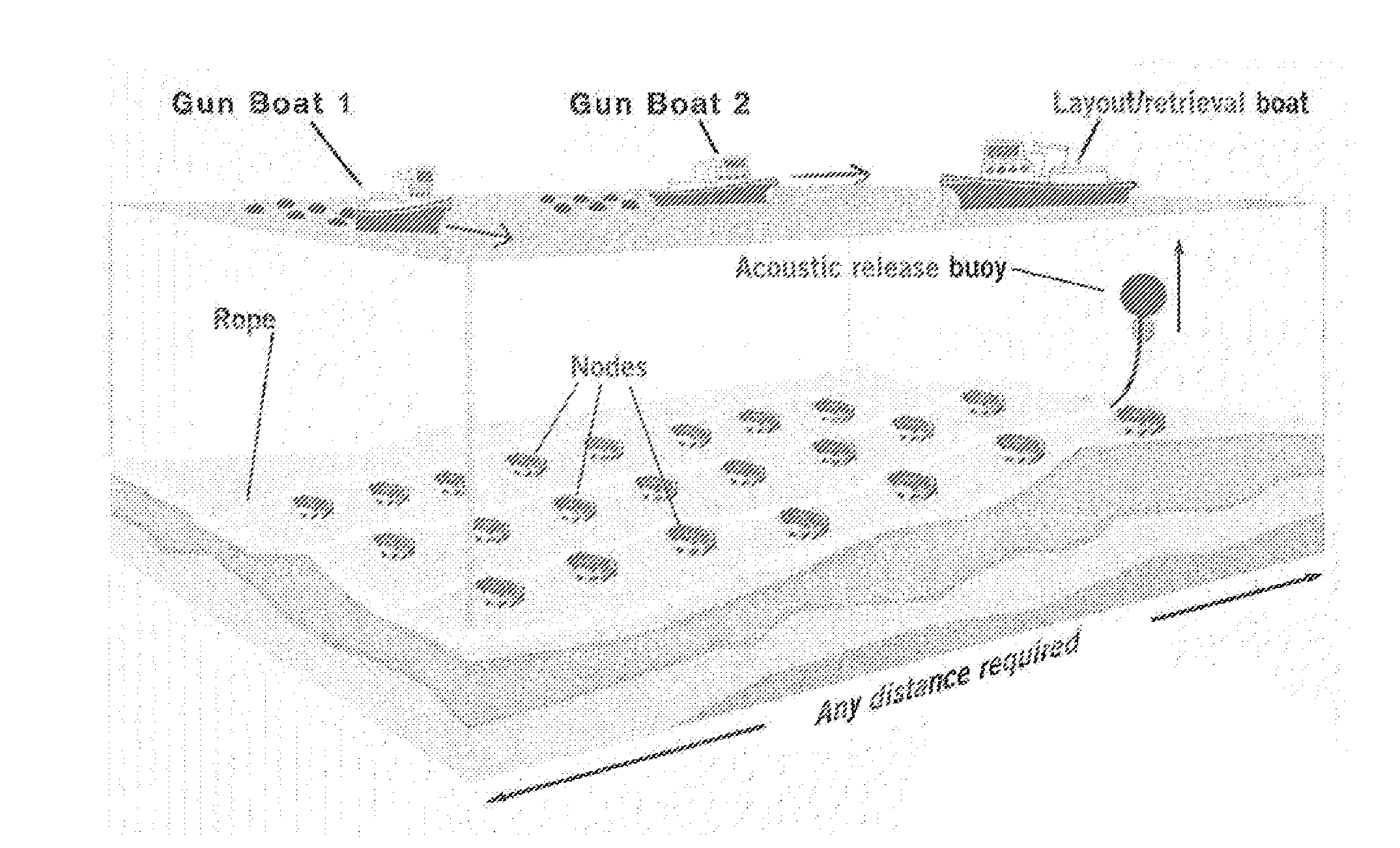
Simultaneous shooting nodal acquisition seismic survey methods
ActiveUS20140198607A1Avoid entrapmentMinimize the possibilitySeismic energy generationSeismology for water-covered areasNODALSeismic survey
A method of performing a seismic survey including: deploying nodal seismic sensors at positions in a survey region; activating a plurality of seismic sources; and using the nodal seismic sensors to record seismic signals generated in response to the activation of the plurality of signals.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
Marine seismic source
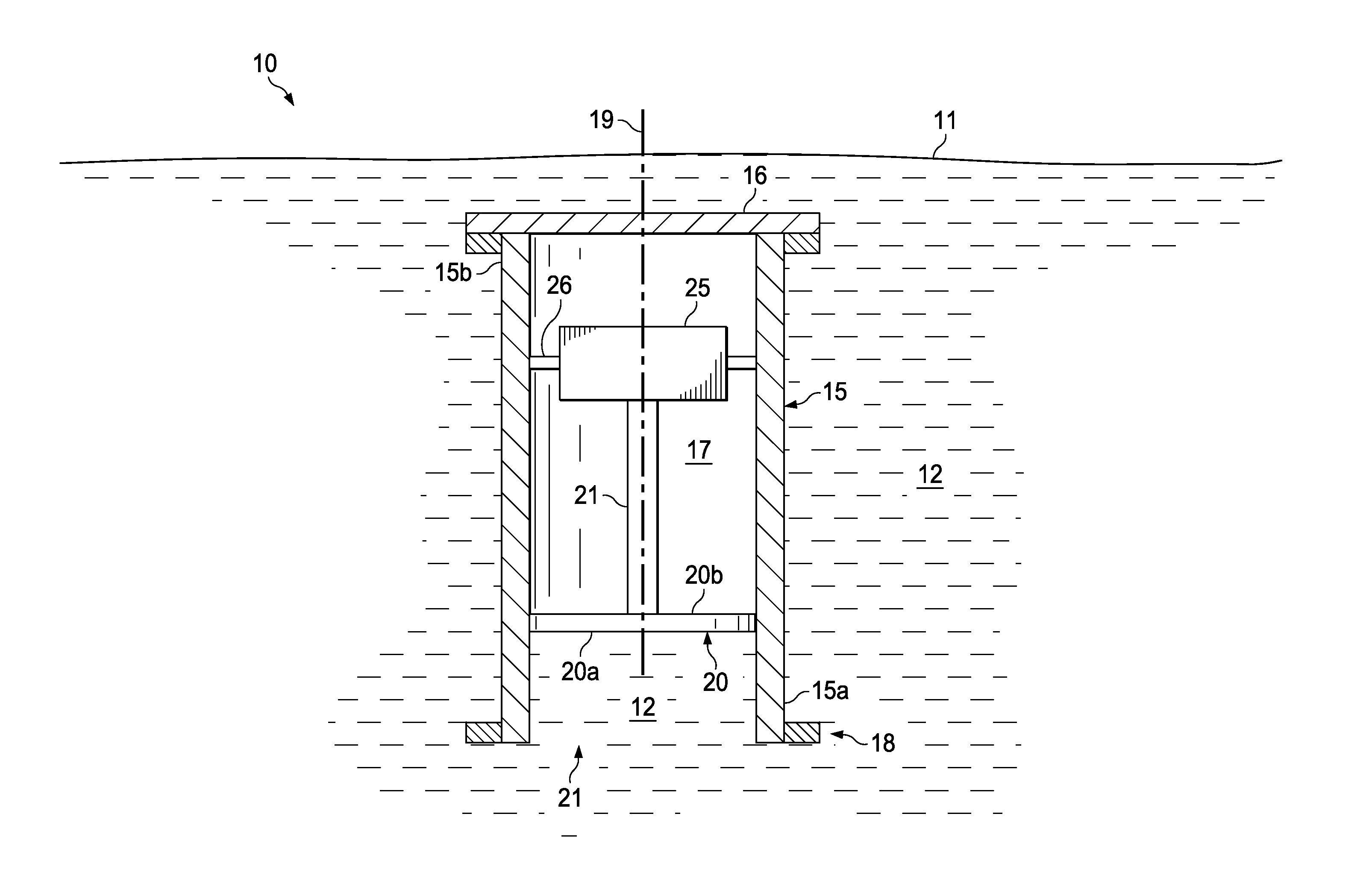
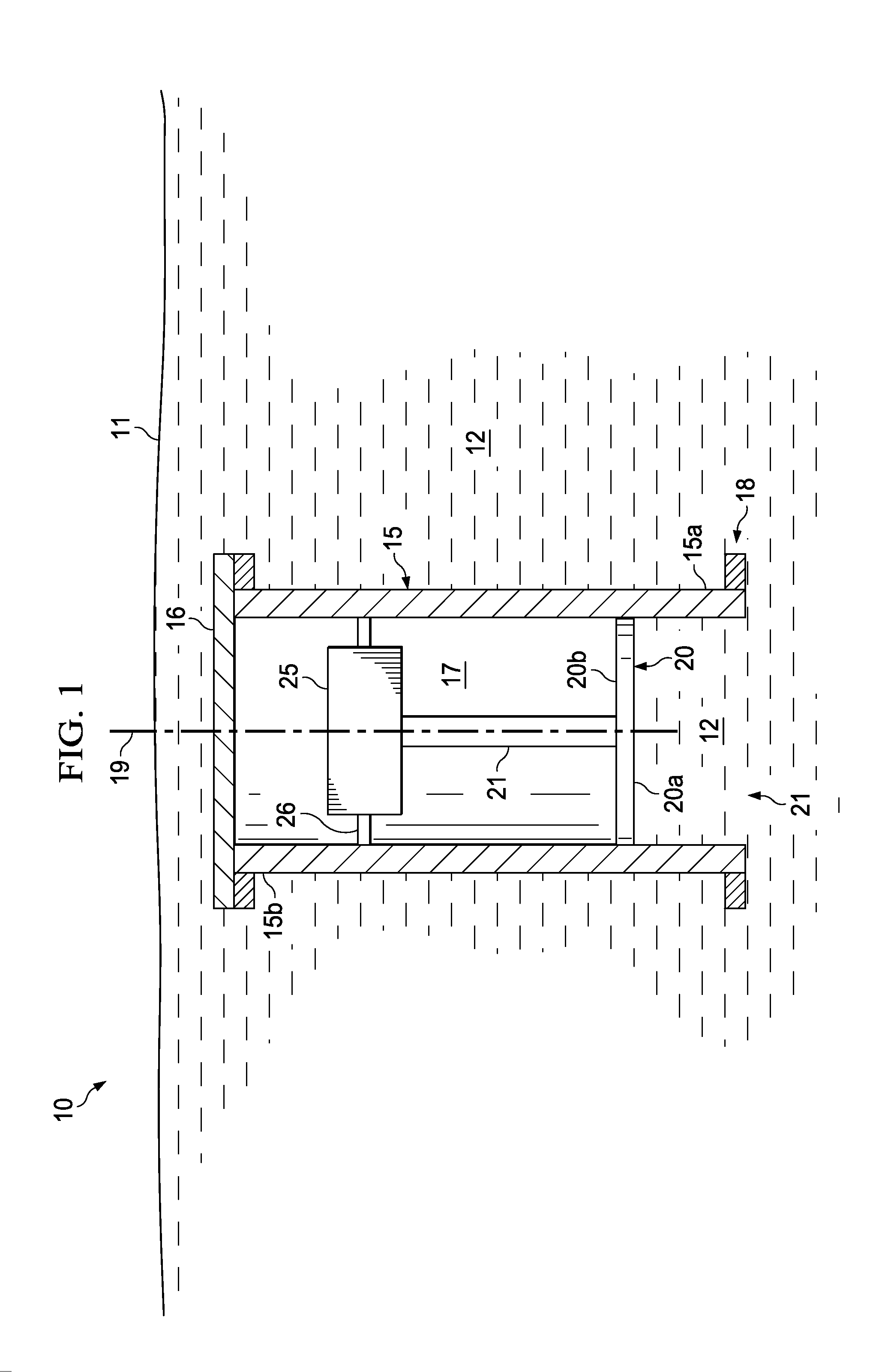
ActiveUS20110162906A1Seismic energy generationSeismology for water-covered areasReciprocating motionEngineering
A marine seismic source comprises a housing having a central axis, an open end, and a closed end opposite the open end. In addition, the seismic source includes a piston extending coaxially through the open end of the housing. The piston is adapted to axially reciprocate relative to the housing. Further, the piston has a first end distal the housing and a second end disposed within the housing.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Driving means for acoustic marine vibrator
InactiveUS7551518B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSeismic energy generationResonanceEngineering
A marine vibrator that in a particular embodiment includes a substantially elliptically shaped outer shell, a driver having a first and second end, at least one outer spring connected between the first end and the second end of the driver, and at least one inner spring connected between the first end and the second end of the driver. One or more masses are attached to the inner spring. At least one transmission element connects the outer spring and the outer shell. The outer and inner springs and the masses attached to the inner spring are selected to generate a first resonance frequency and a second resonance within the frequency range between 1 Hz and 300 Hz.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Method and device for the non-invasive assessement of bones
ActiveUS20050004457A1Difficult to observeSmall sizeMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidBone densityTransducer
A method for the in vivo non-invasive characterization of the material and architectural properties of a bone in which an ultrasonic wave is introduced into a bone in such way as to produce one or more guided wave modes within the bone, and the signals emerging from the bone are stored and analyzed to determine the propagation characteristics of the guided wave / s. These measured guided wave propagation characteristics are then processed to obtain estimates of desired bone properties such as cortical thickness, bone density and bone elastic constants. The invention also includes an unltrasound arrangement with movable transducers.
Owner:OSCARE MEDICAL
Seismic sensor transfer device
ActiveUS7632043B2Pipe laying and repairVehicle with removable loadingMarine engineeringRemotely operated vehicle
A method and apparatus for storing, transporting, and transferring one or more sensor devices is described. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a transfer device having a frame, and a movable platform coupled to the frame. A mesh material may be coupled to the frame and surround at least one side of the movable platform and a mating interface is formed in a side of the frame that is adapted to couple with a remotely operated vehicle in an underwater location.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
Wireless electronic booster, and methods of blasting
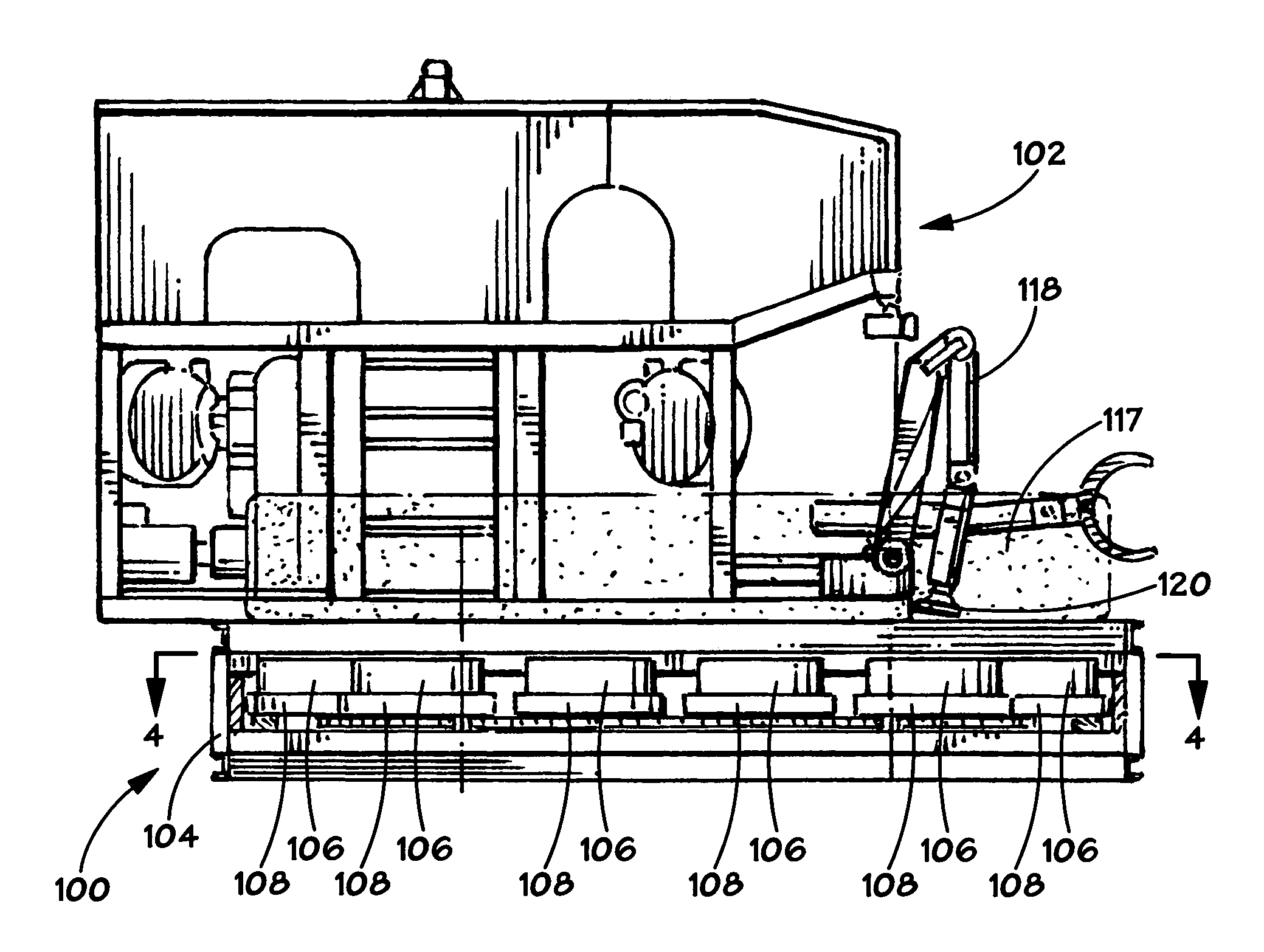
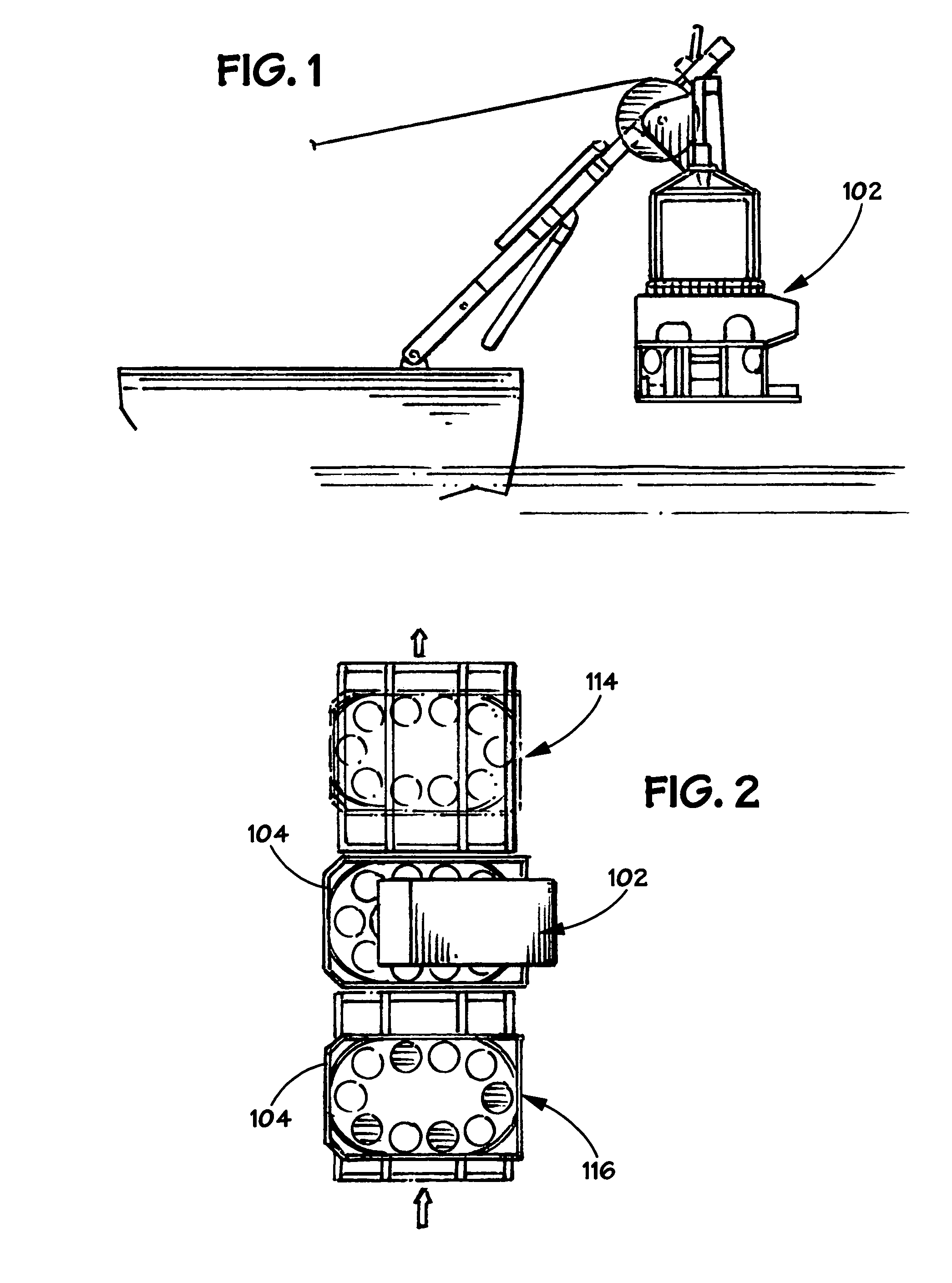
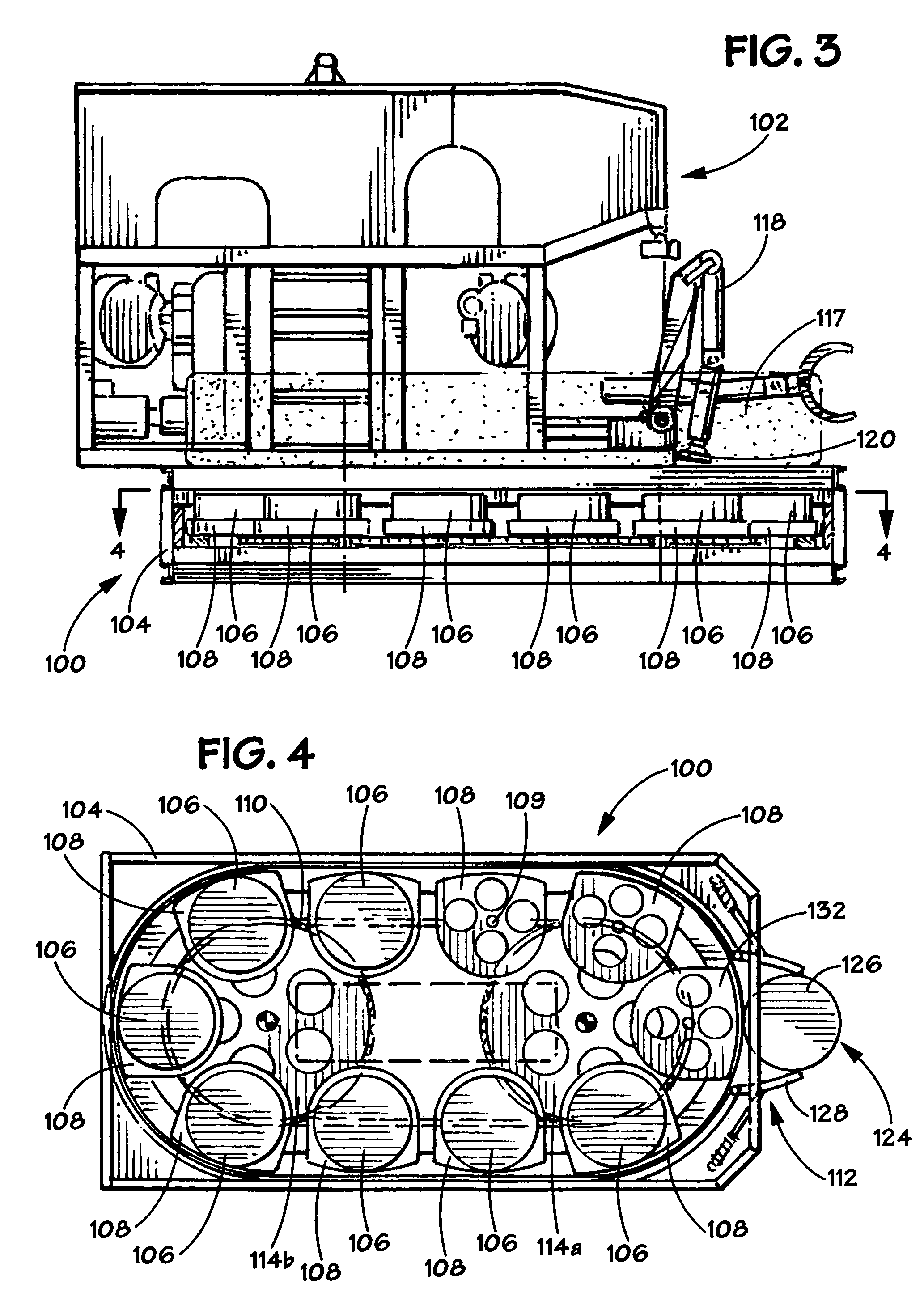
Disclosed herein are boosters that include components sufficient for wireless communications with an associated blasting machine. In selected aspects, there are disclosed wireless electronic boosters that are self-contained and robust. Such boosters are especially suited for underground mining operations, optionally employing automated placement of boosters at a blast site.
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
Acquisition method and device for seismic exploration of a geologic formation by permanent receivers set on the sea bottom
InactiveUS20050098377A1Increases in lifetimeImprove reliabilitySeismic energy generationSeismic signal receiversGeophoneHydrophone
A method and device for seismic exploration of a subsea geologic formation by pickups set on the sea bottom and intermittently connectable to active data acquisition stations (11) brought nearby. Permanent passive reception stations (1) comprising a heavy pedestal provided with housings for seismic pickups (geophones (6), hydrophone (7)) which receive acoustic or seismic signals from the underlying formation are arranged at the bottom of the water body. When collection sessions for the signals received by the pickups are scheduled, mobile active acquisition stations (11) connected to permanent passive reception stations (1) are positioned at the bottom of the water body. The signals picked up are then recorded, for the time required to carry out at least one session of acquisition and recording of the acoustic or seismic signals received by the passive stations in response to the emission of seismic waves by one or more seismic sources. The mobile active acquisition stations (11) are thereafter recovered at the surface and the records acquired by each one are transferred to a central collection laboratory.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
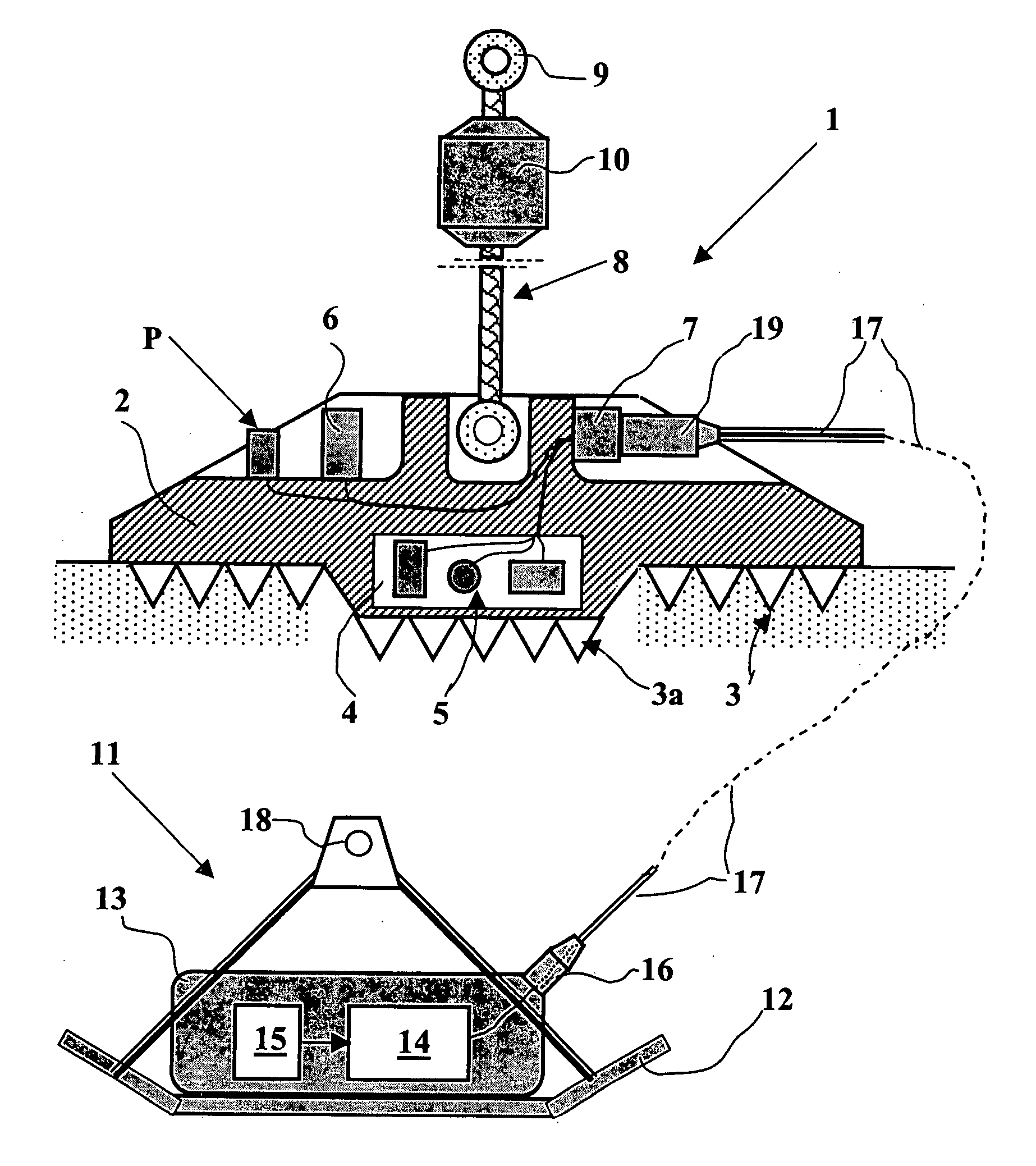
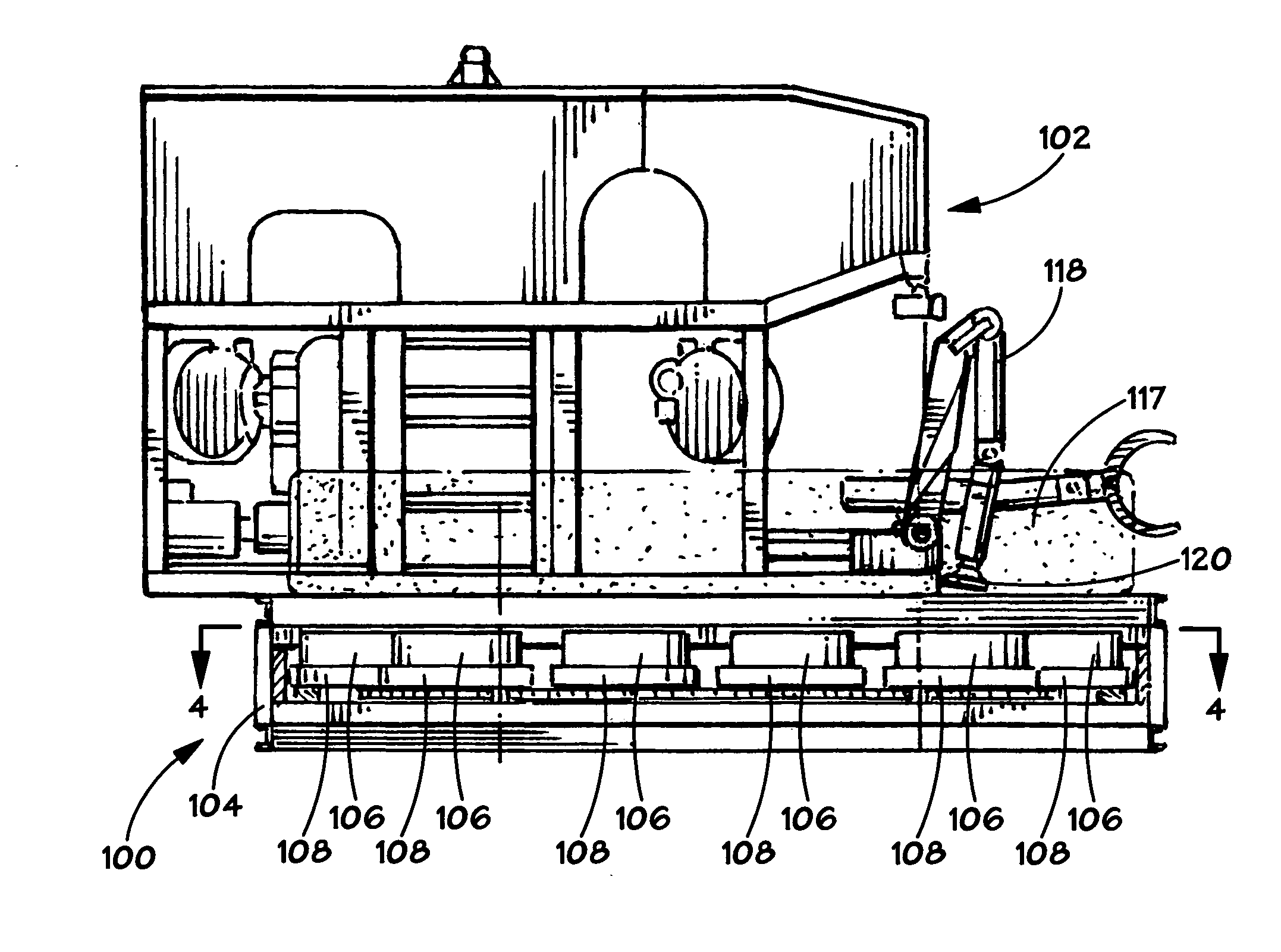
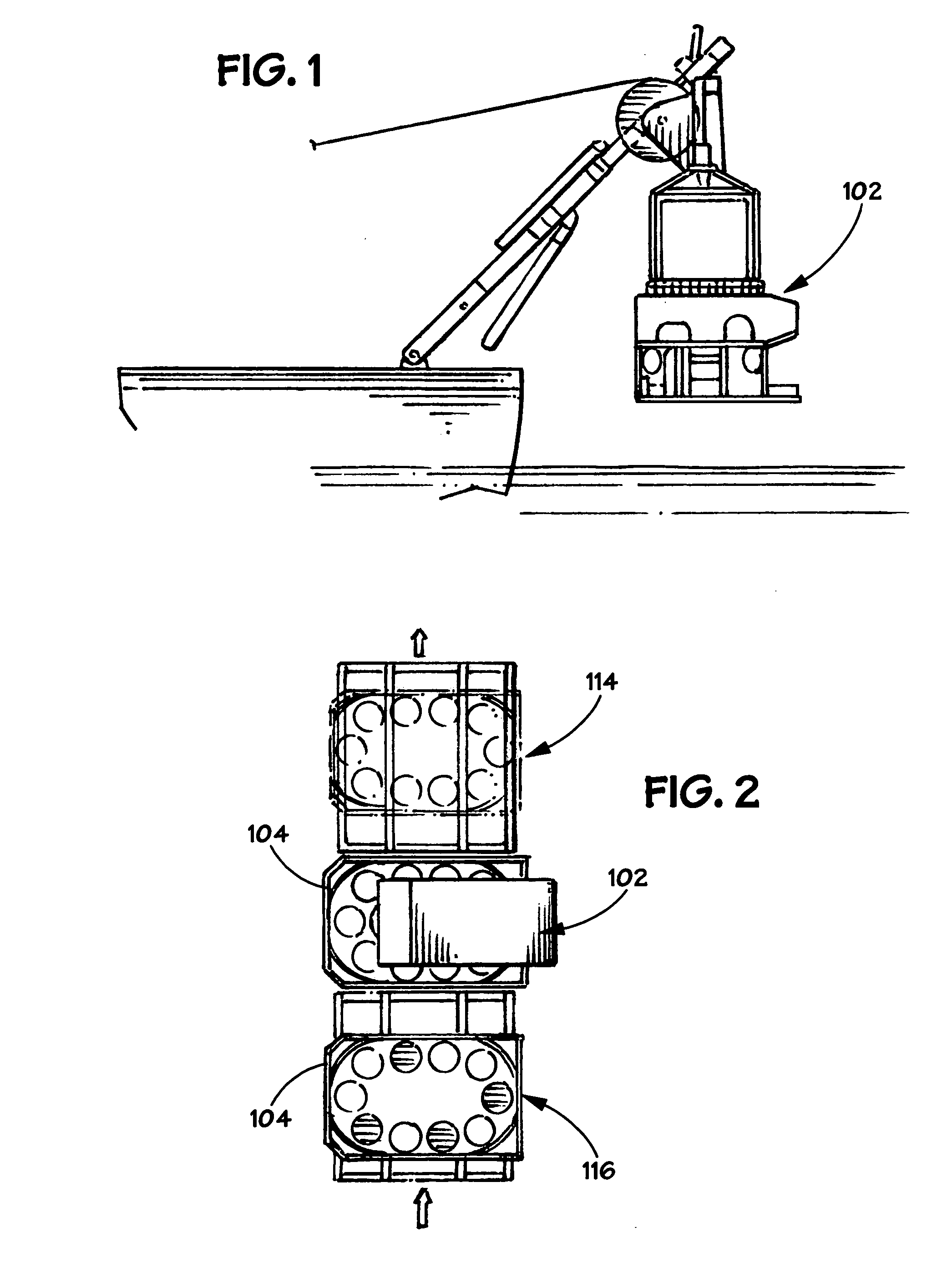
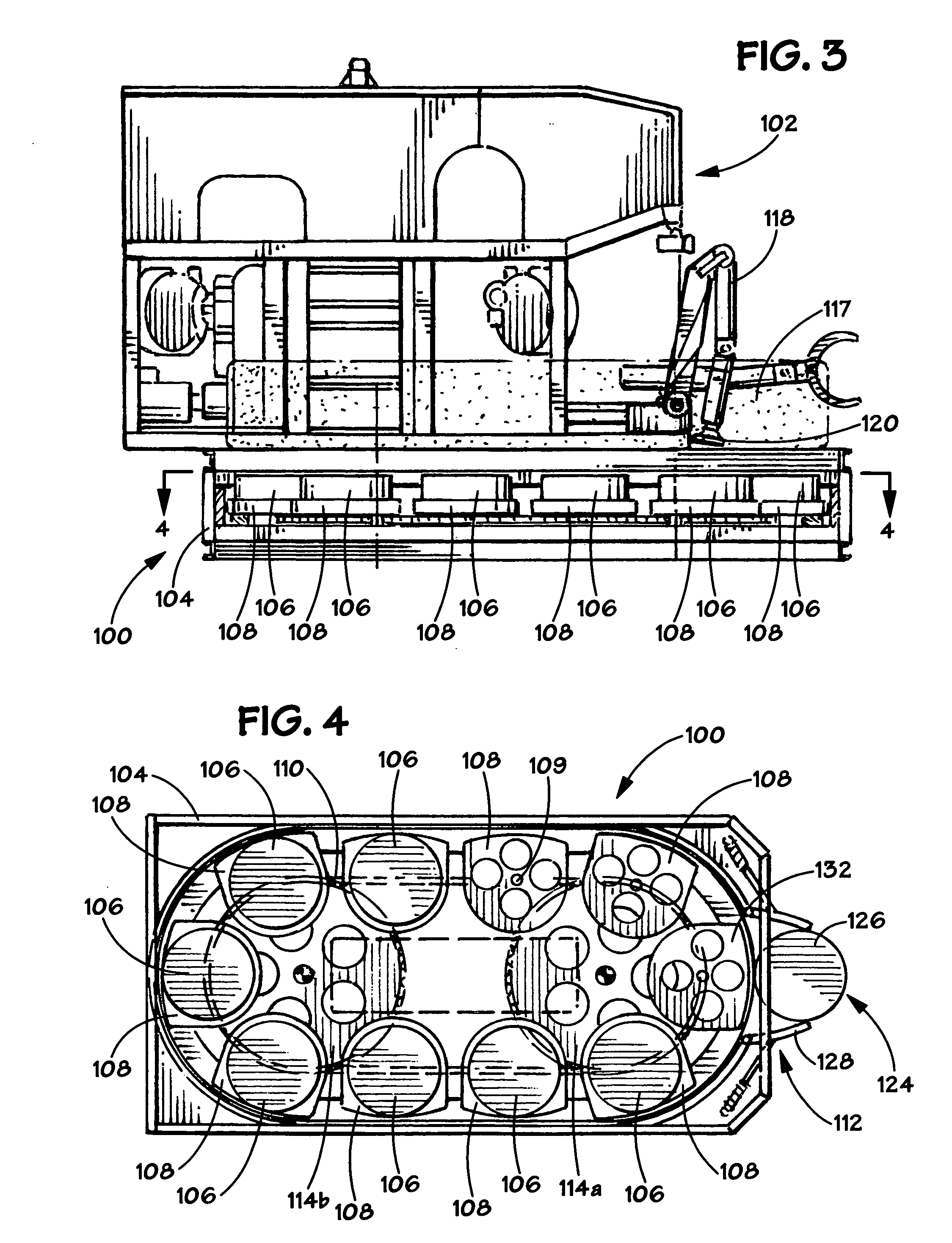
Method and apparatus for installing a sensor array
InactiveUS7210556B2Sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSeismic energy generationSensor arrayActuator
An apparatus and method is provided for transporting, installing, retrieving, and replacing a sensor array of individual sensor pods at a geographically remote location, such as on the sea floor. The apparatus consists of a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), a carousel attached to the ROV, a pod ejector mechanism attached to the carousel, and a manipulator with a manipulator end effector attached to the ROV. The carousel contains a plurality of sensor pod holders, where each sensor pod holder is capable of holding a sensor pod. The pod ejector mechanism is capable of discharging a fresh sensor pod, while the manipulator end effector is capable of lifting a depleted sensor pod and placing the depleted sensor pod in an empty sensor pod holder in the carousel.
Owner:SAIPEM AMERICA
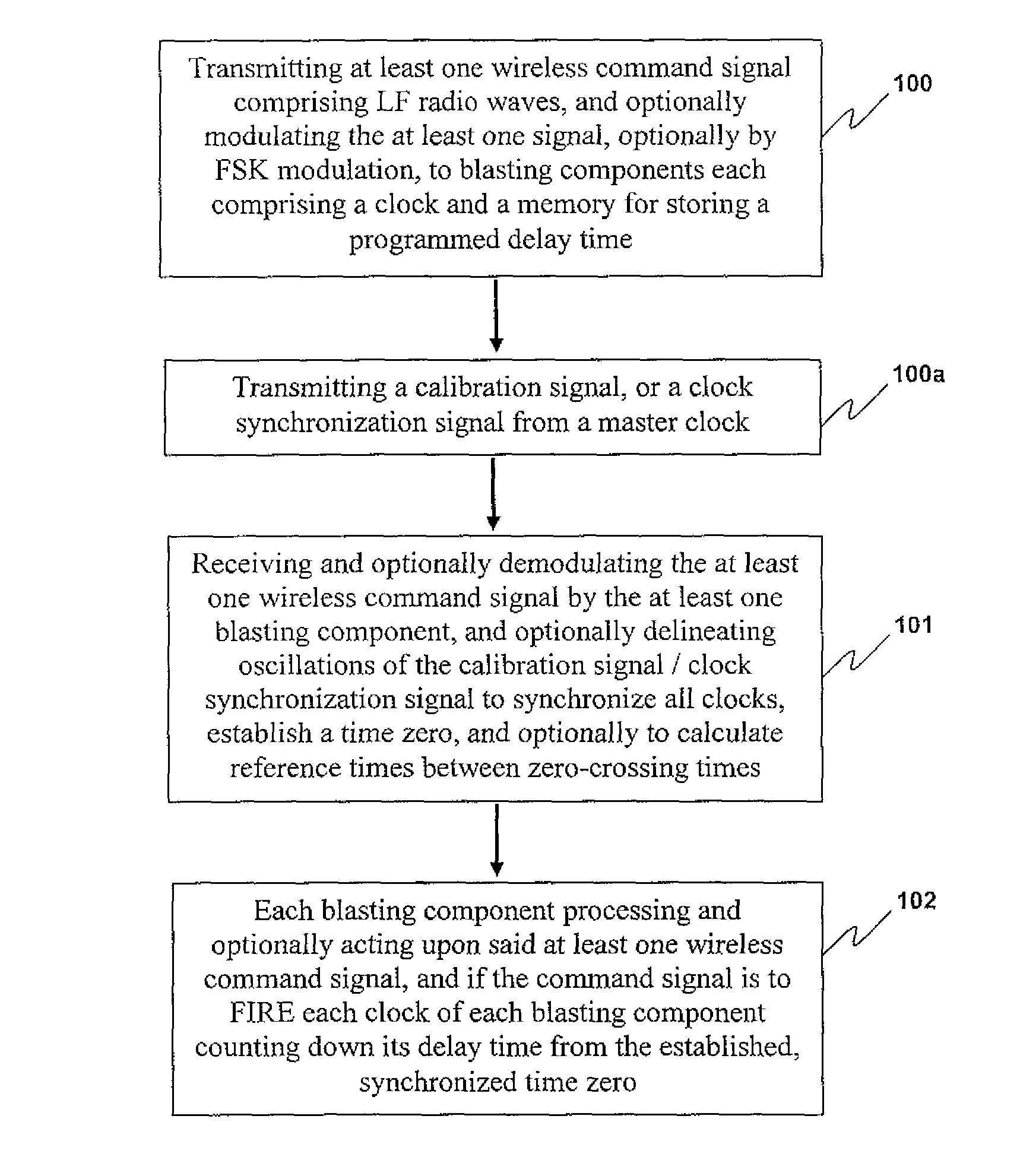
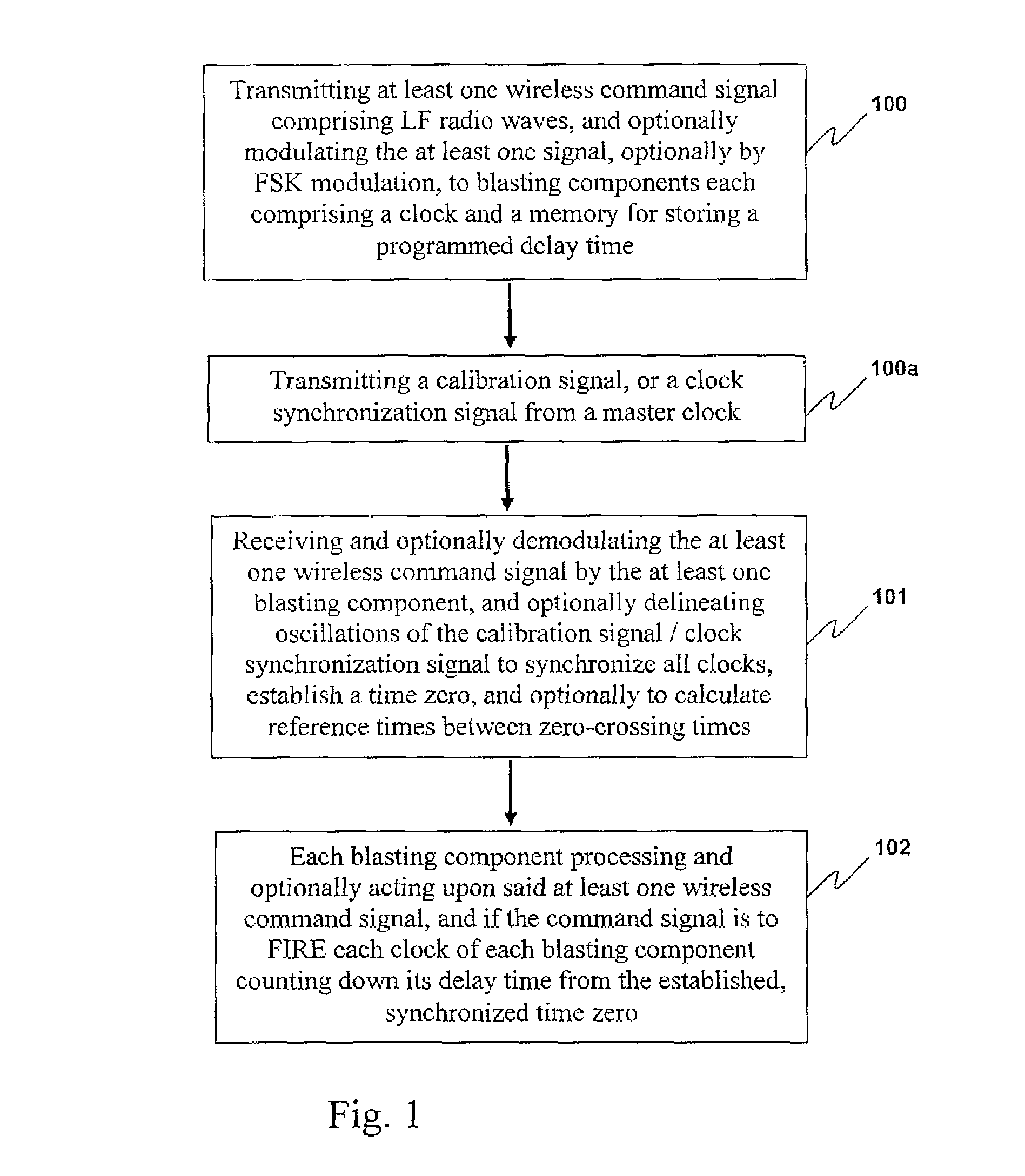
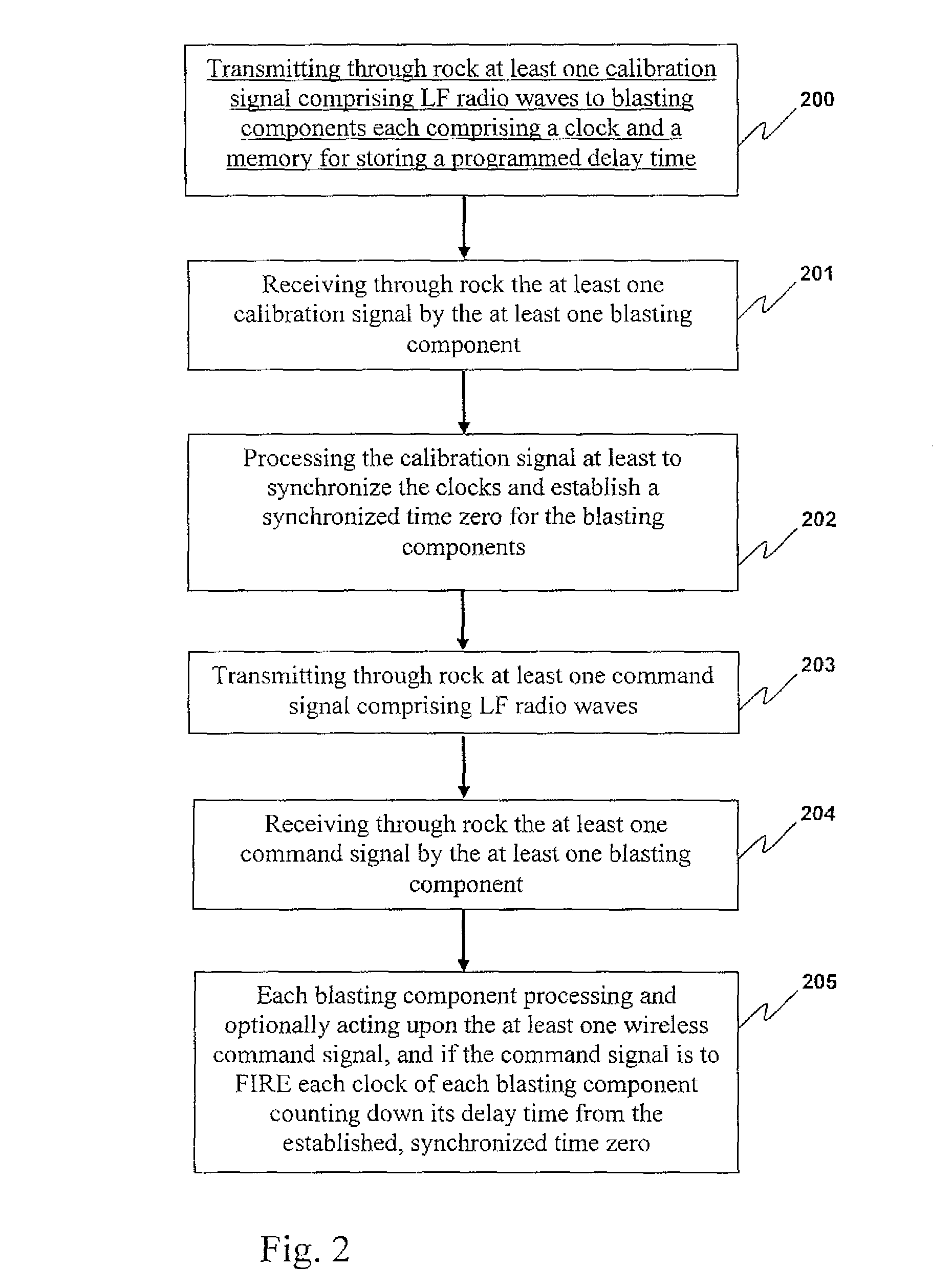
Methods of controlling components of blasting apparatuses, blasting apparatuses, and components thereof
ActiveUS8395878B2Make-and-break ignitionIncandescent ignitionElectrical and Electronics engineeringWireless signal
Disclosed herein are methods for communicating wireless signals between components of a blasting apparatus, with the intention of conducting a blasting event. In preferred embodiments, the methods are particularly suited to through -rock transmission of wireless command signals, and optionally wireless calibration or synchronization signals, thereby to achieve timed actuation of explosive charges positioned below ground under the control of one or more blasting machines located at or above a surface of the ground, with a high degree of accuracy. Further disclosed are blasting apparatuses and components thereof suitable for use, for example, in conducting the methods of the invention.
Owner:ORICA EXPLOSIVES TECH PTY LTD
Control system for marine vibrators and seismic acquisition system using such control system
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Seismic vibratory acquisition method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060018192A1Increase profitSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationSeismic surveyLow frequency band
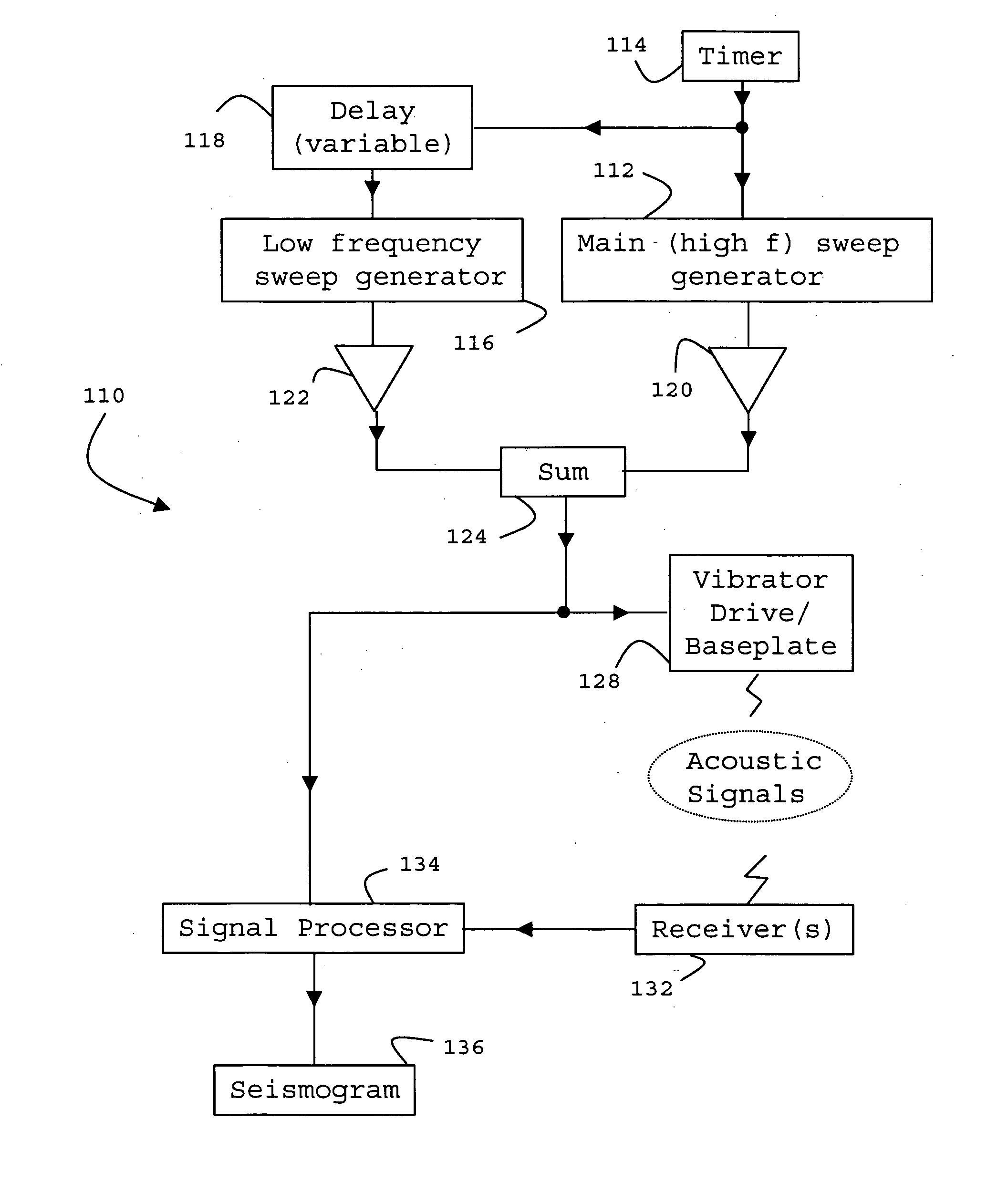
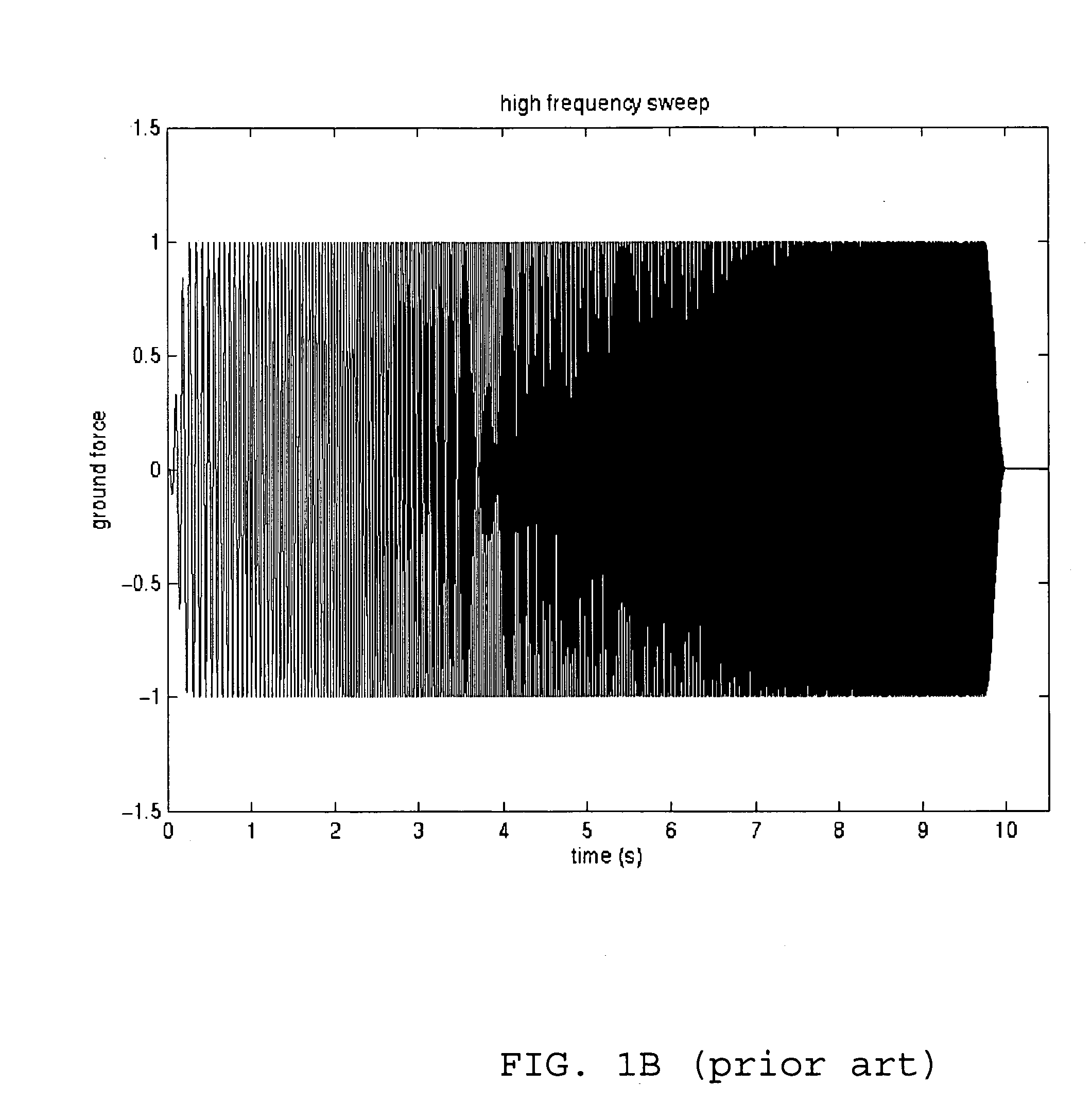
A method and related apparatus are described for generating acoustic signals for use in a vibratory seismic survey, including the step of combining into a drive signal a high frequency sweep signal, which sweeps upwardly through a high frequency band during a first time interval, and a low frequency sweep signal which is of lower amplitude than the high frequency sweep signal and which sweeps upwardly through a low frequency band during a second time interval, wherein the second time interval starts during the first time interval but after the beginning thereof; and applying the drive signal to a mechanical drive system for a vibratable element. The method improves the utilization of a single vibratory source.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
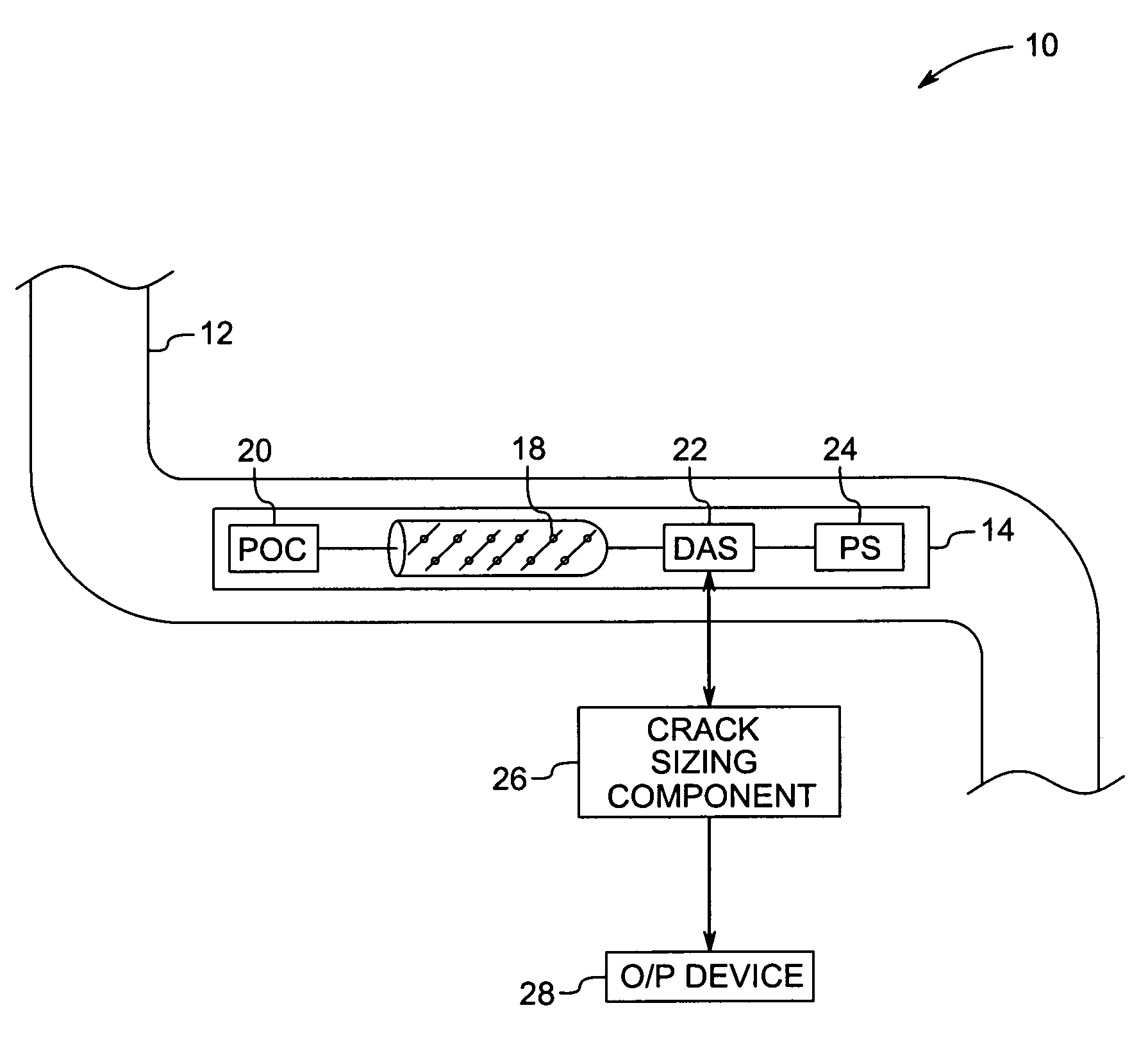
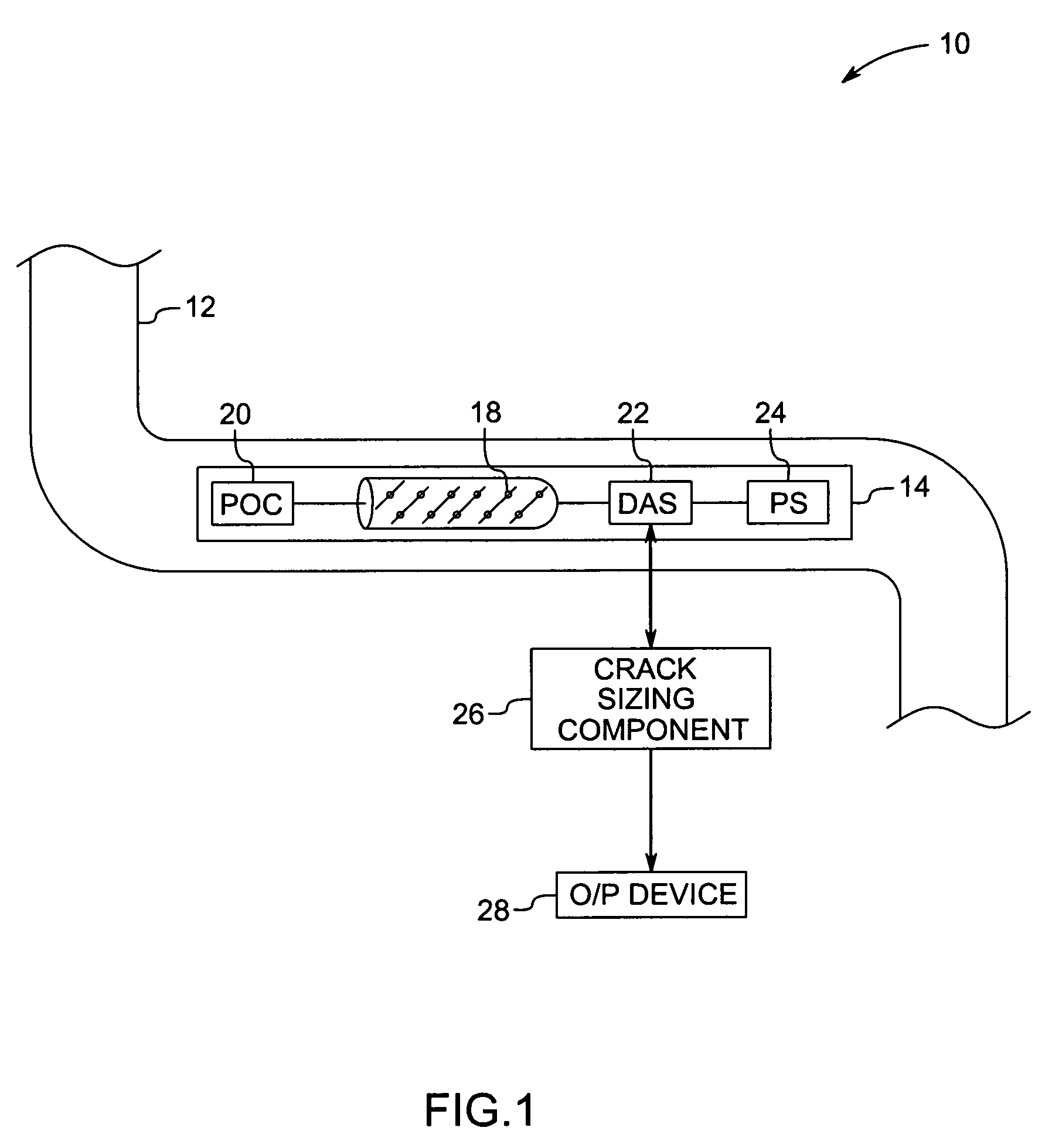
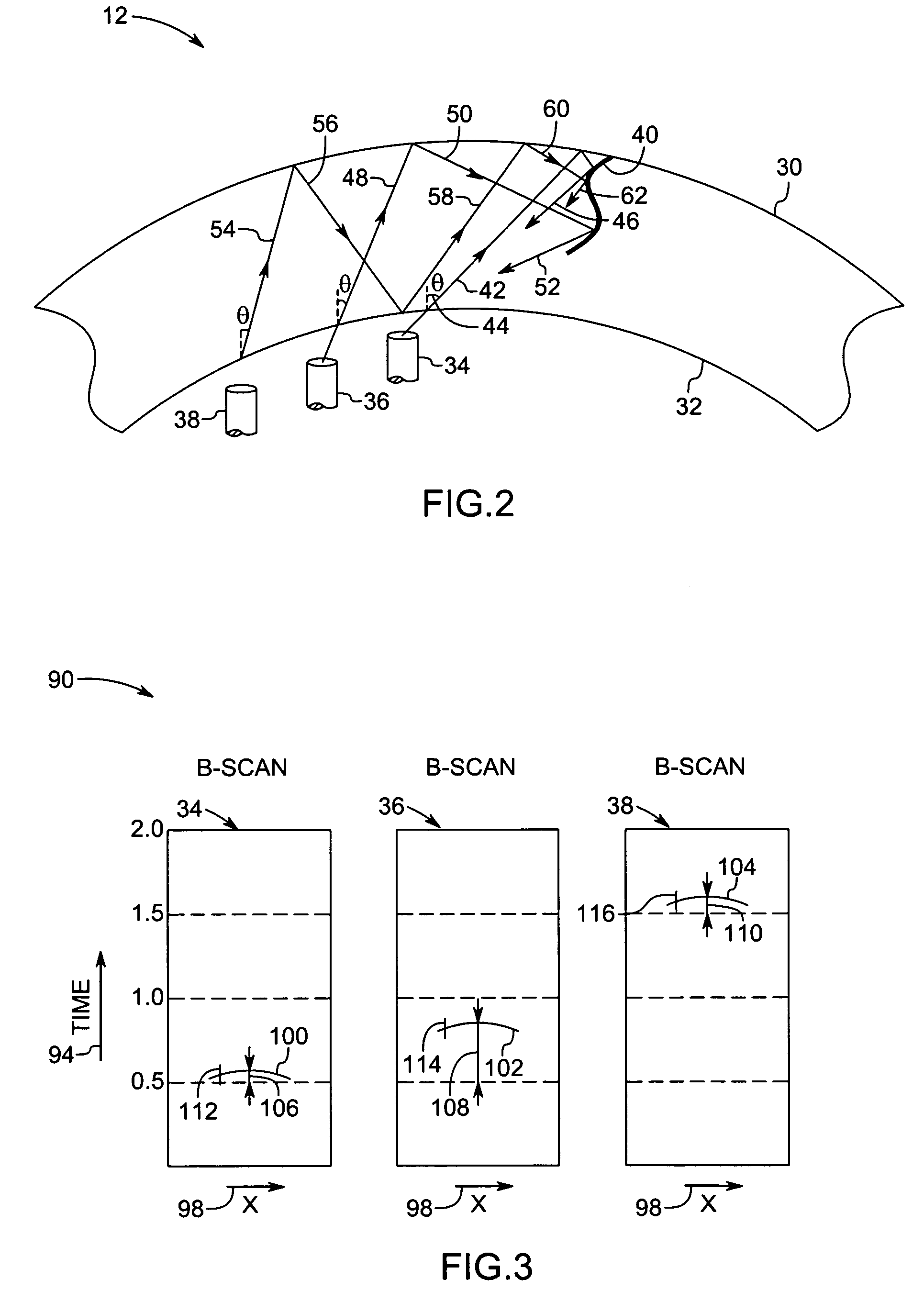
Method and system for inspecting objects using ultrasound scan data
ActiveUS7299697B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationAmplitude response
A method and apparatus for estimating a depth of a crack from ultrasound scan data are provided. The method includes mapping multiple amplitude responses from the ultrasound scan data, each mapped amplitude response being representative of a signal from one of the sensors. The method further includes locating multiple linear responses among the mapped amplitude responses, each linear response being an indicator of a reflected signal from the crack. One or more sensor that corresponds to the linear responses from a given crack is identified. The depth of the crack is estimated using data from the identified sensors.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
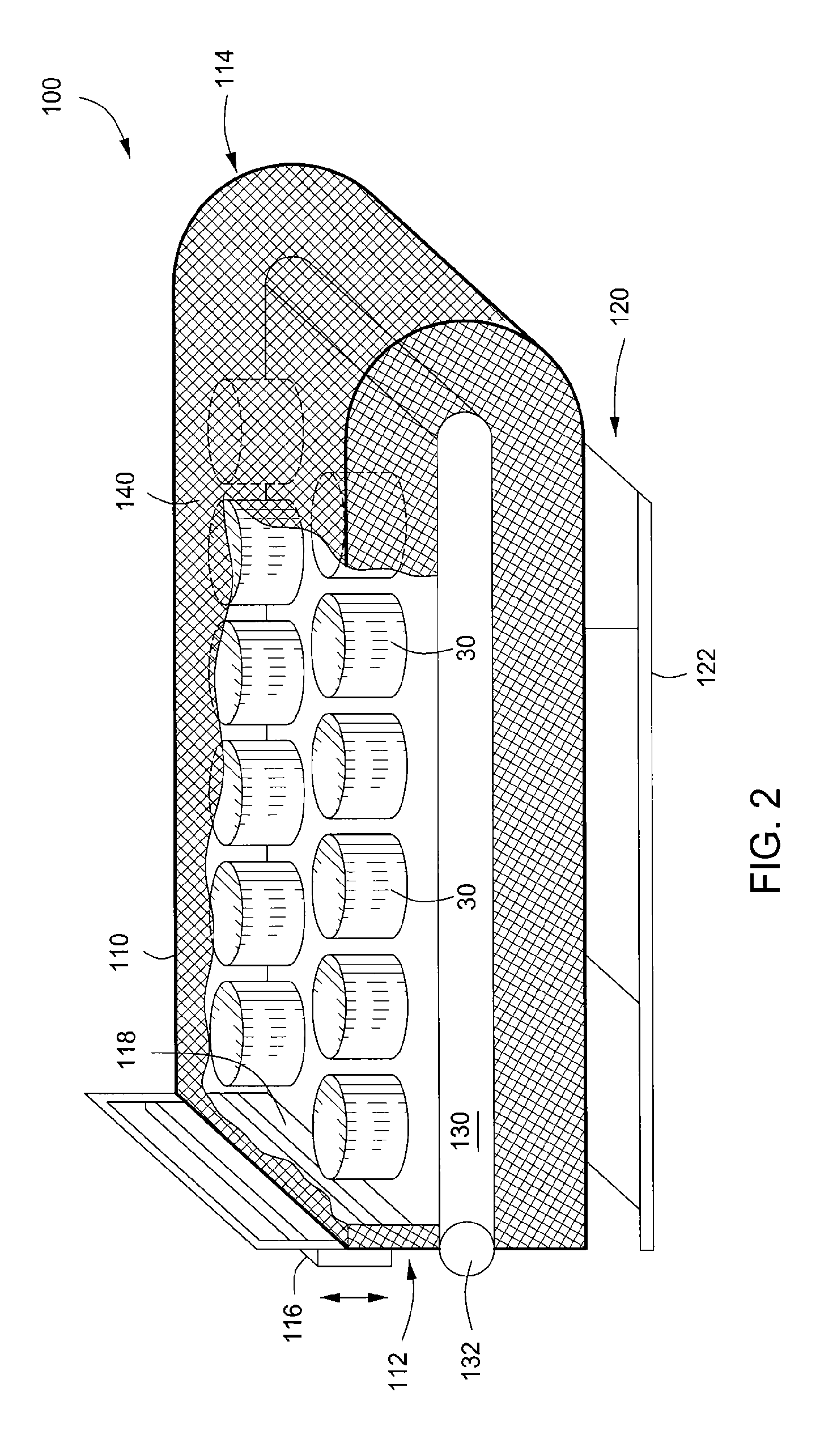
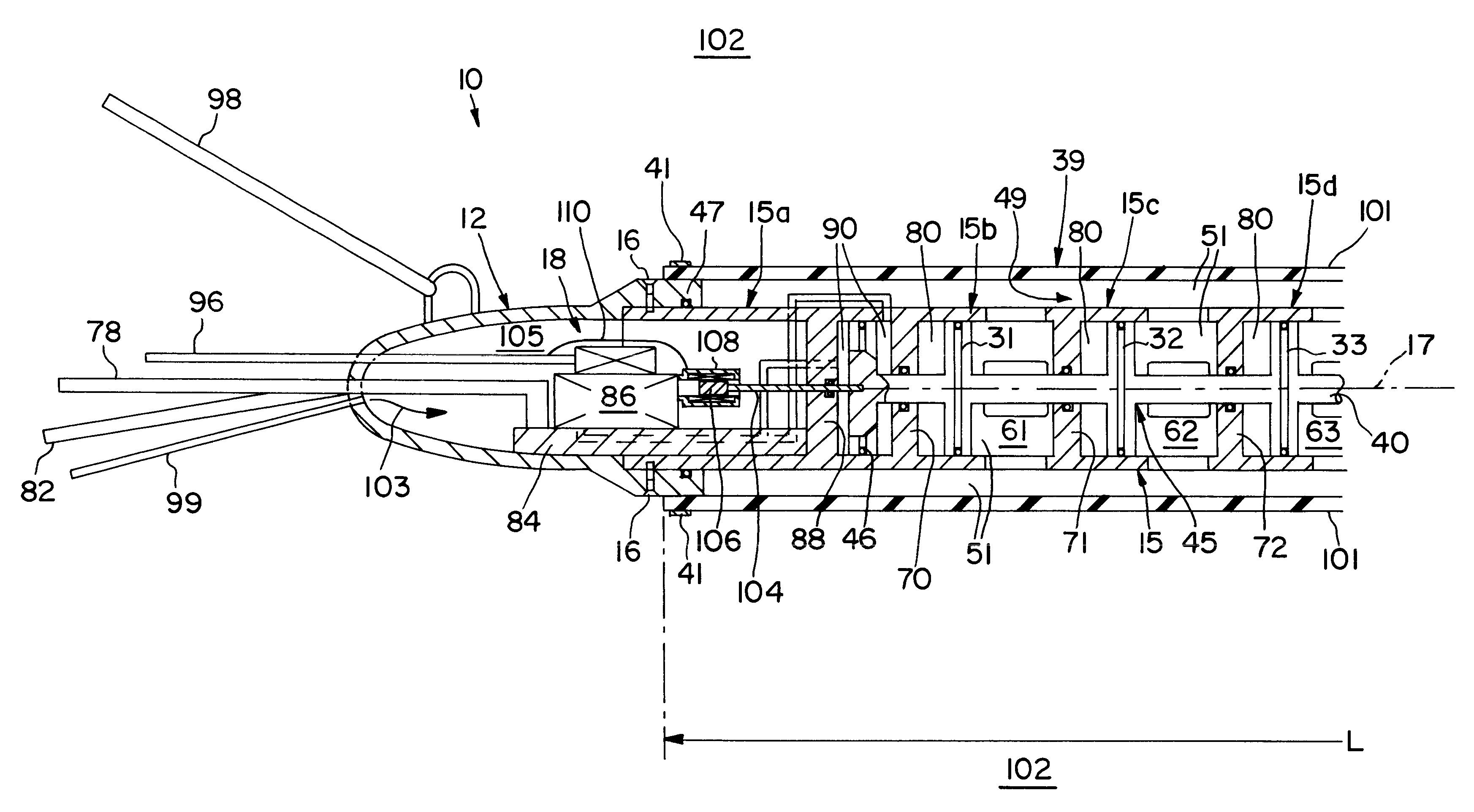
Streamlined, readily towable marine seismic energy source for creating intense swept-frequency and pulse-coded signals in a body of water
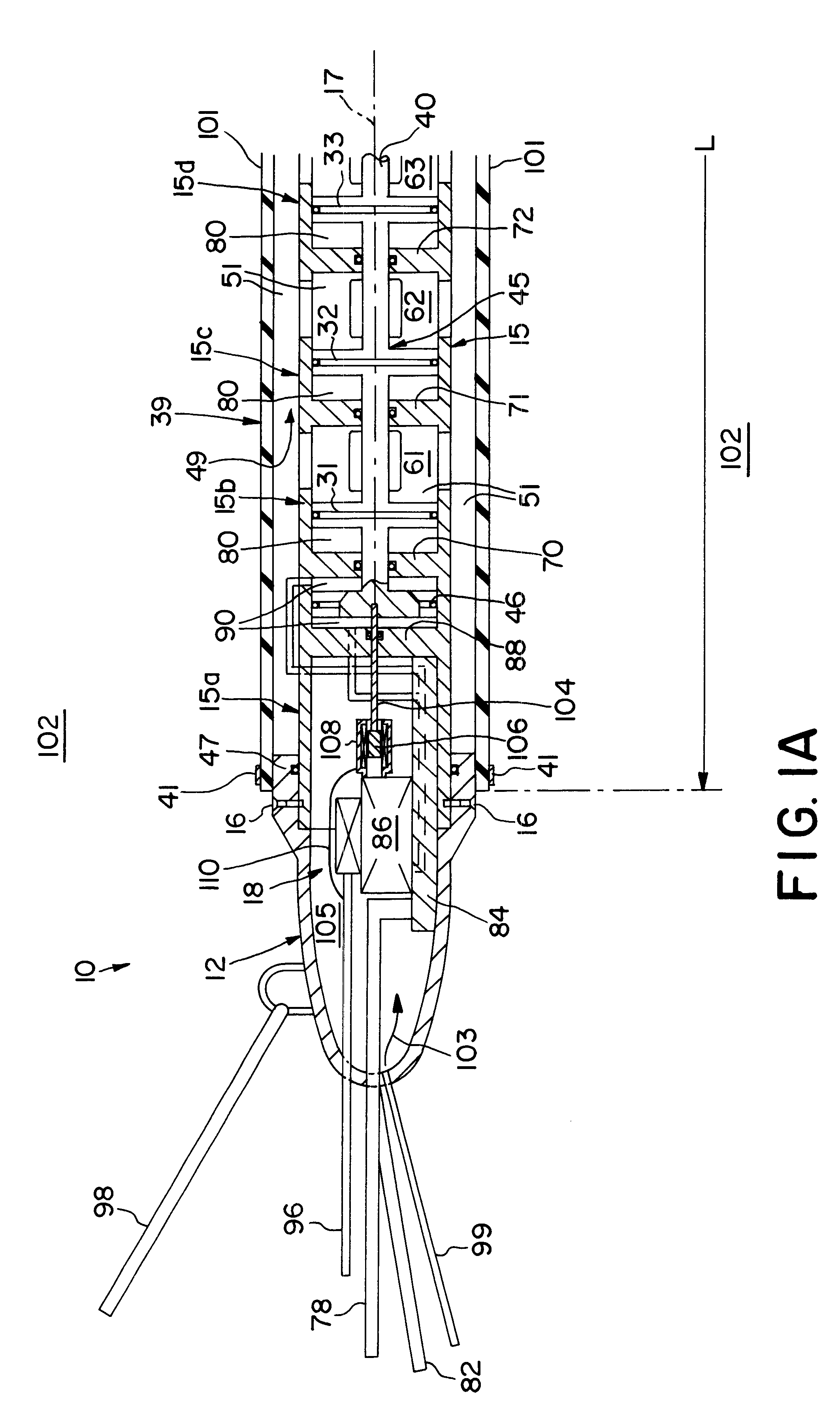
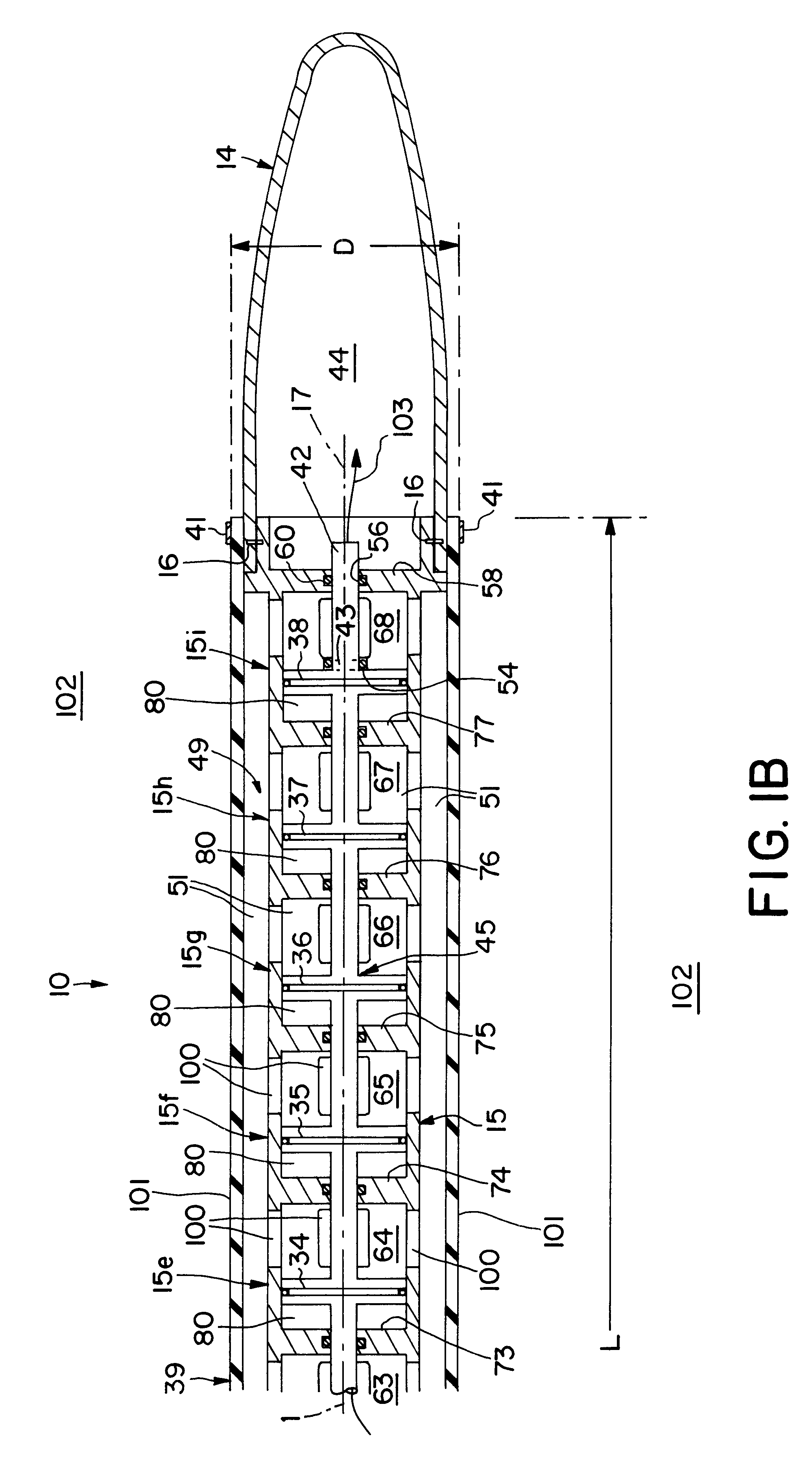
InactiveUS6464035B1Easy to manufactureIncrease surface areaSeismic energy generationSeismology for water-covered areasAmbient waterConfiguration design
Streamlined, towable, marine seismic energy vibrator for creating intense swept-frequency and pulse-coded seismic signals in a body of water has a sleek, fish-like configuration designed for towing with minimum drag. The vibrator has a streamlined hollow towing head and a streamlined hollow tail head mounted onto front and rear of a long cylindrical tubular wall which is modular, comprising cylinder sections joined in end-to-end axial alignment. Within this long tubular cylinder wall is an axially vibratable multi-piston assembly having a plurality of pistons on a long piston rod. One piston is positioned in each of the cylinder chambers. These chambers hive multiple ports opening out through the long cylindrical wall. An elongated circular cylindrical elastomeric bladder forms a water-filled bladder chamber encircling the wall. An actuator piston is vibrated by a remotely controllably hydraulic circuit, thereby vibrating the multi-piston assembly for vibrating water out and in through multiple ports communicating with the water-filled bladder chamber for vibrating the exterior of the bladder shown having diameter "D" of 18 inches and length "L" of 118.5 inches, providing a 6,700 square inch vibration area contacting the ambient water. A multi-piston position sensor enables synchronization of the vibrator with companion sources being towed. An axial passage in the long piston rod feeds low-pressure compressed air into the cylinder chambers forming air cushions behind the pistons vibrating water in these cylinder chambers.
Owner:BOLT TECH CORP
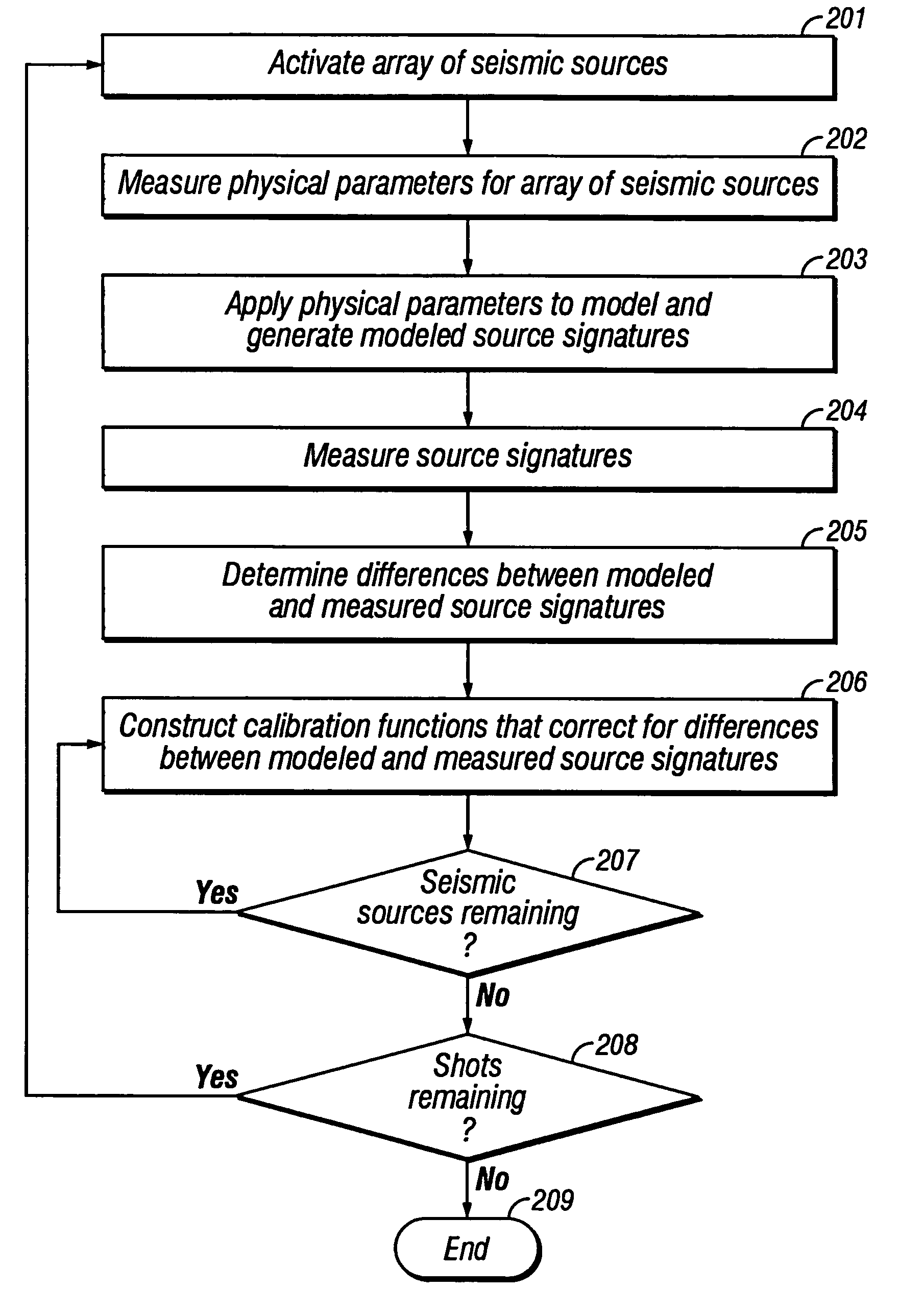
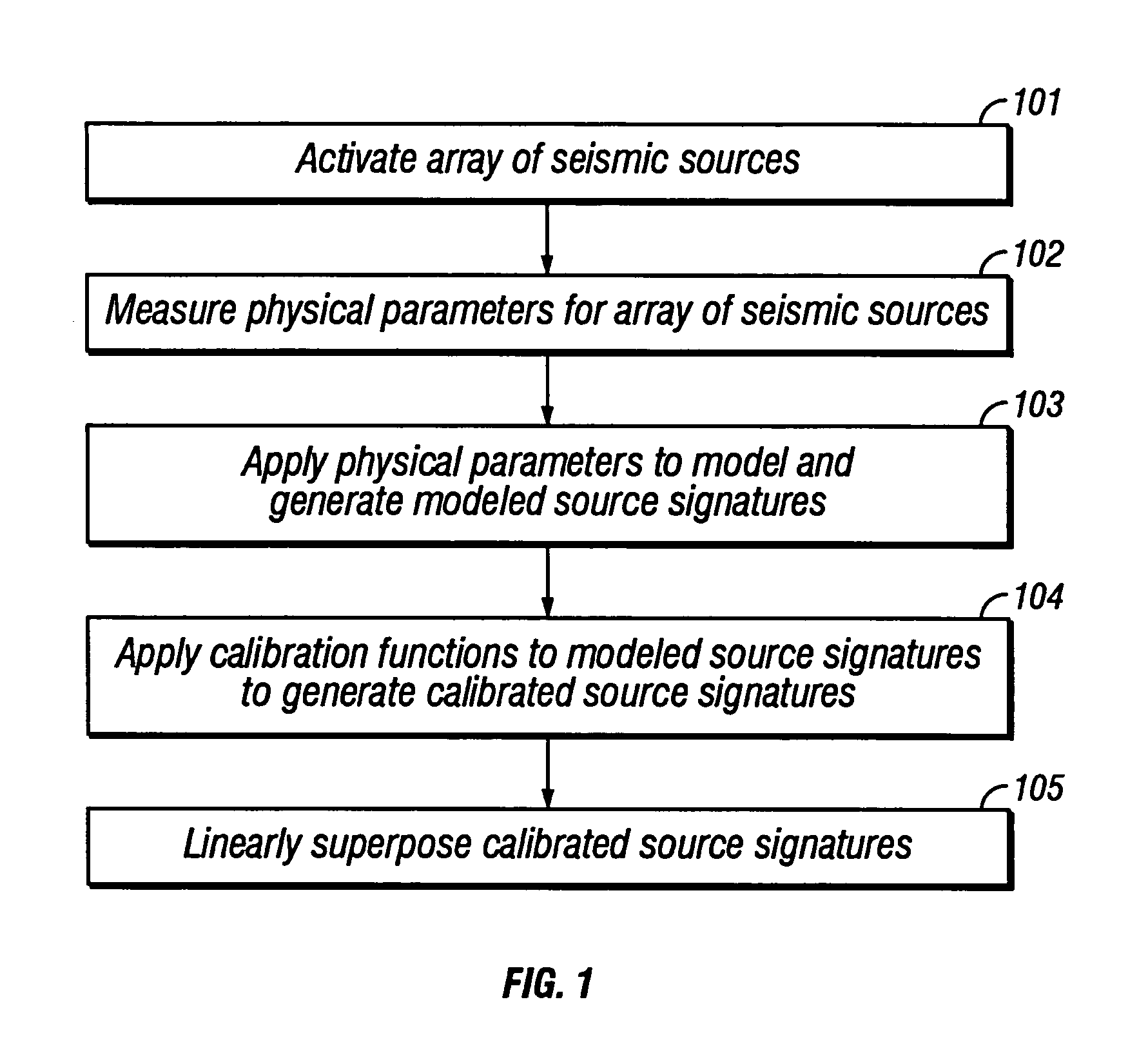
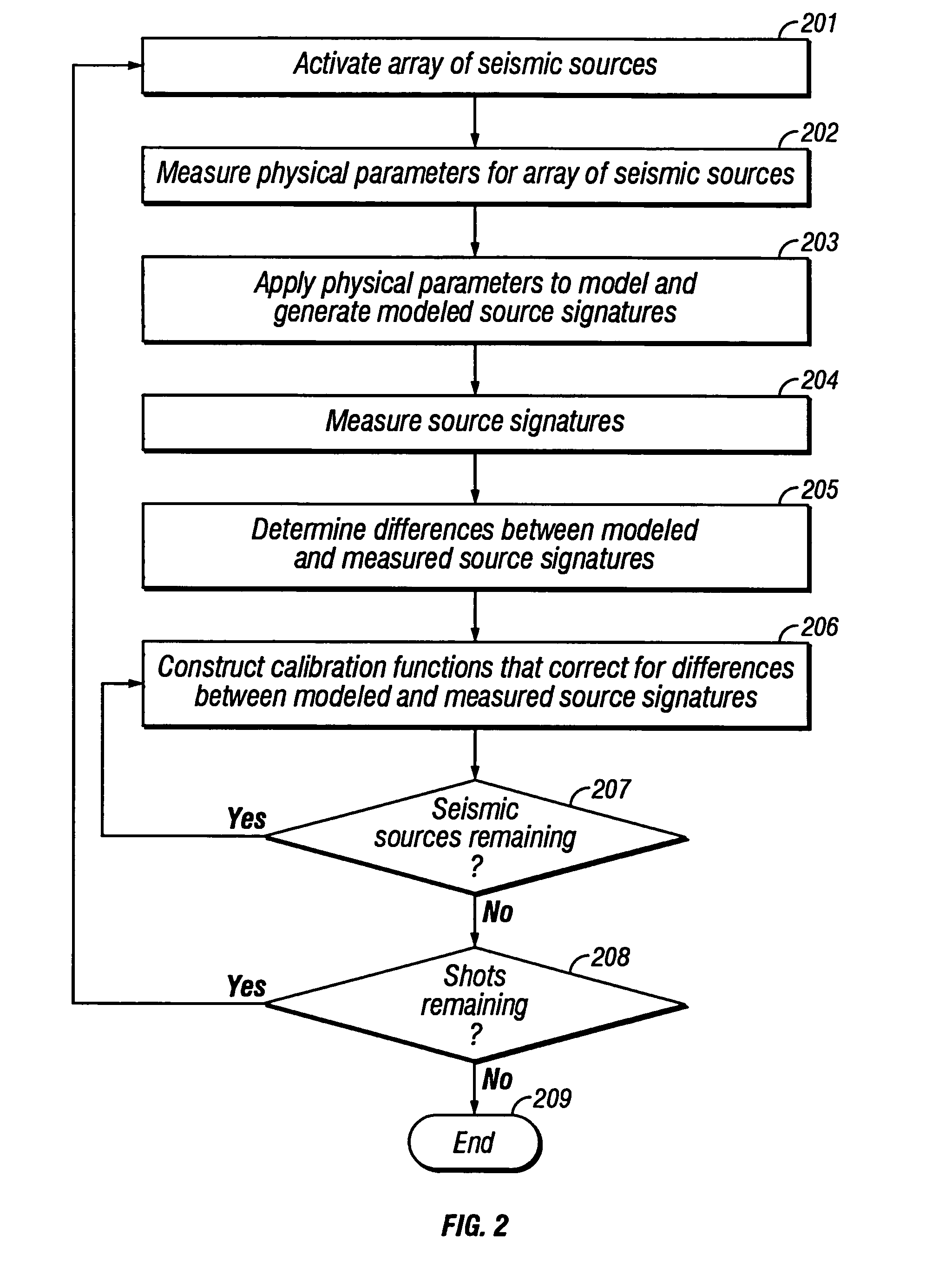
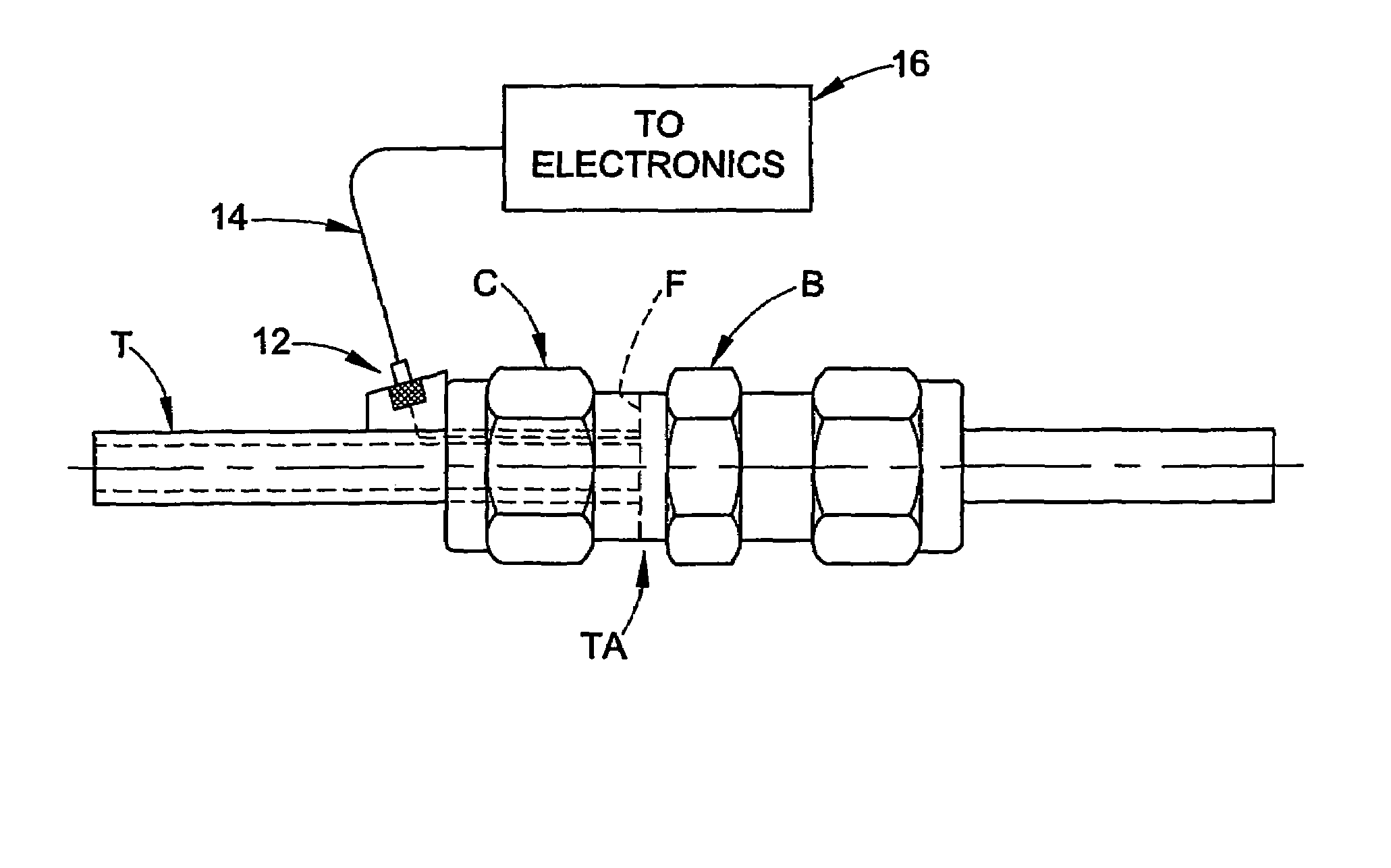
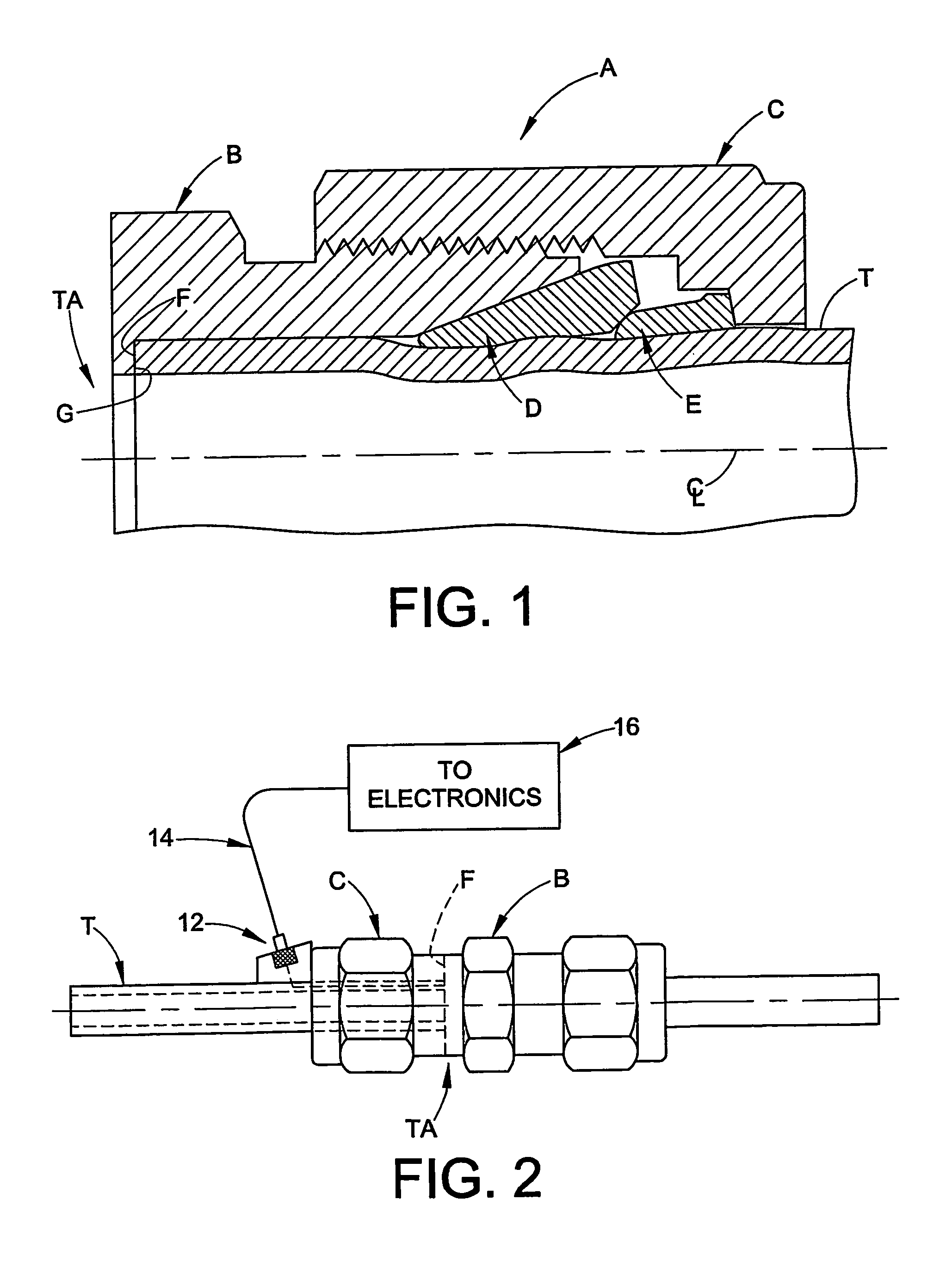
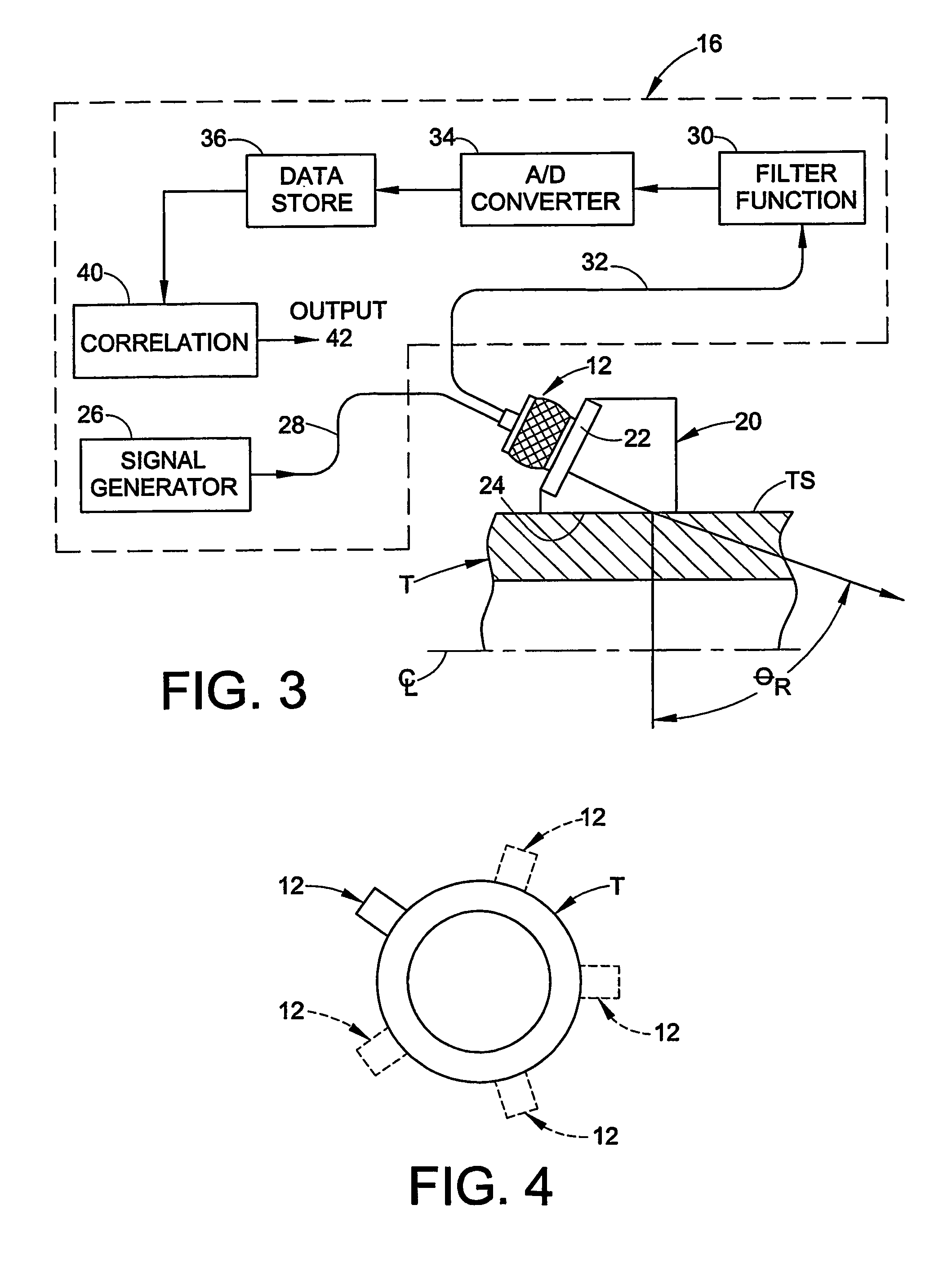
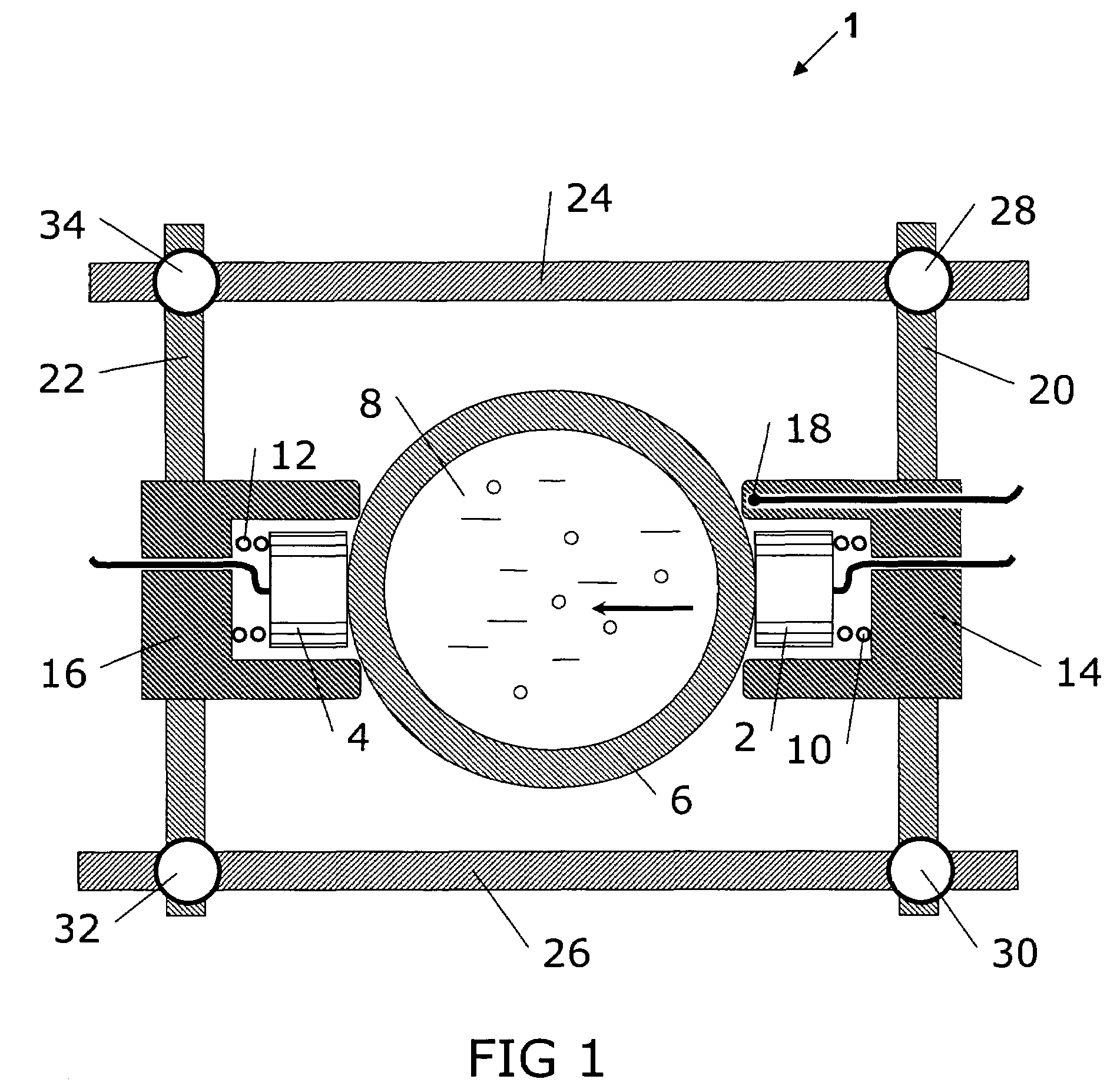
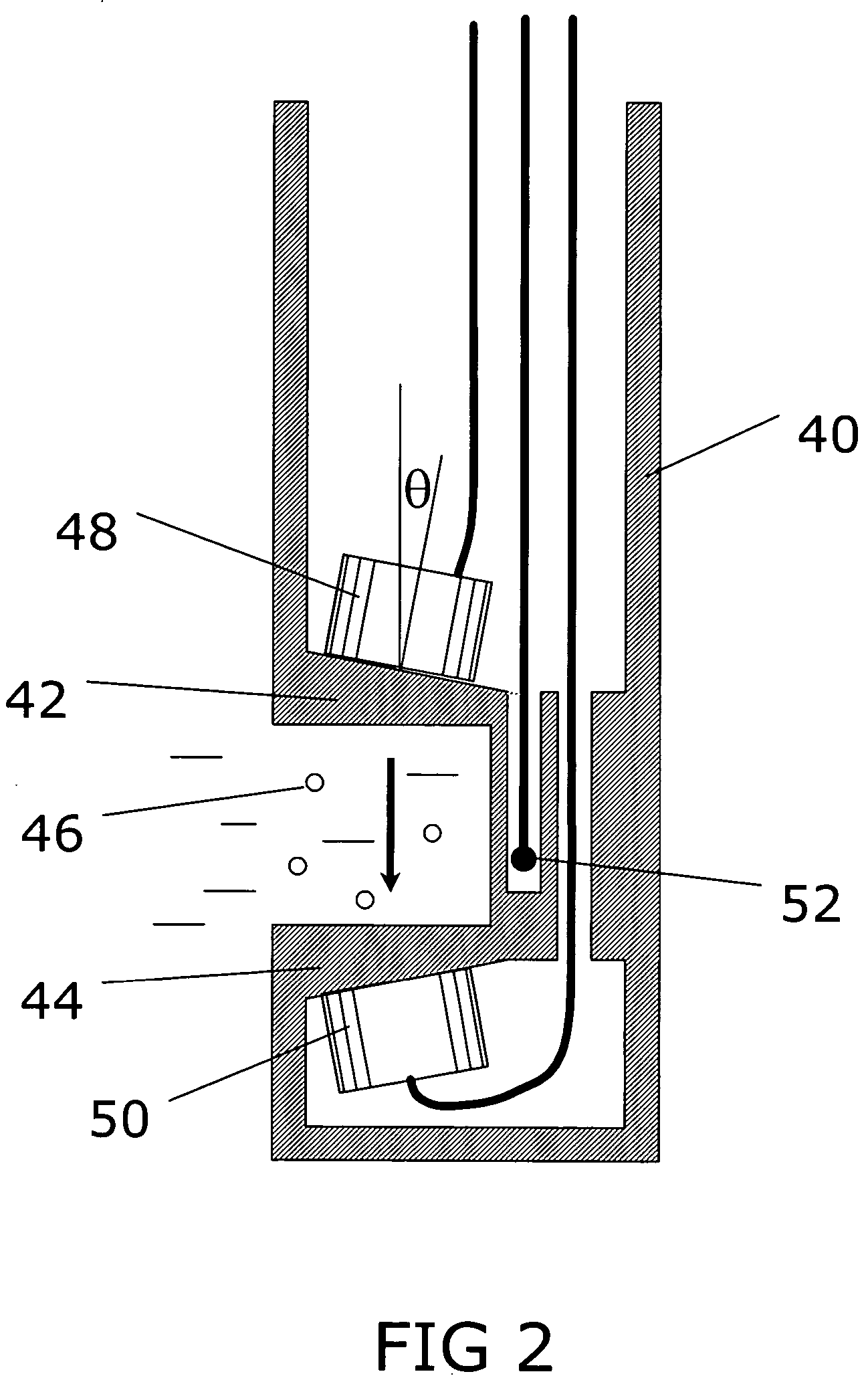
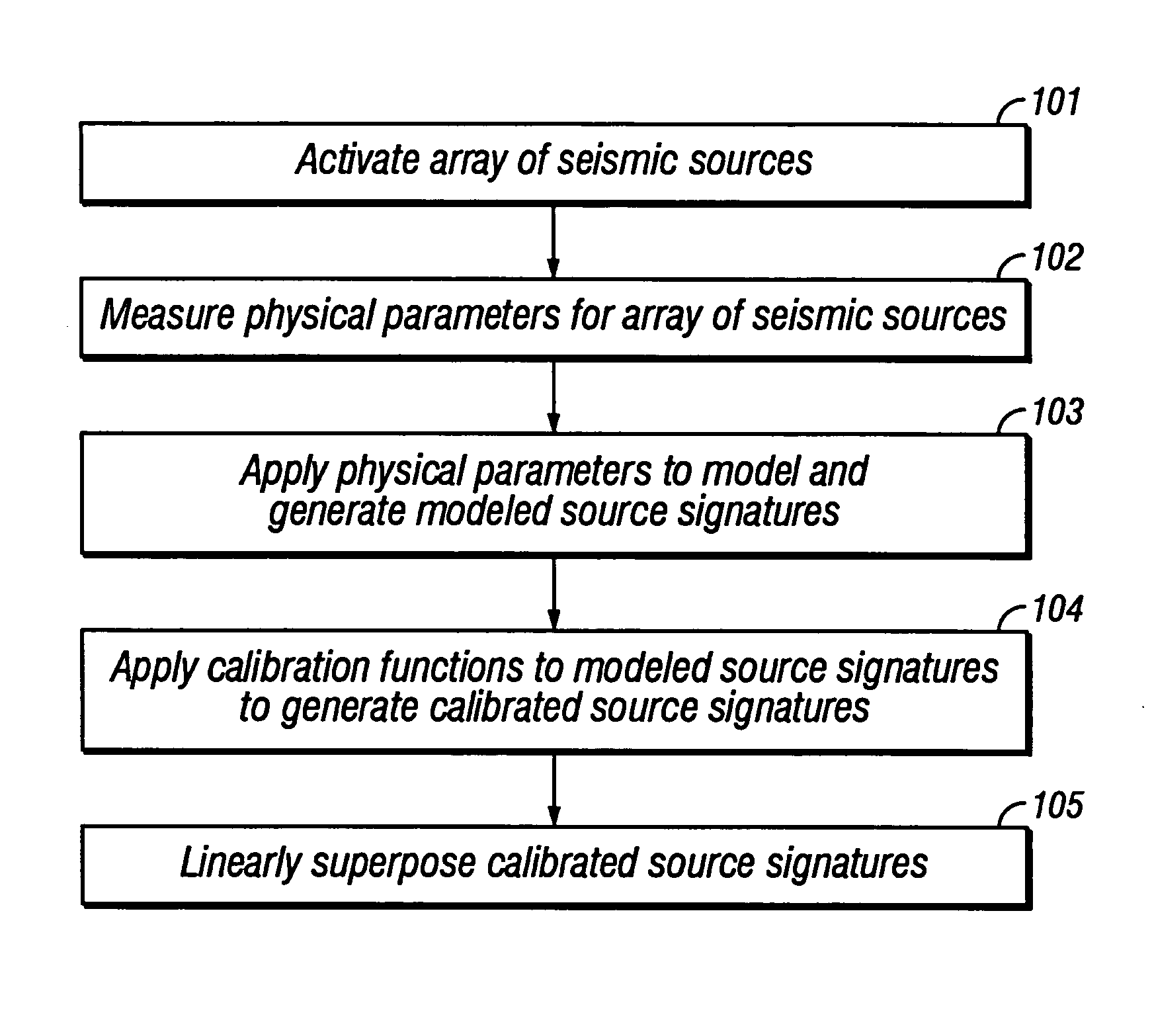
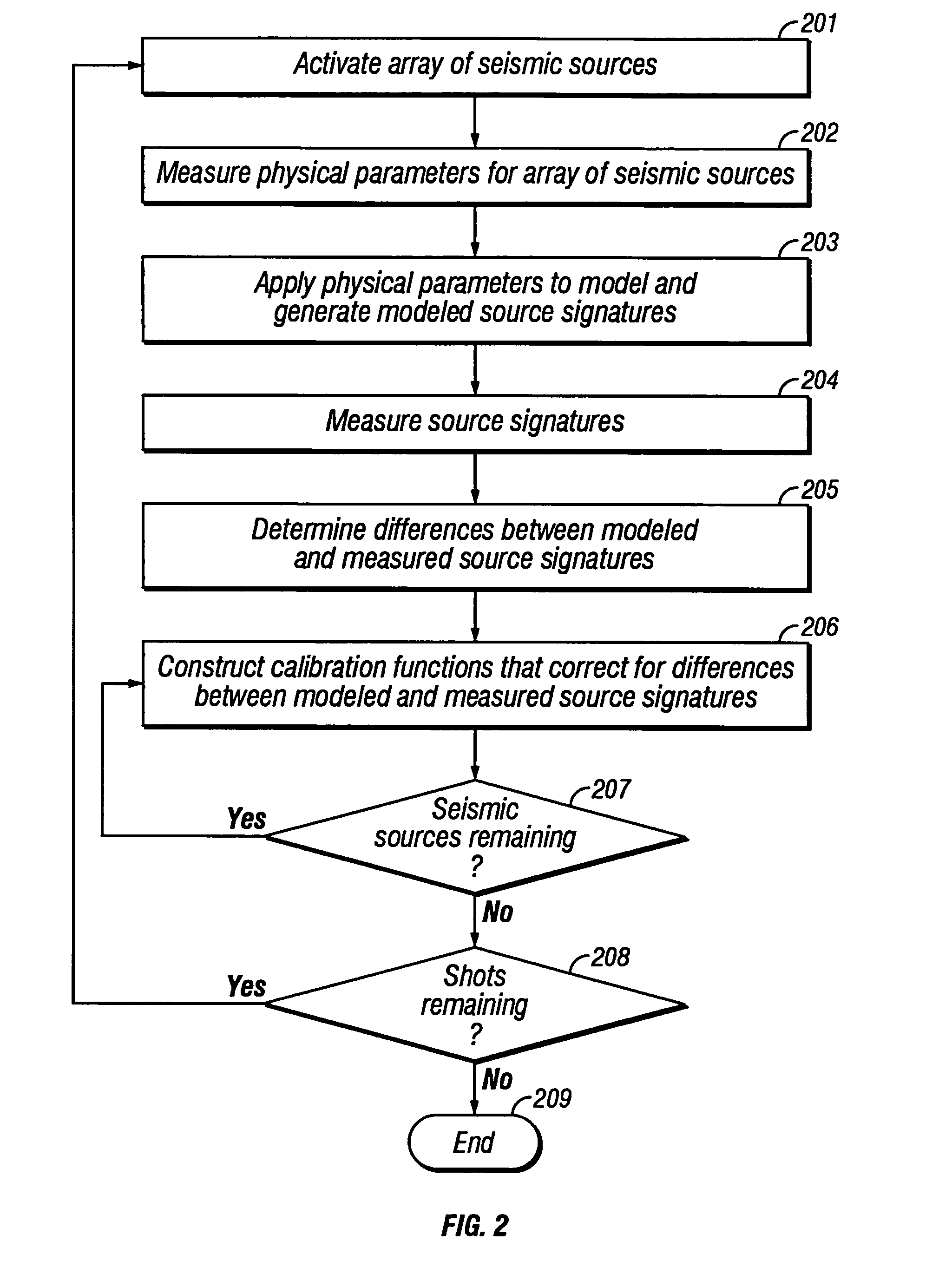
Method of seismic source monitoring using modeled source signatures with calibration functions
Owner:PGS EXPLORATION US
Ultrasonic testing of fitting assembly for fluid conduits with a hand-held apparatus
Hand-held apparatus and method for determining relative and / or absolute axial position of a conduit end within a fluid coupling includes application of input ultrasonic energy in the form of transient shear waves and analyzing the reflected energy. Application of the input energy collected at different radial positions about a first axial location is used with wavelet based correlation techniques to better analyze the reflected energy signals. Quality of the abutment between the conduit end and a surface associated with the coupling may also be determined as a separate or combined feature of the axial position determination.
Owner:SWAGELOK CO
Method and apparatus for installing a sensor array
InactiveUS20050155814A1Sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSeismic energy generationSensor arrayActuator
An apparatus and method is provided for transporting, installing, retrieving, and replacing a sensor array of individual sensor pods at a geographically remote location, such as on the sea floor. The apparatus consists of a remotely operated vehicle (ROV), a carousel attached to the ROV, a pod ejector mechanism attached to the carousel, and a manipulator with a manipulator end effector attached to the ROV. The carousel contains a plurality of sensor pod holders, where each sensor pod holder is capable of holding a sensor pod. The pod ejector mechanism is capable of discharging a fresh sensor pod, while the manipulator end effector is capable of lifting a depleted sensor pod and placing the depleted sensor pod in an empty sensor pod holder in the carousel.
Owner:SAIPEM AMERICA
Ultrasonic monitor of material composition and particle size
InactiveUS7047809B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVibration measurement in fluidUltrasound attenuationMultiple frequency
A method and apparatus for determining the composition of a containerized material, typically a suspension, through which ultrasonic waves are passed. The component ratios and particle sizes of a stationary or flowing material are determined by measuring ultrasonic wave phase and attenuation changes at multiple frequencies and deriving shape features from curves of the phase or attenuation versus frequency. Preferably, the frequency range employed extends below and above the frequency of maximum attenuation of the expected mean particle size in a suspension. The material composition is derived from analysis of the shape features of the derived curves.
Owner:APPLIED SONICS
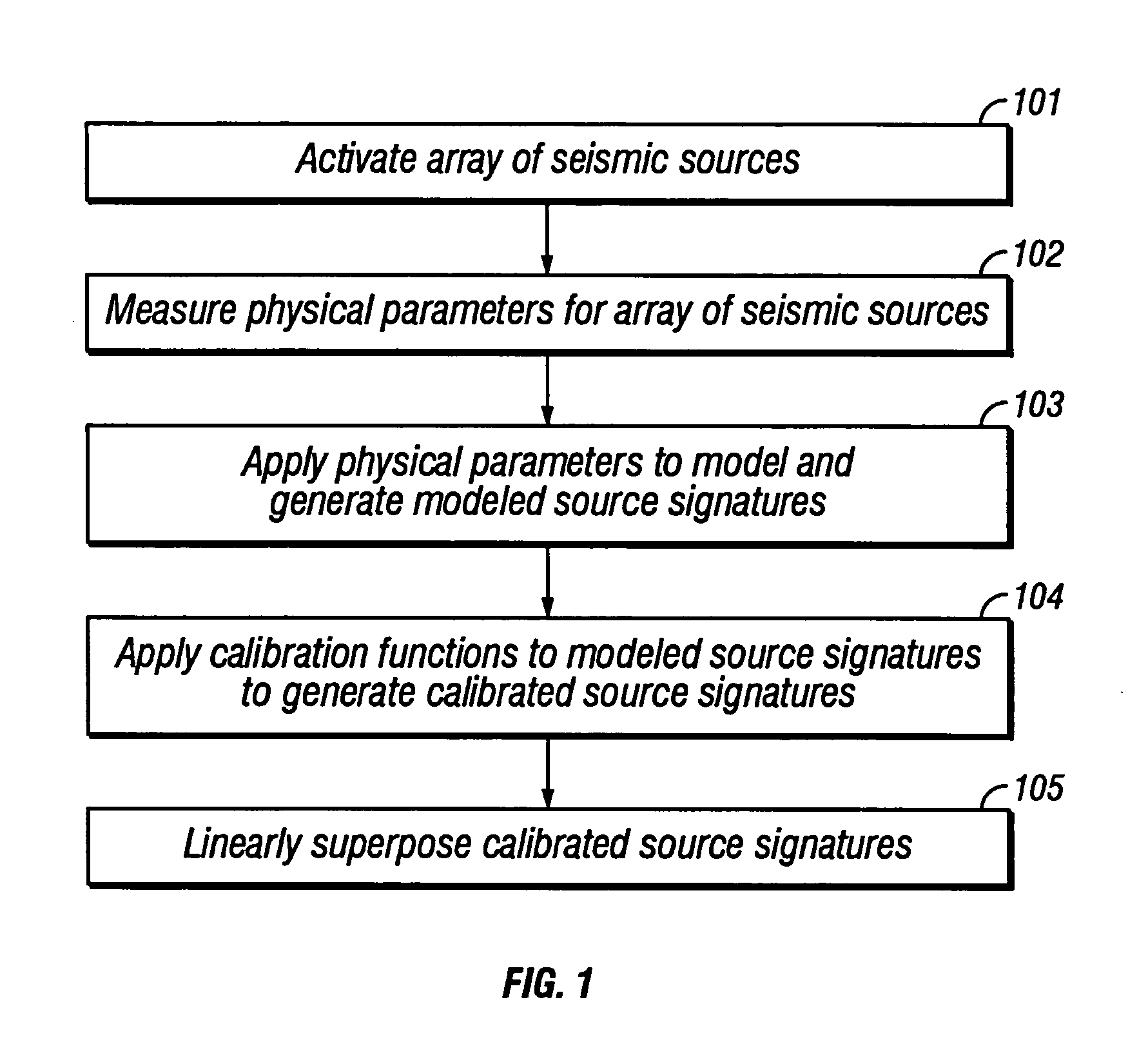
Method of seismic source monitoring using modeled source signatures with calibration functions
Owner:PGS EXPLORATION US
Popular searches
Registering/indicating working of vehicles Digital data processing details Special data processing applications Vehicle safety belts Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangement Hardware monitoring Electric light circuit arrangement Power-operated mechanism Vehicle position/course/altitude control Position/direction control
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com